User login
Advances in Management of Relapsed/Refractory Hairy Cell Leukemia
Pathophysiology
HCL develops from activated, mature memory B-cells that, in most cases, have the acquired mutation in BRAF V600E, which is present in 80% to 90% of patients with classic HCL.1,3,5 BRAF is an integral part of the RAS-BRAF-MEK-ERK cellular pathway that transmits growth factor signals from the cell surface to the nucleus to regulate cell growth and proliferation.6 Mutated BRAF V600E continuously activates BRAF kinase and downstream signaling, resulting in enhanced HCL cell survival and unchecked proliferation.3
Variant HCL (HCLv) is a separate, more virulent disease that lacks BRAF V600E mutation and CD25 expression on flow cytometry.1,7-9 Patients with HCLv have a worse prognosis and poor responses to front-line purine analogs, and a higher proportion of these patients carry the unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) gene (54% vs 17% in HCL).1,10,11 About 30% to 50% have wild-type BRAF and activating mutations in MAP2K1, which encodes aberrant MEK downstream of BRAF.10,12
Most patients with HCL have somatic mutations in the IGHV gene.3,13,14 Patients with unmutated IGHV4-34 and wildtype BRAF have an aggressive form of the disease, even if the HCL cells express CD25 as in classic HCL.1,15 HCL in patients with unmutated IGHV is often refractory to purine analogs and these patients have poor prognosis and rapid progression.16 Other identified mutations include CDKN1B in HCL and MAP2K1 and CCNC3 in HCLv.2
Signs and Symptoms
In many cases, HCL is asymptomatic, and diagnosed when pancytopenia, monocytopenia, and leukopenia are discovered on unrelated blood work.2,3,11 Monocytopenia is a specific presentation of HCL, but not HCLv.11 Typical systemic symptoms include unexplained weight loss and extreme fatigue (80%).1,3 Other symptoms can include fever, recurrent infections, night sweats, splenomegaly and related pain or abdominal fullness, hepatomegaly, and bleeding or bruising due to thrombocytopenia.1,3 Splenomegaly is associated with advanced disease.11
Up to 30% of patients may present with autoimmune disorders such as vasculitis or psoriasis. Although skin involvement is rare with HCL, 10% to 12% of patients will have dermatologic symptoms either due to recurrent infection or autoimmune reactions.1,2 Skin reactions include localized or generalized maculopapular rash, pyoderma gangrenosum (which may be severe), and recurrent bacterial or viral skin infections.17
Diagnosis
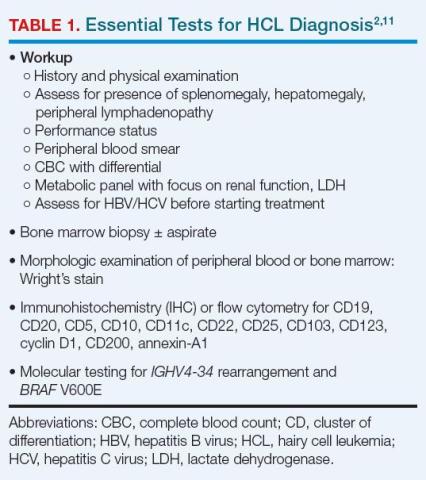
After complete history and physical examination, a diagnosis of HCL is usually made based on flow cytometry for immunophenotyping and molecular testing for BRAF V600E (Table 1).2,17
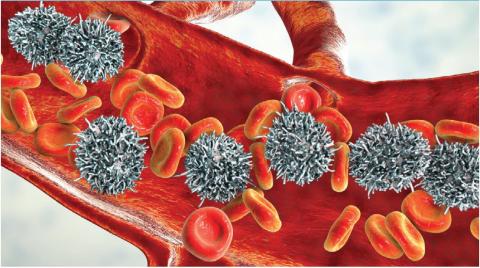
Disease-related fibrosis may impede bone marrow aspiration, and trephine biopsy should be done to make the diagnosis.11 On morphologic examination, HCL cells are small- to medium-sized, with round, oval, or indented, well-defined nuclei. Cytoplasm is pale blue, and cells have small cytoplasmic projections (Figure 1).2,18
On flow cytometry, HCL is positive for B-cell antigens (CD19, CD20, CD22), as well as antigens specific to the disease (CD11c, CD25, CD103, CD123), and by immunohistochemistry (IHC) for cyclin D1 and annexin-A1. CD20, CD123, and CD200 are bright in HCL. The presence of T-cell marker CD103 on B-cells indicates HCL.1-3 HCLv, in contrast, is positive for CD11c and CD103, but usually negative for CD25, CD123, and annexin-A1.2,19
BRAF V600E mutation can be identified using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (PCR), next-generation molecular sequencing, or IHC with a VE1 stain.3,11 IHC for CD20, annexin-1, and VE1 establish the diagnosis, but also are useful in determining the extent to which leukemic cells have infiltrated bone marrow.11
Differential diagnosis of HCL includes HCL variants, splenic marginal zone lymphoma, and splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma.7,11
Indications for Treatment and Criteria for Response
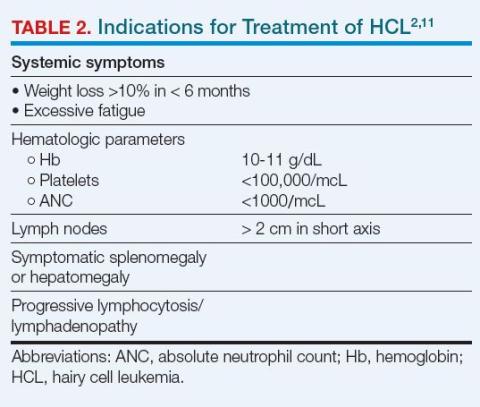
Over time, about 90% of patients with HCL will require treatment. However, not all such patients will require urgent or immediate treatment, and some can be managed with observation and close monitoring.1,11 The indications for initiating treatment generally are systemic symptoms and significant pancytopenia (Table 2).2,11
The optimal response with treatment of HCL is complete response (CR) without minimal residual disease (MRD-free), which minimizes the risk for relapse.1,11 Hematologic and molecular response is assessed using peripheral blood samples; physical examination, ultrasound, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging is used to determine response in lymph nodes, spleen, or liver.1 MRD-free is defined by the absence of HCL cells by the chosen method (IHC, flow cytometry, or PCR).20 Bone marrow aspirate flow cytometry is the most sensitive standard test for MRD detection.1Table 3 summarizes response criteria for HCL.2,11
Initial Treatment of HCL
The purine nucleoside analogs (PNAs) cladribine (± rituximab) and pentostatin are widely recommended for initial treatment.1,2,11 As monotherapy, cladribine and pentostatin are considered similarly effective, with CR in 70% to 90% of patients and durations of response > 10 years.1 Adding the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in 8 weekly doses starting the first day of front-line cladribine (CDAR) improves remission, MRD-free rates, and duration of response (94% MRD-free at 96 months), with minimal added toxicity.21 Rituximab is often added 4 weeks after cladribine, which offers more convenience, an equally high CR rate of 100%, and a 76% MRD-free rate at 3 months.11 Bone marrow biopsy should be delayed for 4 to 6 months to allow a full response to develop with cladribine.1,11
Daily (intravenous or subcutaneous) and weekly cladribine are equally safe and effective.2,11 Pentostatin is administered intravenously every 2 weeks for 3 to 6 months, allowing time for hematologic recovery between doses.1,11 Patient factors to consider when choosing treatment include baseline neutropenia, patient preference, and comorbidities.
Toxicities of PNAs include neutropenia and fever, which typically occur during the first month of treatment and are more frequent in patients with baseline severe neutropenia; T-cell recovery may take years.1 CDAR is associated with higher transient thrombocytopenia, but faster platelet and neutrophil recovery at 4 weeks than cladribine alone.21 Both therapies are immunosuppressive. Patients should be evaluated for existing infections and watched for new infections during treatment. Control of active infection prior to treatment initiation is required.11,23
Patients with confirmed BRAF V600E mutation are candidates for vemurafenib if they are unable to tolerate a PNA, have an active infection, or would like effective vaccinations.2,23-25
Treatment at Relapse
At suspected HCL relapse, patients should be evaluated to determine whether cytopenia is due to recurrent disease or lingering effects from prior treatment. Use of successive flow cytometry over time can clarify whether symptoms are related to disease and need interventional treatment, or will resolve with additional time.1
Patients who have an HCL relapse after initial therapy with cladribine or pentostatin may be candidates for re-treatment with the same or alternate PNA plus rituximab.2 Rituximab
monotherapy has been used for patients unable to tolerate PNA but yields CR rates as low as 13%.26 Repeated courses of PNA therapy yield lower rates and durations of response with each course.1,2
For patients with primary refractory disease (less than CR with initial therapy) or relapse within 2 years of initial therapy, treatment with the BRAF V600E inhibitor vemurafenib off-label, with or without rituximab, is an option.2,5 In HCL, vemurafenib for patients with relapsed or refractory disease achieved CR in 35% and 42% in 2 small trials (N = 54). Relapse-free survival among people with CR was 19 months in 1 of the trials.27 Vemurafenib plus rituximab achieved CR in 87% of patients with relapsed or refractory HCL, and an MRD-free CR rate of 57%. Among patients with CR, 85% were relapse-free at a median follow-up of 34 months.5 Treatment with vemurafenib is not myelotoxic—an advantage for HCL patients. Adverse effects with vemurafenib are often manageable with dose reductions, if needed. A specific concern with vemurafenib is the potential development of secondary skin cancers.5,27,28
Novel Targeted Options and Recommended Use
Promising alternatives for patients with relapsed or refractory HCL include combined BRAF and MEK inhibitors and the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib. The concept of BRAF/MEK inhibition was validated in studies with BRAF-mutated melanoma, in which dabrafenib plus trametinib (the MEK inhibitor) improved overall survival (OS) with less toxicity and better quality of life than vemurafenib.1,29 In a phase 2 trial in HCL, dabrafenib monotherapy demonstrated an overall response rate (ORR) of 80%, including 30% CR.30 In a subsequent phase 2 trial, dabrafenib combined with trametinib was evaluated in refractory or late relapsed HCL. Among 55 enrolled patients, objective response rate was 89%, including 65.5% CR. Nine of 36 patients with CR were MRD-free. Among responding patients, duration of response was 97.7% at 24 months.31 The most common grade ≥ 3 toxicities were hyperglycemia, pyrexia, neutropenia, and pneumonia. Secondary skin cancers were seen in about 5% of patients.31
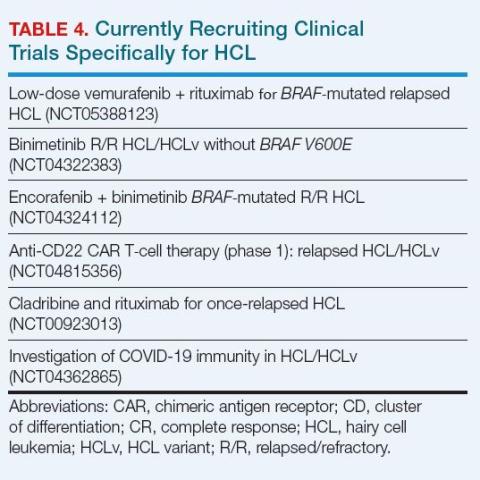
BRAF/MEK inhibitor combinations in HCL offer effective therapy with less myelosuppression than PNAs, making them useful for patients with or at risk for infection.23 Their use in HCL is off-label, as they currently are approved for treatment of BRAF-mutated melanoma and some other tumors.32 A study of encorafenib (a BRAF inhibitor) combined with binimetinib (a MEK inhibitor) is ongoing (Table 4).32
Ibrutinib interrupts B-cell receptor signaling to stop tumor cell growth. In a phase 2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory HCL or HCLv were treated with once-daily oral ibrutinib. Best ORR was 54% (19% CR; 3% MRD-free). Despite the low CR rate, 3-year progression-free survival with ibrutinib was 73% and OS was 85%. Treatment was well-tolerated; cytopenia (including 22% grade ≥ 3 thrombocytopenia and neutropenia) and diarrhea were frequent toxicities.33
Moxetumomab pasudotox is a novel CD22-targeted antibody fused with protein toxin that interrupts protein synthesis in tumor cells.1 As treatment, it was studied in a phase 3 trial of relapsed HCL in heavily pretreated patients, and achieved a CR rate of 41%, including 36% durable CR.34 Although FDA-approved for relapsed or refractory HCL, the drug is being discontinued due to business decisions, not safety or efficacy concerns.2 It is notable that many types of B-cell lymphoma also express CD22.35
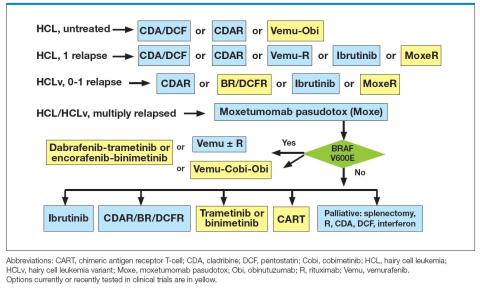
Enrollment in a clinical trial to study possible treatment advances is recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) at first and subsequent relapses of HCL for appropriate patients.2 Figure 2 summarizes an approach to treatment choice and sequencing for patients with HCL.
Supportive Care
Patients being treated for HCL should have supportive care to manage adverse effects of their disease. Such care includes prophylaxis against herpes virus if CD4+ T cells < 200 cells/μL and other prophylactic vaccinations to hepatitis B virus, COVID-19 and Influenza. Patients with neutropeni may require broad-spectrum antibacterial prophylaxis or neutrophil growth factors if neutropenic fever develops. Blood product support is recommended if needed.2 Assessment of anti-COVID-19 antibodies is recommended to optimize immunity, particularly prior to beginning anti-CD20 antibody therapy like rituximab.23
Unmet Needs
Despite improvements in response and survival with newer therapies, not all patients with HCL benefit from these advances. Unmet needs are finding optimal treatment for patients with HCLv, despite some success with MEK inhibitors, and for patients with BRAF mutations other than V600E, who have few options beyond PNAs and rituximab.
- Kreitman RJ, Arons E. Diagnosis and treatment of hairy cell leukemia as the COVID-19 pandemic continues. Blood Rev. 2022;51:100888. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2021.100888
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guideline in oncology: hairy cell leukemia. Version 1.2023. Published August 30, 2022. Accessed March 16, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hairy_cell.pdf
- Janus A, Robak T. Hairy cell leukemia. In: Li W, ed. Leukemia [Internet]. Brisbane: Exon Publications; 2022:chap3. Accessed February 16, 2023. doi:10.36255/exon-publications-leukemia-hairy-cell-leukemia
- Tadmor T, Polliack A. Epidemiology and environmental risk in hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015;28(4):175-179. doi:10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.014
- Tiacci E, De Carolis L, Simonetti E, et al. Vemurafenib plus rituximab in refractory or relapsed hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(19):1810-1823. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa20312986
- Falini B, Martelli MP, Tiacci E. BRAF V600E mutation in hairy cell leukemia: from bench to bedside. Blood. 2016;128(15):1918-1927. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-07-418434
- Matutes E. Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges in hairy cell leukemia-variant: where are we in 2021? Expert Rev Hematol. 2021;14(4):355-363. doi:10.1080/17474086.2021.1908121
- Cawley JC, Burns GF, Hayhoe FG. A chronic lymphoproliferative disorder with distinctive features: a distinct variant of hairy-cell leukaemia. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):547-559. doi:10.1016/0145-2126(80)90066-1
- Xi L, Arons E, Navarro W, et al. Both variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy cell leukemia lack the BRAF V600E mutation. Blood. 2012;119(14):3330-3332. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-09-379339
- Durham BH, Getta B, Dietrich S, et al. Genomic analysis of hairy cell leukemia identifies novel recurrent genetic alterations. Blood. 2017;130(14):1644-1648. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-01-76510711
- Grever MR, Abdel-Wahab O, Andritsos LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2017;129(5):553-560. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-689422
- Waterfall JJ, Arons E, Walker RL, et al. High prevalence of MAP2K1 mutations in variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy-cell leukemias. Nat Genet. 2014;46(1):8-10. doi:10.1038/ng.2828
- Arons E, Sunshine J, Suntum T, Kreitman RJ. Somatic hypermutation and VH gene usage in hairy cell leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2006;133(5):504-512. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06066.x
- Arons E, Roth L, Sapolsky J, Suntum T, Stetler-Stevenson M, Kreitman RJ. Evidence of canonical somatic hypermutation in hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2011;117(18):4844-4851. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-11-316737
- Arons E, Suntum T, Stetler-Stevenson M, Kreitman RJ. VH4-34+ hairy cell leukemia, a new variant with poor prognosis despite standard therapy. Blood. 2009;114(21):4687-4695. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-01-201731
- Forconi F, Sozzi E, Cencini E, et al. Hairy cell leukemias with unmutated IGHV genes define the minor subset refractory to single-agent cladribine and with more aggressive behavior. Blood. 2009;114(21):4696-4702. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-03-212449
- Robak E, Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Robak T. Skin changes in hairy cell leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2021;100(3):615-625. doi:10.1007/s00277-020-04349-z
- Bouroncle BA. Thirty-five years in the progress of hairy cell leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 1994;14(suppl 1):1-12. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7820038/
- Falini B, Tiacci E, Liso A, et al. Simple diagnostic assay for hairy cell leukaemia by immunocytochemical detection of annexin A1 (ANXA1). Lancet. 2004;363(9424): 1869-1870. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16356-3
- Robak T, Robak P. Measurable residual disease in hairy cell leukemia: technical considerations and clinical significance. Front Oncol. 2022;12:976374. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.976374
- Chihara D, Arons E, Stetler-Stevenson M, et al. Randomized phase II study of first-line cladribine with concurrent or delayed rituximab in patients with hairy cell leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(14):1527-1538. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.02250
- Chihara D, Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, et al. Long-term durable remission by cladribine followed by rituximab in patients with hairy cell leukaemia: update of a phase II trial. Br J Haematol. 2016;174(5):760-766. doi:10.1111/bjh.14129
- Grever M, Andritsos L, Banerji V, et al. Hairy cell leukemia and COVID-19 adaptation of treatment guidelines. Leukemia. 2021;35(7):1864-1872. doi:10.1038/s41375-021-01257-7
- Konrat J, Rösler W, Roiss M, et al. BRAF inhibitor treatment of classical hairy cell leukemia allows successful vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. Ann Hematol. 2023;102(2):403-406. doi:10.1007/s00277-022-05026-z
- Park JH, Shukla M, Salcedo JM, et al. First-line chemo-free therapy with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib combined with obinutuzumab is effective in patients with HCL. Blood. 2019;134(suppl 1):Abstract 3998. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2019-124478
- Nieva J, Bethel K, Saven A. Phase 2 study of rituximab in the treatment of cladribine-failed patients with hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2003;102(3):810-813. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-01-0014
- Tiacci E, Park JH, De Carolis L, et al. Targeting mutant BRAF in relapsed or refractory hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1733-1747. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1506583
- Maitre E, Paillassa J, Troussard X. Novel targeted treatments in hairy cell leukemia and other hairy cell-like disorders. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1068981. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1068981
- Grob JJ, Amonkar MM, Karaszewska B, et al. Comparison of dabrafenib and trametinib combination therapy with vemurafenib monotherapy on health-related quality of life in patients with unresectable or metastatic cutaneous BRAF Val600-mutation-positive melanoma (COMBI-v): results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(13):1389-1398. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00087-X
- Tiacci E, De Carolis L, Simonetti E, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib in relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia: a pilot phase-2 clinical trial. Leukemia. 2021;35(11):3314-3318. doi:10.1038/s41375-021-01210-8
- Kreitman RJ, Moreau P, Ravandi F, et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with relapsed/refractory BRAF V600E mutation-positive hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2023;141(9):996-1006. doi:10.1182/blood.2021013658
- Adashek JJ, Menta AK, Reddy NK, Desai AP, Roszik J, Subbiah V. Tissue agnostic activity of BRAF plus MEK inhibitor in BRAF V600E-mutated tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022;21(6):871-878. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0950
- Rogers KA, Andritsos LA, Wei L, et al. Phase 2 study of ibrutinib in classic and variant hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2021;137(25):3473-3483. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009688
- Kreitman RJ, Dearden C, Zinzani PL, et al; Study 1053 investigators. Moxetumomab pasudotox in heavily pre-treated patients with relapsed/refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL): long-term follow-up from the pivotal trial. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):35. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-01004-y
- Leonard JP, Goldenberg DM. Preclinical and clinical evaluation of epratuzumab (anti-CD22 IgG) in B-cell malignancies. Oncogene. 2007;26(25):3704-3713. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210370
Pathophysiology
HCL develops from activated, mature memory B-cells that, in most cases, have the acquired mutation in BRAF V600E, which is present in 80% to 90% of patients with classic HCL.1,3,5 BRAF is an integral part of the RAS-BRAF-MEK-ERK cellular pathway that transmits growth factor signals from the cell surface to the nucleus to regulate cell growth and proliferation.6 Mutated BRAF V600E continuously activates BRAF kinase and downstream signaling, resulting in enhanced HCL cell survival and unchecked proliferation.3
Variant HCL (HCLv) is a separate, more virulent disease that lacks BRAF V600E mutation and CD25 expression on flow cytometry.1,7-9 Patients with HCLv have a worse prognosis and poor responses to front-line purine analogs, and a higher proportion of these patients carry the unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) gene (54% vs 17% in HCL).1,10,11 About 30% to 50% have wild-type BRAF and activating mutations in MAP2K1, which encodes aberrant MEK downstream of BRAF.10,12
Most patients with HCL have somatic mutations in the IGHV gene.3,13,14 Patients with unmutated IGHV4-34 and wildtype BRAF have an aggressive form of the disease, even if the HCL cells express CD25 as in classic HCL.1,15 HCL in patients with unmutated IGHV is often refractory to purine analogs and these patients have poor prognosis and rapid progression.16 Other identified mutations include CDKN1B in HCL and MAP2K1 and CCNC3 in HCLv.2
Signs and Symptoms
In many cases, HCL is asymptomatic, and diagnosed when pancytopenia, monocytopenia, and leukopenia are discovered on unrelated blood work.2,3,11 Monocytopenia is a specific presentation of HCL, but not HCLv.11 Typical systemic symptoms include unexplained weight loss and extreme fatigue (80%).1,3 Other symptoms can include fever, recurrent infections, night sweats, splenomegaly and related pain or abdominal fullness, hepatomegaly, and bleeding or bruising due to thrombocytopenia.1,3 Splenomegaly is associated with advanced disease.11
Up to 30% of patients may present with autoimmune disorders such as vasculitis or psoriasis. Although skin involvement is rare with HCL, 10% to 12% of patients will have dermatologic symptoms either due to recurrent infection or autoimmune reactions.1,2 Skin reactions include localized or generalized maculopapular rash, pyoderma gangrenosum (which may be severe), and recurrent bacterial or viral skin infections.17
Diagnosis
After complete history and physical examination, a diagnosis of HCL is usually made based on flow cytometry for immunophenotyping and molecular testing for BRAF V600E (Table 1).2,17
Disease-related fibrosis may impede bone marrow aspiration, and trephine biopsy should be done to make the diagnosis.11 On morphologic examination, HCL cells are small- to medium-sized, with round, oval, or indented, well-defined nuclei. Cytoplasm is pale blue, and cells have small cytoplasmic projections (Figure 1).2,18
On flow cytometry, HCL is positive for B-cell antigens (CD19, CD20, CD22), as well as antigens specific to the disease (CD11c, CD25, CD103, CD123), and by immunohistochemistry (IHC) for cyclin D1 and annexin-A1. CD20, CD123, and CD200 are bright in HCL. The presence of T-cell marker CD103 on B-cells indicates HCL.1-3 HCLv, in contrast, is positive for CD11c and CD103, but usually negative for CD25, CD123, and annexin-A1.2,19
BRAF V600E mutation can be identified using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (PCR), next-generation molecular sequencing, or IHC with a VE1 stain.3,11 IHC for CD20, annexin-1, and VE1 establish the diagnosis, but also are useful in determining the extent to which leukemic cells have infiltrated bone marrow.11
Differential diagnosis of HCL includes HCL variants, splenic marginal zone lymphoma, and splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma.7,11
Indications for Treatment and Criteria for Response
Over time, about 90% of patients with HCL will require treatment. However, not all such patients will require urgent or immediate treatment, and some can be managed with observation and close monitoring.1,11 The indications for initiating treatment generally are systemic symptoms and significant pancytopenia (Table 2).2,11
The optimal response with treatment of HCL is complete response (CR) without minimal residual disease (MRD-free), which minimizes the risk for relapse.1,11 Hematologic and molecular response is assessed using peripheral blood samples; physical examination, ultrasound, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging is used to determine response in lymph nodes, spleen, or liver.1 MRD-free is defined by the absence of HCL cells by the chosen method (IHC, flow cytometry, or PCR).20 Bone marrow aspirate flow cytometry is the most sensitive standard test for MRD detection.1Table 3 summarizes response criteria for HCL.2,11
Initial Treatment of HCL
The purine nucleoside analogs (PNAs) cladribine (± rituximab) and pentostatin are widely recommended for initial treatment.1,2,11 As monotherapy, cladribine and pentostatin are considered similarly effective, with CR in 70% to 90% of patients and durations of response > 10 years.1 Adding the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in 8 weekly doses starting the first day of front-line cladribine (CDAR) improves remission, MRD-free rates, and duration of response (94% MRD-free at 96 months), with minimal added toxicity.21 Rituximab is often added 4 weeks after cladribine, which offers more convenience, an equally high CR rate of 100%, and a 76% MRD-free rate at 3 months.11 Bone marrow biopsy should be delayed for 4 to 6 months to allow a full response to develop with cladribine.1,11
Daily (intravenous or subcutaneous) and weekly cladribine are equally safe and effective.2,11 Pentostatin is administered intravenously every 2 weeks for 3 to 6 months, allowing time for hematologic recovery between doses.1,11 Patient factors to consider when choosing treatment include baseline neutropenia, patient preference, and comorbidities.
Toxicities of PNAs include neutropenia and fever, which typically occur during the first month of treatment and are more frequent in patients with baseline severe neutropenia; T-cell recovery may take years.1 CDAR is associated with higher transient thrombocytopenia, but faster platelet and neutrophil recovery at 4 weeks than cladribine alone.21 Both therapies are immunosuppressive. Patients should be evaluated for existing infections and watched for new infections during treatment. Control of active infection prior to treatment initiation is required.11,23
Patients with confirmed BRAF V600E mutation are candidates for vemurafenib if they are unable to tolerate a PNA, have an active infection, or would like effective vaccinations.2,23-25
Treatment at Relapse
At suspected HCL relapse, patients should be evaluated to determine whether cytopenia is due to recurrent disease or lingering effects from prior treatment. Use of successive flow cytometry over time can clarify whether symptoms are related to disease and need interventional treatment, or will resolve with additional time.1
Patients who have an HCL relapse after initial therapy with cladribine or pentostatin may be candidates for re-treatment with the same or alternate PNA plus rituximab.2 Rituximab
monotherapy has been used for patients unable to tolerate PNA but yields CR rates as low as 13%.26 Repeated courses of PNA therapy yield lower rates and durations of response with each course.1,2
For patients with primary refractory disease (less than CR with initial therapy) or relapse within 2 years of initial therapy, treatment with the BRAF V600E inhibitor vemurafenib off-label, with or without rituximab, is an option.2,5 In HCL, vemurafenib for patients with relapsed or refractory disease achieved CR in 35% and 42% in 2 small trials (N = 54). Relapse-free survival among people with CR was 19 months in 1 of the trials.27 Vemurafenib plus rituximab achieved CR in 87% of patients with relapsed or refractory HCL, and an MRD-free CR rate of 57%. Among patients with CR, 85% were relapse-free at a median follow-up of 34 months.5 Treatment with vemurafenib is not myelotoxic—an advantage for HCL patients. Adverse effects with vemurafenib are often manageable with dose reductions, if needed. A specific concern with vemurafenib is the potential development of secondary skin cancers.5,27,28
Novel Targeted Options and Recommended Use
Promising alternatives for patients with relapsed or refractory HCL include combined BRAF and MEK inhibitors and the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib. The concept of BRAF/MEK inhibition was validated in studies with BRAF-mutated melanoma, in which dabrafenib plus trametinib (the MEK inhibitor) improved overall survival (OS) with less toxicity and better quality of life than vemurafenib.1,29 In a phase 2 trial in HCL, dabrafenib monotherapy demonstrated an overall response rate (ORR) of 80%, including 30% CR.30 In a subsequent phase 2 trial, dabrafenib combined with trametinib was evaluated in refractory or late relapsed HCL. Among 55 enrolled patients, objective response rate was 89%, including 65.5% CR. Nine of 36 patients with CR were MRD-free. Among responding patients, duration of response was 97.7% at 24 months.31 The most common grade ≥ 3 toxicities were hyperglycemia, pyrexia, neutropenia, and pneumonia. Secondary skin cancers were seen in about 5% of patients.31
BRAF/MEK inhibitor combinations in HCL offer effective therapy with less myelosuppression than PNAs, making them useful for patients with or at risk for infection.23 Their use in HCL is off-label, as they currently are approved for treatment of BRAF-mutated melanoma and some other tumors.32 A study of encorafenib (a BRAF inhibitor) combined with binimetinib (a MEK inhibitor) is ongoing (Table 4).32
Ibrutinib interrupts B-cell receptor signaling to stop tumor cell growth. In a phase 2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory HCL or HCLv were treated with once-daily oral ibrutinib. Best ORR was 54% (19% CR; 3% MRD-free). Despite the low CR rate, 3-year progression-free survival with ibrutinib was 73% and OS was 85%. Treatment was well-tolerated; cytopenia (including 22% grade ≥ 3 thrombocytopenia and neutropenia) and diarrhea were frequent toxicities.33
Moxetumomab pasudotox is a novel CD22-targeted antibody fused with protein toxin that interrupts protein synthesis in tumor cells.1 As treatment, it was studied in a phase 3 trial of relapsed HCL in heavily pretreated patients, and achieved a CR rate of 41%, including 36% durable CR.34 Although FDA-approved for relapsed or refractory HCL, the drug is being discontinued due to business decisions, not safety or efficacy concerns.2 It is notable that many types of B-cell lymphoma also express CD22.35
Enrollment in a clinical trial to study possible treatment advances is recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) at first and subsequent relapses of HCL for appropriate patients.2 Figure 2 summarizes an approach to treatment choice and sequencing for patients with HCL.
Supportive Care
Patients being treated for HCL should have supportive care to manage adverse effects of their disease. Such care includes prophylaxis against herpes virus if CD4+ T cells < 200 cells/μL and other prophylactic vaccinations to hepatitis B virus, COVID-19 and Influenza. Patients with neutropeni may require broad-spectrum antibacterial prophylaxis or neutrophil growth factors if neutropenic fever develops. Blood product support is recommended if needed.2 Assessment of anti-COVID-19 antibodies is recommended to optimize immunity, particularly prior to beginning anti-CD20 antibody therapy like rituximab.23
Unmet Needs
Despite improvements in response and survival with newer therapies, not all patients with HCL benefit from these advances. Unmet needs are finding optimal treatment for patients with HCLv, despite some success with MEK inhibitors, and for patients with BRAF mutations other than V600E, who have few options beyond PNAs and rituximab.
Pathophysiology
HCL develops from activated, mature memory B-cells that, in most cases, have the acquired mutation in BRAF V600E, which is present in 80% to 90% of patients with classic HCL.1,3,5 BRAF is an integral part of the RAS-BRAF-MEK-ERK cellular pathway that transmits growth factor signals from the cell surface to the nucleus to regulate cell growth and proliferation.6 Mutated BRAF V600E continuously activates BRAF kinase and downstream signaling, resulting in enhanced HCL cell survival and unchecked proliferation.3
Variant HCL (HCLv) is a separate, more virulent disease that lacks BRAF V600E mutation and CD25 expression on flow cytometry.1,7-9 Patients with HCLv have a worse prognosis and poor responses to front-line purine analogs, and a higher proportion of these patients carry the unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) gene (54% vs 17% in HCL).1,10,11 About 30% to 50% have wild-type BRAF and activating mutations in MAP2K1, which encodes aberrant MEK downstream of BRAF.10,12
Most patients with HCL have somatic mutations in the IGHV gene.3,13,14 Patients with unmutated IGHV4-34 and wildtype BRAF have an aggressive form of the disease, even if the HCL cells express CD25 as in classic HCL.1,15 HCL in patients with unmutated IGHV is often refractory to purine analogs and these patients have poor prognosis and rapid progression.16 Other identified mutations include CDKN1B in HCL and MAP2K1 and CCNC3 in HCLv.2
Signs and Symptoms
In many cases, HCL is asymptomatic, and diagnosed when pancytopenia, monocytopenia, and leukopenia are discovered on unrelated blood work.2,3,11 Monocytopenia is a specific presentation of HCL, but not HCLv.11 Typical systemic symptoms include unexplained weight loss and extreme fatigue (80%).1,3 Other symptoms can include fever, recurrent infections, night sweats, splenomegaly and related pain or abdominal fullness, hepatomegaly, and bleeding or bruising due to thrombocytopenia.1,3 Splenomegaly is associated with advanced disease.11
Up to 30% of patients may present with autoimmune disorders such as vasculitis or psoriasis. Although skin involvement is rare with HCL, 10% to 12% of patients will have dermatologic symptoms either due to recurrent infection or autoimmune reactions.1,2 Skin reactions include localized or generalized maculopapular rash, pyoderma gangrenosum (which may be severe), and recurrent bacterial or viral skin infections.17
Diagnosis
After complete history and physical examination, a diagnosis of HCL is usually made based on flow cytometry for immunophenotyping and molecular testing for BRAF V600E (Table 1).2,17
Disease-related fibrosis may impede bone marrow aspiration, and trephine biopsy should be done to make the diagnosis.11 On morphologic examination, HCL cells are small- to medium-sized, with round, oval, or indented, well-defined nuclei. Cytoplasm is pale blue, and cells have small cytoplasmic projections (Figure 1).2,18
On flow cytometry, HCL is positive for B-cell antigens (CD19, CD20, CD22), as well as antigens specific to the disease (CD11c, CD25, CD103, CD123), and by immunohistochemistry (IHC) for cyclin D1 and annexin-A1. CD20, CD123, and CD200 are bright in HCL. The presence of T-cell marker CD103 on B-cells indicates HCL.1-3 HCLv, in contrast, is positive for CD11c and CD103, but usually negative for CD25, CD123, and annexin-A1.2,19
BRAF V600E mutation can be identified using droplet digital polymerase chain reaction (PCR), next-generation molecular sequencing, or IHC with a VE1 stain.3,11 IHC for CD20, annexin-1, and VE1 establish the diagnosis, but also are useful in determining the extent to which leukemic cells have infiltrated bone marrow.11
Differential diagnosis of HCL includes HCL variants, splenic marginal zone lymphoma, and splenic diffuse red pulp small B-cell lymphoma.7,11
Indications for Treatment and Criteria for Response
Over time, about 90% of patients with HCL will require treatment. However, not all such patients will require urgent or immediate treatment, and some can be managed with observation and close monitoring.1,11 The indications for initiating treatment generally are systemic symptoms and significant pancytopenia (Table 2).2,11
The optimal response with treatment of HCL is complete response (CR) without minimal residual disease (MRD-free), which minimizes the risk for relapse.1,11 Hematologic and molecular response is assessed using peripheral blood samples; physical examination, ultrasound, computed tomography, or magnetic resonance imaging is used to determine response in lymph nodes, spleen, or liver.1 MRD-free is defined by the absence of HCL cells by the chosen method (IHC, flow cytometry, or PCR).20 Bone marrow aspirate flow cytometry is the most sensitive standard test for MRD detection.1Table 3 summarizes response criteria for HCL.2,11
Initial Treatment of HCL
The purine nucleoside analogs (PNAs) cladribine (± rituximab) and pentostatin are widely recommended for initial treatment.1,2,11 As monotherapy, cladribine and pentostatin are considered similarly effective, with CR in 70% to 90% of patients and durations of response > 10 years.1 Adding the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in 8 weekly doses starting the first day of front-line cladribine (CDAR) improves remission, MRD-free rates, and duration of response (94% MRD-free at 96 months), with minimal added toxicity.21 Rituximab is often added 4 weeks after cladribine, which offers more convenience, an equally high CR rate of 100%, and a 76% MRD-free rate at 3 months.11 Bone marrow biopsy should be delayed for 4 to 6 months to allow a full response to develop with cladribine.1,11
Daily (intravenous or subcutaneous) and weekly cladribine are equally safe and effective.2,11 Pentostatin is administered intravenously every 2 weeks for 3 to 6 months, allowing time for hematologic recovery between doses.1,11 Patient factors to consider when choosing treatment include baseline neutropenia, patient preference, and comorbidities.
Toxicities of PNAs include neutropenia and fever, which typically occur during the first month of treatment and are more frequent in patients with baseline severe neutropenia; T-cell recovery may take years.1 CDAR is associated with higher transient thrombocytopenia, but faster platelet and neutrophil recovery at 4 weeks than cladribine alone.21 Both therapies are immunosuppressive. Patients should be evaluated for existing infections and watched for new infections during treatment. Control of active infection prior to treatment initiation is required.11,23
Patients with confirmed BRAF V600E mutation are candidates for vemurafenib if they are unable to tolerate a PNA, have an active infection, or would like effective vaccinations.2,23-25
Treatment at Relapse
At suspected HCL relapse, patients should be evaluated to determine whether cytopenia is due to recurrent disease or lingering effects from prior treatment. Use of successive flow cytometry over time can clarify whether symptoms are related to disease and need interventional treatment, or will resolve with additional time.1
Patients who have an HCL relapse after initial therapy with cladribine or pentostatin may be candidates for re-treatment with the same or alternate PNA plus rituximab.2 Rituximab
monotherapy has been used for patients unable to tolerate PNA but yields CR rates as low as 13%.26 Repeated courses of PNA therapy yield lower rates and durations of response with each course.1,2
For patients with primary refractory disease (less than CR with initial therapy) or relapse within 2 years of initial therapy, treatment with the BRAF V600E inhibitor vemurafenib off-label, with or without rituximab, is an option.2,5 In HCL, vemurafenib for patients with relapsed or refractory disease achieved CR in 35% and 42% in 2 small trials (N = 54). Relapse-free survival among people with CR was 19 months in 1 of the trials.27 Vemurafenib plus rituximab achieved CR in 87% of patients with relapsed or refractory HCL, and an MRD-free CR rate of 57%. Among patients with CR, 85% were relapse-free at a median follow-up of 34 months.5 Treatment with vemurafenib is not myelotoxic—an advantage for HCL patients. Adverse effects with vemurafenib are often manageable with dose reductions, if needed. A specific concern with vemurafenib is the potential development of secondary skin cancers.5,27,28
Novel Targeted Options and Recommended Use
Promising alternatives for patients with relapsed or refractory HCL include combined BRAF and MEK inhibitors and the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib. The concept of BRAF/MEK inhibition was validated in studies with BRAF-mutated melanoma, in which dabrafenib plus trametinib (the MEK inhibitor) improved overall survival (OS) with less toxicity and better quality of life than vemurafenib.1,29 In a phase 2 trial in HCL, dabrafenib monotherapy demonstrated an overall response rate (ORR) of 80%, including 30% CR.30 In a subsequent phase 2 trial, dabrafenib combined with trametinib was evaluated in refractory or late relapsed HCL. Among 55 enrolled patients, objective response rate was 89%, including 65.5% CR. Nine of 36 patients with CR were MRD-free. Among responding patients, duration of response was 97.7% at 24 months.31 The most common grade ≥ 3 toxicities were hyperglycemia, pyrexia, neutropenia, and pneumonia. Secondary skin cancers were seen in about 5% of patients.31
BRAF/MEK inhibitor combinations in HCL offer effective therapy with less myelosuppression than PNAs, making them useful for patients with or at risk for infection.23 Their use in HCL is off-label, as they currently are approved for treatment of BRAF-mutated melanoma and some other tumors.32 A study of encorafenib (a BRAF inhibitor) combined with binimetinib (a MEK inhibitor) is ongoing (Table 4).32
Ibrutinib interrupts B-cell receptor signaling to stop tumor cell growth. In a phase 2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory HCL or HCLv were treated with once-daily oral ibrutinib. Best ORR was 54% (19% CR; 3% MRD-free). Despite the low CR rate, 3-year progression-free survival with ibrutinib was 73% and OS was 85%. Treatment was well-tolerated; cytopenia (including 22% grade ≥ 3 thrombocytopenia and neutropenia) and diarrhea were frequent toxicities.33
Moxetumomab pasudotox is a novel CD22-targeted antibody fused with protein toxin that interrupts protein synthesis in tumor cells.1 As treatment, it was studied in a phase 3 trial of relapsed HCL in heavily pretreated patients, and achieved a CR rate of 41%, including 36% durable CR.34 Although FDA-approved for relapsed or refractory HCL, the drug is being discontinued due to business decisions, not safety or efficacy concerns.2 It is notable that many types of B-cell lymphoma also express CD22.35
Enrollment in a clinical trial to study possible treatment advances is recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) at first and subsequent relapses of HCL for appropriate patients.2 Figure 2 summarizes an approach to treatment choice and sequencing for patients with HCL.
Supportive Care
Patients being treated for HCL should have supportive care to manage adverse effects of their disease. Such care includes prophylaxis against herpes virus if CD4+ T cells < 200 cells/μL and other prophylactic vaccinations to hepatitis B virus, COVID-19 and Influenza. Patients with neutropeni may require broad-spectrum antibacterial prophylaxis or neutrophil growth factors if neutropenic fever develops. Blood product support is recommended if needed.2 Assessment of anti-COVID-19 antibodies is recommended to optimize immunity, particularly prior to beginning anti-CD20 antibody therapy like rituximab.23
Unmet Needs
Despite improvements in response and survival with newer therapies, not all patients with HCL benefit from these advances. Unmet needs are finding optimal treatment for patients with HCLv, despite some success with MEK inhibitors, and for patients with BRAF mutations other than V600E, who have few options beyond PNAs and rituximab.
- Kreitman RJ, Arons E. Diagnosis and treatment of hairy cell leukemia as the COVID-19 pandemic continues. Blood Rev. 2022;51:100888. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2021.100888
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guideline in oncology: hairy cell leukemia. Version 1.2023. Published August 30, 2022. Accessed March 16, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hairy_cell.pdf
- Janus A, Robak T. Hairy cell leukemia. In: Li W, ed. Leukemia [Internet]. Brisbane: Exon Publications; 2022:chap3. Accessed February 16, 2023. doi:10.36255/exon-publications-leukemia-hairy-cell-leukemia
- Tadmor T, Polliack A. Epidemiology and environmental risk in hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015;28(4):175-179. doi:10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.014
- Tiacci E, De Carolis L, Simonetti E, et al. Vemurafenib plus rituximab in refractory or relapsed hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(19):1810-1823. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa20312986
- Falini B, Martelli MP, Tiacci E. BRAF V600E mutation in hairy cell leukemia: from bench to bedside. Blood. 2016;128(15):1918-1927. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-07-418434
- Matutes E. Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges in hairy cell leukemia-variant: where are we in 2021? Expert Rev Hematol. 2021;14(4):355-363. doi:10.1080/17474086.2021.1908121
- Cawley JC, Burns GF, Hayhoe FG. A chronic lymphoproliferative disorder with distinctive features: a distinct variant of hairy-cell leukaemia. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):547-559. doi:10.1016/0145-2126(80)90066-1
- Xi L, Arons E, Navarro W, et al. Both variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy cell leukemia lack the BRAF V600E mutation. Blood. 2012;119(14):3330-3332. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-09-379339
- Durham BH, Getta B, Dietrich S, et al. Genomic analysis of hairy cell leukemia identifies novel recurrent genetic alterations. Blood. 2017;130(14):1644-1648. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-01-76510711
- Grever MR, Abdel-Wahab O, Andritsos LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2017;129(5):553-560. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-689422
- Waterfall JJ, Arons E, Walker RL, et al. High prevalence of MAP2K1 mutations in variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy-cell leukemias. Nat Genet. 2014;46(1):8-10. doi:10.1038/ng.2828
- Arons E, Sunshine J, Suntum T, Kreitman RJ. Somatic hypermutation and VH gene usage in hairy cell leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2006;133(5):504-512. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06066.x
- Arons E, Roth L, Sapolsky J, Suntum T, Stetler-Stevenson M, Kreitman RJ. Evidence of canonical somatic hypermutation in hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2011;117(18):4844-4851. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-11-316737
- Arons E, Suntum T, Stetler-Stevenson M, Kreitman RJ. VH4-34+ hairy cell leukemia, a new variant with poor prognosis despite standard therapy. Blood. 2009;114(21):4687-4695. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-01-201731
- Forconi F, Sozzi E, Cencini E, et al. Hairy cell leukemias with unmutated IGHV genes define the minor subset refractory to single-agent cladribine and with more aggressive behavior. Blood. 2009;114(21):4696-4702. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-03-212449
- Robak E, Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Robak T. Skin changes in hairy cell leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2021;100(3):615-625. doi:10.1007/s00277-020-04349-z
- Bouroncle BA. Thirty-five years in the progress of hairy cell leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 1994;14(suppl 1):1-12. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7820038/
- Falini B, Tiacci E, Liso A, et al. Simple diagnostic assay for hairy cell leukaemia by immunocytochemical detection of annexin A1 (ANXA1). Lancet. 2004;363(9424): 1869-1870. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16356-3
- Robak T, Robak P. Measurable residual disease in hairy cell leukemia: technical considerations and clinical significance. Front Oncol. 2022;12:976374. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.976374
- Chihara D, Arons E, Stetler-Stevenson M, et al. Randomized phase II study of first-line cladribine with concurrent or delayed rituximab in patients with hairy cell leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(14):1527-1538. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.02250
- Chihara D, Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, et al. Long-term durable remission by cladribine followed by rituximab in patients with hairy cell leukaemia: update of a phase II trial. Br J Haematol. 2016;174(5):760-766. doi:10.1111/bjh.14129
- Grever M, Andritsos L, Banerji V, et al. Hairy cell leukemia and COVID-19 adaptation of treatment guidelines. Leukemia. 2021;35(7):1864-1872. doi:10.1038/s41375-021-01257-7
- Konrat J, Rösler W, Roiss M, et al. BRAF inhibitor treatment of classical hairy cell leukemia allows successful vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. Ann Hematol. 2023;102(2):403-406. doi:10.1007/s00277-022-05026-z
- Park JH, Shukla M, Salcedo JM, et al. First-line chemo-free therapy with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib combined with obinutuzumab is effective in patients with HCL. Blood. 2019;134(suppl 1):Abstract 3998. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2019-124478
- Nieva J, Bethel K, Saven A. Phase 2 study of rituximab in the treatment of cladribine-failed patients with hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2003;102(3):810-813. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-01-0014
- Tiacci E, Park JH, De Carolis L, et al. Targeting mutant BRAF in relapsed or refractory hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1733-1747. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1506583
- Maitre E, Paillassa J, Troussard X. Novel targeted treatments in hairy cell leukemia and other hairy cell-like disorders. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1068981. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1068981
- Grob JJ, Amonkar MM, Karaszewska B, et al. Comparison of dabrafenib and trametinib combination therapy with vemurafenib monotherapy on health-related quality of life in patients with unresectable or metastatic cutaneous BRAF Val600-mutation-positive melanoma (COMBI-v): results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(13):1389-1398. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00087-X
- Tiacci E, De Carolis L, Simonetti E, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib in relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia: a pilot phase-2 clinical trial. Leukemia. 2021;35(11):3314-3318. doi:10.1038/s41375-021-01210-8
- Kreitman RJ, Moreau P, Ravandi F, et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with relapsed/refractory BRAF V600E mutation-positive hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2023;141(9):996-1006. doi:10.1182/blood.2021013658
- Adashek JJ, Menta AK, Reddy NK, Desai AP, Roszik J, Subbiah V. Tissue agnostic activity of BRAF plus MEK inhibitor in BRAF V600E-mutated tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022;21(6):871-878. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0950
- Rogers KA, Andritsos LA, Wei L, et al. Phase 2 study of ibrutinib in classic and variant hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2021;137(25):3473-3483. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009688
- Kreitman RJ, Dearden C, Zinzani PL, et al; Study 1053 investigators. Moxetumomab pasudotox in heavily pre-treated patients with relapsed/refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL): long-term follow-up from the pivotal trial. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):35. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-01004-y
- Leonard JP, Goldenberg DM. Preclinical and clinical evaluation of epratuzumab (anti-CD22 IgG) in B-cell malignancies. Oncogene. 2007;26(25):3704-3713. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210370
- Kreitman RJ, Arons E. Diagnosis and treatment of hairy cell leukemia as the COVID-19 pandemic continues. Blood Rev. 2022;51:100888. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2021.100888
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guideline in oncology: hairy cell leukemia. Version 1.2023. Published August 30, 2022. Accessed March 16, 2023. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/hairy_cell.pdf
- Janus A, Robak T. Hairy cell leukemia. In: Li W, ed. Leukemia [Internet]. Brisbane: Exon Publications; 2022:chap3. Accessed February 16, 2023. doi:10.36255/exon-publications-leukemia-hairy-cell-leukemia
- Tadmor T, Polliack A. Epidemiology and environmental risk in hairy cell leukemia. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2015;28(4):175-179. doi:10.1016/j.beha.2015.10.014
- Tiacci E, De Carolis L, Simonetti E, et al. Vemurafenib plus rituximab in refractory or relapsed hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(19):1810-1823. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa20312986
- Falini B, Martelli MP, Tiacci E. BRAF V600E mutation in hairy cell leukemia: from bench to bedside. Blood. 2016;128(15):1918-1927. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-07-418434
- Matutes E. Diagnostic and therapeutic challenges in hairy cell leukemia-variant: where are we in 2021? Expert Rev Hematol. 2021;14(4):355-363. doi:10.1080/17474086.2021.1908121
- Cawley JC, Burns GF, Hayhoe FG. A chronic lymphoproliferative disorder with distinctive features: a distinct variant of hairy-cell leukaemia. Leuk Res. 1980;4(6):547-559. doi:10.1016/0145-2126(80)90066-1
- Xi L, Arons E, Navarro W, et al. Both variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy cell leukemia lack the BRAF V600E mutation. Blood. 2012;119(14):3330-3332. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-09-379339
- Durham BH, Getta B, Dietrich S, et al. Genomic analysis of hairy cell leukemia identifies novel recurrent genetic alterations. Blood. 2017;130(14):1644-1648. doi:10.1182/blood-2017-01-76510711
- Grever MR, Abdel-Wahab O, Andritsos LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of patients with hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2017;129(5):553-560. doi:10.1182/blood-2016-01-689422
- Waterfall JJ, Arons E, Walker RL, et al. High prevalence of MAP2K1 mutations in variant and IGHV4-34-expressing hairy-cell leukemias. Nat Genet. 2014;46(1):8-10. doi:10.1038/ng.2828
- Arons E, Sunshine J, Suntum T, Kreitman RJ. Somatic hypermutation and VH gene usage in hairy cell leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2006;133(5):504-512. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06066.x
- Arons E, Roth L, Sapolsky J, Suntum T, Stetler-Stevenson M, Kreitman RJ. Evidence of canonical somatic hypermutation in hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2011;117(18):4844-4851. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-11-316737
- Arons E, Suntum T, Stetler-Stevenson M, Kreitman RJ. VH4-34+ hairy cell leukemia, a new variant with poor prognosis despite standard therapy. Blood. 2009;114(21):4687-4695. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-01-201731
- Forconi F, Sozzi E, Cencini E, et al. Hairy cell leukemias with unmutated IGHV genes define the minor subset refractory to single-agent cladribine and with more aggressive behavior. Blood. 2009;114(21):4696-4702. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-03-212449
- Robak E, Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Robak T. Skin changes in hairy cell leukemia. Ann Hematol. 2021;100(3):615-625. doi:10.1007/s00277-020-04349-z
- Bouroncle BA. Thirty-five years in the progress of hairy cell leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 1994;14(suppl 1):1-12. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7820038/
- Falini B, Tiacci E, Liso A, et al. Simple diagnostic assay for hairy cell leukaemia by immunocytochemical detection of annexin A1 (ANXA1). Lancet. 2004;363(9424): 1869-1870. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16356-3
- Robak T, Robak P. Measurable residual disease in hairy cell leukemia: technical considerations and clinical significance. Front Oncol. 2022;12:976374. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.976374
- Chihara D, Arons E, Stetler-Stevenson M, et al. Randomized phase II study of first-line cladribine with concurrent or delayed rituximab in patients with hairy cell leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(14):1527-1538. doi:10.1200/JCO.19.02250
- Chihara D, Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, et al. Long-term durable remission by cladribine followed by rituximab in patients with hairy cell leukaemia: update of a phase II trial. Br J Haematol. 2016;174(5):760-766. doi:10.1111/bjh.14129
- Grever M, Andritsos L, Banerji V, et al. Hairy cell leukemia and COVID-19 adaptation of treatment guidelines. Leukemia. 2021;35(7):1864-1872. doi:10.1038/s41375-021-01257-7
- Konrat J, Rösler W, Roiss M, et al. BRAF inhibitor treatment of classical hairy cell leukemia allows successful vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. Ann Hematol. 2023;102(2):403-406. doi:10.1007/s00277-022-05026-z
- Park JH, Shukla M, Salcedo JM, et al. First-line chemo-free therapy with the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib combined with obinutuzumab is effective in patients with HCL. Blood. 2019;134(suppl 1):Abstract 3998. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2019-124478
- Nieva J, Bethel K, Saven A. Phase 2 study of rituximab in the treatment of cladribine-failed patients with hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2003;102(3):810-813. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-01-0014
- Tiacci E, Park JH, De Carolis L, et al. Targeting mutant BRAF in relapsed or refractory hairy-cell leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(18):1733-1747. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1506583
- Maitre E, Paillassa J, Troussard X. Novel targeted treatments in hairy cell leukemia and other hairy cell-like disorders. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1068981. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1068981
- Grob JJ, Amonkar MM, Karaszewska B, et al. Comparison of dabrafenib and trametinib combination therapy with vemurafenib monotherapy on health-related quality of life in patients with unresectable or metastatic cutaneous BRAF Val600-mutation-positive melanoma (COMBI-v): results of a phase 3, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(13):1389-1398. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00087-X
- Tiacci E, De Carolis L, Simonetti E, et al. Safety and efficacy of the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib in relapsed or refractory hairy cell leukemia: a pilot phase-2 clinical trial. Leukemia. 2021;35(11):3314-3318. doi:10.1038/s41375-021-01210-8
- Kreitman RJ, Moreau P, Ravandi F, et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with relapsed/refractory BRAF V600E mutation-positive hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2023;141(9):996-1006. doi:10.1182/blood.2021013658
- Adashek JJ, Menta AK, Reddy NK, Desai AP, Roszik J, Subbiah V. Tissue agnostic activity of BRAF plus MEK inhibitor in BRAF V600E-mutated tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022;21(6):871-878. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0950
- Rogers KA, Andritsos LA, Wei L, et al. Phase 2 study of ibrutinib in classic and variant hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 2021;137(25):3473-3483. doi:10.1182/blood.2020009688
- Kreitman RJ, Dearden C, Zinzani PL, et al; Study 1053 investigators. Moxetumomab pasudotox in heavily pre-treated patients with relapsed/refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL): long-term follow-up from the pivotal trial. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):35. doi:10.1186/s13045-020-01004-y
- Leonard JP, Goldenberg DM. Preclinical and clinical evaluation of epratuzumab (anti-CD22 IgG) in B-cell malignancies. Oncogene. 2007;26(25):3704-3713. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210370
Multiprong strategy makes clinical trials less White
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – Clinical trials are so White. Only a small percentage of eligible patients participate in clinical trials in the first place, and very few come from racial and ethnic minority groups.
For example, according to the Food and Drug Administration, in trials that resulted in drug approvals from 2017 to 2020, only 2%-5% of participants were Black patients.
When clinical trials lack diverse patient populations, those who are left out have fewer opportunities to get new therapies. Moreover, the scope of the research is limited by smaller phenotypic and genotypic samples, and the trial results are applicable only to more homogeneous patient groups.
There has been a push to include more underrepresented patients in clinical trials. One group reported its success in doing so here at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
a period that included a pandemic-induced hiatus in clinical trials in general.
Alliance member Electra D. Paskett, PhD, from the College of Public Health at the Ohio State University in Columbus, presented accrual data from 117 trials led by the Alliance from 2014 to 2022.
During this period, accrual of racial and ethnic minority patients increased from 13.6% to 25.3% for cancer treatment trials and from 13% to 21.5% for cancer control trials.
Overall, the recruitment program resulted in an absolute increase from 13.5 % to 23.6% of underrepresented populations, which translated into a relative 74.8% improvement.
“We’re focusing now on monitoring accrual of women, rural populations, younger AYAs [adolescents and young adults] and older patients, and we’ll see what strategies we need to implement,” Dr. Packett told this news organization.
The Alliance has implemented a real-time accrual dashboard on its website that allows individual sites to review accrual by trial and overall for all of the identified underrepresented populations, she noted.
Program to increase underrepresented patient accrual
The impetus for the program to increase enrollment of underrepresented patients came from the goal set by Monica M. Bertagnolli, MD, group chair of the Alliance from 2011 to 2022 and currently the director of the U.S. National Cancer Institute.
“Our leader, Dr. Bertagnolli, set out a group-wide goal for accrual of underrepresented minorities to our trials of 20%, and that gave us permission to implement a whole host of new strategies,” Dr. Paskett said in an interview.
“These strategies follow the Accrual of Clinical Trials framework, which essentially says that the interaction between the patient and the provider for going on a clinical trial is not just an interaction between the patient and provider but recognizes, for example, that the provider has coworkers and they have norms and beliefs and attitudes, and the patient comes from a family with their own values. And then there are system-level barriers, and there are community barriers that all relate to this interaction about going on a trial,” Dr. Packett said.
What works?
The study was presented as a poster at the meeting. During the poster discussion session, comoderator Victoria S. Blinder, MD, from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, asked Dr. Paskett, “If you had a certain amount of money and you really wanted to use that resource to focus on one area, where would you put that resource?”
“I’m going to violate the rules of your question,” Dr. Paskett replied.
“You cannot change this problem by focusing on one thing, and that’s what we showed in our Alliance poster, and what I’ve said is based on over 30 years of work in this area,” she said.
She cited what she considered as the two most important components for improving accrual of underrepresented populations: a commitment by leadership to a recruitment goal, and the development of protocols with specific accrual goals for minority populations.
Still, those are only two components of a comprehensive program that includes the aforementioned accrual goal set by Dr. Bertagnolli, as well as the following:
- Funding of minority junior investigators and research that focuses on issues of concern to underrepresented populations.
- Establishment of work groups that focus on specific populations with the Alliance health disparities committee.
- Translation of informational materials for patients.
- Opening studies at National Cancer Institute Community. Oncology Research Program–designated minority underserved sites.
- Real-time monitoring of accrual demographics by the Alliance and at the trial site.
- Closing protocol enrollment to majority populations.
- Increasing the study sample sizes to enroll additional minority participants and to allow for subgroup analyses.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Packett and Dr. Blinder reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
CBSM phone app eases anxiety, depression in cancer patients
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CHICAGO – One-third of patients with cancer also experience anxiety or depression, and an estimated 70% of the 18 million patients with cancer and cancer survivors in the US experience emotional symptoms, including fear of recurrence.
Despite many having these symptoms, few patients with cancer have access to psycho-oncologic support.
A digital cognitive-behavioral stress management (CBSM) application may help to ease some of the burden, reported Allison Ramiller, MPH, of Blue Note Therapeutics in San Francisco, which developed the app version of the program.
In addition, patients assigned to the CBSM app were twice as likely as control persons to report that their symptoms were “much” or “very much” improved after using the app for 12 weeks, Ms. Ramiller reported at an oral abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
However, the investigators did not report baseline characteristics of patients in each of the study arms, which might have helped to clarify the depth of the effects they saw.
The CBSM program was developed by Michael H. Antoni, PhD, and colleagues in the University of Miami Health System. It is based on cognitive-behavioral therapy but also includes stress management and relaxation techniques to help patients cope with cancer-specific stress.
“”It has been clinically validated and shown to benefit patients with cancer,” Ms. Ramiller said. “However, access is a problem,” she said.
“There aren’t enough qualified, trained providers for the need, and patients with cancer encounter barriers to in-person participation, including things like transportation or financial barriers. So to overcome this, we developed a digitized version of CBSM,” she explained.
Impressive and elegant
“Everything about [the study] I thought was very impressive, very elegant, very nicely done,” said invited discussant Raymond U. Osarogiagbon, MBBS, FACP, chief scientist at Baptist Memorial Health Care Corp in Memphis, Tenn.
“They showed efficacy, they showed safety – very nice – user friendliness – very good. Certainly they look like they’re trying to address a highly important, unmet need in a very elegant way. Certainly, they pointed out it needs longer follow-up to see sustainability. We need to see will this work in other settings. Will this be cost-effective? You’ve gotta believe it probably will be,” he said.
CBSM has previously been shown to help patients with cancer reduce stress, improve general and cancer-specific quality of life at various stages of treatment, reduce symptom burden, and improve coping skills, Ms. Ramiller said.
To see whether these benefits could be conveyed digitally rather than in face-to-face encounters, Ms. Ramiller and colleagues worked with Dr. Antoni to develop the CBSM app.
Patients using the app received therapeutic content over 10 sessions with audio, video, and interactive tools that mimicked the sessions they would have received during in-person interventions.
They then compared the app against the control educational app in the randomized, decentralized RESTORE study.
High-quality control
Ms. Ramiller said that the control app set “a high bar.”
“The control also offered 10 interactive self-guided sessions. Both treatment apps were professionally designed and visually similar in styling, and they were presented as digital therapeutic-specific for cancer patients. And they were also in a match condition, meaning they received the same attention from study staff and cadence of reminders, but importantly, only the intervention app was based on CBSM,” she explained.
A total of 449 patients with cancers of stage I–III who were undergoing active systemic treatment or were planning to undergo such treatment within 6 months were randomly assigned to the CBSM app or the control app.
The CBSM app was superior to the control app for the primary outcome of anxiety reduction over baseline, as measured at 4, 8 and 12 weeks by the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System Anxiety Scale (PROMIS-A) (beta = -.03; P = .019).
CBSM was also significantly better than the control app for the secondary endpoints of reducing symptoms of depression, as measured by the PROMIS-D scale (beta = -.02, P = .042), and also at increasing the percentage of patients who reported improvement in anxiety and depression symptoms on the Patient Global Impression of Change instrument (P < .001)
An extension study of the durability of the effects at 3 and 6 months is underway.
The investigators noted that the incremental cost of management of anxiety or depression is greater than $17,000 per patient per year.
“One of the big promises of a digital therapeutic like this is that it could potentially reduce costs,” Ms. Ramiller told the audience, but she acknowledged, “More work is really needed, however, to directly test the potential savings.”
The RESTORE study is funded by Blue Note Therapeutics. Dr. Osarogiagbon owns stock in Gilead, Lilly, and Pfizer, has received honoraria from Biodesix and Medscape, and has a consulting or advisory role for the American Cancer Society AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, LUNGevity, National Cancer Institute, and Triptych Health Partners.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
Huge underuse of germline testing for cancer patients
Information from germline genetic testing could affect a patient’s cancer care. For example, such testing could indicate that targeted therapies would be beneficial, and it would have implications for close relatives who may carry the same genes.
The finding that so few patients with newly diagnosed cancer were tested comes from an analysis of data on more than 1.3 million individuals across two U.S. states. The data were taken from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry.
The rate is “well below guideline recommendations,” said study presenter Allison W. Kurian, MD, department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Innovative care delivery” is needed to tackle the problem, including the streamlining of pretest counseling, making posttest counseling more widely available, and employing long-term follow-up to track patient outcomes, she suggested.
“I do think this is a time for creative solutions of a number of different kinds,” she said. She suggested that lessons could be learned from the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. She also noted that “there have been some interesting studies on embedding genetic counselors in oncology clinics.”
Dr. Kurian presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The current results represent a “missed opportunity for decrease the population-level burden of cancer,” experts noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Clinicians should recommend testing to their patients and provide them with the information necessary to make informed decisions about whether to undergo testing,” Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, and Deborah Schrag, MD, MPH, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, wrote in their editorial.
They suggested novel approaches to widen access, such as use of point-of-care testing, telecounseling, and, in the future, chatbots to respond to patient questions.
“With greater emphasis on overcoming both health system and patient-level barriers to genetic cancer susceptibility testing for patients with cancer, treatment outcomes will improve and cancer diagnoses and related deaths in family members will be prevented,” they concluded.
At the meeting, invited discussant Erin Frances Cobain, MD, assistant professor of medical oncology, University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, referring to breast cancer as an example, said that progress has “stagnated” in recent years.
The study found a higher rate of gene testing among patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, at just over 20%.
Dr. Cobain argued that this was still too low. She pointed out that “a recent study suggested that over 60% of individuals with an incident cancer diagnosis would meet criteria for genetic testing by National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
“This may be because testing is not offered, there may be poor access to genetic counseling resources, or patients may be offered testing but decline it,” she suggested.
One compelling reason to conduct genetic testing for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer is that it may show that they are candidates for treatment with PARP (poly[ADP]-ribose polymerase) inhibitors, which “may have a direct impact on cancer-related mortality,” she pointed out.
“We need increased awareness and access to genetic testing resources for patients with breast cancer, particularly for racial and ethnic minorities,” she said.
Dr. Cobain also noted that finding variants of uncertain significance (VUS) was more likely among patients from racial and ethnic minorities than among White patients. She said such a finding “increases patient and physician anxiety,” and there may be “unclear optimal management recommendations for these patients.”
Details of the study
Germline genetic testing is “increasingly essential for cancer care,” Dr. Kurian said.
It is central to risk-adapted screening and secondary prevention, the use of targeted therapies, including PARP and checkpoint inhibitors, and cascade testing to identify at-risk relatives.
She pointed out that in clinical practice, testing has “evolved rapidly.” Panels include more and more genes. In addition, the cost of these tests is falling, and guidelines have become “more expansive.”
However, “little is known about genetic testing use and results,” Dr. Kurian noted.
The team therefore undertook the SEER-GeneLINK initiative, which involved patients aged ≥ 20 years who were diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2013, and March 31, 2019, and who were reported to statewide SEER registries in California and Georgia.
The team looked for patients for whom germline genetic test results had been reported by the four laboratories that performed the majority of patient testing in the two states. Results were categorized as pathogenic, benign, or VUS.
The results were classified on the basis of current guidelines for testing and/or management as related to breast/ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, other hereditary cancers, or those with no guidelines for testing or management.
Dr. Kurian reported that from an overall population of 1,412,388 patients diagnosed with cancer, 1,369,660 were eligible for inclusion. Of those, about half (51.9%) were women, and the majority (86.3%) were aged 50 years or older.
Many of these patients (61.4%) were non-Hispanic White persons, and slightly fewer than half (49.8%) were deemed to be in medium or high poverty, as determined using U.S. Census tract levels.
Overall, germline genetic testing was performed in 93,052 (6.8%) of patients over the study period.
Women were more likely to have undergone germline mutation testing than men, at 13.9% vs. 2.2%, as were patients aged 20-49 years, at 22.1% vs. 8.2% for those aged 50-69 years, and 3.3% for those aged 70 years and older.
The number of genes for which testing was conducted increased from a median of 2 in 2013 to 34 in 2019. Rates of VUS increased more than that for pathologic variants and substantially more so in non-White patients.
By 2019, the ratio of VUS to pathologic variants stood at 1.7 among White patients, vs. 3.9 among Asian patients, 3.6 among Black patients, and 2.2 among Hispanic patients.
The majority of identified pathologic variants that were related to the diagnosed cancer and genes with testing and/or management guidelines accounted for 67.5% to 94.9% of such variants.
Regarding specific cancer diagnoses, Dr. Kurian said that over the course of the study period, testing rates consistently exceeded 50% only among male breast cancer patients.
There were rapid increases in testing for ovarian cancer, from 28.0% of cases in 2013 to 54.0% in 2019. For pancreatic cancer, rates increased from 1.0% to 19.0% over the same period, and for prostate cancer, rates increased from 0.1% to 4.0%. She suggested that these increases in rates may be related to the approval of PARP inhibitors for use in these indications.
However, there was little change in the rates of germline mutation testing for lung cancer patients, from 01% in 2013 to 0.8% in 2019, and for other cancers, from 0.3% to 2.0%.
The results also revealed racial and ethnic differences in testing after controlling for age, cancer type, and year. Over the course of the study period, 8.0% of White patients underwent genetic testing, compared with 6.0% each for Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients and 5.0% for other patients (P < .001).
With regard specifically to male and female breast cancer and ovarian cancer, testing rates were 31% among White patients, 22% for Asian patients, 25% for Black patients, and 23% for Hispanic patients (P < .001).
Dr. Kurian acknowledged that the study is limited by a lack of testing from other laboratories and direct-to-consumer test data, although a recent survey suggested that this represents fewer than 5% of all germline genetic tests.
She also noted that the SEER registries do not collect data on family history or tumor sequencing.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Kurian has relationships with Adela, Ambry Genetics, Color Genomics, GeneDx/BioReference, Genentech, InVitae, and Myriad Genetics. Other authors report numerous relationships with industry. Dr. Cobain has ties with AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Athenex, Ayala Pharmaceuticals, bioTheranostics, and Immunomedics. Dr. Schrag has relationships with Merck, JAMA, AACR, and Grail. Dr. Stadler has ties with Adverum Biotechnologies, Genentech, Neurogene, Novartis, Optos Plc, Outlook Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Information from germline genetic testing could affect a patient’s cancer care. For example, such testing could indicate that targeted therapies would be beneficial, and it would have implications for close relatives who may carry the same genes.
The finding that so few patients with newly diagnosed cancer were tested comes from an analysis of data on more than 1.3 million individuals across two U.S. states. The data were taken from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry.
The rate is “well below guideline recommendations,” said study presenter Allison W. Kurian, MD, department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Innovative care delivery” is needed to tackle the problem, including the streamlining of pretest counseling, making posttest counseling more widely available, and employing long-term follow-up to track patient outcomes, she suggested.
“I do think this is a time for creative solutions of a number of different kinds,” she said. She suggested that lessons could be learned from the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. She also noted that “there have been some interesting studies on embedding genetic counselors in oncology clinics.”
Dr. Kurian presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The current results represent a “missed opportunity for decrease the population-level burden of cancer,” experts noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Clinicians should recommend testing to their patients and provide them with the information necessary to make informed decisions about whether to undergo testing,” Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, and Deborah Schrag, MD, MPH, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, wrote in their editorial.
They suggested novel approaches to widen access, such as use of point-of-care testing, telecounseling, and, in the future, chatbots to respond to patient questions.
“With greater emphasis on overcoming both health system and patient-level barriers to genetic cancer susceptibility testing for patients with cancer, treatment outcomes will improve and cancer diagnoses and related deaths in family members will be prevented,” they concluded.
At the meeting, invited discussant Erin Frances Cobain, MD, assistant professor of medical oncology, University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, referring to breast cancer as an example, said that progress has “stagnated” in recent years.
The study found a higher rate of gene testing among patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, at just over 20%.
Dr. Cobain argued that this was still too low. She pointed out that “a recent study suggested that over 60% of individuals with an incident cancer diagnosis would meet criteria for genetic testing by National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
“This may be because testing is not offered, there may be poor access to genetic counseling resources, or patients may be offered testing but decline it,” she suggested.
One compelling reason to conduct genetic testing for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer is that it may show that they are candidates for treatment with PARP (poly[ADP]-ribose polymerase) inhibitors, which “may have a direct impact on cancer-related mortality,” she pointed out.
“We need increased awareness and access to genetic testing resources for patients with breast cancer, particularly for racial and ethnic minorities,” she said.
Dr. Cobain also noted that finding variants of uncertain significance (VUS) was more likely among patients from racial and ethnic minorities than among White patients. She said such a finding “increases patient and physician anxiety,” and there may be “unclear optimal management recommendations for these patients.”
Details of the study
Germline genetic testing is “increasingly essential for cancer care,” Dr. Kurian said.
It is central to risk-adapted screening and secondary prevention, the use of targeted therapies, including PARP and checkpoint inhibitors, and cascade testing to identify at-risk relatives.
She pointed out that in clinical practice, testing has “evolved rapidly.” Panels include more and more genes. In addition, the cost of these tests is falling, and guidelines have become “more expansive.”
However, “little is known about genetic testing use and results,” Dr. Kurian noted.
The team therefore undertook the SEER-GeneLINK initiative, which involved patients aged ≥ 20 years who were diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2013, and March 31, 2019, and who were reported to statewide SEER registries in California and Georgia.
The team looked for patients for whom germline genetic test results had been reported by the four laboratories that performed the majority of patient testing in the two states. Results were categorized as pathogenic, benign, or VUS.
The results were classified on the basis of current guidelines for testing and/or management as related to breast/ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, other hereditary cancers, or those with no guidelines for testing or management.
Dr. Kurian reported that from an overall population of 1,412,388 patients diagnosed with cancer, 1,369,660 were eligible for inclusion. Of those, about half (51.9%) were women, and the majority (86.3%) were aged 50 years or older.
Many of these patients (61.4%) were non-Hispanic White persons, and slightly fewer than half (49.8%) were deemed to be in medium or high poverty, as determined using U.S. Census tract levels.
Overall, germline genetic testing was performed in 93,052 (6.8%) of patients over the study period.
Women were more likely to have undergone germline mutation testing than men, at 13.9% vs. 2.2%, as were patients aged 20-49 years, at 22.1% vs. 8.2% for those aged 50-69 years, and 3.3% for those aged 70 years and older.
The number of genes for which testing was conducted increased from a median of 2 in 2013 to 34 in 2019. Rates of VUS increased more than that for pathologic variants and substantially more so in non-White patients.
By 2019, the ratio of VUS to pathologic variants stood at 1.7 among White patients, vs. 3.9 among Asian patients, 3.6 among Black patients, and 2.2 among Hispanic patients.
The majority of identified pathologic variants that were related to the diagnosed cancer and genes with testing and/or management guidelines accounted for 67.5% to 94.9% of such variants.
Regarding specific cancer diagnoses, Dr. Kurian said that over the course of the study period, testing rates consistently exceeded 50% only among male breast cancer patients.
There were rapid increases in testing for ovarian cancer, from 28.0% of cases in 2013 to 54.0% in 2019. For pancreatic cancer, rates increased from 1.0% to 19.0% over the same period, and for prostate cancer, rates increased from 0.1% to 4.0%. She suggested that these increases in rates may be related to the approval of PARP inhibitors for use in these indications.
However, there was little change in the rates of germline mutation testing for lung cancer patients, from 01% in 2013 to 0.8% in 2019, and for other cancers, from 0.3% to 2.0%.
The results also revealed racial and ethnic differences in testing after controlling for age, cancer type, and year. Over the course of the study period, 8.0% of White patients underwent genetic testing, compared with 6.0% each for Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients and 5.0% for other patients (P < .001).
With regard specifically to male and female breast cancer and ovarian cancer, testing rates were 31% among White patients, 22% for Asian patients, 25% for Black patients, and 23% for Hispanic patients (P < .001).
Dr. Kurian acknowledged that the study is limited by a lack of testing from other laboratories and direct-to-consumer test data, although a recent survey suggested that this represents fewer than 5% of all germline genetic tests.
She also noted that the SEER registries do not collect data on family history or tumor sequencing.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Kurian has relationships with Adela, Ambry Genetics, Color Genomics, GeneDx/BioReference, Genentech, InVitae, and Myriad Genetics. Other authors report numerous relationships with industry. Dr. Cobain has ties with AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Athenex, Ayala Pharmaceuticals, bioTheranostics, and Immunomedics. Dr. Schrag has relationships with Merck, JAMA, AACR, and Grail. Dr. Stadler has ties with Adverum Biotechnologies, Genentech, Neurogene, Novartis, Optos Plc, Outlook Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Information from germline genetic testing could affect a patient’s cancer care. For example, such testing could indicate that targeted therapies would be beneficial, and it would have implications for close relatives who may carry the same genes.
The finding that so few patients with newly diagnosed cancer were tested comes from an analysis of data on more than 1.3 million individuals across two U.S. states. The data were taken from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) registry.
The rate is “well below guideline recommendations,” said study presenter Allison W. Kurian, MD, department of medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University.
“Innovative care delivery” is needed to tackle the problem, including the streamlining of pretest counseling, making posttest counseling more widely available, and employing long-term follow-up to track patient outcomes, she suggested.
“I do think this is a time for creative solutions of a number of different kinds,” she said. She suggested that lessons could be learned from the use of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. She also noted that “there have been some interesting studies on embedding genetic counselors in oncology clinics.”
Dr. Kurian presented the study at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO). The study was simultaneously published in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The current results represent a “missed opportunity for decrease the population-level burden of cancer,” experts noted in an accompanying editorial.
“Clinicians should recommend testing to their patients and provide them with the information necessary to make informed decisions about whether to undergo testing,” Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, and Deborah Schrag, MD, MPH, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, wrote in their editorial.
They suggested novel approaches to widen access, such as use of point-of-care testing, telecounseling, and, in the future, chatbots to respond to patient questions.
“With greater emphasis on overcoming both health system and patient-level barriers to genetic cancer susceptibility testing for patients with cancer, treatment outcomes will improve and cancer diagnoses and related deaths in family members will be prevented,” they concluded.
At the meeting, invited discussant Erin Frances Cobain, MD, assistant professor of medical oncology, University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, referring to breast cancer as an example, said that progress has “stagnated” in recent years.
The study found a higher rate of gene testing among patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer, at just over 20%.
Dr. Cobain argued that this was still too low. She pointed out that “a recent study suggested that over 60% of individuals with an incident cancer diagnosis would meet criteria for genetic testing by National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines.
“This may be because testing is not offered, there may be poor access to genetic counseling resources, or patients may be offered testing but decline it,” she suggested.
One compelling reason to conduct genetic testing for patients newly diagnosed with breast cancer is that it may show that they are candidates for treatment with PARP (poly[ADP]-ribose polymerase) inhibitors, which “may have a direct impact on cancer-related mortality,” she pointed out.
“We need increased awareness and access to genetic testing resources for patients with breast cancer, particularly for racial and ethnic minorities,” she said.
Dr. Cobain also noted that finding variants of uncertain significance (VUS) was more likely among patients from racial and ethnic minorities than among White patients. She said such a finding “increases patient and physician anxiety,” and there may be “unclear optimal management recommendations for these patients.”
Details of the study
Germline genetic testing is “increasingly essential for cancer care,” Dr. Kurian said.
It is central to risk-adapted screening and secondary prevention, the use of targeted therapies, including PARP and checkpoint inhibitors, and cascade testing to identify at-risk relatives.
She pointed out that in clinical practice, testing has “evolved rapidly.” Panels include more and more genes. In addition, the cost of these tests is falling, and guidelines have become “more expansive.”
However, “little is known about genetic testing use and results,” Dr. Kurian noted.
The team therefore undertook the SEER-GeneLINK initiative, which involved patients aged ≥ 20 years who were diagnosed with cancer between Jan. 1, 2013, and March 31, 2019, and who were reported to statewide SEER registries in California and Georgia.
The team looked for patients for whom germline genetic test results had been reported by the four laboratories that performed the majority of patient testing in the two states. Results were categorized as pathogenic, benign, or VUS.
The results were classified on the basis of current guidelines for testing and/or management as related to breast/ovarian cancer, gastrointestinal cancer, other hereditary cancers, or those with no guidelines for testing or management.
Dr. Kurian reported that from an overall population of 1,412,388 patients diagnosed with cancer, 1,369,660 were eligible for inclusion. Of those, about half (51.9%) were women, and the majority (86.3%) were aged 50 years or older.
Many of these patients (61.4%) were non-Hispanic White persons, and slightly fewer than half (49.8%) were deemed to be in medium or high poverty, as determined using U.S. Census tract levels.
Overall, germline genetic testing was performed in 93,052 (6.8%) of patients over the study period.
Women were more likely to have undergone germline mutation testing than men, at 13.9% vs. 2.2%, as were patients aged 20-49 years, at 22.1% vs. 8.2% for those aged 50-69 years, and 3.3% for those aged 70 years and older.
The number of genes for which testing was conducted increased from a median of 2 in 2013 to 34 in 2019. Rates of VUS increased more than that for pathologic variants and substantially more so in non-White patients.
By 2019, the ratio of VUS to pathologic variants stood at 1.7 among White patients, vs. 3.9 among Asian patients, 3.6 among Black patients, and 2.2 among Hispanic patients.
The majority of identified pathologic variants that were related to the diagnosed cancer and genes with testing and/or management guidelines accounted for 67.5% to 94.9% of such variants.
Regarding specific cancer diagnoses, Dr. Kurian said that over the course of the study period, testing rates consistently exceeded 50% only among male breast cancer patients.
There were rapid increases in testing for ovarian cancer, from 28.0% of cases in 2013 to 54.0% in 2019. For pancreatic cancer, rates increased from 1.0% to 19.0% over the same period, and for prostate cancer, rates increased from 0.1% to 4.0%. She suggested that these increases in rates may be related to the approval of PARP inhibitors for use in these indications.
However, there was little change in the rates of germline mutation testing for lung cancer patients, from 01% in 2013 to 0.8% in 2019, and for other cancers, from 0.3% to 2.0%.
The results also revealed racial and ethnic differences in testing after controlling for age, cancer type, and year. Over the course of the study period, 8.0% of White patients underwent genetic testing, compared with 6.0% each for Asian, Black, and Hispanic patients and 5.0% for other patients (P < .001).
With regard specifically to male and female breast cancer and ovarian cancer, testing rates were 31% among White patients, 22% for Asian patients, 25% for Black patients, and 23% for Hispanic patients (P < .001).
Dr. Kurian acknowledged that the study is limited by a lack of testing from other laboratories and direct-to-consumer test data, although a recent survey suggested that this represents fewer than 5% of all germline genetic tests.
She also noted that the SEER registries do not collect data on family history or tumor sequencing.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Kurian has relationships with Adela, Ambry Genetics, Color Genomics, GeneDx/BioReference, Genentech, InVitae, and Myriad Genetics. Other authors report numerous relationships with industry. Dr. Cobain has ties with AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Athenex, Ayala Pharmaceuticals, bioTheranostics, and Immunomedics. Dr. Schrag has relationships with Merck, JAMA, AACR, and Grail. Dr. Stadler has ties with Adverum Biotechnologies, Genentech, Neurogene, Novartis, Optos Plc, Outlook Therapeutics, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ASCO 2023
DEI training gives oncology fellows more confidence
The finding comes from a survey conducted after the introduction of DEI training within the Yale Medical Oncology-Hematology Fellowship Program. The study was reported by Norin Ansari, MD, MPH, of Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Dr. Ansari emphasized the DEI curriculum in fellowship programs by highlighting the racial and gender disparities that exist among physicians.
“There is a significant representation problem – only 2%-3% of practicing oncologists are Black or Hispanic/Latino,” she said. “And that representation decreases with each stage in the pipeline of the workforce.”
Dr. Ansari also noted gender disparities in the oncologist workforce, reporting that about one-third of faculty positions are held by women.
The anonymous survey was sent to 29 fellows; 23 responded, including 8 first-year fellows and 13 senior fellows. Over 57% of respondents rated the importance of DEI education as 10 on a 10-point scale (mean, 8.6).
At the start of this year, the responses of senior fellows who had already received some DEI training during the previous year’s lecture series were compared with first-year fellows who had not had any fellowship DEI education.
First-year fellows reported a mean confidence score of 2.5/5 at navigating bias and microaggressions when experienced personally and a mean score of 2.9/5 when they were directed at others. Senior fellows reported mean confidence scores of 3 and 3.2, respectively.
Yale then compared longitudinal data on fellows’ comfort levels in navigating discrimination in 2021, 2022, and 2023 a month before the ASCO meeting.
Fellows were asked to rate their comfort level from 1 to 10 in navigating different types of discrimination, including racial inequality, sexual harassment, and gender discrimination. In these three categories, fellows rated comfortability as a 5 in 2021 and as 7 in 2023 after the DEI training.
“Our first goal is to normalize talking about DEI and to recognize that different people in our workforce have different experiences and how we can be allies for them and for our patients,” Dr. Ansari said. “And I think for long-term goals we want to take stock of who’s at the table, who’s making decisions, and how does that affect our field, our science, and our patients.”
Yale designed the 3-year longitudinal curriculum with two annual core topics: upstander training and journal club for discussion and reflection. An additional two to three training sessions per year will focus on either race, gender, LGBTQ+, disability, religion, or implicit bias training.
The most popular topics among fellows were upstander training, cancer treatment and outcomes disparities, recruitment and retention, and career promotion and pay disparities.
The preferred platforms of content delivery were lectures from experts in the field, affinity groups or mentorship links, small group discussions, and advocacy education.
Gerald Hsu, MD, PhD, with the San Francisco VA Medical Center, discussed the results of Yale’s DEI curriculum assessment, saying it represented “best practices” in the industry. However, he acknowledged that realistically, not everyone will be receptive to DEI training.
Dr. Hsu said that holding medical staff accountable is the only way to truly incorporate DEI into everyday practice.
“Collectively, we need to be holding ourselves to different standards or holding ourselves to some standard,” Dr. Hsu said. “Maybe we need to be setting goals to the degree to which we diversify our training programs and our faculty, and there needs to be consequences to not doing so.”
No funding for the study was reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The finding comes from a survey conducted after the introduction of DEI training within the Yale Medical Oncology-Hematology Fellowship Program. The study was reported by Norin Ansari, MD, MPH, of Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Dr. Ansari emphasized the DEI curriculum in fellowship programs by highlighting the racial and gender disparities that exist among physicians.
“There is a significant representation problem – only 2%-3% of practicing oncologists are Black or Hispanic/Latino,” she said. “And that representation decreases with each stage in the pipeline of the workforce.”
Dr. Ansari also noted gender disparities in the oncologist workforce, reporting that about one-third of faculty positions are held by women.
The anonymous survey was sent to 29 fellows; 23 responded, including 8 first-year fellows and 13 senior fellows. Over 57% of respondents rated the importance of DEI education as 10 on a 10-point scale (mean, 8.6).
At the start of this year, the responses of senior fellows who had already received some DEI training during the previous year’s lecture series were compared with first-year fellows who had not had any fellowship DEI education.
First-year fellows reported a mean confidence score of 2.5/5 at navigating bias and microaggressions when experienced personally and a mean score of 2.9/5 when they were directed at others. Senior fellows reported mean confidence scores of 3 and 3.2, respectively.
Yale then compared longitudinal data on fellows’ comfort levels in navigating discrimination in 2021, 2022, and 2023 a month before the ASCO meeting.
Fellows were asked to rate their comfort level from 1 to 10 in navigating different types of discrimination, including racial inequality, sexual harassment, and gender discrimination. In these three categories, fellows rated comfortability as a 5 in 2021 and as 7 in 2023 after the DEI training.
“Our first goal is to normalize talking about DEI and to recognize that different people in our workforce have different experiences and how we can be allies for them and for our patients,” Dr. Ansari said. “And I think for long-term goals we want to take stock of who’s at the table, who’s making decisions, and how does that affect our field, our science, and our patients.”
Yale designed the 3-year longitudinal curriculum with two annual core topics: upstander training and journal club for discussion and reflection. An additional two to three training sessions per year will focus on either race, gender, LGBTQ+, disability, religion, or implicit bias training.
The most popular topics among fellows were upstander training, cancer treatment and outcomes disparities, recruitment and retention, and career promotion and pay disparities.
The preferred platforms of content delivery were lectures from experts in the field, affinity groups or mentorship links, small group discussions, and advocacy education.
Gerald Hsu, MD, PhD, with the San Francisco VA Medical Center, discussed the results of Yale’s DEI curriculum assessment, saying it represented “best practices” in the industry. However, he acknowledged that realistically, not everyone will be receptive to DEI training.
Dr. Hsu said that holding medical staff accountable is the only way to truly incorporate DEI into everyday practice.
“Collectively, we need to be holding ourselves to different standards or holding ourselves to some standard,” Dr. Hsu said. “Maybe we need to be setting goals to the degree to which we diversify our training programs and our faculty, and there needs to be consequences to not doing so.”
No funding for the study was reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The finding comes from a survey conducted after the introduction of DEI training within the Yale Medical Oncology-Hematology Fellowship Program. The study was reported by Norin Ansari, MD, MPH, of Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Dr. Ansari emphasized the DEI curriculum in fellowship programs by highlighting the racial and gender disparities that exist among physicians.
“There is a significant representation problem – only 2%-3% of practicing oncologists are Black or Hispanic/Latino,” she said. “And that representation decreases with each stage in the pipeline of the workforce.”
Dr. Ansari also noted gender disparities in the oncologist workforce, reporting that about one-third of faculty positions are held by women.
The anonymous survey was sent to 29 fellows; 23 responded, including 8 first-year fellows and 13 senior fellows. Over 57% of respondents rated the importance of DEI education as 10 on a 10-point scale (mean, 8.6).
At the start of this year, the responses of senior fellows who had already received some DEI training during the previous year’s lecture series were compared with first-year fellows who had not had any fellowship DEI education.
First-year fellows reported a mean confidence score of 2.5/5 at navigating bias and microaggressions when experienced personally and a mean score of 2.9/5 when they were directed at others. Senior fellows reported mean confidence scores of 3 and 3.2, respectively.
Yale then compared longitudinal data on fellows’ comfort levels in navigating discrimination in 2021, 2022, and 2023 a month before the ASCO meeting.
Fellows were asked to rate their comfort level from 1 to 10 in navigating different types of discrimination, including racial inequality, sexual harassment, and gender discrimination. In these three categories, fellows rated comfortability as a 5 in 2021 and as 7 in 2023 after the DEI training.
“Our first goal is to normalize talking about DEI and to recognize that different people in our workforce have different experiences and how we can be allies for them and for our patients,” Dr. Ansari said. “And I think for long-term goals we want to take stock of who’s at the table, who’s making decisions, and how does that affect our field, our science, and our patients.”
Yale designed the 3-year longitudinal curriculum with two annual core topics: upstander training and journal club for discussion and reflection. An additional two to three training sessions per year will focus on either race, gender, LGBTQ+, disability, religion, or implicit bias training.
The most popular topics among fellows were upstander training, cancer treatment and outcomes disparities, recruitment and retention, and career promotion and pay disparities.
The preferred platforms of content delivery were lectures from experts in the field, affinity groups or mentorship links, small group discussions, and advocacy education.
Gerald Hsu, MD, PhD, with the San Francisco VA Medical Center, discussed the results of Yale’s DEI curriculum assessment, saying it represented “best practices” in the industry. However, he acknowledged that realistically, not everyone will be receptive to DEI training.
Dr. Hsu said that holding medical staff accountable is the only way to truly incorporate DEI into everyday practice.
“Collectively, we need to be holding ourselves to different standards or holding ourselves to some standard,” Dr. Hsu said. “Maybe we need to be setting goals to the degree to which we diversify our training programs and our faculty, and there needs to be consequences to not doing so.”
No funding for the study was reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2023
Drugmakers are abandoning cheap generics, and now U.S. cancer patients can’t get meds
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
On Nov. 22, three Food and Drug Administration inspectors arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, ADHD pills, blood thinners, and antibiotics. COVID-hangover supply chain issues and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry. Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Joe Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures – undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Mark Ratain, MD, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Stephen Divers, MD, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast, and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin. Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released June 7 found 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Bonny Moore, MD, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Virginia. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives – though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects – are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Mr. McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family – his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight – were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the health care system.
At Dr. Moore’s practice, in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Dr. Moore and colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale – only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big negotiators of such purchases, such as Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February. Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett, with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue. Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim CEO of the Association for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Mr. Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said. Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market. Mr. Sardella testified in May that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical industry product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited 2 months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-mg bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at dr. Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients – ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Mark Einstein, MD, chair of the department of obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive health at New Jersey Medical School, Newark.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic-buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Mr. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations, and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140 million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Mr. Coukell said.
Dr. Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Satyajit Kosuri, MD, recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Dr. Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store 2 years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF – an independent source of health policy research, polling, and journalism. Learn more about KFF.
ACS officer provides ASCO highlights: Targeting hidden cancer, AI in oncology
And it didn’t just sparkle because of the sequined Taylor Swift fans clogging the nearby streets during the meeting.
Arif Kamal, MD, MBA, MHS, who is also an oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said he was impressed by a pair of landmark studies released at the meeting that show hidden cancer can be targeted with “really remarkable outcomes.” He also highlighted sessions that examined the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology, during an interview.
Below are lightly edited excerpts from a conversation with Dr. Kamal:
Question: What are some of most groundbreaking studies released at ASCO?
Answer: One is an interim analysis of the NATALEE trial, which involved patients with early-stage hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative (HR+/HER2–) breast tumors. This phase 3 randomized trial compared maintenance therapy with the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor ribociclib (Kisqali) plus endocrine therapy with an aromatase inhibitor to endocrine therapy alone in patients with node-positive or node-negative and stage II or III HR+/HER– breast cancer.
For a long time, the standard care in these patients has been to use endocrine therapy alone. This is the first big trial to show that upstream usage of additional therapy in early stages is also beneficial for disease-free survival. The 3-year invasive disease-free survival rate was 90.4% in the rebociclib-endocrine therapy group vs. 87.1% for patients who received only endocrine therapy (P = .0014).
Q: How do these findings add to current knowledge?
A: Typically, we let people get metastatic disease before we use CDK4/6 inhibitors. These findings show that systemic treatment beyond endocrine therapy will be helpful in cases where you’ve got smaller disease that has not spread yet.
Even in patients with node-negative breast cancer, micrometastatic disease is clearly there, because the medication killed the negative lymph nodes.
Q: What else struck you as especially important research?
A: The NATALEE findings match what we saw in another study – the ADAURA trial, which looked at adjuvant osimertinib in non–small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR-mutated, stage IB to IIIA disease – cancer that has not spread to the lymph nodes.
This is another example where you have a treatment being used in earlier-stage disease that’s showing really remarkable outcomes. The study found that 5-year overall survival was 88% in an osimertinib group vs. 78% in a placebo group (P < .001). This is a disease where, in stage IB, we wouldn’t even necessarily give these patients treatment at all, other than surgical resection of the tumor and maybe give them a little bit of chemotherapy.
Even in these smaller, early tumors, osimertinib makes a difference.
Q: As a whole, what are these studies telling us about cancer cells that can’t be easily detected?
A: To find a disease-free survival benefit with adding ribociclib in a stage II, stage III setting, particularly in node-negative disease, is remarkable because it says that the cells in hiding are bad actors, and they are going to cause trouble. The study shows that medications can find these cells and reverse that risk of bad outcomes.
If you think about the paradigm of cancer, that’s pretty remarkable because the ADAURA trial does the same thing: You do surgery for [early-stage] lung cancers that have not spread to the lymph nodes and you figure, “Well, I’ve got it all, right? The margins are real big, healthy, clean.” And yet, people still have recurrences, and you ask the same question: “Can any medicine find those few cells, the hundreds of cells that are still left somewhere in hiding?” And the answer is again, yes. It’s changing the paradigm of our understanding of minimal residual disease.
That’s why there’s so much interest in liquid biopsies. Let’s say that after treatment we don’t see any cancer radiologically, but there’s a signal from a liquid biopsy [detecting residual cancer]. These two trials demonstrate that there’s something we can do about it.
Q: There were quite a few studies about artificial intelligence released at ASCO. Where do we stand on that front?
A: We’re just at the beginning of people thinking about the use of generative AI for clinical decision support, clinical trial matching, and pathology review. But AI, at least for now, still has the issue of making up things that aren’t true. That’s not something patients are going to be okay with.
Q: How can AI be helpful to medical providers considering its limitations?
A: AI is going to be very good at the data-to-information transition. You’ll start seeing people use AI to start clinical notes for them and to match patients to the best clinical trials for them. But fundamentally, the clinician’s role will continue to be to check facts and offer wisdom.
Q: Will AI threaten the careers of oncologists?
A: The body of knowledge about oncology is growing exponentially, and no one can actually keep up. There’s so much data that’s out there that needs to be turned into usable information amid a shortage of oncologists. At the same time, the prevalence of cancer is going up, even though mortality is going down.
Synthesis of data is what oncologists are waiting for from AI. They’ll welcome it as opposed to being worried. That’s the sentiment I heard from my colleagues.
Dr. Kamal has no disclosures.
And it didn’t just sparkle because of the sequined Taylor Swift fans clogging the nearby streets during the meeting.
Arif Kamal, MD, MBA, MHS, who is also an oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said he was impressed by a pair of landmark studies released at the meeting that show hidden cancer can be targeted with “really remarkable outcomes.” He also highlighted sessions that examined the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology, during an interview.
Below are lightly edited excerpts from a conversation with Dr. Kamal:
Question: What are some of most groundbreaking studies released at ASCO?
Answer: One is an interim analysis of the NATALEE trial, which involved patients with early-stage hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative (HR+/HER2–) breast tumors. This phase 3 randomized trial compared maintenance therapy with the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor ribociclib (Kisqali) plus endocrine therapy with an aromatase inhibitor to endocrine therapy alone in patients with node-positive or node-negative and stage II or III HR+/HER– breast cancer.
For a long time, the standard care in these patients has been to use endocrine therapy alone. This is the first big trial to show that upstream usage of additional therapy in early stages is also beneficial for disease-free survival. The 3-year invasive disease-free survival rate was 90.4% in the rebociclib-endocrine therapy group vs. 87.1% for patients who received only endocrine therapy (P = .0014).
Q: How do these findings add to current knowledge?
A: Typically, we let people get metastatic disease before we use CDK4/6 inhibitors. These findings show that systemic treatment beyond endocrine therapy will be helpful in cases where you’ve got smaller disease that has not spread yet.
Even in patients with node-negative breast cancer, micrometastatic disease is clearly there, because the medication killed the negative lymph nodes.
Q: What else struck you as especially important research?
A: The NATALEE findings match what we saw in another study – the ADAURA trial, which looked at adjuvant osimertinib in non–small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR-mutated, stage IB to IIIA disease – cancer that has not spread to the lymph nodes.
This is another example where you have a treatment being used in earlier-stage disease that’s showing really remarkable outcomes. The study found that 5-year overall survival was 88% in an osimertinib group vs. 78% in a placebo group (P < .001). This is a disease where, in stage IB, we wouldn’t even necessarily give these patients treatment at all, other than surgical resection of the tumor and maybe give them a little bit of chemotherapy.
Even in these smaller, early tumors, osimertinib makes a difference.
Q: As a whole, what are these studies telling us about cancer cells that can’t be easily detected?
A: To find a disease-free survival benefit with adding ribociclib in a stage II, stage III setting, particularly in node-negative disease, is remarkable because it says that the cells in hiding are bad actors, and they are going to cause trouble. The study shows that medications can find these cells and reverse that risk of bad outcomes.
If you think about the paradigm of cancer, that’s pretty remarkable because the ADAURA trial does the same thing: You do surgery for [early-stage] lung cancers that have not spread to the lymph nodes and you figure, “Well, I’ve got it all, right? The margins are real big, healthy, clean.” And yet, people still have recurrences, and you ask the same question: “Can any medicine find those few cells, the hundreds of cells that are still left somewhere in hiding?” And the answer is again, yes. It’s changing the paradigm of our understanding of minimal residual disease.
That’s why there’s so much interest in liquid biopsies. Let’s say that after treatment we don’t see any cancer radiologically, but there’s a signal from a liquid biopsy [detecting residual cancer]. These two trials demonstrate that there’s something we can do about it.
Q: There were quite a few studies about artificial intelligence released at ASCO. Where do we stand on that front?
A: We’re just at the beginning of people thinking about the use of generative AI for clinical decision support, clinical trial matching, and pathology review. But AI, at least for now, still has the issue of making up things that aren’t true. That’s not something patients are going to be okay with.
Q: How can AI be helpful to medical providers considering its limitations?
A: AI is going to be very good at the data-to-information transition. You’ll start seeing people use AI to start clinical notes for them and to match patients to the best clinical trials for them. But fundamentally, the clinician’s role will continue to be to check facts and offer wisdom.
Q: Will AI threaten the careers of oncologists?
A: The body of knowledge about oncology is growing exponentially, and no one can actually keep up. There’s so much data that’s out there that needs to be turned into usable information amid a shortage of oncologists. At the same time, the prevalence of cancer is going up, even though mortality is going down.
Synthesis of data is what oncologists are waiting for from AI. They’ll welcome it as opposed to being worried. That’s the sentiment I heard from my colleagues.
Dr. Kamal has no disclosures.
And it didn’t just sparkle because of the sequined Taylor Swift fans clogging the nearby streets during the meeting.
Arif Kamal, MD, MBA, MHS, who is also an oncologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C., said he was impressed by a pair of landmark studies released at the meeting that show hidden cancer can be targeted with “really remarkable outcomes.” He also highlighted sessions that examined the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in oncology, during an interview.
Below are lightly edited excerpts from a conversation with Dr. Kamal:
Question: What are some of most groundbreaking studies released at ASCO?
Answer: One is an interim analysis of the NATALEE trial, which involved patients with early-stage hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative (HR+/HER2–) breast tumors. This phase 3 randomized trial compared maintenance therapy with the cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor ribociclib (Kisqali) plus endocrine therapy with an aromatase inhibitor to endocrine therapy alone in patients with node-positive or node-negative and stage II or III HR+/HER– breast cancer.
For a long time, the standard care in these patients has been to use endocrine therapy alone. This is the first big trial to show that upstream usage of additional therapy in early stages is also beneficial for disease-free survival. The 3-year invasive disease-free survival rate was 90.4% in the rebociclib-endocrine therapy group vs. 87.1% for patients who received only endocrine therapy (P = .0014).
Q: How do these findings add to current knowledge?
A: Typically, we let people get metastatic disease before we use CDK4/6 inhibitors. These findings show that systemic treatment beyond endocrine therapy will be helpful in cases where you’ve got smaller disease that has not spread yet.
Even in patients with node-negative breast cancer, micrometastatic disease is clearly there, because the medication killed the negative lymph nodes.
Q: What else struck you as especially important research?
A: The NATALEE findings match what we saw in another study – the ADAURA trial, which looked at adjuvant osimertinib in non–small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR-mutated, stage IB to IIIA disease – cancer that has not spread to the lymph nodes.
This is another example where you have a treatment being used in earlier-stage disease that’s showing really remarkable outcomes. The study found that 5-year overall survival was 88% in an osimertinib group vs. 78% in a placebo group (P < .001). This is a disease where, in stage IB, we wouldn’t even necessarily give these patients treatment at all, other than surgical resection of the tumor and maybe give them a little bit of chemotherapy.
Even in these smaller, early tumors, osimertinib makes a difference.
Q: As a whole, what are these studies telling us about cancer cells that can’t be easily detected?
A: To find a disease-free survival benefit with adding ribociclib in a stage II, stage III setting, particularly in node-negative disease, is remarkable because it says that the cells in hiding are bad actors, and they are going to cause trouble. The study shows that medications can find these cells and reverse that risk of bad outcomes.
If you think about the paradigm of cancer, that’s pretty remarkable because the ADAURA trial does the same thing: You do surgery for [early-stage] lung cancers that have not spread to the lymph nodes and you figure, “Well, I’ve got it all, right? The margins are real big, healthy, clean.” And yet, people still have recurrences, and you ask the same question: “Can any medicine find those few cells, the hundreds of cells that are still left somewhere in hiding?” And the answer is again, yes. It’s changing the paradigm of our understanding of minimal residual disease.
That’s why there’s so much interest in liquid biopsies. Let’s say that after treatment we don’t see any cancer radiologically, but there’s a signal from a liquid biopsy [detecting residual cancer]. These two trials demonstrate that there’s something we can do about it.
Q: There were quite a few studies about artificial intelligence released at ASCO. Where do we stand on that front?
A: We’re just at the beginning of people thinking about the use of generative AI for clinical decision support, clinical trial matching, and pathology review. But AI, at least for now, still has the issue of making up things that aren’t true. That’s not something patients are going to be okay with.
Q: How can AI be helpful to medical providers considering its limitations?
A: AI is going to be very good at the data-to-information transition. You’ll start seeing people use AI to start clinical notes for them and to match patients to the best clinical trials for them. But fundamentally, the clinician’s role will continue to be to check facts and offer wisdom.
Q: Will AI threaten the careers of oncologists?
A: The body of knowledge about oncology is growing exponentially, and no one can actually keep up. There’s so much data that’s out there that needs to be turned into usable information amid a shortage of oncologists. At the same time, the prevalence of cancer is going up, even though mortality is going down.
Synthesis of data is what oncologists are waiting for from AI. They’ll welcome it as opposed to being worried. That’s the sentiment I heard from my colleagues.
Dr. Kamal has no disclosures.
AT ASCO 2023
Widespread carboplatin, cisplatin shortages: NCCN survey
The survey, which included responses from 27 NCCN member institutions, revealed that 93% are experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and that 70% have reported a shortage of cisplatin.
“This is an unacceptable situation,” Robert W. Carlson, MD, NCCN’s chief executive offer, said in the statement released by the network.
“We are hearing from oncologists and pharmacists across the country who have to scramble to find appropriate alternatives for treating their patients with cancer right now,” Dr. Carlson said. And while the survey results show patients are still able to get lifesaving care, “it comes at a burden to our overtaxed medical facilities.”
The NCCN called on the federal government, the pharmaceutical industry, providers, and payers to take steps to “help mitigate any impacts” from this cancer drug shortage.
“We need to work together to improve the current situation and prevent it from happening again in the future,” Dr. Carlson stressed.
Carboplatin and cisplatin, which are frequently used together for systemic treatment, are highly effective therapies prescribed to treat many cancer types, including lung, breast, and prostate cancers, as well as leukemias and lymphomas. An estimated 500,000 new patients with cancer receive these agents each year.
The current survey, conducted over the last week of May, found that 100% of responding centers are able to continue to treat patients who need cisplatin without delays.
The same cannot be said for carboplatin: only 64% of centers said they are still able to continue treating all current patients receiving the platinum-based therapy. Among 19 responding centers, 20% reported that they were continuing carboplatin regimens for some but not all patients. And 16% reported treatment delays from having to obtain prior authorization for modified treatment plans, though none reported denials.
“Carboplatin has been in short supply for months but in the last 4 weeks has reached a critical stage,” according to one survey comment. “Without additional inventory many of our sites will be out of drug by early next week.”
In response to the survey question, “Is your center experiencing a shortage of carboplatin,” others made similar comments:
- “Current shipments from established manufacturers have been paused.”
- “The supply of carboplatin available is not meeting our demands.”
- “Without additional supply in early June, we will have to implement several shortage mitigation strategies.”
Survey respondents also addressed whether manufacturers or suppliers have provided any indication of when these drugs will become readily available again. For both drugs, about 60% of respondents said no. And for those who do receive updates, many noted that the “information is tentative and variable.”
Respondents indicated that other cancer agents, including methotrexate (67%) and 5FU (26%), are also in short supply at their centers.
The shortage and the uncertainty as to when it will end are forcing some centers to develop conservation and mitigation strategies.
The NCCN has broadly outlined how the federal government, the pharmaceutical industry, providers, and payers can help with prevention and mitigation. The NCCN has called on the federal government and the pharmaceutical industry to work to secure a steady supply of core anticancer drugs and has asked payers to “put patients first and provide flexible and efficient systems of providing coverage for alternative therapies replacing anti-cancer drugs that are unavailable or in shortage.”
Overall, the survey results “demonstrate the widespread impact of the chemotherapy shortage,” said Alyssa Schatz, MSW, senior director of policy and advocacy for NCCN. “We hope that by sharing this survey and calling for united action across the oncology community, we can come together to prevent future drug shortages and ensure quality, effective, equitable, and accessible cancer care for all.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The survey, which included responses from 27 NCCN member institutions, revealed that 93% are experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and that 70% have reported a shortage of cisplatin.
“This is an unacceptable situation,” Robert W. Carlson, MD, NCCN’s chief executive offer, said in the statement released by the network.
“We are hearing from oncologists and pharmacists across the country who have to scramble to find appropriate alternatives for treating their patients with cancer right now,” Dr. Carlson said. And while the survey results show patients are still able to get lifesaving care, “it comes at a burden to our overtaxed medical facilities.”
The NCCN called on the federal government, the pharmaceutical industry, providers, and payers to take steps to “help mitigate any impacts” from this cancer drug shortage.
“We need to work together to improve the current situation and prevent it from happening again in the future,” Dr. Carlson stressed.
Carboplatin and cisplatin, which are frequently used together for systemic treatment, are highly effective therapies prescribed to treat many cancer types, including lung, breast, and prostate cancers, as well as leukemias and lymphomas. An estimated 500,000 new patients with cancer receive these agents each year.
The current survey, conducted over the last week of May, found that 100% of responding centers are able to continue to treat patients who need cisplatin without delays.
The same cannot be said for carboplatin: only 64% of centers said they are still able to continue treating all current patients receiving the platinum-based therapy. Among 19 responding centers, 20% reported that they were continuing carboplatin regimens for some but not all patients. And 16% reported treatment delays from having to obtain prior authorization for modified treatment plans, though none reported denials.
“Carboplatin has been in short supply for months but in the last 4 weeks has reached a critical stage,” according to one survey comment. “Without additional inventory many of our sites will be out of drug by early next week.”
In response to the survey question, “Is your center experiencing a shortage of carboplatin,” others made similar comments:
- “Current shipments from established manufacturers have been paused.”
- “The supply of carboplatin available is not meeting our demands.”
- “Without additional supply in early June, we will have to implement several shortage mitigation strategies.”
Survey respondents also addressed whether manufacturers or suppliers have provided any indication of when these drugs will become readily available again. For both drugs, about 60% of respondents said no. And for those who do receive updates, many noted that the “information is tentative and variable.”
Respondents indicated that other cancer agents, including methotrexate (67%) and 5FU (26%), are also in short supply at their centers.
The shortage and the uncertainty as to when it will end are forcing some centers to develop conservation and mitigation strategies.
The NCCN has broadly outlined how the federal government, the pharmaceutical industry, providers, and payers can help with prevention and mitigation. The NCCN has called on the federal government and the pharmaceutical industry to work to secure a steady supply of core anticancer drugs and has asked payers to “put patients first and provide flexible and efficient systems of providing coverage for alternative therapies replacing anti-cancer drugs that are unavailable or in shortage.”
Overall, the survey results “demonstrate the widespread impact of the chemotherapy shortage,” said Alyssa Schatz, MSW, senior director of policy and advocacy for NCCN. “We hope that by sharing this survey and calling for united action across the oncology community, we can come together to prevent future drug shortages and ensure quality, effective, equitable, and accessible cancer care for all.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The survey, which included responses from 27 NCCN member institutions, revealed that 93% are experiencing a shortage of carboplatin and that 70% have reported a shortage of cisplatin.
“This is an unacceptable situation,” Robert W. Carlson, MD, NCCN’s chief executive offer, said in the statement released by the network.
“We are hearing from oncologists and pharmacists across the country who have to scramble to find appropriate alternatives for treating their patients with cancer right now,” Dr. Carlson said. And while the survey results show patients are still able to get lifesaving care, “it comes at a burden to our overtaxed medical facilities.”
The NCCN called on the federal government, the pharmaceutical industry, providers, and payers to take steps to “help mitigate any impacts” from this cancer drug shortage.
“We need to work together to improve the current situation and prevent it from happening again in the future,” Dr. Carlson stressed.
Carboplatin and cisplatin, which are frequently used together for systemic treatment, are highly effective therapies prescribed to treat many cancer types, including lung, breast, and prostate cancers, as well as leukemias and lymphomas. An estimated 500,000 new patients with cancer receive these agents each year.
The current survey, conducted over the last week of May, found that 100% of responding centers are able to continue to treat patients who need cisplatin without delays.
The same cannot be said for carboplatin: only 64% of centers said they are still able to continue treating all current patients receiving the platinum-based therapy. Among 19 responding centers, 20% reported that they were continuing carboplatin regimens for some but not all patients. And 16% reported treatment delays from having to obtain prior authorization for modified treatment plans, though none reported denials.
“Carboplatin has been in short supply for months but in the last 4 weeks has reached a critical stage,” according to one survey comment. “Without additional inventory many of our sites will be out of drug by early next week.”
In response to the survey question, “Is your center experiencing a shortage of carboplatin,” others made similar comments:
- “Current shipments from established manufacturers have been paused.”
- “The supply of carboplatin available is not meeting our demands.”
- “Without additional supply in early June, we will have to implement several shortage mitigation strategies.”
Survey respondents also addressed whether manufacturers or suppliers have provided any indication of when these drugs will become readily available again. For both drugs, about 60% of respondents said no. And for those who do receive updates, many noted that the “information is tentative and variable.”
Respondents indicated that other cancer agents, including methotrexate (67%) and 5FU (26%), are also in short supply at their centers.
The shortage and the uncertainty as to when it will end are forcing some centers to develop conservation and mitigation strategies.
The NCCN has broadly outlined how the federal government, the pharmaceutical industry, providers, and payers can help with prevention and mitigation. The NCCN has called on the federal government and the pharmaceutical industry to work to secure a steady supply of core anticancer drugs and has asked payers to “put patients first and provide flexible and efficient systems of providing coverage for alternative therapies replacing anti-cancer drugs that are unavailable or in shortage.”
Overall, the survey results “demonstrate the widespread impact of the chemotherapy shortage,” said Alyssa Schatz, MSW, senior director of policy and advocacy for NCCN. “We hope that by sharing this survey and calling for united action across the oncology community, we can come together to prevent future drug shortages and ensure quality, effective, equitable, and accessible cancer care for all.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cross-border U.S.-Mexican collaboration drives up ALL survival
A team from a hospital in San Diego combined a previously established training program from the World Health Organization with a new collaboration, which resulted in improvements in care standards and sustainability of care in a center in Tijuana, Mexico, just 23 miles away.
Implementation of the program in 2013 led to a significant 6% improvement in 5-year overall survival for children with ALL.
For patients at standard risk, 5-year overall survival increased from 73% to 100% after implementation of the program.
“This is really remarkable because this survival is the same as we have here in San Diego,” commented Paula Aristizabal, MD, MAS, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, at a press briefing before the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The findings show that “sustained improvements in cancer outcomes in low- and middle-income countries [LMICs] are feasible with innovative cross-border programs, particularly in borders that are shared” between a high- and low-income country, she commented. In other words, “it takes a village in both countries” to drive up standards.
Dr. Aristizabal also noted that the partnership will continue with a particularly focus on improving survival among patients with high-risk disease.
“We like to call it ‘twinning,’ because that means we are twins forever,” she said. “This is not a marriage that can be dissolved.”
‘Huge survival gap’
“The burden of childhood cancer has increased globally, but unfortunately, survival in low- and middle-income countries has not improved at the same level as in high-income countries,” Dr. Aristizabal commented.
This has resulted in a “huge survival gap” between high-income countries and the LMICs. ALL is now a leading cause of death among children in these countries, she commented.
“This study illustrates collaborative strategies that can be put into place today that could greatly improve outcomes for children with cancer globally,” commented Julie R. Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president.
Speaking at the press conference, she added: “As I’ve heard Princess Dina Mired of Jordan say many times: ‘Your ZIP code should not determine if you survive cancer.’ ”
She said the differences in ALL survival between the United States and Mexico are an “example of children being so close in terms of proximity not having the same advantages.”
Also commenting, ASCO President Eric Winer, MD, from the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., asked whether the proximity of the hospitals in San Diego and Tijuana “makes a difference, or do you think this is something that done ... at a distance?”
Dr. Aristizabal said that the proximity between the institutions “has been extremely helpful,” as they can go between hospitals in just 30 minutes.
However, “one of the things that we learned with COVID is that we can do a lot of things remotely,” she answered.
“Some of the projects that we started in Tijuana, through our collaboration with St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, we have been able to implement in many other centers in Mexico,” she said.
Study details
Rady Children’s Hospital partnered with the public sector in Baja California, with the aim of improving outcomes in children’s cancer, she explained.
In 2008, the team collaborated with St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, to establish a training program in the Hospital General Tijuana in Tijuana that shared knowledge, technology, and organizational skills.
The team also consulted on clinical cases and set up education and research programs, all with the aim of building capacity and sustainability in Mexico.
“As the number of leukemia patients increased, we wanted to decrease depending on their international collaborators in the U.S. and ensure long-term sustainability,” Dr. Aristizabal explained.
This led in 2013 to the implementation of the WHO Framework for Action HSS training model, which has several components, including health service delivery.
Combined with the previously established model, the overall goals of the program were to improve health outcomes, systems efficiency, timely access to care, and social and financial risk protection.
Dr. Aristizabal said in an interview that this involved developing highly specific leukemia treatment guidelines, which have now gone through three iterations, as well as guidelines for supportive care.
Working with a local foundation, the team has also “focused on providing psychosocial support, nutritional support, a shelter for families that live 12-14 hours away from the pediatric cancer center, as well as food subsidies, trying to address financial toxicity and food insecurity in these families.”
Impact of the collaboration
To assess the impact of the WHO framework, the researchers conducted a study that involved 109 children with ALL who were treated at Hospital General Tijuana over the preimplementation phase in 2008-2012 and the postimplementation phase in 2013-2017.
The mean age of the patients was 7.04 years, and 50.4% were girls. The majority (67%) were classified as having high-risk disease.
Over the entire study period, the 5-year overall survival rate was 65%. Analysis revealed that between the pre- and postimplementation periods, 5-year overall survival increased from 59% to 65%, which Dr. Aristizabal described as “a significant improvement.”
Among high-risk patients, the improvement in 5-year survival between the pre- and postimplementation period went from 48% to 55%.
“This is an area for improvement,” Dr. Aristizabal said, “and we’re working on additional strategies to help improve survival for high-risk patients.
The study was funded by Rady Children’s Hospital, the Mexican Secretary of Health, and the Patronato Foundation. Dr. Aristizabal and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gralow reported relationships with Genentech and Roche. Dr. Winer reported relationships with Leap Therapeutics, Jounce Therapeutics, Carrick Therapeutics, and Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A team from a hospital in San Diego combined a previously established training program from the World Health Organization with a new collaboration, which resulted in improvements in care standards and sustainability of care in a center in Tijuana, Mexico, just 23 miles away.
Implementation of the program in 2013 led to a significant 6% improvement in 5-year overall survival for children with ALL.
For patients at standard risk, 5-year overall survival increased from 73% to 100% after implementation of the program.
“This is really remarkable because this survival is the same as we have here in San Diego,” commented Paula Aristizabal, MD, MAS, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, at a press briefing before the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The findings show that “sustained improvements in cancer outcomes in low- and middle-income countries [LMICs] are feasible with innovative cross-border programs, particularly in borders that are shared” between a high- and low-income country, she commented. In other words, “it takes a village in both countries” to drive up standards.
Dr. Aristizabal also noted that the partnership will continue with a particularly focus on improving survival among patients with high-risk disease.
“We like to call it ‘twinning,’ because that means we are twins forever,” she said. “This is not a marriage that can be dissolved.”
‘Huge survival gap’
“The burden of childhood cancer has increased globally, but unfortunately, survival in low- and middle-income countries has not improved at the same level as in high-income countries,” Dr. Aristizabal commented.
This has resulted in a “huge survival gap” between high-income countries and the LMICs. ALL is now a leading cause of death among children in these countries, she commented.
“This study illustrates collaborative strategies that can be put into place today that could greatly improve outcomes for children with cancer globally,” commented Julie R. Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president.
Speaking at the press conference, she added: “As I’ve heard Princess Dina Mired of Jordan say many times: ‘Your ZIP code should not determine if you survive cancer.’ ”
She said the differences in ALL survival between the United States and Mexico are an “example of children being so close in terms of proximity not having the same advantages.”
Also commenting, ASCO President Eric Winer, MD, from the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., asked whether the proximity of the hospitals in San Diego and Tijuana “makes a difference, or do you think this is something that done ... at a distance?”
Dr. Aristizabal said that the proximity between the institutions “has been extremely helpful,” as they can go between hospitals in just 30 minutes.
However, “one of the things that we learned with COVID is that we can do a lot of things remotely,” she answered.
“Some of the projects that we started in Tijuana, through our collaboration with St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, we have been able to implement in many other centers in Mexico,” she said.
Study details
Rady Children’s Hospital partnered with the public sector in Baja California, with the aim of improving outcomes in children’s cancer, she explained.
In 2008, the team collaborated with St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, to establish a training program in the Hospital General Tijuana in Tijuana that shared knowledge, technology, and organizational skills.
The team also consulted on clinical cases and set up education and research programs, all with the aim of building capacity and sustainability in Mexico.
“As the number of leukemia patients increased, we wanted to decrease depending on their international collaborators in the U.S. and ensure long-term sustainability,” Dr. Aristizabal explained.
This led in 2013 to the implementation of the WHO Framework for Action HSS training model, which has several components, including health service delivery.
Combined with the previously established model, the overall goals of the program were to improve health outcomes, systems efficiency, timely access to care, and social and financial risk protection.
Dr. Aristizabal said in an interview that this involved developing highly specific leukemia treatment guidelines, which have now gone through three iterations, as well as guidelines for supportive care.
Working with a local foundation, the team has also “focused on providing psychosocial support, nutritional support, a shelter for families that live 12-14 hours away from the pediatric cancer center, as well as food subsidies, trying to address financial toxicity and food insecurity in these families.”
Impact of the collaboration
To assess the impact of the WHO framework, the researchers conducted a study that involved 109 children with ALL who were treated at Hospital General Tijuana over the preimplementation phase in 2008-2012 and the postimplementation phase in 2013-2017.
The mean age of the patients was 7.04 years, and 50.4% were girls. The majority (67%) were classified as having high-risk disease.
Over the entire study period, the 5-year overall survival rate was 65%. Analysis revealed that between the pre- and postimplementation periods, 5-year overall survival increased from 59% to 65%, which Dr. Aristizabal described as “a significant improvement.”
Among high-risk patients, the improvement in 5-year survival between the pre- and postimplementation period went from 48% to 55%.
“This is an area for improvement,” Dr. Aristizabal said, “and we’re working on additional strategies to help improve survival for high-risk patients.
The study was funded by Rady Children’s Hospital, the Mexican Secretary of Health, and the Patronato Foundation. Dr. Aristizabal and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gralow reported relationships with Genentech and Roche. Dr. Winer reported relationships with Leap Therapeutics, Jounce Therapeutics, Carrick Therapeutics, and Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A team from a hospital in San Diego combined a previously established training program from the World Health Organization with a new collaboration, which resulted in improvements in care standards and sustainability of care in a center in Tijuana, Mexico, just 23 miles away.
Implementation of the program in 2013 led to a significant 6% improvement in 5-year overall survival for children with ALL.
For patients at standard risk, 5-year overall survival increased from 73% to 100% after implementation of the program.
“This is really remarkable because this survival is the same as we have here in San Diego,” commented Paula Aristizabal, MD, MAS, a pediatric hematologist/oncologist at Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego, at a press briefing before the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The findings show that “sustained improvements in cancer outcomes in low- and middle-income countries [LMICs] are feasible with innovative cross-border programs, particularly in borders that are shared” between a high- and low-income country, she commented. In other words, “it takes a village in both countries” to drive up standards.
Dr. Aristizabal also noted that the partnership will continue with a particularly focus on improving survival among patients with high-risk disease.
“We like to call it ‘twinning,’ because that means we are twins forever,” she said. “This is not a marriage that can be dissolved.”
‘Huge survival gap’
“The burden of childhood cancer has increased globally, but unfortunately, survival in low- and middle-income countries has not improved at the same level as in high-income countries,” Dr. Aristizabal commented.
This has resulted in a “huge survival gap” between high-income countries and the LMICs. ALL is now a leading cause of death among children in these countries, she commented.
“This study illustrates collaborative strategies that can be put into place today that could greatly improve outcomes for children with cancer globally,” commented Julie R. Gralow, MD, ASCO chief medical officer and executive vice president.
Speaking at the press conference, she added: “As I’ve heard Princess Dina Mired of Jordan say many times: ‘Your ZIP code should not determine if you survive cancer.’ ”
She said the differences in ALL survival between the United States and Mexico are an “example of children being so close in terms of proximity not having the same advantages.”
Also commenting, ASCO President Eric Winer, MD, from the Yale Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn., asked whether the proximity of the hospitals in San Diego and Tijuana “makes a difference, or do you think this is something that done ... at a distance?”
Dr. Aristizabal said that the proximity between the institutions “has been extremely helpful,” as they can go between hospitals in just 30 minutes.
However, “one of the things that we learned with COVID is that we can do a lot of things remotely,” she answered.
“Some of the projects that we started in Tijuana, through our collaboration with St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, we have been able to implement in many other centers in Mexico,” she said.
Study details
Rady Children’s Hospital partnered with the public sector in Baja California, with the aim of improving outcomes in children’s cancer, she explained.
In 2008, the team collaborated with St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, to establish a training program in the Hospital General Tijuana in Tijuana that shared knowledge, technology, and organizational skills.
The team also consulted on clinical cases and set up education and research programs, all with the aim of building capacity and sustainability in Mexico.
“As the number of leukemia patients increased, we wanted to decrease depending on their international collaborators in the U.S. and ensure long-term sustainability,” Dr. Aristizabal explained.
This led in 2013 to the implementation of the WHO Framework for Action HSS training model, which has several components, including health service delivery.
Combined with the previously established model, the overall goals of the program were to improve health outcomes, systems efficiency, timely access to care, and social and financial risk protection.
Dr. Aristizabal said in an interview that this involved developing highly specific leukemia treatment guidelines, which have now gone through three iterations, as well as guidelines for supportive care.
Working with a local foundation, the team has also “focused on providing psychosocial support, nutritional support, a shelter for families that live 12-14 hours away from the pediatric cancer center, as well as food subsidies, trying to address financial toxicity and food insecurity in these families.”
Impact of the collaboration
To assess the impact of the WHO framework, the researchers conducted a study that involved 109 children with ALL who were treated at Hospital General Tijuana over the preimplementation phase in 2008-2012 and the postimplementation phase in 2013-2017.
The mean age of the patients was 7.04 years, and 50.4% were girls. The majority (67%) were classified as having high-risk disease.
Over the entire study period, the 5-year overall survival rate was 65%. Analysis revealed that between the pre- and postimplementation periods, 5-year overall survival increased from 59% to 65%, which Dr. Aristizabal described as “a significant improvement.”
Among high-risk patients, the improvement in 5-year survival between the pre- and postimplementation period went from 48% to 55%.
“This is an area for improvement,” Dr. Aristizabal said, “and we’re working on additional strategies to help improve survival for high-risk patients.
The study was funded by Rady Children’s Hospital, the Mexican Secretary of Health, and the Patronato Foundation. Dr. Aristizabal and coauthors reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gralow reported relationships with Genentech and Roche. Dr. Winer reported relationships with Leap Therapeutics, Jounce Therapeutics, Carrick Therapeutics, and Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2023
Number of cancer survivors with functional limitations doubled in 20 years
Vishal Patel, BS, a student at the Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues identified 51,258 cancer survivors from the National Health Interview Survey, representing a weighted population of approximately 178.8 million from 1999 to 2018.
Most survivors were women (60.2%) and were at least 65 years old (55.4%). In 1999, 3.6 million weighted survivors reported functional limitation. In 2018, the number increased to 8.2 million, a 2.25-fold increase.
The number of survivors who reported no limitations also increased, but not by as much. That group grew 1.34-fold during the study period.
For context, “the 70% prevalence of functional limitation among survivors in 2018 is nearly twice that of the general population,” the authors wrote.
Patients surveyed on function
Functional limitation was defined as “self-reported difficulty performing any of 12 routine physical or social activities without assistance.” Examples of the activities included difficulty sitting for more than 2 hours, difficulty participating in social activities or difficulty pushing or pulling an object the size of a living room chair.
Over the 2 decades analyzed, the adjusted prevalence of functional limitation was highest among survivors of pancreatic cancer (80.3%) and lung cancer (76.5%). Prevalence was lowest for survivors of melanoma (62.2%), breast (61.8%) and prostate (59.5%) cancers.
Not just a result of living longer
Mr. Patel told this publication that one assumption people might make when they read these results is that people are just living longer with cancer and losing functional ability accordingly.
“But, in fact, we found that the youngest [– those less than 65 years–] actually contributed to this trend more than the oldest people, which means it’s not just [happening], because people are getting older,” he said.
Hispanic and Black individuals had disproportionately higher increases in functional limitation; percentage point increases over the 2 decades were 19.5 for Black people, 25.1 for Hispanic people and 12.5 for White people. There may be a couple of reasons for that, Mr. Patel noted.
Those who are Black or Hispanic tend to have less access to cancer survivorship care for reasons including insurance status and historic health care inequities, he noted.
“The other potential reason is that they have had less access to cancer care historically. And if, 20 years ago Black and Hispanic individuals didn’t have access to some chemotherapies, and now they do, maybe it’s the increased access to care that’s causing these functional limitations. Because chemotherapy can sometimes be very toxic. It may be sort of a catch-up toxicity,” he said.
Quality of life beyond survivorship
Mr. Patel said the results seem to call for building on improved survival rates by tracking and improving function.
“It’s good to celebrate that there are more survivors. But now that we can keep people alive longer, maybe we can shift gears to improving their quality of life,” he said.
The more-than-doubling of functional limitations over 2 decades “is a very sobering trend,” he noted, while pointing out that the functional limitations applied to 8 million people in the United States – people whose needs are not being met.
There’s no sign of the trend stopping, he continued. “We saw no downward trend, only an upward trend.”
Increasingly, including functionality as an endpoint in cancer trials, in addition to improvements in mortality, is one place to start, he added.
“Our findings suggest an urgent need for care teams to understand and address function, for researchers to evaluate function as a core outcome in trials, and for health systems and policy makers to reimagine survivorship care, recognizing the burden of cancer and its treatment on physical, psychosocial, and cognitive function,” the authors wrote in their paper. Limitations of the study include the potential for recall bias, lack of cancer staging or treatment information, and the subjective perception of function.
A coauthor reported personal fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, AAA, Blue Earth, Janssen, Lantheus, Myovant, Myriad Genetics, Novartis, Telix, and Sanofi, as well as grants from Pfizer and Bayer during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Vishal Patel, BS, a student at the Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues identified 51,258 cancer survivors from the National Health Interview Survey, representing a weighted population of approximately 178.8 million from 1999 to 2018.
Most survivors were women (60.2%) and were at least 65 years old (55.4%). In 1999, 3.6 million weighted survivors reported functional limitation. In 2018, the number increased to 8.2 million, a 2.25-fold increase.
The number of survivors who reported no limitations also increased, but not by as much. That group grew 1.34-fold during the study period.
For context, “the 70% prevalence of functional limitation among survivors in 2018 is nearly twice that of the general population,” the authors wrote.
Patients surveyed on function
Functional limitation was defined as “self-reported difficulty performing any of 12 routine physical or social activities without assistance.” Examples of the activities included difficulty sitting for more than 2 hours, difficulty participating in social activities or difficulty pushing or pulling an object the size of a living room chair.
Over the 2 decades analyzed, the adjusted prevalence of functional limitation was highest among survivors of pancreatic cancer (80.3%) and lung cancer (76.5%). Prevalence was lowest for survivors of melanoma (62.2%), breast (61.8%) and prostate (59.5%) cancers.
Not just a result of living longer
Mr. Patel told this publication that one assumption people might make when they read these results is that people are just living longer with cancer and losing functional ability accordingly.
“But, in fact, we found that the youngest [– those less than 65 years–] actually contributed to this trend more than the oldest people, which means it’s not just [happening], because people are getting older,” he said.
Hispanic and Black individuals had disproportionately higher increases in functional limitation; percentage point increases over the 2 decades were 19.5 for Black people, 25.1 for Hispanic people and 12.5 for White people. There may be a couple of reasons for that, Mr. Patel noted.
Those who are Black or Hispanic tend to have less access to cancer survivorship care for reasons including insurance status and historic health care inequities, he noted.
“The other potential reason is that they have had less access to cancer care historically. And if, 20 years ago Black and Hispanic individuals didn’t have access to some chemotherapies, and now they do, maybe it’s the increased access to care that’s causing these functional limitations. Because chemotherapy can sometimes be very toxic. It may be sort of a catch-up toxicity,” he said.
Quality of life beyond survivorship
Mr. Patel said the results seem to call for building on improved survival rates by tracking and improving function.
“It’s good to celebrate that there are more survivors. But now that we can keep people alive longer, maybe we can shift gears to improving their quality of life,” he said.
The more-than-doubling of functional limitations over 2 decades “is a very sobering trend,” he noted, while pointing out that the functional limitations applied to 8 million people in the United States – people whose needs are not being met.
There’s no sign of the trend stopping, he continued. “We saw no downward trend, only an upward trend.”
Increasingly, including functionality as an endpoint in cancer trials, in addition to improvements in mortality, is one place to start, he added.
“Our findings suggest an urgent need for care teams to understand and address function, for researchers to evaluate function as a core outcome in trials, and for health systems and policy makers to reimagine survivorship care, recognizing the burden of cancer and its treatment on physical, psychosocial, and cognitive function,” the authors wrote in their paper. Limitations of the study include the potential for recall bias, lack of cancer staging or treatment information, and the subjective perception of function.
A coauthor reported personal fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, AAA, Blue Earth, Janssen, Lantheus, Myovant, Myriad Genetics, Novartis, Telix, and Sanofi, as well as grants from Pfizer and Bayer during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
Vishal Patel, BS, a student at the Dell Medical School at The University of Texas at Austin, and colleagues identified 51,258 cancer survivors from the National Health Interview Survey, representing a weighted population of approximately 178.8 million from 1999 to 2018.
Most survivors were women (60.2%) and were at least 65 years old (55.4%). In 1999, 3.6 million weighted survivors reported functional limitation. In 2018, the number increased to 8.2 million, a 2.25-fold increase.
The number of survivors who reported no limitations also increased, but not by as much. That group grew 1.34-fold during the study period.
For context, “the 70% prevalence of functional limitation among survivors in 2018 is nearly twice that of the general population,” the authors wrote.
Patients surveyed on function
Functional limitation was defined as “self-reported difficulty performing any of 12 routine physical or social activities without assistance.” Examples of the activities included difficulty sitting for more than 2 hours, difficulty participating in social activities or difficulty pushing or pulling an object the size of a living room chair.
Over the 2 decades analyzed, the adjusted prevalence of functional limitation was highest among survivors of pancreatic cancer (80.3%) and lung cancer (76.5%). Prevalence was lowest for survivors of melanoma (62.2%), breast (61.8%) and prostate (59.5%) cancers.
Not just a result of living longer
Mr. Patel told this publication that one assumption people might make when they read these results is that people are just living longer with cancer and losing functional ability accordingly.
“But, in fact, we found that the youngest [– those less than 65 years–] actually contributed to this trend more than the oldest people, which means it’s not just [happening], because people are getting older,” he said.
Hispanic and Black individuals had disproportionately higher increases in functional limitation; percentage point increases over the 2 decades were 19.5 for Black people, 25.1 for Hispanic people and 12.5 for White people. There may be a couple of reasons for that, Mr. Patel noted.
Those who are Black or Hispanic tend to have less access to cancer survivorship care for reasons including insurance status and historic health care inequities, he noted.
“The other potential reason is that they have had less access to cancer care historically. And if, 20 years ago Black and Hispanic individuals didn’t have access to some chemotherapies, and now they do, maybe it’s the increased access to care that’s causing these functional limitations. Because chemotherapy can sometimes be very toxic. It may be sort of a catch-up toxicity,” he said.
Quality of life beyond survivorship
Mr. Patel said the results seem to call for building on improved survival rates by tracking and improving function.
“It’s good to celebrate that there are more survivors. But now that we can keep people alive longer, maybe we can shift gears to improving their quality of life,” he said.
The more-than-doubling of functional limitations over 2 decades “is a very sobering trend,” he noted, while pointing out that the functional limitations applied to 8 million people in the United States – people whose needs are not being met.
There’s no sign of the trend stopping, he continued. “We saw no downward trend, only an upward trend.”
Increasingly, including functionality as an endpoint in cancer trials, in addition to improvements in mortality, is one place to start, he added.
“Our findings suggest an urgent need for care teams to understand and address function, for researchers to evaluate function as a core outcome in trials, and for health systems and policy makers to reimagine survivorship care, recognizing the burden of cancer and its treatment on physical, psychosocial, and cognitive function,” the authors wrote in their paper. Limitations of the study include the potential for recall bias, lack of cancer staging or treatment information, and the subjective perception of function.
A coauthor reported personal fees from Astellas, AstraZeneca, AAA, Blue Earth, Janssen, Lantheus, Myovant, Myriad Genetics, Novartis, Telix, and Sanofi, as well as grants from Pfizer and Bayer during the conduct of the study. No other disclosures were reported.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY