User login
Surgical vs Endoscopic Excision of Large Colon Polyps
Dear colleagues,
We now have the ability to remove almost any large colon polyp endoscopically using a variety of techniques — from the widely used endoscopic mucosal resection to the increasingly prevalent endoscopic submucosal dissection. Yet, in this new era,
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Jeffrey Mosko and Dr. Moamen Gabr discuss the importance of careful polyp selection and argue that almost all polyps can be safely removed endoscopically, with low recurrence rates. In contrast, Dr. Ira Leeds from colorectal surgery offers a counterpoint, urging caution when managing polyps in the cecum and rectum while highlighting the role of minimally invasive surgical approaches. We hope these discussions provide valuable insights to support your approach to managing large colorectal polyps, especially in an era of increasing colon cancer screening.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Advantages of Endoscopic Resection for Large Colon Polyps
BY MOAMEN GABR, MD, MSC, AND JEFFREY D. MOSKO MD, MSC
General Advantages
Endoscopy has revolutionized the management of large colorectal polyps, offering a minimally invasive alternative to surgical resection. The dawn of endoscopic resection in the late 20th century, particularly the evolution of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in Japan, marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of colonic lesions by enabling the removal of lesions that would otherwise necessitate surgery.
Endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps is generally performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to recover at home the same day. This not only minimizes disruption to daily life but also significantly enhances patient satisfaction.
Most procedures are performed under moderate or deep sedation eliminating the need for general anesthesia. This represents a critical benefit, particularly for older or medically frail patients who are at higher risk of anesthesia-related complications.
From an economic perspective, endoscopic resection reduces healthcare costs by eliminating prolonged hospital stays and complex perioperative care. Additionally, preserving the colon’s structure and function avoids long-term consequences such as altered bowel habits or ostomy dependence, common with surgical interventions.
The advantages of endoscopic intervention are clear: safety, cost-effectiveness, organ preservation, and convenience for patients.
Lesion Selection
The superiority of endoscopic resection relies on selecting lesions appropriately, specifically those with a low risk of lymph node metastases. This meticulous process should include assessing a lesion’s size, location, morphology, granularity, microvascular and surface pit pattern using a combination of high-definition white light endoscopy, virtual chromoendoscopy and image magnification (when available).
Gross morphologic assessment utilizes the Paris and LST classifications. Combining the Paris classification, lesion granularity and location is both straightforward and revealing. Ulcerated/excavated lesions (0-III) are concerning for deep invasion. Depressed (0-IIc) morphologies are strongly associated with T1 CRC. Nodular lesions (0-Is or IIa + Is) have a higher risk of T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with flat lesions (0-IIa or 0-IIb). Non-granular lesions (0-Is and 0-IIa + Is) have a higher risk of covert cancer. Finally, the rectosigmoid location is associated with an increased risk of T1 CRC (vs. proximal locations).
Endoscopic surface pattern assessment increases one’s diagnostic accuracy. There are three primary endoscopic surface pattern classifications: NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE), Japanese NBI expert team (JNET), and Kudo pit pattern classifications. Colonic lesions that have a NICE Type 3, JNET 3, or Kudo type Vn pattern should be referred promptly for surgical resection. Lesions with a JNET 2B or Kudo type VI carry a higher risk of superficial T1 CRC but can still be removed endoscopically (see below) in expert centers. All other lesions should undergo endoscopic resection.
Endoscopic Resection Techniques
Endoscopic resection of large colorectal polyps encompasses two primary techniques: EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), each tailored to specific lesion characteristics and operator expertise.
EMR, the technique of choice for the vast majority of lesions, relies on injecting a submucosal cushion to lift the lesion before excision. Recent advances, including enhanced snare designs and underwater EMR, have improved en-bloc resection rates, significantly reducing recurrence and enhancing the efficacy of this technique.
ESD offers unparalleled precision for en-bloc resection of complex lesions, particularly those with fibrosis or high-risk features. Cutting-edge innovations, such as traction devices, have streamlined the procedure, addressing the traditional challenges of ESD. Despite being more time intensive, ESD minimizes recurrence and provides complete histopathological evaluation, critical for the management of malignant or pre-malignant lesions.
For non-lifting polyps, newer techniques such as endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR), using tools like the Full-Thickness Resection Device (FTRD), enable resection of up to 2-3 cm of the colonic or rectal wall. This ensures complete removal of any lesion and its underlying tissue, effectively preventing recurrence.
These advancements demonstrate how endoscopy can tackle even the most challenging colorectal polyps, reinforcing its position as the preferred treatment modality.
Perceived Limitations
With ongoing refinement over the last 2 decades, many of the perceived limitations (below) of endoscopic resection have now been overcome.
- Difficult locations/access: Historically lesions at the anorectal junction, ileocecal valve, appendiceal orifice and anastomoses were preferentially sent for surgery. In spite of unique technical challenges at each of these locations, there is now compelling data supporting EMR for these scenarios. We now also have techniques aimed at enabling the resection of lesions with poor access including patient repositioning, distal attachments, variable endoscope diameter/flexibility, traction and overtube devices.
- Recurrence: In the past, recurrence after endoscopic resection of lesions > 20 mm has been reported to be as high as 20%. With our current systematic approach to complete resection, meticulous examination of the post-resection defect for residual polyp tissue, adjunctive techniques to address submucosal fibrosis (hot avulsion, CAST, submucosal release) and thermal ablation to the resection margin (EMR-T), the risk of recurrence for piecemeal resections can be decreased to < 5%. In fact, some groups argue for the en-bloc resection of all large colorectal lesions based on the extremely low (< 1%) recurrence rates and potential for decreased follow-up.
- Post-resection bleeding: Post-resection bleeding is no longer a major limitation of any endoscopic approach because of the combination of improved intra-procedural hemostatic and resection techniques, optimized electrosurgical technology, and enhanced defect closure capabilities and devices (with prophylactic defect closure now supported by randomized control trial level data).
- Perforation: Deep mural injury, once an endoscopists’ worst fear during resection, is no longer a surgical emergency. It can now be predicted, identified (Sydney classification) and successfully managed. In spite of more widespread aggressive resection strategies, the risk of emergency surgery in patients undergoing EMR and even ESD (where the risk of DMI is significantly higher) is extremely low.
Endoscopic resection for large colorectal polyps is effective, available, minimally invasive and organ sparing making it the standard of care for the management of colonic polyps. With ongoing iteration in techniques, more invasive surgical approaches can be avoided in almost all patients with benign and low-risk T1 colorectal cancers.
Dr. Gabr is associate GI division director at the University of Cincinnati, Ohio. Dr. Mosko is based in the division of gastroenterology at St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Blurred Lines: Polyp Needing Surgical versus Endoscopic Excision
BY IRA LEEDS, MD
I am grateful for the invitation to join in discussion with Dr. Gabr and Dr. Mosko on the ever-increasing role of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). However, as a surgeon, I do carry at least mild trepidation entering one of the literary “safe spaces” of my gastroenterology colleagues.
With the increasing evidentiary support of EMR approaches and the increasing experience of those performing ESD, these two techniques are quickly becoming the options of choice. As these practices become ubiquitous, it is important to recognize both their advantages and limitations, compared with available surgical options. The decision to proceed with EMR and ESD is essentially a turning point away from early surgical referral for a complex lesion. In this discussion, I intend to highlight when EMR and ESD have a clear advantage to early surgical referral, why I believe that early surgical referral is still superior to advanced endoscopic techniques in the rectum, and why the approach for right-sided lesions should hinge on careful shared decision-making.
Endoscopic approaches nearly always beat surgical approaches when considering short-term risks. Even in the best surgical series, colorectal surgery typically leads to complications in 10%-15% of patients, 1%-5% being serious. Moreover, transabdominal surgical interventions (ie, colectomy) require considerable recovery involving at least a few days in the inpatient setting and over a month of activity restrictions. Finally, there is a minority of chronically unwell patients who cannot tolerate surgical intervention but may be fortunate enough to have a lesion that with enhanced attention can be endoscopically resectioned. While EMR and ESD also contribute a disproportionate burden of complications to endoscopy practice, overall complication rates are still favorable when compared with surgical resection.
Moreover, the most feared short-term complication of EMR and ESD, perforation, has the added benefit of a “controlled failure” to colectomy. Advanced endoscopic approaches already require a prepared colon, and patients are given strict return instructions. Hence, the yearly handful of postprocedural perforations that I get called upon to assist with typically tolerate a routine surgical exploration, repair or resection, and recover at rates equal to or better than elective colon resections. For these reasons, lesions that can be endoscopically removed within appropriate risk tolerances, can and should be considered for EMR or ESD at time of diagnosis.
There are two clinical scenarios where this consideration for up-front EMR or ESD requires further caution. First, any rectal lesion considered for advanced endoscopic techniques really needs to be done in multidisciplinary conference with a colorectal surgeon. In the modern era of colorectal surgery, surgeons now have numerous approaches to reach the rectum that bridge the gap between traditional endoscopy and transabdominal resection. For many rectal lesions, transanal laparoscopic and robotic approaches offer the opportunity for local excision. The most commonly practiced approach, transanal minimally invasive microsurgery (TAMIS), provides many of the benefits of endoscopy (eg, same-day discharge, no activity restrictions, limited periprocedural physiologic stress, low complication rates) while providing the surgical precision, repair strategies, and specimen orientation of conventional surgery. Anecdotally, the time it takes to do a high-quality TAMIS excision in the rectum can be substantially less than that required for a comparable ESD.
For rectal lesions in particular, specimen quality is paramount for oncologic prognosis. Regardless of any intrinsic favorable histopathology or deft hand of the endoscopist, a TAMIS approach will typically provide for a deeper partial thickness or even full thickness excision. More times each year than I would like, I find myself at a multidisciplinary tumor board discussing an endoscopically removed rectal lesion done in a piecemeal fashion or insufficient deep ESD where appropriate risk stratification is impossible and we end up offering patients a likely overly aggressive proctectomy or a potentially oncologically unsound re-excision. Consideration of EMR/ESD vs TAMIS up front would allow better sorting of which technique is most suited to which lesion and avoid these diagnostic dilemmas that only seem to be more common as EMR and ESD practices proliferate.
For a different set of reasons, an advanced cecal adenoma may also be more suited to upfront surgical considerations. Right colon lesions can be more challenging for surveillance for a host of reasons. Procedurally, right colon lesions are undeniably more difficult. The thin-walled cecum can be unforgiving for repeated polypectomies. Despite it being an uncomfortable subject for colonoscopists, the evidence suggests that getting to the cecum is not consistent or 100% expected. Finally, patients can be unwilling to undergo serial bowel preparation and endoscopic examination. In contrast, a laparoscopic right colectomy avoids these issues while also attributing little additional risk. Laparoscopic right-colon operations have overall complication rates of less than 10% and major complications of less than 1%. Hospital stays for laparoscopic right colectomy are typically 3 days or less. Finally, surgery reduces both the frequency of surveillance, and a shortened colon makes surveillance easier.
Advanced polypectomy techniques broaden our ability to address even difficult lesions under the ideally aligned degree of invasive procedure. However, like any procedure, these techniques have their own advantages and limitations. There will always be a minority of premalignant colon lesions that are best suited to surgery-first approaches to treatment. In my practice, maintaining open lines of communication and regular interaction with my endoscopy colleagues naturally leads to polyps being addressed in their most suitable fashion.
Dr. Leeds is assistant professor of surgery at the Yale School of Medicine and a staff surgeon at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
We now have the ability to remove almost any large colon polyp endoscopically using a variety of techniques — from the widely used endoscopic mucosal resection to the increasingly prevalent endoscopic submucosal dissection. Yet, in this new era,
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Jeffrey Mosko and Dr. Moamen Gabr discuss the importance of careful polyp selection and argue that almost all polyps can be safely removed endoscopically, with low recurrence rates. In contrast, Dr. Ira Leeds from colorectal surgery offers a counterpoint, urging caution when managing polyps in the cecum and rectum while highlighting the role of minimally invasive surgical approaches. We hope these discussions provide valuable insights to support your approach to managing large colorectal polyps, especially in an era of increasing colon cancer screening.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Advantages of Endoscopic Resection for Large Colon Polyps
BY MOAMEN GABR, MD, MSC, AND JEFFREY D. MOSKO MD, MSC
General Advantages
Endoscopy has revolutionized the management of large colorectal polyps, offering a minimally invasive alternative to surgical resection. The dawn of endoscopic resection in the late 20th century, particularly the evolution of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in Japan, marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of colonic lesions by enabling the removal of lesions that would otherwise necessitate surgery.
Endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps is generally performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to recover at home the same day. This not only minimizes disruption to daily life but also significantly enhances patient satisfaction.
Most procedures are performed under moderate or deep sedation eliminating the need for general anesthesia. This represents a critical benefit, particularly for older or medically frail patients who are at higher risk of anesthesia-related complications.
From an economic perspective, endoscopic resection reduces healthcare costs by eliminating prolonged hospital stays and complex perioperative care. Additionally, preserving the colon’s structure and function avoids long-term consequences such as altered bowel habits or ostomy dependence, common with surgical interventions.
The advantages of endoscopic intervention are clear: safety, cost-effectiveness, organ preservation, and convenience for patients.
Lesion Selection
The superiority of endoscopic resection relies on selecting lesions appropriately, specifically those with a low risk of lymph node metastases. This meticulous process should include assessing a lesion’s size, location, morphology, granularity, microvascular and surface pit pattern using a combination of high-definition white light endoscopy, virtual chromoendoscopy and image magnification (when available).
Gross morphologic assessment utilizes the Paris and LST classifications. Combining the Paris classification, lesion granularity and location is both straightforward and revealing. Ulcerated/excavated lesions (0-III) are concerning for deep invasion. Depressed (0-IIc) morphologies are strongly associated with T1 CRC. Nodular lesions (0-Is or IIa + Is) have a higher risk of T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with flat lesions (0-IIa or 0-IIb). Non-granular lesions (0-Is and 0-IIa + Is) have a higher risk of covert cancer. Finally, the rectosigmoid location is associated with an increased risk of T1 CRC (vs. proximal locations).
Endoscopic surface pattern assessment increases one’s diagnostic accuracy. There are three primary endoscopic surface pattern classifications: NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE), Japanese NBI expert team (JNET), and Kudo pit pattern classifications. Colonic lesions that have a NICE Type 3, JNET 3, or Kudo type Vn pattern should be referred promptly for surgical resection. Lesions with a JNET 2B or Kudo type VI carry a higher risk of superficial T1 CRC but can still be removed endoscopically (see below) in expert centers. All other lesions should undergo endoscopic resection.
Endoscopic Resection Techniques
Endoscopic resection of large colorectal polyps encompasses two primary techniques: EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), each tailored to specific lesion characteristics and operator expertise.
EMR, the technique of choice for the vast majority of lesions, relies on injecting a submucosal cushion to lift the lesion before excision. Recent advances, including enhanced snare designs and underwater EMR, have improved en-bloc resection rates, significantly reducing recurrence and enhancing the efficacy of this technique.
ESD offers unparalleled precision for en-bloc resection of complex lesions, particularly those with fibrosis or high-risk features. Cutting-edge innovations, such as traction devices, have streamlined the procedure, addressing the traditional challenges of ESD. Despite being more time intensive, ESD minimizes recurrence and provides complete histopathological evaluation, critical for the management of malignant or pre-malignant lesions.
For non-lifting polyps, newer techniques such as endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR), using tools like the Full-Thickness Resection Device (FTRD), enable resection of up to 2-3 cm of the colonic or rectal wall. This ensures complete removal of any lesion and its underlying tissue, effectively preventing recurrence.
These advancements demonstrate how endoscopy can tackle even the most challenging colorectal polyps, reinforcing its position as the preferred treatment modality.
Perceived Limitations
With ongoing refinement over the last 2 decades, many of the perceived limitations (below) of endoscopic resection have now been overcome.
- Difficult locations/access: Historically lesions at the anorectal junction, ileocecal valve, appendiceal orifice and anastomoses were preferentially sent for surgery. In spite of unique technical challenges at each of these locations, there is now compelling data supporting EMR for these scenarios. We now also have techniques aimed at enabling the resection of lesions with poor access including patient repositioning, distal attachments, variable endoscope diameter/flexibility, traction and overtube devices.
- Recurrence: In the past, recurrence after endoscopic resection of lesions > 20 mm has been reported to be as high as 20%. With our current systematic approach to complete resection, meticulous examination of the post-resection defect for residual polyp tissue, adjunctive techniques to address submucosal fibrosis (hot avulsion, CAST, submucosal release) and thermal ablation to the resection margin (EMR-T), the risk of recurrence for piecemeal resections can be decreased to < 5%. In fact, some groups argue for the en-bloc resection of all large colorectal lesions based on the extremely low (< 1%) recurrence rates and potential for decreased follow-up.
- Post-resection bleeding: Post-resection bleeding is no longer a major limitation of any endoscopic approach because of the combination of improved intra-procedural hemostatic and resection techniques, optimized electrosurgical technology, and enhanced defect closure capabilities and devices (with prophylactic defect closure now supported by randomized control trial level data).
- Perforation: Deep mural injury, once an endoscopists’ worst fear during resection, is no longer a surgical emergency. It can now be predicted, identified (Sydney classification) and successfully managed. In spite of more widespread aggressive resection strategies, the risk of emergency surgery in patients undergoing EMR and even ESD (where the risk of DMI is significantly higher) is extremely low.
Endoscopic resection for large colorectal polyps is effective, available, minimally invasive and organ sparing making it the standard of care for the management of colonic polyps. With ongoing iteration in techniques, more invasive surgical approaches can be avoided in almost all patients with benign and low-risk T1 colorectal cancers.
Dr. Gabr is associate GI division director at the University of Cincinnati, Ohio. Dr. Mosko is based in the division of gastroenterology at St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Blurred Lines: Polyp Needing Surgical versus Endoscopic Excision
BY IRA LEEDS, MD
I am grateful for the invitation to join in discussion with Dr. Gabr and Dr. Mosko on the ever-increasing role of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). However, as a surgeon, I do carry at least mild trepidation entering one of the literary “safe spaces” of my gastroenterology colleagues.
With the increasing evidentiary support of EMR approaches and the increasing experience of those performing ESD, these two techniques are quickly becoming the options of choice. As these practices become ubiquitous, it is important to recognize both their advantages and limitations, compared with available surgical options. The decision to proceed with EMR and ESD is essentially a turning point away from early surgical referral for a complex lesion. In this discussion, I intend to highlight when EMR and ESD have a clear advantage to early surgical referral, why I believe that early surgical referral is still superior to advanced endoscopic techniques in the rectum, and why the approach for right-sided lesions should hinge on careful shared decision-making.
Endoscopic approaches nearly always beat surgical approaches when considering short-term risks. Even in the best surgical series, colorectal surgery typically leads to complications in 10%-15% of patients, 1%-5% being serious. Moreover, transabdominal surgical interventions (ie, colectomy) require considerable recovery involving at least a few days in the inpatient setting and over a month of activity restrictions. Finally, there is a minority of chronically unwell patients who cannot tolerate surgical intervention but may be fortunate enough to have a lesion that with enhanced attention can be endoscopically resectioned. While EMR and ESD also contribute a disproportionate burden of complications to endoscopy practice, overall complication rates are still favorable when compared with surgical resection.
Moreover, the most feared short-term complication of EMR and ESD, perforation, has the added benefit of a “controlled failure” to colectomy. Advanced endoscopic approaches already require a prepared colon, and patients are given strict return instructions. Hence, the yearly handful of postprocedural perforations that I get called upon to assist with typically tolerate a routine surgical exploration, repair or resection, and recover at rates equal to or better than elective colon resections. For these reasons, lesions that can be endoscopically removed within appropriate risk tolerances, can and should be considered for EMR or ESD at time of diagnosis.
There are two clinical scenarios where this consideration for up-front EMR or ESD requires further caution. First, any rectal lesion considered for advanced endoscopic techniques really needs to be done in multidisciplinary conference with a colorectal surgeon. In the modern era of colorectal surgery, surgeons now have numerous approaches to reach the rectum that bridge the gap between traditional endoscopy and transabdominal resection. For many rectal lesions, transanal laparoscopic and robotic approaches offer the opportunity for local excision. The most commonly practiced approach, transanal minimally invasive microsurgery (TAMIS), provides many of the benefits of endoscopy (eg, same-day discharge, no activity restrictions, limited periprocedural physiologic stress, low complication rates) while providing the surgical precision, repair strategies, and specimen orientation of conventional surgery. Anecdotally, the time it takes to do a high-quality TAMIS excision in the rectum can be substantially less than that required for a comparable ESD.
For rectal lesions in particular, specimen quality is paramount for oncologic prognosis. Regardless of any intrinsic favorable histopathology or deft hand of the endoscopist, a TAMIS approach will typically provide for a deeper partial thickness or even full thickness excision. More times each year than I would like, I find myself at a multidisciplinary tumor board discussing an endoscopically removed rectal lesion done in a piecemeal fashion or insufficient deep ESD where appropriate risk stratification is impossible and we end up offering patients a likely overly aggressive proctectomy or a potentially oncologically unsound re-excision. Consideration of EMR/ESD vs TAMIS up front would allow better sorting of which technique is most suited to which lesion and avoid these diagnostic dilemmas that only seem to be more common as EMR and ESD practices proliferate.
For a different set of reasons, an advanced cecal adenoma may also be more suited to upfront surgical considerations. Right colon lesions can be more challenging for surveillance for a host of reasons. Procedurally, right colon lesions are undeniably more difficult. The thin-walled cecum can be unforgiving for repeated polypectomies. Despite it being an uncomfortable subject for colonoscopists, the evidence suggests that getting to the cecum is not consistent or 100% expected. Finally, patients can be unwilling to undergo serial bowel preparation and endoscopic examination. In contrast, a laparoscopic right colectomy avoids these issues while also attributing little additional risk. Laparoscopic right-colon operations have overall complication rates of less than 10% and major complications of less than 1%. Hospital stays for laparoscopic right colectomy are typically 3 days or less. Finally, surgery reduces both the frequency of surveillance, and a shortened colon makes surveillance easier.
Advanced polypectomy techniques broaden our ability to address even difficult lesions under the ideally aligned degree of invasive procedure. However, like any procedure, these techniques have their own advantages and limitations. There will always be a minority of premalignant colon lesions that are best suited to surgery-first approaches to treatment. In my practice, maintaining open lines of communication and regular interaction with my endoscopy colleagues naturally leads to polyps being addressed in their most suitable fashion.
Dr. Leeds is assistant professor of surgery at the Yale School of Medicine and a staff surgeon at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
We now have the ability to remove almost any large colon polyp endoscopically using a variety of techniques — from the widely used endoscopic mucosal resection to the increasingly prevalent endoscopic submucosal dissection. Yet, in this new era,
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Jeffrey Mosko and Dr. Moamen Gabr discuss the importance of careful polyp selection and argue that almost all polyps can be safely removed endoscopically, with low recurrence rates. In contrast, Dr. Ira Leeds from colorectal surgery offers a counterpoint, urging caution when managing polyps in the cecum and rectum while highlighting the role of minimally invasive surgical approaches. We hope these discussions provide valuable insights to support your approach to managing large colorectal polyps, especially in an era of increasing colon cancer screening.
We also welcome your thoughts on this topic — join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Advantages of Endoscopic Resection for Large Colon Polyps
BY MOAMEN GABR, MD, MSC, AND JEFFREY D. MOSKO MD, MSC
General Advantages
Endoscopy has revolutionized the management of large colorectal polyps, offering a minimally invasive alternative to surgical resection. The dawn of endoscopic resection in the late 20th century, particularly the evolution of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) in Japan, marked a paradigm shift in the treatment of colonic lesions by enabling the removal of lesions that would otherwise necessitate surgery.
Endoscopic resection of colorectal polyps is generally performed in an outpatient setting, allowing patients to recover at home the same day. This not only minimizes disruption to daily life but also significantly enhances patient satisfaction.
Most procedures are performed under moderate or deep sedation eliminating the need for general anesthesia. This represents a critical benefit, particularly for older or medically frail patients who are at higher risk of anesthesia-related complications.
From an economic perspective, endoscopic resection reduces healthcare costs by eliminating prolonged hospital stays and complex perioperative care. Additionally, preserving the colon’s structure and function avoids long-term consequences such as altered bowel habits or ostomy dependence, common with surgical interventions.
The advantages of endoscopic intervention are clear: safety, cost-effectiveness, organ preservation, and convenience for patients.
Lesion Selection
The superiority of endoscopic resection relies on selecting lesions appropriately, specifically those with a low risk of lymph node metastases. This meticulous process should include assessing a lesion’s size, location, morphology, granularity, microvascular and surface pit pattern using a combination of high-definition white light endoscopy, virtual chromoendoscopy and image magnification (when available).
Gross morphologic assessment utilizes the Paris and LST classifications. Combining the Paris classification, lesion granularity and location is both straightforward and revealing. Ulcerated/excavated lesions (0-III) are concerning for deep invasion. Depressed (0-IIc) morphologies are strongly associated with T1 CRC. Nodular lesions (0-Is or IIa + Is) have a higher risk of T1 colorectal cancer (CRC), compared with flat lesions (0-IIa or 0-IIb). Non-granular lesions (0-Is and 0-IIa + Is) have a higher risk of covert cancer. Finally, the rectosigmoid location is associated with an increased risk of T1 CRC (vs. proximal locations).
Endoscopic surface pattern assessment increases one’s diagnostic accuracy. There are three primary endoscopic surface pattern classifications: NBI International Colorectal Endoscopic (NICE), Japanese NBI expert team (JNET), and Kudo pit pattern classifications. Colonic lesions that have a NICE Type 3, JNET 3, or Kudo type Vn pattern should be referred promptly for surgical resection. Lesions with a JNET 2B or Kudo type VI carry a higher risk of superficial T1 CRC but can still be removed endoscopically (see below) in expert centers. All other lesions should undergo endoscopic resection.
Endoscopic Resection Techniques
Endoscopic resection of large colorectal polyps encompasses two primary techniques: EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), each tailored to specific lesion characteristics and operator expertise.
EMR, the technique of choice for the vast majority of lesions, relies on injecting a submucosal cushion to lift the lesion before excision. Recent advances, including enhanced snare designs and underwater EMR, have improved en-bloc resection rates, significantly reducing recurrence and enhancing the efficacy of this technique.
ESD offers unparalleled precision for en-bloc resection of complex lesions, particularly those with fibrosis or high-risk features. Cutting-edge innovations, such as traction devices, have streamlined the procedure, addressing the traditional challenges of ESD. Despite being more time intensive, ESD minimizes recurrence and provides complete histopathological evaluation, critical for the management of malignant or pre-malignant lesions.
For non-lifting polyps, newer techniques such as endoscopic full-thickness resection (eFTR), using tools like the Full-Thickness Resection Device (FTRD), enable resection of up to 2-3 cm of the colonic or rectal wall. This ensures complete removal of any lesion and its underlying tissue, effectively preventing recurrence.
These advancements demonstrate how endoscopy can tackle even the most challenging colorectal polyps, reinforcing its position as the preferred treatment modality.
Perceived Limitations
With ongoing refinement over the last 2 decades, many of the perceived limitations (below) of endoscopic resection have now been overcome.
- Difficult locations/access: Historically lesions at the anorectal junction, ileocecal valve, appendiceal orifice and anastomoses were preferentially sent for surgery. In spite of unique technical challenges at each of these locations, there is now compelling data supporting EMR for these scenarios. We now also have techniques aimed at enabling the resection of lesions with poor access including patient repositioning, distal attachments, variable endoscope diameter/flexibility, traction and overtube devices.
- Recurrence: In the past, recurrence after endoscopic resection of lesions > 20 mm has been reported to be as high as 20%. With our current systematic approach to complete resection, meticulous examination of the post-resection defect for residual polyp tissue, adjunctive techniques to address submucosal fibrosis (hot avulsion, CAST, submucosal release) and thermal ablation to the resection margin (EMR-T), the risk of recurrence for piecemeal resections can be decreased to < 5%. In fact, some groups argue for the en-bloc resection of all large colorectal lesions based on the extremely low (< 1%) recurrence rates and potential for decreased follow-up.
- Post-resection bleeding: Post-resection bleeding is no longer a major limitation of any endoscopic approach because of the combination of improved intra-procedural hemostatic and resection techniques, optimized electrosurgical technology, and enhanced defect closure capabilities and devices (with prophylactic defect closure now supported by randomized control trial level data).
- Perforation: Deep mural injury, once an endoscopists’ worst fear during resection, is no longer a surgical emergency. It can now be predicted, identified (Sydney classification) and successfully managed. In spite of more widespread aggressive resection strategies, the risk of emergency surgery in patients undergoing EMR and even ESD (where the risk of DMI is significantly higher) is extremely low.
Endoscopic resection for large colorectal polyps is effective, available, minimally invasive and organ sparing making it the standard of care for the management of colonic polyps. With ongoing iteration in techniques, more invasive surgical approaches can be avoided in almost all patients with benign and low-risk T1 colorectal cancers.
Dr. Gabr is associate GI division director at the University of Cincinnati, Ohio. Dr. Mosko is based in the division of gastroenterology at St. Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Blurred Lines: Polyp Needing Surgical versus Endoscopic Excision
BY IRA LEEDS, MD
I am grateful for the invitation to join in discussion with Dr. Gabr and Dr. Mosko on the ever-increasing role of endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). However, as a surgeon, I do carry at least mild trepidation entering one of the literary “safe spaces” of my gastroenterology colleagues.
With the increasing evidentiary support of EMR approaches and the increasing experience of those performing ESD, these two techniques are quickly becoming the options of choice. As these practices become ubiquitous, it is important to recognize both their advantages and limitations, compared with available surgical options. The decision to proceed with EMR and ESD is essentially a turning point away from early surgical referral for a complex lesion. In this discussion, I intend to highlight when EMR and ESD have a clear advantage to early surgical referral, why I believe that early surgical referral is still superior to advanced endoscopic techniques in the rectum, and why the approach for right-sided lesions should hinge on careful shared decision-making.
Endoscopic approaches nearly always beat surgical approaches when considering short-term risks. Even in the best surgical series, colorectal surgery typically leads to complications in 10%-15% of patients, 1%-5% being serious. Moreover, transabdominal surgical interventions (ie, colectomy) require considerable recovery involving at least a few days in the inpatient setting and over a month of activity restrictions. Finally, there is a minority of chronically unwell patients who cannot tolerate surgical intervention but may be fortunate enough to have a lesion that with enhanced attention can be endoscopically resectioned. While EMR and ESD also contribute a disproportionate burden of complications to endoscopy practice, overall complication rates are still favorable when compared with surgical resection.
Moreover, the most feared short-term complication of EMR and ESD, perforation, has the added benefit of a “controlled failure” to colectomy. Advanced endoscopic approaches already require a prepared colon, and patients are given strict return instructions. Hence, the yearly handful of postprocedural perforations that I get called upon to assist with typically tolerate a routine surgical exploration, repair or resection, and recover at rates equal to or better than elective colon resections. For these reasons, lesions that can be endoscopically removed within appropriate risk tolerances, can and should be considered for EMR or ESD at time of diagnosis.
There are two clinical scenarios where this consideration for up-front EMR or ESD requires further caution. First, any rectal lesion considered for advanced endoscopic techniques really needs to be done in multidisciplinary conference with a colorectal surgeon. In the modern era of colorectal surgery, surgeons now have numerous approaches to reach the rectum that bridge the gap between traditional endoscopy and transabdominal resection. For many rectal lesions, transanal laparoscopic and robotic approaches offer the opportunity for local excision. The most commonly practiced approach, transanal minimally invasive microsurgery (TAMIS), provides many of the benefits of endoscopy (eg, same-day discharge, no activity restrictions, limited periprocedural physiologic stress, low complication rates) while providing the surgical precision, repair strategies, and specimen orientation of conventional surgery. Anecdotally, the time it takes to do a high-quality TAMIS excision in the rectum can be substantially less than that required for a comparable ESD.
For rectal lesions in particular, specimen quality is paramount for oncologic prognosis. Regardless of any intrinsic favorable histopathology or deft hand of the endoscopist, a TAMIS approach will typically provide for a deeper partial thickness or even full thickness excision. More times each year than I would like, I find myself at a multidisciplinary tumor board discussing an endoscopically removed rectal lesion done in a piecemeal fashion or insufficient deep ESD where appropriate risk stratification is impossible and we end up offering patients a likely overly aggressive proctectomy or a potentially oncologically unsound re-excision. Consideration of EMR/ESD vs TAMIS up front would allow better sorting of which technique is most suited to which lesion and avoid these diagnostic dilemmas that only seem to be more common as EMR and ESD practices proliferate.
For a different set of reasons, an advanced cecal adenoma may also be more suited to upfront surgical considerations. Right colon lesions can be more challenging for surveillance for a host of reasons. Procedurally, right colon lesions are undeniably more difficult. The thin-walled cecum can be unforgiving for repeated polypectomies. Despite it being an uncomfortable subject for colonoscopists, the evidence suggests that getting to the cecum is not consistent or 100% expected. Finally, patients can be unwilling to undergo serial bowel preparation and endoscopic examination. In contrast, a laparoscopic right colectomy avoids these issues while also attributing little additional risk. Laparoscopic right-colon operations have overall complication rates of less than 10% and major complications of less than 1%. Hospital stays for laparoscopic right colectomy are typically 3 days or less. Finally, surgery reduces both the frequency of surveillance, and a shortened colon makes surveillance easier.
Advanced polypectomy techniques broaden our ability to address even difficult lesions under the ideally aligned degree of invasive procedure. However, like any procedure, these techniques have their own advantages and limitations. There will always be a minority of premalignant colon lesions that are best suited to surgery-first approaches to treatment. In my practice, maintaining open lines of communication and regular interaction with my endoscopy colleagues naturally leads to polyps being addressed in their most suitable fashion.
Dr. Leeds is assistant professor of surgery at the Yale School of Medicine and a staff surgeon at the VA Connecticut Healthcare System. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Jumping Jacks and Cold Water: How Pediatricians Are Stepping up in the Youth Mental Health Crisis
A young boy with a habit of screaming when he didn’t get his way is among the patients Joannie Yeh, MD, a primary care physician at Nemours Children’s Health in Media, Pennsylvania, has helped in her practice.
Yeh taught the boy to stretch out his hands into the shape of a starfish, then trace around the edges of his fingers while breathing slowly and deeply. His parents later reported that after using the strategy at home, their son was no longer taking his rage out on his younger siblings.
Interventions like breathing exercises are just a few techniques Yeh hopes more primary care clinicians will teach young patients as mental health issues among this population soar to a national state of emergency, major medical groups say. But many children go without treatment because of shortages of mental health clinicians and long wait-lists for appointments.
“Knowledge of different types of interventions allows pediatricians to offer more options to families — more than just medication alone,” Yeh said. “There are some strategies, like cognitive behavioral therapy, that a therapist is equipped to deliver, but we can help explain them or teach simple skills that borrow from principles of higher-level techniques and can help patients and families while they wait to see a therapist.”
, said Theresa Nguyen, MD, chair of pediatrics at Greater Baltimore Medical Center, Baltimore.
“It kind of sucks if you come in worried and then your doctor says, ‘Okay, let me send you to a psychiatrist who you can’t see for 6 months; let me send you to a therapist who’s going to take a couple of weeks to get in with,’” Nguyen said.
Yeh said over the past few years she has cared for more youth coming in as follow-ups after an emergency department visit for a mental health episode.
“Oftentimes, this is the first time we become aware that the child is struggling,” Yeh said. “We are seeing issues like intentional medication overdose, referrals after other self-harm actions, or even the discovery of a note indicating the intention to do harm to self.”
Suicide deaths among 10- to 14-year-olds tripled between 2007 and 2018 and held steady through 2021, with rates climbing even among children as young as 8 years, according to a research in JAMA Network Open. Meanwhile, one in five high school students seriously contemplated suicide in 2023 (27% girls, 14% boys).
Mental Health Strategies for Kids in Primary Care
While pediatricians cannot replace a mental health professional, they have the unique advantage of maintaining a long-term relationship with patients. Experts said clinicians should take an active role in supporting the mental health of patients through a variety of evidence-based strategies.
Changing Thought Patterns
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) involves identifying and challenging automatic negative thoughts, which can affect a child’s emotional state and lead to behaviors like withdrawal or lashing out.
Yeh recommended asking a child about what is bothering them, pointing out unhelpful and negative thoughts, and then offering a different, positive one instead.
She also often draws a picture of the CBT chart, which is a visual representation of how feelings lead to thoughts, and then behaviors.
“I draw this diagram because it helps give the patients a visual understanding of how their feelings and emotions are connected,” Yeh said.
Tools to Tolerate Stressful Situations
Simple tools like breathing exercises, body scanning, and physical exercise can help children better tolerate distress.
Pediatricians can also recommend families use guided meditations, which have been shown to lower anxiety and increase positive social behavior, said Mollie Grow, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington Medicine and Seattle Children’s Hospital, both in Seattle.
But a child might first need to get negative energy out before they can become calm.
“So I’m like, ‘okay, let’s do actual physical exercise. Give me 10 jumping jacks.’ No one’s nervous after those jumping jacks,” Nguyen said. “When you’ve already been triggered, your nerves have gotten going, and you’re starting to spiral, you can’t slow yourself down enough to do a breathing exercise.”
Nguyen also said that cold water quickly calms the nervous system.
“I’ll run cold water in the office and have them put their hand in it until it’s almost frozen,” and the child or teen is able to think more clearly, Nguyen said. “It’s a real physiological response. It works.”
The Origin of a Feeling
Explaining how symptoms of anxiety, depression, or ADHD work can help children and teens better understand that what they are experiencing is normal and better cope, Yeh said.
Clinicians might teach patients about how shallow breathing — a symptom of anxiety — is a result of the brain scanning for danger, and how slowing breathing tricks the brain into feeling safe again.
Barriers Abound
The use of these interventions in pediatric settings is not yet widespread, Grow said.
But starting in July 2025, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education will require pediatric residencies to include 4 weeks of mental health training. How that requirement is fulfilled will be up to residencies, said Brian Alverson, MD, pediatric program director and vice-chair of education at Nemours Children’s Hospital in Wilmington, Delaware.
Even with training, many pediatricians lack the time to address mental health issues during an office visit, said Carlos Lerner, MD, a professor of clinical pediatrics at University of California, Los Angeles Health. And despite low or sometimes no reimbursement for discussing these issues with patients, “the reality is we end up doing it anyway.”
Treating issues like anxiety and depression “is a daily, constant part of the care that I provide for my patients,” said Lerner. “Whether the pandemic or social media exacerbated it, we are absolutely seeing a rise in mental health issues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A young boy with a habit of screaming when he didn’t get his way is among the patients Joannie Yeh, MD, a primary care physician at Nemours Children’s Health in Media, Pennsylvania, has helped in her practice.
Yeh taught the boy to stretch out his hands into the shape of a starfish, then trace around the edges of his fingers while breathing slowly and deeply. His parents later reported that after using the strategy at home, their son was no longer taking his rage out on his younger siblings.
Interventions like breathing exercises are just a few techniques Yeh hopes more primary care clinicians will teach young patients as mental health issues among this population soar to a national state of emergency, major medical groups say. But many children go without treatment because of shortages of mental health clinicians and long wait-lists for appointments.
“Knowledge of different types of interventions allows pediatricians to offer more options to families — more than just medication alone,” Yeh said. “There are some strategies, like cognitive behavioral therapy, that a therapist is equipped to deliver, but we can help explain them or teach simple skills that borrow from principles of higher-level techniques and can help patients and families while they wait to see a therapist.”
, said Theresa Nguyen, MD, chair of pediatrics at Greater Baltimore Medical Center, Baltimore.
“It kind of sucks if you come in worried and then your doctor says, ‘Okay, let me send you to a psychiatrist who you can’t see for 6 months; let me send you to a therapist who’s going to take a couple of weeks to get in with,’” Nguyen said.
Yeh said over the past few years she has cared for more youth coming in as follow-ups after an emergency department visit for a mental health episode.
“Oftentimes, this is the first time we become aware that the child is struggling,” Yeh said. “We are seeing issues like intentional medication overdose, referrals after other self-harm actions, or even the discovery of a note indicating the intention to do harm to self.”
Suicide deaths among 10- to 14-year-olds tripled between 2007 and 2018 and held steady through 2021, with rates climbing even among children as young as 8 years, according to a research in JAMA Network Open. Meanwhile, one in five high school students seriously contemplated suicide in 2023 (27% girls, 14% boys).
Mental Health Strategies for Kids in Primary Care
While pediatricians cannot replace a mental health professional, they have the unique advantage of maintaining a long-term relationship with patients. Experts said clinicians should take an active role in supporting the mental health of patients through a variety of evidence-based strategies.
Changing Thought Patterns
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) involves identifying and challenging automatic negative thoughts, which can affect a child’s emotional state and lead to behaviors like withdrawal or lashing out.
Yeh recommended asking a child about what is bothering them, pointing out unhelpful and negative thoughts, and then offering a different, positive one instead.
She also often draws a picture of the CBT chart, which is a visual representation of how feelings lead to thoughts, and then behaviors.
“I draw this diagram because it helps give the patients a visual understanding of how their feelings and emotions are connected,” Yeh said.
Tools to Tolerate Stressful Situations
Simple tools like breathing exercises, body scanning, and physical exercise can help children better tolerate distress.
Pediatricians can also recommend families use guided meditations, which have been shown to lower anxiety and increase positive social behavior, said Mollie Grow, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington Medicine and Seattle Children’s Hospital, both in Seattle.
But a child might first need to get negative energy out before they can become calm.
“So I’m like, ‘okay, let’s do actual physical exercise. Give me 10 jumping jacks.’ No one’s nervous after those jumping jacks,” Nguyen said. “When you’ve already been triggered, your nerves have gotten going, and you’re starting to spiral, you can’t slow yourself down enough to do a breathing exercise.”
Nguyen also said that cold water quickly calms the nervous system.
“I’ll run cold water in the office and have them put their hand in it until it’s almost frozen,” and the child or teen is able to think more clearly, Nguyen said. “It’s a real physiological response. It works.”
The Origin of a Feeling
Explaining how symptoms of anxiety, depression, or ADHD work can help children and teens better understand that what they are experiencing is normal and better cope, Yeh said.
Clinicians might teach patients about how shallow breathing — a symptom of anxiety — is a result of the brain scanning for danger, and how slowing breathing tricks the brain into feeling safe again.
Barriers Abound
The use of these interventions in pediatric settings is not yet widespread, Grow said.
But starting in July 2025, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education will require pediatric residencies to include 4 weeks of mental health training. How that requirement is fulfilled will be up to residencies, said Brian Alverson, MD, pediatric program director and vice-chair of education at Nemours Children’s Hospital in Wilmington, Delaware.
Even with training, many pediatricians lack the time to address mental health issues during an office visit, said Carlos Lerner, MD, a professor of clinical pediatrics at University of California, Los Angeles Health. And despite low or sometimes no reimbursement for discussing these issues with patients, “the reality is we end up doing it anyway.”
Treating issues like anxiety and depression “is a daily, constant part of the care that I provide for my patients,” said Lerner. “Whether the pandemic or social media exacerbated it, we are absolutely seeing a rise in mental health issues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A young boy with a habit of screaming when he didn’t get his way is among the patients Joannie Yeh, MD, a primary care physician at Nemours Children’s Health in Media, Pennsylvania, has helped in her practice.
Yeh taught the boy to stretch out his hands into the shape of a starfish, then trace around the edges of his fingers while breathing slowly and deeply. His parents later reported that after using the strategy at home, their son was no longer taking his rage out on his younger siblings.
Interventions like breathing exercises are just a few techniques Yeh hopes more primary care clinicians will teach young patients as mental health issues among this population soar to a national state of emergency, major medical groups say. But many children go without treatment because of shortages of mental health clinicians and long wait-lists for appointments.
“Knowledge of different types of interventions allows pediatricians to offer more options to families — more than just medication alone,” Yeh said. “There are some strategies, like cognitive behavioral therapy, that a therapist is equipped to deliver, but we can help explain them or teach simple skills that borrow from principles of higher-level techniques and can help patients and families while they wait to see a therapist.”
, said Theresa Nguyen, MD, chair of pediatrics at Greater Baltimore Medical Center, Baltimore.
“It kind of sucks if you come in worried and then your doctor says, ‘Okay, let me send you to a psychiatrist who you can’t see for 6 months; let me send you to a therapist who’s going to take a couple of weeks to get in with,’” Nguyen said.
Yeh said over the past few years she has cared for more youth coming in as follow-ups after an emergency department visit for a mental health episode.
“Oftentimes, this is the first time we become aware that the child is struggling,” Yeh said. “We are seeing issues like intentional medication overdose, referrals after other self-harm actions, or even the discovery of a note indicating the intention to do harm to self.”
Suicide deaths among 10- to 14-year-olds tripled between 2007 and 2018 and held steady through 2021, with rates climbing even among children as young as 8 years, according to a research in JAMA Network Open. Meanwhile, one in five high school students seriously contemplated suicide in 2023 (27% girls, 14% boys).
Mental Health Strategies for Kids in Primary Care
While pediatricians cannot replace a mental health professional, they have the unique advantage of maintaining a long-term relationship with patients. Experts said clinicians should take an active role in supporting the mental health of patients through a variety of evidence-based strategies.
Changing Thought Patterns
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) involves identifying and challenging automatic negative thoughts, which can affect a child’s emotional state and lead to behaviors like withdrawal or lashing out.
Yeh recommended asking a child about what is bothering them, pointing out unhelpful and negative thoughts, and then offering a different, positive one instead.
She also often draws a picture of the CBT chart, which is a visual representation of how feelings lead to thoughts, and then behaviors.
“I draw this diagram because it helps give the patients a visual understanding of how their feelings and emotions are connected,” Yeh said.
Tools to Tolerate Stressful Situations
Simple tools like breathing exercises, body scanning, and physical exercise can help children better tolerate distress.
Pediatricians can also recommend families use guided meditations, which have been shown to lower anxiety and increase positive social behavior, said Mollie Grow, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at the University of Washington Medicine and Seattle Children’s Hospital, both in Seattle.
But a child might first need to get negative energy out before they can become calm.
“So I’m like, ‘okay, let’s do actual physical exercise. Give me 10 jumping jacks.’ No one’s nervous after those jumping jacks,” Nguyen said. “When you’ve already been triggered, your nerves have gotten going, and you’re starting to spiral, you can’t slow yourself down enough to do a breathing exercise.”
Nguyen also said that cold water quickly calms the nervous system.
“I’ll run cold water in the office and have them put their hand in it until it’s almost frozen,” and the child or teen is able to think more clearly, Nguyen said. “It’s a real physiological response. It works.”
The Origin of a Feeling
Explaining how symptoms of anxiety, depression, or ADHD work can help children and teens better understand that what they are experiencing is normal and better cope, Yeh said.
Clinicians might teach patients about how shallow breathing — a symptom of anxiety — is a result of the brain scanning for danger, and how slowing breathing tricks the brain into feeling safe again.
Barriers Abound
The use of these interventions in pediatric settings is not yet widespread, Grow said.
But starting in July 2025, the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education will require pediatric residencies to include 4 weeks of mental health training. How that requirement is fulfilled will be up to residencies, said Brian Alverson, MD, pediatric program director and vice-chair of education at Nemours Children’s Hospital in Wilmington, Delaware.
Even with training, many pediatricians lack the time to address mental health issues during an office visit, said Carlos Lerner, MD, a professor of clinical pediatrics at University of California, Los Angeles Health. And despite low or sometimes no reimbursement for discussing these issues with patients, “the reality is we end up doing it anyway.”
Treating issues like anxiety and depression “is a daily, constant part of the care that I provide for my patients,” said Lerner. “Whether the pandemic or social media exacerbated it, we are absolutely seeing a rise in mental health issues.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Red Wine May Not Be a Health Tonic, But Is It a Cancer Risk?
Earlier this month, US surgeon general Vivek Murthy, MD, issued an advisory, calling for alcoholic beverages to carry a warning label about cancer risk. The advisory flagged alcohol as the third leading preventable cause of cancer in the United States, after tobacco and obesity, and highlighted people’s limited awareness about the relationship between alcohol and cancer risk.
But, when it comes to cancer risk, are all types of alcohol created equal?
For many years, red wine seemed to be an outlier, with studies indicating that, in moderation, it might even be good for you. Red wine has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties — most notably, it contains the antioxidant resveratrol. Starting in the 1990s, research began to hint that the compound might protect against heart disease, aging, and cancer, though much of this work was done in animals or test tubes.
The idea that red wine carries health benefits, however, has been called into question more recently. A recent meta-analysis, for instance, suggests that many previous studies touting the health benefits of more moderate drinking were likely biased, potentially leading to “misleading positive health associations.” And one recent study found that alcohol consumption, largely red wine and beer, at all levels was linked to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
Although wine’s health halo is dwindling, there might be an exception: Cancer risk.
Overall, research shows that even light to moderate drinking increases the risk for at least seven types of cancer, but when focusing on red wine, in particular, that risk calculus can look different.
“It’s very complicated and nuanced,” said Timothy Rebbeck, PhD, professor of cancer prevention, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “And ‘complicated and nuanced’ doesn’t work very well in public health messages.”
The Knowns About Alcohol and Cancer Risk
Some things about the relationship between alcohol and cancer risk are crystal clear. “There’s no question that alcohol is a group 1 carcinogen,” Rebbeck said. “Alcohol can cause cancer.”
Groups including the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and American Cancer Society agree that alcohol use is an established cause of seven types of cancer: Those of the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, esophagus (squamous cell carcinoma), liver (hepatocellular carcinoma), breast, and colon/rectum. Heavy drinking — at least 8 standard drinks a week for women and 15 for men — and binge drinking — 4 or more drinks in 2 hours for women and 5 or more for men — only amplify that risk. (A “standard” drink has 14 g of alcohol, which translates to a 5-oz glass of wine.)
“We’re most concerned about high-risk drinking — more than 2 drinks a day — and/or binge drinking,” said Noelle LoConte, MD, of the Division of Hematology, Medical Oncology and Palliative Care, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, who authored a 2018 statement on alcohol and cancer risk from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Compared with not drinking, heavy drinking is linked with a roughly fivefold increase in the risk for oral cavity, pharyngeal, and esophageal cancers, and a 61% increase in the risk for breast cancer, according to LoConte and colleagues.
Things get murkier when it comes to moderate drinking — defined as up to 1 standard drink per day for women and 2 per day for men. There is evidence, LoConte said, that moderate drinking is associated with increased cancer risks, though the magnitude is generally much less than heavier drinking.
Cancer type also matters. One analysis found that the risk for breast cancer increased with even light to moderate alcohol consumption. Compared with no drinking, light to moderate drinking has also been linked to increased risks for oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, and esophageal cancers.
As for whether the type of alcoholic beverage matters, LoConte said, there’s no clear physiological reason that wine would be less risky than beer or liquor. Research indicates that ethanol is the problematic ingredient: Once ingested, it’s metabolized into acetaldehyde, a DNA-damaging substance that’s considered a probable human carcinogen. Ethanol can also alter circulating levels of estrogens and androgens, LoConte said, which is thought to drive its association with breast cancer risk.
“It likely doesn’t matter how you choose to get your ethanol,” she said. “It’s a question of volume.”
Hints That Wine Is an Outlier
Still, some studies suggest that how people ingest ethanol could make a difference.
A study published in August in JAMA Network Open is a case in point. The study found that, among older adults, light to heavy drinkers had an increased risk of dying from cancer, compared with occasional drinkers (though the increased risk among light to moderate drinkers occurred only among people who also had chronic health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, or were of lower socioeconomic status).
Wine drinkers fared differently. Most notably, drinkers who “preferred” wine — consuming over 80% of total ethanol from wine — or those who drank only with meals showed a small reduction in their risk for cancer mortality and all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.94 for both). The small protective association was somewhat stronger among people who reported both patterns (HR, 0.88), especially if they were of lower socioeconomic status (HR, 0.79).
The findings are in line with other research suggesting that wine drinkers may be outliers when it comes to cancer risk. A 2023 meta-analysis of 26 observational studies, for instance, found no association between wine consumption and any cancer type, with the caveat that there was «substantial» heterogeneity among the studies.
This heterogeneity caveat speaks to the inherent limitations of observational research, said Tim Stockwell, PhD, of the Canadian Institute for Substance Use Research, University of Victoria in British Columbia, Canada.
“Individual studies of alcohol and cancer risk do find differences by type of drink, or patterns of drinking,” Stockwell said. “But it’s so hard to unpack the confounding that goes along with the type of person who’s a wine drinker or a beer drinker or a spirit drinker. The beverage of choice seems to come with a lot of baggage.”
Compared with people who favor beer or liquor, he noted, wine aficionados are typically higher-income, exercise more often, smoke less, and have different diets, for example. The “best” studies, Rebbeck said, try to adjust for those differences, but it’s challenging.
The authors of the 2023 meta-analysis noted that “many components in wine could have anticarcinogenic effects” that theoretically could counter the ill effects of ethanol. Besides resveratrol, which is mainly found in red wine, the list includes anthocyanins, quercetin, and tannins. However, the authors also acknowledged that they couldn’t account for whether other lifestyle habits might explain why wine drinkers, overall, showed no increased cancer risks and sometimes lower risks.
Still, groups such as the IARC and ASCO hold that there is no known “safe” level, or type, of alcohol when it comes to cancer.
In the latest Canadian guidelines on alcohol use, the scientific panel calculated that people who have 6 drinks a week throughout adulthood (whatever the source of the alcohol) could shave 11 weeks from their life expectancy, on average, said Stockwell, who was on the guideline panel. Compare that with heavy drinking, where 4 drinks a day could rob the average person of 2 or 3 years. “If you’re drinking a lot, you could get huge benefits from cutting down,” Stockwell explained. “If you’re a moderate drinker, the benefits would obviously be less.”
Stockwell said that choices around drinking and breast cancer risk, specifically, can be “tough.” Unlike many of the other alcohol-associated cancers, he noted, breast cancer is common — so even small relative risk increases may be concerning. Based on a 2020 meta-analysis of 22 cohort studies, the risk for breast cancer rises by about 10%, on average, for every 10 g of alcohol a woman drinks per day. This study also found no evidence that wine is any different from other types of alcohol.
In real life, the calculus around wine consumption and cancer risk will probably vary widely from person to person, Rebbeck said. One woman with a family history of breast cancer might decide that having wine with dinner isn’t worth it. Another with the same family history might see that glass of wine as a stress reliever and opt to focus on other ways to reduce her breast cancer risk — by exercising and maintaining a healthy weight, for example.
“The bottom line is, in human studies, the data on light to moderate drinking and cancer are limited and messy, and you can’t draw firm conclusions from them,” Rebbeck said. “It probably raises risk in some people, but we don’t know who those people are. And the risk increases are relatively small.”
A Conversation Few Are Having
Even with many studies highlighting the connection between alcohol consumption and cancer risk, most people remain unaware about this risk.
A 2023 study by the National Cancer Institute found that only a minority of US adults knew that drinking alcohol is linked to increased cancer risk, and they were much less likely to say that was true of wine: Only 20% did, vs 31% who said that liquor can boost cancer risk. Meanwhile, 10% believed that wine helps prevent cancer. Other studies show that even among cancer survivors and patients undergoing active cancer treatment, many drink — often heavily.
“What we know right now is, physicians almost never talk about this,” LoConte said.
That could be due to time constraints, according to Rebbeck, or clinicians’ perceptions that the subject is too complicated and/or their own confusion about the data. There could also be some “cognitive dissonance” at play, LoConte noted, because many doctors drink alcohol.
It’s critical, she said, that conversations about drinking habits become “normalized,” and that should include informing patients that alcohol use is associated with certain cancers. Again, LoConte said, it’s high-risk drinking that’s most concerning and where reducing intake could have the biggest impact on cancer risk and other health outcomes.
“From a cancer prevention standpoint, it’s probably best not to drink,” she said. “But people don’t make choices based solely on cancer risk. We don’t want to come out with recommendations saying no one should drink. I don’t think the data support that, and people would buck against that advice.”
Rebbeck made a similar point. Even if there’s uncertainty about the risks for a daily glass of wine, he said, people can use that information to make decisions. “Everybody’s preferences and choices are going to be different,” Rebbeck said. “And that’s all we can really do.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier this month, US surgeon general Vivek Murthy, MD, issued an advisory, calling for alcoholic beverages to carry a warning label about cancer risk. The advisory flagged alcohol as the third leading preventable cause of cancer in the United States, after tobacco and obesity, and highlighted people’s limited awareness about the relationship between alcohol and cancer risk.
But, when it comes to cancer risk, are all types of alcohol created equal?
For many years, red wine seemed to be an outlier, with studies indicating that, in moderation, it might even be good for you. Red wine has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties — most notably, it contains the antioxidant resveratrol. Starting in the 1990s, research began to hint that the compound might protect against heart disease, aging, and cancer, though much of this work was done in animals or test tubes.
The idea that red wine carries health benefits, however, has been called into question more recently. A recent meta-analysis, for instance, suggests that many previous studies touting the health benefits of more moderate drinking were likely biased, potentially leading to “misleading positive health associations.” And one recent study found that alcohol consumption, largely red wine and beer, at all levels was linked to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
Although wine’s health halo is dwindling, there might be an exception: Cancer risk.
Overall, research shows that even light to moderate drinking increases the risk for at least seven types of cancer, but when focusing on red wine, in particular, that risk calculus can look different.
“It’s very complicated and nuanced,” said Timothy Rebbeck, PhD, professor of cancer prevention, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “And ‘complicated and nuanced’ doesn’t work very well in public health messages.”
The Knowns About Alcohol and Cancer Risk
Some things about the relationship between alcohol and cancer risk are crystal clear. “There’s no question that alcohol is a group 1 carcinogen,” Rebbeck said. “Alcohol can cause cancer.”
Groups including the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and American Cancer Society agree that alcohol use is an established cause of seven types of cancer: Those of the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, esophagus (squamous cell carcinoma), liver (hepatocellular carcinoma), breast, and colon/rectum. Heavy drinking — at least 8 standard drinks a week for women and 15 for men — and binge drinking — 4 or more drinks in 2 hours for women and 5 or more for men — only amplify that risk. (A “standard” drink has 14 g of alcohol, which translates to a 5-oz glass of wine.)
“We’re most concerned about high-risk drinking — more than 2 drinks a day — and/or binge drinking,” said Noelle LoConte, MD, of the Division of Hematology, Medical Oncology and Palliative Care, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, who authored a 2018 statement on alcohol and cancer risk from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Compared with not drinking, heavy drinking is linked with a roughly fivefold increase in the risk for oral cavity, pharyngeal, and esophageal cancers, and a 61% increase in the risk for breast cancer, according to LoConte and colleagues.
Things get murkier when it comes to moderate drinking — defined as up to 1 standard drink per day for women and 2 per day for men. There is evidence, LoConte said, that moderate drinking is associated with increased cancer risks, though the magnitude is generally much less than heavier drinking.
Cancer type also matters. One analysis found that the risk for breast cancer increased with even light to moderate alcohol consumption. Compared with no drinking, light to moderate drinking has also been linked to increased risks for oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, and esophageal cancers.
As for whether the type of alcoholic beverage matters, LoConte said, there’s no clear physiological reason that wine would be less risky than beer or liquor. Research indicates that ethanol is the problematic ingredient: Once ingested, it’s metabolized into acetaldehyde, a DNA-damaging substance that’s considered a probable human carcinogen. Ethanol can also alter circulating levels of estrogens and androgens, LoConte said, which is thought to drive its association with breast cancer risk.
“It likely doesn’t matter how you choose to get your ethanol,” she said. “It’s a question of volume.”
Hints That Wine Is an Outlier
Still, some studies suggest that how people ingest ethanol could make a difference.
A study published in August in JAMA Network Open is a case in point. The study found that, among older adults, light to heavy drinkers had an increased risk of dying from cancer, compared with occasional drinkers (though the increased risk among light to moderate drinkers occurred only among people who also had chronic health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, or were of lower socioeconomic status).
Wine drinkers fared differently. Most notably, drinkers who “preferred” wine — consuming over 80% of total ethanol from wine — or those who drank only with meals showed a small reduction in their risk for cancer mortality and all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.94 for both). The small protective association was somewhat stronger among people who reported both patterns (HR, 0.88), especially if they were of lower socioeconomic status (HR, 0.79).
The findings are in line with other research suggesting that wine drinkers may be outliers when it comes to cancer risk. A 2023 meta-analysis of 26 observational studies, for instance, found no association between wine consumption and any cancer type, with the caveat that there was «substantial» heterogeneity among the studies.
This heterogeneity caveat speaks to the inherent limitations of observational research, said Tim Stockwell, PhD, of the Canadian Institute for Substance Use Research, University of Victoria in British Columbia, Canada.
“Individual studies of alcohol and cancer risk do find differences by type of drink, or patterns of drinking,” Stockwell said. “But it’s so hard to unpack the confounding that goes along with the type of person who’s a wine drinker or a beer drinker or a spirit drinker. The beverage of choice seems to come with a lot of baggage.”
Compared with people who favor beer or liquor, he noted, wine aficionados are typically higher-income, exercise more often, smoke less, and have different diets, for example. The “best” studies, Rebbeck said, try to adjust for those differences, but it’s challenging.
The authors of the 2023 meta-analysis noted that “many components in wine could have anticarcinogenic effects” that theoretically could counter the ill effects of ethanol. Besides resveratrol, which is mainly found in red wine, the list includes anthocyanins, quercetin, and tannins. However, the authors also acknowledged that they couldn’t account for whether other lifestyle habits might explain why wine drinkers, overall, showed no increased cancer risks and sometimes lower risks.
Still, groups such as the IARC and ASCO hold that there is no known “safe” level, or type, of alcohol when it comes to cancer.
In the latest Canadian guidelines on alcohol use, the scientific panel calculated that people who have 6 drinks a week throughout adulthood (whatever the source of the alcohol) could shave 11 weeks from their life expectancy, on average, said Stockwell, who was on the guideline panel. Compare that with heavy drinking, where 4 drinks a day could rob the average person of 2 or 3 years. “If you’re drinking a lot, you could get huge benefits from cutting down,” Stockwell explained. “If you’re a moderate drinker, the benefits would obviously be less.”
Stockwell said that choices around drinking and breast cancer risk, specifically, can be “tough.” Unlike many of the other alcohol-associated cancers, he noted, breast cancer is common — so even small relative risk increases may be concerning. Based on a 2020 meta-analysis of 22 cohort studies, the risk for breast cancer rises by about 10%, on average, for every 10 g of alcohol a woman drinks per day. This study also found no evidence that wine is any different from other types of alcohol.
In real life, the calculus around wine consumption and cancer risk will probably vary widely from person to person, Rebbeck said. One woman with a family history of breast cancer might decide that having wine with dinner isn’t worth it. Another with the same family history might see that glass of wine as a stress reliever and opt to focus on other ways to reduce her breast cancer risk — by exercising and maintaining a healthy weight, for example.
“The bottom line is, in human studies, the data on light to moderate drinking and cancer are limited and messy, and you can’t draw firm conclusions from them,” Rebbeck said. “It probably raises risk in some people, but we don’t know who those people are. And the risk increases are relatively small.”
A Conversation Few Are Having
Even with many studies highlighting the connection between alcohol consumption and cancer risk, most people remain unaware about this risk.
A 2023 study by the National Cancer Institute found that only a minority of US adults knew that drinking alcohol is linked to increased cancer risk, and they were much less likely to say that was true of wine: Only 20% did, vs 31% who said that liquor can boost cancer risk. Meanwhile, 10% believed that wine helps prevent cancer. Other studies show that even among cancer survivors and patients undergoing active cancer treatment, many drink — often heavily.
“What we know right now is, physicians almost never talk about this,” LoConte said.
That could be due to time constraints, according to Rebbeck, or clinicians’ perceptions that the subject is too complicated and/or their own confusion about the data. There could also be some “cognitive dissonance” at play, LoConte noted, because many doctors drink alcohol.
It’s critical, she said, that conversations about drinking habits become “normalized,” and that should include informing patients that alcohol use is associated with certain cancers. Again, LoConte said, it’s high-risk drinking that’s most concerning and where reducing intake could have the biggest impact on cancer risk and other health outcomes.
“From a cancer prevention standpoint, it’s probably best not to drink,” she said. “But people don’t make choices based solely on cancer risk. We don’t want to come out with recommendations saying no one should drink. I don’t think the data support that, and people would buck against that advice.”
Rebbeck made a similar point. Even if there’s uncertainty about the risks for a daily glass of wine, he said, people can use that information to make decisions. “Everybody’s preferences and choices are going to be different,” Rebbeck said. “And that’s all we can really do.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Earlier this month, US surgeon general Vivek Murthy, MD, issued an advisory, calling for alcoholic beverages to carry a warning label about cancer risk. The advisory flagged alcohol as the third leading preventable cause of cancer in the United States, after tobacco and obesity, and highlighted people’s limited awareness about the relationship between alcohol and cancer risk.
But, when it comes to cancer risk, are all types of alcohol created equal?
For many years, red wine seemed to be an outlier, with studies indicating that, in moderation, it might even be good for you. Red wine has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties — most notably, it contains the antioxidant resveratrol. Starting in the 1990s, research began to hint that the compound might protect against heart disease, aging, and cancer, though much of this work was done in animals or test tubes.
The idea that red wine carries health benefits, however, has been called into question more recently. A recent meta-analysis, for instance, suggests that many previous studies touting the health benefits of more moderate drinking were likely biased, potentially leading to “misleading positive health associations.” And one recent study found that alcohol consumption, largely red wine and beer, at all levels was linked to an increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
Although wine’s health halo is dwindling, there might be an exception: Cancer risk.
Overall, research shows that even light to moderate drinking increases the risk for at least seven types of cancer, but when focusing on red wine, in particular, that risk calculus can look different.
“It’s very complicated and nuanced,” said Timothy Rebbeck, PhD, professor of cancer prevention, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston. “And ‘complicated and nuanced’ doesn’t work very well in public health messages.”
The Knowns About Alcohol and Cancer Risk
Some things about the relationship between alcohol and cancer risk are crystal clear. “There’s no question that alcohol is a group 1 carcinogen,” Rebbeck said. “Alcohol can cause cancer.”
Groups including the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and American Cancer Society agree that alcohol use is an established cause of seven types of cancer: Those of the oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, esophagus (squamous cell carcinoma), liver (hepatocellular carcinoma), breast, and colon/rectum. Heavy drinking — at least 8 standard drinks a week for women and 15 for men — and binge drinking — 4 or more drinks in 2 hours for women and 5 or more for men — only amplify that risk. (A “standard” drink has 14 g of alcohol, which translates to a 5-oz glass of wine.)
“We’re most concerned about high-risk drinking — more than 2 drinks a day — and/or binge drinking,” said Noelle LoConte, MD, of the Division of Hematology, Medical Oncology and Palliative Care, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, who authored a 2018 statement on alcohol and cancer risk from the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Compared with not drinking, heavy drinking is linked with a roughly fivefold increase in the risk for oral cavity, pharyngeal, and esophageal cancers, and a 61% increase in the risk for breast cancer, according to LoConte and colleagues.
Things get murkier when it comes to moderate drinking — defined as up to 1 standard drink per day for women and 2 per day for men. There is evidence, LoConte said, that moderate drinking is associated with increased cancer risks, though the magnitude is generally much less than heavier drinking.
Cancer type also matters. One analysis found that the risk for breast cancer increased with even light to moderate alcohol consumption. Compared with no drinking, light to moderate drinking has also been linked to increased risks for oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, and esophageal cancers.
As for whether the type of alcoholic beverage matters, LoConte said, there’s no clear physiological reason that wine would be less risky than beer or liquor. Research indicates that ethanol is the problematic ingredient: Once ingested, it’s metabolized into acetaldehyde, a DNA-damaging substance that’s considered a probable human carcinogen. Ethanol can also alter circulating levels of estrogens and androgens, LoConte said, which is thought to drive its association with breast cancer risk.
“It likely doesn’t matter how you choose to get your ethanol,” she said. “It’s a question of volume.”
Hints That Wine Is an Outlier
Still, some studies suggest that how people ingest ethanol could make a difference.
A study published in August in JAMA Network Open is a case in point. The study found that, among older adults, light to heavy drinkers had an increased risk of dying from cancer, compared with occasional drinkers (though the increased risk among light to moderate drinkers occurred only among people who also had chronic health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, or were of lower socioeconomic status).
Wine drinkers fared differently. Most notably, drinkers who “preferred” wine — consuming over 80% of total ethanol from wine — or those who drank only with meals showed a small reduction in their risk for cancer mortality and all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 0.94 for both). The small protective association was somewhat stronger among people who reported both patterns (HR, 0.88), especially if they were of lower socioeconomic status (HR, 0.79).
The findings are in line with other research suggesting that wine drinkers may be outliers when it comes to cancer risk. A 2023 meta-analysis of 26 observational studies, for instance, found no association between wine consumption and any cancer type, with the caveat that there was «substantial» heterogeneity among the studies.
This heterogeneity caveat speaks to the inherent limitations of observational research, said Tim Stockwell, PhD, of the Canadian Institute for Substance Use Research, University of Victoria in British Columbia, Canada.
“Individual studies of alcohol and cancer risk do find differences by type of drink, or patterns of drinking,” Stockwell said. “But it’s so hard to unpack the confounding that goes along with the type of person who’s a wine drinker or a beer drinker or a spirit drinker. The beverage of choice seems to come with a lot of baggage.”
Compared with people who favor beer or liquor, he noted, wine aficionados are typically higher-income, exercise more often, smoke less, and have different diets, for example. The “best” studies, Rebbeck said, try to adjust for those differences, but it’s challenging.
The authors of the 2023 meta-analysis noted that “many components in wine could have anticarcinogenic effects” that theoretically could counter the ill effects of ethanol. Besides resveratrol, which is mainly found in red wine, the list includes anthocyanins, quercetin, and tannins. However, the authors also acknowledged that they couldn’t account for whether other lifestyle habits might explain why wine drinkers, overall, showed no increased cancer risks and sometimes lower risks.
Still, groups such as the IARC and ASCO hold that there is no known “safe” level, or type, of alcohol when it comes to cancer.
In the latest Canadian guidelines on alcohol use, the scientific panel calculated that people who have 6 drinks a week throughout adulthood (whatever the source of the alcohol) could shave 11 weeks from their life expectancy, on average, said Stockwell, who was on the guideline panel. Compare that with heavy drinking, where 4 drinks a day could rob the average person of 2 or 3 years. “If you’re drinking a lot, you could get huge benefits from cutting down,” Stockwell explained. “If you’re a moderate drinker, the benefits would obviously be less.”
Stockwell said that choices around drinking and breast cancer risk, specifically, can be “tough.” Unlike many of the other alcohol-associated cancers, he noted, breast cancer is common — so even small relative risk increases may be concerning. Based on a 2020 meta-analysis of 22 cohort studies, the risk for breast cancer rises by about 10%, on average, for every 10 g of alcohol a woman drinks per day. This study also found no evidence that wine is any different from other types of alcohol.
In real life, the calculus around wine consumption and cancer risk will probably vary widely from person to person, Rebbeck said. One woman with a family history of breast cancer might decide that having wine with dinner isn’t worth it. Another with the same family history might see that glass of wine as a stress reliever and opt to focus on other ways to reduce her breast cancer risk — by exercising and maintaining a healthy weight, for example.
“The bottom line is, in human studies, the data on light to moderate drinking and cancer are limited and messy, and you can’t draw firm conclusions from them,” Rebbeck said. “It probably raises risk in some people, but we don’t know who those people are. And the risk increases are relatively small.”
A Conversation Few Are Having
Even with many studies highlighting the connection between alcohol consumption and cancer risk, most people remain unaware about this risk.
A 2023 study by the National Cancer Institute found that only a minority of US adults knew that drinking alcohol is linked to increased cancer risk, and they were much less likely to say that was true of wine: Only 20% did, vs 31% who said that liquor can boost cancer risk. Meanwhile, 10% believed that wine helps prevent cancer. Other studies show that even among cancer survivors and patients undergoing active cancer treatment, many drink — often heavily.
“What we know right now is, physicians almost never talk about this,” LoConte said.
That could be due to time constraints, according to Rebbeck, or clinicians’ perceptions that the subject is too complicated and/or their own confusion about the data. There could also be some “cognitive dissonance” at play, LoConte noted, because many doctors drink alcohol.
It’s critical, she said, that conversations about drinking habits become “normalized,” and that should include informing patients that alcohol use is associated with certain cancers. Again, LoConte said, it’s high-risk drinking that’s most concerning and where reducing intake could have the biggest impact on cancer risk and other health outcomes.
“From a cancer prevention standpoint, it’s probably best not to drink,” she said. “But people don’t make choices based solely on cancer risk. We don’t want to come out with recommendations saying no one should drink. I don’t think the data support that, and people would buck against that advice.”
Rebbeck made a similar point. Even if there’s uncertainty about the risks for a daily glass of wine, he said, people can use that information to make decisions. “Everybody’s preferences and choices are going to be different,” Rebbeck said. “And that’s all we can really do.”
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nutrition, Drugs, or Bariatric Surgery: What’s the Best Approach for Sustained Weight Loss?
Given that more than 100 million US adults have obesity, including 22 million with severe obesity, physicians regularly see patients with the condition in their practices.
Fortunately, doctors have more tools than ever to help their patients. But the question remains: Which method is the safest and most effective? Is it diet and lifestyle changes, one of the recently approved anti-obesity medications (AOMs), bariatric surgery, or a combination approach?
There are no head-to-head trials comparing these three approaches, said Vanita Rahman, MD, clinic director of the Barnard Medical Center, Washington, DC, at the International Conference on Nutrition in Medicine, sponsored by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
Instead, doctors must evaluate the merits and drawbacks of each intervention and decide with their patients which treatment is best for them, she told Medscape Medical News. When she sees patients, Rahman shares the pertinent research with them, so they are able to make an informed choice.
Looking at the Options
In her presentation at the conference, Rahman summarized the guidelines issued by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/The Obesity Society for Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines For Medical Care of Patients with Obesity, including lifestyle changes, AOMs, and bariatric surgery (Table 1).
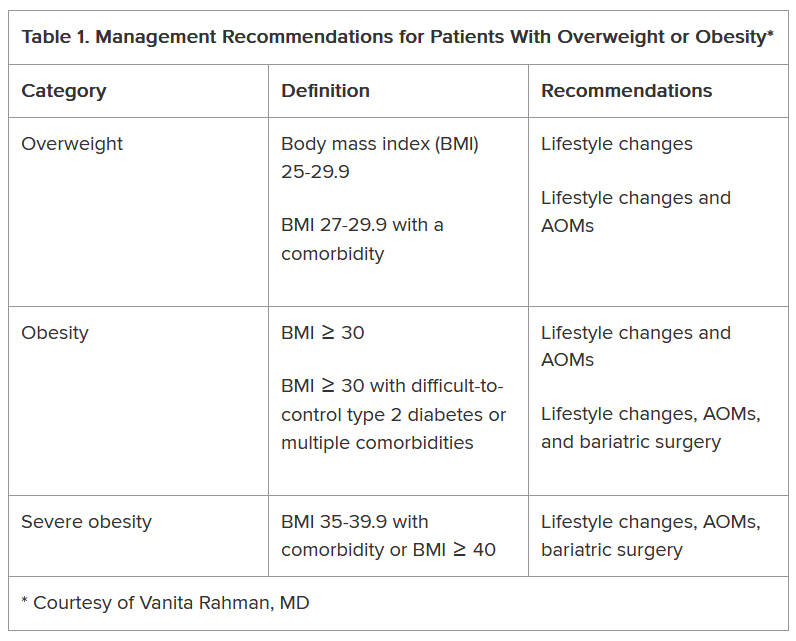
As shown, the current clinical guidelines offer recommendations that consider such factors as the patient’s BMI and presence of one or more comorbidities. Generally, they begin with lifestyle changes for people with overweight, the possibility of an AOM for those with obesity, and bariatric surgery as an option for those with severe obesity-related complications.
“In obesity, we traditionally thought the process was ‘either-or’ — either lifestyle or surgery or medication — and somehow lifestyle is better,” Sheethal Reddy, PhD, a psychologist at the Bariatric Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta, told Medscape Medical News.
Now physicians often use a combination of methods, but lifestyle is foundational to all of them, she said.
“If you don’t make lifestyle changes, none of the approaches will ultimately be effective,” said Reddy, who also is an assistant professor in the Division of General and GI Surgery at Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta.
Lifestyle changes don’t just involve diet and nutrition but include physical exercise.
“Being sedentary affects everything — sleep quality, appetite regulation, and metabolism. Without sufficient exercise, the body isn’t functioning well enough to have a healthy metabolism,” Reddy said.
How Durable Are the Interventions?
Although bariatric surgery has demonstrated effectiveness in helping patients lose weight, many of them regain some or most of it, Rahman said.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found weight regain in 49% of patients who underwent bariatric surgery patients, with the highest prevalence after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Another study of approximately 45,000 patients who underwent bariatric surgery found differences not only in the percentage of total weight loss among Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric band procedures but also in how much of that weight stayed off between 1 and 5 years following the procedure (Table 2).
Weight regain also is a risk with AOMs, if they’re discontinued.
The STEP 1 trial tested the effectiveness of semaglutide — a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist — as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention for weight loss in patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity but not diabetes. Mean weight loss with semaglutide was 17.3% but that figure dropped 11.6 percentage points after treatment was discontinued.
Other studies also have found that patients regain weight after GLP-1 discontinuation.
Tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combination, has shown efficacy with weight reduction, but patients experienced some weight regain upon discontinuation. In one study, patients experienced a mean weight loss of 20.9% after 36 weeks of tirzepatide. In the study’s subsequent 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period, patients who stopped taking the medication experienced a weight regain of 14%, whereas those who remained on the medication lost an additional 5.5% of weight.
GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications do not address the factors that contribute to overweight and obesity, Rahman said. “They simply suppress the appetite; therefore, weight gain occurs after stopping them.”
Patients may stop taking anti-obesity drugs for a variety of reasons, including side effects. Rahman noted that the common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and constipation, whereas rare side effects include gastroparesis, gallbladder and biliary disease, thyroid cancer, and suicidal thoughts. GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications also carry a risk for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, she said.
Moreover, health insurance does not always cover these medications, which likely affects patient access to the drugs and compliance rates.
“Given the side effects and frequent lack of insurance coverage, significant questions remain about long-term safety and feasibility of these agents,” Rahman said.
What About Nutritional Approaches?
The lifestyle interventions in the semaglutide and tirzepatide studies included 500 kcal/d deficit diets, which is difficult for people to maintain, noted Rahman, who is the author of the book Simply Plant Based: Fabulous Food for a Healthy Life.
Additionally, bariatric surgery has been associated with long-term micronutrient deficiencies, including deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, K, B1, and B12, as well as folate, iron, zinc, copper, selenium, and calcium, she said.
The best approach to food from a patient compliance standpoint and to avoid nutrient deficiencies is a whole-food, plant-based diet, Rahman said. She advocates this nutritional approach, along with physical activity, for patients regardless of whether they’ve selected lifestyle intervention alone or combined with an AOM or bariatric surgery to address obesity.
Rahman cited a 5-year heart disease study comparing an intensive lifestyle program involving a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management training, smoking cessation, and group psychosocial support to treatment as usual. Patients in the lifestyle group lost 10.9 kg at 1 year and sustained weight loss of 5.8 kg at 5 years, whereas weight in the control group remained relatively unchanged from baseline.
She also pointed to the findings of a study of patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity that compared standard care with a low-fat, whole-food, plant-based diet with vitamin B12 supplementation. At 6 months, mean BMI reduction was greater in the intervention group than the standard care group (−4.4 vs −0.4).
In her practice, Rahman has seen the benefits of a whole-food, plant-based diet for patients with obesity.
If people are committed to this type of dietary approach and are given the tools and resources to do it effectively, “their thinking changes, their taste buds change, and they grow to enjoy this new way of eating,” she said. “They see results, and it’s a lifestyle that can be sustained long-term.”
Addressing Drivers of Weight Gain
Patients also need help addressing the various factors that may contribute to overweight and obesity, including overconsumption of ultra-processed foods, substandard nutritional quality of restaurant foods, increasing portion sizes, distraction during eating, emotional eating, late-night eating, and cultural/traditional values surrounding food, Rahman noted.
Supatra Tovar, PsyD, RD, a clinical psychologist with a practice in Pasadena, California, agreed that identifying the reasons for weight gain is critical for treatment.
“If you’re not addressing underlying issues, such as a person’s relationship with food, behaviors around food, the tendency to mindlessly eat or emotionally eat or eat to seek comfort, the person’s weight problems won’t ultimately be fully solved by any of the three approaches — dieting, medications, or bariatric surgery,” she said.
Some of her patients “engage in extreme dieting and deprivation, and many who use medications or have had bariatric surgery hardly eat and often develop nutritional deficiencies,” said Tovar, author of the book Deprogram Diet Culture: Rethink Your Relationship with Food, Heal Your Mind, and Live a Diet-Free Life.
The key to healthy and sustained weight loss is to “become attuned to the body’s signals, learn how to honor hunger, stop eating when satisfied, and eat more healthful foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins — especially plant-based proteins — and the body gives signals that this is what it wants,” she said.
Tovar doesn’t give her clients a specific diet or set of portions.
“I teach them to listen to their bodies,” she said. “They’ve lost significant amounts of weight and continued to keep it off because they’ve done this kind of work.”
When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough
For many patients, lifestyle interventions are insufficient to address the degree of overweight and obesity and common comorbidities, said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, associate director and professor, Department of Nutrition Sciences, School of Health Professions, University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Of course, nutritional approaches are very important, not only for weight but also for general health-related reasons,” said Garvey, lead author of the 2016 American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists obesity guidelines. “We’ve seen that the Mediterranean and some plant-based diets can prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes and improve other parameters that reflect metabolic health.”
However, it’s “not common that patients can follow these diets, lose weight, and keep it off,” Garvey cautioned. Up to 50% of weight that’s lost through lifestyle changes is typically regained by 1-year follow-up, with almost all remaining lost weight subsequently regained in the majority of individuals because the person “has to fight against pathophysiological process that drive weight regain,” he noted.
Weight-loss medications can address these pathophysiologic processes by “addressing interactions of satiety hormones with feeding centers in the brain, suppressing the appetite, and making it easier for patients to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.”
Garvey views the weight-loss medications in the same light as drugs for diabetes and hypertension, in that people need to keep taking them to sustain the benefit.
There’s still a role for bariatric surgery because not everyone can tolerate the AOMs or achieve sufficient weight loss.
“Patients with very high BMI who have trouble ambulating might benefit from a combination of bariatric surgery and medication,” Garvey said.
While some side effects are associated with AOMs, being an “alarmist” about them can be detrimental to patients, he warned.
Rahman and Tovar are authors of books about weight loss. Reddy reported no relevant financial relationships. Garvey is a consultant on advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Fractyl Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inogen, Zealand, Allurion, Carmot/Roche, Terns Pharmaceuticals, Neurocrine, Keros Therapeutics, and Regeneron. He is the site principal investigator for multi-centered clinical trials sponsored by his university and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, Neurovalens, and Pfizer. He serves as a consultant on the advisory board for the nonprofit Milken Foundation and is a member of the Data Monitoring Committee for phase 3 clinical trials conducted by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Given that more than 100 million US adults have obesity, including 22 million with severe obesity, physicians regularly see patients with the condition in their practices.
Fortunately, doctors have more tools than ever to help their patients. But the question remains: Which method is the safest and most effective? Is it diet and lifestyle changes, one of the recently approved anti-obesity medications (AOMs), bariatric surgery, or a combination approach?
There are no head-to-head trials comparing these three approaches, said Vanita Rahman, MD, clinic director of the Barnard Medical Center, Washington, DC, at the International Conference on Nutrition in Medicine, sponsored by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
Instead, doctors must evaluate the merits and drawbacks of each intervention and decide with their patients which treatment is best for them, she told Medscape Medical News. When she sees patients, Rahman shares the pertinent research with them, so they are able to make an informed choice.
Looking at the Options
In her presentation at the conference, Rahman summarized the guidelines issued by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/The Obesity Society for Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines For Medical Care of Patients with Obesity, including lifestyle changes, AOMs, and bariatric surgery (Table 1).

As shown, the current clinical guidelines offer recommendations that consider such factors as the patient’s BMI and presence of one or more comorbidities. Generally, they begin with lifestyle changes for people with overweight, the possibility of an AOM for those with obesity, and bariatric surgery as an option for those with severe obesity-related complications.
“In obesity, we traditionally thought the process was ‘either-or’ — either lifestyle or surgery or medication — and somehow lifestyle is better,” Sheethal Reddy, PhD, a psychologist at the Bariatric Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta, told Medscape Medical News.
Now physicians often use a combination of methods, but lifestyle is foundational to all of them, she said.
“If you don’t make lifestyle changes, none of the approaches will ultimately be effective,” said Reddy, who also is an assistant professor in the Division of General and GI Surgery at Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta.
Lifestyle changes don’t just involve diet and nutrition but include physical exercise.
“Being sedentary affects everything — sleep quality, appetite regulation, and metabolism. Without sufficient exercise, the body isn’t functioning well enough to have a healthy metabolism,” Reddy said.
How Durable Are the Interventions?
Although bariatric surgery has demonstrated effectiveness in helping patients lose weight, many of them regain some or most of it, Rahman said.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found weight regain in 49% of patients who underwent bariatric surgery patients, with the highest prevalence after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Another study of approximately 45,000 patients who underwent bariatric surgery found differences not only in the percentage of total weight loss among Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric band procedures but also in how much of that weight stayed off between 1 and 5 years following the procedure (Table 2).

Weight regain also is a risk with AOMs, if they’re discontinued.
The STEP 1 trial tested the effectiveness of semaglutide — a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist — as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention for weight loss in patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity but not diabetes. Mean weight loss with semaglutide was 17.3% but that figure dropped 11.6 percentage points after treatment was discontinued.
Other studies also have found that patients regain weight after GLP-1 discontinuation.
Tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combination, has shown efficacy with weight reduction, but patients experienced some weight regain upon discontinuation. In one study, patients experienced a mean weight loss of 20.9% after 36 weeks of tirzepatide. In the study’s subsequent 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period, patients who stopped taking the medication experienced a weight regain of 14%, whereas those who remained on the medication lost an additional 5.5% of weight.
GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications do not address the factors that contribute to overweight and obesity, Rahman said. “They simply suppress the appetite; therefore, weight gain occurs after stopping them.”
Patients may stop taking anti-obesity drugs for a variety of reasons, including side effects. Rahman noted that the common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and constipation, whereas rare side effects include gastroparesis, gallbladder and biliary disease, thyroid cancer, and suicidal thoughts. GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications also carry a risk for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, she said.
Moreover, health insurance does not always cover these medications, which likely affects patient access to the drugs and compliance rates.
“Given the side effects and frequent lack of insurance coverage, significant questions remain about long-term safety and feasibility of these agents,” Rahman said.
What About Nutritional Approaches?
The lifestyle interventions in the semaglutide and tirzepatide studies included 500 kcal/d deficit diets, which is difficult for people to maintain, noted Rahman, who is the author of the book Simply Plant Based: Fabulous Food for a Healthy Life.
Additionally, bariatric surgery has been associated with long-term micronutrient deficiencies, including deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, K, B1, and B12, as well as folate, iron, zinc, copper, selenium, and calcium, she said.
The best approach to food from a patient compliance standpoint and to avoid nutrient deficiencies is a whole-food, plant-based diet, Rahman said. She advocates this nutritional approach, along with physical activity, for patients regardless of whether they’ve selected lifestyle intervention alone or combined with an AOM or bariatric surgery to address obesity.
Rahman cited a 5-year heart disease study comparing an intensive lifestyle program involving a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management training, smoking cessation, and group psychosocial support to treatment as usual. Patients in the lifestyle group lost 10.9 kg at 1 year and sustained weight loss of 5.8 kg at 5 years, whereas weight in the control group remained relatively unchanged from baseline.
She also pointed to the findings of a study of patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity that compared standard care with a low-fat, whole-food, plant-based diet with vitamin B12 supplementation. At 6 months, mean BMI reduction was greater in the intervention group than the standard care group (−4.4 vs −0.4).
In her practice, Rahman has seen the benefits of a whole-food, plant-based diet for patients with obesity.
If people are committed to this type of dietary approach and are given the tools and resources to do it effectively, “their thinking changes, their taste buds change, and they grow to enjoy this new way of eating,” she said. “They see results, and it’s a lifestyle that can be sustained long-term.”
Addressing Drivers of Weight Gain
Patients also need help addressing the various factors that may contribute to overweight and obesity, including overconsumption of ultra-processed foods, substandard nutritional quality of restaurant foods, increasing portion sizes, distraction during eating, emotional eating, late-night eating, and cultural/traditional values surrounding food, Rahman noted.
Supatra Tovar, PsyD, RD, a clinical psychologist with a practice in Pasadena, California, agreed that identifying the reasons for weight gain is critical for treatment.
“If you’re not addressing underlying issues, such as a person’s relationship with food, behaviors around food, the tendency to mindlessly eat or emotionally eat or eat to seek comfort, the person’s weight problems won’t ultimately be fully solved by any of the three approaches — dieting, medications, or bariatric surgery,” she said.
Some of her patients “engage in extreme dieting and deprivation, and many who use medications or have had bariatric surgery hardly eat and often develop nutritional deficiencies,” said Tovar, author of the book Deprogram Diet Culture: Rethink Your Relationship with Food, Heal Your Mind, and Live a Diet-Free Life.
The key to healthy and sustained weight loss is to “become attuned to the body’s signals, learn how to honor hunger, stop eating when satisfied, and eat more healthful foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins — especially plant-based proteins — and the body gives signals that this is what it wants,” she said.
Tovar doesn’t give her clients a specific diet or set of portions.
“I teach them to listen to their bodies,” she said. “They’ve lost significant amounts of weight and continued to keep it off because they’ve done this kind of work.”
When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough
For many patients, lifestyle interventions are insufficient to address the degree of overweight and obesity and common comorbidities, said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, associate director and professor, Department of Nutrition Sciences, School of Health Professions, University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Of course, nutritional approaches are very important, not only for weight but also for general health-related reasons,” said Garvey, lead author of the 2016 American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists obesity guidelines. “We’ve seen that the Mediterranean and some plant-based diets can prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes and improve other parameters that reflect metabolic health.”
However, it’s “not common that patients can follow these diets, lose weight, and keep it off,” Garvey cautioned. Up to 50% of weight that’s lost through lifestyle changes is typically regained by 1-year follow-up, with almost all remaining lost weight subsequently regained in the majority of individuals because the person “has to fight against pathophysiological process that drive weight regain,” he noted.
Weight-loss medications can address these pathophysiologic processes by “addressing interactions of satiety hormones with feeding centers in the brain, suppressing the appetite, and making it easier for patients to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.”
Garvey views the weight-loss medications in the same light as drugs for diabetes and hypertension, in that people need to keep taking them to sustain the benefit.
There’s still a role for bariatric surgery because not everyone can tolerate the AOMs or achieve sufficient weight loss.
“Patients with very high BMI who have trouble ambulating might benefit from a combination of bariatric surgery and medication,” Garvey said.
While some side effects are associated with AOMs, being an “alarmist” about them can be detrimental to patients, he warned.
Rahman and Tovar are authors of books about weight loss. Reddy reported no relevant financial relationships. Garvey is a consultant on advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Fractyl Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inogen, Zealand, Allurion, Carmot/Roche, Terns Pharmaceuticals, Neurocrine, Keros Therapeutics, and Regeneron. He is the site principal investigator for multi-centered clinical trials sponsored by his university and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, Neurovalens, and Pfizer. He serves as a consultant on the advisory board for the nonprofit Milken Foundation and is a member of the Data Monitoring Committee for phase 3 clinical trials conducted by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Given that more than 100 million US adults have obesity, including 22 million with severe obesity, physicians regularly see patients with the condition in their practices.
Fortunately, doctors have more tools than ever to help their patients. But the question remains: Which method is the safest and most effective? Is it diet and lifestyle changes, one of the recently approved anti-obesity medications (AOMs), bariatric surgery, or a combination approach?
There are no head-to-head trials comparing these three approaches, said Vanita Rahman, MD, clinic director of the Barnard Medical Center, Washington, DC, at the International Conference on Nutrition in Medicine, sponsored by the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine.
Instead, doctors must evaluate the merits and drawbacks of each intervention and decide with their patients which treatment is best for them, she told Medscape Medical News. When she sees patients, Rahman shares the pertinent research with them, so they are able to make an informed choice.
Looking at the Options
In her presentation at the conference, Rahman summarized the guidelines issued by the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/The Obesity Society for Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines For Medical Care of Patients with Obesity, including lifestyle changes, AOMs, and bariatric surgery (Table 1).

As shown, the current clinical guidelines offer recommendations that consider such factors as the patient’s BMI and presence of one or more comorbidities. Generally, they begin with lifestyle changes for people with overweight, the possibility of an AOM for those with obesity, and bariatric surgery as an option for those with severe obesity-related complications.
“In obesity, we traditionally thought the process was ‘either-or’ — either lifestyle or surgery or medication — and somehow lifestyle is better,” Sheethal Reddy, PhD, a psychologist at the Bariatric Center at Emory University Hospital Midtown, Atlanta, told Medscape Medical News.
Now physicians often use a combination of methods, but lifestyle is foundational to all of them, she said.
“If you don’t make lifestyle changes, none of the approaches will ultimately be effective,” said Reddy, who also is an assistant professor in the Division of General and GI Surgery at Emory School of Medicine, Atlanta.
Lifestyle changes don’t just involve diet and nutrition but include physical exercise.
“Being sedentary affects everything — sleep quality, appetite regulation, and metabolism. Without sufficient exercise, the body isn’t functioning well enough to have a healthy metabolism,” Reddy said.
How Durable Are the Interventions?
Although bariatric surgery has demonstrated effectiveness in helping patients lose weight, many of them regain some or most of it, Rahman said.
A systematic review and meta-analysis found weight regain in 49% of patients who underwent bariatric surgery patients, with the highest prevalence after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass.
Another study of approximately 45,000 patients who underwent bariatric surgery found differences not only in the percentage of total weight loss among Roux-en-Y gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, and adjustable gastric band procedures but also in how much of that weight stayed off between 1 and 5 years following the procedure (Table 2).

Weight regain also is a risk with AOMs, if they’re discontinued.
The STEP 1 trial tested the effectiveness of semaglutide — a glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist — as an adjunct to lifestyle intervention for weight loss in patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity but not diabetes. Mean weight loss with semaglutide was 17.3% but that figure dropped 11.6 percentage points after treatment was discontinued.
Other studies also have found that patients regain weight after GLP-1 discontinuation.
Tirzepatide, a GLP-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) combination, has shown efficacy with weight reduction, but patients experienced some weight regain upon discontinuation. In one study, patients experienced a mean weight loss of 20.9% after 36 weeks of tirzepatide. In the study’s subsequent 52-week double-blind, placebo-controlled period, patients who stopped taking the medication experienced a weight regain of 14%, whereas those who remained on the medication lost an additional 5.5% of weight.
GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications do not address the factors that contribute to overweight and obesity, Rahman said. “They simply suppress the appetite; therefore, weight gain occurs after stopping them.”
Patients may stop taking anti-obesity drugs for a variety of reasons, including side effects. Rahman noted that the common side effects include nausea, vomiting, and constipation, whereas rare side effects include gastroparesis, gallbladder and biliary disease, thyroid cancer, and suicidal thoughts. GLP-1 and GLP-1/GIP medications also carry a risk for non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, she said.
Moreover, health insurance does not always cover these medications, which likely affects patient access to the drugs and compliance rates.
“Given the side effects and frequent lack of insurance coverage, significant questions remain about long-term safety and feasibility of these agents,” Rahman said.
What About Nutritional Approaches?
The lifestyle interventions in the semaglutide and tirzepatide studies included 500 kcal/d deficit diets, which is difficult for people to maintain, noted Rahman, who is the author of the book Simply Plant Based: Fabulous Food for a Healthy Life.
Additionally, bariatric surgery has been associated with long-term micronutrient deficiencies, including deficiencies in vitamins A, D, E, K, B1, and B12, as well as folate, iron, zinc, copper, selenium, and calcium, she said.
The best approach to food from a patient compliance standpoint and to avoid nutrient deficiencies is a whole-food, plant-based diet, Rahman said. She advocates this nutritional approach, along with physical activity, for patients regardless of whether they’ve selected lifestyle intervention alone or combined with an AOM or bariatric surgery to address obesity.
Rahman cited a 5-year heart disease study comparing an intensive lifestyle program involving a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management training, smoking cessation, and group psychosocial support to treatment as usual. Patients in the lifestyle group lost 10.9 kg at 1 year and sustained weight loss of 5.8 kg at 5 years, whereas weight in the control group remained relatively unchanged from baseline.
She also pointed to the findings of a study of patients with obesity or with overweight and at least one comorbidity that compared standard care with a low-fat, whole-food, plant-based diet with vitamin B12 supplementation. At 6 months, mean BMI reduction was greater in the intervention group than the standard care group (−4.4 vs −0.4).
In her practice, Rahman has seen the benefits of a whole-food, plant-based diet for patients with obesity.
If people are committed to this type of dietary approach and are given the tools and resources to do it effectively, “their thinking changes, their taste buds change, and they grow to enjoy this new way of eating,” she said. “They see results, and it’s a lifestyle that can be sustained long-term.”
Addressing Drivers of Weight Gain
Patients also need help addressing the various factors that may contribute to overweight and obesity, including overconsumption of ultra-processed foods, substandard nutritional quality of restaurant foods, increasing portion sizes, distraction during eating, emotional eating, late-night eating, and cultural/traditional values surrounding food, Rahman noted.
Supatra Tovar, PsyD, RD, a clinical psychologist with a practice in Pasadena, California, agreed that identifying the reasons for weight gain is critical for treatment.
“If you’re not addressing underlying issues, such as a person’s relationship with food, behaviors around food, the tendency to mindlessly eat or emotionally eat or eat to seek comfort, the person’s weight problems won’t ultimately be fully solved by any of the three approaches — dieting, medications, or bariatric surgery,” she said.
Some of her patients “engage in extreme dieting and deprivation, and many who use medications or have had bariatric surgery hardly eat and often develop nutritional deficiencies,” said Tovar, author of the book Deprogram Diet Culture: Rethink Your Relationship with Food, Heal Your Mind, and Live a Diet-Free Life.
The key to healthy and sustained weight loss is to “become attuned to the body’s signals, learn how to honor hunger, stop eating when satisfied, and eat more healthful foods, such as fruits and vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins — especially plant-based proteins — and the body gives signals that this is what it wants,” she said.
Tovar doesn’t give her clients a specific diet or set of portions.
“I teach them to listen to their bodies,” she said. “They’ve lost significant amounts of weight and continued to keep it off because they’ve done this kind of work.”
When Lifestyle Changes Aren’t Enough
For many patients, lifestyle interventions are insufficient to address the degree of overweight and obesity and common comorbidities, said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, associate director and professor, Department of Nutrition Sciences, School of Health Professions, University of Alabama at Birmingham.
“Of course, nutritional approaches are very important, not only for weight but also for general health-related reasons,” said Garvey, lead author of the 2016 American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists obesity guidelines. “We’ve seen that the Mediterranean and some plant-based diets can prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes and improve other parameters that reflect metabolic health.”
However, it’s “not common that patients can follow these diets, lose weight, and keep it off,” Garvey cautioned. Up to 50% of weight that’s lost through lifestyle changes is typically regained by 1-year follow-up, with almost all remaining lost weight subsequently regained in the majority of individuals because the person “has to fight against pathophysiological process that drive weight regain,” he noted.
Weight-loss medications can address these pathophysiologic processes by “addressing interactions of satiety hormones with feeding centers in the brain, suppressing the appetite, and making it easier for patients to adhere to a reduced-calorie diet.”
Garvey views the weight-loss medications in the same light as drugs for diabetes and hypertension, in that people need to keep taking them to sustain the benefit.
There’s still a role for bariatric surgery because not everyone can tolerate the AOMs or achieve sufficient weight loss.
“Patients with very high BMI who have trouble ambulating might benefit from a combination of bariatric surgery and medication,” Garvey said.
While some side effects are associated with AOMs, being an “alarmist” about them can be detrimental to patients, he warned.
Rahman and Tovar are authors of books about weight loss. Reddy reported no relevant financial relationships. Garvey is a consultant on advisory boards for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Fractyl Health, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inogen, Zealand, Allurion, Carmot/Roche, Terns Pharmaceuticals, Neurocrine, Keros Therapeutics, and Regeneron. He is the site principal investigator for multi-centered clinical trials sponsored by his university and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, Neurovalens, and Pfizer. He serves as a consultant on the advisory board for the nonprofit Milken Foundation and is a member of the Data Monitoring Committee for phase 3 clinical trials conducted by Boehringer-Ingelheim and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientific Publications Face Credibility Crisis
The quality and credibility of scientific publications have received increasing scrutiny. Findings from studies by Maria Ángeles Oviedo-García, PhD, from the Department of Business and Marketing at the University of Seville in Spain, highlight growing concerns about the integrity of published research. Insights from the journal Science and the US blog Retraction Watch reveal similar concerns regarding research integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Spurs Low-Quality Submissions
According to a report in Science, journals are inundated with low-quality contributions such as letters and comments generated by AI. Daniel Prevedello, MD, editor in chief of Neurosurgical Review, announced that the journal would temporarily stop accepting these submissions because of their poor quality.
Neurosurgical Review is not the only journal to experience low-quality submissions. In the journal Oral Oncology Reports (Elsevier), comments comprised 70% of the content, whereas in the International Journal of Surgery Open (Wolters Kluwer), they accounted for nearly half. In Neurosurgical Review, letters, comments, and editorials made up 58% of the total content from January to October 2024, compared with only 9% in the previous year.
This trend benefits authors by allowing them to inflate their publication lists with quickly produced contributions that bypass peer review. Publishers may also profit, as many charge fees to publish comments. Additionally, universities and research institutions find this type of content generation useful as more publications can enhance their reputation.
Concerns Over Peer Reviews
The troubling behavior described by Oviedo-García in the journal Scientometrics raises further doubts. An analysis of 263 peer reviews from 37 journals revealed that reviewers often used identical or very similar phrases in their evaluations, regardless of the content. In one case, the reviewer used the same wording in 52 reviews. This suggests that some reviewers read the studies that they are supposed to evaluate only superficially. Such practices can lead to valueless reviews and jeopardize the integrity of scientific literature. “Some other researchers will probably base their future research on these fake reports, which is frightening, especially when it comes to health and medicine,” Oviedo-García stated.
She suspects that the reviewers may have relied on templates to produce their reports quickly. This allowed them to list this work on their resumes for potential career advantages. Some reviewers have reportedly even “requested” the authors of the studies they reviewed to cite their own scientific work.
AI Complicates Peer Review
The process of research and publication has become increasingly challenging in recent years, and more standard and predatory journals allow anyone to publish their work for a fee. Roger W. Byard, MD, PhD, from the University of Adelaide in Australia, explained this trend in the journal Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology. AI is increasingly being used to generate articles. At international conferences, experts have highlighted claims that AI can complete papers in just a few weeks and dissertations in less than a year. According to the authors of a letter in Critical Care, generative AI is infiltrating the peer review process.
Moreover, the peer review process can be bypassed by publishing research findings on online platforms (eg, preprint servers). Another issue is that some publications have hundreds of authors who can extend their publication list in this manner, even if their contribution to the publication is ambiguous or not substantial.
In a guest article for the Laborjournal, Ulrich Dirnagl, MD, PhD, from the Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany, emphasized that the scientific papers have become so complex that two or three experts often cannot thoroughly assess everything presented. The review process is time-consuming and can take several days for reviewers. Currently, very few people have time, especially because it is an unpaid and anonymous task. Dirnagl stated, “the self-correction of science no longer works as it claims.”
The old Russian saying ‘Dowjerjaj, no prowjerjaj: Trust, but verify’ remains a timeless recommendation that is likely to stay relevant for years to come.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The quality and credibility of scientific publications have received increasing scrutiny. Findings from studies by Maria Ángeles Oviedo-García, PhD, from the Department of Business and Marketing at the University of Seville in Spain, highlight growing concerns about the integrity of published research. Insights from the journal Science and the US blog Retraction Watch reveal similar concerns regarding research integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Spurs Low-Quality Submissions
According to a report in Science, journals are inundated with low-quality contributions such as letters and comments generated by AI. Daniel Prevedello, MD, editor in chief of Neurosurgical Review, announced that the journal would temporarily stop accepting these submissions because of their poor quality.
Neurosurgical Review is not the only journal to experience low-quality submissions. In the journal Oral Oncology Reports (Elsevier), comments comprised 70% of the content, whereas in the International Journal of Surgery Open (Wolters Kluwer), they accounted for nearly half. In Neurosurgical Review, letters, comments, and editorials made up 58% of the total content from January to October 2024, compared with only 9% in the previous year.
This trend benefits authors by allowing them to inflate their publication lists with quickly produced contributions that bypass peer review. Publishers may also profit, as many charge fees to publish comments. Additionally, universities and research institutions find this type of content generation useful as more publications can enhance their reputation.
Concerns Over Peer Reviews
The troubling behavior described by Oviedo-García in the journal Scientometrics raises further doubts. An analysis of 263 peer reviews from 37 journals revealed that reviewers often used identical or very similar phrases in their evaluations, regardless of the content. In one case, the reviewer used the same wording in 52 reviews. This suggests that some reviewers read the studies that they are supposed to evaluate only superficially. Such practices can lead to valueless reviews and jeopardize the integrity of scientific literature. “Some other researchers will probably base their future research on these fake reports, which is frightening, especially when it comes to health and medicine,” Oviedo-García stated.
She suspects that the reviewers may have relied on templates to produce their reports quickly. This allowed them to list this work on their resumes for potential career advantages. Some reviewers have reportedly even “requested” the authors of the studies they reviewed to cite their own scientific work.
AI Complicates Peer Review
The process of research and publication has become increasingly challenging in recent years, and more standard and predatory journals allow anyone to publish their work for a fee. Roger W. Byard, MD, PhD, from the University of Adelaide in Australia, explained this trend in the journal Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology. AI is increasingly being used to generate articles. At international conferences, experts have highlighted claims that AI can complete papers in just a few weeks and dissertations in less than a year. According to the authors of a letter in Critical Care, generative AI is infiltrating the peer review process.
Moreover, the peer review process can be bypassed by publishing research findings on online platforms (eg, preprint servers). Another issue is that some publications have hundreds of authors who can extend their publication list in this manner, even if their contribution to the publication is ambiguous or not substantial.
In a guest article for the Laborjournal, Ulrich Dirnagl, MD, PhD, from the Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany, emphasized that the scientific papers have become so complex that two or three experts often cannot thoroughly assess everything presented. The review process is time-consuming and can take several days for reviewers. Currently, very few people have time, especially because it is an unpaid and anonymous task. Dirnagl stated, “the self-correction of science no longer works as it claims.”
The old Russian saying ‘Dowjerjaj, no prowjerjaj: Trust, but verify’ remains a timeless recommendation that is likely to stay relevant for years to come.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The quality and credibility of scientific publications have received increasing scrutiny. Findings from studies by Maria Ángeles Oviedo-García, PhD, from the Department of Business and Marketing at the University of Seville in Spain, highlight growing concerns about the integrity of published research. Insights from the journal Science and the US blog Retraction Watch reveal similar concerns regarding research integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Spurs Low-Quality Submissions
According to a report in Science, journals are inundated with low-quality contributions such as letters and comments generated by AI. Daniel Prevedello, MD, editor in chief of Neurosurgical Review, announced that the journal would temporarily stop accepting these submissions because of their poor quality.
Neurosurgical Review is not the only journal to experience low-quality submissions. In the journal Oral Oncology Reports (Elsevier), comments comprised 70% of the content, whereas in the International Journal of Surgery Open (Wolters Kluwer), they accounted for nearly half. In Neurosurgical Review, letters, comments, and editorials made up 58% of the total content from January to October 2024, compared with only 9% in the previous year.
This trend benefits authors by allowing them to inflate their publication lists with quickly produced contributions that bypass peer review. Publishers may also profit, as many charge fees to publish comments. Additionally, universities and research institutions find this type of content generation useful as more publications can enhance their reputation.
Concerns Over Peer Reviews
The troubling behavior described by Oviedo-García in the journal Scientometrics raises further doubts. An analysis of 263 peer reviews from 37 journals revealed that reviewers often used identical or very similar phrases in their evaluations, regardless of the content. In one case, the reviewer used the same wording in 52 reviews. This suggests that some reviewers read the studies that they are supposed to evaluate only superficially. Such practices can lead to valueless reviews and jeopardize the integrity of scientific literature. “Some other researchers will probably base their future research on these fake reports, which is frightening, especially when it comes to health and medicine,” Oviedo-García stated.
She suspects that the reviewers may have relied on templates to produce their reports quickly. This allowed them to list this work on their resumes for potential career advantages. Some reviewers have reportedly even “requested” the authors of the studies they reviewed to cite their own scientific work.
AI Complicates Peer Review
The process of research and publication has become increasingly challenging in recent years, and more standard and predatory journals allow anyone to publish their work for a fee. Roger W. Byard, MD, PhD, from the University of Adelaide in Australia, explained this trend in the journal Forensic Science, Medicine and Pathology. AI is increasingly being used to generate articles. At international conferences, experts have highlighted claims that AI can complete papers in just a few weeks and dissertations in less than a year. According to the authors of a letter in Critical Care, generative AI is infiltrating the peer review process.
Moreover, the peer review process can be bypassed by publishing research findings on online platforms (eg, preprint servers). Another issue is that some publications have hundreds of authors who can extend their publication list in this manner, even if their contribution to the publication is ambiguous or not substantial.
In a guest article for the Laborjournal, Ulrich Dirnagl, MD, PhD, from the Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany, emphasized that the scientific papers have become so complex that two or three experts often cannot thoroughly assess everything presented. The review process is time-consuming and can take several days for reviewers. Currently, very few people have time, especially because it is an unpaid and anonymous task. Dirnagl stated, “the self-correction of science no longer works as it claims.”
The old Russian saying ‘Dowjerjaj, no prowjerjaj: Trust, but verify’ remains a timeless recommendation that is likely to stay relevant for years to come.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
MRI-Invisible Prostate Lesions: Are They Dangerous?
MRI-invisible prostate lesions. It sounds like the stuff of science fiction and fantasy, a creation from the minds of H.G. Wells, who wrote The Invisible Man, or J.K. Rowling, who authored the Harry Potter series.
But MRI-invisible prostate lesions are real. And what these lesions may, or may not, indicate is the subject of intense debate.
MRI plays an increasingly important role in detecting and diagnosing prostate cancer, staging prostate cancer as well as monitoring disease progression. However, on occasion, a puzzling phenomenon arises. Certain prostate lesions that appear when pathologists examine biopsied tissue samples under a microscope are not visible on MRI. The prostate tissue will, instead, appear normal to a radiologist’s eye.
Some experts believe these MRI-invisible lesions are nothing to worry about.
If the clinician can’t see the cancer on MRI, then it simply isn’t a threat, according to Mark Emberton, MD, a pioneer in prostate MRIs and director of interventional oncology at University College London, England.
Laurence Klotz, MD, of the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, agreed, noting that “invisible cancers are clinically insignificant and don’t require systematic biopsies.”
Emberton and Klotz compared MRI-invisible lesions to grade group 1 prostate cancer (Gleason score ≤ 6) — the least aggressive category that indicates the cancer that is not likely to spread or kill. For patients on active surveillance, those with MRI-invisible cancers do drastically better than those with visible cancers, Klotz explained.
But other experts in the field are skeptical that MRI-invisible lesions are truly innocuous.
Although statistically an MRI-visible prostate lesion indicates a more aggressive tumor, that is not always the case for every individual, said Brian Helfand, MD, PhD, chief of urology at NorthShore University Health System, Evanston, Illinois.
MRIs can lead to false negatives in about 10%-20% of patients who have clinically significant prostate cancer, though estimates vary.
In one analysis, 16% of men with no suspicious lesions on MRI had clinically significant prostate cancer identified after undergoing a systematic biopsy. Another analysis found that about 35% of MRI-invisible prostate cancers identified via biopsy were clinically significant.
Other studies, however, have indicated that negative MRI results accurately indicate patients at low risk of developing clinically significant cancers. A recent JAMA Oncology analysis, for instance, found that only seven of 233 men (3%) with negative MRI results at baseline who completed 3 years of monitoring were diagnosed with clinically significant prostate cancer.
When a patient has an MRI-invisible prostate tumor, there are a couple of reasons the MRI may not be picking it up, said urologic oncologist Alexander Putnam Cole, MD, assistant professor of surgery, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts. “One is that the cancer is aggressive but just very small,” said Cole.
“Another possibility is that the cancer looks very similar to background prostate tissue, which is something that you might expect if you think about more of a low-grade cancer,” he explained.
The experience level of the radiologist interpreting the MRI can also play into the accuracy of the reading.
But Cole agreed that “in general, MRI visibility is associated with molecular and histologic features of progression and aggressiveness and non-visible cancers are less likely to have aggressive features.”
The genomic profiles of MRI-visible and -invisible cancers bear this out.
According to Todd Morgan, MD, chief of urologic oncology at Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, the gene expression in visible disease tends to be linked to more aggressive prostate tumors whereas gene expression in invisible disease does not.
In one analysis, for instance, researchers found that four genes — PHYHD1, CENPF, ALDH2, and GDF15 — associated with worse progression-free survival and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer also predicted MRI visibility.
“Genes that are associated with visibility are essentially the same genes that are associated with aggressive cancers,” Klotz said.
Next Steps After Negative MRI Result
What do MRI-invisible lesions mean for patient care? If, for instance, a patient has elevated PSA levels but a normal MRI, is a targeted or systematic biopsy warranted?
The overarching message, according to Klotz, is that “you don’t need to find them.” Klotz noted, however, that patients with a negative MRI result should still be followed with periodic repeat imaging.
Several trials support this approach of using MRI to decide who needs a biopsy and delaying a biopsy in men with normal MRIs.
The recent JAMA Oncology analysis found that, among men with negative MRI results, 86% avoided a biopsy over 3 years, with clinically significant prostate cancer detected in only 4% of men across the study period — four in the initial diagnostic phase and seven in the 3-year monitoring phase. However, during the initial diagnostic phase, more than half the men with positive MRI findings had clinically significant prostate cancer detected.
Another recent study found that patients with negative MRI results were much less likely to upgrade to higher Gleason scores over time. Among 522 patients who underwent a systematic and targeted biopsy within 18 months of their grade group 1 designation, 9.2% with negative MRI findings had tumors reclassified as grade group 2 or higher vs 27% with positive MRI findings, and 2.3% with negative MRI findings had tumors reclassified as grade group 3 or higher vs 7.8% with positive MRI findings.
These data suggest that men with grade group 1 cancer and negative MRI result “may be able to avoid confirmatory biopsies until a routine surveillance biopsy in 2-3 years,” according to study author Christian Pavlovich, MD, professor of urologic oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
Cole used MRI findings to triage who gets a biopsy. When a biopsy is warranted, “I usually recommend adding in some systematic sampling of the other side to assess for nonvisible cancers,” he noted.
Sampling prostate tissue outside the target area “adds maybe 1-2 minutes to the procedure and doesn’t drastically increase the morbidity or risks,” Cole said. It also can help “confirm there is cancer in the MRI target and also confirm there is no cancer in the nonvisible areas.”
According to Klotz, if imaging demonstrates progression, patients should receive a biopsy — in most cases, a targeted biopsy only. And, Klotz noted, skipping routine prostate biopsies in men with negative MRI results can save thousands of men from these procedures, which carry risks for infections and sepsis.
Looking beyond Gleason scores for risk prediction, MRI “visibility is a very powerful risk stratifier,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
MRI-invisible prostate lesions. It sounds like the stuff of science fiction and fantasy, a creation from the minds of H.G. Wells, who wrote The Invisible Man, or J.K. Rowling, who authored the Harry Potter series.
But MRI-invisible prostate lesions are real. And what these lesions may, or may not, indicate is the subject of intense debate.
MRI plays an increasingly important role in detecting and diagnosing prostate cancer, staging prostate cancer as well as monitoring disease progression. However, on occasion, a puzzling phenomenon arises. Certain prostate lesions that appear when pathologists examine biopsied tissue samples under a microscope are not visible on MRI. The prostate tissue will, instead, appear normal to a radiologist’s eye.
Some experts believe these MRI-invisible lesions are nothing to worry about.
If the clinician can’t see the cancer on MRI, then it simply isn’t a threat, according to Mark Emberton, MD, a pioneer in prostate MRIs and director of interventional oncology at University College London, England.
Laurence Klotz, MD, of the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, agreed, noting that “invisible cancers are clinically insignificant and don’t require systematic biopsies.”
Emberton and Klotz compared MRI-invisible lesions to grade group 1 prostate cancer (Gleason score ≤ 6) — the least aggressive category that indicates the cancer that is not likely to spread or kill. For patients on active surveillance, those with MRI-invisible cancers do drastically better than those with visible cancers, Klotz explained.
But other experts in the field are skeptical that MRI-invisible lesions are truly innocuous.
Although statistically an MRI-visible prostate lesion indicates a more aggressive tumor, that is not always the case for every individual, said Brian Helfand, MD, PhD, chief of urology at NorthShore University Health System, Evanston, Illinois.
MRIs can lead to false negatives in about 10%-20% of patients who have clinically significant prostate cancer, though estimates vary.
In one analysis, 16% of men with no suspicious lesions on MRI had clinically significant prostate cancer identified after undergoing a systematic biopsy. Another analysis found that about 35% of MRI-invisible prostate cancers identified via biopsy were clinically significant.
Other studies, however, have indicated that negative MRI results accurately indicate patients at low risk of developing clinically significant cancers. A recent JAMA Oncology analysis, for instance, found that only seven of 233 men (3%) with negative MRI results at baseline who completed 3 years of monitoring were diagnosed with clinically significant prostate cancer.
When a patient has an MRI-invisible prostate tumor, there are a couple of reasons the MRI may not be picking it up, said urologic oncologist Alexander Putnam Cole, MD, assistant professor of surgery, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts. “One is that the cancer is aggressive but just very small,” said Cole.
“Another possibility is that the cancer looks very similar to background prostate tissue, which is something that you might expect if you think about more of a low-grade cancer,” he explained.
The experience level of the radiologist interpreting the MRI can also play into the accuracy of the reading.
But Cole agreed that “in general, MRI visibility is associated with molecular and histologic features of progression and aggressiveness and non-visible cancers are less likely to have aggressive features.”
The genomic profiles of MRI-visible and -invisible cancers bear this out.
According to Todd Morgan, MD, chief of urologic oncology at Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, the gene expression in visible disease tends to be linked to more aggressive prostate tumors whereas gene expression in invisible disease does not.
In one analysis, for instance, researchers found that four genes — PHYHD1, CENPF, ALDH2, and GDF15 — associated with worse progression-free survival and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer also predicted MRI visibility.
“Genes that are associated with visibility are essentially the same genes that are associated with aggressive cancers,” Klotz said.
Next Steps After Negative MRI Result
What do MRI-invisible lesions mean for patient care? If, for instance, a patient has elevated PSA levels but a normal MRI, is a targeted or systematic biopsy warranted?
The overarching message, according to Klotz, is that “you don’t need to find them.” Klotz noted, however, that patients with a negative MRI result should still be followed with periodic repeat imaging.
Several trials support this approach of using MRI to decide who needs a biopsy and delaying a biopsy in men with normal MRIs.
The recent JAMA Oncology analysis found that, among men with negative MRI results, 86% avoided a biopsy over 3 years, with clinically significant prostate cancer detected in only 4% of men across the study period — four in the initial diagnostic phase and seven in the 3-year monitoring phase. However, during the initial diagnostic phase, more than half the men with positive MRI findings had clinically significant prostate cancer detected.
Another recent study found that patients with negative MRI results were much less likely to upgrade to higher Gleason scores over time. Among 522 patients who underwent a systematic and targeted biopsy within 18 months of their grade group 1 designation, 9.2% with negative MRI findings had tumors reclassified as grade group 2 or higher vs 27% with positive MRI findings, and 2.3% with negative MRI findings had tumors reclassified as grade group 3 or higher vs 7.8% with positive MRI findings.
These data suggest that men with grade group 1 cancer and negative MRI result “may be able to avoid confirmatory biopsies until a routine surveillance biopsy in 2-3 years,” according to study author Christian Pavlovich, MD, professor of urologic oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
Cole used MRI findings to triage who gets a biopsy. When a biopsy is warranted, “I usually recommend adding in some systematic sampling of the other side to assess for nonvisible cancers,” he noted.
Sampling prostate tissue outside the target area “adds maybe 1-2 minutes to the procedure and doesn’t drastically increase the morbidity or risks,” Cole said. It also can help “confirm there is cancer in the MRI target and also confirm there is no cancer in the nonvisible areas.”
According to Klotz, if imaging demonstrates progression, patients should receive a biopsy — in most cases, a targeted biopsy only. And, Klotz noted, skipping routine prostate biopsies in men with negative MRI results can save thousands of men from these procedures, which carry risks for infections and sepsis.
Looking beyond Gleason scores for risk prediction, MRI “visibility is a very powerful risk stratifier,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
MRI-invisible prostate lesions. It sounds like the stuff of science fiction and fantasy, a creation from the minds of H.G. Wells, who wrote The Invisible Man, or J.K. Rowling, who authored the Harry Potter series.
But MRI-invisible prostate lesions are real. And what these lesions may, or may not, indicate is the subject of intense debate.
MRI plays an increasingly important role in detecting and diagnosing prostate cancer, staging prostate cancer as well as monitoring disease progression. However, on occasion, a puzzling phenomenon arises. Certain prostate lesions that appear when pathologists examine biopsied tissue samples under a microscope are not visible on MRI. The prostate tissue will, instead, appear normal to a radiologist’s eye.
Some experts believe these MRI-invisible lesions are nothing to worry about.
If the clinician can’t see the cancer on MRI, then it simply isn’t a threat, according to Mark Emberton, MD, a pioneer in prostate MRIs and director of interventional oncology at University College London, England.
Laurence Klotz, MD, of the University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada, agreed, noting that “invisible cancers are clinically insignificant and don’t require systematic biopsies.”
Emberton and Klotz compared MRI-invisible lesions to grade group 1 prostate cancer (Gleason score ≤ 6) — the least aggressive category that indicates the cancer that is not likely to spread or kill. For patients on active surveillance, those with MRI-invisible cancers do drastically better than those with visible cancers, Klotz explained.
But other experts in the field are skeptical that MRI-invisible lesions are truly innocuous.
Although statistically an MRI-visible prostate lesion indicates a more aggressive tumor, that is not always the case for every individual, said Brian Helfand, MD, PhD, chief of urology at NorthShore University Health System, Evanston, Illinois.
MRIs can lead to false negatives in about 10%-20% of patients who have clinically significant prostate cancer, though estimates vary.
In one analysis, 16% of men with no suspicious lesions on MRI had clinically significant prostate cancer identified after undergoing a systematic biopsy. Another analysis found that about 35% of MRI-invisible prostate cancers identified via biopsy were clinically significant.
Other studies, however, have indicated that negative MRI results accurately indicate patients at low risk of developing clinically significant cancers. A recent JAMA Oncology analysis, for instance, found that only seven of 233 men (3%) with negative MRI results at baseline who completed 3 years of monitoring were diagnosed with clinically significant prostate cancer.
When a patient has an MRI-invisible prostate tumor, there are a couple of reasons the MRI may not be picking it up, said urologic oncologist Alexander Putnam Cole, MD, assistant professor of surgery, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts. “One is that the cancer is aggressive but just very small,” said Cole.
“Another possibility is that the cancer looks very similar to background prostate tissue, which is something that you might expect if you think about more of a low-grade cancer,” he explained.
The experience level of the radiologist interpreting the MRI can also play into the accuracy of the reading.
But Cole agreed that “in general, MRI visibility is associated with molecular and histologic features of progression and aggressiveness and non-visible cancers are less likely to have aggressive features.”
The genomic profiles of MRI-visible and -invisible cancers bear this out.
According to Todd Morgan, MD, chief of urologic oncology at Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, the gene expression in visible disease tends to be linked to more aggressive prostate tumors whereas gene expression in invisible disease does not.
In one analysis, for instance, researchers found that four genes — PHYHD1, CENPF, ALDH2, and GDF15 — associated with worse progression-free survival and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer also predicted MRI visibility.
“Genes that are associated with visibility are essentially the same genes that are associated with aggressive cancers,” Klotz said.
Next Steps After Negative MRI Result
What do MRI-invisible lesions mean for patient care? If, for instance, a patient has elevated PSA levels but a normal MRI, is a targeted or systematic biopsy warranted?
The overarching message, according to Klotz, is that “you don’t need to find them.” Klotz noted, however, that patients with a negative MRI result should still be followed with periodic repeat imaging.
Several trials support this approach of using MRI to decide who needs a biopsy and delaying a biopsy in men with normal MRIs.
The recent JAMA Oncology analysis found that, among men with negative MRI results, 86% avoided a biopsy over 3 years, with clinically significant prostate cancer detected in only 4% of men across the study period — four in the initial diagnostic phase and seven in the 3-year monitoring phase. However, during the initial diagnostic phase, more than half the men with positive MRI findings had clinically significant prostate cancer detected.
Another recent study found that patients with negative MRI results were much less likely to upgrade to higher Gleason scores over time. Among 522 patients who underwent a systematic and targeted biopsy within 18 months of their grade group 1 designation, 9.2% with negative MRI findings had tumors reclassified as grade group 2 or higher vs 27% with positive MRI findings, and 2.3% with negative MRI findings had tumors reclassified as grade group 3 or higher vs 7.8% with positive MRI findings.
These data suggest that men with grade group 1 cancer and negative MRI result “may be able to avoid confirmatory biopsies until a routine surveillance biopsy in 2-3 years,” according to study author Christian Pavlovich, MD, professor of urologic oncology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
Cole used MRI findings to triage who gets a biopsy. When a biopsy is warranted, “I usually recommend adding in some systematic sampling of the other side to assess for nonvisible cancers,” he noted.
Sampling prostate tissue outside the target area “adds maybe 1-2 minutes to the procedure and doesn’t drastically increase the morbidity or risks,” Cole said. It also can help “confirm there is cancer in the MRI target and also confirm there is no cancer in the nonvisible areas.”
According to Klotz, if imaging demonstrates progression, patients should receive a biopsy — in most cases, a targeted biopsy only. And, Klotz noted, skipping routine prostate biopsies in men with negative MRI results can save thousands of men from these procedures, which carry risks for infections and sepsis.
Looking beyond Gleason scores for risk prediction, MRI “visibility is a very powerful risk stratifier,” he said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Why Aren’t More Primary Care Physicians Prescribing Contraceptives?
In 2024, the Guttmacher Institute reported that eight states enacted or proposed limits on contraceptive access. Currently, more than 19 million women aged 13-44 years in the United States live in “contraceptive deserts” or places that lack access to a full range of birth control methods. About 1.2 million of those women live in counties that don’t have a single health center that has complete birth control services.
Providing contraceptive care in primary care settings has long been deemed a best practice by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). But the percentage of primary care physicians (PCPs) prescribing contraception or offering contraceptive procedures is strikingly low.
Only Half of Family Physicians (FPs) Prescribe Contraceptives
Research by Candice Chen, MD, MPH, and colleagues found that while 73.1% of obstetrician-gynecologists (OB/GYNs) and 72.6% of nurse-midwives prescribed the pill, patch, or vaginal ring; only 51% of FPs, 32.4% of pediatricians, and 19.8% of internal medicine physicians did so. And while 92.8% of OB/GYNs provided intrauterine device (IUD) services, only 16.4% of FPs, 2.6% of internists, and 0.6% of pediatricians did so.
One reason primary care is positioned so well to fill contraception gaps is found in the sheer numbers of PCPs. Chen and colleagues found that while the percentage of FPs prescribing contraception was much smaller (51.4%) than the percentage of OB/GYN prescribers (72.6%), the numbers translate to 72,725 FPs prescribing contraceptives, which is nearly double the number of OB/GYNs prescribing them (36,887).
Access to contraception services took a big hit with the COVID-19 pandemic as did access to healthcare in general. And the 2022 Supreme Court ruling that struck down Roe V. Wade has shaken up the landscape for reproductive services with potential consequences for contraceptive access.
Why Aren’t More PCPs Offering Contraceptive Services?
Reasons for the relatively low numbers of PCPs prescribing contraceptives include lack of training in residency, health systems’ financial choices, insurance barriers, and expectation by some physicians and many patients that birth control belongs in the OB/GYN sector. Access, patient awareness that PCPs can provide the care, expectations, and options vary by states and regions.
Angeline Ti, MD, an FP who teaches in a residency program at Wellstar Douglasville Medical Center in Douglasville, Georgia, told this news organization that the awareness issue might be the easiest change for PCPs as many patients aren’t aware you can get contraceptive services in primary care.
Things PCPs ‘Could Do Tomorrow’
Those physicians who want to add those services might want to start with universal screening, Ti said — having conversations with patients about contraceptive needs and letting them know they don’t have to get those prescriptions from an OB/GYN. The conversations could center on laying out the options and counseling on risks and benefits of various options and providing referrals, if that is the best option. “There are definitely things that you could do tomorrow,” she said.
PCPs should be familiar with the CDC’s Contraceptive Guidance for Health Care Providers and the federal Office of Population Affairs’ Quality Family Planning Recommendations for providers, which offer practice-level information, Ti said.
PCPs should not feel they need to be able to provide same-day contraceptive care to get started. Having nurses and medical assistants and practice managers on board who are passionate about adding the services can also help bring about change with a team approach, she said.
Even when the provider is enthusiastic about providing the care and is trained to do so, however, insurance barriers may exist, Ti acknowledged. For example, at her clinic a common IUD insertion requires prior authorization.
Including Other Providers
Julia Strasser, DrPH, MPH, a member of the core faculty at the Fitzhugh Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity in Washington, DC, told this news organization that including other clinicians could help expand contraceptive services in primary care. Her research showed that the proportion of the contraception workforce that is made up of advanced practice clinicians and nurse practitioners is increasing, whereas the proportion that includes physicians is either static or declining.
A paper by her team found that although OB/GYNs and nurse-midwives were more likely to prescribe the pill, patch, or ring, the largest numbers of contraception prescribers were FPs (72,725) and advanced practice nurses (70,115).
“We also know that pharmacists can safely prescribe contraception, and some states have authorized this practice, but uptake is low and policies vary by state,” she said. “Some health systems have pharmacists embedded in their practice — for example in federally qualified health centers and others.”
It’s important, she said, not to frame the gaps in contraceptive care as a failure on the part of individual clinicians but rather as: “How can we change some of the system-level factors that have gotten us to this point?”
Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, an FP and director of the Robert Graham Center of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said sometimes it’s the health center’s cost analysis that stands in the way. She gave an example from her own health system.
“The health system doesn’t want to pay for us to have the IUDs stored in our offices and provide that procedure because they feel it’s more cost effective if the OB/GYNs do it.” IUD insertions take more appointment time than the standard appointment, which also goes into the cost analysis. “Even though you’re trained to do it, you can’t necessarily do it when you get to the real world,” Jabbarpour said.
She said the thinking is that while OB/GYNs focus on women, FPs cover all ages and family members, so having the equipment and the storage space is best left to the OB/GYNs. She said that thinking may be short sighted.
“We have good data that the highest number of office visits in the United States actually happen in the family physician’s office,” she said. Not providing the services injects a barrier into the system as women are being referred for a simple procedure to a physician they’ve never seen. “That’s not very patient centered,” Jabbarpour noted.
In systems that refer contraceptive procedures to OB/GYNs, doctors also can’t practice skills they learned in residency and then may not feel comfortable performing the procedures when they enter a health system that offers the procedures in primary care.
Number of FPs Prescribing Long-Acting Contraception Growing
Jabbarpour said there has been some improvement in that area in terms of long-acting reversible contraception.
She pointed to a study of recertifying FPs that found that the percent of FPs who offer either IUDs or implants increased from 23.9% in 2018 to 30% in 2022. The share of FPs providing implant insertion increased from 12.9% to 20.8%; those providing IUDs also increased from 22.9% to 25.5% from 2018 to 2022.
FPs also have the advantage of being more widely distributed in rural and remote areas than OB/GYNs, she noted. “They are in almost every county in the United States.”
Jabbarpour said the education must start with health system leaders. If they deem it important to offer these services in primary care, then residency programs will see that their residents must be appropriately trained to provide it.
“Right now, it’s not an expectation of many of the employers that primary care physicians should do this,” she said.
Ti said that expectation should change. The value proposition for all PCPs and health systems, she said, is this: “Most of contraceptive care is well within the scope of primary care providers. This is care that we can do, and it’s care that we should be doing. So why aren’t we doing it?”
Ti, Strasser, and Jabbarpour reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2024, the Guttmacher Institute reported that eight states enacted or proposed limits on contraceptive access. Currently, more than 19 million women aged 13-44 years in the United States live in “contraceptive deserts” or places that lack access to a full range of birth control methods. About 1.2 million of those women live in counties that don’t have a single health center that has complete birth control services.
Providing contraceptive care in primary care settings has long been deemed a best practice by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). But the percentage of primary care physicians (PCPs) prescribing contraception or offering contraceptive procedures is strikingly low.
Only Half of Family Physicians (FPs) Prescribe Contraceptives
Research by Candice Chen, MD, MPH, and colleagues found that while 73.1% of obstetrician-gynecologists (OB/GYNs) and 72.6% of nurse-midwives prescribed the pill, patch, or vaginal ring; only 51% of FPs, 32.4% of pediatricians, and 19.8% of internal medicine physicians did so. And while 92.8% of OB/GYNs provided intrauterine device (IUD) services, only 16.4% of FPs, 2.6% of internists, and 0.6% of pediatricians did so.
One reason primary care is positioned so well to fill contraception gaps is found in the sheer numbers of PCPs. Chen and colleagues found that while the percentage of FPs prescribing contraception was much smaller (51.4%) than the percentage of OB/GYN prescribers (72.6%), the numbers translate to 72,725 FPs prescribing contraceptives, which is nearly double the number of OB/GYNs prescribing them (36,887).
Access to contraception services took a big hit with the COVID-19 pandemic as did access to healthcare in general. And the 2022 Supreme Court ruling that struck down Roe V. Wade has shaken up the landscape for reproductive services with potential consequences for contraceptive access.
Why Aren’t More PCPs Offering Contraceptive Services?
Reasons for the relatively low numbers of PCPs prescribing contraceptives include lack of training in residency, health systems’ financial choices, insurance barriers, and expectation by some physicians and many patients that birth control belongs in the OB/GYN sector. Access, patient awareness that PCPs can provide the care, expectations, and options vary by states and regions.
Angeline Ti, MD, an FP who teaches in a residency program at Wellstar Douglasville Medical Center in Douglasville, Georgia, told this news organization that the awareness issue might be the easiest change for PCPs as many patients aren’t aware you can get contraceptive services in primary care.
Things PCPs ‘Could Do Tomorrow’
Those physicians who want to add those services might want to start with universal screening, Ti said — having conversations with patients about contraceptive needs and letting them know they don’t have to get those prescriptions from an OB/GYN. The conversations could center on laying out the options and counseling on risks and benefits of various options and providing referrals, if that is the best option. “There are definitely things that you could do tomorrow,” she said.
PCPs should be familiar with the CDC’s Contraceptive Guidance for Health Care Providers and the federal Office of Population Affairs’ Quality Family Planning Recommendations for providers, which offer practice-level information, Ti said.
PCPs should not feel they need to be able to provide same-day contraceptive care to get started. Having nurses and medical assistants and practice managers on board who are passionate about adding the services can also help bring about change with a team approach, she said.
Even when the provider is enthusiastic about providing the care and is trained to do so, however, insurance barriers may exist, Ti acknowledged. For example, at her clinic a common IUD insertion requires prior authorization.
Including Other Providers
Julia Strasser, DrPH, MPH, a member of the core faculty at the Fitzhugh Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity in Washington, DC, told this news organization that including other clinicians could help expand contraceptive services in primary care. Her research showed that the proportion of the contraception workforce that is made up of advanced practice clinicians and nurse practitioners is increasing, whereas the proportion that includes physicians is either static or declining.
A paper by her team found that although OB/GYNs and nurse-midwives were more likely to prescribe the pill, patch, or ring, the largest numbers of contraception prescribers were FPs (72,725) and advanced practice nurses (70,115).
“We also know that pharmacists can safely prescribe contraception, and some states have authorized this practice, but uptake is low and policies vary by state,” she said. “Some health systems have pharmacists embedded in their practice — for example in federally qualified health centers and others.”
It’s important, she said, not to frame the gaps in contraceptive care as a failure on the part of individual clinicians but rather as: “How can we change some of the system-level factors that have gotten us to this point?”
Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, an FP and director of the Robert Graham Center of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said sometimes it’s the health center’s cost analysis that stands in the way. She gave an example from her own health system.
“The health system doesn’t want to pay for us to have the IUDs stored in our offices and provide that procedure because they feel it’s more cost effective if the OB/GYNs do it.” IUD insertions take more appointment time than the standard appointment, which also goes into the cost analysis. “Even though you’re trained to do it, you can’t necessarily do it when you get to the real world,” Jabbarpour said.
She said the thinking is that while OB/GYNs focus on women, FPs cover all ages and family members, so having the equipment and the storage space is best left to the OB/GYNs. She said that thinking may be short sighted.
“We have good data that the highest number of office visits in the United States actually happen in the family physician’s office,” she said. Not providing the services injects a barrier into the system as women are being referred for a simple procedure to a physician they’ve never seen. “That’s not very patient centered,” Jabbarpour noted.
In systems that refer contraceptive procedures to OB/GYNs, doctors also can’t practice skills they learned in residency and then may not feel comfortable performing the procedures when they enter a health system that offers the procedures in primary care.
Number of FPs Prescribing Long-Acting Contraception Growing
Jabbarpour said there has been some improvement in that area in terms of long-acting reversible contraception.
She pointed to a study of recertifying FPs that found that the percent of FPs who offer either IUDs or implants increased from 23.9% in 2018 to 30% in 2022. The share of FPs providing implant insertion increased from 12.9% to 20.8%; those providing IUDs also increased from 22.9% to 25.5% from 2018 to 2022.
FPs also have the advantage of being more widely distributed in rural and remote areas than OB/GYNs, she noted. “They are in almost every county in the United States.”
Jabbarpour said the education must start with health system leaders. If they deem it important to offer these services in primary care, then residency programs will see that their residents must be appropriately trained to provide it.
“Right now, it’s not an expectation of many of the employers that primary care physicians should do this,” she said.
Ti said that expectation should change. The value proposition for all PCPs and health systems, she said, is this: “Most of contraceptive care is well within the scope of primary care providers. This is care that we can do, and it’s care that we should be doing. So why aren’t we doing it?”
Ti, Strasser, and Jabbarpour reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In 2024, the Guttmacher Institute reported that eight states enacted or proposed limits on contraceptive access. Currently, more than 19 million women aged 13-44 years in the United States live in “contraceptive deserts” or places that lack access to a full range of birth control methods. About 1.2 million of those women live in counties that don’t have a single health center that has complete birth control services.
Providing contraceptive care in primary care settings has long been deemed a best practice by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). But the percentage of primary care physicians (PCPs) prescribing contraception or offering contraceptive procedures is strikingly low.
Only Half of Family Physicians (FPs) Prescribe Contraceptives
Research by Candice Chen, MD, MPH, and colleagues found that while 73.1% of obstetrician-gynecologists (OB/GYNs) and 72.6% of nurse-midwives prescribed the pill, patch, or vaginal ring; only 51% of FPs, 32.4% of pediatricians, and 19.8% of internal medicine physicians did so. And while 92.8% of OB/GYNs provided intrauterine device (IUD) services, only 16.4% of FPs, 2.6% of internists, and 0.6% of pediatricians did so.
One reason primary care is positioned so well to fill contraception gaps is found in the sheer numbers of PCPs. Chen and colleagues found that while the percentage of FPs prescribing contraception was much smaller (51.4%) than the percentage of OB/GYN prescribers (72.6%), the numbers translate to 72,725 FPs prescribing contraceptives, which is nearly double the number of OB/GYNs prescribing them (36,887).
Access to contraception services took a big hit with the COVID-19 pandemic as did access to healthcare in general. And the 2022 Supreme Court ruling that struck down Roe V. Wade has shaken up the landscape for reproductive services with potential consequences for contraceptive access.
Why Aren’t More PCPs Offering Contraceptive Services?
Reasons for the relatively low numbers of PCPs prescribing contraceptives include lack of training in residency, health systems’ financial choices, insurance barriers, and expectation by some physicians and many patients that birth control belongs in the OB/GYN sector. Access, patient awareness that PCPs can provide the care, expectations, and options vary by states and regions.
Angeline Ti, MD, an FP who teaches in a residency program at Wellstar Douglasville Medical Center in Douglasville, Georgia, told this news organization that the awareness issue might be the easiest change for PCPs as many patients aren’t aware you can get contraceptive services in primary care.
Things PCPs ‘Could Do Tomorrow’
Those physicians who want to add those services might want to start with universal screening, Ti said — having conversations with patients about contraceptive needs and letting them know they don’t have to get those prescriptions from an OB/GYN. The conversations could center on laying out the options and counseling on risks and benefits of various options and providing referrals, if that is the best option. “There are definitely things that you could do tomorrow,” she said.
PCPs should be familiar with the CDC’s Contraceptive Guidance for Health Care Providers and the federal Office of Population Affairs’ Quality Family Planning Recommendations for providers, which offer practice-level information, Ti said.
PCPs should not feel they need to be able to provide same-day contraceptive care to get started. Having nurses and medical assistants and practice managers on board who are passionate about adding the services can also help bring about change with a team approach, she said.
Even when the provider is enthusiastic about providing the care and is trained to do so, however, insurance barriers may exist, Ti acknowledged. For example, at her clinic a common IUD insertion requires prior authorization.
Including Other Providers
Julia Strasser, DrPH, MPH, a member of the core faculty at the Fitzhugh Mullan Institute for Health Workforce Equity in Washington, DC, told this news organization that including other clinicians could help expand contraceptive services in primary care. Her research showed that the proportion of the contraception workforce that is made up of advanced practice clinicians and nurse practitioners is increasing, whereas the proportion that includes physicians is either static or declining.
A paper by her team found that although OB/GYNs and nurse-midwives were more likely to prescribe the pill, patch, or ring, the largest numbers of contraception prescribers were FPs (72,725) and advanced practice nurses (70,115).
“We also know that pharmacists can safely prescribe contraception, and some states have authorized this practice, but uptake is low and policies vary by state,” she said. “Some health systems have pharmacists embedded in their practice — for example in federally qualified health centers and others.”
It’s important, she said, not to frame the gaps in contraceptive care as a failure on the part of individual clinicians but rather as: “How can we change some of the system-level factors that have gotten us to this point?”
Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, an FP and director of the Robert Graham Center of the American Academy of Family Physicians, said sometimes it’s the health center’s cost analysis that stands in the way. She gave an example from her own health system.
“The health system doesn’t want to pay for us to have the IUDs stored in our offices and provide that procedure because they feel it’s more cost effective if the OB/GYNs do it.” IUD insertions take more appointment time than the standard appointment, which also goes into the cost analysis. “Even though you’re trained to do it, you can’t necessarily do it when you get to the real world,” Jabbarpour said.
She said the thinking is that while OB/GYNs focus on women, FPs cover all ages and family members, so having the equipment and the storage space is best left to the OB/GYNs. She said that thinking may be short sighted.
“We have good data that the highest number of office visits in the United States actually happen in the family physician’s office,” she said. Not providing the services injects a barrier into the system as women are being referred for a simple procedure to a physician they’ve never seen. “That’s not very patient centered,” Jabbarpour noted.
In systems that refer contraceptive procedures to OB/GYNs, doctors also can’t practice skills they learned in residency and then may not feel comfortable performing the procedures when they enter a health system that offers the procedures in primary care.
Number of FPs Prescribing Long-Acting Contraception Growing
Jabbarpour said there has been some improvement in that area in terms of long-acting reversible contraception.
She pointed to a study of recertifying FPs that found that the percent of FPs who offer either IUDs or implants increased from 23.9% in 2018 to 30% in 2022. The share of FPs providing implant insertion increased from 12.9% to 20.8%; those providing IUDs also increased from 22.9% to 25.5% from 2018 to 2022.
FPs also have the advantage of being more widely distributed in rural and remote areas than OB/GYNs, she noted. “They are in almost every county in the United States.”
Jabbarpour said the education must start with health system leaders. If they deem it important to offer these services in primary care, then residency programs will see that their residents must be appropriately trained to provide it.
“Right now, it’s not an expectation of many of the employers that primary care physicians should do this,” she said.
Ti said that expectation should change. The value proposition for all PCPs and health systems, she said, is this: “Most of contraceptive care is well within the scope of primary care providers. This is care that we can do, and it’s care that we should be doing. So why aren’t we doing it?”
Ti, Strasser, and Jabbarpour reported no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Dry January: Should Doctors Make It Year-Round?
For millennia in medicine, alcohol, particularly red wine, carried a health halo; in small doses, it has historically been thought to have cardioprotective benefits. Michael Farkouh, MD, a professor of cardiology at Cedars-Sinai, estimates half the physicians still accept people having a drink or two a day. “That is still in practice, though the numbers are reducing,” he said.
But Farkouh no longer drinks alcohol, a position he has come to after getting more involved in research into the substance and his realization that many of the studies touting alcohol’s health benefits were flawed.
Today, alcohol sits alongside asbestos and tobacco as class 1 carcinogens. According to the World Health Organization, it has no known safe ingestible amount. In 2018, a blockbuster report in The Lancet found no amount of any kind of alcohol improves health. In early January, US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy called for adding cancer warnings to alcohol labels.
But the way doctors drink is far from black and white. For physicians, drinking habits are tied up in personal values, professional understanding of a substance with a confusing research history, and the fact alcohol is deeply ingrained in the social fabric of society — and in medicine. As thinking on alcohol shifts, this news organization spoke with physicians about their own drinking habits, how they counsel patients on it, and alcohol’s place in a field that works to keep people healthy.
Cultural Currency
From the days of Hippocrates, who believed alcohol could cure virtually every ailment, alcohol has held a large role in medicine. Through much of the 19th century, patent remedies like Hamlin’s Wizard Oil and the Seven Sutherland Sisters Hair Grower, contained alcohol — sometimes in concentrations exceeding 50%.
The first American Pharmacopoeia, published in 1820, even contained nine wine-based medicines. Throughout the second half of the 19th century, physicians largely debated alcohol’s role in medicine. However, a 1922 poll of members of the American Medical Association found that physicians were still using alcohol as a medicine for everything from heart attacks to animal bites.
Today, alcohol’s presence in medicine is, in some ways, representative of a realized cognitive dissonance.
“In my mind, alcohol has completely lost any illusion of benefit. It is a poison to almost every single organ in our body. Yet I’m currently engaged in a duel of being a physician who drinks in moderation and constantly judging myself for it,” said Tyra Fainstad, MD, an internist and an associate professor at CU Medicine in Denver.
Fainstad said every academic national conference she has attended has had a reception with multiple cash bars — and professional recruitment dinners regularly include at least the offering of alcohol. Private hospitals often have open bars at events.
“Drinking has historically been a way that people unwind, even in medicine,” said addiction psychiatrist Alexis Ritvo, MD. Ritvo — who said she drinks occasionally but much less than she used to after paying attention to how alcohol makes her feel and the harm alcohol can cause — noted that some occasions where alcohol is present socially in medicine don’t bother her. Alcohol is even an option at the addiction psychiatry conference, where attendees can exchange tickets for drinks. But last year, the event provided separate bars for alcoholic and nonalcoholic drinks.
“Our life is full of things that are contradictory or at odds,” Ritvo said. “We want things to either be wrong or right, appropriate or inappropriate, but just like all things, everything’s pretty nuanced.”
But there are examples of alcohol being a part of an event that are downright inappropriate, such as when she attended a fundraiser for a recovery facility that had an open bar.
Farkouh said alcohol at events can exclude others. (He recommends that instead of calling a social gathering “going out for drinks,” someone might say, “We’re getting together.”) He drinks mocktails or nonalcoholic beer at work events where alcohol is served.
Brian Dwinnell, MD, associate dean of student life at CU Medicine, said alcohol can quickly become the focus of an event — something he noticed at an annual kickball game between first- and second-year students that has historically served beer.
In recent years, school leadership has removed alcohol from his institution’s match day celebration and the kickball game. “Initially, there was some pushback from students,” he said of making these events dry, “but now, it’s just sort of accepted, and the events have been just as great as they were when we did provide alcohol.”
How Doctors Drink
Physicians may have a greater understanding of alcohol’s health harms. Still, they don’t necessarily drink less because of it, and whether they should becomes a question not just of health but also of the standards to which society holds medical professionals.
Data suggest physicians tend to drink at rates similar to those among the general population. A recent Medscape Medical News survey found nearly 60% of physicians have started drinking less.
Dwinnell said he is a long-time “wine connoisseur” and drinks on occasion. But he admitted that while he thinks about the health implications of alcohol more — and he has nixed it from various events for medical students — he does not believe his drinking habits have changed much.
Navya Mysore, MD, a family physician in New York City, said she has become interested in wine over the past few years, even taking classes to learn more about it. “I like understanding how it’s made, the regions it’s from, and how to pair it with food,” she said. Mysore admits she drank a little more than usual throughout the pandemic, yet today, she said her relationship with alcohol in moderation is related to family, community, and connection.
Fainstad, who drinks socially, said: “I think there’s an immeasurable quality to the social ritual of it. I think for better or worse — probably for worse — for many generations, alcohol has been a part of many meaningful traditions and rituals that we hold.”
Farkouh was quick to underscore the importance of social connection, and that alcohol reduces stress for some people. “I don’t want to take that away from people,” he said. But he also stated the importance of finding other ways to find social fulfillment and enjoyment — and said it’s essential for societal norms to shift to reflect this.
With emerging data, alcohol’s image in society is shifting. Ireland recently became the first country to pass regulation requiring all alcohol sold there to come with a cancer warning. All the clinicians interviewed for this article spoke about the increased acceptability of choosing not to drink for whatever reason.
In the context of alcohol, Dwinnell often asks his students, “What if you were out at a restaurant and you saw your mother’s surgeon there and they were intoxicated? Are you going to feel comfortable with that individual operating on your mother tomorrow or any time?” He added: “Physicians are held to a higher professional standard than those in other fields — and they should be. This is a high-stakes business.”
Dwinnell’s hypothetical question to students is a good one, albeit perhaps not always a fair one. “It’s important for people to realize that physicians are humans,” Mysore said. “We are people, we have lives, and we may choose to have habits that are not necessarily the healthiest for us.”
Fainstad said there’s no shame in medical professionals drinking on occasion. “You can’t be held accountable for something you don’t know about,” she said, acknowledging the known harms of alcohol and that there is still more to learn. But she does wonder how doctors who drank might be perceived in years to come. “I can imagine in a couple of decades, people could say, ‘Even doctors used to have a glass of wine with dinner.’”
‘Physicians Should Tighten Their Stances on Alcohol’
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines suggest limiting intake to two alcoholic drinks or less daily for men and one drink or less for women or to choose not to drink. Farkouh said he skews toward the latter, encouraging patients to drink as little as possible or nothing at all. “If you take a holistic approach, physicians should tighten their stances on alcohol,” he said.
Ultimately, he said a randomized trial is warranted to address the risk for cardiovascular disease, in particular.
Of course, physicians vary in how they discuss the topic with patients.
Mysore said she regularly educates patients about pour size and ways to swap out alcoholic drinks with nonalcoholic ones. Outside of cases of addiction, she favors the idea of moderation. “I don’t really subscribe to all-or-nothing mindsets. If there’s something that you enjoy having as a part of your life, I don’t think there’s any reason why you need to eliminate it,” she said. “You just need to figure out what moderation looks like for you.”
Ritvo favors motivational interviewing and tries to understand someone’s relationship with alcohol.
Fainstad provides the Dietary Guidelines’ cutoffs to patients and educates them on the poisonous nature of the substance.
Clearer guidance from large governing bodies — potential changes around alcohol in the 2025-230 revision of the US Dietary Guidelines or cancer warnings on booze sold in the United States — are coming and could help streamline messaging.
And although he speaks with urgency about alcohol’s dangers, Farkouh emphasized the need for a judgment-free and patient-centered approach to conversations around drinking: “People have grown up with alcohol being acceptable, and it’s going to take time to change that.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For millennia in medicine, alcohol, particularly red wine, carried a health halo; in small doses, it has historically been thought to have cardioprotective benefits. Michael Farkouh, MD, a professor of cardiology at Cedars-Sinai, estimates half the physicians still accept people having a drink or two a day. “That is still in practice, though the numbers are reducing,” he said.
But Farkouh no longer drinks alcohol, a position he has come to after getting more involved in research into the substance and his realization that many of the studies touting alcohol’s health benefits were flawed.
Today, alcohol sits alongside asbestos and tobacco as class 1 carcinogens. According to the World Health Organization, it has no known safe ingestible amount. In 2018, a blockbuster report in The Lancet found no amount of any kind of alcohol improves health. In early January, US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy called for adding cancer warnings to alcohol labels.
But the way doctors drink is far from black and white. For physicians, drinking habits are tied up in personal values, professional understanding of a substance with a confusing research history, and the fact alcohol is deeply ingrained in the social fabric of society — and in medicine. As thinking on alcohol shifts, this news organization spoke with physicians about their own drinking habits, how they counsel patients on it, and alcohol’s place in a field that works to keep people healthy.
Cultural Currency
From the days of Hippocrates, who believed alcohol could cure virtually every ailment, alcohol has held a large role in medicine. Through much of the 19th century, patent remedies like Hamlin’s Wizard Oil and the Seven Sutherland Sisters Hair Grower, contained alcohol — sometimes in concentrations exceeding 50%.
The first American Pharmacopoeia, published in 1820, even contained nine wine-based medicines. Throughout the second half of the 19th century, physicians largely debated alcohol’s role in medicine. However, a 1922 poll of members of the American Medical Association found that physicians were still using alcohol as a medicine for everything from heart attacks to animal bites.
Today, alcohol’s presence in medicine is, in some ways, representative of a realized cognitive dissonance.
“In my mind, alcohol has completely lost any illusion of benefit. It is a poison to almost every single organ in our body. Yet I’m currently engaged in a duel of being a physician who drinks in moderation and constantly judging myself for it,” said Tyra Fainstad, MD, an internist and an associate professor at CU Medicine in Denver.
Fainstad said every academic national conference she has attended has had a reception with multiple cash bars — and professional recruitment dinners regularly include at least the offering of alcohol. Private hospitals often have open bars at events.
“Drinking has historically been a way that people unwind, even in medicine,” said addiction psychiatrist Alexis Ritvo, MD. Ritvo — who said she drinks occasionally but much less than she used to after paying attention to how alcohol makes her feel and the harm alcohol can cause — noted that some occasions where alcohol is present socially in medicine don’t bother her. Alcohol is even an option at the addiction psychiatry conference, where attendees can exchange tickets for drinks. But last year, the event provided separate bars for alcoholic and nonalcoholic drinks.
“Our life is full of things that are contradictory or at odds,” Ritvo said. “We want things to either be wrong or right, appropriate or inappropriate, but just like all things, everything’s pretty nuanced.”
But there are examples of alcohol being a part of an event that are downright inappropriate, such as when she attended a fundraiser for a recovery facility that had an open bar.
Farkouh said alcohol at events can exclude others. (He recommends that instead of calling a social gathering “going out for drinks,” someone might say, “We’re getting together.”) He drinks mocktails or nonalcoholic beer at work events where alcohol is served.
Brian Dwinnell, MD, associate dean of student life at CU Medicine, said alcohol can quickly become the focus of an event — something he noticed at an annual kickball game between first- and second-year students that has historically served beer.
In recent years, school leadership has removed alcohol from his institution’s match day celebration and the kickball game. “Initially, there was some pushback from students,” he said of making these events dry, “but now, it’s just sort of accepted, and the events have been just as great as they were when we did provide alcohol.”
How Doctors Drink
Physicians may have a greater understanding of alcohol’s health harms. Still, they don’t necessarily drink less because of it, and whether they should becomes a question not just of health but also of the standards to which society holds medical professionals.
Data suggest physicians tend to drink at rates similar to those among the general population. A recent Medscape Medical News survey found nearly 60% of physicians have started drinking less.
Dwinnell said he is a long-time “wine connoisseur” and drinks on occasion. But he admitted that while he thinks about the health implications of alcohol more — and he has nixed it from various events for medical students — he does not believe his drinking habits have changed much.
Navya Mysore, MD, a family physician in New York City, said she has become interested in wine over the past few years, even taking classes to learn more about it. “I like understanding how it’s made, the regions it’s from, and how to pair it with food,” she said. Mysore admits she drank a little more than usual throughout the pandemic, yet today, she said her relationship with alcohol in moderation is related to family, community, and connection.
Fainstad, who drinks socially, said: “I think there’s an immeasurable quality to the social ritual of it. I think for better or worse — probably for worse — for many generations, alcohol has been a part of many meaningful traditions and rituals that we hold.”
Farkouh was quick to underscore the importance of social connection, and that alcohol reduces stress for some people. “I don’t want to take that away from people,” he said. But he also stated the importance of finding other ways to find social fulfillment and enjoyment — and said it’s essential for societal norms to shift to reflect this.
With emerging data, alcohol’s image in society is shifting. Ireland recently became the first country to pass regulation requiring all alcohol sold there to come with a cancer warning. All the clinicians interviewed for this article spoke about the increased acceptability of choosing not to drink for whatever reason.
In the context of alcohol, Dwinnell often asks his students, “What if you were out at a restaurant and you saw your mother’s surgeon there and they were intoxicated? Are you going to feel comfortable with that individual operating on your mother tomorrow or any time?” He added: “Physicians are held to a higher professional standard than those in other fields — and they should be. This is a high-stakes business.”
Dwinnell’s hypothetical question to students is a good one, albeit perhaps not always a fair one. “It’s important for people to realize that physicians are humans,” Mysore said. “We are people, we have lives, and we may choose to have habits that are not necessarily the healthiest for us.”
Fainstad said there’s no shame in medical professionals drinking on occasion. “You can’t be held accountable for something you don’t know about,” she said, acknowledging the known harms of alcohol and that there is still more to learn. But she does wonder how doctors who drank might be perceived in years to come. “I can imagine in a couple of decades, people could say, ‘Even doctors used to have a glass of wine with dinner.’”
‘Physicians Should Tighten Their Stances on Alcohol’
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines suggest limiting intake to two alcoholic drinks or less daily for men and one drink or less for women or to choose not to drink. Farkouh said he skews toward the latter, encouraging patients to drink as little as possible or nothing at all. “If you take a holistic approach, physicians should tighten their stances on alcohol,” he said.
Ultimately, he said a randomized trial is warranted to address the risk for cardiovascular disease, in particular.
Of course, physicians vary in how they discuss the topic with patients.
Mysore said she regularly educates patients about pour size and ways to swap out alcoholic drinks with nonalcoholic ones. Outside of cases of addiction, she favors the idea of moderation. “I don’t really subscribe to all-or-nothing mindsets. If there’s something that you enjoy having as a part of your life, I don’t think there’s any reason why you need to eliminate it,” she said. “You just need to figure out what moderation looks like for you.”
Ritvo favors motivational interviewing and tries to understand someone’s relationship with alcohol.
Fainstad provides the Dietary Guidelines’ cutoffs to patients and educates them on the poisonous nature of the substance.
Clearer guidance from large governing bodies — potential changes around alcohol in the 2025-230 revision of the US Dietary Guidelines or cancer warnings on booze sold in the United States — are coming and could help streamline messaging.
And although he speaks with urgency about alcohol’s dangers, Farkouh emphasized the need for a judgment-free and patient-centered approach to conversations around drinking: “People have grown up with alcohol being acceptable, and it’s going to take time to change that.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For millennia in medicine, alcohol, particularly red wine, carried a health halo; in small doses, it has historically been thought to have cardioprotective benefits. Michael Farkouh, MD, a professor of cardiology at Cedars-Sinai, estimates half the physicians still accept people having a drink or two a day. “That is still in practice, though the numbers are reducing,” he said.
But Farkouh no longer drinks alcohol, a position he has come to after getting more involved in research into the substance and his realization that many of the studies touting alcohol’s health benefits were flawed.
Today, alcohol sits alongside asbestos and tobacco as class 1 carcinogens. According to the World Health Organization, it has no known safe ingestible amount. In 2018, a blockbuster report in The Lancet found no amount of any kind of alcohol improves health. In early January, US Surgeon General Vivek Murthy called for adding cancer warnings to alcohol labels.
But the way doctors drink is far from black and white. For physicians, drinking habits are tied up in personal values, professional understanding of a substance with a confusing research history, and the fact alcohol is deeply ingrained in the social fabric of society — and in medicine. As thinking on alcohol shifts, this news organization spoke with physicians about their own drinking habits, how they counsel patients on it, and alcohol’s place in a field that works to keep people healthy.
Cultural Currency
From the days of Hippocrates, who believed alcohol could cure virtually every ailment, alcohol has held a large role in medicine. Through much of the 19th century, patent remedies like Hamlin’s Wizard Oil and the Seven Sutherland Sisters Hair Grower, contained alcohol — sometimes in concentrations exceeding 50%.
The first American Pharmacopoeia, published in 1820, even contained nine wine-based medicines. Throughout the second half of the 19th century, physicians largely debated alcohol’s role in medicine. However, a 1922 poll of members of the American Medical Association found that physicians were still using alcohol as a medicine for everything from heart attacks to animal bites.
Today, alcohol’s presence in medicine is, in some ways, representative of a realized cognitive dissonance.
“In my mind, alcohol has completely lost any illusion of benefit. It is a poison to almost every single organ in our body. Yet I’m currently engaged in a duel of being a physician who drinks in moderation and constantly judging myself for it,” said Tyra Fainstad, MD, an internist and an associate professor at CU Medicine in Denver.
Fainstad said every academic national conference she has attended has had a reception with multiple cash bars — and professional recruitment dinners regularly include at least the offering of alcohol. Private hospitals often have open bars at events.
“Drinking has historically been a way that people unwind, even in medicine,” said addiction psychiatrist Alexis Ritvo, MD. Ritvo — who said she drinks occasionally but much less than she used to after paying attention to how alcohol makes her feel and the harm alcohol can cause — noted that some occasions where alcohol is present socially in medicine don’t bother her. Alcohol is even an option at the addiction psychiatry conference, where attendees can exchange tickets for drinks. But last year, the event provided separate bars for alcoholic and nonalcoholic drinks.
“Our life is full of things that are contradictory or at odds,” Ritvo said. “We want things to either be wrong or right, appropriate or inappropriate, but just like all things, everything’s pretty nuanced.”
But there are examples of alcohol being a part of an event that are downright inappropriate, such as when she attended a fundraiser for a recovery facility that had an open bar.
Farkouh said alcohol at events can exclude others. (He recommends that instead of calling a social gathering “going out for drinks,” someone might say, “We’re getting together.”) He drinks mocktails or nonalcoholic beer at work events where alcohol is served.
Brian Dwinnell, MD, associate dean of student life at CU Medicine, said alcohol can quickly become the focus of an event — something he noticed at an annual kickball game between first- and second-year students that has historically served beer.
In recent years, school leadership has removed alcohol from his institution’s match day celebration and the kickball game. “Initially, there was some pushback from students,” he said of making these events dry, “but now, it’s just sort of accepted, and the events have been just as great as they were when we did provide alcohol.”
How Doctors Drink
Physicians may have a greater understanding of alcohol’s health harms. Still, they don’t necessarily drink less because of it, and whether they should becomes a question not just of health but also of the standards to which society holds medical professionals.
Data suggest physicians tend to drink at rates similar to those among the general population. A recent Medscape Medical News survey found nearly 60% of physicians have started drinking less.
Dwinnell said he is a long-time “wine connoisseur” and drinks on occasion. But he admitted that while he thinks about the health implications of alcohol more — and he has nixed it from various events for medical students — he does not believe his drinking habits have changed much.
Navya Mysore, MD, a family physician in New York City, said she has become interested in wine over the past few years, even taking classes to learn more about it. “I like understanding how it’s made, the regions it’s from, and how to pair it with food,” she said. Mysore admits she drank a little more than usual throughout the pandemic, yet today, she said her relationship with alcohol in moderation is related to family, community, and connection.
Fainstad, who drinks socially, said: “I think there’s an immeasurable quality to the social ritual of it. I think for better or worse — probably for worse — for many generations, alcohol has been a part of many meaningful traditions and rituals that we hold.”
Farkouh was quick to underscore the importance of social connection, and that alcohol reduces stress for some people. “I don’t want to take that away from people,” he said. But he also stated the importance of finding other ways to find social fulfillment and enjoyment — and said it’s essential for societal norms to shift to reflect this.
With emerging data, alcohol’s image in society is shifting. Ireland recently became the first country to pass regulation requiring all alcohol sold there to come with a cancer warning. All the clinicians interviewed for this article spoke about the increased acceptability of choosing not to drink for whatever reason.
In the context of alcohol, Dwinnell often asks his students, “What if you were out at a restaurant and you saw your mother’s surgeon there and they were intoxicated? Are you going to feel comfortable with that individual operating on your mother tomorrow or any time?” He added: “Physicians are held to a higher professional standard than those in other fields — and they should be. This is a high-stakes business.”
Dwinnell’s hypothetical question to students is a good one, albeit perhaps not always a fair one. “It’s important for people to realize that physicians are humans,” Mysore said. “We are people, we have lives, and we may choose to have habits that are not necessarily the healthiest for us.”
Fainstad said there’s no shame in medical professionals drinking on occasion. “You can’t be held accountable for something you don’t know about,” she said, acknowledging the known harms of alcohol and that there is still more to learn. But she does wonder how doctors who drank might be perceived in years to come. “I can imagine in a couple of decades, people could say, ‘Even doctors used to have a glass of wine with dinner.’”
‘Physicians Should Tighten Their Stances on Alcohol’
The 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines suggest limiting intake to two alcoholic drinks or less daily for men and one drink or less for women or to choose not to drink. Farkouh said he skews toward the latter, encouraging patients to drink as little as possible or nothing at all. “If you take a holistic approach, physicians should tighten their stances on alcohol,” he said.
Ultimately, he said a randomized trial is warranted to address the risk for cardiovascular disease, in particular.
Of course, physicians vary in how they discuss the topic with patients.
Mysore said she regularly educates patients about pour size and ways to swap out alcoholic drinks with nonalcoholic ones. Outside of cases of addiction, she favors the idea of moderation. “I don’t really subscribe to all-or-nothing mindsets. If there’s something that you enjoy having as a part of your life, I don’t think there’s any reason why you need to eliminate it,” she said. “You just need to figure out what moderation looks like for you.”
Ritvo favors motivational interviewing and tries to understand someone’s relationship with alcohol.
Fainstad provides the Dietary Guidelines’ cutoffs to patients and educates them on the poisonous nature of the substance.
Clearer guidance from large governing bodies — potential changes around alcohol in the 2025-230 revision of the US Dietary Guidelines or cancer warnings on booze sold in the United States — are coming and could help streamline messaging.
And although he speaks with urgency about alcohol’s dangers, Farkouh emphasized the need for a judgment-free and patient-centered approach to conversations around drinking: “People have grown up with alcohol being acceptable, and it’s going to take time to change that.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Using AI to ID Osteoporosis: A Medico-Legal Minefield?
Could an artificial intelligence (AI)–driven tool that mines medical records for suspected cases of osteoporosis be so successful that it becomes a potential liability? Yes, according to Christopher White, PhD, executive director of Maridulu Budyari Gumal, the Sydney Partnership for Health, Education, Research, and Enterprise, a research translation center in Liverpool, Australia.
In a thought-provoking presentation at the Endocrine Society’s AI in Healthcare Virtual Summit, White described the results after his fracture liaison team at Prince of Wales Hospital in Randwick, Australia, tried to plug the “osteoporosis treatment gap” by mining medical records to identify patients with the disorder.
‘Be Careful What You Wish For’
White and colleagues developed a robust standalone database over 20 years that informed fracture risk among patients with osteoporosis in Sydney. The database included all relevant clinical information, as well as bone density measurements, on about 30,000 patients and could be interrogated for randomized controlled trial recruitment.
However, a “crisis” occurred around 2011, when the team received a recruitment request for the first head-to-head comparison of alendronate with romosozumab. “We had numerous postmenopausal women in the age range with the required bone density, but we hadn’t captured the severity of their vertebral fracture or how many they actually had,” White told the this news organization. For recruitment into the study, participants must have had at least two moderate or severe vertebral fractures or a proximal vertebral fracture that was sustained between 3 and 24 months before recruitment.
White turned to his hospital’s mainframe, which had coding data and time intervals for patients who were admitted with vertebral or hip fractures. He calculated how many patients who met the study criteria had been discharged and how many of those he thought he’d be able to capture through the mainframe. He was confident he would have enough, but he was wrong. He underrecruited and could not participate in the trial.
Determined not to wind up in a similar situation in the future, he investigated and found that other centers were struggling with similar problems. This led to a collaboration with four investigators who were using AI and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) coding to identify patients at risk for osteoporotic fractures. White, meanwhile, had developed a natural language processing tool called XRAIT that also identified patients at fracture risk. A study comparing the two electronic search programs, which screen medical records for fractures, found that both reliably identified patients who had had a fracture. White and his colleagues concluded that hybrid tools combining XRAIT and AES would likely improve the identification of patients with osteoporosis who would require follow-up or might participate in future trials.
Those patients were not being identified sooner for multiple reasons, White explained. Sometimes, the radiologist would report osteoporosis, but it wouldn’t get coded. Or, in the emergency department, a patient with a fracture would be treated and then sent home, and the possibility of osteoporosis wasn’t reported.
“As we went deeper and deeper with our tools into the medical record, we found more and more patients who hadn’t been coded or reported but who actually had osteoporosis,” White said. “It was incredibly prevalent.”
But the number of patients identified was more than the hospital could comfortably handle.
Ironically, he added, “To my relief and probably not to the benefit of the patients, there was a system upgrade of the radiology reporting system, which was incompatible with the natural language processing technology that I had installed. The AI was turned off at that point, but I had a look over the edge and into the mine pit.”
“The lesson learned,” White told this news organization, is “If you mine the medical record for unidentified patients before you know what to do with the output, you create a medico-legal minefield. You need to be careful what you wish for with technology, because it may actually come true.”
Grappling With the Treatment Gap
An (over)abundance of patients is likely contributing to the “osteoporosis treatment gap” that Australia’s fracture liaison services, which handle many of these patients, are grappling with. One recent meta-analysis showed that not all eligible patients are treated and that not all patients who are treated actually start treatment. Another study showed that only a minority of patients — anywhere between 20% and 40% — who start are still persisting at about 3 years, White said.
Various types of fracture liaison services exist, he noted. The model that has been shown to best promote adherence is the one requiring clinicians to “identify, educate [usually, the primary care physician], evaluate, start treatment, continue treatment, and follow-up at 12 months for to confirm that there is adherence.”
What’s happening now, he said, is that the technology is identifying a high number of vertebral crush fractures, and there’s no education or evaluation. “The radiologist just refers the patient to a primary care physician and hopes for the best. AI isn’t contributing to solving the treatment gap problem; it’s amplifying it. It’s ahead of the ability of organizations to accommodate the findings.”
Solutions, he said, would require support at the top of health systems and organizations, and funding to proceed; data surveys concentrating on vertical integration of the medical record to follow patients wherever they are — eg, hospital, primary care — in their health journeys; a workflow with synchronous diagnosis and treatment planning, delivery, monitoring, and payment; and clinical and community champions advocating and “leading the charge in health tech.”
Furthermore, he advised, organizations need to be “very, very careful with safety and security — that is, managing the digital risks.”
“Oscar Wilde said there are two tragedies in life: One is not getting what one wants, and the other is getting it,” White concluded. “In my career, we’ve moved on from not knowing how to treat osteoporosis to knowing how to treat it. And that is both an asset and a liability.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could an artificial intelligence (AI)–driven tool that mines medical records for suspected cases of osteoporosis be so successful that it becomes a potential liability? Yes, according to Christopher White, PhD, executive director of Maridulu Budyari Gumal, the Sydney Partnership for Health, Education, Research, and Enterprise, a research translation center in Liverpool, Australia.
In a thought-provoking presentation at the Endocrine Society’s AI in Healthcare Virtual Summit, White described the results after his fracture liaison team at Prince of Wales Hospital in Randwick, Australia, tried to plug the “osteoporosis treatment gap” by mining medical records to identify patients with the disorder.
‘Be Careful What You Wish For’
White and colleagues developed a robust standalone database over 20 years that informed fracture risk among patients with osteoporosis in Sydney. The database included all relevant clinical information, as well as bone density measurements, on about 30,000 patients and could be interrogated for randomized controlled trial recruitment.
However, a “crisis” occurred around 2011, when the team received a recruitment request for the first head-to-head comparison of alendronate with romosozumab. “We had numerous postmenopausal women in the age range with the required bone density, but we hadn’t captured the severity of their vertebral fracture or how many they actually had,” White told the this news organization. For recruitment into the study, participants must have had at least two moderate or severe vertebral fractures or a proximal vertebral fracture that was sustained between 3 and 24 months before recruitment.
White turned to his hospital’s mainframe, which had coding data and time intervals for patients who were admitted with vertebral or hip fractures. He calculated how many patients who met the study criteria had been discharged and how many of those he thought he’d be able to capture through the mainframe. He was confident he would have enough, but he was wrong. He underrecruited and could not participate in the trial.
Determined not to wind up in a similar situation in the future, he investigated and found that other centers were struggling with similar problems. This led to a collaboration with four investigators who were using AI and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) coding to identify patients at risk for osteoporotic fractures. White, meanwhile, had developed a natural language processing tool called XRAIT that also identified patients at fracture risk. A study comparing the two electronic search programs, which screen medical records for fractures, found that both reliably identified patients who had had a fracture. White and his colleagues concluded that hybrid tools combining XRAIT and AES would likely improve the identification of patients with osteoporosis who would require follow-up or might participate in future trials.
Those patients were not being identified sooner for multiple reasons, White explained. Sometimes, the radiologist would report osteoporosis, but it wouldn’t get coded. Or, in the emergency department, a patient with a fracture would be treated and then sent home, and the possibility of osteoporosis wasn’t reported.
“As we went deeper and deeper with our tools into the medical record, we found more and more patients who hadn’t been coded or reported but who actually had osteoporosis,” White said. “It was incredibly prevalent.”
But the number of patients identified was more than the hospital could comfortably handle.
Ironically, he added, “To my relief and probably not to the benefit of the patients, there was a system upgrade of the radiology reporting system, which was incompatible with the natural language processing technology that I had installed. The AI was turned off at that point, but I had a look over the edge and into the mine pit.”
“The lesson learned,” White told this news organization, is “If you mine the medical record for unidentified patients before you know what to do with the output, you create a medico-legal minefield. You need to be careful what you wish for with technology, because it may actually come true.”
Grappling With the Treatment Gap
An (over)abundance of patients is likely contributing to the “osteoporosis treatment gap” that Australia’s fracture liaison services, which handle many of these patients, are grappling with. One recent meta-analysis showed that not all eligible patients are treated and that not all patients who are treated actually start treatment. Another study showed that only a minority of patients — anywhere between 20% and 40% — who start are still persisting at about 3 years, White said.
Various types of fracture liaison services exist, he noted. The model that has been shown to best promote adherence is the one requiring clinicians to “identify, educate [usually, the primary care physician], evaluate, start treatment, continue treatment, and follow-up at 12 months for to confirm that there is adherence.”
What’s happening now, he said, is that the technology is identifying a high number of vertebral crush fractures, and there’s no education or evaluation. “The radiologist just refers the patient to a primary care physician and hopes for the best. AI isn’t contributing to solving the treatment gap problem; it’s amplifying it. It’s ahead of the ability of organizations to accommodate the findings.”
Solutions, he said, would require support at the top of health systems and organizations, and funding to proceed; data surveys concentrating on vertical integration of the medical record to follow patients wherever they are — eg, hospital, primary care — in their health journeys; a workflow with synchronous diagnosis and treatment planning, delivery, monitoring, and payment; and clinical and community champions advocating and “leading the charge in health tech.”
Furthermore, he advised, organizations need to be “very, very careful with safety and security — that is, managing the digital risks.”
“Oscar Wilde said there are two tragedies in life: One is not getting what one wants, and the other is getting it,” White concluded. “In my career, we’ve moved on from not knowing how to treat osteoporosis to knowing how to treat it. And that is both an asset and a liability.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Could an artificial intelligence (AI)–driven tool that mines medical records for suspected cases of osteoporosis be so successful that it becomes a potential liability? Yes, according to Christopher White, PhD, executive director of Maridulu Budyari Gumal, the Sydney Partnership for Health, Education, Research, and Enterprise, a research translation center in Liverpool, Australia.
In a thought-provoking presentation at the Endocrine Society’s AI in Healthcare Virtual Summit, White described the results after his fracture liaison team at Prince of Wales Hospital in Randwick, Australia, tried to plug the “osteoporosis treatment gap” by mining medical records to identify patients with the disorder.
‘Be Careful What You Wish For’
White and colleagues developed a robust standalone database over 20 years that informed fracture risk among patients with osteoporosis in Sydney. The database included all relevant clinical information, as well as bone density measurements, on about 30,000 patients and could be interrogated for randomized controlled trial recruitment.
However, a “crisis” occurred around 2011, when the team received a recruitment request for the first head-to-head comparison of alendronate with romosozumab. “We had numerous postmenopausal women in the age range with the required bone density, but we hadn’t captured the severity of their vertebral fracture or how many they actually had,” White told the this news organization. For recruitment into the study, participants must have had at least two moderate or severe vertebral fractures or a proximal vertebral fracture that was sustained between 3 and 24 months before recruitment.
White turned to his hospital’s mainframe, which had coding data and time intervals for patients who were admitted with vertebral or hip fractures. He calculated how many patients who met the study criteria had been discharged and how many of those he thought he’d be able to capture through the mainframe. He was confident he would have enough, but he was wrong. He underrecruited and could not participate in the trial.
Determined not to wind up in a similar situation in the future, he investigated and found that other centers were struggling with similar problems. This led to a collaboration with four investigators who were using AI and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) coding to identify patients at risk for osteoporotic fractures. White, meanwhile, had developed a natural language processing tool called XRAIT that also identified patients at fracture risk. A study comparing the two electronic search programs, which screen medical records for fractures, found that both reliably identified patients who had had a fracture. White and his colleagues concluded that hybrid tools combining XRAIT and AES would likely improve the identification of patients with osteoporosis who would require follow-up or might participate in future trials.
Those patients were not being identified sooner for multiple reasons, White explained. Sometimes, the radiologist would report osteoporosis, but it wouldn’t get coded. Or, in the emergency department, a patient with a fracture would be treated and then sent home, and the possibility of osteoporosis wasn’t reported.
“As we went deeper and deeper with our tools into the medical record, we found more and more patients who hadn’t been coded or reported but who actually had osteoporosis,” White said. “It was incredibly prevalent.”
But the number of patients identified was more than the hospital could comfortably handle.
Ironically, he added, “To my relief and probably not to the benefit of the patients, there was a system upgrade of the radiology reporting system, which was incompatible with the natural language processing technology that I had installed. The AI was turned off at that point, but I had a look over the edge and into the mine pit.”
“The lesson learned,” White told this news organization, is “If you mine the medical record for unidentified patients before you know what to do with the output, you create a medico-legal minefield. You need to be careful what you wish for with technology, because it may actually come true.”
Grappling With the Treatment Gap
An (over)abundance of patients is likely contributing to the “osteoporosis treatment gap” that Australia’s fracture liaison services, which handle many of these patients, are grappling with. One recent meta-analysis showed that not all eligible patients are treated and that not all patients who are treated actually start treatment. Another study showed that only a minority of patients — anywhere between 20% and 40% — who start are still persisting at about 3 years, White said.
Various types of fracture liaison services exist, he noted. The model that has been shown to best promote adherence is the one requiring clinicians to “identify, educate [usually, the primary care physician], evaluate, start treatment, continue treatment, and follow-up at 12 months for to confirm that there is adherence.”
What’s happening now, he said, is that the technology is identifying a high number of vertebral crush fractures, and there’s no education or evaluation. “The radiologist just refers the patient to a primary care physician and hopes for the best. AI isn’t contributing to solving the treatment gap problem; it’s amplifying it. It’s ahead of the ability of organizations to accommodate the findings.”
Solutions, he said, would require support at the top of health systems and organizations, and funding to proceed; data surveys concentrating on vertical integration of the medical record to follow patients wherever they are — eg, hospital, primary care — in their health journeys; a workflow with synchronous diagnosis and treatment planning, delivery, monitoring, and payment; and clinical and community champions advocating and “leading the charge in health tech.”
Furthermore, he advised, organizations need to be “very, very careful with safety and security — that is, managing the digital risks.”
“Oscar Wilde said there are two tragedies in life: One is not getting what one wants, and the other is getting it,” White concluded. “In my career, we’ve moved on from not knowing how to treat osteoporosis to knowing how to treat it. And that is both an asset and a liability.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Using GLP-1s to Meet BMI Goal for Orthopedic Surgery
The woman, in severe pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis, was confined to a wheelchair and had been told that would likely be for life. To qualify for hip replacement surgery, she needed to lose 100 pounds, a seemingly impossible goal. But she wanted to try.
“We tried a couple of medicines — oral medicines off-label — topiramate, phentermine,” said Leslie Golden, MD, MPH, DABM, a family medicine physician and obesity medicine specialist in Watertown, Wisconsin, 42 miles northeast of Madison.
They weren’t enough. But then Golden turned to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and they delivered.
“She did lose a significant amount of weight and was able to get the hip replacement,” said Golden.
It took a couple of years. However, seeing her walk into her office, rather than wheel in, “is still one of the joys of my practice,” Golden said. “She’s so grateful. She felt everyone else had written her off.”
As she told Golden: “If I fell and broke my leg today, they would take me to surgery without concern.”
Because her hip replacement was viewed as a nonemergency procedure, the accepted threshold for elective safe surgery was a body mass index (BMI) < 40. That BMI cutoff can vary from provider to provider and medical facility to medical facility but is often required for other surgeries as well, including kidney and lung transplants, gender-affirming surgery, bariatric surgery, hernia surgery, and in vitro fertilization procedures.
She worked with Rajit Chakravarty, MD, an adult reconstructive surgeon who practices in Watertown and nearby Madison, to oversee the weight loss.
High BMIs & Surgery Issues
High BMIs have long been linked with postsurgery complications, poor wound healing, and other issues, although some research now is questioning some of those associations. Even so, surgeons have long stressed weight loss for their patients with obesity before orthopedic and other procedures.
These days, surgeons are more likely to need to have that talk. In the last decade, the age-adjusted prevalence of severe obesity — a BMI of ≥ 40 — has increased from 7.7% to 9.7% of US adults. The number of joint replacements is also rising — more than 700,000 total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and more than 450,000 total hip arthroplasty (THA), according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. As the population ages, those numbers are expected to increase.
Making the GLP-1 Choice
GLP-1s aren’t the only choice, of course. But they’re often more effective, as Golden found, than other medications. And when his patients with obesity are offered bariatric surgery or GLP-1s, “people definitely want to avoid the bariatric surgery,” Chakravarty said.
With the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of semaglutide (Wegovy) in June 2021 for chronic weight management and then tirzepatide (Zepbound) in November 2023, interest has boomed, he said, among his surgery candidates with a high BMI.
The FDA approved Wegovy based on clinical trials, including one in which participants lost an average of 12.4% of initial body weight compared with those on placebo. It approved Zepbound based on clinical trials, including one in which those on Zepbound lost an average of 18% of their body weight, compared with those on placebo.
The wheelchair-bound woman, now 65, began with a BMI of 63, Golden said. She negotiated a cutoff of 45 with the surgeon and got the go-ahead. Currently, her BMI is 36 as she stayed on the medications.
Beyond the benefit of GLP-1s helping patients meet the BMI cutoff, some research finds fewer postoperative infections and readmissions with their use. This study found the medications did lower both, and another found reduced readmissions and complications.
Growing Partnerships, Increasing Success
Helping patients lose weight isn’t just about lowering the BMI, Chakravarty pointed out. The aim is to improve nutritional health — to teach patients how to eat healthfully for their needs, in turn improving other health barometers. Referring them to an obesity medicine physician helps to meet those goals.
When Daniel Wiznia, MD, a Yale Medicine orthopedic surgeon and codirector of the Avascular Necrosis Program, has a patient who must delay a TKA or THA until they meet a BMI cutoff, he refers that patient to the Yale Medicine Center for Weight Management, New Haven, Connecticut, to learn about weight loss, including the options of anti-obesity medications or bariatric surgery.
Taking the GLP-1s can be a game changer, according to Wiznia and John Morton, MD, MPH, FACS, FASMBS, Yale’s medical director of Bariatric Surgery and professor and vice chair of surgery, who is a physician-director of the center. The program includes other options, such as bariatric surgery, and emphasizes diet and other lifestyle measures. GLP-1s give about a 15% weight loss, Morton said, compared with bariatric surgery providing up to 30%.
Sarah Stombaugh, MD, a family medicine and obesity medicine physician in Charlottesville, Virginia, often gets referrals from two orthopedic surgeons in her community. One recent patient in her early 60s had a BMI of 43.2, too high to qualify for the TKA she needed. On GLP-1s, the initial goal was to decrease a weight of 244 to 225, bringing the BMI to 39.9. The woman did that, then kept losing before her surgery was scheduled, getting to a weight of 210 or a BMI of 37 and staying there for 3 months before the surgery.
She had the TKA, and 5 months out, she is doing well, Stombaugh said. “We do medical weight loss primarily with the GLP-1s because they’re simply the best, the most effective,” Stombaugh said. She does occasionally use oral medications such as naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave).
Stombaugh sees the collaborating trend as still evolving. When she attends obesity medicine conferences, not all her colleagues report they are partnering with surgeons. But she predicts the practice will increase, saying the popularization of what she terms the more effective GLP-1 medications Wegovy and Zepbound is driving it. Partnering with the surgeon requires a conversation at the beginning, when the referral is made, about goals. After that, she sees her patient monthly and sends progress notes to the surgeon.
Golden collaborates with three orthopedic groups in her area, primarily for knee and hip surgeries, but has also helped patients meet the BMI cutoff before spine-related surgeries. She is helping a lung transplant patient now. She has seen several patients who must meet BMI requirements before starting in vitro fertilization, due to the need for conscious sedation for egg retrieval. She has had a few patients who had to meet a BMI cutoff for nonemergency hernia repair.
Insurance Issues
Insurance remains an issue for the pricey medications. “Only about a third of patients are routinely covered with insurance,” Morton said.
However, it’s improving, he said. Golden also finds about a third of private payers cover the medication but tries to use manufacturers’ coupons to help defray the costs (from about $1000 or $1400 to about $500 a month). She has sometimes gotten enough samples to get patients to their BMI goal
Morton consulted for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Olympus, Teleflex, and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The woman, in severe pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis, was confined to a wheelchair and had been told that would likely be for life. To qualify for hip replacement surgery, she needed to lose 100 pounds, a seemingly impossible goal. But she wanted to try.
“We tried a couple of medicines — oral medicines off-label — topiramate, phentermine,” said Leslie Golden, MD, MPH, DABM, a family medicine physician and obesity medicine specialist in Watertown, Wisconsin, 42 miles northeast of Madison.
They weren’t enough. But then Golden turned to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and they delivered.
“She did lose a significant amount of weight and was able to get the hip replacement,” said Golden.
It took a couple of years. However, seeing her walk into her office, rather than wheel in, “is still one of the joys of my practice,” Golden said. “She’s so grateful. She felt everyone else had written her off.”
As she told Golden: “If I fell and broke my leg today, they would take me to surgery without concern.”
Because her hip replacement was viewed as a nonemergency procedure, the accepted threshold for elective safe surgery was a body mass index (BMI) < 40. That BMI cutoff can vary from provider to provider and medical facility to medical facility but is often required for other surgeries as well, including kidney and lung transplants, gender-affirming surgery, bariatric surgery, hernia surgery, and in vitro fertilization procedures.
She worked with Rajit Chakravarty, MD, an adult reconstructive surgeon who practices in Watertown and nearby Madison, to oversee the weight loss.
High BMIs & Surgery Issues
High BMIs have long been linked with postsurgery complications, poor wound healing, and other issues, although some research now is questioning some of those associations. Even so, surgeons have long stressed weight loss for their patients with obesity before orthopedic and other procedures.
These days, surgeons are more likely to need to have that talk. In the last decade, the age-adjusted prevalence of severe obesity — a BMI of ≥ 40 — has increased from 7.7% to 9.7% of US adults. The number of joint replacements is also rising — more than 700,000 total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and more than 450,000 total hip arthroplasty (THA), according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. As the population ages, those numbers are expected to increase.
Making the GLP-1 Choice
GLP-1s aren’t the only choice, of course. But they’re often more effective, as Golden found, than other medications. And when his patients with obesity are offered bariatric surgery or GLP-1s, “people definitely want to avoid the bariatric surgery,” Chakravarty said.
With the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of semaglutide (Wegovy) in June 2021 for chronic weight management and then tirzepatide (Zepbound) in November 2023, interest has boomed, he said, among his surgery candidates with a high BMI.
The FDA approved Wegovy based on clinical trials, including one in which participants lost an average of 12.4% of initial body weight compared with those on placebo. It approved Zepbound based on clinical trials, including one in which those on Zepbound lost an average of 18% of their body weight, compared with those on placebo.
The wheelchair-bound woman, now 65, began with a BMI of 63, Golden said. She negotiated a cutoff of 45 with the surgeon and got the go-ahead. Currently, her BMI is 36 as she stayed on the medications.
Beyond the benefit of GLP-1s helping patients meet the BMI cutoff, some research finds fewer postoperative infections and readmissions with their use. This study found the medications did lower both, and another found reduced readmissions and complications.
Growing Partnerships, Increasing Success
Helping patients lose weight isn’t just about lowering the BMI, Chakravarty pointed out. The aim is to improve nutritional health — to teach patients how to eat healthfully for their needs, in turn improving other health barometers. Referring them to an obesity medicine physician helps to meet those goals.
When Daniel Wiznia, MD, a Yale Medicine orthopedic surgeon and codirector of the Avascular Necrosis Program, has a patient who must delay a TKA or THA until they meet a BMI cutoff, he refers that patient to the Yale Medicine Center for Weight Management, New Haven, Connecticut, to learn about weight loss, including the options of anti-obesity medications or bariatric surgery.
Taking the GLP-1s can be a game changer, according to Wiznia and John Morton, MD, MPH, FACS, FASMBS, Yale’s medical director of Bariatric Surgery and professor and vice chair of surgery, who is a physician-director of the center. The program includes other options, such as bariatric surgery, and emphasizes diet and other lifestyle measures. GLP-1s give about a 15% weight loss, Morton said, compared with bariatric surgery providing up to 30%.
Sarah Stombaugh, MD, a family medicine and obesity medicine physician in Charlottesville, Virginia, often gets referrals from two orthopedic surgeons in her community. One recent patient in her early 60s had a BMI of 43.2, too high to qualify for the TKA she needed. On GLP-1s, the initial goal was to decrease a weight of 244 to 225, bringing the BMI to 39.9. The woman did that, then kept losing before her surgery was scheduled, getting to a weight of 210 or a BMI of 37 and staying there for 3 months before the surgery.
She had the TKA, and 5 months out, she is doing well, Stombaugh said. “We do medical weight loss primarily with the GLP-1s because they’re simply the best, the most effective,” Stombaugh said. She does occasionally use oral medications such as naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave).
Stombaugh sees the collaborating trend as still evolving. When she attends obesity medicine conferences, not all her colleagues report they are partnering with surgeons. But she predicts the practice will increase, saying the popularization of what she terms the more effective GLP-1 medications Wegovy and Zepbound is driving it. Partnering with the surgeon requires a conversation at the beginning, when the referral is made, about goals. After that, she sees her patient monthly and sends progress notes to the surgeon.
Golden collaborates with three orthopedic groups in her area, primarily for knee and hip surgeries, but has also helped patients meet the BMI cutoff before spine-related surgeries. She is helping a lung transplant patient now. She has seen several patients who must meet BMI requirements before starting in vitro fertilization, due to the need for conscious sedation for egg retrieval. She has had a few patients who had to meet a BMI cutoff for nonemergency hernia repair.
Insurance Issues
Insurance remains an issue for the pricey medications. “Only about a third of patients are routinely covered with insurance,” Morton said.
However, it’s improving, he said. Golden also finds about a third of private payers cover the medication but tries to use manufacturers’ coupons to help defray the costs (from about $1000 or $1400 to about $500 a month). She has sometimes gotten enough samples to get patients to their BMI goal
Morton consulted for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Olympus, Teleflex, and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The woman, in severe pain from hip and knee osteoarthritis, was confined to a wheelchair and had been told that would likely be for life. To qualify for hip replacement surgery, she needed to lose 100 pounds, a seemingly impossible goal. But she wanted to try.
“We tried a couple of medicines — oral medicines off-label — topiramate, phentermine,” said Leslie Golden, MD, MPH, DABM, a family medicine physician and obesity medicine specialist in Watertown, Wisconsin, 42 miles northeast of Madison.
They weren’t enough. But then Golden turned to glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, and they delivered.
“She did lose a significant amount of weight and was able to get the hip replacement,” said Golden.
It took a couple of years. However, seeing her walk into her office, rather than wheel in, “is still one of the joys of my practice,” Golden said. “She’s so grateful. She felt everyone else had written her off.”
As she told Golden: “If I fell and broke my leg today, they would take me to surgery without concern.”
Because her hip replacement was viewed as a nonemergency procedure, the accepted threshold for elective safe surgery was a body mass index (BMI) < 40. That BMI cutoff can vary from provider to provider and medical facility to medical facility but is often required for other surgeries as well, including kidney and lung transplants, gender-affirming surgery, bariatric surgery, hernia surgery, and in vitro fertilization procedures.
She worked with Rajit Chakravarty, MD, an adult reconstructive surgeon who practices in Watertown and nearby Madison, to oversee the weight loss.
High BMIs & Surgery Issues
High BMIs have long been linked with postsurgery complications, poor wound healing, and other issues, although some research now is questioning some of those associations. Even so, surgeons have long stressed weight loss for their patients with obesity before orthopedic and other procedures.
These days, surgeons are more likely to need to have that talk. In the last decade, the age-adjusted prevalence of severe obesity — a BMI of ≥ 40 — has increased from 7.7% to 9.7% of US adults. The number of joint replacements is also rising — more than 700,000 total knee arthroplasty (TKA) and more than 450,000 total hip arthroplasty (THA), according to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. As the population ages, those numbers are expected to increase.
Making the GLP-1 Choice
GLP-1s aren’t the only choice, of course. But they’re often more effective, as Golden found, than other medications. And when his patients with obesity are offered bariatric surgery or GLP-1s, “people definitely want to avoid the bariatric surgery,” Chakravarty said.
With the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval of semaglutide (Wegovy) in June 2021 for chronic weight management and then tirzepatide (Zepbound) in November 2023, interest has boomed, he said, among his surgery candidates with a high BMI.
The FDA approved Wegovy based on clinical trials, including one in which participants lost an average of 12.4% of initial body weight compared with those on placebo. It approved Zepbound based on clinical trials, including one in which those on Zepbound lost an average of 18% of their body weight, compared with those on placebo.
The wheelchair-bound woman, now 65, began with a BMI of 63, Golden said. She negotiated a cutoff of 45 with the surgeon and got the go-ahead. Currently, her BMI is 36 as she stayed on the medications.
Beyond the benefit of GLP-1s helping patients meet the BMI cutoff, some research finds fewer postoperative infections and readmissions with their use. This study found the medications did lower both, and another found reduced readmissions and complications.
Growing Partnerships, Increasing Success
Helping patients lose weight isn’t just about lowering the BMI, Chakravarty pointed out. The aim is to improve nutritional health — to teach patients how to eat healthfully for their needs, in turn improving other health barometers. Referring them to an obesity medicine physician helps to meet those goals.
When Daniel Wiznia, MD, a Yale Medicine orthopedic surgeon and codirector of the Avascular Necrosis Program, has a patient who must delay a TKA or THA until they meet a BMI cutoff, he refers that patient to the Yale Medicine Center for Weight Management, New Haven, Connecticut, to learn about weight loss, including the options of anti-obesity medications or bariatric surgery.
Taking the GLP-1s can be a game changer, according to Wiznia and John Morton, MD, MPH, FACS, FASMBS, Yale’s medical director of Bariatric Surgery and professor and vice chair of surgery, who is a physician-director of the center. The program includes other options, such as bariatric surgery, and emphasizes diet and other lifestyle measures. GLP-1s give about a 15% weight loss, Morton said, compared with bariatric surgery providing up to 30%.
Sarah Stombaugh, MD, a family medicine and obesity medicine physician in Charlottesville, Virginia, often gets referrals from two orthopedic surgeons in her community. One recent patient in her early 60s had a BMI of 43.2, too high to qualify for the TKA she needed. On GLP-1s, the initial goal was to decrease a weight of 244 to 225, bringing the BMI to 39.9. The woman did that, then kept losing before her surgery was scheduled, getting to a weight of 210 or a BMI of 37 and staying there for 3 months before the surgery.
She had the TKA, and 5 months out, she is doing well, Stombaugh said. “We do medical weight loss primarily with the GLP-1s because they’re simply the best, the most effective,” Stombaugh said. She does occasionally use oral medications such as naltrexone/bupropion (Contrave).
Stombaugh sees the collaborating trend as still evolving. When she attends obesity medicine conferences, not all her colleagues report they are partnering with surgeons. But she predicts the practice will increase, saying the popularization of what she terms the more effective GLP-1 medications Wegovy and Zepbound is driving it. Partnering with the surgeon requires a conversation at the beginning, when the referral is made, about goals. After that, she sees her patient monthly and sends progress notes to the surgeon.
Golden collaborates with three orthopedic groups in her area, primarily for knee and hip surgeries, but has also helped patients meet the BMI cutoff before spine-related surgeries. She is helping a lung transplant patient now. She has seen several patients who must meet BMI requirements before starting in vitro fertilization, due to the need for conscious sedation for egg retrieval. She has had a few patients who had to meet a BMI cutoff for nonemergency hernia repair.
Insurance Issues
Insurance remains an issue for the pricey medications. “Only about a third of patients are routinely covered with insurance,” Morton said.
However, it’s improving, he said. Golden also finds about a third of private payers cover the medication but tries to use manufacturers’ coupons to help defray the costs (from about $1000 or $1400 to about $500 a month). She has sometimes gotten enough samples to get patients to their BMI goal
Morton consulted for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Olympus, Teleflex, and Johnson & Johnson.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.



