User login
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
More than 50 million US adults report experiencing chronic pain, with nearly 7% experiencing high-impact chronic pain.1-3 Chronic pain negatively affects daily function, results in lost productivity, is a leading cause of disability, and is more prevalent among veterans compared with the general population.1,2,4-6 Estimates from 2021 suggest the prevalence of chronic pain among veterans exceeds 30%; > 11% experienced high-impact chronic pain.1
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) have a prominent role in chronic pain management. Pharmacologic options for treating pain, once a mainstay of therapy, present several challenges for patients and PCPs, including drug-drug interactions and adverse effects.7 The US opioid epidemic and shift to a biopsychosocial model of chronic pain care have increased emphasis on nonpharmacologic treatment options.8,9 These include integrative modalities, which incorporate conventional approaches with an array of complementary health approaches.10-12
Integrative therapy is a prominent feature in whole person care, which may be best exemplified by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of care.13-14 Whole health empowers an individual to take charge of their health and well-being so they can “live their life to the fullest.”14 As implemented in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), whole health includes the use of evidence-based
METHODS
Using a cross-sectional survey design, PCPs and patients with chronic back pain affiliated with the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System were invited to participate in separate but similar surveys to assess knowledge, interest, and use of nonpharmacologic integrative modalities for the treatment of chronic pain. In May, June, and July 2023, 78 PCPs received 3 email
Both survey instruments are available upon request, were developed by the study team, and included a mix of yes/no questions, “select all that apply” items, Likert scale response items, and open-ended questions. For one question about which modalities they would like available, the respondent was instructed to select up to 5 modalities. The instruments were extensively pretested by members of the study team, which included 2 PCPs and a nonveteran with chronic back pain.
The list of integrative modalities included in the survey was derived from the tier 1 and tier 2 complementary and integrative health modalities identified in a VHA Directive on complementary and integrative health.15,16 Tier 1 approaches are considered to have sufficient evidence and must be made available to veterans either within a VA medical facility or in the community. Tier 2 approaches are generally considered safe and may be made available but do not have sufficient evidence to mandate their provision. For participant ease, the integrative modalities were divided into 5 subgroups: manual therapies, energy/biofield therapies, mental health therapies, nutrition counseling, and movement therapies. The clinician survey assessed clinicians’ training and interest, clinical and personal use, and perceived barriers to providing integrative modalities for chronic pain. Professional and personal demographic data were also collected. Similarly, the patient survey assessed use of integrative therapies, perceptions of and interest in integrative modalities, and potential barriers to use. Demographic and health-related information was also collected.
Data analysis included descriptive statistics (eg, frequency counts, means, medians) and visual graphic displays. Separate analyses were conducted for clinicians and patients in addition to a comparative analysis of the use and potential interest in integrative modalities. Analysis were conducted using R software. This study was deemed nonresearch quality improvement by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System facility research oversight board and institutional review board approval was not solicited.
RESULTS
Twenty-eight clinicians completed the survey, yielding a participation rate of 36%. Participating clinicians had a median (IQR) age of 48 years (9.5), 15 self-identified as White (54%), 8 as Asian (29%), 15 as female (54%), 26 as non-Hispanic (93%), and 25 were medical doctors or doctors of osteopathy (89%). Nineteen (68%) worked at the main hospital outpatient clinic, and 9 practiced at community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs). Thirteen respondents (46%) reported having no formal education or training in integrative approaches. Among those with prior training, 8 clinicians had nutrition counseling (29%) and 7 had psychologic therapy training (25%). Thirteen respondents (46%) also reported using integrative modalities for personal health needs: 8 used psychological therapies, 8 used movement therapies, 10 used integrative modalities for stress management or relaxation, and 8 used them for physical symptoms (Table 1).
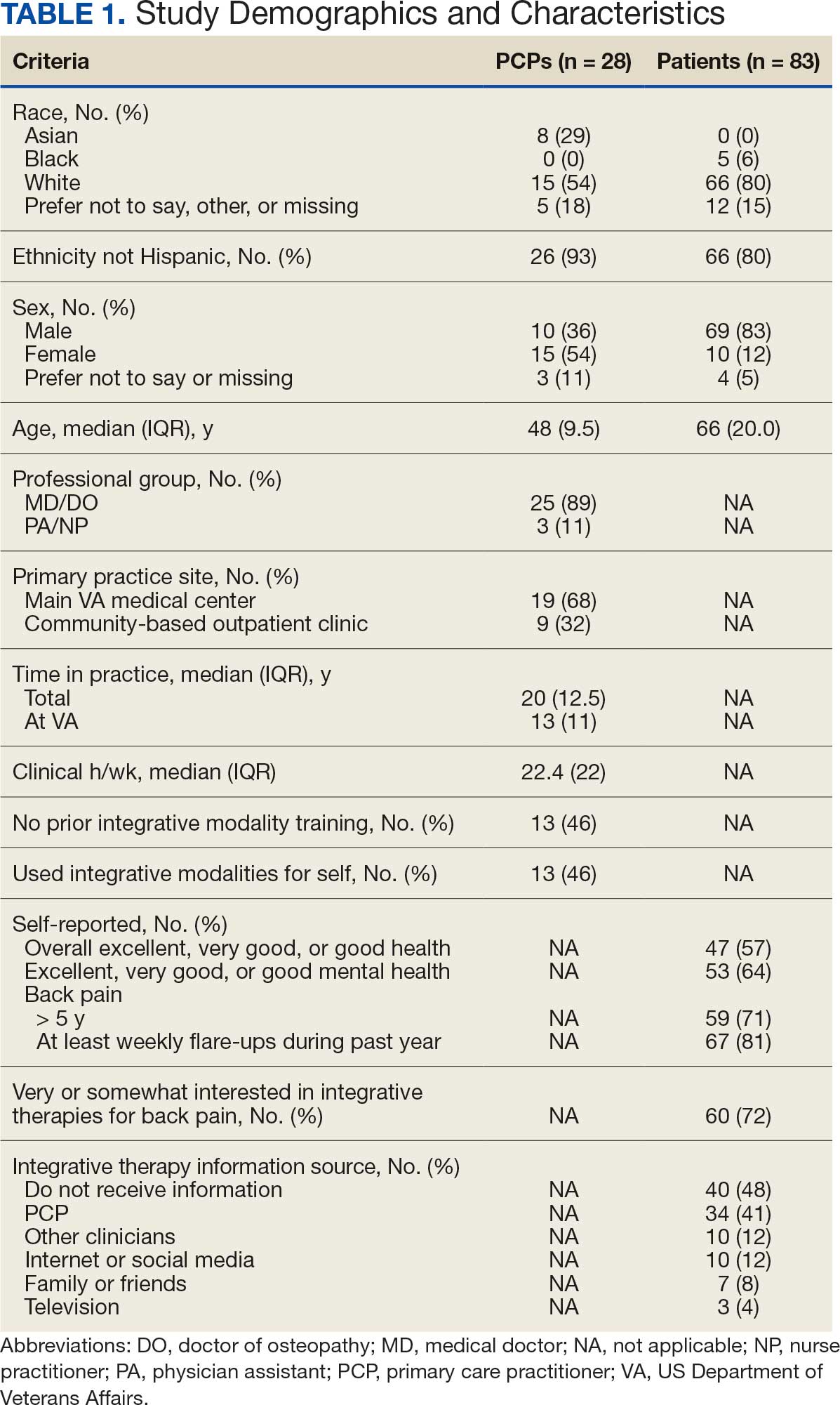
Overall, 85 of 200 patients (43%) responded to the study survey. Two patients indicated they did not have chronic back pain and were excluded. Patients had a median (IQR) age of 66 (20) years, with 66 self-identifying as White (80%), 69 as male (83%), and 66 as non-Hispanic (80%). Forty-four patients (53%) received care at CBOCs. Forty-seven patients reported excellent, very good, or good overall health (57%), while 53 reported excellent, very good, or good mental health (64%). Fifty-nine patients reported back pain duration > 5 years (71%), and 67 (81%) indicated experiencing back pain flare-ups at least once per week over the previous 12 months. Sixty patients (72%) indicated they were somewhat or very interested in using integrative therapies as a back pain treatment; however, 40 patients (48%) indicated they had not received information about these therapies. Among those who indicated they had received information, the most frequently reported source was their PCP (41%). Most patients (72%) also reported feeling somewhat to very comfortable discussing integrative medicine therapies with their PCP.
Integrative Therapy Recommendations and Use
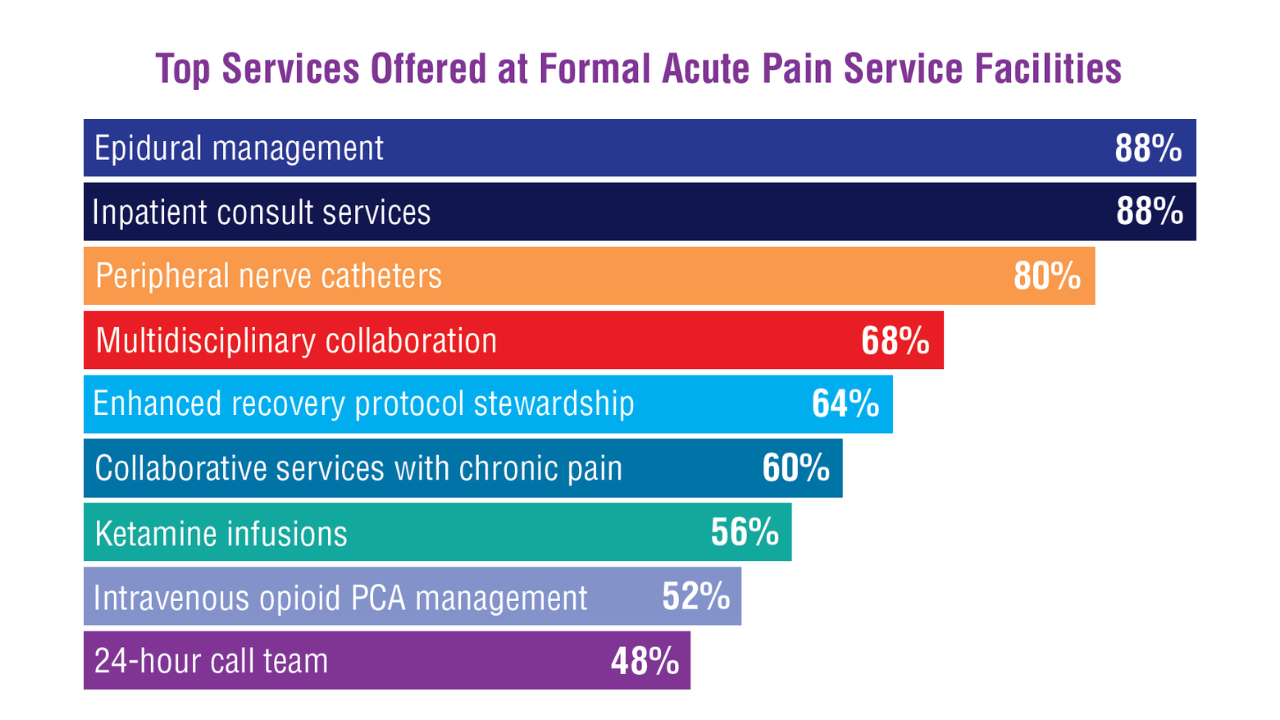
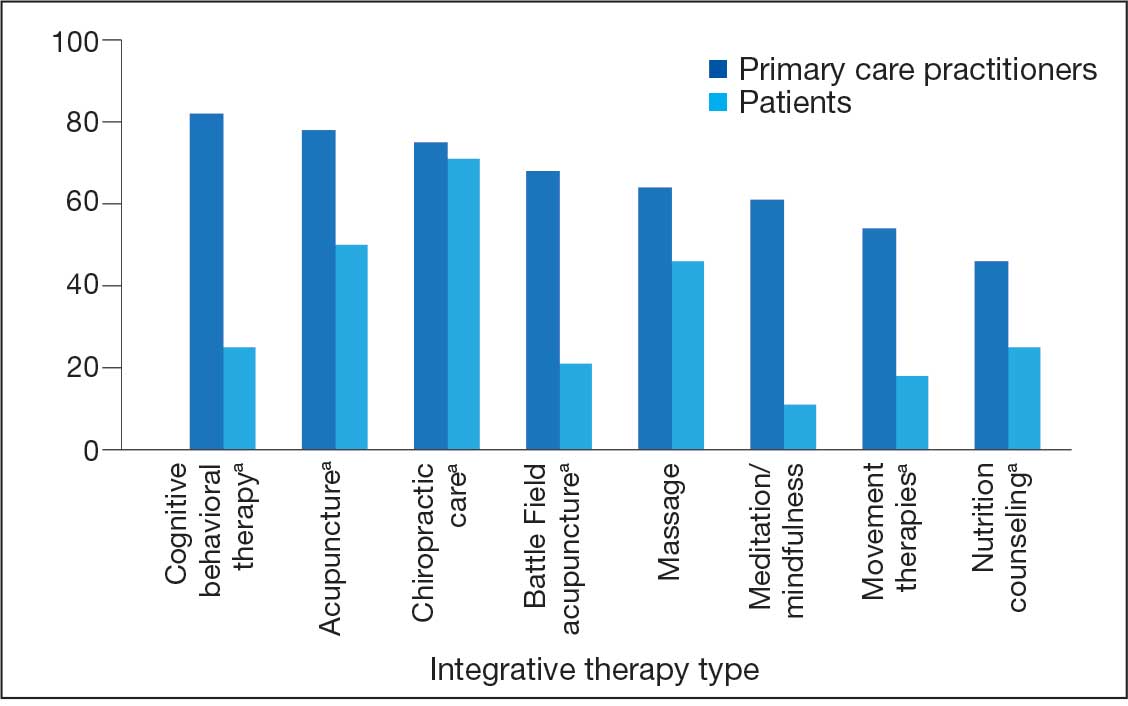
PCPs reported recommending multiple integrative modalities: 23 (82%) recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy, 22 (79%) recommended acupuncture, 21 (75%) recommended chiropractic, 19 (68%) recommended battlefield acupuncture, recommended massage 18 (64%), 17 (61%) recommended meditation or mindfulness, and 15 (54%) recommended movement therapies such as yoga or tai chi/qigong (Figure 1). The only therapies used by at least half of the patients were chiropractic used by 59 patients (71%) and acupuncture by 42 patients (51%). Thirty-eight patients (46%) reported massage use and 21 patients (25%) used cognitive-behavioral therapy (Table 2).
Integrative Therapies Desired
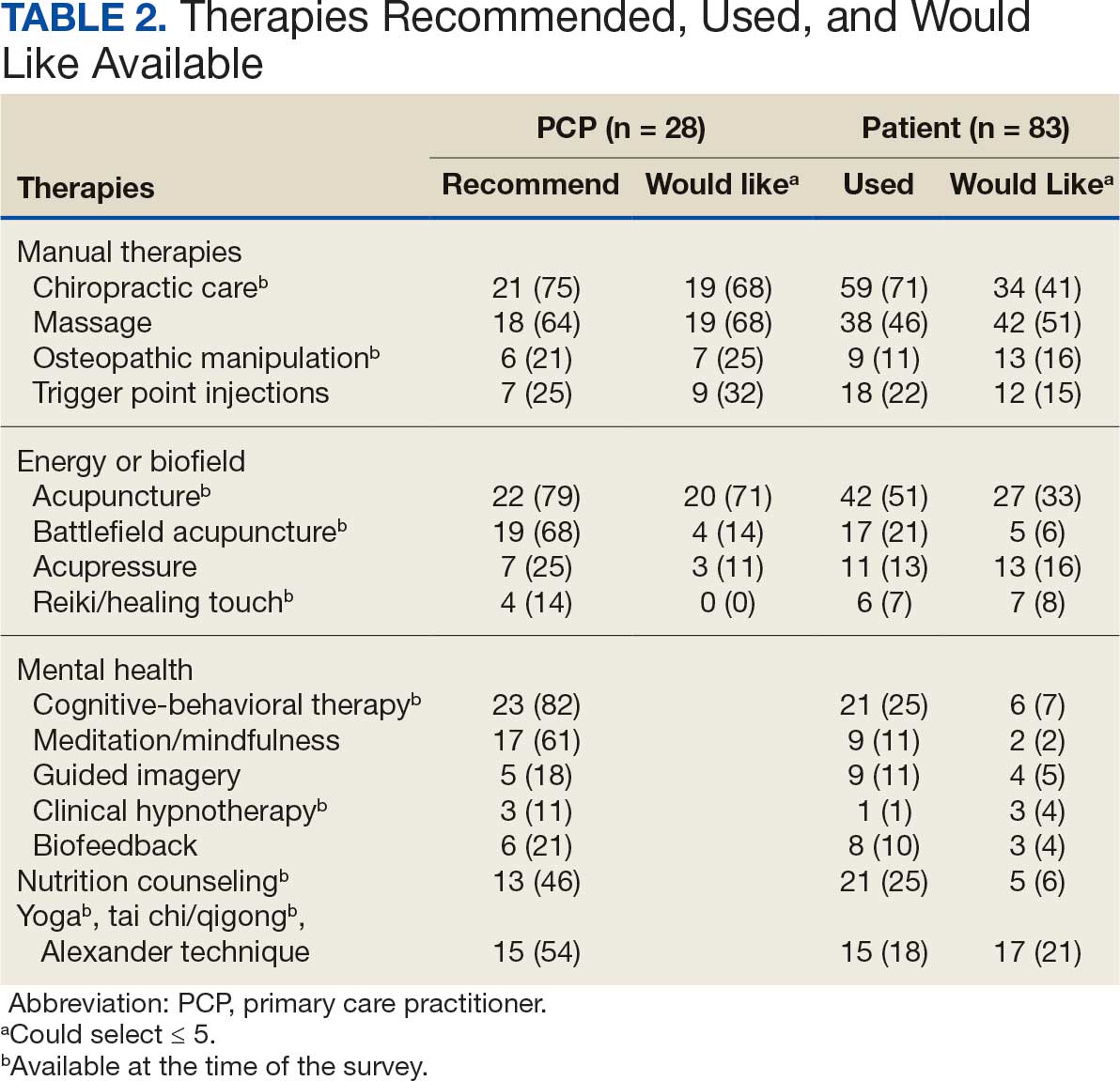
A majority of PCPs identified acupuncture (n = 20, 71%), chiropractic (n = 19, 68%), and massage (n = 19, 68%) as therapies they would most like to have available for patients with chronic pain (Figure 2). Similarly, patients identified massage (n = 42, 51%), chiropractic (n = 34, 41%), and acupuncture (n = 27, 33%) as most desired. Seventeen patients (21%) expressed interest in movement therapies.
Barriers to Integrative Therapies Use
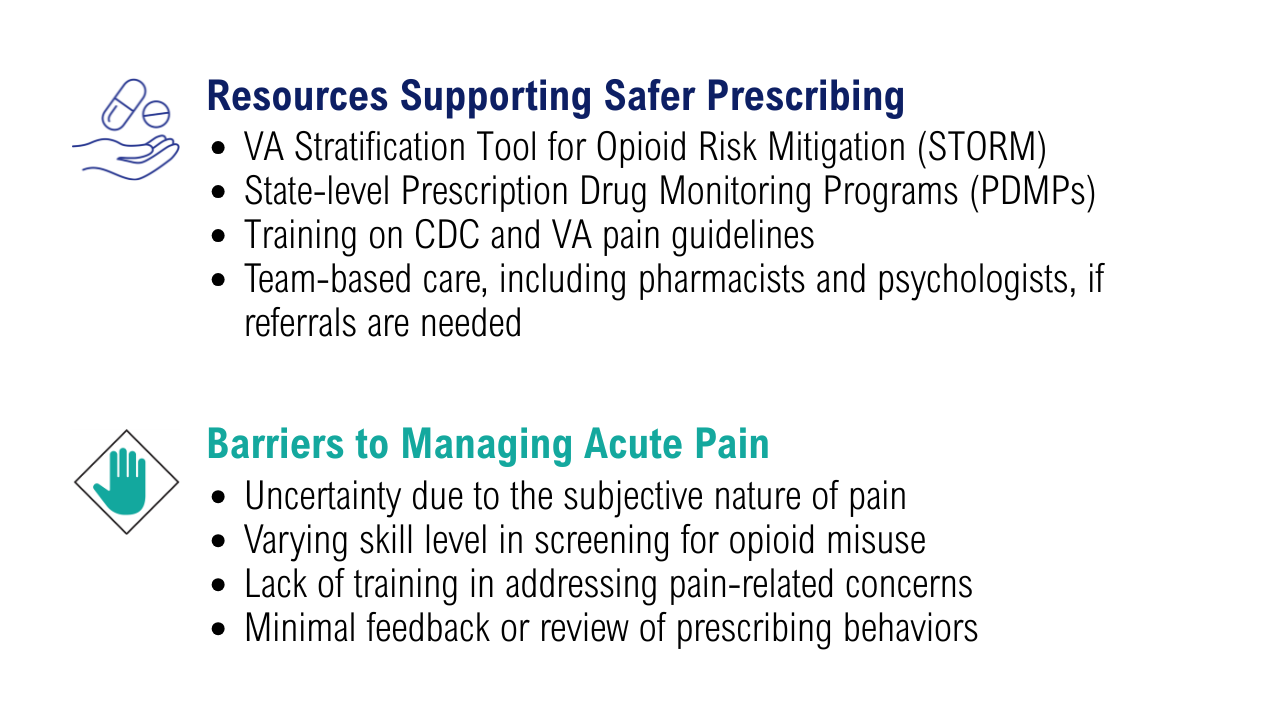
When asked about barriers to use, 26 PCPs (93%) identified access to services as a somewhat or extremely likely barrier, and 22 identified time constraints (79%) (Table 3). However, 17 PCPs (61%) noted lack of familiarity, and 18 (64%) noted a lack of scientific evidence as barriers to recommending integrative modalities. Among patients, 33 (40%) indicated not knowing what services were available at their facility as a barrier, 32 (39%) were not familiar with specific therapies, and 21 (25%) indicated a lack of clarity about the benefits of a specific therapy. Only 14 patients (17%) indicated that there were no obstacles to use.

DISCUSSION
Use of integrative therapies, including complementary treatments, is an increasingly important part of chronic pain management. This survey study suggests VA PCPs are willing to recommend integrative therapies and patients with chronic back pain both desire and use several therapies. Moreover, both groups expressed interest in greater availability of similar therapies. The results also highlight key barriers, such as knowledge gaps, that should be addressed to increase the uptake of integrative modalities for managing chronic pain.
An increasing number of US adults are using complementary health approaches, an important component of integrative therapy.12 This trend includes an increase in use for pain management, from 42.3% in 2002 to 49.2% in 2022; chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage were most frequently used.12 Similarly, chiropractic, acupuncture and massage were most often used by this sample of veterans with chronic back pain and were identified by the highest percentages of PCPs and patients as the therapies they would most like available.
There were areas where the opinions of patients and clinicians differed. As has been seen previously reported, clinicians largely recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy while patients showed less interest.17 Additionally, while patients expressed interest in the availability of movement therapies, such as yoga, PCPs expressed more interest in other strategies, such as trigger point injections. These differences may reflect true preference or a tendency for clinicians and patients to select therapies with which they are more familiar. Additional research is needed to better understand the acceptability and potential use of integrative health treatments across a broad array of therapeutic options.
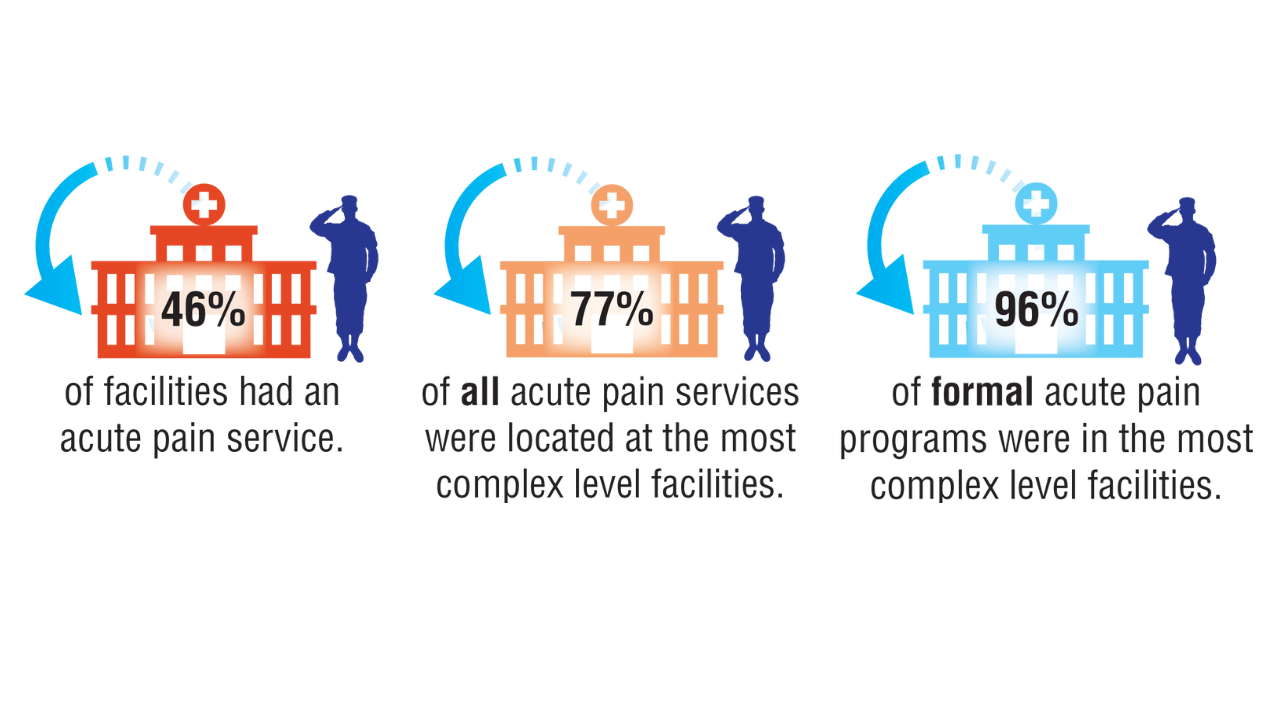
Despite VHA policy requiring facilities to provide certain complementary and integrative health modalities, almost all PCPs identified access to services as a major obstacle.15 Based on evidence and a rigorous vetting process, services currently required on-site, via telehealth, or through community partners include acupuncture and battlefield acupuncture (battlefield auricular acupuncture), biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, medical massage therapy, medication, tai chi/qigong, and yoga. Optional approaches, which may be made available to veterans, include chiropractic and healing touch. Outside the VHA, some states have introduced or enacted legislation mandating insurance coverage of nonpharmacological pain treatments.18 However, these requirements and mandates do not help address challenges such as the availability of trained/qualified practitioners.19,20 Ensuring access to complementary and integrative health treatments requires a more concerted effort to ensure that supply meets demand. It is also important to acknowledge the budgetary and physical space constraints that further limit access to services. Although expansion and integration of integrative medicine services remain a priority within the VA Whole Health program, implementation is contingent on available financial and infrastructure resources.
Time was also identified by PCPs as a barrier to recommending integrative therapies to patients. Developing and implementing time-efficient communication strategies for patient education such as concise talking points and informational handouts could help address this barrier. Furthermore, leveraging existing programs and engaging the entire health care team in patient education and referral could help increase integrative and complementary therapy uptake and use.
Although access and time were identified as major barriers, these findings also suggest that PCP and patient knowledge are another target area for enhancing the use of complementary and integrative therapies. Like prior research, most clinicians identified a lack of familiarity with certain services and a lack of scientific evidence as extremely or somewhat likely to affect their ability to offer integrative services to patients with chronic pain.21 Likewise, about 40% of patients identified being unfamiliar with a specific therapy as one of the major obstacles to receiving integrative therapies, with a similar number identifying PCPs as a source of information. The lack of familiarity may be due in part to the evolving nomenclature, with terms such as alternative, complementary, and integrative used to describe approaches outside what is often considered conventional medicine.10 On the other hand, there has also been considerable expansion in the number of therapies within this domain, along with an expanding evidence base. This suggests a need for targeted educational strategies for clinicians and patients, which can be rapidly deployed and continuously adapted as new therapies and evidence emerge.
Limitations
There are some inherent limitations with a survey-based approach, including sampling, non-response, and social desirability biases. In addition, this study only included PCPs and patients affiliated with a single VA medical center. Steps to mitigate these limitations included maintaining survey anonymity and reporting information about respondent characteristics to enhance transparency about the representativeness of the study findings.
CONCLUSIONS
Expanding the use of nonpharmacological pain treatments, including integrative modalities, is essential for safe and effective chronic pain management and reducing opioid use. Our findings show that VA PCPs and patients with chronic back pain are interested in and have some experience with certain integrative therapies. However, even within the context of a health care system that supports the use of integrative therapies for chronic pain as part of whole person care, increasing uptake will require addressing access and time-related constraints as well as ongoing clinician and patient education.
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, et al. Chronic pain among adults — United States, 2018-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Yong RJ, Mullins PM, Bhattacharyya N. Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain. 2022;163:E328-E332. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002291
- Nahin RL, Feinberg T, Kapos FP, Terman GW. Estimated rates of incident and persistent chronic pain among US adults, 2019-2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2313563. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13563
- Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet. 2024;403:2133-2161. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 5.
- Qureshi AR, Patel M, Neumark S, et al. Prevalence of chronic non-cancer pain among military veterans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ Mil Health. 2025;171:310-314. doi:10.1136/military-2023-002554
- Feldman DE, Nahin RL. Disability among persons with chronic severe back pain: results from a nationally representative population-based sample. J Pain. 2022;23:2144-2154. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.016
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:514-530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367
- van Erp RMA, Huijnen IPJ, Jakobs MLG, Kleijnen J, Smeets RJEM. Effectiveness of primary care interventions using a biopsychosocial approach in chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain Practice. 2019;19:224-241. doi:10.1111/papr.12735
- Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al. Nonpharmacologic therapies for low back pain: a systematic review for an American College of physicians clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:493-505. doi:10.7326/M16-2459
- Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: what’s in a name? National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Updated April 2021. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/complementary-alternative-or-integrative-health-whats-in-a-name.
- Taylor SL, Elwy AR. Complementary and alternative medicine for US veterans and active duty military personnel promising steps to improve their health. Med Care. 2014;52:S1-S4. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000270.
- Nahin RL, Rhee A, Stussman B. Use of complementary health approaches overall and for pain management by US adults. JAMA. 2024;331:613-615. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26775
- Gantt CJ, Donovan N, Khung M. Veterans Affairs’ Whole Health System of Care for transitioning service members and veterans. Mil Med. 2023;188:28-32. doi:10.1093/milmed/usad047
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the Whole Health System of Care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57:53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Department of Veterans Affairs VHA. VHA Policy Directive 1137: Provision of Complementary and Integrative Health. December 2022. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.va.gov/VHApublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10072
- Giannitrapani KF, Holliday JR, Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Taylor SL. Synthesizing the strength of the evidence of complementary and integrative health therapies for pain. Pain Med. 2019;20:1831-1840. doi:10.1093/pm/pnz068
- Belitskaya-Levy I, David Clark J, Shih MC, Bair MJ. Treatment preferences for chronic low back pain: views of veterans and their providers. J Pain Res. 2021;14:161-171. doi:10.2147/JPR.S290400
- Onstott TN, Hurst S, Kronick R, Tsou AC, Groessl E, McMenamin SB. Health insurance mandates for nonpharmacological pain treatments in 7 US states. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:E245737. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5737
- Sullivan M, Leach M, Snow J, Moonaz S. The North American yoga therapy workforce survey. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:39-48. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2017.01.006
- Bolton R, Ritter G, Highland K, Larson MJ. The relationship between capacity and utilization of nonpharmacologic therapies in the US Military Health System. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-07700-4
- Stussman BJ, Nahin RL, Barnes PM, Scott R, Feinberg T, Ward BW. Reasons office-based physicians in the United States recommend common complementary health approaches to patients: an exploratory study using a national survey. J Integr Complement Med. 2022;28:651-663. doi:10.1089/jicm.2022.0493
More than 50 million US adults report experiencing chronic pain, with nearly 7% experiencing high-impact chronic pain.1-3 Chronic pain negatively affects daily function, results in lost productivity, is a leading cause of disability, and is more prevalent among veterans compared with the general population.1,2,4-6 Estimates from 2021 suggest the prevalence of chronic pain among veterans exceeds 30%; > 11% experienced high-impact chronic pain.1
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) have a prominent role in chronic pain management. Pharmacologic options for treating pain, once a mainstay of therapy, present several challenges for patients and PCPs, including drug-drug interactions and adverse effects.7 The US opioid epidemic and shift to a biopsychosocial model of chronic pain care have increased emphasis on nonpharmacologic treatment options.8,9 These include integrative modalities, which incorporate conventional approaches with an array of complementary health approaches.10-12
Integrative therapy is a prominent feature in whole person care, which may be best exemplified by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of care.13-14 Whole health empowers an individual to take charge of their health and well-being so they can “live their life to the fullest.”14 As implemented in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), whole health includes the use of evidence-based
METHODS
Using a cross-sectional survey design, PCPs and patients with chronic back pain affiliated with the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System were invited to participate in separate but similar surveys to assess knowledge, interest, and use of nonpharmacologic integrative modalities for the treatment of chronic pain. In May, June, and July 2023, 78 PCPs received 3 email
Both survey instruments are available upon request, were developed by the study team, and included a mix of yes/no questions, “select all that apply” items, Likert scale response items, and open-ended questions. For one question about which modalities they would like available, the respondent was instructed to select up to 5 modalities. The instruments were extensively pretested by members of the study team, which included 2 PCPs and a nonveteran with chronic back pain.
The list of integrative modalities included in the survey was derived from the tier 1 and tier 2 complementary and integrative health modalities identified in a VHA Directive on complementary and integrative health.15,16 Tier 1 approaches are considered to have sufficient evidence and must be made available to veterans either within a VA medical facility or in the community. Tier 2 approaches are generally considered safe and may be made available but do not have sufficient evidence to mandate their provision. For participant ease, the integrative modalities were divided into 5 subgroups: manual therapies, energy/biofield therapies, mental health therapies, nutrition counseling, and movement therapies. The clinician survey assessed clinicians’ training and interest, clinical and personal use, and perceived barriers to providing integrative modalities for chronic pain. Professional and personal demographic data were also collected. Similarly, the patient survey assessed use of integrative therapies, perceptions of and interest in integrative modalities, and potential barriers to use. Demographic and health-related information was also collected.
Data analysis included descriptive statistics (eg, frequency counts, means, medians) and visual graphic displays. Separate analyses were conducted for clinicians and patients in addition to a comparative analysis of the use and potential interest in integrative modalities. Analysis were conducted using R software. This study was deemed nonresearch quality improvement by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System facility research oversight board and institutional review board approval was not solicited.
RESULTS
Twenty-eight clinicians completed the survey, yielding a participation rate of 36%. Participating clinicians had a median (IQR) age of 48 years (9.5), 15 self-identified as White (54%), 8 as Asian (29%), 15 as female (54%), 26 as non-Hispanic (93%), and 25 were medical doctors or doctors of osteopathy (89%). Nineteen (68%) worked at the main hospital outpatient clinic, and 9 practiced at community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs). Thirteen respondents (46%) reported having no formal education or training in integrative approaches. Among those with prior training, 8 clinicians had nutrition counseling (29%) and 7 had psychologic therapy training (25%). Thirteen respondents (46%) also reported using integrative modalities for personal health needs: 8 used psychological therapies, 8 used movement therapies, 10 used integrative modalities for stress management or relaxation, and 8 used them for physical symptoms (Table 1).

Overall, 85 of 200 patients (43%) responded to the study survey. Two patients indicated they did not have chronic back pain and were excluded. Patients had a median (IQR) age of 66 (20) years, with 66 self-identifying as White (80%), 69 as male (83%), and 66 as non-Hispanic (80%). Forty-four patients (53%) received care at CBOCs. Forty-seven patients reported excellent, very good, or good overall health (57%), while 53 reported excellent, very good, or good mental health (64%). Fifty-nine patients reported back pain duration > 5 years (71%), and 67 (81%) indicated experiencing back pain flare-ups at least once per week over the previous 12 months. Sixty patients (72%) indicated they were somewhat or very interested in using integrative therapies as a back pain treatment; however, 40 patients (48%) indicated they had not received information about these therapies. Among those who indicated they had received information, the most frequently reported source was their PCP (41%). Most patients (72%) also reported feeling somewhat to very comfortable discussing integrative medicine therapies with their PCP.
Integrative Therapy Recommendations and Use
PCPs reported recommending multiple integrative modalities: 23 (82%) recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy, 22 (79%) recommended acupuncture, 21 (75%) recommended chiropractic, 19 (68%) recommended battlefield acupuncture, recommended massage 18 (64%), 17 (61%) recommended meditation or mindfulness, and 15 (54%) recommended movement therapies such as yoga or tai chi/qigong (Figure 1). The only therapies used by at least half of the patients were chiropractic used by 59 patients (71%) and acupuncture by 42 patients (51%). Thirty-eight patients (46%) reported massage use and 21 patients (25%) used cognitive-behavioral therapy (Table 2).


Integrative Therapies Desired
A majority of PCPs identified acupuncture (n = 20, 71%), chiropractic (n = 19, 68%), and massage (n = 19, 68%) as therapies they would most like to have available for patients with chronic pain (Figure 2). Similarly, patients identified massage (n = 42, 51%), chiropractic (n = 34, 41%), and acupuncture (n = 27, 33%) as most desired. Seventeen patients (21%) expressed interest in movement therapies.

Barriers to Integrative Therapies Use
When asked about barriers to use, 26 PCPs (93%) identified access to services as a somewhat or extremely likely barrier, and 22 identified time constraints (79%) (Table 3). However, 17 PCPs (61%) noted lack of familiarity, and 18 (64%) noted a lack of scientific evidence as barriers to recommending integrative modalities. Among patients, 33 (40%) indicated not knowing what services were available at their facility as a barrier, 32 (39%) were not familiar with specific therapies, and 21 (25%) indicated a lack of clarity about the benefits of a specific therapy. Only 14 patients (17%) indicated that there were no obstacles to use.

DISCUSSION
Use of integrative therapies, including complementary treatments, is an increasingly important part of chronic pain management. This survey study suggests VA PCPs are willing to recommend integrative therapies and patients with chronic back pain both desire and use several therapies. Moreover, both groups expressed interest in greater availability of similar therapies. The results also highlight key barriers, such as knowledge gaps, that should be addressed to increase the uptake of integrative modalities for managing chronic pain.
An increasing number of US adults are using complementary health approaches, an important component of integrative therapy.12 This trend includes an increase in use for pain management, from 42.3% in 2002 to 49.2% in 2022; chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage were most frequently used.12 Similarly, chiropractic, acupuncture and massage were most often used by this sample of veterans with chronic back pain and were identified by the highest percentages of PCPs and patients as the therapies they would most like available.
There were areas where the opinions of patients and clinicians differed. As has been seen previously reported, clinicians largely recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy while patients showed less interest.17 Additionally, while patients expressed interest in the availability of movement therapies, such as yoga, PCPs expressed more interest in other strategies, such as trigger point injections. These differences may reflect true preference or a tendency for clinicians and patients to select therapies with which they are more familiar. Additional research is needed to better understand the acceptability and potential use of integrative health treatments across a broad array of therapeutic options.
Despite VHA policy requiring facilities to provide certain complementary and integrative health modalities, almost all PCPs identified access to services as a major obstacle.15 Based on evidence and a rigorous vetting process, services currently required on-site, via telehealth, or through community partners include acupuncture and battlefield acupuncture (battlefield auricular acupuncture), biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, medical massage therapy, medication, tai chi/qigong, and yoga. Optional approaches, which may be made available to veterans, include chiropractic and healing touch. Outside the VHA, some states have introduced or enacted legislation mandating insurance coverage of nonpharmacological pain treatments.18 However, these requirements and mandates do not help address challenges such as the availability of trained/qualified practitioners.19,20 Ensuring access to complementary and integrative health treatments requires a more concerted effort to ensure that supply meets demand. It is also important to acknowledge the budgetary and physical space constraints that further limit access to services. Although expansion and integration of integrative medicine services remain a priority within the VA Whole Health program, implementation is contingent on available financial and infrastructure resources.
Time was also identified by PCPs as a barrier to recommending integrative therapies to patients. Developing and implementing time-efficient communication strategies for patient education such as concise talking points and informational handouts could help address this barrier. Furthermore, leveraging existing programs and engaging the entire health care team in patient education and referral could help increase integrative and complementary therapy uptake and use.
Although access and time were identified as major barriers, these findings also suggest that PCP and patient knowledge are another target area for enhancing the use of complementary and integrative therapies. Like prior research, most clinicians identified a lack of familiarity with certain services and a lack of scientific evidence as extremely or somewhat likely to affect their ability to offer integrative services to patients with chronic pain.21 Likewise, about 40% of patients identified being unfamiliar with a specific therapy as one of the major obstacles to receiving integrative therapies, with a similar number identifying PCPs as a source of information. The lack of familiarity may be due in part to the evolving nomenclature, with terms such as alternative, complementary, and integrative used to describe approaches outside what is often considered conventional medicine.10 On the other hand, there has also been considerable expansion in the number of therapies within this domain, along with an expanding evidence base. This suggests a need for targeted educational strategies for clinicians and patients, which can be rapidly deployed and continuously adapted as new therapies and evidence emerge.
Limitations
There are some inherent limitations with a survey-based approach, including sampling, non-response, and social desirability biases. In addition, this study only included PCPs and patients affiliated with a single VA medical center. Steps to mitigate these limitations included maintaining survey anonymity and reporting information about respondent characteristics to enhance transparency about the representativeness of the study findings.
CONCLUSIONS
Expanding the use of nonpharmacological pain treatments, including integrative modalities, is essential for safe and effective chronic pain management and reducing opioid use. Our findings show that VA PCPs and patients with chronic back pain are interested in and have some experience with certain integrative therapies. However, even within the context of a health care system that supports the use of integrative therapies for chronic pain as part of whole person care, increasing uptake will require addressing access and time-related constraints as well as ongoing clinician and patient education.
More than 50 million US adults report experiencing chronic pain, with nearly 7% experiencing high-impact chronic pain.1-3 Chronic pain negatively affects daily function, results in lost productivity, is a leading cause of disability, and is more prevalent among veterans compared with the general population.1,2,4-6 Estimates from 2021 suggest the prevalence of chronic pain among veterans exceeds 30%; > 11% experienced high-impact chronic pain.1
Primary care practitioners (PCPs) have a prominent role in chronic pain management. Pharmacologic options for treating pain, once a mainstay of therapy, present several challenges for patients and PCPs, including drug-drug interactions and adverse effects.7 The US opioid epidemic and shift to a biopsychosocial model of chronic pain care have increased emphasis on nonpharmacologic treatment options.8,9 These include integrative modalities, which incorporate conventional approaches with an array of complementary health approaches.10-12
Integrative therapy is a prominent feature in whole person care, which may be best exemplified by the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Whole Health System of care.13-14 Whole health empowers an individual to take charge of their health and well-being so they can “live their life to the fullest.”14 As implemented in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), whole health includes the use of evidence-based
METHODS
Using a cross-sectional survey design, PCPs and patients with chronic back pain affiliated with the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System were invited to participate in separate but similar surveys to assess knowledge, interest, and use of nonpharmacologic integrative modalities for the treatment of chronic pain. In May, June, and July 2023, 78 PCPs received 3 email
Both survey instruments are available upon request, were developed by the study team, and included a mix of yes/no questions, “select all that apply” items, Likert scale response items, and open-ended questions. For one question about which modalities they would like available, the respondent was instructed to select up to 5 modalities. The instruments were extensively pretested by members of the study team, which included 2 PCPs and a nonveteran with chronic back pain.
The list of integrative modalities included in the survey was derived from the tier 1 and tier 2 complementary and integrative health modalities identified in a VHA Directive on complementary and integrative health.15,16 Tier 1 approaches are considered to have sufficient evidence and must be made available to veterans either within a VA medical facility or in the community. Tier 2 approaches are generally considered safe and may be made available but do not have sufficient evidence to mandate their provision. For participant ease, the integrative modalities were divided into 5 subgroups: manual therapies, energy/biofield therapies, mental health therapies, nutrition counseling, and movement therapies. The clinician survey assessed clinicians’ training and interest, clinical and personal use, and perceived barriers to providing integrative modalities for chronic pain. Professional and personal demographic data were also collected. Similarly, the patient survey assessed use of integrative therapies, perceptions of and interest in integrative modalities, and potential barriers to use. Demographic and health-related information was also collected.
Data analysis included descriptive statistics (eg, frequency counts, means, medians) and visual graphic displays. Separate analyses were conducted for clinicians and patients in addition to a comparative analysis of the use and potential interest in integrative modalities. Analysis were conducted using R software. This study was deemed nonresearch quality improvement by the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System facility research oversight board and institutional review board approval was not solicited.
RESULTS
Twenty-eight clinicians completed the survey, yielding a participation rate of 36%. Participating clinicians had a median (IQR) age of 48 years (9.5), 15 self-identified as White (54%), 8 as Asian (29%), 15 as female (54%), 26 as non-Hispanic (93%), and 25 were medical doctors or doctors of osteopathy (89%). Nineteen (68%) worked at the main hospital outpatient clinic, and 9 practiced at community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs). Thirteen respondents (46%) reported having no formal education or training in integrative approaches. Among those with prior training, 8 clinicians had nutrition counseling (29%) and 7 had psychologic therapy training (25%). Thirteen respondents (46%) also reported using integrative modalities for personal health needs: 8 used psychological therapies, 8 used movement therapies, 10 used integrative modalities for stress management or relaxation, and 8 used them for physical symptoms (Table 1).

Overall, 85 of 200 patients (43%) responded to the study survey. Two patients indicated they did not have chronic back pain and were excluded. Patients had a median (IQR) age of 66 (20) years, with 66 self-identifying as White (80%), 69 as male (83%), and 66 as non-Hispanic (80%). Forty-four patients (53%) received care at CBOCs. Forty-seven patients reported excellent, very good, or good overall health (57%), while 53 reported excellent, very good, or good mental health (64%). Fifty-nine patients reported back pain duration > 5 years (71%), and 67 (81%) indicated experiencing back pain flare-ups at least once per week over the previous 12 months. Sixty patients (72%) indicated they were somewhat or very interested in using integrative therapies as a back pain treatment; however, 40 patients (48%) indicated they had not received information about these therapies. Among those who indicated they had received information, the most frequently reported source was their PCP (41%). Most patients (72%) also reported feeling somewhat to very comfortable discussing integrative medicine therapies with their PCP.
Integrative Therapy Recommendations and Use
PCPs reported recommending multiple integrative modalities: 23 (82%) recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy, 22 (79%) recommended acupuncture, 21 (75%) recommended chiropractic, 19 (68%) recommended battlefield acupuncture, recommended massage 18 (64%), 17 (61%) recommended meditation or mindfulness, and 15 (54%) recommended movement therapies such as yoga or tai chi/qigong (Figure 1). The only therapies used by at least half of the patients were chiropractic used by 59 patients (71%) and acupuncture by 42 patients (51%). Thirty-eight patients (46%) reported massage use and 21 patients (25%) used cognitive-behavioral therapy (Table 2).


Integrative Therapies Desired
A majority of PCPs identified acupuncture (n = 20, 71%), chiropractic (n = 19, 68%), and massage (n = 19, 68%) as therapies they would most like to have available for patients with chronic pain (Figure 2). Similarly, patients identified massage (n = 42, 51%), chiropractic (n = 34, 41%), and acupuncture (n = 27, 33%) as most desired. Seventeen patients (21%) expressed interest in movement therapies.

Barriers to Integrative Therapies Use
When asked about barriers to use, 26 PCPs (93%) identified access to services as a somewhat or extremely likely barrier, and 22 identified time constraints (79%) (Table 3). However, 17 PCPs (61%) noted lack of familiarity, and 18 (64%) noted a lack of scientific evidence as barriers to recommending integrative modalities. Among patients, 33 (40%) indicated not knowing what services were available at their facility as a barrier, 32 (39%) were not familiar with specific therapies, and 21 (25%) indicated a lack of clarity about the benefits of a specific therapy. Only 14 patients (17%) indicated that there were no obstacles to use.

DISCUSSION
Use of integrative therapies, including complementary treatments, is an increasingly important part of chronic pain management. This survey study suggests VA PCPs are willing to recommend integrative therapies and patients with chronic back pain both desire and use several therapies. Moreover, both groups expressed interest in greater availability of similar therapies. The results also highlight key barriers, such as knowledge gaps, that should be addressed to increase the uptake of integrative modalities for managing chronic pain.
An increasing number of US adults are using complementary health approaches, an important component of integrative therapy.12 This trend includes an increase in use for pain management, from 42.3% in 2002 to 49.2% in 2022; chiropractic care, acupuncture, and massage were most frequently used.12 Similarly, chiropractic, acupuncture and massage were most often used by this sample of veterans with chronic back pain and were identified by the highest percentages of PCPs and patients as the therapies they would most like available.
There were areas where the opinions of patients and clinicians differed. As has been seen previously reported, clinicians largely recommended cognitive-behavioral therapy while patients showed less interest.17 Additionally, while patients expressed interest in the availability of movement therapies, such as yoga, PCPs expressed more interest in other strategies, such as trigger point injections. These differences may reflect true preference or a tendency for clinicians and patients to select therapies with which they are more familiar. Additional research is needed to better understand the acceptability and potential use of integrative health treatments across a broad array of therapeutic options.
Despite VHA policy requiring facilities to provide certain complementary and integrative health modalities, almost all PCPs identified access to services as a major obstacle.15 Based on evidence and a rigorous vetting process, services currently required on-site, via telehealth, or through community partners include acupuncture and battlefield acupuncture (battlefield auricular acupuncture), biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, medical massage therapy, medication, tai chi/qigong, and yoga. Optional approaches, which may be made available to veterans, include chiropractic and healing touch. Outside the VHA, some states have introduced or enacted legislation mandating insurance coverage of nonpharmacological pain treatments.18 However, these requirements and mandates do not help address challenges such as the availability of trained/qualified practitioners.19,20 Ensuring access to complementary and integrative health treatments requires a more concerted effort to ensure that supply meets demand. It is also important to acknowledge the budgetary and physical space constraints that further limit access to services. Although expansion and integration of integrative medicine services remain a priority within the VA Whole Health program, implementation is contingent on available financial and infrastructure resources.
Time was also identified by PCPs as a barrier to recommending integrative therapies to patients. Developing and implementing time-efficient communication strategies for patient education such as concise talking points and informational handouts could help address this barrier. Furthermore, leveraging existing programs and engaging the entire health care team in patient education and referral could help increase integrative and complementary therapy uptake and use.
Although access and time were identified as major barriers, these findings also suggest that PCP and patient knowledge are another target area for enhancing the use of complementary and integrative therapies. Like prior research, most clinicians identified a lack of familiarity with certain services and a lack of scientific evidence as extremely or somewhat likely to affect their ability to offer integrative services to patients with chronic pain.21 Likewise, about 40% of patients identified being unfamiliar with a specific therapy as one of the major obstacles to receiving integrative therapies, with a similar number identifying PCPs as a source of information. The lack of familiarity may be due in part to the evolving nomenclature, with terms such as alternative, complementary, and integrative used to describe approaches outside what is often considered conventional medicine.10 On the other hand, there has also been considerable expansion in the number of therapies within this domain, along with an expanding evidence base. This suggests a need for targeted educational strategies for clinicians and patients, which can be rapidly deployed and continuously adapted as new therapies and evidence emerge.
Limitations
There are some inherent limitations with a survey-based approach, including sampling, non-response, and social desirability biases. In addition, this study only included PCPs and patients affiliated with a single VA medical center. Steps to mitigate these limitations included maintaining survey anonymity and reporting information about respondent characteristics to enhance transparency about the representativeness of the study findings.
CONCLUSIONS
Expanding the use of nonpharmacological pain treatments, including integrative modalities, is essential for safe and effective chronic pain management and reducing opioid use. Our findings show that VA PCPs and patients with chronic back pain are interested in and have some experience with certain integrative therapies. However, even within the context of a health care system that supports the use of integrative therapies for chronic pain as part of whole person care, increasing uptake will require addressing access and time-related constraints as well as ongoing clinician and patient education.
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, et al. Chronic pain among adults — United States, 2018-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Yong RJ, Mullins PM, Bhattacharyya N. Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain. 2022;163:E328-E332. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002291
- Nahin RL, Feinberg T, Kapos FP, Terman GW. Estimated rates of incident and persistent chronic pain among US adults, 2019-2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2313563. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13563
- Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet. 2024;403:2133-2161. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 5.
- Qureshi AR, Patel M, Neumark S, et al. Prevalence of chronic non-cancer pain among military veterans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ Mil Health. 2025;171:310-314. doi:10.1136/military-2023-002554
- Feldman DE, Nahin RL. Disability among persons with chronic severe back pain: results from a nationally representative population-based sample. J Pain. 2022;23:2144-2154. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.016
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:514-530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367
- van Erp RMA, Huijnen IPJ, Jakobs MLG, Kleijnen J, Smeets RJEM. Effectiveness of primary care interventions using a biopsychosocial approach in chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain Practice. 2019;19:224-241. doi:10.1111/papr.12735
- Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al. Nonpharmacologic therapies for low back pain: a systematic review for an American College of physicians clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:493-505. doi:10.7326/M16-2459
- Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: what’s in a name? National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Updated April 2021. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/complementary-alternative-or-integrative-health-whats-in-a-name.
- Taylor SL, Elwy AR. Complementary and alternative medicine for US veterans and active duty military personnel promising steps to improve their health. Med Care. 2014;52:S1-S4. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000270.
- Nahin RL, Rhee A, Stussman B. Use of complementary health approaches overall and for pain management by US adults. JAMA. 2024;331:613-615. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26775
- Gantt CJ, Donovan N, Khung M. Veterans Affairs’ Whole Health System of Care for transitioning service members and veterans. Mil Med. 2023;188:28-32. doi:10.1093/milmed/usad047
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the Whole Health System of Care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57:53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Department of Veterans Affairs VHA. VHA Policy Directive 1137: Provision of Complementary and Integrative Health. December 2022. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.va.gov/VHApublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10072
- Giannitrapani KF, Holliday JR, Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Taylor SL. Synthesizing the strength of the evidence of complementary and integrative health therapies for pain. Pain Med. 2019;20:1831-1840. doi:10.1093/pm/pnz068
- Belitskaya-Levy I, David Clark J, Shih MC, Bair MJ. Treatment preferences for chronic low back pain: views of veterans and their providers. J Pain Res. 2021;14:161-171. doi:10.2147/JPR.S290400
- Onstott TN, Hurst S, Kronick R, Tsou AC, Groessl E, McMenamin SB. Health insurance mandates for nonpharmacological pain treatments in 7 US states. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:E245737. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5737
- Sullivan M, Leach M, Snow J, Moonaz S. The North American yoga therapy workforce survey. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:39-48. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2017.01.006
- Bolton R, Ritter G, Highland K, Larson MJ. The relationship between capacity and utilization of nonpharmacologic therapies in the US Military Health System. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-07700-4
- Stussman BJ, Nahin RL, Barnes PM, Scott R, Feinberg T, Ward BW. Reasons office-based physicians in the United States recommend common complementary health approaches to patients: an exploratory study using a national survey. J Integr Complement Med. 2022;28:651-663. doi:10.1089/jicm.2022.0493
- Rikard SM, Strahan AE, Schmit KM, et al. Chronic pain among adults — United States, 2018-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72:379-385. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7215a1
- Yong RJ, Mullins PM, Bhattacharyya N. Prevalence of chronic pain among adults in the United States. Pain. 2022;163:E328-E332. doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002291
- Nahin RL, Feinberg T, Kapos FP, Terman GW. Estimated rates of incident and persistent chronic pain among US adults, 2019-2020. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6:e2313563. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.13563
- Ferrari AJ, Santomauro DF, Aali A, et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. The Lancet. 2024;403:2133-2161. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 5.
- Qureshi AR, Patel M, Neumark S, et al. Prevalence of chronic non-cancer pain among military veterans: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ Mil Health. 2025;171:310-314. doi:10.1136/military-2023-002554
- Feldman DE, Nahin RL. Disability among persons with chronic severe back pain: results from a nationally representative population-based sample. J Pain. 2022;23:2144-2154. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.016
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, Forciea MA. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:514-530. doi:10.7326/M16-2367
- van Erp RMA, Huijnen IPJ, Jakobs MLG, Kleijnen J, Smeets RJEM. Effectiveness of primary care interventions using a biopsychosocial approach in chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Pain Practice. 2019;19:224-241. doi:10.1111/papr.12735
- Chou R, Deyo R, Friedly J, et al. Nonpharmacologic therapies for low back pain: a systematic review for an American College of physicians clinical practice guideline. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166:493-505. doi:10.7326/M16-2459
- Complementary, alternative, or integrative health: what’s in a name? National Institutes of Health, National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health. Updated April 2021. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/complementary-alternative-or-integrative-health-whats-in-a-name.
- Taylor SL, Elwy AR. Complementary and alternative medicine for US veterans and active duty military personnel promising steps to improve their health. Med Care. 2014;52:S1-S4. doi:10.1097/MLR.0000000000000270.
- Nahin RL, Rhee A, Stussman B. Use of complementary health approaches overall and for pain management by US adults. JAMA. 2024;331:613-615. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.26775
- Gantt CJ, Donovan N, Khung M. Veterans Affairs’ Whole Health System of Care for transitioning service members and veterans. Mil Med. 2023;188:28-32. doi:10.1093/milmed/usad047
- Bokhour BG, Hyde J, Kligler B, et al. From patient outcomes to system change: evaluating the impact of VHA’s implementation of the Whole Health System of Care. Health Serv Res. 2022;57:53-65. doi:10.1111/1475-6773.13938
- Department of Veterans Affairs VHA. VHA Policy Directive 1137: Provision of Complementary and Integrative Health. December 2022. Accessed December 15, 2025. https://www.va.gov/VHApublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=10072
- Giannitrapani KF, Holliday JR, Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Taylor SL. Synthesizing the strength of the evidence of complementary and integrative health therapies for pain. Pain Med. 2019;20:1831-1840. doi:10.1093/pm/pnz068
- Belitskaya-Levy I, David Clark J, Shih MC, Bair MJ. Treatment preferences for chronic low back pain: views of veterans and their providers. J Pain Res. 2021;14:161-171. doi:10.2147/JPR.S290400
- Onstott TN, Hurst S, Kronick R, Tsou AC, Groessl E, McMenamin SB. Health insurance mandates for nonpharmacological pain treatments in 7 US states. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7:E245737. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5737
- Sullivan M, Leach M, Snow J, Moonaz S. The North American yoga therapy workforce survey. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:39-48. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2017.01.006
- Bolton R, Ritter G, Highland K, Larson MJ. The relationship between capacity and utilization of nonpharmacologic therapies in the US Military Health System. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22. doi:10.1186/s12913-022-07700-4
- Stussman BJ, Nahin RL, Barnes PM, Scott R, Feinberg T, Ward BW. Reasons office-based physicians in the United States recommend common complementary health approaches to patients: an exploratory study using a national survey. J Integr Complement Med. 2022;28:651-663. doi:10.1089/jicm.2022.0493
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
Primary Care Clinician and Patient Knowledge, Interest, and Use of Integrative Treatment Options for Chronic Low Back Pain Management
Rural Cancer Survivors Are More Likely to Have Chronic Pain
TOPLINE:
Rural cancer survivors experience significantly higher rates of chronic pain at 43.0% than those among urban survivors at 33.5%. Even after controlling for demographics and health conditions, rural residents showed 21% higher odds of experiencing chronic pain.
METHODOLOGY:
- Chronic pain prevalence among cancer survivors is twice that of the general US population and is associated with numerous negative outcomes. Rural residence is frequently linked to debilitating long-term survivorship effects, and current data lack information on whether chronic pain disparity exists specifically for rural cancer survivors.
- Researchers pooled data from the 2019–2021 and 2023 National Health Interview Survey, a cross–sectional survey conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics.
- Analysis included 5542 adult cancer survivors diagnosed within the previous 5 years, with 51.6% female participants and 48.4% male participants.
- Chronic pain was defined as pain experienced on most or all days over the past 3 months, following National Center for Health Statistics conventions.
- Rural residence classification was based on noncore or nonmetropolitan counties using the modified National Center for Health Statistics Urban–Rural Classification Scheme for Counties.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rural cancer survivors showed significantly higher odds of experiencing chronic pain compared with urban survivors (odds ratio [OR], 1.21; 95% CI, 1.01-1.45).
- Rural survivors were more likely to be non–Hispanic White, have less than a 4-year college degree, have an income below 200% of the federal poverty level, and have slightly more chronic health conditions.
- Having an income below 100% of the federal poverty level was associated with doubled odds of chronic pain (OR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.54-2.77) compared with having an income at least four times the federal poverty level.
- Each additional health condition increased the odds of experiencing chronic pain by 32% (OR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.26-1.39).
IN PRACTICE:
“Policymakers and health systems should work to close this gap by increasing the availability of pain management resources for rural cancer survivors. Approaches could include innovative payment models for integrative medicine in rural areas or supporting rural clinician access to pain specialists,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Hyojin Choi, PhD, Department of Family Medicine, The Robert Larner MD College of Medicine, University of Vermont in Burlington, Vermont. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors note that the cross–sectional design of the study and limited information on individual respondents’ use of multimodal pain treatment options constrain the interpretation of findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not report any relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Rural cancer survivors experience significantly higher rates of chronic pain at 43.0% than those among urban survivors at 33.5%. Even after controlling for demographics and health conditions, rural residents showed 21% higher odds of experiencing chronic pain.
METHODOLOGY:
- Chronic pain prevalence among cancer survivors is twice that of the general US population and is associated with numerous negative outcomes. Rural residence is frequently linked to debilitating long-term survivorship effects, and current data lack information on whether chronic pain disparity exists specifically for rural cancer survivors.
- Researchers pooled data from the 2019–2021 and 2023 National Health Interview Survey, a cross–sectional survey conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics.
- Analysis included 5542 adult cancer survivors diagnosed within the previous 5 years, with 51.6% female participants and 48.4% male participants.
- Chronic pain was defined as pain experienced on most or all days over the past 3 months, following National Center for Health Statistics conventions.
- Rural residence classification was based on noncore or nonmetropolitan counties using the modified National Center for Health Statistics Urban–Rural Classification Scheme for Counties.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rural cancer survivors showed significantly higher odds of experiencing chronic pain compared with urban survivors (odds ratio [OR], 1.21; 95% CI, 1.01-1.45).
- Rural survivors were more likely to be non–Hispanic White, have less than a 4-year college degree, have an income below 200% of the federal poverty level, and have slightly more chronic health conditions.
- Having an income below 100% of the federal poverty level was associated with doubled odds of chronic pain (OR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.54-2.77) compared with having an income at least four times the federal poverty level.
- Each additional health condition increased the odds of experiencing chronic pain by 32% (OR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.26-1.39).
IN PRACTICE:
“Policymakers and health systems should work to close this gap by increasing the availability of pain management resources for rural cancer survivors. Approaches could include innovative payment models for integrative medicine in rural areas or supporting rural clinician access to pain specialists,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Hyojin Choi, PhD, Department of Family Medicine, The Robert Larner MD College of Medicine, University of Vermont in Burlington, Vermont. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors note that the cross–sectional design of the study and limited information on individual respondents’ use of multimodal pain treatment options constrain the interpretation of findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not report any relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Rural cancer survivors experience significantly higher rates of chronic pain at 43.0% than those among urban survivors at 33.5%. Even after controlling for demographics and health conditions, rural residents showed 21% higher odds of experiencing chronic pain.
METHODOLOGY:
- Chronic pain prevalence among cancer survivors is twice that of the general US population and is associated with numerous negative outcomes. Rural residence is frequently linked to debilitating long-term survivorship effects, and current data lack information on whether chronic pain disparity exists specifically for rural cancer survivors.
- Researchers pooled data from the 2019–2021 and 2023 National Health Interview Survey, a cross–sectional survey conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics.
- Analysis included 5542 adult cancer survivors diagnosed within the previous 5 years, with 51.6% female participants and 48.4% male participants.
- Chronic pain was defined as pain experienced on most or all days over the past 3 months, following National Center for Health Statistics conventions.
- Rural residence classification was based on noncore or nonmetropolitan counties using the modified National Center for Health Statistics Urban–Rural Classification Scheme for Counties.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rural cancer survivors showed significantly higher odds of experiencing chronic pain compared with urban survivors (odds ratio [OR], 1.21; 95% CI, 1.01-1.45).
- Rural survivors were more likely to be non–Hispanic White, have less than a 4-year college degree, have an income below 200% of the federal poverty level, and have slightly more chronic health conditions.
- Having an income below 100% of the federal poverty level was associated with doubled odds of chronic pain (OR, 2.07; 95% CI, 1.54-2.77) compared with having an income at least four times the federal poverty level.
- Each additional health condition increased the odds of experiencing chronic pain by 32% (OR, 1.32; 95% CI, 1.26-1.39).
IN PRACTICE:
“Policymakers and health systems should work to close this gap by increasing the availability of pain management resources for rural cancer survivors. Approaches could include innovative payment models for integrative medicine in rural areas or supporting rural clinician access to pain specialists,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Hyojin Choi, PhD, Department of Family Medicine, The Robert Larner MD College of Medicine, University of Vermont in Burlington, Vermont. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors note that the cross–sectional design of the study and limited information on individual respondents’ use of multimodal pain treatment options constrain the interpretation of findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors did not report any relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A True Community: The Vet-to-Vet Program for Chronic Pain
A True Community: The Vet-to-Vet Program for Chronic Pain
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has continued to advance its understanding and treatment of chronic pain. The VHA National Pain Management Strategy emphasizes the significance of the social context of pain while underscoring the importance of self-management.1 This established strategy ensures that all veterans have access to the appropriate pain care in the proper setting.2 VHA has instituted a stepped care model of pain management, delineating the domains of primary care, secondary consultative services, and tertiary care.3 This directive emphasized a biopsychosocial approach to pain management to prioritize the relationship between biological, psychological, and social factors that influence how veterans experience pain and should commensurately influence how it is managed.
The VHA Office of Patient-Centered Care and Cultural Transformation implemented the Whole Health System of Care as part of the Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act, which included a VHA directive to expand pain management.4,5 Reorientation within this system shifts from defining veterans as passive care recipients to viewing them as active partners in their own care and health. This partnership places additional emphasis on peer-led explorations of mission, aspiration, and purpose.6
Peer-led groups, also known as mutual aid, mutual support, and mutual help groups, have historically been successful for patients undergoing treatment for substance use disorders (eg, Alcoholics Anonymous).7 Mutual help groups have 3 defining characteristics. First, they are run by participants, not professionals, though the latter may have been integral in the founding of the groups. Second, participants share a similar problem (eg, disease state, experience, disposition). Finally, there is a reciprocal exchange of information and psychological support among participants.8,9 Mutual help groups that address chronic pain are rare but becoming more common.10-12 Emerging evidence suggests a positive relationship between peer support and improved well-being, self-efficacy, pain management, and pain self-management skills (eg, activity pacing).13-15
Storytelling as a tool for healing has a long history in indigenous and Western medical traditions.16-19 This includes the treatment of chronic disease, including pain.20,21 The use of storytelling in health care overlaps with the role it plays within many mutual help groups focused on chronic disease treatment.22 Storytelling allows an individual to share their experience with a disease, and take a more active role in their health, and facilitate stronger bonds with others.22 In effect, storytelling is not only important to group cohesion—it also plays a role in an individual’s healing.
Vet-to-Vet
The VHA Office of Rural Health funds Vet-to-Vet, a peer-to-peer program to address limited access to care for rural veterans with chronic pain. Similar to the VHA National Pain Management Strategy, Vet-to-Vet is grounded in the significance of the social context of pain and underscores the importance of self-management.1 The program combines pain care, mutual help, and storytelling to support veterans living with chronic pain. While the primary focus of Vet-to-Vet is rural veterans, the program serves any veteran experiencing chronic pain who is isolated from services, including home-bound urban veterans.
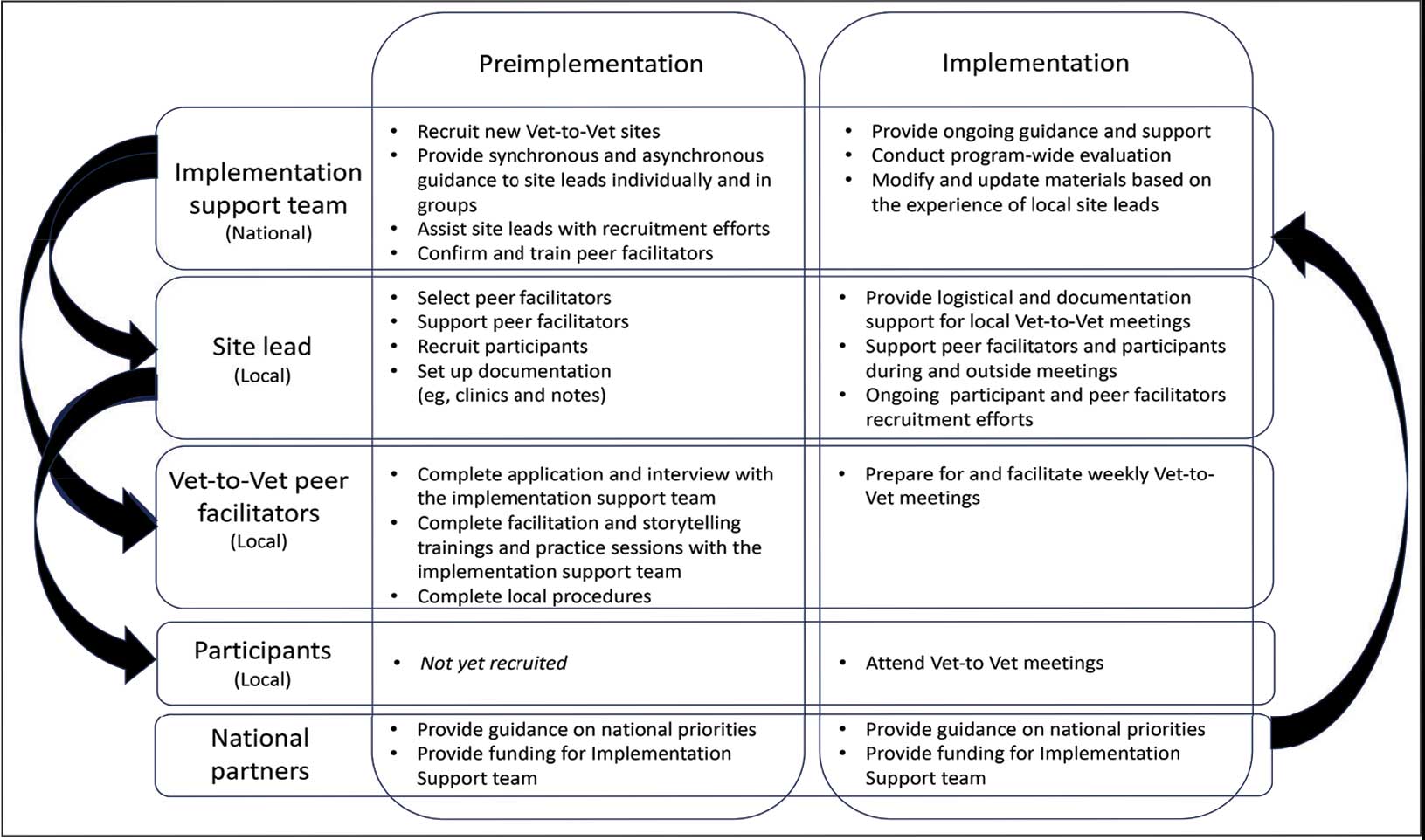
Following mutual help principles, Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators lead weekly online drop-in meetings. Meetings follow the general structure of reiterating group ground rules and sharing an individual pain story, followed by open discussions centered on well-being, chronic pain management, or any topic the group wishes to discuss. Meetings typically end with a mindfulness exercise. The organizational structure that supports Vet-to-Vet includes the implementation support team, site leads, Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators, and national partners (Figure 1).
Implementation Support Team
The implementation support team consists of a principal investigator, coinvestigator, program manager, and program support specialist. The team provides facilitator training, monthly community practice sessions for Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and site leads, and weekly office hours for site leads. The implementation support team also recruits new Vet-to-Vet sites; potential new locations ideally have an existing whole health program, leadership support, committed site and cosite leads, and ≥ 3 peer facilitator volunteers.
Site Leads
Most site and cosite leads are based in whole health or pain management teams and are whole health coaches or peer support specialists. The site lead is responsible for standing up the program and documenting encounters, recruiting and supporting peer facilitators and participants, and overseeing the meeting. During meetings, site leads generally leave their cameras off and only speak when called into the group; the peer facilitators lead the meetings. The implementation support team recommends that site leads dedicate ≥ 4 hours per week to Vet-to-Vet; 2 hours for weekly group meetings and 2 hours for documentation (ie, entering notes into the participants’ electronic health records) and supporting peer facilitators and participants. Cosite lead responsibilities vary by location, with some sites having 2 leads that equally share duties and others having a primary lead and a colead available if the site lead is unable to attend a meeting.
Vet-to-Vet Peer Facilitators
Peer facilitators are the core of the program. They lead meetings from start to finish. Like participants, they also experience chronic pain and are volunteers. The implementation support team encourages sites to establish volunteer peer facilitators, rather than assigning peer support specialists to facilitate meetings. Veterans are eager to connect and give back to their communities, and the Vet-to-Vet peer facilitator role is an opportunity for those unable to work to connect with peers and add meaning to their lives. Even if a VHA employee is a veteran who has chronic pain, they are not eligible to serve as this could create a service provider/service recipient dynamic that is not in the spirit of mutual help.
Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators attend a virtual 3-day training held by the implementation support team prior to starting. These training sessions are available on a quarterly basis and facilitated by the Vet-to-Vet program manager and 2 current peer facilitators. Training content includes established whole health facilitator training materials and program-specific storytelling training materials. Once trained, peer facilitators attend storytelling practice sessions and collaborate with their site leads during weekly meetings.
Participants
Vet-to-Vet participants find the program through direct outreach from site leads, word of mouth, and referrals. The only criteria to join are that the individual is a veteran who experiences chronic pain and is enrolled in the VHA (site leads can assist with enrollment if needed). Participants are not required to have a diagnosis or engage in any other health care. There is no commitment and no end date. Some participants only come once; others have attended for > 3 years. This approach is intended to embrace the idea that the need for support ebbs and flows.
National Partners
The VHA Office of Rural Health provides technical support. The Center for Development and Civic Engagement onboards peer facilitators as VHA volunteers. The Office of Patient-Centered Care and Cultural Transformation provides national guidance and site-level collaboration. The VHA Pain Management, Opioid Safety, and Prescription Drug Monitoring Program supports site recruitment. In addition to the VHA partners, 4 veteran evaluation consultants who have experience with chronic pain but do not participate in Vet-to-Vet meetings provide advice on evaluation activities, such as question development and communication strategies.
Evaluation
This evaluation shares preliminary results from a pilot evaluation of the Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center (RMRVAMC) Vet-to-Vet group. It is intended for program improvement, was deemed nonresearch by the Colorado Multiple Institutional Review Board, and was structured using the RE-AIM (Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance) framework.23 This evaluation focused on capturing measures related to reach and effectiveness, while a forthcoming evaluation includes elements of adoption, implementation, and maintenance.
In 2022, 16 Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and participants completed surveys and interviews to share their experience. Interviews were recorded, transcribed, and coded in ATLAS.ti. A priori codes were based on interview guide questions and emergent descriptive codes were used to identify specific topics which were categorized into RE-AIM domains, barriers, facilitators, what participants learned, how participants applied what they learned to their lives, and participant reported outcomes. This article contains high-level findings from the evaluation; more detailed results will be included in the ongoing evaluation.
Results
The RMRVAMC Vet-to-Vet group has met weekly since April 2022. Four Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and 12 individuals participated in the pilot Vet-to-Vet group and evaluation. The mean age was 62 years, most were men, and half were married. Most participants lived in rural areas with a mean distance of 125 miles to the nearest VAMC. Many experienced multiple kinds of pain, with a mean 4.5 on a 10-point scale (bothered “a lot”). All participants reported that they experienced pain daily.
Participation in Vet-to-Vet meetings was high; 3 of 4 peer facilitators and 7 of 12 participants completed the first 6 months of the program. In interviews, participants described the positive impact of the program. They emphasized the importance of connecting with other veterans and helping one another, with one noting that opportunities to connect with other veterans “just drops off a lot” (peer facilitator 3) after leaving active duty.
Some participants and Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators outlined the content of the sessions (eg, learning about how pain impacts the body and one’s family relationships) and shared the skills they learned (eg, goal setting, self-advocacy) (Table). Most spoke about learning from one another and the power of sharing stories with one peer facilitator sharing how they felt that witnessing another participant’s story “really shifted how I was thinking about things and how I perceived people” (peer facilitator 1).

Participants reported several ways the program impacted their lives, such as learning that they could get help, how to get help, and how to overcome the mental aspects of chronic pain. One veteran shared profound health impacts and attributed the Vet-to-Vet program to having one of the best years of their life. Even those who did not attend many meetings spoke of it positively and stated that it should continue so others could try (Table).
From January 2022 to September 2025, > 80 veterans attended ≥ 1 meeting at RMRVAMC; 29 attended ≥ 1 meeting in the last quarter. There were > 1400 Vet-to-Vet encounters at RMRVAMC, with a mean (SD) of 14.2 (19.2) and a median of 4.5 encounters per participant. Half of the veterans attend ≥ 5 meetings, and one-third attended ≥ 10 meetings.
Since June 2023, 15 additional VHA facilities launched Vet-to-Vet programs. As of October 2025, > 350 veterans have participated in ≥ 1 Vet-to-Vet meeting, totaling > 4500 Vet-to-Vet encounters since the program’s inception (Figure 2).
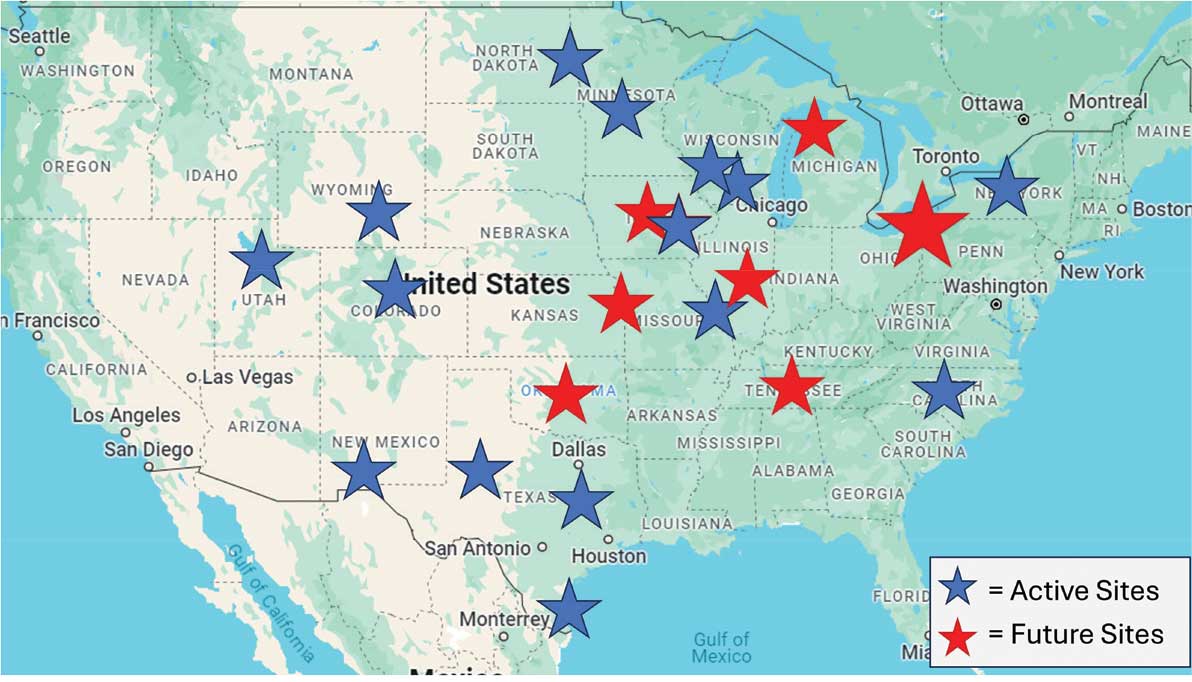
Challenges
The RMRVAMC site and cosite leads are part of the national implementation team and dedicate substantial time to developing the program: 40 and 10 hours per week, respectively. Site leads at new locations do not receive funding for Vet-to-Vet activities and are recommended to dedicate only 4 hours per week to the program. Formally embedding Vet-to-Vet into the site leads’ roles is critical for sustainment.
The Vet-to-Vet model has changed. The initial Vet-to-Vet cohort included the 6-week Taking Charge of My Life and Health curriculum prior to moving to the mutual help format.24 While this curriculum still informs peer facilitator training, it is not used in new groups. It has anecdotally been reported that this change was positive, but the impact of this adaptation is unknown.
This evaluation cohort was small (16 participants) and initial patient reported and administrative outcomes were inconclusive. However, most veterans who stopped participating in Vet-to-Vet spoke fondly of their experiences with the program.
CONCLUSIONS
Vet-to-Vet is a promising new initiative to support self-management and social connection in chronic pain care. The program employs a mutual help approach and storytelling to empower veterans living with chronic pain. The effectiveness of these strategies will be evaluated, which will inform its continued growth. The program's current goals focus on sustainment at existing sites and expansion to new sites to reach more rural veterans across the VA enterprise. While Vet-to-Vet is designed to serve those who experience chronic pain, a partnership with the Office of Whole Health has established goals to begin expanding this model to other chronic conditions in 2026.
- Kerns RD, Philip EJ, Lee AW, Rosenberger PH. Implementation of the Veterans Health Administration national pain management strategy. Transl Behav Med. 2011;1:635-643. doi:10.1007/s13142-011-0094-3
- Pain Management, Opioid Safety, and PDMP (PMOP). US Department of Veterans Affairs. Updated August 21, 2025. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/PAINMANAGEMENT/Providers/IntegratedTeambasedPainCare.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VHA Directive 2009-053. October 28, 2009. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/PAINMANAGEMENT/docs/VHA09PainDirective.pdf
- Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016, S524, 114th Cong (2015-2016). Pub L No. 114-198. July 22, 2016. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/senate-bill/524
- Bokhour B, Hyde J, Zeliadt, Mohr D. Whole Health System of Care Evaluation. US Department of Veterans Affairs. February 18, 2020. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/WHOLEHEALTH/docs/EPCC_WHSevaluation_FinalReport_508.pdf
- Gaudet T, Kligler B. Whole health in the whole system of the veterans administration: how will we know we have reached this future state? J Altern Complement Med. 2019;25:S7-S11. doi:10.1089/acm.2018.29061.gau
- Kelly JF, Yeterian JD. The role of mutual-help groups in extending the framework of treatment. Alcohol Res Health. 2011;33:350-355.
- Humphreys K. Self-help/mutual aid organizations: the view from Mars. Subst Use Misuse. 1997;32:2105-2109. doi:10.3109/10826089709035622
- Chinman M, Kloos B, O’Connell M, Davidson L. Service providers’ views of psychiatric mutual support groups. J Community Psychol. 2002;30:349-366. doi:10.1002/jcop.10010
- Shue SA, McGuire AB, Matthias MS. Facilitators and barriers to implementation of a peer support intervention for patients with chronic pain: a qualitative study. Pain Med. 2019;20:1311-1320. doi:10.1093/pm/pny229
- Pester BD, Tankha H, Caño A, et al. Facing pain together: a randomized controlled trial of the effects of Facebook support groups on adults with chronic pain. J Pain. 2022;23:2121-2134. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.013
- Matthias MS, McGuire AB, Kukla M, Daggy J, Myers LJ, Bair MJ. A brief peer support intervention for veterans with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a pilot study of feasibility and effectiveness. Pain Med. 2015;16:81-87. doi:10.1111/pme.12571
- Finlay KA, Elander J. Reflecting the transition from pain management services to chronic pain support group attendance: an interpretative phenomenological analysis. Br J Health Psychol. 2016;21:660-676. doi:10.1111/bjhp.12194
- Finlay KA, Peacock S, Elander J. Developing successful social support: an interpretative phenomenological analysis of mechanisms and processes in a chronic pain support group. Psychol Health. 2018;33:846-871. doi:10.1080/08870446.2017.1421188
- Farr M, Brant H, Patel R, et al. Experiences of patient-led chronic pain peer support groups after pain management programs: a qualitative study. Pain Med. 2021;22:2884-2895. doi:10.1093/pm/pnab189
- Mehl-Madrona L. Narrative Medicine: The Use of History and Story in the Healing Process. Bear & Company; 2007.
- Fioretti C, Mazzocco K, Riva S, Oliveri S, Masiero M, Pravettoni G. Research studies on patients’ illness experience using the Narrative Medicine approach: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e011220. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011220
- Hall JM, Powell J. Understanding the person through narrative. Nurs Res Pract. 2011;2011:293837. doi:10.1155/2011/293837
- Ricks L, Kitchens S, Goodrich T, Hancock E. My story: the use of narrative therapy in individual and group counseling. J Creat Ment Health. 2014;9:99-110. doi:10.1080/15401383.2013.870947
- Hydén L-C. Illness and narrative. Sociol Health Illn. 1997;19:48-69. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9566.1997.tb00015.x
- Georgiadis E, Johnson MI. Incorporating personal narratives in positive psychology interventions to manage chronic pain. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023;4:1253310. doi:10.3389/fpain.2023.1253310
- Gucciardi E, Jean-Pierre N, Karam G, Sidani S. Designing and delivering facilitated storytelling interventions for chronic disease self-management: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:249. doi:10.1186/s12913-016-1474-7
- Glasgow RE, Vogt TM, Boles SM. Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: the RE-AIM framework. Am J Public Health. 1999;89:1322-1327. doi:10.2105/ajph.89.9.1322
- Abadi M, Richard B, Shamblen S, et al. Achieving whole health: a preliminary study of TCMLH, a group-based program promoting self-care and empowerment among veterans. Health Educ Behav. 2022;49:347-357. doi:10.1177/10901981211011043
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has continued to advance its understanding and treatment of chronic pain. The VHA National Pain Management Strategy emphasizes the significance of the social context of pain while underscoring the importance of self-management.1 This established strategy ensures that all veterans have access to the appropriate pain care in the proper setting.2 VHA has instituted a stepped care model of pain management, delineating the domains of primary care, secondary consultative services, and tertiary care.3 This directive emphasized a biopsychosocial approach to pain management to prioritize the relationship between biological, psychological, and social factors that influence how veterans experience pain and should commensurately influence how it is managed.
The VHA Office of Patient-Centered Care and Cultural Transformation implemented the Whole Health System of Care as part of the Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act, which included a VHA directive to expand pain management.4,5 Reorientation within this system shifts from defining veterans as passive care recipients to viewing them as active partners in their own care and health. This partnership places additional emphasis on peer-led explorations of mission, aspiration, and purpose.6
Peer-led groups, also known as mutual aid, mutual support, and mutual help groups, have historically been successful for patients undergoing treatment for substance use disorders (eg, Alcoholics Anonymous).7 Mutual help groups have 3 defining characteristics. First, they are run by participants, not professionals, though the latter may have been integral in the founding of the groups. Second, participants share a similar problem (eg, disease state, experience, disposition). Finally, there is a reciprocal exchange of information and psychological support among participants.8,9 Mutual help groups that address chronic pain are rare but becoming more common.10-12 Emerging evidence suggests a positive relationship between peer support and improved well-being, self-efficacy, pain management, and pain self-management skills (eg, activity pacing).13-15
Storytelling as a tool for healing has a long history in indigenous and Western medical traditions.16-19 This includes the treatment of chronic disease, including pain.20,21 The use of storytelling in health care overlaps with the role it plays within many mutual help groups focused on chronic disease treatment.22 Storytelling allows an individual to share their experience with a disease, and take a more active role in their health, and facilitate stronger bonds with others.22 In effect, storytelling is not only important to group cohesion—it also plays a role in an individual’s healing.
Vet-to-Vet
The VHA Office of Rural Health funds Vet-to-Vet, a peer-to-peer program to address limited access to care for rural veterans with chronic pain. Similar to the VHA National Pain Management Strategy, Vet-to-Vet is grounded in the significance of the social context of pain and underscores the importance of self-management.1 The program combines pain care, mutual help, and storytelling to support veterans living with chronic pain. While the primary focus of Vet-to-Vet is rural veterans, the program serves any veteran experiencing chronic pain who is isolated from services, including home-bound urban veterans.
Following mutual help principles, Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators lead weekly online drop-in meetings. Meetings follow the general structure of reiterating group ground rules and sharing an individual pain story, followed by open discussions centered on well-being, chronic pain management, or any topic the group wishes to discuss. Meetings typically end with a mindfulness exercise. The organizational structure that supports Vet-to-Vet includes the implementation support team, site leads, Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators, and national partners (Figure 1).

Implementation Support Team
The implementation support team consists of a principal investigator, coinvestigator, program manager, and program support specialist. The team provides facilitator training, monthly community practice sessions for Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and site leads, and weekly office hours for site leads. The implementation support team also recruits new Vet-to-Vet sites; potential new locations ideally have an existing whole health program, leadership support, committed site and cosite leads, and ≥ 3 peer facilitator volunteers.
Site Leads
Most site and cosite leads are based in whole health or pain management teams and are whole health coaches or peer support specialists. The site lead is responsible for standing up the program and documenting encounters, recruiting and supporting peer facilitators and participants, and overseeing the meeting. During meetings, site leads generally leave their cameras off and only speak when called into the group; the peer facilitators lead the meetings. The implementation support team recommends that site leads dedicate ≥ 4 hours per week to Vet-to-Vet; 2 hours for weekly group meetings and 2 hours for documentation (ie, entering notes into the participants’ electronic health records) and supporting peer facilitators and participants. Cosite lead responsibilities vary by location, with some sites having 2 leads that equally share duties and others having a primary lead and a colead available if the site lead is unable to attend a meeting.
Vet-to-Vet Peer Facilitators
Peer facilitators are the core of the program. They lead meetings from start to finish. Like participants, they also experience chronic pain and are volunteers. The implementation support team encourages sites to establish volunteer peer facilitators, rather than assigning peer support specialists to facilitate meetings. Veterans are eager to connect and give back to their communities, and the Vet-to-Vet peer facilitator role is an opportunity for those unable to work to connect with peers and add meaning to their lives. Even if a VHA employee is a veteran who has chronic pain, they are not eligible to serve as this could create a service provider/service recipient dynamic that is not in the spirit of mutual help.
Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators attend a virtual 3-day training held by the implementation support team prior to starting. These training sessions are available on a quarterly basis and facilitated by the Vet-to-Vet program manager and 2 current peer facilitators. Training content includes established whole health facilitator training materials and program-specific storytelling training materials. Once trained, peer facilitators attend storytelling practice sessions and collaborate with their site leads during weekly meetings.
Participants
Vet-to-Vet participants find the program through direct outreach from site leads, word of mouth, and referrals. The only criteria to join are that the individual is a veteran who experiences chronic pain and is enrolled in the VHA (site leads can assist with enrollment if needed). Participants are not required to have a diagnosis or engage in any other health care. There is no commitment and no end date. Some participants only come once; others have attended for > 3 years. This approach is intended to embrace the idea that the need for support ebbs and flows.
National Partners
The VHA Office of Rural Health provides technical support. The Center for Development and Civic Engagement onboards peer facilitators as VHA volunteers. The Office of Patient-Centered Care and Cultural Transformation provides national guidance and site-level collaboration. The VHA Pain Management, Opioid Safety, and Prescription Drug Monitoring Program supports site recruitment. In addition to the VHA partners, 4 veteran evaluation consultants who have experience with chronic pain but do not participate in Vet-to-Vet meetings provide advice on evaluation activities, such as question development and communication strategies.
Evaluation
This evaluation shares preliminary results from a pilot evaluation of the Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center (RMRVAMC) Vet-to-Vet group. It is intended for program improvement, was deemed nonresearch by the Colorado Multiple Institutional Review Board, and was structured using the RE-AIM (Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance) framework.23 This evaluation focused on capturing measures related to reach and effectiveness, while a forthcoming evaluation includes elements of adoption, implementation, and maintenance.
In 2022, 16 Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and participants completed surveys and interviews to share their experience. Interviews were recorded, transcribed, and coded in ATLAS.ti. A priori codes were based on interview guide questions and emergent descriptive codes were used to identify specific topics which were categorized into RE-AIM domains, barriers, facilitators, what participants learned, how participants applied what they learned to their lives, and participant reported outcomes. This article contains high-level findings from the evaluation; more detailed results will be included in the ongoing evaluation.
Results
The RMRVAMC Vet-to-Vet group has met weekly since April 2022. Four Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and 12 individuals participated in the pilot Vet-to-Vet group and evaluation. The mean age was 62 years, most were men, and half were married. Most participants lived in rural areas with a mean distance of 125 miles to the nearest VAMC. Many experienced multiple kinds of pain, with a mean 4.5 on a 10-point scale (bothered “a lot”). All participants reported that they experienced pain daily.
Participation in Vet-to-Vet meetings was high; 3 of 4 peer facilitators and 7 of 12 participants completed the first 6 months of the program. In interviews, participants described the positive impact of the program. They emphasized the importance of connecting with other veterans and helping one another, with one noting that opportunities to connect with other veterans “just drops off a lot” (peer facilitator 3) after leaving active duty.
Some participants and Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators outlined the content of the sessions (eg, learning about how pain impacts the body and one’s family relationships) and shared the skills they learned (eg, goal setting, self-advocacy) (Table). Most spoke about learning from one another and the power of sharing stories with one peer facilitator sharing how they felt that witnessing another participant’s story “really shifted how I was thinking about things and how I perceived people” (peer facilitator 1).

Participants reported several ways the program impacted their lives, such as learning that they could get help, how to get help, and how to overcome the mental aspects of chronic pain. One veteran shared profound health impacts and attributed the Vet-to-Vet program to having one of the best years of their life. Even those who did not attend many meetings spoke of it positively and stated that it should continue so others could try (Table).
From January 2022 to September 2025, > 80 veterans attended ≥ 1 meeting at RMRVAMC; 29 attended ≥ 1 meeting in the last quarter. There were > 1400 Vet-to-Vet encounters at RMRVAMC, with a mean (SD) of 14.2 (19.2) and a median of 4.5 encounters per participant. Half of the veterans attend ≥ 5 meetings, and one-third attended ≥ 10 meetings.
Since June 2023, 15 additional VHA facilities launched Vet-to-Vet programs. As of October 2025, > 350 veterans have participated in ≥ 1 Vet-to-Vet meeting, totaling > 4500 Vet-to-Vet encounters since the program’s inception (Figure 2).

Challenges
The RMRVAMC site and cosite leads are part of the national implementation team and dedicate substantial time to developing the program: 40 and 10 hours per week, respectively. Site leads at new locations do not receive funding for Vet-to-Vet activities and are recommended to dedicate only 4 hours per week to the program. Formally embedding Vet-to-Vet into the site leads’ roles is critical for sustainment.
The Vet-to-Vet model has changed. The initial Vet-to-Vet cohort included the 6-week Taking Charge of My Life and Health curriculum prior to moving to the mutual help format.24 While this curriculum still informs peer facilitator training, it is not used in new groups. It has anecdotally been reported that this change was positive, but the impact of this adaptation is unknown.
This evaluation cohort was small (16 participants) and initial patient reported and administrative outcomes were inconclusive. However, most veterans who stopped participating in Vet-to-Vet spoke fondly of their experiences with the program.
CONCLUSIONS
Vet-to-Vet is a promising new initiative to support self-management and social connection in chronic pain care. The program employs a mutual help approach and storytelling to empower veterans living with chronic pain. The effectiveness of these strategies will be evaluated, which will inform its continued growth. The program's current goals focus on sustainment at existing sites and expansion to new sites to reach more rural veterans across the VA enterprise. While Vet-to-Vet is designed to serve those who experience chronic pain, a partnership with the Office of Whole Health has established goals to begin expanding this model to other chronic conditions in 2026.
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has continued to advance its understanding and treatment of chronic pain. The VHA National Pain Management Strategy emphasizes the significance of the social context of pain while underscoring the importance of self-management.1 This established strategy ensures that all veterans have access to the appropriate pain care in the proper setting.2 VHA has instituted a stepped care model of pain management, delineating the domains of primary care, secondary consultative services, and tertiary care.3 This directive emphasized a biopsychosocial approach to pain management to prioritize the relationship between biological, psychological, and social factors that influence how veterans experience pain and should commensurately influence how it is managed.
The VHA Office of Patient-Centered Care and Cultural Transformation implemented the Whole Health System of Care as part of the Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act, which included a VHA directive to expand pain management.4,5 Reorientation within this system shifts from defining veterans as passive care recipients to viewing them as active partners in their own care and health. This partnership places additional emphasis on peer-led explorations of mission, aspiration, and purpose.6
Peer-led groups, also known as mutual aid, mutual support, and mutual help groups, have historically been successful for patients undergoing treatment for substance use disorders (eg, Alcoholics Anonymous).7 Mutual help groups have 3 defining characteristics. First, they are run by participants, not professionals, though the latter may have been integral in the founding of the groups. Second, participants share a similar problem (eg, disease state, experience, disposition). Finally, there is a reciprocal exchange of information and psychological support among participants.8,9 Mutual help groups that address chronic pain are rare but becoming more common.10-12 Emerging evidence suggests a positive relationship between peer support and improved well-being, self-efficacy, pain management, and pain self-management skills (eg, activity pacing).13-15
Storytelling as a tool for healing has a long history in indigenous and Western medical traditions.16-19 This includes the treatment of chronic disease, including pain.20,21 The use of storytelling in health care overlaps with the role it plays within many mutual help groups focused on chronic disease treatment.22 Storytelling allows an individual to share their experience with a disease, and take a more active role in their health, and facilitate stronger bonds with others.22 In effect, storytelling is not only important to group cohesion—it also plays a role in an individual’s healing.
Vet-to-Vet
The VHA Office of Rural Health funds Vet-to-Vet, a peer-to-peer program to address limited access to care for rural veterans with chronic pain. Similar to the VHA National Pain Management Strategy, Vet-to-Vet is grounded in the significance of the social context of pain and underscores the importance of self-management.1 The program combines pain care, mutual help, and storytelling to support veterans living with chronic pain. While the primary focus of Vet-to-Vet is rural veterans, the program serves any veteran experiencing chronic pain who is isolated from services, including home-bound urban veterans.
Following mutual help principles, Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators lead weekly online drop-in meetings. Meetings follow the general structure of reiterating group ground rules and sharing an individual pain story, followed by open discussions centered on well-being, chronic pain management, or any topic the group wishes to discuss. Meetings typically end with a mindfulness exercise. The organizational structure that supports Vet-to-Vet includes the implementation support team, site leads, Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators, and national partners (Figure 1).

Implementation Support Team
The implementation support team consists of a principal investigator, coinvestigator, program manager, and program support specialist. The team provides facilitator training, monthly community practice sessions for Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and site leads, and weekly office hours for site leads. The implementation support team also recruits new Vet-to-Vet sites; potential new locations ideally have an existing whole health program, leadership support, committed site and cosite leads, and ≥ 3 peer facilitator volunteers.
Site Leads
Most site and cosite leads are based in whole health or pain management teams and are whole health coaches or peer support specialists. The site lead is responsible for standing up the program and documenting encounters, recruiting and supporting peer facilitators and participants, and overseeing the meeting. During meetings, site leads generally leave their cameras off and only speak when called into the group; the peer facilitators lead the meetings. The implementation support team recommends that site leads dedicate ≥ 4 hours per week to Vet-to-Vet; 2 hours for weekly group meetings and 2 hours for documentation (ie, entering notes into the participants’ electronic health records) and supporting peer facilitators and participants. Cosite lead responsibilities vary by location, with some sites having 2 leads that equally share duties and others having a primary lead and a colead available if the site lead is unable to attend a meeting.
Vet-to-Vet Peer Facilitators
Peer facilitators are the core of the program. They lead meetings from start to finish. Like participants, they also experience chronic pain and are volunteers. The implementation support team encourages sites to establish volunteer peer facilitators, rather than assigning peer support specialists to facilitate meetings. Veterans are eager to connect and give back to their communities, and the Vet-to-Vet peer facilitator role is an opportunity for those unable to work to connect with peers and add meaning to their lives. Even if a VHA employee is a veteran who has chronic pain, they are not eligible to serve as this could create a service provider/service recipient dynamic that is not in the spirit of mutual help.
Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators attend a virtual 3-day training held by the implementation support team prior to starting. These training sessions are available on a quarterly basis and facilitated by the Vet-to-Vet program manager and 2 current peer facilitators. Training content includes established whole health facilitator training materials and program-specific storytelling training materials. Once trained, peer facilitators attend storytelling practice sessions and collaborate with their site leads during weekly meetings.
Participants
Vet-to-Vet participants find the program through direct outreach from site leads, word of mouth, and referrals. The only criteria to join are that the individual is a veteran who experiences chronic pain and is enrolled in the VHA (site leads can assist with enrollment if needed). Participants are not required to have a diagnosis or engage in any other health care. There is no commitment and no end date. Some participants only come once; others have attended for > 3 years. This approach is intended to embrace the idea that the need for support ebbs and flows.
National Partners
The VHA Office of Rural Health provides technical support. The Center for Development and Civic Engagement onboards peer facilitators as VHA volunteers. The Office of Patient-Centered Care and Cultural Transformation provides national guidance and site-level collaboration. The VHA Pain Management, Opioid Safety, and Prescription Drug Monitoring Program supports site recruitment. In addition to the VHA partners, 4 veteran evaluation consultants who have experience with chronic pain but do not participate in Vet-to-Vet meetings provide advice on evaluation activities, such as question development and communication strategies.
Evaluation
This evaluation shares preliminary results from a pilot evaluation of the Rocky Mountain Regional VA Medical Center (RMRVAMC) Vet-to-Vet group. It is intended for program improvement, was deemed nonresearch by the Colorado Multiple Institutional Review Board, and was structured using the RE-AIM (Reach, Effectiveness, Adoption, Implementation, and Maintenance) framework.23 This evaluation focused on capturing measures related to reach and effectiveness, while a forthcoming evaluation includes elements of adoption, implementation, and maintenance.
In 2022, 16 Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and participants completed surveys and interviews to share their experience. Interviews were recorded, transcribed, and coded in ATLAS.ti. A priori codes were based on interview guide questions and emergent descriptive codes were used to identify specific topics which were categorized into RE-AIM domains, barriers, facilitators, what participants learned, how participants applied what they learned to their lives, and participant reported outcomes. This article contains high-level findings from the evaluation; more detailed results will be included in the ongoing evaluation.
Results
The RMRVAMC Vet-to-Vet group has met weekly since April 2022. Four Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators and 12 individuals participated in the pilot Vet-to-Vet group and evaluation. The mean age was 62 years, most were men, and half were married. Most participants lived in rural areas with a mean distance of 125 miles to the nearest VAMC. Many experienced multiple kinds of pain, with a mean 4.5 on a 10-point scale (bothered “a lot”). All participants reported that they experienced pain daily.
Participation in Vet-to-Vet meetings was high; 3 of 4 peer facilitators and 7 of 12 participants completed the first 6 months of the program. In interviews, participants described the positive impact of the program. They emphasized the importance of connecting with other veterans and helping one another, with one noting that opportunities to connect with other veterans “just drops off a lot” (peer facilitator 3) after leaving active duty.
Some participants and Vet-to-Vet peer facilitators outlined the content of the sessions (eg, learning about how pain impacts the body and one’s family relationships) and shared the skills they learned (eg, goal setting, self-advocacy) (Table). Most spoke about learning from one another and the power of sharing stories with one peer facilitator sharing how they felt that witnessing another participant’s story “really shifted how I was thinking about things and how I perceived people” (peer facilitator 1).

Participants reported several ways the program impacted their lives, such as learning that they could get help, how to get help, and how to overcome the mental aspects of chronic pain. One veteran shared profound health impacts and attributed the Vet-to-Vet program to having one of the best years of their life. Even those who did not attend many meetings spoke of it positively and stated that it should continue so others could try (Table).
From January 2022 to September 2025, > 80 veterans attended ≥ 1 meeting at RMRVAMC; 29 attended ≥ 1 meeting in the last quarter. There were > 1400 Vet-to-Vet encounters at RMRVAMC, with a mean (SD) of 14.2 (19.2) and a median of 4.5 encounters per participant. Half of the veterans attend ≥ 5 meetings, and one-third attended ≥ 10 meetings.
Since June 2023, 15 additional VHA facilities launched Vet-to-Vet programs. As of October 2025, > 350 veterans have participated in ≥ 1 Vet-to-Vet meeting, totaling > 4500 Vet-to-Vet encounters since the program’s inception (Figure 2).

Challenges
The RMRVAMC site and cosite leads are part of the national implementation team and dedicate substantial time to developing the program: 40 and 10 hours per week, respectively. Site leads at new locations do not receive funding for Vet-to-Vet activities and are recommended to dedicate only 4 hours per week to the program. Formally embedding Vet-to-Vet into the site leads’ roles is critical for sustainment.
The Vet-to-Vet model has changed. The initial Vet-to-Vet cohort included the 6-week Taking Charge of My Life and Health curriculum prior to moving to the mutual help format.24 While this curriculum still informs peer facilitator training, it is not used in new groups. It has anecdotally been reported that this change was positive, but the impact of this adaptation is unknown.
This evaluation cohort was small (16 participants) and initial patient reported and administrative outcomes were inconclusive. However, most veterans who stopped participating in Vet-to-Vet spoke fondly of their experiences with the program.
CONCLUSIONS
Vet-to-Vet is a promising new initiative to support self-management and social connection in chronic pain care. The program employs a mutual help approach and storytelling to empower veterans living with chronic pain. The effectiveness of these strategies will be evaluated, which will inform its continued growth. The program's current goals focus on sustainment at existing sites and expansion to new sites to reach more rural veterans across the VA enterprise. While Vet-to-Vet is designed to serve those who experience chronic pain, a partnership with the Office of Whole Health has established goals to begin expanding this model to other chronic conditions in 2026.
- Kerns RD, Philip EJ, Lee AW, Rosenberger PH. Implementation of the Veterans Health Administration national pain management strategy. Transl Behav Med. 2011;1:635-643. doi:10.1007/s13142-011-0094-3
- Pain Management, Opioid Safety, and PDMP (PMOP). US Department of Veterans Affairs. Updated August 21, 2025. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/PAINMANAGEMENT/Providers/IntegratedTeambasedPainCare.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VHA Directive 2009-053. October 28, 2009. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/PAINMANAGEMENT/docs/VHA09PainDirective.pdf
- Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016, S524, 114th Cong (2015-2016). Pub L No. 114-198. July 22, 2016. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/senate-bill/524
- Bokhour B, Hyde J, Zeliadt, Mohr D. Whole Health System of Care Evaluation. US Department of Veterans Affairs. February 18, 2020. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/WHOLEHEALTH/docs/EPCC_WHSevaluation_FinalReport_508.pdf
- Gaudet T, Kligler B. Whole health in the whole system of the veterans administration: how will we know we have reached this future state? J Altern Complement Med. 2019;25:S7-S11. doi:10.1089/acm.2018.29061.gau
- Kelly JF, Yeterian JD. The role of mutual-help groups in extending the framework of treatment. Alcohol Res Health. 2011;33:350-355.
- Humphreys K. Self-help/mutual aid organizations: the view from Mars. Subst Use Misuse. 1997;32:2105-2109. doi:10.3109/10826089709035622
- Chinman M, Kloos B, O’Connell M, Davidson L. Service providers’ views of psychiatric mutual support groups. J Community Psychol. 2002;30:349-366. doi:10.1002/jcop.10010
- Shue SA, McGuire AB, Matthias MS. Facilitators and barriers to implementation of a peer support intervention for patients with chronic pain: a qualitative study. Pain Med. 2019;20:1311-1320. doi:10.1093/pm/pny229
- Pester BD, Tankha H, Caño A, et al. Facing pain together: a randomized controlled trial of the effects of Facebook support groups on adults with chronic pain. J Pain. 2022;23:2121-2134. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.013
- Matthias MS, McGuire AB, Kukla M, Daggy J, Myers LJ, Bair MJ. A brief peer support intervention for veterans with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a pilot study of feasibility and effectiveness. Pain Med. 2015;16:81-87. doi:10.1111/pme.12571
- Finlay KA, Elander J. Reflecting the transition from pain management services to chronic pain support group attendance: an interpretative phenomenological analysis. Br J Health Psychol. 2016;21:660-676. doi:10.1111/bjhp.12194
- Finlay KA, Peacock S, Elander J. Developing successful social support: an interpretative phenomenological analysis of mechanisms and processes in a chronic pain support group. Psychol Health. 2018;33:846-871. doi:10.1080/08870446.2017.1421188
- Farr M, Brant H, Patel R, et al. Experiences of patient-led chronic pain peer support groups after pain management programs: a qualitative study. Pain Med. 2021;22:2884-2895. doi:10.1093/pm/pnab189
- Mehl-Madrona L. Narrative Medicine: The Use of History and Story in the Healing Process. Bear & Company; 2007.
- Fioretti C, Mazzocco K, Riva S, Oliveri S, Masiero M, Pravettoni G. Research studies on patients’ illness experience using the Narrative Medicine approach: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e011220. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011220
- Hall JM, Powell J. Understanding the person through narrative. Nurs Res Pract. 2011;2011:293837. doi:10.1155/2011/293837
- Ricks L, Kitchens S, Goodrich T, Hancock E. My story: the use of narrative therapy in individual and group counseling. J Creat Ment Health. 2014;9:99-110. doi:10.1080/15401383.2013.870947
- Hydén L-C. Illness and narrative. Sociol Health Illn. 1997;19:48-69. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9566.1997.tb00015.x
- Georgiadis E, Johnson MI. Incorporating personal narratives in positive psychology interventions to manage chronic pain. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023;4:1253310. doi:10.3389/fpain.2023.1253310
- Gucciardi E, Jean-Pierre N, Karam G, Sidani S. Designing and delivering facilitated storytelling interventions for chronic disease self-management: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:249. doi:10.1186/s12913-016-1474-7
- Glasgow RE, Vogt TM, Boles SM. Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: the RE-AIM framework. Am J Public Health. 1999;89:1322-1327. doi:10.2105/ajph.89.9.1322
- Abadi M, Richard B, Shamblen S, et al. Achieving whole health: a preliminary study of TCMLH, a group-based program promoting self-care and empowerment among veterans. Health Educ Behav. 2022;49:347-357. doi:10.1177/10901981211011043
- Kerns RD, Philip EJ, Lee AW, Rosenberger PH. Implementation of the Veterans Health Administration national pain management strategy. Transl Behav Med. 2011;1:635-643. doi:10.1007/s13142-011-0094-3
- Pain Management, Opioid Safety, and PDMP (PMOP). US Department of Veterans Affairs. Updated August 21, 2025. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/PAINMANAGEMENT/Providers/IntegratedTeambasedPainCare.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. VHA Directive 2009-053. October 28, 2009. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/PAINMANAGEMENT/docs/VHA09PainDirective.pdf
- Comprehensive Addiction and Recovery Act of 2016, S524, 114th Cong (2015-2016). Pub L No. 114-198. July 22, 2016. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/114th-congress/senate-bill/524
- Bokhour B, Hyde J, Zeliadt, Mohr D. Whole Health System of Care Evaluation. US Department of Veterans Affairs. February 18, 2020. Accessed September 25, 2025. https://www.va.gov/WHOLEHEALTH/docs/EPCC_WHSevaluation_FinalReport_508.pdf
- Gaudet T, Kligler B. Whole health in the whole system of the veterans administration: how will we know we have reached this future state? J Altern Complement Med. 2019;25:S7-S11. doi:10.1089/acm.2018.29061.gau
- Kelly JF, Yeterian JD. The role of mutual-help groups in extending the framework of treatment. Alcohol Res Health. 2011;33:350-355.
- Humphreys K. Self-help/mutual aid organizations: the view from Mars. Subst Use Misuse. 1997;32:2105-2109. doi:10.3109/10826089709035622
- Chinman M, Kloos B, O’Connell M, Davidson L. Service providers’ views of psychiatric mutual support groups. J Community Psychol. 2002;30:349-366. doi:10.1002/jcop.10010
- Shue SA, McGuire AB, Matthias MS. Facilitators and barriers to implementation of a peer support intervention for patients with chronic pain: a qualitative study. Pain Med. 2019;20:1311-1320. doi:10.1093/pm/pny229
- Pester BD, Tankha H, Caño A, et al. Facing pain together: a randomized controlled trial of the effects of Facebook support groups on adults with chronic pain. J Pain. 2022;23:2121-2134. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2022.07.013
- Matthias MS, McGuire AB, Kukla M, Daggy J, Myers LJ, Bair MJ. A brief peer support intervention for veterans with chronic musculoskeletal pain: a pilot study of feasibility and effectiveness. Pain Med. 2015;16:81-87. doi:10.1111/pme.12571
- Finlay KA, Elander J. Reflecting the transition from pain management services to chronic pain support group attendance: an interpretative phenomenological analysis. Br J Health Psychol. 2016;21:660-676. doi:10.1111/bjhp.12194
- Finlay KA, Peacock S, Elander J. Developing successful social support: an interpretative phenomenological analysis of mechanisms and processes in a chronic pain support group. Psychol Health. 2018;33:846-871. doi:10.1080/08870446.2017.1421188
- Farr M, Brant H, Patel R, et al. Experiences of patient-led chronic pain peer support groups after pain management programs: a qualitative study. Pain Med. 2021;22:2884-2895. doi:10.1093/pm/pnab189
- Mehl-Madrona L. Narrative Medicine: The Use of History and Story in the Healing Process. Bear & Company; 2007.
- Fioretti C, Mazzocco K, Riva S, Oliveri S, Masiero M, Pravettoni G. Research studies on patients’ illness experience using the Narrative Medicine approach: a systematic review. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e011220. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011220
- Hall JM, Powell J. Understanding the person through narrative. Nurs Res Pract. 2011;2011:293837. doi:10.1155/2011/293837
- Ricks L, Kitchens S, Goodrich T, Hancock E. My story: the use of narrative therapy in individual and group counseling. J Creat Ment Health. 2014;9:99-110. doi:10.1080/15401383.2013.870947
- Hydén L-C. Illness and narrative. Sociol Health Illn. 1997;19:48-69. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9566.1997.tb00015.x
- Georgiadis E, Johnson MI. Incorporating personal narratives in positive psychology interventions to manage chronic pain. Front Pain Res (Lausanne). 2023;4:1253310. doi:10.3389/fpain.2023.1253310
- Gucciardi E, Jean-Pierre N, Karam G, Sidani S. Designing and delivering facilitated storytelling interventions for chronic disease self-management: a scoping review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:249. doi:10.1186/s12913-016-1474-7
- Glasgow RE, Vogt TM, Boles SM. Evaluating the public health impact of health promotion interventions: the RE-AIM framework. Am J Public Health. 1999;89:1322-1327. doi:10.2105/ajph.89.9.1322
- Abadi M, Richard B, Shamblen S, et al. Achieving whole health: a preliminary study of TCMLH, a group-based program promoting self-care and empowerment among veterans. Health Educ Behav. 2022;49:347-357. doi:10.1177/10901981211011043
A True Community: The Vet-to-Vet Program for Chronic Pain
A True Community: The Vet-to-Vet Program for Chronic Pain
Time to Reconsider Tramadol for Chronic Pain?
Time to Reconsider Tramadol for Chronic Pain?
Tramadol, a commonly prescribed opioid often viewed as a safer option for chronic pain, provided limited pain relief while increasing the risk for serious adverse effects, results of a new analysis showed.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis, investigators found that tramadol offered clinically insignificant pain relief, while doubling the likelihood of serious adverse events, most commonly cardiac complications.
"Given the limited analgesic benefits and increased risk of harm, tramadol use for chronic pain should be reconsidered," Jehad Ahmad Barakji, MD, of the Centre for Clinical Intervention Research at Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, Denmark, told Medscape Medical News.
"Across different chronic pain conditions, tramadol's pain-relieving effect appears modest, and while some patients may experience relief, most will not gain substantial benefit," he added.
However, the researchers cautioned that the certainty of the evidence was low-to-moderate and that the quality of the underlying trials varied substantially.
The study was published on October 7 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
Popularity Outpacing Proof
Tramadol, a dual-action opioid that modulates serotonin and norepinephrine pathways, has long been promoted as a middle-ground analgesic - less addictive than morphine but stronger than nonopioid medications. It is approved for moderate-to-severe pain, including postoperative and chronic conditions.
Prescriptions have risen sharply worldwide, fueled by perceptions of safety and a belief that tramadol carries a lower risk for dependence. A recent global analysis estimated that nearly 18% of adults have used tramadol in their lifetime, and > 80% of those users combined it with at least 1 other substance.
Despite its widespread use, evidence supporting tramadol's long-term effectiveness and safety in chronic pain has been limited and inconsistent. Previous research has largely focused on short-term or condition-specific outcomes, such as osteoarthritis or neuropathic pain, leaving uncertainty about the drug's overall risk-benefit profile.
Small Benefit, Big Risk
The current study is the first comprehensive systematic review to evaluate tramadol alone for chronic pain using both meta-analysis and trail sequential analysis, provided a broader view of efficacy and safety across pain types.
"We sought to fill this gap by evaluating the totality of evidence to guide clinical practice," Barakji said.
The analysis included 19 randomized, placebo-controlled trials with 6569 adults. The average participant age was 56 years, and study durations ranged from 4 to 16 weeks. Pain intensity was typically assessed with the 0-10 numeric rating scale (NRS), while function and quality of life were measured with validated patient-reported tools.
Across the pooled analysis, participants receiving tramadol experienced an average pain reduction of 0.9 points on the NRS compared with placebo - a difference below the 1-point threshold considered clinically meaningful. About 7% more patients in the tramadol groups achieved noticeable pain relief, but investigators said the benefit was modest and uncertain.
Serious adverse events were twice as common among tramadol users, most often involving cardiac complications such as chest pain, coronary artery disease, or heart failure. Nonserious adverse effects, including nausea, dizziness, constipation, and drowsiness, were frequent and contributed to higher discontinuation rates among tramadol recipients.
The researchers acknowledged that most included trials were at a high risk for bias due to incomplete outcome reporting, small sample sizes, and inconsistent assessment methods, factors that may have exaggerated benefits and underestimated harms.
Reevaluating Tramadol's Role
Commenting on the research, Jessica Otte, MD, clinical associate professor in the Department of Family Medicine at The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, said the new review stands out for examining tramadol's use across a range of chronic pain conditions, an area where clinicians often struggle to help patients achieve meaningful and sustained relief.
Otte, who has studied the drug's safety and effectiveness through The University of British Columbia's Therapeutics Initiative, said the Danish team's analysis expands on earlier research that largely focused on single pain conditions. The findings, she said, add weight to growing evidence that challenges tramadol's perceived advantages over other analgesics.
"This review doesn't change the narrative but strengthens it: Tramdol's reputation as a safer or uniquely effective opioid is increasingly difficult to defend," she told Medscape Medical News.
While she believes the study makes an important contribution, Otte said the results should be interpreted with caution because of gaps in the underlying evidence. The Danish authors noted similar concerns, and Otte agreed that many of the included trials had methodological shortcomings.
"A lot of the studies had biases that made use less certain about what was reported," she said. "Many outcomes that matter to patients - like quality of life, functional improvement, or withdrawal - were either inconsistently measured or not reported at all."
She added that patients assigned to tramadol were more likely to discontinue early, both overall and because of adverse effects, raising concern about tolerability and attrition bias.
Also commenting, Houman Danesh, MD, professor and medical director of pain management at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said the review provides moderate-certainty evidence that tramadol increases the risk for serious adverse events; but its broad approach - evaluating efficacy and safety across multiple chronic pain conditions - could be a confounding factor.
"Tramadol may benefit some conditions more than others," he noted, which could alter the overall risk-benefit profile.
In his clinical experience, Danesh said severe complications such as cardiac events are uncommon. He explained that heart rhythm disturbances occasionally associated with tramadol generally arise when patients are taking other medications that affect cardiac conduction.
Danesh emphasized that clinicians should weigh the study alongside other research and their own experience when deciding whether to prescribe the drug.
"It's important to take this study into consideration," he said, "but there are multiple studies that support the use of tramadol, and we have to look at the totality of the evidence."
Written by Carla Cantor.
The authors declared no competing interests and received no specific grant from any funding agency. Otte and Danesh reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tramadol, a commonly prescribed opioid often viewed as a safer option for chronic pain, provided limited pain relief while increasing the risk for serious adverse effects, results of a new analysis showed.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis, investigators found that tramadol offered clinically insignificant pain relief, while doubling the likelihood of serious adverse events, most commonly cardiac complications.
"Given the limited analgesic benefits and increased risk of harm, tramadol use for chronic pain should be reconsidered," Jehad Ahmad Barakji, MD, of the Centre for Clinical Intervention Research at Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, Denmark, told Medscape Medical News.
"Across different chronic pain conditions, tramadol's pain-relieving effect appears modest, and while some patients may experience relief, most will not gain substantial benefit," he added.
However, the researchers cautioned that the certainty of the evidence was low-to-moderate and that the quality of the underlying trials varied substantially.
The study was published on October 7 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
Popularity Outpacing Proof
Tramadol, a dual-action opioid that modulates serotonin and norepinephrine pathways, has long been promoted as a middle-ground analgesic - less addictive than morphine but stronger than nonopioid medications. It is approved for moderate-to-severe pain, including postoperative and chronic conditions.
Prescriptions have risen sharply worldwide, fueled by perceptions of safety and a belief that tramadol carries a lower risk for dependence. A recent global analysis estimated that nearly 18% of adults have used tramadol in their lifetime, and > 80% of those users combined it with at least 1 other substance.
Despite its widespread use, evidence supporting tramadol's long-term effectiveness and safety in chronic pain has been limited and inconsistent. Previous research has largely focused on short-term or condition-specific outcomes, such as osteoarthritis or neuropathic pain, leaving uncertainty about the drug's overall risk-benefit profile.
Small Benefit, Big Risk
The current study is the first comprehensive systematic review to evaluate tramadol alone for chronic pain using both meta-analysis and trail sequential analysis, provided a broader view of efficacy and safety across pain types.
"We sought to fill this gap by evaluating the totality of evidence to guide clinical practice," Barakji said.
The analysis included 19 randomized, placebo-controlled trials with 6569 adults. The average participant age was 56 years, and study durations ranged from 4 to 16 weeks. Pain intensity was typically assessed with the 0-10 numeric rating scale (NRS), while function and quality of life were measured with validated patient-reported tools.
Across the pooled analysis, participants receiving tramadol experienced an average pain reduction of 0.9 points on the NRS compared with placebo - a difference below the 1-point threshold considered clinically meaningful. About 7% more patients in the tramadol groups achieved noticeable pain relief, but investigators said the benefit was modest and uncertain.
Serious adverse events were twice as common among tramadol users, most often involving cardiac complications such as chest pain, coronary artery disease, or heart failure. Nonserious adverse effects, including nausea, dizziness, constipation, and drowsiness, were frequent and contributed to higher discontinuation rates among tramadol recipients.
The researchers acknowledged that most included trials were at a high risk for bias due to incomplete outcome reporting, small sample sizes, and inconsistent assessment methods, factors that may have exaggerated benefits and underestimated harms.
Reevaluating Tramadol's Role
Commenting on the research, Jessica Otte, MD, clinical associate professor in the Department of Family Medicine at The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, said the new review stands out for examining tramadol's use across a range of chronic pain conditions, an area where clinicians often struggle to help patients achieve meaningful and sustained relief.
Otte, who has studied the drug's safety and effectiveness through The University of British Columbia's Therapeutics Initiative, said the Danish team's analysis expands on earlier research that largely focused on single pain conditions. The findings, she said, add weight to growing evidence that challenges tramadol's perceived advantages over other analgesics.
"This review doesn't change the narrative but strengthens it: Tramdol's reputation as a safer or uniquely effective opioid is increasingly difficult to defend," she told Medscape Medical News.
While she believes the study makes an important contribution, Otte said the results should be interpreted with caution because of gaps in the underlying evidence. The Danish authors noted similar concerns, and Otte agreed that many of the included trials had methodological shortcomings.
"A lot of the studies had biases that made use less certain about what was reported," she said. "Many outcomes that matter to patients - like quality of life, functional improvement, or withdrawal - were either inconsistently measured or not reported at all."
She added that patients assigned to tramadol were more likely to discontinue early, both overall and because of adverse effects, raising concern about tolerability and attrition bias.
Also commenting, Houman Danesh, MD, professor and medical director of pain management at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said the review provides moderate-certainty evidence that tramadol increases the risk for serious adverse events; but its broad approach - evaluating efficacy and safety across multiple chronic pain conditions - could be a confounding factor.
"Tramadol may benefit some conditions more than others," he noted, which could alter the overall risk-benefit profile.
In his clinical experience, Danesh said severe complications such as cardiac events are uncommon. He explained that heart rhythm disturbances occasionally associated with tramadol generally arise when patients are taking other medications that affect cardiac conduction.
Danesh emphasized that clinicians should weigh the study alongside other research and their own experience when deciding whether to prescribe the drug.
"It's important to take this study into consideration," he said, "but there are multiple studies that support the use of tramadol, and we have to look at the totality of the evidence."
Written by Carla Cantor.
The authors declared no competing interests and received no specific grant from any funding agency. Otte and Danesh reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tramadol, a commonly prescribed opioid often viewed as a safer option for chronic pain, provided limited pain relief while increasing the risk for serious adverse effects, results of a new analysis showed.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis, investigators found that tramadol offered clinically insignificant pain relief, while doubling the likelihood of serious adverse events, most commonly cardiac complications.
"Given the limited analgesic benefits and increased risk of harm, tramadol use for chronic pain should be reconsidered," Jehad Ahmad Barakji, MD, of the Centre for Clinical Intervention Research at Rigshospitalet in Copenhagen, Denmark, told Medscape Medical News.
"Across different chronic pain conditions, tramadol's pain-relieving effect appears modest, and while some patients may experience relief, most will not gain substantial benefit," he added.
However, the researchers cautioned that the certainty of the evidence was low-to-moderate and that the quality of the underlying trials varied substantially.
The study was published on October 7 in BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
Popularity Outpacing Proof
Tramadol, a dual-action opioid that modulates serotonin and norepinephrine pathways, has long been promoted as a middle-ground analgesic - less addictive than morphine but stronger than nonopioid medications. It is approved for moderate-to-severe pain, including postoperative and chronic conditions.
Prescriptions have risen sharply worldwide, fueled by perceptions of safety and a belief that tramadol carries a lower risk for dependence. A recent global analysis estimated that nearly 18% of adults have used tramadol in their lifetime, and > 80% of those users combined it with at least 1 other substance.
Despite its widespread use, evidence supporting tramadol's long-term effectiveness and safety in chronic pain has been limited and inconsistent. Previous research has largely focused on short-term or condition-specific outcomes, such as osteoarthritis or neuropathic pain, leaving uncertainty about the drug's overall risk-benefit profile.
Small Benefit, Big Risk
The current study is the first comprehensive systematic review to evaluate tramadol alone for chronic pain using both meta-analysis and trail sequential analysis, provided a broader view of efficacy and safety across pain types.
"We sought to fill this gap by evaluating the totality of evidence to guide clinical practice," Barakji said.
The analysis included 19 randomized, placebo-controlled trials with 6569 adults. The average participant age was 56 years, and study durations ranged from 4 to 16 weeks. Pain intensity was typically assessed with the 0-10 numeric rating scale (NRS), while function and quality of life were measured with validated patient-reported tools.
Across the pooled analysis, participants receiving tramadol experienced an average pain reduction of 0.9 points on the NRS compared with placebo - a difference below the 1-point threshold considered clinically meaningful. About 7% more patients in the tramadol groups achieved noticeable pain relief, but investigators said the benefit was modest and uncertain.
Serious adverse events were twice as common among tramadol users, most often involving cardiac complications such as chest pain, coronary artery disease, or heart failure. Nonserious adverse effects, including nausea, dizziness, constipation, and drowsiness, were frequent and contributed to higher discontinuation rates among tramadol recipients.
The researchers acknowledged that most included trials were at a high risk for bias due to incomplete outcome reporting, small sample sizes, and inconsistent assessment methods, factors that may have exaggerated benefits and underestimated harms.
Reevaluating Tramadol's Role
Commenting on the research, Jessica Otte, MD, clinical associate professor in the Department of Family Medicine at The University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, said the new review stands out for examining tramadol's use across a range of chronic pain conditions, an area where clinicians often struggle to help patients achieve meaningful and sustained relief.
Otte, who has studied the drug's safety and effectiveness through The University of British Columbia's Therapeutics Initiative, said the Danish team's analysis expands on earlier research that largely focused on single pain conditions. The findings, she said, add weight to growing evidence that challenges tramadol's perceived advantages over other analgesics.
"This review doesn't change the narrative but strengthens it: Tramdol's reputation as a safer or uniquely effective opioid is increasingly difficult to defend," she told Medscape Medical News.
While she believes the study makes an important contribution, Otte said the results should be interpreted with caution because of gaps in the underlying evidence. The Danish authors noted similar concerns, and Otte agreed that many of the included trials had methodological shortcomings.
"A lot of the studies had biases that made use less certain about what was reported," she said. "Many outcomes that matter to patients - like quality of life, functional improvement, or withdrawal - were either inconsistently measured or not reported at all."
She added that patients assigned to tramadol were more likely to discontinue early, both overall and because of adverse effects, raising concern about tolerability and attrition bias.
Also commenting, Houman Danesh, MD, professor and medical director of pain management at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, said the review provides moderate-certainty evidence that tramadol increases the risk for serious adverse events; but its broad approach - evaluating efficacy and safety across multiple chronic pain conditions - could be a confounding factor.
"Tramadol may benefit some conditions more than others," he noted, which could alter the overall risk-benefit profile.
In his clinical experience, Danesh said severe complications such as cardiac events are uncommon. He explained that heart rhythm disturbances occasionally associated with tramadol generally arise when patients are taking other medications that affect cardiac conduction.
Danesh emphasized that clinicians should weigh the study alongside other research and their own experience when deciding whether to prescribe the drug.
"It's important to take this study into consideration," he said, "but there are multiple studies that support the use of tramadol, and we have to look at the totality of the evidence."
Written by Carla Cantor.
The authors declared no competing interests and received no specific grant from any funding agency. Otte and Danesh reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Time to Reconsider Tramadol for Chronic Pain?
Time to Reconsider Tramadol for Chronic Pain?
Data Trends 2025: Acute Pain
Data Trends 2025: Acute Pain
Click to view more from Federal Health Care Data Trends 2025.
- Baumann L, et al. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2023;27(9):437-444. doi:10.1007/s11916-023-01127-0
- Reif S, et al. Mil Med. 2018;183(9-10):e330-e337. doi:10.1093/milmed/usx200
- Sharp LK, e t a l . Pain. 2023;164( 4 ) : 749-757. doi:10.1097/j .pain.0000000000002759
- Dalton MK, et al. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021;91(2S Suppl 2):S213-S220. doi:10.1097/TA.0000000000003133
- Mahyar L, et al. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2024;49(2):117-121. doi:10.1136/rapm-2023-104610
- Gupta K, et al. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2025;51(1):103. doi:10.1007/s00068-025-02778-x
- Mariano ER, et al. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2022;47(2):118-127. doi:10.1136/rapm-2021-103083
Click to view more from Federal Health Care Data Trends 2025.
Click to view more from Federal Health Care Data Trends 2025.
- Baumann L, et al. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2023;27(9):437-444. doi:10.1007/s11916-023-01127-0
- Reif S, et al. Mil Med. 2018;183(9-10):e330-e337. doi:10.1093/milmed/usx200
- Sharp LK, e t a l . Pain. 2023;164( 4 ) : 749-757. doi:10.1097/j .pain.0000000000002759
- Dalton MK, et al. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021;91(2S Suppl 2):S213-S220. doi:10.1097/TA.0000000000003133
- Mahyar L, et al. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2024;49(2):117-121. doi:10.1136/rapm-2023-104610
- Gupta K, et al. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2025;51(1):103. doi:10.1007/s00068-025-02778-x
- Mariano ER, et al. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2022;47(2):118-127. doi:10.1136/rapm-2021-103083
- Baumann L, et al. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2023;27(9):437-444. doi:10.1007/s11916-023-01127-0
- Reif S, et al. Mil Med. 2018;183(9-10):e330-e337. doi:10.1093/milmed/usx200
- Sharp LK, e t a l . Pain. 2023;164( 4 ) : 749-757. doi:10.1097/j .pain.0000000000002759
- Dalton MK, et al. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2021;91(2S Suppl 2):S213-S220. doi:10.1097/TA.0000000000003133
- Mahyar L, et al. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2024;49(2):117-121. doi:10.1136/rapm-2023-104610
- Gupta K, et al. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2025;51(1):103. doi:10.1007/s00068-025-02778-x
- Mariano ER, et al. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2022;47(2):118-127. doi:10.1136/rapm-2021-103083
Data Trends 2025: Acute Pain
Data Trends 2025: Acute Pain
Sports Injuries of the Hip in Primary Care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.
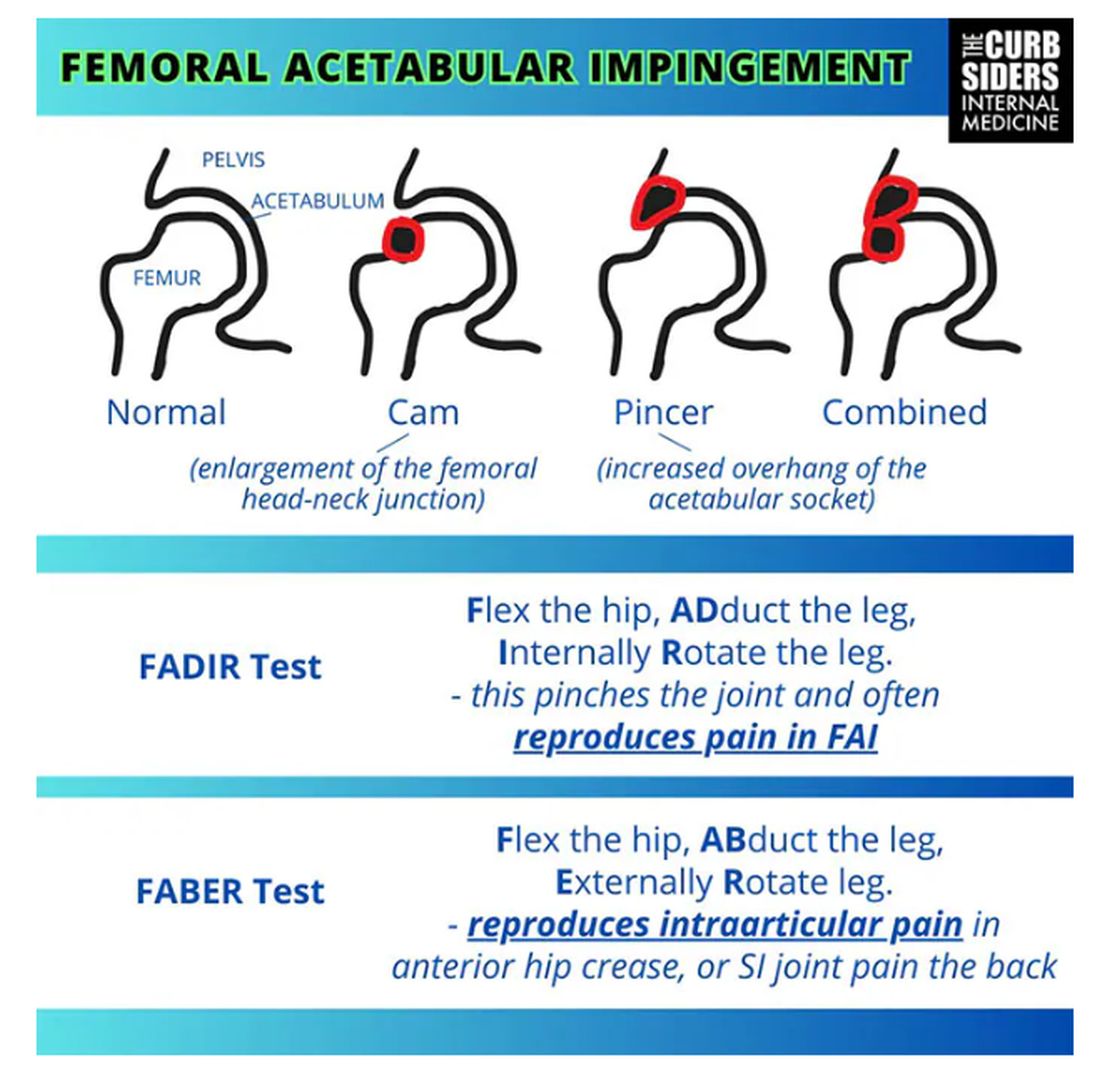
Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.
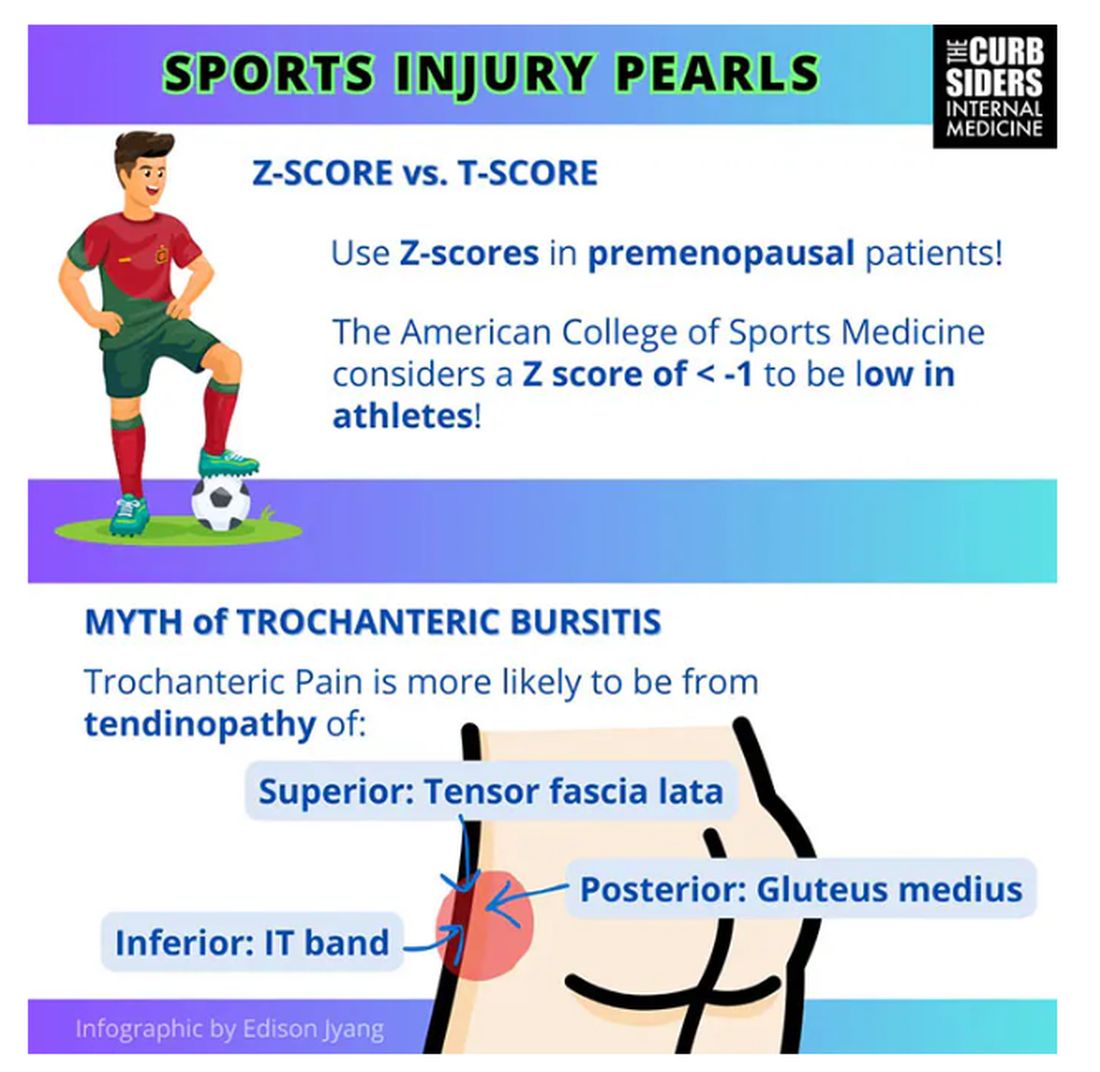
Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
More Americans Than Ever Suffer From Chronic Pain
More Americans than ever are hurting with enduring, life-restricting pain. Like obesity, this condition is on the rise, according to figures in a new National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Data Brief from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Both types increased with age and with decreasing urbanization level. Women were more likely than men to have HICP (23.2% vs 7.3%).
Like obesity, chronic pain is multifactorial and is best managed with multidisciplinary intervention, said Jianguo Cheng, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology and medical director of the Cleveland Clinic Consortium for Pain in Ohio. “It’s a complex mix of genetic, biological, and psychosocial dimensions that can cause ongoing pain out of proportion to the original limited injury that triggered it.”
While today’s longer lifespans are the primary driver of the increase, noted Martin Cheatle, PhD, an associate professor of psychiatry, anesthesiology, and critical care and director of behavioral medicine at the Penn Pain Medicine Center at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, another important factor is the more than 100 million Americans who suffer from obesity. “Obesity is a major risk factor for chronic pain conditions including advancing joint disease, low back pain, and diabetic neuropathies,” he said.
Age is an amplifier, agreed Beth Darnall, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology and perioperative and pain medicine and director of the Pain Relief Innovations Lab at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California, but the increases in chronic pain and HICP cut across age strata.
“Across the board we see striking increases in chronic pain, such as a 5% increase for those 65 and older, and a nearly 2% increase in HICP in that same age group,” Darnall said, referencing the changes from 2019 data in the new NCHS Data Brief. “And an almost 4% increase was observed for the youngest adult age category,18 to 29. Some of our research is now focusing on how to best treat chronic pain in young adults.”
The rise in chronic pain is broadly linked to the overall decline in the health of the US population, as indicated by the CDC 2024’s Chronic Disease Prevalence in the US: Sociodemographic and Geographic Variations by Zip Code Tabulation Area.
The Opioid Crisis and COVID
Beginning in 2016, in response to the opioid crisis and CDC guidelines, opioid prescribing for chronic pain rapidly dropped, both in terms of new prescriptions and tapering of doses of long-term users. “Reduced opioid prescribing yielded benefits for some patients but created new problems and harms for other patients,” said Darnall. Cheng added that the CDC’s recommendations on opioid prescribing were widely misinterpreted and were applied to patients with painful conditions such as cancer and sickle cell disease who were not intended to be affected by the guidelines. “In addition, although medical opioid prescribing dropped by 50%, overdose deaths from non-medical opioid sources increased by more 50%.”
Currently, most opioid overdoses are related to heroin, fentanyl, and newer drugs of abuse such as xylazine. “Most pain clinicians would agree that opioids are not first-line therapy for chronic non-cancer pain, but in a select number of well-vetted patients, opioids can be very effective in improving functionality and quality of life as part of a multimodal approach to pain care,” Cheatle said.
The impact of the opioid crisis is complex, said Cheatle, noting that only 8%-10% of pain patients on long-term opioid therapy develop a use disorder. “However, opioids were overly prescribed due to clinicians’ lack of training in core competencies of pain management and the insurance companies’ refusal to adequately cover non-opioid therapies such as acupuncture, cognitive behavioral therapy, extended physical therapy, and medical massage,” he said.
He pointed out that in the late 1990s there were more than 1000 multidisciplinary pain centers, whereas currently there are many fewer owing to lack of insurance reimbursement. “This results in more possibly avoidable invasive surgeries, which can further contribute to the increase in chronic pain.”
The COVID pandemic further exacerbated the pain problem and delayed access to timely medical interventions for many people. Some adopted a more sedentary lifestyle, already entrenched in today’s technology-driven society, leading in turn to weight gain and more chronic pain. “The isolation and lack of normal human connections during the pandemic could exacerbate pain and loss of autonomy,” Cheatle said. And some individuals developed painful neurologic conditions related to long-haul COVID, for which there is no effective treatment.
Best Approach
“Historically, pain has been treated as a purely biomedical issue. Bringing a biopsychosocial perspective to pain care can support pain relief,” said Darnall. Multiple national clinical guidance documents have called for a comprehensive approach that considers the whole person: their circumstances, their needs, their stressors, and their environment. “And we must provide patients meaningful access to the lowest-risk, non-pharmacologic treatments first – and ideally early on,” she said.
Even effective medications rarely make a person pain free, so other approaches are needed in tandem, Darnall said. Support for stronger patient competency in self-management of chronic pain is mounting.
“It’s vitally important that we help people know how to help themselves have less pain – how to steer their mind and body toward relief by using pain relief skills,” she said. “By so doing they can cultivate a critical level of control over their pain and are less at its mercy, which supports good mood and is shown to help people be more active as the impacts of pain diminish.”
Darnall outlined a recent development in the primary care setting that involves offering patients a brief program in pain-relief skills training. Within Veterans Affairs primary care, for example, patients receive several 30-minute sessions in pain reduction techniques. Outside of the VA, primary care clinics are incorporating an evidence-based, one-session 2-hour pain relief skills class called Empowered Relief, as standard care.
The class teaches participants three pain management skills and creates a personalized plan for each that includes a free app for ongoing daily use.
Since pain causes agitation in the central nervous system, manifested as fast heart rate, rapid breathing, muscle tension, and distress, people learn various ways to calm the central nervous system – with, for example, a sound technology known as binaural audio to deepen the relaxation response. “They also learn to identify and target worry about pain and develop self-soothing actions to interrupt unhelpful patterns,” Darnall said.
Data from randomized chronic pain studies, including one by her group using a virtual reality training program for lower back pain, show that 3 months after the training program people report clinically meaningful reductions in pain intensity, pain interference with daily activities, and sleep disturbance, as well as pain-related distress, anxiety, and fatigue
While psychological and complementary approaches have been effective in improving function and mood, there are barriers to accessing them, said Cheatle, such as lack of insurance coverage and the stigma associated with nontraditional, especially psychological, care.
Prevention
Good lifestyle behaviors promote better health as people age. “Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, prioritizing good sleep, and avoiding smoking and alcohol use can support better health and buffer against chronic diseases and pain,” Darnall said.
Cheatle noted the importance of maintaining a safe work environment and avoiding injury risks by, for example, wearing a seatbelt or a cycling helmet.
The Future
“We need to ensure all individuals have access to effective, low-burden pain treatments, including evidence-based treatments they can receive from home so as to minimize treatment disparities.” Darnall said. Also needed is better comprehensive treatment for acute and chronic pain alike. “If we treat acute pain better, we will have fewer people transitioning to the chronic pain state.”
To that end, added Cheng, healthcare professionals in every specialty from doctors and nurses to psychologists and chiropractors need to develop co-competencies in pain management.
For Cheatle, the near future looks bleak. “There are some pioneering bioengineering approaches to reduce chronic pain and novel pharmacologic agents such as calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibitors for intractable migraines, but just changing insurance reimbursement for a comprehensive approach to chronic pain care and bolstering healthcare provider education on core pain competencies will benefit the over 50 million adults who suffer from chronic pain.”
Cheng, however, is more sanguine. “I don’t expect miracles in 10 years’ time, but we’re making rapid progress in understanding the genetics of chronic pain and the mechanisms of disease and therapy. We’re developing biomarkers to help in prognosis and monitor disease progress.” In the meantime, he pointed to an expanding array of non-pharmaceutical options, including neuromodulatory approaches such as nerve blocks and spinal cord stimulation.
Cheng, Cheatle, and Darnall disclosed no relevant competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
More Americans than ever are hurting with enduring, life-restricting pain. Like obesity, this condition is on the rise, according to figures in a new National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Data Brief from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Both types increased with age and with decreasing urbanization level. Women were more likely than men to have HICP (23.2% vs 7.3%).
Like obesity, chronic pain is multifactorial and is best managed with multidisciplinary intervention, said Jianguo Cheng, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology and medical director of the Cleveland Clinic Consortium for Pain in Ohio. “It’s a complex mix of genetic, biological, and psychosocial dimensions that can cause ongoing pain out of proportion to the original limited injury that triggered it.”
While today’s longer lifespans are the primary driver of the increase, noted Martin Cheatle, PhD, an associate professor of psychiatry, anesthesiology, and critical care and director of behavioral medicine at the Penn Pain Medicine Center at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, another important factor is the more than 100 million Americans who suffer from obesity. “Obesity is a major risk factor for chronic pain conditions including advancing joint disease, low back pain, and diabetic neuropathies,” he said.
Age is an amplifier, agreed Beth Darnall, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology and perioperative and pain medicine and director of the Pain Relief Innovations Lab at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California, but the increases in chronic pain and HICP cut across age strata.
“Across the board we see striking increases in chronic pain, such as a 5% increase for those 65 and older, and a nearly 2% increase in HICP in that same age group,” Darnall said, referencing the changes from 2019 data in the new NCHS Data Brief. “And an almost 4% increase was observed for the youngest adult age category,18 to 29. Some of our research is now focusing on how to best treat chronic pain in young adults.”
The rise in chronic pain is broadly linked to the overall decline in the health of the US population, as indicated by the CDC 2024’s Chronic Disease Prevalence in the US: Sociodemographic and Geographic Variations by Zip Code Tabulation Area.
The Opioid Crisis and COVID
Beginning in 2016, in response to the opioid crisis and CDC guidelines, opioid prescribing for chronic pain rapidly dropped, both in terms of new prescriptions and tapering of doses of long-term users. “Reduced opioid prescribing yielded benefits for some patients but created new problems and harms for other patients,” said Darnall. Cheng added that the CDC’s recommendations on opioid prescribing were widely misinterpreted and were applied to patients with painful conditions such as cancer and sickle cell disease who were not intended to be affected by the guidelines. “In addition, although medical opioid prescribing dropped by 50%, overdose deaths from non-medical opioid sources increased by more 50%.”
Currently, most opioid overdoses are related to heroin, fentanyl, and newer drugs of abuse such as xylazine. “Most pain clinicians would agree that opioids are not first-line therapy for chronic non-cancer pain, but in a select number of well-vetted patients, opioids can be very effective in improving functionality and quality of life as part of a multimodal approach to pain care,” Cheatle said.
The impact of the opioid crisis is complex, said Cheatle, noting that only 8%-10% of pain patients on long-term opioid therapy develop a use disorder. “However, opioids were overly prescribed due to clinicians’ lack of training in core competencies of pain management and the insurance companies’ refusal to adequately cover non-opioid therapies such as acupuncture, cognitive behavioral therapy, extended physical therapy, and medical massage,” he said.
He pointed out that in the late 1990s there were more than 1000 multidisciplinary pain centers, whereas currently there are many fewer owing to lack of insurance reimbursement. “This results in more possibly avoidable invasive surgeries, which can further contribute to the increase in chronic pain.”
The COVID pandemic further exacerbated the pain problem and delayed access to timely medical interventions for many people. Some adopted a more sedentary lifestyle, already entrenched in today’s technology-driven society, leading in turn to weight gain and more chronic pain. “The isolation and lack of normal human connections during the pandemic could exacerbate pain and loss of autonomy,” Cheatle said. And some individuals developed painful neurologic conditions related to long-haul COVID, for which there is no effective treatment.
Best Approach
“Historically, pain has been treated as a purely biomedical issue. Bringing a biopsychosocial perspective to pain care can support pain relief,” said Darnall. Multiple national clinical guidance documents have called for a comprehensive approach that considers the whole person: their circumstances, their needs, their stressors, and their environment. “And we must provide patients meaningful access to the lowest-risk, non-pharmacologic treatments first – and ideally early on,” she said.
Even effective medications rarely make a person pain free, so other approaches are needed in tandem, Darnall said. Support for stronger patient competency in self-management of chronic pain is mounting.
“It’s vitally important that we help people know how to help themselves have less pain – how to steer their mind and body toward relief by using pain relief skills,” she said. “By so doing they can cultivate a critical level of control over their pain and are less at its mercy, which supports good mood and is shown to help people be more active as the impacts of pain diminish.”
Darnall outlined a recent development in the primary care setting that involves offering patients a brief program in pain-relief skills training. Within Veterans Affairs primary care, for example, patients receive several 30-minute sessions in pain reduction techniques. Outside of the VA, primary care clinics are incorporating an evidence-based, one-session 2-hour pain relief skills class called Empowered Relief, as standard care.
The class teaches participants three pain management skills and creates a personalized plan for each that includes a free app for ongoing daily use.
Since pain causes agitation in the central nervous system, manifested as fast heart rate, rapid breathing, muscle tension, and distress, people learn various ways to calm the central nervous system – with, for example, a sound technology known as binaural audio to deepen the relaxation response. “They also learn to identify and target worry about pain and develop self-soothing actions to interrupt unhelpful patterns,” Darnall said.
Data from randomized chronic pain studies, including one by her group using a virtual reality training program for lower back pain, show that 3 months after the training program people report clinically meaningful reductions in pain intensity, pain interference with daily activities, and sleep disturbance, as well as pain-related distress, anxiety, and fatigue
While psychological and complementary approaches have been effective in improving function and mood, there are barriers to accessing them, said Cheatle, such as lack of insurance coverage and the stigma associated with nontraditional, especially psychological, care.
Prevention
Good lifestyle behaviors promote better health as people age. “Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, prioritizing good sleep, and avoiding smoking and alcohol use can support better health and buffer against chronic diseases and pain,” Darnall said.
Cheatle noted the importance of maintaining a safe work environment and avoiding injury risks by, for example, wearing a seatbelt or a cycling helmet.
The Future
“We need to ensure all individuals have access to effective, low-burden pain treatments, including evidence-based treatments they can receive from home so as to minimize treatment disparities.” Darnall said. Also needed is better comprehensive treatment for acute and chronic pain alike. “If we treat acute pain better, we will have fewer people transitioning to the chronic pain state.”
To that end, added Cheng, healthcare professionals in every specialty from doctors and nurses to psychologists and chiropractors need to develop co-competencies in pain management.
For Cheatle, the near future looks bleak. “There are some pioneering bioengineering approaches to reduce chronic pain and novel pharmacologic agents such as calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibitors for intractable migraines, but just changing insurance reimbursement for a comprehensive approach to chronic pain care and bolstering healthcare provider education on core pain competencies will benefit the over 50 million adults who suffer from chronic pain.”
Cheng, however, is more sanguine. “I don’t expect miracles in 10 years’ time, but we’re making rapid progress in understanding the genetics of chronic pain and the mechanisms of disease and therapy. We’re developing biomarkers to help in prognosis and monitor disease progress.” In the meantime, he pointed to an expanding array of non-pharmaceutical options, including neuromodulatory approaches such as nerve blocks and spinal cord stimulation.
Cheng, Cheatle, and Darnall disclosed no relevant competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
More Americans than ever are hurting with enduring, life-restricting pain. Like obesity, this condition is on the rise, according to figures in a new National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Data Brief from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Both types increased with age and with decreasing urbanization level. Women were more likely than men to have HICP (23.2% vs 7.3%).
Like obesity, chronic pain is multifactorial and is best managed with multidisciplinary intervention, said Jianguo Cheng, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology and medical director of the Cleveland Clinic Consortium for Pain in Ohio. “It’s a complex mix of genetic, biological, and psychosocial dimensions that can cause ongoing pain out of proportion to the original limited injury that triggered it.”
While today’s longer lifespans are the primary driver of the increase, noted Martin Cheatle, PhD, an associate professor of psychiatry, anesthesiology, and critical care and director of behavioral medicine at the Penn Pain Medicine Center at the University of Pennsylvania’s Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, another important factor is the more than 100 million Americans who suffer from obesity. “Obesity is a major risk factor for chronic pain conditions including advancing joint disease, low back pain, and diabetic neuropathies,” he said.
Age is an amplifier, agreed Beth Darnall, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology and perioperative and pain medicine and director of the Pain Relief Innovations Lab at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California, but the increases in chronic pain and HICP cut across age strata.
“Across the board we see striking increases in chronic pain, such as a 5% increase for those 65 and older, and a nearly 2% increase in HICP in that same age group,” Darnall said, referencing the changes from 2019 data in the new NCHS Data Brief. “And an almost 4% increase was observed for the youngest adult age category,18 to 29. Some of our research is now focusing on how to best treat chronic pain in young adults.”
The rise in chronic pain is broadly linked to the overall decline in the health of the US population, as indicated by the CDC 2024’s Chronic Disease Prevalence in the US: Sociodemographic and Geographic Variations by Zip Code Tabulation Area.
The Opioid Crisis and COVID
Beginning in 2016, in response to the opioid crisis and CDC guidelines, opioid prescribing for chronic pain rapidly dropped, both in terms of new prescriptions and tapering of doses of long-term users. “Reduced opioid prescribing yielded benefits for some patients but created new problems and harms for other patients,” said Darnall. Cheng added that the CDC’s recommendations on opioid prescribing were widely misinterpreted and were applied to patients with painful conditions such as cancer and sickle cell disease who were not intended to be affected by the guidelines. “In addition, although medical opioid prescribing dropped by 50%, overdose deaths from non-medical opioid sources increased by more 50%.”
Currently, most opioid overdoses are related to heroin, fentanyl, and newer drugs of abuse such as xylazine. “Most pain clinicians would agree that opioids are not first-line therapy for chronic non-cancer pain, but in a select number of well-vetted patients, opioids can be very effective in improving functionality and quality of life as part of a multimodal approach to pain care,” Cheatle said.
The impact of the opioid crisis is complex, said Cheatle, noting that only 8%-10% of pain patients on long-term opioid therapy develop a use disorder. “However, opioids were overly prescribed due to clinicians’ lack of training in core competencies of pain management and the insurance companies’ refusal to adequately cover non-opioid therapies such as acupuncture, cognitive behavioral therapy, extended physical therapy, and medical massage,” he said.
He pointed out that in the late 1990s there were more than 1000 multidisciplinary pain centers, whereas currently there are many fewer owing to lack of insurance reimbursement. “This results in more possibly avoidable invasive surgeries, which can further contribute to the increase in chronic pain.”
The COVID pandemic further exacerbated the pain problem and delayed access to timely medical interventions for many people. Some adopted a more sedentary lifestyle, already entrenched in today’s technology-driven society, leading in turn to weight gain and more chronic pain. “The isolation and lack of normal human connections during the pandemic could exacerbate pain and loss of autonomy,” Cheatle said. And some individuals developed painful neurologic conditions related to long-haul COVID, for which there is no effective treatment.
Best Approach
“Historically, pain has been treated as a purely biomedical issue. Bringing a biopsychosocial perspective to pain care can support pain relief,” said Darnall. Multiple national clinical guidance documents have called for a comprehensive approach that considers the whole person: their circumstances, their needs, their stressors, and their environment. “And we must provide patients meaningful access to the lowest-risk, non-pharmacologic treatments first – and ideally early on,” she said.
Even effective medications rarely make a person pain free, so other approaches are needed in tandem, Darnall said. Support for stronger patient competency in self-management of chronic pain is mounting.
“It’s vitally important that we help people know how to help themselves have less pain – how to steer their mind and body toward relief by using pain relief skills,” she said. “By so doing they can cultivate a critical level of control over their pain and are less at its mercy, which supports good mood and is shown to help people be more active as the impacts of pain diminish.”
Darnall outlined a recent development in the primary care setting that involves offering patients a brief program in pain-relief skills training. Within Veterans Affairs primary care, for example, patients receive several 30-minute sessions in pain reduction techniques. Outside of the VA, primary care clinics are incorporating an evidence-based, one-session 2-hour pain relief skills class called Empowered Relief, as standard care.
The class teaches participants three pain management skills and creates a personalized plan for each that includes a free app for ongoing daily use.
Since pain causes agitation in the central nervous system, manifested as fast heart rate, rapid breathing, muscle tension, and distress, people learn various ways to calm the central nervous system – with, for example, a sound technology known as binaural audio to deepen the relaxation response. “They also learn to identify and target worry about pain and develop self-soothing actions to interrupt unhelpful patterns,” Darnall said.
Data from randomized chronic pain studies, including one by her group using a virtual reality training program for lower back pain, show that 3 months after the training program people report clinically meaningful reductions in pain intensity, pain interference with daily activities, and sleep disturbance, as well as pain-related distress, anxiety, and fatigue
While psychological and complementary approaches have been effective in improving function and mood, there are barriers to accessing them, said Cheatle, such as lack of insurance coverage and the stigma associated with nontraditional, especially psychological, care.
Prevention
Good lifestyle behaviors promote better health as people age. “Maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, prioritizing good sleep, and avoiding smoking and alcohol use can support better health and buffer against chronic diseases and pain,” Darnall said.
Cheatle noted the importance of maintaining a safe work environment and avoiding injury risks by, for example, wearing a seatbelt or a cycling helmet.
The Future
“We need to ensure all individuals have access to effective, low-burden pain treatments, including evidence-based treatments they can receive from home so as to minimize treatment disparities.” Darnall said. Also needed is better comprehensive treatment for acute and chronic pain alike. “If we treat acute pain better, we will have fewer people transitioning to the chronic pain state.”
To that end, added Cheng, healthcare professionals in every specialty from doctors and nurses to psychologists and chiropractors need to develop co-competencies in pain management.
For Cheatle, the near future looks bleak. “There are some pioneering bioengineering approaches to reduce chronic pain and novel pharmacologic agents such as calcitonin gene-related peptide inhibitors for intractable migraines, but just changing insurance reimbursement for a comprehensive approach to chronic pain care and bolstering healthcare provider education on core pain competencies will benefit the over 50 million adults who suffer from chronic pain.”
Cheng, however, is more sanguine. “I don’t expect miracles in 10 years’ time, but we’re making rapid progress in understanding the genetics of chronic pain and the mechanisms of disease and therapy. We’re developing biomarkers to help in prognosis and monitor disease progress.” In the meantime, he pointed to an expanding array of non-pharmaceutical options, including neuromodulatory approaches such as nerve blocks and spinal cord stimulation.
Cheng, Cheatle, and Darnall disclosed no relevant competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Total Intravenous Anesthesia Enables Earlier Facial Nerve Monitoring Than Sevoflurane in Ear Surgery
TOPLINE:
Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) enables earlier intraoperative monitoring of facial nerve activity than sevoflurane anesthesia during ear surgery, with reduced patient-ventilator dyssynchrony and fewer requirements for postoperative antiemetics.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the difference in the timeliness of intraoperative monitoring of facial nerve activity during ear surgery with TIVA vs sevoflurane anesthesia.
- They included 98 patients aged 18-74 years undergoing ear surgery between November 2021 and November 2022; patients were randomly assigned to receive either TIVA or sevoflurane during the procedure. Of these, 92 were included in the final analysis.
- Neuromuscular function was monitored quantitatively throughout anesthesia with train-of-four counts and train-of-four ratios.
- The time from the administration of rocuronium to the start of facial nerve monitoring was recorded.
- The primary outcome measure focused on the recovery index, defined as the time interval between a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 and 0.75; the key secondary outcome was the time to reach a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 from rocuronium administration.
TAKEAWAY:
- The time to reach a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 was achieved earlier with TIVA than with sevoflurane (34 minutes vs 51 minutes; P < .001).
- Patient-ventilator dyssynchrony occurred less frequently in the TIVA group than in the sevoflurane group (15% vs 39%; P = .01).
- Postoperative requests for antiemetics were less frequent in the TIVA group than in the sevoflurane group (2% vs 17%; P = .03).
IN PRACTICE:
“We suggest that TIVA may be a better choice than sevoflurane anesthesia to meet an earlier request” for intraoperative facial nerve monitoring by surgeons, the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yu Jeong Bang, MD, of the Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine at Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, in Seoul, Republic of Korea. It was published online on November 27, 2024, in The Canadian Journal of Anesthesia.
LIMITATIONS:
A careful interpretation of results may be necessary when clinicians use balanced anesthesia, such as sevoflurane with adjuvants like opioids or nonopioids. The feasibility of intraoperative facial nerve monitoring was decided by the surgeon during surgery, and the lowest stimulation intensity threshold for electromyography amplitude was not detected, as it was not the focus of this study. Although patients requiring intraoperative facial nerve monitoring during ear surgery were enrolled, some did not undergo the procedure based on the surgeon’s judgment.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) enables earlier intraoperative monitoring of facial nerve activity than sevoflurane anesthesia during ear surgery, with reduced patient-ventilator dyssynchrony and fewer requirements for postoperative antiemetics.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the difference in the timeliness of intraoperative monitoring of facial nerve activity during ear surgery with TIVA vs sevoflurane anesthesia.
- They included 98 patients aged 18-74 years undergoing ear surgery between November 2021 and November 2022; patients were randomly assigned to receive either TIVA or sevoflurane during the procedure. Of these, 92 were included in the final analysis.
- Neuromuscular function was monitored quantitatively throughout anesthesia with train-of-four counts and train-of-four ratios.
- The time from the administration of rocuronium to the start of facial nerve monitoring was recorded.
- The primary outcome measure focused on the recovery index, defined as the time interval between a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 and 0.75; the key secondary outcome was the time to reach a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 from rocuronium administration.
TAKEAWAY:
- The time to reach a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 was achieved earlier with TIVA than with sevoflurane (34 minutes vs 51 minutes; P < .001).
- Patient-ventilator dyssynchrony occurred less frequently in the TIVA group than in the sevoflurane group (15% vs 39%; P = .01).
- Postoperative requests for antiemetics were less frequent in the TIVA group than in the sevoflurane group (2% vs 17%; P = .03).
IN PRACTICE:
“We suggest that TIVA may be a better choice than sevoflurane anesthesia to meet an earlier request” for intraoperative facial nerve monitoring by surgeons, the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yu Jeong Bang, MD, of the Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine at Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, in Seoul, Republic of Korea. It was published online on November 27, 2024, in The Canadian Journal of Anesthesia.
LIMITATIONS:
A careful interpretation of results may be necessary when clinicians use balanced anesthesia, such as sevoflurane with adjuvants like opioids or nonopioids. The feasibility of intraoperative facial nerve monitoring was decided by the surgeon during surgery, and the lowest stimulation intensity threshold for electromyography amplitude was not detected, as it was not the focus of this study. Although patients requiring intraoperative facial nerve monitoring during ear surgery were enrolled, some did not undergo the procedure based on the surgeon’s judgment.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Total intravenous anesthesia (TIVA) enables earlier intraoperative monitoring of facial nerve activity than sevoflurane anesthesia during ear surgery, with reduced patient-ventilator dyssynchrony and fewer requirements for postoperative antiemetics.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the difference in the timeliness of intraoperative monitoring of facial nerve activity during ear surgery with TIVA vs sevoflurane anesthesia.
- They included 98 patients aged 18-74 years undergoing ear surgery between November 2021 and November 2022; patients were randomly assigned to receive either TIVA or sevoflurane during the procedure. Of these, 92 were included in the final analysis.
- Neuromuscular function was monitored quantitatively throughout anesthesia with train-of-four counts and train-of-four ratios.
- The time from the administration of rocuronium to the start of facial nerve monitoring was recorded.
- The primary outcome measure focused on the recovery index, defined as the time interval between a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 and 0.75; the key secondary outcome was the time to reach a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 from rocuronium administration.
TAKEAWAY:
- The time to reach a train-of-four ratio of 0.25 was achieved earlier with TIVA than with sevoflurane (34 minutes vs 51 minutes; P < .001).
- Patient-ventilator dyssynchrony occurred less frequently in the TIVA group than in the sevoflurane group (15% vs 39%; P = .01).
- Postoperative requests for antiemetics were less frequent in the TIVA group than in the sevoflurane group (2% vs 17%; P = .03).
IN PRACTICE:
“We suggest that TIVA may be a better choice than sevoflurane anesthesia to meet an earlier request” for intraoperative facial nerve monitoring by surgeons, the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yu Jeong Bang, MD, of the Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine at Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, in Seoul, Republic of Korea. It was published online on November 27, 2024, in The Canadian Journal of Anesthesia.
LIMITATIONS:
A careful interpretation of results may be necessary when clinicians use balanced anesthesia, such as sevoflurane with adjuvants like opioids or nonopioids. The feasibility of intraoperative facial nerve monitoring was decided by the surgeon during surgery, and the lowest stimulation intensity threshold for electromyography amplitude was not detected, as it was not the focus of this study. Although patients requiring intraoperative facial nerve monitoring during ear surgery were enrolled, some did not undergo the procedure based on the surgeon’s judgment.
DISCLOSURES:
This study did not receive any funding. The authors disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Managing Return-to-Work Barriers for People With Long COVID
Although some patients experience symptoms so severe that they cannot work under any conditions, medical providers and employers can help ensure many patients with long COVID can stay in the workforce.
Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems. By the end of 2023, at least 400 million people worldwide were estimated to have long COVID.
As members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers and health advocates living with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions, we have published one of the first research studies of people with long COVID and their desire to work, the specific needs they have, and what doctors and employers can do to create a path for returning to the workforce.
In our recent paper, we document the barriers and facilitators that individuals living with long COVID experience when attempting to return to work. Our recommendations are based on these findings and include recommendations for both medical providers and employers.
If you are a medical provider:
- Ensure you adequately document your patients’ COVID cases, any long COVID diagnoses, and the functional impairment that long COVID causes. Remember that you can diagnose a patient with long COVID on the basis of their symptoms, and clinical guidelines do not require a record of a positive COVID-19 test, which many patients lack owing to testing barriers.
- Keep up to date on research on long COVID and related infection-associated chronic conditions — for example, through the Project ECHO Long COVID and Fatiguing Illness Recovery Program — and learn about pacing and other treatment options.
If you are an employer:
- Utilize a return-to-work model in which any worker with suspected or confirmed COVID discusses support they may need with their employer when they return to work, with additional check-in dates scheduled to reevaluate supports as needed. Planning for this collaborative and iterative evaluation of return-to-work supports for all workers with COVID-19 is important because it may not be immediately clear to a worker whether they have developed long COVID or are generally recuperating from the illness.
- Do not require medical documentation of a SARS-CoV-2 infection or a Long COVID diagnosis to access accommodations — this is owing to disparities in accessing documentation.
- Tailor job responsibilities, provide remote options, allow flexible hours, and provide longer-range deadlines to account for symptoms for people with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions.
- Provide accommodations to any caregivers of people with long COVID in your workplace.
- If requiring in-person work, make the workplace as safe as possible through ventilation and masking requirements, which will help ensure fewer of your workers develop long COVID, and those already with infection-associated chronic conditions will not get worse.
Our findings and recommendations are specific to long COVID, but they can and should apply to other disabilities. Given that our study’s sample was predominately White and working in jobs that did not require substantial physical labor, additional recommendations may be needed for other populations and workers who have labor-intensive jobs.
510 Study Participants
Long COVID is characterized as a relapsing-remitting illness, often described as episodic, in which an individual’s symptoms may fluctuate. Symptoms can become more or less severe depending on tasks, exertion, and social support in addition to physiologic processes and medical intervention. In our paper, we illustrate how the long COVID return-to-work experience and individuals’ symptoms can be shaped by workplace, home, and medical environments.
We randomly selected 510 participants from a global survey of people living with long COVID and systematically analyzed their open-ended responses using established qualitative analysis methods. In this study, we specifically analyzed what patients wrote about their return-to-work experiences, considering how work experiences and relapsing and remitting long COVID symptoms intersected with personal lives and medical care.
Most of the study participants identified as White, were 30-60 years old (ie, in their key earning years), and had at least a baccalaureate degree. Participants lived in the United States (38%), United Kingdom (25%), continental Europe (8%), Canada (4%), or other countries (25%). Most participants worked in professions that did not require substantial physical labor, and individuals in those fields may experience even greater return-to-work barriers than are reported in this study.
Key Findings
Through our qualitative analysis, we identified four primary return-to-work themes:
1. People living with long COVID have a strong desire and financial need to return to work.
The participants in our study described how they had experienced financial hardship because they could not successfully return to work and may have incurred new expenses with long COVID. They also often wrote how they wanted to return to work because their jobs provided meaning and structure for their lives. Some people in this study shared how they had tried to return to their jobs but relapsed. As a result, they considered leaving the workforce.
2. Workers’ long COVID symptoms intersect with organization of work and home life.
Most of the people in our study were employed in positions that did not require substantial physical labor. Even so, workers described how their long COVID symptoms were exacerbated by some job tasks. Computer screen time; reading dense material or writing (including emails); and conversations and meetings, regardless of whether they were in-person or via phone or video conferencing, could trigger or make symptoms worse. Workers who needed to stand for long periods of time, such as teachers and healthcare workers, and workers who needed to do lifting as part of their jobs described how these requirements were too taxing and could lead to relapses.
Because of the relapsing and remitting nature of many long COVID symptoms, people reported how it could be difficult to predict how job tasks, long hours, or pressing deadlines may exacerbate symptoms, which would require them to take time off work. For these participants, “pushing through” symptoms only made the symptoms worse. However, people in the study who were allowed to work from home reported how pacing, elevating their legs, and conserving energy (especially by not commuting) was key to doing their jobs well.
Some people in the study described how they were only able to return to work because they had substantial support from family or partners at home. These individuals shared how the people they lived with did most of the cooking, cleaning, and other household tasks so that the person living with long COVID could conserve their energy for work. This reorganization of home life notably shifted household tasks and caregiving to other people in the household, but without this shift, the individual’s long COVID symptoms may be too severe to work.
3. People with long COVID experience disbelief and stigma at work and healthcare settings.
Some people in our study described how their colleagues, supervisors, and human resource managers insinuated that they were fabricating or exaggerating their symptoms. This made it hard for workers to communicate what support they needed and could limit access to necessary work accommodations.
Many people in our study also described how medical providers did not believe that they had long COVID despite experiencing debilitating symptoms, often because they did not have a positive COVID-19 test to prove they had had an acute infection. Many people with long COVID may not have a positive COVID-19 test because:
- They could not access a test because testing access was limited at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are transportation and cost barriers to tests, many health insurance providers no longer cover tests; and there are fewer public testing sites since the World Health Organization declared an end to the public health emergency;
- There is a high probability of false-negative results for viral and antibody tests (especially during the first wave of the pandemic and for individuals with limited immune response); and
- People can develop long COVID after asymptomatic acute infection.
Although healthcare providers can provide a long COVID diagnosis without a positive COVID-19 test on the basis of a patient’s presentation of symptoms and clinical history, many people in our study said that their providers would not provide this diagnosis, which restricted access to worker’s compensation, paid time off, and job accommodations.
Many people in the study also reported that their medical providers misdiagnosed them with a mental health disorder, such as anxiety, instead of long COVID. Although some people with long COVID may experience poor mental health as a natural consequence of dealing with a debilitating medical condition or may have neuropsychiatric symptoms as part of their long COVID, long COVID is not caused by an underlying psychiatric illness.
4. Support of medical providers is key to successful return to work for people living with long COVID.
Some people in our study described how they were able to get workplace accommodations or access workers’ compensation or sick leave because their medical providers recognized they had long COVID and provided them with this documentation. Some of these participants did not have a positive COVID-19 test, but their medical providers were able to diagnose them with long COVID on the basis of symptom presentation and clinical history. This documentation was critical for helping workers remain financially stable and able to return to work.
Conclusion
While we continue to search for treatment and cures for long COVID and work to provide a robust social safety net, it is crucial to address the stigma, inaccessibility, and lack of support often experienced by patients in their workplaces. Disabled people have long faced these issues; long COVID may be an opportunity to revolutionize the workplace to ensure an inclusive and accessible environment that can improve the lives of all workers.
For more on how to best be inclusive of employees with long COVID, read Harvard Business Review’s “Long Covid at Work: A Manager’s Guide” and visit the Job Accommodation Network webpage dedicated to long COVID.
Additional discussion about our study and applying the findings to improve work and medical care can be found by listening to the Healthy Work podcast episode titled “Supporting Long COVID at Work.”
Elisabeth Stelson, Gina Assaf, and Lisa McCorkell are members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers. Dr Stelson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Gina Assaf is Research Lead, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC. Lisa McCorkell is a long COVID patient; Cofounder, Team Lead, Researcher, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Although some patients experience symptoms so severe that they cannot work under any conditions, medical providers and employers can help ensure many patients with long COVID can stay in the workforce.
Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems. By the end of 2023, at least 400 million people worldwide were estimated to have long COVID.
As members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers and health advocates living with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions, we have published one of the first research studies of people with long COVID and their desire to work, the specific needs they have, and what doctors and employers can do to create a path for returning to the workforce.
In our recent paper, we document the barriers and facilitators that individuals living with long COVID experience when attempting to return to work. Our recommendations are based on these findings and include recommendations for both medical providers and employers.
If you are a medical provider:
- Ensure you adequately document your patients’ COVID cases, any long COVID diagnoses, and the functional impairment that long COVID causes. Remember that you can diagnose a patient with long COVID on the basis of their symptoms, and clinical guidelines do not require a record of a positive COVID-19 test, which many patients lack owing to testing barriers.
- Keep up to date on research on long COVID and related infection-associated chronic conditions — for example, through the Project ECHO Long COVID and Fatiguing Illness Recovery Program — and learn about pacing and other treatment options.
If you are an employer:
- Utilize a return-to-work model in which any worker with suspected or confirmed COVID discusses support they may need with their employer when they return to work, with additional check-in dates scheduled to reevaluate supports as needed. Planning for this collaborative and iterative evaluation of return-to-work supports for all workers with COVID-19 is important because it may not be immediately clear to a worker whether they have developed long COVID or are generally recuperating from the illness.
- Do not require medical documentation of a SARS-CoV-2 infection or a Long COVID diagnosis to access accommodations — this is owing to disparities in accessing documentation.
- Tailor job responsibilities, provide remote options, allow flexible hours, and provide longer-range deadlines to account for symptoms for people with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions.
- Provide accommodations to any caregivers of people with long COVID in your workplace.
- If requiring in-person work, make the workplace as safe as possible through ventilation and masking requirements, which will help ensure fewer of your workers develop long COVID, and those already with infection-associated chronic conditions will not get worse.
Our findings and recommendations are specific to long COVID, but they can and should apply to other disabilities. Given that our study’s sample was predominately White and working in jobs that did not require substantial physical labor, additional recommendations may be needed for other populations and workers who have labor-intensive jobs.
510 Study Participants
Long COVID is characterized as a relapsing-remitting illness, often described as episodic, in which an individual’s symptoms may fluctuate. Symptoms can become more or less severe depending on tasks, exertion, and social support in addition to physiologic processes and medical intervention. In our paper, we illustrate how the long COVID return-to-work experience and individuals’ symptoms can be shaped by workplace, home, and medical environments.
We randomly selected 510 participants from a global survey of people living with long COVID and systematically analyzed their open-ended responses using established qualitative analysis methods. In this study, we specifically analyzed what patients wrote about their return-to-work experiences, considering how work experiences and relapsing and remitting long COVID symptoms intersected with personal lives and medical care.
Most of the study participants identified as White, were 30-60 years old (ie, in their key earning years), and had at least a baccalaureate degree. Participants lived in the United States (38%), United Kingdom (25%), continental Europe (8%), Canada (4%), or other countries (25%). Most participants worked in professions that did not require substantial physical labor, and individuals in those fields may experience even greater return-to-work barriers than are reported in this study.
Key Findings
Through our qualitative analysis, we identified four primary return-to-work themes:
1. People living with long COVID have a strong desire and financial need to return to work.
The participants in our study described how they had experienced financial hardship because they could not successfully return to work and may have incurred new expenses with long COVID. They also often wrote how they wanted to return to work because their jobs provided meaning and structure for their lives. Some people in this study shared how they had tried to return to their jobs but relapsed. As a result, they considered leaving the workforce.
2. Workers’ long COVID symptoms intersect with organization of work and home life.
Most of the people in our study were employed in positions that did not require substantial physical labor. Even so, workers described how their long COVID symptoms were exacerbated by some job tasks. Computer screen time; reading dense material or writing (including emails); and conversations and meetings, regardless of whether they were in-person or via phone or video conferencing, could trigger or make symptoms worse. Workers who needed to stand for long periods of time, such as teachers and healthcare workers, and workers who needed to do lifting as part of their jobs described how these requirements were too taxing and could lead to relapses.
Because of the relapsing and remitting nature of many long COVID symptoms, people reported how it could be difficult to predict how job tasks, long hours, or pressing deadlines may exacerbate symptoms, which would require them to take time off work. For these participants, “pushing through” symptoms only made the symptoms worse. However, people in the study who were allowed to work from home reported how pacing, elevating their legs, and conserving energy (especially by not commuting) was key to doing their jobs well.
Some people in the study described how they were only able to return to work because they had substantial support from family or partners at home. These individuals shared how the people they lived with did most of the cooking, cleaning, and other household tasks so that the person living with long COVID could conserve their energy for work. This reorganization of home life notably shifted household tasks and caregiving to other people in the household, but without this shift, the individual’s long COVID symptoms may be too severe to work.
3. People with long COVID experience disbelief and stigma at work and healthcare settings.
Some people in our study described how their colleagues, supervisors, and human resource managers insinuated that they were fabricating or exaggerating their symptoms. This made it hard for workers to communicate what support they needed and could limit access to necessary work accommodations.
Many people in our study also described how medical providers did not believe that they had long COVID despite experiencing debilitating symptoms, often because they did not have a positive COVID-19 test to prove they had had an acute infection. Many people with long COVID may not have a positive COVID-19 test because:
- They could not access a test because testing access was limited at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are transportation and cost barriers to tests, many health insurance providers no longer cover tests; and there are fewer public testing sites since the World Health Organization declared an end to the public health emergency;
- There is a high probability of false-negative results for viral and antibody tests (especially during the first wave of the pandemic and for individuals with limited immune response); and
- People can develop long COVID after asymptomatic acute infection.
Although healthcare providers can provide a long COVID diagnosis without a positive COVID-19 test on the basis of a patient’s presentation of symptoms and clinical history, many people in our study said that their providers would not provide this diagnosis, which restricted access to worker’s compensation, paid time off, and job accommodations.
Many people in the study also reported that their medical providers misdiagnosed them with a mental health disorder, such as anxiety, instead of long COVID. Although some people with long COVID may experience poor mental health as a natural consequence of dealing with a debilitating medical condition or may have neuropsychiatric symptoms as part of their long COVID, long COVID is not caused by an underlying psychiatric illness.
4. Support of medical providers is key to successful return to work for people living with long COVID.
Some people in our study described how they were able to get workplace accommodations or access workers’ compensation or sick leave because their medical providers recognized they had long COVID and provided them with this documentation. Some of these participants did not have a positive COVID-19 test, but their medical providers were able to diagnose them with long COVID on the basis of symptom presentation and clinical history. This documentation was critical for helping workers remain financially stable and able to return to work.
Conclusion
While we continue to search for treatment and cures for long COVID and work to provide a robust social safety net, it is crucial to address the stigma, inaccessibility, and lack of support often experienced by patients in their workplaces. Disabled people have long faced these issues; long COVID may be an opportunity to revolutionize the workplace to ensure an inclusive and accessible environment that can improve the lives of all workers.
For more on how to best be inclusive of employees with long COVID, read Harvard Business Review’s “Long Covid at Work: A Manager’s Guide” and visit the Job Accommodation Network webpage dedicated to long COVID.
Additional discussion about our study and applying the findings to improve work and medical care can be found by listening to the Healthy Work podcast episode titled “Supporting Long COVID at Work.”
Elisabeth Stelson, Gina Assaf, and Lisa McCorkell are members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers. Dr Stelson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Gina Assaf is Research Lead, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC. Lisa McCorkell is a long COVID patient; Cofounder, Team Lead, Researcher, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Although some patients experience symptoms so severe that they cannot work under any conditions, medical providers and employers can help ensure many patients with long COVID can stay in the workforce.
Long COVID is an infection-associated chronic condition that occurs after SARS-CoV-2 infection and is present for at least 3 months as a continuous, relapsing and remitting, or progressive disease state that affects one or more organ systems. By the end of 2023, at least 400 million people worldwide were estimated to have long COVID.
As members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers and health advocates living with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions, we have published one of the first research studies of people with long COVID and their desire to work, the specific needs they have, and what doctors and employers can do to create a path for returning to the workforce.
In our recent paper, we document the barriers and facilitators that individuals living with long COVID experience when attempting to return to work. Our recommendations are based on these findings and include recommendations for both medical providers and employers.
If you are a medical provider:
- Ensure you adequately document your patients’ COVID cases, any long COVID diagnoses, and the functional impairment that long COVID causes. Remember that you can diagnose a patient with long COVID on the basis of their symptoms, and clinical guidelines do not require a record of a positive COVID-19 test, which many patients lack owing to testing barriers.
- Keep up to date on research on long COVID and related infection-associated chronic conditions — for example, through the Project ECHO Long COVID and Fatiguing Illness Recovery Program — and learn about pacing and other treatment options.
If you are an employer:
- Utilize a return-to-work model in which any worker with suspected or confirmed COVID discusses support they may need with their employer when they return to work, with additional check-in dates scheduled to reevaluate supports as needed. Planning for this collaborative and iterative evaluation of return-to-work supports for all workers with COVID-19 is important because it may not be immediately clear to a worker whether they have developed long COVID or are generally recuperating from the illness.
- Do not require medical documentation of a SARS-CoV-2 infection or a Long COVID diagnosis to access accommodations — this is owing to disparities in accessing documentation.
- Tailor job responsibilities, provide remote options, allow flexible hours, and provide longer-range deadlines to account for symptoms for people with long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions.
- Provide accommodations to any caregivers of people with long COVID in your workplace.
- If requiring in-person work, make the workplace as safe as possible through ventilation and masking requirements, which will help ensure fewer of your workers develop long COVID, and those already with infection-associated chronic conditions will not get worse.
Our findings and recommendations are specific to long COVID, but they can and should apply to other disabilities. Given that our study’s sample was predominately White and working in jobs that did not require substantial physical labor, additional recommendations may be needed for other populations and workers who have labor-intensive jobs.
510 Study Participants
Long COVID is characterized as a relapsing-remitting illness, often described as episodic, in which an individual’s symptoms may fluctuate. Symptoms can become more or less severe depending on tasks, exertion, and social support in addition to physiologic processes and medical intervention. In our paper, we illustrate how the long COVID return-to-work experience and individuals’ symptoms can be shaped by workplace, home, and medical environments.
We randomly selected 510 participants from a global survey of people living with long COVID and systematically analyzed their open-ended responses using established qualitative analysis methods. In this study, we specifically analyzed what patients wrote about their return-to-work experiences, considering how work experiences and relapsing and remitting long COVID symptoms intersected with personal lives and medical care.
Most of the study participants identified as White, were 30-60 years old (ie, in their key earning years), and had at least a baccalaureate degree. Participants lived in the United States (38%), United Kingdom (25%), continental Europe (8%), Canada (4%), or other countries (25%). Most participants worked in professions that did not require substantial physical labor, and individuals in those fields may experience even greater return-to-work barriers than are reported in this study.
Key Findings
Through our qualitative analysis, we identified four primary return-to-work themes:
1. People living with long COVID have a strong desire and financial need to return to work.
The participants in our study described how they had experienced financial hardship because they could not successfully return to work and may have incurred new expenses with long COVID. They also often wrote how they wanted to return to work because their jobs provided meaning and structure for their lives. Some people in this study shared how they had tried to return to their jobs but relapsed. As a result, they considered leaving the workforce.
2. Workers’ long COVID symptoms intersect with organization of work and home life.
Most of the people in our study were employed in positions that did not require substantial physical labor. Even so, workers described how their long COVID symptoms were exacerbated by some job tasks. Computer screen time; reading dense material or writing (including emails); and conversations and meetings, regardless of whether they were in-person or via phone or video conferencing, could trigger or make symptoms worse. Workers who needed to stand for long periods of time, such as teachers and healthcare workers, and workers who needed to do lifting as part of their jobs described how these requirements were too taxing and could lead to relapses.
Because of the relapsing and remitting nature of many long COVID symptoms, people reported how it could be difficult to predict how job tasks, long hours, or pressing deadlines may exacerbate symptoms, which would require them to take time off work. For these participants, “pushing through” symptoms only made the symptoms worse. However, people in the study who were allowed to work from home reported how pacing, elevating their legs, and conserving energy (especially by not commuting) was key to doing their jobs well.
Some people in the study described how they were only able to return to work because they had substantial support from family or partners at home. These individuals shared how the people they lived with did most of the cooking, cleaning, and other household tasks so that the person living with long COVID could conserve their energy for work. This reorganization of home life notably shifted household tasks and caregiving to other people in the household, but without this shift, the individual’s long COVID symptoms may be too severe to work.
3. People with long COVID experience disbelief and stigma at work and healthcare settings.
Some people in our study described how their colleagues, supervisors, and human resource managers insinuated that they were fabricating or exaggerating their symptoms. This made it hard for workers to communicate what support they needed and could limit access to necessary work accommodations.
Many people in our study also described how medical providers did not believe that they had long COVID despite experiencing debilitating symptoms, often because they did not have a positive COVID-19 test to prove they had had an acute infection. Many people with long COVID may not have a positive COVID-19 test because:
- They could not access a test because testing access was limited at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, there are transportation and cost barriers to tests, many health insurance providers no longer cover tests; and there are fewer public testing sites since the World Health Organization declared an end to the public health emergency;
- There is a high probability of false-negative results for viral and antibody tests (especially during the first wave of the pandemic and for individuals with limited immune response); and
- People can develop long COVID after asymptomatic acute infection.
Although healthcare providers can provide a long COVID diagnosis without a positive COVID-19 test on the basis of a patient’s presentation of symptoms and clinical history, many people in our study said that their providers would not provide this diagnosis, which restricted access to worker’s compensation, paid time off, and job accommodations.
Many people in the study also reported that their medical providers misdiagnosed them with a mental health disorder, such as anxiety, instead of long COVID. Although some people with long COVID may experience poor mental health as a natural consequence of dealing with a debilitating medical condition or may have neuropsychiatric symptoms as part of their long COVID, long COVID is not caused by an underlying psychiatric illness.
4. Support of medical providers is key to successful return to work for people living with long COVID.
Some people in our study described how they were able to get workplace accommodations or access workers’ compensation or sick leave because their medical providers recognized they had long COVID and provided them with this documentation. Some of these participants did not have a positive COVID-19 test, but their medical providers were able to diagnose them with long COVID on the basis of symptom presentation and clinical history. This documentation was critical for helping workers remain financially stable and able to return to work.
Conclusion
While we continue to search for treatment and cures for long COVID and work to provide a robust social safety net, it is crucial to address the stigma, inaccessibility, and lack of support often experienced by patients in their workplaces. Disabled people have long faced these issues; long COVID may be an opportunity to revolutionize the workplace to ensure an inclusive and accessible environment that can improve the lives of all workers.
For more on how to best be inclusive of employees with long COVID, read Harvard Business Review’s “Long Covid at Work: A Manager’s Guide” and visit the Job Accommodation Network webpage dedicated to long COVID.
Additional discussion about our study and applying the findings to improve work and medical care can be found by listening to the Healthy Work podcast episode titled “Supporting Long COVID at Work.”
Elisabeth Stelson, Gina Assaf, and Lisa McCorkell are members of the Patient-Led Research Collaborative, an international group of more than 60 researchers. Dr Stelson, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Gina Assaf is Research Lead, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC. Lisa McCorkell is a long COVID patient; Cofounder, Team Lead, Researcher, Patient-Led Research Collaborative, Washington, DC.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Can GPs Recognize and Respond to Domestic Abuse?
Domestic abuse is a leading cause of violence against women in Europe. In France alone, 122 women were killed by their partner or ex-partner in 2021. A 2024 study led by French GP Dr Noémie Deparis, who has expertise in domestic violence, revealed that female victims often want their GPs to recognize signs of abuse and offer support.
In this interview with Medscape, Deparis provides practical advice for doctors on identifying the subtle signs of domestic violence and offering compassionate, effective support to affected patients.
How can GPs identify victims of domestic abuse during consultations? What are the signs and symptoms they should look out for?
GPs play an important role in identifying victims of domestic violence or child abuse. They need to be alert to any signs that might suggest violence. Physical signs may include unexplained or recurring injuries, scars, and bruising in unusual areas such as the torso, back, or face. Delays in seeking care for their injuries may also be a cause for concern.
There are also psychological signs to look out for, including anxiety, depression, sleep problems, and lowered self-esteem. Other signs can include a change in the patient’s behavior or avoidance behavior. A partner who dominates the consultation, prevents the victim from speaking freely, or watches her excessively could also be an indicator.
There are also contextual signs to look out for — for example, frequent consultations for chronic pain, and multiple reasons for vague, unexplained symptoms such as headaches, abdominal pain, and chronic fatigue. A medical history that is incompatible with the explanations given by the patient can also be a warning sign, as can medical nomadism, where a patient consults with multiple GPs for the same symptoms over a period of time.
It is crucial to remember that domestic violence can affect individuals across all sociocultural backgrounds, ages, and sexual orientations. Every GP’s patient population includes people who may have experienced domestic violence. In my practice, I’ve developed the habit of reminding myself that when there’s a patient I don’t understand or the situation isn’t clear, it’s often a signal to ask the question.
How can GPs initiate conversations on the topic sensitively, should they have concerns?
For GPs to be able to ask the question systematically when they suspect violence, the most important point is that they themselves should be comfortable with the question they are asking. Obviously, the question must be asked in a nonjudgmental way and in a safe and confidential environment.
The question can be asked systematically, with a direct question and a routine to normalize the topic. For example: “This is a question I ask all my patients: Have you ever experienced violence in your life?”
GPs can also approach the subject in a more general way. For example: “You seem to be under a lot of stress recently. Is everything okay at home?” or “Sometimes when patients come in with these symptoms, they may be under pressure or experiencing stress in their lives. Could this be the case for you?”
It is essential to express understanding without insistence, depending on the patient’s response.
Are there specific protocols or guidelines in Europe for recognizing and addressing such cases?
I don’t know enough about the particularities of each European country, but in France since 2022, the French National Authority for Health has recommended systematic screening for domestic violence. The French National Medical Council has also issued recommendations for medical certificates and reporting to the judicial authorities of victims of violence without their consent in cases of control and risk of serious and imminent danger.
The French College of General Practitioners has recently published practical information sheets to help GPs deal with violence. For more than 5 years, the Déclic Violence website has been regularly updated to help GPs deal with and support victims of violence. Across France, an increasing number of women’s centers are being set up in every region. These centers serve as essential resources, not only for women experiencing violence but also for professionals assisting them.
Could you describe what happens in Europe once a GP confirms that a patient is a victim of domestic violence, including what steps they would take and what support is available?
When a doctor confirms a situation of violence, it is important to provide an active listening ear, a safe space, and immediate support adapted to the victim’s situation and wishes. All the information brought to our attention must be written in the medical file, both the facts reported and the physical or psychological clinical findings. This information should enable us to draw up a descriptive medical certificate at the time of the consultation, if the victim so wishes, or at a later date.
It is important not to be left on your own and to refer the victim to other health professionals; to legal, judicial, or social aid structures; to local or national associations; or to a victim support number.
How can GPs ensure that their involvement helps victims to access broader support systems such as shelters or counseling services?
As in many areas of medical care, GPs have an important role to play in coordinating the efforts of all the professionals involved. Victims of domestic violence often require long-term monitoring, with periods of improvement and setbacks. In my consultations, I often use the concept of the cycle of violence to help patients recognize the powerful control mechanisms at play. Collaboration with support networks ensures that the victim is not isolated after their GP consultation.
What role can GPs play in documenting cases to assist with legal or social interventions?
GPs play a crucial role in documenting cases of domestic violence to support legal and social interventions. This involves maintaining detailed, objective medical records that include descriptions of injuries, the patient’s account in their own words, psychological observations, and findings from physical examinations.
GPs can issue legally recognized medical certificates detailing the injuries and their consistency. Photographic evidence, with patient consent, can further substantiate claims. GPs also contribute to risk assessments, identifying immediate dangers to the victim or others, which inform protective actions by social services or law enforcement.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Domestic abuse is a leading cause of violence against women in Europe. In France alone, 122 women were killed by their partner or ex-partner in 2021. A 2024 study led by French GP Dr Noémie Deparis, who has expertise in domestic violence, revealed that female victims often want their GPs to recognize signs of abuse and offer support.
In this interview with Medscape, Deparis provides practical advice for doctors on identifying the subtle signs of domestic violence and offering compassionate, effective support to affected patients.
How can GPs identify victims of domestic abuse during consultations? What are the signs and symptoms they should look out for?
GPs play an important role in identifying victims of domestic violence or child abuse. They need to be alert to any signs that might suggest violence. Physical signs may include unexplained or recurring injuries, scars, and bruising in unusual areas such as the torso, back, or face. Delays in seeking care for their injuries may also be a cause for concern.
There are also psychological signs to look out for, including anxiety, depression, sleep problems, and lowered self-esteem. Other signs can include a change in the patient’s behavior or avoidance behavior. A partner who dominates the consultation, prevents the victim from speaking freely, or watches her excessively could also be an indicator.
There are also contextual signs to look out for — for example, frequent consultations for chronic pain, and multiple reasons for vague, unexplained symptoms such as headaches, abdominal pain, and chronic fatigue. A medical history that is incompatible with the explanations given by the patient can also be a warning sign, as can medical nomadism, where a patient consults with multiple GPs for the same symptoms over a period of time.
It is crucial to remember that domestic violence can affect individuals across all sociocultural backgrounds, ages, and sexual orientations. Every GP’s patient population includes people who may have experienced domestic violence. In my practice, I’ve developed the habit of reminding myself that when there’s a patient I don’t understand or the situation isn’t clear, it’s often a signal to ask the question.
How can GPs initiate conversations on the topic sensitively, should they have concerns?
For GPs to be able to ask the question systematically when they suspect violence, the most important point is that they themselves should be comfortable with the question they are asking. Obviously, the question must be asked in a nonjudgmental way and in a safe and confidential environment.
The question can be asked systematically, with a direct question and a routine to normalize the topic. For example: “This is a question I ask all my patients: Have you ever experienced violence in your life?”
GPs can also approach the subject in a more general way. For example: “You seem to be under a lot of stress recently. Is everything okay at home?” or “Sometimes when patients come in with these symptoms, they may be under pressure or experiencing stress in their lives. Could this be the case for you?”
It is essential to express understanding without insistence, depending on the patient’s response.
Are there specific protocols or guidelines in Europe for recognizing and addressing such cases?
I don’t know enough about the particularities of each European country, but in France since 2022, the French National Authority for Health has recommended systematic screening for domestic violence. The French National Medical Council has also issued recommendations for medical certificates and reporting to the judicial authorities of victims of violence without their consent in cases of control and risk of serious and imminent danger.
The French College of General Practitioners has recently published practical information sheets to help GPs deal with violence. For more than 5 years, the Déclic Violence website has been regularly updated to help GPs deal with and support victims of violence. Across France, an increasing number of women’s centers are being set up in every region. These centers serve as essential resources, not only for women experiencing violence but also for professionals assisting them.
Could you describe what happens in Europe once a GP confirms that a patient is a victim of domestic violence, including what steps they would take and what support is available?
When a doctor confirms a situation of violence, it is important to provide an active listening ear, a safe space, and immediate support adapted to the victim’s situation and wishes. All the information brought to our attention must be written in the medical file, both the facts reported and the physical or psychological clinical findings. This information should enable us to draw up a descriptive medical certificate at the time of the consultation, if the victim so wishes, or at a later date.
It is important not to be left on your own and to refer the victim to other health professionals; to legal, judicial, or social aid structures; to local or national associations; or to a victim support number.
How can GPs ensure that their involvement helps victims to access broader support systems such as shelters or counseling services?
As in many areas of medical care, GPs have an important role to play in coordinating the efforts of all the professionals involved. Victims of domestic violence often require long-term monitoring, with periods of improvement and setbacks. In my consultations, I often use the concept of the cycle of violence to help patients recognize the powerful control mechanisms at play. Collaboration with support networks ensures that the victim is not isolated after their GP consultation.
What role can GPs play in documenting cases to assist with legal or social interventions?
GPs play a crucial role in documenting cases of domestic violence to support legal and social interventions. This involves maintaining detailed, objective medical records that include descriptions of injuries, the patient’s account in their own words, psychological observations, and findings from physical examinations.
GPs can issue legally recognized medical certificates detailing the injuries and their consistency. Photographic evidence, with patient consent, can further substantiate claims. GPs also contribute to risk assessments, identifying immediate dangers to the victim or others, which inform protective actions by social services or law enforcement.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Domestic abuse is a leading cause of violence against women in Europe. In France alone, 122 women were killed by their partner or ex-partner in 2021. A 2024 study led by French GP Dr Noémie Deparis, who has expertise in domestic violence, revealed that female victims often want their GPs to recognize signs of abuse and offer support.
In this interview with Medscape, Deparis provides practical advice for doctors on identifying the subtle signs of domestic violence and offering compassionate, effective support to affected patients.
How can GPs identify victims of domestic abuse during consultations? What are the signs and symptoms they should look out for?
GPs play an important role in identifying victims of domestic violence or child abuse. They need to be alert to any signs that might suggest violence. Physical signs may include unexplained or recurring injuries, scars, and bruising in unusual areas such as the torso, back, or face. Delays in seeking care for their injuries may also be a cause for concern.
There are also psychological signs to look out for, including anxiety, depression, sleep problems, and lowered self-esteem. Other signs can include a change in the patient’s behavior or avoidance behavior. A partner who dominates the consultation, prevents the victim from speaking freely, or watches her excessively could also be an indicator.
There are also contextual signs to look out for — for example, frequent consultations for chronic pain, and multiple reasons for vague, unexplained symptoms such as headaches, abdominal pain, and chronic fatigue. A medical history that is incompatible with the explanations given by the patient can also be a warning sign, as can medical nomadism, where a patient consults with multiple GPs for the same symptoms over a period of time.
It is crucial to remember that domestic violence can affect individuals across all sociocultural backgrounds, ages, and sexual orientations. Every GP’s patient population includes people who may have experienced domestic violence. In my practice, I’ve developed the habit of reminding myself that when there’s a patient I don’t understand or the situation isn’t clear, it’s often a signal to ask the question.
How can GPs initiate conversations on the topic sensitively, should they have concerns?
For GPs to be able to ask the question systematically when they suspect violence, the most important point is that they themselves should be comfortable with the question they are asking. Obviously, the question must be asked in a nonjudgmental way and in a safe and confidential environment.
The question can be asked systematically, with a direct question and a routine to normalize the topic. For example: “This is a question I ask all my patients: Have you ever experienced violence in your life?”
GPs can also approach the subject in a more general way. For example: “You seem to be under a lot of stress recently. Is everything okay at home?” or “Sometimes when patients come in with these symptoms, they may be under pressure or experiencing stress in their lives. Could this be the case for you?”
It is essential to express understanding without insistence, depending on the patient’s response.
Are there specific protocols or guidelines in Europe for recognizing and addressing such cases?
I don’t know enough about the particularities of each European country, but in France since 2022, the French National Authority for Health has recommended systematic screening for domestic violence. The French National Medical Council has also issued recommendations for medical certificates and reporting to the judicial authorities of victims of violence without their consent in cases of control and risk of serious and imminent danger.
The French College of General Practitioners has recently published practical information sheets to help GPs deal with violence. For more than 5 years, the Déclic Violence website has been regularly updated to help GPs deal with and support victims of violence. Across France, an increasing number of women’s centers are being set up in every region. These centers serve as essential resources, not only for women experiencing violence but also for professionals assisting them.
Could you describe what happens in Europe once a GP confirms that a patient is a victim of domestic violence, including what steps they would take and what support is available?
When a doctor confirms a situation of violence, it is important to provide an active listening ear, a safe space, and immediate support adapted to the victim’s situation and wishes. All the information brought to our attention must be written in the medical file, both the facts reported and the physical or psychological clinical findings. This information should enable us to draw up a descriptive medical certificate at the time of the consultation, if the victim so wishes, or at a later date.
It is important not to be left on your own and to refer the victim to other health professionals; to legal, judicial, or social aid structures; to local or national associations; or to a victim support number.
How can GPs ensure that their involvement helps victims to access broader support systems such as shelters or counseling services?
As in many areas of medical care, GPs have an important role to play in coordinating the efforts of all the professionals involved. Victims of domestic violence often require long-term monitoring, with periods of improvement and setbacks. In my consultations, I often use the concept of the cycle of violence to help patients recognize the powerful control mechanisms at play. Collaboration with support networks ensures that the victim is not isolated after their GP consultation.
What role can GPs play in documenting cases to assist with legal or social interventions?
GPs play a crucial role in documenting cases of domestic violence to support legal and social interventions. This involves maintaining detailed, objective medical records that include descriptions of injuries, the patient’s account in their own words, psychological observations, and findings from physical examinations.
GPs can issue legally recognized medical certificates detailing the injuries and their consistency. Photographic evidence, with patient consent, can further substantiate claims. GPs also contribute to risk assessments, identifying immediate dangers to the victim or others, which inform protective actions by social services or law enforcement.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.