User login
Contraceptive Care Clinic Focuses on Military Readiness
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
SAN DIEGO — Not surprisingly, the contraception clinic at Madigan Army Medical Center near Tacoma, Wash., is popular among female soldiers seeking to avoid pregnancy. However, about half of the patients drop by for other reasons, the military pharmacist who runs the program told colleagues here at the Joint Federal Pharmacy Seminar.
“They come to suppress menstruation, to get help with pain, to get help with PCOS [polycystic ovary syndrome] symptoms. They're coming for a wide range of indications that we use contraception to treat,” said Sarah Abel, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist.
Regardless of the reason, Abel emphasized that contraceptives can significantly impact the ability of female soldiers to do their jobs. “If you have heavy periods and can't make it in work, or you have endometriosis and requiring a lot of doctor's appointments, or you're deployed and you get pregnant, these are all situations where contraceptive care matters,” she said. Rates of unintended pregnancy are higher in servicewomen than in the general population.
Abel, who opened the medical center’s contraceptive clinic about 10 years ago, stressed that it’s crucial to military readiness considering that the percentage of women in the American military is approaching 20%.
Thanks to a 2022 edict, military hospitals and clinics are required to offer walk-in contraceptive services with same-day access, no requirements for appointments or referrals. An announcement about the mandate noted that these contraceptive services, such as preventing unplanned pregnancy and decreasing menstrual periods, “support the overall well-being of the force and optimize personal warrior readiness.”
As Abel noted, 29 states and Washington D.C. allow pharmacists to prescribe contraception to outpatients, although the requirements vary. “Can we start practicing at the top of our license and start prescribing in the outpatient setting? Absolutely we should,” she said. “Pharmacists have a very unique opportunity to be a part of this.”
Abel also shared that setting up a contraceptive program requires patience and education. “I cannot tell you how many women have come to me who don't know the different names of their body parts, women who've had two babies that don't understand how their body works. So, I constantly find myself taking extra time to do general sexual education,” she said.
There are many lessons to impart to patients about sexual health. For example, birth control drugs and devices do not prevent transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). “So I have bowls of condoms literally everywhere because condoms are the only thing that protects against STIs,” Abel said.
In terms of devices, “we have diaphragms available and cervical caps,” she said. “The Caya diaphragm is a TRICARE-covered benefit. It’s a small purple diaphragm, one size fits most. We can prescribe it, and it is good for 2 years. Unfortunately, spermicide, which you have to use with these things, is not a TRICARE-covered benefit.”
Hormonal contraceptives are also available, with Abel recommending the continuous monophasic type for most women. “Please don't tell women they have to have their periods. They don't,” she said. “What I'm trying to do is give a woman some stability in her hormones. She can know and expect what she's going to feel like. She's not going to wake up and say, ‘Oh God, today's the day. I'm going to be like this for a week.’”
Patches are another option, and a flurry of patients have been asking about them because of recent TikTok videos promoting their use. “We have the Xulane patch, our bread and butter. They wear it on their shoulder, their hip, their butt, or their back. They leave it in place for a week at a time. And every week, they will change that patch. I usually have to walk patients through a whole month to help them understand how that works.”
Another option, the NuvaRing, is notable because it’s linked to low amounts of breakthrough bleeding Abel noted. An extended form is now available that doesn’t need to be removed during menstrual periods.
Medroxyprogesterone injections, which are linked to bone loss, and subdermal implants, which may be less effective in women over 130% of their ideal weight are also available, she said.
Finally, IUDs are an option, although when they fail, they’re linked to ectopic pregnancies.
Abel has no disclosures.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Building Trust: Enhancing Rural Women Veterans’ Healthcare Experiences Through Need-Supportive Patient-Centered Communication
Background
Rural women veterans often confront unique healthcare barriers—geographic isolation, gender-related stigma, and limited provider cultural sensitivity that undermine trust and engagement. In response, we co-designed an interprofessional communication curriculum to promote relational, patient-centered care grounded in psychological need support.
Innovation
Anchored in Self Determination Theory (SDT), this curriculum equips nurses and social workers with need-supportive communication strategies that nurture autonomy, competence, and relatedness, integrating two transformative learning methods for enhancing respectful and inclusive listening:
- Cultural humility reflections for veteran-centered care—personal narratives, storytelling, and power-awareness discussions to build lifelong reflective practices.
- Medical improv simulations—adaptive improvisational role plays for healthcare environments fostering presence, adaptability, empathy, trust-building, and real-time responsiveness.
Delivered via a multiday health professions learning lab, the training combines asynchronous workshops with in-person facilitated interactions. Core modules cover SDT foundations, need supportive dialogue, veteran-centered cultural humility, and shared decision-making practices that uplift rural women veterans’ voices. Using Kirkpatrick’s Four Level Model, we assess impact at multiple tiers:
- Reaction: Participant satisfaction and perceived training relevance.
- Learning: Pre/post assessments track SDT knowledge and communication skills gains.
- Behavior: Observe simulations and self-reported changes in communication practices.
- Results: Qualitative satisfaction metrics and care engagement trends among rural women veterans.
Results
A pilot cohort (N = 20) across two rural sites is pending implementation. pre/post surveys will assess any improved confidence in applying need supportive communication and the most effective component in building empathetic presence. Feedback measures will also indicate the significance of combined uses of medical improv and cultural humility on deepened relational capacity and trust.
Discussion
This program operationalizes SDT within healthcare communications, integrating cultural humility and improvisation learning modalities to enhance care quality for rural women veterans, ultimately strengthening provider-patient connections. Using health professions learning lab environments can foster sustained behavioral impacts. Future iterations will expand to additional rural VA sites, co-designing with the voices of women veterans through focus groups.
Background
Rural women veterans often confront unique healthcare barriers—geographic isolation, gender-related stigma, and limited provider cultural sensitivity that undermine trust and engagement. In response, we co-designed an interprofessional communication curriculum to promote relational, patient-centered care grounded in psychological need support.
Innovation
Anchored in Self Determination Theory (SDT), this curriculum equips nurses and social workers with need-supportive communication strategies that nurture autonomy, competence, and relatedness, integrating two transformative learning methods for enhancing respectful and inclusive listening:
- Cultural humility reflections for veteran-centered care—personal narratives, storytelling, and power-awareness discussions to build lifelong reflective practices.
- Medical improv simulations—adaptive improvisational role plays for healthcare environments fostering presence, adaptability, empathy, trust-building, and real-time responsiveness.
Delivered via a multiday health professions learning lab, the training combines asynchronous workshops with in-person facilitated interactions. Core modules cover SDT foundations, need supportive dialogue, veteran-centered cultural humility, and shared decision-making practices that uplift rural women veterans’ voices. Using Kirkpatrick’s Four Level Model, we assess impact at multiple tiers:
- Reaction: Participant satisfaction and perceived training relevance.
- Learning: Pre/post assessments track SDT knowledge and communication skills gains.
- Behavior: Observe simulations and self-reported changes in communication practices.
- Results: Qualitative satisfaction metrics and care engagement trends among rural women veterans.
Results
A pilot cohort (N = 20) across two rural sites is pending implementation. pre/post surveys will assess any improved confidence in applying need supportive communication and the most effective component in building empathetic presence. Feedback measures will also indicate the significance of combined uses of medical improv and cultural humility on deepened relational capacity and trust.
Discussion
This program operationalizes SDT within healthcare communications, integrating cultural humility and improvisation learning modalities to enhance care quality for rural women veterans, ultimately strengthening provider-patient connections. Using health professions learning lab environments can foster sustained behavioral impacts. Future iterations will expand to additional rural VA sites, co-designing with the voices of women veterans through focus groups.
Background
Rural women veterans often confront unique healthcare barriers—geographic isolation, gender-related stigma, and limited provider cultural sensitivity that undermine trust and engagement. In response, we co-designed an interprofessional communication curriculum to promote relational, patient-centered care grounded in psychological need support.
Innovation
Anchored in Self Determination Theory (SDT), this curriculum equips nurses and social workers with need-supportive communication strategies that nurture autonomy, competence, and relatedness, integrating two transformative learning methods for enhancing respectful and inclusive listening:
- Cultural humility reflections for veteran-centered care—personal narratives, storytelling, and power-awareness discussions to build lifelong reflective practices.
- Medical improv simulations—adaptive improvisational role plays for healthcare environments fostering presence, adaptability, empathy, trust-building, and real-time responsiveness.
Delivered via a multiday health professions learning lab, the training combines asynchronous workshops with in-person facilitated interactions. Core modules cover SDT foundations, need supportive dialogue, veteran-centered cultural humility, and shared decision-making practices that uplift rural women veterans’ voices. Using Kirkpatrick’s Four Level Model, we assess impact at multiple tiers:
- Reaction: Participant satisfaction and perceived training relevance.
- Learning: Pre/post assessments track SDT knowledge and communication skills gains.
- Behavior: Observe simulations and self-reported changes in communication practices.
- Results: Qualitative satisfaction metrics and care engagement trends among rural women veterans.
Results
A pilot cohort (N = 20) across two rural sites is pending implementation. pre/post surveys will assess any improved confidence in applying need supportive communication and the most effective component in building empathetic presence. Feedback measures will also indicate the significance of combined uses of medical improv and cultural humility on deepened relational capacity and trust.
Discussion
This program operationalizes SDT within healthcare communications, integrating cultural humility and improvisation learning modalities to enhance care quality for rural women veterans, ultimately strengthening provider-patient connections. Using health professions learning lab environments can foster sustained behavioral impacts. Future iterations will expand to additional rural VA sites, co-designing with the voices of women veterans through focus groups.
UK Approves Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer
UK Approves Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has approved tisotumab vedotin (Genmab AS) for adults with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer.
The decision, made via the International Recognition Procedure, applies to patients whose disease has progressed after prior systemic therapy. It provides a new treatment option for a high-risk group with limited alternatives.
How the Treatment Works
Tisotumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate that combines a tissue factor-directed human monoclonal antibody with monomethyl auristatin E, a microtubule-disrupting agent. The therapy targets tissue factor, which is overexpressed in a several solid tumours, including recurrent cervical cancer.
It is administered as a 30-minute intravenous infusion once every 3 weeks.
What Trials Showed
The approval is based on evidence from multiple clinical studies demonstrating tisotumab vedotin's efficacy in previously treated patients.
In the phase 2 innovaTV 204 study, 102 patients were enrolled and 101 received at least 1 dose of tisotumab vedotin. The confirmed objective response rate was 24%, including seven complete responses and 17 partial responses, demonstrating clinically meaningful activity in a heavily pretreated population.
Further evidence came from the phase 3 innovaTV-301 trial, which randomly assigned 502 patients to receive either tisotumab vedotin or investigator's-choice chemotherapy.
Median overall survival was 11.5 months with the new therapy compared with 9.5 months in the chemotherapy arm, translating to roughly a 30% reduction in the risk for death. The confirmed objective response rate was also significantly higher with tisotumab vedotin—17.8% vs 5.2%—underscoring its advantage over standard treatment options.
Safety and Tolerability
Ocular toxicity and peripheral neuropathy were the most notable adverse reactions.
Common treatment-related events in the phase 2 study included alopecia (38%), epistaxis (30%), nausea, conjunctivitis (26%), and fatigue (26%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events occurred in about 28% of patients. Clinicians should be alert to conjunctivitis and keratitis as well as sensory neuropathic symptoms (numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in the hands and feet).
Julian Beach, interim executive director of healthcare quality and access at the MHRA, said that patient safety is the agency's "top priority." "We will continue to monitor its safety closely as it becomes more widely used," he added.
The Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflets will be published on the MHRA website within 7 days of approval.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has approved tisotumab vedotin (Genmab AS) for adults with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer.
The decision, made via the International Recognition Procedure, applies to patients whose disease has progressed after prior systemic therapy. It provides a new treatment option for a high-risk group with limited alternatives.
How the Treatment Works
Tisotumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate that combines a tissue factor-directed human monoclonal antibody with monomethyl auristatin E, a microtubule-disrupting agent. The therapy targets tissue factor, which is overexpressed in a several solid tumours, including recurrent cervical cancer.
It is administered as a 30-minute intravenous infusion once every 3 weeks.
What Trials Showed
The approval is based on evidence from multiple clinical studies demonstrating tisotumab vedotin's efficacy in previously treated patients.
In the phase 2 innovaTV 204 study, 102 patients were enrolled and 101 received at least 1 dose of tisotumab vedotin. The confirmed objective response rate was 24%, including seven complete responses and 17 partial responses, demonstrating clinically meaningful activity in a heavily pretreated population.
Further evidence came from the phase 3 innovaTV-301 trial, which randomly assigned 502 patients to receive either tisotumab vedotin or investigator's-choice chemotherapy.
Median overall survival was 11.5 months with the new therapy compared with 9.5 months in the chemotherapy arm, translating to roughly a 30% reduction in the risk for death. The confirmed objective response rate was also significantly higher with tisotumab vedotin—17.8% vs 5.2%—underscoring its advantage over standard treatment options.
Safety and Tolerability
Ocular toxicity and peripheral neuropathy were the most notable adverse reactions.
Common treatment-related events in the phase 2 study included alopecia (38%), epistaxis (30%), nausea, conjunctivitis (26%), and fatigue (26%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events occurred in about 28% of patients. Clinicians should be alert to conjunctivitis and keratitis as well as sensory neuropathic symptoms (numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in the hands and feet).
Julian Beach, interim executive director of healthcare quality and access at the MHRA, said that patient safety is the agency's "top priority." "We will continue to monitor its safety closely as it becomes more widely used," he added.
The Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflets will be published on the MHRA website within 7 days of approval.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has approved tisotumab vedotin (Genmab AS) for adults with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer.
The decision, made via the International Recognition Procedure, applies to patients whose disease has progressed after prior systemic therapy. It provides a new treatment option for a high-risk group with limited alternatives.
How the Treatment Works
Tisotumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate that combines a tissue factor-directed human monoclonal antibody with monomethyl auristatin E, a microtubule-disrupting agent. The therapy targets tissue factor, which is overexpressed in a several solid tumours, including recurrent cervical cancer.
It is administered as a 30-minute intravenous infusion once every 3 weeks.
What Trials Showed
The approval is based on evidence from multiple clinical studies demonstrating tisotumab vedotin's efficacy in previously treated patients.
In the phase 2 innovaTV 204 study, 102 patients were enrolled and 101 received at least 1 dose of tisotumab vedotin. The confirmed objective response rate was 24%, including seven complete responses and 17 partial responses, demonstrating clinically meaningful activity in a heavily pretreated population.
Further evidence came from the phase 3 innovaTV-301 trial, which randomly assigned 502 patients to receive either tisotumab vedotin or investigator's-choice chemotherapy.
Median overall survival was 11.5 months with the new therapy compared with 9.5 months in the chemotherapy arm, translating to roughly a 30% reduction in the risk for death. The confirmed objective response rate was also significantly higher with tisotumab vedotin—17.8% vs 5.2%—underscoring its advantage over standard treatment options.
Safety and Tolerability
Ocular toxicity and peripheral neuropathy were the most notable adverse reactions.
Common treatment-related events in the phase 2 study included alopecia (38%), epistaxis (30%), nausea, conjunctivitis (26%), and fatigue (26%).
Grade 3 or higher treatment-related adverse events occurred in about 28% of patients. Clinicians should be alert to conjunctivitis and keratitis as well as sensory neuropathic symptoms (numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in the hands and feet).
Julian Beach, interim executive director of healthcare quality and access at the MHRA, said that patient safety is the agency's "top priority." "We will continue to monitor its safety closely as it becomes more widely used," he added.
The Summary of Product Characteristics and Patient Information Leaflets will be published on the MHRA website within 7 days of approval.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
UK Approves Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer
UK Approves Targeted Therapy for Cervical Cancer
Research Focuses on Mental Health Needs of Women Veterans
The more than 2 million women US veterans are the fastest-growing military population. While research into women veterans has traditionally lagged, more recently studies have begun to focus on their needs impacts of combat and service on women. These studies have found that women veterans preferred tailored solutions focused on women veterans.
A November 2025 study is one of the first to examine the impact of combat on women veterans. It found that those in combat roles had higher levels of depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), dissociation, and overall poorer health compared with civilians and noncombat women military personnel. Previous research had found that women veterans had higher rates of lifetime and past-year PTSD (13.4%) compared with female civilians (8.0%), male veterans (7.7%), and male civilians (3.4%). A 2020 US Department of Veterans (VA) study of 4,928,638 men and 448,455 women similarly found that women had nearly twice the rates of depression and anxiety compared with men.
For many veterans, mental health issues may develop or be exacerbated in their return to civilian life. That transition can be especially confusing and isolating for women veterans, according to a 2024 study: “They neither fit in the military due to gendered relations centered on masculinity, or civilian life where they are largely misunderstood as ‘veterans.’ This ‘no woman’s land’ is poorly understood.” Few programs for transitioning veterans have been found effective for women veterans because they’ve been developed for a largely male veteran population. That includes mental health support programs.
Some women may prefer women-only groups, and even that choice may be dependent on their background, service history, socioeconomic level, and other factors. They may feel more comfortable in women-only groups if they’ve experienced MST. Others who have served in combat may choose mixed-gender programs. One study found that some women benefited from being in a mixed-gender group because it enabled them to work on difficulties with men in a safe environment. Other research has found that women veterans with substance use disorders are reluctant to seek help alongside men in the same facilities.
Accessing care may be especially challenging for rural women veterans. However, separate facilities and women-only groups are not always available, particularly in rural areas where there may be very few women veterans. And even if they are available, rural women are often up against barriers that urban women do not face, such as having to travel long distances to get care. Clinicians also may be hard to find in rural areas. Some participants in a 2025 study were hampered not only by a lack of female practitioners, but practitioners who were well trained to understand and treat the unique needs of female veterans: “[It’s] incredibly difficult to find a mental health practitioner that understands a veteran’s unique experience as a woman,” a participant said.
The more than 2 million women US veterans are the fastest-growing military population. While research into women veterans has traditionally lagged, more recently studies have begun to focus on their needs impacts of combat and service on women. These studies have found that women veterans preferred tailored solutions focused on women veterans.
A November 2025 study is one of the first to examine the impact of combat on women veterans. It found that those in combat roles had higher levels of depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), dissociation, and overall poorer health compared with civilians and noncombat women military personnel. Previous research had found that women veterans had higher rates of lifetime and past-year PTSD (13.4%) compared with female civilians (8.0%), male veterans (7.7%), and male civilians (3.4%). A 2020 US Department of Veterans (VA) study of 4,928,638 men and 448,455 women similarly found that women had nearly twice the rates of depression and anxiety compared with men.
For many veterans, mental health issues may develop or be exacerbated in their return to civilian life. That transition can be especially confusing and isolating for women veterans, according to a 2024 study: “They neither fit in the military due to gendered relations centered on masculinity, or civilian life where they are largely misunderstood as ‘veterans.’ This ‘no woman’s land’ is poorly understood.” Few programs for transitioning veterans have been found effective for women veterans because they’ve been developed for a largely male veteran population. That includes mental health support programs.
Some women may prefer women-only groups, and even that choice may be dependent on their background, service history, socioeconomic level, and other factors. They may feel more comfortable in women-only groups if they’ve experienced MST. Others who have served in combat may choose mixed-gender programs. One study found that some women benefited from being in a mixed-gender group because it enabled them to work on difficulties with men in a safe environment. Other research has found that women veterans with substance use disorders are reluctant to seek help alongside men in the same facilities.
Accessing care may be especially challenging for rural women veterans. However, separate facilities and women-only groups are not always available, particularly in rural areas where there may be very few women veterans. And even if they are available, rural women are often up against barriers that urban women do not face, such as having to travel long distances to get care. Clinicians also may be hard to find in rural areas. Some participants in a 2025 study were hampered not only by a lack of female practitioners, but practitioners who were well trained to understand and treat the unique needs of female veterans: “[It’s] incredibly difficult to find a mental health practitioner that understands a veteran’s unique experience as a woman,” a participant said.
The more than 2 million women US veterans are the fastest-growing military population. While research into women veterans has traditionally lagged, more recently studies have begun to focus on their needs impacts of combat and service on women. These studies have found that women veterans preferred tailored solutions focused on women veterans.
A November 2025 study is one of the first to examine the impact of combat on women veterans. It found that those in combat roles had higher levels of depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), dissociation, and overall poorer health compared with civilians and noncombat women military personnel. Previous research had found that women veterans had higher rates of lifetime and past-year PTSD (13.4%) compared with female civilians (8.0%), male veterans (7.7%), and male civilians (3.4%). A 2020 US Department of Veterans (VA) study of 4,928,638 men and 448,455 women similarly found that women had nearly twice the rates of depression and anxiety compared with men.
For many veterans, mental health issues may develop or be exacerbated in their return to civilian life. That transition can be especially confusing and isolating for women veterans, according to a 2024 study: “They neither fit in the military due to gendered relations centered on masculinity, or civilian life where they are largely misunderstood as ‘veterans.’ This ‘no woman’s land’ is poorly understood.” Few programs for transitioning veterans have been found effective for women veterans because they’ve been developed for a largely male veteran population. That includes mental health support programs.
Some women may prefer women-only groups, and even that choice may be dependent on their background, service history, socioeconomic level, and other factors. They may feel more comfortable in women-only groups if they’ve experienced MST. Others who have served in combat may choose mixed-gender programs. One study found that some women benefited from being in a mixed-gender group because it enabled them to work on difficulties with men in a safe environment. Other research has found that women veterans with substance use disorders are reluctant to seek help alongside men in the same facilities.
Accessing care may be especially challenging for rural women veterans. However, separate facilities and women-only groups are not always available, particularly in rural areas where there may be very few women veterans. And even if they are available, rural women are often up against barriers that urban women do not face, such as having to travel long distances to get care. Clinicians also may be hard to find in rural areas. Some participants in a 2025 study were hampered not only by a lack of female practitioners, but practitioners who were well trained to understand and treat the unique needs of female veterans: “[It’s] incredibly difficult to find a mental health practitioner that understands a veteran’s unique experience as a woman,” a participant said.
Socioeconomic Status Linked to Psychiatric Disorders in Older Women Veterans
TOPLINE: Psychiatric disorders affect 37.8% of veteran vs 37.3% of nonveteran in a study of > 42,000 women aged ≥ 65 years. Most differences between veterans and nonveterans were statistically insignificant after removing confounders.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers analyzed 42,031 Women's Health Initiative (WHI) participants aged > 65 years at enrollment (1993-1998), including 1,512 veterans and 40,519 non-veterans, through linked WHI-Medicare databases with approximately 15 years of follow-up.
Analysis included multivariable logistic and Cox regression models to evaluate characteristics associated with prevalent and incident psychiatric disorders, respectively.
Participants were followed from WHI enrollment until first psychiatric diagnosis, with censoring at death, end of follow-up, or December 31, 2013.
Investigators examined relationships between individual-level and neighborhood-level socioeconomic status indicators with psychiatric disorders before and after stratification by veteran status.
TAKEAWAY:
The overall prevalence of psychiatric disorders was 37.3%, with an incidence rate of 25.5 per 1,000 person-years, showing no significant differences between veterans and non-veterans (odds ratio [OR], 0.95; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-0.06).
There was a higher prevalence of psychiatric disorders for women veterans with technical, sales, or administrative occupations (adjusted OR [aOR], 1.72; 95 % CI, 1.02, 2.89) and those with “other” occupations (aOR, 2.09; 95 % CI, 1.13, 3.88) when compared with women veterans with managerial or professional occupations.
Mood and anxiety disorders emerged as the leading types of psychiatric conditions among both veteran and nonveteran women.
IN PRACTICE: "Although interaction effects by veteran status were nonsignificant,” the authors of the study explained, “lower education, household income, and neighborhood socioeconomic status were associated with higher frequencies of psychiatric disorders only among women non-veterans.”
SOURCE: The study was led by Jack Tsai and the US Department of Veterans Affairs National Center on Homelessness Among Veterans in Washington, DC. It was published online in Journal of Affective Disorders.
LIMITATIONS: The study faced several limitations including potential selection and survival biases, as findings correspond only to Women's Health Initiative participants who survived until age 65 or later. Information bias likely occurred due to self-reported measures and sole reliance on International Classification of Disease, 9th revision, Clinical Modification diagnostic codes from Medicare claims. Additionally, socioeconomic status indicators assessed at enrollment may not reflect early life or midlife exposures that could influence psychiatric diagnoses.
DISCLOSURES: The Women’s Health Initiative program received funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services through grants 75N92021D00001, 75N92021D00002, 75N92021D00003, 75N92021D00004, and 75N92021D00005.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: Psychiatric disorders affect 37.8% of veteran vs 37.3% of nonveteran in a study of > 42,000 women aged ≥ 65 years. Most differences between veterans and nonveterans were statistically insignificant after removing confounders.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers analyzed 42,031 Women's Health Initiative (WHI) participants aged > 65 years at enrollment (1993-1998), including 1,512 veterans and 40,519 non-veterans, through linked WHI-Medicare databases with approximately 15 years of follow-up.
Analysis included multivariable logistic and Cox regression models to evaluate characteristics associated with prevalent and incident psychiatric disorders, respectively.
Participants were followed from WHI enrollment until first psychiatric diagnosis, with censoring at death, end of follow-up, or December 31, 2013.
Investigators examined relationships between individual-level and neighborhood-level socioeconomic status indicators with psychiatric disorders before and after stratification by veteran status.
TAKEAWAY:
The overall prevalence of psychiatric disorders was 37.3%, with an incidence rate of 25.5 per 1,000 person-years, showing no significant differences between veterans and non-veterans (odds ratio [OR], 0.95; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-0.06).
There was a higher prevalence of psychiatric disorders for women veterans with technical, sales, or administrative occupations (adjusted OR [aOR], 1.72; 95 % CI, 1.02, 2.89) and those with “other” occupations (aOR, 2.09; 95 % CI, 1.13, 3.88) when compared with women veterans with managerial or professional occupations.
Mood and anxiety disorders emerged as the leading types of psychiatric conditions among both veteran and nonveteran women.
IN PRACTICE: "Although interaction effects by veteran status were nonsignificant,” the authors of the study explained, “lower education, household income, and neighborhood socioeconomic status were associated with higher frequencies of psychiatric disorders only among women non-veterans.”
SOURCE: The study was led by Jack Tsai and the US Department of Veterans Affairs National Center on Homelessness Among Veterans in Washington, DC. It was published online in Journal of Affective Disorders.
LIMITATIONS: The study faced several limitations including potential selection and survival biases, as findings correspond only to Women's Health Initiative participants who survived until age 65 or later. Information bias likely occurred due to self-reported measures and sole reliance on International Classification of Disease, 9th revision, Clinical Modification diagnostic codes from Medicare claims. Additionally, socioeconomic status indicators assessed at enrollment may not reflect early life or midlife exposures that could influence psychiatric diagnoses.
DISCLOSURES: The Women’s Health Initiative program received funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services through grants 75N92021D00001, 75N92021D00002, 75N92021D00003, 75N92021D00004, and 75N92021D00005.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
TOPLINE: Psychiatric disorders affect 37.8% of veteran vs 37.3% of nonveteran in a study of > 42,000 women aged ≥ 65 years. Most differences between veterans and nonveterans were statistically insignificant after removing confounders.
METHODOLOGY:
Researchers analyzed 42,031 Women's Health Initiative (WHI) participants aged > 65 years at enrollment (1993-1998), including 1,512 veterans and 40,519 non-veterans, through linked WHI-Medicare databases with approximately 15 years of follow-up.
Analysis included multivariable logistic and Cox regression models to evaluate characteristics associated with prevalent and incident psychiatric disorders, respectively.
Participants were followed from WHI enrollment until first psychiatric diagnosis, with censoring at death, end of follow-up, or December 31, 2013.
Investigators examined relationships between individual-level and neighborhood-level socioeconomic status indicators with psychiatric disorders before and after stratification by veteran status.
TAKEAWAY:
The overall prevalence of psychiatric disorders was 37.3%, with an incidence rate of 25.5 per 1,000 person-years, showing no significant differences between veterans and non-veterans (odds ratio [OR], 0.95; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-0.06).
There was a higher prevalence of psychiatric disorders for women veterans with technical, sales, or administrative occupations (adjusted OR [aOR], 1.72; 95 % CI, 1.02, 2.89) and those with “other” occupations (aOR, 2.09; 95 % CI, 1.13, 3.88) when compared with women veterans with managerial or professional occupations.
Mood and anxiety disorders emerged as the leading types of psychiatric conditions among both veteran and nonveteran women.
IN PRACTICE: "Although interaction effects by veteran status were nonsignificant,” the authors of the study explained, “lower education, household income, and neighborhood socioeconomic status were associated with higher frequencies of psychiatric disorders only among women non-veterans.”
SOURCE: The study was led by Jack Tsai and the US Department of Veterans Affairs National Center on Homelessness Among Veterans in Washington, DC. It was published online in Journal of Affective Disorders.
LIMITATIONS: The study faced several limitations including potential selection and survival biases, as findings correspond only to Women's Health Initiative participants who survived until age 65 or later. Information bias likely occurred due to self-reported measures and sole reliance on International Classification of Disease, 9th revision, Clinical Modification diagnostic codes from Medicare claims. Additionally, socioeconomic status indicators assessed at enrollment may not reflect early life or midlife exposures that could influence psychiatric diagnoses.
DISCLOSURES: The Women’s Health Initiative program received funding from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services through grants 75N92021D00001, 75N92021D00002, 75N92021D00003, 75N92021D00004, and 75N92021D00005.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death among women in the United States.1 Most CVD is due to the buildup of plaque (ie, cholesterol, proteins, calcium, and inflammatory cells) in artery walls.2 The plaque may lead to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), which includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and aortic atherosclerotic disease.2,3 Control and reduction of ASCVD risk factors, including high cholesterol levels, elevated blood pressure, insulin resistance, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle, can contribute to a reduction in ASCVD morbidity and mortality.2 People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have an increased prevalence of lipid abnormalities, contributing to their high risk of ASCVD.4,5
The prescribing of statins (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzmye A reductase inhibitors) is the cornerstone of lipid-lowering therapy and cardiovascular risk reduction for primary and secondary prevention of ASCVD.6 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend moderate- to high-intensity statins for primary prevention in patients with T2DM and high-intensity statins for secondary prevention in those with or without diabetes when not contraindicated.4,5,7 Despite eligibility according to guideline recommendations, research predominantly shows that women are less likely to receive statin therapy; however, this trend is improving. [6,8-11] To explain the sex differences in statin use, Nanna et al found that there is a combination of women being offered statin therapy less frequently, declining therapy more frequently, and discontinuing treatment more frequently.11 One possibility for discontinuing treatment could be statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), which occur in about 10% of patients.12 The incidence of adverse effects (AEs) may be related to the way statins are metabolized.
Pharmacogenomic testing is free for veterans through the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) PHASER program, which offers information and recommendations for a panel of 11 gene variants. The panel includes genes related to common medication classes such as anticoagulants, antiplatelets, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, antidepressants, and statins. The VA PHASER panel includes the solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, which is predominantly expressed in the liver and facilitates the hepatic uptake of most statins.13,14 A reduced function of SLCO1B1 can lead to higher statin levels, resulting in increased concentrations that may potentially cause SAMS.13,14 Some alleles associated with reduced function include SLCO1B1*5, *15, *23, *31, and *46 to *49, whereas others are associated with increased function, such as SLCO1B1 *14 and *20 (Appendix).15 Supporting evidence shows the SLCO1B1*5 nucleotide polymorphism increases plasma levels of simvastatin and atorvastatin, affecting effectiveness or toxicity. 13 Females tend to have a lower body weight and higher percentage of body fat compared with males, which might lead to higher concentrations of lipophilic drugs, including atorvastatin and simvastatin, which may be exacerbated by decreased function of SLCO1B1*5.15 With pharmacogenomic testing, therapeutic recommendations can be made to improve the overall safety and efficacy of statins, thus improving adherence using a patient-specific approach.14,15
Methods
Carl Vinson VA Medical Center (CVVAMC) serves about 42,000 veterans in Central and South Georgia, of which about 15% are female. Of the female veterans enrolled in care, 63% identify as Black, 27% White, and 1.5% as Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, or Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander. The 2020 Veterans Chartbook report showed that female veterans and minority racial and ethnic groups had worse access to health care and higher mortality rates than their male and non-Hispanic White counterparts.16
The Primary Care Equity Dashboard (PCED) was developed to engage the VA health care workforce in the process of identifying and addressing inequities in local patient populations.17 Using electronic quality measure data, the PCED provides Veterans Integrated Service Network-level and facility-level performance on several metrics.18 The PCED had not been previously used at the CVVAMC, and few publications or quality improvement projects regarding its use have been reported by the VA Office of Health Equity. PCED helped identify disparities when comparing female to male patients in the prescribing of statin therapy for patients with CVD and statin therapy for patients with T2DM.
VA PHASER pharmacogenomic analyses provided an opportunity to expand this quality improvement project. Sanford Health and the VA collaborated on the PHASER program to offer free genetic testing for veterans. The program launched in 2019 and expanded to various VA sites, including CVVAMC in March 2023. This program has been extended to December 31, 2025.
The primary objective of this quality improvement project was to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk. Secondary outcomes included increased pharmacogenomic testing and the assessment of pharmacogenomic results related to statin therapy. This project was approved by the CVVAMC Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. The PCED was used to identify female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD without an active prescription for a statin between July and October 2023. A review of Computerized Patient Record System patient charts was completed to screen for prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria. Veterans were included if they were assigned female at birth, were enrolled in care at CVVAMC, and had a diagnosis of T2DM or CVD (history of myocardial infarction, coronary bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other revascularization in any setting).
Veterans were excluded if they were currently pregnant, trying to conceive, breastfeeding, had a T1DM diagnosis, had previously documented hypersensitivity to a statin, active liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis, previously documented statin-associated rhabdomyolysis or autoimmune myopathy, an active prescription for a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, or previously documented statin intolerance (defined as the inability to tolerate ≥ 3 statins, with ≥ 1 prescribed at low intensity or alternate-day dosing). The female veterans were compared to 2 comparators: the facility's male veterans and the VA national average, identified via the PCED.
Once a veteran was screened, they were telephoned between October 2023 and February 2024 and provided education on statin use and pharmacogenomic testing using a standardized note template. An order was placed for participants who provided verbal consent for pharmacogenomic testing. Those who agreed to statin initiation were referred to a clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) who contacted them at a later date to prescribe a statin following the recommendations of the 2019 ACC/AHA and 2023 ADA guidelines and pharmacogenomic testing, if applicable.4,5,7 Appropriate monitoring and follow-up occurred at the discretion of each CPP. Data collection included: age, race, diagnoses (T2DM, CVD, or both), baseline lipid panel (total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein), hepatic function, name and dose of statin, reasons for declining statin therapy, and pharmacogenomic testing results related to SLCO1B1.
Results
At baseline in July 2023, 77.8% of female veterans with T2DM were prescribed a statin, which exceeded the national VA average (77.0%), but was below the rate for male veterans (78.7%) in the facility comparator group.17 Additionally, 82.2% of females with CVD were prescribed a statin, which was below the national VA average of 86.0% and the 84.9% of male veterans in the facility comparator group.17 The PCED identified 189 female veterans from July 2023 to October 2023 who may benefit from statin therapy. Thirty-three females met the exclusion criteria. Of the 156 included veterans, 129 (82.7%) were successfully contacted and 27 (17.3%) could not be reached by telephone after 3 attempts (Figure 1). The 129 female veterans contacted had a mean age of 59 years and the majority were Black (82.9%) (Table 1).
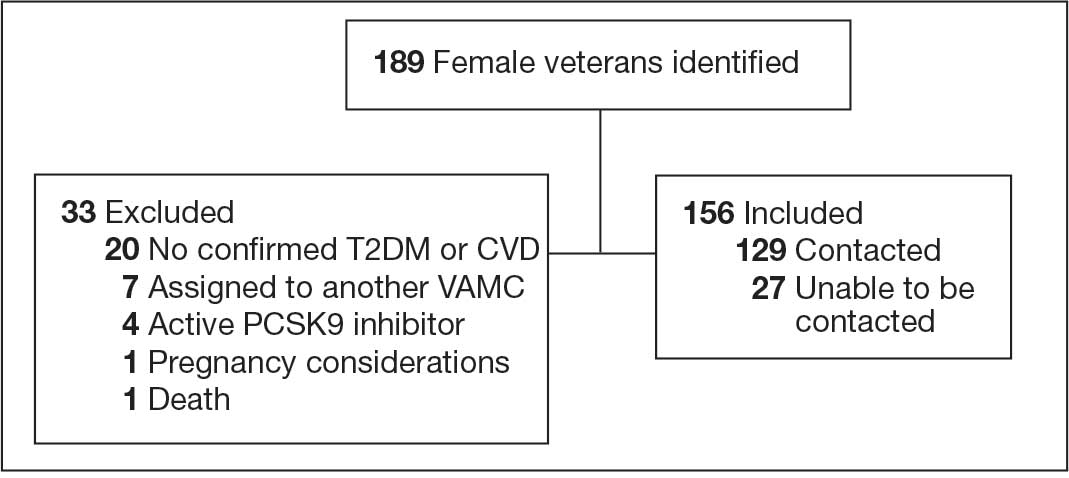
Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/
kexin type 9; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; VAMC, Veterans Affairs medical center.
Primary Outcomes
Of the 129 contacted veterans, 31 (24.0%) had a non-VA statin prescription, 13 (10.1%) had an active VA statin prescription, and 85 (65.9%) did not have a statin prescription, despite being eligible. Statin adherence was confirmed with participants, and the medication list was updated accordingly.
Of the 85 veterans with no active statin therapy, 37 (43.5%) accepted a new statin prescription and 48 (56.5%) declined. There were various reasons provided for declining statin therapy: 17 participants (35.4%) declined due to concern for AEs (Table 2).

From July 2023 to March 2024, the percentage of female veterans with active statin therapy with T2DM increased from 77.8% to 79.0%. For those with active statin therapy with CVD, usage increased from 82.2% to 90.2%, which exceeded the national VA average and facility male comparator group (Figures 2 and 3).17
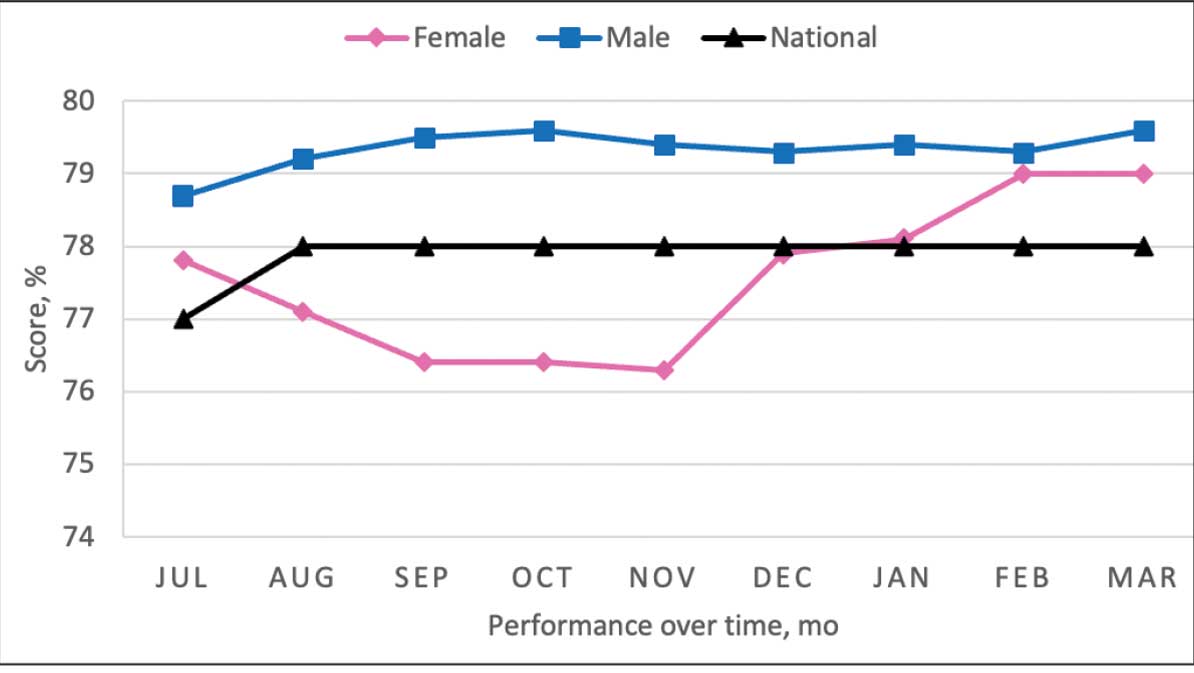
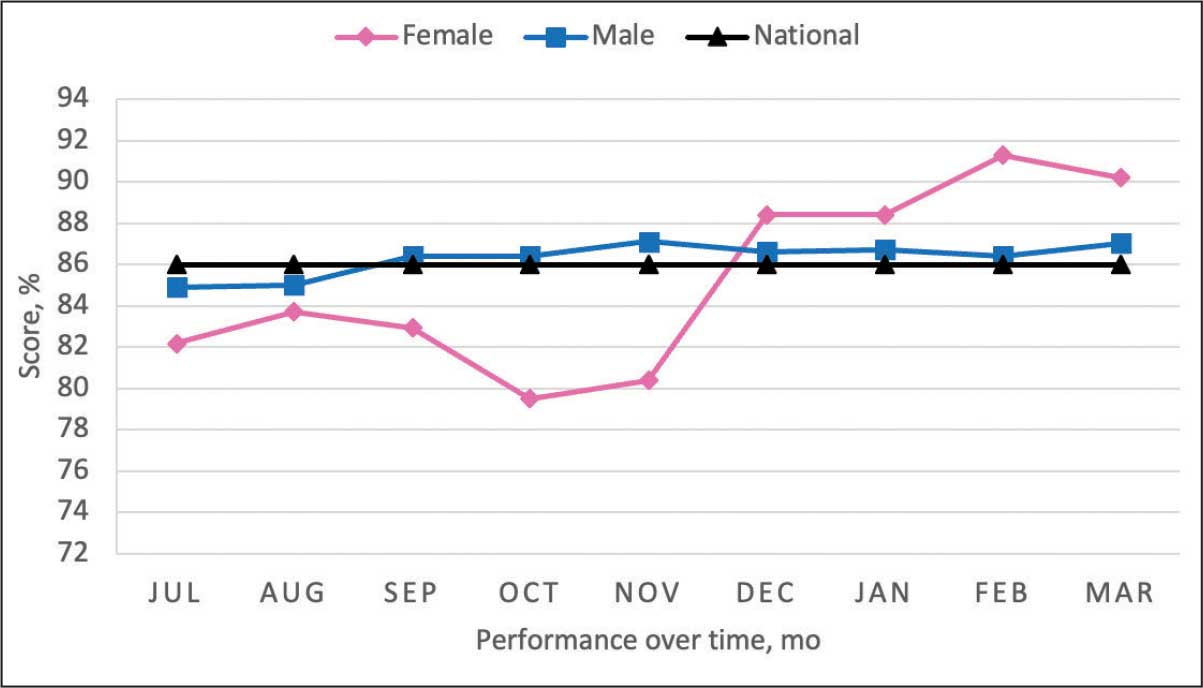
Secondary Outcomes
Seventy-one of 129 veterans (55.0%) gave verbal consent, and 47 (66.2%) completed the pharmacogenomic testing; 58 (45.0%) declined. Five veterans (10.6%) had a known SLCO1B1 allele variant present. One veteran required a change in statin therapy based on the results (eAppendix).
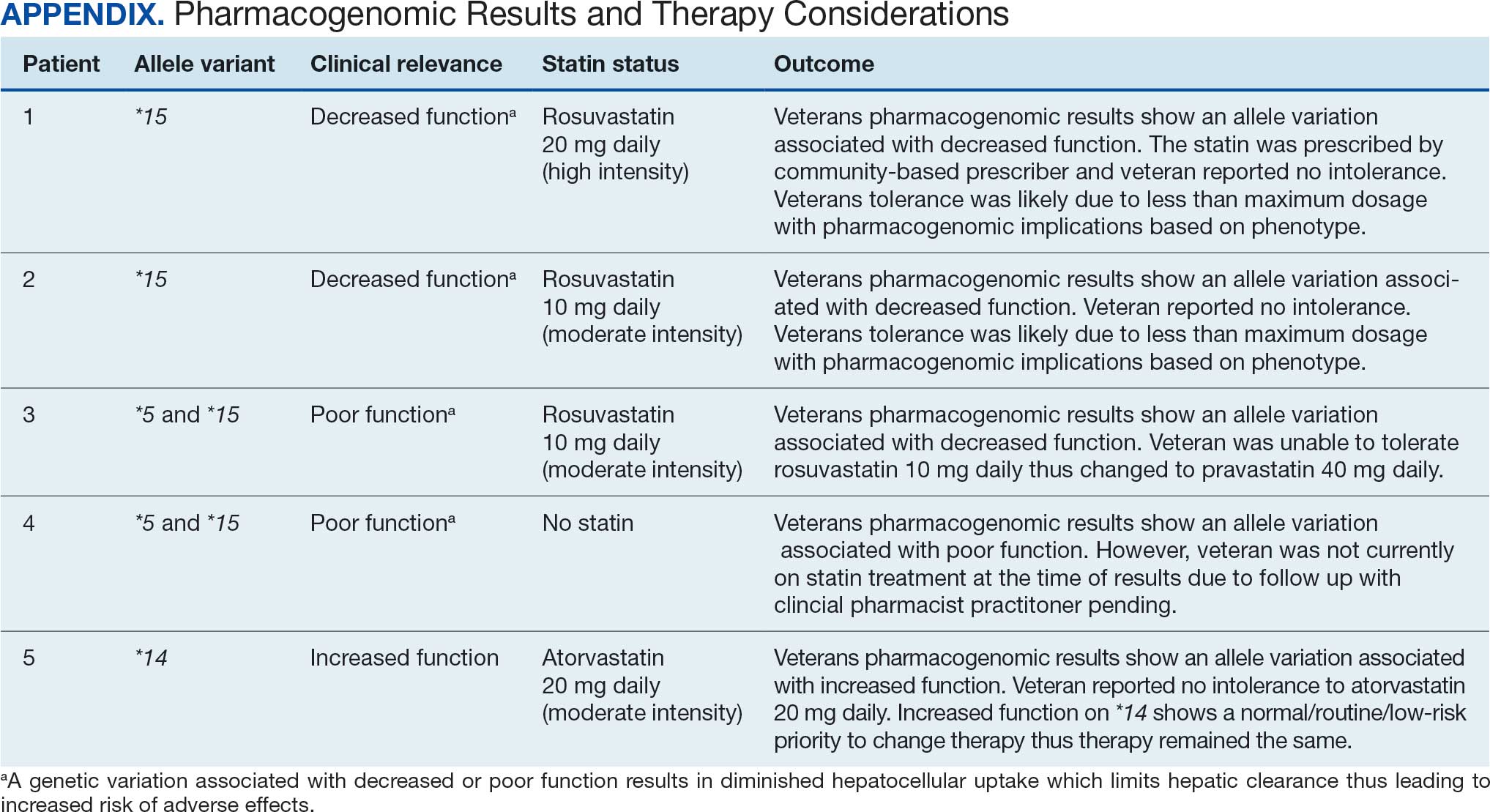
Discussion
This project aimed to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk and increase pharmacogenomic testing using the PCED and care managed by CPPs. The results of this quality improvement project illustrated that both metrics have improved at CVVAMC as a result of the intervention. The results in both metrics now exceed the PCED national VA average, and the CVD metric also exceeds that of the facility male comparator group. While there was only a 1.2% increase from July 2023 to March 2024 for patients with T2DM, there was an 8.0% increase for patients with CVD. Despite standardized education on statin use, more veterans declined therapy than accepted it, mostly due to concern for AEs. Recording the reasons for declining statin therapy offered valuable insight that can be used in additional discussions with veterans and clinicians.
Pharmacogenomics gives clinicians the unique opportunity to take a proactive approach to better predict drug responses, potentially allowing for less trial and error with medications, fewer AEs, greater trust in the clinician, and improved medication adherence. The CPPs incorporated pharmacogenomic testing into their practice, which led to identifying 5 SLCO1B1 gene abnormalities. The PCED served as a powerful tool for advancing equity-focused quality improvement initiatives on a local level and was crucial in prioritizing the detection of veterans potentially receiving suboptimal care.
Limitations
The nature of “cold calls” made it challenging to establish contact for inclusion in this study. An alternative to increase engagement could have been scheduled phone or face-to-face visits. While the use of the PCED was crucial, data did not account for statins listed in the non-VA medication list. All 31 patients with statins prescribed outside the VA had a start date added to provide the most accurate representation of the data moving forward.
Another limitation in this project was its small sample size and population. CVVAMC serves about 6200 female veterans, with roughly 63% identifying as Black. The preponderance of Black individuals (83%) in this project is typical for the female patient population at CVVAMC but may not reflect the demographics of other populations. Other limitations to this project consisted of scheduling conflicts. Appointments for laboratory draws at community-based outpatient clinics were subject to availability, which resulted in some delay in completion of pharmacogenomic testing.
Conclusions
CPPs can help reduce inequity in health care delivery. Increased incorporation of the PCED into regular practice within the VA is recommended to continue addressing sex disparities in statin use, diabetes control, blood pressure management, cancer screenings, and vaccination needs. CVVAMC plans to expand its use through another quality improvement project focused on reducing sex disparities in blood pressure management. Improving educational resources made available to veterans on the importance of statin therapy and potential to mitigate AEs through use of the VA PHASER program also would be helpful. This project successfully improved CVVAMC metrics for female veterans appropriately prescribed statin therapy and increased access to pharmacogenomic testing. Most importantly, it helped close the sex-based gap in CVD risk reduction care.
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2018. Nat Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-114.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical practice guideline for the management of dyslipidemia for cardiovascular risk reduction. Published June 2020. Accessed August 25, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/lipids/VADODDyslipidemiaCPG5087212020.pdf
- Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). American Heart Association. Accessed August 26, 2025. https:// www.heart.org/en/professional/quality-improvement/ascvd
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S144-S174. doi:10.2337/dc22-S010
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes. 2022;41(1):4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Buchanan CH, Brown EA, Bishu KG, et al. The magnitude and potential causes of gender disparities in statin therapy in veterans with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year nationwide longitudinal cohort study. Womens Health Issues. 2022;32:274-283. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2021.10.003
- Ahmed F, Lin J, Ahmed T, et al. Health disparities: statin prescribing patterns among patients with diabetes in a family medicine clinic. Health Equity. 2022;6:291-297. doi:10.1089/heq.2021.0144
- Metser G, Bradley C, Moise N, Liyanage-Don N, Kronish I, Ye S. Gaps and disparities in primary prevention statin prescription during outpatient care. Am J Cardiol. 2021;161:36-41. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.08.070
- Nanna MG, Wang TY, Xiang Q, et al. Sex differences in the use of statins in community practice. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(8):e005562. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.005562
- Kitzmiller JP, Mikulik EB, Dauki AM, Murkherjee C, Luzum JA. Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2016;9:97-106. doi:10.2147/PGPM.S86013
- Türkmen D, Masoli JAH, Kuo CL, Bowden J, Melzer D, Pilling LC. Statin treatment effectiveness and the SLCO1B1*5 reduced function genotype: long-term outcomes in women and men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88:3230-3240. doi:10.1111/bcp.15245
- Cooper-DeHoff RM, Niemi M, Ramsey LB, et al. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and statin-associated musculoskeletal symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;111:1007-1021. doi:10.1002/cpt.2557
- Ramsey LB, Gong L, Lee SB, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: SLCO1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023;113:782-793. doi:10.1002/cpt.2705
- National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report: Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); November 2020.
- Procario G. Primary Care Equity Dashboard [database online]. Power Bi. 2023. Accessed August 26, 2025. https://app.powerbigov.us
- Hausmann LRM, Lamorte C, Estock JL. Understanding the context for incorporating equity into quality improvement throughout a national health care system. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):312-320. doi:10.1089/heq.2023.0009
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death among women in the United States.1 Most CVD is due to the buildup of plaque (ie, cholesterol, proteins, calcium, and inflammatory cells) in artery walls.2 The plaque may lead to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), which includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and aortic atherosclerotic disease.2,3 Control and reduction of ASCVD risk factors, including high cholesterol levels, elevated blood pressure, insulin resistance, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle, can contribute to a reduction in ASCVD morbidity and mortality.2 People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have an increased prevalence of lipid abnormalities, contributing to their high risk of ASCVD.4,5
The prescribing of statins (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzmye A reductase inhibitors) is the cornerstone of lipid-lowering therapy and cardiovascular risk reduction for primary and secondary prevention of ASCVD.6 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend moderate- to high-intensity statins for primary prevention in patients with T2DM and high-intensity statins for secondary prevention in those with or without diabetes when not contraindicated.4,5,7 Despite eligibility according to guideline recommendations, research predominantly shows that women are less likely to receive statin therapy; however, this trend is improving. [6,8-11] To explain the sex differences in statin use, Nanna et al found that there is a combination of women being offered statin therapy less frequently, declining therapy more frequently, and discontinuing treatment more frequently.11 One possibility for discontinuing treatment could be statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), which occur in about 10% of patients.12 The incidence of adverse effects (AEs) may be related to the way statins are metabolized.
Pharmacogenomic testing is free for veterans through the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) PHASER program, which offers information and recommendations for a panel of 11 gene variants. The panel includes genes related to common medication classes such as anticoagulants, antiplatelets, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, antidepressants, and statins. The VA PHASER panel includes the solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, which is predominantly expressed in the liver and facilitates the hepatic uptake of most statins.13,14 A reduced function of SLCO1B1 can lead to higher statin levels, resulting in increased concentrations that may potentially cause SAMS.13,14 Some alleles associated with reduced function include SLCO1B1*5, *15, *23, *31, and *46 to *49, whereas others are associated with increased function, such as SLCO1B1 *14 and *20 (Appendix).15 Supporting evidence shows the SLCO1B1*5 nucleotide polymorphism increases plasma levels of simvastatin and atorvastatin, affecting effectiveness or toxicity. 13 Females tend to have a lower body weight and higher percentage of body fat compared with males, which might lead to higher concentrations of lipophilic drugs, including atorvastatin and simvastatin, which may be exacerbated by decreased function of SLCO1B1*5.15 With pharmacogenomic testing, therapeutic recommendations can be made to improve the overall safety and efficacy of statins, thus improving adherence using a patient-specific approach.14,15
Methods
Carl Vinson VA Medical Center (CVVAMC) serves about 42,000 veterans in Central and South Georgia, of which about 15% are female. Of the female veterans enrolled in care, 63% identify as Black, 27% White, and 1.5% as Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, or Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander. The 2020 Veterans Chartbook report showed that female veterans and minority racial and ethnic groups had worse access to health care and higher mortality rates than their male and non-Hispanic White counterparts.16
The Primary Care Equity Dashboard (PCED) was developed to engage the VA health care workforce in the process of identifying and addressing inequities in local patient populations.17 Using electronic quality measure data, the PCED provides Veterans Integrated Service Network-level and facility-level performance on several metrics.18 The PCED had not been previously used at the CVVAMC, and few publications or quality improvement projects regarding its use have been reported by the VA Office of Health Equity. PCED helped identify disparities when comparing female to male patients in the prescribing of statin therapy for patients with CVD and statin therapy for patients with T2DM.
VA PHASER pharmacogenomic analyses provided an opportunity to expand this quality improvement project. Sanford Health and the VA collaborated on the PHASER program to offer free genetic testing for veterans. The program launched in 2019 and expanded to various VA sites, including CVVAMC in March 2023. This program has been extended to December 31, 2025.
The primary objective of this quality improvement project was to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk. Secondary outcomes included increased pharmacogenomic testing and the assessment of pharmacogenomic results related to statin therapy. This project was approved by the CVVAMC Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. The PCED was used to identify female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD without an active prescription for a statin between July and October 2023. A review of Computerized Patient Record System patient charts was completed to screen for prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria. Veterans were included if they were assigned female at birth, were enrolled in care at CVVAMC, and had a diagnosis of T2DM or CVD (history of myocardial infarction, coronary bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other revascularization in any setting).
Veterans were excluded if they were currently pregnant, trying to conceive, breastfeeding, had a T1DM diagnosis, had previously documented hypersensitivity to a statin, active liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis, previously documented statin-associated rhabdomyolysis or autoimmune myopathy, an active prescription for a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, or previously documented statin intolerance (defined as the inability to tolerate ≥ 3 statins, with ≥ 1 prescribed at low intensity or alternate-day dosing). The female veterans were compared to 2 comparators: the facility's male veterans and the VA national average, identified via the PCED.
Once a veteran was screened, they were telephoned between October 2023 and February 2024 and provided education on statin use and pharmacogenomic testing using a standardized note template. An order was placed for participants who provided verbal consent for pharmacogenomic testing. Those who agreed to statin initiation were referred to a clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) who contacted them at a later date to prescribe a statin following the recommendations of the 2019 ACC/AHA and 2023 ADA guidelines and pharmacogenomic testing, if applicable.4,5,7 Appropriate monitoring and follow-up occurred at the discretion of each CPP. Data collection included: age, race, diagnoses (T2DM, CVD, or both), baseline lipid panel (total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein), hepatic function, name and dose of statin, reasons for declining statin therapy, and pharmacogenomic testing results related to SLCO1B1.
Results
At baseline in July 2023, 77.8% of female veterans with T2DM were prescribed a statin, which exceeded the national VA average (77.0%), but was below the rate for male veterans (78.7%) in the facility comparator group.17 Additionally, 82.2% of females with CVD were prescribed a statin, which was below the national VA average of 86.0% and the 84.9% of male veterans in the facility comparator group.17 The PCED identified 189 female veterans from July 2023 to October 2023 who may benefit from statin therapy. Thirty-three females met the exclusion criteria. Of the 156 included veterans, 129 (82.7%) were successfully contacted and 27 (17.3%) could not be reached by telephone after 3 attempts (Figure 1). The 129 female veterans contacted had a mean age of 59 years and the majority were Black (82.9%) (Table 1).


Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/
kexin type 9; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; VAMC, Veterans Affairs medical center.
Primary Outcomes
Of the 129 contacted veterans, 31 (24.0%) had a non-VA statin prescription, 13 (10.1%) had an active VA statin prescription, and 85 (65.9%) did not have a statin prescription, despite being eligible. Statin adherence was confirmed with participants, and the medication list was updated accordingly.
Of the 85 veterans with no active statin therapy, 37 (43.5%) accepted a new statin prescription and 48 (56.5%) declined. There were various reasons provided for declining statin therapy: 17 participants (35.4%) declined due to concern for AEs (Table 2).

From July 2023 to March 2024, the percentage of female veterans with active statin therapy with T2DM increased from 77.8% to 79.0%. For those with active statin therapy with CVD, usage increased from 82.2% to 90.2%, which exceeded the national VA average and facility male comparator group (Figures 2 and 3).17


Secondary Outcomes
Seventy-one of 129 veterans (55.0%) gave verbal consent, and 47 (66.2%) completed the pharmacogenomic testing; 58 (45.0%) declined. Five veterans (10.6%) had a known SLCO1B1 allele variant present. One veteran required a change in statin therapy based on the results (eAppendix).

Discussion
This project aimed to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk and increase pharmacogenomic testing using the PCED and care managed by CPPs. The results of this quality improvement project illustrated that both metrics have improved at CVVAMC as a result of the intervention. The results in both metrics now exceed the PCED national VA average, and the CVD metric also exceeds that of the facility male comparator group. While there was only a 1.2% increase from July 2023 to March 2024 for patients with T2DM, there was an 8.0% increase for patients with CVD. Despite standardized education on statin use, more veterans declined therapy than accepted it, mostly due to concern for AEs. Recording the reasons for declining statin therapy offered valuable insight that can be used in additional discussions with veterans and clinicians.
Pharmacogenomics gives clinicians the unique opportunity to take a proactive approach to better predict drug responses, potentially allowing for less trial and error with medications, fewer AEs, greater trust in the clinician, and improved medication adherence. The CPPs incorporated pharmacogenomic testing into their practice, which led to identifying 5 SLCO1B1 gene abnormalities. The PCED served as a powerful tool for advancing equity-focused quality improvement initiatives on a local level and was crucial in prioritizing the detection of veterans potentially receiving suboptimal care.
Limitations
The nature of “cold calls” made it challenging to establish contact for inclusion in this study. An alternative to increase engagement could have been scheduled phone or face-to-face visits. While the use of the PCED was crucial, data did not account for statins listed in the non-VA medication list. All 31 patients with statins prescribed outside the VA had a start date added to provide the most accurate representation of the data moving forward.
Another limitation in this project was its small sample size and population. CVVAMC serves about 6200 female veterans, with roughly 63% identifying as Black. The preponderance of Black individuals (83%) in this project is typical for the female patient population at CVVAMC but may not reflect the demographics of other populations. Other limitations to this project consisted of scheduling conflicts. Appointments for laboratory draws at community-based outpatient clinics were subject to availability, which resulted in some delay in completion of pharmacogenomic testing.
Conclusions
CPPs can help reduce inequity in health care delivery. Increased incorporation of the PCED into regular practice within the VA is recommended to continue addressing sex disparities in statin use, diabetes control, blood pressure management, cancer screenings, and vaccination needs. CVVAMC plans to expand its use through another quality improvement project focused on reducing sex disparities in blood pressure management. Improving educational resources made available to veterans on the importance of statin therapy and potential to mitigate AEs through use of the VA PHASER program also would be helpful. This project successfully improved CVVAMC metrics for female veterans appropriately prescribed statin therapy and increased access to pharmacogenomic testing. Most importantly, it helped close the sex-based gap in CVD risk reduction care.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death among women in the United States.1 Most CVD is due to the buildup of plaque (ie, cholesterol, proteins, calcium, and inflammatory cells) in artery walls.2 The plaque may lead to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), which includes coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral artery disease, and aortic atherosclerotic disease.2,3 Control and reduction of ASCVD risk factors, including high cholesterol levels, elevated blood pressure, insulin resistance, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle, can contribute to a reduction in ASCVD morbidity and mortality.2 People with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) have an increased prevalence of lipid abnormalities, contributing to their high risk of ASCVD.4,5
The prescribing of statins (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzmye A reductase inhibitors) is the cornerstone of lipid-lowering therapy and cardiovascular risk reduction for primary and secondary prevention of ASCVD.6 The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) recommend moderate- to high-intensity statins for primary prevention in patients with T2DM and high-intensity statins for secondary prevention in those with or without diabetes when not contraindicated.4,5,7 Despite eligibility according to guideline recommendations, research predominantly shows that women are less likely to receive statin therapy; however, this trend is improving. [6,8-11] To explain the sex differences in statin use, Nanna et al found that there is a combination of women being offered statin therapy less frequently, declining therapy more frequently, and discontinuing treatment more frequently.11 One possibility for discontinuing treatment could be statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), which occur in about 10% of patients.12 The incidence of adverse effects (AEs) may be related to the way statins are metabolized.
Pharmacogenomic testing is free for veterans through the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) PHASER program, which offers information and recommendations for a panel of 11 gene variants. The panel includes genes related to common medication classes such as anticoagulants, antiplatelets, proton pump inhibitors, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, antidepressants, and statins. The VA PHASER panel includes the solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) gene, which is predominantly expressed in the liver and facilitates the hepatic uptake of most statins.13,14 A reduced function of SLCO1B1 can lead to higher statin levels, resulting in increased concentrations that may potentially cause SAMS.13,14 Some alleles associated with reduced function include SLCO1B1*5, *15, *23, *31, and *46 to *49, whereas others are associated with increased function, such as SLCO1B1 *14 and *20 (Appendix).15 Supporting evidence shows the SLCO1B1*5 nucleotide polymorphism increases plasma levels of simvastatin and atorvastatin, affecting effectiveness or toxicity. 13 Females tend to have a lower body weight and higher percentage of body fat compared with males, which might lead to higher concentrations of lipophilic drugs, including atorvastatin and simvastatin, which may be exacerbated by decreased function of SLCO1B1*5.15 With pharmacogenomic testing, therapeutic recommendations can be made to improve the overall safety and efficacy of statins, thus improving adherence using a patient-specific approach.14,15
Methods
Carl Vinson VA Medical Center (CVVAMC) serves about 42,000 veterans in Central and South Georgia, of which about 15% are female. Of the female veterans enrolled in care, 63% identify as Black, 27% White, and 1.5% as Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, or Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander. The 2020 Veterans Chartbook report showed that female veterans and minority racial and ethnic groups had worse access to health care and higher mortality rates than their male and non-Hispanic White counterparts.16
The Primary Care Equity Dashboard (PCED) was developed to engage the VA health care workforce in the process of identifying and addressing inequities in local patient populations.17 Using electronic quality measure data, the PCED provides Veterans Integrated Service Network-level and facility-level performance on several metrics.18 The PCED had not been previously used at the CVVAMC, and few publications or quality improvement projects regarding its use have been reported by the VA Office of Health Equity. PCED helped identify disparities when comparing female to male patients in the prescribing of statin therapy for patients with CVD and statin therapy for patients with T2DM.
VA PHASER pharmacogenomic analyses provided an opportunity to expand this quality improvement project. Sanford Health and the VA collaborated on the PHASER program to offer free genetic testing for veterans. The program launched in 2019 and expanded to various VA sites, including CVVAMC in March 2023. This program has been extended to December 31, 2025.
The primary objective of this quality improvement project was to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk. Secondary outcomes included increased pharmacogenomic testing and the assessment of pharmacogenomic results related to statin therapy. This project was approved by the CVVAMC Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee. The PCED was used to identify female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD without an active prescription for a statin between July and October 2023. A review of Computerized Patient Record System patient charts was completed to screen for prespecified inclusion and exclusion criteria. Veterans were included if they were assigned female at birth, were enrolled in care at CVVAMC, and had a diagnosis of T2DM or CVD (history of myocardial infarction, coronary bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, or other revascularization in any setting).
Veterans were excluded if they were currently pregnant, trying to conceive, breastfeeding, had a T1DM diagnosis, had previously documented hypersensitivity to a statin, active liver failure or decompensated cirrhosis, previously documented statin-associated rhabdomyolysis or autoimmune myopathy, an active prescription for a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, or previously documented statin intolerance (defined as the inability to tolerate ≥ 3 statins, with ≥ 1 prescribed at low intensity or alternate-day dosing). The female veterans were compared to 2 comparators: the facility's male veterans and the VA national average, identified via the PCED.
Once a veteran was screened, they were telephoned between October 2023 and February 2024 and provided education on statin use and pharmacogenomic testing using a standardized note template. An order was placed for participants who provided verbal consent for pharmacogenomic testing. Those who agreed to statin initiation were referred to a clinical pharmacist practitioner (CPP) who contacted them at a later date to prescribe a statin following the recommendations of the 2019 ACC/AHA and 2023 ADA guidelines and pharmacogenomic testing, if applicable.4,5,7 Appropriate monitoring and follow-up occurred at the discretion of each CPP. Data collection included: age, race, diagnoses (T2DM, CVD, or both), baseline lipid panel (total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoprotein), hepatic function, name and dose of statin, reasons for declining statin therapy, and pharmacogenomic testing results related to SLCO1B1.
Results
At baseline in July 2023, 77.8% of female veterans with T2DM were prescribed a statin, which exceeded the national VA average (77.0%), but was below the rate for male veterans (78.7%) in the facility comparator group.17 Additionally, 82.2% of females with CVD were prescribed a statin, which was below the national VA average of 86.0% and the 84.9% of male veterans in the facility comparator group.17 The PCED identified 189 female veterans from July 2023 to October 2023 who may benefit from statin therapy. Thirty-three females met the exclusion criteria. Of the 156 included veterans, 129 (82.7%) were successfully contacted and 27 (17.3%) could not be reached by telephone after 3 attempts (Figure 1). The 129 female veterans contacted had a mean age of 59 years and the majority were Black (82.9%) (Table 1).


Abbreviations: CVD, cardiovascular disease; PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/
kexin type 9; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; VAMC, Veterans Affairs medical center.
Primary Outcomes
Of the 129 contacted veterans, 31 (24.0%) had a non-VA statin prescription, 13 (10.1%) had an active VA statin prescription, and 85 (65.9%) did not have a statin prescription, despite being eligible. Statin adherence was confirmed with participants, and the medication list was updated accordingly.
Of the 85 veterans with no active statin therapy, 37 (43.5%) accepted a new statin prescription and 48 (56.5%) declined. There were various reasons provided for declining statin therapy: 17 participants (35.4%) declined due to concern for AEs (Table 2).

From July 2023 to March 2024, the percentage of female veterans with active statin therapy with T2DM increased from 77.8% to 79.0%. For those with active statin therapy with CVD, usage increased from 82.2% to 90.2%, which exceeded the national VA average and facility male comparator group (Figures 2 and 3).17


Secondary Outcomes
Seventy-one of 129 veterans (55.0%) gave verbal consent, and 47 (66.2%) completed the pharmacogenomic testing; 58 (45.0%) declined. Five veterans (10.6%) had a known SLCO1B1 allele variant present. One veteran required a change in statin therapy based on the results (eAppendix).

Discussion
This project aimed to increase statin prescribing among female veterans with T2DM and/or CVD to reduce cardiovascular risk and increase pharmacogenomic testing using the PCED and care managed by CPPs. The results of this quality improvement project illustrated that both metrics have improved at CVVAMC as a result of the intervention. The results in both metrics now exceed the PCED national VA average, and the CVD metric also exceeds that of the facility male comparator group. While there was only a 1.2% increase from July 2023 to March 2024 for patients with T2DM, there was an 8.0% increase for patients with CVD. Despite standardized education on statin use, more veterans declined therapy than accepted it, mostly due to concern for AEs. Recording the reasons for declining statin therapy offered valuable insight that can be used in additional discussions with veterans and clinicians.
Pharmacogenomics gives clinicians the unique opportunity to take a proactive approach to better predict drug responses, potentially allowing for less trial and error with medications, fewer AEs, greater trust in the clinician, and improved medication adherence. The CPPs incorporated pharmacogenomic testing into their practice, which led to identifying 5 SLCO1B1 gene abnormalities. The PCED served as a powerful tool for advancing equity-focused quality improvement initiatives on a local level and was crucial in prioritizing the detection of veterans potentially receiving suboptimal care.
Limitations
The nature of “cold calls” made it challenging to establish contact for inclusion in this study. An alternative to increase engagement could have been scheduled phone or face-to-face visits. While the use of the PCED was crucial, data did not account for statins listed in the non-VA medication list. All 31 patients with statins prescribed outside the VA had a start date added to provide the most accurate representation of the data moving forward.
Another limitation in this project was its small sample size and population. CVVAMC serves about 6200 female veterans, with roughly 63% identifying as Black. The preponderance of Black individuals (83%) in this project is typical for the female patient population at CVVAMC but may not reflect the demographics of other populations. Other limitations to this project consisted of scheduling conflicts. Appointments for laboratory draws at community-based outpatient clinics were subject to availability, which resulted in some delay in completion of pharmacogenomic testing.
Conclusions
CPPs can help reduce inequity in health care delivery. Increased incorporation of the PCED into regular practice within the VA is recommended to continue addressing sex disparities in statin use, diabetes control, blood pressure management, cancer screenings, and vaccination needs. CVVAMC plans to expand its use through another quality improvement project focused on reducing sex disparities in blood pressure management. Improving educational resources made available to veterans on the importance of statin therapy and potential to mitigate AEs through use of the VA PHASER program also would be helpful. This project successfully improved CVVAMC metrics for female veterans appropriately prescribed statin therapy and increased access to pharmacogenomic testing. Most importantly, it helped close the sex-based gap in CVD risk reduction care.
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2018. Nat Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-114.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical practice guideline for the management of dyslipidemia for cardiovascular risk reduction. Published June 2020. Accessed August 25, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/lipids/VADODDyslipidemiaCPG5087212020.pdf
- Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). American Heart Association. Accessed August 26, 2025. https:// www.heart.org/en/professional/quality-improvement/ascvd
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S144-S174. doi:10.2337/dc22-S010
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes. 2022;41(1):4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Buchanan CH, Brown EA, Bishu KG, et al. The magnitude and potential causes of gender disparities in statin therapy in veterans with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year nationwide longitudinal cohort study. Womens Health Issues. 2022;32:274-283. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2021.10.003
- Ahmed F, Lin J, Ahmed T, et al. Health disparities: statin prescribing patterns among patients with diabetes in a family medicine clinic. Health Equity. 2022;6:291-297. doi:10.1089/heq.2021.0144
- Metser G, Bradley C, Moise N, Liyanage-Don N, Kronish I, Ye S. Gaps and disparities in primary prevention statin prescription during outpatient care. Am J Cardiol. 2021;161:36-41. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.08.070
- Nanna MG, Wang TY, Xiang Q, et al. Sex differences in the use of statins in community practice. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(8):e005562. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.005562
- Kitzmiller JP, Mikulik EB, Dauki AM, Murkherjee C, Luzum JA. Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2016;9:97-106. doi:10.2147/PGPM.S86013
- Türkmen D, Masoli JAH, Kuo CL, Bowden J, Melzer D, Pilling LC. Statin treatment effectiveness and the SLCO1B1*5 reduced function genotype: long-term outcomes in women and men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88:3230-3240. doi:10.1111/bcp.15245
- Cooper-DeHoff RM, Niemi M, Ramsey LB, et al. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and statin-associated musculoskeletal symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;111:1007-1021. doi:10.1002/cpt.2557
- Ramsey LB, Gong L, Lee SB, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: SLCO1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023;113:782-793. doi:10.1002/cpt.2705
- National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report: Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); November 2020.
- Procario G. Primary Care Equity Dashboard [database online]. Power Bi. 2023. Accessed August 26, 2025. https://app.powerbigov.us
- Hausmann LRM, Lamorte C, Estock JL. Understanding the context for incorporating equity into quality improvement throughout a national health care system. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):312-320. doi:10.1089/heq.2023.0009
- Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2018. Nat Vital Stat Rep. 2021;70:1-114.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, US Department of Defense. VA/DoD Clinical practice guideline for the management of dyslipidemia for cardiovascular risk reduction. Published June 2020. Accessed August 25, 2025. https://www.healthquality.va.gov/guidelines/CD/lipids/VADODDyslipidemiaCPG5087212020.pdf
- Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). American Heart Association. Accessed August 26, 2025. https:// www.heart.org/en/professional/quality-improvement/ascvd
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(Suppl 1):S144-S174. doi:10.2337/dc22-S010
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes— 2023 abridged for primary care providers. Clinical Diabetes. 2022;41(1):4-31. doi:10.2337/cd23-as01
- Virani SS, Woodard LD, Ramsey DJ, et al. Gender disparities in evidence-based statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115:21-26. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2014.09.041
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/ AHA Guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/ American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596-e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678
- Buchanan CH, Brown EA, Bishu KG, et al. The magnitude and potential causes of gender disparities in statin therapy in veterans with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year nationwide longitudinal cohort study. Womens Health Issues. 2022;32:274-283. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2021.10.003
- Ahmed F, Lin J, Ahmed T, et al. Health disparities: statin prescribing patterns among patients with diabetes in a family medicine clinic. Health Equity. 2022;6:291-297. doi:10.1089/heq.2021.0144
- Metser G, Bradley C, Moise N, Liyanage-Don N, Kronish I, Ye S. Gaps and disparities in primary prevention statin prescription during outpatient care. Am J Cardiol. 2021;161:36-41. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2021.08.070
- Nanna MG, Wang TY, Xiang Q, et al. Sex differences in the use of statins in community practice. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2019;12(8):e005562. doi:10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.118.005562
- Kitzmiller JP, Mikulik EB, Dauki AM, Murkherjee C, Luzum JA. Pharmacogenomics of statins: understanding susceptibility to adverse effects. Pharmgenomics Pers Med. 2016;9:97-106. doi:10.2147/PGPM.S86013
- Türkmen D, Masoli JAH, Kuo CL, Bowden J, Melzer D, Pilling LC. Statin treatment effectiveness and the SLCO1B1*5 reduced function genotype: long-term outcomes in women and men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88:3230-3240. doi:10.1111/bcp.15245
- Cooper-DeHoff RM, Niemi M, Ramsey LB, et al. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and statin-associated musculoskeletal symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;111:1007-1021. doi:10.1002/cpt.2557
- Ramsey LB, Gong L, Lee SB, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: SLCO1B1. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2023;113:782-793. doi:10.1002/cpt.2705
- National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report: Chartbook on Healthcare for Veterans. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); November 2020.
- Procario G. Primary Care Equity Dashboard [database online]. Power Bi. 2023. Accessed August 26, 2025. https://app.powerbigov.us
- Hausmann LRM, Lamorte C, Estock JL. Understanding the context for incorporating equity into quality improvement throughout a national health care system. Health Equity. 2023;7(1):312-320. doi:10.1089/heq.2023.0009
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
Reducing Sex Disparities in Statin Therapy Among Female Veterans With Type 2 Diabetes and/or Cardiovascular Disease
AI in Mammography: Inside the Tangible Benefits Ready Now
In this Practical AI column, we’ve explored everything from large language models to the nuances of trial matching, but one of the most immediate and impactful applications of AI is unfolding right now in breast imaging. For oncologists, this isn’t an abstract future — with new screening guidelines, dense-breast mandates, and a shrinking radiology workforce, it’s the imaging reports and patient questions landing in your clinic today.
Here is what oncologists need to know, and how to put it to work for their patients.
Why AI in Mammography Matters
More than 200 million women undergo breast cancer screening each year. In the US alone, 10% of the 40 million women screened annually require additional diagnostic imaging, and 4%–5% of these women are eventually diagnosed with breast cancer.
Two major shifts are redefining breast cancer screening in the US: The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends biennial screening from age 40 to 74 years, and notifying patients of breast density is a federal requirement as of September 10, 2024. That means more mammograms, more patient questions, and more downstream oncology decisions. Patients will increasingly ask about “dense” breast results and what to do next. Add a national radiologist shortage into the mix, and the pressure on timely callbacks, biopsies, and treatment planning will only grow.
Can AI Help Without Compromising Care?
The short answer is yes. With AI, we may be able to transform these rate-limiting steps into opportunities for earlier detection, decentralized screening, and smarter triage and save hundreds of thousands of women from an unnecessary diagnostic procedure, if implemented deliberately.
Don’t Confuse Today’s AI With Yesterday’s CAD
Think of older computer-aided detection (CAD) like a 1990s chemotherapy drug: It sometimes helped, but it came with significant toxicity and rarely delivered consistent survival benefits. Today’s deep-learning AI is closer to targeted therapy — trained on millions of “trial participants” (mammograms), more precise, and applied in specific contexts where it adds value. If you once dismissed CAD as noise, it’s time to revisit what AI can now offer.
The role of AI is broader than drawing boxes. It provides second readings, worklist triage, risk prediction, density assessment, and decision support. FDA has cleared several AI tools for both 2D and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which include iCAD ProFound (DBT), ScreenPoint Transpara (2D/DBT), and Lunit INSIGHT DBT.
Some of the strongest evidence for AI in mammography is as a second reader during screening. Large trials show that AI plus one radiologist can match reading from two radiologists, cutting workload by about 40%. For example, the MASAI randomized trial showed that AI-supported screening achieved similar cancer detection but cut human screen-reading workload about 44% vs standard double reading (39,996 vs 40,024 participants). The primary interval cancer outcomes are maturing, but the safety analysis is reassuring.
Reducing second reads and arbitration time are important for clinicians because it frees capacity for callbacks and diagnostic workups. This will be especially key given that screening now starts at age 40. That will mean about 21 to 22 million more women are newly eligible, translating to about 10 to 11 million additional mammograms each year under biennial screening.
Another important area where AI can make its mark in mammography is triage and time to diagnosis. The results from a randomized implementation study showed that AI-prioritized worklists accelerated time to additional imaging and biopsy diagnosis without harming efficiency for others — exactly the kind of outcome patients feel.
Multiple studies have demonstrated improved diagnostic performance and shorter reading times when AI supports DBT interpretation, which is important because DBT can otherwise be time intensive.
We are also seeing rapid advancement in risk-based screening, moving beyond a single dense vs not dense approach. Deep-learning risk models, such as Mirai, predict 1- to 5-year breast cancer risk directly from the mammogram, and these tools are now being assessed prospectively to guide supplemental MRI. Cost-effectiveness modeling supports risk-stratified intervals vs one-size-fits-all schedules.
Finally, automated density tools, such as Transpara Density and Volpara, offer objective, reproducible volumetric measures that map to the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System, which is useful for Mammography Quality Standards Act-required reporting and as inputs to risk calculators.
While early evidence suggests AI may help surface future or interval cancers earlier, including more invasive tumors, the definitive impacts on interval cancer rates and mortality require longitudinal follow-up, which is now in progress.
Pitfalls to Watch For
Bias is real. Studies show false-positive differences by race, age, and density. AI can even infer racial identity from images, potentially amplifying disparities. Performance can also shift by vendor, demographics, and prevalence.
A Radiology study of 4855 DBT exams showed that an algorithm produced more false-positive case scores in Black patients and older patients (aged 71-80 years) patients and in women with extremely dense breasts. This can happen because AI can infer proxies for race directly from images, even when humans cannot, and this can propagate disparities if not addressed. External validations and reviews emphasize that performance can shift with device manufacturer, demographics, and prevalence, which is why all tools need to undergo local validation and calibration.
Here’s a pragmatic adoption checklist before going live with an AI tool.
- Confirm FDA clearance: Verify the name and version of the algorithm, imaging modes (2D vs DBT), and operating points. Confirm 510(k) numbers.
- Local validation: Test on your patient mix and vendor stack (Hologic, GE, Siemens, Fuji). Compare this to your baseline recall rate, positive predictive value of recall (PPV1), cancer detection rate, and reading time. Commit to recalibration if drift occurs.
- Equity plan: Monitor false-positive and negative false-rates by age, race/ethnicity, and density; document corrective actions if disparities emerge. (This isn’t optional.)
- Workflow clarity: Is AI a second reader, an additional reader, or a triage tool? Who arbitrates discordance? What’s the escalation path for high-risk or interval cancer-like patterns?
- Regulatory strategy: Confirm whether the vendor has (or will file) a Predetermined Change Control Plan so models can be updated safely without repeated submissions. Also confirm how you’ll be notified about performance-relevant changes.
- Data governance: Audit logs of AI outputs, retention, protected health information handling, and the patient communication policy for AI-assisted reads.
After going live, set up a quarterly dashboard. It should include cancer detection rate per 1000 patients, recall rate, PPV1, interval cancer rate (as it matures), reading time, and turnaround time to diagnostic imaging or biopsy — all stratified by age, race/ethnicity, and density.
Here, I dissect what this discussion means through the lens of Moravec’s paradox (machines excel at what clinicians find hard, and vice versa) and offer a possible playbook for putting these tools to work.
What to Tell Patients
When speaking with patients, emphasize that a radiologist still reads their mammogram. AI helps with consistency and efficiency; it doesn’t replace human oversight. Patients with dense breasts should still expect a standard notice; discussion of individualized risk factors, such as family history, genetics, and prior biopsies; and consideration of supplemental imaging if risk warrants. But it’s also important to tell these patients that while dense breasts are common, they do not automatically mean high cancer risk.
As for screening schedules, remind patients that screening is at least biennial from 40 to 74 years of age per the USPSTF guidelines; however, specialty groups may recommend starting on an annual schedule at 40.
What You Can Implement Now
There are multiple practical use cases you can introduce now. One is to use AI as a second reader or an additional reader safety net to preserve detection while reducing human workload. This helps your breast center absorb screening expansion to age 40 without diluting quality. Another is to turn on AI triage to shorten the time to callback and biopsy for the few who need it most — patients notice and appreciate faster answers. You can also begin adopting automated density plus risk models to move beyond “dense/not dense.” For selected patients, AI-informed risk can justify MRI or tailored intervals.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet (for your next leadership or tumor-board meeting).
Do:
- Use AI as a second or additional reader or triage tool, not as a black box.
- Track cancer detection rate, recall, PPV1, interval cancers, and reading time, stratified by age, race, and breast density.
- Pair automated density with AI risk to personalize screening and supplemental imaging.
- Enroll patients in future clinical trials, such as PRISM, the first large-scale randomized controlled trial of AI for screening mammography. This US-based, $16 million, seven-site study is funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Don’t:
- Assume “AI = CAD.” The 2015 CAD story is over; modern deep learning systems are different and require different oversight.
- Go live without a local validation and equity plan or without clarity on software updates.
- Forget to remind patients that screening starts at age 40, and dense breast notifications are now universal. Use the visit to discuss risk, supplemental imaging, and why a human still directs their care.
The Bottom Line
AI won’t replace radiologists or read mammograms for us — just as PET scans didn’t replace oncologists and stethoscopes didn’t make cardiologists obsolete. What it will do is catch what the tired human eye might miss, shave days off anxious waiting, and turn breast density into data instead of doubt. For oncologists, that means staging sooner, enrolling smarter, and spending more time talking with patients instead of chasing callbacks.
In short, AI may not take the picture, but it helps us frame the story, making it sharper, faster, and with fewer blind spots. By pairing this powerful technology with rigorous, equity-focused local validation and transparent governance under the FDA’s emerging Predetermined Change Control Plan framework, we can realize the tangible benefits of practical AI for our patients without widening disparities.
Now, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, how about we add on AI to that pink ribbon — how cool would that be?
Thoughts? Drop me a line at Arturo.AI.MedTech@gmail.com. Let’s keep the conversation — and pink ribbons — going.
Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD, MSEd, is the co-founder and chief medical AI officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as Systemwide Chief of Hematology and Oncology at St. Luke’s University Health Network, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this Practical AI column, we’ve explored everything from large language models to the nuances of trial matching, but one of the most immediate and impactful applications of AI is unfolding right now in breast imaging. For oncologists, this isn’t an abstract future — with new screening guidelines, dense-breast mandates, and a shrinking radiology workforce, it’s the imaging reports and patient questions landing in your clinic today.
Here is what oncologists need to know, and how to put it to work for their patients.
Why AI in Mammography Matters
More than 200 million women undergo breast cancer screening each year. In the US alone, 10% of the 40 million women screened annually require additional diagnostic imaging, and 4%–5% of these women are eventually diagnosed with breast cancer.
Two major shifts are redefining breast cancer screening in the US: The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends biennial screening from age 40 to 74 years, and notifying patients of breast density is a federal requirement as of September 10, 2024. That means more mammograms, more patient questions, and more downstream oncology decisions. Patients will increasingly ask about “dense” breast results and what to do next. Add a national radiologist shortage into the mix, and the pressure on timely callbacks, biopsies, and treatment planning will only grow.
Can AI Help Without Compromising Care?
The short answer is yes. With AI, we may be able to transform these rate-limiting steps into opportunities for earlier detection, decentralized screening, and smarter triage and save hundreds of thousands of women from an unnecessary diagnostic procedure, if implemented deliberately.
Don’t Confuse Today’s AI With Yesterday’s CAD
Think of older computer-aided detection (CAD) like a 1990s chemotherapy drug: It sometimes helped, but it came with significant toxicity and rarely delivered consistent survival benefits. Today’s deep-learning AI is closer to targeted therapy — trained on millions of “trial participants” (mammograms), more precise, and applied in specific contexts where it adds value. If you once dismissed CAD as noise, it’s time to revisit what AI can now offer.
The role of AI is broader than drawing boxes. It provides second readings, worklist triage, risk prediction, density assessment, and decision support. FDA has cleared several AI tools for both 2D and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which include iCAD ProFound (DBT), ScreenPoint Transpara (2D/DBT), and Lunit INSIGHT DBT.
Some of the strongest evidence for AI in mammography is as a second reader during screening. Large trials show that AI plus one radiologist can match reading from two radiologists, cutting workload by about 40%. For example, the MASAI randomized trial showed that AI-supported screening achieved similar cancer detection but cut human screen-reading workload about 44% vs standard double reading (39,996 vs 40,024 participants). The primary interval cancer outcomes are maturing, but the safety analysis is reassuring.
Reducing second reads and arbitration time are important for clinicians because it frees capacity for callbacks and diagnostic workups. This will be especially key given that screening now starts at age 40. That will mean about 21 to 22 million more women are newly eligible, translating to about 10 to 11 million additional mammograms each year under biennial screening.
Another important area where AI can make its mark in mammography is triage and time to diagnosis. The results from a randomized implementation study showed that AI-prioritized worklists accelerated time to additional imaging and biopsy diagnosis without harming efficiency for others — exactly the kind of outcome patients feel.
Multiple studies have demonstrated improved diagnostic performance and shorter reading times when AI supports DBT interpretation, which is important because DBT can otherwise be time intensive.
We are also seeing rapid advancement in risk-based screening, moving beyond a single dense vs not dense approach. Deep-learning risk models, such as Mirai, predict 1- to 5-year breast cancer risk directly from the mammogram, and these tools are now being assessed prospectively to guide supplemental MRI. Cost-effectiveness modeling supports risk-stratified intervals vs one-size-fits-all schedules.
Finally, automated density tools, such as Transpara Density and Volpara, offer objective, reproducible volumetric measures that map to the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System, which is useful for Mammography Quality Standards Act-required reporting and as inputs to risk calculators.
While early evidence suggests AI may help surface future or interval cancers earlier, including more invasive tumors, the definitive impacts on interval cancer rates and mortality require longitudinal follow-up, which is now in progress.
Pitfalls to Watch For
Bias is real. Studies show false-positive differences by race, age, and density. AI can even infer racial identity from images, potentially amplifying disparities. Performance can also shift by vendor, demographics, and prevalence.
A Radiology study of 4855 DBT exams showed that an algorithm produced more false-positive case scores in Black patients and older patients (aged 71-80 years) patients and in women with extremely dense breasts. This can happen because AI can infer proxies for race directly from images, even when humans cannot, and this can propagate disparities if not addressed. External validations and reviews emphasize that performance can shift with device manufacturer, demographics, and prevalence, which is why all tools need to undergo local validation and calibration.
Here’s a pragmatic adoption checklist before going live with an AI tool.
- Confirm FDA clearance: Verify the name and version of the algorithm, imaging modes (2D vs DBT), and operating points. Confirm 510(k) numbers.
- Local validation: Test on your patient mix and vendor stack (Hologic, GE, Siemens, Fuji). Compare this to your baseline recall rate, positive predictive value of recall (PPV1), cancer detection rate, and reading time. Commit to recalibration if drift occurs.
- Equity plan: Monitor false-positive and negative false-rates by age, race/ethnicity, and density; document corrective actions if disparities emerge. (This isn’t optional.)
- Workflow clarity: Is AI a second reader, an additional reader, or a triage tool? Who arbitrates discordance? What’s the escalation path for high-risk or interval cancer-like patterns?
- Regulatory strategy: Confirm whether the vendor has (or will file) a Predetermined Change Control Plan so models can be updated safely without repeated submissions. Also confirm how you’ll be notified about performance-relevant changes.
- Data governance: Audit logs of AI outputs, retention, protected health information handling, and the patient communication policy for AI-assisted reads.
After going live, set up a quarterly dashboard. It should include cancer detection rate per 1000 patients, recall rate, PPV1, interval cancer rate (as it matures), reading time, and turnaround time to diagnostic imaging or biopsy — all stratified by age, race/ethnicity, and density.
Here, I dissect what this discussion means through the lens of Moravec’s paradox (machines excel at what clinicians find hard, and vice versa) and offer a possible playbook for putting these tools to work.
What to Tell Patients
When speaking with patients, emphasize that a radiologist still reads their mammogram. AI helps with consistency and efficiency; it doesn’t replace human oversight. Patients with dense breasts should still expect a standard notice; discussion of individualized risk factors, such as family history, genetics, and prior biopsies; and consideration of supplemental imaging if risk warrants. But it’s also important to tell these patients that while dense breasts are common, they do not automatically mean high cancer risk.
As for screening schedules, remind patients that screening is at least biennial from 40 to 74 years of age per the USPSTF guidelines; however, specialty groups may recommend starting on an annual schedule at 40.
What You Can Implement Now
There are multiple practical use cases you can introduce now. One is to use AI as a second reader or an additional reader safety net to preserve detection while reducing human workload. This helps your breast center absorb screening expansion to age 40 without diluting quality. Another is to turn on AI triage to shorten the time to callback and biopsy for the few who need it most — patients notice and appreciate faster answers. You can also begin adopting automated density plus risk models to move beyond “dense/not dense.” For selected patients, AI-informed risk can justify MRI or tailored intervals.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet (for your next leadership or tumor-board meeting).
Do:
- Use AI as a second or additional reader or triage tool, not as a black box.
- Track cancer detection rate, recall, PPV1, interval cancers, and reading time, stratified by age, race, and breast density.
- Pair automated density with AI risk to personalize screening and supplemental imaging.
- Enroll patients in future clinical trials, such as PRISM, the first large-scale randomized controlled trial of AI for screening mammography. This US-based, $16 million, seven-site study is funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Don’t:
- Assume “AI = CAD.” The 2015 CAD story is over; modern deep learning systems are different and require different oversight.
- Go live without a local validation and equity plan or without clarity on software updates.
- Forget to remind patients that screening starts at age 40, and dense breast notifications are now universal. Use the visit to discuss risk, supplemental imaging, and why a human still directs their care.
The Bottom Line
AI won’t replace radiologists or read mammograms for us — just as PET scans didn’t replace oncologists and stethoscopes didn’t make cardiologists obsolete. What it will do is catch what the tired human eye might miss, shave days off anxious waiting, and turn breast density into data instead of doubt. For oncologists, that means staging sooner, enrolling smarter, and spending more time talking with patients instead of chasing callbacks.
In short, AI may not take the picture, but it helps us frame the story, making it sharper, faster, and with fewer blind spots. By pairing this powerful technology with rigorous, equity-focused local validation and transparent governance under the FDA’s emerging Predetermined Change Control Plan framework, we can realize the tangible benefits of practical AI for our patients without widening disparities.
Now, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, how about we add on AI to that pink ribbon — how cool would that be?
Thoughts? Drop me a line at Arturo.AI.MedTech@gmail.com. Let’s keep the conversation — and pink ribbons — going.
Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD, MSEd, is the co-founder and chief medical AI officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as Systemwide Chief of Hematology and Oncology at St. Luke’s University Health Network, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In this Practical AI column, we’ve explored everything from large language models to the nuances of trial matching, but one of the most immediate and impactful applications of AI is unfolding right now in breast imaging. For oncologists, this isn’t an abstract future — with new screening guidelines, dense-breast mandates, and a shrinking radiology workforce, it’s the imaging reports and patient questions landing in your clinic today.
Here is what oncologists need to know, and how to put it to work for their patients.
Why AI in Mammography Matters
More than 200 million women undergo breast cancer screening each year. In the US alone, 10% of the 40 million women screened annually require additional diagnostic imaging, and 4%–5% of these women are eventually diagnosed with breast cancer.
Two major shifts are redefining breast cancer screening in the US: The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) now recommends biennial screening from age 40 to 74 years, and notifying patients of breast density is a federal requirement as of September 10, 2024. That means more mammograms, more patient questions, and more downstream oncology decisions. Patients will increasingly ask about “dense” breast results and what to do next. Add a national radiologist shortage into the mix, and the pressure on timely callbacks, biopsies, and treatment planning will only grow.
Can AI Help Without Compromising Care?
The short answer is yes. With AI, we may be able to transform these rate-limiting steps into opportunities for earlier detection, decentralized screening, and smarter triage and save hundreds of thousands of women from an unnecessary diagnostic procedure, if implemented deliberately.
Don’t Confuse Today’s AI With Yesterday’s CAD
Think of older computer-aided detection (CAD) like a 1990s chemotherapy drug: It sometimes helped, but it came with significant toxicity and rarely delivered consistent survival benefits. Today’s deep-learning AI is closer to targeted therapy — trained on millions of “trial participants” (mammograms), more precise, and applied in specific contexts where it adds value. If you once dismissed CAD as noise, it’s time to revisit what AI can now offer.
The role of AI is broader than drawing boxes. It provides second readings, worklist triage, risk prediction, density assessment, and decision support. FDA has cleared several AI tools for both 2D and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), which include iCAD ProFound (DBT), ScreenPoint Transpara (2D/DBT), and Lunit INSIGHT DBT.
Some of the strongest evidence for AI in mammography is as a second reader during screening. Large trials show that AI plus one radiologist can match reading from two radiologists, cutting workload by about 40%. For example, the MASAI randomized trial showed that AI-supported screening achieved similar cancer detection but cut human screen-reading workload about 44% vs standard double reading (39,996 vs 40,024 participants). The primary interval cancer outcomes are maturing, but the safety analysis is reassuring.
Reducing second reads and arbitration time are important for clinicians because it frees capacity for callbacks and diagnostic workups. This will be especially key given that screening now starts at age 40. That will mean about 21 to 22 million more women are newly eligible, translating to about 10 to 11 million additional mammograms each year under biennial screening.
Another important area where AI can make its mark in mammography is triage and time to diagnosis. The results from a randomized implementation study showed that AI-prioritized worklists accelerated time to additional imaging and biopsy diagnosis without harming efficiency for others — exactly the kind of outcome patients feel.
Multiple studies have demonstrated improved diagnostic performance and shorter reading times when AI supports DBT interpretation, which is important because DBT can otherwise be time intensive.
We are also seeing rapid advancement in risk-based screening, moving beyond a single dense vs not dense approach. Deep-learning risk models, such as Mirai, predict 1- to 5-year breast cancer risk directly from the mammogram, and these tools are now being assessed prospectively to guide supplemental MRI. Cost-effectiveness modeling supports risk-stratified intervals vs one-size-fits-all schedules.
Finally, automated density tools, such as Transpara Density and Volpara, offer objective, reproducible volumetric measures that map to the Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System, which is useful for Mammography Quality Standards Act-required reporting and as inputs to risk calculators.
While early evidence suggests AI may help surface future or interval cancers earlier, including more invasive tumors, the definitive impacts on interval cancer rates and mortality require longitudinal follow-up, which is now in progress.
Pitfalls to Watch For
Bias is real. Studies show false-positive differences by race, age, and density. AI can even infer racial identity from images, potentially amplifying disparities. Performance can also shift by vendor, demographics, and prevalence.
A Radiology study of 4855 DBT exams showed that an algorithm produced more false-positive case scores in Black patients and older patients (aged 71-80 years) patients and in women with extremely dense breasts. This can happen because AI can infer proxies for race directly from images, even when humans cannot, and this can propagate disparities if not addressed. External validations and reviews emphasize that performance can shift with device manufacturer, demographics, and prevalence, which is why all tools need to undergo local validation and calibration.
Here’s a pragmatic adoption checklist before going live with an AI tool.
- Confirm FDA clearance: Verify the name and version of the algorithm, imaging modes (2D vs DBT), and operating points. Confirm 510(k) numbers.
- Local validation: Test on your patient mix and vendor stack (Hologic, GE, Siemens, Fuji). Compare this to your baseline recall rate, positive predictive value of recall (PPV1), cancer detection rate, and reading time. Commit to recalibration if drift occurs.
- Equity plan: Monitor false-positive and negative false-rates by age, race/ethnicity, and density; document corrective actions if disparities emerge. (This isn’t optional.)
- Workflow clarity: Is AI a second reader, an additional reader, or a triage tool? Who arbitrates discordance? What’s the escalation path for high-risk or interval cancer-like patterns?
- Regulatory strategy: Confirm whether the vendor has (or will file) a Predetermined Change Control Plan so models can be updated safely without repeated submissions. Also confirm how you’ll be notified about performance-relevant changes.
- Data governance: Audit logs of AI outputs, retention, protected health information handling, and the patient communication policy for AI-assisted reads.
After going live, set up a quarterly dashboard. It should include cancer detection rate per 1000 patients, recall rate, PPV1, interval cancer rate (as it matures), reading time, and turnaround time to diagnostic imaging or biopsy — all stratified by age, race/ethnicity, and density.
Here, I dissect what this discussion means through the lens of Moravec’s paradox (machines excel at what clinicians find hard, and vice versa) and offer a possible playbook for putting these tools to work.
What to Tell Patients
When speaking with patients, emphasize that a radiologist still reads their mammogram. AI helps with consistency and efficiency; it doesn’t replace human oversight. Patients with dense breasts should still expect a standard notice; discussion of individualized risk factors, such as family history, genetics, and prior biopsies; and consideration of supplemental imaging if risk warrants. But it’s also important to tell these patients that while dense breasts are common, they do not automatically mean high cancer risk.
As for screening schedules, remind patients that screening is at least biennial from 40 to 74 years of age per the USPSTF guidelines; however, specialty groups may recommend starting on an annual schedule at 40.
What You Can Implement Now
There are multiple practical use cases you can introduce now. One is to use AI as a second reader or an additional reader safety net to preserve detection while reducing human workload. This helps your breast center absorb screening expansion to age 40 without diluting quality. Another is to turn on AI triage to shorten the time to callback and biopsy for the few who need it most — patients notice and appreciate faster answers. You can also begin adopting automated density plus risk models to move beyond “dense/not dense.” For selected patients, AI-informed risk can justify MRI or tailored intervals.
Here’s a quick cheat sheet (for your next leadership or tumor-board meeting).
Do:
- Use AI as a second or additional reader or triage tool, not as a black box.
- Track cancer detection rate, recall, PPV1, interval cancers, and reading time, stratified by age, race, and breast density.
- Pair automated density with AI risk to personalize screening and supplemental imaging.
- Enroll patients in future clinical trials, such as PRISM, the first large-scale randomized controlled trial of AI for screening mammography. This US-based, $16 million, seven-site study is funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Don’t:
- Assume “AI = CAD.” The 2015 CAD story is over; modern deep learning systems are different and require different oversight.
- Go live without a local validation and equity plan or without clarity on software updates.
- Forget to remind patients that screening starts at age 40, and dense breast notifications are now universal. Use the visit to discuss risk, supplemental imaging, and why a human still directs their care.
The Bottom Line
AI won’t replace radiologists or read mammograms for us — just as PET scans didn’t replace oncologists and stethoscopes didn’t make cardiologists obsolete. What it will do is catch what the tired human eye might miss, shave days off anxious waiting, and turn breast density into data instead of doubt. For oncologists, that means staging sooner, enrolling smarter, and spending more time talking with patients instead of chasing callbacks.
In short, AI may not take the picture, but it helps us frame the story, making it sharper, faster, and with fewer blind spots. By pairing this powerful technology with rigorous, equity-focused local validation and transparent governance under the FDA’s emerging Predetermined Change Control Plan framework, we can realize the tangible benefits of practical AI for our patients without widening disparities.
Now, during Breast Cancer Awareness Month, how about we add on AI to that pink ribbon — how cool would that be?
Thoughts? Drop me a line at Arturo.AI.MedTech@gmail.com. Let’s keep the conversation — and pink ribbons — going.
Arturo Loaiza-Bonilla, MD, MSEd, is the co-founder and chief medical AI officer at Massive Bio, a company connecting patients to clinical trials using artificial intelligence. His research and professional interests focus on precision medicine, clinical trial design, digital health, entrepreneurship, and patient advocacy. Dr Loaiza-Bonilla serves as Systemwide Chief of Hematology and Oncology at St. Luke’s University Health Network, where he maintains a connection to patient care by attending to patients 2 days a week.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Unique Presentation of Postpartum Hypereosinophilic Syndrome With Atypical Features and Therapeutic Challenges
Unique Presentation of Postpartum Hypereosinophilic Syndrome With Atypical Features and Therapeutic Challenges
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is defined by marked, persistent absolute eosinophil count (AEC) > 1500 cells/μL on ≥ 2 peripheral smears separated by ≥ 1 month with evidence of accompanied end-organ damage, in the absence of other causes of eosinophilia such as malignancy, atopy, or parasitic infections.1-5 Hypereosinophilic infiltration can impact almost every organ system; however, the most profound complications in patients with HES are related to leukemias and cardiac manifestations of the disease.3,4 Although rare, the associated morbidity and mortality of HES are considerable, making prompt recognition and treatment essential. Management involves targeted therapy based on pathologic classification of HES and on decreasing associated inflammation, fibrosis, and end-organ damage.3,5-7
The patient in this case report met the diagnostic criteria for HES. However, this patient had several clinical and laboratory features that made it difficult to characterize a specific HES variant. Moreover, she had additional immunomodulating factors in the setting of pregnancy. This is the first documented case of HES of undetermined etiology diagnosed postpartum and managed in the setting of a new pregnancy.2,8
CASE PRESENTATION
A 32-year-old female active-duty military service member with allergic rhinitis and a history of childhood eczema was referred to allergy/immunology for evaluation of a new, progressive pruritic rash. Symptoms started 3 months after the birth of her first child, with a new diffuse erythematous skin rash sparing her palms, soles, and mucosal surfaces. Given her history of atopy, the rash was initially treated as severe atopic dermatitis with appropriate topical medications. The rash gradually worsened, with the development of intermittent facial swelling, night sweats, dyspnea, recurrent epigastric abdominal pain, and nausea with vomiting, resulting in decreased oral intake and weight loss.
The patient was hospitalized and received an expedited multidisciplinary evaluation by dermatology, hematology/oncology, and gastroenterology. Her AEC of 4787 cells/μL peaked on admission and was markedly elevated from the 1070 cells/μL reported in the third trimester of her pregnancy. She was found to have mature eosinophilia on skin biopsy (Figure 1), endoscopic duodenal biopsy (Figure 2), peripheral blood smear (Figure 3), and bone marrow biopsy (Figure 4).
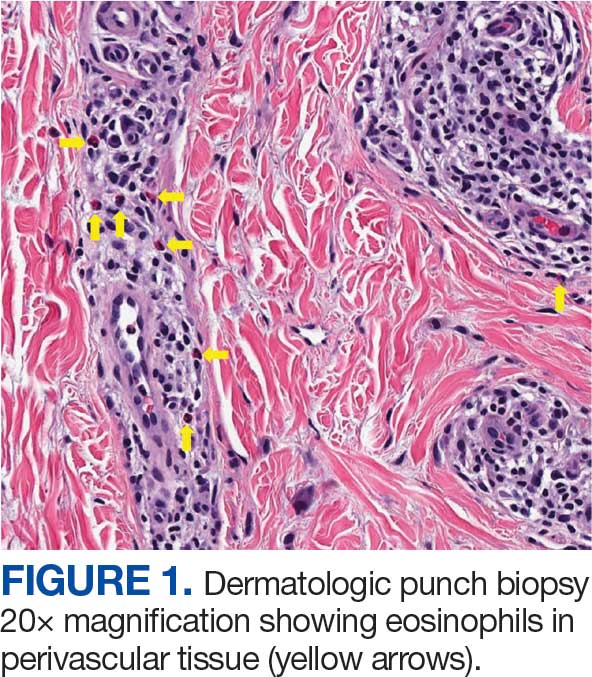
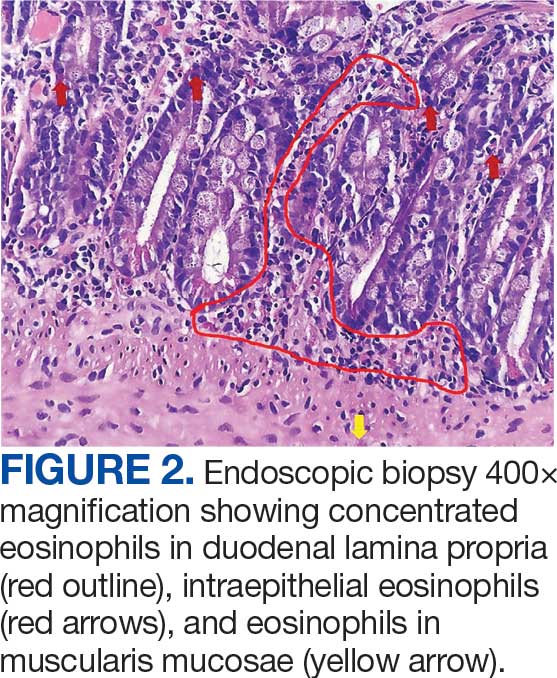
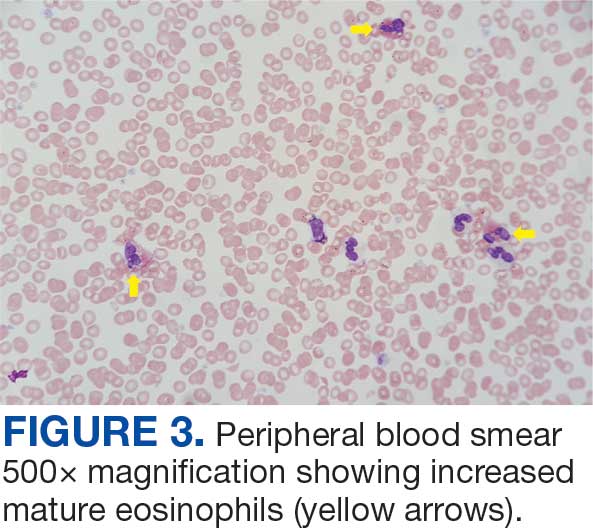
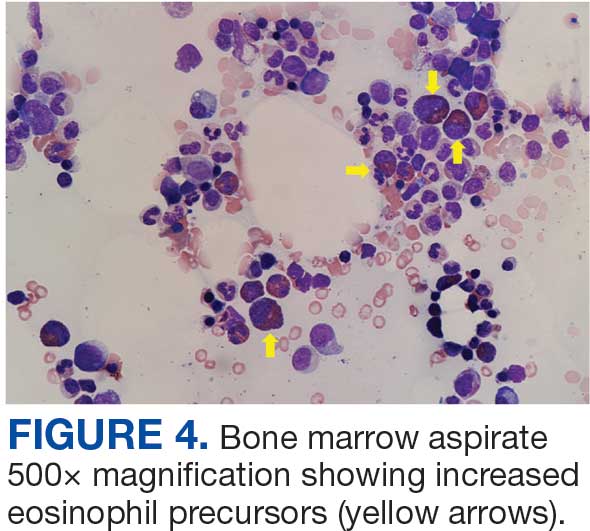
Radiographic imaging of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed hepatomegaly without detectable neoplasm. There was no clinical evidence of cardiac involvement, and evaluation with electrocardiography and echocardiography did not indicate myocarditis. Extensive laboratory testing revealed no genetic mutations indicative of familial, myeloproliferative, or lymphocytic variants of HES.
The patient received topical emollients, omeprazole 40 mg daily, and ondansetron 8 mg 3 times daily as needed for symptom management, and was started on oral prednisone 40 mg daily with improvement in dyspnea, night sweats, and gastrointestinal complaints. During the patient's 6-day hospitalization and treatment, her AECs gradually decreased to 2110 cells/μL, and decreased to 1600 cells/μL over the course of a month, remaining in the hypereosinophilic range. The patient was discovered to be pregnant while symptoms were improving, resulting in stepwise discontinuation of oral steroids, but she reported continued improvement in symptoms.
DISCUSSION
Peripheral eosinophilia has a broad differential diagnoses, including HES, parasitic infections, atopic hypersensitivity diseases, eosinophilic lung diseases, eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases, vasculitides such as eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, genetic syndromes predisposing to eosinophilia, episodic angioedema with eosinophilia, and chronic metabolic disease with adrenal insufficiency.1-5 HES, although rare, is a disease process with potentially devastating associated morbidity and mortality if not promptly recognized and treated. HES is further delineated by hypereosinophilia with associated eosinophil-mediated organ damage or dysfunction.3-5
Clinical manifestations of HES can differ greatly depending on the HES variant and degree of organ involvement at the time of diagnosis and throughout the disease course. Patients with HES, as well as those with asymptomatic eosinophilia or hypereosinophilia, should be closely monitored for disease progression. In addition to trending peripheral AECs, clinicians should screen for symptoms of organ involvement and perform targeted evaluation of the suspected organs to promptly identify early signs of organ involvement and initiate treatment.1-4 Recommendations regarding screening intervals vary widely from monthly to annually, depending on a patient’s specific clinical picture.
HES has been subdivided into clinically relevant variants, including myeloproliferative (M-HES), T lymphocytic (L-HES), organ-restricted (or overlap) HES, familial HES, idiopathic HES, and specific syndromes with associated hypereosinophilia.3-5,9 Patients with M-HES have elevated circulating leukocyte precursors and clinical manifestations, including but not limited to hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The most commonly associated genetic mutations include the FIP1L1-PDGFR-α fusion, BCR-ABL1, PDGFRA/B, JAK2, KIT, and FGFR1.3-6 L-HES usually has predominant skin and soft tissue involvement secondary to immunoglobulin E-mediated actions with clonal expansion of T cells (most commonly CD3-4+ or CD3+CD4-CD8-).3,5,6 Familial HES, a rare variant, follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern and is usually present at birth. It involves chromosome 5, which contains genes coding for cytokines that drive eosinophilic proliferation, including interleukin (IL)-3, IL-5, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.5,9 Hypereosinophilia in the setting of end-organ damage restricted to a single organ is considered organ-restricted HES. There can be significant hepatic and gastrointestinal dysfunction, with or without malabsorption.
HES can also manifest with hematologic malignancy, restrictive obliterative cardiomyopathies, renal injury manifested by hematuria and electrolyte derangements, and neurologic complications including hemiparesis, dysarthria, and even coma.6 Endothelial damage due to eosinophil-driven inflammation can result in thrombus formation and increased risk of thromboembolic events in various organs.3 Idiopathic HES, otherwise known as HES of unknown etiology or significance, is a diagnosis of exclusion and constitutes a cohort of patients who do not fit into the other delineated categories.3-5 These patients often have multisystem involvement, making classification and treatment a challenge.5
The patient described in this case met the diagnostic criteria for HES, but her complicated clinical and laboratory features were challenging to characterize into a specific variant of HES. Organ-restricted HES was ruled out due to skin, marrow, and duodenal infiltration. She also had the potential for lung involvement based on her clinical symptoms, however no biopsy was obtained. Laboratory testing revealed no deletions or mutations indicative of familial, myeloproliferative, or lymphocytic variants. Her multisystem involvement without an underlying associated syndrome suggests idiopathic HES or HES of undetermined significance.1-5
Most patients with HES are diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50 years.10 While HES has its peak incidence in the fourth decade of life, acute onset of new symptoms 3 months postpartum makes this an unusual presentation. In this unique case, it is important to highlight the role of the physiologic changes of pregnancy in inflammatory mediation. The physiologic changes that occur in pregnancy to ensure fetal tolerance can have profound implications for leukocyte count, AEC, and subsequent inflammatory responses. The phenomenon of inflammatory amelioration during pregnancy is well-documented, but there has only been 1 known published case report discussing decreasing HES symptoms during pregnancy with prepregnancy and postpartum hypereosinophilia.8 It is suggested that this amelioration is secondary to cortisol and progesterone shifts that occur in pregnancy. Physiologic increases in adrenocorticotropic hormone in pregnancy leads to subsequent secretion of endogenous steroids by the adrenal cortex. In turn, pregnancy can lead to leukocytosis and eosinopenia.8 Overall, pregnancy can have beneficial immunomodulating properties in the spectrum of hypereosinophilic syndromes. Even so, this patient with HES diagnosed postpartum remains at risk for the sequelae of hypereosinophilia, regardless of potential for AEC reduction during pregnancy. Therefore, treatment considerations need to be made with the safety of the maternal-fetal dyad as a priority.
Treatment
The treatment of symptomatic HES without acute life-threatening features or associated malignancy is generally determined by clinical variant.2-4 There is insufficient data to support initiation of treatment solely based on persistently elevated AEC. Patients with peripheral eosinophilia and hypereosinophilia should be monitored periodically with appropriate subspecialist evaluation for occult end-organ involvement, and targeted therapies should be deferred until an HES diagnosis.1-4 First-line therapy in most HES variants is systemic glucocorticoids.2,3,7 Since the disease course for this patient did not precisely match an HES variant, it was challenging to ascertain the optimal personalized treatment regimen. The approach to therapy was further complicated by newly identified pregnancy necessitating cessation of systemic glucocorticoids. In addition to glucocorticoids, hydroxyurea and interferon-α are among treatments historically used for HES, with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-5 becoming more common.1-4 Although this patient may ultimately benefit from an IL-5 targeting biologic medication such as mepolizumab, safety in pregnancy is not well-studied and may require close clinical monitoring with treatment deferred until after delivery if possible.3,7,8,11
Military service members with frequent geographic relocation have additional barriers to timely diagnosis with often-limited access to subspecialty care depending on the duty station. While the patient was able to receive care at a large military medical center with many subspecialists, prompt recognition and timely referral to specialists would be even more critical at a smaller treatment facility. Depending on the severity and variant of HES, patients may warrant evaluation and treatment by hematology/oncology, cardiology, pulmonology, and immunology. Although HES can present in young children and older adults, this condition is most often diagnosed during the third and fourth decades of life, putting clinicians on the front line of hypereosinophilia identification and evaluation.10 Military physicians have the additional duty to not only think ahead in their diverse clinical settings to ensure proper care for patients, but also maintain a broad differential inclusive of more rare disease processes such as HES.
CONCLUSIONS
This case emphasizes how uncontrolled or untreated HES can lead to significant end-organ damage involving multiple systems and high morbidity. Prompt recognition of hypereosinophilia with potential HES can help expedite coordination of multidisciplinary care across multiple specialties to minimize delays in diagnosis and treatment. Doing so may minimize associated morbidity and mortality, especially in individuals located at more remote duty stations or deployed to austere environments.
- Cogan E, Roufosse F. Clinical management of the hypereosinophilic syndromes. Expert Rev Hematol. 2012;5:275-290. doi: 10.1586/ehm.12.14
- Klion A. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: approach to treatment in the era of precision medicine. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2018;2018:326-331. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2018.1.326
- Shomali W, Gotlib J. World health organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2022;97:129-148. doi:10.1002/ajh.26352
- Helbig G, Klion AD. Hypereosinophilic syndromes - an enigmatic group of disorders with an intriguing clinical spectrum and challenging treatment. Blood Rev. 2021;49:100809. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2021.100809
- Valent P, Klion AD, Horny HP, et al. Contemporary consensus proposal on criteria and classification of eosinophilic disorders and related syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:607-612.e9. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.02.019
- Roufosse FE, Goldman M, Cogan E. Hypereosinophilic syndromes. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:37. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-37
- Pitlick MM, Li JT, Pongdee T. Current and emerging biologic therapies targeting eosinophilic disorders. World Allergy Organ J. 2022;15:100676. doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2022.10067
- Ault P, Cortes J, Lynn A, Keating M, Verstovsek S. Pregnancy in a patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2009;33:186-187. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2008.05.013
- Rioux JD, Stone VA, Daly MJ, et al. Familial eosinophilia maps to the cytokine gene cluster on human chromosomal region 5q31-q33. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63:1086-1094. doi:10.1086/302053
- Williams KW, Ware J, Abiodun A, et al. Hypereosinophilia in children and adults: a retrospective comparison. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016;4:941-947.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2016.03.020
- Pane F, Lefevre G, Kwon N, et al. Characterization of disease flares and impact of mepolizumab in patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Front Immunol. 2022;13:935996. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.935996
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is defined by marked, persistent absolute eosinophil count (AEC) > 1500 cells/μL on ≥ 2 peripheral smears separated by ≥ 1 month with evidence of accompanied end-organ damage, in the absence of other causes of eosinophilia such as malignancy, atopy, or parasitic infections.1-5 Hypereosinophilic infiltration can impact almost every organ system; however, the most profound complications in patients with HES are related to leukemias and cardiac manifestations of the disease.3,4 Although rare, the associated morbidity and mortality of HES are considerable, making prompt recognition and treatment essential. Management involves targeted therapy based on pathologic classification of HES and on decreasing associated inflammation, fibrosis, and end-organ damage.3,5-7
The patient in this case report met the diagnostic criteria for HES. However, this patient had several clinical and laboratory features that made it difficult to characterize a specific HES variant. Moreover, she had additional immunomodulating factors in the setting of pregnancy. This is the first documented case of HES of undetermined etiology diagnosed postpartum and managed in the setting of a new pregnancy.2,8
CASE PRESENTATION
A 32-year-old female active-duty military service member with allergic rhinitis and a history of childhood eczema was referred to allergy/immunology for evaluation of a new, progressive pruritic rash. Symptoms started 3 months after the birth of her first child, with a new diffuse erythematous skin rash sparing her palms, soles, and mucosal surfaces. Given her history of atopy, the rash was initially treated as severe atopic dermatitis with appropriate topical medications. The rash gradually worsened, with the development of intermittent facial swelling, night sweats, dyspnea, recurrent epigastric abdominal pain, and nausea with vomiting, resulting in decreased oral intake and weight loss.
The patient was hospitalized and received an expedited multidisciplinary evaluation by dermatology, hematology/oncology, and gastroenterology. Her AEC of 4787 cells/μL peaked on admission and was markedly elevated from the 1070 cells/μL reported in the third trimester of her pregnancy. She was found to have mature eosinophilia on skin biopsy (Figure 1), endoscopic duodenal biopsy (Figure 2), peripheral blood smear (Figure 3), and bone marrow biopsy (Figure 4).




Radiographic imaging of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed hepatomegaly without detectable neoplasm. There was no clinical evidence of cardiac involvement, and evaluation with electrocardiography and echocardiography did not indicate myocarditis. Extensive laboratory testing revealed no genetic mutations indicative of familial, myeloproliferative, or lymphocytic variants of HES.
The patient received topical emollients, omeprazole 40 mg daily, and ondansetron 8 mg 3 times daily as needed for symptom management, and was started on oral prednisone 40 mg daily with improvement in dyspnea, night sweats, and gastrointestinal complaints. During the patient's 6-day hospitalization and treatment, her AECs gradually decreased to 2110 cells/μL, and decreased to 1600 cells/μL over the course of a month, remaining in the hypereosinophilic range. The patient was discovered to be pregnant while symptoms were improving, resulting in stepwise discontinuation of oral steroids, but she reported continued improvement in symptoms.
DISCUSSION
Peripheral eosinophilia has a broad differential diagnoses, including HES, parasitic infections, atopic hypersensitivity diseases, eosinophilic lung diseases, eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases, vasculitides such as eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, genetic syndromes predisposing to eosinophilia, episodic angioedema with eosinophilia, and chronic metabolic disease with adrenal insufficiency.1-5 HES, although rare, is a disease process with potentially devastating associated morbidity and mortality if not promptly recognized and treated. HES is further delineated by hypereosinophilia with associated eosinophil-mediated organ damage or dysfunction.3-5
Clinical manifestations of HES can differ greatly depending on the HES variant and degree of organ involvement at the time of diagnosis and throughout the disease course. Patients with HES, as well as those with asymptomatic eosinophilia or hypereosinophilia, should be closely monitored for disease progression. In addition to trending peripheral AECs, clinicians should screen for symptoms of organ involvement and perform targeted evaluation of the suspected organs to promptly identify early signs of organ involvement and initiate treatment.1-4 Recommendations regarding screening intervals vary widely from monthly to annually, depending on a patient’s specific clinical picture.
HES has been subdivided into clinically relevant variants, including myeloproliferative (M-HES), T lymphocytic (L-HES), organ-restricted (or overlap) HES, familial HES, idiopathic HES, and specific syndromes with associated hypereosinophilia.3-5,9 Patients with M-HES have elevated circulating leukocyte precursors and clinical manifestations, including but not limited to hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The most commonly associated genetic mutations include the FIP1L1-PDGFR-α fusion, BCR-ABL1, PDGFRA/B, JAK2, KIT, and FGFR1.3-6 L-HES usually has predominant skin and soft tissue involvement secondary to immunoglobulin E-mediated actions with clonal expansion of T cells (most commonly CD3-4+ or CD3+CD4-CD8-).3,5,6 Familial HES, a rare variant, follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern and is usually present at birth. It involves chromosome 5, which contains genes coding for cytokines that drive eosinophilic proliferation, including interleukin (IL)-3, IL-5, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.5,9 Hypereosinophilia in the setting of end-organ damage restricted to a single organ is considered organ-restricted HES. There can be significant hepatic and gastrointestinal dysfunction, with or without malabsorption.
HES can also manifest with hematologic malignancy, restrictive obliterative cardiomyopathies, renal injury manifested by hematuria and electrolyte derangements, and neurologic complications including hemiparesis, dysarthria, and even coma.6 Endothelial damage due to eosinophil-driven inflammation can result in thrombus formation and increased risk of thromboembolic events in various organs.3 Idiopathic HES, otherwise known as HES of unknown etiology or significance, is a diagnosis of exclusion and constitutes a cohort of patients who do not fit into the other delineated categories.3-5 These patients often have multisystem involvement, making classification and treatment a challenge.5
The patient described in this case met the diagnostic criteria for HES, but her complicated clinical and laboratory features were challenging to characterize into a specific variant of HES. Organ-restricted HES was ruled out due to skin, marrow, and duodenal infiltration. She also had the potential for lung involvement based on her clinical symptoms, however no biopsy was obtained. Laboratory testing revealed no deletions or mutations indicative of familial, myeloproliferative, or lymphocytic variants. Her multisystem involvement without an underlying associated syndrome suggests idiopathic HES or HES of undetermined significance.1-5
Most patients with HES are diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50 years.10 While HES has its peak incidence in the fourth decade of life, acute onset of new symptoms 3 months postpartum makes this an unusual presentation. In this unique case, it is important to highlight the role of the physiologic changes of pregnancy in inflammatory mediation. The physiologic changes that occur in pregnancy to ensure fetal tolerance can have profound implications for leukocyte count, AEC, and subsequent inflammatory responses. The phenomenon of inflammatory amelioration during pregnancy is well-documented, but there has only been 1 known published case report discussing decreasing HES symptoms during pregnancy with prepregnancy and postpartum hypereosinophilia.8 It is suggested that this amelioration is secondary to cortisol and progesterone shifts that occur in pregnancy. Physiologic increases in adrenocorticotropic hormone in pregnancy leads to subsequent secretion of endogenous steroids by the adrenal cortex. In turn, pregnancy can lead to leukocytosis and eosinopenia.8 Overall, pregnancy can have beneficial immunomodulating properties in the spectrum of hypereosinophilic syndromes. Even so, this patient with HES diagnosed postpartum remains at risk for the sequelae of hypereosinophilia, regardless of potential for AEC reduction during pregnancy. Therefore, treatment considerations need to be made with the safety of the maternal-fetal dyad as a priority.
Treatment
The treatment of symptomatic HES without acute life-threatening features or associated malignancy is generally determined by clinical variant.2-4 There is insufficient data to support initiation of treatment solely based on persistently elevated AEC. Patients with peripheral eosinophilia and hypereosinophilia should be monitored periodically with appropriate subspecialist evaluation for occult end-organ involvement, and targeted therapies should be deferred until an HES diagnosis.1-4 First-line therapy in most HES variants is systemic glucocorticoids.2,3,7 Since the disease course for this patient did not precisely match an HES variant, it was challenging to ascertain the optimal personalized treatment regimen. The approach to therapy was further complicated by newly identified pregnancy necessitating cessation of systemic glucocorticoids. In addition to glucocorticoids, hydroxyurea and interferon-α are among treatments historically used for HES, with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-5 becoming more common.1-4 Although this patient may ultimately benefit from an IL-5 targeting biologic medication such as mepolizumab, safety in pregnancy is not well-studied and may require close clinical monitoring with treatment deferred until after delivery if possible.3,7,8,11
Military service members with frequent geographic relocation have additional barriers to timely diagnosis with often-limited access to subspecialty care depending on the duty station. While the patient was able to receive care at a large military medical center with many subspecialists, prompt recognition and timely referral to specialists would be even more critical at a smaller treatment facility. Depending on the severity and variant of HES, patients may warrant evaluation and treatment by hematology/oncology, cardiology, pulmonology, and immunology. Although HES can present in young children and older adults, this condition is most often diagnosed during the third and fourth decades of life, putting clinicians on the front line of hypereosinophilia identification and evaluation.10 Military physicians have the additional duty to not only think ahead in their diverse clinical settings to ensure proper care for patients, but also maintain a broad differential inclusive of more rare disease processes such as HES.
CONCLUSIONS
This case emphasizes how uncontrolled or untreated HES can lead to significant end-organ damage involving multiple systems and high morbidity. Prompt recognition of hypereosinophilia with potential HES can help expedite coordination of multidisciplinary care across multiple specialties to minimize delays in diagnosis and treatment. Doing so may minimize associated morbidity and mortality, especially in individuals located at more remote duty stations or deployed to austere environments.
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is defined by marked, persistent absolute eosinophil count (AEC) > 1500 cells/μL on ≥ 2 peripheral smears separated by ≥ 1 month with evidence of accompanied end-organ damage, in the absence of other causes of eosinophilia such as malignancy, atopy, or parasitic infections.1-5 Hypereosinophilic infiltration can impact almost every organ system; however, the most profound complications in patients with HES are related to leukemias and cardiac manifestations of the disease.3,4 Although rare, the associated morbidity and mortality of HES are considerable, making prompt recognition and treatment essential. Management involves targeted therapy based on pathologic classification of HES and on decreasing associated inflammation, fibrosis, and end-organ damage.3,5-7
The patient in this case report met the diagnostic criteria for HES. However, this patient had several clinical and laboratory features that made it difficult to characterize a specific HES variant. Moreover, she had additional immunomodulating factors in the setting of pregnancy. This is the first documented case of HES of undetermined etiology diagnosed postpartum and managed in the setting of a new pregnancy.2,8
CASE PRESENTATION
A 32-year-old female active-duty military service member with allergic rhinitis and a history of childhood eczema was referred to allergy/immunology for evaluation of a new, progressive pruritic rash. Symptoms started 3 months after the birth of her first child, with a new diffuse erythematous skin rash sparing her palms, soles, and mucosal surfaces. Given her history of atopy, the rash was initially treated as severe atopic dermatitis with appropriate topical medications. The rash gradually worsened, with the development of intermittent facial swelling, night sweats, dyspnea, recurrent epigastric abdominal pain, and nausea with vomiting, resulting in decreased oral intake and weight loss.
The patient was hospitalized and received an expedited multidisciplinary evaluation by dermatology, hematology/oncology, and gastroenterology. Her AEC of 4787 cells/μL peaked on admission and was markedly elevated from the 1070 cells/μL reported in the third trimester of her pregnancy. She was found to have mature eosinophilia on skin biopsy (Figure 1), endoscopic duodenal biopsy (Figure 2), peripheral blood smear (Figure 3), and bone marrow biopsy (Figure 4).




Radiographic imaging of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis revealed hepatomegaly without detectable neoplasm. There was no clinical evidence of cardiac involvement, and evaluation with electrocardiography and echocardiography did not indicate myocarditis. Extensive laboratory testing revealed no genetic mutations indicative of familial, myeloproliferative, or lymphocytic variants of HES.
The patient received topical emollients, omeprazole 40 mg daily, and ondansetron 8 mg 3 times daily as needed for symptom management, and was started on oral prednisone 40 mg daily with improvement in dyspnea, night sweats, and gastrointestinal complaints. During the patient's 6-day hospitalization and treatment, her AECs gradually decreased to 2110 cells/μL, and decreased to 1600 cells/μL over the course of a month, remaining in the hypereosinophilic range. The patient was discovered to be pregnant while symptoms were improving, resulting in stepwise discontinuation of oral steroids, but she reported continued improvement in symptoms.
DISCUSSION
Peripheral eosinophilia has a broad differential diagnoses, including HES, parasitic infections, atopic hypersensitivity diseases, eosinophilic lung diseases, eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases, vasculitides such as eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, genetic syndromes predisposing to eosinophilia, episodic angioedema with eosinophilia, and chronic metabolic disease with adrenal insufficiency.1-5 HES, although rare, is a disease process with potentially devastating associated morbidity and mortality if not promptly recognized and treated. HES is further delineated by hypereosinophilia with associated eosinophil-mediated organ damage or dysfunction.3-5
Clinical manifestations of HES can differ greatly depending on the HES variant and degree of organ involvement at the time of diagnosis and throughout the disease course. Patients with HES, as well as those with asymptomatic eosinophilia or hypereosinophilia, should be closely monitored for disease progression. In addition to trending peripheral AECs, clinicians should screen for symptoms of organ involvement and perform targeted evaluation of the suspected organs to promptly identify early signs of organ involvement and initiate treatment.1-4 Recommendations regarding screening intervals vary widely from monthly to annually, depending on a patient’s specific clinical picture.
HES has been subdivided into clinically relevant variants, including myeloproliferative (M-HES), T lymphocytic (L-HES), organ-restricted (or overlap) HES, familial HES, idiopathic HES, and specific syndromes with associated hypereosinophilia.3-5,9 Patients with M-HES have elevated circulating leukocyte precursors and clinical manifestations, including but not limited to hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The most commonly associated genetic mutations include the FIP1L1-PDGFR-α fusion, BCR-ABL1, PDGFRA/B, JAK2, KIT, and FGFR1.3-6 L-HES usually has predominant skin and soft tissue involvement secondary to immunoglobulin E-mediated actions with clonal expansion of T cells (most commonly CD3-4+ or CD3+CD4-CD8-).3,5,6 Familial HES, a rare variant, follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern and is usually present at birth. It involves chromosome 5, which contains genes coding for cytokines that drive eosinophilic proliferation, including interleukin (IL)-3, IL-5, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor.5,9 Hypereosinophilia in the setting of end-organ damage restricted to a single organ is considered organ-restricted HES. There can be significant hepatic and gastrointestinal dysfunction, with or without malabsorption.
HES can also manifest with hematologic malignancy, restrictive obliterative cardiomyopathies, renal injury manifested by hematuria and electrolyte derangements, and neurologic complications including hemiparesis, dysarthria, and even coma.6 Endothelial damage due to eosinophil-driven inflammation can result in thrombus formation and increased risk of thromboembolic events in various organs.3 Idiopathic HES, otherwise known as HES of unknown etiology or significance, is a diagnosis of exclusion and constitutes a cohort of patients who do not fit into the other delineated categories.3-5 These patients often have multisystem involvement, making classification and treatment a challenge.5
The patient described in this case met the diagnostic criteria for HES, but her complicated clinical and laboratory features were challenging to characterize into a specific variant of HES. Organ-restricted HES was ruled out due to skin, marrow, and duodenal infiltration. She also had the potential for lung involvement based on her clinical symptoms, however no biopsy was obtained. Laboratory testing revealed no deletions or mutations indicative of familial, myeloproliferative, or lymphocytic variants. Her multisystem involvement without an underlying associated syndrome suggests idiopathic HES or HES of undetermined significance.1-5
Most patients with HES are diagnosed between the ages of 20 and 50 years.10 While HES has its peak incidence in the fourth decade of life, acute onset of new symptoms 3 months postpartum makes this an unusual presentation. In this unique case, it is important to highlight the role of the physiologic changes of pregnancy in inflammatory mediation. The physiologic changes that occur in pregnancy to ensure fetal tolerance can have profound implications for leukocyte count, AEC, and subsequent inflammatory responses. The phenomenon of inflammatory amelioration during pregnancy is well-documented, but there has only been 1 known published case report discussing decreasing HES symptoms during pregnancy with prepregnancy and postpartum hypereosinophilia.8 It is suggested that this amelioration is secondary to cortisol and progesterone shifts that occur in pregnancy. Physiologic increases in adrenocorticotropic hormone in pregnancy leads to subsequent secretion of endogenous steroids by the adrenal cortex. In turn, pregnancy can lead to leukocytosis and eosinopenia.8 Overall, pregnancy can have beneficial immunomodulating properties in the spectrum of hypereosinophilic syndromes. Even so, this patient with HES diagnosed postpartum remains at risk for the sequelae of hypereosinophilia, regardless of potential for AEC reduction during pregnancy. Therefore, treatment considerations need to be made with the safety of the maternal-fetal dyad as a priority.
Treatment
The treatment of symptomatic HES without acute life-threatening features or associated malignancy is generally determined by clinical variant.2-4 There is insufficient data to support initiation of treatment solely based on persistently elevated AEC. Patients with peripheral eosinophilia and hypereosinophilia should be monitored periodically with appropriate subspecialist evaluation for occult end-organ involvement, and targeted therapies should be deferred until an HES diagnosis.1-4 First-line therapy in most HES variants is systemic glucocorticoids.2,3,7 Since the disease course for this patient did not precisely match an HES variant, it was challenging to ascertain the optimal personalized treatment regimen. The approach to therapy was further complicated by newly identified pregnancy necessitating cessation of systemic glucocorticoids. In addition to glucocorticoids, hydroxyurea and interferon-α are among treatments historically used for HES, with tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting IL-5 becoming more common.1-4 Although this patient may ultimately benefit from an IL-5 targeting biologic medication such as mepolizumab, safety in pregnancy is not well-studied and may require close clinical monitoring with treatment deferred until after delivery if possible.3,7,8,11
Military service members with frequent geographic relocation have additional barriers to timely diagnosis with often-limited access to subspecialty care depending on the duty station. While the patient was able to receive care at a large military medical center with many subspecialists, prompt recognition and timely referral to specialists would be even more critical at a smaller treatment facility. Depending on the severity and variant of HES, patients may warrant evaluation and treatment by hematology/oncology, cardiology, pulmonology, and immunology. Although HES can present in young children and older adults, this condition is most often diagnosed during the third and fourth decades of life, putting clinicians on the front line of hypereosinophilia identification and evaluation.10 Military physicians have the additional duty to not only think ahead in their diverse clinical settings to ensure proper care for patients, but also maintain a broad differential inclusive of more rare disease processes such as HES.
CONCLUSIONS
This case emphasizes how uncontrolled or untreated HES can lead to significant end-organ damage involving multiple systems and high morbidity. Prompt recognition of hypereosinophilia with potential HES can help expedite coordination of multidisciplinary care across multiple specialties to minimize delays in diagnosis and treatment. Doing so may minimize associated morbidity and mortality, especially in individuals located at more remote duty stations or deployed to austere environments.
- Cogan E, Roufosse F. Clinical management of the hypereosinophilic syndromes. Expert Rev Hematol. 2012;5:275-290. doi: 10.1586/ehm.12.14
- Klion A. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: approach to treatment in the era of precision medicine. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2018;2018:326-331. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2018.1.326
- Shomali W, Gotlib J. World health organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2022;97:129-148. doi:10.1002/ajh.26352
- Helbig G, Klion AD. Hypereosinophilic syndromes - an enigmatic group of disorders with an intriguing clinical spectrum and challenging treatment. Blood Rev. 2021;49:100809. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2021.100809
- Valent P, Klion AD, Horny HP, et al. Contemporary consensus proposal on criteria and classification of eosinophilic disorders and related syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:607-612.e9. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.02.019
- Roufosse FE, Goldman M, Cogan E. Hypereosinophilic syndromes. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:37. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-37
- Pitlick MM, Li JT, Pongdee T. Current and emerging biologic therapies targeting eosinophilic disorders. World Allergy Organ J. 2022;15:100676. doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2022.10067
- Ault P, Cortes J, Lynn A, Keating M, Verstovsek S. Pregnancy in a patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2009;33:186-187. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2008.05.013
- Rioux JD, Stone VA, Daly MJ, et al. Familial eosinophilia maps to the cytokine gene cluster on human chromosomal region 5q31-q33. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63:1086-1094. doi:10.1086/302053
- Williams KW, Ware J, Abiodun A, et al. Hypereosinophilia in children and adults: a retrospective comparison. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016;4:941-947.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2016.03.020
- Pane F, Lefevre G, Kwon N, et al. Characterization of disease flares and impact of mepolizumab in patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Front Immunol. 2022;13:935996. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.935996
- Cogan E, Roufosse F. Clinical management of the hypereosinophilic syndromes. Expert Rev Hematol. 2012;5:275-290. doi: 10.1586/ehm.12.14
- Klion A. Hypereosinophilic syndrome: approach to treatment in the era of precision medicine. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2018;2018:326-331. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2018.1.326
- Shomali W, Gotlib J. World health organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol. 2022;97:129-148. doi:10.1002/ajh.26352
- Helbig G, Klion AD. Hypereosinophilic syndromes - an enigmatic group of disorders with an intriguing clinical spectrum and challenging treatment. Blood Rev. 2021;49:100809. doi:10.1016/j.blre.2021.100809
- Valent P, Klion AD, Horny HP, et al. Contemporary consensus proposal on criteria and classification of eosinophilic disorders and related syndromes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;130:607-612.e9. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2012.02.019
- Roufosse FE, Goldman M, Cogan E. Hypereosinophilic syndromes. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007;2:37. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-2-37
- Pitlick MM, Li JT, Pongdee T. Current and emerging biologic therapies targeting eosinophilic disorders. World Allergy Organ J. 2022;15:100676. doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2022.10067
- Ault P, Cortes J, Lynn A, Keating M, Verstovsek S. Pregnancy in a patient with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Leuk Res. 2009;33:186-187. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2008.05.013
- Rioux JD, Stone VA, Daly MJ, et al. Familial eosinophilia maps to the cytokine gene cluster on human chromosomal region 5q31-q33. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63:1086-1094. doi:10.1086/302053
- Williams KW, Ware J, Abiodun A, et al. Hypereosinophilia in children and adults: a retrospective comparison. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016;4:941-947.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2016.03.020
- Pane F, Lefevre G, Kwon N, et al. Characterization of disease flares and impact of mepolizumab in patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome. Front Immunol. 2022;13:935996. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.935996
Unique Presentation of Postpartum Hypereosinophilic Syndrome With Atypical Features and Therapeutic Challenges
Unique Presentation of Postpartum Hypereosinophilic Syndrome With Atypical Features and Therapeutic Challenges
Evaluation of Subcutaneous Contraception for Patient Self-Administration at North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System
Evaluation of Subcutaneous Contraception for Patient Self-Administration at North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System
Medroxyprogesterone acetate is an injectable medication indicated for contraception and management of endometriosis-associated pain in females of reproductive age.1 Medroxyprogesterone inhibits gonadotropin secretion, which prevents follicular maturation and ovulation. This leads to endometrial thinning and a contraceptive effect. Adverse drug reactions (ADRs), such as weight gain, menstrual bleeding irregularities, and bone loss appear to be dose- and time-related. Two formulations of medroxyprogesterone acetate are available: 150 mg depot medroxyprogesterone acetate intramuscular (DMPA-IM) and 104 mg DMPA subcutaneous (DMPA-SC).2 Originally, medroxyprogesterone acetate injections required administration by a health care worker. While the current labeling for DMPA-SC still indicates a requirement for administration by a health care worker, data show that the medication can be safe and effective when self-administered.3
Self-Administered Contraception
The 2019 World Health Organization (WHO) guideline on self-care interventions recommends making self-administered injectable contraception available to individuals of reproductive age.3 The WHO recommendation is based on evidence from the Depo Self-Administration Study, which included 401 patients randomized 1:1 to receive self-administered or clinic-administered DMPA-SC. This study concluded that self-administration improved continuation of contraception.4
The North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System (NFSGVHS) is the largest US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system, serving > 22,000 female veterans. All primary care practitioners (PCP) have been trained in women’s health (WH).
The WH patient-aligned care team (PACT) clinical pharmacy practitioner (CPP) proposed using DMPA-SC for outpatient self-administration to increase access, improve patient satisfaction, and reduce burden on patients and nurses for administration appointments. The Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee (P&T), WH Medical Director, and Chief of Gynecology approved the proposal. DMPA-SC was added to the ordering menu with order sets. The order set included instructions that outlined the 12-week dosing interval, instructions to contact the prescriber if the injection was > 2 weeks overdue (aligning with dosing recommendations for administration every 12 to 14 weeks), and an optional order for a home pregnancy test if necessary. These instructions were designed to ensure proper self-administration of the medication and timely follow-up care.
The gynecology and PACT health care practitioners (HCPs), including physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and medical assistants, received DMPA-SC education, which consisted of a review of medication, ADRs, contraindications, and administration. An NFSGVHS procedure was developed to ensure patients received self-administration education. DMPA-SC prescriptions were mailed to patients with scheduled nursing appointments. The patient would then bring DMPA-SC to the nursing appointment where they received administration instruction and completed the first injection under nurse supervision to ensure appropriate technique. Patients were offered supplementary educational documents and a calendar to keep track of injection days. The patients were responsible for ordering refills and administering subsequent injections at home. Once all stakeholders received education and order sets were in place, prescribers and nurses could begin offering the option for initiation of self-administered DMPA-SC to patients. All conversions or new prescriptions were initiated by prescribers as a part of usual care.
Medication Use Evaluation
A medication use evaluation was conducted about 1 year after the rollout to assess use, adherence, and impact of DMPA-SC for patient-self administration as a new contraceptive option for NFSGVHS patients.
A retrospective chart review was conducted for patients dispensed DMPA-SC from June 1, 2022, to July 1, 2023. Baseline body mass index (BMI), recorded prior to initiation of DMPA-SC, was compared with the most recent BMI on record at the completion of the study to evaluate weight change. Nursing visit attendance for the first injection was also assessed. Adherence was evaluated by reviewing the date of the initial DMPA-SC prescription, the date of the patient's first nursing visit, and subsequent refill patterns. A 2-week margin of error was established to account for the flexibility within the recommended dosing interval and delays in postal service delivery.
Forty patients were initiated on DMPA-SC for patient self-administration. The mean age of patients was 37.2 years. All 40 patients were female. Twenty-two patients (55%) identified as Black, 17 (43%) as White, and 1 (3%) as Asian. The majority (90%) of patients were non-Hispanic. The mean baseline BMI was 30 and BMI after DMPA-SC initiation was 30.4.
Twenty-eight (70%) patients had a nursing appointment, adhering to the NFSGVHS protocol. Five patients (13%) discontinued use and switched to DMPA-IM administered by an HCP and 4 (10%) discontinued use following an ADR (hives, mood changes, bruising, and menometrorrhagia). Of the 31 patients who continued therapy, 25 (81%) were refilling appropriately (Table).

Six patients with unidentified reasons for nonadherence were contacted to determine if there were unmet contraceptive needs. This subgroup included patients with an active prescription for DMPA-SC that did not meet refill expectations. Nonadherence was mostly due to forgetfulness, however 1 patient was unable to refill her DMPA-SC in a timely manner due to an outside hospital admission and another was unreachable. These conversations were documented in the electronic health record (EHR) and all patients requesting follow-up, reinitiation of therapy, or alternative regimens, the appropriate parties were notified to coordinate care.
Discussion
The uptake in DMPA-SC prescribing suggests prescribers and patients have embraced self-administration as an option for contraception. Most patients were appropriately scheduled for nursing appointments to reinforce education and ensure appropriate self-injection technique, as outlined in the NFSGVHS procedure.
The need to improve adherence to NFSGVHS procedure was identified because not all patients had scheduled nursing appointments. This is concerning because some patients may have started self-injecting DMPA-SC without proper education, which could lead to improper injection technique and diminished effectiveness. Nursing appointments ensure appropriate self-injection techniques and reinforce the importance of refilling every 12 weeks for proper effectiveness. Nonadherence to contraceptive therapy may result in unintended pregnancy, although no pregnancies were reported by patients in this study. Pharmacist involvement in DMPA-SC initiation and follow-up monitoring may help ensure adherence to local procedure for initiation and improve patient adherence.
There is limited evidence comparing weight gain related to DMPA-SC vs DMPA-IM. However, in a small, 2-year, randomized study, weight changes were considered comparable for both cohorts with a mean increase of 3.5 kg in the DMPA-IM group vs 3.4 kg in the DMPA-SC group.5 While our analysis did not formally evaluate weight changes, BMI data were collected to evaluate for evidence of weight change. The duration of therapy varied per patient and may not have been long enough to see comparable weight changes.
Strengths of this project include the use of the PACT multidisciplinary approach in primary care including physicians, pharmacists, and nurses. The NFSGVHS EHR is comprehensive, and data including appointments and pharmacy refill information was readily available for collection and evaluation. Limitations included inconsistent documentation in the patient’s EHR which made collection of some data difficult.
Cost Estimates
NFSGVHS had 231 patients prescribed DMPA-IM at the time of DMPA-SC rollout and 40 patients initiated DMPA-SC therapy in the first year. There are possible cost savings associated with the use of DMPA-SC compared to DMPA-IM. Although DMPA-IM costs about $120 annually and DMPA-SC costs about $252 annually, this does not account for indirect costs such as supplies, overhead cost, nursing visits, and patient travel.6 Additionally, allowing patients to self-administer the DMPA-SC injection at home provides nurses time to care for other patients.
Moving forward, the PACT and gynecology teams will receive instruction on the importance of adhering to NFSGVHS procedures to ensure new patients prescribed DMPA-SC receive education and present for nursing appointments to ensure appropriate self-injection.
DMPA has historically been administered in the clinic setting by an HCP; therefore, the prescriber was available to assess adherence to therapy based on patient’s attendance to scheduled clinic appointments. Some prescribers may feel apprehensive about shifting the onus of medication adherence to the patient when prescribing DMPA-SC. However, this model is comparable to any other prescription form of birth control, such as combined hormonal contraceptive pills, where the prescriber expects the patient to take the medication as prescribed and refill their prescriptions in a timely manner to avoid gaps in therapy. The findings of this project suggest the majority of patients who were prescribed self-administered DMPA-SC for contraception were adherent to therapy. The utility of self-administration of DMPA-SC for other labeled or off-label indications was not evaluated; however, it is possible that patients who are motivated to self-administer the medication (regardless of indication) would also demonstrate similar adherence rates.
Conclusions
The majority of patients who started DMPA-SC tolerated the medication well and continued to refill therapy within the recommended time period. Patient self-administration of DMPA-SC can enhance access by removing barriers to administration, increase patient autonomy and contraceptive continuation rates. Overall, the increase in DMPA-SC prescriptions suggests that patients and HCPs support the option for DMPA-SC self-administration at NFSGVHS.
- Depo-SubQ Provera. Package insert. Pharmacia & Upjohn Co; 2019.
- Kaunitz AM. Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate. UpToDate. Updated June 12, 2025. Accessed July 11, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/depot-medroxyprogesterone-acetate-dmpa-formulations-patient-selection-and-drug-administration
- World Health Organization. WHO guideline on self-care interventions for health and well-being, 2022 revision. World Health Organization. 2022. Accessed July 17, 2025. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/357828/9789240052192-eng.pdf
- Kohn JE, Simons HR, Della Badia L, et al. Increased 1-year continuation of DMPA among women randomized to self-administration: results from a randomized controlled trial at Planned Parenthood. Contraception. 2018;97(3):198-204. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2017.11.009
- Kaunitz AM, Darney PD, Ross D, Wolter KD, Speroff L. Subcutaneous DMPA vs. intramuscular DMPA: a 2-year randomized study of contraceptive efficacy and bone mineral density. Contraception. 2009;80(1):7-17. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2009.02.005
- UpToDate, Lexidrug. Medroxyprogesterone acetate. Accessed July 16, 2025. https://online.lexi.com
Medroxyprogesterone acetate is an injectable medication indicated for contraception and management of endometriosis-associated pain in females of reproductive age.1 Medroxyprogesterone inhibits gonadotropin secretion, which prevents follicular maturation and ovulation. This leads to endometrial thinning and a contraceptive effect. Adverse drug reactions (ADRs), such as weight gain, menstrual bleeding irregularities, and bone loss appear to be dose- and time-related. Two formulations of medroxyprogesterone acetate are available: 150 mg depot medroxyprogesterone acetate intramuscular (DMPA-IM) and 104 mg DMPA subcutaneous (DMPA-SC).2 Originally, medroxyprogesterone acetate injections required administration by a health care worker. While the current labeling for DMPA-SC still indicates a requirement for administration by a health care worker, data show that the medication can be safe and effective when self-administered.3
Self-Administered Contraception
The 2019 World Health Organization (WHO) guideline on self-care interventions recommends making self-administered injectable contraception available to individuals of reproductive age.3 The WHO recommendation is based on evidence from the Depo Self-Administration Study, which included 401 patients randomized 1:1 to receive self-administered or clinic-administered DMPA-SC. This study concluded that self-administration improved continuation of contraception.4
The North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System (NFSGVHS) is the largest US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system, serving > 22,000 female veterans. All primary care practitioners (PCP) have been trained in women’s health (WH).
The WH patient-aligned care team (PACT) clinical pharmacy practitioner (CPP) proposed using DMPA-SC for outpatient self-administration to increase access, improve patient satisfaction, and reduce burden on patients and nurses for administration appointments. The Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee (P&T), WH Medical Director, and Chief of Gynecology approved the proposal. DMPA-SC was added to the ordering menu with order sets. The order set included instructions that outlined the 12-week dosing interval, instructions to contact the prescriber if the injection was > 2 weeks overdue (aligning with dosing recommendations for administration every 12 to 14 weeks), and an optional order for a home pregnancy test if necessary. These instructions were designed to ensure proper self-administration of the medication and timely follow-up care.
The gynecology and PACT health care practitioners (HCPs), including physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and medical assistants, received DMPA-SC education, which consisted of a review of medication, ADRs, contraindications, and administration. An NFSGVHS procedure was developed to ensure patients received self-administration education. DMPA-SC prescriptions were mailed to patients with scheduled nursing appointments. The patient would then bring DMPA-SC to the nursing appointment where they received administration instruction and completed the first injection under nurse supervision to ensure appropriate technique. Patients were offered supplementary educational documents and a calendar to keep track of injection days. The patients were responsible for ordering refills and administering subsequent injections at home. Once all stakeholders received education and order sets were in place, prescribers and nurses could begin offering the option for initiation of self-administered DMPA-SC to patients. All conversions or new prescriptions were initiated by prescribers as a part of usual care.
Medication Use Evaluation
A medication use evaluation was conducted about 1 year after the rollout to assess use, adherence, and impact of DMPA-SC for patient-self administration as a new contraceptive option for NFSGVHS patients.
A retrospective chart review was conducted for patients dispensed DMPA-SC from June 1, 2022, to July 1, 2023. Baseline body mass index (BMI), recorded prior to initiation of DMPA-SC, was compared with the most recent BMI on record at the completion of the study to evaluate weight change. Nursing visit attendance for the first injection was also assessed. Adherence was evaluated by reviewing the date of the initial DMPA-SC prescription, the date of the patient's first nursing visit, and subsequent refill patterns. A 2-week margin of error was established to account for the flexibility within the recommended dosing interval and delays in postal service delivery.
Forty patients were initiated on DMPA-SC for patient self-administration. The mean age of patients was 37.2 years. All 40 patients were female. Twenty-two patients (55%) identified as Black, 17 (43%) as White, and 1 (3%) as Asian. The majority (90%) of patients were non-Hispanic. The mean baseline BMI was 30 and BMI after DMPA-SC initiation was 30.4.
Twenty-eight (70%) patients had a nursing appointment, adhering to the NFSGVHS protocol. Five patients (13%) discontinued use and switched to DMPA-IM administered by an HCP and 4 (10%) discontinued use following an ADR (hives, mood changes, bruising, and menometrorrhagia). Of the 31 patients who continued therapy, 25 (81%) were refilling appropriately (Table).

Six patients with unidentified reasons for nonadherence were contacted to determine if there were unmet contraceptive needs. This subgroup included patients with an active prescription for DMPA-SC that did not meet refill expectations. Nonadherence was mostly due to forgetfulness, however 1 patient was unable to refill her DMPA-SC in a timely manner due to an outside hospital admission and another was unreachable. These conversations were documented in the electronic health record (EHR) and all patients requesting follow-up, reinitiation of therapy, or alternative regimens, the appropriate parties were notified to coordinate care.
Discussion
The uptake in DMPA-SC prescribing suggests prescribers and patients have embraced self-administration as an option for contraception. Most patients were appropriately scheduled for nursing appointments to reinforce education and ensure appropriate self-injection technique, as outlined in the NFSGVHS procedure.
The need to improve adherence to NFSGVHS procedure was identified because not all patients had scheduled nursing appointments. This is concerning because some patients may have started self-injecting DMPA-SC without proper education, which could lead to improper injection technique and diminished effectiveness. Nursing appointments ensure appropriate self-injection techniques and reinforce the importance of refilling every 12 weeks for proper effectiveness. Nonadherence to contraceptive therapy may result in unintended pregnancy, although no pregnancies were reported by patients in this study. Pharmacist involvement in DMPA-SC initiation and follow-up monitoring may help ensure adherence to local procedure for initiation and improve patient adherence.
There is limited evidence comparing weight gain related to DMPA-SC vs DMPA-IM. However, in a small, 2-year, randomized study, weight changes were considered comparable for both cohorts with a mean increase of 3.5 kg in the DMPA-IM group vs 3.4 kg in the DMPA-SC group.5 While our analysis did not formally evaluate weight changes, BMI data were collected to evaluate for evidence of weight change. The duration of therapy varied per patient and may not have been long enough to see comparable weight changes.
Strengths of this project include the use of the PACT multidisciplinary approach in primary care including physicians, pharmacists, and nurses. The NFSGVHS EHR is comprehensive, and data including appointments and pharmacy refill information was readily available for collection and evaluation. Limitations included inconsistent documentation in the patient’s EHR which made collection of some data difficult.
Cost Estimates
NFSGVHS had 231 patients prescribed DMPA-IM at the time of DMPA-SC rollout and 40 patients initiated DMPA-SC therapy in the first year. There are possible cost savings associated with the use of DMPA-SC compared to DMPA-IM. Although DMPA-IM costs about $120 annually and DMPA-SC costs about $252 annually, this does not account for indirect costs such as supplies, overhead cost, nursing visits, and patient travel.6 Additionally, allowing patients to self-administer the DMPA-SC injection at home provides nurses time to care for other patients.
Moving forward, the PACT and gynecology teams will receive instruction on the importance of adhering to NFSGVHS procedures to ensure new patients prescribed DMPA-SC receive education and present for nursing appointments to ensure appropriate self-injection.
DMPA has historically been administered in the clinic setting by an HCP; therefore, the prescriber was available to assess adherence to therapy based on patient’s attendance to scheduled clinic appointments. Some prescribers may feel apprehensive about shifting the onus of medication adherence to the patient when prescribing DMPA-SC. However, this model is comparable to any other prescription form of birth control, such as combined hormonal contraceptive pills, where the prescriber expects the patient to take the medication as prescribed and refill their prescriptions in a timely manner to avoid gaps in therapy. The findings of this project suggest the majority of patients who were prescribed self-administered DMPA-SC for contraception were adherent to therapy. The utility of self-administration of DMPA-SC for other labeled or off-label indications was not evaluated; however, it is possible that patients who are motivated to self-administer the medication (regardless of indication) would also demonstrate similar adherence rates.
Conclusions
The majority of patients who started DMPA-SC tolerated the medication well and continued to refill therapy within the recommended time period. Patient self-administration of DMPA-SC can enhance access by removing barriers to administration, increase patient autonomy and contraceptive continuation rates. Overall, the increase in DMPA-SC prescriptions suggests that patients and HCPs support the option for DMPA-SC self-administration at NFSGVHS.
Medroxyprogesterone acetate is an injectable medication indicated for contraception and management of endometriosis-associated pain in females of reproductive age.1 Medroxyprogesterone inhibits gonadotropin secretion, which prevents follicular maturation and ovulation. This leads to endometrial thinning and a contraceptive effect. Adverse drug reactions (ADRs), such as weight gain, menstrual bleeding irregularities, and bone loss appear to be dose- and time-related. Two formulations of medroxyprogesterone acetate are available: 150 mg depot medroxyprogesterone acetate intramuscular (DMPA-IM) and 104 mg DMPA subcutaneous (DMPA-SC).2 Originally, medroxyprogesterone acetate injections required administration by a health care worker. While the current labeling for DMPA-SC still indicates a requirement for administration by a health care worker, data show that the medication can be safe and effective when self-administered.3
Self-Administered Contraception
The 2019 World Health Organization (WHO) guideline on self-care interventions recommends making self-administered injectable contraception available to individuals of reproductive age.3 The WHO recommendation is based on evidence from the Depo Self-Administration Study, which included 401 patients randomized 1:1 to receive self-administered or clinic-administered DMPA-SC. This study concluded that self-administration improved continuation of contraception.4
The North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System (NFSGVHS) is the largest US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) health care system, serving > 22,000 female veterans. All primary care practitioners (PCP) have been trained in women’s health (WH).
The WH patient-aligned care team (PACT) clinical pharmacy practitioner (CPP) proposed using DMPA-SC for outpatient self-administration to increase access, improve patient satisfaction, and reduce burden on patients and nurses for administration appointments. The Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee (P&T), WH Medical Director, and Chief of Gynecology approved the proposal. DMPA-SC was added to the ordering menu with order sets. The order set included instructions that outlined the 12-week dosing interval, instructions to contact the prescriber if the injection was > 2 weeks overdue (aligning with dosing recommendations for administration every 12 to 14 weeks), and an optional order for a home pregnancy test if necessary. These instructions were designed to ensure proper self-administration of the medication and timely follow-up care.
The gynecology and PACT health care practitioners (HCPs), including physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and medical assistants, received DMPA-SC education, which consisted of a review of medication, ADRs, contraindications, and administration. An NFSGVHS procedure was developed to ensure patients received self-administration education. DMPA-SC prescriptions were mailed to patients with scheduled nursing appointments. The patient would then bring DMPA-SC to the nursing appointment where they received administration instruction and completed the first injection under nurse supervision to ensure appropriate technique. Patients were offered supplementary educational documents and a calendar to keep track of injection days. The patients were responsible for ordering refills and administering subsequent injections at home. Once all stakeholders received education and order sets were in place, prescribers and nurses could begin offering the option for initiation of self-administered DMPA-SC to patients. All conversions or new prescriptions were initiated by prescribers as a part of usual care.
Medication Use Evaluation
A medication use evaluation was conducted about 1 year after the rollout to assess use, adherence, and impact of DMPA-SC for patient-self administration as a new contraceptive option for NFSGVHS patients.
A retrospective chart review was conducted for patients dispensed DMPA-SC from June 1, 2022, to July 1, 2023. Baseline body mass index (BMI), recorded prior to initiation of DMPA-SC, was compared with the most recent BMI on record at the completion of the study to evaluate weight change. Nursing visit attendance for the first injection was also assessed. Adherence was evaluated by reviewing the date of the initial DMPA-SC prescription, the date of the patient's first nursing visit, and subsequent refill patterns. A 2-week margin of error was established to account for the flexibility within the recommended dosing interval and delays in postal service delivery.
Forty patients were initiated on DMPA-SC for patient self-administration. The mean age of patients was 37.2 years. All 40 patients were female. Twenty-two patients (55%) identified as Black, 17 (43%) as White, and 1 (3%) as Asian. The majority (90%) of patients were non-Hispanic. The mean baseline BMI was 30 and BMI after DMPA-SC initiation was 30.4.
Twenty-eight (70%) patients had a nursing appointment, adhering to the NFSGVHS protocol. Five patients (13%) discontinued use and switched to DMPA-IM administered by an HCP and 4 (10%) discontinued use following an ADR (hives, mood changes, bruising, and menometrorrhagia). Of the 31 patients who continued therapy, 25 (81%) were refilling appropriately (Table).

Six patients with unidentified reasons for nonadherence were contacted to determine if there were unmet contraceptive needs. This subgroup included patients with an active prescription for DMPA-SC that did not meet refill expectations. Nonadherence was mostly due to forgetfulness, however 1 patient was unable to refill her DMPA-SC in a timely manner due to an outside hospital admission and another was unreachable. These conversations were documented in the electronic health record (EHR) and all patients requesting follow-up, reinitiation of therapy, or alternative regimens, the appropriate parties were notified to coordinate care.
Discussion
The uptake in DMPA-SC prescribing suggests prescribers and patients have embraced self-administration as an option for contraception. Most patients were appropriately scheduled for nursing appointments to reinforce education and ensure appropriate self-injection technique, as outlined in the NFSGVHS procedure.
The need to improve adherence to NFSGVHS procedure was identified because not all patients had scheduled nursing appointments. This is concerning because some patients may have started self-injecting DMPA-SC without proper education, which could lead to improper injection technique and diminished effectiveness. Nursing appointments ensure appropriate self-injection techniques and reinforce the importance of refilling every 12 weeks for proper effectiveness. Nonadherence to contraceptive therapy may result in unintended pregnancy, although no pregnancies were reported by patients in this study. Pharmacist involvement in DMPA-SC initiation and follow-up monitoring may help ensure adherence to local procedure for initiation and improve patient adherence.
There is limited evidence comparing weight gain related to DMPA-SC vs DMPA-IM. However, in a small, 2-year, randomized study, weight changes were considered comparable for both cohorts with a mean increase of 3.5 kg in the DMPA-IM group vs 3.4 kg in the DMPA-SC group.5 While our analysis did not formally evaluate weight changes, BMI data were collected to evaluate for evidence of weight change. The duration of therapy varied per patient and may not have been long enough to see comparable weight changes.
Strengths of this project include the use of the PACT multidisciplinary approach in primary care including physicians, pharmacists, and nurses. The NFSGVHS EHR is comprehensive, and data including appointments and pharmacy refill information was readily available for collection and evaluation. Limitations included inconsistent documentation in the patient’s EHR which made collection of some data difficult.
Cost Estimates
NFSGVHS had 231 patients prescribed DMPA-IM at the time of DMPA-SC rollout and 40 patients initiated DMPA-SC therapy in the first year. There are possible cost savings associated with the use of DMPA-SC compared to DMPA-IM. Although DMPA-IM costs about $120 annually and DMPA-SC costs about $252 annually, this does not account for indirect costs such as supplies, overhead cost, nursing visits, and patient travel.6 Additionally, allowing patients to self-administer the DMPA-SC injection at home provides nurses time to care for other patients.
Moving forward, the PACT and gynecology teams will receive instruction on the importance of adhering to NFSGVHS procedures to ensure new patients prescribed DMPA-SC receive education and present for nursing appointments to ensure appropriate self-injection.
DMPA has historically been administered in the clinic setting by an HCP; therefore, the prescriber was available to assess adherence to therapy based on patient’s attendance to scheduled clinic appointments. Some prescribers may feel apprehensive about shifting the onus of medication adherence to the patient when prescribing DMPA-SC. However, this model is comparable to any other prescription form of birth control, such as combined hormonal contraceptive pills, where the prescriber expects the patient to take the medication as prescribed and refill their prescriptions in a timely manner to avoid gaps in therapy. The findings of this project suggest the majority of patients who were prescribed self-administered DMPA-SC for contraception were adherent to therapy. The utility of self-administration of DMPA-SC for other labeled or off-label indications was not evaluated; however, it is possible that patients who are motivated to self-administer the medication (regardless of indication) would also demonstrate similar adherence rates.
Conclusions
The majority of patients who started DMPA-SC tolerated the medication well and continued to refill therapy within the recommended time period. Patient self-administration of DMPA-SC can enhance access by removing barriers to administration, increase patient autonomy and contraceptive continuation rates. Overall, the increase in DMPA-SC prescriptions suggests that patients and HCPs support the option for DMPA-SC self-administration at NFSGVHS.
- Depo-SubQ Provera. Package insert. Pharmacia & Upjohn Co; 2019.
- Kaunitz AM. Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate. UpToDate. Updated June 12, 2025. Accessed July 11, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/depot-medroxyprogesterone-acetate-dmpa-formulations-patient-selection-and-drug-administration
- World Health Organization. WHO guideline on self-care interventions for health and well-being, 2022 revision. World Health Organization. 2022. Accessed July 17, 2025. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/357828/9789240052192-eng.pdf
- Kohn JE, Simons HR, Della Badia L, et al. Increased 1-year continuation of DMPA among women randomized to self-administration: results from a randomized controlled trial at Planned Parenthood. Contraception. 2018;97(3):198-204. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2017.11.009
- Kaunitz AM, Darney PD, Ross D, Wolter KD, Speroff L. Subcutaneous DMPA vs. intramuscular DMPA: a 2-year randomized study of contraceptive efficacy and bone mineral density. Contraception. 2009;80(1):7-17. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2009.02.005
- UpToDate, Lexidrug. Medroxyprogesterone acetate. Accessed July 16, 2025. https://online.lexi.com
- Depo-SubQ Provera. Package insert. Pharmacia & Upjohn Co; 2019.
- Kaunitz AM. Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate. UpToDate. Updated June 12, 2025. Accessed July 11, 2025. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/depot-medroxyprogesterone-acetate-dmpa-formulations-patient-selection-and-drug-administration
- World Health Organization. WHO guideline on self-care interventions for health and well-being, 2022 revision. World Health Organization. 2022. Accessed July 17, 2025. https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/357828/9789240052192-eng.pdf
- Kohn JE, Simons HR, Della Badia L, et al. Increased 1-year continuation of DMPA among women randomized to self-administration: results from a randomized controlled trial at Planned Parenthood. Contraception. 2018;97(3):198-204. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2017.11.009
- Kaunitz AM, Darney PD, Ross D, Wolter KD, Speroff L. Subcutaneous DMPA vs. intramuscular DMPA: a 2-year randomized study of contraceptive efficacy and bone mineral density. Contraception. 2009;80(1):7-17. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2009.02.005
- UpToDate, Lexidrug. Medroxyprogesterone acetate. Accessed July 16, 2025. https://online.lexi.com
Evaluation of Subcutaneous Contraception for Patient Self-Administration at North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System
Evaluation of Subcutaneous Contraception for Patient Self-Administration at North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System