User login
‘Alarming’ increase in fake pills laced with fentanyl, methamphetamine, DEA warns
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has issued a public safety alert over an “alarming” increase in fake prescription pills laced with the synthetic opioid fentanyl or the stimulant methamphetamine.
“The United States is facing an unprecedented crisis of overdose deaths fueled by illegally manufactured fentanyl and methamphetamine,” DEA Administrator Anne Milgram said in the alert.
“Counterfeit pills that contain these dangerous and extremely addictive drugs are more lethal and more accessible than ever before. DEA is focusing resources on taking down the violent drug traffickers causing the greatest harm and posing the greatest threat to the safety and health of Americans,” Ms. Milgram said.
Criminal drug networks are mass-producing fake fentanyl- and methamphetamine-laced pills and deceptively marketing them as legitimate prescription pills, the DEA warns.
such as oxycodone (Oxycontin, Percocet), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and alprazolam (Xanax); or stimulants like amphetamines (Adderall).
The agency has seized fake pills in every U.S. state. More than 9.5 million fake pills have been seized so far this year – more than the last 2 years combined.
The number of seized counterfeit pills with fentanyl has jumped nearly 430% since 2019. DEA lab tests reveal that two out of every five pills with fentanyl contain a potentially lethal dose.
These deadly pills are widely accessible and often sold on social media and e-commerce platforms – making them available to anyone with a smartphone, including minors, the DEA warns.
More than 93,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States last year, according to federal statistics, and fentanyl is the primary driver of this alarming increase in overdose deaths, the DEA says.
The agency has launched a “One Pill Can Kill” public awareness campaign to educate the public of the dangers of counterfeit pills purchased outside of a licensed pharmacy. These pills are “illegal, dangerous, and potentially lethal,” the DEA warns.
This alert does not apply to legitimate pharmaceutical medications prescribed by doctors and dispensed by licensed pharmacists, the DEA says.
“The legitimate prescription supply chain is not impacted. Anyone filling a prescription at a licensed pharmacy can be confident that the medications they receive are safe when taken as directed by a medical professional,” the agency says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has issued a public safety alert over an “alarming” increase in fake prescription pills laced with the synthetic opioid fentanyl or the stimulant methamphetamine.
“The United States is facing an unprecedented crisis of overdose deaths fueled by illegally manufactured fentanyl and methamphetamine,” DEA Administrator Anne Milgram said in the alert.
“Counterfeit pills that contain these dangerous and extremely addictive drugs are more lethal and more accessible than ever before. DEA is focusing resources on taking down the violent drug traffickers causing the greatest harm and posing the greatest threat to the safety and health of Americans,” Ms. Milgram said.
Criminal drug networks are mass-producing fake fentanyl- and methamphetamine-laced pills and deceptively marketing them as legitimate prescription pills, the DEA warns.
such as oxycodone (Oxycontin, Percocet), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and alprazolam (Xanax); or stimulants like amphetamines (Adderall).
The agency has seized fake pills in every U.S. state. More than 9.5 million fake pills have been seized so far this year – more than the last 2 years combined.
The number of seized counterfeit pills with fentanyl has jumped nearly 430% since 2019. DEA lab tests reveal that two out of every five pills with fentanyl contain a potentially lethal dose.
These deadly pills are widely accessible and often sold on social media and e-commerce platforms – making them available to anyone with a smartphone, including minors, the DEA warns.
More than 93,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States last year, according to federal statistics, and fentanyl is the primary driver of this alarming increase in overdose deaths, the DEA says.
The agency has launched a “One Pill Can Kill” public awareness campaign to educate the public of the dangers of counterfeit pills purchased outside of a licensed pharmacy. These pills are “illegal, dangerous, and potentially lethal,” the DEA warns.
This alert does not apply to legitimate pharmaceutical medications prescribed by doctors and dispensed by licensed pharmacists, the DEA says.
“The legitimate prescription supply chain is not impacted. Anyone filling a prescription at a licensed pharmacy can be confident that the medications they receive are safe when taken as directed by a medical professional,” the agency says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration has issued a public safety alert over an “alarming” increase in fake prescription pills laced with the synthetic opioid fentanyl or the stimulant methamphetamine.
“The United States is facing an unprecedented crisis of overdose deaths fueled by illegally manufactured fentanyl and methamphetamine,” DEA Administrator Anne Milgram said in the alert.
“Counterfeit pills that contain these dangerous and extremely addictive drugs are more lethal and more accessible than ever before. DEA is focusing resources on taking down the violent drug traffickers causing the greatest harm and posing the greatest threat to the safety and health of Americans,” Ms. Milgram said.
Criminal drug networks are mass-producing fake fentanyl- and methamphetamine-laced pills and deceptively marketing them as legitimate prescription pills, the DEA warns.
such as oxycodone (Oxycontin, Percocet), hydrocodone (Vicodin), and alprazolam (Xanax); or stimulants like amphetamines (Adderall).
The agency has seized fake pills in every U.S. state. More than 9.5 million fake pills have been seized so far this year – more than the last 2 years combined.
The number of seized counterfeit pills with fentanyl has jumped nearly 430% since 2019. DEA lab tests reveal that two out of every five pills with fentanyl contain a potentially lethal dose.
These deadly pills are widely accessible and often sold on social media and e-commerce platforms – making them available to anyone with a smartphone, including minors, the DEA warns.
More than 93,000 people died of a drug overdose in the United States last year, according to federal statistics, and fentanyl is the primary driver of this alarming increase in overdose deaths, the DEA says.
The agency has launched a “One Pill Can Kill” public awareness campaign to educate the public of the dangers of counterfeit pills purchased outside of a licensed pharmacy. These pills are “illegal, dangerous, and potentially lethal,” the DEA warns.
This alert does not apply to legitimate pharmaceutical medications prescribed by doctors and dispensed by licensed pharmacists, the DEA says.
“The legitimate prescription supply chain is not impacted. Anyone filling a prescription at a licensed pharmacy can be confident that the medications they receive are safe when taken as directed by a medical professional,” the agency says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One in three children fall short of sleep recommendations
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
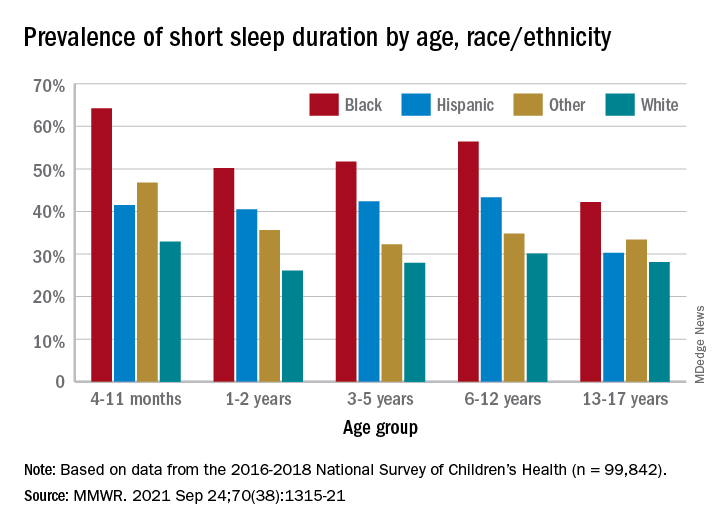
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
Just over one-third of children in the United States get less sleep than recommended, with higher rates occurring among several racial/ethnic and socioeconomic groups, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

, Anne G. Wheaton, PhD, and Angelika H. Claussen, PhD, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Unlike previous reports, this analysis showed that adolescents were less likely than infants to have short sleep duration, 31.2% vs. 40.3%. These latest data are based on the 2016-2018 editions of the National Survey of Children’s Health, and the “difference might be explained by NSCH’s reliance on parent report rather than self-report with Youth Risk Behavior Surveys,” they suggested.
Black children had the highest prevalence of any group included in the study, as parents reported that 50.8% of all ages were not getting the recommended amount of sleep, compared with 39.1% among Hispanics, 34.6% for other races, and 28.8% for Whites. The figure for Black infants was 64.2%, almost double the prevalence for White infants (32.9%), said Dr. Wheaton and Dr. Claussen of the CDC.
Short sleep duration also was more common in children from lower-income families and among those with less educated parents. Geography had an effect as well, with prevalence “highest in the Southeast, similar to geographic variation in adequate sleep observed for adults,” they noted.
Previous research has shown that “sleep disparity was associated with various social determinants of health (e.g., poverty, food insecurity, and perceived racism), which can increase chronic and acute stress and result in environmental and psychological factors that negatively affect sleep duration and can compound long-term health risks,” the investigators wrote.
Short sleep duration by age group was defined as less the following amounts: Twelve hours for infants (4-11 months), 11 hours for children aged 1-2 years, 10 hours for children aged 3-5 years, 9 hours for children aged 6-12, and 8 hours for adolescents (13-17 years), they explained. Responses for the survey’s sleep-duration question totaled 99,842 for the 3 years included.
FROM MMWR
Differences in Care by Race in Older Nursing Home Residents With Dementia
Study Overview
Objective. To examine differences in care, specifically hospitalization towards the end of life, among nursing home residents with dementia who were Black compared with those who were White.
Design. Population based cohort study in the US. The study included all decedents with Alzheimer’s disease or related dementia (ADRD) who resided in a nursing home from 2014 to 2017. Decedents from nursing homes were identified by death within 1 day of an identified nursing home stay or within 8 days of a hospital transfer from nursing home. Data were obtained from Minimum Data Set 3.0 (MDS) which contains clinical data from all Medicaid or Medicare certified nursing homes, and from the Medicare Beneficiary Summary File (MBSF) and Medicare Provider and Analysis and Review (MedPAR) which contains hospitalization events for all Medicare Beneficiaries. These files were linked to identify nursing home residents with ADRD who were hospitalized at the end of life. ADRD diagnosis was identified from the chronic condition list from the MBSF and from MDS diagnosis list.
Setting and participants. The study included 665 033 residents from 14 595 nursing homes who died during the study period. Resident race was categorized as White or Black based on the MBSF. Severe cognitive impairment was identified using the MDS that categorized residents as severe or not using the Brief Interview for Mental Status and the Cognitive Performance Scale. The mean (SD) age of the study population was 86.7 (9.2) years for White residents and 82.6 (11.1) years for Black residents. Of the participants, 68.8% and 61.2% were female for Black and White residents, respectively. Approximately 23.4% of White and 32.5% of Black residents had severe cognitive impairment. For nursing home characteristics, 71.5% of the 14 595 nursing homes represented were for profit; average bedside was 109.5 (57.0) and occupancy rate was on average 81.2% (14.3%).
Main outcome measures. The study outcome measure was any hospitalization within 30 days prior to death. The outcome was selected as an indicator of quality of care because as older adults living with ADRD experience progressive worsening of cognitive symptoms, at the end of life when dementia is severe, advance care planning and communication with health care proxies and surrogates often result in coordinated care that avoids acute hospitalizations, which are often burdensome to both patient and family and may yield poorer quality of life.
Main results. The study found that approximately 29.5% of White decedents and 40.7% of Black decedents were hospitalized towards the end of life. Nursing homes with a higher proportion of Black residents were more likely to have residents hospitalized towards the end of life with 35% of residents hospitalized in the highest quartile (27% Black) compared with 17% hospitalized for nursing homes in the lowest quartile (0% Black).After adjusting for covariates, Black residents were 7.9% more likely to be hospitalized in the last 30 days of life compared with White residents. Blacks with severe cognitive impairment has elevated risk of hospitalization by 4.9% when compared with White residents. After accounting for nursing home facility–level characteristics, nursing homes with a low proportion of Black residents had a 5.2% higher risk of hospitalizations compared with nursing homes with no Black residents, and nursing homes with a higher percentage of Black residents had a 13.3% higher risk of hospitalization compared with nursing homes with no Black residents.
Conclusion. Race is associated with care disparities in older nursing home residents with dementia. This study suggests that hospitalization towards the end of life as a quality of care marker differs across nursing homes, and nursing homes with a higher proportion of Black residents were more likely to be hospitalized. This suggests that these nursing homes may have fewer resources and delivered poorer quality of care, and that disparities in health systems or institutions contribute to differences in quality of care for this vulnerable group.
Commentary
Disparities of health status, health care, and affordability across race and ethnicity have persisted throughout the past 20 years.1 There is further evidence to support systemic differences that can contribute to differences in health outcomes.2 Although changes in health care policy such as the Affordable Care Act have expanded health care coverage, and instituted changes that aims to improve health care quality and reduce disparities, it is clear that factors contributing to disparities in care are structural and perhaps systemic. The latest evidence comes in this study that examines racial disparities in health care quality in one of the most vulnerable populations—older adults with Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The finding that Black nursing home residents, when compared with White residents, often has higher risk of hospitalization at the end of life, even among those with severe dementia where better coordinated care, clear goals of care and perhaps instituting palliative care would result in lower rate of hospitalization. The disparities were observed across nursing homes as well, where nursing homes with higher proportion of Black residents appear to have lower quality of care.
These findings are consistent with prior work that has examined differences in Black and White population on uptake of palliative care, discussion, and the documentation of advance care planning.3 Factors that may contribute to these differences include mistrust of the health care system among minorities, and not being connected to adequate health care resources. Family members and surrogate health care decision makers may consider receiving more aggressive care as advocating for better health care for their family members.4 These differences may contribute to the differences in hospitalization rates among residents within the same nursing home; however, the differences between nursing homes even after accounting for individual differences may indicate more widespread systemic differences that is associated with race. Policy changes that will address these differences are needed to level these differences so that quality care can be delivered regardless of race.5 For this vulnerable population with a terminal illness, approaches to enhance uptake of palliative approaches and care delivery for dementia patients at terminal stage are needed and understanding and targeting factors that contribute to low uptake of these approaches will enhance end of life care. Understanding the differences in resources and systems of care in nursing homes and perhaps how palliative care is integrated in these settings will be important to address care disparities that occurs across nursing homes.
Applications for Clinical Practice
Clinicians who take care of this population of older adults with advanced dementia should be aware of the potential for racial disparities that may lead to differences in the quality of care. The underlying reasons for these differences could be targeted so that older adults in all racial groups may have equal access to quality care including palliative approaches that avoid aggressive care for terminal illnesses across settings that may yield better care and quality of life. Policy makers and health systems leaders need to consider the current realities with racial disparities that policies need to address these differences so that they may not continue to persist in our systems of care.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Mahajan S, Caraballo C, Lu Y, et al. Trends in Differences in Health Status and Health Care Access and Affordability by Race and Ethnicity in the United States, 1999-2018. JAMA. 2021;326(7):637-648. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.9907
2. Gill TM, Zang EX, Murphy TE, et al. Association Between Neighborhood Disadvantage and Functional Well-being in Community-Living Older Persons. [published online ahead of print, 2021 Aug 23]. JAMA Intern Med. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.4260
3. Bazargan M, Bazargan-Hejazi S. Disparities in Palliative and Hospice Care and Completion of Advance Care Planning and Directives Among Non-Hispanic Blacks: A Scoping Review of Recent Literature. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(6):688-718. doi:10.1177/1049909120966585
4. Siler S, Arora K, Doyon K, Fischer SM. Spirituality and the Illness Experience: Perspectives of African American Older Adults. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(6):618-625. doi:10.1177/1049909120988280
5. Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs. Black-white disparities in health care. JAMA. 1990;263(17):2344-2346. doi:10.1001/jama.1990.03440170066038
Study Overview
Objective. To examine differences in care, specifically hospitalization towards the end of life, among nursing home residents with dementia who were Black compared with those who were White.
Design. Population based cohort study in the US. The study included all decedents with Alzheimer’s disease or related dementia (ADRD) who resided in a nursing home from 2014 to 2017. Decedents from nursing homes were identified by death within 1 day of an identified nursing home stay or within 8 days of a hospital transfer from nursing home. Data were obtained from Minimum Data Set 3.0 (MDS) which contains clinical data from all Medicaid or Medicare certified nursing homes, and from the Medicare Beneficiary Summary File (MBSF) and Medicare Provider and Analysis and Review (MedPAR) which contains hospitalization events for all Medicare Beneficiaries. These files were linked to identify nursing home residents with ADRD who were hospitalized at the end of life. ADRD diagnosis was identified from the chronic condition list from the MBSF and from MDS diagnosis list.
Setting and participants. The study included 665 033 residents from 14 595 nursing homes who died during the study period. Resident race was categorized as White or Black based on the MBSF. Severe cognitive impairment was identified using the MDS that categorized residents as severe or not using the Brief Interview for Mental Status and the Cognitive Performance Scale. The mean (SD) age of the study population was 86.7 (9.2) years for White residents and 82.6 (11.1) years for Black residents. Of the participants, 68.8% and 61.2% were female for Black and White residents, respectively. Approximately 23.4% of White and 32.5% of Black residents had severe cognitive impairment. For nursing home characteristics, 71.5% of the 14 595 nursing homes represented were for profit; average bedside was 109.5 (57.0) and occupancy rate was on average 81.2% (14.3%).
Main outcome measures. The study outcome measure was any hospitalization within 30 days prior to death. The outcome was selected as an indicator of quality of care because as older adults living with ADRD experience progressive worsening of cognitive symptoms, at the end of life when dementia is severe, advance care planning and communication with health care proxies and surrogates often result in coordinated care that avoids acute hospitalizations, which are often burdensome to both patient and family and may yield poorer quality of life.
Main results. The study found that approximately 29.5% of White decedents and 40.7% of Black decedents were hospitalized towards the end of life. Nursing homes with a higher proportion of Black residents were more likely to have residents hospitalized towards the end of life with 35% of residents hospitalized in the highest quartile (27% Black) compared with 17% hospitalized for nursing homes in the lowest quartile (0% Black).After adjusting for covariates, Black residents were 7.9% more likely to be hospitalized in the last 30 days of life compared with White residents. Blacks with severe cognitive impairment has elevated risk of hospitalization by 4.9% when compared with White residents. After accounting for nursing home facility–level characteristics, nursing homes with a low proportion of Black residents had a 5.2% higher risk of hospitalizations compared with nursing homes with no Black residents, and nursing homes with a higher percentage of Black residents had a 13.3% higher risk of hospitalization compared with nursing homes with no Black residents.
Conclusion. Race is associated with care disparities in older nursing home residents with dementia. This study suggests that hospitalization towards the end of life as a quality of care marker differs across nursing homes, and nursing homes with a higher proportion of Black residents were more likely to be hospitalized. This suggests that these nursing homes may have fewer resources and delivered poorer quality of care, and that disparities in health systems or institutions contribute to differences in quality of care for this vulnerable group.
Commentary
Disparities of health status, health care, and affordability across race and ethnicity have persisted throughout the past 20 years.1 There is further evidence to support systemic differences that can contribute to differences in health outcomes.2 Although changes in health care policy such as the Affordable Care Act have expanded health care coverage, and instituted changes that aims to improve health care quality and reduce disparities, it is clear that factors contributing to disparities in care are structural and perhaps systemic. The latest evidence comes in this study that examines racial disparities in health care quality in one of the most vulnerable populations—older adults with Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The finding that Black nursing home residents, when compared with White residents, often has higher risk of hospitalization at the end of life, even among those with severe dementia where better coordinated care, clear goals of care and perhaps instituting palliative care would result in lower rate of hospitalization. The disparities were observed across nursing homes as well, where nursing homes with higher proportion of Black residents appear to have lower quality of care.
These findings are consistent with prior work that has examined differences in Black and White population on uptake of palliative care, discussion, and the documentation of advance care planning.3 Factors that may contribute to these differences include mistrust of the health care system among minorities, and not being connected to adequate health care resources. Family members and surrogate health care decision makers may consider receiving more aggressive care as advocating for better health care for their family members.4 These differences may contribute to the differences in hospitalization rates among residents within the same nursing home; however, the differences between nursing homes even after accounting for individual differences may indicate more widespread systemic differences that is associated with race. Policy changes that will address these differences are needed to level these differences so that quality care can be delivered regardless of race.5 For this vulnerable population with a terminal illness, approaches to enhance uptake of palliative approaches and care delivery for dementia patients at terminal stage are needed and understanding and targeting factors that contribute to low uptake of these approaches will enhance end of life care. Understanding the differences in resources and systems of care in nursing homes and perhaps how palliative care is integrated in these settings will be important to address care disparities that occurs across nursing homes.
Applications for Clinical Practice
Clinicians who take care of this population of older adults with advanced dementia should be aware of the potential for racial disparities that may lead to differences in the quality of care. The underlying reasons for these differences could be targeted so that older adults in all racial groups may have equal access to quality care including palliative approaches that avoid aggressive care for terminal illnesses across settings that may yield better care and quality of life. Policy makers and health systems leaders need to consider the current realities with racial disparities that policies need to address these differences so that they may not continue to persist in our systems of care.
Financial disclosures: None.
Study Overview
Objective. To examine differences in care, specifically hospitalization towards the end of life, among nursing home residents with dementia who were Black compared with those who were White.
Design. Population based cohort study in the US. The study included all decedents with Alzheimer’s disease or related dementia (ADRD) who resided in a nursing home from 2014 to 2017. Decedents from nursing homes were identified by death within 1 day of an identified nursing home stay or within 8 days of a hospital transfer from nursing home. Data were obtained from Minimum Data Set 3.0 (MDS) which contains clinical data from all Medicaid or Medicare certified nursing homes, and from the Medicare Beneficiary Summary File (MBSF) and Medicare Provider and Analysis and Review (MedPAR) which contains hospitalization events for all Medicare Beneficiaries. These files were linked to identify nursing home residents with ADRD who were hospitalized at the end of life. ADRD diagnosis was identified from the chronic condition list from the MBSF and from MDS diagnosis list.
Setting and participants. The study included 665 033 residents from 14 595 nursing homes who died during the study period. Resident race was categorized as White or Black based on the MBSF. Severe cognitive impairment was identified using the MDS that categorized residents as severe or not using the Brief Interview for Mental Status and the Cognitive Performance Scale. The mean (SD) age of the study population was 86.7 (9.2) years for White residents and 82.6 (11.1) years for Black residents. Of the participants, 68.8% and 61.2% were female for Black and White residents, respectively. Approximately 23.4% of White and 32.5% of Black residents had severe cognitive impairment. For nursing home characteristics, 71.5% of the 14 595 nursing homes represented were for profit; average bedside was 109.5 (57.0) and occupancy rate was on average 81.2% (14.3%).
Main outcome measures. The study outcome measure was any hospitalization within 30 days prior to death. The outcome was selected as an indicator of quality of care because as older adults living with ADRD experience progressive worsening of cognitive symptoms, at the end of life when dementia is severe, advance care planning and communication with health care proxies and surrogates often result in coordinated care that avoids acute hospitalizations, which are often burdensome to both patient and family and may yield poorer quality of life.
Main results. The study found that approximately 29.5% of White decedents and 40.7% of Black decedents were hospitalized towards the end of life. Nursing homes with a higher proportion of Black residents were more likely to have residents hospitalized towards the end of life with 35% of residents hospitalized in the highest quartile (27% Black) compared with 17% hospitalized for nursing homes in the lowest quartile (0% Black).After adjusting for covariates, Black residents were 7.9% more likely to be hospitalized in the last 30 days of life compared with White residents. Blacks with severe cognitive impairment has elevated risk of hospitalization by 4.9% when compared with White residents. After accounting for nursing home facility–level characteristics, nursing homes with a low proportion of Black residents had a 5.2% higher risk of hospitalizations compared with nursing homes with no Black residents, and nursing homes with a higher percentage of Black residents had a 13.3% higher risk of hospitalization compared with nursing homes with no Black residents.
Conclusion. Race is associated with care disparities in older nursing home residents with dementia. This study suggests that hospitalization towards the end of life as a quality of care marker differs across nursing homes, and nursing homes with a higher proportion of Black residents were more likely to be hospitalized. This suggests that these nursing homes may have fewer resources and delivered poorer quality of care, and that disparities in health systems or institutions contribute to differences in quality of care for this vulnerable group.
Commentary
Disparities of health status, health care, and affordability across race and ethnicity have persisted throughout the past 20 years.1 There is further evidence to support systemic differences that can contribute to differences in health outcomes.2 Although changes in health care policy such as the Affordable Care Act have expanded health care coverage, and instituted changes that aims to improve health care quality and reduce disparities, it is clear that factors contributing to disparities in care are structural and perhaps systemic. The latest evidence comes in this study that examines racial disparities in health care quality in one of the most vulnerable populations—older adults with Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The finding that Black nursing home residents, when compared with White residents, often has higher risk of hospitalization at the end of life, even among those with severe dementia where better coordinated care, clear goals of care and perhaps instituting palliative care would result in lower rate of hospitalization. The disparities were observed across nursing homes as well, where nursing homes with higher proportion of Black residents appear to have lower quality of care.
These findings are consistent with prior work that has examined differences in Black and White population on uptake of palliative care, discussion, and the documentation of advance care planning.3 Factors that may contribute to these differences include mistrust of the health care system among minorities, and not being connected to adequate health care resources. Family members and surrogate health care decision makers may consider receiving more aggressive care as advocating for better health care for their family members.4 These differences may contribute to the differences in hospitalization rates among residents within the same nursing home; however, the differences between nursing homes even after accounting for individual differences may indicate more widespread systemic differences that is associated with race. Policy changes that will address these differences are needed to level these differences so that quality care can be delivered regardless of race.5 For this vulnerable population with a terminal illness, approaches to enhance uptake of palliative approaches and care delivery for dementia patients at terminal stage are needed and understanding and targeting factors that contribute to low uptake of these approaches will enhance end of life care. Understanding the differences in resources and systems of care in nursing homes and perhaps how palliative care is integrated in these settings will be important to address care disparities that occurs across nursing homes.
Applications for Clinical Practice
Clinicians who take care of this population of older adults with advanced dementia should be aware of the potential for racial disparities that may lead to differences in the quality of care. The underlying reasons for these differences could be targeted so that older adults in all racial groups may have equal access to quality care including palliative approaches that avoid aggressive care for terminal illnesses across settings that may yield better care and quality of life. Policy makers and health systems leaders need to consider the current realities with racial disparities that policies need to address these differences so that they may not continue to persist in our systems of care.
Financial disclosures: None.
1. Mahajan S, Caraballo C, Lu Y, et al. Trends in Differences in Health Status and Health Care Access and Affordability by Race and Ethnicity in the United States, 1999-2018. JAMA. 2021;326(7):637-648. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.9907
2. Gill TM, Zang EX, Murphy TE, et al. Association Between Neighborhood Disadvantage and Functional Well-being in Community-Living Older Persons. [published online ahead of print, 2021 Aug 23]. JAMA Intern Med. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.4260
3. Bazargan M, Bazargan-Hejazi S. Disparities in Palliative and Hospice Care and Completion of Advance Care Planning and Directives Among Non-Hispanic Blacks: A Scoping Review of Recent Literature. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(6):688-718. doi:10.1177/1049909120966585
4. Siler S, Arora K, Doyon K, Fischer SM. Spirituality and the Illness Experience: Perspectives of African American Older Adults. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(6):618-625. doi:10.1177/1049909120988280
5. Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs. Black-white disparities in health care. JAMA. 1990;263(17):2344-2346. doi:10.1001/jama.1990.03440170066038
1. Mahajan S, Caraballo C, Lu Y, et al. Trends in Differences in Health Status and Health Care Access and Affordability by Race and Ethnicity in the United States, 1999-2018. JAMA. 2021;326(7):637-648. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.9907
2. Gill TM, Zang EX, Murphy TE, et al. Association Between Neighborhood Disadvantage and Functional Well-being in Community-Living Older Persons. [published online ahead of print, 2021 Aug 23]. JAMA Intern Med. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.4260
3. Bazargan M, Bazargan-Hejazi S. Disparities in Palliative and Hospice Care and Completion of Advance Care Planning and Directives Among Non-Hispanic Blacks: A Scoping Review of Recent Literature. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(6):688-718. doi:10.1177/1049909120966585
4. Siler S, Arora K, Doyon K, Fischer SM. Spirituality and the Illness Experience: Perspectives of African American Older Adults. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(6):618-625. doi:10.1177/1049909120988280
5. Council on Ethical and Judicial Affairs. Black-white disparities in health care. JAMA. 1990;263(17):2344-2346. doi:10.1001/jama.1990.03440170066038
Dopamine and reward: The story of social media
How often do you find yourself on social media? The first thing I do when I wake up is check my email and text messages, as well as my Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram notifications.
Some 150,000 messages are shared on Facebook each minute; 293 million daily active users worldwide were recorded on Snapchat during the second quarter of 2021; 127.2 million monthly active users in the United States are projected to be on Instagram by 2023.
Social media has gained the hearts and wonder of many around the world. It’s absolutely incredible how ingrained it has become in our lives as a medium for creativity, outlet for communication, and platform for information. In fact, these online network tools have now become essential during COVID-19 to ensure productive workflow, keep in touch with our loved ones, and, overall, maintain social capital. Social media has truly emerged as a powerful form of living beyond our physical selves.
Yet, increased (and addictive) social media use is associated with negative health outcomes, especially among adolescents. For example, in a study reporting parent and adolescent accounts of social media use, it was reported that social media use was associated with hyperactivity/impulsivity, depression, anxiety, loneliness, and a fear of missing out. Furthermore, a meta-analysis investigating the relationship between social media use and depressive symptoms among adolescents found a small but significant and positive relationship between the two. However, additional research is required to elucidate this association.
Notwithstanding, the addictive nature of social media has previously been called out as analogous to the addictive nature of gambling. Let’s think about it. Whether you’re on Instagram, TikTok, or a similar platform, you can’t help but scroll from one video to the next. It’s one 5- to 10-second video after the next, and before you know it, you’ve spent the past hour going through random videos – but you can’t stop. Why is that so?
Social media actually “rewires” our brain such that we expect instant gratification. In other words, when we get a notification, message, like, or share, we expect fast and short-term pleasure/reward because the brain will produce a “hit of dopamine.” However, it is important to note that the reward system is not delimited to the dopaminergic pathway and, in fact, should be understood as a complex network system (i.e., governed by changes in brain morphology through addiction and excessive behavior). Given the quick pace of the social media world, the reward pathways in our brain change and there’s an increasing demand for attention, perpetuating an addictive mindset.
When we refresh our page, we expect instant gratification. But what happens when we don’t get a like, or a message, or some sort of “reward”? Recounts of social media use by adolescents have likened online attention to popularity. Accordingly, a lack of constant attention on social media has created a vicious cycle of anxiety, loneliness, and depression because of a failure to receive “virtual” reward. Taken together, social media may be harmful because it distorts our self-image, and while social media platforms help connect us, they can also ironically make us feel isolated, lower our self-confidence, and diminish our overall sense of well-being.
As the platforms for communication and information have evolved so rapidly over the past decade, there is a need to establish boundaries between what is beneficial and what is potentially detrimental to our mental health. While social media companies should play a role in mitigating addictive social network behavior, it would also seem counterintuitive to the general business model. In that case, who takes charge? This multifaceted problem requires a multidisciplinary approach.
Leanna M.W. Lui is an MSc candidate at the University of Toronto.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How often do you find yourself on social media? The first thing I do when I wake up is check my email and text messages, as well as my Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram notifications.
Some 150,000 messages are shared on Facebook each minute; 293 million daily active users worldwide were recorded on Snapchat during the second quarter of 2021; 127.2 million monthly active users in the United States are projected to be on Instagram by 2023.
Social media has gained the hearts and wonder of many around the world. It’s absolutely incredible how ingrained it has become in our lives as a medium for creativity, outlet for communication, and platform for information. In fact, these online network tools have now become essential during COVID-19 to ensure productive workflow, keep in touch with our loved ones, and, overall, maintain social capital. Social media has truly emerged as a powerful form of living beyond our physical selves.
Yet, increased (and addictive) social media use is associated with negative health outcomes, especially among adolescents. For example, in a study reporting parent and adolescent accounts of social media use, it was reported that social media use was associated with hyperactivity/impulsivity, depression, anxiety, loneliness, and a fear of missing out. Furthermore, a meta-analysis investigating the relationship between social media use and depressive symptoms among adolescents found a small but significant and positive relationship between the two. However, additional research is required to elucidate this association.
Notwithstanding, the addictive nature of social media has previously been called out as analogous to the addictive nature of gambling. Let’s think about it. Whether you’re on Instagram, TikTok, or a similar platform, you can’t help but scroll from one video to the next. It’s one 5- to 10-second video after the next, and before you know it, you’ve spent the past hour going through random videos – but you can’t stop. Why is that so?
Social media actually “rewires” our brain such that we expect instant gratification. In other words, when we get a notification, message, like, or share, we expect fast and short-term pleasure/reward because the brain will produce a “hit of dopamine.” However, it is important to note that the reward system is not delimited to the dopaminergic pathway and, in fact, should be understood as a complex network system (i.e., governed by changes in brain morphology through addiction and excessive behavior). Given the quick pace of the social media world, the reward pathways in our brain change and there’s an increasing demand for attention, perpetuating an addictive mindset.
When we refresh our page, we expect instant gratification. But what happens when we don’t get a like, or a message, or some sort of “reward”? Recounts of social media use by adolescents have likened online attention to popularity. Accordingly, a lack of constant attention on social media has created a vicious cycle of anxiety, loneliness, and depression because of a failure to receive “virtual” reward. Taken together, social media may be harmful because it distorts our self-image, and while social media platforms help connect us, they can also ironically make us feel isolated, lower our self-confidence, and diminish our overall sense of well-being.
As the platforms for communication and information have evolved so rapidly over the past decade, there is a need to establish boundaries between what is beneficial and what is potentially detrimental to our mental health. While social media companies should play a role in mitigating addictive social network behavior, it would also seem counterintuitive to the general business model. In that case, who takes charge? This multifaceted problem requires a multidisciplinary approach.
Leanna M.W. Lui is an MSc candidate at the University of Toronto.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How often do you find yourself on social media? The first thing I do when I wake up is check my email and text messages, as well as my Facebook, Snapchat, and Instagram notifications.
Some 150,000 messages are shared on Facebook each minute; 293 million daily active users worldwide were recorded on Snapchat during the second quarter of 2021; 127.2 million monthly active users in the United States are projected to be on Instagram by 2023.
Social media has gained the hearts and wonder of many around the world. It’s absolutely incredible how ingrained it has become in our lives as a medium for creativity, outlet for communication, and platform for information. In fact, these online network tools have now become essential during COVID-19 to ensure productive workflow, keep in touch with our loved ones, and, overall, maintain social capital. Social media has truly emerged as a powerful form of living beyond our physical selves.
Yet, increased (and addictive) social media use is associated with negative health outcomes, especially among adolescents. For example, in a study reporting parent and adolescent accounts of social media use, it was reported that social media use was associated with hyperactivity/impulsivity, depression, anxiety, loneliness, and a fear of missing out. Furthermore, a meta-analysis investigating the relationship between social media use and depressive symptoms among adolescents found a small but significant and positive relationship between the two. However, additional research is required to elucidate this association.
Notwithstanding, the addictive nature of social media has previously been called out as analogous to the addictive nature of gambling. Let’s think about it. Whether you’re on Instagram, TikTok, or a similar platform, you can’t help but scroll from one video to the next. It’s one 5- to 10-second video after the next, and before you know it, you’ve spent the past hour going through random videos – but you can’t stop. Why is that so?
Social media actually “rewires” our brain such that we expect instant gratification. In other words, when we get a notification, message, like, or share, we expect fast and short-term pleasure/reward because the brain will produce a “hit of dopamine.” However, it is important to note that the reward system is not delimited to the dopaminergic pathway and, in fact, should be understood as a complex network system (i.e., governed by changes in brain morphology through addiction and excessive behavior). Given the quick pace of the social media world, the reward pathways in our brain change and there’s an increasing demand for attention, perpetuating an addictive mindset.
When we refresh our page, we expect instant gratification. But what happens when we don’t get a like, or a message, or some sort of “reward”? Recounts of social media use by adolescents have likened online attention to popularity. Accordingly, a lack of constant attention on social media has created a vicious cycle of anxiety, loneliness, and depression because of a failure to receive “virtual” reward. Taken together, social media may be harmful because it distorts our self-image, and while social media platforms help connect us, they can also ironically make us feel isolated, lower our self-confidence, and diminish our overall sense of well-being.
As the platforms for communication and information have evolved so rapidly over the past decade, there is a need to establish boundaries between what is beneficial and what is potentially detrimental to our mental health. While social media companies should play a role in mitigating addictive social network behavior, it would also seem counterintuitive to the general business model. In that case, who takes charge? This multifaceted problem requires a multidisciplinary approach.
Leanna M.W. Lui is an MSc candidate at the University of Toronto.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
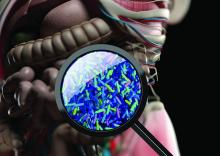
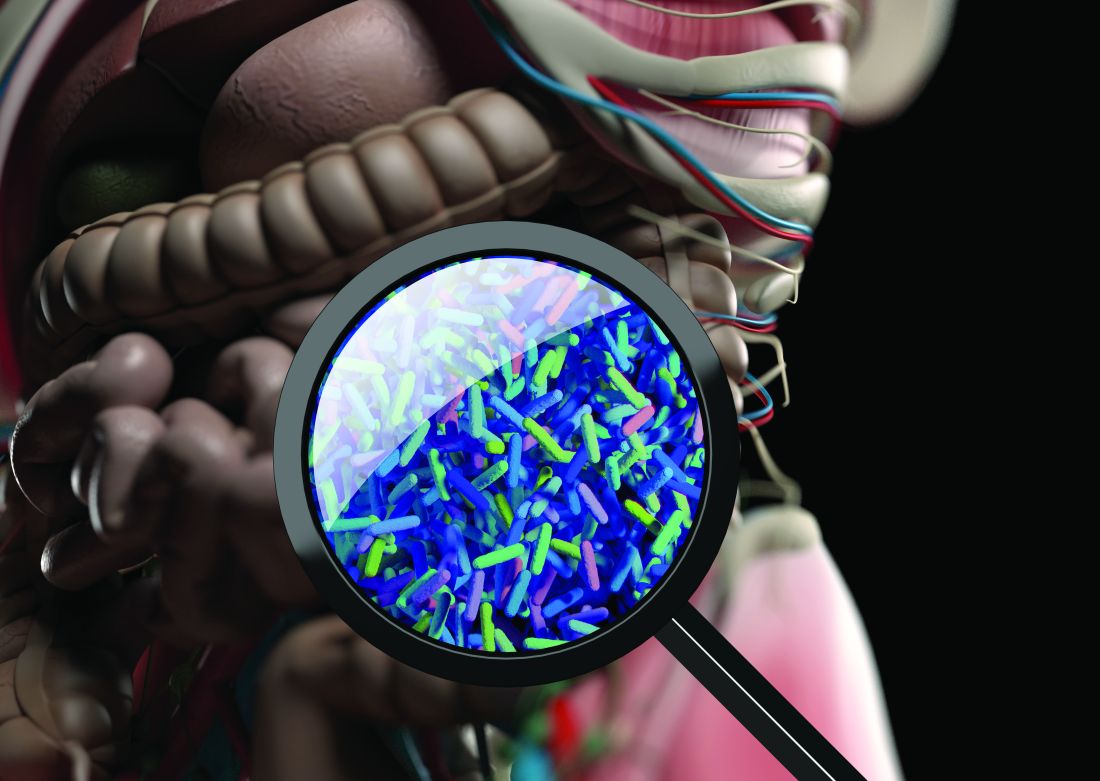
Gut health ‘vitally important’ for mental health
Disturbances in gut microbiota are associated with depletion of anti-inflammatory bacteria and proliferation of proinflammatory bacteria, a pattern tied to several major psychiatric disorders including depression, bipolar disorder (BD), schizophrenia, and anxiety, new research shows.
A meta-analysis of 59 studies, encompassing roughly 2,600 patients with psychiatric conditions, showed a decrease in microbial richness in patients with psychiatric conditions versus controls.
In addition, those with depression, anxiety, BD, and psychosis had a similar set of abnormalities in the microbiota, particularly lower levels of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus – two types of bacteria that have an anti-inflammatory effect in gut – and higher levels of Eggerthella, a bacterium with proinflammatory effects.
“The wealth of evidence we have summarized clearly demonstrates that the gut microbiota is vitally important to the wider mental health of individuals,” lead author Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, Centre for Affective Disorders, King’s College London, said in an interview.
“While it is still too early to recommend specific interventions, it’s clear that clinicians need to place a greater awareness of gut health when considering the treatment of certain psychiatric disorders,” she said.
The study was published online Sept. 15, 2021, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Reliable biomarkers
“Evidence of gut microbiota perturbations has accumulated for multiple psychiatric disorders, with microbiota signatures proposed as potential biomarkers,” the authors wrote.
However, “while there is a wealth of evidence to suggest that abnormalities within the composition of the gut microbiota are connected to a number of psychiatric disorders, there haven’t been any attempts to evaluate the specificity of this evidence – that is, if these changes are unique to specific disorders or shared across many,” Ms. Nikolova said.
Previous research in individual disorders has identified “patterns that may be promising biomarker targets,” with the potential to “improve diagnostic accuracy, guide treatment, and assist the monitoring of treatment response,” the authors noted.
“We wanted to see if we could reliably establish biomarkers for individual conditions in an effort to further our understanding of the relationship between mental illness and gut microbiota,” said Ms. Nikolova.
The researchers wanted to “evaluate the specificity and reproducibility of gut microbiota alterations and delineate those with potential to become biomarkers.”
They identified 59 studies (64 case-control comparisons; n = 2,643 patients, 2,336 controls). Most (54.2%) were conducted in East Asia, followed by Westernized populations (40.7%) and Africa (1.7%).
These studies evaluated diversity or abundance of gut microbes in adult populations encompassing an array of psychiatric disorders: major depressive disorder (MDD), BD, psychosis and schizophrenia, eating disorders (anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa), anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), PTSD, and ADHD.
Although studies were similar in exclusion criteria, few attempted to minimize dietary changes or control dietary intake. In addition, use of psychiatric medication also “varied substantially.”
The researchers conducted several analyses, with primary outcomes consisting of “community-level measures of gut microbiota composition (alpha and beta diversity) as well as taxonomic findings at the phylum, family, and genus levels (relative abundance).”
Alpha diversity provides a “summary of the microbial community in individual samples,” which “can be compared across groups to evaluate the role of a particular factor (in this case psychiatric diagnosis) on the richness (number of species) and evenness (how well each species is represented) in the sample.”
Beta diversity, on the other hand, “measures interindividual (between samples) diversity that assesses similarity of communities, compared with the other samples analyzed.”
Control samples consisted of participants without the relevant condition.
Biological overlap?
The alpha-diversity meta-analysis encompassed 34 studies (n = 1,519 patients, 1,429 controls). The researchers found significant decreases in microbial richness in patients, compared with controls (observed species standardized mean difference, −0.26; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.06; Chao1 SMD, −0.5; 95% CI, −0.79 to −0.21). On the other hand, when they examined each diagnosis separately, they found consistent decreases only in bipolar disorder. There was a small, nonsignificant decrease in phylogenetic diversity between groups.
MDD, psychosis, and schizophrenia were the only conditions in which differences in beta diversity were consistently observed.
“These findings suggest there is reliable evidence for differences in the shared phylogenetic structure in MDD and psychosis and schizophrenia compared with controls,” the authors write.
However, “method of measurement and method of patient classification (symptom vs. diagnosis based) may affect findings,” they added.
When they focused on relative abundance, they found “little evidence” of disorder specificity, but rather a “transdiagnostic pattern of microbiota signatures.”
In particular, depleted levels of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus and enriched levels of Eggerthella were “consistently shared” between MDD, BD, psychosis and schizophrenia, and anxiety, “suggesting these disorders are characterized by a reduction of anti-inflammatory butyrate-producing bacteria, while proinflammatory genera are enriched.”
“The finding that these perturbations do not appear to be disorder-specific suggests that the microbiota is affected in a similar manner by conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and psychosis,” said Ms. Nikolova.
“We have seen similar findings from previous meta-analyses of inflammatory marker studies and genetic studies, for example, suggesting that there is a biological overlap between these conditions, which we have now also seen in the microbiota.”
The authors highlighted potential confounders, including study region and medication use.
Conditions such as MDD, psychosis, and schizophrenia were “largely investigated in the East,” while anorexia nervosa and OCD were primarily investigated in the West.
Moreover, comparing results from medication-free studies with those in which 80% or more of patients were taking psychiatric medication showed increases in bacterial families Lactobacillaceae, Klebsiella, Streptococcus, and Megasphaera only in medicated groups, and decreases in Dialister.
In light of these confounders, the findings should be considered “preliminary,” the investigators noted.
Greater standardization needed
Commenting on the study, Emeran Mayer, MD, director of the Oppenheimer Center for Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience at the University of California, Los Angeles, said it is “intriguing to speculate that low-grade immune activation due to reduced production of butyrate may be such a generalized factor affecting microbial composition shared similarly in several brain disorders. However, such a mechanism has not been confirmed in mechanistic studies to date.”
In addition, the study “lumps together a large number of studies and heterogeneous patient populations, with and without centrally acting medication, without adequate dietary history, studied in different ethnic populations, studied with highly variable collection and analysis methods, including highly variable sample and study sizes for different diseases, and using only measures of microbial composition but not function,” cautioned Dr. Mayer, who was not involved in the research.
Future studies “with much greater standardization of subject populations and clinical and biological analyses techniques should be performed to reevaluate the results of the current study and confirm or reject the main hypotheses,” asserted Dr. Mayer, who is also the founding director of the UCLA Brain Gut Microbiome Center.
Ms. Nikolova is funded by a Medical Research Council PhD Studentship. Other sources of funding include the National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley National Health Service Foundation Trust and King’s College London. Ms. Nikolova has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mayer is a scientific advisory board member of Danone, Axial Therapeutics, Viome, Amare, Mahana Therapeutics, Pendulum, Bloom Biosciences, and APC Microbiome Ireland.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
Disturbances in gut microbiota are associated with depletion of anti-inflammatory bacteria and proliferation of proinflammatory bacteria, a pattern tied to several major psychiatric disorders including depression, bipolar disorder (BD), schizophrenia, and anxiety, new research shows.
A meta-analysis of 59 studies, encompassing roughly 2,600 patients with psychiatric conditions, showed a decrease in microbial richness in patients with psychiatric conditions versus controls.
In addition, those with depression, anxiety, BD, and psychosis had a similar set of abnormalities in the microbiota, particularly lower levels of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus – two types of bacteria that have an anti-inflammatory effect in gut – and higher levels of Eggerthella, a bacterium with proinflammatory effects.
“The wealth of evidence we have summarized clearly demonstrates that the gut microbiota is vitally important to the wider mental health of individuals,” lead author Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, Centre for Affective Disorders, King’s College London, said in an interview.
“While it is still too early to recommend specific interventions, it’s clear that clinicians need to place a greater awareness of gut health when considering the treatment of certain psychiatric disorders,” she said.
The study was published online Sept. 15, 2021, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Reliable biomarkers
“Evidence of gut microbiota perturbations has accumulated for multiple psychiatric disorders, with microbiota signatures proposed as potential biomarkers,” the authors wrote.
However, “while there is a wealth of evidence to suggest that abnormalities within the composition of the gut microbiota are connected to a number of psychiatric disorders, there haven’t been any attempts to evaluate the specificity of this evidence – that is, if these changes are unique to specific disorders or shared across many,” Ms. Nikolova said.
Previous research in individual disorders has identified “patterns that may be promising biomarker targets,” with the potential to “improve diagnostic accuracy, guide treatment, and assist the monitoring of treatment response,” the authors noted.
“We wanted to see if we could reliably establish biomarkers for individual conditions in an effort to further our understanding of the relationship between mental illness and gut microbiota,” said Ms. Nikolova.
The researchers wanted to “evaluate the specificity and reproducibility of gut microbiota alterations and delineate those with potential to become biomarkers.”
They identified 59 studies (64 case-control comparisons; n = 2,643 patients, 2,336 controls). Most (54.2%) were conducted in East Asia, followed by Westernized populations (40.7%) and Africa (1.7%).
These studies evaluated diversity or abundance of gut microbes in adult populations encompassing an array of psychiatric disorders: major depressive disorder (MDD), BD, psychosis and schizophrenia, eating disorders (anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa), anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), PTSD, and ADHD.
Although studies were similar in exclusion criteria, few attempted to minimize dietary changes or control dietary intake. In addition, use of psychiatric medication also “varied substantially.”
The researchers conducted several analyses, with primary outcomes consisting of “community-level measures of gut microbiota composition (alpha and beta diversity) as well as taxonomic findings at the phylum, family, and genus levels (relative abundance).”
Alpha diversity provides a “summary of the microbial community in individual samples,” which “can be compared across groups to evaluate the role of a particular factor (in this case psychiatric diagnosis) on the richness (number of species) and evenness (how well each species is represented) in the sample.”
Beta diversity, on the other hand, “measures interindividual (between samples) diversity that assesses similarity of communities, compared with the other samples analyzed.”
Control samples consisted of participants without the relevant condition.
Biological overlap?
The alpha-diversity meta-analysis encompassed 34 studies (n = 1,519 patients, 1,429 controls). The researchers found significant decreases in microbial richness in patients, compared with controls (observed species standardized mean difference, −0.26; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.06; Chao1 SMD, −0.5; 95% CI, −0.79 to −0.21). On the other hand, when they examined each diagnosis separately, they found consistent decreases only in bipolar disorder. There was a small, nonsignificant decrease in phylogenetic diversity between groups.
MDD, psychosis, and schizophrenia were the only conditions in which differences in beta diversity were consistently observed.
“These findings suggest there is reliable evidence for differences in the shared phylogenetic structure in MDD and psychosis and schizophrenia compared with controls,” the authors write.
However, “method of measurement and method of patient classification (symptom vs. diagnosis based) may affect findings,” they added.
When they focused on relative abundance, they found “little evidence” of disorder specificity, but rather a “transdiagnostic pattern of microbiota signatures.”
In particular, depleted levels of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus and enriched levels of Eggerthella were “consistently shared” between MDD, BD, psychosis and schizophrenia, and anxiety, “suggesting these disorders are characterized by a reduction of anti-inflammatory butyrate-producing bacteria, while proinflammatory genera are enriched.”
“The finding that these perturbations do not appear to be disorder-specific suggests that the microbiota is affected in a similar manner by conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and psychosis,” said Ms. Nikolova.
“We have seen similar findings from previous meta-analyses of inflammatory marker studies and genetic studies, for example, suggesting that there is a biological overlap between these conditions, which we have now also seen in the microbiota.”
The authors highlighted potential confounders, including study region and medication use.
Conditions such as MDD, psychosis, and schizophrenia were “largely investigated in the East,” while anorexia nervosa and OCD were primarily investigated in the West.
Moreover, comparing results from medication-free studies with those in which 80% or more of patients were taking psychiatric medication showed increases in bacterial families Lactobacillaceae, Klebsiella, Streptococcus, and Megasphaera only in medicated groups, and decreases in Dialister.
In light of these confounders, the findings should be considered “preliminary,” the investigators noted.
Greater standardization needed
Commenting on the study, Emeran Mayer, MD, director of the Oppenheimer Center for Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience at the University of California, Los Angeles, said it is “intriguing to speculate that low-grade immune activation due to reduced production of butyrate may be such a generalized factor affecting microbial composition shared similarly in several brain disorders. However, such a mechanism has not been confirmed in mechanistic studies to date.”
In addition, the study “lumps together a large number of studies and heterogeneous patient populations, with and without centrally acting medication, without adequate dietary history, studied in different ethnic populations, studied with highly variable collection and analysis methods, including highly variable sample and study sizes for different diseases, and using only measures of microbial composition but not function,” cautioned Dr. Mayer, who was not involved in the research.
Future studies “with much greater standardization of subject populations and clinical and biological analyses techniques should be performed to reevaluate the results of the current study and confirm or reject the main hypotheses,” asserted Dr. Mayer, who is also the founding director of the UCLA Brain Gut Microbiome Center.
Ms. Nikolova is funded by a Medical Research Council PhD Studentship. Other sources of funding include the National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley National Health Service Foundation Trust and King’s College London. Ms. Nikolova has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mayer is a scientific advisory board member of Danone, Axial Therapeutics, Viome, Amare, Mahana Therapeutics, Pendulum, Bloom Biosciences, and APC Microbiome Ireland.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
Disturbances in gut microbiota are associated with depletion of anti-inflammatory bacteria and proliferation of proinflammatory bacteria, a pattern tied to several major psychiatric disorders including depression, bipolar disorder (BD), schizophrenia, and anxiety, new research shows.
A meta-analysis of 59 studies, encompassing roughly 2,600 patients with psychiatric conditions, showed a decrease in microbial richness in patients with psychiatric conditions versus controls.
In addition, those with depression, anxiety, BD, and psychosis had a similar set of abnormalities in the microbiota, particularly lower levels of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus – two types of bacteria that have an anti-inflammatory effect in gut – and higher levels of Eggerthella, a bacterium with proinflammatory effects.
“The wealth of evidence we have summarized clearly demonstrates that the gut microbiota is vitally important to the wider mental health of individuals,” lead author Viktoriya Nikolova, MRes, Centre for Affective Disorders, King’s College London, said in an interview.
“While it is still too early to recommend specific interventions, it’s clear that clinicians need to place a greater awareness of gut health when considering the treatment of certain psychiatric disorders,” she said.
The study was published online Sept. 15, 2021, in JAMA Psychiatry.
Reliable biomarkers
“Evidence of gut microbiota perturbations has accumulated for multiple psychiatric disorders, with microbiota signatures proposed as potential biomarkers,” the authors wrote.
However, “while there is a wealth of evidence to suggest that abnormalities within the composition of the gut microbiota are connected to a number of psychiatric disorders, there haven’t been any attempts to evaluate the specificity of this evidence – that is, if these changes are unique to specific disorders or shared across many,” Ms. Nikolova said.
Previous research in individual disorders has identified “patterns that may be promising biomarker targets,” with the potential to “improve diagnostic accuracy, guide treatment, and assist the monitoring of treatment response,” the authors noted.
“We wanted to see if we could reliably establish biomarkers for individual conditions in an effort to further our understanding of the relationship between mental illness and gut microbiota,” said Ms. Nikolova.
The researchers wanted to “evaluate the specificity and reproducibility of gut microbiota alterations and delineate those with potential to become biomarkers.”
They identified 59 studies (64 case-control comparisons; n = 2,643 patients, 2,336 controls). Most (54.2%) were conducted in East Asia, followed by Westernized populations (40.7%) and Africa (1.7%).
These studies evaluated diversity or abundance of gut microbes in adult populations encompassing an array of psychiatric disorders: major depressive disorder (MDD), BD, psychosis and schizophrenia, eating disorders (anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa), anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), PTSD, and ADHD.
Although studies were similar in exclusion criteria, few attempted to minimize dietary changes or control dietary intake. In addition, use of psychiatric medication also “varied substantially.”
The researchers conducted several analyses, with primary outcomes consisting of “community-level measures of gut microbiota composition (alpha and beta diversity) as well as taxonomic findings at the phylum, family, and genus levels (relative abundance).”
Alpha diversity provides a “summary of the microbial community in individual samples,” which “can be compared across groups to evaluate the role of a particular factor (in this case psychiatric diagnosis) on the richness (number of species) and evenness (how well each species is represented) in the sample.”
Beta diversity, on the other hand, “measures interindividual (between samples) diversity that assesses similarity of communities, compared with the other samples analyzed.”
Control samples consisted of participants without the relevant condition.
Biological overlap?
The alpha-diversity meta-analysis encompassed 34 studies (n = 1,519 patients, 1,429 controls). The researchers found significant decreases in microbial richness in patients, compared with controls (observed species standardized mean difference, −0.26; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.06; Chao1 SMD, −0.5; 95% CI, −0.79 to −0.21). On the other hand, when they examined each diagnosis separately, they found consistent decreases only in bipolar disorder. There was a small, nonsignificant decrease in phylogenetic diversity between groups.
MDD, psychosis, and schizophrenia were the only conditions in which differences in beta diversity were consistently observed.
“These findings suggest there is reliable evidence for differences in the shared phylogenetic structure in MDD and psychosis and schizophrenia compared with controls,” the authors write.
However, “method of measurement and method of patient classification (symptom vs. diagnosis based) may affect findings,” they added.
When they focused on relative abundance, they found “little evidence” of disorder specificity, but rather a “transdiagnostic pattern of microbiota signatures.”
In particular, depleted levels of Faecalibacterium and Coprococcus and enriched levels of Eggerthella were “consistently shared” between MDD, BD, psychosis and schizophrenia, and anxiety, “suggesting these disorders are characterized by a reduction of anti-inflammatory butyrate-producing bacteria, while proinflammatory genera are enriched.”
“The finding that these perturbations do not appear to be disorder-specific suggests that the microbiota is affected in a similar manner by conditions such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and psychosis,” said Ms. Nikolova.
“We have seen similar findings from previous meta-analyses of inflammatory marker studies and genetic studies, for example, suggesting that there is a biological overlap between these conditions, which we have now also seen in the microbiota.”
The authors highlighted potential confounders, including study region and medication use.
Conditions such as MDD, psychosis, and schizophrenia were “largely investigated in the East,” while anorexia nervosa and OCD were primarily investigated in the West.
Moreover, comparing results from medication-free studies with those in which 80% or more of patients were taking psychiatric medication showed increases in bacterial families Lactobacillaceae, Klebsiella, Streptococcus, and Megasphaera only in medicated groups, and decreases in Dialister.
In light of these confounders, the findings should be considered “preliminary,” the investigators noted.
Greater standardization needed
Commenting on the study, Emeran Mayer, MD, director of the Oppenheimer Center for Neurobiology of Stress and Resilience at the University of California, Los Angeles, said it is “intriguing to speculate that low-grade immune activation due to reduced production of butyrate may be such a generalized factor affecting microbial composition shared similarly in several brain disorders. However, such a mechanism has not been confirmed in mechanistic studies to date.”
In addition, the study “lumps together a large number of studies and heterogeneous patient populations, with and without centrally acting medication, without adequate dietary history, studied in different ethnic populations, studied with highly variable collection and analysis methods, including highly variable sample and study sizes for different diseases, and using only measures of microbial composition but not function,” cautioned Dr. Mayer, who was not involved in the research.
Future studies “with much greater standardization of subject populations and clinical and biological analyses techniques should be performed to reevaluate the results of the current study and confirm or reject the main hypotheses,” asserted Dr. Mayer, who is also the founding director of the UCLA Brain Gut Microbiome Center.
Ms. Nikolova is funded by a Medical Research Council PhD Studentship. Other sources of funding include the National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley National Health Service Foundation Trust and King’s College London. Ms. Nikolova has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mayer is a scientific advisory board member of Danone, Axial Therapeutics, Viome, Amare, Mahana Therapeutics, Pendulum, Bloom Biosciences, and APC Microbiome Ireland.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com .
Pandemic affected home life of nearly 70% of female physicians with children
The survey, conducted by the Robert Graham Center and the American Board of Family Medicine from May to June 2020, examined the professional and personal experiences of being a mother and a primary care physician during the pandemic.
“The pandemic was hard for everyone, but for women who had children in the home, and it didn’t really matter what age, it seemed like the emotional impact was much harder,” study author Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, said in an interview.
The results of the survey of 89 female physicians who worked in the primary care specialty were published in the Journal of Mother Studies.
Dr. Jabbapour and her colleagues found that 67% of female physicians with children said the pandemic had a great “impact” on their home life compared with 25% of those without children. Furthermore, 41% of physician moms said COVID-19 greatly affected their work life, as opposed to 17% of their counterparts without children.
“Women are going into medicine at much higher rates. In primary care, it’s becoming close to the majority,” said Dr. Jabbarpour, a family physician and medical director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “That has important workforce implications. If we’re not supporting our female physicians and they are greater than 50% of the physician workforce and they’re burning out, who’s going to have a doctor anymore?”
Child care challenges
Researchers found that the emotional toll female physicians experienced early on in the pandemic was indicative of the challenges they were facing. Some of those challenges included managing anxiety, increased stress from both work and home, and social isolation from friends and family.
Another challenge physician mothers had to deal with was fulfilling child care and homeschooling needs, as many women didn’t know what to do with their children and didn’t have external support from their employers.
Child care options vanished for many people during the pandemic, Emily Kaye, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
“I think it was incredibly challenging for everyone and uniquely challenging for women who were young mothers, specifically with respect to child care” said Dr. Kaye, assistant professor in the department of oncology at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. “Many women were expected to just continue plugging on in the absence of any reasonable or safe form of child care.”
Some of the changes physician-mothers said they were required to make at home or in their personal lives included physical changes related to their family safety, such as decontaminating themselves in their garages before heading home after a shift. Some also reported that they had to find new ways to maintain emotional and mental health because of social isolation from family and friends.
The survey results, which were taken early on in the pandemic, highlight the need for health policies that support physician mothers and families, as women shoulder the burden of parenting and domestic responsibilities in heterosexual relationships, the researchers said.
“I’m hoping that people pay attention and start to implement more family friendly policies within their workplaces,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “But during a pandemic, it was essential for [female health care workers] to go in, and they had nowhere to put their kids. [Therefore], the choice became leaving young children alone at home, putting them into daycare facilities that did remain open without knowing if they were [safe], or quitting their jobs. None of those choices are good.”
Community support as a potential solution
Dr. Kaye said she believes that there should be a “long overdue investment” in community support, affordable and accessible child care, flexible spending, paid family leave, and other forms of caregiving support.
“In order to keep women physicians in the workforce, we need to have a significant increase in investment in the social safety net in this country,” Dr. Kaye said.
Researchers said more studies should evaluate the role the COVID-19 pandemic had on the primary care workforce in the U.S., “with a specific emphasis on how the pandemic impacted mothers, and should more intentionally consider the further intersections of race and ethnicity in the experiences of physician-mothers.”
“I think people are burning out and then there’s all this anti-science, anti-health sentiment out there, which makes it harder,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “If we did repeat this study now, I think things would be even more dire in the voices of the women that we heard.”
Dr. Jabbarpour and Dr. Kaye reported no disclosures.
The survey, conducted by the Robert Graham Center and the American Board of Family Medicine from May to June 2020, examined the professional and personal experiences of being a mother and a primary care physician during the pandemic.
“The pandemic was hard for everyone, but for women who had children in the home, and it didn’t really matter what age, it seemed like the emotional impact was much harder,” study author Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, said in an interview.
The results of the survey of 89 female physicians who worked in the primary care specialty were published in the Journal of Mother Studies.
Dr. Jabbapour and her colleagues found that 67% of female physicians with children said the pandemic had a great “impact” on their home life compared with 25% of those without children. Furthermore, 41% of physician moms said COVID-19 greatly affected their work life, as opposed to 17% of their counterparts without children.
“Women are going into medicine at much higher rates. In primary care, it’s becoming close to the majority,” said Dr. Jabbarpour, a family physician and medical director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “That has important workforce implications. If we’re not supporting our female physicians and they are greater than 50% of the physician workforce and they’re burning out, who’s going to have a doctor anymore?”
Child care challenges
Researchers found that the emotional toll female physicians experienced early on in the pandemic was indicative of the challenges they were facing. Some of those challenges included managing anxiety, increased stress from both work and home, and social isolation from friends and family.
Another challenge physician mothers had to deal with was fulfilling child care and homeschooling needs, as many women didn’t know what to do with their children and didn’t have external support from their employers.
Child care options vanished for many people during the pandemic, Emily Kaye, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
“I think it was incredibly challenging for everyone and uniquely challenging for women who were young mothers, specifically with respect to child care” said Dr. Kaye, assistant professor in the department of oncology at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. “Many women were expected to just continue plugging on in the absence of any reasonable or safe form of child care.”
Some of the changes physician-mothers said they were required to make at home or in their personal lives included physical changes related to their family safety, such as decontaminating themselves in their garages before heading home after a shift. Some also reported that they had to find new ways to maintain emotional and mental health because of social isolation from family and friends.
The survey results, which were taken early on in the pandemic, highlight the need for health policies that support physician mothers and families, as women shoulder the burden of parenting and domestic responsibilities in heterosexual relationships, the researchers said.
“I’m hoping that people pay attention and start to implement more family friendly policies within their workplaces,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “But during a pandemic, it was essential for [female health care workers] to go in, and they had nowhere to put their kids. [Therefore], the choice became leaving young children alone at home, putting them into daycare facilities that did remain open without knowing if they were [safe], or quitting their jobs. None of those choices are good.”
Community support as a potential solution
Dr. Kaye said she believes that there should be a “long overdue investment” in community support, affordable and accessible child care, flexible spending, paid family leave, and other forms of caregiving support.
“In order to keep women physicians in the workforce, we need to have a significant increase in investment in the social safety net in this country,” Dr. Kaye said.
Researchers said more studies should evaluate the role the COVID-19 pandemic had on the primary care workforce in the U.S., “with a specific emphasis on how the pandemic impacted mothers, and should more intentionally consider the further intersections of race and ethnicity in the experiences of physician-mothers.”
“I think people are burning out and then there’s all this anti-science, anti-health sentiment out there, which makes it harder,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “If we did repeat this study now, I think things would be even more dire in the voices of the women that we heard.”
Dr. Jabbarpour and Dr. Kaye reported no disclosures.
The survey, conducted by the Robert Graham Center and the American Board of Family Medicine from May to June 2020, examined the professional and personal experiences of being a mother and a primary care physician during the pandemic.
“The pandemic was hard for everyone, but for women who had children in the home, and it didn’t really matter what age, it seemed like the emotional impact was much harder,” study author Yalda Jabbarpour, MD, said in an interview.
The results of the survey of 89 female physicians who worked in the primary care specialty were published in the Journal of Mother Studies.
Dr. Jabbapour and her colleagues found that 67% of female physicians with children said the pandemic had a great “impact” on their home life compared with 25% of those without children. Furthermore, 41% of physician moms said COVID-19 greatly affected their work life, as opposed to 17% of their counterparts without children.
“Women are going into medicine at much higher rates. In primary care, it’s becoming close to the majority,” said Dr. Jabbarpour, a family physician and medical director of the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies. “That has important workforce implications. If we’re not supporting our female physicians and they are greater than 50% of the physician workforce and they’re burning out, who’s going to have a doctor anymore?”
Child care challenges
Researchers found that the emotional toll female physicians experienced early on in the pandemic was indicative of the challenges they were facing. Some of those challenges included managing anxiety, increased stress from both work and home, and social isolation from friends and family.
Another challenge physician mothers had to deal with was fulfilling child care and homeschooling needs, as many women didn’t know what to do with their children and didn’t have external support from their employers.
Child care options vanished for many people during the pandemic, Emily Kaye, MD, MPH, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview.
“I think it was incredibly challenging for everyone and uniquely challenging for women who were young mothers, specifically with respect to child care” said Dr. Kaye, assistant professor in the department of oncology at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. “Many women were expected to just continue plugging on in the absence of any reasonable or safe form of child care.”
Some of the changes physician-mothers said they were required to make at home or in their personal lives included physical changes related to their family safety, such as decontaminating themselves in their garages before heading home after a shift. Some also reported that they had to find new ways to maintain emotional and mental health because of social isolation from family and friends.
The survey results, which were taken early on in the pandemic, highlight the need for health policies that support physician mothers and families, as women shoulder the burden of parenting and domestic responsibilities in heterosexual relationships, the researchers said.
“I’m hoping that people pay attention and start to implement more family friendly policies within their workplaces,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “But during a pandemic, it was essential for [female health care workers] to go in, and they had nowhere to put their kids. [Therefore], the choice became leaving young children alone at home, putting them into daycare facilities that did remain open without knowing if they were [safe], or quitting their jobs. None of those choices are good.”
Community support as a potential solution
Dr. Kaye said she believes that there should be a “long overdue investment” in community support, affordable and accessible child care, flexible spending, paid family leave, and other forms of caregiving support.
“In order to keep women physicians in the workforce, we need to have a significant increase in investment in the social safety net in this country,” Dr. Kaye said.
Researchers said more studies should evaluate the role the COVID-19 pandemic had on the primary care workforce in the U.S., “with a specific emphasis on how the pandemic impacted mothers, and should more intentionally consider the further intersections of race and ethnicity in the experiences of physician-mothers.”
“I think people are burning out and then there’s all this anti-science, anti-health sentiment out there, which makes it harder,” Dr. Jabbarpour said. “If we did repeat this study now, I think things would be even more dire in the voices of the women that we heard.”
Dr. Jabbarpour and Dr. Kaye reported no disclosures.
FROM JOURNAL OF MOTHER STUDIES
How to engage soldiers, veterans in psychiatric treatment
Deployments in places such as Afghanistan and Iraq, and traumatic events such as the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks affect everyone, but military personnel and veterans face unique circumstances that can present challenges to treatment. Much progress has been made in recent years in treating people with posttraumatic stress disorder and helping them recover after traumatic events.
To explore some of those changes and challenges, this news organization interviewed Col. (Ret.) Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, who retired from the Army in 2010 after assignments and missions that took her to Korea, Somalia, Iraq, and Cuba, about her approaches to treating soldiers and veterans.
Dr. Ritchie is chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, and a professor of psychiatry at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Md., and at Georgetown University and George Washington University, both in Washington.
She is the author of 250 publications, including the book, “Forensic and Ethical Issues in Military Behavioral Health” (Fort Sam Houston, Tex.: Borden Institute, 2015). In addition, Dr. Ritchie is coeditor of “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Related Diseases in Combat Veterans” (New York: Springer, 2015) and “Psychiatrists in Combat, Clinicians Experience in the War Zone” (New York: Springer, 2017).
Question: What are some of the interventions available in the aftermath of traumatic events?
Answer: What we thought the standard of care should be after a traumatic event was to have what’s called a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD). It was basically getting the members of the group who had been traumatized by a school shooting or plane crash, or the Oklahoma City bombing, getting them all together literally a few hours after the event, and having them tell what happened. And the idea is to get it all out. But what we discovered is that this could actually make people worse, because you’d be hearing not only about your own trauma, but other people’s traumas, and that it was too soon for the event.
So prior to 9/11, we had organized a conference, which was held in October 2001, just a month after 9/11. At that conference, we worked on mass violence and early intervention, which is the name of the book that came out from the (National Institute of Mental Health) as a result. It focused on basic principles of safety and security and communication, and knowing where your family was, rather than reliving the trauma. Now, we did think that sometimes you could have a CISD that would be helpful, but only when it was people who knew each other well, like an ED group who would work with each other or soldiers who served together.
Q: What was your involvement in the aftermath of the Sept. 11 attacks?
A: At the time of 9/11, I was assigned at the Pentagon, but I wasn’t there. When the plane hit, I was actually across the river at the Navy’s Bureau of Medicine and Surgery. And then for the next 3 weeks, all I did was work at the Pentagon. We used some of these principles of early intervention but not focusing on telling us what happened right afterward. We focused on how the service members and their families were coping in the here and now, and how they could support each other.
We knew that soldiers would not come out of their offices to go to a therapist. They are too strong for that. So, we did what was called “therapy by walking around.” We went to the service members’ offices.
There was also a Family Assistance Center. That was for the families of the people who died. And that was very helpful because you had all the services there in one place – medical care, mental health care, therapy dogs, massage, the people who collected the DNA to identify remains. You had it in one place, the Sheraton in Crystal City, Va.. That has become a model now, especially for mass transportation fatalities. There are a lot more in the literature about Family Assistance Centers now, mainly formed by the National Transportation Safety Board.
Right after 9/11, we went to war in Afghanistan, and later in Iraq, and we had a lot of soldiers who developed both PTSD and traumatic brain injury (TBI). One of the good things that the military can do is they can really innovate with both medical treatment and mental health treatment because they don’t have to ask for an insurance company to pay for it. So for some years, starting in about 2004, Congress allocated a large sum of money every year to the Department of Defense to focus on treatment for PTSD and TBI.
And as a result of that, a couple of things happened. One was that the treatments that we had, we were able to study much better, exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy. We were able to do large trials, and then we continued with the use of medications when necessary. There are only two (Food and Drug Administration)–approved medicines for the treatment of PTSD: sertraline and paroxetine, but many others are used.
We also learned what didn’t work and what soldiers would not take. Most of these medications have sexual side effects. If you’re a young, healthy soldier, you really don’t want to be taking something that causes you erectile dysfunction, or in women a loss of libido. So many people wouldn’t take these therapies. As for exposure therapy, if you got into it and completed the program, usually your PTSD symptoms went down. But many people couldn’t complete it. In the exposure therapy, you’re talking about whatever trauma you’ve been through – maybe your best friend died next to you, and you don’t want to talk about that all the time.
When I talk to patients about this, I say the first bucket is medication, the second bucket is therapy, and the third bucket is everything else. And everything else includes meditation, yoga, exercise, and it also involves working with animals. There are programs where you’re paired with a service dog, who helps calm you down, and you feel protected.
One of my favorites is called Warrior Canine Connection, where a soldier with PTSD trains a puppy to become a service animal. And in the training of the dog, you have to learn to control your emotions, you have to modulate your voice, you have to appear calm. Often soldiers have a background that they’re familiar with animals, especially dogs. So that’s been very successful.
A couple of other (treatments) to mention one is called stellate ganglion block, where a little lidocaine is injected into the back of the cervical spine. It was used initially for pain control, and they found that it was actually very helpful for PTSD. Another thing we’ve learned is that pain and PTSD often go hand in hand, because if you’re in pain, you’ll be feeling awful, you won’t sleep well, you’ll have more nightmares. But if you can control both of them together, then that’s going to help.
Q: One issue that veterans may face is moral injury. Can you talk about that?
A: Moral injury is a term that was first used after Vietnam. Moral injury is not a psychiatric diagnosis. It is feelings of shame and guilt that can be very corrosive and can lead to suicide. It overlaps with PTSD. You feel either you’ve let yourself down, or the government has let you down. And this can be very corrosive. Another thing that could happen is, say, you switched your tour of duty with a buddy, and he got killed and you didn’t. A very common scenario is you’re manning a checkpoint, and a car comes at you and doesn’t stop like it’s supposed to. You do what you’ve been trained to do, which is open fire, and check on the car afterward. And there’s four little kids and their parents in the car all dead. And that is something that even though that was your sort of duty, that it still eats at you because you have kids the same age as the ones who were dead in the car.
You can still have these feelings of shame and guilt, and it will often bleed into your relationships with your family. And that can lead to distance and divorce, which is a further risk factor for suicide.
Q: Are there are any specific treatments that have been designed for moral injury, different from PTSD or other conditions?
A: The Armed Services has set up a number of intensive programs at different places, and each is a little bit different. They usually integrate moral injury in with some of the other treatments. There was one at Fort Bliss, Tex., that had reiki; they had art therapy. And they had the chaplains working on moral injury. So there’s no medical treatment for it, but there certainly is talking about it, and for some people to go to a chaplain can be very helpful.
There’s a Military Health System Centers of Excellence, which is a place by the new Walter Reed on the campus, they have a marvelous wall full of masks. And the masks have been painted by soldiers with usually a combination of PTSD, TBI, and although it’s not an official psychiatric diagnosis, moral injury. They’re able to draw and paint. Another thing that’s been used quite a bit as writing therapy, and journaling, and just writing down how you feel about something, because you can do that without retraumatizing anybody else, except perhaps if you are working with a therapist.
Q: For therapists who are treating soldiers, veterans, are there specific challenges that they should be aware of? Are these patients maybe different from the patients that they might otherwise see? Are there specific pieces of advice as to how to engage them?
A: There are a few things that are different. One is that many people in the military are not used to talking about their feelings. And that’s especially if you’ve got a young man who only grunts and says: “Hooah!” That is going to be hard to break through. And that’s why some of these other ways of reaching somebody is very effective. Also, the military likes to have physical activity; they’re usually not comfortable sitting in a chair. If you’re a civilian psychiatrist, I don’t expect you to go bungee jumping with your patients. But what I’d recommend is that you recommend to your patients that they stay active.
Another thing about veterans is that they like to be self-sufficient. They really don’t like to ask for help, although they might ask for help for their buddy. After the Pentagon and 9/11, when I was working with senior officers, they never needed any help. No, but their buddy over here might, so I could help them in the guise of providing care for their buddy in a group setting. We could work with everybody and enhance cohesion, morale, bonding, “we’re all in this together” type of feeling.
I think one thing that’s really improved is that there is less stigma around PTSD. People are more willing to present for help, and some people have called PTSD the Purple Heart of mental disorders. People don’t feel like it’s as bad as having depression or anxiety. Even though PTSD often has depression and anxiety components to it – they run hand in hand – still, it’s sort of more honorable if you’ve been at war and have gotten PTSD.
Q: How have you been faring yourself, in the face of the 9/11 anniversary and recent events in Afghanistan?
A: (The Sept. 11 weekend) was very sad for me – and a lot of my colleagues [with] the combination of the 20th anniversary of 9/11, and the recent development. Fortunately, I have friends and people I can talk to. I walked with a colleague of mine who was in the Army. I’m following my own rule of the three buckets, so we took a walk around the hospital center for about 45 minutes, and we have five fish ponds here. And we went and looked at the fish, and talked to the fish. At the National Rehab Hospital, they were playing the guitar. So there’s are a variety of things that people can do.
Deployments in places such as Afghanistan and Iraq, and traumatic events such as the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks affect everyone, but military personnel and veterans face unique circumstances that can present challenges to treatment. Much progress has been made in recent years in treating people with posttraumatic stress disorder and helping them recover after traumatic events.
To explore some of those changes and challenges, this news organization interviewed Col. (Ret.) Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, who retired from the Army in 2010 after assignments and missions that took her to Korea, Somalia, Iraq, and Cuba, about her approaches to treating soldiers and veterans.
Dr. Ritchie is chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, and a professor of psychiatry at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Md., and at Georgetown University and George Washington University, both in Washington.
She is the author of 250 publications, including the book, “Forensic and Ethical Issues in Military Behavioral Health” (Fort Sam Houston, Tex.: Borden Institute, 2015). In addition, Dr. Ritchie is coeditor of “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Related Diseases in Combat Veterans” (New York: Springer, 2015) and “Psychiatrists in Combat, Clinicians Experience in the War Zone” (New York: Springer, 2017).
Question: What are some of the interventions available in the aftermath of traumatic events?
Answer: What we thought the standard of care should be after a traumatic event was to have what’s called a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD). It was basically getting the members of the group who had been traumatized by a school shooting or plane crash, or the Oklahoma City bombing, getting them all together literally a few hours after the event, and having them tell what happened. And the idea is to get it all out. But what we discovered is that this could actually make people worse, because you’d be hearing not only about your own trauma, but other people’s traumas, and that it was too soon for the event.
So prior to 9/11, we had organized a conference, which was held in October 2001, just a month after 9/11. At that conference, we worked on mass violence and early intervention, which is the name of the book that came out from the (National Institute of Mental Health) as a result. It focused on basic principles of safety and security and communication, and knowing where your family was, rather than reliving the trauma. Now, we did think that sometimes you could have a CISD that would be helpful, but only when it was people who knew each other well, like an ED group who would work with each other or soldiers who served together.
Q: What was your involvement in the aftermath of the Sept. 11 attacks?
A: At the time of 9/11, I was assigned at the Pentagon, but I wasn’t there. When the plane hit, I was actually across the river at the Navy’s Bureau of Medicine and Surgery. And then for the next 3 weeks, all I did was work at the Pentagon. We used some of these principles of early intervention but not focusing on telling us what happened right afterward. We focused on how the service members and their families were coping in the here and now, and how they could support each other.
We knew that soldiers would not come out of their offices to go to a therapist. They are too strong for that. So, we did what was called “therapy by walking around.” We went to the service members’ offices.
There was also a Family Assistance Center. That was for the families of the people who died. And that was very helpful because you had all the services there in one place – medical care, mental health care, therapy dogs, massage, the people who collected the DNA to identify remains. You had it in one place, the Sheraton in Crystal City, Va.. That has become a model now, especially for mass transportation fatalities. There are a lot more in the literature about Family Assistance Centers now, mainly formed by the National Transportation Safety Board.
Right after 9/11, we went to war in Afghanistan, and later in Iraq, and we had a lot of soldiers who developed both PTSD and traumatic brain injury (TBI). One of the good things that the military can do is they can really innovate with both medical treatment and mental health treatment because they don’t have to ask for an insurance company to pay for it. So for some years, starting in about 2004, Congress allocated a large sum of money every year to the Department of Defense to focus on treatment for PTSD and TBI.
And as a result of that, a couple of things happened. One was that the treatments that we had, we were able to study much better, exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy. We were able to do large trials, and then we continued with the use of medications when necessary. There are only two (Food and Drug Administration)–approved medicines for the treatment of PTSD: sertraline and paroxetine, but many others are used.
We also learned what didn’t work and what soldiers would not take. Most of these medications have sexual side effects. If you’re a young, healthy soldier, you really don’t want to be taking something that causes you erectile dysfunction, or in women a loss of libido. So many people wouldn’t take these therapies. As for exposure therapy, if you got into it and completed the program, usually your PTSD symptoms went down. But many people couldn’t complete it. In the exposure therapy, you’re talking about whatever trauma you’ve been through – maybe your best friend died next to you, and you don’t want to talk about that all the time.
When I talk to patients about this, I say the first bucket is medication, the second bucket is therapy, and the third bucket is everything else. And everything else includes meditation, yoga, exercise, and it also involves working with animals. There are programs where you’re paired with a service dog, who helps calm you down, and you feel protected.
One of my favorites is called Warrior Canine Connection, where a soldier with PTSD trains a puppy to become a service animal. And in the training of the dog, you have to learn to control your emotions, you have to modulate your voice, you have to appear calm. Often soldiers have a background that they’re familiar with animals, especially dogs. So that’s been very successful.
A couple of other (treatments) to mention one is called stellate ganglion block, where a little lidocaine is injected into the back of the cervical spine. It was used initially for pain control, and they found that it was actually very helpful for PTSD. Another thing we’ve learned is that pain and PTSD often go hand in hand, because if you’re in pain, you’ll be feeling awful, you won’t sleep well, you’ll have more nightmares. But if you can control both of them together, then that’s going to help.
Q: One issue that veterans may face is moral injury. Can you talk about that?
A: Moral injury is a term that was first used after Vietnam. Moral injury is not a psychiatric diagnosis. It is feelings of shame and guilt that can be very corrosive and can lead to suicide. It overlaps with PTSD. You feel either you’ve let yourself down, or the government has let you down. And this can be very corrosive. Another thing that could happen is, say, you switched your tour of duty with a buddy, and he got killed and you didn’t. A very common scenario is you’re manning a checkpoint, and a car comes at you and doesn’t stop like it’s supposed to. You do what you’ve been trained to do, which is open fire, and check on the car afterward. And there’s four little kids and their parents in the car all dead. And that is something that even though that was your sort of duty, that it still eats at you because you have kids the same age as the ones who were dead in the car.
You can still have these feelings of shame and guilt, and it will often bleed into your relationships with your family. And that can lead to distance and divorce, which is a further risk factor for suicide.
Q: Are there are any specific treatments that have been designed for moral injury, different from PTSD or other conditions?
A: The Armed Services has set up a number of intensive programs at different places, and each is a little bit different. They usually integrate moral injury in with some of the other treatments. There was one at Fort Bliss, Tex., that had reiki; they had art therapy. And they had the chaplains working on moral injury. So there’s no medical treatment for it, but there certainly is talking about it, and for some people to go to a chaplain can be very helpful.
There’s a Military Health System Centers of Excellence, which is a place by the new Walter Reed on the campus, they have a marvelous wall full of masks. And the masks have been painted by soldiers with usually a combination of PTSD, TBI, and although it’s not an official psychiatric diagnosis, moral injury. They’re able to draw and paint. Another thing that’s been used quite a bit as writing therapy, and journaling, and just writing down how you feel about something, because you can do that without retraumatizing anybody else, except perhaps if you are working with a therapist.
Q: For therapists who are treating soldiers, veterans, are there specific challenges that they should be aware of? Are these patients maybe different from the patients that they might otherwise see? Are there specific pieces of advice as to how to engage them?
A: There are a few things that are different. One is that many people in the military are not used to talking about their feelings. And that’s especially if you’ve got a young man who only grunts and says: “Hooah!” That is going to be hard to break through. And that’s why some of these other ways of reaching somebody is very effective. Also, the military likes to have physical activity; they’re usually not comfortable sitting in a chair. If you’re a civilian psychiatrist, I don’t expect you to go bungee jumping with your patients. But what I’d recommend is that you recommend to your patients that they stay active.
Another thing about veterans is that they like to be self-sufficient. They really don’t like to ask for help, although they might ask for help for their buddy. After the Pentagon and 9/11, when I was working with senior officers, they never needed any help. No, but their buddy over here might, so I could help them in the guise of providing care for their buddy in a group setting. We could work with everybody and enhance cohesion, morale, bonding, “we’re all in this together” type of feeling.
I think one thing that’s really improved is that there is less stigma around PTSD. People are more willing to present for help, and some people have called PTSD the Purple Heart of mental disorders. People don’t feel like it’s as bad as having depression or anxiety. Even though PTSD often has depression and anxiety components to it – they run hand in hand – still, it’s sort of more honorable if you’ve been at war and have gotten PTSD.
Q: How have you been faring yourself, in the face of the 9/11 anniversary and recent events in Afghanistan?
A: (The Sept. 11 weekend) was very sad for me – and a lot of my colleagues [with] the combination of the 20th anniversary of 9/11, and the recent development. Fortunately, I have friends and people I can talk to. I walked with a colleague of mine who was in the Army. I’m following my own rule of the three buckets, so we took a walk around the hospital center for about 45 minutes, and we have five fish ponds here. And we went and looked at the fish, and talked to the fish. At the National Rehab Hospital, they were playing the guitar. So there’s are a variety of things that people can do.
Deployments in places such as Afghanistan and Iraq, and traumatic events such as the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks affect everyone, but military personnel and veterans face unique circumstances that can present challenges to treatment. Much progress has been made in recent years in treating people with posttraumatic stress disorder and helping them recover after traumatic events.
To explore some of those changes and challenges, this news organization interviewed Col. (Ret.) Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, MPH, who retired from the Army in 2010 after assignments and missions that took her to Korea, Somalia, Iraq, and Cuba, about her approaches to treating soldiers and veterans.
Dr. Ritchie is chief of psychiatry at Medstar Washington Hospital Center, and a professor of psychiatry at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences in Bethesda, Md., and at Georgetown University and George Washington University, both in Washington.
She is the author of 250 publications, including the book, “Forensic and Ethical Issues in Military Behavioral Health” (Fort Sam Houston, Tex.: Borden Institute, 2015). In addition, Dr. Ritchie is coeditor of “Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder and Related Diseases in Combat Veterans” (New York: Springer, 2015) and “Psychiatrists in Combat, Clinicians Experience in the War Zone” (New York: Springer, 2017).
Question: What are some of the interventions available in the aftermath of traumatic events?
Answer: What we thought the standard of care should be after a traumatic event was to have what’s called a critical incident stress debriefing (CISD). It was basically getting the members of the group who had been traumatized by a school shooting or plane crash, or the Oklahoma City bombing, getting them all together literally a few hours after the event, and having them tell what happened. And the idea is to get it all out. But what we discovered is that this could actually make people worse, because you’d be hearing not only about your own trauma, but other people’s traumas, and that it was too soon for the event.
So prior to 9/11, we had organized a conference, which was held in October 2001, just a month after 9/11. At that conference, we worked on mass violence and early intervention, which is the name of the book that came out from the (National Institute of Mental Health) as a result. It focused on basic principles of safety and security and communication, and knowing where your family was, rather than reliving the trauma. Now, we did think that sometimes you could have a CISD that would be helpful, but only when it was people who knew each other well, like an ED group who would work with each other or soldiers who served together.
Q: What was your involvement in the aftermath of the Sept. 11 attacks?
A: At the time of 9/11, I was assigned at the Pentagon, but I wasn’t there. When the plane hit, I was actually across the river at the Navy’s Bureau of Medicine and Surgery. And then for the next 3 weeks, all I did was work at the Pentagon. We used some of these principles of early intervention but not focusing on telling us what happened right afterward. We focused on how the service members and their families were coping in the here and now, and how they could support each other.
We knew that soldiers would not come out of their offices to go to a therapist. They are too strong for that. So, we did what was called “therapy by walking around.” We went to the service members’ offices.
There was also a Family Assistance Center. That was for the families of the people who died. And that was very helpful because you had all the services there in one place – medical care, mental health care, therapy dogs, massage, the people who collected the DNA to identify remains. You had it in one place, the Sheraton in Crystal City, Va.. That has become a model now, especially for mass transportation fatalities. There are a lot more in the literature about Family Assistance Centers now, mainly formed by the National Transportation Safety Board.
Right after 9/11, we went to war in Afghanistan, and later in Iraq, and we had a lot of soldiers who developed both PTSD and traumatic brain injury (TBI). One of the good things that the military can do is they can really innovate with both medical treatment and mental health treatment because they don’t have to ask for an insurance company to pay for it. So for some years, starting in about 2004, Congress allocated a large sum of money every year to the Department of Defense to focus on treatment for PTSD and TBI.
And as a result of that, a couple of things happened. One was that the treatments that we had, we were able to study much better, exposure therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy. We were able to do large trials, and then we continued with the use of medications when necessary. There are only two (Food and Drug Administration)–approved medicines for the treatment of PTSD: sertraline and paroxetine, but many others are used.
We also learned what didn’t work and what soldiers would not take. Most of these medications have sexual side effects. If you’re a young, healthy soldier, you really don’t want to be taking something that causes you erectile dysfunction, or in women a loss of libido. So many people wouldn’t take these therapies. As for exposure therapy, if you got into it and completed the program, usually your PTSD symptoms went down. But many people couldn’t complete it. In the exposure therapy, you’re talking about whatever trauma you’ve been through – maybe your best friend died next to you, and you don’t want to talk about that all the time.
When I talk to patients about this, I say the first bucket is medication, the second bucket is therapy, and the third bucket is everything else. And everything else includes meditation, yoga, exercise, and it also involves working with animals. There are programs where you’re paired with a service dog, who helps calm you down, and you feel protected.
One of my favorites is called Warrior Canine Connection, where a soldier with PTSD trains a puppy to become a service animal. And in the training of the dog, you have to learn to control your emotions, you have to modulate your voice, you have to appear calm. Often soldiers have a background that they’re familiar with animals, especially dogs. So that’s been very successful.
A couple of other (treatments) to mention one is called stellate ganglion block, where a little lidocaine is injected into the back of the cervical spine. It was used initially for pain control, and they found that it was actually very helpful for PTSD. Another thing we’ve learned is that pain and PTSD often go hand in hand, because if you’re in pain, you’ll be feeling awful, you won’t sleep well, you’ll have more nightmares. But if you can control both of them together, then that’s going to help.
Q: One issue that veterans may face is moral injury. Can you talk about that?
A: Moral injury is a term that was first used after Vietnam. Moral injury is not a psychiatric diagnosis. It is feelings of shame and guilt that can be very corrosive and can lead to suicide. It overlaps with PTSD. You feel either you’ve let yourself down, or the government has let you down. And this can be very corrosive. Another thing that could happen is, say, you switched your tour of duty with a buddy, and he got killed and you didn’t. A very common scenario is you’re manning a checkpoint, and a car comes at you and doesn’t stop like it’s supposed to. You do what you’ve been trained to do, which is open fire, and check on the car afterward. And there’s four little kids and their parents in the car all dead. And that is something that even though that was your sort of duty, that it still eats at you because you have kids the same age as the ones who were dead in the car.
You can still have these feelings of shame and guilt, and it will often bleed into your relationships with your family. And that can lead to distance and divorce, which is a further risk factor for suicide.
Q: Are there are any specific treatments that have been designed for moral injury, different from PTSD or other conditions?
A: The Armed Services has set up a number of intensive programs at different places, and each is a little bit different. They usually integrate moral injury in with some of the other treatments. There was one at Fort Bliss, Tex., that had reiki; they had art therapy. And they had the chaplains working on moral injury. So there’s no medical treatment for it, but there certainly is talking about it, and for some people to go to a chaplain can be very helpful.
There’s a Military Health System Centers of Excellence, which is a place by the new Walter Reed on the campus, they have a marvelous wall full of masks. And the masks have been painted by soldiers with usually a combination of PTSD, TBI, and although it’s not an official psychiatric diagnosis, moral injury. They’re able to draw and paint. Another thing that’s been used quite a bit as writing therapy, and journaling, and just writing down how you feel about something, because you can do that without retraumatizing anybody else, except perhaps if you are working with a therapist.
Q: For therapists who are treating soldiers, veterans, are there specific challenges that they should be aware of? Are these patients maybe different from the patients that they might otherwise see? Are there specific pieces of advice as to how to engage them?
A: There are a few things that are different. One is that many people in the military are not used to talking about their feelings. And that’s especially if you’ve got a young man who only grunts and says: “Hooah!” That is going to be hard to break through. And that’s why some of these other ways of reaching somebody is very effective. Also, the military likes to have physical activity; they’re usually not comfortable sitting in a chair. If you’re a civilian psychiatrist, I don’t expect you to go bungee jumping with your patients. But what I’d recommend is that you recommend to your patients that they stay active.
Another thing about veterans is that they like to be self-sufficient. They really don’t like to ask for help, although they might ask for help for their buddy. After the Pentagon and 9/11, when I was working with senior officers, they never needed any help. No, but their buddy over here might, so I could help them in the guise of providing care for their buddy in a group setting. We could work with everybody and enhance cohesion, morale, bonding, “we’re all in this together” type of feeling.
I think one thing that’s really improved is that there is less stigma around PTSD. People are more willing to present for help, and some people have called PTSD the Purple Heart of mental disorders. People don’t feel like it’s as bad as having depression or anxiety. Even though PTSD often has depression and anxiety components to it – they run hand in hand – still, it’s sort of more honorable if you’ve been at war and have gotten PTSD.
Q: How have you been faring yourself, in the face of the 9/11 anniversary and recent events in Afghanistan?
A: (The Sept. 11 weekend) was very sad for me – and a lot of my colleagues [with] the combination of the 20th anniversary of 9/11, and the recent development. Fortunately, I have friends and people I can talk to. I walked with a colleague of mine who was in the Army. I’m following my own rule of the three buckets, so we took a walk around the hospital center for about 45 minutes, and we have five fish ponds here. And we went and looked at the fish, and talked to the fish. At the National Rehab Hospital, they were playing the guitar. So there’s are a variety of things that people can do.
A new name for BPD?
Michael A. Cummings, MD, has never liked the term “borderline personality disorder” (BPD). In his view, it’s a misnomer and needs to be changed.
“What is it bordering on? It’s not bordering on something, it’s a disorder on its own,” said Dr. Cummings of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD grew out of the concept that patients were bordering on something, perhaps becoming bipolar. “In many ways, I don’t think it is even a personality disorder. It appears to be an inherent temperament that evolves into an inability to regulate mood.”
In his view, this puts it in the category of a mood dysregulation disorder.
Changing the label would not necessarily improve treatment, he added. However, transitioning from a pejorative to a more neutral label could make it easier for people to say, “this is just a type of mood disorder. It’s not necessarily easy, but it’s workable,” said Dr. Cummings.
Others in the field contend that the term fits the condition. BPD “describes how it encompasses a lot of complex psychological difficulties, undermining functioning of patients in a specific way,” said Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass. The disorder was identified because of its relationship with other known psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Choi-Kain. “There’s an element of BPD that borders on mood disorders because moods are so unstable with BPD. It also borders on trauma-related disorders. It borders on psychotic disorders because there’s sometimes stress-induced experiences of losing contact with realistic thinking.”
If anything needs to change, it’s the attitude toward the disorder, not the name. “I don’t think the term itself is pejorative. But I think that associations with the term have been very stigmatizing. For a long time, there was an attitude that these patients could not be treated or had negative therapeutic reactions.”
Data suggest that these patients are highly prevalent in clinical settings. “And I interpret that as them seeking the care that they need rather than resisting care or not responding to care,” said Dr. Choi-Kain.
Michael A. Cummings, MD, has never liked the term “borderline personality disorder” (BPD). In his view, it’s a misnomer and needs to be changed.
“What is it bordering on? It’s not bordering on something, it’s a disorder on its own,” said Dr. Cummings of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD grew out of the concept that patients were bordering on something, perhaps becoming bipolar. “In many ways, I don’t think it is even a personality disorder. It appears to be an inherent temperament that evolves into an inability to regulate mood.”
In his view, this puts it in the category of a mood dysregulation disorder.
Changing the label would not necessarily improve treatment, he added. However, transitioning from a pejorative to a more neutral label could make it easier for people to say, “this is just a type of mood disorder. It’s not necessarily easy, but it’s workable,” said Dr. Cummings.
Others in the field contend that the term fits the condition. BPD “describes how it encompasses a lot of complex psychological difficulties, undermining functioning of patients in a specific way,” said Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass. The disorder was identified because of its relationship with other known psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Choi-Kain. “There’s an element of BPD that borders on mood disorders because moods are so unstable with BPD. It also borders on trauma-related disorders. It borders on psychotic disorders because there’s sometimes stress-induced experiences of losing contact with realistic thinking.”
If anything needs to change, it’s the attitude toward the disorder, not the name. “I don’t think the term itself is pejorative. But I think that associations with the term have been very stigmatizing. For a long time, there was an attitude that these patients could not be treated or had negative therapeutic reactions.”
Data suggest that these patients are highly prevalent in clinical settings. “And I interpret that as them seeking the care that they need rather than resisting care or not responding to care,” said Dr. Choi-Kain.
Michael A. Cummings, MD, has never liked the term “borderline personality disorder” (BPD). In his view, it’s a misnomer and needs to be changed.
“What is it bordering on? It’s not bordering on something, it’s a disorder on its own,” said Dr. Cummings of the department of psychiatry at the University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD grew out of the concept that patients were bordering on something, perhaps becoming bipolar. “In many ways, I don’t think it is even a personality disorder. It appears to be an inherent temperament that evolves into an inability to regulate mood.”
In his view, this puts it in the category of a mood dysregulation disorder.
Changing the label would not necessarily improve treatment, he added. However, transitioning from a pejorative to a more neutral label could make it easier for people to say, “this is just a type of mood disorder. It’s not necessarily easy, but it’s workable,” said Dr. Cummings.
Others in the field contend that the term fits the condition. BPD “describes how it encompasses a lot of complex psychological difficulties, undermining functioning of patients in a specific way,” said Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute, McLean Hospital, Belmont, Mass. The disorder was identified because of its relationship with other known psychiatric disorders, said Dr. Choi-Kain. “There’s an element of BPD that borders on mood disorders because moods are so unstable with BPD. It also borders on trauma-related disorders. It borders on psychotic disorders because there’s sometimes stress-induced experiences of losing contact with realistic thinking.”
If anything needs to change, it’s the attitude toward the disorder, not the name. “I don’t think the term itself is pejorative. But I think that associations with the term have been very stigmatizing. For a long time, there was an attitude that these patients could not be treated or had negative therapeutic reactions.”
Data suggest that these patients are highly prevalent in clinical settings. “And I interpret that as them seeking the care that they need rather than resisting care or not responding to care,” said Dr. Choi-Kain.
Trust is key in treating borderline personality disorder
Difficulties associated with treating borderline personality disorder (BPD) make for an uneasy alliance between patient and clinician. Deep-seated anxiety and trust issues often lead to patients skipping visits or raging at those who treat them, leaving clinicians frustrated and ready to give up or relying on a pill to make the patient better.
John M. Oldham, MD, MS, recalls one patient he almost lost, a woman who was struggling with aggressive behavior. Initially cooperative and punctual, the patient gradually became distrustful, grilling Dr. Oldham on his training and credentials. “As the questions continued, she slipped from being very cooperative to being enraged and attacking me,” said Dr. Oldham, Distinguished Emeritus Professor in the Menninger department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College in Houston.
Dr. Oldham eventually drew her back in by earning her trust. “There’s no magic to this,” he acknowledged. “You try to be as alert and informed and vigilant for anything you say that produces a negative or concerning reaction in the patient.”
This interactive approach to BPD treatment has been gaining traction in a profession that often looks to medications to alleviate specific symptoms. It’s so effective that it sometimes even surprises the patient, Dr. Oldham noted. “When you approach them like this, they can begin to settle down,” which was the case with the female patient he once treated.
About 1.4% of the U.S. population has BPD, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Conceptualized by the late John G. Gunderson, MD, BPD initially was seen as floating on the borderline between psychosis and neurosis. Clinicians now understand that this isn’t the case. The patients need, as Dr. Gunderson once pointed out, constant vigilance because of attachment issues and childhood trauma.
A stable therapeutic alliance between patient and physician, sometimes in combination with evidence-based therapies, is a formula for success, some experts say.
A misunderstood condition
Although there is some degree of heritable risk, BPD patients are often the product of an invalidating environment in childhood. “As kids, we’re guided and nurtured by caring adults to provide models of reasonable, trustworthy behavior. If those role models are missing or just so inconsistent and unpredictable, the patient doesn’t end up with a sturdy self-image. Instead, they’re adrift, trying to figure out who will be helpful and be a meaningful, trustworthy companion and adviser,” Dr. Oldham said.
Emotional or affective instability and impulsivity, sometimes impulsive aggression, often characterize their condition. “Brain-imaging studies have revealed that certain nerve pathways that are necessary to regulate emotions are impoverished in patients with BPD,” Dr. Oldham said.
An analogy is a car going too fast, with a runaway engine that’s running too hot – and the brakes don’t work, he added.
“People think these patients are trying to create big drama, that they’re putting on a big show. That’s not accurate,” he continued. These patients don’t have the ability to stop the trigger that leads to their emotional storms. They also don’t have the ability to regulate themselves. “We may say, it’s a beautiful day outside, but I still have to go to work. Someone with BPD may say: It’s a beautiful day; I’m going to the beach,” Dr. Oldham explained.
A person with BPD might sound coherent when arguing with someone else. But their words are driven by the storm they can’t turn off.
This can lead to their own efforts to turn off the intensity. They might become self-injurious or push other people away. It’s one of the ironies of this condition because BPD patients desperately want to trust others but are scared to do so. “They look for any little signal – that someone else will hurt, disappoint, or leave them. Eventually their relationships unravel,” Dr. Oldham saod.
For some, suicide is sometimes a final solution.
Those traits make it difficult for a therapist to connect with a patient. “This is a very difficult group of people to treat and to establish treatment,” said Michael A. Cummings, MD, of the department of psychiatry at University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD patients tend to idealize people who are attempting to help them. When they become frustrated or disappointed in some way, “they then devalue the caregiver or the treatment and not infrequently, fall out of treatment,” Dr. Cummings said. It can be a very taxing experience, particularly for younger, less experienced therapists.
Medication only goes so far
Psychiatrists tend to look at BPD patients as receptor sites for molecules, assessing symptoms they can prescribe for, Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass., said in an interview.
Yet, BPD is not a molecular problem, principally. It’s an interpersonal disorder. When BPD is a co-occurring disorder, as is often the case, the depressive, anxiety, or other disorder can mask the BPD, he added, citing his 2018 paper on tensions in psychiatry between the biomedical and biopsychosocial models (Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2018 Jun;41[2]:237-48).
In one longitudinal study (J Pers Disord. 2005 Oct;19[5]:487-504), the presence of BPD strongly predicted the persistence of depression. BPD comorbid with depression is often a recipe for treatment-resistant depression, which results in higher costs, more utilization of resources, and higher suicide rates. Too often, psychiatrists diagnose the depression but miss the BPD. They keep trying molecular approaches with prescription drugs – even though it’s really the interpersonal issues of BPD that need to be addressed, said Dr. Plakun, who is a member of the Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry’s Psychotherapy Committee, and founder and past leader of the American Psychiatric Association’s Psychotherapy Caucus.
Medication can be helpful as a short-term adjunctive therapy. Long term, it’s not a sustainable approach, said Dr. Oldham. “If a patient is in a particularly stressful period, in the middle of a stormy breakup or having a depressive episode or talking about suicide, a time-limited course of an antidepressant may be helpful,” he said. They could also benefit from an anxiety-related drug or medication to help them sleep.
What you don’t want is for the patient to start relying on medications to help them feel better. The problem is, many are suffering so much that they’ll go to their primary care doctor and say, “I’m suffering from anxiety,” and get an antianxiety drug. Or they’re depressed or in pain and end up with a cocktail of medications. “And that’s just going to make matters worse,” Dr. Oldham said.
Psychotherapy as a first-line approach
APA practice guidelines and others worldwide have all come to the same conclusion about BPD. , who chaired an APA committee that developed an evidence-based practice guideline for patients with BPD.
Psychotherapy keeps the patient from firing you, he asserted. “Because of the lack of trust, they push away. They’re very scared, and this fear also applies to therapist. The goal is to help the patient learn to trust you. To do that, you need to develop a strong therapeutic alliance.”
In crafting the APA’s practice guideline, Dr. Oldham and his colleagues studied a variety of approaches, including mentalization-based therapy (MBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which was developed by Marsha Linehan, PhD. Since then, other approaches have demonstrated efficacy in randomized clinical trials, including schema-based therapy (SBT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP).
Those treatments might complement the broader goal of establishing a strong alliance with the patient, Dr. Oldham said. Manualized approaches can help prepackage a program that allows clinicians and patients to look at their problems in an objective, nonpejorative way, Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., said in an interview. DBT, for example, focuses on emotion dysregulation. MBT addresses how the patient sees themselves through others and their interactions with others. “It destigmatizes a problem as a clinical entity rather than an interpersonal problem between the patient and the clinician,” Dr. Choi-Kain said.
The choice of approach depends on several factors: the patient’s needs and preferences, and the therapist’s skills and experience, said Dr. Oldham. Some patients don’t do well with DBT because it involves a lot of homework and didactic work. Others do better with TFP because they want to understand what drives their behavior.
Dr. Cummings recalled how one of his patients used TFP to look inward and heal.
He first met the patient when she was in her early 30s. “She had made some progress, but I remember she was still struggling mightily with relationship issues and with identifying her role in relationships,” he said. The patient was becoming increasingly aware that she was going to end up alone and didn’t want that as an outcome.
Adapting to a TFP model, “she worked very hard trying to understand herself as she related to other people, understanding her own emotional volatility, and some of her proneness to behavioral problems,” Dr. Cummings said. The patient also had to learn how to negotiate her relationships to the point where she didn’t end up destroying them and alienating people.
Customizing the treatment
Physicians can choose from one of these manualized forms of treatment to see what’s appropriate and what works for the patient. “You can individualize the treatment, borrowing from these approaches and shaping it based on what your patient needs,” Dr. Oldham recommended.
Recently, the field of psychiatry has seen the benefits of combining manualized, evidence-based approaches with general psychiatric management (GPM), a method conceived by Dr. Gunderson. GPM “reflects a sensitive understanding of mental illness, offering ‘non attacking’ or collaborative work with the patient and a sensitive recognition of appropriate interventions or corrections to help the patient stay in treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
It aims to conceptualize BPD in a clinically objective way, medicalizing the disorder so it’s something that the patient has, rather than something he or she is, explained Dr. Choi-Kain, who worked with Dr. Gunderson to train clinicians on using this approach. Using a framework that’s compatible with good medical practices, the clinician tries to define the problem together with the patient, “really assessing whether or not the treatment works, setting goals, managing safety, and trying to promote functioning, something we need to pay more attention to with BPD,” she said.
For these patients, the goal is to have positive, corrective experiences in the real world, reinforcing their hopes and what they’re capable of, and an interface with the world that makes them feel like contributors, she said.
Cycle of rupture and repair
Many people with BPD struggle with the desire to find and feel love, but also deal with their rage and hate. Hence, therapists must prepare themselves for the experience of sometimes being hated, said Dr. Plakun. The patient needs to feel they’re in a safe enough space to express those feelings, activating a cycle of “rupture and repair,” he continued.
The key in working with these patients is to avoid any language that will make them feel attacked or criticized, said Dr. Oldham.
A patient may get furious and say “I don’t know what you’re talking about. I didn’t say that.” When in truth, the psychiatrist is flat accurate about what the patient said. Instead of arguing with the patient, a physician can back up and say: “Help me understand what you’re feeling right now. What did I say that made you feel that you couldn’t trust me? Help me understand you. I may have made a mistake,” he advised.
Trust is a key ingredient in an alliance-based intervention for suicidal patients with BPD that Dr. Plakun has frequently written about. A bond he had with a deeply suicidal patient helped her overcome her grief and come to terms with an abusive childhood.
“She had a horrible history of abuse and had BPD and bipolar disorder. Even controlled with medications her life was still awful. She contemplated suicide relentlessly.” Working through her history of sexual abuse, the patient discovered that much of what she and clinicians thought of as a depressive illness was in fact intense grief about the irreparable damage that had taken place during childhood.
Through their work she was able to mourn, and her depression and BPD improved.
Developing a trusting relationship with the patient isn’t a starting point; it’s the goal, he emphasized.
“You don’t prescribe trust to someone. It’s earned.” Through the shared journey of therapy, as the patient suffers from inevitable injuries and ruptures and as the therapist reveals his or her imperfections, opportunities arise to nonjudgmentally examine and repair ruptures. This lead to gains in trust, he said.
It’s not just about genes
Many in the psychiatric and psychological communities tend to develop a very nihilistic view of BPD patients, observed Dr. Cummings. “They’ll say: ‘Oh, well, it’s hopeless. There’s nothing that can be done.’ That isn’t true,” he said.
Epidemiologic studies of these individuals have shown that many of these patients no longer meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD by the time they reach middle age. This means they get better over time, noted Dr. Cummings.
Dr. Plakun’s hope is that the field will evolve in a direction that recognizes the importance of psychosocial treatments like psychotherapy, in addition to biomedical treatments. The drive to medicate still exists, which can contribute to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of BPD, he said. “Although there are manualized, evidence-based treatments, few clinicians learn even one of these for BPD, not to mention those for other disorders.”
In 1996, Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, the current director of the National Institutes of Health, predicted that the decoding of the human genome would transform treatment of medical and mental disorders [and] “that we would discover the ways in which genes equal disease,” said Dr. Plakun. What the science has since shown, is genes by environmental interaction lead to disease and health.
Nature and nurture both matter. “And I don’t think we’re paying enough attention to the nurture side,” Dr. Plakun said.
The solution is a return to a biopsychosocial model, recognizing that psychotherapy is an essential part of treatment of BPD and other conditions, and an essential clinician skill, he said.
Dr. Oldham is coeditor of the “Textbook of Personality Disorders”, 3rd edition (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2021).Dr. Choi-Kain is coeditor with Dr. Gunderson of “Applications of Good Psychiatric Management for Borderline Personality Disorder: A Practical Guide” (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2019).
Dr. Cummings and Dr. Plakun had no disclosures.
Difficulties associated with treating borderline personality disorder (BPD) make for an uneasy alliance between patient and clinician. Deep-seated anxiety and trust issues often lead to patients skipping visits or raging at those who treat them, leaving clinicians frustrated and ready to give up or relying on a pill to make the patient better.
John M. Oldham, MD, MS, recalls one patient he almost lost, a woman who was struggling with aggressive behavior. Initially cooperative and punctual, the patient gradually became distrustful, grilling Dr. Oldham on his training and credentials. “As the questions continued, she slipped from being very cooperative to being enraged and attacking me,” said Dr. Oldham, Distinguished Emeritus Professor in the Menninger department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College in Houston.
Dr. Oldham eventually drew her back in by earning her trust. “There’s no magic to this,” he acknowledged. “You try to be as alert and informed and vigilant for anything you say that produces a negative or concerning reaction in the patient.”
This interactive approach to BPD treatment has been gaining traction in a profession that often looks to medications to alleviate specific symptoms. It’s so effective that it sometimes even surprises the patient, Dr. Oldham noted. “When you approach them like this, they can begin to settle down,” which was the case with the female patient he once treated.
About 1.4% of the U.S. population has BPD, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Conceptualized by the late John G. Gunderson, MD, BPD initially was seen as floating on the borderline between psychosis and neurosis. Clinicians now understand that this isn’t the case. The patients need, as Dr. Gunderson once pointed out, constant vigilance because of attachment issues and childhood trauma.
A stable therapeutic alliance between patient and physician, sometimes in combination with evidence-based therapies, is a formula for success, some experts say.
A misunderstood condition
Although there is some degree of heritable risk, BPD patients are often the product of an invalidating environment in childhood. “As kids, we’re guided and nurtured by caring adults to provide models of reasonable, trustworthy behavior. If those role models are missing or just so inconsistent and unpredictable, the patient doesn’t end up with a sturdy self-image. Instead, they’re adrift, trying to figure out who will be helpful and be a meaningful, trustworthy companion and adviser,” Dr. Oldham said.
Emotional or affective instability and impulsivity, sometimes impulsive aggression, often characterize their condition. “Brain-imaging studies have revealed that certain nerve pathways that are necessary to regulate emotions are impoverished in patients with BPD,” Dr. Oldham said.
An analogy is a car going too fast, with a runaway engine that’s running too hot – and the brakes don’t work, he added.
“People think these patients are trying to create big drama, that they’re putting on a big show. That’s not accurate,” he continued. These patients don’t have the ability to stop the trigger that leads to their emotional storms. They also don’t have the ability to regulate themselves. “We may say, it’s a beautiful day outside, but I still have to go to work. Someone with BPD may say: It’s a beautiful day; I’m going to the beach,” Dr. Oldham explained.
A person with BPD might sound coherent when arguing with someone else. But their words are driven by the storm they can’t turn off.
This can lead to their own efforts to turn off the intensity. They might become self-injurious or push other people away. It’s one of the ironies of this condition because BPD patients desperately want to trust others but are scared to do so. “They look for any little signal – that someone else will hurt, disappoint, or leave them. Eventually their relationships unravel,” Dr. Oldham saod.
For some, suicide is sometimes a final solution.
Those traits make it difficult for a therapist to connect with a patient. “This is a very difficult group of people to treat and to establish treatment,” said Michael A. Cummings, MD, of the department of psychiatry at University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD patients tend to idealize people who are attempting to help them. When they become frustrated or disappointed in some way, “they then devalue the caregiver or the treatment and not infrequently, fall out of treatment,” Dr. Cummings said. It can be a very taxing experience, particularly for younger, less experienced therapists.
Medication only goes so far
Psychiatrists tend to look at BPD patients as receptor sites for molecules, assessing symptoms they can prescribe for, Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass., said in an interview.
Yet, BPD is not a molecular problem, principally. It’s an interpersonal disorder. When BPD is a co-occurring disorder, as is often the case, the depressive, anxiety, or other disorder can mask the BPD, he added, citing his 2018 paper on tensions in psychiatry between the biomedical and biopsychosocial models (Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2018 Jun;41[2]:237-48).
In one longitudinal study (J Pers Disord. 2005 Oct;19[5]:487-504), the presence of BPD strongly predicted the persistence of depression. BPD comorbid with depression is often a recipe for treatment-resistant depression, which results in higher costs, more utilization of resources, and higher suicide rates. Too often, psychiatrists diagnose the depression but miss the BPD. They keep trying molecular approaches with prescription drugs – even though it’s really the interpersonal issues of BPD that need to be addressed, said Dr. Plakun, who is a member of the Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry’s Psychotherapy Committee, and founder and past leader of the American Psychiatric Association’s Psychotherapy Caucus.
Medication can be helpful as a short-term adjunctive therapy. Long term, it’s not a sustainable approach, said Dr. Oldham. “If a patient is in a particularly stressful period, in the middle of a stormy breakup or having a depressive episode or talking about suicide, a time-limited course of an antidepressant may be helpful,” he said. They could also benefit from an anxiety-related drug or medication to help them sleep.
What you don’t want is for the patient to start relying on medications to help them feel better. The problem is, many are suffering so much that they’ll go to their primary care doctor and say, “I’m suffering from anxiety,” and get an antianxiety drug. Or they’re depressed or in pain and end up with a cocktail of medications. “And that’s just going to make matters worse,” Dr. Oldham said.
Psychotherapy as a first-line approach
APA practice guidelines and others worldwide have all come to the same conclusion about BPD. , who chaired an APA committee that developed an evidence-based practice guideline for patients with BPD.
Psychotherapy keeps the patient from firing you, he asserted. “Because of the lack of trust, they push away. They’re very scared, and this fear also applies to therapist. The goal is to help the patient learn to trust you. To do that, you need to develop a strong therapeutic alliance.”
In crafting the APA’s practice guideline, Dr. Oldham and his colleagues studied a variety of approaches, including mentalization-based therapy (MBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which was developed by Marsha Linehan, PhD. Since then, other approaches have demonstrated efficacy in randomized clinical trials, including schema-based therapy (SBT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP).
Those treatments might complement the broader goal of establishing a strong alliance with the patient, Dr. Oldham said. Manualized approaches can help prepackage a program that allows clinicians and patients to look at their problems in an objective, nonpejorative way, Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., said in an interview. DBT, for example, focuses on emotion dysregulation. MBT addresses how the patient sees themselves through others and their interactions with others. “It destigmatizes a problem as a clinical entity rather than an interpersonal problem between the patient and the clinician,” Dr. Choi-Kain said.
The choice of approach depends on several factors: the patient’s needs and preferences, and the therapist’s skills and experience, said Dr. Oldham. Some patients don’t do well with DBT because it involves a lot of homework and didactic work. Others do better with TFP because they want to understand what drives their behavior.
Dr. Cummings recalled how one of his patients used TFP to look inward and heal.
He first met the patient when she was in her early 30s. “She had made some progress, but I remember she was still struggling mightily with relationship issues and with identifying her role in relationships,” he said. The patient was becoming increasingly aware that she was going to end up alone and didn’t want that as an outcome.
Adapting to a TFP model, “she worked very hard trying to understand herself as she related to other people, understanding her own emotional volatility, and some of her proneness to behavioral problems,” Dr. Cummings said. The patient also had to learn how to negotiate her relationships to the point where she didn’t end up destroying them and alienating people.
Customizing the treatment
Physicians can choose from one of these manualized forms of treatment to see what’s appropriate and what works for the patient. “You can individualize the treatment, borrowing from these approaches and shaping it based on what your patient needs,” Dr. Oldham recommended.
Recently, the field of psychiatry has seen the benefits of combining manualized, evidence-based approaches with general psychiatric management (GPM), a method conceived by Dr. Gunderson. GPM “reflects a sensitive understanding of mental illness, offering ‘non attacking’ or collaborative work with the patient and a sensitive recognition of appropriate interventions or corrections to help the patient stay in treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
It aims to conceptualize BPD in a clinically objective way, medicalizing the disorder so it’s something that the patient has, rather than something he or she is, explained Dr. Choi-Kain, who worked with Dr. Gunderson to train clinicians on using this approach. Using a framework that’s compatible with good medical practices, the clinician tries to define the problem together with the patient, “really assessing whether or not the treatment works, setting goals, managing safety, and trying to promote functioning, something we need to pay more attention to with BPD,” she said.
For these patients, the goal is to have positive, corrective experiences in the real world, reinforcing their hopes and what they’re capable of, and an interface with the world that makes them feel like contributors, she said.
Cycle of rupture and repair
Many people with BPD struggle with the desire to find and feel love, but also deal with their rage and hate. Hence, therapists must prepare themselves for the experience of sometimes being hated, said Dr. Plakun. The patient needs to feel they’re in a safe enough space to express those feelings, activating a cycle of “rupture and repair,” he continued.
The key in working with these patients is to avoid any language that will make them feel attacked or criticized, said Dr. Oldham.
A patient may get furious and say “I don’t know what you’re talking about. I didn’t say that.” When in truth, the psychiatrist is flat accurate about what the patient said. Instead of arguing with the patient, a physician can back up and say: “Help me understand what you’re feeling right now. What did I say that made you feel that you couldn’t trust me? Help me understand you. I may have made a mistake,” he advised.
Trust is a key ingredient in an alliance-based intervention for suicidal patients with BPD that Dr. Plakun has frequently written about. A bond he had with a deeply suicidal patient helped her overcome her grief and come to terms with an abusive childhood.
“She had a horrible history of abuse and had BPD and bipolar disorder. Even controlled with medications her life was still awful. She contemplated suicide relentlessly.” Working through her history of sexual abuse, the patient discovered that much of what she and clinicians thought of as a depressive illness was in fact intense grief about the irreparable damage that had taken place during childhood.
Through their work she was able to mourn, and her depression and BPD improved.
Developing a trusting relationship with the patient isn’t a starting point; it’s the goal, he emphasized.
“You don’t prescribe trust to someone. It’s earned.” Through the shared journey of therapy, as the patient suffers from inevitable injuries and ruptures and as the therapist reveals his or her imperfections, opportunities arise to nonjudgmentally examine and repair ruptures. This lead to gains in trust, he said.
It’s not just about genes
Many in the psychiatric and psychological communities tend to develop a very nihilistic view of BPD patients, observed Dr. Cummings. “They’ll say: ‘Oh, well, it’s hopeless. There’s nothing that can be done.’ That isn’t true,” he said.
Epidemiologic studies of these individuals have shown that many of these patients no longer meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD by the time they reach middle age. This means they get better over time, noted Dr. Cummings.
Dr. Plakun’s hope is that the field will evolve in a direction that recognizes the importance of psychosocial treatments like psychotherapy, in addition to biomedical treatments. The drive to medicate still exists, which can contribute to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of BPD, he said. “Although there are manualized, evidence-based treatments, few clinicians learn even one of these for BPD, not to mention those for other disorders.”
In 1996, Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, the current director of the National Institutes of Health, predicted that the decoding of the human genome would transform treatment of medical and mental disorders [and] “that we would discover the ways in which genes equal disease,” said Dr. Plakun. What the science has since shown, is genes by environmental interaction lead to disease and health.
Nature and nurture both matter. “And I don’t think we’re paying enough attention to the nurture side,” Dr. Plakun said.
The solution is a return to a biopsychosocial model, recognizing that psychotherapy is an essential part of treatment of BPD and other conditions, and an essential clinician skill, he said.
Dr. Oldham is coeditor of the “Textbook of Personality Disorders”, 3rd edition (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2021).Dr. Choi-Kain is coeditor with Dr. Gunderson of “Applications of Good Psychiatric Management for Borderline Personality Disorder: A Practical Guide” (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2019).
Dr. Cummings and Dr. Plakun had no disclosures.
Difficulties associated with treating borderline personality disorder (BPD) make for an uneasy alliance between patient and clinician. Deep-seated anxiety and trust issues often lead to patients skipping visits or raging at those who treat them, leaving clinicians frustrated and ready to give up or relying on a pill to make the patient better.
John M. Oldham, MD, MS, recalls one patient he almost lost, a woman who was struggling with aggressive behavior. Initially cooperative and punctual, the patient gradually became distrustful, grilling Dr. Oldham on his training and credentials. “As the questions continued, she slipped from being very cooperative to being enraged and attacking me,” said Dr. Oldham, Distinguished Emeritus Professor in the Menninger department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Baylor College in Houston.
Dr. Oldham eventually drew her back in by earning her trust. “There’s no magic to this,” he acknowledged. “You try to be as alert and informed and vigilant for anything you say that produces a negative or concerning reaction in the patient.”
This interactive approach to BPD treatment has been gaining traction in a profession that often looks to medications to alleviate specific symptoms. It’s so effective that it sometimes even surprises the patient, Dr. Oldham noted. “When you approach them like this, they can begin to settle down,” which was the case with the female patient he once treated.
About 1.4% of the U.S. population has BPD, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. Conceptualized by the late John G. Gunderson, MD, BPD initially was seen as floating on the borderline between psychosis and neurosis. Clinicians now understand that this isn’t the case. The patients need, as Dr. Gunderson once pointed out, constant vigilance because of attachment issues and childhood trauma.
A stable therapeutic alliance between patient and physician, sometimes in combination with evidence-based therapies, is a formula for success, some experts say.
A misunderstood condition
Although there is some degree of heritable risk, BPD patients are often the product of an invalidating environment in childhood. “As kids, we’re guided and nurtured by caring adults to provide models of reasonable, trustworthy behavior. If those role models are missing or just so inconsistent and unpredictable, the patient doesn’t end up with a sturdy self-image. Instead, they’re adrift, trying to figure out who will be helpful and be a meaningful, trustworthy companion and adviser,” Dr. Oldham said.
Emotional or affective instability and impulsivity, sometimes impulsive aggression, often characterize their condition. “Brain-imaging studies have revealed that certain nerve pathways that are necessary to regulate emotions are impoverished in patients with BPD,” Dr. Oldham said.
An analogy is a car going too fast, with a runaway engine that’s running too hot – and the brakes don’t work, he added.
“People think these patients are trying to create big drama, that they’re putting on a big show. That’s not accurate,” he continued. These patients don’t have the ability to stop the trigger that leads to their emotional storms. They also don’t have the ability to regulate themselves. “We may say, it’s a beautiful day outside, but I still have to go to work. Someone with BPD may say: It’s a beautiful day; I’m going to the beach,” Dr. Oldham explained.
A person with BPD might sound coherent when arguing with someone else. But their words are driven by the storm they can’t turn off.
This can lead to their own efforts to turn off the intensity. They might become self-injurious or push other people away. It’s one of the ironies of this condition because BPD patients desperately want to trust others but are scared to do so. “They look for any little signal – that someone else will hurt, disappoint, or leave them. Eventually their relationships unravel,” Dr. Oldham saod.
For some, suicide is sometimes a final solution.
Those traits make it difficult for a therapist to connect with a patient. “This is a very difficult group of people to treat and to establish treatment,” said Michael A. Cummings, MD, of the department of psychiatry at University of California, Riverside, and a psychopharmacology consultant with the California Department of State Hospitals’ Psychopharmacology Resource Network.
BPD patients tend to idealize people who are attempting to help them. When they become frustrated or disappointed in some way, “they then devalue the caregiver or the treatment and not infrequently, fall out of treatment,” Dr. Cummings said. It can be a very taxing experience, particularly for younger, less experienced therapists.
Medication only goes so far
Psychiatrists tend to look at BPD patients as receptor sites for molecules, assessing symptoms they can prescribe for, Eric M. Plakun, MD, DLFAPA, FACPsych, medical director/CEO of the Austen Riggs Center in Stockbridge, Mass., said in an interview.
Yet, BPD is not a molecular problem, principally. It’s an interpersonal disorder. When BPD is a co-occurring disorder, as is often the case, the depressive, anxiety, or other disorder can mask the BPD, he added, citing his 2018 paper on tensions in psychiatry between the biomedical and biopsychosocial models (Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2018 Jun;41[2]:237-48).
In one longitudinal study (J Pers Disord. 2005 Oct;19[5]:487-504), the presence of BPD strongly predicted the persistence of depression. BPD comorbid with depression is often a recipe for treatment-resistant depression, which results in higher costs, more utilization of resources, and higher suicide rates. Too often, psychiatrists diagnose the depression but miss the BPD. They keep trying molecular approaches with prescription drugs – even though it’s really the interpersonal issues of BPD that need to be addressed, said Dr. Plakun, who is a member of the Group for the Advancement of Psychiatry’s Psychotherapy Committee, and founder and past leader of the American Psychiatric Association’s Psychotherapy Caucus.
Medication can be helpful as a short-term adjunctive therapy. Long term, it’s not a sustainable approach, said Dr. Oldham. “If a patient is in a particularly stressful period, in the middle of a stormy breakup or having a depressive episode or talking about suicide, a time-limited course of an antidepressant may be helpful,” he said. They could also benefit from an anxiety-related drug or medication to help them sleep.
What you don’t want is for the patient to start relying on medications to help them feel better. The problem is, many are suffering so much that they’ll go to their primary care doctor and say, “I’m suffering from anxiety,” and get an antianxiety drug. Or they’re depressed or in pain and end up with a cocktail of medications. “And that’s just going to make matters worse,” Dr. Oldham said.
Psychotherapy as a first-line approach
APA practice guidelines and others worldwide have all come to the same conclusion about BPD. , who chaired an APA committee that developed an evidence-based practice guideline for patients with BPD.
Psychotherapy keeps the patient from firing you, he asserted. “Because of the lack of trust, they push away. They’re very scared, and this fear also applies to therapist. The goal is to help the patient learn to trust you. To do that, you need to develop a strong therapeutic alliance.”
In crafting the APA’s practice guideline, Dr. Oldham and his colleagues studied a variety of approaches, including mentalization-based therapy (MBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT), which was developed by Marsha Linehan, PhD. Since then, other approaches have demonstrated efficacy in randomized clinical trials, including schema-based therapy (SBT), cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), and transference-focused psychotherapy (TFP).
Those treatments might complement the broader goal of establishing a strong alliance with the patient, Dr. Oldham said. Manualized approaches can help prepackage a program that allows clinicians and patients to look at their problems in an objective, nonpejorative way, Lois W. Choi-Kain, MD, MEd, director of the Gunderson Personality Disorders Institute at McLean Hospital in Belmont, Mass., said in an interview. DBT, for example, focuses on emotion dysregulation. MBT addresses how the patient sees themselves through others and their interactions with others. “It destigmatizes a problem as a clinical entity rather than an interpersonal problem between the patient and the clinician,” Dr. Choi-Kain said.
The choice of approach depends on several factors: the patient’s needs and preferences, and the therapist’s skills and experience, said Dr. Oldham. Some patients don’t do well with DBT because it involves a lot of homework and didactic work. Others do better with TFP because they want to understand what drives their behavior.
Dr. Cummings recalled how one of his patients used TFP to look inward and heal.
He first met the patient when she was in her early 30s. “She had made some progress, but I remember she was still struggling mightily with relationship issues and with identifying her role in relationships,” he said. The patient was becoming increasingly aware that she was going to end up alone and didn’t want that as an outcome.
Adapting to a TFP model, “she worked very hard trying to understand herself as she related to other people, understanding her own emotional volatility, and some of her proneness to behavioral problems,” Dr. Cummings said. The patient also had to learn how to negotiate her relationships to the point where she didn’t end up destroying them and alienating people.
Customizing the treatment
Physicians can choose from one of these manualized forms of treatment to see what’s appropriate and what works for the patient. “You can individualize the treatment, borrowing from these approaches and shaping it based on what your patient needs,” Dr. Oldham recommended.
Recently, the field of psychiatry has seen the benefits of combining manualized, evidence-based approaches with general psychiatric management (GPM), a method conceived by Dr. Gunderson. GPM “reflects a sensitive understanding of mental illness, offering ‘non attacking’ or collaborative work with the patient and a sensitive recognition of appropriate interventions or corrections to help the patient stay in treatment,” said Dr. Oldham.
It aims to conceptualize BPD in a clinically objective way, medicalizing the disorder so it’s something that the patient has, rather than something he or she is, explained Dr. Choi-Kain, who worked with Dr. Gunderson to train clinicians on using this approach. Using a framework that’s compatible with good medical practices, the clinician tries to define the problem together with the patient, “really assessing whether or not the treatment works, setting goals, managing safety, and trying to promote functioning, something we need to pay more attention to with BPD,” she said.
For these patients, the goal is to have positive, corrective experiences in the real world, reinforcing their hopes and what they’re capable of, and an interface with the world that makes them feel like contributors, she said.
Cycle of rupture and repair
Many people with BPD struggle with the desire to find and feel love, but also deal with their rage and hate. Hence, therapists must prepare themselves for the experience of sometimes being hated, said Dr. Plakun. The patient needs to feel they’re in a safe enough space to express those feelings, activating a cycle of “rupture and repair,” he continued.
The key in working with these patients is to avoid any language that will make them feel attacked or criticized, said Dr. Oldham.
A patient may get furious and say “I don’t know what you’re talking about. I didn’t say that.” When in truth, the psychiatrist is flat accurate about what the patient said. Instead of arguing with the patient, a physician can back up and say: “Help me understand what you’re feeling right now. What did I say that made you feel that you couldn’t trust me? Help me understand you. I may have made a mistake,” he advised.
Trust is a key ingredient in an alliance-based intervention for suicidal patients with BPD that Dr. Plakun has frequently written about. A bond he had with a deeply suicidal patient helped her overcome her grief and come to terms with an abusive childhood.
“She had a horrible history of abuse and had BPD and bipolar disorder. Even controlled with medications her life was still awful. She contemplated suicide relentlessly.” Working through her history of sexual abuse, the patient discovered that much of what she and clinicians thought of as a depressive illness was in fact intense grief about the irreparable damage that had taken place during childhood.
Through their work she was able to mourn, and her depression and BPD improved.
Developing a trusting relationship with the patient isn’t a starting point; it’s the goal, he emphasized.
“You don’t prescribe trust to someone. It’s earned.” Through the shared journey of therapy, as the patient suffers from inevitable injuries and ruptures and as the therapist reveals his or her imperfections, opportunities arise to nonjudgmentally examine and repair ruptures. This lead to gains in trust, he said.
It’s not just about genes
Many in the psychiatric and psychological communities tend to develop a very nihilistic view of BPD patients, observed Dr. Cummings. “They’ll say: ‘Oh, well, it’s hopeless. There’s nothing that can be done.’ That isn’t true,” he said.
Epidemiologic studies of these individuals have shown that many of these patients no longer meet the diagnostic criteria for BPD by the time they reach middle age. This means they get better over time, noted Dr. Cummings.
Dr. Plakun’s hope is that the field will evolve in a direction that recognizes the importance of psychosocial treatments like psychotherapy, in addition to biomedical treatments. The drive to medicate still exists, which can contribute to underdiagnosis and undertreatment of BPD, he said. “Although there are manualized, evidence-based treatments, few clinicians learn even one of these for BPD, not to mention those for other disorders.”
In 1996, Francis S. Collins, MD, PhD, the current director of the National Institutes of Health, predicted that the decoding of the human genome would transform treatment of medical and mental disorders [and] “that we would discover the ways in which genes equal disease,” said Dr. Plakun. What the science has since shown, is genes by environmental interaction lead to disease and health.
Nature and nurture both matter. “And I don’t think we’re paying enough attention to the nurture side,” Dr. Plakun said.
The solution is a return to a biopsychosocial model, recognizing that psychotherapy is an essential part of treatment of BPD and other conditions, and an essential clinician skill, he said.
Dr. Oldham is coeditor of the “Textbook of Personality Disorders”, 3rd edition (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2021).Dr. Choi-Kain is coeditor with Dr. Gunderson of “Applications of Good Psychiatric Management for Borderline Personality Disorder: A Practical Guide” (Washington: American Psychiatric Association Publishing, 2019).
Dr. Cummings and Dr. Plakun had no disclosures.
Parent-led intervention linked with decreased autism symptoms in at-risk infants
These findings, which were published in JAMA Pediatrics, were the first evidence worldwide that a preemptive intervention during infancy could lead to such a significant improvement in children’s social development, resulting in “three times fewer diagnoses of autism at age 3,” said lead author Andrew Whitehouse, PhD, in a statement.
“No trial of a preemptive infant intervention, applied prior to diagnosis, has to date shown such an effect to impact diagnostic outcomes – until now,” he said.
Study intervention is a nontraditonal approach
Dr. Whitehouse, who is professor of Autism Research at Telethon Kids and University of Western Australia, and Director of CliniKids in Perth, said the intervention is a departure from traditional approaches. “Traditionally, therapy seeks to train children to learn ‘typical’ behaviors,” he said in an email. “The difference of this therapy is that we help parents understand the unique abilities of their baby, and to use these strengths as a foundation for future development.”
Dr. Whitehouse’s study included 103 children (aged approximately 12 months), who displayed at least three of five behaviors indicating a high likelihood of ASD as defined by the Social Attention and Communication Surveillance–Revised (SACS-R) 12-month checklist. The infants were randomized to receive either usual care or the intervention, which is called the iBASIS–Video Interaction to Promote Positive Parenting (iBASIS-VIPP). Usual care was delivered by community physicians, whereas the intervention involved 10 sessions delivered at home by a trained therapist.
“The iBASIS-VIPP uses video-feedback as a means of helping parents recognize their baby’s communication cues so they can respond in a way that builds their social communication development,” Dr. Whitehouse explained in an interview. “The therapist then provides guidance to the parent as to how their baby is communicating with them, and they can communicate back to have back-and-forth conversations.”
“We know these back-and-forth conversations are crucial to support early social communication development, and are a precursor to more complex skills, such as verbal language,” he added.
Reassessment of the children at age 3 years showed a “small but enduring” benefit of the intervention, noted the authors. Children in the intervention group had a reduction in ASD symptom severity (P = .04), and reduced odds of ASD classification, compared with children receiving usual care (6.7% vs. 20.5%; odds ratio, 0.18; P = .02).
The findings provide “initial evidence of efficacy for a new clinical model that uses a specific developmentally focused intervention,” noted the authors. “The children falling below the diagnostic threshold still had developmental difficulties, but by working with each child’s unique differences, rather than trying to counter them, the therapy has effectively supported their development through the early childhood years,” noted Dr. Whitehouse in a statement.
Other research has shown benefits of new study approach
This is a “solid” study, “but, as acknowledged by the authors, the main effects are small in magnitude, and longer-term outcomes will be important to capture,” said Jessica Brian, PhD, C Psych, associate professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Toronto, colead at the Autism Research Centre, and psychologist and clinician-investigator at Holland Bloorview Kids Rehab Hospital in Toronto.
Dr. Brian said she and her coauthors of a paper published in Autism Research and others have shown that the kind of approach used in the new study can be helpful for enhancing different areas of toddler development, but “the specific finding of reduced likelihood of a clinical ASD diagnosis is a bit different.”
The goal of reducing the likelihood of an ASD diagnosis “needs to be considered carefully, from the perspective of autism acceptance,” she added. “From an acceptance lens, the primary objective of early intervention in ASD might be better positioned as aiming to enhance or support a young child’s development, help them make developmental progress, build on their strengths, optimize outcomes, or reduce impairment. … I think the authors do a good job of balancing this perspective.”
New study shows value of parent-mediated interventions
Overall, Dr. Brian, who coauthored the Canadian Paediatric Society’s position statement on ASD diagnosis, lauded the findings as good news.
“It shows the value of using parent-mediated interventions, which are far less costly and are more resource-efficient than most therapist-delivered models.”
“In cases where parent-mediated approaches are made available to families prior to diagnosis, there is potential for strong effects, when the brain is most amenable to learning. Such models may also be an ideal fit before diagnosis, since they are less resource-intensive than therapist-delivered models, which may only be funded by governments once a diagnosis is confirmed,” she said.
“Finally, parent-mediated programs have the potential to support parents during what, for many families, is a particularly challenging time as they identify their child’s developmental differences or receive a diagnosis. Such programs have potential to increase parents’ confidence in parenting a young child with unique learning needs.”
What Dr. Brian thought was missing from the paper was acknowledgment that, “despite early developmental gains from parent-mediated interventions, it is likely that most children with ASD will need additional supports throughout development.”
This study was sponsored by the Telethon Kids Institute. Dr. Whitehouse reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Brian codeveloped a parent-mediated intervention for toddlers with probable or confirmed ASD (the Social ABCs), for which she does not receive any royalties.
These findings, which were published in JAMA Pediatrics, were the first evidence worldwide that a preemptive intervention during infancy could lead to such a significant improvement in children’s social development, resulting in “three times fewer diagnoses of autism at age 3,” said lead author Andrew Whitehouse, PhD, in a statement.
“No trial of a preemptive infant intervention, applied prior to diagnosis, has to date shown such an effect to impact diagnostic outcomes – until now,” he said.
Study intervention is a nontraditonal approach
Dr. Whitehouse, who is professor of Autism Research at Telethon Kids and University of Western Australia, and Director of CliniKids in Perth, said the intervention is a departure from traditional approaches. “Traditionally, therapy seeks to train children to learn ‘typical’ behaviors,” he said in an email. “The difference of this therapy is that we help parents understand the unique abilities of their baby, and to use these strengths as a foundation for future development.”
Dr. Whitehouse’s study included 103 children (aged approximately 12 months), who displayed at least three of five behaviors indicating a high likelihood of ASD as defined by the Social Attention and Communication Surveillance–Revised (SACS-R) 12-month checklist. The infants were randomized to receive either usual care or the intervention, which is called the iBASIS–Video Interaction to Promote Positive Parenting (iBASIS-VIPP). Usual care was delivered by community physicians, whereas the intervention involved 10 sessions delivered at home by a trained therapist.
“The iBASIS-VIPP uses video-feedback as a means of helping parents recognize their baby’s communication cues so they can respond in a way that builds their social communication development,” Dr. Whitehouse explained in an interview. “The therapist then provides guidance to the parent as to how their baby is communicating with them, and they can communicate back to have back-and-forth conversations.”
“We know these back-and-forth conversations are crucial to support early social communication development, and are a precursor to more complex skills, such as verbal language,” he added.
Reassessment of the children at age 3 years showed a “small but enduring” benefit of the intervention, noted the authors. Children in the intervention group had a reduction in ASD symptom severity (P = .04), and reduced odds of ASD classification, compared with children receiving usual care (6.7% vs. 20.5%; odds ratio, 0.18; P = .02).
The findings provide “initial evidence of efficacy for a new clinical model that uses a specific developmentally focused intervention,” noted the authors. “The children falling below the diagnostic threshold still had developmental difficulties, but by working with each child’s unique differences, rather than trying to counter them, the therapy has effectively supported their development through the early childhood years,” noted Dr. Whitehouse in a statement.
Other research has shown benefits of new study approach
This is a “solid” study, “but, as acknowledged by the authors, the main effects are small in magnitude, and longer-term outcomes will be important to capture,” said Jessica Brian, PhD, C Psych, associate professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Toronto, colead at the Autism Research Centre, and psychologist and clinician-investigator at Holland Bloorview Kids Rehab Hospital in Toronto.
Dr. Brian said she and her coauthors of a paper published in Autism Research and others have shown that the kind of approach used in the new study can be helpful for enhancing different areas of toddler development, but “the specific finding of reduced likelihood of a clinical ASD diagnosis is a bit different.”
The goal of reducing the likelihood of an ASD diagnosis “needs to be considered carefully, from the perspective of autism acceptance,” she added. “From an acceptance lens, the primary objective of early intervention in ASD might be better positioned as aiming to enhance or support a young child’s development, help them make developmental progress, build on their strengths, optimize outcomes, or reduce impairment. … I think the authors do a good job of balancing this perspective.”
New study shows value of parent-mediated interventions
Overall, Dr. Brian, who coauthored the Canadian Paediatric Society’s position statement on ASD diagnosis, lauded the findings as good news.
“It shows the value of using parent-mediated interventions, which are far less costly and are more resource-efficient than most therapist-delivered models.”
“In cases where parent-mediated approaches are made available to families prior to diagnosis, there is potential for strong effects, when the brain is most amenable to learning. Such models may also be an ideal fit before diagnosis, since they are less resource-intensive than therapist-delivered models, which may only be funded by governments once a diagnosis is confirmed,” she said.
“Finally, parent-mediated programs have the potential to support parents during what, for many families, is a particularly challenging time as they identify their child’s developmental differences or receive a diagnosis. Such programs have potential to increase parents’ confidence in parenting a young child with unique learning needs.”
What Dr. Brian thought was missing from the paper was acknowledgment that, “despite early developmental gains from parent-mediated interventions, it is likely that most children with ASD will need additional supports throughout development.”
This study was sponsored by the Telethon Kids Institute. Dr. Whitehouse reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Brian codeveloped a parent-mediated intervention for toddlers with probable or confirmed ASD (the Social ABCs), for which she does not receive any royalties.
These findings, which were published in JAMA Pediatrics, were the first evidence worldwide that a preemptive intervention during infancy could lead to such a significant improvement in children’s social development, resulting in “three times fewer diagnoses of autism at age 3,” said lead author Andrew Whitehouse, PhD, in a statement.
“No trial of a preemptive infant intervention, applied prior to diagnosis, has to date shown such an effect to impact diagnostic outcomes – until now,” he said.
Study intervention is a nontraditonal approach
Dr. Whitehouse, who is professor of Autism Research at Telethon Kids and University of Western Australia, and Director of CliniKids in Perth, said the intervention is a departure from traditional approaches. “Traditionally, therapy seeks to train children to learn ‘typical’ behaviors,” he said in an email. “The difference of this therapy is that we help parents understand the unique abilities of their baby, and to use these strengths as a foundation for future development.”
Dr. Whitehouse’s study included 103 children (aged approximately 12 months), who displayed at least three of five behaviors indicating a high likelihood of ASD as defined by the Social Attention and Communication Surveillance–Revised (SACS-R) 12-month checklist. The infants were randomized to receive either usual care or the intervention, which is called the iBASIS–Video Interaction to Promote Positive Parenting (iBASIS-VIPP). Usual care was delivered by community physicians, whereas the intervention involved 10 sessions delivered at home by a trained therapist.
“The iBASIS-VIPP uses video-feedback as a means of helping parents recognize their baby’s communication cues so they can respond in a way that builds their social communication development,” Dr. Whitehouse explained in an interview. “The therapist then provides guidance to the parent as to how their baby is communicating with them, and they can communicate back to have back-and-forth conversations.”
“We know these back-and-forth conversations are crucial to support early social communication development, and are a precursor to more complex skills, such as verbal language,” he added.
Reassessment of the children at age 3 years showed a “small but enduring” benefit of the intervention, noted the authors. Children in the intervention group had a reduction in ASD symptom severity (P = .04), and reduced odds of ASD classification, compared with children receiving usual care (6.7% vs. 20.5%; odds ratio, 0.18; P = .02).
The findings provide “initial evidence of efficacy for a new clinical model that uses a specific developmentally focused intervention,” noted the authors. “The children falling below the diagnostic threshold still had developmental difficulties, but by working with each child’s unique differences, rather than trying to counter them, the therapy has effectively supported their development through the early childhood years,” noted Dr. Whitehouse in a statement.
Other research has shown benefits of new study approach
This is a “solid” study, “but, as acknowledged by the authors, the main effects are small in magnitude, and longer-term outcomes will be important to capture,” said Jessica Brian, PhD, C Psych, associate professor in the department of pediatrics at the University of Toronto, colead at the Autism Research Centre, and psychologist and clinician-investigator at Holland Bloorview Kids Rehab Hospital in Toronto.
Dr. Brian said she and her coauthors of a paper published in Autism Research and others have shown that the kind of approach used in the new study can be helpful for enhancing different areas of toddler development, but “the specific finding of reduced likelihood of a clinical ASD diagnosis is a bit different.”
The goal of reducing the likelihood of an ASD diagnosis “needs to be considered carefully, from the perspective of autism acceptance,” she added. “From an acceptance lens, the primary objective of early intervention in ASD might be better positioned as aiming to enhance or support a young child’s development, help them make developmental progress, build on their strengths, optimize outcomes, or reduce impairment. … I think the authors do a good job of balancing this perspective.”
New study shows value of parent-mediated interventions
Overall, Dr. Brian, who coauthored the Canadian Paediatric Society’s position statement on ASD diagnosis, lauded the findings as good news.
“It shows the value of using parent-mediated interventions, which are far less costly and are more resource-efficient than most therapist-delivered models.”
“In cases where parent-mediated approaches are made available to families prior to diagnosis, there is potential for strong effects, when the brain is most amenable to learning. Such models may also be an ideal fit before diagnosis, since they are less resource-intensive than therapist-delivered models, which may only be funded by governments once a diagnosis is confirmed,” she said.
“Finally, parent-mediated programs have the potential to support parents during what, for many families, is a particularly challenging time as they identify their child’s developmental differences or receive a diagnosis. Such programs have potential to increase parents’ confidence in parenting a young child with unique learning needs.”
What Dr. Brian thought was missing from the paper was acknowledgment that, “despite early developmental gains from parent-mediated interventions, it is likely that most children with ASD will need additional supports throughout development.”
This study was sponsored by the Telethon Kids Institute. Dr. Whitehouse reported no conflicts of interest. Dr. Brian codeveloped a parent-mediated intervention for toddlers with probable or confirmed ASD (the Social ABCs), for which she does not receive any royalties.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS