User login
New international guidelines on opioid deprescribing
An expert panel of pain management clinicians has released what they say are the first international guidelines for general practitioners on opioid analgesic deprescribing in adults.
The recommendations describe best practices for stopping opioid therapy and emphasize slow tapering and individualized deprescribing plans tailored to each patient.
Developed by general practitioners, pain specialists, addiction specialists, pharmacists, registered nurses, consumers, and physiotherapists, the guidelines note that deprescribing may not be appropriate for every patient and that stopping abruptly can be associated with an increased risk of overdose.
“Internationally, we were seeing significant harms from opioids but also significant harms from unsolicited and abrupt opioid cessation,” said lead author Aili Langford, PhD, who conducted the study as a doctoral student at the University of Sydney. “It was clear that recommendations to support safe and person-centered opioid deprescribing were required.”
The findings were published online in the Medical Journal of Australia.
Deprescribing plan
The consensus guidelines include 11 recommendations for deprescribing in adult patients who take at least one opioid for any type of pain.
Recommendations include implementing a deprescribing plan when opioids are first prescribed and gradual and individualized deprescribing, with regular monitoring and review.
Clinicians should consider opioid deprescribing in patients who experience no clinically meaningful improvement in function, quality of life, or pain at high risk with opioid therapy, they note. Patients who are at high risk for opioid-related harm are also good candidates for deprescribing.
Stopping opioid therapy is not recommended for patients with severe opioid use disorder (OUD). In those patients, medication-assisted OUD treatment and other evidence-based interventions are recommended.
“Opioids can be effective in pain management,” co-author Carl Schneider, PhD, an associate professor of pharmacy at the University of Sydney, said in a press release. “However, over the longer term, the risk of harms may outweigh the benefits.”
A ‘global problem’
Commenting on the guidelines, Orman Trent Hall, DO, assistant professor of addiction medicine, department of psychiatry and behavioral health at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said they are similar to recommendations published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2016 and 2022 but offer additional information that could be helpful.
“This new guideline provides more explicit advice about tapering and withdrawal management, which may be useful to practitioners. The opioid crisis is a global problem, and while individual countries may require local solutions, the new international guideline may offer a framework for approaching this issue,” he said.
The guideline’s emphasis on the potential risks of deprescribing in some patients is also key, Dr. Hall added. Patients who are tapering off opioid therapy may have worsening pain and loss of function that can affect their quality of life.
“Patients may also experience psychological harm and increased risk of opioid use disorder and death by suicide following opioid deprescribing,” Dr. Hall said. “Therefore, it is important for providers to carefully weigh the risks of prescribing and deprescribing and engage patients with person-centered communication and shared decision-making.”
The work was funded by grants from the University of Sydney and the National Health and Medical Research Council. Full disclosures are available in the original article. Dr. Hall has provided expert opinion to the health care consultancy firm Lumanity and Emergent BioSolutions regarding the overdose crisis.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An expert panel of pain management clinicians has released what they say are the first international guidelines for general practitioners on opioid analgesic deprescribing in adults.
The recommendations describe best practices for stopping opioid therapy and emphasize slow tapering and individualized deprescribing plans tailored to each patient.
Developed by general practitioners, pain specialists, addiction specialists, pharmacists, registered nurses, consumers, and physiotherapists, the guidelines note that deprescribing may not be appropriate for every patient and that stopping abruptly can be associated with an increased risk of overdose.
“Internationally, we were seeing significant harms from opioids but also significant harms from unsolicited and abrupt opioid cessation,” said lead author Aili Langford, PhD, who conducted the study as a doctoral student at the University of Sydney. “It was clear that recommendations to support safe and person-centered opioid deprescribing were required.”
The findings were published online in the Medical Journal of Australia.
Deprescribing plan
The consensus guidelines include 11 recommendations for deprescribing in adult patients who take at least one opioid for any type of pain.
Recommendations include implementing a deprescribing plan when opioids are first prescribed and gradual and individualized deprescribing, with regular monitoring and review.
Clinicians should consider opioid deprescribing in patients who experience no clinically meaningful improvement in function, quality of life, or pain at high risk with opioid therapy, they note. Patients who are at high risk for opioid-related harm are also good candidates for deprescribing.
Stopping opioid therapy is not recommended for patients with severe opioid use disorder (OUD). In those patients, medication-assisted OUD treatment and other evidence-based interventions are recommended.
“Opioids can be effective in pain management,” co-author Carl Schneider, PhD, an associate professor of pharmacy at the University of Sydney, said in a press release. “However, over the longer term, the risk of harms may outweigh the benefits.”
A ‘global problem’
Commenting on the guidelines, Orman Trent Hall, DO, assistant professor of addiction medicine, department of psychiatry and behavioral health at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said they are similar to recommendations published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2016 and 2022 but offer additional information that could be helpful.
“This new guideline provides more explicit advice about tapering and withdrawal management, which may be useful to practitioners. The opioid crisis is a global problem, and while individual countries may require local solutions, the new international guideline may offer a framework for approaching this issue,” he said.
The guideline’s emphasis on the potential risks of deprescribing in some patients is also key, Dr. Hall added. Patients who are tapering off opioid therapy may have worsening pain and loss of function that can affect their quality of life.
“Patients may also experience psychological harm and increased risk of opioid use disorder and death by suicide following opioid deprescribing,” Dr. Hall said. “Therefore, it is important for providers to carefully weigh the risks of prescribing and deprescribing and engage patients with person-centered communication and shared decision-making.”
The work was funded by grants from the University of Sydney and the National Health and Medical Research Council. Full disclosures are available in the original article. Dr. Hall has provided expert opinion to the health care consultancy firm Lumanity and Emergent BioSolutions regarding the overdose crisis.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
An expert panel of pain management clinicians has released what they say are the first international guidelines for general practitioners on opioid analgesic deprescribing in adults.
The recommendations describe best practices for stopping opioid therapy and emphasize slow tapering and individualized deprescribing plans tailored to each patient.
Developed by general practitioners, pain specialists, addiction specialists, pharmacists, registered nurses, consumers, and physiotherapists, the guidelines note that deprescribing may not be appropriate for every patient and that stopping abruptly can be associated with an increased risk of overdose.
“Internationally, we were seeing significant harms from opioids but also significant harms from unsolicited and abrupt opioid cessation,” said lead author Aili Langford, PhD, who conducted the study as a doctoral student at the University of Sydney. “It was clear that recommendations to support safe and person-centered opioid deprescribing were required.”
The findings were published online in the Medical Journal of Australia.
Deprescribing plan
The consensus guidelines include 11 recommendations for deprescribing in adult patients who take at least one opioid for any type of pain.
Recommendations include implementing a deprescribing plan when opioids are first prescribed and gradual and individualized deprescribing, with regular monitoring and review.
Clinicians should consider opioid deprescribing in patients who experience no clinically meaningful improvement in function, quality of life, or pain at high risk with opioid therapy, they note. Patients who are at high risk for opioid-related harm are also good candidates for deprescribing.
Stopping opioid therapy is not recommended for patients with severe opioid use disorder (OUD). In those patients, medication-assisted OUD treatment and other evidence-based interventions are recommended.
“Opioids can be effective in pain management,” co-author Carl Schneider, PhD, an associate professor of pharmacy at the University of Sydney, said in a press release. “However, over the longer term, the risk of harms may outweigh the benefits.”
A ‘global problem’
Commenting on the guidelines, Orman Trent Hall, DO, assistant professor of addiction medicine, department of psychiatry and behavioral health at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, said they are similar to recommendations published by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in 2016 and 2022 but offer additional information that could be helpful.
“This new guideline provides more explicit advice about tapering and withdrawal management, which may be useful to practitioners. The opioid crisis is a global problem, and while individual countries may require local solutions, the new international guideline may offer a framework for approaching this issue,” he said.
The guideline’s emphasis on the potential risks of deprescribing in some patients is also key, Dr. Hall added. Patients who are tapering off opioid therapy may have worsening pain and loss of function that can affect their quality of life.
“Patients may also experience psychological harm and increased risk of opioid use disorder and death by suicide following opioid deprescribing,” Dr. Hall said. “Therefore, it is important for providers to carefully weigh the risks of prescribing and deprescribing and engage patients with person-centered communication and shared decision-making.”
The work was funded by grants from the University of Sydney and the National Health and Medical Research Council. Full disclosures are available in the original article. Dr. Hall has provided expert opinion to the health care consultancy firm Lumanity and Emergent BioSolutions regarding the overdose crisis.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New DEA CME mandate affects 2 million prescribers
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.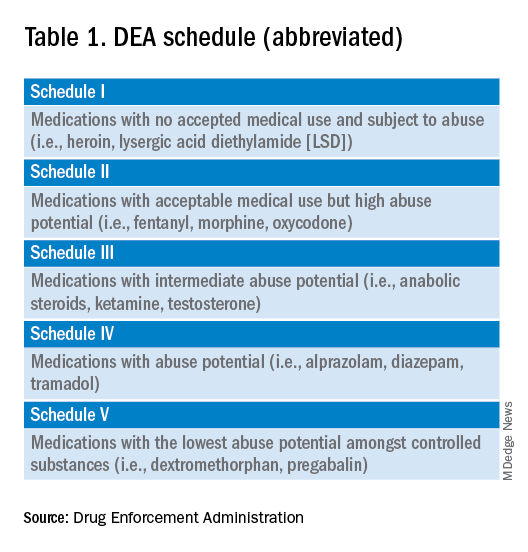
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 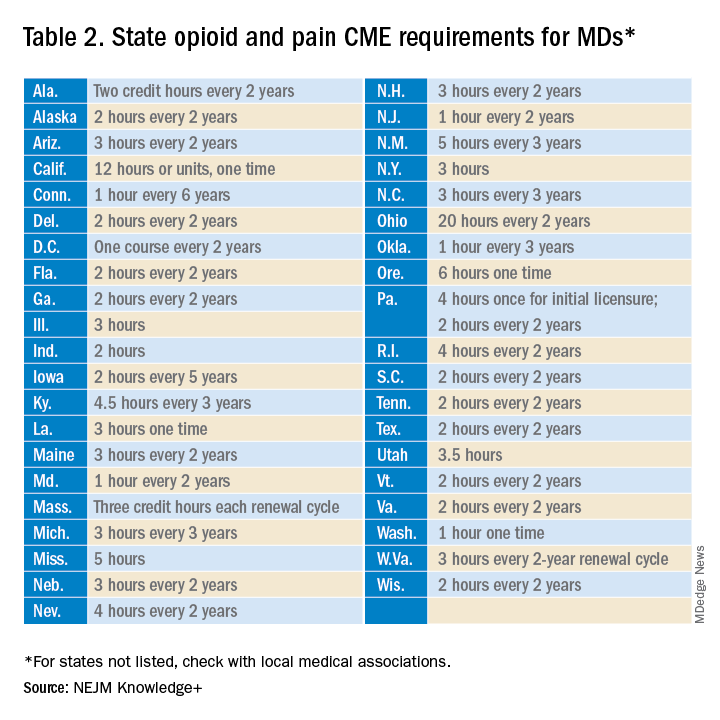
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).
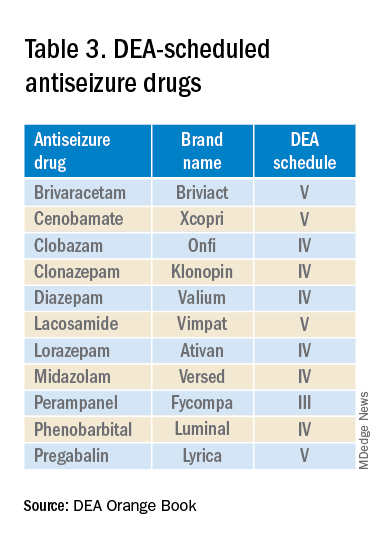
Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).

Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2023 mandates that all Drug Enforcement Administration–registered physicians and health care providers complete a one-time, 8-hour CME training on managing and treating opioid and other substance abuse disorders. This requirement goes into effect on June 27, 2023. New DEA registrants must also comply. Veterinarians are exempt.
A DEA registration is required to prescribe any controlled substance. The DEA categorizes these as Schedule I-V, with V being the least likely to be abused (Table 1). For example, opioids like fentanyl, oxycodone, and morphine are Schedule II. Medications without abuse potential are not scheduled.
Will 16 million hours of opioid education save lives?
One should not underestimate the sweeping scope of this new federal requirement. DEA registrants include physicians and other health care providers such as nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and dentists. That is 8 hours per provider x 2 million providers: 16 million hours of CME!
Many states already require 1 or more hours of opioid training and pain management as part of their relicensure requirements (Table 2). To avoid redundancy, the DEA-mandated 8-hour training satisfies the various states’ requirements. 
An uncompensated mandate
Physicians are no strangers to lifelong learning and most eagerly pursue educational opportunities. Though some physicians may have CME time and stipends allocated by their employers, many others, such as the approximately 50,000 locum tenens doctors, do not. However, as enthusiastic as these physicians may be about this new CME course, they will likely lose a day of seeing patients (and income) to comply with this new obligation.
Not just pain doctors
The mandate’s broad brush includes many health care providers who hold DEA certificates but do not prescribe opioids. For example, as a general neurologist and epileptologist, I do not treat patients with chronic pain and cannot remember the last time I wrote an opioid prescription. However, I frequently prescribe lacosamide, a Schedule V drug. A surprisingly large number of antiseizure drugs are Schedule III, IV, or V drugs (Table 3).

Real-world abuse?
How often scheduled antiseizure drugs are diverted or abused in an epilepsy population is unknown but appears to be infrequent. For example, perampanel abuse has not been reported despite its classification as a Schedule III drug. Anecdotally, in more than 40 years of clinical practice, I have never known a patient with epilepsy to abuse their antiseizure medications.
Take the course
Many organizations are happy to charge for the new 8-hour course. For example, the Tennessee Medical Association offers the training for $299 online or $400 in person. Materials from Elite Learning satisfy the 8-hour requirement for $80. However, NEJM Knowledge+ provides a complimentary 10-hour DEA-compliant course.
I recently completed the NEJM course. The information was thorough and took the whole 10 hours to finish. As excellent as it was, the content was only tangentially relevant to my clinical practice.
Conclusions
To obtain or renew a DEA certificate, neurologists, epilepsy specialists, and many other health care providers must comply with the new 8-hour CME opioid training mandate. Because the course requires 1 day to complete, health care providers would be prudent to obtain their CME well before their DEA certificate expires.
Though efforts to control the morbidity and mortality of the opioid epidemic are laudatory, perhaps the training should be more targeted to physicians who actually prescribe opioids rather than every DEA registrant. In the meantime, whether 16 million CME hours will save lives remains to be seen.
Dr. Wilner is professor of neurology at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis. He reported a conflict of interest with Accordant Health Services.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pharmacotherapy underprescribed for alcohol use disorder
Health care providers are missing opportunities to give medical treatment to high-risk individuals hospitalized for alcohol use disorder (AUD), a national analysis of Medicare beneficiaries reported.
Increasing such patients’ access to psychiatric care and addiction medicine, as well as encouraging medication prescribing by generalists and nonaddiction specialists, are remedial strategies recommended by lead author Eden Y. Bernstein, MD, of the division of general internal medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues.
“Hospitalizations for alcohol use disorder are common,” Dr. Bernstein said in an interview. “Our work shows they represent an underutilized opportunity to engage patients with appropriate treatment, including initiation of medications for alcohol use disorder.”
There is a pressing need for such treatment strategies since 29 million U.S. adults have AUD, and alcohol contributes to more than 140,000 deaths annually, the authors noted.
Rarely initiated either at hospital discharge or during follow-up care, medical therapy for AUD was more likely to be provided to younger patients and those involved with psychiatric care or addiction medicine, Dr. Bernstein’s group reported in Annals of Internal Medicine.Hospital admissions, they argued, give patients more access to clinicians and social workers and the vulnerability experienced during hospitalization may motivate behavioral change.
National study
The cohort included 28,601 AUD hospitalizations for 20,401 unique Medicare patients from 2015 to 2017. About 30% of admissions were for women and about 72% for non-Hispanic Blacks. Discharge initiation of medication for AUD was defined as a pharmacy claim for naltrexone, acamprosate, or disulfiram from the day before discharge to 2 days after.
Overall, just 206 patients (0.7%) initiated medication for AUD within 2 days of discharge and 364 (1.3%) started it within 30 days. Among those discharged with a primary diagnosis of AUD, only 70 (2.3%) started medical therapy within 2 days.
The most predictive demographic factor for discharge medication for AUD was younger age: 18-39 years versus 75 years and older (adjusted odds ratio, 3.87; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-11.16).
Initiation of medication for AUD should involve a long-term treatment plan, according to Dr. Bernstein’s group, and if that is not feasible during hospitalization, patients should be referred for outpatient treatment.
An accompanying editorial agrees that the results offer strong evidence of a missed opportunity to address AUD at a potential flexion point. “Hospitalization is a critical touch point for identifying and treating AUD,” wrote Michael F. Mayo-Smith, MD, MPH, of White River Junction (Vt.) VA Medical Center, and Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., and David Lawrence, MD, of the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
An intentional discharge protocol can be effective, they noted, as evidenced by a 2014 report in which this approach increased medication-assisted treatment from 0% to 64% in tandem with a decrease in all-cause, 30-day readmission rates.
“There is also growing interest in inpatient addiction consultation services, which have shown [medication] for AUD treatment initiation rates of up to 70% as well as improved engagement in posthospital treatment,” Dr. Mayo-Smith and Dr. Lawrence wrote.
Minority populations need particular attention, they added. “Unfortunately, the availability of evidence-based treatments for AUD does not by itself lead to improved care. We need strategies for widespread adoption so that patients can realize the benefits of these treatments.”
Dr. Bernstein reported funding support from a National Research Service Award and the Massachusetts General Hospital division of general internal medicine; he disclosed fees from Alosa Health. One coauthor was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Another was supported by the National Institute on Aging and reported relationships with the American College of Cardiology, Boston OIAC Pepper Center, American Heart Association, and US Deprescribing Research Network. Dr. Mayo-Smith disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Lawrence reported fees related to presentations at DDW 2023 and the California Society of Addiction Medicine 2022.
Health care providers are missing opportunities to give medical treatment to high-risk individuals hospitalized for alcohol use disorder (AUD), a national analysis of Medicare beneficiaries reported.
Increasing such patients’ access to psychiatric care and addiction medicine, as well as encouraging medication prescribing by generalists and nonaddiction specialists, are remedial strategies recommended by lead author Eden Y. Bernstein, MD, of the division of general internal medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues.
“Hospitalizations for alcohol use disorder are common,” Dr. Bernstein said in an interview. “Our work shows they represent an underutilized opportunity to engage patients with appropriate treatment, including initiation of medications for alcohol use disorder.”
There is a pressing need for such treatment strategies since 29 million U.S. adults have AUD, and alcohol contributes to more than 140,000 deaths annually, the authors noted.
Rarely initiated either at hospital discharge or during follow-up care, medical therapy for AUD was more likely to be provided to younger patients and those involved with psychiatric care or addiction medicine, Dr. Bernstein’s group reported in Annals of Internal Medicine.Hospital admissions, they argued, give patients more access to clinicians and social workers and the vulnerability experienced during hospitalization may motivate behavioral change.
National study
The cohort included 28,601 AUD hospitalizations for 20,401 unique Medicare patients from 2015 to 2017. About 30% of admissions were for women and about 72% for non-Hispanic Blacks. Discharge initiation of medication for AUD was defined as a pharmacy claim for naltrexone, acamprosate, or disulfiram from the day before discharge to 2 days after.
Overall, just 206 patients (0.7%) initiated medication for AUD within 2 days of discharge and 364 (1.3%) started it within 30 days. Among those discharged with a primary diagnosis of AUD, only 70 (2.3%) started medical therapy within 2 days.
The most predictive demographic factor for discharge medication for AUD was younger age: 18-39 years versus 75 years and older (adjusted odds ratio, 3.87; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-11.16).
Initiation of medication for AUD should involve a long-term treatment plan, according to Dr. Bernstein’s group, and if that is not feasible during hospitalization, patients should be referred for outpatient treatment.
An accompanying editorial agrees that the results offer strong evidence of a missed opportunity to address AUD at a potential flexion point. “Hospitalization is a critical touch point for identifying and treating AUD,” wrote Michael F. Mayo-Smith, MD, MPH, of White River Junction (Vt.) VA Medical Center, and Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., and David Lawrence, MD, of the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
An intentional discharge protocol can be effective, they noted, as evidenced by a 2014 report in which this approach increased medication-assisted treatment from 0% to 64% in tandem with a decrease in all-cause, 30-day readmission rates.
“There is also growing interest in inpatient addiction consultation services, which have shown [medication] for AUD treatment initiation rates of up to 70% as well as improved engagement in posthospital treatment,” Dr. Mayo-Smith and Dr. Lawrence wrote.
Minority populations need particular attention, they added. “Unfortunately, the availability of evidence-based treatments for AUD does not by itself lead to improved care. We need strategies for widespread adoption so that patients can realize the benefits of these treatments.”
Dr. Bernstein reported funding support from a National Research Service Award and the Massachusetts General Hospital division of general internal medicine; he disclosed fees from Alosa Health. One coauthor was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Another was supported by the National Institute on Aging and reported relationships with the American College of Cardiology, Boston OIAC Pepper Center, American Heart Association, and US Deprescribing Research Network. Dr. Mayo-Smith disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Lawrence reported fees related to presentations at DDW 2023 and the California Society of Addiction Medicine 2022.
Health care providers are missing opportunities to give medical treatment to high-risk individuals hospitalized for alcohol use disorder (AUD), a national analysis of Medicare beneficiaries reported.
Increasing such patients’ access to psychiatric care and addiction medicine, as well as encouraging medication prescribing by generalists and nonaddiction specialists, are remedial strategies recommended by lead author Eden Y. Bernstein, MD, of the division of general internal medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and colleagues.
“Hospitalizations for alcohol use disorder are common,” Dr. Bernstein said in an interview. “Our work shows they represent an underutilized opportunity to engage patients with appropriate treatment, including initiation of medications for alcohol use disorder.”
There is a pressing need for such treatment strategies since 29 million U.S. adults have AUD, and alcohol contributes to more than 140,000 deaths annually, the authors noted.
Rarely initiated either at hospital discharge or during follow-up care, medical therapy for AUD was more likely to be provided to younger patients and those involved with psychiatric care or addiction medicine, Dr. Bernstein’s group reported in Annals of Internal Medicine.Hospital admissions, they argued, give patients more access to clinicians and social workers and the vulnerability experienced during hospitalization may motivate behavioral change.
National study
The cohort included 28,601 AUD hospitalizations for 20,401 unique Medicare patients from 2015 to 2017. About 30% of admissions were for women and about 72% for non-Hispanic Blacks. Discharge initiation of medication for AUD was defined as a pharmacy claim for naltrexone, acamprosate, or disulfiram from the day before discharge to 2 days after.
Overall, just 206 patients (0.7%) initiated medication for AUD within 2 days of discharge and 364 (1.3%) started it within 30 days. Among those discharged with a primary diagnosis of AUD, only 70 (2.3%) started medical therapy within 2 days.
The most predictive demographic factor for discharge medication for AUD was younger age: 18-39 years versus 75 years and older (adjusted odds ratio, 3.87; 95% confidence interval, 1.34-11.16).
Initiation of medication for AUD should involve a long-term treatment plan, according to Dr. Bernstein’s group, and if that is not feasible during hospitalization, patients should be referred for outpatient treatment.
An accompanying editorial agrees that the results offer strong evidence of a missed opportunity to address AUD at a potential flexion point. “Hospitalization is a critical touch point for identifying and treating AUD,” wrote Michael F. Mayo-Smith, MD, MPH, of White River Junction (Vt.) VA Medical Center, and Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., and David Lawrence, MD, of the VA Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System and the University of California, Los Angeles.
An intentional discharge protocol can be effective, they noted, as evidenced by a 2014 report in which this approach increased medication-assisted treatment from 0% to 64% in tandem with a decrease in all-cause, 30-day readmission rates.
“There is also growing interest in inpatient addiction consultation services, which have shown [medication] for AUD treatment initiation rates of up to 70% as well as improved engagement in posthospital treatment,” Dr. Mayo-Smith and Dr. Lawrence wrote.
Minority populations need particular attention, they added. “Unfortunately, the availability of evidence-based treatments for AUD does not by itself lead to improved care. We need strategies for widespread adoption so that patients can realize the benefits of these treatments.”
Dr. Bernstein reported funding support from a National Research Service Award and the Massachusetts General Hospital division of general internal medicine; he disclosed fees from Alosa Health. One coauthor was supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Another was supported by the National Institute on Aging and reported relationships with the American College of Cardiology, Boston OIAC Pepper Center, American Heart Association, and US Deprescribing Research Network. Dr. Mayo-Smith disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Lawrence reported fees related to presentations at DDW 2023 and the California Society of Addiction Medicine 2022.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Tips for addressing uptick in mental health visits: Primary care providers collaborate, innovate
This growth in the number of patients needing behavioral health–related care is likely driven by multiple factors, including a shortage of mental health care providers, an increasing incidence of psychiatric illness, and destigmatization of mental health in general, suggested Swetha P. Iruku, MD, MPH, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine family physician in Philadelphia.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention noted that “the COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with mental health challenges related to the morbidity and mortality caused by the disease and to mitigation activities, including the impact of physical distancing and stay-at-home orders,” in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
From June 24 to 30, 2020, U.S. adults reported considerably elevated adverse mental health conditions associated with COVID-19, and symptoms of anxiety disorder and depressive disorder climbed during the months of April through June of the same year, compared with the same period in 2019, they wrote.
Even before the pandemic got underway, multiple studies of national data published this year suggested mental issues were on the rise in the United States. For example, the proportion of adult patient visits to primary care providers that addressed mental health concerns rose from 10.7% to 15.9% from 2006 to 2018, according to research published in Health Affairs. Plus, the number and proportion of pediatric acute care hospitalizations because of mental health diagnoses increased significantly between 2009 and 2019, according to a paper published in JAMA.
“I truly believe that we can’t, as primary care physicians, take care of someone’s physical health without also taking care of their mental health,” Dr. Iruku said in an interview. “It’s all intertwined.”
To rise to this challenge, PCPs first need a collaborative mindset, she suggested, as well as familiarity with available resources, both locally and virtually.
This article examines strategies for managing mental illness in primary care, outlines clinical resources, and reviews related educational opportunities.
In addition, clinical pearls are shared by Dr. Iruku and five other clinicians who provide or have provided mental health care to primary care patients or work in close collaboration with a primary care practice, including a clinical psychologist, a nurse practitioner licensed in psychiatric health, a pediatrician, and a licensed clinical social worker.
Build a network
Most of the providers interviewed cited the importance of collaboration in mental health care, particularly for complex cases.
“I would recommend [that primary care providers get] to know the psychiatric providers [in their area],” said Jessica Viton, DNP, FNP, PMHNP, who delivers mental health care through a community-based primary care practice in Colorado which she requested remain anonymous.
Dr. Iruku suggested making an in-person connection first, if possible.
“So much of what we do is ‘see one, do one, teach one,’ so learn a little bit, then go off and trial,” she said. “[It can be valuable] having someone in your back pocket that you can contact in the case of an emergency, or in a situation where you just don’t know how to tackle it.”
Screen for depression and anxiety
William J. Sieber, PhD, a clinical psychologist, director of integrated behavioral health, and professor in the department of family medicine and public health and the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said primary care providers should screen all adult patients for depression and anxiety with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) and General Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7), respectively.
To save time, he suggested a cascading approach.
“In primary care, everybody’s in a hurry,” Dr. Sieber said. “[With the cascading approach,] the first two items [from each questionnaire] are given, and if a person endorses either of those items … then they are asked to complete the other items.”
Jennifer Mullally, MD, a pediatrician at Sanford Health in Fargo, N.D., uses this cascading approach to depression and anxiety screening with all her patients aged 13-18. For younger kids, she screens only those who present with signs or symptoms of mental health issues, or if the parent shares a concern.
This approach differs slightly from U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations, which suggest screening for anxiety in patients aged 8-18 years and depression in patients aged 12-18 years.
Use other screening tools only as needed
Dr. Sieber, the research director for the division of family medicine at UC San Diego, collaborates regularly with primary care providers via hallway consultations, by sharing cases, and through providing oversight of psychiatric care at 13 primary care practices within the UC San Diego network. He recommended against routine screening beyond depression and anxiety in the primary care setting.
“There are a lot of screening tools,” Dr. Sieber said. “It depends on what you’re presented with. The challenge in primary care is you’re going to see all kinds of things. It’s not like running a depression clinic.”
Other than the PHQ-9 and GAD-7, he suggested primary care providers establish familiarity with screening tools for posttraumatic stress disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, noting again that these should be used only when one of the conditions is already suspected.
Dr. Mullally follows a similar approach with her pediatric population. In addition to the GAD-7, she investigates whether a patient has anxiety with the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED). For depression, she couples the PHQ-9 with the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
While additional screening tools like these are readily available online, Dr. Viton suggested that they should be employed only if the provider is trained to interpret and respond to those findings, and only if they know which tool to use, and when.
For example, she has recently observed PCPs diagnosing adults with ADHD using a three-question test, when in fact a full-length, standardized instrument should be administered by a provider with necessary training.
She also pointed out that bipolar disorder continues to be underdiagnosed, possibly because of providers detecting depression using a questionnaire like the PHQ-9, while failing to inquire about manic episodes.
Leverage online resources
If depression is confirmed, Dr. Iruku often directs the patient to the Mayo Clinic Depression Medication Choice Decision Aid. This website steers patients through medication options based on their answers to a questionnaire. Choices are listed alongside possible adverse effects.
For clinician use, Dr. Iruku recommended The Waco Guide to Psychopharmacology in Primary Care, which aids clinical decision-making for mental illness and substance abuse. The app processes case details to suggest first-, second-, and third-line pharmacotherapies, as well as modifications based on patient needs.
Even with tools like these, however, a referral may be needed.
“[Primary care providers] may not be the best fit for what the patient is looking for, from a mental health or behavioral standpoint,” Dr. Sieber said.
In this case, he encourages patients to visit Psychology Today, a “quite popular portal” that helps patients locate a suitable provider based on location, insurance, driving radius, and mental health concern. This usually generates 10-20 options, Dr. Sieber said, although results can vary.
“It may be discouraging, because maybe only three [providers] pop up based on your criteria, and the closest one is miles away,” he said.
Consider virtual support
If no local psychiatric help is available, Dr. Sieber suggested virtual support, highlighting that “it’s much easier now than it was 3 or 4 years ago” to connect patients with external mental health care.
But this strategy should be reserved for cases of actual need instead of pure convenience, cautioned Dr. Viton, who noted that virtual visits may fail to capture the nuance of an in-person meeting, as body language, mode of dress, and other clues can provide insights into mental health status.
“Occasionally, I think you do have to have an in-person visit, especially when you’re developing a rapport with someone,” Dr. Viton said.
Claire McArdle, a licensed clinical social worker in Fort Collins, Colo., noted that virtual care from an outside provider may also impede the collaboration needed to effectively address mental illness.
In her 11 years in primary care at Associates in Family Medicine, Ms. McArdle had countless interactions with colleagues seeking support when managing a complex case. “I’m coaching providers, front desk staff, and nursing staff on how to interact with patients [with] behavioral health needs,” she said, citing the multitude of nonmedical factors that need to be considered, such as family relationships and patient preferences.
These unscheduled conversations with colleagues throughout the day are impossible to have when sharing a case with an unknown, remote peer.
Ms. McArdle speaks from experience. She recently resigned from Associates in Family Medicine to start her own private therapy practice after her former employer was acquired by VillageMD, a national provider that terminated employment of most other social workers in the practice and began outsourcing mental health care to Mindoula Health, a virtual provider.
Dr. Sieber offered a similar perspective on in-person collaboration as the psychiatric specialist at his center. He routinely offers on-site support for both providers and patients, serving as “another set of eyes and ears” when there is a concern about patient safety or directly managing care when a patient is hospitalized for mental illness.
While virtual solutions may fall short of in-person management, they can offer care at a scale and cost impossible through traditional practice.
This could even be free. Zero-cost, automated software now allows individuals who are uninsured or unable to afford care at least one avenue to manage their mental health concerns.
For example, Bliss is a free, 8-session, interactive online therapy program for depression that was created by the Centre for Interactive Mental Health Solutions. The program offers a tool for monitoring mood and quizzes to test understanding of personal mental health management, among other features.
More advanced programs are emerging as artificial intelligence (AI) enables dialogues between humans and machines. This is the case with Woebot, an app that asks the user about their mood throughout the day, and responds with evidence-based strategies for managing concerns, all for free at press time.
Keep learning
A range of educational options and professional resources are available for primary care providers who would like to improve their knowledge of mental health care. These include formal fellowships in primary care psychiatry/behavioral health integration, free mental health webinars, and various other opportunities.
Eric Eschweiler, DNP, APRN, FNP-C, PHN, completed the University of California, Irvine, Train New Trainers (TNT) Primary Care Psychiatry (PCP) Fellowship in 2016, when he was working as a solo nurse practitioner.
“I was drowning in practice,” said Dr. Eschweiler, director of nursing and public health outreach services at Riverside-San Bernardino County Indian Health, Grand Terrace, Calif., in an interview. “I was a solo NP. There was no physician on site. We were seeing a lot of [individuals with] schizoaffective [disorder] in downtown San Bernardino, the homeless, unhoused – a lot of substance use. I felt I needed to have the skills to be able to treat them effectively. That’s what the fellowship did.”
The skills Dr. Eschweiler learned from participating in his fellowship allowed him to manage more cases of mental illness without need for referral. When a referral was needed for a complex or severe case, he had the confidence to bridge care and collaborate more effectively with psychiatric specialists.
“It was awesome, because we were able to communicate using the same language,” Dr. Eschweiler said of these collaborations. “It’s [about] talking that same language, starting those initial treatments, and then moving forward with specialty care, and vice versa. [Psychiatric specialists] would send me patients that needed medical care because of the types of medications they were taking. And I was then very well aware of those side effects and other issues that might come up from those treatments. So it’s a two-way street.”
Dr. Eschweiler was so impressed by his fellowship that he has since ushered multiple providers through the program since transitioning to an administrative role as director of nursing.
In Fargo, where psychiatric care is sparse and wait times for referral can be months long, Dr. Mullally, like Dr. Eschweiler, knew that she needed more training in mental health.
“I don’t feel like we get enough training in residency,” Dr. Mullally said. “So you do need to look at your options for further CME.”
Out of several CME courses she has taken to further her understanding of pediatric psychiatry, Dr. Mullally recommended The Reach Institute above all others, as their courses involve in-depth discussions and valuable handouts, particularly for medication selection.
“I think that a lot of the other CMEs tend to involve a lot more PowerPoint presentations,” Dr. Mullally said. “And you don’t necessarily leave with a lot of good documents. I still use my Reach handouts. I have them sitting right next to me. I use them every single day.”
Providers interested in The Reach Institute, however, should be prepared to invest both time and money, she added, citing a 2-3 day commitment, and calling it “not cheap.” To overcome these barriers, she suggested that providers get their institution to support their attendance.
For a lighter commitment, Dr. Iruku recommended the American Academy of Family Physicians CME portal, as this offers 13 online, accredited courses covering a range of topics, from adolescent health to substance abuse disorders.
Dr. Sieber suggested that primary care providers join the Collaborative Family Healthcare Association, which aims to integrate physical and behavioral health in routine practice. CFHA, of which he is a member, offers a “bevy of different resources” for interested providers, including a conference in Phoenix this October.
The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
This growth in the number of patients needing behavioral health–related care is likely driven by multiple factors, including a shortage of mental health care providers, an increasing incidence of psychiatric illness, and destigmatization of mental health in general, suggested Swetha P. Iruku, MD, MPH, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine family physician in Philadelphia.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention noted that “the COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with mental health challenges related to the morbidity and mortality caused by the disease and to mitigation activities, including the impact of physical distancing and stay-at-home orders,” in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
From June 24 to 30, 2020, U.S. adults reported considerably elevated adverse mental health conditions associated with COVID-19, and symptoms of anxiety disorder and depressive disorder climbed during the months of April through June of the same year, compared with the same period in 2019, they wrote.
Even before the pandemic got underway, multiple studies of national data published this year suggested mental issues were on the rise in the United States. For example, the proportion of adult patient visits to primary care providers that addressed mental health concerns rose from 10.7% to 15.9% from 2006 to 2018, according to research published in Health Affairs. Plus, the number and proportion of pediatric acute care hospitalizations because of mental health diagnoses increased significantly between 2009 and 2019, according to a paper published in JAMA.
“I truly believe that we can’t, as primary care physicians, take care of someone’s physical health without also taking care of their mental health,” Dr. Iruku said in an interview. “It’s all intertwined.”
To rise to this challenge, PCPs first need a collaborative mindset, she suggested, as well as familiarity with available resources, both locally and virtually.
This article examines strategies for managing mental illness in primary care, outlines clinical resources, and reviews related educational opportunities.
In addition, clinical pearls are shared by Dr. Iruku and five other clinicians who provide or have provided mental health care to primary care patients or work in close collaboration with a primary care practice, including a clinical psychologist, a nurse practitioner licensed in psychiatric health, a pediatrician, and a licensed clinical social worker.
Build a network
Most of the providers interviewed cited the importance of collaboration in mental health care, particularly for complex cases.
“I would recommend [that primary care providers get] to know the psychiatric providers [in their area],” said Jessica Viton, DNP, FNP, PMHNP, who delivers mental health care through a community-based primary care practice in Colorado which she requested remain anonymous.
Dr. Iruku suggested making an in-person connection first, if possible.
“So much of what we do is ‘see one, do one, teach one,’ so learn a little bit, then go off and trial,” she said. “[It can be valuable] having someone in your back pocket that you can contact in the case of an emergency, or in a situation where you just don’t know how to tackle it.”
Screen for depression and anxiety
William J. Sieber, PhD, a clinical psychologist, director of integrated behavioral health, and professor in the department of family medicine and public health and the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said primary care providers should screen all adult patients for depression and anxiety with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) and General Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7), respectively.
To save time, he suggested a cascading approach.
“In primary care, everybody’s in a hurry,” Dr. Sieber said. “[With the cascading approach,] the first two items [from each questionnaire] are given, and if a person endorses either of those items … then they are asked to complete the other items.”
Jennifer Mullally, MD, a pediatrician at Sanford Health in Fargo, N.D., uses this cascading approach to depression and anxiety screening with all her patients aged 13-18. For younger kids, she screens only those who present with signs or symptoms of mental health issues, or if the parent shares a concern.
This approach differs slightly from U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations, which suggest screening for anxiety in patients aged 8-18 years and depression in patients aged 12-18 years.
Use other screening tools only as needed
Dr. Sieber, the research director for the division of family medicine at UC San Diego, collaborates regularly with primary care providers via hallway consultations, by sharing cases, and through providing oversight of psychiatric care at 13 primary care practices within the UC San Diego network. He recommended against routine screening beyond depression and anxiety in the primary care setting.
“There are a lot of screening tools,” Dr. Sieber said. “It depends on what you’re presented with. The challenge in primary care is you’re going to see all kinds of things. It’s not like running a depression clinic.”
Other than the PHQ-9 and GAD-7, he suggested primary care providers establish familiarity with screening tools for posttraumatic stress disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, noting again that these should be used only when one of the conditions is already suspected.
Dr. Mullally follows a similar approach with her pediatric population. In addition to the GAD-7, she investigates whether a patient has anxiety with the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED). For depression, she couples the PHQ-9 with the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
While additional screening tools like these are readily available online, Dr. Viton suggested that they should be employed only if the provider is trained to interpret and respond to those findings, and only if they know which tool to use, and when.
For example, she has recently observed PCPs diagnosing adults with ADHD using a three-question test, when in fact a full-length, standardized instrument should be administered by a provider with necessary training.
She also pointed out that bipolar disorder continues to be underdiagnosed, possibly because of providers detecting depression using a questionnaire like the PHQ-9, while failing to inquire about manic episodes.
Leverage online resources
If depression is confirmed, Dr. Iruku often directs the patient to the Mayo Clinic Depression Medication Choice Decision Aid. This website steers patients through medication options based on their answers to a questionnaire. Choices are listed alongside possible adverse effects.
For clinician use, Dr. Iruku recommended The Waco Guide to Psychopharmacology in Primary Care, which aids clinical decision-making for mental illness and substance abuse. The app processes case details to suggest first-, second-, and third-line pharmacotherapies, as well as modifications based on patient needs.
Even with tools like these, however, a referral may be needed.
“[Primary care providers] may not be the best fit for what the patient is looking for, from a mental health or behavioral standpoint,” Dr. Sieber said.
In this case, he encourages patients to visit Psychology Today, a “quite popular portal” that helps patients locate a suitable provider based on location, insurance, driving radius, and mental health concern. This usually generates 10-20 options, Dr. Sieber said, although results can vary.
“It may be discouraging, because maybe only three [providers] pop up based on your criteria, and the closest one is miles away,” he said.
Consider virtual support
If no local psychiatric help is available, Dr. Sieber suggested virtual support, highlighting that “it’s much easier now than it was 3 or 4 years ago” to connect patients with external mental health care.
But this strategy should be reserved for cases of actual need instead of pure convenience, cautioned Dr. Viton, who noted that virtual visits may fail to capture the nuance of an in-person meeting, as body language, mode of dress, and other clues can provide insights into mental health status.
“Occasionally, I think you do have to have an in-person visit, especially when you’re developing a rapport with someone,” Dr. Viton said.
Claire McArdle, a licensed clinical social worker in Fort Collins, Colo., noted that virtual care from an outside provider may also impede the collaboration needed to effectively address mental illness.
In her 11 years in primary care at Associates in Family Medicine, Ms. McArdle had countless interactions with colleagues seeking support when managing a complex case. “I’m coaching providers, front desk staff, and nursing staff on how to interact with patients [with] behavioral health needs,” she said, citing the multitude of nonmedical factors that need to be considered, such as family relationships and patient preferences.
These unscheduled conversations with colleagues throughout the day are impossible to have when sharing a case with an unknown, remote peer.
Ms. McArdle speaks from experience. She recently resigned from Associates in Family Medicine to start her own private therapy practice after her former employer was acquired by VillageMD, a national provider that terminated employment of most other social workers in the practice and began outsourcing mental health care to Mindoula Health, a virtual provider.
Dr. Sieber offered a similar perspective on in-person collaboration as the psychiatric specialist at his center. He routinely offers on-site support for both providers and patients, serving as “another set of eyes and ears” when there is a concern about patient safety or directly managing care when a patient is hospitalized for mental illness.
While virtual solutions may fall short of in-person management, they can offer care at a scale and cost impossible through traditional practice.
This could even be free. Zero-cost, automated software now allows individuals who are uninsured or unable to afford care at least one avenue to manage their mental health concerns.
For example, Bliss is a free, 8-session, interactive online therapy program for depression that was created by the Centre for Interactive Mental Health Solutions. The program offers a tool for monitoring mood and quizzes to test understanding of personal mental health management, among other features.
More advanced programs are emerging as artificial intelligence (AI) enables dialogues between humans and machines. This is the case with Woebot, an app that asks the user about their mood throughout the day, and responds with evidence-based strategies for managing concerns, all for free at press time.
Keep learning
A range of educational options and professional resources are available for primary care providers who would like to improve their knowledge of mental health care. These include formal fellowships in primary care psychiatry/behavioral health integration, free mental health webinars, and various other opportunities.
Eric Eschweiler, DNP, APRN, FNP-C, PHN, completed the University of California, Irvine, Train New Trainers (TNT) Primary Care Psychiatry (PCP) Fellowship in 2016, when he was working as a solo nurse practitioner.
“I was drowning in practice,” said Dr. Eschweiler, director of nursing and public health outreach services at Riverside-San Bernardino County Indian Health, Grand Terrace, Calif., in an interview. “I was a solo NP. There was no physician on site. We were seeing a lot of [individuals with] schizoaffective [disorder] in downtown San Bernardino, the homeless, unhoused – a lot of substance use. I felt I needed to have the skills to be able to treat them effectively. That’s what the fellowship did.”
The skills Dr. Eschweiler learned from participating in his fellowship allowed him to manage more cases of mental illness without need for referral. When a referral was needed for a complex or severe case, he had the confidence to bridge care and collaborate more effectively with psychiatric specialists.
“It was awesome, because we were able to communicate using the same language,” Dr. Eschweiler said of these collaborations. “It’s [about] talking that same language, starting those initial treatments, and then moving forward with specialty care, and vice versa. [Psychiatric specialists] would send me patients that needed medical care because of the types of medications they were taking. And I was then very well aware of those side effects and other issues that might come up from those treatments. So it’s a two-way street.”
Dr. Eschweiler was so impressed by his fellowship that he has since ushered multiple providers through the program since transitioning to an administrative role as director of nursing.
In Fargo, where psychiatric care is sparse and wait times for referral can be months long, Dr. Mullally, like Dr. Eschweiler, knew that she needed more training in mental health.
“I don’t feel like we get enough training in residency,” Dr. Mullally said. “So you do need to look at your options for further CME.”
Out of several CME courses she has taken to further her understanding of pediatric psychiatry, Dr. Mullally recommended The Reach Institute above all others, as their courses involve in-depth discussions and valuable handouts, particularly for medication selection.
“I think that a lot of the other CMEs tend to involve a lot more PowerPoint presentations,” Dr. Mullally said. “And you don’t necessarily leave with a lot of good documents. I still use my Reach handouts. I have them sitting right next to me. I use them every single day.”
Providers interested in The Reach Institute, however, should be prepared to invest both time and money, she added, citing a 2-3 day commitment, and calling it “not cheap.” To overcome these barriers, she suggested that providers get their institution to support their attendance.
For a lighter commitment, Dr. Iruku recommended the American Academy of Family Physicians CME portal, as this offers 13 online, accredited courses covering a range of topics, from adolescent health to substance abuse disorders.
Dr. Sieber suggested that primary care providers join the Collaborative Family Healthcare Association, which aims to integrate physical and behavioral health in routine practice. CFHA, of which he is a member, offers a “bevy of different resources” for interested providers, including a conference in Phoenix this October.
The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
This growth in the number of patients needing behavioral health–related care is likely driven by multiple factors, including a shortage of mental health care providers, an increasing incidence of psychiatric illness, and destigmatization of mental health in general, suggested Swetha P. Iruku, MD, MPH, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine family physician in Philadelphia.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention noted that “the COVID-19 pandemic has been associated with mental health challenges related to the morbidity and mortality caused by the disease and to mitigation activities, including the impact of physical distancing and stay-at-home orders,” in a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
From June 24 to 30, 2020, U.S. adults reported considerably elevated adverse mental health conditions associated with COVID-19, and symptoms of anxiety disorder and depressive disorder climbed during the months of April through June of the same year, compared with the same period in 2019, they wrote.
Even before the pandemic got underway, multiple studies of national data published this year suggested mental issues were on the rise in the United States. For example, the proportion of adult patient visits to primary care providers that addressed mental health concerns rose from 10.7% to 15.9% from 2006 to 2018, according to research published in Health Affairs. Plus, the number and proportion of pediatric acute care hospitalizations because of mental health diagnoses increased significantly between 2009 and 2019, according to a paper published in JAMA.
“I truly believe that we can’t, as primary care physicians, take care of someone’s physical health without also taking care of their mental health,” Dr. Iruku said in an interview. “It’s all intertwined.”
To rise to this challenge, PCPs first need a collaborative mindset, she suggested, as well as familiarity with available resources, both locally and virtually.
This article examines strategies for managing mental illness in primary care, outlines clinical resources, and reviews related educational opportunities.
In addition, clinical pearls are shared by Dr. Iruku and five other clinicians who provide or have provided mental health care to primary care patients or work in close collaboration with a primary care practice, including a clinical psychologist, a nurse practitioner licensed in psychiatric health, a pediatrician, and a licensed clinical social worker.
Build a network
Most of the providers interviewed cited the importance of collaboration in mental health care, particularly for complex cases.
“I would recommend [that primary care providers get] to know the psychiatric providers [in their area],” said Jessica Viton, DNP, FNP, PMHNP, who delivers mental health care through a community-based primary care practice in Colorado which she requested remain anonymous.
Dr. Iruku suggested making an in-person connection first, if possible.
“So much of what we do is ‘see one, do one, teach one,’ so learn a little bit, then go off and trial,” she said. “[It can be valuable] having someone in your back pocket that you can contact in the case of an emergency, or in a situation where you just don’t know how to tackle it.”
Screen for depression and anxiety
William J. Sieber, PhD, a clinical psychologist, director of integrated behavioral health, and professor in the department of family medicine and public health and the department of psychiatry at the University of California, San Diego, said primary care providers should screen all adult patients for depression and anxiety with the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) and General Anxiety Disorder Assessment (GAD-7), respectively.
To save time, he suggested a cascading approach.
“In primary care, everybody’s in a hurry,” Dr. Sieber said. “[With the cascading approach,] the first two items [from each questionnaire] are given, and if a person endorses either of those items … then they are asked to complete the other items.”
Jennifer Mullally, MD, a pediatrician at Sanford Health in Fargo, N.D., uses this cascading approach to depression and anxiety screening with all her patients aged 13-18. For younger kids, she screens only those who present with signs or symptoms of mental health issues, or if the parent shares a concern.
This approach differs slightly from U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendations, which suggest screening for anxiety in patients aged 8-18 years and depression in patients aged 12-18 years.
Use other screening tools only as needed
Dr. Sieber, the research director for the division of family medicine at UC San Diego, collaborates regularly with primary care providers via hallway consultations, by sharing cases, and through providing oversight of psychiatric care at 13 primary care practices within the UC San Diego network. He recommended against routine screening beyond depression and anxiety in the primary care setting.
“There are a lot of screening tools,” Dr. Sieber said. “It depends on what you’re presented with. The challenge in primary care is you’re going to see all kinds of things. It’s not like running a depression clinic.”
Other than the PHQ-9 and GAD-7, he suggested primary care providers establish familiarity with screening tools for posttraumatic stress disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, noting again that these should be used only when one of the conditions is already suspected.
Dr. Mullally follows a similar approach with her pediatric population. In addition to the GAD-7, she investigates whether a patient has anxiety with the Screen for Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED). For depression, she couples the PHQ-9 with the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale.
While additional screening tools like these are readily available online, Dr. Viton suggested that they should be employed only if the provider is trained to interpret and respond to those findings, and only if they know which tool to use, and when.
For example, she has recently observed PCPs diagnosing adults with ADHD using a three-question test, when in fact a full-length, standardized instrument should be administered by a provider with necessary training.
She also pointed out that bipolar disorder continues to be underdiagnosed, possibly because of providers detecting depression using a questionnaire like the PHQ-9, while failing to inquire about manic episodes.
Leverage online resources
If depression is confirmed, Dr. Iruku often directs the patient to the Mayo Clinic Depression Medication Choice Decision Aid. This website steers patients through medication options based on their answers to a questionnaire. Choices are listed alongside possible adverse effects.
For clinician use, Dr. Iruku recommended The Waco Guide to Psychopharmacology in Primary Care, which aids clinical decision-making for mental illness and substance abuse. The app processes case details to suggest first-, second-, and third-line pharmacotherapies, as well as modifications based on patient needs.
Even with tools like these, however, a referral may be needed.
“[Primary care providers] may not be the best fit for what the patient is looking for, from a mental health or behavioral standpoint,” Dr. Sieber said.
In this case, he encourages patients to visit Psychology Today, a “quite popular portal” that helps patients locate a suitable provider based on location, insurance, driving radius, and mental health concern. This usually generates 10-20 options, Dr. Sieber said, although results can vary.
“It may be discouraging, because maybe only three [providers] pop up based on your criteria, and the closest one is miles away,” he said.
Consider virtual support
If no local psychiatric help is available, Dr. Sieber suggested virtual support, highlighting that “it’s much easier now than it was 3 or 4 years ago” to connect patients with external mental health care.
But this strategy should be reserved for cases of actual need instead of pure convenience, cautioned Dr. Viton, who noted that virtual visits may fail to capture the nuance of an in-person meeting, as body language, mode of dress, and other clues can provide insights into mental health status.
“Occasionally, I think you do have to have an in-person visit, especially when you’re developing a rapport with someone,” Dr. Viton said.
Claire McArdle, a licensed clinical social worker in Fort Collins, Colo., noted that virtual care from an outside provider may also impede the collaboration needed to effectively address mental illness.
In her 11 years in primary care at Associates in Family Medicine, Ms. McArdle had countless interactions with colleagues seeking support when managing a complex case. “I’m coaching providers, front desk staff, and nursing staff on how to interact with patients [with] behavioral health needs,” she said, citing the multitude of nonmedical factors that need to be considered, such as family relationships and patient preferences.
These unscheduled conversations with colleagues throughout the day are impossible to have when sharing a case with an unknown, remote peer.
Ms. McArdle speaks from experience. She recently resigned from Associates in Family Medicine to start her own private therapy practice after her former employer was acquired by VillageMD, a national provider that terminated employment of most other social workers in the practice and began outsourcing mental health care to Mindoula Health, a virtual provider.
Dr. Sieber offered a similar perspective on in-person collaboration as the psychiatric specialist at his center. He routinely offers on-site support for both providers and patients, serving as “another set of eyes and ears” when there is a concern about patient safety or directly managing care when a patient is hospitalized for mental illness.
While virtual solutions may fall short of in-person management, they can offer care at a scale and cost impossible through traditional practice.
This could even be free. Zero-cost, automated software now allows individuals who are uninsured or unable to afford care at least one avenue to manage their mental health concerns.
For example, Bliss is a free, 8-session, interactive online therapy program for depression that was created by the Centre for Interactive Mental Health Solutions. The program offers a tool for monitoring mood and quizzes to test understanding of personal mental health management, among other features.
More advanced programs are emerging as artificial intelligence (AI) enables dialogues between humans and machines. This is the case with Woebot, an app that asks the user about their mood throughout the day, and responds with evidence-based strategies for managing concerns, all for free at press time.
Keep learning
A range of educational options and professional resources are available for primary care providers who would like to improve their knowledge of mental health care. These include formal fellowships in primary care psychiatry/behavioral health integration, free mental health webinars, and various other opportunities.
Eric Eschweiler, DNP, APRN, FNP-C, PHN, completed the University of California, Irvine, Train New Trainers (TNT) Primary Care Psychiatry (PCP) Fellowship in 2016, when he was working as a solo nurse practitioner.
“I was drowning in practice,” said Dr. Eschweiler, director of nursing and public health outreach services at Riverside-San Bernardino County Indian Health, Grand Terrace, Calif., in an interview. “I was a solo NP. There was no physician on site. We were seeing a lot of [individuals with] schizoaffective [disorder] in downtown San Bernardino, the homeless, unhoused – a lot of substance use. I felt I needed to have the skills to be able to treat them effectively. That’s what the fellowship did.”
The skills Dr. Eschweiler learned from participating in his fellowship allowed him to manage more cases of mental illness without need for referral. When a referral was needed for a complex or severe case, he had the confidence to bridge care and collaborate more effectively with psychiatric specialists.
“It was awesome, because we were able to communicate using the same language,” Dr. Eschweiler said of these collaborations. “It’s [about] talking that same language, starting those initial treatments, and then moving forward with specialty care, and vice versa. [Psychiatric specialists] would send me patients that needed medical care because of the types of medications they were taking. And I was then very well aware of those side effects and other issues that might come up from those treatments. So it’s a two-way street.”
Dr. Eschweiler was so impressed by his fellowship that he has since ushered multiple providers through the program since transitioning to an administrative role as director of nursing.
In Fargo, where psychiatric care is sparse and wait times for referral can be months long, Dr. Mullally, like Dr. Eschweiler, knew that she needed more training in mental health.
“I don’t feel like we get enough training in residency,” Dr. Mullally said. “So you do need to look at your options for further CME.”
Out of several CME courses she has taken to further her understanding of pediatric psychiatry, Dr. Mullally recommended The Reach Institute above all others, as their courses involve in-depth discussions and valuable handouts, particularly for medication selection.
“I think that a lot of the other CMEs tend to involve a lot more PowerPoint presentations,” Dr. Mullally said. “And you don’t necessarily leave with a lot of good documents. I still use my Reach handouts. I have them sitting right next to me. I use them every single day.”
Providers interested in The Reach Institute, however, should be prepared to invest both time and money, she added, citing a 2-3 day commitment, and calling it “not cheap.” To overcome these barriers, she suggested that providers get their institution to support their attendance.
For a lighter commitment, Dr. Iruku recommended the American Academy of Family Physicians CME portal, as this offers 13 online, accredited courses covering a range of topics, from adolescent health to substance abuse disorders.
Dr. Sieber suggested that primary care providers join the Collaborative Family Healthcare Association, which aims to integrate physical and behavioral health in routine practice. CFHA, of which he is a member, offers a “bevy of different resources” for interested providers, including a conference in Phoenix this October.
The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Are you a physician ... or a vending machine?
When we address this problem with patients, some become immediately defensive, making it difficult to modify treatment regimens. It’s almost as if people believe that they have a “right” to their medications and nobody should dare take them away. Even when I think the interaction goes relatively smoothly, the outcome usually shows otherwise.
I will decrease gabapentin from 3,200 mg per day and they will come back with cyclobenzaprine from the urgent care center down the block.
I try to stop an abused amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, and not only do the drugs show up in the urine toxicology test a month later (from the brother’s girlfriend’s sister) but the screening will be positive for cocaine (from the sister’s boyfriend’s brother) and probably alprazolam, too.
People want what they want, and I believe what they want is the overwhelming need not to feel, and especially to not feel our natural and uncomfortable states of pain, sadness, anxiety, fatigue, and discomfort (sometimes all at once). They will use anything orally or intravenously or nasally to make those feelings go away.
I am an addiction specialist so I write this commentary out of care and concern and recognition of how much, pain both physical and psychic, people suffer.
Perhaps we as physicians are conditioned to believe that we must prescribe “something” to the patient who is uncomfortable and sitting in front of us. In general we are sympathetic to the needs of those who come to us in distress, and we try our best to help reduce their symptoms.
I know that we cannot simply “fire” people, because these patients are ours to take care of; they are our responsibility, though this is our overused response to “difficult” patients.
And I know that we have insufficient replacements for these medications. We stopped prescribing oxycodone and now people are on gabapentin in the highest doses, diversion is up, and so is its abuse.
Many of us regularly teach about breathing and mindfulness. I discuss trauma and talk therapy. I order physical therapy and walking regimens and podcasts. But our relationship is transactional, and in prescribing a medication, I have shown them that I am hearing them. I hate this feeling of being trapped.
I spend much of my day negotiating and drive home at night feeling like nothing more than a vending machine.
Dr. Hambright is with the department of addiction medicine at Samaritan Daytop Village, Ellenville, N.Y., and Samadhi Recovery Community Outreach Center, Kingston, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When we address this problem with patients, some become immediately defensive, making it difficult to modify treatment regimens. It’s almost as if people believe that they have a “right” to their medications and nobody should dare take them away. Even when I think the interaction goes relatively smoothly, the outcome usually shows otherwise.
I will decrease gabapentin from 3,200 mg per day and they will come back with cyclobenzaprine from the urgent care center down the block.
I try to stop an abused amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, and not only do the drugs show up in the urine toxicology test a month later (from the brother’s girlfriend’s sister) but the screening will be positive for cocaine (from the sister’s boyfriend’s brother) and probably alprazolam, too.
People want what they want, and I believe what they want is the overwhelming need not to feel, and especially to not feel our natural and uncomfortable states of pain, sadness, anxiety, fatigue, and discomfort (sometimes all at once). They will use anything orally or intravenously or nasally to make those feelings go away.
I am an addiction specialist so I write this commentary out of care and concern and recognition of how much, pain both physical and psychic, people suffer.
Perhaps we as physicians are conditioned to believe that we must prescribe “something” to the patient who is uncomfortable and sitting in front of us. In general we are sympathetic to the needs of those who come to us in distress, and we try our best to help reduce their symptoms.
I know that we cannot simply “fire” people, because these patients are ours to take care of; they are our responsibility, though this is our overused response to “difficult” patients.
And I know that we have insufficient replacements for these medications. We stopped prescribing oxycodone and now people are on gabapentin in the highest doses, diversion is up, and so is its abuse.
Many of us regularly teach about breathing and mindfulness. I discuss trauma and talk therapy. I order physical therapy and walking regimens and podcasts. But our relationship is transactional, and in prescribing a medication, I have shown them that I am hearing them. I hate this feeling of being trapped.
I spend much of my day negotiating and drive home at night feeling like nothing more than a vending machine.
Dr. Hambright is with the department of addiction medicine at Samaritan Daytop Village, Ellenville, N.Y., and Samadhi Recovery Community Outreach Center, Kingston, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When we address this problem with patients, some become immediately defensive, making it difficult to modify treatment regimens. It’s almost as if people believe that they have a “right” to their medications and nobody should dare take them away. Even when I think the interaction goes relatively smoothly, the outcome usually shows otherwise.
I will decrease gabapentin from 3,200 mg per day and they will come back with cyclobenzaprine from the urgent care center down the block.
I try to stop an abused amphetamine and dextroamphetamine, and not only do the drugs show up in the urine toxicology test a month later (from the brother’s girlfriend’s sister) but the screening will be positive for cocaine (from the sister’s boyfriend’s brother) and probably alprazolam, too.
People want what they want, and I believe what they want is the overwhelming need not to feel, and especially to not feel our natural and uncomfortable states of pain, sadness, anxiety, fatigue, and discomfort (sometimes all at once). They will use anything orally or intravenously or nasally to make those feelings go away.
I am an addiction specialist so I write this commentary out of care and concern and recognition of how much, pain both physical and psychic, people suffer.
Perhaps we as physicians are conditioned to believe that we must prescribe “something” to the patient who is uncomfortable and sitting in front of us. In general we are sympathetic to the needs of those who come to us in distress, and we try our best to help reduce their symptoms.
I know that we cannot simply “fire” people, because these patients are ours to take care of; they are our responsibility, though this is our overused response to “difficult” patients.
And I know that we have insufficient replacements for these medications. We stopped prescribing oxycodone and now people are on gabapentin in the highest doses, diversion is up, and so is its abuse.
Many of us regularly teach about breathing and mindfulness. I discuss trauma and talk therapy. I order physical therapy and walking regimens and podcasts. But our relationship is transactional, and in prescribing a medication, I have shown them that I am hearing them. I hate this feeling of being trapped.
I spend much of my day negotiating and drive home at night feeling like nothing more than a vending machine.
Dr. Hambright is with the department of addiction medicine at Samaritan Daytop Village, Ellenville, N.Y., and Samadhi Recovery Community Outreach Center, Kingston, N.Y. She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dramatic rise in hallucinogen use among young adults
With the exception of lysergic acid diethylamide,
In 2018, the prevalence of young adults’ past-year use of non-LSD hallucinogens was 3.4%. By 2021, it had jumped to 6.6%.
The increase in non-LSD hallucinogen use occurred while LSD use remained stable at around 4% in 2018 and 2021.
“While non-LSD hallucinogen use remains substantially less prevalent than use of substances such as alcohol and cannabis, a doubling of prevalence in just three years is a dramatic increase and raises possible public health concerns,” co-author Megan Patrick, PhD, with the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research, Ann Arbor, said in a news release.
The results were published online in the journal Addiction.
Health concerns
The estimates are derived from the Monitoring the Future study, which includes annual assessments of adolescent and adult health in the United States.
The analysis focused on 11,304 persons (52% female) aged 9-30 years from the U.S. general population who were interviewed between 2018 and 2021.
Participants were asked about past 12-month use of LSD, as well as use of non-LSD hallucinogens, such as psilocybin.
From 2018 to 2021, past 12-month use of LSD remained relatively stable; it was 3.7% in 2018 and 4.2% in 2021.
However, non-LSD hallucinogen use increased in prevalence from 3.4% to 6.6% from 2018 to 2021.
Across years, the odds of non-LSD use were higher among males, White people, and individuals from households with higher parental education – a proxy for higher socioeconomic status.
The most commonly used non-LSD hallucinogen was psilocybin.
The survey did not ask whether young adults used non-LSD hallucinogens for therapeutic or medical reasons.
“The use of psychedelic and hallucinogenic drugs for a range of therapeutic uses is increasing, given accumulating yet still preliminary data from randomized trials on clinical effectiveness,” lead author Katherine Keyes, PhD, with Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, New York, said in the release.
“With increased visibility for medical and therapeutic use, however, potentially comes diversion and unregulated product availability, as well as a lack of understanding among the public of potential risks,” Dr. Keyes added.
“However, approved therapeutic use of psychedelics under a trained health professional’s care remains uncommon in the United States, thus the trends we observe here are undoubtedly in nonmedical and nontherapeutic use,” Dr. Keyes noted.
Dr. Patrick said the increased use of hallucinogens raises “concern for young adult health” and is not without risk. While hallucinogen dependence has historically been rare in the U.S. population, it could become more common as use increases, she noted.
The researchers will continue to track these trends to see whether the increases continue.
“We need additional research, including about the motives for hallucinogen use and how young adults are using these substances, in order to be able to mitigate the associated negative consequences,” Dr. Patrick said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Keyes and Dr. Patrick have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With the exception of lysergic acid diethylamide,
In 2018, the prevalence of young adults’ past-year use of non-LSD hallucinogens was 3.4%. By 2021, it had jumped to 6.6%.
The increase in non-LSD hallucinogen use occurred while LSD use remained stable at around 4% in 2018 and 2021.
“While non-LSD hallucinogen use remains substantially less prevalent than use of substances such as alcohol and cannabis, a doubling of prevalence in just three years is a dramatic increase and raises possible public health concerns,” co-author Megan Patrick, PhD, with the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research, Ann Arbor, said in a news release.
The results were published online in the journal Addiction.
Health concerns
The estimates are derived from the Monitoring the Future study, which includes annual assessments of adolescent and adult health in the United States.
The analysis focused on 11,304 persons (52% female) aged 9-30 years from the U.S. general population who were interviewed between 2018 and 2021.
Participants were asked about past 12-month use of LSD, as well as use of non-LSD hallucinogens, such as psilocybin.
From 2018 to 2021, past 12-month use of LSD remained relatively stable; it was 3.7% in 2018 and 4.2% in 2021.
However, non-LSD hallucinogen use increased in prevalence from 3.4% to 6.6% from 2018 to 2021.
Across years, the odds of non-LSD use were higher among males, White people, and individuals from households with higher parental education – a proxy for higher socioeconomic status.
The most commonly used non-LSD hallucinogen was psilocybin.
The survey did not ask whether young adults used non-LSD hallucinogens for therapeutic or medical reasons.
“The use of psychedelic and hallucinogenic drugs for a range of therapeutic uses is increasing, given accumulating yet still preliminary data from randomized trials on clinical effectiveness,” lead author Katherine Keyes, PhD, with Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, New York, said in the release.
“With increased visibility for medical and therapeutic use, however, potentially comes diversion and unregulated product availability, as well as a lack of understanding among the public of potential risks,” Dr. Keyes added.
“However, approved therapeutic use of psychedelics under a trained health professional’s care remains uncommon in the United States, thus the trends we observe here are undoubtedly in nonmedical and nontherapeutic use,” Dr. Keyes noted.
Dr. Patrick said the increased use of hallucinogens raises “concern for young adult health” and is not without risk. While hallucinogen dependence has historically been rare in the U.S. population, it could become more common as use increases, she noted.
The researchers will continue to track these trends to see whether the increases continue.
“We need additional research, including about the motives for hallucinogen use and how young adults are using these substances, in order to be able to mitigate the associated negative consequences,” Dr. Patrick said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Keyes and Dr. Patrick have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
With the exception of lysergic acid diethylamide,
In 2018, the prevalence of young adults’ past-year use of non-LSD hallucinogens was 3.4%. By 2021, it had jumped to 6.6%.
The increase in non-LSD hallucinogen use occurred while LSD use remained stable at around 4% in 2018 and 2021.
“While non-LSD hallucinogen use remains substantially less prevalent than use of substances such as alcohol and cannabis, a doubling of prevalence in just three years is a dramatic increase and raises possible public health concerns,” co-author Megan Patrick, PhD, with the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research, Ann Arbor, said in a news release.
The results were published online in the journal Addiction.
Health concerns
The estimates are derived from the Monitoring the Future study, which includes annual assessments of adolescent and adult health in the United States.
The analysis focused on 11,304 persons (52% female) aged 9-30 years from the U.S. general population who were interviewed between 2018 and 2021.
Participants were asked about past 12-month use of LSD, as well as use of non-LSD hallucinogens, such as psilocybin.
From 2018 to 2021, past 12-month use of LSD remained relatively stable; it was 3.7% in 2018 and 4.2% in 2021.
However, non-LSD hallucinogen use increased in prevalence from 3.4% to 6.6% from 2018 to 2021.
Across years, the odds of non-LSD use were higher among males, White people, and individuals from households with higher parental education – a proxy for higher socioeconomic status.
The most commonly used non-LSD hallucinogen was psilocybin.
The survey did not ask whether young adults used non-LSD hallucinogens for therapeutic or medical reasons.
“The use of psychedelic and hallucinogenic drugs for a range of therapeutic uses is increasing, given accumulating yet still preliminary data from randomized trials on clinical effectiveness,” lead author Katherine Keyes, PhD, with Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, New York, said in the release.
“With increased visibility for medical and therapeutic use, however, potentially comes diversion and unregulated product availability, as well as a lack of understanding among the public of potential risks,” Dr. Keyes added.
“However, approved therapeutic use of psychedelics under a trained health professional’s care remains uncommon in the United States, thus the trends we observe here are undoubtedly in nonmedical and nontherapeutic use,” Dr. Keyes noted.
Dr. Patrick said the increased use of hallucinogens raises “concern for young adult health” and is not without risk. While hallucinogen dependence has historically been rare in the U.S. population, it could become more common as use increases, she noted.
The researchers will continue to track these trends to see whether the increases continue.
“We need additional research, including about the motives for hallucinogen use and how young adults are using these substances, in order to be able to mitigate the associated negative consequences,” Dr. Patrick said.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Drug Abuse, part of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Keyes and Dr. Patrick have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ADDICTION
Could semaglutide treat addiction as well as obesity?
As demand for semaglutide for weight loss grew following approval of Wegovy by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2021, anecdotal reports of unexpected potential added benefits also began to surface.
Some patients taking these drugs for type 2 diabetes or weight loss also lost interest in addictive and compulsive behaviors such as drinking alcohol, smoking, shopping, nail biting, and skin picking, as reported in articles in the New York Times and The Atlantic, among others.
There is also some preliminary research to support these observations.
This news organization invited three experts to weigh in.
Recent and upcoming studies
The senior author of a recent randomized controlled trial of 127 patients with alcohol use disorder (AUD), Anders Fink-Jensen, MD, said: “I hope that GLP-1 analogs in the future can be used against AUD, but before that can happen, several GLP-1 trials [are needed to] prove an effect on alcohol intake.”
His study involved patients who received exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon, AstraZeneca), the first-generation GLP-1 agonist approved for type 2 diabetes, over 26 weeks, but treatment did not reduce the number of heavy drinking days (the primary outcome), compared with placebo.
However, in post hoc, exploratory analyses, heavy drinking days and total alcohol intake were significantly reduced in the subgroup of patients with AUD and obesity (body mass index > 30 kg/m2).
The participants were also shown pictures of alcohol or neutral subjects while they underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging. Those who had received exenatide, compared with placebo, had significantly less activation of brain reward centers when shown the pictures of alcohol.
“Something is happening in the brain and activation of the reward center is hampered by the GLP-1 compound,” Dr. Fink-Jensen, a clinical psychologist at the Psychiatric Centre Copenhagen, remarked in an email.
“If patients with AUD already fulfill the criteria for semaglutide (or other GLP-1 analogs) by having type 2 diabetes and/or a BMI over 30 kg/m2, they can of course use the compound right now,” he noted.
His team is also beginning a study in patients with AUD and a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 to investigate the effects on alcohol intake of semaglutide up to 2.4 mg weekly, the maximum dose currently approved for obesity in the United States.
“Based on the potency of exenatide and semaglutide,” Dr. Fink-Jensen said, “we expect that semaglutide will cause a stronger reduction in alcohol intake” than exenatide.
Animal studies have also shown that GLP-1 agonists suppress alcohol-induced reward, alcohol intake, motivation to consume alcohol, alcohol seeking, and relapse drinking of alcohol, Elisabet Jerlhag Holm, PhD, noted.
Interestingly, these agents also suppress the reward, intake, and motivation to consume other addictive drugs like cocaine, amphetamine, nicotine, and some opioids, Jerlhag Holm, professor, department of pharmacology, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, noted in an email.
In a recently published preclinical study, her group provides evidence to help explain anecdotal reports from patients with obesity treated with semaglutide who claim they also reduced their alcohol intake. In the study, semaglutide both reduced alcohol intake (and relapse-like drinking) and decreased body weight of rats of both sexes.
“Future research should explore the possibility of semaglutide decreasing alcohol intake in patients with AUD, particularly those who are overweight,” said Prof. Holm.
“AUD is a heterogenous disorder, and one medication is most likely not helpful for all AUD patients,” she added. “Therefore, an arsenal of different medications is beneficial when treating AUD.”
Janice J. Hwang, MD, MHS, echoed these thoughts: “Anecdotally, there are a lot of reports from patients (and in the news) that this class of medication [GLP-1 agonists] impacts cravings and could impact addictive behaviors.”
“I would say, overall, the jury is still out,” as to whether anecdotal reports of GLP-1 agonists curbing addictions will be borne out in randomized controlled trials.
“I think it is much too early to tell” whether these drugs might be approved for treating addictions without more solid clinical trial data, noted Dr. Hwang, who is an associate professor of medicine and chief, division of endocrinology and metabolism, at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Meanwhile, another research group at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, led by psychiatrist Christian Hendershot, PhD, is conducting a clinical trial in 48 participants with AUD who are also smokers.
They aim to determine if patients who receive semaglutide at escalating doses (0.25 mg to 1.0 mg per week via subcutaneous injection) over 9 weeks will consume less alcohol (the primary outcome) and smoke less (a secondary outcome) than those who receive a sham placebo injection. Results are expected in October 2023.
Dr. Fink-Jensen has received an unrestricted research grant from Novo Nordisk to investigate the effects of GLP-1 receptor stimulation on weight gain and metabolic disturbances in patients with schizophrenia treated with an antipsychotic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As demand for semaglutide for weight loss grew following approval of Wegovy by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2021, anecdotal reports of unexpected potential added benefits also began to surface.
Some patients taking these drugs for type 2 diabetes or weight loss also lost interest in addictive and compulsive behaviors such as drinking alcohol, smoking, shopping, nail biting, and skin picking, as reported in articles in the New York Times and The Atlantic, among others.
There is also some preliminary research to support these observations.
This news organization invited three experts to weigh in.
Recent and upcoming studies
The senior author of a recent randomized controlled trial of 127 patients with alcohol use disorder (AUD), Anders Fink-Jensen, MD, said: “I hope that GLP-1 analogs in the future can be used against AUD, but before that can happen, several GLP-1 trials [are needed to] prove an effect on alcohol intake.”
His study involved patients who received exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon, AstraZeneca), the first-generation GLP-1 agonist approved for type 2 diabetes, over 26 weeks, but treatment did not reduce the number of heavy drinking days (the primary outcome), compared with placebo.
However, in post hoc, exploratory analyses, heavy drinking days and total alcohol intake were significantly reduced in the subgroup of patients with AUD and obesity (body mass index > 30 kg/m2).
The participants were also shown pictures of alcohol or neutral subjects while they underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging. Those who had received exenatide, compared with placebo, had significantly less activation of brain reward centers when shown the pictures of alcohol.
“Something is happening in the brain and activation of the reward center is hampered by the GLP-1 compound,” Dr. Fink-Jensen, a clinical psychologist at the Psychiatric Centre Copenhagen, remarked in an email.
“If patients with AUD already fulfill the criteria for semaglutide (or other GLP-1 analogs) by having type 2 diabetes and/or a BMI over 30 kg/m2, they can of course use the compound right now,” he noted.
His team is also beginning a study in patients with AUD and a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 to investigate the effects on alcohol intake of semaglutide up to 2.4 mg weekly, the maximum dose currently approved for obesity in the United States.
“Based on the potency of exenatide and semaglutide,” Dr. Fink-Jensen said, “we expect that semaglutide will cause a stronger reduction in alcohol intake” than exenatide.
Animal studies have also shown that GLP-1 agonists suppress alcohol-induced reward, alcohol intake, motivation to consume alcohol, alcohol seeking, and relapse drinking of alcohol, Elisabet Jerlhag Holm, PhD, noted.
Interestingly, these agents also suppress the reward, intake, and motivation to consume other addictive drugs like cocaine, amphetamine, nicotine, and some opioids, Jerlhag Holm, professor, department of pharmacology, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, noted in an email.
In a recently published preclinical study, her group provides evidence to help explain anecdotal reports from patients with obesity treated with semaglutide who claim they also reduced their alcohol intake. In the study, semaglutide both reduced alcohol intake (and relapse-like drinking) and decreased body weight of rats of both sexes.
“Future research should explore the possibility of semaglutide decreasing alcohol intake in patients with AUD, particularly those who are overweight,” said Prof. Holm.
“AUD is a heterogenous disorder, and one medication is most likely not helpful for all AUD patients,” she added. “Therefore, an arsenal of different medications is beneficial when treating AUD.”
Janice J. Hwang, MD, MHS, echoed these thoughts: “Anecdotally, there are a lot of reports from patients (and in the news) that this class of medication [GLP-1 agonists] impacts cravings and could impact addictive behaviors.”
“I would say, overall, the jury is still out,” as to whether anecdotal reports of GLP-1 agonists curbing addictions will be borne out in randomized controlled trials.
“I think it is much too early to tell” whether these drugs might be approved for treating addictions without more solid clinical trial data, noted Dr. Hwang, who is an associate professor of medicine and chief, division of endocrinology and metabolism, at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Meanwhile, another research group at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, led by psychiatrist Christian Hendershot, PhD, is conducting a clinical trial in 48 participants with AUD who are also smokers.
They aim to determine if patients who receive semaglutide at escalating doses (0.25 mg to 1.0 mg per week via subcutaneous injection) over 9 weeks will consume less alcohol (the primary outcome) and smoke less (a secondary outcome) than those who receive a sham placebo injection. Results are expected in October 2023.
Dr. Fink-Jensen has received an unrestricted research grant from Novo Nordisk to investigate the effects of GLP-1 receptor stimulation on weight gain and metabolic disturbances in patients with schizophrenia treated with an antipsychotic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As demand for semaglutide for weight loss grew following approval of Wegovy by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2021, anecdotal reports of unexpected potential added benefits also began to surface.
Some patients taking these drugs for type 2 diabetes or weight loss also lost interest in addictive and compulsive behaviors such as drinking alcohol, smoking, shopping, nail biting, and skin picking, as reported in articles in the New York Times and The Atlantic, among others.
There is also some preliminary research to support these observations.
This news organization invited three experts to weigh in.
Recent and upcoming studies
The senior author of a recent randomized controlled trial of 127 patients with alcohol use disorder (AUD), Anders Fink-Jensen, MD, said: “I hope that GLP-1 analogs in the future can be used against AUD, but before that can happen, several GLP-1 trials [are needed to] prove an effect on alcohol intake.”
His study involved patients who received exenatide (Byetta, Bydureon, AstraZeneca), the first-generation GLP-1 agonist approved for type 2 diabetes, over 26 weeks, but treatment did not reduce the number of heavy drinking days (the primary outcome), compared with placebo.
However, in post hoc, exploratory analyses, heavy drinking days and total alcohol intake were significantly reduced in the subgroup of patients with AUD and obesity (body mass index > 30 kg/m2).
The participants were also shown pictures of alcohol or neutral subjects while they underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging. Those who had received exenatide, compared with placebo, had significantly less activation of brain reward centers when shown the pictures of alcohol.
“Something is happening in the brain and activation of the reward center is hampered by the GLP-1 compound,” Dr. Fink-Jensen, a clinical psychologist at the Psychiatric Centre Copenhagen, remarked in an email.
“If patients with AUD already fulfill the criteria for semaglutide (or other GLP-1 analogs) by having type 2 diabetes and/or a BMI over 30 kg/m2, they can of course use the compound right now,” he noted.
His team is also beginning a study in patients with AUD and a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 to investigate the effects on alcohol intake of semaglutide up to 2.4 mg weekly, the maximum dose currently approved for obesity in the United States.
“Based on the potency of exenatide and semaglutide,” Dr. Fink-Jensen said, “we expect that semaglutide will cause a stronger reduction in alcohol intake” than exenatide.
Animal studies have also shown that GLP-1 agonists suppress alcohol-induced reward, alcohol intake, motivation to consume alcohol, alcohol seeking, and relapse drinking of alcohol, Elisabet Jerlhag Holm, PhD, noted.
Interestingly, these agents also suppress the reward, intake, and motivation to consume other addictive drugs like cocaine, amphetamine, nicotine, and some opioids, Jerlhag Holm, professor, department of pharmacology, University of Gothenburg, Sweden, noted in an email.
In a recently published preclinical study, her group provides evidence to help explain anecdotal reports from patients with obesity treated with semaglutide who claim they also reduced their alcohol intake. In the study, semaglutide both reduced alcohol intake (and relapse-like drinking) and decreased body weight of rats of both sexes.
“Future research should explore the possibility of semaglutide decreasing alcohol intake in patients with AUD, particularly those who are overweight,” said Prof. Holm.
“AUD is a heterogenous disorder, and one medication is most likely not helpful for all AUD patients,” she added. “Therefore, an arsenal of different medications is beneficial when treating AUD.”
Janice J. Hwang, MD, MHS, echoed these thoughts: “Anecdotally, there are a lot of reports from patients (and in the news) that this class of medication [GLP-1 agonists] impacts cravings and could impact addictive behaviors.”
“I would say, overall, the jury is still out,” as to whether anecdotal reports of GLP-1 agonists curbing addictions will be borne out in randomized controlled trials.
“I think it is much too early to tell” whether these drugs might be approved for treating addictions without more solid clinical trial data, noted Dr. Hwang, who is an associate professor of medicine and chief, division of endocrinology and metabolism, at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Meanwhile, another research group at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, led by psychiatrist Christian Hendershot, PhD, is conducting a clinical trial in 48 participants with AUD who are also smokers.
They aim to determine if patients who receive semaglutide at escalating doses (0.25 mg to 1.0 mg per week via subcutaneous injection) over 9 weeks will consume less alcohol (the primary outcome) and smoke less (a secondary outcome) than those who receive a sham placebo injection. Results are expected in October 2023.
Dr. Fink-Jensen has received an unrestricted research grant from Novo Nordisk to investigate the effects of GLP-1 receptor stimulation on weight gain and metabolic disturbances in patients with schizophrenia treated with an antipsychotic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Alcohol dependence in teens tied to subsequent depression
TOPLINE
Alcohol dependence, but not consumption, at age 18 years increases the risk for depression at age 24 years.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included 3,902 mostly White adolescents, about 58% female, born in England from April 1991 to December 1992, who were part of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) that examined genetic and environmental determinants of health and development.
- Participants completed the self-report Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) between the ages of 16 and 23 years, a period when average alcohol use increases rapidly.
- The primary outcome was probability for depression at age 24 years, using the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), a self-administered computerized clinical assessment of common mental disorder symptoms during the past week.
- Researchers assessed frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption as well as alcohol dependence.
- Confounders included sex, housing type, maternal education and depressive symptoms, parents’ alcohol use, conduct problems at age 4 years, being bullied, and smoking status.
TAKEAWAYS
- After adjustments, alcohol dependence at age 18 years was associated with depression at age 24 years (unstandardized probit coefficient 0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.02-0.25; P = .019)
- The relationship appeared to persist for alcohol dependence at each age of the growth curve (17-22 years).
- There was no evidence that frequency or quantity of alcohol consumption at age 18 was significantly associated with depression at age 24, suggesting these factors may not increase the risk for later depression unless there are also features of dependency.
IN PRACTICE
“Our findings suggest that preventing alcohol dependence during adolescence, or treating it early, could reduce the risk of depression,” which could have important public health implications, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS
The study was carried out by researchers at the University of Bristol; University College London; Critical Thinking Unit, Public Health Directorate, NHS; University of Nottingham, all in the United Kingdom. It was published online in Lancet Psychiatry
LIMITATIONS
There was substantial attrition in the ALSPAC cohort from birth to age 24 years. The sample was recruited from one U.K. region and most participants were White. Measures of alcohol consumption and dependence excluded some features of abuse. And as this is an observational study, the possibility of residual confounding can’t be excluded.
DISCLOSURES
The investigators report no relevant disclosures. The study received support from the UK Medical Research Council and Alcohol Research UK.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
Alcohol dependence, but not consumption, at age 18 years increases the risk for depression at age 24 years.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included 3,902 mostly White adolescents, about 58% female, born in England from April 1991 to December 1992, who were part of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) that examined genetic and environmental determinants of health and development.
- Participants completed the self-report Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) between the ages of 16 and 23 years, a period when average alcohol use increases rapidly.
- The primary outcome was probability for depression at age 24 years, using the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), a self-administered computerized clinical assessment of common mental disorder symptoms during the past week.
- Researchers assessed frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption as well as alcohol dependence.
- Confounders included sex, housing type, maternal education and depressive symptoms, parents’ alcohol use, conduct problems at age 4 years, being bullied, and smoking status.
TAKEAWAYS
- After adjustments, alcohol dependence at age 18 years was associated with depression at age 24 years (unstandardized probit coefficient 0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.02-0.25; P = .019)
- The relationship appeared to persist for alcohol dependence at each age of the growth curve (17-22 years).
- There was no evidence that frequency or quantity of alcohol consumption at age 18 was significantly associated with depression at age 24, suggesting these factors may not increase the risk for later depression unless there are also features of dependency.
IN PRACTICE
“Our findings suggest that preventing alcohol dependence during adolescence, or treating it early, could reduce the risk of depression,” which could have important public health implications, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS
The study was carried out by researchers at the University of Bristol; University College London; Critical Thinking Unit, Public Health Directorate, NHS; University of Nottingham, all in the United Kingdom. It was published online in Lancet Psychiatry
LIMITATIONS
There was substantial attrition in the ALSPAC cohort from birth to age 24 years. The sample was recruited from one U.K. region and most participants were White. Measures of alcohol consumption and dependence excluded some features of abuse. And as this is an observational study, the possibility of residual confounding can’t be excluded.
DISCLOSURES
The investigators report no relevant disclosures. The study received support from the UK Medical Research Council and Alcohol Research UK.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
Alcohol dependence, but not consumption, at age 18 years increases the risk for depression at age 24 years.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included 3,902 mostly White adolescents, about 58% female, born in England from April 1991 to December 1992, who were part of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) that examined genetic and environmental determinants of health and development.
- Participants completed the self-report Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) between the ages of 16 and 23 years, a period when average alcohol use increases rapidly.
- The primary outcome was probability for depression at age 24 years, using the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), a self-administered computerized clinical assessment of common mental disorder symptoms during the past week.
- Researchers assessed frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption as well as alcohol dependence.
- Confounders included sex, housing type, maternal education and depressive symptoms, parents’ alcohol use, conduct problems at age 4 years, being bullied, and smoking status.
TAKEAWAYS
- After adjustments, alcohol dependence at age 18 years was associated with depression at age 24 years (unstandardized probit coefficient 0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.02-0.25; P = .019)
- The relationship appeared to persist for alcohol dependence at each age of the growth curve (17-22 years).
- There was no evidence that frequency or quantity of alcohol consumption at age 18 was significantly associated with depression at age 24, suggesting these factors may not increase the risk for later depression unless there are also features of dependency.
IN PRACTICE
“Our findings suggest that preventing alcohol dependence during adolescence, or treating it early, could reduce the risk of depression,” which could have important public health implications, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS
The study was carried out by researchers at the University of Bristol; University College London; Critical Thinking Unit, Public Health Directorate, NHS; University of Nottingham, all in the United Kingdom. It was published online in Lancet Psychiatry
LIMITATIONS
There was substantial attrition in the ALSPAC cohort from birth to age 24 years. The sample was recruited from one U.K. region and most participants were White. Measures of alcohol consumption and dependence excluded some features of abuse. And as this is an observational study, the possibility of residual confounding can’t be excluded.
DISCLOSURES
The investigators report no relevant disclosures. The study received support from the UK Medical Research Council and Alcohol Research UK.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How has cannabis legalization affected pregnant mothers?
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A population-based study shows that the rate of cannabis-related acute care use during pregnancy increased from 11 per 100,000 pregnancies before legalization to 20 per 100,000 pregnancies afterward: an increase of 82%. Absolute increases were small, however.
“Our findings are consistent with studies highlighting that cannabis use during pregnancy has been increasing in North America, and this study suggests that cannabis legalization might contribute to and accelerate such trends,” study author Daniel Myran, MD, MPH, a public health and preventive medicine physician at the University of Ottawa in Ontario, said in an interview.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Risks for newborns
In a 2019 study, 7% of U.S. women reported using cannabis during pregnancy during 2016-2017, which was double the rate of 3.4% for 2002-2003.
Dr. Myran and colleagues hypothesized that legalizing nonmedical cannabis has affected the drug’s use during pregnancy in Ontario. “We also hypothesized that hospital care for cannabis use would be associated with adverse neonatal outcomes, even after adjusting for other important risk factors that may differ between people with and without cannabis use,” he said.
The researchers’ repeated cross-sectional analysis evaluated changes in the number of pregnant people who received acute care from January 2015 to July 2021 among all patients who were eligible for Ontario’s public health coverage. The final study cohort included 691,242 pregnant patients, of whom 533 had at least one pregnancy with cannabis-related acute care visits. These mothers had a mean age of 24 years vs. 30 for their counterparts with no such visits.
Using segmented regression, the researchers compared changes in the quarterly rate of pregnant people with acute care related to cannabis use (the primary outcome) with those of acute care for mental health conditions or for noncannabis substance use (the control conditions).
“Severe morning sickness was a major risk factor for care in the emergency department or hospital for cannabis use,” said Dr. Myran. “Prior work has found that people who use cannabis during pregnancy often state that it was used to manage challenging symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness.”
Most acute care events (72.2%) were emergency department visits. The most common reasons for acute care were harmful cannabis use (57.6%), followed by cannabis dependence or withdrawal (21.5%), and acute cannabis intoxication (12.8%).
Compared with pregnancies without acute care, those with acute care related to cannabis had higher rates of adverse neonatal outcomes such as birth before 37 weeks’ gestational age (16.9% vs. 7.2%), birth weight at or below the bottom fifth percentile after adjustment for gestational age (12.1% vs. 4.4%), and neonatal intensive care unit admission in the first 28 days of life (31.5% vs. 13%).
An adjusted analysis found that patients younger than 35 years and those living in rural settings or the lowest-income neighborhoods had higher odds of acute cannabis-related care during pregnancy. Patients who received acute care for any substance use or schizophrenia before pregnancy or who accessed outpatient mental health services before pregnancy had higher risk for cannabis-related acute care during pregnancy. Mothers receiving acute care for cannabis also had higher risk for acute care for hyperemesis gravidarum during pregnancy (30.9%).
The rate of acute care for other types of substance use such as alcohol and opioids did not change after cannabis legalization, and acute care for mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression during pregnancy declined by 14%, Dr. Myran noted.
“Physicians who care for pregnant people should consider increasing screening for cannabis use during pregnancy,” said Dr. Myran. “In addition, repeated nonstigmatizing screening and counseling may be indicated for higher-risk groups identified in the study, including pregnancies with severe morning sickness.”
The U.S. perspective
Commenting on the study, M. Camille Hoffman, MD, MSc, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at the University of Colorado in Aurora, said that the findings likely indicate that legalization has made cannabis users less reluctant to come forward for urgent care. “They cannot really claim that this is equivalent to more use, just that more people are willing to present,” she said. Dr. Hoffman was not involved in the study.
The Canadian results do not align perfectly with what is seen in the United States. “It does suggest that there may be more cannabinoid hyperemesis being coded as hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a pregnancy-specific condition vs. a cannabis-dependence-related one,” said Dr. Hoffman.
Literature in the United States often includes tobacco use as a covariate, she added. “This study does not appear to do that,” she said. “Rather, it uses any substance use. Because of this, it is difficult to really know the contribution of cannabis to the adverse pregnancy outcomes vs. the combination of tobacco and cannabis.”
Finally, she pointed out, the proportion of those presenting for acute care for substance use in the 2 years before conception was 22% for acute care visits for cannabis vs 1% for no acute care visits. “This suggests to me that this was a highly vulnerable group before the legalization of cannabis as well. The overall absolute difference is nine in total per 100,000 – hardly enough to draw any real conclusions. Again, maybe those nine were simply more willing to come forth with concerns with cannabis being legal.”
There is no known safe level of cannabis consumption, and its use by pregnant women has been linked to later neurodevelopmental issues in their offspring. A 2022 U.S. study suggested that cannabis exposure in the womb may leave children later in life at risk for autism, psychiatric disorders, and problematic substance abuse, particularly as they enter peak periods of vulnerability in late adolescence.
As to the impact of legalization in certain U.S. states, a 2022 study found that women perceived legalization to mean greater access to cannabis, increased acceptance of use, and greater trust in cannabis retailers. In line with Dr. Hoffman’s view, this study suggested that legalization made pregnant women more willing to discuss cannabis use during pregnancy honestly with their care providers.
In the United States, prenatal cannabis use is still included in definitions of child abuse or neglect and can lead to termination of parental rights, even in states with full legalization.
“These findings highlight the need for ongoing monitoring of markers of cannabis use during pregnancy after legalization,” said Dr. Myran. He also called for effective policies in regions with legal cannabis, such as increased warning labels on cannabis products.
This study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the University of Ottawa site of ICES, which is funded by an annual grant from the Ontario Ministry of Health and Ministry of Long-Term Care. Dr. Myran reports a speaker fee from McMaster University. Dr. Hoffman reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CMAJ
Higher buprenorphine doses help OUD patients stay in treatment
SAN FRANCISCO – . Eighty-five percent of patients who were titrated up to 32 mg remained in treatment for 1 year vs. 22% of those who never went higher than 16 mg, and those on higher doses stayed in treatment 3.83 times longer than those who didn’t.
“Simply put, we demonstrated better retention in treatment if patients were given higher buprenorphine doses when they complained of opioid craving,” said Andrew Gilbert, a medical student at California Northstate University, Elk Grove, Calif. He is lead author of a poster presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
There’s an ongoing debate over ideal doses of buprenorphine (Suboxone), an opioid that’s used to help treat withdrawal symptoms in users of drugs such as heroin and fentanyl. Some sources recommend lower doses. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration, for example, says “ideally, average dosing does not exceed 16 mg” in a guide to the drug’s usage, referring to the sublingual form. (A long-lasting injectable is also available.) Drugs.com says 24 mg is the maximum, and “higher doses have not shown a clinical advantage.
However, some emergency departments have begun providing doses up to 28 mg or higher amid the increased use of the powerful opioid fentanyl. “There are mountains of evidence demonstrating the safety of higher doses at 32 mg, and even several-fold higher than that,” study coauthor Phillip Summers MD, MPH, medical director of the harm-reduction organization Safer Alternatives Thru Networking and Education, Sacramento, Calif., said in an interview. “The question is: Is there clinical benefit to these higher doses?”
‘Significantly higher’ retention
For the new study, researchers tracked 328 patients who were treated for opioid use disorder at the Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento from 2010 to 2017. They were followed until 2022. Their average age was 36, 37.2% were female, 75.0% were White, and 24.1% had a history of overdose.
Clinicians titrated up the doses of buprenorphine to address withdrawal and craving. Five patients never went past 4 mg, and two of them stayed in treatment for a year. Nine of 19 who went up to 8 mg stayed in treatment for 1 year, and 4 of 21 did among those who reached 12 mg.
“Our data suggest that the highest rate of patient dropout is at the beginning of treatment, and that there is significantly higher treatment retention in patients on greater than 24 mg or higher of buprenorphine,” the researchers wrote.
Mr. Gilbert said clinicians start at 8 mg the first day in patients who haven’t taken buprenorphine before, then they go to 16 mg the second day. “We then reevaluate in at least 1 week, oftentimes sooner if the patient’s opioid craving is uncontrolled, and determine if 16 mg is too low, too high, or the correct dosage for the patient.”
If a dose of over 32 mg is needed, clinicians turn to the long-lasting injectable form of the drug, study coauthor Neil Flynn MD, MPH, former medical director of the Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento, said in an interview. “We controlled craving with this form for every patient that did not have opioid craving relief with 32 mg. We believe this form achieved opioid craving cessation due to increased buprenorphine blood levels and increased ratio of unmetabolized buprenorphine to metabolized buprenorphine in our patients.”
According to Dr. Summers, it’s clear that too-low doses hurt the recovery process. “If we prescribe subtherapeutic doses of buprenorphine, our patients will experience opioid craving, which leads to treatment dropout and most likely to relapse. Higher doses of buprenorphine are more likely to cease opioid cravings, leading patients to remain in treatment for longer periods of time.”
Mr. Gilbert said buprenorphine has few side effects, which include decreased libido and hot flashes in both men and women. Testosterone therapy can relieve these symptoms in men, he said, but “unfortunately, we do not have any good medications for reversing this side effect in women. Further research should investigate eliminating this side effect in women.”
Mr. Gilbert declined to comment on the extra cost of higher doses since that is outside the scope of the study.
Medication is the ‘star’
In an interview, addiction specialist Dave Cundiff, MD, MPH, of Ilwaco, Wash., praised the study and agreed with its conclusions about the value of high doses of buprenorphine.
“They’re confirming what the science has already shown, but the world does not accept,” he said, adding that “for opioid use disorder, the medication is the star of the show, although counseling is a necessary adjunct for some patients.”
Dr. Cundiff said he’s coauthored a pending review article that finds that studies support higher doses of buprenorphine.
MaryAnne Murray, DNP, EdD, MBA, a psychiatric mental health nurse practitioner who’s married to Dr. Cundiff, said in an interview that the evolution of the opioid epidemic supports the use of higher doses. “The old way we used to do with heroin users was to wait until they’re in moderate withdrawal, and then start up buprenorphine, usually slowly. With fentanyl, it takes longer, and the wait is often less bearable – unbearable for many people.”
Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento funded the study. The authors, Dr. Cundiff, and Dr. Murray have no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – . Eighty-five percent of patients who were titrated up to 32 mg remained in treatment for 1 year vs. 22% of those who never went higher than 16 mg, and those on higher doses stayed in treatment 3.83 times longer than those who didn’t.
“Simply put, we demonstrated better retention in treatment if patients were given higher buprenorphine doses when they complained of opioid craving,” said Andrew Gilbert, a medical student at California Northstate University, Elk Grove, Calif. He is lead author of a poster presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
There’s an ongoing debate over ideal doses of buprenorphine (Suboxone), an opioid that’s used to help treat withdrawal symptoms in users of drugs such as heroin and fentanyl. Some sources recommend lower doses. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration, for example, says “ideally, average dosing does not exceed 16 mg” in a guide to the drug’s usage, referring to the sublingual form. (A long-lasting injectable is also available.) Drugs.com says 24 mg is the maximum, and “higher doses have not shown a clinical advantage.
However, some emergency departments have begun providing doses up to 28 mg or higher amid the increased use of the powerful opioid fentanyl. “There are mountains of evidence demonstrating the safety of higher doses at 32 mg, and even several-fold higher than that,” study coauthor Phillip Summers MD, MPH, medical director of the harm-reduction organization Safer Alternatives Thru Networking and Education, Sacramento, Calif., said in an interview. “The question is: Is there clinical benefit to these higher doses?”
‘Significantly higher’ retention
For the new study, researchers tracked 328 patients who were treated for opioid use disorder at the Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento from 2010 to 2017. They were followed until 2022. Their average age was 36, 37.2% were female, 75.0% were White, and 24.1% had a history of overdose.
Clinicians titrated up the doses of buprenorphine to address withdrawal and craving. Five patients never went past 4 mg, and two of them stayed in treatment for a year. Nine of 19 who went up to 8 mg stayed in treatment for 1 year, and 4 of 21 did among those who reached 12 mg.
“Our data suggest that the highest rate of patient dropout is at the beginning of treatment, and that there is significantly higher treatment retention in patients on greater than 24 mg or higher of buprenorphine,” the researchers wrote.
Mr. Gilbert said clinicians start at 8 mg the first day in patients who haven’t taken buprenorphine before, then they go to 16 mg the second day. “We then reevaluate in at least 1 week, oftentimes sooner if the patient’s opioid craving is uncontrolled, and determine if 16 mg is too low, too high, or the correct dosage for the patient.”
If a dose of over 32 mg is needed, clinicians turn to the long-lasting injectable form of the drug, study coauthor Neil Flynn MD, MPH, former medical director of the Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento, said in an interview. “We controlled craving with this form for every patient that did not have opioid craving relief with 32 mg. We believe this form achieved opioid craving cessation due to increased buprenorphine blood levels and increased ratio of unmetabolized buprenorphine to metabolized buprenorphine in our patients.”
According to Dr. Summers, it’s clear that too-low doses hurt the recovery process. “If we prescribe subtherapeutic doses of buprenorphine, our patients will experience opioid craving, which leads to treatment dropout and most likely to relapse. Higher doses of buprenorphine are more likely to cease opioid cravings, leading patients to remain in treatment for longer periods of time.”
Mr. Gilbert said buprenorphine has few side effects, which include decreased libido and hot flashes in both men and women. Testosterone therapy can relieve these symptoms in men, he said, but “unfortunately, we do not have any good medications for reversing this side effect in women. Further research should investigate eliminating this side effect in women.”
Mr. Gilbert declined to comment on the extra cost of higher doses since that is outside the scope of the study.
Medication is the ‘star’
In an interview, addiction specialist Dave Cundiff, MD, MPH, of Ilwaco, Wash., praised the study and agreed with its conclusions about the value of high doses of buprenorphine.
“They’re confirming what the science has already shown, but the world does not accept,” he said, adding that “for opioid use disorder, the medication is the star of the show, although counseling is a necessary adjunct for some patients.”
Dr. Cundiff said he’s coauthored a pending review article that finds that studies support higher doses of buprenorphine.
MaryAnne Murray, DNP, EdD, MBA, a psychiatric mental health nurse practitioner who’s married to Dr. Cundiff, said in an interview that the evolution of the opioid epidemic supports the use of higher doses. “The old way we used to do with heroin users was to wait until they’re in moderate withdrawal, and then start up buprenorphine, usually slowly. With fentanyl, it takes longer, and the wait is often less bearable – unbearable for many people.”
Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento funded the study. The authors, Dr. Cundiff, and Dr. Murray have no disclosures.
SAN FRANCISCO – . Eighty-five percent of patients who were titrated up to 32 mg remained in treatment for 1 year vs. 22% of those who never went higher than 16 mg, and those on higher doses stayed in treatment 3.83 times longer than those who didn’t.
“Simply put, we demonstrated better retention in treatment if patients were given higher buprenorphine doses when they complained of opioid craving,” said Andrew Gilbert, a medical student at California Northstate University, Elk Grove, Calif. He is lead author of a poster presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Psychiatric Association.
There’s an ongoing debate over ideal doses of buprenorphine (Suboxone), an opioid that’s used to help treat withdrawal symptoms in users of drugs such as heroin and fentanyl. Some sources recommend lower doses. The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration, for example, says “ideally, average dosing does not exceed 16 mg” in a guide to the drug’s usage, referring to the sublingual form. (A long-lasting injectable is also available.) Drugs.com says 24 mg is the maximum, and “higher doses have not shown a clinical advantage.
However, some emergency departments have begun providing doses up to 28 mg or higher amid the increased use of the powerful opioid fentanyl. “There are mountains of evidence demonstrating the safety of higher doses at 32 mg, and even several-fold higher than that,” study coauthor Phillip Summers MD, MPH, medical director of the harm-reduction organization Safer Alternatives Thru Networking and Education, Sacramento, Calif., said in an interview. “The question is: Is there clinical benefit to these higher doses?”
‘Significantly higher’ retention
For the new study, researchers tracked 328 patients who were treated for opioid use disorder at the Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento from 2010 to 2017. They were followed until 2022. Their average age was 36, 37.2% were female, 75.0% were White, and 24.1% had a history of overdose.
Clinicians titrated up the doses of buprenorphine to address withdrawal and craving. Five patients never went past 4 mg, and two of them stayed in treatment for a year. Nine of 19 who went up to 8 mg stayed in treatment for 1 year, and 4 of 21 did among those who reached 12 mg.
“Our data suggest that the highest rate of patient dropout is at the beginning of treatment, and that there is significantly higher treatment retention in patients on greater than 24 mg or higher of buprenorphine,” the researchers wrote.
Mr. Gilbert said clinicians start at 8 mg the first day in patients who haven’t taken buprenorphine before, then they go to 16 mg the second day. “We then reevaluate in at least 1 week, oftentimes sooner if the patient’s opioid craving is uncontrolled, and determine if 16 mg is too low, too high, or the correct dosage for the patient.”
If a dose of over 32 mg is needed, clinicians turn to the long-lasting injectable form of the drug, study coauthor Neil Flynn MD, MPH, former medical director of the Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento, said in an interview. “We controlled craving with this form for every patient that did not have opioid craving relief with 32 mg. We believe this form achieved opioid craving cessation due to increased buprenorphine blood levels and increased ratio of unmetabolized buprenorphine to metabolized buprenorphine in our patients.”
According to Dr. Summers, it’s clear that too-low doses hurt the recovery process. “If we prescribe subtherapeutic doses of buprenorphine, our patients will experience opioid craving, which leads to treatment dropout and most likely to relapse. Higher doses of buprenorphine are more likely to cease opioid cravings, leading patients to remain in treatment for longer periods of time.”
Mr. Gilbert said buprenorphine has few side effects, which include decreased libido and hot flashes in both men and women. Testosterone therapy can relieve these symptoms in men, he said, but “unfortunately, we do not have any good medications for reversing this side effect in women. Further research should investigate eliminating this side effect in women.”
Mr. Gilbert declined to comment on the extra cost of higher doses since that is outside the scope of the study.
Medication is the ‘star’
In an interview, addiction specialist Dave Cundiff, MD, MPH, of Ilwaco, Wash., praised the study and agreed with its conclusions about the value of high doses of buprenorphine.
“They’re confirming what the science has already shown, but the world does not accept,” he said, adding that “for opioid use disorder, the medication is the star of the show, although counseling is a necessary adjunct for some patients.”
Dr. Cundiff said he’s coauthored a pending review article that finds that studies support higher doses of buprenorphine.
MaryAnne Murray, DNP, EdD, MBA, a psychiatric mental health nurse practitioner who’s married to Dr. Cundiff, said in an interview that the evolution of the opioid epidemic supports the use of higher doses. “The old way we used to do with heroin users was to wait until they’re in moderate withdrawal, and then start up buprenorphine, usually slowly. With fentanyl, it takes longer, and the wait is often less bearable – unbearable for many people.”
Transitions Buprenorphine Clinic of Sacramento funded the study. The authors, Dr. Cundiff, and Dr. Murray have no disclosures.
AT APA 2023




