User login
How To Navigate Your First Job
In a special episode live from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024, host Dr. Matthew Whitson talks with returning guest Dr. Janice Jou. Dr. Jou is a transplant hematologist at the Portland VA and currently serves as professor of medicine and fellowship program director at Oregon Health & Science University. Don’t miss her insight as she shares advice all about what she wishes she knew when going into her first job in gastroenterology. Dr. Jou also answers questions from the audience on topics including “when to say no” and the importance of encouraging emotional transparency with fellows and faculty.
Catch up with past episodes and subscribe wherever you listen to podcasts. You can also listen by clicking on the episode name below.
- Episode 5: Janice Jou: Live from #DDW2024 with tips for your first job
- Episode 4: Loren Rabinowitz and Rachel Issaka: Building research collaborations
- Episode 3: Andy Tau: How to treat GI emergencies
- Episode 2: Laurel Fisher and Asma Khapra: Advancing and advocating for women in GI
- Episode 1: Barbara Jung: Unpacking mentorship with AGA’s president
In a special episode live from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024, host Dr. Matthew Whitson talks with returning guest Dr. Janice Jou. Dr. Jou is a transplant hematologist at the Portland VA and currently serves as professor of medicine and fellowship program director at Oregon Health & Science University. Don’t miss her insight as she shares advice all about what she wishes she knew when going into her first job in gastroenterology. Dr. Jou also answers questions from the audience on topics including “when to say no” and the importance of encouraging emotional transparency with fellows and faculty.
Catch up with past episodes and subscribe wherever you listen to podcasts. You can also listen by clicking on the episode name below.
- Episode 5: Janice Jou: Live from #DDW2024 with tips for your first job
- Episode 4: Loren Rabinowitz and Rachel Issaka: Building research collaborations
- Episode 3: Andy Tau: How to treat GI emergencies
- Episode 2: Laurel Fisher and Asma Khapra: Advancing and advocating for women in GI
- Episode 1: Barbara Jung: Unpacking mentorship with AGA’s president
In a special episode live from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024, host Dr. Matthew Whitson talks with returning guest Dr. Janice Jou. Dr. Jou is a transplant hematologist at the Portland VA and currently serves as professor of medicine and fellowship program director at Oregon Health & Science University. Don’t miss her insight as she shares advice all about what she wishes she knew when going into her first job in gastroenterology. Dr. Jou also answers questions from the audience on topics including “when to say no” and the importance of encouraging emotional transparency with fellows and faculty.
Catch up with past episodes and subscribe wherever you listen to podcasts. You can also listen by clicking on the episode name below.
- Episode 5: Janice Jou: Live from #DDW2024 with tips for your first job
- Episode 4: Loren Rabinowitz and Rachel Issaka: Building research collaborations
- Episode 3: Andy Tau: How to treat GI emergencies
- Episode 2: Laurel Fisher and Asma Khapra: Advancing and advocating for women in GI
- Episode 1: Barbara Jung: Unpacking mentorship with AGA’s president
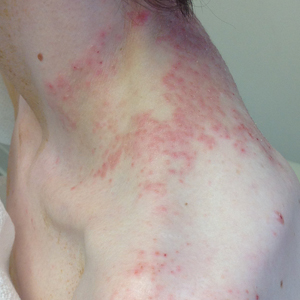
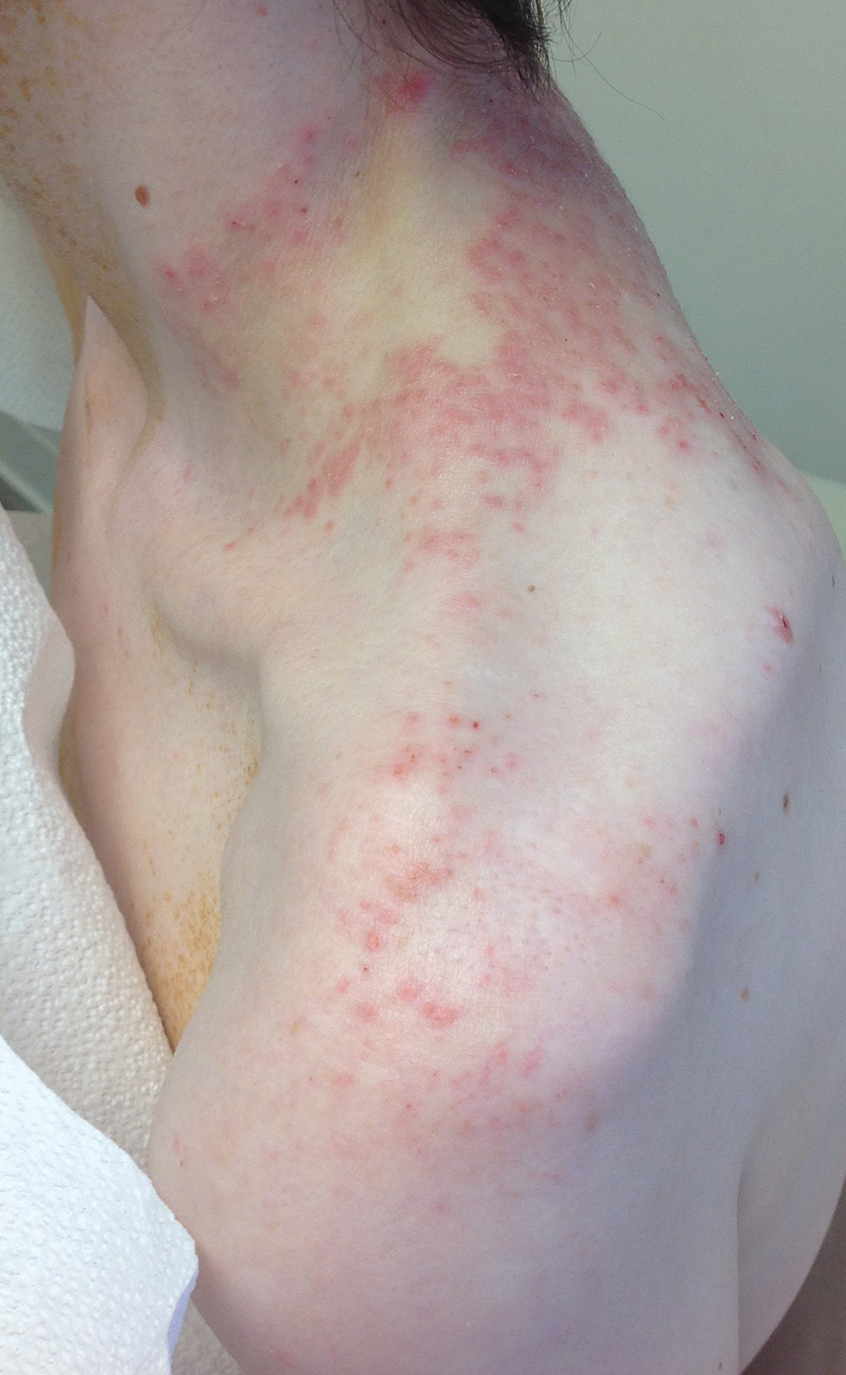
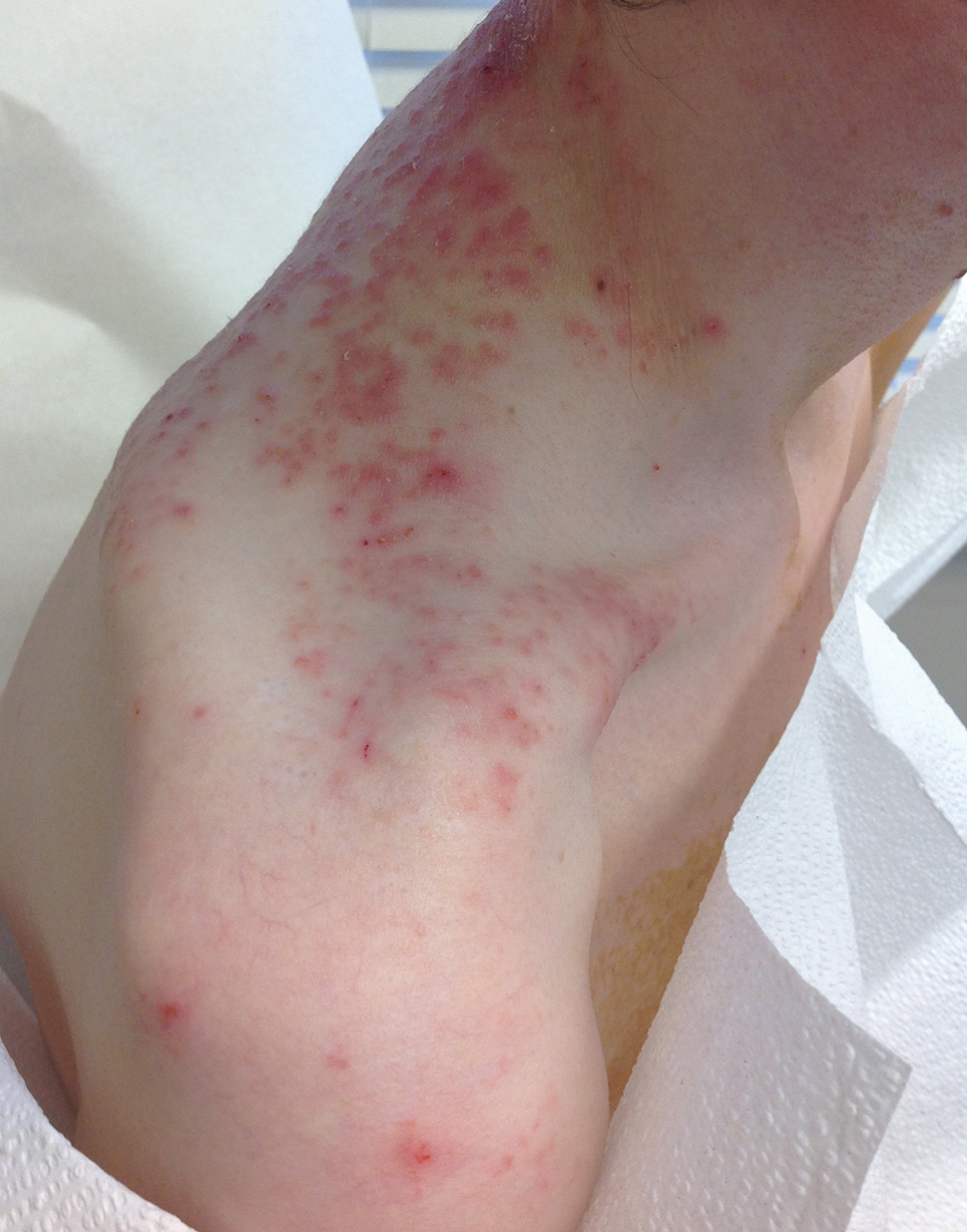
Pruritic Rash on the Neck and Back
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
A comprehensive metabolic panel collected from our patient 1 month earlier did not reveal any abnormalities. Serum methylmalonic acid and homocysteine were both elevated at 417 nmol/L (reference range [for those aged 2–59 years], 55–335 nmol/L) and 23 μmol/L (reference range, 5–15 μmol/L), respectively. Serum folate and 25-hydroxyvitamin D were low at 3.1 ng/mL (reference range, >4.8 ng/mL) and 5 ng/mL (reference range, 30–80 ng/mL), respectively. Vitamin B12 was within reference range. Two 4-mm punch biopsies collected from the upper back showed spongiotic dermatitis.
Our patient’s histopathology results along with the rash distribution and medical history of anorexia increased suspicion for prurigo pigmentosa. A trial of oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 2 weeks was prescribed. At 2-week follow-up, the patient’s mother revealed a history of ketosis in her daughter, solidifying the diagnosis. The patient was counseled on maintaining a healthy diet to prevent future breakouts. The patient’s rash resolved with diet modification and doxycycline; however, it recurred upon relapse of anorexia 4 months later.
Prurigo pigmentosa, originally identified in Japan by Nagashima et al,1 is an uncommon recurrent inflammatory disorder predominantly observed in young adults of Asian descent. Subsequently, it was reported to occur among individuals from different ethnic backgrounds, indicating potential underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis in Western countries.2 Although a direct pathogenic cause for prurigo pigmentosa has not been identified, a strong association has been linked to diet, specifically when ketosis is induced, such as in ketogenic diets and anorexia nervosa.3-5 Other possible causes include sunlight exposure, clothing friction, and sweating.1,5 The disease course is characterized by intermittent flares and spontaneous resolution, with recurrence in most cases. During the active phase, intensely pruritic, papulovesicular or urticarial papules are predominant and most often are localized to the upper body and torso, including the back, shoulders, neck, and chest.5 These flares can persist for several days but eventually subside, leaving behind a characteristic reticular pigmentation that can persist for months.5 First-line treatment often involves the use of tetracycline antibiotics, such as minocycline or doxycycline. 2,4,5 Dapsone often is used with successful resolution. 6 Dietary modifications also have been found to be effective in treating prurigo pigmentosa, particularly in patients presenting with dietary insufficiency.6,7 Increased carbohydrate intake has been shown to promote resolution. 6 Topical corticosteroids demonstrate limited efficacy in controlling flares.6,8
Histopathology has been variably described, with initial findings reported as nonspecific.1 However, it was later described as a distinct inflammatory disease of the skin with histologically distinct stages.2,9 Early stages reveal scattered dermal, dermal papillary, and perivascular neutrophilic infiltration.9 The lesions then progress and become fully developed, at which point neutrophilic infiltration becomes more prominent, accompanied by the presence of intraepidermal neutrophils and spongiosis. As the lesions resolve, the infiltration transitions to lymphocytic, and lichenoid changes can sometimes be appreciated along with epidermal hyperplasia, hyperpigmentation, and dermal melanophages.9 Although these findings aid in the diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa, a clinicopathologic correlation is necessary to establish a definitive diagnosis.
Because prurigo pigmentosa is rare, it often is misdiagnosed as another condition with a similar presentation and nonspecific biopsy findings.6 Allergic contact dermatitis is a common type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction that manifests similar to prurigo pigmentosa with pruritus and a well-demarcated distribution10 that is related to the pattern of allergen exposure; in the case of allergic contact dermatitis related to textiles, a well-demarcated rash will appear in the distribution area of the associated clothing (eg, shirt, pants, shorts).11 Development of allergy involves exposure and sensitization to an allergen, followed by subsequent re-exposure that results in cutaneous T-cell activation and inflammation. 10 Histopathology shows nonspecific spongiotic inflammation, and the gold standard for diagnosis is patch testing to identify the causative substance(s). Definitive treatment includes avoidance of identified allergies; however, if patients are unable to avoid the allergen or the cause is unknown, then corticosteroids, antihistamines, and/or calcineurin inhibitors are beneficial in controlling symptoms and flares.10
Pityrosporum folliculitis (also known as Malassezia folliculitis) is a fungal acneform condition that arises from overgrowth of normal skin flora Malassezia yeast,12 which may be due to occlusion of follicles or disruption of the normal flora composition. Clinically, the manifestation may resemble prurigo pigmentosa in distribution and presence of intense pruritus. However, pustular lesions and involvement of the face can aid in differentiating Pityrosporum from prurigo pigmentosa, which can be confirmed via periodic acid–Schiff staining with numerous round yeasts within affected follicles. Oral antifungal therapy typically yields rapid improvement and resolution of symptoms.12
Urticaria and prurigo pigmentosa share similar clinical characteristics, with symptoms of intense pruritus and urticarial lesions on the trunk.2,13 Urticaria is an IgEmediated type I hypersensitivity reaction characterized by wheals (ie, edematous red or pink lesions of variable size and shape that typically resolve spontaneously within 24–48 hours).13 Notably, urticaria will improve and in some cases completely resolve with antihistamines or anti-IgE antibody treatment, which may aid in distinguishing it from prurigo pigmentosa, as the latter typically exhibits limited response to such treatment.2 Histopathology also can assist in the diagnosis by ruling out other causes of similar rash; however, biopsies are not routinely done unless other inflammatory conditions are of high suspicion.13
Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune, subepidermal, blistering dermatosis that is most common among the elderly.14 It is characterized by the presence of IgG antibodies that target BP180 and BP230, which initiate inflammatory cascades that lead to tissue damage and blister formation. It typically manifests as pruritic blistering eruptions, primarily on the limbs and trunk, but may involve the head, neck, or palmoplantar regions.14 Although blistering eruptions are the prodrome of the disease, some cases may present with nonspecific urticarial or eczematous lesions14,15 that may resemble prurigo pigmentosa. The diagnosis is confirmed through direct immunofluorescence microscopy of biopsied lesions, which reveals IgG and/or C3 deposits along the dermoepidermal junction.14 Management of bullous pemphigoid involves timely initiation of dapsone or systemic corticosteroids, which have demonstrated high efficacy in controlling the disease and its associated symptoms.15
Our patient achieved a favorable response to diet modification and doxycycline therapy consistent with the diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa. Unfortunately, the condition recurred following a relapse of anorexia. Management of prurigo pigmentosa necessitates not only accurate diagnosis but also addressing any underlying factors that may contribute to disease exacerbation. We anticipate the eating disorder will pose a major challenge in achieving long-term control of prurigo pigmentosa.
- Nagashima M, Ohshiro A, Shimizu N. A peculiar pruriginous dermatosis with gross reticular pigmentation. Jpn J Dermatol. 1971;81:38-39.
- Boer A, Asgari M. Prurigo pigmentosa: an underdiagnosed disease? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:405-409. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.29334
- Michaels JD, Hoss E, DiCaudo DJ, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa after a strict ketogenic diet. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;32:248-251. doi:10.1111/pde.12275
- Teraki Y, Teraki E, Kawashima M, et al. Ketosis is involved in the origin of prurigo pigmentosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:509-511. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90460-0
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79-87. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.003
- Wong M, Lee E, Wu Y, et al. Treatment of prurigo pigmentosa with diet modification: a medical case study. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2018;77:114-117.
- Almaani N, Al-Tarawneh AH, Msallam H. Prurigo pigmentosa: a clinicopathological report of three Middle Eastern patients. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2018;2018:9406797. doi:10.1155/2018/9406797
- Kim JK, Chung WK, Chang SE, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: clinicopathological study and analysis of 50 cases in Korea. J Dermatol. 2012;39:891-897. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01640.x
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient diagnosis and evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1029-1040. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1139
- Lazarov A, Cordoba M, Plosk N, et al. Atypical and unusual clinical manifestations of contact dermatitis to clothing (textile contact dermatitis)—case presentation and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9. doi:10.5070/d30kd1d259
- Rubenstein RM, Malerich SA. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) folliculitis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:37-41.
- Bernstein JA, Lang DM, Khan DA, et al. The diagnosis and management of acute and chronic urticaria: 2014 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1270-1277. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.02.036
- della Torre R, Combescure C, Cortés B, et al. Clinical presentation and diagnostic delay in bullous pemphigoid: a prospective nationwide cohort. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1111-1117. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11108.x
- Alonso-Llamazares J, Rogers RS 3rd, Oursler JR, et al. Bullous pemphigoid presenting as generalized pruritus: observations in six patients. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:508-514.
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
A comprehensive metabolic panel collected from our patient 1 month earlier did not reveal any abnormalities. Serum methylmalonic acid and homocysteine were both elevated at 417 nmol/L (reference range [for those aged 2–59 years], 55–335 nmol/L) and 23 μmol/L (reference range, 5–15 μmol/L), respectively. Serum folate and 25-hydroxyvitamin D were low at 3.1 ng/mL (reference range, >4.8 ng/mL) and 5 ng/mL (reference range, 30–80 ng/mL), respectively. Vitamin B12 was within reference range. Two 4-mm punch biopsies collected from the upper back showed spongiotic dermatitis.
Our patient’s histopathology results along with the rash distribution and medical history of anorexia increased suspicion for prurigo pigmentosa. A trial of oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 2 weeks was prescribed. At 2-week follow-up, the patient’s mother revealed a history of ketosis in her daughter, solidifying the diagnosis. The patient was counseled on maintaining a healthy diet to prevent future breakouts. The patient’s rash resolved with diet modification and doxycycline; however, it recurred upon relapse of anorexia 4 months later.
Prurigo pigmentosa, originally identified in Japan by Nagashima et al,1 is an uncommon recurrent inflammatory disorder predominantly observed in young adults of Asian descent. Subsequently, it was reported to occur among individuals from different ethnic backgrounds, indicating potential underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis in Western countries.2 Although a direct pathogenic cause for prurigo pigmentosa has not been identified, a strong association has been linked to diet, specifically when ketosis is induced, such as in ketogenic diets and anorexia nervosa.3-5 Other possible causes include sunlight exposure, clothing friction, and sweating.1,5 The disease course is characterized by intermittent flares and spontaneous resolution, with recurrence in most cases. During the active phase, intensely pruritic, papulovesicular or urticarial papules are predominant and most often are localized to the upper body and torso, including the back, shoulders, neck, and chest.5 These flares can persist for several days but eventually subside, leaving behind a characteristic reticular pigmentation that can persist for months.5 First-line treatment often involves the use of tetracycline antibiotics, such as minocycline or doxycycline. 2,4,5 Dapsone often is used with successful resolution. 6 Dietary modifications also have been found to be effective in treating prurigo pigmentosa, particularly in patients presenting with dietary insufficiency.6,7 Increased carbohydrate intake has been shown to promote resolution. 6 Topical corticosteroids demonstrate limited efficacy in controlling flares.6,8
Histopathology has been variably described, with initial findings reported as nonspecific.1 However, it was later described as a distinct inflammatory disease of the skin with histologically distinct stages.2,9 Early stages reveal scattered dermal, dermal papillary, and perivascular neutrophilic infiltration.9 The lesions then progress and become fully developed, at which point neutrophilic infiltration becomes more prominent, accompanied by the presence of intraepidermal neutrophils and spongiosis. As the lesions resolve, the infiltration transitions to lymphocytic, and lichenoid changes can sometimes be appreciated along with epidermal hyperplasia, hyperpigmentation, and dermal melanophages.9 Although these findings aid in the diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa, a clinicopathologic correlation is necessary to establish a definitive diagnosis.
Because prurigo pigmentosa is rare, it often is misdiagnosed as another condition with a similar presentation and nonspecific biopsy findings.6 Allergic contact dermatitis is a common type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction that manifests similar to prurigo pigmentosa with pruritus and a well-demarcated distribution10 that is related to the pattern of allergen exposure; in the case of allergic contact dermatitis related to textiles, a well-demarcated rash will appear in the distribution area of the associated clothing (eg, shirt, pants, shorts).11 Development of allergy involves exposure and sensitization to an allergen, followed by subsequent re-exposure that results in cutaneous T-cell activation and inflammation. 10 Histopathology shows nonspecific spongiotic inflammation, and the gold standard for diagnosis is patch testing to identify the causative substance(s). Definitive treatment includes avoidance of identified allergies; however, if patients are unable to avoid the allergen or the cause is unknown, then corticosteroids, antihistamines, and/or calcineurin inhibitors are beneficial in controlling symptoms and flares.10
Pityrosporum folliculitis (also known as Malassezia folliculitis) is a fungal acneform condition that arises from overgrowth of normal skin flora Malassezia yeast,12 which may be due to occlusion of follicles or disruption of the normal flora composition. Clinically, the manifestation may resemble prurigo pigmentosa in distribution and presence of intense pruritus. However, pustular lesions and involvement of the face can aid in differentiating Pityrosporum from prurigo pigmentosa, which can be confirmed via periodic acid–Schiff staining with numerous round yeasts within affected follicles. Oral antifungal therapy typically yields rapid improvement and resolution of symptoms.12
Urticaria and prurigo pigmentosa share similar clinical characteristics, with symptoms of intense pruritus and urticarial lesions on the trunk.2,13 Urticaria is an IgEmediated type I hypersensitivity reaction characterized by wheals (ie, edematous red or pink lesions of variable size and shape that typically resolve spontaneously within 24–48 hours).13 Notably, urticaria will improve and in some cases completely resolve with antihistamines or anti-IgE antibody treatment, which may aid in distinguishing it from prurigo pigmentosa, as the latter typically exhibits limited response to such treatment.2 Histopathology also can assist in the diagnosis by ruling out other causes of similar rash; however, biopsies are not routinely done unless other inflammatory conditions are of high suspicion.13
Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune, subepidermal, blistering dermatosis that is most common among the elderly.14 It is characterized by the presence of IgG antibodies that target BP180 and BP230, which initiate inflammatory cascades that lead to tissue damage and blister formation. It typically manifests as pruritic blistering eruptions, primarily on the limbs and trunk, but may involve the head, neck, or palmoplantar regions.14 Although blistering eruptions are the prodrome of the disease, some cases may present with nonspecific urticarial or eczematous lesions14,15 that may resemble prurigo pigmentosa. The diagnosis is confirmed through direct immunofluorescence microscopy of biopsied lesions, which reveals IgG and/or C3 deposits along the dermoepidermal junction.14 Management of bullous pemphigoid involves timely initiation of dapsone or systemic corticosteroids, which have demonstrated high efficacy in controlling the disease and its associated symptoms.15
Our patient achieved a favorable response to diet modification and doxycycline therapy consistent with the diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa. Unfortunately, the condition recurred following a relapse of anorexia. Management of prurigo pigmentosa necessitates not only accurate diagnosis but also addressing any underlying factors that may contribute to disease exacerbation. We anticipate the eating disorder will pose a major challenge in achieving long-term control of prurigo pigmentosa.
The Diagnosis: Prurigo Pigmentosa
A comprehensive metabolic panel collected from our patient 1 month earlier did not reveal any abnormalities. Serum methylmalonic acid and homocysteine were both elevated at 417 nmol/L (reference range [for those aged 2–59 years], 55–335 nmol/L) and 23 μmol/L (reference range, 5–15 μmol/L), respectively. Serum folate and 25-hydroxyvitamin D were low at 3.1 ng/mL (reference range, >4.8 ng/mL) and 5 ng/mL (reference range, 30–80 ng/mL), respectively. Vitamin B12 was within reference range. Two 4-mm punch biopsies collected from the upper back showed spongiotic dermatitis.
Our patient’s histopathology results along with the rash distribution and medical history of anorexia increased suspicion for prurigo pigmentosa. A trial of oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for 2 weeks was prescribed. At 2-week follow-up, the patient’s mother revealed a history of ketosis in her daughter, solidifying the diagnosis. The patient was counseled on maintaining a healthy diet to prevent future breakouts. The patient’s rash resolved with diet modification and doxycycline; however, it recurred upon relapse of anorexia 4 months later.
Prurigo pigmentosa, originally identified in Japan by Nagashima et al,1 is an uncommon recurrent inflammatory disorder predominantly observed in young adults of Asian descent. Subsequently, it was reported to occur among individuals from different ethnic backgrounds, indicating potential underdiagnosis or misdiagnosis in Western countries.2 Although a direct pathogenic cause for prurigo pigmentosa has not been identified, a strong association has been linked to diet, specifically when ketosis is induced, such as in ketogenic diets and anorexia nervosa.3-5 Other possible causes include sunlight exposure, clothing friction, and sweating.1,5 The disease course is characterized by intermittent flares and spontaneous resolution, with recurrence in most cases. During the active phase, intensely pruritic, papulovesicular or urticarial papules are predominant and most often are localized to the upper body and torso, including the back, shoulders, neck, and chest.5 These flares can persist for several days but eventually subside, leaving behind a characteristic reticular pigmentation that can persist for months.5 First-line treatment often involves the use of tetracycline antibiotics, such as minocycline or doxycycline. 2,4,5 Dapsone often is used with successful resolution. 6 Dietary modifications also have been found to be effective in treating prurigo pigmentosa, particularly in patients presenting with dietary insufficiency.6,7 Increased carbohydrate intake has been shown to promote resolution. 6 Topical corticosteroids demonstrate limited efficacy in controlling flares.6,8
Histopathology has been variably described, with initial findings reported as nonspecific.1 However, it was later described as a distinct inflammatory disease of the skin with histologically distinct stages.2,9 Early stages reveal scattered dermal, dermal papillary, and perivascular neutrophilic infiltration.9 The lesions then progress and become fully developed, at which point neutrophilic infiltration becomes more prominent, accompanied by the presence of intraepidermal neutrophils and spongiosis. As the lesions resolve, the infiltration transitions to lymphocytic, and lichenoid changes can sometimes be appreciated along with epidermal hyperplasia, hyperpigmentation, and dermal melanophages.9 Although these findings aid in the diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa, a clinicopathologic correlation is necessary to establish a definitive diagnosis.
Because prurigo pigmentosa is rare, it often is misdiagnosed as another condition with a similar presentation and nonspecific biopsy findings.6 Allergic contact dermatitis is a common type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction that manifests similar to prurigo pigmentosa with pruritus and a well-demarcated distribution10 that is related to the pattern of allergen exposure; in the case of allergic contact dermatitis related to textiles, a well-demarcated rash will appear in the distribution area of the associated clothing (eg, shirt, pants, shorts).11 Development of allergy involves exposure and sensitization to an allergen, followed by subsequent re-exposure that results in cutaneous T-cell activation and inflammation. 10 Histopathology shows nonspecific spongiotic inflammation, and the gold standard for diagnosis is patch testing to identify the causative substance(s). Definitive treatment includes avoidance of identified allergies; however, if patients are unable to avoid the allergen or the cause is unknown, then corticosteroids, antihistamines, and/or calcineurin inhibitors are beneficial in controlling symptoms and flares.10
Pityrosporum folliculitis (also known as Malassezia folliculitis) is a fungal acneform condition that arises from overgrowth of normal skin flora Malassezia yeast,12 which may be due to occlusion of follicles or disruption of the normal flora composition. Clinically, the manifestation may resemble prurigo pigmentosa in distribution and presence of intense pruritus. However, pustular lesions and involvement of the face can aid in differentiating Pityrosporum from prurigo pigmentosa, which can be confirmed via periodic acid–Schiff staining with numerous round yeasts within affected follicles. Oral antifungal therapy typically yields rapid improvement and resolution of symptoms.12
Urticaria and prurigo pigmentosa share similar clinical characteristics, with symptoms of intense pruritus and urticarial lesions on the trunk.2,13 Urticaria is an IgEmediated type I hypersensitivity reaction characterized by wheals (ie, edematous red or pink lesions of variable size and shape that typically resolve spontaneously within 24–48 hours).13 Notably, urticaria will improve and in some cases completely resolve with antihistamines or anti-IgE antibody treatment, which may aid in distinguishing it from prurigo pigmentosa, as the latter typically exhibits limited response to such treatment.2 Histopathology also can assist in the diagnosis by ruling out other causes of similar rash; however, biopsies are not routinely done unless other inflammatory conditions are of high suspicion.13
Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune, subepidermal, blistering dermatosis that is most common among the elderly.14 It is characterized by the presence of IgG antibodies that target BP180 and BP230, which initiate inflammatory cascades that lead to tissue damage and blister formation. It typically manifests as pruritic blistering eruptions, primarily on the limbs and trunk, but may involve the head, neck, or palmoplantar regions.14 Although blistering eruptions are the prodrome of the disease, some cases may present with nonspecific urticarial or eczematous lesions14,15 that may resemble prurigo pigmentosa. The diagnosis is confirmed through direct immunofluorescence microscopy of biopsied lesions, which reveals IgG and/or C3 deposits along the dermoepidermal junction.14 Management of bullous pemphigoid involves timely initiation of dapsone or systemic corticosteroids, which have demonstrated high efficacy in controlling the disease and its associated symptoms.15
Our patient achieved a favorable response to diet modification and doxycycline therapy consistent with the diagnosis of prurigo pigmentosa. Unfortunately, the condition recurred following a relapse of anorexia. Management of prurigo pigmentosa necessitates not only accurate diagnosis but also addressing any underlying factors that may contribute to disease exacerbation. We anticipate the eating disorder will pose a major challenge in achieving long-term control of prurigo pigmentosa.
- Nagashima M, Ohshiro A, Shimizu N. A peculiar pruriginous dermatosis with gross reticular pigmentation. Jpn J Dermatol. 1971;81:38-39.
- Boer A, Asgari M. Prurigo pigmentosa: an underdiagnosed disease? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:405-409. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.29334
- Michaels JD, Hoss E, DiCaudo DJ, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa after a strict ketogenic diet. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;32:248-251. doi:10.1111/pde.12275
- Teraki Y, Teraki E, Kawashima M, et al. Ketosis is involved in the origin of prurigo pigmentosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:509-511. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90460-0
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79-87. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.003
- Wong M, Lee E, Wu Y, et al. Treatment of prurigo pigmentosa with diet modification: a medical case study. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2018;77:114-117.
- Almaani N, Al-Tarawneh AH, Msallam H. Prurigo pigmentosa: a clinicopathological report of three Middle Eastern patients. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2018;2018:9406797. doi:10.1155/2018/9406797
- Kim JK, Chung WK, Chang SE, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: clinicopathological study and analysis of 50 cases in Korea. J Dermatol. 2012;39:891-897. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01640.x
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient diagnosis and evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1029-1040. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1139
- Lazarov A, Cordoba M, Plosk N, et al. Atypical and unusual clinical manifestations of contact dermatitis to clothing (textile contact dermatitis)—case presentation and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9. doi:10.5070/d30kd1d259
- Rubenstein RM, Malerich SA. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) folliculitis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:37-41.
- Bernstein JA, Lang DM, Khan DA, et al. The diagnosis and management of acute and chronic urticaria: 2014 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1270-1277. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.02.036
- della Torre R, Combescure C, Cortés B, et al. Clinical presentation and diagnostic delay in bullous pemphigoid: a prospective nationwide cohort. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1111-1117. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11108.x
- Alonso-Llamazares J, Rogers RS 3rd, Oursler JR, et al. Bullous pemphigoid presenting as generalized pruritus: observations in six patients. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:508-514.
- Nagashima M, Ohshiro A, Shimizu N. A peculiar pruriginous dermatosis with gross reticular pigmentation. Jpn J Dermatol. 1971;81:38-39.
- Boer A, Asgari M. Prurigo pigmentosa: an underdiagnosed disease? Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2006;72:405-409. doi:10.4103/0378-6323.29334
- Michaels JD, Hoss E, DiCaudo DJ, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa after a strict ketogenic diet. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;32:248-251. doi:10.1111/pde.12275
- Teraki Y, Teraki E, Kawashima M, et al. Ketosis is involved in the origin of prurigo pigmentosa. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:509-511. doi:10.1016/s0190-9622(96)90460-0
- Böer A, Misago N, Wolter M, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: a distinctive inflammatory disease of the skin. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:117-129. doi:10.1097/00000372-200304000-00005
- Mufti A, Mirali S, Abduelmula A, et al. Clinical manifestations and treatment outcomes in prurigo pigmentosa (Nagashima disease): a systematic review of the literature. JAAD Int. 2021;3:79-87. doi:10.1016/j.jdin.2021.03.003
- Wong M, Lee E, Wu Y, et al. Treatment of prurigo pigmentosa with diet modification: a medical case study. Hawaii J Med Public Health. 2018;77:114-117.
- Almaani N, Al-Tarawneh AH, Msallam H. Prurigo pigmentosa: a clinicopathological report of three Middle Eastern patients. Case Rep Dermatol Med. 2018;2018:9406797. doi:10.1155/2018/9406797
- Kim JK, Chung WK, Chang SE, et al. Prurigo pigmentosa: clinicopathological study and analysis of 50 cases in Korea. J Dermatol. 2012;39:891-897. doi:10.1111/j.1346-8138.2012.01640.x
- Mowad CM, Anderson B, Scheinman P, et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: patient diagnosis and evaluation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;74:1029-1040. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2015.02.1139
- Lazarov A, Cordoba M, Plosk N, et al. Atypical and unusual clinical manifestations of contact dermatitis to clothing (textile contact dermatitis)—case presentation and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2003;9. doi:10.5070/d30kd1d259
- Rubenstein RM, Malerich SA. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) folliculitis. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014;7:37-41.
- Bernstein JA, Lang DM, Khan DA, et al. The diagnosis and management of acute and chronic urticaria: 2014 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133:1270-1277. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.02.036
- della Torre R, Combescure C, Cortés B, et al. Clinical presentation and diagnostic delay in bullous pemphigoid: a prospective nationwide cohort. Br J Dermatol. 2012;167:1111-1117. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11108.x
- Alonso-Llamazares J, Rogers RS 3rd, Oursler JR, et al. Bullous pemphigoid presenting as generalized pruritus: observations in six patients. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:508-514.
A 43-year-old woman presented with a pruritic rash across the neck and back of 6 months’ duration that progressively worsened. She had a medical history of anorexia nervosa, herpes zoster with a recent flare, and peripheral neuropathy. Physical examination showed numerous red scaly papules across the upper back and shoulders that coalesced in a reticular pattern. No similar papules were seen elsewhere on the body.
New Models Predict Time From Mild Cognitive Impairment to Dementia
Using a large, real-world population, researchers have developed models that predict cognitive decline in amyloid-positive patients with either mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia.
The models may help clinicians better answer common questions from their patients about their rate of cognitive decline, noted the investigators, led by Pieter J. van der Veere, MD, Alzheimer Center and Department of Neurology, Amsterdam Neuroscience, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Easy-to-Use Prototype
On average, it takes 4 years for MCI to progress to dementia. While new disease-modifying drugs targeting amyloid may slow progression, whether this effect is clinically meaningful is debatable, the investigators noted.
Earlier published models predicting cognitive decline either are limited to patients with MCI or haven’t been developed for easy clinical use, they added.
For the single-center study, researchers selected 961 amyloid-positive patients, mean age 65 years, who had at least two longitudinal Mini-Mental State Examinations (MMSEs). Of these, 310 had MCI, and 651 had mild dementia; 48% were women, and over 90% were White.
Researchers used linear mixed modeling to predict MMSE over time. They included age, sex, baseline MMSE, apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 status, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) beta-amyloid (Aß) 1-42 and plasma phosphorylated-tau markers, and MRI total brain and hippocampal volume measures in the various models, including the final biomarker prediction models.
At follow-up, investigators found that the yearly decline in MMSEs increased in patients with both MCI and mild dementia. In MCI, the average MMSE declined from 26.4 (95% confidence interval [CI], 26.2-26.7) at baseline to 21.0 (95% CI, 20.2-21.7) after 5 years.
In mild dementia, the average MMSE declined from 22.4 (95% CI, 22.0-22.7) to 7.8 (95% CI, 6.8-8.9) at 5 years.
The predicted mean time to reach an MMSE of 20 (indicating mild dementia) for a hypothetical patient with MCI and a baseline MMSE of 28 and CSF Aß 1-42 of 925 pg/mL was 6 years (95% CI, 5.4-6.7 years).
However, with a hypothetical drug treatment that reduces the rate of decline by 30%, the patient would not reach the stage of moderate dementia for 8.6 years.
For a hypothetical patient with mild dementia with a baseline MMSE of 20 and CSF Aß 1-42 of 625 pg/mL, the predicted mean time to reach an MMSE of 15 was 2.3 years (95% CI, 2.1-2.5), or 3.3 years if decline is reduced by 30% with drug treatment.
External validation of the prediction models using data from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, a longitudinal cohort of patients not cognitively impaired or with MCI or dementia, showed comparable performance between the model-building approaches.
Researchers have incorporated the models in an easy-to-use calculator as a prototype tool that physicians can use to discuss prognosis, the uncertainty surrounding the predictions, and the impact of intervention strategies with patients.
Future prediction models may be able to predict patient-reported outcomes such as quality of life and daily functioning, the researchers noted.
“Until then, there is an important role for clinicians in translating the observed and predicted cognitive functions,” they wrote.
Compared with other studies predicting the MMSE decline using different statistical techniques, these new models showed similar or even better predictive performance while requiring less or similar information, the investigators noted.
The study used MMSE as a measure of cognition, but there may be intraindividual variation in these measures among cognitively normal patients, and those with cognitive decline may score lower if measurements are taken later in the day. Another study limitation was that the models were built for use in memory clinics, so generalizability to the general population could be limited.
The study was supported by Eisai, ZonMW, and Health~Holland Top Sector Life Sciences & Health. See paper for financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Using a large, real-world population, researchers have developed models that predict cognitive decline in amyloid-positive patients with either mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia.
The models may help clinicians better answer common questions from their patients about their rate of cognitive decline, noted the investigators, led by Pieter J. van der Veere, MD, Alzheimer Center and Department of Neurology, Amsterdam Neuroscience, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Easy-to-Use Prototype
On average, it takes 4 years for MCI to progress to dementia. While new disease-modifying drugs targeting amyloid may slow progression, whether this effect is clinically meaningful is debatable, the investigators noted.
Earlier published models predicting cognitive decline either are limited to patients with MCI or haven’t been developed for easy clinical use, they added.
For the single-center study, researchers selected 961 amyloid-positive patients, mean age 65 years, who had at least two longitudinal Mini-Mental State Examinations (MMSEs). Of these, 310 had MCI, and 651 had mild dementia; 48% were women, and over 90% were White.
Researchers used linear mixed modeling to predict MMSE over time. They included age, sex, baseline MMSE, apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 status, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) beta-amyloid (Aß) 1-42 and plasma phosphorylated-tau markers, and MRI total brain and hippocampal volume measures in the various models, including the final biomarker prediction models.
At follow-up, investigators found that the yearly decline in MMSEs increased in patients with both MCI and mild dementia. In MCI, the average MMSE declined from 26.4 (95% confidence interval [CI], 26.2-26.7) at baseline to 21.0 (95% CI, 20.2-21.7) after 5 years.
In mild dementia, the average MMSE declined from 22.4 (95% CI, 22.0-22.7) to 7.8 (95% CI, 6.8-8.9) at 5 years.
The predicted mean time to reach an MMSE of 20 (indicating mild dementia) for a hypothetical patient with MCI and a baseline MMSE of 28 and CSF Aß 1-42 of 925 pg/mL was 6 years (95% CI, 5.4-6.7 years).
However, with a hypothetical drug treatment that reduces the rate of decline by 30%, the patient would not reach the stage of moderate dementia for 8.6 years.
For a hypothetical patient with mild dementia with a baseline MMSE of 20 and CSF Aß 1-42 of 625 pg/mL, the predicted mean time to reach an MMSE of 15 was 2.3 years (95% CI, 2.1-2.5), or 3.3 years if decline is reduced by 30% with drug treatment.
External validation of the prediction models using data from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, a longitudinal cohort of patients not cognitively impaired or with MCI or dementia, showed comparable performance between the model-building approaches.
Researchers have incorporated the models in an easy-to-use calculator as a prototype tool that physicians can use to discuss prognosis, the uncertainty surrounding the predictions, and the impact of intervention strategies with patients.
Future prediction models may be able to predict patient-reported outcomes such as quality of life and daily functioning, the researchers noted.
“Until then, there is an important role for clinicians in translating the observed and predicted cognitive functions,” they wrote.
Compared with other studies predicting the MMSE decline using different statistical techniques, these new models showed similar or even better predictive performance while requiring less or similar information, the investigators noted.
The study used MMSE as a measure of cognition, but there may be intraindividual variation in these measures among cognitively normal patients, and those with cognitive decline may score lower if measurements are taken later in the day. Another study limitation was that the models were built for use in memory clinics, so generalizability to the general population could be limited.
The study was supported by Eisai, ZonMW, and Health~Holland Top Sector Life Sciences & Health. See paper for financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Using a large, real-world population, researchers have developed models that predict cognitive decline in amyloid-positive patients with either mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia.
The models may help clinicians better answer common questions from their patients about their rate of cognitive decline, noted the investigators, led by Pieter J. van der Veere, MD, Alzheimer Center and Department of Neurology, Amsterdam Neuroscience, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
The findings were published online in Neurology.
Easy-to-Use Prototype
On average, it takes 4 years for MCI to progress to dementia. While new disease-modifying drugs targeting amyloid may slow progression, whether this effect is clinically meaningful is debatable, the investigators noted.
Earlier published models predicting cognitive decline either are limited to patients with MCI or haven’t been developed for easy clinical use, they added.
For the single-center study, researchers selected 961 amyloid-positive patients, mean age 65 years, who had at least two longitudinal Mini-Mental State Examinations (MMSEs). Of these, 310 had MCI, and 651 had mild dementia; 48% were women, and over 90% were White.
Researchers used linear mixed modeling to predict MMSE over time. They included age, sex, baseline MMSE, apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 status, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) beta-amyloid (Aß) 1-42 and plasma phosphorylated-tau markers, and MRI total brain and hippocampal volume measures in the various models, including the final biomarker prediction models.
At follow-up, investigators found that the yearly decline in MMSEs increased in patients with both MCI and mild dementia. In MCI, the average MMSE declined from 26.4 (95% confidence interval [CI], 26.2-26.7) at baseline to 21.0 (95% CI, 20.2-21.7) after 5 years.
In mild dementia, the average MMSE declined from 22.4 (95% CI, 22.0-22.7) to 7.8 (95% CI, 6.8-8.9) at 5 years.
The predicted mean time to reach an MMSE of 20 (indicating mild dementia) for a hypothetical patient with MCI and a baseline MMSE of 28 and CSF Aß 1-42 of 925 pg/mL was 6 years (95% CI, 5.4-6.7 years).
However, with a hypothetical drug treatment that reduces the rate of decline by 30%, the patient would not reach the stage of moderate dementia for 8.6 years.
For a hypothetical patient with mild dementia with a baseline MMSE of 20 and CSF Aß 1-42 of 625 pg/mL, the predicted mean time to reach an MMSE of 15 was 2.3 years (95% CI, 2.1-2.5), or 3.3 years if decline is reduced by 30% with drug treatment.
External validation of the prediction models using data from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, a longitudinal cohort of patients not cognitively impaired or with MCI or dementia, showed comparable performance between the model-building approaches.
Researchers have incorporated the models in an easy-to-use calculator as a prototype tool that physicians can use to discuss prognosis, the uncertainty surrounding the predictions, and the impact of intervention strategies with patients.
Future prediction models may be able to predict patient-reported outcomes such as quality of life and daily functioning, the researchers noted.
“Until then, there is an important role for clinicians in translating the observed and predicted cognitive functions,” they wrote.
Compared with other studies predicting the MMSE decline using different statistical techniques, these new models showed similar or even better predictive performance while requiring less or similar information, the investigators noted.
The study used MMSE as a measure of cognition, but there may be intraindividual variation in these measures among cognitively normal patients, and those with cognitive decline may score lower if measurements are taken later in the day. Another study limitation was that the models were built for use in memory clinics, so generalizability to the general population could be limited.
The study was supported by Eisai, ZonMW, and Health~Holland Top Sector Life Sciences & Health. See paper for financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
FDA Calls AstraZeneca’s NSCLC Trial Design Into Question
The trial in question, AEGEAN, investigated perioperative durvalumab for resectable NSCLC tumors across 802 patients. Patients without EGFR or ALK mutations were randomly assigned to receive durvalumab before surgery alongside platinum-containing chemotherapy and after surgery for a year as monotherapy or to receive chemotherapy and surgery alone.
Patients receiving durvalumab demonstrated better event-free survival at 1 year (73.4% vs 64.5% without durvalumab) and a better pathologic complete response rate (17.2% vs 4.3% without). Currently, AstraZeneca is seeking to add the indication for durvalumab to those the agent already has.
However, at the July 25 ODAC meeting, the committee explained that the AEGEAN trial design makes it impossible to tell whether patients benefited from durvalumab before surgery, after it, or at both points.
Mounting evidence, including from AstraZeneca’s own studies, suggests that the benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as durvalumab, comes before surgery. That means prescribing durvalumab after surgery could be exposing patients to serious side effects and financial toxicity, with potentially no clinical benefit, “magnifying the risk of potential overtreatment,” the committee cautioned.
When AEGEAN was being designed in 2018, FDA requested that AstraZeneca address the uncertainty surrounding when to use durvalumab by including separate neoadjuvant and adjuvant arms, or at least an arm where patients were treated with neoadjuvant durvalumab alone to compare with treatment both before and after surgery.
The company didn’t follow through and, during the July 25 meeting, the committee wanted answers. “Why did you not comply with this?” asked ODAC committee acting chair Daniel Spratt, MD, a radiation oncologist at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio.
AstraZeneca personnel explained that doing so would have required many more subjects, made the trial more expensive, and added about 2 years to AEGEAN.
One speaker noted that the company, which makes more than $4 billion a year on durvalumab, would have taken about 2 days to recoup that added cost. Others wondered whether the motive was to sell durvalumab for as long as possible across a patient’s course of treatment.
Perhaps the biggest reason the company ignored the request is that “it wasn’t our understanding at that time that this was a barrier to approval,” an AstraZeneca regulatory affairs specialist said.
To this end, the agency asked its advisory panel to vote on whether it should require — instead of simply request, as it did with AstraZeneca — companies to prove that patients need immunotherapy both before and after surgery in resectable NSCLC.
The 11-member panel voted unanimously that it should make this a requirement, and several members said it should do so in other cancers as well.
However, when the agency asked whether durvalumab’s resectable NSCLC approval should be delayed until AstraZeneca conducts a trial to answer the neoadjuvant vs adjuvant question, the panel members didn’t think so.
The consensus was that because AEGEAN showed a decent benefit, patients and physicians should have it as an option, and approval shouldn’t be delayed. The panel said that the bigger question about the benefit of maintenance therapy should be left to future studies.
FDA usually follows the advice of its advisory panels.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The trial in question, AEGEAN, investigated perioperative durvalumab for resectable NSCLC tumors across 802 patients. Patients without EGFR or ALK mutations were randomly assigned to receive durvalumab before surgery alongside platinum-containing chemotherapy and after surgery for a year as monotherapy or to receive chemotherapy and surgery alone.
Patients receiving durvalumab demonstrated better event-free survival at 1 year (73.4% vs 64.5% without durvalumab) and a better pathologic complete response rate (17.2% vs 4.3% without). Currently, AstraZeneca is seeking to add the indication for durvalumab to those the agent already has.
However, at the July 25 ODAC meeting, the committee explained that the AEGEAN trial design makes it impossible to tell whether patients benefited from durvalumab before surgery, after it, or at both points.
Mounting evidence, including from AstraZeneca’s own studies, suggests that the benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as durvalumab, comes before surgery. That means prescribing durvalumab after surgery could be exposing patients to serious side effects and financial toxicity, with potentially no clinical benefit, “magnifying the risk of potential overtreatment,” the committee cautioned.
When AEGEAN was being designed in 2018, FDA requested that AstraZeneca address the uncertainty surrounding when to use durvalumab by including separate neoadjuvant and adjuvant arms, or at least an arm where patients were treated with neoadjuvant durvalumab alone to compare with treatment both before and after surgery.
The company didn’t follow through and, during the July 25 meeting, the committee wanted answers. “Why did you not comply with this?” asked ODAC committee acting chair Daniel Spratt, MD, a radiation oncologist at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio.
AstraZeneca personnel explained that doing so would have required many more subjects, made the trial more expensive, and added about 2 years to AEGEAN.
One speaker noted that the company, which makes more than $4 billion a year on durvalumab, would have taken about 2 days to recoup that added cost. Others wondered whether the motive was to sell durvalumab for as long as possible across a patient’s course of treatment.
Perhaps the biggest reason the company ignored the request is that “it wasn’t our understanding at that time that this was a barrier to approval,” an AstraZeneca regulatory affairs specialist said.
To this end, the agency asked its advisory panel to vote on whether it should require — instead of simply request, as it did with AstraZeneca — companies to prove that patients need immunotherapy both before and after surgery in resectable NSCLC.
The 11-member panel voted unanimously that it should make this a requirement, and several members said it should do so in other cancers as well.
However, when the agency asked whether durvalumab’s resectable NSCLC approval should be delayed until AstraZeneca conducts a trial to answer the neoadjuvant vs adjuvant question, the panel members didn’t think so.
The consensus was that because AEGEAN showed a decent benefit, patients and physicians should have it as an option, and approval shouldn’t be delayed. The panel said that the bigger question about the benefit of maintenance therapy should be left to future studies.
FDA usually follows the advice of its advisory panels.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The trial in question, AEGEAN, investigated perioperative durvalumab for resectable NSCLC tumors across 802 patients. Patients without EGFR or ALK mutations were randomly assigned to receive durvalumab before surgery alongside platinum-containing chemotherapy and after surgery for a year as monotherapy or to receive chemotherapy and surgery alone.
Patients receiving durvalumab demonstrated better event-free survival at 1 year (73.4% vs 64.5% without durvalumab) and a better pathologic complete response rate (17.2% vs 4.3% without). Currently, AstraZeneca is seeking to add the indication for durvalumab to those the agent already has.
However, at the July 25 ODAC meeting, the committee explained that the AEGEAN trial design makes it impossible to tell whether patients benefited from durvalumab before surgery, after it, or at both points.
Mounting evidence, including from AstraZeneca’s own studies, suggests that the benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitors, such as durvalumab, comes before surgery. That means prescribing durvalumab after surgery could be exposing patients to serious side effects and financial toxicity, with potentially no clinical benefit, “magnifying the risk of potential overtreatment,” the committee cautioned.
When AEGEAN was being designed in 2018, FDA requested that AstraZeneca address the uncertainty surrounding when to use durvalumab by including separate neoadjuvant and adjuvant arms, or at least an arm where patients were treated with neoadjuvant durvalumab alone to compare with treatment both before and after surgery.
The company didn’t follow through and, during the July 25 meeting, the committee wanted answers. “Why did you not comply with this?” asked ODAC committee acting chair Daniel Spratt, MD, a radiation oncologist at Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio.
AstraZeneca personnel explained that doing so would have required many more subjects, made the trial more expensive, and added about 2 years to AEGEAN.
One speaker noted that the company, which makes more than $4 billion a year on durvalumab, would have taken about 2 days to recoup that added cost. Others wondered whether the motive was to sell durvalumab for as long as possible across a patient’s course of treatment.
Perhaps the biggest reason the company ignored the request is that “it wasn’t our understanding at that time that this was a barrier to approval,” an AstraZeneca regulatory affairs specialist said.
To this end, the agency asked its advisory panel to vote on whether it should require — instead of simply request, as it did with AstraZeneca — companies to prove that patients need immunotherapy both before and after surgery in resectable NSCLC.
The 11-member panel voted unanimously that it should make this a requirement, and several members said it should do so in other cancers as well.
However, when the agency asked whether durvalumab’s resectable NSCLC approval should be delayed until AstraZeneca conducts a trial to answer the neoadjuvant vs adjuvant question, the panel members didn’t think so.
The consensus was that because AEGEAN showed a decent benefit, patients and physicians should have it as an option, and approval shouldn’t be delayed. The panel said that the bigger question about the benefit of maintenance therapy should be left to future studies.
FDA usually follows the advice of its advisory panels.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Advantages of a Pediatric Rheumatology/Dermatology Clinic Evaluated
results from a retrospective cohort study showed.
“This finding highlights the complexity of patients referred to this clinic,” the study’s first author, Jessica Crockett, a fourth-year medical student at UCSF, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Integrated care models such as rheumatology/dermatology clinics (RDCs) have been shown to facilitate complete clinical evaluations, establish new or revised diagnoses, and streamline care for adult patients with complex autoimmune skin diseases. However, few pediatric RDCs exist nationwide, and data therefore is quite limited.”
To advance the understanding of pediatric RDC practice patterns, the influence of the care model on patient care, and professional development for trainees and clinicians, Ms. Crockett collaborated with senior author Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at UCSF, and colleagues to evaluate a cohort of 71 patients who received care at the UCSF pediatric RDC. The clinic, which was launched in 2017, includes two dermatologists, two rheumatologists, trainees, a social worker, and a nurse. Team members participate in a preclinic conference to review patient data and images, discuss relevant literature, and develop an approach to each patient.
In a separate part of the study, the researchers distributed a survey to 17 pediatric dermatologists who participate in unique RDCs in North America. Respondents were asked to describe the variability of clinical operations, participants, administrative/clinical support, and educational value for participating physicians and trainees.
Of the 71 patients cared for at the UCSF pediatric RDC, 69% were female, 44% were White, 51% were aged 13-21 years, 42% were aged 3-12 years, and 7% were aged 0-11 years at their first clinic visit. The top four primary RDC diagnoses were linear morphea (33%), lupus (23%), psoriasis (13%), and juvenile dermatomyositis (10%).
Nearly one in four patients (17, or 24%) presented to the RDC without a confirmed diagnosis. A diagnosis was established at the first RDC visit for 7 of these 17 patients (41%). Among 54 patients who presented with an established diagnosis, the first RDC visit confirmed the diagnosis for 52 (96%) and revised it for 2 (4%). “Initial pediatric RDC evaluation significantly influenced patient care by confirming or revising preexisting diagnoses, rendering new diagnoses, and streamlining additional laboratory and imaging recommendations,” the researchers wrote in their poster.
The evaluation also resulted in modified disease management in the form of systemic medication changes or dosage adjustments as well as the initiation of novel therapies. For example, systemic medication changes were made during the first RDC visit in 34 of the 46 patients (74%) who were on systemic medication at presentation.
“Seeing complex patients together in real time allows specialists and other team members (social work, nursing, PT/OT, for example) to share ideas, communicate clearly to families, and efficiently develop recommendations,” Ms. Crockett said of the UCSF pediatric RDC. “Exposure to other specialists while caring for patients enhances medical knowledge, communication skills, and professional competency of faculty and trainees alike.”
In the survey portion of the study, each of the 17 dermatologists reported that the pediatric RDC is valuable for patient care, and 88% believed the RDC was a valuable use of their time. However, only 59% of respondents reported having administrative support, and only 29% had a dedicated clinic coordinator or navigator.
“We were surprised to find that only a quarter of pediatric RDCs incorporate an educational conference,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization. “We have found that assembling the care team prior to seeing patients to review clinical data, discuss relevant literature, and define the clinical questions for each patient is an integral part of the clinical operation. The trainees are involved in these conference presentations, and it really enhances their understanding of the complex diagnoses we manage in this clinic and the issues faced by affected children and families. The preclinical conference increases efficiency, positively influences patient care, and supports professional development for all participants.”
The study was indirectly supported by a fellowship grant awarded to Ms. Crockett from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a retrospective cohort study showed.
“This finding highlights the complexity of patients referred to this clinic,” the study’s first author, Jessica Crockett, a fourth-year medical student at UCSF, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Integrated care models such as rheumatology/dermatology clinics (RDCs) have been shown to facilitate complete clinical evaluations, establish new or revised diagnoses, and streamline care for adult patients with complex autoimmune skin diseases. However, few pediatric RDCs exist nationwide, and data therefore is quite limited.”
To advance the understanding of pediatric RDC practice patterns, the influence of the care model on patient care, and professional development for trainees and clinicians, Ms. Crockett collaborated with senior author Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at UCSF, and colleagues to evaluate a cohort of 71 patients who received care at the UCSF pediatric RDC. The clinic, which was launched in 2017, includes two dermatologists, two rheumatologists, trainees, a social worker, and a nurse. Team members participate in a preclinic conference to review patient data and images, discuss relevant literature, and develop an approach to each patient.
In a separate part of the study, the researchers distributed a survey to 17 pediatric dermatologists who participate in unique RDCs in North America. Respondents were asked to describe the variability of clinical operations, participants, administrative/clinical support, and educational value for participating physicians and trainees.
Of the 71 patients cared for at the UCSF pediatric RDC, 69% were female, 44% were White, 51% were aged 13-21 years, 42% were aged 3-12 years, and 7% were aged 0-11 years at their first clinic visit. The top four primary RDC diagnoses were linear morphea (33%), lupus (23%), psoriasis (13%), and juvenile dermatomyositis (10%).
Nearly one in four patients (17, or 24%) presented to the RDC without a confirmed diagnosis. A diagnosis was established at the first RDC visit for 7 of these 17 patients (41%). Among 54 patients who presented with an established diagnosis, the first RDC visit confirmed the diagnosis for 52 (96%) and revised it for 2 (4%). “Initial pediatric RDC evaluation significantly influenced patient care by confirming or revising preexisting diagnoses, rendering new diagnoses, and streamlining additional laboratory and imaging recommendations,” the researchers wrote in their poster.
The evaluation also resulted in modified disease management in the form of systemic medication changes or dosage adjustments as well as the initiation of novel therapies. For example, systemic medication changes were made during the first RDC visit in 34 of the 46 patients (74%) who were on systemic medication at presentation.
“Seeing complex patients together in real time allows specialists and other team members (social work, nursing, PT/OT, for example) to share ideas, communicate clearly to families, and efficiently develop recommendations,” Ms. Crockett said of the UCSF pediatric RDC. “Exposure to other specialists while caring for patients enhances medical knowledge, communication skills, and professional competency of faculty and trainees alike.”
In the survey portion of the study, each of the 17 dermatologists reported that the pediatric RDC is valuable for patient care, and 88% believed the RDC was a valuable use of their time. However, only 59% of respondents reported having administrative support, and only 29% had a dedicated clinic coordinator or navigator.
“We were surprised to find that only a quarter of pediatric RDCs incorporate an educational conference,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization. “We have found that assembling the care team prior to seeing patients to review clinical data, discuss relevant literature, and define the clinical questions for each patient is an integral part of the clinical operation. The trainees are involved in these conference presentations, and it really enhances their understanding of the complex diagnoses we manage in this clinic and the issues faced by affected children and families. The preclinical conference increases efficiency, positively influences patient care, and supports professional development for all participants.”
The study was indirectly supported by a fellowship grant awarded to Ms. Crockett from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
results from a retrospective cohort study showed.
“This finding highlights the complexity of patients referred to this clinic,” the study’s first author, Jessica Crockett, a fourth-year medical student at UCSF, told this news organization following the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Integrated care models such as rheumatology/dermatology clinics (RDCs) have been shown to facilitate complete clinical evaluations, establish new or revised diagnoses, and streamline care for adult patients with complex autoimmune skin diseases. However, few pediatric RDCs exist nationwide, and data therefore is quite limited.”
To advance the understanding of pediatric RDC practice patterns, the influence of the care model on patient care, and professional development for trainees and clinicians, Ms. Crockett collaborated with senior author Kelly Cordoro, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at UCSF, and colleagues to evaluate a cohort of 71 patients who received care at the UCSF pediatric RDC. The clinic, which was launched in 2017, includes two dermatologists, two rheumatologists, trainees, a social worker, and a nurse. Team members participate in a preclinic conference to review patient data and images, discuss relevant literature, and develop an approach to each patient.
In a separate part of the study, the researchers distributed a survey to 17 pediatric dermatologists who participate in unique RDCs in North America. Respondents were asked to describe the variability of clinical operations, participants, administrative/clinical support, and educational value for participating physicians and trainees.
Of the 71 patients cared for at the UCSF pediatric RDC, 69% were female, 44% were White, 51% were aged 13-21 years, 42% were aged 3-12 years, and 7% were aged 0-11 years at their first clinic visit. The top four primary RDC diagnoses were linear morphea (33%), lupus (23%), psoriasis (13%), and juvenile dermatomyositis (10%).
Nearly one in four patients (17, or 24%) presented to the RDC without a confirmed diagnosis. A diagnosis was established at the first RDC visit for 7 of these 17 patients (41%). Among 54 patients who presented with an established diagnosis, the first RDC visit confirmed the diagnosis for 52 (96%) and revised it for 2 (4%). “Initial pediatric RDC evaluation significantly influenced patient care by confirming or revising preexisting diagnoses, rendering new diagnoses, and streamlining additional laboratory and imaging recommendations,” the researchers wrote in their poster.
The evaluation also resulted in modified disease management in the form of systemic medication changes or dosage adjustments as well as the initiation of novel therapies. For example, systemic medication changes were made during the first RDC visit in 34 of the 46 patients (74%) who were on systemic medication at presentation.
“Seeing complex patients together in real time allows specialists and other team members (social work, nursing, PT/OT, for example) to share ideas, communicate clearly to families, and efficiently develop recommendations,” Ms. Crockett said of the UCSF pediatric RDC. “Exposure to other specialists while caring for patients enhances medical knowledge, communication skills, and professional competency of faculty and trainees alike.”
In the survey portion of the study, each of the 17 dermatologists reported that the pediatric RDC is valuable for patient care, and 88% believed the RDC was a valuable use of their time. However, only 59% of respondents reported having administrative support, and only 29% had a dedicated clinic coordinator or navigator.
“We were surprised to find that only a quarter of pediatric RDCs incorporate an educational conference,” Dr. Cordoro told this news organization. “We have found that assembling the care team prior to seeing patients to review clinical data, discuss relevant literature, and define the clinical questions for each patient is an integral part of the clinical operation. The trainees are involved in these conference presentations, and it really enhances their understanding of the complex diagnoses we manage in this clinic and the issues faced by affected children and families. The preclinical conference increases efficiency, positively influences patient care, and supports professional development for all participants.”
The study was indirectly supported by a fellowship grant awarded to Ms. Crockett from the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Underserved Families Share Ways to Improve Access to Pediatric Dermatologists
, a theme emerged that surprised lead study author Lucinda L. Kohn, MD, MHS.
“Most families said that racial concordance didn’t matter that much, but they did place high value on being heard,” Dr. Kohn, of the Department of Dermatology at the University of Colorado, Aurora, told this news organization following the Society for Pediatric Dermatology annual meeting, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Being heard means that their experience was respected; that their questions and worries were anticipated, addressed, and answered; and that their feelings were acknowledged.”
As a way to understand these families’ knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about access to pediatric dermatology care and how the hospital system and medical team could better support them, Dr. Kohn and colleagues conducted in-depth, semi-structured interviews with 32 English-speaking parents and/or guardians of children who received care at the Children’s Hospital Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus pediatric dermatology clinic. The researchers conducted and recorded the 30- to 60-minute interviews via Zoom or phone call from October 17, 2023, to January 23, 2024. Domains of interest included participant background and experiences, communication preferences, and experience accessing pediatric dermatology care. Next, Dr. Kohn and colleagues used a reflexive, team-based inductive approach to carry out a thematic analysis from the interviews.
The mean age of the 32 study participants was 38.9 years; 14 (43.75%) identified as Hispanic, 11 (34.38%) as Black, and 12 (37.50%) as American Indian/Alaska Native (response categories were not mutually exclusive). Several themes emerged from analysis of the interviews. Barriers to receiving pediatric dermatology care included distrust of the healthcare system, generational and community lack of awareness about dermatology, distance to the hospital, and household income.
“One family mentioned that they needed to save up for 3 months to be able to afford the drive, hotel, and food needed for their child to attend their pediatric dermatology visit,” Dr. Kohn said. “As we know, most pediatric dermatology visits are 10-15 minutes long, so that they needed to cut groceries for 3 months to be able to see a pediatric dermatologist for 10-15 minutes is just heart wrenching. Families also didn’t understand the large teams that we have in medicine: The medical students, residents, nurses, medical assistants, attendings, and physician extenders.”
One key facilitator to receiving pediatric dermatology care was the family’s perception that the provider shares their minoritized experience because of similarities in skin tone. “When it’s your own race, whether it’s Black, Hispanic, or you know, we feel like when it’s someone like me, they will look out for me more,” one study participant said. Other facilitators expressed by the study participants included increased representation from the family’s community at all levels of healthcare (“the more you see providers and people in a space that look like you, I think the more welcoming it will feel,” one said) and normalizing dermatology care (“letting it be known that going to the dermatologist is just like going to a regular doctor,” another said).
Dr. Kohn acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center qualitative design. “Qualitative studies are not generalizable, but they do dive into the lived experiences of a few,” she said. “There aren’t a lot of qualitative studies in derm, so even though this was a very simple study, we hope the findings will help us to support our most diverse and underserved families access the pediatric dermatology care that they need.”
The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures. The study was recognized as an award-winning poster at the meeting.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a theme emerged that surprised lead study author Lucinda L. Kohn, MD, MHS.
“Most families said that racial concordance didn’t matter that much, but they did place high value on being heard,” Dr. Kohn, of the Department of Dermatology at the University of Colorado, Aurora, told this news organization following the Society for Pediatric Dermatology annual meeting, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Being heard means that their experience was respected; that their questions and worries were anticipated, addressed, and answered; and that their feelings were acknowledged.”
As a way to understand these families’ knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about access to pediatric dermatology care and how the hospital system and medical team could better support them, Dr. Kohn and colleagues conducted in-depth, semi-structured interviews with 32 English-speaking parents and/or guardians of children who received care at the Children’s Hospital Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus pediatric dermatology clinic. The researchers conducted and recorded the 30- to 60-minute interviews via Zoom or phone call from October 17, 2023, to January 23, 2024. Domains of interest included participant background and experiences, communication preferences, and experience accessing pediatric dermatology care. Next, Dr. Kohn and colleagues used a reflexive, team-based inductive approach to carry out a thematic analysis from the interviews.
The mean age of the 32 study participants was 38.9 years; 14 (43.75%) identified as Hispanic, 11 (34.38%) as Black, and 12 (37.50%) as American Indian/Alaska Native (response categories were not mutually exclusive). Several themes emerged from analysis of the interviews. Barriers to receiving pediatric dermatology care included distrust of the healthcare system, generational and community lack of awareness about dermatology, distance to the hospital, and household income.
“One family mentioned that they needed to save up for 3 months to be able to afford the drive, hotel, and food needed for their child to attend their pediatric dermatology visit,” Dr. Kohn said. “As we know, most pediatric dermatology visits are 10-15 minutes long, so that they needed to cut groceries for 3 months to be able to see a pediatric dermatologist for 10-15 minutes is just heart wrenching. Families also didn’t understand the large teams that we have in medicine: The medical students, residents, nurses, medical assistants, attendings, and physician extenders.”
One key facilitator to receiving pediatric dermatology care was the family’s perception that the provider shares their minoritized experience because of similarities in skin tone. “When it’s your own race, whether it’s Black, Hispanic, or you know, we feel like when it’s someone like me, they will look out for me more,” one study participant said. Other facilitators expressed by the study participants included increased representation from the family’s community at all levels of healthcare (“the more you see providers and people in a space that look like you, I think the more welcoming it will feel,” one said) and normalizing dermatology care (“letting it be known that going to the dermatologist is just like going to a regular doctor,” another said).
Dr. Kohn acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center qualitative design. “Qualitative studies are not generalizable, but they do dive into the lived experiences of a few,” she said. “There aren’t a lot of qualitative studies in derm, so even though this was a very simple study, we hope the findings will help us to support our most diverse and underserved families access the pediatric dermatology care that they need.”
The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures. The study was recognized as an award-winning poster at the meeting.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, a theme emerged that surprised lead study author Lucinda L. Kohn, MD, MHS.
“Most families said that racial concordance didn’t matter that much, but they did place high value on being heard,” Dr. Kohn, of the Department of Dermatology at the University of Colorado, Aurora, told this news organization following the Society for Pediatric Dermatology annual meeting, where the study was presented during a poster session. “Being heard means that their experience was respected; that their questions and worries were anticipated, addressed, and answered; and that their feelings were acknowledged.”
As a way to understand these families’ knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about access to pediatric dermatology care and how the hospital system and medical team could better support them, Dr. Kohn and colleagues conducted in-depth, semi-structured interviews with 32 English-speaking parents and/or guardians of children who received care at the Children’s Hospital Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus pediatric dermatology clinic. The researchers conducted and recorded the 30- to 60-minute interviews via Zoom or phone call from October 17, 2023, to January 23, 2024. Domains of interest included participant background and experiences, communication preferences, and experience accessing pediatric dermatology care. Next, Dr. Kohn and colleagues used a reflexive, team-based inductive approach to carry out a thematic analysis from the interviews.
The mean age of the 32 study participants was 38.9 years; 14 (43.75%) identified as Hispanic, 11 (34.38%) as Black, and 12 (37.50%) as American Indian/Alaska Native (response categories were not mutually exclusive). Several themes emerged from analysis of the interviews. Barriers to receiving pediatric dermatology care included distrust of the healthcare system, generational and community lack of awareness about dermatology, distance to the hospital, and household income.
“One family mentioned that they needed to save up for 3 months to be able to afford the drive, hotel, and food needed for their child to attend their pediatric dermatology visit,” Dr. Kohn said. “As we know, most pediatric dermatology visits are 10-15 minutes long, so that they needed to cut groceries for 3 months to be able to see a pediatric dermatologist for 10-15 minutes is just heart wrenching. Families also didn’t understand the large teams that we have in medicine: The medical students, residents, nurses, medical assistants, attendings, and physician extenders.”
One key facilitator to receiving pediatric dermatology care was the family’s perception that the provider shares their minoritized experience because of similarities in skin tone. “When it’s your own race, whether it’s Black, Hispanic, or you know, we feel like when it’s someone like me, they will look out for me more,” one study participant said. Other facilitators expressed by the study participants included increased representation from the family’s community at all levels of healthcare (“the more you see providers and people in a space that look like you, I think the more welcoming it will feel,” one said) and normalizing dermatology care (“letting it be known that going to the dermatologist is just like going to a regular doctor,” another said).
Dr. Kohn acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center qualitative design. “Qualitative studies are not generalizable, but they do dive into the lived experiences of a few,” she said. “There aren’t a lot of qualitative studies in derm, so even though this was a very simple study, we hope the findings will help us to support our most diverse and underserved families access the pediatric dermatology care that they need.”
The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures. The study was recognized as an award-winning poster at the meeting.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Study Finds Gout Drug Effective for Aphthous Ulcers in Children
“Complex aphthous stomatitis in children is typically treated with topical supportive care, which is often not effective,” one of the study investigators, Ananya Shah, a third-year medical student at the University of Rochester School of Medicine & Dentistry, Rochester, New York, told this news organization following the Society for Pediatric Dermatology annual meeting, where the study was presented during a poster session. “There is limited research on CAS and its treatment in children. Colchicine is often used for treatment of CAS in adults, but its use in children has not been studied.”
Ms. Shah, in collaboration with Hilary Kunkel, MD, Nessa Aghazadeh, MD, and Megha Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, retrospectively reviewed the charts of 20 children diagnosed with CAS who were treated with colchicine, an anti-inflammatory drug often used to treat gout, at the clinic between 2000 and 2023. Treatment responses were defined as no response, partial response, and complete response. Half of the patients were girls, and their median age at presentation was 5 years.
Ulcers were most commonly located in the buccal mucosa (80%), followed by the gingiva (50%), the mucosal lip (50%), and the palate (40%). Nearly all patients (95%) reported that the CAS caused difficulties with eating or drinking. Other effects on their quality of life included weight loss (35%), bleeding (30%), and difficulty brushing teeth (25%). “I was surprised by how much CAS impacts pediatric patients’ quality of life,” Ms. Shah said. “Almost all of the patients experienced trouble with basic activities of daily living, including eating and drinking. In addition, CAS negatively impacted mental health and led to missed school for patients.”
The researchers had follow-up data on responses to colchicine for 14 of the 20 patients. Of these, 12 (86%) had symptom improvement, 5 (36%) had a complete response, 8 (57%) had a partial response, and 1 (7%) did not respond. Nine patients (64%) experienced side effects. Of these, six had diarrhea, two had nausea, and one had constipation.
“Colchicine should be considered as a treatment in pediatric patients who have refractory complex aphthous stomatitis as it is generally well tolerated with minimal side effects,” Ms. Shah said. She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center, retrospective design.
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Complex aphthous stomatitis in children is typically treated with topical supportive care, which is often not effective,” one of the study investigators, Ananya Shah, a third-year medical student at the University of Rochester School of Medicine & Dentistry, Rochester, New York, told this news organization following the Society for Pediatric Dermatology annual meeting, where the study was presented during a poster session. “There is limited research on CAS and its treatment in children. Colchicine is often used for treatment of CAS in adults, but its use in children has not been studied.”
Ms. Shah, in collaboration with Hilary Kunkel, MD, Nessa Aghazadeh, MD, and Megha Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, retrospectively reviewed the charts of 20 children diagnosed with CAS who were treated with colchicine, an anti-inflammatory drug often used to treat gout, at the clinic between 2000 and 2023. Treatment responses were defined as no response, partial response, and complete response. Half of the patients were girls, and their median age at presentation was 5 years.
Ulcers were most commonly located in the buccal mucosa (80%), followed by the gingiva (50%), the mucosal lip (50%), and the palate (40%). Nearly all patients (95%) reported that the CAS caused difficulties with eating or drinking. Other effects on their quality of life included weight loss (35%), bleeding (30%), and difficulty brushing teeth (25%). “I was surprised by how much CAS impacts pediatric patients’ quality of life,” Ms. Shah said. “Almost all of the patients experienced trouble with basic activities of daily living, including eating and drinking. In addition, CAS negatively impacted mental health and led to missed school for patients.”
The researchers had follow-up data on responses to colchicine for 14 of the 20 patients. Of these, 12 (86%) had symptom improvement, 5 (36%) had a complete response, 8 (57%) had a partial response, and 1 (7%) did not respond. Nine patients (64%) experienced side effects. Of these, six had diarrhea, two had nausea, and one had constipation.
“Colchicine should be considered as a treatment in pediatric patients who have refractory complex aphthous stomatitis as it is generally well tolerated with minimal side effects,” Ms. Shah said. She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center, retrospective design.
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Complex aphthous stomatitis in children is typically treated with topical supportive care, which is often not effective,” one of the study investigators, Ananya Shah, a third-year medical student at the University of Rochester School of Medicine & Dentistry, Rochester, New York, told this news organization following the Society for Pediatric Dermatology annual meeting, where the study was presented during a poster session. “There is limited research on CAS and its treatment in children. Colchicine is often used for treatment of CAS in adults, but its use in children has not been studied.”
Ms. Shah, in collaboration with Hilary Kunkel, MD, Nessa Aghazadeh, MD, and Megha Tollefson, MD, of the Department of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, retrospectively reviewed the charts of 20 children diagnosed with CAS who were treated with colchicine, an anti-inflammatory drug often used to treat gout, at the clinic between 2000 and 2023. Treatment responses were defined as no response, partial response, and complete response. Half of the patients were girls, and their median age at presentation was 5 years.
Ulcers were most commonly located in the buccal mucosa (80%), followed by the gingiva (50%), the mucosal lip (50%), and the palate (40%). Nearly all patients (95%) reported that the CAS caused difficulties with eating or drinking. Other effects on their quality of life included weight loss (35%), bleeding (30%), and difficulty brushing teeth (25%). “I was surprised by how much CAS impacts pediatric patients’ quality of life,” Ms. Shah said. “Almost all of the patients experienced trouble with basic activities of daily living, including eating and drinking. In addition, CAS negatively impacted mental health and led to missed school for patients.”
The researchers had follow-up data on responses to colchicine for 14 of the 20 patients. Of these, 12 (86%) had symptom improvement, 5 (36%) had a complete response, 8 (57%) had a partial response, and 1 (7%) did not respond. Nine patients (64%) experienced side effects. Of these, six had diarrhea, two had nausea, and one had constipation.
“Colchicine should be considered as a treatment in pediatric patients who have refractory complex aphthous stomatitis as it is generally well tolerated with minimal side effects,” Ms. Shah said. She acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including its single-center, retrospective design.
The researchers reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Safety Standards a Top Priority for ASLMS President
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, began her term as president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) during the organization’s annual meeting in April 2024.
After earning her medical degree from Albany Medical College, Albany, New York, Dr. Ortiz, a native of Los Angeles, completed her dermatology residency training at the University of California, Irvine, and the university’s Beckman Laser Institute. Next, she completed a laser and cosmetic dermatology fellowship at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, all in Boston, and acquired additional fellowship training in Mohs micrographic surgery at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Dr. Ortiz is currently director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and a clinical professor of dermatology at UCSD.
She has authored more than 60 publications on new innovations in cutaneous surgery and is a frequent speaker at meetings of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), and ASLMS, and she cochairs the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in San Diego. Dr. Ortiz has received several awards, including the 2024 Castle Connolly Top Doctor Award and the Exceptional Women in Medicine Award; Newsweek America’s Best Dermatologists; the ASLMS Dr. Horace Furumoto Young Investigator Award, the ASLMS Best of Session Award for Cutaneous Applications, and the ASDS President’s Outstanding Service Award. Her primary research focuses on the laser treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
In an interview, Dr. Ortiz spoke about her goals as ASLMS president and other topics related to dermatology.
Who inspired you most to become a doctor?
I’ve wanted to become a doctor for as long as I can remember. My fascination with science and the idea of helping people improve their health were driving forces. However, my biggest influence early on was my uncle, who was a pediatrician. His dedication and passion for medicine deeply inspired me and solidified my desire to pursue a career in healthcare.
I understand that a bout with chickenpox as a teenager influenced your decision to specialize in dermatology.
It’s an interesting and somewhat humorous story. When I was 18, I contracted chickenpox and ended up with scars on my face. It was a tough experience as a teenager, but it’s fascinating how such events can shape your life. In my quest for help, I opened the Yellow Pages and randomly chose a dermatologist nearby, who turned out to be Gary Lask, MD, director of lasers at UCLA [University of California, Los Angeles]. During our visit, I mentioned that I was premed, and he encouraged me to consider dermatology. About 6 years later, as a second-year medical student, I realized my passion for dermatology. I reached out to Dr. Lask and told him: “You were right. I want to be a dermatologist. Now, you have to help me get in!” Today, he remains my mentor, and I am deeply grateful for his guidance and support on this journey.
One of the initiatives for your term as ASLMS president includes a focus on safety standards for lasers and energy-based devices. Why is this important now?
Working at the university, I frequently encounter severe complications arising from the improper use of lasers and energy-based devices. As these procedures gain popularity, more providers are offering them, yet often without adequate training. As the world’s premier laser society, it is our duty to ensure patient safety. In the ever-evolving field of laser medicine, it is crucial that we continually strive to enhance the regulation of laser usage, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care with minimal risk.
One of the suggestions you have for the safety initiative is to offer a rigorous laser safety certification course with continuing education opportunities as a way foster a culture of heightened safety standards. Please explain what would be included in such a course and how it would align with current efforts to report adverse events such as the ASDS-Northwestern University Cutaneous Procedures Adverse Events Reporting (CAPER) registry and the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Program.
A laser safety certification task force has been established to determine the best approach for developing a comprehensive course. The task force aims to assess the necessity of a formal safety certification in our industry, identify the resources needed to support such a certification, establish general safety protocols to form the content foundation, address potential legal concerns, and outline the process for formal certification program recognition. This exploratory work is expected to conclude by the end of the year. The proposed course may include modules on the fundamentals of laser physics, safe operation techniques, patient selection and management, and emergency protocols. Continuing education opportunities would be considered to keep practitioners updated on the latest advancements and safety protocols in laser medicine, thereby fostering a culture of heightened safety standards.
Another initiative for your term is the rollout of a tattoo removal program for former gang members based on the UCSD Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program. Please tell us more about your vision for this national program.
UCSD Dermatology, in collaboration with UCSD Global Health, has been involved in the Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program for the past decade. This initiative supports and rehabilitates former gang members by offering laser tattoo removal, helping them reintegrate into society. My vision is to equip our members with the necessary protocols to implement this outreach initiative in their own communities. By providing opportunities for reform and growth, we aim to foster safer and more inclusive communities nationwide.
You were one of the first clinicians to use a laser to treat basal cell carcinoma (BCC). Who are the ideal candidates for this procedure? Is the technique ready for wide clinical adoption? If not, what kind of studies are needed to make it so?
My research passion lies in optimizing laser treatments for BCC. During my fellowship with R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Mathew Avram, MD, at the MGH Wellman Center for Photomedicine, we conducted a pilot study using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, achieving a 92% clearance rate after one treatment. Inspired by these results, we conducted a larger multicenter study, which demonstrated a 90% clearance rate after a single treatment. I now incorporate this technique into my daily practice. The ideal candidates for this procedure are patients with BCC that do not meet the Mohs Appropriate Use Criteria, such as those with nodular or superficial BCC subtypes on the body, individuals who are poor surgical candidates, or those who are surgically exhausted. However, I do not recommend this treatment for patients who are primarily concerned about facial scarring, particularly younger individuals; in such cases, Mohs surgery still remains the preferred option. While I believe this technique is ready for broader clinical adoption, it requires an understanding of laser endpoints. We are also exploring antibody-targeted gold nanorods to enhance the selectivity and standardization of the treatment.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
My patients are my greatest inspiration. Their trust and dedication motivate me to stay at the forefront of dermatologic advancements, ensuring I provide the most cutting-edge and safe treatments possible. Their commitment drives my relentless pursuit of continuous learning and innovation in the field.
What’s the best advice you can give to female dermatologists seeking leadership positions at the local, state, or national level?
My best advice is to have the courage to ask for what you seek. Societies are always looking for members who are eager to participate and contribute. If you express your interest in becoming more involved, there is likely a position available for you. The more you are willing to contribute to a society, the more likely you will be noticed and excel into higher leadership positions. Take initiative, show your commitment, and don’t hesitate to step forward when opportunities arise.
What’s the one tried-and-true laser- or energy-based procedure that you consider a “must” for your dermatology practice? And why?
Determining a single “must-have” laser- or energy-based procedure is a challenging question as it greatly depends on the specific needs of your patient population. However, one of the most common concerns among patients involves issues like redness and pigmentation. Therefore, having a versatile laser or an intense pulsed light device that effectively targets both red and brown pigmentation is indispensable for most practices.
In your view, what are the top three trends in aesthetic dermatology?
Over the years, I have observed several key trends in aesthetic dermatology:
- Minimally invasive procedures. There is a growing preference for less invasive treatments. Patients increasingly desire minimal downtime while still achieving significant results.
- Advancements in laser and energy-based devices for darker skin. There have been substantial advancements in technologies that are safer and more effective for darker skin tones. These developments play a crucial role in addressing diverse patient needs and providing inclusive dermatologic care.
- Natural aesthetic. I am hopeful that the trend toward an overdone appearance is fading. There seems to be a shift back towards a more natural and conservative aesthetic, emphasizing subtle enhancements over dramatic changes.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
I am most excited to see how artificial intelligence and robotics play a role in energy-based devices.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is also cochair of the MOAS.
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, began her term as president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) during the organization’s annual meeting in April 2024.
After earning her medical degree from Albany Medical College, Albany, New York, Dr. Ortiz, a native of Los Angeles, completed her dermatology residency training at the University of California, Irvine, and the university’s Beckman Laser Institute. Next, she completed a laser and cosmetic dermatology fellowship at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, all in Boston, and acquired additional fellowship training in Mohs micrographic surgery at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Dr. Ortiz is currently director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and a clinical professor of dermatology at UCSD.
She has authored more than 60 publications on new innovations in cutaneous surgery and is a frequent speaker at meetings of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), and ASLMS, and she cochairs the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in San Diego. Dr. Ortiz has received several awards, including the 2024 Castle Connolly Top Doctor Award and the Exceptional Women in Medicine Award; Newsweek America’s Best Dermatologists; the ASLMS Dr. Horace Furumoto Young Investigator Award, the ASLMS Best of Session Award for Cutaneous Applications, and the ASDS President’s Outstanding Service Award. Her primary research focuses on the laser treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
In an interview, Dr. Ortiz spoke about her goals as ASLMS president and other topics related to dermatology.
Who inspired you most to become a doctor?
I’ve wanted to become a doctor for as long as I can remember. My fascination with science and the idea of helping people improve their health were driving forces. However, my biggest influence early on was my uncle, who was a pediatrician. His dedication and passion for medicine deeply inspired me and solidified my desire to pursue a career in healthcare.
I understand that a bout with chickenpox as a teenager influenced your decision to specialize in dermatology.
It’s an interesting and somewhat humorous story. When I was 18, I contracted chickenpox and ended up with scars on my face. It was a tough experience as a teenager, but it’s fascinating how such events can shape your life. In my quest for help, I opened the Yellow Pages and randomly chose a dermatologist nearby, who turned out to be Gary Lask, MD, director of lasers at UCLA [University of California, Los Angeles]. During our visit, I mentioned that I was premed, and he encouraged me to consider dermatology. About 6 years later, as a second-year medical student, I realized my passion for dermatology. I reached out to Dr. Lask and told him: “You were right. I want to be a dermatologist. Now, you have to help me get in!” Today, he remains my mentor, and I am deeply grateful for his guidance and support on this journey.
One of the initiatives for your term as ASLMS president includes a focus on safety standards for lasers and energy-based devices. Why is this important now?
Working at the university, I frequently encounter severe complications arising from the improper use of lasers and energy-based devices. As these procedures gain popularity, more providers are offering them, yet often without adequate training. As the world’s premier laser society, it is our duty to ensure patient safety. In the ever-evolving field of laser medicine, it is crucial that we continually strive to enhance the regulation of laser usage, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care with minimal risk.
One of the suggestions you have for the safety initiative is to offer a rigorous laser safety certification course with continuing education opportunities as a way foster a culture of heightened safety standards. Please explain what would be included in such a course and how it would align with current efforts to report adverse events such as the ASDS-Northwestern University Cutaneous Procedures Adverse Events Reporting (CAPER) registry and the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Program.
A laser safety certification task force has been established to determine the best approach for developing a comprehensive course. The task force aims to assess the necessity of a formal safety certification in our industry, identify the resources needed to support such a certification, establish general safety protocols to form the content foundation, address potential legal concerns, and outline the process for formal certification program recognition. This exploratory work is expected to conclude by the end of the year. The proposed course may include modules on the fundamentals of laser physics, safe operation techniques, patient selection and management, and emergency protocols. Continuing education opportunities would be considered to keep practitioners updated on the latest advancements and safety protocols in laser medicine, thereby fostering a culture of heightened safety standards.
Another initiative for your term is the rollout of a tattoo removal program for former gang members based on the UCSD Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program. Please tell us more about your vision for this national program.
UCSD Dermatology, in collaboration with UCSD Global Health, has been involved in the Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program for the past decade. This initiative supports and rehabilitates former gang members by offering laser tattoo removal, helping them reintegrate into society. My vision is to equip our members with the necessary protocols to implement this outreach initiative in their own communities. By providing opportunities for reform and growth, we aim to foster safer and more inclusive communities nationwide.
You were one of the first clinicians to use a laser to treat basal cell carcinoma (BCC). Who are the ideal candidates for this procedure? Is the technique ready for wide clinical adoption? If not, what kind of studies are needed to make it so?
My research passion lies in optimizing laser treatments for BCC. During my fellowship with R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Mathew Avram, MD, at the MGH Wellman Center for Photomedicine, we conducted a pilot study using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, achieving a 92% clearance rate after one treatment. Inspired by these results, we conducted a larger multicenter study, which demonstrated a 90% clearance rate after a single treatment. I now incorporate this technique into my daily practice. The ideal candidates for this procedure are patients with BCC that do not meet the Mohs Appropriate Use Criteria, such as those with nodular or superficial BCC subtypes on the body, individuals who are poor surgical candidates, or those who are surgically exhausted. However, I do not recommend this treatment for patients who are primarily concerned about facial scarring, particularly younger individuals; in such cases, Mohs surgery still remains the preferred option. While I believe this technique is ready for broader clinical adoption, it requires an understanding of laser endpoints. We are also exploring antibody-targeted gold nanorods to enhance the selectivity and standardization of the treatment.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
My patients are my greatest inspiration. Their trust and dedication motivate me to stay at the forefront of dermatologic advancements, ensuring I provide the most cutting-edge and safe treatments possible. Their commitment drives my relentless pursuit of continuous learning and innovation in the field.
What’s the best advice you can give to female dermatologists seeking leadership positions at the local, state, or national level?
My best advice is to have the courage to ask for what you seek. Societies are always looking for members who are eager to participate and contribute. If you express your interest in becoming more involved, there is likely a position available for you. The more you are willing to contribute to a society, the more likely you will be noticed and excel into higher leadership positions. Take initiative, show your commitment, and don’t hesitate to step forward when opportunities arise.
What’s the one tried-and-true laser- or energy-based procedure that you consider a “must” for your dermatology practice? And why?
Determining a single “must-have” laser- or energy-based procedure is a challenging question as it greatly depends on the specific needs of your patient population. However, one of the most common concerns among patients involves issues like redness and pigmentation. Therefore, having a versatile laser or an intense pulsed light device that effectively targets both red and brown pigmentation is indispensable for most practices.
In your view, what are the top three trends in aesthetic dermatology?
Over the years, I have observed several key trends in aesthetic dermatology:
- Minimally invasive procedures. There is a growing preference for less invasive treatments. Patients increasingly desire minimal downtime while still achieving significant results.
- Advancements in laser and energy-based devices for darker skin. There have been substantial advancements in technologies that are safer and more effective for darker skin tones. These developments play a crucial role in addressing diverse patient needs and providing inclusive dermatologic care.
- Natural aesthetic. I am hopeful that the trend toward an overdone appearance is fading. There seems to be a shift back towards a more natural and conservative aesthetic, emphasizing subtle enhancements over dramatic changes.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
I am most excited to see how artificial intelligence and robotics play a role in energy-based devices.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is also cochair of the MOAS.
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, began her term as president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery (ASLMS) during the organization’s annual meeting in April 2024.
After earning her medical degree from Albany Medical College, Albany, New York, Dr. Ortiz, a native of Los Angeles, completed her dermatology residency training at the University of California, Irvine, and the university’s Beckman Laser Institute. Next, she completed a laser and cosmetic dermatology fellowship at Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, and the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, all in Boston, and acquired additional fellowship training in Mohs micrographic surgery at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). Dr. Ortiz is currently director of laser and cosmetic dermatology and a clinical professor of dermatology at UCSD.
She has authored more than 60 publications on new innovations in cutaneous surgery and is a frequent speaker at meetings of the American Academy of Dermatology, the American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), and ASLMS, and she cochairs the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium in San Diego. Dr. Ortiz has received several awards, including the 2024 Castle Connolly Top Doctor Award and the Exceptional Women in Medicine Award; Newsweek America’s Best Dermatologists; the ASLMS Dr. Horace Furumoto Young Investigator Award, the ASLMS Best of Session Award for Cutaneous Applications, and the ASDS President’s Outstanding Service Award. Her primary research focuses on the laser treatment of nonmelanoma skin cancer.
In an interview, Dr. Ortiz spoke about her goals as ASLMS president and other topics related to dermatology.
Who inspired you most to become a doctor?
I’ve wanted to become a doctor for as long as I can remember. My fascination with science and the idea of helping people improve their health were driving forces. However, my biggest influence early on was my uncle, who was a pediatrician. His dedication and passion for medicine deeply inspired me and solidified my desire to pursue a career in healthcare.
I understand that a bout with chickenpox as a teenager influenced your decision to specialize in dermatology.
It’s an interesting and somewhat humorous story. When I was 18, I contracted chickenpox and ended up with scars on my face. It was a tough experience as a teenager, but it’s fascinating how such events can shape your life. In my quest for help, I opened the Yellow Pages and randomly chose a dermatologist nearby, who turned out to be Gary Lask, MD, director of lasers at UCLA [University of California, Los Angeles]. During our visit, I mentioned that I was premed, and he encouraged me to consider dermatology. About 6 years later, as a second-year medical student, I realized my passion for dermatology. I reached out to Dr. Lask and told him: “You were right. I want to be a dermatologist. Now, you have to help me get in!” Today, he remains my mentor, and I am deeply grateful for his guidance and support on this journey.
One of the initiatives for your term as ASLMS president includes a focus on safety standards for lasers and energy-based devices. Why is this important now?
Working at the university, I frequently encounter severe complications arising from the improper use of lasers and energy-based devices. As these procedures gain popularity, more providers are offering them, yet often without adequate training. As the world’s premier laser society, it is our duty to ensure patient safety. In the ever-evolving field of laser medicine, it is crucial that we continually strive to enhance the regulation of laser usage, ensuring that patients receive the highest standard of care with minimal risk.
One of the suggestions you have for the safety initiative is to offer a rigorous laser safety certification course with continuing education opportunities as a way foster a culture of heightened safety standards. Please explain what would be included in such a course and how it would align with current efforts to report adverse events such as the ASDS-Northwestern University Cutaneous Procedures Adverse Events Reporting (CAPER) registry and the Food and Drug Administration’s MedWatch Program.
A laser safety certification task force has been established to determine the best approach for developing a comprehensive course. The task force aims to assess the necessity of a formal safety certification in our industry, identify the resources needed to support such a certification, establish general safety protocols to form the content foundation, address potential legal concerns, and outline the process for formal certification program recognition. This exploratory work is expected to conclude by the end of the year. The proposed course may include modules on the fundamentals of laser physics, safe operation techniques, patient selection and management, and emergency protocols. Continuing education opportunities would be considered to keep practitioners updated on the latest advancements and safety protocols in laser medicine, thereby fostering a culture of heightened safety standards.
Another initiative for your term is the rollout of a tattoo removal program for former gang members based on the UCSD Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program. Please tell us more about your vision for this national program.
UCSD Dermatology, in collaboration with UCSD Global Health, has been involved in the Clean Slate Tattoo Removal Program for the past decade. This initiative supports and rehabilitates former gang members by offering laser tattoo removal, helping them reintegrate into society. My vision is to equip our members with the necessary protocols to implement this outreach initiative in their own communities. By providing opportunities for reform and growth, we aim to foster safer and more inclusive communities nationwide.
You were one of the first clinicians to use a laser to treat basal cell carcinoma (BCC). Who are the ideal candidates for this procedure? Is the technique ready for wide clinical adoption? If not, what kind of studies are needed to make it so?
My research passion lies in optimizing laser treatments for BCC. During my fellowship with R. Rox Anderson, MD, and Mathew Avram, MD, at the MGH Wellman Center for Photomedicine, we conducted a pilot study using the 1064-nm Nd:YAG laser, achieving a 92% clearance rate after one treatment. Inspired by these results, we conducted a larger multicenter study, which demonstrated a 90% clearance rate after a single treatment. I now incorporate this technique into my daily practice. The ideal candidates for this procedure are patients with BCC that do not meet the Mohs Appropriate Use Criteria, such as those with nodular or superficial BCC subtypes on the body, individuals who are poor surgical candidates, or those who are surgically exhausted. However, I do not recommend this treatment for patients who are primarily concerned about facial scarring, particularly younger individuals; in such cases, Mohs surgery still remains the preferred option. While I believe this technique is ready for broader clinical adoption, it requires an understanding of laser endpoints. We are also exploring antibody-targeted gold nanorods to enhance the selectivity and standardization of the treatment.
Who inspires you most in your work today?
My patients are my greatest inspiration. Their trust and dedication motivate me to stay at the forefront of dermatologic advancements, ensuring I provide the most cutting-edge and safe treatments possible. Their commitment drives my relentless pursuit of continuous learning and innovation in the field.
What’s the best advice you can give to female dermatologists seeking leadership positions at the local, state, or national level?
My best advice is to have the courage to ask for what you seek. Societies are always looking for members who are eager to participate and contribute. If you express your interest in becoming more involved, there is likely a position available for you. The more you are willing to contribute to a society, the more likely you will be noticed and excel into higher leadership positions. Take initiative, show your commitment, and don’t hesitate to step forward when opportunities arise.
What’s the one tried-and-true laser- or energy-based procedure that you consider a “must” for your dermatology practice? And why?
Determining a single “must-have” laser- or energy-based procedure is a challenging question as it greatly depends on the specific needs of your patient population. However, one of the most common concerns among patients involves issues like redness and pigmentation. Therefore, having a versatile laser or an intense pulsed light device that effectively targets both red and brown pigmentation is indispensable for most practices.
In your view, what are the top three trends in aesthetic dermatology?
Over the years, I have observed several key trends in aesthetic dermatology:
- Minimally invasive procedures. There is a growing preference for less invasive treatments. Patients increasingly desire minimal downtime while still achieving significant results.
- Advancements in laser and energy-based devices for darker skin. There have been substantial advancements in technologies that are safer and more effective for darker skin tones. These developments play a crucial role in addressing diverse patient needs and providing inclusive dermatologic care.
- Natural aesthetic. I am hopeful that the trend toward an overdone appearance is fading. There seems to be a shift back towards a more natural and conservative aesthetic, emphasizing subtle enhancements over dramatic changes.
What development in dermatology are you most excited about in the next 5 years?
I am most excited to see how artificial intelligence and robotics play a role in energy-based devices.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies. She is also cochair of the MOAS.
Retirement Planning for Gastroenterologists
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Navigating as a GI Locum: My Path and Guide to This Alternative Practice Model
My successful career in academic gastroenterology makes me a natural proponent of the academic model of practice. However, in my current role as a locum tenens, I have witnessed the versatility that locum assignments offer gastroenterologists, particularly when flexibility in their professional lives is paramount.
The locum tenens industry is a growing feature of the healthcare staffing landscape. My perspective is unique, transitioning from professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at an academic medical center to a self-employed locum gastroenterologist.
As chief, I hired locums to offer additional coverage to the faculty staffing as our division, inclusive of GI fellowship and endoscopy volume, expanded. I recruited, supervised, and assigned responsibilities to the locums. Not only were these physicians professional and competent, but they also contributed to my division’s forward evolution. Based on this experience, I was confident that I could successfully perform as a locum gastroenterologist myself.
My work as a locum these past 5 years has been a positive professional transition for me. I have enjoyed meeting and working with new colleagues, including international locums who travel to work in the United States. I have also witnessed how early-career and mid-career gastroenterologists have taken advantage of this flexible and well-remunerated work.
What It Entails to Be a Locum Tenens
I suspect you have been on the receiving end of emails and postcards from locum tenens companies recruiting for potential assignments and have wondered about the specifics. Essentially, a locum physician functions as an independent contractor who accepts a temporary position at a healthcare organization to provide clinical staffing support during periods of staffing disruption.
Assignments vary in geographic location, facility work site (outpatient vs inpatient), hours, required skills, cadence of assignment, and expected length of staffing need. The locum physician has complete control over selecting the assignment location, the intensity of responsibilities, and the time they wish to commit to the position. Temporal flexibility offers locums the opportunity to commit from a few weeks per year to a full-time commitment. Locums can also combine multiple assignments in different regions or states to match the targeted number of weeks they wish to commit to and the financial goal they have set.
I have met physicians working a few weeks a year during time off from their permanent jobs to supplement their incomes, as well as fully employed physicians leveraging locum placements to explore locations or practices that they have an interest in. Gastroenterologists facing planned or unplanned life events may find the role enticing as locum opportunities offer an elevated level of flexibility and autonomy.
The Role of the Locum Tenens Company
Locum tenens companies have arrangements with healthcare facilities to provide temporary staffing. They aim to recruit prospective physicians, establish a collaborative relationship, and align these physicians with a locum assignment that benefits all parties.
Once the physician has completed the company’s credentialing packet, the company facilitates credentialing for new state medical licensures and the specific healthcare facility. The company conducts all negotiations, communications, and financial arrangements between the locum physician and the facility. Locum physicians do not communicate directly with the facility, at least not initially. The company also provides medical malpractice coverage through an established insurance broker. The company arranges travel (flights, car rentals, and hotels) for the assignment, and the healthcare facility reimburses the company.
Lastly, the company arranges a phone interview between the locum physician and the facility’s gastroenterologist or medical director for a more detailed description of expected responsibilities and level of staffing for endoscopy before the locum physician decides whether the job is a “good fit” for their skills and objectives. It is critical at this point that the locum physician does their due diligence, asking thoughtful questions to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the role before committing.
What Does It Mean to Be an Independent Contractor
An independent contractor is contracted to perform work but is not an employee of an organization (ie, self-employed). This is an important distinction when it comes to the IRS, tax obligations, and allowable deductions.
Initially, this may seem confusing, but some websites review the specifics of these significant taxation differences. Because you are an independent contractor, your paycheck depicts your compensation without any deductions taken. At year’s end, you receive form 1099 rather than the more familiar W-2. The most critical difference is that as a W-2 employed person, you and the employer each contribute half of the obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes owed, but as an independent contractor you are required to pay the entire obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Also important to consider is that although the locum tenens company facilitates necessary documentation, travel, and work schedules, you will be responsible for tracking your work-related finances, and maintaining your CME. This is not difficult but requires attention throughout the year and is manageable with a bit of organizing. A simple example is that meals are deductible on your taxes and can be easily tallied by the government’s per diem rate found at www.gsa.gov — so it is not necessary to save receipts. While it is important to become familiar with these financial nuances as they will affect your net income, they are not as intimidating or complex as you may initially believe.
Primary Benefits of Locum Tenens Assignments
In my experience, the benefits of working as a locum gastroenterologist include the opportunity to remain engaged in a gratifying career while having enhanced autonomy and flexibility. You can construct a schedule in a location most pleasing to you that fits your financial needs. You may work just a few weeks per year to full-time. You can uniquely plan for your desired personal time and alternative professional ambitions. If you choose to transition back to traditional full-time employment, the pivot remains feasible because you have demonstrated attractive professional attributes such as adaptability in different settings, maintenance of necessary skill sets, and collaboration with medical staffing of various complexities.
Quick Points to Consider
- Review the tax obligations and deductions before signing on to your first assignment.
- Healthcare benefits are not provided. If you must purchase healthcare, your healthcare premiums are 100% deductible.
- Malpractice insurance is provided through the locum tenens company.
- The points on flights, hotels, and car rentals remain in your accounts and can be used by you for personal travel in the future.
- You may be able to negotiate hourly rates and terms of responsibilities in certain instances. There’s no harm in requesting.
- Before accepting an assignment, review the website and location of the facility, accessibility to airports, frequency of flights, the physician directory, and services available.
- If your plans change and you are unable to complete a scheduled assignment previously confirmed, you must notify the locum tenens company within a specified window from the start date (usually 30 days) to avoid penalty.
Institutions utilizing locum physicians generally are doing so because their staffing is not optimal; for example, there may have been a transition in leadership or the facility may be located in a rural area. Self-awareness is key; recognize that you are essentially a guest who may need to adapt to the prevailing culture and make do with the resources at hand. You are not there to step in, innovate, or institute changes. Most often the office staff, nurses, and other physicians are very grateful that you are present and a part of the team.
Dr. Bartholomew is a gastroenterologist based in Sarasota, Florida. She has no conflicts to declare in relation to this article.
My successful career in academic gastroenterology makes me a natural proponent of the academic model of practice. However, in my current role as a locum tenens, I have witnessed the versatility that locum assignments offer gastroenterologists, particularly when flexibility in their professional lives is paramount.
The locum tenens industry is a growing feature of the healthcare staffing landscape. My perspective is unique, transitioning from professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at an academic medical center to a self-employed locum gastroenterologist.
As chief, I hired locums to offer additional coverage to the faculty staffing as our division, inclusive of GI fellowship and endoscopy volume, expanded. I recruited, supervised, and assigned responsibilities to the locums. Not only were these physicians professional and competent, but they also contributed to my division’s forward evolution. Based on this experience, I was confident that I could successfully perform as a locum gastroenterologist myself.
My work as a locum these past 5 years has been a positive professional transition for me. I have enjoyed meeting and working with new colleagues, including international locums who travel to work in the United States. I have also witnessed how early-career and mid-career gastroenterologists have taken advantage of this flexible and well-remunerated work.
What It Entails to Be a Locum Tenens
I suspect you have been on the receiving end of emails and postcards from locum tenens companies recruiting for potential assignments and have wondered about the specifics. Essentially, a locum physician functions as an independent contractor who accepts a temporary position at a healthcare organization to provide clinical staffing support during periods of staffing disruption.
Assignments vary in geographic location, facility work site (outpatient vs inpatient), hours, required skills, cadence of assignment, and expected length of staffing need. The locum physician has complete control over selecting the assignment location, the intensity of responsibilities, and the time they wish to commit to the position. Temporal flexibility offers locums the opportunity to commit from a few weeks per year to a full-time commitment. Locums can also combine multiple assignments in different regions or states to match the targeted number of weeks they wish to commit to and the financial goal they have set.
I have met physicians working a few weeks a year during time off from their permanent jobs to supplement their incomes, as well as fully employed physicians leveraging locum placements to explore locations or practices that they have an interest in. Gastroenterologists facing planned or unplanned life events may find the role enticing as locum opportunities offer an elevated level of flexibility and autonomy.
The Role of the Locum Tenens Company
Locum tenens companies have arrangements with healthcare facilities to provide temporary staffing. They aim to recruit prospective physicians, establish a collaborative relationship, and align these physicians with a locum assignment that benefits all parties.
Once the physician has completed the company’s credentialing packet, the company facilitates credentialing for new state medical licensures and the specific healthcare facility. The company conducts all negotiations, communications, and financial arrangements between the locum physician and the facility. Locum physicians do not communicate directly with the facility, at least not initially. The company also provides medical malpractice coverage through an established insurance broker. The company arranges travel (flights, car rentals, and hotels) for the assignment, and the healthcare facility reimburses the company.
Lastly, the company arranges a phone interview between the locum physician and the facility’s gastroenterologist or medical director for a more detailed description of expected responsibilities and level of staffing for endoscopy before the locum physician decides whether the job is a “good fit” for their skills and objectives. It is critical at this point that the locum physician does their due diligence, asking thoughtful questions to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the role before committing.
What Does It Mean to Be an Independent Contractor
An independent contractor is contracted to perform work but is not an employee of an organization (ie, self-employed). This is an important distinction when it comes to the IRS, tax obligations, and allowable deductions.
Initially, this may seem confusing, but some websites review the specifics of these significant taxation differences. Because you are an independent contractor, your paycheck depicts your compensation without any deductions taken. At year’s end, you receive form 1099 rather than the more familiar W-2. The most critical difference is that as a W-2 employed person, you and the employer each contribute half of the obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes owed, but as an independent contractor you are required to pay the entire obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Also important to consider is that although the locum tenens company facilitates necessary documentation, travel, and work schedules, you will be responsible for tracking your work-related finances, and maintaining your CME. This is not difficult but requires attention throughout the year and is manageable with a bit of organizing. A simple example is that meals are deductible on your taxes and can be easily tallied by the government’s per diem rate found at www.gsa.gov — so it is not necessary to save receipts. While it is important to become familiar with these financial nuances as they will affect your net income, they are not as intimidating or complex as you may initially believe.
Primary Benefits of Locum Tenens Assignments
In my experience, the benefits of working as a locum gastroenterologist include the opportunity to remain engaged in a gratifying career while having enhanced autonomy and flexibility. You can construct a schedule in a location most pleasing to you that fits your financial needs. You may work just a few weeks per year to full-time. You can uniquely plan for your desired personal time and alternative professional ambitions. If you choose to transition back to traditional full-time employment, the pivot remains feasible because you have demonstrated attractive professional attributes such as adaptability in different settings, maintenance of necessary skill sets, and collaboration with medical staffing of various complexities.
Quick Points to Consider
- Review the tax obligations and deductions before signing on to your first assignment.
- Healthcare benefits are not provided. If you must purchase healthcare, your healthcare premiums are 100% deductible.
- Malpractice insurance is provided through the locum tenens company.
- The points on flights, hotels, and car rentals remain in your accounts and can be used by you for personal travel in the future.
- You may be able to negotiate hourly rates and terms of responsibilities in certain instances. There’s no harm in requesting.
- Before accepting an assignment, review the website and location of the facility, accessibility to airports, frequency of flights, the physician directory, and services available.
- If your plans change and you are unable to complete a scheduled assignment previously confirmed, you must notify the locum tenens company within a specified window from the start date (usually 30 days) to avoid penalty.
Institutions utilizing locum physicians generally are doing so because their staffing is not optimal; for example, there may have been a transition in leadership or the facility may be located in a rural area. Self-awareness is key; recognize that you are essentially a guest who may need to adapt to the prevailing culture and make do with the resources at hand. You are not there to step in, innovate, or institute changes. Most often the office staff, nurses, and other physicians are very grateful that you are present and a part of the team.
Dr. Bartholomew is a gastroenterologist based in Sarasota, Florida. She has no conflicts to declare in relation to this article.
My successful career in academic gastroenterology makes me a natural proponent of the academic model of practice. However, in my current role as a locum tenens, I have witnessed the versatility that locum assignments offer gastroenterologists, particularly when flexibility in their professional lives is paramount.
The locum tenens industry is a growing feature of the healthcare staffing landscape. My perspective is unique, transitioning from professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at an academic medical center to a self-employed locum gastroenterologist.
As chief, I hired locums to offer additional coverage to the faculty staffing as our division, inclusive of GI fellowship and endoscopy volume, expanded. I recruited, supervised, and assigned responsibilities to the locums. Not only were these physicians professional and competent, but they also contributed to my division’s forward evolution. Based on this experience, I was confident that I could successfully perform as a locum gastroenterologist myself.
My work as a locum these past 5 years has been a positive professional transition for me. I have enjoyed meeting and working with new colleagues, including international locums who travel to work in the United States. I have also witnessed how early-career and mid-career gastroenterologists have taken advantage of this flexible and well-remunerated work.
What It Entails to Be a Locum Tenens
I suspect you have been on the receiving end of emails and postcards from locum tenens companies recruiting for potential assignments and have wondered about the specifics. Essentially, a locum physician functions as an independent contractor who accepts a temporary position at a healthcare organization to provide clinical staffing support during periods of staffing disruption.
Assignments vary in geographic location, facility work site (outpatient vs inpatient), hours, required skills, cadence of assignment, and expected length of staffing need. The locum physician has complete control over selecting the assignment location, the intensity of responsibilities, and the time they wish to commit to the position. Temporal flexibility offers locums the opportunity to commit from a few weeks per year to a full-time commitment. Locums can also combine multiple assignments in different regions or states to match the targeted number of weeks they wish to commit to and the financial goal they have set.
I have met physicians working a few weeks a year during time off from their permanent jobs to supplement their incomes, as well as fully employed physicians leveraging locum placements to explore locations or practices that they have an interest in. Gastroenterologists facing planned or unplanned life events may find the role enticing as locum opportunities offer an elevated level of flexibility and autonomy.
The Role of the Locum Tenens Company
Locum tenens companies have arrangements with healthcare facilities to provide temporary staffing. They aim to recruit prospective physicians, establish a collaborative relationship, and align these physicians with a locum assignment that benefits all parties.
Once the physician has completed the company’s credentialing packet, the company facilitates credentialing for new state medical licensures and the specific healthcare facility. The company conducts all negotiations, communications, and financial arrangements between the locum physician and the facility. Locum physicians do not communicate directly with the facility, at least not initially. The company also provides medical malpractice coverage through an established insurance broker. The company arranges travel (flights, car rentals, and hotels) for the assignment, and the healthcare facility reimburses the company.
Lastly, the company arranges a phone interview between the locum physician and the facility’s gastroenterologist or medical director for a more detailed description of expected responsibilities and level of staffing for endoscopy before the locum physician decides whether the job is a “good fit” for their skills and objectives. It is critical at this point that the locum physician does their due diligence, asking thoughtful questions to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the role before committing.
What Does It Mean to Be an Independent Contractor
An independent contractor is contracted to perform work but is not an employee of an organization (ie, self-employed). This is an important distinction when it comes to the IRS, tax obligations, and allowable deductions.
Initially, this may seem confusing, but some websites review the specifics of these significant taxation differences. Because you are an independent contractor, your paycheck depicts your compensation without any deductions taken. At year’s end, you receive form 1099 rather than the more familiar W-2. The most critical difference is that as a W-2 employed person, you and the employer each contribute half of the obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes owed, but as an independent contractor you are required to pay the entire obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Also important to consider is that although the locum tenens company facilitates necessary documentation, travel, and work schedules, you will be responsible for tracking your work-related finances, and maintaining your CME. This is not difficult but requires attention throughout the year and is manageable with a bit of organizing. A simple example is that meals are deductible on your taxes and can be easily tallied by the government’s per diem rate found at www.gsa.gov — so it is not necessary to save receipts. While it is important to become familiar with these financial nuances as they will affect your net income, they are not as intimidating or complex as you may initially believe.
Primary Benefits of Locum Tenens Assignments
In my experience, the benefits of working as a locum gastroenterologist include the opportunity to remain engaged in a gratifying career while having enhanced autonomy and flexibility. You can construct a schedule in a location most pleasing to you that fits your financial needs. You may work just a few weeks per year to full-time. You can uniquely plan for your desired personal time and alternative professional ambitions. If you choose to transition back to traditional full-time employment, the pivot remains feasible because you have demonstrated attractive professional attributes such as adaptability in different settings, maintenance of necessary skill sets, and collaboration with medical staffing of various complexities.
Quick Points to Consider
- Review the tax obligations and deductions before signing on to your first assignment.
- Healthcare benefits are not provided. If you must purchase healthcare, your healthcare premiums are 100% deductible.
- Malpractice insurance is provided through the locum tenens company.
- The points on flights, hotels, and car rentals remain in your accounts and can be used by you for personal travel in the future.
- You may be able to negotiate hourly rates and terms of responsibilities in certain instances. There’s no harm in requesting.
- Before accepting an assignment, review the website and location of the facility, accessibility to airports, frequency of flights, the physician directory, and services available.
- If your plans change and you are unable to complete a scheduled assignment previously confirmed, you must notify the locum tenens company within a specified window from the start date (usually 30 days) to avoid penalty.
Institutions utilizing locum physicians generally are doing so because their staffing is not optimal; for example, there may have been a transition in leadership or the facility may be located in a rural area. Self-awareness is key; recognize that you are essentially a guest who may need to adapt to the prevailing culture and make do with the resources at hand. You are not there to step in, innovate, or institute changes. Most often the office staff, nurses, and other physicians are very grateful that you are present and a part of the team.
Dr. Bartholomew is a gastroenterologist based in Sarasota, Florida. She has no conflicts to declare in relation to this article.