User login
Why it’s so hard to prevent physician suicide
Kip Wenger, DO, an emergency physician and systems medical director of Team Health, Knoxville, Tenn., was asked to see a patient in the emergency department. He was shocked when he realized who the patient was – a 33-year-old female physician friend and colleague.
She was bleeding from multiple self-inflicted injuries and ultimately died. “I was devastated and couldn’t wrap my head around what had just happened,” Dr. Wenger told this news organization.
It’s important for physicians to be aware of warning signs in their colleagues, such as showing up late, being irritable and short-tempered with staff, missing shifts, making mistakes, or receiving an increasing number of patient complaints, Dr. Wenger says.
Dr. Wenger had had dinner with her several weeks earlier and saw some subtle changes. He had known her as a “positive, upbeat person,” but her demeanor was different during dinner.
“There were no typical telltale signs – she was talking about her plans for the future, including buying a new bicycle – but she wasn’t herself and seemed to become tearful when I hugged her at the end of the evening,” he said. He later heard from another colleague that she had shared feeling “hopeless.”
The scope of the problem
According to the American Society for Suicide Prevention, roughly 300-400 physicians die by suicide annually. Although one study suggests a lower number, official reports likely underestimate suicides, study author Katherine Gold, MD, MSW, associate professor of family medicine, obstetrics, and gynecology, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, MBBS, professor of psychiatry, University of California, Davis, concurs, suggesting that some single-car accidents involving physicians might be suicides. Perry Lin, MD, assistant clinical professor, Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine, Ohio University, Athens, and national co-chair of the Physician Suicide Awareness Committee of the American Association of Suicidology, says that some death certificates state that the deceased died of “accidental causes” because the physician who completes the certificate, possibly a colleague, is reluctant to list the actual cause of death to protect his colleague’s memory or the family’s feelings.
In general, and among physicians, White men older than 65 “represent the largest percentage of people who die from suicide nationwide,” says Dr. Lin.
But younger people are also susceptible, Dr. Lin adds. One of the most vulnerable periods for potential suicide is during the first few months of residency. This dovetails with the findings of Medscape’s 2022 report Suicide: A Tragedy of the Profession. In that report, a difference was found between frequency of suicidal thoughts in younger physicians, compared with older physicians (14% in those < 35 years vs. 8% for those ≥ 45 years).
Hurdles to preventing physician suicide
“The best thing that can happen in our profession is upstream intervention – if people seek help before they get to the point of suicidality, recognizing they’re under stress and duress and that they might be going down a bad pathway,” says Dr. Lin. But research suggests that many physicians don’t do so.
Gary Price, MD, attending surgeon and clinical assistant professor of surgery, Yale–New Haven Hospital, Connecticut, and president of the Physicians Foundation, says his organization has identified barriers that prevent physicians from seeking help.
Physicians feel they may put their licensure at risk if they admit to receiving help for mental issues. These concerns were expressed by respondents in Medscape’s above mentioned 2022 report, many of whom didn’t seek treatment for depression, burnout, or suicidal thoughts lest it affect their professional standing when renewing their license or seeking credentialing.
Although organizations and societies are advocating against these questions, a recent study found that almost 70% of U.S. states and territories continue to ask physicians about their mental health, and 28% ask for diagnoses (beyond current impairments) – a violation of the Americans With Disabilities Act.
“Mental health illness is different from mental health impairment,” Ryan Mire, MD, a Nashville, Tenn.–based internist, said in an interview. “As physicians, we’re comfortable with licensing boards asking whether the physician has any condition that might impair their care for patients, but not about a history of mental illness.”
The second barrier, says Dr. Price, is that hospital credentialing committees sometimes ask similar questions, as do commercial and malpractice insurers.
Another roadblock is that in some states, undergoing treatment for a mental health problem could be subject to discovery by a plaintiff’s attorney in a malpractice case, even if the physician’s mental health history had no effect on patient care. But that’s uncommon, says Daniel Shapiro, PhD, author of “Delivering Doctor Amelia,” a book about his treatment of a suicidal physician who underwent a malpractice lawsuit. “I’ve never seen that happen.”
A final barrier is that many employers require employees to receive treatment within their own institution or health system. “Physicians may be reluctant to get help where they work, with colleagues and friends knowing about their illness or being involved with their care,” says Dr. Price.
In 2022, the American College of Physicians (ACP) issued a toolkit to help members encourage licensing and credentialing boards to remove questions about mental health on applications and include language that supports receiving treatment, Dr. Mire says.
Layers of vulnerability
There are few data regarding relative risk among particular races or ethnicities, “but we know racism is a social stressor,” says Dr. Mire. “Obviously, people from historically disadvantaged populations tend to have societal stressors like discrimination and racism that add an extra layer of burden.”
Intersectionality – having multiple intersecting risk factors – may confer even higher risk. “For example, if you’re a female physician from a historically marginalized race and a resident dealing with the ‘hidden curriculum’ of trying to be resilient, you have multiple layers of vulnerability.”
There are also limited data regarding which specialties or work environments are associated with highest risk. “Obviously, challenges exist in every segment of medicine and at different ages, stages, and work environments, and they intersect with each individual physician’s personal risk factors,” says Dr. Mire, president of the ACP and assistant clinical professor of clinical medical education, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis.
Pamela Wible, MD, is an Oregon-based retired physician who herself went through a suicidal period about 11 years into her career that motivated her to embrace a new vision of clinical practice and change her practice model. After a series of physician suicides in her area, she began to speak and write openly about physician suicide, and since her retirement from clinical practice, she makes herself available on a full-time basis to distressed physicians. “When I address a conference of a particular medical specialty or a group in a particular geographical region, I focus on the specific vulnerabilities in that specialty or region,” she says.
What increases the chances of suicide?
“Many factors, both within and outside the professional setting, affect someone’s decision to die by suicide – after all, physicians have the same stressors as other people, like family, finances, and their own health,” Dr. Mire says. When it comes to non–work-related factors, marital stressors and comorbid psychiatric illness particularly raise the risk, says Dr. Lin.
But certain drivers are specific to the practice of medicine, with burnout and depression first in line.
Dr. Shapiro, who is vice dean for faculty and administrative affairs, Penn State University, Hershey, and the Garner James Cline Professor of Medical Humanism, conducts burnout evaluations throughout the country. “Simple depression screeners prior to the pandemic showed about a 10% major depression rate in physicians,” he told this news organization. “Now, we’re seeing a 30%-33% depression rate, even in those who weren’t frontline providers during the pandemic.”
Dr. Price agrees, noting that burnout in physicians has gone from 40% to 60% since the pandemic. But burnout doesn’t always lead to suicide. It’s when burnout progresses to depression, becomes more severe, and is untreated that the suicidal risk arises, he emphasizes.
Additionally, being a doctor isn’t “just a profession” but a “calling and identity,” says Dr. Gold. Job-related problems (for example, a malpractice suit, complaints to the medical board, loss of autonomy, changing work demands) can raise suicidal risk.
And job-related problems can inform the location of suicide, says Dr. Wible, who is the author of “Physicians Suicide Letters – Answered.”
“A work-related catalyst makes it more likely that the person will attempt or complete suicide in the work setting. Physicians have stepped off hospital rooftops, shot or stabbed themselves in hospital parking lots, or [hanged] themselves in hospital chapels. Perhaps it’s because they’re choosing to die in the place where they’ve been most wounded.”
You are not at fault
“If you’re feeling suicidal, you might feel utterly alone, but if there’s one message I can give you, it’s that you’re not alone, and there are many things you can do to mitigate your pain and despair,” Dr. Wible says. “And you’re not defective. It’s the health care system that’s defective. You have nothing to be ashamed of.”
Some institutions have a “buddy system” that pairs clinicians to provide mutual peer support. A partner who notices concerning signs can refer the other partner for help. Physicians can also be paired with a “buddy,” even without a formal institutional structure.
A “buddy” is a step in the right direction, but Dr. Shapiro cautions it might be necessary to consult a trained professional for serious depression or suicidality. Several states provide connection to local resources. Employee assistance programs (EAPs) might be helpful, although many physicians don’t trust their institution’s EAP. Or physicians can ask colleagues to recommend a “doctor’s doctor” who specializes in treating physicians, suggests Dr. Yellowlees, author of “Physician Suicide: Cases and Commentaries.”
In Medscape’s 2022 report, almost all respondents who reported having suicidal colleagues said they offered help, including emotional support, practical assistance, referrals, speaking to family members, or even personally taking the colleague to the ED or to a therapist.
To enhance physicians’ ability to help each other, Dr. Lin recommends “gatekeeper training,” which has been shown to reduce suicide. “This strategy utilizes a peer-to-peer model, but, rather than a single ‘peer buddy,’ everyone is a ‘gatekeeper’ trained in approaches, such as QPR – Question, Persuade, Refer. ‘Gatekeepers’ are taught how to recognize warning signs of suicide, question the potentially suicidal individual, persuade him/her to get help, and provide referrals.”
Other ways to prevent suicide
Dr. Lin advises physicians to “create a personalized safety plan and write down signs and clues that they may be going down the wrong path and what they can do – like breathing exercises, relaxation – and identifying people to talk to, places to go, or phone numbers to call, if those initial measures aren’t enough.” The plan is private and allows the physician to determine at what point help is needed and who should be consulted. “Sometimes, when a person is in acute stress, even looking up a phone number can seem insurmountable. But having it on paper lowers the barrier, making it more achievable.”
Resources should be posted in places where physicians gather so that those who don’t already have a safety plan have easy access to that information, he suggests.
In addition, consideration may be given to reaching out for support if a colleague has died by suicide, experts suggest. Whether offered by one’s institution, a peer arrangement, spiritual counseling, or psychotherapy, one may need help dealing with the trauma, guilt, and grief that often accompany this type of loss.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Kip Wenger, DO, an emergency physician and systems medical director of Team Health, Knoxville, Tenn., was asked to see a patient in the emergency department. He was shocked when he realized who the patient was – a 33-year-old female physician friend and colleague.
She was bleeding from multiple self-inflicted injuries and ultimately died. “I was devastated and couldn’t wrap my head around what had just happened,” Dr. Wenger told this news organization.
It’s important for physicians to be aware of warning signs in their colleagues, such as showing up late, being irritable and short-tempered with staff, missing shifts, making mistakes, or receiving an increasing number of patient complaints, Dr. Wenger says.
Dr. Wenger had had dinner with her several weeks earlier and saw some subtle changes. He had known her as a “positive, upbeat person,” but her demeanor was different during dinner.
“There were no typical telltale signs – she was talking about her plans for the future, including buying a new bicycle – but she wasn’t herself and seemed to become tearful when I hugged her at the end of the evening,” he said. He later heard from another colleague that she had shared feeling “hopeless.”
The scope of the problem
According to the American Society for Suicide Prevention, roughly 300-400 physicians die by suicide annually. Although one study suggests a lower number, official reports likely underestimate suicides, study author Katherine Gold, MD, MSW, associate professor of family medicine, obstetrics, and gynecology, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, MBBS, professor of psychiatry, University of California, Davis, concurs, suggesting that some single-car accidents involving physicians might be suicides. Perry Lin, MD, assistant clinical professor, Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine, Ohio University, Athens, and national co-chair of the Physician Suicide Awareness Committee of the American Association of Suicidology, says that some death certificates state that the deceased died of “accidental causes” because the physician who completes the certificate, possibly a colleague, is reluctant to list the actual cause of death to protect his colleague’s memory or the family’s feelings.
In general, and among physicians, White men older than 65 “represent the largest percentage of people who die from suicide nationwide,” says Dr. Lin.
But younger people are also susceptible, Dr. Lin adds. One of the most vulnerable periods for potential suicide is during the first few months of residency. This dovetails with the findings of Medscape’s 2022 report Suicide: A Tragedy of the Profession. In that report, a difference was found between frequency of suicidal thoughts in younger physicians, compared with older physicians (14% in those < 35 years vs. 8% for those ≥ 45 years).
Hurdles to preventing physician suicide
“The best thing that can happen in our profession is upstream intervention – if people seek help before they get to the point of suicidality, recognizing they’re under stress and duress and that they might be going down a bad pathway,” says Dr. Lin. But research suggests that many physicians don’t do so.
Gary Price, MD, attending surgeon and clinical assistant professor of surgery, Yale–New Haven Hospital, Connecticut, and president of the Physicians Foundation, says his organization has identified barriers that prevent physicians from seeking help.
Physicians feel they may put their licensure at risk if they admit to receiving help for mental issues. These concerns were expressed by respondents in Medscape’s above mentioned 2022 report, many of whom didn’t seek treatment for depression, burnout, or suicidal thoughts lest it affect their professional standing when renewing their license or seeking credentialing.
Although organizations and societies are advocating against these questions, a recent study found that almost 70% of U.S. states and territories continue to ask physicians about their mental health, and 28% ask for diagnoses (beyond current impairments) – a violation of the Americans With Disabilities Act.
“Mental health illness is different from mental health impairment,” Ryan Mire, MD, a Nashville, Tenn.–based internist, said in an interview. “As physicians, we’re comfortable with licensing boards asking whether the physician has any condition that might impair their care for patients, but not about a history of mental illness.”
The second barrier, says Dr. Price, is that hospital credentialing committees sometimes ask similar questions, as do commercial and malpractice insurers.
Another roadblock is that in some states, undergoing treatment for a mental health problem could be subject to discovery by a plaintiff’s attorney in a malpractice case, even if the physician’s mental health history had no effect on patient care. But that’s uncommon, says Daniel Shapiro, PhD, author of “Delivering Doctor Amelia,” a book about his treatment of a suicidal physician who underwent a malpractice lawsuit. “I’ve never seen that happen.”
A final barrier is that many employers require employees to receive treatment within their own institution or health system. “Physicians may be reluctant to get help where they work, with colleagues and friends knowing about their illness or being involved with their care,” says Dr. Price.
In 2022, the American College of Physicians (ACP) issued a toolkit to help members encourage licensing and credentialing boards to remove questions about mental health on applications and include language that supports receiving treatment, Dr. Mire says.
Layers of vulnerability
There are few data regarding relative risk among particular races or ethnicities, “but we know racism is a social stressor,” says Dr. Mire. “Obviously, people from historically disadvantaged populations tend to have societal stressors like discrimination and racism that add an extra layer of burden.”
Intersectionality – having multiple intersecting risk factors – may confer even higher risk. “For example, if you’re a female physician from a historically marginalized race and a resident dealing with the ‘hidden curriculum’ of trying to be resilient, you have multiple layers of vulnerability.”
There are also limited data regarding which specialties or work environments are associated with highest risk. “Obviously, challenges exist in every segment of medicine and at different ages, stages, and work environments, and they intersect with each individual physician’s personal risk factors,” says Dr. Mire, president of the ACP and assistant clinical professor of clinical medical education, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis.
Pamela Wible, MD, is an Oregon-based retired physician who herself went through a suicidal period about 11 years into her career that motivated her to embrace a new vision of clinical practice and change her practice model. After a series of physician suicides in her area, she began to speak and write openly about physician suicide, and since her retirement from clinical practice, she makes herself available on a full-time basis to distressed physicians. “When I address a conference of a particular medical specialty or a group in a particular geographical region, I focus on the specific vulnerabilities in that specialty or region,” she says.
What increases the chances of suicide?
“Many factors, both within and outside the professional setting, affect someone’s decision to die by suicide – after all, physicians have the same stressors as other people, like family, finances, and their own health,” Dr. Mire says. When it comes to non–work-related factors, marital stressors and comorbid psychiatric illness particularly raise the risk, says Dr. Lin.
But certain drivers are specific to the practice of medicine, with burnout and depression first in line.
Dr. Shapiro, who is vice dean for faculty and administrative affairs, Penn State University, Hershey, and the Garner James Cline Professor of Medical Humanism, conducts burnout evaluations throughout the country. “Simple depression screeners prior to the pandemic showed about a 10% major depression rate in physicians,” he told this news organization. “Now, we’re seeing a 30%-33% depression rate, even in those who weren’t frontline providers during the pandemic.”
Dr. Price agrees, noting that burnout in physicians has gone from 40% to 60% since the pandemic. But burnout doesn’t always lead to suicide. It’s when burnout progresses to depression, becomes more severe, and is untreated that the suicidal risk arises, he emphasizes.
Additionally, being a doctor isn’t “just a profession” but a “calling and identity,” says Dr. Gold. Job-related problems (for example, a malpractice suit, complaints to the medical board, loss of autonomy, changing work demands) can raise suicidal risk.
And job-related problems can inform the location of suicide, says Dr. Wible, who is the author of “Physicians Suicide Letters – Answered.”
“A work-related catalyst makes it more likely that the person will attempt or complete suicide in the work setting. Physicians have stepped off hospital rooftops, shot or stabbed themselves in hospital parking lots, or [hanged] themselves in hospital chapels. Perhaps it’s because they’re choosing to die in the place where they’ve been most wounded.”
You are not at fault
“If you’re feeling suicidal, you might feel utterly alone, but if there’s one message I can give you, it’s that you’re not alone, and there are many things you can do to mitigate your pain and despair,” Dr. Wible says. “And you’re not defective. It’s the health care system that’s defective. You have nothing to be ashamed of.”
Some institutions have a “buddy system” that pairs clinicians to provide mutual peer support. A partner who notices concerning signs can refer the other partner for help. Physicians can also be paired with a “buddy,” even without a formal institutional structure.
A “buddy” is a step in the right direction, but Dr. Shapiro cautions it might be necessary to consult a trained professional for serious depression or suicidality. Several states provide connection to local resources. Employee assistance programs (EAPs) might be helpful, although many physicians don’t trust their institution’s EAP. Or physicians can ask colleagues to recommend a “doctor’s doctor” who specializes in treating physicians, suggests Dr. Yellowlees, author of “Physician Suicide: Cases and Commentaries.”
In Medscape’s 2022 report, almost all respondents who reported having suicidal colleagues said they offered help, including emotional support, practical assistance, referrals, speaking to family members, or even personally taking the colleague to the ED or to a therapist.
To enhance physicians’ ability to help each other, Dr. Lin recommends “gatekeeper training,” which has been shown to reduce suicide. “This strategy utilizes a peer-to-peer model, but, rather than a single ‘peer buddy,’ everyone is a ‘gatekeeper’ trained in approaches, such as QPR – Question, Persuade, Refer. ‘Gatekeepers’ are taught how to recognize warning signs of suicide, question the potentially suicidal individual, persuade him/her to get help, and provide referrals.”
Other ways to prevent suicide
Dr. Lin advises physicians to “create a personalized safety plan and write down signs and clues that they may be going down the wrong path and what they can do – like breathing exercises, relaxation – and identifying people to talk to, places to go, or phone numbers to call, if those initial measures aren’t enough.” The plan is private and allows the physician to determine at what point help is needed and who should be consulted. “Sometimes, when a person is in acute stress, even looking up a phone number can seem insurmountable. But having it on paper lowers the barrier, making it more achievable.”
Resources should be posted in places where physicians gather so that those who don’t already have a safety plan have easy access to that information, he suggests.
In addition, consideration may be given to reaching out for support if a colleague has died by suicide, experts suggest. Whether offered by one’s institution, a peer arrangement, spiritual counseling, or psychotherapy, one may need help dealing with the trauma, guilt, and grief that often accompany this type of loss.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Kip Wenger, DO, an emergency physician and systems medical director of Team Health, Knoxville, Tenn., was asked to see a patient in the emergency department. He was shocked when he realized who the patient was – a 33-year-old female physician friend and colleague.
She was bleeding from multiple self-inflicted injuries and ultimately died. “I was devastated and couldn’t wrap my head around what had just happened,” Dr. Wenger told this news organization.
It’s important for physicians to be aware of warning signs in their colleagues, such as showing up late, being irritable and short-tempered with staff, missing shifts, making mistakes, or receiving an increasing number of patient complaints, Dr. Wenger says.
Dr. Wenger had had dinner with her several weeks earlier and saw some subtle changes. He had known her as a “positive, upbeat person,” but her demeanor was different during dinner.
“There were no typical telltale signs – she was talking about her plans for the future, including buying a new bicycle – but she wasn’t herself and seemed to become tearful when I hugged her at the end of the evening,” he said. He later heard from another colleague that she had shared feeling “hopeless.”
The scope of the problem
According to the American Society for Suicide Prevention, roughly 300-400 physicians die by suicide annually. Although one study suggests a lower number, official reports likely underestimate suicides, study author Katherine Gold, MD, MSW, associate professor of family medicine, obstetrics, and gynecology, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview.
Peter Yellowlees, MD, MBBS, professor of psychiatry, University of California, Davis, concurs, suggesting that some single-car accidents involving physicians might be suicides. Perry Lin, MD, assistant clinical professor, Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine, Ohio University, Athens, and national co-chair of the Physician Suicide Awareness Committee of the American Association of Suicidology, says that some death certificates state that the deceased died of “accidental causes” because the physician who completes the certificate, possibly a colleague, is reluctant to list the actual cause of death to protect his colleague’s memory or the family’s feelings.
In general, and among physicians, White men older than 65 “represent the largest percentage of people who die from suicide nationwide,” says Dr. Lin.
But younger people are also susceptible, Dr. Lin adds. One of the most vulnerable periods for potential suicide is during the first few months of residency. This dovetails with the findings of Medscape’s 2022 report Suicide: A Tragedy of the Profession. In that report, a difference was found between frequency of suicidal thoughts in younger physicians, compared with older physicians (14% in those < 35 years vs. 8% for those ≥ 45 years).
Hurdles to preventing physician suicide
“The best thing that can happen in our profession is upstream intervention – if people seek help before they get to the point of suicidality, recognizing they’re under stress and duress and that they might be going down a bad pathway,” says Dr. Lin. But research suggests that many physicians don’t do so.
Gary Price, MD, attending surgeon and clinical assistant professor of surgery, Yale–New Haven Hospital, Connecticut, and president of the Physicians Foundation, says his organization has identified barriers that prevent physicians from seeking help.
Physicians feel they may put their licensure at risk if they admit to receiving help for mental issues. These concerns were expressed by respondents in Medscape’s above mentioned 2022 report, many of whom didn’t seek treatment for depression, burnout, or suicidal thoughts lest it affect their professional standing when renewing their license or seeking credentialing.
Although organizations and societies are advocating against these questions, a recent study found that almost 70% of U.S. states and territories continue to ask physicians about their mental health, and 28% ask for diagnoses (beyond current impairments) – a violation of the Americans With Disabilities Act.
“Mental health illness is different from mental health impairment,” Ryan Mire, MD, a Nashville, Tenn.–based internist, said in an interview. “As physicians, we’re comfortable with licensing boards asking whether the physician has any condition that might impair their care for patients, but not about a history of mental illness.”
The second barrier, says Dr. Price, is that hospital credentialing committees sometimes ask similar questions, as do commercial and malpractice insurers.
Another roadblock is that in some states, undergoing treatment for a mental health problem could be subject to discovery by a plaintiff’s attorney in a malpractice case, even if the physician’s mental health history had no effect on patient care. But that’s uncommon, says Daniel Shapiro, PhD, author of “Delivering Doctor Amelia,” a book about his treatment of a suicidal physician who underwent a malpractice lawsuit. “I’ve never seen that happen.”
A final barrier is that many employers require employees to receive treatment within their own institution or health system. “Physicians may be reluctant to get help where they work, with colleagues and friends knowing about their illness or being involved with their care,” says Dr. Price.
In 2022, the American College of Physicians (ACP) issued a toolkit to help members encourage licensing and credentialing boards to remove questions about mental health on applications and include language that supports receiving treatment, Dr. Mire says.
Layers of vulnerability
There are few data regarding relative risk among particular races or ethnicities, “but we know racism is a social stressor,” says Dr. Mire. “Obviously, people from historically disadvantaged populations tend to have societal stressors like discrimination and racism that add an extra layer of burden.”
Intersectionality – having multiple intersecting risk factors – may confer even higher risk. “For example, if you’re a female physician from a historically marginalized race and a resident dealing with the ‘hidden curriculum’ of trying to be resilient, you have multiple layers of vulnerability.”
There are also limited data regarding which specialties or work environments are associated with highest risk. “Obviously, challenges exist in every segment of medicine and at different ages, stages, and work environments, and they intersect with each individual physician’s personal risk factors,” says Dr. Mire, president of the ACP and assistant clinical professor of clinical medical education, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis.
Pamela Wible, MD, is an Oregon-based retired physician who herself went through a suicidal period about 11 years into her career that motivated her to embrace a new vision of clinical practice and change her practice model. After a series of physician suicides in her area, she began to speak and write openly about physician suicide, and since her retirement from clinical practice, she makes herself available on a full-time basis to distressed physicians. “When I address a conference of a particular medical specialty or a group in a particular geographical region, I focus on the specific vulnerabilities in that specialty or region,” she says.
What increases the chances of suicide?
“Many factors, both within and outside the professional setting, affect someone’s decision to die by suicide – after all, physicians have the same stressors as other people, like family, finances, and their own health,” Dr. Mire says. When it comes to non–work-related factors, marital stressors and comorbid psychiatric illness particularly raise the risk, says Dr. Lin.
But certain drivers are specific to the practice of medicine, with burnout and depression first in line.
Dr. Shapiro, who is vice dean for faculty and administrative affairs, Penn State University, Hershey, and the Garner James Cline Professor of Medical Humanism, conducts burnout evaluations throughout the country. “Simple depression screeners prior to the pandemic showed about a 10% major depression rate in physicians,” he told this news organization. “Now, we’re seeing a 30%-33% depression rate, even in those who weren’t frontline providers during the pandemic.”
Dr. Price agrees, noting that burnout in physicians has gone from 40% to 60% since the pandemic. But burnout doesn’t always lead to suicide. It’s when burnout progresses to depression, becomes more severe, and is untreated that the suicidal risk arises, he emphasizes.
Additionally, being a doctor isn’t “just a profession” but a “calling and identity,” says Dr. Gold. Job-related problems (for example, a malpractice suit, complaints to the medical board, loss of autonomy, changing work demands) can raise suicidal risk.
And job-related problems can inform the location of suicide, says Dr. Wible, who is the author of “Physicians Suicide Letters – Answered.”
“A work-related catalyst makes it more likely that the person will attempt or complete suicide in the work setting. Physicians have stepped off hospital rooftops, shot or stabbed themselves in hospital parking lots, or [hanged] themselves in hospital chapels. Perhaps it’s because they’re choosing to die in the place where they’ve been most wounded.”
You are not at fault
“If you’re feeling suicidal, you might feel utterly alone, but if there’s one message I can give you, it’s that you’re not alone, and there are many things you can do to mitigate your pain and despair,” Dr. Wible says. “And you’re not defective. It’s the health care system that’s defective. You have nothing to be ashamed of.”
Some institutions have a “buddy system” that pairs clinicians to provide mutual peer support. A partner who notices concerning signs can refer the other partner for help. Physicians can also be paired with a “buddy,” even without a formal institutional structure.
A “buddy” is a step in the right direction, but Dr. Shapiro cautions it might be necessary to consult a trained professional for serious depression or suicidality. Several states provide connection to local resources. Employee assistance programs (EAPs) might be helpful, although many physicians don’t trust their institution’s EAP. Or physicians can ask colleagues to recommend a “doctor’s doctor” who specializes in treating physicians, suggests Dr. Yellowlees, author of “Physician Suicide: Cases and Commentaries.”
In Medscape’s 2022 report, almost all respondents who reported having suicidal colleagues said they offered help, including emotional support, practical assistance, referrals, speaking to family members, or even personally taking the colleague to the ED or to a therapist.
To enhance physicians’ ability to help each other, Dr. Lin recommends “gatekeeper training,” which has been shown to reduce suicide. “This strategy utilizes a peer-to-peer model, but, rather than a single ‘peer buddy,’ everyone is a ‘gatekeeper’ trained in approaches, such as QPR – Question, Persuade, Refer. ‘Gatekeepers’ are taught how to recognize warning signs of suicide, question the potentially suicidal individual, persuade him/her to get help, and provide referrals.”
Other ways to prevent suicide
Dr. Lin advises physicians to “create a personalized safety plan and write down signs and clues that they may be going down the wrong path and what they can do – like breathing exercises, relaxation – and identifying people to talk to, places to go, or phone numbers to call, if those initial measures aren’t enough.” The plan is private and allows the physician to determine at what point help is needed and who should be consulted. “Sometimes, when a person is in acute stress, even looking up a phone number can seem insurmountable. But having it on paper lowers the barrier, making it more achievable.”
Resources should be posted in places where physicians gather so that those who don’t already have a safety plan have easy access to that information, he suggests.
In addition, consideration may be given to reaching out for support if a colleague has died by suicide, experts suggest. Whether offered by one’s institution, a peer arrangement, spiritual counseling, or psychotherapy, one may need help dealing with the trauma, guilt, and grief that often accompany this type of loss.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hypertensive pregnancy disorders tied to double hypertension risk
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) are associated with a greater than twofold risk of developing hypertension a decade later, new research suggests.
Investigators prospectively studied patients who had and who had not experienced HDP 10 years earlier; most self-identified as Black. They found that those with a history of HDP had a 2.4-fold higher risk for new hypertension than those without such a history.
Patients who developed hypertension showed greater left ventricular (LV) remodeling (including greater relative wall thickness), worse diastolic function, more abnormal longitudinal strain, and higher effective arterial elastance than those without hypertension, regardless of the presence or absence of an HDP history.
“We know that patients with preeclampsia are at a higher risk for heart disease later in life, and it seems to be driven by the development of new hypertension,” lead author Lisa Levine, MD, MSCE, director, pregnancy and heart disease program, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
It is critically important to “study a more diverse population, including a larger percentage of Black patients, since HDP and CVD both disproportionately affect Black women,” Dr. Levine said. “And it is important to screen patients for hypertension, getting them into primary care for visits, getting them diagnosed sooner, and treating them early for hypertension.”
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Understudied population
HDP includes gestational hypertension and preeclampsia, Dr. Levine explained. “We already know that patients who have had preeclampsia are at higher risk for stroke, heart failure [HF], and myocardial infarction later in life,” she said. The goal of this study was to see whether, instead of waiting 20-30 years, they could look only 10 years later to see which patients would be at highest risk for future heart disease, Dr. Levine said.
In particular, it’s known that cardiovascular disease (CVD) and HDP “disproportionately affect Black women,” Dr. Levine continued. “What makes our study different from other studies is that we focused predominantly on the Black African American population, since it’s understudied and also at highest risk for preeclampsia and heart disease,” she said.
They set out to “evaluate differences in CV risk factors as well as subclinical CVD among a well-characterized group of racially diverse patients with and without a history of HDP 10 years earlier,” the authors state.
To investigate the question, the researchers performed a prospective, cross-sectional study between April 2016 and December 2019 of patients with and without a diagnosis of HDP during a previous pregnancy at least 10 years earlier (from 2005 to 2007). Patients were drawn from a parent cohort in a previously performed observational study of patients with preeclampsia or HDP and normotensive control subjects.
The current study focused on 135 patients (85% Black), 84 with a history of HDP and 51 without. Of the Black patients, 91.7% had a history of HDP, compared with 8.3% of the White patients.
During an in-person visit, the researchers assessed participants’ blood pressure and other clinical risk factors for CVD, including fasting glucose and lipids. They also used noninvasive means to measure cardiac and vascular structure and function.
Importance of routine screening
The risk for new hypertension was 2.4 times higher in patients with a history of HDP than in those without HDP, with stage 2 hypertension noted in 56.0% of patients with and in 23.5% without HDP (P < .001). This equates to a relative risk of 2.4 (95% confidence interval, 1.39-4.14), even after adjustment for race, maternal age, body mass index, and history of preterm birth.
“Importantly, 18% of patients with a history of HDP met criteria for a new diagnosis of hypertension identified through the study visit,” the authors report.
There were no differences in many cardiac measures (left ventricular (LV) structure, global longitudinal strain, diastolic function, arterial stiffness, or endothelial function) between patients with and without a history of HDP.
However, patients with chronic hypertension (CHTN), regardless of HDP history, had other cardiac abnormalities, including greater LV remodeling, worse diastolic function, and higher effective arterial elastance.
“The data regarding increased risk of hypertension after HDP is not a novel finding, however our cohort is unique in the high baseline rate of stage 2 hypertension, even among patients without a history of HDP,” the authors comment.
In fact, when they looked at the diagnosis of either stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, they found that more than 80% of patients with and 60% of patients without a history of HDP had hypertension. Notably, among patients with a history of HDP, only 39% had a formal diagnosis of either stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, further highlighting “the importance of routine screening for CHTN in this population,” they state.
“Further studies should evaluate the optimal time period to screen for postpartum hypertension and a monitoring plan for these at-risk women,” Dr. Levine added.
‘Opportunity of a lifetime’
Commenting for this news organization, Malamo Countouris, MD, MS, assistant professor of medicine and codirector, postpartum hypertension program, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said hypertension is “underrecognized and undertreated among young, premenopausal, Black women.”
Pregnancy “gives us a clue, through HDP, as to who is high risk to develop chronic hypertension and subsequent subclinical structural cardiac changes in the decade after delivery,” said Dr. Countouris, who was not involved with the study.
“The jury is still out on whether HDP contributes independently to cardiovascular changes in the years after delivery. Ongoing research is needed to clarify the unique or compounding contributions of pregnancy complications and hypertension,” she added.
In an accompanying editorial , Josephine Chou, MD, MS, director of cardio-obstetrics and codirector of maternal cardiology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., called the study a “laudable contribution to understanding of HDP and hypertension within the first decade after pregnancy,” saying that it “paves the way for future efforts to improve postpartum CV care, enabling us to grasp this opportunity of a lifetime to ultimately reduce maternal and pregnancy-related morbidity and mortality.”
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the American Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Foundation. Dr. Levine reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Countouris reports receiving funding from the American Heart Association. Dr. Chou reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) are associated with a greater than twofold risk of developing hypertension a decade later, new research suggests.
Investigators prospectively studied patients who had and who had not experienced HDP 10 years earlier; most self-identified as Black. They found that those with a history of HDP had a 2.4-fold higher risk for new hypertension than those without such a history.
Patients who developed hypertension showed greater left ventricular (LV) remodeling (including greater relative wall thickness), worse diastolic function, more abnormal longitudinal strain, and higher effective arterial elastance than those without hypertension, regardless of the presence or absence of an HDP history.
“We know that patients with preeclampsia are at a higher risk for heart disease later in life, and it seems to be driven by the development of new hypertension,” lead author Lisa Levine, MD, MSCE, director, pregnancy and heart disease program, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
It is critically important to “study a more diverse population, including a larger percentage of Black patients, since HDP and CVD both disproportionately affect Black women,” Dr. Levine said. “And it is important to screen patients for hypertension, getting them into primary care for visits, getting them diagnosed sooner, and treating them early for hypertension.”
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Understudied population
HDP includes gestational hypertension and preeclampsia, Dr. Levine explained. “We already know that patients who have had preeclampsia are at higher risk for stroke, heart failure [HF], and myocardial infarction later in life,” she said. The goal of this study was to see whether, instead of waiting 20-30 years, they could look only 10 years later to see which patients would be at highest risk for future heart disease, Dr. Levine said.
In particular, it’s known that cardiovascular disease (CVD) and HDP “disproportionately affect Black women,” Dr. Levine continued. “What makes our study different from other studies is that we focused predominantly on the Black African American population, since it’s understudied and also at highest risk for preeclampsia and heart disease,” she said.
They set out to “evaluate differences in CV risk factors as well as subclinical CVD among a well-characterized group of racially diverse patients with and without a history of HDP 10 years earlier,” the authors state.
To investigate the question, the researchers performed a prospective, cross-sectional study between April 2016 and December 2019 of patients with and without a diagnosis of HDP during a previous pregnancy at least 10 years earlier (from 2005 to 2007). Patients were drawn from a parent cohort in a previously performed observational study of patients with preeclampsia or HDP and normotensive control subjects.
The current study focused on 135 patients (85% Black), 84 with a history of HDP and 51 without. Of the Black patients, 91.7% had a history of HDP, compared with 8.3% of the White patients.
During an in-person visit, the researchers assessed participants’ blood pressure and other clinical risk factors for CVD, including fasting glucose and lipids. They also used noninvasive means to measure cardiac and vascular structure and function.
Importance of routine screening
The risk for new hypertension was 2.4 times higher in patients with a history of HDP than in those without HDP, with stage 2 hypertension noted in 56.0% of patients with and in 23.5% without HDP (P < .001). This equates to a relative risk of 2.4 (95% confidence interval, 1.39-4.14), even after adjustment for race, maternal age, body mass index, and history of preterm birth.
“Importantly, 18% of patients with a history of HDP met criteria for a new diagnosis of hypertension identified through the study visit,” the authors report.
There were no differences in many cardiac measures (left ventricular (LV) structure, global longitudinal strain, diastolic function, arterial stiffness, or endothelial function) between patients with and without a history of HDP.
However, patients with chronic hypertension (CHTN), regardless of HDP history, had other cardiac abnormalities, including greater LV remodeling, worse diastolic function, and higher effective arterial elastance.
“The data regarding increased risk of hypertension after HDP is not a novel finding, however our cohort is unique in the high baseline rate of stage 2 hypertension, even among patients without a history of HDP,” the authors comment.
In fact, when they looked at the diagnosis of either stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, they found that more than 80% of patients with and 60% of patients without a history of HDP had hypertension. Notably, among patients with a history of HDP, only 39% had a formal diagnosis of either stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, further highlighting “the importance of routine screening for CHTN in this population,” they state.
“Further studies should evaluate the optimal time period to screen for postpartum hypertension and a monitoring plan for these at-risk women,” Dr. Levine added.
‘Opportunity of a lifetime’
Commenting for this news organization, Malamo Countouris, MD, MS, assistant professor of medicine and codirector, postpartum hypertension program, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said hypertension is “underrecognized and undertreated among young, premenopausal, Black women.”
Pregnancy “gives us a clue, through HDP, as to who is high risk to develop chronic hypertension and subsequent subclinical structural cardiac changes in the decade after delivery,” said Dr. Countouris, who was not involved with the study.
“The jury is still out on whether HDP contributes independently to cardiovascular changes in the years after delivery. Ongoing research is needed to clarify the unique or compounding contributions of pregnancy complications and hypertension,” she added.
In an accompanying editorial , Josephine Chou, MD, MS, director of cardio-obstetrics and codirector of maternal cardiology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., called the study a “laudable contribution to understanding of HDP and hypertension within the first decade after pregnancy,” saying that it “paves the way for future efforts to improve postpartum CV care, enabling us to grasp this opportunity of a lifetime to ultimately reduce maternal and pregnancy-related morbidity and mortality.”
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the American Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Foundation. Dr. Levine reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Countouris reports receiving funding from the American Heart Association. Dr. Chou reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (HDP) are associated with a greater than twofold risk of developing hypertension a decade later, new research suggests.
Investigators prospectively studied patients who had and who had not experienced HDP 10 years earlier; most self-identified as Black. They found that those with a history of HDP had a 2.4-fold higher risk for new hypertension than those without such a history.
Patients who developed hypertension showed greater left ventricular (LV) remodeling (including greater relative wall thickness), worse diastolic function, more abnormal longitudinal strain, and higher effective arterial elastance than those without hypertension, regardless of the presence or absence of an HDP history.
“We know that patients with preeclampsia are at a higher risk for heart disease later in life, and it seems to be driven by the development of new hypertension,” lead author Lisa Levine, MD, MSCE, director, pregnancy and heart disease program, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
It is critically important to “study a more diverse population, including a larger percentage of Black patients, since HDP and CVD both disproportionately affect Black women,” Dr. Levine said. “And it is important to screen patients for hypertension, getting them into primary care for visits, getting them diagnosed sooner, and treating them early for hypertension.”
The study was published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Understudied population
HDP includes gestational hypertension and preeclampsia, Dr. Levine explained. “We already know that patients who have had preeclampsia are at higher risk for stroke, heart failure [HF], and myocardial infarction later in life,” she said. The goal of this study was to see whether, instead of waiting 20-30 years, they could look only 10 years later to see which patients would be at highest risk for future heart disease, Dr. Levine said.
In particular, it’s known that cardiovascular disease (CVD) and HDP “disproportionately affect Black women,” Dr. Levine continued. “What makes our study different from other studies is that we focused predominantly on the Black African American population, since it’s understudied and also at highest risk for preeclampsia and heart disease,” she said.
They set out to “evaluate differences in CV risk factors as well as subclinical CVD among a well-characterized group of racially diverse patients with and without a history of HDP 10 years earlier,” the authors state.
To investigate the question, the researchers performed a prospective, cross-sectional study between April 2016 and December 2019 of patients with and without a diagnosis of HDP during a previous pregnancy at least 10 years earlier (from 2005 to 2007). Patients were drawn from a parent cohort in a previously performed observational study of patients with preeclampsia or HDP and normotensive control subjects.
The current study focused on 135 patients (85% Black), 84 with a history of HDP and 51 without. Of the Black patients, 91.7% had a history of HDP, compared with 8.3% of the White patients.
During an in-person visit, the researchers assessed participants’ blood pressure and other clinical risk factors for CVD, including fasting glucose and lipids. They also used noninvasive means to measure cardiac and vascular structure and function.
Importance of routine screening
The risk for new hypertension was 2.4 times higher in patients with a history of HDP than in those without HDP, with stage 2 hypertension noted in 56.0% of patients with and in 23.5% without HDP (P < .001). This equates to a relative risk of 2.4 (95% confidence interval, 1.39-4.14), even after adjustment for race, maternal age, body mass index, and history of preterm birth.
“Importantly, 18% of patients with a history of HDP met criteria for a new diagnosis of hypertension identified through the study visit,” the authors report.
There were no differences in many cardiac measures (left ventricular (LV) structure, global longitudinal strain, diastolic function, arterial stiffness, or endothelial function) between patients with and without a history of HDP.
However, patients with chronic hypertension (CHTN), regardless of HDP history, had other cardiac abnormalities, including greater LV remodeling, worse diastolic function, and higher effective arterial elastance.
“The data regarding increased risk of hypertension after HDP is not a novel finding, however our cohort is unique in the high baseline rate of stage 2 hypertension, even among patients without a history of HDP,” the authors comment.
In fact, when they looked at the diagnosis of either stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, they found that more than 80% of patients with and 60% of patients without a history of HDP had hypertension. Notably, among patients with a history of HDP, only 39% had a formal diagnosis of either stage 1 or stage 2 hypertension, further highlighting “the importance of routine screening for CHTN in this population,” they state.
“Further studies should evaluate the optimal time period to screen for postpartum hypertension and a monitoring plan for these at-risk women,” Dr. Levine added.
‘Opportunity of a lifetime’
Commenting for this news organization, Malamo Countouris, MD, MS, assistant professor of medicine and codirector, postpartum hypertension program, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, said hypertension is “underrecognized and undertreated among young, premenopausal, Black women.”
Pregnancy “gives us a clue, through HDP, as to who is high risk to develop chronic hypertension and subsequent subclinical structural cardiac changes in the decade after delivery,” said Dr. Countouris, who was not involved with the study.
“The jury is still out on whether HDP contributes independently to cardiovascular changes in the years after delivery. Ongoing research is needed to clarify the unique or compounding contributions of pregnancy complications and hypertension,” she added.
In an accompanying editorial , Josephine Chou, MD, MS, director of cardio-obstetrics and codirector of maternal cardiology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn., called the study a “laudable contribution to understanding of HDP and hypertension within the first decade after pregnancy,” saying that it “paves the way for future efforts to improve postpartum CV care, enabling us to grasp this opportunity of a lifetime to ultimately reduce maternal and pregnancy-related morbidity and mortality.”
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the American Association of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Foundation. Dr. Levine reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper. Dr. Countouris reports receiving funding from the American Heart Association. Dr. Chou reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Air pollution tied to ventricular arrhythmias in those with ICDs
Ventricular arrhythmias more commonly occur on days when there are higher levels of air pollution, especially with fine particulate matter (PM), a new study suggests.
The investigators studied the relationship between air pollution and ventricular arrhythmias in Piacenza, Italy by examining 5-year data on patients who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD).
They found a significant association between PM2.5 levels and ventricular arrhythmias, especially those treated with direct current shock. Moreover, higher levels of PM2.5 and PM10 were associated with increased risk of all ventricular arrhythmias.
“These data confirm that environmental pollution is not only a climate emergency but also a public health problem,” lead author Alessia Zanni, currently at Maggiore Hospital, Bologna, Italy, and previously at Piacenza Hospital, said in an interview.
“The study suggests that the survival of patients with heart disease is affected not only by pharmacological therapies and advances in cardiology, but also by the air that they breathe,” she said.
The results were presented at European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure 2022.
More ED visits
The World Health Organization estimates around 7 million people die every year from exposure to polluted air, “as 91% of the world’s population lives in areas where air contaminants exceed safety levels,” Dr. Zanni said. Furthermore, “air pollution has been defined as the fourth-highest ranking risk factor for mortality – more important than LDL cholesterol, obesity, physical activity, or alcohol use.”
She noted that Piacenza has “historically been very attentive to the issues of early defibrillation and cardiac arrest.” Her group had previously found a correlation between out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and air pollution in the general population.
Moreover, her group recently observed that ED visits for patients with ICDs “tended to cluster; on some special days, many patients with ICDs had cardiac arrhythmias, and during those days, air pollution levels were particularly high.”
Her group therefore decided to compare the concentration of air pollutants on days when patients suffered from an arrhythmia event versus pollution levels on days without an arrhythmia, she said.
Further piece in a complex puzzle
The researchers studied 146 patients with ICDs between January 2013 and December 2017, assigning exposures (short, mid, and long term) to these patients based on their residential addresses.
They extracted day-by-day urban PM10, PM2.5, CO, NO2, and O3 levels from the Environmental Protection Agency monitoring stations and then, using time-stratified case-crossover analysis methodology, they calculated the association of ventricular arrhythmia onset with 0- to 7-day moving averages of the various air pollutants prior to the event.
Patients had received their ICD to control cardiac dysfunction brought on by previous myocardial infarction (n = 93), genetic or inflammatory conditions (n = 53), secondary prevention after a lethal arrhythmia (n = 67), and primary prevention (n = 79).
Of the 440 ventricular arrhythmias recorded, 322 were treated with antitachycardia pacing, while the remaining 118 were treated with direct current shock.
The researchers found a significant association between PM2.5 levels and ventricular arrhythmia treated with shock, corresponding to a 15% increased risk or every additional 10mg/m3 (P < .019).
They also found that, when PM2.5 concentrations were elevated by 1 mg/m3 for an entire week, compared with average levels, there was a 2.4% higher likelihood of ventricular arrhythmias, regardless of the temperature, and when PM10 was 1 mg/m3 above average for a week, there was a 2.1% increased risk for arrhythmias (odds ratio, 1,024; 95% confidence interval, 1,009-1,040] and OR, 1,021; 95% CI, 1,009-1,033, respectively), Dr. Zanni reported.
“Since the majority of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest causes still remain unclear, our data add a further piece to the complex puzzle of cardiac arrest triggers,” Dr. Zanni commented. “We think that particulate matter can cause acute inflammation of the heart muscle and potentially act as a trigger for lethal cardiac arrhythmias.
“As these toxic particles are emitted from power plants, industries, and cars, we think that cardiovascular research should highlight these new findings to promote green projects among the general population, clarifying the risks to the health of the human being, and we think strategies to prevent air pollutant exposure in high-risk patients [with previous cardiac disease] should be developed,” she added.
Further, “we advise patients at risk, during days with high PM2.5 (> 35 mg/m3) and PM10 (> 50 mg/m3) to use a mask of the N95 type outdoors, to reduce time spent outdoors – particularly in traffic – and to improve home air filtration,” Dr. Zanni said.
Entering the mainstream
In a comment, Joel Kaufman, MD, MPH, professor of internal medicine and environmental health, University of Washington, Seattle, said the study “adds to a fairly substantial literature already on this topic of short-term exposure to air pollution.”
The evidence that air pollutants “can be a trigger of worsening of cardiovascular disease is fairly consistent at this time, and although the effect sizes are small, they are consistent,” said Dr. Kaufman, who was the chair of the writing group for the American Heart Association’s 2020 policy statement, “Guidance to Reduce Cardiovascular Burden of Ambient Air Pollutants.”
“The research into this issue has become clearer during the past 10 years but still is not in the mainstream of most cardiologists’ awareness. They tend to focus more on controlling cholesterol and performing procedures, etc., but there are modifiable risk factors like air pollution that are increasingly recognized as being part of the picture,” said Dr. Kaufman, who was not involved with the current study.
Dr. Zanni added: “It is important that politics work hand in hand with the scientific community in order to win the battle against global warming, which will reduce the number of cardiovascular deaths – the leading cause of death worldwide – as well as environmental integrity.”
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Dr. Zanni and coauthors and Dr. Kaufman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ventricular arrhythmias more commonly occur on days when there are higher levels of air pollution, especially with fine particulate matter (PM), a new study suggests.
The investigators studied the relationship between air pollution and ventricular arrhythmias in Piacenza, Italy by examining 5-year data on patients who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD).
They found a significant association between PM2.5 levels and ventricular arrhythmias, especially those treated with direct current shock. Moreover, higher levels of PM2.5 and PM10 were associated with increased risk of all ventricular arrhythmias.
“These data confirm that environmental pollution is not only a climate emergency but also a public health problem,” lead author Alessia Zanni, currently at Maggiore Hospital, Bologna, Italy, and previously at Piacenza Hospital, said in an interview.
“The study suggests that the survival of patients with heart disease is affected not only by pharmacological therapies and advances in cardiology, but also by the air that they breathe,” she said.
The results were presented at European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure 2022.
More ED visits
The World Health Organization estimates around 7 million people die every year from exposure to polluted air, “as 91% of the world’s population lives in areas where air contaminants exceed safety levels,” Dr. Zanni said. Furthermore, “air pollution has been defined as the fourth-highest ranking risk factor for mortality – more important than LDL cholesterol, obesity, physical activity, or alcohol use.”
She noted that Piacenza has “historically been very attentive to the issues of early defibrillation and cardiac arrest.” Her group had previously found a correlation between out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and air pollution in the general population.
Moreover, her group recently observed that ED visits for patients with ICDs “tended to cluster; on some special days, many patients with ICDs had cardiac arrhythmias, and during those days, air pollution levels were particularly high.”
Her group therefore decided to compare the concentration of air pollutants on days when patients suffered from an arrhythmia event versus pollution levels on days without an arrhythmia, she said.
Further piece in a complex puzzle
The researchers studied 146 patients with ICDs between January 2013 and December 2017, assigning exposures (short, mid, and long term) to these patients based on their residential addresses.
They extracted day-by-day urban PM10, PM2.5, CO, NO2, and O3 levels from the Environmental Protection Agency monitoring stations and then, using time-stratified case-crossover analysis methodology, they calculated the association of ventricular arrhythmia onset with 0- to 7-day moving averages of the various air pollutants prior to the event.
Patients had received their ICD to control cardiac dysfunction brought on by previous myocardial infarction (n = 93), genetic or inflammatory conditions (n = 53), secondary prevention after a lethal arrhythmia (n = 67), and primary prevention (n = 79).
Of the 440 ventricular arrhythmias recorded, 322 were treated with antitachycardia pacing, while the remaining 118 were treated with direct current shock.
The researchers found a significant association between PM2.5 levels and ventricular arrhythmia treated with shock, corresponding to a 15% increased risk or every additional 10mg/m3 (P < .019).
They also found that, when PM2.5 concentrations were elevated by 1 mg/m3 for an entire week, compared with average levels, there was a 2.4% higher likelihood of ventricular arrhythmias, regardless of the temperature, and when PM10 was 1 mg/m3 above average for a week, there was a 2.1% increased risk for arrhythmias (odds ratio, 1,024; 95% confidence interval, 1,009-1,040] and OR, 1,021; 95% CI, 1,009-1,033, respectively), Dr. Zanni reported.
“Since the majority of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest causes still remain unclear, our data add a further piece to the complex puzzle of cardiac arrest triggers,” Dr. Zanni commented. “We think that particulate matter can cause acute inflammation of the heart muscle and potentially act as a trigger for lethal cardiac arrhythmias.
“As these toxic particles are emitted from power plants, industries, and cars, we think that cardiovascular research should highlight these new findings to promote green projects among the general population, clarifying the risks to the health of the human being, and we think strategies to prevent air pollutant exposure in high-risk patients [with previous cardiac disease] should be developed,” she added.
Further, “we advise patients at risk, during days with high PM2.5 (> 35 mg/m3) and PM10 (> 50 mg/m3) to use a mask of the N95 type outdoors, to reduce time spent outdoors – particularly in traffic – and to improve home air filtration,” Dr. Zanni said.
Entering the mainstream
In a comment, Joel Kaufman, MD, MPH, professor of internal medicine and environmental health, University of Washington, Seattle, said the study “adds to a fairly substantial literature already on this topic of short-term exposure to air pollution.”
The evidence that air pollutants “can be a trigger of worsening of cardiovascular disease is fairly consistent at this time, and although the effect sizes are small, they are consistent,” said Dr. Kaufman, who was the chair of the writing group for the American Heart Association’s 2020 policy statement, “Guidance to Reduce Cardiovascular Burden of Ambient Air Pollutants.”
“The research into this issue has become clearer during the past 10 years but still is not in the mainstream of most cardiologists’ awareness. They tend to focus more on controlling cholesterol and performing procedures, etc., but there are modifiable risk factors like air pollution that are increasingly recognized as being part of the picture,” said Dr. Kaufman, who was not involved with the current study.
Dr. Zanni added: “It is important that politics work hand in hand with the scientific community in order to win the battle against global warming, which will reduce the number of cardiovascular deaths – the leading cause of death worldwide – as well as environmental integrity.”
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Dr. Zanni and coauthors and Dr. Kaufman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ventricular arrhythmias more commonly occur on days when there are higher levels of air pollution, especially with fine particulate matter (PM), a new study suggests.
The investigators studied the relationship between air pollution and ventricular arrhythmias in Piacenza, Italy by examining 5-year data on patients who received an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD).
They found a significant association between PM2.5 levels and ventricular arrhythmias, especially those treated with direct current shock. Moreover, higher levels of PM2.5 and PM10 were associated with increased risk of all ventricular arrhythmias.
“These data confirm that environmental pollution is not only a climate emergency but also a public health problem,” lead author Alessia Zanni, currently at Maggiore Hospital, Bologna, Italy, and previously at Piacenza Hospital, said in an interview.
“The study suggests that the survival of patients with heart disease is affected not only by pharmacological therapies and advances in cardiology, but also by the air that they breathe,” she said.
The results were presented at European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure 2022.
More ED visits
The World Health Organization estimates around 7 million people die every year from exposure to polluted air, “as 91% of the world’s population lives in areas where air contaminants exceed safety levels,” Dr. Zanni said. Furthermore, “air pollution has been defined as the fourth-highest ranking risk factor for mortality – more important than LDL cholesterol, obesity, physical activity, or alcohol use.”
She noted that Piacenza has “historically been very attentive to the issues of early defibrillation and cardiac arrest.” Her group had previously found a correlation between out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and air pollution in the general population.
Moreover, her group recently observed that ED visits for patients with ICDs “tended to cluster; on some special days, many patients with ICDs had cardiac arrhythmias, and during those days, air pollution levels were particularly high.”
Her group therefore decided to compare the concentration of air pollutants on days when patients suffered from an arrhythmia event versus pollution levels on days without an arrhythmia, she said.
Further piece in a complex puzzle
The researchers studied 146 patients with ICDs between January 2013 and December 2017, assigning exposures (short, mid, and long term) to these patients based on their residential addresses.
They extracted day-by-day urban PM10, PM2.5, CO, NO2, and O3 levels from the Environmental Protection Agency monitoring stations and then, using time-stratified case-crossover analysis methodology, they calculated the association of ventricular arrhythmia onset with 0- to 7-day moving averages of the various air pollutants prior to the event.
Patients had received their ICD to control cardiac dysfunction brought on by previous myocardial infarction (n = 93), genetic or inflammatory conditions (n = 53), secondary prevention after a lethal arrhythmia (n = 67), and primary prevention (n = 79).
Of the 440 ventricular arrhythmias recorded, 322 were treated with antitachycardia pacing, while the remaining 118 were treated with direct current shock.
The researchers found a significant association between PM2.5 levels and ventricular arrhythmia treated with shock, corresponding to a 15% increased risk or every additional 10mg/m3 (P < .019).
They also found that, when PM2.5 concentrations were elevated by 1 mg/m3 for an entire week, compared with average levels, there was a 2.4% higher likelihood of ventricular arrhythmias, regardless of the temperature, and when PM10 was 1 mg/m3 above average for a week, there was a 2.1% increased risk for arrhythmias (odds ratio, 1,024; 95% confidence interval, 1,009-1,040] and OR, 1,021; 95% CI, 1,009-1,033, respectively), Dr. Zanni reported.
“Since the majority of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest causes still remain unclear, our data add a further piece to the complex puzzle of cardiac arrest triggers,” Dr. Zanni commented. “We think that particulate matter can cause acute inflammation of the heart muscle and potentially act as a trigger for lethal cardiac arrhythmias.
“As these toxic particles are emitted from power plants, industries, and cars, we think that cardiovascular research should highlight these new findings to promote green projects among the general population, clarifying the risks to the health of the human being, and we think strategies to prevent air pollutant exposure in high-risk patients [with previous cardiac disease] should be developed,” she added.
Further, “we advise patients at risk, during days with high PM2.5 (> 35 mg/m3) and PM10 (> 50 mg/m3) to use a mask of the N95 type outdoors, to reduce time spent outdoors – particularly in traffic – and to improve home air filtration,” Dr. Zanni said.
Entering the mainstream
In a comment, Joel Kaufman, MD, MPH, professor of internal medicine and environmental health, University of Washington, Seattle, said the study “adds to a fairly substantial literature already on this topic of short-term exposure to air pollution.”
The evidence that air pollutants “can be a trigger of worsening of cardiovascular disease is fairly consistent at this time, and although the effect sizes are small, they are consistent,” said Dr. Kaufman, who was the chair of the writing group for the American Heart Association’s 2020 policy statement, “Guidance to Reduce Cardiovascular Burden of Ambient Air Pollutants.”
“The research into this issue has become clearer during the past 10 years but still is not in the mainstream of most cardiologists’ awareness. They tend to focus more on controlling cholesterol and performing procedures, etc., but there are modifiable risk factors like air pollution that are increasingly recognized as being part of the picture,” said Dr. Kaufman, who was not involved with the current study.
Dr. Zanni added: “It is important that politics work hand in hand with the scientific community in order to win the battle against global warming, which will reduce the number of cardiovascular deaths – the leading cause of death worldwide – as well as environmental integrity.”
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Dr. Zanni and coauthors and Dr. Kaufman reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC HEART FAILURE 2022
Youth with bipolar disorder at high risk of eating disorders
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.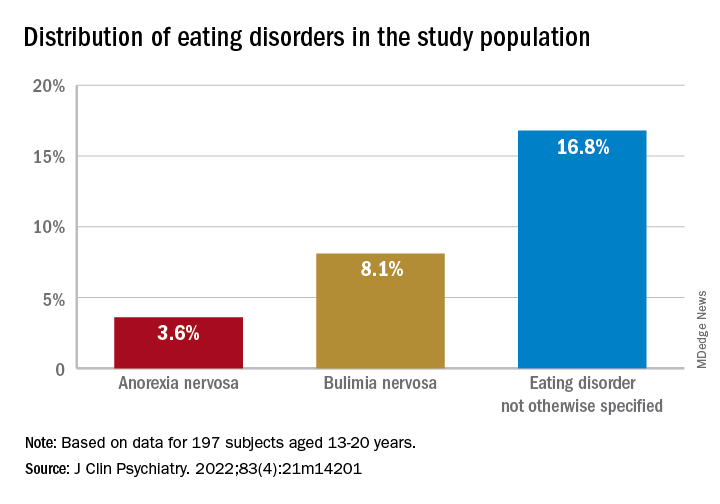
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.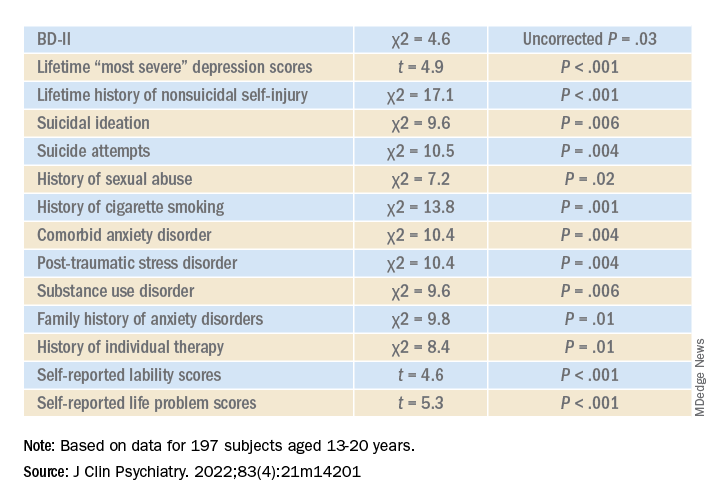
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”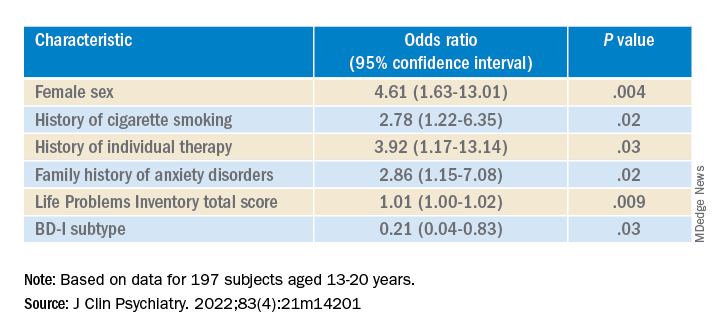
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators studied close to 200 youth with BD and found that more than 25% had a lifetime ED, which included anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and an ED not otherwise specified (NOS).
Those with comorbid EDs were more likely to be female and to have BD-II subtype. Their presentations were also more complicated and included a history of suicidality, additional psychiatric conditions, smoking, and a history of sexual abuse, as well as more severe depression and emotional instability.
“We think the take-home message is that, in addition to other more recognized psychiatric comorbidities, youth with BD are also vulnerable to developing EDs. Thus, clinicians should be routinely monitoring for eating, appetite, and body image disturbances when working with this population,” lead author Diana Khoubaeva, research analyst at the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, and senior author Benjamin Goldstein, MD, PhD, director of the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder, wrote in an e-mail to this news organization.
“Given the more complicated clinical picture of youth with co-occurring BD and EDs, this combination warrants careful attention,” the investigators note.
The study was published online May 11 in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Lack of research
“From the existing literature, we learned that EDs are not uncommon in individuals with BD, and that they are often associated with a more severe clinical profile,” say the researchers. “However, the majority of these studies have been limited to adult samples, and there was a real scarcity of studies that examined this co-occurrence in youth.”
This is “surprising” because EDs often have their onset in adolescence, so the researchers decided to explore the issue in their “fairly large sample of youth with BD.”
To investigate the issue, the researchers studied 197 youth (aged 13-20 years) with a diagnosis of BD (BD-I, BD-II, or BD-NOS) who were recruited between 2009 and 2017 (mean [standard deviation] age, 16.69 [1.50] years; 67.5% female).
ED diagnoses included both current and lifetime AN, BN, and ED-NOS. The researchers used the Kiddie Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia for School Age Children, Present and Lifetime Version (K-SADS-PL) to determine the diagnosis of BD.
They also collected information about comorbid psychiatric disorders, as well as substance use disorders and cigarette smoking. The Life Problems Inventory (LPI) was used to identify dimensional borderline personality traits.
Information about physical and sexual abuse, suicidal ideation, nonsuicidal self-injury (NSSI), and affect regulation were obtained from other measurement tools. Participants’ height and weight were measured to calculate body mass index.
Neurobiological and environmental factors
Of the total sample, 24.84% had received a diagnosis of ED in their lifetime.
Moreover, 28.9% had a lifetime history of binge eating. Of these, 17.7% also had been diagnosed with an ED.
Participants with BD-II were significantly more likely than those with BD-I to report both current and lifetime BN. There were no significant differences by BD subtype in AN, ED-NOS, or binge eating.
Higher correlates of clinical characteristics, psychiatric morbidity, treatment history, and dimensional traits in those with vs. those without an ED are detailed in the accompanying table.
The ED group scored significantly higher on all LPI scores, including impulsivity, emotional dysregulation, identity confusion, and interpersonal problems, compared to those without an ED. They also were less likely to report lifetime lithium use (chi2 = 7.9, P = .01).
Multivariate analysis revealed that lifetime EDs were significantly associated with female sex, history of cigarette smoking, history of individual therapy, family history of anxiety, and LPI total score and were negatively associated with BD-I subtype.
“The comorbidity [between EDs and BD] could be driven by both neurobiological and environmental factors,” Dr. Khoubaeva and Dr. Goldstein noted. EDs and BD “are both illnesses that are fundamentally linked with dysfunction in reward systems – that is, there are imbalances in terms of too much or too little reward seeking.”
They added that individuals affected by these conditions have “ongoing challenges with instability of emotions and ability to manage emotions; and eating too much or too little can be a manifestation of coping with emotions.”
In addition, medications commonly used to treat BD “are known to have side effects such as weight/appetite/metabolic changes, which may make it harder to regulate eating, and which may exacerbate preexisting body image challenges.”
The researchers recommend implementing trauma-informed care, assessing and addressing suicidality and self-injury, and prioritizing therapies that target emotional dysregulation, such as dialectical behavioral therapy.
‘Clarion call’
Commenting on the study, Roger McIntyre, MD, professor of psychiatry and pharmacology, University of Toronto, and head of the Mood Disorders Psychopharmacology Unit, said the study is “the first of its kind to comprehensively characterize the prevalence of ED in youth living with BD.
“It could be hypothesized that EDs have overlapping domain disturbances of cognitive dysfunction, such as executive function and impulse control, as well as cognitive reward processes,” said Dr. McIntyre, who is the chairman and executive director of the Brain and Cognitive Discover Foundation, Toronto, and was not involved with the study.
“The data are a clarion call for clinicians to routinely screen for EDs in youth with BD and, when present, to be aware of the greater complexity, severity, and risk in this patient subpopulation. The higher prevalence of ED in youth with BD-II is an additional reminder of the severity, morbidity, and complexity of BD-II,” Dr. McIntyre said.
The study received no direct funding. It was supported by philanthropic donations to the Centre for Youth Bipolar Disorder and the CAMH Discovery Fund. Dr. Goldstein reports grant support from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, National Institute of Mental Health, and the departments of psychiatry at the University of Toronto and Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre. He also acknowledges his position as RBC investments chair in Children›s Mental Health and Developmental Psychopathology at CAMH, a joint Hospital-University chair among the University of Toronto, CAMH, and the CAMH Foundation. Ms. Khoubaeva reports no relevant financial relationships. The other authors’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. McIntyre has received research grant support from CIHR/GACD/National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC); speaker/consultation fees from Lundbeck, Janssen, Alkermes, Neumora Therapeutics, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Purdue, Pfizer, Otsuka, Takeda, Neurocrine, Sunovion, Bausch Health, Axsome, Novo Nordisk, Kris, Sanofi, Eisai, Intra-Cellular, NewBridge Pharmaceuticals, Abbvie, and Atai Life Sciences. Dr. McIntyre is a CEO of Braxia Scientific.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Antipsychotic tied to dose-related weight gain, higher cholesterol
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.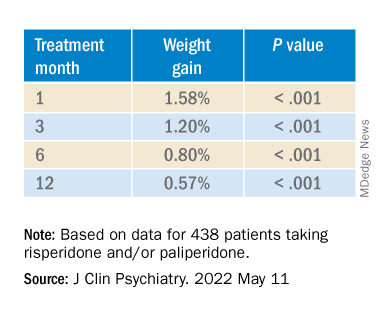
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.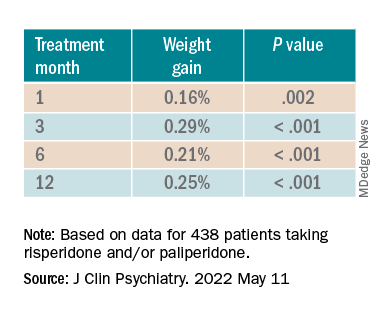
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.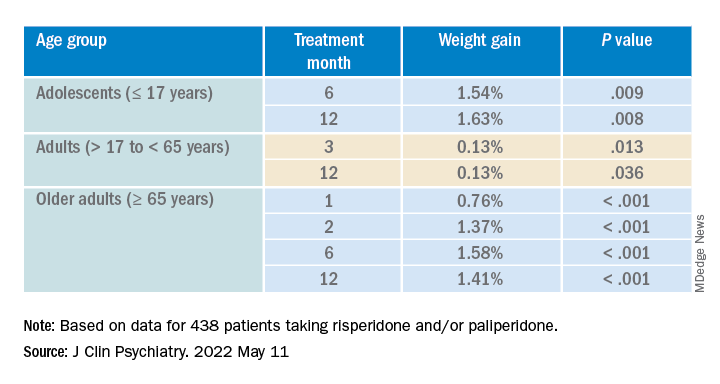
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research suggests.
Investigators analyzed 1-year data for more than 400 patients who were taking risperidone and/or its metabolite paliperidone (Invega). Results showed increments of 1 mg of risperidone-equivalent doses were associated with an increase of 0.25% of weight within a year of follow-up.
“Although our findings report a positive and statistically significant dose-dependence of weight gain and cholesterol, both total and LDL [cholesterol], the size of the predicted changes of metabolic effects is clinically nonrelevant,” lead author Marianna Piras, PharmD, Centre for Psychiatric Neuroscience, Lausanne (Switzerland) University Hospital, said in an interview.
“Therefore, dose lowering would not have a beneficial effect on attenuating weight gain or cholesterol increases and could lead to psychiatric decompensation,” said Ms. Piras, who is also a PhD candidate in the unit of pharmacogenetics and clinical psychopharmacology at the University of Lausanne.
However, she added that because dose increments could increase risk for significant weight gain in the first month of treatment – the dose can be increased typically in a range of 1-10 grams – and strong dose increments could contribute to metabolic worsening over time, “risperidone minimum effective doses should be preferred.”
The findings were published online in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
‘Serious public health issue’
Compared with the general population, patients with mental illness present with a greater prevalence of metabolic disorders. In addition, several psychotropic medications, including antipsychotics, can induce metabolic alterations such as weight gain, the investigators noted.
Antipsychotic-induced metabolic adverse effects “constitute a serious public health issue” because they are risk factors for cardiovascular diseases such as obesity and/or dyslipidemia, “which have been associated with a 10-year reduced life expectancy in the psychiatric population,” Ms. Piras said.
“The dose-dependence of metabolic adverse effects is a debated subject that needs to be assessed for each psychotropic drug known to induce weight gain,” she added.
Several previous studies have examined whether there is a dose-related effect of antipsychotics on metabolic parameters, “with some results suggesting that [weight gain] seems to develop even when low off-label doses are prescribed,” Ms. Piras noted.
She and her colleagues had already studied dose-related metabolic effects of quetiapine (Seroquel) and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
Risperidone is an antipsychotic with a “medium to high metabolic risk profile,” the researchers note, and few studies have examined the impact of risperidone on metabolic parameters other than weight gain.
For the current analysis, they analyzed data from a longitudinal study that included 438 patients (mean age, 40.7 years; 50.7% men) who started treatment with risperidone and/or paliperidone between 2007 and 2018.
The participants had diagnoses of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, depression, “other,” or “unknown.”
Clinical follow-up periods were up to a year, but were no shorter than 3 weeks. The investigators also assessed the data at different time intervals at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months “to appreciate the evolution of the metabolic parameters.”
In addition, they collected demographic and clinical information, such as comorbidities, and measured patients’ weight, height, waist circumference, blood pressure, plasma glucose, and lipids at baseline and at 1, 3, and 12 months and then annually. Weight, waist circumference, and BP were also assessed at 2 and 6 months.
Doses of paliperidone were converted into risperidone-equivalent doses.
Significant weight gain over time
The mean duration of follow-up for the participants, of whom 374 were being treated with risperidone and 64 with paliperidone, was 153 days. Close to half (48.2%) were taking other psychotropic medications known to be associated with some degree of metabolic risk.
Patients were divided into two cohorts based on their daily dose intake (DDI): less than 3 mg/day (n = 201) and at least 3 mg/day (n = 237).
In the overall cohort, a “significant effect of time on weight change was found for each time point,” the investigators reported.
When the researchers looked at the changes according to DDI, they found that each 1-mg dose increase was associated with incremental weight gain at each time point.
Patients who had 5% or greater weight gain in the first month continued to gain weight more than patients who did not reach that threshold, leading the researchers to call that early threshold a “strong predictor of important weight gain in the long term.” There was a weight gain of 6.68% at 3 months, of 7.36% at 6 months, and of 7.7% at 12 months.
After the patients were stratified by age, there were differences in the effect of DDI on various age groups at different time points.
Dose was shown to have a significant effect on weight gain for women at all four time points (P ≥ .001), but for men only at 3 months (P = .003).
For each additional 1-mg dose, there was a 0.05 mmol/L (1.93 mg/dL) increase in total cholesterol (P = .018) after 1 year and a 0.04 mmol/L (1.54 mg/dL) increase in LDL cholesterol (P = .011).
There were no significant effects of time or DDI on triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, glucose levels, and systolic BP, and there was a negative effect of DDI on diastolic BP (P = .001).
The findings “provide evidence for a small dose effect of risperidone” on weight gain and total and LDL cholesterol levels, the investigators note.
Ms. Piras added that because each antipsychotic differs in its metabolic risk profile, “further analyses on other antipsychotics are ongoing in our laboratory, so far confirming our findings.”
Small increases, big changes
Commenting on the study, Erika Nurmi, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences at the Semel Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, Los Angeles, said the study is “unique in the field.”
It “leverages real-world data from a large patient registry to ask a long-unanswered question: Are weight and metabolic adverse effects proportional to dose? Big data approaches like these are very powerful, given the large number of participants that can be included,” said Dr. Nurmi, who was not involved with the research.
However, she cautioned, the “biggest drawback [is that] these data are by nature much more complex and prone to confounding effects.”
In this case, a “critical confounder” for the study was that the majority of individuals taking higher risperidone doses were also taking other drugs known to cause weight gain, whereas the majority of those on lower risperidone doses were not. “This difference may explain the dose relationship observed,” she said.
Because real-world, big data are “valuable but also messy, conclusions drawn from them must be interpreted with caution,” Dr. Nurmi said.
She added that it is generally wise to use the lowest effective dose possible.
“Clinicians should appreciate that even small doses of antipsychotics can cause big changes in weight. Risks and benefits of medications must be carefully considered in clinical practice,” Dr. Nurmi said.
The research was funded in part by the Swiss National Research Foundation. Piras reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Nurmi reported no relevant financial relationships, but she is an unpaid member of the Tourette Association of America’s medical advisory board and of the Myriad Genetics scientific advisory board.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
Hearing, vision loss combo a colossal risk for cognitive decline
The combination of hearing loss and vision loss is linked to an eightfold increased risk of cognitive impairment, new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data on more than 5 million U.S. seniors. Adjusted results show that participants with hearing impairment alone had more than twice the odds of also having cognitive impairment, while those with vision impairment alone had more than triple the odds of cognitive impairment.
However, those with dual sensory impairment (DSI) had an eightfold higher risk for cognitive impairment.
In addition, half of the participants with DSI also had cognitive impairment. Of those with cognitive impairment, 16% had DSI, compared with only about 2% of their peers without cognitive impairment.
“The findings of the present study may inform interventions that can support older people with concurrent sensory impairment and cognitive impairment,” said lead author Esme Fuller-Thomson, PhD, professor, Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work, University of Toronto.
“Special attention, in particular, should be given to those aged 65-74 who have serious hearing and/or vision impairment [because], if the relationship with dementia is found to be causal, such interventions can potentially mitigate the development of cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fuller-Thomson, who is also director of the Institute for Life Course and Aging and a professor in the department of family and community medicine and faculty of nursing, all at the University of Toronto.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Sensory isolation
Hearing and vision impairment increase with age; it is estimated that one-third of U.S. adults between the ages of 65 and 74 experience hearing loss, and 4% experience vision impairment, the investigators note.
“The link between dual hearing loss and seeing loss and mental health problems such as depression and social isolation have been well researched, but we were very interested in the link between dual sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Additionally, “there have been several studies in the past decade linking hearing loss to dementia and cognitive decline, but less attention has been paid to cognitive problems among those with DSI, despite this group being particularly isolated,” she said. Existing research into DSI suggests an association with cognitive decline; the current investigators sought to expand on this previous work.
To do so, they used merged data from 10 consecutive waves from 2008 to 2017 of the American Community Survey (ACS), which was conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. The ACS is a nationally representative sample of 3.5 million randomly selected U.S. addresses and includes community-dwelling adults and those residing in institutional settings.
Participants aged 65 or older (n = 5,405,135; 56.4% women) were asked yes/no questions regarding serious cognitive impairment, hearing impairment, and vision impairment. A proxy, such as a family member or nursing home staff member, provided answers for individuals not capable of self-report.
Potential confounding variables included age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, and household income.
Potential mechanisms
Results showed that, among those with cognitive impairment, there was a higher prevalence of hearing impairment, vision impairment, and DSI than among their peers without cognitive impairment; in addition, a lower percentage of these persons had no sensory impairment (P < .001).
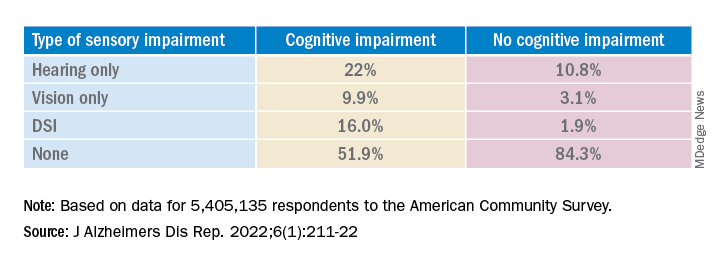
The prevalence of DSI climbed with age, from 1.5% for respondents aged 65-74 years to 2.6% for those aged 75-84 and to 10.8% in those 85 years and older.
Individuals with higher levels of poverty also had higher levels of DSI. Among those who had not completed high school, the prevalence of DSI was higher, compared with high school or university graduates (6.3% vs. 3.1% and 1.85, respectively).
After controlling for age, race, education, and income, the researchers found “substantially” higher odds of cognitive impairment in those with vs. those without sensory impairments.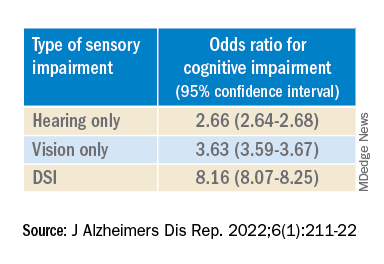
“The magnitude of the odds of cognitive impairment by sensory impairment was greatest for the youngest cohort (age 65-74) and lowest for the oldest cohort (age 85+),” the investigators wrote. Among participants in the youngest cohort, there was a “dose-response relationship” for those with hearing impairment only, visual impairment only, and DSI.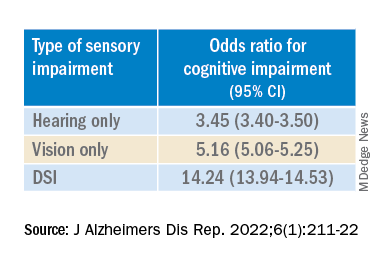
Because the study was observational, it “does not provide sufficient information to determine the reasons behind the observed link between sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said. However, there are “several potential causal mechanisms [that] warrant future research.”
The “sensory deprivation hypothesis” suggests that DSI could cause cognitive deterioration because of decreased auditory and visual input. The “resource allocation hypothesis” posits that hearing- or vision-impaired older adults “may use more cognitive resources to accommodate for sensory deficits, allocating fewer cognitive resources for higher-order memory processes,” the researchers wrote. Hearing impairment “may also lead to social disengagement among older adults, hastening cognitive decline due to isolation and lack of stimulation,” they added.
Reverse causality is also possible. In the “cognitive load on perception” hypothesis, cognitive decline may lead to declines in hearing and vision because of “decreased resources for sensory processing.”
In addition, the association may be noncausal. “The ‘common cause hypothesis’ theorizes that sensory impairment and cognitive impairment may be due to shared age-related degeneration of the central nervous system ... or frailty,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Parallel findings
The results are similar to those from a study conducted by Phillip Hwang, PhD, of the department of anatomy and neurobiology, Boston University, and colleagues that was published online in JAMA Network Open.
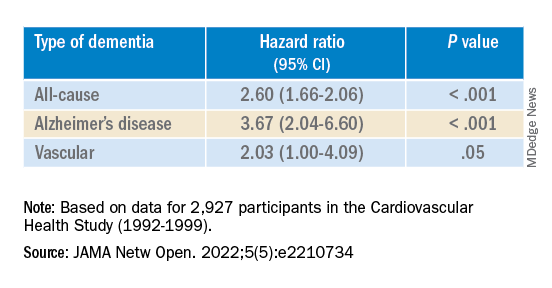
They analyzed data on 8 years of follow-up of 2,927 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study (mean age, 74.6 years; 58.2% women).
Compared with no sensory impairment, DSI was associated with increased risk for all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, but not with vascular dementia.
“Future work in health care guidelines could consider incorporating screening of sensory impairment in older adults as part of risk assessment for dementia,” Nicholas Reed, AuD, and Esther Oh, MD, PhD, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Accurate testing
Commenting on both studies, Heather Whitson, MD, professor of medicine (geriatrics) and ophthalmology and director at the Duke University Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development, Durham, N.C., said both “add further strength to the evidence base, which has really converged in the last few years to support that there is a link between sensory health and cognitive health.”
However, “we still don’t know whether hearing/vision loss causes cognitive decline, though there are plausible ways that sensory loss could affect cognitive abilities like memory, language, and executive function,” she said
Dr. Whitson, who was not involved with the research, is also codirector of the Duke/University of North Carolina Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and the Durham VA Medical Center.
“The big question is whether we can improve patients’ cognitive performance by treating or accommodating their sensory impairments,” she said. “If safe and feasible things like hearing aids or cataract surgery improve cognitive health, even a little bit, it would be a huge benefit to society, because sensory loss is very common, and there are many treatment options,” Dr. Whitson added.
Dr. Fuller-Thomson emphasized that practitioners should “consider the full impact of sensory impairment on cognitive testing methods, as both auditory and visual testing methods may fail to take hearing and vision impairment into account.”
Thus, “when performing cognitive tests on older adults with sensory impairments, practitioners should ensure they are communicating audibly and/or using visual speech cues for hearing-impaired individuals, eliminating items from cognitive tests that rely on vision for those who are visually impaired, and using physical cues for individuals with hearing or dual sensory impairment, as this can help increase the accuracy of testing and prevent confounding,” she said.
The study by Fuller-Thomson et al. was funded by a donation from Janis Rotman. Its investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. The study by Hwang et al. was funded by contracts from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Hwang reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Reed received grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and has served on the advisory board of Neosensory outside the submitted work. Dr. Oh and Dr. Whitson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of hearing loss and vision loss is linked to an eightfold increased risk of cognitive impairment, new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data on more than 5 million U.S. seniors. Adjusted results show that participants with hearing impairment alone had more than twice the odds of also having cognitive impairment, while those with vision impairment alone had more than triple the odds of cognitive impairment.
However, those with dual sensory impairment (DSI) had an eightfold higher risk for cognitive impairment.
In addition, half of the participants with DSI also had cognitive impairment. Of those with cognitive impairment, 16% had DSI, compared with only about 2% of their peers without cognitive impairment.
“The findings of the present study may inform interventions that can support older people with concurrent sensory impairment and cognitive impairment,” said lead author Esme Fuller-Thomson, PhD, professor, Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work, University of Toronto.
“Special attention, in particular, should be given to those aged 65-74 who have serious hearing and/or vision impairment [because], if the relationship with dementia is found to be causal, such interventions can potentially mitigate the development of cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fuller-Thomson, who is also director of the Institute for Life Course and Aging and a professor in the department of family and community medicine and faculty of nursing, all at the University of Toronto.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Sensory isolation
Hearing and vision impairment increase with age; it is estimated that one-third of U.S. adults between the ages of 65 and 74 experience hearing loss, and 4% experience vision impairment, the investigators note.
“The link between dual hearing loss and seeing loss and mental health problems such as depression and social isolation have been well researched, but we were very interested in the link between dual sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Additionally, “there have been several studies in the past decade linking hearing loss to dementia and cognitive decline, but less attention has been paid to cognitive problems among those with DSI, despite this group being particularly isolated,” she said. Existing research into DSI suggests an association with cognitive decline; the current investigators sought to expand on this previous work.
To do so, they used merged data from 10 consecutive waves from 2008 to 2017 of the American Community Survey (ACS), which was conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. The ACS is a nationally representative sample of 3.5 million randomly selected U.S. addresses and includes community-dwelling adults and those residing in institutional settings.
Participants aged 65 or older (n = 5,405,135; 56.4% women) were asked yes/no questions regarding serious cognitive impairment, hearing impairment, and vision impairment. A proxy, such as a family member or nursing home staff member, provided answers for individuals not capable of self-report.
Potential confounding variables included age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, and household income.
Potential mechanisms
Results showed that, among those with cognitive impairment, there was a higher prevalence of hearing impairment, vision impairment, and DSI than among their peers without cognitive impairment; in addition, a lower percentage of these persons had no sensory impairment (P < .001).

The prevalence of DSI climbed with age, from 1.5% for respondents aged 65-74 years to 2.6% for those aged 75-84 and to 10.8% in those 85 years and older.
Individuals with higher levels of poverty also had higher levels of DSI. Among those who had not completed high school, the prevalence of DSI was higher, compared with high school or university graduates (6.3% vs. 3.1% and 1.85, respectively).
After controlling for age, race, education, and income, the researchers found “substantially” higher odds of cognitive impairment in those with vs. those without sensory impairments.
“The magnitude of the odds of cognitive impairment by sensory impairment was greatest for the youngest cohort (age 65-74) and lowest for the oldest cohort (age 85+),” the investigators wrote. Among participants in the youngest cohort, there was a “dose-response relationship” for those with hearing impairment only, visual impairment only, and DSI.
Because the study was observational, it “does not provide sufficient information to determine the reasons behind the observed link between sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said. However, there are “several potential causal mechanisms [that] warrant future research.”
The “sensory deprivation hypothesis” suggests that DSI could cause cognitive deterioration because of decreased auditory and visual input. The “resource allocation hypothesis” posits that hearing- or vision-impaired older adults “may use more cognitive resources to accommodate for sensory deficits, allocating fewer cognitive resources for higher-order memory processes,” the researchers wrote. Hearing impairment “may also lead to social disengagement among older adults, hastening cognitive decline due to isolation and lack of stimulation,” they added.
Reverse causality is also possible. In the “cognitive load on perception” hypothesis, cognitive decline may lead to declines in hearing and vision because of “decreased resources for sensory processing.”
In addition, the association may be noncausal. “The ‘common cause hypothesis’ theorizes that sensory impairment and cognitive impairment may be due to shared age-related degeneration of the central nervous system ... or frailty,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Parallel findings
The results are similar to those from a study conducted by Phillip Hwang, PhD, of the department of anatomy and neurobiology, Boston University, and colleagues that was published online in JAMA Network Open.

They analyzed data on 8 years of follow-up of 2,927 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study (mean age, 74.6 years; 58.2% women).
Compared with no sensory impairment, DSI was associated with increased risk for all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, but not with vascular dementia.
“Future work in health care guidelines could consider incorporating screening of sensory impairment in older adults as part of risk assessment for dementia,” Nicholas Reed, AuD, and Esther Oh, MD, PhD, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Accurate testing
Commenting on both studies, Heather Whitson, MD, professor of medicine (geriatrics) and ophthalmology and director at the Duke University Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development, Durham, N.C., said both “add further strength to the evidence base, which has really converged in the last few years to support that there is a link between sensory health and cognitive health.”
However, “we still don’t know whether hearing/vision loss causes cognitive decline, though there are plausible ways that sensory loss could affect cognitive abilities like memory, language, and executive function,” she said
Dr. Whitson, who was not involved with the research, is also codirector of the Duke/University of North Carolina Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and the Durham VA Medical Center.
“The big question is whether we can improve patients’ cognitive performance by treating or accommodating their sensory impairments,” she said. “If safe and feasible things like hearing aids or cataract surgery improve cognitive health, even a little bit, it would be a huge benefit to society, because sensory loss is very common, and there are many treatment options,” Dr. Whitson added.
Dr. Fuller-Thomson emphasized that practitioners should “consider the full impact of sensory impairment on cognitive testing methods, as both auditory and visual testing methods may fail to take hearing and vision impairment into account.”
Thus, “when performing cognitive tests on older adults with sensory impairments, practitioners should ensure they are communicating audibly and/or using visual speech cues for hearing-impaired individuals, eliminating items from cognitive tests that rely on vision for those who are visually impaired, and using physical cues for individuals with hearing or dual sensory impairment, as this can help increase the accuracy of testing and prevent confounding,” she said.
The study by Fuller-Thomson et al. was funded by a donation from Janis Rotman. Its investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. The study by Hwang et al. was funded by contracts from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Hwang reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Reed received grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and has served on the advisory board of Neosensory outside the submitted work. Dr. Oh and Dr. Whitson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The combination of hearing loss and vision loss is linked to an eightfold increased risk of cognitive impairment, new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data on more than 5 million U.S. seniors. Adjusted results show that participants with hearing impairment alone had more than twice the odds of also having cognitive impairment, while those with vision impairment alone had more than triple the odds of cognitive impairment.
However, those with dual sensory impairment (DSI) had an eightfold higher risk for cognitive impairment.
In addition, half of the participants with DSI also had cognitive impairment. Of those with cognitive impairment, 16% had DSI, compared with only about 2% of their peers without cognitive impairment.
“The findings of the present study may inform interventions that can support older people with concurrent sensory impairment and cognitive impairment,” said lead author Esme Fuller-Thomson, PhD, professor, Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work, University of Toronto.
“Special attention, in particular, should be given to those aged 65-74 who have serious hearing and/or vision impairment [because], if the relationship with dementia is found to be causal, such interventions can potentially mitigate the development of cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Fuller-Thomson, who is also director of the Institute for Life Course and Aging and a professor in the department of family and community medicine and faculty of nursing, all at the University of Toronto.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease Reports.
Sensory isolation
Hearing and vision impairment increase with age; it is estimated that one-third of U.S. adults between the ages of 65 and 74 experience hearing loss, and 4% experience vision impairment, the investigators note.
“The link between dual hearing loss and seeing loss and mental health problems such as depression and social isolation have been well researched, but we were very interested in the link between dual sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Additionally, “there have been several studies in the past decade linking hearing loss to dementia and cognitive decline, but less attention has been paid to cognitive problems among those with DSI, despite this group being particularly isolated,” she said. Existing research into DSI suggests an association with cognitive decline; the current investigators sought to expand on this previous work.
To do so, they used merged data from 10 consecutive waves from 2008 to 2017 of the American Community Survey (ACS), which was conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. The ACS is a nationally representative sample of 3.5 million randomly selected U.S. addresses and includes community-dwelling adults and those residing in institutional settings.
Participants aged 65 or older (n = 5,405,135; 56.4% women) were asked yes/no questions regarding serious cognitive impairment, hearing impairment, and vision impairment. A proxy, such as a family member or nursing home staff member, provided answers for individuals not capable of self-report.
Potential confounding variables included age, race/ethnicity, sex, education, and household income.
Potential mechanisms
Results showed that, among those with cognitive impairment, there was a higher prevalence of hearing impairment, vision impairment, and DSI than among their peers without cognitive impairment; in addition, a lower percentage of these persons had no sensory impairment (P < .001).

The prevalence of DSI climbed with age, from 1.5% for respondents aged 65-74 years to 2.6% for those aged 75-84 and to 10.8% in those 85 years and older.
Individuals with higher levels of poverty also had higher levels of DSI. Among those who had not completed high school, the prevalence of DSI was higher, compared with high school or university graduates (6.3% vs. 3.1% and 1.85, respectively).
After controlling for age, race, education, and income, the researchers found “substantially” higher odds of cognitive impairment in those with vs. those without sensory impairments.
“The magnitude of the odds of cognitive impairment by sensory impairment was greatest for the youngest cohort (age 65-74) and lowest for the oldest cohort (age 85+),” the investigators wrote. Among participants in the youngest cohort, there was a “dose-response relationship” for those with hearing impairment only, visual impairment only, and DSI.
Because the study was observational, it “does not provide sufficient information to determine the reasons behind the observed link between sensory loss and cognitive problems,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said. However, there are “several potential causal mechanisms [that] warrant future research.”
The “sensory deprivation hypothesis” suggests that DSI could cause cognitive deterioration because of decreased auditory and visual input. The “resource allocation hypothesis” posits that hearing- or vision-impaired older adults “may use more cognitive resources to accommodate for sensory deficits, allocating fewer cognitive resources for higher-order memory processes,” the researchers wrote. Hearing impairment “may also lead to social disengagement among older adults, hastening cognitive decline due to isolation and lack of stimulation,” they added.
Reverse causality is also possible. In the “cognitive load on perception” hypothesis, cognitive decline may lead to declines in hearing and vision because of “decreased resources for sensory processing.”
In addition, the association may be noncausal. “The ‘common cause hypothesis’ theorizes that sensory impairment and cognitive impairment may be due to shared age-related degeneration of the central nervous system ... or frailty,” Dr. Fuller-Thomson said.
Parallel findings
The results are similar to those from a study conducted by Phillip Hwang, PhD, of the department of anatomy and neurobiology, Boston University, and colleagues that was published online in JAMA Network Open.

They analyzed data on 8 years of follow-up of 2,927 participants in the Cardiovascular Health Study (mean age, 74.6 years; 58.2% women).
Compared with no sensory impairment, DSI was associated with increased risk for all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, but not with vascular dementia.
“Future work in health care guidelines could consider incorporating screening of sensory impairment in older adults as part of risk assessment for dementia,” Nicholas Reed, AuD, and Esther Oh, MD, PhD, both of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Accurate testing
Commenting on both studies, Heather Whitson, MD, professor of medicine (geriatrics) and ophthalmology and director at the Duke University Center for the Study of Aging and Human Development, Durham, N.C., said both “add further strength to the evidence base, which has really converged in the last few years to support that there is a link between sensory health and cognitive health.”
However, “we still don’t know whether hearing/vision loss causes cognitive decline, though there are plausible ways that sensory loss could affect cognitive abilities like memory, language, and executive function,” she said
Dr. Whitson, who was not involved with the research, is also codirector of the Duke/University of North Carolina Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and the Durham VA Medical Center.
“The big question is whether we can improve patients’ cognitive performance by treating or accommodating their sensory impairments,” she said. “If safe and feasible things like hearing aids or cataract surgery improve cognitive health, even a little bit, it would be a huge benefit to society, because sensory loss is very common, and there are many treatment options,” Dr. Whitson added.
Dr. Fuller-Thomson emphasized that practitioners should “consider the full impact of sensory impairment on cognitive testing methods, as both auditory and visual testing methods may fail to take hearing and vision impairment into account.”
Thus, “when performing cognitive tests on older adults with sensory impairments, practitioners should ensure they are communicating audibly and/or using visual speech cues for hearing-impaired individuals, eliminating items from cognitive tests that rely on vision for those who are visually impaired, and using physical cues for individuals with hearing or dual sensory impairment, as this can help increase the accuracy of testing and prevent confounding,” she said.
The study by Fuller-Thomson et al. was funded by a donation from Janis Rotman. Its investigators have reported no relevant financial relationships. The study by Hwang et al. was funded by contracts from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the National Institute on Aging. Dr. Hwang reports no relevant financial relationships. The other investigators’ disclosures are listed in the original article. Dr. Reed received grants from the National Institute on Aging during the conduct of the study and has served on the advisory board of Neosensory outside the submitted work. Dr. Oh and Dr. Whitson report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE REPORTS
Very high HDL-C: Too much of a good thing?
A new study suggests that .
Investigators studied close to 10,000 patients with CAD in two separate cohorts. After adjusting for an array of covariates, they found that individuals with HDL-C levels greater than 80 mg/dL had a 96% higher risk for all-cause mortality and a 71% higher risk for cardiovascular mortality than those with HDL-C levels between 40 and 60 mg/dL.
A U-shaped association was found, with higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with both very low and very high, compared with midrange, HDL-C values.
“Very high HDL levels are associated with increased risk of adverse outcomes, not lower risk, as previously thought. This is true not only in the general population, but also in people with known coronary artery disease,” senior author Arshed A. Quyyumi, MD, professor of medicine, division of cardiology, Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization.
“Physicians have to be cognizant of the fact that, at levels of HDL-C above 80 mg/dL, they [should be] more aggressive with risk reduction and not believe that the patient is at ‘low risk’ because of high levels of ‘good’ cholesterol,” said Dr. Quyyumi, director of the Emory Clinical Cardiovascular Research Institute.
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Inverse association?
HDL-C levels have “historically been inversely associated with increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk; however, recent studies have questioned the efficacy of therapies designed to increase HDL-C levels,” the authors wrote. Moreover, genetic variants associated with HDL-C have not been found to be linked to CVD risk.
Whether “very high HDL-C levels in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) are associated with mortality risk remains unknown,” they wrote. In this study, the researchers investigated not only the potential risk of elevated HDL-C levels in these patients, but also the association of known HDL-C genetic variants with this risk.
To do so, they analyzed data from a subset of patients with CAD in two independent study groups: the UK Biobank (UKB; n = 14,478; mean [standard deviation] age, 61.2 [5.8] years; 76.2% male; 93.8% White) and the Emory Cardiovascular Biobank (EmCAB; n = 5,467; mean age, 63.8 [12.3] years; 66.4% male; 73.2% White). Participants were followed prospectively for a median of 8.9 (interquartile range, 8.0-9.7) years and 6.7 (IQR, 4.0-10.8) years, respectively.
Additional data collected included medical and medication history and demographic characteristics, which were used as covariates, as well as genomic information.
Of the UKB cohort, 12.4% and 7.9% sustained all-cause or cardiovascular death, respectively, during the follow-up period, and 1.8% of participants had an HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL.
Among these participants with very high HDL-C levels, 16.9% and 8.6% had all-cause or cardiovascular death, respectively. Compared with the reference category (HDL-C level of 40-60 mg/dL), those with low HDL-C levels (≤ 30 mg/dL) had an expected higher risk for both all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, even after adjustment for covariates (hazard ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.07-1.64 and HR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.09-1.85, respectively; P = .009).
“Importantly,” the authors stated, “compared with the reference category, individuals with very high HDL-C levels (>80 mg/dL) also had a higher risk of all-cause death (HR, 1.58 [1.16-2.14], P = .004).”
Although cardiovascular death rates were not significantly greater in unadjusted analyses, after adjustment, the highest HDL-C group had an increased risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death (HR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.42-2.71; P < .001 and HR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.09-2.68, respectively; P = .02).
Compared with females, males with HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL had a higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death.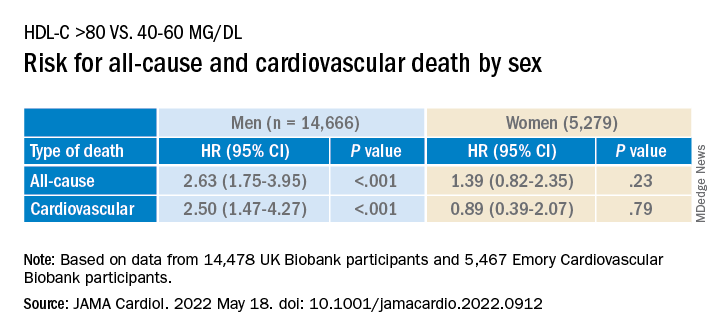
Similar findings were obtained in the EmCAB patients, 1.6% of whom had HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL. During the follow-up period, 26.9% and 13.8% of participants sustained all-cause and cardiovascular death, respectively. Of those with HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL, 30.0% and 16.7% experienced all-cause and cardiovascular death, respectively.
Compared with those with HDL-C levels of 40-60 mg/dL, those in the lowest (≤30 mg/dL) and highest (>80 mg/dL) groups had a “significant or near-significant greater risk for all-cause death in both unadjusted and fully adjusted models.
“Using adjusted HR curves, a U-shaped association between HDL-C and adverse events was evident with higher mortality at both very high and low HDL-C levels,” the authors noted.
Compared with patients without diabetes, those with diabetes and an HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL had a higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death, and patients younger than 65 years had a higher risk for cardiovascular death than patients 65 years and older.
The researchers found a “positive linear association” between the HDL-C genetic risk score (GRS) and HDL levels, wherein a 1-SD higher HDL-C GRS was associated with a 3.03 mg/dL higher HDL-C level (2.83-3.22; P < .001; R 2 = 0.06).
The HDL-C GRS was not associated with the risk for all-cause or cardiovascular death in unadjusted models, and after the HDL-C GRS was added to the fully adjusted models, the association with HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL was not attenuated, “indicating that HDL-C genetic variations in the GRS do not contribute substantially to the risk.”
“Potential mechanisms through which very high HDL-C might cause adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CAD need to be studied,” Dr. Quyyumi said. “Whether the functional capacity of the HDL particle is altered when the level is very high remains unknown. Whether it is more able to oxidize and thus shift from being protective to harmful also needs to be investigated.”
Red flag
Commenting for this news organization, Sadiya Sana Khan, MD, MSc, assistant professor of medicine (cardiology) and preventive medicine (epidemiology), Northwestern University, Chicago, said: “I think the most important point [of the study] is to identify people with very high HDL-C. This can serve as a reminder to discuss heart-healthy lifestyles and discussion of statin therapy if needed, based on LDL-C.”
In an accompanying editorial coauthored with Gregg Fonarow, MD, Ahmanson-UCLA Cardiomyopathy Center, University of California, Los Angeles, the pair wrote: “Although the present findings may be related to residual confounding, high HDL-C levels should not automatically be assumed to be protective.”
They advised clinicians to “use HDL-C levels as a surrogate marker, with very low and very high levels as a red flag to target for more intensive primary and secondary prevention, as the maxim for HDL-C as ‘good’ cholesterol only holds for HDL-C levels of 80 mg/dL or less.”
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Abraham J. & Phyllis Katz Foundation. Dr. Quyyumi and coauthors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Khan reports receiving grants from the American Heart Association and the National Institutes of Health outside the submitted work. Dr. Fonarow reports receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study suggests that .
Investigators studied close to 10,000 patients with CAD in two separate cohorts. After adjusting for an array of covariates, they found that individuals with HDL-C levels greater than 80 mg/dL had a 96% higher risk for all-cause mortality and a 71% higher risk for cardiovascular mortality than those with HDL-C levels between 40 and 60 mg/dL.
A U-shaped association was found, with higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with both very low and very high, compared with midrange, HDL-C values.
“Very high HDL levels are associated with increased risk of adverse outcomes, not lower risk, as previously thought. This is true not only in the general population, but also in people with known coronary artery disease,” senior author Arshed A. Quyyumi, MD, professor of medicine, division of cardiology, Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization.
“Physicians have to be cognizant of the fact that, at levels of HDL-C above 80 mg/dL, they [should be] more aggressive with risk reduction and not believe that the patient is at ‘low risk’ because of high levels of ‘good’ cholesterol,” said Dr. Quyyumi, director of the Emory Clinical Cardiovascular Research Institute.
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Inverse association?
HDL-C levels have “historically been inversely associated with increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk; however, recent studies have questioned the efficacy of therapies designed to increase HDL-C levels,” the authors wrote. Moreover, genetic variants associated with HDL-C have not been found to be linked to CVD risk.
Whether “very high HDL-C levels in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) are associated with mortality risk remains unknown,” they wrote. In this study, the researchers investigated not only the potential risk of elevated HDL-C levels in these patients, but also the association of known HDL-C genetic variants with this risk.
To do so, they analyzed data from a subset of patients with CAD in two independent study groups: the UK Biobank (UKB; n = 14,478; mean [standard deviation] age, 61.2 [5.8] years; 76.2% male; 93.8% White) and the Emory Cardiovascular Biobank (EmCAB; n = 5,467; mean age, 63.8 [12.3] years; 66.4% male; 73.2% White). Participants were followed prospectively for a median of 8.9 (interquartile range, 8.0-9.7) years and 6.7 (IQR, 4.0-10.8) years, respectively.
Additional data collected included medical and medication history and demographic characteristics, which were used as covariates, as well as genomic information.
Of the UKB cohort, 12.4% and 7.9% sustained all-cause or cardiovascular death, respectively, during the follow-up period, and 1.8% of participants had an HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL.
Among these participants with very high HDL-C levels, 16.9% and 8.6% had all-cause or cardiovascular death, respectively. Compared with the reference category (HDL-C level of 40-60 mg/dL), those with low HDL-C levels (≤ 30 mg/dL) had an expected higher risk for both all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, even after adjustment for covariates (hazard ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.07-1.64 and HR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.09-1.85, respectively; P = .009).
“Importantly,” the authors stated, “compared with the reference category, individuals with very high HDL-C levels (>80 mg/dL) also had a higher risk of all-cause death (HR, 1.58 [1.16-2.14], P = .004).”
Although cardiovascular death rates were not significantly greater in unadjusted analyses, after adjustment, the highest HDL-C group had an increased risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death (HR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.42-2.71; P < .001 and HR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.09-2.68, respectively; P = .02).
Compared with females, males with HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL had a higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death.
Similar findings were obtained in the EmCAB patients, 1.6% of whom had HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL. During the follow-up period, 26.9% and 13.8% of participants sustained all-cause and cardiovascular death, respectively. Of those with HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL, 30.0% and 16.7% experienced all-cause and cardiovascular death, respectively.
Compared with those with HDL-C levels of 40-60 mg/dL, those in the lowest (≤30 mg/dL) and highest (>80 mg/dL) groups had a “significant or near-significant greater risk for all-cause death in both unadjusted and fully adjusted models.
“Using adjusted HR curves, a U-shaped association between HDL-C and adverse events was evident with higher mortality at both very high and low HDL-C levels,” the authors noted.
Compared with patients without diabetes, those with diabetes and an HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL had a higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death, and patients younger than 65 years had a higher risk for cardiovascular death than patients 65 years and older.
The researchers found a “positive linear association” between the HDL-C genetic risk score (GRS) and HDL levels, wherein a 1-SD higher HDL-C GRS was associated with a 3.03 mg/dL higher HDL-C level (2.83-3.22; P < .001; R 2 = 0.06).
The HDL-C GRS was not associated with the risk for all-cause or cardiovascular death in unadjusted models, and after the HDL-C GRS was added to the fully adjusted models, the association with HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL was not attenuated, “indicating that HDL-C genetic variations in the GRS do not contribute substantially to the risk.”
“Potential mechanisms through which very high HDL-C might cause adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CAD need to be studied,” Dr. Quyyumi said. “Whether the functional capacity of the HDL particle is altered when the level is very high remains unknown. Whether it is more able to oxidize and thus shift from being protective to harmful also needs to be investigated.”
Red flag
Commenting for this news organization, Sadiya Sana Khan, MD, MSc, assistant professor of medicine (cardiology) and preventive medicine (epidemiology), Northwestern University, Chicago, said: “I think the most important point [of the study] is to identify people with very high HDL-C. This can serve as a reminder to discuss heart-healthy lifestyles and discussion of statin therapy if needed, based on LDL-C.”
In an accompanying editorial coauthored with Gregg Fonarow, MD, Ahmanson-UCLA Cardiomyopathy Center, University of California, Los Angeles, the pair wrote: “Although the present findings may be related to residual confounding, high HDL-C levels should not automatically be assumed to be protective.”
They advised clinicians to “use HDL-C levels as a surrogate marker, with very low and very high levels as a red flag to target for more intensive primary and secondary prevention, as the maxim for HDL-C as ‘good’ cholesterol only holds for HDL-C levels of 80 mg/dL or less.”
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Abraham J. & Phyllis Katz Foundation. Dr. Quyyumi and coauthors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Khan reports receiving grants from the American Heart Association and the National Institutes of Health outside the submitted work. Dr. Fonarow reports receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study suggests that .
Investigators studied close to 10,000 patients with CAD in two separate cohorts. After adjusting for an array of covariates, they found that individuals with HDL-C levels greater than 80 mg/dL had a 96% higher risk for all-cause mortality and a 71% higher risk for cardiovascular mortality than those with HDL-C levels between 40 and 60 mg/dL.
A U-shaped association was found, with higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with both very low and very high, compared with midrange, HDL-C values.
“Very high HDL levels are associated with increased risk of adverse outcomes, not lower risk, as previously thought. This is true not only in the general population, but also in people with known coronary artery disease,” senior author Arshed A. Quyyumi, MD, professor of medicine, division of cardiology, Emory University, Atlanta, told this news organization.
“Physicians have to be cognizant of the fact that, at levels of HDL-C above 80 mg/dL, they [should be] more aggressive with risk reduction and not believe that the patient is at ‘low risk’ because of high levels of ‘good’ cholesterol,” said Dr. Quyyumi, director of the Emory Clinical Cardiovascular Research Institute.
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Inverse association?
HDL-C levels have “historically been inversely associated with increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk; however, recent studies have questioned the efficacy of therapies designed to increase HDL-C levels,” the authors wrote. Moreover, genetic variants associated with HDL-C have not been found to be linked to CVD risk.
Whether “very high HDL-C levels in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) are associated with mortality risk remains unknown,” they wrote. In this study, the researchers investigated not only the potential risk of elevated HDL-C levels in these patients, but also the association of known HDL-C genetic variants with this risk.
To do so, they analyzed data from a subset of patients with CAD in two independent study groups: the UK Biobank (UKB; n = 14,478; mean [standard deviation] age, 61.2 [5.8] years; 76.2% male; 93.8% White) and the Emory Cardiovascular Biobank (EmCAB; n = 5,467; mean age, 63.8 [12.3] years; 66.4% male; 73.2% White). Participants were followed prospectively for a median of 8.9 (interquartile range, 8.0-9.7) years and 6.7 (IQR, 4.0-10.8) years, respectively.
Additional data collected included medical and medication history and demographic characteristics, which were used as covariates, as well as genomic information.
Of the UKB cohort, 12.4% and 7.9% sustained all-cause or cardiovascular death, respectively, during the follow-up period, and 1.8% of participants had an HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL.
Among these participants with very high HDL-C levels, 16.9% and 8.6% had all-cause or cardiovascular death, respectively. Compared with the reference category (HDL-C level of 40-60 mg/dL), those with low HDL-C levels (≤ 30 mg/dL) had an expected higher risk for both all-cause and cardiovascular mortality, even after adjustment for covariates (hazard ratio, 1.33; 95% confidence interval, 1.07-1.64 and HR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.09-1.85, respectively; P = .009).
“Importantly,” the authors stated, “compared with the reference category, individuals with very high HDL-C levels (>80 mg/dL) also had a higher risk of all-cause death (HR, 1.58 [1.16-2.14], P = .004).”
Although cardiovascular death rates were not significantly greater in unadjusted analyses, after adjustment, the highest HDL-C group had an increased risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death (HR, 1.96; 95% CI, 1.42-2.71; P < .001 and HR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.09-2.68, respectively; P = .02).
Compared with females, males with HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL had a higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death.
Similar findings were obtained in the EmCAB patients, 1.6% of whom had HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL. During the follow-up period, 26.9% and 13.8% of participants sustained all-cause and cardiovascular death, respectively. Of those with HDL-C levels above 80 mg/dL, 30.0% and 16.7% experienced all-cause and cardiovascular death, respectively.
Compared with those with HDL-C levels of 40-60 mg/dL, those in the lowest (≤30 mg/dL) and highest (>80 mg/dL) groups had a “significant or near-significant greater risk for all-cause death in both unadjusted and fully adjusted models.
“Using adjusted HR curves, a U-shaped association between HDL-C and adverse events was evident with higher mortality at both very high and low HDL-C levels,” the authors noted.
Compared with patients without diabetes, those with diabetes and an HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL had a higher risk for all-cause and cardiovascular death, and patients younger than 65 years had a higher risk for cardiovascular death than patients 65 years and older.
The researchers found a “positive linear association” between the HDL-C genetic risk score (GRS) and HDL levels, wherein a 1-SD higher HDL-C GRS was associated with a 3.03 mg/dL higher HDL-C level (2.83-3.22; P < .001; R 2 = 0.06).
The HDL-C GRS was not associated with the risk for all-cause or cardiovascular death in unadjusted models, and after the HDL-C GRS was added to the fully adjusted models, the association with HDL-C level above 80 mg/dL was not attenuated, “indicating that HDL-C genetic variations in the GRS do not contribute substantially to the risk.”
“Potential mechanisms through which very high HDL-C might cause adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CAD need to be studied,” Dr. Quyyumi said. “Whether the functional capacity of the HDL particle is altered when the level is very high remains unknown. Whether it is more able to oxidize and thus shift from being protective to harmful also needs to be investigated.”
Red flag
Commenting for this news organization, Sadiya Sana Khan, MD, MSc, assistant professor of medicine (cardiology) and preventive medicine (epidemiology), Northwestern University, Chicago, said: “I think the most important point [of the study] is to identify people with very high HDL-C. This can serve as a reminder to discuss heart-healthy lifestyles and discussion of statin therapy if needed, based on LDL-C.”
In an accompanying editorial coauthored with Gregg Fonarow, MD, Ahmanson-UCLA Cardiomyopathy Center, University of California, Los Angeles, the pair wrote: “Although the present findings may be related to residual confounding, high HDL-C levels should not automatically be assumed to be protective.”
They advised clinicians to “use HDL-C levels as a surrogate marker, with very low and very high levels as a red flag to target for more intensive primary and secondary prevention, as the maxim for HDL-C as ‘good’ cholesterol only holds for HDL-C levels of 80 mg/dL or less.”
This study was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the American Heart Association, and the Abraham J. & Phyllis Katz Foundation. Dr. Quyyumi and coauthors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Khan reports receiving grants from the American Heart Association and the National Institutes of Health outside the submitted work. Dr. Fonarow reports receiving personal fees from Abbott, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cytokinetics, Edwards, Janssen, Medtronic, Merck, and Novartis outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
Are physician white coats becoming obsolete? How docs dress for work now
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, Trisha Pasricha, MD, a gastroenterologist and research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, was talking to a patient who had been hospitalized for a peptic ulcer.
Like other physicians in her institution, Dr. Pasricha was wearing scrubs instead of a white coat, out of concern that the white coat might be more prone to accumulating or transmitting COVID-19 pathogens. Her badge identified her as a physician, and she introduced herself clearly as “Dr. Pasricha.”
The patient “required an emergent procedure, which I discussed with him,” Dr. Pasricha told this news organization. “I went over what the procedure entailed, the risks and benefits, and the need for informed consent. The patient nodded and seemed to understand, but at the end of the discussion he said: ‘That all sounds fine, but I need to speak to the doctor first.’ ”
Dr. Pasricha was taken aback. She wondered: “Who did he think I was the whole time that I was reviewing medical concerns, explaining medical concepts, and describing a procedure in a way that a physician would describe it?”
She realized the reason he didn’t correctly identify her was that, clad only in scrubs, she was less easily recognizable as a physician. And to be misidentified as technicians, nurses, physician assistants, or other health care professionals, according to Dr. Pasricha.
Dr. Pasricha said she has been the recipient of this “implicit bias” not only from patients but also from members of the health care team, and added that other female colleagues have told her that they’ve had similar experiences, especially when they’re not wearing a white coat.
Changing times, changing trends
When COVID-19 began to spread, “there was an initial concern that COVID-19 was passed through surfaces, and concerns about whether white coats could carry viral particles,” according to Jordan Steinberg, MD, PhD, surgical director of the craniofacial program at Nicklaus Children’s Pediatric Specialists/Nicklaus Children’s Health System, Miami. “Hospitals didn’t want to launder the white coats as frequently as scrubs, due to cost concerns. There was also a concern raised that a necktie might dangle in patients’ faces, coming in closer contact with pathogens, so more physicians were wearing scrubs.”
Yet even before the pandemic, physician attire in hospital and outpatient settings had started to change. Dr. Steinberg, who is also a clinical associate professor at Florida International University, Miami, told this news organization that, in his previous appointment at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, he and his colleagues “had noticed in our institution, as well as other facilities, an increasing trend that moved from white coats worn over professional attire toward more casual dress among medical staff – increased wearing of casual fleece or softshell jackets with the institutional logo.”
This was especially true with trainees and the “younger generation,” who were preferring “what I would almost call ‘warm-up clothes,’ gym clothes, and less shirt-tie-white-coat attire for men or white-coats-and-business attire for women.” Dr. Steinberg thinks that some physicians prefer the fleece with the institutional logo “because it’s like wearing your favorite sports team jersey. It gives a sense of belonging.”
Todd Shaffer, MD, MBA, a family physician at University Physicians Associates, Truman Medical Centers and the Lakewood Medical Pavilion, Kansas City, Mo., has been at his institution for 30 years and has seen a similar trend. “At one point, things were very formal,” he told this news organization. But attire was already becoming less formal before the pandemic, and new changes took place during the pandemic, as physicians began wearing scrubs instead of white coats because of fears of viral contamination.
Now, there is less concern about potential viral contamination with the white coat. Yet many physicians continue to wear scrubs – especially those who interact with patients with COVID – and it has become more acceptable to do so, or to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) over ordinary clothing, but it is less common in routine clinical practice, said Dr. Shaffer, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
“The world has changed since COVID. People feel more comfortable dressing more casually during professional Zoom calls, when they have the convenience of working from home,” said Dr. Shaffer, who is also a professor of family medicine at University of Missouri–Kansas City.
Dr. Shaffer himself hasn’t worn a white coat for years. “I’m more likely to wear medium casual pants. I’ve bought some nicer shirts, so I still look professional and upbeat. I don’t always tuck in my shirt, and I don’t dress as formally.” He wears PPE and a mask and/or face shield when treating patients with COVID-19. And he wears a white coat “when someone wants a photograph taken with the doctors – with the stethoscope draped around my neck.”
Traditional symbol of medicine
Because of the changing mores, Dr. Steinberg and colleagues at Johns Hopkins wondered if there might still be a role for professional attire and white coats and what patients prefer. To investigate the question, they surveyed 487 U.S. adults in the spring of 2020.
Respondents were asked where and how frequently they see health care professionals wearing white coats, scrubs, and fleece or softshell jackets. They were also shown photographs depicting models wearing various types of attire commonly seen in health care settings and were asked to rank the “health care provider’s” level of experience, professionalism, and friendliness.
The majority of participants said they had seen health care practitioners in white coats “most of the time,” in scrubs “sometimes,” and in fleece or softshell jackets “rarely.” Models in white coats were regarded by respondents as more experienced and professional, although those in softshell jackets were perceived as friendlier.
There were age as well as regional differences in the responses, Dr. Steinberg said. Older respondents were significantly more likely than their younger counterparts to perceive a model wearing a white coat over business attire as being more experienced, and – in all regions of the United States except the West coast – respondents gave lower professionalism scores to providers wearing fleece jackets with scrubs underneath.
Respondents tended to prefer surgeons wearing a white coat with scrubs underneath, while a white coat over business attire was the preferred dress code for family physicians and dermatologists.
“People tended to respond as if there was a more professional element in the white coat. The age-old symbol of the white coat still marked something important,” Dr. Steinberg said. “Our data suggest that the white coat isn’t ready to die just yet. People still see an air of authority and a traditional symbol of medicine. Nevertheless, I do think it will become less common than it used to be, especially in certain regions of the country.”
Organic, subtle changes
Christopher Petrilli, MD, assistant professor at New York University, conducted research in 2018 regarding physician attire by surveying over 4,000 patients in 10 U.S. academic hospitals. His team found that most patients continued to prefer physicians to wear formal attire under a white coat, especially older respondents.
Dr. Petrilli and colleagues have been studying the issue of physician attire since 2015. “The big issue when we did our initial study – which might not be accurate anymore – is that few hospitals actually had a uniform dress code,” said Dr. Petrilli, the medical director of clinical documentation improvement and the clinical lead of value-based medicine at NYU Langone Hospitals. “When we looked at ‘honor roll hospitals’ during our study, we cold-called these hospitals and also looked online for their dress code policies. Except for the Mayo Clinic, hospitals that had dress code policies were more generic.”
For example, the American Medical Association guidance merely states that attire should be “clean, unsoiled, and appropriate to the setting of care” and recommends weighing research findings regarding textile transmission of health care–associated infections when individual institutions determine their dress code policies. The AMA’s last policy discussion took place in 2015 and its guidance has not changed since the pandemic.
Regardless of what institutions and patients prefer, some research suggests that many physicians would prefer to stay with wearing scrubs rather than reverting to the white coat. One study of 151 hospitalists, conducted in Ireland, found that three-quarters wanted scrubs to remain standard attire, despite the fact that close to half had experienced changes in patients› perception in the absence of their white coat and “professional attire.”
Jennifer Workman, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics, division of pediatric critical care, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said in an interview that, as the pandemic has “waxed and waned, some trends have reverted to what they were prepandemic, but other physicians have stayed with wearing scrubs.”
Much depends on practice setting, said Dr. Workman, who is also the medical director of pediatric sepsis at Intermountain Care. In pediatrics, for example, many physicians prefer not to wear white coats when they are interacting with young children or adolescents.
Like Dr. Shaffer, Dr. Workman has seen changes in physicians’ attire during video meetings, where they often dress more casually, perhaps wearing sweatshirts. And in the hospital, more are continuing to wear scrubs. “But I don’t see it as people trying to consciously experiment or push boundaries,” she said. “I see it as a more organic, subtle shift.”
Dr. Petrilli thinks that, at this juncture, it’s “pretty heterogeneous as to who is going to return to formal attire and a white coat and who won’t.” Further research needs to be done into currently evolving trends. “We need a more thorough survey looking at changes. We need to ask [physician respondents]: ‘What is your current attire, and how has it changed?’ ”
Navigating the gender divide
In their study, Dr. Steinberg and colleagues found that respondents perceived a male model wearing business attire underneath any type of outerwear (white coat or fleece) to be significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire. Respondents also perceived males wearing scrubs to be more professional than females wearing scrubs.
Male models in white coats over business attire were also more likely to be identified as physicians, compared with female models in the same attire. Females were also more likely to be misidentified as nonphysician health care professionals.
Shikha Jain, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Illinois Cancer Center in Chicago, said that Dr. Steinberg’s study confirmed experiences that she and other female physicians have had. Wearing a white coat makes it more likely that a patient will identify you as a physician, but women are less likely to be identified as physicians, regardless of what they wear.
“I think that individuals of color and especially people with intersectional identities – such as women of color – are even more frequently targeted and stereotyped. Numerous studies have shown that a person of color is less likely to be seen as an authority figure, and studies have shown that physicians of color are less likely to be identified as ‘physicians,’ compared to a Caucasian individual,” she said.
Does that mean that female physicians should revert back to prepandemic white coats rather than scrubs or more casual attire? Not necessarily, according to Dr. Jain.
“The typical dress code guidance is that physicians should dress ‘professionally,’ but what that means is a question that needs to be addressed,” Dr. Jain said. “Medicine has evolved from the days of house calls, in which one’s patient population is a very small, intimate group of people in the physician’s community. Yet now, we’ve given rebirth to the ‘house call’ when we do telemedicine with a patient in his or her home. And in the old days, doctors often had offices their homes and now, with telemedicine, patients often see the interior of their physician’s home.” As the delivery of medicine evolves, concepts of “professionalism” – what is defined as “casual” and what is defined as “formal” – is also evolving.
The more important issue, according to Dr. Jain, is to “continue the conversation” about the discrepancies between how men and women are treated in medicine. Attire is one arena in which this issue plays out, and it’s a “bigger picture” that goes beyond the white coat.
Dr. Jain has been “told by patients that a particular outfit doesn’t make me look like a doctor or that scrubs make me look younger. I don’t think my male colleagues have been subjected to these types of remarks, but my female colleagues have heard them as well.”
Even fellow health care providers have commented on Dr. Jain’s clothing. She was presenting at a major medical conference via video and was wearing a similar outfit to the one she wore for her headshot. “Thirty seconds before beginning my talk, one of the male physicians said: ‘Are you wearing the same outfit you wore for your headshot?’ I can’t imagine a man commenting that another man was wearing the same jacket or tie that he wore in the photograph. I found it odd that this was something that someone felt the need to comment on right before I was about to address a large group of people in a professional capacity.”
Addressing these systemic issues “needs to be done and amplified not only by women but also by men in medicine,” said Dr. Jain, founder and director of Women in Medicine, an organization consisting of women physicians whose goal is to “find and implement solutions to gender inequity.”
Dr. Jain said the organization offers an Inclusive Leadership Development Lab – a course specifically for men in health care leadership positions to learn how to be more equitable, inclusive leaders.
A personal decision
Dr. Pasricha hopes she “handled the patient’s misidentification graciously.” She explained to him that she would be the physician conducting the procedure. The patient was initially “a little embarrassed” that he had misidentified her, but she put him at ease and “we moved forward quickly.”
At this point, although some of her colleagues have continued to wear scrubs or have returned to wearing fleeces with hospital logos, Dr. Pasricha prefers to wear a white coat in both inpatient and outpatient settings because it reduces the likelihood of misidentification.
And white coats can be more convenient – for example, Dr. Jain likes the fact that the white coat has pockets where she can put her stethoscope and other items, while some of her professional clothes don’t always have pockets.
Dr. Jain noted that there are some institutions where everyone seems to wear white coats, not only the physician – “from the chaplain to the phlebotomist to the social worker.” In those settings, the white coat no longer distinguishes physicians from nonphysicians, and so wearing a white coat may not confer additional credibility as a physician.
Nevertheless, “if you want to wear a white coat, if you feel it gives you that added level of authority, if you feel it tells people more clearly that you’re a physician, by all means go ahead and do so,” she said. “There’s no ‘one-size-fits-all’ strategy or solution. What’s more important than your clothing is your professionalism.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, Trisha Pasricha, MD, a gastroenterologist and research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, was talking to a patient who had been hospitalized for a peptic ulcer.
Like other physicians in her institution, Dr. Pasricha was wearing scrubs instead of a white coat, out of concern that the white coat might be more prone to accumulating or transmitting COVID-19 pathogens. Her badge identified her as a physician, and she introduced herself clearly as “Dr. Pasricha.”
The patient “required an emergent procedure, which I discussed with him,” Dr. Pasricha told this news organization. “I went over what the procedure entailed, the risks and benefits, and the need for informed consent. The patient nodded and seemed to understand, but at the end of the discussion he said: ‘That all sounds fine, but I need to speak to the doctor first.’ ”
Dr. Pasricha was taken aback. She wondered: “Who did he think I was the whole time that I was reviewing medical concerns, explaining medical concepts, and describing a procedure in a way that a physician would describe it?”
She realized the reason he didn’t correctly identify her was that, clad only in scrubs, she was less easily recognizable as a physician. And to be misidentified as technicians, nurses, physician assistants, or other health care professionals, according to Dr. Pasricha.
Dr. Pasricha said she has been the recipient of this “implicit bias” not only from patients but also from members of the health care team, and added that other female colleagues have told her that they’ve had similar experiences, especially when they’re not wearing a white coat.
Changing times, changing trends
When COVID-19 began to spread, “there was an initial concern that COVID-19 was passed through surfaces, and concerns about whether white coats could carry viral particles,” according to Jordan Steinberg, MD, PhD, surgical director of the craniofacial program at Nicklaus Children’s Pediatric Specialists/Nicklaus Children’s Health System, Miami. “Hospitals didn’t want to launder the white coats as frequently as scrubs, due to cost concerns. There was also a concern raised that a necktie might dangle in patients’ faces, coming in closer contact with pathogens, so more physicians were wearing scrubs.”
Yet even before the pandemic, physician attire in hospital and outpatient settings had started to change. Dr. Steinberg, who is also a clinical associate professor at Florida International University, Miami, told this news organization that, in his previous appointment at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, he and his colleagues “had noticed in our institution, as well as other facilities, an increasing trend that moved from white coats worn over professional attire toward more casual dress among medical staff – increased wearing of casual fleece or softshell jackets with the institutional logo.”
This was especially true with trainees and the “younger generation,” who were preferring “what I would almost call ‘warm-up clothes,’ gym clothes, and less shirt-tie-white-coat attire for men or white-coats-and-business attire for women.” Dr. Steinberg thinks that some physicians prefer the fleece with the institutional logo “because it’s like wearing your favorite sports team jersey. It gives a sense of belonging.”
Todd Shaffer, MD, MBA, a family physician at University Physicians Associates, Truman Medical Centers and the Lakewood Medical Pavilion, Kansas City, Mo., has been at his institution for 30 years and has seen a similar trend. “At one point, things were very formal,” he told this news organization. But attire was already becoming less formal before the pandemic, and new changes took place during the pandemic, as physicians began wearing scrubs instead of white coats because of fears of viral contamination.
Now, there is less concern about potential viral contamination with the white coat. Yet many physicians continue to wear scrubs – especially those who interact with patients with COVID – and it has become more acceptable to do so, or to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) over ordinary clothing, but it is less common in routine clinical practice, said Dr. Shaffer, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
“The world has changed since COVID. People feel more comfortable dressing more casually during professional Zoom calls, when they have the convenience of working from home,” said Dr. Shaffer, who is also a professor of family medicine at University of Missouri–Kansas City.
Dr. Shaffer himself hasn’t worn a white coat for years. “I’m more likely to wear medium casual pants. I’ve bought some nicer shirts, so I still look professional and upbeat. I don’t always tuck in my shirt, and I don’t dress as formally.” He wears PPE and a mask and/or face shield when treating patients with COVID-19. And he wears a white coat “when someone wants a photograph taken with the doctors – with the stethoscope draped around my neck.”
Traditional symbol of medicine
Because of the changing mores, Dr. Steinberg and colleagues at Johns Hopkins wondered if there might still be a role for professional attire and white coats and what patients prefer. To investigate the question, they surveyed 487 U.S. adults in the spring of 2020.
Respondents were asked where and how frequently they see health care professionals wearing white coats, scrubs, and fleece or softshell jackets. They were also shown photographs depicting models wearing various types of attire commonly seen in health care settings and were asked to rank the “health care provider’s” level of experience, professionalism, and friendliness.
The majority of participants said they had seen health care practitioners in white coats “most of the time,” in scrubs “sometimes,” and in fleece or softshell jackets “rarely.” Models in white coats were regarded by respondents as more experienced and professional, although those in softshell jackets were perceived as friendlier.
There were age as well as regional differences in the responses, Dr. Steinberg said. Older respondents were significantly more likely than their younger counterparts to perceive a model wearing a white coat over business attire as being more experienced, and – in all regions of the United States except the West coast – respondents gave lower professionalism scores to providers wearing fleece jackets with scrubs underneath.
Respondents tended to prefer surgeons wearing a white coat with scrubs underneath, while a white coat over business attire was the preferred dress code for family physicians and dermatologists.
“People tended to respond as if there was a more professional element in the white coat. The age-old symbol of the white coat still marked something important,” Dr. Steinberg said. “Our data suggest that the white coat isn’t ready to die just yet. People still see an air of authority and a traditional symbol of medicine. Nevertheless, I do think it will become less common than it used to be, especially in certain regions of the country.”
Organic, subtle changes
Christopher Petrilli, MD, assistant professor at New York University, conducted research in 2018 regarding physician attire by surveying over 4,000 patients in 10 U.S. academic hospitals. His team found that most patients continued to prefer physicians to wear formal attire under a white coat, especially older respondents.
Dr. Petrilli and colleagues have been studying the issue of physician attire since 2015. “The big issue when we did our initial study – which might not be accurate anymore – is that few hospitals actually had a uniform dress code,” said Dr. Petrilli, the medical director of clinical documentation improvement and the clinical lead of value-based medicine at NYU Langone Hospitals. “When we looked at ‘honor roll hospitals’ during our study, we cold-called these hospitals and also looked online for their dress code policies. Except for the Mayo Clinic, hospitals that had dress code policies were more generic.”
For example, the American Medical Association guidance merely states that attire should be “clean, unsoiled, and appropriate to the setting of care” and recommends weighing research findings regarding textile transmission of health care–associated infections when individual institutions determine their dress code policies. The AMA’s last policy discussion took place in 2015 and its guidance has not changed since the pandemic.
Regardless of what institutions and patients prefer, some research suggests that many physicians would prefer to stay with wearing scrubs rather than reverting to the white coat. One study of 151 hospitalists, conducted in Ireland, found that three-quarters wanted scrubs to remain standard attire, despite the fact that close to half had experienced changes in patients› perception in the absence of their white coat and “professional attire.”
Jennifer Workman, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics, division of pediatric critical care, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said in an interview that, as the pandemic has “waxed and waned, some trends have reverted to what they were prepandemic, but other physicians have stayed with wearing scrubs.”
Much depends on practice setting, said Dr. Workman, who is also the medical director of pediatric sepsis at Intermountain Care. In pediatrics, for example, many physicians prefer not to wear white coats when they are interacting with young children or adolescents.
Like Dr. Shaffer, Dr. Workman has seen changes in physicians’ attire during video meetings, where they often dress more casually, perhaps wearing sweatshirts. And in the hospital, more are continuing to wear scrubs. “But I don’t see it as people trying to consciously experiment or push boundaries,” she said. “I see it as a more organic, subtle shift.”
Dr. Petrilli thinks that, at this juncture, it’s “pretty heterogeneous as to who is going to return to formal attire and a white coat and who won’t.” Further research needs to be done into currently evolving trends. “We need a more thorough survey looking at changes. We need to ask [physician respondents]: ‘What is your current attire, and how has it changed?’ ”
Navigating the gender divide
In their study, Dr. Steinberg and colleagues found that respondents perceived a male model wearing business attire underneath any type of outerwear (white coat or fleece) to be significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire. Respondents also perceived males wearing scrubs to be more professional than females wearing scrubs.
Male models in white coats over business attire were also more likely to be identified as physicians, compared with female models in the same attire. Females were also more likely to be misidentified as nonphysician health care professionals.
Shikha Jain, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Illinois Cancer Center in Chicago, said that Dr. Steinberg’s study confirmed experiences that she and other female physicians have had. Wearing a white coat makes it more likely that a patient will identify you as a physician, but women are less likely to be identified as physicians, regardless of what they wear.
“I think that individuals of color and especially people with intersectional identities – such as women of color – are even more frequently targeted and stereotyped. Numerous studies have shown that a person of color is less likely to be seen as an authority figure, and studies have shown that physicians of color are less likely to be identified as ‘physicians,’ compared to a Caucasian individual,” she said.
Does that mean that female physicians should revert back to prepandemic white coats rather than scrubs or more casual attire? Not necessarily, according to Dr. Jain.
“The typical dress code guidance is that physicians should dress ‘professionally,’ but what that means is a question that needs to be addressed,” Dr. Jain said. “Medicine has evolved from the days of house calls, in which one’s patient population is a very small, intimate group of people in the physician’s community. Yet now, we’ve given rebirth to the ‘house call’ when we do telemedicine with a patient in his or her home. And in the old days, doctors often had offices their homes and now, with telemedicine, patients often see the interior of their physician’s home.” As the delivery of medicine evolves, concepts of “professionalism” – what is defined as “casual” and what is defined as “formal” – is also evolving.
The more important issue, according to Dr. Jain, is to “continue the conversation” about the discrepancies between how men and women are treated in medicine. Attire is one arena in which this issue plays out, and it’s a “bigger picture” that goes beyond the white coat.
Dr. Jain has been “told by patients that a particular outfit doesn’t make me look like a doctor or that scrubs make me look younger. I don’t think my male colleagues have been subjected to these types of remarks, but my female colleagues have heard them as well.”
Even fellow health care providers have commented on Dr. Jain’s clothing. She was presenting at a major medical conference via video and was wearing a similar outfit to the one she wore for her headshot. “Thirty seconds before beginning my talk, one of the male physicians said: ‘Are you wearing the same outfit you wore for your headshot?’ I can’t imagine a man commenting that another man was wearing the same jacket or tie that he wore in the photograph. I found it odd that this was something that someone felt the need to comment on right before I was about to address a large group of people in a professional capacity.”
Addressing these systemic issues “needs to be done and amplified not only by women but also by men in medicine,” said Dr. Jain, founder and director of Women in Medicine, an organization consisting of women physicians whose goal is to “find and implement solutions to gender inequity.”
Dr. Jain said the organization offers an Inclusive Leadership Development Lab – a course specifically for men in health care leadership positions to learn how to be more equitable, inclusive leaders.
A personal decision
Dr. Pasricha hopes she “handled the patient’s misidentification graciously.” She explained to him that she would be the physician conducting the procedure. The patient was initially “a little embarrassed” that he had misidentified her, but she put him at ease and “we moved forward quickly.”
At this point, although some of her colleagues have continued to wear scrubs or have returned to wearing fleeces with hospital logos, Dr. Pasricha prefers to wear a white coat in both inpatient and outpatient settings because it reduces the likelihood of misidentification.
And white coats can be more convenient – for example, Dr. Jain likes the fact that the white coat has pockets where she can put her stethoscope and other items, while some of her professional clothes don’t always have pockets.
Dr. Jain noted that there are some institutions where everyone seems to wear white coats, not only the physician – “from the chaplain to the phlebotomist to the social worker.” In those settings, the white coat no longer distinguishes physicians from nonphysicians, and so wearing a white coat may not confer additional credibility as a physician.
Nevertheless, “if you want to wear a white coat, if you feel it gives you that added level of authority, if you feel it tells people more clearly that you’re a physician, by all means go ahead and do so,” she said. “There’s no ‘one-size-fits-all’ strategy or solution. What’s more important than your clothing is your professionalism.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, Trisha Pasricha, MD, a gastroenterologist and research fellow at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, was talking to a patient who had been hospitalized for a peptic ulcer.
Like other physicians in her institution, Dr. Pasricha was wearing scrubs instead of a white coat, out of concern that the white coat might be more prone to accumulating or transmitting COVID-19 pathogens. Her badge identified her as a physician, and she introduced herself clearly as “Dr. Pasricha.”
The patient “required an emergent procedure, which I discussed with him,” Dr. Pasricha told this news organization. “I went over what the procedure entailed, the risks and benefits, and the need for informed consent. The patient nodded and seemed to understand, but at the end of the discussion he said: ‘That all sounds fine, but I need to speak to the doctor first.’ ”
Dr. Pasricha was taken aback. She wondered: “Who did he think I was the whole time that I was reviewing medical concerns, explaining medical concepts, and describing a procedure in a way that a physician would describe it?”
She realized the reason he didn’t correctly identify her was that, clad only in scrubs, she was less easily recognizable as a physician. And to be misidentified as technicians, nurses, physician assistants, or other health care professionals, according to Dr. Pasricha.
Dr. Pasricha said she has been the recipient of this “implicit bias” not only from patients but also from members of the health care team, and added that other female colleagues have told her that they’ve had similar experiences, especially when they’re not wearing a white coat.
Changing times, changing trends
When COVID-19 began to spread, “there was an initial concern that COVID-19 was passed through surfaces, and concerns about whether white coats could carry viral particles,” according to Jordan Steinberg, MD, PhD, surgical director of the craniofacial program at Nicklaus Children’s Pediatric Specialists/Nicklaus Children’s Health System, Miami. “Hospitals didn’t want to launder the white coats as frequently as scrubs, due to cost concerns. There was also a concern raised that a necktie might dangle in patients’ faces, coming in closer contact with pathogens, so more physicians were wearing scrubs.”
Yet even before the pandemic, physician attire in hospital and outpatient settings had started to change. Dr. Steinberg, who is also a clinical associate professor at Florida International University, Miami, told this news organization that, in his previous appointment at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, he and his colleagues “had noticed in our institution, as well as other facilities, an increasing trend that moved from white coats worn over professional attire toward more casual dress among medical staff – increased wearing of casual fleece or softshell jackets with the institutional logo.”
This was especially true with trainees and the “younger generation,” who were preferring “what I would almost call ‘warm-up clothes,’ gym clothes, and less shirt-tie-white-coat attire for men or white-coats-and-business attire for women.” Dr. Steinberg thinks that some physicians prefer the fleece with the institutional logo “because it’s like wearing your favorite sports team jersey. It gives a sense of belonging.”
Todd Shaffer, MD, MBA, a family physician at University Physicians Associates, Truman Medical Centers and the Lakewood Medical Pavilion, Kansas City, Mo., has been at his institution for 30 years and has seen a similar trend. “At one point, things were very formal,” he told this news organization. But attire was already becoming less formal before the pandemic, and new changes took place during the pandemic, as physicians began wearing scrubs instead of white coats because of fears of viral contamination.
Now, there is less concern about potential viral contamination with the white coat. Yet many physicians continue to wear scrubs – especially those who interact with patients with COVID – and it has become more acceptable to do so, or to wear personal protective equipment (PPE) over ordinary clothing, but it is less common in routine clinical practice, said Dr. Shaffer, a member of the board of directors of the American Academy of Family Physicians.
“The world has changed since COVID. People feel more comfortable dressing more casually during professional Zoom calls, when they have the convenience of working from home,” said Dr. Shaffer, who is also a professor of family medicine at University of Missouri–Kansas City.
Dr. Shaffer himself hasn’t worn a white coat for years. “I’m more likely to wear medium casual pants. I’ve bought some nicer shirts, so I still look professional and upbeat. I don’t always tuck in my shirt, and I don’t dress as formally.” He wears PPE and a mask and/or face shield when treating patients with COVID-19. And he wears a white coat “when someone wants a photograph taken with the doctors – with the stethoscope draped around my neck.”
Traditional symbol of medicine
Because of the changing mores, Dr. Steinberg and colleagues at Johns Hopkins wondered if there might still be a role for professional attire and white coats and what patients prefer. To investigate the question, they surveyed 487 U.S. adults in the spring of 2020.
Respondents were asked where and how frequently they see health care professionals wearing white coats, scrubs, and fleece or softshell jackets. They were also shown photographs depicting models wearing various types of attire commonly seen in health care settings and were asked to rank the “health care provider’s” level of experience, professionalism, and friendliness.
The majority of participants said they had seen health care practitioners in white coats “most of the time,” in scrubs “sometimes,” and in fleece or softshell jackets “rarely.” Models in white coats were regarded by respondents as more experienced and professional, although those in softshell jackets were perceived as friendlier.
There were age as well as regional differences in the responses, Dr. Steinberg said. Older respondents were significantly more likely than their younger counterparts to perceive a model wearing a white coat over business attire as being more experienced, and – in all regions of the United States except the West coast – respondents gave lower professionalism scores to providers wearing fleece jackets with scrubs underneath.
Respondents tended to prefer surgeons wearing a white coat with scrubs underneath, while a white coat over business attire was the preferred dress code for family physicians and dermatologists.
“People tended to respond as if there was a more professional element in the white coat. The age-old symbol of the white coat still marked something important,” Dr. Steinberg said. “Our data suggest that the white coat isn’t ready to die just yet. People still see an air of authority and a traditional symbol of medicine. Nevertheless, I do think it will become less common than it used to be, especially in certain regions of the country.”
Organic, subtle changes
Christopher Petrilli, MD, assistant professor at New York University, conducted research in 2018 regarding physician attire by surveying over 4,000 patients in 10 U.S. academic hospitals. His team found that most patients continued to prefer physicians to wear formal attire under a white coat, especially older respondents.
Dr. Petrilli and colleagues have been studying the issue of physician attire since 2015. “The big issue when we did our initial study – which might not be accurate anymore – is that few hospitals actually had a uniform dress code,” said Dr. Petrilli, the medical director of clinical documentation improvement and the clinical lead of value-based medicine at NYU Langone Hospitals. “When we looked at ‘honor roll hospitals’ during our study, we cold-called these hospitals and also looked online for their dress code policies. Except for the Mayo Clinic, hospitals that had dress code policies were more generic.”
For example, the American Medical Association guidance merely states that attire should be “clean, unsoiled, and appropriate to the setting of care” and recommends weighing research findings regarding textile transmission of health care–associated infections when individual institutions determine their dress code policies. The AMA’s last policy discussion took place in 2015 and its guidance has not changed since the pandemic.
Regardless of what institutions and patients prefer, some research suggests that many physicians would prefer to stay with wearing scrubs rather than reverting to the white coat. One study of 151 hospitalists, conducted in Ireland, found that three-quarters wanted scrubs to remain standard attire, despite the fact that close to half had experienced changes in patients› perception in the absence of their white coat and “professional attire.”
Jennifer Workman, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics, division of pediatric critical care, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, said in an interview that, as the pandemic has “waxed and waned, some trends have reverted to what they were prepandemic, but other physicians have stayed with wearing scrubs.”
Much depends on practice setting, said Dr. Workman, who is also the medical director of pediatric sepsis at Intermountain Care. In pediatrics, for example, many physicians prefer not to wear white coats when they are interacting with young children or adolescents.
Like Dr. Shaffer, Dr. Workman has seen changes in physicians’ attire during video meetings, where they often dress more casually, perhaps wearing sweatshirts. And in the hospital, more are continuing to wear scrubs. “But I don’t see it as people trying to consciously experiment or push boundaries,” she said. “I see it as a more organic, subtle shift.”
Dr. Petrilli thinks that, at this juncture, it’s “pretty heterogeneous as to who is going to return to formal attire and a white coat and who won’t.” Further research needs to be done into currently evolving trends. “We need a more thorough survey looking at changes. We need to ask [physician respondents]: ‘What is your current attire, and how has it changed?’ ”
Navigating the gender divide
In their study, Dr. Steinberg and colleagues found that respondents perceived a male model wearing business attire underneath any type of outerwear (white coat or fleece) to be significantly more professional than a female model wearing the same attire. Respondents also perceived males wearing scrubs to be more professional than females wearing scrubs.
Male models in white coats over business attire were also more likely to be identified as physicians, compared with female models in the same attire. Females were also more likely to be misidentified as nonphysician health care professionals.
Shikha Jain, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Illinois Cancer Center in Chicago, said that Dr. Steinberg’s study confirmed experiences that she and other female physicians have had. Wearing a white coat makes it more likely that a patient will identify you as a physician, but women are less likely to be identified as physicians, regardless of what they wear.
“I think that individuals of color and especially people with intersectional identities – such as women of color – are even more frequently targeted and stereotyped. Numerous studies have shown that a person of color is less likely to be seen as an authority figure, and studies have shown that physicians of color are less likely to be identified as ‘physicians,’ compared to a Caucasian individual,” she said.
Does that mean that female physicians should revert back to prepandemic white coats rather than scrubs or more casual attire? Not necessarily, according to Dr. Jain.
“The typical dress code guidance is that physicians should dress ‘professionally,’ but what that means is a question that needs to be addressed,” Dr. Jain said. “Medicine has evolved from the days of house calls, in which one’s patient population is a very small, intimate group of people in the physician’s community. Yet now, we’ve given rebirth to the ‘house call’ when we do telemedicine with a patient in his or her home. And in the old days, doctors often had offices their homes and now, with telemedicine, patients often see the interior of their physician’s home.” As the delivery of medicine evolves, concepts of “professionalism” – what is defined as “casual” and what is defined as “formal” – is also evolving.
The more important issue, according to Dr. Jain, is to “continue the conversation” about the discrepancies between how men and women are treated in medicine. Attire is one arena in which this issue plays out, and it’s a “bigger picture” that goes beyond the white coat.
Dr. Jain has been “told by patients that a particular outfit doesn’t make me look like a doctor or that scrubs make me look younger. I don’t think my male colleagues have been subjected to these types of remarks, but my female colleagues have heard them as well.”
Even fellow health care providers have commented on Dr. Jain’s clothing. She was presenting at a major medical conference via video and was wearing a similar outfit to the one she wore for her headshot. “Thirty seconds before beginning my talk, one of the male physicians said: ‘Are you wearing the same outfit you wore for your headshot?’ I can’t imagine a man commenting that another man was wearing the same jacket or tie that he wore in the photograph. I found it odd that this was something that someone felt the need to comment on right before I was about to address a large group of people in a professional capacity.”
Addressing these systemic issues “needs to be done and amplified not only by women but also by men in medicine,” said Dr. Jain, founder and director of Women in Medicine, an organization consisting of women physicians whose goal is to “find and implement solutions to gender inequity.”
Dr. Jain said the organization offers an Inclusive Leadership Development Lab – a course specifically for men in health care leadership positions to learn how to be more equitable, inclusive leaders.
A personal decision
Dr. Pasricha hopes she “handled the patient’s misidentification graciously.” She explained to him that she would be the physician conducting the procedure. The patient was initially “a little embarrassed” that he had misidentified her, but she put him at ease and “we moved forward quickly.”
At this point, although some of her colleagues have continued to wear scrubs or have returned to wearing fleeces with hospital logos, Dr. Pasricha prefers to wear a white coat in both inpatient and outpatient settings because it reduces the likelihood of misidentification.
And white coats can be more convenient – for example, Dr. Jain likes the fact that the white coat has pockets where she can put her stethoscope and other items, while some of her professional clothes don’t always have pockets.
Dr. Jain noted that there are some institutions where everyone seems to wear white coats, not only the physician – “from the chaplain to the phlebotomist to the social worker.” In those settings, the white coat no longer distinguishes physicians from nonphysicians, and so wearing a white coat may not confer additional credibility as a physician.
Nevertheless, “if you want to wear a white coat, if you feel it gives you that added level of authority, if you feel it tells people more clearly that you’re a physician, by all means go ahead and do so,” she said. “There’s no ‘one-size-fits-all’ strategy or solution. What’s more important than your clothing is your professionalism.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Burnout ‘highly prevalent’ in psychiatrists across the globe
Burnout in psychiatrists is “highly prevalent” across the globe, new research shows.
In a review and meta-analysis of 36 studies and more than 5,000 psychiatrists in European countries, as well as the United States, Australia, New Zealand, India, Turkey, and Thailand,
“Our review showed that regardless of the identification method of burnout, its prevalence among psychiatrists is high and ranges from 25% to 50%,” lead author Kirill Bykov, MD, a PhD candidate at the Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), Moscow, Russian Federation, told this news organization.
There was a “high heterogeneity of studies in terms of statistics, screening methods, burnout definitions, and cutoff points in the included studies, which necessitates the unification of future research methodology, but not to the detriment of the development of the theoretical background,” Dr. Bykov said.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
‘Unresolved problem’
Although burnout is a serious and prevalent problem among health care workers, little research has focused on burnout in mental health workers compared with other professionals, the investigators noted.
A previous systematic review and meta-analysis that focused specifically on burnout in psychiatrists was limited by methodologic concerns, including that the only burnout screening instrument used in the included studies was the full-length (22-item) MBI.
The current researchers surmised that “the integration of different empirical studies of psychiatrists’ burnout prevalence [remained] an unresolved problem.”
Dr. Bykov noted the current review was “investigator-initiated” and was a part of his PhD dissertation.
“Studying the works devoted to the burnout of psychiatrists, I drew attention to the varying prevalence rates of this phenomenon among them. This prompted me to conduct a systematic review of the literature and summarize the available data,” he said.
Unlike the previous review, the current one “does not contain restrictions regarding the place of research, publication language, covered burnout concepts, definitions, and screening instruments. Thus, its results will be helpful for practitioners and scientists around the world,” Dr. Bykov added.
Among the inclusion criteria was that a study should be empirical and quantitative, contain at least 20 practicing psychiatrists as participants, use a valid and reliable burnout screening instrument, have at least one burnout metric extractable specifically with regard to psychiatrists, and have a national survey or a response rate among psychiatrists of 20% or greater.
Qualitative or review articles or studies consisting of psychiatric trainees (such as medical students or residents) or nonpracticing psychiatrists were excluded.
Pooled prevalence
The researchers included 36 studies that comprised 5,481 participants (51.3% were women; mean age, 46.7 years). All studies had from 20 to 1,157 participants. They were employed in an array of settings in 19 countries.
In 22 studies, survey years ranged from 1996 to 2018; 14 studies did not report the year of data collection.
Most studies (75%) used some version of the MBI, and 19 studies used the full-length 22-item MBI Human Service Survey (MBI-HSS) . The survey rates emotional exhaustion (EE), depersonalization (DP), and low personal achievement (PA) on a 7-point Likert scale from 0 (“never”) to 6 (“almost every day”).
Other instruments included the CBI, the 16-item Oldenburg Burnout Inventory, the 21-item Tedium Measure, the 30-item Professional Quality of Life measure, the Rohland et al. Single-Item Measure of Self-Perceived Burnout, and the 21-item Brief Burnout Questionnaire.
Only three studies were free of methodologic limitations. The remaining 33 studies had some problems, such as not reporting the response rate or comparability between responders and nonresponders.
Results showed that the overall prevalence of burnout, as measured by the MBI and the CBI, was 25.9% (range, 11.1%-40.75%) and 50.3% (range, 30.9%-69.8%), respectively.
The pooled prevalence for burnout components is shown in the table.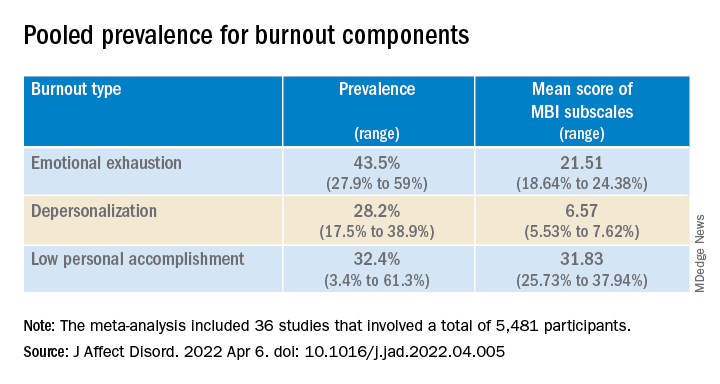
European psychiatrists had lower EE scores (20.82; 95% confidence interval, 7.24-4.41) compared with their non-European counterparts (24.99; 95% CI, 23.05-26.94; P = .045).
‘Carry the hope’
In a comment, Christine Crawford, MD, associate medical director of the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), said she was surprised the burnout numbers weren’t higher.
Many colleagues she interacts with “have been experiencing pretty significant burnout that has only been exacerbated by the pandemic and ever-growing demand for mental health providers, and there aren’t enough to meet that demand,” said Dr. Crawford, a psychiatrist at Boston Medical Center’s Outpatient Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Clinic and at Codman Square Health Center. She was not involved with the current research.
Dr. Crawford noted that much of the data was from Europeans. Speaking to the experience of U.S.-based psychiatrists, she said there is a “greater appreciation for what we do as mental health providers, due to the growing conversations around mental health and normalizing mental health conditions.”
On the other hand, there is “a lack of parity in reimbursement rates. Although the general public values mental health, the medical system doesn’t value mental health providers in the same way as physicians in other specialties,” Dr. Crawford said. Feeling devalued can contribute to burnout, she added.
One way to counter burnout is to remember “that our role is to carry the hope. We can be hopeful for the patient that the treatment will work or the medications can provide some relief,” Dr. Crawford noted.
Psychiatrists “may need to hold on tightly to that hope because we may not receive that instant gratification from the patient or receive praise or see the change from the patient during that time, which can be challenging,” she said.
“But it’s important for us to keep in mind that, even in that moment when the patient can’t see it, we can work alongside the patient to create the vision of hope and what it will look like in the future,” said Dr. Crawford.
In the 2022 Medscape Psychiatrist Lifestyle, Happiness & Burnout Report, an annual online survey of Medscape member physicians, 47% of respondents reported burnout – which was up from 42% the previous year.
The investigators received no funding for this work. They and Dr. Crawford report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Burnout in psychiatrists is “highly prevalent” across the globe, new research shows.
In a review and meta-analysis of 36 studies and more than 5,000 psychiatrists in European countries, as well as the United States, Australia, New Zealand, India, Turkey, and Thailand,
“Our review showed that regardless of the identification method of burnout, its prevalence among psychiatrists is high and ranges from 25% to 50%,” lead author Kirill Bykov, MD, a PhD candidate at the Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), Moscow, Russian Federation, told this news organization.
There was a “high heterogeneity of studies in terms of statistics, screening methods, burnout definitions, and cutoff points in the included studies, which necessitates the unification of future research methodology, but not to the detriment of the development of the theoretical background,” Dr. Bykov said.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
‘Unresolved problem’
Although burnout is a serious and prevalent problem among health care workers, little research has focused on burnout in mental health workers compared with other professionals, the investigators noted.
A previous systematic review and meta-analysis that focused specifically on burnout in psychiatrists was limited by methodologic concerns, including that the only burnout screening instrument used in the included studies was the full-length (22-item) MBI.
The current researchers surmised that “the integration of different empirical studies of psychiatrists’ burnout prevalence [remained] an unresolved problem.”
Dr. Bykov noted the current review was “investigator-initiated” and was a part of his PhD dissertation.
“Studying the works devoted to the burnout of psychiatrists, I drew attention to the varying prevalence rates of this phenomenon among them. This prompted me to conduct a systematic review of the literature and summarize the available data,” he said.
Unlike the previous review, the current one “does not contain restrictions regarding the place of research, publication language, covered burnout concepts, definitions, and screening instruments. Thus, its results will be helpful for practitioners and scientists around the world,” Dr. Bykov added.
Among the inclusion criteria was that a study should be empirical and quantitative, contain at least 20 practicing psychiatrists as participants, use a valid and reliable burnout screening instrument, have at least one burnout metric extractable specifically with regard to psychiatrists, and have a national survey or a response rate among psychiatrists of 20% or greater.
Qualitative or review articles or studies consisting of psychiatric trainees (such as medical students or residents) or nonpracticing psychiatrists were excluded.
Pooled prevalence
The researchers included 36 studies that comprised 5,481 participants (51.3% were women; mean age, 46.7 years). All studies had from 20 to 1,157 participants. They were employed in an array of settings in 19 countries.
In 22 studies, survey years ranged from 1996 to 2018; 14 studies did not report the year of data collection.
Most studies (75%) used some version of the MBI, and 19 studies used the full-length 22-item MBI Human Service Survey (MBI-HSS) . The survey rates emotional exhaustion (EE), depersonalization (DP), and low personal achievement (PA) on a 7-point Likert scale from 0 (“never”) to 6 (“almost every day”).
Other instruments included the CBI, the 16-item Oldenburg Burnout Inventory, the 21-item Tedium Measure, the 30-item Professional Quality of Life measure, the Rohland et al. Single-Item Measure of Self-Perceived Burnout, and the 21-item Brief Burnout Questionnaire.
Only three studies were free of methodologic limitations. The remaining 33 studies had some problems, such as not reporting the response rate or comparability between responders and nonresponders.
Results showed that the overall prevalence of burnout, as measured by the MBI and the CBI, was 25.9% (range, 11.1%-40.75%) and 50.3% (range, 30.9%-69.8%), respectively.
The pooled prevalence for burnout components is shown in the table.
European psychiatrists had lower EE scores (20.82; 95% confidence interval, 7.24-4.41) compared with their non-European counterparts (24.99; 95% CI, 23.05-26.94; P = .045).
‘Carry the hope’
In a comment, Christine Crawford, MD, associate medical director of the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), said she was surprised the burnout numbers weren’t higher.
Many colleagues she interacts with “have been experiencing pretty significant burnout that has only been exacerbated by the pandemic and ever-growing demand for mental health providers, and there aren’t enough to meet that demand,” said Dr. Crawford, a psychiatrist at Boston Medical Center’s Outpatient Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Clinic and at Codman Square Health Center. She was not involved with the current research.
Dr. Crawford noted that much of the data was from Europeans. Speaking to the experience of U.S.-based psychiatrists, she said there is a “greater appreciation for what we do as mental health providers, due to the growing conversations around mental health and normalizing mental health conditions.”
On the other hand, there is “a lack of parity in reimbursement rates. Although the general public values mental health, the medical system doesn’t value mental health providers in the same way as physicians in other specialties,” Dr. Crawford said. Feeling devalued can contribute to burnout, she added.
One way to counter burnout is to remember “that our role is to carry the hope. We can be hopeful for the patient that the treatment will work or the medications can provide some relief,” Dr. Crawford noted.
Psychiatrists “may need to hold on tightly to that hope because we may not receive that instant gratification from the patient or receive praise or see the change from the patient during that time, which can be challenging,” she said.
“But it’s important for us to keep in mind that, even in that moment when the patient can’t see it, we can work alongside the patient to create the vision of hope and what it will look like in the future,” said Dr. Crawford.
In the 2022 Medscape Psychiatrist Lifestyle, Happiness & Burnout Report, an annual online survey of Medscape member physicians, 47% of respondents reported burnout – which was up from 42% the previous year.
The investigators received no funding for this work. They and Dr. Crawford report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Burnout in psychiatrists is “highly prevalent” across the globe, new research shows.
In a review and meta-analysis of 36 studies and more than 5,000 psychiatrists in European countries, as well as the United States, Australia, New Zealand, India, Turkey, and Thailand,
“Our review showed that regardless of the identification method of burnout, its prevalence among psychiatrists is high and ranges from 25% to 50%,” lead author Kirill Bykov, MD, a PhD candidate at the Peoples’ Friendship University of Russia (RUDN University), Moscow, Russian Federation, told this news organization.
There was a “high heterogeneity of studies in terms of statistics, screening methods, burnout definitions, and cutoff points in the included studies, which necessitates the unification of future research methodology, but not to the detriment of the development of the theoretical background,” Dr. Bykov said.
The findings were published online in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
‘Unresolved problem’
Although burnout is a serious and prevalent problem among health care workers, little research has focused on burnout in mental health workers compared with other professionals, the investigators noted.
A previous systematic review and meta-analysis that focused specifically on burnout in psychiatrists was limited by methodologic concerns, including that the only burnout screening instrument used in the included studies was the full-length (22-item) MBI.
The current researchers surmised that “the integration of different empirical studies of psychiatrists’ burnout prevalence [remained] an unresolved problem.”
Dr. Bykov noted the current review was “investigator-initiated” and was a part of his PhD dissertation.
“Studying the works devoted to the burnout of psychiatrists, I drew attention to the varying prevalence rates of this phenomenon among them. This prompted me to conduct a systematic review of the literature and summarize the available data,” he said.
Unlike the previous review, the current one “does not contain restrictions regarding the place of research, publication language, covered burnout concepts, definitions, and screening instruments. Thus, its results will be helpful for practitioners and scientists around the world,” Dr. Bykov added.
Among the inclusion criteria was that a study should be empirical and quantitative, contain at least 20 practicing psychiatrists as participants, use a valid and reliable burnout screening instrument, have at least one burnout metric extractable specifically with regard to psychiatrists, and have a national survey or a response rate among psychiatrists of 20% or greater.
Qualitative or review articles or studies consisting of psychiatric trainees (such as medical students or residents) or nonpracticing psychiatrists were excluded.
Pooled prevalence
The researchers included 36 studies that comprised 5,481 participants (51.3% were women; mean age, 46.7 years). All studies had from 20 to 1,157 participants. They were employed in an array of settings in 19 countries.
In 22 studies, survey years ranged from 1996 to 2018; 14 studies did not report the year of data collection.
Most studies (75%) used some version of the MBI, and 19 studies used the full-length 22-item MBI Human Service Survey (MBI-HSS) . The survey rates emotional exhaustion (EE), depersonalization (DP), and low personal achievement (PA) on a 7-point Likert scale from 0 (“never”) to 6 (“almost every day”).
Other instruments included the CBI, the 16-item Oldenburg Burnout Inventory, the 21-item Tedium Measure, the 30-item Professional Quality of Life measure, the Rohland et al. Single-Item Measure of Self-Perceived Burnout, and the 21-item Brief Burnout Questionnaire.
Only three studies were free of methodologic limitations. The remaining 33 studies had some problems, such as not reporting the response rate or comparability between responders and nonresponders.
Results showed that the overall prevalence of burnout, as measured by the MBI and the CBI, was 25.9% (range, 11.1%-40.75%) and 50.3% (range, 30.9%-69.8%), respectively.
The pooled prevalence for burnout components is shown in the table.
European psychiatrists had lower EE scores (20.82; 95% confidence interval, 7.24-4.41) compared with their non-European counterparts (24.99; 95% CI, 23.05-26.94; P = .045).
‘Carry the hope’
In a comment, Christine Crawford, MD, associate medical director of the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), said she was surprised the burnout numbers weren’t higher.
Many colleagues she interacts with “have been experiencing pretty significant burnout that has only been exacerbated by the pandemic and ever-growing demand for mental health providers, and there aren’t enough to meet that demand,” said Dr. Crawford, a psychiatrist at Boston Medical Center’s Outpatient Child and Adolescent Psychiatry Clinic and at Codman Square Health Center. She was not involved with the current research.
Dr. Crawford noted that much of the data was from Europeans. Speaking to the experience of U.S.-based psychiatrists, she said there is a “greater appreciation for what we do as mental health providers, due to the growing conversations around mental health and normalizing mental health conditions.”
On the other hand, there is “a lack of parity in reimbursement rates. Although the general public values mental health, the medical system doesn’t value mental health providers in the same way as physicians in other specialties,” Dr. Crawford said. Feeling devalued can contribute to burnout, she added.
One way to counter burnout is to remember “that our role is to carry the hope. We can be hopeful for the patient that the treatment will work or the medications can provide some relief,” Dr. Crawford noted.
Psychiatrists “may need to hold on tightly to that hope because we may not receive that instant gratification from the patient or receive praise or see the change from the patient during that time, which can be challenging,” she said.
“But it’s important for us to keep in mind that, even in that moment when the patient can’t see it, we can work alongside the patient to create the vision of hope and what it will look like in the future,” said Dr. Crawford.
In the 2022 Medscape Psychiatrist Lifestyle, Happiness & Burnout Report, an annual online survey of Medscape member physicians, 47% of respondents reported burnout – which was up from 42% the previous year.
The investigators received no funding for this work. They and Dr. Crawford report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF AFFECTIVE DISORDERS
Do personality traits predict cognitive decline?
new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data from almost 2,000 individuals enrolled in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP) – a longitudinal study of older adults living in the greater Chicago metropolitan region and northeastern Illinois – with recruitment that began in 1997 and continues through today. Participants received a personality assessment as well as annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
Those with high scores on measures of conscientiousness were significantly less likely to progress from normal cognition to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) during the study. In fact, scoring an extra 1 standard deviation on the conscientiousness scale was associated with a 22% lower risk of transitioning from no cognitive impairment (NCI) to MCI. On the other hand, scoring an additional 1 SD on a neuroticism scale was associated with a 12% increased risk of transitioning to MCI.
Participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored high on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, tended to maintain normal cognitive functioning longer than other participants.
“Personality traits reflect relatively enduring patterns of thinking and behaving, which may cumulatively affect engagement in healthy and unhealthy behaviors and thought patterns across the lifespan,” lead author Tomiko Yoneda, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of medical social sciences, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
“The accumulation of lifelong experiences may then contribute to susceptibility of particular diseases or disorders, such as mild cognitive impairment, or contribute to individual differences in the ability to withstand age-related neurological changes,” she added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Competing risk factors
Personality traits “reflect an individual’s persistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving,” Dr. Yoneda said.
“For example, conscientiousness is characterized by competence, dutifulness, and self-discipline, while neuroticism is characterized by anxiety, depressive symptoms, and emotional instability. Likewise, individuals high in extraversion tend to be enthusiastic, gregarious, talkative, and assertive,” she added.
Previous research “suggests that low conscientiousness and high neuroticism are associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment,” she continued. However, “there is also an increased risk of death in older adulthood – in other words, these outcomes are ‘competing risk factors.’”
Dr. Yoneda said her team wanted to “examine the impact of personality traits on the simultaneous risk of transitioning to mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and death.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 1,954 participants in MAP (mean age at baseline 80 years, 73.7% female, 86.8% White), who received a personality assessment and annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
To assess personality traits – in particular, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion – the researchers used the NEO Five Factor Inventory (NEO-FFI). They also used multistate survival modeling to examine the potential association between these traits and transitions from one cognitive status category to another (NCI, MCI, and dementia) and to death.
Cognitive healthspan
By the end of the study, over half of the sample (54%) had died.
Most transitions showed “relative stability in cognitive status across measurement occasions.”
- NCI to NCI (n = 7,368)
- MCI to MCI (n = 1,244)
- Dementia to dementia (n = 876)
There were 725 “backward transitions” from MCI to NCI, “which may reflect improvement or within-person variability in cognitive functioning, or learning effects,” the authors note.
There were only 114 “backward transitions” from dementia to MCI and only 12 from dementia to NCI, “suggesting that improvement in cognitive status was relatively rare, particularly once an individual progresses to dementia.”
After adjusting for demographics, depressive symptoms, and apolipoprotein (APOE) ε4 allele, the researchers found that personality traits were the most important factors in the transition from NCI to MCI.
Higher conscientiousness was associated with a decreased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.85). Conversely, higher neuroticism was associated with an increased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21) and a significantly decreased likelihood of transition back from MCI to NCI (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.81-1.00).
Scoring ~6 points on a conscientiousness scale ranging from 0-48 (that is, 1 SD on the scale) was significantly associated with ~22% lower risk of transitioning forward from NCI to MCI, while scoring ~7 more points on a neuroticism scale (1 SD) was significantly associated with ~12% higher risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI.
Higher extraversion was associated with an increased likelihood of transitioning from MCI back to NCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22), and although extraversion was not associated with a longer total lifespan, participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored low on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, maintained normal cognitive function longer than other participants.
“Our results suggest that high conscientiousness and low neuroticism may protect individuals against mild cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Yoneda.
Importantly, individuals who were either higher in conscientiousness, higher in extraversion, or lower in neuroticism had more years of “cognitive healthspan,” meaning more years without cognitive impairment,” she added.
In addition, “individuals lower in neuroticism and higher in extraversion were more likely to recover after receiving an MCI diagnosis, suggesting that these traits may be protective even after an individual starts to progress to dementia,” she said.
The authors note that the study focused on only three of the Big Five personality traits, while the other 2 – openness to experience and agreeableness – may also be associated with cognitive aging processes and mortality.
Nevertheless, given the current results, alongside extensive research in the personality field, aiming to increase conscientiousness through persistent behavioral change is one potential strategy for promoting healthy cognitive aging, Dr. Yoneda said.
‘Invaluable window’
In a comment, Brent Roberts, PhD, professor of psychology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, said the study provides an “invaluable window into how personality affects the process of decline and either accelerates it, as in the role of neuroticism, or decelerates it, as in the role of conscientiousness.”
“I think the most fascinating finding was the fact that extraversion was related to transitioning from MCI back to NCI. These types of transitions have simply not been part of prior research, and it provides utterly unique insights and opportunities for interventions that may actually help people recover from a decline,” said Dr. Roberts, who was not involved in the research.
Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, called the paper “novel” because it investigated the transitions between normal cognition and mild impairment and between mild impairment and dementia.
Dr. Sexton, who was associated with this research team, cautioned that is it observational, “so it can illuminate associations or correlations, but not causes. As a result, we can’t say for sure what the mechanisms are behind these potential connections between personality and cognition, and more research is needed.”
The research was supported by the Alzheimer Society Research Program, Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Yoneda and co-authors, Dr. Roberts, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data from almost 2,000 individuals enrolled in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP) – a longitudinal study of older adults living in the greater Chicago metropolitan region and northeastern Illinois – with recruitment that began in 1997 and continues through today. Participants received a personality assessment as well as annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
Those with high scores on measures of conscientiousness were significantly less likely to progress from normal cognition to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) during the study. In fact, scoring an extra 1 standard deviation on the conscientiousness scale was associated with a 22% lower risk of transitioning from no cognitive impairment (NCI) to MCI. On the other hand, scoring an additional 1 SD on a neuroticism scale was associated with a 12% increased risk of transitioning to MCI.
Participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored high on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, tended to maintain normal cognitive functioning longer than other participants.
“Personality traits reflect relatively enduring patterns of thinking and behaving, which may cumulatively affect engagement in healthy and unhealthy behaviors and thought patterns across the lifespan,” lead author Tomiko Yoneda, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of medical social sciences, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
“The accumulation of lifelong experiences may then contribute to susceptibility of particular diseases or disorders, such as mild cognitive impairment, or contribute to individual differences in the ability to withstand age-related neurological changes,” she added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Competing risk factors
Personality traits “reflect an individual’s persistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving,” Dr. Yoneda said.
“For example, conscientiousness is characterized by competence, dutifulness, and self-discipline, while neuroticism is characterized by anxiety, depressive symptoms, and emotional instability. Likewise, individuals high in extraversion tend to be enthusiastic, gregarious, talkative, and assertive,” she added.
Previous research “suggests that low conscientiousness and high neuroticism are associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment,” she continued. However, “there is also an increased risk of death in older adulthood – in other words, these outcomes are ‘competing risk factors.’”
Dr. Yoneda said her team wanted to “examine the impact of personality traits on the simultaneous risk of transitioning to mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and death.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 1,954 participants in MAP (mean age at baseline 80 years, 73.7% female, 86.8% White), who received a personality assessment and annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
To assess personality traits – in particular, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion – the researchers used the NEO Five Factor Inventory (NEO-FFI). They also used multistate survival modeling to examine the potential association between these traits and transitions from one cognitive status category to another (NCI, MCI, and dementia) and to death.
Cognitive healthspan
By the end of the study, over half of the sample (54%) had died.
Most transitions showed “relative stability in cognitive status across measurement occasions.”
- NCI to NCI (n = 7,368)
- MCI to MCI (n = 1,244)
- Dementia to dementia (n = 876)
There were 725 “backward transitions” from MCI to NCI, “which may reflect improvement or within-person variability in cognitive functioning, or learning effects,” the authors note.
There were only 114 “backward transitions” from dementia to MCI and only 12 from dementia to NCI, “suggesting that improvement in cognitive status was relatively rare, particularly once an individual progresses to dementia.”
After adjusting for demographics, depressive symptoms, and apolipoprotein (APOE) ε4 allele, the researchers found that personality traits were the most important factors in the transition from NCI to MCI.
Higher conscientiousness was associated with a decreased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.85). Conversely, higher neuroticism was associated with an increased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21) and a significantly decreased likelihood of transition back from MCI to NCI (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.81-1.00).
Scoring ~6 points on a conscientiousness scale ranging from 0-48 (that is, 1 SD on the scale) was significantly associated with ~22% lower risk of transitioning forward from NCI to MCI, while scoring ~7 more points on a neuroticism scale (1 SD) was significantly associated with ~12% higher risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI.
Higher extraversion was associated with an increased likelihood of transitioning from MCI back to NCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22), and although extraversion was not associated with a longer total lifespan, participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored low on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, maintained normal cognitive function longer than other participants.
“Our results suggest that high conscientiousness and low neuroticism may protect individuals against mild cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Yoneda.
Importantly, individuals who were either higher in conscientiousness, higher in extraversion, or lower in neuroticism had more years of “cognitive healthspan,” meaning more years without cognitive impairment,” she added.
In addition, “individuals lower in neuroticism and higher in extraversion were more likely to recover after receiving an MCI diagnosis, suggesting that these traits may be protective even after an individual starts to progress to dementia,” she said.
The authors note that the study focused on only three of the Big Five personality traits, while the other 2 – openness to experience and agreeableness – may also be associated with cognitive aging processes and mortality.
Nevertheless, given the current results, alongside extensive research in the personality field, aiming to increase conscientiousness through persistent behavioral change is one potential strategy for promoting healthy cognitive aging, Dr. Yoneda said.
‘Invaluable window’
In a comment, Brent Roberts, PhD, professor of psychology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, said the study provides an “invaluable window into how personality affects the process of decline and either accelerates it, as in the role of neuroticism, or decelerates it, as in the role of conscientiousness.”
“I think the most fascinating finding was the fact that extraversion was related to transitioning from MCI back to NCI. These types of transitions have simply not been part of prior research, and it provides utterly unique insights and opportunities for interventions that may actually help people recover from a decline,” said Dr. Roberts, who was not involved in the research.
Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, called the paper “novel” because it investigated the transitions between normal cognition and mild impairment and between mild impairment and dementia.
Dr. Sexton, who was associated with this research team, cautioned that is it observational, “so it can illuminate associations or correlations, but not causes. As a result, we can’t say for sure what the mechanisms are behind these potential connections between personality and cognition, and more research is needed.”
The research was supported by the Alzheimer Society Research Program, Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Yoneda and co-authors, Dr. Roberts, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
new research shows.
Investigators analyzed data from almost 2,000 individuals enrolled in the Rush Memory and Aging Project (MAP) – a longitudinal study of older adults living in the greater Chicago metropolitan region and northeastern Illinois – with recruitment that began in 1997 and continues through today. Participants received a personality assessment as well as annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
Those with high scores on measures of conscientiousness were significantly less likely to progress from normal cognition to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) during the study. In fact, scoring an extra 1 standard deviation on the conscientiousness scale was associated with a 22% lower risk of transitioning from no cognitive impairment (NCI) to MCI. On the other hand, scoring an additional 1 SD on a neuroticism scale was associated with a 12% increased risk of transitioning to MCI.
Participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored high on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, tended to maintain normal cognitive functioning longer than other participants.
“Personality traits reflect relatively enduring patterns of thinking and behaving, which may cumulatively affect engagement in healthy and unhealthy behaviors and thought patterns across the lifespan,” lead author Tomiko Yoneda, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of medical social sciences, Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
“The accumulation of lifelong experiences may then contribute to susceptibility of particular diseases or disorders, such as mild cognitive impairment, or contribute to individual differences in the ability to withstand age-related neurological changes,” she added.
The study was published online in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology.
Competing risk factors
Personality traits “reflect an individual’s persistent patterns of thinking, feeling, and behaving,” Dr. Yoneda said.
“For example, conscientiousness is characterized by competence, dutifulness, and self-discipline, while neuroticism is characterized by anxiety, depressive symptoms, and emotional instability. Likewise, individuals high in extraversion tend to be enthusiastic, gregarious, talkative, and assertive,” she added.
Previous research “suggests that low conscientiousness and high neuroticism are associated with an increased risk of cognitive impairment,” she continued. However, “there is also an increased risk of death in older adulthood – in other words, these outcomes are ‘competing risk factors.’”
Dr. Yoneda said her team wanted to “examine the impact of personality traits on the simultaneous risk of transitioning to mild cognitive impairment, dementia, and death.”
For the study, the researchers analyzed data from 1,954 participants in MAP (mean age at baseline 80 years, 73.7% female, 86.8% White), who received a personality assessment and annual assessments of their cognitive abilities.
To assess personality traits – in particular, conscientiousness, neuroticism, and extraversion – the researchers used the NEO Five Factor Inventory (NEO-FFI). They also used multistate survival modeling to examine the potential association between these traits and transitions from one cognitive status category to another (NCI, MCI, and dementia) and to death.
Cognitive healthspan
By the end of the study, over half of the sample (54%) had died.
Most transitions showed “relative stability in cognitive status across measurement occasions.”
- NCI to NCI (n = 7,368)
- MCI to MCI (n = 1,244)
- Dementia to dementia (n = 876)
There were 725 “backward transitions” from MCI to NCI, “which may reflect improvement or within-person variability in cognitive functioning, or learning effects,” the authors note.
There were only 114 “backward transitions” from dementia to MCI and only 12 from dementia to NCI, “suggesting that improvement in cognitive status was relatively rare, particularly once an individual progresses to dementia.”
After adjusting for demographics, depressive symptoms, and apolipoprotein (APOE) ε4 allele, the researchers found that personality traits were the most important factors in the transition from NCI to MCI.
Higher conscientiousness was associated with a decreased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-0.85). Conversely, higher neuroticism was associated with an increased risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.04-1.21) and a significantly decreased likelihood of transition back from MCI to NCI (HR, 0.90; 95% CI, 0.81-1.00).
Scoring ~6 points on a conscientiousness scale ranging from 0-48 (that is, 1 SD on the scale) was significantly associated with ~22% lower risk of transitioning forward from NCI to MCI, while scoring ~7 more points on a neuroticism scale (1 SD) was significantly associated with ~12% higher risk of transitioning from NCI to MCI.
Higher extraversion was associated with an increased likelihood of transitioning from MCI back to NCI (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 1.03-1.22), and although extraversion was not associated with a longer total lifespan, participants who scored high on extraversion, as well as those who scored low on conscientiousness or low on neuroticism, maintained normal cognitive function longer than other participants.
“Our results suggest that high conscientiousness and low neuroticism may protect individuals against mild cognitive impairment,” said Dr. Yoneda.
Importantly, individuals who were either higher in conscientiousness, higher in extraversion, or lower in neuroticism had more years of “cognitive healthspan,” meaning more years without cognitive impairment,” she added.
In addition, “individuals lower in neuroticism and higher in extraversion were more likely to recover after receiving an MCI diagnosis, suggesting that these traits may be protective even after an individual starts to progress to dementia,” she said.
The authors note that the study focused on only three of the Big Five personality traits, while the other 2 – openness to experience and agreeableness – may also be associated with cognitive aging processes and mortality.
Nevertheless, given the current results, alongside extensive research in the personality field, aiming to increase conscientiousness through persistent behavioral change is one potential strategy for promoting healthy cognitive aging, Dr. Yoneda said.
‘Invaluable window’
In a comment, Brent Roberts, PhD, professor of psychology, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, said the study provides an “invaluable window into how personality affects the process of decline and either accelerates it, as in the role of neuroticism, or decelerates it, as in the role of conscientiousness.”
“I think the most fascinating finding was the fact that extraversion was related to transitioning from MCI back to NCI. These types of transitions have simply not been part of prior research, and it provides utterly unique insights and opportunities for interventions that may actually help people recover from a decline,” said Dr. Roberts, who was not involved in the research.
Claire Sexton, DPhil, Alzheimer’s Association director of scientific programs and outreach, called the paper “novel” because it investigated the transitions between normal cognition and mild impairment and between mild impairment and dementia.
Dr. Sexton, who was associated with this research team, cautioned that is it observational, “so it can illuminate associations or correlations, but not causes. As a result, we can’t say for sure what the mechanisms are behind these potential connections between personality and cognition, and more research is needed.”
The research was supported by the Alzheimer Society Research Program, Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council, and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Yoneda and co-authors, Dr. Roberts, and Dr. Sexton have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PERSONALITY AND SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY



