User login
Is it time for yet another COVID booster? It’s complicated
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Possible bivalent vaccine link to strokes in people over 65
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
who got the shot, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Food and Drug Administration said in a joint news release.
The release did not recommend people change their vaccine practices, saying the database finding probably did not represent a “true clinical risk.” The CDC said everybody, including people over 65, should stay up to date on their COVID vaccines, including the bivalent booster.
The news release said the Vaccine Safety Datalink (VSD), “a near real-time surveillance system,” raised a safety concern about the Pfizer/BioNTech booster.
“Rapid-response investigation of the signal in the VSD raised a question of whether people 65 and older who have received the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine, Bivalent were more likely to have an ischemic stroke in the 21 days following vaccination compared with days 22-44 following vaccination,” the news release said.
Ischemic strokes are blockages of blood to the brain, often caused by blood clots.
“Although the totality of the data currently suggests that it is very unlikely that the signal in VSD (Vaccine Safety Datalink) represents a true clinical risk, we believe it is important to share this information with the public, as we have in the past, when one of our safety monitoring systems detects a signal,” the release said.
No higher likelihood of strokes linked to the Pfizer bivalent vaccine had been found by Pfizer/BioNTech, the Department of Veterans Affairs, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System maintained by the CDC and the FDA, or other agencies that monitor reactions of vaccines, the news release said. No safety issues about strokes have been identified with the Moderna bivalent vaccine.
CNN, citing a CDC official, reported that about 550,000 seniors who got Pfizer bivalent boosters were tracked by the VSD, and 130 of them had strokes within 3 weeks of getting the shot. None of those 130 people died, CNN said. The official spoke on the condition of anonymity because they weren’t authorized to share the data.
The issue will be discussed at the January meeting of the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee.
In a joint statement, Pfizer and BioNTech said: “Neither Pfizer and BioNTech nor the CDC or FDA have observed similar findings across numerous other monitoring systems in the U.S. and globally and there is no evidence to conclude that ischemic stroke is associated with the use of the companies’ COVID-19 vaccines.”
Bivalent boosters contain two strains of vaccine – one to protect against the original COVID-19 virus and another targeting Omicron subvariants.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Children and COVID: ED visits and hospitalizations start to fall again
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.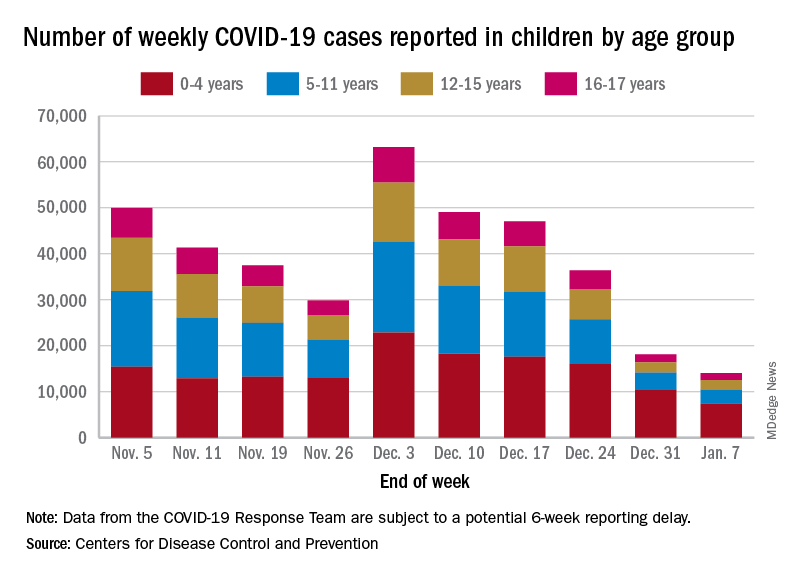
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for COVID-19 in children appear to be following the declining trend set by weekly cases since early December, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
. New cases took a different path that had the weekly total falling through November before taking a big jump during the week of Nov. 27 to Dec. 3 – the count doubled from 30,000 the previous week to 63,000 – and then decreased again, the CDC reported.
The proportion of ED visits with COVID, which was down to 1.0% of all ED visits (7-day average) for children aged 0-4 years on Nov. 4, was up to 3.2% on Jan. 3 but slipped to 2.5% as of Jan. 10. The patterns for older children are similar, with some differences in timing and lower peaks (1.7% for 12- to 15-year-olds and 1.9% for those aged 16-17), according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The trend for new hospital admissions of children with confirmed COVID showed a similar rise through December, and the latest data for the very beginning of January suggest an even faster drop, although there is more of a reporting lag with hospitalization data, compared with ED visits, the CDC noted.
The most current data (Dec. 30 to Jan. 5) available from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association show less volatility in the number of weekly cases through November and December, with the peak being about 48,000 in mid-December. The AAP/CHA totals for the last 2 weeks, however, were both higher than the CDC’s corresponding counts, which are more preliminary and subject to revision.
The CDC puts the total number of COVID cases in children at 16.7 million – about 17.2% of all cases – as of Jan. 11, with 1,981 deaths reported so far. The AAP and CHA are not tracking deaths, but their case total as of Jan. 5 was 15.2 million, which represents 18.1% of cases in all ages. The AAP/CHA report is based on data reported publicly by an ever-decreasing number of states and territories.
Add this to the list of long COVID symptoms: Stigma
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Most people with long COVID find they’re facing stigma due to their condition, according to a new report from researchers in the United Kingdom. In short: Relatives and friends may not believe they’re truly sick.
The U.K. team found that more than three-quarters of people studied had experienced stigma often or always.
In fact, 95% of people with long COVID faced at least one type of stigma at least sometimes, according to the study, published in November in the journal PLOS One.
Those conclusions had surprised the study’s lead researcher, Marija Pantelic, PhD, a public health lecturer at Brighton and Sussex Medical School, England.
“After years of working on HIV-related stigma, I was shocked to see how many people were turning a blind eye to and dismissing the difficulties experienced by people with long COVID,” Dr. Pantelic says. “It has also been clear to me from the start that this stigma is detrimental not just for people’s dignity, but also public health.”
Even some doctors argue that the growing attention paid to long COVID is excessive.
“It’s often normal to experience mild fatigue or weaknesses for weeks after being sick and inactive and not eating well. Calling these cases long COVID is the medicalization of modern life,” Marty Makary, MD, a surgeon and public policy researcher at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, wrote in a commentary in the Wall Street Journal.
Other doctors strongly disagree, including Alba Azola, MD, codirector of the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team and an expert in the stigma surrounding long COVID.
“Putting that spin on things, it’s just hurting people,” she says.
One example is people who cannot return to work.
“A lot of their family members tell me that they’re being lazy,” Dr. Azola says. “That’s part of the public stigma, that these are people just trying to get out of work.”
Some experts say the U.K. study represents a landmark.
“When you have data like this on long COVID stigma, it becomes more difficult to deny its existence or address it,” says Naomi Torres-Mackie, PhD, a clinical psychologist at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York. She also is head of research at the New York–based Mental Health Coalition, a group of experts working to end the stigma surrounding mental health.
She recalls her first patient with long COVID.
“She experienced the discomfort and pain itself, and then she had this crushing feeling that it wasn’t valid, or real. She felt very alone in it,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Another one of her patients is working at her job from home but facing doubt about her condition from her employers.
“Every month, her medical doctor has to produce a letter confirming her medical condition,” Dr. Torres-Mackie says.
Taking part in the British stigma survey were 1,166 people, including 966 residents of the United Kingdom, with the average age of 48. Nearly 85% were female, and more than three-quarters were educated at the university level or higher.
Half of them said they had a clinical diagnosis of long COVID.
More than 60% of them said that at least some of the time, they were cautious about who they talked to about their condition. And fully 34% of those who did disclose their diagnosis said that they regretted having done so.
That’s a difficult experience for those with long COVID, says Leonard Jason, PhD, a professor of psychology at DePaul University in Chicago.
“It’s like they’re traumatized by the initial experience of being sick, and retraumatized by the response of others to them,” he says.
Unexplained illnesses are not well-regarded by the general public, Dr. Jason says.
He gave the example of multiple sclerosis. Before the 1980s, those with MS were considered to have a psychological illness, he says. “Then, in the 1980s, there were biomarkers that said, ‘Here’s the evidence.’ ”
The British study described three types of stigma stemming from the long COVID diagnosis of those questioned:
- Enacted stigma: People were directly treated unfairly because of their condition.
- Internalized stigma: People felt embarrassed by that condition.
- Anticipated stigma: People expected they would be treated poorly because of their diagnosis.
Dr. Azola calls the medical community a major problem when it comes to dealing with long COVID.
“What I see with my patients is medical trauma,” she says. They may have symptoms that send them to the emergency room, and then the tests come back negative. “Instead of tracking the patients’ symptoms, patients get told, ‘Everything looks good, you can go home, this is a panic attack,’ ” she says.
Some people go online to search for treatments, sometimes launching GoFundMe campaigns to raise money for unreliable treatments.
Long COVID patients may have gone through 5 to 10 doctors before they arrive for treatment with the Johns Hopkins Post-Acute COVID-19 Team. The clinic began in April 2020 remotely and in August of that year in person.
Today, the clinic staff spends an hour with a first-time long COVID patient, hearing their stories and helping relieve anxiety, Dr. Azola says.
The phenomenon of long COVID is similar to what patients have had with chronic fatigue syndrome, lupus, or fibromyalgia, where people have symptoms that are hard to explain, says Jennifer Chevinsky, MD, deputy public health officer for Riverside County, Calif.
“Stigma within medicine or health care is nothing new,” she says.
In Chicago, Dr. Jason notes that the federal government’s decision to invest hundreds of millions of dollars in long COVID research “shows the government is helping destigmatize it.”
Dr. Pantelic says she and her colleagues are continuing their research.
“We are interested in understanding the impacts of this stigma, and how to mitigate any adverse outcomes for patients and services,” she says.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
PLOS ONE
Which treatments improve long-term outcomes of critical COVID illness?
, according to new data.
However, survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation, convalescent plasma, or lopinavir-ritonavir, and survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine.
“After critically ill patients leave the hospital, there’s a high risk of readmission, death after discharge, or exacerbations of chronic illness,” study author Patrick Lawler, MD, a clinician-scientist at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre at University Health Network and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“When looking at the impact of treatment, we don’t want to improve short-term outcomes yet worsen long-term disability,” he said. “That long-term, 6-month horizon is what matters most to patients.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Investigating treatments
The investigators analyzed data from an ongoing platform trial called Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community Acquired Pneumonia (REMAP-CAP). The trial is evaluating treatments for patients with severe pneumonia in pandemic and nonpandemic settings.
In the trial, patients are randomly assigned to receive one or more interventions within the following six treatment domains: immune modulators, convalescent plasma, antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, antivirals, and corticosteroids. The trial’s primary outcome for patients with COVID-19 is hospital survival and organ support–free days up to 21 days. Researchers previously observed improvement after treatment with IL-6 receptor antagonists (which are immune modulators).
For this study, the research team analyzed data for 4,869 critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled between March 2020 and June 2021 at 197 sites in 14 countries. A 180-day follow-up was completed in March 2022. The critically ill patients had been admitted to an intensive care unit and had received respiratory or cardiovascular organ support.
The researchers examined survival through day 180. A hazard ratio of less than 1 represented improved survival, and an HR greater than 1 represented harm. Futility was represented by a relative improvement in outcome of less than 20%, which was shown by an HR greater than 0.83.
Among the 4,869 patients, 4,107 patients had a known mortality status, and 2,590 were alive at day 180. Among the 1,517 patients who died by day 180, 91 deaths (6%) occurred between hospital discharge and day 180.
Overall, use of IL-6 receptor antagonists (either tocilizumab or sarilumab) had a greater than 99.9% probability of improving 6-month survival, and use of antiplatelet agents (aspirin or a P2Y12 inhibitor such as clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor) had a 95% probability of improving 6-month survival, compared with control therapies.
In contrast, long-term survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation (11.5%), convalescent plasma (54.7%), or lopinavir-ritonavir (31.9%). The probability of trial-defined statistical futility was high for anticoagulation (99.9%), convalescent plasma (99.2%), and lopinavir-ritonavir (96.6%).
Long-term survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine, with a posterior probability of harm of 96.9%. In addition, the combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine had a 96.8% probability of harm.
Corticosteroids didn’t improve long-term outcomes, although enrollment in the treatment domain was terminated early in response to external evidence. The probability of improving 6-month survival ranged from 57.1% to 61.6% for various hydrocortisone dosing strategies.
Consistent treatment effects
When considered along with previously reported short-term results from the REMAP-CAP trial, the findings indicate that initial in-hospital treatment effects were consistent for most therapies through 6 months.
“We were very relieved to see that treatments with a favorable benefit for patients in the short term also appeared to be beneficial through 180 days,” said Dr. Lawler. “This supports the current clinical practice strategy in providing treatment to critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
In a subgroup analysis of 989 patients, health-related quality of life at day 180 was higher among those treated with IL-6 receptor antagonists and antiplatelet agents. The average quality-of-life score for the lopinavir-ritonavir group was lower than for control patients.
Among 720 survivors, 273 patients (37.9%) had moderate, severe, or complete disability at day 180. IL-6 receptor antagonists had a 92.6% probability of reducing disability, and anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) had a 90.8% probability of reducing disability. However, lopinavir-ritonavir had a 91.7% probability of worsening disability.
The REMAP-CAP trial investigators will continue to assess treatment domains and long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients. They will evaluate additional data regarding disability, quality of life, and long-COVID outcomes.
“Reassuring” results
Commenting on the study, Angela Cheung, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Toronto General Research Institute, said, “It is important to look at the longer-term effects of these therapies, as sometimes we may improve things in the short term, but that may not translate to longer-term gains. Historically, most trials conducted in this patient population assess only short outcomes, such as organ failure or 28-day mortality.”
Dr. Cheung, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as the co-lead for the Canadian COVID-19 Prospective Cohort Study (CANCOV) and the Recovering From COVID-19 Lingering Symptoms Adaptive Integrative Medicine Trial (RECLAIM). These studies are also analyzing long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients.
“It is reassuring to see that the 6-month outcomes are consistent with the short-term outcomes,” she said. “This study will help guide critical care medicine physicians in their treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
The study was supported by numerous grants and funds, including the Canadian Institute of Health Research COVID-19 Rapid Research Funding. Amgen and Eisai also provided funding. Dr. Lawler received grants from Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Novartis, CorEvitas, Partners Healthcare, and the American College of Cardiology outside the submitted work. Dr. Cheung has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
However, survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation, convalescent plasma, or lopinavir-ritonavir, and survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine.
“After critically ill patients leave the hospital, there’s a high risk of readmission, death after discharge, or exacerbations of chronic illness,” study author Patrick Lawler, MD, a clinician-scientist at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre at University Health Network and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“When looking at the impact of treatment, we don’t want to improve short-term outcomes yet worsen long-term disability,” he said. “That long-term, 6-month horizon is what matters most to patients.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Investigating treatments
The investigators analyzed data from an ongoing platform trial called Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community Acquired Pneumonia (REMAP-CAP). The trial is evaluating treatments for patients with severe pneumonia in pandemic and nonpandemic settings.
In the trial, patients are randomly assigned to receive one or more interventions within the following six treatment domains: immune modulators, convalescent plasma, antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, antivirals, and corticosteroids. The trial’s primary outcome for patients with COVID-19 is hospital survival and organ support–free days up to 21 days. Researchers previously observed improvement after treatment with IL-6 receptor antagonists (which are immune modulators).
For this study, the research team analyzed data for 4,869 critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled between March 2020 and June 2021 at 197 sites in 14 countries. A 180-day follow-up was completed in March 2022. The critically ill patients had been admitted to an intensive care unit and had received respiratory or cardiovascular organ support.
The researchers examined survival through day 180. A hazard ratio of less than 1 represented improved survival, and an HR greater than 1 represented harm. Futility was represented by a relative improvement in outcome of less than 20%, which was shown by an HR greater than 0.83.
Among the 4,869 patients, 4,107 patients had a known mortality status, and 2,590 were alive at day 180. Among the 1,517 patients who died by day 180, 91 deaths (6%) occurred between hospital discharge and day 180.
Overall, use of IL-6 receptor antagonists (either tocilizumab or sarilumab) had a greater than 99.9% probability of improving 6-month survival, and use of antiplatelet agents (aspirin or a P2Y12 inhibitor such as clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor) had a 95% probability of improving 6-month survival, compared with control therapies.
In contrast, long-term survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation (11.5%), convalescent plasma (54.7%), or lopinavir-ritonavir (31.9%). The probability of trial-defined statistical futility was high for anticoagulation (99.9%), convalescent plasma (99.2%), and lopinavir-ritonavir (96.6%).
Long-term survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine, with a posterior probability of harm of 96.9%. In addition, the combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine had a 96.8% probability of harm.
Corticosteroids didn’t improve long-term outcomes, although enrollment in the treatment domain was terminated early in response to external evidence. The probability of improving 6-month survival ranged from 57.1% to 61.6% for various hydrocortisone dosing strategies.
Consistent treatment effects
When considered along with previously reported short-term results from the REMAP-CAP trial, the findings indicate that initial in-hospital treatment effects were consistent for most therapies through 6 months.
“We were very relieved to see that treatments with a favorable benefit for patients in the short term also appeared to be beneficial through 180 days,” said Dr. Lawler. “This supports the current clinical practice strategy in providing treatment to critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
In a subgroup analysis of 989 patients, health-related quality of life at day 180 was higher among those treated with IL-6 receptor antagonists and antiplatelet agents. The average quality-of-life score for the lopinavir-ritonavir group was lower than for control patients.
Among 720 survivors, 273 patients (37.9%) had moderate, severe, or complete disability at day 180. IL-6 receptor antagonists had a 92.6% probability of reducing disability, and anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) had a 90.8% probability of reducing disability. However, lopinavir-ritonavir had a 91.7% probability of worsening disability.
The REMAP-CAP trial investigators will continue to assess treatment domains and long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients. They will evaluate additional data regarding disability, quality of life, and long-COVID outcomes.
“Reassuring” results
Commenting on the study, Angela Cheung, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Toronto General Research Institute, said, “It is important to look at the longer-term effects of these therapies, as sometimes we may improve things in the short term, but that may not translate to longer-term gains. Historically, most trials conducted in this patient population assess only short outcomes, such as organ failure or 28-day mortality.”
Dr. Cheung, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as the co-lead for the Canadian COVID-19 Prospective Cohort Study (CANCOV) and the Recovering From COVID-19 Lingering Symptoms Adaptive Integrative Medicine Trial (RECLAIM). These studies are also analyzing long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients.
“It is reassuring to see that the 6-month outcomes are consistent with the short-term outcomes,” she said. “This study will help guide critical care medicine physicians in their treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
The study was supported by numerous grants and funds, including the Canadian Institute of Health Research COVID-19 Rapid Research Funding. Amgen and Eisai also provided funding. Dr. Lawler received grants from Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Novartis, CorEvitas, Partners Healthcare, and the American College of Cardiology outside the submitted work. Dr. Cheung has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to new data.
However, survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation, convalescent plasma, or lopinavir-ritonavir, and survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine.
“After critically ill patients leave the hospital, there’s a high risk of readmission, death after discharge, or exacerbations of chronic illness,” study author Patrick Lawler, MD, a clinician-scientist at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre at University Health Network and an assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto, said in an interview.
“When looking at the impact of treatment, we don’t want to improve short-term outcomes yet worsen long-term disability,” he said. “That long-term, 6-month horizon is what matters most to patients.”
The study was published online in JAMA.
Investigating treatments
The investigators analyzed data from an ongoing platform trial called Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community Acquired Pneumonia (REMAP-CAP). The trial is evaluating treatments for patients with severe pneumonia in pandemic and nonpandemic settings.
In the trial, patients are randomly assigned to receive one or more interventions within the following six treatment domains: immune modulators, convalescent plasma, antiplatelet therapy, anticoagulation, antivirals, and corticosteroids. The trial’s primary outcome for patients with COVID-19 is hospital survival and organ support–free days up to 21 days. Researchers previously observed improvement after treatment with IL-6 receptor antagonists (which are immune modulators).
For this study, the research team analyzed data for 4,869 critically ill adult patients with COVID-19 who were enrolled between March 2020 and June 2021 at 197 sites in 14 countries. A 180-day follow-up was completed in March 2022. The critically ill patients had been admitted to an intensive care unit and had received respiratory or cardiovascular organ support.
The researchers examined survival through day 180. A hazard ratio of less than 1 represented improved survival, and an HR greater than 1 represented harm. Futility was represented by a relative improvement in outcome of less than 20%, which was shown by an HR greater than 0.83.
Among the 4,869 patients, 4,107 patients had a known mortality status, and 2,590 were alive at day 180. Among the 1,517 patients who died by day 180, 91 deaths (6%) occurred between hospital discharge and day 180.
Overall, use of IL-6 receptor antagonists (either tocilizumab or sarilumab) had a greater than 99.9% probability of improving 6-month survival, and use of antiplatelet agents (aspirin or a P2Y12 inhibitor such as clopidogrel, prasugrel, or ticagrelor) had a 95% probability of improving 6-month survival, compared with control therapies.
In contrast, long-term survival wasn’t improved with therapeutic anticoagulation (11.5%), convalescent plasma (54.7%), or lopinavir-ritonavir (31.9%). The probability of trial-defined statistical futility was high for anticoagulation (99.9%), convalescent plasma (99.2%), and lopinavir-ritonavir (96.6%).
Long-term survival was worsened with hydroxychloroquine, with a posterior probability of harm of 96.9%. In addition, the combination of lopinavir-ritonavir and hydroxychloroquine had a 96.8% probability of harm.
Corticosteroids didn’t improve long-term outcomes, although enrollment in the treatment domain was terminated early in response to external evidence. The probability of improving 6-month survival ranged from 57.1% to 61.6% for various hydrocortisone dosing strategies.
Consistent treatment effects
When considered along with previously reported short-term results from the REMAP-CAP trial, the findings indicate that initial in-hospital treatment effects were consistent for most therapies through 6 months.
“We were very relieved to see that treatments with a favorable benefit for patients in the short term also appeared to be beneficial through 180 days,” said Dr. Lawler. “This supports the current clinical practice strategy in providing treatment to critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
In a subgroup analysis of 989 patients, health-related quality of life at day 180 was higher among those treated with IL-6 receptor antagonists and antiplatelet agents. The average quality-of-life score for the lopinavir-ritonavir group was lower than for control patients.
Among 720 survivors, 273 patients (37.9%) had moderate, severe, or complete disability at day 180. IL-6 receptor antagonists had a 92.6% probability of reducing disability, and anakinra (an IL-1 receptor antagonist) had a 90.8% probability of reducing disability. However, lopinavir-ritonavir had a 91.7% probability of worsening disability.
The REMAP-CAP trial investigators will continue to assess treatment domains and long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients. They will evaluate additional data regarding disability, quality of life, and long-COVID outcomes.
“Reassuring” results
Commenting on the study, Angela Cheung, MD, PhD, a professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and senior scientist at the Toronto General Research Institute, said, “It is important to look at the longer-term effects of these therapies, as sometimes we may improve things in the short term, but that may not translate to longer-term gains. Historically, most trials conducted in this patient population assess only short outcomes, such as organ failure or 28-day mortality.”
Dr. Cheung, who wasn’t involved with this study, serves as the co-lead for the Canadian COVID-19 Prospective Cohort Study (CANCOV) and the Recovering From COVID-19 Lingering Symptoms Adaptive Integrative Medicine Trial (RECLAIM). These studies are also analyzing long-term outcomes among COVID-19 patients.
“It is reassuring to see that the 6-month outcomes are consistent with the short-term outcomes,” she said. “This study will help guide critical care medicine physicians in their treatment of critically ill patients with COVID-19.”
The study was supported by numerous grants and funds, including the Canadian Institute of Health Research COVID-19 Rapid Research Funding. Amgen and Eisai also provided funding. Dr. Lawler received grants from Canadian Institutes for Health Research and the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Novartis, CorEvitas, Partners Healthcare, and the American College of Cardiology outside the submitted work. Dr. Cheung has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA
Pandemic may be limiting ED access for sexual assault
“In 2020, we hoped that the COVID pandemic would only last a few months. However, as it continued, we became increasingly concerned about limited health care access for survivors of sexual assault throughout the ongoing crisis,” study author Katherine A. Muldoon, PhD, MPH, a senior clinical research associate at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute in Ontario, told this news organization.
“Unexpectedly, we found a 20%-25% increase in the number of survivors of sexual assault presenting for emergency care before the lockdown protocols were enacted,” she added. “After lockdown, the numbers dropped by 50%-60% and fluctuated throughout ... the pandemic.”
As they develop new lockdown protocols, public health officials and governments should incorporate warnings of the risks of violence and state that survivors should still present for urgent care when needed, said Dr. Muldoon. “COVID-19 lockdown protocols have limited access to health care for survivors worldwide, and barriers are likely greater in low-resource settings and those heavily affected by COVID-19.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Both sexes affected
The researchers analyzed linked health administrative data from 197 EDs in Ontario from January 2019 to September 2021. They used 10 bimonthly time periods to compare differences in the frequency and rates of ED visits for sexual assault in 2020-2021 (during the pandemic), compared with baseline prepandemic rates in 2019.
Sexual assault was defined by 27 ICD-10 procedure and diagnoses codes.
More than 14 million ED presentations occurred during the study period, including 10,523 for sexual assault. The median age was 23 years for female patients and 15 years for males. Most encounters (88.4%) were among females.
During the 2 months before the pandemic (Jan. 11 to Mar. 10, 2020), the rates of ED encounters for sexual assault among females were significantly higher than prepandemic levels (8.4 vs. 6.9 cases per 100,000; age-adjusted rate ratio [aRR], 1.22), whereas during the first 2 months of the pandemic (Mar. 11 to May 10, 2020), rates were significantly lower (4.2 vs. 8.3 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.51).
Among males, rates were higher during the 2 months before the pandemic, but not significantly different, compared with prepandemic levels (1.2 vs. 1.0 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.19). However, the rates decreased significantly during the first 2 months of the pandemic (0.5 vs. 1.2 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.39).
For the 12 months starting July 11, 2020, rates were the same as in 2019. In the final time period (July 11 to Sept. 10, 2021), however, the rates were significantly higher than during prepandemic levels (1.5 vs. 1.1 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.40).
Further analyses showed a similar pattern for all age groups, community sizes, and income quintiles. Rates were predominantly above prepandemic levels for the 2 months leading up to the pandemic and below expected levels from the beginning of the pandemic onward. However, from July 11 to Sept. 10, 2020 (during a trough in the summer, when sexual assaults are generally higher), and from May 11 to Sept. 10, 2021 (also during a trough and the summer), the rates returned to prepandemic levels.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many changes to society and health care delivery and access,” the authors wrote. “We recommend that the decision-making regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic include antiviolence considerations to evaluate how policies and protocols affect the risk of violence and ensure that those who need health care can access services without concern.”
“Specialized and trauma-informed clinics are the best solution for encouraging survivors to come for urgent care following a sexual assault,” said Dr. Muldoon. “Clinicians should be prepared and trained to provide the best possible care for survivors of violence and ensure that getting care is not retraumatizing. Fostering conversations about the common experience of violence and destigmatizing those exposed to violence remain the most important ways to create safer spaces and societies.”
Dedicated care pathways
Commenting on the study, Samuel A. McLean, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Trauma Recovery and professor of emergency medicine, psychiatry, and anesthesiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “This important work documents a reduction in visits by sexual assault survivors for emergency care and forensic evidence collection during times of pandemic surge. It’s impossible to know for certain if this reduction in visits is entirely due to a reduction in sexual assaults, but a number of lines of circumstantial evidence make this unlikely.”
The results highlight the importance of ensuring that sexual assault care is maintained during surges in emergency care volume, added Dr. McLean, who was not involved with the current study. “This can be done via methods such as dedicated care pathways that avoid prolonged survivor wait times for care, and public health messaging that informs the public of the continued ready access to care during surges. Evidence, including data cited by the authors, suggests that these same care-seeking reductions are occurring in the United States and elsewhere.”
The study was supported by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-term Care Applied Health Research Question Fund. Dr. Muldoon, study coauthors, and Dr. McLean report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“In 2020, we hoped that the COVID pandemic would only last a few months. However, as it continued, we became increasingly concerned about limited health care access for survivors of sexual assault throughout the ongoing crisis,” study author Katherine A. Muldoon, PhD, MPH, a senior clinical research associate at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute in Ontario, told this news organization.
“Unexpectedly, we found a 20%-25% increase in the number of survivors of sexual assault presenting for emergency care before the lockdown protocols were enacted,” she added. “After lockdown, the numbers dropped by 50%-60% and fluctuated throughout ... the pandemic.”
As they develop new lockdown protocols, public health officials and governments should incorporate warnings of the risks of violence and state that survivors should still present for urgent care when needed, said Dr. Muldoon. “COVID-19 lockdown protocols have limited access to health care for survivors worldwide, and barriers are likely greater in low-resource settings and those heavily affected by COVID-19.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Both sexes affected
The researchers analyzed linked health administrative data from 197 EDs in Ontario from January 2019 to September 2021. They used 10 bimonthly time periods to compare differences in the frequency and rates of ED visits for sexual assault in 2020-2021 (during the pandemic), compared with baseline prepandemic rates in 2019.
Sexual assault was defined by 27 ICD-10 procedure and diagnoses codes.
More than 14 million ED presentations occurred during the study period, including 10,523 for sexual assault. The median age was 23 years for female patients and 15 years for males. Most encounters (88.4%) were among females.
During the 2 months before the pandemic (Jan. 11 to Mar. 10, 2020), the rates of ED encounters for sexual assault among females were significantly higher than prepandemic levels (8.4 vs. 6.9 cases per 100,000; age-adjusted rate ratio [aRR], 1.22), whereas during the first 2 months of the pandemic (Mar. 11 to May 10, 2020), rates were significantly lower (4.2 vs. 8.3 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.51).
Among males, rates were higher during the 2 months before the pandemic, but not significantly different, compared with prepandemic levels (1.2 vs. 1.0 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.19). However, the rates decreased significantly during the first 2 months of the pandemic (0.5 vs. 1.2 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.39).
For the 12 months starting July 11, 2020, rates were the same as in 2019. In the final time period (July 11 to Sept. 10, 2021), however, the rates were significantly higher than during prepandemic levels (1.5 vs. 1.1 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.40).
Further analyses showed a similar pattern for all age groups, community sizes, and income quintiles. Rates were predominantly above prepandemic levels for the 2 months leading up to the pandemic and below expected levels from the beginning of the pandemic onward. However, from July 11 to Sept. 10, 2020 (during a trough in the summer, when sexual assaults are generally higher), and from May 11 to Sept. 10, 2021 (also during a trough and the summer), the rates returned to prepandemic levels.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many changes to society and health care delivery and access,” the authors wrote. “We recommend that the decision-making regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic include antiviolence considerations to evaluate how policies and protocols affect the risk of violence and ensure that those who need health care can access services without concern.”
“Specialized and trauma-informed clinics are the best solution for encouraging survivors to come for urgent care following a sexual assault,” said Dr. Muldoon. “Clinicians should be prepared and trained to provide the best possible care for survivors of violence and ensure that getting care is not retraumatizing. Fostering conversations about the common experience of violence and destigmatizing those exposed to violence remain the most important ways to create safer spaces and societies.”
Dedicated care pathways
Commenting on the study, Samuel A. McLean, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Trauma Recovery and professor of emergency medicine, psychiatry, and anesthesiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “This important work documents a reduction in visits by sexual assault survivors for emergency care and forensic evidence collection during times of pandemic surge. It’s impossible to know for certain if this reduction in visits is entirely due to a reduction in sexual assaults, but a number of lines of circumstantial evidence make this unlikely.”
The results highlight the importance of ensuring that sexual assault care is maintained during surges in emergency care volume, added Dr. McLean, who was not involved with the current study. “This can be done via methods such as dedicated care pathways that avoid prolonged survivor wait times for care, and public health messaging that informs the public of the continued ready access to care during surges. Evidence, including data cited by the authors, suggests that these same care-seeking reductions are occurring in the United States and elsewhere.”
The study was supported by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-term Care Applied Health Research Question Fund. Dr. Muldoon, study coauthors, and Dr. McLean report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“In 2020, we hoped that the COVID pandemic would only last a few months. However, as it continued, we became increasingly concerned about limited health care access for survivors of sexual assault throughout the ongoing crisis,” study author Katherine A. Muldoon, PhD, MPH, a senior clinical research associate at the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute in Ontario, told this news organization.
“Unexpectedly, we found a 20%-25% increase in the number of survivors of sexual assault presenting for emergency care before the lockdown protocols were enacted,” she added. “After lockdown, the numbers dropped by 50%-60% and fluctuated throughout ... the pandemic.”
As they develop new lockdown protocols, public health officials and governments should incorporate warnings of the risks of violence and state that survivors should still present for urgent care when needed, said Dr. Muldoon. “COVID-19 lockdown protocols have limited access to health care for survivors worldwide, and barriers are likely greater in low-resource settings and those heavily affected by COVID-19.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open.
Both sexes affected
The researchers analyzed linked health administrative data from 197 EDs in Ontario from January 2019 to September 2021. They used 10 bimonthly time periods to compare differences in the frequency and rates of ED visits for sexual assault in 2020-2021 (during the pandemic), compared with baseline prepandemic rates in 2019.
Sexual assault was defined by 27 ICD-10 procedure and diagnoses codes.
More than 14 million ED presentations occurred during the study period, including 10,523 for sexual assault. The median age was 23 years for female patients and 15 years for males. Most encounters (88.4%) were among females.
During the 2 months before the pandemic (Jan. 11 to Mar. 10, 2020), the rates of ED encounters for sexual assault among females were significantly higher than prepandemic levels (8.4 vs. 6.9 cases per 100,000; age-adjusted rate ratio [aRR], 1.22), whereas during the first 2 months of the pandemic (Mar. 11 to May 10, 2020), rates were significantly lower (4.2 vs. 8.3 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.51).
Among males, rates were higher during the 2 months before the pandemic, but not significantly different, compared with prepandemic levels (1.2 vs. 1.0 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.19). However, the rates decreased significantly during the first 2 months of the pandemic (0.5 vs. 1.2 cases per 100,000; aRR, 0.39).
For the 12 months starting July 11, 2020, rates were the same as in 2019. In the final time period (July 11 to Sept. 10, 2021), however, the rates were significantly higher than during prepandemic levels (1.5 vs. 1.1 cases per 100,000; aRR, 1.40).
Further analyses showed a similar pattern for all age groups, community sizes, and income quintiles. Rates were predominantly above prepandemic levels for the 2 months leading up to the pandemic and below expected levels from the beginning of the pandemic onward. However, from July 11 to Sept. 10, 2020 (during a trough in the summer, when sexual assaults are generally higher), and from May 11 to Sept. 10, 2021 (also during a trough and the summer), the rates returned to prepandemic levels.
“The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many changes to society and health care delivery and access,” the authors wrote. “We recommend that the decision-making regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic include antiviolence considerations to evaluate how policies and protocols affect the risk of violence and ensure that those who need health care can access services without concern.”
“Specialized and trauma-informed clinics are the best solution for encouraging survivors to come for urgent care following a sexual assault,” said Dr. Muldoon. “Clinicians should be prepared and trained to provide the best possible care for survivors of violence and ensure that getting care is not retraumatizing. Fostering conversations about the common experience of violence and destigmatizing those exposed to violence remain the most important ways to create safer spaces and societies.”
Dedicated care pathways
Commenting on the study, Samuel A. McLean, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Trauma Recovery and professor of emergency medicine, psychiatry, and anesthesiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said, “This important work documents a reduction in visits by sexual assault survivors for emergency care and forensic evidence collection during times of pandemic surge. It’s impossible to know for certain if this reduction in visits is entirely due to a reduction in sexual assaults, but a number of lines of circumstantial evidence make this unlikely.”
The results highlight the importance of ensuring that sexual assault care is maintained during surges in emergency care volume, added Dr. McLean, who was not involved with the current study. “This can be done via methods such as dedicated care pathways that avoid prolonged survivor wait times for care, and public health messaging that informs the public of the continued ready access to care during surges. Evidence, including data cited by the authors, suggests that these same care-seeking reductions are occurring in the United States and elsewhere.”
The study was supported by the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-term Care Applied Health Research Question Fund. Dr. Muldoon, study coauthors, and Dr. McLean report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Spikes out: A COVID mystery
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
To date, it has been a mystery, like “Glass Onion.” And in the spirit of all the great mysteries, to get to the bottom of this, we’ll need to round up the usual suspects.
Appearing in Circulation, a new study does a great job of systematically evaluating multiple hypotheses linking vaccination to myocarditis, and eliminating them, Poirot-style, one by one until only one remains. We’ll get there.
But first, let’s review the suspects. Why do the mRNA vaccines cause myocarditis in a small subset of people?
There are a few leading candidates.
Number one: antibody responses. There are two flavors here. The quantitative hypothesis suggests that some people simply generate too many antibodies to the vaccine, leading to increased inflammation and heart damage.
The qualitative hypothesis suggests that maybe it’s the nature of the antibodies generated rather than the amount; they might cross-react with some protein on the surface of heart cells for instance.
Or maybe it is driven by T-cell responses, which, of course, are independent of antibody levels.
There’s the idea that myocarditis is due to excessive cytokine release – sort of like what we see in the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
Or it could be due to the viral antigens themselves – the spike protein the mRNA codes for that is generated after vaccination.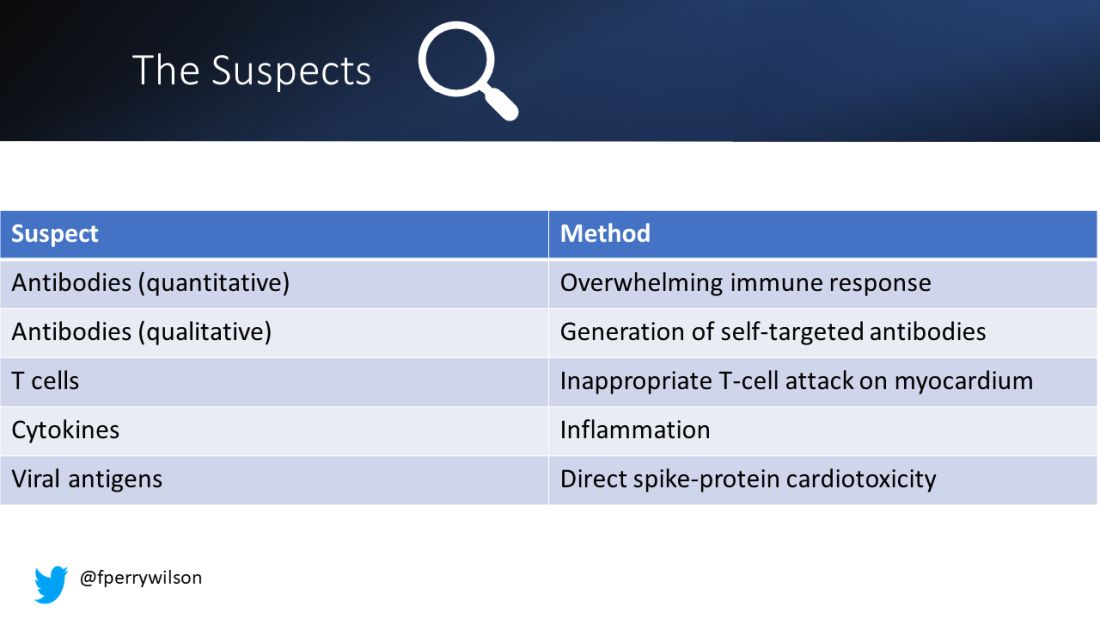
To tease all these possibilities apart, researchers led by Lael Yonker at Mass General performed a case-control study. Sixteen children with postvaccine myocarditis were matched by age to 45 control children who had been vaccinated without complications.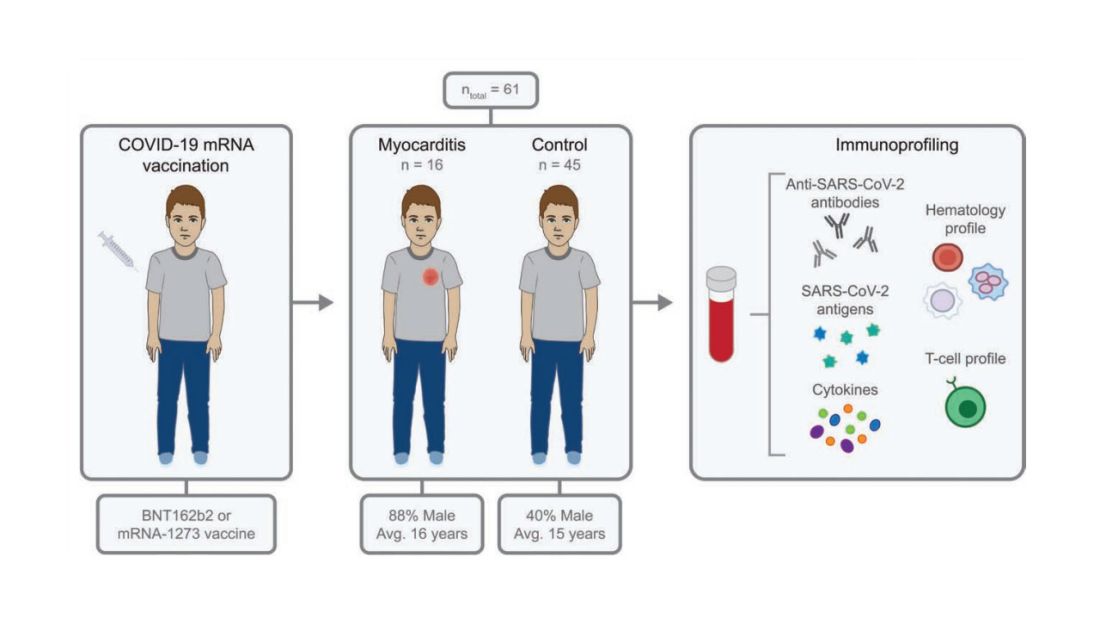
The matching was OK, but as you can see here, there were more boys in the myocarditis group, and the time from vaccination was a bit shorter in that group as well. We’ll keep that in mind as we go through the results.
OK, let’s start eliminating suspects.
First, quantitative antibodies. Seems unlikely. Absolute antibody titers were really no different in the myocarditis vs. the control group.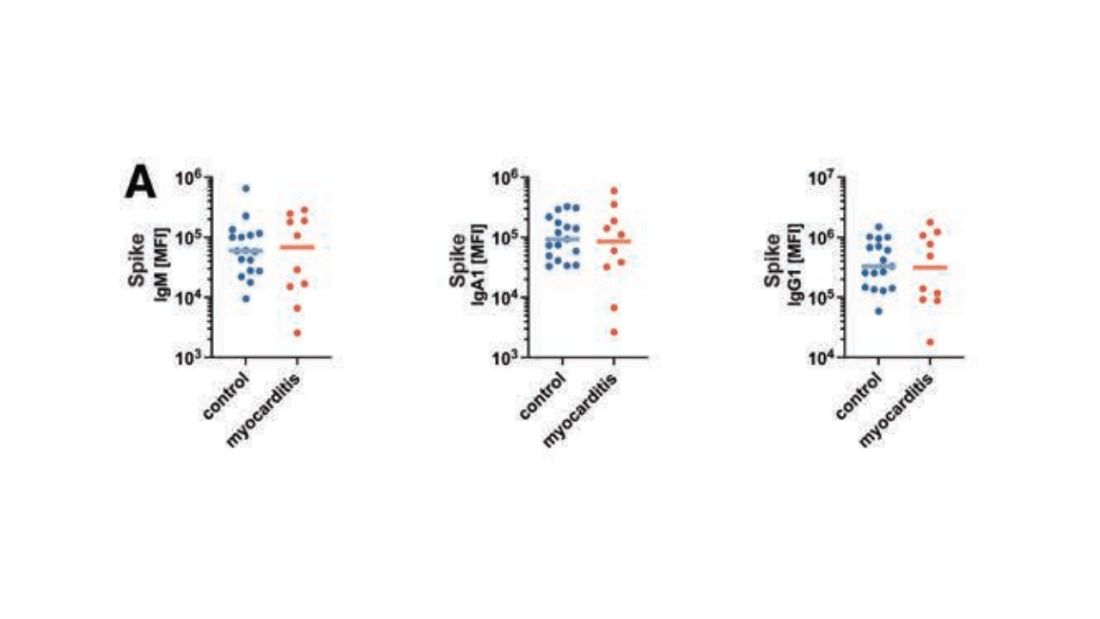
What about the quality of the antibodies? Would the kids with myocarditis have more self-recognizing antibodies present? It doesn’t appear so. Autoantibody levels were similar in the two groups.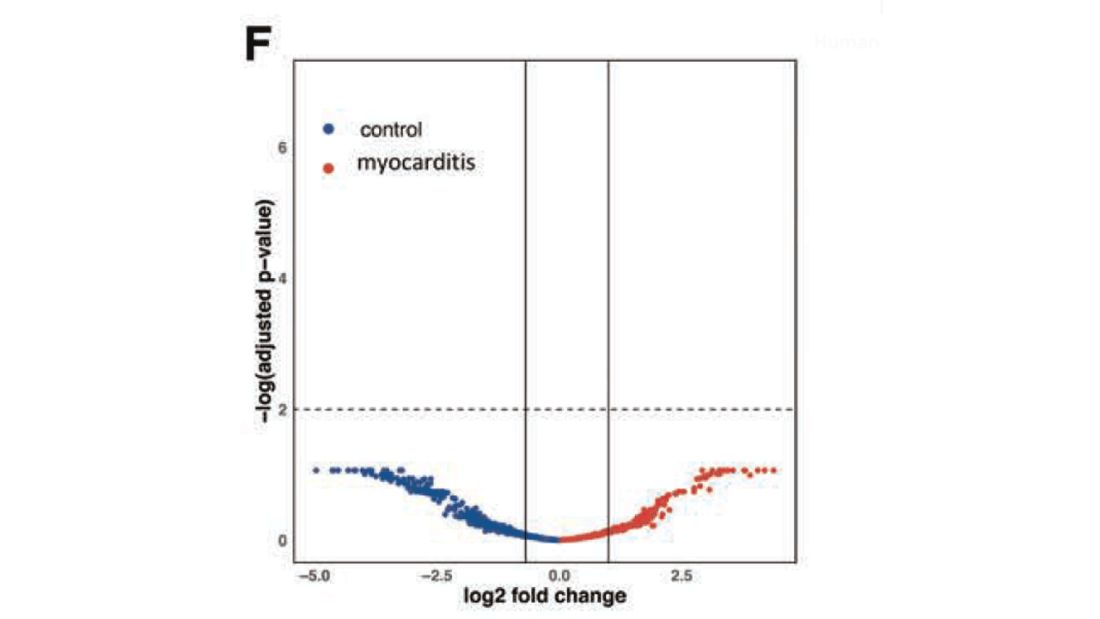
Take antibodies off the list.
T-cell responses come next, and, again, no major differences here, save for one specific T-cell subtype that was moderately elevated in the myocarditis group. Not what I would call a smoking gun, frankly.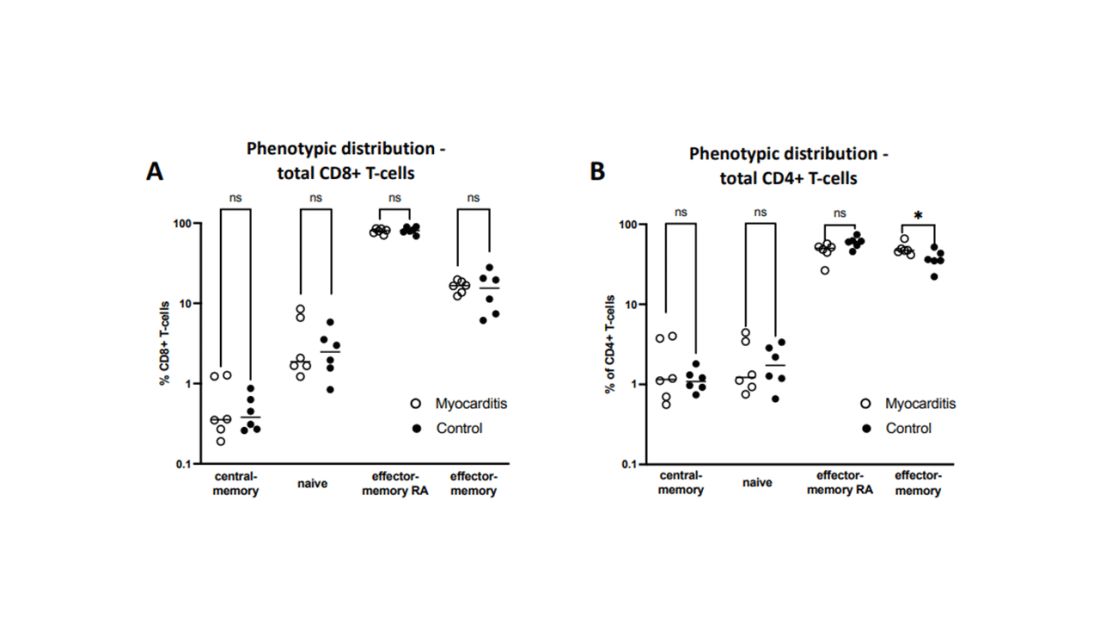
Cytokines give us a bit more to chew on. Levels of interleukin (IL)-8, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and IL-10 were all substantially higher in the kids with myocarditis.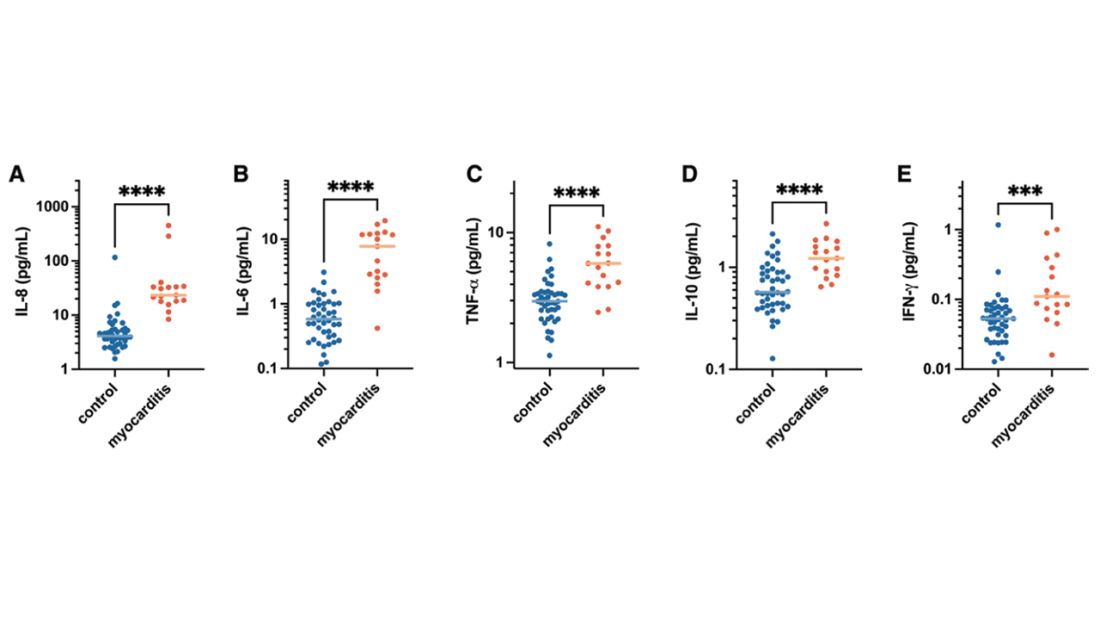
But the thing about cytokines is that they are not particularly specific. OK, kids with myocarditis have more systemic inflammation than kids without; that’s not really surprising. It still leaves us with the question of what is causing all this inflammation? Who is the arch-villain? The kingpin? The don?
It’s the analyses of antigens – the protein products of vaccination – that may hold the key here.
In 12 out of 16 kids with myocarditis, the researchers were able to measure free spike protein in the blood – that is to say spike protein, not bound by antispike antibodies.
These free spikes were present in – wait for it – zero of the 45 control patients. That makes spike protein itself our prime suspect. J’accuse free spike protein!
Of course, all good detectives need to wrap up the case with a good story: How was it all done?
And here’s where we could use Agatha Christie’s help. How could this all work? The vaccine gets injected; mRNA is taken up into cells, where spike protein is generated and released, generating antibody and T-cell responses all the while. Those responses rapidly clear that spike protein from the system – this has been demonstrated in multiple studies – in adults, at least. But in some small number of people, apparently, spike protein is not cleared. Why? It makes no damn sense. Compels me, though. Some have suggested that inadvertent intravenous injection of vaccine, compared with the appropriate intramuscular route, might distribute the vaccine to sites with less immune surveillance. But that is definitely not proven yet.
We are on the path for sure, but this is, as Benoit Blanc would say, a twisted web – and we are not finished untangling it. Not yet.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, “How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t,” is available for preorder now. He reports no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
To date, it has been a mystery, like “Glass Onion.” And in the spirit of all the great mysteries, to get to the bottom of this, we’ll need to round up the usual suspects.
Appearing in Circulation, a new study does a great job of systematically evaluating multiple hypotheses linking vaccination to myocarditis, and eliminating them, Poirot-style, one by one until only one remains. We’ll get there.
But first, let’s review the suspects. Why do the mRNA vaccines cause myocarditis in a small subset of people?
There are a few leading candidates.
Number one: antibody responses. There are two flavors here. The quantitative hypothesis suggests that some people simply generate too many antibodies to the vaccine, leading to increased inflammation and heart damage.
The qualitative hypothesis suggests that maybe it’s the nature of the antibodies generated rather than the amount; they might cross-react with some protein on the surface of heart cells for instance.
Or maybe it is driven by T-cell responses, which, of course, are independent of antibody levels.
There’s the idea that myocarditis is due to excessive cytokine release – sort of like what we see in the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
Or it could be due to the viral antigens themselves – the spike protein the mRNA codes for that is generated after vaccination.
To tease all these possibilities apart, researchers led by Lael Yonker at Mass General performed a case-control study. Sixteen children with postvaccine myocarditis were matched by age to 45 control children who had been vaccinated without complications.
The matching was OK, but as you can see here, there were more boys in the myocarditis group, and the time from vaccination was a bit shorter in that group as well. We’ll keep that in mind as we go through the results.
OK, let’s start eliminating suspects.
First, quantitative antibodies. Seems unlikely. Absolute antibody titers were really no different in the myocarditis vs. the control group.
What about the quality of the antibodies? Would the kids with myocarditis have more self-recognizing antibodies present? It doesn’t appear so. Autoantibody levels were similar in the two groups.
Take antibodies off the list.
T-cell responses come next, and, again, no major differences here, save for one specific T-cell subtype that was moderately elevated in the myocarditis group. Not what I would call a smoking gun, frankly.
Cytokines give us a bit more to chew on. Levels of interleukin (IL)-8, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and IL-10 were all substantially higher in the kids with myocarditis.
But the thing about cytokines is that they are not particularly specific. OK, kids with myocarditis have more systemic inflammation than kids without; that’s not really surprising. It still leaves us with the question of what is causing all this inflammation? Who is the arch-villain? The kingpin? The don?
It’s the analyses of antigens – the protein products of vaccination – that may hold the key here.
In 12 out of 16 kids with myocarditis, the researchers were able to measure free spike protein in the blood – that is to say spike protein, not bound by antispike antibodies.
These free spikes were present in – wait for it – zero of the 45 control patients. That makes spike protein itself our prime suspect. J’accuse free spike protein!
Of course, all good detectives need to wrap up the case with a good story: How was it all done?
And here’s where we could use Agatha Christie’s help. How could this all work? The vaccine gets injected; mRNA is taken up into cells, where spike protein is generated and released, generating antibody and T-cell responses all the while. Those responses rapidly clear that spike protein from the system – this has been demonstrated in multiple studies – in adults, at least. But in some small number of people, apparently, spike protein is not cleared. Why? It makes no damn sense. Compels me, though. Some have suggested that inadvertent intravenous injection of vaccine, compared with the appropriate intramuscular route, might distribute the vaccine to sites with less immune surveillance. But that is definitely not proven yet.
We are on the path for sure, but this is, as Benoit Blanc would say, a twisted web – and we are not finished untangling it. Not yet.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, “How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t,” is available for preorder now. He reports no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr. F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
To date, it has been a mystery, like “Glass Onion.” And in the spirit of all the great mysteries, to get to the bottom of this, we’ll need to round up the usual suspects.
Appearing in Circulation, a new study does a great job of systematically evaluating multiple hypotheses linking vaccination to myocarditis, and eliminating them, Poirot-style, one by one until only one remains. We’ll get there.
But first, let’s review the suspects. Why do the mRNA vaccines cause myocarditis in a small subset of people?
There are a few leading candidates.
Number one: antibody responses. There are two flavors here. The quantitative hypothesis suggests that some people simply generate too many antibodies to the vaccine, leading to increased inflammation and heart damage.
The qualitative hypothesis suggests that maybe it’s the nature of the antibodies generated rather than the amount; they might cross-react with some protein on the surface of heart cells for instance.
Or maybe it is driven by T-cell responses, which, of course, are independent of antibody levels.
There’s the idea that myocarditis is due to excessive cytokine release – sort of like what we see in the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children.
Or it could be due to the viral antigens themselves – the spike protein the mRNA codes for that is generated after vaccination.
To tease all these possibilities apart, researchers led by Lael Yonker at Mass General performed a case-control study. Sixteen children with postvaccine myocarditis were matched by age to 45 control children who had been vaccinated without complications.
The matching was OK, but as you can see here, there were more boys in the myocarditis group, and the time from vaccination was a bit shorter in that group as well. We’ll keep that in mind as we go through the results.
OK, let’s start eliminating suspects.
First, quantitative antibodies. Seems unlikely. Absolute antibody titers were really no different in the myocarditis vs. the control group.
What about the quality of the antibodies? Would the kids with myocarditis have more self-recognizing antibodies present? It doesn’t appear so. Autoantibody levels were similar in the two groups.
Take antibodies off the list.
T-cell responses come next, and, again, no major differences here, save for one specific T-cell subtype that was moderately elevated in the myocarditis group. Not what I would call a smoking gun, frankly.
Cytokines give us a bit more to chew on. Levels of interleukin (IL)-8, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, and IL-10 were all substantially higher in the kids with myocarditis.
But the thing about cytokines is that they are not particularly specific. OK, kids with myocarditis have more systemic inflammation than kids without; that’s not really surprising. It still leaves us with the question of what is causing all this inflammation? Who is the arch-villain? The kingpin? The don?
It’s the analyses of antigens – the protein products of vaccination – that may hold the key here.
In 12 out of 16 kids with myocarditis, the researchers were able to measure free spike protein in the blood – that is to say spike protein, not bound by antispike antibodies.
These free spikes were present in – wait for it – zero of the 45 control patients. That makes spike protein itself our prime suspect. J’accuse free spike protein!
Of course, all good detectives need to wrap up the case with a good story: How was it all done?
And here’s where we could use Agatha Christie’s help. How could this all work? The vaccine gets injected; mRNA is taken up into cells, where spike protein is generated and released, generating antibody and T-cell responses all the while. Those responses rapidly clear that spike protein from the system – this has been demonstrated in multiple studies – in adults, at least. But in some small number of people, apparently, spike protein is not cleared. Why? It makes no damn sense. Compels me, though. Some have suggested that inadvertent intravenous injection of vaccine, compared with the appropriate intramuscular route, might distribute the vaccine to sites with less immune surveillance. But that is definitely not proven yet.
We are on the path for sure, but this is, as Benoit Blanc would say, a twisted web – and we are not finished untangling it. Not yet.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator. His science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and here. He tweets @fperrywilson and his new book, “How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t,” is available for preorder now. He reports no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Omicron subvariant is ‘crazy infectious,’ COVID expert warns
“It’s crazy infectious,” said Paula Cannon, PhD, a virologist at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “All the things that have protected you for the past couple of years, I don’t think are going to protect you against this new crop of variants.”
XBB.1.5 is spreading quickly in the United States. It accounted for 27.6% of cases in the country in the week ending on Jan. 7, up from about 1% of cases at one point in December, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s especially prevalent in the Northeast, now accounting for more than 70% of the cases in that region.
It’s spreading across the globe, too. Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, technical lead of the World Health Organization, has called XBB.1.5 is “the most transmissible subvariant that has been detected yet.”
Ashish Jha, MD, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, tweeted a few days ago that the spread of XBB.1.5 is “stunning” but cautioned that it’s unclear if the symptoms of infection will be more severe than for previous variants.
“Whether we’ll have an XBB.1.5 wave (and if yes, how big) will depend on many factors including immunity of the population, people’s actions, etc.,” he tweeted.
He urged people to get up to date on their boosters, wear a snug-fitting mask, and avoid crowded indoor spaces. He noted that people who haven’t been infected recently or haven’t gotten the bivalent booster likely have little protection against infection.
The symptoms for XBB.1.5 appear to be the same as for other versions of COVID-19. However, it’s less common for people infected with XBB.1.5 to report losing their sense of taste and smell, USA Today reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“It’s crazy infectious,” said Paula Cannon, PhD, a virologist at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “All the things that have protected you for the past couple of years, I don’t think are going to protect you against this new crop of variants.”
XBB.1.5 is spreading quickly in the United States. It accounted for 27.6% of cases in the country in the week ending on Jan. 7, up from about 1% of cases at one point in December, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s especially prevalent in the Northeast, now accounting for more than 70% of the cases in that region.
It’s spreading across the globe, too. Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, technical lead of the World Health Organization, has called XBB.1.5 is “the most transmissible subvariant that has been detected yet.”
Ashish Jha, MD, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, tweeted a few days ago that the spread of XBB.1.5 is “stunning” but cautioned that it’s unclear if the symptoms of infection will be more severe than for previous variants.
“Whether we’ll have an XBB.1.5 wave (and if yes, how big) will depend on many factors including immunity of the population, people’s actions, etc.,” he tweeted.
He urged people to get up to date on their boosters, wear a snug-fitting mask, and avoid crowded indoor spaces. He noted that people who haven’t been infected recently or haven’t gotten the bivalent booster likely have little protection against infection.
The symptoms for XBB.1.5 appear to be the same as for other versions of COVID-19. However, it’s less common for people infected with XBB.1.5 to report losing their sense of taste and smell, USA Today reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
“It’s crazy infectious,” said Paula Cannon, PhD, a virologist at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles. “All the things that have protected you for the past couple of years, I don’t think are going to protect you against this new crop of variants.”
XBB.1.5 is spreading quickly in the United States. It accounted for 27.6% of cases in the country in the week ending on Jan. 7, up from about 1% of cases at one point in December, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It’s especially prevalent in the Northeast, now accounting for more than 70% of the cases in that region.
It’s spreading across the globe, too. Maria Van Kerkhove, PhD, technical lead of the World Health Organization, has called XBB.1.5 is “the most transmissible subvariant that has been detected yet.”
Ashish Jha, MD, the White House COVID-19 response coordinator, tweeted a few days ago that the spread of XBB.1.5 is “stunning” but cautioned that it’s unclear if the symptoms of infection will be more severe than for previous variants.
“Whether we’ll have an XBB.1.5 wave (and if yes, how big) will depend on many factors including immunity of the population, people’s actions, etc.,” he tweeted.
He urged people to get up to date on their boosters, wear a snug-fitting mask, and avoid crowded indoor spaces. He noted that people who haven’t been infected recently or haven’t gotten the bivalent booster likely have little protection against infection.
The symptoms for XBB.1.5 appear to be the same as for other versions of COVID-19. However, it’s less common for people infected with XBB.1.5 to report losing their sense of taste and smell, USA Today reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Autopsies show COVID virus invades entire body
A study on the subject was published in the journal Nature. The researchers completed autopsies from April 2020 to March 2021 of 44 unvaccinated people who had severe COVID-19. The median age was 62.5 years old, and 30% were female. Extensive brain sampling was done for 11 cases.
Because of its nature as a respiratory illness, SARS-CoV-2 was most widespread in the respiratory system such as in the lungs. But it was also found in 79 other body locations, including the heart, kidneys, liver, muscles, nerves, reproductive tract, and eyes.
The researchers said their work shows the SARS-CoV-2 “is capable of infecting and replicating within the human brain.” They also said their results indicate the virus spreads via the blood early during infection, which “seeds the virus throughout the body following infection of the respiratory tract.”
The authors noted that, while the virus was found outside the respiratory tract, they did not find signs of inflammation beyond the respiratory system.
The results will help narrow down treatments for long COVID, and particularly support the idea of using the antiviral drug Paxlovid to treat long COVID, according to a blog post from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. A clinical trial is already underway examining the treatment, and results are expected in January 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A study on the subject was published in the journal Nature. The researchers completed autopsies from April 2020 to March 2021 of 44 unvaccinated people who had severe COVID-19. The median age was 62.5 years old, and 30% were female. Extensive brain sampling was done for 11 cases.
Because of its nature as a respiratory illness, SARS-CoV-2 was most widespread in the respiratory system such as in the lungs. But it was also found in 79 other body locations, including the heart, kidneys, liver, muscles, nerves, reproductive tract, and eyes.
The researchers said their work shows the SARS-CoV-2 “is capable of infecting and replicating within the human brain.” They also said their results indicate the virus spreads via the blood early during infection, which “seeds the virus throughout the body following infection of the respiratory tract.”
The authors noted that, while the virus was found outside the respiratory tract, they did not find signs of inflammation beyond the respiratory system.
The results will help narrow down treatments for long COVID, and particularly support the idea of using the antiviral drug Paxlovid to treat long COVID, according to a blog post from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. A clinical trial is already underway examining the treatment, and results are expected in January 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
A study on the subject was published in the journal Nature. The researchers completed autopsies from April 2020 to March 2021 of 44 unvaccinated people who had severe COVID-19. The median age was 62.5 years old, and 30% were female. Extensive brain sampling was done for 11 cases.
Because of its nature as a respiratory illness, SARS-CoV-2 was most widespread in the respiratory system such as in the lungs. But it was also found in 79 other body locations, including the heart, kidneys, liver, muscles, nerves, reproductive tract, and eyes.
The researchers said their work shows the SARS-CoV-2 “is capable of infecting and replicating within the human brain.” They also said their results indicate the virus spreads via the blood early during infection, which “seeds the virus throughout the body following infection of the respiratory tract.”
The authors noted that, while the virus was found outside the respiratory tract, they did not find signs of inflammation beyond the respiratory system.
The results will help narrow down treatments for long COVID, and particularly support the idea of using the antiviral drug Paxlovid to treat long COVID, according to a blog post from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. A clinical trial is already underway examining the treatment, and results are expected in January 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM NATURE
Advanced Primary Care program boosts COVID-19 results
The better outcomes were seen in higher vaccination rates and fewer infections, hospitalizations, and deaths from the disease, according to study authors, led by Emily Gruber, MBA, MPH, with the Maryland Primary Care Program, Maryland Department of Health in Baltimore.
The results were published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study population was divided into MDPCP participants (n = 208,146) and a matched cohort (n = 37,203) of beneficiaries not attributed to MDPCP practices but who met eligibility criteria for study participation from Jan. 1, 2020, through Dec. 31, 2021.
More vaccinations, more antibody treatments
Researchers broke down the comparisons of better outcomes: 84.47% of MDPCP beneficiaries were fully vaccinated vs. 77.93% of nonparticipating beneficiaries (P less than .001). COVID-19–positive program beneficiaries also received monoclonal antibody treatment more often (8.45% vs. 6.11%; P less than .001).
Plus, program participants received more care via telehealth (62.95% vs. 54.53%; P less than .001) compared with those not participating.
Regarding secondary outcomes, MDPCP beneficiaries had lower rates of COVID cases (6.55% vs. 7.09%; P less than .001), lower rates of COVID-19 hospitalizations (1.81% vs. 2.06%; P = .001), and lower rates of death due to COVID-19 (0.56% vs. 0.77%; P less than .001).
Program components
Enrollment in the MDPCP is voluntary, and primary care practices can apply each year to be part of the program.
The model integrates primary care and public health in the pandemic response. It was created by the Maryland Department of Health (MDH) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
It expands the role of primary care to include services such as expanded care management, integrated behavioral health, data-driven care, and screenings and referrals to address social needs.
Coauthor Howard Haft, MD, MMM, with the Maryland Department of Public Health, said in an interview that among the most important factors in the program’s success were giving providers vaccines to distribute and then giving providers data on how many patients are vaccinated, and who’s not vaccinated but at high risk, and how those rates compare to other practices.
As to whether this could be a widespread model, Dr. Haft said, “It’s highly replicable.”
“Every state in the nation overall has all of these resources. It’s a matter of having the operational and political will to put those resources together. Almost every state has the technological ability to use their health information exchange to help tie pieces together.”
Vaccines and testing made available to providers
Making ample vaccines and testing available to providers in their offices helped patients get those services in a place they trust, Dr. Haft said.
The model also included a payment system for providers that included a significant amount of non–visit-based payments when many locations were closed in the height of the pandemic.
“That helped financially,” as did providing free telehealth platforms to practices with training on how to use them, Dr. Haft said.
‘Innovative and important’
Renu Tipirneni, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Michigan and at the Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor, said Maryland is out front putting into practice what practices nationwide aspire to do – coordinating physical and mental health and social needs and integrating primary and public health. Dr. Tipirneni, who was not involved with the study, said she was impressed the researchers were able to show statistically significant improvement with COVID-19 outcomes in the first 2 years.
“In terms of health outcomes, we often have to wait longer to see good outcomes,” she said. “It’s a really innovative and important model.”
She said states can learn from each other and this model is an example.
Integrating primary care and public health and addressing social needs may be the biggest challenges for states, she said, as those realms typically have been siloed.
“But they may be the key components to achieving these outcomes,” she said.
Take-home message
The most important benefit of the program is that data suggest it saves lives, according to Dr. Haft. While the actual difference between COVID deaths in the program and nonprogram groups was small, multiplying that savings across the nation shows substantial potential benefit, he explained.
“At a time when we were losing lives at an unconscionable rate, we were able to make a difference in saving lives,” Dr. Haft said.
Authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
The study received financial support from the Maryland Department of Health.
Dr. Tiperneni is helping evaluate Michigan’s Medicaid contract.
The better outcomes were seen in higher vaccination rates and fewer infections, hospitalizations, and deaths from the disease, according to study authors, led by Emily Gruber, MBA, MPH, with the Maryland Primary Care Program, Maryland Department of Health in Baltimore.
The results were published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study population was divided into MDPCP participants (n = 208,146) and a matched cohort (n = 37,203) of beneficiaries not attributed to MDPCP practices but who met eligibility criteria for study participation from Jan. 1, 2020, through Dec. 31, 2021.
More vaccinations, more antibody treatments
Researchers broke down the comparisons of better outcomes: 84.47% of MDPCP beneficiaries were fully vaccinated vs. 77.93% of nonparticipating beneficiaries (P less than .001). COVID-19–positive program beneficiaries also received monoclonal antibody treatment more often (8.45% vs. 6.11%; P less than .001).
Plus, program participants received more care via telehealth (62.95% vs. 54.53%; P less than .001) compared with those not participating.
Regarding secondary outcomes, MDPCP beneficiaries had lower rates of COVID cases (6.55% vs. 7.09%; P less than .001), lower rates of COVID-19 hospitalizations (1.81% vs. 2.06%; P = .001), and lower rates of death due to COVID-19 (0.56% vs. 0.77%; P less than .001).
Program components
Enrollment in the MDPCP is voluntary, and primary care practices can apply each year to be part of the program.
The model integrates primary care and public health in the pandemic response. It was created by the Maryland Department of Health (MDH) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
It expands the role of primary care to include services such as expanded care management, integrated behavioral health, data-driven care, and screenings and referrals to address social needs.
Coauthor Howard Haft, MD, MMM, with the Maryland Department of Public Health, said in an interview that among the most important factors in the program’s success were giving providers vaccines to distribute and then giving providers data on how many patients are vaccinated, and who’s not vaccinated but at high risk, and how those rates compare to other practices.
As to whether this could be a widespread model, Dr. Haft said, “It’s highly replicable.”
“Every state in the nation overall has all of these resources. It’s a matter of having the operational and political will to put those resources together. Almost every state has the technological ability to use their health information exchange to help tie pieces together.”
Vaccines and testing made available to providers
Making ample vaccines and testing available to providers in their offices helped patients get those services in a place they trust, Dr. Haft said.
The model also included a payment system for providers that included a significant amount of non–visit-based payments when many locations were closed in the height of the pandemic.
“That helped financially,” as did providing free telehealth platforms to practices with training on how to use them, Dr. Haft said.
‘Innovative and important’
Renu Tipirneni, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Michigan and at the Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor, said Maryland is out front putting into practice what practices nationwide aspire to do – coordinating physical and mental health and social needs and integrating primary and public health. Dr. Tipirneni, who was not involved with the study, said she was impressed the researchers were able to show statistically significant improvement with COVID-19 outcomes in the first 2 years.
“In terms of health outcomes, we often have to wait longer to see good outcomes,” she said. “It’s a really innovative and important model.”
She said states can learn from each other and this model is an example.
Integrating primary care and public health and addressing social needs may be the biggest challenges for states, she said, as those realms typically have been siloed.
“But they may be the key components to achieving these outcomes,” she said.
Take-home message
The most important benefit of the program is that data suggest it saves lives, according to Dr. Haft. While the actual difference between COVID deaths in the program and nonprogram groups was small, multiplying that savings across the nation shows substantial potential benefit, he explained.
“At a time when we were losing lives at an unconscionable rate, we were able to make a difference in saving lives,” Dr. Haft said.
Authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
The study received financial support from the Maryland Department of Health.
Dr. Tiperneni is helping evaluate Michigan’s Medicaid contract.
The better outcomes were seen in higher vaccination rates and fewer infections, hospitalizations, and deaths from the disease, according to study authors, led by Emily Gruber, MBA, MPH, with the Maryland Primary Care Program, Maryland Department of Health in Baltimore.
The results were published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study population was divided into MDPCP participants (n = 208,146) and a matched cohort (n = 37,203) of beneficiaries not attributed to MDPCP practices but who met eligibility criteria for study participation from Jan. 1, 2020, through Dec. 31, 2021.
More vaccinations, more antibody treatments
Researchers broke down the comparisons of better outcomes: 84.47% of MDPCP beneficiaries were fully vaccinated vs. 77.93% of nonparticipating beneficiaries (P less than .001). COVID-19–positive program beneficiaries also received monoclonal antibody treatment more often (8.45% vs. 6.11%; P less than .001).
Plus, program participants received more care via telehealth (62.95% vs. 54.53%; P less than .001) compared with those not participating.
Regarding secondary outcomes, MDPCP beneficiaries had lower rates of COVID cases (6.55% vs. 7.09%; P less than .001), lower rates of COVID-19 hospitalizations (1.81% vs. 2.06%; P = .001), and lower rates of death due to COVID-19 (0.56% vs. 0.77%; P less than .001).
Program components
Enrollment in the MDPCP is voluntary, and primary care practices can apply each year to be part of the program.
The model integrates primary care and public health in the pandemic response. It was created by the Maryland Department of Health (MDH) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
It expands the role of primary care to include services such as expanded care management, integrated behavioral health, data-driven care, and screenings and referrals to address social needs.
Coauthor Howard Haft, MD, MMM, with the Maryland Department of Public Health, said in an interview that among the most important factors in the program’s success were giving providers vaccines to distribute and then giving providers data on how many patients are vaccinated, and who’s not vaccinated but at high risk, and how those rates compare to other practices.
As to whether this could be a widespread model, Dr. Haft said, “It’s highly replicable.”
“Every state in the nation overall has all of these resources. It’s a matter of having the operational and political will to put those resources together. Almost every state has the technological ability to use their health information exchange to help tie pieces together.”
Vaccines and testing made available to providers
Making ample vaccines and testing available to providers in their offices helped patients get those services in a place they trust, Dr. Haft said.
The model also included a payment system for providers that included a significant amount of non–visit-based payments when many locations were closed in the height of the pandemic.
“That helped financially,” as did providing free telehealth platforms to practices with training on how to use them, Dr. Haft said.
‘Innovative and important’
Renu Tipirneni, MD, an assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Michigan and at the Institute for Healthcare Policy and Innovation in Ann Arbor, said Maryland is out front putting into practice what practices nationwide aspire to do – coordinating physical and mental health and social needs and integrating primary and public health. Dr. Tipirneni, who was not involved with the study, said she was impressed the researchers were able to show statistically significant improvement with COVID-19 outcomes in the first 2 years.
“In terms of health outcomes, we often have to wait longer to see good outcomes,” she said. “It’s a really innovative and important model.”
She said states can learn from each other and this model is an example.
Integrating primary care and public health and addressing social needs may be the biggest challenges for states, she said, as those realms typically have been siloed.
“But they may be the key components to achieving these outcomes,” she said.
Take-home message
The most important benefit of the program is that data suggest it saves lives, according to Dr. Haft. While the actual difference between COVID deaths in the program and nonprogram groups was small, multiplying that savings across the nation shows substantial potential benefit, he explained.
“At a time when we were losing lives at an unconscionable rate, we were able to make a difference in saving lives,” Dr. Haft said.
Authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
The study received financial support from the Maryland Department of Health.
Dr. Tiperneni is helping evaluate Michigan’s Medicaid contract.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN