User login
Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Migraine: A Revolution in Progress
Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Migraine: A Revolution in Progress
In assessing chronic medical disorders that adversely affect quality of life, including disorders such as malaria, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and sickle cell anemia, the World Health Organization has ranked migraine as the number 1 disorder for women. The diagnosis of chronic migraine (CM) implies an established history of migraine, including 15 or more days of headache per month. This clinical variant accounts for a disproportionate share of the public health burden generally imposed by migraine. One of the great paradoxes of migraine is that, despite this outsized burden, as few as 5% of the millions of Americans with CM seek medical attention, are diagnosed accurately, and receive appropriate therapy.
Why is this? The answer lies in part with the relatively recent formal recognition of CM as a distinct primary headache disorder. Not until the 2006 revision of the International Classification of Headache Disorders were widely accepted diagnostic criteria for CM available. Without such criteria in place, meaningful clinical research (and therapeutic research in particular) is impossible. As recently as 2009, we consequently lacked any evidence-based therapies for suppression of CM. In what may be a therapeutic revolution unrivaled in almost any other area of clinical medicine, within 15 years we have identified and introduced into general clinical practice no fewer than 6 new evidence-based therapies for suppression of CM that are safe, generally well tolerated, and effective. Those therapies are onabotulinumtoxin A, an orally administered atogepant, the 3 subcutaneously self-administered anti–calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibodies (erenumab, galcanezumab, and fremanezumab), and the intravenously administered anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody eptinenzumab. A seventh and older therapy, topiramate, could be included in that group, except tolerability issues reduce its utility.
As we presently lack adequate active vs active comparator trials, at this point there is no “best” among these 6 CM therapies. Each is effective in reducing migraine burden substantially in a large proportion of patients. In many cases, the onset of the positive treatment response is gratifyingly rapid. Are they disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) that, in addition to suppressing symptoms, can alter the disorder’s biologic underpinnings and its long-term course? Put another way, does their benefit extend beyond the period of time the patient is actively on treatment? Given their relative newness, the answer is unknown. However, preliminary evidence suggests that onabotulinumtoxin A may qualify as a DMT. The US Food and Drug Administration indicated onabotulinumtoxin A for CM in 2010, and it is the first of the group introduced into clinical practice.
Complicating clinical use of these 6 therapies for suppression of CM have been various proscriptions emanating from the health care insurance industry. Chief among these has been the oft-encountered mandate that, for 1 of these 6 evidence-based treatments to be authorized for coverage, the patient with CM first must fail an “adequate” trial of multiple older, generic, and less costly therapies commonly used for prophylaxis in episodic migraine. But, with the exception of frequently difficult-to-tolerate topiramate, these therapies have no meaningful evidence base for use in CM. Furthermore, some limited evidence suggests that the efficacy of the evidence-based treatments may be less robust in patients whose CM has been longstanding. Therefore, spending many months prescribing a succession of therapies lacking an evidence base seems counterproductive and contrary to the patient’s best interests, when evidence-based therapies are available. In addition, the higher cost of evidence-based therapies may be offset by their reduction in the direct medical costs that result from clinical improvement.
The American Headache Society (AHS) recently published a position statement recommending that the CGRP-targeting medications─both the small molecule gepants and the large molecule monoclonal antibodies─be considered first-line treatment for migraine prevention. An estimated 40% of patients with migraine require prevention therapy. The soundness of the AHS recommendation is especially evident in the sizeable subset of that population with CM; for treatment of CM, this list of recommended first-line therapies logically can be extended to include onabotulinumtoxin A. In their consensus statement the AHS acknowledged the relatively higher cost of these therapies but noted the resulting reduction in direct and indirect costs could justify their use.
Migraine ranks near or at the top of the list of chronic medical disorders that adversely impact public health. CM, a common variant of migraine, is particularly adept at eroding quality of life. Presently available are 6 safe and typically well-tolerated therapies, known to be effective for treating CM and potentially capable of modifying its long-term course. Although the cost of these exceeds the cost of older generic therapies commonly used for migraine prophylaxis, those older therapies generally lack any meaningful evidence base for use in CM. In addition, prescription of these older therapies may delay easing the CM patient’s migraine burden without any associated reduction in long-term net cost. Both medically and financially, a strong case can be made for designating these 6 medications as first-line therapy for CM. Insurers, the ball is now in your court.
In assessing chronic medical disorders that adversely affect quality of life, including disorders such as malaria, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and sickle cell anemia, the World Health Organization has ranked migraine as the number 1 disorder for women. The diagnosis of chronic migraine (CM) implies an established history of migraine, including 15 or more days of headache per month. This clinical variant accounts for a disproportionate share of the public health burden generally imposed by migraine. One of the great paradoxes of migraine is that, despite this outsized burden, as few as 5% of the millions of Americans with CM seek medical attention, are diagnosed accurately, and receive appropriate therapy.
Why is this? The answer lies in part with the relatively recent formal recognition of CM as a distinct primary headache disorder. Not until the 2006 revision of the International Classification of Headache Disorders were widely accepted diagnostic criteria for CM available. Without such criteria in place, meaningful clinical research (and therapeutic research in particular) is impossible. As recently as 2009, we consequently lacked any evidence-based therapies for suppression of CM. In what may be a therapeutic revolution unrivaled in almost any other area of clinical medicine, within 15 years we have identified and introduced into general clinical practice no fewer than 6 new evidence-based therapies for suppression of CM that are safe, generally well tolerated, and effective. Those therapies are onabotulinumtoxin A, an orally administered atogepant, the 3 subcutaneously self-administered anti–calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibodies (erenumab, galcanezumab, and fremanezumab), and the intravenously administered anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody eptinenzumab. A seventh and older therapy, topiramate, could be included in that group, except tolerability issues reduce its utility.
As we presently lack adequate active vs active comparator trials, at this point there is no “best” among these 6 CM therapies. Each is effective in reducing migraine burden substantially in a large proportion of patients. In many cases, the onset of the positive treatment response is gratifyingly rapid. Are they disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) that, in addition to suppressing symptoms, can alter the disorder’s biologic underpinnings and its long-term course? Put another way, does their benefit extend beyond the period of time the patient is actively on treatment? Given their relative newness, the answer is unknown. However, preliminary evidence suggests that onabotulinumtoxin A may qualify as a DMT. The US Food and Drug Administration indicated onabotulinumtoxin A for CM in 2010, and it is the first of the group introduced into clinical practice.
Complicating clinical use of these 6 therapies for suppression of CM have been various proscriptions emanating from the health care insurance industry. Chief among these has been the oft-encountered mandate that, for 1 of these 6 evidence-based treatments to be authorized for coverage, the patient with CM first must fail an “adequate” trial of multiple older, generic, and less costly therapies commonly used for prophylaxis in episodic migraine. But, with the exception of frequently difficult-to-tolerate topiramate, these therapies have no meaningful evidence base for use in CM. Furthermore, some limited evidence suggests that the efficacy of the evidence-based treatments may be less robust in patients whose CM has been longstanding. Therefore, spending many months prescribing a succession of therapies lacking an evidence base seems counterproductive and contrary to the patient’s best interests, when evidence-based therapies are available. In addition, the higher cost of evidence-based therapies may be offset by their reduction in the direct medical costs that result from clinical improvement.
The American Headache Society (AHS) recently published a position statement recommending that the CGRP-targeting medications─both the small molecule gepants and the large molecule monoclonal antibodies─be considered first-line treatment for migraine prevention. An estimated 40% of patients with migraine require prevention therapy. The soundness of the AHS recommendation is especially evident in the sizeable subset of that population with CM; for treatment of CM, this list of recommended first-line therapies logically can be extended to include onabotulinumtoxin A. In their consensus statement the AHS acknowledged the relatively higher cost of these therapies but noted the resulting reduction in direct and indirect costs could justify their use.
Migraine ranks near or at the top of the list of chronic medical disorders that adversely impact public health. CM, a common variant of migraine, is particularly adept at eroding quality of life. Presently available are 6 safe and typically well-tolerated therapies, known to be effective for treating CM and potentially capable of modifying its long-term course. Although the cost of these exceeds the cost of older generic therapies commonly used for migraine prophylaxis, those older therapies generally lack any meaningful evidence base for use in CM. In addition, prescription of these older therapies may delay easing the CM patient’s migraine burden without any associated reduction in long-term net cost. Both medically and financially, a strong case can be made for designating these 6 medications as first-line therapy for CM. Insurers, the ball is now in your court.
In assessing chronic medical disorders that adversely affect quality of life, including disorders such as malaria, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, and sickle cell anemia, the World Health Organization has ranked migraine as the number 1 disorder for women. The diagnosis of chronic migraine (CM) implies an established history of migraine, including 15 or more days of headache per month. This clinical variant accounts for a disproportionate share of the public health burden generally imposed by migraine. One of the great paradoxes of migraine is that, despite this outsized burden, as few as 5% of the millions of Americans with CM seek medical attention, are diagnosed accurately, and receive appropriate therapy.
Why is this? The answer lies in part with the relatively recent formal recognition of CM as a distinct primary headache disorder. Not until the 2006 revision of the International Classification of Headache Disorders were widely accepted diagnostic criteria for CM available. Without such criteria in place, meaningful clinical research (and therapeutic research in particular) is impossible. As recently as 2009, we consequently lacked any evidence-based therapies for suppression of CM. In what may be a therapeutic revolution unrivaled in almost any other area of clinical medicine, within 15 years we have identified and introduced into general clinical practice no fewer than 6 new evidence-based therapies for suppression of CM that are safe, generally well tolerated, and effective. Those therapies are onabotulinumtoxin A, an orally administered atogepant, the 3 subcutaneously self-administered anti–calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) monoclonal antibodies (erenumab, galcanezumab, and fremanezumab), and the intravenously administered anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody eptinenzumab. A seventh and older therapy, topiramate, could be included in that group, except tolerability issues reduce its utility.
As we presently lack adequate active vs active comparator trials, at this point there is no “best” among these 6 CM therapies. Each is effective in reducing migraine burden substantially in a large proportion of patients. In many cases, the onset of the positive treatment response is gratifyingly rapid. Are they disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) that, in addition to suppressing symptoms, can alter the disorder’s biologic underpinnings and its long-term course? Put another way, does their benefit extend beyond the period of time the patient is actively on treatment? Given their relative newness, the answer is unknown. However, preliminary evidence suggests that onabotulinumtoxin A may qualify as a DMT. The US Food and Drug Administration indicated onabotulinumtoxin A for CM in 2010, and it is the first of the group introduced into clinical practice.
Complicating clinical use of these 6 therapies for suppression of CM have been various proscriptions emanating from the health care insurance industry. Chief among these has been the oft-encountered mandate that, for 1 of these 6 evidence-based treatments to be authorized for coverage, the patient with CM first must fail an “adequate” trial of multiple older, generic, and less costly therapies commonly used for prophylaxis in episodic migraine. But, with the exception of frequently difficult-to-tolerate topiramate, these therapies have no meaningful evidence base for use in CM. Furthermore, some limited evidence suggests that the efficacy of the evidence-based treatments may be less robust in patients whose CM has been longstanding. Therefore, spending many months prescribing a succession of therapies lacking an evidence base seems counterproductive and contrary to the patient’s best interests, when evidence-based therapies are available. In addition, the higher cost of evidence-based therapies may be offset by their reduction in the direct medical costs that result from clinical improvement.
The American Headache Society (AHS) recently published a position statement recommending that the CGRP-targeting medications─both the small molecule gepants and the large molecule monoclonal antibodies─be considered first-line treatment for migraine prevention. An estimated 40% of patients with migraine require prevention therapy. The soundness of the AHS recommendation is especially evident in the sizeable subset of that population with CM; for treatment of CM, this list of recommended first-line therapies logically can be extended to include onabotulinumtoxin A. In their consensus statement the AHS acknowledged the relatively higher cost of these therapies but noted the resulting reduction in direct and indirect costs could justify their use.
Migraine ranks near or at the top of the list of chronic medical disorders that adversely impact public health. CM, a common variant of migraine, is particularly adept at eroding quality of life. Presently available are 6 safe and typically well-tolerated therapies, known to be effective for treating CM and potentially capable of modifying its long-term course. Although the cost of these exceeds the cost of older generic therapies commonly used for migraine prophylaxis, those older therapies generally lack any meaningful evidence base for use in CM. In addition, prescription of these older therapies may delay easing the CM patient’s migraine burden without any associated reduction in long-term net cost. Both medically and financially, a strong case can be made for designating these 6 medications as first-line therapy for CM. Insurers, the ball is now in your court.
Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Migraine: A Revolution in Progress
Pharmacologic Treatment of Chronic Migraine: A Revolution in Progress
Maternal Immunization to Prevent Serious Respiratory Illness
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.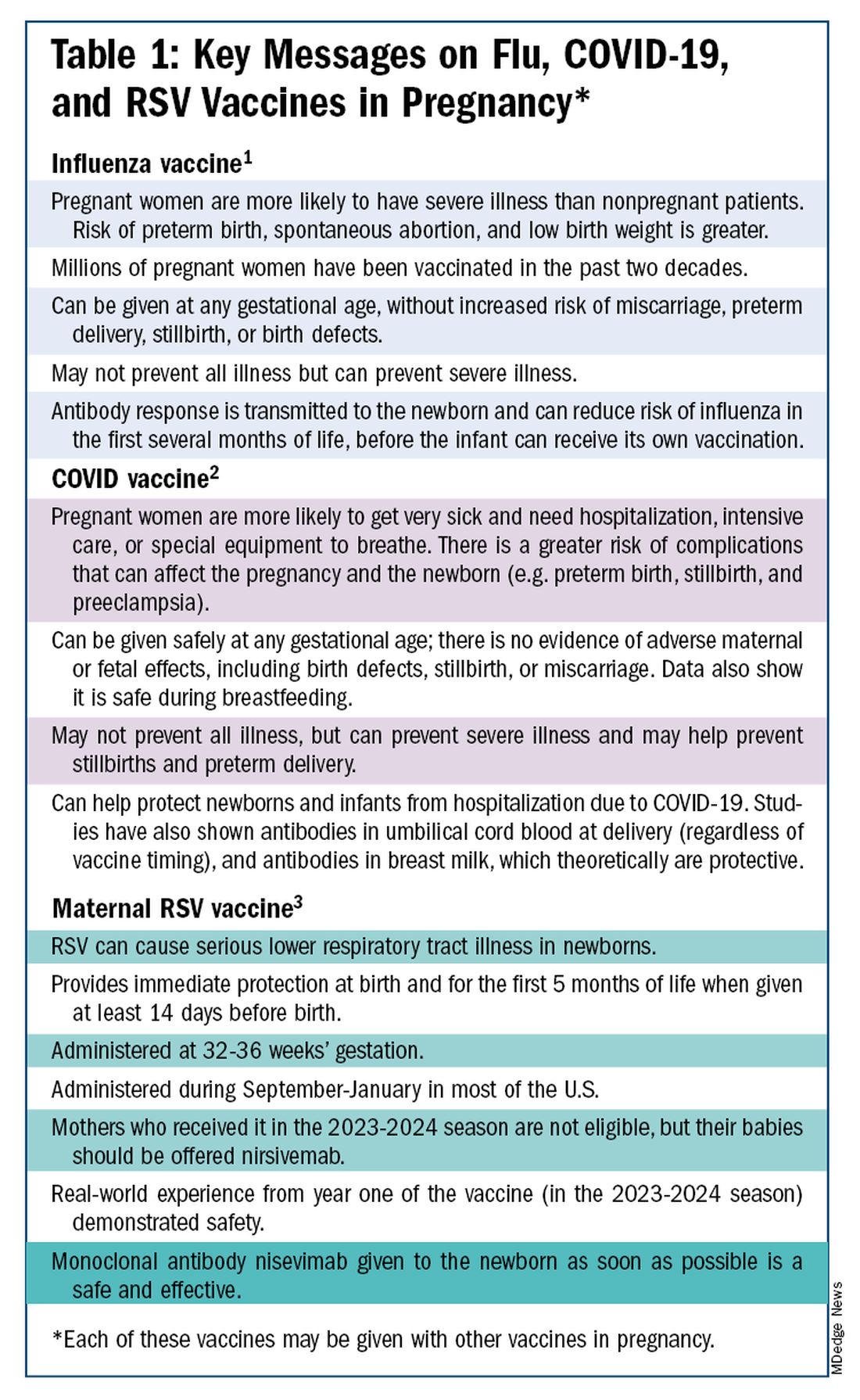
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Revolutionizing Headache Medicine: The Role of Artificial Intelligence
As we move further into the 21st century, technology continues to revolutionize various facets of our lives. Healthcare is a prime example. Advances in technology have dramatically reshaped the way we develop medications, diagnose diseases, and enhance patient care. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and the widespread adoption of digital health technologies have marked a significant milestone in improving the quality of care. AI, with its ability to leverage algorithms, deep learning, and machine learning to process data, make decisions, and perform tasks autonomously, is becoming an integral part of modern society. It is embedded in various technologies that we rely on daily, from smartphones and smart home devices to content recommendations on streaming services and social media platforms.
In healthcare, AI has applications in numerous fields, such as radiology. AI streamlines processes such as organizing patient appointments, optimizing radiation protocols for safety and efficiency, and enhancing the documentation process through advanced image analysis. AI technology plays an integral role in imaging tasks like image enhancement, lesion detection, and precise measurement. In difficult-to-interpret radiologic studies, such as some mammography images, it can be a crucial aid to the radiologist. Additionally, the use of AI has significantly improved remote patient monitoring that enables healthcare professionals to monitor and assess patient conditions without needing in-person visits. Remote patient monitoring gained prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to be a valuable tool in post pandemic care. Study results have highlighted that AI-driven ambient dictation tools have increased provider engagement with patients during consultations while reducing the time spent documenting in electronic health records.
Like many other medical specialties, headache medicine also uses AI. Most prominently, AI has been used in models and engines in assisting with headache diagnoses. A noteworthy example of AI in headache medicine is the development of an online, computer-based diagnostic engine (CDE) by Rapoport et al, called BonTriage. This tool is designed to diagnose headaches by employing a rule set based on the International Classification of Headache Disorders-3 (ICHD-3) criteria for primary headache disorders while also evaluating secondary headaches and medication overuse headaches. By leveraging machine learning, the CDE has the potential to streamline the diagnostic process, reducing the number of questions needed to reach a diagnosis and making the experience more efficient. This information can then be printed as a PDF file and taken by the patient to a healthcare professional for further discussion, fostering a more accurate, fluid, and conversational consultation.
A study was conducted to evaluate the accuracy of the CDE. Participants were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 sequences: (1) using the CDE followed by a structured standard interview with a headache specialist using the same ICHD-3 criteria or (2) starting with the structured standard interview followed by the CDE. The results demonstrated nearly perfect agreement in diagnosing migraine and probable migraine between the CDE and structured standard interview (κ = 0.82, 95% CI: 0.74, 0.90). The CDE demonstrated a diagnostic accuracy of 91.6% (95% CI: 86.9%, 95.0%), a sensitivity rate of 89.0% (95% CI: 82.5%, 93.7%), and a specificity rate of 97.0% (95% CI: 89.5%, 99.6%).
A diagnostic engine such as this can save time that clinicians spend on documentation and allow more time for discussion with the patient. For instance, a patient can take the printout received from the CDE to an appointment; the printout gives a detailed history plus information about social and psychological issues, a list of medications taken, and results of previous testing. The CDE system was originally designed to help patients see a specialist in the environment of a nationwide lack of headache specialists. There are currently 45 million patients with headaches who are seeking treatment with only around 550 certified headache specialists in the United States. The CDE printed information can help a patient obtain a consultation from a clinician quickly and start evaluation and treatment earlier. This expert online consultation is currently free of charge.
Kwon et al developed a machine learning–based model designed to automatically classify headache disorders using data from a questionnaire. Their model was able to predict diagnoses for conditions such as migraine, tension-type headaches, trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia, epicranial headache, and thunderclap headaches. The model was trained on data from 2162 patients, all diagnosed by headache specialists, and achieved an overall accuracy of 81%, with a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 95% for diagnosing migraines. However, the model’s performance was less robust when applied to other headache disorders.
Katsuki et al developed an AI model to help non specialists accurately diagnose headaches. This model analyzed 17 variables and was trained on data from 2800 patients, with additional testing and refinement using data from another 200 patients. To evaluate its effectiveness, 2 groups of non-headache specialists each assessed 50 patients: 1 group relied solely on their expertise, while the other used the AI model. The group without AI assistance achieved an overall accuracy of 46% (κ = 0.21), while the group using the AI model significantly improved, reaching an overall accuracy of 83.2% (κ = 0.68).
Building on their work with AI for diagnosing headaches, Katsuki et al conducted a study using a smartphone application that tracked user-reported headache events alongside local weather data. The AI model revealed that lower barometric pressure, higher humidity, and increased rainfall were linked to the onset of headache attacks. The application also identified triggers for headaches in specific weather patterns, such as a drop in barometric pressure noted 6 hours before headache onset. The application of AI in monitoring weather changes could be crucial, especially given concerns that the rising frequency of severe weather events due to climate change may be exacerbating the severity and burden of migraine. Additionally, recent post hoc analyses of fremanezumab clinical trials have provided further evidence that weather changes can trigger headaches.
Rapoport and colleagues have also developed an application called Migraine Mentor, which accurately tracks headaches, triggers, health data, and response to medication on a smartphone. The patient spends 3 minutes a day answering a few questions about their day and whether they had a headache or took any medication. At 1 or 2 months, Migraine Mentor can generate a detailed report with data and current trends that is sent to the patient, which the patient can then share with the clinician. The application also reminds patients when to document data and take medication.
However, although the use of AI in headache medicine appears promising, caution must be exercised to ensure proper results and information are disseminated. One rapidly expanding application of AI is the widely popular ChatGPT. ChatGPT, which stands for generative pretraining transformer, is a type of large language model (LLM). An LLM is a deep learning algorithm designed to recognize, translate, predict, summarize, and generate text responses based on a given prompt. This model is trained on an extensive dataset that includes a diverse array of books, articles, and websites, exposing it to various language structures and styles. This training enables ChatGPT to generate responses that closely mimic human communication. LLMs are being used more and more in medicine to assist with generating patient documentation and educational materials.
However, Dr Fred Cohen published a perspective piece detailing how LLMs (such as ChatGPT) can produce misleading and inaccurate answers. In his example, he tasked ChatGPT to describe the epidemiology of migraines in penguins; the AI model generated a well-written and highly believable manuscript titled, “Migraine Under the Ice: Understanding Headaches in Antarctica's Feathered Friends.” The manuscript highlights that migraines are more prevalent in male penguins compared to females, with the peak age of onset occurring between 4 and 5 years. Additionally, emperor and king penguins are identified as being more susceptible to developing migraines compared to other penguin species. The paper was fictitious (as no studies on migraine in penguins have been written to date), exemplifying that these models can produce nonfactual materials.
For years, technological advancements have been reshaping many aspects of life, and medicine is no exception. AI has been successfully applied to streamline medical documentation, develop new drug targets, and deepen our understanding of various diseases. The field of headache medicine now also uses AI. Recent developments show significant promise, with AI aiding in the diagnosis of migraine and other headache disorders. AI models have even been used in the identification of potential drug targets for migraine treatment. Although there are still limitations to overcome, the future of AI in headache medicine appears bright.
If you would like to read more about Dr. Cohen’s work on AI and migraine, please visit fredcohenmd.com or TikTok @fredcohenmd.
As we move further into the 21st century, technology continues to revolutionize various facets of our lives. Healthcare is a prime example. Advances in technology have dramatically reshaped the way we develop medications, diagnose diseases, and enhance patient care. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and the widespread adoption of digital health technologies have marked a significant milestone in improving the quality of care. AI, with its ability to leverage algorithms, deep learning, and machine learning to process data, make decisions, and perform tasks autonomously, is becoming an integral part of modern society. It is embedded in various technologies that we rely on daily, from smartphones and smart home devices to content recommendations on streaming services and social media platforms.
In healthcare, AI has applications in numerous fields, such as radiology. AI streamlines processes such as organizing patient appointments, optimizing radiation protocols for safety and efficiency, and enhancing the documentation process through advanced image analysis. AI technology plays an integral role in imaging tasks like image enhancement, lesion detection, and precise measurement. In difficult-to-interpret radiologic studies, such as some mammography images, it can be a crucial aid to the radiologist. Additionally, the use of AI has significantly improved remote patient monitoring that enables healthcare professionals to monitor and assess patient conditions without needing in-person visits. Remote patient monitoring gained prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to be a valuable tool in post pandemic care. Study results have highlighted that AI-driven ambient dictation tools have increased provider engagement with patients during consultations while reducing the time spent documenting in electronic health records.
Like many other medical specialties, headache medicine also uses AI. Most prominently, AI has been used in models and engines in assisting with headache diagnoses. A noteworthy example of AI in headache medicine is the development of an online, computer-based diagnostic engine (CDE) by Rapoport et al, called BonTriage. This tool is designed to diagnose headaches by employing a rule set based on the International Classification of Headache Disorders-3 (ICHD-3) criteria for primary headache disorders while also evaluating secondary headaches and medication overuse headaches. By leveraging machine learning, the CDE has the potential to streamline the diagnostic process, reducing the number of questions needed to reach a diagnosis and making the experience more efficient. This information can then be printed as a PDF file and taken by the patient to a healthcare professional for further discussion, fostering a more accurate, fluid, and conversational consultation.
A study was conducted to evaluate the accuracy of the CDE. Participants were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 sequences: (1) using the CDE followed by a structured standard interview with a headache specialist using the same ICHD-3 criteria or (2) starting with the structured standard interview followed by the CDE. The results demonstrated nearly perfect agreement in diagnosing migraine and probable migraine between the CDE and structured standard interview (κ = 0.82, 95% CI: 0.74, 0.90). The CDE demonstrated a diagnostic accuracy of 91.6% (95% CI: 86.9%, 95.0%), a sensitivity rate of 89.0% (95% CI: 82.5%, 93.7%), and a specificity rate of 97.0% (95% CI: 89.5%, 99.6%).
A diagnostic engine such as this can save time that clinicians spend on documentation and allow more time for discussion with the patient. For instance, a patient can take the printout received from the CDE to an appointment; the printout gives a detailed history plus information about social and psychological issues, a list of medications taken, and results of previous testing. The CDE system was originally designed to help patients see a specialist in the environment of a nationwide lack of headache specialists. There are currently 45 million patients with headaches who are seeking treatment with only around 550 certified headache specialists in the United States. The CDE printed information can help a patient obtain a consultation from a clinician quickly and start evaluation and treatment earlier. This expert online consultation is currently free of charge.
Kwon et al developed a machine learning–based model designed to automatically classify headache disorders using data from a questionnaire. Their model was able to predict diagnoses for conditions such as migraine, tension-type headaches, trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia, epicranial headache, and thunderclap headaches. The model was trained on data from 2162 patients, all diagnosed by headache specialists, and achieved an overall accuracy of 81%, with a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 95% for diagnosing migraines. However, the model’s performance was less robust when applied to other headache disorders.
Katsuki et al developed an AI model to help non specialists accurately diagnose headaches. This model analyzed 17 variables and was trained on data from 2800 patients, with additional testing and refinement using data from another 200 patients. To evaluate its effectiveness, 2 groups of non-headache specialists each assessed 50 patients: 1 group relied solely on their expertise, while the other used the AI model. The group without AI assistance achieved an overall accuracy of 46% (κ = 0.21), while the group using the AI model significantly improved, reaching an overall accuracy of 83.2% (κ = 0.68).
Building on their work with AI for diagnosing headaches, Katsuki et al conducted a study using a smartphone application that tracked user-reported headache events alongside local weather data. The AI model revealed that lower barometric pressure, higher humidity, and increased rainfall were linked to the onset of headache attacks. The application also identified triggers for headaches in specific weather patterns, such as a drop in barometric pressure noted 6 hours before headache onset. The application of AI in monitoring weather changes could be crucial, especially given concerns that the rising frequency of severe weather events due to climate change may be exacerbating the severity and burden of migraine. Additionally, recent post hoc analyses of fremanezumab clinical trials have provided further evidence that weather changes can trigger headaches.
Rapoport and colleagues have also developed an application called Migraine Mentor, which accurately tracks headaches, triggers, health data, and response to medication on a smartphone. The patient spends 3 minutes a day answering a few questions about their day and whether they had a headache or took any medication. At 1 or 2 months, Migraine Mentor can generate a detailed report with data and current trends that is sent to the patient, which the patient can then share with the clinician. The application also reminds patients when to document data and take medication.
However, although the use of AI in headache medicine appears promising, caution must be exercised to ensure proper results and information are disseminated. One rapidly expanding application of AI is the widely popular ChatGPT. ChatGPT, which stands for generative pretraining transformer, is a type of large language model (LLM). An LLM is a deep learning algorithm designed to recognize, translate, predict, summarize, and generate text responses based on a given prompt. This model is trained on an extensive dataset that includes a diverse array of books, articles, and websites, exposing it to various language structures and styles. This training enables ChatGPT to generate responses that closely mimic human communication. LLMs are being used more and more in medicine to assist with generating patient documentation and educational materials.
However, Dr Fred Cohen published a perspective piece detailing how LLMs (such as ChatGPT) can produce misleading and inaccurate answers. In his example, he tasked ChatGPT to describe the epidemiology of migraines in penguins; the AI model generated a well-written and highly believable manuscript titled, “Migraine Under the Ice: Understanding Headaches in Antarctica's Feathered Friends.” The manuscript highlights that migraines are more prevalent in male penguins compared to females, with the peak age of onset occurring between 4 and 5 years. Additionally, emperor and king penguins are identified as being more susceptible to developing migraines compared to other penguin species. The paper was fictitious (as no studies on migraine in penguins have been written to date), exemplifying that these models can produce nonfactual materials.
For years, technological advancements have been reshaping many aspects of life, and medicine is no exception. AI has been successfully applied to streamline medical documentation, develop new drug targets, and deepen our understanding of various diseases. The field of headache medicine now also uses AI. Recent developments show significant promise, with AI aiding in the diagnosis of migraine and other headache disorders. AI models have even been used in the identification of potential drug targets for migraine treatment. Although there are still limitations to overcome, the future of AI in headache medicine appears bright.
If you would like to read more about Dr. Cohen’s work on AI and migraine, please visit fredcohenmd.com or TikTok @fredcohenmd.
As we move further into the 21st century, technology continues to revolutionize various facets of our lives. Healthcare is a prime example. Advances in technology have dramatically reshaped the way we develop medications, diagnose diseases, and enhance patient care. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and the widespread adoption of digital health technologies have marked a significant milestone in improving the quality of care. AI, with its ability to leverage algorithms, deep learning, and machine learning to process data, make decisions, and perform tasks autonomously, is becoming an integral part of modern society. It is embedded in various technologies that we rely on daily, from smartphones and smart home devices to content recommendations on streaming services and social media platforms.
In healthcare, AI has applications in numerous fields, such as radiology. AI streamlines processes such as organizing patient appointments, optimizing radiation protocols for safety and efficiency, and enhancing the documentation process through advanced image analysis. AI technology plays an integral role in imaging tasks like image enhancement, lesion detection, and precise measurement. In difficult-to-interpret radiologic studies, such as some mammography images, it can be a crucial aid to the radiologist. Additionally, the use of AI has significantly improved remote patient monitoring that enables healthcare professionals to monitor and assess patient conditions without needing in-person visits. Remote patient monitoring gained prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic and continues to be a valuable tool in post pandemic care. Study results have highlighted that AI-driven ambient dictation tools have increased provider engagement with patients during consultations while reducing the time spent documenting in electronic health records.
Like many other medical specialties, headache medicine also uses AI. Most prominently, AI has been used in models and engines in assisting with headache diagnoses. A noteworthy example of AI in headache medicine is the development of an online, computer-based diagnostic engine (CDE) by Rapoport et al, called BonTriage. This tool is designed to diagnose headaches by employing a rule set based on the International Classification of Headache Disorders-3 (ICHD-3) criteria for primary headache disorders while also evaluating secondary headaches and medication overuse headaches. By leveraging machine learning, the CDE has the potential to streamline the diagnostic process, reducing the number of questions needed to reach a diagnosis and making the experience more efficient. This information can then be printed as a PDF file and taken by the patient to a healthcare professional for further discussion, fostering a more accurate, fluid, and conversational consultation.
A study was conducted to evaluate the accuracy of the CDE. Participants were randomly assigned to 1 of 2 sequences: (1) using the CDE followed by a structured standard interview with a headache specialist using the same ICHD-3 criteria or (2) starting with the structured standard interview followed by the CDE. The results demonstrated nearly perfect agreement in diagnosing migraine and probable migraine between the CDE and structured standard interview (κ = 0.82, 95% CI: 0.74, 0.90). The CDE demonstrated a diagnostic accuracy of 91.6% (95% CI: 86.9%, 95.0%), a sensitivity rate of 89.0% (95% CI: 82.5%, 93.7%), and a specificity rate of 97.0% (95% CI: 89.5%, 99.6%).
A diagnostic engine such as this can save time that clinicians spend on documentation and allow more time for discussion with the patient. For instance, a patient can take the printout received from the CDE to an appointment; the printout gives a detailed history plus information about social and psychological issues, a list of medications taken, and results of previous testing. The CDE system was originally designed to help patients see a specialist in the environment of a nationwide lack of headache specialists. There are currently 45 million patients with headaches who are seeking treatment with only around 550 certified headache specialists in the United States. The CDE printed information can help a patient obtain a consultation from a clinician quickly and start evaluation and treatment earlier. This expert online consultation is currently free of charge.
Kwon et al developed a machine learning–based model designed to automatically classify headache disorders using data from a questionnaire. Their model was able to predict diagnoses for conditions such as migraine, tension-type headaches, trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia, epicranial headache, and thunderclap headaches. The model was trained on data from 2162 patients, all diagnosed by headache specialists, and achieved an overall accuracy of 81%, with a sensitivity of 88% and a specificity of 95% for diagnosing migraines. However, the model’s performance was less robust when applied to other headache disorders.
Katsuki et al developed an AI model to help non specialists accurately diagnose headaches. This model analyzed 17 variables and was trained on data from 2800 patients, with additional testing and refinement using data from another 200 patients. To evaluate its effectiveness, 2 groups of non-headache specialists each assessed 50 patients: 1 group relied solely on their expertise, while the other used the AI model. The group without AI assistance achieved an overall accuracy of 46% (κ = 0.21), while the group using the AI model significantly improved, reaching an overall accuracy of 83.2% (κ = 0.68).
Building on their work with AI for diagnosing headaches, Katsuki et al conducted a study using a smartphone application that tracked user-reported headache events alongside local weather data. The AI model revealed that lower barometric pressure, higher humidity, and increased rainfall were linked to the onset of headache attacks. The application also identified triggers for headaches in specific weather patterns, such as a drop in barometric pressure noted 6 hours before headache onset. The application of AI in monitoring weather changes could be crucial, especially given concerns that the rising frequency of severe weather events due to climate change may be exacerbating the severity and burden of migraine. Additionally, recent post hoc analyses of fremanezumab clinical trials have provided further evidence that weather changes can trigger headaches.
Rapoport and colleagues have also developed an application called Migraine Mentor, which accurately tracks headaches, triggers, health data, and response to medication on a smartphone. The patient spends 3 minutes a day answering a few questions about their day and whether they had a headache or took any medication. At 1 or 2 months, Migraine Mentor can generate a detailed report with data and current trends that is sent to the patient, which the patient can then share with the clinician. The application also reminds patients when to document data and take medication.
However, although the use of AI in headache medicine appears promising, caution must be exercised to ensure proper results and information are disseminated. One rapidly expanding application of AI is the widely popular ChatGPT. ChatGPT, which stands for generative pretraining transformer, is a type of large language model (LLM). An LLM is a deep learning algorithm designed to recognize, translate, predict, summarize, and generate text responses based on a given prompt. This model is trained on an extensive dataset that includes a diverse array of books, articles, and websites, exposing it to various language structures and styles. This training enables ChatGPT to generate responses that closely mimic human communication. LLMs are being used more and more in medicine to assist with generating patient documentation and educational materials.
However, Dr Fred Cohen published a perspective piece detailing how LLMs (such as ChatGPT) can produce misleading and inaccurate answers. In his example, he tasked ChatGPT to describe the epidemiology of migraines in penguins; the AI model generated a well-written and highly believable manuscript titled, “Migraine Under the Ice: Understanding Headaches in Antarctica's Feathered Friends.” The manuscript highlights that migraines are more prevalent in male penguins compared to females, with the peak age of onset occurring between 4 and 5 years. Additionally, emperor and king penguins are identified as being more susceptible to developing migraines compared to other penguin species. The paper was fictitious (as no studies on migraine in penguins have been written to date), exemplifying that these models can produce nonfactual materials.
For years, technological advancements have been reshaping many aspects of life, and medicine is no exception. AI has been successfully applied to streamline medical documentation, develop new drug targets, and deepen our understanding of various diseases. The field of headache medicine now also uses AI. Recent developments show significant promise, with AI aiding in the diagnosis of migraine and other headache disorders. AI models have even been used in the identification of potential drug targets for migraine treatment. Although there are still limitations to overcome, the future of AI in headache medicine appears bright.
If you would like to read more about Dr. Cohen’s work on AI and migraine, please visit fredcohenmd.com or TikTok @fredcohenmd.
Viral Season 2024-2025: Try for An Ounce of Prevention
We are quickly approaching the typical cold and flu season. But can we call anything typical since 2020? Since 2020, there have been different recommendations for prevention, testing, return to work, and treatment since our world was rocked by the pandemic. Now that we are in the “post-pandemic” era, family physicians and other primary care professionals are the front line for discussions on prevention, evaluation, and treatment of the typical upper-respiratory infections, influenza, and COVID-19.
Let’s start with prevention. We have all heard the old adage, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. In primary care, we need to focus on prevention. Vaccination is often one of our best tools against the myriad of infections we are hoping to help patients prevent during cold and flu season. Most recently, we have fall vaccinations aimed to prevent COVID-19, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
The number and timing of each of these vaccinations has different recommendations based on a variety of factors including age, pregnancy status, and whether or not the patient is immunocompromised. For the 2024-2025 season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended updated vaccines for both influenza and COVID-19.1
They have also updated the RSV vaccine recommendations to “People 75 or older, or between 60-74 with certain chronic health conditions or living in a nursing home should get one dose of the RSV vaccine to provide an extra layer of protection.”2
In addition to vaccines as prevention, there is also hygiene, staying home when sick and away from others who are sick, following guidelines for where and when to wear a face mask, and the general tools of eating well, and getting sufficient sleep and exercise to help maintain the healthiest immune system.
Despite the best of intentions, there will still be many who experience viral infections in this upcoming season. The CDC is currently recommending persons to stay away from others for at least 24 hours after their symptoms improve and they are fever-free without antipyretics. In addition to isolation while sick, general symptom management is something that we can recommend for all of these illnesses.
There is more to consider, though, as our patients face these illnesses. The first question is how to determine the diagnosis — and if that diagnosis is even necessary. Unfortunately, many of these viral illnesses can look the same. They can all cause fevers, chills, and other upper respiratory symptoms. They are all fairly contagious. All of these viruses can cause serious illness associated with additional complications. It is not truly possible to determine which virus someone has by symptoms alone, our patients can have multiple viruses at the same time and diagnosis of one does not preclude having another.3
Instead, we truly do need a test for diagnosis. In-office testing is available for RSV, influenza, and COVID-19. Additionally, despite not being as freely available as they were during the pandemic, patients are able to do home COVID tests and then call in with their results. At the time of writing this, at-home rapid influenza tests have also been approved by the FDA but are not yet readily available to the public. These tests are important for determining if the patient is eligible for treatment. Both influenza and COVID-19 have antiviral treatments available to help decrease the severity of the illness and potentially the length of illness and time contagious. According to the CDC, both treatments are underutilized.
This could be because of a lack of testing and diagnosis. It may also be because of a lack of familiarity with the available treatments.4,5
Influenza treatment is recommended as soon as possible for those with suspected or confirmed diagnosis, immediately for anyone hospitalized, anyone with severe, complicated, or progressing illness, and for those at high risk of severe illness including but not limited to those under 2 years old, those over 65, those who are pregnant, and those with many chronic conditions.
Treatment can also be used for those who are not high risk when diagnosed within 48 hours. In the United States, four antivirals are recommended to treat influenza: oseltamivir phosphate, zanamivir, peramivir, and baloxavir marboxil. For COVID-19, treatments are also available for mild or moderate disease in those at risk for severe disease. Both remdesivir and nimatrelvir with ritonavir are treatment options that can be used for COVID-19 infection. Unfortunately, no specific antiviral is available for the other viral illnesses we see often during this season.
In primary care, we have some important roles to play. We need to continue to discuss all methods of prevention. Not only do vaccine recommendations change at least annually, our patients’ situations change and we have to reassess them. Additionally, people often need to hear things more than once before committing — so it never hurts to continue having those conversations. Combining the conversation about vaccines with other prevention measures is also important so that it does not seem like we are only recommending one thing. We should also start talking about treatment options before our patients are sick. We can communicate what is available as long as they let us know they are sick early. We can also be there to help our patients determine when they are at risk for severe illness and when they should consider a higher level of care.
The availability of home testing gives us the opportunity to provide these treatments via telehealth and even potentially in times when these illnesses are everywhere — with standing orders with our clinical teams. Although it is a busy time for us in the clinic, “cold and flu” season is definitely one of those times when our primary care relationship can truly help our patients.
References
1. CDC Recommends Updated 2024-2025 COVID-19 and Flu Vaccines for Fall/Winter Virus Season. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2024/s-t0627-vaccine-recommendations.html. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
2. CDC Updates RSV Vaccination Recommendation for Adults. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2024/s-0626-vaccination-adults.html. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
3. Similarities and Differences between Flu and COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/flu-vs-covid19.htm. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
4. Respiratory Virus Guidance. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/guidance/index.html. Accessed August 9, 2024. Source: National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
5. Provider Toolkit: Preparing Patients for the Fall and Winter Virus Season. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/hcp/tools-resources/index.html. Accessed August 9, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
We are quickly approaching the typical cold and flu season. But can we call anything typical since 2020? Since 2020, there have been different recommendations for prevention, testing, return to work, and treatment since our world was rocked by the pandemic. Now that we are in the “post-pandemic” era, family physicians and other primary care professionals are the front line for discussions on prevention, evaluation, and treatment of the typical upper-respiratory infections, influenza, and COVID-19.
Let’s start with prevention. We have all heard the old adage, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. In primary care, we need to focus on prevention. Vaccination is often one of our best tools against the myriad of infections we are hoping to help patients prevent during cold and flu season. Most recently, we have fall vaccinations aimed to prevent COVID-19, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
The number and timing of each of these vaccinations has different recommendations based on a variety of factors including age, pregnancy status, and whether or not the patient is immunocompromised. For the 2024-2025 season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended updated vaccines for both influenza and COVID-19.1
They have also updated the RSV vaccine recommendations to “People 75 or older, or between 60-74 with certain chronic health conditions or living in a nursing home should get one dose of the RSV vaccine to provide an extra layer of protection.”2
In addition to vaccines as prevention, there is also hygiene, staying home when sick and away from others who are sick, following guidelines for where and when to wear a face mask, and the general tools of eating well, and getting sufficient sleep and exercise to help maintain the healthiest immune system.
Despite the best of intentions, there will still be many who experience viral infections in this upcoming season. The CDC is currently recommending persons to stay away from others for at least 24 hours after their symptoms improve and they are fever-free without antipyretics. In addition to isolation while sick, general symptom management is something that we can recommend for all of these illnesses.
There is more to consider, though, as our patients face these illnesses. The first question is how to determine the diagnosis — and if that diagnosis is even necessary. Unfortunately, many of these viral illnesses can look the same. They can all cause fevers, chills, and other upper respiratory symptoms. They are all fairly contagious. All of these viruses can cause serious illness associated with additional complications. It is not truly possible to determine which virus someone has by symptoms alone, our patients can have multiple viruses at the same time and diagnosis of one does not preclude having another.3
Instead, we truly do need a test for diagnosis. In-office testing is available for RSV, influenza, and COVID-19. Additionally, despite not being as freely available as they were during the pandemic, patients are able to do home COVID tests and then call in with their results. At the time of writing this, at-home rapid influenza tests have also been approved by the FDA but are not yet readily available to the public. These tests are important for determining if the patient is eligible for treatment. Both influenza and COVID-19 have antiviral treatments available to help decrease the severity of the illness and potentially the length of illness and time contagious. According to the CDC, both treatments are underutilized.
This could be because of a lack of testing and diagnosis. It may also be because of a lack of familiarity with the available treatments.4,5
Influenza treatment is recommended as soon as possible for those with suspected or confirmed diagnosis, immediately for anyone hospitalized, anyone with severe, complicated, or progressing illness, and for those at high risk of severe illness including but not limited to those under 2 years old, those over 65, those who are pregnant, and those with many chronic conditions.
Treatment can also be used for those who are not high risk when diagnosed within 48 hours. In the United States, four antivirals are recommended to treat influenza: oseltamivir phosphate, zanamivir, peramivir, and baloxavir marboxil. For COVID-19, treatments are also available for mild or moderate disease in those at risk for severe disease. Both remdesivir and nimatrelvir with ritonavir are treatment options that can be used for COVID-19 infection. Unfortunately, no specific antiviral is available for the other viral illnesses we see often during this season.
In primary care, we have some important roles to play. We need to continue to discuss all methods of prevention. Not only do vaccine recommendations change at least annually, our patients’ situations change and we have to reassess them. Additionally, people often need to hear things more than once before committing — so it never hurts to continue having those conversations. Combining the conversation about vaccines with other prevention measures is also important so that it does not seem like we are only recommending one thing. We should also start talking about treatment options before our patients are sick. We can communicate what is available as long as they let us know they are sick early. We can also be there to help our patients determine when they are at risk for severe illness and when they should consider a higher level of care.
The availability of home testing gives us the opportunity to provide these treatments via telehealth and even potentially in times when these illnesses are everywhere — with standing orders with our clinical teams. Although it is a busy time for us in the clinic, “cold and flu” season is definitely one of those times when our primary care relationship can truly help our patients.
References
1. CDC Recommends Updated 2024-2025 COVID-19 and Flu Vaccines for Fall/Winter Virus Season. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2024/s-t0627-vaccine-recommendations.html. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
2. CDC Updates RSV Vaccination Recommendation for Adults. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2024/s-0626-vaccination-adults.html. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
3. Similarities and Differences between Flu and COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/flu-vs-covid19.htm. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
4. Respiratory Virus Guidance. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/guidance/index.html. Accessed August 9, 2024. Source: National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
5. Provider Toolkit: Preparing Patients for the Fall and Winter Virus Season. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/hcp/tools-resources/index.html. Accessed August 9, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
We are quickly approaching the typical cold and flu season. But can we call anything typical since 2020? Since 2020, there have been different recommendations for prevention, testing, return to work, and treatment since our world was rocked by the pandemic. Now that we are in the “post-pandemic” era, family physicians and other primary care professionals are the front line for discussions on prevention, evaluation, and treatment of the typical upper-respiratory infections, influenza, and COVID-19.
Let’s start with prevention. We have all heard the old adage, an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. In primary care, we need to focus on prevention. Vaccination is often one of our best tools against the myriad of infections we are hoping to help patients prevent during cold and flu season. Most recently, we have fall vaccinations aimed to prevent COVID-19, influenza, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
The number and timing of each of these vaccinations has different recommendations based on a variety of factors including age, pregnancy status, and whether or not the patient is immunocompromised. For the 2024-2025 season, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has recommended updated vaccines for both influenza and COVID-19.1
They have also updated the RSV vaccine recommendations to “People 75 or older, or between 60-74 with certain chronic health conditions or living in a nursing home should get one dose of the RSV vaccine to provide an extra layer of protection.”2
In addition to vaccines as prevention, there is also hygiene, staying home when sick and away from others who are sick, following guidelines for where and when to wear a face mask, and the general tools of eating well, and getting sufficient sleep and exercise to help maintain the healthiest immune system.
Despite the best of intentions, there will still be many who experience viral infections in this upcoming season. The CDC is currently recommending persons to stay away from others for at least 24 hours after their symptoms improve and they are fever-free without antipyretics. In addition to isolation while sick, general symptom management is something that we can recommend for all of these illnesses.
There is more to consider, though, as our patients face these illnesses. The first question is how to determine the diagnosis — and if that diagnosis is even necessary. Unfortunately, many of these viral illnesses can look the same. They can all cause fevers, chills, and other upper respiratory symptoms. They are all fairly contagious. All of these viruses can cause serious illness associated with additional complications. It is not truly possible to determine which virus someone has by symptoms alone, our patients can have multiple viruses at the same time and diagnosis of one does not preclude having another.3
Instead, we truly do need a test for diagnosis. In-office testing is available for RSV, influenza, and COVID-19. Additionally, despite not being as freely available as they were during the pandemic, patients are able to do home COVID tests and then call in with their results. At the time of writing this, at-home rapid influenza tests have also been approved by the FDA but are not yet readily available to the public. These tests are important for determining if the patient is eligible for treatment. Both influenza and COVID-19 have antiviral treatments available to help decrease the severity of the illness and potentially the length of illness and time contagious. According to the CDC, both treatments are underutilized.
This could be because of a lack of testing and diagnosis. It may also be because of a lack of familiarity with the available treatments.4,5
Influenza treatment is recommended as soon as possible for those with suspected or confirmed diagnosis, immediately for anyone hospitalized, anyone with severe, complicated, or progressing illness, and for those at high risk of severe illness including but not limited to those under 2 years old, those over 65, those who are pregnant, and those with many chronic conditions.
Treatment can also be used for those who are not high risk when diagnosed within 48 hours. In the United States, four antivirals are recommended to treat influenza: oseltamivir phosphate, zanamivir, peramivir, and baloxavir marboxil. For COVID-19, treatments are also available for mild or moderate disease in those at risk for severe disease. Both remdesivir and nimatrelvir with ritonavir are treatment options that can be used for COVID-19 infection. Unfortunately, no specific antiviral is available for the other viral illnesses we see often during this season.
In primary care, we have some important roles to play. We need to continue to discuss all methods of prevention. Not only do vaccine recommendations change at least annually, our patients’ situations change and we have to reassess them. Additionally, people often need to hear things more than once before committing — so it never hurts to continue having those conversations. Combining the conversation about vaccines with other prevention measures is also important so that it does not seem like we are only recommending one thing. We should also start talking about treatment options before our patients are sick. We can communicate what is available as long as they let us know they are sick early. We can also be there to help our patients determine when they are at risk for severe illness and when they should consider a higher level of care.
The availability of home testing gives us the opportunity to provide these treatments via telehealth and even potentially in times when these illnesses are everywhere — with standing orders with our clinical teams. Although it is a busy time for us in the clinic, “cold and flu” season is definitely one of those times when our primary care relationship can truly help our patients.
References
1. CDC Recommends Updated 2024-2025 COVID-19 and Flu Vaccines for Fall/Winter Virus Season. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2024/s-t0627-vaccine-recommendations.html. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
2. CDC Updates RSV Vaccination Recommendation for Adults. https://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2024/s-0626-vaccination-adults.html. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
3. Similarities and Differences between Flu and COVID-19. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/symptoms/flu-vs-covid19.htm. Accessed August 8, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
4. Respiratory Virus Guidance. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/guidance/index.html. Accessed August 9, 2024. Source: National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
5. Provider Toolkit: Preparing Patients for the Fall and Winter Virus Season. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/hcp/tools-resources/index.html. Accessed August 9, 2024. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Migraine Treatment Outcomes
Outcomes of Acute and Preventive Migraine Therapy Based on Patient Sex
I previously have addressed myths about migraine as they pertain to men and women. When I found an interesting study recently published in Cephalalgia investigating the effectiveness of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRP-R) antagonists (gepants) for acute care and prevention of episodic migraine and CGRP monoclonal antibodies for preventive treatment of episodic and chronic migraine in men and women, I thought I would discuss it here.
The study’s aim was to discern if patient sex contributed to outcomes in each specific treatment arm. Female sex hormones have been recognized as factors in promoting migraine, and women show increased severity, persistence, and comorbidity in migraine profiles, and increased prevalence of migraine relative to men.
Gepants used for acute therapy (ubrogepant, rimegepant, zavegepant) and preventive therapy (atogepant, rimegepant) were studied in this trial. Erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and eptinezumab are monoclonal antibodies that either sit on the CGRP receptor (erenumab) or inactivate the CGRP ligand (fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and eptinezumab) and are used for migraine prevention. CGRP-based therapies are not effective in all patients and understanding which patient groups respond preferentially could reduce trial and error in treatment selection. The effectiveness of treatments targeting CGRP or the CGRP receptor may not be uniform in men and women, highlighting the need for further research and understanding of CGRP neurobiology in both sexes.
Key findings:
- In the trial by Porreca et al: In women, the 3 gepants approved by the FDA for the acute care of migraine (ubrogepant, rimegepant, zavegepant) produced a statistically significant drug effect for the 2-hour pain freedom (2h-PF) endpoint, with an average drug effect of 9.5% (CI: 7.4 to 11.6) and an average number needed to treat (NNT) of 11.
- Men did not show statistically significant effects with the acute use of gepants. The average drug effect was 2.8%, and the average NNT was 36.
- For both men and women, CGRP-targeting therapies for prevention of migraine (the 4 monoclonal antibodies) were equally effective; however, possible sex differences remain uncertain and need further study.
- In patients with chronic migraine, CGRP/CGRP-R antibodies were similarly effective in both men and women.
- For the 2-hour freedom from most bothersome symptom (2h-MBS) endpoint when gepants were given acutely, the effects were much better in women than men, with an average drug effect of 10.2% and an average NNT of 10.
- In men, these medications produced observed treatment effects on 2h-MBS with an average drug effect of 3.2% and an average NNT of 32.
- In men, 5 out of 12 estimates favored placebo over the active treatment, suggesting a treatment with little to no effect.
- The pooled treatment effects for women were 3 times as large, at 9.2% and 10.2%, respectively.
- The placebo response rates for 2 of the 3 ubrogepant studies and one of 2 zavegepant studies were higher in men than in women.
The study concludes that, while small molecule CGRP-R antagonists are dramatically effective for acute therapy of migraine in women, available data do not demonstrate effectiveness in men. The treatment effect was found to always favor active treatment numerically for both men and women for prevention of episodic and chronic migraine. The data highlight possible differential effects of CGRP-targeted therapies in different patient populations and the need for increased understanding of CGRP neurobiology in men and women. The study also emphasizes the need to understand which patient groups preferentially respond to CGRP-based therapies to reduce trial and error in treatment. Note that rimegepant data on prevention were not available for analysis at the time of the writing.
It would be interesting to perform a meta-analysis of multiple well-done, large, real-world studies to see if the same differences and similarities are found in men versus women for acute care of migraine and prevention of episodic and chronic migraine. I suspect that we would find that acute care results favor women but that some men do well.
The Effectiveness of Prednisolone for Treating Medication Overuse Headache
I often discuss medication overuse headache (MOH), as it is difficult to diagnose and treat, so I wanted to comment on another pertinent study. It is a post hoc analysis of the Registry for Load and Management of Medication Overuse Headache (RELEASE). The RELEASE trial is an ongoing, multicenter, observational, cohort study of MOH that has been conducted in Korea since April 2020. Findings were recently published in Headache by Lee et al.
MOH is a secondary headache disorder that develops in patients with a preexisting primary headache when they overuse acute care headache medications of any type except gepants. This includes prescription medications such as triptans, ergots, butalbital-containing medications; opioids; aspirin; acetaminophen; any type of combination medication often containing caffeine; or a combination of medications. This condition significantly impacts patients’ quality of life and productivity, usually increasing the frequency of headaches per month and leading to higher healthcare-related costs.
Treating MOH is challenging due to the lack of high-quality drug trials specifically designed for MOH and doctor inexperience. Current evidence is based largely on subgroup analyses of drug trials for the treatment of chronic migraine that contain these patient types.
Withdrawal of acute care headache medications that are being overused has traditionally been considered an important aspect of MOH treatment, although this may be changing. Withdrawal symptoms, such as increased intensity of headache pain, frequency of headaches, and other symptoms like agitation and sleep disturbance, can prevent patients from discontinuing overused medications. Systemic corticosteroids are widely used to reduce these withdrawal headaches, but clinical trials are sparse and have failed to meet proper endpoints. Despite this, corticosteroids have shown potential benefits, such as decreasing withdrawal headaches, reducing the use of rescue medications, and lowering headache intensity at certain time points after treatment.
Given these findings, this published study hypothesized that prednisolone may play a role in converting MOH to non-MOH at 3 months after treatment. The objective was to evaluate the outcome of prednisolone therapy in reversing medication overuse at 3 months posttreatment in patients with MOH using prospective multicenter registry data. Prednisolone was prescribed to 59 out of 309 patients (19.1%) enrolled during this observational study period, with doses ranging from 10 to 40 mg/day for 5-14 days. Of these patients, 228 (73.8%) completed the 3-month follow-up period.
Key findings:
- The MOH reversal rates at 3 months postbaseline were 76% (31/41) in the prednisolone group and 57.8% (108/187) in the no prednisolone group (p = 0.034).
- The steroid effect remained significant (adjusted odds ratio, 2.78; 95% confidence interval 1.27-6.1, p = 0.010) after adjusting for the number of monthly headache days at baseline, mode of discontinuation of overused medication, use of early preventive medications, and the number of combined preventive medications.
The study had several strengths, including the multicenter collection of data, prospective follow-ups, and comprehensiveness of data acquisition. However, it also had significant limitations, such as the noninterventional, observational nature of the study, potential bias in steroid prescription (every doctor prescribed what they wanted), and heterogeneity in the patient population. Also, there were a variety of treatments, and they were not standardized. Further external validation may be necessary before generalizing the study results.
Despite these limitations, the results do suggest that prednisolone may be one part of a valid treatment option for patients with MOH. I suspect, if the proper studies are done, we will see that using a good preventive medication, with few adverse events, and with careful education of the patient, formal detoxification will not be necessary when treating many patients with MOH. This has been my experience with MOH treatment utilizing the newer anti-CGRP preventive medications, including the older monoclonal antibodies and the newer gepants.
Outcomes of Acute and Preventive Migraine Therapy Based on Patient Sex
I previously have addressed myths about migraine as they pertain to men and women. When I found an interesting study recently published in Cephalalgia investigating the effectiveness of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRP-R) antagonists (gepants) for acute care and prevention of episodic migraine and CGRP monoclonal antibodies for preventive treatment of episodic and chronic migraine in men and women, I thought I would discuss it here.
The study’s aim was to discern if patient sex contributed to outcomes in each specific treatment arm. Female sex hormones have been recognized as factors in promoting migraine, and women show increased severity, persistence, and comorbidity in migraine profiles, and increased prevalence of migraine relative to men.
Gepants used for acute therapy (ubrogepant, rimegepant, zavegepant) and preventive therapy (atogepant, rimegepant) were studied in this trial. Erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and eptinezumab are monoclonal antibodies that either sit on the CGRP receptor (erenumab) or inactivate the CGRP ligand (fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and eptinezumab) and are used for migraine prevention. CGRP-based therapies are not effective in all patients and understanding which patient groups respond preferentially could reduce trial and error in treatment selection. The effectiveness of treatments targeting CGRP or the CGRP receptor may not be uniform in men and women, highlighting the need for further research and understanding of CGRP neurobiology in both sexes.
Key findings:
- In the trial by Porreca et al: In women, the 3 gepants approved by the FDA for the acute care of migraine (ubrogepant, rimegepant, zavegepant) produced a statistically significant drug effect for the 2-hour pain freedom (2h-PF) endpoint, with an average drug effect of 9.5% (CI: 7.4 to 11.6) and an average number needed to treat (NNT) of 11.
- Men did not show statistically significant effects with the acute use of gepants. The average drug effect was 2.8%, and the average NNT was 36.
- For both men and women, CGRP-targeting therapies for prevention of migraine (the 4 monoclonal antibodies) were equally effective; however, possible sex differences remain uncertain and need further study.
- In patients with chronic migraine, CGRP/CGRP-R antibodies were similarly effective in both men and women.
- For the 2-hour freedom from most bothersome symptom (2h-MBS) endpoint when gepants were given acutely, the effects were much better in women than men, with an average drug effect of 10.2% and an average NNT of 10.
- In men, these medications produced observed treatment effects on 2h-MBS with an average drug effect of 3.2% and an average NNT of 32.
- In men, 5 out of 12 estimates favored placebo over the active treatment, suggesting a treatment with little to no effect.
- The pooled treatment effects for women were 3 times as large, at 9.2% and 10.2%, respectively.
- The placebo response rates for 2 of the 3 ubrogepant studies and one of 2 zavegepant studies were higher in men than in women.
The study concludes that, while small molecule CGRP-R antagonists are dramatically effective for acute therapy of migraine in women, available data do not demonstrate effectiveness in men. The treatment effect was found to always favor active treatment numerically for both men and women for prevention of episodic and chronic migraine. The data highlight possible differential effects of CGRP-targeted therapies in different patient populations and the need for increased understanding of CGRP neurobiology in men and women. The study also emphasizes the need to understand which patient groups preferentially respond to CGRP-based therapies to reduce trial and error in treatment. Note that rimegepant data on prevention were not available for analysis at the time of the writing.
It would be interesting to perform a meta-analysis of multiple well-done, large, real-world studies to see if the same differences and similarities are found in men versus women for acute care of migraine and prevention of episodic and chronic migraine. I suspect that we would find that acute care results favor women but that some men do well.
The Effectiveness of Prednisolone for Treating Medication Overuse Headache
I often discuss medication overuse headache (MOH), as it is difficult to diagnose and treat, so I wanted to comment on another pertinent study. It is a post hoc analysis of the Registry for Load and Management of Medication Overuse Headache (RELEASE). The RELEASE trial is an ongoing, multicenter, observational, cohort study of MOH that has been conducted in Korea since April 2020. Findings were recently published in Headache by Lee et al.
MOH is a secondary headache disorder that develops in patients with a preexisting primary headache when they overuse acute care headache medications of any type except gepants. This includes prescription medications such as triptans, ergots, butalbital-containing medications; opioids; aspirin; acetaminophen; any type of combination medication often containing caffeine; or a combination of medications. This condition significantly impacts patients’ quality of life and productivity, usually increasing the frequency of headaches per month and leading to higher healthcare-related costs.
Treating MOH is challenging due to the lack of high-quality drug trials specifically designed for MOH and doctor inexperience. Current evidence is based largely on subgroup analyses of drug trials for the treatment of chronic migraine that contain these patient types.
Withdrawal of acute care headache medications that are being overused has traditionally been considered an important aspect of MOH treatment, although this may be changing. Withdrawal symptoms, such as increased intensity of headache pain, frequency of headaches, and other symptoms like agitation and sleep disturbance, can prevent patients from discontinuing overused medications. Systemic corticosteroids are widely used to reduce these withdrawal headaches, but clinical trials are sparse and have failed to meet proper endpoints. Despite this, corticosteroids have shown potential benefits, such as decreasing withdrawal headaches, reducing the use of rescue medications, and lowering headache intensity at certain time points after treatment.
Given these findings, this published study hypothesized that prednisolone may play a role in converting MOH to non-MOH at 3 months after treatment. The objective was to evaluate the outcome of prednisolone therapy in reversing medication overuse at 3 months posttreatment in patients with MOH using prospective multicenter registry data. Prednisolone was prescribed to 59 out of 309 patients (19.1%) enrolled during this observational study period, with doses ranging from 10 to 40 mg/day for 5-14 days. Of these patients, 228 (73.8%) completed the 3-month follow-up period.
Key findings:
- The MOH reversal rates at 3 months postbaseline were 76% (31/41) in the prednisolone group and 57.8% (108/187) in the no prednisolone group (p = 0.034).
- The steroid effect remained significant (adjusted odds ratio, 2.78; 95% confidence interval 1.27-6.1, p = 0.010) after adjusting for the number of monthly headache days at baseline, mode of discontinuation of overused medication, use of early preventive medications, and the number of combined preventive medications.
The study had several strengths, including the multicenter collection of data, prospective follow-ups, and comprehensiveness of data acquisition. However, it also had significant limitations, such as the noninterventional, observational nature of the study, potential bias in steroid prescription (every doctor prescribed what they wanted), and heterogeneity in the patient population. Also, there were a variety of treatments, and they were not standardized. Further external validation may be necessary before generalizing the study results.
Despite these limitations, the results do suggest that prednisolone may be one part of a valid treatment option for patients with MOH. I suspect, if the proper studies are done, we will see that using a good preventive medication, with few adverse events, and with careful education of the patient, formal detoxification will not be necessary when treating many patients with MOH. This has been my experience with MOH treatment utilizing the newer anti-CGRP preventive medications, including the older monoclonal antibodies and the newer gepants.
Outcomes of Acute and Preventive Migraine Therapy Based on Patient Sex
I previously have addressed myths about migraine as they pertain to men and women. When I found an interesting study recently published in Cephalalgia investigating the effectiveness of calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor (CGRP-R) antagonists (gepants) for acute care and prevention of episodic migraine and CGRP monoclonal antibodies for preventive treatment of episodic and chronic migraine in men and women, I thought I would discuss it here.
The study’s aim was to discern if patient sex contributed to outcomes in each specific treatment arm. Female sex hormones have been recognized as factors in promoting migraine, and women show increased severity, persistence, and comorbidity in migraine profiles, and increased prevalence of migraine relative to men.
Gepants used for acute therapy (ubrogepant, rimegepant, zavegepant) and preventive therapy (atogepant, rimegepant) were studied in this trial. Erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and eptinezumab are monoclonal antibodies that either sit on the CGRP receptor (erenumab) or inactivate the CGRP ligand (fremanezumab, galcanezumab, and eptinezumab) and are used for migraine prevention. CGRP-based therapies are not effective in all patients and understanding which patient groups respond preferentially could reduce trial and error in treatment selection. The effectiveness of treatments targeting CGRP or the CGRP receptor may not be uniform in men and women, highlighting the need for further research and understanding of CGRP neurobiology in both sexes.
Key findings:
- In the trial by Porreca et al: In women, the 3 gepants approved by the FDA for the acute care of migraine (ubrogepant, rimegepant, zavegepant) produced a statistically significant drug effect for the 2-hour pain freedom (2h-PF) endpoint, with an average drug effect of 9.5% (CI: 7.4 to 11.6) and an average number needed to treat (NNT) of 11.
- Men did not show statistically significant effects with the acute use of gepants. The average drug effect was 2.8%, and the average NNT was 36.
- For both men and women, CGRP-targeting therapies for prevention of migraine (the 4 monoclonal antibodies) were equally effective; however, possible sex differences remain uncertain and need further study.
- In patients with chronic migraine, CGRP/CGRP-R antibodies were similarly effective in both men and women.
- For the 2-hour freedom from most bothersome symptom (2h-MBS) endpoint when gepants were given acutely, the effects were much better in women than men, with an average drug effect of 10.2% and an average NNT of 10.
- In men, these medications produced observed treatment effects on 2h-MBS with an average drug effect of 3.2% and an average NNT of 32.
- In men, 5 out of 12 estimates favored placebo over the active treatment, suggesting a treatment with little to no effect.
- The pooled treatment effects for women were 3 times as large, at 9.2% and 10.2%, respectively.
- The placebo response rates for 2 of the 3 ubrogepant studies and one of 2 zavegepant studies were higher in men than in women.
The study concludes that, while small molecule CGRP-R antagonists are dramatically effective for acute therapy of migraine in women, available data do not demonstrate effectiveness in men. The treatment effect was found to always favor active treatment numerically for both men and women for prevention of episodic and chronic migraine. The data highlight possible differential effects of CGRP-targeted therapies in different patient populations and the need for increased understanding of CGRP neurobiology in men and women. The study also emphasizes the need to understand which patient groups preferentially respond to CGRP-based therapies to reduce trial and error in treatment. Note that rimegepant data on prevention were not available for analysis at the time of the writing.
It would be interesting to perform a meta-analysis of multiple well-done, large, real-world studies to see if the same differences and similarities are found in men versus women for acute care of migraine and prevention of episodic and chronic migraine. I suspect that we would find that acute care results favor women but that some men do well.
The Effectiveness of Prednisolone for Treating Medication Overuse Headache
I often discuss medication overuse headache (MOH), as it is difficult to diagnose and treat, so I wanted to comment on another pertinent study. It is a post hoc analysis of the Registry for Load and Management of Medication Overuse Headache (RELEASE). The RELEASE trial is an ongoing, multicenter, observational, cohort study of MOH that has been conducted in Korea since April 2020. Findings were recently published in Headache by Lee et al.
MOH is a secondary headache disorder that develops in patients with a preexisting primary headache when they overuse acute care headache medications of any type except gepants. This includes prescription medications such as triptans, ergots, butalbital-containing medications; opioids; aspirin; acetaminophen; any type of combination medication often containing caffeine; or a combination of medications. This condition significantly impacts patients’ quality of life and productivity, usually increasing the frequency of headaches per month and leading to higher healthcare-related costs.
Treating MOH is challenging due to the lack of high-quality drug trials specifically designed for MOH and doctor inexperience. Current evidence is based largely on subgroup analyses of drug trials for the treatment of chronic migraine that contain these patient types.
Withdrawal of acute care headache medications that are being overused has traditionally been considered an important aspect of MOH treatment, although this may be changing. Withdrawal symptoms, such as increased intensity of headache pain, frequency of headaches, and other symptoms like agitation and sleep disturbance, can prevent patients from discontinuing overused medications. Systemic corticosteroids are widely used to reduce these withdrawal headaches, but clinical trials are sparse and have failed to meet proper endpoints. Despite this, corticosteroids have shown potential benefits, such as decreasing withdrawal headaches, reducing the use of rescue medications, and lowering headache intensity at certain time points after treatment.
Given these findings, this published study hypothesized that prednisolone may play a role in converting MOH to non-MOH at 3 months after treatment. The objective was to evaluate the outcome of prednisolone therapy in reversing medication overuse at 3 months posttreatment in patients with MOH using prospective multicenter registry data. Prednisolone was prescribed to 59 out of 309 patients (19.1%) enrolled during this observational study period, with doses ranging from 10 to 40 mg/day for 5-14 days. Of these patients, 228 (73.8%) completed the 3-month follow-up period.
Key findings:
- The MOH reversal rates at 3 months postbaseline were 76% (31/41) in the prednisolone group and 57.8% (108/187) in the no prednisolone group (p = 0.034).
- The steroid effect remained significant (adjusted odds ratio, 2.78; 95% confidence interval 1.27-6.1, p = 0.010) after adjusting for the number of monthly headache days at baseline, mode of discontinuation of overused medication, use of early preventive medications, and the number of combined preventive medications.
The study had several strengths, including the multicenter collection of data, prospective follow-ups, and comprehensiveness of data acquisition. However, it also had significant limitations, such as the noninterventional, observational nature of the study, potential bias in steroid prescription (every doctor prescribed what they wanted), and heterogeneity in the patient population. Also, there were a variety of treatments, and they were not standardized. Further external validation may be necessary before generalizing the study results.
Despite these limitations, the results do suggest that prednisolone may be one part of a valid treatment option for patients with MOH. I suspect, if the proper studies are done, we will see that using a good preventive medication, with few adverse events, and with careful education of the patient, formal detoxification will not be necessary when treating many patients with MOH. This has been my experience with MOH treatment utilizing the newer anti-CGRP preventive medications, including the older monoclonal antibodies and the newer gepants.
Getting Reluctant Patients to ‘Yes’ on COVID Vaccination
No matter how much we’d like to leave it in the dust, COVID-19 remains prevalent and potent. Tens of thousands of people still contract COVID per week in the United States. Hundreds die. And those who don’t may still develop long COVID.
Pleas from public health officials for people to get a COVID vaccine or booster shot have been ignored by many people. About 80% of eligible Americans haven’t taken any kind of COVID booster. Meantime, the virus continues to mutate, eroding the efficacy of the vaccine’s past versions.
How to get more people to get the jab? Vaccine hesitancy, said infectious disease specialist William Schaffner, MD, is likely rooted in a lack of trust in authority, whether it’s public health officials or politicians.
Dr. Schaffner, professor of infectious diseases at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee, and former medical director of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases, recommended five strategies physicians can try when discussing the importance of staying up to date on COVID vaccines with patients.
#1: Be Patient With Your Patient
First and foremost, if doctors are feeling reluctance from their patients, they need to know “what they shouldn’t do,” Dr. Schaffner said.
When a patient initially doesn’t want the vaccine, doctors shouldn’t express surprise. “Do not scold or berate or belittle. Do not give the impression the patient is somehow wrong or has failed a test of some sort,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Step back and affirm that they understand what the patient is saying so they feel reassured, even if they don’t agree or it’s based on falsehoods about the vaccine.
He said patients need to feel “the doctor heard them; it’s okay to tell the doctor this.” When you affirm what the patient says, it puts them at ease and provides a smoother road to eventually getting them to say “yes.”
But if there’s still a roadblock, don’t bulldoze them. “You don’t want to punish the patient ... let them know you’ll continue to hear them,” Dr. Schaffner said.
#2: Always Acknowledge a Concern
Fear of side effects is great among some patients, even if the risks are low, Dr. Schaffner said. Patients may be hesitant because they’re afraid they’ll become one of the “two or three in a million” who suffer extremely rare side effects from the vaccine, Dr. Schaffner said.
In that case, doctors should acknowledge their concern is valid, he said. Never be dismissive. Ask the patients how they feel about the vaccine, listen to their responses, and let them know “I hear you. This is a new mRNA vaccine…you have concern about that,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Doctors can segue into how there’s little reason to wait for some elusive perfectly risk-free vaccine when they can help themselves right now.
“The adverse events that occur with vaccines occur within 2 months [and are typically mild]. I don’t know of a single vaccine that has genuinely long-term implications,” Dr. Schaffner said. “We should remember that old French philosopher Voltaire. He admonished us: Waiting for perfection is the great enemy of the current good.”
#3: Make a Strong Recommendation
Here’s something that may seem obvious: Don’t treat the vaccine as an afterthought. “Survey after survey tells us this ... it has everything to do with the strength of the recommendation,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Doctors typically make strong treatment recommendations such conditions as diabetes or high blood pressure, but “when it comes to vaccines, they’re often rather nonchalant,” he said.
If a patient is eligible for a vaccine, doctors should tell the patient they need to get it — not that you think they should get it. “Doctors have to make a firm recommendation: ‘You’re eligible for a vaccine ... and you need to get it ... you’ll receive it on your way out.’ It then becomes a distinct and strong recommendation,” he said.
#4: Appeal to Patients’ Hearts, Not Their Minds
In the opening of Charles Dickens’s novel “Hard Times,” the stern school superintendent, Mr. Gradgrind, scolds his students by beating their brow with the notion that, “Facts alone are wanted in life. Plant nothing else and root out everything else.”
The idea that facts alone can sway a vaccine-resistant patient is wrong. “It often doesn’t happen that way,” Dr. Schaffner said. “I don’t think facts do that. Psychologists tell us, yes, information is important, but it’s rarely sufficient to change behavior.”
Data and studies are foundational to medicine, but the key is to change how a patient feels about the data they’re presented with, not how they think about it. “Don’t attack their brain so much but their heart,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Dr. Schaffner has stressed with his patients that the COVID vaccine has become “the social norm,” suggesting virtually everyone he knows has received it and had no problem.
Once questions have been answered about whether the vaccine works and its various side effects, doctors could remind the patient, “You know, everyone in my office is getting the vaccine, and we’re trying to provide this protection to every patient,” he said.
You’re then delving deeper into their emotions and crossing a barrier that facts alone can’t breach.
#5: Make it Personal
Lead by example and personalize the fight against the virus. This allows doctors to act as if they’re building an alliance with their patients by framing the vaccine not as something that only affects them but can also confer benefits to a broader social circle.
Even after using these methods, patients may remain resistant, apprehensive, or even indifferent. In cases like these, Dr. Schaffner said it’s a good idea to let it go for the time being.
Let the patient know they “have access to you and can keep speaking with you about it” in the future, he said. “It takes more time, and you have to be cognizant of the nature of the conversation.”
Everybody is unique, but with trust, patience, and awareness of the patient’s feelings, doctors have a better shot at finding common ground with their patients and convincing them the vaccine is in their best interest, he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No matter how much we’d like to leave it in the dust, COVID-19 remains prevalent and potent. Tens of thousands of people still contract COVID per week in the United States. Hundreds die. And those who don’t may still develop long COVID.
Pleas from public health officials for people to get a COVID vaccine or booster shot have been ignored by many people. About 80% of eligible Americans haven’t taken any kind of COVID booster. Meantime, the virus continues to mutate, eroding the efficacy of the vaccine’s past versions.
How to get more people to get the jab? Vaccine hesitancy, said infectious disease specialist William Schaffner, MD, is likely rooted in a lack of trust in authority, whether it’s public health officials or politicians.
Dr. Schaffner, professor of infectious diseases at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee, and former medical director of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases, recommended five strategies physicians can try when discussing the importance of staying up to date on COVID vaccines with patients.
#1: Be Patient With Your Patient
First and foremost, if doctors are feeling reluctance from their patients, they need to know “what they shouldn’t do,” Dr. Schaffner said.
When a patient initially doesn’t want the vaccine, doctors shouldn’t express surprise. “Do not scold or berate or belittle. Do not give the impression the patient is somehow wrong or has failed a test of some sort,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Step back and affirm that they understand what the patient is saying so they feel reassured, even if they don’t agree or it’s based on falsehoods about the vaccine.
He said patients need to feel “the doctor heard them; it’s okay to tell the doctor this.” When you affirm what the patient says, it puts them at ease and provides a smoother road to eventually getting them to say “yes.”
But if there’s still a roadblock, don’t bulldoze them. “You don’t want to punish the patient ... let them know you’ll continue to hear them,” Dr. Schaffner said.
#2: Always Acknowledge a Concern
Fear of side effects is great among some patients, even if the risks are low, Dr. Schaffner said. Patients may be hesitant because they’re afraid they’ll become one of the “two or three in a million” who suffer extremely rare side effects from the vaccine, Dr. Schaffner said.
In that case, doctors should acknowledge their concern is valid, he said. Never be dismissive. Ask the patients how they feel about the vaccine, listen to their responses, and let them know “I hear you. This is a new mRNA vaccine…you have concern about that,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Doctors can segue into how there’s little reason to wait for some elusive perfectly risk-free vaccine when they can help themselves right now.
“The adverse events that occur with vaccines occur within 2 months [and are typically mild]. I don’t know of a single vaccine that has genuinely long-term implications,” Dr. Schaffner said. “We should remember that old French philosopher Voltaire. He admonished us: Waiting for perfection is the great enemy of the current good.”
#3: Make a Strong Recommendation
Here’s something that may seem obvious: Don’t treat the vaccine as an afterthought. “Survey after survey tells us this ... it has everything to do with the strength of the recommendation,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Doctors typically make strong treatment recommendations such conditions as diabetes or high blood pressure, but “when it comes to vaccines, they’re often rather nonchalant,” he said.
If a patient is eligible for a vaccine, doctors should tell the patient they need to get it — not that you think they should get it. “Doctors have to make a firm recommendation: ‘You’re eligible for a vaccine ... and you need to get it ... you’ll receive it on your way out.’ It then becomes a distinct and strong recommendation,” he said.
#4: Appeal to Patients’ Hearts, Not Their Minds
In the opening of Charles Dickens’s novel “Hard Times,” the stern school superintendent, Mr. Gradgrind, scolds his students by beating their brow with the notion that, “Facts alone are wanted in life. Plant nothing else and root out everything else.”
The idea that facts alone can sway a vaccine-resistant patient is wrong. “It often doesn’t happen that way,” Dr. Schaffner said. “I don’t think facts do that. Psychologists tell us, yes, information is important, but it’s rarely sufficient to change behavior.”
Data and studies are foundational to medicine, but the key is to change how a patient feels about the data they’re presented with, not how they think about it. “Don’t attack their brain so much but their heart,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Dr. Schaffner has stressed with his patients that the COVID vaccine has become “the social norm,” suggesting virtually everyone he knows has received it and had no problem.
Once questions have been answered about whether the vaccine works and its various side effects, doctors could remind the patient, “You know, everyone in my office is getting the vaccine, and we’re trying to provide this protection to every patient,” he said.
You’re then delving deeper into their emotions and crossing a barrier that facts alone can’t breach.
#5: Make it Personal
Lead by example and personalize the fight against the virus. This allows doctors to act as if they’re building an alliance with their patients by framing the vaccine not as something that only affects them but can also confer benefits to a broader social circle.
Even after using these methods, patients may remain resistant, apprehensive, or even indifferent. In cases like these, Dr. Schaffner said it’s a good idea to let it go for the time being.
Let the patient know they “have access to you and can keep speaking with you about it” in the future, he said. “It takes more time, and you have to be cognizant of the nature of the conversation.”
Everybody is unique, but with trust, patience, and awareness of the patient’s feelings, doctors have a better shot at finding common ground with their patients and convincing them the vaccine is in their best interest, he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No matter how much we’d like to leave it in the dust, COVID-19 remains prevalent and potent. Tens of thousands of people still contract COVID per week in the United States. Hundreds die. And those who don’t may still develop long COVID.
Pleas from public health officials for people to get a COVID vaccine or booster shot have been ignored by many people. About 80% of eligible Americans haven’t taken any kind of COVID booster. Meantime, the virus continues to mutate, eroding the efficacy of the vaccine’s past versions.
How to get more people to get the jab? Vaccine hesitancy, said infectious disease specialist William Schaffner, MD, is likely rooted in a lack of trust in authority, whether it’s public health officials or politicians.
Dr. Schaffner, professor of infectious diseases at the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee, and former medical director of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases, recommended five strategies physicians can try when discussing the importance of staying up to date on COVID vaccines with patients.
#1: Be Patient With Your Patient
First and foremost, if doctors are feeling reluctance from their patients, they need to know “what they shouldn’t do,” Dr. Schaffner said.
When a patient initially doesn’t want the vaccine, doctors shouldn’t express surprise. “Do not scold or berate or belittle. Do not give the impression the patient is somehow wrong or has failed a test of some sort,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Step back and affirm that they understand what the patient is saying so they feel reassured, even if they don’t agree or it’s based on falsehoods about the vaccine.
He said patients need to feel “the doctor heard them; it’s okay to tell the doctor this.” When you affirm what the patient says, it puts them at ease and provides a smoother road to eventually getting them to say “yes.”
But if there’s still a roadblock, don’t bulldoze them. “You don’t want to punish the patient ... let them know you’ll continue to hear them,” Dr. Schaffner said.
#2: Always Acknowledge a Concern
Fear of side effects is great among some patients, even if the risks are low, Dr. Schaffner said. Patients may be hesitant because they’re afraid they’ll become one of the “two or three in a million” who suffer extremely rare side effects from the vaccine, Dr. Schaffner said.
In that case, doctors should acknowledge their concern is valid, he said. Never be dismissive. Ask the patients how they feel about the vaccine, listen to their responses, and let them know “I hear you. This is a new mRNA vaccine…you have concern about that,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Doctors can segue into how there’s little reason to wait for some elusive perfectly risk-free vaccine when they can help themselves right now.
“The adverse events that occur with vaccines occur within 2 months [and are typically mild]. I don’t know of a single vaccine that has genuinely long-term implications,” Dr. Schaffner said. “We should remember that old French philosopher Voltaire. He admonished us: Waiting for perfection is the great enemy of the current good.”
#3: Make a Strong Recommendation
Here’s something that may seem obvious: Don’t treat the vaccine as an afterthought. “Survey after survey tells us this ... it has everything to do with the strength of the recommendation,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Doctors typically make strong treatment recommendations such conditions as diabetes or high blood pressure, but “when it comes to vaccines, they’re often rather nonchalant,” he said.
If a patient is eligible for a vaccine, doctors should tell the patient they need to get it — not that you think they should get it. “Doctors have to make a firm recommendation: ‘You’re eligible for a vaccine ... and you need to get it ... you’ll receive it on your way out.’ It then becomes a distinct and strong recommendation,” he said.
#4: Appeal to Patients’ Hearts, Not Their Minds
In the opening of Charles Dickens’s novel “Hard Times,” the stern school superintendent, Mr. Gradgrind, scolds his students by beating their brow with the notion that, “Facts alone are wanted in life. Plant nothing else and root out everything else.”
The idea that facts alone can sway a vaccine-resistant patient is wrong. “It often doesn’t happen that way,” Dr. Schaffner said. “I don’t think facts do that. Psychologists tell us, yes, information is important, but it’s rarely sufficient to change behavior.”
Data and studies are foundational to medicine, but the key is to change how a patient feels about the data they’re presented with, not how they think about it. “Don’t attack their brain so much but their heart,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Dr. Schaffner has stressed with his patients that the COVID vaccine has become “the social norm,” suggesting virtually everyone he knows has received it and had no problem.
Once questions have been answered about whether the vaccine works and its various side effects, doctors could remind the patient, “You know, everyone in my office is getting the vaccine, and we’re trying to provide this protection to every patient,” he said.
You’re then delving deeper into their emotions and crossing a barrier that facts alone can’t breach.
#5: Make it Personal
Lead by example and personalize the fight against the virus. This allows doctors to act as if they’re building an alliance with their patients by framing the vaccine not as something that only affects them but can also confer benefits to a broader social circle.
Even after using these methods, patients may remain resistant, apprehensive, or even indifferent. In cases like these, Dr. Schaffner said it’s a good idea to let it go for the time being.
Let the patient know they “have access to you and can keep speaking with you about it” in the future, he said. “It takes more time, and you have to be cognizant of the nature of the conversation.”
Everybody is unique, but with trust, patience, and awareness of the patient’s feelings, doctors have a better shot at finding common ground with their patients and convincing them the vaccine is in their best interest, he said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 Is a Very Weird Virus
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).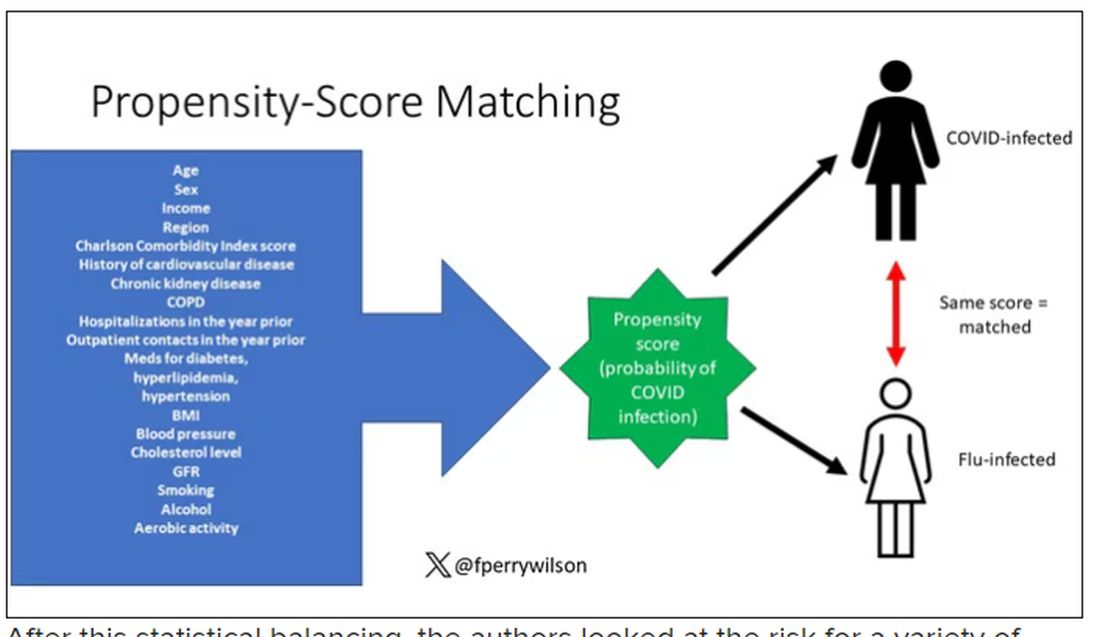
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.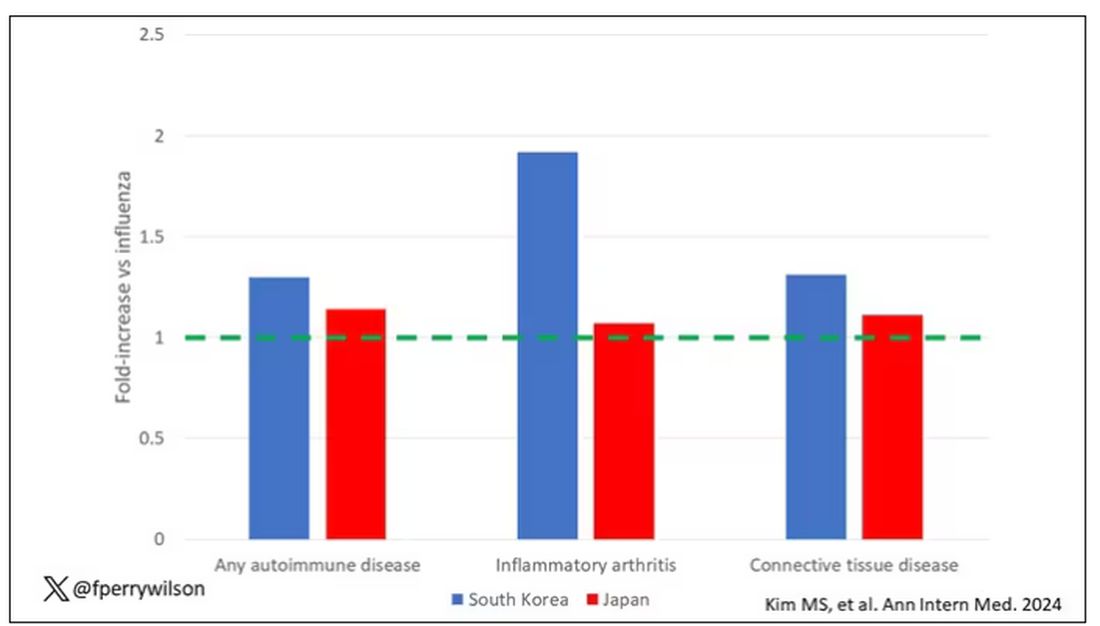
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.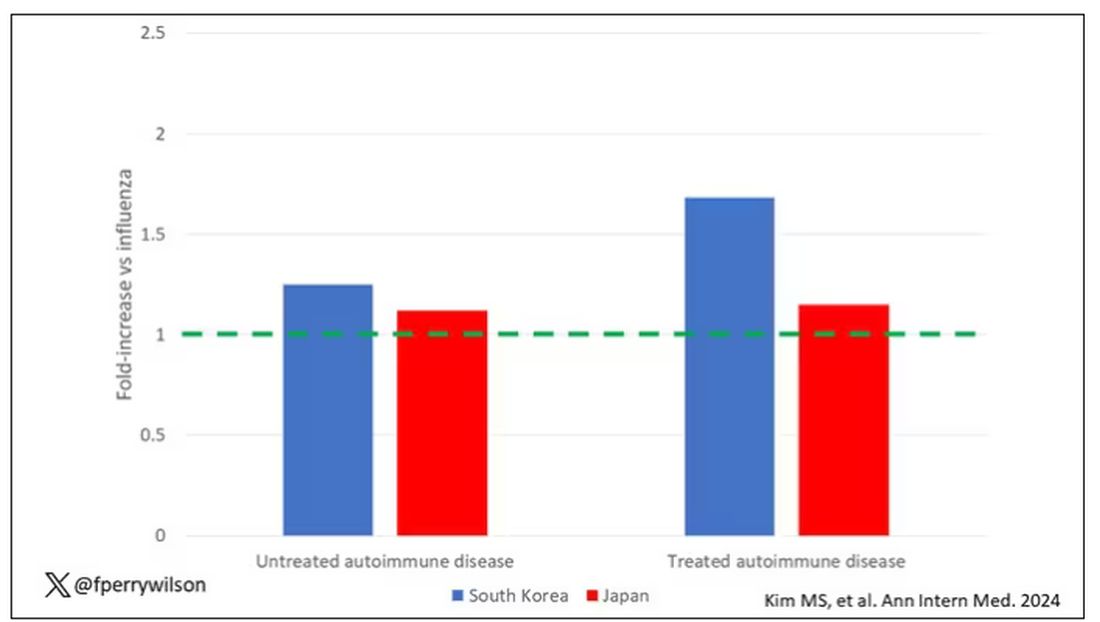
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.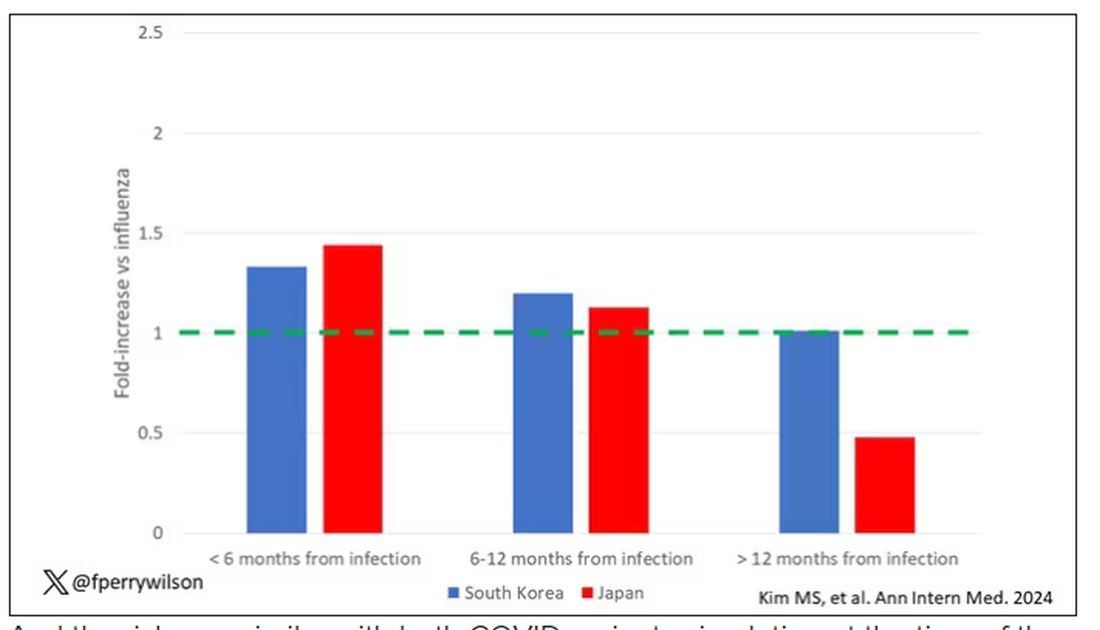
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?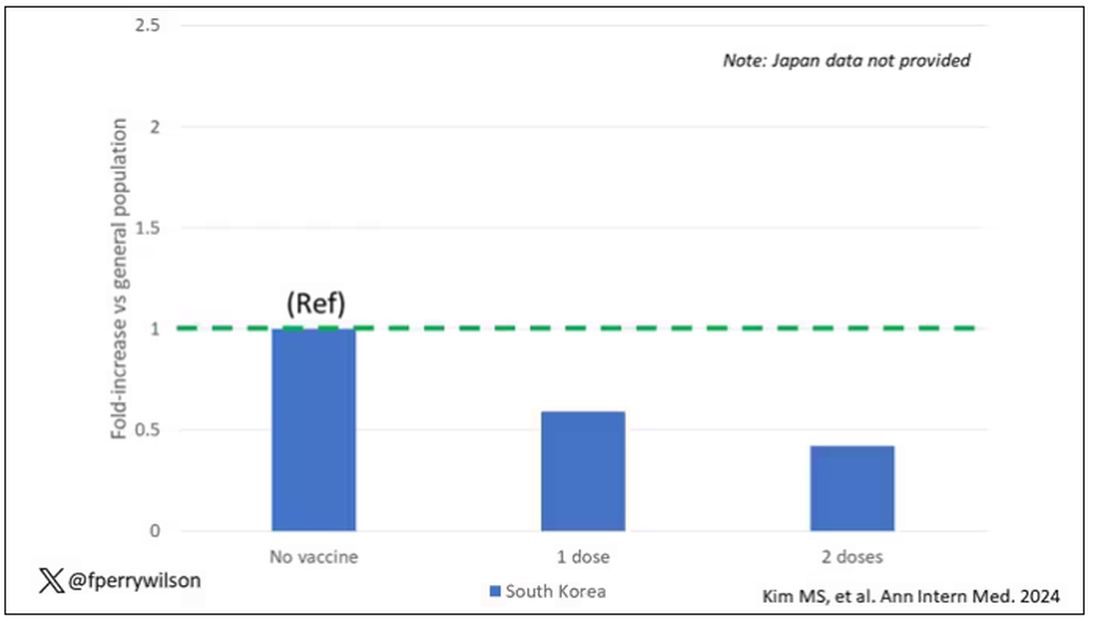
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
In the early days of the pandemic, before we really understood what COVID was, two specialties in the hospital had a foreboding sense that something was very strange about this virus. The first was the pulmonologists, who noticed the striking levels of hypoxemia — low oxygen in the blood — and the rapidity with which patients who had previously been stable would crash in the intensive care unit.
The second, and I mark myself among this group, were the nephrologists. The dialysis machines stopped working right. I remember rounding on patients in the hospital who were on dialysis for kidney failure in the setting of severe COVID infection and seeing clots forming on the dialysis filters. Some patients could barely get in a full treatment because the filters would clog so quickly.
We knew it was worse than flu because of the mortality rates, but these oddities made us realize that it was different too — not just a particularly nasty respiratory virus but one that had effects on the body that we hadn’t really seen before.
That’s why I’ve always been interested in studies that compare what happens to patients after COVID infection vs what happens to patients after other respiratory infections. This week, we’ll look at an intriguing study that suggests that COVID may lead to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and vasculitis.
The study appears in the Annals of Internal Medicine and is made possible by the universal electronic health record systems of South Korea and Japan, who collaborated to create a truly staggering cohort of more than 20 million individuals living in those countries from 2020 to 2021.
The exposure of interest? COVID infection, experienced by just under 5% of that cohort over the study period. (Remember, there was a time when COVID infections were relatively controlled, particularly in some countries.)
The researchers wanted to compare the risk for autoimmune disease among COVID-infected individuals against two control groups. The first control group was the general population. This is interesting but a difficult analysis, because people who become infected with COVID might be very different from the general population. The second control group was people infected with influenza. I like this a lot better; the risk factors for COVID and influenza are quite similar, and the fact that this group was diagnosed with flu means at least that they are getting medical care and are sort of “in the system,” so to speak.
But it’s not enough to simply identify these folks and see who ends up with more autoimmune disease. The authors used propensity score matching to pair individuals infected with COVID with individuals from the control groups who were very similar to them. I’ve talked about this strategy before, but the basic idea is that you build a model predicting the likelihood of infection with COVID, based on a slew of factors — and the slew these authors used is pretty big, as shown below — and then stick people with similar risk for COVID together, with one member of the pair having had COVID and the other having eluded it (at least for the study period).
After this statistical balancing, the authors looked at the risk for a variety of autoimmune diseases.
Compared with those infected with flu, those infected with COVID were more likely to be diagnosed with any autoimmune condition, connective tissue disease, and, in Japan at least, inflammatory arthritis.
The authors acknowledge that being diagnosed with a disease might not be the same as actually having the disease, so in another analysis they looked only at people who received treatment for the autoimmune conditions, and the signals were even stronger in that group.
This risk seemed to be highest in the 6 months following the COVID infection, which makes sense biologically if we think that the infection is somehow screwing up the immune system.
And the risk was similar with both COVID variants circulating at the time of the study.
The only factor that reduced the risk? You guessed it: vaccination. This is a particularly interesting finding because the exposure cohort was defined by having been infected with COVID. Therefore, the mechanism of protection is not prevention of infection; it’s something else. Perhaps vaccination helps to get the immune system in a state to respond to COVID infection more… appropriately?
Yes, this study is observational. We can’t draw causal conclusions here. But it does reinforce my long-held belief that COVID is a weird virus, one with effects that are different from the respiratory viruses we are used to. I can’t say for certain whether COVID causes immune system dysfunction that puts someone at risk for autoimmunity — not from this study. But I can say it wouldn’t surprise me.
Dr. F. Perry Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Long COVID: Another Great Pretender
Has COVID replaced syphilis as the great imitator? At the turn of the 20th century, Sir William Osler was quoted as saying, “He who knows syphilis knows medicine.”
If you have any doubts about the “imitator” analogy, simply use any broad search engine or AI portal and enter “what is the differential diagnosis of primary syphilis, or secondary syphilis, or tertiary syphilis?” A plethora of diseases across many body systems appears.
Another Great Pretender?
Did you or do you now have long COVID? How do you know? Do you even know what long COVID is? How would you diagnosis it?
When asked about long COVID, this is what large language model source bard.google.com had to say:
Long COVID, also known as post-COVID conditions or PASC, is a complex condition that can occur in people who have had COVID-19, even if their initial illness was mild or even asymptomatic. It’s characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can last for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
Symptoms of long COVID can include: fatigue, shortness of breath, brain fog (trouble thinking or concentrating), loss of smell or taste, sleep problems, muscle pain, joint pain, headache, dizziness, depression or anxiety, heart palpitations, gastrointestinal problems.
Duh!!! It reads much like a continuation of the symptoms of acute COVID. Bard continued:
The exact cause of long COVID is still unknown, but there are several theories. One possibility is that the virus itself can damage organs and tissues, leading to ongoing symptoms. Another possibility is that the immune system’s response to the virus can continue to cause inflammation even after the virus is gone.
Human intelligence source Wikipedia says this:
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after infection, but other definitions put the start of long COVID at four weeks.
Highly varied, including post-exertional malaise (symptoms made worse with effort), fatigue, muscle pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cognitive dysfunction (brain fog).
Acute COVID to Long COVID
The World Health Organization estimates that 36 million people in the European region have developed long COVID in the first 3 years of the pandemic. That›s a lot.
We all know that the common signs and symptoms of acute COVID-19 include fever or chills, a dry cough and shortness of breath, feeling very tired, muscle or body aches, headache, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Except for the taste and smell findings, every one of these symptoms or signs could indicate a different virus infection or even some type of allergy. My point is the nonspecificity in this list.
Uncommon signs and symptoms of acute COVID include a flat skin rash covered with small bumps, discolored swollen areas on the fingers and toes (COVID toes), and hives. The skin of hands, wrists, or ankles also can be affected. Blisters, itchiness, rough skin, or pus can be seen.
Severe confusion (delirium) might be the main or only symptom of COVID-19 in older people. This COVID-19 symptom is linked with a high risk for poor outcomes, including death. Pink eye (conjunctivitis) can be a COVID-19 symptom. Other eye problems linked to COVID-19 are light sensitivity, sore eyes, and itchy eyes. Acute myocarditis, tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss have been reported. And 1-4 weeks after the onset of COVID-19 infection, a patient may experience de novo reactive synovitis and arthritis of any joints.
So, take your pick. Myriad symptoms, signs, diseases, diagnoses, and organ systems — still present, recurring, just appearing, apparently de novo, or after asymptomatic infection. We have so much still to learn.
What big-time symptoms, signs, and major diseases are not on any of these lists? Obviously, cancer, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, obesity, bone diseases, and competitive infections. But be patient; the lingering effects of direct tissue invasion by the virus as well as a wide range of immunologic reactions may just be getting started. Mitochondrial damage, especially in muscles, is increasingly a pathophysiologic suspect.
Human diseases can be physical or mental; and in COVID, that twain not only meet but mix and mingle freely, and may even merge into psychosoma. Don’t ever forget that. Consider “fatigue.” Who among us, COVID or NOVID, does not experience that from time to time?
Or consider brain fog as a common reported symptom of COVID. What on earth is that actually? How can a person know they have brain fog, or whether they had it and are over it?
We need one or more lab or other diagnostic tests that can objectively confirm the diagnosis of long COVID.
Useful Progress?
A recent research paper in Science reported intriguing chemical findings that seemed to point a finger at some form of complement dysregulation as a potential disease marker for long COVID. Unfortunately, some critics have pointed out that this entire study may be invalid or irrelevant because the New York cohort was recruited in 2020, before vaccines were available. The Zurich cohort was recruited up until April 2021, so some may have been vaccinated.
Then this news organization came along in early January 2024 with an article about COVID causing not only more than a million American deaths but also more than 5000 deaths from long COVID. We physicians don’t really know what long COVID even is, but we have to sign death certificates blaming thousands of deaths on it anyway? And rolling back the clock to 2020: Are patients dying from COVID or with COVID, according to death certificates?Now, armed with the knowledge that “documented serious post–COVID-19 conditions include cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurological, renal, endocrine, hematological, and gastrointestinal complications, as well as death,” CDC has published clear and fairly concise instructions on how to address post-acute COVID sequelae on death certificates.
In late January, this news organization painted a hopeful picture by naming four phenotypes of long COVID, suggesting that such divisions might further our understanding, including prognosis, and even therapy for this condition. Among the clinical phenotypes of (1) chronic fatigue–like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; (2) respiratory syndrome (which includes cough and difficulty breathing); (3) chronic pain; and (4) neurosensorial syndrome (which causes an altered sense of taste and smell), overlap is clearly possible but isn›t addressed.
I see these recent developments as needed and useful progress, but we are still left with…not much. So, when you tell me that you do or do not have long COVID, I will say to you, “How do you know?”
I also say: She/he/they who know COVID know medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Has COVID replaced syphilis as the great imitator? At the turn of the 20th century, Sir William Osler was quoted as saying, “He who knows syphilis knows medicine.”
If you have any doubts about the “imitator” analogy, simply use any broad search engine or AI portal and enter “what is the differential diagnosis of primary syphilis, or secondary syphilis, or tertiary syphilis?” A plethora of diseases across many body systems appears.
Another Great Pretender?
Did you or do you now have long COVID? How do you know? Do you even know what long COVID is? How would you diagnosis it?
When asked about long COVID, this is what large language model source bard.google.com had to say:
Long COVID, also known as post-COVID conditions or PASC, is a complex condition that can occur in people who have had COVID-19, even if their initial illness was mild or even asymptomatic. It’s characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can last for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
Symptoms of long COVID can include: fatigue, shortness of breath, brain fog (trouble thinking or concentrating), loss of smell or taste, sleep problems, muscle pain, joint pain, headache, dizziness, depression or anxiety, heart palpitations, gastrointestinal problems.
Duh!!! It reads much like a continuation of the symptoms of acute COVID. Bard continued:
The exact cause of long COVID is still unknown, but there are several theories. One possibility is that the virus itself can damage organs and tissues, leading to ongoing symptoms. Another possibility is that the immune system’s response to the virus can continue to cause inflammation even after the virus is gone.
Human intelligence source Wikipedia says this:
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after infection, but other definitions put the start of long COVID at four weeks.
Highly varied, including post-exertional malaise (symptoms made worse with effort), fatigue, muscle pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cognitive dysfunction (brain fog).
Acute COVID to Long COVID
The World Health Organization estimates that 36 million people in the European region have developed long COVID in the first 3 years of the pandemic. That›s a lot.
We all know that the common signs and symptoms of acute COVID-19 include fever or chills, a dry cough and shortness of breath, feeling very tired, muscle or body aches, headache, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Except for the taste and smell findings, every one of these symptoms or signs could indicate a different virus infection or even some type of allergy. My point is the nonspecificity in this list.
Uncommon signs and symptoms of acute COVID include a flat skin rash covered with small bumps, discolored swollen areas on the fingers and toes (COVID toes), and hives. The skin of hands, wrists, or ankles also can be affected. Blisters, itchiness, rough skin, or pus can be seen.
Severe confusion (delirium) might be the main or only symptom of COVID-19 in older people. This COVID-19 symptom is linked with a high risk for poor outcomes, including death. Pink eye (conjunctivitis) can be a COVID-19 symptom. Other eye problems linked to COVID-19 are light sensitivity, sore eyes, and itchy eyes. Acute myocarditis, tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss have been reported. And 1-4 weeks after the onset of COVID-19 infection, a patient may experience de novo reactive synovitis and arthritis of any joints.
So, take your pick. Myriad symptoms, signs, diseases, diagnoses, and organ systems — still present, recurring, just appearing, apparently de novo, or after asymptomatic infection. We have so much still to learn.
What big-time symptoms, signs, and major diseases are not on any of these lists? Obviously, cancer, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, obesity, bone diseases, and competitive infections. But be patient; the lingering effects of direct tissue invasion by the virus as well as a wide range of immunologic reactions may just be getting started. Mitochondrial damage, especially in muscles, is increasingly a pathophysiologic suspect.
Human diseases can be physical or mental; and in COVID, that twain not only meet but mix and mingle freely, and may even merge into psychosoma. Don’t ever forget that. Consider “fatigue.” Who among us, COVID or NOVID, does not experience that from time to time?
Or consider brain fog as a common reported symptom of COVID. What on earth is that actually? How can a person know they have brain fog, or whether they had it and are over it?
We need one or more lab or other diagnostic tests that can objectively confirm the diagnosis of long COVID.
Useful Progress?
A recent research paper in Science reported intriguing chemical findings that seemed to point a finger at some form of complement dysregulation as a potential disease marker for long COVID. Unfortunately, some critics have pointed out that this entire study may be invalid or irrelevant because the New York cohort was recruited in 2020, before vaccines were available. The Zurich cohort was recruited up until April 2021, so some may have been vaccinated.
Then this news organization came along in early January 2024 with an article about COVID causing not only more than a million American deaths but also more than 5000 deaths from long COVID. We physicians don’t really know what long COVID even is, but we have to sign death certificates blaming thousands of deaths on it anyway? And rolling back the clock to 2020: Are patients dying from COVID or with COVID, according to death certificates?Now, armed with the knowledge that “documented serious post–COVID-19 conditions include cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurological, renal, endocrine, hematological, and gastrointestinal complications, as well as death,” CDC has published clear and fairly concise instructions on how to address post-acute COVID sequelae on death certificates.
In late January, this news organization painted a hopeful picture by naming four phenotypes of long COVID, suggesting that such divisions might further our understanding, including prognosis, and even therapy for this condition. Among the clinical phenotypes of (1) chronic fatigue–like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; (2) respiratory syndrome (which includes cough and difficulty breathing); (3) chronic pain; and (4) neurosensorial syndrome (which causes an altered sense of taste and smell), overlap is clearly possible but isn›t addressed.
I see these recent developments as needed and useful progress, but we are still left with…not much. So, when you tell me that you do or do not have long COVID, I will say to you, “How do you know?”
I also say: She/he/they who know COVID know medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Has COVID replaced syphilis as the great imitator? At the turn of the 20th century, Sir William Osler was quoted as saying, “He who knows syphilis knows medicine.”
If you have any doubts about the “imitator” analogy, simply use any broad search engine or AI portal and enter “what is the differential diagnosis of primary syphilis, or secondary syphilis, or tertiary syphilis?” A plethora of diseases across many body systems appears.
Another Great Pretender?
Did you or do you now have long COVID? How do you know? Do you even know what long COVID is? How would you diagnosis it?
When asked about long COVID, this is what large language model source bard.google.com had to say:
Long COVID, also known as post-COVID conditions or PASC, is a complex condition that can occur in people who have had COVID-19, even if their initial illness was mild or even asymptomatic. It’s characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can last for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection.
Symptoms of long COVID can include: fatigue, shortness of breath, brain fog (trouble thinking or concentrating), loss of smell or taste, sleep problems, muscle pain, joint pain, headache, dizziness, depression or anxiety, heart palpitations, gastrointestinal problems.
Duh!!! It reads much like a continuation of the symptoms of acute COVID. Bard continued:
The exact cause of long COVID is still unknown, but there are several theories. One possibility is that the virus itself can damage organs and tissues, leading to ongoing symptoms. Another possibility is that the immune system’s response to the virus can continue to cause inflammation even after the virus is gone.
Human intelligence source Wikipedia says this:
Long COVID or long-haul COVID is a group of health problems persisting or developing after an initial COVID-19 infection. Symptoms can last weeks, months or years and are often debilitating. The World Health Organization defines long COVID as starting three months after infection, but other definitions put the start of long COVID at four weeks.
Highly varied, including post-exertional malaise (symptoms made worse with effort), fatigue, muscle pain, shortness of breath, chest pain, and cognitive dysfunction (brain fog).
Acute COVID to Long COVID
The World Health Organization estimates that 36 million people in the European region have developed long COVID in the first 3 years of the pandemic. That›s a lot.
We all know that the common signs and symptoms of acute COVID-19 include fever or chills, a dry cough and shortness of breath, feeling very tired, muscle or body aches, headache, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, congestion, runny nose, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Except for the taste and smell findings, every one of these symptoms or signs could indicate a different virus infection or even some type of allergy. My point is the nonspecificity in this list.
Uncommon signs and symptoms of acute COVID include a flat skin rash covered with small bumps, discolored swollen areas on the fingers and toes (COVID toes), and hives. The skin of hands, wrists, or ankles also can be affected. Blisters, itchiness, rough skin, or pus can be seen.
Severe confusion (delirium) might be the main or only symptom of COVID-19 in older people. This COVID-19 symptom is linked with a high risk for poor outcomes, including death. Pink eye (conjunctivitis) can be a COVID-19 symptom. Other eye problems linked to COVID-19 are light sensitivity, sore eyes, and itchy eyes. Acute myocarditis, tinnitus, vertigo, and hearing loss have been reported. And 1-4 weeks after the onset of COVID-19 infection, a patient may experience de novo reactive synovitis and arthritis of any joints.
So, take your pick. Myriad symptoms, signs, diseases, diagnoses, and organ systems — still present, recurring, just appearing, apparently de novo, or after asymptomatic infection. We have so much still to learn.
What big-time symptoms, signs, and major diseases are not on any of these lists? Obviously, cancer, atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, obesity, bone diseases, and competitive infections. But be patient; the lingering effects of direct tissue invasion by the virus as well as a wide range of immunologic reactions may just be getting started. Mitochondrial damage, especially in muscles, is increasingly a pathophysiologic suspect.
Human diseases can be physical or mental; and in COVID, that twain not only meet but mix and mingle freely, and may even merge into psychosoma. Don’t ever forget that. Consider “fatigue.” Who among us, COVID or NOVID, does not experience that from time to time?
Or consider brain fog as a common reported symptom of COVID. What on earth is that actually? How can a person know they have brain fog, or whether they had it and are over it?
We need one or more lab or other diagnostic tests that can objectively confirm the diagnosis of long COVID.
Useful Progress?
A recent research paper in Science reported intriguing chemical findings that seemed to point a finger at some form of complement dysregulation as a potential disease marker for long COVID. Unfortunately, some critics have pointed out that this entire study may be invalid or irrelevant because the New York cohort was recruited in 2020, before vaccines were available. The Zurich cohort was recruited up until April 2021, so some may have been vaccinated.
Then this news organization came along in early January 2024 with an article about COVID causing not only more than a million American deaths but also more than 5000 deaths from long COVID. We physicians don’t really know what long COVID even is, but we have to sign death certificates blaming thousands of deaths on it anyway? And rolling back the clock to 2020: Are patients dying from COVID or with COVID, according to death certificates?Now, armed with the knowledge that “documented serious post–COVID-19 conditions include cardiovascular, pulmonary, neurological, renal, endocrine, hematological, and gastrointestinal complications, as well as death,” CDC has published clear and fairly concise instructions on how to address post-acute COVID sequelae on death certificates.
In late January, this news organization painted a hopeful picture by naming four phenotypes of long COVID, suggesting that such divisions might further our understanding, including prognosis, and even therapy for this condition. Among the clinical phenotypes of (1) chronic fatigue–like syndrome, headache, and memory loss; (2) respiratory syndrome (which includes cough and difficulty breathing); (3) chronic pain; and (4) neurosensorial syndrome (which causes an altered sense of taste and smell), overlap is clearly possible but isn›t addressed.
I see these recent developments as needed and useful progress, but we are still left with…not much. So, when you tell me that you do or do not have long COVID, I will say to you, “How do you know?”
I also say: She/he/they who know COVID know medicine.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
GLP-1s for Obesity: Your Questions Answered
The arrival of GLP-1 receptor agonists has revolutionized treatment options for people with obesity and medical practice.
This news organization recently hosted a panel of experts across specialties — including endocrinology, gastroenterology, and obesity medicine — to discuss these potentially life-changing medications and to answer questions from the audience.
Because of the flood of queries from our audience, we asked our panelists to address some of the questions that didn’t make the recording. Their answers are below.
Beverly Tchang, MD, endocrinologist, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City
Audience member: Can you initiate glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists (GLP-1 RAs) as a primary drug in a patient with obesity and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes?
BT: We often prescribe GLP-1 RAs to individuals with type 2 diabetes as a first-line medication. Guidelines from the American Diabetes Association are really emphasizing a patient-centered approach, and metformin may not be the best first-line medication anymore.
Audience member:
BT: GLP-1 RAs do not need to be renally dosed, but I still recommend conferring with the patient’s nephrologist because the glomerular filtration rate might decrease in the setting of dehydration. Because GLP1s suppress the thirst, not just appetite, patients can go all day without drinking water and not feel thirsty.
Michael Camilleri, MD, gastroenterologist, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota
Audience member: Should GLP-1 RAs be held for 1 week or 4 weeks prior to surgery to reduce the patient’s risk for aspiration? And is tapering required?
MC: For a patient taking liraglutide, I would hold the drug for 1 week prior to surgery. For patients taking other GLP-1 RAs, including extended exenatide, I advise holding for between 2 and 3 weeks before the procedure. It’s also important to make sure the patient’s diabetes is well-controlled with other medications — not GLP-1 RAs — during this period.
After surgery, you can restart GLP-1 RA therapy once there is recovery of oral food intake and normal bowel function.
Audience member: Is treatment with GLP-1 RAs appropriate for a patient with a family history of colon cancer but an otherwise unremarkable medical and family history?
MC: I have not seen a contraindication to receiving GLP-1 RAs based on a family history of colorectal cancer or other malignancies. An analysis of the French national healthcare insurance system database has suggested 1-3 years use of GLP-1 RAs (exenatide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide) may be linked with increased occurrence of thyroid cancer. Data from 37 randomized controlled trials and 19 real-world studies having 16,839 patients in placebo control group, 16,550 patients in active control group, and 13,330 patients in real-world studies were analyzed in a 2023 systematic review and meta-analysis. Compared to placebo or active control treatments, occurrence of pancreatic cancer, thyroid cancer, and all neoplasms — benign, malignant, and otherwise unspecified — were similar in the semaglutide group.
Toshi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, family physician, Zucker School of Medicine, Hempstead, New York
Audience member: What do you do about elevated liver functions after starting treatment with GLP-1 RAs, and what do you do when a patient has reached their weight loss goal?
TI-M: I recommend monitoring the liver function tests, evaluating for underlying causes, such as viral hepatitis, alcohol-related damage, or problems with other medications, and consulting a gastroenterologist or liver specialist if necessary. It’s also important to discuss the risk-benefit of continuing on the GP-1 RA for that particular patient.
Audience member: What effects will GLP-1 RAs have on sleep-disordered breathing/obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)? Are you aware of any ongoing trials addressing this subject?
TI-M: GLP-1 RAs may have beneficial effects on sleep-disordered breathing and OSA through weight loss, which can lead to a reduction in excess adipose tissue, and improvements in metabolic parameters. In terms of studies, a 2023 paper addressed this question, but more research is needed.
Audience member: Is it within a psychiatric provider’s scope of practice to prescribe GLP-1 agents for the reduction of weight gain associated with psychiatric medications?
TI-M: Obesity medicine is an interdisciplinary process. Numerous medications prescribed for mental health can contribute to obesity, and psychiatrists can play a role in collaborating with a patient’s primary care provider and/or obesity medicine specialist to determine which medications can be adjusted or replaced. It is important to remember that obesity management is not just about medications. It requires managing nutrition and activity in addition to behavioral health issues and social determinants of health. If the clinician has had the training to manage these pillars and is comfortable managing this chronic illness — similar to diabetes, hypertension, and other conditions — then this is a possibility. Otherwise, team-based care is appropriate.
Holly Lofton, MD, obesity medicine, NYU Langone Health, New York City
Audience member: Can we safely use them on patients who have had bariatric surgery and regularly develop dumping syndrome?
HL: These medications can be used after bariatric surgery in patients who meet the criteria for pharmacologic treatment. If a patient is having postoperative symptoms of dumping syndrome or excessive gastrointestinal losses from vomiting or diarrhea, dietary adjustments and other methods of managing the dumping syndrome in gastric bypass patients should be initiated before considering GLP-1 RAs because these patients do not have a functioning pylorus in their alimentary tract and these drugs are not indicated to treat dumping syndrome. The first-line approach typically involves reducing the patient’s intake of simple carbohydrates but can also include medications or surgical intervention when appropriate.
Audience member: Would teaching a patient to fast intermittently while they’re on GLP-1 RAs help them preserve weight loss if they choose to wean off the medication?
HL: Personally, I feel it is best to use the titration period and the time in which the patient is actively losing weight when on GLP-1 RAs. These are the best periods to help develop an individualized treatment plan, one that includes nutrition, activity, behavior modification, and resistance training. The patient’s lifestyle plan will likely change based on their environment and other factors. Intermittent fasting can be a part of such a plan. There is no consensus as to exactly which eating pattern will help patients maintain weight once they lose the physiologic benefit of the weight loss medications. However, studies have been published that demonstrate an average weight regain of 66% or greater when patients go from taking the maximum dose of a GLP-1 RA to taking none at all. Thus, patients should still be followed closely for weight regain when they discontinue a GLP-1 RA.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The arrival of GLP-1 receptor agonists has revolutionized treatment options for people with obesity and medical practice.
This news organization recently hosted a panel of experts across specialties — including endocrinology, gastroenterology, and obesity medicine — to discuss these potentially life-changing medications and to answer questions from the audience.
Because of the flood of queries from our audience, we asked our panelists to address some of the questions that didn’t make the recording. Their answers are below.
Beverly Tchang, MD, endocrinologist, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City
Audience member: Can you initiate glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists (GLP-1 RAs) as a primary drug in a patient with obesity and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes?
BT: We often prescribe GLP-1 RAs to individuals with type 2 diabetes as a first-line medication. Guidelines from the American Diabetes Association are really emphasizing a patient-centered approach, and metformin may not be the best first-line medication anymore.
Audience member:
BT: GLP-1 RAs do not need to be renally dosed, but I still recommend conferring with the patient’s nephrologist because the glomerular filtration rate might decrease in the setting of dehydration. Because GLP1s suppress the thirst, not just appetite, patients can go all day without drinking water and not feel thirsty.
Michael Camilleri, MD, gastroenterologist, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota
Audience member: Should GLP-1 RAs be held for 1 week or 4 weeks prior to surgery to reduce the patient’s risk for aspiration? And is tapering required?
MC: For a patient taking liraglutide, I would hold the drug for 1 week prior to surgery. For patients taking other GLP-1 RAs, including extended exenatide, I advise holding for between 2 and 3 weeks before the procedure. It’s also important to make sure the patient’s diabetes is well-controlled with other medications — not GLP-1 RAs — during this period.
After surgery, you can restart GLP-1 RA therapy once there is recovery of oral food intake and normal bowel function.
Audience member: Is treatment with GLP-1 RAs appropriate for a patient with a family history of colon cancer but an otherwise unremarkable medical and family history?
MC: I have not seen a contraindication to receiving GLP-1 RAs based on a family history of colorectal cancer or other malignancies. An analysis of the French national healthcare insurance system database has suggested 1-3 years use of GLP-1 RAs (exenatide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide) may be linked with increased occurrence of thyroid cancer. Data from 37 randomized controlled trials and 19 real-world studies having 16,839 patients in placebo control group, 16,550 patients in active control group, and 13,330 patients in real-world studies were analyzed in a 2023 systematic review and meta-analysis. Compared to placebo or active control treatments, occurrence of pancreatic cancer, thyroid cancer, and all neoplasms — benign, malignant, and otherwise unspecified — were similar in the semaglutide group.
Toshi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, family physician, Zucker School of Medicine, Hempstead, New York
Audience member: What do you do about elevated liver functions after starting treatment with GLP-1 RAs, and what do you do when a patient has reached their weight loss goal?
TI-M: I recommend monitoring the liver function tests, evaluating for underlying causes, such as viral hepatitis, alcohol-related damage, or problems with other medications, and consulting a gastroenterologist or liver specialist if necessary. It’s also important to discuss the risk-benefit of continuing on the GP-1 RA for that particular patient.
Audience member: What effects will GLP-1 RAs have on sleep-disordered breathing/obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)? Are you aware of any ongoing trials addressing this subject?
TI-M: GLP-1 RAs may have beneficial effects on sleep-disordered breathing and OSA through weight loss, which can lead to a reduction in excess adipose tissue, and improvements in metabolic parameters. In terms of studies, a 2023 paper addressed this question, but more research is needed.
Audience member: Is it within a psychiatric provider’s scope of practice to prescribe GLP-1 agents for the reduction of weight gain associated with psychiatric medications?
TI-M: Obesity medicine is an interdisciplinary process. Numerous medications prescribed for mental health can contribute to obesity, and psychiatrists can play a role in collaborating with a patient’s primary care provider and/or obesity medicine specialist to determine which medications can be adjusted or replaced. It is important to remember that obesity management is not just about medications. It requires managing nutrition and activity in addition to behavioral health issues and social determinants of health. If the clinician has had the training to manage these pillars and is comfortable managing this chronic illness — similar to diabetes, hypertension, and other conditions — then this is a possibility. Otherwise, team-based care is appropriate.
Holly Lofton, MD, obesity medicine, NYU Langone Health, New York City
Audience member: Can we safely use them on patients who have had bariatric surgery and regularly develop dumping syndrome?
HL: These medications can be used after bariatric surgery in patients who meet the criteria for pharmacologic treatment. If a patient is having postoperative symptoms of dumping syndrome or excessive gastrointestinal losses from vomiting or diarrhea, dietary adjustments and other methods of managing the dumping syndrome in gastric bypass patients should be initiated before considering GLP-1 RAs because these patients do not have a functioning pylorus in their alimentary tract and these drugs are not indicated to treat dumping syndrome. The first-line approach typically involves reducing the patient’s intake of simple carbohydrates but can also include medications or surgical intervention when appropriate.
Audience member: Would teaching a patient to fast intermittently while they’re on GLP-1 RAs help them preserve weight loss if they choose to wean off the medication?
HL: Personally, I feel it is best to use the titration period and the time in which the patient is actively losing weight when on GLP-1 RAs. These are the best periods to help develop an individualized treatment plan, one that includes nutrition, activity, behavior modification, and resistance training. The patient’s lifestyle plan will likely change based on their environment and other factors. Intermittent fasting can be a part of such a plan. There is no consensus as to exactly which eating pattern will help patients maintain weight once they lose the physiologic benefit of the weight loss medications. However, studies have been published that demonstrate an average weight regain of 66% or greater when patients go from taking the maximum dose of a GLP-1 RA to taking none at all. Thus, patients should still be followed closely for weight regain when they discontinue a GLP-1 RA.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The arrival of GLP-1 receptor agonists has revolutionized treatment options for people with obesity and medical practice.
This news organization recently hosted a panel of experts across specialties — including endocrinology, gastroenterology, and obesity medicine — to discuss these potentially life-changing medications and to answer questions from the audience.
Because of the flood of queries from our audience, we asked our panelists to address some of the questions that didn’t make the recording. Their answers are below.
Beverly Tchang, MD, endocrinologist, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York City
Audience member: Can you initiate glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists (GLP-1 RAs) as a primary drug in a patient with obesity and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes?
BT: We often prescribe GLP-1 RAs to individuals with type 2 diabetes as a first-line medication. Guidelines from the American Diabetes Association are really emphasizing a patient-centered approach, and metformin may not be the best first-line medication anymore.
Audience member:
BT: GLP-1 RAs do not need to be renally dosed, but I still recommend conferring with the patient’s nephrologist because the glomerular filtration rate might decrease in the setting of dehydration. Because GLP1s suppress the thirst, not just appetite, patients can go all day without drinking water and not feel thirsty.
Michael Camilleri, MD, gastroenterologist, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota
Audience member: Should GLP-1 RAs be held for 1 week or 4 weeks prior to surgery to reduce the patient’s risk for aspiration? And is tapering required?
MC: For a patient taking liraglutide, I would hold the drug for 1 week prior to surgery. For patients taking other GLP-1 RAs, including extended exenatide, I advise holding for between 2 and 3 weeks before the procedure. It’s also important to make sure the patient’s diabetes is well-controlled with other medications — not GLP-1 RAs — during this period.
After surgery, you can restart GLP-1 RA therapy once there is recovery of oral food intake and normal bowel function.
Audience member: Is treatment with GLP-1 RAs appropriate for a patient with a family history of colon cancer but an otherwise unremarkable medical and family history?
MC: I have not seen a contraindication to receiving GLP-1 RAs based on a family history of colorectal cancer or other malignancies. An analysis of the French national healthcare insurance system database has suggested 1-3 years use of GLP-1 RAs (exenatide, liraglutide, and dulaglutide) may be linked with increased occurrence of thyroid cancer. Data from 37 randomized controlled trials and 19 real-world studies having 16,839 patients in placebo control group, 16,550 patients in active control group, and 13,330 patients in real-world studies were analyzed in a 2023 systematic review and meta-analysis. Compared to placebo or active control treatments, occurrence of pancreatic cancer, thyroid cancer, and all neoplasms — benign, malignant, and otherwise unspecified — were similar in the semaglutide group.
Toshi Iroku-Malize, MD, MPH, MBA, FAAFP, family physician, Zucker School of Medicine, Hempstead, New York
Audience member: What do you do about elevated liver functions after starting treatment with GLP-1 RAs, and what do you do when a patient has reached their weight loss goal?
TI-M: I recommend monitoring the liver function tests, evaluating for underlying causes, such as viral hepatitis, alcohol-related damage, or problems with other medications, and consulting a gastroenterologist or liver specialist if necessary. It’s also important to discuss the risk-benefit of continuing on the GP-1 RA for that particular patient.
Audience member: What effects will GLP-1 RAs have on sleep-disordered breathing/obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)? Are you aware of any ongoing trials addressing this subject?
TI-M: GLP-1 RAs may have beneficial effects on sleep-disordered breathing and OSA through weight loss, which can lead to a reduction in excess adipose tissue, and improvements in metabolic parameters. In terms of studies, a 2023 paper addressed this question, but more research is needed.
Audience member: Is it within a psychiatric provider’s scope of practice to prescribe GLP-1 agents for the reduction of weight gain associated with psychiatric medications?
TI-M: Obesity medicine is an interdisciplinary process. Numerous medications prescribed for mental health can contribute to obesity, and psychiatrists can play a role in collaborating with a patient’s primary care provider and/or obesity medicine specialist to determine which medications can be adjusted or replaced. It is important to remember that obesity management is not just about medications. It requires managing nutrition and activity in addition to behavioral health issues and social determinants of health. If the clinician has had the training to manage these pillars and is comfortable managing this chronic illness — similar to diabetes, hypertension, and other conditions — then this is a possibility. Otherwise, team-based care is appropriate.
Holly Lofton, MD, obesity medicine, NYU Langone Health, New York City
Audience member: Can we safely use them on patients who have had bariatric surgery and regularly develop dumping syndrome?
HL: These medications can be used after bariatric surgery in patients who meet the criteria for pharmacologic treatment. If a patient is having postoperative symptoms of dumping syndrome or excessive gastrointestinal losses from vomiting or diarrhea, dietary adjustments and other methods of managing the dumping syndrome in gastric bypass patients should be initiated before considering GLP-1 RAs because these patients do not have a functioning pylorus in their alimentary tract and these drugs are not indicated to treat dumping syndrome. The first-line approach typically involves reducing the patient’s intake of simple carbohydrates but can also include medications or surgical intervention when appropriate.
Audience member: Would teaching a patient to fast intermittently while they’re on GLP-1 RAs help them preserve weight loss if they choose to wean off the medication?
HL: Personally, I feel it is best to use the titration period and the time in which the patient is actively losing weight when on GLP-1 RAs. These are the best periods to help develop an individualized treatment plan, one that includes nutrition, activity, behavior modification, and resistance training. The patient’s lifestyle plan will likely change based on their environment and other factors. Intermittent fasting can be a part of such a plan. There is no consensus as to exactly which eating pattern will help patients maintain weight once they lose the physiologic benefit of the weight loss medications. However, studies have been published that demonstrate an average weight regain of 66% or greater when patients go from taking the maximum dose of a GLP-1 RA to taking none at all. Thus, patients should still be followed closely for weight regain when they discontinue a GLP-1 RA.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Dispelling Common Headache Myths
Patients may be familiar with several myths and have misconceptions about headaches and migraine, which often arise due to a combination of factors, including limited understanding of the conditions, cultural beliefs, misinformation, and the complex nature of headaches. Being aware of these myths and seeking accurate information help patients to better understand and manage their headaches.
Myth: Migraine Is the Most Common Type of Headache
This is not true. The most common type of headache is tension-type headache, and it's the kind of headache that almost everyone has from time to time. Between 40% and 80% of the US population have had some form of tension-type headache, but only about 13% of the adult population have migraine. Stress can make muscles in the head and neck tense and knotted, and these muscles can be the source of a tension-type headache. Sometimes these headaches are not at all related to muscles or stress. Neck position may also be a factor. Pain from this type of headache is usually felt on both sides of the head and presents more often as steady, dull pressure or pain that’s usually mild to moderate in intensity. The pain can be in the forehead and eyes or further back in the head. Tension-type headaches are not usually associated with nausea, vomiting, or light and sound sensitivity.
When a tension-type headache is really severe, patients could consider this headache a migraine. Clinicians can easily distinguish tension-type headache from migraine, which often presents on one side of the head, with moderate or severe intensity, is throbbing, and is associated with nausea, vomiting, and light and sound sensitivity.
Myth: Only Adults Get Headaches
False. Headaches aren’t experienced just by adults. However, unlike adults, children find it harder to explain their headaches. It is true that adults have more migraines than children; children’s migraines are often hard for doctors to recognize. A 6- to 9-year-old child is 50% less likely than an adult to have migraine, and their attacks are more often bilateral, are shorter, and respond to sleep quickly.
Myth: Migraines Are Just Really Bad Headaches
False. They are bad, but that is only a small part of the story. A migraine attack is different from other headaches; they actually are 1 of the 3 primary headache disorders, along with tension-type headache and cluster headache. A moderate or severe headache is one of the many characteristics of migraine, and some patients do not even have a headache during a migraine attack. Migraine is an inherited disease of the brain and other parts of the nervous system and can feel much worse than a normal headache. During a migraine attack, the brain does not process sensory data, such as lights, sound, or touch, properly. Patients might even experience visual, sensory, or speech problems (ie, auras) and sometime see flashing lights or zigzag lines that blink on and off or blind spots in their vision. Patients with migraine are often nauseated and severely bothered by light, sound, and even smells. Migraine headaches can last between 4 and 72 hours on average, causing disability, tiredness, and inability to think clearly or work productively, which adds to the burden of the disease. So, migraine is not just a headache.
Myth: More Women Than Men Experience Migraine
This is true. Epidemiologic data show a 3-fold higher incidence of migraine in women than men, starting from puberty and throughout life. From about 6 to 12 years, boys have a slightly higher incidence than girls, but then migraine occurrence levels off and becomes a disease primarily of women. The modulation of neuronal and vascular reactivity by hormones (namely estrogens and progesterone) is a crucial aspect of migraine in some women only. These hormones exert influence on a spectrum of neuromediators and neurotransmitters, potentially leading to functional and structural variations in specific brain regions associated with migraine pathogenesis. Beyond their central effects, sex hormones also modulate vascular tone. Therefore, migraine follows a pattern throughout a woman’s life corresponding to the fluctuation of estrogen. Within a year of their first menstrual period, many girls with migraine have their first attack. They are more likely to have a migraine attack just before and at the start of menses, and at other times of the month as well. They feel better when pregnant and worse after they stop breastfeeding, and they start to feel worse prior to menopause. Then they improve a few years after menopause.
While men are less at risk of having migraine, they’re more likely to have cluster headache than women (although this type of headache is rare compared with other headaches like migraine). Only about 0.1% or less of the population of adults in the US experience this type of headache. Cluster headache gets its name from the clustering of attacks occurring 2 to 6 times per day for 4 to 10 weeks and disappearing as quickly as they came. This headache pain is felt exclusively in or behind 1 eye and rarely elsewhere, on the same side of the head. There is also a clustering of other symptoms called autonomic findings, such as tearing and redness of 1 eye, stuffiness and running in 1 nostril, sweating over 1 eyebrow, drooping of 1 eyelid, and a small pupil—all on the same side of the head the pain is radiating from. Most patients have only some of these findings. Cluster headaches tend to occur every year around the same time (circannual). When a patient is in a cycle of cluster headaches, they often occur at the same time each day (circadian). These set times of the year and of the day are caused by the biological clock deep down under the brain in the hypothalamus.
Myth: All Headaches Are Psychological
This is not true. Usually the underlying cause of migraine is genetically-inherited, but each attack may be triggered by an underlying cause (eg, drop in barometric pressure, menses, certain food/drinks, lack of sleep, stress, etc). Even tension-type headaches can be triggered by muscles in the head and neck becoming tense, stressful events, or jaw issues, which in turn send out pain signals that are felt on both sides of the head.
Many years ago (ie, 1950s-1960s), it was thought that the underlying cause of migraine in women was psychological issues; that has been disproven many times. Both men and women have migraine, and they both can have coexisting psychological issues (ie, depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric problems).
Myth: Migraines Aren’t Serious
Most types of migraine in and of themselves are not serious; however, chronic migraine can continue for years and is debilitating and disabling—becoming a serious issue for patients. These patients usually take many medications, are obese, can have big changes in weight and severe insomnia, don’t exercise enough, and develop other illnesses. Migraine can severely impact quality of life; many people living with migraine have reported reduced productivity while at work, lack of promotion, loss of jobs, and a disruption in their family, social, and leisure activities.
Migraine attacks vary from one person to another and can be quite different from one attack to another in the same person. Hemiplegic migraine, a rare and distinct subtype that is sometimes inherited, is characterized by neurologic symptoms (multiple auras, including a significant weakness or paralysis on 1 side of the body). Although these patients seem much sicker and have multiple types of auras and 1-sided weakness with a prolonged headache, most recover without serious consequences.
Myth: Lack of Sleep Causes Migraine
Yes, lack of sleep is a known trigger for migraine in many people, but lack of sleep is not the cause of migraine. Sleep deprivation and irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain, potentially triggering migraine in susceptible individuals. Additionally, inadequate sleep may contribute to increased stress and tension, which are also common triggers for migraine. In fact, many people with migraine do have sleep issues, which can range from trouble falling asleep to early morning awakening without being able to get back to sleep or frequently interrupted sleep each night. Correcting the sleep problem is part of the migraine therapy. Patients should be checked for sleep apnea if they wake with headache in the morning. Medication overuse headache should also be considered.
Establishing a regular sleep routine and ensuring an adequate amount of sleep can be important components of managing migraine symptoms, particularly for those who find a connection between their sleep patterns and the onset of a migraine attack. However, the relationship between sleep and migraine can vary widely among individuals, and other factors may also contribute to migraine triggers.
Myth: Caffeine Causes Migraine
This is a myth; caffeine does not cause migraine but definitely can be a trigger for some people. Coffee and caffeine and migraine have a complex relationship: excessive caffeine consumption or withdrawal can trigger migraine attacks, but caffeine can also help alleviate headaches (including migraine) due to its analgesic properties. Caffeine is a major component of many over-the-counter medicines for migraine. Some people find drinking coffee or a soda or taking a caffeine tablet at the onset of a migraine attack lowers the intensity of a migraine headache. Regular use of caffeine, either as “treatment” or for pleasure, is not advised in patients with migraine. Most doctors limit caffeine to a regular cup of coffee or tea per day, with no caffeine-containing sodas or chocolate in their patients with migraine; caffeine withdrawal is also a frequent migraine trigger. Patients can notice withdrawal headaches when they stop coffee, even if they are only consuming 1 cup per day. Most people drink a lot more.
Myth: Headache Medicine Will Cure Migraine
False. There currently is no “cure” for migraine. There are several medicines available that certainly can help prevent, abort, or control symptoms of migraine. Some of these medications include over-the-counter analgesics; triptans (like sumatriptan or rizatriptan); gepants, which are small molecule CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) antagonists; CGRP antibodies given by injection; antidepressants; antiseizure medicines; and beta-blockers.
Myth: You Cannot Take Any Migraine Medications During Pregnancy
Migraine medications, such as triptans, are relatively safe during pregnancy, particularly after the first trimester. Acetaminophen in low doses is safe as well, but some of the preventive antiseizure medications should be avoided due to the risk of halting the pregnancy or producing a congenital malformation. Noninvasive wearable devices (such as Nerivio), biofeedback training, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques are particularly appealing to pregnant women as they have high efficacy with virtually no lasting side effects.
Although patients who are pregnant might have an increased flurry of migraine headaches in the first trimester of their pregnancy, they will most likely have a decreased number of attacks in the next 2 trimesters of their pregnancy, making them feel really well. The first trimester is a dangerous time for fetuses to be exposed to certain medicines that are foreign to them, as their organs are still being formed. There are medicines that doctors feel are less problematic both for acute care and prevention of migraine during pregnancy; therefore, patients with a history of migraine should always consult with their obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist (or other doctor they usually see for their migraine care) before taking any medication if they are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
Effective nonpharmaceutical options are available for all patients with migraine, whether pregnant or not. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes getting 7 to 10 hours of sleep each night, drinking plenty of water each day, getting ample nutrition from healthy foods, and eliminating as many sources of extra stress as possible can help reduce the risk of a migraine, even when exposed to a known trigger.
Medications may also lead to headaches by a phenomenon called medication overuse headache, if the rescue medication is taken too often. Clinicians recommend no more than 2 days per week of any acute care medication and taking a good preventive medication if needed.
Myth: “Migraine Diets” Cure Migraine
This is false. Avoiding known food triggers can reduce the risk of a migraine attack, but a diet regimen is not a cure. Although eating healthy foods and avoiding certain kinds of food that trigger migraine can eliminate triggering the episodes, there are other factors to take into account. For instance, the migraine diet cannot address a lack of sleep, stress, or hormonal changes a person experiences. Only very few patients with migraine can say their medication has cured their migraine, but it could happen.
Myth: Dietary Supplements Can Cure Migraine
This myth is not true. Supplements can help migraine headache or prevent triggering it, but they won’t cure it. Supplements, such as magnesium, vitamin D3, coenzyme Q10, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), feverfew, melatonin, and vitamin B2 are important additions to the migraine treatment armamentarium, but no one specific vitamin/mineral or supplement has been proven to help prevent or relieve migraine for everyone. They help some people immensely and do little for others, just as with any pharmacologic agent.
Myth: It’s Not a Migraine Unless You Experience Aura
This is not true, as most migraines present without aura. Migraine with typical aura affects 30% of patients with migraine.
Myth: Researchers No Longer Investigate Migraine
False; there are several ongoing studies working to address the pathophysiology of migraine and find new treatment options. Recently, neuromodulation devices have entered the market. One such device from Theranica (called Nerivio) now has clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration for acute and preventive migraine treatment from age 12 and up. One phase 4 study by Theranica shows that Nerivio appears to be safe during pregnancy.
Several migraine studies of note include the following:
OnabotulinumtoxinA as a treatment for hemiplegic migraine: This project aims to evaluate the response to onabotulinumtoxinA treatments in patients with hemiplegic migraine evaluated at Mayo Clinic.
Occipital nerve stimulation for migraine: OPTIMISE. This study is evaluating the safety and efficacy of occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) using the Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) Precision™ System in the management of intractable chronic migraine, when used in conjunction with antimigraine medications.
The Medication Overuse Treatment Strategy trial: This study is comparing the outcomes among patients randomized to 1 of the 2 treatment strategies for treating patients who have chronic migraine with medication overuse.
Metformin is being investigated as a treatment for the prevention of episodic migraine.
Myth: Migraine Cannot Be Diagnosed Without an Imaging Exam
This is false. Migraine is a clinical diagnosis and does not need any imaging to confirm. Imaging is indicated only if the symptoms are not clear or if there are neurologic symptoms or warning signs accompanying the migraine. In such cases, imaging would be warranted to rule out other pathologies. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed to rule out other pathology, not to diagnose migraine. A clinician must identify a pattern in the patient’s history according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Headache Society to diagnose migraine, which include that the patient had 5 previous attacks without aura or 2 attacks with aura.
Summary
Headaches, especially migraine, can be unpleasant and disabling and can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. However, pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical interventions that can help are available. Lifestyle changes, including diet, sleep, and stress reduction can ease symptoms and reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. As researchers continue to investigate the pathophysiology of migraine, they are sure to identify better treatments and, perhaps one day—a cure.
Patients may be familiar with several myths and have misconceptions about headaches and migraine, which often arise due to a combination of factors, including limited understanding of the conditions, cultural beliefs, misinformation, and the complex nature of headaches. Being aware of these myths and seeking accurate information help patients to better understand and manage their headaches.
Myth: Migraine Is the Most Common Type of Headache
This is not true. The most common type of headache is tension-type headache, and it's the kind of headache that almost everyone has from time to time. Between 40% and 80% of the US population have had some form of tension-type headache, but only about 13% of the adult population have migraine. Stress can make muscles in the head and neck tense and knotted, and these muscles can be the source of a tension-type headache. Sometimes these headaches are not at all related to muscles or stress. Neck position may also be a factor. Pain from this type of headache is usually felt on both sides of the head and presents more often as steady, dull pressure or pain that’s usually mild to moderate in intensity. The pain can be in the forehead and eyes or further back in the head. Tension-type headaches are not usually associated with nausea, vomiting, or light and sound sensitivity.
When a tension-type headache is really severe, patients could consider this headache a migraine. Clinicians can easily distinguish tension-type headache from migraine, which often presents on one side of the head, with moderate or severe intensity, is throbbing, and is associated with nausea, vomiting, and light and sound sensitivity.
Myth: Only Adults Get Headaches
False. Headaches aren’t experienced just by adults. However, unlike adults, children find it harder to explain their headaches. It is true that adults have more migraines than children; children’s migraines are often hard for doctors to recognize. A 6- to 9-year-old child is 50% less likely than an adult to have migraine, and their attacks are more often bilateral, are shorter, and respond to sleep quickly.
Myth: Migraines Are Just Really Bad Headaches
False. They are bad, but that is only a small part of the story. A migraine attack is different from other headaches; they actually are 1 of the 3 primary headache disorders, along with tension-type headache and cluster headache. A moderate or severe headache is one of the many characteristics of migraine, and some patients do not even have a headache during a migraine attack. Migraine is an inherited disease of the brain and other parts of the nervous system and can feel much worse than a normal headache. During a migraine attack, the brain does not process sensory data, such as lights, sound, or touch, properly. Patients might even experience visual, sensory, or speech problems (ie, auras) and sometime see flashing lights or zigzag lines that blink on and off or blind spots in their vision. Patients with migraine are often nauseated and severely bothered by light, sound, and even smells. Migraine headaches can last between 4 and 72 hours on average, causing disability, tiredness, and inability to think clearly or work productively, which adds to the burden of the disease. So, migraine is not just a headache.
Myth: More Women Than Men Experience Migraine
This is true. Epidemiologic data show a 3-fold higher incidence of migraine in women than men, starting from puberty and throughout life. From about 6 to 12 years, boys have a slightly higher incidence than girls, but then migraine occurrence levels off and becomes a disease primarily of women. The modulation of neuronal and vascular reactivity by hormones (namely estrogens and progesterone) is a crucial aspect of migraine in some women only. These hormones exert influence on a spectrum of neuromediators and neurotransmitters, potentially leading to functional and structural variations in specific brain regions associated with migraine pathogenesis. Beyond their central effects, sex hormones also modulate vascular tone. Therefore, migraine follows a pattern throughout a woman’s life corresponding to the fluctuation of estrogen. Within a year of their first menstrual period, many girls with migraine have their first attack. They are more likely to have a migraine attack just before and at the start of menses, and at other times of the month as well. They feel better when pregnant and worse after they stop breastfeeding, and they start to feel worse prior to menopause. Then they improve a few years after menopause.
While men are less at risk of having migraine, they’re more likely to have cluster headache than women (although this type of headache is rare compared with other headaches like migraine). Only about 0.1% or less of the population of adults in the US experience this type of headache. Cluster headache gets its name from the clustering of attacks occurring 2 to 6 times per day for 4 to 10 weeks and disappearing as quickly as they came. This headache pain is felt exclusively in or behind 1 eye and rarely elsewhere, on the same side of the head. There is also a clustering of other symptoms called autonomic findings, such as tearing and redness of 1 eye, stuffiness and running in 1 nostril, sweating over 1 eyebrow, drooping of 1 eyelid, and a small pupil—all on the same side of the head the pain is radiating from. Most patients have only some of these findings. Cluster headaches tend to occur every year around the same time (circannual). When a patient is in a cycle of cluster headaches, they often occur at the same time each day (circadian). These set times of the year and of the day are caused by the biological clock deep down under the brain in the hypothalamus.
Myth: All Headaches Are Psychological
This is not true. Usually the underlying cause of migraine is genetically-inherited, but each attack may be triggered by an underlying cause (eg, drop in barometric pressure, menses, certain food/drinks, lack of sleep, stress, etc). Even tension-type headaches can be triggered by muscles in the head and neck becoming tense, stressful events, or jaw issues, which in turn send out pain signals that are felt on both sides of the head.
Many years ago (ie, 1950s-1960s), it was thought that the underlying cause of migraine in women was psychological issues; that has been disproven many times. Both men and women have migraine, and they both can have coexisting psychological issues (ie, depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric problems).
Myth: Migraines Aren’t Serious
Most types of migraine in and of themselves are not serious; however, chronic migraine can continue for years and is debilitating and disabling—becoming a serious issue for patients. These patients usually take many medications, are obese, can have big changes in weight and severe insomnia, don’t exercise enough, and develop other illnesses. Migraine can severely impact quality of life; many people living with migraine have reported reduced productivity while at work, lack of promotion, loss of jobs, and a disruption in their family, social, and leisure activities.
Migraine attacks vary from one person to another and can be quite different from one attack to another in the same person. Hemiplegic migraine, a rare and distinct subtype that is sometimes inherited, is characterized by neurologic symptoms (multiple auras, including a significant weakness or paralysis on 1 side of the body). Although these patients seem much sicker and have multiple types of auras and 1-sided weakness with a prolonged headache, most recover without serious consequences.
Myth: Lack of Sleep Causes Migraine
Yes, lack of sleep is a known trigger for migraine in many people, but lack of sleep is not the cause of migraine. Sleep deprivation and irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain, potentially triggering migraine in susceptible individuals. Additionally, inadequate sleep may contribute to increased stress and tension, which are also common triggers for migraine. In fact, many people with migraine do have sleep issues, which can range from trouble falling asleep to early morning awakening without being able to get back to sleep or frequently interrupted sleep each night. Correcting the sleep problem is part of the migraine therapy. Patients should be checked for sleep apnea if they wake with headache in the morning. Medication overuse headache should also be considered.
Establishing a regular sleep routine and ensuring an adequate amount of sleep can be important components of managing migraine symptoms, particularly for those who find a connection between their sleep patterns and the onset of a migraine attack. However, the relationship between sleep and migraine can vary widely among individuals, and other factors may also contribute to migraine triggers.
Myth: Caffeine Causes Migraine
This is a myth; caffeine does not cause migraine but definitely can be a trigger for some people. Coffee and caffeine and migraine have a complex relationship: excessive caffeine consumption or withdrawal can trigger migraine attacks, but caffeine can also help alleviate headaches (including migraine) due to its analgesic properties. Caffeine is a major component of many over-the-counter medicines for migraine. Some people find drinking coffee or a soda or taking a caffeine tablet at the onset of a migraine attack lowers the intensity of a migraine headache. Regular use of caffeine, either as “treatment” or for pleasure, is not advised in patients with migraine. Most doctors limit caffeine to a regular cup of coffee or tea per day, with no caffeine-containing sodas or chocolate in their patients with migraine; caffeine withdrawal is also a frequent migraine trigger. Patients can notice withdrawal headaches when they stop coffee, even if they are only consuming 1 cup per day. Most people drink a lot more.
Myth: Headache Medicine Will Cure Migraine
False. There currently is no “cure” for migraine. There are several medicines available that certainly can help prevent, abort, or control symptoms of migraine. Some of these medications include over-the-counter analgesics; triptans (like sumatriptan or rizatriptan); gepants, which are small molecule CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) antagonists; CGRP antibodies given by injection; antidepressants; antiseizure medicines; and beta-blockers.
Myth: You Cannot Take Any Migraine Medications During Pregnancy
Migraine medications, such as triptans, are relatively safe during pregnancy, particularly after the first trimester. Acetaminophen in low doses is safe as well, but some of the preventive antiseizure medications should be avoided due to the risk of halting the pregnancy or producing a congenital malformation. Noninvasive wearable devices (such as Nerivio), biofeedback training, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques are particularly appealing to pregnant women as they have high efficacy with virtually no lasting side effects.
Although patients who are pregnant might have an increased flurry of migraine headaches in the first trimester of their pregnancy, they will most likely have a decreased number of attacks in the next 2 trimesters of their pregnancy, making them feel really well. The first trimester is a dangerous time for fetuses to be exposed to certain medicines that are foreign to them, as their organs are still being formed. There are medicines that doctors feel are less problematic both for acute care and prevention of migraine during pregnancy; therefore, patients with a history of migraine should always consult with their obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist (or other doctor they usually see for their migraine care) before taking any medication if they are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
Effective nonpharmaceutical options are available for all patients with migraine, whether pregnant or not. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes getting 7 to 10 hours of sleep each night, drinking plenty of water each day, getting ample nutrition from healthy foods, and eliminating as many sources of extra stress as possible can help reduce the risk of a migraine, even when exposed to a known trigger.
Medications may also lead to headaches by a phenomenon called medication overuse headache, if the rescue medication is taken too often. Clinicians recommend no more than 2 days per week of any acute care medication and taking a good preventive medication if needed.
Myth: “Migraine Diets” Cure Migraine
This is false. Avoiding known food triggers can reduce the risk of a migraine attack, but a diet regimen is not a cure. Although eating healthy foods and avoiding certain kinds of food that trigger migraine can eliminate triggering the episodes, there are other factors to take into account. For instance, the migraine diet cannot address a lack of sleep, stress, or hormonal changes a person experiences. Only very few patients with migraine can say their medication has cured their migraine, but it could happen.
Myth: Dietary Supplements Can Cure Migraine
This myth is not true. Supplements can help migraine headache or prevent triggering it, but they won’t cure it. Supplements, such as magnesium, vitamin D3, coenzyme Q10, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), feverfew, melatonin, and vitamin B2 are important additions to the migraine treatment armamentarium, but no one specific vitamin/mineral or supplement has been proven to help prevent or relieve migraine for everyone. They help some people immensely and do little for others, just as with any pharmacologic agent.
Myth: It’s Not a Migraine Unless You Experience Aura
This is not true, as most migraines present without aura. Migraine with typical aura affects 30% of patients with migraine.
Myth: Researchers No Longer Investigate Migraine
False; there are several ongoing studies working to address the pathophysiology of migraine and find new treatment options. Recently, neuromodulation devices have entered the market. One such device from Theranica (called Nerivio) now has clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration for acute and preventive migraine treatment from age 12 and up. One phase 4 study by Theranica shows that Nerivio appears to be safe during pregnancy.
Several migraine studies of note include the following:
OnabotulinumtoxinA as a treatment for hemiplegic migraine: This project aims to evaluate the response to onabotulinumtoxinA treatments in patients with hemiplegic migraine evaluated at Mayo Clinic.
Occipital nerve stimulation for migraine: OPTIMISE. This study is evaluating the safety and efficacy of occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) using the Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) Precision™ System in the management of intractable chronic migraine, when used in conjunction with antimigraine medications.
The Medication Overuse Treatment Strategy trial: This study is comparing the outcomes among patients randomized to 1 of the 2 treatment strategies for treating patients who have chronic migraine with medication overuse.
Metformin is being investigated as a treatment for the prevention of episodic migraine.
Myth: Migraine Cannot Be Diagnosed Without an Imaging Exam
This is false. Migraine is a clinical diagnosis and does not need any imaging to confirm. Imaging is indicated only if the symptoms are not clear or if there are neurologic symptoms or warning signs accompanying the migraine. In such cases, imaging would be warranted to rule out other pathologies. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed to rule out other pathology, not to diagnose migraine. A clinician must identify a pattern in the patient’s history according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Headache Society to diagnose migraine, which include that the patient had 5 previous attacks without aura or 2 attacks with aura.
Summary
Headaches, especially migraine, can be unpleasant and disabling and can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. However, pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical interventions that can help are available. Lifestyle changes, including diet, sleep, and stress reduction can ease symptoms and reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. As researchers continue to investigate the pathophysiology of migraine, they are sure to identify better treatments and, perhaps one day—a cure.
Patients may be familiar with several myths and have misconceptions about headaches and migraine, which often arise due to a combination of factors, including limited understanding of the conditions, cultural beliefs, misinformation, and the complex nature of headaches. Being aware of these myths and seeking accurate information help patients to better understand and manage their headaches.
Myth: Migraine Is the Most Common Type of Headache
This is not true. The most common type of headache is tension-type headache, and it's the kind of headache that almost everyone has from time to time. Between 40% and 80% of the US population have had some form of tension-type headache, but only about 13% of the adult population have migraine. Stress can make muscles in the head and neck tense and knotted, and these muscles can be the source of a tension-type headache. Sometimes these headaches are not at all related to muscles or stress. Neck position may also be a factor. Pain from this type of headache is usually felt on both sides of the head and presents more often as steady, dull pressure or pain that’s usually mild to moderate in intensity. The pain can be in the forehead and eyes or further back in the head. Tension-type headaches are not usually associated with nausea, vomiting, or light and sound sensitivity.
When a tension-type headache is really severe, patients could consider this headache a migraine. Clinicians can easily distinguish tension-type headache from migraine, which often presents on one side of the head, with moderate or severe intensity, is throbbing, and is associated with nausea, vomiting, and light and sound sensitivity.
Myth: Only Adults Get Headaches
False. Headaches aren’t experienced just by adults. However, unlike adults, children find it harder to explain their headaches. It is true that adults have more migraines than children; children’s migraines are often hard for doctors to recognize. A 6- to 9-year-old child is 50% less likely than an adult to have migraine, and their attacks are more often bilateral, are shorter, and respond to sleep quickly.
Myth: Migraines Are Just Really Bad Headaches
False. They are bad, but that is only a small part of the story. A migraine attack is different from other headaches; they actually are 1 of the 3 primary headache disorders, along with tension-type headache and cluster headache. A moderate or severe headache is one of the many characteristics of migraine, and some patients do not even have a headache during a migraine attack. Migraine is an inherited disease of the brain and other parts of the nervous system and can feel much worse than a normal headache. During a migraine attack, the brain does not process sensory data, such as lights, sound, or touch, properly. Patients might even experience visual, sensory, or speech problems (ie, auras) and sometime see flashing lights or zigzag lines that blink on and off or blind spots in their vision. Patients with migraine are often nauseated and severely bothered by light, sound, and even smells. Migraine headaches can last between 4 and 72 hours on average, causing disability, tiredness, and inability to think clearly or work productively, which adds to the burden of the disease. So, migraine is not just a headache.
Myth: More Women Than Men Experience Migraine
This is true. Epidemiologic data show a 3-fold higher incidence of migraine in women than men, starting from puberty and throughout life. From about 6 to 12 years, boys have a slightly higher incidence than girls, but then migraine occurrence levels off and becomes a disease primarily of women. The modulation of neuronal and vascular reactivity by hormones (namely estrogens and progesterone) is a crucial aspect of migraine in some women only. These hormones exert influence on a spectrum of neuromediators and neurotransmitters, potentially leading to functional and structural variations in specific brain regions associated with migraine pathogenesis. Beyond their central effects, sex hormones also modulate vascular tone. Therefore, migraine follows a pattern throughout a woman’s life corresponding to the fluctuation of estrogen. Within a year of their first menstrual period, many girls with migraine have their first attack. They are more likely to have a migraine attack just before and at the start of menses, and at other times of the month as well. They feel better when pregnant and worse after they stop breastfeeding, and they start to feel worse prior to menopause. Then they improve a few years after menopause.
While men are less at risk of having migraine, they’re more likely to have cluster headache than women (although this type of headache is rare compared with other headaches like migraine). Only about 0.1% or less of the population of adults in the US experience this type of headache. Cluster headache gets its name from the clustering of attacks occurring 2 to 6 times per day for 4 to 10 weeks and disappearing as quickly as they came. This headache pain is felt exclusively in or behind 1 eye and rarely elsewhere, on the same side of the head. There is also a clustering of other symptoms called autonomic findings, such as tearing and redness of 1 eye, stuffiness and running in 1 nostril, sweating over 1 eyebrow, drooping of 1 eyelid, and a small pupil—all on the same side of the head the pain is radiating from. Most patients have only some of these findings. Cluster headaches tend to occur every year around the same time (circannual). When a patient is in a cycle of cluster headaches, they often occur at the same time each day (circadian). These set times of the year and of the day are caused by the biological clock deep down under the brain in the hypothalamus.
Myth: All Headaches Are Psychological
This is not true. Usually the underlying cause of migraine is genetically-inherited, but each attack may be triggered by an underlying cause (eg, drop in barometric pressure, menses, certain food/drinks, lack of sleep, stress, etc). Even tension-type headaches can be triggered by muscles in the head and neck becoming tense, stressful events, or jaw issues, which in turn send out pain signals that are felt on both sides of the head.
Many years ago (ie, 1950s-1960s), it was thought that the underlying cause of migraine in women was psychological issues; that has been disproven many times. Both men and women have migraine, and they both can have coexisting psychological issues (ie, depression, anxiety, and other psychiatric problems).
Myth: Migraines Aren’t Serious
Most types of migraine in and of themselves are not serious; however, chronic migraine can continue for years and is debilitating and disabling—becoming a serious issue for patients. These patients usually take many medications, are obese, can have big changes in weight and severe insomnia, don’t exercise enough, and develop other illnesses. Migraine can severely impact quality of life; many people living with migraine have reported reduced productivity while at work, lack of promotion, loss of jobs, and a disruption in their family, social, and leisure activities.
Migraine attacks vary from one person to another and can be quite different from one attack to another in the same person. Hemiplegic migraine, a rare and distinct subtype that is sometimes inherited, is characterized by neurologic symptoms (multiple auras, including a significant weakness or paralysis on 1 side of the body). Although these patients seem much sicker and have multiple types of auras and 1-sided weakness with a prolonged headache, most recover without serious consequences.
Myth: Lack of Sleep Causes Migraine
Yes, lack of sleep is a known trigger for migraine in many people, but lack of sleep is not the cause of migraine. Sleep deprivation and irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain, potentially triggering migraine in susceptible individuals. Additionally, inadequate sleep may contribute to increased stress and tension, which are also common triggers for migraine. In fact, many people with migraine do have sleep issues, which can range from trouble falling asleep to early morning awakening without being able to get back to sleep or frequently interrupted sleep each night. Correcting the sleep problem is part of the migraine therapy. Patients should be checked for sleep apnea if they wake with headache in the morning. Medication overuse headache should also be considered.
Establishing a regular sleep routine and ensuring an adequate amount of sleep can be important components of managing migraine symptoms, particularly for those who find a connection between their sleep patterns and the onset of a migraine attack. However, the relationship between sleep and migraine can vary widely among individuals, and other factors may also contribute to migraine triggers.
Myth: Caffeine Causes Migraine
This is a myth; caffeine does not cause migraine but definitely can be a trigger for some people. Coffee and caffeine and migraine have a complex relationship: excessive caffeine consumption or withdrawal can trigger migraine attacks, but caffeine can also help alleviate headaches (including migraine) due to its analgesic properties. Caffeine is a major component of many over-the-counter medicines for migraine. Some people find drinking coffee or a soda or taking a caffeine tablet at the onset of a migraine attack lowers the intensity of a migraine headache. Regular use of caffeine, either as “treatment” or for pleasure, is not advised in patients with migraine. Most doctors limit caffeine to a regular cup of coffee or tea per day, with no caffeine-containing sodas or chocolate in their patients with migraine; caffeine withdrawal is also a frequent migraine trigger. Patients can notice withdrawal headaches when they stop coffee, even if they are only consuming 1 cup per day. Most people drink a lot more.
Myth: Headache Medicine Will Cure Migraine
False. There currently is no “cure” for migraine. There are several medicines available that certainly can help prevent, abort, or control symptoms of migraine. Some of these medications include over-the-counter analgesics; triptans (like sumatriptan or rizatriptan); gepants, which are small molecule CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) antagonists; CGRP antibodies given by injection; antidepressants; antiseizure medicines; and beta-blockers.
Myth: You Cannot Take Any Migraine Medications During Pregnancy
Migraine medications, such as triptans, are relatively safe during pregnancy, particularly after the first trimester. Acetaminophen in low doses is safe as well, but some of the preventive antiseizure medications should be avoided due to the risk of halting the pregnancy or producing a congenital malformation. Noninvasive wearable devices (such as Nerivio), biofeedback training, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques are particularly appealing to pregnant women as they have high efficacy with virtually no lasting side effects.
Although patients who are pregnant might have an increased flurry of migraine headaches in the first trimester of their pregnancy, they will most likely have a decreased number of attacks in the next 2 trimesters of their pregnancy, making them feel really well. The first trimester is a dangerous time for fetuses to be exposed to certain medicines that are foreign to them, as their organs are still being formed. There are medicines that doctors feel are less problematic both for acute care and prevention of migraine during pregnancy; therefore, patients with a history of migraine should always consult with their obstetrician-gynecologist and a neurologist (or other doctor they usually see for their migraine care) before taking any medication if they are planning a pregnancy or are pregnant.
Effective nonpharmaceutical options are available for all patients with migraine, whether pregnant or not. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, which includes getting 7 to 10 hours of sleep each night, drinking plenty of water each day, getting ample nutrition from healthy foods, and eliminating as many sources of extra stress as possible can help reduce the risk of a migraine, even when exposed to a known trigger.
Medications may also lead to headaches by a phenomenon called medication overuse headache, if the rescue medication is taken too often. Clinicians recommend no more than 2 days per week of any acute care medication and taking a good preventive medication if needed.
Myth: “Migraine Diets” Cure Migraine
This is false. Avoiding known food triggers can reduce the risk of a migraine attack, but a diet regimen is not a cure. Although eating healthy foods and avoiding certain kinds of food that trigger migraine can eliminate triggering the episodes, there are other factors to take into account. For instance, the migraine diet cannot address a lack of sleep, stress, or hormonal changes a person experiences. Only very few patients with migraine can say their medication has cured their migraine, but it could happen.
Myth: Dietary Supplements Can Cure Migraine
This myth is not true. Supplements can help migraine headache or prevent triggering it, but they won’t cure it. Supplements, such as magnesium, vitamin D3, coenzyme Q10, vitamin B2 (riboflavin), feverfew, melatonin, and vitamin B2 are important additions to the migraine treatment armamentarium, but no one specific vitamin/mineral or supplement has been proven to help prevent or relieve migraine for everyone. They help some people immensely and do little for others, just as with any pharmacologic agent.
Myth: It’s Not a Migraine Unless You Experience Aura
This is not true, as most migraines present without aura. Migraine with typical aura affects 30% of patients with migraine.
Myth: Researchers No Longer Investigate Migraine
False; there are several ongoing studies working to address the pathophysiology of migraine and find new treatment options. Recently, neuromodulation devices have entered the market. One such device from Theranica (called Nerivio) now has clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration for acute and preventive migraine treatment from age 12 and up. One phase 4 study by Theranica shows that Nerivio appears to be safe during pregnancy.
Several migraine studies of note include the following:
OnabotulinumtoxinA as a treatment for hemiplegic migraine: This project aims to evaluate the response to onabotulinumtoxinA treatments in patients with hemiplegic migraine evaluated at Mayo Clinic.
Occipital nerve stimulation for migraine: OPTIMISE. This study is evaluating the safety and efficacy of occipital nerve stimulation (ONS) using the Boston Scientific Corporation (BSC) Precision™ System in the management of intractable chronic migraine, when used in conjunction with antimigraine medications.
The Medication Overuse Treatment Strategy trial: This study is comparing the outcomes among patients randomized to 1 of the 2 treatment strategies for treating patients who have chronic migraine with medication overuse.
Metformin is being investigated as a treatment for the prevention of episodic migraine.
Myth: Migraine Cannot Be Diagnosed Without an Imaging Exam
This is false. Migraine is a clinical diagnosis and does not need any imaging to confirm. Imaging is indicated only if the symptoms are not clear or if there are neurologic symptoms or warning signs accompanying the migraine. In such cases, imaging would be warranted to rule out other pathologies. A magnetic resonance imaging scan is performed to rule out other pathology, not to diagnose migraine. A clinician must identify a pattern in the patient’s history according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Headache Society to diagnose migraine, which include that the patient had 5 previous attacks without aura or 2 attacks with aura.
Summary
Headaches, especially migraine, can be unpleasant and disabling and can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. However, pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical interventions that can help are available. Lifestyle changes, including diet, sleep, and stress reduction can ease symptoms and reduce the frequency of migraine attacks. As researchers continue to investigate the pathophysiology of migraine, they are sure to identify better treatments and, perhaps one day—a cure.








