User login
ART Linked With Congenital Heart Defects in Newborns
The rate of congenital heart defects is higher in newborns conceived using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) than in newborns conceived without assistance. This finding comes from a population-based cohort study led by Dr. Nona Sargisian, a gynecologist at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and colleagues, which was published in the European Heart Journal.
The researchers analyzed more than 7 million results of all live-born children in Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway between 1984 and 2015. They found that congenital heart defects occurred more frequently in the ART newborn group (1.85%) than in naturally conceived newborns (1.15%).
The study also revealed that the risk for congenital heart defects in multiple births is higher than in single births, with and without the use of ART. However, the result that congenital heart defects occur more often in ART newborns remained significant when comparing single births from both groups (1.62% vs 1.11%).
Relatively Low Prevalence
Barbara Sonntag, MD, PhD, a gynecologist at Amedes Fertility Center in Hamburg, Germany, referred to a “clinically relevant risk increase” with a relatively low prevalence of the condition.
“When 1000 children are born, an abnormality occurs in 18 children after ART, compared with 11 children born after natural conception,” she told the Science Media Center.
Dr. Sonntag emphasized that the risk is particularly increased by a multiple pregnancy. A statement about causality is not possible based on the study, but multiple pregnancies are generally associated with increased risks during pregnancy and for the children.
The large and robust dataset confirms long-known findings, said Georg Griesinger, MD, PhD, medical director of the fertility centers of the University Medical Center Schleswig-Holstein in Lübeck and Manhagen, Germany.
The key figures can be found in single births, he explained. “Among single births conceived by ART, the rate of severe congenital heart defects was 1.62% compared with 1.11% in spontaneously conceived single births, an increase in risk by 1.19 times. For severe heart defects, the rate was 0.31% in ART single births, compared with 0.25% in spontaneously conceived single births.”
The increased risks are consistent with existing literature. Therefore, the current study does not reveal any new risk signals, said Dr. Griesinger.
Single Embryo Transfer
The “risks are small but present,” according to Michael von Wolff, MD, head of gynecological endocrinology and reproductive medicine at Bern University Hospital in Switzerland. “Therefore, ART therapy should only be carried out after exhausting conservative treatments,” he recommended. For example, ovarian stimulation with low-dose hormone preparations could be an option.
Dr. Griesinger pointed out that, in absolute numbers, all maternal and fetal or neonatal risks are significantly increased in twins and higher-order multiples, compared with the estimated risk association within the actual ART treatment.
“For this reason, reproductive medicine specialists have been advocating for single-embryo transfer for years to promote the occurrence of single pregnancies through ART,” said Dr. Griesinger.
The study “emphasizes the importance of single embryo transfer to avoid the higher risks associated with multiple pregnancies,” according to Rocío Núñez Calonge, PhD, scientific director of the International Reproduction Unit in Alicante, Spain.
Dr. Sonntag also sees a “strong additional call to avoid multiple pregnancies through a predominant strategy of single-embryo transfer in the data. The increased rate of childhood birth defects is already part of the information provided before assisted reproduction.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The rate of congenital heart defects is higher in newborns conceived using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) than in newborns conceived without assistance. This finding comes from a population-based cohort study led by Dr. Nona Sargisian, a gynecologist at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and colleagues, which was published in the European Heart Journal.
The researchers analyzed more than 7 million results of all live-born children in Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway between 1984 and 2015. They found that congenital heart defects occurred more frequently in the ART newborn group (1.85%) than in naturally conceived newborns (1.15%).
The study also revealed that the risk for congenital heart defects in multiple births is higher than in single births, with and without the use of ART. However, the result that congenital heart defects occur more often in ART newborns remained significant when comparing single births from both groups (1.62% vs 1.11%).
Relatively Low Prevalence
Barbara Sonntag, MD, PhD, a gynecologist at Amedes Fertility Center in Hamburg, Germany, referred to a “clinically relevant risk increase” with a relatively low prevalence of the condition.
“When 1000 children are born, an abnormality occurs in 18 children after ART, compared with 11 children born after natural conception,” she told the Science Media Center.
Dr. Sonntag emphasized that the risk is particularly increased by a multiple pregnancy. A statement about causality is not possible based on the study, but multiple pregnancies are generally associated with increased risks during pregnancy and for the children.
The large and robust dataset confirms long-known findings, said Georg Griesinger, MD, PhD, medical director of the fertility centers of the University Medical Center Schleswig-Holstein in Lübeck and Manhagen, Germany.
The key figures can be found in single births, he explained. “Among single births conceived by ART, the rate of severe congenital heart defects was 1.62% compared with 1.11% in spontaneously conceived single births, an increase in risk by 1.19 times. For severe heart defects, the rate was 0.31% in ART single births, compared with 0.25% in spontaneously conceived single births.”
The increased risks are consistent with existing literature. Therefore, the current study does not reveal any new risk signals, said Dr. Griesinger.
Single Embryo Transfer
The “risks are small but present,” according to Michael von Wolff, MD, head of gynecological endocrinology and reproductive medicine at Bern University Hospital in Switzerland. “Therefore, ART therapy should only be carried out after exhausting conservative treatments,” he recommended. For example, ovarian stimulation with low-dose hormone preparations could be an option.
Dr. Griesinger pointed out that, in absolute numbers, all maternal and fetal or neonatal risks are significantly increased in twins and higher-order multiples, compared with the estimated risk association within the actual ART treatment.
“For this reason, reproductive medicine specialists have been advocating for single-embryo transfer for years to promote the occurrence of single pregnancies through ART,” said Dr. Griesinger.
The study “emphasizes the importance of single embryo transfer to avoid the higher risks associated with multiple pregnancies,” according to Rocío Núñez Calonge, PhD, scientific director of the International Reproduction Unit in Alicante, Spain.
Dr. Sonntag also sees a “strong additional call to avoid multiple pregnancies through a predominant strategy of single-embryo transfer in the data. The increased rate of childhood birth defects is already part of the information provided before assisted reproduction.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The rate of congenital heart defects is higher in newborns conceived using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) than in newborns conceived without assistance. This finding comes from a population-based cohort study led by Dr. Nona Sargisian, a gynecologist at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and colleagues, which was published in the European Heart Journal.
The researchers analyzed more than 7 million results of all live-born children in Denmark, Finland, Sweden, and Norway between 1984 and 2015. They found that congenital heart defects occurred more frequently in the ART newborn group (1.85%) than in naturally conceived newborns (1.15%).
The study also revealed that the risk for congenital heart defects in multiple births is higher than in single births, with and without the use of ART. However, the result that congenital heart defects occur more often in ART newborns remained significant when comparing single births from both groups (1.62% vs 1.11%).
Relatively Low Prevalence
Barbara Sonntag, MD, PhD, a gynecologist at Amedes Fertility Center in Hamburg, Germany, referred to a “clinically relevant risk increase” with a relatively low prevalence of the condition.
“When 1000 children are born, an abnormality occurs in 18 children after ART, compared with 11 children born after natural conception,” she told the Science Media Center.
Dr. Sonntag emphasized that the risk is particularly increased by a multiple pregnancy. A statement about causality is not possible based on the study, but multiple pregnancies are generally associated with increased risks during pregnancy and for the children.
The large and robust dataset confirms long-known findings, said Georg Griesinger, MD, PhD, medical director of the fertility centers of the University Medical Center Schleswig-Holstein in Lübeck and Manhagen, Germany.
The key figures can be found in single births, he explained. “Among single births conceived by ART, the rate of severe congenital heart defects was 1.62% compared with 1.11% in spontaneously conceived single births, an increase in risk by 1.19 times. For severe heart defects, the rate was 0.31% in ART single births, compared with 0.25% in spontaneously conceived single births.”
The increased risks are consistent with existing literature. Therefore, the current study does not reveal any new risk signals, said Dr. Griesinger.
Single Embryo Transfer
The “risks are small but present,” according to Michael von Wolff, MD, head of gynecological endocrinology and reproductive medicine at Bern University Hospital in Switzerland. “Therefore, ART therapy should only be carried out after exhausting conservative treatments,” he recommended. For example, ovarian stimulation with low-dose hormone preparations could be an option.
Dr. Griesinger pointed out that, in absolute numbers, all maternal and fetal or neonatal risks are significantly increased in twins and higher-order multiples, compared with the estimated risk association within the actual ART treatment.
“For this reason, reproductive medicine specialists have been advocating for single-embryo transfer for years to promote the occurrence of single pregnancies through ART,” said Dr. Griesinger.
The study “emphasizes the importance of single embryo transfer to avoid the higher risks associated with multiple pregnancies,” according to Rocío Núñez Calonge, PhD, scientific director of the International Reproduction Unit in Alicante, Spain.
Dr. Sonntag also sees a “strong additional call to avoid multiple pregnancies through a predominant strategy of single-embryo transfer in the data. The increased rate of childhood birth defects is already part of the information provided before assisted reproduction.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EUROPEAN HEART JOURNAL
Is Wildfire Smoke More Toxic Than General Air Pollution?
Wildfire-related air pollution in Europe kills more than non-wildfire air pollution. As climate change exacerbates the frequency and violence of wildfires, researchers are studying the health implications of mitigation methods such as prescribed fires.
Presenting at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), Cathryn Tonne, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona, Spain, said wildfire-related PM2.5 is more toxic than general PM2.5, leading to significantly higher mortality rates.
Prescribed, controlled fires have been employed worldwide to reduce the chance of uncontrolled, catastrophic fires. However, researchers wonder whether the techniques reduce the overall fire-related PM2.5 or add up to it. “Prescribed fire increases ecosystem resilience and can reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire,” said Jason Sacks, MPH, an epidemiologist in the Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment in the Office of Research and Development at the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), at the congress. “But it also leads to poorer air quality and health impacts, and we still don’t know what this means at a regional scale.”
Wildfire Pollution Kills More Than Other Air Pollution
Researchers at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona used a large dataset of daily mortality data from 32 European countries collected through the EARLY-ADAPT project. They utilized the SILAM model to derive daily average concentrations of wildfire-related PM2.5, non-fire PM2.5, and total PM2.5 levels. They also employed GEOSTAT population grids at a 1-km resolution to calculate the attributable number of deaths across different regions, specifically focusing on data from 2006, 2011, and 2018.
The data analysis indicated that the relative risk per unit of PM2.5 is substantially larger for wildfire-related PM2.5, compared with non-fire PM2.5. “We essentially assume that wildfire smoke PM2.5 has the same toxicity as total PM2.5, but it’s increasingly clear that’s likely not the case,” Dr. Tonne said, presenting the study.
When employing exposure-response functions (ERFs) specific to wildfire smoke, researchers found that the attributable deaths from all causes of wildfire PM2.5 were approximately 10 times larger than those calculated using total PM2.5 exposure estimates. Dr. Tonne explained that this stark difference highlights the critical need for tailored ERFs that accurately reflect the unique health risks posed by wildfire smoke.
“Respiratory mortality usually has the strongest relative risks, and we’re seeing that in this study as well,” Dr. Tonne said. “Wildfire smoke seems to operate through quite immediate mechanisms, likely through inflammation and oxidative stress.”
One significant challenge of the study was the lack of uniform spatial resolution across all countries involved in the analysis. This inconsistency may affect how accurately mortality estimates can be attributed to specific PM2.5 sources. Additionally, the study had limited statistical power for generating age- and sex-specific mortality estimates, which could obscure important demographic differences in vulnerability to wildfire smoke exposure. The analysis was also constrained to data available only up to 2020, thereby excluding critical wildfire events from subsequent years, such as those in 2022 and 2023, which may have further elucidated the health impacts of wildfire smoke in Europe.
Fires Prescription
Prescribed fires or controlled burns are intentional fires set by land managers under carefully managed conditions.
Historically, many forested areas have been subjected to fire suppression practices, which allow combustible materials like dry leaves, twigs, and shrubs to accumulate over time. This buildup leads to a higher likelihood of severe, uncontrollable wildfires. Prescribed fires can reduce these fuel loads and improve the health and resilience of ecosystems.
They release fewer pollutants and emissions than the large-scale, unmanageable wildfires they help prevent because they happen at lower temperatures. But they still introduce pollutants in the air that can negatively affect nearby communities’ health.
People with preexisting respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are particularly vulnerable to smoke, which can trigger health issues like breathing difficulties, coughing, and eye irritation. The cumulative impact of increased burns raises concerns about long-term air quality, especially in densely populated areas. “We need to understand if we’re actually tipping the scale to having less wildfire smoke or just increasing the total amount of smoke.”
Mitigation strategies include accurately picking the right timing and weather conditions to determine when and where to conduct controlled burns and effective and timely communication to inform local communities about upcoming burns, the potential for smoke exposure, and how to protect themselves.
There is a growing need to improve public messaging around prescribed fires, Mr. Sacks said, because often the message communicated is oversimplified, such as “there will be smoke, but don’t worry. But that’s not the message we want to convey, especially for people with asthma or COPD.”
Instead, he said public health agencies should provide clearer, science-based guidance on the risks for smoke exposure and practical steps people can take to reduce their risk.
What Can Doctors Do?
Chris Carlsten, MD, director of the Centre for Lung Health and professor and head of the Respiratory Medicine Division at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, told this news organization that determining whether an exacerbation of a respiratory condition is caused by fire exposure or other factors, such as viral infections, is complex because both can trigger similar responses and may complement each other. “It’s very difficult for any individual to know whether, when they’re having an exacerbation of asthma or COPD, that’s due to the fire,” he said. Fire smoke also increases infection risks, further complicating diagnosis.
Dr. Carlsten suggested that physicians could recommend preventative use of inhalers for at-risk patients when wildfires occur rather than waiting for symptoms to worsen. “That is a really interesting idea that could be practical.” Still, he advises caution, stressing that patients should consult their providers because not all may react well to increased inhaler use.
He also highlighted a significant shift in the healthcare landscape, noting that traditionally, the focus has been on the cardiovascular impacts of pollution, particularly traffic-related pollution. However, as wildfire smoke becomes a growing issue, the focus is shifting back to respiratory problems, with profound implications for healthcare resources, budgets, and drug approvals based on the burden of respiratory disease. “Fire smoke is becoming more of a problem. This swing back to respiratory has huge implications for healthcare systems and respiratory disease burden.”
Mr. Sacks and Dr. Carlsten reported no relevant financial relationships. The study presented by Dr. Tonne received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 101057131.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Wildfire-related air pollution in Europe kills more than non-wildfire air pollution. As climate change exacerbates the frequency and violence of wildfires, researchers are studying the health implications of mitigation methods such as prescribed fires.
Presenting at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), Cathryn Tonne, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona, Spain, said wildfire-related PM2.5 is more toxic than general PM2.5, leading to significantly higher mortality rates.
Prescribed, controlled fires have been employed worldwide to reduce the chance of uncontrolled, catastrophic fires. However, researchers wonder whether the techniques reduce the overall fire-related PM2.5 or add up to it. “Prescribed fire increases ecosystem resilience and can reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire,” said Jason Sacks, MPH, an epidemiologist in the Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment in the Office of Research and Development at the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), at the congress. “But it also leads to poorer air quality and health impacts, and we still don’t know what this means at a regional scale.”
Wildfire Pollution Kills More Than Other Air Pollution
Researchers at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona used a large dataset of daily mortality data from 32 European countries collected through the EARLY-ADAPT project. They utilized the SILAM model to derive daily average concentrations of wildfire-related PM2.5, non-fire PM2.5, and total PM2.5 levels. They also employed GEOSTAT population grids at a 1-km resolution to calculate the attributable number of deaths across different regions, specifically focusing on data from 2006, 2011, and 2018.
The data analysis indicated that the relative risk per unit of PM2.5 is substantially larger for wildfire-related PM2.5, compared with non-fire PM2.5. “We essentially assume that wildfire smoke PM2.5 has the same toxicity as total PM2.5, but it’s increasingly clear that’s likely not the case,” Dr. Tonne said, presenting the study.
When employing exposure-response functions (ERFs) specific to wildfire smoke, researchers found that the attributable deaths from all causes of wildfire PM2.5 were approximately 10 times larger than those calculated using total PM2.5 exposure estimates. Dr. Tonne explained that this stark difference highlights the critical need for tailored ERFs that accurately reflect the unique health risks posed by wildfire smoke.
“Respiratory mortality usually has the strongest relative risks, and we’re seeing that in this study as well,” Dr. Tonne said. “Wildfire smoke seems to operate through quite immediate mechanisms, likely through inflammation and oxidative stress.”
One significant challenge of the study was the lack of uniform spatial resolution across all countries involved in the analysis. This inconsistency may affect how accurately mortality estimates can be attributed to specific PM2.5 sources. Additionally, the study had limited statistical power for generating age- and sex-specific mortality estimates, which could obscure important demographic differences in vulnerability to wildfire smoke exposure. The analysis was also constrained to data available only up to 2020, thereby excluding critical wildfire events from subsequent years, such as those in 2022 and 2023, which may have further elucidated the health impacts of wildfire smoke in Europe.
Fires Prescription
Prescribed fires or controlled burns are intentional fires set by land managers under carefully managed conditions.
Historically, many forested areas have been subjected to fire suppression practices, which allow combustible materials like dry leaves, twigs, and shrubs to accumulate over time. This buildup leads to a higher likelihood of severe, uncontrollable wildfires. Prescribed fires can reduce these fuel loads and improve the health and resilience of ecosystems.
They release fewer pollutants and emissions than the large-scale, unmanageable wildfires they help prevent because they happen at lower temperatures. But they still introduce pollutants in the air that can negatively affect nearby communities’ health.
People with preexisting respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are particularly vulnerable to smoke, which can trigger health issues like breathing difficulties, coughing, and eye irritation. The cumulative impact of increased burns raises concerns about long-term air quality, especially in densely populated areas. “We need to understand if we’re actually tipping the scale to having less wildfire smoke or just increasing the total amount of smoke.”
Mitigation strategies include accurately picking the right timing and weather conditions to determine when and where to conduct controlled burns and effective and timely communication to inform local communities about upcoming burns, the potential for smoke exposure, and how to protect themselves.
There is a growing need to improve public messaging around prescribed fires, Mr. Sacks said, because often the message communicated is oversimplified, such as “there will be smoke, but don’t worry. But that’s not the message we want to convey, especially for people with asthma or COPD.”
Instead, he said public health agencies should provide clearer, science-based guidance on the risks for smoke exposure and practical steps people can take to reduce their risk.
What Can Doctors Do?
Chris Carlsten, MD, director of the Centre for Lung Health and professor and head of the Respiratory Medicine Division at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, told this news organization that determining whether an exacerbation of a respiratory condition is caused by fire exposure or other factors, such as viral infections, is complex because both can trigger similar responses and may complement each other. “It’s very difficult for any individual to know whether, when they’re having an exacerbation of asthma or COPD, that’s due to the fire,” he said. Fire smoke also increases infection risks, further complicating diagnosis.
Dr. Carlsten suggested that physicians could recommend preventative use of inhalers for at-risk patients when wildfires occur rather than waiting for symptoms to worsen. “That is a really interesting idea that could be practical.” Still, he advises caution, stressing that patients should consult their providers because not all may react well to increased inhaler use.
He also highlighted a significant shift in the healthcare landscape, noting that traditionally, the focus has been on the cardiovascular impacts of pollution, particularly traffic-related pollution. However, as wildfire smoke becomes a growing issue, the focus is shifting back to respiratory problems, with profound implications for healthcare resources, budgets, and drug approvals based on the burden of respiratory disease. “Fire smoke is becoming more of a problem. This swing back to respiratory has huge implications for healthcare systems and respiratory disease burden.”
Mr. Sacks and Dr. Carlsten reported no relevant financial relationships. The study presented by Dr. Tonne received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 101057131.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Wildfire-related air pollution in Europe kills more than non-wildfire air pollution. As climate change exacerbates the frequency and violence of wildfires, researchers are studying the health implications of mitigation methods such as prescribed fires.
Presenting at the annual congress of the European Respiratory Society (ERS), Cathryn Tonne, PhD, an environmental epidemiologist at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona, Spain, said wildfire-related PM2.5 is more toxic than general PM2.5, leading to significantly higher mortality rates.
Prescribed, controlled fires have been employed worldwide to reduce the chance of uncontrolled, catastrophic fires. However, researchers wonder whether the techniques reduce the overall fire-related PM2.5 or add up to it. “Prescribed fire increases ecosystem resilience and can reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfire,” said Jason Sacks, MPH, an epidemiologist in the Center for Public Health and Environmental Assessment in the Office of Research and Development at the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), at the congress. “But it also leads to poorer air quality and health impacts, and we still don’t know what this means at a regional scale.”
Wildfire Pollution Kills More Than Other Air Pollution
Researchers at the Instituto de Salud Global de Barcelona used a large dataset of daily mortality data from 32 European countries collected through the EARLY-ADAPT project. They utilized the SILAM model to derive daily average concentrations of wildfire-related PM2.5, non-fire PM2.5, and total PM2.5 levels. They also employed GEOSTAT population grids at a 1-km resolution to calculate the attributable number of deaths across different regions, specifically focusing on data from 2006, 2011, and 2018.
The data analysis indicated that the relative risk per unit of PM2.5 is substantially larger for wildfire-related PM2.5, compared with non-fire PM2.5. “We essentially assume that wildfire smoke PM2.5 has the same toxicity as total PM2.5, but it’s increasingly clear that’s likely not the case,” Dr. Tonne said, presenting the study.
When employing exposure-response functions (ERFs) specific to wildfire smoke, researchers found that the attributable deaths from all causes of wildfire PM2.5 were approximately 10 times larger than those calculated using total PM2.5 exposure estimates. Dr. Tonne explained that this stark difference highlights the critical need for tailored ERFs that accurately reflect the unique health risks posed by wildfire smoke.
“Respiratory mortality usually has the strongest relative risks, and we’re seeing that in this study as well,” Dr. Tonne said. “Wildfire smoke seems to operate through quite immediate mechanisms, likely through inflammation and oxidative stress.”
One significant challenge of the study was the lack of uniform spatial resolution across all countries involved in the analysis. This inconsistency may affect how accurately mortality estimates can be attributed to specific PM2.5 sources. Additionally, the study had limited statistical power for generating age- and sex-specific mortality estimates, which could obscure important demographic differences in vulnerability to wildfire smoke exposure. The analysis was also constrained to data available only up to 2020, thereby excluding critical wildfire events from subsequent years, such as those in 2022 and 2023, which may have further elucidated the health impacts of wildfire smoke in Europe.
Fires Prescription
Prescribed fires or controlled burns are intentional fires set by land managers under carefully managed conditions.
Historically, many forested areas have been subjected to fire suppression practices, which allow combustible materials like dry leaves, twigs, and shrubs to accumulate over time. This buildup leads to a higher likelihood of severe, uncontrollable wildfires. Prescribed fires can reduce these fuel loads and improve the health and resilience of ecosystems.
They release fewer pollutants and emissions than the large-scale, unmanageable wildfires they help prevent because they happen at lower temperatures. But they still introduce pollutants in the air that can negatively affect nearby communities’ health.
People with preexisting respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are particularly vulnerable to smoke, which can trigger health issues like breathing difficulties, coughing, and eye irritation. The cumulative impact of increased burns raises concerns about long-term air quality, especially in densely populated areas. “We need to understand if we’re actually tipping the scale to having less wildfire smoke or just increasing the total amount of smoke.”
Mitigation strategies include accurately picking the right timing and weather conditions to determine when and where to conduct controlled burns and effective and timely communication to inform local communities about upcoming burns, the potential for smoke exposure, and how to protect themselves.
There is a growing need to improve public messaging around prescribed fires, Mr. Sacks said, because often the message communicated is oversimplified, such as “there will be smoke, but don’t worry. But that’s not the message we want to convey, especially for people with asthma or COPD.”
Instead, he said public health agencies should provide clearer, science-based guidance on the risks for smoke exposure and practical steps people can take to reduce their risk.
What Can Doctors Do?
Chris Carlsten, MD, director of the Centre for Lung Health and professor and head of the Respiratory Medicine Division at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, told this news organization that determining whether an exacerbation of a respiratory condition is caused by fire exposure or other factors, such as viral infections, is complex because both can trigger similar responses and may complement each other. “It’s very difficult for any individual to know whether, when they’re having an exacerbation of asthma or COPD, that’s due to the fire,” he said. Fire smoke also increases infection risks, further complicating diagnosis.
Dr. Carlsten suggested that physicians could recommend preventative use of inhalers for at-risk patients when wildfires occur rather than waiting for symptoms to worsen. “That is a really interesting idea that could be practical.” Still, he advises caution, stressing that patients should consult their providers because not all may react well to increased inhaler use.
He also highlighted a significant shift in the healthcare landscape, noting that traditionally, the focus has been on the cardiovascular impacts of pollution, particularly traffic-related pollution. However, as wildfire smoke becomes a growing issue, the focus is shifting back to respiratory problems, with profound implications for healthcare resources, budgets, and drug approvals based on the burden of respiratory disease. “Fire smoke is becoming more of a problem. This swing back to respiratory has huge implications for healthcare systems and respiratory disease burden.”
Mr. Sacks and Dr. Carlsten reported no relevant financial relationships. The study presented by Dr. Tonne received funding from the European Union’s Horizon Europe research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 101057131.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ERS 2024
How Doctors Can Overcome Vaccine Hesitancy Through Empathy, Storytelling, and Patient-Centered Communication
When Kimberly Fisher, MD, was a junior doctor, she got fired up when patients showed hesitancy about vaccines. She responded by providing numbers, data, and facts that proved vaccines were safe and effective in preventing life-threatening diseases. But she soon realized that regurgitating scientific evidence wasn’t a winning strategy. “I’ve made the mistake of launching into a let me tell you all the things that I know that you don’t know kind of lecture,” Dr. Fisher, now an associate professor of medicine at UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, a pulmonary physician, and a researcher interested in patient-provider communication, told this news organization. “Through experience and research, I have learned that when you do that, they stop listening.”
She said when patients give reasons for not getting vaccinated that are factually wrong and rooted in misinformation, the most common reaction is to correct that information and not let it stand. “That is important; it just can’t be the first thing you do,” she said.
Diane Arnaout, MD, a pediatrician at Cook Children’s Pediatrics in Fort Worth, Texas, said listening to some patients explaining why vaccine injections are poisonous or a conspiracy can be exhausting and frustrating, but she agrees that presenting scientific facts alone won’t change people’s minds. “Even in my worst days, I take the time to stop talking for a moment and let the parents talk about what concerns them because if you just get mad and put a wall up, then that trust is gone, possibly forever, not just about vaccines.”
The Default Option
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fisher has dedicated much of her time researching vaccine hesitancy. One of the most “fascinating and unexpected” findings of her work was that people are more likely to get vaccinated if a healthcare provider recommends that they get vaccinated in a “presumptive style,” which means that the provider uses language that presupposes that the person’s going to get vaccinated. “Rather than asking whether they wanted to get the vaccine conveying that the option of not getting it is just as valid, you make vaccination the default option,” she suggested.
The strategy wins many undecided, but it might not work on the most reluctant. “The presumptive recommendation is very directive, and if that works, great, but if it doesn’t, you need to shift to almost the opposite strategy, showing empathy and understanding about the person’s reasons for not wanting to be vaccinated,” Dr. Fisher said.
Find One Thing to Agree On
During a focus group on COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy that Dr. Fisher conducted in December 2021, most physicians expressed frustration that some patients remained resistant despite their best efforts. However, one participant shared an approach she found effective with even the most hesitant patients. The physician would listen carefully and express understanding, and even if what the patient said wasn’t accurate, she would find a kernel of truth to agree with and align herself with the patient. By doing this, she made patients feel like they were a team.
The example she gave was if a patient said, “I don’t know. I’ve heard different things and don’t feel comfortable taking the vaccine,” she might respond with something like, “I think it’s great that you’re thinking critically about this before making a decision. I was the same way — I wanted to fully understand the data before getting vaccinated. I also wouldn’t want to take something if I thought it wasn’t safe. It’s good that you’re being thorough.” Acknowledging their careful thought process, the physician helped patients feel seen and understood only after she introduced additional information to guide them toward understanding why the vaccine might be beneficial.
Focus on the Disease
Dr. Arnaout’s frustration grows when at the end of an appointment some parents object to vaccines with irrational and misguided concerns. “You’ve trusted me with everything else we’ve discussed today — whether it’s a diaper rash or an ear infection — so why wouldn’t you trust me on this? Sometimes it feels almost offensive — why trust my medical expertise on everything else but not vaccines?” she said.
The answer, she believes, is that vaccines are preventive, and when the threat of disease feels distant, it’s hard to see the necessity of a painful shot for your healthy child. “But if your baby were dying from meningitis, the needles we use to deliver life-saving medications in the hospital would feel absolutely necessary. It’s hard as a parent to inflict pain for something you’ve never personally seen.”
Dr. Arnaout thinks it is important to bring the focus on the disease the vaccine prevents. “Let’s talk about measles — how if a baby in my waiting room has measles and coughs, the virus can stay suspended in the air for 2 hours, and 100% of unvaccinated people in that room will get measles.”
She said sharing personal stories can also help physicians connect with their patients. “I talk to parents every day about their vaccine concerns, and I’ve found that if I take the time to explain why we vaccinate, they start to understand. I also tell them, ‘I vaccinated my children for everything on time and give them the flu shot every year. Why would I offer your child something I wouldn’t give my own?’ That personal decision, made without hesitation, resonates with parents.”
Wired for Stories
Medical professionals have a professional necessity to think and speak with precision. Their training is based on analyzing studies and data, and they develop a specialized vocabulary to describe their findings accurately.
But the human brain is naturally inclined to process and make sense of information through the structure and narrative of stories. We instinctively organize reality into a “shape of a story” rather than just isolated facts, explained Ben Riggs, senior communications specialist at Kettering Health, Dayton, Ohio, a nonfiction writing coach and author. Storytelling also taps into the emotional, rather than just the rational, parts of the brain. This emotional connection helps make the information more memorable and impactful for the listener.
Mr. Riggs said that moving from this world of precision and accuracy to one that also requires effective communication with those who haven’t had that same training is much like learning a new language. “If they can’t speak in a way that non-scientists understand, it’s like the old saying: If a tree falls in the woods and no one hears it, does it make a sound?”
Metaphors can help doctors translate scientific facts into language that meets people where they are, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their health. They can help physicians transform abstract concepts into vivid, tangible mental images that are easier for people to understand and relate to, Mr. Riggs explained. “We are predominantly concrete thinkers. Metaphors can create concrete scenes and do much of the heavy lifting when communicating complex ideas.”
“It’s important to align yourself with the other person by showing that you care, that you’re truly listening, and understand their perspective,” concluded Dr. Fisher. “Acknowledge their point of view and emphasize that they have autonomy in the decision-making process. This can open people up to hearing your perspective. You also need to know when to let go don’t cause a rift in the relationship.”
Dr. Fisher, Dr. Arnaout, and Mr. Riggs reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Kimberly Fisher, MD, was a junior doctor, she got fired up when patients showed hesitancy about vaccines. She responded by providing numbers, data, and facts that proved vaccines were safe and effective in preventing life-threatening diseases. But she soon realized that regurgitating scientific evidence wasn’t a winning strategy. “I’ve made the mistake of launching into a let me tell you all the things that I know that you don’t know kind of lecture,” Dr. Fisher, now an associate professor of medicine at UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, a pulmonary physician, and a researcher interested in patient-provider communication, told this news organization. “Through experience and research, I have learned that when you do that, they stop listening.”
She said when patients give reasons for not getting vaccinated that are factually wrong and rooted in misinformation, the most common reaction is to correct that information and not let it stand. “That is important; it just can’t be the first thing you do,” she said.
Diane Arnaout, MD, a pediatrician at Cook Children’s Pediatrics in Fort Worth, Texas, said listening to some patients explaining why vaccine injections are poisonous or a conspiracy can be exhausting and frustrating, but she agrees that presenting scientific facts alone won’t change people’s minds. “Even in my worst days, I take the time to stop talking for a moment and let the parents talk about what concerns them because if you just get mad and put a wall up, then that trust is gone, possibly forever, not just about vaccines.”
The Default Option
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fisher has dedicated much of her time researching vaccine hesitancy. One of the most “fascinating and unexpected” findings of her work was that people are more likely to get vaccinated if a healthcare provider recommends that they get vaccinated in a “presumptive style,” which means that the provider uses language that presupposes that the person’s going to get vaccinated. “Rather than asking whether they wanted to get the vaccine conveying that the option of not getting it is just as valid, you make vaccination the default option,” she suggested.
The strategy wins many undecided, but it might not work on the most reluctant. “The presumptive recommendation is very directive, and if that works, great, but if it doesn’t, you need to shift to almost the opposite strategy, showing empathy and understanding about the person’s reasons for not wanting to be vaccinated,” Dr. Fisher said.
Find One Thing to Agree On
During a focus group on COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy that Dr. Fisher conducted in December 2021, most physicians expressed frustration that some patients remained resistant despite their best efforts. However, one participant shared an approach she found effective with even the most hesitant patients. The physician would listen carefully and express understanding, and even if what the patient said wasn’t accurate, she would find a kernel of truth to agree with and align herself with the patient. By doing this, she made patients feel like they were a team.
The example she gave was if a patient said, “I don’t know. I’ve heard different things and don’t feel comfortable taking the vaccine,” she might respond with something like, “I think it’s great that you’re thinking critically about this before making a decision. I was the same way — I wanted to fully understand the data before getting vaccinated. I also wouldn’t want to take something if I thought it wasn’t safe. It’s good that you’re being thorough.” Acknowledging their careful thought process, the physician helped patients feel seen and understood only after she introduced additional information to guide them toward understanding why the vaccine might be beneficial.
Focus on the Disease
Dr. Arnaout’s frustration grows when at the end of an appointment some parents object to vaccines with irrational and misguided concerns. “You’ve trusted me with everything else we’ve discussed today — whether it’s a diaper rash or an ear infection — so why wouldn’t you trust me on this? Sometimes it feels almost offensive — why trust my medical expertise on everything else but not vaccines?” she said.
The answer, she believes, is that vaccines are preventive, and when the threat of disease feels distant, it’s hard to see the necessity of a painful shot for your healthy child. “But if your baby were dying from meningitis, the needles we use to deliver life-saving medications in the hospital would feel absolutely necessary. It’s hard as a parent to inflict pain for something you’ve never personally seen.”
Dr. Arnaout thinks it is important to bring the focus on the disease the vaccine prevents. “Let’s talk about measles — how if a baby in my waiting room has measles and coughs, the virus can stay suspended in the air for 2 hours, and 100% of unvaccinated people in that room will get measles.”
She said sharing personal stories can also help physicians connect with their patients. “I talk to parents every day about their vaccine concerns, and I’ve found that if I take the time to explain why we vaccinate, they start to understand. I also tell them, ‘I vaccinated my children for everything on time and give them the flu shot every year. Why would I offer your child something I wouldn’t give my own?’ That personal decision, made without hesitation, resonates with parents.”
Wired for Stories
Medical professionals have a professional necessity to think and speak with precision. Their training is based on analyzing studies and data, and they develop a specialized vocabulary to describe their findings accurately.
But the human brain is naturally inclined to process and make sense of information through the structure and narrative of stories. We instinctively organize reality into a “shape of a story” rather than just isolated facts, explained Ben Riggs, senior communications specialist at Kettering Health, Dayton, Ohio, a nonfiction writing coach and author. Storytelling also taps into the emotional, rather than just the rational, parts of the brain. This emotional connection helps make the information more memorable and impactful for the listener.
Mr. Riggs said that moving from this world of precision and accuracy to one that also requires effective communication with those who haven’t had that same training is much like learning a new language. “If they can’t speak in a way that non-scientists understand, it’s like the old saying: If a tree falls in the woods and no one hears it, does it make a sound?”
Metaphors can help doctors translate scientific facts into language that meets people where they are, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their health. They can help physicians transform abstract concepts into vivid, tangible mental images that are easier for people to understand and relate to, Mr. Riggs explained. “We are predominantly concrete thinkers. Metaphors can create concrete scenes and do much of the heavy lifting when communicating complex ideas.”
“It’s important to align yourself with the other person by showing that you care, that you’re truly listening, and understand their perspective,” concluded Dr. Fisher. “Acknowledge their point of view and emphasize that they have autonomy in the decision-making process. This can open people up to hearing your perspective. You also need to know when to let go don’t cause a rift in the relationship.”
Dr. Fisher, Dr. Arnaout, and Mr. Riggs reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Kimberly Fisher, MD, was a junior doctor, she got fired up when patients showed hesitancy about vaccines. She responded by providing numbers, data, and facts that proved vaccines were safe and effective in preventing life-threatening diseases. But she soon realized that regurgitating scientific evidence wasn’t a winning strategy. “I’ve made the mistake of launching into a let me tell you all the things that I know that you don’t know kind of lecture,” Dr. Fisher, now an associate professor of medicine at UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, Massachusetts, a pulmonary physician, and a researcher interested in patient-provider communication, told this news organization. “Through experience and research, I have learned that when you do that, they stop listening.”
She said when patients give reasons for not getting vaccinated that are factually wrong and rooted in misinformation, the most common reaction is to correct that information and not let it stand. “That is important; it just can’t be the first thing you do,” she said.
Diane Arnaout, MD, a pediatrician at Cook Children’s Pediatrics in Fort Worth, Texas, said listening to some patients explaining why vaccine injections are poisonous or a conspiracy can be exhausting and frustrating, but she agrees that presenting scientific facts alone won’t change people’s minds. “Even in my worst days, I take the time to stop talking for a moment and let the parents talk about what concerns them because if you just get mad and put a wall up, then that trust is gone, possibly forever, not just about vaccines.”
The Default Option
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, Dr. Fisher has dedicated much of her time researching vaccine hesitancy. One of the most “fascinating and unexpected” findings of her work was that people are more likely to get vaccinated if a healthcare provider recommends that they get vaccinated in a “presumptive style,” which means that the provider uses language that presupposes that the person’s going to get vaccinated. “Rather than asking whether they wanted to get the vaccine conveying that the option of not getting it is just as valid, you make vaccination the default option,” she suggested.
The strategy wins many undecided, but it might not work on the most reluctant. “The presumptive recommendation is very directive, and if that works, great, but if it doesn’t, you need to shift to almost the opposite strategy, showing empathy and understanding about the person’s reasons for not wanting to be vaccinated,” Dr. Fisher said.
Find One Thing to Agree On
During a focus group on COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy that Dr. Fisher conducted in December 2021, most physicians expressed frustration that some patients remained resistant despite their best efforts. However, one participant shared an approach she found effective with even the most hesitant patients. The physician would listen carefully and express understanding, and even if what the patient said wasn’t accurate, she would find a kernel of truth to agree with and align herself with the patient. By doing this, she made patients feel like they were a team.
The example she gave was if a patient said, “I don’t know. I’ve heard different things and don’t feel comfortable taking the vaccine,” she might respond with something like, “I think it’s great that you’re thinking critically about this before making a decision. I was the same way — I wanted to fully understand the data before getting vaccinated. I also wouldn’t want to take something if I thought it wasn’t safe. It’s good that you’re being thorough.” Acknowledging their careful thought process, the physician helped patients feel seen and understood only after she introduced additional information to guide them toward understanding why the vaccine might be beneficial.
Focus on the Disease
Dr. Arnaout’s frustration grows when at the end of an appointment some parents object to vaccines with irrational and misguided concerns. “You’ve trusted me with everything else we’ve discussed today — whether it’s a diaper rash or an ear infection — so why wouldn’t you trust me on this? Sometimes it feels almost offensive — why trust my medical expertise on everything else but not vaccines?” she said.
The answer, she believes, is that vaccines are preventive, and when the threat of disease feels distant, it’s hard to see the necessity of a painful shot for your healthy child. “But if your baby were dying from meningitis, the needles we use to deliver life-saving medications in the hospital would feel absolutely necessary. It’s hard as a parent to inflict pain for something you’ve never personally seen.”
Dr. Arnaout thinks it is important to bring the focus on the disease the vaccine prevents. “Let’s talk about measles — how if a baby in my waiting room has measles and coughs, the virus can stay suspended in the air for 2 hours, and 100% of unvaccinated people in that room will get measles.”
She said sharing personal stories can also help physicians connect with their patients. “I talk to parents every day about their vaccine concerns, and I’ve found that if I take the time to explain why we vaccinate, they start to understand. I also tell them, ‘I vaccinated my children for everything on time and give them the flu shot every year. Why would I offer your child something I wouldn’t give my own?’ That personal decision, made without hesitation, resonates with parents.”
Wired for Stories
Medical professionals have a professional necessity to think and speak with precision. Their training is based on analyzing studies and data, and they develop a specialized vocabulary to describe their findings accurately.
But the human brain is naturally inclined to process and make sense of information through the structure and narrative of stories. We instinctively organize reality into a “shape of a story” rather than just isolated facts, explained Ben Riggs, senior communications specialist at Kettering Health, Dayton, Ohio, a nonfiction writing coach and author. Storytelling also taps into the emotional, rather than just the rational, parts of the brain. This emotional connection helps make the information more memorable and impactful for the listener.
Mr. Riggs said that moving from this world of precision and accuracy to one that also requires effective communication with those who haven’t had that same training is much like learning a new language. “If they can’t speak in a way that non-scientists understand, it’s like the old saying: If a tree falls in the woods and no one hears it, does it make a sound?”
Metaphors can help doctors translate scientific facts into language that meets people where they are, allowing patients to make informed decisions about their health. They can help physicians transform abstract concepts into vivid, tangible mental images that are easier for people to understand and relate to, Mr. Riggs explained. “We are predominantly concrete thinkers. Metaphors can create concrete scenes and do much of the heavy lifting when communicating complex ideas.”
“It’s important to align yourself with the other person by showing that you care, that you’re truly listening, and understand their perspective,” concluded Dr. Fisher. “Acknowledge their point of view and emphasize that they have autonomy in the decision-making process. This can open people up to hearing your perspective. You also need to know when to let go don’t cause a rift in the relationship.”
Dr. Fisher, Dr. Arnaout, and Mr. Riggs reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
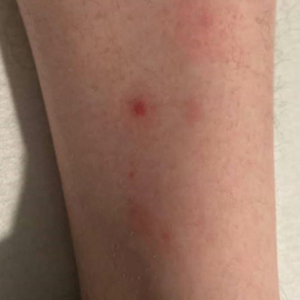
Down Syndrome: Several Cutaneous Conditions Common, Study Finds
TOPLINE:
(DS) in a 10-year retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 1529 patients with DS from eight outpatient dermatology clinics in the United States and Canada between 2011 and 2021.
- In total, 50.8% of patients were children (0-12 years), 25.2% were adolescents (13-17 years), and 24% were adults (≥ 18 years).
- The researchers evaluated skin conditions in the patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Eczematous dermatitis was the most common diagnosis, affecting 26% of patients, followed by folliculitis (19.3%) and seborrheic dermatitis (15.6%). Dermatophyte infections were diagnosed in 13%.
- Alopecia areata was the most common autoimmune skin condition, diagnosed in 178 patients (11.6%); 135 (75.8%) were children. Vitiligo was diagnosed in 66 patients (4.3%).
- The most common cutaneous infections were onychomycosis (5.9%), tinea pedis (5%), and verruca vulgaris/other viral warts (5%).
- High-risk medication use was reported in 4.3% of patients; acne vulgaris, hidradenitis suppurativa, and eczematous dermatitis were the most common associated conditions with such medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Children, adolescents, and adults with DS are most often found to have eczematous, adnexal, and autoimmune skin conditions at outpatient dermatology visits,” the authors wrote. Their findings, they added, “offer valuable insights for clinicians and researchers, aiding in the improved prioritization of screening, diagnosis, and management, as well as facilitating both basic science and clinical research into prevalent skin conditions in individuals with DS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tasya Rakasiwi, of the Department of Dermatology, Dartmouth Health, Manchester, New Hampshire, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Over 50% of the patients were children, potentially resulting in bias toward pediatric diagnoses and younger ages of presentation. Race, ethnicity, and sociodemographic factors were not captured, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Medical codes often do not capture disease phenotype or severity, and the manual conversion of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9 to ICD-10 codes may introduce potential conversion errors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
(DS) in a 10-year retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 1529 patients with DS from eight outpatient dermatology clinics in the United States and Canada between 2011 and 2021.
- In total, 50.8% of patients were children (0-12 years), 25.2% were adolescents (13-17 years), and 24% were adults (≥ 18 years).
- The researchers evaluated skin conditions in the patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Eczematous dermatitis was the most common diagnosis, affecting 26% of patients, followed by folliculitis (19.3%) and seborrheic dermatitis (15.6%). Dermatophyte infections were diagnosed in 13%.
- Alopecia areata was the most common autoimmune skin condition, diagnosed in 178 patients (11.6%); 135 (75.8%) were children. Vitiligo was diagnosed in 66 patients (4.3%).
- The most common cutaneous infections were onychomycosis (5.9%), tinea pedis (5%), and verruca vulgaris/other viral warts (5%).
- High-risk medication use was reported in 4.3% of patients; acne vulgaris, hidradenitis suppurativa, and eczematous dermatitis were the most common associated conditions with such medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Children, adolescents, and adults with DS are most often found to have eczematous, adnexal, and autoimmune skin conditions at outpatient dermatology visits,” the authors wrote. Their findings, they added, “offer valuable insights for clinicians and researchers, aiding in the improved prioritization of screening, diagnosis, and management, as well as facilitating both basic science and clinical research into prevalent skin conditions in individuals with DS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tasya Rakasiwi, of the Department of Dermatology, Dartmouth Health, Manchester, New Hampshire, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Over 50% of the patients were children, potentially resulting in bias toward pediatric diagnoses and younger ages of presentation. Race, ethnicity, and sociodemographic factors were not captured, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Medical codes often do not capture disease phenotype or severity, and the manual conversion of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9 to ICD-10 codes may introduce potential conversion errors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
(DS) in a 10-year retrospective study.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a multicenter retrospective study of 1529 patients with DS from eight outpatient dermatology clinics in the United States and Canada between 2011 and 2021.
- In total, 50.8% of patients were children (0-12 years), 25.2% were adolescents (13-17 years), and 24% were adults (≥ 18 years).
- The researchers evaluated skin conditions in the patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Eczematous dermatitis was the most common diagnosis, affecting 26% of patients, followed by folliculitis (19.3%) and seborrheic dermatitis (15.6%). Dermatophyte infections were diagnosed in 13%.
- Alopecia areata was the most common autoimmune skin condition, diagnosed in 178 patients (11.6%); 135 (75.8%) were children. Vitiligo was diagnosed in 66 patients (4.3%).
- The most common cutaneous infections were onychomycosis (5.9%), tinea pedis (5%), and verruca vulgaris/other viral warts (5%).
- High-risk medication use was reported in 4.3% of patients; acne vulgaris, hidradenitis suppurativa, and eczematous dermatitis were the most common associated conditions with such medications.
IN PRACTICE:
“Children, adolescents, and adults with DS are most often found to have eczematous, adnexal, and autoimmune skin conditions at outpatient dermatology visits,” the authors wrote. Their findings, they added, “offer valuable insights for clinicians and researchers, aiding in the improved prioritization of screening, diagnosis, and management, as well as facilitating both basic science and clinical research into prevalent skin conditions in individuals with DS.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Tasya Rakasiwi, of the Department of Dermatology, Dartmouth Health, Manchester, New Hampshire, and was published online in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Over 50% of the patients were children, potentially resulting in bias toward pediatric diagnoses and younger ages of presentation. Race, ethnicity, and sociodemographic factors were not captured, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Medical codes often do not capture disease phenotype or severity, and the manual conversion of International Classification of Diseases (ICD) 9 to ICD-10 codes may introduce potential conversion errors.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Reduced Vaccination Rates Contribute to Rising Pertussis Numbers
New data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show significant spikes in pertussis cases compared with last year, especially in several urban areas including New York, Illinois, Florida, and Colorado.
Notably, the current pertussis case count in Illinois as of September 21, 2024, was five times higher than the total cases in 2023 (1058 vs 50). New York City alone had reported 624 cases as of September 21, compared with 38 cases in 2023.
Additional data from the CDC on vaccination coverage and exemptions of school-aged children showed an increase from 3.0% last year to 3.3% in 2024 of children who were exempted from recommended vaccination requirements. Although nearly 93% of kindergarteners in the United States received recommended vaccines (including Tdap), similar to last year, this number shows a steady decline from 94% in the 2021-2021 school year and 93% in the 2021-2022 school year, according to previous CDC reports.
What’s Happening in the Clinic
Clinical experience and the most recent CDC data point to under vaccination as a driver of the increased pertussis cases this year, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the division of infectious disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
Although the pertussis vaccination rates in infancy are still very good, clinicians are seeing a drop-off in school-aged children and adults, and the lingering anti-vaccine efforts from the COVID-19 pandemic period are undoubtedly playing a part, said Dr. Cennimo. “Unfortunately, pertussis is contagious, and the vaccine effectiveness wears off. Having decreased numbers of people protected results in more rapid spread,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo agreed that the number of cases in the United States is underreported, and even higher than the data suggest. “I’m sure of it; the initial clinical presentation may be mistaken for a viral upper respiratory tract infection (common cold),” he told this news organization.
Many older children and adults with pertussis do not manifest the classic “whooping cough” seen in infants and young children, so making a clinical diagnosis can be difficult, he said. “One classical component of the illness is a prolonged cough. I have wondered if some people now reporting a lingering cough had pertussis that was missed,” Dr. Cennimo noted.
“Clinicians should stress the value of boosters in a vaccine-preventable illness where we know immunity wanes overtime,” Dr. Cennimo said. “We have a great remedy in the Tdap vaccine, which we should all be getting very 10 years,” he said.
He also emphasized that clinicians remind pregnant women of the current recommendations to receive the Tdap vaccine for every pregnancy. “Vaccination during pregnancy is the best way to protect both the pregnant person and the newborn.
Even for the vaccine hesitant, this vaccine has a long track record of safety so should not be a significant concern,” he said.
The ultimate take-home message is not a new one, and applies to all illnesses, Dr. Cennimo told this news organization. Simply put, “Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing is not just for COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show significant spikes in pertussis cases compared with last year, especially in several urban areas including New York, Illinois, Florida, and Colorado.
Notably, the current pertussis case count in Illinois as of September 21, 2024, was five times higher than the total cases in 2023 (1058 vs 50). New York City alone had reported 624 cases as of September 21, compared with 38 cases in 2023.
Additional data from the CDC on vaccination coverage and exemptions of school-aged children showed an increase from 3.0% last year to 3.3% in 2024 of children who were exempted from recommended vaccination requirements. Although nearly 93% of kindergarteners in the United States received recommended vaccines (including Tdap), similar to last year, this number shows a steady decline from 94% in the 2021-2021 school year and 93% in the 2021-2022 school year, according to previous CDC reports.
What’s Happening in the Clinic
Clinical experience and the most recent CDC data point to under vaccination as a driver of the increased pertussis cases this year, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the division of infectious disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
Although the pertussis vaccination rates in infancy are still very good, clinicians are seeing a drop-off in school-aged children and adults, and the lingering anti-vaccine efforts from the COVID-19 pandemic period are undoubtedly playing a part, said Dr. Cennimo. “Unfortunately, pertussis is contagious, and the vaccine effectiveness wears off. Having decreased numbers of people protected results in more rapid spread,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo agreed that the number of cases in the United States is underreported, and even higher than the data suggest. “I’m sure of it; the initial clinical presentation may be mistaken for a viral upper respiratory tract infection (common cold),” he told this news organization.
Many older children and adults with pertussis do not manifest the classic “whooping cough” seen in infants and young children, so making a clinical diagnosis can be difficult, he said. “One classical component of the illness is a prolonged cough. I have wondered if some people now reporting a lingering cough had pertussis that was missed,” Dr. Cennimo noted.
“Clinicians should stress the value of boosters in a vaccine-preventable illness where we know immunity wanes overtime,” Dr. Cennimo said. “We have a great remedy in the Tdap vaccine, which we should all be getting very 10 years,” he said.
He also emphasized that clinicians remind pregnant women of the current recommendations to receive the Tdap vaccine for every pregnancy. “Vaccination during pregnancy is the best way to protect both the pregnant person and the newborn.
Even for the vaccine hesitant, this vaccine has a long track record of safety so should not be a significant concern,” he said.
The ultimate take-home message is not a new one, and applies to all illnesses, Dr. Cennimo told this news organization. Simply put, “Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing is not just for COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) show significant spikes in pertussis cases compared with last year, especially in several urban areas including New York, Illinois, Florida, and Colorado.
Notably, the current pertussis case count in Illinois as of September 21, 2024, was five times higher than the total cases in 2023 (1058 vs 50). New York City alone had reported 624 cases as of September 21, compared with 38 cases in 2023.
Additional data from the CDC on vaccination coverage and exemptions of school-aged children showed an increase from 3.0% last year to 3.3% in 2024 of children who were exempted from recommended vaccination requirements. Although nearly 93% of kindergarteners in the United States received recommended vaccines (including Tdap), similar to last year, this number shows a steady decline from 94% in the 2021-2021 school year and 93% in the 2021-2022 school year, according to previous CDC reports.
What’s Happening in the Clinic
Clinical experience and the most recent CDC data point to under vaccination as a driver of the increased pertussis cases this year, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the division of infectious disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
Although the pertussis vaccination rates in infancy are still very good, clinicians are seeing a drop-off in school-aged children and adults, and the lingering anti-vaccine efforts from the COVID-19 pandemic period are undoubtedly playing a part, said Dr. Cennimo. “Unfortunately, pertussis is contagious, and the vaccine effectiveness wears off. Having decreased numbers of people protected results in more rapid spread,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo agreed that the number of cases in the United States is underreported, and even higher than the data suggest. “I’m sure of it; the initial clinical presentation may be mistaken for a viral upper respiratory tract infection (common cold),” he told this news organization.
Many older children and adults with pertussis do not manifest the classic “whooping cough” seen in infants and young children, so making a clinical diagnosis can be difficult, he said. “One classical component of the illness is a prolonged cough. I have wondered if some people now reporting a lingering cough had pertussis that was missed,” Dr. Cennimo noted.
“Clinicians should stress the value of boosters in a vaccine-preventable illness where we know immunity wanes overtime,” Dr. Cennimo said. “We have a great remedy in the Tdap vaccine, which we should all be getting very 10 years,” he said.
He also emphasized that clinicians remind pregnant women of the current recommendations to receive the Tdap vaccine for every pregnancy. “Vaccination during pregnancy is the best way to protect both the pregnant person and the newborn.
Even for the vaccine hesitant, this vaccine has a long track record of safety so should not be a significant concern,” he said.
The ultimate take-home message is not a new one, and applies to all illnesses, Dr. Cennimo told this news organization. Simply put, “Stay home if you are sick. Social distancing is not just for COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Statins for MS (Not)
Hidden behind all of the new drugs and breakthroughs reported at the 2024 ECTRIMS meetings was one paper that caught my attention.
It was that, after several years of study, simvastatin had no benefit for multiple sclerosis.
Statins for MS (and for Alzheimer’s disease) have been bandied about for some time, with arguments based on theoretical ideas, and small studies, that they’d have a beneficial effect on the disease – maybe from anti-inflammatory and other properties. In addition, they offered the benefit of being widely available and comparatively inexpensive.
Because of those studies, 15-20 years ago I used them off label for MS in a handful of patients – sometimes as an adjunct to their current treatment (limited at that point to interferons and Copaxone), or in patients who couldn’t afford the FDA-approved drugs. Although not without their drawbacks, the statins are relatively well understood and tolerated.
At some point, for reasons I’ve long forgotten, they all came off of them (at least for MS purposes). Maybe for side effects, or lack of benefit, or because new medications, with much clearer efficacies, were rolling out.
Now it seems pretty clear that statins don’t work for MS.
So was it a bad idea to try? No. Without asking questions we don’t find answers. If they’d worked out it would have been great, another tool on the neurology workbench to reach for in the right situation. It might also have led us to new avenues in MS treatment.
But it didn’t, and that’s fine. Although they don’t get the attention, we learn as much (sometimes more) from negative studies as we do from positive ones. If we put people on every drug that initially showed promise for their conditions, my patients would have a pretty huge medication list. For Alzheimer’s disease alone I remember studies that once suggested ibuprofen, statins, estrogen, nicotine, and several vitamins might be effective (“might” being the key word). Today we’re looking at the PDE5 inhibitors and semaglutide. The jury is still out on them, but whichever way it goes we’ll still learn something.
The statins are good drugs. Their benefits in cardiac and cerebrovascular disease can’t be disputed (I’m sure someone would, but that’s not the point of this piece). But, like all drugs, they don’t work for everything.
We learn from both and keep moving forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Hidden behind all of the new drugs and breakthroughs reported at the 2024 ECTRIMS meetings was one paper that caught my attention.
It was that, after several years of study, simvastatin had no benefit for multiple sclerosis.
Statins for MS (and for Alzheimer’s disease) have been bandied about for some time, with arguments based on theoretical ideas, and small studies, that they’d have a beneficial effect on the disease – maybe from anti-inflammatory and other properties. In addition, they offered the benefit of being widely available and comparatively inexpensive.
Because of those studies, 15-20 years ago I used them off label for MS in a handful of patients – sometimes as an adjunct to their current treatment (limited at that point to interferons and Copaxone), or in patients who couldn’t afford the FDA-approved drugs. Although not without their drawbacks, the statins are relatively well understood and tolerated.
At some point, for reasons I’ve long forgotten, they all came off of them (at least for MS purposes). Maybe for side effects, or lack of benefit, or because new medications, with much clearer efficacies, were rolling out.
Now it seems pretty clear that statins don’t work for MS.
So was it a bad idea to try? No. Without asking questions we don’t find answers. If they’d worked out it would have been great, another tool on the neurology workbench to reach for in the right situation. It might also have led us to new avenues in MS treatment.
But it didn’t, and that’s fine. Although they don’t get the attention, we learn as much (sometimes more) from negative studies as we do from positive ones. If we put people on every drug that initially showed promise for their conditions, my patients would have a pretty huge medication list. For Alzheimer’s disease alone I remember studies that once suggested ibuprofen, statins, estrogen, nicotine, and several vitamins might be effective (“might” being the key word). Today we’re looking at the PDE5 inhibitors and semaglutide. The jury is still out on them, but whichever way it goes we’ll still learn something.
The statins are good drugs. Their benefits in cardiac and cerebrovascular disease can’t be disputed (I’m sure someone would, but that’s not the point of this piece). But, like all drugs, they don’t work for everything.
We learn from both and keep moving forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Hidden behind all of the new drugs and breakthroughs reported at the 2024 ECTRIMS meetings was one paper that caught my attention.
It was that, after several years of study, simvastatin had no benefit for multiple sclerosis.
Statins for MS (and for Alzheimer’s disease) have been bandied about for some time, with arguments based on theoretical ideas, and small studies, that they’d have a beneficial effect on the disease – maybe from anti-inflammatory and other properties. In addition, they offered the benefit of being widely available and comparatively inexpensive.
Because of those studies, 15-20 years ago I used them off label for MS in a handful of patients – sometimes as an adjunct to their current treatment (limited at that point to interferons and Copaxone), or in patients who couldn’t afford the FDA-approved drugs. Although not without their drawbacks, the statins are relatively well understood and tolerated.
At some point, for reasons I’ve long forgotten, they all came off of them (at least for MS purposes). Maybe for side effects, or lack of benefit, or because new medications, with much clearer efficacies, were rolling out.
Now it seems pretty clear that statins don’t work for MS.
So was it a bad idea to try? No. Without asking questions we don’t find answers. If they’d worked out it would have been great, another tool on the neurology workbench to reach for in the right situation. It might also have led us to new avenues in MS treatment.
But it didn’t, and that’s fine. Although they don’t get the attention, we learn as much (sometimes more) from negative studies as we do from positive ones. If we put people on every drug that initially showed promise for their conditions, my patients would have a pretty huge medication list. For Alzheimer’s disease alone I remember studies that once suggested ibuprofen, statins, estrogen, nicotine, and several vitamins might be effective (“might” being the key word). Today we’re looking at the PDE5 inhibitors and semaglutide. The jury is still out on them, but whichever way it goes we’ll still learn something.
The statins are good drugs. Their benefits in cardiac and cerebrovascular disease can’t be disputed (I’m sure someone would, but that’s not the point of this piece). But, like all drugs, they don’t work for everything.
We learn from both and keep moving forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Arizona.
Disseminated Gonococcal Infection of Pharyngeal Origin: Test All Anatomic Sites
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2 Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.
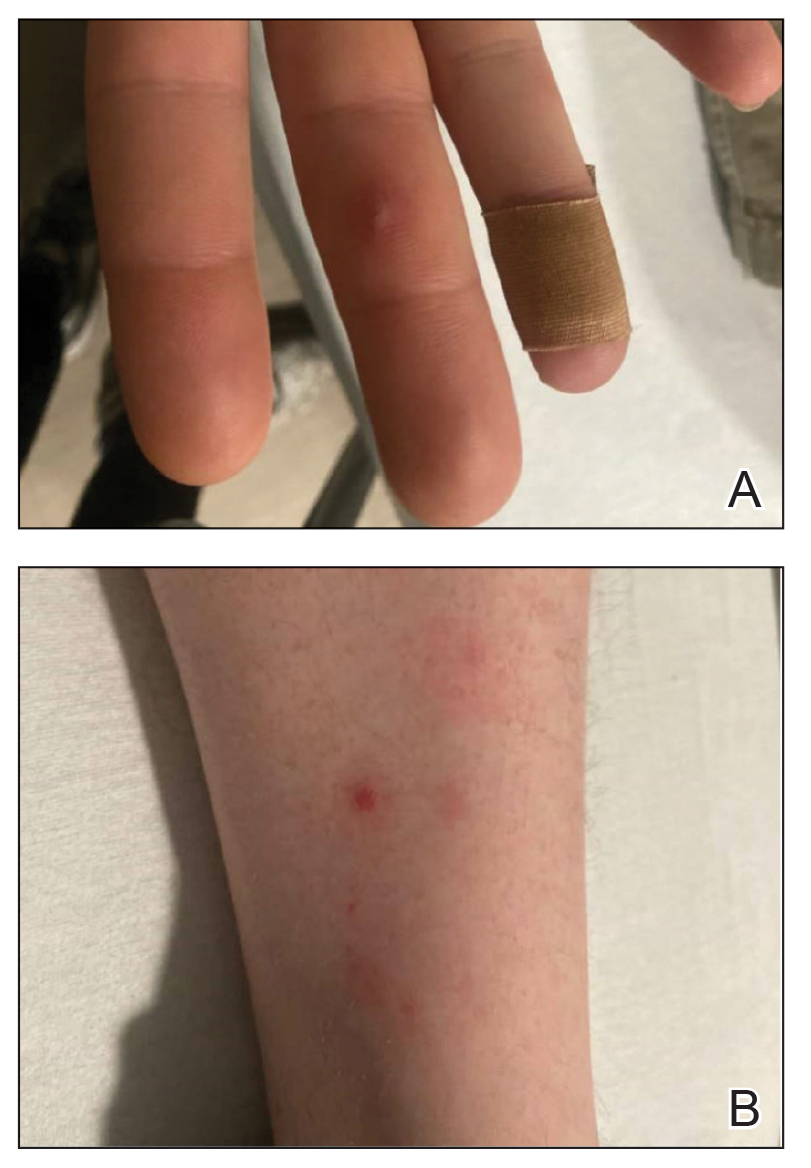
A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.
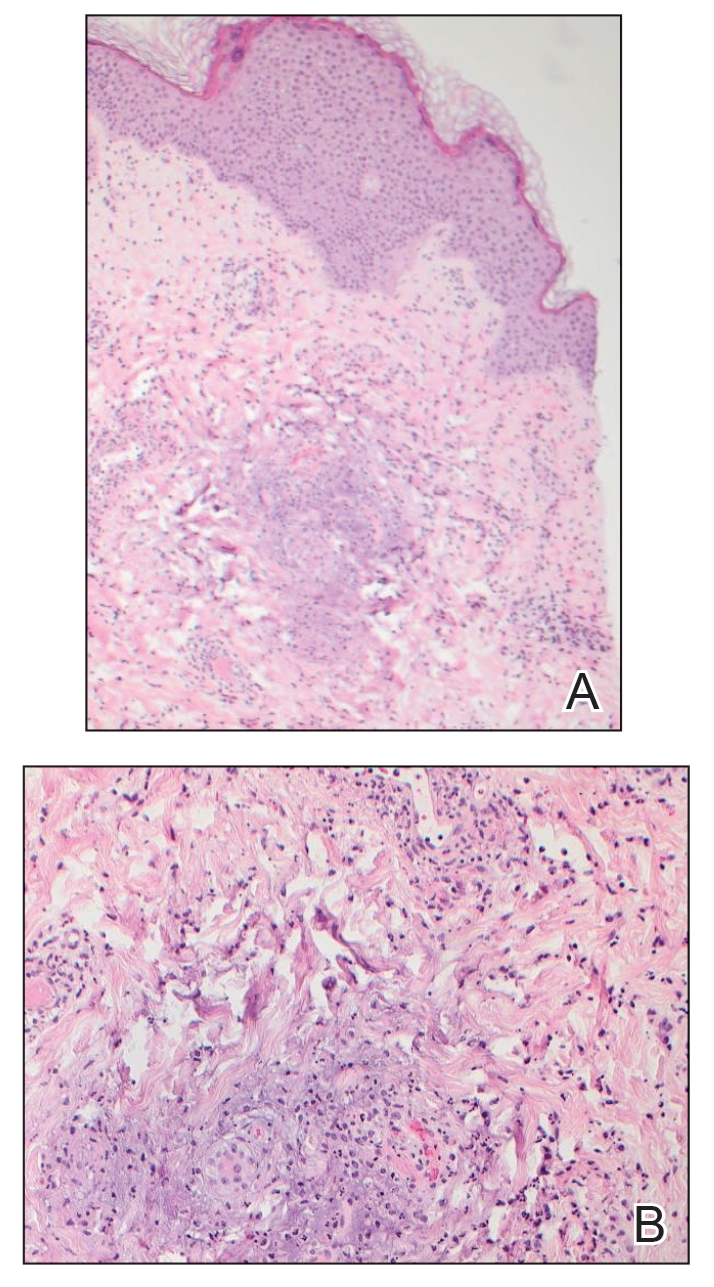
Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2 Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.

A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.

Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
To the Editor:
Gonococcal infections, which are caused by the sexually transmitted, gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae, are a current and increasing threat to public health. Between 2012 and 2021, the rate of gonococcal infection in the United States increased 137.8% in men and 64.9% in women,1 with an estimated 1.5 million new gonococcal infections occurring each year in the United States as of 2021.2 Neisseria gonorrhoeae is the second most common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI), and patients with gonococcal infection frequently are coinfected with Chlamydia trachomatis, which is the most common bacterial STI. Uncomplicated gonococcal infection (also known as gonorrhea) most commonly causes asymptomatic cervicovaginal infection in women and symptomatic urethral infection in men.2 Other uncomplicated manifestations include rectal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with anal pruritus, anal discharge, or tenesmus, and oropharyngeal infection, which can be asymptomatic or manifest with throat pain. If uncomplicated gonococcal infections are left untreated or are incompletely treated, serious complications including septic arthritis, myositis, osteomyelitis, myocarditis, endocarditis, and meningitis might occur.2-5 Ascending, locally invasive infections can cause epididymitis or pelvic inflammatory disease, which is an important cause of infertility in women.2,3 Gonococcal conjunctivitis also can occur, particularly when neonates are exposed to bacteria during vaginal delivery. Although rare, gonococcal bacteria can disseminate widely, with an estimated 0.5% to 3% of uncomplicated gonococcal infections progressing to disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI).3-6 Because DGI can mimic other systemic conditions, including a variety of bacterial and viral infections as well as inflammatory conditions, it can be difficult to diagnose without a high index of clinical suspicion. We present a case of DGI diagnosed based on dermatologic expertise and pharyngeal molecular testing.
A 30-year-old man presented to the emergency department with a rash on the extremeities as well as emesis, fever, sore throat, and severe arthralgia in the wrists, hands, knees, and feet of 2 days’ duration. The patient also had experienced several months of dysuria. He reported daily use of the recreational drug ketamine, multiple new male sexual partners, and unprotected oral and receptive anal sex in recent months. He denied any history of STIs. Physical examination demonstrated tender edematous wrists and fingers, papulovesicles on erythematous bases on the palms, and purpuric macules scattered on the legs (Figure 1). The patient also had tonsillar edema with notable white tonsillar exudate.

A shave biopsy performed on a papulovesicular lesion on the right thigh showed an intact epidermis with minimal spongiosis and no viral cytopathic changes. There was dermal edema with a moderate superficial and deep neutrophilic infiltrate, mild karyorrhexis, and focal dermal necrosis (Figure 2). Rare acute vasculitis with intravascular fibrin was seen. Periodic acid-Schiff stain for fungi, Gram stain for bacteria, and immunostains for human herpesviruses 1 and 2 were negative.

Laboratory studies revealed neutrophil-predominant leukocytosis (white blood cell count, 13.89×109/L [reference range, 4.5–11.0×109/L] with 78.2% neutrophils [reference range, 40.0%–70.0%]) as well as an elevated C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (19.98 mg/dL [reference range, <0.05 mg/dL] and 38 mm/h [reference range, 0–15 mm/h], respectively). His liver enzymes, kidney function, prothrombin time, and international normalized ratio were all normal. Urinalysis showed trace amounts of blood and protein, and urine culture was negative for pathogenic bacteria. A rapid plasma reagin test and a fifth-generation HIV antibody test were nonreactive, and bacterial blood cultures were negative for other infectious diseases. Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) performed on a swab from a papulovesicular lesion was negative for human herpesviruses 1 and 2, varicella-zoster virus, orthopoxvirus, and mpox (monkeypox) virus. Based on recommendations from dermatology, NAATs for C trachomatis and N gonorrhoeae were performed on urine and on swabs from the patient’s rectum and pharynx; N gonorrhoeae was detected at the pharynx, but the other sites were negative for both bacteria. A diagnosis of DGI was made based on these results as well as the patient’s clinical presentation of fever, arthralgia, and papulovesicular skin lesions. The patient was treated with 1 g of intravenous ceftriaxone while in the hospital, but unfortunately, he was lost to follow-up and did not complete the full 1-week treatment course.
Disseminated gonococcal infection (also known as arthritis-dermatitis syndrome) is characterized by the abrupt onset of fever, skin lesions, and arthralgia in a symmetric and migratory distribution. Tenosynovitis involving the extensor tendons of the wrists, fingers, knees, and ankles (particularly the Achilles tendon) is characteristic. Skin manifestations usually include hemorrhagic vesicles and papulovesicles limited to the extremities, often with an acral distribution,2-5 though other cutaneous lesions have been described in DGI, including macules, purpura, periurethral abscesses, multifocal cellulitis, and necrotizing fasciitis.7 It is important to consider DGI in a patient who presents with acute systemic symptoms and any of these cutaneous manifestations, even in the absence of joint pain.
Diagnosis of DGI can be difficult, and surveillance is limited in the United States; therefore, the risk factors are somewhat unclear and might be changing. Traditional risk factors for DGI have included immunosuppression due to terminal complement deficiency, female sex, recent menstruation, and pregnancy, but recent data have shown that male sex, HIV infection, use of methamphetamines and other drugs, and use of the monoclonal antibody eculizumab for treatment of complement disorders have been associated with DGI.2,6-8 In the past decade, uncomplicated gonococcal infections have disproportionately affected Black patients, men who have sex with men, adults aged 20 to 25 years, and individuals living in the southern United States.1 It is unclear if the changing demographics of patients with DGI represent true risk factors for dissemination or simply reflect the changing demographics of patients at risk for uncomplicated gonococcal infection.6
Dermatologic expertise in the recognition of cutaneous manifestations of DGI is particularly important due to the limitations of diagnostic tools. The organism is fastidious and difficult to grow in vitro, thus cultures for N gonorrhoeae are not sensitive and require specialized media (eg, Thayer-Martin, modified New York City, or chocolate agar medium with additional antimicrobial agents).3 Molecular assays such as NAATs are more sensitive and specific than culture but are not 100% accurate.2,3,5 Finally, sterile sites such as joints, blood, or cerebrospinal fluid can be difficult to access, and specimens are not always available for specific microbial diagnosis; therefore, even when a gonococcal infection is identified at a mucosal source, physicians must use their clinical judgment to determine whether the mucosal infection is the cause of DGI or if the patient has a separate additional illness.
Once a diagnosis of gonococcal infection is made, any isolated gonococcal bacteria should be tested for antimicrobial susceptibility due to rising rates of drug resistance. Since at least the 1980s, N gonorrhoeae has steadily evolved to have some degree of resistance to most antimicrobials, and epidemiologic evidence indicates that this evolution is continuing.2 Current Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommendations are to treat uncomplicated gonococcal infections with 1 dose of ceftriaxone 500 mg intramuscularly in individuals weighing less than 150 kg (increase to 1 g in those ≥150 kg). Disseminated gonococcal infection requires more aggressive treatment with ceftriaxone 1 g intravenously or intramuscularly every 24 hours for at least 7 days and at a higher dose and for longer duration for patients with endocarditis or meningitis.2 If there is notable clinical improvement after 24 to 48 hours and antimicrobial susceptibility testing confirms an oral agent is appropriate, the patient can be switched to that oral agent to complete treatment. Also, if chlamydia has not been excluded in patients with any type of gonococcal infection, they also should be treated for chlamydia with doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, per CDC guidelines.2 Dermatologists should advocate for patients to be treated for DGI even if the diagnosis is clinical because of the potential for untreated or undertreated patients to progress, to develop additional antimicrobial resistant bacteria, and/or to transmit the infection to others.
This case highlights 2 important points about gonococcal infections and DGI. First, it is important to test and screen patients for gonococcal infection at genitourinary, rectal, and pharyngeal sites. Despite our patient’s report of dysuria, gonococcal infection was only detected via NAAT at the pharynx. As of 2021, CDC guidelines recommend not only testing for gonococcal infection in symptomatic patients at all mucosal sites but also screening all mucosal sites in asymptomatic individuals at high risk.2 Second, dermatologists’ specialized knowledge of cutaneous manifestations provides a valuable tool in the clinical diagnosis of DGI. In this patient, it was the dermatology team’s high index of concern for DGI that led to NAAT testing at all mucosal sites and resulted in an accurate diagnosis. Ultimately, dermatologists play an important role in the diagnosis and management of DGI.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually transmitted disease surveillance, 2021. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2022/2021-STD-Surveillance-Report-PDF_ARCHIVED-2-16-24.pdf
- Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70:1-187. doi:10.15585/mmwr.rr7004a1
- Skerlev M, Čulav-Košćak I. Gonorrhea: new challenges. Clin Dermatol. 2014;32:275-281. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.08.010
- Mehrany K, Kist JM, O’Connor WJ, et al. Disseminated gonococcemia. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:208-209. doi:10.1046/j.1365-4362.2003.01720.x
- Sciaudone M, Cope A, Mobley V, et al. Ten years of disseminated gonococcal infections in North Carolina: a review of cases from a large tertiary care hospital. Sex Transm Dis. 2023;50:410-414. doi:10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001794
- Weston EJ, Heidenga BL, Farley MM, et al. Surveillance for disseminated gonococcal infections, Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs)—United States, 2015-2019. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;75:953-958. doi:10.1093/cid/ciac052
- Beatrous SV, Grisoli SB, Riahi RR, et al. Cutaneous manifestations of disseminated gonococcemia. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030/qt33b24006
- Nettleton WD, Kent JB, Macomber K, et al. Notes from the field: ongoing cluster of highly related disseminated gonococcal infections—southwest Michigan, 2019. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:353-354. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6912az
Practice Points
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections of the genitourinary system, rectum, and pharynx can disseminate and cause fever, joint pain, and hemorrhagic papulovesicles that can mimic other serious conditions and require dermatologic expertise to confirm.
- Patients with suspected disseminated gonococcal infection (DGI) as well as patients who are asymptomatic and at increased risk should have all possible anatomic sites of infection—the genitourinary system, rectum, and pharynx—tested with the appropriate molecular assays and culture when appropriate.
- Appropriate recognition and treatment of DGI is vital, as undertreatment can result in serious complications and contribute to the increasing global public health threat of antimicrobial-resistant gonococcal infections.
Caregiver Surveys on Firearms, Suicide Offer Pediatricians Prevention Opportunities
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , according to researchers who presented their findings at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2024 National Conference.
An estimated 4.6 million US homes with children have firearms that are loaded and unlocked, a risk factor for youth suicide, yet only about half of parents of suicidal children had been screened for gun ownership in the hospital even as most would be receptive to both firearm screening and counseling, found one study in Texas.
In another study in Colorado, nearly all firearm owners believed that securely storing guns reduces the risk for firearm injury or death, but owners were less likely than non-owners to believe suicide is preventable or that removing a gun from the home reduces the risk for injury or death.
“Previous studies have shown that when pediatricians discuss the importance of armed safe storage guidance with families, families are actually more likely to go home and store firearms safely — storing them locked, unloaded, and separate from the ammunition,” said study author Taylor Rosenbaum, MD, a former pediatric fellow at Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston and now an assistant professor at Children’s Hospital University of Miami. “However, previous studies have also shown that pediatricians really are not discussing firearm safe storage with our patients and their families, and we see this both in the outpatient setting, but especially in the inpatient setting for youth suicides, which have risen since 2020 and now are the second leading cause of death for those who are 10-24 years old in the United States.”
Firearm Safety Is a Necessary Conversation
The leading cause of death among children and teens aged 1-19 years is actually firearms, which are also the most fatal method for suicide. While only 4% of all suicide attempts in youth are fatal, 90% of those attempted with a firearm are fatal, Dr. Rosenbaum said. In addition, she said, 80% of the guns used in attempted suicide by children and teens belonged to a family member, and an estimated 70% of firearm-related suicides in youth can be prevented with safe storage of guns.
“This really gives us, as pediatricians, something actionable to do during these hospitalizations” for suicidal ideation or attempts, Dr. Rosenbaum said. “We know that when pediatricians discuss the importance of firearm safe storage guidance with families, they’re more likely to store their firearm safely,” Dr. Rosenbaum said. “We also know that families are not being screened for firearm ownership, that caregivers of youth who are in the hospital for suicidal thoughts or actions want their healthcare team to be screening for firearms, to be giving them information on how to safely secure their firearms, and to be providing free firearm blocks.”
Nathan Boonstra, MD, a general pediatrician at Blank Children’s Hospital, Des Moines, Iowa, said these findings are encouraging in terms of the opportunity pediatricians have.
“There is so much politicization around even basic firearm safety that pediatricians might shy away from the topic, but this research is reassuring that parents are receptive to our advice on safe gun storage,” said Dr. Boonstra, who was not involved in any of this presented research. “It’s especially important for pediatricians to address home firearms when their patient has a history of suicidal ideation or an attempt.”
Reducing the Risk
The Colorado findings similarly reinforce the opportunity physicians have to help caregivers reduce suicide risk, according to Maya Haasz, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and emergency medicine at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Only 60% of firearm owners believed that removing firearms from the home in times of mental health crisis can decrease the risk of suicide,” she said. “These findings are really concerning, but what we found on the flip side was that 93% of firearm owners actually believe that secure storage can overall decrease the risk for firearm injury and death. So overall, we are underestimating the risk for suicide in our community, and we’re also underestimating our ability to prevent it.”
That presents an opportunity, Dr. Haasz said, “to educate families both about the preventability of suicide but also to have specific strategies, like secure storage and temporary removable requirements from the home, that can prevent suicide.”
Dr. Boonstra found it “disheartening that so many children live in a house with an unlocked and even loaded firearm when the evidence is so clear that this is a significant risk factor for youth suicide,” he said. “It’s also disheartening, though not too surprising, that families with a firearm are less likely to think that youth suicide can be prevented.”
Survey Results
Dr. Rosenbaum’s team conducted the survey in Houston with caregivers whose children were 8-21 years old and hospitalized for suicidal ideation or attempts at a large children’s hospital and two nearby community hospitals between June 2023 and May 2024. The respondents were 46% White and 23% Black, and 47% of the population were Hispanic, all but three of whom were not gun owners.
Among 244 potential participants, only 150 were eligible and approached, and 100 of these completed the surveys, including 26% firearm owners and 68% non-owners. Most of the youth (74%) were aged 14-17 years, and about three in four respondents were their mothers. Only half of the respondents (51%) said the healthcare provider had asked them whether they owned a gun.
One of the key findings Dr. Rosenbaum highlighted was the receptiveness of firearm-owning caregivers to advice from healthcare providers about ownership. If the healthcare team advised parents not to have any guns in the home for the safety of their child with self-arm, 58% of the firearm owners would follow the advice and 27% would consider it, with none saying they would be offended by it.
Among the firearm owners, 81% said their guns were safely secured where they did not believe their child could access it, which meant one in five youth had unsecured access to firearms. Most of the gun owners (77%), like the non-owners (70%), were “not at all worried” about their child getting ahold of a gun in the home, though 11.5% of the firearm owners were “very worried” about it. Interestingly, more gun owners (19%) were very worried about their children accessing a gun outside their home, a concern shared by 37% of non-owners. Nearly twice as many gun owners (46%) as non-owners (25%) were not at all worried about their child getting a gun outside the home.
The vast majority of respondents — 88% of gun owners and 91% of non-owners — felt it was “very important for the healthcare team to ask parents of children with suicidal ideation/attempts about firearms in the home.” Similarly, high proportions believed it was important for the healthcare team to counsel those parents on safe gun storage. Although only 69% of firearm owners believed it was important to distribute firearm locks in the hospital, 81% would be interested in receiving a free one. Significantly more of the non-owners (80%; P = .02) believed free lock distribution was important, and 72% of non-owners would also be interested in one.
About half the respondents (55%) preferred to hear firearm counseling one-on-one from a provider, whereas 31% would like written information and 27% would be interested in a video. In terms of what information parents preferred to receive, a little over half of owners (54%) and non-owners (56%) were interested in how or when (50% and 40%, respectively) to discuss the topic with their child. Only about a third (35% owners and 37% non-owners) wanted information on how to discuss the topic with the parents of their child’s friends.
The survey’s biggest limitations after its small size were the selection bias of those willing to complete the survey and potential response bias from the self-reported data.
The study of Colorado caregivers, just published in Pediatrics, surveyed 512 Colorado caregivers in April-May 2023 to learn about their beliefs and perceptions regarding firearms, firearm storage and risk, and youth suicide (2024 Oct 1;154[4]:e2024066930. doi: 10.1542/peds.2024-066930). Just over half the respondents (52%) had grown up in a household with firearms, and 44% currently lived in a household with a gun. The sample was 43% men and 88% White, predominantly non-Hispanic (75%), with 11% living in rural areas and 19% who currently or previously served in the military. Most (79%) had a child age 12 or younger in the home.
Only about one in four caregivers (24%) correctly answered that suicide is the leading cause of firearm death in Colorado, with similar rates of correct responses among both firearm owners and non-firearm owners. Both groups were also similarly likely (64% overall) to be concerned about youth suicide in their community, though those from homes with firearms were less likely to be concerned about youth suicide in their own family (28%) than those from homes without firearms (39%; P = .013).
In addition, caregivers from homes with versus without firearms were considerably less likely to believe suicide can be prevented (48% vs 69%) and were less likely to believe that temporarily removing a firearm from the home reduces the risk for gun injury or death (60% vs 78%; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Firearm owners were also much less likely than non-owners to believe keeping a gun in the home makes it more dangerous (7% vs 29%) and over twice as likely to think keeping a firearm makes their home safer (52% vs 22%; P < .001). The vast majority of respondents (89%) believed secure storage of guns reduces the risk for injury or death, though the response was higher for firearm owners (93%) than for non-owners (86%; P < .001).
“Our finding that most firearm owners believe that secure firearm storage is protective against firearm injury is a promising messaging strategy,” the authors wrote. “It presents a preventive education opportunity for adults living with children who have mental health concerns, who may benefit most from secure in-home storage and/or temporary and voluntary storage of firearms away from home.”
Firearm Injuries
A separate study at the AAP conference underscored the devastating impact of firearm injuries even among those who survive, whether self-inflicted or not, and the potential for reducing healthcare treatment and costs from effective prevention efforts. A national analysis of pediatric inpatient data from 2017 to 2020 calculated how much greater the burden of healthcare treatment and costs is for firearm injuries of any kind compared with penetrating traumas and blunt traumas.
“As a surgical resident, I have seen these patients who make it into the trauma bed that we are then faced to care for,” said Colleen Nofi, DO, PhD, MBA, a general surgery resident at Cohen Children’s Medical Center at Northwell Health in New York. “Anecdotally, we understand that the devastation and injury caused by bullets far outweighs the injuries caused by other trauma mechanisms,” but the actual calculation of the burden hasn’t been studied.
Among 6615 firearm injuries, 9787 penetrating traumas and 66,003 blunt traumas examined from the National Inpatient Sample Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Database, 11% of firearm traumas required a transfusion of red blood cells, compared with 1.4% of penetrating traumas and 3% of blunt traumas (P < .001). Patients with firearm injuries also had a longer length of stay — 10.8 days compared with 8.3 for patients with penetrating trauma and 9.8 for those with blunt trauma — and significantly higher rates of CPR, pericardiotomy, chest tube, exploratory laparotomy and/or thoracotomy, colorectal surgery, small bowel surgery, ostomy formation, splenectomy, hepatic resection, tracheostomy, and feeding tube placement.
Pulmonary complications were higher for firearm injuries (4.9%) than for penetrating trauma (0.6%) or blunt trauma (2.9%), and septicemia rates were also higher (1.7% vs 0.2% and 1%, respectively). Cardiac, neurologic, and urinary complications were also significantly and substantially higher for firearm injuries, 6.9% of which resulted in death compared with 0.2% of penetrating traumas and 1.2% of blunt traumas.
The costs from firearm injuries were also significantly higher than the costs from other traumas; “firearm injury remained independently predictive of greater hospital costs, even when controlling for injury severity as well as age, sex, race, insurance, region, hospital type, and household income.
“These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted prevention, supportive measures, and resource allocation to mitigate the devastating impact of firearm injuries on children and healthcare systems alike,” Dr. Nofi said.
The Colorado study was funded by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment and a National Institutes of Health grant to Dr. Haasz. The Texas study and the one from Northwell Health did not note any external funding. Dr. Haasz, Dr. Rosenbaum, Dr. Boonstra, and Dr. Nofi had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , according to researchers who presented their findings at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2024 National Conference.
An estimated 4.6 million US homes with children have firearms that are loaded and unlocked, a risk factor for youth suicide, yet only about half of parents of suicidal children had been screened for gun ownership in the hospital even as most would be receptive to both firearm screening and counseling, found one study in Texas.
In another study in Colorado, nearly all firearm owners believed that securely storing guns reduces the risk for firearm injury or death, but owners were less likely than non-owners to believe suicide is preventable or that removing a gun from the home reduces the risk for injury or death.
“Previous studies have shown that when pediatricians discuss the importance of armed safe storage guidance with families, families are actually more likely to go home and store firearms safely — storing them locked, unloaded, and separate from the ammunition,” said study author Taylor Rosenbaum, MD, a former pediatric fellow at Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston and now an assistant professor at Children’s Hospital University of Miami. “However, previous studies have also shown that pediatricians really are not discussing firearm safe storage with our patients and their families, and we see this both in the outpatient setting, but especially in the inpatient setting for youth suicides, which have risen since 2020 and now are the second leading cause of death for those who are 10-24 years old in the United States.”
Firearm Safety Is a Necessary Conversation
The leading cause of death among children and teens aged 1-19 years is actually firearms, which are also the most fatal method for suicide. While only 4% of all suicide attempts in youth are fatal, 90% of those attempted with a firearm are fatal, Dr. Rosenbaum said. In addition, she said, 80% of the guns used in attempted suicide by children and teens belonged to a family member, and an estimated 70% of firearm-related suicides in youth can be prevented with safe storage of guns.
“This really gives us, as pediatricians, something actionable to do during these hospitalizations” for suicidal ideation or attempts, Dr. Rosenbaum said. “We know that when pediatricians discuss the importance of firearm safe storage guidance with families, they’re more likely to store their firearm safely,” Dr. Rosenbaum said. “We also know that families are not being screened for firearm ownership, that caregivers of youth who are in the hospital for suicidal thoughts or actions want their healthcare team to be screening for firearms, to be giving them information on how to safely secure their firearms, and to be providing free firearm blocks.”
Nathan Boonstra, MD, a general pediatrician at Blank Children’s Hospital, Des Moines, Iowa, said these findings are encouraging in terms of the opportunity pediatricians have.
“There is so much politicization around even basic firearm safety that pediatricians might shy away from the topic, but this research is reassuring that parents are receptive to our advice on safe gun storage,” said Dr. Boonstra, who was not involved in any of this presented research. “It’s especially important for pediatricians to address home firearms when their patient has a history of suicidal ideation or an attempt.”
Reducing the Risk
The Colorado findings similarly reinforce the opportunity physicians have to help caregivers reduce suicide risk, according to Maya Haasz, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and emergency medicine at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Only 60% of firearm owners believed that removing firearms from the home in times of mental health crisis can decrease the risk of suicide,” she said. “These findings are really concerning, but what we found on the flip side was that 93% of firearm owners actually believe that secure storage can overall decrease the risk for firearm injury and death. So overall, we are underestimating the risk for suicide in our community, and we’re also underestimating our ability to prevent it.”
That presents an opportunity, Dr. Haasz said, “to educate families both about the preventability of suicide but also to have specific strategies, like secure storage and temporary removable requirements from the home, that can prevent suicide.”
Dr. Boonstra found it “disheartening that so many children live in a house with an unlocked and even loaded firearm when the evidence is so clear that this is a significant risk factor for youth suicide,” he said. “It’s also disheartening, though not too surprising, that families with a firearm are less likely to think that youth suicide can be prevented.”
Survey Results
Dr. Rosenbaum’s team conducted the survey in Houston with caregivers whose children were 8-21 years old and hospitalized for suicidal ideation or attempts at a large children’s hospital and two nearby community hospitals between June 2023 and May 2024. The respondents were 46% White and 23% Black, and 47% of the population were Hispanic, all but three of whom were not gun owners.
Among 244 potential participants, only 150 were eligible and approached, and 100 of these completed the surveys, including 26% firearm owners and 68% non-owners. Most of the youth (74%) were aged 14-17 years, and about three in four respondents were their mothers. Only half of the respondents (51%) said the healthcare provider had asked them whether they owned a gun.
One of the key findings Dr. Rosenbaum highlighted was the receptiveness of firearm-owning caregivers to advice from healthcare providers about ownership. If the healthcare team advised parents not to have any guns in the home for the safety of their child with self-arm, 58% of the firearm owners would follow the advice and 27% would consider it, with none saying they would be offended by it.
Among the firearm owners, 81% said their guns were safely secured where they did not believe their child could access it, which meant one in five youth had unsecured access to firearms. Most of the gun owners (77%), like the non-owners (70%), were “not at all worried” about their child getting ahold of a gun in the home, though 11.5% of the firearm owners were “very worried” about it. Interestingly, more gun owners (19%) were very worried about their children accessing a gun outside their home, a concern shared by 37% of non-owners. Nearly twice as many gun owners (46%) as non-owners (25%) were not at all worried about their child getting a gun outside the home.
The vast majority of respondents — 88% of gun owners and 91% of non-owners — felt it was “very important for the healthcare team to ask parents of children with suicidal ideation/attempts about firearms in the home.” Similarly, high proportions believed it was important for the healthcare team to counsel those parents on safe gun storage. Although only 69% of firearm owners believed it was important to distribute firearm locks in the hospital, 81% would be interested in receiving a free one. Significantly more of the non-owners (80%; P = .02) believed free lock distribution was important, and 72% of non-owners would also be interested in one.
About half the respondents (55%) preferred to hear firearm counseling one-on-one from a provider, whereas 31% would like written information and 27% would be interested in a video. In terms of what information parents preferred to receive, a little over half of owners (54%) and non-owners (56%) were interested in how or when (50% and 40%, respectively) to discuss the topic with their child. Only about a third (35% owners and 37% non-owners) wanted information on how to discuss the topic with the parents of their child’s friends.
The survey’s biggest limitations after its small size were the selection bias of those willing to complete the survey and potential response bias from the self-reported data.
The study of Colorado caregivers, just published in Pediatrics, surveyed 512 Colorado caregivers in April-May 2023 to learn about their beliefs and perceptions regarding firearms, firearm storage and risk, and youth suicide (2024 Oct 1;154[4]:e2024066930. doi: 10.1542/peds.2024-066930). Just over half the respondents (52%) had grown up in a household with firearms, and 44% currently lived in a household with a gun. The sample was 43% men and 88% White, predominantly non-Hispanic (75%), with 11% living in rural areas and 19% who currently or previously served in the military. Most (79%) had a child age 12 or younger in the home.
Only about one in four caregivers (24%) correctly answered that suicide is the leading cause of firearm death in Colorado, with similar rates of correct responses among both firearm owners and non-firearm owners. Both groups were also similarly likely (64% overall) to be concerned about youth suicide in their community, though those from homes with firearms were less likely to be concerned about youth suicide in their own family (28%) than those from homes without firearms (39%; P = .013).
In addition, caregivers from homes with versus without firearms were considerably less likely to believe suicide can be prevented (48% vs 69%) and were less likely to believe that temporarily removing a firearm from the home reduces the risk for gun injury or death (60% vs 78%; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Firearm owners were also much less likely than non-owners to believe keeping a gun in the home makes it more dangerous (7% vs 29%) and over twice as likely to think keeping a firearm makes their home safer (52% vs 22%; P < .001). The vast majority of respondents (89%) believed secure storage of guns reduces the risk for injury or death, though the response was higher for firearm owners (93%) than for non-owners (86%; P < .001).
“Our finding that most firearm owners believe that secure firearm storage is protective against firearm injury is a promising messaging strategy,” the authors wrote. “It presents a preventive education opportunity for adults living with children who have mental health concerns, who may benefit most from secure in-home storage and/or temporary and voluntary storage of firearms away from home.”
Firearm Injuries
A separate study at the AAP conference underscored the devastating impact of firearm injuries even among those who survive, whether self-inflicted or not, and the potential for reducing healthcare treatment and costs from effective prevention efforts. A national analysis of pediatric inpatient data from 2017 to 2020 calculated how much greater the burden of healthcare treatment and costs is for firearm injuries of any kind compared with penetrating traumas and blunt traumas.
“As a surgical resident, I have seen these patients who make it into the trauma bed that we are then faced to care for,” said Colleen Nofi, DO, PhD, MBA, a general surgery resident at Cohen Children’s Medical Center at Northwell Health in New York. “Anecdotally, we understand that the devastation and injury caused by bullets far outweighs the injuries caused by other trauma mechanisms,” but the actual calculation of the burden hasn’t been studied.
Among 6615 firearm injuries, 9787 penetrating traumas and 66,003 blunt traumas examined from the National Inpatient Sample Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Database, 11% of firearm traumas required a transfusion of red blood cells, compared with 1.4% of penetrating traumas and 3% of blunt traumas (P < .001). Patients with firearm injuries also had a longer length of stay — 10.8 days compared with 8.3 for patients with penetrating trauma and 9.8 for those with blunt trauma — and significantly higher rates of CPR, pericardiotomy, chest tube, exploratory laparotomy and/or thoracotomy, colorectal surgery, small bowel surgery, ostomy formation, splenectomy, hepatic resection, tracheostomy, and feeding tube placement.
Pulmonary complications were higher for firearm injuries (4.9%) than for penetrating trauma (0.6%) or blunt trauma (2.9%), and septicemia rates were also higher (1.7% vs 0.2% and 1%, respectively). Cardiac, neurologic, and urinary complications were also significantly and substantially higher for firearm injuries, 6.9% of which resulted in death compared with 0.2% of penetrating traumas and 1.2% of blunt traumas.
The costs from firearm injuries were also significantly higher than the costs from other traumas; “firearm injury remained independently predictive of greater hospital costs, even when controlling for injury severity as well as age, sex, race, insurance, region, hospital type, and household income.
“These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted prevention, supportive measures, and resource allocation to mitigate the devastating impact of firearm injuries on children and healthcare systems alike,” Dr. Nofi said.
The Colorado study was funded by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment and a National Institutes of Health grant to Dr. Haasz. The Texas study and the one from Northwell Health did not note any external funding. Dr. Haasz, Dr. Rosenbaum, Dr. Boonstra, and Dr. Nofi had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO, FLORIDA — , according to researchers who presented their findings at the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) 2024 National Conference.
An estimated 4.6 million US homes with children have firearms that are loaded and unlocked, a risk factor for youth suicide, yet only about half of parents of suicidal children had been screened for gun ownership in the hospital even as most would be receptive to both firearm screening and counseling, found one study in Texas.
In another study in Colorado, nearly all firearm owners believed that securely storing guns reduces the risk for firearm injury or death, but owners were less likely than non-owners to believe suicide is preventable or that removing a gun from the home reduces the risk for injury or death.
“Previous studies have shown that when pediatricians discuss the importance of armed safe storage guidance with families, families are actually more likely to go home and store firearms safely — storing them locked, unloaded, and separate from the ammunition,” said study author Taylor Rosenbaum, MD, a former pediatric fellow at Baylor College of Medicine/Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston and now an assistant professor at Children’s Hospital University of Miami. “However, previous studies have also shown that pediatricians really are not discussing firearm safe storage with our patients and their families, and we see this both in the outpatient setting, but especially in the inpatient setting for youth suicides, which have risen since 2020 and now are the second leading cause of death for those who are 10-24 years old in the United States.”
Firearm Safety Is a Necessary Conversation
The leading cause of death among children and teens aged 1-19 years is actually firearms, which are also the most fatal method for suicide. While only 4% of all suicide attempts in youth are fatal, 90% of those attempted with a firearm are fatal, Dr. Rosenbaum said. In addition, she said, 80% of the guns used in attempted suicide by children and teens belonged to a family member, and an estimated 70% of firearm-related suicides in youth can be prevented with safe storage of guns.
“This really gives us, as pediatricians, something actionable to do during these hospitalizations” for suicidal ideation or attempts, Dr. Rosenbaum said. “We know that when pediatricians discuss the importance of firearm safe storage guidance with families, they’re more likely to store their firearm safely,” Dr. Rosenbaum said. “We also know that families are not being screened for firearm ownership, that caregivers of youth who are in the hospital for suicidal thoughts or actions want their healthcare team to be screening for firearms, to be giving them information on how to safely secure their firearms, and to be providing free firearm blocks.”
Nathan Boonstra, MD, a general pediatrician at Blank Children’s Hospital, Des Moines, Iowa, said these findings are encouraging in terms of the opportunity pediatricians have.
“There is so much politicization around even basic firearm safety that pediatricians might shy away from the topic, but this research is reassuring that parents are receptive to our advice on safe gun storage,” said Dr. Boonstra, who was not involved in any of this presented research. “It’s especially important for pediatricians to address home firearms when their patient has a history of suicidal ideation or an attempt.”
Reducing the Risk
The Colorado findings similarly reinforce the opportunity physicians have to help caregivers reduce suicide risk, according to Maya Haasz, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics and emergency medicine at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, Colorado.
“Only 60% of firearm owners believed that removing firearms from the home in times of mental health crisis can decrease the risk of suicide,” she said. “These findings are really concerning, but what we found on the flip side was that 93% of firearm owners actually believe that secure storage can overall decrease the risk for firearm injury and death. So overall, we are underestimating the risk for suicide in our community, and we’re also underestimating our ability to prevent it.”
That presents an opportunity, Dr. Haasz said, “to educate families both about the preventability of suicide but also to have specific strategies, like secure storage and temporary removable requirements from the home, that can prevent suicide.”
Dr. Boonstra found it “disheartening that so many children live in a house with an unlocked and even loaded firearm when the evidence is so clear that this is a significant risk factor for youth suicide,” he said. “It’s also disheartening, though not too surprising, that families with a firearm are less likely to think that youth suicide can be prevented.”
Survey Results
Dr. Rosenbaum’s team conducted the survey in Houston with caregivers whose children were 8-21 years old and hospitalized for suicidal ideation or attempts at a large children’s hospital and two nearby community hospitals between June 2023 and May 2024. The respondents were 46% White and 23% Black, and 47% of the population were Hispanic, all but three of whom were not gun owners.
Among 244 potential participants, only 150 were eligible and approached, and 100 of these completed the surveys, including 26% firearm owners and 68% non-owners. Most of the youth (74%) were aged 14-17 years, and about three in four respondents were their mothers. Only half of the respondents (51%) said the healthcare provider had asked them whether they owned a gun.
One of the key findings Dr. Rosenbaum highlighted was the receptiveness of firearm-owning caregivers to advice from healthcare providers about ownership. If the healthcare team advised parents not to have any guns in the home for the safety of their child with self-arm, 58% of the firearm owners would follow the advice and 27% would consider it, with none saying they would be offended by it.
Among the firearm owners, 81% said their guns were safely secured where they did not believe their child could access it, which meant one in five youth had unsecured access to firearms. Most of the gun owners (77%), like the non-owners (70%), were “not at all worried” about their child getting ahold of a gun in the home, though 11.5% of the firearm owners were “very worried” about it. Interestingly, more gun owners (19%) were very worried about their children accessing a gun outside their home, a concern shared by 37% of non-owners. Nearly twice as many gun owners (46%) as non-owners (25%) were not at all worried about their child getting a gun outside the home.
The vast majority of respondents — 88% of gun owners and 91% of non-owners — felt it was “very important for the healthcare team to ask parents of children with suicidal ideation/attempts about firearms in the home.” Similarly, high proportions believed it was important for the healthcare team to counsel those parents on safe gun storage. Although only 69% of firearm owners believed it was important to distribute firearm locks in the hospital, 81% would be interested in receiving a free one. Significantly more of the non-owners (80%; P = .02) believed free lock distribution was important, and 72% of non-owners would also be interested in one.
About half the respondents (55%) preferred to hear firearm counseling one-on-one from a provider, whereas 31% would like written information and 27% would be interested in a video. In terms of what information parents preferred to receive, a little over half of owners (54%) and non-owners (56%) were interested in how or when (50% and 40%, respectively) to discuss the topic with their child. Only about a third (35% owners and 37% non-owners) wanted information on how to discuss the topic with the parents of their child’s friends.
The survey’s biggest limitations after its small size were the selection bias of those willing to complete the survey and potential response bias from the self-reported data.
The study of Colorado caregivers, just published in Pediatrics, surveyed 512 Colorado caregivers in April-May 2023 to learn about their beliefs and perceptions regarding firearms, firearm storage and risk, and youth suicide (2024 Oct 1;154[4]:e2024066930. doi: 10.1542/peds.2024-066930). Just over half the respondents (52%) had grown up in a household with firearms, and 44% currently lived in a household with a gun. The sample was 43% men and 88% White, predominantly non-Hispanic (75%), with 11% living in rural areas and 19% who currently or previously served in the military. Most (79%) had a child age 12 or younger in the home.
Only about one in four caregivers (24%) correctly answered that suicide is the leading cause of firearm death in Colorado, with similar rates of correct responses among both firearm owners and non-firearm owners. Both groups were also similarly likely (64% overall) to be concerned about youth suicide in their community, though those from homes with firearms were less likely to be concerned about youth suicide in their own family (28%) than those from homes without firearms (39%; P = .013).
In addition, caregivers from homes with versus without firearms were considerably less likely to believe suicide can be prevented (48% vs 69%) and were less likely to believe that temporarily removing a firearm from the home reduces the risk for gun injury or death (60% vs 78%; P < .001 for both comparisons).
Firearm owners were also much less likely than non-owners to believe keeping a gun in the home makes it more dangerous (7% vs 29%) and over twice as likely to think keeping a firearm makes their home safer (52% vs 22%; P < .001). The vast majority of respondents (89%) believed secure storage of guns reduces the risk for injury or death, though the response was higher for firearm owners (93%) than for non-owners (86%; P < .001).
“Our finding that most firearm owners believe that secure firearm storage is protective against firearm injury is a promising messaging strategy,” the authors wrote. “It presents a preventive education opportunity for adults living with children who have mental health concerns, who may benefit most from secure in-home storage and/or temporary and voluntary storage of firearms away from home.”
Firearm Injuries
A separate study at the AAP conference underscored the devastating impact of firearm injuries even among those who survive, whether self-inflicted or not, and the potential for reducing healthcare treatment and costs from effective prevention efforts. A national analysis of pediatric inpatient data from 2017 to 2020 calculated how much greater the burden of healthcare treatment and costs is for firearm injuries of any kind compared with penetrating traumas and blunt traumas.
“As a surgical resident, I have seen these patients who make it into the trauma bed that we are then faced to care for,” said Colleen Nofi, DO, PhD, MBA, a general surgery resident at Cohen Children’s Medical Center at Northwell Health in New York. “Anecdotally, we understand that the devastation and injury caused by bullets far outweighs the injuries caused by other trauma mechanisms,” but the actual calculation of the burden hasn’t been studied.
Among 6615 firearm injuries, 9787 penetrating traumas and 66,003 blunt traumas examined from the National Inpatient Sample Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project Database, 11% of firearm traumas required a transfusion of red blood cells, compared with 1.4% of penetrating traumas and 3% of blunt traumas (P < .001). Patients with firearm injuries also had a longer length of stay — 10.8 days compared with 8.3 for patients with penetrating trauma and 9.8 for those with blunt trauma — and significantly higher rates of CPR, pericardiotomy, chest tube, exploratory laparotomy and/or thoracotomy, colorectal surgery, small bowel surgery, ostomy formation, splenectomy, hepatic resection, tracheostomy, and feeding tube placement.
Pulmonary complications were higher for firearm injuries (4.9%) than for penetrating trauma (0.6%) or blunt trauma (2.9%), and septicemia rates were also higher (1.7% vs 0.2% and 1%, respectively). Cardiac, neurologic, and urinary complications were also significantly and substantially higher for firearm injuries, 6.9% of which resulted in death compared with 0.2% of penetrating traumas and 1.2% of blunt traumas.
The costs from firearm injuries were also significantly higher than the costs from other traumas; “firearm injury remained independently predictive of greater hospital costs, even when controlling for injury severity as well as age, sex, race, insurance, region, hospital type, and household income.
“These findings underscore the urgent need for targeted prevention, supportive measures, and resource allocation to mitigate the devastating impact of firearm injuries on children and healthcare systems alike,” Dr. Nofi said.
The Colorado study was funded by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment and a National Institutes of Health grant to Dr. Haasz. The Texas study and the one from Northwell Health did not note any external funding. Dr. Haasz, Dr. Rosenbaum, Dr. Boonstra, and Dr. Nofi had no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
From AAP 2024
Erenumab Reduces Nonopioid Medication Overuse Headache in Chronic Migraine
In a recent study of 6 monthly injections of 140 mg erenumab (Aimovig, Amgen), most patients with chronic migraine and nonopioid medication overuse headache (MOH) achieved remission. Published online in JAMA Neurology, the study is the first prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled attempt to investigate patients with chronic migraine and MOH related to nonopioid medications, according to lead author Stewart J. Tepper, MD, and his coauthors.
Prior Studies Did Not Focus on MOH
Several prior phase 2 and 3 trials of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) ligand or receptor inhibitors that have been FDA-approved for migraine prevention have been performed. These drugs include erenumab, fremanezumab (Ajovy, Teva), galcanezumab (Emgality, Lilly), and eptinezumab (Vyepti, Lundbeck), for patients with and without medication overuse, said Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was not involved with the new study. Dr. Rapoport is a clinical professor of neurology at the David Geffen School of Medicine of the University of California, in Los Angeles; past president of the International Headache Society; and founder and director emeritus of The New England Center for Headache in Stamford, Connecticut.
“But we could not call them patients with MOH because they weren’t studied prospectively, so that they had medication overuse according to International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) criteria,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Phase 4, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
In the present clinical trial, investigators enrolled 584 patients with nonopioid MOH and history of failing at least one preventive treatment. After a 4-week baseline phase, researchers randomized patients 1:1:1 to 6 months’ treatment with erenumab 70 mg, erenumab 140 mg, or placebo.
Investigators defined remission as either of the following through months 4-6:
- < 10 mean monthly acute headache medication days per month (AHMD)
- < 14 mean monthly headache days (MHD)
In the primary analysis, 69.1% of patients in the 140 mg cohort achieved remission (P < .001) versus placebo. Remission rates in the 70 mg and the placebo cohorts were 60.3% (P < .13) and 52.6%, respectively. AHMD for the 140-mg, 70-mg, and placebo groups fell by 9.4, 7.8, and 6.6 days per month, respectively. Migraine Physical Function Impact Diary (non-EU sites) and Headache Impact Test-6 (EU sites) scores also showed greater improvement for patients treated with erenumab.
No new safety signals emerged, although erenumab-treated participants experienced 2-2.5 times as much COVID-19 disease.
Regarding the primary endpoint, said Dr. Rapoport, the 70-mg dose might also have yielded statistically significant improvement over placebo with a larger sample size. “I have seen that the higher dose of erenumab can be superior for efficacy than the lower in some of the double-blind trials,” he said. The 52.6% placebo response rate was rather high, he added, but not necessarily higher than in other migraine prevention trials.
“Placebo is a type of treatment,” Dr. Rapoport said. “It’s not as strong as the actual medication, which is specific for prevention, but it does work on the brain to some extent.”
He was more concerned, however, that authors did not counsel study patients about reducing or discontinuing their overused medications in a unified manner. Rather, it was left to individual investigators’ discretion, in different countries, as to whether to educate patients about the harms of medication overuse. “The fascinating aspect of this paper was that no patient was asked to detoxify from the overused medication,” said Dr. Rapoport, “and yet so many patients no longer had MOH at 6 months.”
Detox Versus No Detox
In a pioneering study of migraine medication overuse headache (then called rebound headache) published by Lee Kudrow, MD, in Advances in Neurology in 1982, patients who discontinued the overused medication fared much better than those who did not. Adding amitriptyline for migraine prevention further improved results, mostly in those who discontinued their overused medication.
Anticipating possible concerns, the authors wrote that their approach “may also be seen as a strength, as it represents a scenario closer to real life and avoids undue interference with the physician-patient relationship.” Indeed, said Dr. Rapoport, study results are perhaps more impressive because they were achieved through treatment with erenumab alone, without detoxification.
Managing Chronic Migraine and MOH
Until erenumab’s 2018 approval, migraine prevention options were limited to tricyclic antidepressants, beta blockers, and antiseizure medicines – though these medicines never seemed to work very well without detoxification, said Dr. Rapoport. Neurologists still use these categories for migraine prevention, he added, “because insurance companies insist that before we give the more expensive, newer medications like those that block CGRP, patients must fail 2 of those 3 categories of older medications which are not approved for chronic migraine.” Only onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) is FDA-approved for chronic migraine. “There has been no head-to-head comparison of it and any of the monoclonal antibodies against CGRP,” he said.
In a March 2024 publication in Headache, the American Headache Society stated that requiring patients to fail older drugs is inappropriate, and that CGRP inhibitors, though costly, should be first-line for headache prevention. The key advantage of any drug that blocks CGRP in treating MOH is that unlike older drugs, CGRP inhibitors appear to work well even without detoxification, said Dr. Rapoport.
Additional study limitations included the possibility that the 24-week treatment period might not have allowed complete evaluation of long-term efficacy, the authors wrote. “These are usually pretty sick patients,” said Dr. Rapoport, who acknowledged the difficulty of keeping placebo patients off preventive medication altogether for 6 months. The study was extended to 12 months, and the results of an opiate overusers cohort also will be published.
Authors noted that according to a study published in Headache in 2022, most Americans with chronic migraine commonly go without preventive medications. Moreover, such medications do not always work. Accordingly, Dr. Rapoport said, the study duration was reasonable provided patients understood that they had a 33% chance of receiving no effective preventive medication over 6 months.
Extending the study’s month-long baseline period to 3 months before starting erenumab might have been helpful, he added, as that is the timeframe required to confirm MOH diagnosis according to ICHD-3. “However,” said Dr. Rapoport, “3 months with only usual medications, and then 1/3 of patients going 6-12 months with only placebo, would be tough for some patients.”
Dr. Rapoport reports no relevant financial conflicts.
In a recent study of 6 monthly injections of 140 mg erenumab (Aimovig, Amgen), most patients with chronic migraine and nonopioid medication overuse headache (MOH) achieved remission. Published online in JAMA Neurology, the study is the first prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled attempt to investigate patients with chronic migraine and MOH related to nonopioid medications, according to lead author Stewart J. Tepper, MD, and his coauthors.
Prior Studies Did Not Focus on MOH
Several prior phase 2 and 3 trials of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) ligand or receptor inhibitors that have been FDA-approved for migraine prevention have been performed. These drugs include erenumab, fremanezumab (Ajovy, Teva), galcanezumab (Emgality, Lilly), and eptinezumab (Vyepti, Lundbeck), for patients with and without medication overuse, said Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was not involved with the new study. Dr. Rapoport is a clinical professor of neurology at the David Geffen School of Medicine of the University of California, in Los Angeles; past president of the International Headache Society; and founder and director emeritus of The New England Center for Headache in Stamford, Connecticut.
“But we could not call them patients with MOH because they weren’t studied prospectively, so that they had medication overuse according to International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) criteria,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Phase 4, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
In the present clinical trial, investigators enrolled 584 patients with nonopioid MOH and history of failing at least one preventive treatment. After a 4-week baseline phase, researchers randomized patients 1:1:1 to 6 months’ treatment with erenumab 70 mg, erenumab 140 mg, or placebo.
Investigators defined remission as either of the following through months 4-6:
- < 10 mean monthly acute headache medication days per month (AHMD)
- < 14 mean monthly headache days (MHD)
In the primary analysis, 69.1% of patients in the 140 mg cohort achieved remission (P < .001) versus placebo. Remission rates in the 70 mg and the placebo cohorts were 60.3% (P < .13) and 52.6%, respectively. AHMD for the 140-mg, 70-mg, and placebo groups fell by 9.4, 7.8, and 6.6 days per month, respectively. Migraine Physical Function Impact Diary (non-EU sites) and Headache Impact Test-6 (EU sites) scores also showed greater improvement for patients treated with erenumab.
No new safety signals emerged, although erenumab-treated participants experienced 2-2.5 times as much COVID-19 disease.
Regarding the primary endpoint, said Dr. Rapoport, the 70-mg dose might also have yielded statistically significant improvement over placebo with a larger sample size. “I have seen that the higher dose of erenumab can be superior for efficacy than the lower in some of the double-blind trials,” he said. The 52.6% placebo response rate was rather high, he added, but not necessarily higher than in other migraine prevention trials.
“Placebo is a type of treatment,” Dr. Rapoport said. “It’s not as strong as the actual medication, which is specific for prevention, but it does work on the brain to some extent.”
He was more concerned, however, that authors did not counsel study patients about reducing or discontinuing their overused medications in a unified manner. Rather, it was left to individual investigators’ discretion, in different countries, as to whether to educate patients about the harms of medication overuse. “The fascinating aspect of this paper was that no patient was asked to detoxify from the overused medication,” said Dr. Rapoport, “and yet so many patients no longer had MOH at 6 months.”
Detox Versus No Detox
In a pioneering study of migraine medication overuse headache (then called rebound headache) published by Lee Kudrow, MD, in Advances in Neurology in 1982, patients who discontinued the overused medication fared much better than those who did not. Adding amitriptyline for migraine prevention further improved results, mostly in those who discontinued their overused medication.
Anticipating possible concerns, the authors wrote that their approach “may also be seen as a strength, as it represents a scenario closer to real life and avoids undue interference with the physician-patient relationship.” Indeed, said Dr. Rapoport, study results are perhaps more impressive because they were achieved through treatment with erenumab alone, without detoxification.
Managing Chronic Migraine and MOH
Until erenumab’s 2018 approval, migraine prevention options were limited to tricyclic antidepressants, beta blockers, and antiseizure medicines – though these medicines never seemed to work very well without detoxification, said Dr. Rapoport. Neurologists still use these categories for migraine prevention, he added, “because insurance companies insist that before we give the more expensive, newer medications like those that block CGRP, patients must fail 2 of those 3 categories of older medications which are not approved for chronic migraine.” Only onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) is FDA-approved for chronic migraine. “There has been no head-to-head comparison of it and any of the monoclonal antibodies against CGRP,” he said.
In a March 2024 publication in Headache, the American Headache Society stated that requiring patients to fail older drugs is inappropriate, and that CGRP inhibitors, though costly, should be first-line for headache prevention. The key advantage of any drug that blocks CGRP in treating MOH is that unlike older drugs, CGRP inhibitors appear to work well even without detoxification, said Dr. Rapoport.
Additional study limitations included the possibility that the 24-week treatment period might not have allowed complete evaluation of long-term efficacy, the authors wrote. “These are usually pretty sick patients,” said Dr. Rapoport, who acknowledged the difficulty of keeping placebo patients off preventive medication altogether for 6 months. The study was extended to 12 months, and the results of an opiate overusers cohort also will be published.
Authors noted that according to a study published in Headache in 2022, most Americans with chronic migraine commonly go without preventive medications. Moreover, such medications do not always work. Accordingly, Dr. Rapoport said, the study duration was reasonable provided patients understood that they had a 33% chance of receiving no effective preventive medication over 6 months.
Extending the study’s month-long baseline period to 3 months before starting erenumab might have been helpful, he added, as that is the timeframe required to confirm MOH diagnosis according to ICHD-3. “However,” said Dr. Rapoport, “3 months with only usual medications, and then 1/3 of patients going 6-12 months with only placebo, would be tough for some patients.”
Dr. Rapoport reports no relevant financial conflicts.
In a recent study of 6 monthly injections of 140 mg erenumab (Aimovig, Amgen), most patients with chronic migraine and nonopioid medication overuse headache (MOH) achieved remission. Published online in JAMA Neurology, the study is the first prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled attempt to investigate patients with chronic migraine and MOH related to nonopioid medications, according to lead author Stewart J. Tepper, MD, and his coauthors.
Prior Studies Did Not Focus on MOH
Several prior phase 2 and 3 trials of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) ligand or receptor inhibitors that have been FDA-approved for migraine prevention have been performed. These drugs include erenumab, fremanezumab (Ajovy, Teva), galcanezumab (Emgality, Lilly), and eptinezumab (Vyepti, Lundbeck), for patients with and without medication overuse, said Alan M. Rapoport, MD, who was not involved with the new study. Dr. Rapoport is a clinical professor of neurology at the David Geffen School of Medicine of the University of California, in Los Angeles; past president of the International Headache Society; and founder and director emeritus of The New England Center for Headache in Stamford, Connecticut.
“But we could not call them patients with MOH because they weren’t studied prospectively, so that they had medication overuse according to International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD-3) criteria,” said Dr. Rapoport.
Phase 4, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
In the present clinical trial, investigators enrolled 584 patients with nonopioid MOH and history of failing at least one preventive treatment. After a 4-week baseline phase, researchers randomized patients 1:1:1 to 6 months’ treatment with erenumab 70 mg, erenumab 140 mg, or placebo.
Investigators defined remission as either of the following through months 4-6:
- < 10 mean monthly acute headache medication days per month (AHMD)
- < 14 mean monthly headache days (MHD)
In the primary analysis, 69.1% of patients in the 140 mg cohort achieved remission (P < .001) versus placebo. Remission rates in the 70 mg and the placebo cohorts were 60.3% (P < .13) and 52.6%, respectively. AHMD for the 140-mg, 70-mg, and placebo groups fell by 9.4, 7.8, and 6.6 days per month, respectively. Migraine Physical Function Impact Diary (non-EU sites) and Headache Impact Test-6 (EU sites) scores also showed greater improvement for patients treated with erenumab.
No new safety signals emerged, although erenumab-treated participants experienced 2-2.5 times as much COVID-19 disease.
Regarding the primary endpoint, said Dr. Rapoport, the 70-mg dose might also have yielded statistically significant improvement over placebo with a larger sample size. “I have seen that the higher dose of erenumab can be superior for efficacy than the lower in some of the double-blind trials,” he said. The 52.6% placebo response rate was rather high, he added, but not necessarily higher than in other migraine prevention trials.
“Placebo is a type of treatment,” Dr. Rapoport said. “It’s not as strong as the actual medication, which is specific for prevention, but it does work on the brain to some extent.”
He was more concerned, however, that authors did not counsel study patients about reducing or discontinuing their overused medications in a unified manner. Rather, it was left to individual investigators’ discretion, in different countries, as to whether to educate patients about the harms of medication overuse. “The fascinating aspect of this paper was that no patient was asked to detoxify from the overused medication,” said Dr. Rapoport, “and yet so many patients no longer had MOH at 6 months.”
Detox Versus No Detox
In a pioneering study of migraine medication overuse headache (then called rebound headache) published by Lee Kudrow, MD, in Advances in Neurology in 1982, patients who discontinued the overused medication fared much better than those who did not. Adding amitriptyline for migraine prevention further improved results, mostly in those who discontinued their overused medication.
Anticipating possible concerns, the authors wrote that their approach “may also be seen as a strength, as it represents a scenario closer to real life and avoids undue interference with the physician-patient relationship.” Indeed, said Dr. Rapoport, study results are perhaps more impressive because they were achieved through treatment with erenumab alone, without detoxification.
Managing Chronic Migraine and MOH
Until erenumab’s 2018 approval, migraine prevention options were limited to tricyclic antidepressants, beta blockers, and antiseizure medicines – though these medicines never seemed to work very well without detoxification, said Dr. Rapoport. Neurologists still use these categories for migraine prevention, he added, “because insurance companies insist that before we give the more expensive, newer medications like those that block CGRP, patients must fail 2 of those 3 categories of older medications which are not approved for chronic migraine.” Only onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) is FDA-approved for chronic migraine. “There has been no head-to-head comparison of it and any of the monoclonal antibodies against CGRP,” he said.
In a March 2024 publication in Headache, the American Headache Society stated that requiring patients to fail older drugs is inappropriate, and that CGRP inhibitors, though costly, should be first-line for headache prevention. The key advantage of any drug that blocks CGRP in treating MOH is that unlike older drugs, CGRP inhibitors appear to work well even without detoxification, said Dr. Rapoport.
Additional study limitations included the possibility that the 24-week treatment period might not have allowed complete evaluation of long-term efficacy, the authors wrote. “These are usually pretty sick patients,” said Dr. Rapoport, who acknowledged the difficulty of keeping placebo patients off preventive medication altogether for 6 months. The study was extended to 12 months, and the results of an opiate overusers cohort also will be published.
Authors noted that according to a study published in Headache in 2022, most Americans with chronic migraine commonly go without preventive medications. Moreover, such medications do not always work. Accordingly, Dr. Rapoport said, the study duration was reasonable provided patients understood that they had a 33% chance of receiving no effective preventive medication over 6 months.
Extending the study’s month-long baseline period to 3 months before starting erenumab might have been helpful, he added, as that is the timeframe required to confirm MOH diagnosis according to ICHD-3. “However,” said Dr. Rapoport, “3 months with only usual medications, and then 1/3 of patients going 6-12 months with only placebo, would be tough for some patients.”
Dr. Rapoport reports no relevant financial conflicts.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
FDA OKs Next-Gen Cologuard Test for CRC Screening
Developed in collaboration with Mayo Clinic, the company noted in the news release announcing its approval that this noninvasive test “raises the performance bar.”
The company says the enhanced sensitivity will help minimize unnecessary follow-up colonoscopy procedures by reducing the odds of a false-positive screening test.
Enhanced sample stability components also will give patients more time to return their sample to the lab.
Cologuard Plus tests for three novel methylated DNA markers and fecal hemoglobin.
The BLUE-C Study
The FDA’s approval was based on the results of the BLUE-C study involving more than 20,000 adults at average risk for CRC that compared the next-generation mt-sDNA test with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and colonoscopy.
According to the BLUE-C results, the sensitivities of Cologuard Plus were 95% for CRC and 43% for advanced precancerous lesions, at 94% specificity with no findings on colonoscopy.
The BLUE-C results also showed that the test significantly outperformed FIT for sensitivity for CRC overall, CRC stages I-III, high-grade dysplasia, and advanced precancerous lesions.
“To meaningfully improve outcomes in colorectal cancer, we must catch cancer early — when it is most treatable — and find advanced precancers, which can prevent cases of this cancer,” Thomas F. Imperiale, MD, AGAF, professor of medicine at the Indiana University School of Medicine and research scientist at the Regenstrief Institute, said in the news release.
“The high colorectal cancer sensitivity and specificity of the Cologuard Plus test gives me confidence in the test’s ability to do just that while simultaneously maintaining a low risk of false positives. This makes the Cologuard Plus test a strong option for first-line screening of average risk patients,” said Dr. Imperiale, who served as principal investigator of the BLUE-C study.
The company plans to launch Cologuard Plus in 2025.
They anticipate that it will be covered by Medicare and included in the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines and within quality measures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Developed in collaboration with Mayo Clinic, the company noted in the news release announcing its approval that this noninvasive test “raises the performance bar.”
The company says the enhanced sensitivity will help minimize unnecessary follow-up colonoscopy procedures by reducing the odds of a false-positive screening test.
Enhanced sample stability components also will give patients more time to return their sample to the lab.
Cologuard Plus tests for three novel methylated DNA markers and fecal hemoglobin.
The BLUE-C Study
The FDA’s approval was based on the results of the BLUE-C study involving more than 20,000 adults at average risk for CRC that compared the next-generation mt-sDNA test with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and colonoscopy.
According to the BLUE-C results, the sensitivities of Cologuard Plus were 95% for CRC and 43% for advanced precancerous lesions, at 94% specificity with no findings on colonoscopy.
The BLUE-C results also showed that the test significantly outperformed FIT for sensitivity for CRC overall, CRC stages I-III, high-grade dysplasia, and advanced precancerous lesions.
“To meaningfully improve outcomes in colorectal cancer, we must catch cancer early — when it is most treatable — and find advanced precancers, which can prevent cases of this cancer,” Thomas F. Imperiale, MD, AGAF, professor of medicine at the Indiana University School of Medicine and research scientist at the Regenstrief Institute, said in the news release.
“The high colorectal cancer sensitivity and specificity of the Cologuard Plus test gives me confidence in the test’s ability to do just that while simultaneously maintaining a low risk of false positives. This makes the Cologuard Plus test a strong option for first-line screening of average risk patients,” said Dr. Imperiale, who served as principal investigator of the BLUE-C study.
The company plans to launch Cologuard Plus in 2025.
They anticipate that it will be covered by Medicare and included in the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines and within quality measures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Developed in collaboration with Mayo Clinic, the company noted in the news release announcing its approval that this noninvasive test “raises the performance bar.”
The company says the enhanced sensitivity will help minimize unnecessary follow-up colonoscopy procedures by reducing the odds of a false-positive screening test.
Enhanced sample stability components also will give patients more time to return their sample to the lab.
Cologuard Plus tests for three novel methylated DNA markers and fecal hemoglobin.
The BLUE-C Study
The FDA’s approval was based on the results of the BLUE-C study involving more than 20,000 adults at average risk for CRC that compared the next-generation mt-sDNA test with a fecal immunochemical test (FIT) and colonoscopy.
According to the BLUE-C results, the sensitivities of Cologuard Plus were 95% for CRC and 43% for advanced precancerous lesions, at 94% specificity with no findings on colonoscopy.
The BLUE-C results also showed that the test significantly outperformed FIT for sensitivity for CRC overall, CRC stages I-III, high-grade dysplasia, and advanced precancerous lesions.
“To meaningfully improve outcomes in colorectal cancer, we must catch cancer early — when it is most treatable — and find advanced precancers, which can prevent cases of this cancer,” Thomas F. Imperiale, MD, AGAF, professor of medicine at the Indiana University School of Medicine and research scientist at the Regenstrief Institute, said in the news release.
“The high colorectal cancer sensitivity and specificity of the Cologuard Plus test gives me confidence in the test’s ability to do just that while simultaneously maintaining a low risk of false positives. This makes the Cologuard Plus test a strong option for first-line screening of average risk patients,” said Dr. Imperiale, who served as principal investigator of the BLUE-C study.
The company plans to launch Cologuard Plus in 2025.
They anticipate that it will be covered by Medicare and included in the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines and within quality measures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.