User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Periorbital Orange Spots
The Diagnosis: Orange Palpebral Spots
The clinical presentation of our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of orange palpebral spots (OPSs), an uncommon discoloration that most often appears in White patients in the fifth or sixth decades of life. Orange palpebral spots were first described in 2008 by Assouly et al1 in 27 patients (23 females and 4 males). In 2015, Belliveau et al2 expanded the designation to yellow-orange palpebral spots because they felt the term more fully expressed the color variations depicted in their patients; however, this term more frequently is used in ophthalmology.
Orange palpebral spots commonly appear as asymptomatic, yellow-orange, symmetric lesions with a predilection for the recessed areas of the superior eyelids but also can present on the canthi and inferior eyelids. The discolorations are more easily visible on fair skin and have been reported to measure from 10 to 15 mm in the long axis.3 Assouly et al1 described the orange spots as having indistinct margins, with borders similar to “sand on a sea shore.” Orange palpebral spots can be a persistent discoloration, and there are no reports of spontaneous regression. No known association with malignancy or systemic illness has been reported.
Case reports of OPSs describe histologic similarities between specimens, including increased adipose tissue and pigment-laden macrophages in the superficial dermis.2 The pigmented deposits sometimes may be found in the basal keratinocytes of the epidermis and turn black with Fontana-Masson stain.1 No inflammatory infiltrates, necrosis, or xanthomization are characteristically found. Stains for iron, mucin, and amyloid also have been negative.2
The cause of pigmentation in OPSs is unknown; however, lipofuscin deposits and high-situated adipocytes in the reticular dermis colored by carotenoids have been proposed as possible mechanisms.1 No unifying cause for pigmentation in the serum (eg, cholesterol, triglycerides, thyroid-stimulating hormone, free retinol, vitamin E, carotenoids) was found in 11 of 27 patients with OPSs assessed by Assouly et al.1 In one case, lipofuscin, a degradation product of lysosomes, was detected by microscopic autofluorescence in the superficial dermis. However, lipofuscin typically is a breakdown product associated with aging, and OPSs have been present in patients as young as 28 years.1 Local trauma related to eye rubbing is another theory that has been proposed due to the finding of melanin in the superficial dermis. However, the absence of hemosiderin deposits as well as the extensive duration of the discolorations makes local trauma a less likely explanation for the etiology of OPSs.2
The clinical differential diagnosis for OPSs includes xanthelasma, jaundice, and carotenoderma. Xanthelasma presents as elevated yellow plaques usually found over the medial aspect of the eyes. In contrast, OPSs are nonelevated with both orange and yellow hues typically present. Histologic samples of xanthelasma are characterized by lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells) in the dermis in contrast to the adipose tissue seen in OPSs that has not been phagocytized.1,2 The lack of scleral icterus made jaundice an unlikely diagnosis in our patient. Bilirubin elevations substantial enough to cause skin discoloration also would be expected to discolor the conjunctiva. In carotenoderma, carotenoids are deposited in the sweat and sebum of the stratum corneum with the orange pigmentation most prominent in regions of increased sweating such as the palms, soles, and nasolabial folds.4 Our patient’s lack of discoloration in places other than the periorbital region made carotenoderma less likely.
In the study by Assouly et al,1 10 of 11 patients who underwent laboratory analysis self-reported eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables, though no standardized questionnaire was given. One patient was found to have an elevated vitamin E level, and in 5 cases there was an elevated level of β-cryptoxanthin. The significance of these elevations in such a small minority is unknown, and increased β-cryptoxanthin has been attributed to increased consumption of citrus fruits during the winter season. Our patient reported ingesting a daily oral supplement rich in carotenoids that constituted 60% of the daily value of vitamin E including mixed tocopherols as well as 90% of the daily value of vitamin A with many sources of carotenoids including beta-carotenes, lutein/zeaxanthin, lycopene, and astaxanthin. An invasive biopsy was not taken in this case, as OPSs largely are diagnosed clinically. Greater awareness and recognition of OPSs may help to identify common underlying causes for this unique diagnosis.
- Assouly P, Cavelier-Balloy B, Dupré T. Orange palpebral spots. Dermatology. 2008;216:166-170.
- Belliveau MJ, Odashiro AN, Harvey JT. Yellow-orange palpebral spots. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:2139-2140.
- Kluger N, Guillot B. Bilateral orange discoloration of the upper eyelids: a quiz. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:211-212.
- Maharshak N, Shapiro J, Trau H. Carotenoderma—a review of the current literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:178-181.
The Diagnosis: Orange Palpebral Spots
The clinical presentation of our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of orange palpebral spots (OPSs), an uncommon discoloration that most often appears in White patients in the fifth or sixth decades of life. Orange palpebral spots were first described in 2008 by Assouly et al1 in 27 patients (23 females and 4 males). In 2015, Belliveau et al2 expanded the designation to yellow-orange palpebral spots because they felt the term more fully expressed the color variations depicted in their patients; however, this term more frequently is used in ophthalmology.
Orange palpebral spots commonly appear as asymptomatic, yellow-orange, symmetric lesions with a predilection for the recessed areas of the superior eyelids but also can present on the canthi and inferior eyelids. The discolorations are more easily visible on fair skin and have been reported to measure from 10 to 15 mm in the long axis.3 Assouly et al1 described the orange spots as having indistinct margins, with borders similar to “sand on a sea shore.” Orange palpebral spots can be a persistent discoloration, and there are no reports of spontaneous regression. No known association with malignancy or systemic illness has been reported.
Case reports of OPSs describe histologic similarities between specimens, including increased adipose tissue and pigment-laden macrophages in the superficial dermis.2 The pigmented deposits sometimes may be found in the basal keratinocytes of the epidermis and turn black with Fontana-Masson stain.1 No inflammatory infiltrates, necrosis, or xanthomization are characteristically found. Stains for iron, mucin, and amyloid also have been negative.2
The cause of pigmentation in OPSs is unknown; however, lipofuscin deposits and high-situated adipocytes in the reticular dermis colored by carotenoids have been proposed as possible mechanisms.1 No unifying cause for pigmentation in the serum (eg, cholesterol, triglycerides, thyroid-stimulating hormone, free retinol, vitamin E, carotenoids) was found in 11 of 27 patients with OPSs assessed by Assouly et al.1 In one case, lipofuscin, a degradation product of lysosomes, was detected by microscopic autofluorescence in the superficial dermis. However, lipofuscin typically is a breakdown product associated with aging, and OPSs have been present in patients as young as 28 years.1 Local trauma related to eye rubbing is another theory that has been proposed due to the finding of melanin in the superficial dermis. However, the absence of hemosiderin deposits as well as the extensive duration of the discolorations makes local trauma a less likely explanation for the etiology of OPSs.2
The clinical differential diagnosis for OPSs includes xanthelasma, jaundice, and carotenoderma. Xanthelasma presents as elevated yellow plaques usually found over the medial aspect of the eyes. In contrast, OPSs are nonelevated with both orange and yellow hues typically present. Histologic samples of xanthelasma are characterized by lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells) in the dermis in contrast to the adipose tissue seen in OPSs that has not been phagocytized.1,2 The lack of scleral icterus made jaundice an unlikely diagnosis in our patient. Bilirubin elevations substantial enough to cause skin discoloration also would be expected to discolor the conjunctiva. In carotenoderma, carotenoids are deposited in the sweat and sebum of the stratum corneum with the orange pigmentation most prominent in regions of increased sweating such as the palms, soles, and nasolabial folds.4 Our patient’s lack of discoloration in places other than the periorbital region made carotenoderma less likely.
In the study by Assouly et al,1 10 of 11 patients who underwent laboratory analysis self-reported eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables, though no standardized questionnaire was given. One patient was found to have an elevated vitamin E level, and in 5 cases there was an elevated level of β-cryptoxanthin. The significance of these elevations in such a small minority is unknown, and increased β-cryptoxanthin has been attributed to increased consumption of citrus fruits during the winter season. Our patient reported ingesting a daily oral supplement rich in carotenoids that constituted 60% of the daily value of vitamin E including mixed tocopherols as well as 90% of the daily value of vitamin A with many sources of carotenoids including beta-carotenes, lutein/zeaxanthin, lycopene, and astaxanthin. An invasive biopsy was not taken in this case, as OPSs largely are diagnosed clinically. Greater awareness and recognition of OPSs may help to identify common underlying causes for this unique diagnosis.
The Diagnosis: Orange Palpebral Spots
The clinical presentation of our patient was consistent with a diagnosis of orange palpebral spots (OPSs), an uncommon discoloration that most often appears in White patients in the fifth or sixth decades of life. Orange palpebral spots were first described in 2008 by Assouly et al1 in 27 patients (23 females and 4 males). In 2015, Belliveau et al2 expanded the designation to yellow-orange palpebral spots because they felt the term more fully expressed the color variations depicted in their patients; however, this term more frequently is used in ophthalmology.
Orange palpebral spots commonly appear as asymptomatic, yellow-orange, symmetric lesions with a predilection for the recessed areas of the superior eyelids but also can present on the canthi and inferior eyelids. The discolorations are more easily visible on fair skin and have been reported to measure from 10 to 15 mm in the long axis.3 Assouly et al1 described the orange spots as having indistinct margins, with borders similar to “sand on a sea shore.” Orange palpebral spots can be a persistent discoloration, and there are no reports of spontaneous regression. No known association with malignancy or systemic illness has been reported.
Case reports of OPSs describe histologic similarities between specimens, including increased adipose tissue and pigment-laden macrophages in the superficial dermis.2 The pigmented deposits sometimes may be found in the basal keratinocytes of the epidermis and turn black with Fontana-Masson stain.1 No inflammatory infiltrates, necrosis, or xanthomization are characteristically found. Stains for iron, mucin, and amyloid also have been negative.2
The cause of pigmentation in OPSs is unknown; however, lipofuscin deposits and high-situated adipocytes in the reticular dermis colored by carotenoids have been proposed as possible mechanisms.1 No unifying cause for pigmentation in the serum (eg, cholesterol, triglycerides, thyroid-stimulating hormone, free retinol, vitamin E, carotenoids) was found in 11 of 27 patients with OPSs assessed by Assouly et al.1 In one case, lipofuscin, a degradation product of lysosomes, was detected by microscopic autofluorescence in the superficial dermis. However, lipofuscin typically is a breakdown product associated with aging, and OPSs have been present in patients as young as 28 years.1 Local trauma related to eye rubbing is another theory that has been proposed due to the finding of melanin in the superficial dermis. However, the absence of hemosiderin deposits as well as the extensive duration of the discolorations makes local trauma a less likely explanation for the etiology of OPSs.2
The clinical differential diagnosis for OPSs includes xanthelasma, jaundice, and carotenoderma. Xanthelasma presents as elevated yellow plaques usually found over the medial aspect of the eyes. In contrast, OPSs are nonelevated with both orange and yellow hues typically present. Histologic samples of xanthelasma are characterized by lipid-laden macrophages (foam cells) in the dermis in contrast to the adipose tissue seen in OPSs that has not been phagocytized.1,2 The lack of scleral icterus made jaundice an unlikely diagnosis in our patient. Bilirubin elevations substantial enough to cause skin discoloration also would be expected to discolor the conjunctiva. In carotenoderma, carotenoids are deposited in the sweat and sebum of the stratum corneum with the orange pigmentation most prominent in regions of increased sweating such as the palms, soles, and nasolabial folds.4 Our patient’s lack of discoloration in places other than the periorbital region made carotenoderma less likely.
In the study by Assouly et al,1 10 of 11 patients who underwent laboratory analysis self-reported eating a diet rich in fruit and vegetables, though no standardized questionnaire was given. One patient was found to have an elevated vitamin E level, and in 5 cases there was an elevated level of β-cryptoxanthin. The significance of these elevations in such a small minority is unknown, and increased β-cryptoxanthin has been attributed to increased consumption of citrus fruits during the winter season. Our patient reported ingesting a daily oral supplement rich in carotenoids that constituted 60% of the daily value of vitamin E including mixed tocopherols as well as 90% of the daily value of vitamin A with many sources of carotenoids including beta-carotenes, lutein/zeaxanthin, lycopene, and astaxanthin. An invasive biopsy was not taken in this case, as OPSs largely are diagnosed clinically. Greater awareness and recognition of OPSs may help to identify common underlying causes for this unique diagnosis.
- Assouly P, Cavelier-Balloy B, Dupré T. Orange palpebral spots. Dermatology. 2008;216:166-170.
- Belliveau MJ, Odashiro AN, Harvey JT. Yellow-orange palpebral spots. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:2139-2140.
- Kluger N, Guillot B. Bilateral orange discoloration of the upper eyelids: a quiz. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:211-212.
- Maharshak N, Shapiro J, Trau H. Carotenoderma—a review of the current literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:178-181.
- Assouly P, Cavelier-Balloy B, Dupré T. Orange palpebral spots. Dermatology. 2008;216:166-170.
- Belliveau MJ, Odashiro AN, Harvey JT. Yellow-orange palpebral spots. Ophthalmology. 2015;122:2139-2140.
- Kluger N, Guillot B. Bilateral orange discoloration of the upper eyelids: a quiz. Acta Derm Venereol. 2011;91:211-212.
- Maharshak N, Shapiro J, Trau H. Carotenoderma—a review of the current literature. Int J Dermatol. 2003;42:178-181.
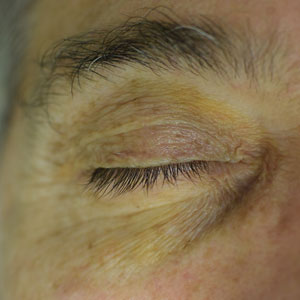
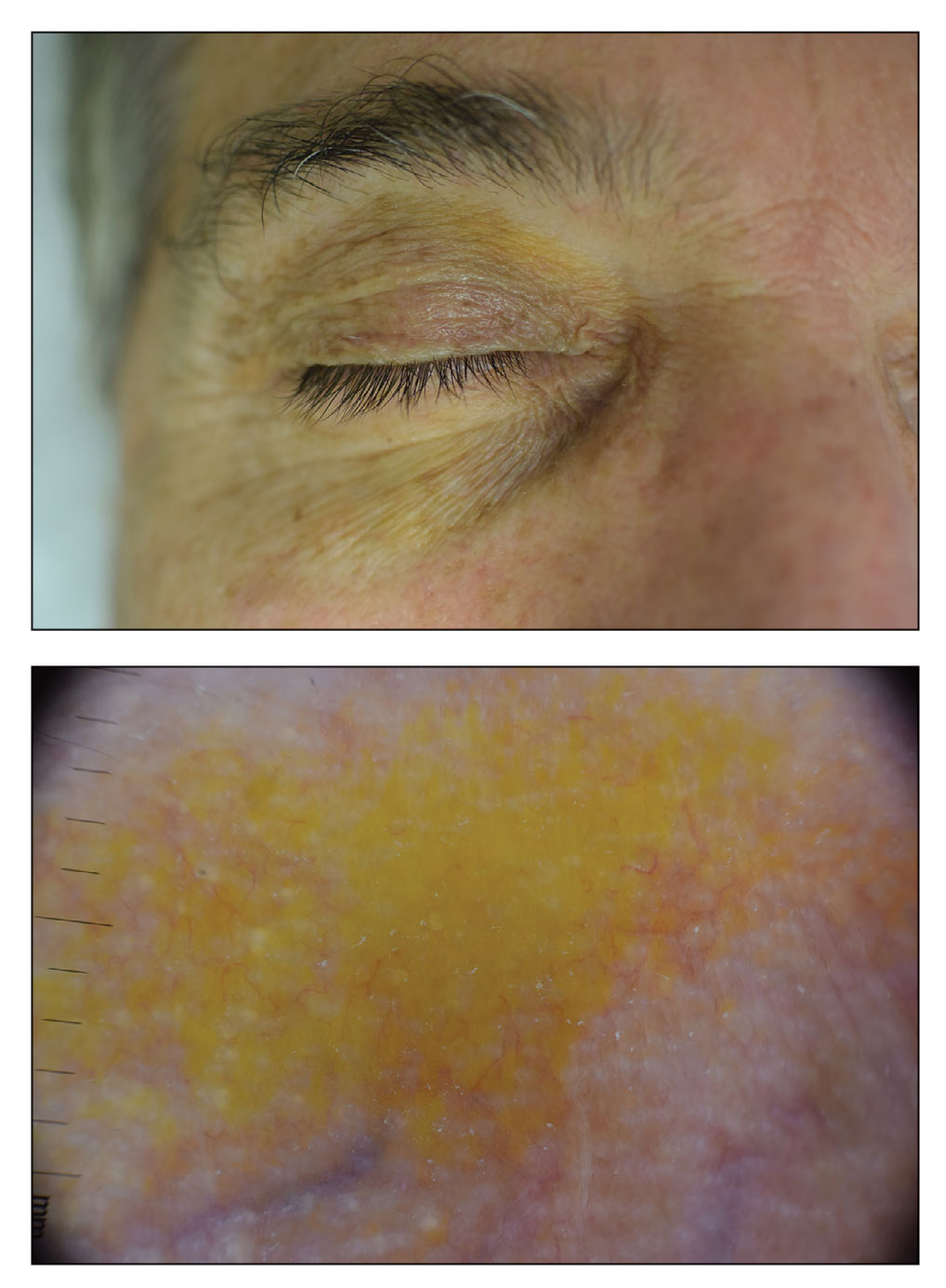
A 63-year-old White man with a history of melanoma presented to our dermatology clinic for evaluation of gradually worsening yellow discoloration around the eyes of 2 years’ duration. Physical examination revealed periorbital yellow-orange patches (top). The discolorations were nonelevated and nonpalpable. Dermoscopy revealed yellow blotches with sparing of the hair follicles (bottom). The remainder of the skin examination was unremarkable.
Despite limits, COVID vaccines protect CLL patients
These findings don’t reveal whether the T-cell boost actually provides extra protection against COVID-19. Still, the study suggests that patients with CLL should be vaccinated no matter which medications they’re taking, coauthor and hematologist/oncologist Clemens-Martin Wendtner, MD, of the Munich (Germany) Clinic, said in an interview.
“Do not defer or pause treatment,” said Dr. Wendtner, whose study was published in Blood Advances.
Patients with CLL appear to have among the weakest responses to the COVID-19 vaccine among people with various types of blood cancer. A meta-analysis published in 2022 found that seropositivity rates following vaccination were just 51% in patients with CLL, compared with 80%-90% in those with acute leukemia and 76%-80% of those with myeloma.
“Usually, the response rate to vaccination among the nonimmunocompromised would be 95%,” Dr. Wendtner said.
Research has also suggested that patients treated with B-cell pathway inhibitors and anti-CD20 antibodies are especially likely to have poorer responses to COVID-19 vaccines, no surprise considering that their job is to dampen the immune system. But there’s an unanswered question, according to Dr. Wendtner: Does “just measuring B-cell response tell us everything about the immune response?”
The new prospective, single-institution study aims to answer that question in patients who each received two types of vaccines. Researchers compared peripheral blood mononuclear cell transcriptional response with antibody and T-cell response rates in 15 patients with CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma following vaccination with both the Pfizer-BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines.
The average antibody response was limited. “Overall, 7/15 of patients failed to mount a humoral response even after three-dose vaccination,” the researchers reported. All of the patients were “heavily pretreated” with CLL medications such as venetoclax, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.
By contrast, the T-cell response was much stronger: 80% of patients (12/15) had a robust response, a number that grew to 90% (14/15) after a booster. This response is “almost ideal” considering that the response in a nonimmunocompromised person would be about 99%, Dr. Wendtner said.
The study also revealed that vaccine responses were weaker in patients who took a combination of a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor and venetoclax within a year.
Four patients developed COVID-19 infections with the Omicron variant about 6 months after vaccination. All had mild symptoms. A lone patient had a history of COVID-19 infection prior to vaccination.
The researchers noted that the study had several limitations, including its small size, its reliance on a single institution, and the differences in treatments and vaccination protocols among the patient population.
Broadly speaking, the study showed that “a vaccine is not in vain” in patients with CLL, “although the doctor might not detect an antibody response,” Dr. Wendtner said. He added that mixing vaccine types should provide more protection. Start with a viral vector vaccine followed by an mRNA vaccine or vice versa, he suggested.
In an interview, infectious disease physician Joshua A. Hill, MD, from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, who wasn’t involved with the study, said it makes “important and interesting observations to reinforce other studies with similar findings.”
Specifically, Dr. Hill said, “despite the absence of a robust antibody response some of these patients who are on active treatment, patients can still generate robust cellular immune responses in the form of T-cell immunity. Our understanding is that having T cell immunity will provide important additional protection for developing severe disease, although is less easily tested.”
As for the best vaccination strategies, Dr. Hill said “patients should get vaccinated as soon as they are eligible, according to standard guidelines. If patients have not yet started therapy, they should get their indicated vaccines before starting treatment whenever possible.”
The German study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the Bavarian State Ministry of Science and Art. Dr. Wendtner disclosed consultant fees from AstraZeneca and BioNTech, and another author disclosed consultant fees from AstraZeneca. The other authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Hill disclosed consultant fees from Moderna, Pfizer, and Gilead.
These findings don’t reveal whether the T-cell boost actually provides extra protection against COVID-19. Still, the study suggests that patients with CLL should be vaccinated no matter which medications they’re taking, coauthor and hematologist/oncologist Clemens-Martin Wendtner, MD, of the Munich (Germany) Clinic, said in an interview.
“Do not defer or pause treatment,” said Dr. Wendtner, whose study was published in Blood Advances.
Patients with CLL appear to have among the weakest responses to the COVID-19 vaccine among people with various types of blood cancer. A meta-analysis published in 2022 found that seropositivity rates following vaccination were just 51% in patients with CLL, compared with 80%-90% in those with acute leukemia and 76%-80% of those with myeloma.
“Usually, the response rate to vaccination among the nonimmunocompromised would be 95%,” Dr. Wendtner said.
Research has also suggested that patients treated with B-cell pathway inhibitors and anti-CD20 antibodies are especially likely to have poorer responses to COVID-19 vaccines, no surprise considering that their job is to dampen the immune system. But there’s an unanswered question, according to Dr. Wendtner: Does “just measuring B-cell response tell us everything about the immune response?”
The new prospective, single-institution study aims to answer that question in patients who each received two types of vaccines. Researchers compared peripheral blood mononuclear cell transcriptional response with antibody and T-cell response rates in 15 patients with CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma following vaccination with both the Pfizer-BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines.
The average antibody response was limited. “Overall, 7/15 of patients failed to mount a humoral response even after three-dose vaccination,” the researchers reported. All of the patients were “heavily pretreated” with CLL medications such as venetoclax, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.
By contrast, the T-cell response was much stronger: 80% of patients (12/15) had a robust response, a number that grew to 90% (14/15) after a booster. This response is “almost ideal” considering that the response in a nonimmunocompromised person would be about 99%, Dr. Wendtner said.
The study also revealed that vaccine responses were weaker in patients who took a combination of a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor and venetoclax within a year.
Four patients developed COVID-19 infections with the Omicron variant about 6 months after vaccination. All had mild symptoms. A lone patient had a history of COVID-19 infection prior to vaccination.
The researchers noted that the study had several limitations, including its small size, its reliance on a single institution, and the differences in treatments and vaccination protocols among the patient population.
Broadly speaking, the study showed that “a vaccine is not in vain” in patients with CLL, “although the doctor might not detect an antibody response,” Dr. Wendtner said. He added that mixing vaccine types should provide more protection. Start with a viral vector vaccine followed by an mRNA vaccine or vice versa, he suggested.
In an interview, infectious disease physician Joshua A. Hill, MD, from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, who wasn’t involved with the study, said it makes “important and interesting observations to reinforce other studies with similar findings.”
Specifically, Dr. Hill said, “despite the absence of a robust antibody response some of these patients who are on active treatment, patients can still generate robust cellular immune responses in the form of T-cell immunity. Our understanding is that having T cell immunity will provide important additional protection for developing severe disease, although is less easily tested.”
As for the best vaccination strategies, Dr. Hill said “patients should get vaccinated as soon as they are eligible, according to standard guidelines. If patients have not yet started therapy, they should get their indicated vaccines before starting treatment whenever possible.”
The German study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the Bavarian State Ministry of Science and Art. Dr. Wendtner disclosed consultant fees from AstraZeneca and BioNTech, and another author disclosed consultant fees from AstraZeneca. The other authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Hill disclosed consultant fees from Moderna, Pfizer, and Gilead.
These findings don’t reveal whether the T-cell boost actually provides extra protection against COVID-19. Still, the study suggests that patients with CLL should be vaccinated no matter which medications they’re taking, coauthor and hematologist/oncologist Clemens-Martin Wendtner, MD, of the Munich (Germany) Clinic, said in an interview.
“Do not defer or pause treatment,” said Dr. Wendtner, whose study was published in Blood Advances.
Patients with CLL appear to have among the weakest responses to the COVID-19 vaccine among people with various types of blood cancer. A meta-analysis published in 2022 found that seropositivity rates following vaccination were just 51% in patients with CLL, compared with 80%-90% in those with acute leukemia and 76%-80% of those with myeloma.
“Usually, the response rate to vaccination among the nonimmunocompromised would be 95%,” Dr. Wendtner said.
Research has also suggested that patients treated with B-cell pathway inhibitors and anti-CD20 antibodies are especially likely to have poorer responses to COVID-19 vaccines, no surprise considering that their job is to dampen the immune system. But there’s an unanswered question, according to Dr. Wendtner: Does “just measuring B-cell response tell us everything about the immune response?”
The new prospective, single-institution study aims to answer that question in patients who each received two types of vaccines. Researchers compared peripheral blood mononuclear cell transcriptional response with antibody and T-cell response rates in 15 patients with CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma following vaccination with both the Pfizer-BioNTech and AstraZeneca vaccines.
The average antibody response was limited. “Overall, 7/15 of patients failed to mount a humoral response even after three-dose vaccination,” the researchers reported. All of the patients were “heavily pretreated” with CLL medications such as venetoclax, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody.
By contrast, the T-cell response was much stronger: 80% of patients (12/15) had a robust response, a number that grew to 90% (14/15) after a booster. This response is “almost ideal” considering that the response in a nonimmunocompromised person would be about 99%, Dr. Wendtner said.
The study also revealed that vaccine responses were weaker in patients who took a combination of a Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor and venetoclax within a year.
Four patients developed COVID-19 infections with the Omicron variant about 6 months after vaccination. All had mild symptoms. A lone patient had a history of COVID-19 infection prior to vaccination.
The researchers noted that the study had several limitations, including its small size, its reliance on a single institution, and the differences in treatments and vaccination protocols among the patient population.
Broadly speaking, the study showed that “a vaccine is not in vain” in patients with CLL, “although the doctor might not detect an antibody response,” Dr. Wendtner said. He added that mixing vaccine types should provide more protection. Start with a viral vector vaccine followed by an mRNA vaccine or vice versa, he suggested.
In an interview, infectious disease physician Joshua A. Hill, MD, from Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Seattle, who wasn’t involved with the study, said it makes “important and interesting observations to reinforce other studies with similar findings.”
Specifically, Dr. Hill said, “despite the absence of a robust antibody response some of these patients who are on active treatment, patients can still generate robust cellular immune responses in the form of T-cell immunity. Our understanding is that having T cell immunity will provide important additional protection for developing severe disease, although is less easily tested.”
As for the best vaccination strategies, Dr. Hill said “patients should get vaccinated as soon as they are eligible, according to standard guidelines. If patients have not yet started therapy, they should get their indicated vaccines before starting treatment whenever possible.”
The German study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and the Bavarian State Ministry of Science and Art. Dr. Wendtner disclosed consultant fees from AstraZeneca and BioNTech, and another author disclosed consultant fees from AstraZeneca. The other authors reported no disclosures. Dr. Hill disclosed consultant fees from Moderna, Pfizer, and Gilead.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Commenting on weight’s not rude. It’s dangerous.
It was the start of the fall semester of my sophomore year of college.
At my small women’s college, the previous semester’s gossip had been about our classmate, S*. She had gone from being very thin to noticeably gaining a lot of weight in a few months. The rumors were that S was pregnant and gave birth over summer break. As a busy biology premed major, this was my first time hearing the news. So when I saw her standing in the hallway, back to her previous weight, I was excited for her.
In true extravert fashion, I commented on the baby and her new size. But no sooner had the words left my mouth than I regretted them.
The hall grew awkwardly silent as S’s face flushed and she asked, “Excuse me?!” Instantly I knew that the rumors weren’t true.
Thankfully, at that moment, the classroom opened and we walked in. Whew! After class, S asked if we could talk. She explained that she had a thyroid tumor and struggled to adjust to the treatments, which caused her weight fluctuations. She had never been pregnant.
My awkward statement had been the first time anyone on campus had directly mentioned her weight, though she suspected that people were talking about her. We became fast friends after this rocky beginning. Although we lost touch after college, S taught me an invaluable lesson about making assumptions about people’s weight: Ask before you assume.
Now, years later, as an internist and obesity specialist, this lesson continues to be reinforced daily.
In daily life, comments about weight can be perceived as rude. In the clinical setting, however, assumptions about weight are a form of weight bias. Weight bias can lead to weight stigma and even be dangerous to health care.
Let’s discuss the insidious influence of weight bias in health care through two commonly used phrases and then look at a few solutions to address weight bias in health care individually and systematically.
Common weight bias assumptions
“Great job, you lost weight!” In checking your patient’s vital signs, you notice that this patient with obesity has a significant weight change. You congratulate them upon entering the room. Unfortunately, their weight loss was a result of minimal eating after losing a loved one. This isn’t healthy weight loss. One of the adverse effects of weight bias is that it infers that weight loss is always a good thing, especially in people with larger bodies. This is a dangerous presumption. Let’s remember that the body favors fat storage, hence why “unintentional weight loss” is a recognized medical condition prompting evaluation. We have to be careful not to celebrate weight loss “at all costs,” such as fad diets that haven’t been shown to improve health outcomes.
Furthermore, patients who lose weight quickly (more than 4-8 lb/month) require closer follow-up and evaluation for secondary causes of weight loss. Patients may lose weight at a faster rate with the new antiobesity medications, but clinicians still should ensure that age-appropriate health maintenance screening is done and be vigilant for secondary causes of weight changes.
“Have you tried losing weight yet?” Three times. That’s how many times Chanté Burkett went to her doctor about her painful, enlarging firm stomach. She was advised to continue working on weight loss, which she did diligently. But Ms. Burkett’s abdomen kept growing and her concerns were dismissed. A visit to urgent care and a CT scan revealed that Ms. Burkett’s excess abdominal “fat” was a 13-lb mucinous cystadenoma. Sadly, cases like hers aren’t rare, isolated events. Weight bias can cause anchoring on one diagnosis, preventing consideration of other diagnostic possibilities. Even worse, anchoring will lead to the wrong intervention, such as prescribing weight loss for presumed increased adiposity instead of ordering the appropriate testing.
It’s also essential to recognize that, even if someone does have the disease of obesity, weight loss isn’t the solution to every medical concern. Even if weight loss is helpful, other, more pressing treatments may still be necessary. Telling a person with obesity who has an acute complaint to “just lose weight” is comparable to telling a patient with coronary artery disease who presents with an 80% vessel occlusion and chest pain to follow a low-fat diet. In both cases, you need to address the acute concern appropriately, then focus on the chronic treatment.
Ways to reduce clinical weight bias
How do you reduce clinical weight bias?
Ask, don’t assume. The information from the scale is simply data. Instead of judging it positively or negatively and creating a story, ask the patient. An unbiased way to approach the conversation is to say, “Great to see you. You seem [positive adjective of choice]. How have you been?” Wait until the vitals section to objectively discuss weight unless the patient offers the discussion earlier or their chief complaint lists a weight-related concern.
Order necessary tests to evaluate weight. Weight is the vital sign that people wear externally, so we feel that we can readily interpret it without any further assessment. However, resist the urge to interpret scale data without context. Keeping an open mind helps prevent anchoring and missing critical clues in the clinical history.
Address weight changes effectively. Sometimes there is an indication to prescribe weight loss as part of the treatment plan. However, remember that weight loss isn’t simply “calories in vs. calories out.” Obesity is a complex medical disease that requires a multimodal treatment approach. As clinicians, we have access to the most powerful tools for weight loss. Unfortunately, weight bias contributes to limited prescribing of metabolic medications (“antiobesity medications” or AOMs). In addition, systemic weight bias prevents insurance coverage of AOMs. The Treat and Reduce Obesity Act has been introduced into Congress to help improve life-transforming access to AOMs.
Acknowledge your bias. Our experiences make us all susceptible to bias. The Harvard Weight Implicit Association Test is free and a helpful way to assess your level of weight bias. I take it annually to ensure that I remain objective in my practice.
Addressing weight bias needs to extend beyond the individual level.
Systemically, health care needs to address the following:
Language. Use people-centered language. For example, “People aren’t obese. They have obesity.”
Accessibility. Health care settings must be comfortable and accessible for people of all sizes. Furthermore, improvements to access the services that comprehensive obesity care requires, such as AOMs, bariatric procedures and bariatric surgery, mental health care, nutrition, fitness specialists, health coaches, and more, are needed.
Education. Medical students and trainees have to learn the newest obesity science and know how to treat obesity effectively. Acknowledge and address biased tools. Recent data have shown that some of our screening tools, such as body mass index, have inherent bias. It’s time to focus on using improved diagnostic tools and personalized treatments.
We are at a pivotal time in our scientific understanding of body weight regulation and the disease of obesity. Clinical weight bias is primarily rooted in flawed science influenced by biased cultural norms and other forms of discrimination, such as racial and gender bias. We must move past assumptions to give our patients the optimal individualized care they need. So next time you observe a weight change, instead of commenting on their weight, say, “Great to see you! How have you been?”
S*: Initial has been changed to protect privacy.
Dr. Gonsahn-Bollie is an integrative obesity specialist focused on individualized solutions for emotional and biological overeating. Connect with her at www.embraceyouweightloss.com or on Instagram @embraceyoumd. Her bestselling book, “Embrace You: Your Guide to Transforming Weight Loss Misconceptions Into Lifelong Wellness”, was Healthline.com’s Best Overall Weight Loss Book of 2022 and one of Livestrong.com’s 8 Best Weight-Loss Books to Read in 2022. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
It was the start of the fall semester of my sophomore year of college.
At my small women’s college, the previous semester’s gossip had been about our classmate, S*. She had gone from being very thin to noticeably gaining a lot of weight in a few months. The rumors were that S was pregnant and gave birth over summer break. As a busy biology premed major, this was my first time hearing the news. So when I saw her standing in the hallway, back to her previous weight, I was excited for her.
In true extravert fashion, I commented on the baby and her new size. But no sooner had the words left my mouth than I regretted them.
The hall grew awkwardly silent as S’s face flushed and she asked, “Excuse me?!” Instantly I knew that the rumors weren’t true.
Thankfully, at that moment, the classroom opened and we walked in. Whew! After class, S asked if we could talk. She explained that she had a thyroid tumor and struggled to adjust to the treatments, which caused her weight fluctuations. She had never been pregnant.
My awkward statement had been the first time anyone on campus had directly mentioned her weight, though she suspected that people were talking about her. We became fast friends after this rocky beginning. Although we lost touch after college, S taught me an invaluable lesson about making assumptions about people’s weight: Ask before you assume.
Now, years later, as an internist and obesity specialist, this lesson continues to be reinforced daily.
In daily life, comments about weight can be perceived as rude. In the clinical setting, however, assumptions about weight are a form of weight bias. Weight bias can lead to weight stigma and even be dangerous to health care.
Let’s discuss the insidious influence of weight bias in health care through two commonly used phrases and then look at a few solutions to address weight bias in health care individually and systematically.
Common weight bias assumptions
“Great job, you lost weight!” In checking your patient’s vital signs, you notice that this patient with obesity has a significant weight change. You congratulate them upon entering the room. Unfortunately, their weight loss was a result of minimal eating after losing a loved one. This isn’t healthy weight loss. One of the adverse effects of weight bias is that it infers that weight loss is always a good thing, especially in people with larger bodies. This is a dangerous presumption. Let’s remember that the body favors fat storage, hence why “unintentional weight loss” is a recognized medical condition prompting evaluation. We have to be careful not to celebrate weight loss “at all costs,” such as fad diets that haven’t been shown to improve health outcomes.
Furthermore, patients who lose weight quickly (more than 4-8 lb/month) require closer follow-up and evaluation for secondary causes of weight loss. Patients may lose weight at a faster rate with the new antiobesity medications, but clinicians still should ensure that age-appropriate health maintenance screening is done and be vigilant for secondary causes of weight changes.
“Have you tried losing weight yet?” Three times. That’s how many times Chanté Burkett went to her doctor about her painful, enlarging firm stomach. She was advised to continue working on weight loss, which she did diligently. But Ms. Burkett’s abdomen kept growing and her concerns were dismissed. A visit to urgent care and a CT scan revealed that Ms. Burkett’s excess abdominal “fat” was a 13-lb mucinous cystadenoma. Sadly, cases like hers aren’t rare, isolated events. Weight bias can cause anchoring on one diagnosis, preventing consideration of other diagnostic possibilities. Even worse, anchoring will lead to the wrong intervention, such as prescribing weight loss for presumed increased adiposity instead of ordering the appropriate testing.
It’s also essential to recognize that, even if someone does have the disease of obesity, weight loss isn’t the solution to every medical concern. Even if weight loss is helpful, other, more pressing treatments may still be necessary. Telling a person with obesity who has an acute complaint to “just lose weight” is comparable to telling a patient with coronary artery disease who presents with an 80% vessel occlusion and chest pain to follow a low-fat diet. In both cases, you need to address the acute concern appropriately, then focus on the chronic treatment.
Ways to reduce clinical weight bias
How do you reduce clinical weight bias?
Ask, don’t assume. The information from the scale is simply data. Instead of judging it positively or negatively and creating a story, ask the patient. An unbiased way to approach the conversation is to say, “Great to see you. You seem [positive adjective of choice]. How have you been?” Wait until the vitals section to objectively discuss weight unless the patient offers the discussion earlier or their chief complaint lists a weight-related concern.
Order necessary tests to evaluate weight. Weight is the vital sign that people wear externally, so we feel that we can readily interpret it without any further assessment. However, resist the urge to interpret scale data without context. Keeping an open mind helps prevent anchoring and missing critical clues in the clinical history.
Address weight changes effectively. Sometimes there is an indication to prescribe weight loss as part of the treatment plan. However, remember that weight loss isn’t simply “calories in vs. calories out.” Obesity is a complex medical disease that requires a multimodal treatment approach. As clinicians, we have access to the most powerful tools for weight loss. Unfortunately, weight bias contributes to limited prescribing of metabolic medications (“antiobesity medications” or AOMs). In addition, systemic weight bias prevents insurance coverage of AOMs. The Treat and Reduce Obesity Act has been introduced into Congress to help improve life-transforming access to AOMs.
Acknowledge your bias. Our experiences make us all susceptible to bias. The Harvard Weight Implicit Association Test is free and a helpful way to assess your level of weight bias. I take it annually to ensure that I remain objective in my practice.
Addressing weight bias needs to extend beyond the individual level.
Systemically, health care needs to address the following:
Language. Use people-centered language. For example, “People aren’t obese. They have obesity.”
Accessibility. Health care settings must be comfortable and accessible for people of all sizes. Furthermore, improvements to access the services that comprehensive obesity care requires, such as AOMs, bariatric procedures and bariatric surgery, mental health care, nutrition, fitness specialists, health coaches, and more, are needed.
Education. Medical students and trainees have to learn the newest obesity science and know how to treat obesity effectively. Acknowledge and address biased tools. Recent data have shown that some of our screening tools, such as body mass index, have inherent bias. It’s time to focus on using improved diagnostic tools and personalized treatments.
We are at a pivotal time in our scientific understanding of body weight regulation and the disease of obesity. Clinical weight bias is primarily rooted in flawed science influenced by biased cultural norms and other forms of discrimination, such as racial and gender bias. We must move past assumptions to give our patients the optimal individualized care they need. So next time you observe a weight change, instead of commenting on their weight, say, “Great to see you! How have you been?”
S*: Initial has been changed to protect privacy.
Dr. Gonsahn-Bollie is an integrative obesity specialist focused on individualized solutions for emotional and biological overeating. Connect with her at www.embraceyouweightloss.com or on Instagram @embraceyoumd. Her bestselling book, “Embrace You: Your Guide to Transforming Weight Loss Misconceptions Into Lifelong Wellness”, was Healthline.com’s Best Overall Weight Loss Book of 2022 and one of Livestrong.com’s 8 Best Weight-Loss Books to Read in 2022. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
It was the start of the fall semester of my sophomore year of college.
At my small women’s college, the previous semester’s gossip had been about our classmate, S*. She had gone from being very thin to noticeably gaining a lot of weight in a few months. The rumors were that S was pregnant and gave birth over summer break. As a busy biology premed major, this was my first time hearing the news. So when I saw her standing in the hallway, back to her previous weight, I was excited for her.
In true extravert fashion, I commented on the baby and her new size. But no sooner had the words left my mouth than I regretted them.
The hall grew awkwardly silent as S’s face flushed and she asked, “Excuse me?!” Instantly I knew that the rumors weren’t true.
Thankfully, at that moment, the classroom opened and we walked in. Whew! After class, S asked if we could talk. She explained that she had a thyroid tumor and struggled to adjust to the treatments, which caused her weight fluctuations. She had never been pregnant.
My awkward statement had been the first time anyone on campus had directly mentioned her weight, though she suspected that people were talking about her. We became fast friends after this rocky beginning. Although we lost touch after college, S taught me an invaluable lesson about making assumptions about people’s weight: Ask before you assume.
Now, years later, as an internist and obesity specialist, this lesson continues to be reinforced daily.
In daily life, comments about weight can be perceived as rude. In the clinical setting, however, assumptions about weight are a form of weight bias. Weight bias can lead to weight stigma and even be dangerous to health care.
Let’s discuss the insidious influence of weight bias in health care through two commonly used phrases and then look at a few solutions to address weight bias in health care individually and systematically.
Common weight bias assumptions
“Great job, you lost weight!” In checking your patient’s vital signs, you notice that this patient with obesity has a significant weight change. You congratulate them upon entering the room. Unfortunately, their weight loss was a result of minimal eating after losing a loved one. This isn’t healthy weight loss. One of the adverse effects of weight bias is that it infers that weight loss is always a good thing, especially in people with larger bodies. This is a dangerous presumption. Let’s remember that the body favors fat storage, hence why “unintentional weight loss” is a recognized medical condition prompting evaluation. We have to be careful not to celebrate weight loss “at all costs,” such as fad diets that haven’t been shown to improve health outcomes.
Furthermore, patients who lose weight quickly (more than 4-8 lb/month) require closer follow-up and evaluation for secondary causes of weight loss. Patients may lose weight at a faster rate with the new antiobesity medications, but clinicians still should ensure that age-appropriate health maintenance screening is done and be vigilant for secondary causes of weight changes.
“Have you tried losing weight yet?” Three times. That’s how many times Chanté Burkett went to her doctor about her painful, enlarging firm stomach. She was advised to continue working on weight loss, which she did diligently. But Ms. Burkett’s abdomen kept growing and her concerns were dismissed. A visit to urgent care and a CT scan revealed that Ms. Burkett’s excess abdominal “fat” was a 13-lb mucinous cystadenoma. Sadly, cases like hers aren’t rare, isolated events. Weight bias can cause anchoring on one diagnosis, preventing consideration of other diagnostic possibilities. Even worse, anchoring will lead to the wrong intervention, such as prescribing weight loss for presumed increased adiposity instead of ordering the appropriate testing.
It’s also essential to recognize that, even if someone does have the disease of obesity, weight loss isn’t the solution to every medical concern. Even if weight loss is helpful, other, more pressing treatments may still be necessary. Telling a person with obesity who has an acute complaint to “just lose weight” is comparable to telling a patient with coronary artery disease who presents with an 80% vessel occlusion and chest pain to follow a low-fat diet. In both cases, you need to address the acute concern appropriately, then focus on the chronic treatment.
Ways to reduce clinical weight bias
How do you reduce clinical weight bias?
Ask, don’t assume. The information from the scale is simply data. Instead of judging it positively or negatively and creating a story, ask the patient. An unbiased way to approach the conversation is to say, “Great to see you. You seem [positive adjective of choice]. How have you been?” Wait until the vitals section to objectively discuss weight unless the patient offers the discussion earlier or their chief complaint lists a weight-related concern.
Order necessary tests to evaluate weight. Weight is the vital sign that people wear externally, so we feel that we can readily interpret it without any further assessment. However, resist the urge to interpret scale data without context. Keeping an open mind helps prevent anchoring and missing critical clues in the clinical history.
Address weight changes effectively. Sometimes there is an indication to prescribe weight loss as part of the treatment plan. However, remember that weight loss isn’t simply “calories in vs. calories out.” Obesity is a complex medical disease that requires a multimodal treatment approach. As clinicians, we have access to the most powerful tools for weight loss. Unfortunately, weight bias contributes to limited prescribing of metabolic medications (“antiobesity medications” or AOMs). In addition, systemic weight bias prevents insurance coverage of AOMs. The Treat and Reduce Obesity Act has been introduced into Congress to help improve life-transforming access to AOMs.
Acknowledge your bias. Our experiences make us all susceptible to bias. The Harvard Weight Implicit Association Test is free and a helpful way to assess your level of weight bias. I take it annually to ensure that I remain objective in my practice.
Addressing weight bias needs to extend beyond the individual level.
Systemically, health care needs to address the following:
Language. Use people-centered language. For example, “People aren’t obese. They have obesity.”
Accessibility. Health care settings must be comfortable and accessible for people of all sizes. Furthermore, improvements to access the services that comprehensive obesity care requires, such as AOMs, bariatric procedures and bariatric surgery, mental health care, nutrition, fitness specialists, health coaches, and more, are needed.
Education. Medical students and trainees have to learn the newest obesity science and know how to treat obesity effectively. Acknowledge and address biased tools. Recent data have shown that some of our screening tools, such as body mass index, have inherent bias. It’s time to focus on using improved diagnostic tools and personalized treatments.
We are at a pivotal time in our scientific understanding of body weight regulation and the disease of obesity. Clinical weight bias is primarily rooted in flawed science influenced by biased cultural norms and other forms of discrimination, such as racial and gender bias. We must move past assumptions to give our patients the optimal individualized care they need. So next time you observe a weight change, instead of commenting on their weight, say, “Great to see you! How have you been?”
S*: Initial has been changed to protect privacy.
Dr. Gonsahn-Bollie is an integrative obesity specialist focused on individualized solutions for emotional and biological overeating. Connect with her at www.embraceyouweightloss.com or on Instagram @embraceyoumd. Her bestselling book, “Embrace You: Your Guide to Transforming Weight Loss Misconceptions Into Lifelong Wellness”, was Healthline.com’s Best Overall Weight Loss Book of 2022 and one of Livestrong.com’s 8 Best Weight-Loss Books to Read in 2022. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Ozempic face’: Accepting wrinkles for improved health
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Last week, a number of patients emailed me regarding their concerns about this phenomenon known as Ozempic face. I went on to read about what this meant. I live in Los Angeles, where most people appear to be on semaglutide (Ozempic). It’s the phenomenon where people lose weight relatively rapidly, making their faces thin out. Then what happens, apparently, is they look older because their face is more wrinkled and baggier. They might have to have further plastic surgery. I say that with slight sarcasm because of where I live.
I want to talk about what I think about this, living here where there’s a great pressure to prescribe semaglutide off label, and what I think about it for my patients with diabetes.
Historically, we haven’t had much in terms of effective medication for treating obesity, and frankly, now we do. We now have agents that are effective, that have relatively few side effects, and that have become part of what’s out there. People now want to use these agents, semaglutide, and there’s been a great need for these agents.
The problem, however, is twofold. One, as we all know, is that it has basically caused a shortage of medication for treating our patients who actually have type 2 diabetes and really need these medications to manage their disease. Then we have people who want these medications who can’t pay for them. Insurance doesn’t cover obesity medications, which is problematic and actually quite frustrating for people who, I think, really would benefit from using these medications.
What I tell people, frankly, is that until I have enough supply for my patients with type 2 diabetes, who need these agents to control their blood sugars, I want to keep this class of drugs available to them. I also hope we’re able to expand it more and more with improving insurance coverage – and that’s a big if, if you ask me – both for people who have prediabetes and for patients who are overweight and obese, because I think it’s really hard for people to lose weight.
It’s frustrating, and for many people, being overweight and obese causes all sorts of other health issues, not only diabetes. I believe that these drugs are both safe and effective and should be more available. I do think we need to be careful in terms of who we prescribe them to, at least at the moment. Hopefully, we’ll be able to expand their use.
Anything that can encourage our population to lose weight and maintain that weight loss is very important. We need to couple weight loss medications with lifestyle interventions. I think people can out-eat any medication; therefore, it’s very important to encourage our patients to eat better, to exercise more, and to do all the other things they need to do to reduce their risks for other comorbidities.
I am incredibly happy to have these newer agents on the market. I tell my patients – at least those who have diabetes – that they have to accept looking a little bit too thin for the benefits that we can see in using these medications.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts, and three books, on diabetes, and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations. She has ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, MannKind Corporation, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, and Zafgen. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Last week, a number of patients emailed me regarding their concerns about this phenomenon known as Ozempic face. I went on to read about what this meant. I live in Los Angeles, where most people appear to be on semaglutide (Ozempic). It’s the phenomenon where people lose weight relatively rapidly, making their faces thin out. Then what happens, apparently, is they look older because their face is more wrinkled and baggier. They might have to have further plastic surgery. I say that with slight sarcasm because of where I live.
I want to talk about what I think about this, living here where there’s a great pressure to prescribe semaglutide off label, and what I think about it for my patients with diabetes.
Historically, we haven’t had much in terms of effective medication for treating obesity, and frankly, now we do. We now have agents that are effective, that have relatively few side effects, and that have become part of what’s out there. People now want to use these agents, semaglutide, and there’s been a great need for these agents.
The problem, however, is twofold. One, as we all know, is that it has basically caused a shortage of medication for treating our patients who actually have type 2 diabetes and really need these medications to manage their disease. Then we have people who want these medications who can’t pay for them. Insurance doesn’t cover obesity medications, which is problematic and actually quite frustrating for people who, I think, really would benefit from using these medications.
What I tell people, frankly, is that until I have enough supply for my patients with type 2 diabetes, who need these agents to control their blood sugars, I want to keep this class of drugs available to them. I also hope we’re able to expand it more and more with improving insurance coverage – and that’s a big if, if you ask me – both for people who have prediabetes and for patients who are overweight and obese, because I think it’s really hard for people to lose weight.
It’s frustrating, and for many people, being overweight and obese causes all sorts of other health issues, not only diabetes. I believe that these drugs are both safe and effective and should be more available. I do think we need to be careful in terms of who we prescribe them to, at least at the moment. Hopefully, we’ll be able to expand their use.
Anything that can encourage our population to lose weight and maintain that weight loss is very important. We need to couple weight loss medications with lifestyle interventions. I think people can out-eat any medication; therefore, it’s very important to encourage our patients to eat better, to exercise more, and to do all the other things they need to do to reduce their risks for other comorbidities.
I am incredibly happy to have these newer agents on the market. I tell my patients – at least those who have diabetes – that they have to accept looking a little bit too thin for the benefits that we can see in using these medications.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts, and three books, on diabetes, and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations. She has ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, MannKind Corporation, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, and Zafgen. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Last week, a number of patients emailed me regarding their concerns about this phenomenon known as Ozempic face. I went on to read about what this meant. I live in Los Angeles, where most people appear to be on semaglutide (Ozempic). It’s the phenomenon where people lose weight relatively rapidly, making their faces thin out. Then what happens, apparently, is they look older because their face is more wrinkled and baggier. They might have to have further plastic surgery. I say that with slight sarcasm because of where I live.
I want to talk about what I think about this, living here where there’s a great pressure to prescribe semaglutide off label, and what I think about it for my patients with diabetes.
Historically, we haven’t had much in terms of effective medication for treating obesity, and frankly, now we do. We now have agents that are effective, that have relatively few side effects, and that have become part of what’s out there. People now want to use these agents, semaglutide, and there’s been a great need for these agents.
The problem, however, is twofold. One, as we all know, is that it has basically caused a shortage of medication for treating our patients who actually have type 2 diabetes and really need these medications to manage their disease. Then we have people who want these medications who can’t pay for them. Insurance doesn’t cover obesity medications, which is problematic and actually quite frustrating for people who, I think, really would benefit from using these medications.
What I tell people, frankly, is that until I have enough supply for my patients with type 2 diabetes, who need these agents to control their blood sugars, I want to keep this class of drugs available to them. I also hope we’re able to expand it more and more with improving insurance coverage – and that’s a big if, if you ask me – both for people who have prediabetes and for patients who are overweight and obese, because I think it’s really hard for people to lose weight.
It’s frustrating, and for many people, being overweight and obese causes all sorts of other health issues, not only diabetes. I believe that these drugs are both safe and effective and should be more available. I do think we need to be careful in terms of who we prescribe them to, at least at the moment. Hopefully, we’ll be able to expand their use.
Anything that can encourage our population to lose weight and maintain that weight loss is very important. We need to couple weight loss medications with lifestyle interventions. I think people can out-eat any medication; therefore, it’s very important to encourage our patients to eat better, to exercise more, and to do all the other things they need to do to reduce their risks for other comorbidities.
I am incredibly happy to have these newer agents on the market. I tell my patients – at least those who have diabetes – that they have to accept looking a little bit too thin for the benefits that we can see in using these medications.
Thank you.
Dr. Peters is professor of medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and director of the USC clinical diabetes programs. She has published more than 200 articles, reviews, and abstracts, and three books, on diabetes, and has been an investigator for more than 40 research studies. She has spoken internationally at over 400 programs and serves on many committees of several professional organizations. She has ties with Abbott Diabetes Care, AstraZeneca Becton Dickinson, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Livongo, MannKind Corporation, Medscape, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Omada Health, OptumHealth, Sanofi, and Zafgen. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Accelerated pacing a possible strategy for HFpEF?
Evidence supporting medications that slow the heart rate (HR), notably beta-blockers, is overwhelming in heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction. Underwhelming, however, is clinical trial support for such agents in patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Indeed, at least for some such patients, a treatment that modestly accelerates resting HR may be a more promising strategy, suggests an early line of research that challenges prevalent thinking about HFpEF therapy.
In a small, randomized test of the idea, patients with HFpEF and standard pacemakers set to a backup resting HR a bit higher than a standard of care 60 bpm, usually to about 75 bpm, reaped important quality of life benefits.
More strikingly, their natriuretic peptide levels and burden of atrial fibrillation (AFib) fell significantly, the latter by 27% over 1 year.
The trial enrolled only HFpEF patients with pacemakers previously implanted for sick sinus syndrome or atrioventricular block. But researchers say their 107-patient study called myPACE – if confirmed in larger, multicenter trials – lays the groundwork for a device therapy that is broadly useful, potentially, in patients with “preclinical or overt” HFpEF.
Indeed, some of the intervention’s “quite substantial” benefits rivaled or surpassed what his group has observed with available HFpEF drug therapies, including the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, observed Markus Meyer, MD, PhD, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Moreover, the study may be “the first to show that, with this approach, we can actually also reduce atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Meyer said his group is “confident” that the HR-modulation strategy will be successful in appropriate clinical trials and that “pacemakers, in the end, will become a treatment modality for HFpEF.”
Meyer is senior author on the trial’s publication in JAMA Cardiology in JAMA Cardiology (2023 Feb 1. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2022.5320), with lead author Margaret Infeld, MD, University of Vermont, Burlington.
The trial entered pacemaker patients with HFpEF of stage B or C – that is, either asymptomatic with structural disease or fully symptomatic. But, Dr. Meyer said, “we saw that the treatment effect was much more pronounced in the patients who had overt heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.”
Challenging beta-blocker dogma
The study, the report states, “contradicts canonical thinking” by suggesting HFpEF patients may benefit from a higher resting heart rate, which would presumably shorten diastolic filling time. It also “may help reduce the overprescription of beta-blockers to allow higher heart rates in this population.”
Indeed, Dr. Meyer observed, no one really knows whether beta-blockers work in HFpEF, “because they really have never been studied in a sufficiently powered randomized controlled trial.”
The current study “basically rewrites what we know about the pathophysiology of this form of clinical heart failure,” said Michael R. Zile, MD, Medical University of South Carolina and Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Charleston, who was not part of the trial or report.
Previously in HFpEF, Dr. Zile said in an interview, “everybody thought you needed to make diastole longer to give the ventricle a longer time to fill. And none of that really made any sense. It was just sort of accepted as dogma.”
The idea led to widespread use of beta-blockers in HFpEF but “turned out just not to be true.” Indeed, European and North American guidelines, Dr. Zile observed, “have all taken beta-blockers out of the equation for HFpEF” except for treating comorbidities that can be associated with HFpEF, like hypertension or AFib.
Many patients with HFpEF and chronotropic incompetence could be provided with standard pacemakers with primarily conduction-system pacing but are not getting them, he observed.
The current study might help change that. No one is suggesting, based on the current study, “that we start putting pacemakers in every single patient with HFpEF,” Dr. Zile said. Still, for HFpEF patients already with a pacemaker, the study provides “reasonable assurance” that its criteria for elevated resting HR may well improve symptoms.
Moreover, it suggests such pacemakers, programmed as in the study, might potentially give a boost to HFpEF patients without chronotropic incompetence but with persisting symptoms despite guideline-directed drug therapy. That’s certainly worth exploring in further trials, Dr. Zile said.
How the study worked
The single-center trial entered 107 participants with HFpEF and pacemakers set, at baseline, to a backup resting HR of 60 bpm; their age averaged 75 and 48% were women. Only patients with devices for atrial pacing, conduction-system pacing, or biventricular pacing – which are unlikely to promote ventricular dyssynchrony – were included.
They were randomly assigned, double-blind, to have their devices set to an accelerated backup rate or to be continued at 60 bpm. The backup resting rate set for the intervention group’s 50 patients was individualized based on height and other factors; the median was 75 bpm.
Scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire, the primary endpoint, improved in the intervention group, compared with baseline, by about 11 points after 1 month and by 15 points after 1 year (P < .001).
The scores in the usual-care group deteriorated by half a point and by 3.5 points at 1 month and 1 year (P = .03), respectively.
Consistent advantages for the accelerated-HR strategy were evident throughout the major secondary endpoints. For example, levels of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide fell an average 109 pg/dL after 1 month in the accelerated-HR group and rose a mean of 128 pg/dL in the usual-care group (P = .02).
Mean daily pacemaker-monitored activity level rose by 47 minutes by 1 year in the accelerated-HR group, compared with a drop of 22 minutes for those assigned to the standard-care rate (P < .001).
AFib was detected in 18% of intervention patients at the 1-year follow-up, down from 31% at baseline. Their risk ratio for AFib at 1 year was 0.73 (95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.99, P = .04), compared with the control group.
In other patients with HFpEF “we have done pacing studies where we just ramped up the pacing rate, and we see that these pressures in the left atrium actually drop immediately,” Dr. Meyer said. It’s that “unburdening of the atria,” he added, that probably leads to the reduction in AFib.
Dr. Meyer reported holding a patent for pacemakers for HFpEF licensed to Medtronic. Dr. Zile said he consults for Medtronic and has no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Evidence supporting medications that slow the heart rate (HR), notably beta-blockers, is overwhelming in heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction. Underwhelming, however, is clinical trial support for such agents in patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Indeed, at least for some such patients, a treatment that modestly accelerates resting HR may be a more promising strategy, suggests an early line of research that challenges prevalent thinking about HFpEF therapy.
In a small, randomized test of the idea, patients with HFpEF and standard pacemakers set to a backup resting HR a bit higher than a standard of care 60 bpm, usually to about 75 bpm, reaped important quality of life benefits.
More strikingly, their natriuretic peptide levels and burden of atrial fibrillation (AFib) fell significantly, the latter by 27% over 1 year.
The trial enrolled only HFpEF patients with pacemakers previously implanted for sick sinus syndrome or atrioventricular block. But researchers say their 107-patient study called myPACE – if confirmed in larger, multicenter trials – lays the groundwork for a device therapy that is broadly useful, potentially, in patients with “preclinical or overt” HFpEF.
Indeed, some of the intervention’s “quite substantial” benefits rivaled or surpassed what his group has observed with available HFpEF drug therapies, including the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, observed Markus Meyer, MD, PhD, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Moreover, the study may be “the first to show that, with this approach, we can actually also reduce atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Meyer said his group is “confident” that the HR-modulation strategy will be successful in appropriate clinical trials and that “pacemakers, in the end, will become a treatment modality for HFpEF.”
Meyer is senior author on the trial’s publication in JAMA Cardiology in JAMA Cardiology (2023 Feb 1. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2022.5320), with lead author Margaret Infeld, MD, University of Vermont, Burlington.
The trial entered pacemaker patients with HFpEF of stage B or C – that is, either asymptomatic with structural disease or fully symptomatic. But, Dr. Meyer said, “we saw that the treatment effect was much more pronounced in the patients who had overt heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.”
Challenging beta-blocker dogma
The study, the report states, “contradicts canonical thinking” by suggesting HFpEF patients may benefit from a higher resting heart rate, which would presumably shorten diastolic filling time. It also “may help reduce the overprescription of beta-blockers to allow higher heart rates in this population.”
Indeed, Dr. Meyer observed, no one really knows whether beta-blockers work in HFpEF, “because they really have never been studied in a sufficiently powered randomized controlled trial.”
The current study “basically rewrites what we know about the pathophysiology of this form of clinical heart failure,” said Michael R. Zile, MD, Medical University of South Carolina and Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Charleston, who was not part of the trial or report.
Previously in HFpEF, Dr. Zile said in an interview, “everybody thought you needed to make diastole longer to give the ventricle a longer time to fill. And none of that really made any sense. It was just sort of accepted as dogma.”
The idea led to widespread use of beta-blockers in HFpEF but “turned out just not to be true.” Indeed, European and North American guidelines, Dr. Zile observed, “have all taken beta-blockers out of the equation for HFpEF” except for treating comorbidities that can be associated with HFpEF, like hypertension or AFib.
Many patients with HFpEF and chronotropic incompetence could be provided with standard pacemakers with primarily conduction-system pacing but are not getting them, he observed.
The current study might help change that. No one is suggesting, based on the current study, “that we start putting pacemakers in every single patient with HFpEF,” Dr. Zile said. Still, for HFpEF patients already with a pacemaker, the study provides “reasonable assurance” that its criteria for elevated resting HR may well improve symptoms.
Moreover, it suggests such pacemakers, programmed as in the study, might potentially give a boost to HFpEF patients without chronotropic incompetence but with persisting symptoms despite guideline-directed drug therapy. That’s certainly worth exploring in further trials, Dr. Zile said.
How the study worked
The single-center trial entered 107 participants with HFpEF and pacemakers set, at baseline, to a backup resting HR of 60 bpm; their age averaged 75 and 48% were women. Only patients with devices for atrial pacing, conduction-system pacing, or biventricular pacing – which are unlikely to promote ventricular dyssynchrony – were included.
They were randomly assigned, double-blind, to have their devices set to an accelerated backup rate or to be continued at 60 bpm. The backup resting rate set for the intervention group’s 50 patients was individualized based on height and other factors; the median was 75 bpm.
Scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire, the primary endpoint, improved in the intervention group, compared with baseline, by about 11 points after 1 month and by 15 points after 1 year (P < .001).
The scores in the usual-care group deteriorated by half a point and by 3.5 points at 1 month and 1 year (P = .03), respectively.
Consistent advantages for the accelerated-HR strategy were evident throughout the major secondary endpoints. For example, levels of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide fell an average 109 pg/dL after 1 month in the accelerated-HR group and rose a mean of 128 pg/dL in the usual-care group (P = .02).
Mean daily pacemaker-monitored activity level rose by 47 minutes by 1 year in the accelerated-HR group, compared with a drop of 22 minutes for those assigned to the standard-care rate (P < .001).
AFib was detected in 18% of intervention patients at the 1-year follow-up, down from 31% at baseline. Their risk ratio for AFib at 1 year was 0.73 (95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.99, P = .04), compared with the control group.
In other patients with HFpEF “we have done pacing studies where we just ramped up the pacing rate, and we see that these pressures in the left atrium actually drop immediately,” Dr. Meyer said. It’s that “unburdening of the atria,” he added, that probably leads to the reduction in AFib.
Dr. Meyer reported holding a patent for pacemakers for HFpEF licensed to Medtronic. Dr. Zile said he consults for Medtronic and has no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Evidence supporting medications that slow the heart rate (HR), notably beta-blockers, is overwhelming in heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction. Underwhelming, however, is clinical trial support for such agents in patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Indeed, at least for some such patients, a treatment that modestly accelerates resting HR may be a more promising strategy, suggests an early line of research that challenges prevalent thinking about HFpEF therapy.
In a small, randomized test of the idea, patients with HFpEF and standard pacemakers set to a backup resting HR a bit higher than a standard of care 60 bpm, usually to about 75 bpm, reaped important quality of life benefits.
More strikingly, their natriuretic peptide levels and burden of atrial fibrillation (AFib) fell significantly, the latter by 27% over 1 year.
The trial enrolled only HFpEF patients with pacemakers previously implanted for sick sinus syndrome or atrioventricular block. But researchers say their 107-patient study called myPACE – if confirmed in larger, multicenter trials – lays the groundwork for a device therapy that is broadly useful, potentially, in patients with “preclinical or overt” HFpEF.
Indeed, some of the intervention’s “quite substantial” benefits rivaled or surpassed what his group has observed with available HFpEF drug therapies, including the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, observed Markus Meyer, MD, PhD, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Moreover, the study may be “the first to show that, with this approach, we can actually also reduce atrial fibrillation,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Meyer said his group is “confident” that the HR-modulation strategy will be successful in appropriate clinical trials and that “pacemakers, in the end, will become a treatment modality for HFpEF.”
Meyer is senior author on the trial’s publication in JAMA Cardiology in JAMA Cardiology (2023 Feb 1. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2022.5320), with lead author Margaret Infeld, MD, University of Vermont, Burlington.
The trial entered pacemaker patients with HFpEF of stage B or C – that is, either asymptomatic with structural disease or fully symptomatic. But, Dr. Meyer said, “we saw that the treatment effect was much more pronounced in the patients who had overt heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.”
Challenging beta-blocker dogma
The study, the report states, “contradicts canonical thinking” by suggesting HFpEF patients may benefit from a higher resting heart rate, which would presumably shorten diastolic filling time. It also “may help reduce the overprescription of beta-blockers to allow higher heart rates in this population.”
Indeed, Dr. Meyer observed, no one really knows whether beta-blockers work in HFpEF, “because they really have never been studied in a sufficiently powered randomized controlled trial.”
The current study “basically rewrites what we know about the pathophysiology of this form of clinical heart failure,” said Michael R. Zile, MD, Medical University of South Carolina and Veterans Affairs Medical Center, both in Charleston, who was not part of the trial or report.
Previously in HFpEF, Dr. Zile said in an interview, “everybody thought you needed to make diastole longer to give the ventricle a longer time to fill. And none of that really made any sense. It was just sort of accepted as dogma.”
The idea led to widespread use of beta-blockers in HFpEF but “turned out just not to be true.” Indeed, European and North American guidelines, Dr. Zile observed, “have all taken beta-blockers out of the equation for HFpEF” except for treating comorbidities that can be associated with HFpEF, like hypertension or AFib.
Many patients with HFpEF and chronotropic incompetence could be provided with standard pacemakers with primarily conduction-system pacing but are not getting them, he observed.
The current study might help change that. No one is suggesting, based on the current study, “that we start putting pacemakers in every single patient with HFpEF,” Dr. Zile said. Still, for HFpEF patients already with a pacemaker, the study provides “reasonable assurance” that its criteria for elevated resting HR may well improve symptoms.
Moreover, it suggests such pacemakers, programmed as in the study, might potentially give a boost to HFpEF patients without chronotropic incompetence but with persisting symptoms despite guideline-directed drug therapy. That’s certainly worth exploring in further trials, Dr. Zile said.
How the study worked
The single-center trial entered 107 participants with HFpEF and pacemakers set, at baseline, to a backup resting HR of 60 bpm; their age averaged 75 and 48% were women. Only patients with devices for atrial pacing, conduction-system pacing, or biventricular pacing – which are unlikely to promote ventricular dyssynchrony – were included.
They were randomly assigned, double-blind, to have their devices set to an accelerated backup rate or to be continued at 60 bpm. The backup resting rate set for the intervention group’s 50 patients was individualized based on height and other factors; the median was 75 bpm.
Scores on the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire, the primary endpoint, improved in the intervention group, compared with baseline, by about 11 points after 1 month and by 15 points after 1 year (P < .001).
The scores in the usual-care group deteriorated by half a point and by 3.5 points at 1 month and 1 year (P = .03), respectively.
Consistent advantages for the accelerated-HR strategy were evident throughout the major secondary endpoints. For example, levels of N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide fell an average 109 pg/dL after 1 month in the accelerated-HR group and rose a mean of 128 pg/dL in the usual-care group (P = .02).
Mean daily pacemaker-monitored activity level rose by 47 minutes by 1 year in the accelerated-HR group, compared with a drop of 22 minutes for those assigned to the standard-care rate (P < .001).
AFib was detected in 18% of intervention patients at the 1-year follow-up, down from 31% at baseline. Their risk ratio for AFib at 1 year was 0.73 (95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.99, P = .04), compared with the control group.
In other patients with HFpEF “we have done pacing studies where we just ramped up the pacing rate, and we see that these pressures in the left atrium actually drop immediately,” Dr. Meyer said. It’s that “unburdening of the atria,” he added, that probably leads to the reduction in AFib.
Dr. Meyer reported holding a patent for pacemakers for HFpEF licensed to Medtronic. Dr. Zile said he consults for Medtronic and has no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
Longer diabetes duration links with increased heart failure
The longer people had diabetes, the greater their rate of incident heart failure, suggests a recently published review of prospectively collected observational data from nearly 24,000 people with diabetes in the UK Biobank.
The findings “add to the growing body of evidence suggesting that duration of diabetes is an important and independent determinant of heart failure among patients with diabetes,” comments Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, MD, PhD, in an accompanying editorial.
Collectively, the new UK Biobank results and prior findings, “provide additional persuasive evidence that the link between duration of diabetes and heart failure is real,” although the physiological mechanisms behind the relationship remain incompletely understood, wrote Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui, an endocrinologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
“The duration of diabetes may reflect cumulative effects of various adverse processes in the setting of diabetes” that result in “intrinsic myocardial lesions,” he suggested. These adverse processes might include not only hyperglycemia, but also glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, hyperinsulinemia, advanced glycosylation end products, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, cardiac autonomic neuropathy, and coronary microvascular dysfunction. Long-duration diabetes may also contribute to declining kidney function, which can further worsen heart failure risk.
The upshot is that clinicians may need to consider more systematically the duration of diabetes when assessing people with diabetes for heart failure.
Existing risk-assessment tools for predicting heart failure in people with diabetes “have not always accounted for diabetes duration,” Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui noted.
Intensify heart failure detection with longer diabetes duration
“Active heart failure detection should perhaps be intensified with increased diabetes duration,” Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui suggested in his editorial. He noted that a 2022 consensus report by the American Diabetes Association recommends clinicians measure natriuretic peptide or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin in all people with diabetes “on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest heart failure stages and implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic heart failure.”
The UK Biobank study was run by investigators primarily based in China and included data from 23,754 people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and no heart failure at baseline. The prospectively collected data allowed for a median follow-up of 11.7 years, during which time 2,081 people developed incident heart failure.
In an analysis that divided participants into four categories of diabetes duration (< 5 years, 5-9 years, 10-14 years, and ≥ 15 years) and adjusted for potential confounders, heart failure incidence showed a significant 32% increased incidence among those with diabetes for at least 15 years, compared with those with diabetes for less than 5 years. People with a diabetes duration of 5-14 years showed a trend toward having more incident heart failure, compared with those with diabetes for less than 5 years, but the difference was not significant.
An adjusted analysis also showed poor glycemic control at baseline (hemoglobin A1c ≥ 8.0%) significantly linked with a 46% increased incidence of heart failure, compared with those with baseline A1c less than 7.0%.
Additive effect?
When the authors analyzed the effect of both these variables, they saw a roughly additive effect.
Patients with diabetes for at least 15 years and a baseline A1c of at least 8.0% had a 98% increased incidence of heart failure, compared with those who had diabetes for less than 5 years and a baseline A1c less than 7.0%, after adjustment. This association was independent of age, sex, and race.
These findings “highlight the paramount role of the duration of diabetes and its interaction with glycemic control in the development of heart failure,” the authors concluded. “Long duration of diabetes and poor glycemic control may result in structural and functional changes in the myocardium, which is likely to underlie the pathogenesis of heart failure among individuals with diabetes.”
In his editorial, Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui lauded the report for its “robust” analyses that included a large sample and accounted for key confounders, such as glycemic control. However, he also cited eight “shortcomings” of the study, including its sole reliance on A1c levels to identify diabetes, a likely underestimation of diabetes duration, the lumping together of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and lack of a subanalysis of incident heart failure in those with preserved or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction.
Among prior reports of evidence also suggesting an effect of diabetes duration on incident heart failure, Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui cited a study he led, published in 2021, that analyzed prospective, longitudinal, observational data from 9,734 adults enrolled in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. The results showed that, compared with those without diabetes, the incidence of heart failure rose with longer diabetes duration, with the highest risk among those with diabetes for at least 15 years, who had a 2.8-fold increase in heart failure versus the reference group. Each 5-year increase in diabetes duration was associated with a significant 17% relative increase in heart failure incidence.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and editorialist reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The longer people had diabetes, the greater their rate of incident heart failure, suggests a recently published review of prospectively collected observational data from nearly 24,000 people with diabetes in the UK Biobank.
The findings “add to the growing body of evidence suggesting that duration of diabetes is an important and independent determinant of heart failure among patients with diabetes,” comments Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, MD, PhD, in an accompanying editorial.
Collectively, the new UK Biobank results and prior findings, “provide additional persuasive evidence that the link between duration of diabetes and heart failure is real,” although the physiological mechanisms behind the relationship remain incompletely understood, wrote Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui, an endocrinologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
“The duration of diabetes may reflect cumulative effects of various adverse processes in the setting of diabetes” that result in “intrinsic myocardial lesions,” he suggested. These adverse processes might include not only hyperglycemia, but also glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, hyperinsulinemia, advanced glycosylation end products, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, cardiac autonomic neuropathy, and coronary microvascular dysfunction. Long-duration diabetes may also contribute to declining kidney function, which can further worsen heart failure risk.
The upshot is that clinicians may need to consider more systematically the duration of diabetes when assessing people with diabetes for heart failure.
Existing risk-assessment tools for predicting heart failure in people with diabetes “have not always accounted for diabetes duration,” Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui noted.
Intensify heart failure detection with longer diabetes duration
“Active heart failure detection should perhaps be intensified with increased diabetes duration,” Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui suggested in his editorial. He noted that a 2022 consensus report by the American Diabetes Association recommends clinicians measure natriuretic peptide or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin in all people with diabetes “on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest heart failure stages and implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic heart failure.”
The UK Biobank study was run by investigators primarily based in China and included data from 23,754 people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and no heart failure at baseline. The prospectively collected data allowed for a median follow-up of 11.7 years, during which time 2,081 people developed incident heart failure.
In an analysis that divided participants into four categories of diabetes duration (< 5 years, 5-9 years, 10-14 years, and ≥ 15 years) and adjusted for potential confounders, heart failure incidence showed a significant 32% increased incidence among those with diabetes for at least 15 years, compared with those with diabetes for less than 5 years. People with a diabetes duration of 5-14 years showed a trend toward having more incident heart failure, compared with those with diabetes for less than 5 years, but the difference was not significant.
An adjusted analysis also showed poor glycemic control at baseline (hemoglobin A1c ≥ 8.0%) significantly linked with a 46% increased incidence of heart failure, compared with those with baseline A1c less than 7.0%.
Additive effect?
When the authors analyzed the effect of both these variables, they saw a roughly additive effect.
Patients with diabetes for at least 15 years and a baseline A1c of at least 8.0% had a 98% increased incidence of heart failure, compared with those who had diabetes for less than 5 years and a baseline A1c less than 7.0%, after adjustment. This association was independent of age, sex, and race.
These findings “highlight the paramount role of the duration of diabetes and its interaction with glycemic control in the development of heart failure,” the authors concluded. “Long duration of diabetes and poor glycemic control may result in structural and functional changes in the myocardium, which is likely to underlie the pathogenesis of heart failure among individuals with diabetes.”
In his editorial, Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui lauded the report for its “robust” analyses that included a large sample and accounted for key confounders, such as glycemic control. However, he also cited eight “shortcomings” of the study, including its sole reliance on A1c levels to identify diabetes, a likely underestimation of diabetes duration, the lumping together of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and lack of a subanalysis of incident heart failure in those with preserved or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction.
Among prior reports of evidence also suggesting an effect of diabetes duration on incident heart failure, Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui cited a study he led, published in 2021, that analyzed prospective, longitudinal, observational data from 9,734 adults enrolled in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. The results showed that, compared with those without diabetes, the incidence of heart failure rose with longer diabetes duration, with the highest risk among those with diabetes for at least 15 years, who had a 2.8-fold increase in heart failure versus the reference group. Each 5-year increase in diabetes duration was associated with a significant 17% relative increase in heart failure incidence.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and editorialist reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The longer people had diabetes, the greater their rate of incident heart failure, suggests a recently published review of prospectively collected observational data from nearly 24,000 people with diabetes in the UK Biobank.
The findings “add to the growing body of evidence suggesting that duration of diabetes is an important and independent determinant of heart failure among patients with diabetes,” comments Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, MD, PhD, in an accompanying editorial.
Collectively, the new UK Biobank results and prior findings, “provide additional persuasive evidence that the link between duration of diabetes and heart failure is real,” although the physiological mechanisms behind the relationship remain incompletely understood, wrote Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui, an endocrinologist at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore.
“The duration of diabetes may reflect cumulative effects of various adverse processes in the setting of diabetes” that result in “intrinsic myocardial lesions,” he suggested. These adverse processes might include not only hyperglycemia, but also glucotoxicity, lipotoxicity, hyperinsulinemia, advanced glycosylation end products, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, cardiac autonomic neuropathy, and coronary microvascular dysfunction. Long-duration diabetes may also contribute to declining kidney function, which can further worsen heart failure risk.
The upshot is that clinicians may need to consider more systematically the duration of diabetes when assessing people with diabetes for heart failure.
Existing risk-assessment tools for predicting heart failure in people with diabetes “have not always accounted for diabetes duration,” Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui noted.
Intensify heart failure detection with longer diabetes duration
“Active heart failure detection should perhaps be intensified with increased diabetes duration,” Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui suggested in his editorial. He noted that a 2022 consensus report by the American Diabetes Association recommends clinicians measure natriuretic peptide or high-sensitivity cardiac troponin in all people with diabetes “on at least a yearly basis to identify the earliest heart failure stages and implement strategies to prevent transition to symptomatic heart failure.”
The UK Biobank study was run by investigators primarily based in China and included data from 23,754 people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and no heart failure at baseline. The prospectively collected data allowed for a median follow-up of 11.7 years, during which time 2,081 people developed incident heart failure.
In an analysis that divided participants into four categories of diabetes duration (< 5 years, 5-9 years, 10-14 years, and ≥ 15 years) and adjusted for potential confounders, heart failure incidence showed a significant 32% increased incidence among those with diabetes for at least 15 years, compared with those with diabetes for less than 5 years. People with a diabetes duration of 5-14 years showed a trend toward having more incident heart failure, compared with those with diabetes for less than 5 years, but the difference was not significant.
An adjusted analysis also showed poor glycemic control at baseline (hemoglobin A1c ≥ 8.0%) significantly linked with a 46% increased incidence of heart failure, compared with those with baseline A1c less than 7.0%.
Additive effect?
When the authors analyzed the effect of both these variables, they saw a roughly additive effect.
Patients with diabetes for at least 15 years and a baseline A1c of at least 8.0% had a 98% increased incidence of heart failure, compared with those who had diabetes for less than 5 years and a baseline A1c less than 7.0%, after adjustment. This association was independent of age, sex, and race.
These findings “highlight the paramount role of the duration of diabetes and its interaction with glycemic control in the development of heart failure,” the authors concluded. “Long duration of diabetes and poor glycemic control may result in structural and functional changes in the myocardium, which is likely to underlie the pathogenesis of heart failure among individuals with diabetes.”
In his editorial, Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui lauded the report for its “robust” analyses that included a large sample and accounted for key confounders, such as glycemic control. However, he also cited eight “shortcomings” of the study, including its sole reliance on A1c levels to identify diabetes, a likely underestimation of diabetes duration, the lumping together of people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and lack of a subanalysis of incident heart failure in those with preserved or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction.
Among prior reports of evidence also suggesting an effect of diabetes duration on incident heart failure, Dr. Echouffo-Tcheugui cited a study he led, published in 2021, that analyzed prospective, longitudinal, observational data from 9,734 adults enrolled in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. The results showed that, compared with those without diabetes, the incidence of heart failure rose with longer diabetes duration, with the highest risk among those with diabetes for at least 15 years, who had a 2.8-fold increase in heart failure versus the reference group. Each 5-year increase in diabetes duration was associated with a significant 17% relative increase in heart failure incidence.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and editorialist reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM
New developments and barriers to palliative care
As we enter into this new year, it is a good time to review the past few years of living through a pandemic and the impact this has had on the field of palliative care.
According to the World Health Organization, “Palliative care is an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families who are facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, by the prevention and relief of suffering through early identification, assessment and treatment of pain and other problems whether physical, psychosocial and spiritual.”1 They identify a global need and recognize palliative care as a “human right to health and as a standard of care particularly for individuals living with a serious illness.1 However, the WHO goes further to recognize palliative care as an essential part of the response team during crises and health emergencies like a pandemic, noting that a response team without palliative care is “medically deficient and ethically indefensible.”2
The need for palliative care in the United States is projected to grow significantly in the next decades.3 However, there has been insufficient staffing to meet these needs, even prior to the pandemic.4 The demand for palliative care reached further unprecedented levels during the pandemic as palliative care teams played an integral role and were well situated to support not only patients and families with COVID-19,5 but to also support the well-being of health care teams caring for COVID-19 patients.6,7
A recent survey that was conducted by the Center to Advance Palliative Care among palliative care leadership captured the experiences of leading their teams through a pandemic. Below are the results of this survey, which highlighted important issues and developments to palliative care during the pandemic.6
Increasing need for palliative care
One of the main findings from the national survey of palliative care leaders corroborated that the demands for palliative care have increased significantly from 2020 through the pandemic.
As with many areas in the health care system, the pandemic has emphasized the strain and short staffing of the palliative care teams. In the survey, 61% of leaders reported that palliative care consults significantly increased from prepandemic levels. But only 26% of these leaders said they had the staffing support to meet these needs.
Value of palliative care
The value of palliative care along with understanding of the role of palliative care has been better recognized during the pandemic and has been evidenced by the increase in palliative care referrals from clinical providers, compared with prepandemic levels. In addition, data collected showed that earlier palliative care consultations reduced length of hospital stay, decreased ICU admissions, and improved patient, family, and provider satisfaction.
Well-being of the workforce
The pandemic has been a tremendously stressful time for the health care workforce that has undoubtedly led to burnout. A nationwide study of physicians,8 found that 61% of physicians experienced burnout. This is a significant increase from prepandemic levels with impacts on mental health (that is, anxiety, depression). This study did not include palliative care specialists, but the CAPC survey indicates a similar feeling of burnout. Because of this, some palliative care specialists have left the field altogether, or are leaving leadership positions because of burnout and exhaustion from the pandemic. This was featured as a concern among palliative care leaders, where 93% reported concern for the emotional well-being of the palliative care team.
Telehealth
A permanent operational change that has been well-utilized and implemented across multiple health care settings has been providing palliative care through telehealth. Prior to the pandemic, the baseline use of telehealth was less than 5% with the use now greater than 75% – a modality that is favored by both patients and clinicians. This has offered a broader scope of practice, reaching individuals who may have no other means, have limitations to accessing palliative care, or were in circumstances where patients required isolation during the pandemic. However, there are limitations to this platform, including in equity of access to devices and ease of use for those with limited exposure to technology.9
Barriers to implementation
Although the important role and value of palliative care has been well recognized, there have been barriers identified in a qualitative study of the integration of palliative care into COVID-19 action plans that are mentioned below.5
- Patients and families were identified as barriers to integration of palliative care if they were not open to palliative care referral, mainly because of misperceptions of palliative care as end-of-life care.
- Palliative care knowledge among providers was identified as another barrier to integration of palliative care. There are still misperceptions among providers that palliative care is end-of-life care and palliative care involvement is stigmatized as hastening death. In addition, some felt that COVID-19 was not a traditional “palliative diagnosis” thus were less likely to integrate palliative care into care plans.
- Lack of availability of a primary provider to conduct primary palliative care and lack of motivation “not to give up” were identified as other barriers. On the other hand, palliative care provider availability and accessibility to care teams affected the integration into COVID-19 care plans.
- COVID-19 itself was identified to be a barrier because of the uncertainty of illness trajectory and outcomes, which made it difficult for doctors to ascertain when to involve palliative care.
- Leadership and institution were important factors to consider in integration of palliative care into long-term care plans, which depended on leadership engagement and institutional culture.
Takeaways
The past few years have taught us a lot, but there is still much to learn. The COVID-19 pandemic has called attention to the challenges and barriers of health care delivery and has magnified the needs of the health care system including its infrastructure, preparedness, and staffing, including the field of palliative care. More work needs to be done, but leaders have taken steps to initiate national and international preparedness plans including the integration of palliative care, which has been identified as a vital role in any humanitarian crises.10,11
Dr. Kang is a geriatrician and palliative care provider at the University of Washington, Seattle, in the division of geriatrics and gerontology. She has no conflicts related to the content of this article.
References
1. Palliative care. World Health Organization. Aug 5, 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/palliative-care
2. World Health Organization. Integrating palliative care and symptom relief into the response to humanitarian emergencies and crises: A WHO guide. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/274565.
3. Hughes MT, Smith TJ. The growth of palliative care in the United States. Annual Review Public Health. 2014;35:459-75.
4. Pastrana T et al. The impact of COVID-19 on palliative care workers across the world: A qualitative analysis of responses to open-ended questions. Palliative and Supportive Care. 2021:1-6.
5. Wentlandt K et al. Identifying barriers and facilitators to palliative care integration in the management of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A qualitative study. Palliat Med. 2022;36(6):945-54.
6. Rogers M et al. Palliative care leadership during the pandemic: Results from a recent survey. Center to Advance Palliative Care. 2022 Sept 8. https://www.capc.org/blog/palliative-care-leadership-during-the-pandemic-results-from-a-recent-survey
7. Fogelman P. Reflections form a palliative care program leader two years into the pandemic. Center to Advance Palliative Care. 2023 Jan 15. https://www.capc.org/blog/reflections-from-a-palliative-care-program-leader-two-years-into-the-pandemic
8. 2021 survey of America’s physicians Covid-19 impact edition: A year later. The Physicians Foundation. 2021.
9. Caraceni A et al. Telemedicine for outpatient palliative care during Covid-19 pandemics: A longitudinal study. BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care. 2022;0:1-7.
10. Bausewein C et al. National strategy for palliative care of severely ill and dying people and their relatives in pandemics (PallPan) in Germany – study protocol of a mixed-methods project. BMC Palliative Care. 2022;21(10).
11. Powell RA et al. Palliative care in humanitarian crises: Always something to offer. The Lancet. 2017;389(10078):1498-9.
As we enter into this new year, it is a good time to review the past few years of living through a pandemic and the impact this has had on the field of palliative care.
According to the World Health Organization, “Palliative care is an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families who are facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, by the prevention and relief of suffering through early identification, assessment and treatment of pain and other problems whether physical, psychosocial and spiritual.”1 They identify a global need and recognize palliative care as a “human right to health and as a standard of care particularly for individuals living with a serious illness.1 However, the WHO goes further to recognize palliative care as an essential part of the response team during crises and health emergencies like a pandemic, noting that a response team without palliative care is “medically deficient and ethically indefensible.”2
The need for palliative care in the United States is projected to grow significantly in the next decades.3 However, there has been insufficient staffing to meet these needs, even prior to the pandemic.4 The demand for palliative care reached further unprecedented levels during the pandemic as palliative care teams played an integral role and were well situated to support not only patients and families with COVID-19,5 but to also support the well-being of health care teams caring for COVID-19 patients.6,7
A recent survey that was conducted by the Center to Advance Palliative Care among palliative care leadership captured the experiences of leading their teams through a pandemic. Below are the results of this survey, which highlighted important issues and developments to palliative care during the pandemic.6
Increasing need for palliative care
One of the main findings from the national survey of palliative care leaders corroborated that the demands for palliative care have increased significantly from 2020 through the pandemic.
As with many areas in the health care system, the pandemic has emphasized the strain and short staffing of the palliative care teams. In the survey, 61% of leaders reported that palliative care consults significantly increased from prepandemic levels. But only 26% of these leaders said they had the staffing support to meet these needs.
Value of palliative care
The value of palliative care along with understanding of the role of palliative care has been better recognized during the pandemic and has been evidenced by the increase in palliative care referrals from clinical providers, compared with prepandemic levels. In addition, data collected showed that earlier palliative care consultations reduced length of hospital stay, decreased ICU admissions, and improved patient, family, and provider satisfaction.
Well-being of the workforce
The pandemic has been a tremendously stressful time for the health care workforce that has undoubtedly led to burnout. A nationwide study of physicians,8 found that 61% of physicians experienced burnout. This is a significant increase from prepandemic levels with impacts on mental health (that is, anxiety, depression). This study did not include palliative care specialists, but the CAPC survey indicates a similar feeling of burnout. Because of this, some palliative care specialists have left the field altogether, or are leaving leadership positions because of burnout and exhaustion from the pandemic. This was featured as a concern among palliative care leaders, where 93% reported concern for the emotional well-being of the palliative care team.
Telehealth
A permanent operational change that has been well-utilized and implemented across multiple health care settings has been providing palliative care through telehealth. Prior to the pandemic, the baseline use of telehealth was less than 5% with the use now greater than 75% – a modality that is favored by both patients and clinicians. This has offered a broader scope of practice, reaching individuals who may have no other means, have limitations to accessing palliative care, or were in circumstances where patients required isolation during the pandemic. However, there are limitations to this platform, including in equity of access to devices and ease of use for those with limited exposure to technology.9
Barriers to implementation
Although the important role and value of palliative care has been well recognized, there have been barriers identified in a qualitative study of the integration of palliative care into COVID-19 action plans that are mentioned below.5
- Patients and families were identified as barriers to integration of palliative care if they were not open to palliative care referral, mainly because of misperceptions of palliative care as end-of-life care.
- Palliative care knowledge among providers was identified as another barrier to integration of palliative care. There are still misperceptions among providers that palliative care is end-of-life care and palliative care involvement is stigmatized as hastening death. In addition, some felt that COVID-19 was not a traditional “palliative diagnosis” thus were less likely to integrate palliative care into care plans.
- Lack of availability of a primary provider to conduct primary palliative care and lack of motivation “not to give up” were identified as other barriers. On the other hand, palliative care provider availability and accessibility to care teams affected the integration into COVID-19 care plans.
- COVID-19 itself was identified to be a barrier because of the uncertainty of illness trajectory and outcomes, which made it difficult for doctors to ascertain when to involve palliative care.
- Leadership and institution were important factors to consider in integration of palliative care into long-term care plans, which depended on leadership engagement and institutional culture.
Takeaways
The past few years have taught us a lot, but there is still much to learn. The COVID-19 pandemic has called attention to the challenges and barriers of health care delivery and has magnified the needs of the health care system including its infrastructure, preparedness, and staffing, including the field of palliative care. More work needs to be done, but leaders have taken steps to initiate national and international preparedness plans including the integration of palliative care, which has been identified as a vital role in any humanitarian crises.10,11
Dr. Kang is a geriatrician and palliative care provider at the University of Washington, Seattle, in the division of geriatrics and gerontology. She has no conflicts related to the content of this article.
References
1. Palliative care. World Health Organization. Aug 5, 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/palliative-care
2. World Health Organization. Integrating palliative care and symptom relief into the response to humanitarian emergencies and crises: A WHO guide. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/274565.
3. Hughes MT, Smith TJ. The growth of palliative care in the United States. Annual Review Public Health. 2014;35:459-75.
4. Pastrana T et al. The impact of COVID-19 on palliative care workers across the world: A qualitative analysis of responses to open-ended questions. Palliative and Supportive Care. 2021:1-6.
5. Wentlandt K et al. Identifying barriers and facilitators to palliative care integration in the management of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A qualitative study. Palliat Med. 2022;36(6):945-54.
6. Rogers M et al. Palliative care leadership during the pandemic: Results from a recent survey. Center to Advance Palliative Care. 2022 Sept 8. https://www.capc.org/blog/palliative-care-leadership-during-the-pandemic-results-from-a-recent-survey
7. Fogelman P. Reflections form a palliative care program leader two years into the pandemic. Center to Advance Palliative Care. 2023 Jan 15. https://www.capc.org/blog/reflections-from-a-palliative-care-program-leader-two-years-into-the-pandemic
8. 2021 survey of America’s physicians Covid-19 impact edition: A year later. The Physicians Foundation. 2021.
9. Caraceni A et al. Telemedicine for outpatient palliative care during Covid-19 pandemics: A longitudinal study. BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care. 2022;0:1-7.
10. Bausewein C et al. National strategy for palliative care of severely ill and dying people and their relatives in pandemics (PallPan) in Germany – study protocol of a mixed-methods project. BMC Palliative Care. 2022;21(10).
11. Powell RA et al. Palliative care in humanitarian crises: Always something to offer. The Lancet. 2017;389(10078):1498-9.
As we enter into this new year, it is a good time to review the past few years of living through a pandemic and the impact this has had on the field of palliative care.
According to the World Health Organization, “Palliative care is an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and their families who are facing the problems associated with life-threatening illness, by the prevention and relief of suffering through early identification, assessment and treatment of pain and other problems whether physical, psychosocial and spiritual.”1 They identify a global need and recognize palliative care as a “human right to health and as a standard of care particularly for individuals living with a serious illness.1 However, the WHO goes further to recognize palliative care as an essential part of the response team during crises and health emergencies like a pandemic, noting that a response team without palliative care is “medically deficient and ethically indefensible.”2
The need for palliative care in the United States is projected to grow significantly in the next decades.3 However, there has been insufficient staffing to meet these needs, even prior to the pandemic.4 The demand for palliative care reached further unprecedented levels during the pandemic as palliative care teams played an integral role and were well situated to support not only patients and families with COVID-19,5 but to also support the well-being of health care teams caring for COVID-19 patients.6,7
A recent survey that was conducted by the Center to Advance Palliative Care among palliative care leadership captured the experiences of leading their teams through a pandemic. Below are the results of this survey, which highlighted important issues and developments to palliative care during the pandemic.6
Increasing need for palliative care
One of the main findings from the national survey of palliative care leaders corroborated that the demands for palliative care have increased significantly from 2020 through the pandemic.
As with many areas in the health care system, the pandemic has emphasized the strain and short staffing of the palliative care teams. In the survey, 61% of leaders reported that palliative care consults significantly increased from prepandemic levels. But only 26% of these leaders said they had the staffing support to meet these needs.
Value of palliative care
The value of palliative care along with understanding of the role of palliative care has been better recognized during the pandemic and has been evidenced by the increase in palliative care referrals from clinical providers, compared with prepandemic levels. In addition, data collected showed that earlier palliative care consultations reduced length of hospital stay, decreased ICU admissions, and improved patient, family, and provider satisfaction.
Well-being of the workforce
The pandemic has been a tremendously stressful time for the health care workforce that has undoubtedly led to burnout. A nationwide study of physicians,8 found that 61% of physicians experienced burnout. This is a significant increase from prepandemic levels with impacts on mental health (that is, anxiety, depression). This study did not include palliative care specialists, but the CAPC survey indicates a similar feeling of burnout. Because of this, some palliative care specialists have left the field altogether, or are leaving leadership positions because of burnout and exhaustion from the pandemic. This was featured as a concern among palliative care leaders, where 93% reported concern for the emotional well-being of the palliative care team.
Telehealth
A permanent operational change that has been well-utilized and implemented across multiple health care settings has been providing palliative care through telehealth. Prior to the pandemic, the baseline use of telehealth was less than 5% with the use now greater than 75% – a modality that is favored by both patients and clinicians. This has offered a broader scope of practice, reaching individuals who may have no other means, have limitations to accessing palliative care, or were in circumstances where patients required isolation during the pandemic. However, there are limitations to this platform, including in equity of access to devices and ease of use for those with limited exposure to technology.9
Barriers to implementation
Although the important role and value of palliative care has been well recognized, there have been barriers identified in a qualitative study of the integration of palliative care into COVID-19 action plans that are mentioned below.5
- Patients and families were identified as barriers to integration of palliative care if they were not open to palliative care referral, mainly because of misperceptions of palliative care as end-of-life care.
- Palliative care knowledge among providers was identified as another barrier to integration of palliative care. There are still misperceptions among providers that palliative care is end-of-life care and palliative care involvement is stigmatized as hastening death. In addition, some felt that COVID-19 was not a traditional “palliative diagnosis” thus were less likely to integrate palliative care into care plans.
- Lack of availability of a primary provider to conduct primary palliative care and lack of motivation “not to give up” were identified as other barriers. On the other hand, palliative care provider availability and accessibility to care teams affected the integration into COVID-19 care plans.
- COVID-19 itself was identified to be a barrier because of the uncertainty of illness trajectory and outcomes, which made it difficult for doctors to ascertain when to involve palliative care.
- Leadership and institution were important factors to consider in integration of palliative care into long-term care plans, which depended on leadership engagement and institutional culture.
Takeaways
The past few years have taught us a lot, but there is still much to learn. The COVID-19 pandemic has called attention to the challenges and barriers of health care delivery and has magnified the needs of the health care system including its infrastructure, preparedness, and staffing, including the field of palliative care. More work needs to be done, but leaders have taken steps to initiate national and international preparedness plans including the integration of palliative care, which has been identified as a vital role in any humanitarian crises.10,11
Dr. Kang is a geriatrician and palliative care provider at the University of Washington, Seattle, in the division of geriatrics and gerontology. She has no conflicts related to the content of this article.
References
1. Palliative care. World Health Organization. Aug 5, 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/palliative-care
2. World Health Organization. Integrating palliative care and symptom relief into the response to humanitarian emergencies and crises: A WHO guide. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2018. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/274565.
3. Hughes MT, Smith TJ. The growth of palliative care in the United States. Annual Review Public Health. 2014;35:459-75.
4. Pastrana T et al. The impact of COVID-19 on palliative care workers across the world: A qualitative analysis of responses to open-ended questions. Palliative and Supportive Care. 2021:1-6.
5. Wentlandt K et al. Identifying barriers and facilitators to palliative care integration in the management of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A qualitative study. Palliat Med. 2022;36(6):945-54.
6. Rogers M et al. Palliative care leadership during the pandemic: Results from a recent survey. Center to Advance Palliative Care. 2022 Sept 8. https://www.capc.org/blog/palliative-care-leadership-during-the-pandemic-results-from-a-recent-survey
7. Fogelman P. Reflections form a palliative care program leader two years into the pandemic. Center to Advance Palliative Care. 2023 Jan 15. https://www.capc.org/blog/reflections-from-a-palliative-care-program-leader-two-years-into-the-pandemic
8. 2021 survey of America’s physicians Covid-19 impact edition: A year later. The Physicians Foundation. 2021.
9. Caraceni A et al. Telemedicine for outpatient palliative care during Covid-19 pandemics: A longitudinal study. BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care. 2022;0:1-7.
10. Bausewein C et al. National strategy for palliative care of severely ill and dying people and their relatives in pandemics (PallPan) in Germany – study protocol of a mixed-methods project. BMC Palliative Care. 2022;21(10).
11. Powell RA et al. Palliative care in humanitarian crises: Always something to offer. The Lancet. 2017;389(10078):1498-9.
Frequent visits to green spaces linked to lower use of some meds
Frequent visits to green spaces such as parks and community gardens are associated with a reduced use of certain prescription medications among city dwellers, a new analysis suggests.
In a cross-sectional cohort study, frequent green space visits were associated with less frequent use of psychotropic, antihypertensive, and asthma medications in urban environments.
Viewing green or so called “blue” spaces (views of lakes, rivers, or other water views) from the home was not associated with reduced medication use.
The growing scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of nature exposure is likely to increase the availability of high-quality green spaces in urban environments and promote the use of these spaces, lead author Anu W. Turunen, PhD, from the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, Kuopio, Finland, told this news organization.
This might be one way to improve health and well-being among city dwellers, Dr. Turunen added.
The findings were published online in Occupational and Environmental Medicine.
Nature exposure a timely topic
Exposure to natural environments is thought to be beneficial for human health, but the evidence is inconsistent, Dr. Turunen said.
“The potential health benefits of nature exposure is a very timely topic in environmental epidemiology. Scientific evidence indicates that residential exposure to greenery and water bodies might be beneficial, especially for mental, cardiovascular, and respiratory health, but the findings are partly inconsistent and thus, more detailed information is needed,” she said.
In the current cross-sectional study, the investigators surveyed 16,000 residents of three urban areas in Finland – Helsinki, Espoo, and Vantaa – over the period of 12 months from 2015 to 2016, about their exposure to green and blue spaces.
Of this number, 43% responded, resulting in 7,321 participants.
In the questionnaire, green areas were defined as forests, parks, fields, meadows, boglands, and rocks, as well as any playgrounds or playing fields within those areas, and blue areas were defined as sea, lakes, and rivers.
Residents were asked about their use of anxiolytics, hypnotics, antidepressants, antihypertensives, and asthma medication within the past 7 to 52 weeks.
They were also asked if they had any green and blue views from any of the windows of their home, and if so, how often did they look out of those windows, selecting “seldom” to “often.”
They were also asked about how much time they spent outdoors in green spaces during the months of May and September. If so, did they spend any of that time exercising? Options ranged from never to five or more times a week.
In addition, amounts of residential green and blue spaces located within a 1 km radius of the respondents’ homes were assessed from land use and land cover data.
Covariates included health behaviors, outdoor air pollution and noise, and socioeconomic status, including household income and educational attainment.
Results showed that the presence of green and blue spaces at home, and the amount of time spent viewing them, had no association with the use of the prescribed medicines.
However, greater frequency of green space visits was associated with lower odds of using the medications surveyed.
For psychotropic medications, the odds ratios were 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.82) for 3-4 times per week and 0.78 (95% CI, 0.63-0.96) for 5 or more times per week.
For antihypertensive meds, the ORs were 0.64 (95% CI, 0.52-0.78) for 3-4 times per week and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.48-0.74) for 5 or more times per week.
For asthma medications, the ORs were 0.74 (95% CI, 0.58-0.94) for 3-4 times per week and 0.76 (95% CI, 0.59-0.99) for 5 or more times per week.
The observed associations were attenuated by body mass index.
“We observed that those who reported visiting green spaces often had a slightly lower BMI than those who visited green spaces less often,” Dr. Turunen said. However, no consistent interactions with socioeconomic status indicators were observed.
“We are hoping to see new results from different countries and different settings,” she noted. “Longitudinal studies, especially, are needed. In epidemiology, a large body of consistent evidence is needed to draw strong conclusions and to make recommendations.”
Evidence mounts on the benefits of nature
There is growing evidence that exposure to nature could benefit human health, especially mental and cardiovascular health, says Jochem Klompmaker, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of environmental health at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
Dr. Klompmaker has researched the association between exposure to green spaces and health outcomes related to neurological diseases.
In a study recently published in JAMA Network Open, and reported by this news organization, Dr. Klompmaker and his team found that among a large cohort of about 6.7 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries in the United States aged 65 or older, living in areas rich with greenery, parks, and waterways was associated with fewer hospitalizations for certain neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and related dementias.
Commenting on the current study, Dr. Klompmaker noted its strengths.
“A particular strength of this study is that they used data about the amount of green and blue spaces around the residential addresses of the participants, data about green space visit frequency, and data about green and blue views from home. Most other studies only have data about the amount of green and blue spaces in general,” he said.
“The strong protective associations of frequency of green space visits make sense to me and indicate the importance of one’s actual nature exposure,” he added. “Like the results of our study, these results provide clinicians with more evidence of the importance of being close to nature and of encouraging patients to take more walks. If they live near a park, that could be a good place to be more physically active and reduce stress levels.”
The study was supported by the Academy of Finland and the Ministry of the Environment. Dr. Turunen and Dr. Klompmaker report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Frequent visits to green spaces such as parks and community gardens are associated with a reduced use of certain prescription medications among city dwellers, a new analysis suggests.
In a cross-sectional cohort study, frequent green space visits were associated with less frequent use of psychotropic, antihypertensive, and asthma medications in urban environments.
Viewing green or so called “blue” spaces (views of lakes, rivers, or other water views) from the home was not associated with reduced medication use.
The growing scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of nature exposure is likely to increase the availability of high-quality green spaces in urban environments and promote the use of these spaces, lead author Anu W. Turunen, PhD, from the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, Kuopio, Finland, told this news organization.
This might be one way to improve health and well-being among city dwellers, Dr. Turunen added.
The findings were published online in Occupational and Environmental Medicine.
Nature exposure a timely topic
Exposure to natural environments is thought to be beneficial for human health, but the evidence is inconsistent, Dr. Turunen said.
“The potential health benefits of nature exposure is a very timely topic in environmental epidemiology. Scientific evidence indicates that residential exposure to greenery and water bodies might be beneficial, especially for mental, cardiovascular, and respiratory health, but the findings are partly inconsistent and thus, more detailed information is needed,” she said.
In the current cross-sectional study, the investigators surveyed 16,000 residents of three urban areas in Finland – Helsinki, Espoo, and Vantaa – over the period of 12 months from 2015 to 2016, about their exposure to green and blue spaces.
Of this number, 43% responded, resulting in 7,321 participants.
In the questionnaire, green areas were defined as forests, parks, fields, meadows, boglands, and rocks, as well as any playgrounds or playing fields within those areas, and blue areas were defined as sea, lakes, and rivers.
Residents were asked about their use of anxiolytics, hypnotics, antidepressants, antihypertensives, and asthma medication within the past 7 to 52 weeks.
They were also asked if they had any green and blue views from any of the windows of their home, and if so, how often did they look out of those windows, selecting “seldom” to “often.”
They were also asked about how much time they spent outdoors in green spaces during the months of May and September. If so, did they spend any of that time exercising? Options ranged from never to five or more times a week.
In addition, amounts of residential green and blue spaces located within a 1 km radius of the respondents’ homes were assessed from land use and land cover data.
Covariates included health behaviors, outdoor air pollution and noise, and socioeconomic status, including household income and educational attainment.
Results showed that the presence of green and blue spaces at home, and the amount of time spent viewing them, had no association with the use of the prescribed medicines.
However, greater frequency of green space visits was associated with lower odds of using the medications surveyed.
For psychotropic medications, the odds ratios were 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.82) for 3-4 times per week and 0.78 (95% CI, 0.63-0.96) for 5 or more times per week.
For antihypertensive meds, the ORs were 0.64 (95% CI, 0.52-0.78) for 3-4 times per week and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.48-0.74) for 5 or more times per week.
For asthma medications, the ORs were 0.74 (95% CI, 0.58-0.94) for 3-4 times per week and 0.76 (95% CI, 0.59-0.99) for 5 or more times per week.
The observed associations were attenuated by body mass index.
“We observed that those who reported visiting green spaces often had a slightly lower BMI than those who visited green spaces less often,” Dr. Turunen said. However, no consistent interactions with socioeconomic status indicators were observed.
“We are hoping to see new results from different countries and different settings,” she noted. “Longitudinal studies, especially, are needed. In epidemiology, a large body of consistent evidence is needed to draw strong conclusions and to make recommendations.”
Evidence mounts on the benefits of nature
There is growing evidence that exposure to nature could benefit human health, especially mental and cardiovascular health, says Jochem Klompmaker, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of environmental health at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
Dr. Klompmaker has researched the association between exposure to green spaces and health outcomes related to neurological diseases.
In a study recently published in JAMA Network Open, and reported by this news organization, Dr. Klompmaker and his team found that among a large cohort of about 6.7 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries in the United States aged 65 or older, living in areas rich with greenery, parks, and waterways was associated with fewer hospitalizations for certain neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and related dementias.
Commenting on the current study, Dr. Klompmaker noted its strengths.
“A particular strength of this study is that they used data about the amount of green and blue spaces around the residential addresses of the participants, data about green space visit frequency, and data about green and blue views from home. Most other studies only have data about the amount of green and blue spaces in general,” he said.
“The strong protective associations of frequency of green space visits make sense to me and indicate the importance of one’s actual nature exposure,” he added. “Like the results of our study, these results provide clinicians with more evidence of the importance of being close to nature and of encouraging patients to take more walks. If they live near a park, that could be a good place to be more physically active and reduce stress levels.”
The study was supported by the Academy of Finland and the Ministry of the Environment. Dr. Turunen and Dr. Klompmaker report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Frequent visits to green spaces such as parks and community gardens are associated with a reduced use of certain prescription medications among city dwellers, a new analysis suggests.
In a cross-sectional cohort study, frequent green space visits were associated with less frequent use of psychotropic, antihypertensive, and asthma medications in urban environments.
Viewing green or so called “blue” spaces (views of lakes, rivers, or other water views) from the home was not associated with reduced medication use.
The growing scientific evidence supporting the health benefits of nature exposure is likely to increase the availability of high-quality green spaces in urban environments and promote the use of these spaces, lead author Anu W. Turunen, PhD, from the Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, Kuopio, Finland, told this news organization.
This might be one way to improve health and well-being among city dwellers, Dr. Turunen added.
The findings were published online in Occupational and Environmental Medicine.
Nature exposure a timely topic
Exposure to natural environments is thought to be beneficial for human health, but the evidence is inconsistent, Dr. Turunen said.
“The potential health benefits of nature exposure is a very timely topic in environmental epidemiology. Scientific evidence indicates that residential exposure to greenery and water bodies might be beneficial, especially for mental, cardiovascular, and respiratory health, but the findings are partly inconsistent and thus, more detailed information is needed,” she said.
In the current cross-sectional study, the investigators surveyed 16,000 residents of three urban areas in Finland – Helsinki, Espoo, and Vantaa – over the period of 12 months from 2015 to 2016, about their exposure to green and blue spaces.
Of this number, 43% responded, resulting in 7,321 participants.
In the questionnaire, green areas were defined as forests, parks, fields, meadows, boglands, and rocks, as well as any playgrounds or playing fields within those areas, and blue areas were defined as sea, lakes, and rivers.
Residents were asked about their use of anxiolytics, hypnotics, antidepressants, antihypertensives, and asthma medication within the past 7 to 52 weeks.
They were also asked if they had any green and blue views from any of the windows of their home, and if so, how often did they look out of those windows, selecting “seldom” to “often.”
They were also asked about how much time they spent outdoors in green spaces during the months of May and September. If so, did they spend any of that time exercising? Options ranged from never to five or more times a week.
In addition, amounts of residential green and blue spaces located within a 1 km radius of the respondents’ homes were assessed from land use and land cover data.
Covariates included health behaviors, outdoor air pollution and noise, and socioeconomic status, including household income and educational attainment.
Results showed that the presence of green and blue spaces at home, and the amount of time spent viewing them, had no association with the use of the prescribed medicines.
However, greater frequency of green space visits was associated with lower odds of using the medications surveyed.
For psychotropic medications, the odds ratios were 0.67 (95% confidence interval, 0.55-0.82) for 3-4 times per week and 0.78 (95% CI, 0.63-0.96) for 5 or more times per week.
For antihypertensive meds, the ORs were 0.64 (95% CI, 0.52-0.78) for 3-4 times per week and 0.59 (95% CI, 0.48-0.74) for 5 or more times per week.
For asthma medications, the ORs were 0.74 (95% CI, 0.58-0.94) for 3-4 times per week and 0.76 (95% CI, 0.59-0.99) for 5 or more times per week.
The observed associations were attenuated by body mass index.
“We observed that those who reported visiting green spaces often had a slightly lower BMI than those who visited green spaces less often,” Dr. Turunen said. However, no consistent interactions with socioeconomic status indicators were observed.
“We are hoping to see new results from different countries and different settings,” she noted. “Longitudinal studies, especially, are needed. In epidemiology, a large body of consistent evidence is needed to draw strong conclusions and to make recommendations.”
Evidence mounts on the benefits of nature
There is growing evidence that exposure to nature could benefit human health, especially mental and cardiovascular health, says Jochem Klompmaker, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher in the department of environmental health at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston.
Dr. Klompmaker has researched the association between exposure to green spaces and health outcomes related to neurological diseases.
In a study recently published in JAMA Network Open, and reported by this news organization, Dr. Klompmaker and his team found that among a large cohort of about 6.7 million fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries in the United States aged 65 or older, living in areas rich with greenery, parks, and waterways was associated with fewer hospitalizations for certain neurological disorders, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and related dementias.
Commenting on the current study, Dr. Klompmaker noted its strengths.
“A particular strength of this study is that they used data about the amount of green and blue spaces around the residential addresses of the participants, data about green space visit frequency, and data about green and blue views from home. Most other studies only have data about the amount of green and blue spaces in general,” he said.
“The strong protective associations of frequency of green space visits make sense to me and indicate the importance of one’s actual nature exposure,” he added. “Like the results of our study, these results provide clinicians with more evidence of the importance of being close to nature and of encouraging patients to take more walks. If they live near a park, that could be a good place to be more physically active and reduce stress levels.”
The study was supported by the Academy of Finland and the Ministry of the Environment. Dr. Turunen and Dr. Klompmaker report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Legacy ICDs exposed to MRI still shock, pace as needed
Functions like sensing and pacing in implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) tend to resist interference from the energy fields generated by MRI, as long as device programming is properly adjusted before the scan.
That applies even to patients with older “legacy” devices implanted before the 2015 advent of MRI-conditional ICDs despite, in practice, prevalent but misguided resistance to obtaining MRI scans in such cases.
Less is known whether such non–MRI-conditional devices, once exposed to MRI, will then reliably deliver antiarrhythmic shocks or antitachycardia pacing (ATP) when needed.
A new cohort study has tried to fill in some of that knowledge gap. It showed no evidence of an excess risk for death or ICD failure to deliver therapy within about 2 years of clinically indicated MRI scans in 629 patients with non–MRI-conditional devices.
The findings, published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine, come with caveats. For example, they’re based on the experience of one, albeit major, center and on MRIs that were for varied indications using 1.5-tesla equipment only.
Despite such safety evidence for appropriately adjusted non–MRI-conditional ICDs, many patients with the devices don›t receive clinically indicated MRI scans due to “perceived risk” that the ICDs won’t then reliably deliver appropriate therapy, observe the authors, led by Joshua Ra, MD, University of California, San Francisco.
Any such risks are “largely theoretical,” but may still explain “why some institutions are shying away from offering MRI exams” to patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs, Dr. Ra told this news organization.
Many such hospitals refer such patients to more experienced centers, creating “significant logistical barriers in terms of patient access to these MRIs,” he said. “That seems to still be prevalent, unfortunately.”
The current findings “provide another layer of reassurance” that MRI scans in patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs don’t impair a device’s ability to deliver shocks or ATP, Dr. Ra said.
The cohort consisted of 629 patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs who underwent 813 clinically indicated MRI exams from 2003 to early 2015 at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Scans performed within 4 weeks of device implantation were excluded because, the report notes, that’s when spontaneous lead dislodgements or changes to device parameters are most likely to occur. Also excluded were patients with permanent epicardial leads, abandoned leads, or subcutaneous ICD lead systems, the report states.
Still, Dr. Ra said, the cohort is fairly representative of “the modern patient population” of non–MRI-conditional ICD recipients.
A total of 4,177 arrhythmia episodes were documented during a median 2.2 years between scans and last device interrogation prior to pulse-generator change-out or lead exchange.
Of note, Dr. Ra observed, the arrhythmias were confirmed in only 85% of the cohort. Most of the remainder were referral patients who were lost to follow-up whose devices were unavailable for interrogation.
Device therapy terminated “nearly all” documented spontaneous arrhythmias in that 85% of patients, the report states. They included 757 episodes of ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF), including 130 that were shocked and the remainder that were managed with ATP. There were also 105 supraventricular tachycardias, all successfully terminated with shocks.
There were no cases of VT or VF detection delay from undersensing or instances of syncope because of “abnormalities” in device detection of arrhythmias, the report states.
Of the 210 known deaths, which occurred a median 1.7 years after the scan, about half were noncardiac and more than a third were cardiac but nonarrhythmic.
Ten patients died from arrhythmia-related cardiac causes, representing 5% of deaths; but 7% of deaths were of undetermined cause.
“No direct relationship of deaths attributable to prior MRI exposure was found or reported,” the report states.
The researchers informally compared outcomes between older and more recently implanted non–MRI-conditional ICDs, the latter presumably with more modern design features. Their data, based on device interrogations, Dr. Ra said, “seem to suggest there were no differences.”
The study was supported by Johns Hopkins University and the National Institutes of Health. Author disclosures are available at apconline.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Functions like sensing and pacing in implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) tend to resist interference from the energy fields generated by MRI, as long as device programming is properly adjusted before the scan.
That applies even to patients with older “legacy” devices implanted before the 2015 advent of MRI-conditional ICDs despite, in practice, prevalent but misguided resistance to obtaining MRI scans in such cases.
Less is known whether such non–MRI-conditional devices, once exposed to MRI, will then reliably deliver antiarrhythmic shocks or antitachycardia pacing (ATP) when needed.
A new cohort study has tried to fill in some of that knowledge gap. It showed no evidence of an excess risk for death or ICD failure to deliver therapy within about 2 years of clinically indicated MRI scans in 629 patients with non–MRI-conditional devices.
The findings, published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine, come with caveats. For example, they’re based on the experience of one, albeit major, center and on MRIs that were for varied indications using 1.5-tesla equipment only.
Despite such safety evidence for appropriately adjusted non–MRI-conditional ICDs, many patients with the devices don›t receive clinically indicated MRI scans due to “perceived risk” that the ICDs won’t then reliably deliver appropriate therapy, observe the authors, led by Joshua Ra, MD, University of California, San Francisco.
Any such risks are “largely theoretical,” but may still explain “why some institutions are shying away from offering MRI exams” to patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs, Dr. Ra told this news organization.
Many such hospitals refer such patients to more experienced centers, creating “significant logistical barriers in terms of patient access to these MRIs,” he said. “That seems to still be prevalent, unfortunately.”
The current findings “provide another layer of reassurance” that MRI scans in patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs don’t impair a device’s ability to deliver shocks or ATP, Dr. Ra said.
The cohort consisted of 629 patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs who underwent 813 clinically indicated MRI exams from 2003 to early 2015 at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Scans performed within 4 weeks of device implantation were excluded because, the report notes, that’s when spontaneous lead dislodgements or changes to device parameters are most likely to occur. Also excluded were patients with permanent epicardial leads, abandoned leads, or subcutaneous ICD lead systems, the report states.
Still, Dr. Ra said, the cohort is fairly representative of “the modern patient population” of non–MRI-conditional ICD recipients.
A total of 4,177 arrhythmia episodes were documented during a median 2.2 years between scans and last device interrogation prior to pulse-generator change-out or lead exchange.
Of note, Dr. Ra observed, the arrhythmias were confirmed in only 85% of the cohort. Most of the remainder were referral patients who were lost to follow-up whose devices were unavailable for interrogation.
Device therapy terminated “nearly all” documented spontaneous arrhythmias in that 85% of patients, the report states. They included 757 episodes of ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF), including 130 that were shocked and the remainder that were managed with ATP. There were also 105 supraventricular tachycardias, all successfully terminated with shocks.
There were no cases of VT or VF detection delay from undersensing or instances of syncope because of “abnormalities” in device detection of arrhythmias, the report states.
Of the 210 known deaths, which occurred a median 1.7 years after the scan, about half were noncardiac and more than a third were cardiac but nonarrhythmic.
Ten patients died from arrhythmia-related cardiac causes, representing 5% of deaths; but 7% of deaths were of undetermined cause.
“No direct relationship of deaths attributable to prior MRI exposure was found or reported,” the report states.
The researchers informally compared outcomes between older and more recently implanted non–MRI-conditional ICDs, the latter presumably with more modern design features. Their data, based on device interrogations, Dr. Ra said, “seem to suggest there were no differences.”
The study was supported by Johns Hopkins University and the National Institutes of Health. Author disclosures are available at apconline.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Functions like sensing and pacing in implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) tend to resist interference from the energy fields generated by MRI, as long as device programming is properly adjusted before the scan.
That applies even to patients with older “legacy” devices implanted before the 2015 advent of MRI-conditional ICDs despite, in practice, prevalent but misguided resistance to obtaining MRI scans in such cases.
Less is known whether such non–MRI-conditional devices, once exposed to MRI, will then reliably deliver antiarrhythmic shocks or antitachycardia pacing (ATP) when needed.
A new cohort study has tried to fill in some of that knowledge gap. It showed no evidence of an excess risk for death or ICD failure to deliver therapy within about 2 years of clinically indicated MRI scans in 629 patients with non–MRI-conditional devices.
The findings, published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine, come with caveats. For example, they’re based on the experience of one, albeit major, center and on MRIs that were for varied indications using 1.5-tesla equipment only.
Despite such safety evidence for appropriately adjusted non–MRI-conditional ICDs, many patients with the devices don›t receive clinically indicated MRI scans due to “perceived risk” that the ICDs won’t then reliably deliver appropriate therapy, observe the authors, led by Joshua Ra, MD, University of California, San Francisco.
Any such risks are “largely theoretical,” but may still explain “why some institutions are shying away from offering MRI exams” to patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs, Dr. Ra told this news organization.
Many such hospitals refer such patients to more experienced centers, creating “significant logistical barriers in terms of patient access to these MRIs,” he said. “That seems to still be prevalent, unfortunately.”
The current findings “provide another layer of reassurance” that MRI scans in patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs don’t impair a device’s ability to deliver shocks or ATP, Dr. Ra said.
The cohort consisted of 629 patients with non–MRI-conditional ICDs who underwent 813 clinically indicated MRI exams from 2003 to early 2015 at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
Scans performed within 4 weeks of device implantation were excluded because, the report notes, that’s when spontaneous lead dislodgements or changes to device parameters are most likely to occur. Also excluded were patients with permanent epicardial leads, abandoned leads, or subcutaneous ICD lead systems, the report states.
Still, Dr. Ra said, the cohort is fairly representative of “the modern patient population” of non–MRI-conditional ICD recipients.
A total of 4,177 arrhythmia episodes were documented during a median 2.2 years between scans and last device interrogation prior to pulse-generator change-out or lead exchange.
Of note, Dr. Ra observed, the arrhythmias were confirmed in only 85% of the cohort. Most of the remainder were referral patients who were lost to follow-up whose devices were unavailable for interrogation.
Device therapy terminated “nearly all” documented spontaneous arrhythmias in that 85% of patients, the report states. They included 757 episodes of ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF), including 130 that were shocked and the remainder that were managed with ATP. There were also 105 supraventricular tachycardias, all successfully terminated with shocks.
There were no cases of VT or VF detection delay from undersensing or instances of syncope because of “abnormalities” in device detection of arrhythmias, the report states.
Of the 210 known deaths, which occurred a median 1.7 years after the scan, about half were noncardiac and more than a third were cardiac but nonarrhythmic.
Ten patients died from arrhythmia-related cardiac causes, representing 5% of deaths; but 7% of deaths were of undetermined cause.
“No direct relationship of deaths attributable to prior MRI exposure was found or reported,” the report states.
The researchers informally compared outcomes between older and more recently implanted non–MRI-conditional ICDs, the latter presumably with more modern design features. Their data, based on device interrogations, Dr. Ra said, “seem to suggest there were no differences.”
The study was supported by Johns Hopkins University and the National Institutes of Health. Author disclosures are available at apconline.org.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new blood pressure target in primary care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. There are very few things that we treat more often than hypertension, so you’d think the guidelines would have been clear a long time ago. Less than 10 years ago, in 2014, JNC 8 (Eighth Joint National Committee) recommended target blood pressure for individuals under 60 to be less than 140/90, and for those older than 60, less than 150/90.
Then, based primarily on the SPRINT trial (which included only people with or at significantly elevated risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease), in 2017 the American Heart Association’s hypertension guidelines lowered the target BP to less than 130/80 for most individuals. It’s a little more nuanced than that, but most of us don’t remember the nuance. I’ve written about my reservations with that statement in the AHA’s journal, Circulation.
Now the American Academy of Family Physicians has updated its recommendations, and they recommend a BP less than 140/90. This is not a small change, as it often takes additional medication to achieve lower BP targets, and additional medicines lead to additional adverse effects. I’m going share with you some details from the new guideline, and then I’m going share my opinion about it.
The AAFP guideline applies to adults with hypertension, with or without cardiovascular disease. In the comprehensive literature review, the trials ran for an average of 3.7 years, and about 75% of the patients in the trials did not have preexisting cardiovascular disease.
The key to their recommendations is that target BPs lower than 140/90 did not show a statistically significant decrease in total mortality. In regard to serious adverse events, though, lower targets led to a nominal increase that didn’t reach statistical significance. Serious adverse events were defined as death or events that required hospitalization or resulted in significant disability. In regard to all other adverse events, including syncope and hypotension, there was a significant increase, with a relative risk of 1.44 (a 44% increase in adverse events). This reflected an absolute risk increase of 3%, compared with the standard target group (specifically 9.8% vs. 6.8%), with a number needed to harm of 33 over 3.7 years.
Another potential harm of low BP targets was the need for an average of one additional medicine to reach lower BP targets. One systematic review cited an eightfold higher withdrawal rate because of adverse events in the lower-target BP groups.
The AAFP guidelines said that, in the comprehensive review of the literature, while there was no difference in mortality or stroke with lower BP targets, a small additional benefit was observed in myocardial infarction – a 16% lower incidence, with a number needed to treat of 137 over 3.7 years.
So that’s the background. Let me now go over the specifics of the AAFP recommendations.
AAFP gives a strong recommendation for a standard BP target of less than 140/90. They go on to say – and grade this next statement as a weak recommendation – that, while treating to a lower BP target does not provide additional mortality benefit, a target BP of less than 135/85 can be considered to lower the risk for MI, noting that lower BP may increase harms. They state that the lower BP target could be considered based on patient preferences and values.
The AAFP guideline is incredibly helpful. The difference in the recommendations of two large societies – American Heart Association and AAFP — stems from two things. I believe that AHA focused on the composite endpoints in trials such as SPRINT, which included only high-risk patients, and the AAFP uses mortality as the driving endpoint in a broader group of patients that included both high- and lower-risk patients.
In addition, it appears that the two organizations weigh adverse events differently in coming to their conclusions. Clearly, we see more adverse events when aiming for a lower BP level, and in my experience, patients care a lot about adverse events.
Interestingly, the International Society of Hypertension recommends an “essential” BP target of less than 140/90 for most individuals, and for those under 65, they provide the option of an “optimal” BP of less than 130/80. Remember that for certain comorbidities there are also other guidelines out there. The American Diabetes Association this year revised its target BP to less than 130/80 for people with diabetes; for prevention of recurrent stroke, guidelines from the AHA/American Stroke Association in 2021 recommend BP less than 130/80, and the International Society for Hypertension as well as the AHA recommends a BP of less than 130/80 for those with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
To repeat, though, the main topic for today is that as a general target, the AAFP guidelines recommend a BP less than 140/90.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 2/7/2023.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. There are very few things that we treat more often than hypertension, so you’d think the guidelines would have been clear a long time ago. Less than 10 years ago, in 2014, JNC 8 (Eighth Joint National Committee) recommended target blood pressure for individuals under 60 to be less than 140/90, and for those older than 60, less than 150/90.
Then, based primarily on the SPRINT trial (which included only people with or at significantly elevated risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease), in 2017 the American Heart Association’s hypertension guidelines lowered the target BP to less than 130/80 for most individuals. It’s a little more nuanced than that, but most of us don’t remember the nuance. I’ve written about my reservations with that statement in the AHA’s journal, Circulation.
Now the American Academy of Family Physicians has updated its recommendations, and they recommend a BP less than 140/90. This is not a small change, as it often takes additional medication to achieve lower BP targets, and additional medicines lead to additional adverse effects. I’m going share with you some details from the new guideline, and then I’m going share my opinion about it.
The AAFP guideline applies to adults with hypertension, with or without cardiovascular disease. In the comprehensive literature review, the trials ran for an average of 3.7 years, and about 75% of the patients in the trials did not have preexisting cardiovascular disease.
The key to their recommendations is that target BPs lower than 140/90 did not show a statistically significant decrease in total mortality. In regard to serious adverse events, though, lower targets led to a nominal increase that didn’t reach statistical significance. Serious adverse events were defined as death or events that required hospitalization or resulted in significant disability. In regard to all other adverse events, including syncope and hypotension, there was a significant increase, with a relative risk of 1.44 (a 44% increase in adverse events). This reflected an absolute risk increase of 3%, compared with the standard target group (specifically 9.8% vs. 6.8%), with a number needed to harm of 33 over 3.7 years.
Another potential harm of low BP targets was the need for an average of one additional medicine to reach lower BP targets. One systematic review cited an eightfold higher withdrawal rate because of adverse events in the lower-target BP groups.
The AAFP guidelines said that, in the comprehensive review of the literature, while there was no difference in mortality or stroke with lower BP targets, a small additional benefit was observed in myocardial infarction – a 16% lower incidence, with a number needed to treat of 137 over 3.7 years.
So that’s the background. Let me now go over the specifics of the AAFP recommendations.
AAFP gives a strong recommendation for a standard BP target of less than 140/90. They go on to say – and grade this next statement as a weak recommendation – that, while treating to a lower BP target does not provide additional mortality benefit, a target BP of less than 135/85 can be considered to lower the risk for MI, noting that lower BP may increase harms. They state that the lower BP target could be considered based on patient preferences and values.
The AAFP guideline is incredibly helpful. The difference in the recommendations of two large societies – American Heart Association and AAFP — stems from two things. I believe that AHA focused on the composite endpoints in trials such as SPRINT, which included only high-risk patients, and the AAFP uses mortality as the driving endpoint in a broader group of patients that included both high- and lower-risk patients.
In addition, it appears that the two organizations weigh adverse events differently in coming to their conclusions. Clearly, we see more adverse events when aiming for a lower BP level, and in my experience, patients care a lot about adverse events.
Interestingly, the International Society of Hypertension recommends an “essential” BP target of less than 140/90 for most individuals, and for those under 65, they provide the option of an “optimal” BP of less than 130/80. Remember that for certain comorbidities there are also other guidelines out there. The American Diabetes Association this year revised its target BP to less than 130/80 for people with diabetes; for prevention of recurrent stroke, guidelines from the AHA/American Stroke Association in 2021 recommend BP less than 130/80, and the International Society for Hypertension as well as the AHA recommends a BP of less than 130/80 for those with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
To repeat, though, the main topic for today is that as a general target, the AAFP guidelines recommend a BP less than 140/90.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 2/7/2023.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I’m Dr. Neil Skolnik. There are very few things that we treat more often than hypertension, so you’d think the guidelines would have been clear a long time ago. Less than 10 years ago, in 2014, JNC 8 (Eighth Joint National Committee) recommended target blood pressure for individuals under 60 to be less than 140/90, and for those older than 60, less than 150/90.
Then, based primarily on the SPRINT trial (which included only people with or at significantly elevated risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease), in 2017 the American Heart Association’s hypertension guidelines lowered the target BP to less than 130/80 for most individuals. It’s a little more nuanced than that, but most of us don’t remember the nuance. I’ve written about my reservations with that statement in the AHA’s journal, Circulation.
Now the American Academy of Family Physicians has updated its recommendations, and they recommend a BP less than 140/90. This is not a small change, as it often takes additional medication to achieve lower BP targets, and additional medicines lead to additional adverse effects. I’m going share with you some details from the new guideline, and then I’m going share my opinion about it.
The AAFP guideline applies to adults with hypertension, with or without cardiovascular disease. In the comprehensive literature review, the trials ran for an average of 3.7 years, and about 75% of the patients in the trials did not have preexisting cardiovascular disease.
The key to their recommendations is that target BPs lower than 140/90 did not show a statistically significant decrease in total mortality. In regard to serious adverse events, though, lower targets led to a nominal increase that didn’t reach statistical significance. Serious adverse events were defined as death or events that required hospitalization or resulted in significant disability. In regard to all other adverse events, including syncope and hypotension, there was a significant increase, with a relative risk of 1.44 (a 44% increase in adverse events). This reflected an absolute risk increase of 3%, compared with the standard target group (specifically 9.8% vs. 6.8%), with a number needed to harm of 33 over 3.7 years.
Another potential harm of low BP targets was the need for an average of one additional medicine to reach lower BP targets. One systematic review cited an eightfold higher withdrawal rate because of adverse events in the lower-target BP groups.
The AAFP guidelines said that, in the comprehensive review of the literature, while there was no difference in mortality or stroke with lower BP targets, a small additional benefit was observed in myocardial infarction – a 16% lower incidence, with a number needed to treat of 137 over 3.7 years.
So that’s the background. Let me now go over the specifics of the AAFP recommendations.
AAFP gives a strong recommendation for a standard BP target of less than 140/90. They go on to say – and grade this next statement as a weak recommendation – that, while treating to a lower BP target does not provide additional mortality benefit, a target BP of less than 135/85 can be considered to lower the risk for MI, noting that lower BP may increase harms. They state that the lower BP target could be considered based on patient preferences and values.
The AAFP guideline is incredibly helpful. The difference in the recommendations of two large societies – American Heart Association and AAFP — stems from two things. I believe that AHA focused on the composite endpoints in trials such as SPRINT, which included only high-risk patients, and the AAFP uses mortality as the driving endpoint in a broader group of patients that included both high- and lower-risk patients.
In addition, it appears that the two organizations weigh adverse events differently in coming to their conclusions. Clearly, we see more adverse events when aiming for a lower BP level, and in my experience, patients care a lot about adverse events.
Interestingly, the International Society of Hypertension recommends an “essential” BP target of less than 140/90 for most individuals, and for those under 65, they provide the option of an “optimal” BP of less than 130/80. Remember that for certain comorbidities there are also other guidelines out there. The American Diabetes Association this year revised its target BP to less than 130/80 for people with diabetes; for prevention of recurrent stroke, guidelines from the AHA/American Stroke Association in 2021 recommend BP less than 130/80, and the International Society for Hypertension as well as the AHA recommends a BP of less than 130/80 for those with established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
To repeat, though, the main topic for today is that as a general target, the AAFP guidelines recommend a BP less than 140/90.
Dr. Skolnik is professor, department of family medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director, department of family medicine, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. He disclosed conflicts of interest with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, and Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*This article was updated on 2/7/2023.