User login
Novel therapy shows promise for treating skin-predominant dermatomyositis
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
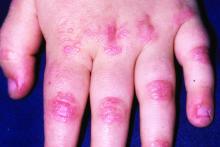
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – in a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial, according to results presented as a late-breaker at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“These findings support the inhibition of IFN-beta as a promising therapeutic strategy in skin-predominant disease,” said principal investigator Aaron Mangold, MD, associate professor of dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, Ariz.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune inflammatory condition that typically involves both skeletal muscles and skin, is a challenging disease with a diverse set of potential complications.
Immunosuppressive and immunomodulatory agents are used with mixed success for myositis, but skin manifestations, which include papular eruptions, heliotrope rash, photoerythema, burning, and pruritus, are often the most troublesome and the most difficult to control. Treatment options other than immunomodulators that target cutaneous involvement – which include steroids, emollients, and photoprotection – are generally modestly effective, according to Dr. Mangold.
Targeting an elevated cytokine
Interest in IFN-beta, which is elevated in the blood of individuals with dermatomyositis, was triggered by evidence that this cytokine plays an important role in driving the skin inflammation, Dr. Mangold explained.
“The blood concentrations of IFN-beta are positively correlated with cutaneous disease activity and severity,” he said.
The study drug, currently known as PF-06823859 (Dazukibart), “is a potent, selective humanized IgG1-neutralizing antibody directed at IFN-beta,” Dr. Mangold said. A dose-ranging phase 1 study published 2 years ago provided evidence of acceptable pharmacokinetics and safety in healthy individuals to support treatment studies for disorders associated with elevated IFN-beta levels. In addition to dermatomyositis, this includes systemic lupus erythematosus.
In this phase 2 trial, patients whose condition was not improved by at least one standard-care therapy for skin manifestations of dermatomyositis were eligible if they had moderate to severe disease as measured with the Cutaneous Dermatomyositis Disease Area and Severity Index (CDASI), according to Dr. Mangold. During the study, patients were allowed to remain on a disease modifying antirheumatic drug and/or prednisone if they had been on stable doses and did not change the dose.
After a screening run-in, the trial had two blinded stages. In stage 1, 30 patients were randomly assigned either to 600 mg of PF-06823859 or to placebo, both administered intravenously every 4 weeks. A second cohort of 25 patients was randomly assigned in stage 2 to placebo, 150 mg of PF-06823859, or 600 mg of PF-06823859. The primary endpoint assessed at 12 weeks was a greater than 5-point reduction in CDASI score or greater than 40% CDASI improvement from baseline.
Both endpoints are associated with a clinically meaningful response in regard to an improved quality of life, Dr. Mangold noted.
Both doses better than placebo
In results from the stage 1 portion, the mean reduction in CDASI at 12 weeks after three doses of the assigned therapy was 18.8 points in the active-treatment group versus 3.9 points in the placebo group. In pooled data from stage 1 and 2, the reductions were 16.6 points, 19.2 points, and 2.9 points for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively. Both doses achieved a highly significant advantage over placebo.
For both stages and doses, the response curves of the active-treatment groups and the placebo group diverged almost immediately. By 4 weeks, both measures of CDASI reductions on active therapy were significantly improved relative to placebo, and the response curves had a consistent downward slope through the end of the 12-week study, Dr. Mangold reported.
The majority of patients responded by either of the primary endpoint criteria. For a CDASI reduction of greater than 5 points, the response rates were 100% and 96% for the 150-mg and 600-mg doses of PF-06823859, respectively. The placebo response was 35.7%. For the CDASI reduction of greater than 40%, the rates were 80%, 82.1%, and 7.1% for the 150-mg, 600-mg, and placebo arms, respectively.
“There were no major safety concerns. Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild, and adverse events did not have a relationship to dose,” Dr. Mangold said. Notably, there were no cases of herpes zoster, and infections of any kind were low in all study groups.
A phase 3 study is being planned with the 600-mg dose, according to Dr. Mangold, but he acknowledged that regulatory authorities have generally required endpoints for both cutaneous and muscle manifestations in previous trials of therapies for dermatomyositis.
It is not yet certain that “there will be a carve-out for skin,” he said in answer to a question about investigations moving forward. So far, studies have been focused on skin response. However, a meaningful degree of benefit against muscle involvement, which has not yet been well studied, has not been ruled out.
Even though this is a phase 2 trial with small numbers, it was controlled and blinded, and the potential of an inhibitor of IFN-beta to control the skin manifestations of dermatomyositis “is kind of a big deal,” said Paul Nghiem, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology, University of Washington, Seattle.
“There is definitely an unmet need for better therapies to control the skin involvement,” Dr. Nghiem said.
Hensin Tsao, MD, PhD, clinical director of the Melanoma and Pigmented Lesion Center at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, agreed. Like Dr. Nghiem, Dr. Tsao was a panelist during the late-breaker session where the study was presented, and he was impressed by the data.
“This is something that is definitely newsworthy,” Dr. Tsao said.
Dr. Mangold reports financial relationships with Actelion, Amgen, Corbus, Eli Lilly, Incyte, miRagen, Novartis, Regeneron, Solagenix, Sun Pharmaceuticals, Teva, and Pfizer, which provided funding for this trial. Both Dr. Nghiem and Dr. Tsao reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
Treatment of craniofacial hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Hyperhidrosis has a significant impact on a person’s physical, psychological, and social aspects of life. The lack of treatment options and associated stigma limits access to care and treatment options.
Primary hyperhidrosis does not have an underlying cause; is symmetrical; can worsen with anxiety, fear, or stress; and may have a familial component. Palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis are the most common types of hyperhidrosis. The incidence of craniofacial hyperhidrosis has not been clearly defined but it is most commonly reported on the forehead, where the concentration of eccrine sweat glands is highest.
Treatment options for craniofacial hyperhidrosis include topical aluminum chloride, which blocks the eccrine sweat duct or causes eccrine cell atrophy. Although this option is a common treatment for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis, use on the face has not been thoroughly studied, and may also cause skin irritation.
Topical and oral glycopyrrolate can be effective for all types of hyperhidrosis, but must be used daily and can have systemic side effects, with variable efficacy and longevity. Oral oxybutynin, beta-blockers, clonidine, and benzodiazepines have also been used with some limited studies available in patients with generalized hyperhidrosis.
Surgical treatments such as videothoracoscopy sympathectomy can be used in severe or recalcitrant cases of hyperhidrosis with good efficacy. However, surgical complications and inherent surgical risks limit these treatment options unless other modalities are exhausted.
OnabotulinumtoxinA is Food and Drug Administration approved for treating severe primary axillary hyperhidrosis, but is used off label for palmar, plantar, and craniofacial hyperhidrosis with great results and few side effects. Clinical pearls and guidelines for the use of botulinum toxin A in craniofacial hyperhidrosis were outlined by Wolosker and colleagues in a review article. As with any injection of neurotoxin, knowledge of the facial anatomy is critical to avoiding muscle paralysis.
double diluted. Treatment effects usually last 3 months, similar to cosmetic uses. Wolosker uses a dilution of 100 U botulinum toxin in 1.0 mL saline, which I find slightly more difficult to control and more likely to have loss of toxin.
In my experience, I have found the following dosing to be most effective with the least side effects for the following (dosages vary and can be titrated up to response):
- Upper lip: 6-10 U.
- Chin: 6-10 U.
- Forehead: 15-30 U. (Avoid 1 cm above the brow unless risks of brow drop are reviewed and acceptable to the patient. In my experience patients would rather have a lower brow than obstructive sweating in their brow that can irritate the eyes, blur vision, and smudge skincare and makeup.)
- Nose: 10 U
- Cheeks: 10 U per side (staying very superficial with injections).
- Scalp: 30-50 U (using serial injections 1-2 cm apart in the area affected by hyperhidrosis).
Side effects include temporary erythema, bruising, and edema, as well as muscle paralysis and asymmetry if proper injection technique is not used, the dose is not diluted properly, or the injection is too deep.
There are scattered case studies of symbiotic techniques to help the penetration of botulinum toxin when treating craniofacial hyperhidrosis, including microneedling, radiofrequency, long-pulsed diode laser, and ultrasound. But the safety and efficacy of these procedures have not been properly evaluated.
In all of my patients with craniofacial hyperhidrosis treated with botulinum toxin, quality of life is significantly improved with almost no complications. Botulinum toxin is a safe, relatively quick in-office procedure to treat craniofacial hyperhidrosis that can be used to help patients – particularly those who experience anxiety or have social and occupational impairment related to their disease.
This procedure is cosmetic in nature, and therefore, not covered by insurance.
Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Write to her at dermnews@mdedge.com. She had no relevant disclosures.
References
Parashar K et al. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2023 Mar;24(2):187-98.
Doolittle J et al. Arch Dermatol Res. 2016 Dec;308(10):743-9.
Wolosker N et al. J Vasc Bras. 2020 Nov 16;19:e20190152.
Garcia-Souto F et al. Dermatol Ther. 2021 Jan;34(1):e14658.
Ebrahim H et al. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2022 Sep;15(9):40-4.
Campanati A et al. Toxins (Basel). 2022 May 27;14(6):3727.
Studies validate IL-17 as hidradenitis suppurativa drug target
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – In two phase 3 trials, bimekizumab, a monoclonal antibody targeting two types of interleukin-17 — IL-17A and IL-17F — reduced the abscess and inflammatory nodule count better than placebo in the chronic inflammatory skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), according to results presented together during a late-breaker session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
“We are very excited to add this data to what we already have around IL-17 inhibition. This clearly validates this target for the control of HS,” reported lead investigator Alexa B. Kimball, MD, MPH, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
The trials, called BE HEARD I and BE HEARD II, enrolled 505 and 509 patients with HS, respectively. About 50% of patients in BE HEARD I and 60% of patients in BE HEARD II had Hurley stage 3 disease, which is the most severe of the three stratifications. The remainder were in Hurley stage 2. The mean duration of HS was 8.3 and 7.1 years, respectively.
Patients in both studies were randomized to one of four groups – either to a dosing regimen of 320 mg of bimekizumab administered by subcutaneous injection or to a placebo group. Both trials comprised double-blind 16-week initial and 32-week maintenance treatment periods.
In one experimental group, bimekizumab was given once every 2 weeks for the full course of the 48-week study (Q2W/Q2W). In another, patients started on the every-2-week schedule for 16 weeks and then were switched to every-4-week dosing (Q2W/Q4W). In the third group, patients started and remained on the every-4-week schedule (Q4W/Q4W). Patients in a fourth group started on placebo and switched at 16 weeks to the every-2-week bimekizumab schedule (placebo/Q2W).
Results at primary endpoint
The primary endpoint was HiSCR50, signifying a 50% reduction from baseline in abscess and inflammatory nodule count on the Hidradenitis Suppurativa Clinical Response (HiSCR) assessment tool. At 16 weeks, the initial Q2W dose in two of the groups outperformed the placebo in both BE HEARD I (47.8% vs. 28.7%) and BE HEARD II (52.0% vs. 32.2%). The response rates in the Q4W arm in BE HEARD I (45.3%) and BE HEARD II (53.8%) were also higher than the placebo, but the difference was only significant in BE HEARD II.
At 48 weeks, the proportion of patients with an HiSCR50 response climbed in all groups in both trials. The patterns were generally the same with slightly higher numerical responses among the groups that received the every-2-week dosing schedule relative to the every-4-week schedule.
In BE HEARD I at 48 weeks, the HiSCR50 response rate was about 60% for those who started and remained on every-2-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q2W) or were switched at 16 weeks to every-4-week bimekizumab (Q2W/Q4W). For those who started and remained on every-4-week bimekizumab and the group started on placebo and switched to every-2-week bimekizumab, the response rates were 52.7% and 45.3%, respectively.
In BE HEARD II, the HiSCR50 response rates were higher in all groups, including the placebo, and the patterns of response were similar at 48 weeks. Most patients reached the HiSCR50 response – 79.8% (Q2W/Q2W), 78.4% (Q2W/Q4W), 76.7% (Q4W/Q4W), and 65.9 % (placebo/Q2W) of patients.
It is notable that, although there was rapid increase in the proportion of placebo patients reaching HiSCR50 after the switch at 16 weeks, there appeared to be an advantage at 48 weeks for starting on full-dose bimekizumab over starting on placebo.
In this trial, patients were listed as nonresponders if they received antibiotics at any time and for any reason after randomization. This might have concealed an even greater benefit of bimekizumab, Dr. Kimball said, but the study design element was considered necessary to isolate the activity of the study drug.
“In future HS trials, it will be helpful to address the difficulty of handling the impact of antibiotics and pain medications [in assessing results],” Dr. Kimball said.
Clinically meaningful secondary endpoint
For HS patients, the secondary endpoint of HiSCR75 might be considered the most meaningful, according to Dr. Kimball. She said that this higher bar not only documents a higher level of efficacy but correlates with meaningful improvement in quality of life. In the two trials combined, more than 55% of patients on continuous bimekizumab achieved HiSCR75 at week 48 in the observed case analysis, according to a news release from biopharmaceutical company UCB, developer of bimekizumab.
In BE HEARD I, the HiSCR75 rates were 33.4% and 24.7% for the every-2-week and every-4-week bimekizumab doses, respectively. The 33.4% response was statistically superior to placebo (18.4%). In BE HEARD II, both the every-2-week dose (35.7%) and the every-4-week dose (33.7%) were superior to the 15.6% response in placebo patients.
The improvements in quality of life as measured with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), reflected the changes in disease activity. Relative to about a 3-point reduction from baseline in the placebo groups of the two trials, the 5-point reduction for either the 2-week or 4-week bimekizumab groups in each clinical trial were highly significant, Dr. Kimball said.
Bimekizumab was relatively well tolerated, although it shares the increased risk for candidiasis observed with this agent when used in psoriasis and with other IL-17 inhibitors, such as secukinumab (Cosentyx), in general. The risk of candidiasis appeared to be dose related, but cases were generally mild and easily managed, according to Dr. Kimball. She noted that only three patients discontinued treatment for this reason. Discontinuations for a treatment-related adverse event overall was less than 4% at 16 weeks.
This is only the third phase 3 trial ever completed in patients with HS. In fact, Dr. Kimball has led all of the phase 3 trials so far, including clinical studies of adalimumab (Humira), published in 2016, and of secukinumab, published earlier this year. All were positive studies.
“This is amazing news for our patients,” Dr. Kimball said. HS remains a challenging disease, even with a growing number of options showing benefit in large studies, she said, and the high rate of response, particularly at the level of HiSCR75, “is a huge milestone for what we can achieve.”
Multiple treatment options important
Her assessment was echoed by other experts, including Christopher J. Sayed, MD, an associate professor of dermatology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, who publishes frequently about this disease.
“It is incredibly exciting to see the strong phase 3 data on bimekizumab, particularly the deep responses at the HiSCR75 in a majority of patients after the first year,” he said.
Importantly, he does not see the growing array of treatment options as necessarily competitive for a disease with heterogeneous manifestations and variable responses to any one agent.
“While this may be a major step forward, it will still be critical to see more drugs come along for those who do not respond fully enough or have comorbidities that prevent the use of IL-17 and TNF [tumor necrosis factor] antagonists,” he said.
Bimekizumab is not approved for any indication in the United States; it is approved for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy in the EU/EEA, where it is marketed as Bimzelx, according to UCB. Dr. Kimball reports financial relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, Kymera, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Sayed reports financial relationships with AbbVie, InflaRx, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
Novel single-use patch shows promise for primary axillary hyperhidrosis
NEW ORLEANS – , results from a pivotal randomized trial showed.
“This is a new kind of device that is going to be a nice tool to have for treating patients who have hyperhidrosis of the axilla,” the study’s lead investigator, David M. Pariser, MD, who practices dermatology in Norfolk, Va., said during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In a study known as SAHARA, investigators at 11 sites evaluated the efficacy of the targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) patch, a single-use disposable device. The patch consists of a thin sodium layer on an adhesive overlay. It’s applied to the dry axilla, and as the patient sweats during treatment, the sweat reacts with the sodium. According to Dr. Pariser, this interaction generates precisely targeted thermal energy that targets sweat glands, leading to a reduction in excessive sweat production for up to three months.
The researchers enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 and randomized them to either an active TAT or a sham patch for up to 3 minutes. Their mean age was about 33 years, and slightly more than half were women. “If significant discomfort or pain was noted, [the patch] treatment was halted; otherwise, it was left on for 3 minutes,” said Dr. Pariser, professor of dermatology at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk. “The treated area was thoroughly cleaned after treatment, and the TAT patch was deactivated. This process was repeated on the other axilla.”
The HDSS, Gravimetric Sweat Production (GSP), and quality of life assessments for bother and impact were measured through 12 weeks. The quality of life assessments were an exploratory endpoint and scored from 0 to 4, with 4 being extremely bothered or impacted and 0 not being bothered or impacted at all. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of treated patients achieving a 1 or 2 on the HDSS at week 4, compared with sham treatment.
Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients with an improvement of at least 2 grades from baseline to 4 weeks in HDSS by treatment group; mean improvement in the quality of life scale bother by treatment group; mean improvement in the quality of life scale impact by treatment group; and the proportion of subjects with at least 50% improvement in GSP from baseline to 4 weeks in the active patch group only.
Adverse events (AEs) were divided into 3 categories: AEs at the treatment site (or skin reactions within the treated part of the axilla); procedure-related AEs (those that are the result of treatment, but not in the treated part of the axilla), and non-axillary AEs.
Dr. Pariser reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group versus 44.2% of those in the sham group improved to an HDSS score of 1 or 2 (P = .0332) and that 43.2% of those in the active patch group versus 16.3% of those in the sham group (P = .0107) achieved a 2-point or greater HDSS improvement. In addition, 9.1% of those in the active patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” he commented.
In other findings, 60.5% of patients in the active patch group showed at least a 50% reduction in GSP, compared with 32.6% of those in the sham group (P = .0102), with mean reductions of 57.3 mg/5min and 18.2 mg/5min, respectively (P = .0036). As for quality-of-life outcome scores, bother associated with hyperhidrosis was reduced by 1.52 points in active versus 0.61 in sham subjects (P = .0005), while impact was reduced by 1.44 in active versus 0.57 in sham subjects (P = .0004).
Adverse events
A total of 13 patients in the active patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site, including six with erythema; four with erosion; two with burning, itching or stinging; and one with underarm odor. “The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” said Dr. Pariser said.
Most adverse events resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all were mild to moderate. No serious adverse events occurred. Only five adverse events occurred in the sham group.
The TAT patch is currently undergoing review by the Food and Drug Administration, and according to Dr. Pariser, no other body sites have been treated with the device.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, characterized hyperhidrosis as “an exceedingly common medical condition that is commonly overlooked even though it has a tremendous burden on quality of life. I should know, as both someone who manages a large cohort of these patients but also as someone who suffers from it.”
Treatment options “have historically been limited, many of which are off-label and some which are difficult to access due to cost and/or duration/frequency of treatment,” added Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study. “The TAT patch offers a new, targeted, in-office, practical procedure-based approach to treat primary axillary hyperhidrosis. Innovation is certainly welcomed and needed, and I am curious to see how this technology is employed in practice once approved.”
The device is being developed by Candesant Biomedical. Dr. Pariser disclosed that he is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – , results from a pivotal randomized trial showed.
“This is a new kind of device that is going to be a nice tool to have for treating patients who have hyperhidrosis of the axilla,” the study’s lead investigator, David M. Pariser, MD, who practices dermatology in Norfolk, Va., said during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In a study known as SAHARA, investigators at 11 sites evaluated the efficacy of the targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) patch, a single-use disposable device. The patch consists of a thin sodium layer on an adhesive overlay. It’s applied to the dry axilla, and as the patient sweats during treatment, the sweat reacts with the sodium. According to Dr. Pariser, this interaction generates precisely targeted thermal energy that targets sweat glands, leading to a reduction in excessive sweat production for up to three months.
The researchers enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 and randomized them to either an active TAT or a sham patch for up to 3 minutes. Their mean age was about 33 years, and slightly more than half were women. “If significant discomfort or pain was noted, [the patch] treatment was halted; otherwise, it was left on for 3 minutes,” said Dr. Pariser, professor of dermatology at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk. “The treated area was thoroughly cleaned after treatment, and the TAT patch was deactivated. This process was repeated on the other axilla.”
The HDSS, Gravimetric Sweat Production (GSP), and quality of life assessments for bother and impact were measured through 12 weeks. The quality of life assessments were an exploratory endpoint and scored from 0 to 4, with 4 being extremely bothered or impacted and 0 not being bothered or impacted at all. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of treated patients achieving a 1 or 2 on the HDSS at week 4, compared with sham treatment.
Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients with an improvement of at least 2 grades from baseline to 4 weeks in HDSS by treatment group; mean improvement in the quality of life scale bother by treatment group; mean improvement in the quality of life scale impact by treatment group; and the proportion of subjects with at least 50% improvement in GSP from baseline to 4 weeks in the active patch group only.
Adverse events (AEs) were divided into 3 categories: AEs at the treatment site (or skin reactions within the treated part of the axilla); procedure-related AEs (those that are the result of treatment, but not in the treated part of the axilla), and non-axillary AEs.
Dr. Pariser reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group versus 44.2% of those in the sham group improved to an HDSS score of 1 or 2 (P = .0332) and that 43.2% of those in the active patch group versus 16.3% of those in the sham group (P = .0107) achieved a 2-point or greater HDSS improvement. In addition, 9.1% of those in the active patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” he commented.
In other findings, 60.5% of patients in the active patch group showed at least a 50% reduction in GSP, compared with 32.6% of those in the sham group (P = .0102), with mean reductions of 57.3 mg/5min and 18.2 mg/5min, respectively (P = .0036). As for quality-of-life outcome scores, bother associated with hyperhidrosis was reduced by 1.52 points in active versus 0.61 in sham subjects (P = .0005), while impact was reduced by 1.44 in active versus 0.57 in sham subjects (P = .0004).
Adverse events
A total of 13 patients in the active patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site, including six with erythema; four with erosion; two with burning, itching or stinging; and one with underarm odor. “The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” said Dr. Pariser said.
Most adverse events resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all were mild to moderate. No serious adverse events occurred. Only five adverse events occurred in the sham group.
The TAT patch is currently undergoing review by the Food and Drug Administration, and according to Dr. Pariser, no other body sites have been treated with the device.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, characterized hyperhidrosis as “an exceedingly common medical condition that is commonly overlooked even though it has a tremendous burden on quality of life. I should know, as both someone who manages a large cohort of these patients but also as someone who suffers from it.”
Treatment options “have historically been limited, many of which are off-label and some which are difficult to access due to cost and/or duration/frequency of treatment,” added Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study. “The TAT patch offers a new, targeted, in-office, practical procedure-based approach to treat primary axillary hyperhidrosis. Innovation is certainly welcomed and needed, and I am curious to see how this technology is employed in practice once approved.”
The device is being developed by Candesant Biomedical. Dr. Pariser disclosed that he is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – , results from a pivotal randomized trial showed.
“This is a new kind of device that is going to be a nice tool to have for treating patients who have hyperhidrosis of the axilla,” the study’s lead investigator, David M. Pariser, MD, who practices dermatology in Norfolk, Va., said during a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
In a study known as SAHARA, investigators at 11 sites evaluated the efficacy of the targeted alkali thermolysis (TAT) patch, a single-use disposable device. The patch consists of a thin sodium layer on an adhesive overlay. It’s applied to the dry axilla, and as the patient sweats during treatment, the sweat reacts with the sodium. According to Dr. Pariser, this interaction generates precisely targeted thermal energy that targets sweat glands, leading to a reduction in excessive sweat production for up to three months.
The researchers enrolled 110 individuals with Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale (HDSS) scores of 3 or 4 and randomized them to either an active TAT or a sham patch for up to 3 minutes. Their mean age was about 33 years, and slightly more than half were women. “If significant discomfort or pain was noted, [the patch] treatment was halted; otherwise, it was left on for 3 minutes,” said Dr. Pariser, professor of dermatology at Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk. “The treated area was thoroughly cleaned after treatment, and the TAT patch was deactivated. This process was repeated on the other axilla.”
The HDSS, Gravimetric Sweat Production (GSP), and quality of life assessments for bother and impact were measured through 12 weeks. The quality of life assessments were an exploratory endpoint and scored from 0 to 4, with 4 being extremely bothered or impacted and 0 not being bothered or impacted at all. The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of treated patients achieving a 1 or 2 on the HDSS at week 4, compared with sham treatment.
Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients with an improvement of at least 2 grades from baseline to 4 weeks in HDSS by treatment group; mean improvement in the quality of life scale bother by treatment group; mean improvement in the quality of life scale impact by treatment group; and the proportion of subjects with at least 50% improvement in GSP from baseline to 4 weeks in the active patch group only.
Adverse events (AEs) were divided into 3 categories: AEs at the treatment site (or skin reactions within the treated part of the axilla); procedure-related AEs (those that are the result of treatment, but not in the treated part of the axilla), and non-axillary AEs.
Dr. Pariser reported that at 4 weeks, 63.6% of patients in the active patch group versus 44.2% of those in the sham group improved to an HDSS score of 1 or 2 (P = .0332) and that 43.2% of those in the active patch group versus 16.3% of those in the sham group (P = .0107) achieved a 2-point or greater HDSS improvement. In addition, 9.1% of those in the active patch group achieved a 3-point improvement on the HDSS, compared with none in the sham group. “That’s an amazing improvement; you’re basically going from moderate or severe to none,” he commented.
In other findings, 60.5% of patients in the active patch group showed at least a 50% reduction in GSP, compared with 32.6% of those in the sham group (P = .0102), with mean reductions of 57.3 mg/5min and 18.2 mg/5min, respectively (P = .0036). As for quality-of-life outcome scores, bother associated with hyperhidrosis was reduced by 1.52 points in active versus 0.61 in sham subjects (P = .0005), while impact was reduced by 1.44 in active versus 0.57 in sham subjects (P = .0004).
Adverse events
A total of 13 patients in the active patch group experienced AEs at the treatment site, including six with erythema; four with erosion; two with burning, itching or stinging; and one with underarm odor. “The two procedure-related AEs in the TAT-treated group were compensatory sweating and irritant contact dermatitis due to the adhesive,” said Dr. Pariser said.
Most adverse events resolved in fewer than 2 weeks, and all were mild to moderate. No serious adverse events occurred. Only five adverse events occurred in the sham group.
The TAT patch is currently undergoing review by the Food and Drug Administration, and according to Dr. Pariser, no other body sites have been treated with the device.
Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, who was asked to comment on the study, characterized hyperhidrosis as “an exceedingly common medical condition that is commonly overlooked even though it has a tremendous burden on quality of life. I should know, as both someone who manages a large cohort of these patients but also as someone who suffers from it.”
Treatment options “have historically been limited, many of which are off-label and some which are difficult to access due to cost and/or duration/frequency of treatment,” added Dr. Friedman, who was not involved with the study. “The TAT patch offers a new, targeted, in-office, practical procedure-based approach to treat primary axillary hyperhidrosis. Innovation is certainly welcomed and needed, and I am curious to see how this technology is employed in practice once approved.”
The device is being developed by Candesant Biomedical. Dr. Pariser disclosed that he is a consultant or investigator for Bickel Biotechnology, Biofrontera AG, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene Corporation, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Sanofi.
Dr. Friedman reported having no relevant disclosures.
AT AAD 2023
JAK inhibitor safety warnings drawn from rheumatologic data may be misleading in dermatology
NEW ORLEANS – , even though the basis for all the risks is a rheumatoid arthritis study, according to a critical review at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Given the fact that the postmarketing RA study was specifically enriched with high-risk patients by requiring an age at enrollment of at least 50 years and the presence of at least one cardiovascular risk factor, the extrapolation of these risks to dermatologic indications is “not necessarily data-driven,” said Brett A. King, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The recently approved deucravacitinib is the only JAK inhibitor that has so far been exempt from these warnings. Instead, based on the ORAL Surveillance study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the Food and Drug Administration requires a boxed warning in nearly identical language for all the other JAK inhibitors. Relative to tofacitinib, the JAK inhibitor tested in ORAL Surveillance, many of these drugs differ by JAK selectivity and other characteristics that are likely relevant to risk of adverse events, Dr. King said. The same language has even been applied to topical ruxolitinib cream.
Basis of boxed warnings
In ORAL Surveillance, about 4,300 high-risk patients with RA were randomized to one of two doses of tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg) twice daily or a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor. All patients in the trial were taking methotrexate, and almost 60% were taking concomitant corticosteroids. The average body mass index of the study population was about 30 kg/m2.
After a median 4 years of follow-up (about 5,000 patient-years), the incidence of many of the adverse events tracked in the study were higher in the tofacitinib groups, including serious infections, MACE, thromboembolic events, and cancer. Dr. King did not challenge the importance of these data, but he questioned whether they are reasonably extrapolated to dermatologic indications, particularly as many of those treated are younger than those common to an RA population.
In fact, despite a study enriched for a higher risk of many events tracked, most adverse events were only slightly elevated, Dr. King pointed out. For example, the incidence of MACE over the 4 years of follow-up was 3.4% among those taking any dose of tofacitinib versus 2.5% of those randomized to TNF inhibitor. Rates of cancer were 4.2% versus 2.9%, respectively. There were also absolute increases in the number of serious infections and thromboembolic events for tofacitinib relative to TNF inhibitor.
Dr. King acknowledged that the numbers in ORAL Surveillance associated tofacitinib with a higher risk of serious events than TNF inhibitor in patients with RA, but he believes that “JAK inhibitor safety is almost certainly not the same in dermatology as it is in rheumatology patients.”
Evidence of difference in dermatology
There is some evidence to back this up. Dr. King cited a recently published study in RMD Open that evaluated the safety profile of the JAK inhibitor upadacitinib in nearly 7,000 patients over 15,000 patient-years of follow-up. Drug safety data were evaluated with up to 5.5 years of follow-up from 12 clinical trials of the four diseases for which upadacitinib is now indicated. Three were rheumatologic (RA, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis), and the fourth was atopic dermatitis (AD). Fourteen outcomes, including numerous types of infection, MACE, hepatic complications, and malignancy, were compared with methotrexate and the TNF inhibitor adalimumab.
For the RA diseases, upadacitinib was associated with a greater risk than comparators for several outcomes, including serious infections. But in AD, there was a smaller increased risk of adverse outcomes for the JAK inhibitor relative to comparators.
When evaluated by risk of adverse events across indications, for MACE, the exposure-adjusted event rates for upadacitinib were less than 0.1 in patients treated for AD over the observation period versus 0.3 and 0.4 for RA and psoriatic arthritis, respectively. Similarly, for venous thromboembolism, the rates for upadacitinib were again less than 0.1 in patients with AD versus 0.4 and 0.2 in RA and psoriatic arthritis, respectively.
Referring back to the postmarketing study, Dr. King emphasized that it is essential to consider how the boxed warning for JAK inhibitors was generated before applying them to dermatologic indications.
“Is a 30-year-old patient with a dermatologic disorder possibly at the same risk as the patients in the study from which we got the boxed warning? The answer is simply no,” he said.
Like the tofacitinib data in the ORAL Surveillance study, the upadacitinib clinical trial data are not necessarily relevant to other JAK inhibitors. In fact, Dr. King pointed out that the safety profiles of the available JAK inhibitors are not identical, an observation that is consistent with differences in JAK inhibitor selectivity that has implications for off-target events.
Dr. King does not dismiss the potential risks outlined in the current regulatory cautions about the use of JAK inhibitors, but he believes that dermatologists should be cognizant of “where the black box warning comes from.”
“We need to think carefully about the risk-to-benefit ratio in older patients or patients with risk factors, such as obesity and diabetes,” he said. But the safety profile of JAK inhibitors “is almost certainly better” than the profile suggested in boxed warnings applied to JAK inhibitors for dermatologic indications, he advised.
Risk-benefit considerations in dermatology
This position was supported by numerous other experts when asked for their perspectives. “I fully agree,” said Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, system chair of dermatology and immunology, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai, New York.
Like Dr. King, Dr. Guttman-Yassky did not dismiss the potential risks of JAK inhibitors when treating dermatologic diseases.
“While JAK inhibitors need monitoring as advised, adopting a boxed warning from an RA study for patients who are older [is problematic],” she commented. A study with the nonselective tofacitinib in this population “cannot be compared to more selective inhibitors in a much younger population, such as those treated [for] alopecia areata or atopic dermatitis.”
George Z. Han, MD, PhD, an associate professor of dermatology, Zucker School of Medicine, Hofstra, Northwell Medical Center, New Hyde Park, New York, also agreed but added some caveats.
“The comments about the ORAL Surveillance study are salient,” he said in an interview. “This kind of data should not directly be extrapolated to other patient types or to other medications.” However, one of Dr. Han’s most important caveats involves long-term use.
“JAK inhibitors are still relatively narrow-therapeutic-window drugs that in a dose-dependent fashion could lead to negative effects, including thromboembolic events, abnormalities in red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and lipids,” he said. While doses used in dermatology “are generally below the level of any major concern,” Dr. Han cautioned that “we lack definitive data” on long-term use, and this is important for understanding “any potential small risk of rare events, such as malignancy or thromboembolism.”
Saakshi Khattri, MD, a colleague of Dr. Guttman-Yassky at Mount Sinai, said the risks of JAK inhibitors should not be underestimated, but she also agreed that risk “needs to be delivered in the right context.” Dr. Khattri, who is board certified in both dermatology and rheumatology, noted the safety profiles of available JAK inhibitors differ and that extrapolating safety from an RA study to dermatologic indications does not make sense. “Different diseases, different age groups,” she said.
Dr. King has reported financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Han reports financial relationships with Amgen, Athenex, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bond Avillion, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, PellePharm, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Khattri has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – , even though the basis for all the risks is a rheumatoid arthritis study, according to a critical review at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Given the fact that the postmarketing RA study was specifically enriched with high-risk patients by requiring an age at enrollment of at least 50 years and the presence of at least one cardiovascular risk factor, the extrapolation of these risks to dermatologic indications is “not necessarily data-driven,” said Brett A. King, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The recently approved deucravacitinib is the only JAK inhibitor that has so far been exempt from these warnings. Instead, based on the ORAL Surveillance study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the Food and Drug Administration requires a boxed warning in nearly identical language for all the other JAK inhibitors. Relative to tofacitinib, the JAK inhibitor tested in ORAL Surveillance, many of these drugs differ by JAK selectivity and other characteristics that are likely relevant to risk of adverse events, Dr. King said. The same language has even been applied to topical ruxolitinib cream.
Basis of boxed warnings
In ORAL Surveillance, about 4,300 high-risk patients with RA were randomized to one of two doses of tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg) twice daily or a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor. All patients in the trial were taking methotrexate, and almost 60% were taking concomitant corticosteroids. The average body mass index of the study population was about 30 kg/m2.
After a median 4 years of follow-up (about 5,000 patient-years), the incidence of many of the adverse events tracked in the study were higher in the tofacitinib groups, including serious infections, MACE, thromboembolic events, and cancer. Dr. King did not challenge the importance of these data, but he questioned whether they are reasonably extrapolated to dermatologic indications, particularly as many of those treated are younger than those common to an RA population.
In fact, despite a study enriched for a higher risk of many events tracked, most adverse events were only slightly elevated, Dr. King pointed out. For example, the incidence of MACE over the 4 years of follow-up was 3.4% among those taking any dose of tofacitinib versus 2.5% of those randomized to TNF inhibitor. Rates of cancer were 4.2% versus 2.9%, respectively. There were also absolute increases in the number of serious infections and thromboembolic events for tofacitinib relative to TNF inhibitor.
Dr. King acknowledged that the numbers in ORAL Surveillance associated tofacitinib with a higher risk of serious events than TNF inhibitor in patients with RA, but he believes that “JAK inhibitor safety is almost certainly not the same in dermatology as it is in rheumatology patients.”
Evidence of difference in dermatology
There is some evidence to back this up. Dr. King cited a recently published study in RMD Open that evaluated the safety profile of the JAK inhibitor upadacitinib in nearly 7,000 patients over 15,000 patient-years of follow-up. Drug safety data were evaluated with up to 5.5 years of follow-up from 12 clinical trials of the four diseases for which upadacitinib is now indicated. Three were rheumatologic (RA, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis), and the fourth was atopic dermatitis (AD). Fourteen outcomes, including numerous types of infection, MACE, hepatic complications, and malignancy, were compared with methotrexate and the TNF inhibitor adalimumab.
For the RA diseases, upadacitinib was associated with a greater risk than comparators for several outcomes, including serious infections. But in AD, there was a smaller increased risk of adverse outcomes for the JAK inhibitor relative to comparators.
When evaluated by risk of adverse events across indications, for MACE, the exposure-adjusted event rates for upadacitinib were less than 0.1 in patients treated for AD over the observation period versus 0.3 and 0.4 for RA and psoriatic arthritis, respectively. Similarly, for venous thromboembolism, the rates for upadacitinib were again less than 0.1 in patients with AD versus 0.4 and 0.2 in RA and psoriatic arthritis, respectively.
Referring back to the postmarketing study, Dr. King emphasized that it is essential to consider how the boxed warning for JAK inhibitors was generated before applying them to dermatologic indications.
“Is a 30-year-old patient with a dermatologic disorder possibly at the same risk as the patients in the study from which we got the boxed warning? The answer is simply no,” he said.
Like the tofacitinib data in the ORAL Surveillance study, the upadacitinib clinical trial data are not necessarily relevant to other JAK inhibitors. In fact, Dr. King pointed out that the safety profiles of the available JAK inhibitors are not identical, an observation that is consistent with differences in JAK inhibitor selectivity that has implications for off-target events.
Dr. King does not dismiss the potential risks outlined in the current regulatory cautions about the use of JAK inhibitors, but he believes that dermatologists should be cognizant of “where the black box warning comes from.”
“We need to think carefully about the risk-to-benefit ratio in older patients or patients with risk factors, such as obesity and diabetes,” he said. But the safety profile of JAK inhibitors “is almost certainly better” than the profile suggested in boxed warnings applied to JAK inhibitors for dermatologic indications, he advised.
Risk-benefit considerations in dermatology
This position was supported by numerous other experts when asked for their perspectives. “I fully agree,” said Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, system chair of dermatology and immunology, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai, New York.
Like Dr. King, Dr. Guttman-Yassky did not dismiss the potential risks of JAK inhibitors when treating dermatologic diseases.
“While JAK inhibitors need monitoring as advised, adopting a boxed warning from an RA study for patients who are older [is problematic],” she commented. A study with the nonselective tofacitinib in this population “cannot be compared to more selective inhibitors in a much younger population, such as those treated [for] alopecia areata or atopic dermatitis.”
George Z. Han, MD, PhD, an associate professor of dermatology, Zucker School of Medicine, Hofstra, Northwell Medical Center, New Hyde Park, New York, also agreed but added some caveats.
“The comments about the ORAL Surveillance study are salient,” he said in an interview. “This kind of data should not directly be extrapolated to other patient types or to other medications.” However, one of Dr. Han’s most important caveats involves long-term use.
“JAK inhibitors are still relatively narrow-therapeutic-window drugs that in a dose-dependent fashion could lead to negative effects, including thromboembolic events, abnormalities in red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and lipids,” he said. While doses used in dermatology “are generally below the level of any major concern,” Dr. Han cautioned that “we lack definitive data” on long-term use, and this is important for understanding “any potential small risk of rare events, such as malignancy or thromboembolism.”
Saakshi Khattri, MD, a colleague of Dr. Guttman-Yassky at Mount Sinai, said the risks of JAK inhibitors should not be underestimated, but she also agreed that risk “needs to be delivered in the right context.” Dr. Khattri, who is board certified in both dermatology and rheumatology, noted the safety profiles of available JAK inhibitors differ and that extrapolating safety from an RA study to dermatologic indications does not make sense. “Different diseases, different age groups,” she said.
Dr. King has reported financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Han reports financial relationships with Amgen, Athenex, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bond Avillion, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, PellePharm, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Khattri has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
NEW ORLEANS – , even though the basis for all the risks is a rheumatoid arthritis study, according to a critical review at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Given the fact that the postmarketing RA study was specifically enriched with high-risk patients by requiring an age at enrollment of at least 50 years and the presence of at least one cardiovascular risk factor, the extrapolation of these risks to dermatologic indications is “not necessarily data-driven,” said Brett A. King, MD, PhD, associate professor of dermatology, Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
The recently approved deucravacitinib is the only JAK inhibitor that has so far been exempt from these warnings. Instead, based on the ORAL Surveillance study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the Food and Drug Administration requires a boxed warning in nearly identical language for all the other JAK inhibitors. Relative to tofacitinib, the JAK inhibitor tested in ORAL Surveillance, many of these drugs differ by JAK selectivity and other characteristics that are likely relevant to risk of adverse events, Dr. King said. The same language has even been applied to topical ruxolitinib cream.
Basis of boxed warnings
In ORAL Surveillance, about 4,300 high-risk patients with RA were randomized to one of two doses of tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg) twice daily or a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor. All patients in the trial were taking methotrexate, and almost 60% were taking concomitant corticosteroids. The average body mass index of the study population was about 30 kg/m2.
After a median 4 years of follow-up (about 5,000 patient-years), the incidence of many of the adverse events tracked in the study were higher in the tofacitinib groups, including serious infections, MACE, thromboembolic events, and cancer. Dr. King did not challenge the importance of these data, but he questioned whether they are reasonably extrapolated to dermatologic indications, particularly as many of those treated are younger than those common to an RA population.
In fact, despite a study enriched for a higher risk of many events tracked, most adverse events were only slightly elevated, Dr. King pointed out. For example, the incidence of MACE over the 4 years of follow-up was 3.4% among those taking any dose of tofacitinib versus 2.5% of those randomized to TNF inhibitor. Rates of cancer were 4.2% versus 2.9%, respectively. There were also absolute increases in the number of serious infections and thromboembolic events for tofacitinib relative to TNF inhibitor.
Dr. King acknowledged that the numbers in ORAL Surveillance associated tofacitinib with a higher risk of serious events than TNF inhibitor in patients with RA, but he believes that “JAK inhibitor safety is almost certainly not the same in dermatology as it is in rheumatology patients.”
Evidence of difference in dermatology
There is some evidence to back this up. Dr. King cited a recently published study in RMD Open that evaluated the safety profile of the JAK inhibitor upadacitinib in nearly 7,000 patients over 15,000 patient-years of follow-up. Drug safety data were evaluated with up to 5.5 years of follow-up from 12 clinical trials of the four diseases for which upadacitinib is now indicated. Three were rheumatologic (RA, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis), and the fourth was atopic dermatitis (AD). Fourteen outcomes, including numerous types of infection, MACE, hepatic complications, and malignancy, were compared with methotrexate and the TNF inhibitor adalimumab.
For the RA diseases, upadacitinib was associated with a greater risk than comparators for several outcomes, including serious infections. But in AD, there was a smaller increased risk of adverse outcomes for the JAK inhibitor relative to comparators.
When evaluated by risk of adverse events across indications, for MACE, the exposure-adjusted event rates for upadacitinib were less than 0.1 in patients treated for AD over the observation period versus 0.3 and 0.4 for RA and psoriatic arthritis, respectively. Similarly, for venous thromboembolism, the rates for upadacitinib were again less than 0.1 in patients with AD versus 0.4 and 0.2 in RA and psoriatic arthritis, respectively.
Referring back to the postmarketing study, Dr. King emphasized that it is essential to consider how the boxed warning for JAK inhibitors was generated before applying them to dermatologic indications.
“Is a 30-year-old patient with a dermatologic disorder possibly at the same risk as the patients in the study from which we got the boxed warning? The answer is simply no,” he said.
Like the tofacitinib data in the ORAL Surveillance study, the upadacitinib clinical trial data are not necessarily relevant to other JAK inhibitors. In fact, Dr. King pointed out that the safety profiles of the available JAK inhibitors are not identical, an observation that is consistent with differences in JAK inhibitor selectivity that has implications for off-target events.
Dr. King does not dismiss the potential risks outlined in the current regulatory cautions about the use of JAK inhibitors, but he believes that dermatologists should be cognizant of “where the black box warning comes from.”
“We need to think carefully about the risk-to-benefit ratio in older patients or patients with risk factors, such as obesity and diabetes,” he said. But the safety profile of JAK inhibitors “is almost certainly better” than the profile suggested in boxed warnings applied to JAK inhibitors for dermatologic indications, he advised.
Risk-benefit considerations in dermatology
This position was supported by numerous other experts when asked for their perspectives. “I fully agree,” said Emma Guttman-Yassky, MD, PhD, system chair of dermatology and immunology, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai, New York.
Like Dr. King, Dr. Guttman-Yassky did not dismiss the potential risks of JAK inhibitors when treating dermatologic diseases.
“While JAK inhibitors need monitoring as advised, adopting a boxed warning from an RA study for patients who are older [is problematic],” she commented. A study with the nonselective tofacitinib in this population “cannot be compared to more selective inhibitors in a much younger population, such as those treated [for] alopecia areata or atopic dermatitis.”
George Z. Han, MD, PhD, an associate professor of dermatology, Zucker School of Medicine, Hofstra, Northwell Medical Center, New Hyde Park, New York, also agreed but added some caveats.
“The comments about the ORAL Surveillance study are salient,” he said in an interview. “This kind of data should not directly be extrapolated to other patient types or to other medications.” However, one of Dr. Han’s most important caveats involves long-term use.
“JAK inhibitors are still relatively narrow-therapeutic-window drugs that in a dose-dependent fashion could lead to negative effects, including thromboembolic events, abnormalities in red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and lipids,” he said. While doses used in dermatology “are generally below the level of any major concern,” Dr. Han cautioned that “we lack definitive data” on long-term use, and this is important for understanding “any potential small risk of rare events, such as malignancy or thromboembolism.”
Saakshi Khattri, MD, a colleague of Dr. Guttman-Yassky at Mount Sinai, said the risks of JAK inhibitors should not be underestimated, but she also agreed that risk “needs to be delivered in the right context.” Dr. Khattri, who is board certified in both dermatology and rheumatology, noted the safety profiles of available JAK inhibitors differ and that extrapolating safety from an RA study to dermatologic indications does not make sense. “Different diseases, different age groups,” she said.
Dr. King has reported financial relationships with more than 15 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Guttman-Yassky has reported financial relationships with more than 20 pharmaceutical companies, including companies that make JAK inhibitors. Dr. Han reports financial relationships with Amgen, Athenex, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bond Avillion, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, PellePharm, Pfizer, and UCB. Dr. Khattri has reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Arcutis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen, Leo, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AAD 2023
How to become wise
The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing. – Socrates
At what age is one supposed to be wise? I feel like I’m falling behind. I’ve crossed the middle of life and can check the prerequisite experiences: Joy, tragedy, love, adventure, love again. I lived a jetsetter life with an overnight bag always packed. I’ve sported the “Dad AF” tee with a fully loaded dad-pack. I’ve seen the 50 states and had my picture wrapped on a city bus (super-weird when you pull up next to one). Yet, when a moment arrives to pop in pithy advice for a resident or drop a few reassuring lines for a grieving friend, I’m often unable to find the words. If life were a video game, I’ve not earned the wisdom level yet.
Who are the wise men and women in your life? It’s difficult to list them. This is because it’s a complex attribute and hard to explain. It’s also because the wise who walk among us are rare. Wise is more than being brilliant at bullous diseases or knowing how to sleep train a baby. Nor is wise the buddy who purchased $1,000 of Bitcoin in 2010 (although stay close with him, he probably owns a jet). Neither content experts nor lucky friends rise to the appellation. Both experience and empathy.
The ancients considered wisdom to be one of the vital virtues. It was personified in high-profile gods like Apollo and Athena. It’s rare and important enough to be seen as spiritual. It features heavily in the Bible, the Bhagavad Gita, the Meditations of Marcus Aurelius. In some cultures the wise are called elders or sages. In all cultures they are helpful, respected, sought after, appreciated. We need more wise people in this game of life. I want to be one. But there’s no Coursera for it.
To become wise you have to pass through many levels, put in a lot of reps, suffer through many sleepless nights. Like the third molar, also known as the wisdom tooth, it takes years. You also have to emerge stronger and smarter through those experiences. FDR would not have become one of the wisest presidents in history had it not been for his trials, and victories, over polio. Osler missed Cushing syndrome multiple times before he got it right. It seems you have to go to the mountain, like Batman, and fight a few battles to realize your full wisdom potential.
You must also reflect on your experiences and hone your insight. The management sage Peter Drucker would write what he expected to happen after a decision. Then he’d return to it to hone his intuition and judgment.
Lastly, you have to use your powers for good. Using insight to win your NCAA bracket pool isn’t wisdom. Helping a friend whose marriage is falling apart or colleague whose patient is suing them or a resident whose excision hit an arteriole surely is.
I’ve got a ways to go before anyone puts me on their wise friend list. I’m working on it though. Perhaps you will too – we are desperately short-staffed in this area. For now, I can start with writing better condolences.
“Who maintains that it is not a heavy blow? But it is part of being human.” – Seneca
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing. – Socrates
At what age is one supposed to be wise? I feel like I’m falling behind. I’ve crossed the middle of life and can check the prerequisite experiences: Joy, tragedy, love, adventure, love again. I lived a jetsetter life with an overnight bag always packed. I’ve sported the “Dad AF” tee with a fully loaded dad-pack. I’ve seen the 50 states and had my picture wrapped on a city bus (super-weird when you pull up next to one). Yet, when a moment arrives to pop in pithy advice for a resident or drop a few reassuring lines for a grieving friend, I’m often unable to find the words. If life were a video game, I’ve not earned the wisdom level yet.
Who are the wise men and women in your life? It’s difficult to list them. This is because it’s a complex attribute and hard to explain. It’s also because the wise who walk among us are rare. Wise is more than being brilliant at bullous diseases or knowing how to sleep train a baby. Nor is wise the buddy who purchased $1,000 of Bitcoin in 2010 (although stay close with him, he probably owns a jet). Neither content experts nor lucky friends rise to the appellation. Both experience and empathy.
The ancients considered wisdom to be one of the vital virtues. It was personified in high-profile gods like Apollo and Athena. It’s rare and important enough to be seen as spiritual. It features heavily in the Bible, the Bhagavad Gita, the Meditations of Marcus Aurelius. In some cultures the wise are called elders or sages. In all cultures they are helpful, respected, sought after, appreciated. We need more wise people in this game of life. I want to be one. But there’s no Coursera for it.
To become wise you have to pass through many levels, put in a lot of reps, suffer through many sleepless nights. Like the third molar, also known as the wisdom tooth, it takes years. You also have to emerge stronger and smarter through those experiences. FDR would not have become one of the wisest presidents in history had it not been for his trials, and victories, over polio. Osler missed Cushing syndrome multiple times before he got it right. It seems you have to go to the mountain, like Batman, and fight a few battles to realize your full wisdom potential.
You must also reflect on your experiences and hone your insight. The management sage Peter Drucker would write what he expected to happen after a decision. Then he’d return to it to hone his intuition and judgment.
Lastly, you have to use your powers for good. Using insight to win your NCAA bracket pool isn’t wisdom. Helping a friend whose marriage is falling apart or colleague whose patient is suing them or a resident whose excision hit an arteriole surely is.
I’ve got a ways to go before anyone puts me on their wise friend list. I’m working on it though. Perhaps you will too – we are desperately short-staffed in this area. For now, I can start with writing better condolences.
“Who maintains that it is not a heavy blow? But it is part of being human.” – Seneca
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing. – Socrates
At what age is one supposed to be wise? I feel like I’m falling behind. I’ve crossed the middle of life and can check the prerequisite experiences: Joy, tragedy, love, adventure, love again. I lived a jetsetter life with an overnight bag always packed. I’ve sported the “Dad AF” tee with a fully loaded dad-pack. I’ve seen the 50 states and had my picture wrapped on a city bus (super-weird when you pull up next to one). Yet, when a moment arrives to pop in pithy advice for a resident or drop a few reassuring lines for a grieving friend, I’m often unable to find the words. If life were a video game, I’ve not earned the wisdom level yet.
Who are the wise men and women in your life? It’s difficult to list them. This is because it’s a complex attribute and hard to explain. It’s also because the wise who walk among us are rare. Wise is more than being brilliant at bullous diseases or knowing how to sleep train a baby. Nor is wise the buddy who purchased $1,000 of Bitcoin in 2010 (although stay close with him, he probably owns a jet). Neither content experts nor lucky friends rise to the appellation. Both experience and empathy.
The ancients considered wisdom to be one of the vital virtues. It was personified in high-profile gods like Apollo and Athena. It’s rare and important enough to be seen as spiritual. It features heavily in the Bible, the Bhagavad Gita, the Meditations of Marcus Aurelius. In some cultures the wise are called elders or sages. In all cultures they are helpful, respected, sought after, appreciated. We need more wise people in this game of life. I want to be one. But there’s no Coursera for it.
To become wise you have to pass through many levels, put in a lot of reps, suffer through many sleepless nights. Like the third molar, also known as the wisdom tooth, it takes years. You also have to emerge stronger and smarter through those experiences. FDR would not have become one of the wisest presidents in history had it not been for his trials, and victories, over polio. Osler missed Cushing syndrome multiple times before he got it right. It seems you have to go to the mountain, like Batman, and fight a few battles to realize your full wisdom potential.
You must also reflect on your experiences and hone your insight. The management sage Peter Drucker would write what he expected to happen after a decision. Then he’d return to it to hone his intuition and judgment.
Lastly, you have to use your powers for good. Using insight to win your NCAA bracket pool isn’t wisdom. Helping a friend whose marriage is falling apart or colleague whose patient is suing them or a resident whose excision hit an arteriole surely is.
I’ve got a ways to go before anyone puts me on their wise friend list. I’m working on it though. Perhaps you will too – we are desperately short-staffed in this area. For now, I can start with writing better condolences.
“Who maintains that it is not a heavy blow? But it is part of being human.” – Seneca
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at dermnews@mdedge.com.
Study finds quality of topical steroid withdrawal videos on YouTube subpar
NEW ORLEANS –
“Video-sharing platforms such as YouTube are a great place for patients to connect and find community with others dealing with the same conditions,” senior author Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during an e-poster session. “There is no doubt tremendous value in viewing the shared experience; however, it is important that medical advice be evidence based and validated. Seeking said advice from a medical professional such as a board-certified dermatologist will no doubt increase the likelihood that said guidance is supported by the literature and most importantly, will do no harm.”
Noting a trend of increased user-created content on social media and Internet sites about topical steroid withdrawal in recent years, Dr. Friedman, first author Erika McCormick, a fourth-year medical student at George Washington University, and colleagues used the keywords “topical steroid withdrawal” on YouTube to search for and analyze the top 10 most viewed videos on the subject.
Two independent reviewers used the modified DISCERN (mDISCERN) tool and the Global Quality Scale (GQS) to assess reliability and quality/scientific accuracy of videos, respectively. Average scores were generated for each video and the researchers used one way ANOVA, unpaired t-tests, and linear regression to analyze the ratings. For mDISCERN criteria, a point is given per each of five criteria for a possible score between 0 and 5. Examples of criteria included “Are the aims clear and achieved?” and “Is the information presented both balanced and unbiased”? For GQS, a score from 1 to 5 is designated based on criteria ranging from “poor quality, poor flow, most information missing” to “excellent quality and flow, very useful for patients.”
The researchers found that the mean combined mDISCERN score of the 10 videos was a 2, which indicates poor reliability and shortcomings. Similarly, the combined mean GQS score was 2.5, which suggests poor to moderate quality of videos, missing discussion of important topics, and limited use to patients. The researchers found no correlation between mDISCERN or GQS scores and length of video, duration on YouTube, or number of views, subscribers, or likes.
“We were disheartened that patient testimonial videos had the poorest quality and reliability of the information sources,” Ms. McCormick said in an interview. “Videos that included medical research and information from dermatologists had significantly higher quality and reliability scores than the remainder of videos.” Accurate information online is essential to help patients recognize topical steroid withdrawal and seek medical care, she continued.
Conversely, wide viewership of unreliable information “may contribute to fear of topical corticosteroids and dissuade use in patients with primary skin diseases that may benefit from this common treatment,” Dr. Friedman said. “Dermatologists must be aware of the content patients are consuming online, should guide patients in appraising quality and reliability of online resources, and must provide valid sources of additional information for their patients.” One such resource he recommended is the National Eczema Association, which has created online content for patients about topical steroid withdrawal.
Doris Day, MD, a New York–based dermatologist who was asked to comment on the study, said that many patients rely on YouTube as a go-to resource, with videos that can be watched at times of their choosing. “Oftentimes, the person on the video is relatable and has some general knowledge but is lacking the information that would be relevant and important for the individual patient,” said Dr. Day, who was not involved with the study. “The downside of this is that the person who takes that advice may not use the prescription properly or for the correct amount of time, which can lead to either undertreating or, even worse, overtreatment, which can have permanent consequences.”
One possible solution is for more doctors to create videos for YouTube, she added, “but that doesn’t guarantee that those would be the ones patients would choose to watch.” Another solution “is to have YouTube add qualifiers indicating that the information being discussed is not medical,” she suggested. “Ideally, patients will get all the information they need while they are in the office and also have clear written instructions and even a video they can review at a later time, made by the office, to help them feel they are getting personalized care and the attention they need.”
Ms. McCormick’s research is funded by a grant from Galderma. Dr. Friedman and Dr. Day had no relevant disclosures to report.
NEW ORLEANS –
“Video-sharing platforms such as YouTube are a great place for patients to connect and find community with others dealing with the same conditions,” senior author Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during an e-poster session. “There is no doubt tremendous value in viewing the shared experience; however, it is important that medical advice be evidence based and validated. Seeking said advice from a medical professional such as a board-certified dermatologist will no doubt increase the likelihood that said guidance is supported by the literature and most importantly, will do no harm.”
Noting a trend of increased user-created content on social media and Internet sites about topical steroid withdrawal in recent years, Dr. Friedman, first author Erika McCormick, a fourth-year medical student at George Washington University, and colleagues used the keywords “topical steroid withdrawal” on YouTube to search for and analyze the top 10 most viewed videos on the subject.
Two independent reviewers used the modified DISCERN (mDISCERN) tool and the Global Quality Scale (GQS) to assess reliability and quality/scientific accuracy of videos, respectively. Average scores were generated for each video and the researchers used one way ANOVA, unpaired t-tests, and linear regression to analyze the ratings. For mDISCERN criteria, a point is given per each of five criteria for a possible score between 0 and 5. Examples of criteria included “Are the aims clear and achieved?” and “Is the information presented both balanced and unbiased”? For GQS, a score from 1 to 5 is designated based on criteria ranging from “poor quality, poor flow, most information missing” to “excellent quality and flow, very useful for patients.”
The researchers found that the mean combined mDISCERN score of the 10 videos was a 2, which indicates poor reliability and shortcomings. Similarly, the combined mean GQS score was 2.5, which suggests poor to moderate quality of videos, missing discussion of important topics, and limited use to patients. The researchers found no correlation between mDISCERN or GQS scores and length of video, duration on YouTube, or number of views, subscribers, or likes.
“We were disheartened that patient testimonial videos had the poorest quality and reliability of the information sources,” Ms. McCormick said in an interview. “Videos that included medical research and information from dermatologists had significantly higher quality and reliability scores than the remainder of videos.” Accurate information online is essential to help patients recognize topical steroid withdrawal and seek medical care, she continued.
Conversely, wide viewership of unreliable information “may contribute to fear of topical corticosteroids and dissuade use in patients with primary skin diseases that may benefit from this common treatment,” Dr. Friedman said. “Dermatologists must be aware of the content patients are consuming online, should guide patients in appraising quality and reliability of online resources, and must provide valid sources of additional information for their patients.” One such resource he recommended is the National Eczema Association, which has created online content for patients about topical steroid withdrawal.
Doris Day, MD, a New York–based dermatologist who was asked to comment on the study, said that many patients rely on YouTube as a go-to resource, with videos that can be watched at times of their choosing. “Oftentimes, the person on the video is relatable and has some general knowledge but is lacking the information that would be relevant and important for the individual patient,” said Dr. Day, who was not involved with the study. “The downside of this is that the person who takes that advice may not use the prescription properly or for the correct amount of time, which can lead to either undertreating or, even worse, overtreatment, which can have permanent consequences.”
One possible solution is for more doctors to create videos for YouTube, she added, “but that doesn’t guarantee that those would be the ones patients would choose to watch.” Another solution “is to have YouTube add qualifiers indicating that the information being discussed is not medical,” she suggested. “Ideally, patients will get all the information they need while they are in the office and also have clear written instructions and even a video they can review at a later time, made by the office, to help them feel they are getting personalized care and the attention they need.”
Ms. McCormick’s research is funded by a grant from Galderma. Dr. Friedman and Dr. Day had no relevant disclosures to report.
NEW ORLEANS –
“Video-sharing platforms such as YouTube are a great place for patients to connect and find community with others dealing with the same conditions,” senior author Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology, where the study was presented during an e-poster session. “There is no doubt tremendous value in viewing the shared experience; however, it is important that medical advice be evidence based and validated. Seeking said advice from a medical professional such as a board-certified dermatologist will no doubt increase the likelihood that said guidance is supported by the literature and most importantly, will do no harm.”
Noting a trend of increased user-created content on social media and Internet sites about topical steroid withdrawal in recent years, Dr. Friedman, first author Erika McCormick, a fourth-year medical student at George Washington University, and colleagues used the keywords “topical steroid withdrawal” on YouTube to search for and analyze the top 10 most viewed videos on the subject.
Two independent reviewers used the modified DISCERN (mDISCERN) tool and the Global Quality Scale (GQS) to assess reliability and quality/scientific accuracy of videos, respectively. Average scores were generated for each video and the researchers used one way ANOVA, unpaired t-tests, and linear regression to analyze the ratings. For mDISCERN criteria, a point is given per each of five criteria for a possible score between 0 and 5. Examples of criteria included “Are the aims clear and achieved?” and “Is the information presented both balanced and unbiased”? For GQS, a score from 1 to 5 is designated based on criteria ranging from “poor quality, poor flow, most information missing” to “excellent quality and flow, very useful for patients.”
The researchers found that the mean combined mDISCERN score of the 10 videos was a 2, which indicates poor reliability and shortcomings. Similarly, the combined mean GQS score was 2.5, which suggests poor to moderate quality of videos, missing discussion of important topics, and limited use to patients. The researchers found no correlation between mDISCERN or GQS scores and length of video, duration on YouTube, or number of views, subscribers, or likes.
“We were disheartened that patient testimonial videos had the poorest quality and reliability of the information sources,” Ms. McCormick said in an interview. “Videos that included medical research and information from dermatologists had significantly higher quality and reliability scores than the remainder of videos.” Accurate information online is essential to help patients recognize topical steroid withdrawal and seek medical care, she continued.
Conversely, wide viewership of unreliable information “may contribute to fear of topical corticosteroids and dissuade use in patients with primary skin diseases that may benefit from this common treatment,” Dr. Friedman said. “Dermatologists must be aware of the content patients are consuming online, should guide patients in appraising quality and reliability of online resources, and must provide valid sources of additional information for their patients.” One such resource he recommended is the National Eczema Association, which has created online content for patients about topical steroid withdrawal.
Doris Day, MD, a New York–based dermatologist who was asked to comment on the study, said that many patients rely on YouTube as a go-to resource, with videos that can be watched at times of their choosing. “Oftentimes, the person on the video is relatable and has some general knowledge but is lacking the information that would be relevant and important for the individual patient,” said Dr. Day, who was not involved with the study. “The downside of this is that the person who takes that advice may not use the prescription properly or for the correct amount of time, which can lead to either undertreating or, even worse, overtreatment, which can have permanent consequences.”
One possible solution is for more doctors to create videos for YouTube, she added, “but that doesn’t guarantee that those would be the ones patients would choose to watch.” Another solution “is to have YouTube add qualifiers indicating that the information being discussed is not medical,” she suggested. “Ideally, patients will get all the information they need while they are in the office and also have clear written instructions and even a video they can review at a later time, made by the office, to help them feel they are getting personalized care and the attention they need.”
Ms. McCormick’s research is funded by a grant from Galderma. Dr. Friedman and Dr. Day had no relevant disclosures to report.
AT AAD 2023
Nearly one in three patients with IBD affected by skin lesions
People with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) commonly develop skin lesions linked to their condition, but until now few researchers looked at how common they are.
, according to the prospective, single-center study.
“Skin lesions in IBD patients are much more prevalent than it is generally accepted. The lesions may be related to the pathogenesis of IBD, but it is very important to know that the modern biological therapies may also cause skin lesions,” said senior study author Laimas Jonaitis, MD, PhD, professor in the department of gastroenterology at Lithuanian University of Health Sciences in Kaunas.
“If the gastroenterologist is experienced and has enough competence, he or she may establish the diagnosis, but in all other cases it is wise and advisable to refer the patient to the dermatologist,” Dr. Jonaitis said. A referral should include the history and full treatment for IBD.
The results were presented as a poster at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation, held in Copenhagen and virtually.
Dr. Jonaitis and colleagues conducted a literature analysis to determine the prevalence of extra-abdominal manifestations of IBD. The lack of published data prompted them to survey 152 consecutive patients with IBD receiving outpatient treatment at their institution. The patients completed questionnaires from January to October 2022 about any cutaneous lesions.
The mean age of patients was 42 years, and 58% were men. A majority, 72%, had ulcerative colitis, and 28% had Crohn’s disease.
Prevalence of skin lesions
A total of 43% of participants reported skin lesions, but only 30% of patients had lesions considered related to IBD or IBD therapy due to their emergence after the patient’s IBD diagnosis.
By IBD diagnosis, 29% of patients with ulcerative colitis and 33% of patients with Crohn’s disease had lesions related to their condition. The difference in skin lesion prevalence between the two groups was not significant (P > .05), the researchers noted.
The team further investigated the types of skin lesions deemed to be associated with IBD or IBD therapy.
Overall, they found psoriasis in nine patients, eczema in nine, erythema nodosum in six, pyoderma gangrenosum in five, allergic rash in four, and vitiligo in two. They found acne, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and hemorrhagic vasculitis in one patient each.
Specifically, among patients with ulcerative colitis, skin lesions were reported in 8 of 27 with left-sided colitis, 2 of 15 with ulcerative colitis proctitis, and 22 of 67 patients with pancolitis. The difference between the groups of proctitis and pancolitis was significant (P = .03).
Within the group with Crohn’s disease, skin lesions were reported in 3 of 15 patients with ileitis, 4 of 10 with colitis, and 7 of 17 with ileocolitis. The difference among these groups was not significant (P > .05).
The most common skin lesions observed in Crohn’s disease were erythema nodosum and eczema, and in ulcerative colitis, psoriasis and eczema, the researchers reported.
They also noted that the cutaneous lesions were significantly more prevalent in extensive ulcerative colitis compared with distal disease.
Skin lesions add to patient misery
“Skin lesions are considered a burden to patients with IBD and add to their suffering,” said Sara Mesilhy, MBBS, a gastroenterologist with the Royal College of Physicians in the United Kingdom, who was not affiliated with the research.
The severity and location of the disease appears to play a role because researchers found extensive ulcerative colitis may carry a higher risk for the development of skin lesions, Dr. Mesilhy noted.
The first step when facing skin lesions is to control the disease activity via the best treatment option, Dr. Mesilhy suggested.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Jonaitis and Dr. Mesilhy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
People with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) commonly develop skin lesions linked to their condition, but until now few researchers looked at how common they are.
, according to the prospective, single-center study.
“Skin lesions in IBD patients are much more prevalent than it is generally accepted. The lesions may be related to the pathogenesis of IBD, but it is very important to know that the modern biological therapies may also cause skin lesions,” said senior study author Laimas Jonaitis, MD, PhD, professor in the department of gastroenterology at Lithuanian University of Health Sciences in Kaunas.
“If the gastroenterologist is experienced and has enough competence, he or she may establish the diagnosis, but in all other cases it is wise and advisable to refer the patient to the dermatologist,” Dr. Jonaitis said. A referral should include the history and full treatment for IBD.
The results were presented as a poster at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation, held in Copenhagen and virtually.
Dr. Jonaitis and colleagues conducted a literature analysis to determine the prevalence of extra-abdominal manifestations of IBD. The lack of published data prompted them to survey 152 consecutive patients with IBD receiving outpatient treatment at their institution. The patients completed questionnaires from January to October 2022 about any cutaneous lesions.
The mean age of patients was 42 years, and 58% were men. A majority, 72%, had ulcerative colitis, and 28% had Crohn’s disease.
Prevalence of skin lesions
A total of 43% of participants reported skin lesions, but only 30% of patients had lesions considered related to IBD or IBD therapy due to their emergence after the patient’s IBD diagnosis.
By IBD diagnosis, 29% of patients with ulcerative colitis and 33% of patients with Crohn’s disease had lesions related to their condition. The difference in skin lesion prevalence between the two groups was not significant (P > .05), the researchers noted.
The team further investigated the types of skin lesions deemed to be associated with IBD or IBD therapy.
Overall, they found psoriasis in nine patients, eczema in nine, erythema nodosum in six, pyoderma gangrenosum in five, allergic rash in four, and vitiligo in two. They found acne, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and hemorrhagic vasculitis in one patient each.
Specifically, among patients with ulcerative colitis, skin lesions were reported in 8 of 27 with left-sided colitis, 2 of 15 with ulcerative colitis proctitis, and 22 of 67 patients with pancolitis. The difference between the groups of proctitis and pancolitis was significant (P = .03).
Within the group with Crohn’s disease, skin lesions were reported in 3 of 15 patients with ileitis, 4 of 10 with colitis, and 7 of 17 with ileocolitis. The difference among these groups was not significant (P > .05).
The most common skin lesions observed in Crohn’s disease were erythema nodosum and eczema, and in ulcerative colitis, psoriasis and eczema, the researchers reported.
They also noted that the cutaneous lesions were significantly more prevalent in extensive ulcerative colitis compared with distal disease.
Skin lesions add to patient misery
“Skin lesions are considered a burden to patients with IBD and add to their suffering,” said Sara Mesilhy, MBBS, a gastroenterologist with the Royal College of Physicians in the United Kingdom, who was not affiliated with the research.
The severity and location of the disease appears to play a role because researchers found extensive ulcerative colitis may carry a higher risk for the development of skin lesions, Dr. Mesilhy noted.
The first step when facing skin lesions is to control the disease activity via the best treatment option, Dr. Mesilhy suggested.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Jonaitis and Dr. Mesilhy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
People with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) commonly develop skin lesions linked to their condition, but until now few researchers looked at how common they are.
, according to the prospective, single-center study.
“Skin lesions in IBD patients are much more prevalent than it is generally accepted. The lesions may be related to the pathogenesis of IBD, but it is very important to know that the modern biological therapies may also cause skin lesions,” said senior study author Laimas Jonaitis, MD, PhD, professor in the department of gastroenterology at Lithuanian University of Health Sciences in Kaunas.
“If the gastroenterologist is experienced and has enough competence, he or she may establish the diagnosis, but in all other cases it is wise and advisable to refer the patient to the dermatologist,” Dr. Jonaitis said. A referral should include the history and full treatment for IBD.
The results were presented as a poster at the annual congress of the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation, held in Copenhagen and virtually.
Dr. Jonaitis and colleagues conducted a literature analysis to determine the prevalence of extra-abdominal manifestations of IBD. The lack of published data prompted them to survey 152 consecutive patients with IBD receiving outpatient treatment at their institution. The patients completed questionnaires from January to October 2022 about any cutaneous lesions.
The mean age of patients was 42 years, and 58% were men. A majority, 72%, had ulcerative colitis, and 28% had Crohn’s disease.
Prevalence of skin lesions
A total of 43% of participants reported skin lesions, but only 30% of patients had lesions considered related to IBD or IBD therapy due to their emergence after the patient’s IBD diagnosis.
By IBD diagnosis, 29% of patients with ulcerative colitis and 33% of patients with Crohn’s disease had lesions related to their condition. The difference in skin lesion prevalence between the two groups was not significant (P > .05), the researchers noted.
The team further investigated the types of skin lesions deemed to be associated with IBD or IBD therapy.
Overall, they found psoriasis in nine patients, eczema in nine, erythema nodosum in six, pyoderma gangrenosum in five, allergic rash in four, and vitiligo in two. They found acne, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, and hemorrhagic vasculitis in one patient each.
Specifically, among patients with ulcerative colitis, skin lesions were reported in 8 of 27 with left-sided colitis, 2 of 15 with ulcerative colitis proctitis, and 22 of 67 patients with pancolitis. The difference between the groups of proctitis and pancolitis was significant (P = .03).
Within the group with Crohn’s disease, skin lesions were reported in 3 of 15 patients with ileitis, 4 of 10 with colitis, and 7 of 17 with ileocolitis. The difference among these groups was not significant (P > .05).
The most common skin lesions observed in Crohn’s disease were erythema nodosum and eczema, and in ulcerative colitis, psoriasis and eczema, the researchers reported.
They also noted that the cutaneous lesions were significantly more prevalent in extensive ulcerative colitis compared with distal disease.
Skin lesions add to patient misery
“Skin lesions are considered a burden to patients with IBD and add to their suffering,” said Sara Mesilhy, MBBS, a gastroenterologist with the Royal College of Physicians in the United Kingdom, who was not affiliated with the research.
The severity and location of the disease appears to play a role because researchers found extensive ulcerative colitis may carry a higher risk for the development of skin lesions, Dr. Mesilhy noted.
The first step when facing skin lesions is to control the disease activity via the best treatment option, Dr. Mesilhy suggested.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Jonaitis and Dr. Mesilhy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECCO 2023
Silicone-based film for radiation dermatitis: It works, so why isn’t it used?
Radiation dermatitis is one of the most common side effects of radiotherapy for women with breast cancer. Results from a phase 3 trial add to previous evidence from smaller trials that show that a silicone-based film can protect skin from this side effect.
But it is not being used much in clinical practice. Instead, radiation dermatitis is usually treated after the fact, most often with aqueous creams.
said Edward Chow, MBBS, PhD, of the department of radiation oncology, Odette Cancer Centre, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, who was the senior author of the phase 3 study published recently in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Other doctors think that because radiation dermatitis isn’t life-threatening it isn’t as important, but the condition does affect the quality of life for patients,” Dr. Chow said. “If we can lessen the pain and discomfort, why wouldn’t we as physicians?”
Dr. Chow’s open-label, multicenter trial was conducted in 376 women with large breasts (bra cup size C or larger) who were undergoing radiotherapy after lumpectomy or mastectomy. The primary endpoint was grade 2 or 3 radiation dermatitis using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. (Grade 2 is described as moderate, whereas grade 3 is severe.)
The film significantly reduced the incidence of grade 2 or 3 radiation dermatitis, down to 15.5% compared with 45.6% in patients receiving standard care (odds ratio, 0.20, 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.34, P < .0001).
There was also a significant reduction in grade 3 radiation dermatitis (2.8% vs. 13.6%; OR, 0.19; P < .0002) and moist desquamation (8% vs. 19.2%; OR, 0.36; P = .002).
“The film was remarkably effective and helped protect patients from potentially debilitating side effects,” commented Corey Speers, MD, PhD, a radiation oncologist with University Hospitals, Cleveland, who saw the study data presented during a plenary session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
He believes that preventing radiation dermatitis before it develops is the best way to care for patients.
“[Radiation dermatitis] is usually associated with pain and discomfort and can lead to more serious issues like infection or delayed wound healing, and unfortunately, there aren’t effective treatments for it once it’s developed, so preventing it is our most effective strategy,” Dr. Speers said.
One reason for the film not being used much could be that it takes time apply the film, suggested Patries Herst, PhD, department of radiation therapy, University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand. She was the lead author of a study published in 2014 that also analyzed the effectiveness of the film in preventing radiation dermatitis.
In their trial, a research radiation therapist applied the film to women when they were starting their radiotherapy. The film is applied to a portion of the breast or chest wall, and Dr. Herst emphasized the importance of applying the film correctly, making sure the film is not stretched during application and not overlapping other pieces of the film, while also making sure that it conforms to the breast shape. The film was replaced when it would curl too much around the sides, approximately every 1 or 2 weeks.
“Radiation therapy itself is very short. And so you have about 10 minutes for every patient,” she explained.
“But applying the film adds 20-30 minutes and it’s really awkward to apply properly,” Dr. Herst said. “You have to tap it in and then have to maybe cut it so that it fits better. And hospitals say, ‘We don’t have the time’ and that is still the biggest issue that we’re seeing right now.”
In Dr. Chow’s study, the average time spent applying the film on lumpectomy patients was 55 minutes and was slightly shorter at 45 minutes for mastectomy patients. He acknowledged that it does take time that staff at most hospitals and clinics simply don’t have.
Dr. Chow suggested that perhaps a family member or other caregiver could apply the film, and he referenced an educational video from the manufacturer that provides in-depth instructions on the correct way to apply the film for radiotherapy patients. However, this could lead to errors and a waste of product if not the film was not applied properly.
The cost of Mepitel film may also be a deterrent. Dr. Chow’s study noted that, during the entire course of radiotherapy, the cost for the film was about $80-$100 per patient. However, he believes the benefits outweigh the cost.
In addition, there have been issues with supplies, and it has been difficult for people to get their hands on the actual product.
Currently, the Mayo Clinic is also conducting a study testing Mepitel Film for radiation dermatitis in breast cancer patients following mastectomy. Mayo Clinic principal investigator Kimberly Corbin, MD, could not go into great detail about the ongoing trial, but she said it has been difficult to get the product.
“We have been using the film at Mayo for a number of years,” Dr. Corbin said, but we “have found that it is challenging to get supplies.”
“While we have generally been able to have some supply established through our store here, we know that is not typical and it is difficult for patients to access,” she said. In addition, “there are not a ton of centers with experience in application.”
A representative with Mölnlycke Health Care, Allyson Bower-Willner, could not comment on the distribution of Mepitel film in the United States or if the company plans to increase the amount of product shipped. The film is available “to a limited set of customers,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Radiation dermatitis is one of the most common side effects of radiotherapy for women with breast cancer. Results from a phase 3 trial add to previous evidence from smaller trials that show that a silicone-based film can protect skin from this side effect.
But it is not being used much in clinical practice. Instead, radiation dermatitis is usually treated after the fact, most often with aqueous creams.
said Edward Chow, MBBS, PhD, of the department of radiation oncology, Odette Cancer Centre, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, who was the senior author of the phase 3 study published recently in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Other doctors think that because radiation dermatitis isn’t life-threatening it isn’t as important, but the condition does affect the quality of life for patients,” Dr. Chow said. “If we can lessen the pain and discomfort, why wouldn’t we as physicians?”
Dr. Chow’s open-label, multicenter trial was conducted in 376 women with large breasts (bra cup size C or larger) who were undergoing radiotherapy after lumpectomy or mastectomy. The primary endpoint was grade 2 or 3 radiation dermatitis using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. (Grade 2 is described as moderate, whereas grade 3 is severe.)
The film significantly reduced the incidence of grade 2 or 3 radiation dermatitis, down to 15.5% compared with 45.6% in patients receiving standard care (odds ratio, 0.20, 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.34, P < .0001).
There was also a significant reduction in grade 3 radiation dermatitis (2.8% vs. 13.6%; OR, 0.19; P < .0002) and moist desquamation (8% vs. 19.2%; OR, 0.36; P = .002).
“The film was remarkably effective and helped protect patients from potentially debilitating side effects,” commented Corey Speers, MD, PhD, a radiation oncologist with University Hospitals, Cleveland, who saw the study data presented during a plenary session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
He believes that preventing radiation dermatitis before it develops is the best way to care for patients.
“[Radiation dermatitis] is usually associated with pain and discomfort and can lead to more serious issues like infection or delayed wound healing, and unfortunately, there aren’t effective treatments for it once it’s developed, so preventing it is our most effective strategy,” Dr. Speers said.
One reason for the film not being used much could be that it takes time apply the film, suggested Patries Herst, PhD, department of radiation therapy, University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand. She was the lead author of a study published in 2014 that also analyzed the effectiveness of the film in preventing radiation dermatitis.
In their trial, a research radiation therapist applied the film to women when they were starting their radiotherapy. The film is applied to a portion of the breast or chest wall, and Dr. Herst emphasized the importance of applying the film correctly, making sure the film is not stretched during application and not overlapping other pieces of the film, while also making sure that it conforms to the breast shape. The film was replaced when it would curl too much around the sides, approximately every 1 or 2 weeks.
“Radiation therapy itself is very short. And so you have about 10 minutes for every patient,” she explained.
“But applying the film adds 20-30 minutes and it’s really awkward to apply properly,” Dr. Herst said. “You have to tap it in and then have to maybe cut it so that it fits better. And hospitals say, ‘We don’t have the time’ and that is still the biggest issue that we’re seeing right now.”
In Dr. Chow’s study, the average time spent applying the film on lumpectomy patients was 55 minutes and was slightly shorter at 45 minutes for mastectomy patients. He acknowledged that it does take time that staff at most hospitals and clinics simply don’t have.
Dr. Chow suggested that perhaps a family member or other caregiver could apply the film, and he referenced an educational video from the manufacturer that provides in-depth instructions on the correct way to apply the film for radiotherapy patients. However, this could lead to errors and a waste of product if not the film was not applied properly.
The cost of Mepitel film may also be a deterrent. Dr. Chow’s study noted that, during the entire course of radiotherapy, the cost for the film was about $80-$100 per patient. However, he believes the benefits outweigh the cost.
In addition, there have been issues with supplies, and it has been difficult for people to get their hands on the actual product.
Currently, the Mayo Clinic is also conducting a study testing Mepitel Film for radiation dermatitis in breast cancer patients following mastectomy. Mayo Clinic principal investigator Kimberly Corbin, MD, could not go into great detail about the ongoing trial, but she said it has been difficult to get the product.
“We have been using the film at Mayo for a number of years,” Dr. Corbin said, but we “have found that it is challenging to get supplies.”
“While we have generally been able to have some supply established through our store here, we know that is not typical and it is difficult for patients to access,” she said. In addition, “there are not a ton of centers with experience in application.”
A representative with Mölnlycke Health Care, Allyson Bower-Willner, could not comment on the distribution of Mepitel film in the United States or if the company plans to increase the amount of product shipped. The film is available “to a limited set of customers,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Radiation dermatitis is one of the most common side effects of radiotherapy for women with breast cancer. Results from a phase 3 trial add to previous evidence from smaller trials that show that a silicone-based film can protect skin from this side effect.
But it is not being used much in clinical practice. Instead, radiation dermatitis is usually treated after the fact, most often with aqueous creams.
said Edward Chow, MBBS, PhD, of the department of radiation oncology, Odette Cancer Centre, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, who was the senior author of the phase 3 study published recently in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
“Other doctors think that because radiation dermatitis isn’t life-threatening it isn’t as important, but the condition does affect the quality of life for patients,” Dr. Chow said. “If we can lessen the pain and discomfort, why wouldn’t we as physicians?”
Dr. Chow’s open-label, multicenter trial was conducted in 376 women with large breasts (bra cup size C or larger) who were undergoing radiotherapy after lumpectomy or mastectomy. The primary endpoint was grade 2 or 3 radiation dermatitis using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. (Grade 2 is described as moderate, whereas grade 3 is severe.)
The film significantly reduced the incidence of grade 2 or 3 radiation dermatitis, down to 15.5% compared with 45.6% in patients receiving standard care (odds ratio, 0.20, 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.34, P < .0001).
There was also a significant reduction in grade 3 radiation dermatitis (2.8% vs. 13.6%; OR, 0.19; P < .0002) and moist desquamation (8% vs. 19.2%; OR, 0.36; P = .002).
“The film was remarkably effective and helped protect patients from potentially debilitating side effects,” commented Corey Speers, MD, PhD, a radiation oncologist with University Hospitals, Cleveland, who saw the study data presented during a plenary session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
He believes that preventing radiation dermatitis before it develops is the best way to care for patients.
“[Radiation dermatitis] is usually associated with pain and discomfort and can lead to more serious issues like infection or delayed wound healing, and unfortunately, there aren’t effective treatments for it once it’s developed, so preventing it is our most effective strategy,” Dr. Speers said.
One reason for the film not being used much could be that it takes time apply the film, suggested Patries Herst, PhD, department of radiation therapy, University of Otago, Wellington, New Zealand. She was the lead author of a study published in 2014 that also analyzed the effectiveness of the film in preventing radiation dermatitis.
In their trial, a research radiation therapist applied the film to women when they were starting their radiotherapy. The film is applied to a portion of the breast or chest wall, and Dr. Herst emphasized the importance of applying the film correctly, making sure the film is not stretched during application and not overlapping other pieces of the film, while also making sure that it conforms to the breast shape. The film was replaced when it would curl too much around the sides, approximately every 1 or 2 weeks.
“Radiation therapy itself is very short. And so you have about 10 minutes for every patient,” she explained.
“But applying the film adds 20-30 minutes and it’s really awkward to apply properly,” Dr. Herst said. “You have to tap it in and then have to maybe cut it so that it fits better. And hospitals say, ‘We don’t have the time’ and that is still the biggest issue that we’re seeing right now.”
In Dr. Chow’s study, the average time spent applying the film on lumpectomy patients was 55 minutes and was slightly shorter at 45 minutes for mastectomy patients. He acknowledged that it does take time that staff at most hospitals and clinics simply don’t have.
Dr. Chow suggested that perhaps a family member or other caregiver could apply the film, and he referenced an educational video from the manufacturer that provides in-depth instructions on the correct way to apply the film for radiotherapy patients. However, this could lead to errors and a waste of product if not the film was not applied properly.
The cost of Mepitel film may also be a deterrent. Dr. Chow’s study noted that, during the entire course of radiotherapy, the cost for the film was about $80-$100 per patient. However, he believes the benefits outweigh the cost.
In addition, there have been issues with supplies, and it has been difficult for people to get their hands on the actual product.
Currently, the Mayo Clinic is also conducting a study testing Mepitel Film for radiation dermatitis in breast cancer patients following mastectomy. Mayo Clinic principal investigator Kimberly Corbin, MD, could not go into great detail about the ongoing trial, but she said it has been difficult to get the product.
“We have been using the film at Mayo for a number of years,” Dr. Corbin said, but we “have found that it is challenging to get supplies.”
“While we have generally been able to have some supply established through our store here, we know that is not typical and it is difficult for patients to access,” she said. In addition, “there are not a ton of centers with experience in application.”
A representative with Mölnlycke Health Care, Allyson Bower-Willner, could not comment on the distribution of Mepitel film in the United States or if the company plans to increase the amount of product shipped. The film is available “to a limited set of customers,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
White male presents with pruritic, scaly, erythematous patches on his feet and left hand
Two feet–one hand syndrome
This condition, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection caused by a dermatophyte, and presents as a superficial annular or circular rash with a raised, scaly border.
Symptoms include dryness and itchiness, and the lesions may appear red-pink on lighter skin and gray-brown on darker skin types. Although these infections can arise in a variety of combinations, two feet–one hand syndrome occurs in about 60% of cases. Trichophyton rubrum is the most common agent.
Diagnosis is made by patient history, dermoscopic visualization, and staining of skin scraping with KOH or fungal culture. Dermatophytes prefer moist, warm environments, so this disease is prevalent in tropical conditions and associated with moist public areas such as locker rooms and showers. As a result, tinea pedis is also nicknamed “athlete’s foot” for its common presentation in athletes. The fungus spreads easily through contact and can survive on infected surfaces, so patients often self-inoculate by touching/scratching the affected area then touching another body part. Cautions that should be taken to avoid transmission include not sharing personal care products, washing the area and keeping it dry, and avoiding close, humid environments.
The syndrome is highly associated with onychomycosis, which can be more difficult to treat and often requires oral antifungals. Tinea manuum is commonly misdiagnosed as hand dermatitis or eczema and treated with topical steroids, which will exacerbate or flare the tinea.
Two feet–one hand syndrome can typically be treated with over-the-counter topical antifungal medications such as miconazole or clotrimazole. Topical ketoconazole may be prescribed, and oral terbinafine or itraconazole are used in more severe cases when a larger body surface area is affected or in immunocompromised patients.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University, Davie, Fla.; Kiran C. Patel, Tampa Bay Regional Campus; and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
Cleveland Clinic. Tinea manuum: Symptoms, causes & treatment. 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24063-tinea-manuum.
Ugalde-Trejo NX et al. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2022 Nov 17. doi: 10.1007/s12281-022-00447-9.
Mizumoto J. Cureus. 2021 Dec 27;13(12):e20758.
Two feet–one hand syndrome
This condition, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection caused by a dermatophyte, and presents as a superficial annular or circular rash with a raised, scaly border.
Symptoms include dryness and itchiness, and the lesions may appear red-pink on lighter skin and gray-brown on darker skin types. Although these infections can arise in a variety of combinations, two feet–one hand syndrome occurs in about 60% of cases. Trichophyton rubrum is the most common agent.
Diagnosis is made by patient history, dermoscopic visualization, and staining of skin scraping with KOH or fungal culture. Dermatophytes prefer moist, warm environments, so this disease is prevalent in tropical conditions and associated with moist public areas such as locker rooms and showers. As a result, tinea pedis is also nicknamed “athlete’s foot” for its common presentation in athletes. The fungus spreads easily through contact and can survive on infected surfaces, so patients often self-inoculate by touching/scratching the affected area then touching another body part. Cautions that should be taken to avoid transmission include not sharing personal care products, washing the area and keeping it dry, and avoiding close, humid environments.
The syndrome is highly associated with onychomycosis, which can be more difficult to treat and often requires oral antifungals. Tinea manuum is commonly misdiagnosed as hand dermatitis or eczema and treated with topical steroids, which will exacerbate or flare the tinea.
Two feet–one hand syndrome can typically be treated with over-the-counter topical antifungal medications such as miconazole or clotrimazole. Topical ketoconazole may be prescribed, and oral terbinafine or itraconazole are used in more severe cases when a larger body surface area is affected or in immunocompromised patients.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University, Davie, Fla.; Kiran C. Patel, Tampa Bay Regional Campus; and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
Cleveland Clinic. Tinea manuum: Symptoms, causes & treatment. 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24063-tinea-manuum.
Ugalde-Trejo NX et al. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2022 Nov 17. doi: 10.1007/s12281-022-00447-9.
Mizumoto J. Cureus. 2021 Dec 27;13(12):e20758.
Two feet–one hand syndrome
This condition, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection caused by a dermatophyte, and presents as a superficial annular or circular rash with a raised, scaly border.
Symptoms include dryness and itchiness, and the lesions may appear red-pink on lighter skin and gray-brown on darker skin types. Although these infections can arise in a variety of combinations, two feet–one hand syndrome occurs in about 60% of cases. Trichophyton rubrum is the most common agent.
Diagnosis is made by patient history, dermoscopic visualization, and staining of skin scraping with KOH or fungal culture. Dermatophytes prefer moist, warm environments, so this disease is prevalent in tropical conditions and associated with moist public areas such as locker rooms and showers. As a result, tinea pedis is also nicknamed “athlete’s foot” for its common presentation in athletes. The fungus spreads easily through contact and can survive on infected surfaces, so patients often self-inoculate by touching/scratching the affected area then touching another body part. Cautions that should be taken to avoid transmission include not sharing personal care products, washing the area and keeping it dry, and avoiding close, humid environments.
The syndrome is highly associated with onychomycosis, which can be more difficult to treat and often requires oral antifungals. Tinea manuum is commonly misdiagnosed as hand dermatitis or eczema and treated with topical steroids, which will exacerbate or flare the tinea.
Two feet–one hand syndrome can typically be treated with over-the-counter topical antifungal medications such as miconazole or clotrimazole. Topical ketoconazole may be prescribed, and oral terbinafine or itraconazole are used in more severe cases when a larger body surface area is affected or in immunocompromised patients.
This case and photo were submitted by Lucas Shapiro, BS, Nova Southeastern University, Davie, Fla.; Kiran C. Patel, Tampa Bay Regional Campus; and Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to dermnews@mdedge.com.
References
Cleveland Clinic. Tinea manuum: Symptoms, causes & treatment. 2022. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/24063-tinea-manuum.
Ugalde-Trejo NX et al. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2022 Nov 17. doi: 10.1007/s12281-022-00447-9.
Mizumoto J. Cureus. 2021 Dec 27;13(12):e20758.