User login
ACC/AHA issue updated atrial fibrillation guideline
The American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) have issued an updated guideline for preventing and optimally managing atrial fibrillation (AF).
The 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
“The new guideline has important changes,” including a new way to classify AF, Jose Joglar, MD, professor of cardiac electrophysiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, and chair of the writing committee, said in an interview.
The previous classification was largely based only on arrhythmia duration and tended to emphasize specific therapeutic interventions rather than a more holistic and multidisciplinary management approach, Dr. Joglar explained.
, from prevention, lifestyle and risk factor modification, screening, and therapy.
Stage 1: At risk for AF due to the presence of risk factors
Stage 2: Pre-AF, with evidence of structural or electrical findings predisposing to AF
Stage 3: AF, including paroxysmal (3A), persistent (3B), long-standing persistent (3C), successful AF ablation (3D)
Stage 4: Permanent AF
The updated guideline recognizes lifestyle and risk factor modification as a “pillar” of AF management and offers “more prescriptive” recommendations, including management of obesity, weight loss, physical activity, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, hypertension, and other comorbidities.
“We should not only be telling patients they need to be healthy, which doesn’t mean much to a patient, we need to tell them precisely what they need to do. For example, how much exercise to do or how much weight to lose to have a benefit,” Dr. Joglar said in an interview.
The good news for many people, he noted, is that coffee, which has had a “bad reputation,” is okay, as the latest data show it doesn’t seem to exacerbate AF.
The new guideline continues to endorse use of the CHA2DS2-VASc score as the predictor of choice to determine the risk of stroke, but it also allows for flexibility to use other calculators when uncertainty exists or when other risk factors, such as kidney disease, need to be included.
With the emergence of “new and consistent” evidence, the guideline also emphasizes the importance of early and continued management of patients with AF with a focus on maintaining sinus rhythm and minimizing AF burden.
Catheter ablation of AF is given a class 1 indication as first-line therapy in selected patients, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
That’s based on recent randomized studies that have shown catheter ablation to be “superior to pharmacological therapy” for rhythm control in appropriately selected patients, Dr. Joglar told this news organization.
“There’s no need to try pharmacological therapies after a discussion between the patient and doctor and they decide that they want to proceed with the most effective intervention,” he added.
The new guideline also upgrades the class of recommendation for left atrial appendage occlusion devices to 2a, compared with the 2019 AF Focused Update, for use of these devices in patients with long-term contraindications to anticoagulation.
It also provides updated recommendations for AF detected via implantable devices and wearables as well as recommendations for patients with AF identified during medical illness or surgery.
Development of the guideline had no commercial funding. Disclosures for the writing group are available with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) have issued an updated guideline for preventing and optimally managing atrial fibrillation (AF).
The 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
“The new guideline has important changes,” including a new way to classify AF, Jose Joglar, MD, professor of cardiac electrophysiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, and chair of the writing committee, said in an interview.
The previous classification was largely based only on arrhythmia duration and tended to emphasize specific therapeutic interventions rather than a more holistic and multidisciplinary management approach, Dr. Joglar explained.
, from prevention, lifestyle and risk factor modification, screening, and therapy.
Stage 1: At risk for AF due to the presence of risk factors
Stage 2: Pre-AF, with evidence of structural or electrical findings predisposing to AF
Stage 3: AF, including paroxysmal (3A), persistent (3B), long-standing persistent (3C), successful AF ablation (3D)
Stage 4: Permanent AF
The updated guideline recognizes lifestyle and risk factor modification as a “pillar” of AF management and offers “more prescriptive” recommendations, including management of obesity, weight loss, physical activity, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, hypertension, and other comorbidities.
“We should not only be telling patients they need to be healthy, which doesn’t mean much to a patient, we need to tell them precisely what they need to do. For example, how much exercise to do or how much weight to lose to have a benefit,” Dr. Joglar said in an interview.
The good news for many people, he noted, is that coffee, which has had a “bad reputation,” is okay, as the latest data show it doesn’t seem to exacerbate AF.
The new guideline continues to endorse use of the CHA2DS2-VASc score as the predictor of choice to determine the risk of stroke, but it also allows for flexibility to use other calculators when uncertainty exists or when other risk factors, such as kidney disease, need to be included.
With the emergence of “new and consistent” evidence, the guideline also emphasizes the importance of early and continued management of patients with AF with a focus on maintaining sinus rhythm and minimizing AF burden.
Catheter ablation of AF is given a class 1 indication as first-line therapy in selected patients, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
That’s based on recent randomized studies that have shown catheter ablation to be “superior to pharmacological therapy” for rhythm control in appropriately selected patients, Dr. Joglar told this news organization.
“There’s no need to try pharmacological therapies after a discussion between the patient and doctor and they decide that they want to proceed with the most effective intervention,” he added.
The new guideline also upgrades the class of recommendation for left atrial appendage occlusion devices to 2a, compared with the 2019 AF Focused Update, for use of these devices in patients with long-term contraindications to anticoagulation.
It also provides updated recommendations for AF detected via implantable devices and wearables as well as recommendations for patients with AF identified during medical illness or surgery.
Development of the guideline had no commercial funding. Disclosures for the writing group are available with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) have issued an updated guideline for preventing and optimally managing atrial fibrillation (AF).
The 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology and Circulation.
“The new guideline has important changes,” including a new way to classify AF, Jose Joglar, MD, professor of cardiac electrophysiology at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Texas, and chair of the writing committee, said in an interview.
The previous classification was largely based only on arrhythmia duration and tended to emphasize specific therapeutic interventions rather than a more holistic and multidisciplinary management approach, Dr. Joglar explained.
, from prevention, lifestyle and risk factor modification, screening, and therapy.
Stage 1: At risk for AF due to the presence of risk factors
Stage 2: Pre-AF, with evidence of structural or electrical findings predisposing to AF
Stage 3: AF, including paroxysmal (3A), persistent (3B), long-standing persistent (3C), successful AF ablation (3D)
Stage 4: Permanent AF
The updated guideline recognizes lifestyle and risk factor modification as a “pillar” of AF management and offers “more prescriptive” recommendations, including management of obesity, weight loss, physical activity, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, hypertension, and other comorbidities.
“We should not only be telling patients they need to be healthy, which doesn’t mean much to a patient, we need to tell them precisely what they need to do. For example, how much exercise to do or how much weight to lose to have a benefit,” Dr. Joglar said in an interview.
The good news for many people, he noted, is that coffee, which has had a “bad reputation,” is okay, as the latest data show it doesn’t seem to exacerbate AF.
The new guideline continues to endorse use of the CHA2DS2-VASc score as the predictor of choice to determine the risk of stroke, but it also allows for flexibility to use other calculators when uncertainty exists or when other risk factors, such as kidney disease, need to be included.
With the emergence of “new and consistent” evidence, the guideline also emphasizes the importance of early and continued management of patients with AF with a focus on maintaining sinus rhythm and minimizing AF burden.
Catheter ablation of AF is given a class 1 indication as first-line therapy in selected patients, including those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.
That’s based on recent randomized studies that have shown catheter ablation to be “superior to pharmacological therapy” for rhythm control in appropriately selected patients, Dr. Joglar told this news organization.
“There’s no need to try pharmacological therapies after a discussion between the patient and doctor and they decide that they want to proceed with the most effective intervention,” he added.
The new guideline also upgrades the class of recommendation for left atrial appendage occlusion devices to 2a, compared with the 2019 AF Focused Update, for use of these devices in patients with long-term contraindications to anticoagulation.
It also provides updated recommendations for AF detected via implantable devices and wearables as well as recommendations for patients with AF identified during medical illness or surgery.
Development of the guideline had no commercial funding. Disclosures for the writing group are available with the original articles.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vagus nerve stimulation promising in POTS
TOPLINE:
possibly through decreased antiadrenergic autoantibodies and inflammatory cytokines, and improved cardiac autonomic function, in a small proof-of-concept study.
METHODOLOGY:
The double-blind study included 25 female patients with POTS, a syndrome of orthostatic intolerance (mean age 31 years and 81% Caucasian), who were randomly assigned to transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) to the right tragus or sham stimulation to the earlobe, a site devoid of vagal innervation.
After training, patients delivered the tVNS themselves at a frequency of 20 Hz and pulse width of 200 ms during 1-hour daily sessions over 2 months.
At baseline and 2 months, patients underwent a tilt test to determine postural tachycardia; they remained supine for 25 minutes, followed by 10 minutes of standing, as tolerated.
Researchers used electrocardiogram data to examine heart rate and blood samples to assess serum cytokines and antiautonomic autoantibodies.
The primary outcome was a comparison of orthostatic tachycardia (standing – supine) between the two arms at 2 months.
TAKEAWAY:
At 2 months, postural tachycardia was significantly less in the active vs sham arm (mean postural increase in heart rate 17.6 beats/min vs 31.7 beats/min; P = .01).
There was a significant decrease in beta 1-adrenergic receptor (beta 1-AR; P = .01) and alpha-1-AR (P = .04) autoantibody activity in the active vs sham group, which may account at least in part for the reduced orthostatic tachycardia, although the exact mechanisms for this effect have not been clearly defined, the authors said.
Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels were significantly decreased in the active group relative to the sham group (8.3 pg/mL vs 13.9 pg/mL; P = .01).
As for heart rate variability, change in low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF) from supine to standing was significantly decreased, and postural change in LF/HF ratio, a surrogate for sympathovagal balance, was significantly lower in the active group compared with the sham group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Collectively, these data suggest that tVNS, a low-cost, low-risk intervention, applied for a short period of time in selected patients with POTS, may result in a significant amelioration of their disease,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Stavros Stavrakis, MD, PhD, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology..
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a small sample size, included only females, and extended only up to 2 months. As there was no improvement on the overall score from the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS-31) questionnaire, researchers can’t conclude tVNS improved patient reported outcomes. The study used 1 hour of daily stimulation but the optimal duration and ideal timing of tVNS is yet to be determined.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, NIH/National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and individual donations from Francie Fitzgerald and family through the OU Foundation Fund. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
possibly through decreased antiadrenergic autoantibodies and inflammatory cytokines, and improved cardiac autonomic function, in a small proof-of-concept study.
METHODOLOGY:
The double-blind study included 25 female patients with POTS, a syndrome of orthostatic intolerance (mean age 31 years and 81% Caucasian), who were randomly assigned to transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) to the right tragus or sham stimulation to the earlobe, a site devoid of vagal innervation.
After training, patients delivered the tVNS themselves at a frequency of 20 Hz and pulse width of 200 ms during 1-hour daily sessions over 2 months.
At baseline and 2 months, patients underwent a tilt test to determine postural tachycardia; they remained supine for 25 minutes, followed by 10 minutes of standing, as tolerated.
Researchers used electrocardiogram data to examine heart rate and blood samples to assess serum cytokines and antiautonomic autoantibodies.
The primary outcome was a comparison of orthostatic tachycardia (standing – supine) between the two arms at 2 months.
TAKEAWAY:
At 2 months, postural tachycardia was significantly less in the active vs sham arm (mean postural increase in heart rate 17.6 beats/min vs 31.7 beats/min; P = .01).
There was a significant decrease in beta 1-adrenergic receptor (beta 1-AR; P = .01) and alpha-1-AR (P = .04) autoantibody activity in the active vs sham group, which may account at least in part for the reduced orthostatic tachycardia, although the exact mechanisms for this effect have not been clearly defined, the authors said.
Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels were significantly decreased in the active group relative to the sham group (8.3 pg/mL vs 13.9 pg/mL; P = .01).
As for heart rate variability, change in low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF) from supine to standing was significantly decreased, and postural change in LF/HF ratio, a surrogate for sympathovagal balance, was significantly lower in the active group compared with the sham group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Collectively, these data suggest that tVNS, a low-cost, low-risk intervention, applied for a short period of time in selected patients with POTS, may result in a significant amelioration of their disease,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Stavros Stavrakis, MD, PhD, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology..
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a small sample size, included only females, and extended only up to 2 months. As there was no improvement on the overall score from the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS-31) questionnaire, researchers can’t conclude tVNS improved patient reported outcomes. The study used 1 hour of daily stimulation but the optimal duration and ideal timing of tVNS is yet to be determined.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, NIH/National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and individual donations from Francie Fitzgerald and family through the OU Foundation Fund. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
possibly through decreased antiadrenergic autoantibodies and inflammatory cytokines, and improved cardiac autonomic function, in a small proof-of-concept study.
METHODOLOGY:
The double-blind study included 25 female patients with POTS, a syndrome of orthostatic intolerance (mean age 31 years and 81% Caucasian), who were randomly assigned to transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) to the right tragus or sham stimulation to the earlobe, a site devoid of vagal innervation.
After training, patients delivered the tVNS themselves at a frequency of 20 Hz and pulse width of 200 ms during 1-hour daily sessions over 2 months.
At baseline and 2 months, patients underwent a tilt test to determine postural tachycardia; they remained supine for 25 minutes, followed by 10 minutes of standing, as tolerated.
Researchers used electrocardiogram data to examine heart rate and blood samples to assess serum cytokines and antiautonomic autoantibodies.
The primary outcome was a comparison of orthostatic tachycardia (standing – supine) between the two arms at 2 months.
TAKEAWAY:
At 2 months, postural tachycardia was significantly less in the active vs sham arm (mean postural increase in heart rate 17.6 beats/min vs 31.7 beats/min; P = .01).
There was a significant decrease in beta 1-adrenergic receptor (beta 1-AR; P = .01) and alpha-1-AR (P = .04) autoantibody activity in the active vs sham group, which may account at least in part for the reduced orthostatic tachycardia, although the exact mechanisms for this effect have not been clearly defined, the authors said.
Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels were significantly decreased in the active group relative to the sham group (8.3 pg/mL vs 13.9 pg/mL; P = .01).
As for heart rate variability, change in low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF) from supine to standing was significantly decreased, and postural change in LF/HF ratio, a surrogate for sympathovagal balance, was significantly lower in the active group compared with the sham group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Collectively, these data suggest that tVNS, a low-cost, low-risk intervention, applied for a short period of time in selected patients with POTS, may result in a significant amelioration of their disease,” the authors conclude.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Stavros Stavrakis, MD, PhD, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology..
LIMITATIONS:
The study had a small sample size, included only females, and extended only up to 2 months. As there was no improvement on the overall score from the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score 31 (COMPASS-31) questionnaire, researchers can’t conclude tVNS improved patient reported outcomes. The study used 1 hour of daily stimulation but the optimal duration and ideal timing of tVNS is yet to be determined.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, NIH/National Institute of General Medical Sciences, and individual donations from Francie Fitzgerald and family through the OU Foundation Fund. The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Less severe strokes with LAA closure vs. DOAC in AFib?
TOPLINE:
Left atrial appendage closure was associated with about half as many disabling or fatal strokes and lower mortality after a stroke, compared with dual oral anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), new observational research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective registry analysis included 447 adult patients with nonvalvular AFib, mean age 74 years, who were hospitalized with an ischemic stroke, 322 of whom were receiving direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy, mostly (84%) apixaban or rivaroxaban, and 125 were treated with left atrial appendage closure (LAAC), almost all (97%) with Watchman or Watchman-FLX devices.
- All patients received standard stroke care, monitoring, and treatment as well as physical therapy/rehabilitation.
- For the primary outcome, researchers used the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) to determine disabling (mRS score of 3-5) and fatal (mRS score of 6) strokes at discharge and at 3 months.
- The study adjusted for age, smoking, paroxysmal AFib, prior major bleeding, prior hemorrhagic stroke, medication adherence, and other risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- (38.3% vs. 70.3%; P < .001) and at 3 months (33.3% vs. 56.2%; P < .001), even though the LAAC group had more baseline comorbidity, for example, older age, more smokers, and more prior major bleeding.
- There was no significant difference in mortality between groups during hospitalization, but at 3 months, mortality was lower in the LAAC group (14.7% vs. 32.1%; P = .002).
- Multivariate linear regression analysis showed LAAC independently predicted more favorable mRS at discharge (2.8) and 3 months (1.4) (both P < .001) and was associated with less all-cause death at 3 months (odds ratio, 0.28; 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.64; P = .002).
- Including those that excluded the 14.4% of LAAC patients who also received DOAC therapy, sensitivity analyses patients who got reduced dose DOACs and nonadherent patients yielded nearly identical outcomes to the full cohort analysis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Despite a higher baseline risk profile, patients treated with LAAC who developed IS had better outcomes than those receiving DOAC prophylaxis,” the authors conclude, adding that several ongoing prospective trials could, “shed light on the mechanism(s) responsible for differences in stroke severity.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Mohit K. Turagam, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite sensitivity analyses and adjustment for risk factors, selection bias, missing data, and other confounding factors could have affected outcomes. The study didn’t evaluate recurrent IS or type and intensity of rehabilitation on outcomes. Lack of imaging data comparing stroke infarct size and volume limits understanding of exact mechanism driving higher stroke severity with DOACs. Because patients who died before reaching hospital weren’t captured in the registry, the actual mortality may be higher than reported.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Turagam has served as a consultant for Biosense Webster and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Left atrial appendage closure was associated with about half as many disabling or fatal strokes and lower mortality after a stroke, compared with dual oral anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), new observational research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective registry analysis included 447 adult patients with nonvalvular AFib, mean age 74 years, who were hospitalized with an ischemic stroke, 322 of whom were receiving direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy, mostly (84%) apixaban or rivaroxaban, and 125 were treated with left atrial appendage closure (LAAC), almost all (97%) with Watchman or Watchman-FLX devices.
- All patients received standard stroke care, monitoring, and treatment as well as physical therapy/rehabilitation.
- For the primary outcome, researchers used the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) to determine disabling (mRS score of 3-5) and fatal (mRS score of 6) strokes at discharge and at 3 months.
- The study adjusted for age, smoking, paroxysmal AFib, prior major bleeding, prior hemorrhagic stroke, medication adherence, and other risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- (38.3% vs. 70.3%; P < .001) and at 3 months (33.3% vs. 56.2%; P < .001), even though the LAAC group had more baseline comorbidity, for example, older age, more smokers, and more prior major bleeding.
- There was no significant difference in mortality between groups during hospitalization, but at 3 months, mortality was lower in the LAAC group (14.7% vs. 32.1%; P = .002).
- Multivariate linear regression analysis showed LAAC independently predicted more favorable mRS at discharge (2.8) and 3 months (1.4) (both P < .001) and was associated with less all-cause death at 3 months (odds ratio, 0.28; 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.64; P = .002).
- Including those that excluded the 14.4% of LAAC patients who also received DOAC therapy, sensitivity analyses patients who got reduced dose DOACs and nonadherent patients yielded nearly identical outcomes to the full cohort analysis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Despite a higher baseline risk profile, patients treated with LAAC who developed IS had better outcomes than those receiving DOAC prophylaxis,” the authors conclude, adding that several ongoing prospective trials could, “shed light on the mechanism(s) responsible for differences in stroke severity.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Mohit K. Turagam, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite sensitivity analyses and adjustment for risk factors, selection bias, missing data, and other confounding factors could have affected outcomes. The study didn’t evaluate recurrent IS or type and intensity of rehabilitation on outcomes. Lack of imaging data comparing stroke infarct size and volume limits understanding of exact mechanism driving higher stroke severity with DOACs. Because patients who died before reaching hospital weren’t captured in the registry, the actual mortality may be higher than reported.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Turagam has served as a consultant for Biosense Webster and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Left atrial appendage closure was associated with about half as many disabling or fatal strokes and lower mortality after a stroke, compared with dual oral anticoagulant therapy in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), new observational research shows.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective registry analysis included 447 adult patients with nonvalvular AFib, mean age 74 years, who were hospitalized with an ischemic stroke, 322 of whom were receiving direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) therapy, mostly (84%) apixaban or rivaroxaban, and 125 were treated with left atrial appendage closure (LAAC), almost all (97%) with Watchman or Watchman-FLX devices.
- All patients received standard stroke care, monitoring, and treatment as well as physical therapy/rehabilitation.
- For the primary outcome, researchers used the modified Rankin Scale (mRS) to determine disabling (mRS score of 3-5) and fatal (mRS score of 6) strokes at discharge and at 3 months.
- The study adjusted for age, smoking, paroxysmal AFib, prior major bleeding, prior hemorrhagic stroke, medication adherence, and other risk factors.
TAKEAWAY:
- (38.3% vs. 70.3%; P < .001) and at 3 months (33.3% vs. 56.2%; P < .001), even though the LAAC group had more baseline comorbidity, for example, older age, more smokers, and more prior major bleeding.
- There was no significant difference in mortality between groups during hospitalization, but at 3 months, mortality was lower in the LAAC group (14.7% vs. 32.1%; P = .002).
- Multivariate linear regression analysis showed LAAC independently predicted more favorable mRS at discharge (2.8) and 3 months (1.4) (both P < .001) and was associated with less all-cause death at 3 months (odds ratio, 0.28; 95% confidence interval, 0.12-0.64; P = .002).
- Including those that excluded the 14.4% of LAAC patients who also received DOAC therapy, sensitivity analyses patients who got reduced dose DOACs and nonadherent patients yielded nearly identical outcomes to the full cohort analysis.
IN PRACTICE:
“Despite a higher baseline risk profile, patients treated with LAAC who developed IS had better outcomes than those receiving DOAC prophylaxis,” the authors conclude, adding that several ongoing prospective trials could, “shed light on the mechanism(s) responsible for differences in stroke severity.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Mohit K. Turagam, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues. It was published online in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Despite sensitivity analyses and adjustment for risk factors, selection bias, missing data, and other confounding factors could have affected outcomes. The study didn’t evaluate recurrent IS or type and intensity of rehabilitation on outcomes. Lack of imaging data comparing stroke infarct size and volume limits understanding of exact mechanism driving higher stroke severity with DOACs. Because patients who died before reaching hospital weren’t captured in the registry, the actual mortality may be higher than reported.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Turagam has served as a consultant for Biosense Webster and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Apixaban cuts stroke but ups bleeding in subclinical AFib: ARTESIA
in the ARTESIA study.
The results appear to contrast somewhat with the recently reported NOAH-AFNET 6 trial, which failed to show a reduction in stroke with the anticoagulant edoxaban versus placebo in a similar patient group, but that trial was stopped early and so was underpowered.
However, the lead investigators of both trials say the studies actually show consistent results – both found a lower rate of stroke than expected in this population, but the confidence intervals for stroke reduction with anticoagulation overlap, suggesting there is likely some effect, albeit less than that in clinical AFib.
The big question is whether the reduction in stroke with anticoagulation outweighs the increase in major bleeding.
A new meta-analysis of the two trials showed that “oral anticoagulation with edoxaban or apixaban reduces the risk of ischemic stroke by approximately one-third and increases major bleeding by roughly double.”
In absolute numbers, there were three fewer ischemic strokes per 1,000 patient-years with anticoagulation in the two trials combined, at the cost of seven more major bleeds.
The lead investigators of the two trials have somewhat different opinions on how these findings may translate into clinical practice.
Jeff Healey, MD, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., lead investigator of the ARTESIA trial, believes that the risks and benefits need to be assessed in individual patients, but there should be some patient groups that will benefit from anticoagulation treatment.
“In patients with pacemakers or implantable loop recorders with continuous monitoring, subclinical AF[ib] is detected in about one third of patients, so this is extremely common,” he said in an interview. “The question is whether this is just a normal feature of getting older or is this like AF[ib] that we see in the clinic which increases stroke risk, and I think we can conclude from ARTESIA that this subclinical AF[ib] is associated with an increased risk of stroke, although that is lower than the risk with clinical AF[ib], and that it can be reduced by anticoagulation.”
Until recently it hasn’t been possible to quantify the risk associated with subclinical AFib, he noted. “But now we have a rich dataset to use to see if we can tease out some specifics on this. Future analyses of this dataset will help define patients where the benefits outweigh the risks of bleeding. For now, I think we can look at the data in a qualitative way and consider the totality of risk factors in each patient – their bleeding risk, stroke risk, how much AF[ib] they have, and make a decision as to whether to give anticoagulation or not.”
But Paulus Kirchhof, MD, University Heart and Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), lead investigator of the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial said: “Both trials showed the stroke rate is low in these patients – about 1% per year – and that anticoagulation can reduce it a bit further at the expense of increasing major bleeding. I don’t believe the AF[ib] episodes picked up on these devices constitute a sufficient stroke risk to warrant anticoagulation, given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Kirchhof suggests an alternate approach of performing further traditional AFib monitoring on these patients.
“I think going forward in my practice, when we come across this device-detected AF[ib], we will do further investigations with an established method for detecting AF[ib] involving surface ECG monitoring – maybe a 3-day or 7-day Holter. If that shows AF[ib], then we will be on firm ground to start anticoagulation. If that doesn’t show AF[ib], we will probably not use anticoagulation.”
The ARTESIA trial and the meta-analysis of the two trials were both presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Both studies were also simultaneously published online – ARTESIA in the New England Journal of Medicine and the meta-analysis in Circulation.
ARTESIA
For the ARTESIA study, 4012 patients with device-detected AFib and other clinical risk factors for stroke were randomly assigned to treatment with apixaban (5 mg twice daily) or aspirin (81 mg daily).
After a mean follow-up of 3.5 years, the primary endpoint – stroke or systemic embolism – occurred in 55 patients in the apixaban group (0.78% per patient-year), compared with 86 patients in the aspirin group (1.24% per patient-year), giving a hazard ratio of 0.63 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.88; P = .007).
“The risk of stroke or systemic embolism was lower by 37% with apixaban than with aspirin, and the risk of disabling or fatal stroke was lower by 49%,” Dr. Healey reported.
In the “on-treatment” population, the rate of major bleeding was 1.71% per patient-year in the apixaban group and 0.94% per patient-year in the aspirin group (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.26-2.57; P = .001).
Fatal bleeding occurred in five patients in the apixaban group and eight patients in the aspirin group. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 12 patients with apixaban and 15 patients with aspirin.
One of the main findings of the trial is the lower-than-expected risk of ischemic stroke in this population – about 1% per year in the aspirin group, which was reduced to 0.64% per year in the apixaban group.
The authors noted that “simply counting strokes as compared with bleeding events might suggest a neutral overall effect. With apixaban as compared with aspirin, 31 fewer cases of stroke or systemic embolism were seen in the intention-to-treat analysis, as compared with 39 more major bleeding events in the on-treatment analysis.”
However, they pointed out that strokes involve permanent loss of brain tissue, whereas major bleeding is usually reversible, with most patients having complete recovery, which was the case in this study.
“Thus, on the basis of the considerably greater severity of the stroke events prevented than the bleeding events caused, we believe that these findings favor consideration of the use of oral anticoagulation for patients with risk factors for stroke in whom subclinical atrial fibrillation develops,” they concluded.
First well-powered trial addressing this question
Discussing the ARTESIA trial at an AHA press conference, Christine Albert, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said: “I want to emphasize how important this trial is.”
She explained that current guidelines do not recommend any treatment for patients with device-detected AFib that is not shown on ECG, even though it is known this confers some excess risk of stroke.
“ARTESIA is the first well-powered, long-term trial looking at this question,” she said. “It found a clear reduction in the risk of stroke/systemic embolism with apixaban vs aspirin, but there was also a significant amount of bleeding – about an 80% increase. The question is whether the benefit on stroke is worth it given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Albert highlighted the low absolute risk of stroke in this study population of around 1.2%, pointing out that even with the 37% relative reduction with anticoagulation, stroke is only reduced in absolute terms by 0.4%.
“We are going to have to take this back to committees and guidelines and look at the balance between the benefit on stroke and the increase in bleeding,” she concluded.
Noting that observational studies have shown that the duration of AFib impacts the risk of stroke, Dr. Albert suggested that patients with longer-duration AFib may benefit from anticoagulation to a greater extent; and given that the bleeding seen in ARTESIA was mainly GI bleeding, it might be possible to screen out patients at high risk of GI bleeding.
She also pointed out that a lot of patients discontinued anticoagulation treatment in both ARTESIA and NOAH-AFNET 6, showing that this is not an easy strategy for elderly patients.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the ARTESIA trial, Emma Svennberg, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also concluded that, “going forward, we must balance the increased bleeding risks with the risk for disabling strokes,” and that “future substudies and meta-analyses may provide further insights regarding treatment benefits in specific subgroups.”
NOAH-AFNET 6: New subgroup analysis
The previously reported NOAH-AFNET 6 study randomly assigned 2,538 patients with subclinical AFib and additional risk factors for stroke to anticoagulation with edoxaban or placebo. The trial was stopped early, so it was underpowered – but it found no difference between groups in the incidence of the composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism, or death from cardiovascular causes or in the incidence of stroke, although there was higher risk of major bleeding.
Again, there was a low rate of stroke in this trial with just 49 strokes in total in the whole study. The NOAH-AFNET-6 investigators concluded that these patients should not receive anticoagulation because the risk of bleeding outweighed any potential benefits.
A new subanalysis of the 259 patients who had durations of subclinical AFib of 24 hours or longer in the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was presented at the AHA meeting, and simultaneously published online in the European Heart Journal.
This showed that the rate of stroke also appeared low in patients with these long durations of subclinical AFib, and that there was no interaction between the duration of subclinical AFib and the efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulation.
But with such a low number of events in the study as a whole and in the long duration subclinical AFib subgroup (in which there were just two strokes in each treatment group), this analysis was unlikely to show a difference, Dr. Kirchhof commented.
The subgroup analysis did, however, show that patients experiencing subclinical AFib durations of 24 hours or more were more likely to develop clinical AFib over time than those with shorter durations, suggesting the need for regular ECGs in these patients.
Dr. Kirchhof said better methods are needed to detect patients with subclinical AFib at high risk of stroke. “I don’t think our clinical stroke risk factor scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc are sufficient to detect high-risk patients. Patients in both NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESIA had a median CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, but they had a stroke rate of just 1% per year,” he noted.
The meta-analysis of the two trials showed that the results from both are consistent, with an overall reduction in ischemic stroke with oral anticoagulation (relative risk, 0.68). Oral anticoagulation also reduced a composite of cardiovascular death, all-cause stroke, peripheral arterial embolism, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary embolism (RR, 0.85).
There was no significant difference in cardiovascular death (RR, 0.95) or all-cause mortality (RR, 1.08), but anticoagulation significantly increased major bleeding (RR, 1.62).
Aspirin use complicates results
Dr. Healey said further analyses of the ARTESIA data will try to tease out the effect of concomitant aspirin use in the trial.
He explained that patients in this trial were allowed to take a single antiplatelet agent on top of study therapy.
“It is difficult to work out the exact use of antiplatelet therapy as it changed throughout the study,” he said. “About two-thirds were taking antiplatelet agents at the time of enrollment into the trial, but this decreased throughout the study. Many clinicians stopped open-label antiplatelet therapy during the trial when new evidence came out to suggest that there was no added benefit of adding aspirin on top of anticoagulants.
“We need to look carefully as to what impact that may have had,” Dr. Healey added. “We know from other studies that adding an antiplatelet on top of an anticoagulant doesn’t do much to thromboembolic events, but it approximately doubles the risk of major bleeding.”
In contrast, the NOAH-AFNET trial did not allow aspirin use in the anticoagulation group and aspirin was taken by around half the patients in the placebo group who had an indication for its use.
The authors of the meta-analysis pointed out that the omission of aspirin in nearly half of the control patients in NOAH-AFNET 6 and the early termination of the trial may have led to a slightly higher estimate for excess major bleeding with anticoagulation.
The ARTESIA study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network, Hamilton Health Sciences, the Advancing Clinical Trials Network and the Population Health Research Institute. Dr. Healey reported research grants and speaking fees from BMS/Pfizer Alliance, Servier, Novartis, Boston Scientific, Medtronic; and acts as a consultant to Bayer, Servier and Boston Scientific. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was an investigator-initiated trial funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Daiichi Sankyo Europe. Dr. Kirchhof reported research support from several drug and device companies active in AFib. He is also listed as an inventor on two patents held by the University of Hamburg on AFib therapy and AFib markers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in the ARTESIA study.
The results appear to contrast somewhat with the recently reported NOAH-AFNET 6 trial, which failed to show a reduction in stroke with the anticoagulant edoxaban versus placebo in a similar patient group, but that trial was stopped early and so was underpowered.
However, the lead investigators of both trials say the studies actually show consistent results – both found a lower rate of stroke than expected in this population, but the confidence intervals for stroke reduction with anticoagulation overlap, suggesting there is likely some effect, albeit less than that in clinical AFib.
The big question is whether the reduction in stroke with anticoagulation outweighs the increase in major bleeding.
A new meta-analysis of the two trials showed that “oral anticoagulation with edoxaban or apixaban reduces the risk of ischemic stroke by approximately one-third and increases major bleeding by roughly double.”
In absolute numbers, there were three fewer ischemic strokes per 1,000 patient-years with anticoagulation in the two trials combined, at the cost of seven more major bleeds.
The lead investigators of the two trials have somewhat different opinions on how these findings may translate into clinical practice.
Jeff Healey, MD, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., lead investigator of the ARTESIA trial, believes that the risks and benefits need to be assessed in individual patients, but there should be some patient groups that will benefit from anticoagulation treatment.
“In patients with pacemakers or implantable loop recorders with continuous monitoring, subclinical AF[ib] is detected in about one third of patients, so this is extremely common,” he said in an interview. “The question is whether this is just a normal feature of getting older or is this like AF[ib] that we see in the clinic which increases stroke risk, and I think we can conclude from ARTESIA that this subclinical AF[ib] is associated with an increased risk of stroke, although that is lower than the risk with clinical AF[ib], and that it can be reduced by anticoagulation.”
Until recently it hasn’t been possible to quantify the risk associated with subclinical AFib, he noted. “But now we have a rich dataset to use to see if we can tease out some specifics on this. Future analyses of this dataset will help define patients where the benefits outweigh the risks of bleeding. For now, I think we can look at the data in a qualitative way and consider the totality of risk factors in each patient – their bleeding risk, stroke risk, how much AF[ib] they have, and make a decision as to whether to give anticoagulation or not.”
But Paulus Kirchhof, MD, University Heart and Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), lead investigator of the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial said: “Both trials showed the stroke rate is low in these patients – about 1% per year – and that anticoagulation can reduce it a bit further at the expense of increasing major bleeding. I don’t believe the AF[ib] episodes picked up on these devices constitute a sufficient stroke risk to warrant anticoagulation, given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Kirchhof suggests an alternate approach of performing further traditional AFib monitoring on these patients.
“I think going forward in my practice, when we come across this device-detected AF[ib], we will do further investigations with an established method for detecting AF[ib] involving surface ECG monitoring – maybe a 3-day or 7-day Holter. If that shows AF[ib], then we will be on firm ground to start anticoagulation. If that doesn’t show AF[ib], we will probably not use anticoagulation.”
The ARTESIA trial and the meta-analysis of the two trials were both presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Both studies were also simultaneously published online – ARTESIA in the New England Journal of Medicine and the meta-analysis in Circulation.
ARTESIA
For the ARTESIA study, 4012 patients with device-detected AFib and other clinical risk factors for stroke were randomly assigned to treatment with apixaban (5 mg twice daily) or aspirin (81 mg daily).
After a mean follow-up of 3.5 years, the primary endpoint – stroke or systemic embolism – occurred in 55 patients in the apixaban group (0.78% per patient-year), compared with 86 patients in the aspirin group (1.24% per patient-year), giving a hazard ratio of 0.63 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.88; P = .007).
“The risk of stroke or systemic embolism was lower by 37% with apixaban than with aspirin, and the risk of disabling or fatal stroke was lower by 49%,” Dr. Healey reported.
In the “on-treatment” population, the rate of major bleeding was 1.71% per patient-year in the apixaban group and 0.94% per patient-year in the aspirin group (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.26-2.57; P = .001).
Fatal bleeding occurred in five patients in the apixaban group and eight patients in the aspirin group. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 12 patients with apixaban and 15 patients with aspirin.
One of the main findings of the trial is the lower-than-expected risk of ischemic stroke in this population – about 1% per year in the aspirin group, which was reduced to 0.64% per year in the apixaban group.
The authors noted that “simply counting strokes as compared with bleeding events might suggest a neutral overall effect. With apixaban as compared with aspirin, 31 fewer cases of stroke or systemic embolism were seen in the intention-to-treat analysis, as compared with 39 more major bleeding events in the on-treatment analysis.”
However, they pointed out that strokes involve permanent loss of brain tissue, whereas major bleeding is usually reversible, with most patients having complete recovery, which was the case in this study.
“Thus, on the basis of the considerably greater severity of the stroke events prevented than the bleeding events caused, we believe that these findings favor consideration of the use of oral anticoagulation for patients with risk factors for stroke in whom subclinical atrial fibrillation develops,” they concluded.
First well-powered trial addressing this question
Discussing the ARTESIA trial at an AHA press conference, Christine Albert, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said: “I want to emphasize how important this trial is.”
She explained that current guidelines do not recommend any treatment for patients with device-detected AFib that is not shown on ECG, even though it is known this confers some excess risk of stroke.
“ARTESIA is the first well-powered, long-term trial looking at this question,” she said. “It found a clear reduction in the risk of stroke/systemic embolism with apixaban vs aspirin, but there was also a significant amount of bleeding – about an 80% increase. The question is whether the benefit on stroke is worth it given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Albert highlighted the low absolute risk of stroke in this study population of around 1.2%, pointing out that even with the 37% relative reduction with anticoagulation, stroke is only reduced in absolute terms by 0.4%.
“We are going to have to take this back to committees and guidelines and look at the balance between the benefit on stroke and the increase in bleeding,” she concluded.
Noting that observational studies have shown that the duration of AFib impacts the risk of stroke, Dr. Albert suggested that patients with longer-duration AFib may benefit from anticoagulation to a greater extent; and given that the bleeding seen in ARTESIA was mainly GI bleeding, it might be possible to screen out patients at high risk of GI bleeding.
She also pointed out that a lot of patients discontinued anticoagulation treatment in both ARTESIA and NOAH-AFNET 6, showing that this is not an easy strategy for elderly patients.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the ARTESIA trial, Emma Svennberg, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also concluded that, “going forward, we must balance the increased bleeding risks with the risk for disabling strokes,” and that “future substudies and meta-analyses may provide further insights regarding treatment benefits in specific subgroups.”
NOAH-AFNET 6: New subgroup analysis
The previously reported NOAH-AFNET 6 study randomly assigned 2,538 patients with subclinical AFib and additional risk factors for stroke to anticoagulation with edoxaban or placebo. The trial was stopped early, so it was underpowered – but it found no difference between groups in the incidence of the composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism, or death from cardiovascular causes or in the incidence of stroke, although there was higher risk of major bleeding.
Again, there was a low rate of stroke in this trial with just 49 strokes in total in the whole study. The NOAH-AFNET-6 investigators concluded that these patients should not receive anticoagulation because the risk of bleeding outweighed any potential benefits.
A new subanalysis of the 259 patients who had durations of subclinical AFib of 24 hours or longer in the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was presented at the AHA meeting, and simultaneously published online in the European Heart Journal.
This showed that the rate of stroke also appeared low in patients with these long durations of subclinical AFib, and that there was no interaction between the duration of subclinical AFib and the efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulation.
But with such a low number of events in the study as a whole and in the long duration subclinical AFib subgroup (in which there were just two strokes in each treatment group), this analysis was unlikely to show a difference, Dr. Kirchhof commented.
The subgroup analysis did, however, show that patients experiencing subclinical AFib durations of 24 hours or more were more likely to develop clinical AFib over time than those with shorter durations, suggesting the need for regular ECGs in these patients.
Dr. Kirchhof said better methods are needed to detect patients with subclinical AFib at high risk of stroke. “I don’t think our clinical stroke risk factor scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc are sufficient to detect high-risk patients. Patients in both NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESIA had a median CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, but they had a stroke rate of just 1% per year,” he noted.
The meta-analysis of the two trials showed that the results from both are consistent, with an overall reduction in ischemic stroke with oral anticoagulation (relative risk, 0.68). Oral anticoagulation also reduced a composite of cardiovascular death, all-cause stroke, peripheral arterial embolism, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary embolism (RR, 0.85).
There was no significant difference in cardiovascular death (RR, 0.95) or all-cause mortality (RR, 1.08), but anticoagulation significantly increased major bleeding (RR, 1.62).
Aspirin use complicates results
Dr. Healey said further analyses of the ARTESIA data will try to tease out the effect of concomitant aspirin use in the trial.
He explained that patients in this trial were allowed to take a single antiplatelet agent on top of study therapy.
“It is difficult to work out the exact use of antiplatelet therapy as it changed throughout the study,” he said. “About two-thirds were taking antiplatelet agents at the time of enrollment into the trial, but this decreased throughout the study. Many clinicians stopped open-label antiplatelet therapy during the trial when new evidence came out to suggest that there was no added benefit of adding aspirin on top of anticoagulants.
“We need to look carefully as to what impact that may have had,” Dr. Healey added. “We know from other studies that adding an antiplatelet on top of an anticoagulant doesn’t do much to thromboembolic events, but it approximately doubles the risk of major bleeding.”
In contrast, the NOAH-AFNET trial did not allow aspirin use in the anticoagulation group and aspirin was taken by around half the patients in the placebo group who had an indication for its use.
The authors of the meta-analysis pointed out that the omission of aspirin in nearly half of the control patients in NOAH-AFNET 6 and the early termination of the trial may have led to a slightly higher estimate for excess major bleeding with anticoagulation.
The ARTESIA study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network, Hamilton Health Sciences, the Advancing Clinical Trials Network and the Population Health Research Institute. Dr. Healey reported research grants and speaking fees from BMS/Pfizer Alliance, Servier, Novartis, Boston Scientific, Medtronic; and acts as a consultant to Bayer, Servier and Boston Scientific. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was an investigator-initiated trial funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Daiichi Sankyo Europe. Dr. Kirchhof reported research support from several drug and device companies active in AFib. He is also listed as an inventor on two patents held by the University of Hamburg on AFib therapy and AFib markers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in the ARTESIA study.
The results appear to contrast somewhat with the recently reported NOAH-AFNET 6 trial, which failed to show a reduction in stroke with the anticoagulant edoxaban versus placebo in a similar patient group, but that trial was stopped early and so was underpowered.
However, the lead investigators of both trials say the studies actually show consistent results – both found a lower rate of stroke than expected in this population, but the confidence intervals for stroke reduction with anticoagulation overlap, suggesting there is likely some effect, albeit less than that in clinical AFib.
The big question is whether the reduction in stroke with anticoagulation outweighs the increase in major bleeding.
A new meta-analysis of the two trials showed that “oral anticoagulation with edoxaban or apixaban reduces the risk of ischemic stroke by approximately one-third and increases major bleeding by roughly double.”
In absolute numbers, there were three fewer ischemic strokes per 1,000 patient-years with anticoagulation in the two trials combined, at the cost of seven more major bleeds.
The lead investigators of the two trials have somewhat different opinions on how these findings may translate into clinical practice.
Jeff Healey, MD, Population Health Research Institute, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., lead investigator of the ARTESIA trial, believes that the risks and benefits need to be assessed in individual patients, but there should be some patient groups that will benefit from anticoagulation treatment.
“In patients with pacemakers or implantable loop recorders with continuous monitoring, subclinical AF[ib] is detected in about one third of patients, so this is extremely common,” he said in an interview. “The question is whether this is just a normal feature of getting older or is this like AF[ib] that we see in the clinic which increases stroke risk, and I think we can conclude from ARTESIA that this subclinical AF[ib] is associated with an increased risk of stroke, although that is lower than the risk with clinical AF[ib], and that it can be reduced by anticoagulation.”
Until recently it hasn’t been possible to quantify the risk associated with subclinical AFib, he noted. “But now we have a rich dataset to use to see if we can tease out some specifics on this. Future analyses of this dataset will help define patients where the benefits outweigh the risks of bleeding. For now, I think we can look at the data in a qualitative way and consider the totality of risk factors in each patient – their bleeding risk, stroke risk, how much AF[ib] they have, and make a decision as to whether to give anticoagulation or not.”
But Paulus Kirchhof, MD, University Heart and Vascular Center Hamburg (Germany), lead investigator of the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial said: “Both trials showed the stroke rate is low in these patients – about 1% per year – and that anticoagulation can reduce it a bit further at the expense of increasing major bleeding. I don’t believe the AF[ib] episodes picked up on these devices constitute a sufficient stroke risk to warrant anticoagulation, given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Kirchhof suggests an alternate approach of performing further traditional AFib monitoring on these patients.
“I think going forward in my practice, when we come across this device-detected AF[ib], we will do further investigations with an established method for detecting AF[ib] involving surface ECG monitoring – maybe a 3-day or 7-day Holter. If that shows AF[ib], then we will be on firm ground to start anticoagulation. If that doesn’t show AF[ib], we will probably not use anticoagulation.”
The ARTESIA trial and the meta-analysis of the two trials were both presented at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association. Both studies were also simultaneously published online – ARTESIA in the New England Journal of Medicine and the meta-analysis in Circulation.
ARTESIA
For the ARTESIA study, 4012 patients with device-detected AFib and other clinical risk factors for stroke were randomly assigned to treatment with apixaban (5 mg twice daily) or aspirin (81 mg daily).
After a mean follow-up of 3.5 years, the primary endpoint – stroke or systemic embolism – occurred in 55 patients in the apixaban group (0.78% per patient-year), compared with 86 patients in the aspirin group (1.24% per patient-year), giving a hazard ratio of 0.63 (95% confidence interval, 0.45-0.88; P = .007).
“The risk of stroke or systemic embolism was lower by 37% with apixaban than with aspirin, and the risk of disabling or fatal stroke was lower by 49%,” Dr. Healey reported.
In the “on-treatment” population, the rate of major bleeding was 1.71% per patient-year in the apixaban group and 0.94% per patient-year in the aspirin group (HR, 1.80; 95% CI, 1.26-2.57; P = .001).
Fatal bleeding occurred in five patients in the apixaban group and eight patients in the aspirin group. Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in 12 patients with apixaban and 15 patients with aspirin.
One of the main findings of the trial is the lower-than-expected risk of ischemic stroke in this population – about 1% per year in the aspirin group, which was reduced to 0.64% per year in the apixaban group.
The authors noted that “simply counting strokes as compared with bleeding events might suggest a neutral overall effect. With apixaban as compared with aspirin, 31 fewer cases of stroke or systemic embolism were seen in the intention-to-treat analysis, as compared with 39 more major bleeding events in the on-treatment analysis.”
However, they pointed out that strokes involve permanent loss of brain tissue, whereas major bleeding is usually reversible, with most patients having complete recovery, which was the case in this study.
“Thus, on the basis of the considerably greater severity of the stroke events prevented than the bleeding events caused, we believe that these findings favor consideration of the use of oral anticoagulation for patients with risk factors for stroke in whom subclinical atrial fibrillation develops,” they concluded.
First well-powered trial addressing this question
Discussing the ARTESIA trial at an AHA press conference, Christine Albert, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said: “I want to emphasize how important this trial is.”
She explained that current guidelines do not recommend any treatment for patients with device-detected AFib that is not shown on ECG, even though it is known this confers some excess risk of stroke.
“ARTESIA is the first well-powered, long-term trial looking at this question,” she said. “It found a clear reduction in the risk of stroke/systemic embolism with apixaban vs aspirin, but there was also a significant amount of bleeding – about an 80% increase. The question is whether the benefit on stroke is worth it given the bleeding risk.”
Dr. Albert highlighted the low absolute risk of stroke in this study population of around 1.2%, pointing out that even with the 37% relative reduction with anticoagulation, stroke is only reduced in absolute terms by 0.4%.
“We are going to have to take this back to committees and guidelines and look at the balance between the benefit on stroke and the increase in bleeding,” she concluded.
Noting that observational studies have shown that the duration of AFib impacts the risk of stroke, Dr. Albert suggested that patients with longer-duration AFib may benefit from anticoagulation to a greater extent; and given that the bleeding seen in ARTESIA was mainly GI bleeding, it might be possible to screen out patients at high risk of GI bleeding.
She also pointed out that a lot of patients discontinued anticoagulation treatment in both ARTESIA and NOAH-AFNET 6, showing that this is not an easy strategy for elderly patients.
In an editorial accompanying publication of the ARTESIA trial, Emma Svennberg, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also concluded that, “going forward, we must balance the increased bleeding risks with the risk for disabling strokes,” and that “future substudies and meta-analyses may provide further insights regarding treatment benefits in specific subgroups.”
NOAH-AFNET 6: New subgroup analysis
The previously reported NOAH-AFNET 6 study randomly assigned 2,538 patients with subclinical AFib and additional risk factors for stroke to anticoagulation with edoxaban or placebo. The trial was stopped early, so it was underpowered – but it found no difference between groups in the incidence of the composite endpoint of stroke, systemic embolism, or death from cardiovascular causes or in the incidence of stroke, although there was higher risk of major bleeding.
Again, there was a low rate of stroke in this trial with just 49 strokes in total in the whole study. The NOAH-AFNET-6 investigators concluded that these patients should not receive anticoagulation because the risk of bleeding outweighed any potential benefits.
A new subanalysis of the 259 patients who had durations of subclinical AFib of 24 hours or longer in the NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was presented at the AHA meeting, and simultaneously published online in the European Heart Journal.
This showed that the rate of stroke also appeared low in patients with these long durations of subclinical AFib, and that there was no interaction between the duration of subclinical AFib and the efficacy and safety of oral anticoagulation.
But with such a low number of events in the study as a whole and in the long duration subclinical AFib subgroup (in which there were just two strokes in each treatment group), this analysis was unlikely to show a difference, Dr. Kirchhof commented.
The subgroup analysis did, however, show that patients experiencing subclinical AFib durations of 24 hours or more were more likely to develop clinical AFib over time than those with shorter durations, suggesting the need for regular ECGs in these patients.
Dr. Kirchhof said better methods are needed to detect patients with subclinical AFib at high risk of stroke. “I don’t think our clinical stroke risk factor scores such as CHA2DS2-VASc are sufficient to detect high-risk patients. Patients in both NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESIA had a median CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, but they had a stroke rate of just 1% per year,” he noted.
The meta-analysis of the two trials showed that the results from both are consistent, with an overall reduction in ischemic stroke with oral anticoagulation (relative risk, 0.68). Oral anticoagulation also reduced a composite of cardiovascular death, all-cause stroke, peripheral arterial embolism, myocardial infarction, or pulmonary embolism (RR, 0.85).
There was no significant difference in cardiovascular death (RR, 0.95) or all-cause mortality (RR, 1.08), but anticoagulation significantly increased major bleeding (RR, 1.62).
Aspirin use complicates results
Dr. Healey said further analyses of the ARTESIA data will try to tease out the effect of concomitant aspirin use in the trial.
He explained that patients in this trial were allowed to take a single antiplatelet agent on top of study therapy.
“It is difficult to work out the exact use of antiplatelet therapy as it changed throughout the study,” he said. “About two-thirds were taking antiplatelet agents at the time of enrollment into the trial, but this decreased throughout the study. Many clinicians stopped open-label antiplatelet therapy during the trial when new evidence came out to suggest that there was no added benefit of adding aspirin on top of anticoagulants.
“We need to look carefully as to what impact that may have had,” Dr. Healey added. “We know from other studies that adding an antiplatelet on top of an anticoagulant doesn’t do much to thromboembolic events, but it approximately doubles the risk of major bleeding.”
In contrast, the NOAH-AFNET trial did not allow aspirin use in the anticoagulation group and aspirin was taken by around half the patients in the placebo group who had an indication for its use.
The authors of the meta-analysis pointed out that the omission of aspirin in nearly half of the control patients in NOAH-AFNET 6 and the early termination of the trial may have led to a slightly higher estimate for excess major bleeding with anticoagulation.
The ARTESIA study was supported by the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance, the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network, Hamilton Health Sciences, the Advancing Clinical Trials Network and the Population Health Research Institute. Dr. Healey reported research grants and speaking fees from BMS/Pfizer Alliance, Servier, Novartis, Boston Scientific, Medtronic; and acts as a consultant to Bayer, Servier and Boston Scientific. The NOAH-AFNET 6 trial was an investigator-initiated trial funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research and Daiichi Sankyo Europe. Dr. Kirchhof reported research support from several drug and device companies active in AFib. He is also listed as an inventor on two patents held by the University of Hamburg on AFib therapy and AFib markers.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Impressive bleeding profile with factor XI inhibitor in AFib: AZALEA
; the risk of stroke was moderate to high.
The trial was stopped earlier this year because of an “overwhelming” reduction in bleeding with abelacimab in comparison to rivaroxaban. Abelacimab is a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month.
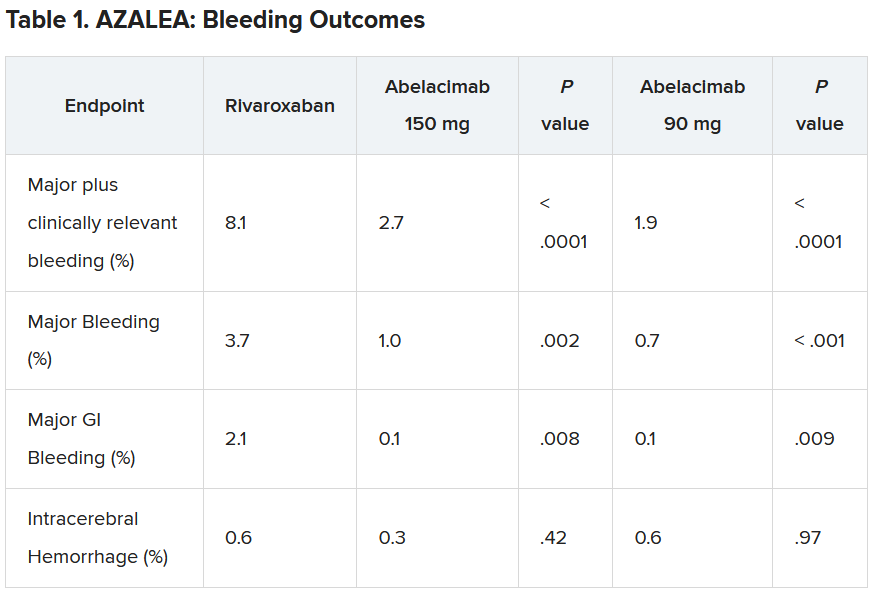
“Details of the bleeding results have now shown that the 150-mg dose of abelacimab, which is the dose being carried forward to phase 3 trials, was associated with a 67% reduction in major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, the primary endpoint of the study.”
In addition, major bleeding was reduced by 74%, and major gastrointestinal bleeding was reduced by 93%.
“We are seeing really profound reductions in bleeding with this agent vs. a NOAC [novel oral anticoagulant],” lead AZALEA investigator Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Major bleeding – effectively the type of bleeding that results in hospitalization – is reduced by more than two-thirds, and major GI bleeding – which is the most common type of bleeding experienced by AF patients on anticoagulants – is almost eliminated. This gives us real hope that we have finally found an anticoagulant that is remarkably safe and will allow us to use anticoagulation in our most vulnerable patients,” he said.
Dr. Ruff presented the full results from the AZALEA trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He noted that AFib is one of the most common medical conditions in the world and that it confers an increased risk of stroke. Anticoagulants reduce this risk very effectively, and while the NOACS, such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, are safer than warfarin, significant bleeding still occurs, and “shockingly,” he said, between 30% and 60% of patients are not prescribed an anticoagulant or discontinue treatment because of bleeding concerns.
“Clearly, we need safer anticoagulants to protect these patients. Factor XI inhibitors, of which abelacimab is one, have emerged as the most promising agents, as they are thought to provide precision anticoagulation,” Dr. Ruff said.
He explained that factor XI appears to be involved in the formation of thrombus, which blocks arteries and causes strokes and myocardial infarction (thrombosis), but not in the healing process of blood vessels after injury (hemostasis). So, it is believed that inhibiting factor XI should reduce thrombotic events without causing excess bleeding.
AZALEA, which is the largest and longest trial of a factor XI inhibitor to date, enrolled 1,287 adults with AF who were at moderate to high risk of stroke.
They were randomly assigned to receive one of three treatments: oral rivaroxaban 20 mg daily; abelacimab 90 mg; or abelacimab 150 mg. Abelacimab was given monthly by injection.
Both doses of abelacimab inhibited factor XI almost completely; 97% inhibition was achieved with the 90-mg dose, and 99% inhibition was achieved with the 150-mg dose.
Results showed that after a median follow-up of 1.8 years, there was a clear reduction in all bleeding endpoints with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban.
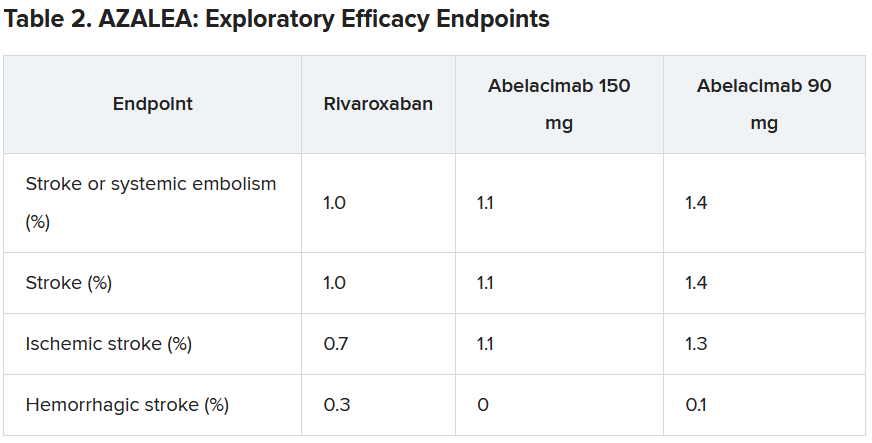
Dr. Ruff explained that the trial was powered to detect differences in bleeding, not stroke, but the investigators approached this in an exploratory way.
“As expected, the numbers were low, with just 25 strokes (23 ischemic strokes) across all three groups in the trial. So, because of this very low rate, we are really not able to compare how abelacimab compares with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke,” he commented.
He did, however, suggest that the low stroke rate in the study was encouraging.
“If we look at the same population without anticoagulation, the stroke rate would be about 7% per year. And we see here in this trial that in all three arms, the stroke rate was just above 1% per year. I think this shows that all the patients in the trial were getting highly effective anticoagulation,” he said.
“But what this trial doesn’t answer – because the numbers are so low – is exactly how effective factor XI inhibition with abelacimab is, compared to NOACs in reducing stroke rates. That requires dedicated phase 3 trials.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that there are some reassuring data from phase 2 trials in venous thromboembolism (VTE), in which the 150-mg dose of abelacimab was associated with an 80% reduction in VTE, compared with enoxaparin. “Historically in the development of anticoagulants, efficacy in VTE has translated into efficacy in stroke prevention, so that is very encouraging,” he commented.
“So, I think our results along with the VTE results are encouraging, but the precision regarding the relative efficacy compared to NOACs is still an open question that needs to be clarified in phase 3 trials,” he concluded.
Several phase 3 trials are now underway with abelacimab and two other small-molecule orally available factor XI inhibitors, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer).
The designated discussant of the AZALEA study at the AHA meeting, Manesh Patel. MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., described the results as “an important step forward.”
“This trial, with the prior data in this field, show that factor XI inhibition as a target is biologically possible (studies showing > 95% inhibition), significantly less bleeding than NOACS. We await the phase 3 studies, but having significantly less bleeding and similar or less stroke would be a substantial step forward for the field,” he said.
John Alexander, MD, also from Duke University, said: “There were clinically important reductions in bleeding with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban. This is consistent to what we’ve seen with comparisons between other factor XI inhibitors and other factor Xa inhibitors.”
On the exploratory efficacy results, Dr. Alexander agreed with Dr. Ruff that it was not possible to get any idea of how abelacimab compared with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke. “The hazard ratio and confidence intervals comparing abelacimab and rivaroxaban include substantial lower rates, no difference, and substantially higher rates,” he noted.
“We need to wait for the results of phase 3 trials, with abelacimab and other factor XI inhibitors, to understand how well factor XI inhibition prevents stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Alexander added. “These trials are ongoing.”
Dr. Ruff concluded: “Assuming the data from ongoing phase 3 trials confirm the benefit of factor XI inhibitors for stroke prevention in people with AF, it will really be transformative for the field of cardiology.
“Our first mission in treating people with AF is to prevent stroke, and our ability to do this with a remarkably safe anticoagulant such as abelacimab would be an incredible advance,” he concluded.
Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AF executive committee for BMS/Janssen (milvexian), and has been on an advisory board for Bayer (asundexian). Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an advisor to Bayer and Janssen. Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
; the risk of stroke was moderate to high.
The trial was stopped earlier this year because of an “overwhelming” reduction in bleeding with abelacimab in comparison to rivaroxaban. Abelacimab is a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month.
“Details of the bleeding results have now shown that the 150-mg dose of abelacimab, which is the dose being carried forward to phase 3 trials, was associated with a 67% reduction in major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, the primary endpoint of the study.”
In addition, major bleeding was reduced by 74%, and major gastrointestinal bleeding was reduced by 93%.
“We are seeing really profound reductions in bleeding with this agent vs. a NOAC [novel oral anticoagulant],” lead AZALEA investigator Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Major bleeding – effectively the type of bleeding that results in hospitalization – is reduced by more than two-thirds, and major GI bleeding – which is the most common type of bleeding experienced by AF patients on anticoagulants – is almost eliminated. This gives us real hope that we have finally found an anticoagulant that is remarkably safe and will allow us to use anticoagulation in our most vulnerable patients,” he said.
Dr. Ruff presented the full results from the AZALEA trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He noted that AFib is one of the most common medical conditions in the world and that it confers an increased risk of stroke. Anticoagulants reduce this risk very effectively, and while the NOACS, such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, are safer than warfarin, significant bleeding still occurs, and “shockingly,” he said, between 30% and 60% of patients are not prescribed an anticoagulant or discontinue treatment because of bleeding concerns.
“Clearly, we need safer anticoagulants to protect these patients. Factor XI inhibitors, of which abelacimab is one, have emerged as the most promising agents, as they are thought to provide precision anticoagulation,” Dr. Ruff said.
He explained that factor XI appears to be involved in the formation of thrombus, which blocks arteries and causes strokes and myocardial infarction (thrombosis), but not in the healing process of blood vessels after injury (hemostasis). So, it is believed that inhibiting factor XI should reduce thrombotic events without causing excess bleeding.
AZALEA, which is the largest and longest trial of a factor XI inhibitor to date, enrolled 1,287 adults with AF who were at moderate to high risk of stroke.
They were randomly assigned to receive one of three treatments: oral rivaroxaban 20 mg daily; abelacimab 90 mg; or abelacimab 150 mg. Abelacimab was given monthly by injection.
Both doses of abelacimab inhibited factor XI almost completely; 97% inhibition was achieved with the 90-mg dose, and 99% inhibition was achieved with the 150-mg dose.
Results showed that after a median follow-up of 1.8 years, there was a clear reduction in all bleeding endpoints with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban.
Dr. Ruff explained that the trial was powered to detect differences in bleeding, not stroke, but the investigators approached this in an exploratory way.
“As expected, the numbers were low, with just 25 strokes (23 ischemic strokes) across all three groups in the trial. So, because of this very low rate, we are really not able to compare how abelacimab compares with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke,” he commented.
He did, however, suggest that the low stroke rate in the study was encouraging.
“If we look at the same population without anticoagulation, the stroke rate would be about 7% per year. And we see here in this trial that in all three arms, the stroke rate was just above 1% per year. I think this shows that all the patients in the trial were getting highly effective anticoagulation,” he said.
“But what this trial doesn’t answer – because the numbers are so low – is exactly how effective factor XI inhibition with abelacimab is, compared to NOACs in reducing stroke rates. That requires dedicated phase 3 trials.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that there are some reassuring data from phase 2 trials in venous thromboembolism (VTE), in which the 150-mg dose of abelacimab was associated with an 80% reduction in VTE, compared with enoxaparin. “Historically in the development of anticoagulants, efficacy in VTE has translated into efficacy in stroke prevention, so that is very encouraging,” he commented.
“So, I think our results along with the VTE results are encouraging, but the precision regarding the relative efficacy compared to NOACs is still an open question that needs to be clarified in phase 3 trials,” he concluded.
Several phase 3 trials are now underway with abelacimab and two other small-molecule orally available factor XI inhibitors, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer).
The designated discussant of the AZALEA study at the AHA meeting, Manesh Patel. MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., described the results as “an important step forward.”
“This trial, with the prior data in this field, show that factor XI inhibition as a target is biologically possible (studies showing > 95% inhibition), significantly less bleeding than NOACS. We await the phase 3 studies, but having significantly less bleeding and similar or less stroke would be a substantial step forward for the field,” he said.
John Alexander, MD, also from Duke University, said: “There were clinically important reductions in bleeding with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban. This is consistent to what we’ve seen with comparisons between other factor XI inhibitors and other factor Xa inhibitors.”
On the exploratory efficacy results, Dr. Alexander agreed with Dr. Ruff that it was not possible to get any idea of how abelacimab compared with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke. “The hazard ratio and confidence intervals comparing abelacimab and rivaroxaban include substantial lower rates, no difference, and substantially higher rates,” he noted.
“We need to wait for the results of phase 3 trials, with abelacimab and other factor XI inhibitors, to understand how well factor XI inhibition prevents stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Alexander added. “These trials are ongoing.”
Dr. Ruff concluded: “Assuming the data from ongoing phase 3 trials confirm the benefit of factor XI inhibitors for stroke prevention in people with AF, it will really be transformative for the field of cardiology.
“Our first mission in treating people with AF is to prevent stroke, and our ability to do this with a remarkably safe anticoagulant such as abelacimab would be an incredible advance,” he concluded.
Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AF executive committee for BMS/Janssen (milvexian), and has been on an advisory board for Bayer (asundexian). Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an advisor to Bayer and Janssen. Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
; the risk of stroke was moderate to high.
The trial was stopped earlier this year because of an “overwhelming” reduction in bleeding with abelacimab in comparison to rivaroxaban. Abelacimab is a monoclonal antibody given by subcutaneous injection once a month.
“Details of the bleeding results have now shown that the 150-mg dose of abelacimab, which is the dose being carried forward to phase 3 trials, was associated with a 67% reduction in major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, the primary endpoint of the study.”
In addition, major bleeding was reduced by 74%, and major gastrointestinal bleeding was reduced by 93%.
“We are seeing really profound reductions in bleeding with this agent vs. a NOAC [novel oral anticoagulant],” lead AZALEA investigator Christian Ruff, MD, professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Major bleeding – effectively the type of bleeding that results in hospitalization – is reduced by more than two-thirds, and major GI bleeding – which is the most common type of bleeding experienced by AF patients on anticoagulants – is almost eliminated. This gives us real hope that we have finally found an anticoagulant that is remarkably safe and will allow us to use anticoagulation in our most vulnerable patients,” he said.
Dr. Ruff presented the full results from the AZALEA trial at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
He noted that AFib is one of the most common medical conditions in the world and that it confers an increased risk of stroke. Anticoagulants reduce this risk very effectively, and while the NOACS, such as apixaban and rivaroxaban, are safer than warfarin, significant bleeding still occurs, and “shockingly,” he said, between 30% and 60% of patients are not prescribed an anticoagulant or discontinue treatment because of bleeding concerns.
“Clearly, we need safer anticoagulants to protect these patients. Factor XI inhibitors, of which abelacimab is one, have emerged as the most promising agents, as they are thought to provide precision anticoagulation,” Dr. Ruff said.
He explained that factor XI appears to be involved in the formation of thrombus, which blocks arteries and causes strokes and myocardial infarction (thrombosis), but not in the healing process of blood vessels after injury (hemostasis). So, it is believed that inhibiting factor XI should reduce thrombotic events without causing excess bleeding.
AZALEA, which is the largest and longest trial of a factor XI inhibitor to date, enrolled 1,287 adults with AF who were at moderate to high risk of stroke.
They were randomly assigned to receive one of three treatments: oral rivaroxaban 20 mg daily; abelacimab 90 mg; or abelacimab 150 mg. Abelacimab was given monthly by injection.
Both doses of abelacimab inhibited factor XI almost completely; 97% inhibition was achieved with the 90-mg dose, and 99% inhibition was achieved with the 150-mg dose.
Results showed that after a median follow-up of 1.8 years, there was a clear reduction in all bleeding endpoints with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban.
Dr. Ruff explained that the trial was powered to detect differences in bleeding, not stroke, but the investigators approached this in an exploratory way.
“As expected, the numbers were low, with just 25 strokes (23 ischemic strokes) across all three groups in the trial. So, because of this very low rate, we are really not able to compare how abelacimab compares with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke,” he commented.
He did, however, suggest that the low stroke rate in the study was encouraging.
“If we look at the same population without anticoagulation, the stroke rate would be about 7% per year. And we see here in this trial that in all three arms, the stroke rate was just above 1% per year. I think this shows that all the patients in the trial were getting highly effective anticoagulation,” he said.
“But what this trial doesn’t answer – because the numbers are so low – is exactly how effective factor XI inhibition with abelacimab is, compared to NOACs in reducing stroke rates. That requires dedicated phase 3 trials.”
Dr. Ruff pointed out that there are some reassuring data from phase 2 trials in venous thromboembolism (VTE), in which the 150-mg dose of abelacimab was associated with an 80% reduction in VTE, compared with enoxaparin. “Historically in the development of anticoagulants, efficacy in VTE has translated into efficacy in stroke prevention, so that is very encouraging,” he commented.
“So, I think our results along with the VTE results are encouraging, but the precision regarding the relative efficacy compared to NOACs is still an open question that needs to be clarified in phase 3 trials,” he concluded.
Several phase 3 trials are now underway with abelacimab and two other small-molecule orally available factor XI inhibitors, milvexian (BMS/Janssen) and asundexian (Bayer).
The designated discussant of the AZALEA study at the AHA meeting, Manesh Patel. MD, Duke University, Durham, N.C., described the results as “an important step forward.”
“This trial, with the prior data in this field, show that factor XI inhibition as a target is biologically possible (studies showing > 95% inhibition), significantly less bleeding than NOACS. We await the phase 3 studies, but having significantly less bleeding and similar or less stroke would be a substantial step forward for the field,” he said.
John Alexander, MD, also from Duke University, said: “There were clinically important reductions in bleeding with both doses of abelacimab, compared with rivaroxaban. This is consistent to what we’ve seen with comparisons between other factor XI inhibitors and other factor Xa inhibitors.”
On the exploratory efficacy results, Dr. Alexander agreed with Dr. Ruff that it was not possible to get any idea of how abelacimab compared with rivaroxaban in reducing stroke. “The hazard ratio and confidence intervals comparing abelacimab and rivaroxaban include substantial lower rates, no difference, and substantially higher rates,” he noted.
“We need to wait for the results of phase 3 trials, with abelacimab and other factor XI inhibitors, to understand how well factor XI inhibition prevents stroke and systemic embolism in patients with atrial fibrillation,” Dr. Alexander added. “These trials are ongoing.”
Dr. Ruff concluded: “Assuming the data from ongoing phase 3 trials confirm the benefit of factor XI inhibitors for stroke prevention in people with AF, it will really be transformative for the field of cardiology.
“Our first mission in treating people with AF is to prevent stroke, and our ability to do this with a remarkably safe anticoagulant such as abelacimab would be an incredible advance,” he concluded.
Dr. Ruff receives research funding from Anthos for abelacimab trials, is on an AF executive committee for BMS/Janssen (milvexian), and has been on an advisory board for Bayer (asundexian). Dr. Patel has received grants from and acts as an advisor to Bayer and Janssen. Dr. Alexander receives research funding from Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2023
Atrial fibrillation linked to dementia, especially when diagnosed before age 65 years
TOPLINE:
Adults with atrial fibrillation (AFib) are at increased risk for dementia, especially when AFib occurs before age 65 years, new research shows. Investigators note the findings highlight the importance of monitoring cognitive function in adults with AF.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective, population-based cohort study leveraged data from 433,746 UK Biobank participants (55% women), including 30,601 with AFib, who were followed for a median of 12.6 years
- Incident cases of dementia were determined through linkage from multiple databases.
- Cox proportional hazards models and propensity score matching were used to estimate the association between age at onset of AFib and incident dementia.
TAKEAWAY:
- During follow-up, new-onset dementia occurred in 5,898 participants (2,546 with Alzheimer’s disease [AD] and 1,211 with vascular dementia [VD]), of which, 1,031 had AFib (350 with AD; 320 with VD).
- Compared with participants without AFib, those with AFib had a 42% higher risk for all-cause dementia (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.42; P < .001) and more than double the risk for VD (aHR, 2.06; P < .001), but no significantly higher risk for AD.
- Younger age at AFib onset was associated with higher risks for all-cause dementia, AD and VD, with aHRs per 10-year decrease of 1.23, 1.27, and 1.35, respectively (P < .001 for all).
- After propensity score matching, AFib onset before age 65 years had the highest risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 1.82; P < .001), followed by AF onset at age 65-74 years (aHR, 1.47; P < .001). Similar results were seen in AD and VD.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings indicate that careful monitoring of cognitive function for patients with a younger [AFib] onset age, particularly those diagnosed with [AFib] before age 65 years, is important to attenuate the risk of subsequent dementia,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Wenya Zhang, with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because the study was observational, a cause-effect relationship cannot be established. Despite the adjustment for many underlying confounders, residual unidentified confounders may still exist. The vast majority of participants were White. The analyses did not consider the potential impact of effective treatment of AFib on dementia risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adults with atrial fibrillation (AFib) are at increased risk for dementia, especially when AFib occurs before age 65 years, new research shows. Investigators note the findings highlight the importance of monitoring cognitive function in adults with AF.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective, population-based cohort study leveraged data from 433,746 UK Biobank participants (55% women), including 30,601 with AFib, who were followed for a median of 12.6 years
- Incident cases of dementia were determined through linkage from multiple databases.
- Cox proportional hazards models and propensity score matching were used to estimate the association between age at onset of AFib and incident dementia.
TAKEAWAY:
- During follow-up, new-onset dementia occurred in 5,898 participants (2,546 with Alzheimer’s disease [AD] and 1,211 with vascular dementia [VD]), of which, 1,031 had AFib (350 with AD; 320 with VD).
- Compared with participants without AFib, those with AFib had a 42% higher risk for all-cause dementia (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.42; P < .001) and more than double the risk for VD (aHR, 2.06; P < .001), but no significantly higher risk for AD.
- Younger age at AFib onset was associated with higher risks for all-cause dementia, AD and VD, with aHRs per 10-year decrease of 1.23, 1.27, and 1.35, respectively (P < .001 for all).
- After propensity score matching, AFib onset before age 65 years had the highest risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 1.82; P < .001), followed by AF onset at age 65-74 years (aHR, 1.47; P < .001). Similar results were seen in AD and VD.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings indicate that careful monitoring of cognitive function for patients with a younger [AFib] onset age, particularly those diagnosed with [AFib] before age 65 years, is important to attenuate the risk of subsequent dementia,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Wenya Zhang, with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because the study was observational, a cause-effect relationship cannot be established. Despite the adjustment for many underlying confounders, residual unidentified confounders may still exist. The vast majority of participants were White. The analyses did not consider the potential impact of effective treatment of AFib on dementia risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adults with atrial fibrillation (AFib) are at increased risk for dementia, especially when AFib occurs before age 65 years, new research shows. Investigators note the findings highlight the importance of monitoring cognitive function in adults with AF.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective, population-based cohort study leveraged data from 433,746 UK Biobank participants (55% women), including 30,601 with AFib, who were followed for a median of 12.6 years
- Incident cases of dementia were determined through linkage from multiple databases.
- Cox proportional hazards models and propensity score matching were used to estimate the association between age at onset of AFib and incident dementia.
TAKEAWAY:
- During follow-up, new-onset dementia occurred in 5,898 participants (2,546 with Alzheimer’s disease [AD] and 1,211 with vascular dementia [VD]), of which, 1,031 had AFib (350 with AD; 320 with VD).
- Compared with participants without AFib, those with AFib had a 42% higher risk for all-cause dementia (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.42; P < .001) and more than double the risk for VD (aHR, 2.06; P < .001), but no significantly higher risk for AD.
- Younger age at AFib onset was associated with higher risks for all-cause dementia, AD and VD, with aHRs per 10-year decrease of 1.23, 1.27, and 1.35, respectively (P < .001 for all).
- After propensity score matching, AFib onset before age 65 years had the highest risk for all-cause dementia (aHR, 1.82; P < .001), followed by AF onset at age 65-74 years (aHR, 1.47; P < .001). Similar results were seen in AD and VD.
IN PRACTICE:
“The findings indicate that careful monitoring of cognitive function for patients with a younger [AFib] onset age, particularly those diagnosed with [AFib] before age 65 years, is important to attenuate the risk of subsequent dementia,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study, with first author Wenya Zhang, with the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Because the study was observational, a cause-effect relationship cannot be established. Despite the adjustment for many underlying confounders, residual unidentified confounders may still exist. The vast majority of participants were White. The analyses did not consider the potential impact of effective treatment of AFib on dementia risk.
DISCLOSURES:
The study had no commercial funding. The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For AFib cardioversion in obesity, dual energy might be the answer
PHILADELPHIA – , a multicenter randomized trial shows.
When treated with dual direct current cardioversion (DCCV), only 2% of patients with obesity failed to cardiovert on the first shock versus 14% (P = .002) of those treated with a conventional single DCCV, reported Joshua D. Aymond, MD, a fellow in electrophysiology at Ochsner Health, New Orleans.
Of the 14 patients in the single DCCV arm who did not convert on the first shock, 12 cardioverted when switched to dual energy. The remaining two cardioverted on the second dual shock.
In the dual DCCV group, of the two patients who did not cardiovert on the first dual shock, one did on the second. The other also cardioverted on a second shock, but this second shock was not delivered for 2 weeks, during which time the patient received a course of amiodarone-based anti-arrhythmic therapy.
No disadvantages seen with dual energy
The greater efficacy of a first shock with dual DCCV was achieved with no apparent disadvantages. There were no differences in post-procedure chest discomfort and no procedure-related adverse events in either arm, Dr. Aymond said.
The rising prevalence of obesity in the United States has created the need for a more effective first-line strategy for AF, noted Dr. Aymond, who presented the results of this study at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
Cardioversion, which he characterized as the treatment of choice for AF, “fails to restore sinus rhythm in 20% to 35% of obese patients versus less than 10% of non-obese patients,” he said. The higher failure rate in patients with obesity is becoming a more common clinical issue not only due to the rising rates of obesity but a corresponding rise in AF, which is a related phenomenon.
“The risk of atrial fibrillation is increased by 50% relative to those who are not obese,” Dr. Aymond explained.
In this study, 200 patients at three participating centers were randomized to single DCCV or double DCCV after exclusions that included ventricular tachycardia and respiratory instability. The baseline characteristics were comparable. All 101 patients in the single DCCV group and 99 patients in the dual DCCV group were available for the intention-to-treat analysis.
200 vs. 400 joules delivered across the heart
In the study protocol, patients were fitted with four chest pads, two located adjacent but above the heart and two adjacent but below the heart. For single DCCV, 200 joules of energy were delivered from the upper right pad to the lower left pad across the heart. For dual DCCV, another 200 joules were delivered simultaneously from the upper left to the lower right across the heart. The total dose in the dual DCCV group was 400 joules.
The primary outcome was restoration of sinus rhythm of any duration immediately after DCCV. Safety, including clinical events, was a secondary outcome. Only the patients were blinded to the energy they received.
On univariate analysis, the odds ratio for successful cardioversion with dual DCCV was nearly eightfold higher (OR 7.8; P = .008) than single DCCV. On a simple multivariable analysis, when the researchers controlled for just age, sex, and body mass index, the odds ratio rose (OR 8.5; P = .007).
On a comprehensive multivariable analysis adding control for such characteristics as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), obstructive sleep apnea, and antiarrhythmic drugs, the advantage of dual DCCV climbed above 12-fold (OR 12.6; P = .03).
The study is addressing a relevant and persistent question, said the AHA-invited discussant Jose A. Joglar, MD, program director, Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
Dr. Joglar pointed out that alternatives to single DCCV for patients more difficult to cardiovert have been “sought for decades.” He noted that a variety of techniques, including dual DCCV, have been evaluated in small studies and case reports.
Alternatives for obese outlined
Several have shown promise, Dr. Joglar said. As one of several examples, he cited a 20-patient study that randomized patients to adhesive patches, like those employed in the Aymond trial, or handheld paddles. Both patches and paddles were applied with manual pressure while a 200-joule shock was delivered. The proportion of patients who cardioverted on the first shock was almost two times higher in the group after the first shock with the paddles (50% vs. 27%; P = .01). Dr. Joglar said the study supports the principle that 200 joules delivered by adhesive patches is inadequate for treatment of AF in many patients with obesity.
Dr. Joglar also cited studies suggesting that single DCCV delivered with higher energy than 200 joules appears to improve cardioversion success rates, but he indicated that this study with dual DCCV in the front-line setting provides evidence for another alternative.
“This is the first such trial with dual defibrillators as an initial strategy,” he said, calling the groups well matched and the superiority of dual DCCV “impressive.” He cautioned that the study size was well powered for the endpoint but perhaps small for evaluating relative safety.
Yet, “the study adds credibility and confidence for the use of dual DCCV, especially in difficult or refractory patients,” he said. He is less certain that it establishes dual DCCV as a standard first-line therapy in all patients with obesity. This would require additional studies to compare it to other types of strategies such as those he mentioned.
As an option for improving cardioversion in first-line treatment, dual DCCV “can be added to a list of other techniques, such as manual pressure or a higher initial dose with single DCCV,” he said.
Dr. Aymond and Dr. Joglar report no potential conflicts of interest.
PHILADELPHIA – , a multicenter randomized trial shows.
When treated with dual direct current cardioversion (DCCV), only 2% of patients with obesity failed to cardiovert on the first shock versus 14% (P = .002) of those treated with a conventional single DCCV, reported Joshua D. Aymond, MD, a fellow in electrophysiology at Ochsner Health, New Orleans.
Of the 14 patients in the single DCCV arm who did not convert on the first shock, 12 cardioverted when switched to dual energy. The remaining two cardioverted on the second dual shock.
In the dual DCCV group, of the two patients who did not cardiovert on the first dual shock, one did on the second. The other also cardioverted on a second shock, but this second shock was not delivered for 2 weeks, during which time the patient received a course of amiodarone-based anti-arrhythmic therapy.
No disadvantages seen with dual energy
The greater efficacy of a first shock with dual DCCV was achieved with no apparent disadvantages. There were no differences in post-procedure chest discomfort and no procedure-related adverse events in either arm, Dr. Aymond said.
The rising prevalence of obesity in the United States has created the need for a more effective first-line strategy for AF, noted Dr. Aymond, who presented the results of this study at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
Cardioversion, which he characterized as the treatment of choice for AF, “fails to restore sinus rhythm in 20% to 35% of obese patients versus less than 10% of non-obese patients,” he said. The higher failure rate in patients with obesity is becoming a more common clinical issue not only due to the rising rates of obesity but a corresponding rise in AF, which is a related phenomenon.
“The risk of atrial fibrillation is increased by 50% relative to those who are not obese,” Dr. Aymond explained.
In this study, 200 patients at three participating centers were randomized to single DCCV or double DCCV after exclusions that included ventricular tachycardia and respiratory instability. The baseline characteristics were comparable. All 101 patients in the single DCCV group and 99 patients in the dual DCCV group were available for the intention-to-treat analysis.
200 vs. 400 joules delivered across the heart
In the study protocol, patients were fitted with four chest pads, two located adjacent but above the heart and two adjacent but below the heart. For single DCCV, 200 joules of energy were delivered from the upper right pad to the lower left pad across the heart. For dual DCCV, another 200 joules were delivered simultaneously from the upper left to the lower right across the heart. The total dose in the dual DCCV group was 400 joules.
The primary outcome was restoration of sinus rhythm of any duration immediately after DCCV. Safety, including clinical events, was a secondary outcome. Only the patients were blinded to the energy they received.
On univariate analysis, the odds ratio for successful cardioversion with dual DCCV was nearly eightfold higher (OR 7.8; P = .008) than single DCCV. On a simple multivariable analysis, when the researchers controlled for just age, sex, and body mass index, the odds ratio rose (OR 8.5; P = .007).
On a comprehensive multivariable analysis adding control for such characteristics as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), obstructive sleep apnea, and antiarrhythmic drugs, the advantage of dual DCCV climbed above 12-fold (OR 12.6; P = .03).
The study is addressing a relevant and persistent question, said the AHA-invited discussant Jose A. Joglar, MD, program director, Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
Dr. Joglar pointed out that alternatives to single DCCV for patients more difficult to cardiovert have been “sought for decades.” He noted that a variety of techniques, including dual DCCV, have been evaluated in small studies and case reports.
Alternatives for obese outlined
Several have shown promise, Dr. Joglar said. As one of several examples, he cited a 20-patient study that randomized patients to adhesive patches, like those employed in the Aymond trial, or handheld paddles. Both patches and paddles were applied with manual pressure while a 200-joule shock was delivered. The proportion of patients who cardioverted on the first shock was almost two times higher in the group after the first shock with the paddles (50% vs. 27%; P = .01). Dr. Joglar said the study supports the principle that 200 joules delivered by adhesive patches is inadequate for treatment of AF in many patients with obesity.
Dr. Joglar also cited studies suggesting that single DCCV delivered with higher energy than 200 joules appears to improve cardioversion success rates, but he indicated that this study with dual DCCV in the front-line setting provides evidence for another alternative.
“This is the first such trial with dual defibrillators as an initial strategy,” he said, calling the groups well matched and the superiority of dual DCCV “impressive.” He cautioned that the study size was well powered for the endpoint but perhaps small for evaluating relative safety.
Yet, “the study adds credibility and confidence for the use of dual DCCV, especially in difficult or refractory patients,” he said. He is less certain that it establishes dual DCCV as a standard first-line therapy in all patients with obesity. This would require additional studies to compare it to other types of strategies such as those he mentioned.
As an option for improving cardioversion in first-line treatment, dual DCCV “can be added to a list of other techniques, such as manual pressure or a higher initial dose with single DCCV,” he said.
Dr. Aymond and Dr. Joglar report no potential conflicts of interest.
PHILADELPHIA – , a multicenter randomized trial shows.
When treated with dual direct current cardioversion (DCCV), only 2% of patients with obesity failed to cardiovert on the first shock versus 14% (P = .002) of those treated with a conventional single DCCV, reported Joshua D. Aymond, MD, a fellow in electrophysiology at Ochsner Health, New Orleans.
Of the 14 patients in the single DCCV arm who did not convert on the first shock, 12 cardioverted when switched to dual energy. The remaining two cardioverted on the second dual shock.
In the dual DCCV group, of the two patients who did not cardiovert on the first dual shock, one did on the second. The other also cardioverted on a second shock, but this second shock was not delivered for 2 weeks, during which time the patient received a course of amiodarone-based anti-arrhythmic therapy.
No disadvantages seen with dual energy
The greater efficacy of a first shock with dual DCCV was achieved with no apparent disadvantages. There were no differences in post-procedure chest discomfort and no procedure-related adverse events in either arm, Dr. Aymond said.
The rising prevalence of obesity in the United States has created the need for a more effective first-line strategy for AF, noted Dr. Aymond, who presented the results of this study at the annual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
Cardioversion, which he characterized as the treatment of choice for AF, “fails to restore sinus rhythm in 20% to 35% of obese patients versus less than 10% of non-obese patients,” he said. The higher failure rate in patients with obesity is becoming a more common clinical issue not only due to the rising rates of obesity but a corresponding rise in AF, which is a related phenomenon.
“The risk of atrial fibrillation is increased by 50% relative to those who are not obese,” Dr. Aymond explained.
In this study, 200 patients at three participating centers were randomized to single DCCV or double DCCV after exclusions that included ventricular tachycardia and respiratory instability. The baseline characteristics were comparable. All 101 patients in the single DCCV group and 99 patients in the dual DCCV group were available for the intention-to-treat analysis.
200 vs. 400 joules delivered across the heart
In the study protocol, patients were fitted with four chest pads, two located adjacent but above the heart and two adjacent but below the heart. For single DCCV, 200 joules of energy were delivered from the upper right pad to the lower left pad across the heart. For dual DCCV, another 200 joules were delivered simultaneously from the upper left to the lower right across the heart. The total dose in the dual DCCV group was 400 joules.
The primary outcome was restoration of sinus rhythm of any duration immediately after DCCV. Safety, including clinical events, was a secondary outcome. Only the patients were blinded to the energy they received.
On univariate analysis, the odds ratio for successful cardioversion with dual DCCV was nearly eightfold higher (OR 7.8; P = .008) than single DCCV. On a simple multivariable analysis, when the researchers controlled for just age, sex, and body mass index, the odds ratio rose (OR 8.5; P = .007).
On a comprehensive multivariable analysis adding control for such characteristics as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), obstructive sleep apnea, and antiarrhythmic drugs, the advantage of dual DCCV climbed above 12-fold (OR 12.6; P = .03).
The study is addressing a relevant and persistent question, said the AHA-invited discussant Jose A. Joglar, MD, program director, Clinical Cardiac Electrophysiology Fellowship, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
Dr. Joglar pointed out that alternatives to single DCCV for patients more difficult to cardiovert have been “sought for decades.” He noted that a variety of techniques, including dual DCCV, have been evaluated in small studies and case reports.
Alternatives for obese outlined
Several have shown promise, Dr. Joglar said. As one of several examples, he cited a 20-patient study that randomized patients to adhesive patches, like those employed in the Aymond trial, or handheld paddles. Both patches and paddles were applied with manual pressure while a 200-joule shock was delivered. The proportion of patients who cardioverted on the first shock was almost two times higher in the group after the first shock with the paddles (50% vs. 27%; P = .01). Dr. Joglar said the study supports the principle that 200 joules delivered by adhesive patches is inadequate for treatment of AF in many patients with obesity.
Dr. Joglar also cited studies suggesting that single DCCV delivered with higher energy than 200 joules appears to improve cardioversion success rates, but he indicated that this study with dual DCCV in the front-line setting provides evidence for another alternative.
“This is the first such trial with dual defibrillators as an initial strategy,” he said, calling the groups well matched and the superiority of dual DCCV “impressive.” He cautioned that the study size was well powered for the endpoint but perhaps small for evaluating relative safety.
Yet, “the study adds credibility and confidence for the use of dual DCCV, especially in difficult or refractory patients,” he said. He is less certain that it establishes dual DCCV as a standard first-line therapy in all patients with obesity. This would require additional studies to compare it to other types of strategies such as those he mentioned.
As an option for improving cardioversion in first-line treatment, dual DCCV “can be added to a list of other techniques, such as manual pressure or a higher initial dose with single DCCV,” he said.
Dr. Aymond and Dr. Joglar report no potential conflicts of interest.
AT AHA 2023
Pregnancy in rheumatic disease quadruples risk of cardiovascular events
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.
Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.
Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
SAN DIEGO – Pregnant individuals with autoimmune rheumatic diseases (ARDs) are at least four times more likely to experience an acute cardiovascular event (CVE) than are pregnant individuals without these conditions, according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Pregnant individuals with primary antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) had a 15-fold increase in CVE risk.
Patients who experienced CVEs were also more likely to experience preterm birth and other adverse pregnancy outcomes (APOs).
Rashmi Dhital, MD, a rheumatology fellow at the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues examined the medical records of pregnant individuals in California who had delivered singleton live-born infants from 2005 to 2020. Using data from the Study of Outcomes in Mothers and Infants (SOMI) database, an administrative population-based birth cohort in California, they identified more than 7 million individuals, 19,340 with ARDs and 7,758 with APS.
They then analyzed how many patients experienced an acute CVE during pregnancy and up to 6 weeks after giving birth.
CVEs occurred in 2.0% of patients with ARDs, 6.9% of individuals with APS, and 0.4% of women without these conditions. CVE risk was four times higher in the ARDs group (adjusted relative risk, 4.1; 95% confidence interval, 3.7-4.5) and nearly 15 times higher in the APS group (aRR, 14.7; 95% CI, 13.5-16.0) than in the comparison group. Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) had a sixfold higher risk of CVE, which was further exacerbated by concomitant APS (18-fold higher risk) or lupus nephritis (15-fold higher risk).
Dr. Dhital also classified CVEs as either venous thromboembolism and non-VTE events. Pregnant patients with APS had a high risk for VTE-only CVE (40-fold greater) and a 3.7-fold higher risk of non-VTE events, compared with pregnant patients without these conditions. Patients with SLE along with lupus nephritis had a 20-fold increased risk of VTE-only CVE and an 11-fold higher risk of non-VTE CVE.
Although the study grouped rheumatic diseases together, “lupus is generally driving these results,” Sharon Kolasinski, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, noted in an interview. She moderated the plenary session where the research was presented. “If you take out lupus, then what is the risk? That would be an interesting question.”
Between 25% and 30% of all CVEs occurred in the postpartum period, highlighting the importance of close monitoring of cardiovascular risks and events in women with ARDs or APS both during pregnancy and postpartum, Dr. Dhital noted.
Recognizing these risks “can sometimes be challenging due to a lower suspicion of CVE in younger patients, and also symptoms overlap with normal pregnancy,” Dr. Dhital said during her plenary presentation. Working with other clinical teams could help physicians detect these risks in patients.
“It’s important for us to remember that there’s increased risk of cardiovascular events in pregnancy in our patients. It’s uncommon, but it’s not zero,” added Dr. Kolasinski, and this study highlighted when physicians should be more focused about that risk.
Dr. Dhital noted there were some limitations to the study that are inherent in using administrative databases for research that relies on ICD codes, including “the availability of information on disease activity, medications, and labs, which may restrict clinical interpretation.”
SOMI data reinforced by National Inpatient Sample study
The findings were complemented by a study using the National Inpatient Sample database to explore CVE risk in pregnant individuals with various rheumatic diseases. Lead author Karun Shrestha, MD, a resident physician at St. Barnabas Hospital in New York, and colleagues identified delivery hospitalizations from 2016 to 2019 for individuals with SLE, RA, and systemic vasculitis and looked for CVEs including preeclampsia, peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), heart failure, stroke, cardiac arrhythmias, and VTE.
Out of over 3.4 million delivery hospitalizations, researchers identified 5,900 individuals with SLE, 4,895 with RA, and 325 with vasculitis. After adjusting for confounding factors such as race, age, insurance, and other comorbidities, SLE was identified as an independent risk factor for preeclampsia (odds ratio, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.1-2.1), arrhythmia (OR, 3.17; 95% CI, 1.73-5.79), and venous thrombosis (OR, 8.4; 95% CI, 2.9-22.1). Vasculitis was tied to increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 4.7; 95% CI, 2-11.3), stroke (OR, 513.3; 95% CI, 114-2,284), heart failure (OR, 24.17; 95% CI, 4.68-124.6), and PPCM (OR, 66.7; 95% CI, 8.7-509.4). RA was tied to an increased risk for preeclampsia (OR, 1.5; 95% CI, 1.05-2.1).
Patients with SLE or vasculitis had longer, more costly hospital stays, compared with those without these conditions, and they experienced higher rates of in-hospital mortality. While previous research has demonstrated that patients with SLE have higher risk of cardiac events, there is less literature on CVE risk in pregnancies for vasculitis, Dr. Shrestha said in an interview.
“It’s something to work on,” he said.
Adverse pregnancy outcomes higher with ARDs, APS
In a second abstract also led by Dr. Dhital using SOMI data, researchers found that pregnant individuals with ARDs or APS had a higher risk of experiencing an APO – preterm birth or small-for-gestational age – than individuals without these conditions. CVEs exacerbated that risk, regardless of underlying chronic health conditions.
Over half of patients with an ARD and a CVE during pregnancy experienced an APO – most commonly preterm birth. More than one in four pregnant individuals without ARD or APS who experienced a CVE also had an APO.
After differentiating CVEs as either VTE and non-VTE events, patients with ARD and a non-VTE CVE had a fivefold greater risk of early preterm birth (< 32 weeks) and a threefold higher risk of moderate preterm birth (32 to < 34 weeks).
“These findings highlight the need for close monitoring and management of pregnant women, not only for adverse outcomes, but also for cardiovascular risks and events, in order to identify those at the highest risk for adverse outcomes,” the authors wrote. “This need is particularly significant for individuals with ARDs, as 53.4% of our population with an ARD and CVE in pregnancy experienced an APO.”
Dr. Dhital, Dr. Kolasinski, and Dr. Shrestha disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT ACR 2023
Outcomes of PF ablation for AFib similar between sexes
TOPLINE:
results of a large registry study show.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included all 1,568 patients (mean age 64.5 years and 35.3% women) in the MANIFEST-PF registry, which includes 24 European centers that began using PFA for treating AFib after regulatory approval in 2021.
- Researchers categorized patients by sex and evaluated them for clinical outcomes of PFA, including freedom from AFib and adverse events.
- All patients underwent pulmonary vein isolation (Farawave, Boston Scientific) and were followed up at 3, 6, and 12 months.
- The primary effectiveness outcome was freedom from atrial arrhythmia outside the 90-day blanking period lasting 30 seconds or longer.
- The primary safety outcome included the composite of acute (less than 7 days post-procedure) and chronic (more than 7 days post-procedure) major adverse events, including atrioesophageal fistula, symptomatic pulmonary vein stenosis, cardiac tamponade/perforation requiring intervention or surgery, stroke or systemic thromboembolism, persistent phrenic nerve injury, vascular access complications requiring surgery, coronary artery spasm, and death.
TAKEAWAY:
- There was no significant difference in 12-month recurrence of atrial arrhythmia between male and female patients (79.0% vs 76.3%; P = .28), with greater overall effectiveness in the paroxysmal AFib cohort (men, 82.5% vs women, 80.2%; P = .30) than in the persistent AF/long-standing persistent AFib cohort (men, 73.3% vs women, 67.3%; P = .40).
- Repeated ablation rates were similar between sexes (men, 8.3% vs women, 10.0%; P = .32).
- Among patients who underwent repeat ablation, pulmonary vein isolation durability was higher in female than in male patients (per vein, 82.6% vs 68.1%; P = .15 and per patient, 63.0% vs 37.8%; P = .005).
- Major adverse events occurred in 2.5% of women and 1.5% of men (P = .19), with such events mostly consisting of cardiac tamponade (women, 1.4% vs men, 1.0%; P = .46) and stroke (0.4% vs 0.4%, P > .99), and with no atrioesophageal fistulas or symptomatic pulmonary valve stenosis in either group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results are important, as women are underrepresented in prior ablation studies and the results have been mixed with regards to both safety and effectiveness using conventional ablation strategies such as radiofrequency or cryoablation,” lead author Mohit Turagam, MD, associate professor of medicine (cardiology), Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, said in a press release.
In an accompanying commentary, Peter M. Kistler, MBBS, PhD, Department of Cardiology, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, and a colleague said that the study authors should be congratulated “for presenting much-needed data on sex-specific outcomes in catheter ablation,” which “reassuringly” suggest that success and safety for AFib ablation are comparable between the sexes, although the study does have “important limitations.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Turagam and colleagues. It was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Researchers can’t rule out the possibility that treatment selection and unmeasured confounders between sexes affected the validity of the study findings. The median number of follow-up 24-hour Holter monitors used for AFib monitoring was only two, which may have resulted in inaccurate estimates of AFib recurrence rates and treatment effectiveness.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Boston Scientific Corporation, the PFA device manufacturer. Turagam has no relevant conflicts of interest; see paper for disclosures of other study authors. The commentary authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
results of a large registry study show.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included all 1,568 patients (mean age 64.5 years and 35.3% women) in the MANIFEST-PF registry, which includes 24 European centers that began using PFA for treating AFib after regulatory approval in 2021.
- Researchers categorized patients by sex and evaluated them for clinical outcomes of PFA, including freedom from AFib and adverse events.
- All patients underwent pulmonary vein isolation (Farawave, Boston Scientific) and were followed up at 3, 6, and 12 months.
- The primary effectiveness outcome was freedom from atrial arrhythmia outside the 90-day blanking period lasting 30 seconds or longer.
- The primary safety outcome included the composite of acute (less than 7 days post-procedure) and chronic (more than 7 days post-procedure) major adverse events, including atrioesophageal fistula, symptomatic pulmonary vein stenosis, cardiac tamponade/perforation requiring intervention or surgery, stroke or systemic thromboembolism, persistent phrenic nerve injury, vascular access complications requiring surgery, coronary artery spasm, and death.
TAKEAWAY:
- There was no significant difference in 12-month recurrence of atrial arrhythmia between male and female patients (79.0% vs 76.3%; P = .28), with greater overall effectiveness in the paroxysmal AFib cohort (men, 82.5% vs women, 80.2%; P = .30) than in the persistent AF/long-standing persistent AFib cohort (men, 73.3% vs women, 67.3%; P = .40).
- Repeated ablation rates were similar between sexes (men, 8.3% vs women, 10.0%; P = .32).
- Among patients who underwent repeat ablation, pulmonary vein isolation durability was higher in female than in male patients (per vein, 82.6% vs 68.1%; P = .15 and per patient, 63.0% vs 37.8%; P = .005).
- Major adverse events occurred in 2.5% of women and 1.5% of men (P = .19), with such events mostly consisting of cardiac tamponade (women, 1.4% vs men, 1.0%; P = .46) and stroke (0.4% vs 0.4%, P > .99), and with no atrioesophageal fistulas or symptomatic pulmonary valve stenosis in either group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results are important, as women are underrepresented in prior ablation studies and the results have been mixed with regards to both safety and effectiveness using conventional ablation strategies such as radiofrequency or cryoablation,” lead author Mohit Turagam, MD, associate professor of medicine (cardiology), Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, said in a press release.
In an accompanying commentary, Peter M. Kistler, MBBS, PhD, Department of Cardiology, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, and a colleague said that the study authors should be congratulated “for presenting much-needed data on sex-specific outcomes in catheter ablation,” which “reassuringly” suggest that success and safety for AFib ablation are comparable between the sexes, although the study does have “important limitations.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Turagam and colleagues. It was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Researchers can’t rule out the possibility that treatment selection and unmeasured confounders between sexes affected the validity of the study findings. The median number of follow-up 24-hour Holter monitors used for AFib monitoring was only two, which may have resulted in inaccurate estimates of AFib recurrence rates and treatment effectiveness.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Boston Scientific Corporation, the PFA device manufacturer. Turagam has no relevant conflicts of interest; see paper for disclosures of other study authors. The commentary authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
results of a large registry study show.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included all 1,568 patients (mean age 64.5 years and 35.3% women) in the MANIFEST-PF registry, which includes 24 European centers that began using PFA for treating AFib after regulatory approval in 2021.
- Researchers categorized patients by sex and evaluated them for clinical outcomes of PFA, including freedom from AFib and adverse events.
- All patients underwent pulmonary vein isolation (Farawave, Boston Scientific) and were followed up at 3, 6, and 12 months.
- The primary effectiveness outcome was freedom from atrial arrhythmia outside the 90-day blanking period lasting 30 seconds or longer.
- The primary safety outcome included the composite of acute (less than 7 days post-procedure) and chronic (more than 7 days post-procedure) major adverse events, including atrioesophageal fistula, symptomatic pulmonary vein stenosis, cardiac tamponade/perforation requiring intervention or surgery, stroke or systemic thromboembolism, persistent phrenic nerve injury, vascular access complications requiring surgery, coronary artery spasm, and death.
TAKEAWAY:
- There was no significant difference in 12-month recurrence of atrial arrhythmia between male and female patients (79.0% vs 76.3%; P = .28), with greater overall effectiveness in the paroxysmal AFib cohort (men, 82.5% vs women, 80.2%; P = .30) than in the persistent AF/long-standing persistent AFib cohort (men, 73.3% vs women, 67.3%; P = .40).
- Repeated ablation rates were similar between sexes (men, 8.3% vs women, 10.0%; P = .32).
- Among patients who underwent repeat ablation, pulmonary vein isolation durability was higher in female than in male patients (per vein, 82.6% vs 68.1%; P = .15 and per patient, 63.0% vs 37.8%; P = .005).
- Major adverse events occurred in 2.5% of women and 1.5% of men (P = .19), with such events mostly consisting of cardiac tamponade (women, 1.4% vs men, 1.0%; P = .46) and stroke (0.4% vs 0.4%, P > .99), and with no atrioesophageal fistulas or symptomatic pulmonary valve stenosis in either group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These results are important, as women are underrepresented in prior ablation studies and the results have been mixed with regards to both safety and effectiveness using conventional ablation strategies such as radiofrequency or cryoablation,” lead author Mohit Turagam, MD, associate professor of medicine (cardiology), Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, said in a press release.
In an accompanying commentary, Peter M. Kistler, MBBS, PhD, Department of Cardiology, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, and a colleague said that the study authors should be congratulated “for presenting much-needed data on sex-specific outcomes in catheter ablation,” which “reassuringly” suggest that success and safety for AFib ablation are comparable between the sexes, although the study does have “important limitations.”
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Turagam and colleagues. It was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Researchers can’t rule out the possibility that treatment selection and unmeasured confounders between sexes affected the validity of the study findings. The median number of follow-up 24-hour Holter monitors used for AFib monitoring was only two, which may have resulted in inaccurate estimates of AFib recurrence rates and treatment effectiveness.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Boston Scientific Corporation, the PFA device manufacturer. Turagam has no relevant conflicts of interest; see paper for disclosures of other study authors. The commentary authors have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AF tied to 45% increase in mild cognitive impairment
TOPLINE:
results of a new study suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- From over 4.3 million people in the UK primary electronic health record (EHR) database, researchers identified 233,833 (5.4%) with AF (mean age, 74.2 years) and randomly selected one age- and sex-matched control person without AF for each AF case patient.
- The primary outcome was incidence of mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
- The authors adjusted for age, sex, year at study entry, socioeconomic status, smoking, and a number of comorbid conditions.
- During a median of 5.3 years of follow-up, there were 4,269 incident MCI cases among both AF and non-AF patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Individuals with AF had a higher risk of MCI than that of those without AF (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.45; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.35-1.56).
- Besides AF, older age (risk ratio [RR], 1.08) and history of depression (RR, 1.44) were associated with greater risk of MCI, as were female sex, greater socioeconomic deprivation, stroke, and multimorbidity, including, for example, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and peripheral artery disease (all P < .001).
- Individuals with AF who received oral anticoagulants or amiodarone were not at increased risk of MCI, as was the case for those treated with digoxin.
- Individuals with AF and MCI were at greater risk of dementia (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.09-1.42). Sex, smoking, chronic kidney disease, and multi-comorbidity were among factors linked to elevated dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings emphasize the association of multi-comorbidity and cardiovascular risk factors with development of MCI and progression to dementia in AF patients, the authors wrote. They noted that the data suggest combining anticoagulation and symptom and comorbidity management may prevent cognitive deterioration.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Sheng-Chia Chung, PhD, Institute of Health informatics Research, University College London, and colleagues. It was published online Oct. 25, 2023, as a research letter in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC): Advances.
LIMITATIONS:
The EHR dataset may have lacked granularity and detail, and some risk factors or comorbidities may not have been measured. While those with AF receiving digoxin or amiodarone treatment had no higher risk of MCI than their non-AF peers, the study’s observational design and very wide confidence intervals for these subgroups prevent making solid inferences about causality or a potential protective role of these drugs.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Chung is supported by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Author Rui Providencia, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Health informatics Research, University College London, is supported by the University College London British Heart Foundation and NIHR. All other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
results of a new study suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- From over 4.3 million people in the UK primary electronic health record (EHR) database, researchers identified 233,833 (5.4%) with AF (mean age, 74.2 years) and randomly selected one age- and sex-matched control person without AF for each AF case patient.
- The primary outcome was incidence of mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
- The authors adjusted for age, sex, year at study entry, socioeconomic status, smoking, and a number of comorbid conditions.
- During a median of 5.3 years of follow-up, there were 4,269 incident MCI cases among both AF and non-AF patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Individuals with AF had a higher risk of MCI than that of those without AF (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.45; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.35-1.56).
- Besides AF, older age (risk ratio [RR], 1.08) and history of depression (RR, 1.44) were associated with greater risk of MCI, as were female sex, greater socioeconomic deprivation, stroke, and multimorbidity, including, for example, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and peripheral artery disease (all P < .001).
- Individuals with AF who received oral anticoagulants or amiodarone were not at increased risk of MCI, as was the case for those treated with digoxin.
- Individuals with AF and MCI were at greater risk of dementia (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.09-1.42). Sex, smoking, chronic kidney disease, and multi-comorbidity were among factors linked to elevated dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings emphasize the association of multi-comorbidity and cardiovascular risk factors with development of MCI and progression to dementia in AF patients, the authors wrote. They noted that the data suggest combining anticoagulation and symptom and comorbidity management may prevent cognitive deterioration.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Sheng-Chia Chung, PhD, Institute of Health informatics Research, University College London, and colleagues. It was published online Oct. 25, 2023, as a research letter in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC): Advances.
LIMITATIONS:
The EHR dataset may have lacked granularity and detail, and some risk factors or comorbidities may not have been measured. While those with AF receiving digoxin or amiodarone treatment had no higher risk of MCI than their non-AF peers, the study’s observational design and very wide confidence intervals for these subgroups prevent making solid inferences about causality or a potential protective role of these drugs.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Chung is supported by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Author Rui Providencia, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Health informatics Research, University College London, is supported by the University College London British Heart Foundation and NIHR. All other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
results of a new study suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- From over 4.3 million people in the UK primary electronic health record (EHR) database, researchers identified 233,833 (5.4%) with AF (mean age, 74.2 years) and randomly selected one age- and sex-matched control person without AF for each AF case patient.
- The primary outcome was incidence of mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
- The authors adjusted for age, sex, year at study entry, socioeconomic status, smoking, and a number of comorbid conditions.
- During a median of 5.3 years of follow-up, there were 4,269 incident MCI cases among both AF and non-AF patients.
TAKEAWAY:
- Individuals with AF had a higher risk of MCI than that of those without AF (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.45; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.35-1.56).
- Besides AF, older age (risk ratio [RR], 1.08) and history of depression (RR, 1.44) were associated with greater risk of MCI, as were female sex, greater socioeconomic deprivation, stroke, and multimorbidity, including, for example, diabetes, hypercholesterolemia, and peripheral artery disease (all P < .001).
- Individuals with AF who received oral anticoagulants or amiodarone were not at increased risk of MCI, as was the case for those treated with digoxin.
- Individuals with AF and MCI were at greater risk of dementia (aHR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.09-1.42). Sex, smoking, chronic kidney disease, and multi-comorbidity were among factors linked to elevated dementia risk.
IN PRACTICE:
The findings emphasize the association of multi-comorbidity and cardiovascular risk factors with development of MCI and progression to dementia in AF patients, the authors wrote. They noted that the data suggest combining anticoagulation and symptom and comorbidity management may prevent cognitive deterioration.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Sheng-Chia Chung, PhD, Institute of Health informatics Research, University College London, and colleagues. It was published online Oct. 25, 2023, as a research letter in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC): Advances.
LIMITATIONS:
The EHR dataset may have lacked granularity and detail, and some risk factors or comorbidities may not have been measured. While those with AF receiving digoxin or amiodarone treatment had no higher risk of MCI than their non-AF peers, the study’s observational design and very wide confidence intervals for these subgroups prevent making solid inferences about causality or a potential protective role of these drugs.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Chung is supported by the National Institute of Health and Care Research (NIHR) Author Rui Providencia, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Health informatics Research, University College London, is supported by the University College London British Heart Foundation and NIHR. All other authors report no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.