User login
A Paradigm Shift in Evaluating and Investigating the Etiology of Bloating
Introduction
Abdominal bloating is a common condition affecting up to 3.5% of people globally (4.6% in women and 2.4% in men),1 with 13.9% of the US population reporting bloating in the past 7 days.2 The prevalence of bloating and distention exceeds 50% when linked to disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBIs) such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia (FD).3,4 According to the Rome IV criteria, functional bloating and distention (FABD) patients are characterized by recurrent symptoms of abdominal fullness or pressure (bloating), or a visible increase in abdominal girth (distention) occurring at least 1 day per week for 3 consecutive months with an onset of 6 months and without predominant pain or altered bowel habits.5
Prolonged abdominal bloating and distention (ABD) can significantly impact quality of life and work productivity and can lead to increased medical consultations.2 Multiple pathophysiological mechanisms are involved in ABD that complicate the clinical management.4 There is an unmet need to understand the underlying mechanisms that lead to the development of ABD such as, food intolerance, abnormal viscerosomatic reflex, visceral hypersensitivity, and gut microbial dysbiosis. Recent advancements and acceptance of a multidisciplinary management of ABD have shifted the paradigm from merely treating symptoms to subtyping the condition and identifying overlaps with other DGBIs in order to individualize treatment that addresses the underlying pathophysiological mechanism. The recent American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical update provided insights into the best practice advice for evaluating and managing ABD based on a review of current literature and on expert opinion of coauthors.6 This article aims to deliberate a practical approach to diagnostic strategies and treatment options based on etiology to refine clinical care of patients with ABD.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
ABD can result from various pathophysiological mechanisms. This section highlights the major causes (illustrated in Figure 1).
Food intolerances
Understanding food intolerances is crucial for diagnosing and managing patients with ABD. Disaccharidase deficiency is common (e.g., lactase deficiency is found in 35%-40% of adults).7 It can be undiagnosed in patients presenting with IBS symptoms, given the overlap in presentation with a prevalence of 9% of pan-disaccharidase deficiency. Sucrase-deficient patients must often adjust sugar and carbohydrate/starch intake to relieve symptoms.7 Deficiencies in lactase and sucrase activity, along with the consumption of some artificial sweeteners (e.g., sugar alcohols and sorbitol) and fructans can lead to bloating and distention. These substances increase osmotic load, fluid retention, microbial fermentation, and visceral hypersensitivity, leading to gas production and abdominal distention. One prospective study of symptomatic patients with various DGBIs (n = 1372) reported a prevalence of lactose intolerance and malabsorption at 51% and 32%, respectively.8 Furthermore, fructose intolerance and malabsorption prevalence were 60% and 45%, respectively.8 Notably, lactase deficiency does not always cause ABD, as not all individuals with lactase deficiency experience these symptoms after consuming lactose. Patients with celiac disease (CD), non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), and gluten intolerance can also experience bloating and distention, with or without changes in bowel habits.9 In some patients with self-reported NCGS, symptoms may be due to fructans in gluten-rich foods rather than gluten itself, thus recommending the elimination of fructans may help improve symptoms.9
Visceral hypersensitivity
Visceral hypersensitivity is explained by an increased perception of gut mechano-chemical stimulation, which typically manifests in an aggravated feeling of pain, nausea, distension, and ABD.10 In the gut, food particles and gut bacteria and their derived molecules interact with neuroimmune and enteroendocrine cells causing visceral sensitivity by the proximity of gut’s neurons to immune cells activated by them and leading to inflammatory reactions (Figure 1). 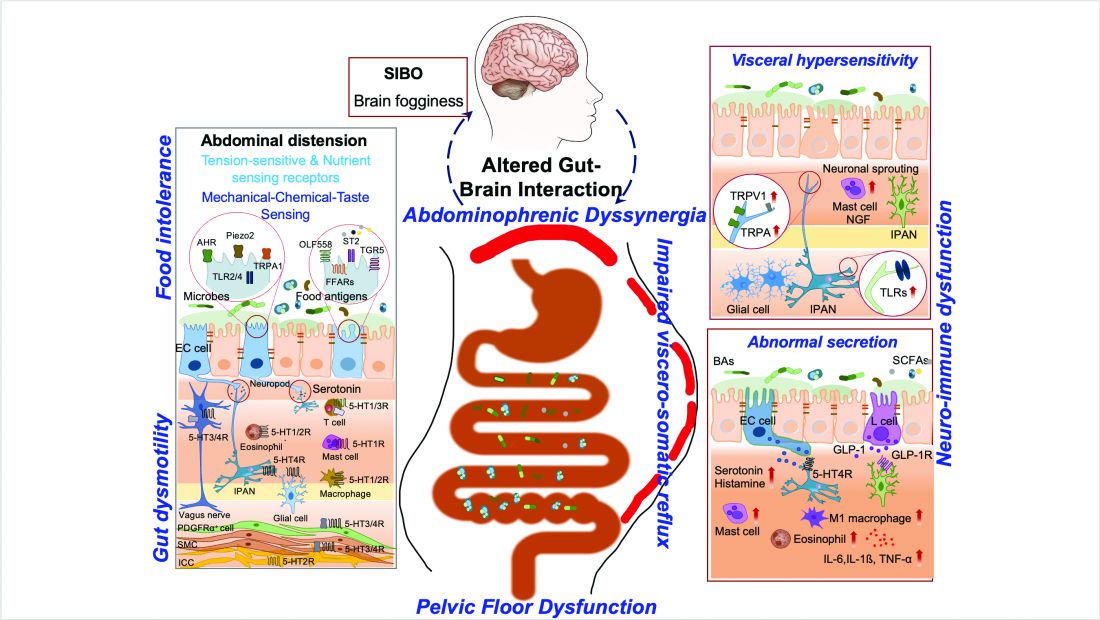
Pelvic floor dysfunction
Patients with anorectal motor dysfunction often experience difficulty in effectively evacuating both gas and stool, leading to ABD.12 Impaired ability to expel gas and stool results in prolonged balloon expulsion times, which correlates with symptoms of distention in patients with constipation.
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia is characterized as a paradoxical viscerosomatic reflex response to minimal gaseous distention in individuals with FABD.13 In this condition, the diaphragm contracts (descends), and the anterior abdominal wall muscles relax in response to the presence of gas. This response is opposite to the normal physiological response to increased intraluminal gas, where the diaphragm relaxes and the anterior abdominal muscles contract to increase the craniocaudal capacity of the abdominal cavity without causing abdominal protrusion.13 Patients with FABD exhibit significant abdominal wall protrusion and diaphragmatic descent even with relatively small increases in intraluminal gas.11 Understanding the role of abdominophrenic dyssynergia in abdominal bloating and distention is essential for effective diagnosis and management of the patients.
Gut dysmotility
Gut dysmotility is a crucial factor that can contribute to FABD. Gut dysmotility affects the movement of contents through the GI tract, accumulating gas and stool, directly contributing to bloating and distention. A prospective study involving over 2000 patients with functional constipation and constipation predominant-IBS (IBS-C) found that more than 90% of these patients reported symptoms of bloating.14 Furthermore, in IBS-C patients, those with prolonged colonic transit exhibited greater abdominal distention compared to those with normal gut transit times. In patients with gastroparesis, delayed gastric emptying resulting in prolonged retention of stomach contents is the main factor in the generation of bloating symptoms.4
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
SIBO is overrepresented in various conditions, including IBS, FD, diabetes, gastrointestinal (GI) surgery patients and obesity, and can play an important role in generating ABD. Excess bacteria in the small intestine ferment carbohydrates, producing gas that stretches and distends the small intestine, leading to these symptoms. Additionally, altered sensation and abnormal viscerosomatic reflexes may contribute to SIBO-related bloating.4 One recent study noted decreased duodenal phylogenetic diversity in individuals who developed postprandial bloating.15 Increased methane levels caused by intestinal methanogen overgrowth, primarily the archaea Methanobrevibacter smithii, is possibly responsible for ABD in patients with IBS-C.16 Testing for SIBO in patients with ABD is generally only recommended if there are clear risk factors or severe symptoms warranting a test-and-treat approach.
Practical Diagnosis
Diagnosing ABD typically does not require extensive laboratory testing, imaging, or endoscopy unless there are alarm features or significant changes in symptoms. Here is the AGA clinical update on best practice advice6 for when to conduct further testing:
Diagnostic tests should be considered if patients exhibit:
- Recent onset or worsening of dyspepsia or abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GI bleeding
- Unintentional weight loss exceeding 10% of body weight
- Chronic diarrhea
- Family history of GI malignancy, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease
Physical examination
If visible abdominal distention is present, a thorough abdominal examination can help identify potential issues:
- Tympany to percussion suggests bowel dilation.
- Abnormal bowel sounds may indicate obstruction or ileus.
- A succussion splash could indicate the presence of ascites and obstruction.
- Any abnormalities discovered during the physical exam should prompt further investigation with imaging, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound, to evaluate for ascites, masses, or increased bowel gas due to ileus, obstruction, or pseudo-obstruction.
Radiologic imaging, laboratory testing and endoscopy
- An abdominal x-ray may reveal an increased stool burden, suggesting the need for further evaluation of slow transit constipation or a pelvic floor disorder, particularly in patients with functional constipation, IBS-mixed, or IBS-C.
- Hyperglycemia, weight gain, and bloating can be a presenting sign of ovarian cancer therefore all women should continue pelvic exams as dictated by the gynecologic societies. The need for an annual pelvic exam should be discussed with health care professionals especially in those with family history of ovarian cancer.
- An upper endoscopy may be warranted for patients over 40 years old with dyspeptic symptoms and abdominal bloating or distention, especially in regions with a high prevalence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Chronic pancreatitis, indicated by bloating and pain, may necessitate fecal elastase testing to assess pancreatic function.
The expert review in the AGA clinical update provides step-by-step advice regarding the best practices6 for diagnosis and identifying who to test for ABD.
Treatment Options
The following sections highlight recent best practice advice on therapeutic approaches for treating ABD.
Dietary interventions
Specific foods may trigger bloating and abdominal distention, especially in patients with overlapping DGBIs. However, only a few studies have evaluated dietary restriction specifically for patients with primary ABD. Restricting non-absorbable sugars led to symptomatic improvement in 81% of patients with FABD who had documented sugar malabsorption.17 Two studies have shown that IBS patients treated with a low-fermentable, oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides (FODMAP) diet noted improvement in ABD and that restricting fructans initially may be the most optimal.18 A recent study showed that the Mediterranean diet improved IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain and bloating.19 It should be noted restrictive diets are efficacious but come with short- and long-term challenges. If empiric treatment and/or therapeutic testing do not resolve symptoms, a referral to a dietitian can be useful. Dietitians can provide tailored dietary advice, ensuring patients avoid trigger foods while maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet.
Prokinetics and laxatives
Prokinetic agents are used to treat symptoms of FD, gastroparesis, chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC), and IBS. A meta-analysis of 13 trials found all constipation medications superior to placebo for treating abdominal bloating in patients with IBS-C.20
Probiotics
Treatment with probiotics is recommended for bloating or distention. One double-blind placebo-controlled trial with two separate probiotics, Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, showed improvements in global GI symptoms of patients with DGBI at 8 weeks versus placebo, with improvements in bloating symptoms.21
Antibiotics
The most commonly studied antibiotic for treating bloating is rifaximin.22 Global symptomatic improvement in IBS patients treated with antibiotics has correlated with the normalization of hydrogen levels in lactulose hydrogen breath tests.22 Patients with non-constipation IBS randomized to rifaximin 550 mg three times daily for 14 days had a greater proportion of relief of IBS-related bloating compared to placebo for at least 2 of the first 4 weeks after treatment.22 Future research warrants use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics study for FABD as the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may deplete commensals forever, resulting in metabolic disorders.
Biofeedback therapy
Anorectal biofeedback therapy may help with ABD, particularly in patients with IBS-C and chronic constipation. One study noted that post-biofeedback therapy, myoelectric activity of the intercostals and diaphragm decreased, and internal oblique myoelectric activity increased.23 This study also showed ascent of the diaphragm and decreased girth, improving distention.
Central neuromodulators
As bloating results from multiple disturbed mechanisms, including altered gut-brain interaction, these symptoms can be amplified by psychological states such as anxiety, depression, or somatization. Central neuromodulators reduce the perception of visceral signals, re-regulate brain-gut control mechanisms, and improve psychological comorbidities.6 A large study of FD patients demonstrated that both amitriptyline (50 mg daily) and escitalopram (10 mg daily) significantly improved postprandial bloating compared to placebo.24 Antidepressants that activate noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways, including tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and venlafaxine), show the greatest benefit in reducing visceral sensations.6
Brain-gut behavioral therapies
A recent multidisciplinary consensus report supports a myriad of potential brain-gut behavioral therapies (BGBTs) for treating DGBI.25 These therapies, including hypnotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other modalities, may be combined with central neuromodulators and other GI treatments in a safe, noninvasive, and complementary fashion. BGBTs do not need to be symptom-specific, as they improve overall quality of life, anxiety, stress, and the burden associated with DGBIs. To date, none of the BGBTs have focused exclusively on FABD; however, prescription-based psychological therapies are now FDA-approved for use on smart apps, improving global symptoms that include bloating in IBS and FD.
Recent AGA clinical update best practices should be considered for the clinical care of patients with ABD.6
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
ABD are highly prevalent and significantly impact patients with various GI and metabolic disorders. Although our understanding of these symptoms is still evolving, evidence increasingly points to the dysregulation of the gut-brain axis and supports the application of the biopsychosocial model in treatment. This model addresses diet, motility, visceral sensitivity, pelvic floor disorders and psychosocial factors, providing a comprehensive approach to patient care.
Physician-scientists around the globe face numerous challenges when evaluating patients with these symptoms. However, the recent AGA clinical update on the best practice guidelines offers step-by-step diagnostic tests and treatment options to assist physicians in making informed decisions. . More comprehensive, large-scale, and longitudinal studies using metabolomics, capsule technologies for discovery of dysbiosis, mass spectrometry, and imaging data are needed to identify the exact contributors to disease pathogenesis, particularly those that can be targeted with pharmacologic agents. Collaborative work between gastroenterologists, dietitians, gut-brain behavioral therapists, endocrinologists, is crucial for clinical care of patients with ABD.
Careful attention to the patient’s primary symptoms and physical examination, combined with advancements in targeted diagnostics like the analysis of microbial markers, metabolites, and molecular signals, can significantly enhance patient clinical outcomes. Additionally, education and effective communication using a patient-centered care model are essential for guiding practical evaluation and individualized treatment.
Dr. Singh is assistant professor (research) at the University of Nevada, Reno, School of Medicine. Dr. Moshiree is director of motility at Atrium Health, and clinical professor of medicine, Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, North Carolina.
References
1. Ballou S et al. Prevalence and associated factors of bloating: Results from the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2023 June. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.049.
2. Oh JE et al. Abdominal bloating in the United States: Results of a survey of 88,795 Americans examining prevalence and healthcare seeking. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.10.031.
3. Drossman DA et al. Neuromodulators for functional gastrointestinal disorders (disorders of gut-brain interaction): A Rome Foundation Working Team Report. Gastroenterology. 2018 Mar. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.279.
4. Lacy BE et al. Management of chronic abdominal distension and bloating. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.056.
5. Mearin F et al. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031.
6. Moshiree B et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on evaluation and management of belching, abdominal bloating, and distention: expert review. Gastroenterology. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.04.039.
7. Viswanathan L and Rao SS. Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in adults: evaluation and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2023 May. doi: 10.1007/s11894-023-00870-z.
8. Wilder-Smith CH et al. Fructose and lactose intolerance and malabsorption testing: the relationship with symptoms in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1111/apt.12306.
9. Skodje GI et al. Fructan, rather than gluten, induces symptoms in patients with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.040.
10. Singh R et al. Current treatment options and therapeutic insights for gastrointestinal dysmotility and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.808195.
11. Accarino A et al. Abdominal distention results from caudo-ventral redistribution of contents. Gastroenterology 2009 May. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.01.067.
12. Shim L et al. Prolonged balloon expulsion is predictive of abdominal distension in bloating. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.54.
13. Villoria A et al. Abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in patients with abdominal bloating and distension. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 May. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.408.
14. Neri L and Iovino P. Laxative Inadequate Relief Survey Group. Bloating is associated with worse quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and treatment responsiveness among patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and functional constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12758.
15. Saffouri GB et al. Small intestinal microbial dysbiosis underlies symptoms associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat Commun. 2019 May. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09964-7.
16. Villanueva-Millan MJ et al. Methanogens and hydrogen sulfide producing bacteria guide distinct gut microbe profiles and irritable bowel syndrome subtypes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001997.
17. Fernández-Bañares F et al. Sugar malabsorption in functional abdominal bloating: a pilot study on the long-term effect of dietary treatment. Clin Nutr. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.11.010.
18. Böhn L et al. Diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome as well as traditional dietary advice: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.054.
19. Staudacher HM et al. Clinical trial: A Mediterranean diet is feasible and improves gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Feb. doi: 10.1111/apt.17791.
20. Nelson AD et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: efficacy of licensed drugs for abdominal bloating in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1111/apt.16437.
21. Ringel-Kulka T et al. Probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 versus placebo for the symptoms of bloating in patients with functional bowel disorders: a double-blind study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31820ca4d6.
22. Pimentel M et al. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1004409.
23. Iovino P et al. Pelvic floor biofeedback is an effective treatment for severe bloating in disorders of gut-brain interaction with outlet dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2022 May. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14264.
24. Talley NJ et al. Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: A multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.020.
25. Keefer L et al. A Rome Working Team Report on brain-gut behavior therapies for disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.015.
Introduction
Abdominal bloating is a common condition affecting up to 3.5% of people globally (4.6% in women and 2.4% in men),1 with 13.9% of the US population reporting bloating in the past 7 days.2 The prevalence of bloating and distention exceeds 50% when linked to disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBIs) such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia (FD).3,4 According to the Rome IV criteria, functional bloating and distention (FABD) patients are characterized by recurrent symptoms of abdominal fullness or pressure (bloating), or a visible increase in abdominal girth (distention) occurring at least 1 day per week for 3 consecutive months with an onset of 6 months and without predominant pain or altered bowel habits.5
Prolonged abdominal bloating and distention (ABD) can significantly impact quality of life and work productivity and can lead to increased medical consultations.2 Multiple pathophysiological mechanisms are involved in ABD that complicate the clinical management.4 There is an unmet need to understand the underlying mechanisms that lead to the development of ABD such as, food intolerance, abnormal viscerosomatic reflex, visceral hypersensitivity, and gut microbial dysbiosis. Recent advancements and acceptance of a multidisciplinary management of ABD have shifted the paradigm from merely treating symptoms to subtyping the condition and identifying overlaps with other DGBIs in order to individualize treatment that addresses the underlying pathophysiological mechanism. The recent American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical update provided insights into the best practice advice for evaluating and managing ABD based on a review of current literature and on expert opinion of coauthors.6 This article aims to deliberate a practical approach to diagnostic strategies and treatment options based on etiology to refine clinical care of patients with ABD.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
ABD can result from various pathophysiological mechanisms. This section highlights the major causes (illustrated in Figure 1).
Food intolerances
Understanding food intolerances is crucial for diagnosing and managing patients with ABD. Disaccharidase deficiency is common (e.g., lactase deficiency is found in 35%-40% of adults).7 It can be undiagnosed in patients presenting with IBS symptoms, given the overlap in presentation with a prevalence of 9% of pan-disaccharidase deficiency. Sucrase-deficient patients must often adjust sugar and carbohydrate/starch intake to relieve symptoms.7 Deficiencies in lactase and sucrase activity, along with the consumption of some artificial sweeteners (e.g., sugar alcohols and sorbitol) and fructans can lead to bloating and distention. These substances increase osmotic load, fluid retention, microbial fermentation, and visceral hypersensitivity, leading to gas production and abdominal distention. One prospective study of symptomatic patients with various DGBIs (n = 1372) reported a prevalence of lactose intolerance and malabsorption at 51% and 32%, respectively.8 Furthermore, fructose intolerance and malabsorption prevalence were 60% and 45%, respectively.8 Notably, lactase deficiency does not always cause ABD, as not all individuals with lactase deficiency experience these symptoms after consuming lactose. Patients with celiac disease (CD), non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), and gluten intolerance can also experience bloating and distention, with or without changes in bowel habits.9 In some patients with self-reported NCGS, symptoms may be due to fructans in gluten-rich foods rather than gluten itself, thus recommending the elimination of fructans may help improve symptoms.9
Visceral hypersensitivity
Visceral hypersensitivity is explained by an increased perception of gut mechano-chemical stimulation, which typically manifests in an aggravated feeling of pain, nausea, distension, and ABD.10 In the gut, food particles and gut bacteria and their derived molecules interact with neuroimmune and enteroendocrine cells causing visceral sensitivity by the proximity of gut’s neurons to immune cells activated by them and leading to inflammatory reactions (Figure 1). 
Pelvic floor dysfunction
Patients with anorectal motor dysfunction often experience difficulty in effectively evacuating both gas and stool, leading to ABD.12 Impaired ability to expel gas and stool results in prolonged balloon expulsion times, which correlates with symptoms of distention in patients with constipation.
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia is characterized as a paradoxical viscerosomatic reflex response to minimal gaseous distention in individuals with FABD.13 In this condition, the diaphragm contracts (descends), and the anterior abdominal wall muscles relax in response to the presence of gas. This response is opposite to the normal physiological response to increased intraluminal gas, where the diaphragm relaxes and the anterior abdominal muscles contract to increase the craniocaudal capacity of the abdominal cavity without causing abdominal protrusion.13 Patients with FABD exhibit significant abdominal wall protrusion and diaphragmatic descent even with relatively small increases in intraluminal gas.11 Understanding the role of abdominophrenic dyssynergia in abdominal bloating and distention is essential for effective diagnosis and management of the patients.
Gut dysmotility
Gut dysmotility is a crucial factor that can contribute to FABD. Gut dysmotility affects the movement of contents through the GI tract, accumulating gas and stool, directly contributing to bloating and distention. A prospective study involving over 2000 patients with functional constipation and constipation predominant-IBS (IBS-C) found that more than 90% of these patients reported symptoms of bloating.14 Furthermore, in IBS-C patients, those with prolonged colonic transit exhibited greater abdominal distention compared to those with normal gut transit times. In patients with gastroparesis, delayed gastric emptying resulting in prolonged retention of stomach contents is the main factor in the generation of bloating symptoms.4
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
SIBO is overrepresented in various conditions, including IBS, FD, diabetes, gastrointestinal (GI) surgery patients and obesity, and can play an important role in generating ABD. Excess bacteria in the small intestine ferment carbohydrates, producing gas that stretches and distends the small intestine, leading to these symptoms. Additionally, altered sensation and abnormal viscerosomatic reflexes may contribute to SIBO-related bloating.4 One recent study noted decreased duodenal phylogenetic diversity in individuals who developed postprandial bloating.15 Increased methane levels caused by intestinal methanogen overgrowth, primarily the archaea Methanobrevibacter smithii, is possibly responsible for ABD in patients with IBS-C.16 Testing for SIBO in patients with ABD is generally only recommended if there are clear risk factors or severe symptoms warranting a test-and-treat approach.
Practical Diagnosis
Diagnosing ABD typically does not require extensive laboratory testing, imaging, or endoscopy unless there are alarm features or significant changes in symptoms. Here is the AGA clinical update on best practice advice6 for when to conduct further testing:
Diagnostic tests should be considered if patients exhibit:
- Recent onset or worsening of dyspepsia or abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GI bleeding
- Unintentional weight loss exceeding 10% of body weight
- Chronic diarrhea
- Family history of GI malignancy, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease
Physical examination
If visible abdominal distention is present, a thorough abdominal examination can help identify potential issues:
- Tympany to percussion suggests bowel dilation.
- Abnormal bowel sounds may indicate obstruction or ileus.
- A succussion splash could indicate the presence of ascites and obstruction.
- Any abnormalities discovered during the physical exam should prompt further investigation with imaging, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound, to evaluate for ascites, masses, or increased bowel gas due to ileus, obstruction, or pseudo-obstruction.
Radiologic imaging, laboratory testing and endoscopy
- An abdominal x-ray may reveal an increased stool burden, suggesting the need for further evaluation of slow transit constipation or a pelvic floor disorder, particularly in patients with functional constipation, IBS-mixed, or IBS-C.
- Hyperglycemia, weight gain, and bloating can be a presenting sign of ovarian cancer therefore all women should continue pelvic exams as dictated by the gynecologic societies. The need for an annual pelvic exam should be discussed with health care professionals especially in those with family history of ovarian cancer.
- An upper endoscopy may be warranted for patients over 40 years old with dyspeptic symptoms and abdominal bloating or distention, especially in regions with a high prevalence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Chronic pancreatitis, indicated by bloating and pain, may necessitate fecal elastase testing to assess pancreatic function.
The expert review in the AGA clinical update provides step-by-step advice regarding the best practices6 for diagnosis and identifying who to test for ABD.
Treatment Options
The following sections highlight recent best practice advice on therapeutic approaches for treating ABD.
Dietary interventions
Specific foods may trigger bloating and abdominal distention, especially in patients with overlapping DGBIs. However, only a few studies have evaluated dietary restriction specifically for patients with primary ABD. Restricting non-absorbable sugars led to symptomatic improvement in 81% of patients with FABD who had documented sugar malabsorption.17 Two studies have shown that IBS patients treated with a low-fermentable, oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides (FODMAP) diet noted improvement in ABD and that restricting fructans initially may be the most optimal.18 A recent study showed that the Mediterranean diet improved IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain and bloating.19 It should be noted restrictive diets are efficacious but come with short- and long-term challenges. If empiric treatment and/or therapeutic testing do not resolve symptoms, a referral to a dietitian can be useful. Dietitians can provide tailored dietary advice, ensuring patients avoid trigger foods while maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet.
Prokinetics and laxatives
Prokinetic agents are used to treat symptoms of FD, gastroparesis, chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC), and IBS. A meta-analysis of 13 trials found all constipation medications superior to placebo for treating abdominal bloating in patients with IBS-C.20
Probiotics
Treatment with probiotics is recommended for bloating or distention. One double-blind placebo-controlled trial with two separate probiotics, Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, showed improvements in global GI symptoms of patients with DGBI at 8 weeks versus placebo, with improvements in bloating symptoms.21
Antibiotics
The most commonly studied antibiotic for treating bloating is rifaximin.22 Global symptomatic improvement in IBS patients treated with antibiotics has correlated with the normalization of hydrogen levels in lactulose hydrogen breath tests.22 Patients with non-constipation IBS randomized to rifaximin 550 mg three times daily for 14 days had a greater proportion of relief of IBS-related bloating compared to placebo for at least 2 of the first 4 weeks after treatment.22 Future research warrants use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics study for FABD as the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may deplete commensals forever, resulting in metabolic disorders.
Biofeedback therapy
Anorectal biofeedback therapy may help with ABD, particularly in patients with IBS-C and chronic constipation. One study noted that post-biofeedback therapy, myoelectric activity of the intercostals and diaphragm decreased, and internal oblique myoelectric activity increased.23 This study also showed ascent of the diaphragm and decreased girth, improving distention.
Central neuromodulators
As bloating results from multiple disturbed mechanisms, including altered gut-brain interaction, these symptoms can be amplified by psychological states such as anxiety, depression, or somatization. Central neuromodulators reduce the perception of visceral signals, re-regulate brain-gut control mechanisms, and improve psychological comorbidities.6 A large study of FD patients demonstrated that both amitriptyline (50 mg daily) and escitalopram (10 mg daily) significantly improved postprandial bloating compared to placebo.24 Antidepressants that activate noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways, including tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and venlafaxine), show the greatest benefit in reducing visceral sensations.6
Brain-gut behavioral therapies
A recent multidisciplinary consensus report supports a myriad of potential brain-gut behavioral therapies (BGBTs) for treating DGBI.25 These therapies, including hypnotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other modalities, may be combined with central neuromodulators and other GI treatments in a safe, noninvasive, and complementary fashion. BGBTs do not need to be symptom-specific, as they improve overall quality of life, anxiety, stress, and the burden associated with DGBIs. To date, none of the BGBTs have focused exclusively on FABD; however, prescription-based psychological therapies are now FDA-approved for use on smart apps, improving global symptoms that include bloating in IBS and FD.
Recent AGA clinical update best practices should be considered for the clinical care of patients with ABD.6
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
ABD are highly prevalent and significantly impact patients with various GI and metabolic disorders. Although our understanding of these symptoms is still evolving, evidence increasingly points to the dysregulation of the gut-brain axis and supports the application of the biopsychosocial model in treatment. This model addresses diet, motility, visceral sensitivity, pelvic floor disorders and psychosocial factors, providing a comprehensive approach to patient care.
Physician-scientists around the globe face numerous challenges when evaluating patients with these symptoms. However, the recent AGA clinical update on the best practice guidelines offers step-by-step diagnostic tests and treatment options to assist physicians in making informed decisions. . More comprehensive, large-scale, and longitudinal studies using metabolomics, capsule technologies for discovery of dysbiosis, mass spectrometry, and imaging data are needed to identify the exact contributors to disease pathogenesis, particularly those that can be targeted with pharmacologic agents. Collaborative work between gastroenterologists, dietitians, gut-brain behavioral therapists, endocrinologists, is crucial for clinical care of patients with ABD.
Careful attention to the patient’s primary symptoms and physical examination, combined with advancements in targeted diagnostics like the analysis of microbial markers, metabolites, and molecular signals, can significantly enhance patient clinical outcomes. Additionally, education and effective communication using a patient-centered care model are essential for guiding practical evaluation and individualized treatment.
Dr. Singh is assistant professor (research) at the University of Nevada, Reno, School of Medicine. Dr. Moshiree is director of motility at Atrium Health, and clinical professor of medicine, Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, North Carolina.
References
1. Ballou S et al. Prevalence and associated factors of bloating: Results from the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2023 June. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.049.
2. Oh JE et al. Abdominal bloating in the United States: Results of a survey of 88,795 Americans examining prevalence and healthcare seeking. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.10.031.
3. Drossman DA et al. Neuromodulators for functional gastrointestinal disorders (disorders of gut-brain interaction): A Rome Foundation Working Team Report. Gastroenterology. 2018 Mar. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.279.
4. Lacy BE et al. Management of chronic abdominal distension and bloating. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.056.
5. Mearin F et al. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031.
6. Moshiree B et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on evaluation and management of belching, abdominal bloating, and distention: expert review. Gastroenterology. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.04.039.
7. Viswanathan L and Rao SS. Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in adults: evaluation and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2023 May. doi: 10.1007/s11894-023-00870-z.
8. Wilder-Smith CH et al. Fructose and lactose intolerance and malabsorption testing: the relationship with symptoms in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1111/apt.12306.
9. Skodje GI et al. Fructan, rather than gluten, induces symptoms in patients with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.040.
10. Singh R et al. Current treatment options and therapeutic insights for gastrointestinal dysmotility and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.808195.
11. Accarino A et al. Abdominal distention results from caudo-ventral redistribution of contents. Gastroenterology 2009 May. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.01.067.
12. Shim L et al. Prolonged balloon expulsion is predictive of abdominal distension in bloating. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.54.
13. Villoria A et al. Abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in patients with abdominal bloating and distension. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 May. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.408.
14. Neri L and Iovino P. Laxative Inadequate Relief Survey Group. Bloating is associated with worse quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and treatment responsiveness among patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and functional constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12758.
15. Saffouri GB et al. Small intestinal microbial dysbiosis underlies symptoms associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat Commun. 2019 May. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09964-7.
16. Villanueva-Millan MJ et al. Methanogens and hydrogen sulfide producing bacteria guide distinct gut microbe profiles and irritable bowel syndrome subtypes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001997.
17. Fernández-Bañares F et al. Sugar malabsorption in functional abdominal bloating: a pilot study on the long-term effect of dietary treatment. Clin Nutr. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.11.010.
18. Böhn L et al. Diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome as well as traditional dietary advice: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.054.
19. Staudacher HM et al. Clinical trial: A Mediterranean diet is feasible and improves gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Feb. doi: 10.1111/apt.17791.
20. Nelson AD et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: efficacy of licensed drugs for abdominal bloating in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1111/apt.16437.
21. Ringel-Kulka T et al. Probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 versus placebo for the symptoms of bloating in patients with functional bowel disorders: a double-blind study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31820ca4d6.
22. Pimentel M et al. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1004409.
23. Iovino P et al. Pelvic floor biofeedback is an effective treatment for severe bloating in disorders of gut-brain interaction with outlet dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2022 May. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14264.
24. Talley NJ et al. Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: A multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.020.
25. Keefer L et al. A Rome Working Team Report on brain-gut behavior therapies for disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.015.
Introduction
Abdominal bloating is a common condition affecting up to 3.5% of people globally (4.6% in women and 2.4% in men),1 with 13.9% of the US population reporting bloating in the past 7 days.2 The prevalence of bloating and distention exceeds 50% when linked to disorders of gut-brain interaction (DGBIs) such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), constipation, gastroparesis, and functional dyspepsia (FD).3,4 According to the Rome IV criteria, functional bloating and distention (FABD) patients are characterized by recurrent symptoms of abdominal fullness or pressure (bloating), or a visible increase in abdominal girth (distention) occurring at least 1 day per week for 3 consecutive months with an onset of 6 months and without predominant pain or altered bowel habits.5
Prolonged abdominal bloating and distention (ABD) can significantly impact quality of life and work productivity and can lead to increased medical consultations.2 Multiple pathophysiological mechanisms are involved in ABD that complicate the clinical management.4 There is an unmet need to understand the underlying mechanisms that lead to the development of ABD such as, food intolerance, abnormal viscerosomatic reflex, visceral hypersensitivity, and gut microbial dysbiosis. Recent advancements and acceptance of a multidisciplinary management of ABD have shifted the paradigm from merely treating symptoms to subtyping the condition and identifying overlaps with other DGBIs in order to individualize treatment that addresses the underlying pathophysiological mechanism. The recent American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) clinical update provided insights into the best practice advice for evaluating and managing ABD based on a review of current literature and on expert opinion of coauthors.6 This article aims to deliberate a practical approach to diagnostic strategies and treatment options based on etiology to refine clinical care of patients with ABD.
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
ABD can result from various pathophysiological mechanisms. This section highlights the major causes (illustrated in Figure 1).
Food intolerances
Understanding food intolerances is crucial for diagnosing and managing patients with ABD. Disaccharidase deficiency is common (e.g., lactase deficiency is found in 35%-40% of adults).7 It can be undiagnosed in patients presenting with IBS symptoms, given the overlap in presentation with a prevalence of 9% of pan-disaccharidase deficiency. Sucrase-deficient patients must often adjust sugar and carbohydrate/starch intake to relieve symptoms.7 Deficiencies in lactase and sucrase activity, along with the consumption of some artificial sweeteners (e.g., sugar alcohols and sorbitol) and fructans can lead to bloating and distention. These substances increase osmotic load, fluid retention, microbial fermentation, and visceral hypersensitivity, leading to gas production and abdominal distention. One prospective study of symptomatic patients with various DGBIs (n = 1372) reported a prevalence of lactose intolerance and malabsorption at 51% and 32%, respectively.8 Furthermore, fructose intolerance and malabsorption prevalence were 60% and 45%, respectively.8 Notably, lactase deficiency does not always cause ABD, as not all individuals with lactase deficiency experience these symptoms after consuming lactose. Patients with celiac disease (CD), non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), and gluten intolerance can also experience bloating and distention, with or without changes in bowel habits.9 In some patients with self-reported NCGS, symptoms may be due to fructans in gluten-rich foods rather than gluten itself, thus recommending the elimination of fructans may help improve symptoms.9
Visceral hypersensitivity
Visceral hypersensitivity is explained by an increased perception of gut mechano-chemical stimulation, which typically manifests in an aggravated feeling of pain, nausea, distension, and ABD.10 In the gut, food particles and gut bacteria and their derived molecules interact with neuroimmune and enteroendocrine cells causing visceral sensitivity by the proximity of gut’s neurons to immune cells activated by them and leading to inflammatory reactions (Figure 1). 
Pelvic floor dysfunction
Patients with anorectal motor dysfunction often experience difficulty in effectively evacuating both gas and stool, leading to ABD.12 Impaired ability to expel gas and stool results in prolonged balloon expulsion times, which correlates with symptoms of distention in patients with constipation.
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia
Abdominophrenic dyssynergia is characterized as a paradoxical viscerosomatic reflex response to minimal gaseous distention in individuals with FABD.13 In this condition, the diaphragm contracts (descends), and the anterior abdominal wall muscles relax in response to the presence of gas. This response is opposite to the normal physiological response to increased intraluminal gas, where the diaphragm relaxes and the anterior abdominal muscles contract to increase the craniocaudal capacity of the abdominal cavity without causing abdominal protrusion.13 Patients with FABD exhibit significant abdominal wall protrusion and diaphragmatic descent even with relatively small increases in intraluminal gas.11 Understanding the role of abdominophrenic dyssynergia in abdominal bloating and distention is essential for effective diagnosis and management of the patients.
Gut dysmotility
Gut dysmotility is a crucial factor that can contribute to FABD. Gut dysmotility affects the movement of contents through the GI tract, accumulating gas and stool, directly contributing to bloating and distention. A prospective study involving over 2000 patients with functional constipation and constipation predominant-IBS (IBS-C) found that more than 90% of these patients reported symptoms of bloating.14 Furthermore, in IBS-C patients, those with prolonged colonic transit exhibited greater abdominal distention compared to those with normal gut transit times. In patients with gastroparesis, delayed gastric emptying resulting in prolonged retention of stomach contents is the main factor in the generation of bloating symptoms.4
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
SIBO is overrepresented in various conditions, including IBS, FD, diabetes, gastrointestinal (GI) surgery patients and obesity, and can play an important role in generating ABD. Excess bacteria in the small intestine ferment carbohydrates, producing gas that stretches and distends the small intestine, leading to these symptoms. Additionally, altered sensation and abnormal viscerosomatic reflexes may contribute to SIBO-related bloating.4 One recent study noted decreased duodenal phylogenetic diversity in individuals who developed postprandial bloating.15 Increased methane levels caused by intestinal methanogen overgrowth, primarily the archaea Methanobrevibacter smithii, is possibly responsible for ABD in patients with IBS-C.16 Testing for SIBO in patients with ABD is generally only recommended if there are clear risk factors or severe symptoms warranting a test-and-treat approach.
Practical Diagnosis
Diagnosing ABD typically does not require extensive laboratory testing, imaging, or endoscopy unless there are alarm features or significant changes in symptoms. Here is the AGA clinical update on best practice advice6 for when to conduct further testing:
Diagnostic tests should be considered if patients exhibit:
- Recent onset or worsening of dyspepsia or abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- GI bleeding
- Unintentional weight loss exceeding 10% of body weight
- Chronic diarrhea
- Family history of GI malignancy, celiac disease, or inflammatory bowel disease
Physical examination
If visible abdominal distention is present, a thorough abdominal examination can help identify potential issues:
- Tympany to percussion suggests bowel dilation.
- Abnormal bowel sounds may indicate obstruction or ileus.
- A succussion splash could indicate the presence of ascites and obstruction.
- Any abnormalities discovered during the physical exam should prompt further investigation with imaging, such as a computed tomography (CT) scan or ultrasound, to evaluate for ascites, masses, or increased bowel gas due to ileus, obstruction, or pseudo-obstruction.
Radiologic imaging, laboratory testing and endoscopy
- An abdominal x-ray may reveal an increased stool burden, suggesting the need for further evaluation of slow transit constipation or a pelvic floor disorder, particularly in patients with functional constipation, IBS-mixed, or IBS-C.
- Hyperglycemia, weight gain, and bloating can be a presenting sign of ovarian cancer therefore all women should continue pelvic exams as dictated by the gynecologic societies. The need for an annual pelvic exam should be discussed with health care professionals especially in those with family history of ovarian cancer.
- An upper endoscopy may be warranted for patients over 40 years old with dyspeptic symptoms and abdominal bloating or distention, especially in regions with a high prevalence of Helicobacter pylori.
- Chronic pancreatitis, indicated by bloating and pain, may necessitate fecal elastase testing to assess pancreatic function.
The expert review in the AGA clinical update provides step-by-step advice regarding the best practices6 for diagnosis and identifying who to test for ABD.
Treatment Options
The following sections highlight recent best practice advice on therapeutic approaches for treating ABD.
Dietary interventions
Specific foods may trigger bloating and abdominal distention, especially in patients with overlapping DGBIs. However, only a few studies have evaluated dietary restriction specifically for patients with primary ABD. Restricting non-absorbable sugars led to symptomatic improvement in 81% of patients with FABD who had documented sugar malabsorption.17 Two studies have shown that IBS patients treated with a low-fermentable, oligo-, di-, and monosaccharides (FODMAP) diet noted improvement in ABD and that restricting fructans initially may be the most optimal.18 A recent study showed that the Mediterranean diet improved IBS symptoms, including abdominal pain and bloating.19 It should be noted restrictive diets are efficacious but come with short- and long-term challenges. If empiric treatment and/or therapeutic testing do not resolve symptoms, a referral to a dietitian can be useful. Dietitians can provide tailored dietary advice, ensuring patients avoid trigger foods while maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet.
Prokinetics and laxatives
Prokinetic agents are used to treat symptoms of FD, gastroparesis, chronic idiopathic constipation (CIC), and IBS. A meta-analysis of 13 trials found all constipation medications superior to placebo for treating abdominal bloating in patients with IBS-C.20
Probiotics
Treatment with probiotics is recommended for bloating or distention. One double-blind placebo-controlled trial with two separate probiotics, Bifidobacterium lactis and Lactobacillus acidophilus, showed improvements in global GI symptoms of patients with DGBI at 8 weeks versus placebo, with improvements in bloating symptoms.21
Antibiotics
The most commonly studied antibiotic for treating bloating is rifaximin.22 Global symptomatic improvement in IBS patients treated with antibiotics has correlated with the normalization of hydrogen levels in lactulose hydrogen breath tests.22 Patients with non-constipation IBS randomized to rifaximin 550 mg three times daily for 14 days had a greater proportion of relief of IBS-related bloating compared to placebo for at least 2 of the first 4 weeks after treatment.22 Future research warrants use of narrow-spectrum antibiotics study for FABD as the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics may deplete commensals forever, resulting in metabolic disorders.
Biofeedback therapy
Anorectal biofeedback therapy may help with ABD, particularly in patients with IBS-C and chronic constipation. One study noted that post-biofeedback therapy, myoelectric activity of the intercostals and diaphragm decreased, and internal oblique myoelectric activity increased.23 This study also showed ascent of the diaphragm and decreased girth, improving distention.
Central neuromodulators
As bloating results from multiple disturbed mechanisms, including altered gut-brain interaction, these symptoms can be amplified by psychological states such as anxiety, depression, or somatization. Central neuromodulators reduce the perception of visceral signals, re-regulate brain-gut control mechanisms, and improve psychological comorbidities.6 A large study of FD patients demonstrated that both amitriptyline (50 mg daily) and escitalopram (10 mg daily) significantly improved postprandial bloating compared to placebo.24 Antidepressants that activate noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways, including tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (e.g., duloxetine and venlafaxine), show the greatest benefit in reducing visceral sensations.6
Brain-gut behavioral therapies
A recent multidisciplinary consensus report supports a myriad of potential brain-gut behavioral therapies (BGBTs) for treating DGBI.25 These therapies, including hypnotherapy, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), and other modalities, may be combined with central neuromodulators and other GI treatments in a safe, noninvasive, and complementary fashion. BGBTs do not need to be symptom-specific, as they improve overall quality of life, anxiety, stress, and the burden associated with DGBIs. To date, none of the BGBTs have focused exclusively on FABD; however, prescription-based psychological therapies are now FDA-approved for use on smart apps, improving global symptoms that include bloating in IBS and FD.
Recent AGA clinical update best practices should be considered for the clinical care of patients with ABD.6
Conclusion and Future Perspectives
ABD are highly prevalent and significantly impact patients with various GI and metabolic disorders. Although our understanding of these symptoms is still evolving, evidence increasingly points to the dysregulation of the gut-brain axis and supports the application of the biopsychosocial model in treatment. This model addresses diet, motility, visceral sensitivity, pelvic floor disorders and psychosocial factors, providing a comprehensive approach to patient care.
Physician-scientists around the globe face numerous challenges when evaluating patients with these symptoms. However, the recent AGA clinical update on the best practice guidelines offers step-by-step diagnostic tests and treatment options to assist physicians in making informed decisions. . More comprehensive, large-scale, and longitudinal studies using metabolomics, capsule technologies for discovery of dysbiosis, mass spectrometry, and imaging data are needed to identify the exact contributors to disease pathogenesis, particularly those that can be targeted with pharmacologic agents. Collaborative work between gastroenterologists, dietitians, gut-brain behavioral therapists, endocrinologists, is crucial for clinical care of patients with ABD.
Careful attention to the patient’s primary symptoms and physical examination, combined with advancements in targeted diagnostics like the analysis of microbial markers, metabolites, and molecular signals, can significantly enhance patient clinical outcomes. Additionally, education and effective communication using a patient-centered care model are essential for guiding practical evaluation and individualized treatment.
Dr. Singh is assistant professor (research) at the University of Nevada, Reno, School of Medicine. Dr. Moshiree is director of motility at Atrium Health, and clinical professor of medicine, Wake Forest Medical University, Charlotte, North Carolina.
References
1. Ballou S et al. Prevalence and associated factors of bloating: Results from the Rome Foundation Global Epidemiology Study. Gastroenterology. 2023 June. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.049.
2. Oh JE et al. Abdominal bloating in the United States: Results of a survey of 88,795 Americans examining prevalence and healthcare seeking. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.10.031.
3. Drossman DA et al. Neuromodulators for functional gastrointestinal disorders (disorders of gut-brain interaction): A Rome Foundation Working Team Report. Gastroenterology. 2018 Mar. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.279.
4. Lacy BE et al. Management of chronic abdominal distension and bloating. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.056.
5. Mearin F et al. Bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031.
6. Moshiree B et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on evaluation and management of belching, abdominal bloating, and distention: expert review. Gastroenterology. 2023 Sep. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.04.039.
7. Viswanathan L and Rao SS. Intestinal disaccharidase deficiency in adults: evaluation and treatment. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2023 May. doi: 10.1007/s11894-023-00870-z.
8. Wilder-Smith CH et al. Fructose and lactose intolerance and malabsorption testing: the relationship with symptoms in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jun. doi: 10.1111/apt.12306.
9. Skodje GI et al. Fructan, rather than gluten, induces symptoms in patients with self-reported non-celiac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.040.
10. Singh R et al. Current treatment options and therapeutic insights for gastrointestinal dysmotility and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.808195.
11. Accarino A et al. Abdominal distention results from caudo-ventral redistribution of contents. Gastroenterology 2009 May. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.01.067.
12. Shim L et al. Prolonged balloon expulsion is predictive of abdominal distension in bloating. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.54.
13. Villoria A et al. Abdomino-phrenic dyssynergia in patients with abdominal bloating and distension. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011 May. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.408.
14. Neri L and Iovino P. Laxative Inadequate Relief Survey Group. Bloating is associated with worse quality of life, treatment satisfaction, and treatment responsiveness among patients with constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome and functional constipation. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12758.
15. Saffouri GB et al. Small intestinal microbial dysbiosis underlies symptoms associated with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Nat Commun. 2019 May. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09964-7.
16. Villanueva-Millan MJ et al. Methanogens and hydrogen sulfide producing bacteria guide distinct gut microbe profiles and irritable bowel syndrome subtypes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001997.
17. Fernández-Bañares F et al. Sugar malabsorption in functional abdominal bloating: a pilot study on the long-term effect of dietary treatment. Clin Nutr. 2006 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.11.010.
18. Böhn L et al. Diet low in FODMAPs reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome as well as traditional dietary advice: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterology. 2015 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.054.
19. Staudacher HM et al. Clinical trial: A Mediterranean diet is feasible and improves gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2024 Feb. doi: 10.1111/apt.17791.
20. Nelson AD et al. Systematic review and network meta-analysis: efficacy of licensed drugs for abdominal bloating in irritable bowel syndrome with constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Jul. doi: 10.1111/apt.16437.
21. Ringel-Kulka T et al. Probiotic bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 versus placebo for the symptoms of bloating in patients with functional bowel disorders: a double-blind study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2011 Jul. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e31820ca4d6.
22. Pimentel M et al. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N Engl J Med. 2011 Jan. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1004409.
23. Iovino P et al. Pelvic floor biofeedback is an effective treatment for severe bloating in disorders of gut-brain interaction with outlet dysfunction. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2022 May. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14264.
24. Talley NJ et al. Effect of amitriptyline and escitalopram on functional dyspepsia: A multicenter, randomized controlled study. Gastroenterology. 2015 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.020.
25. Keefer L et al. A Rome Working Team Report on brain-gut behavior therapies for disorders of gut-brain interaction. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jan. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.015.
Advanced Tissue Resection in Gastroenterology: Indications, Role, and Outcomes
Endoscopists are often faced with unique challenges in the management and resection of various gastrointestinal tract lesions. These challenges could be lesion-related, endoscopist-related, or practice-related (see Table 1). (ATR). Not only does this organ-sparing approach offer a less invasive alternative to surgery, but it has also proved to have outcomes comparable to those of surgical standard of practice in specific scenarios. 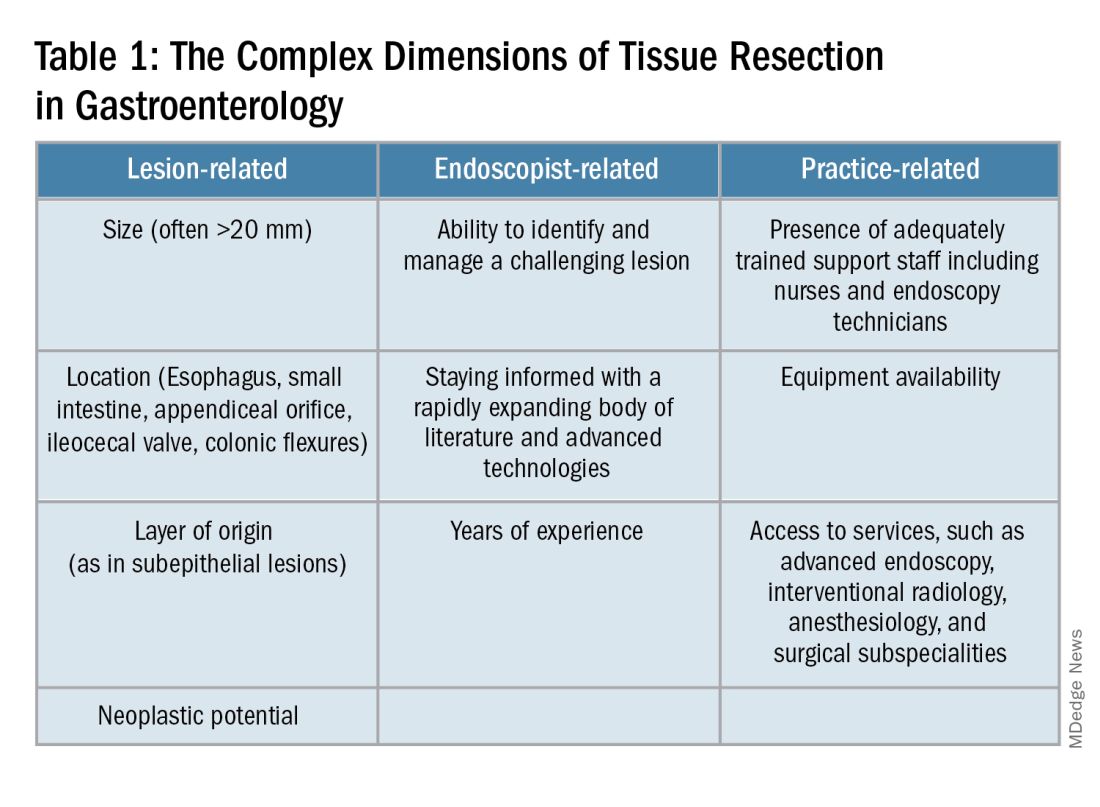
When Do You Refer to an Advanced Endoscopist?
One of the most critical steps in caring for patients with complex lesions is the ability to accurately determine whether a referral to an advanced endoscopist is warranted. The initial assessment of a lesion should always involve a careful assessment that risk stratifies the lesion depending on the location, size, neoplastic potential, and the feasibility of standard endoscopic resection compared to the need for surgical input.
A practical example in the case of colonic polyps is highlighted by the American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) guidelines recommending the referral of patients with polyps’ size ≥ 20 mm, challenging polypectomy location, or recurrent polyp at a prior polypectomy site to an endoscopic referral center.1 In the case of subepithelial lesions without endoscopic characteristics of benign etiology (i.e., lipomas, pancreatic rests, etc.), the threshold for referral to advanced endoscopists for further diagnostic testing by means of endoscopic ultrasonography or for therapeutic ATR should be lower.
Endoscopic tissue resection follows a spectrum, which often involves deeper layers of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) as we progress along this spectrum (see Figure 1). 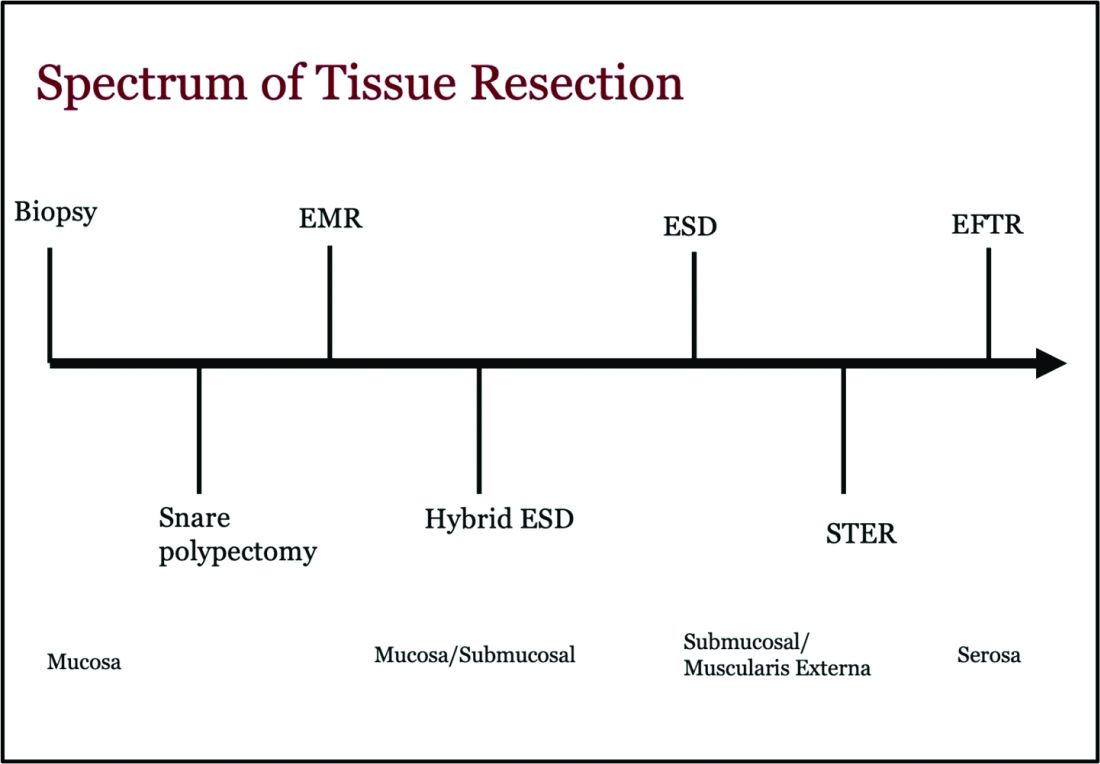
ATR, a term encompassing a variety of endoscopic techniques ranging from endoscopic mucosal resection to full thickness resection, has gained traction over the last years given the ability to effectively remove various lesions in a precise time and cost-effective manner while maintaining the integrity of the GIT and avoiding major surgery. The indications for ATR vary depending on the technique, but generally include the presence of large or poorly positioned lesions, particularly in high-risk areas of the GIT such as the esophagus and small intestine, lesions extending beyond the mucosal layer or originating from deeper layers, and when en bloc resection of select lesions is necessary.
For providers referring patients for ATR, we recommend a few important endoscopic pearls when caring for these patients.
1) Biopsy the lesion if there is concern for malignancy — While some studies have noted increased fibrosis during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and some guidelines recommend against biopsies pre ESD, we believe that when there is high pretest probability for malignancy, a biopsy should be obtained. This should involve the area that is most concerning for malignancy (at the margin or center).2
2) While marking a lesion with tattoo is helpful for surgical planning and for lesions difficult to locate endoscopically, we stress the importance of placing tattoos 3 to 5 centimeters distal to the lesion and avoiding tattooing the lesion itself, which has been shown to induce fibrosis and can make resection challenging. Based on an international Delphi consensus, expert recommendations on when and how to endoscopically tattoo a lesion can be instrumental in adequately localizing the lesion, allowing for endoscopic resection, and preventing unnecessary surgeries.3
3) If you encounter a lesion that you are not sure can be resected safely and efficaciously, we recommend against attempting resection that may result in partial resection. This can also induce fibrosis and scarring and limit future attempts at resection.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
EMR is currently utilized for curative treatment of a wide array of GIT lesions limited to the mucosal layer, whether metaplastic, dysplastic, or even in cases with early mucosal cancer, where the risk of submucosal and lymphatic invasion is minimal.4 This makes EMR a versatile and proven therapy, often serving as the first-line treatment for many GIT lesions.
EMR has various techniques that could be categorized into suction or non-suction (lift and cut) techniques. In the suction technique, devices like multiband mucosectomy (MBM) are commonly used, especially in nodular Barrett’s dysplasia, forming a pseudopolyp for subsequent resection. The procedure is characterized by its safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to its widespread adoption in clinical practice. In the lift and cut approach, a submucosal injection is utilized to separate the muscularis propria from the lesion, thereby reducing the risk of perforation. Different solutions, such as normal saline, hypertonic saline, 50% dextrose, or proprietary submucosal injection solutions, are employed for submucosal injection.5
The non-suction technique using a snare to resect polyps after injection is more often used in colonic and small intestinal EMR. Resection can be done via thermal energy in the form of cut or coagulation; however, there is rising data on the use of piecemeal cold snare resection for select flat polyps of the colon.6 There is also promising data on the role of underwater EMR, a common technique employed for colonic lesions, particularly if the lesion does not lift well with submucosal injection.7
Adverse events associated with EMR include bleeding (7%-8%) and perforation (0.9%-2%).8-9 Adequate submucosal fluid injection is crucial to prevent perforations. However, the main limitation of EMR is the piecemeal nature of resections for lesions larger than 20 mm, leading to compromised histopathologic evaluation for complete excision, especially in cases with superficial submucosal invasion (SMI). This can result in residual or recurrent tissue, reportedly 8% to 20%.10 Despite this limitation, EMR remains a reliable strategy, and recurrent lesions are generally manageable through repeat sessions. The importance of EMR as a therapeutic modality lies in its role in addressing lesions with favorable characteristics, where the risk of SMI is low.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
ESD is an evolving technique that can be utilized for submucosal lesions of the GIT, lesions not amenable to EMR due to submucosal fibrosis, when en bloc removal of a lesion is needed for accurate histopathological diagnosis, and when other techniques fail.11-12
ESD was only recently adopted in the United States, requires specialized training, and usually is a lengthier procedure than EMR.13 Compared to EMR, it has higher en bloc resection rates and lower recurrence rates, making it curative for lesions with superficial SMI and favorable histologic features.4,14 The safety profile of ESD appears favorable, with most of the adverse events managed successfully by endoscopic methods. Major complications include intraoperative and delayed perforation, intraoperative and delayed bleeding, aspiration pneumonia, thromboembolism, and stricture formation in the case of circumferential lesions.15
Despite being technically challenging, ESD may provide a cost-effective long-term solution by avoiding surgery, reducing the need for additional interventions by minimizing recurrence rates. Given the technical complexity of ESD, particularly the submucosal dissection portion, techniques such as hybrid ESD developed. Hybrid ESD combines snaring with circumferential mucosal incision and partial submucosal dissection. Although it promises shorter procedure times, reduced complication rates like perforation, and similar recurrence rates compared to traditional ESD, studies have shown lower success rates in en bloc resection.16-17
Both EMR and ESD are considered complementary strategies, and the choice between them should be dictated by lesion characteristics, patient preferences, and local expertise.
Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection (STER)
STER has emerged as a well-established technique for the endoscopic resection of GI subepithelial tumors (SETs) originating from the muscularis propria layer. The standard STER procedure involves a series of steps including submucosal elevation proximal to the SET, mucosotomy, creation of a submucosal tunnel, dissection of the SET within the tunnel, enucleation from the deep muscle layer, and subsequent specimen retrieval followed by mucosal closure.
This technique is typically recommended for SETs smaller than 3.5 cm, particularly those located in the mid or distal esophagus, cardia, or along the greater curvature of the gastric body.18 However, STER may pose technical challenges for larger SETs or lesions in anatomically difficult locations, where surgical resection is recommended instead.19 Notably, recent large-scale meta-analyses have showcased the favorable complete resection and en bloc resection rates of STER in treating GI SETs.20
Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection (EFTR)
EFTR has emerged as a valuable technique in the endoscopic management of gastrointestinal lesions, particularly SETs and lesions not amenable to EMR or ESD due to fibrosis. EFTR involves the resection of all layers of the GIT from mucosa to serosa, and therefore is well-suited for SETs arising from the muscularis propria (MP).20
EFTR entails two main concepts: tissue resection and complete defect closure. Conventional EFTR consists of several steps, which include mucosal and submucosal pre-cutting, circumferential incision, and dissection through the MP or serosa. This results in a full thickness defect, for which closure of the wall defect is achieved using standard endoscopic clips or a combination of clips and endoloops or endoscopic suturing.21 For lesions less than 2 cm, EFTR can be performed in a single step using a cap-mounted full thickness resection device (FTRD). This results in deployment of over-the-scope clip over the target lesion followed by snaring the lesions above the clip.21
Location of the SET generally dictates the specific modality of ATR. For example, esophageal SETs may be more amenable to STER given that the lesion typically runs parallel with the lumen of the tubular esophagus, which allows for easier dissection without the need of full or partial retroflexion. While gastric SETs can be resected with STER, it may be challenging and more effectively addressed with EFTR, particularly when the entire lesion can be grasped into the full-thickness resection device.22 Limited data exists for duodenal EFTR, and colorectal SETs closure is particularly challenging.
Conclusion
It is key to emphasize that ATR cannot be safely established in practice without the incorporation of a multidisciplinary team (surgeons, radiologists, etc.), specialized tools, and trained personnel. This requires dedicated endoscopic rooms, careful patient selection, and a comprehensive approach to patient care before, during, and after these procedures.
Moreover, it is important to note that some patients may require post-procedure hospitalization for observation to ensure no early complications are encountered. Optimal surveillance strategies after ATR rely heavily on the potential for residual or recurrent disease, underlying pathology, and the expertise of the advanced endoscopist. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and technological advances of devices will further enhance the efficacy and safety of ATR in gastroenterology.
Dr. Madi (@MahMadi90) is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri. Dr. Rengarajan (@ArvindRenga) and Dr. Bazarbashi (@AhmadBazarbashi) are based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and no funding was required for this project.
References
1. Copland AP, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on appropriate and tailored polypectomy: Expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.012.
2. Lee SP, et al. Effect of preceding biopsy on the results of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal laterally spreading tumor. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05625-3.
3. Medina-Prado L, et al. When and how to use endoscopic tattooing in the colon: An international Delphi agreement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.024.
4. Rashid MU, et al. EMR and ESD: Indications, techniques and results. Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101742.
5. Castro R, et al. Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.777.
6. Rex DK. Best practices for resection of diminutive and small polyps in the colorectum. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2019.06.004.
7. Lv XH, et al. Underwater EMR for nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.10.044.
8. Fujiya M, et al. Efficacy and adverse events of EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colon neoplasms: a meta-analysis of studies comparing EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.034.
9. Kandel P, Wallace MB. Colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.05.006.
10. Kemper G, et al; ENDOCARE Study Group. Endoscopic techniques to reduce recurrence rates after colorectal EMR: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08574-z.
11. Goto O, et al. Expanding indications for ESD: submucosal disease (SMT/carcinoid tumors). Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.11.006.
12. Wang K, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection, indication, methods and perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1111/den.14474.
13. Herreros de Tejada A. ESD training: A challenging path to excellence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014 Apr 16. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i4.112.
14. Chiba H, et al. Safety and efficacy of simultaneous colorectal ESD for large synchronous colorectal lesions. Endosc Int Open. 2017 Jul. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-110567.
15. Mannath J, Ragunath K. Endoscopic mucosal resection: who and how? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep. doi: 10.1177/1756283X10388683.
16. Wang XY, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: An alternative resection modality for large laterally spreading tumors in the cecum? BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01766-w.
17. McCarty TR, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) compared with conventional ESD for colorectal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1055/a-1266-1855.
18. Jain D, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria. Ann Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.20524/aog.2017.0128.
19. Lv XH, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017 Jan. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4978-7.
20. Cao B, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021 Jan. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.6989/2020.
21. Cai M, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.12.013.
22. Brigic A, et al. A systematic review regarding the feasibility and safety of endoscopic full thickness resection (EFTR) for colonic lesions. Surg Endosc. 2013 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2946-z.
Endoscopists are often faced with unique challenges in the management and resection of various gastrointestinal tract lesions. These challenges could be lesion-related, endoscopist-related, or practice-related (see Table 1). (ATR). Not only does this organ-sparing approach offer a less invasive alternative to surgery, but it has also proved to have outcomes comparable to those of surgical standard of practice in specific scenarios. 
When Do You Refer to an Advanced Endoscopist?
One of the most critical steps in caring for patients with complex lesions is the ability to accurately determine whether a referral to an advanced endoscopist is warranted. The initial assessment of a lesion should always involve a careful assessment that risk stratifies the lesion depending on the location, size, neoplastic potential, and the feasibility of standard endoscopic resection compared to the need for surgical input.
A practical example in the case of colonic polyps is highlighted by the American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) guidelines recommending the referral of patients with polyps’ size ≥ 20 mm, challenging polypectomy location, or recurrent polyp at a prior polypectomy site to an endoscopic referral center.1 In the case of subepithelial lesions without endoscopic characteristics of benign etiology (i.e., lipomas, pancreatic rests, etc.), the threshold for referral to advanced endoscopists for further diagnostic testing by means of endoscopic ultrasonography or for therapeutic ATR should be lower.
Endoscopic tissue resection follows a spectrum, which often involves deeper layers of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) as we progress along this spectrum (see Figure 1). 
ATR, a term encompassing a variety of endoscopic techniques ranging from endoscopic mucosal resection to full thickness resection, has gained traction over the last years given the ability to effectively remove various lesions in a precise time and cost-effective manner while maintaining the integrity of the GIT and avoiding major surgery. The indications for ATR vary depending on the technique, but generally include the presence of large or poorly positioned lesions, particularly in high-risk areas of the GIT such as the esophagus and small intestine, lesions extending beyond the mucosal layer or originating from deeper layers, and when en bloc resection of select lesions is necessary.
For providers referring patients for ATR, we recommend a few important endoscopic pearls when caring for these patients.
1) Biopsy the lesion if there is concern for malignancy — While some studies have noted increased fibrosis during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and some guidelines recommend against biopsies pre ESD, we believe that when there is high pretest probability for malignancy, a biopsy should be obtained. This should involve the area that is most concerning for malignancy (at the margin or center).2
2) While marking a lesion with tattoo is helpful for surgical planning and for lesions difficult to locate endoscopically, we stress the importance of placing tattoos 3 to 5 centimeters distal to the lesion and avoiding tattooing the lesion itself, which has been shown to induce fibrosis and can make resection challenging. Based on an international Delphi consensus, expert recommendations on when and how to endoscopically tattoo a lesion can be instrumental in adequately localizing the lesion, allowing for endoscopic resection, and preventing unnecessary surgeries.3
3) If you encounter a lesion that you are not sure can be resected safely and efficaciously, we recommend against attempting resection that may result in partial resection. This can also induce fibrosis and scarring and limit future attempts at resection.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
EMR is currently utilized for curative treatment of a wide array of GIT lesions limited to the mucosal layer, whether metaplastic, dysplastic, or even in cases with early mucosal cancer, where the risk of submucosal and lymphatic invasion is minimal.4 This makes EMR a versatile and proven therapy, often serving as the first-line treatment for many GIT lesions.
EMR has various techniques that could be categorized into suction or non-suction (lift and cut) techniques. In the suction technique, devices like multiband mucosectomy (MBM) are commonly used, especially in nodular Barrett’s dysplasia, forming a pseudopolyp for subsequent resection. The procedure is characterized by its safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to its widespread adoption in clinical practice. In the lift and cut approach, a submucosal injection is utilized to separate the muscularis propria from the lesion, thereby reducing the risk of perforation. Different solutions, such as normal saline, hypertonic saline, 50% dextrose, or proprietary submucosal injection solutions, are employed for submucosal injection.5
The non-suction technique using a snare to resect polyps after injection is more often used in colonic and small intestinal EMR. Resection can be done via thermal energy in the form of cut or coagulation; however, there is rising data on the use of piecemeal cold snare resection for select flat polyps of the colon.6 There is also promising data on the role of underwater EMR, a common technique employed for colonic lesions, particularly if the lesion does not lift well with submucosal injection.7
Adverse events associated with EMR include bleeding (7%-8%) and perforation (0.9%-2%).8-9 Adequate submucosal fluid injection is crucial to prevent perforations. However, the main limitation of EMR is the piecemeal nature of resections for lesions larger than 20 mm, leading to compromised histopathologic evaluation for complete excision, especially in cases with superficial submucosal invasion (SMI). This can result in residual or recurrent tissue, reportedly 8% to 20%.10 Despite this limitation, EMR remains a reliable strategy, and recurrent lesions are generally manageable through repeat sessions. The importance of EMR as a therapeutic modality lies in its role in addressing lesions with favorable characteristics, where the risk of SMI is low.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
ESD is an evolving technique that can be utilized for submucosal lesions of the GIT, lesions not amenable to EMR due to submucosal fibrosis, when en bloc removal of a lesion is needed for accurate histopathological diagnosis, and when other techniques fail.11-12
ESD was only recently adopted in the United States, requires specialized training, and usually is a lengthier procedure than EMR.13 Compared to EMR, it has higher en bloc resection rates and lower recurrence rates, making it curative for lesions with superficial SMI and favorable histologic features.4,14 The safety profile of ESD appears favorable, with most of the adverse events managed successfully by endoscopic methods. Major complications include intraoperative and delayed perforation, intraoperative and delayed bleeding, aspiration pneumonia, thromboembolism, and stricture formation in the case of circumferential lesions.15
Despite being technically challenging, ESD may provide a cost-effective long-term solution by avoiding surgery, reducing the need for additional interventions by minimizing recurrence rates. Given the technical complexity of ESD, particularly the submucosal dissection portion, techniques such as hybrid ESD developed. Hybrid ESD combines snaring with circumferential mucosal incision and partial submucosal dissection. Although it promises shorter procedure times, reduced complication rates like perforation, and similar recurrence rates compared to traditional ESD, studies have shown lower success rates in en bloc resection.16-17
Both EMR and ESD are considered complementary strategies, and the choice between them should be dictated by lesion characteristics, patient preferences, and local expertise.
Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection (STER)
STER has emerged as a well-established technique for the endoscopic resection of GI subepithelial tumors (SETs) originating from the muscularis propria layer. The standard STER procedure involves a series of steps including submucosal elevation proximal to the SET, mucosotomy, creation of a submucosal tunnel, dissection of the SET within the tunnel, enucleation from the deep muscle layer, and subsequent specimen retrieval followed by mucosal closure.
This technique is typically recommended for SETs smaller than 3.5 cm, particularly those located in the mid or distal esophagus, cardia, or along the greater curvature of the gastric body.18 However, STER may pose technical challenges for larger SETs or lesions in anatomically difficult locations, where surgical resection is recommended instead.19 Notably, recent large-scale meta-analyses have showcased the favorable complete resection and en bloc resection rates of STER in treating GI SETs.20
Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection (EFTR)
EFTR has emerged as a valuable technique in the endoscopic management of gastrointestinal lesions, particularly SETs and lesions not amenable to EMR or ESD due to fibrosis. EFTR involves the resection of all layers of the GIT from mucosa to serosa, and therefore is well-suited for SETs arising from the muscularis propria (MP).20
EFTR entails two main concepts: tissue resection and complete defect closure. Conventional EFTR consists of several steps, which include mucosal and submucosal pre-cutting, circumferential incision, and dissection through the MP or serosa. This results in a full thickness defect, for which closure of the wall defect is achieved using standard endoscopic clips or a combination of clips and endoloops or endoscopic suturing.21 For lesions less than 2 cm, EFTR can be performed in a single step using a cap-mounted full thickness resection device (FTRD). This results in deployment of over-the-scope clip over the target lesion followed by snaring the lesions above the clip.21
Location of the SET generally dictates the specific modality of ATR. For example, esophageal SETs may be more amenable to STER given that the lesion typically runs parallel with the lumen of the tubular esophagus, which allows for easier dissection without the need of full or partial retroflexion. While gastric SETs can be resected with STER, it may be challenging and more effectively addressed with EFTR, particularly when the entire lesion can be grasped into the full-thickness resection device.22 Limited data exists for duodenal EFTR, and colorectal SETs closure is particularly challenging.
Conclusion
It is key to emphasize that ATR cannot be safely established in practice without the incorporation of a multidisciplinary team (surgeons, radiologists, etc.), specialized tools, and trained personnel. This requires dedicated endoscopic rooms, careful patient selection, and a comprehensive approach to patient care before, during, and after these procedures.
Moreover, it is important to note that some patients may require post-procedure hospitalization for observation to ensure no early complications are encountered. Optimal surveillance strategies after ATR rely heavily on the potential for residual or recurrent disease, underlying pathology, and the expertise of the advanced endoscopist. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and technological advances of devices will further enhance the efficacy and safety of ATR in gastroenterology.
Dr. Madi (@MahMadi90) is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri. Dr. Rengarajan (@ArvindRenga) and Dr. Bazarbashi (@AhmadBazarbashi) are based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and no funding was required for this project.
References
1. Copland AP, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on appropriate and tailored polypectomy: Expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.012.
2. Lee SP, et al. Effect of preceding biopsy on the results of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal laterally spreading tumor. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05625-3.
3. Medina-Prado L, et al. When and how to use endoscopic tattooing in the colon: An international Delphi agreement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.024.
4. Rashid MU, et al. EMR and ESD: Indications, techniques and results. Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101742.
5. Castro R, et al. Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.777.
6. Rex DK. Best practices for resection of diminutive and small polyps in the colorectum. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2019.06.004.
7. Lv XH, et al. Underwater EMR for nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.10.044.
8. Fujiya M, et al. Efficacy and adverse events of EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colon neoplasms: a meta-analysis of studies comparing EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.034.
9. Kandel P, Wallace MB. Colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.05.006.
10. Kemper G, et al; ENDOCARE Study Group. Endoscopic techniques to reduce recurrence rates after colorectal EMR: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08574-z.
11. Goto O, et al. Expanding indications for ESD: submucosal disease (SMT/carcinoid tumors). Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.11.006.
12. Wang K, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection, indication, methods and perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1111/den.14474.
13. Herreros de Tejada A. ESD training: A challenging path to excellence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014 Apr 16. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i4.112.
14. Chiba H, et al. Safety and efficacy of simultaneous colorectal ESD for large synchronous colorectal lesions. Endosc Int Open. 2017 Jul. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-110567.
15. Mannath J, Ragunath K. Endoscopic mucosal resection: who and how? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep. doi: 10.1177/1756283X10388683.
16. Wang XY, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: An alternative resection modality for large laterally spreading tumors in the cecum? BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01766-w.
17. McCarty TR, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) compared with conventional ESD for colorectal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1055/a-1266-1855.
18. Jain D, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria. Ann Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.20524/aog.2017.0128.
19. Lv XH, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017 Jan. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4978-7.
20. Cao B, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021 Jan. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.6989/2020.
21. Cai M, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.12.013.
22. Brigic A, et al. A systematic review regarding the feasibility and safety of endoscopic full thickness resection (EFTR) for colonic lesions. Surg Endosc. 2013 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2946-z.
Endoscopists are often faced with unique challenges in the management and resection of various gastrointestinal tract lesions. These challenges could be lesion-related, endoscopist-related, or practice-related (see Table 1). (ATR). Not only does this organ-sparing approach offer a less invasive alternative to surgery, but it has also proved to have outcomes comparable to those of surgical standard of practice in specific scenarios. 
When Do You Refer to an Advanced Endoscopist?
One of the most critical steps in caring for patients with complex lesions is the ability to accurately determine whether a referral to an advanced endoscopist is warranted. The initial assessment of a lesion should always involve a careful assessment that risk stratifies the lesion depending on the location, size, neoplastic potential, and the feasibility of standard endoscopic resection compared to the need for surgical input.
A practical example in the case of colonic polyps is highlighted by the American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) guidelines recommending the referral of patients with polyps’ size ≥ 20 mm, challenging polypectomy location, or recurrent polyp at a prior polypectomy site to an endoscopic referral center.1 In the case of subepithelial lesions without endoscopic characteristics of benign etiology (i.e., lipomas, pancreatic rests, etc.), the threshold for referral to advanced endoscopists for further diagnostic testing by means of endoscopic ultrasonography or for therapeutic ATR should be lower.
Endoscopic tissue resection follows a spectrum, which often involves deeper layers of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) as we progress along this spectrum (see Figure 1). 
ATR, a term encompassing a variety of endoscopic techniques ranging from endoscopic mucosal resection to full thickness resection, has gained traction over the last years given the ability to effectively remove various lesions in a precise time and cost-effective manner while maintaining the integrity of the GIT and avoiding major surgery. The indications for ATR vary depending on the technique, but generally include the presence of large or poorly positioned lesions, particularly in high-risk areas of the GIT such as the esophagus and small intestine, lesions extending beyond the mucosal layer or originating from deeper layers, and when en bloc resection of select lesions is necessary.
For providers referring patients for ATR, we recommend a few important endoscopic pearls when caring for these patients.
1) Biopsy the lesion if there is concern for malignancy — While some studies have noted increased fibrosis during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and some guidelines recommend against biopsies pre ESD, we believe that when there is high pretest probability for malignancy, a biopsy should be obtained. This should involve the area that is most concerning for malignancy (at the margin or center).2
2) While marking a lesion with tattoo is helpful for surgical planning and for lesions difficult to locate endoscopically, we stress the importance of placing tattoos 3 to 5 centimeters distal to the lesion and avoiding tattooing the lesion itself, which has been shown to induce fibrosis and can make resection challenging. Based on an international Delphi consensus, expert recommendations on when and how to endoscopically tattoo a lesion can be instrumental in adequately localizing the lesion, allowing for endoscopic resection, and preventing unnecessary surgeries.3
3) If you encounter a lesion that you are not sure can be resected safely and efficaciously, we recommend against attempting resection that may result in partial resection. This can also induce fibrosis and scarring and limit future attempts at resection.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
EMR is currently utilized for curative treatment of a wide array of GIT lesions limited to the mucosal layer, whether metaplastic, dysplastic, or even in cases with early mucosal cancer, where the risk of submucosal and lymphatic invasion is minimal.4 This makes EMR a versatile and proven therapy, often serving as the first-line treatment for many GIT lesions.
EMR has various techniques that could be categorized into suction or non-suction (lift and cut) techniques. In the suction technique, devices like multiband mucosectomy (MBM) are commonly used, especially in nodular Barrett’s dysplasia, forming a pseudopolyp for subsequent resection. The procedure is characterized by its safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to its widespread adoption in clinical practice. In the lift and cut approach, a submucosal injection is utilized to separate the muscularis propria from the lesion, thereby reducing the risk of perforation. Different solutions, such as normal saline, hypertonic saline, 50% dextrose, or proprietary submucosal injection solutions, are employed for submucosal injection.5
The non-suction technique using a snare to resect polyps after injection is more often used in colonic and small intestinal EMR. Resection can be done via thermal energy in the form of cut or coagulation; however, there is rising data on the use of piecemeal cold snare resection for select flat polyps of the colon.6 There is also promising data on the role of underwater EMR, a common technique employed for colonic lesions, particularly if the lesion does not lift well with submucosal injection.7
Adverse events associated with EMR include bleeding (7%-8%) and perforation (0.9%-2%).8-9 Adequate submucosal fluid injection is crucial to prevent perforations. However, the main limitation of EMR is the piecemeal nature of resections for lesions larger than 20 mm, leading to compromised histopathologic evaluation for complete excision, especially in cases with superficial submucosal invasion (SMI). This can result in residual or recurrent tissue, reportedly 8% to 20%.10 Despite this limitation, EMR remains a reliable strategy, and recurrent lesions are generally manageable through repeat sessions. The importance of EMR as a therapeutic modality lies in its role in addressing lesions with favorable characteristics, where the risk of SMI is low.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
ESD is an evolving technique that can be utilized for submucosal lesions of the GIT, lesions not amenable to EMR due to submucosal fibrosis, when en bloc removal of a lesion is needed for accurate histopathological diagnosis, and when other techniques fail.11-12
ESD was only recently adopted in the United States, requires specialized training, and usually is a lengthier procedure than EMR.13 Compared to EMR, it has higher en bloc resection rates and lower recurrence rates, making it curative for lesions with superficial SMI and favorable histologic features.4,14 The safety profile of ESD appears favorable, with most of the adverse events managed successfully by endoscopic methods. Major complications include intraoperative and delayed perforation, intraoperative and delayed bleeding, aspiration pneumonia, thromboembolism, and stricture formation in the case of circumferential lesions.15
Despite being technically challenging, ESD may provide a cost-effective long-term solution by avoiding surgery, reducing the need for additional interventions by minimizing recurrence rates. Given the technical complexity of ESD, particularly the submucosal dissection portion, techniques such as hybrid ESD developed. Hybrid ESD combines snaring with circumferential mucosal incision and partial submucosal dissection. Although it promises shorter procedure times, reduced complication rates like perforation, and similar recurrence rates compared to traditional ESD, studies have shown lower success rates in en bloc resection.16-17
Both EMR and ESD are considered complementary strategies, and the choice between them should be dictated by lesion characteristics, patient preferences, and local expertise.
Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection (STER)
STER has emerged as a well-established technique for the endoscopic resection of GI subepithelial tumors (SETs) originating from the muscularis propria layer. The standard STER procedure involves a series of steps including submucosal elevation proximal to the SET, mucosotomy, creation of a submucosal tunnel, dissection of the SET within the tunnel, enucleation from the deep muscle layer, and subsequent specimen retrieval followed by mucosal closure.
This technique is typically recommended for SETs smaller than 3.5 cm, particularly those located in the mid or distal esophagus, cardia, or along the greater curvature of the gastric body.18 However, STER may pose technical challenges for larger SETs or lesions in anatomically difficult locations, where surgical resection is recommended instead.19 Notably, recent large-scale meta-analyses have showcased the favorable complete resection and en bloc resection rates of STER in treating GI SETs.20
Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection (EFTR)
EFTR has emerged as a valuable technique in the endoscopic management of gastrointestinal lesions, particularly SETs and lesions not amenable to EMR or ESD due to fibrosis. EFTR involves the resection of all layers of the GIT from mucosa to serosa, and therefore is well-suited for SETs arising from the muscularis propria (MP).20
EFTR entails two main concepts: tissue resection and complete defect closure. Conventional EFTR consists of several steps, which include mucosal and submucosal pre-cutting, circumferential incision, and dissection through the MP or serosa. This results in a full thickness defect, for which closure of the wall defect is achieved using standard endoscopic clips or a combination of clips and endoloops or endoscopic suturing.21 For lesions less than 2 cm, EFTR can be performed in a single step using a cap-mounted full thickness resection device (FTRD). This results in deployment of over-the-scope clip over the target lesion followed by snaring the lesions above the clip.21
Location of the SET generally dictates the specific modality of ATR. For example, esophageal SETs may be more amenable to STER given that the lesion typically runs parallel with the lumen of the tubular esophagus, which allows for easier dissection without the need of full or partial retroflexion. While gastric SETs can be resected with STER, it may be challenging and more effectively addressed with EFTR, particularly when the entire lesion can be grasped into the full-thickness resection device.22 Limited data exists for duodenal EFTR, and colorectal SETs closure is particularly challenging.
Conclusion
It is key to emphasize that ATR cannot be safely established in practice without the incorporation of a multidisciplinary team (surgeons, radiologists, etc.), specialized tools, and trained personnel. This requires dedicated endoscopic rooms, careful patient selection, and a comprehensive approach to patient care before, during, and after these procedures.
Moreover, it is important to note that some patients may require post-procedure hospitalization for observation to ensure no early complications are encountered. Optimal surveillance strategies after ATR rely heavily on the potential for residual or recurrent disease, underlying pathology, and the expertise of the advanced endoscopist. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and technological advances of devices will further enhance the efficacy and safety of ATR in gastroenterology.
Dr. Madi (@MahMadi90) is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri. Dr. Rengarajan (@ArvindRenga) and Dr. Bazarbashi (@AhmadBazarbashi) are based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and no funding was required for this project.
References
1. Copland AP, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on appropriate and tailored polypectomy: Expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.012.
2. Lee SP, et al. Effect of preceding biopsy on the results of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal laterally spreading tumor. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05625-3.
3. Medina-Prado L, et al. When and how to use endoscopic tattooing in the colon: An international Delphi agreement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.024.
4. Rashid MU, et al. EMR and ESD: Indications, techniques and results. Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101742.
5. Castro R, et al. Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.777.
6. Rex DK. Best practices for resection of diminutive and small polyps in the colorectum. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2019.06.004.
7. Lv XH, et al. Underwater EMR for nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.10.044.
8. Fujiya M, et al. Efficacy and adverse events of EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colon neoplasms: a meta-analysis of studies comparing EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.034.
9. Kandel P, Wallace MB. Colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.05.006.
10. Kemper G, et al; ENDOCARE Study Group. Endoscopic techniques to reduce recurrence rates after colorectal EMR: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08574-z.
11. Goto O, et al. Expanding indications for ESD: submucosal disease (SMT/carcinoid tumors). Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.11.006.
12. Wang K, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection, indication, methods and perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1111/den.14474.
13. Herreros de Tejada A. ESD training: A challenging path to excellence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014 Apr 16. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i4.112.
14. Chiba H, et al. Safety and efficacy of simultaneous colorectal ESD for large synchronous colorectal lesions. Endosc Int Open. 2017 Jul. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-110567.
15. Mannath J, Ragunath K. Endoscopic mucosal resection: who and how? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep. doi: 10.1177/1756283X10388683.
16. Wang XY, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: An alternative resection modality for large laterally spreading tumors in the cecum? BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01766-w.
17. McCarty TR, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) compared with conventional ESD for colorectal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1055/a-1266-1855.
18. Jain D, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria. Ann Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.20524/aog.2017.0128.
19. Lv XH, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017 Jan. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4978-7.
20. Cao B, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021 Jan. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.6989/2020.
21. Cai M, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.12.013.
22. Brigic A, et al. A systematic review regarding the feasibility and safety of endoscopic full thickness resection (EFTR) for colonic lesions. Surg Endosc. 2013 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2946-z.
Elevate Your Career: AGA Women in GI Regional Workshops Await
As a woman in a dynamic and ever-changing profession, balancing life as a powerhouse physician or scientist is no easy feat. AGA recognizes the challenges you face and is committed to addressing them directly at the AGA Women in GI Regional Workshops. The program has been expanded to six workshops in 2024.
. Participate in candid discussions regarding the challenges you face as a woman navigating the 21st century healthcare environment. Derive inspiration from your community and cultivate meaningful connections that will carry you beyond the workshop.
You may choose to join us in person or virtually, whatever fits into your busy schedule. We are also pleased to offer grants of $300 to support travel and registration fees for trainee and early career women. Additional details for the Maria Leo-Lieber Travel Award may be found in your confirmation email.
Register today for the final three workshops.
Rocky Mountain West
Saturday, Sept. 8
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Aug. 23
Deadline to register: Aug. 30
Southwest
Saturday, Sept. 14
Houston, Texas
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Aug. 30
Deadline to register: Sept. 6
Southeast
Saturday, Nov. 2
Coral Gables, Florida
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Oct. 8
Deadline to register: Oct. 25
This program is supported by Janssen.
As a woman in a dynamic and ever-changing profession, balancing life as a powerhouse physician or scientist is no easy feat. AGA recognizes the challenges you face and is committed to addressing them directly at the AGA Women in GI Regional Workshops. The program has been expanded to six workshops in 2024.
. Participate in candid discussions regarding the challenges you face as a woman navigating the 21st century healthcare environment. Derive inspiration from your community and cultivate meaningful connections that will carry you beyond the workshop.
You may choose to join us in person or virtually, whatever fits into your busy schedule. We are also pleased to offer grants of $300 to support travel and registration fees for trainee and early career women. Additional details for the Maria Leo-Lieber Travel Award may be found in your confirmation email.
Register today for the final three workshops.
Rocky Mountain West
Saturday, Sept. 8
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Aug. 23
Deadline to register: Aug. 30
Southwest
Saturday, Sept. 14
Houston, Texas
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Aug. 30
Deadline to register: Sept. 6
Southeast
Saturday, Nov. 2
Coral Gables, Florida
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Oct. 8
Deadline to register: Oct. 25
This program is supported by Janssen.
As a woman in a dynamic and ever-changing profession, balancing life as a powerhouse physician or scientist is no easy feat. AGA recognizes the challenges you face and is committed to addressing them directly at the AGA Women in GI Regional Workshops. The program has been expanded to six workshops in 2024.
. Participate in candid discussions regarding the challenges you face as a woman navigating the 21st century healthcare environment. Derive inspiration from your community and cultivate meaningful connections that will carry you beyond the workshop.
You may choose to join us in person or virtually, whatever fits into your busy schedule. We are also pleased to offer grants of $300 to support travel and registration fees for trainee and early career women. Additional details for the Maria Leo-Lieber Travel Award may be found in your confirmation email.
Register today for the final three workshops.
Rocky Mountain West
Saturday, Sept. 8
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Aug. 23
Deadline to register: Aug. 30
Southwest
Saturday, Sept. 14
Houston, Texas
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Aug. 30
Deadline to register: Sept. 6
Southeast
Saturday, Nov. 2
Coral Gables, Florida
Deadline to apply for a travel grant: Oct. 8
Deadline to register: Oct. 25
This program is supported by Janssen.
How To Navigate Your First Job
In a special episode live from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024, host Dr. Matthew Whitson talks with returning guest Dr. Janice Jou. Dr. Jou is a transplant hematologist at the Portland VA and currently serves as professor of medicine and fellowship program director at Oregon Health & Science University. Don’t miss her insight as she shares advice all about what she wishes she knew when going into her first job in gastroenterology. Dr. Jou also answers questions from the audience on topics including “when to say no” and the importance of encouraging emotional transparency with fellows and faculty.
Catch up with past episodes and subscribe wherever you listen to podcasts. You can also listen by clicking on the episode name below.
- Episode 5: Janice Jou: Live from #DDW2024 with tips for your first job
- Episode 4: Loren Rabinowitz and Rachel Issaka: Building research collaborations
- Episode 3: Andy Tau: How to treat GI emergencies
- Episode 2: Laurel Fisher and Asma Khapra: Advancing and advocating for women in GI
- Episode 1: Barbara Jung: Unpacking mentorship with AGA’s president
In a special episode live from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024, host Dr. Matthew Whitson talks with returning guest Dr. Janice Jou. Dr. Jou is a transplant hematologist at the Portland VA and currently serves as professor of medicine and fellowship program director at Oregon Health & Science University. Don’t miss her insight as she shares advice all about what she wishes she knew when going into her first job in gastroenterology. Dr. Jou also answers questions from the audience on topics including “when to say no” and the importance of encouraging emotional transparency with fellows and faculty.
Catch up with past episodes and subscribe wherever you listen to podcasts. You can also listen by clicking on the episode name below.
- Episode 5: Janice Jou: Live from #DDW2024 with tips for your first job
- Episode 4: Loren Rabinowitz and Rachel Issaka: Building research collaborations
- Episode 3: Andy Tau: How to treat GI emergencies
- Episode 2: Laurel Fisher and Asma Khapra: Advancing and advocating for women in GI
- Episode 1: Barbara Jung: Unpacking mentorship with AGA’s president
In a special episode live from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024, host Dr. Matthew Whitson talks with returning guest Dr. Janice Jou. Dr. Jou is a transplant hematologist at the Portland VA and currently serves as professor of medicine and fellowship program director at Oregon Health & Science University. Don’t miss her insight as she shares advice all about what she wishes she knew when going into her first job in gastroenterology. Dr. Jou also answers questions from the audience on topics including “when to say no” and the importance of encouraging emotional transparency with fellows and faculty.
Catch up with past episodes and subscribe wherever you listen to podcasts. You can also listen by clicking on the episode name below.
- Episode 5: Janice Jou: Live from #DDW2024 with tips for your first job
- Episode 4: Loren Rabinowitz and Rachel Issaka: Building research collaborations
- Episode 3: Andy Tau: How to treat GI emergencies
- Episode 2: Laurel Fisher and Asma Khapra: Advancing and advocating for women in GI
- Episode 1: Barbara Jung: Unpacking mentorship with AGA’s president
Retirement Planning for Gastroenterologists
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Retirement planning starts the day we start our careers. Whenever we start any project, it is always worthwhile to learn how the project works, what we want to pursue and achieve with the project, how to exit the project, and when is the right time to exit.
As physicians, gastroenterologists go through several years of vigorous training, years spent studying, researching, practicing, and juggling between work and life, trying to lead a well-balanced life. With all the years of medical training, we do not get the same level of education in financial planning in order to attain financial stability, financial empowerment, or resources that we need to put in place for a successful retirement.
Many physicians like to work and provide services as long as they can, provided the physical and mental capacity permits. Retirement planning should start as early as possible — at your first job, with the first paycheck. Having a strategic plan and understanding several personal factors can help one make this journey successful.
Financial Planning
Financial planning starts with investments in 401k, IRA, defined benefit, and defined contribution plans, as early as possible and to the maximum extent possible. It is beneficial to contribute at the first opportunity and contribute enough to the employer retirement plan to earn the full employer match. Also consider capital investment opportunities that match your risk appetite and returns, as these compound and grow over time. This can be done by adjusting personal expenses and lifestyle, giving priority to savings and future wealth management, and auto-escalation of permitted retirement contributions annually.
Assessing your financial situation periodically to determine retirement needs based on how long you intend to work and preferred lifestyle post retirement (travel, leisurely activities, etc.) is important. It is also pertinent to align revenue earned, expenses made, and wealth saved to support post-retirement life. Consider hiring a financial advisor who has the best interests in your personal wealth management. These are usually found with reputable institutions at a fixed percentage cost. Finding a trustworthy knowledgeable advisor is the key. Learning from your colleagues, networking, and learning from friends in and out of healthcare are good resources to find the right financial advisor.
Healthcare expenses should be planned as well as part of financial planning. Short-term and long-term disability and long-term care expenses should be investigated when planning for healthcare needs.
Transition Planning
Timing of retirement is based on factors such as age, financial status, personal health and preferences. The transition can be facilitated by better communication with colleagues, partners, employer, staff, and patients. Identifying a successor and planning for continuity of care of the patients, such as transitioning patients to another provider, is important as well. This may involve hiring a new associate, merging with another practice, or selling the practice.
Healthcare Coverage
One of the biggest expenses with retirement is healthcare coverage. Healthcare coverage options need to be analyzed which may include Medicare eligibility, enrollment, potential needs after retirement, including preventative care, treatment of chronic conditions, long term care services, and unexpected health outcomes and consequences.
Lifestyle and Travel Planning
Reflect on the retirement lifestyle, hobbies, and passions to be explored. Some activities like volunteer work, continuing educational opportunities, and advisory work, will help maintain physical and mental health. Consider downsizing living arrangements to align with retirement lifestyle goals which may include relocating to a different area as it fits your needs.
Legal and Estate Planning
Review and update legal documents including power of attorney, healthcare directives, will, trusts, and periodically ensure that these documents reflect your wishes.
Professional Development
Retirement may not mean quitting work completely. Some may look at this as an opportunity for professional development and pivoting to a different career that suits their lifestyle and needs. Gastroenterologists may contribute to the field and stay connected by being mentors, advisors, or, industry partners; being involved in national organizations; leading purposeful projects; or teaching part-time or on a volunteer basis.
Emotional and Social Support
Being a physician and a leader on treatment teams after so many years, some may feel lonely and unproductive with a lack of purpose in retirement; while others are excited about the free time they gained to pursue other activities and projects.
The process can be emotionally challenging even for well-prepared individuals. Finding friends, family, and professionals who can support you through this process will be helpful as you go through the uncertainties, anxiety, and fear during this phase of life. Think of developing hobbies and interests and nurturing networks outside of work environment that will keep you engaged and content during this transition.
Gastroenterologists can plan for a financially secure, emotionally fulfilling, and professionally satisfying transition tailored to their needs and preferences. Seeking help from financial advisors, legal experts, mentors, and other professionals who can provide valuable advice, support, and guidance is crucial during this process.
Do what you love and love what you do.
Dr. Appalaneni is a gastroenterologist at Dayton Gastroenterology in Beavercreek, Ohio, and a clinical assistant professor at Boonshoft School of Medicine, Wright State University in Dayton, Ohio. This article is not a financial planning document, nor legal advice; these are the author’s learnings, experiences, and opinions and are not considered financial advice.
Navigating as a GI Locum: My Path and Guide to This Alternative Practice Model
My successful career in academic gastroenterology makes me a natural proponent of the academic model of practice. However, in my current role as a locum tenens, I have witnessed the versatility that locum assignments offer gastroenterologists, particularly when flexibility in their professional lives is paramount.
The locum tenens industry is a growing feature of the healthcare staffing landscape. My perspective is unique, transitioning from professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at an academic medical center to a self-employed locum gastroenterologist.
As chief, I hired locums to offer additional coverage to the faculty staffing as our division, inclusive of GI fellowship and endoscopy volume, expanded. I recruited, supervised, and assigned responsibilities to the locums. Not only were these physicians professional and competent, but they also contributed to my division’s forward evolution. Based on this experience, I was confident that I could successfully perform as a locum gastroenterologist myself.
My work as a locum these past 5 years has been a positive professional transition for me. I have enjoyed meeting and working with new colleagues, including international locums who travel to work in the United States. I have also witnessed how early-career and mid-career gastroenterologists have taken advantage of this flexible and well-remunerated work.
What It Entails to Be a Locum Tenens
I suspect you have been on the receiving end of emails and postcards from locum tenens companies recruiting for potential assignments and have wondered about the specifics. Essentially, a locum physician functions as an independent contractor who accepts a temporary position at a healthcare organization to provide clinical staffing support during periods of staffing disruption.
Assignments vary in geographic location, facility work site (outpatient vs inpatient), hours, required skills, cadence of assignment, and expected length of staffing need. The locum physician has complete control over selecting the assignment location, the intensity of responsibilities, and the time they wish to commit to the position. Temporal flexibility offers locums the opportunity to commit from a few weeks per year to a full-time commitment. Locums can also combine multiple assignments in different regions or states to match the targeted number of weeks they wish to commit to and the financial goal they have set.
I have met physicians working a few weeks a year during time off from their permanent jobs to supplement their incomes, as well as fully employed physicians leveraging locum placements to explore locations or practices that they have an interest in. Gastroenterologists facing planned or unplanned life events may find the role enticing as locum opportunities offer an elevated level of flexibility and autonomy.
The Role of the Locum Tenens Company
Locum tenens companies have arrangements with healthcare facilities to provide temporary staffing. They aim to recruit prospective physicians, establish a collaborative relationship, and align these physicians with a locum assignment that benefits all parties.
Once the physician has completed the company’s credentialing packet, the company facilitates credentialing for new state medical licensures and the specific healthcare facility. The company conducts all negotiations, communications, and financial arrangements between the locum physician and the facility. Locum physicians do not communicate directly with the facility, at least not initially. The company also provides medical malpractice coverage through an established insurance broker. The company arranges travel (flights, car rentals, and hotels) for the assignment, and the healthcare facility reimburses the company.
Lastly, the company arranges a phone interview between the locum physician and the facility’s gastroenterologist or medical director for a more detailed description of expected responsibilities and level of staffing for endoscopy before the locum physician decides whether the job is a “good fit” for their skills and objectives. It is critical at this point that the locum physician does their due diligence, asking thoughtful questions to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the role before committing.
What Does It Mean to Be an Independent Contractor
An independent contractor is contracted to perform work but is not an employee of an organization (ie, self-employed). This is an important distinction when it comes to the IRS, tax obligations, and allowable deductions.
Initially, this may seem confusing, but some websites review the specifics of these significant taxation differences. Because you are an independent contractor, your paycheck depicts your compensation without any deductions taken. At year’s end, you receive form 1099 rather than the more familiar W-2. The most critical difference is that as a W-2 employed person, you and the employer each contribute half of the obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes owed, but as an independent contractor you are required to pay the entire obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Also important to consider is that although the locum tenens company facilitates necessary documentation, travel, and work schedules, you will be responsible for tracking your work-related finances, and maintaining your CME. This is not difficult but requires attention throughout the year and is manageable with a bit of organizing. A simple example is that meals are deductible on your taxes and can be easily tallied by the government’s per diem rate found at www.gsa.gov — so it is not necessary to save receipts. While it is important to become familiar with these financial nuances as they will affect your net income, they are not as intimidating or complex as you may initially believe.
Primary Benefits of Locum Tenens Assignments
In my experience, the benefits of working as a locum gastroenterologist include the opportunity to remain engaged in a gratifying career while having enhanced autonomy and flexibility. You can construct a schedule in a location most pleasing to you that fits your financial needs. You may work just a few weeks per year to full-time. You can uniquely plan for your desired personal time and alternative professional ambitions. If you choose to transition back to traditional full-time employment, the pivot remains feasible because you have demonstrated attractive professional attributes such as adaptability in different settings, maintenance of necessary skill sets, and collaboration with medical staffing of various complexities.
Quick Points to Consider
- Review the tax obligations and deductions before signing on to your first assignment.
- Healthcare benefits are not provided. If you must purchase healthcare, your healthcare premiums are 100% deductible.
- Malpractice insurance is provided through the locum tenens company.
- The points on flights, hotels, and car rentals remain in your accounts and can be used by you for personal travel in the future.
- You may be able to negotiate hourly rates and terms of responsibilities in certain instances. There’s no harm in requesting.
- Before accepting an assignment, review the website and location of the facility, accessibility to airports, frequency of flights, the physician directory, and services available.
- If your plans change and you are unable to complete a scheduled assignment previously confirmed, you must notify the locum tenens company within a specified window from the start date (usually 30 days) to avoid penalty.
Institutions utilizing locum physicians generally are doing so because their staffing is not optimal; for example, there may have been a transition in leadership or the facility may be located in a rural area. Self-awareness is key; recognize that you are essentially a guest who may need to adapt to the prevailing culture and make do with the resources at hand. You are not there to step in, innovate, or institute changes. Most often the office staff, nurses, and other physicians are very grateful that you are present and a part of the team.
Dr. Bartholomew is a gastroenterologist based in Sarasota, Florida. She has no conflicts to declare in relation to this article.
My successful career in academic gastroenterology makes me a natural proponent of the academic model of practice. However, in my current role as a locum tenens, I have witnessed the versatility that locum assignments offer gastroenterologists, particularly when flexibility in their professional lives is paramount.
The locum tenens industry is a growing feature of the healthcare staffing landscape. My perspective is unique, transitioning from professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at an academic medical center to a self-employed locum gastroenterologist.
As chief, I hired locums to offer additional coverage to the faculty staffing as our division, inclusive of GI fellowship and endoscopy volume, expanded. I recruited, supervised, and assigned responsibilities to the locums. Not only were these physicians professional and competent, but they also contributed to my division’s forward evolution. Based on this experience, I was confident that I could successfully perform as a locum gastroenterologist myself.
My work as a locum these past 5 years has been a positive professional transition for me. I have enjoyed meeting and working with new colleagues, including international locums who travel to work in the United States. I have also witnessed how early-career and mid-career gastroenterologists have taken advantage of this flexible and well-remunerated work.
What It Entails to Be a Locum Tenens
I suspect you have been on the receiving end of emails and postcards from locum tenens companies recruiting for potential assignments and have wondered about the specifics. Essentially, a locum physician functions as an independent contractor who accepts a temporary position at a healthcare organization to provide clinical staffing support during periods of staffing disruption.
Assignments vary in geographic location, facility work site (outpatient vs inpatient), hours, required skills, cadence of assignment, and expected length of staffing need. The locum physician has complete control over selecting the assignment location, the intensity of responsibilities, and the time they wish to commit to the position. Temporal flexibility offers locums the opportunity to commit from a few weeks per year to a full-time commitment. Locums can also combine multiple assignments in different regions or states to match the targeted number of weeks they wish to commit to and the financial goal they have set.
I have met physicians working a few weeks a year during time off from their permanent jobs to supplement their incomes, as well as fully employed physicians leveraging locum placements to explore locations or practices that they have an interest in. Gastroenterologists facing planned or unplanned life events may find the role enticing as locum opportunities offer an elevated level of flexibility and autonomy.
The Role of the Locum Tenens Company
Locum tenens companies have arrangements with healthcare facilities to provide temporary staffing. They aim to recruit prospective physicians, establish a collaborative relationship, and align these physicians with a locum assignment that benefits all parties.
Once the physician has completed the company’s credentialing packet, the company facilitates credentialing for new state medical licensures and the specific healthcare facility. The company conducts all negotiations, communications, and financial arrangements between the locum physician and the facility. Locum physicians do not communicate directly with the facility, at least not initially. The company also provides medical malpractice coverage through an established insurance broker. The company arranges travel (flights, car rentals, and hotels) for the assignment, and the healthcare facility reimburses the company.
Lastly, the company arranges a phone interview between the locum physician and the facility’s gastroenterologist or medical director for a more detailed description of expected responsibilities and level of staffing for endoscopy before the locum physician decides whether the job is a “good fit” for their skills and objectives. It is critical at this point that the locum physician does their due diligence, asking thoughtful questions to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the role before committing.
What Does It Mean to Be an Independent Contractor
An independent contractor is contracted to perform work but is not an employee of an organization (ie, self-employed). This is an important distinction when it comes to the IRS, tax obligations, and allowable deductions.
Initially, this may seem confusing, but some websites review the specifics of these significant taxation differences. Because you are an independent contractor, your paycheck depicts your compensation without any deductions taken. At year’s end, you receive form 1099 rather than the more familiar W-2. The most critical difference is that as a W-2 employed person, you and the employer each contribute half of the obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes owed, but as an independent contractor you are required to pay the entire obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Also important to consider is that although the locum tenens company facilitates necessary documentation, travel, and work schedules, you will be responsible for tracking your work-related finances, and maintaining your CME. This is not difficult but requires attention throughout the year and is manageable with a bit of organizing. A simple example is that meals are deductible on your taxes and can be easily tallied by the government’s per diem rate found at www.gsa.gov — so it is not necessary to save receipts. While it is important to become familiar with these financial nuances as they will affect your net income, they are not as intimidating or complex as you may initially believe.
Primary Benefits of Locum Tenens Assignments
In my experience, the benefits of working as a locum gastroenterologist include the opportunity to remain engaged in a gratifying career while having enhanced autonomy and flexibility. You can construct a schedule in a location most pleasing to you that fits your financial needs. You may work just a few weeks per year to full-time. You can uniquely plan for your desired personal time and alternative professional ambitions. If you choose to transition back to traditional full-time employment, the pivot remains feasible because you have demonstrated attractive professional attributes such as adaptability in different settings, maintenance of necessary skill sets, and collaboration with medical staffing of various complexities.
Quick Points to Consider
- Review the tax obligations and deductions before signing on to your first assignment.
- Healthcare benefits are not provided. If you must purchase healthcare, your healthcare premiums are 100% deductible.
- Malpractice insurance is provided through the locum tenens company.
- The points on flights, hotels, and car rentals remain in your accounts and can be used by you for personal travel in the future.
- You may be able to negotiate hourly rates and terms of responsibilities in certain instances. There’s no harm in requesting.
- Before accepting an assignment, review the website and location of the facility, accessibility to airports, frequency of flights, the physician directory, and services available.
- If your plans change and you are unable to complete a scheduled assignment previously confirmed, you must notify the locum tenens company within a specified window from the start date (usually 30 days) to avoid penalty.
Institutions utilizing locum physicians generally are doing so because their staffing is not optimal; for example, there may have been a transition in leadership or the facility may be located in a rural area. Self-awareness is key; recognize that you are essentially a guest who may need to adapt to the prevailing culture and make do with the resources at hand. You are not there to step in, innovate, or institute changes. Most often the office staff, nurses, and other physicians are very grateful that you are present and a part of the team.
Dr. Bartholomew is a gastroenterologist based in Sarasota, Florida. She has no conflicts to declare in relation to this article.
My successful career in academic gastroenterology makes me a natural proponent of the academic model of practice. However, in my current role as a locum tenens, I have witnessed the versatility that locum assignments offer gastroenterologists, particularly when flexibility in their professional lives is paramount.
The locum tenens industry is a growing feature of the healthcare staffing landscape. My perspective is unique, transitioning from professor of medicine and chief of gastroenterology at an academic medical center to a self-employed locum gastroenterologist.
As chief, I hired locums to offer additional coverage to the faculty staffing as our division, inclusive of GI fellowship and endoscopy volume, expanded. I recruited, supervised, and assigned responsibilities to the locums. Not only were these physicians professional and competent, but they also contributed to my division’s forward evolution. Based on this experience, I was confident that I could successfully perform as a locum gastroenterologist myself.
My work as a locum these past 5 years has been a positive professional transition for me. I have enjoyed meeting and working with new colleagues, including international locums who travel to work in the United States. I have also witnessed how early-career and mid-career gastroenterologists have taken advantage of this flexible and well-remunerated work.
What It Entails to Be a Locum Tenens
I suspect you have been on the receiving end of emails and postcards from locum tenens companies recruiting for potential assignments and have wondered about the specifics. Essentially, a locum physician functions as an independent contractor who accepts a temporary position at a healthcare organization to provide clinical staffing support during periods of staffing disruption.
Assignments vary in geographic location, facility work site (outpatient vs inpatient), hours, required skills, cadence of assignment, and expected length of staffing need. The locum physician has complete control over selecting the assignment location, the intensity of responsibilities, and the time they wish to commit to the position. Temporal flexibility offers locums the opportunity to commit from a few weeks per year to a full-time commitment. Locums can also combine multiple assignments in different regions or states to match the targeted number of weeks they wish to commit to and the financial goal they have set.
I have met physicians working a few weeks a year during time off from their permanent jobs to supplement their incomes, as well as fully employed physicians leveraging locum placements to explore locations or practices that they have an interest in. Gastroenterologists facing planned or unplanned life events may find the role enticing as locum opportunities offer an elevated level of flexibility and autonomy.
The Role of the Locum Tenens Company
Locum tenens companies have arrangements with healthcare facilities to provide temporary staffing. They aim to recruit prospective physicians, establish a collaborative relationship, and align these physicians with a locum assignment that benefits all parties.
Once the physician has completed the company’s credentialing packet, the company facilitates credentialing for new state medical licensures and the specific healthcare facility. The company conducts all negotiations, communications, and financial arrangements between the locum physician and the facility. Locum physicians do not communicate directly with the facility, at least not initially. The company also provides medical malpractice coverage through an established insurance broker. The company arranges travel (flights, car rentals, and hotels) for the assignment, and the healthcare facility reimburses the company.
Lastly, the company arranges a phone interview between the locum physician and the facility’s gastroenterologist or medical director for a more detailed description of expected responsibilities and level of staffing for endoscopy before the locum physician decides whether the job is a “good fit” for their skills and objectives. It is critical at this point that the locum physician does their due diligence, asking thoughtful questions to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the role before committing.
What Does It Mean to Be an Independent Contractor
An independent contractor is contracted to perform work but is not an employee of an organization (ie, self-employed). This is an important distinction when it comes to the IRS, tax obligations, and allowable deductions.
Initially, this may seem confusing, but some websites review the specifics of these significant taxation differences. Because you are an independent contractor, your paycheck depicts your compensation without any deductions taken. At year’s end, you receive form 1099 rather than the more familiar W-2. The most critical difference is that as a W-2 employed person, you and the employer each contribute half of the obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes owed, but as an independent contractor you are required to pay the entire obligated Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Also important to consider is that although the locum tenens company facilitates necessary documentation, travel, and work schedules, you will be responsible for tracking your work-related finances, and maintaining your CME. This is not difficult but requires attention throughout the year and is manageable with a bit of organizing. A simple example is that meals are deductible on your taxes and can be easily tallied by the government’s per diem rate found at www.gsa.gov — so it is not necessary to save receipts. While it is important to become familiar with these financial nuances as they will affect your net income, they are not as intimidating or complex as you may initially believe.
Primary Benefits of Locum Tenens Assignments
In my experience, the benefits of working as a locum gastroenterologist include the opportunity to remain engaged in a gratifying career while having enhanced autonomy and flexibility. You can construct a schedule in a location most pleasing to you that fits your financial needs. You may work just a few weeks per year to full-time. You can uniquely plan for your desired personal time and alternative professional ambitions. If you choose to transition back to traditional full-time employment, the pivot remains feasible because you have demonstrated attractive professional attributes such as adaptability in different settings, maintenance of necessary skill sets, and collaboration with medical staffing of various complexities.
Quick Points to Consider
- Review the tax obligations and deductions before signing on to your first assignment.
- Healthcare benefits are not provided. If you must purchase healthcare, your healthcare premiums are 100% deductible.
- Malpractice insurance is provided through the locum tenens company.
- The points on flights, hotels, and car rentals remain in your accounts and can be used by you for personal travel in the future.
- You may be able to negotiate hourly rates and terms of responsibilities in certain instances. There’s no harm in requesting.
- Before accepting an assignment, review the website and location of the facility, accessibility to airports, frequency of flights, the physician directory, and services available.
- If your plans change and you are unable to complete a scheduled assignment previously confirmed, you must notify the locum tenens company within a specified window from the start date (usually 30 days) to avoid penalty.
Institutions utilizing locum physicians generally are doing so because their staffing is not optimal; for example, there may have been a transition in leadership or the facility may be located in a rural area. Self-awareness is key; recognize that you are essentially a guest who may need to adapt to the prevailing culture and make do with the resources at hand. You are not there to step in, innovate, or institute changes. Most often the office staff, nurses, and other physicians are very grateful that you are present and a part of the team.
Dr. Bartholomew is a gastroenterologist based in Sarasota, Florida. She has no conflicts to declare in relation to this article.
Navigating and Negotiating Maternity/Paternity Leave in Private Practice
Marybeth Spanarkel, MD, a Duke University School of Medicine alumna (1979), completed her internal medicine and gastroenterology training at the University of Pennsylvania, National Institutes of Health, and Johns Hopkins. Initially groomed for an academic role, she chose a clinical position in private practice at Duke Regional Hospital in Durham, North Carolina, where she worked for 25 years.
At age 59, Dr. Spanarkel suffered a neck injury leading to permanent C5-6 radiculopathy, which abruptly ended her career as a clinical gastroenterologist. Since then, she has been a passionate advocate for ergonomic reform in endoscopy. Currently, she is the senior medical adviser and cofounder of ColoWrap, a device designed to improve colonoscopy procedures and reduce ergonomic risk.

Dr. Spanarkel spoke with GI & Hepatology News about the issues that gastroenterologists should consider when negotiating maternity/paternity leave in private practice.
Would you share with the readers your experience with maternity leave in private practice?
As a mother of four, I had two children during my GI fellowship, and received my full salary each time for a 3-month maternity leave. My third child arrived in the time period between leaving my academic position and starting in private practice. My fourth child was born after 2 years in private practice, and I took 3 weeks off. Fortunately, I was not asked to pay upfront overhead fees in my 15-person practice. However, my reduced productivity during that time was factored into my salary calculations, leading to a decreased income for the following 6 months.
How does pregnancy affect your performance and productivity as a GI physician?
“We” may be having a baby, but “You” are pregnant. While some may experience few symptoms, most pregnant doctors deal with problems such as nausea and extreme fatigue, especially in the first trimester. The third trimester may result in reduced physical agility, particularly when performing procedures. Even in uncomplicated pregnancies, balancing the physiologic changes with the demands of a full-time GI role can be strenuous. And this doesn’t even take into account potential infertility issues, pregnancy complications, or newborn concerns that physicians may encounter.
And after childbirth?
Post childbirth, despite a supportive partner, the primary responsibilities such as feeding, nursing support, and bonding often fall on the biological mother. These duties are superimposed on the doctor’s own recovery and postpartum changes. While the United States commonly recognizes 3 months as a standard maternity leave, some European countries advocate for up to 12 months, demonstrating again that this is not an “overnight” transition.
In the past, GI doctors were mostly male, but now there’s a growing number of females in the field. Despite this shift, studies still highlight continued gender disparities in salaries and leadership opportunities, and support for pregnancy-related issues has been largely under-addressed.1,2,3
How do academic centers manage maternity leave?
In academic centers or large healthcare settings, maternity leave policies are more standardized compared with private practice. Doctors are salaried depending on their level of training and experience and then they are assigned a mix of clinical, research, teaching, and/or administrative duties.
Typically, maternity leave in these centers is a standard 3-month period, often combining paid time off (PTO) with unpaid or paid leave. In some cases, short- or long-term disability payments are available, especially for complications. But, the financial impact of a doctor’s maternity leave on the overall unit is usually minimal due to the number of participants in the system. The extra workload is diffused over a larger number of doctors, so the new schedule is generally manageable.4 And since the salary of the employee/physician includes a portion of nonclinical time (administrative, teaching, research), the actual decrease in revenue isn’t that dramatic.
How about maternity leave in private practice?
Maternity leave in private practice, especially if there is only a small number of partners, is handled entirely differently. Think of a household budget (rent, utilities, salaries, benefits, insurance) that is shared by “roommates,” the other partners in the group. To understand how maternity leave affects a private practice, you have to understand how your private practice operates.
Typically, newly hired private practice physicians receive a set salary, with the expectation that their patient revenue will eventually cover both their share of overhead and their salary. The practice might set a monthly quota, offering a bonus for exceeding it, or they may retain the extra revenue until the physician becomes a full partner.
Income in private practice is almost entirely generated by seeing patients and performing procedures, as opposed to non-reimbursable activities such as committee meetings or lectures. Physicians learn to be highly efficient with their time, a standard also expected of their employees. They have more control over their schedules, vacation time, and patient/procedure load. Since income is affected only after overhead costs are covered, each doctor’s approach to workload and pace doesn’t typically concern the other partners. Some physicians may be highly aggressive and efficient (and thus increase their salaries), while others may prefer a slower pace due to external responsibilities.
This arrangement is often seen as fair because the established practice helps you get started by providing the environment for you to generate revenue. This includes patient referrals, office space, and staff. In return, the practice not only hopes you will achieve its goals/quotas but may expect a return on its investment in you.
Additionally, access to shared passive revenue streams, such as a pathology lab, clinical research trials, or facility fees from an endoscopy center, may only be available once a certain level of productivity or full partnership is reached.
The initial years in private practice can be seen as a trial period. Your professional reputation, liability, and patient population are more directly in your own hands. Decision-making, patient management, and potential complications are more wholly your responsibility, which can feel isolating. However, providing excellent care can build your reputation, as satisfied patients will seek you out and generate more referrals. During this time, you need to demonstrate to your prospective partners your commitment to delivering high-quality patient care and to meeting certain minimum standards of volume. If clinical medicine is your passion, the right private practice role can be a fulfilling platform where you do what you love to do and simultaneously are well compensated for it.
How does taking maternity affect shared overhead?
Any physician requiring “leave” will affect the overall revenue of a practice. Issues regarding maternity leave in private practice can also be applied to adoption, paternity, surrogacy, foster care, or medical leave. For instance, if the cumulative overhead is $100k per month in a practice with five doctors, each doctor contributes $20k monthly, totaling $240k each annually.
For example, Dr. “Jones” generates $480k in charges/collections, so after paying his share of overhead, his salary is $240k for the year. In contrast, Dr. “Smith” works more intensely, doubling the patients and procedures of Dr. “Jones,” and generates $960k. After deducting the overhead, his salary is $720k, more than twice his partner’s salary.
Let’s say the practice is considering hiring a new doctor who is 2 months pregnant. If he/she generates $380k in charges in the first year but owes $240k in shared overhead, his/her salary would be $140k, which is not very attractive as a “starting salary” for a highly competent, well-trained GI physician. In extreme cases, with high overhead and low productivity, there might be no revenue for salary once the overhead is paid.
In private practice, is there hesitancy hiring a pregnant person?
While it’s illegal to inquire about pregnancy during employment interviews, partners in private practice might still hesitate to hire a pregnant person. Concerns include sharing overhead costs, handling extra calls or emergencies, and wanting new physicians to contribute equally.
However, this viewpoint can be shortsighted. , as older partners might also face personal or medical needs. Adopting a flexible, empathetic approach toward partners can foster goodwill, potentially enhancing revenue, teamwork, and patient care over a long-term career. The value of empathy should not be underestimated.
What should you consider when you are applying for a new private practice job?
When applying for a private practice position, here are some key points to consider:
- If possible, have your children while employed by a large healthcare system with an established leave policy.
- In a private practice job, ensure the employment contract clearly outlines the terms of medical leave (maternity, paternity, adoption, illness), including details on overhead, benefits, salary, call schedule, and the path to full partnership. Consider having a lawyer review the contract.
- Inquire about how other types of leave, like sabbatical, personal, family, military, or medical, are managed. Understand the implications for salary and overhead, for example, in cases of a partner needing extended leave for surgery or rehabilitation.
- Review the requirements for becoming a full partner, particularly if this includes potential future passive income sources. Does maternity leave (or other types of leave) alter this path?
- Examine the entire benefit package, with a focus on long-term disability policies, considering the statistics on both temporary and permanent disability among GI doctors.5
- Negotiate terms for overhead during leave. Options might include a long term or interest-free loan to cover the 3-month sum, a 50% reduction in overhead charges, or “overhead protection insurance” where a designated policy covers overhead for partners on medical leave.
Remember, a brief leave in a 30-year career is relatively minor. Prioritize taking enough time for yourself and your child. Concentrate on long term fairness when engaged in salary negotiations. Don’t rush back; there will be time later to compensate for a temporary decrease in salary, but limited opportunities to spend age-specific time with your young child.
References
1. Butkus R, et al. Achieving Gender Equity in Physician Compensation and Career Advancement: A Position Paper of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2018 May 15. doi: 10.7326/M17-3438.
2. American Medical Association. Advancing Gender Equity in Medicine: Resources for physicians. 2024 Feb 28.
3. Devi J, et al. Fixing the leaky pipeline: gender imbalance in gastroenterology in Asia-Pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Sept. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16353.
4. Mahadevan U, et al. Closing the gender gap: building a successful career and leadership in research as a female gastroenterologist. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00135-2.
5. Murphy R. Know your maternity leave options. 2024 Apr 4.
Marybeth Spanarkel, MD, a Duke University School of Medicine alumna (1979), completed her internal medicine and gastroenterology training at the University of Pennsylvania, National Institutes of Health, and Johns Hopkins. Initially groomed for an academic role, she chose a clinical position in private practice at Duke Regional Hospital in Durham, North Carolina, where she worked for 25 years.
At age 59, Dr. Spanarkel suffered a neck injury leading to permanent C5-6 radiculopathy, which abruptly ended her career as a clinical gastroenterologist. Since then, she has been a passionate advocate for ergonomic reform in endoscopy. Currently, she is the senior medical adviser and cofounder of ColoWrap, a device designed to improve colonoscopy procedures and reduce ergonomic risk.

Dr. Spanarkel spoke with GI & Hepatology News about the issues that gastroenterologists should consider when negotiating maternity/paternity leave in private practice.
Would you share with the readers your experience with maternity leave in private practice?
As a mother of four, I had two children during my GI fellowship, and received my full salary each time for a 3-month maternity leave. My third child arrived in the time period between leaving my academic position and starting in private practice. My fourth child was born after 2 years in private practice, and I took 3 weeks off. Fortunately, I was not asked to pay upfront overhead fees in my 15-person practice. However, my reduced productivity during that time was factored into my salary calculations, leading to a decreased income for the following 6 months.
How does pregnancy affect your performance and productivity as a GI physician?
“We” may be having a baby, but “You” are pregnant. While some may experience few symptoms, most pregnant doctors deal with problems such as nausea and extreme fatigue, especially in the first trimester. The third trimester may result in reduced physical agility, particularly when performing procedures. Even in uncomplicated pregnancies, balancing the physiologic changes with the demands of a full-time GI role can be strenuous. And this doesn’t even take into account potential infertility issues, pregnancy complications, or newborn concerns that physicians may encounter.
And after childbirth?
Post childbirth, despite a supportive partner, the primary responsibilities such as feeding, nursing support, and bonding often fall on the biological mother. These duties are superimposed on the doctor’s own recovery and postpartum changes. While the United States commonly recognizes 3 months as a standard maternity leave, some European countries advocate for up to 12 months, demonstrating again that this is not an “overnight” transition.
In the past, GI doctors were mostly male, but now there’s a growing number of females in the field. Despite this shift, studies still highlight continued gender disparities in salaries and leadership opportunities, and support for pregnancy-related issues has been largely under-addressed.1,2,3
How do academic centers manage maternity leave?
In academic centers or large healthcare settings, maternity leave policies are more standardized compared with private practice. Doctors are salaried depending on their level of training and experience and then they are assigned a mix of clinical, research, teaching, and/or administrative duties.
Typically, maternity leave in these centers is a standard 3-month period, often combining paid time off (PTO) with unpaid or paid leave. In some cases, short- or long-term disability payments are available, especially for complications. But, the financial impact of a doctor’s maternity leave on the overall unit is usually minimal due to the number of participants in the system. The extra workload is diffused over a larger number of doctors, so the new schedule is generally manageable.4 And since the salary of the employee/physician includes a portion of nonclinical time (administrative, teaching, research), the actual decrease in revenue isn’t that dramatic.
How about maternity leave in private practice?
Maternity leave in private practice, especially if there is only a small number of partners, is handled entirely differently. Think of a household budget (rent, utilities, salaries, benefits, insurance) that is shared by “roommates,” the other partners in the group. To understand how maternity leave affects a private practice, you have to understand how your private practice operates.
Typically, newly hired private practice physicians receive a set salary, with the expectation that their patient revenue will eventually cover both their share of overhead and their salary. The practice might set a monthly quota, offering a bonus for exceeding it, or they may retain the extra revenue until the physician becomes a full partner.
Income in private practice is almost entirely generated by seeing patients and performing procedures, as opposed to non-reimbursable activities such as committee meetings or lectures. Physicians learn to be highly efficient with their time, a standard also expected of their employees. They have more control over their schedules, vacation time, and patient/procedure load. Since income is affected only after overhead costs are covered, each doctor’s approach to workload and pace doesn’t typically concern the other partners. Some physicians may be highly aggressive and efficient (and thus increase their salaries), while others may prefer a slower pace due to external responsibilities.
This arrangement is often seen as fair because the established practice helps you get started by providing the environment for you to generate revenue. This includes patient referrals, office space, and staff. In return, the practice not only hopes you will achieve its goals/quotas but may expect a return on its investment in you.
Additionally, access to shared passive revenue streams, such as a pathology lab, clinical research trials, or facility fees from an endoscopy center, may only be available once a certain level of productivity or full partnership is reached.
The initial years in private practice can be seen as a trial period. Your professional reputation, liability, and patient population are more directly in your own hands. Decision-making, patient management, and potential complications are more wholly your responsibility, which can feel isolating. However, providing excellent care can build your reputation, as satisfied patients will seek you out and generate more referrals. During this time, you need to demonstrate to your prospective partners your commitment to delivering high-quality patient care and to meeting certain minimum standards of volume. If clinical medicine is your passion, the right private practice role can be a fulfilling platform where you do what you love to do and simultaneously are well compensated for it.
How does taking maternity affect shared overhead?
Any physician requiring “leave” will affect the overall revenue of a practice. Issues regarding maternity leave in private practice can also be applied to adoption, paternity, surrogacy, foster care, or medical leave. For instance, if the cumulative overhead is $100k per month in a practice with five doctors, each doctor contributes $20k monthly, totaling $240k each annually.
For example, Dr. “Jones” generates $480k in charges/collections, so after paying his share of overhead, his salary is $240k for the year. In contrast, Dr. “Smith” works more intensely, doubling the patients and procedures of Dr. “Jones,” and generates $960k. After deducting the overhead, his salary is $720k, more than twice his partner’s salary.
Let’s say the practice is considering hiring a new doctor who is 2 months pregnant. If he/she generates $380k in charges in the first year but owes $240k in shared overhead, his/her salary would be $140k, which is not very attractive as a “starting salary” for a highly competent, well-trained GI physician. In extreme cases, with high overhead and low productivity, there might be no revenue for salary once the overhead is paid.
In private practice, is there hesitancy hiring a pregnant person?
While it’s illegal to inquire about pregnancy during employment interviews, partners in private practice might still hesitate to hire a pregnant person. Concerns include sharing overhead costs, handling extra calls or emergencies, and wanting new physicians to contribute equally.
However, this viewpoint can be shortsighted. , as older partners might also face personal or medical needs. Adopting a flexible, empathetic approach toward partners can foster goodwill, potentially enhancing revenue, teamwork, and patient care over a long-term career. The value of empathy should not be underestimated.
What should you consider when you are applying for a new private practice job?
When applying for a private practice position, here are some key points to consider:
- If possible, have your children while employed by a large healthcare system with an established leave policy.
- In a private practice job, ensure the employment contract clearly outlines the terms of medical leave (maternity, paternity, adoption, illness), including details on overhead, benefits, salary, call schedule, and the path to full partnership. Consider having a lawyer review the contract.
- Inquire about how other types of leave, like sabbatical, personal, family, military, or medical, are managed. Understand the implications for salary and overhead, for example, in cases of a partner needing extended leave for surgery or rehabilitation.
- Review the requirements for becoming a full partner, particularly if this includes potential future passive income sources. Does maternity leave (or other types of leave) alter this path?
- Examine the entire benefit package, with a focus on long-term disability policies, considering the statistics on both temporary and permanent disability among GI doctors.5
- Negotiate terms for overhead during leave. Options might include a long term or interest-free loan to cover the 3-month sum, a 50% reduction in overhead charges, or “overhead protection insurance” where a designated policy covers overhead for partners on medical leave.
Remember, a brief leave in a 30-year career is relatively minor. Prioritize taking enough time for yourself and your child. Concentrate on long term fairness when engaged in salary negotiations. Don’t rush back; there will be time later to compensate for a temporary decrease in salary, but limited opportunities to spend age-specific time with your young child.
References
1. Butkus R, et al. Achieving Gender Equity in Physician Compensation and Career Advancement: A Position Paper of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2018 May 15. doi: 10.7326/M17-3438.
2. American Medical Association. Advancing Gender Equity in Medicine: Resources for physicians. 2024 Feb 28.
3. Devi J, et al. Fixing the leaky pipeline: gender imbalance in gastroenterology in Asia-Pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Sept. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16353.
4. Mahadevan U, et al. Closing the gender gap: building a successful career and leadership in research as a female gastroenterologist. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00135-2.
5. Murphy R. Know your maternity leave options. 2024 Apr 4.
Marybeth Spanarkel, MD, a Duke University School of Medicine alumna (1979), completed her internal medicine and gastroenterology training at the University of Pennsylvania, National Institutes of Health, and Johns Hopkins. Initially groomed for an academic role, she chose a clinical position in private practice at Duke Regional Hospital in Durham, North Carolina, where she worked for 25 years.
At age 59, Dr. Spanarkel suffered a neck injury leading to permanent C5-6 radiculopathy, which abruptly ended her career as a clinical gastroenterologist. Since then, she has been a passionate advocate for ergonomic reform in endoscopy. Currently, she is the senior medical adviser and cofounder of ColoWrap, a device designed to improve colonoscopy procedures and reduce ergonomic risk.

Dr. Spanarkel spoke with GI & Hepatology News about the issues that gastroenterologists should consider when negotiating maternity/paternity leave in private practice.
Would you share with the readers your experience with maternity leave in private practice?
As a mother of four, I had two children during my GI fellowship, and received my full salary each time for a 3-month maternity leave. My third child arrived in the time period between leaving my academic position and starting in private practice. My fourth child was born after 2 years in private practice, and I took 3 weeks off. Fortunately, I was not asked to pay upfront overhead fees in my 15-person practice. However, my reduced productivity during that time was factored into my salary calculations, leading to a decreased income for the following 6 months.
How does pregnancy affect your performance and productivity as a GI physician?
“We” may be having a baby, but “You” are pregnant. While some may experience few symptoms, most pregnant doctors deal with problems such as nausea and extreme fatigue, especially in the first trimester. The third trimester may result in reduced physical agility, particularly when performing procedures. Even in uncomplicated pregnancies, balancing the physiologic changes with the demands of a full-time GI role can be strenuous. And this doesn’t even take into account potential infertility issues, pregnancy complications, or newborn concerns that physicians may encounter.
And after childbirth?
Post childbirth, despite a supportive partner, the primary responsibilities such as feeding, nursing support, and bonding often fall on the biological mother. These duties are superimposed on the doctor’s own recovery and postpartum changes. While the United States commonly recognizes 3 months as a standard maternity leave, some European countries advocate for up to 12 months, demonstrating again that this is not an “overnight” transition.
In the past, GI doctors were mostly male, but now there’s a growing number of females in the field. Despite this shift, studies still highlight continued gender disparities in salaries and leadership opportunities, and support for pregnancy-related issues has been largely under-addressed.1,2,3
How do academic centers manage maternity leave?
In academic centers or large healthcare settings, maternity leave policies are more standardized compared with private practice. Doctors are salaried depending on their level of training and experience and then they are assigned a mix of clinical, research, teaching, and/or administrative duties.
Typically, maternity leave in these centers is a standard 3-month period, often combining paid time off (PTO) with unpaid or paid leave. In some cases, short- or long-term disability payments are available, especially for complications. But, the financial impact of a doctor’s maternity leave on the overall unit is usually minimal due to the number of participants in the system. The extra workload is diffused over a larger number of doctors, so the new schedule is generally manageable.4 And since the salary of the employee/physician includes a portion of nonclinical time (administrative, teaching, research), the actual decrease in revenue isn’t that dramatic.
How about maternity leave in private practice?
Maternity leave in private practice, especially if there is only a small number of partners, is handled entirely differently. Think of a household budget (rent, utilities, salaries, benefits, insurance) that is shared by “roommates,” the other partners in the group. To understand how maternity leave affects a private practice, you have to understand how your private practice operates.
Typically, newly hired private practice physicians receive a set salary, with the expectation that their patient revenue will eventually cover both their share of overhead and their salary. The practice might set a monthly quota, offering a bonus for exceeding it, or they may retain the extra revenue until the physician becomes a full partner.
Income in private practice is almost entirely generated by seeing patients and performing procedures, as opposed to non-reimbursable activities such as committee meetings or lectures. Physicians learn to be highly efficient with their time, a standard also expected of their employees. They have more control over their schedules, vacation time, and patient/procedure load. Since income is affected only after overhead costs are covered, each doctor’s approach to workload and pace doesn’t typically concern the other partners. Some physicians may be highly aggressive and efficient (and thus increase their salaries), while others may prefer a slower pace due to external responsibilities.
This arrangement is often seen as fair because the established practice helps you get started by providing the environment for you to generate revenue. This includes patient referrals, office space, and staff. In return, the practice not only hopes you will achieve its goals/quotas but may expect a return on its investment in you.
Additionally, access to shared passive revenue streams, such as a pathology lab, clinical research trials, or facility fees from an endoscopy center, may only be available once a certain level of productivity or full partnership is reached.
The initial years in private practice can be seen as a trial period. Your professional reputation, liability, and patient population are more directly in your own hands. Decision-making, patient management, and potential complications are more wholly your responsibility, which can feel isolating. However, providing excellent care can build your reputation, as satisfied patients will seek you out and generate more referrals. During this time, you need to demonstrate to your prospective partners your commitment to delivering high-quality patient care and to meeting certain minimum standards of volume. If clinical medicine is your passion, the right private practice role can be a fulfilling platform where you do what you love to do and simultaneously are well compensated for it.
How does taking maternity affect shared overhead?
Any physician requiring “leave” will affect the overall revenue of a practice. Issues regarding maternity leave in private practice can also be applied to adoption, paternity, surrogacy, foster care, or medical leave. For instance, if the cumulative overhead is $100k per month in a practice with five doctors, each doctor contributes $20k monthly, totaling $240k each annually.
For example, Dr. “Jones” generates $480k in charges/collections, so after paying his share of overhead, his salary is $240k for the year. In contrast, Dr. “Smith” works more intensely, doubling the patients and procedures of Dr. “Jones,” and generates $960k. After deducting the overhead, his salary is $720k, more than twice his partner’s salary.
Let’s say the practice is considering hiring a new doctor who is 2 months pregnant. If he/she generates $380k in charges in the first year but owes $240k in shared overhead, his/her salary would be $140k, which is not very attractive as a “starting salary” for a highly competent, well-trained GI physician. In extreme cases, with high overhead and low productivity, there might be no revenue for salary once the overhead is paid.
In private practice, is there hesitancy hiring a pregnant person?
While it’s illegal to inquire about pregnancy during employment interviews, partners in private practice might still hesitate to hire a pregnant person. Concerns include sharing overhead costs, handling extra calls or emergencies, and wanting new physicians to contribute equally.
However, this viewpoint can be shortsighted. , as older partners might also face personal or medical needs. Adopting a flexible, empathetic approach toward partners can foster goodwill, potentially enhancing revenue, teamwork, and patient care over a long-term career. The value of empathy should not be underestimated.
What should you consider when you are applying for a new private practice job?
When applying for a private practice position, here are some key points to consider:
- If possible, have your children while employed by a large healthcare system with an established leave policy.
- In a private practice job, ensure the employment contract clearly outlines the terms of medical leave (maternity, paternity, adoption, illness), including details on overhead, benefits, salary, call schedule, and the path to full partnership. Consider having a lawyer review the contract.
- Inquire about how other types of leave, like sabbatical, personal, family, military, or medical, are managed. Understand the implications for salary and overhead, for example, in cases of a partner needing extended leave for surgery or rehabilitation.
- Review the requirements for becoming a full partner, particularly if this includes potential future passive income sources. Does maternity leave (or other types of leave) alter this path?
- Examine the entire benefit package, with a focus on long-term disability policies, considering the statistics on both temporary and permanent disability among GI doctors.5
- Negotiate terms for overhead during leave. Options might include a long term or interest-free loan to cover the 3-month sum, a 50% reduction in overhead charges, or “overhead protection insurance” where a designated policy covers overhead for partners on medical leave.
Remember, a brief leave in a 30-year career is relatively minor. Prioritize taking enough time for yourself and your child. Concentrate on long term fairness when engaged in salary negotiations. Don’t rush back; there will be time later to compensate for a temporary decrease in salary, but limited opportunities to spend age-specific time with your young child.
References
1. Butkus R, et al. Achieving Gender Equity in Physician Compensation and Career Advancement: A Position Paper of the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2018 May 15. doi: 10.7326/M17-3438.
2. American Medical Association. Advancing Gender Equity in Medicine: Resources for physicians. 2024 Feb 28.
3. Devi J, et al. Fixing the leaky pipeline: gender imbalance in gastroenterology in Asia-Pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 Sept. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16353.
4. Mahadevan U, et al. Closing the gender gap: building a successful career and leadership in research as a female gastroenterologist. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jun. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00135-2.
5. Murphy R. Know your maternity leave options. 2024 Apr 4.
Endoscopic Management of Barrett’s Esophagus
Introduction
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is characterized by the replacement of squamous epithelium by columnar metaplasia of the distal esophagus (>1 cm length). It is a precancerous condition, with 3%-5% of patients with BE developing esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) in their lifetime. EAC is one of the cancers with high morbidity and mortality (5-year survival < 20%), and its incidence has been on the rise. Studies examining the natural history of BE have demonstrated that the progression happens through a metaplasia-dysplasia-neoplasia sequence. Therefore, early detection of BE and timely management to prevent progression to EAC is crucial.
Grades of Dysplasia
The current gold standard for the diagnosis of BE neoplasia includes a high-quality endoscopic evaluation and biopsies. Biopsies should be obtained from any visible lesions (nodules, ulcers) followed by a random 4-quadrant fashion (Seattle protocol) interval of the entire length of the BE segment. It is essential to pay attention to the results of the biopsy that have been obtained since it will not only determine the surveillance interval but is crucial in planning any necessary endoscopic therapy. The possible results of the biopsy and its implications are:
- No intestinal metaplasia (IM): This would rule out Barrett’s esophagus and no further surveillance would be necessary. A recent population-based study of over 1 million patients showed a 55% and 61% reduced risk of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) cancer and deaths respectively after a negative endoscopy.1
- Intestinal metaplasia with no dysplasia (non-dysplastic BE): Biopsies confirm presence of intestinal metaplasia in the biopsies without any evidence of dysplasia. While the rate of progression to EAC is low (0.07%-0.25%), it is not absent and thus surveillance would be indicated. Current guidelines suggest repeating an endoscopy with biopsy in 5 years if the length of BE is < 3 cm or 3 years if length of BE ≥ 3 cm.2
- Indeterminate for dysplasia (BE-IND): Biopsies confirm IM but are not able to definitively rule out dysplasia. This can be seen in about 4%-8% of the biopsies obtained. The progression rates to EAC are reported to be comparable or lower to low-grade dysplasia (LGD), so the current recommendation is to intensify acid reduction therapy and repeat endoscopy in 6 months. If repeat endoscopy downgrades to non-dysplastic, then can follow surveillance according to NDBE protocol; otherwise recommend continuing surveillance every 12 months.
- Low-grade dysplasia (BE-LGD): Biopsies confirm IM but also show tightly packed overlapping basal nuclei with hyperchromasia and irregular contours, basal stratification of nuclei, and diminished goblet and columnar cell mucus. There is significant inter-observer variability reported,3 and thus the slides must be reviewed by a second pathologist with experience in BE to confirm the findings. Once confirmed, based on risk factors such as presence of multifocal LGD, persistence of LGD, presence of visible lesions, etc., the patient can be offered Barrett’s endoscopic therapy (BET) or undergo continued surveillance. The decision of pursuing one or the other would be dependent on patient preference and shared decision-making between the patient and the provider.
- High-grade dysplasia (BE-HGD): Biopsies confirm IM with cells showing greater degree of cytologic and architectural alterations of dysplasia than LGD but without overt neoplastic features. Over 40% of the patients would progress to EAC and thus the current recommendations would be to recommend BET in these patients.4
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC): Biopsies demonstrate neoplasia. If the neoplastic changes are limited to the mucosa (T1a) on endoscopic ultrasound or cross-sectional imaging, then BET is suggested. If there is involvement of submucosa, then depending on the depth of invasion, absence of high-risk features (poor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion), BET can be considered as an alternative to esophagectomy.
Lesion Detection on Endoscopy
Data from large population-based studies with at least 3 years of follow-up reported that 58%-66% of EAC detected during endoscopy were diagnosed within 1 year of an index Barrett’s esophagus screening endoscopy, or post-endoscopy Barrett’s neoplasia, and were considered likely to have been missed during index endoscopy.5 This underscores the importance of careful and systematic endoscopic examination during an upper endoscopy.
Studies have also demonstrated that longer examination time was associated with significantly higher detection of HGD/EAC.6,7 Careful examination of the tubular esophagus and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) should be performed in forward and retroflexed views looking for any subtle areas of nodularity, loop distortion, variability in vascular patterns, mucosal changes concerning for dysplasia or neoplasia. Use of high-definition white light endoscopy (HD-WLE) and virtual chromoendoscopy techniques such as narrow banding imaging (NBI) or blue laser imaging (BLI) are currently recommended in the guidelines.2 Spray chromoendoscopy using acetic acid can also be utilized. Another exciting development is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in detecting and diagnosing BE associated lesions and neoplasia.
Barrett’s Endoscopic Therapy (BET)
Patients with visible lesions, dysplasia, or early EAC are candidates for BET (Table 1). 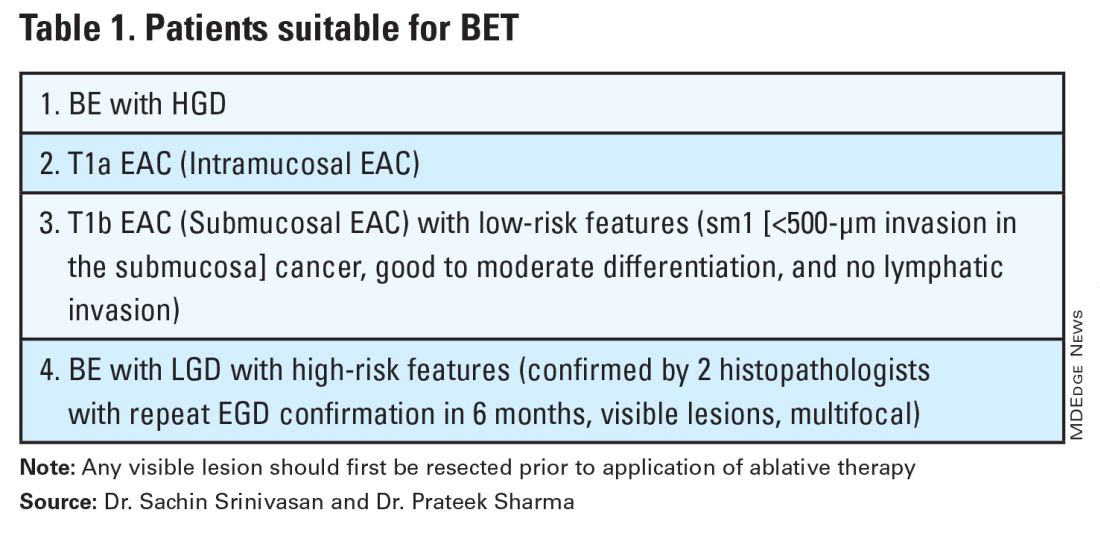
BET involves resective and ablative modalities. The resective modalities include endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and are the modalities of choice for nodular or raised lesions.
EMR involves endoscopic resection of abnormal mucosa using either lift-assisted technique or multi-band ligation (Figure 1). 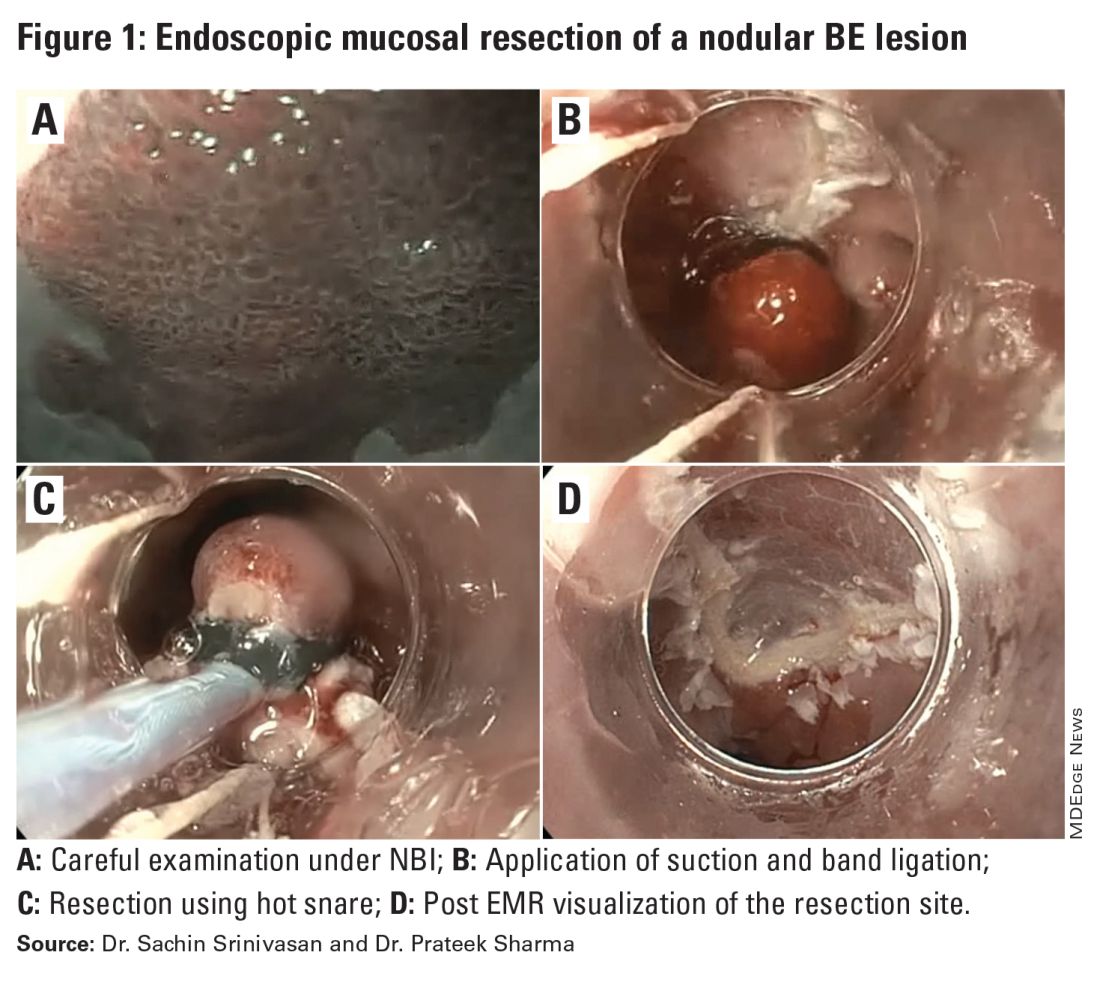
ESD, on the other hand, involves submucosal dissection and perimeter resection of the lesion, thus providing the advantage of an en-bloc resection. In a recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 40 patients undergoing ESD vs EMR for HGD/EAC, ESD was better for curative resection (R0) (58%) compared with EMR (12%); however, the remission rates at 3 months were comparable with two perforations reported in the ESD group while there were no complications in the EMR group.8
There is an apparent learning curve when it comes to these advanced techniques, and with more experience, we are seeing comparable results for both these modalities. However, given the complexity and time required for the procedure, current practices typically involve preserving ESD for lesions > 2 cm, those having a likelihood of cancer in the superficial submucosa, or those that EMR cannot remove due to underlying fibrosis or post-EMR recurrence.
The ablative modalities include radiofrequency ablation (RFA), cryotherapy, and hybrid argon plasma coagulation (hybrid APC). These modalities are used for flat lesions, and as therapy following endoscopic resection of nodular lesions to treat residual flat segment of BE. RFA, one of the earliest introduced endoscopic modalities, involves applying directed and controlled heat energy to ablate lesions. Current devices allow circumferential or focal application of RFA. It is a safe and effective modality with good complete eradication of IM (CE-IM) (71%-93%) and complete eradication of dysplasia (CE-D) (91%-100%) rates. These results have been sustained even at 2 years, with the most recent long-term data from a registry study showing a relapse rate of 6% for dysplasia and 19% for IM after 8 years, suggesting durability of this treatment.9
Cryotherapy involves the application of liquid nitrogen or rapidly expanding CO2 to the abnormal mucosa, leading to the rapid freezing and thawing that leads to the death of the cells. Cryogen can be applied as a spray or using a balloon with the spray nozzle in the center. This modality can be used to treat focal lesions and/or larger segments. While it has not been systematically compared with RFA, rates of CE-IM up to 81% and CE-D up to 97% are reported. Hybrid APC involves the use of submucosal saline injection to provide a protective cushion before APC is applied. It has CE-IM rate of 69% and CE-D rate of 67%-86%.10 In a recent RCT of 101 patients randomized to RFA or hybrid APC, CE-IM rates were similar (RFA:74.2% vs hAPC: 82.9%).11
Recently, another technique called radiofrequency vapor ablation (RFVA) is being evaluated, which involves ablating BE segment using vapor at 100° C generated with an RF electrode. A proof-of-concept study of 15 patients showed median squamous conversion of 55% (IQR 33-74) and 98% (IQR 56-99) for 1- and 3-second applications, respectively, with no reported adverse events.12
Barrett’s Refractory to Endoscopic Therapy
Failure of BET is defined as persistent columnar lined epithelium (intestinal metaplasia) with inadequate response, after adequate attempts at endoscopic ablation therapy (after resection) with at least four ablation sessions.13 If encountered, special attention must be given to check compliance with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), previous incomplete resection, and presence of large hiatal hernia. If CE-IM is not achieved after multiple sessions, change of ablative modality is typically considered. In addition, careful examination for visible lesions should be performed and even if a small one is noted, this should be first resected prior to application of any ablative therapy.
Currently there are no guideline recommendations regarding the preference of one endoscopic modality over another or consideration of potential endoscopic or surgical fundoplication. These modalities primarily rely on technologies available at an institution and the preference of a provider based on their training and experience. Most studies indicate 1-3 sessions (~ 3 months apart) of ablative treatment before achieving CE-IM.
Success and Adverse Events of BET
In a recent real-world study of over 27,000 patients with dysplastic BE, 5295 underwent BET. Analysis showed that patients with HGD/EAC who had BET had a significantly lower 3-year mortality (HGD: RR, 0.59; 95%CI, 0.49-0.71; EAC: RR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.44-0.65) compared with those who did not undergo BET. Esophageal strictures were the most common adverse event and were noted in 6.5%, followed by chest pain (1.8%), upper GI bleeding (0.47%), and esophageal perforation (0.2%).14
In general, adverse events can be divided into immediate and delayed adverse events. Immediate adverse events typically involve bleeding and perforation that can occur during or shortly after the procedure. These are reported at higher rates with resective modalities compared with ablative therapies. Standard endoscopic techniques involving coagulation grasper or clips can be used to achieve hemostasis. Endoscopic suturing devices offer the ability to contain any perforation. The need for surgical intervention is small and limited to adverse events not detected during the procedure.
Delayed adverse events such as stricture and stenosis are higher for resective modalities (up to 30%), especially when involving more significant than 75% of the esophageal circumference. Post-procedural pain/dysphagia is most common after ablative therapies. Dysphagia reported after any endoscopic therapy should be promptly evaluated, and sequential dilation until the goal esophageal lumen is achieved should be performed every 2-4 weeks.
Recurrences and Surveillance After BET
What is established is that recurrences can occur and may be subtle, therefore detailed endoscopic surveillance is required. In a prospective study, recurrence rates of 15%-16% for IM and 3%-5% for any dysplasia were reported, with the majority being in the first 2 years after achieving CE-IM.15 A systematic review of 21 studies looking at the location of recurrences suggested that the majority (56%) occur in the distal esophagus. Of those that occur in the esophagus, about 80% of them were in the distal 2 cm of the esophagus and only 50% of the recurrences were visible recurrences, thus reiterating the importance of meticulous examination and systematic biopsies.16
On the contrary, a recent single-center study of 217 patients who had achieved CE-IM with 5.5 years of follow-up demonstrated a 26% and 8% recurrence of IM and dysplasia, respectively. One hundred percent of the recurrence in the esophagus was reported as visible.17 Therefore, follow-up endoscopy surveillance protocol after CE-IM should still involve meticulous examination, biopsy of visible lesions, and systematic biopsies for non-visible lesions from the original BE segment, similar to those patients who have not needed BET.
Current guidelines based on expert consensus and evidence recommend surveillance after CE-IM based on original most advanced histology:2
1. LGD: 1 year, 3 years, and every 2 years after that.
2. HGD/EAC: 3 months, 6 months, 12 months, and annually after that.
There is no clear guideline on when to stop surveillance since the longest available follow-up is around 10 years, and recurrences are still detected. A potential surveillance endpoint may be based on age and comorbidities, especially those that would preclude a patient from being a candidate for BET.
When Should a Patient Be Referred?
BE patients with visible lesions and/or dysplastic changes in the biopsy who would require BET should be considered for referral to high-volume centers. Studies have shown higher success for CE-IM and lower rates of adverse events and recurrences in these patients managed at expert centers. The presence of a multidisciplinary team involving pathologists, surgeons, and oncologists is critical and offers a timely opportunity in case of need for a high-risk patient.
Conclusion
BE is a precursor to EAC, with rising incidence and poor 5-year survival. Endoscopic diagnosis is the gold standard and requires a high-quality examination and biopsies. Based on histopathology, a systematic surveillance and BET plan should be performed to achieve CE-IM in patients with dysplasia. Once CE-IM is achieved, regular surveillance should be performed with careful attention to recurrences and complications from the BET modalities.
Dr. Srinivasan and Dr. Sharma are based at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, Kansas, and the Kansas City Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri. Dr. Srinivasan has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Sharma disclosed research grants from ERBE, Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Olympus, and Medtronic. He has served as a consultant for Takeda, Samsung Bioepis, Olympus, and Lumendi, and reports other funding from Medtronic, Fujifilm Medical Systems USA, and Salix.
References
1. Holmberg D, et al. Incidence and mortality in upper gastrointestinal cancer after negative endoscopy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(2):431-438.e4.
2. Shaheen NJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus: An updated ACG guideline. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr;117(4):559-587.
3. Pech O, et al. Inter-observer variability in the diagnosis of low-grade dysplasia in pathologists: A comparison between experienced and inexperienced pathologists. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006 Apr;63(5):AB130.
4. Krishnamoorthi R, et al. Factors associated with progression of Barrett’s esophagus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jul;16(7):1046-1055.e8.
5. Visrodia K, et al. Magnitude of missed esophageal adenocarcinoma after Barrett’s esophagus diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar;150(3):599-607.e7; quiz e14-5.
6. Perisetti A, Sharma P. Tips for improving the identification of neoplastic visible lesions in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb;97(2):248-250.
7. Gupta N, et al. Longer inspection time is associated with increased detection of high-grade dysplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Sep;76(3):531-538.
8. Terheggen G, et al. A randomised trial of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for early Barrett’s neoplasia. Gut. 2017 May;66(5):783-793.
9. Wolfson P, et al. Endoscopic eradication therapy for Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia: A final 10-year report from the UK National HALO Radiofrequency Ablation Registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Aug;96(2):223-233.
10. Rösch T, et al. 1151 Multicenter feasibility study of combined injection and argon plasma coagulation (hybrid-APC) in the ablation therapy of neoplastic Barrett esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(5):AB154.
11. Knabe M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus hybrid argon plasma coagulation in Barrett’s esophagus: A prospective randomised trial. Surg Endosc. 2023;37(10):7803-7811.
12. Van Munster SN, et al. Radiofrequency vapor ablation for Barrett’s esophagus: Feasibility, safety, and proof of concept in a stepwise study with in vitro, animal, and the first in-human application. Endoscopy. 2021 Nov;53(11):1162-1168.
13. Emura F, et al. Rio de Janeiro global consensus on landmarks, definitions, and classifications in Barrett’s esophagus: World Endoscopy Organization Delphi study. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jul;163(1):84-96.e2.
14. Singh RR, et al. Real-world evidence of safety and effectiveness of Barrett’s endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Aug;98(2):155-161.e1.
15. Wani S, et al. Recurrence Is rare following complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia in patients with Barrett’s esophagus and peaks at 18 months. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;18(11):2609-2617.e2.
16. Duvvuri A, et al. Mo1273 Location and pattern of recurrences in patients with Barrett’s esophagus after endoscopic therapy: A systematic review and critical analysis of the published literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(6):AB410-1.
17. He T, et al. Location and appearance of dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus recurrence after endoscopic eradication therapy: No additional yield from random biopsy sampling neosquamous mucosa. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Nov;98(5):722-732.
Introduction
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is characterized by the replacement of squamous epithelium by columnar metaplasia of the distal esophagus (>1 cm length). It is a precancerous condition, with 3%-5% of patients with BE developing esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) in their lifetime. EAC is one of the cancers with high morbidity and mortality (5-year survival < 20%), and its incidence has been on the rise. Studies examining the natural history of BE have demonstrated that the progression happens through a metaplasia-dysplasia-neoplasia sequence. Therefore, early detection of BE and timely management to prevent progression to EAC is crucial.
Grades of Dysplasia
The current gold standard for the diagnosis of BE neoplasia includes a high-quality endoscopic evaluation and biopsies. Biopsies should be obtained from any visible lesions (nodules, ulcers) followed by a random 4-quadrant fashion (Seattle protocol) interval of the entire length of the BE segment. It is essential to pay attention to the results of the biopsy that have been obtained since it will not only determine the surveillance interval but is crucial in planning any necessary endoscopic therapy. The possible results of the biopsy and its implications are:
- No intestinal metaplasia (IM): This would rule out Barrett’s esophagus and no further surveillance would be necessary. A recent population-based study of over 1 million patients showed a 55% and 61% reduced risk of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) cancer and deaths respectively after a negative endoscopy.1
- Intestinal metaplasia with no dysplasia (non-dysplastic BE): Biopsies confirm presence of intestinal metaplasia in the biopsies without any evidence of dysplasia. While the rate of progression to EAC is low (0.07%-0.25%), it is not absent and thus surveillance would be indicated. Current guidelines suggest repeating an endoscopy with biopsy in 5 years if the length of BE is < 3 cm or 3 years if length of BE ≥ 3 cm.2
- Indeterminate for dysplasia (BE-IND): Biopsies confirm IM but are not able to definitively rule out dysplasia. This can be seen in about 4%-8% of the biopsies obtained. The progression rates to EAC are reported to be comparable or lower to low-grade dysplasia (LGD), so the current recommendation is to intensify acid reduction therapy and repeat endoscopy in 6 months. If repeat endoscopy downgrades to non-dysplastic, then can follow surveillance according to NDBE protocol; otherwise recommend continuing surveillance every 12 months.
- Low-grade dysplasia (BE-LGD): Biopsies confirm IM but also show tightly packed overlapping basal nuclei with hyperchromasia and irregular contours, basal stratification of nuclei, and diminished goblet and columnar cell mucus. There is significant inter-observer variability reported,3 and thus the slides must be reviewed by a second pathologist with experience in BE to confirm the findings. Once confirmed, based on risk factors such as presence of multifocal LGD, persistence of LGD, presence of visible lesions, etc., the patient can be offered Barrett’s endoscopic therapy (BET) or undergo continued surveillance. The decision of pursuing one or the other would be dependent on patient preference and shared decision-making between the patient and the provider.
- High-grade dysplasia (BE-HGD): Biopsies confirm IM with cells showing greater degree of cytologic and architectural alterations of dysplasia than LGD but without overt neoplastic features. Over 40% of the patients would progress to EAC and thus the current recommendations would be to recommend BET in these patients.4
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC): Biopsies demonstrate neoplasia. If the neoplastic changes are limited to the mucosa (T1a) on endoscopic ultrasound or cross-sectional imaging, then BET is suggested. If there is involvement of submucosa, then depending on the depth of invasion, absence of high-risk features (poor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion), BET can be considered as an alternative to esophagectomy.
Lesion Detection on Endoscopy
Data from large population-based studies with at least 3 years of follow-up reported that 58%-66% of EAC detected during endoscopy were diagnosed within 1 year of an index Barrett’s esophagus screening endoscopy, or post-endoscopy Barrett’s neoplasia, and were considered likely to have been missed during index endoscopy.5 This underscores the importance of careful and systematic endoscopic examination during an upper endoscopy.
Studies have also demonstrated that longer examination time was associated with significantly higher detection of HGD/EAC.6,7 Careful examination of the tubular esophagus and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) should be performed in forward and retroflexed views looking for any subtle areas of nodularity, loop distortion, variability in vascular patterns, mucosal changes concerning for dysplasia or neoplasia. Use of high-definition white light endoscopy (HD-WLE) and virtual chromoendoscopy techniques such as narrow banding imaging (NBI) or blue laser imaging (BLI) are currently recommended in the guidelines.2 Spray chromoendoscopy using acetic acid can also be utilized. Another exciting development is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in detecting and diagnosing BE associated lesions and neoplasia.
Barrett’s Endoscopic Therapy (BET)
Patients with visible lesions, dysplasia, or early EAC are candidates for BET (Table 1). 
BET involves resective and ablative modalities. The resective modalities include endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and are the modalities of choice for nodular or raised lesions.
EMR involves endoscopic resection of abnormal mucosa using either lift-assisted technique or multi-band ligation (Figure 1). 
ESD, on the other hand, involves submucosal dissection and perimeter resection of the lesion, thus providing the advantage of an en-bloc resection. In a recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 40 patients undergoing ESD vs EMR for HGD/EAC, ESD was better for curative resection (R0) (58%) compared with EMR (12%); however, the remission rates at 3 months were comparable with two perforations reported in the ESD group while there were no complications in the EMR group.8
There is an apparent learning curve when it comes to these advanced techniques, and with more experience, we are seeing comparable results for both these modalities. However, given the complexity and time required for the procedure, current practices typically involve preserving ESD for lesions > 2 cm, those having a likelihood of cancer in the superficial submucosa, or those that EMR cannot remove due to underlying fibrosis or post-EMR recurrence.
The ablative modalities include radiofrequency ablation (RFA), cryotherapy, and hybrid argon plasma coagulation (hybrid APC). These modalities are used for flat lesions, and as therapy following endoscopic resection of nodular lesions to treat residual flat segment of BE. RFA, one of the earliest introduced endoscopic modalities, involves applying directed and controlled heat energy to ablate lesions. Current devices allow circumferential or focal application of RFA. It is a safe and effective modality with good complete eradication of IM (CE-IM) (71%-93%) and complete eradication of dysplasia (CE-D) (91%-100%) rates. These results have been sustained even at 2 years, with the most recent long-term data from a registry study showing a relapse rate of 6% for dysplasia and 19% for IM after 8 years, suggesting durability of this treatment.9
Cryotherapy involves the application of liquid nitrogen or rapidly expanding CO2 to the abnormal mucosa, leading to the rapid freezing and thawing that leads to the death of the cells. Cryogen can be applied as a spray or using a balloon with the spray nozzle in the center. This modality can be used to treat focal lesions and/or larger segments. While it has not been systematically compared with RFA, rates of CE-IM up to 81% and CE-D up to 97% are reported. Hybrid APC involves the use of submucosal saline injection to provide a protective cushion before APC is applied. It has CE-IM rate of 69% and CE-D rate of 67%-86%.10 In a recent RCT of 101 patients randomized to RFA or hybrid APC, CE-IM rates were similar (RFA:74.2% vs hAPC: 82.9%).11
Recently, another technique called radiofrequency vapor ablation (RFVA) is being evaluated, which involves ablating BE segment using vapor at 100° C generated with an RF electrode. A proof-of-concept study of 15 patients showed median squamous conversion of 55% (IQR 33-74) and 98% (IQR 56-99) for 1- and 3-second applications, respectively, with no reported adverse events.12
Barrett’s Refractory to Endoscopic Therapy
Failure of BET is defined as persistent columnar lined epithelium (intestinal metaplasia) with inadequate response, after adequate attempts at endoscopic ablation therapy (after resection) with at least four ablation sessions.13 If encountered, special attention must be given to check compliance with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), previous incomplete resection, and presence of large hiatal hernia. If CE-IM is not achieved after multiple sessions, change of ablative modality is typically considered. In addition, careful examination for visible lesions should be performed and even if a small one is noted, this should be first resected prior to application of any ablative therapy.
Currently there are no guideline recommendations regarding the preference of one endoscopic modality over another or consideration of potential endoscopic or surgical fundoplication. These modalities primarily rely on technologies available at an institution and the preference of a provider based on their training and experience. Most studies indicate 1-3 sessions (~ 3 months apart) of ablative treatment before achieving CE-IM.
Success and Adverse Events of BET
In a recent real-world study of over 27,000 patients with dysplastic BE, 5295 underwent BET. Analysis showed that patients with HGD/EAC who had BET had a significantly lower 3-year mortality (HGD: RR, 0.59; 95%CI, 0.49-0.71; EAC: RR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.44-0.65) compared with those who did not undergo BET. Esophageal strictures were the most common adverse event and were noted in 6.5%, followed by chest pain (1.8%), upper GI bleeding (0.47%), and esophageal perforation (0.2%).14
In general, adverse events can be divided into immediate and delayed adverse events. Immediate adverse events typically involve bleeding and perforation that can occur during or shortly after the procedure. These are reported at higher rates with resective modalities compared with ablative therapies. Standard endoscopic techniques involving coagulation grasper or clips can be used to achieve hemostasis. Endoscopic suturing devices offer the ability to contain any perforation. The need for surgical intervention is small and limited to adverse events not detected during the procedure.
Delayed adverse events such as stricture and stenosis are higher for resective modalities (up to 30%), especially when involving more significant than 75% of the esophageal circumference. Post-procedural pain/dysphagia is most common after ablative therapies. Dysphagia reported after any endoscopic therapy should be promptly evaluated, and sequential dilation until the goal esophageal lumen is achieved should be performed every 2-4 weeks.
Recurrences and Surveillance After BET
What is established is that recurrences can occur and may be subtle, therefore detailed endoscopic surveillance is required. In a prospective study, recurrence rates of 15%-16% for IM and 3%-5% for any dysplasia were reported, with the majority being in the first 2 years after achieving CE-IM.15 A systematic review of 21 studies looking at the location of recurrences suggested that the majority (56%) occur in the distal esophagus. Of those that occur in the esophagus, about 80% of them were in the distal 2 cm of the esophagus and only 50% of the recurrences were visible recurrences, thus reiterating the importance of meticulous examination and systematic biopsies.16
On the contrary, a recent single-center study of 217 patients who had achieved CE-IM with 5.5 years of follow-up demonstrated a 26% and 8% recurrence of IM and dysplasia, respectively. One hundred percent of the recurrence in the esophagus was reported as visible.17 Therefore, follow-up endoscopy surveillance protocol after CE-IM should still involve meticulous examination, biopsy of visible lesions, and systematic biopsies for non-visible lesions from the original BE segment, similar to those patients who have not needed BET.
Current guidelines based on expert consensus and evidence recommend surveillance after CE-IM based on original most advanced histology:2
1. LGD: 1 year, 3 years, and every 2 years after that.
2. HGD/EAC: 3 months, 6 months, 12 months, and annually after that.
There is no clear guideline on when to stop surveillance since the longest available follow-up is around 10 years, and recurrences are still detected. A potential surveillance endpoint may be based on age and comorbidities, especially those that would preclude a patient from being a candidate for BET.
When Should a Patient Be Referred?
BE patients with visible lesions and/or dysplastic changes in the biopsy who would require BET should be considered for referral to high-volume centers. Studies have shown higher success for CE-IM and lower rates of adverse events and recurrences in these patients managed at expert centers. The presence of a multidisciplinary team involving pathologists, surgeons, and oncologists is critical and offers a timely opportunity in case of need for a high-risk patient.
Conclusion
BE is a precursor to EAC, with rising incidence and poor 5-year survival. Endoscopic diagnosis is the gold standard and requires a high-quality examination and biopsies. Based on histopathology, a systematic surveillance and BET plan should be performed to achieve CE-IM in patients with dysplasia. Once CE-IM is achieved, regular surveillance should be performed with careful attention to recurrences and complications from the BET modalities.
Dr. Srinivasan and Dr. Sharma are based at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, Kansas, and the Kansas City Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri. Dr. Srinivasan has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Sharma disclosed research grants from ERBE, Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Olympus, and Medtronic. He has served as a consultant for Takeda, Samsung Bioepis, Olympus, and Lumendi, and reports other funding from Medtronic, Fujifilm Medical Systems USA, and Salix.
References
1. Holmberg D, et al. Incidence and mortality in upper gastrointestinal cancer after negative endoscopy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(2):431-438.e4.
2. Shaheen NJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus: An updated ACG guideline. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr;117(4):559-587.
3. Pech O, et al. Inter-observer variability in the diagnosis of low-grade dysplasia in pathologists: A comparison between experienced and inexperienced pathologists. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006 Apr;63(5):AB130.
4. Krishnamoorthi R, et al. Factors associated with progression of Barrett’s esophagus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jul;16(7):1046-1055.e8.
5. Visrodia K, et al. Magnitude of missed esophageal adenocarcinoma after Barrett’s esophagus diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar;150(3):599-607.e7; quiz e14-5.
6. Perisetti A, Sharma P. Tips for improving the identification of neoplastic visible lesions in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb;97(2):248-250.
7. Gupta N, et al. Longer inspection time is associated with increased detection of high-grade dysplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Sep;76(3):531-538.
8. Terheggen G, et al. A randomised trial of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for early Barrett’s neoplasia. Gut. 2017 May;66(5):783-793.
9. Wolfson P, et al. Endoscopic eradication therapy for Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia: A final 10-year report from the UK National HALO Radiofrequency Ablation Registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Aug;96(2):223-233.
10. Rösch T, et al. 1151 Multicenter feasibility study of combined injection and argon plasma coagulation (hybrid-APC) in the ablation therapy of neoplastic Barrett esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(5):AB154.
11. Knabe M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus hybrid argon plasma coagulation in Barrett’s esophagus: A prospective randomised trial. Surg Endosc. 2023;37(10):7803-7811.
12. Van Munster SN, et al. Radiofrequency vapor ablation for Barrett’s esophagus: Feasibility, safety, and proof of concept in a stepwise study with in vitro, animal, and the first in-human application. Endoscopy. 2021 Nov;53(11):1162-1168.
13. Emura F, et al. Rio de Janeiro global consensus on landmarks, definitions, and classifications in Barrett’s esophagus: World Endoscopy Organization Delphi study. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jul;163(1):84-96.e2.
14. Singh RR, et al. Real-world evidence of safety and effectiveness of Barrett’s endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Aug;98(2):155-161.e1.
15. Wani S, et al. Recurrence Is rare following complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia in patients with Barrett’s esophagus and peaks at 18 months. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;18(11):2609-2617.e2.
16. Duvvuri A, et al. Mo1273 Location and pattern of recurrences in patients with Barrett’s esophagus after endoscopic therapy: A systematic review and critical analysis of the published literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(6):AB410-1.
17. He T, et al. Location and appearance of dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus recurrence after endoscopic eradication therapy: No additional yield from random biopsy sampling neosquamous mucosa. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Nov;98(5):722-732.
Introduction
Barrett’s esophagus (BE) is characterized by the replacement of squamous epithelium by columnar metaplasia of the distal esophagus (>1 cm length). It is a precancerous condition, with 3%-5% of patients with BE developing esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) in their lifetime. EAC is one of the cancers with high morbidity and mortality (5-year survival < 20%), and its incidence has been on the rise. Studies examining the natural history of BE have demonstrated that the progression happens through a metaplasia-dysplasia-neoplasia sequence. Therefore, early detection of BE and timely management to prevent progression to EAC is crucial.
Grades of Dysplasia
The current gold standard for the diagnosis of BE neoplasia includes a high-quality endoscopic evaluation and biopsies. Biopsies should be obtained from any visible lesions (nodules, ulcers) followed by a random 4-quadrant fashion (Seattle protocol) interval of the entire length of the BE segment. It is essential to pay attention to the results of the biopsy that have been obtained since it will not only determine the surveillance interval but is crucial in planning any necessary endoscopic therapy. The possible results of the biopsy and its implications are:
- No intestinal metaplasia (IM): This would rule out Barrett’s esophagus and no further surveillance would be necessary. A recent population-based study of over 1 million patients showed a 55% and 61% reduced risk of upper gastrointestinal (UGI) cancer and deaths respectively after a negative endoscopy.1
- Intestinal metaplasia with no dysplasia (non-dysplastic BE): Biopsies confirm presence of intestinal metaplasia in the biopsies without any evidence of dysplasia. While the rate of progression to EAC is low (0.07%-0.25%), it is not absent and thus surveillance would be indicated. Current guidelines suggest repeating an endoscopy with biopsy in 5 years if the length of BE is < 3 cm or 3 years if length of BE ≥ 3 cm.2
- Indeterminate for dysplasia (BE-IND): Biopsies confirm IM but are not able to definitively rule out dysplasia. This can be seen in about 4%-8% of the biopsies obtained. The progression rates to EAC are reported to be comparable or lower to low-grade dysplasia (LGD), so the current recommendation is to intensify acid reduction therapy and repeat endoscopy in 6 months. If repeat endoscopy downgrades to non-dysplastic, then can follow surveillance according to NDBE protocol; otherwise recommend continuing surveillance every 12 months.
- Low-grade dysplasia (BE-LGD): Biopsies confirm IM but also show tightly packed overlapping basal nuclei with hyperchromasia and irregular contours, basal stratification of nuclei, and diminished goblet and columnar cell mucus. There is significant inter-observer variability reported,3 and thus the slides must be reviewed by a second pathologist with experience in BE to confirm the findings. Once confirmed, based on risk factors such as presence of multifocal LGD, persistence of LGD, presence of visible lesions, etc., the patient can be offered Barrett’s endoscopic therapy (BET) or undergo continued surveillance. The decision of pursuing one or the other would be dependent on patient preference and shared decision-making between the patient and the provider.
- High-grade dysplasia (BE-HGD): Biopsies confirm IM with cells showing greater degree of cytologic and architectural alterations of dysplasia than LGD but without overt neoplastic features. Over 40% of the patients would progress to EAC and thus the current recommendations would be to recommend BET in these patients.4
- Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC): Biopsies demonstrate neoplasia. If the neoplastic changes are limited to the mucosa (T1a) on endoscopic ultrasound or cross-sectional imaging, then BET is suggested. If there is involvement of submucosa, then depending on the depth of invasion, absence of high-risk features (poor differentiation, lymphovascular invasion), BET can be considered as an alternative to esophagectomy.
Lesion Detection on Endoscopy
Data from large population-based studies with at least 3 years of follow-up reported that 58%-66% of EAC detected during endoscopy were diagnosed within 1 year of an index Barrett’s esophagus screening endoscopy, or post-endoscopy Barrett’s neoplasia, and were considered likely to have been missed during index endoscopy.5 This underscores the importance of careful and systematic endoscopic examination during an upper endoscopy.
Studies have also demonstrated that longer examination time was associated with significantly higher detection of HGD/EAC.6,7 Careful examination of the tubular esophagus and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) should be performed in forward and retroflexed views looking for any subtle areas of nodularity, loop distortion, variability in vascular patterns, mucosal changes concerning for dysplasia or neoplasia. Use of high-definition white light endoscopy (HD-WLE) and virtual chromoendoscopy techniques such as narrow banding imaging (NBI) or blue laser imaging (BLI) are currently recommended in the guidelines.2 Spray chromoendoscopy using acetic acid can also be utilized. Another exciting development is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in detecting and diagnosing BE associated lesions and neoplasia.
Barrett’s Endoscopic Therapy (BET)
Patients with visible lesions, dysplasia, or early EAC are candidates for BET (Table 1). 
BET involves resective and ablative modalities. The resective modalities include endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and are the modalities of choice for nodular or raised lesions.
EMR involves endoscopic resection of abnormal mucosa using either lift-assisted technique or multi-band ligation (Figure 1). 
ESD, on the other hand, involves submucosal dissection and perimeter resection of the lesion, thus providing the advantage of an en-bloc resection. In a recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) of 40 patients undergoing ESD vs EMR for HGD/EAC, ESD was better for curative resection (R0) (58%) compared with EMR (12%); however, the remission rates at 3 months were comparable with two perforations reported in the ESD group while there were no complications in the EMR group.8
There is an apparent learning curve when it comes to these advanced techniques, and with more experience, we are seeing comparable results for both these modalities. However, given the complexity and time required for the procedure, current practices typically involve preserving ESD for lesions > 2 cm, those having a likelihood of cancer in the superficial submucosa, or those that EMR cannot remove due to underlying fibrosis or post-EMR recurrence.
The ablative modalities include radiofrequency ablation (RFA), cryotherapy, and hybrid argon plasma coagulation (hybrid APC). These modalities are used for flat lesions, and as therapy following endoscopic resection of nodular lesions to treat residual flat segment of BE. RFA, one of the earliest introduced endoscopic modalities, involves applying directed and controlled heat energy to ablate lesions. Current devices allow circumferential or focal application of RFA. It is a safe and effective modality with good complete eradication of IM (CE-IM) (71%-93%) and complete eradication of dysplasia (CE-D) (91%-100%) rates. These results have been sustained even at 2 years, with the most recent long-term data from a registry study showing a relapse rate of 6% for dysplasia and 19% for IM after 8 years, suggesting durability of this treatment.9
Cryotherapy involves the application of liquid nitrogen or rapidly expanding CO2 to the abnormal mucosa, leading to the rapid freezing and thawing that leads to the death of the cells. Cryogen can be applied as a spray or using a balloon with the spray nozzle in the center. This modality can be used to treat focal lesions and/or larger segments. While it has not been systematically compared with RFA, rates of CE-IM up to 81% and CE-D up to 97% are reported. Hybrid APC involves the use of submucosal saline injection to provide a protective cushion before APC is applied. It has CE-IM rate of 69% and CE-D rate of 67%-86%.10 In a recent RCT of 101 patients randomized to RFA or hybrid APC, CE-IM rates were similar (RFA:74.2% vs hAPC: 82.9%).11
Recently, another technique called radiofrequency vapor ablation (RFVA) is being evaluated, which involves ablating BE segment using vapor at 100° C generated with an RF electrode. A proof-of-concept study of 15 patients showed median squamous conversion of 55% (IQR 33-74) and 98% (IQR 56-99) for 1- and 3-second applications, respectively, with no reported adverse events.12
Barrett’s Refractory to Endoscopic Therapy
Failure of BET is defined as persistent columnar lined epithelium (intestinal metaplasia) with inadequate response, after adequate attempts at endoscopic ablation therapy (after resection) with at least four ablation sessions.13 If encountered, special attention must be given to check compliance with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), previous incomplete resection, and presence of large hiatal hernia. If CE-IM is not achieved after multiple sessions, change of ablative modality is typically considered. In addition, careful examination for visible lesions should be performed and even if a small one is noted, this should be first resected prior to application of any ablative therapy.
Currently there are no guideline recommendations regarding the preference of one endoscopic modality over another or consideration of potential endoscopic or surgical fundoplication. These modalities primarily rely on technologies available at an institution and the preference of a provider based on their training and experience. Most studies indicate 1-3 sessions (~ 3 months apart) of ablative treatment before achieving CE-IM.
Success and Adverse Events of BET
In a recent real-world study of over 27,000 patients with dysplastic BE, 5295 underwent BET. Analysis showed that patients with HGD/EAC who had BET had a significantly lower 3-year mortality (HGD: RR, 0.59; 95%CI, 0.49-0.71; EAC: RR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.44-0.65) compared with those who did not undergo BET. Esophageal strictures were the most common adverse event and were noted in 6.5%, followed by chest pain (1.8%), upper GI bleeding (0.47%), and esophageal perforation (0.2%).14
In general, adverse events can be divided into immediate and delayed adverse events. Immediate adverse events typically involve bleeding and perforation that can occur during or shortly after the procedure. These are reported at higher rates with resective modalities compared with ablative therapies. Standard endoscopic techniques involving coagulation grasper or clips can be used to achieve hemostasis. Endoscopic suturing devices offer the ability to contain any perforation. The need for surgical intervention is small and limited to adverse events not detected during the procedure.
Delayed adverse events such as stricture and stenosis are higher for resective modalities (up to 30%), especially when involving more significant than 75% of the esophageal circumference. Post-procedural pain/dysphagia is most common after ablative therapies. Dysphagia reported after any endoscopic therapy should be promptly evaluated, and sequential dilation until the goal esophageal lumen is achieved should be performed every 2-4 weeks.
Recurrences and Surveillance After BET
What is established is that recurrences can occur and may be subtle, therefore detailed endoscopic surveillance is required. In a prospective study, recurrence rates of 15%-16% for IM and 3%-5% for any dysplasia were reported, with the majority being in the first 2 years after achieving CE-IM.15 A systematic review of 21 studies looking at the location of recurrences suggested that the majority (56%) occur in the distal esophagus. Of those that occur in the esophagus, about 80% of them were in the distal 2 cm of the esophagus and only 50% of the recurrences were visible recurrences, thus reiterating the importance of meticulous examination and systematic biopsies.16
On the contrary, a recent single-center study of 217 patients who had achieved CE-IM with 5.5 years of follow-up demonstrated a 26% and 8% recurrence of IM and dysplasia, respectively. One hundred percent of the recurrence in the esophagus was reported as visible.17 Therefore, follow-up endoscopy surveillance protocol after CE-IM should still involve meticulous examination, biopsy of visible lesions, and systematic biopsies for non-visible lesions from the original BE segment, similar to those patients who have not needed BET.
Current guidelines based on expert consensus and evidence recommend surveillance after CE-IM based on original most advanced histology:2
1. LGD: 1 year, 3 years, and every 2 years after that.
2. HGD/EAC: 3 months, 6 months, 12 months, and annually after that.
There is no clear guideline on when to stop surveillance since the longest available follow-up is around 10 years, and recurrences are still detected. A potential surveillance endpoint may be based on age and comorbidities, especially those that would preclude a patient from being a candidate for BET.
When Should a Patient Be Referred?
BE patients with visible lesions and/or dysplastic changes in the biopsy who would require BET should be considered for referral to high-volume centers. Studies have shown higher success for CE-IM and lower rates of adverse events and recurrences in these patients managed at expert centers. The presence of a multidisciplinary team involving pathologists, surgeons, and oncologists is critical and offers a timely opportunity in case of need for a high-risk patient.
Conclusion
BE is a precursor to EAC, with rising incidence and poor 5-year survival. Endoscopic diagnosis is the gold standard and requires a high-quality examination and biopsies. Based on histopathology, a systematic surveillance and BET plan should be performed to achieve CE-IM in patients with dysplasia. Once CE-IM is achieved, regular surveillance should be performed with careful attention to recurrences and complications from the BET modalities.
Dr. Srinivasan and Dr. Sharma are based at the University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, Kansas, and the Kansas City Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri. Dr. Srinivasan has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Sharma disclosed research grants from ERBE, Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Olympus, and Medtronic. He has served as a consultant for Takeda, Samsung Bioepis, Olympus, and Lumendi, and reports other funding from Medtronic, Fujifilm Medical Systems USA, and Salix.
References
1. Holmberg D, et al. Incidence and mortality in upper gastrointestinal cancer after negative endoscopy for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(2):431-438.e4.
2. Shaheen NJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus: An updated ACG guideline. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022 Apr;117(4):559-587.
3. Pech O, et al. Inter-observer variability in the diagnosis of low-grade dysplasia in pathologists: A comparison between experienced and inexperienced pathologists. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006 Apr;63(5):AB130.
4. Krishnamoorthi R, et al. Factors associated with progression of Barrett’s esophagus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jul;16(7):1046-1055.e8.
5. Visrodia K, et al. Magnitude of missed esophageal adenocarcinoma after Barrett’s esophagus diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar;150(3):599-607.e7; quiz e14-5.
6. Perisetti A, Sharma P. Tips for improving the identification of neoplastic visible lesions in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Feb;97(2):248-250.
7. Gupta N, et al. Longer inspection time is associated with increased detection of high-grade dysplasia and esophageal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012 Sep;76(3):531-538.
8. Terheggen G, et al. A randomised trial of endoscopic submucosal dissection versus endoscopic mucosal resection for early Barrett’s neoplasia. Gut. 2017 May;66(5):783-793.
9. Wolfson P, et al. Endoscopic eradication therapy for Barrett’s esophagus-related neoplasia: A final 10-year report from the UK National HALO Radiofrequency Ablation Registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Aug;96(2):223-233.
10. Rösch T, et al. 1151 Multicenter feasibility study of combined injection and argon plasma coagulation (hybrid-APC) in the ablation therapy of neoplastic Barrett esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85(5):AB154.
11. Knabe M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus hybrid argon plasma coagulation in Barrett’s esophagus: A prospective randomised trial. Surg Endosc. 2023;37(10):7803-7811.
12. Van Munster SN, et al. Radiofrequency vapor ablation for Barrett’s esophagus: Feasibility, safety, and proof of concept in a stepwise study with in vitro, animal, and the first in-human application. Endoscopy. 2021 Nov;53(11):1162-1168.
13. Emura F, et al. Rio de Janeiro global consensus on landmarks, definitions, and classifications in Barrett’s esophagus: World Endoscopy Organization Delphi study. Gastroenterology. 2022 Jul;163(1):84-96.e2.
14. Singh RR, et al. Real-world evidence of safety and effectiveness of Barrett’s endoscopic therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Aug;98(2):155-161.e1.
15. Wani S, et al. Recurrence Is rare following complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia in patients with Barrett’s esophagus and peaks at 18 months. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;18(11):2609-2617.e2.
16. Duvvuri A, et al. Mo1273 Location and pattern of recurrences in patients with Barrett’s esophagus after endoscopic therapy: A systematic review and critical analysis of the published literature. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91(6):AB410-1.
17. He T, et al. Location and appearance of dysplastic Barrett’s esophagus recurrence after endoscopic eradication therapy: No additional yield from random biopsy sampling neosquamous mucosa. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Nov;98(5):722-732.
May 2024 – ICYMI
Gastroenterology
January 2024
Hirano I, et al; ASCENT WORKING GROUP. Ascending to New Heights for Novel Therapeutics for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690772; PMCID: PMC10872872.
Åkerström JH, et al. Antireflux Surgery Versus Antireflux Medication and Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):132-138.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.050. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690771.
Barnes EL, et al; AGA Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Pouchitis and Inflammatory Pouch Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):59-85. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.015. PMID: 38128971.
February 2024
Yoo HW, et al. Helicobacter pylori Treatment and Gastric Cancer Risk After Endoscopic Resection of Dysplasia: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):313-322.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37863270.
Yang J, et al. High Soluble Fiber Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):323-337.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37858797.
Young E, et al. Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging Improves Colonic Adenoma Detection: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):338-340.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Oct 14. PMID: 37839498.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
January 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; Dutch Familial Pancreatic Cancer Surveillance Study work group. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms in High-Risk Individuals: Incidence, Growth Rate, and Malignancy Risk. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):62-71.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.03.035. Epub 2023 Apr 7. PMID: 37031711.
Reddy CA, et al. Achalasia is Strongly Associated With Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Other Allergic Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):34-41.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.06.013. Epub 2023 Jun 28. PMID: 37391057; PMCID: PMC10753026.
Thiruvengadam NR, et al. The Clinical Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Surveillance of Incidentally Detected Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: A Microsimulation Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.05.028. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 19;: PMID: 37302442.
February 2024
Goodoory VC, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Mesalamine in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):243-251.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Feb 27. PMID: 36858143.
Brenner DM, et al. Development and Current State of Digital Therapeutics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.013. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743035.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
January 2024
Ramirez PR, et al. Gaps and Improvement Opportunities in Post-Colonoscopy Communication. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1):90-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 22.
Gonzaga ER, et al. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the Management of Gastroparesis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan; 26(1): 46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 13.
Wang D, et al. Sphincterotomy vs Sham Procedure for Pain Relief in Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1): 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Nov 8.
Gastro Hep Advances
January 2024
Adeniran E, et al. Intense and Sustained Alcohol Consumption Associated With Acute Pancreatitis Warrants Early Intervention. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1):61-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.017. Epub 2023 Sep 2.
Alkhouri N, et al. A Novel Prescription Digital Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.019. Epub 2023 Oct 1.
Gastroenterology
January 2024
Hirano I, et al; ASCENT WORKING GROUP. Ascending to New Heights for Novel Therapeutics for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690772; PMCID: PMC10872872.
Åkerström JH, et al. Antireflux Surgery Versus Antireflux Medication and Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):132-138.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.050. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690771.
Barnes EL, et al; AGA Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Pouchitis and Inflammatory Pouch Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):59-85. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.015. PMID: 38128971.
February 2024
Yoo HW, et al. Helicobacter pylori Treatment and Gastric Cancer Risk After Endoscopic Resection of Dysplasia: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):313-322.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37863270.
Yang J, et al. High Soluble Fiber Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):323-337.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37858797.
Young E, et al. Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging Improves Colonic Adenoma Detection: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):338-340.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Oct 14. PMID: 37839498.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
January 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; Dutch Familial Pancreatic Cancer Surveillance Study work group. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms in High-Risk Individuals: Incidence, Growth Rate, and Malignancy Risk. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):62-71.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.03.035. Epub 2023 Apr 7. PMID: 37031711.
Reddy CA, et al. Achalasia is Strongly Associated With Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Other Allergic Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):34-41.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.06.013. Epub 2023 Jun 28. PMID: 37391057; PMCID: PMC10753026.
Thiruvengadam NR, et al. The Clinical Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Surveillance of Incidentally Detected Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: A Microsimulation Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.05.028. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 19;: PMID: 37302442.
February 2024
Goodoory VC, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Mesalamine in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):243-251.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Feb 27. PMID: 36858143.
Brenner DM, et al. Development and Current State of Digital Therapeutics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.013. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743035.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
January 2024
Ramirez PR, et al. Gaps and Improvement Opportunities in Post-Colonoscopy Communication. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1):90-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 22.
Gonzaga ER, et al. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the Management of Gastroparesis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan; 26(1): 46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 13.
Wang D, et al. Sphincterotomy vs Sham Procedure for Pain Relief in Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1): 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Nov 8.
Gastro Hep Advances
January 2024
Adeniran E, et al. Intense and Sustained Alcohol Consumption Associated With Acute Pancreatitis Warrants Early Intervention. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1):61-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.017. Epub 2023 Sep 2.
Alkhouri N, et al. A Novel Prescription Digital Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.019. Epub 2023 Oct 1.
Gastroenterology
January 2024
Hirano I, et al; ASCENT WORKING GROUP. Ascending to New Heights for Novel Therapeutics for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690772; PMCID: PMC10872872.
Åkerström JH, et al. Antireflux Surgery Versus Antireflux Medication and Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):132-138.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.050. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690771.
Barnes EL, et al; AGA Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Pouchitis and Inflammatory Pouch Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):59-85. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.015. PMID: 38128971.
February 2024
Yoo HW, et al. Helicobacter pylori Treatment and Gastric Cancer Risk After Endoscopic Resection of Dysplasia: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):313-322.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37863270.
Yang J, et al. High Soluble Fiber Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):323-337.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37858797.
Young E, et al. Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging Improves Colonic Adenoma Detection: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):338-340.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Oct 14. PMID: 37839498.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
January 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; Dutch Familial Pancreatic Cancer Surveillance Study work group. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms in High-Risk Individuals: Incidence, Growth Rate, and Malignancy Risk. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):62-71.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.03.035. Epub 2023 Apr 7. PMID: 37031711.
Reddy CA, et al. Achalasia is Strongly Associated With Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Other Allergic Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):34-41.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.06.013. Epub 2023 Jun 28. PMID: 37391057; PMCID: PMC10753026.
Thiruvengadam NR, et al. The Clinical Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Surveillance of Incidentally Detected Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: A Microsimulation Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.05.028. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 19;: PMID: 37302442.
February 2024
Goodoory VC, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Mesalamine in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):243-251.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Feb 27. PMID: 36858143.
Brenner DM, et al. Development and Current State of Digital Therapeutics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.013. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743035.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
January 2024
Ramirez PR, et al. Gaps and Improvement Opportunities in Post-Colonoscopy Communication. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1):90-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 22.
Gonzaga ER, et al. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the Management of Gastroparesis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan; 26(1): 46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 13.
Wang D, et al. Sphincterotomy vs Sham Procedure for Pain Relief in Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1): 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Nov 8.
Gastro Hep Advances
January 2024
Adeniran E, et al. Intense and Sustained Alcohol Consumption Associated With Acute Pancreatitis Warrants Early Intervention. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1):61-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.017. Epub 2023 Sep 2.
Alkhouri N, et al. A Novel Prescription Digital Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.019. Epub 2023 Oct 1.
The AGA Future Leaders Program: A Mentee-Mentor Triad Perspective
Two of us (Parakkal Deepak and Edward L. Barnes) were part of the American Gastroenterological Association’s (AGA) Future Leaders Program (FLP) class of 2022-2023, and our mentor was Aasma Shaukat. We were invited to share our experiences as participants in the FLP and its impact in our careers.
Why Was the Future Leaders Program Conceived?
To understand this, one must first understand that the AGA, like all other GI professional organizations, relies on volunteer leaders to develop its long-term vision and execute this through strategic initiatives and programs. and understand the governance structure of the AGA to help lead it to face these challenges effectively.
The AGA FLP was thus conceived and launched in 2014-2015 by the founding chairs, Byron Cryer, MD, who is a professor of medicine and associate dean for faculty diversity at University of Texas Southwestern Medical School and Suzanne Rose, MD, MSEd, AGAF, who is a professor of medicine and senior vice dean for medical education at Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. They envisioned a leadership pathway that would position early career GIs on a track to positively affect the AGA and the field of GI.
How Does One Apply for the Program?
Our FLP cohort applications were invited in October of 2021 and mentees accepted into the program in November 2021. The application process is competitive – applicants are encouraged to detail why they feel they would benefit from the FLP, what existing skillsets they have that can be further enhanced through the program, and what their long-term vision is for their growth as leaders, both within their institution and within the AGA. This is further accompanied by letters of support from their divisional chiefs and other key supervisors within the division who are intimately aware of their leadership potential and career trajectory. This process identified 18 future leaders for our class of 2022-2023.
What Is Involved?
Following acceptance into the AGA Future Leaders Program, we embarked on a series of virtual and in-person meetings with our mentorship triads (one mentor and two mentees) and other mentorship teams over the 18-month program (see Figure). These meetings covered highly focused topics ranging from the role of advocacy in leadership to negotiation and developing a business plan, with ample opportunities for individually tailored mentorship within the mentorship triads.
We also completed personality assessments that helped us understand our strengths and areas of improvement, and ways to use the information to hone our leadership styles.
A large portion of programming and the mentorship experience during the AGA Future Leaders Program is focused on a leadership project that is aimed at addressing a societal driver of interest for the AGA. Examples of these societal drivers of interest include maximizing the role of women in gastroenterology, the role of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology, burnout, and the impact of climate change on gastroenterology. Mentorship triads propose novel methods for addressing these critical issues, outlining the roles that the AGA and other stakeholders may embrace to address these anticipated growing challenges head on.
Our mentorship triad was asked to address the issue of ending disparities within gastroenterology. Given our research and clinical interest in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), we immediately recognized an opportunity to evaluate and potentially offer solutions for the geographic disparities that exist in the field of IBD. These disparities affect access to care for patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, leading to delays in diagnosis and ultimately effective therapy decisions.
In addition to developing a proposal for the AGA to expand access to care to major IBD centers in rural areas where these disparities exist, we also initiated an examination of geographic disparities in our own multidisciplinary IBD centers (abstract accepted for presentation at Digestive Diseases Week 2024). This allowed us to expand our respective research footprints at our institutions, utilizing new methods of geocoding to directly measure factors affecting clinical outcomes in IBD. Given our in-depth evaluation of this topic as part of our Future Leaders Program training, at the suggestion of our mentor, our mentorship triad also published a commentary on geographic disparities in the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion sections of Gastroenterology and Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.1, 2
Impact on the Field and Our Careers
Our mentorship triad had the unique experience of having a mentor who had previously participated in the Future Leaders Program as a mentee. As the Future Leaders Program has now enrolled 72 participants, these occasions will likely become more frequent, given the opportunities for career development and growth within the AGA (and our field) that are available after participating in the Future Leaders Program.
To have a mentor with this insight of having been a mentee in the program was invaluable, given her direct experience and understanding of the growth opportunities available, and opportunities to maximize participation in the Future Leaders Program. Additionally, as evidenced by Dr. Shaukat’s recommendations to grow our initial assignment into published commentaries, need statements for our field, and ultimately growing research projects, her keen insights as a mentor were a critical component of our individual growth in the program and the success of our mentorship triad. We benefited from networking with peers and learning about their work, which can lead to future collaborations. We had access to the highly accomplished mentors from diverse settings and learned models of leadership, while developing skills to foster our own leadership style.
In terms of programmatic impact, more than 90% of FLP alumni are serving in AGA leadership on committees, task forces, editorial boards, and councils. What is also important is the impact of content developed by mentee-mentor triads during the FLP cohorts over time. More than 700 GIs have benefited from online leadership development content created by the FLP. Based on our experience, we highly recommend all early career GI physicians to apply!
Dr. Parakkal (@P_DeepakIBDMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis (Mo.) School of Medicine. He is supported by a Junior Faculty Development Award from the American College of Gastroenterology and IBD Plexus of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. He has received research support under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from AbbVie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Prometheus Biosciences, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Roche-Genentech, and CorEvitas LLC. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Scipher Medicine, Fresenius Kabi, Roche-Genentech, and CorEvitas LLC. Dr. Barnes (@EdBarnesMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. He is supported by National Institutes of Health K23DK127157-01, and has served as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, and Target RWE. Dr. Shaukat (@AasmaShaukatMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology, New York University, New York. She has served as a consultant for Iterative health, Motus, Freenome, and Geneoscopy. Research support by the Steve and Alex Cohen Foundation.
References
1. Deepak P, Barnes EL, Shaukat A. Health Disparities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Care Driven by Rural Versus Urban Residence: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Gastroenterology. 2023 July. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.017.
2. Deepak P, Barnes EL, Shaukat A. Health Disparities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Care Driven by Rural Versus Urban Residence: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 July. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.006.
Two of us (Parakkal Deepak and Edward L. Barnes) were part of the American Gastroenterological Association’s (AGA) Future Leaders Program (FLP) class of 2022-2023, and our mentor was Aasma Shaukat. We were invited to share our experiences as participants in the FLP and its impact in our careers.
Why Was the Future Leaders Program Conceived?
To understand this, one must first understand that the AGA, like all other GI professional organizations, relies on volunteer leaders to develop its long-term vision and execute this through strategic initiatives and programs. and understand the governance structure of the AGA to help lead it to face these challenges effectively.
The AGA FLP was thus conceived and launched in 2014-2015 by the founding chairs, Byron Cryer, MD, who is a professor of medicine and associate dean for faculty diversity at University of Texas Southwestern Medical School and Suzanne Rose, MD, MSEd, AGAF, who is a professor of medicine and senior vice dean for medical education at Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. They envisioned a leadership pathway that would position early career GIs on a track to positively affect the AGA and the field of GI.
How Does One Apply for the Program?
Our FLP cohort applications were invited in October of 2021 and mentees accepted into the program in November 2021. The application process is competitive – applicants are encouraged to detail why they feel they would benefit from the FLP, what existing skillsets they have that can be further enhanced through the program, and what their long-term vision is for their growth as leaders, both within their institution and within the AGA. This is further accompanied by letters of support from their divisional chiefs and other key supervisors within the division who are intimately aware of their leadership potential and career trajectory. This process identified 18 future leaders for our class of 2022-2023.
What Is Involved?
Following acceptance into the AGA Future Leaders Program, we embarked on a series of virtual and in-person meetings with our mentorship triads (one mentor and two mentees) and other mentorship teams over the 18-month program (see Figure). These meetings covered highly focused topics ranging from the role of advocacy in leadership to negotiation and developing a business plan, with ample opportunities for individually tailored mentorship within the mentorship triads.

We also completed personality assessments that helped us understand our strengths and areas of improvement, and ways to use the information to hone our leadership styles.
A large portion of programming and the mentorship experience during the AGA Future Leaders Program is focused on a leadership project that is aimed at addressing a societal driver of interest for the AGA. Examples of these societal drivers of interest include maximizing the role of women in gastroenterology, the role of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology, burnout, and the impact of climate change on gastroenterology. Mentorship triads propose novel methods for addressing these critical issues, outlining the roles that the AGA and other stakeholders may embrace to address these anticipated growing challenges head on.
Our mentorship triad was asked to address the issue of ending disparities within gastroenterology. Given our research and clinical interest in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), we immediately recognized an opportunity to evaluate and potentially offer solutions for the geographic disparities that exist in the field of IBD. These disparities affect access to care for patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, leading to delays in diagnosis and ultimately effective therapy decisions.
In addition to developing a proposal for the AGA to expand access to care to major IBD centers in rural areas where these disparities exist, we also initiated an examination of geographic disparities in our own multidisciplinary IBD centers (abstract accepted for presentation at Digestive Diseases Week 2024). This allowed us to expand our respective research footprints at our institutions, utilizing new methods of geocoding to directly measure factors affecting clinical outcomes in IBD. Given our in-depth evaluation of this topic as part of our Future Leaders Program training, at the suggestion of our mentor, our mentorship triad also published a commentary on geographic disparities in the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion sections of Gastroenterology and Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.1, 2
Impact on the Field and Our Careers
Our mentorship triad had the unique experience of having a mentor who had previously participated in the Future Leaders Program as a mentee. As the Future Leaders Program has now enrolled 72 participants, these occasions will likely become more frequent, given the opportunities for career development and growth within the AGA (and our field) that are available after participating in the Future Leaders Program.
To have a mentor with this insight of having been a mentee in the program was invaluable, given her direct experience and understanding of the growth opportunities available, and opportunities to maximize participation in the Future Leaders Program. Additionally, as evidenced by Dr. Shaukat’s recommendations to grow our initial assignment into published commentaries, need statements for our field, and ultimately growing research projects, her keen insights as a mentor were a critical component of our individual growth in the program and the success of our mentorship triad. We benefited from networking with peers and learning about their work, which can lead to future collaborations. We had access to the highly accomplished mentors from diverse settings and learned models of leadership, while developing skills to foster our own leadership style.
In terms of programmatic impact, more than 90% of FLP alumni are serving in AGA leadership on committees, task forces, editorial boards, and councils. What is also important is the impact of content developed by mentee-mentor triads during the FLP cohorts over time. More than 700 GIs have benefited from online leadership development content created by the FLP. Based on our experience, we highly recommend all early career GI physicians to apply!
Dr. Parakkal (@P_DeepakIBDMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis (Mo.) School of Medicine. He is supported by a Junior Faculty Development Award from the American College of Gastroenterology and IBD Plexus of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. He has received research support under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from AbbVie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Prometheus Biosciences, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Roche-Genentech, and CorEvitas LLC. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Scipher Medicine, Fresenius Kabi, Roche-Genentech, and CorEvitas LLC. Dr. Barnes (@EdBarnesMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. He is supported by National Institutes of Health K23DK127157-01, and has served as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, and Target RWE. Dr. Shaukat (@AasmaShaukatMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology, New York University, New York. She has served as a consultant for Iterative health, Motus, Freenome, and Geneoscopy. Research support by the Steve and Alex Cohen Foundation.
References
1. Deepak P, Barnes EL, Shaukat A. Health Disparities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Care Driven by Rural Versus Urban Residence: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Gastroenterology. 2023 July. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.017.
2. Deepak P, Barnes EL, Shaukat A. Health Disparities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Care Driven by Rural Versus Urban Residence: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 July. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.006.
Two of us (Parakkal Deepak and Edward L. Barnes) were part of the American Gastroenterological Association’s (AGA) Future Leaders Program (FLP) class of 2022-2023, and our mentor was Aasma Shaukat. We were invited to share our experiences as participants in the FLP and its impact in our careers.
Why Was the Future Leaders Program Conceived?
To understand this, one must first understand that the AGA, like all other GI professional organizations, relies on volunteer leaders to develop its long-term vision and execute this through strategic initiatives and programs. and understand the governance structure of the AGA to help lead it to face these challenges effectively.
The AGA FLP was thus conceived and launched in 2014-2015 by the founding chairs, Byron Cryer, MD, who is a professor of medicine and associate dean for faculty diversity at University of Texas Southwestern Medical School and Suzanne Rose, MD, MSEd, AGAF, who is a professor of medicine and senior vice dean for medical education at Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. They envisioned a leadership pathway that would position early career GIs on a track to positively affect the AGA and the field of GI.
How Does One Apply for the Program?
Our FLP cohort applications were invited in October of 2021 and mentees accepted into the program in November 2021. The application process is competitive – applicants are encouraged to detail why they feel they would benefit from the FLP, what existing skillsets they have that can be further enhanced through the program, and what their long-term vision is for their growth as leaders, both within their institution and within the AGA. This is further accompanied by letters of support from their divisional chiefs and other key supervisors within the division who are intimately aware of their leadership potential and career trajectory. This process identified 18 future leaders for our class of 2022-2023.
What Is Involved?
Following acceptance into the AGA Future Leaders Program, we embarked on a series of virtual and in-person meetings with our mentorship triads (one mentor and two mentees) and other mentorship teams over the 18-month program (see Figure). These meetings covered highly focused topics ranging from the role of advocacy in leadership to negotiation and developing a business plan, with ample opportunities for individually tailored mentorship within the mentorship triads.

We also completed personality assessments that helped us understand our strengths and areas of improvement, and ways to use the information to hone our leadership styles.
A large portion of programming and the mentorship experience during the AGA Future Leaders Program is focused on a leadership project that is aimed at addressing a societal driver of interest for the AGA. Examples of these societal drivers of interest include maximizing the role of women in gastroenterology, the role of artificial intelligence in gastroenterology, burnout, and the impact of climate change on gastroenterology. Mentorship triads propose novel methods for addressing these critical issues, outlining the roles that the AGA and other stakeholders may embrace to address these anticipated growing challenges head on.
Our mentorship triad was asked to address the issue of ending disparities within gastroenterology. Given our research and clinical interest in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), we immediately recognized an opportunity to evaluate and potentially offer solutions for the geographic disparities that exist in the field of IBD. These disparities affect access to care for patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, leading to delays in diagnosis and ultimately effective therapy decisions.
In addition to developing a proposal for the AGA to expand access to care to major IBD centers in rural areas where these disparities exist, we also initiated an examination of geographic disparities in our own multidisciplinary IBD centers (abstract accepted for presentation at Digestive Diseases Week 2024). This allowed us to expand our respective research footprints at our institutions, utilizing new methods of geocoding to directly measure factors affecting clinical outcomes in IBD. Given our in-depth evaluation of this topic as part of our Future Leaders Program training, at the suggestion of our mentor, our mentorship triad also published a commentary on geographic disparities in the Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion sections of Gastroenterology and Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.1, 2
Impact on the Field and Our Careers
Our mentorship triad had the unique experience of having a mentor who had previously participated in the Future Leaders Program as a mentee. As the Future Leaders Program has now enrolled 72 participants, these occasions will likely become more frequent, given the opportunities for career development and growth within the AGA (and our field) that are available after participating in the Future Leaders Program.
To have a mentor with this insight of having been a mentee in the program was invaluable, given her direct experience and understanding of the growth opportunities available, and opportunities to maximize participation in the Future Leaders Program. Additionally, as evidenced by Dr. Shaukat’s recommendations to grow our initial assignment into published commentaries, need statements for our field, and ultimately growing research projects, her keen insights as a mentor were a critical component of our individual growth in the program and the success of our mentorship triad. We benefited from networking with peers and learning about their work, which can lead to future collaborations. We had access to the highly accomplished mentors from diverse settings and learned models of leadership, while developing skills to foster our own leadership style.
In terms of programmatic impact, more than 90% of FLP alumni are serving in AGA leadership on committees, task forces, editorial boards, and councils. What is also important is the impact of content developed by mentee-mentor triads during the FLP cohorts over time. More than 700 GIs have benefited from online leadership development content created by the FLP. Based on our experience, we highly recommend all early career GI physicians to apply!
Dr. Parakkal (@P_DeepakIBDMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis (Mo.) School of Medicine. He is supported by a Junior Faculty Development Award from the American College of Gastroenterology and IBD Plexus of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation. He has received research support under a sponsored research agreement unrelated to the data in the paper from AbbVie, Arena Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Prometheus Biosciences, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Roche-Genentech, and CorEvitas LLC. He has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Scipher Medicine, Fresenius Kabi, Roche-Genentech, and CorEvitas LLC. Dr. Barnes (@EdBarnesMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. He is supported by National Institutes of Health K23DK127157-01, and has served as a consultant for Eli Lilly, Bristol-Meyers Squibb, and Target RWE. Dr. Shaukat (@AasmaShaukatMD) is based in the division of gastroenterology, New York University, New York. She has served as a consultant for Iterative health, Motus, Freenome, and Geneoscopy. Research support by the Steve and Alex Cohen Foundation.
References
1. Deepak P, Barnes EL, Shaukat A. Health Disparities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Care Driven by Rural Versus Urban Residence: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Gastroenterology. 2023 July. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.017.
2. Deepak P, Barnes EL, Shaukat A. Health Disparities in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Care Driven by Rural Versus Urban Residence: Challenges and Potential Solutions. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 July. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.04.006.
















