User login
APA, others lobby to make COVID-19 telehealth waivers permanent
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is calling on Congress to permanently lift restrictions that have allowed unfettered delivery of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic, which experts say has been a boon to patients and physicians alike.
“We ask Congress to extend the telehealth waiver authority under COVID-19 beyond the emergency and to study its impact while doing so,” said APA President Jeffrey Geller, MD, in a May 27 video briefing with congressional staff and reporters.
The APA is also seeking to make permanent certain waivers granted by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on April 30, including elimination of geographic restrictions on behavioral health and allowing patients be seen at home, said Dr. Geller.
The APA also is asking for the elimination of the rule that requires clinicians to have an initial face-to-face meeting with patients before they can prescribe controlled substances, Dr. Geller said. The Drug Enforcement Administration waived that requirement, known as the Ryan Haight Act, on March 17 for the duration of the national emergency.
Telemedicine has supporters on both sides of the aisle in Congress, including Rep. Paul Tonko (D-N.Y.) who said at the APA briefing he would fight to make the waivers permanent.
“The expanded use of telehealth has enormous potential during normal times as well, especially in behavioral health,” said Mr. Tonko. “I am pushing fiercely for these current flexibilities to be extended for a reasonable time after the public health emergency so that we can have time to evaluate which should be made permanent,” he said.
Dr. Geller, other clinicians, and advocates in the briefing praised CMS for facilitating telepsychiatry for Medicare. That follows in the footsteps of most private insurers, who have also relaxed requirements into the summer, according to the Medical Group Management Association.
Game changer
The Medicare waivers “have dramatically changed the entire scene for someone like myself as a clinician to allow me to see my patients in a much easier way,” said Peter Yellowlees, MBBS, MD, chief wellness officer, University of California Davis Health. Within 2 weeks in March, the health system converted almost all of its regular outpatient visits to telemedicine, he said.
Dr. Yellowlees added government still needs to address, what he called, outdated HIPAA regulations that ban certain technologies.
“It makes no sense that I can talk to someone on an iPhone, but the moment I talk to them on FaceTime, it’s illegal,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a former president of the American Telemedicine Association.
Dr. Geller said that “psychiatric care provided by telehealth is as effective as in-person psychiatric services,” adding that “some patients prefer telepsychiatry because of its convenience and as a means of reducing stigma associated with seeking help for mental health.”
Shabana Khan, MD, a child psychiatrist and director of telepsychiatry at New York University Langone Health, said audio and video conferencing are helping address a shortage and maldistribution of child and adolescent psychiatrists.
Americans’ mental health is suffering during the pandemic. The U.S. Census Bureau recently released data showing that half of those surveyed reported depressed mood and that one-third are reporting anxiety, depression, or both, as reported by the Washington Post.
“At this very time that anxiety, depression, substance use, and other mental health problems are rising, our nation’s already strained mental health system is really being pushed to the brink,” said Jodi Kwarciany, manager for mental health policy for the National Alliance on Mental Illness, during the briefing.
Telemedicine can help “by connecting people to providers at the time and the place and using the technology that works best for them,” she said, adding that NAMI would press policymakers to address barriers to access.
The clinicians on the briefing said they’ve observed that some patients are more comfortable with video or audio interactions than with in-person visits.
Increased access to care
Telepsychiatry seems to be convincing some to reconsider therapy, since they can do it at home, said Dr. Yellowlees. he said.
For instance, he said, he has been able to consult by phone and video with several patients who receive care through the Indian Health Service who had not be able to get into the physical clinic.
Dr. Yellowlees said video sessions also may encourage patients to be more, not less, talkative. “Video is actually counterintuitively a very intimate experience,” he said, in part because of the perceived distance and people’s tendency to be less inhibited on technology platforms.“It’s less embarrassing,” he said. “If you’ve got really dramatic, difficult, traumatic things to talk about, it’s slightly easier to talk to someone who’s slightly further apart from you on video,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“Individuals who have a significant amount of anxiety may actually feel more comfortable with the distance that this technology affords,” agreed Dr. Khan. She said telemedicine had made sessions more comfortable for some of her patients with autism spectrum disorder.
Dr. Geller said audio and video have been important to his practice during the pandemic. One of his patients never leaves the house and does not use computers. “He spends his time sequestered at home listening to records on his record player,” said Dr. Geller. But he’s been amenable to phone sessions. “What I’ve found with him, and I’ve found with several other patients, is that they actually talk more easily when they’re not face to face,” he said.
Far fewer no-shows
Another plus for his New England–based practice during the last few months: patients have not been anxious about missing sessions because of the weather. The clinicians all noted that telepsychiatry seemed to reduce missed visits.
Dr. Yellowlees said that no-show rates had decreased by half at UC Davis. “That means no significant loss of income,” during the pandemic, he said.
“The no-show rate is incredibly low, particularly because when you call the patients and they don’t remember they had an appointment, you have the appointment anyway, most of the time,” said Dr. Geller.
For Dr. Khan, being able to conduct audio and video sessions during the pandemic has meant keeping up continuity of care.
As a result of the pandemic, many college students in New York City had to go home – often to another state. The waivers granted by New York’s Medicaid program and other insurers have allowed Dr. Khan to continue care for these patients.
The NYU clinic also operates day programs in rural areas 5 hours from the city. Dr. Khan recently evaluated a 12-year-old girl with significant anxiety and low mood, both of which had worsened.
“She would not have been able to access care otherwise,” said Dr. Khan. And for rural patients who do not have access to broadband or smartphones, audio visits “have been immensely helpful,” she said.
Dr. Khan, Dr. Geller, and Dr. Yellowlees have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is calling on Congress to permanently lift restrictions that have allowed unfettered delivery of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic, which experts say has been a boon to patients and physicians alike.
“We ask Congress to extend the telehealth waiver authority under COVID-19 beyond the emergency and to study its impact while doing so,” said APA President Jeffrey Geller, MD, in a May 27 video briefing with congressional staff and reporters.
The APA is also seeking to make permanent certain waivers granted by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on April 30, including elimination of geographic restrictions on behavioral health and allowing patients be seen at home, said Dr. Geller.
The APA also is asking for the elimination of the rule that requires clinicians to have an initial face-to-face meeting with patients before they can prescribe controlled substances, Dr. Geller said. The Drug Enforcement Administration waived that requirement, known as the Ryan Haight Act, on March 17 for the duration of the national emergency.
Telemedicine has supporters on both sides of the aisle in Congress, including Rep. Paul Tonko (D-N.Y.) who said at the APA briefing he would fight to make the waivers permanent.
“The expanded use of telehealth has enormous potential during normal times as well, especially in behavioral health,” said Mr. Tonko. “I am pushing fiercely for these current flexibilities to be extended for a reasonable time after the public health emergency so that we can have time to evaluate which should be made permanent,” he said.
Dr. Geller, other clinicians, and advocates in the briefing praised CMS for facilitating telepsychiatry for Medicare. That follows in the footsteps of most private insurers, who have also relaxed requirements into the summer, according to the Medical Group Management Association.
Game changer
The Medicare waivers “have dramatically changed the entire scene for someone like myself as a clinician to allow me to see my patients in a much easier way,” said Peter Yellowlees, MBBS, MD, chief wellness officer, University of California Davis Health. Within 2 weeks in March, the health system converted almost all of its regular outpatient visits to telemedicine, he said.
Dr. Yellowlees added government still needs to address, what he called, outdated HIPAA regulations that ban certain technologies.
“It makes no sense that I can talk to someone on an iPhone, but the moment I talk to them on FaceTime, it’s illegal,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a former president of the American Telemedicine Association.
Dr. Geller said that “psychiatric care provided by telehealth is as effective as in-person psychiatric services,” adding that “some patients prefer telepsychiatry because of its convenience and as a means of reducing stigma associated with seeking help for mental health.”
Shabana Khan, MD, a child psychiatrist and director of telepsychiatry at New York University Langone Health, said audio and video conferencing are helping address a shortage and maldistribution of child and adolescent psychiatrists.
Americans’ mental health is suffering during the pandemic. The U.S. Census Bureau recently released data showing that half of those surveyed reported depressed mood and that one-third are reporting anxiety, depression, or both, as reported by the Washington Post.
“At this very time that anxiety, depression, substance use, and other mental health problems are rising, our nation’s already strained mental health system is really being pushed to the brink,” said Jodi Kwarciany, manager for mental health policy for the National Alliance on Mental Illness, during the briefing.
Telemedicine can help “by connecting people to providers at the time and the place and using the technology that works best for them,” she said, adding that NAMI would press policymakers to address barriers to access.
The clinicians on the briefing said they’ve observed that some patients are more comfortable with video or audio interactions than with in-person visits.
Increased access to care
Telepsychiatry seems to be convincing some to reconsider therapy, since they can do it at home, said Dr. Yellowlees. he said.
For instance, he said, he has been able to consult by phone and video with several patients who receive care through the Indian Health Service who had not be able to get into the physical clinic.
Dr. Yellowlees said video sessions also may encourage patients to be more, not less, talkative. “Video is actually counterintuitively a very intimate experience,” he said, in part because of the perceived distance and people’s tendency to be less inhibited on technology platforms.“It’s less embarrassing,” he said. “If you’ve got really dramatic, difficult, traumatic things to talk about, it’s slightly easier to talk to someone who’s slightly further apart from you on video,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“Individuals who have a significant amount of anxiety may actually feel more comfortable with the distance that this technology affords,” agreed Dr. Khan. She said telemedicine had made sessions more comfortable for some of her patients with autism spectrum disorder.
Dr. Geller said audio and video have been important to his practice during the pandemic. One of his patients never leaves the house and does not use computers. “He spends his time sequestered at home listening to records on his record player,” said Dr. Geller. But he’s been amenable to phone sessions. “What I’ve found with him, and I’ve found with several other patients, is that they actually talk more easily when they’re not face to face,” he said.
Far fewer no-shows
Another plus for his New England–based practice during the last few months: patients have not been anxious about missing sessions because of the weather. The clinicians all noted that telepsychiatry seemed to reduce missed visits.
Dr. Yellowlees said that no-show rates had decreased by half at UC Davis. “That means no significant loss of income,” during the pandemic, he said.
“The no-show rate is incredibly low, particularly because when you call the patients and they don’t remember they had an appointment, you have the appointment anyway, most of the time,” said Dr. Geller.
For Dr. Khan, being able to conduct audio and video sessions during the pandemic has meant keeping up continuity of care.
As a result of the pandemic, many college students in New York City had to go home – often to another state. The waivers granted by New York’s Medicaid program and other insurers have allowed Dr. Khan to continue care for these patients.
The NYU clinic also operates day programs in rural areas 5 hours from the city. Dr. Khan recently evaluated a 12-year-old girl with significant anxiety and low mood, both of which had worsened.
“She would not have been able to access care otherwise,” said Dr. Khan. And for rural patients who do not have access to broadband or smartphones, audio visits “have been immensely helpful,” she said.
Dr. Khan, Dr. Geller, and Dr. Yellowlees have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) is calling on Congress to permanently lift restrictions that have allowed unfettered delivery of telehealth services during the COVID-19 pandemic, which experts say has been a boon to patients and physicians alike.
“We ask Congress to extend the telehealth waiver authority under COVID-19 beyond the emergency and to study its impact while doing so,” said APA President Jeffrey Geller, MD, in a May 27 video briefing with congressional staff and reporters.
The APA is also seeking to make permanent certain waivers granted by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on April 30, including elimination of geographic restrictions on behavioral health and allowing patients be seen at home, said Dr. Geller.
The APA also is asking for the elimination of the rule that requires clinicians to have an initial face-to-face meeting with patients before they can prescribe controlled substances, Dr. Geller said. The Drug Enforcement Administration waived that requirement, known as the Ryan Haight Act, on March 17 for the duration of the national emergency.
Telemedicine has supporters on both sides of the aisle in Congress, including Rep. Paul Tonko (D-N.Y.) who said at the APA briefing he would fight to make the waivers permanent.
“The expanded use of telehealth has enormous potential during normal times as well, especially in behavioral health,” said Mr. Tonko. “I am pushing fiercely for these current flexibilities to be extended for a reasonable time after the public health emergency so that we can have time to evaluate which should be made permanent,” he said.
Dr. Geller, other clinicians, and advocates in the briefing praised CMS for facilitating telepsychiatry for Medicare. That follows in the footsteps of most private insurers, who have also relaxed requirements into the summer, according to the Medical Group Management Association.
Game changer
The Medicare waivers “have dramatically changed the entire scene for someone like myself as a clinician to allow me to see my patients in a much easier way,” said Peter Yellowlees, MBBS, MD, chief wellness officer, University of California Davis Health. Within 2 weeks in March, the health system converted almost all of its regular outpatient visits to telemedicine, he said.
Dr. Yellowlees added government still needs to address, what he called, outdated HIPAA regulations that ban certain technologies.
“It makes no sense that I can talk to someone on an iPhone, but the moment I talk to them on FaceTime, it’s illegal,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a former president of the American Telemedicine Association.
Dr. Geller said that “psychiatric care provided by telehealth is as effective as in-person psychiatric services,” adding that “some patients prefer telepsychiatry because of its convenience and as a means of reducing stigma associated with seeking help for mental health.”
Shabana Khan, MD, a child psychiatrist and director of telepsychiatry at New York University Langone Health, said audio and video conferencing are helping address a shortage and maldistribution of child and adolescent psychiatrists.
Americans’ mental health is suffering during the pandemic. The U.S. Census Bureau recently released data showing that half of those surveyed reported depressed mood and that one-third are reporting anxiety, depression, or both, as reported by the Washington Post.
“At this very time that anxiety, depression, substance use, and other mental health problems are rising, our nation’s already strained mental health system is really being pushed to the brink,” said Jodi Kwarciany, manager for mental health policy for the National Alliance on Mental Illness, during the briefing.
Telemedicine can help “by connecting people to providers at the time and the place and using the technology that works best for them,” she said, adding that NAMI would press policymakers to address barriers to access.
The clinicians on the briefing said they’ve observed that some patients are more comfortable with video or audio interactions than with in-person visits.
Increased access to care
Telepsychiatry seems to be convincing some to reconsider therapy, since they can do it at home, said Dr. Yellowlees. he said.
For instance, he said, he has been able to consult by phone and video with several patients who receive care through the Indian Health Service who had not be able to get into the physical clinic.
Dr. Yellowlees said video sessions also may encourage patients to be more, not less, talkative. “Video is actually counterintuitively a very intimate experience,” he said, in part because of the perceived distance and people’s tendency to be less inhibited on technology platforms.“It’s less embarrassing,” he said. “If you’ve got really dramatic, difficult, traumatic things to talk about, it’s slightly easier to talk to someone who’s slightly further apart from you on video,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
“Individuals who have a significant amount of anxiety may actually feel more comfortable with the distance that this technology affords,” agreed Dr. Khan. She said telemedicine had made sessions more comfortable for some of her patients with autism spectrum disorder.
Dr. Geller said audio and video have been important to his practice during the pandemic. One of his patients never leaves the house and does not use computers. “He spends his time sequestered at home listening to records on his record player,” said Dr. Geller. But he’s been amenable to phone sessions. “What I’ve found with him, and I’ve found with several other patients, is that they actually talk more easily when they’re not face to face,” he said.
Far fewer no-shows
Another plus for his New England–based practice during the last few months: patients have not been anxious about missing sessions because of the weather. The clinicians all noted that telepsychiatry seemed to reduce missed visits.
Dr. Yellowlees said that no-show rates had decreased by half at UC Davis. “That means no significant loss of income,” during the pandemic, he said.
“The no-show rate is incredibly low, particularly because when you call the patients and they don’t remember they had an appointment, you have the appointment anyway, most of the time,” said Dr. Geller.
For Dr. Khan, being able to conduct audio and video sessions during the pandemic has meant keeping up continuity of care.
As a result of the pandemic, many college students in New York City had to go home – often to another state. The waivers granted by New York’s Medicaid program and other insurers have allowed Dr. Khan to continue care for these patients.
The NYU clinic also operates day programs in rural areas 5 hours from the city. Dr. Khan recently evaluated a 12-year-old girl with significant anxiety and low mood, both of which had worsened.
“She would not have been able to access care otherwise,” said Dr. Khan. And for rural patients who do not have access to broadband or smartphones, audio visits “have been immensely helpful,” she said.
Dr. Khan, Dr. Geller, and Dr. Yellowlees have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 may increase risk of preterm birth and cesarean delivery
Among 57 hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection who underwent vaginal or cesarean delivery, 7 had spontaneous preterm or respiratory-indicated preterm delivery, a rate of 12%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. For comparison, 7% of patients had preterm delivery in 2019, researchers reported “We also noted a high cesarean delivery rate in the study population (39% vs. 27% in the same area in 2019), mainly as a result of maternal respiratory-indicated urgent delivery,” wrote Valeria M. Savasi, MD, PhD, of the University of Milan and Luigi Sacco Hospital, also in Milan, and colleagues.
Data do not indicate that pregnant women are more susceptible to severe COVID-19 infection, nor have studies suggested an increased risk of miscarriage, congenital anomalies, or early pregnancy loss in pregnant patients with COVID-19, the authors wrote. Studies have described an increased risk of preterm birth, however.
To study clinical features of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential factors associated with severe disease and iatrogenic delivery, Dr. Savasi and colleagues conducted a prospective study of 77 women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection who were admitted during pregnancy or the immediate postpartum period in 12 maternity hospitals in northern Italy between Feb. 23 and March 28, 2020.
The investigators classified patients as having severe disease if they underwent urgent delivery based on maternal respiratory function or if they were admitted to an ICU or subintensive care department. In all, 14 patients (18%) were classified as having severe disease.
“Three patients were intubated after emergency cesarean delivery performed for maternal deterioration, and one patient underwent extracorporeal membrane oxygenation,” Dr. Savasi and colleagues reported. The results are consistent with epidemiologic data in the nonpregnant population with COVID-19 disease.
Of 11 patients with severe disease who underwent urgent delivery for respiratory compromise, 6 had significant postpartum improvement in clinical conditions. No maternal deaths occurred.
“Increased BMI [body mass index] was a significant risk factor for severe disease,” Dr. Savasi and colleagues wrote. “Fever and dyspnea on admission were symptoms significantly associated with subsequent severe maternal respiratory deterioration.”
Most patients (65%) were admitted during the third trimester, and 20 patients were still pregnant at discharge.
“Nine newborns were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit,” the authors wrote. “Interestingly, besides prematurity, fetal oxygenation and well-being at delivery were not apparently affected by the maternal acute conditions.” Three newborns with vaginal delivery and one with cesarean delivery tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The newborns may have been infected after delivery, Dr. Savasi and colleagues added. For all newborns, rooming-in and breastfeeding were performed, and none developed respiratory symptoms.
Criteria for hospital admission and therapeutic protocols may have varied between hospitals, the authors noted. In addition, the study included 12 patients who were asymptomatic and admitted for obstetric indications. These patients were tested for SARS-CoV-2 because of contact with an infected individual. Most patients were symptomatic, however, which explains the high rate of maternal severe outcomes. Hospitals have since adopted a universal SARS-CoV-2 screening policy for hospitalized pregnant patients.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle, commented in an interview that Savasi et al. describe one of the larger COVID-19 in pregnancy cohorts to date with rates of severe disease and delivery for respiratory compromise, which is remarkably similar to Washington state (severe disease, 18% vs. nearly 15%; delivery for respiratory compromise, 16% vs. 20%). As in Washington state, Italian women with a higher prepregnancy BMI were overrepresented in the severe disease group.
“Data are beginning to emerge that identify women who were overweight or obese prior to pregnancy as a high risk group for developing severe COVID-19. These data are similar to known associations between obesity and critical illness in pregnancy during the 2009 ‘swine flu’ (influenza A virus, H1N1) pandemic,” she said.
“This study and others indicate that the late second and third trimesters may be a time when women are more likely to be symptomatic from COVID-19. It remains unclear if women in the first trimester are protected from severe COVID-19 outcomes or have outcomes similar to nonpregnant women,” concluded Dr. Waldorf.
One study author disclosed receiving funds from Lo Li Pharma and Zambongroup. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Savasi VM et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003979.
Among 57 hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection who underwent vaginal or cesarean delivery, 7 had spontaneous preterm or respiratory-indicated preterm delivery, a rate of 12%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. For comparison, 7% of patients had preterm delivery in 2019, researchers reported “We also noted a high cesarean delivery rate in the study population (39% vs. 27% in the same area in 2019), mainly as a result of maternal respiratory-indicated urgent delivery,” wrote Valeria M. Savasi, MD, PhD, of the University of Milan and Luigi Sacco Hospital, also in Milan, and colleagues.
Data do not indicate that pregnant women are more susceptible to severe COVID-19 infection, nor have studies suggested an increased risk of miscarriage, congenital anomalies, or early pregnancy loss in pregnant patients with COVID-19, the authors wrote. Studies have described an increased risk of preterm birth, however.
To study clinical features of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential factors associated with severe disease and iatrogenic delivery, Dr. Savasi and colleagues conducted a prospective study of 77 women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection who were admitted during pregnancy or the immediate postpartum period in 12 maternity hospitals in northern Italy between Feb. 23 and March 28, 2020.
The investigators classified patients as having severe disease if they underwent urgent delivery based on maternal respiratory function or if they were admitted to an ICU or subintensive care department. In all, 14 patients (18%) were classified as having severe disease.
“Three patients were intubated after emergency cesarean delivery performed for maternal deterioration, and one patient underwent extracorporeal membrane oxygenation,” Dr. Savasi and colleagues reported. The results are consistent with epidemiologic data in the nonpregnant population with COVID-19 disease.
Of 11 patients with severe disease who underwent urgent delivery for respiratory compromise, 6 had significant postpartum improvement in clinical conditions. No maternal deaths occurred.
“Increased BMI [body mass index] was a significant risk factor for severe disease,” Dr. Savasi and colleagues wrote. “Fever and dyspnea on admission were symptoms significantly associated with subsequent severe maternal respiratory deterioration.”
Most patients (65%) were admitted during the third trimester, and 20 patients were still pregnant at discharge.
“Nine newborns were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit,” the authors wrote. “Interestingly, besides prematurity, fetal oxygenation and well-being at delivery were not apparently affected by the maternal acute conditions.” Three newborns with vaginal delivery and one with cesarean delivery tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The newborns may have been infected after delivery, Dr. Savasi and colleagues added. For all newborns, rooming-in and breastfeeding were performed, and none developed respiratory symptoms.
Criteria for hospital admission and therapeutic protocols may have varied between hospitals, the authors noted. In addition, the study included 12 patients who were asymptomatic and admitted for obstetric indications. These patients were tested for SARS-CoV-2 because of contact with an infected individual. Most patients were symptomatic, however, which explains the high rate of maternal severe outcomes. Hospitals have since adopted a universal SARS-CoV-2 screening policy for hospitalized pregnant patients.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle, commented in an interview that Savasi et al. describe one of the larger COVID-19 in pregnancy cohorts to date with rates of severe disease and delivery for respiratory compromise, which is remarkably similar to Washington state (severe disease, 18% vs. nearly 15%; delivery for respiratory compromise, 16% vs. 20%). As in Washington state, Italian women with a higher prepregnancy BMI were overrepresented in the severe disease group.
“Data are beginning to emerge that identify women who were overweight or obese prior to pregnancy as a high risk group for developing severe COVID-19. These data are similar to known associations between obesity and critical illness in pregnancy during the 2009 ‘swine flu’ (influenza A virus, H1N1) pandemic,” she said.
“This study and others indicate that the late second and third trimesters may be a time when women are more likely to be symptomatic from COVID-19. It remains unclear if women in the first trimester are protected from severe COVID-19 outcomes or have outcomes similar to nonpregnant women,” concluded Dr. Waldorf.
One study author disclosed receiving funds from Lo Li Pharma and Zambongroup. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Savasi VM et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003979.
Among 57 hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection who underwent vaginal or cesarean delivery, 7 had spontaneous preterm or respiratory-indicated preterm delivery, a rate of 12%, according to a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology. For comparison, 7% of patients had preterm delivery in 2019, researchers reported “We also noted a high cesarean delivery rate in the study population (39% vs. 27% in the same area in 2019), mainly as a result of maternal respiratory-indicated urgent delivery,” wrote Valeria M. Savasi, MD, PhD, of the University of Milan and Luigi Sacco Hospital, also in Milan, and colleagues.
Data do not indicate that pregnant women are more susceptible to severe COVID-19 infection, nor have studies suggested an increased risk of miscarriage, congenital anomalies, or early pregnancy loss in pregnant patients with COVID-19, the authors wrote. Studies have described an increased risk of preterm birth, however.
To study clinical features of maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential factors associated with severe disease and iatrogenic delivery, Dr. Savasi and colleagues conducted a prospective study of 77 women with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection who were admitted during pregnancy or the immediate postpartum period in 12 maternity hospitals in northern Italy between Feb. 23 and March 28, 2020.
The investigators classified patients as having severe disease if they underwent urgent delivery based on maternal respiratory function or if they were admitted to an ICU or subintensive care department. In all, 14 patients (18%) were classified as having severe disease.
“Three patients were intubated after emergency cesarean delivery performed for maternal deterioration, and one patient underwent extracorporeal membrane oxygenation,” Dr. Savasi and colleagues reported. The results are consistent with epidemiologic data in the nonpregnant population with COVID-19 disease.
Of 11 patients with severe disease who underwent urgent delivery for respiratory compromise, 6 had significant postpartum improvement in clinical conditions. No maternal deaths occurred.
“Increased BMI [body mass index] was a significant risk factor for severe disease,” Dr. Savasi and colleagues wrote. “Fever and dyspnea on admission were symptoms significantly associated with subsequent severe maternal respiratory deterioration.”
Most patients (65%) were admitted during the third trimester, and 20 patients were still pregnant at discharge.
“Nine newborns were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit,” the authors wrote. “Interestingly, besides prematurity, fetal oxygenation and well-being at delivery were not apparently affected by the maternal acute conditions.” Three newborns with vaginal delivery and one with cesarean delivery tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. The newborns may have been infected after delivery, Dr. Savasi and colleagues added. For all newborns, rooming-in and breastfeeding were performed, and none developed respiratory symptoms.
Criteria for hospital admission and therapeutic protocols may have varied between hospitals, the authors noted. In addition, the study included 12 patients who were asymptomatic and admitted for obstetric indications. These patients were tested for SARS-CoV-2 because of contact with an infected individual. Most patients were symptomatic, however, which explains the high rate of maternal severe outcomes. Hospitals have since adopted a universal SARS-CoV-2 screening policy for hospitalized pregnant patients.
Kristina Adams Waldorf, MD, professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Washington, Seattle, commented in an interview that Savasi et al. describe one of the larger COVID-19 in pregnancy cohorts to date with rates of severe disease and delivery for respiratory compromise, which is remarkably similar to Washington state (severe disease, 18% vs. nearly 15%; delivery for respiratory compromise, 16% vs. 20%). As in Washington state, Italian women with a higher prepregnancy BMI were overrepresented in the severe disease group.
“Data are beginning to emerge that identify women who were overweight or obese prior to pregnancy as a high risk group for developing severe COVID-19. These data are similar to known associations between obesity and critical illness in pregnancy during the 2009 ‘swine flu’ (influenza A virus, H1N1) pandemic,” she said.
“This study and others indicate that the late second and third trimesters may be a time when women are more likely to be symptomatic from COVID-19. It remains unclear if women in the first trimester are protected from severe COVID-19 outcomes or have outcomes similar to nonpregnant women,” concluded Dr. Waldorf.
One study author disclosed receiving funds from Lo Li Pharma and Zambongroup. The other authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Dr. Waldorf said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Savasi VM et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003979.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Scientific doubt tempers COVID-19 vaccine optimism
US government and industry projections that a COVID-19 vaccine will be ready by this fall or even January would take compressing what usually takes at least a decade into months, with little room for error or safety surprises.
“If all the cards fall into the right place and all the stars are aligned, you definitely could get a vaccine by December or January,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said last week.
But Fauci said a more realistic timeline is still 12 to 18 months, and experts interviewed by Medscape Medical News agree. They say that although recent developments are encouraging, history and scientific reason say the day when a COVID-19 vaccine is widely available will not come this year and may not come by the end of 2021.
The encouraging signals come primarily from two recent announcements: the $1.2 billion United States backing last week of one vaccine platform and the announcement on May 18 that the first human trials of another have produced some positive phase 1 results.
Recent developments
On May 21, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under “Operation Warp Speed” announced that the US will give AstraZeneca $1.2 billion “to make available at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine called AZD1222, with the first doses delivered as early as October 2020.”
On May 18, the Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Moderna announced that phase 1 clinical results showed that its vaccine candidate, which uses a new messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, appeared safe. Eight participants in the human trials were able to produce neutralizing antibodies that researchers believe are important in developing protection from the virus.
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Tal Zaks, MD, PhD told CNN that if the vaccine candidate does well in phase 2, “it could be ready by January 2021.”
The two candidates are among 10 in clinical trials for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The AstraZeneca/ AZD1222 candidate (also called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, in collaboration with the University of Oxford) has entered phase 2/3.
Moderna’s candidate and another being developed in Beijing, China, are in phase 2, WHO reports. As of yesterday, 115 other candidates are in preclinical evaluation.
Maria Elena Bottazzi, PhD, associate dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, told Medscape Medical News it’s important to realize that, in the case of the $1.2 billion US investment, “what they’re talking about is manufacturing.”
The idea, she said, is to pay AstraZeneca up front so that manufacturing can start before it is known whether the vaccine candidate is safe or effective, the reverse of how the clinical trial process usually works.
That way, if the candidate is deemed safe and effective, time is not lost by then deciding how to make it and distribute it.
By the end of this year, she said, “Maybe we will have many vaccines made and stored in a refrigerator somewhere. But between now and December, there’s absolutely no way you can show efficacy of the vaccine at the same time you confirm that it’s safe.”
“Take these things with a grain of salt”
Animal testing for the AstraZeneca candidate, made in partnership with the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, has yielded lackluster results, according to results on the preprint server BioRxiv, which have not been peer-reviewed.
“The results were not bad, but they were not gangbusters,” Bottazzi said. The results show the vaccine offered only partial protection.
“Partial protection is better than no protection,” she noted. “You have to take these things with a grain of salt. We don’t know what’s going to happen in humans.”
As for the Moderna candidate, Bottazzi said, “the good news is they found an appropriate safety profile. But from an eight-person group to make the extrapolation that they have efficacy — it’s unrealistic.”
Nicole Lurie, MD, MSPH, is senior adviser to the CEO for the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI), a nongovernmental organization funded by the Wellcome Trust, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the European Commission, and eight countries (Australia, Belgium, Canada, Ethiopia, Germany, Japan, Norway, and the United Kingdom) charged with supporting development of vaccines for pathogens on WHO’s priority list.
She and her colleagues write in a paper published online in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 30 that “it typically takes multiple candidates and many years to produce a licensed vaccine.”
The fastest time for developing a vaccine to date is 4 years, for the mumps vaccine, licensed in 1967.
As to whether she would expect a rollout of any vaccine by the end of the year, Lurie told Medscape Medical News, “If everything goes according to plan in every way, shape or form, well then maybe you can get there. But I wouldn’t hold my breath.”
Lurie and her colleagues write that “it’s far from certain that these new platforms will be scalable or that existing capacity can provide sufficient quantities of vaccine fast enough.”
On a call with reporters today, leaders of some of the words largest pharmaceutical companies said that one of the key bottlenecks is the sheer number of vials needed in order to distribute billions of doses of a successful vaccine.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, said, “Typically we are producing vaccines in single-dose vials. We are exploring with governments right now if it would be more convenient if there were 5-dose vials or 10-dose vials. I think we can resolve a significant part of the bottleneck.”
Despite the challenges, experts interviewed for this article agree that it will be possible to make a vaccine for COVID-19. They don’t expect attempts to meet the same complications that HIV researchers have seen over decades as the virus continues to confound with mutations.
Fred Ledley, MD, director of the Center for Integration of Science and Industry at Bentley University in Waltham, Massachusetts, told Medscape Medical News, “There doesn’t appear to be anything terribly diabolical about this virus. The mutation rate doesn’t appear to be anything like HIV. It appears to have some big, ugly proteins on the surface, which is good for vaccines — proteins with a lot of physical features look distinguishable from healthy cells. Signs all point to that it should be possible to make a vaccine.”
History raises safety concerns
However, Ledley said, “The idea of doing it in 6 months is largely unrealistic.”
He says 18 months is more realistic, primarily because of the sheer number of people that would have to be enrolled in a phase 3 study to truly test whether the endpoints are being met.
Vaccines are given to healthy volunteers. If safety signals arise, they may not be apparent until massive numbers of people are tested in phase 3.
“You’re never going to see the rates cut to 0%, but to see the difference between 10 people getting sick and seven people getting sick, takes very, very large numbers,” Ledley said. “There’s no way that can be done in 6 months. You’re talking about tens of thousands of people enrolled.”
He notes at this point it’s unclear what the endpoints will be and what the safety thresholds will be after consideration of risks and benefit.
Another big question for Ledley: “We don’t know what type of immunity we need to protect us against the virus. Do you just need the antibodies in your blood or do you need cells that are primed to attack the virus? Is it more of a chemical clearance or do the cells need to physically go in and digest the virus?”
History also points to the need for rigorous safety precautions that scientists fear could be compromised as trial phases overlap and processes are run in parallel instead of one step at a time.
An early batch of the Salk vaccine for polio in 1955, for example, turned out to be contaminated and caused paralysis in some children and 10 deaths, he points out.
CEPI’s Lurie adds that early candidates for another coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), “caused a reaction in the lungs that was very dangerous” before development was halted.
She also pointed to previous findings that a vaccine for dengue fever could worsen the disease in some people through a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
Lurie and colleagues write in their paper that “it’s critical that vaccines also be developed using the tried-and-true methods, even if they may take longer to enter clinical trials or to result in large numbers of doses.”
Live attenuated vaccine
Raul Andino, PhD, a virologist at the University of California San Francisco, is among the scientists working with a tried-and-true method — a live attenuated vaccine — and he told Medscape Medical News he’s predicting it will take 2 years to develop.
He said it is cheaper to produce because scientists just have to learn how to grow the virus. Because the technology is already proven, a live attenuated vaccine could be rapidly produced on a worldwide scale.
The hope is also that a live attenuated vaccine would be given once in a lifetime and therefore be more affordable, especially in poorer countries.
“While a Moderna vaccine might be good for Europe and the United States,” he said, “It’s not going to be good for Africa, India, Brazil.”
Andino said, “I would bet money” that the front-runner vaccines so far will not be one-time vaccines.
He points out that most of the vaccine candidates are trying to protect people from disease. While there’s nothing wrong with that, he said, “In my opinion that is the lower-hanging fruit.”
“In my mind we need something that interrupts the chain of transmission and induces protection,” Andino said, important for developing herd immunity.
The reason this type of approach takes longer is because you are introducing a weakened form of the virus to the body and you have to make sure it doesn’t cause disease, not just in a small test population, but in populations who may be more susceptible to the disease, Andino said.
A call for unified strategies
Universities, countries, international consortiums, and public-private partnerships are all racing to find several safe and effective vaccines as no one entity will likely be able to provide the global solution.
Some of the efforts involve overlap of entities but with different focuses.
Along with “Operation Warp Speed” and CEPI, other collaborations include Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, whose core partners include WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the Gates Foundation; and “Accelerating Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) partnership,” led by the National Institutes of Health.
Industry partners in ACTIV (18 biopharmaceutical companies), according to a May 18 article published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association, have said they will contribute their respective clinical trial capacities, regardless of which agent is studied.
Some, however, have called for more streamlining of efforts.
“Ideally we’d be working together,” Lurie told Medscape Medical News.
“I’m hopeful we will find ways to collaborate scientifically,” she said. “The US government’s responsibility is to make doses for the US. CEPI’s responsibility is to make doses for the world. A big focus of CEPI is to make sure we have manufacturing capacity outside of the US so those doses can be available to the world and they don’t get seized by wealthy countries.”
Bottazzi, Ledley, Lurie, and Andino report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
US government and industry projections that a COVID-19 vaccine will be ready by this fall or even January would take compressing what usually takes at least a decade into months, with little room for error or safety surprises.
“If all the cards fall into the right place and all the stars are aligned, you definitely could get a vaccine by December or January,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said last week.
But Fauci said a more realistic timeline is still 12 to 18 months, and experts interviewed by Medscape Medical News agree. They say that although recent developments are encouraging, history and scientific reason say the day when a COVID-19 vaccine is widely available will not come this year and may not come by the end of 2021.
The encouraging signals come primarily from two recent announcements: the $1.2 billion United States backing last week of one vaccine platform and the announcement on May 18 that the first human trials of another have produced some positive phase 1 results.
Recent developments
On May 21, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under “Operation Warp Speed” announced that the US will give AstraZeneca $1.2 billion “to make available at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine called AZD1222, with the first doses delivered as early as October 2020.”
On May 18, the Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Moderna announced that phase 1 clinical results showed that its vaccine candidate, which uses a new messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, appeared safe. Eight participants in the human trials were able to produce neutralizing antibodies that researchers believe are important in developing protection from the virus.
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Tal Zaks, MD, PhD told CNN that if the vaccine candidate does well in phase 2, “it could be ready by January 2021.”
The two candidates are among 10 in clinical trials for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The AstraZeneca/ AZD1222 candidate (also called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, in collaboration with the University of Oxford) has entered phase 2/3.
Moderna’s candidate and another being developed in Beijing, China, are in phase 2, WHO reports. As of yesterday, 115 other candidates are in preclinical evaluation.
Maria Elena Bottazzi, PhD, associate dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, told Medscape Medical News it’s important to realize that, in the case of the $1.2 billion US investment, “what they’re talking about is manufacturing.”
The idea, she said, is to pay AstraZeneca up front so that manufacturing can start before it is known whether the vaccine candidate is safe or effective, the reverse of how the clinical trial process usually works.
That way, if the candidate is deemed safe and effective, time is not lost by then deciding how to make it and distribute it.
By the end of this year, she said, “Maybe we will have many vaccines made and stored in a refrigerator somewhere. But between now and December, there’s absolutely no way you can show efficacy of the vaccine at the same time you confirm that it’s safe.”
“Take these things with a grain of salt”
Animal testing for the AstraZeneca candidate, made in partnership with the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, has yielded lackluster results, according to results on the preprint server BioRxiv, which have not been peer-reviewed.
“The results were not bad, but they were not gangbusters,” Bottazzi said. The results show the vaccine offered only partial protection.
“Partial protection is better than no protection,” she noted. “You have to take these things with a grain of salt. We don’t know what’s going to happen in humans.”
As for the Moderna candidate, Bottazzi said, “the good news is they found an appropriate safety profile. But from an eight-person group to make the extrapolation that they have efficacy — it’s unrealistic.”
Nicole Lurie, MD, MSPH, is senior adviser to the CEO for the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI), a nongovernmental organization funded by the Wellcome Trust, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the European Commission, and eight countries (Australia, Belgium, Canada, Ethiopia, Germany, Japan, Norway, and the United Kingdom) charged with supporting development of vaccines for pathogens on WHO’s priority list.
She and her colleagues write in a paper published online in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 30 that “it typically takes multiple candidates and many years to produce a licensed vaccine.”
The fastest time for developing a vaccine to date is 4 years, for the mumps vaccine, licensed in 1967.
As to whether she would expect a rollout of any vaccine by the end of the year, Lurie told Medscape Medical News, “If everything goes according to plan in every way, shape or form, well then maybe you can get there. But I wouldn’t hold my breath.”
Lurie and her colleagues write that “it’s far from certain that these new platforms will be scalable or that existing capacity can provide sufficient quantities of vaccine fast enough.”
On a call with reporters today, leaders of some of the words largest pharmaceutical companies said that one of the key bottlenecks is the sheer number of vials needed in order to distribute billions of doses of a successful vaccine.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, said, “Typically we are producing vaccines in single-dose vials. We are exploring with governments right now if it would be more convenient if there were 5-dose vials or 10-dose vials. I think we can resolve a significant part of the bottleneck.”
Despite the challenges, experts interviewed for this article agree that it will be possible to make a vaccine for COVID-19. They don’t expect attempts to meet the same complications that HIV researchers have seen over decades as the virus continues to confound with mutations.
Fred Ledley, MD, director of the Center for Integration of Science and Industry at Bentley University in Waltham, Massachusetts, told Medscape Medical News, “There doesn’t appear to be anything terribly diabolical about this virus. The mutation rate doesn’t appear to be anything like HIV. It appears to have some big, ugly proteins on the surface, which is good for vaccines — proteins with a lot of physical features look distinguishable from healthy cells. Signs all point to that it should be possible to make a vaccine.”
History raises safety concerns
However, Ledley said, “The idea of doing it in 6 months is largely unrealistic.”
He says 18 months is more realistic, primarily because of the sheer number of people that would have to be enrolled in a phase 3 study to truly test whether the endpoints are being met.
Vaccines are given to healthy volunteers. If safety signals arise, they may not be apparent until massive numbers of people are tested in phase 3.
“You’re never going to see the rates cut to 0%, but to see the difference between 10 people getting sick and seven people getting sick, takes very, very large numbers,” Ledley said. “There’s no way that can be done in 6 months. You’re talking about tens of thousands of people enrolled.”
He notes at this point it’s unclear what the endpoints will be and what the safety thresholds will be after consideration of risks and benefit.
Another big question for Ledley: “We don’t know what type of immunity we need to protect us against the virus. Do you just need the antibodies in your blood or do you need cells that are primed to attack the virus? Is it more of a chemical clearance or do the cells need to physically go in and digest the virus?”
History also points to the need for rigorous safety precautions that scientists fear could be compromised as trial phases overlap and processes are run in parallel instead of one step at a time.
An early batch of the Salk vaccine for polio in 1955, for example, turned out to be contaminated and caused paralysis in some children and 10 deaths, he points out.
CEPI’s Lurie adds that early candidates for another coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), “caused a reaction in the lungs that was very dangerous” before development was halted.
She also pointed to previous findings that a vaccine for dengue fever could worsen the disease in some people through a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
Lurie and colleagues write in their paper that “it’s critical that vaccines also be developed using the tried-and-true methods, even if they may take longer to enter clinical trials or to result in large numbers of doses.”
Live attenuated vaccine
Raul Andino, PhD, a virologist at the University of California San Francisco, is among the scientists working with a tried-and-true method — a live attenuated vaccine — and he told Medscape Medical News he’s predicting it will take 2 years to develop.
He said it is cheaper to produce because scientists just have to learn how to grow the virus. Because the technology is already proven, a live attenuated vaccine could be rapidly produced on a worldwide scale.
The hope is also that a live attenuated vaccine would be given once in a lifetime and therefore be more affordable, especially in poorer countries.
“While a Moderna vaccine might be good for Europe and the United States,” he said, “It’s not going to be good for Africa, India, Brazil.”
Andino said, “I would bet money” that the front-runner vaccines so far will not be one-time vaccines.
He points out that most of the vaccine candidates are trying to protect people from disease. While there’s nothing wrong with that, he said, “In my opinion that is the lower-hanging fruit.”
“In my mind we need something that interrupts the chain of transmission and induces protection,” Andino said, important for developing herd immunity.
The reason this type of approach takes longer is because you are introducing a weakened form of the virus to the body and you have to make sure it doesn’t cause disease, not just in a small test population, but in populations who may be more susceptible to the disease, Andino said.
A call for unified strategies
Universities, countries, international consortiums, and public-private partnerships are all racing to find several safe and effective vaccines as no one entity will likely be able to provide the global solution.
Some of the efforts involve overlap of entities but with different focuses.
Along with “Operation Warp Speed” and CEPI, other collaborations include Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, whose core partners include WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the Gates Foundation; and “Accelerating Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) partnership,” led by the National Institutes of Health.
Industry partners in ACTIV (18 biopharmaceutical companies), according to a May 18 article published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association, have said they will contribute their respective clinical trial capacities, regardless of which agent is studied.
Some, however, have called for more streamlining of efforts.
“Ideally we’d be working together,” Lurie told Medscape Medical News.
“I’m hopeful we will find ways to collaborate scientifically,” she said. “The US government’s responsibility is to make doses for the US. CEPI’s responsibility is to make doses for the world. A big focus of CEPI is to make sure we have manufacturing capacity outside of the US so those doses can be available to the world and they don’t get seized by wealthy countries.”
Bottazzi, Ledley, Lurie, and Andino report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
US government and industry projections that a COVID-19 vaccine will be ready by this fall or even January would take compressing what usually takes at least a decade into months, with little room for error or safety surprises.
“If all the cards fall into the right place and all the stars are aligned, you definitely could get a vaccine by December or January,” Anthony Fauci, MD, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said last week.
But Fauci said a more realistic timeline is still 12 to 18 months, and experts interviewed by Medscape Medical News agree. They say that although recent developments are encouraging, history and scientific reason say the day when a COVID-19 vaccine is widely available will not come this year and may not come by the end of 2021.
The encouraging signals come primarily from two recent announcements: the $1.2 billion United States backing last week of one vaccine platform and the announcement on May 18 that the first human trials of another have produced some positive phase 1 results.
Recent developments
On May 21, the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under “Operation Warp Speed” announced that the US will give AstraZeneca $1.2 billion “to make available at least 300 million doses of a coronavirus vaccine called AZD1222, with the first doses delivered as early as October 2020.”
On May 18, the Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Moderna announced that phase 1 clinical results showed that its vaccine candidate, which uses a new messenger RNA (mRNA) technology, appeared safe. Eight participants in the human trials were able to produce neutralizing antibodies that researchers believe are important in developing protection from the virus.
Moderna Chief Medical Officer Tal Zaks, MD, PhD told CNN that if the vaccine candidate does well in phase 2, “it could be ready by January 2021.”
The two candidates are among 10 in clinical trials for the SARS-CoV-2 virus, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). The AstraZeneca/ AZD1222 candidate (also called ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, in collaboration with the University of Oxford) has entered phase 2/3.
Moderna’s candidate and another being developed in Beijing, China, are in phase 2, WHO reports. As of yesterday, 115 other candidates are in preclinical evaluation.
Maria Elena Bottazzi, PhD, associate dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, told Medscape Medical News it’s important to realize that, in the case of the $1.2 billion US investment, “what they’re talking about is manufacturing.”
The idea, she said, is to pay AstraZeneca up front so that manufacturing can start before it is known whether the vaccine candidate is safe or effective, the reverse of how the clinical trial process usually works.
That way, if the candidate is deemed safe and effective, time is not lost by then deciding how to make it and distribute it.
By the end of this year, she said, “Maybe we will have many vaccines made and stored in a refrigerator somewhere. But between now and December, there’s absolutely no way you can show efficacy of the vaccine at the same time you confirm that it’s safe.”
“Take these things with a grain of salt”
Animal testing for the AstraZeneca candidate, made in partnership with the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom, has yielded lackluster results, according to results on the preprint server BioRxiv, which have not been peer-reviewed.
“The results were not bad, but they were not gangbusters,” Bottazzi said. The results show the vaccine offered only partial protection.
“Partial protection is better than no protection,” she noted. “You have to take these things with a grain of salt. We don’t know what’s going to happen in humans.”
As for the Moderna candidate, Bottazzi said, “the good news is they found an appropriate safety profile. But from an eight-person group to make the extrapolation that they have efficacy — it’s unrealistic.”
Nicole Lurie, MD, MSPH, is senior adviser to the CEO for the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI), a nongovernmental organization funded by the Wellcome Trust, the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, the European Commission, and eight countries (Australia, Belgium, Canada, Ethiopia, Germany, Japan, Norway, and the United Kingdom) charged with supporting development of vaccines for pathogens on WHO’s priority list.
She and her colleagues write in a paper published online in the New England Journal of Medicine on March 30 that “it typically takes multiple candidates and many years to produce a licensed vaccine.”
The fastest time for developing a vaccine to date is 4 years, for the mumps vaccine, licensed in 1967.
As to whether she would expect a rollout of any vaccine by the end of the year, Lurie told Medscape Medical News, “If everything goes according to plan in every way, shape or form, well then maybe you can get there. But I wouldn’t hold my breath.”
Lurie and her colleagues write that “it’s far from certain that these new platforms will be scalable or that existing capacity can provide sufficient quantities of vaccine fast enough.”
On a call with reporters today, leaders of some of the words largest pharmaceutical companies said that one of the key bottlenecks is the sheer number of vials needed in order to distribute billions of doses of a successful vaccine.
Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla, DVM, PhD, said, “Typically we are producing vaccines in single-dose vials. We are exploring with governments right now if it would be more convenient if there were 5-dose vials or 10-dose vials. I think we can resolve a significant part of the bottleneck.”
Despite the challenges, experts interviewed for this article agree that it will be possible to make a vaccine for COVID-19. They don’t expect attempts to meet the same complications that HIV researchers have seen over decades as the virus continues to confound with mutations.
Fred Ledley, MD, director of the Center for Integration of Science and Industry at Bentley University in Waltham, Massachusetts, told Medscape Medical News, “There doesn’t appear to be anything terribly diabolical about this virus. The mutation rate doesn’t appear to be anything like HIV. It appears to have some big, ugly proteins on the surface, which is good for vaccines — proteins with a lot of physical features look distinguishable from healthy cells. Signs all point to that it should be possible to make a vaccine.”
History raises safety concerns
However, Ledley said, “The idea of doing it in 6 months is largely unrealistic.”
He says 18 months is more realistic, primarily because of the sheer number of people that would have to be enrolled in a phase 3 study to truly test whether the endpoints are being met.
Vaccines are given to healthy volunteers. If safety signals arise, they may not be apparent until massive numbers of people are tested in phase 3.
“You’re never going to see the rates cut to 0%, but to see the difference between 10 people getting sick and seven people getting sick, takes very, very large numbers,” Ledley said. “There’s no way that can be done in 6 months. You’re talking about tens of thousands of people enrolled.”
He notes at this point it’s unclear what the endpoints will be and what the safety thresholds will be after consideration of risks and benefit.
Another big question for Ledley: “We don’t know what type of immunity we need to protect us against the virus. Do you just need the antibodies in your blood or do you need cells that are primed to attack the virus? Is it more of a chemical clearance or do the cells need to physically go in and digest the virus?”
History also points to the need for rigorous safety precautions that scientists fear could be compromised as trial phases overlap and processes are run in parallel instead of one step at a time.
An early batch of the Salk vaccine for polio in 1955, for example, turned out to be contaminated and caused paralysis in some children and 10 deaths, he points out.
CEPI’s Lurie adds that early candidates for another coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), “caused a reaction in the lungs that was very dangerous” before development was halted.
She also pointed to previous findings that a vaccine for dengue fever could worsen the disease in some people through a phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement.
Lurie and colleagues write in their paper that “it’s critical that vaccines also be developed using the tried-and-true methods, even if they may take longer to enter clinical trials or to result in large numbers of doses.”
Live attenuated vaccine
Raul Andino, PhD, a virologist at the University of California San Francisco, is among the scientists working with a tried-and-true method — a live attenuated vaccine — and he told Medscape Medical News he’s predicting it will take 2 years to develop.
He said it is cheaper to produce because scientists just have to learn how to grow the virus. Because the technology is already proven, a live attenuated vaccine could be rapidly produced on a worldwide scale.
The hope is also that a live attenuated vaccine would be given once in a lifetime and therefore be more affordable, especially in poorer countries.
“While a Moderna vaccine might be good for Europe and the United States,” he said, “It’s not going to be good for Africa, India, Brazil.”
Andino said, “I would bet money” that the front-runner vaccines so far will not be one-time vaccines.
He points out that most of the vaccine candidates are trying to protect people from disease. While there’s nothing wrong with that, he said, “In my opinion that is the lower-hanging fruit.”
“In my mind we need something that interrupts the chain of transmission and induces protection,” Andino said, important for developing herd immunity.
The reason this type of approach takes longer is because you are introducing a weakened form of the virus to the body and you have to make sure it doesn’t cause disease, not just in a small test population, but in populations who may be more susceptible to the disease, Andino said.
A call for unified strategies
Universities, countries, international consortiums, and public-private partnerships are all racing to find several safe and effective vaccines as no one entity will likely be able to provide the global solution.
Some of the efforts involve overlap of entities but with different focuses.
Along with “Operation Warp Speed” and CEPI, other collaborations include Gavi the Vaccine Alliance, whose core partners include WHO, UNICEF, the World Bank, and the Gates Foundation; and “Accelerating Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) partnership,” led by the National Institutes of Health.
Industry partners in ACTIV (18 biopharmaceutical companies), according to a May 18 article published online in the Journal of the American Medical Association, have said they will contribute their respective clinical trial capacities, regardless of which agent is studied.
Some, however, have called for more streamlining of efforts.
“Ideally we’d be working together,” Lurie told Medscape Medical News.
“I’m hopeful we will find ways to collaborate scientifically,” she said. “The US government’s responsibility is to make doses for the US. CEPI’s responsibility is to make doses for the world. A big focus of CEPI is to make sure we have manufacturing capacity outside of the US so those doses can be available to the world and they don’t get seized by wealthy countries.”
Bottazzi, Ledley, Lurie, and Andino report no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
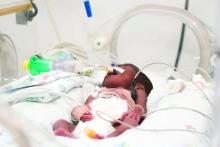
Placental injury reported in women with COVID-19
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Neonates appear healthy so far
Neonates appear healthy so far
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
Maternal vascular malperfusion and intervillous thrombi were more common in the placentas of women infected with SARS-CoV-2, compared with historic controls, report researchers who conducted the first-of-its-kind case series in the English literature. Nevertheless, the neonates in the report appear to be healthy so far and all tested negative for the virus.
Although the series examining placentas from 16 women is small, it carries a larger implication – that increased antenatal surveillance for pregnant women infected with SARS-CoV-2 may be indicated, the researchers noted.
Furthermore, the results could align with other reports of coagulation and vascular abnormalities among people with COVID-19. “I would say that our findings fit into that larger picture of vascular injury. This is developing, and there are some significant ways that these feeder vessels to the placenta are different, but if this is the emerging paradigm, our findings can fit into it,” Jeffrey A. Goldstein, MD, PhD, assistant professor of pathology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview.
The research was published in the American Journal of Clinical Pathology.
Prior case series reported in Wuhan, China, do not currently suggest that pregnant women are more likely to experience severe COVID-19, in contrast to observations during severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreaks. “However,” the researchers noted, “adverse perinatal outcomes have been reported, including increased risks of miscarriage, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and stillbirth.”
To learn more, Dr. Goldstein, lead author Elisheva D. Shanes, MD, and colleagues examined the histology of placentas from women with COVID-19 giving birth between March 18 and May 5, 2020. They compared these placentas with over 17,000 historic controls and 215 women who had their placentas evaluated as part of a melanoma history study.
A total of 10 women were diagnosed with COVID-19 upon presentation to labor and delivery, 4 others were diagnosed approximately 1 month before delivery and the remaining 2 within 1 week of delivery. Ten of the patients were symptomatic and two required oxygen. None of the patients received intubation or died. A total of 14 patients delivered at term, 1 delivered at 34 weeks, and the remaining case experienced a 16-week intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD). The IUFD was excluded from subsequent statistical analysis.
The neonates each had a 5-minute Apgar score of 9. Most infants were discharged on the first or second day of life, and there were no neonatal deaths.
Key findings
Of the 15 placentas, 12 featured maternal vascular malperfusion. This rate was significantly higher than historic controls (P = .046) and melanoma study controls (P = .001).
Specific features varied between groups, with decidual arteriopathy, atherosis and fibrinoid necrosis of maternal vessels, and mural hypertrophy of membrane arterioles observed more often in COVID-19 cases than in all historical controls. In addition, peripheral infarctions, decidual arteriopathy, atherosis, and fibrinoid necrosis, and mural hypertrophy being more common in COVID-19 cases than in placentas of women with a history of melanoma.
In contrast, features of fetal vascular malperfusion were observed in 12 of 15 cases, but not at rates significantly different from the control groups. Chorangiosis, villous edema, and intervillous thrombi also were more common in the COVID-19 cohort.
Dr. Goldstein was surprised they did not observe much acute or chronic inflammation. “We see chronic inflammation in the placenta in response to many viruses, such as cytomegalovirus, so you might expect similar findings, but we didn’t see any increase above the controls.”
There are a couple of case reports of histiocytic intervillositis – a particularly severe form of chronic inflammation – associated with COVID-19, “but we didn’t see that in our study,” he added.
Clinical implications
The healthy neonatal outcomes reported in the study occurred despite the placental injury, which may be caused by the redundancy built into placentas for delivering oxygen and nutrients and for removing waste.
The negative COVID-19 test results in all infants also supports existing evidence that vertical transmission of the virus is uncommon. The finding also suggests that any damage to the placenta is likely related to maternal infection.
Only one mother in the COVID-19 cohort was hypertensive, which surprised the researchers because intervillous thrombi have been associated with maternal high blood pressure. “In the context of research suggesting an increase of thrombotic and thromboembolic disorders in COVID-19,” the researchers noted, “these may represent placental formation or deposition of thrombi in response to the virus.”
One of the priorities for the researchers going forward is to monitor the longer-term outcomes of the infants, Dr. Goldstein said. “We know the people in utero during the 1918-1919 flu pandemic had higher rates of heart disease and other long-term problems, so we want to be on the lookout for something similar.”
Valuable insight
“This is a comprehensive case series of this topic, with findings worth noting and sharing in a timely fashion,” Karen Mestan, MD, associate professor of pediatrics within the division of neonatology at Northwestern University, said when asked to comment on the study.
“The information is valuable to neonatologists as the short- and long-term effects of COVID-19 exposure on newborn infants are still largely unknown,” she added. “Details of placental pathology provide emerging insight and may help us understand mother-baby vertical transmission during the current pandemic.”
Dr. Goldstein and Dr. Mestan had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Shanes ED et al. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020 May 22. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaa089.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY
Whether to test laboring women for SARS-CoV-2 may hinge on regional prevalence
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
at the time of admission, research published online in Obstetrics & Gynecology suggests.
In Los Angeles, researchers stopped universal testing after none of the first 80 asymptomatic women had positive results. Researchers in Chicago, on the other hand, found a positive rate of approximately 1.6% among 614 asymptomatic patients and continue to test all patients.
“Decisions regarding universal testing need to be made in the context of regional prevalence of COVID-19 infection, with recognition that a ‘one-size-fits-all’ approach is unlikely to be justifiable,” Torri D. Metz, MD,of University of Utah Health in Salt Lake City said in an editorial accompanying research letters that described the experience in Los Angeles and Chicago. “In the setting of low population prevalence of COVID-19 infection or in locations with limited testing availability, deferring universal testing may represent the better part of valor when weighing risks, benefits, economic burden, and unintended consequences of testing for SARS-CoV-2 infection. In high-prevalence regions, universal testing may be a valuable addition to obstetric care that will prevent infections in health care workers and neonates.”
Testing all patients also may provide valuable population-level surveillance, added Dr. Metz, who is an associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology, a maternal-fetal medicine subspecialist, and vice-chair of research in obstetrics and gynecology.
One week of data
After New York hospitals reported an approximately 13% prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among asymptomatic laboring women, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles changed its policy from testing only women with COVID-19 symptoms to testing all women beginning April 4, 2020. “Data from New York made us very concerned about the possibility of asymptomatic infections among our own pregnant patients,” Mariam Naqvi, MD, a maternal-fetal medicine specialist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, said in a news release. “This would have implications for them, their babies, their households, and for the health of our staff caring for them.”
In 1 week, 82 pregnant women admitted to the obstetric unit were tested for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of two women who reported COVID-19 symptoms, one tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Of the remaining 80 asymptomatic women, none tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection, and all remained symptom free throughout their hospitalizations,” Dr. Naqvi and colleagues reported. “One asymptomatic patient had an inadequate nasopharyngeal specimen and declined repeat testing.”
Precautions taken during universal testing meant that all members of the treatment team used valuable personal protective equipment. In some cases, mothers and newborns were separated until test results were available.
“We discontinued universal testing after a 7-day period, because we could not justify continued testing of asymptomatic women in the absence of positive test results for SARS-CoV-2 infection,” they noted. “Though universal testing did not yield enough positive results on our obstetric unit to warrant continued testing at this time, our approach may change if local rates of infection increase.”
20 days of testing
In a prospective case series of pregnant women admitted to Northwestern Memorial Hospital in Chicago from April 8 to April 27, 2020, universal testing did detect asymptomatic infections. Women with scheduled admissions were tested 12-36 hours before admission in a drive-through testing center, and women with unscheduled admissions received a test that has a 2- to 3-hour turnaround time. In addition, patients were screened for symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, cough, sore throat, body aches, chills, new-onset vomiting, diarrhea, loss of taste or smell, and red or painful eyes.
“Asymptomatic women with pending tests were managed on the routine labor floor, but health care workers used personal protective equipment that included a respirator during the second stage of labor and delivery until the test result became available,” wrote Emily S. Miller, MD, MPH, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues.
During the first 20 days of universal testing, 635 pregnant women were admitted, and 23 (3.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 21 women with COVID-19 symptoms, 13 (62%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Of 614 women who were asymptomatic, 10 (1.6%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. “Our data corroborate the observation that pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection on admission do not seem to be reliably identified using symptom screening alone,” the researchers wrote.
Unintended consequences
Despite a lack of effective treatments for mild to moderate COVID-19, “knowledge of the disease state allows ... health care workers to wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid exposure,” Dr. Metz wrote. It also allows “women to be counseled about ways to decrease transmission to neonates” and enables close monitoring of patients with infection.
At the same time, universal testing may have unintended consequences for infected patients, such as stigmatization, separation from the newborn, and delays in care related to health care providers spending more time donning personal protective equipment or changes in medical decision-making regarding cesarean delivery, she emphasized.
“Obstetricians should remain aware of disease prevalence in their communities and consider universal screening of asymptomatic women on an ongoing basis as new ‘hot spots’ for COVID-19 infection are identified,” Dr. Metz concluded.
One of Dr. Naqvi’s coauthors disclosed receiving funds from Contemporary OB/GYN, Keneka, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and serving as a board examiner for the American Board of Obstetrics and Gynecology; her coauthors did not report any relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Metz disclosed that money was paid to her institution from Pfizer and GestVision for work related to an RSV vaccination trial and a preeclampsia test, respectively. Dr. Miller and colleagues did not report any potential conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Naqvi M et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003987; Miller ES et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003983; Metz TD. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 May 19. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003972.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Domestic violence amid COVID-19: Helping your patients from afar
Roger R., MD, a primary care physician from Philadelphia, set up a telemedicine appointment with a 24-year-old female patient who was experiencing headaches and was worried she might have COVID-19.
During the televisit, Dr. R. noticed that “Tonya” (not her real name) had a purplish bruise under her right eye. When asked how she got the bruise, Tonya said she had bumped into a dresser. The physician suspected abuse. He then heard a man’s voice in the background and thought it might belong to the abuser. “Is this a good time for you to talk?” he asked Tonya.
Tonya hesitated.
“When might be a better time?”
Tonya suggested an alternate time, and the physician called her then. During the visit, she shared that her fiancé, a car salesman who was also sheltering at home, was punching her.
“He always had a bad temper. Once he shoved me, but he’s never hit me before. And when he was upset, we used to go out to eat and he calmed down. Now, we’re stuck inside, we can’t even get away from each other to go to work, and he’s getting scary,” she told the doctor.
The physician asked if she would like to be connected with a domestic violence counselor. When Tonya agreed, he called Jessica DuBois Palardy, a licensed social worker and the program supervisor at STOP Intimate Partner Violence, a Philadelphia-based collaborative project of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Lutheran Settlement House’s Bilingual Domestic Violence Program.
A ‘horrifying’ trend
Tonya’s story is not unique. A United Nations report shows that there has been a “horrifying global surge in domestic violence” linked to “lockdowns imposed by the governments responding to the COVID-19 pandemic.” The United States is no exception – 2,345 calls were placed to the National Domestic Violence Hotline during March 16–April 6, 2020.
Carole Warshaw, MD, director of the National Center on Domestic Violence, Trauma, and Mental Health in Chicago, said, “We know that intimate partner violence is increasing among people sheltering at home, and that abuse has become more severe.”
Even in nonabusive situations, being confined together at close quarters, often amid family stress and financial hardship, can be wearing, and tempers can flare. In an abusive relationship, “the main contributor to violence during shelter-in-place restrictions is that the isolation gives abusers more opportunities for controlling their partners, who have fewer options for accessing safety and support,” Dr. Warshaw said.
It is critical to “approach every clinical encounter knowing that domestic violence may be at play,” she emphasized.
Physicians might be the most important lifeline
Physicians are already facing myriad COVID-19–related challenges, and having another concern to keep in mind may be daunting.
“We’re in uncharted territory and we’re all trying to figure out how to navigate this time, how to practice medicine via phone and video conferences, and how to deal with the financial repercussions of the pandemic – not to mention concern for the health of our families,” said Peter F. Cronholm, MD, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “So maintaining vigilance is often difficult. Nevertheless, it’s important not to let this critical issue fall to the wayside.”
Marcella Nyachogo, MSW, a licensed social worker and assistant director of the Bilingual Domestic Violence Program, noted that physicians and other health care providers “may be the only people the patient interacts with, since the abuser may cut the survivor off from family and friends. And because the survivor isn’t leaving the house, he or she doesn’t have an opportunity to interact with coworkers or others – which makes health care providers the most important lifeline.”
COVID-19 as a weapon of abuse
Carey Watson, MD, regional medical director of the Family Violence Prevention Program at Kaiser Permanente in northern California, points to a disturbing trend in COVID-19–related abuse.
“Unfortunately, I’m hearing more and more accounts of how the illness itself can be one more weapon in the abuser’s arsenal,” she said.
Experts say that increasingly, abusers are claiming that their partner, who is employed in an “essential” job outside the home, is carrying the virus, and they are using this as a means of control and manipulation.
This is especially true of abusive partners of health care providers, Dr. Watson noted. She recounted the story of a divorced nurse whose husband did not allow her to have contact with their children, allegedly out of concern that she might have COVID-19, and would threaten her with a gun when she protested.
“It is important to keep this abusive tactic in mind, not only when dealing with patients but also with fellow physicians and health care professionals, and check in to see if everything is okay – especially if they seem particularly stressed out or distant,” Dr. Watson recommended.
Trust your clinical gut
How can you tell if your patients might be experiencing abuse when you’re not seeing them in person?
Pay attention to subtle signals and “trust your clinical gut when something doesn’t feel right,” Ms. Nyachogo advised.
If a patient’s demeanor is jittery or anxious or if someone next to him or her is answering all the questions or interrupting the visit, these could be red flags.
Dr. Cronholm added that telemedicine visits offer a “rare window into a patient’s home life that would not be available in an office visit.” For example, a house in disarray, the presence of broken objects, or the presence of another person hovering in the background suggests the need for further exploration.
“The main thing for all providers to keep in mind is ‘first, do no harm,’ ” Ms. Nyachogo emphasized.
“Our agency has been working for years with medical professionals in how to screen and connect folks with help most effectively and safely, and – although the specific situations posed by COVID are new – the overall approach is the same, which is to proceed with caution in how you approach the subject and how you make referrals,” she said.
Begin by asking if it is a convenient time to talk.
“This question takes the onus off the patient, who may not know how to communicate that she has no privacy or is in the middle of an argument,” explained Elsa Swenson, program manager of Home Free community program, which serves individuals experiencing domestic violence. The program is part of Minnesota-based Missions Inc. Programs, which serves those experiencing domestic abuse and chemical dependency.
If the patient indicates that it isn’t a convenient time to talk, find out when would be a better time. “This might be difficult for busy physicians and may not be what they’re accustomed to when calling a patient at home, but the patient’s circumstances are unknown to you, so it’s essential to organize around their ability to talk,” Ms. Swenson noted.
‘Are you alone?’
Another important piece of information is whether the patient has privacy – which can be tricky if the abuser is standing right there.
“You don’t want to tip the abuser off to your concerns, so you need to frame the question in a neutral way,” Dr. Watson advised.
For example, you might say that HIPAA laws require that you conduct the consultation with no one else present, and find out if there is a location in the house where the patient can have privacy.
It might be easier to talk on the phone than via video, suggests Florence Remes, a New Jersey–based licensed social worker who specializes in domestic violence. Going into another room and playing music or turning on the television might make it less obvious that a call is taking place, and the abuser would be less likely to overhear the caller’s conversation.
Dr. Watson suggested that questions about abuse might be included with other questions and asked in a simple yes/no format. “I’d like to ask you some standard questions I’m asking everyone during the pandemic. Do you have a cough or fever? Do you have any other physical symptoms? Do you have access to hand sanitizer? How is your sleep? Are you experiencing stress? Do you feel safe at home?”
The abuser, if present, will only hear the patient’s “yes” or “no” without knowing the question. If the patient indicates that she is being abused but is unable to talk, a later time can be arranged to further explore the issue.
Technology is a double-edged sword
Modern technologies have been a great boon to patients and physicians during this time of social distancing, allowing ongoing contact and health care when it would not otherwise have been possible. On the other hand, technology is fraught with potential dangers that can jeopardize the patient’s safety and compromise privacy.
Ms. Remes recounted the story of “Susan,” a client with whom she had been conducting teletherapy visits using an approved HIPAA-compliant telemedicine forum. Susan was working from home because of shelter-in-place restrictions. Her husband had been abusive, and Susan was concerned he might be “sabotaging” the household’s WiFi to isolate her from outside sources of support.
At the recommendation of Ms. Remes, Susan continued sessions either via phone calls or by using the WhatsApp program on her cellphone. Many of the requirements governing HIPAA privacy regulations have been temporarily relaxed, and clinicians can use non–encrypted forms of transmission, such as FaceTime, WhatsApp, or Skype, if no other platform is available.
But even cellphones have risks, Dr. Warshaw noted. The patient’s abuser might track texts or look at call logs – especially on unsecured platforms. It’s advisable to ask patients about who has access to their phone and computer and discuss ways to increase security.
Follow the patient’s lead
Proceed slowly and start with nonthreatening questions, Ms. Palardy advised. “I notice you have some injuries; can you tell me how you got them? Did someone hurt you? What does your relationship look like when you argue? Is there anything that makes you feel uncomfortable or unsafe?”
Emphasizing that you are asking these questions because of care and concern is reassuring and helps patients to feel they are not alone, Ms. Nyachogo pointed out.
“As your doctor, I’m worried about your health and (if relevant) your children’s safety. I can help connect you with counseling and support, legal resources, and a shelter, and everything is free and confidential. Would you be interested?” she said.
If the client acknowledges abuse, “follow their lead, but don’t push too hard,” Ms. Nyachogo warned.
“It is the client’s choice whether or not to take action,” she noted. “I’ve met survivors who said that it wasn’t until a doctor or nurse expressed concern about bruises that it even occurred to them that they were being abused. Some lied to the doctor about how they got hurt – but the question planted a seed, even though it might have taken years to follow up on the referral,” she said.
What if the patient doesn’t want to get help?
If a patient is not ready to seek help, you can create a home-safety plan. This might include setting follow-up times. If you don’t hear from him or her, you should then call the police. Or you might create a “code word,” such as “apple pie.” If the patient uses that word during a session, you know her life is in danger, Ms. Remes suggested.
Providing written information about how to get help is important but can be problematic if the abuser finds it.
Ms. Nyachogo recommends e-mailing follow-up materials that cover a variety of topics, such as keeping safe during the COVID-19 pandemic, relaxation, healthy eating, getting exercise while homebound, activities for children, and suggestions for hotlines and other resources if one is feeling suicidal or unsafe.
“If you present these as your ‘standard’ follow-up materials, the abuser is less likely to become suspicious,” Ms. Nyachogo noted.
Resources are available during COVID-19
All of the experts emphasize that resources for victims of domestic violence remain available during the COVID-19 pandemic, although some shelters may be operating at reduced capacity. Some agencies are finding alternatives to group shelters, such as hotels or Airbnb, which carry less risk of catching COVID-19.
Referring a patient to domestic violence resources is a delicate process. “You don’t want referring the patient for help to further endanger their life,” Ms. Nyachogo said.
The more you can take the burden off the patient, the better. If she is interested in getting help, you can call a domestic violence counselor or advocate while she is on the phone.
“This type of ‘warm handoff’ is what Tonya’s physician did,” Ms. Palardy recounted.
A warm handoff requires that physicians be familiar with domestic violence resources, Dr. Warshaw emphasized.
“Don’t wait until you are working with someone who needs help to find out where to refer them. Take the time to proactively research local agencies specializing in domestic violence and have their phone numbers on hand, so you can offer resources immediately if the person is interested,” she advised. The National Domestic Violence Hotline can also assist with safety planning and access to local resources.
‘Thinking on your feet’ critical for physicians
Addressing domestic violence during this unprecedented time requires “thinking on your feet” about novel forms of detection and intervention, Dr. Watson said. This involves a combination of clinical acumen, creativity, and finely honed intuition.
Ms. Nyachogo added, “Keeping an eye on domestic violence can feel like an extra burden, but don’t forget that it is lifesaving work.”
Resources
National Domestic Violence Hotline
- 800-799-SAFE (7233)
- The patient can also text LOVEIS to 22522.
National Center on Domestic Violence, Trauma, and Mental Health
- Provides resources for health care, mental health, and substance use treatment and recovery support providers on responding to domestic violence and other trauma.
- Provides resources for professionals and patients regarding access to substance use and mental health care during the COVID-1 pandemic.
- Provides support for parents, caregivers, and children during the pandemic.
- Provides resources for advocates serving families affected by domestic violence.
- A state-by-state guide to local resources
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Research Institute
STOP Intimate Partner Violence (IPV)
New Jersey Coalition for Domestic Violence
American Bar Association COVID-19 resources for communities
- Text HOME to 741741.
National Network to End Domestic Violence (NNEDV) COVID-19 Technology Safety
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Roger R., MD, a primary care physician from Philadelphia, set up a telemedicine appointment with a 24-year-old female patient who was experiencing headaches and was worried she might have COVID-19.
During the televisit, Dr. R. noticed that “Tonya” (not her real name) had a purplish bruise under her right eye. When asked how she got the bruise, Tonya said she had bumped into a dresser. The physician suspected abuse. He then heard a man’s voice in the background and thought it might belong to the abuser. “Is this a good time for you to talk?” he asked Tonya.
Tonya hesitated.
“When might be a better time?”
Tonya suggested an alternate time, and the physician called her then. During the visit, she shared that her fiancé, a car salesman who was also sheltering at home, was punching her.
“He always had a bad temper. Once he shoved me, but he’s never hit me before. And when he was upset, we used to go out to eat and he calmed down. Now, we’re stuck inside, we can’t even get away from each other to go to work, and he’s getting scary,” she told the doctor.
The physician asked if she would like to be connected with a domestic violence counselor. When Tonya agreed, he called Jessica DuBois Palardy, a licensed social worker and the program supervisor at STOP Intimate Partner Violence, a Philadelphia-based collaborative project of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Lutheran Settlement House’s Bilingual Domestic Violence Program.
A ‘horrifying’ trend
Tonya’s story is not unique. A United Nations report shows that there has been a “horrifying global surge in domestic violence” linked to “lockdowns imposed by the governments responding to the COVID-19 pandemic.” The United States is no exception – 2,345 calls were placed to the National Domestic Violence Hotline during March 16–April 6, 2020.
Carole Warshaw, MD, director of the National Center on Domestic Violence, Trauma, and Mental Health in Chicago, said, “We know that intimate partner violence is increasing among people sheltering at home, and that abuse has become more severe.”
Even in nonabusive situations, being confined together at close quarters, often amid family stress and financial hardship, can be wearing, and tempers can flare. In an abusive relationship, “the main contributor to violence during shelter-in-place restrictions is that the isolation gives abusers more opportunities for controlling their partners, who have fewer options for accessing safety and support,” Dr. Warshaw said.
It is critical to “approach every clinical encounter knowing that domestic violence may be at play,” she emphasized.
Physicians might be the most important lifeline
Physicians are already facing myriad COVID-19–related challenges, and having another concern to keep in mind may be daunting.
“We’re in uncharted territory and we’re all trying to figure out how to navigate this time, how to practice medicine via phone and video conferences, and how to deal with the financial repercussions of the pandemic – not to mention concern for the health of our families,” said Peter F. Cronholm, MD, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “So maintaining vigilance is often difficult. Nevertheless, it’s important not to let this critical issue fall to the wayside.”
Marcella Nyachogo, MSW, a licensed social worker and assistant director of the Bilingual Domestic Violence Program, noted that physicians and other health care providers “may be the only people the patient interacts with, since the abuser may cut the survivor off from family and friends. And because the survivor isn’t leaving the house, he or she doesn’t have an opportunity to interact with coworkers or others – which makes health care providers the most important lifeline.”
COVID-19 as a weapon of abuse
Carey Watson, MD, regional medical director of the Family Violence Prevention Program at Kaiser Permanente in northern California, points to a disturbing trend in COVID-19–related abuse.
“Unfortunately, I’m hearing more and more accounts of how the illness itself can be one more weapon in the abuser’s arsenal,” she said.
Experts say that increasingly, abusers are claiming that their partner, who is employed in an “essential” job outside the home, is carrying the virus, and they are using this as a means of control and manipulation.
This is especially true of abusive partners of health care providers, Dr. Watson noted. She recounted the story of a divorced nurse whose husband did not allow her to have contact with their children, allegedly out of concern that she might have COVID-19, and would threaten her with a gun when she protested.
“It is important to keep this abusive tactic in mind, not only when dealing with patients but also with fellow physicians and health care professionals, and check in to see if everything is okay – especially if they seem particularly stressed out or distant,” Dr. Watson recommended.
Trust your clinical gut
How can you tell if your patients might be experiencing abuse when you’re not seeing them in person?
Pay attention to subtle signals and “trust your clinical gut when something doesn’t feel right,” Ms. Nyachogo advised.
If a patient’s demeanor is jittery or anxious or if someone next to him or her is answering all the questions or interrupting the visit, these could be red flags.
Dr. Cronholm added that telemedicine visits offer a “rare window into a patient’s home life that would not be available in an office visit.” For example, a house in disarray, the presence of broken objects, or the presence of another person hovering in the background suggests the need for further exploration.
“The main thing for all providers to keep in mind is ‘first, do no harm,’ ” Ms. Nyachogo emphasized.
“Our agency has been working for years with medical professionals in how to screen and connect folks with help most effectively and safely, and – although the specific situations posed by COVID are new – the overall approach is the same, which is to proceed with caution in how you approach the subject and how you make referrals,” she said.
Begin by asking if it is a convenient time to talk.
“This question takes the onus off the patient, who may not know how to communicate that she has no privacy or is in the middle of an argument,” explained Elsa Swenson, program manager of Home Free community program, which serves individuals experiencing domestic violence. The program is part of Minnesota-based Missions Inc. Programs, which serves those experiencing domestic abuse and chemical dependency.
If the patient indicates that it isn’t a convenient time to talk, find out when would be a better time. “This might be difficult for busy physicians and may not be what they’re accustomed to when calling a patient at home, but the patient’s circumstances are unknown to you, so it’s essential to organize around their ability to talk,” Ms. Swenson noted.
‘Are you alone?’
Another important piece of information is whether the patient has privacy – which can be tricky if the abuser is standing right there.
“You don’t want to tip the abuser off to your concerns, so you need to frame the question in a neutral way,” Dr. Watson advised.
For example, you might say that HIPAA laws require that you conduct the consultation with no one else present, and find out if there is a location in the house where the patient can have privacy.
It might be easier to talk on the phone than via video, suggests Florence Remes, a New Jersey–based licensed social worker who specializes in domestic violence. Going into another room and playing music or turning on the television might make it less obvious that a call is taking place, and the abuser would be less likely to overhear the caller’s conversation.
Dr. Watson suggested that questions about abuse might be included with other questions and asked in a simple yes/no format. “I’d like to ask you some standard questions I’m asking everyone during the pandemic. Do you have a cough or fever? Do you have any other physical symptoms? Do you have access to hand sanitizer? How is your sleep? Are you experiencing stress? Do you feel safe at home?”
The abuser, if present, will only hear the patient’s “yes” or “no” without knowing the question. If the patient indicates that she is being abused but is unable to talk, a later time can be arranged to further explore the issue.
Technology is a double-edged sword
Modern technologies have been a great boon to patients and physicians during this time of social distancing, allowing ongoing contact and health care when it would not otherwise have been possible. On the other hand, technology is fraught with potential dangers that can jeopardize the patient’s safety and compromise privacy.
Ms. Remes recounted the story of “Susan,” a client with whom she had been conducting teletherapy visits using an approved HIPAA-compliant telemedicine forum. Susan was working from home because of shelter-in-place restrictions. Her husband had been abusive, and Susan was concerned he might be “sabotaging” the household’s WiFi to isolate her from outside sources of support.
At the recommendation of Ms. Remes, Susan continued sessions either via phone calls or by using the WhatsApp program on her cellphone. Many of the requirements governing HIPAA privacy regulations have been temporarily relaxed, and clinicians can use non–encrypted forms of transmission, such as FaceTime, WhatsApp, or Skype, if no other platform is available.
But even cellphones have risks, Dr. Warshaw noted. The patient’s abuser might track texts or look at call logs – especially on unsecured platforms. It’s advisable to ask patients about who has access to their phone and computer and discuss ways to increase security.
Follow the patient’s lead
Proceed slowly and start with nonthreatening questions, Ms. Palardy advised. “I notice you have some injuries; can you tell me how you got them? Did someone hurt you? What does your relationship look like when you argue? Is there anything that makes you feel uncomfortable or unsafe?”
Emphasizing that you are asking these questions because of care and concern is reassuring and helps patients to feel they are not alone, Ms. Nyachogo pointed out.
“As your doctor, I’m worried about your health and (if relevant) your children’s safety. I can help connect you with counseling and support, legal resources, and a shelter, and everything is free and confidential. Would you be interested?” she said.
If the client acknowledges abuse, “follow their lead, but don’t push too hard,” Ms. Nyachogo warned.
“It is the client’s choice whether or not to take action,” she noted. “I’ve met survivors who said that it wasn’t until a doctor or nurse expressed concern about bruises that it even occurred to them that they were being abused. Some lied to the doctor about how they got hurt – but the question planted a seed, even though it might have taken years to follow up on the referral,” she said.
What if the patient doesn’t want to get help?
If a patient is not ready to seek help, you can create a home-safety plan. This might include setting follow-up times. If you don’t hear from him or her, you should then call the police. Or you might create a “code word,” such as “apple pie.” If the patient uses that word during a session, you know her life is in danger, Ms. Remes suggested.
Providing written information about how to get help is important but can be problematic if the abuser finds it.
Ms. Nyachogo recommends e-mailing follow-up materials that cover a variety of topics, such as keeping safe during the COVID-19 pandemic, relaxation, healthy eating, getting exercise while homebound, activities for children, and suggestions for hotlines and other resources if one is feeling suicidal or unsafe.
“If you present these as your ‘standard’ follow-up materials, the abuser is less likely to become suspicious,” Ms. Nyachogo noted.
Resources are available during COVID-19
All of the experts emphasize that resources for victims of domestic violence remain available during the COVID-19 pandemic, although some shelters may be operating at reduced capacity. Some agencies are finding alternatives to group shelters, such as hotels or Airbnb, which carry less risk of catching COVID-19.
Referring a patient to domestic violence resources is a delicate process. “You don’t want referring the patient for help to further endanger their life,” Ms. Nyachogo said.
The more you can take the burden off the patient, the better. If she is interested in getting help, you can call a domestic violence counselor or advocate while she is on the phone.
“This type of ‘warm handoff’ is what Tonya’s physician did,” Ms. Palardy recounted.
A warm handoff requires that physicians be familiar with domestic violence resources, Dr. Warshaw emphasized.
“Don’t wait until you are working with someone who needs help to find out where to refer them. Take the time to proactively research local agencies specializing in domestic violence and have their phone numbers on hand, so you can offer resources immediately if the person is interested,” she advised. The National Domestic Violence Hotline can also assist with safety planning and access to local resources.
‘Thinking on your feet’ critical for physicians
Addressing domestic violence during this unprecedented time requires “thinking on your feet” about novel forms of detection and intervention, Dr. Watson said. This involves a combination of clinical acumen, creativity, and finely honed intuition.
Ms. Nyachogo added, “Keeping an eye on domestic violence can feel like an extra burden, but don’t forget that it is lifesaving work.”
Resources
National Domestic Violence Hotline
- 800-799-SAFE (7233)
- The patient can also text LOVEIS to 22522.
National Center on Domestic Violence, Trauma, and Mental Health
- Provides resources for health care, mental health, and substance use treatment and recovery support providers on responding to domestic violence and other trauma.
- Provides resources for professionals and patients regarding access to substance use and mental health care during the COVID-1 pandemic.
- Provides support for parents, caregivers, and children during the pandemic.
- Provides resources for advocates serving families affected by domestic violence.
- A state-by-state guide to local resources
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Research Institute
STOP Intimate Partner Violence (IPV)
New Jersey Coalition for Domestic Violence
American Bar Association COVID-19 resources for communities
- Text HOME to 741741.
National Network to End Domestic Violence (NNEDV) COVID-19 Technology Safety
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Roger R., MD, a primary care physician from Philadelphia, set up a telemedicine appointment with a 24-year-old female patient who was experiencing headaches and was worried she might have COVID-19.
During the televisit, Dr. R. noticed that “Tonya” (not her real name) had a purplish bruise under her right eye. When asked how she got the bruise, Tonya said she had bumped into a dresser. The physician suspected abuse. He then heard a man’s voice in the background and thought it might belong to the abuser. “Is this a good time for you to talk?” he asked Tonya.
Tonya hesitated.
“When might be a better time?”
Tonya suggested an alternate time, and the physician called her then. During the visit, she shared that her fiancé, a car salesman who was also sheltering at home, was punching her.
“He always had a bad temper. Once he shoved me, but he’s never hit me before. And when he was upset, we used to go out to eat and he calmed down. Now, we’re stuck inside, we can’t even get away from each other to go to work, and he’s getting scary,” she told the doctor.
The physician asked if she would like to be connected with a domestic violence counselor. When Tonya agreed, he called Jessica DuBois Palardy, a licensed social worker and the program supervisor at STOP Intimate Partner Violence, a Philadelphia-based collaborative project of the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Lutheran Settlement House’s Bilingual Domestic Violence Program.
A ‘horrifying’ trend
Tonya’s story is not unique. A United Nations report shows that there has been a “horrifying global surge in domestic violence” linked to “lockdowns imposed by the governments responding to the COVID-19 pandemic.” The United States is no exception – 2,345 calls were placed to the National Domestic Violence Hotline during March 16–April 6, 2020.
Carole Warshaw, MD, director of the National Center on Domestic Violence, Trauma, and Mental Health in Chicago, said, “We know that intimate partner violence is increasing among people sheltering at home, and that abuse has become more severe.”
Even in nonabusive situations, being confined together at close quarters, often amid family stress and financial hardship, can be wearing, and tempers can flare. In an abusive relationship, “the main contributor to violence during shelter-in-place restrictions is that the isolation gives abusers more opportunities for controlling their partners, who have fewer options for accessing safety and support,” Dr. Warshaw said.
It is critical to “approach every clinical encounter knowing that domestic violence may be at play,” she emphasized.
Physicians might be the most important lifeline
Physicians are already facing myriad COVID-19–related challenges, and having another concern to keep in mind may be daunting.
“We’re in uncharted territory and we’re all trying to figure out how to navigate this time, how to practice medicine via phone and video conferences, and how to deal with the financial repercussions of the pandemic – not to mention concern for the health of our families,” said Peter F. Cronholm, MD, associate professor of family medicine and community health at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “So maintaining vigilance is often difficult. Nevertheless, it’s important not to let this critical issue fall to the wayside.”
Marcella Nyachogo, MSW, a licensed social worker and assistant director of the Bilingual Domestic Violence Program, noted that physicians and other health care providers “may be the only people the patient interacts with, since the abuser may cut the survivor off from family and friends. And because the survivor isn’t leaving the house, he or she doesn’t have an opportunity to interact with coworkers or others – which makes health care providers the most important lifeline.”
COVID-19 as a weapon of abuse
Carey Watson, MD, regional medical director of the Family Violence Prevention Program at Kaiser Permanente in northern California, points to a disturbing trend in COVID-19–related abuse.
“Unfortunately, I’m hearing more and more accounts of how the illness itself can be one more weapon in the abuser’s arsenal,” she said.
Experts say that increasingly, abusers are claiming that their partner, who is employed in an “essential” job outside the home, is carrying the virus, and they are using this as a means of control and manipulation.
This is especially true of abusive partners of health care providers, Dr. Watson noted. She recounted the story of a divorced nurse whose husband did not allow her to have contact with their children, allegedly out of concern that she might have COVID-19, and would threaten her with a gun when she protested.
“It is important to keep this abusive tactic in mind, not only when dealing with patients but also with fellow physicians and health care professionals, and check in to see if everything is okay – especially if they seem particularly stressed out or distant,” Dr. Watson recommended.
Trust your clinical gut
How can you tell if your patients might be experiencing abuse when you’re not seeing them in person?
Pay attention to subtle signals and “trust your clinical gut when something doesn’t feel right,” Ms. Nyachogo advised.
If a patient’s demeanor is jittery or anxious or if someone next to him or her is answering all the questions or interrupting the visit, these could be red flags.
Dr. Cronholm added that telemedicine visits offer a “rare window into a patient’s home life that would not be available in an office visit.” For example, a house in disarray, the presence of broken objects, or the presence of another person hovering in the background suggests the need for further exploration.
“The main thing for all providers to keep in mind is ‘first, do no harm,’ ” Ms. Nyachogo emphasized.
“Our agency has been working for years with medical professionals in how to screen and connect folks with help most effectively and safely, and – although the specific situations posed by COVID are new – the overall approach is the same, which is to proceed with caution in how you approach the subject and how you make referrals,” she said.
Begin by asking if it is a convenient time to talk.
“This question takes the onus off the patient, who may not know how to communicate that she has no privacy or is in the middle of an argument,” explained Elsa Swenson, program manager of Home Free community program, which serves individuals experiencing domestic violence. The program is part of Minnesota-based Missions Inc. Programs, which serves those experiencing domestic abuse and chemical dependency.
If the patient indicates that it isn’t a convenient time to talk, find out when would be a better time. “This might be difficult for busy physicians and may not be what they’re accustomed to when calling a patient at home, but the patient’s circumstances are unknown to you, so it’s essential to organize around their ability to talk,” Ms. Swenson noted.
‘Are you alone?’
Another important piece of information is whether the patient has privacy – which can be tricky if the abuser is standing right there.
“You don’t want to tip the abuser off to your concerns, so you need to frame the question in a neutral way,” Dr. Watson advised.
For example, you might say that HIPAA laws require that you conduct the consultation with no one else present, and find out if there is a location in the house where the patient can have privacy.
It might be easier to talk on the phone than via video, suggests Florence Remes, a New Jersey–based licensed social worker who specializes in domestic violence. Going into another room and playing music or turning on the television might make it less obvious that a call is taking place, and the abuser would be less likely to overhear the caller’s conversation.
Dr. Watson suggested that questions about abuse might be included with other questions and asked in a simple yes/no format. “I’d like to ask you some standard questions I’m asking everyone during the pandemic. Do you have a cough or fever? Do you have any other physical symptoms? Do you have access to hand sanitizer? How is your sleep? Are you experiencing stress? Do you feel safe at home?”
The abuser, if present, will only hear the patient’s “yes” or “no” without knowing the question. If the patient indicates that she is being abused but is unable to talk, a later time can be arranged to further explore the issue.
Technology is a double-edged sword
Modern technologies have been a great boon to patients and physicians during this time of social distancing, allowing ongoing contact and health care when it would not otherwise have been possible. On the other hand, technology is fraught with potential dangers that can jeopardize the patient’s safety and compromise privacy.
Ms. Remes recounted the story of “Susan,” a client with whom she had been conducting teletherapy visits using an approved HIPAA-compliant telemedicine forum. Susan was working from home because of shelter-in-place restrictions. Her husband had been abusive, and Susan was concerned he might be “sabotaging” the household’s WiFi to isolate her from outside sources of support.
At the recommendation of Ms. Remes, Susan continued sessions either via phone calls or by using the WhatsApp program on her cellphone. Many of the requirements governing HIPAA privacy regulations have been temporarily relaxed, and clinicians can use non–encrypted forms of transmission, such as FaceTime, WhatsApp, or Skype, if no other platform is available.
But even cellphones have risks, Dr. Warshaw noted. The patient’s abuser might track texts or look at call logs – especially on unsecured platforms. It’s advisable to ask patients about who has access to their phone and computer and discuss ways to increase security.
Follow the patient’s lead
Proceed slowly and start with nonthreatening questions, Ms. Palardy advised. “I notice you have some injuries; can you tell me how you got them? Did someone hurt you? What does your relationship look like when you argue? Is there anything that makes you feel uncomfortable or unsafe?”
Emphasizing that you are asking these questions because of care and concern is reassuring and helps patients to feel they are not alone, Ms. Nyachogo pointed out.
“As your doctor, I’m worried about your health and (if relevant) your children’s safety. I can help connect you with counseling and support, legal resources, and a shelter, and everything is free and confidential. Would you be interested?” she said.
If the client acknowledges abuse, “follow their lead, but don’t push too hard,” Ms. Nyachogo warned.
“It is the client’s choice whether or not to take action,” she noted. “I’ve met survivors who said that it wasn’t until a doctor or nurse expressed concern about bruises that it even occurred to them that they were being abused. Some lied to the doctor about how they got hurt – but the question planted a seed, even though it might have taken years to follow up on the referral,” she said.
What if the patient doesn’t want to get help?
If a patient is not ready to seek help, you can create a home-safety plan. This might include setting follow-up times. If you don’t hear from him or her, you should then call the police. Or you might create a “code word,” such as “apple pie.” If the patient uses that word during a session, you know her life is in danger, Ms. Remes suggested.
Providing written information about how to get help is important but can be problematic if the abuser finds it.
Ms. Nyachogo recommends e-mailing follow-up materials that cover a variety of topics, such as keeping safe during the COVID-19 pandemic, relaxation, healthy eating, getting exercise while homebound, activities for children, and suggestions for hotlines and other resources if one is feeling suicidal or unsafe.
“If you present these as your ‘standard’ follow-up materials, the abuser is less likely to become suspicious,” Ms. Nyachogo noted.
Resources are available during COVID-19
All of the experts emphasize that resources for victims of domestic violence remain available during the COVID-19 pandemic, although some shelters may be operating at reduced capacity. Some agencies are finding alternatives to group shelters, such as hotels or Airbnb, which carry less risk of catching COVID-19.
Referring a patient to domestic violence resources is a delicate process. “You don’t want referring the patient for help to further endanger their life,” Ms. Nyachogo said.
The more you can take the burden off the patient, the better. If she is interested in getting help, you can call a domestic violence counselor or advocate while she is on the phone.
“This type of ‘warm handoff’ is what Tonya’s physician did,” Ms. Palardy recounted.
A warm handoff requires that physicians be familiar with domestic violence resources, Dr. Warshaw emphasized.
“Don’t wait until you are working with someone who needs help to find out where to refer them. Take the time to proactively research local agencies specializing in domestic violence and have their phone numbers on hand, so you can offer resources immediately if the person is interested,” she advised. The National Domestic Violence Hotline can also assist with safety planning and access to local resources.
‘Thinking on your feet’ critical for physicians
Addressing domestic violence during this unprecedented time requires “thinking on your feet” about novel forms of detection and intervention, Dr. Watson said. This involves a combination of clinical acumen, creativity, and finely honed intuition.
Ms. Nyachogo added, “Keeping an eye on domestic violence can feel like an extra burden, but don’t forget that it is lifesaving work.”
Resources
National Domestic Violence Hotline
- 800-799-SAFE (7233)
- The patient can also text LOVEIS to 22522.
National Center on Domestic Violence, Trauma, and Mental Health
- Provides resources for health care, mental health, and substance use treatment and recovery support providers on responding to domestic violence and other trauma.
- Provides resources for professionals and patients regarding access to substance use and mental health care during the COVID-1 pandemic.
- Provides support for parents, caregivers, and children during the pandemic.
- Provides resources for advocates serving families affected by domestic violence.
- A state-by-state guide to local resources
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia Research Institute
STOP Intimate Partner Violence (IPV)
New Jersey Coalition for Domestic Violence
American Bar Association COVID-19 resources for communities
- Text HOME to 741741.
National Network to End Domestic Violence (NNEDV) COVID-19 Technology Safety
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Seek safe strategies to diagnose gestational diabetes during pandemic
Clinicians and pregnant women are less likely to prescribe and undergo the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to diagnose gestational diabetes in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a review by H. David McIntyre, MD, of the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, and Robert G. Moses, MD, of Wollongong (Australia) Hospital.
National and international discussions of whether a one- or two-step test for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is optimal, and which women should be tested are ongoing, but the potential for exposure risks to COVID-19 are impacting the test process, they wrote in a commentary published in Diabetes Care.
“Any national or local guidelines should be developed with the primary aim of being protective for pregnant women and workable in the current health crisis,” they wrote.
Key concerns expressed by women and health care providers include the need for travel to be tested, the possible need for two visits, and the several hours spent in a potentially high-risk specimen collection center.
“Further, a GDM diagnosis generally involves additional health service visits for diabetes education, glucose monitoring review, and fetal ultrasonography, all of which carry exposure risks during a pandemic,” Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses noted.
Professional societies in the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia have issued guidance to clinicians for modifying GDM diagnoses criteria during the pandemic that aim to reduce the need for the oral glucose tolerance test both during and after pregnancy.
Pandemic guidelines for all three of these countries support the identification of GDM using early pregnancy hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of at least 41 mmol/mol (5.9%).
Then, professionals in the United Kingdom recommend testing based on risk factors and diagnosing GDM based on any of these criteria: HbA1c of at least 39 mmol/mol (5.7%), fasting venous plasma glucose of at least 5.6 mmol/L (preferred), or random VPG of at least 9.0 mmol/L.
The revised testing pathway for Canada accepts an HbA1c of at least 39 mmol/mol (5.7%) and/or random VPG of at least 11.1 mmol/L.
“The revised Australian pathway does not include HbA1c but recommends a fasting VPG with progression to OGTT only if this result is 4.7-5.0 mmol/L,” Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses explained.
Overall, the revised guidelines for GDM testing will likely miss some women and only identify those with higher levels of hyperglycemia, the authors wrote. In addition, “the evidence base for these revised pathways is limited and that each alternative strategy should be evaluated over the course of the current pandemic.”
Validation of new testing strategies are needed, and the pandemic may provide and opportunity to adopt an alternative to the OGTT. The World Health Organization has not issued revised guidance for other methods of testing, but fasting VPG alone may be the simplest and most cost effective, at least for the short term, they noted.
“In this ‘new COVID world,’ GDM should not be ignored but pragmatically merits a lower priority than the avoidance of exposure to the COVID-19 virus,” although no single alternative strategy applies in all countries and situations, the authors concluded. Pragmatic measures and documentation of outcomes at the local level will offer the “least worst” solution while the pandemic continues.
The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: McIntyre HD, Moses RG. Diabetes Care. 2020 May. doi: 10.2337/dci20-0026.
A major concern against the backdrop of COVID-19 is ensuring long-term health while urgent care is – understandably so – being prioritized over preventive care. We can already see the impact that the decrease in primary care has had: Rates of childhood vaccination appear to have dropped; the cancellation or indefinite delay of elective medical procedures has meant a reduction in preventive cancer screenings, such as colonoscopies and mammograms; and concerns about COVID-19 may be keeping those experiencing cardiac events from seeking emergency care.
However, an outcropping of the coronavirus pandemic is an ingenuity to adapt to our new “normal.” Medical licenses have been recognized across state lines to allow much-needed professionals to practice in the hardest-hit areas. Doctors retrofitted a sleep apnea machine to be used as a makeshift ventilator. Those in the wearable device market now have a greater onus to deliver on quality, utility, security, and accuracy.
Obstetricians have had to dramatically change delivery of ante-, intra- and postpartum care. The recent commentary by Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses focuses on one particular area of concern: screening, diagnosis, and management of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Screening and diagnosis are mainstays to reduce the adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes of diabetes in pregnancy. Although there is no universally accepted approach to evaluating GDM, all current methods utilize an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), which requires significant time spent in a clinical office setting, thus increasing risk for COVID-19 exposure.
Several countries have adopted modified GDM criteria within the last months. At the time of this writing, the United States has not. Although not testing women for GDM, which is what Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses point out may be happening in countries with modified guidelines, seems questionable, perhaps we should think differently about our approach.
More than 20 years ago, it was reported that jelly beans could be used as an alternative to the 50-g GDM screening test (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Nov;181[5 Pt 1]:1154‐7; Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Dec;173[6]:1889‐92); more recently, candy twists were used with similar results (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Apr;212[4]:522.e1-5). In addition, a number of articles have reported on the utility of capillary whole blood glucose measurements to screen for GDM in developing and resource-limited countries (Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13[5]:586‐91; Acta Diabetol. 2016 Feb;53[1]:91‐7; Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012 Feb;14[2]:131-4). Therefore, rather than forgo GDM screening, women could self-administer a jelly bean test at home, measure blood sugar with a glucometer, and depending on the results, have an OGTT. Importantly, this would allow ob.gyns. to maintain medical standards while managing patients via telemedicine.
We have evidence that GDM can establish poor health for generations. We know that people with underlying conditions have greater morbidity and mortality from infectious diseases. We recognize that accurate screening and diagnosis is the key to prevention and management. Rather than accept a “least worst” scenario, as Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses state, we must find ways to provide the best possible care under the current circumstances.
E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the University of Maryland School of Medicine. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. He is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board.
A major concern against the backdrop of COVID-19 is ensuring long-term health while urgent care is – understandably so – being prioritized over preventive care. We can already see the impact that the decrease in primary care has had: Rates of childhood vaccination appear to have dropped; the cancellation or indefinite delay of elective medical procedures has meant a reduction in preventive cancer screenings, such as colonoscopies and mammograms; and concerns about COVID-19 may be keeping those experiencing cardiac events from seeking emergency care.
However, an outcropping of the coronavirus pandemic is an ingenuity to adapt to our new “normal.” Medical licenses have been recognized across state lines to allow much-needed professionals to practice in the hardest-hit areas. Doctors retrofitted a sleep apnea machine to be used as a makeshift ventilator. Those in the wearable device market now have a greater onus to deliver on quality, utility, security, and accuracy.
Obstetricians have had to dramatically change delivery of ante-, intra- and postpartum care. The recent commentary by Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses focuses on one particular area of concern: screening, diagnosis, and management of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Screening and diagnosis are mainstays to reduce the adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes of diabetes in pregnancy. Although there is no universally accepted approach to evaluating GDM, all current methods utilize an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), which requires significant time spent in a clinical office setting, thus increasing risk for COVID-19 exposure.
Several countries have adopted modified GDM criteria within the last months. At the time of this writing, the United States has not. Although not testing women for GDM, which is what Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses point out may be happening in countries with modified guidelines, seems questionable, perhaps we should think differently about our approach.
More than 20 years ago, it was reported that jelly beans could be used as an alternative to the 50-g GDM screening test (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Nov;181[5 Pt 1]:1154‐7; Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Dec;173[6]:1889‐92); more recently, candy twists were used with similar results (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Apr;212[4]:522.e1-5). In addition, a number of articles have reported on the utility of capillary whole blood glucose measurements to screen for GDM in developing and resource-limited countries (Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13[5]:586‐91; Acta Diabetol. 2016 Feb;53[1]:91‐7; Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012 Feb;14[2]:131-4). Therefore, rather than forgo GDM screening, women could self-administer a jelly bean test at home, measure blood sugar with a glucometer, and depending on the results, have an OGTT. Importantly, this would allow ob.gyns. to maintain medical standards while managing patients via telemedicine.
We have evidence that GDM can establish poor health for generations. We know that people with underlying conditions have greater morbidity and mortality from infectious diseases. We recognize that accurate screening and diagnosis is the key to prevention and management. Rather than accept a “least worst” scenario, as Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses state, we must find ways to provide the best possible care under the current circumstances.
E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the University of Maryland School of Medicine. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. He is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board.
A major concern against the backdrop of COVID-19 is ensuring long-term health while urgent care is – understandably so – being prioritized over preventive care. We can already see the impact that the decrease in primary care has had: Rates of childhood vaccination appear to have dropped; the cancellation or indefinite delay of elective medical procedures has meant a reduction in preventive cancer screenings, such as colonoscopies and mammograms; and concerns about COVID-19 may be keeping those experiencing cardiac events from seeking emergency care.
However, an outcropping of the coronavirus pandemic is an ingenuity to adapt to our new “normal.” Medical licenses have been recognized across state lines to allow much-needed professionals to practice in the hardest-hit areas. Doctors retrofitted a sleep apnea machine to be used as a makeshift ventilator. Those in the wearable device market now have a greater onus to deliver on quality, utility, security, and accuracy.
Obstetricians have had to dramatically change delivery of ante-, intra- and postpartum care. The recent commentary by Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses focuses on one particular area of concern: screening, diagnosis, and management of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
Screening and diagnosis are mainstays to reduce the adverse maternal and neonatal outcomes of diabetes in pregnancy. Although there is no universally accepted approach to evaluating GDM, all current methods utilize an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), which requires significant time spent in a clinical office setting, thus increasing risk for COVID-19 exposure.
Several countries have adopted modified GDM criteria within the last months. At the time of this writing, the United States has not. Although not testing women for GDM, which is what Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses point out may be happening in countries with modified guidelines, seems questionable, perhaps we should think differently about our approach.
More than 20 years ago, it was reported that jelly beans could be used as an alternative to the 50-g GDM screening test (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Nov;181[5 Pt 1]:1154‐7; Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1995 Dec;173[6]:1889‐92); more recently, candy twists were used with similar results (Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Apr;212[4]:522.e1-5). In addition, a number of articles have reported on the utility of capillary whole blood glucose measurements to screen for GDM in developing and resource-limited countries (Diabetes Technol Ther. 2011;13[5]:586‐91; Acta Diabetol. 2016 Feb;53[1]:91‐7; Diabetes Technol Ther. 2012 Feb;14[2]:131-4). Therefore, rather than forgo GDM screening, women could self-administer a jelly bean test at home, measure blood sugar with a glucometer, and depending on the results, have an OGTT. Importantly, this would allow ob.gyns. to maintain medical standards while managing patients via telemedicine.
We have evidence that GDM can establish poor health for generations. We know that people with underlying conditions have greater morbidity and mortality from infectious diseases. We recognize that accurate screening and diagnosis is the key to prevention and management. Rather than accept a “least worst” scenario, as Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses state, we must find ways to provide the best possible care under the current circumstances.
E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the University of Maryland School of Medicine. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. He is a member of the Ob.Gyn. News editorial advisory board.
Clinicians and pregnant women are less likely to prescribe and undergo the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to diagnose gestational diabetes in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a review by H. David McIntyre, MD, of the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, and Robert G. Moses, MD, of Wollongong (Australia) Hospital.
National and international discussions of whether a one- or two-step test for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is optimal, and which women should be tested are ongoing, but the potential for exposure risks to COVID-19 are impacting the test process, they wrote in a commentary published in Diabetes Care.
“Any national or local guidelines should be developed with the primary aim of being protective for pregnant women and workable in the current health crisis,” they wrote.
Key concerns expressed by women and health care providers include the need for travel to be tested, the possible need for two visits, and the several hours spent in a potentially high-risk specimen collection center.
“Further, a GDM diagnosis generally involves additional health service visits for diabetes education, glucose monitoring review, and fetal ultrasonography, all of which carry exposure risks during a pandemic,” Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses noted.
Professional societies in the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia have issued guidance to clinicians for modifying GDM diagnoses criteria during the pandemic that aim to reduce the need for the oral glucose tolerance test both during and after pregnancy.
Pandemic guidelines for all three of these countries support the identification of GDM using early pregnancy hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of at least 41 mmol/mol (5.9%).
Then, professionals in the United Kingdom recommend testing based on risk factors and diagnosing GDM based on any of these criteria: HbA1c of at least 39 mmol/mol (5.7%), fasting venous plasma glucose of at least 5.6 mmol/L (preferred), or random VPG of at least 9.0 mmol/L.
The revised testing pathway for Canada accepts an HbA1c of at least 39 mmol/mol (5.7%) and/or random VPG of at least 11.1 mmol/L.
“The revised Australian pathway does not include HbA1c but recommends a fasting VPG with progression to OGTT only if this result is 4.7-5.0 mmol/L,” Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses explained.
Overall, the revised guidelines for GDM testing will likely miss some women and only identify those with higher levels of hyperglycemia, the authors wrote. In addition, “the evidence base for these revised pathways is limited and that each alternative strategy should be evaluated over the course of the current pandemic.”
Validation of new testing strategies are needed, and the pandemic may provide and opportunity to adopt an alternative to the OGTT. The World Health Organization has not issued revised guidance for other methods of testing, but fasting VPG alone may be the simplest and most cost effective, at least for the short term, they noted.
“In this ‘new COVID world,’ GDM should not be ignored but pragmatically merits a lower priority than the avoidance of exposure to the COVID-19 virus,” although no single alternative strategy applies in all countries and situations, the authors concluded. Pragmatic measures and documentation of outcomes at the local level will offer the “least worst” solution while the pandemic continues.
The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: McIntyre HD, Moses RG. Diabetes Care. 2020 May. doi: 10.2337/dci20-0026.
Clinicians and pregnant women are less likely to prescribe and undergo the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) to diagnose gestational diabetes in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a review by H. David McIntyre, MD, of the University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, and Robert G. Moses, MD, of Wollongong (Australia) Hospital.
National and international discussions of whether a one- or two-step test for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is optimal, and which women should be tested are ongoing, but the potential for exposure risks to COVID-19 are impacting the test process, they wrote in a commentary published in Diabetes Care.
“Any national or local guidelines should be developed with the primary aim of being protective for pregnant women and workable in the current health crisis,” they wrote.
Key concerns expressed by women and health care providers include the need for travel to be tested, the possible need for two visits, and the several hours spent in a potentially high-risk specimen collection center.
“Further, a GDM diagnosis generally involves additional health service visits for diabetes education, glucose monitoring review, and fetal ultrasonography, all of which carry exposure risks during a pandemic,” Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses noted.
Professional societies in the United Kingdom, Canada, and Australia have issued guidance to clinicians for modifying GDM diagnoses criteria during the pandemic that aim to reduce the need for the oral glucose tolerance test both during and after pregnancy.
Pandemic guidelines for all three of these countries support the identification of GDM using early pregnancy hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) of at least 41 mmol/mol (5.9%).
Then, professionals in the United Kingdom recommend testing based on risk factors and diagnosing GDM based on any of these criteria: HbA1c of at least 39 mmol/mol (5.7%), fasting venous plasma glucose of at least 5.6 mmol/L (preferred), or random VPG of at least 9.0 mmol/L.
The revised testing pathway for Canada accepts an HbA1c of at least 39 mmol/mol (5.7%) and/or random VPG of at least 11.1 mmol/L.
“The revised Australian pathway does not include HbA1c but recommends a fasting VPG with progression to OGTT only if this result is 4.7-5.0 mmol/L,” Dr. McIntyre and Dr. Moses explained.
Overall, the revised guidelines for GDM testing will likely miss some women and only identify those with higher levels of hyperglycemia, the authors wrote. In addition, “the evidence base for these revised pathways is limited and that each alternative strategy should be evaluated over the course of the current pandemic.”
Validation of new testing strategies are needed, and the pandemic may provide and opportunity to adopt an alternative to the OGTT. The World Health Organization has not issued revised guidance for other methods of testing, but fasting VPG alone may be the simplest and most cost effective, at least for the short term, they noted.
“In this ‘new COVID world,’ GDM should not be ignored but pragmatically merits a lower priority than the avoidance of exposure to the COVID-19 virus,” although no single alternative strategy applies in all countries and situations, the authors concluded. Pragmatic measures and documentation of outcomes at the local level will offer the “least worst” solution while the pandemic continues.
The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: McIntyre HD, Moses RG. Diabetes Care. 2020 May. doi: 10.2337/dci20-0026.
COVID-19: Psychiatrists assess geriatric harm from social distancing
One of the greatest tragedies of the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic has been the failure of health policy makers to anticipate and mitigate the enormous havoc the policy of social distancing would wreak on mental health and cognitive function in older persons, speakers agreed at a webinar on COVID-19, social distancing, and its impact on social and mental health in the elderly hosted by the International Psychogeriatric Association in collaboration with INTERDEM.
“Social distancing” is a two-edged sword: It is for now and the foreseeable future the only available effective strategy for protecting against infection in the older population most vulnerable to severe forms of COVID-19. Yet social distancing also has caused many elderly – particularly those in nursing homes and other long-term care facilities – to plunge into a profound experience of loneliness, isolation, distress, feelings of abandonment, anxiety, depression, and accelerated cognitive deterioration. And this needn’t have happened, the mental health professionals asserted.
“When are we going to get rid of the term ‘social distancing?’ ” asked IPA President William E. Reichman, MD. “Many have appreciated – including the World Health Organization – that the real issue is physical distancing to prevent contagion. And physical distancing doesn’t have to mean social distancing.”
Social connectedness between elderly persons and their peers and family members can be maintained and should be emphatically encouraged during the physical distancing required by the pandemic, said Myrra Vernooij-Dassen, PhD, of Radboud University in Nigmegen, the Netherlands, and chair of INTERDEM, a pan-European network of dementia researchers.
This can be achieved using readily available technologies, including the telephone and videoconferencing, as well as by creating opportunities for supervised masked visits between a family member and an elderly loved one in outdoor courtyards or gardens within long-term care facilities. And yet, as the pandemic seized hold in many parts of the world, family members were blocked from entry to these facilities, she observed.
Impact on mental health, cognition
Dr. Vernooij-Dassen noted that studies of previous quarantine periods as well as preliminary findings during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrate an inverse relationship between social isolation measures and cognitive functioning in the elderly.
“ Conversely, epidemiologic data indicate that a socially integrated lifestyle had a favorable influence on cognitive functioning and could even delay onset of dementia,” she said.
INTERDEM is backing two ongoing studies evaluating the hypothesis that interventions fostering increased social interaction among elderly individuals can delay onset of dementia or favorably affect its course. The proposed mechanism of benefit is stimulation of brain plasticity to enhance cognitive reserve.
“This is a hypothesis of hope. We know that social interaction for humans is like water to plants – we really, really need it,” she explained.
Diego de Leo, MD, PhD, emeritus professor of psychiatry and former director of the Australian Institute for Suicide Research and Prevention at Griffith University in Brisbane, was living in hard-hit Padua, Italy, during the first surge of COVID-19. He described his anecdotal experience.
“What I hear from many Italian colleagues and friends and directors of mental health services is that emergency admissions related to mental disorders declined during the first wave of the COVID pandemic. For example, not many people attended emergency departments due to suicide attempts; there was a very marked decrease in the number of suicide attempts during the worst days of the pandemic,” he said.
People with psychiatric conditions were afraid to go to the hospital because they thought they would contract the infection and die there. That’s changing now, however.
“Now there is an increased number of admissions to mental health units. A new wave. It has been a U-shaped curve. And we’re now witnessing an increasing number of fatal suicides due to persistent fears, due to people imagining that there is no more room for them, and no more future for them from a financial point of view – which is the major negative outcome of this crisis. It will be a disaster for many families,” the psychiatrist continued.
A noteworthy phenomenon in northern Italy was that, when tablets were made available to nursing home residents in an effort to enhance their connectedness to the outside world, those with dementia often became so frustrated and confused by their difficulty in using the devices that they developed a hypokinetic delirium marked by refusal to eat or leave their bed, he reported.
It’s far too early to have reliable data on suicide trends in response to the pandemic, according to Dr. de Leo. But one thing is for sure: The strategy of social distancing employed to curb COVID-19 has increased the prevalence of known risk factors for suicide in older individuals, including loneliness, anxiety, and depression; increased alcohol use; and a perception of being a burden on society. Dr. de Leo directs a foundation dedicated to helping people experiencing traumatic bereavement, and in one recent week, the foundation was contacted by eight families in the province of Padua with a recent death by suicide apparently related to fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s an unusually high spike in suicide in a province with a population of 1 million.
“People probably preferred to end the agitation, the fear, the extreme anxiety about their destiny by deciding to prematurely truncate their life. That has been reported by nursing staff,” he said.
The Italian government has determined that, to date, 36% of all COVID-related deaths have occurred in people aged 85 years or older, and 84% of deaths were in individuals aged at least 70 years. And in Milan and the surrounding province of Lombardy, it’s estimated that COVID-19 has taken the lives of 25% of all nursing home residents. The North American experience has been uncomfortably similar.
“Almost 80% of COVID deaths in Canada have occurred in congregate settings,” observed Dr. Reichman, professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto, and president and CEO of Baycrest Health Sciences, a geriatric research center.
“Certainly, the appalling number of deaths in nursing homes is the No. 1 horror of the pandemic,” declared Carmelle Peisah, MBBS, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of New South Wales in Kensington, Australia.
The fire next time
The conventional wisdom holds that COVID-19 has caused all sorts of mayhem in the delivery of elder care. Not so, in Dr. Reichman’s view.
“I would suggest that the pandemic has not caused many of the problems we talk about, it’s actually revealed problems that have always been there under the surface. For example, many older people, even before COVID-19, were socially isolated, socially distant. They had difficulty connecting with their relatives, difficulty accessing transportation to get to the store to buy food and see their doctors, and to interact with other older people,” the psychiatrist said.
“I would say as well that the pandemic didn’t cause the problems we’ve seen in long-term congregate senior care. The pandemic revealed them. We’ve had facilities where older people were severely crowded together, which compromises their quality of life, even when there’s not a pandemic. We’ve had difficulty staffing these kinds of environments with people that are paid an honest wage for the very hard work that they do. In many of these settings they’re inadequately trained, not only in infection prevention and control but in all other aspects of care. And the pandemic has revealed that many of these organizations are not properly funded. The government doesn’t support them well enough across jurisdictions, and they can’t raise enough philanthropic funds to provide the kind of quality of life that residents demand,” Dr. Reichman continued.
Could the pandemic spur improved elder care? His hope is that health care professionals, politicians, and society at large will learn from the devastation left by the first surge of the pandemic and will lobby for the resources necessary for much-needed improvements in geriatric care.
“We need to be better prepared should there be not only a second wave of this pandemic, but for other pandemics to come,” Dr. Reichman concluded.
The speakers indicated they had no financial conflicts regarding their presentations.
One of the greatest tragedies of the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic has been the failure of health policy makers to anticipate and mitigate the enormous havoc the policy of social distancing would wreak on mental health and cognitive function in older persons, speakers agreed at a webinar on COVID-19, social distancing, and its impact on social and mental health in the elderly hosted by the International Psychogeriatric Association in collaboration with INTERDEM.
“Social distancing” is a two-edged sword: It is for now and the foreseeable future the only available effective strategy for protecting against infection in the older population most vulnerable to severe forms of COVID-19. Yet social distancing also has caused many elderly – particularly those in nursing homes and other long-term care facilities – to plunge into a profound experience of loneliness, isolation, distress, feelings of abandonment, anxiety, depression, and accelerated cognitive deterioration. And this needn’t have happened, the mental health professionals asserted.
“When are we going to get rid of the term ‘social distancing?’ ” asked IPA President William E. Reichman, MD. “Many have appreciated – including the World Health Organization – that the real issue is physical distancing to prevent contagion. And physical distancing doesn’t have to mean social distancing.”
Social connectedness between elderly persons and their peers and family members can be maintained and should be emphatically encouraged during the physical distancing required by the pandemic, said Myrra Vernooij-Dassen, PhD, of Radboud University in Nigmegen, the Netherlands, and chair of INTERDEM, a pan-European network of dementia researchers.
This can be achieved using readily available technologies, including the telephone and videoconferencing, as well as by creating opportunities for supervised masked visits between a family member and an elderly loved one in outdoor courtyards or gardens within long-term care facilities. And yet, as the pandemic seized hold in many parts of the world, family members were blocked from entry to these facilities, she observed.
Impact on mental health, cognition
Dr. Vernooij-Dassen noted that studies of previous quarantine periods as well as preliminary findings during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrate an inverse relationship between social isolation measures and cognitive functioning in the elderly.
“ Conversely, epidemiologic data indicate that a socially integrated lifestyle had a favorable influence on cognitive functioning and could even delay onset of dementia,” she said.
INTERDEM is backing two ongoing studies evaluating the hypothesis that interventions fostering increased social interaction among elderly individuals can delay onset of dementia or favorably affect its course. The proposed mechanism of benefit is stimulation of brain plasticity to enhance cognitive reserve.
“This is a hypothesis of hope. We know that social interaction for humans is like water to plants – we really, really need it,” she explained.
Diego de Leo, MD, PhD, emeritus professor of psychiatry and former director of the Australian Institute for Suicide Research and Prevention at Griffith University in Brisbane, was living in hard-hit Padua, Italy, during the first surge of COVID-19. He described his anecdotal experience.
“What I hear from many Italian colleagues and friends and directors of mental health services is that emergency admissions related to mental disorders declined during the first wave of the COVID pandemic. For example, not many people attended emergency departments due to suicide attempts; there was a very marked decrease in the number of suicide attempts during the worst days of the pandemic,” he said.
People with psychiatric conditions were afraid to go to the hospital because they thought they would contract the infection and die there. That’s changing now, however.
“Now there is an increased number of admissions to mental health units. A new wave. It has been a U-shaped curve. And we’re now witnessing an increasing number of fatal suicides due to persistent fears, due to people imagining that there is no more room for them, and no more future for them from a financial point of view – which is the major negative outcome of this crisis. It will be a disaster for many families,” the psychiatrist continued.
A noteworthy phenomenon in northern Italy was that, when tablets were made available to nursing home residents in an effort to enhance their connectedness to the outside world, those with dementia often became so frustrated and confused by their difficulty in using the devices that they developed a hypokinetic delirium marked by refusal to eat or leave their bed, he reported.
It’s far too early to have reliable data on suicide trends in response to the pandemic, according to Dr. de Leo. But one thing is for sure: The strategy of social distancing employed to curb COVID-19 has increased the prevalence of known risk factors for suicide in older individuals, including loneliness, anxiety, and depression; increased alcohol use; and a perception of being a burden on society. Dr. de Leo directs a foundation dedicated to helping people experiencing traumatic bereavement, and in one recent week, the foundation was contacted by eight families in the province of Padua with a recent death by suicide apparently related to fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s an unusually high spike in suicide in a province with a population of 1 million.
“People probably preferred to end the agitation, the fear, the extreme anxiety about their destiny by deciding to prematurely truncate their life. That has been reported by nursing staff,” he said.
The Italian government has determined that, to date, 36% of all COVID-related deaths have occurred in people aged 85 years or older, and 84% of deaths were in individuals aged at least 70 years. And in Milan and the surrounding province of Lombardy, it’s estimated that COVID-19 has taken the lives of 25% of all nursing home residents. The North American experience has been uncomfortably similar.
“Almost 80% of COVID deaths in Canada have occurred in congregate settings,” observed Dr. Reichman, professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto, and president and CEO of Baycrest Health Sciences, a geriatric research center.
“Certainly, the appalling number of deaths in nursing homes is the No. 1 horror of the pandemic,” declared Carmelle Peisah, MBBS, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of New South Wales in Kensington, Australia.
The fire next time
The conventional wisdom holds that COVID-19 has caused all sorts of mayhem in the delivery of elder care. Not so, in Dr. Reichman’s view.
“I would suggest that the pandemic has not caused many of the problems we talk about, it’s actually revealed problems that have always been there under the surface. For example, many older people, even before COVID-19, were socially isolated, socially distant. They had difficulty connecting with their relatives, difficulty accessing transportation to get to the store to buy food and see their doctors, and to interact with other older people,” the psychiatrist said.
“I would say as well that the pandemic didn’t cause the problems we’ve seen in long-term congregate senior care. The pandemic revealed them. We’ve had facilities where older people were severely crowded together, which compromises their quality of life, even when there’s not a pandemic. We’ve had difficulty staffing these kinds of environments with people that are paid an honest wage for the very hard work that they do. In many of these settings they’re inadequately trained, not only in infection prevention and control but in all other aspects of care. And the pandemic has revealed that many of these organizations are not properly funded. The government doesn’t support them well enough across jurisdictions, and they can’t raise enough philanthropic funds to provide the kind of quality of life that residents demand,” Dr. Reichman continued.
Could the pandemic spur improved elder care? His hope is that health care professionals, politicians, and society at large will learn from the devastation left by the first surge of the pandemic and will lobby for the resources necessary for much-needed improvements in geriatric care.
“We need to be better prepared should there be not only a second wave of this pandemic, but for other pandemics to come,” Dr. Reichman concluded.
The speakers indicated they had no financial conflicts regarding their presentations.
One of the greatest tragedies of the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic has been the failure of health policy makers to anticipate and mitigate the enormous havoc the policy of social distancing would wreak on mental health and cognitive function in older persons, speakers agreed at a webinar on COVID-19, social distancing, and its impact on social and mental health in the elderly hosted by the International Psychogeriatric Association in collaboration with INTERDEM.
“Social distancing” is a two-edged sword: It is for now and the foreseeable future the only available effective strategy for protecting against infection in the older population most vulnerable to severe forms of COVID-19. Yet social distancing also has caused many elderly – particularly those in nursing homes and other long-term care facilities – to plunge into a profound experience of loneliness, isolation, distress, feelings of abandonment, anxiety, depression, and accelerated cognitive deterioration. And this needn’t have happened, the mental health professionals asserted.
“When are we going to get rid of the term ‘social distancing?’ ” asked IPA President William E. Reichman, MD. “Many have appreciated – including the World Health Organization – that the real issue is physical distancing to prevent contagion. And physical distancing doesn’t have to mean social distancing.”
Social connectedness between elderly persons and their peers and family members can be maintained and should be emphatically encouraged during the physical distancing required by the pandemic, said Myrra Vernooij-Dassen, PhD, of Radboud University in Nigmegen, the Netherlands, and chair of INTERDEM, a pan-European network of dementia researchers.
This can be achieved using readily available technologies, including the telephone and videoconferencing, as well as by creating opportunities for supervised masked visits between a family member and an elderly loved one in outdoor courtyards or gardens within long-term care facilities. And yet, as the pandemic seized hold in many parts of the world, family members were blocked from entry to these facilities, she observed.
Impact on mental health, cognition
Dr. Vernooij-Dassen noted that studies of previous quarantine periods as well as preliminary findings during the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrate an inverse relationship between social isolation measures and cognitive functioning in the elderly.
“ Conversely, epidemiologic data indicate that a socially integrated lifestyle had a favorable influence on cognitive functioning and could even delay onset of dementia,” she said.
INTERDEM is backing two ongoing studies evaluating the hypothesis that interventions fostering increased social interaction among elderly individuals can delay onset of dementia or favorably affect its course. The proposed mechanism of benefit is stimulation of brain plasticity to enhance cognitive reserve.
“This is a hypothesis of hope. We know that social interaction for humans is like water to plants – we really, really need it,” she explained.
Diego de Leo, MD, PhD, emeritus professor of psychiatry and former director of the Australian Institute for Suicide Research and Prevention at Griffith University in Brisbane, was living in hard-hit Padua, Italy, during the first surge of COVID-19. He described his anecdotal experience.
“What I hear from many Italian colleagues and friends and directors of mental health services is that emergency admissions related to mental disorders declined during the first wave of the COVID pandemic. For example, not many people attended emergency departments due to suicide attempts; there was a very marked decrease in the number of suicide attempts during the worst days of the pandemic,” he said.
People with psychiatric conditions were afraid to go to the hospital because they thought they would contract the infection and die there. That’s changing now, however.
“Now there is an increased number of admissions to mental health units. A new wave. It has been a U-shaped curve. And we’re now witnessing an increasing number of fatal suicides due to persistent fears, due to people imagining that there is no more room for them, and no more future for them from a financial point of view – which is the major negative outcome of this crisis. It will be a disaster for many families,” the psychiatrist continued.
A noteworthy phenomenon in northern Italy was that, when tablets were made available to nursing home residents in an effort to enhance their connectedness to the outside world, those with dementia often became so frustrated and confused by their difficulty in using the devices that they developed a hypokinetic delirium marked by refusal to eat or leave their bed, he reported.
It’s far too early to have reliable data on suicide trends in response to the pandemic, according to Dr. de Leo. But one thing is for sure: The strategy of social distancing employed to curb COVID-19 has increased the prevalence of known risk factors for suicide in older individuals, including loneliness, anxiety, and depression; increased alcohol use; and a perception of being a burden on society. Dr. de Leo directs a foundation dedicated to helping people experiencing traumatic bereavement, and in one recent week, the foundation was contacted by eight families in the province of Padua with a recent death by suicide apparently related to fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. That’s an unusually high spike in suicide in a province with a population of 1 million.
“People probably preferred to end the agitation, the fear, the extreme anxiety about their destiny by deciding to prematurely truncate their life. That has been reported by nursing staff,” he said.
The Italian government has determined that, to date, 36% of all COVID-related deaths have occurred in people aged 85 years or older, and 84% of deaths were in individuals aged at least 70 years. And in Milan and the surrounding province of Lombardy, it’s estimated that COVID-19 has taken the lives of 25% of all nursing home residents. The North American experience has been uncomfortably similar.
“Almost 80% of COVID deaths in Canada have occurred in congregate settings,” observed Dr. Reichman, professor of psychiatry at the University of Toronto, and president and CEO of Baycrest Health Sciences, a geriatric research center.
“Certainly, the appalling number of deaths in nursing homes is the No. 1 horror of the pandemic,” declared Carmelle Peisah, MBBS, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of New South Wales in Kensington, Australia.
The fire next time
The conventional wisdom holds that COVID-19 has caused all sorts of mayhem in the delivery of elder care. Not so, in Dr. Reichman’s view.
“I would suggest that the pandemic has not caused many of the problems we talk about, it’s actually revealed problems that have always been there under the surface. For example, many older people, even before COVID-19, were socially isolated, socially distant. They had difficulty connecting with their relatives, difficulty accessing transportation to get to the store to buy food and see their doctors, and to interact with other older people,” the psychiatrist said.
“I would say as well that the pandemic didn’t cause the problems we’ve seen in long-term congregate senior care. The pandemic revealed them. We’ve had facilities where older people were severely crowded together, which compromises their quality of life, even when there’s not a pandemic. We’ve had difficulty staffing these kinds of environments with people that are paid an honest wage for the very hard work that they do. In many of these settings they’re inadequately trained, not only in infection prevention and control but in all other aspects of care. And the pandemic has revealed that many of these organizations are not properly funded. The government doesn’t support them well enough across jurisdictions, and they can’t raise enough philanthropic funds to provide the kind of quality of life that residents demand,” Dr. Reichman continued.
Could the pandemic spur improved elder care? His hope is that health care professionals, politicians, and society at large will learn from the devastation left by the first surge of the pandemic and will lobby for the resources necessary for much-needed improvements in geriatric care.
“We need to be better prepared should there be not only a second wave of this pandemic, but for other pandemics to come,” Dr. Reichman concluded.
The speakers indicated they had no financial conflicts regarding their presentations.
Is HIPAA critical?
Ignorance may be bliss for some. But as I sit here in my scenic social isolation on the Maine coast I find that, like most people, what I don’t know unsettles me. How is the COVID-19 virus spread? Does my wife’s wipe down of the doorknobs after I return from the grocery store really make us any less likely to contract the virus? Is wearing my homemade bandana face mask doing anything to protect me? I suspect not, but I wear it as a statement of courtesy and solidarity to my fellow community members.
Does the 6-foot rule make any sense? I’ve read that it is based on a study dating back to the 1930s. I’ve seen images of the 25-foot droplet plume blasting out from a sneeze and understand that, as a bicyclist, I may be generating a shower of droplets in my wake. But, are those droplets a threat to anyone I pedal by if I am symptom free? What does being a carrier mean when we are talking about COVID-19?
What makes me more vulnerable to this particular virus as an apparently healthy septuagenarian? What collection of misfortunes have fallen on those younger victims of the pandemic? How often was it genetic?
Of course, none of us has the information yet that can provide us answers. This vacuum has attracted scores of “experts” bold enough or careless enough to venture an opinion. They may have also issued a caveat, but how often have the media failed to include it in the report or buried it in the fine print at the end of the story?
My discomfort with this information void has left me and you and everyone else to our imaginations to craft our own explanations. So, I try to piece together a construct based on what I can glean from what I read and see in the news because like most people I fortunately have no first-hand information about even a single case. The number of deaths is horrifying, but may not have hit close to home and given most of us a real personal sense of the illness and its character.
Maine is a small state with just over a million inhabitants, and most of us have some connection to one another. It may be that a person is the second cousin of someone who used to live 2 miles down the road. But, there is some feeling of familiarity. We have had deaths related to COVID-19, but very scanty information other than the county about where they occurred and whether the victim was a resident of an extended care facility. We are told very little if any details about exposure as officials invoke HIPAA regulations that leave us in the dark. Other than one vague reference to a “traveling salesman” who may have introduced the virus to several nursing homes, there has been very little information about how the virus may have been spread here in Maine. Even national reports of the deaths of high-profile entertainers and retired athletes are usually draped in the same haze of privacy.
Most of us don’t need to know the names and street addresses of the victims but a few anonymous narratives that include some general information on how epidemiologists believe clusters began and propagated would help us understand our risks with just a glimmer of clarity.
Of course the epidemiologists may not have the answers we are seeking because they too are struggling to untangle connections hampered by concerns of privacy. There is no question that privacy must remain an important part of the physician-patient relationship. But a pandemic has thrown us into a situation where common sense demands that HIPAA be interpreted with an emphasis on the greater good. Finding that balance between privacy and public knowledge will continue to be one of our greatest challenges.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Ignorance may be bliss for some. But as I sit here in my scenic social isolation on the Maine coast I find that, like most people, what I don’t know unsettles me. How is the COVID-19 virus spread? Does my wife’s wipe down of the doorknobs after I return from the grocery store really make us any less likely to contract the virus? Is wearing my homemade bandana face mask doing anything to protect me? I suspect not, but I wear it as a statement of courtesy and solidarity to my fellow community members.
Does the 6-foot rule make any sense? I’ve read that it is based on a study dating back to the 1930s. I’ve seen images of the 25-foot droplet plume blasting out from a sneeze and understand that, as a bicyclist, I may be generating a shower of droplets in my wake. But, are those droplets a threat to anyone I pedal by if I am symptom free? What does being a carrier mean when we are talking about COVID-19?
What makes me more vulnerable to this particular virus as an apparently healthy septuagenarian? What collection of misfortunes have fallen on those younger victims of the pandemic? How often was it genetic?
Of course, none of us has the information yet that can provide us answers. This vacuum has attracted scores of “experts” bold enough or careless enough to venture an opinion. They may have also issued a caveat, but how often have the media failed to include it in the report or buried it in the fine print at the end of the story?
My discomfort with this information void has left me and you and everyone else to our imaginations to craft our own explanations. So, I try to piece together a construct based on what I can glean from what I read and see in the news because like most people I fortunately have no first-hand information about even a single case. The number of deaths is horrifying, but may not have hit close to home and given most of us a real personal sense of the illness and its character.
Maine is a small state with just over a million inhabitants, and most of us have some connection to one another. It may be that a person is the second cousin of someone who used to live 2 miles down the road. But, there is some feeling of familiarity. We have had deaths related to COVID-19, but very scanty information other than the county about where they occurred and whether the victim was a resident of an extended care facility. We are told very little if any details about exposure as officials invoke HIPAA regulations that leave us in the dark. Other than one vague reference to a “traveling salesman” who may have introduced the virus to several nursing homes, there has been very little information about how the virus may have been spread here in Maine. Even national reports of the deaths of high-profile entertainers and retired athletes are usually draped in the same haze of privacy.
Most of us don’t need to know the names and street addresses of the victims but a few anonymous narratives that include some general information on how epidemiologists believe clusters began and propagated would help us understand our risks with just a glimmer of clarity.
Of course the epidemiologists may not have the answers we are seeking because they too are struggling to untangle connections hampered by concerns of privacy. There is no question that privacy must remain an important part of the physician-patient relationship. But a pandemic has thrown us into a situation where common sense demands that HIPAA be interpreted with an emphasis on the greater good. Finding that balance between privacy and public knowledge will continue to be one of our greatest challenges.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Ignorance may be bliss for some. But as I sit here in my scenic social isolation on the Maine coast I find that, like most people, what I don’t know unsettles me. How is the COVID-19 virus spread? Does my wife’s wipe down of the doorknobs after I return from the grocery store really make us any less likely to contract the virus? Is wearing my homemade bandana face mask doing anything to protect me? I suspect not, but I wear it as a statement of courtesy and solidarity to my fellow community members.
Does the 6-foot rule make any sense? I’ve read that it is based on a study dating back to the 1930s. I’ve seen images of the 25-foot droplet plume blasting out from a sneeze and understand that, as a bicyclist, I may be generating a shower of droplets in my wake. But, are those droplets a threat to anyone I pedal by if I am symptom free? What does being a carrier mean when we are talking about COVID-19?
What makes me more vulnerable to this particular virus as an apparently healthy septuagenarian? What collection of misfortunes have fallen on those younger victims of the pandemic? How often was it genetic?
Of course, none of us has the information yet that can provide us answers. This vacuum has attracted scores of “experts” bold enough or careless enough to venture an opinion. They may have also issued a caveat, but how often have the media failed to include it in the report or buried it in the fine print at the end of the story?
My discomfort with this information void has left me and you and everyone else to our imaginations to craft our own explanations. So, I try to piece together a construct based on what I can glean from what I read and see in the news because like most people I fortunately have no first-hand information about even a single case. The number of deaths is horrifying, but may not have hit close to home and given most of us a real personal sense of the illness and its character.
Maine is a small state with just over a million inhabitants, and most of us have some connection to one another. It may be that a person is the second cousin of someone who used to live 2 miles down the road. But, there is some feeling of familiarity. We have had deaths related to COVID-19, but very scanty information other than the county about where they occurred and whether the victim was a resident of an extended care facility. We are told very little if any details about exposure as officials invoke HIPAA regulations that leave us in the dark. Other than one vague reference to a “traveling salesman” who may have introduced the virus to several nursing homes, there has been very little information about how the virus may have been spread here in Maine. Even national reports of the deaths of high-profile entertainers and retired athletes are usually draped in the same haze of privacy.
Most of us don’t need to know the names and street addresses of the victims but a few anonymous narratives that include some general information on how epidemiologists believe clusters began and propagated would help us understand our risks with just a glimmer of clarity.
Of course the epidemiologists may not have the answers we are seeking because they too are struggling to untangle connections hampered by concerns of privacy. There is no question that privacy must remain an important part of the physician-patient relationship. But a pandemic has thrown us into a situation where common sense demands that HIPAA be interpreted with an emphasis on the greater good. Finding that balance between privacy and public knowledge will continue to be one of our greatest challenges.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Armchair epidemiology
Real epidemiologists are out knocking on doors, chasing down contacts, or hunched over their computers trying to make sense out of screens full of data and maps. A few are trying valiantly to talk some sense into our elected officials.
This leaves the rest of us with time on our hands to fabricate our own less-than-scientific explanations for the behavior of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. So I have decided to put on hold my current mental challenge of choosing which pasta shape to pair with the sauce I’ve prepared from an online recipe. Here is my educated guess based on what I can glean from media sources that may have been filtered through a variety politically biased lenses. Remember, I did go to medical school; however, when I was in college the DNA helix was still just theoretical.
From those halcyon days of mid-February when our attention was focused on the Diamond Princess quarantined in Yokohama Harbor, it didn’t take a board-certified epidemiologist to suspect that the virus was spreading through the ventilating system in the ship’s tight quarters. Subsequent outbreaks on U.S. and French military ships suggests a similar explanation.
While still not proven, it sounds like SARS-CoV-2 jumped to humans from bats. It should not surprise us that having evolved in a dense population of mammals it would thrive in other high-density populations such as New York and nursing homes. Because we have lacked a robust testing capability, it has been less obvious until recently that, while it is easily transmitted, the virus has infected many who are asymptomatic (“Antibody surveys suggesting vast undercount of coronavirus infections may be unreliable,” Gretchen Vogel, Science, April 21, 2020). Subsequent surveys seem to confirm this higher level carrier state; it suggests that the virus is far less deadly than was previously suggested. However, it seems to be a crafty little bug attacking just about any organ system it lands on.
I don’t think any of us are surprised that the elderly population with weakened immune systems, particularly those in congregate housing, has been much more vulnerable. However, many of the deaths among younger apparently healthy people have defied explanation. The anecdotal observations that physicians, particularly those who practice in-your-face medicine (e.g., ophthalmologists and otolaryngologists) may be more vulnerable raises the issue of viral load. It may be that, although it can be extremely contagious, the virus is not terribly dangerous for most people until the inoculum dose of the virus reaches a certain level. To my knowledge this dose is unknown.
A published survey of more than 300 outbreaks from 120 Chinese cities also may support my suspicion that viral load is of critical importance. The researchers found that all the “identified outbreaks of three or more cases occurred in an indoor environment, which confirms that sharing indoor space is a major SARS-CoV-2 infection risk” (Huan Qian et al. “Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2,” MedRxiv. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.04.20053058). Again, this data shouldn’t surprise us when we look back at what little we know about the outbreaks in the confined spaces on cruise ships and in nursing homes.
I’m not sure that we have any data that helps us determine whether wearing a mask in an outdoor space has any more than symbolic value when we are talking about this particular virus. We may read that the virus in a droplet can survive on the surface it lands on for 8 minutes, and we can see those slow motion videos of the impressive plume of snot spray released by a sneeze. It would seem obvious that even outside someone within 10 feet of the sneeze has a good chance of being infected. However, how much of a threat is the asymptomatic carrier who passes within three feet of you while you are out on lovely summer day stroll? This armchair epidemiologist suspects that, when we are talking about an outside space, the 6-foot guideline for small groups of a dozen or less is overly restrictive. But until we know, I’m staying put in my armchair ... outside on the porch overlooking Casco Bay.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” He has no disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Real epidemiologists are out knocking on doors, chasing down contacts, or hunched over their computers trying to make sense out of screens full of data and maps. A few are trying valiantly to talk some sense into our elected officials.
This leaves the rest of us with time on our hands to fabricate our own less-than-scientific explanations for the behavior of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. So I have decided to put on hold my current mental challenge of choosing which pasta shape to pair with the sauce I’ve prepared from an online recipe. Here is my educated guess based on what I can glean from media sources that may have been filtered through a variety politically biased lenses. Remember, I did go to medical school; however, when I was in college the DNA helix was still just theoretical.
From those halcyon days of mid-February when our attention was focused on the Diamond Princess quarantined in Yokohama Harbor, it didn’t take a board-certified epidemiologist to suspect that the virus was spreading through the ventilating system in the ship’s tight quarters. Subsequent outbreaks on U.S. and French military ships suggests a similar explanation.
While still not proven, it sounds like SARS-CoV-2 jumped to humans from bats. It should not surprise us that having evolved in a dense population of mammals it would thrive in other high-density populations such as New York and nursing homes. Because we have lacked a robust testing capability, it has been less obvious until recently that, while it is easily transmitted, the virus has infected many who are asymptomatic (“Antibody surveys suggesting vast undercount of coronavirus infections may be unreliable,” Gretchen Vogel, Science, April 21, 2020). Subsequent surveys seem to confirm this higher level carrier state; it suggests that the virus is far less deadly than was previously suggested. However, it seems to be a crafty little bug attacking just about any organ system it lands on.
I don’t think any of us are surprised that the elderly population with weakened immune systems, particularly those in congregate housing, has been much more vulnerable. However, many of the deaths among younger apparently healthy people have defied explanation. The anecdotal observations that physicians, particularly those who practice in-your-face medicine (e.g., ophthalmologists and otolaryngologists) may be more vulnerable raises the issue of viral load. It may be that, although it can be extremely contagious, the virus is not terribly dangerous for most people until the inoculum dose of the virus reaches a certain level. To my knowledge this dose is unknown.
A published survey of more than 300 outbreaks from 120 Chinese cities also may support my suspicion that viral load is of critical importance. The researchers found that all the “identified outbreaks of three or more cases occurred in an indoor environment, which confirms that sharing indoor space is a major SARS-CoV-2 infection risk” (Huan Qian et al. “Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2,” MedRxiv. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.04.20053058). Again, this data shouldn’t surprise us when we look back at what little we know about the outbreaks in the confined spaces on cruise ships and in nursing homes.
I’m not sure that we have any data that helps us determine whether wearing a mask in an outdoor space has any more than symbolic value when we are talking about this particular virus. We may read that the virus in a droplet can survive on the surface it lands on for 8 minutes, and we can see those slow motion videos of the impressive plume of snot spray released by a sneeze. It would seem obvious that even outside someone within 10 feet of the sneeze has a good chance of being infected. However, how much of a threat is the asymptomatic carrier who passes within three feet of you while you are out on lovely summer day stroll? This armchair epidemiologist suspects that, when we are talking about an outside space, the 6-foot guideline for small groups of a dozen or less is overly restrictive. But until we know, I’m staying put in my armchair ... outside on the porch overlooking Casco Bay.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” He has no disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Real epidemiologists are out knocking on doors, chasing down contacts, or hunched over their computers trying to make sense out of screens full of data and maps. A few are trying valiantly to talk some sense into our elected officials.
This leaves the rest of us with time on our hands to fabricate our own less-than-scientific explanations for the behavior of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. So I have decided to put on hold my current mental challenge of choosing which pasta shape to pair with the sauce I’ve prepared from an online recipe. Here is my educated guess based on what I can glean from media sources that may have been filtered through a variety politically biased lenses. Remember, I did go to medical school; however, when I was in college the DNA helix was still just theoretical.
From those halcyon days of mid-February when our attention was focused on the Diamond Princess quarantined in Yokohama Harbor, it didn’t take a board-certified epidemiologist to suspect that the virus was spreading through the ventilating system in the ship’s tight quarters. Subsequent outbreaks on U.S. and French military ships suggests a similar explanation.
While still not proven, it sounds like SARS-CoV-2 jumped to humans from bats. It should not surprise us that having evolved in a dense population of mammals it would thrive in other high-density populations such as New York and nursing homes. Because we have lacked a robust testing capability, it has been less obvious until recently that, while it is easily transmitted, the virus has infected many who are asymptomatic (“Antibody surveys suggesting vast undercount of coronavirus infections may be unreliable,” Gretchen Vogel, Science, April 21, 2020). Subsequent surveys seem to confirm this higher level carrier state; it suggests that the virus is far less deadly than was previously suggested. However, it seems to be a crafty little bug attacking just about any organ system it lands on.
I don’t think any of us are surprised that the elderly population with weakened immune systems, particularly those in congregate housing, has been much more vulnerable. However, many of the deaths among younger apparently healthy people have defied explanation. The anecdotal observations that physicians, particularly those who practice in-your-face medicine (e.g., ophthalmologists and otolaryngologists) may be more vulnerable raises the issue of viral load. It may be that, although it can be extremely contagious, the virus is not terribly dangerous for most people until the inoculum dose of the virus reaches a certain level. To my knowledge this dose is unknown.
A published survey of more than 300 outbreaks from 120 Chinese cities also may support my suspicion that viral load is of critical importance. The researchers found that all the “identified outbreaks of three or more cases occurred in an indoor environment, which confirms that sharing indoor space is a major SARS-CoV-2 infection risk” (Huan Qian et al. “Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2,” MedRxiv. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1101/2020.04.04.20053058). Again, this data shouldn’t surprise us when we look back at what little we know about the outbreaks in the confined spaces on cruise ships and in nursing homes.
I’m not sure that we have any data that helps us determine whether wearing a mask in an outdoor space has any more than symbolic value when we are talking about this particular virus. We may read that the virus in a droplet can survive on the surface it lands on for 8 minutes, and we can see those slow motion videos of the impressive plume of snot spray released by a sneeze. It would seem obvious that even outside someone within 10 feet of the sneeze has a good chance of being infected. However, how much of a threat is the asymptomatic carrier who passes within three feet of you while you are out on lovely summer day stroll? This armchair epidemiologist suspects that, when we are talking about an outside space, the 6-foot guideline for small groups of a dozen or less is overly restrictive. But until we know, I’m staying put in my armchair ... outside on the porch overlooking Casco Bay.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” He has no disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.