User login
Official news magazine of the Society of Hospital Medicine
Copyright by Society of Hospital Medicine or related companies. All rights reserved. ISSN 1553-085X
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-hospitalist')]


Opioid prescribing mapped: Alabama highest, New York lowest
Medicare beneficiaries in Alabama were more likely to get a prescription for an opioid than in any other state in 2019, based on newly released data.
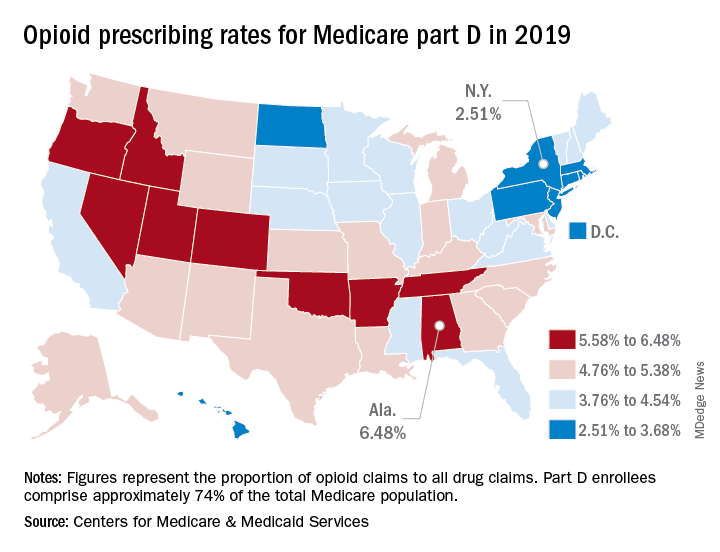
That year, opioids represented 6.48% of all drug claims for part D enrollees in the state, just ahead of Utah at 6.41%. Idaho, at 6.07%, was the only other state with an opioid prescribing rate over 6%, while Oklahoma came in at an even 6.0%, according to the latest update of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ dataset.
The lowest rate in 2019 belonged to New York, where 2.51% of drug claims, including original prescriptions and refills, involved an opioid. Rhode Island was next at 2.87%, followed by New Jersey (3.23%), Massachusetts (3.26%), and North Dakota (3.39%),
Altogether, Medicare part D processed 1.5 billion drug claims in 2019, of which 66.1 million, or 4.41%, involved opioids. Both of the opioid numbers were down from 2018, when opioids represented 4.68% (70.2 million) of the 1.5 billion total claims, and from 2014, when opioids were involved in 5.73% (81,026,831) of the 1.41 billion drug claims, the CMS data show. That works out to 5.77% fewer opioids in 2019, compared with 2014, despite the increase in total volume.
from 2014 to 2019, with Hawaii showing the smallest decline as it slipped 0.41 percentage points from 3.9% to 3.49%, according to the CMS.
In 2019, part D beneficiaries in Vermont were the most likely to receive a long-acting opioid, which accounted for 20.14% of all opioid prescriptions in the state, while Kentucky had the lowest share of prescriptions written for long-acting forms at 6.41%. The national average was 11.02%, dropping from 11.79% in 2018 and 12.75% in 2014, the CMS reported.
Medicare beneficiaries in Alabama were more likely to get a prescription for an opioid than in any other state in 2019, based on newly released data.

That year, opioids represented 6.48% of all drug claims for part D enrollees in the state, just ahead of Utah at 6.41%. Idaho, at 6.07%, was the only other state with an opioid prescribing rate over 6%, while Oklahoma came in at an even 6.0%, according to the latest update of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ dataset.
The lowest rate in 2019 belonged to New York, where 2.51% of drug claims, including original prescriptions and refills, involved an opioid. Rhode Island was next at 2.87%, followed by New Jersey (3.23%), Massachusetts (3.26%), and North Dakota (3.39%),
Altogether, Medicare part D processed 1.5 billion drug claims in 2019, of which 66.1 million, or 4.41%, involved opioids. Both of the opioid numbers were down from 2018, when opioids represented 4.68% (70.2 million) of the 1.5 billion total claims, and from 2014, when opioids were involved in 5.73% (81,026,831) of the 1.41 billion drug claims, the CMS data show. That works out to 5.77% fewer opioids in 2019, compared with 2014, despite the increase in total volume.
from 2014 to 2019, with Hawaii showing the smallest decline as it slipped 0.41 percentage points from 3.9% to 3.49%, according to the CMS.
In 2019, part D beneficiaries in Vermont were the most likely to receive a long-acting opioid, which accounted for 20.14% of all opioid prescriptions in the state, while Kentucky had the lowest share of prescriptions written for long-acting forms at 6.41%. The national average was 11.02%, dropping from 11.79% in 2018 and 12.75% in 2014, the CMS reported.
Medicare beneficiaries in Alabama were more likely to get a prescription for an opioid than in any other state in 2019, based on newly released data.

That year, opioids represented 6.48% of all drug claims for part D enrollees in the state, just ahead of Utah at 6.41%. Idaho, at 6.07%, was the only other state with an opioid prescribing rate over 6%, while Oklahoma came in at an even 6.0%, according to the latest update of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ dataset.
The lowest rate in 2019 belonged to New York, where 2.51% of drug claims, including original prescriptions and refills, involved an opioid. Rhode Island was next at 2.87%, followed by New Jersey (3.23%), Massachusetts (3.26%), and North Dakota (3.39%),
Altogether, Medicare part D processed 1.5 billion drug claims in 2019, of which 66.1 million, or 4.41%, involved opioids. Both of the opioid numbers were down from 2018, when opioids represented 4.68% (70.2 million) of the 1.5 billion total claims, and from 2014, when opioids were involved in 5.73% (81,026,831) of the 1.41 billion drug claims, the CMS data show. That works out to 5.77% fewer opioids in 2019, compared with 2014, despite the increase in total volume.
from 2014 to 2019, with Hawaii showing the smallest decline as it slipped 0.41 percentage points from 3.9% to 3.49%, according to the CMS.
In 2019, part D beneficiaries in Vermont were the most likely to receive a long-acting opioid, which accounted for 20.14% of all opioid prescriptions in the state, while Kentucky had the lowest share of prescriptions written for long-acting forms at 6.41%. The national average was 11.02%, dropping from 11.79% in 2018 and 12.75% in 2014, the CMS reported.
Antibody cocktail reduces chance of developing COVID
A one-time dose of two long-acting monoclonal antibodies reduced the risk of developing symptomatic COVID by 77% in comparison with placebo (P < .001) in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in adults, according to researchers who presented results at IDWeek 2021, an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The mix of tixagevimab and cilgavimab (AZD7442, Astra Zeneca) in a 300-mg dose is delivered in two intramuscular injections.
“This is the first long-acting combination of monoclonal antibodies that represents a potential new option to augment COVID-19 prevention,” said lead author Myron J. Levin, MD, a professor and pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who presented the findings of the PROVENT trial.
Both antibodies were taken from B cells donated by patients who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2, and they work synergistically, Dr. Levin said.
“The combination of them is better than adding results of each individually,” he said. “In vitro experiments have already shown that variants of interest and concern, including the Delta variant, are successfully neutralized by this cocktail.”
The trial was conducted in 87 sites in the United States, the United Kingdom, Spain, France, and Belgium. Participants included 5,197 unvaccinated adults who had never been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and either were at higher risk for inadequate response to COVID-19 vaccines because they were immunocompromised or were at high risk for exposure.
“Efficacy was observed through at least 3 months,” Dr. Levin said. “Preliminary pharmacokinetic modeling predicts potential protection for up to 12 months.”
Raymund Razonable, MD, an infectious disease expert with the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., who was not involved with the trial, told this news organization he was particularly interested in this combination because the developers made use of novel technology that extends the half-life of the antibodies and because of the large number of participants in the study.
Modeling that shows protection could last up to a year is novel and important, he said.
“People won’t need frequent injections,” Dr. Razonable said. With postexposure prophylaxis monoclonal cocktails, people may be given a dose a month, he noted.
Dr. Razonable said, “This is something intended to prevent COVID in people who are unvaccinated. The downside to that is we want people to get vaccinated. The best strategy so far is really vaccination.”
He said AZD7442 could potentially help fill the void for patients who are not able to respond to the COVID vaccines, including some who are immunocompromised or are undergoing chemotherapy.
Dr. Razonable said that, although the 77% reduction for developing symptomatic COVID-19 (95% confidence interval vs. placebo, 46.0-90.0; P < .001) is impressive, it is a reduction in relative risk. Still unknown is how much an individual’s absolute risk is reduced.
He also said it would be helpful to know how many people in the study population were immunocompromised, “because I think that’s where this product will be useful for prevention.”
The primary study endpoints were the first case of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR-positive symptomatic illness post dose and prior to day 183 (efficacy) as well as the safety of the product.
The cocktail appeared to be well tolerated. Adverse events occurred in 35% of participants administered AZD7442 and in 34% of the placebo group. Injection-site reactions occurred in 2.4% of the AZD7442 group and in 2.1% of the placebo group. There was one case of severe or critical COVID-19; two COVID-19–related deaths occurred in the placebo group.
AZD7442 is being developed with the help of funding from the U.S. government. Dr. Levin has received support from GlaxoSmithKline companies. Many of the coauthors are employed by AstraZeneca and hold stock in the company. Dr. Razonable has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A one-time dose of two long-acting monoclonal antibodies reduced the risk of developing symptomatic COVID by 77% in comparison with placebo (P < .001) in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in adults, according to researchers who presented results at IDWeek 2021, an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The mix of tixagevimab and cilgavimab (AZD7442, Astra Zeneca) in a 300-mg dose is delivered in two intramuscular injections.
“This is the first long-acting combination of monoclonal antibodies that represents a potential new option to augment COVID-19 prevention,” said lead author Myron J. Levin, MD, a professor and pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who presented the findings of the PROVENT trial.
Both antibodies were taken from B cells donated by patients who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2, and they work synergistically, Dr. Levin said.
“The combination of them is better than adding results of each individually,” he said. “In vitro experiments have already shown that variants of interest and concern, including the Delta variant, are successfully neutralized by this cocktail.”
The trial was conducted in 87 sites in the United States, the United Kingdom, Spain, France, and Belgium. Participants included 5,197 unvaccinated adults who had never been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and either were at higher risk for inadequate response to COVID-19 vaccines because they were immunocompromised or were at high risk for exposure.
“Efficacy was observed through at least 3 months,” Dr. Levin said. “Preliminary pharmacokinetic modeling predicts potential protection for up to 12 months.”
Raymund Razonable, MD, an infectious disease expert with the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., who was not involved with the trial, told this news organization he was particularly interested in this combination because the developers made use of novel technology that extends the half-life of the antibodies and because of the large number of participants in the study.
Modeling that shows protection could last up to a year is novel and important, he said.
“People won’t need frequent injections,” Dr. Razonable said. With postexposure prophylaxis monoclonal cocktails, people may be given a dose a month, he noted.
Dr. Razonable said, “This is something intended to prevent COVID in people who are unvaccinated. The downside to that is we want people to get vaccinated. The best strategy so far is really vaccination.”
He said AZD7442 could potentially help fill the void for patients who are not able to respond to the COVID vaccines, including some who are immunocompromised or are undergoing chemotherapy.
Dr. Razonable said that, although the 77% reduction for developing symptomatic COVID-19 (95% confidence interval vs. placebo, 46.0-90.0; P < .001) is impressive, it is a reduction in relative risk. Still unknown is how much an individual’s absolute risk is reduced.
He also said it would be helpful to know how many people in the study population were immunocompromised, “because I think that’s where this product will be useful for prevention.”
The primary study endpoints were the first case of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR-positive symptomatic illness post dose and prior to day 183 (efficacy) as well as the safety of the product.
The cocktail appeared to be well tolerated. Adverse events occurred in 35% of participants administered AZD7442 and in 34% of the placebo group. Injection-site reactions occurred in 2.4% of the AZD7442 group and in 2.1% of the placebo group. There was one case of severe or critical COVID-19; two COVID-19–related deaths occurred in the placebo group.
AZD7442 is being developed with the help of funding from the U.S. government. Dr. Levin has received support from GlaxoSmithKline companies. Many of the coauthors are employed by AstraZeneca and hold stock in the company. Dr. Razonable has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A one-time dose of two long-acting monoclonal antibodies reduced the risk of developing symptomatic COVID by 77% in comparison with placebo (P < .001) in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in adults, according to researchers who presented results at IDWeek 2021, an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
The mix of tixagevimab and cilgavimab (AZD7442, Astra Zeneca) in a 300-mg dose is delivered in two intramuscular injections.
“This is the first long-acting combination of monoclonal antibodies that represents a potential new option to augment COVID-19 prevention,” said lead author Myron J. Levin, MD, a professor and pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who presented the findings of the PROVENT trial.
Both antibodies were taken from B cells donated by patients who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2, and they work synergistically, Dr. Levin said.
“The combination of them is better than adding results of each individually,” he said. “In vitro experiments have already shown that variants of interest and concern, including the Delta variant, are successfully neutralized by this cocktail.”
The trial was conducted in 87 sites in the United States, the United Kingdom, Spain, France, and Belgium. Participants included 5,197 unvaccinated adults who had never been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and either were at higher risk for inadequate response to COVID-19 vaccines because they were immunocompromised or were at high risk for exposure.
“Efficacy was observed through at least 3 months,” Dr. Levin said. “Preliminary pharmacokinetic modeling predicts potential protection for up to 12 months.”
Raymund Razonable, MD, an infectious disease expert with the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., who was not involved with the trial, told this news organization he was particularly interested in this combination because the developers made use of novel technology that extends the half-life of the antibodies and because of the large number of participants in the study.
Modeling that shows protection could last up to a year is novel and important, he said.
“People won’t need frequent injections,” Dr. Razonable said. With postexposure prophylaxis monoclonal cocktails, people may be given a dose a month, he noted.
Dr. Razonable said, “This is something intended to prevent COVID in people who are unvaccinated. The downside to that is we want people to get vaccinated. The best strategy so far is really vaccination.”
He said AZD7442 could potentially help fill the void for patients who are not able to respond to the COVID vaccines, including some who are immunocompromised or are undergoing chemotherapy.
Dr. Razonable said that, although the 77% reduction for developing symptomatic COVID-19 (95% confidence interval vs. placebo, 46.0-90.0; P < .001) is impressive, it is a reduction in relative risk. Still unknown is how much an individual’s absolute risk is reduced.
He also said it would be helpful to know how many people in the study population were immunocompromised, “because I think that’s where this product will be useful for prevention.”
The primary study endpoints were the first case of SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR-positive symptomatic illness post dose and prior to day 183 (efficacy) as well as the safety of the product.
The cocktail appeared to be well tolerated. Adverse events occurred in 35% of participants administered AZD7442 and in 34% of the placebo group. Injection-site reactions occurred in 2.4% of the AZD7442 group and in 2.1% of the placebo group. There was one case of severe or critical COVID-19; two COVID-19–related deaths occurred in the placebo group.
AZD7442 is being developed with the help of funding from the U.S. government. Dr. Levin has received support from GlaxoSmithKline companies. Many of the coauthors are employed by AstraZeneca and hold stock in the company. Dr. Razonable has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccine controversies: How can hospitalists help?
On April 1, Houston Methodist Hospital in Houston, Texas, announced a new policy that all of its staff would need to be vaccinated against COVID-19 by June 7 in order to hold onto their jobs. Most responded positively but an estimated 150 staff members who did not comply either resigned or were terminated. A lawsuit by employees opposed to the vaccine mandate was dismissed by Federal District Court Judge Lynn Hughes in June, although a subsequent lawsuit was filed Aug. 16.
Vaccines have been shown to dramatically reduce both the incidence and the severity of COVID infections. Vaccinations of health care workers, especially those who have direct contact with patients, are demonstrated to be effective strategies to significantly reduce, although not eliminate, the possibility of viral transmissions to patients – or to health care workers themselves – thus saving lives.
Hospitalists, in their central role in the care of hospitalized patients, and often with primary responsibility for managing their hospital’s COVID-19 caseloads, may find themselves encountering conversations about the vaccine, its safety, effectiveness, and mandates with their peers, other hospital staff, patients, and families, and their communities. They can play key roles in advocating for the vaccine, answering questions, clarifying the science, and dispelling misinformation – for those who are willing to listen.
Becker’s Hospital Review, which has kept an ongoing tally of announced vaccine mandate policies in hospitals, health systems, and health departments nationwide, reported on Aug. 13 that 1,850 or 30% of U.S. hospitals, had announced vaccine mandates.1 Often exceptions can be made, such as for medical or religious reasons, or with other declarations or opt-out provisions. But in many settings, mandating COVID vaccinations won’t be easy.
Amith Skandhan, MD, SFHM, FACP, a hospitalist at Southeast Health Medical Center in Dothan, Ala., and a core faculty member in the internal medicine residency program at Alabama College of Osteopathic Medicine, said that implementing vaccine mandates will be more difficult in smaller health systems, in rural communities, and in states with lower vaccination rates and greater vaccine controversy.
Alabama has the lowest vaccination rates in the country, reflected in the recent rise in COVID cases and hospitalizations, even higher than during the surge of late 2020, Dr. Skandhan said. “In June we had one COVID patient in this hospital.” By late August the number was 119 COVID patients and climbing.
But where he works, in a health system where staffing is already spread thin, a vaccine mandate would be challenging. “What if our staff started leaving? It’s only 10 minutes from here to the Florida or Georgia border,” Dr. Skandhan said. Health care workers opposed to vaccinations would have the option of easily seeking work elsewhere.
When contacted for this article, he had been off work for several days but was mentally preparing himself to go back. “I’m not even following the [COVID-19] numbers but I am prepared for the worst. I know it will be mostly COVID. People just don’t realize what goes into this work.”
Dr. Skandhan, who said he was the third or fourth person in Alabama to receive the COVID vaccine, often finds himself feeling frustrated and angry – in the midst of a surge in cases that could have been prevented – that such a beneficial medical advance for bringing the pandemic under control became so politicized. “It is imperative that we find out why this mistrust exists and work to address it. It has to be done.”
Protecting health care professionals
On July 26, the Society of Hospital Medicine joined 50 other health care organizations including the American Medical Association, American Nurses Association, and American Academy of Pediatrics in advocating for all health care employers to require their employees to be vaccinated against COVID, in order to protect the safety of all patients and residents of health care facilities.2
“As an organization, we support vaccinating health care workers, including hospitalists, to help stop the spread of COVID-19 and the increasingly dominant Delta variant,” said SHM’s chief executive officer Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, in a prepared statement. “We aim to uphold the highest standards among hospitalists and other health care providers to help protect our fellow health care professionals, our patients, and our communities.”
To that end, Dr. Skandhan has started conversations with hospital staff who he knows are not vaccinated. “For some, we’re not able to have a civil conversation, but in most cases I can help to persuade people.” The reasons people give for not getting vaccinated are not based in science, he said. “I am worried about the safety of our hospitalists and staff nurses.” But unvaccinated frontline workers are also putting their patients at risk. “Can we say why they’re hesitating? Can we have an honest discourse? If we can’t do that with our colleagues, how can we blame the patients?”
Dr. Skandhan encourages hospitalists to start simply in their own hospitals, trying to influence their own departments and colleagues. “If you can convince one or two more every week, you can start a chain reaction. Have that conversation. Use your trust.” For some hospitalized patients, the vaccination conversation comes too late, after their infection, but even some of them might consider obtaining it down the road or trying to persuade family members to get vaccinated.
Adult hospitalists, however, may not have received training in how to effectively address vaccine fears and misconceptions among their patients, he said. Because the patients they see in the hospital are already very sick, they don’t get a lot of practice talking about vaccines except, perhaps, for the influenza vaccine.
Pediatric hospitalists have more experience with such conversations involving their patients’ parents, Dr. Skandhan said. “It comes more naturally to them. We need to learn quickly from them about how to talk about vaccines with our patients.”
Pediatric training and experience
Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, FAAP, a pediatric hospitalist at the Cleveland Clinic and the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist, agrees that pediatricians and pediatric hospitalists often have received more training in how to lead vaccination conversations. She often talks about vaccines with the parents of hospitalized children relative to chicken pox, measles, and other diseases of childhood.
Pediatric hospitalists may also ask to administer the hepatitis B vaccine to newborn babies, along with other preventive treatments such as eye drops and vitamin K shots. “I often encourage the influenza vaccine prior to the patient’s hospital discharge, especially for kids with chronic conditions, asthma, diabetes, or premature birth. We talk about how the influenza vaccine isn’t perfect, but it helps to prevent more serious disease,” she said.
“A lot of vaccine hesitancy comes from misunderstandings about the role of vaccines,” she said. People forget that for years children have been getting vaccines before starting school. “Misinformation and opinions about vaccines have existed for decades. What’s new today is the abundance of sources for obtaining these opinions. My job is to inform families of scientific facts and to address their concerns.”
It has become more common recently for parents to say they don’t want their kids to get vaccinated, Dr. Kumar said. Another group is better described as vaccine hesitant and just needs more information. “I may not, by the time they leave the hospital, convince them to allow me to administer the vaccine. But in the discharge summary, I document that I had this conversation. I’ve done my due diligence and tried to start a larger dialogue. I say: ‘I encourage you to continue this discussion with the pediatrician you trust.’ I also communicate with the outpatient team,” she said.
“But it’s our responsibility, because we’re the ones seeing these patients, to do whatever we can to keep our patients from getting sick. A lot of challenging conversations we have with families are just trying to find out where they’re at with the issue – which can lead to productive dialogue.”
Ariel Carpenter, MD, a 4th-year resident in internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Louisville (Ky.), and a future pediatric hospitalist, agreed that her combined training in med-peds has been helpful preparation for the vaccine conversation. That training has included techniques of motivational interviewing. In pediatrics, she explained, the communication is a little softer. “I try to approach my patients in a family-centered way.”
Dr. Carpenter recently wrote a personal essay for Louisville Medicine magazine from the perspective of growing up homeschooled by a mother who didn’t believe in vaccines.3 As a teenager, she independently obtained the complete childhood vaccine series so that she could do medical shadowing and volunteering. In medical school she became a passionate vaccine advocate, eventually persuading her mother to change her mind on the subject in time for the COVID vaccine.
“There’s not one answer to the vaccination dilemma,” she said. “Different approaches are required because there are so many different reasons for it. Based on my own life experience, I try to approach patients where they are – not from a place of data and science. What worked in my own family, and works with my patients, is first to establish trust. If they trust you, they’re more likely to listen. Simply ask their worries and concerns,” Dr. Carpenter said.
“A lot of them haven’t had the opportunity before to sit down with a physician they trust and have their worries listened to. They don’t feel heard in our medical system. So I remind myself that I need to understand my patients first – before inserting myself into the conversation.”
Many patients she sees are in an information bubble, with a very different understanding of the issue than their doctors. “A lot of well-meaning people feel they are making the safer choice. Very few truly don’t care about protecting others. But they don’t feel the urgency about that and see the vaccine as the scarier option right now.”
Frontline vaccine advocates
Hospitalists are the frontline advocates within their hospital system, in a position to lead, so they need to make vaccines a priority, Dr. Carpenter said. They should also make sure that their hospitals have ready access to the vaccine, so patients who agree to receive it are able to get it quickly. “In our hospital they can get the shot within a few hours if the opportunity arises. We stocked the Johnson & Johnson vaccine so that they wouldn’t have to connect with another health care provider in order to get a second dose.”
Hospitals should also invest in access to vaccine counseling training and personnel. “Fund a nurse clinician who can screen and counsel hospitalized patients for vaccination. If they meet resistance, they can then refer to the dedicated physician of the day to have the conversation,” she said. “But if we don’t mention it, patients will assume we don’t feel strongly about it.”
Because hospitalists are front and center in treating COVID, they need to be the experts and the people offering guidance, said Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, FAAFP, section chief for hospital medicine at the Carilion Clinic in Roanoke, Va. “What we’re trying to do is spread awareness. We educated physician groups, learners, and clinical teams during the initial phase, and now mostly patients and their families.” COVID vaccine reluctance is hard to overcome, Dr. Odeti said. People feel the vaccine was developed very quickly. But there are different ways to present it.
“Like most doctors, I thought people would jump on a vaccine to get past the pandemic. I was surprised and then disappointed. Right now, the pandemic is among the unvaccinated. So we face these encounters, and we’re doing our best to overcome the misinformation. My organization is 100% supportive. We talk about these issues every day.”
Carilion, effective Oct. 1, has required unvaccinated employees to get weekly COVID tests and wear an N95 mask while working, and has developed Facebook pages, other social media, and an Internet presence to address these issues. “We’ve gone to the local African-American community with physician leaders active in that community. We had a Spanish language roundtable,” Dr. Odeti said.
Dr. Skandhan reported that the Wiregrass regional chapter of SHM recently organized a successful statewide community educational event aimed at empowering community leaders to address vaccine misinformation and mistrust. “We surveyed religious leaders and pastors regarding the causes of vaccine hesitancy and reached out to physicians active in community awareness.” Based on that input, a presentation by the faith leaders was developed. Legislators from the Alabama State Senate’s Healthcare Policy Committee were also invited to the presentation and discussion.
Trying to stay positive
It’s important to try to stay positive, Dr. Odeti said. “We have to be empathetic with every patient. We have to keep working at this, since there’s no way out of the pandemic except through vaccinations. But it all creates stress for hospitalists. Our job is made significantly more difficult by the vaccine controversy.”
Jennifer Cowart, MD, a hospitalist at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., has been outspoken in her community about vaccination and masking issues, talking to reporters, attending rallies and press conferences, posting on social media, and speaking in favor of mask policies at a local school board meeting. She is part of an informal local group called Doctors Fighting COVID, which meets online to strategize how to share its expertise, including writing a recent letter about masks to Jacksonville’s mayor.
“In July, when we saw the Delta variant surging locally, we held a webinar via local media, taking calls about the vaccine from the community. I’m trying not to make this a political issue, but we are health officials.” Dr. Cowart said she also tries not to raise her voice when speaking with vaccine opponents and tries to remain empathetic. “Even though inwardly I’m screaming, I try to stay calm. The misinformation is real. People are afraid and feeling pressure. I do my best, but I’m human, too.”
Hospitalists need to pull whatever levers they can to help advance understanding of vaccines, Dr. Cowart said. “In the hospital, our biggest issue is time. We often don’t have it, with a long list of patients to see. But every patient encounter is an opportunity to talk to patients, whether they have COVID or something else.” Sometimes, she might go back to a patient’s room after rounds to resume the conversation.
Hospital nurses have been trained and entrusted to do tobacco abatement counseling, she said, so why not mobilize them for vaccine education? “Or respiratory therapists, who do inhaler training, could talk about what it’s like to care for COVID patients. There’s a whole bunch of staff in the hospital who could be mobilized,” she said.
“I feel passionate about vaccines, as a hospitalist, as a medical educator, as a daughter, as a responsible member of society,” said Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, SFHM, MACP, director of continuing medical education at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “I see this as a personal and societal responsibility. When I speak about the vaccine among groups of doctors, I say we need to stay in our lane regarding our skills at interpreting the science and not undermining it.”
Some health care worker hesitancy is from distrust of pharmaceutical companies, or of federal agencies, she said. “Our research has highlighted to me the widespread inequity issues in our health care system. We should also take a long, hard look at how we teach the scientific method to health professionals. That will be part of a pandemic retrospective.”
Sometimes with people who are vaccine deliberative, whether health care workers or patients, there is a small window of opportunity. “We need to hear people and respond to them as people. Then, if they are willing to get vaccinated, we need to accomplish that as quickly and easily as possible,” Dr. Barrett said. “I see them make a face and say, ‘Well, okay, I’ll do it.’ We need to get the vaccine to them that same day. We should be able to accomplish that.”
References
1. Gamble M. 30% of US hospitals mandate vaccination for employment. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2021 Aug 13. www.beckershospitalreview.com/workforce/covid-19-vaccination-needed-to-work-at-30-of-us-hospitals.html .
2. Society of Hospital Medicine signs on to joint statement in support of health worker COVID-19 vaccine mandates. Press release. 2021 Jul 26. www.hospitalmedicine.org/news-publications/press-releases/society-of-hospital-medicine-signs-on-to-joint-statement-of-support-of-health-worker-covid-19-vaccine-mandates/.
3. Carpenter A. A physician’s lessons from an unvaccinated childhood. Louisville Medicine. 2021 July;69(2):26-7. https://viewer.joomag.com/louisville-medicine-volume-69-issue-2/0045988001624974172?short&.
Lessons for hospitalists from the vaccination controversy
1. Remain up-to-date on information about the COVID infection, its treatment, and vaccination efficacy data.
2. Hospitalists should take advantage of their positions to lead conversations in their facilities about the importance of COVID vaccinations.
3. Other professionals in the hospital, with some additional training and support, could take on the role of providing vaccine education and support – with a physician to back them up on difficult cases.
4. It’s important to listen to people’s concerns, try to build trust, and establish dialogue before starting to convey a lot of information. People need to feel heard.
5. If you are successful in persuading someone to take the vaccine, a shot should be promptly and easily accessible to them.
6. Pediatric hospitalists may have more experience and skill with vaccine discussions, which they should share with their peers who treat adults.
On April 1, Houston Methodist Hospital in Houston, Texas, announced a new policy that all of its staff would need to be vaccinated against COVID-19 by June 7 in order to hold onto their jobs. Most responded positively but an estimated 150 staff members who did not comply either resigned or were terminated. A lawsuit by employees opposed to the vaccine mandate was dismissed by Federal District Court Judge Lynn Hughes in June, although a subsequent lawsuit was filed Aug. 16.
Vaccines have been shown to dramatically reduce both the incidence and the severity of COVID infections. Vaccinations of health care workers, especially those who have direct contact with patients, are demonstrated to be effective strategies to significantly reduce, although not eliminate, the possibility of viral transmissions to patients – or to health care workers themselves – thus saving lives.
Hospitalists, in their central role in the care of hospitalized patients, and often with primary responsibility for managing their hospital’s COVID-19 caseloads, may find themselves encountering conversations about the vaccine, its safety, effectiveness, and mandates with their peers, other hospital staff, patients, and families, and their communities. They can play key roles in advocating for the vaccine, answering questions, clarifying the science, and dispelling misinformation – for those who are willing to listen.
Becker’s Hospital Review, which has kept an ongoing tally of announced vaccine mandate policies in hospitals, health systems, and health departments nationwide, reported on Aug. 13 that 1,850 or 30% of U.S. hospitals, had announced vaccine mandates.1 Often exceptions can be made, such as for medical or religious reasons, or with other declarations or opt-out provisions. But in many settings, mandating COVID vaccinations won’t be easy.
Amith Skandhan, MD, SFHM, FACP, a hospitalist at Southeast Health Medical Center in Dothan, Ala., and a core faculty member in the internal medicine residency program at Alabama College of Osteopathic Medicine, said that implementing vaccine mandates will be more difficult in smaller health systems, in rural communities, and in states with lower vaccination rates and greater vaccine controversy.
Alabama has the lowest vaccination rates in the country, reflected in the recent rise in COVID cases and hospitalizations, even higher than during the surge of late 2020, Dr. Skandhan said. “In June we had one COVID patient in this hospital.” By late August the number was 119 COVID patients and climbing.
But where he works, in a health system where staffing is already spread thin, a vaccine mandate would be challenging. “What if our staff started leaving? It’s only 10 minutes from here to the Florida or Georgia border,” Dr. Skandhan said. Health care workers opposed to vaccinations would have the option of easily seeking work elsewhere.
When contacted for this article, he had been off work for several days but was mentally preparing himself to go back. “I’m not even following the [COVID-19] numbers but I am prepared for the worst. I know it will be mostly COVID. People just don’t realize what goes into this work.”
Dr. Skandhan, who said he was the third or fourth person in Alabama to receive the COVID vaccine, often finds himself feeling frustrated and angry – in the midst of a surge in cases that could have been prevented – that such a beneficial medical advance for bringing the pandemic under control became so politicized. “It is imperative that we find out why this mistrust exists and work to address it. It has to be done.”
Protecting health care professionals
On July 26, the Society of Hospital Medicine joined 50 other health care organizations including the American Medical Association, American Nurses Association, and American Academy of Pediatrics in advocating for all health care employers to require their employees to be vaccinated against COVID, in order to protect the safety of all patients and residents of health care facilities.2
“As an organization, we support vaccinating health care workers, including hospitalists, to help stop the spread of COVID-19 and the increasingly dominant Delta variant,” said SHM’s chief executive officer Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, in a prepared statement. “We aim to uphold the highest standards among hospitalists and other health care providers to help protect our fellow health care professionals, our patients, and our communities.”
To that end, Dr. Skandhan has started conversations with hospital staff who he knows are not vaccinated. “For some, we’re not able to have a civil conversation, but in most cases I can help to persuade people.” The reasons people give for not getting vaccinated are not based in science, he said. “I am worried about the safety of our hospitalists and staff nurses.” But unvaccinated frontline workers are also putting their patients at risk. “Can we say why they’re hesitating? Can we have an honest discourse? If we can’t do that with our colleagues, how can we blame the patients?”
Dr. Skandhan encourages hospitalists to start simply in their own hospitals, trying to influence their own departments and colleagues. “If you can convince one or two more every week, you can start a chain reaction. Have that conversation. Use your trust.” For some hospitalized patients, the vaccination conversation comes too late, after their infection, but even some of them might consider obtaining it down the road or trying to persuade family members to get vaccinated.
Adult hospitalists, however, may not have received training in how to effectively address vaccine fears and misconceptions among their patients, he said. Because the patients they see in the hospital are already very sick, they don’t get a lot of practice talking about vaccines except, perhaps, for the influenza vaccine.
Pediatric hospitalists have more experience with such conversations involving their patients’ parents, Dr. Skandhan said. “It comes more naturally to them. We need to learn quickly from them about how to talk about vaccines with our patients.”
Pediatric training and experience
Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, FAAP, a pediatric hospitalist at the Cleveland Clinic and the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist, agrees that pediatricians and pediatric hospitalists often have received more training in how to lead vaccination conversations. She often talks about vaccines with the parents of hospitalized children relative to chicken pox, measles, and other diseases of childhood.
Pediatric hospitalists may also ask to administer the hepatitis B vaccine to newborn babies, along with other preventive treatments such as eye drops and vitamin K shots. “I often encourage the influenza vaccine prior to the patient’s hospital discharge, especially for kids with chronic conditions, asthma, diabetes, or premature birth. We talk about how the influenza vaccine isn’t perfect, but it helps to prevent more serious disease,” she said.
“A lot of vaccine hesitancy comes from misunderstandings about the role of vaccines,” she said. People forget that for years children have been getting vaccines before starting school. “Misinformation and opinions about vaccines have existed for decades. What’s new today is the abundance of sources for obtaining these opinions. My job is to inform families of scientific facts and to address their concerns.”
It has become more common recently for parents to say they don’t want their kids to get vaccinated, Dr. Kumar said. Another group is better described as vaccine hesitant and just needs more information. “I may not, by the time they leave the hospital, convince them to allow me to administer the vaccine. But in the discharge summary, I document that I had this conversation. I’ve done my due diligence and tried to start a larger dialogue. I say: ‘I encourage you to continue this discussion with the pediatrician you trust.’ I also communicate with the outpatient team,” she said.
“But it’s our responsibility, because we’re the ones seeing these patients, to do whatever we can to keep our patients from getting sick. A lot of challenging conversations we have with families are just trying to find out where they’re at with the issue – which can lead to productive dialogue.”
Ariel Carpenter, MD, a 4th-year resident in internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Louisville (Ky.), and a future pediatric hospitalist, agreed that her combined training in med-peds has been helpful preparation for the vaccine conversation. That training has included techniques of motivational interviewing. In pediatrics, she explained, the communication is a little softer. “I try to approach my patients in a family-centered way.”
Dr. Carpenter recently wrote a personal essay for Louisville Medicine magazine from the perspective of growing up homeschooled by a mother who didn’t believe in vaccines.3 As a teenager, she independently obtained the complete childhood vaccine series so that she could do medical shadowing and volunteering. In medical school she became a passionate vaccine advocate, eventually persuading her mother to change her mind on the subject in time for the COVID vaccine.
“There’s not one answer to the vaccination dilemma,” she said. “Different approaches are required because there are so many different reasons for it. Based on my own life experience, I try to approach patients where they are – not from a place of data and science. What worked in my own family, and works with my patients, is first to establish trust. If they trust you, they’re more likely to listen. Simply ask their worries and concerns,” Dr. Carpenter said.
“A lot of them haven’t had the opportunity before to sit down with a physician they trust and have their worries listened to. They don’t feel heard in our medical system. So I remind myself that I need to understand my patients first – before inserting myself into the conversation.”
Many patients she sees are in an information bubble, with a very different understanding of the issue than their doctors. “A lot of well-meaning people feel they are making the safer choice. Very few truly don’t care about protecting others. But they don’t feel the urgency about that and see the vaccine as the scarier option right now.”
Frontline vaccine advocates
Hospitalists are the frontline advocates within their hospital system, in a position to lead, so they need to make vaccines a priority, Dr. Carpenter said. They should also make sure that their hospitals have ready access to the vaccine, so patients who agree to receive it are able to get it quickly. “In our hospital they can get the shot within a few hours if the opportunity arises. We stocked the Johnson & Johnson vaccine so that they wouldn’t have to connect with another health care provider in order to get a second dose.”
Hospitals should also invest in access to vaccine counseling training and personnel. “Fund a nurse clinician who can screen and counsel hospitalized patients for vaccination. If they meet resistance, they can then refer to the dedicated physician of the day to have the conversation,” she said. “But if we don’t mention it, patients will assume we don’t feel strongly about it.”
Because hospitalists are front and center in treating COVID, they need to be the experts and the people offering guidance, said Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, FAAFP, section chief for hospital medicine at the Carilion Clinic in Roanoke, Va. “What we’re trying to do is spread awareness. We educated physician groups, learners, and clinical teams during the initial phase, and now mostly patients and their families.” COVID vaccine reluctance is hard to overcome, Dr. Odeti said. People feel the vaccine was developed very quickly. But there are different ways to present it.
“Like most doctors, I thought people would jump on a vaccine to get past the pandemic. I was surprised and then disappointed. Right now, the pandemic is among the unvaccinated. So we face these encounters, and we’re doing our best to overcome the misinformation. My organization is 100% supportive. We talk about these issues every day.”
Carilion, effective Oct. 1, has required unvaccinated employees to get weekly COVID tests and wear an N95 mask while working, and has developed Facebook pages, other social media, and an Internet presence to address these issues. “We’ve gone to the local African-American community with physician leaders active in that community. We had a Spanish language roundtable,” Dr. Odeti said.
Dr. Skandhan reported that the Wiregrass regional chapter of SHM recently organized a successful statewide community educational event aimed at empowering community leaders to address vaccine misinformation and mistrust. “We surveyed religious leaders and pastors regarding the causes of vaccine hesitancy and reached out to physicians active in community awareness.” Based on that input, a presentation by the faith leaders was developed. Legislators from the Alabama State Senate’s Healthcare Policy Committee were also invited to the presentation and discussion.
Trying to stay positive
It’s important to try to stay positive, Dr. Odeti said. “We have to be empathetic with every patient. We have to keep working at this, since there’s no way out of the pandemic except through vaccinations. But it all creates stress for hospitalists. Our job is made significantly more difficult by the vaccine controversy.”
Jennifer Cowart, MD, a hospitalist at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., has been outspoken in her community about vaccination and masking issues, talking to reporters, attending rallies and press conferences, posting on social media, and speaking in favor of mask policies at a local school board meeting. She is part of an informal local group called Doctors Fighting COVID, which meets online to strategize how to share its expertise, including writing a recent letter about masks to Jacksonville’s mayor.
“In July, when we saw the Delta variant surging locally, we held a webinar via local media, taking calls about the vaccine from the community. I’m trying not to make this a political issue, but we are health officials.” Dr. Cowart said she also tries not to raise her voice when speaking with vaccine opponents and tries to remain empathetic. “Even though inwardly I’m screaming, I try to stay calm. The misinformation is real. People are afraid and feeling pressure. I do my best, but I’m human, too.”
Hospitalists need to pull whatever levers they can to help advance understanding of vaccines, Dr. Cowart said. “In the hospital, our biggest issue is time. We often don’t have it, with a long list of patients to see. But every patient encounter is an opportunity to talk to patients, whether they have COVID or something else.” Sometimes, she might go back to a patient’s room after rounds to resume the conversation.
Hospital nurses have been trained and entrusted to do tobacco abatement counseling, she said, so why not mobilize them for vaccine education? “Or respiratory therapists, who do inhaler training, could talk about what it’s like to care for COVID patients. There’s a whole bunch of staff in the hospital who could be mobilized,” she said.
“I feel passionate about vaccines, as a hospitalist, as a medical educator, as a daughter, as a responsible member of society,” said Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, SFHM, MACP, director of continuing medical education at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “I see this as a personal and societal responsibility. When I speak about the vaccine among groups of doctors, I say we need to stay in our lane regarding our skills at interpreting the science and not undermining it.”
Some health care worker hesitancy is from distrust of pharmaceutical companies, or of federal agencies, she said. “Our research has highlighted to me the widespread inequity issues in our health care system. We should also take a long, hard look at how we teach the scientific method to health professionals. That will be part of a pandemic retrospective.”
Sometimes with people who are vaccine deliberative, whether health care workers or patients, there is a small window of opportunity. “We need to hear people and respond to them as people. Then, if they are willing to get vaccinated, we need to accomplish that as quickly and easily as possible,” Dr. Barrett said. “I see them make a face and say, ‘Well, okay, I’ll do it.’ We need to get the vaccine to them that same day. We should be able to accomplish that.”
References
1. Gamble M. 30% of US hospitals mandate vaccination for employment. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2021 Aug 13. www.beckershospitalreview.com/workforce/covid-19-vaccination-needed-to-work-at-30-of-us-hospitals.html .
2. Society of Hospital Medicine signs on to joint statement in support of health worker COVID-19 vaccine mandates. Press release. 2021 Jul 26. www.hospitalmedicine.org/news-publications/press-releases/society-of-hospital-medicine-signs-on-to-joint-statement-of-support-of-health-worker-covid-19-vaccine-mandates/.
3. Carpenter A. A physician’s lessons from an unvaccinated childhood. Louisville Medicine. 2021 July;69(2):26-7. https://viewer.joomag.com/louisville-medicine-volume-69-issue-2/0045988001624974172?short&.
Lessons for hospitalists from the vaccination controversy
1. Remain up-to-date on information about the COVID infection, its treatment, and vaccination efficacy data.
2. Hospitalists should take advantage of their positions to lead conversations in their facilities about the importance of COVID vaccinations.
3. Other professionals in the hospital, with some additional training and support, could take on the role of providing vaccine education and support – with a physician to back them up on difficult cases.
4. It’s important to listen to people’s concerns, try to build trust, and establish dialogue before starting to convey a lot of information. People need to feel heard.
5. If you are successful in persuading someone to take the vaccine, a shot should be promptly and easily accessible to them.
6. Pediatric hospitalists may have more experience and skill with vaccine discussions, which they should share with their peers who treat adults.
On April 1, Houston Methodist Hospital in Houston, Texas, announced a new policy that all of its staff would need to be vaccinated against COVID-19 by June 7 in order to hold onto their jobs. Most responded positively but an estimated 150 staff members who did not comply either resigned or were terminated. A lawsuit by employees opposed to the vaccine mandate was dismissed by Federal District Court Judge Lynn Hughes in June, although a subsequent lawsuit was filed Aug. 16.
Vaccines have been shown to dramatically reduce both the incidence and the severity of COVID infections. Vaccinations of health care workers, especially those who have direct contact with patients, are demonstrated to be effective strategies to significantly reduce, although not eliminate, the possibility of viral transmissions to patients – or to health care workers themselves – thus saving lives.
Hospitalists, in their central role in the care of hospitalized patients, and often with primary responsibility for managing their hospital’s COVID-19 caseloads, may find themselves encountering conversations about the vaccine, its safety, effectiveness, and mandates with their peers, other hospital staff, patients, and families, and their communities. They can play key roles in advocating for the vaccine, answering questions, clarifying the science, and dispelling misinformation – for those who are willing to listen.
Becker’s Hospital Review, which has kept an ongoing tally of announced vaccine mandate policies in hospitals, health systems, and health departments nationwide, reported on Aug. 13 that 1,850 or 30% of U.S. hospitals, had announced vaccine mandates.1 Often exceptions can be made, such as for medical or religious reasons, or with other declarations or opt-out provisions. But in many settings, mandating COVID vaccinations won’t be easy.
Amith Skandhan, MD, SFHM, FACP, a hospitalist at Southeast Health Medical Center in Dothan, Ala., and a core faculty member in the internal medicine residency program at Alabama College of Osteopathic Medicine, said that implementing vaccine mandates will be more difficult in smaller health systems, in rural communities, and in states with lower vaccination rates and greater vaccine controversy.
Alabama has the lowest vaccination rates in the country, reflected in the recent rise in COVID cases and hospitalizations, even higher than during the surge of late 2020, Dr. Skandhan said. “In June we had one COVID patient in this hospital.” By late August the number was 119 COVID patients and climbing.
But where he works, in a health system where staffing is already spread thin, a vaccine mandate would be challenging. “What if our staff started leaving? It’s only 10 minutes from here to the Florida or Georgia border,” Dr. Skandhan said. Health care workers opposed to vaccinations would have the option of easily seeking work elsewhere.
When contacted for this article, he had been off work for several days but was mentally preparing himself to go back. “I’m not even following the [COVID-19] numbers but I am prepared for the worst. I know it will be mostly COVID. People just don’t realize what goes into this work.”
Dr. Skandhan, who said he was the third or fourth person in Alabama to receive the COVID vaccine, often finds himself feeling frustrated and angry – in the midst of a surge in cases that could have been prevented – that such a beneficial medical advance for bringing the pandemic under control became so politicized. “It is imperative that we find out why this mistrust exists and work to address it. It has to be done.”
Protecting health care professionals
On July 26, the Society of Hospital Medicine joined 50 other health care organizations including the American Medical Association, American Nurses Association, and American Academy of Pediatrics in advocating for all health care employers to require their employees to be vaccinated against COVID, in order to protect the safety of all patients and residents of health care facilities.2
“As an organization, we support vaccinating health care workers, including hospitalists, to help stop the spread of COVID-19 and the increasingly dominant Delta variant,” said SHM’s chief executive officer Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, in a prepared statement. “We aim to uphold the highest standards among hospitalists and other health care providers to help protect our fellow health care professionals, our patients, and our communities.”
To that end, Dr. Skandhan has started conversations with hospital staff who he knows are not vaccinated. “For some, we’re not able to have a civil conversation, but in most cases I can help to persuade people.” The reasons people give for not getting vaccinated are not based in science, he said. “I am worried about the safety of our hospitalists and staff nurses.” But unvaccinated frontline workers are also putting their patients at risk. “Can we say why they’re hesitating? Can we have an honest discourse? If we can’t do that with our colleagues, how can we blame the patients?”
Dr. Skandhan encourages hospitalists to start simply in their own hospitals, trying to influence their own departments and colleagues. “If you can convince one or two more every week, you can start a chain reaction. Have that conversation. Use your trust.” For some hospitalized patients, the vaccination conversation comes too late, after their infection, but even some of them might consider obtaining it down the road or trying to persuade family members to get vaccinated.
Adult hospitalists, however, may not have received training in how to effectively address vaccine fears and misconceptions among their patients, he said. Because the patients they see in the hospital are already very sick, they don’t get a lot of practice talking about vaccines except, perhaps, for the influenza vaccine.
Pediatric hospitalists have more experience with such conversations involving their patients’ parents, Dr. Skandhan said. “It comes more naturally to them. We need to learn quickly from them about how to talk about vaccines with our patients.”
Pediatric training and experience
Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, FAAP, a pediatric hospitalist at the Cleveland Clinic and the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist, agrees that pediatricians and pediatric hospitalists often have received more training in how to lead vaccination conversations. She often talks about vaccines with the parents of hospitalized children relative to chicken pox, measles, and other diseases of childhood.
Pediatric hospitalists may also ask to administer the hepatitis B vaccine to newborn babies, along with other preventive treatments such as eye drops and vitamin K shots. “I often encourage the influenza vaccine prior to the patient’s hospital discharge, especially for kids with chronic conditions, asthma, diabetes, or premature birth. We talk about how the influenza vaccine isn’t perfect, but it helps to prevent more serious disease,” she said.
“A lot of vaccine hesitancy comes from misunderstandings about the role of vaccines,” she said. People forget that for years children have been getting vaccines before starting school. “Misinformation and opinions about vaccines have existed for decades. What’s new today is the abundance of sources for obtaining these opinions. My job is to inform families of scientific facts and to address their concerns.”
It has become more common recently for parents to say they don’t want their kids to get vaccinated, Dr. Kumar said. Another group is better described as vaccine hesitant and just needs more information. “I may not, by the time they leave the hospital, convince them to allow me to administer the vaccine. But in the discharge summary, I document that I had this conversation. I’ve done my due diligence and tried to start a larger dialogue. I say: ‘I encourage you to continue this discussion with the pediatrician you trust.’ I also communicate with the outpatient team,” she said.
“But it’s our responsibility, because we’re the ones seeing these patients, to do whatever we can to keep our patients from getting sick. A lot of challenging conversations we have with families are just trying to find out where they’re at with the issue – which can lead to productive dialogue.”
Ariel Carpenter, MD, a 4th-year resident in internal medicine and pediatrics at the University of Louisville (Ky.), and a future pediatric hospitalist, agreed that her combined training in med-peds has been helpful preparation for the vaccine conversation. That training has included techniques of motivational interviewing. In pediatrics, she explained, the communication is a little softer. “I try to approach my patients in a family-centered way.”
Dr. Carpenter recently wrote a personal essay for Louisville Medicine magazine from the perspective of growing up homeschooled by a mother who didn’t believe in vaccines.3 As a teenager, she independently obtained the complete childhood vaccine series so that she could do medical shadowing and volunteering. In medical school she became a passionate vaccine advocate, eventually persuading her mother to change her mind on the subject in time for the COVID vaccine.
“There’s not one answer to the vaccination dilemma,” she said. “Different approaches are required because there are so many different reasons for it. Based on my own life experience, I try to approach patients where they are – not from a place of data and science. What worked in my own family, and works with my patients, is first to establish trust. If they trust you, they’re more likely to listen. Simply ask their worries and concerns,” Dr. Carpenter said.
“A lot of them haven’t had the opportunity before to sit down with a physician they trust and have their worries listened to. They don’t feel heard in our medical system. So I remind myself that I need to understand my patients first – before inserting myself into the conversation.”
Many patients she sees are in an information bubble, with a very different understanding of the issue than their doctors. “A lot of well-meaning people feel they are making the safer choice. Very few truly don’t care about protecting others. But they don’t feel the urgency about that and see the vaccine as the scarier option right now.”
Frontline vaccine advocates
Hospitalists are the frontline advocates within their hospital system, in a position to lead, so they need to make vaccines a priority, Dr. Carpenter said. They should also make sure that their hospitals have ready access to the vaccine, so patients who agree to receive it are able to get it quickly. “In our hospital they can get the shot within a few hours if the opportunity arises. We stocked the Johnson & Johnson vaccine so that they wouldn’t have to connect with another health care provider in order to get a second dose.”
Hospitals should also invest in access to vaccine counseling training and personnel. “Fund a nurse clinician who can screen and counsel hospitalized patients for vaccination. If they meet resistance, they can then refer to the dedicated physician of the day to have the conversation,” she said. “But if we don’t mention it, patients will assume we don’t feel strongly about it.”
Because hospitalists are front and center in treating COVID, they need to be the experts and the people offering guidance, said Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, FAAFP, section chief for hospital medicine at the Carilion Clinic in Roanoke, Va. “What we’re trying to do is spread awareness. We educated physician groups, learners, and clinical teams during the initial phase, and now mostly patients and their families.” COVID vaccine reluctance is hard to overcome, Dr. Odeti said. People feel the vaccine was developed very quickly. But there are different ways to present it.
“Like most doctors, I thought people would jump on a vaccine to get past the pandemic. I was surprised and then disappointed. Right now, the pandemic is among the unvaccinated. So we face these encounters, and we’re doing our best to overcome the misinformation. My organization is 100% supportive. We talk about these issues every day.”
Carilion, effective Oct. 1, has required unvaccinated employees to get weekly COVID tests and wear an N95 mask while working, and has developed Facebook pages, other social media, and an Internet presence to address these issues. “We’ve gone to the local African-American community with physician leaders active in that community. We had a Spanish language roundtable,” Dr. Odeti said.
Dr. Skandhan reported that the Wiregrass regional chapter of SHM recently organized a successful statewide community educational event aimed at empowering community leaders to address vaccine misinformation and mistrust. “We surveyed religious leaders and pastors regarding the causes of vaccine hesitancy and reached out to physicians active in community awareness.” Based on that input, a presentation by the faith leaders was developed. Legislators from the Alabama State Senate’s Healthcare Policy Committee were also invited to the presentation and discussion.
Trying to stay positive
It’s important to try to stay positive, Dr. Odeti said. “We have to be empathetic with every patient. We have to keep working at this, since there’s no way out of the pandemic except through vaccinations. But it all creates stress for hospitalists. Our job is made significantly more difficult by the vaccine controversy.”
Jennifer Cowart, MD, a hospitalist at Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Fla., has been outspoken in her community about vaccination and masking issues, talking to reporters, attending rallies and press conferences, posting on social media, and speaking in favor of mask policies at a local school board meeting. She is part of an informal local group called Doctors Fighting COVID, which meets online to strategize how to share its expertise, including writing a recent letter about masks to Jacksonville’s mayor.
“In July, when we saw the Delta variant surging locally, we held a webinar via local media, taking calls about the vaccine from the community. I’m trying not to make this a political issue, but we are health officials.” Dr. Cowart said she also tries not to raise her voice when speaking with vaccine opponents and tries to remain empathetic. “Even though inwardly I’m screaming, I try to stay calm. The misinformation is real. People are afraid and feeling pressure. I do my best, but I’m human, too.”
Hospitalists need to pull whatever levers they can to help advance understanding of vaccines, Dr. Cowart said. “In the hospital, our biggest issue is time. We often don’t have it, with a long list of patients to see. But every patient encounter is an opportunity to talk to patients, whether they have COVID or something else.” Sometimes, she might go back to a patient’s room after rounds to resume the conversation.
Hospital nurses have been trained and entrusted to do tobacco abatement counseling, she said, so why not mobilize them for vaccine education? “Or respiratory therapists, who do inhaler training, could talk about what it’s like to care for COVID patients. There’s a whole bunch of staff in the hospital who could be mobilized,” she said.
“I feel passionate about vaccines, as a hospitalist, as a medical educator, as a daughter, as a responsible member of society,” said Eileen Barrett, MD, MPH, SFHM, MACP, director of continuing medical education at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque. “I see this as a personal and societal responsibility. When I speak about the vaccine among groups of doctors, I say we need to stay in our lane regarding our skills at interpreting the science and not undermining it.”
Some health care worker hesitancy is from distrust of pharmaceutical companies, or of federal agencies, she said. “Our research has highlighted to me the widespread inequity issues in our health care system. We should also take a long, hard look at how we teach the scientific method to health professionals. That will be part of a pandemic retrospective.”
Sometimes with people who are vaccine deliberative, whether health care workers or patients, there is a small window of opportunity. “We need to hear people and respond to them as people. Then, if they are willing to get vaccinated, we need to accomplish that as quickly and easily as possible,” Dr. Barrett said. “I see them make a face and say, ‘Well, okay, I’ll do it.’ We need to get the vaccine to them that same day. We should be able to accomplish that.”
References
1. Gamble M. 30% of US hospitals mandate vaccination for employment. Becker’s Hospital Review. 2021 Aug 13. www.beckershospitalreview.com/workforce/covid-19-vaccination-needed-to-work-at-30-of-us-hospitals.html .
2. Society of Hospital Medicine signs on to joint statement in support of health worker COVID-19 vaccine mandates. Press release. 2021 Jul 26. www.hospitalmedicine.org/news-publications/press-releases/society-of-hospital-medicine-signs-on-to-joint-statement-of-support-of-health-worker-covid-19-vaccine-mandates/.
3. Carpenter A. A physician’s lessons from an unvaccinated childhood. Louisville Medicine. 2021 July;69(2):26-7. https://viewer.joomag.com/louisville-medicine-volume-69-issue-2/0045988001624974172?short&.
Lessons for hospitalists from the vaccination controversy
1. Remain up-to-date on information about the COVID infection, its treatment, and vaccination efficacy data.
2. Hospitalists should take advantage of their positions to lead conversations in their facilities about the importance of COVID vaccinations.
3. Other professionals in the hospital, with some additional training and support, could take on the role of providing vaccine education and support – with a physician to back them up on difficult cases.
4. It’s important to listen to people’s concerns, try to build trust, and establish dialogue before starting to convey a lot of information. People need to feel heard.
5. If you are successful in persuading someone to take the vaccine, a shot should be promptly and easily accessible to them.
6. Pediatric hospitalists may have more experience and skill with vaccine discussions, which they should share with their peers who treat adults.
CVST after COVID-19 vaccine: New data confirm high mortality rate
, confirming the severity of the reaction and the associated high mortality rate.
The new series comes from an international registry of consecutive patients who experienced CVST within 28 days of COVID-19 vaccination between March 29 and June 18, 2021, from 81 hospitals in 19 countries.
The cases are described in an article published online on Sept. 28. in JAMA Neurology.
“This is a reliable description on the clinical condition of these patients with CVST associated with COVID-19 vaccination. It is striking that this a much worse condition than CVST not associated with COVID-19 vaccination, with a much higher rate of intracerebral hemorrhage and coma and a much higher mortality rate,” senior author Jonathan M. Coutinho, MD, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, told this news organization.
These data confirm the observations from an earlier U.K. cohort in which cases of cerebral venous thrombosis linked to COVID-19 vaccination occurred.
“This is the biggest series, and as an international series, it gives a broader perspective from a larger range of countries,” Dr. Coutinho said. “All the data together show that, although this side effect is rare, the consequences are very severe,” he added.
In the current study, the researchers regarded CVST as being linked to the vaccine if it was accompanied by thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS), as evidenced by thrombosis and new-onset thrombocytopenia.
In the cohort of 116 patients with CVST after COVID-19 vaccination, 78 (67.2%) had thrombosis with TTS and were thus classified as having had a vaccine-related adverse event. These patients were frequently comatose at presentation (24%) and often had intracerebral hemorrhage (68%) and concomitant thromboembolism (36%); 47% died during hospitalization.
These patients were compared with the 38 patients in the same cohort who had CVST but in whom there was no indication of concomitant thrombosis and thrombocytopenia. The case patients were also compared with a control group of 207 patients with CVST who were included in a separate international registry before the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mortality rates were much higher among the patients deemed to have had a vaccine-related CVST. The in-hospital mortality rate was 47%, compared with 5% among the patients in the same cohort who did not have TTS and 3.9% among the prepandemic control group.
The mortality rate was even higher (61%) among patients in the TTS group for whom the diagnosis was made before the condition garnered attention in the scientific community. The mortality rate was 42% among patients diagnosed later.
Of the 78 patients in whom CVST and TTS occurred after COVID-19 vaccination in this cohort, 76 had received the AstraZeneca vaccine (in 75 patients, CVST and TTS occurred after the first vaccination; in one patient, they occurred after the second vaccination). One patient had received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, and one had received the Pfizer vaccine.
“After more analysis, the case after the Pfizer vaccination is not believed to be caused by the vaccine,” Dr. Coutinho said. “In that case, the patient had a platelet count just below the lower limit and was taking an immunomodulator drug that is known to be associated with thrombocytopenia.”
For two patients who received the AstraZeneca vaccine, there was also an alternative explanation for the thrombocytopenia.
Dr. Coutinho also pointed out that the Johnson & Johnson vaccine has been used mainly in the United States, and these data were largely from other countries.
The median time from vaccination to CVST symptom onset was 9 days in the TTS group. The median platelet count at hospital admission among patients with postvaccination CVST-TTS was 45. Three patients presented with a normal platelet count and developed thrombocytopenia during admission; two patients presented with mild thrombocytopenia, 30 presented with moderate thrombocytopenia, and 43 presented with severe thrombocytopenia.
Antibodies against platelet factor 4 (PF4) were measured in 69 patients with TTS, of whom 63 (91%) tested positive (the one patient in whom TTS occurred after the patient received the Pfizer vaccine did not test positive). However, the researchers note that sensitivity varies among different PF4 ELISA tests. Findings of platelet activation assays were positive in all 36 tested patients.
In the TTS group, 52 patients (67%) received immunomodulation therapy, most often intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG). Among patients treated with IVIG, the mortality rate was lower (28%).
Different from CVST linked to natural COVID-19 infection
Dr. Coutinho noted that CVST can occur in natural SARS-CoV-2 infection but that vaccine-associated CVST is very different.
“In natural COVID-19 infection, there is an increased risk of thrombosis, and some patients can get CVST as a part of this, but in these cases, this is not accompanied by thrombocytopenia. While the CVST in natural COVID-19 infection is also associated with a bad prognosis, this is more to do with the underlying disease. It is normally the very sick COVID patients who develop CVST, and these patients usually die from the underlying disease rather than the CVST itself,” he explained.
“Clinicians need to be aware of vaccine-related CVST, as it requires very specific and rapid treatment,” Dr. Coutinho stressed.
“Patients presenting with an extremely severe headache (unlike any headache they’ve had before) or with seizures or a focal deficit (weakness in arm or problems with speaking or vision) within 4 weeks of an adenovirus COVID-19 vaccination should ring alarm bells. It is important to do diagnostics quickly, with a platelet count the most important first step, and a rapid CT/MRI scan,” he said.
Other tests that should be conducted are D-dimer for thrombosis and the PF4 antibody test. But results for the PF4 antibody test can take days to come back, and clinicians shouldn’t wait for that, Dr. Coutinho notes.
“Specific treatment needs to be given immediately – with anticoagulation (preferably nonheparin) and immunomodulation with IVIG to stop the immune reaction. Platelets should not be given – that may seem counterintuitive in patients with a low platelet count, but giving platelets makes it worse,” he said.
Is there a geographic difference?
Dr. Coutinho pointed out that fewer cases of this vaccine-related CVST are being reported at the current time.
“We are not sure why this is the case. These adenovirus vaccines are not being used much now in Western countries, but our collaboration covers many less developed countries in South America and Asia, which are relying heavily on these vaccines. We are now shifting focus to these countries, but so far we have only seen a handful of cases from these areas,” he said.
He suggested that this may be because these countries started their vaccination programs later and are vaccinating their elderly (who are not so susceptible to this side effect) first, or it may be because of some environmental or genetic factor that has not yet been discovered.
“This is now an important research question – is the risk of vaccine-induced CVST the same in different countries or ethnicities? This could influence decisions on future vaccine strategies,” Dr. Coutinho said.
“So far, female sex is the strongest risk factor for vaccine-induced CVST. In our cohort, 81% of cases were in women. In addition, 95% were White, but that doesn’t allow us to conclude that this is a risk factor, as the majority of people who have been vaccinated are White. So, we have no clear insight into that yet,” he said.
In a comment for this news organization, the lead author of the previous U.K. report of a series of 70 cases of cerebral venous thrombosis linked to COVID-19 vaccination, Richard Perry, PhD, University College Hospital, London, described this new report as “an excellent study, with many of the same strengths and weaknesses as our study and has very similar results.”
Dr. Perry noted that the two studies used slightly different definitions of vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia, but the cases reported appear to be very similar overall. “It is reassuring and gratifying to see that they have made such similar observations,” he said.
“And as they have drawn their cases from a broad range of countries whereas ours were all from the U.K., this provides evidence that the observations from both studies are reasonably generalizable,” he added.
Dr. Perry pointed out that this new report states that TTS occurred in one patient after the patient had received a second dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine. “I would like to know more about this case, because we didn’t see any cases after a second dose in our cohort,” he said.
Dr. Coutinho responded that he didn’t believe this was the first reported case after the second dose.
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Coutinho has received grants paid to his institution from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bayer and payments paid to his institution for data safety monitoring board participation by Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, confirming the severity of the reaction and the associated high mortality rate.
The new series comes from an international registry of consecutive patients who experienced CVST within 28 days of COVID-19 vaccination between March 29 and June 18, 2021, from 81 hospitals in 19 countries.
The cases are described in an article published online on Sept. 28. in JAMA Neurology.
“This is a reliable description on the clinical condition of these patients with CVST associated with COVID-19 vaccination. It is striking that this a much worse condition than CVST not associated with COVID-19 vaccination, with a much higher rate of intracerebral hemorrhage and coma and a much higher mortality rate,” senior author Jonathan M. Coutinho, MD, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, told this news organization.
These data confirm the observations from an earlier U.K. cohort in which cases of cerebral venous thrombosis linked to COVID-19 vaccination occurred.
“This is the biggest series, and as an international series, it gives a broader perspective from a larger range of countries,” Dr. Coutinho said. “All the data together show that, although this side effect is rare, the consequences are very severe,” he added.
In the current study, the researchers regarded CVST as being linked to the vaccine if it was accompanied by thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS), as evidenced by thrombosis and new-onset thrombocytopenia.
In the cohort of 116 patients with CVST after COVID-19 vaccination, 78 (67.2%) had thrombosis with TTS and were thus classified as having had a vaccine-related adverse event. These patients were frequently comatose at presentation (24%) and often had intracerebral hemorrhage (68%) and concomitant thromboembolism (36%); 47% died during hospitalization.
These patients were compared with the 38 patients in the same cohort who had CVST but in whom there was no indication of concomitant thrombosis and thrombocytopenia. The case patients were also compared with a control group of 207 patients with CVST who were included in a separate international registry before the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mortality rates were much higher among the patients deemed to have had a vaccine-related CVST. The in-hospital mortality rate was 47%, compared with 5% among the patients in the same cohort who did not have TTS and 3.9% among the prepandemic control group.
The mortality rate was even higher (61%) among patients in the TTS group for whom the diagnosis was made before the condition garnered attention in the scientific community. The mortality rate was 42% among patients diagnosed later.
Of the 78 patients in whom CVST and TTS occurred after COVID-19 vaccination in this cohort, 76 had received the AstraZeneca vaccine (in 75 patients, CVST and TTS occurred after the first vaccination; in one patient, they occurred after the second vaccination). One patient had received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, and one had received the Pfizer vaccine.
“After more analysis, the case after the Pfizer vaccination is not believed to be caused by the vaccine,” Dr. Coutinho said. “In that case, the patient had a platelet count just below the lower limit and was taking an immunomodulator drug that is known to be associated with thrombocytopenia.”
For two patients who received the AstraZeneca vaccine, there was also an alternative explanation for the thrombocytopenia.
Dr. Coutinho also pointed out that the Johnson & Johnson vaccine has been used mainly in the United States, and these data were largely from other countries.
The median time from vaccination to CVST symptom onset was 9 days in the TTS group. The median platelet count at hospital admission among patients with postvaccination CVST-TTS was 45. Three patients presented with a normal platelet count and developed thrombocytopenia during admission; two patients presented with mild thrombocytopenia, 30 presented with moderate thrombocytopenia, and 43 presented with severe thrombocytopenia.
Antibodies against platelet factor 4 (PF4) were measured in 69 patients with TTS, of whom 63 (91%) tested positive (the one patient in whom TTS occurred after the patient received the Pfizer vaccine did not test positive). However, the researchers note that sensitivity varies among different PF4 ELISA tests. Findings of platelet activation assays were positive in all 36 tested patients.
In the TTS group, 52 patients (67%) received immunomodulation therapy, most often intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG). Among patients treated with IVIG, the mortality rate was lower (28%).
Different from CVST linked to natural COVID-19 infection
Dr. Coutinho noted that CVST can occur in natural SARS-CoV-2 infection but that vaccine-associated CVST is very different.
“In natural COVID-19 infection, there is an increased risk of thrombosis, and some patients can get CVST as a part of this, but in these cases, this is not accompanied by thrombocytopenia. While the CVST in natural COVID-19 infection is also associated with a bad prognosis, this is more to do with the underlying disease. It is normally the very sick COVID patients who develop CVST, and these patients usually die from the underlying disease rather than the CVST itself,” he explained.
“Clinicians need to be aware of vaccine-related CVST, as it requires very specific and rapid treatment,” Dr. Coutinho stressed.
“Patients presenting with an extremely severe headache (unlike any headache they’ve had before) or with seizures or a focal deficit (weakness in arm or problems with speaking or vision) within 4 weeks of an adenovirus COVID-19 vaccination should ring alarm bells. It is important to do diagnostics quickly, with a platelet count the most important first step, and a rapid CT/MRI scan,” he said.
Other tests that should be conducted are D-dimer for thrombosis and the PF4 antibody test. But results for the PF4 antibody test can take days to come back, and clinicians shouldn’t wait for that, Dr. Coutinho notes.
“Specific treatment needs to be given immediately – with anticoagulation (preferably nonheparin) and immunomodulation with IVIG to stop the immune reaction. Platelets should not be given – that may seem counterintuitive in patients with a low platelet count, but giving platelets makes it worse,” he said.
Is there a geographic difference?
Dr. Coutinho pointed out that fewer cases of this vaccine-related CVST are being reported at the current time.
“We are not sure why this is the case. These adenovirus vaccines are not being used much now in Western countries, but our collaboration covers many less developed countries in South America and Asia, which are relying heavily on these vaccines. We are now shifting focus to these countries, but so far we have only seen a handful of cases from these areas,” he said.
He suggested that this may be because these countries started their vaccination programs later and are vaccinating their elderly (who are not so susceptible to this side effect) first, or it may be because of some environmental or genetic factor that has not yet been discovered.
“This is now an important research question – is the risk of vaccine-induced CVST the same in different countries or ethnicities? This could influence decisions on future vaccine strategies,” Dr. Coutinho said.
“So far, female sex is the strongest risk factor for vaccine-induced CVST. In our cohort, 81% of cases were in women. In addition, 95% were White, but that doesn’t allow us to conclude that this is a risk factor, as the majority of people who have been vaccinated are White. So, we have no clear insight into that yet,” he said.
In a comment for this news organization, the lead author of the previous U.K. report of a series of 70 cases of cerebral venous thrombosis linked to COVID-19 vaccination, Richard Perry, PhD, University College Hospital, London, described this new report as “an excellent study, with many of the same strengths and weaknesses as our study and has very similar results.”
Dr. Perry noted that the two studies used slightly different definitions of vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia, but the cases reported appear to be very similar overall. “It is reassuring and gratifying to see that they have made such similar observations,” he said.
“And as they have drawn their cases from a broad range of countries whereas ours were all from the U.K., this provides evidence that the observations from both studies are reasonably generalizable,” he added.
Dr. Perry pointed out that this new report states that TTS occurred in one patient after the patient had received a second dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine. “I would like to know more about this case, because we didn’t see any cases after a second dose in our cohort,” he said.
Dr. Coutinho responded that he didn’t believe this was the first reported case after the second dose.
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Coutinho has received grants paid to his institution from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bayer and payments paid to his institution for data safety monitoring board participation by Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, confirming the severity of the reaction and the associated high mortality rate.
The new series comes from an international registry of consecutive patients who experienced CVST within 28 days of COVID-19 vaccination between March 29 and June 18, 2021, from 81 hospitals in 19 countries.
The cases are described in an article published online on Sept. 28. in JAMA Neurology.
“This is a reliable description on the clinical condition of these patients with CVST associated with COVID-19 vaccination. It is striking that this a much worse condition than CVST not associated with COVID-19 vaccination, with a much higher rate of intracerebral hemorrhage and coma and a much higher mortality rate,” senior author Jonathan M. Coutinho, MD, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, told this news organization.
These data confirm the observations from an earlier U.K. cohort in which cases of cerebral venous thrombosis linked to COVID-19 vaccination occurred.
“This is the biggest series, and as an international series, it gives a broader perspective from a larger range of countries,” Dr. Coutinho said. “All the data together show that, although this side effect is rare, the consequences are very severe,” he added.
In the current study, the researchers regarded CVST as being linked to the vaccine if it was accompanied by thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome (TTS), as evidenced by thrombosis and new-onset thrombocytopenia.
In the cohort of 116 patients with CVST after COVID-19 vaccination, 78 (67.2%) had thrombosis with TTS and were thus classified as having had a vaccine-related adverse event. These patients were frequently comatose at presentation (24%) and often had intracerebral hemorrhage (68%) and concomitant thromboembolism (36%); 47% died during hospitalization.
These patients were compared with the 38 patients in the same cohort who had CVST but in whom there was no indication of concomitant thrombosis and thrombocytopenia. The case patients were also compared with a control group of 207 patients with CVST who were included in a separate international registry before the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mortality rates were much higher among the patients deemed to have had a vaccine-related CVST. The in-hospital mortality rate was 47%, compared with 5% among the patients in the same cohort who did not have TTS and 3.9% among the prepandemic control group.
The mortality rate was even higher (61%) among patients in the TTS group for whom the diagnosis was made before the condition garnered attention in the scientific community. The mortality rate was 42% among patients diagnosed later.
Of the 78 patients in whom CVST and TTS occurred after COVID-19 vaccination in this cohort, 76 had received the AstraZeneca vaccine (in 75 patients, CVST and TTS occurred after the first vaccination; in one patient, they occurred after the second vaccination). One patient had received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine, and one had received the Pfizer vaccine.
“After more analysis, the case after the Pfizer vaccination is not believed to be caused by the vaccine,” Dr. Coutinho said. “In that case, the patient had a platelet count just below the lower limit and was taking an immunomodulator drug that is known to be associated with thrombocytopenia.”
For two patients who received the AstraZeneca vaccine, there was also an alternative explanation for the thrombocytopenia.
Dr. Coutinho also pointed out that the Johnson & Johnson vaccine has been used mainly in the United States, and these data were largely from other countries.
The median time from vaccination to CVST symptom onset was 9 days in the TTS group. The median platelet count at hospital admission among patients with postvaccination CVST-TTS was 45. Three patients presented with a normal platelet count and developed thrombocytopenia during admission; two patients presented with mild thrombocytopenia, 30 presented with moderate thrombocytopenia, and 43 presented with severe thrombocytopenia.
Antibodies against platelet factor 4 (PF4) were measured in 69 patients with TTS, of whom 63 (91%) tested positive (the one patient in whom TTS occurred after the patient received the Pfizer vaccine did not test positive). However, the researchers note that sensitivity varies among different PF4 ELISA tests. Findings of platelet activation assays were positive in all 36 tested patients.
In the TTS group, 52 patients (67%) received immunomodulation therapy, most often intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG). Among patients treated with IVIG, the mortality rate was lower (28%).
Different from CVST linked to natural COVID-19 infection
Dr. Coutinho noted that CVST can occur in natural SARS-CoV-2 infection but that vaccine-associated CVST is very different.
“In natural COVID-19 infection, there is an increased risk of thrombosis, and some patients can get CVST as a part of this, but in these cases, this is not accompanied by thrombocytopenia. While the CVST in natural COVID-19 infection is also associated with a bad prognosis, this is more to do with the underlying disease. It is normally the very sick COVID patients who develop CVST, and these patients usually die from the underlying disease rather than the CVST itself,” he explained.
“Clinicians need to be aware of vaccine-related CVST, as it requires very specific and rapid treatment,” Dr. Coutinho stressed.
“Patients presenting with an extremely severe headache (unlike any headache they’ve had before) or with seizures or a focal deficit (weakness in arm or problems with speaking or vision) within 4 weeks of an adenovirus COVID-19 vaccination should ring alarm bells. It is important to do diagnostics quickly, with a platelet count the most important first step, and a rapid CT/MRI scan,” he said.
Other tests that should be conducted are D-dimer for thrombosis and the PF4 antibody test. But results for the PF4 antibody test can take days to come back, and clinicians shouldn’t wait for that, Dr. Coutinho notes.
“Specific treatment needs to be given immediately – with anticoagulation (preferably nonheparin) and immunomodulation with IVIG to stop the immune reaction. Platelets should not be given – that may seem counterintuitive in patients with a low platelet count, but giving platelets makes it worse,” he said.
Is there a geographic difference?
Dr. Coutinho pointed out that fewer cases of this vaccine-related CVST are being reported at the current time.
“We are not sure why this is the case. These adenovirus vaccines are not being used much now in Western countries, but our collaboration covers many less developed countries in South America and Asia, which are relying heavily on these vaccines. We are now shifting focus to these countries, but so far we have only seen a handful of cases from these areas,” he said.
He suggested that this may be because these countries started their vaccination programs later and are vaccinating their elderly (who are not so susceptible to this side effect) first, or it may be because of some environmental or genetic factor that has not yet been discovered.
“This is now an important research question – is the risk of vaccine-induced CVST the same in different countries or ethnicities? This could influence decisions on future vaccine strategies,” Dr. Coutinho said.
“So far, female sex is the strongest risk factor for vaccine-induced CVST. In our cohort, 81% of cases were in women. In addition, 95% were White, but that doesn’t allow us to conclude that this is a risk factor, as the majority of people who have been vaccinated are White. So, we have no clear insight into that yet,” he said.
In a comment for this news organization, the lead author of the previous U.K. report of a series of 70 cases of cerebral venous thrombosis linked to COVID-19 vaccination, Richard Perry, PhD, University College Hospital, London, described this new report as “an excellent study, with many of the same strengths and weaknesses as our study and has very similar results.”
Dr. Perry noted that the two studies used slightly different definitions of vaccine-induced thrombotic thrombocytopenia, but the cases reported appear to be very similar overall. “It is reassuring and gratifying to see that they have made such similar observations,” he said.
“And as they have drawn their cases from a broad range of countries whereas ours were all from the U.K., this provides evidence that the observations from both studies are reasonably generalizable,” he added.
Dr. Perry pointed out that this new report states that TTS occurred in one patient after the patient had received a second dose of the AstraZeneca vaccine. “I would like to know more about this case, because we didn’t see any cases after a second dose in our cohort,” he said.
Dr. Coutinho responded that he didn’t believe this was the first reported case after the second dose.
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Coutinho has received grants paid to his institution from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bayer and payments paid to his institution for data safety monitoring board participation by Bayer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two Colorado nurses admit to stealing drugs from hospital patients
, according to the US Attorney’s Office in Denver.
Alicia Nickel-Tangeman, 44, formerly of Woodland Park, Colo., pled guilty to four counts of obtaining controlled substances using fraud and deception. She gained access to rooms of patients who weren’t assigned to her and diverted drugs from their pain-on-demand devices, according to federal officials.
The defendant told patients she was conducting a study on the pumps that deliver drugs to relieve pain when the patient pushes a button, the officials stated. She would open the machine and would remove a portion of the drug with a syringe. She obtained drugs in this way from three patients on four occasions, a press release stated.
When questioned by law enforcement, Ms. Nickel-Tangeman continued to lie about her conduct and produced a false email address to substantiate her claims, the Department of Justice reported. She is scheduled to be sentenced November 30.
Ms. Nickel-Tangeman’s LinkedIn profile shows that she was a nurse with UCHealth in Colorado for 17 years, ending in May 2019.
Katie Muhs, 34, of Littleton, Colo., was convicted of a felony for using fraud and deception to divert fentanyl for her personal use while serving as an intensive care nurse.
The defendant admitted that between June and September 2019 she stole fentanyl by removing it from the IV bags of patients using a syringe. She also admitted to stealing fentanyl that remained in vials after fentanyl had been administered to patients. She would replace the stolen drug with saline and would “then have a fellow nurse witness her ‘waste,’ or dispose of the saline.”
U.S. District Judge Raymond Moore sentenced Ms. Muhs to 3 months of probation as a result of “the defendant’s confession and her cooperation in disclosing full information on her diversion, which is a matter potentially affecting the public health and the integrity of the health care system. The felony offense is punishable by up to four years of imprisonment and a fine of $250,000, per count.”
In pleading guilty to the single count in the case, Ms. Muhs admitted that on September 8, 2019, “she removed a bag of fentanyl from the automated medication control machine at the hospital under a different nurse’s login credentials. She then removed fentanyl from the IV bag for personal use.”
In April, the Colorado Court of Appeals denied her request for unemployment benefits. Court documents reveal that Ms. Muhs lost her job at St. Anthony Hospital after it was discovered that she stole and self-injected fentanyl while working as a registered nurse there.
The investigations in these cases were conducted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the Office of Criminal Investigations, and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
“We want it to be known that healthcare professionals who take advantage of patients in need by stealing their medications will be held accountable to the law,” said Deanne Reuter, DEA Denver Field Division special agent in charge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the US Attorney’s Office in Denver.
Alicia Nickel-Tangeman, 44, formerly of Woodland Park, Colo., pled guilty to four counts of obtaining controlled substances using fraud and deception. She gained access to rooms of patients who weren’t assigned to her and diverted drugs from their pain-on-demand devices, according to federal officials.
The defendant told patients she was conducting a study on the pumps that deliver drugs to relieve pain when the patient pushes a button, the officials stated. She would open the machine and would remove a portion of the drug with a syringe. She obtained drugs in this way from three patients on four occasions, a press release stated.
When questioned by law enforcement, Ms. Nickel-Tangeman continued to lie about her conduct and produced a false email address to substantiate her claims, the Department of Justice reported. She is scheduled to be sentenced November 30.
Ms. Nickel-Tangeman’s LinkedIn profile shows that she was a nurse with UCHealth in Colorado for 17 years, ending in May 2019.
Katie Muhs, 34, of Littleton, Colo., was convicted of a felony for using fraud and deception to divert fentanyl for her personal use while serving as an intensive care nurse.
The defendant admitted that between June and September 2019 she stole fentanyl by removing it from the IV bags of patients using a syringe. She also admitted to stealing fentanyl that remained in vials after fentanyl had been administered to patients. She would replace the stolen drug with saline and would “then have a fellow nurse witness her ‘waste,’ or dispose of the saline.”
U.S. District Judge Raymond Moore sentenced Ms. Muhs to 3 months of probation as a result of “the defendant’s confession and her cooperation in disclosing full information on her diversion, which is a matter potentially affecting the public health and the integrity of the health care system. The felony offense is punishable by up to four years of imprisonment and a fine of $250,000, per count.”
In pleading guilty to the single count in the case, Ms. Muhs admitted that on September 8, 2019, “she removed a bag of fentanyl from the automated medication control machine at the hospital under a different nurse’s login credentials. She then removed fentanyl from the IV bag for personal use.”
In April, the Colorado Court of Appeals denied her request for unemployment benefits. Court documents reveal that Ms. Muhs lost her job at St. Anthony Hospital after it was discovered that she stole and self-injected fentanyl while working as a registered nurse there.
The investigations in these cases were conducted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the Office of Criminal Investigations, and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
“We want it to be known that healthcare professionals who take advantage of patients in need by stealing their medications will be held accountable to the law,” said Deanne Reuter, DEA Denver Field Division special agent in charge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to the US Attorney’s Office in Denver.
Alicia Nickel-Tangeman, 44, formerly of Woodland Park, Colo., pled guilty to four counts of obtaining controlled substances using fraud and deception. She gained access to rooms of patients who weren’t assigned to her and diverted drugs from their pain-on-demand devices, according to federal officials.
The defendant told patients she was conducting a study on the pumps that deliver drugs to relieve pain when the patient pushes a button, the officials stated. She would open the machine and would remove a portion of the drug with a syringe. She obtained drugs in this way from three patients on four occasions, a press release stated.
When questioned by law enforcement, Ms. Nickel-Tangeman continued to lie about her conduct and produced a false email address to substantiate her claims, the Department of Justice reported. She is scheduled to be sentenced November 30.
Ms. Nickel-Tangeman’s LinkedIn profile shows that she was a nurse with UCHealth in Colorado for 17 years, ending in May 2019.
Katie Muhs, 34, of Littleton, Colo., was convicted of a felony for using fraud and deception to divert fentanyl for her personal use while serving as an intensive care nurse.
The defendant admitted that between June and September 2019 she stole fentanyl by removing it from the IV bags of patients using a syringe. She also admitted to stealing fentanyl that remained in vials after fentanyl had been administered to patients. She would replace the stolen drug with saline and would “then have a fellow nurse witness her ‘waste,’ or dispose of the saline.”
U.S. District Judge Raymond Moore sentenced Ms. Muhs to 3 months of probation as a result of “the defendant’s confession and her cooperation in disclosing full information on her diversion, which is a matter potentially affecting the public health and the integrity of the health care system. The felony offense is punishable by up to four years of imprisonment and a fine of $250,000, per count.”
In pleading guilty to the single count in the case, Ms. Muhs admitted that on September 8, 2019, “she removed a bag of fentanyl from the automated medication control machine at the hospital under a different nurse’s login credentials. She then removed fentanyl from the IV bag for personal use.”
In April, the Colorado Court of Appeals denied her request for unemployment benefits. Court documents reveal that Ms. Muhs lost her job at St. Anthony Hospital after it was discovered that she stole and self-injected fentanyl while working as a registered nurse there.
The investigations in these cases were conducted by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the Office of Criminal Investigations, and the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA).
“We want it to be known that healthcare professionals who take advantage of patients in need by stealing their medications will be held accountable to the law,” said Deanne Reuter, DEA Denver Field Division special agent in charge.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MDs doing wrong-site surgery: Why is it still happening?
In July 2021, University Hospitals, in Cleveland, announced that its staff had transplanted a kidney into the wrong patient. Although the patient who received the kidney was recovering well, the patient who was supposed to have received the kidney was skipped over. As a result of the error, two employees were placed on administrative leave and the incident was being investigated, the hospital announced.
In April 2020, an interventional radiologist at Boca Raton Regional Hospital, in Boca Raton, Fla., was sued for allegedly placing a stent into the wrong kidney of an 80-year-old patient. Using fluoroscopic guidance, the doctor removed an old stent from the right side but incorrectly replaced it with a new stent on the left side, according to an interview conducted by this news organization with the patient’s lawyers at Searcy Law, in West Palm Beach.
“The problem is that it is so rare that doctors don’t focus on it,” says Mary R. Kwaan, MD, a colorectal surgeon at UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles.
A 2006 study in which Kwaan was the lead author concluded that there was one wrong-site surgery for every 112,994 surgeries. Those mistakes can add up. A 2006 study estimated that 25 to 52 wrong-site surgeries were performed each week in the United States.
“Many surgeons don’t think it can happen to them, so they don’t take extra precautions,” says David Mayer, MD, executive director of the MedStar Institute for Quality and Safety, in Washington, DC. “When they make a wrong-site error, usually the first thing they say is, ‘I never thought this would happen to me,’ ” he says.
Wrong-site surgeries are considered sentinel events -- the worst kinds of medical errors. The Sullivan Group, a patient safety consultancy based in Colorado, reports that in 2013, 2.7% of patients who were involved in wrong-site surgeries died and 41% experienced some type of permanent injury. The mean malpractice payment was $127,000.
Some malpractice payments are much higher. In 2013, a Maryland ob.gyn paid a $1.42 million malpractice award for removing the wrong ovary from a woman in 2009. In 2017, a Pennsylvania urologist paid $870,000 for removing the wrong testicle from a man in 2013.
Wrong-site surgery often involves experienced surgeons
One might think that wrong-site surgeries usually involve younger or less-experienced surgeons, but that’s not the case; two thirds of the surgeons who perform wrong-site surgeries are in their 40s and 50s, compared with fewer than 25% younger than 40.
In a rather chilling statistic, in a 2013 survey, 12.4% of doctors who were involved in sentinel events in general had claims for more than one event.
These errors are more common in certain specialties. In a study reported in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Spine, 25% of orthopedic surgeons reported performing at least one wrong-site surgery during their career.
Within orthopedics, spine surgery is ground zero for wrong-site surgery. “Finding the site in spine surgery can be more difficult than in common left-right orthopedic procedures,” says Joseph A. Bosco III, a New York City orthopedist.
A 2007 study found that 25% of neurosurgeons had performed wrong-site surgeries. In Missouri in 2013, for example, a 53-year-old patient who was scheduled to undergo a left-sided craniotomy bypass allegedly underwent a right-sided craniotomy and was unable to speak after surgery.
Wrong-site surgeries are also performed by general surgeons, urologists, cardiologists, otolaryngologists, and ophthalmologists. A 2021 lawsuit accused a Tampa urologist of removing the patient’s wrong testicle. And a 2019 lawsuit accused a Chicago ophthalmologist of operating on the wrong eye to remove a cyst.
It’s not just the surgeon’s mistake
Mistakes are not only made by the surgeon in the operating room (OR). They can be made by staff when scheduling a surgery, radiologists and pathologists when writing their reports for surgery, and by team members in the OR.
Many people are prone to confusing left and right. A 2020 study found that 14.9% of people had difficulty distinguishing left from right; other studies have shown higher rates. Distractions increase the likelihood of mistakes. In a 2015 study, background noise in a hospital ward made it more difficult for medical students to make left-right judgments.
OR personnel can be confused when patients are turned around. “To operate on the back of someone’s leg, the surgeon may turn the patient from supine to prone, and so left becomes right,” says Samuel C. Seiden, MD, an anesthesiologist in Roseville, Calif., who has studied wrong-site surgery.
Operative site markings that are drawn on the skin can be rubbed off when surgical prep is applied, and markings aren’t usually possible for procedures such as spine surgeries. Surgical draping can make it harder to distinguish the patient’s left and right, and a busy surgeon relying on memory may confuse cases and perform wrong-patient surgery.
A push to eliminate wrong-site surgery
In 2004, the Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals and many surgery centers, decided to do something about wrong-site surgery and related surgical errors. It released a universal protocol, which requires hospitals to take three steps to prevent errors: perform preoperative verification that is based on patient care documents; mark the operative site; and take a time-out just before surgery, during which the team should consider whether a mistake is about to be made.
Two years after the Joint Commission published its protocol, Dr. Seiden led a study to determine what effect it had had. The investigators found that wrong-site cases had decreased by only about one third. Preventing wrong-site surgery “turns out to be more complicated to eradicate than anybody thought,” Mark Chassin, MD, president of the Joint Commission, stated a few years later.
Why did the protocol have only a limited effect? Dr. Seiden says that it has been hard to change doctors’ traditional attitudes against standardization. “Some have had an attitude that checklists are for dummies, but that is changing,” he says.
For instance, some surgical teams were not paying attention during time-outs. “The time-out should be like the invocation of the National Anthem,” an orthopedic surgeon from Iowa wrote. “All other activities should stop.”
Even had surgeons followed the universal protocol, about one third of wrong-site surgeries would not have been identified, according to Dr. Kwaan’s study, which was published in the same year as Dr. Seiden’s. As an example, when the wrong kidney was removed at Methodist Hospital, in St. Louis Park, Minn., the hospital said it was following a protocol set by the Minnesota Hospital Association.
Redoubling efforts
In 2009, the Joint Commission decided to take another tack. It encouraged hospitals to make root-cause analyses not only of wrong-site surgeries but also of near misses, which are much more plentiful. It used the insights gained to change surgical routines and protocols.
The Safe Surgery Project, a collaboration between the Joint Commission’s Center for Transforming Healthcare and eight hospitals and surgery centers, reduced the number of errors and near misses by 46% in the scheduling area, 63% in pre-op, and 51% in the OR area.
From that project, the center developed the Targeted Solutions Tool, which basically uses the same methodology that the project used. The center told this news organization that 79 healthcare organizations have used the tool and have reduced the number of errors and near misses by 56% in scheduling, 24% in pre-op, and 48% in the OR.
For this approach to work, however, surgical teams must report their errors to the hospital, which had not been done before. A 2008 study by the Office of the Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services found that surgical staff did not report 86% of adverse events to their hospitals. Reasons given included lack of time, fear of punitive action, and skepticism that reporting would do any good.
Unlike some other adverse events, it’s hard to keep wrong-site surgeries secret from patients, because they can usually see the scars from it, but some surgeons invent ways to cover it up from patients, too, Dr. Mayer says. One wrong-side hernia repair was corrected in mid operation. Afterward, the surgeon told the patient that he had found another hernia on the other side and had fixed that one, too.
Changing the culture
Reformers argue that wrong-site surgeries can be prevented by changing the culture of the hospital or surgery center. “We have to think of wrong-site surgeries as a failure of the system, not of the individual,” says Ron Savrin, MD, a general surgeon in Chagrin Falls, Ohio, who is a surgery subject matter expert for the Sullivan Group. “It should never be only up to one individual to stop an error from occurring.”
Seeing oneself as part of a team can reduce errors. Although other people can introduce errors that make a person look bad, they can also stop the errors that might otherwise have occurred. Punishing individuals for making errors does little good in stopping errors.
“It’s human nature to want to punish somebody for making a mistake, and it’s hard to change that mentality,” Dr. Savrin says. He recalls that when he was a resident, “the morbidity and mortality conferences could be very difficult for anyone who made a mistake, but I think that attitude is changing.”
Studies have found wide variation in the number of wrong-site surgeries among hospitals. A recent Pennsylvania study found an average of one wrong-site surgery or near miss per hospital per year, but about one third of hospitals did not report any.
Wrong-site surgeries are often concentrated in certain hospitals -- even prestigious teaching hospitals are not immune. A decade ago, Rhode Island Hospital had five wrong-site surgeries in 2 years, and Boston’s Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center had three wrong-spine surgeries within 2 months.
Other ways to reduce errors
Dr. Seiden thinks reform efforts should take a page from his own specialty. Anesthesiology has developed a variety of forcing functions, which are simple changes in technology that can stop errors. An example is the use of a valve that will not deliver a drug unless certain steps are followed.
The StartBox System, a new way to prevent surgical errors, delivers the surgery blade only after all safety information has been provided. Tested by 11 orthopedic surgeons performing 487 procedures, the system identified 17 near misses.
Another approach is to film time-outs so as to enforce compliance with protocols and help with root-cause analyses. NYU-Langone Medical Center, in New York City, not only films the time-out but also grades OR teams on compliance, says Dr. Bosco, who is vice chair of clinical affairs in the department of orthopedic surgery at the hospital.
In addition, more states are requiring hospitals to report adverse events, including wrong-site surgeries. According to the National Academy for State Health Policy, 28 states require the reporting of adverse events. However, only six states identify facilities in public reports; 16 states publish only aggregate data; and five states do not report error data to the public.
The goal is zero errors
Are there fewer wrong-site surgeries now? “My sense is that surgeons, hospitals, and surgery centers are taking wrong-site errors more seriously,” Dr. Savrin says.
Because reported information is spotty and no major studies on incidence have been conducted in recent years, “we don’t have a clear idea,” he says, “but my best guess is that the rate is declining.
“Absolute zero preventable errors has to be our goal,” Dr. Savrin says “We might not get there, but we can’t stop trying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In July 2021, University Hospitals, in Cleveland, announced that its staff had transplanted a kidney into the wrong patient. Although the patient who received the kidney was recovering well, the patient who was supposed to have received the kidney was skipped over. As a result of the error, two employees were placed on administrative leave and the incident was being investigated, the hospital announced.
In April 2020, an interventional radiologist at Boca Raton Regional Hospital, in Boca Raton, Fla., was sued for allegedly placing a stent into the wrong kidney of an 80-year-old patient. Using fluoroscopic guidance, the doctor removed an old stent from the right side but incorrectly replaced it with a new stent on the left side, according to an interview conducted by this news organization with the patient’s lawyers at Searcy Law, in West Palm Beach.
“The problem is that it is so rare that doctors don’t focus on it,” says Mary R. Kwaan, MD, a colorectal surgeon at UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles.
A 2006 study in which Kwaan was the lead author concluded that there was one wrong-site surgery for every 112,994 surgeries. Those mistakes can add up. A 2006 study estimated that 25 to 52 wrong-site surgeries were performed each week in the United States.
“Many surgeons don’t think it can happen to them, so they don’t take extra precautions,” says David Mayer, MD, executive director of the MedStar Institute for Quality and Safety, in Washington, DC. “When they make a wrong-site error, usually the first thing they say is, ‘I never thought this would happen to me,’ ” he says.
Wrong-site surgeries are considered sentinel events -- the worst kinds of medical errors. The Sullivan Group, a patient safety consultancy based in Colorado, reports that in 2013, 2.7% of patients who were involved in wrong-site surgeries died and 41% experienced some type of permanent injury. The mean malpractice payment was $127,000.
Some malpractice payments are much higher. In 2013, a Maryland ob.gyn paid a $1.42 million malpractice award for removing the wrong ovary from a woman in 2009. In 2017, a Pennsylvania urologist paid $870,000 for removing the wrong testicle from a man in 2013.
Wrong-site surgery often involves experienced surgeons
One might think that wrong-site surgeries usually involve younger or less-experienced surgeons, but that’s not the case; two thirds of the surgeons who perform wrong-site surgeries are in their 40s and 50s, compared with fewer than 25% younger than 40.
In a rather chilling statistic, in a 2013 survey, 12.4% of doctors who were involved in sentinel events in general had claims for more than one event.
These errors are more common in certain specialties. In a study reported in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Spine, 25% of orthopedic surgeons reported performing at least one wrong-site surgery during their career.
Within orthopedics, spine surgery is ground zero for wrong-site surgery. “Finding the site in spine surgery can be more difficult than in common left-right orthopedic procedures,” says Joseph A. Bosco III, a New York City orthopedist.
A 2007 study found that 25% of neurosurgeons had performed wrong-site surgeries. In Missouri in 2013, for example, a 53-year-old patient who was scheduled to undergo a left-sided craniotomy bypass allegedly underwent a right-sided craniotomy and was unable to speak after surgery.
Wrong-site surgeries are also performed by general surgeons, urologists, cardiologists, otolaryngologists, and ophthalmologists. A 2021 lawsuit accused a Tampa urologist of removing the patient’s wrong testicle. And a 2019 lawsuit accused a Chicago ophthalmologist of operating on the wrong eye to remove a cyst.
It’s not just the surgeon’s mistake
Mistakes are not only made by the surgeon in the operating room (OR). They can be made by staff when scheduling a surgery, radiologists and pathologists when writing their reports for surgery, and by team members in the OR.
Many people are prone to confusing left and right. A 2020 study found that 14.9% of people had difficulty distinguishing left from right; other studies have shown higher rates. Distractions increase the likelihood of mistakes. In a 2015 study, background noise in a hospital ward made it more difficult for medical students to make left-right judgments.
OR personnel can be confused when patients are turned around. “To operate on the back of someone’s leg, the surgeon may turn the patient from supine to prone, and so left becomes right,” says Samuel C. Seiden, MD, an anesthesiologist in Roseville, Calif., who has studied wrong-site surgery.
Operative site markings that are drawn on the skin can be rubbed off when surgical prep is applied, and markings aren’t usually possible for procedures such as spine surgeries. Surgical draping can make it harder to distinguish the patient’s left and right, and a busy surgeon relying on memory may confuse cases and perform wrong-patient surgery.
A push to eliminate wrong-site surgery
In 2004, the Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals and many surgery centers, decided to do something about wrong-site surgery and related surgical errors. It released a universal protocol, which requires hospitals to take three steps to prevent errors: perform preoperative verification that is based on patient care documents; mark the operative site; and take a time-out just before surgery, during which the team should consider whether a mistake is about to be made.
Two years after the Joint Commission published its protocol, Dr. Seiden led a study to determine what effect it had had. The investigators found that wrong-site cases had decreased by only about one third. Preventing wrong-site surgery “turns out to be more complicated to eradicate than anybody thought,” Mark Chassin, MD, president of the Joint Commission, stated a few years later.
Why did the protocol have only a limited effect? Dr. Seiden says that it has been hard to change doctors’ traditional attitudes against standardization. “Some have had an attitude that checklists are for dummies, but that is changing,” he says.
For instance, some surgical teams were not paying attention during time-outs. “The time-out should be like the invocation of the National Anthem,” an orthopedic surgeon from Iowa wrote. “All other activities should stop.”
Even had surgeons followed the universal protocol, about one third of wrong-site surgeries would not have been identified, according to Dr. Kwaan’s study, which was published in the same year as Dr. Seiden’s. As an example, when the wrong kidney was removed at Methodist Hospital, in St. Louis Park, Minn., the hospital said it was following a protocol set by the Minnesota Hospital Association.
Redoubling efforts
In 2009, the Joint Commission decided to take another tack. It encouraged hospitals to make root-cause analyses not only of wrong-site surgeries but also of near misses, which are much more plentiful. It used the insights gained to change surgical routines and protocols.
The Safe Surgery Project, a collaboration between the Joint Commission’s Center for Transforming Healthcare and eight hospitals and surgery centers, reduced the number of errors and near misses by 46% in the scheduling area, 63% in pre-op, and 51% in the OR area.
From that project, the center developed the Targeted Solutions Tool, which basically uses the same methodology that the project used. The center told this news organization that 79 healthcare organizations have used the tool and have reduced the number of errors and near misses by 56% in scheduling, 24% in pre-op, and 48% in the OR.
For this approach to work, however, surgical teams must report their errors to the hospital, which had not been done before. A 2008 study by the Office of the Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services found that surgical staff did not report 86% of adverse events to their hospitals. Reasons given included lack of time, fear of punitive action, and skepticism that reporting would do any good.
Unlike some other adverse events, it’s hard to keep wrong-site surgeries secret from patients, because they can usually see the scars from it, but some surgeons invent ways to cover it up from patients, too, Dr. Mayer says. One wrong-side hernia repair was corrected in mid operation. Afterward, the surgeon told the patient that he had found another hernia on the other side and had fixed that one, too.
Changing the culture
Reformers argue that wrong-site surgeries can be prevented by changing the culture of the hospital or surgery center. “We have to think of wrong-site surgeries as a failure of the system, not of the individual,” says Ron Savrin, MD, a general surgeon in Chagrin Falls, Ohio, who is a surgery subject matter expert for the Sullivan Group. “It should never be only up to one individual to stop an error from occurring.”
Seeing oneself as part of a team can reduce errors. Although other people can introduce errors that make a person look bad, they can also stop the errors that might otherwise have occurred. Punishing individuals for making errors does little good in stopping errors.
“It’s human nature to want to punish somebody for making a mistake, and it’s hard to change that mentality,” Dr. Savrin says. He recalls that when he was a resident, “the morbidity and mortality conferences could be very difficult for anyone who made a mistake, but I think that attitude is changing.”
Studies have found wide variation in the number of wrong-site surgeries among hospitals. A recent Pennsylvania study found an average of one wrong-site surgery or near miss per hospital per year, but about one third of hospitals did not report any.
Wrong-site surgeries are often concentrated in certain hospitals -- even prestigious teaching hospitals are not immune. A decade ago, Rhode Island Hospital had five wrong-site surgeries in 2 years, and Boston’s Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center had three wrong-spine surgeries within 2 months.
Other ways to reduce errors
Dr. Seiden thinks reform efforts should take a page from his own specialty. Anesthesiology has developed a variety of forcing functions, which are simple changes in technology that can stop errors. An example is the use of a valve that will not deliver a drug unless certain steps are followed.
The StartBox System, a new way to prevent surgical errors, delivers the surgery blade only after all safety information has been provided. Tested by 11 orthopedic surgeons performing 487 procedures, the system identified 17 near misses.
Another approach is to film time-outs so as to enforce compliance with protocols and help with root-cause analyses. NYU-Langone Medical Center, in New York City, not only films the time-out but also grades OR teams on compliance, says Dr. Bosco, who is vice chair of clinical affairs in the department of orthopedic surgery at the hospital.
In addition, more states are requiring hospitals to report adverse events, including wrong-site surgeries. According to the National Academy for State Health Policy, 28 states require the reporting of adverse events. However, only six states identify facilities in public reports; 16 states publish only aggregate data; and five states do not report error data to the public.
The goal is zero errors
Are there fewer wrong-site surgeries now? “My sense is that surgeons, hospitals, and surgery centers are taking wrong-site errors more seriously,” Dr. Savrin says.
Because reported information is spotty and no major studies on incidence have been conducted in recent years, “we don’t have a clear idea,” he says, “but my best guess is that the rate is declining.
“Absolute zero preventable errors has to be our goal,” Dr. Savrin says “We might not get there, but we can’t stop trying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In July 2021, University Hospitals, in Cleveland, announced that its staff had transplanted a kidney into the wrong patient. Although the patient who received the kidney was recovering well, the patient who was supposed to have received the kidney was skipped over. As a result of the error, two employees were placed on administrative leave and the incident was being investigated, the hospital announced.
In April 2020, an interventional radiologist at Boca Raton Regional Hospital, in Boca Raton, Fla., was sued for allegedly placing a stent into the wrong kidney of an 80-year-old patient. Using fluoroscopic guidance, the doctor removed an old stent from the right side but incorrectly replaced it with a new stent on the left side, according to an interview conducted by this news organization with the patient’s lawyers at Searcy Law, in West Palm Beach.
“The problem is that it is so rare that doctors don’t focus on it,” says Mary R. Kwaan, MD, a colorectal surgeon at UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles.
A 2006 study in which Kwaan was the lead author concluded that there was one wrong-site surgery for every 112,994 surgeries. Those mistakes can add up. A 2006 study estimated that 25 to 52 wrong-site surgeries were performed each week in the United States.
“Many surgeons don’t think it can happen to them, so they don’t take extra precautions,” says David Mayer, MD, executive director of the MedStar Institute for Quality and Safety, in Washington, DC. “When they make a wrong-site error, usually the first thing they say is, ‘I never thought this would happen to me,’ ” he says.
Wrong-site surgeries are considered sentinel events -- the worst kinds of medical errors. The Sullivan Group, a patient safety consultancy based in Colorado, reports that in 2013, 2.7% of patients who were involved in wrong-site surgeries died and 41% experienced some type of permanent injury. The mean malpractice payment was $127,000.
Some malpractice payments are much higher. In 2013, a Maryland ob.gyn paid a $1.42 million malpractice award for removing the wrong ovary from a woman in 2009. In 2017, a Pennsylvania urologist paid $870,000 for removing the wrong testicle from a man in 2013.
Wrong-site surgery often involves experienced surgeons
One might think that wrong-site surgeries usually involve younger or less-experienced surgeons, but that’s not the case; two thirds of the surgeons who perform wrong-site surgeries are in their 40s and 50s, compared with fewer than 25% younger than 40.
In a rather chilling statistic, in a 2013 survey, 12.4% of doctors who were involved in sentinel events in general had claims for more than one event.
These errors are more common in certain specialties. In a study reported in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Spine, 25% of orthopedic surgeons reported performing at least one wrong-site surgery during their career.
Within orthopedics, spine surgery is ground zero for wrong-site surgery. “Finding the site in spine surgery can be more difficult than in common left-right orthopedic procedures,” says Joseph A. Bosco III, a New York City orthopedist.
A 2007 study found that 25% of neurosurgeons had performed wrong-site surgeries. In Missouri in 2013, for example, a 53-year-old patient who was scheduled to undergo a left-sided craniotomy bypass allegedly underwent a right-sided craniotomy and was unable to speak after surgery.
Wrong-site surgeries are also performed by general surgeons, urologists, cardiologists, otolaryngologists, and ophthalmologists. A 2021 lawsuit accused a Tampa urologist of removing the patient’s wrong testicle. And a 2019 lawsuit accused a Chicago ophthalmologist of operating on the wrong eye to remove a cyst.
It’s not just the surgeon’s mistake
Mistakes are not only made by the surgeon in the operating room (OR). They can be made by staff when scheduling a surgery, radiologists and pathologists when writing their reports for surgery, and by team members in the OR.
Many people are prone to confusing left and right. A 2020 study found that 14.9% of people had difficulty distinguishing left from right; other studies have shown higher rates. Distractions increase the likelihood of mistakes. In a 2015 study, background noise in a hospital ward made it more difficult for medical students to make left-right judgments.
OR personnel can be confused when patients are turned around. “To operate on the back of someone’s leg, the surgeon may turn the patient from supine to prone, and so left becomes right,” says Samuel C. Seiden, MD, an anesthesiologist in Roseville, Calif., who has studied wrong-site surgery.
Operative site markings that are drawn on the skin can be rubbed off when surgical prep is applied, and markings aren’t usually possible for procedures such as spine surgeries. Surgical draping can make it harder to distinguish the patient’s left and right, and a busy surgeon relying on memory may confuse cases and perform wrong-patient surgery.
A push to eliminate wrong-site surgery
In 2004, the Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals and many surgery centers, decided to do something about wrong-site surgery and related surgical errors. It released a universal protocol, which requires hospitals to take three steps to prevent errors: perform preoperative verification that is based on patient care documents; mark the operative site; and take a time-out just before surgery, during which the team should consider whether a mistake is about to be made.
Two years after the Joint Commission published its protocol, Dr. Seiden led a study to determine what effect it had had. The investigators found that wrong-site cases had decreased by only about one third. Preventing wrong-site surgery “turns out to be more complicated to eradicate than anybody thought,” Mark Chassin, MD, president of the Joint Commission, stated a few years later.
Why did the protocol have only a limited effect? Dr. Seiden says that it has been hard to change doctors’ traditional attitudes against standardization. “Some have had an attitude that checklists are for dummies, but that is changing,” he says.
For instance, some surgical teams were not paying attention during time-outs. “The time-out should be like the invocation of the National Anthem,” an orthopedic surgeon from Iowa wrote. “All other activities should stop.”
Even had surgeons followed the universal protocol, about one third of wrong-site surgeries would not have been identified, according to Dr. Kwaan’s study, which was published in the same year as Dr. Seiden’s. As an example, when the wrong kidney was removed at Methodist Hospital, in St. Louis Park, Minn., the hospital said it was following a protocol set by the Minnesota Hospital Association.
Redoubling efforts
In 2009, the Joint Commission decided to take another tack. It encouraged hospitals to make root-cause analyses not only of wrong-site surgeries but also of near misses, which are much more plentiful. It used the insights gained to change surgical routines and protocols.
The Safe Surgery Project, a collaboration between the Joint Commission’s Center for Transforming Healthcare and eight hospitals and surgery centers, reduced the number of errors and near misses by 46% in the scheduling area, 63% in pre-op, and 51% in the OR area.
From that project, the center developed the Targeted Solutions Tool, which basically uses the same methodology that the project used. The center told this news organization that 79 healthcare organizations have used the tool and have reduced the number of errors and near misses by 56% in scheduling, 24% in pre-op, and 48% in the OR.
For this approach to work, however, surgical teams must report their errors to the hospital, which had not been done before. A 2008 study by the Office of the Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services found that surgical staff did not report 86% of adverse events to their hospitals. Reasons given included lack of time, fear of punitive action, and skepticism that reporting would do any good.
Unlike some other adverse events, it’s hard to keep wrong-site surgeries secret from patients, because they can usually see the scars from it, but some surgeons invent ways to cover it up from patients, too, Dr. Mayer says. One wrong-side hernia repair was corrected in mid operation. Afterward, the surgeon told the patient that he had found another hernia on the other side and had fixed that one, too.
Changing the culture
Reformers argue that wrong-site surgeries can be prevented by changing the culture of the hospital or surgery center. “We have to think of wrong-site surgeries as a failure of the system, not of the individual,” says Ron Savrin, MD, a general surgeon in Chagrin Falls, Ohio, who is a surgery subject matter expert for the Sullivan Group. “It should never be only up to one individual to stop an error from occurring.”
Seeing oneself as part of a team can reduce errors. Although other people can introduce errors that make a person look bad, they can also stop the errors that might otherwise have occurred. Punishing individuals for making errors does little good in stopping errors.
“It’s human nature to want to punish somebody for making a mistake, and it’s hard to change that mentality,” Dr. Savrin says. He recalls that when he was a resident, “the morbidity and mortality conferences could be very difficult for anyone who made a mistake, but I think that attitude is changing.”
Studies have found wide variation in the number of wrong-site surgeries among hospitals. A recent Pennsylvania study found an average of one wrong-site surgery or near miss per hospital per year, but about one third of hospitals did not report any.
Wrong-site surgeries are often concentrated in certain hospitals -- even prestigious teaching hospitals are not immune. A decade ago, Rhode Island Hospital had five wrong-site surgeries in 2 years, and Boston’s Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center had three wrong-spine surgeries within 2 months.
Other ways to reduce errors
Dr. Seiden thinks reform efforts should take a page from his own specialty. Anesthesiology has developed a variety of forcing functions, which are simple changes in technology that can stop errors. An example is the use of a valve that will not deliver a drug unless certain steps are followed.
The StartBox System, a new way to prevent surgical errors, delivers the surgery blade only after all safety information has been provided. Tested by 11 orthopedic surgeons performing 487 procedures, the system identified 17 near misses.
Another approach is to film time-outs so as to enforce compliance with protocols and help with root-cause analyses. NYU-Langone Medical Center, in New York City, not only films the time-out but also grades OR teams on compliance, says Dr. Bosco, who is vice chair of clinical affairs in the department of orthopedic surgery at the hospital.
In addition, more states are requiring hospitals to report adverse events, including wrong-site surgeries. According to the National Academy for State Health Policy, 28 states require the reporting of adverse events. However, only six states identify facilities in public reports; 16 states publish only aggregate data; and five states do not report error data to the public.
The goal is zero errors
Are there fewer wrong-site surgeries now? “My sense is that surgeons, hospitals, and surgery centers are taking wrong-site errors more seriously,” Dr. Savrin says.
Because reported information is spotty and no major studies on incidence have been conducted in recent years, “we don’t have a clear idea,” he says, “but my best guess is that the rate is declining.
“Absolute zero preventable errors has to be our goal,” Dr. Savrin says “We might not get there, but we can’t stop trying.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Age, C-reactive protein predict COVID-19 death in diabetes
The data, from the retrospective ACCREDIT cohort study, were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2021) by Daniel Kevin Llanera, MD.
The combination of older age and high levels of the inflammatory marker CRP were linked to a tripled risk for death by day 7 after hospitalization for COVID-19 among people with diabetes. But, in contrast to other studies, recent A1c and body mass index did not predict COVID-19 outcomes.
“Both of these variables are easily available upon admission to hospital,” Dr. Llanera, who now works at Imperial College, London, said in an EASD press release.
“This means we can easily identify patients early on in their hospital stay who will likely require more aggressive interventions to try and improve survival.”
“It makes sense that CRP and age are important,” said Simon Heller, MB BChir, DM, of the University of Sheffield, England. “It may be that diabetes alone overwhelmed the additional effects of obesity and A1c.
“Certainly in other studies, age was the overwhelming bad prognostic sign among people with diabetes, and perhaps long-term diabetes has effects on the immune system which we haven’t yet identified.”
Kidney disease in younger patients also linked to poorer outcomes
The study, conducted when Dr. Llanera worked for the Countess of Chester NHS Foundation Trust, involved 1,004 patients with diabetes admitted with COVID-19 to seven hospitals in northwest England from Jan. 1 through June 30, 2020. The patients were a mean age of 74.1 years, 60.7% were male, and 45% were in the most deprived quintile based on the U.K. government deprivation index. Overall, 56.2% had macrovascular complications and 49.6% had microvascular complications.
They had a median BMI of 27.6 kg/m2, which is lower than that reported in previous studies and might explain the difference, Dr. Llanera noted.
The primary outcome, death within 7 days of admission, occurred in 24%. By day 30, 33% had died. These rates are higher than the rate found in previous studies, possibly because of greater socioeconomic deprivation and older age of the population, Dr. Llanera speculated.
A total of 7.5% of patients received intensive care by day 7 and 9.8% required intravenous insulin infusions.
On univariate analysis, insulin infusion was found to be protective, with those receiving it half as likely to die as those who didn’t need IV insulin (odds ratio [OR], 0.5).
In contrast, chronic kidney disease in people younger than 70 years increased the risk of death more than twofold (OR, 2.74), as did type 2 diabetes compared with other diabetes types (OR, 2.52).
As in previous studies, use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers were not associated with COVID-19 outcomes, nor was the presence of diabetes-related complications.
In multivariate analysis, CRP and age emerged as the most significant predictors of the primary outcome, with those deemed high risk by a logistic regression model having an OR of 3.44 for death by day 7 compared with those at lower risk based on the two factors.
Data for glycemic control during the time of hospitalization weren’t available for this study, Dr. Llanera said in response to a question.
“We didn’t look into glycemic control during admission, just at entry, so I can’t answer whether strict glucose control is of benefit. I think it’s worth exploring further whether the use of IV insulin may be of benefit.”
Dr. Llanera also pointed out that people with diabetic kidney disease are in a chronic proinflammatory state and have immune dysregulation, thus potentially hindering their ability to “fight off” the virus.
“In addition, ACE2 receptors are upregulated in the kidneys of patients with diabetic kidney disease. These are molecules that facilitate entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. This may lead to direct attack of the kidneys by the virus, possibly leading to worse overall outcomes,” he said.
Dr. Llanera has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heller has reported serving as consultant or speaker for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Mannkind, Zealand, MSD, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data, from the retrospective ACCREDIT cohort study, were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2021) by Daniel Kevin Llanera, MD.
The combination of older age and high levels of the inflammatory marker CRP were linked to a tripled risk for death by day 7 after hospitalization for COVID-19 among people with diabetes. But, in contrast to other studies, recent A1c and body mass index did not predict COVID-19 outcomes.
“Both of these variables are easily available upon admission to hospital,” Dr. Llanera, who now works at Imperial College, London, said in an EASD press release.
“This means we can easily identify patients early on in their hospital stay who will likely require more aggressive interventions to try and improve survival.”
“It makes sense that CRP and age are important,” said Simon Heller, MB BChir, DM, of the University of Sheffield, England. “It may be that diabetes alone overwhelmed the additional effects of obesity and A1c.
“Certainly in other studies, age was the overwhelming bad prognostic sign among people with diabetes, and perhaps long-term diabetes has effects on the immune system which we haven’t yet identified.”
Kidney disease in younger patients also linked to poorer outcomes
The study, conducted when Dr. Llanera worked for the Countess of Chester NHS Foundation Trust, involved 1,004 patients with diabetes admitted with COVID-19 to seven hospitals in northwest England from Jan. 1 through June 30, 2020. The patients were a mean age of 74.1 years, 60.7% were male, and 45% were in the most deprived quintile based on the U.K. government deprivation index. Overall, 56.2% had macrovascular complications and 49.6% had microvascular complications.
They had a median BMI of 27.6 kg/m2, which is lower than that reported in previous studies and might explain the difference, Dr. Llanera noted.
The primary outcome, death within 7 days of admission, occurred in 24%. By day 30, 33% had died. These rates are higher than the rate found in previous studies, possibly because of greater socioeconomic deprivation and older age of the population, Dr. Llanera speculated.
A total of 7.5% of patients received intensive care by day 7 and 9.8% required intravenous insulin infusions.
On univariate analysis, insulin infusion was found to be protective, with those receiving it half as likely to die as those who didn’t need IV insulin (odds ratio [OR], 0.5).
In contrast, chronic kidney disease in people younger than 70 years increased the risk of death more than twofold (OR, 2.74), as did type 2 diabetes compared with other diabetes types (OR, 2.52).
As in previous studies, use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers were not associated with COVID-19 outcomes, nor was the presence of diabetes-related complications.
In multivariate analysis, CRP and age emerged as the most significant predictors of the primary outcome, with those deemed high risk by a logistic regression model having an OR of 3.44 for death by day 7 compared with those at lower risk based on the two factors.
Data for glycemic control during the time of hospitalization weren’t available for this study, Dr. Llanera said in response to a question.
“We didn’t look into glycemic control during admission, just at entry, so I can’t answer whether strict glucose control is of benefit. I think it’s worth exploring further whether the use of IV insulin may be of benefit.”
Dr. Llanera also pointed out that people with diabetic kidney disease are in a chronic proinflammatory state and have immune dysregulation, thus potentially hindering their ability to “fight off” the virus.
“In addition, ACE2 receptors are upregulated in the kidneys of patients with diabetic kidney disease. These are molecules that facilitate entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. This may lead to direct attack of the kidneys by the virus, possibly leading to worse overall outcomes,” he said.
Dr. Llanera has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heller has reported serving as consultant or speaker for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Mannkind, Zealand, MSD, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The data, from the retrospective ACCREDIT cohort study, were presented at the virtual annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD 2021) by Daniel Kevin Llanera, MD.
The combination of older age and high levels of the inflammatory marker CRP were linked to a tripled risk for death by day 7 after hospitalization for COVID-19 among people with diabetes. But, in contrast to other studies, recent A1c and body mass index did not predict COVID-19 outcomes.
“Both of these variables are easily available upon admission to hospital,” Dr. Llanera, who now works at Imperial College, London, said in an EASD press release.
“This means we can easily identify patients early on in their hospital stay who will likely require more aggressive interventions to try and improve survival.”
“It makes sense that CRP and age are important,” said Simon Heller, MB BChir, DM, of the University of Sheffield, England. “It may be that diabetes alone overwhelmed the additional effects of obesity and A1c.
“Certainly in other studies, age was the overwhelming bad prognostic sign among people with diabetes, and perhaps long-term diabetes has effects on the immune system which we haven’t yet identified.”
Kidney disease in younger patients also linked to poorer outcomes
The study, conducted when Dr. Llanera worked for the Countess of Chester NHS Foundation Trust, involved 1,004 patients with diabetes admitted with COVID-19 to seven hospitals in northwest England from Jan. 1 through June 30, 2020. The patients were a mean age of 74.1 years, 60.7% were male, and 45% were in the most deprived quintile based on the U.K. government deprivation index. Overall, 56.2% had macrovascular complications and 49.6% had microvascular complications.
They had a median BMI of 27.6 kg/m2, which is lower than that reported in previous studies and might explain the difference, Dr. Llanera noted.
The primary outcome, death within 7 days of admission, occurred in 24%. By day 30, 33% had died. These rates are higher than the rate found in previous studies, possibly because of greater socioeconomic deprivation and older age of the population, Dr. Llanera speculated.
A total of 7.5% of patients received intensive care by day 7 and 9.8% required intravenous insulin infusions.
On univariate analysis, insulin infusion was found to be protective, with those receiving it half as likely to die as those who didn’t need IV insulin (odds ratio [OR], 0.5).
In contrast, chronic kidney disease in people younger than 70 years increased the risk of death more than twofold (OR, 2.74), as did type 2 diabetes compared with other diabetes types (OR, 2.52).
As in previous studies, use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers were not associated with COVID-19 outcomes, nor was the presence of diabetes-related complications.
In multivariate analysis, CRP and age emerged as the most significant predictors of the primary outcome, with those deemed high risk by a logistic regression model having an OR of 3.44 for death by day 7 compared with those at lower risk based on the two factors.
Data for glycemic control during the time of hospitalization weren’t available for this study, Dr. Llanera said in response to a question.
“We didn’t look into glycemic control during admission, just at entry, so I can’t answer whether strict glucose control is of benefit. I think it’s worth exploring further whether the use of IV insulin may be of benefit.”
Dr. Llanera also pointed out that people with diabetic kidney disease are in a chronic proinflammatory state and have immune dysregulation, thus potentially hindering their ability to “fight off” the virus.
“In addition, ACE2 receptors are upregulated in the kidneys of patients with diabetic kidney disease. These are molecules that facilitate entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the cells. This may lead to direct attack of the kidneys by the virus, possibly leading to worse overall outcomes,” he said.
Dr. Llanera has reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Heller has reported serving as consultant or speaker for Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Sanofi Aventis, Mannkind, Zealand, MSD, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 hospitalization 80% more likely for smokers
Observational data was analyzed alongside hospital coronavirus test data and UK Biobank genetic information for the first time, and the findings are published in Thorax.
The data cover 421,469 people overall. Of these, 3.2% took a polymerase chain reaction swab test, 0.4% of these tested positive, 0.2% of them required hospitalization for COVID-19, and 0.1% of them died because of COVID-19.
When it came to smoking status, 59% had never smoked, 37% were ex-smokers, and 3% were current smokers.
Current smokers were 80% more likely to be admitted to hospital, and significantly more likely to die from COVID-19, than nonsmokers.
Time to quit
Heavy smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day were 6.11 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than people who had never smoked.
Analysis also showed those with a genetic predisposition to being smokers had a 45% higher infection risk, and 60% higher hospitalization risk.
The authors wrote: “Overall, the congruence of observational analyses indicating associations with recent smoking behaviors and [Mendelian randomization] analyses indicating associations with lifelong predisposition to smoking and smoking heaviness support a causal effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity.”
In a linked podcast, lead researcher Dr. Ashley Clift, said: “Our results strongly suggest that smoking is related to your risk of getting severe COVID, and just as smoking affects your risk of heart disease, different cancers, and all those other conditions we know smoking is linked to, it appears that it’s the same for COVID. So now might be as good a time as any to quit cigarettes and quit smoking.”
These results contrast with previous studies that have suggested a protective effect of smoking against COVID-19. In a linked editorial, Anthony Laverty, PhD, and Christopher Millet, PhD, Imperial College London, wrote: “The idea that tobacco smoking may protect against COVID-19 was always an improbable one.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Observational data was analyzed alongside hospital coronavirus test data and UK Biobank genetic information for the first time, and the findings are published in Thorax.
The data cover 421,469 people overall. Of these, 3.2% took a polymerase chain reaction swab test, 0.4% of these tested positive, 0.2% of them required hospitalization for COVID-19, and 0.1% of them died because of COVID-19.
When it came to smoking status, 59% had never smoked, 37% were ex-smokers, and 3% were current smokers.
Current smokers were 80% more likely to be admitted to hospital, and significantly more likely to die from COVID-19, than nonsmokers.
Time to quit
Heavy smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day were 6.11 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than people who had never smoked.
Analysis also showed those with a genetic predisposition to being smokers had a 45% higher infection risk, and 60% higher hospitalization risk.
The authors wrote: “Overall, the congruence of observational analyses indicating associations with recent smoking behaviors and [Mendelian randomization] analyses indicating associations with lifelong predisposition to smoking and smoking heaviness support a causal effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity.”
In a linked podcast, lead researcher Dr. Ashley Clift, said: “Our results strongly suggest that smoking is related to your risk of getting severe COVID, and just as smoking affects your risk of heart disease, different cancers, and all those other conditions we know smoking is linked to, it appears that it’s the same for COVID. So now might be as good a time as any to quit cigarettes and quit smoking.”
These results contrast with previous studies that have suggested a protective effect of smoking against COVID-19. In a linked editorial, Anthony Laverty, PhD, and Christopher Millet, PhD, Imperial College London, wrote: “The idea that tobacco smoking may protect against COVID-19 was always an improbable one.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Observational data was analyzed alongside hospital coronavirus test data and UK Biobank genetic information for the first time, and the findings are published in Thorax.
The data cover 421,469 people overall. Of these, 3.2% took a polymerase chain reaction swab test, 0.4% of these tested positive, 0.2% of them required hospitalization for COVID-19, and 0.1% of them died because of COVID-19.
When it came to smoking status, 59% had never smoked, 37% were ex-smokers, and 3% were current smokers.
Current smokers were 80% more likely to be admitted to hospital, and significantly more likely to die from COVID-19, than nonsmokers.
Time to quit
Heavy smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day were 6.11 times more likely to die from COVID-19 than people who had never smoked.
Analysis also showed those with a genetic predisposition to being smokers had a 45% higher infection risk, and 60% higher hospitalization risk.
The authors wrote: “Overall, the congruence of observational analyses indicating associations with recent smoking behaviors and [Mendelian randomization] analyses indicating associations with lifelong predisposition to smoking and smoking heaviness support a causal effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity.”
In a linked podcast, lead researcher Dr. Ashley Clift, said: “Our results strongly suggest that smoking is related to your risk of getting severe COVID, and just as smoking affects your risk of heart disease, different cancers, and all those other conditions we know smoking is linked to, it appears that it’s the same for COVID. So now might be as good a time as any to quit cigarettes and quit smoking.”
These results contrast with previous studies that have suggested a protective effect of smoking against COVID-19. In a linked editorial, Anthony Laverty, PhD, and Christopher Millet, PhD, Imperial College London, wrote: “The idea that tobacco smoking may protect against COVID-19 was always an improbable one.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth models of care for pediatric hospital medicine
PHM 2021 session
Let’s Go Virtual! Developing, Implementing, and Evaluating Telehealth Models of Care for Pediatric Hospital Medicine
Presenters
Brooke Geyer, DO; Christina Olson, MD; and Amy Willis, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Geyer, Dr. Olson, and Dr. Willis of the University of Colorado presented and facilitated a workshop discussing the role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine. Participants were given a brief introduction to the basics of telehealth practices before breaking up into small groups to explore the process of developing, implementing, and evaluating a telehealth model in a pediatric hospital. For each of these topics, the presenters led the breakout groups through a discussion of Colorado’s successful telehealth models, including virtual nocturnists, health system resource optimization, and virtual transitions of care, as well as addressed the participants’ questions unique to their telehealth experiences. The session emphasized the emerging role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine and that “telehealth is here to stay, and we have an opportunity to redesign health care forever.”
Key takeaways
- Telehealth is more than just synchronous virtual patient care, it encompasses asynchronous care, remote patient monitoring, education, policy, and more.
- Telehealth standards of care are the same as in-person care.
- Development and implementation of a telehealth model in pediatric hospital medicine is feasible with appropriate planning and conversations with key stakeholders.
- Evaluation and refinement of telehealth models is an iterative process that will take time, much like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles in quality improvement work.
Dr. Scott is a second-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at New York–Presbyterian Columbia/Cornell. Her academic interests are in curriculum development and evaluation in medical education with a focus on telemedicine.
PHM 2021 session
Let’s Go Virtual! Developing, Implementing, and Evaluating Telehealth Models of Care for Pediatric Hospital Medicine
Presenters
Brooke Geyer, DO; Christina Olson, MD; and Amy Willis, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Geyer, Dr. Olson, and Dr. Willis of the University of Colorado presented and facilitated a workshop discussing the role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine. Participants were given a brief introduction to the basics of telehealth practices before breaking up into small groups to explore the process of developing, implementing, and evaluating a telehealth model in a pediatric hospital. For each of these topics, the presenters led the breakout groups through a discussion of Colorado’s successful telehealth models, including virtual nocturnists, health system resource optimization, and virtual transitions of care, as well as addressed the participants’ questions unique to their telehealth experiences. The session emphasized the emerging role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine and that “telehealth is here to stay, and we have an opportunity to redesign health care forever.”
Key takeaways
- Telehealth is more than just synchronous virtual patient care, it encompasses asynchronous care, remote patient monitoring, education, policy, and more.
- Telehealth standards of care are the same as in-person care.
- Development and implementation of a telehealth model in pediatric hospital medicine is feasible with appropriate planning and conversations with key stakeholders.
- Evaluation and refinement of telehealth models is an iterative process that will take time, much like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles in quality improvement work.
Dr. Scott is a second-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at New York–Presbyterian Columbia/Cornell. Her academic interests are in curriculum development and evaluation in medical education with a focus on telemedicine.
PHM 2021 session
Let’s Go Virtual! Developing, Implementing, and Evaluating Telehealth Models of Care for Pediatric Hospital Medicine
Presenters
Brooke Geyer, DO; Christina Olson, MD; and Amy Willis, MD, FAAP
Session summary
Dr. Geyer, Dr. Olson, and Dr. Willis of the University of Colorado presented and facilitated a workshop discussing the role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine. Participants were given a brief introduction to the basics of telehealth practices before breaking up into small groups to explore the process of developing, implementing, and evaluating a telehealth model in a pediatric hospital. For each of these topics, the presenters led the breakout groups through a discussion of Colorado’s successful telehealth models, including virtual nocturnists, health system resource optimization, and virtual transitions of care, as well as addressed the participants’ questions unique to their telehealth experiences. The session emphasized the emerging role of telehealth in pediatric hospital medicine and that “telehealth is here to stay, and we have an opportunity to redesign health care forever.”
Key takeaways
- Telehealth is more than just synchronous virtual patient care, it encompasses asynchronous care, remote patient monitoring, education, policy, and more.
- Telehealth standards of care are the same as in-person care.
- Development and implementation of a telehealth model in pediatric hospital medicine is feasible with appropriate planning and conversations with key stakeholders.
- Evaluation and refinement of telehealth models is an iterative process that will take time, much like Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles in quality improvement work.
Dr. Scott is a second-year pediatric hospital medicine fellow at New York–Presbyterian Columbia/Cornell. Her academic interests are in curriculum development and evaluation in medical education with a focus on telemedicine.
Children and COVID: New cases topped 200,000 after 3 weeks of declines
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.
Weekly COVID-19 cases in children dropped again, but the count remained above 200,000 for the fifth consecutive week, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

based on the data in the AAP/CHA joint weekly report on COVID in children.
In the most recent week, Sept. 17-23, there were almost 207,000 new cases of COVID-19 in children, which represented 26.7% of all cases reported in the 46 states that are currently posting data by age on their COVID dashboards, the AAP and CHA said. (New York has never reported such data by age, and Alabama, Nebraska, and Texas have not updated their websites since July 29, June 24, and Aug. 26, respectively.)
The decline in new vaccinations among children, however, began before the summer surge in new cases hit its peak – 251,781 during the week of Aug. 27 to Sept. 2 – and has continued for 7 straight weeks in children aged 12-17 years, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
There were about 172,000 COVID vaccine initiations in children aged 12-17 for the week of Sept. 21-27, the lowest number since April, before it was approved for use in 12- to 15-year-olds. That figure is down by almost a third from the previous week and by more than two-thirds since early August, just before the decline in vaccinations began, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
The cumulative vaccine situation looks like this: Just over 13 million children under age 18 years have received at least one dose as of Sept. 27, and almost 10.6 million are fully vaccinated. By age group, 53.9% of 12- to 15-year-olds and 61.6% of 16- to 17-year-olds have received at least one dose, with corresponding figures of 43.3% and 51.3% for full vaccination, the CDC said.
COVID-related hospital admissions also continue to fall after peaking at 0.51 children aged 0-17 per 100,000 population on Sept. 4. The admission rate was down to 0.45 per 100,000 as of Sept. 17, and the latest 7-day average (Sept. 19-25) was 258 admissions, compared with a peak of 371 for the week of Aug. 29 to Sept. 4, the CDC reported.
“Although we have seen slight improvements in COVID-19 volumes in the past week, we are at the beginning of an anticipated increase in” multi-inflammatory syndrome in children, Margaret Rush, MD, president of Monroe Carell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., said at a recent hearing of the House Committee on Energy and Commerce’s Oversight subcommittee. That increase would be expected to produce “a secondary wave of seriously ill children 3-6 weeks after acute infection peaks in the community,” the American Hospital Association said.
Meanwhile, Dr. Rush noted, there are signs that seasonal viruses are coming into play. “With the emergence of the Delta variant, we’ve experienced a steep increase in COVID-19 hospitalizations among children on top of an early surge of [respiratory syncytial virus], a serious respiratory illness we usually see in the winter months,” she said in a prepared statement before her testimony.








