User login
Maternal COVID-19 May Not Harm Baby’s Neural Development
TOPLINE:
Fetuses exposed in utero to SARS-CoV-2 are not at an increased risk for neurodevelopmental problems in early childhood.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective study aimed to assess whether in utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, is associated with abnormal neurodevelopment among children at ages 12, 18, and 24 months.
- It included 2003 pregnant individuals (mean age, 33.3 years) from the ASPIRE cohort who were enrolled before 10 weeks’ gestation and followed through 24 months post partum; 10.8% of them were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy, as determined via self-reported data or dried blood spot cards.
- The birth mothers were required to complete the Ages & Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition (ASQ-3), a validated screening tool for neurodevelopmental delays, at 12, 18, and 24 months postpartum.
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes were available for 1757, 1522, and 1523 children at ages 12, 18, and 24 months, respectively.
- The primary outcome was a score below the cutoff on the ASQ-3 across any of the following developmental domains: Communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem-solving, and social skills.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of abnormal ASQ-3 scores did not differ between children who were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in utero and those who were not, at ages 12 (P = .39), 18 (P = .58), and 24 (P = .45) months.
- No association was observed between in utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and abnormal ASQ-3 scores among children in any of the age groups.
- The lack of an association between exposure to SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy and abnormal neurodevelopment remained unchanged even when factors such as preterm delivery and the sex of the infant were considered.
- Supplemental analyses found no difference in risk based on the trimester of infection, presence of fever, or incidence of breakthrough infection following vaccination.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this prospective cohort study of pregnant individuals and offspring, in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with abnormal neurodevelopmental screening scores of children through age 24 months. These findings are critical considering the novelty of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to the human species, the global scale of the initial COVID-19 outbreak, the now-endemic nature of the virus indicating ongoing relevance for pregnant individuals,” the authors of the study wrote.
“While the scientific consensus resists a link between in utero COVID-19 exposure and impaired offspring neurodevelopment, the question remains whether societal responses to the pandemic impacted developmental trajectories,” the researchers added. “Certain studies comparing infants from a pandemic cohort with historic controls have raised concerns about lower ASQ-3 scores among children living during the pandemic. Critically, socioeconomic factors influence vulnerability, not only to infection itself but also regarding the ability to deploy resources in times of stress (eg, school closures) to mitigate sources of developmental harm. Our data support this theory, with the observed independent protective association of increasing household income with childhood ASQ-3 scores. Additional research is warranted to clarify the potential impact of societal measures on early development and the differential impact of these measures on different communities.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Eleni G. Jaswa, MD, MSc, of the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences at the University of California, San Francisco. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations of the research included the use of self-reported data and dried blood spot cards for determining exposure to SARS-CoV-2, which may have led to misclassification. The ASQ-3 is a modestly sensitive tool for detecting developmental delays that may have affected the study’s power to detect associations. The sample size of this study, while larger than many, may still have been underpowered to detect small differences in neurodevelopmental outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The ASPIRE cohort was supported by research grants provided to the University of California, San Francisco, and by the Start Small Foundation, the California Breast Cancer Research Program, the COVID Catalyst Award, and other sources. Some authors reported receiving grants, royalties, and personal fees, serving on medical advisory boards, and having other ties with several institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Fetuses exposed in utero to SARS-CoV-2 are not at an increased risk for neurodevelopmental problems in early childhood.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective study aimed to assess whether in utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, is associated with abnormal neurodevelopment among children at ages 12, 18, and 24 months.
- It included 2003 pregnant individuals (mean age, 33.3 years) from the ASPIRE cohort who were enrolled before 10 weeks’ gestation and followed through 24 months post partum; 10.8% of them were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy, as determined via self-reported data or dried blood spot cards.
- The birth mothers were required to complete the Ages & Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition (ASQ-3), a validated screening tool for neurodevelopmental delays, at 12, 18, and 24 months postpartum.
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes were available for 1757, 1522, and 1523 children at ages 12, 18, and 24 months, respectively.
- The primary outcome was a score below the cutoff on the ASQ-3 across any of the following developmental domains: Communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem-solving, and social skills.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of abnormal ASQ-3 scores did not differ between children who were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in utero and those who were not, at ages 12 (P = .39), 18 (P = .58), and 24 (P = .45) months.
- No association was observed between in utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and abnormal ASQ-3 scores among children in any of the age groups.
- The lack of an association between exposure to SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy and abnormal neurodevelopment remained unchanged even when factors such as preterm delivery and the sex of the infant were considered.
- Supplemental analyses found no difference in risk based on the trimester of infection, presence of fever, or incidence of breakthrough infection following vaccination.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this prospective cohort study of pregnant individuals and offspring, in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with abnormal neurodevelopmental screening scores of children through age 24 months. These findings are critical considering the novelty of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to the human species, the global scale of the initial COVID-19 outbreak, the now-endemic nature of the virus indicating ongoing relevance for pregnant individuals,” the authors of the study wrote.
“While the scientific consensus resists a link between in utero COVID-19 exposure and impaired offspring neurodevelopment, the question remains whether societal responses to the pandemic impacted developmental trajectories,” the researchers added. “Certain studies comparing infants from a pandemic cohort with historic controls have raised concerns about lower ASQ-3 scores among children living during the pandemic. Critically, socioeconomic factors influence vulnerability, not only to infection itself but also regarding the ability to deploy resources in times of stress (eg, school closures) to mitigate sources of developmental harm. Our data support this theory, with the observed independent protective association of increasing household income with childhood ASQ-3 scores. Additional research is warranted to clarify the potential impact of societal measures on early development and the differential impact of these measures on different communities.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Eleni G. Jaswa, MD, MSc, of the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences at the University of California, San Francisco. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations of the research included the use of self-reported data and dried blood spot cards for determining exposure to SARS-CoV-2, which may have led to misclassification. The ASQ-3 is a modestly sensitive tool for detecting developmental delays that may have affected the study’s power to detect associations. The sample size of this study, while larger than many, may still have been underpowered to detect small differences in neurodevelopmental outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The ASPIRE cohort was supported by research grants provided to the University of California, San Francisco, and by the Start Small Foundation, the California Breast Cancer Research Program, the COVID Catalyst Award, and other sources. Some authors reported receiving grants, royalties, and personal fees, serving on medical advisory boards, and having other ties with several institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Fetuses exposed in utero to SARS-CoV-2 are not at an increased risk for neurodevelopmental problems in early childhood.
METHODOLOGY:
- This prospective study aimed to assess whether in utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19, is associated with abnormal neurodevelopment among children at ages 12, 18, and 24 months.
- It included 2003 pregnant individuals (mean age, 33.3 years) from the ASPIRE cohort who were enrolled before 10 weeks’ gestation and followed through 24 months post partum; 10.8% of them were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy, as determined via self-reported data or dried blood spot cards.
- The birth mothers were required to complete the Ages & Stages Questionnaires, Third Edition (ASQ-3), a validated screening tool for neurodevelopmental delays, at 12, 18, and 24 months postpartum.
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes were available for 1757, 1522, and 1523 children at ages 12, 18, and 24 months, respectively.
- The primary outcome was a score below the cutoff on the ASQ-3 across any of the following developmental domains: Communication, gross motor, fine motor, problem-solving, and social skills.
TAKEAWAY:
- The prevalence of abnormal ASQ-3 scores did not differ between children who were exposed to SARS-CoV-2 in utero and those who were not, at ages 12 (P = .39), 18 (P = .58), and 24 (P = .45) months.
- No association was observed between in utero exposure to SARS-CoV-2 and abnormal ASQ-3 scores among children in any of the age groups.
- The lack of an association between exposure to SARS-CoV-2 during pregnancy and abnormal neurodevelopment remained unchanged even when factors such as preterm delivery and the sex of the infant were considered.
- Supplemental analyses found no difference in risk based on the trimester of infection, presence of fever, or incidence of breakthrough infection following vaccination.
IN PRACTICE:
“In this prospective cohort study of pregnant individuals and offspring, in utero exposure to maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with abnormal neurodevelopmental screening scores of children through age 24 months. These findings are critical considering the novelty of the SARS-CoV-2 virus to the human species, the global scale of the initial COVID-19 outbreak, the now-endemic nature of the virus indicating ongoing relevance for pregnant individuals,” the authors of the study wrote.
“While the scientific consensus resists a link between in utero COVID-19 exposure and impaired offspring neurodevelopment, the question remains whether societal responses to the pandemic impacted developmental trajectories,” the researchers added. “Certain studies comparing infants from a pandemic cohort with historic controls have raised concerns about lower ASQ-3 scores among children living during the pandemic. Critically, socioeconomic factors influence vulnerability, not only to infection itself but also regarding the ability to deploy resources in times of stress (eg, school closures) to mitigate sources of developmental harm. Our data support this theory, with the observed independent protective association of increasing household income with childhood ASQ-3 scores. Additional research is warranted to clarify the potential impact of societal measures on early development and the differential impact of these measures on different communities.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Eleni G. Jaswa, MD, MSc, of the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology & Reproductive Sciences at the University of California, San Francisco. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations of the research included the use of self-reported data and dried blood spot cards for determining exposure to SARS-CoV-2, which may have led to misclassification. The ASQ-3 is a modestly sensitive tool for detecting developmental delays that may have affected the study’s power to detect associations. The sample size of this study, while larger than many, may still have been underpowered to detect small differences in neurodevelopmental outcomes.
DISCLOSURES:
The ASPIRE cohort was supported by research grants provided to the University of California, San Francisco, and by the Start Small Foundation, the California Breast Cancer Research Program, the COVID Catalyst Award, and other sources. Some authors reported receiving grants, royalties, and personal fees, serving on medical advisory boards, and having other ties with several institutions.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Avoid Too Low or High Vitamin D Levels for Best Pregnancy Outcomes in Lupus
TOPLINE:
Both low and high levels of maternal 25-hydroxy [25(OH)] vitamin D are linked to an increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with levels of 40-59 ng/mL being associated with the lowest risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed 260 pregnancies in the Hopkins Lupus Cohort to examine the association between 25(OH) vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with SLE.
- The participants were required to have serum vitamin D levels measured during pregnancy and pregnancy-related outcomes data.
- The 25(OH) vitamin D levels were measured at visits every 6 weeks, and the participants were divided into six subgroups on the basis of the mean 25(OH) vitamin D levels: < 20 ng/dL, 20-29 ng/dL, 30-39 ng/dL, 40-49 ng/dL, 50-59 ng/dL, and ≥ 60 ng/dL.
- The adverse pregnancy outcomes included miscarriage, preterm delivery, and restricted intrauterine growth of the fetus.
- This study used a time-to-event analysis to assess the association between time-varying 25(OH) vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Adverse pregnancy outcomes were observed in 45.3% of pregnancies; the risks for miscarriage and preterm delivery were significantly different across the six subgroups with varying vitamin D levels (P = .0045 and P = .0007, respectively).
- A U-shaped curve association was observed between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes, with the highest risk seen in patients with the lowest or highest levels of vitamin D during pregnancy, while the lowest risk was seen in those with vitamin D levels between 40 and 59 ng/mL.
- Low 25(OH) vitamin D levels during the second trimester resulted in premature delivery in 9 out of 10 pregnancies; however, a relationship between vitamin D levels in the first trimester and pregnancy outcomes was not observed.
- The time-to-event analysis showed that the U-shaped association between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes was still observed even after accounting for lupus disease activity; however, the elevated risk seen in individuals with the highest levels of vitamin D was no longer statistically significant.
IN PRACTICE:
“We recommend monitoring of maternal serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels throughout SLE pregnancies and supplementing patients with vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency, aiming for 25(OH) vitamin D range of 40-59 ng/mL. Over supplementation should be avoided,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Nima Madanchi, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and was published online on September 23, 2024, in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
This study could not prove a cause-and-effect relationship between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes. This study included only clinically identified pregnancies, potentially missing very early miscarriages. It also could not adjust for parity due to the unknown parity of the index pregnancy.
DISCLOSURES:
This Hopkins Lupus Cohort was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both low and high levels of maternal 25-hydroxy [25(OH)] vitamin D are linked to an increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with levels of 40-59 ng/mL being associated with the lowest risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed 260 pregnancies in the Hopkins Lupus Cohort to examine the association between 25(OH) vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with SLE.
- The participants were required to have serum vitamin D levels measured during pregnancy and pregnancy-related outcomes data.
- The 25(OH) vitamin D levels were measured at visits every 6 weeks, and the participants were divided into six subgroups on the basis of the mean 25(OH) vitamin D levels: < 20 ng/dL, 20-29 ng/dL, 30-39 ng/dL, 40-49 ng/dL, 50-59 ng/dL, and ≥ 60 ng/dL.
- The adverse pregnancy outcomes included miscarriage, preterm delivery, and restricted intrauterine growth of the fetus.
- This study used a time-to-event analysis to assess the association between time-varying 25(OH) vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Adverse pregnancy outcomes were observed in 45.3% of pregnancies; the risks for miscarriage and preterm delivery were significantly different across the six subgroups with varying vitamin D levels (P = .0045 and P = .0007, respectively).
- A U-shaped curve association was observed between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes, with the highest risk seen in patients with the lowest or highest levels of vitamin D during pregnancy, while the lowest risk was seen in those with vitamin D levels between 40 and 59 ng/mL.
- Low 25(OH) vitamin D levels during the second trimester resulted in premature delivery in 9 out of 10 pregnancies; however, a relationship between vitamin D levels in the first trimester and pregnancy outcomes was not observed.
- The time-to-event analysis showed that the U-shaped association between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes was still observed even after accounting for lupus disease activity; however, the elevated risk seen in individuals with the highest levels of vitamin D was no longer statistically significant.
IN PRACTICE:
“We recommend monitoring of maternal serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels throughout SLE pregnancies and supplementing patients with vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency, aiming for 25(OH) vitamin D range of 40-59 ng/mL. Over supplementation should be avoided,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Nima Madanchi, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and was published online on September 23, 2024, in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
This study could not prove a cause-and-effect relationship between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes. This study included only clinically identified pregnancies, potentially missing very early miscarriages. It also could not adjust for parity due to the unknown parity of the index pregnancy.
DISCLOSURES:
This Hopkins Lupus Cohort was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Both low and high levels of maternal 25-hydroxy [25(OH)] vitamin D are linked to an increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), with levels of 40-59 ng/mL being associated with the lowest risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed 260 pregnancies in the Hopkins Lupus Cohort to examine the association between 25(OH) vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with SLE.
- The participants were required to have serum vitamin D levels measured during pregnancy and pregnancy-related outcomes data.
- The 25(OH) vitamin D levels were measured at visits every 6 weeks, and the participants were divided into six subgroups on the basis of the mean 25(OH) vitamin D levels: < 20 ng/dL, 20-29 ng/dL, 30-39 ng/dL, 40-49 ng/dL, 50-59 ng/dL, and ≥ 60 ng/dL.
- The adverse pregnancy outcomes included miscarriage, preterm delivery, and restricted intrauterine growth of the fetus.
- This study used a time-to-event analysis to assess the association between time-varying 25(OH) vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
TAKEAWAY:
- Adverse pregnancy outcomes were observed in 45.3% of pregnancies; the risks for miscarriage and preterm delivery were significantly different across the six subgroups with varying vitamin D levels (P = .0045 and P = .0007, respectively).
- A U-shaped curve association was observed between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes, with the highest risk seen in patients with the lowest or highest levels of vitamin D during pregnancy, while the lowest risk was seen in those with vitamin D levels between 40 and 59 ng/mL.
- Low 25(OH) vitamin D levels during the second trimester resulted in premature delivery in 9 out of 10 pregnancies; however, a relationship between vitamin D levels in the first trimester and pregnancy outcomes was not observed.
- The time-to-event analysis showed that the U-shaped association between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes was still observed even after accounting for lupus disease activity; however, the elevated risk seen in individuals with the highest levels of vitamin D was no longer statistically significant.
IN PRACTICE:
“We recommend monitoring of maternal serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels throughout SLE pregnancies and supplementing patients with vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency, aiming for 25(OH) vitamin D range of 40-59 ng/mL. Over supplementation should be avoided,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Nima Madanchi, MD, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and was published online on September 23, 2024, in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
This study could not prove a cause-and-effect relationship between vitamin D levels and adverse pregnancy outcomes. This study included only clinically identified pregnancies, potentially missing very early miscarriages. It also could not adjust for parity due to the unknown parity of the index pregnancy.
DISCLOSURES:
This Hopkins Lupus Cohort was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Live Rotavirus Vaccine Safe for Newborns of Biologic-Treated Moms With IBD
No adverse events or impairment of the immune system emerged in babies at 7 days, 1 month, and 9 months post vaccination, in findings from a small Canadian study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The study found normal extended immune function testing in infants despite third-trimester maternal biologic therapy and regardless of circulating drug levels. The data provide reassurance about live rotavirus vaccination in this population and may also offer insights into the safety of other live vaccines in biologic-exposed individuals, wrote investigators led by gastroenterologist Cynthia H. Seow, MD, a professor in the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada.
“Despite the well-established safety and effectiveness of non–live vaccination in individuals with IBD, including those on immunomodulators and biologic therapy, vaccine uptake in pregnant women with IBD and their infants remains suboptimal,” Seow said in an interview. This largely arises from maternal and physician concerns regarding transplacental transfer of IBD therapies and their impact on the safety of vaccination.
“These concerns were heightened after reports emerged of five fatal outcomes following the administration of the live Bacille Calmette-Guérin [BCG] vaccine in biologic-exposed infants. However, it had already been reported that inadvertent administration of the live oral rotavirus vaccine, a very different vaccine in terms of target and mechanism of action, in biologic-exposed individuals had not been associated with significant adverse effects,” she said.
They undertook their analysis with the hypothesis that vaccination would carry low risk, although the live oral vaccine is not currently recommended in biologic-exposed infants. “Yet rotavirus is a leading cause of severe, dehydrating diarrhea in children under the age of 5 years globally, and vaccination has led to significant reductions in hospitalizations and mortality,” Seow added.
Provision of the vaccine to anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–exposed infants has been incorporated into the Canadian Public Health and Immunization guidelines, as the majority of the biologic-exposed infants were exposed to anti-TNF agents. “And with collection of further data, we expect that this will be extended to other biologic agent exposure. These data are important to pregnant women with IBD as they help to normalize their care. Pregnancy is difficult enough without having to remember exceptions to care,” Seow said.
“Before some of the studies came out, broad guidelines recommended that live vaccines should not be used in biologic-exposed infants, but this had been thought to be overly zealous and too conservative, and the risk was thought to be low,” said Elizabeth Spencer, MD, an assistant professor of pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, in an interview. Spencer was not involved in the Canadian study.
“At our center, we had some moms on biologics during pregnancy who forgot and had their babies vaccinated for rotavirus, and the babies were all fine,” she said.
The safety of this vaccine has been confirmed by several small studies and recently the PIANO Helmsley Global Consensus on Pregnancy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, which was presented at Digestive Disease Week 2024. The consensus encompasses preconception counseling and the safety of IBD medications during pregnancy and lactation.
“Another concern, however, was that giving a live GI bug like rotavirus to babies might overstimulate their immune systems and provoke IBD,” Spencer added. “While a number of population-based studies in the US and Europe showed that was not the case, at least in the general population, there was a suggestion that, down the road, vaccination might be mildly protective against IBD in some cases.”
She added the caveat that these studies were not done in mothers and their babies with IBD, who might be inherently at greater risk for IBD. “So, a question for future research would be, ‘Is immune stimulation of the gut in IBD moms and their babies a good or a bad thing for their gut?’ ”
Spencer conceded that “the data present a bit of a blurry picture, but I think it’s always better just to vaccinate according to the regular schedule. The current data say there is no added risk, but it would be nice to look specifically at risk in moms with IBD and their children.”
The Study
The prospective cohort study is a substudy of a larger 2023 one that included biologic use in a range of maternal illnesses, not just IBD.
For the current study, Seow and colleagues identified 57 infants born to 52 mothers with IBD attending a pregnancy clinic at the University of Calgary in the period 2019-2023. Almost 81% of the mothers had Crohn’s disease, and the median duration of IBD was 10 years. The median gestational age at delivery was 39 weeks, and almost 60% of deliveries were vaginal. The infants had been exposed in utero to infliximab (n = 21), adalimumab (n = 19), vedolizumab (n = 10), and ustekinumab (n = 7) in the third trimester.
The 57 biologic-exposed infants underwent standardized clinical assessments, drug concentration, and immune function testing. The live oral rotavirus vaccine series was provided to 50 infants, with the first dose at a median of 13 weeks of age. Immunologic assessments validated for age were normal in all infants despite median infliximab concentrations of 6.1 μg/mL (range, 0.4-28.8 μg/mL), adalimumab concentrations of 1.7 μg/mL (range, 0.7-7.9 μg/mL), ustekinumab concentrations of 0.6 μg/mL (range, 0-1.1), and undetectable for vedolizumab at 10.7 weeks of age.
As anticipated, infant immune function was normal regardless of circulating drug levels.
The overall message, said Seow, is “healthy mum equals healthy baby. Be more concerned regarding active inflammation than active medications. In almost all circumstances, treat to target in pregnancy as you would in the nonpregnant state.” She added, however, that further studies are needed to determine the safety and optimal timing of other live vaccines, such as the BCG, in the presence of biologic therapy.
This study was funded by the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute. Seow reported advisory/speaker’s fees for Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmascience, and Lilly, as well as funding from Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, Crohn’s and Colitis Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Calgary Health Trust, and data safety monitoring from New South Wales Government Health, Australia. Multiple coauthors disclosed similar consulting or speaker relationships with private industry. Spencer had no competing interests with regard to her comments.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No adverse events or impairment of the immune system emerged in babies at 7 days, 1 month, and 9 months post vaccination, in findings from a small Canadian study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The study found normal extended immune function testing in infants despite third-trimester maternal biologic therapy and regardless of circulating drug levels. The data provide reassurance about live rotavirus vaccination in this population and may also offer insights into the safety of other live vaccines in biologic-exposed individuals, wrote investigators led by gastroenterologist Cynthia H. Seow, MD, a professor in the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada.
“Despite the well-established safety and effectiveness of non–live vaccination in individuals with IBD, including those on immunomodulators and biologic therapy, vaccine uptake in pregnant women with IBD and their infants remains suboptimal,” Seow said in an interview. This largely arises from maternal and physician concerns regarding transplacental transfer of IBD therapies and their impact on the safety of vaccination.
“These concerns were heightened after reports emerged of five fatal outcomes following the administration of the live Bacille Calmette-Guérin [BCG] vaccine in biologic-exposed infants. However, it had already been reported that inadvertent administration of the live oral rotavirus vaccine, a very different vaccine in terms of target and mechanism of action, in biologic-exposed individuals had not been associated with significant adverse effects,” she said.
They undertook their analysis with the hypothesis that vaccination would carry low risk, although the live oral vaccine is not currently recommended in biologic-exposed infants. “Yet rotavirus is a leading cause of severe, dehydrating diarrhea in children under the age of 5 years globally, and vaccination has led to significant reductions in hospitalizations and mortality,” Seow added.
Provision of the vaccine to anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–exposed infants has been incorporated into the Canadian Public Health and Immunization guidelines, as the majority of the biologic-exposed infants were exposed to anti-TNF agents. “And with collection of further data, we expect that this will be extended to other biologic agent exposure. These data are important to pregnant women with IBD as they help to normalize their care. Pregnancy is difficult enough without having to remember exceptions to care,” Seow said.
“Before some of the studies came out, broad guidelines recommended that live vaccines should not be used in biologic-exposed infants, but this had been thought to be overly zealous and too conservative, and the risk was thought to be low,” said Elizabeth Spencer, MD, an assistant professor of pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, in an interview. Spencer was not involved in the Canadian study.
“At our center, we had some moms on biologics during pregnancy who forgot and had their babies vaccinated for rotavirus, and the babies were all fine,” she said.
The safety of this vaccine has been confirmed by several small studies and recently the PIANO Helmsley Global Consensus on Pregnancy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, which was presented at Digestive Disease Week 2024. The consensus encompasses preconception counseling and the safety of IBD medications during pregnancy and lactation.
“Another concern, however, was that giving a live GI bug like rotavirus to babies might overstimulate their immune systems and provoke IBD,” Spencer added. “While a number of population-based studies in the US and Europe showed that was not the case, at least in the general population, there was a suggestion that, down the road, vaccination might be mildly protective against IBD in some cases.”
She added the caveat that these studies were not done in mothers and their babies with IBD, who might be inherently at greater risk for IBD. “So, a question for future research would be, ‘Is immune stimulation of the gut in IBD moms and their babies a good or a bad thing for their gut?’ ”
Spencer conceded that “the data present a bit of a blurry picture, but I think it’s always better just to vaccinate according to the regular schedule. The current data say there is no added risk, but it would be nice to look specifically at risk in moms with IBD and their children.”
The Study
The prospective cohort study is a substudy of a larger 2023 one that included biologic use in a range of maternal illnesses, not just IBD.
For the current study, Seow and colleagues identified 57 infants born to 52 mothers with IBD attending a pregnancy clinic at the University of Calgary in the period 2019-2023. Almost 81% of the mothers had Crohn’s disease, and the median duration of IBD was 10 years. The median gestational age at delivery was 39 weeks, and almost 60% of deliveries were vaginal. The infants had been exposed in utero to infliximab (n = 21), adalimumab (n = 19), vedolizumab (n = 10), and ustekinumab (n = 7) in the third trimester.
The 57 biologic-exposed infants underwent standardized clinical assessments, drug concentration, and immune function testing. The live oral rotavirus vaccine series was provided to 50 infants, with the first dose at a median of 13 weeks of age. Immunologic assessments validated for age were normal in all infants despite median infliximab concentrations of 6.1 μg/mL (range, 0.4-28.8 μg/mL), adalimumab concentrations of 1.7 μg/mL (range, 0.7-7.9 μg/mL), ustekinumab concentrations of 0.6 μg/mL (range, 0-1.1), and undetectable for vedolizumab at 10.7 weeks of age.
As anticipated, infant immune function was normal regardless of circulating drug levels.
The overall message, said Seow, is “healthy mum equals healthy baby. Be more concerned regarding active inflammation than active medications. In almost all circumstances, treat to target in pregnancy as you would in the nonpregnant state.” She added, however, that further studies are needed to determine the safety and optimal timing of other live vaccines, such as the BCG, in the presence of biologic therapy.
This study was funded by the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute. Seow reported advisory/speaker’s fees for Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmascience, and Lilly, as well as funding from Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, Crohn’s and Colitis Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Calgary Health Trust, and data safety monitoring from New South Wales Government Health, Australia. Multiple coauthors disclosed similar consulting or speaker relationships with private industry. Spencer had no competing interests with regard to her comments.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No adverse events or impairment of the immune system emerged in babies at 7 days, 1 month, and 9 months post vaccination, in findings from a small Canadian study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
The study found normal extended immune function testing in infants despite third-trimester maternal biologic therapy and regardless of circulating drug levels. The data provide reassurance about live rotavirus vaccination in this population and may also offer insights into the safety of other live vaccines in biologic-exposed individuals, wrote investigators led by gastroenterologist Cynthia H. Seow, MD, a professor in the Cumming School of Medicine at the University of Calgary in Alberta, Canada.
“Despite the well-established safety and effectiveness of non–live vaccination in individuals with IBD, including those on immunomodulators and biologic therapy, vaccine uptake in pregnant women with IBD and their infants remains suboptimal,” Seow said in an interview. This largely arises from maternal and physician concerns regarding transplacental transfer of IBD therapies and their impact on the safety of vaccination.
“These concerns were heightened after reports emerged of five fatal outcomes following the administration of the live Bacille Calmette-Guérin [BCG] vaccine in biologic-exposed infants. However, it had already been reported that inadvertent administration of the live oral rotavirus vaccine, a very different vaccine in terms of target and mechanism of action, in biologic-exposed individuals had not been associated with significant adverse effects,” she said.
They undertook their analysis with the hypothesis that vaccination would carry low risk, although the live oral vaccine is not currently recommended in biologic-exposed infants. “Yet rotavirus is a leading cause of severe, dehydrating diarrhea in children under the age of 5 years globally, and vaccination has led to significant reductions in hospitalizations and mortality,” Seow added.
Provision of the vaccine to anti–tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–exposed infants has been incorporated into the Canadian Public Health and Immunization guidelines, as the majority of the biologic-exposed infants were exposed to anti-TNF agents. “And with collection of further data, we expect that this will be extended to other biologic agent exposure. These data are important to pregnant women with IBD as they help to normalize their care. Pregnancy is difficult enough without having to remember exceptions to care,” Seow said.
“Before some of the studies came out, broad guidelines recommended that live vaccines should not be used in biologic-exposed infants, but this had been thought to be overly zealous and too conservative, and the risk was thought to be low,” said Elizabeth Spencer, MD, an assistant professor of pediatrics in the Division of Pediatric Gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City, in an interview. Spencer was not involved in the Canadian study.
“At our center, we had some moms on biologics during pregnancy who forgot and had their babies vaccinated for rotavirus, and the babies were all fine,” she said.
The safety of this vaccine has been confirmed by several small studies and recently the PIANO Helmsley Global Consensus on Pregnancy and Inflammatory Bowel Disease, which was presented at Digestive Disease Week 2024. The consensus encompasses preconception counseling and the safety of IBD medications during pregnancy and lactation.
“Another concern, however, was that giving a live GI bug like rotavirus to babies might overstimulate their immune systems and provoke IBD,” Spencer added. “While a number of population-based studies in the US and Europe showed that was not the case, at least in the general population, there was a suggestion that, down the road, vaccination might be mildly protective against IBD in some cases.”
She added the caveat that these studies were not done in mothers and their babies with IBD, who might be inherently at greater risk for IBD. “So, a question for future research would be, ‘Is immune stimulation of the gut in IBD moms and their babies a good or a bad thing for their gut?’ ”
Spencer conceded that “the data present a bit of a blurry picture, but I think it’s always better just to vaccinate according to the regular schedule. The current data say there is no added risk, but it would be nice to look specifically at risk in moms with IBD and their children.”
The Study
The prospective cohort study is a substudy of a larger 2023 one that included biologic use in a range of maternal illnesses, not just IBD.
For the current study, Seow and colleagues identified 57 infants born to 52 mothers with IBD attending a pregnancy clinic at the University of Calgary in the period 2019-2023. Almost 81% of the mothers had Crohn’s disease, and the median duration of IBD was 10 years. The median gestational age at delivery was 39 weeks, and almost 60% of deliveries were vaginal. The infants had been exposed in utero to infliximab (n = 21), adalimumab (n = 19), vedolizumab (n = 10), and ustekinumab (n = 7) in the third trimester.
The 57 biologic-exposed infants underwent standardized clinical assessments, drug concentration, and immune function testing. The live oral rotavirus vaccine series was provided to 50 infants, with the first dose at a median of 13 weeks of age. Immunologic assessments validated for age were normal in all infants despite median infliximab concentrations of 6.1 μg/mL (range, 0.4-28.8 μg/mL), adalimumab concentrations of 1.7 μg/mL (range, 0.7-7.9 μg/mL), ustekinumab concentrations of 0.6 μg/mL (range, 0-1.1), and undetectable for vedolizumab at 10.7 weeks of age.
As anticipated, infant immune function was normal regardless of circulating drug levels.
The overall message, said Seow, is “healthy mum equals healthy baby. Be more concerned regarding active inflammation than active medications. In almost all circumstances, treat to target in pregnancy as you would in the nonpregnant state.” She added, however, that further studies are needed to determine the safety and optimal timing of other live vaccines, such as the BCG, in the presence of biologic therapy.
This study was funded by the Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute. Seow reported advisory/speaker’s fees for Janssen, AbbVie, Takeda, Pfizer, Fresenius Kabi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pharmascience, and Lilly, as well as funding from Alberta Children’s Hospital Research Institute, Crohn’s and Colitis Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and Calgary Health Trust, and data safety monitoring from New South Wales Government Health, Australia. Multiple coauthors disclosed similar consulting or speaker relationships with private industry. Spencer had no competing interests with regard to her comments.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Maternal Serum Folate Levels During Pregnancy Linked to Congenital Heart Disease Risk
TOPLINE:
Maternal serum folate levels during early to midpregnancy show a U-shaped association with congenital heart disease (CHD) risk in offspring. Both low and high folate levels are linked to an increased risk, with vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further exacerbating this risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study with 129 participants with CHD and 516 matched control participants from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital in China between 2015 and 2018.
- Maternal serum levels of folate, vitamin B12, and homocysteine were measured at around 16 weeks of gestation using a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay.
- CHD was confirmed using echocardiography, and the participants were matched by maternal age at a ratio of 1:4.
- Covariates included periconceptional folic acid supplementation, maternal education, occupation, parity, abortion history, pregnancy complications, and genetic polymorphisms related to folate metabolism.
- Conditional logistic regression was used to assess the associations, with adjustments for various covariates and sensitivity analyses excluding participants with missing genetic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- A U-shaped association was found between maternal serum folate levels and CHD risk in offspring, with both low and high levels linked to increased risk (P < .001).
- Low maternal folate levels were associated with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 3.09 (95% CI, 1.88-5.08) for CHD risk, whereas high levels had an aOR of 1.81 (95% CI, 1.07-3.06).
- Using World Health Organization criteria, folate deficiency (< 5.9 ng/mL) had an aOR of 18.97 (95% CI, 3.87-93.11) and elevated levels (> 20 ng/mL) had an aOR of 5.71 (95% CI, 2.72-11.98) for CHD risk.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further increased the risk associated with both low and high maternal folate levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insufficient folate and vitamin B12 can lead to increased homocysteine levels, which is harmful to the cardiovascular system. Thus, homocysteine might act as a central mediator in the relationships between deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12 and the risk of CHD. Additionally, the role of folate extends beyond homocysteine mediation, contributing independently to placental implantation and vascular remodeling, irrespective of vitamin B12 and homocysteine levels,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yanji Qu, PhD, and Jie Li, PhD, Global Health Research Center, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included the measurement of maternal serum folate levels at a single time point, which may not reflect preconception and early postconception periods. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to other populations as participants were recruited from a single cardiac referral center in Southern China. Additionally, the lack of dietary intake data limited the ability to account for related biases. The sample size, while relatively large for CHD research, may lack sufficient power for stratified analyses.
DISCLOSURES:
One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Maternal serum folate levels during early to midpregnancy show a U-shaped association with congenital heart disease (CHD) risk in offspring. Both low and high folate levels are linked to an increased risk, with vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further exacerbating this risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study with 129 participants with CHD and 516 matched control participants from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital in China between 2015 and 2018.
- Maternal serum levels of folate, vitamin B12, and homocysteine were measured at around 16 weeks of gestation using a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay.
- CHD was confirmed using echocardiography, and the participants were matched by maternal age at a ratio of 1:4.
- Covariates included periconceptional folic acid supplementation, maternal education, occupation, parity, abortion history, pregnancy complications, and genetic polymorphisms related to folate metabolism.
- Conditional logistic regression was used to assess the associations, with adjustments for various covariates and sensitivity analyses excluding participants with missing genetic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- A U-shaped association was found between maternal serum folate levels and CHD risk in offspring, with both low and high levels linked to increased risk (P < .001).
- Low maternal folate levels were associated with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 3.09 (95% CI, 1.88-5.08) for CHD risk, whereas high levels had an aOR of 1.81 (95% CI, 1.07-3.06).
- Using World Health Organization criteria, folate deficiency (< 5.9 ng/mL) had an aOR of 18.97 (95% CI, 3.87-93.11) and elevated levels (> 20 ng/mL) had an aOR of 5.71 (95% CI, 2.72-11.98) for CHD risk.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further increased the risk associated with both low and high maternal folate levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insufficient folate and vitamin B12 can lead to increased homocysteine levels, which is harmful to the cardiovascular system. Thus, homocysteine might act as a central mediator in the relationships between deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12 and the risk of CHD. Additionally, the role of folate extends beyond homocysteine mediation, contributing independently to placental implantation and vascular remodeling, irrespective of vitamin B12 and homocysteine levels,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yanji Qu, PhD, and Jie Li, PhD, Global Health Research Center, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included the measurement of maternal serum folate levels at a single time point, which may not reflect preconception and early postconception periods. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to other populations as participants were recruited from a single cardiac referral center in Southern China. Additionally, the lack of dietary intake data limited the ability to account for related biases. The sample size, while relatively large for CHD research, may lack sufficient power for stratified analyses.
DISCLOSURES:
One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Maternal serum folate levels during early to midpregnancy show a U-shaped association with congenital heart disease (CHD) risk in offspring. Both low and high folate levels are linked to an increased risk, with vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further exacerbating this risk.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a case-control study with 129 participants with CHD and 516 matched control participants from Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital in China between 2015 and 2018.
- Maternal serum levels of folate, vitamin B12, and homocysteine were measured at around 16 weeks of gestation using a chemiluminescence microparticle immunoassay.
- CHD was confirmed using echocardiography, and the participants were matched by maternal age at a ratio of 1:4.
- Covariates included periconceptional folic acid supplementation, maternal education, occupation, parity, abortion history, pregnancy complications, and genetic polymorphisms related to folate metabolism.
- Conditional logistic regression was used to assess the associations, with adjustments for various covariates and sensitivity analyses excluding participants with missing genetic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- A U-shaped association was found between maternal serum folate levels and CHD risk in offspring, with both low and high levels linked to increased risk (P < .001).
- Low maternal folate levels were associated with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 3.09 (95% CI, 1.88-5.08) for CHD risk, whereas high levels had an aOR of 1.81 (95% CI, 1.07-3.06).
- Using World Health Organization criteria, folate deficiency (< 5.9 ng/mL) had an aOR of 18.97 (95% CI, 3.87-93.11) and elevated levels (> 20 ng/mL) had an aOR of 5.71 (95% CI, 2.72-11.98) for CHD risk.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels further increased the risk associated with both low and high maternal folate levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insufficient folate and vitamin B12 can lead to increased homocysteine levels, which is harmful to the cardiovascular system. Thus, homocysteine might act as a central mediator in the relationships between deficiencies in folate and vitamin B12 and the risk of CHD. Additionally, the role of folate extends beyond homocysteine mediation, contributing independently to placental implantation and vascular remodeling, irrespective of vitamin B12 and homocysteine levels,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Yanji Qu, PhD, and Jie Li, PhD, Global Health Research Center, Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s limitations included the measurement of maternal serum folate levels at a single time point, which may not reflect preconception and early postconception periods. The study’s findings may not be generalizable to other populations as participants were recruited from a single cardiac referral center in Southern China. Additionally, the lack of dietary intake data limited the ability to account for related biases. The sample size, while relatively large for CHD research, may lack sufficient power for stratified analyses.
DISCLOSURES:
One coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute outside the submitted work. Additional disclosures are noted in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Underutilized Mifepristone Shows Promise in Care of Early Pregnancy Loss
TOPLINE:
Mifepristone plus misoprostol reduces the need for subsequent uterine aspiration and emergency department visits in the management of early pregnancy loss. Despite its effectiveness, mifepristone remains underutilized, with 8.6% of patients receiving it in 2022.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using national insurance claims data of US patients with commercial insurance.
- More than 31,000 pregnant women (mean age, 32.7 years) with a diagnosis of early pregnancy loss between 2015 and 2022 were included.
- The diagnosis of patients included having a missed abortion (72.3%), spontaneous abortion (26.9%), or both (0.8%).
- Researchers compared the outcomes of individuals who received a combination of mifepristone and misoprostol vs those who received misoprostol alone. The outcome measures included the need for subsequent procedural management (uterine aspiration), return visits to the emergency department or an outpatient clinic, hospitalizations, and complications within 6 weeks of initial diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- The use of mifepristone was more common in outpatient clinics than in emergency departments (3.4% vs 0.9%; P < .001).
- The use of mifepristone plus misoprostol vs misoprostol alone was linked to a lower incidence of subsequent procedural management (10.5% vs 14.0%; P = .002) and fewer emergency department visits (3.5% vs 7.9%; P < .001).
- The multivariable analysis showed that the use of mifepristone was linked to decreased odds of subsequent procedural management (adjusted odds ratio, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.57-0.87).
- Despite its effectiveness, mifepristone was used in only 8.6% of those receiving medication management for early pregnancy loss in 2022.
IN PRACTICE:
“Continued efforts are needed to reduce barriers to mifepristone use for medication management of EPL,” the authors wrote.
“Any practitioner who cares for patients experiencing early pregnancy loss should consider mifepristone pretreatment to misoprostol to be the standard of care for medication management. Provision of the evidence-based standard of care with the use of mifepristone for early pregnancy loss is an opportunity to advocate for an essential strategy in improving sexual and reproductive health in the US,” wrote Sarita Sonalkar, MD, MPH, and Rachel McKean, MD, MPH, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in an invited commentary.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lyndsey S. Benson, MD, MS, of the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the accuracy of the diagnosis of early pregnancy loss and procedure codes because claims data are intended for billing purposes and may be incomplete or inaccurate. The use of de-identified data meant that specific gestational durations, exact dosing, or routes of misoprostol administration could not be determined. The findings may not be generalizable to those with public insurance or no insurance.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported in part by a grant from a Women’s Reproductive Health Research grant from the National Institutes of Health Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute for Child Health and Human Development. One author reported serving as an adviser and investigator, while another reported receiving personal fees and serving as an expert witness, contributing editor, and course instructor outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mifepristone plus misoprostol reduces the need for subsequent uterine aspiration and emergency department visits in the management of early pregnancy loss. Despite its effectiveness, mifepristone remains underutilized, with 8.6% of patients receiving it in 2022.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using national insurance claims data of US patients with commercial insurance.
- More than 31,000 pregnant women (mean age, 32.7 years) with a diagnosis of early pregnancy loss between 2015 and 2022 were included.
- The diagnosis of patients included having a missed abortion (72.3%), spontaneous abortion (26.9%), or both (0.8%).
- Researchers compared the outcomes of individuals who received a combination of mifepristone and misoprostol vs those who received misoprostol alone. The outcome measures included the need for subsequent procedural management (uterine aspiration), return visits to the emergency department or an outpatient clinic, hospitalizations, and complications within 6 weeks of initial diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- The use of mifepristone was more common in outpatient clinics than in emergency departments (3.4% vs 0.9%; P < .001).
- The use of mifepristone plus misoprostol vs misoprostol alone was linked to a lower incidence of subsequent procedural management (10.5% vs 14.0%; P = .002) and fewer emergency department visits (3.5% vs 7.9%; P < .001).
- The multivariable analysis showed that the use of mifepristone was linked to decreased odds of subsequent procedural management (adjusted odds ratio, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.57-0.87).
- Despite its effectiveness, mifepristone was used in only 8.6% of those receiving medication management for early pregnancy loss in 2022.
IN PRACTICE:
“Continued efforts are needed to reduce barriers to mifepristone use for medication management of EPL,” the authors wrote.
“Any practitioner who cares for patients experiencing early pregnancy loss should consider mifepristone pretreatment to misoprostol to be the standard of care for medication management. Provision of the evidence-based standard of care with the use of mifepristone for early pregnancy loss is an opportunity to advocate for an essential strategy in improving sexual and reproductive health in the US,” wrote Sarita Sonalkar, MD, MPH, and Rachel McKean, MD, MPH, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in an invited commentary.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lyndsey S. Benson, MD, MS, of the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the accuracy of the diagnosis of early pregnancy loss and procedure codes because claims data are intended for billing purposes and may be incomplete or inaccurate. The use of de-identified data meant that specific gestational durations, exact dosing, or routes of misoprostol administration could not be determined. The findings may not be generalizable to those with public insurance or no insurance.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported in part by a grant from a Women’s Reproductive Health Research grant from the National Institutes of Health Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute for Child Health and Human Development. One author reported serving as an adviser and investigator, while another reported receiving personal fees and serving as an expert witness, contributing editor, and course instructor outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mifepristone plus misoprostol reduces the need for subsequent uterine aspiration and emergency department visits in the management of early pregnancy loss. Despite its effectiveness, mifepristone remains underutilized, with 8.6% of patients receiving it in 2022.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using national insurance claims data of US patients with commercial insurance.
- More than 31,000 pregnant women (mean age, 32.7 years) with a diagnosis of early pregnancy loss between 2015 and 2022 were included.
- The diagnosis of patients included having a missed abortion (72.3%), spontaneous abortion (26.9%), or both (0.8%).
- Researchers compared the outcomes of individuals who received a combination of mifepristone and misoprostol vs those who received misoprostol alone. The outcome measures included the need for subsequent procedural management (uterine aspiration), return visits to the emergency department or an outpatient clinic, hospitalizations, and complications within 6 weeks of initial diagnosis.
TAKEAWAY:
- The use of mifepristone was more common in outpatient clinics than in emergency departments (3.4% vs 0.9%; P < .001).
- The use of mifepristone plus misoprostol vs misoprostol alone was linked to a lower incidence of subsequent procedural management (10.5% vs 14.0%; P = .002) and fewer emergency department visits (3.5% vs 7.9%; P < .001).
- The multivariable analysis showed that the use of mifepristone was linked to decreased odds of subsequent procedural management (adjusted odds ratio, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.57-0.87).
- Despite its effectiveness, mifepristone was used in only 8.6% of those receiving medication management for early pregnancy loss in 2022.
IN PRACTICE:
“Continued efforts are needed to reduce barriers to mifepristone use for medication management of EPL,” the authors wrote.
“Any practitioner who cares for patients experiencing early pregnancy loss should consider mifepristone pretreatment to misoprostol to be the standard of care for medication management. Provision of the evidence-based standard of care with the use of mifepristone for early pregnancy loss is an opportunity to advocate for an essential strategy in improving sexual and reproductive health in the US,” wrote Sarita Sonalkar, MD, MPH, and Rachel McKean, MD, MPH, of the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, in an invited commentary.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Lyndsey S. Benson, MD, MS, of the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was limited by the accuracy of the diagnosis of early pregnancy loss and procedure codes because claims data are intended for billing purposes and may be incomplete or inaccurate. The use of de-identified data meant that specific gestational durations, exact dosing, or routes of misoprostol administration could not be determined. The findings may not be generalizable to those with public insurance or no insurance.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported in part by a grant from a Women’s Reproductive Health Research grant from the National Institutes of Health Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute for Child Health and Human Development. One author reported serving as an adviser and investigator, while another reported receiving personal fees and serving as an expert witness, contributing editor, and course instructor outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Maternal Immunization to Prevent Serious Respiratory Illness
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.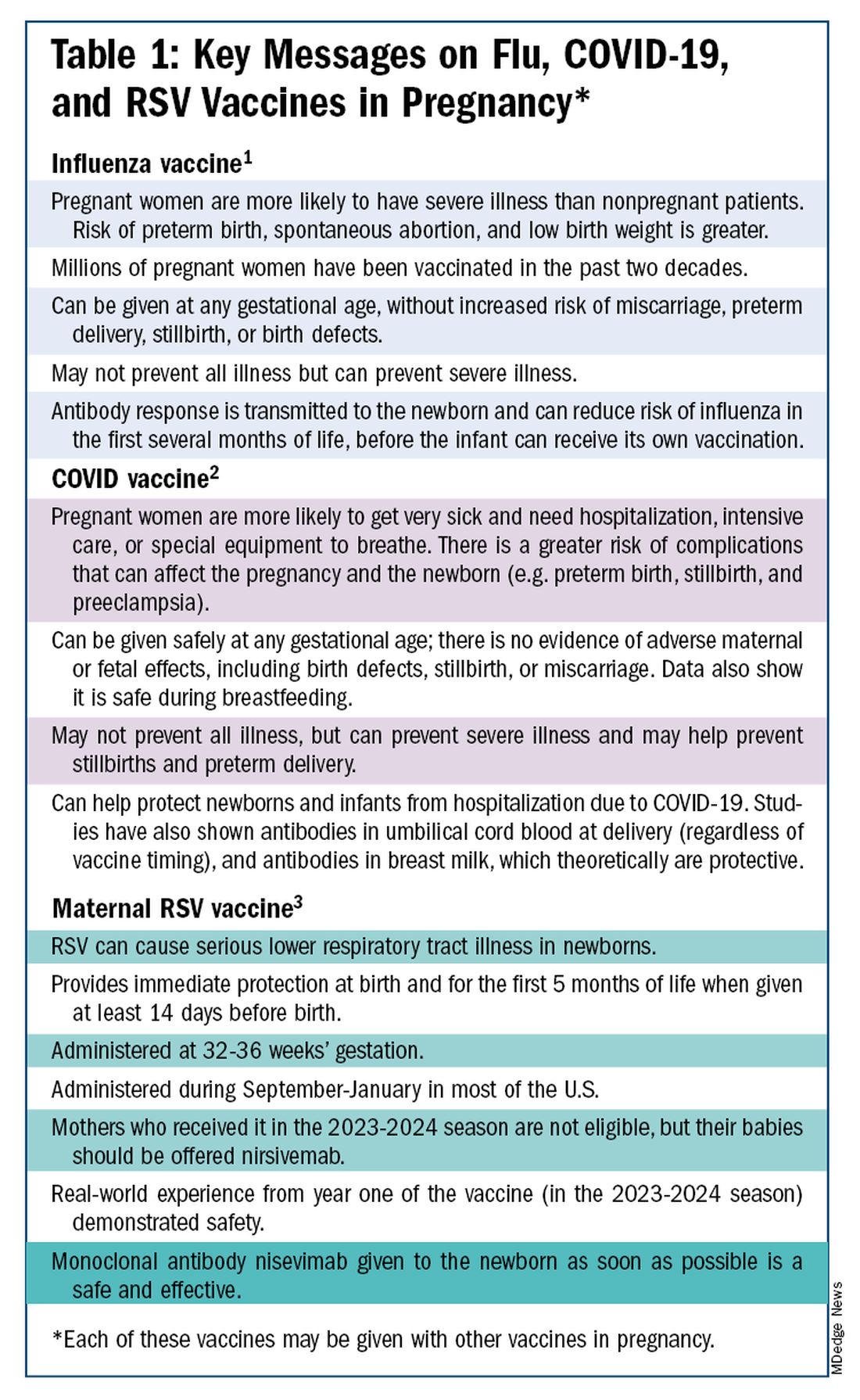
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Editor’s Note: Sadly, this is the last column in the Master Class Obstetrics series. This award-winning column has been part of Ob.Gyn. News for 20 years. The deep discussion of cutting-edge topics in obstetrics by specialists and researchers will be missed as will the leadership and curation of topics by Dr. E. Albert Reece.
Introduction: The Need for Increased Vigilance About Maternal Immunization
Viruses are becoming increasingly prevalent in our world and the consequences of viral infections are implicated in a growing number of disease states. It is well established that certain cancers are caused by viruses and it is increasingly evident that viral infections can trigger the development of chronic illness. In pregnant women, viruses such as cytomegalovirus can cause infection in utero and lead to long-term impairments for the baby.
Likewise, it appears that the virulence of viruses is increasing, whether it be the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in children or the severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronaviruses in adults. Clearly, our environment is changing, with increases in population growth and urbanization, for instance, and an intensification of climate change and its effects. Viruses are part of this changing background.
Vaccines are our most powerful tool to protect people of all ages against viral threats, and fortunately, we benefit from increasing expertise in vaccinology. Since 1974, the University of Maryland School of Medicine has a Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health that has conducted research on vaccines to defend against the Zika virus, H1N1, Ebola, and SARS-CoV-2.
We’re not alone. Other vaccinology centers across the country — as well as the National Institutes of Health at the national level, through its National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases — are doing research and developing vaccines to combat viral diseases.
In this column, we are focused on viral diseases in pregnancy and the role that vaccines can play in preventing serious respiratory illness in mothers and their newborns. I have invited Laura E. Riley, MD, the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine, to address the importance of maternal immunization and how we can best counsel our patients and improve immunization rates.
As Dr. Riley explains, we are in a new era, and it behooves us all to be more vigilant about recommending vaccines, combating misperceptions, addressing patients’ knowledge gaps, and administering vaccines whenever possible.
Dr. Reece is the former Dean of Medicine & University Executive VP, and The Distinguished University and Endowed Professor & Director of the Center for Advanced Research Training and Innovation (CARTI) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, as well as senior scientist at the Center for Birth Defects Research.
The alarming decline in maternal immunization rates that occurred in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic means that, now more than ever, we must fully embrace our responsibility to recommend immunizations in pregnancy and to communicate what is known about their efficacy and safety. Data show that vaccination rates drop when we do not offer vaccines in our offices, so whenever possible, we should administer them as well.
The ob.gyn. is the patient’s most trusted person in pregnancy. When patients decline or express hesitancy about vaccines, it is incumbent upon us to ask why. Oftentimes, we can identify areas in which patients lack knowledge or have misperceptions and we can successfully educate the patient or change their perspective or misunderstanding concerning the importance of vaccination for themselves and their babies. (See Table 1.) We can also successfully address concerns about safety.
The safety of COVID-19 vaccinations in pregnancy is now backed by several years of data from multiple studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
Data also show that pregnant patients are more likely than patients who are not pregnant to need hospitalization and intensive care when infected with SARS-CoV-2 and are at risk of having complications that can affect pregnancy and the newborn, including preterm birth and stillbirth. Vaccination has been shown to reduce the risk of severe illness and the risk of such adverse obstetrical outcomes, in addition to providing protection for the infant early on.
Similarly, influenza has long been more likely to be severe in pregnant patients, with an increased risk of poor obstetrical outcomes. Vaccines similarly provide “two for one protection,” protecting both mother and baby, and are, of course, backed by many years of safety and efficacy data.
With the new maternal respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine, now in its second year of availability, the goal is to protect the baby from RSV-caused serious lower respiratory tract illness. The illness has contributed to tens of thousands of annual hospitalizations and up to several hundred deaths every year in children younger than 5 years — particularly in those under age 6 months.
The RSV monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is available for the newborn as an alternative to maternal immunization but the maternal vaccine is optimal in that it will provide immediate rather than delayed protection for the newborn. The maternal vaccine is recommended during weeks 32-36 of pregnancy in mothers who were not vaccinated during last year’s RSV season. With real-world experience from year one, the available safety data are reassuring.
Counseling About Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccination
The COVID-19 pandemic took a toll on vaccination interest/receptivity broadly in pregnant and nonpregnant people. Among pregnant individuals, influenza vaccination coverage declined from 71% in the 2019-2020 influenza season to 56% in the 2021-2022 season, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Vaccine Safety Datalink.4 Coverage for the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 influenza seasons was even worse: well under 50%.5
Fewer pregnant women have received updated COVID-19 vaccines. Only 13% of pregnant persons overall received the updated 2023-2024 COVID-19 booster vaccine (through March 30, 2024), according to the CDC.6
Maternal immunization for influenza has been recommended in the United States since 2004 (part of the recommendation that everyone over the age of 6 months receive an annual flu vaccine), and flu vaccines have been given to millions of pregnant women, but the H1N1 pandemic of 2009 reinforced its value as a priority for prenatal care. Most of the women who became severely ill from the H1N1 virus were young and healthy, without co-existing conditions known to increase risk.7
It became clearer during the H1N1 pandemic that pregnancy itself — which is associated with physiologic changes such as decreased lung capacity, increased nasal congestion and changes in the immune system – is its own significant risk factor for severe illness from the influenza virus. This increased risk applies to COVID-19 as well.
As COVID-19 has become endemic, with hospitalizations and deaths not reaching the levels of previous surges — and with mask-wearing and other preventive measures having declined — patients understandably have become more complacent. Some patients are vaccine deniers, but in my practice, these patients are a much smaller group than those who believe COVID-19 “is no big deal,” especially if they have had infections recently.
This is why it’s important to actively listen to concerns and to ask patients who decline a vaccination why they are hesitant. Blanket messages about vaccine efficacy and safety are the first step, but individualized, more pointed conversations based on the patient’s personal experiences and beliefs have become increasingly important.
I routinely tell pregnant patients about the risks of COVID-19 and I explain that it has been difficult to predict who will develop severe illness. Sometimes more conversation is needed. For those who are still hesitant or who tell me they feel protected by a recent infection, for instance, I provide more detail on the unique risks of pregnancy — the fact that “pregnancy is different” — and that natural immunity wanes while the protection afforded by immunization is believed to last longer. Many women are also concerned about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine, so having safety data at your fingertips is helpful. (See Table 2.)
The fact that influenza and COVID-19 vaccination protect the newborn as well as the mother is something that I find is underappreciated by many patients. Explaining that infants likely benefit from the passage of antibodies across the placenta should be part of patient counseling.
Counseling About RSV Vaccination
Importantly, for the 2024-2025 RSV season, the maternal RSV vaccine (Abrysvo, Pfizer) is recommended only for pregnant women who did not receive the vaccine during the 2023-2024 season. When more research is done and more data are obtained showing how long the immune response persists post vaccination, it may be that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will approve the maternal RSV vaccine for use in every pregnancy.
The later timing of the vaccination recommendation — 32-36 weeks’ gestation — reflects a conservative approach taken by the FDA in response to data from one of the pivotal trials showing a numerical trend toward more preterm deliveries among vaccinated compared with unvaccinated patients. This imbalance in the original trial, which administered the vaccine during 24-36 weeks of gestation, was seen only in low-income countries with no temporal association, however.
In our experience at two Weill Cornell Medical College–associated hospitals we did not see this trend. Our cohort study of almost 3000 pregnant patients who delivered at 32 weeks’ gestation or later found no increased risk of preterm birth among the 35% of patients who received the RSV vaccine during the 2023-2024 RSV season. We also did not see any difference in preeclampsia, in contrast with original trial data that showed a signal for increased risk.11
When fewer than 2 weeks have elapsed between maternal vaccination and delivery, the monoclonal antibody nirsevimab is recommended for the newborn — ideally before the newborn leaves the hospital. Nirsevimab is also recommended for newborns of mothers who decline vaccination or were not candidates (e.g. vaccinated in a previous pregnancy), or when there is concern about the adequacy of the maternal immune response to the vaccine (e.g. in cases of immunosuppression).
While there was a limited supply of the monoclonal antibody last year, limitations are not expected this year, especially after October.
The ultimate goal is that patients choose the vaccine or the immunoglobulin, given the severity of RSV disease. Patient preferences should be considered. However, given that it takes 2 weeks after vaccination for protection to build up, I stress to patients that if they’ve vaccinated themselves, their newborn will leave the hospital with protection. If nirsevimab is relied upon, I explain, their newborn may not be protected for some period of time.
Take-home Messages
- When patients decline or are hesitant about vaccines, ask why. Listen actively, and work to correct misperceptions and knowledge gaps.
- Whenever possible, offer vaccines in your practice. Vaccination rates drop when this does not occur.
- COVID-vaccine safety is backed by many studies showing no increase in birth defects, preterm delivery, miscarriage, or stillbirth.
- Pregnant women are more likely to have severe illness from the influenza and SARS-CoV-2 viruses. Vaccines can prevent severe illness and can protect the newborn as well as the mother.
- Recommend/administer the maternal RSV vaccine at 32-36 weeks’ gestation in women who did not receive the vaccine in the 2023-2024 season. If mothers aren’t eligible their babies should be offered nirsevimab.
Dr. Riley is the Given Foundation Professor and Chair of Obstetrics and Gynecology at Weill Cornell Medicine and the obstetrician and gynecologist-in-chief at New York Presbyterian Hospital. She disclosed that she has provided one-time consultations to Pfizer (Abrysvo RSV vaccine) and GSK (cytomegalovirus vaccine), and is providing consultant education on CMV for Moderna. She is chair of ACOG’s task force on immunization and emerging infectious diseases, serves on the medical advisory board for MAVEN, and serves as an editor or editorial board member for several medical publications.
References
1. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 741: Maternal Immunization. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(6):e214-e217.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccination for People Who are Pregnant or Breastfeeding. https://www.cdc.gov/covid/vaccines/pregnant-or-breastfeeding.html.
3. ACOG Practice Advisory on Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination, September 2023. (Updated August 2024).4. Irving S et al. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10(Suppl 2):ofad500.1002.
5. Flu Vaccination Dashboard, CDC, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases.
6. Weekly COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard, CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/covidvaxview/weekly-dashboard/index.html
7. Louie JK et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:27-35. 8. Ciapponi A et al. Vaccine. 2021;39(40):5891-908.
9. Prasad S et al. Nature Communications. 2022;13:2414. 10. Fleming-Dutra KE et al. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 2023;50(2):279-97. 11. Mouen S et al. JAMA Network Open 2024;7(7):e2419268.
Vitamin D in Pregnancy Results in Stronger Bones for Kids
TOPLINE:
Gestational supplementation of 1000 IU/d cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) from early pregnancy until delivery increases the bone mineral content, bone mineral density (BMD), and bone mineral apparent density in children at age 6-7 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blinded, placebo-controlled MAVIDOS trial of gestational vitamin D supplementation previously showed increased BMD at age 4 years (but no difference at birth), and it is unclear how the effect may persist or change over time.
- In the original trial, researchers randomized 1134 pregnant women with singleton pregnancy from three UK hospitals from 2008 to 2014, and the 723 children born to mothers recruited in Southampton were invited to continue in offspring follow-up.
- Mothers were randomly assigned to receive either 1000-IU/d vitamin D or placebo from 14-17 weeks’ gestation until delivery; women in the placebo arm could take up to 400-IU/d vitamin D.
- In this post hoc analysis, among 454 children who were followed up at age 6-7 years, 447 had a usable whole body and lumbar spine dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan (placebo group: n = 216; 48% boys; 98% White mothers and vitamin D group: n = 231; 56% boys; 96% White mothers).
- Offspring follow-up measures at birth and 4 and 6-7 years were bone area, bone mineral content, BMD, and bone mineral apparent density, derived from a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan of whole body less head (WBLH), as well as fat and lean mass.
TAKEAWAY:
- The effect of gestational vitamin D supplementation on bone outcomes in children was similar at ages 4 and 6-7 years.
- At age 6-7 years, gestational vitamin D supplementation resulted in higher WBLH bone mineral content (0.15 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.26) and BMD (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.06-0.31) than placebo.
- The WBLH bone mineral apparent density (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.32) was also higher in the vitamin D group.
- The lean mass was greater in the vitamin D group (0.09 SD; 95% CI, 0.00-0.17) than in the placebo group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that pregnancy vitamin D supplementation may be an important population health strategy to improve bone health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rebecca J. Moon, PhD, MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, England. It was published online in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
LIMITATIONS:
Only individuals with baseline vitamin D levels of 25-100 nmol/L were eligible, excluding those with severe deficiency who might have benefited the most from supplementation. The participants were mostly White and well-educated, commonly overweight, which may have limited generalizability to other populations. Only 47% of the original cohort participated in the follow-up phase. Differences in maternal age, smoking status, and education between participants who remained in the study and those who did not may have introduced bias and affected generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis UK, Medical Research Council, Bupa Foundation, and National Institute for Health and Care Research, Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, and other sources. Some authors disclosed receiving travel reimbursement, speaker or lecture fees, honoraria, research funding, or personal or consultancy fees from Alliance for Better Bone Health and various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device, healthcare, and food and nutrition companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Gestational supplementation of 1000 IU/d cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) from early pregnancy until delivery increases the bone mineral content, bone mineral density (BMD), and bone mineral apparent density in children at age 6-7 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blinded, placebo-controlled MAVIDOS trial of gestational vitamin D supplementation previously showed increased BMD at age 4 years (but no difference at birth), and it is unclear how the effect may persist or change over time.
- In the original trial, researchers randomized 1134 pregnant women with singleton pregnancy from three UK hospitals from 2008 to 2014, and the 723 children born to mothers recruited in Southampton were invited to continue in offspring follow-up.
- Mothers were randomly assigned to receive either 1000-IU/d vitamin D or placebo from 14-17 weeks’ gestation until delivery; women in the placebo arm could take up to 400-IU/d vitamin D.
- In this post hoc analysis, among 454 children who were followed up at age 6-7 years, 447 had a usable whole body and lumbar spine dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan (placebo group: n = 216; 48% boys; 98% White mothers and vitamin D group: n = 231; 56% boys; 96% White mothers).
- Offspring follow-up measures at birth and 4 and 6-7 years were bone area, bone mineral content, BMD, and bone mineral apparent density, derived from a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan of whole body less head (WBLH), as well as fat and lean mass.
TAKEAWAY:
- The effect of gestational vitamin D supplementation on bone outcomes in children was similar at ages 4 and 6-7 years.
- At age 6-7 years, gestational vitamin D supplementation resulted in higher WBLH bone mineral content (0.15 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.26) and BMD (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.06-0.31) than placebo.
- The WBLH bone mineral apparent density (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.32) was also higher in the vitamin D group.
- The lean mass was greater in the vitamin D group (0.09 SD; 95% CI, 0.00-0.17) than in the placebo group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that pregnancy vitamin D supplementation may be an important population health strategy to improve bone health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rebecca J. Moon, PhD, MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, England. It was published online in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
LIMITATIONS:
Only individuals with baseline vitamin D levels of 25-100 nmol/L were eligible, excluding those with severe deficiency who might have benefited the most from supplementation. The participants were mostly White and well-educated, commonly overweight, which may have limited generalizability to other populations. Only 47% of the original cohort participated in the follow-up phase. Differences in maternal age, smoking status, and education between participants who remained in the study and those who did not may have introduced bias and affected generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis UK, Medical Research Council, Bupa Foundation, and National Institute for Health and Care Research, Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, and other sources. Some authors disclosed receiving travel reimbursement, speaker or lecture fees, honoraria, research funding, or personal or consultancy fees from Alliance for Better Bone Health and various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device, healthcare, and food and nutrition companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Gestational supplementation of 1000 IU/d cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) from early pregnancy until delivery increases the bone mineral content, bone mineral density (BMD), and bone mineral apparent density in children at age 6-7 years.
METHODOLOGY:
- The double-blinded, placebo-controlled MAVIDOS trial of gestational vitamin D supplementation previously showed increased BMD at age 4 years (but no difference at birth), and it is unclear how the effect may persist or change over time.
- In the original trial, researchers randomized 1134 pregnant women with singleton pregnancy from three UK hospitals from 2008 to 2014, and the 723 children born to mothers recruited in Southampton were invited to continue in offspring follow-up.
- Mothers were randomly assigned to receive either 1000-IU/d vitamin D or placebo from 14-17 weeks’ gestation until delivery; women in the placebo arm could take up to 400-IU/d vitamin D.
- In this post hoc analysis, among 454 children who were followed up at age 6-7 years, 447 had a usable whole body and lumbar spine dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan (placebo group: n = 216; 48% boys; 98% White mothers and vitamin D group: n = 231; 56% boys; 96% White mothers).
- Offspring follow-up measures at birth and 4 and 6-7 years were bone area, bone mineral content, BMD, and bone mineral apparent density, derived from a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan of whole body less head (WBLH), as well as fat and lean mass.
TAKEAWAY:
- The effect of gestational vitamin D supplementation on bone outcomes in children was similar at ages 4 and 6-7 years.
- At age 6-7 years, gestational vitamin D supplementation resulted in higher WBLH bone mineral content (0.15 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.26) and BMD (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.06-0.31) than placebo.
- The WBLH bone mineral apparent density (0.18 SD; 95% CI, 0.04-0.32) was also higher in the vitamin D group.
- The lean mass was greater in the vitamin D group (0.09 SD; 95% CI, 0.00-0.17) than in the placebo group.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings suggest that pregnancy vitamin D supplementation may be an important population health strategy to improve bone health,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Rebecca J. Moon, PhD, MRC Lifecourse Epidemiology Centre, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, England. It was published online in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
LIMITATIONS:
Only individuals with baseline vitamin D levels of 25-100 nmol/L were eligible, excluding those with severe deficiency who might have benefited the most from supplementation. The participants were mostly White and well-educated, commonly overweight, which may have limited generalizability to other populations. Only 47% of the original cohort participated in the follow-up phase. Differences in maternal age, smoking status, and education between participants who remained in the study and those who did not may have introduced bias and affected generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by Versus Arthritis UK, Medical Research Council, Bupa Foundation, and National Institute for Health and Care Research, Southampton Biomedical Research Centre, and other sources. Some authors disclosed receiving travel reimbursement, speaker or lecture fees, honoraria, research funding, or personal or consultancy fees from Alliance for Better Bone Health and various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device, healthcare, and food and nutrition companies outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heightened Amygdala Activity Tied to Postpartum Depression
MILAN, ITALY — Pregnant women with heightened amygdala activity have a reduced capacity to regulate emotions and report more symptoms of depression than those with lower activity in this brain region, a new imaging study suggested.
If validated, these findings could pave the way for identifying women at higher risk for postpartum depression, said lead researcher Franziska Weinmar, MSc, from the University of Tübingen in Germany.
The study was presented at the 37th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress.
Differences in Brain Activity
During pregnancy and the peripartum period, rising hormone levels create a “psychoneuroendocrinological window of vulnerability” for mental health in which 80% of women can develop transitory “baby blues,” and about one in seven develop more serious postpartum depression, Ms. Weinmar told this news organization.
The study included 47 women — 15 pregnant women and 32 nonpregnant controls. The nonpregnant women had normal menstrual cycles; 16 were in the early follicular phase with low estradiol levels (231.7 pmol/L), and 16 had high estradiol levels (516.6 pmol/L) after administration of estradiol.
To examine brain activity, participants were asked to view negative emotional images while undergoing functional MRI. They were then asked to use cognitive reappraisal to regulate their emotional response to the images.
The findings showed that both pregnant and nonpregnant women were equally successful at emotional regulation, but this process involved different brain activity in pregnant vs their nonpregnant counterpart.
All women had increased left middle frontal gyrus activity when regulating their emotions, but there was a difference in the amygdala between the pregnancy group and controls, Ms. Weinmar noted.
This suggests that pregnant women may have to exert more neural effort in emotional regulation, she said. “And pregnant women with higher amygdala activity were less able to regulate their emotions successfully compared to those with less amygdala activity.”
Linear regression analyses were performed to assess the relation of brain activity during down-regulation, regulation success, and self-reported depression scores, and this showed that higher amygdala activity was also associated with higher depression scores.
“We need to be cautious in interpreting this,” said Ms. Weinmar. “This is a small sample, and we are the first to undertake this work.”
Nonetheless, she said that if the findings are confirmed by larger studies, pregnant women could be assessed “in the waiting room” using existing questionnaires that evaluate emotional regulation.
If a woman has difficulties with emotion regulation, “there are adaptive strategies, like cognitive reappraisal that a counseling psychotherapist can help with,” said Ms. Weinmar.
“I could also imagine group sessions, for example, or online courses,” she said, adding that obstetricians could also be trained to identify these women.
Commenting on the findings in a press release, Susana Carmona, PhD, from Gregorio Marañón Hospital in Madrid, Spain, said research like this is crucial for gaining insight into one of the most intense physiological processes a human can undergo: pregnancy. It’s remarkable how much remains unknown.
“Recently, the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] approved the first treatment for postpartum depression. However, we still have a long way to go in characterizing what happens in the brain during pregnancy, identifying biomarkers that can indicate the risk of developing perinatal mental disorders, and designing strategies to prevent mother and infant suffering during the delicate and critical peripartum period,” Dr. Carmona added.
The study was supported by the Center for Integrative Neuroscience in Tübingen, Germany, and the International Research Training Group “Women’s Mental Health Across the Reproductive Years” (IRTG 2804). Ms. Weinmar and Dr. Carmona reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN, ITALY — Pregnant women with heightened amygdala activity have a reduced capacity to regulate emotions and report more symptoms of depression than those with lower activity in this brain region, a new imaging study suggested.
If validated, these findings could pave the way for identifying women at higher risk for postpartum depression, said lead researcher Franziska Weinmar, MSc, from the University of Tübingen in Germany.
The study was presented at the 37th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress.
Differences in Brain Activity
During pregnancy and the peripartum period, rising hormone levels create a “psychoneuroendocrinological window of vulnerability” for mental health in which 80% of women can develop transitory “baby blues,” and about one in seven develop more serious postpartum depression, Ms. Weinmar told this news organization.
The study included 47 women — 15 pregnant women and 32 nonpregnant controls. The nonpregnant women had normal menstrual cycles; 16 were in the early follicular phase with low estradiol levels (231.7 pmol/L), and 16 had high estradiol levels (516.6 pmol/L) after administration of estradiol.
To examine brain activity, participants were asked to view negative emotional images while undergoing functional MRI. They were then asked to use cognitive reappraisal to regulate their emotional response to the images.
The findings showed that both pregnant and nonpregnant women were equally successful at emotional regulation, but this process involved different brain activity in pregnant vs their nonpregnant counterpart.
All women had increased left middle frontal gyrus activity when regulating their emotions, but there was a difference in the amygdala between the pregnancy group and controls, Ms. Weinmar noted.
This suggests that pregnant women may have to exert more neural effort in emotional regulation, she said. “And pregnant women with higher amygdala activity were less able to regulate their emotions successfully compared to those with less amygdala activity.”
Linear regression analyses were performed to assess the relation of brain activity during down-regulation, regulation success, and self-reported depression scores, and this showed that higher amygdala activity was also associated with higher depression scores.
“We need to be cautious in interpreting this,” said Ms. Weinmar. “This is a small sample, and we are the first to undertake this work.”
Nonetheless, she said that if the findings are confirmed by larger studies, pregnant women could be assessed “in the waiting room” using existing questionnaires that evaluate emotional regulation.
If a woman has difficulties with emotion regulation, “there are adaptive strategies, like cognitive reappraisal that a counseling psychotherapist can help with,” said Ms. Weinmar.
“I could also imagine group sessions, for example, or online courses,” she said, adding that obstetricians could also be trained to identify these women.
Commenting on the findings in a press release, Susana Carmona, PhD, from Gregorio Marañón Hospital in Madrid, Spain, said research like this is crucial for gaining insight into one of the most intense physiological processes a human can undergo: pregnancy. It’s remarkable how much remains unknown.
“Recently, the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] approved the first treatment for postpartum depression. However, we still have a long way to go in characterizing what happens in the brain during pregnancy, identifying biomarkers that can indicate the risk of developing perinatal mental disorders, and designing strategies to prevent mother and infant suffering during the delicate and critical peripartum period,” Dr. Carmona added.
The study was supported by the Center for Integrative Neuroscience in Tübingen, Germany, and the International Research Training Group “Women’s Mental Health Across the Reproductive Years” (IRTG 2804). Ms. Weinmar and Dr. Carmona reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
MILAN, ITALY — Pregnant women with heightened amygdala activity have a reduced capacity to regulate emotions and report more symptoms of depression than those with lower activity in this brain region, a new imaging study suggested.
If validated, these findings could pave the way for identifying women at higher risk for postpartum depression, said lead researcher Franziska Weinmar, MSc, from the University of Tübingen in Germany.
The study was presented at the 37th European College of Neuropsychopharmacology Congress.
Differences in Brain Activity
During pregnancy and the peripartum period, rising hormone levels create a “psychoneuroendocrinological window of vulnerability” for mental health in which 80% of women can develop transitory “baby blues,” and about one in seven develop more serious postpartum depression, Ms. Weinmar told this news organization.
The study included 47 women — 15 pregnant women and 32 nonpregnant controls. The nonpregnant women had normal menstrual cycles; 16 were in the early follicular phase with low estradiol levels (231.7 pmol/L), and 16 had high estradiol levels (516.6 pmol/L) after administration of estradiol.
To examine brain activity, participants were asked to view negative emotional images while undergoing functional MRI. They were then asked to use cognitive reappraisal to regulate their emotional response to the images.
The findings showed that both pregnant and nonpregnant women were equally successful at emotional regulation, but this process involved different brain activity in pregnant vs their nonpregnant counterpart.
All women had increased left middle frontal gyrus activity when regulating their emotions, but there was a difference in the amygdala between the pregnancy group and controls, Ms. Weinmar noted.
This suggests that pregnant women may have to exert more neural effort in emotional regulation, she said. “And pregnant women with higher amygdala activity were less able to regulate their emotions successfully compared to those with less amygdala activity.”
Linear regression analyses were performed to assess the relation of brain activity during down-regulation, regulation success, and self-reported depression scores, and this showed that higher amygdala activity was also associated with higher depression scores.
“We need to be cautious in interpreting this,” said Ms. Weinmar. “This is a small sample, and we are the first to undertake this work.”
Nonetheless, she said that if the findings are confirmed by larger studies, pregnant women could be assessed “in the waiting room” using existing questionnaires that evaluate emotional regulation.
If a woman has difficulties with emotion regulation, “there are adaptive strategies, like cognitive reappraisal that a counseling psychotherapist can help with,” said Ms. Weinmar.
“I could also imagine group sessions, for example, or online courses,” she said, adding that obstetricians could also be trained to identify these women.
Commenting on the findings in a press release, Susana Carmona, PhD, from Gregorio Marañón Hospital in Madrid, Spain, said research like this is crucial for gaining insight into one of the most intense physiological processes a human can undergo: pregnancy. It’s remarkable how much remains unknown.
“Recently, the FDA [Food and Drug Administration] approved the first treatment for postpartum depression. However, we still have a long way to go in characterizing what happens in the brain during pregnancy, identifying biomarkers that can indicate the risk of developing perinatal mental disorders, and designing strategies to prevent mother and infant suffering during the delicate and critical peripartum period,” Dr. Carmona added.
The study was supported by the Center for Integrative Neuroscience in Tübingen, Germany, and the International Research Training Group “Women’s Mental Health Across the Reproductive Years” (IRTG 2804). Ms. Weinmar and Dr. Carmona reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECNP 2024
Severe Maternal Morbidity Three Times Higher in Surrogate Gestational Carriers
Gestational carriers face a significantly higher risk for severe maternal morbidity and other pregnancy complications than those conceiving naturally or via in vitro fertilization (IVF), according to a recent Canadian study.
These findings suggest that more work is needed to ensure careful selection of gestational carriers, reported lead author Maria P. Velez, MD, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“Although a gestational carrier should ideally be a healthy person, with a demonstrated low-risk obstetric history, it is not clear whether this occurs in practice,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. “Moreover, the risk for maternal and neonatal adversity is largely unknown in this group.”
Study Compared Gestational Carriage With IVF and Unassisted Conception
To address these knowledge gaps, Dr. Velez and colleagues conducted a population-based cohort study in Ontario using linked administrative datasets. All singleton births at more than 20 weeks’ gestation with mothers aged 18-50 years were included from April 2012 to March 2021. Multifetal pregnancies were excluded, as were women with a history of infertility diagnosis without fertility treatment, and those who underwent intrauterine insemination or ovulation induction.
Outcomes were compared across three groups: Unassisted conception, IVF, and gestational carriage. The primary maternal outcome was severe maternal morbidity, defined by a validated composite of 41 unique indicators. The primary infant outcome was severe neonatal morbidity, comprising 19 unique indicators.
Secondary outcomes were hypertensive disorders, elective cesarean delivery, emergent cesarean delivery, preterm birth at less than 37 weeks, preterm birth at more than 32 weeks, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Logistic regression analysis adjusted for a range of covariates, including age, obesity, tobacco/drug dependence, chronic hypertension, and others. The final dataset included 846,124 births by unassisted conception (97.6%), 16,087 by IVF (1.8%), and 806 by gestational carriage (0.1%).
The weighted relative risk (wRR) for severe maternal morbidity was more than three times higher in gestational carriers than in those conceiving naturally (wRR, 3.30; 95% CI, 2.59-4.20) and 86% higher than in those conceiving via IVF (wRR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.36-2.55). These stem from absolute risks of 2.3%, 4.3%, and 7.8% for unassisted, IVF, and surrogate pregnancies, respectively.
Moreover, surrogates were 75% more likely to have hypertensive disorders, 79% more likely to have preterm birth at less than 37 weeks, and almost three times as likely to have postpartum hemorrhage.
These same three secondary outcomes were also significantly more common when comparing surrogate with IVF pregnancies, albeit to a lesser degree. In contrast, surrogate pregnancies were associated with a 21% lower risk for elective cesarean delivery than IVF pregnancies (wRR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.68-0.93).
Severe neonatal morbidity was not significantly different between the groups. These findings add to a mixed body of evidence surrounding both maternal and neonatal outcomes with gestational carriers, according to the investigators.
“Prior small studies [by Söderström-Anttila et al. and Swanson et al.] reported varying risks for preterm birth in singleton gestational carriage pregnancies, whereas a recent large US registry reported no increased risk for preterm birth compared with IVF, after accounting for multifetal pregnancy,” they wrote. “This study excluded multifetal pregnancies, a common occurrence after IVF, with reported higher risks for adverse outcomes. Accordingly, adverse maternal and newborn outcomes may have been underestimated herein.”
Causes of Worse Outcomes Remain Unclear
While the present findings suggest greater maternal morbidity among surrogates, potential causes of these adverse outcomes remain unclear.
The investigators suggested that implantation of a nonautologous embryo could be playing a role, as oocyte donation has been linked with an increased risk for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
“We don’t know exactly why that can happen,” Dr. Velez said in an interview. “Maybe that embryo can be associated with an immunological response that could be associated with higher morbidity during pregnancy. We need, however, other studies that can continue testing that hypothesis.”
In the meantime, more care is needed in surrogate selection, according to Dr. Velez.
“In our study, we found that there were patients, for example, who had more than three prior C-sections, which is one of the contraindications for gestational carriers, and patients who had more than five [prior] pregnancies, which is also another limitation in the guidelines for choosing these patients,” she said. “Definitely we need to be more vigilant when we accept these gestational carriers.”
But improving surrogate selection may be easier said than done.
The quantitative thresholds cited by Dr. Velez come from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine guidelines. Alternative guidance documents from the Canadian Fertility and Andrology Society and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists are less prescriptive; instead, they offer qualitative recommendations concerning obstetric history and risk assessment.
And then there is the regulatory specter looming over the entire field, evidenced by the many times that these publications cite ethical and legal considerations — far more than the average medical guidance document — when making clinical decisions related to surrogacy.
Present Study Offers Much-Needed Data in Understudied Field
According to Kate Swanson, MD, a perinatologist, clinical geneticist, and associate professor at the University of California San Francisco, the present study may help steer medical societies and healthcare providers away from these potential sand traps and toward conversations grounded in scientific data.
“I think one of the reasons that the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine and the maternal-fetal medicine community in general hasn’t been interested in this subject is that they see it as a social/ethical/legal issue rather than a medical one,” Dr. Swanson said in an interview. “One of the real benefits of this article is that it shows that this is a medical issue that the obstetric community needs to pay attention to.”
These new data could help guide decisions about risk and candidacy with both potential gestational carriers and intended parents, she said.
Still, it’s hard — if not impossible — to disentangle the medical and legal aspects of surrogacy, as shown when analyzing the present study.
In Canada, where it was conducted, intended parents are forbidden from paying surrogates for their services beyond out-of-pocket costs directly related to pregnancy. Meanwhile, surrogacy laws vary widely across the United States; some states (eg, Louisiana) allow only altruistic surrogacy like Canada, while other states (eg, California) permit commercial surrogacy with no legal limits on compensation.
Dr. Swanson and Dr. Velez offered starkly different views on this topic.
“I think there should be more regulations in terms of compensating [gestational carriers],” Dr. Velez said. “I don’t think being a gestational carrier should be like a job or a way of making a living.”
Dr. Swanson, who has published multiple studies on gestational carriage and experienced the process as an intended parent, said compensation beyond expenses is essential.
“I do think it’s incredibly reasonable to pay someone — a woman is taking on quite a lot of inconvenience and risk — in order to perform this service for another family,” she said. “I think it’s incredibly appropriate to compensate her for all of that.”
Reasons for compensation go beyond the ethical, Dr. Swanson added, and may explain some of the findings from the present study.
“A lot of these gestational carriers [in the present dataset] wouldn’t necessarily meet criteria through the American Society of Reproductive Medicine,” Dr. Swanson said, pointing out surrogates who had never had a pregnancy before or reported the use of tobacco or other drugs. “Really, it shows me that a lot of the people participating as gestational carriers were maybe not ideal candidates. I think one of the reasons that we might see that in this Canadian population is ... that you can’t compensate someone, so I think their pool of people willing to be gestational carriers is a lot smaller, and they may be a little bit less selective sometimes.”
Dr. Velez acknowledged that the present study was limited by a shortage of potentially relevant information concerning the surrogacy selection process, including underlying reasons for becoming a gestational carrier. More work is needed to understand the health and outcomes of these women, she said, including topics ranging from immunologic mechanisms to mental health.
She also called for more discussions surrounding maternal safety, with participation from all stakeholders, including governments, surrogates, intended parents, and physicians too.
This study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Swanson disclosed a relationship with Mitera.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gestational carriers face a significantly higher risk for severe maternal morbidity and other pregnancy complications than those conceiving naturally or via in vitro fertilization (IVF), according to a recent Canadian study.
These findings suggest that more work is needed to ensure careful selection of gestational carriers, reported lead author Maria P. Velez, MD, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“Although a gestational carrier should ideally be a healthy person, with a demonstrated low-risk obstetric history, it is not clear whether this occurs in practice,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. “Moreover, the risk for maternal and neonatal adversity is largely unknown in this group.”
Study Compared Gestational Carriage With IVF and Unassisted Conception
To address these knowledge gaps, Dr. Velez and colleagues conducted a population-based cohort study in Ontario using linked administrative datasets. All singleton births at more than 20 weeks’ gestation with mothers aged 18-50 years were included from April 2012 to March 2021. Multifetal pregnancies were excluded, as were women with a history of infertility diagnosis without fertility treatment, and those who underwent intrauterine insemination or ovulation induction.
Outcomes were compared across three groups: Unassisted conception, IVF, and gestational carriage. The primary maternal outcome was severe maternal morbidity, defined by a validated composite of 41 unique indicators. The primary infant outcome was severe neonatal morbidity, comprising 19 unique indicators.
Secondary outcomes were hypertensive disorders, elective cesarean delivery, emergent cesarean delivery, preterm birth at less than 37 weeks, preterm birth at more than 32 weeks, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Logistic regression analysis adjusted for a range of covariates, including age, obesity, tobacco/drug dependence, chronic hypertension, and others. The final dataset included 846,124 births by unassisted conception (97.6%), 16,087 by IVF (1.8%), and 806 by gestational carriage (0.1%).
The weighted relative risk (wRR) for severe maternal morbidity was more than three times higher in gestational carriers than in those conceiving naturally (wRR, 3.30; 95% CI, 2.59-4.20) and 86% higher than in those conceiving via IVF (wRR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.36-2.55). These stem from absolute risks of 2.3%, 4.3%, and 7.8% for unassisted, IVF, and surrogate pregnancies, respectively.
Moreover, surrogates were 75% more likely to have hypertensive disorders, 79% more likely to have preterm birth at less than 37 weeks, and almost three times as likely to have postpartum hemorrhage.
These same three secondary outcomes were also significantly more common when comparing surrogate with IVF pregnancies, albeit to a lesser degree. In contrast, surrogate pregnancies were associated with a 21% lower risk for elective cesarean delivery than IVF pregnancies (wRR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.68-0.93).
Severe neonatal morbidity was not significantly different between the groups. These findings add to a mixed body of evidence surrounding both maternal and neonatal outcomes with gestational carriers, according to the investigators.
“Prior small studies [by Söderström-Anttila et al. and Swanson et al.] reported varying risks for preterm birth in singleton gestational carriage pregnancies, whereas a recent large US registry reported no increased risk for preterm birth compared with IVF, after accounting for multifetal pregnancy,” they wrote. “This study excluded multifetal pregnancies, a common occurrence after IVF, with reported higher risks for adverse outcomes. Accordingly, adverse maternal and newborn outcomes may have been underestimated herein.”
Causes of Worse Outcomes Remain Unclear
While the present findings suggest greater maternal morbidity among surrogates, potential causes of these adverse outcomes remain unclear.
The investigators suggested that implantation of a nonautologous embryo could be playing a role, as oocyte donation has been linked with an increased risk for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
“We don’t know exactly why that can happen,” Dr. Velez said in an interview. “Maybe that embryo can be associated with an immunological response that could be associated with higher morbidity during pregnancy. We need, however, other studies that can continue testing that hypothesis.”
In the meantime, more care is needed in surrogate selection, according to Dr. Velez.
“In our study, we found that there were patients, for example, who had more than three prior C-sections, which is one of the contraindications for gestational carriers, and patients who had more than five [prior] pregnancies, which is also another limitation in the guidelines for choosing these patients,” she said. “Definitely we need to be more vigilant when we accept these gestational carriers.”
But improving surrogate selection may be easier said than done.
The quantitative thresholds cited by Dr. Velez come from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine guidelines. Alternative guidance documents from the Canadian Fertility and Andrology Society and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists are less prescriptive; instead, they offer qualitative recommendations concerning obstetric history and risk assessment.
And then there is the regulatory specter looming over the entire field, evidenced by the many times that these publications cite ethical and legal considerations — far more than the average medical guidance document — when making clinical decisions related to surrogacy.
Present Study Offers Much-Needed Data in Understudied Field
According to Kate Swanson, MD, a perinatologist, clinical geneticist, and associate professor at the University of California San Francisco, the present study may help steer medical societies and healthcare providers away from these potential sand traps and toward conversations grounded in scientific data.
“I think one of the reasons that the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine and the maternal-fetal medicine community in general hasn’t been interested in this subject is that they see it as a social/ethical/legal issue rather than a medical one,” Dr. Swanson said in an interview. “One of the real benefits of this article is that it shows that this is a medical issue that the obstetric community needs to pay attention to.”
These new data could help guide decisions about risk and candidacy with both potential gestational carriers and intended parents, she said.
Still, it’s hard — if not impossible — to disentangle the medical and legal aspects of surrogacy, as shown when analyzing the present study.
In Canada, where it was conducted, intended parents are forbidden from paying surrogates for their services beyond out-of-pocket costs directly related to pregnancy. Meanwhile, surrogacy laws vary widely across the United States; some states (eg, Louisiana) allow only altruistic surrogacy like Canada, while other states (eg, California) permit commercial surrogacy with no legal limits on compensation.
Dr. Swanson and Dr. Velez offered starkly different views on this topic.
“I think there should be more regulations in terms of compensating [gestational carriers],” Dr. Velez said. “I don’t think being a gestational carrier should be like a job or a way of making a living.”
Dr. Swanson, who has published multiple studies on gestational carriage and experienced the process as an intended parent, said compensation beyond expenses is essential.
“I do think it’s incredibly reasonable to pay someone — a woman is taking on quite a lot of inconvenience and risk — in order to perform this service for another family,” she said. “I think it’s incredibly appropriate to compensate her for all of that.”
Reasons for compensation go beyond the ethical, Dr. Swanson added, and may explain some of the findings from the present study.
“A lot of these gestational carriers [in the present dataset] wouldn’t necessarily meet criteria through the American Society of Reproductive Medicine,” Dr. Swanson said, pointing out surrogates who had never had a pregnancy before or reported the use of tobacco or other drugs. “Really, it shows me that a lot of the people participating as gestational carriers were maybe not ideal candidates. I think one of the reasons that we might see that in this Canadian population is ... that you can’t compensate someone, so I think their pool of people willing to be gestational carriers is a lot smaller, and they may be a little bit less selective sometimes.”
Dr. Velez acknowledged that the present study was limited by a shortage of potentially relevant information concerning the surrogacy selection process, including underlying reasons for becoming a gestational carrier. More work is needed to understand the health and outcomes of these women, she said, including topics ranging from immunologic mechanisms to mental health.
She also called for more discussions surrounding maternal safety, with participation from all stakeholders, including governments, surrogates, intended parents, and physicians too.
This study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Swanson disclosed a relationship with Mitera.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gestational carriers face a significantly higher risk for severe maternal morbidity and other pregnancy complications than those conceiving naturally or via in vitro fertilization (IVF), according to a recent Canadian study.
These findings suggest that more work is needed to ensure careful selection of gestational carriers, reported lead author Maria P. Velez, MD, PhD, of McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues.
“Although a gestational carrier should ideally be a healthy person, with a demonstrated low-risk obstetric history, it is not clear whether this occurs in practice,” the investigators wrote in Annals of Internal Medicine. “Moreover, the risk for maternal and neonatal adversity is largely unknown in this group.”
Study Compared Gestational Carriage With IVF and Unassisted Conception
To address these knowledge gaps, Dr. Velez and colleagues conducted a population-based cohort study in Ontario using linked administrative datasets. All singleton births at more than 20 weeks’ gestation with mothers aged 18-50 years were included from April 2012 to March 2021. Multifetal pregnancies were excluded, as were women with a history of infertility diagnosis without fertility treatment, and those who underwent intrauterine insemination or ovulation induction.
Outcomes were compared across three groups: Unassisted conception, IVF, and gestational carriage. The primary maternal outcome was severe maternal morbidity, defined by a validated composite of 41 unique indicators. The primary infant outcome was severe neonatal morbidity, comprising 19 unique indicators.
Secondary outcomes were hypertensive disorders, elective cesarean delivery, emergent cesarean delivery, preterm birth at less than 37 weeks, preterm birth at more than 32 weeks, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Logistic regression analysis adjusted for a range of covariates, including age, obesity, tobacco/drug dependence, chronic hypertension, and others. The final dataset included 846,124 births by unassisted conception (97.6%), 16,087 by IVF (1.8%), and 806 by gestational carriage (0.1%).
The weighted relative risk (wRR) for severe maternal morbidity was more than three times higher in gestational carriers than in those conceiving naturally (wRR, 3.30; 95% CI, 2.59-4.20) and 86% higher than in those conceiving via IVF (wRR, 1.86; 95% CI, 1.36-2.55). These stem from absolute risks of 2.3%, 4.3%, and 7.8% for unassisted, IVF, and surrogate pregnancies, respectively.
Moreover, surrogates were 75% more likely to have hypertensive disorders, 79% more likely to have preterm birth at less than 37 weeks, and almost three times as likely to have postpartum hemorrhage.
These same three secondary outcomes were also significantly more common when comparing surrogate with IVF pregnancies, albeit to a lesser degree. In contrast, surrogate pregnancies were associated with a 21% lower risk for elective cesarean delivery than IVF pregnancies (wRR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.68-0.93).
Severe neonatal morbidity was not significantly different between the groups. These findings add to a mixed body of evidence surrounding both maternal and neonatal outcomes with gestational carriers, according to the investigators.
“Prior small studies [by Söderström-Anttila et al. and Swanson et al.] reported varying risks for preterm birth in singleton gestational carriage pregnancies, whereas a recent large US registry reported no increased risk for preterm birth compared with IVF, after accounting for multifetal pregnancy,” they wrote. “This study excluded multifetal pregnancies, a common occurrence after IVF, with reported higher risks for adverse outcomes. Accordingly, adverse maternal and newborn outcomes may have been underestimated herein.”
Causes of Worse Outcomes Remain Unclear
While the present findings suggest greater maternal morbidity among surrogates, potential causes of these adverse outcomes remain unclear.
The investigators suggested that implantation of a nonautologous embryo could be playing a role, as oocyte donation has been linked with an increased risk for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
“We don’t know exactly why that can happen,” Dr. Velez said in an interview. “Maybe that embryo can be associated with an immunological response that could be associated with higher morbidity during pregnancy. We need, however, other studies that can continue testing that hypothesis.”
In the meantime, more care is needed in surrogate selection, according to Dr. Velez.
“In our study, we found that there were patients, for example, who had more than three prior C-sections, which is one of the contraindications for gestational carriers, and patients who had more than five [prior] pregnancies, which is also another limitation in the guidelines for choosing these patients,” she said. “Definitely we need to be more vigilant when we accept these gestational carriers.”
But improving surrogate selection may be easier said than done.
The quantitative thresholds cited by Dr. Velez come from the American Society for Reproductive Medicine guidelines. Alternative guidance documents from the Canadian Fertility and Andrology Society and American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists are less prescriptive; instead, they offer qualitative recommendations concerning obstetric history and risk assessment.
And then there is the regulatory specter looming over the entire field, evidenced by the many times that these publications cite ethical and legal considerations — far more than the average medical guidance document — when making clinical decisions related to surrogacy.
Present Study Offers Much-Needed Data in Understudied Field
According to Kate Swanson, MD, a perinatologist, clinical geneticist, and associate professor at the University of California San Francisco, the present study may help steer medical societies and healthcare providers away from these potential sand traps and toward conversations grounded in scientific data.
“I think one of the reasons that the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine and the maternal-fetal medicine community in general hasn’t been interested in this subject is that they see it as a social/ethical/legal issue rather than a medical one,” Dr. Swanson said in an interview. “One of the real benefits of this article is that it shows that this is a medical issue that the obstetric community needs to pay attention to.”
These new data could help guide decisions about risk and candidacy with both potential gestational carriers and intended parents, she said.
Still, it’s hard — if not impossible — to disentangle the medical and legal aspects of surrogacy, as shown when analyzing the present study.
In Canada, where it was conducted, intended parents are forbidden from paying surrogates for their services beyond out-of-pocket costs directly related to pregnancy. Meanwhile, surrogacy laws vary widely across the United States; some states (eg, Louisiana) allow only altruistic surrogacy like Canada, while other states (eg, California) permit commercial surrogacy with no legal limits on compensation.
Dr. Swanson and Dr. Velez offered starkly different views on this topic.
“I think there should be more regulations in terms of compensating [gestational carriers],” Dr. Velez said. “I don’t think being a gestational carrier should be like a job or a way of making a living.”
Dr. Swanson, who has published multiple studies on gestational carriage and experienced the process as an intended parent, said compensation beyond expenses is essential.
“I do think it’s incredibly reasonable to pay someone — a woman is taking on quite a lot of inconvenience and risk — in order to perform this service for another family,” she said. “I think it’s incredibly appropriate to compensate her for all of that.”
Reasons for compensation go beyond the ethical, Dr. Swanson added, and may explain some of the findings from the present study.
“A lot of these gestational carriers [in the present dataset] wouldn’t necessarily meet criteria through the American Society of Reproductive Medicine,” Dr. Swanson said, pointing out surrogates who had never had a pregnancy before or reported the use of tobacco or other drugs. “Really, it shows me that a lot of the people participating as gestational carriers were maybe not ideal candidates. I think one of the reasons that we might see that in this Canadian population is ... that you can’t compensate someone, so I think their pool of people willing to be gestational carriers is a lot smaller, and they may be a little bit less selective sometimes.”
Dr. Velez acknowledged that the present study was limited by a shortage of potentially relevant information concerning the surrogacy selection process, including underlying reasons for becoming a gestational carrier. More work is needed to understand the health and outcomes of these women, she said, including topics ranging from immunologic mechanisms to mental health.
She also called for more discussions surrounding maternal safety, with participation from all stakeholders, including governments, surrogates, intended parents, and physicians too.
This study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. The investigators disclosed no conflicts of interest. Dr. Swanson disclosed a relationship with Mitera.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Doulas Support Moms-to-Be and Try to Fit Into the Obstetric Care Team
It’s well known that the United States enjoys the dubious distinction of having the worst maternal morbidity and mortality rates among industrialized nations. Maternal mortality in this country increased by 14% from 2018 to 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics.
But a current trend of engaging birth doulas — nonmedical guides offering continuous one-on-one physical and psychological support in the pre-, peri,- and postnatal periods — may be poised to brighten that dismal statistical landscape.
Recent research has shown that mothers matched with a doula are less likely to have a low birth weight baby, less likely to experience a birth complication, and significantly more likely to initiate breastfeeding.
Doula services — even delivered digitally — are seen to lower healthcare costs, reduce cesarean sections, decrease maternal anxiety and depression, and improve communication between healthcare providers and low-income, racially/ethnically diverse pregnant women. Doulas can be especially helpful for mothers dealing with the psychological fallout of miscarriage or stillbirth. They can guide patients in the postpartum period, when problems can arise and when some mothers are lost to medical follow-up, and provide an ongoing source of patient information for the ob.gyn.
“Research has shown that in addition to better outcomes, doula care can shorten labor time and increase patient satisfaction,” said ob.gyn. Layan Alrahmani, MD, in an interview. A maternal-fetal medicine specialist with a focus on high-risk pregnancies among low-income women at Loyola Medicine in Maywood, Illinois, Dr. Alrahmani welcomes doulas to her patients’ antenatal visits.
“Many of my patients who are looking to avoid an epidural will work with a labor doula, in order to stay home as long as possible and to have one-on-one coaching through the pain as things progress,” said Susan Rothenberg, MD, an assistant professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and an ob/gyn at Mount Sinai Downtown Union Square in New York City. She added, “When a woman’s partner is squeamish or potentially unavailable, a labor doula can be a great option.”
Another ob.gyn. who enthusiastically embraces doula care is L. Joy Baker, MD, who practices in LaGrange, Georgia, and is affiliated with Wellstar West Georgia Medical Center. “I love it when my patients have a doula. A doula answers a patient’s questions throughout the pregnancy and amplifies the mother’s voice in the medical system and the clinical setting,” Dr. Baker told this news organization.
“They provide important details on patients’ food, housing, and transportation status when the mothers themselves would not bring those up in a short appointment with their doctors,” she said. Dr. Baker called for more recognition of their merit, especially for first-time and high-risk moms.
Efua B. Leke, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine and chief of obstetrics at Ben Taub Hospital in Houston, Texas, also believes a major benefit of doulas is improved flow of information. “We know that having doulas participate in maternal care can ease communication between pregnant and parturient mothers and their clinical team,” Dr. Leke said. “This is especially important for under-resourced pregnant women for whom morbidity tends to be disparately higher.”
Doulas can also take pressure off embattled ob.gyn. clinical staff. “Our volume of patients is huge, so we have to keep appointments brief,” Dr. Baker said. “The US is currently 8000 ob.gyn.s short, and to make matters worse, we’re seeing more and more obstetrical care deserts.”
Still largely underutilized, doula care is seen by its proponents as important in light of the drastic shortage of ob.gyn.s and the shrinking presence of maternity care in many US counties.
According to a recent March of Dimes report, access to maternity care is waning, with more than 35% of US counties offering no community obstetrical care and 52% providing no maternity care in local hospitals. That translates to long distances and extended travel time for mothers seeking care.
Growth Remains Slow
Although many believe doulas could become part of the solution to the lack of access to maternity care, their acceptance seems to be slow growing. In a 2012 national survey by Declercq and associates, about 6% of mothers used a doula during childbirth, up from 3% in a 2006 national survey. Of those who were familiar with but lacking doula care, just 27% would have chosen to have this service.
“I’d estimate that doulas are still involved in only about 6%-8% of births,” said Shaconna Haley, MA, a certified holistic doula and doula trainer in Atlanta, Georgia.
And are there enough practicing doulas in the United States to put a dent in the current shortfall in pregnancy care? Although no reliable estimate of their numbers exists, a centralized online doula registration service listed 9000 registered practitioners in 2018. Contrast that with the approximately 3.6 million live births in 2023.
Potential for Friction?
Although generally seen as benign and helpful, the presence of a doula can add another layer of people for hard-pressed medical staff to deal with. Can their attendance occasionally lead to an adversarial encounter? Yes, said Dr. Baker, especially in the case of assertive questioning or suggestions directed at medical staff. “There can be some mistrust on the part of clinicians when nonmedical persons start raising concerns and asking questions. Staff can get a little prickly at this.”
In the view of Melissa A. Simon, MD, MPH, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology, preventive medicine, and medical social sciences at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, Illinois, simple, preventable communication breakdown is often the cause of occasional antagonism. “As in all team care approaches, it’s helpful to have upfront conversations with the birthing person, the doula, and any care team members or support people who will be present in the birthing room. These conversations should be about expectations.”
According to Ms. Haley, “As long as the focus stays firmly on the client/patient and not on the other team members, there should be no friction. Medical staff should be aware there will be a doula in attendance and ideally there should be a collaborative team and plan in place before the birth.”
In Dr. Leke’s experience, doulas do not hinder the medical team as long as clinical roles are well clarified and the patient is engaged in her care plan. “Friction can occur when doulas are functioning outside of their scope of practice, such as speaking to the healthcare team on behalf of the mother instead empowering the mother to speak up herself,” she said. “Or, when the healthcare team doesn’t understand the doula’s scope of practice or recognize the doula as a member of the team.”
Added Dr. Rothenberg, “I’ve occasionally run into doulas who imagine I have an ulterior motive when making recommendations to patients when that’s completely untrue. It’s common for women to decide to become doulas because they didn’t feel listened to during their own birthing experience, and for a few of them, it’s hard to not project that onto their clients’ labor situations, creating conflict where it doesn’t need to exist.”
Barriers and Challenges
Unfortunately, the barriers of cost and access remain high for pregnant and birthing mothers from lower socioeconomic echelons who have no or limited insurance. “There also are very few multilingual doulas or doulas from diverse racial-ethnic backgrounds and identities,” Dr. Simon pointed out.
Yet by all indications, Medicaid members who receive doula services experience positive maternal outcomes, even those at higher risk for pregnancy complications.
As for Medicaid coverage of doula services, in a recent Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services report, just 11 state Medicaid programs were reimbursing doula services, whereas an additional five were in the process of implementing reimbursement.
Doula care is not covered by all private insurance plans either, Dr. Simon said. “Although there are maternity care bundles with payment models that help integrate doula care, and there are ways to use your flexible spending account to cover it.”
Some hospitals may undertake independent initiatives. Dr. Baker’s center is offering antenatal and peripartum doula support for under-resourced mothers thanks to a Health Resources and Services Administration grant.*
But for now, doula services are largely limited to middle- and high-income women able to afford the associated out-of-pocket costs. These mothers are disproportionately White, and the doulas serving them tend to be of the same race and socioeconomic class.
The Future
Dr. Simon foresees an optimal scenario in which a team of doulas works with all birthing persons on a hospital labor floor as well as with a team of clinicians. “It takes a true team approach to ensure an optimal birthing experience and optimal birth outcomes,” she said.
Despite the many challenges ahead, doulas will probably become a permanent fixture in pregnancy, birth, and postpartum care, said Dr. Baker. “Doula care is going to be a game changer, and obstetricians welcome doulas to the obstetrical care team.”
Dr. Alrahmani, Dr. Baker, Ms. Haley, Dr. Leke, Dr. Rothenberg, and Dr. Simon declared no conflicts of interest relevant to their comments.
*This story was updated on October 1, 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s well known that the United States enjoys the dubious distinction of having the worst maternal morbidity and mortality rates among industrialized nations. Maternal mortality in this country increased by 14% from 2018 to 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics.
But a current trend of engaging birth doulas — nonmedical guides offering continuous one-on-one physical and psychological support in the pre-, peri,- and postnatal periods — may be poised to brighten that dismal statistical landscape.
Recent research has shown that mothers matched with a doula are less likely to have a low birth weight baby, less likely to experience a birth complication, and significantly more likely to initiate breastfeeding.
Doula services — even delivered digitally — are seen to lower healthcare costs, reduce cesarean sections, decrease maternal anxiety and depression, and improve communication between healthcare providers and low-income, racially/ethnically diverse pregnant women. Doulas can be especially helpful for mothers dealing with the psychological fallout of miscarriage or stillbirth. They can guide patients in the postpartum period, when problems can arise and when some mothers are lost to medical follow-up, and provide an ongoing source of patient information for the ob.gyn.
“Research has shown that in addition to better outcomes, doula care can shorten labor time and increase patient satisfaction,” said ob.gyn. Layan Alrahmani, MD, in an interview. A maternal-fetal medicine specialist with a focus on high-risk pregnancies among low-income women at Loyola Medicine in Maywood, Illinois, Dr. Alrahmani welcomes doulas to her patients’ antenatal visits.
“Many of my patients who are looking to avoid an epidural will work with a labor doula, in order to stay home as long as possible and to have one-on-one coaching through the pain as things progress,” said Susan Rothenberg, MD, an assistant professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and an ob/gyn at Mount Sinai Downtown Union Square in New York City. She added, “When a woman’s partner is squeamish or potentially unavailable, a labor doula can be a great option.”
Another ob.gyn. who enthusiastically embraces doula care is L. Joy Baker, MD, who practices in LaGrange, Georgia, and is affiliated with Wellstar West Georgia Medical Center. “I love it when my patients have a doula. A doula answers a patient’s questions throughout the pregnancy and amplifies the mother’s voice in the medical system and the clinical setting,” Dr. Baker told this news organization.
“They provide important details on patients’ food, housing, and transportation status when the mothers themselves would not bring those up in a short appointment with their doctors,” she said. Dr. Baker called for more recognition of their merit, especially for first-time and high-risk moms.
Efua B. Leke, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine and chief of obstetrics at Ben Taub Hospital in Houston, Texas, also believes a major benefit of doulas is improved flow of information. “We know that having doulas participate in maternal care can ease communication between pregnant and parturient mothers and their clinical team,” Dr. Leke said. “This is especially important for under-resourced pregnant women for whom morbidity tends to be disparately higher.”
Doulas can also take pressure off embattled ob.gyn. clinical staff. “Our volume of patients is huge, so we have to keep appointments brief,” Dr. Baker said. “The US is currently 8000 ob.gyn.s short, and to make matters worse, we’re seeing more and more obstetrical care deserts.”
Still largely underutilized, doula care is seen by its proponents as important in light of the drastic shortage of ob.gyn.s and the shrinking presence of maternity care in many US counties.
According to a recent March of Dimes report, access to maternity care is waning, with more than 35% of US counties offering no community obstetrical care and 52% providing no maternity care in local hospitals. That translates to long distances and extended travel time for mothers seeking care.
Growth Remains Slow
Although many believe doulas could become part of the solution to the lack of access to maternity care, their acceptance seems to be slow growing. In a 2012 national survey by Declercq and associates, about 6% of mothers used a doula during childbirth, up from 3% in a 2006 national survey. Of those who were familiar with but lacking doula care, just 27% would have chosen to have this service.
“I’d estimate that doulas are still involved in only about 6%-8% of births,” said Shaconna Haley, MA, a certified holistic doula and doula trainer in Atlanta, Georgia.
And are there enough practicing doulas in the United States to put a dent in the current shortfall in pregnancy care? Although no reliable estimate of their numbers exists, a centralized online doula registration service listed 9000 registered practitioners in 2018. Contrast that with the approximately 3.6 million live births in 2023.
Potential for Friction?
Although generally seen as benign and helpful, the presence of a doula can add another layer of people for hard-pressed medical staff to deal with. Can their attendance occasionally lead to an adversarial encounter? Yes, said Dr. Baker, especially in the case of assertive questioning or suggestions directed at medical staff. “There can be some mistrust on the part of clinicians when nonmedical persons start raising concerns and asking questions. Staff can get a little prickly at this.”
In the view of Melissa A. Simon, MD, MPH, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology, preventive medicine, and medical social sciences at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, Illinois, simple, preventable communication breakdown is often the cause of occasional antagonism. “As in all team care approaches, it’s helpful to have upfront conversations with the birthing person, the doula, and any care team members or support people who will be present in the birthing room. These conversations should be about expectations.”
According to Ms. Haley, “As long as the focus stays firmly on the client/patient and not on the other team members, there should be no friction. Medical staff should be aware there will be a doula in attendance and ideally there should be a collaborative team and plan in place before the birth.”
In Dr. Leke’s experience, doulas do not hinder the medical team as long as clinical roles are well clarified and the patient is engaged in her care plan. “Friction can occur when doulas are functioning outside of their scope of practice, such as speaking to the healthcare team on behalf of the mother instead empowering the mother to speak up herself,” she said. “Or, when the healthcare team doesn’t understand the doula’s scope of practice or recognize the doula as a member of the team.”
Added Dr. Rothenberg, “I’ve occasionally run into doulas who imagine I have an ulterior motive when making recommendations to patients when that’s completely untrue. It’s common for women to decide to become doulas because they didn’t feel listened to during their own birthing experience, and for a few of them, it’s hard to not project that onto their clients’ labor situations, creating conflict where it doesn’t need to exist.”
Barriers and Challenges
Unfortunately, the barriers of cost and access remain high for pregnant and birthing mothers from lower socioeconomic echelons who have no or limited insurance. “There also are very few multilingual doulas or doulas from diverse racial-ethnic backgrounds and identities,” Dr. Simon pointed out.
Yet by all indications, Medicaid members who receive doula services experience positive maternal outcomes, even those at higher risk for pregnancy complications.
As for Medicaid coverage of doula services, in a recent Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services report, just 11 state Medicaid programs were reimbursing doula services, whereas an additional five were in the process of implementing reimbursement.
Doula care is not covered by all private insurance plans either, Dr. Simon said. “Although there are maternity care bundles with payment models that help integrate doula care, and there are ways to use your flexible spending account to cover it.”
Some hospitals may undertake independent initiatives. Dr. Baker’s center is offering antenatal and peripartum doula support for under-resourced mothers thanks to a Health Resources and Services Administration grant.*
But for now, doula services are largely limited to middle- and high-income women able to afford the associated out-of-pocket costs. These mothers are disproportionately White, and the doulas serving them tend to be of the same race and socioeconomic class.
The Future
Dr. Simon foresees an optimal scenario in which a team of doulas works with all birthing persons on a hospital labor floor as well as with a team of clinicians. “It takes a true team approach to ensure an optimal birthing experience and optimal birth outcomes,” she said.
Despite the many challenges ahead, doulas will probably become a permanent fixture in pregnancy, birth, and postpartum care, said Dr. Baker. “Doula care is going to be a game changer, and obstetricians welcome doulas to the obstetrical care team.”
Dr. Alrahmani, Dr. Baker, Ms. Haley, Dr. Leke, Dr. Rothenberg, and Dr. Simon declared no conflicts of interest relevant to their comments.
*This story was updated on October 1, 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s well known that the United States enjoys the dubious distinction of having the worst maternal morbidity and mortality rates among industrialized nations. Maternal mortality in this country increased by 14% from 2018 to 2020, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s National Center for Health Statistics.
But a current trend of engaging birth doulas — nonmedical guides offering continuous one-on-one physical and psychological support in the pre-, peri,- and postnatal periods — may be poised to brighten that dismal statistical landscape.
Recent research has shown that mothers matched with a doula are less likely to have a low birth weight baby, less likely to experience a birth complication, and significantly more likely to initiate breastfeeding.
Doula services — even delivered digitally — are seen to lower healthcare costs, reduce cesarean sections, decrease maternal anxiety and depression, and improve communication between healthcare providers and low-income, racially/ethnically diverse pregnant women. Doulas can be especially helpful for mothers dealing with the psychological fallout of miscarriage or stillbirth. They can guide patients in the postpartum period, when problems can arise and when some mothers are lost to medical follow-up, and provide an ongoing source of patient information for the ob.gyn.
“Research has shown that in addition to better outcomes, doula care can shorten labor time and increase patient satisfaction,” said ob.gyn. Layan Alrahmani, MD, in an interview. A maternal-fetal medicine specialist with a focus on high-risk pregnancies among low-income women at Loyola Medicine in Maywood, Illinois, Dr. Alrahmani welcomes doulas to her patients’ antenatal visits.
“Many of my patients who are looking to avoid an epidural will work with a labor doula, in order to stay home as long as possible and to have one-on-one coaching through the pain as things progress,” said Susan Rothenberg, MD, an assistant professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive science at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and an ob/gyn at Mount Sinai Downtown Union Square in New York City. She added, “When a woman’s partner is squeamish or potentially unavailable, a labor doula can be a great option.”
Another ob.gyn. who enthusiastically embraces doula care is L. Joy Baker, MD, who practices in LaGrange, Georgia, and is affiliated with Wellstar West Georgia Medical Center. “I love it when my patients have a doula. A doula answers a patient’s questions throughout the pregnancy and amplifies the mother’s voice in the medical system and the clinical setting,” Dr. Baker told this news organization.
“They provide important details on patients’ food, housing, and transportation status when the mothers themselves would not bring those up in a short appointment with their doctors,” she said. Dr. Baker called for more recognition of their merit, especially for first-time and high-risk moms.
Efua B. Leke, MD, MPH, an assistant professor at Baylor College of Medicine and chief of obstetrics at Ben Taub Hospital in Houston, Texas, also believes a major benefit of doulas is improved flow of information. “We know that having doulas participate in maternal care can ease communication between pregnant and parturient mothers and their clinical team,” Dr. Leke said. “This is especially important for under-resourced pregnant women for whom morbidity tends to be disparately higher.”
Doulas can also take pressure off embattled ob.gyn. clinical staff. “Our volume of patients is huge, so we have to keep appointments brief,” Dr. Baker said. “The US is currently 8000 ob.gyn.s short, and to make matters worse, we’re seeing more and more obstetrical care deserts.”
Still largely underutilized, doula care is seen by its proponents as important in light of the drastic shortage of ob.gyn.s and the shrinking presence of maternity care in many US counties.
According to a recent March of Dimes report, access to maternity care is waning, with more than 35% of US counties offering no community obstetrical care and 52% providing no maternity care in local hospitals. That translates to long distances and extended travel time for mothers seeking care.
Growth Remains Slow
Although many believe doulas could become part of the solution to the lack of access to maternity care, their acceptance seems to be slow growing. In a 2012 national survey by Declercq and associates, about 6% of mothers used a doula during childbirth, up from 3% in a 2006 national survey. Of those who were familiar with but lacking doula care, just 27% would have chosen to have this service.
“I’d estimate that doulas are still involved in only about 6%-8% of births,” said Shaconna Haley, MA, a certified holistic doula and doula trainer in Atlanta, Georgia.
And are there enough practicing doulas in the United States to put a dent in the current shortfall in pregnancy care? Although no reliable estimate of their numbers exists, a centralized online doula registration service listed 9000 registered practitioners in 2018. Contrast that with the approximately 3.6 million live births in 2023.
Potential for Friction?
Although generally seen as benign and helpful, the presence of a doula can add another layer of people for hard-pressed medical staff to deal with. Can their attendance occasionally lead to an adversarial encounter? Yes, said Dr. Baker, especially in the case of assertive questioning or suggestions directed at medical staff. “There can be some mistrust on the part of clinicians when nonmedical persons start raising concerns and asking questions. Staff can get a little prickly at this.”
In the view of Melissa A. Simon, MD, MPH, a professor of obstetrics and gynecology, preventive medicine, and medical social sciences at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, Illinois, simple, preventable communication breakdown is often the cause of occasional antagonism. “As in all team care approaches, it’s helpful to have upfront conversations with the birthing person, the doula, and any care team members or support people who will be present in the birthing room. These conversations should be about expectations.”
According to Ms. Haley, “As long as the focus stays firmly on the client/patient and not on the other team members, there should be no friction. Medical staff should be aware there will be a doula in attendance and ideally there should be a collaborative team and plan in place before the birth.”
In Dr. Leke’s experience, doulas do not hinder the medical team as long as clinical roles are well clarified and the patient is engaged in her care plan. “Friction can occur when doulas are functioning outside of their scope of practice, such as speaking to the healthcare team on behalf of the mother instead empowering the mother to speak up herself,” she said. “Or, when the healthcare team doesn’t understand the doula’s scope of practice or recognize the doula as a member of the team.”
Added Dr. Rothenberg, “I’ve occasionally run into doulas who imagine I have an ulterior motive when making recommendations to patients when that’s completely untrue. It’s common for women to decide to become doulas because they didn’t feel listened to during their own birthing experience, and for a few of them, it’s hard to not project that onto their clients’ labor situations, creating conflict where it doesn’t need to exist.”
Barriers and Challenges
Unfortunately, the barriers of cost and access remain high for pregnant and birthing mothers from lower socioeconomic echelons who have no or limited insurance. “There also are very few multilingual doulas or doulas from diverse racial-ethnic backgrounds and identities,” Dr. Simon pointed out.
Yet by all indications, Medicaid members who receive doula services experience positive maternal outcomes, even those at higher risk for pregnancy complications.
As for Medicaid coverage of doula services, in a recent Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services report, just 11 state Medicaid programs were reimbursing doula services, whereas an additional five were in the process of implementing reimbursement.
Doula care is not covered by all private insurance plans either, Dr. Simon said. “Although there are maternity care bundles with payment models that help integrate doula care, and there are ways to use your flexible spending account to cover it.”
Some hospitals may undertake independent initiatives. Dr. Baker’s center is offering antenatal and peripartum doula support for under-resourced mothers thanks to a Health Resources and Services Administration grant.*
But for now, doula services are largely limited to middle- and high-income women able to afford the associated out-of-pocket costs. These mothers are disproportionately White, and the doulas serving them tend to be of the same race and socioeconomic class.
The Future
Dr. Simon foresees an optimal scenario in which a team of doulas works with all birthing persons on a hospital labor floor as well as with a team of clinicians. “It takes a true team approach to ensure an optimal birthing experience and optimal birth outcomes,” she said.
Despite the many challenges ahead, doulas will probably become a permanent fixture in pregnancy, birth, and postpartum care, said Dr. Baker. “Doula care is going to be a game changer, and obstetricians welcome doulas to the obstetrical care team.”
Dr. Alrahmani, Dr. Baker, Ms. Haley, Dr. Leke, Dr. Rothenberg, and Dr. Simon declared no conflicts of interest relevant to their comments.
*This story was updated on October 1, 2024.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.





