User login
Norgestrel for nonprescription contraception: What you and your patients need to know
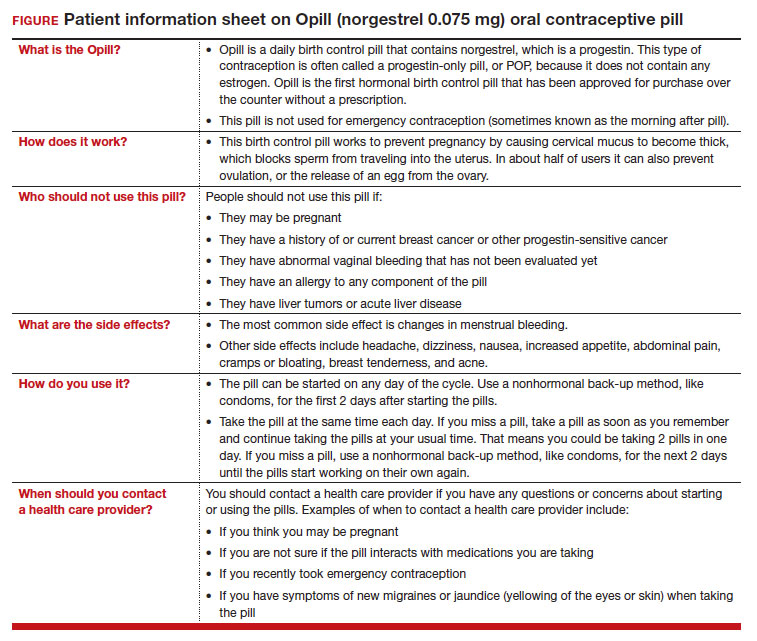
On July 13, 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved norgestrel 0.075 mg (Opill, HRA Pharma, Paris, France) as the first nonprescription oral contraceptive pill (FIGURE). This progestin-only pill was originally FDA approved in 1973, with prescription required, and was available as Ovrette until 2005, when product distribution ceased for marketing reasons and not for safety or effectiveness concerns.1 In recent years, studies have been conducted to support converted approval from prescription to nonprescription to increase access to safe and effective contraception. Overall, norgestrel is more effective than other currently available nonprescription contraceptive options when used as directed, and widespread accessibility to this method has the potential to decrease the risk of unintended pregnancies. This product is expected to be available in drugstores, convenience stores, grocery stores, and online in 2024.
How it works
The indication for norgestrel 0.075 mg is pregnancy prevention in people with the capacity to become pregnant; this product is not intended for emergency contraception. Norgestrel is a racemic mixture of 2 isomers, of which only levonorgestrel is bioactive. The mechanism of action for contraception is primarily through cervical mucus thickening, which inhibits sperm movement through the cervix. About 50% of users also have an additional contraceptive effect of ovulation suppression.2
Instructions for use. In the package label, users are instructed to take the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill daily, preferably at the same time each day and no more than 3 hours from the time taken on the previous day. This method can be started on any day of the cycle, and backup contraception (a barrier method) should be used for the first 48 hours after starting the method if it has been more than 5 days since menstrual bleeding started.3 Product instructions indicate that, if users miss a dose, they should take the next dose as soon as possible. If a pill is taken 3 hours or more later than the usual time, they should take a pill immediately and then resume the next pill at the usual time. In addition, backup contraception is recommended for 48 hours.2
Based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, no examinations or tests are required prior to initiation of progestin-only pills for safe and effective use.3
Efficacy
The product label indicates that the pregnancy rate is approximately 2 per 100 women-years based on over 21,000 28-day exposure cycles from 8 US clinical studies.2 In a recent review by Glasier and colleagues, the authors identified 13 trials that assessed the efficacy of the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill, all published several decades ago.4 Given that breastfeeding can have contraceptive impact through ovulation inhibition, studies that included breastfeeding participants were evaluated separately. Six studies without breastfeeding participants included 3,184 women who provided more than 35,000 months of use. The overall failure rates ranged from 0 to 2.4 per hundred woman-years with typical use; an aggregate Pearl Index was calculated to be 2.2 based on the total numbers of pregnancies and cycles. The remaining 7 studies included individuals who were breastfeeding for at least part of their study participation. These studies included 5,445 women, and the 12-month life table cumulative pregnancy rates in this group ranged from 0.0% to 3.4%. This review noted that the available studies are limited by incomplete descriptions of study participant information and differences in reporting of failure rates; however, the overall data support the effectiveness of the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill for pregnancy prevention.
Continue to: Norgestrel’s mechanism of action on ovarian activity and cervical mucus...
Norgestrel’s mechanism of action on ovarian activity and cervical mucus
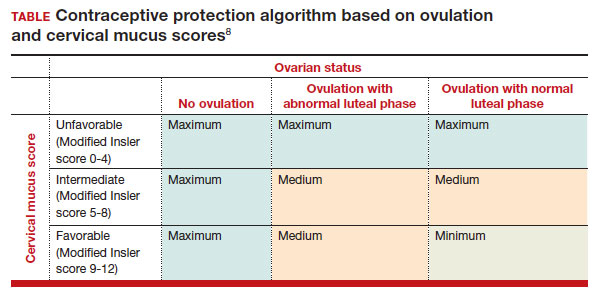
More recently, a prospective, multicenter randomized, crossover study was performed to better understand this pill’s impact on cervical mucus and ovulation during preparation for nonprescription approval. In this study, participants were evaluated with frequent transvaginal ultrasonography, cervical mucus, and blood assessments (including levels of follicular-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, progesterone, and estradiol) for three 28-day cycles. Cervical mucus was scored on a modified Insler scale to indicate if the mucus was favorable (Insler score ≥9), intermediate (Insler score 5-8), or unfavorable to fertility (Insler score ≤4).5
In the first cycle, participants were instructed to use the pills as prescribed (described as “correct use”). During this cycle, most participants (n = 34/51; 67%) did not ovulate, confirming that norgestrel 0.075 mg does impact ovulation.6 Most participants also had unfavorable cervical mucus (n = 39/51; 76%).6 Overall, 94% had full protection against pregnancy, either through lack of ovulation (n = 9), unfavorable mucus (n = 14), or both (n = 25). The remaining 3 participants ovulated and had intermediate mucus scores; ultimately, these participants were considered to have medium protection against pregnancy.7,8 (See the contraceptive protection algorithm [TABLE]).8
In the second and third cycles, the investigators evaluated ovulation and cervical mucus changes in the setting of either a delayed (by 6 hours) or missed dose midcycle.8 Of the 46 participants with evaluable data during the intervention cycles, 32 (70%) did not ovulate in each of the delayed- and missed-dose cycles. Most participants (n = 27; 59%) also demonstrated unfavorable mucus scores (modified Insler score ≤4) over the entire cycle despite delaying or missing a pill. There was no significant change to the cervical mucus score when comparing the scores on the days before, during, and after the delayed or missed pills (P = .26), nor when comparing between delayed pill use and missed pill use (P = .45). With the delayed pill intervention, 4 (9%) had reduced contraceptive protection (ie, medium protection) based on ovulation with intermediate mucus scores. With the missed pill intervention, 5 (11%) had reduced protection, of whom 3 had medium protection and 2 had minimum protection with ovulation and favorable mucus scores. Overall, this study shows that delaying or missing one pill may not impact contraceptive efficacy as much as previously thought given the strict 3-hour window for progestin-only pills. However, these findings are theoretical as information about pregnancy outcomes with delaying or missing pills are lacking.
Safety
Progestin-only methods are one of the safest options for contraception, with few contraindications to use; those listed include known or suspected pregnancy, known or suspected carcinoma of the breast or other progestinsensitive cancer, undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding, hypersensitivity to any component of the product, benign or malignant liver tumors, and acute liver disease.2
The CDC Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use guidelines offer guidance for progestin-only pills, indicating a category 3 (theoretical or proven risks usually outweigh the advantages) or category 4 (unacceptable health risk, method not to be used) for only a select number of additional conditions. These conditions include a history of malabsorptive bariatric surgery (category 3) and concurrent use of medications that induce hepatic enzyme activity (category 3)— such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, barbiturates, primidone, topiramate, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, and rifabutin.9 These conditions are included primarily due to concerns of decreased effectivenessof the contraception and not necessarily because of evidence of harm with use.
The prevalence of consumers with contraindications to progestin-only pills appears to be low. In a large database study, only 4.36% seeking preventive care and 2.29% seeking both preventive and contraceptive services had a contraindication to progestin-only pills.10 Therefore, candidates for norgestrel use include individuals who have commonly encountered conditions, including those who9:
- have recently given birth
- are breastfeeding
- have a history of venous thromboembolism
- smoke
- have cardiovascular disease, hypertension, migraines with aura, or longstanding diabetes.
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects (AEs) related to norgestrel use are bleeding changes.2 In the initial clinical studies for FDA approval, about half of enrolled participants reported a change in bleeding; about 9% discontinued the contraceptive due to bleeding. Breakthrough bleeding and spotting were reported by 48.6% and 47.3% of participants, respectively. About 6.1% had amenorrhea in their first cycle; 28.7% of participants had amenorrhea overall. Other reported AEs were headache, dizziness, nausea, increased appetite, abdominal pain, cramps or bloating, breast tenderness, and acne.
- Brand name: Opill
- Class: Progestin-only contraception
- Indication: Pregnancy prevention
- Approval date: Initial approval in 1973, nonprescription approval on July 13, 2023
- Availability date: 2024
- Manufacturer: Perrigo Company, HRA Pharma, Paris, France
- Dosage forms: 0.075 mg tablet
Continue to: FDA approval required determining appropriate direct-to-patient classification...
FDA approval required determining appropriate direct-to-patient classification
As part of the process for obtaining nonprescription approval, studies needed to determine that patients can safely and effectively use norgestrel without talking to a health care provider first. As part of that process, label comprehension, self-selection, and actualuse studies were required to demonstrate that consumers can use the package information to determine their eligibility and take the medication appropriately.
The ACCESS study Research Q: Do patients appropriately determine if the contraceptive is right for them?
Study A: Yes, 99% of the time. In the Adherence with Continuous-dose Oral Contraceptive: Evaluation of Self-Selection and Use (ACCESS) pivotal study, which evaluated prescription to nonprescription approval, participants were asked to review the label and determine whether the product was appropriate for them to use based on their health history.11 Approximately 99% of participants (n = 1,234/1,246) were able to correctly self-select whether norgestrel was appropriate for their own use.12
Research Q: After beginning the contraceptive, do patients adhere to correct use?
Study A: Yes, more than 90% of the time (and that remained true for subpopulations).
In the next phase of the ACCESS study, eligible participants from the self-selection population who purchased norgestrel and reported using the product at least once in their e-diary over a 6-month study period comprised the “User Population.”12 The overall adherence to daily pill intake was 92.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 92.3–92.6%) among the 883 participants who contributed more than 90,000 days of study participation, and adherence was similarly high in subpopulations of individuals with low health literacy (92.6%; 95% CI, 92.1–93.0), adolescents aged 12–14 years (91.8%; 95% CI, 91.0–92.5%), and adolescents aged 15–17 years (91.9%; 95% CI, 91.4%–92.3%).
Research Q: When a pill was missed, did patients use backup contraception?
Study A: Yes, 97% of the time.
When including whether participants followed label instructions for mitigating behaviors when the pill was missed (eg, take a pill as soon as they remember, use backup contraception for 2 days after restarting the pill), adherence was 97.1% (95% CI, 97.0–97.2%). Most participants missed a single day of taking pills, and the most common reported reason for missing pills was issues with resupply as participants needed to get new packs from their enrolled research site, which should be less of a barrier when these pills are available over the counter.
Clinical implications of expanded access
Opportunities to expand access to effective contraception have become more critical in the increasingly restrictive environment for abortion care in the post-Dobbs era, and the availability of norgestrel to patients without prescription can advance contraceptive equity. Patients encounter many barriers to accessing prescription contraception, such as lack of insurance; difficulty with scheduling an appointment or getting to a clinic; not having a regular clinician or clinic; or health care providers requiring a visit, exam, or test prior to prescribing contraception.13,14 For patients who face these challenges, an alternative option is to use a nonprescription contraceptive, such as barrier or fertility awareness–based methods, which are typically associated with higher failure rates. With the introduction of norgestrel as a nonprescription contraceptive product, people can have direct access to a more effective contraceptive option.
A follow-up study of participants who had participated in the ACCESS actual-use study demonstrated that most (83%) would be likely to use the nonprescription method if available in the future for many reasons, including convenience, ease of access, ability to save time and money, not needing to visit a clinic, and flexibility of accessing the pills while traveling or having someone else get their pills for them.14 Furthermore, a nonprescription method could be beneficial for people who have concerns about privacy, such as adolescents or individuals affected by contraception sabotage (an act that can intentionally limit or prohibit a person's contraception access or use, ie, damaging condoms or hiding a person’s contraception method). This expansion of access can ultimately lead to a decrease in unintended pregnancies. In a model using the ACCESS actual-use data, about 1,500 to 34,000 unintended pregnancies would be prevented per year based on varying model parameters, with all scenarios demonstrating a benefit to nonprescription access to norgestrel.15
After norgestrel is available, where will patients be able to seek more information?
Patients who have questions or concerns about starting or taking norgestrel should talk to their clinician or a pharmacist for additional information (FIGURE 2). Examples of situations when additional clinical evaluation or counseling are recommended include:
- when a person is taking any medications with possible drug-drug interactions
- if a person is starting norgestrel after taking an emergency contraceptive in the last 5 days
- if there is a concern about pregnancy
- when there are any questions about adverse effects while taking norgestrel.
Bottom line
The nonprescription approval of norgestrel, a progestin-only pill, has the potential to greatly expand patient access to a safe and effective contraceptive method and advance contraceptive equity. The availability of informational materials for consumers about potential issues that may arise (for instance, changes in bleeding) will be important for initiation and continuation of this method. As this product is not yet available for purchase, several unknown factors remain, such as the cost and ease of accessibility in stores or online, that will ultimately determine its public health impact on unintended pregnancies. ●
- US Food and Drug Administration. 82 FR 49380. Determination that Ovrette (norgestrel) tablet, 0.075 milligrams, was not withdrawn from sale for reasons of safety or effectiveness. October 25, 2017. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.federalregister.gov/d/2017-23125
- US Food and Drug Administration. Opill tablets (norgestrel tablets) package label. August 2017. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label /2017/017031s035s036lbl.pdf
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. US selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No. RR-4):1-66.
- Glasier A, Sober S, Gasloli R, et al. A review of the effectiveness of a progestogen-only pill containing norgestrel 75 µg/day. Contraception. 2022;105:1-6.
- Edelman A, Hemon A, Creinin M, et al. Assessing the pregnancy protective impact of scheduled nonadherence to a novel progestin-only pill: protocol for a prospective, multicenter, randomized, crossover study. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021;10:e292208.
- Glasier A, Edelman A, Creinin MD, et al. Mechanism of action of norgestrel 0.075 mg a progestogen-only pill. I. Effect on ovarian activity. Contraception. 2022;112:37-42.
- Han L, Creinin MD, Hemon A, et al. Mechanism of action of a 0.075 mg norgestrel progestogen-only pill 2. Effect on cervical mucus and theoretical risk of conception. Contraception. 2022;112:43-47.
- Glasier A, Edelman A, Creinin MD, et al. The effect of deliberate non-adherence to a norgestrel progestin-only pill: a randomized, crossover study. Contraception. 2023;117:1-6.
- Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No RR-3):1-104.
- Dutton C, Kim R, Janiak E. Prevalence of contraindications to progestin-only contraceptive pills in a multi-institution patient database. Contraception. 2021;103:367-370.
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Adherence with Continuous-dose Oral Contraceptive Evaluation of Self-Selection and Use (ACCESS). Accessed December 5, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study /NCT04112095
- HRA Pharma. Opill (norgestrel 0.075 mg tablets) for Rx-toOTC switch. Sponsor Briefing Documents. Joint Meeting of the Nonprescription Drugs Advisory Committee and the Obstetrics, Reproductive, and Urology Drugs Advisory Committee. Meeting dates: 9-10 May 2023. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/media/167893 /download
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion No. 788: Over-the-counter access to hormonal contraception. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:e96-105.
- Grindlay K, Key K, Zuniga C, et al. Interest in continued use after participation in a study of over-the-counter progestin-only pills in the United States. Womens Health Rep. 2022;3:904-914.
- Guillard H, Laurora I, Sober S, et al. Modeling the potential benefit of an over-the-counter progestin-only pill in preventing unintended pregnancies in the U.S. Contraception. 2023;117:7-12.
On July 13, 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved norgestrel 0.075 mg (Opill, HRA Pharma, Paris, France) as the first nonprescription oral contraceptive pill (FIGURE). This progestin-only pill was originally FDA approved in 1973, with prescription required, and was available as Ovrette until 2005, when product distribution ceased for marketing reasons and not for safety or effectiveness concerns.1 In recent years, studies have been conducted to support converted approval from prescription to nonprescription to increase access to safe and effective contraception. Overall, norgestrel is more effective than other currently available nonprescription contraceptive options when used as directed, and widespread accessibility to this method has the potential to decrease the risk of unintended pregnancies. This product is expected to be available in drugstores, convenience stores, grocery stores, and online in 2024.

How it works
The indication for norgestrel 0.075 mg is pregnancy prevention in people with the capacity to become pregnant; this product is not intended for emergency contraception. Norgestrel is a racemic mixture of 2 isomers, of which only levonorgestrel is bioactive. The mechanism of action for contraception is primarily through cervical mucus thickening, which inhibits sperm movement through the cervix. About 50% of users also have an additional contraceptive effect of ovulation suppression.2
Instructions for use. In the package label, users are instructed to take the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill daily, preferably at the same time each day and no more than 3 hours from the time taken on the previous day. This method can be started on any day of the cycle, and backup contraception (a barrier method) should be used for the first 48 hours after starting the method if it has been more than 5 days since menstrual bleeding started.3 Product instructions indicate that, if users miss a dose, they should take the next dose as soon as possible. If a pill is taken 3 hours or more later than the usual time, they should take a pill immediately and then resume the next pill at the usual time. In addition, backup contraception is recommended for 48 hours.2
Based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, no examinations or tests are required prior to initiation of progestin-only pills for safe and effective use.3
Efficacy
The product label indicates that the pregnancy rate is approximately 2 per 100 women-years based on over 21,000 28-day exposure cycles from 8 US clinical studies.2 In a recent review by Glasier and colleagues, the authors identified 13 trials that assessed the efficacy of the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill, all published several decades ago.4 Given that breastfeeding can have contraceptive impact through ovulation inhibition, studies that included breastfeeding participants were evaluated separately. Six studies without breastfeeding participants included 3,184 women who provided more than 35,000 months of use. The overall failure rates ranged from 0 to 2.4 per hundred woman-years with typical use; an aggregate Pearl Index was calculated to be 2.2 based on the total numbers of pregnancies and cycles. The remaining 7 studies included individuals who were breastfeeding for at least part of their study participation. These studies included 5,445 women, and the 12-month life table cumulative pregnancy rates in this group ranged from 0.0% to 3.4%. This review noted that the available studies are limited by incomplete descriptions of study participant information and differences in reporting of failure rates; however, the overall data support the effectiveness of the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill for pregnancy prevention.
Continue to: Norgestrel’s mechanism of action on ovarian activity and cervical mucus...
Norgestrel’s mechanism of action on ovarian activity and cervical mucus
More recently, a prospective, multicenter randomized, crossover study was performed to better understand this pill’s impact on cervical mucus and ovulation during preparation for nonprescription approval. In this study, participants were evaluated with frequent transvaginal ultrasonography, cervical mucus, and blood assessments (including levels of follicular-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, progesterone, and estradiol) for three 28-day cycles. Cervical mucus was scored on a modified Insler scale to indicate if the mucus was favorable (Insler score ≥9), intermediate (Insler score 5-8), or unfavorable to fertility (Insler score ≤4).5
In the first cycle, participants were instructed to use the pills as prescribed (described as “correct use”). During this cycle, most participants (n = 34/51; 67%) did not ovulate, confirming that norgestrel 0.075 mg does impact ovulation.6 Most participants also had unfavorable cervical mucus (n = 39/51; 76%).6 Overall, 94% had full protection against pregnancy, either through lack of ovulation (n = 9), unfavorable mucus (n = 14), or both (n = 25). The remaining 3 participants ovulated and had intermediate mucus scores; ultimately, these participants were considered to have medium protection against pregnancy.7,8 (See the contraceptive protection algorithm [TABLE]).8

In the second and third cycles, the investigators evaluated ovulation and cervical mucus changes in the setting of either a delayed (by 6 hours) or missed dose midcycle.8 Of the 46 participants with evaluable data during the intervention cycles, 32 (70%) did not ovulate in each of the delayed- and missed-dose cycles. Most participants (n = 27; 59%) also demonstrated unfavorable mucus scores (modified Insler score ≤4) over the entire cycle despite delaying or missing a pill. There was no significant change to the cervical mucus score when comparing the scores on the days before, during, and after the delayed or missed pills (P = .26), nor when comparing between delayed pill use and missed pill use (P = .45). With the delayed pill intervention, 4 (9%) had reduced contraceptive protection (ie, medium protection) based on ovulation with intermediate mucus scores. With the missed pill intervention, 5 (11%) had reduced protection, of whom 3 had medium protection and 2 had minimum protection with ovulation and favorable mucus scores. Overall, this study shows that delaying or missing one pill may not impact contraceptive efficacy as much as previously thought given the strict 3-hour window for progestin-only pills. However, these findings are theoretical as information about pregnancy outcomes with delaying or missing pills are lacking.
Safety
Progestin-only methods are one of the safest options for contraception, with few contraindications to use; those listed include known or suspected pregnancy, known or suspected carcinoma of the breast or other progestinsensitive cancer, undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding, hypersensitivity to any component of the product, benign or malignant liver tumors, and acute liver disease.2
The CDC Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use guidelines offer guidance for progestin-only pills, indicating a category 3 (theoretical or proven risks usually outweigh the advantages) or category 4 (unacceptable health risk, method not to be used) for only a select number of additional conditions. These conditions include a history of malabsorptive bariatric surgery (category 3) and concurrent use of medications that induce hepatic enzyme activity (category 3)— such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, barbiturates, primidone, topiramate, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, and rifabutin.9 These conditions are included primarily due to concerns of decreased effectivenessof the contraception and not necessarily because of evidence of harm with use.
The prevalence of consumers with contraindications to progestin-only pills appears to be low. In a large database study, only 4.36% seeking preventive care and 2.29% seeking both preventive and contraceptive services had a contraindication to progestin-only pills.10 Therefore, candidates for norgestrel use include individuals who have commonly encountered conditions, including those who9:
- have recently given birth
- are breastfeeding
- have a history of venous thromboembolism
- smoke
- have cardiovascular disease, hypertension, migraines with aura, or longstanding diabetes.
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects (AEs) related to norgestrel use are bleeding changes.2 In the initial clinical studies for FDA approval, about half of enrolled participants reported a change in bleeding; about 9% discontinued the contraceptive due to bleeding. Breakthrough bleeding and spotting were reported by 48.6% and 47.3% of participants, respectively. About 6.1% had amenorrhea in their first cycle; 28.7% of participants had amenorrhea overall. Other reported AEs were headache, dizziness, nausea, increased appetite, abdominal pain, cramps or bloating, breast tenderness, and acne.
- Brand name: Opill
- Class: Progestin-only contraception
- Indication: Pregnancy prevention
- Approval date: Initial approval in 1973, nonprescription approval on July 13, 2023
- Availability date: 2024
- Manufacturer: Perrigo Company, HRA Pharma, Paris, France
- Dosage forms: 0.075 mg tablet
Continue to: FDA approval required determining appropriate direct-to-patient classification...
FDA approval required determining appropriate direct-to-patient classification
As part of the process for obtaining nonprescription approval, studies needed to determine that patients can safely and effectively use norgestrel without talking to a health care provider first. As part of that process, label comprehension, self-selection, and actualuse studies were required to demonstrate that consumers can use the package information to determine their eligibility and take the medication appropriately.
The ACCESS study Research Q: Do patients appropriately determine if the contraceptive is right for them?
Study A: Yes, 99% of the time. In the Adherence with Continuous-dose Oral Contraceptive: Evaluation of Self-Selection and Use (ACCESS) pivotal study, which evaluated prescription to nonprescription approval, participants were asked to review the label and determine whether the product was appropriate for them to use based on their health history.11 Approximately 99% of participants (n = 1,234/1,246) were able to correctly self-select whether norgestrel was appropriate for their own use.12
Research Q: After beginning the contraceptive, do patients adhere to correct use?
Study A: Yes, more than 90% of the time (and that remained true for subpopulations).
In the next phase of the ACCESS study, eligible participants from the self-selection population who purchased norgestrel and reported using the product at least once in their e-diary over a 6-month study period comprised the “User Population.”12 The overall adherence to daily pill intake was 92.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 92.3–92.6%) among the 883 participants who contributed more than 90,000 days of study participation, and adherence was similarly high in subpopulations of individuals with low health literacy (92.6%; 95% CI, 92.1–93.0), adolescents aged 12–14 years (91.8%; 95% CI, 91.0–92.5%), and adolescents aged 15–17 years (91.9%; 95% CI, 91.4%–92.3%).
Research Q: When a pill was missed, did patients use backup contraception?
Study A: Yes, 97% of the time.
When including whether participants followed label instructions for mitigating behaviors when the pill was missed (eg, take a pill as soon as they remember, use backup contraception for 2 days after restarting the pill), adherence was 97.1% (95% CI, 97.0–97.2%). Most participants missed a single day of taking pills, and the most common reported reason for missing pills was issues with resupply as participants needed to get new packs from their enrolled research site, which should be less of a barrier when these pills are available over the counter.
Clinical implications of expanded access
Opportunities to expand access to effective contraception have become more critical in the increasingly restrictive environment for abortion care in the post-Dobbs era, and the availability of norgestrel to patients without prescription can advance contraceptive equity. Patients encounter many barriers to accessing prescription contraception, such as lack of insurance; difficulty with scheduling an appointment or getting to a clinic; not having a regular clinician or clinic; or health care providers requiring a visit, exam, or test prior to prescribing contraception.13,14 For patients who face these challenges, an alternative option is to use a nonprescription contraceptive, such as barrier or fertility awareness–based methods, which are typically associated with higher failure rates. With the introduction of norgestrel as a nonprescription contraceptive product, people can have direct access to a more effective contraceptive option.
A follow-up study of participants who had participated in the ACCESS actual-use study demonstrated that most (83%) would be likely to use the nonprescription method if available in the future for many reasons, including convenience, ease of access, ability to save time and money, not needing to visit a clinic, and flexibility of accessing the pills while traveling or having someone else get their pills for them.14 Furthermore, a nonprescription method could be beneficial for people who have concerns about privacy, such as adolescents or individuals affected by contraception sabotage (an act that can intentionally limit or prohibit a person's contraception access or use, ie, damaging condoms or hiding a person’s contraception method). This expansion of access can ultimately lead to a decrease in unintended pregnancies. In a model using the ACCESS actual-use data, about 1,500 to 34,000 unintended pregnancies would be prevented per year based on varying model parameters, with all scenarios demonstrating a benefit to nonprescription access to norgestrel.15
After norgestrel is available, where will patients be able to seek more information?
Patients who have questions or concerns about starting or taking norgestrel should talk to their clinician or a pharmacist for additional information (FIGURE 2). Examples of situations when additional clinical evaluation or counseling are recommended include:
- when a person is taking any medications with possible drug-drug interactions
- if a person is starting norgestrel after taking an emergency contraceptive in the last 5 days
- if there is a concern about pregnancy
- when there are any questions about adverse effects while taking norgestrel.
Bottom line
The nonprescription approval of norgestrel, a progestin-only pill, has the potential to greatly expand patient access to a safe and effective contraceptive method and advance contraceptive equity. The availability of informational materials for consumers about potential issues that may arise (for instance, changes in bleeding) will be important for initiation and continuation of this method. As this product is not yet available for purchase, several unknown factors remain, such as the cost and ease of accessibility in stores or online, that will ultimately determine its public health impact on unintended pregnancies. ●
On July 13, 2023, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved norgestrel 0.075 mg (Opill, HRA Pharma, Paris, France) as the first nonprescription oral contraceptive pill (FIGURE). This progestin-only pill was originally FDA approved in 1973, with prescription required, and was available as Ovrette until 2005, when product distribution ceased for marketing reasons and not for safety or effectiveness concerns.1 In recent years, studies have been conducted to support converted approval from prescription to nonprescription to increase access to safe and effective contraception. Overall, norgestrel is more effective than other currently available nonprescription contraceptive options when used as directed, and widespread accessibility to this method has the potential to decrease the risk of unintended pregnancies. This product is expected to be available in drugstores, convenience stores, grocery stores, and online in 2024.

How it works
The indication for norgestrel 0.075 mg is pregnancy prevention in people with the capacity to become pregnant; this product is not intended for emergency contraception. Norgestrel is a racemic mixture of 2 isomers, of which only levonorgestrel is bioactive. The mechanism of action for contraception is primarily through cervical mucus thickening, which inhibits sperm movement through the cervix. About 50% of users also have an additional contraceptive effect of ovulation suppression.2
Instructions for use. In the package label, users are instructed to take the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill daily, preferably at the same time each day and no more than 3 hours from the time taken on the previous day. This method can be started on any day of the cycle, and backup contraception (a barrier method) should be used for the first 48 hours after starting the method if it has been more than 5 days since menstrual bleeding started.3 Product instructions indicate that, if users miss a dose, they should take the next dose as soon as possible. If a pill is taken 3 hours or more later than the usual time, they should take a pill immediately and then resume the next pill at the usual time. In addition, backup contraception is recommended for 48 hours.2
Based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, no examinations or tests are required prior to initiation of progestin-only pills for safe and effective use.3
Efficacy
The product label indicates that the pregnancy rate is approximately 2 per 100 women-years based on over 21,000 28-day exposure cycles from 8 US clinical studies.2 In a recent review by Glasier and colleagues, the authors identified 13 trials that assessed the efficacy of the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill, all published several decades ago.4 Given that breastfeeding can have contraceptive impact through ovulation inhibition, studies that included breastfeeding participants were evaluated separately. Six studies without breastfeeding participants included 3,184 women who provided more than 35,000 months of use. The overall failure rates ranged from 0 to 2.4 per hundred woman-years with typical use; an aggregate Pearl Index was calculated to be 2.2 based on the total numbers of pregnancies and cycles. The remaining 7 studies included individuals who were breastfeeding for at least part of their study participation. These studies included 5,445 women, and the 12-month life table cumulative pregnancy rates in this group ranged from 0.0% to 3.4%. This review noted that the available studies are limited by incomplete descriptions of study participant information and differences in reporting of failure rates; however, the overall data support the effectiveness of the norgestrel 0.075 mg pill for pregnancy prevention.
Continue to: Norgestrel’s mechanism of action on ovarian activity and cervical mucus...
Norgestrel’s mechanism of action on ovarian activity and cervical mucus
More recently, a prospective, multicenter randomized, crossover study was performed to better understand this pill’s impact on cervical mucus and ovulation during preparation for nonprescription approval. In this study, participants were evaluated with frequent transvaginal ultrasonography, cervical mucus, and blood assessments (including levels of follicular-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, progesterone, and estradiol) for three 28-day cycles. Cervical mucus was scored on a modified Insler scale to indicate if the mucus was favorable (Insler score ≥9), intermediate (Insler score 5-8), or unfavorable to fertility (Insler score ≤4).5
In the first cycle, participants were instructed to use the pills as prescribed (described as “correct use”). During this cycle, most participants (n = 34/51; 67%) did not ovulate, confirming that norgestrel 0.075 mg does impact ovulation.6 Most participants also had unfavorable cervical mucus (n = 39/51; 76%).6 Overall, 94% had full protection against pregnancy, either through lack of ovulation (n = 9), unfavorable mucus (n = 14), or both (n = 25). The remaining 3 participants ovulated and had intermediate mucus scores; ultimately, these participants were considered to have medium protection against pregnancy.7,8 (See the contraceptive protection algorithm [TABLE]).8

In the second and third cycles, the investigators evaluated ovulation and cervical mucus changes in the setting of either a delayed (by 6 hours) or missed dose midcycle.8 Of the 46 participants with evaluable data during the intervention cycles, 32 (70%) did not ovulate in each of the delayed- and missed-dose cycles. Most participants (n = 27; 59%) also demonstrated unfavorable mucus scores (modified Insler score ≤4) over the entire cycle despite delaying or missing a pill. There was no significant change to the cervical mucus score when comparing the scores on the days before, during, and after the delayed or missed pills (P = .26), nor when comparing between delayed pill use and missed pill use (P = .45). With the delayed pill intervention, 4 (9%) had reduced contraceptive protection (ie, medium protection) based on ovulation with intermediate mucus scores. With the missed pill intervention, 5 (11%) had reduced protection, of whom 3 had medium protection and 2 had minimum protection with ovulation and favorable mucus scores. Overall, this study shows that delaying or missing one pill may not impact contraceptive efficacy as much as previously thought given the strict 3-hour window for progestin-only pills. However, these findings are theoretical as information about pregnancy outcomes with delaying or missing pills are lacking.
Safety
Progestin-only methods are one of the safest options for contraception, with few contraindications to use; those listed include known or suspected pregnancy, known or suspected carcinoma of the breast or other progestinsensitive cancer, undiagnosed abnormal uterine bleeding, hypersensitivity to any component of the product, benign or malignant liver tumors, and acute liver disease.2
The CDC Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use guidelines offer guidance for progestin-only pills, indicating a category 3 (theoretical or proven risks usually outweigh the advantages) or category 4 (unacceptable health risk, method not to be used) for only a select number of additional conditions. These conditions include a history of malabsorptive bariatric surgery (category 3) and concurrent use of medications that induce hepatic enzyme activity (category 3)— such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, barbiturates, primidone, topiramate, oxcarbazepine, rifampin, and rifabutin.9 These conditions are included primarily due to concerns of decreased effectivenessof the contraception and not necessarily because of evidence of harm with use.
The prevalence of consumers with contraindications to progestin-only pills appears to be low. In a large database study, only 4.36% seeking preventive care and 2.29% seeking both preventive and contraceptive services had a contraindication to progestin-only pills.10 Therefore, candidates for norgestrel use include individuals who have commonly encountered conditions, including those who9:
- have recently given birth
- are breastfeeding
- have a history of venous thromboembolism
- smoke
- have cardiovascular disease, hypertension, migraines with aura, or longstanding diabetes.
Adverse effects
The most common adverse effects (AEs) related to norgestrel use are bleeding changes.2 In the initial clinical studies for FDA approval, about half of enrolled participants reported a change in bleeding; about 9% discontinued the contraceptive due to bleeding. Breakthrough bleeding and spotting were reported by 48.6% and 47.3% of participants, respectively. About 6.1% had amenorrhea in their first cycle; 28.7% of participants had amenorrhea overall. Other reported AEs were headache, dizziness, nausea, increased appetite, abdominal pain, cramps or bloating, breast tenderness, and acne.
- Brand name: Opill
- Class: Progestin-only contraception
- Indication: Pregnancy prevention
- Approval date: Initial approval in 1973, nonprescription approval on July 13, 2023
- Availability date: 2024
- Manufacturer: Perrigo Company, HRA Pharma, Paris, France
- Dosage forms: 0.075 mg tablet
Continue to: FDA approval required determining appropriate direct-to-patient classification...
FDA approval required determining appropriate direct-to-patient classification
As part of the process for obtaining nonprescription approval, studies needed to determine that patients can safely and effectively use norgestrel without talking to a health care provider first. As part of that process, label comprehension, self-selection, and actualuse studies were required to demonstrate that consumers can use the package information to determine their eligibility and take the medication appropriately.
The ACCESS study Research Q: Do patients appropriately determine if the contraceptive is right for them?
Study A: Yes, 99% of the time. In the Adherence with Continuous-dose Oral Contraceptive: Evaluation of Self-Selection and Use (ACCESS) pivotal study, which evaluated prescription to nonprescription approval, participants were asked to review the label and determine whether the product was appropriate for them to use based on their health history.11 Approximately 99% of participants (n = 1,234/1,246) were able to correctly self-select whether norgestrel was appropriate for their own use.12
Research Q: After beginning the contraceptive, do patients adhere to correct use?
Study A: Yes, more than 90% of the time (and that remained true for subpopulations).
In the next phase of the ACCESS study, eligible participants from the self-selection population who purchased norgestrel and reported using the product at least once in their e-diary over a 6-month study period comprised the “User Population.”12 The overall adherence to daily pill intake was 92.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 92.3–92.6%) among the 883 participants who contributed more than 90,000 days of study participation, and adherence was similarly high in subpopulations of individuals with low health literacy (92.6%; 95% CI, 92.1–93.0), adolescents aged 12–14 years (91.8%; 95% CI, 91.0–92.5%), and adolescents aged 15–17 years (91.9%; 95% CI, 91.4%–92.3%).
Research Q: When a pill was missed, did patients use backup contraception?
Study A: Yes, 97% of the time.
When including whether participants followed label instructions for mitigating behaviors when the pill was missed (eg, take a pill as soon as they remember, use backup contraception for 2 days after restarting the pill), adherence was 97.1% (95% CI, 97.0–97.2%). Most participants missed a single day of taking pills, and the most common reported reason for missing pills was issues with resupply as participants needed to get new packs from their enrolled research site, which should be less of a barrier when these pills are available over the counter.
Clinical implications of expanded access
Opportunities to expand access to effective contraception have become more critical in the increasingly restrictive environment for abortion care in the post-Dobbs era, and the availability of norgestrel to patients without prescription can advance contraceptive equity. Patients encounter many barriers to accessing prescription contraception, such as lack of insurance; difficulty with scheduling an appointment or getting to a clinic; not having a regular clinician or clinic; or health care providers requiring a visit, exam, or test prior to prescribing contraception.13,14 For patients who face these challenges, an alternative option is to use a nonprescription contraceptive, such as barrier or fertility awareness–based methods, which are typically associated with higher failure rates. With the introduction of norgestrel as a nonprescription contraceptive product, people can have direct access to a more effective contraceptive option.
A follow-up study of participants who had participated in the ACCESS actual-use study demonstrated that most (83%) would be likely to use the nonprescription method if available in the future for many reasons, including convenience, ease of access, ability to save time and money, not needing to visit a clinic, and flexibility of accessing the pills while traveling or having someone else get their pills for them.14 Furthermore, a nonprescription method could be beneficial for people who have concerns about privacy, such as adolescents or individuals affected by contraception sabotage (an act that can intentionally limit or prohibit a person's contraception access or use, ie, damaging condoms or hiding a person’s contraception method). This expansion of access can ultimately lead to a decrease in unintended pregnancies. In a model using the ACCESS actual-use data, about 1,500 to 34,000 unintended pregnancies would be prevented per year based on varying model parameters, with all scenarios demonstrating a benefit to nonprescription access to norgestrel.15
After norgestrel is available, where will patients be able to seek more information?
Patients who have questions or concerns about starting or taking norgestrel should talk to their clinician or a pharmacist for additional information (FIGURE 2). Examples of situations when additional clinical evaluation or counseling are recommended include:
- when a person is taking any medications with possible drug-drug interactions
- if a person is starting norgestrel after taking an emergency contraceptive in the last 5 days
- if there is a concern about pregnancy
- when there are any questions about adverse effects while taking norgestrel.
Bottom line
The nonprescription approval of norgestrel, a progestin-only pill, has the potential to greatly expand patient access to a safe and effective contraceptive method and advance contraceptive equity. The availability of informational materials for consumers about potential issues that may arise (for instance, changes in bleeding) will be important for initiation and continuation of this method. As this product is not yet available for purchase, several unknown factors remain, such as the cost and ease of accessibility in stores or online, that will ultimately determine its public health impact on unintended pregnancies. ●
- US Food and Drug Administration. 82 FR 49380. Determination that Ovrette (norgestrel) tablet, 0.075 milligrams, was not withdrawn from sale for reasons of safety or effectiveness. October 25, 2017. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.federalregister.gov/d/2017-23125
- US Food and Drug Administration. Opill tablets (norgestrel tablets) package label. August 2017. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label /2017/017031s035s036lbl.pdf
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. US selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No. RR-4):1-66.
- Glasier A, Sober S, Gasloli R, et al. A review of the effectiveness of a progestogen-only pill containing norgestrel 75 µg/day. Contraception. 2022;105:1-6.
- Edelman A, Hemon A, Creinin M, et al. Assessing the pregnancy protective impact of scheduled nonadherence to a novel progestin-only pill: protocol for a prospective, multicenter, randomized, crossover study. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021;10:e292208.
- Glasier A, Edelman A, Creinin MD, et al. Mechanism of action of norgestrel 0.075 mg a progestogen-only pill. I. Effect on ovarian activity. Contraception. 2022;112:37-42.
- Han L, Creinin MD, Hemon A, et al. Mechanism of action of a 0.075 mg norgestrel progestogen-only pill 2. Effect on cervical mucus and theoretical risk of conception. Contraception. 2022;112:43-47.
- Glasier A, Edelman A, Creinin MD, et al. The effect of deliberate non-adherence to a norgestrel progestin-only pill: a randomized, crossover study. Contraception. 2023;117:1-6.
- Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No RR-3):1-104.
- Dutton C, Kim R, Janiak E. Prevalence of contraindications to progestin-only contraceptive pills in a multi-institution patient database. Contraception. 2021;103:367-370.
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Adherence with Continuous-dose Oral Contraceptive Evaluation of Self-Selection and Use (ACCESS). Accessed December 5, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study /NCT04112095
- HRA Pharma. Opill (norgestrel 0.075 mg tablets) for Rx-toOTC switch. Sponsor Briefing Documents. Joint Meeting of the Nonprescription Drugs Advisory Committee and the Obstetrics, Reproductive, and Urology Drugs Advisory Committee. Meeting dates: 9-10 May 2023. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/media/167893 /download
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion No. 788: Over-the-counter access to hormonal contraception. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:e96-105.
- Grindlay K, Key K, Zuniga C, et al. Interest in continued use after participation in a study of over-the-counter progestin-only pills in the United States. Womens Health Rep. 2022;3:904-914.
- Guillard H, Laurora I, Sober S, et al. Modeling the potential benefit of an over-the-counter progestin-only pill in preventing unintended pregnancies in the U.S. Contraception. 2023;117:7-12.
- US Food and Drug Administration. 82 FR 49380. Determination that Ovrette (norgestrel) tablet, 0.075 milligrams, was not withdrawn from sale for reasons of safety or effectiveness. October 25, 2017. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.federalregister.gov/d/2017-23125
- US Food and Drug Administration. Opill tablets (norgestrel tablets) package label. August 2017. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label /2017/017031s035s036lbl.pdf
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. US selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No. RR-4):1-66.
- Glasier A, Sober S, Gasloli R, et al. A review of the effectiveness of a progestogen-only pill containing norgestrel 75 µg/day. Contraception. 2022;105:1-6.
- Edelman A, Hemon A, Creinin M, et al. Assessing the pregnancy protective impact of scheduled nonadherence to a novel progestin-only pill: protocol for a prospective, multicenter, randomized, crossover study. JMIR Res Protoc. 2021;10:e292208.
- Glasier A, Edelman A, Creinin MD, et al. Mechanism of action of norgestrel 0.075 mg a progestogen-only pill. I. Effect on ovarian activity. Contraception. 2022;112:37-42.
- Han L, Creinin MD, Hemon A, et al. Mechanism of action of a 0.075 mg norgestrel progestogen-only pill 2. Effect on cervical mucus and theoretical risk of conception. Contraception. 2022;112:43-47.
- Glasier A, Edelman A, Creinin MD, et al. The effect of deliberate non-adherence to a norgestrel progestin-only pill: a randomized, crossover study. Contraception. 2023;117:1-6.
- Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No RR-3):1-104.
- Dutton C, Kim R, Janiak E. Prevalence of contraindications to progestin-only contraceptive pills in a multi-institution patient database. Contraception. 2021;103:367-370.
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Adherence with Continuous-dose Oral Contraceptive Evaluation of Self-Selection and Use (ACCESS). Accessed December 5, 2023. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study /NCT04112095
- HRA Pharma. Opill (norgestrel 0.075 mg tablets) for Rx-toOTC switch. Sponsor Briefing Documents. Joint Meeting of the Nonprescription Drugs Advisory Committee and the Obstetrics, Reproductive, and Urology Drugs Advisory Committee. Meeting dates: 9-10 May 2023. Accessed December 5, 2023. https://www.fda.gov/media/167893 /download
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Committee Opinion No. 788: Over-the-counter access to hormonal contraception. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134:e96-105.
- Grindlay K, Key K, Zuniga C, et al. Interest in continued use after participation in a study of over-the-counter progestin-only pills in the United States. Womens Health Rep. 2022;3:904-914.
- Guillard H, Laurora I, Sober S, et al. Modeling the potential benefit of an over-the-counter progestin-only pill in preventing unintended pregnancies in the U.S. Contraception. 2023;117:7-12.
Case Q: How can I best remove my patient’s difficult-to-find implant?
Individuals spend close to half of their lives preventing, or planning for, pregnancy. As such, contraception plays a major role in patient-provider interactions. Contraception counseling and management is a common scenario encountered in the general gynecologist’s practice. Luckily, we have 2 evidence-based guidelines developed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that support the provision of contraceptive care:
- US Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use (US-MEC),1 which provides guidance on which patients can safely use a method
- US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR),2 which provides method-specific guidance on how to use a method (including how to: initiate or start a method; manage adherence issues, such as a missed pill, etc; and manage common issues like breakthrough bleeding).
Both of these guidelines are updated routinely and are publicly available online or for free, through smartphone applications.
While most contraceptive care is straightforward, there are circumstances that require additional consideration. In the concluding part of this series on contraceptive conundrums, we review 2 clinical cases, existing evidence to guide management decisions, and our recommendations.
CASE 1 Patient presents with hard-to-remove implant
A 44-year-old patient (G2P2) with a new diagnosis of estrogen and progesterone-receptor–positive breast cancer is undergoing her evaluation with her oncologist who recommends removal of her contraceptive implant, which has been in place for 2 years. She presents to your office for removal; however, the device is no longer palpable.
What are your next steps?
Conundrum 1. Should you attempt to remove it?
No, never attempt implant removal if you cannot palpate or localize it. Localization of the implant needs to occur prior to any attempt. However, we recommend checking the contra-lateral arm before sending the patient to obtain imaging, especially if you have no formal documentation regarding in which arm the implant was placed. The next step is identifying what type of implant the patient likely has so you can correctly interpret imaging studies.
Conundrum 2. What type of subdermal contraceptive device is it likely to be?
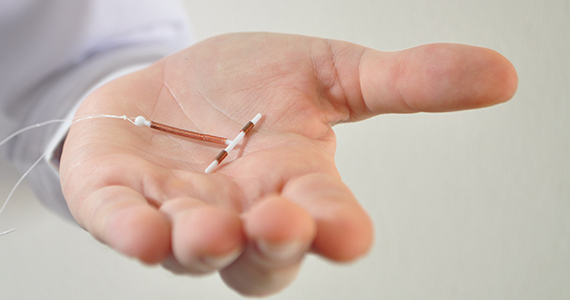
Currently, the only subdermal contraceptive device available for placement in the United States is the 68-mg etonogestrel implant, marketed with the brand name Nexplanon. This device was initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2001 and measures 4 cm in length by 2 mm in diameter. It is placed in the medial upper arm, about 8 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle and 3 cm posterior to the sulcus between the biceps and triceps muscles. (The implant should no longer be placed over the bicipital groove.) The implant is impregnated with 15 mg of barium sulfate, making it radiopaque and able to be seen on imaging modalities such as ultrasonography (10–18 mHz high frequency transducer) and x-ray (arm anteroposterior and lateral) for localization in cases in which the device becomes nonpalpable.3
Clinicians also may encounter devices which are no longer marketed in the United States, or which are only available in other countries, and thus should be aware of the appearance and imaging characteristics. It is important to let your imaging team know these characteristics as well:
- From 2006–2010, a 68-mg etonogestrel implant marketed under the name Implanon was available in the United States.4 It has the same dimensions and general placement recommendations as the Nexplanon etonogestrel device but is not able to be seen via imaging.
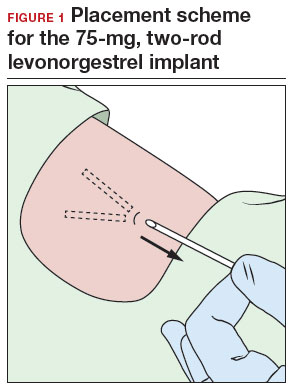
- A 2-arm, 75-mg levonorgestrel (LNG) device known as Jadelle (or, Norplant II; FIGURE 1) received FDA approval in 1996 and is currently only available overseas.5 It is also placed in the upper, inner arm in a V-shape using a single incision, and has dimensions similar to the etonogestrel implants.
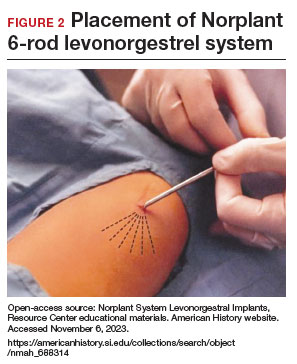
- From 1990– 2002, the 6-rod device known as Norplant was available in the United States. Each rod measured 3.4 cm in length and contained 36 mg of LNG (FIGURE 2).
Continue to: How do you approach removal of a deep contraceptive implant?...
How do you approach removal of a deep contraceptive implant?
Clinicians who are not trained in deep or difficult implant removal should refer patients to a trained provider (eg, a complex family planning subspecialist), or if not available, partner with a health care practitioner that has expertise in the anatomy of the upper arm (eg, vascular surgery, orthopedics, or interventional radiology). A resource for finding a nearby trained provider is the Organon Information Center (1-877-467-5266). However, when these services are not readily available, consider the following 3-step approach to complex implant removal.
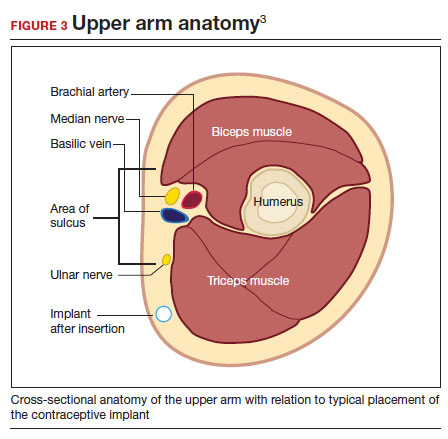
- Be familiar with the anatomy of the upper arm (FIGURE 3). Nonpalpable implants may be close to or under the biceps or triceps fascia or be near critically important and fragile structures like the neurovascular bundle of the upper arm. Prior to attempting a difficult implant removal, ensure that you are well acquainted with critical structures in the upper arm.
- Locate the device. Prior to attempting removal, localize the device using either x-ray or ultrasonography, depending on local availability. Ultrasound offers the advantage of mapping the location in 3 dimensions, with the ability to map the device with skin markings immediately prior to removal. Typically, a highfrequency transducer (15- or 18-MHz) is used, such as for breast imaging, either in a clinician’s office or in coordination with radiology. If device removal is attempted the same day, the proximal, midportion, and distal aspects of the device should be marked with a skin pen, and it should be noted what position the arm is in when the device is marked (eg, arm flexed at elbow and externally rotated so that the wrist is parallel to the ear).
Rarely, if a device is not seen in the expected extremity, imaging of the contralateral arm or a chest x-ray can be undertaken to rule out mis-documented laterality or a migrated device. Lastly, if no device is seen, and the patient has no memory of device removal, you can obtain the patient’s etonogestrel levels. (Resource: Merck National Service Center, 1-877-888-4231.)
Removal procedure. For nonpalpable implants, strong consideration should be given to performing the procedure with ultrasonography guidance. Rarely, fluoroscopic guidance may be useful for orientation in challenging cases, which may require coordination with other services, such as interventional radiology.
Cleaning and anesthetizing the site is similar to routine removal of a palpable implant. A 2- to 3-mm skin incision is made, either at the distal end of the implant (if one end is amenable to traditional pop-out technique) or over the midportion of the device (if a clinician has experience using the “U” technique).6 The incision should be parallel to the long axis of the implant and not perpendicular, to facilitate extension of the incision if needed during the procedure. Straight or curved hemostat clamps can then be used for blunt dissection of the subcutaneous tissues and to grasp the end of the device. Experienced clinicians may have access to a modified vasectomy clamp (with a
Indications for referral. Typically, referral to a complex family planning specialist or vascular surgeon is required for cases that involve dissection of the muscular fascia or where dissection would be in close proximity to critical neurologic or vascular structures.
CASE 1 Conclusion
Ultrasonography of the patient’s extremity demonstrated a
CASE 2 Patient enquires about immediate IUD insertion
A 28-year-old patient (G1P0) arrives at your clinic for a contraceptive consultation. They report a condom break during intercourse 4 days ago. Prior to that they used condoms consistently with each act of intercourse. They have used combined hormonal contraceptive pills in the past but had difficulty remembering to take them consistently. The patient and their partner have been mutually monogamous for 6 months and have no plans for pregnancy. Last menstrual period was 12 days ago. Their cycles are regular but heavy and painful. They are interested in using a hormonal IUD for contraception and would love to get it today.
- Do not attempt removal of a nonpalpable implant without prior localization via imaging
- Ultrasound-guided removal procedures using a “U” technique are successful for many deep implant removals but require specialized equipment and training
- Referral to a complex family planning specialist or other specialist is highly recommended for implants located below the triceps fascia or close to the nerves and vessels of the upper arm
- Never attempt to remove a nonpalpable implant prior to determining its location via imaging
Continue to: Is same-day IUD an option?...
Is same-day IUD an option?
Yes. This patient needs EC given the recent condom break, but they are still eligible for having an IUD placed today if their pregnancy test is negative and after counseling of the potential risks and benefits. According to the US-SPR it is reasonable to insert an IUD at any time during the cycle as long as you are reasonably certain the patient is not pregnant.7
Options for EC are:
- 1.5-mg oral LNG pill
- 30-mg oral UPA pill
- copper IUD (cu-IUD).
If they are interested in the cu-IUD for long-term contraception, by having a cu-IUD placed they can get both their needs met—EC and an ongoing method of contraception. Any patient receiving EC, whether a pill or an IUD, should be counseled to repeat a home urine pregnancy test in 2 to 4 weeks.
Given the favorable non–contraceptive benefits associated with 52-mg LNG-IUDs, many clinicians and patients have advocated for additional evidence regarding the use of hormonal IUDs alone for EC.
What is the evidence concerning LNG-IUD placement as EC?
The 52-mg LNG-IUD has not been mechanistically proven to work as an EC, but growing evidence exists showing that it is safe for same-day or “quick start” placement even in a population seeking EC—if their pregnancy test result is negative at the time of presentation.
Turok and colleagues performed a noninferiority trial comparing 1-month pregnancy rates after placement of either an LNG-IUD or a cu-IUD for EC.8 This study concluded that the LNG-IUD (which resulted in 1 pregnancy in 317 users; pregnancy rate, 0.3%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01–1.70) is noninferior to cu-IUD (0 pregnancies in 321 users; pregnancy rate, 0%; 95% CI, 0.0–1.1) for EC. Although encouraging, only a small percentage of the study population seeking EC who received an IUD were actually at high risk of pregnancy (eg, they were not mid-cycle or were recently using contraception), which is why it is difficult to determine if the LNG-IUD actually works mechanistically as an EC. More likely, the LNG-IUD helps prevent pregnancy due to its ongoing contraceptive effect.9 Ongoing acts of intercourse post–oral EC initiation without starting a method of contraception is one of the main reasons for EC failure, which is why starting a method immediately is so effective at preventing pregnancy.10
A systematic review conducted by Ramanadhan and colleagues concluded that Turok’s 2021 trial is the only relevant study specific to 52-mg LNG-IUD use as EC, but they also mention that its results are limited in the strength of its conclusions due to biases in randomization, including11:
- the study groups were not balanced in that there was a 10% difference in reported use of contraception at last intercourse, which means that the LNG-IUD group had a lower baseline risk of pregnancy
- and a rare primary outcome (ie, pregnancy, which requires a larger sample size to know if the method works as an EC).
The review authors concluded that more studies are needed to further validate the effectiveness of using the 52-mg LNG-IUD as EC. Thus, for those at highest risk of pregnancy from recent unprotected sex and desiring a 52-mg IUD, it is probably best to continue combining oral EC with a 52-mg LNG-IUD and utilizing the LNG-IUD only as EC on a limited, case-by-case basis.
What we recommend
For anyone with a negative pregnancy test on the day of presentation, the studies mentioned further support the practice of same-day placement of a 52-mg LNG-IUD. However, those seeking EC who are at highest risk for an unplanned pregnancy (ie, the unprotected sex was mid-cycle), we recommend co-administering the LNG-IUD with oral LNG for EC.
CASE 2 Conclusion
After a conversation with the patient about all contraceptive options, through shared decision making the patient decided to take 1.5 mg of oral LNG and have a 52-mg LNG-IUD placed in the office today. They do not wish to be pregnant at this time and would choose termination if they became pregnant. They understood their pregnancy risk and opted to plan a urine pregnancy test at home in 2 weeks with a clear understanding that they should return to clinic immediately if the test is positive. ●
- A copper IUD is the most effective method of emergency contraception (EC).
- 52-mg LNG-IUDs are an emerging consideration for EC, but evidence is still lacking that they work as EC (or whether they just prevent pregnancy after placement for subsequent acts of intercourse). Clinicians should utilize shared decision making and advise patients to repeat a pregnancy test at home in 2 to 4 weeks
- Any patient receiving EC, whether a pill or an IUD, should be counseled to repeat a home urine pregnancy test in 2 to 4 weeks
- Any type of IUD can be placed same day if the clinician is reasonably sure the patient is not pregnant
- It appears safe to co-administer the 52-mg LNG-IUD with oral EC for those seeking emergency contraception but also want to use an LNG-IUD for contraception going forward
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr .rr6504a1
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health. US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR). Accessed October 11, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth /contraception/mmwr/spr/summary.html
- Nexplanon [package insert]. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck; 2018.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Implanon (etonogestrel implant) 2006. Accessed November 6, 2023. https://www .accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2006 /021529s000_Lbl.pdf
- US Food and Drug Administration. Jadelle (levonorgestrel implant) 2016. Accessed November 6, 2023. https://www. accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/020544s 010lbl.pdf
- Chen MJ, Creinin MD. Removal of a nonpalpable etonogestrel implant with preprocedure ultrasonography and modified vasectomy clamp. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:935-938.
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep Morb Mortal Wkly. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6504a1
- Turok DK, Gero A, Simmons RG, et al. Levonorgestrel vs. copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:335-344. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/33503342/
- Kaiser JE, Turok DK, Gero A, et al. One-year pregnancy and continuation rates after placement of levonorgestrel or copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;228:438.e1-438.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022 .11.1296
- Sander PM, Raymond EG, Weaver MA. Emergency contraceptive use as a marker of future risky sex, pregnancy, and sexually transmitted infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:146.e1-e6.
- Ramanadhan S, Goldstuck N, Henderson JT, et al. Progestin intrauterine devices versus copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;2:CD013744. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858 .CD013744.pub2
Individuals spend close to half of their lives preventing, or planning for, pregnancy. As such, contraception plays a major role in patient-provider interactions. Contraception counseling and management is a common scenario encountered in the general gynecologist’s practice. Luckily, we have 2 evidence-based guidelines developed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that support the provision of contraceptive care:
- US Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use (US-MEC),1 which provides guidance on which patients can safely use a method
- US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR),2 which provides method-specific guidance on how to use a method (including how to: initiate or start a method; manage adherence issues, such as a missed pill, etc; and manage common issues like breakthrough bleeding).
Both of these guidelines are updated routinely and are publicly available online or for free, through smartphone applications.
While most contraceptive care is straightforward, there are circumstances that require additional consideration. In the concluding part of this series on contraceptive conundrums, we review 2 clinical cases, existing evidence to guide management decisions, and our recommendations.
CASE 1 Patient presents with hard-to-remove implant
A 44-year-old patient (G2P2) with a new diagnosis of estrogen and progesterone-receptor–positive breast cancer is undergoing her evaluation with her oncologist who recommends removal of her contraceptive implant, which has been in place for 2 years. She presents to your office for removal; however, the device is no longer palpable.
What are your next steps?
Conundrum 1. Should you attempt to remove it?
No, never attempt implant removal if you cannot palpate or localize it. Localization of the implant needs to occur prior to any attempt. However, we recommend checking the contra-lateral arm before sending the patient to obtain imaging, especially if you have no formal documentation regarding in which arm the implant was placed. The next step is identifying what type of implant the patient likely has so you can correctly interpret imaging studies.
Conundrum 2. What type of subdermal contraceptive device is it likely to be?
Currently, the only subdermal contraceptive device available for placement in the United States is the 68-mg etonogestrel implant, marketed with the brand name Nexplanon. This device was initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2001 and measures 4 cm in length by 2 mm in diameter. It is placed in the medial upper arm, about 8 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle and 3 cm posterior to the sulcus between the biceps and triceps muscles. (The implant should no longer be placed over the bicipital groove.) The implant is impregnated with 15 mg of barium sulfate, making it radiopaque and able to be seen on imaging modalities such as ultrasonography (10–18 mHz high frequency transducer) and x-ray (arm anteroposterior and lateral) for localization in cases in which the device becomes nonpalpable.3
Clinicians also may encounter devices which are no longer marketed in the United States, or which are only available in other countries, and thus should be aware of the appearance and imaging characteristics. It is important to let your imaging team know these characteristics as well:
- From 2006–2010, a 68-mg etonogestrel implant marketed under the name Implanon was available in the United States.4 It has the same dimensions and general placement recommendations as the Nexplanon etonogestrel device but is not able to be seen via imaging.
- A 2-arm, 75-mg levonorgestrel (LNG) device known as Jadelle (or, Norplant II; FIGURE 1) received FDA approval in 1996 and is currently only available overseas.5 It is also placed in the upper, inner arm in a V-shape using a single incision, and has dimensions similar to the etonogestrel implants.
- From 1990– 2002, the 6-rod device known as Norplant was available in the United States. Each rod measured 3.4 cm in length and contained 36 mg of LNG (FIGURE 2).


Continue to: How do you approach removal of a deep contraceptive implant?...
How do you approach removal of a deep contraceptive implant?
Clinicians who are not trained in deep or difficult implant removal should refer patients to a trained provider (eg, a complex family planning subspecialist), or if not available, partner with a health care practitioner that has expertise in the anatomy of the upper arm (eg, vascular surgery, orthopedics, or interventional radiology). A resource for finding a nearby trained provider is the Organon Information Center (1-877-467-5266). However, when these services are not readily available, consider the following 3-step approach to complex implant removal.
- Be familiar with the anatomy of the upper arm (FIGURE 3). Nonpalpable implants may be close to or under the biceps or triceps fascia or be near critically important and fragile structures like the neurovascular bundle of the upper arm. Prior to attempting a difficult implant removal, ensure that you are well acquainted with critical structures in the upper arm.
- Locate the device. Prior to attempting removal, localize the device using either x-ray or ultrasonography, depending on local availability. Ultrasound offers the advantage of mapping the location in 3 dimensions, with the ability to map the device with skin markings immediately prior to removal. Typically, a highfrequency transducer (15- or 18-MHz) is used, such as for breast imaging, either in a clinician’s office or in coordination with radiology. If device removal is attempted the same day, the proximal, midportion, and distal aspects of the device should be marked with a skin pen, and it should be noted what position the arm is in when the device is marked (eg, arm flexed at elbow and externally rotated so that the wrist is parallel to the ear).

Rarely, if a device is not seen in the expected extremity, imaging of the contralateral arm or a chest x-ray can be undertaken to rule out mis-documented laterality or a migrated device. Lastly, if no device is seen, and the patient has no memory of device removal, you can obtain the patient’s etonogestrel levels. (Resource: Merck National Service Center, 1-877-888-4231.)
Removal procedure. For nonpalpable implants, strong consideration should be given to performing the procedure with ultrasonography guidance. Rarely, fluoroscopic guidance may be useful for orientation in challenging cases, which may require coordination with other services, such as interventional radiology.
Cleaning and anesthetizing the site is similar to routine removal of a palpable implant. A 2- to 3-mm skin incision is made, either at the distal end of the implant (if one end is amenable to traditional pop-out technique) or over the midportion of the device (if a clinician has experience using the “U” technique).6 The incision should be parallel to the long axis of the implant and not perpendicular, to facilitate extension of the incision if needed during the procedure. Straight or curved hemostat clamps can then be used for blunt dissection of the subcutaneous tissues and to grasp the end of the device. Experienced clinicians may have access to a modified vasectomy clamp (with a
Indications for referral. Typically, referral to a complex family planning specialist or vascular surgeon is required for cases that involve dissection of the muscular fascia or where dissection would be in close proximity to critical neurologic or vascular structures.
CASE 1 Conclusion
Ultrasonography of the patient’s extremity demonstrated a
CASE 2 Patient enquires about immediate IUD insertion
A 28-year-old patient (G1P0) arrives at your clinic for a contraceptive consultation. They report a condom break during intercourse 4 days ago. Prior to that they used condoms consistently with each act of intercourse. They have used combined hormonal contraceptive pills in the past but had difficulty remembering to take them consistently. The patient and their partner have been mutually monogamous for 6 months and have no plans for pregnancy. Last menstrual period was 12 days ago. Their cycles are regular but heavy and painful. They are interested in using a hormonal IUD for contraception and would love to get it today.
- Do not attempt removal of a nonpalpable implant without prior localization via imaging
- Ultrasound-guided removal procedures using a “U” technique are successful for many deep implant removals but require specialized equipment and training
- Referral to a complex family planning specialist or other specialist is highly recommended for implants located below the triceps fascia or close to the nerves and vessels of the upper arm
- Never attempt to remove a nonpalpable implant prior to determining its location via imaging
Continue to: Is same-day IUD an option?...
Is same-day IUD an option?
Yes. This patient needs EC given the recent condom break, but they are still eligible for having an IUD placed today if their pregnancy test is negative and after counseling of the potential risks and benefits. According to the US-SPR it is reasonable to insert an IUD at any time during the cycle as long as you are reasonably certain the patient is not pregnant.7
Options for EC are:
- 1.5-mg oral LNG pill
- 30-mg oral UPA pill
- copper IUD (cu-IUD).
If they are interested in the cu-IUD for long-term contraception, by having a cu-IUD placed they can get both their needs met—EC and an ongoing method of contraception. Any patient receiving EC, whether a pill or an IUD, should be counseled to repeat a home urine pregnancy test in 2 to 4 weeks.
Given the favorable non–contraceptive benefits associated with 52-mg LNG-IUDs, many clinicians and patients have advocated for additional evidence regarding the use of hormonal IUDs alone for EC.
What is the evidence concerning LNG-IUD placement as EC?
The 52-mg LNG-IUD has not been mechanistically proven to work as an EC, but growing evidence exists showing that it is safe for same-day or “quick start” placement even in a population seeking EC—if their pregnancy test result is negative at the time of presentation.
Turok and colleagues performed a noninferiority trial comparing 1-month pregnancy rates after placement of either an LNG-IUD or a cu-IUD for EC.8 This study concluded that the LNG-IUD (which resulted in 1 pregnancy in 317 users; pregnancy rate, 0.3%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01–1.70) is noninferior to cu-IUD (0 pregnancies in 321 users; pregnancy rate, 0%; 95% CI, 0.0–1.1) for EC. Although encouraging, only a small percentage of the study population seeking EC who received an IUD were actually at high risk of pregnancy (eg, they were not mid-cycle or were recently using contraception), which is why it is difficult to determine if the LNG-IUD actually works mechanistically as an EC. More likely, the LNG-IUD helps prevent pregnancy due to its ongoing contraceptive effect.9 Ongoing acts of intercourse post–oral EC initiation without starting a method of contraception is one of the main reasons for EC failure, which is why starting a method immediately is so effective at preventing pregnancy.10
A systematic review conducted by Ramanadhan and colleagues concluded that Turok’s 2021 trial is the only relevant study specific to 52-mg LNG-IUD use as EC, but they also mention that its results are limited in the strength of its conclusions due to biases in randomization, including11:
- the study groups were not balanced in that there was a 10% difference in reported use of contraception at last intercourse, which means that the LNG-IUD group had a lower baseline risk of pregnancy
- and a rare primary outcome (ie, pregnancy, which requires a larger sample size to know if the method works as an EC).
The review authors concluded that more studies are needed to further validate the effectiveness of using the 52-mg LNG-IUD as EC. Thus, for those at highest risk of pregnancy from recent unprotected sex and desiring a 52-mg IUD, it is probably best to continue combining oral EC with a 52-mg LNG-IUD and utilizing the LNG-IUD only as EC on a limited, case-by-case basis.
What we recommend
For anyone with a negative pregnancy test on the day of presentation, the studies mentioned further support the practice of same-day placement of a 52-mg LNG-IUD. However, those seeking EC who are at highest risk for an unplanned pregnancy (ie, the unprotected sex was mid-cycle), we recommend co-administering the LNG-IUD with oral LNG for EC.
CASE 2 Conclusion
After a conversation with the patient about all contraceptive options, through shared decision making the patient decided to take 1.5 mg of oral LNG and have a 52-mg LNG-IUD placed in the office today. They do not wish to be pregnant at this time and would choose termination if they became pregnant. They understood their pregnancy risk and opted to plan a urine pregnancy test at home in 2 weeks with a clear understanding that they should return to clinic immediately if the test is positive. ●
- A copper IUD is the most effective method of emergency contraception (EC).
- 52-mg LNG-IUDs are an emerging consideration for EC, but evidence is still lacking that they work as EC (or whether they just prevent pregnancy after placement for subsequent acts of intercourse). Clinicians should utilize shared decision making and advise patients to repeat a pregnancy test at home in 2 to 4 weeks
- Any patient receiving EC, whether a pill or an IUD, should be counseled to repeat a home urine pregnancy test in 2 to 4 weeks
- Any type of IUD can be placed same day if the clinician is reasonably sure the patient is not pregnant
- It appears safe to co-administer the 52-mg LNG-IUD with oral EC for those seeking emergency contraception but also want to use an LNG-IUD for contraception going forward
Individuals spend close to half of their lives preventing, or planning for, pregnancy. As such, contraception plays a major role in patient-provider interactions. Contraception counseling and management is a common scenario encountered in the general gynecologist’s practice. Luckily, we have 2 evidence-based guidelines developed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that support the provision of contraceptive care:
- US Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use (US-MEC),1 which provides guidance on which patients can safely use a method
- US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR),2 which provides method-specific guidance on how to use a method (including how to: initiate or start a method; manage adherence issues, such as a missed pill, etc; and manage common issues like breakthrough bleeding).
Both of these guidelines are updated routinely and are publicly available online or for free, through smartphone applications.
While most contraceptive care is straightforward, there are circumstances that require additional consideration. In the concluding part of this series on contraceptive conundrums, we review 2 clinical cases, existing evidence to guide management decisions, and our recommendations.
CASE 1 Patient presents with hard-to-remove implant
A 44-year-old patient (G2P2) with a new diagnosis of estrogen and progesterone-receptor–positive breast cancer is undergoing her evaluation with her oncologist who recommends removal of her contraceptive implant, which has been in place for 2 years. She presents to your office for removal; however, the device is no longer palpable.
What are your next steps?
Conundrum 1. Should you attempt to remove it?
No, never attempt implant removal if you cannot palpate or localize it. Localization of the implant needs to occur prior to any attempt. However, we recommend checking the contra-lateral arm before sending the patient to obtain imaging, especially if you have no formal documentation regarding in which arm the implant was placed. The next step is identifying what type of implant the patient likely has so you can correctly interpret imaging studies.
Conundrum 2. What type of subdermal contraceptive device is it likely to be?
Currently, the only subdermal contraceptive device available for placement in the United States is the 68-mg etonogestrel implant, marketed with the brand name Nexplanon. This device was initially approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2001 and measures 4 cm in length by 2 mm in diameter. It is placed in the medial upper arm, about 8 cm proximal to the medial epicondyle and 3 cm posterior to the sulcus between the biceps and triceps muscles. (The implant should no longer be placed over the bicipital groove.) The implant is impregnated with 15 mg of barium sulfate, making it radiopaque and able to be seen on imaging modalities such as ultrasonography (10–18 mHz high frequency transducer) and x-ray (arm anteroposterior and lateral) for localization in cases in which the device becomes nonpalpable.3
Clinicians also may encounter devices which are no longer marketed in the United States, or which are only available in other countries, and thus should be aware of the appearance and imaging characteristics. It is important to let your imaging team know these characteristics as well:
- From 2006–2010, a 68-mg etonogestrel implant marketed under the name Implanon was available in the United States.4 It has the same dimensions and general placement recommendations as the Nexplanon etonogestrel device but is not able to be seen via imaging.
- A 2-arm, 75-mg levonorgestrel (LNG) device known as Jadelle (or, Norplant II; FIGURE 1) received FDA approval in 1996 and is currently only available overseas.5 It is also placed in the upper, inner arm in a V-shape using a single incision, and has dimensions similar to the etonogestrel implants.
- From 1990– 2002, the 6-rod device known as Norplant was available in the United States. Each rod measured 3.4 cm in length and contained 36 mg of LNG (FIGURE 2).


Continue to: How do you approach removal of a deep contraceptive implant?...
How do you approach removal of a deep contraceptive implant?
Clinicians who are not trained in deep or difficult implant removal should refer patients to a trained provider (eg, a complex family planning subspecialist), or if not available, partner with a health care practitioner that has expertise in the anatomy of the upper arm (eg, vascular surgery, orthopedics, or interventional radiology). A resource for finding a nearby trained provider is the Organon Information Center (1-877-467-5266). However, when these services are not readily available, consider the following 3-step approach to complex implant removal.
- Be familiar with the anatomy of the upper arm (FIGURE 3). Nonpalpable implants may be close to or under the biceps or triceps fascia or be near critically important and fragile structures like the neurovascular bundle of the upper arm. Prior to attempting a difficult implant removal, ensure that you are well acquainted with critical structures in the upper arm.
- Locate the device. Prior to attempting removal, localize the device using either x-ray or ultrasonography, depending on local availability. Ultrasound offers the advantage of mapping the location in 3 dimensions, with the ability to map the device with skin markings immediately prior to removal. Typically, a highfrequency transducer (15- or 18-MHz) is used, such as for breast imaging, either in a clinician’s office or in coordination with radiology. If device removal is attempted the same day, the proximal, midportion, and distal aspects of the device should be marked with a skin pen, and it should be noted what position the arm is in when the device is marked (eg, arm flexed at elbow and externally rotated so that the wrist is parallel to the ear).

Rarely, if a device is not seen in the expected extremity, imaging of the contralateral arm or a chest x-ray can be undertaken to rule out mis-documented laterality or a migrated device. Lastly, if no device is seen, and the patient has no memory of device removal, you can obtain the patient’s etonogestrel levels. (Resource: Merck National Service Center, 1-877-888-4231.)
Removal procedure. For nonpalpable implants, strong consideration should be given to performing the procedure with ultrasonography guidance. Rarely, fluoroscopic guidance may be useful for orientation in challenging cases, which may require coordination with other services, such as interventional radiology.
Cleaning and anesthetizing the site is similar to routine removal of a palpable implant. A 2- to 3-mm skin incision is made, either at the distal end of the implant (if one end is amenable to traditional pop-out technique) or over the midportion of the device (if a clinician has experience using the “U” technique).6 The incision should be parallel to the long axis of the implant and not perpendicular, to facilitate extension of the incision if needed during the procedure. Straight or curved hemostat clamps can then be used for blunt dissection of the subcutaneous tissues and to grasp the end of the device. Experienced clinicians may have access to a modified vasectomy clamp (with a
Indications for referral. Typically, referral to a complex family planning specialist or vascular surgeon is required for cases that involve dissection of the muscular fascia or where dissection would be in close proximity to critical neurologic or vascular structures.
CASE 1 Conclusion
Ultrasonography of the patient’s extremity demonstrated a
CASE 2 Patient enquires about immediate IUD insertion
A 28-year-old patient (G1P0) arrives at your clinic for a contraceptive consultation. They report a condom break during intercourse 4 days ago. Prior to that they used condoms consistently with each act of intercourse. They have used combined hormonal contraceptive pills in the past but had difficulty remembering to take them consistently. The patient and their partner have been mutually monogamous for 6 months and have no plans for pregnancy. Last menstrual period was 12 days ago. Their cycles are regular but heavy and painful. They are interested in using a hormonal IUD for contraception and would love to get it today.
- Do not attempt removal of a nonpalpable implant without prior localization via imaging
- Ultrasound-guided removal procedures using a “U” technique are successful for many deep implant removals but require specialized equipment and training
- Referral to a complex family planning specialist or other specialist is highly recommended for implants located below the triceps fascia or close to the nerves and vessels of the upper arm
- Never attempt to remove a nonpalpable implant prior to determining its location via imaging
Continue to: Is same-day IUD an option?...
Is same-day IUD an option?
Yes. This patient needs EC given the recent condom break, but they are still eligible for having an IUD placed today if their pregnancy test is negative and after counseling of the potential risks and benefits. According to the US-SPR it is reasonable to insert an IUD at any time during the cycle as long as you are reasonably certain the patient is not pregnant.7
Options for EC are:
- 1.5-mg oral LNG pill
- 30-mg oral UPA pill
- copper IUD (cu-IUD).
If they are interested in the cu-IUD for long-term contraception, by having a cu-IUD placed they can get both their needs met—EC and an ongoing method of contraception. Any patient receiving EC, whether a pill or an IUD, should be counseled to repeat a home urine pregnancy test in 2 to 4 weeks.
Given the favorable non–contraceptive benefits associated with 52-mg LNG-IUDs, many clinicians and patients have advocated for additional evidence regarding the use of hormonal IUDs alone for EC.
What is the evidence concerning LNG-IUD placement as EC?
The 52-mg LNG-IUD has not been mechanistically proven to work as an EC, but growing evidence exists showing that it is safe for same-day or “quick start” placement even in a population seeking EC—if their pregnancy test result is negative at the time of presentation.
Turok and colleagues performed a noninferiority trial comparing 1-month pregnancy rates after placement of either an LNG-IUD or a cu-IUD for EC.8 This study concluded that the LNG-IUD (which resulted in 1 pregnancy in 317 users; pregnancy rate, 0.3%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.01–1.70) is noninferior to cu-IUD (0 pregnancies in 321 users; pregnancy rate, 0%; 95% CI, 0.0–1.1) for EC. Although encouraging, only a small percentage of the study population seeking EC who received an IUD were actually at high risk of pregnancy (eg, they were not mid-cycle or were recently using contraception), which is why it is difficult to determine if the LNG-IUD actually works mechanistically as an EC. More likely, the LNG-IUD helps prevent pregnancy due to its ongoing contraceptive effect.9 Ongoing acts of intercourse post–oral EC initiation without starting a method of contraception is one of the main reasons for EC failure, which is why starting a method immediately is so effective at preventing pregnancy.10
A systematic review conducted by Ramanadhan and colleagues concluded that Turok’s 2021 trial is the only relevant study specific to 52-mg LNG-IUD use as EC, but they also mention that its results are limited in the strength of its conclusions due to biases in randomization, including11:
- the study groups were not balanced in that there was a 10% difference in reported use of contraception at last intercourse, which means that the LNG-IUD group had a lower baseline risk of pregnancy
- and a rare primary outcome (ie, pregnancy, which requires a larger sample size to know if the method works as an EC).
The review authors concluded that more studies are needed to further validate the effectiveness of using the 52-mg LNG-IUD as EC. Thus, for those at highest risk of pregnancy from recent unprotected sex and desiring a 52-mg IUD, it is probably best to continue combining oral EC with a 52-mg LNG-IUD and utilizing the LNG-IUD only as EC on a limited, case-by-case basis.
What we recommend
For anyone with a negative pregnancy test on the day of presentation, the studies mentioned further support the practice of same-day placement of a 52-mg LNG-IUD. However, those seeking EC who are at highest risk for an unplanned pregnancy (ie, the unprotected sex was mid-cycle), we recommend co-administering the LNG-IUD with oral LNG for EC.
CASE 2 Conclusion
After a conversation with the patient about all contraceptive options, through shared decision making the patient decided to take 1.5 mg of oral LNG and have a 52-mg LNG-IUD placed in the office today. They do not wish to be pregnant at this time and would choose termination if they became pregnant. They understood their pregnancy risk and opted to plan a urine pregnancy test at home in 2 weeks with a clear understanding that they should return to clinic immediately if the test is positive. ●
- A copper IUD is the most effective method of emergency contraception (EC).
- 52-mg LNG-IUDs are an emerging consideration for EC, but evidence is still lacking that they work as EC (or whether they just prevent pregnancy after placement for subsequent acts of intercourse). Clinicians should utilize shared decision making and advise patients to repeat a pregnancy test at home in 2 to 4 weeks
- Any patient receiving EC, whether a pill or an IUD, should be counseled to repeat a home urine pregnancy test in 2 to 4 weeks
- Any type of IUD can be placed same day if the clinician is reasonably sure the patient is not pregnant
- It appears safe to co-administer the 52-mg LNG-IUD with oral EC for those seeking emergency contraception but also want to use an LNG-IUD for contraception going forward
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr .rr6504a1
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health. US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR). Accessed October 11, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth /contraception/mmwr/spr/summary.html
- Nexplanon [package insert]. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck; 2018.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Implanon (etonogestrel implant) 2006. Accessed November 6, 2023. https://www .accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2006 /021529s000_Lbl.pdf
- US Food and Drug Administration. Jadelle (levonorgestrel implant) 2016. Accessed November 6, 2023. https://www. accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/020544s 010lbl.pdf
- Chen MJ, Creinin MD. Removal of a nonpalpable etonogestrel implant with preprocedure ultrasonography and modified vasectomy clamp. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:935-938.
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep Morb Mortal Wkly. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6504a1
- Turok DK, Gero A, Simmons RG, et al. Levonorgestrel vs. copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:335-344. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/33503342/
- Kaiser JE, Turok DK, Gero A, et al. One-year pregnancy and continuation rates after placement of levonorgestrel or copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;228:438.e1-438.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022 .11.1296
- Sander PM, Raymond EG, Weaver MA. Emergency contraceptive use as a marker of future risky sex, pregnancy, and sexually transmitted infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:146.e1-e6.
- Ramanadhan S, Goldstuck N, Henderson JT, et al. Progestin intrauterine devices versus copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;2:CD013744. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858 .CD013744.pub2
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr .rr6504a1
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health. US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR). Accessed October 11, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth /contraception/mmwr/spr/summary.html
- Nexplanon [package insert]. Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck; 2018.
- US Food and Drug Administration. Implanon (etonogestrel implant) 2006. Accessed November 6, 2023. https://www .accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2006 /021529s000_Lbl.pdf
- US Food and Drug Administration. Jadelle (levonorgestrel implant) 2016. Accessed November 6, 2023. https://www. accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/020544s 010lbl.pdf
- Chen MJ, Creinin MD. Removal of a nonpalpable etonogestrel implant with preprocedure ultrasonography and modified vasectomy clamp. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;126:935-938.
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep Morb Mortal Wkly. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6504a1
- Turok DK, Gero A, Simmons RG, et al. Levonorgestrel vs. copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:335-344. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm .nih.gov/33503342/
- Kaiser JE, Turok DK, Gero A, et al. One-year pregnancy and continuation rates after placement of levonorgestrel or copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2023;228:438.e1-438.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022 .11.1296
- Sander PM, Raymond EG, Weaver MA. Emergency contraceptive use as a marker of future risky sex, pregnancy, and sexually transmitted infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2009;201:146.e1-e6.
- Ramanadhan S, Goldstuck N, Henderson JT, et al. Progestin intrauterine devices versus copper intrauterine devices for emergency contraception. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023;2:CD013744. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858 .CD013744.pub2
FDA mandates five changes to iPLEDGE program for isotretinoin
In a letter dated Nov. 30, 2023, the .
The development follows a March 2023 joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee about iPLEDGE REMS requirements, which included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes to the REMS program, aimed at minimizing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while continuing to maintain safe use of the highly teratogenic drug for patients.
The five changes include the following:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests must be performed in a specially certified (i.e., Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments [CLIA]) laboratory. In the opinion of John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, this change “may make it easier to perform pregnancy tests in a clinic setting without needing to send the patient to a separate lab,” he said in an interview.
- Allow prescribers the option of using home pregnancy testing for their patients during and after isotretinoin treatment. Prescribers who rely on the patient to perform a home pregnancy test need to take steps to minimize patients falsifying the results of these tests. According to Dr. Barbieri, this means that two pregnancy tests prior to starting isotretinoin must be done in a lab or office setting. “However, all the pregnancy tests on therapy can be either in a medical setting or using a home pregnancy test,” he told this news organization. “This option facilitates the use of telemedicine so that patients would not need to come in; they can just share a pregnancy test with their name and date with their dermatologist.”
- Remove the waiting period requirement — also known as the “19-day lockout” — for patients if they do not obtain isotretinoin within the first 7-day prescription window. According to Dr. Barbieri, this change helps to ensure that patients can begin isotretinoin in a timely manner. “Insurance and pharmacy delays that are no fault of the patient can commonly cause missed initial window periods,” he said. “Allowing for immediate repeat of a pregnancy test to start a new window period, rather than requiring the patient to wait 19 more days, can ensure patient safety and pregnancy prevention without negatively impacting access.”
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement to remove the objective to document the pregnancy and fetal outcomes for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling in patients who cannot become pregnant from monthly to only at enrollment. Dr. Barbieri characterized this change as “major” and said that it could eliminate the need for monthly visits for persons of non–childbearing potential. “This could substantially reduce logistical burdens for patients and reduce wait times to see a dermatologist,” he said.
Future changes to iPLEDGE that Dr. Barbieri would like to see include allowing for home pregnancy tests prior to starting therapy — particularly the test after the 30-day window period. “In addition, it would be good to be able to reduce the 30-day waiting period prior to therapy to something shorter,” such as 14 days, which would still “reliably exclude pregnancy, particularly for those on stable long-acting reversible contraception,” he said. There are also opportunities to improve the iPLEDGE website functionality and to ensure that the website is accessible to patients with limited English proficiency, he added.
He also recommended greater transparency by the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group and inclusion of input from diverse stakeholders such as dermatologists, patients, and pharmacists.
Dr. Barbieri reported personal fees from Dexcel Pharma.
In a letter dated Nov. 30, 2023, the .
The development follows a March 2023 joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee about iPLEDGE REMS requirements, which included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes to the REMS program, aimed at minimizing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while continuing to maintain safe use of the highly teratogenic drug for patients.
The five changes include the following:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests must be performed in a specially certified (i.e., Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments [CLIA]) laboratory. In the opinion of John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, this change “may make it easier to perform pregnancy tests in a clinic setting without needing to send the patient to a separate lab,” he said in an interview.
- Allow prescribers the option of using home pregnancy testing for their patients during and after isotretinoin treatment. Prescribers who rely on the patient to perform a home pregnancy test need to take steps to minimize patients falsifying the results of these tests. According to Dr. Barbieri, this means that two pregnancy tests prior to starting isotretinoin must be done in a lab or office setting. “However, all the pregnancy tests on therapy can be either in a medical setting or using a home pregnancy test,” he told this news organization. “This option facilitates the use of telemedicine so that patients would not need to come in; they can just share a pregnancy test with their name and date with their dermatologist.”
- Remove the waiting period requirement — also known as the “19-day lockout” — for patients if they do not obtain isotretinoin within the first 7-day prescription window. According to Dr. Barbieri, this change helps to ensure that patients can begin isotretinoin in a timely manner. “Insurance and pharmacy delays that are no fault of the patient can commonly cause missed initial window periods,” he said. “Allowing for immediate repeat of a pregnancy test to start a new window period, rather than requiring the patient to wait 19 more days, can ensure patient safety and pregnancy prevention without negatively impacting access.”
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement to remove the objective to document the pregnancy and fetal outcomes for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling in patients who cannot become pregnant from monthly to only at enrollment. Dr. Barbieri characterized this change as “major” and said that it could eliminate the need for monthly visits for persons of non–childbearing potential. “This could substantially reduce logistical burdens for patients and reduce wait times to see a dermatologist,” he said.
Future changes to iPLEDGE that Dr. Barbieri would like to see include allowing for home pregnancy tests prior to starting therapy — particularly the test after the 30-day window period. “In addition, it would be good to be able to reduce the 30-day waiting period prior to therapy to something shorter,” such as 14 days, which would still “reliably exclude pregnancy, particularly for those on stable long-acting reversible contraception,” he said. There are also opportunities to improve the iPLEDGE website functionality and to ensure that the website is accessible to patients with limited English proficiency, he added.
He also recommended greater transparency by the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group and inclusion of input from diverse stakeholders such as dermatologists, patients, and pharmacists.
Dr. Barbieri reported personal fees from Dexcel Pharma.
In a letter dated Nov. 30, 2023, the .
The development follows a March 2023 joint meeting of the FDA’s Drug Safety and Risk Management Advisory Committee and the Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee about iPLEDGE REMS requirements, which included feedback from patients and dermatologists and recommendations for changes to the REMS program, aimed at minimizing the burden of the program on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while continuing to maintain safe use of the highly teratogenic drug for patients.
The five changes include the following:
- Remove the requirement that pregnancy tests must be performed in a specially certified (i.e., Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments [CLIA]) laboratory. In the opinion of John S. Barbieri, MD, MBA, director of the Advanced Acne Therapeutics Clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, this change “may make it easier to perform pregnancy tests in a clinic setting without needing to send the patient to a separate lab,” he said in an interview.
- Allow prescribers the option of using home pregnancy testing for their patients during and after isotretinoin treatment. Prescribers who rely on the patient to perform a home pregnancy test need to take steps to minimize patients falsifying the results of these tests. According to Dr. Barbieri, this means that two pregnancy tests prior to starting isotretinoin must be done in a lab or office setting. “However, all the pregnancy tests on therapy can be either in a medical setting or using a home pregnancy test,” he told this news organization. “This option facilitates the use of telemedicine so that patients would not need to come in; they can just share a pregnancy test with their name and date with their dermatologist.”
- Remove the waiting period requirement — also known as the “19-day lockout” — for patients if they do not obtain isotretinoin within the first 7-day prescription window. According to Dr. Barbieri, this change helps to ensure that patients can begin isotretinoin in a timely manner. “Insurance and pharmacy delays that are no fault of the patient can commonly cause missed initial window periods,” he said. “Allowing for immediate repeat of a pregnancy test to start a new window period, rather than requiring the patient to wait 19 more days, can ensure patient safety and pregnancy prevention without negatively impacting access.”
- Revise the pregnancy registry requirement to remove the objective to document the pregnancy and fetal outcomes for each pregnancy.
- Revise the requirement for prescribers to document patient counseling in patients who cannot become pregnant from monthly to only at enrollment. Dr. Barbieri characterized this change as “major” and said that it could eliminate the need for monthly visits for persons of non–childbearing potential. “This could substantially reduce logistical burdens for patients and reduce wait times to see a dermatologist,” he said.
Future changes to iPLEDGE that Dr. Barbieri would like to see include allowing for home pregnancy tests prior to starting therapy — particularly the test after the 30-day window period. “In addition, it would be good to be able to reduce the 30-day waiting period prior to therapy to something shorter,” such as 14 days, which would still “reliably exclude pregnancy, particularly for those on stable long-acting reversible contraception,” he said. There are also opportunities to improve the iPLEDGE website functionality and to ensure that the website is accessible to patients with limited English proficiency, he added.
He also recommended greater transparency by the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group and inclusion of input from diverse stakeholders such as dermatologists, patients, and pharmacists.
Dr. Barbieri reported personal fees from Dexcel Pharma.
Does taking an NSAID while on hormonal contraception increase VTE risk?
Meaidi A, Mascolo A, Sessa M, et al. Venous thromboembolism with use of hormonal contraception and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: nationwide cohort study. BMJ. 2023;382:e074450. doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-074450
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Combination (estrogen plus progestin) hormonal contraceptives as well as non–aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increase the risk of VTE events, including lower extremity clots and pulmonary embolism. Taking contraceptives formulated with ethinyl estradiol increases hepatic production of clotting factors on a dose-related basis. Newer progestins, including desogestrel and drospirenone, also may contribute to an elevated VTE risk, although this association is controversial.1 NSAIDs promote platelet aggregation, thereby activating the clotting system and formation of clots. Although studies that assessed the association between NSAID use and thrombosis have focused on arterial clots, a substantial literature suggests that NSAIDs, including older NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen), also increase VTE risk.2
Although combination contraceptives (oral contraceptives, patches, vaginal rings) and NSAIDs are both commonly used by reproductive-age women, little data have assessed the impact of concomitant use of these medications on VTE risk. Accordingly, investigators in Denmark, using national databases, conducted a retrospective cohort study to assess the impact that independent as well as concomitant use of these medications have on VTE risk.
Details of the study
Meaidi and colleagues included in the cohort reproductive-age women living in Denmark between 1996 and 2017 with no history of thrombosis, thrombophilia, cancer, tubal sterilization, hysterectomy, bilateral oophorectomy, or infertility treatment. National prescription data were used to assess exposure to hormonal contraception.
The investigators classified hormonal contraception into 3 VTE risk categories:
- high risk—estrogen-progestin patches and vaginal rings; oral contraceptives containing 50 µg of ethinyl estradiol; or the progestins desogestrel, drospirenone, gestodene, or cyproterone (with the latter 2 progestins not available in the United States)
- medium risk—all other combination oral contraceptives, including those formulated with the progestins norethindrone, norethindrone acetate, norgestrel, and levonorgestrel, as well as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate
- low/no risk—progestin-only pills, implants, and progestin-containing intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Because in Denmark NSAIDs are prescribed as a single package containing no more than 30 tablets, time exposed to non–aspirin NSAIDs was assumed to last 1 week from the prescription date.
The authors considered first-time diagnoses of lower limb venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism that were made in hospitals to represent VTE. They also constructed a subgroup of VTE patients in whom the diagnosis was either confirmed with imaging or followed by prescription of an anticoagulant.
To address potential confounding, the authors adjusted their analysis based on age, calendar year, educational attainment, occurrence of pregnancy, surgery, hypertension, diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, migraine, systemic connective tissue diseases, inflammatory polyarthropathies, and use of tranexamic acid (a medication that may increase VTE risk). They also censored (temporarily excluded women from analysis) episodes associated with a transiently elevated risk of VTE: pregnancy and 6 months following delivery, 12 weeks after other pregnancy terminations, 8 weeks following any surgery involving hospital admission, and 8 weeks following prescription of tranexamic acid.
Continue to: VTEs associated with risk category of hormonal contraception used...
VTEs associated with risk category of hormonal contraception used
Results. The overall cohort included more than 2 million women who were followed for a median of 10 years. During 21.0 million person-years, 8,710 VTE events were diagnosed; almost one-third of these were pulmonary embolisms, with the remainder diagnosed as lower extremity VTE. Of these 8,710 women diagnosed with VTE, 7,043 (81%) were confirmed with either diagnostic imaging or prescription of an anticoagulant. Unfortunately, 228 women (2.6%) died within 30 days of the diagnosis of VTE.
The investigators identified concomitant use of hormonal contraception and NSAIDs in more than 500,000 women. Among women with such concomitant use, 58% were using contraceptives that were high risk while 23% used medium-risk and 19% used low/no-risk contraceptives. Ibuprofen (60%) was the most commonly used NSAID, followed by diclofenac (20%) and naproxen (6%). Between 97% and 98% of high-risk and medium-risk contraceptives were combination pills; 89% of low/no-risk contraceptives were progestin IUDs.
Compared with nonuse of both hormonal contraceptives and NSAIDs, incidence rate ratios of VTE adjusted for age, calendar year, and education were 8.1 (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.9–9.6) for use of NSAIDs only, 4.2 (95% CI, 4.0–4.4) for use of high-risk contraceptives only, 3.0 (95% CI, 2.8–3.2) for medium-risk contraceptive use, and 1.1 (95% CI, 1.0–1.3) for use of low/no-risk hormonal contraception. Risk of VTE was approximately twice as high with the use of diclofenac only compared with the risks associated with ibuprofen or naproxen use only.
With respect to concomitant use of NSAIDs and hormonal contraception, incidence rate ratios of VTE were 50.6 (95% CI, 44.2–57.8), 26.1 (95% CI, 19.6–34.7), and 5.7 (95% CI, 3.3–10.1), respectively, with use of high-risk, medium-risk, and low/no-risk hormonal contraceptives. Adjusting for time updated information on occurrences of migraine, connective tissue disorder, inflammatory polyarthropathies, endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, hypertension, and diabetes did not materially affect these associations.
When analysis was limited to women without these occurring conditions, rate ratios were somewhat higher (5.7 and 4.1) for use of high-risk and medium-risk contraceptives only. Incidence rate ratios in this subcohort of healthier women were substantially higher for NSAID use only (15.0), and 111.7, 43.2, and 13.0, respectively, for concomitant use of NSAIDs with high-risk, medium-risk, and low/no-risk contraceptives. In this analysis of healthier women, diclofenac continued to be associated with substantially higher risks of VTE than ibuprofen or naproxen. When the stricter definition of VTE (confirmed cases) was used, adjusted rate ratios remained similar.
Absolute risks of VTE
Although some of the elevated rate ratios noted in this study might appear alarming, it is important to keep in mind that the baseline incidence of VTE in healthy reproductive-age women is low. Accordingly, as the authors pointed out, even among women who used NSAIDs concomitantly with high-risk combination hormonal contraceptives, the absolute risk of VTE was 2/10,000.
Study strengths and limitations
Strengths of this analysis by Meaidi and colleagues include the use of large, essentially all-inclusive national registries. In addition, nationwide Danish registry data that indicate a diagnosis of VTE have been found to have a high positive predictive value.3 Another strength is the large number of potentially confounding factors that the authors controlled for.
One potential limitation of their analysis is that the use of only prescribed NSAIDs was considered. Fortunately, however, the prevalence of over-the-counter ibuprofen use in Denmark is not high enough to materially affect the authors’ findings.4 Another potential limitation was that information on smoking and body mass index was not available for most of the women included in the study cohort. The authors countered this limitation by pointing out that, in Denmark, smoking and obesity are highly correlated with educational status, and that all analyses were adjusted for educational status. ●
It is important for clinicians and our patients to recognize that pregnancy—the condition prevented by hormonal contraception— is associated with far higher risks of VTE (10–14 VTE events per 10,000 deliveries) than the use of any modern hormonal contraceptive.5 Although concomitant use of combination contraceptives and NSAIDs increases VTE risk, the absolute risk is modest, particularly when the NSAID is ibuprofen or naproxen (these are the non–aspirin NSAIDs most commonly used in the United States6). Women who regularly take NSAIDs can minimize VTE risk by choosing hormonal contraceptives with little or no impact on the risk of VTE: the progestin implant, progestin IUDs, and progestinonly pills.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, MSCP
- Reid RL. Oral hormonal contraception and venous thromboembolism (VTE). Contraception. 2014;89:235-236. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.02.002
- Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Wijarnpreecha K, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54:736-742. doi:10.1093 /rheumatology/keu408
- Sundbøll J, Adelborg K, Munch T, et al. Positive predictive value of cardiovascular diagnoses in the Danish National Patient Registry: a validation study. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e012832. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012832
- Gaster N, Hallas J, Pottegård A, et al. The validity of Danish prescription data to measure use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and quantification of bias due to non-prescription drug use. Clin Epidemiol. 2021;13:569-579. doi:10.2147/CLEP.S311450
- Maughan BC, Marin M, Han J, et al. Venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and the postpartum period: risk factors, diagnostic testing, and treatment. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2022;77:433-444. doi:10.1097/OGX.0000000000001043
- Chu A. Ibuprofen, naproxen, and more: the 8 most common NSAIDs. GoodRx. July 20, 2023. Accessed October 4, 2023. https://www.goodrx.com/classes/nsaids/nsaid-list
Meaidi A, Mascolo A, Sessa M, et al. Venous thromboembolism with use of hormonal contraception and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: nationwide cohort study. BMJ. 2023;382:e074450. doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-074450
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Combination (estrogen plus progestin) hormonal contraceptives as well as non–aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increase the risk of VTE events, including lower extremity clots and pulmonary embolism. Taking contraceptives formulated with ethinyl estradiol increases hepatic production of clotting factors on a dose-related basis. Newer progestins, including desogestrel and drospirenone, also may contribute to an elevated VTE risk, although this association is controversial.1 NSAIDs promote platelet aggregation, thereby activating the clotting system and formation of clots. Although studies that assessed the association between NSAID use and thrombosis have focused on arterial clots, a substantial literature suggests that NSAIDs, including older NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen), also increase VTE risk.2
Although combination contraceptives (oral contraceptives, patches, vaginal rings) and NSAIDs are both commonly used by reproductive-age women, little data have assessed the impact of concomitant use of these medications on VTE risk. Accordingly, investigators in Denmark, using national databases, conducted a retrospective cohort study to assess the impact that independent as well as concomitant use of these medications have on VTE risk.
Details of the study
Meaidi and colleagues included in the cohort reproductive-age women living in Denmark between 1996 and 2017 with no history of thrombosis, thrombophilia, cancer, tubal sterilization, hysterectomy, bilateral oophorectomy, or infertility treatment. National prescription data were used to assess exposure to hormonal contraception.
The investigators classified hormonal contraception into 3 VTE risk categories:
- high risk—estrogen-progestin patches and vaginal rings; oral contraceptives containing 50 µg of ethinyl estradiol; or the progestins desogestrel, drospirenone, gestodene, or cyproterone (with the latter 2 progestins not available in the United States)
- medium risk—all other combination oral contraceptives, including those formulated with the progestins norethindrone, norethindrone acetate, norgestrel, and levonorgestrel, as well as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate
- low/no risk—progestin-only pills, implants, and progestin-containing intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Because in Denmark NSAIDs are prescribed as a single package containing no more than 30 tablets, time exposed to non–aspirin NSAIDs was assumed to last 1 week from the prescription date.
The authors considered first-time diagnoses of lower limb venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism that were made in hospitals to represent VTE. They also constructed a subgroup of VTE patients in whom the diagnosis was either confirmed with imaging or followed by prescription of an anticoagulant.
To address potential confounding, the authors adjusted their analysis based on age, calendar year, educational attainment, occurrence of pregnancy, surgery, hypertension, diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, migraine, systemic connective tissue diseases, inflammatory polyarthropathies, and use of tranexamic acid (a medication that may increase VTE risk). They also censored (temporarily excluded women from analysis) episodes associated with a transiently elevated risk of VTE: pregnancy and 6 months following delivery, 12 weeks after other pregnancy terminations, 8 weeks following any surgery involving hospital admission, and 8 weeks following prescription of tranexamic acid.
Continue to: VTEs associated with risk category of hormonal contraception used...
VTEs associated with risk category of hormonal contraception used
Results. The overall cohort included more than 2 million women who were followed for a median of 10 years. During 21.0 million person-years, 8,710 VTE events were diagnosed; almost one-third of these were pulmonary embolisms, with the remainder diagnosed as lower extremity VTE. Of these 8,710 women diagnosed with VTE, 7,043 (81%) were confirmed with either diagnostic imaging or prescription of an anticoagulant. Unfortunately, 228 women (2.6%) died within 30 days of the diagnosis of VTE.
The investigators identified concomitant use of hormonal contraception and NSAIDs in more than 500,000 women. Among women with such concomitant use, 58% were using contraceptives that were high risk while 23% used medium-risk and 19% used low/no-risk contraceptives. Ibuprofen (60%) was the most commonly used NSAID, followed by diclofenac (20%) and naproxen (6%). Between 97% and 98% of high-risk and medium-risk contraceptives were combination pills; 89% of low/no-risk contraceptives were progestin IUDs.
Compared with nonuse of both hormonal contraceptives and NSAIDs, incidence rate ratios of VTE adjusted for age, calendar year, and education were 8.1 (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.9–9.6) for use of NSAIDs only, 4.2 (95% CI, 4.0–4.4) for use of high-risk contraceptives only, 3.0 (95% CI, 2.8–3.2) for medium-risk contraceptive use, and 1.1 (95% CI, 1.0–1.3) for use of low/no-risk hormonal contraception. Risk of VTE was approximately twice as high with the use of diclofenac only compared with the risks associated with ibuprofen or naproxen use only.
With respect to concomitant use of NSAIDs and hormonal contraception, incidence rate ratios of VTE were 50.6 (95% CI, 44.2–57.8), 26.1 (95% CI, 19.6–34.7), and 5.7 (95% CI, 3.3–10.1), respectively, with use of high-risk, medium-risk, and low/no-risk hormonal contraceptives. Adjusting for time updated information on occurrences of migraine, connective tissue disorder, inflammatory polyarthropathies, endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, hypertension, and diabetes did not materially affect these associations.
When analysis was limited to women without these occurring conditions, rate ratios were somewhat higher (5.7 and 4.1) for use of high-risk and medium-risk contraceptives only. Incidence rate ratios in this subcohort of healthier women were substantially higher for NSAID use only (15.0), and 111.7, 43.2, and 13.0, respectively, for concomitant use of NSAIDs with high-risk, medium-risk, and low/no-risk contraceptives. In this analysis of healthier women, diclofenac continued to be associated with substantially higher risks of VTE than ibuprofen or naproxen. When the stricter definition of VTE (confirmed cases) was used, adjusted rate ratios remained similar.
Absolute risks of VTE
Although some of the elevated rate ratios noted in this study might appear alarming, it is important to keep in mind that the baseline incidence of VTE in healthy reproductive-age women is low. Accordingly, as the authors pointed out, even among women who used NSAIDs concomitantly with high-risk combination hormonal contraceptives, the absolute risk of VTE was 2/10,000.
Study strengths and limitations
Strengths of this analysis by Meaidi and colleagues include the use of large, essentially all-inclusive national registries. In addition, nationwide Danish registry data that indicate a diagnosis of VTE have been found to have a high positive predictive value.3 Another strength is the large number of potentially confounding factors that the authors controlled for.
One potential limitation of their analysis is that the use of only prescribed NSAIDs was considered. Fortunately, however, the prevalence of over-the-counter ibuprofen use in Denmark is not high enough to materially affect the authors’ findings.4 Another potential limitation was that information on smoking and body mass index was not available for most of the women included in the study cohort. The authors countered this limitation by pointing out that, in Denmark, smoking and obesity are highly correlated with educational status, and that all analyses were adjusted for educational status. ●
It is important for clinicians and our patients to recognize that pregnancy—the condition prevented by hormonal contraception— is associated with far higher risks of VTE (10–14 VTE events per 10,000 deliveries) than the use of any modern hormonal contraceptive.5 Although concomitant use of combination contraceptives and NSAIDs increases VTE risk, the absolute risk is modest, particularly when the NSAID is ibuprofen or naproxen (these are the non–aspirin NSAIDs most commonly used in the United States6). Women who regularly take NSAIDs can minimize VTE risk by choosing hormonal contraceptives with little or no impact on the risk of VTE: the progestin implant, progestin IUDs, and progestinonly pills.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, MSCP
Meaidi A, Mascolo A, Sessa M, et al. Venous thromboembolism with use of hormonal contraception and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: nationwide cohort study. BMJ. 2023;382:e074450. doi:10.1136/bmj-2022-074450
EXPERT COMMENTARY
Combination (estrogen plus progestin) hormonal contraceptives as well as non–aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) increase the risk of VTE events, including lower extremity clots and pulmonary embolism. Taking contraceptives formulated with ethinyl estradiol increases hepatic production of clotting factors on a dose-related basis. Newer progestins, including desogestrel and drospirenone, also may contribute to an elevated VTE risk, although this association is controversial.1 NSAIDs promote platelet aggregation, thereby activating the clotting system and formation of clots. Although studies that assessed the association between NSAID use and thrombosis have focused on arterial clots, a substantial literature suggests that NSAIDs, including older NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen), also increase VTE risk.2
Although combination contraceptives (oral contraceptives, patches, vaginal rings) and NSAIDs are both commonly used by reproductive-age women, little data have assessed the impact of concomitant use of these medications on VTE risk. Accordingly, investigators in Denmark, using national databases, conducted a retrospective cohort study to assess the impact that independent as well as concomitant use of these medications have on VTE risk.
Details of the study
Meaidi and colleagues included in the cohort reproductive-age women living in Denmark between 1996 and 2017 with no history of thrombosis, thrombophilia, cancer, tubal sterilization, hysterectomy, bilateral oophorectomy, or infertility treatment. National prescription data were used to assess exposure to hormonal contraception.
The investigators classified hormonal contraception into 3 VTE risk categories:
- high risk—estrogen-progestin patches and vaginal rings; oral contraceptives containing 50 µg of ethinyl estradiol; or the progestins desogestrel, drospirenone, gestodene, or cyproterone (with the latter 2 progestins not available in the United States)
- medium risk—all other combination oral contraceptives, including those formulated with the progestins norethindrone, norethindrone acetate, norgestrel, and levonorgestrel, as well as depot medroxyprogesterone acetate
- low/no risk—progestin-only pills, implants, and progestin-containing intrauterine devices (IUDs).
Because in Denmark NSAIDs are prescribed as a single package containing no more than 30 tablets, time exposed to non–aspirin NSAIDs was assumed to last 1 week from the prescription date.
The authors considered first-time diagnoses of lower limb venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism that were made in hospitals to represent VTE. They also constructed a subgroup of VTE patients in whom the diagnosis was either confirmed with imaging or followed by prescription of an anticoagulant.
To address potential confounding, the authors adjusted their analysis based on age, calendar year, educational attainment, occurrence of pregnancy, surgery, hypertension, diabetes, polycystic ovary syndrome, endometriosis, migraine, systemic connective tissue diseases, inflammatory polyarthropathies, and use of tranexamic acid (a medication that may increase VTE risk). They also censored (temporarily excluded women from analysis) episodes associated with a transiently elevated risk of VTE: pregnancy and 6 months following delivery, 12 weeks after other pregnancy terminations, 8 weeks following any surgery involving hospital admission, and 8 weeks following prescription of tranexamic acid.
Continue to: VTEs associated with risk category of hormonal contraception used...
VTEs associated with risk category of hormonal contraception used
Results. The overall cohort included more than 2 million women who were followed for a median of 10 years. During 21.0 million person-years, 8,710 VTE events were diagnosed; almost one-third of these were pulmonary embolisms, with the remainder diagnosed as lower extremity VTE. Of these 8,710 women diagnosed with VTE, 7,043 (81%) were confirmed with either diagnostic imaging or prescription of an anticoagulant. Unfortunately, 228 women (2.6%) died within 30 days of the diagnosis of VTE.
The investigators identified concomitant use of hormonal contraception and NSAIDs in more than 500,000 women. Among women with such concomitant use, 58% were using contraceptives that were high risk while 23% used medium-risk and 19% used low/no-risk contraceptives. Ibuprofen (60%) was the most commonly used NSAID, followed by diclofenac (20%) and naproxen (6%). Between 97% and 98% of high-risk and medium-risk contraceptives were combination pills; 89% of low/no-risk contraceptives were progestin IUDs.
Compared with nonuse of both hormonal contraceptives and NSAIDs, incidence rate ratios of VTE adjusted for age, calendar year, and education were 8.1 (95% confidence interval [CI], 6.9–9.6) for use of NSAIDs only, 4.2 (95% CI, 4.0–4.4) for use of high-risk contraceptives only, 3.0 (95% CI, 2.8–3.2) for medium-risk contraceptive use, and 1.1 (95% CI, 1.0–1.3) for use of low/no-risk hormonal contraception. Risk of VTE was approximately twice as high with the use of diclofenac only compared with the risks associated with ibuprofen or naproxen use only.
With respect to concomitant use of NSAIDs and hormonal contraception, incidence rate ratios of VTE were 50.6 (95% CI, 44.2–57.8), 26.1 (95% CI, 19.6–34.7), and 5.7 (95% CI, 3.3–10.1), respectively, with use of high-risk, medium-risk, and low/no-risk hormonal contraceptives. Adjusting for time updated information on occurrences of migraine, connective tissue disorder, inflammatory polyarthropathies, endometriosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, hypertension, and diabetes did not materially affect these associations.
When analysis was limited to women without these occurring conditions, rate ratios were somewhat higher (5.7 and 4.1) for use of high-risk and medium-risk contraceptives only. Incidence rate ratios in this subcohort of healthier women were substantially higher for NSAID use only (15.0), and 111.7, 43.2, and 13.0, respectively, for concomitant use of NSAIDs with high-risk, medium-risk, and low/no-risk contraceptives. In this analysis of healthier women, diclofenac continued to be associated with substantially higher risks of VTE than ibuprofen or naproxen. When the stricter definition of VTE (confirmed cases) was used, adjusted rate ratios remained similar.
Absolute risks of VTE
Although some of the elevated rate ratios noted in this study might appear alarming, it is important to keep in mind that the baseline incidence of VTE in healthy reproductive-age women is low. Accordingly, as the authors pointed out, even among women who used NSAIDs concomitantly with high-risk combination hormonal contraceptives, the absolute risk of VTE was 2/10,000.
Study strengths and limitations
Strengths of this analysis by Meaidi and colleagues include the use of large, essentially all-inclusive national registries. In addition, nationwide Danish registry data that indicate a diagnosis of VTE have been found to have a high positive predictive value.3 Another strength is the large number of potentially confounding factors that the authors controlled for.
One potential limitation of their analysis is that the use of only prescribed NSAIDs was considered. Fortunately, however, the prevalence of over-the-counter ibuprofen use in Denmark is not high enough to materially affect the authors’ findings.4 Another potential limitation was that information on smoking and body mass index was not available for most of the women included in the study cohort. The authors countered this limitation by pointing out that, in Denmark, smoking and obesity are highly correlated with educational status, and that all analyses were adjusted for educational status. ●
It is important for clinicians and our patients to recognize that pregnancy—the condition prevented by hormonal contraception— is associated with far higher risks of VTE (10–14 VTE events per 10,000 deliveries) than the use of any modern hormonal contraceptive.5 Although concomitant use of combination contraceptives and NSAIDs increases VTE risk, the absolute risk is modest, particularly when the NSAID is ibuprofen or naproxen (these are the non–aspirin NSAIDs most commonly used in the United States6). Women who regularly take NSAIDs can minimize VTE risk by choosing hormonal contraceptives with little or no impact on the risk of VTE: the progestin implant, progestin IUDs, and progestinonly pills.
ANDREW M. KAUNITZ, MD, MSCP
- Reid RL. Oral hormonal contraception and venous thromboembolism (VTE). Contraception. 2014;89:235-236. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.02.002
- Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Wijarnpreecha K, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54:736-742. doi:10.1093 /rheumatology/keu408
- Sundbøll J, Adelborg K, Munch T, et al. Positive predictive value of cardiovascular diagnoses in the Danish National Patient Registry: a validation study. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e012832. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012832
- Gaster N, Hallas J, Pottegård A, et al. The validity of Danish prescription data to measure use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and quantification of bias due to non-prescription drug use. Clin Epidemiol. 2021;13:569-579. doi:10.2147/CLEP.S311450
- Maughan BC, Marin M, Han J, et al. Venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and the postpartum period: risk factors, diagnostic testing, and treatment. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2022;77:433-444. doi:10.1097/OGX.0000000000001043
- Chu A. Ibuprofen, naproxen, and more: the 8 most common NSAIDs. GoodRx. July 20, 2023. Accessed October 4, 2023. https://www.goodrx.com/classes/nsaids/nsaid-list
- Reid RL. Oral hormonal contraception and venous thromboembolism (VTE). Contraception. 2014;89:235-236. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.02.002
- Ungprasert P, Srivali N, Wijarnpreecha K, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54:736-742. doi:10.1093 /rheumatology/keu408
- Sundbøll J, Adelborg K, Munch T, et al. Positive predictive value of cardiovascular diagnoses in the Danish National Patient Registry: a validation study. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e012832. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012832
- Gaster N, Hallas J, Pottegård A, et al. The validity of Danish prescription data to measure use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and quantification of bias due to non-prescription drug use. Clin Epidemiol. 2021;13:569-579. doi:10.2147/CLEP.S311450
- Maughan BC, Marin M, Han J, et al. Venous thromboembolism during pregnancy and the postpartum period: risk factors, diagnostic testing, and treatment. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2022;77:433-444. doi:10.1097/OGX.0000000000001043
- Chu A. Ibuprofen, naproxen, and more: the 8 most common NSAIDs. GoodRx. July 20, 2023. Accessed October 4, 2023. https://www.goodrx.com/classes/nsaids/nsaid-list
Case Q: How soon after taking emergency contraception can a patient begin hormonal contraception?
Individuals spend close to half of their lives preventing, or planning for, pregnancy. As such, contraception plays a major role in patient-provider interactions. Contraception counseling and management is a common scenario encountered in the general gynecologist’s practice. Luckily, we have two evidence-based guidelines developed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that support the provision of contraceptive care:
- US Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use (US-MEC),1 which provides guidance on which patients can safely use a method
- US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR),2 which provides method-specific guidance on how to use a method (including how to: initiate or start a method; manage adherence issues, such as a missed pill, etc; and manage common issues like breakthrough bleeding). Both of these guidelines are updated routinely and are publicly available online or for free, through smartphone applications.
While most contraceptive care is straightforward, there are circumstances that require additional consideration. In this 3-part series we review 3 clinical cases, existing evidence to guide management decisions, and our recommendations. In part 1, we focus on restarting hormonal contraception after ulipristal acetate administration. In parts 2 and 3, we will discuss removal of a nonpalpable contraceptive implant and the consideration of a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) for emergency contraception.
- After using ulipristal acetate for emergency contraception, advise patients to wait at least 5 days to initiate hormonal contraception and about the importance of abstaining or using a back-up method for another 7 days with the start of their hormonal contraceptive method
CASE Meeting emergency and follow-up contraception needs
A 27-year-old woman (G0) presents to you after having unprotected intercourse 4 days ago. She does not formally track her menstrual cycles and is unsure when her last menstrual period was. She is not using contraception but is interested in starting a method. After counseling, she elects to take a dose of oral ulipristal acetate (UPA; Ella) now for emergency contraception and would like to start a combined oral contraceptive (COC) pill moving forward.
How soon after taking UPA should you tell her to start the combined hormonal pill?
Effectiveness of hormonal contraception following UPA
UPA does not appear to decrease the efficacy of COCs when started around the same time. However, immediately starting a hormonal contraceptive can decrease the effectiveness of UPA, and as such, it is recommended to take UPA and then abstain or use a backup method for 7 days before initiating a hormonal contraceptive method.1 By obtaining some additional information from your patient and with the use of shared decision making, though, your patient may be able to start their contraceptive method earlier than 5 days after UPA.
What is UPA
UPA is a progesterone receptor modulator used for emergency contraception intenhded to prevent pregnancy after unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure.3 It works by delaying follicular rupture at least 5 days, if taken before the peak of the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge. If taken after that timeframe, it does not work. Since UPA competes for the progesterone receptor, there is a concern that the effectiveness of UPA may be decreased if a progestin-containing form of contraception is started immediately after taking UPA, or vice versa.4 Several studies have now specifically looked at the interaction between UPA and progestin-containing contraceptives, including at how UPA is impacted by the contraceptive method, and conversely, how the contraceptive method is impacted by UPA.5-8
Data on types of hormonal contraception. Brache and colleagues demonstrated that UPA users who started a desogestrel progestin-only pill (DSG POP) the next day had higher rates of ovulation within 5 days of taking UPA (45%), compared with those who the next day started a placebo pill (3%).6 This type of progestin-only pill is not available in the United States.
A study by Edelman and colleagues demonstrated similar findings in those starting a COC pill containing estrogen and progestin. When taking a COC two days after UPA use, more participants had evidence of follicular rupture in less than 5 days.5 It should be noted that these studies focused on ovulation, which—while necessary for conception to occur—is a surrogate biomarker for pregnancy risk. Additional studies have looked at the impact of UPA on the COC and have not found that UPA impacts ovulation suppression of the COC with its initiation or use.8
Considering unprotected intercourse and UPA timing. Of course, the risk of pregnancy is reliant on cycle timing plus the presence of viable sperm in the reproductive tract. Sperm have been shown to only be viable in the reproductive tract for 5 days, which could result in fertilization and subsequent pregnancy. Longevity of an egg is much shorter, at 12 to 24 hours after ovulation. For this patient, her exposure was 4 days ago, but sperm are only viable for approximately 5 days—she could consider taking the UPA now and then starting a COC earlier than 5 days since she only needs an extra day or two of protection from the UPA from the sperm in her reproductive tract. Your patient’s involvement in this decision making is paramount, as only they can prioritize their desire to avoid pregnancy from their recent act of unprotected intercourse versus their immediate needs for starting their method of contraception. It is important that individuals abstain from sexual activity or use an additional back-up method during the first 7 days of starting their method of contraception.
Continue to: Counseling considerations for the case patient...
Counseling considerations for the case patient
For a patient planning to start or resume a hormonal contraceptive method after taking UPA, the waiting period recommended by the CDC (5 days) is most beneficial for patients who are uncertain about their menstrual cycle timing in relation to the act of unprotected intercourse that already occurred and need to prioritize maximum effectiveness of emergency contraception.
Patients with unsure cycle-sex timing planning to self-start or resume a short-term hormonal contraceptive method (eg, pills, patches, or rings), should be counseled to wait 5 days after the most recent act of unprotected sex, before taking their hormonal contraceptive method.7 Patients with unsure cycle-sex timing planning to use provider-dependent hormonal contraceptive methods (eg, those requiring a prescription, including a progestin-contraceptive implant or depot medroxyprogesterone acetate) should also be counseled to wait. Timing of levonorgestrel and copper intrauterine devices are addressed in part 3 of this series.
However, if your patient has a good understanding of their menstrual cycle, and the primary concern is exposure from subsequent sexual encounters and not the recent unprotected intercourse, it is advisable to provide UPA and immediately initiate a contraceptive method. One of the primary reasons for emergency contraception failure is that its effectiveness is limited to the most recent act of unprotected sexual intercourse and does not extend to subsequent acts throughout the month.
For these patients with sure cycle-sex timing who are planning to start or resume short-or long-term contraceptive methods, and whose primary concern is to prevent pregnancy risk from subsequent sexual encounters, immediately initiating a contraceptive method is advisable. For provider-dependent methods, we must weigh the risk of unintended pregnancy from the act of intercourse that already occurred (and the potential to increase that risk by initiating a method that could compromise UPA efficacy) versus the future risk of pregnancy if the patient cannot return for a contraception visit.7
In short, starting the contraceptive method at the time of UPA use can be considered after shared decision making with the patient and understanding what their primary concerns are.
Important point
Counsel on using backup barrier contraception after UPA
Oral emergency contraception only covers that one act of unprotected intercourse and does not continue to protect a patient from pregnancy for the rest of their cycle. When taken before ovulation, UPA works by delaying follicular development and rupture for at least 5 days. Patients who continue to have unprotected intercourse after taking UPA are at a high risk of an unintended pregnancy from this ‘stalled’ follicle that will eventually ovulate. Follicular maturation resumes after UPA’s effects wane, and the patient is primed for ovulation (and therefore unintended pregnancy) if ongoing unprotected intercourse occurs for the rest of their cycle.
Therefore, it is important to counsel patients on the need, if they do not desire a pregnancy, to abstain or start a method of contraception.
Final question
What about starting or resuming non–hormonal contraceptive methods?
Non-hormonal contraceptive methods can be started immediately with UPA use.1
CASE Resolved
After shared decision making, the patient decides to start using the COC pill. You prescribe her both UPA for emergency contraception and a combined hormonal contraceptive pill. Given her unsure cycle-sex timing, she expresses to you that her most important priority is preventing unintended pregnancy. You counsel her to set a reminder on her phone to start taking the pill 5 days from her most recent act of unprotected intercourse. You also counsel her to use a back-up barrier method of contraception for 7 days after starting her COC pill. ●

- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6504a1
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health. US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR). Accessed October 11, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth /contraception/mmwr/spr/summary.html
- Ella [package insert]. Charleston, SC; Afaxys, Inc. 2014.
- Salcedo J, Rodriguez MI, Curtis KM, et al. When can a woman resume or initiate contraception after taking emergency contraceptive pills? A systematic review. Contraception. 2013;87:602-604. https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.contraception.2012.08.013
- Edelman AB, Jensen JT, McCrimmon S, et al. Combined oral contraceptive interference with the ability of ulipristal acetate to delay ovulation: a prospective cohort study. Contraception. 2018;98:463-466. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.08.003
- Brache V, Cochon L, Duijkers IJM, et al. A prospective, randomized, pharmacodynamic study of quick-starting a desogestrel progestin-only pill following ulipristal acetate for emergency contraception. Hum Reprod Oxf Engl. 2015;30:2785-2793. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep /dev241
- Cameron ST, Berger C, Michie L, et al. The effects on ovarian activity of ulipristal acetate when ‘quickstarting’ a combined oral contraceptive pill: a prospective, randomized, doubleblind parallel-arm, placebo-controlled study. Hum Reprod. 2015;30:1566-1572. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev115
- Banh C, Rautenberg T, Diujkers I, et al. The effects on ovarian activity of delaying versus immediately restarting combined oral contraception after missing three pills and taking ulipristal acetate 30 mg. Contraception. 2020;102:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2020.05.013
- American Society for Emergency Contraception. Providing ongoing hormonal contraception after use of emergency contraceptive pills. September 2016. Accessed October 11, 2023. chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj /https://www.americansocietyforec.org/_files/ugd/7f2e0b _ff1bc90bea204644ba28d1b0e6a6a6a8.pdf
Individuals spend close to half of their lives preventing, or planning for, pregnancy. As such, contraception plays a major role in patient-provider interactions. Contraception counseling and management is a common scenario encountered in the general gynecologist’s practice. Luckily, we have two evidence-based guidelines developed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that support the provision of contraceptive care:
- US Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use (US-MEC),1 which provides guidance on which patients can safely use a method
- US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR),2 which provides method-specific guidance on how to use a method (including how to: initiate or start a method; manage adherence issues, such as a missed pill, etc; and manage common issues like breakthrough bleeding). Both of these guidelines are updated routinely and are publicly available online or for free, through smartphone applications.
While most contraceptive care is straightforward, there are circumstances that require additional consideration. In this 3-part series we review 3 clinical cases, existing evidence to guide management decisions, and our recommendations. In part 1, we focus on restarting hormonal contraception after ulipristal acetate administration. In parts 2 and 3, we will discuss removal of a nonpalpable contraceptive implant and the consideration of a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) for emergency contraception.
- After using ulipristal acetate for emergency contraception, advise patients to wait at least 5 days to initiate hormonal contraception and about the importance of abstaining or using a back-up method for another 7 days with the start of their hormonal contraceptive method
CASE Meeting emergency and follow-up contraception needs
A 27-year-old woman (G0) presents to you after having unprotected intercourse 4 days ago. She does not formally track her menstrual cycles and is unsure when her last menstrual period was. She is not using contraception but is interested in starting a method. After counseling, she elects to take a dose of oral ulipristal acetate (UPA; Ella) now for emergency contraception and would like to start a combined oral contraceptive (COC) pill moving forward.
How soon after taking UPA should you tell her to start the combined hormonal pill?
Effectiveness of hormonal contraception following UPA
UPA does not appear to decrease the efficacy of COCs when started around the same time. However, immediately starting a hormonal contraceptive can decrease the effectiveness of UPA, and as such, it is recommended to take UPA and then abstain or use a backup method for 7 days before initiating a hormonal contraceptive method.1 By obtaining some additional information from your patient and with the use of shared decision making, though, your patient may be able to start their contraceptive method earlier than 5 days after UPA.
What is UPA
UPA is a progesterone receptor modulator used for emergency contraception intenhded to prevent pregnancy after unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure.3 It works by delaying follicular rupture at least 5 days, if taken before the peak of the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge. If taken after that timeframe, it does not work. Since UPA competes for the progesterone receptor, there is a concern that the effectiveness of UPA may be decreased if a progestin-containing form of contraception is started immediately after taking UPA, or vice versa.4 Several studies have now specifically looked at the interaction between UPA and progestin-containing contraceptives, including at how UPA is impacted by the contraceptive method, and conversely, how the contraceptive method is impacted by UPA.5-8
Data on types of hormonal contraception. Brache and colleagues demonstrated that UPA users who started a desogestrel progestin-only pill (DSG POP) the next day had higher rates of ovulation within 5 days of taking UPA (45%), compared with those who the next day started a placebo pill (3%).6 This type of progestin-only pill is not available in the United States.
A study by Edelman and colleagues demonstrated similar findings in those starting a COC pill containing estrogen and progestin. When taking a COC two days after UPA use, more participants had evidence of follicular rupture in less than 5 days.5 It should be noted that these studies focused on ovulation, which—while necessary for conception to occur—is a surrogate biomarker for pregnancy risk. Additional studies have looked at the impact of UPA on the COC and have not found that UPA impacts ovulation suppression of the COC with its initiation or use.8
Considering unprotected intercourse and UPA timing. Of course, the risk of pregnancy is reliant on cycle timing plus the presence of viable sperm in the reproductive tract. Sperm have been shown to only be viable in the reproductive tract for 5 days, which could result in fertilization and subsequent pregnancy. Longevity of an egg is much shorter, at 12 to 24 hours after ovulation. For this patient, her exposure was 4 days ago, but sperm are only viable for approximately 5 days—she could consider taking the UPA now and then starting a COC earlier than 5 days since she only needs an extra day or two of protection from the UPA from the sperm in her reproductive tract. Your patient’s involvement in this decision making is paramount, as only they can prioritize their desire to avoid pregnancy from their recent act of unprotected intercourse versus their immediate needs for starting their method of contraception. It is important that individuals abstain from sexual activity or use an additional back-up method during the first 7 days of starting their method of contraception.
Continue to: Counseling considerations for the case patient...
Counseling considerations for the case patient
For a patient planning to start or resume a hormonal contraceptive method after taking UPA, the waiting period recommended by the CDC (5 days) is most beneficial for patients who are uncertain about their menstrual cycle timing in relation to the act of unprotected intercourse that already occurred and need to prioritize maximum effectiveness of emergency contraception.
Patients with unsure cycle-sex timing planning to self-start or resume a short-term hormonal contraceptive method (eg, pills, patches, or rings), should be counseled to wait 5 days after the most recent act of unprotected sex, before taking their hormonal contraceptive method.7 Patients with unsure cycle-sex timing planning to use provider-dependent hormonal contraceptive methods (eg, those requiring a prescription, including a progestin-contraceptive implant or depot medroxyprogesterone acetate) should also be counseled to wait. Timing of levonorgestrel and copper intrauterine devices are addressed in part 3 of this series.
However, if your patient has a good understanding of their menstrual cycle, and the primary concern is exposure from subsequent sexual encounters and not the recent unprotected intercourse, it is advisable to provide UPA and immediately initiate a contraceptive method. One of the primary reasons for emergency contraception failure is that its effectiveness is limited to the most recent act of unprotected sexual intercourse and does not extend to subsequent acts throughout the month.
For these patients with sure cycle-sex timing who are planning to start or resume short-or long-term contraceptive methods, and whose primary concern is to prevent pregnancy risk from subsequent sexual encounters, immediately initiating a contraceptive method is advisable. For provider-dependent methods, we must weigh the risk of unintended pregnancy from the act of intercourse that already occurred (and the potential to increase that risk by initiating a method that could compromise UPA efficacy) versus the future risk of pregnancy if the patient cannot return for a contraception visit.7
In short, starting the contraceptive method at the time of UPA use can be considered after shared decision making with the patient and understanding what their primary concerns are.
Important point
Counsel on using backup barrier contraception after UPA
Oral emergency contraception only covers that one act of unprotected intercourse and does not continue to protect a patient from pregnancy for the rest of their cycle. When taken before ovulation, UPA works by delaying follicular development and rupture for at least 5 days. Patients who continue to have unprotected intercourse after taking UPA are at a high risk of an unintended pregnancy from this ‘stalled’ follicle that will eventually ovulate. Follicular maturation resumes after UPA’s effects wane, and the patient is primed for ovulation (and therefore unintended pregnancy) if ongoing unprotected intercourse occurs for the rest of their cycle.
Therefore, it is important to counsel patients on the need, if they do not desire a pregnancy, to abstain or start a method of contraception.
Final question
What about starting or resuming non–hormonal contraceptive methods?
Non-hormonal contraceptive methods can be started immediately with UPA use.1
CASE Resolved
After shared decision making, the patient decides to start using the COC pill. You prescribe her both UPA for emergency contraception and a combined hormonal contraceptive pill. Given her unsure cycle-sex timing, she expresses to you that her most important priority is preventing unintended pregnancy. You counsel her to set a reminder on her phone to start taking the pill 5 days from her most recent act of unprotected intercourse. You also counsel her to use a back-up barrier method of contraception for 7 days after starting her COC pill. ●

Individuals spend close to half of their lives preventing, or planning for, pregnancy. As such, contraception plays a major role in patient-provider interactions. Contraception counseling and management is a common scenario encountered in the general gynecologist’s practice. Luckily, we have two evidence-based guidelines developed by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) that support the provision of contraceptive care:
- US Medical Eligibility for Contraceptive Use (US-MEC),1 which provides guidance on which patients can safely use a method
- US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR),2 which provides method-specific guidance on how to use a method (including how to: initiate or start a method; manage adherence issues, such as a missed pill, etc; and manage common issues like breakthrough bleeding). Both of these guidelines are updated routinely and are publicly available online or for free, through smartphone applications.
While most contraceptive care is straightforward, there are circumstances that require additional consideration. In this 3-part series we review 3 clinical cases, existing evidence to guide management decisions, and our recommendations. In part 1, we focus on restarting hormonal contraception after ulipristal acetate administration. In parts 2 and 3, we will discuss removal of a nonpalpable contraceptive implant and the consideration of a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (LNG-IUD) for emergency contraception.
- After using ulipristal acetate for emergency contraception, advise patients to wait at least 5 days to initiate hormonal contraception and about the importance of abstaining or using a back-up method for another 7 days with the start of their hormonal contraceptive method
CASE Meeting emergency and follow-up contraception needs
A 27-year-old woman (G0) presents to you after having unprotected intercourse 4 days ago. She does not formally track her menstrual cycles and is unsure when her last menstrual period was. She is not using contraception but is interested in starting a method. After counseling, she elects to take a dose of oral ulipristal acetate (UPA; Ella) now for emergency contraception and would like to start a combined oral contraceptive (COC) pill moving forward.
How soon after taking UPA should you tell her to start the combined hormonal pill?
Effectiveness of hormonal contraception following UPA
UPA does not appear to decrease the efficacy of COCs when started around the same time. However, immediately starting a hormonal contraceptive can decrease the effectiveness of UPA, and as such, it is recommended to take UPA and then abstain or use a backup method for 7 days before initiating a hormonal contraceptive method.1 By obtaining some additional information from your patient and with the use of shared decision making, though, your patient may be able to start their contraceptive method earlier than 5 days after UPA.
What is UPA
UPA is a progesterone receptor modulator used for emergency contraception intenhded to prevent pregnancy after unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure.3 It works by delaying follicular rupture at least 5 days, if taken before the peak of the luteinizing hormone (LH) surge. If taken after that timeframe, it does not work. Since UPA competes for the progesterone receptor, there is a concern that the effectiveness of UPA may be decreased if a progestin-containing form of contraception is started immediately after taking UPA, or vice versa.4 Several studies have now specifically looked at the interaction between UPA and progestin-containing contraceptives, including at how UPA is impacted by the contraceptive method, and conversely, how the contraceptive method is impacted by UPA.5-8
Data on types of hormonal contraception. Brache and colleagues demonstrated that UPA users who started a desogestrel progestin-only pill (DSG POP) the next day had higher rates of ovulation within 5 days of taking UPA (45%), compared with those who the next day started a placebo pill (3%).6 This type of progestin-only pill is not available in the United States.
A study by Edelman and colleagues demonstrated similar findings in those starting a COC pill containing estrogen and progestin. When taking a COC two days after UPA use, more participants had evidence of follicular rupture in less than 5 days.5 It should be noted that these studies focused on ovulation, which—while necessary for conception to occur—is a surrogate biomarker for pregnancy risk. Additional studies have looked at the impact of UPA on the COC and have not found that UPA impacts ovulation suppression of the COC with its initiation or use.8
Considering unprotected intercourse and UPA timing. Of course, the risk of pregnancy is reliant on cycle timing plus the presence of viable sperm in the reproductive tract. Sperm have been shown to only be viable in the reproductive tract for 5 days, which could result in fertilization and subsequent pregnancy. Longevity of an egg is much shorter, at 12 to 24 hours after ovulation. For this patient, her exposure was 4 days ago, but sperm are only viable for approximately 5 days—she could consider taking the UPA now and then starting a COC earlier than 5 days since she only needs an extra day or two of protection from the UPA from the sperm in her reproductive tract. Your patient’s involvement in this decision making is paramount, as only they can prioritize their desire to avoid pregnancy from their recent act of unprotected intercourse versus their immediate needs for starting their method of contraception. It is important that individuals abstain from sexual activity or use an additional back-up method during the first 7 days of starting their method of contraception.
Continue to: Counseling considerations for the case patient...
Counseling considerations for the case patient
For a patient planning to start or resume a hormonal contraceptive method after taking UPA, the waiting period recommended by the CDC (5 days) is most beneficial for patients who are uncertain about their menstrual cycle timing in relation to the act of unprotected intercourse that already occurred and need to prioritize maximum effectiveness of emergency contraception.
Patients with unsure cycle-sex timing planning to self-start or resume a short-term hormonal contraceptive method (eg, pills, patches, or rings), should be counseled to wait 5 days after the most recent act of unprotected sex, before taking their hormonal contraceptive method.7 Patients with unsure cycle-sex timing planning to use provider-dependent hormonal contraceptive methods (eg, those requiring a prescription, including a progestin-contraceptive implant or depot medroxyprogesterone acetate) should also be counseled to wait. Timing of levonorgestrel and copper intrauterine devices are addressed in part 3 of this series.
However, if your patient has a good understanding of their menstrual cycle, and the primary concern is exposure from subsequent sexual encounters and not the recent unprotected intercourse, it is advisable to provide UPA and immediately initiate a contraceptive method. One of the primary reasons for emergency contraception failure is that its effectiveness is limited to the most recent act of unprotected sexual intercourse and does not extend to subsequent acts throughout the month.
For these patients with sure cycle-sex timing who are planning to start or resume short-or long-term contraceptive methods, and whose primary concern is to prevent pregnancy risk from subsequent sexual encounters, immediately initiating a contraceptive method is advisable. For provider-dependent methods, we must weigh the risk of unintended pregnancy from the act of intercourse that already occurred (and the potential to increase that risk by initiating a method that could compromise UPA efficacy) versus the future risk of pregnancy if the patient cannot return for a contraception visit.7
In short, starting the contraceptive method at the time of UPA use can be considered after shared decision making with the patient and understanding what their primary concerns are.
Important point
Counsel on using backup barrier contraception after UPA
Oral emergency contraception only covers that one act of unprotected intercourse and does not continue to protect a patient from pregnancy for the rest of their cycle. When taken before ovulation, UPA works by delaying follicular development and rupture for at least 5 days. Patients who continue to have unprotected intercourse after taking UPA are at a high risk of an unintended pregnancy from this ‘stalled’ follicle that will eventually ovulate. Follicular maturation resumes after UPA’s effects wane, and the patient is primed for ovulation (and therefore unintended pregnancy) if ongoing unprotected intercourse occurs for the rest of their cycle.
Therefore, it is important to counsel patients on the need, if they do not desire a pregnancy, to abstain or start a method of contraception.
Final question
What about starting or resuming non–hormonal contraceptive methods?
Non-hormonal contraceptive methods can be started immediately with UPA use.1
CASE Resolved
After shared decision making, the patient decides to start using the COC pill. You prescribe her both UPA for emergency contraception and a combined hormonal contraceptive pill. Given her unsure cycle-sex timing, she expresses to you that her most important priority is preventing unintended pregnancy. You counsel her to set a reminder on her phone to start taking the pill 5 days from her most recent act of unprotected intercourse. You also counsel her to use a back-up barrier method of contraception for 7 days after starting her COC pill. ●

- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6504a1
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health. US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR). Accessed October 11, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth /contraception/mmwr/spr/summary.html
- Ella [package insert]. Charleston, SC; Afaxys, Inc. 2014.
- Salcedo J, Rodriguez MI, Curtis KM, et al. When can a woman resume or initiate contraception after taking emergency contraceptive pills? A systematic review. Contraception. 2013;87:602-604. https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.contraception.2012.08.013
- Edelman AB, Jensen JT, McCrimmon S, et al. Combined oral contraceptive interference with the ability of ulipristal acetate to delay ovulation: a prospective cohort study. Contraception. 2018;98:463-466. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.08.003
- Brache V, Cochon L, Duijkers IJM, et al. A prospective, randomized, pharmacodynamic study of quick-starting a desogestrel progestin-only pill following ulipristal acetate for emergency contraception. Hum Reprod Oxf Engl. 2015;30:2785-2793. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep /dev241
- Cameron ST, Berger C, Michie L, et al. The effects on ovarian activity of ulipristal acetate when ‘quickstarting’ a combined oral contraceptive pill: a prospective, randomized, doubleblind parallel-arm, placebo-controlled study. Hum Reprod. 2015;30:1566-1572. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev115
- Banh C, Rautenberg T, Diujkers I, et al. The effects on ovarian activity of delaying versus immediately restarting combined oral contraception after missing three pills and taking ulipristal acetate 30 mg. Contraception. 2020;102:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2020.05.013
- American Society for Emergency Contraception. Providing ongoing hormonal contraception after use of emergency contraceptive pills. September 2016. Accessed October 11, 2023. chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj /https://www.americansocietyforec.org/_files/ugd/7f2e0b _ff1bc90bea204644ba28d1b0e6a6a6a8.pdf
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2016;65:1-66. https://doi .org/10.15585/mmwr.rr6504a1
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Division of Reproductive Health. US Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use (US-SPR). Accessed October 11, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/reproductivehealth /contraception/mmwr/spr/summary.html
- Ella [package insert]. Charleston, SC; Afaxys, Inc. 2014.
- Salcedo J, Rodriguez MI, Curtis KM, et al. When can a woman resume or initiate contraception after taking emergency contraceptive pills? A systematic review. Contraception. 2013;87:602-604. https://doi.org/10.1016 /j.contraception.2012.08.013
- Edelman AB, Jensen JT, McCrimmon S, et al. Combined oral contraceptive interference with the ability of ulipristal acetate to delay ovulation: a prospective cohort study. Contraception. 2018;98:463-466. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2018.08.003
- Brache V, Cochon L, Duijkers IJM, et al. A prospective, randomized, pharmacodynamic study of quick-starting a desogestrel progestin-only pill following ulipristal acetate for emergency contraception. Hum Reprod Oxf Engl. 2015;30:2785-2793. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep /dev241
- Cameron ST, Berger C, Michie L, et al. The effects on ovarian activity of ulipristal acetate when ‘quickstarting’ a combined oral contraceptive pill: a prospective, randomized, doubleblind parallel-arm, placebo-controlled study. Hum Reprod. 2015;30:1566-1572. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev115
- Banh C, Rautenberg T, Diujkers I, et al. The effects on ovarian activity of delaying versus immediately restarting combined oral contraception after missing three pills and taking ulipristal acetate 30 mg. Contraception. 2020;102:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2020.05.013
- American Society for Emergency Contraception. Providing ongoing hormonal contraception after use of emergency contraceptive pills. September 2016. Accessed October 11, 2023. chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj /https://www.americansocietyforec.org/_files/ugd/7f2e0b _ff1bc90bea204644ba28d1b0e6a6a6a8.pdf
Why aren’t doctors managing pain during gynecologic procedures?
During a fellowship rotation in gynecology, Rebekah D. Fenton, MD, asked the attending physicians what pain management options they could offer patients for insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD). Their answer surprised her: None.
The research on the effectiveness of pain management techniques during the procedure were not strong enough to warrant providing potential relief.
But Dr. Fenton knew the attending physician was wrong: She’d received the drug lidocaine during a recent visit to her own ob.gyn. to get an IUD placed. The local anesthetic enabled her to avoid the experiences of many patients who often withstand debilitating cramping and pain during insertion, side effects that can last for hours after the procedure has ended.
By not teaching her how to administer pain treatment options such as lidocaine gel or injection, “they made the decision for me, whether I could give patients this option,” said Dr. Fenton, now an adolescent medicine specialist at Alivio Medical Center in Chicago.
As a result, patients undergoing IUD placements, biopsies, hysteroscopies, and pelvic exams are often subject to pain that could be mitigated.
Some research suggests simple numbing agents, including lidocaine, may induce less pain without the need for full anesthesia. But clinicians don’t always present these options.
During gynecologic procedures, the amount of pain a patient can expect is often downplayed by clinicians. Because every patient experiences the sensation differently, discussing options for pain management and the range of possible pain is paramount in building patient-clinician trust, and ultimately providing the best care for patients in the long run, according to Megan Wasson, DO, chair of the department of medical and surgical gynecology at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Phoenix.
“It comes down to shared decision-making so the patient is aware of the pain that should be expected and what avenue they want to go down,” Dr. Wasson said. “It’s not a one-size-fits-all.”
Lack of uniform protocols
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has clear guidelines for pain management during pregnancy and delivery but not for many routine gynecologic procedures. Some experts say not offering options for pain management based on lack of efficacy evidence can undermine a patient’s experience.
ACOG does have recommendations for reducing dilation pain during a hysteroscopy, including providing intravaginal misoprostol and estrogen. The organization also recommends performing a vaginoscopy instead if possible because the procedure is typically less painful than is a hysteroscopy.
For an IUD placement, ACOG states that the procedure “may cause temporary discomfort” and recommends that patients take over-the-counter pain relief before a procedure. The most recent clinical bulletin on the topic, published in 2016, states routine misoprostol is not recommended for IUD placement, although it may be considered with difficult insertions for management of pain.
A clinical inquiry published in 2020 outlined the efficacy of several pain options that practitioners can weigh with patients. The inquiry cited a 2019 meta-analysis of 38 studies that found lidocaine-prilocaine cream to be the most effective option for pain management during IUD placement, reducing insertion pain by nearly 30%. The inquiry concluded that a combination of 600 mcg of misoprostol and 4% lidocaine gel may be effective, while lower dosages of both drugs were not effective. A 2018 clinical trial cited in the analysis found that though a 20-cc 1% lidocaine paracervical block on its own did not reduce pain, the block mixed with sodium bicarbonate reduced pain during IUD insertion by 22%.
Some doctors make the decision to not use lidocaine without offering it to patients first, according to Dr. Fenton. Instead, clinicians should discuss any potential drawbacks, such as pain from administering the numbing agent with a needle or the procedure taking extra time while the patient waits for the lidocaine to kick in.
“That always felt unfair, to make that decision for [the patient],” Dr. Fenton said.
Often clinicians won’t know how a patient will respond to a procedure: A 2014 secondary analysis of a clinical trial compared how patients rated their pain after an IUD procedure to the amount of pain physicians perceived the procedure to cause. They found that the average pain scores patients reported were nearly twice as high as clinician expectations were.
ACOG’s guideline states that the evidence backing paracervical blocks and lidocaine to IUD insertion pain is controversial. The American College of Physicians also cites “low-quality evidence” to support patient reports of pain and discomfort during pelvic exams. Some studies have found up to 60% of women report these negative experiences.
The varying evidence highlights the need for a personalized approach – one that includes patients – to pain management for routine gynecological procedures.
“Usually patients are pretty good predictors,” said Lisa Bayer, MD, MPH, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland. “They can anticipate what different things are going to feel like based on previous experiences.”
Making patients part of the discussion
Clinicians should have open discussions with patients about their past experiences and current anxieties about a gynecologic procedure, according to Dr. Bayer.
“Part of it is just creating a really safe environment of trust as a medical provider,” she said.
A study published in 2016 of more than 800 patients undergoing oocyte retrieval, which has clear protocols for pain management, found that previous negative gynecologic experiences were significantly correlated to greater amounts of pain reported during the procedure.
If pain isn’t properly managed, patients may avoid care in the future, putting them at risk for unplanned pregnancies, skipped cancer screenings, and complications from undiagnosed conditions and infections, Dr. Bayer added. Clinician offices will not always have access to all pain management options, so making referrals to another physician who has access to the appropriate technique may be the best thing for the patient, Dr. Bayer said.
Downplaying the experience
Informing a patient that she will feel only a little discomfort during a procedure – when a clinician doesn’t know how exactly the patient will react – can also result in distrust.
When a clinician says, “ ’It’s only going to be a little cramp, it’s only going to be a little pinch,’ we know extreme pain is a possibility, we’ve seen it,” Dr. Fenton said. “But if we choose to disregard that [possibility], it feels invalidating for patients.”
Failing to fully explain the possible pain scale can also directly interfere with the procedure at hand.
“My first concern is if they aren’t anticipating the amount of pain they are going to experience, they may move; For biopsies and IUD insertions, we need them to be still,” Dr. Wasson said. “If they are unable to tolerate the procedure, we’ve put them through pain and not been able to accomplish the primary goal.”
Managing both pain and what patients can expect is even more crucial for adolescent and teenage patients who are often having their first gynecologic experience.
“We’re framing what these experiences look like,” Dr. Fenton said. “That means there are opportunities for creating a space that builds trust and security for the patients moving forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a fellowship rotation in gynecology, Rebekah D. Fenton, MD, asked the attending physicians what pain management options they could offer patients for insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD). Their answer surprised her: None.
The research on the effectiveness of pain management techniques during the procedure were not strong enough to warrant providing potential relief.
But Dr. Fenton knew the attending physician was wrong: She’d received the drug lidocaine during a recent visit to her own ob.gyn. to get an IUD placed. The local anesthetic enabled her to avoid the experiences of many patients who often withstand debilitating cramping and pain during insertion, side effects that can last for hours after the procedure has ended.
By not teaching her how to administer pain treatment options such as lidocaine gel or injection, “they made the decision for me, whether I could give patients this option,” said Dr. Fenton, now an adolescent medicine specialist at Alivio Medical Center in Chicago.
As a result, patients undergoing IUD placements, biopsies, hysteroscopies, and pelvic exams are often subject to pain that could be mitigated.
Some research suggests simple numbing agents, including lidocaine, may induce less pain without the need for full anesthesia. But clinicians don’t always present these options.
During gynecologic procedures, the amount of pain a patient can expect is often downplayed by clinicians. Because every patient experiences the sensation differently, discussing options for pain management and the range of possible pain is paramount in building patient-clinician trust, and ultimately providing the best care for patients in the long run, according to Megan Wasson, DO, chair of the department of medical and surgical gynecology at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Phoenix.
“It comes down to shared decision-making so the patient is aware of the pain that should be expected and what avenue they want to go down,” Dr. Wasson said. “It’s not a one-size-fits-all.”
Lack of uniform protocols
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has clear guidelines for pain management during pregnancy and delivery but not for many routine gynecologic procedures. Some experts say not offering options for pain management based on lack of efficacy evidence can undermine a patient’s experience.
ACOG does have recommendations for reducing dilation pain during a hysteroscopy, including providing intravaginal misoprostol and estrogen. The organization also recommends performing a vaginoscopy instead if possible because the procedure is typically less painful than is a hysteroscopy.
For an IUD placement, ACOG states that the procedure “may cause temporary discomfort” and recommends that patients take over-the-counter pain relief before a procedure. The most recent clinical bulletin on the topic, published in 2016, states routine misoprostol is not recommended for IUD placement, although it may be considered with difficult insertions for management of pain.
A clinical inquiry published in 2020 outlined the efficacy of several pain options that practitioners can weigh with patients. The inquiry cited a 2019 meta-analysis of 38 studies that found lidocaine-prilocaine cream to be the most effective option for pain management during IUD placement, reducing insertion pain by nearly 30%. The inquiry concluded that a combination of 600 mcg of misoprostol and 4% lidocaine gel may be effective, while lower dosages of both drugs were not effective. A 2018 clinical trial cited in the analysis found that though a 20-cc 1% lidocaine paracervical block on its own did not reduce pain, the block mixed with sodium bicarbonate reduced pain during IUD insertion by 22%.
Some doctors make the decision to not use lidocaine without offering it to patients first, according to Dr. Fenton. Instead, clinicians should discuss any potential drawbacks, such as pain from administering the numbing agent with a needle or the procedure taking extra time while the patient waits for the lidocaine to kick in.
“That always felt unfair, to make that decision for [the patient],” Dr. Fenton said.
Often clinicians won’t know how a patient will respond to a procedure: A 2014 secondary analysis of a clinical trial compared how patients rated their pain after an IUD procedure to the amount of pain physicians perceived the procedure to cause. They found that the average pain scores patients reported were nearly twice as high as clinician expectations were.
ACOG’s guideline states that the evidence backing paracervical blocks and lidocaine to IUD insertion pain is controversial. The American College of Physicians also cites “low-quality evidence” to support patient reports of pain and discomfort during pelvic exams. Some studies have found up to 60% of women report these negative experiences.
The varying evidence highlights the need for a personalized approach – one that includes patients – to pain management for routine gynecological procedures.
“Usually patients are pretty good predictors,” said Lisa Bayer, MD, MPH, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland. “They can anticipate what different things are going to feel like based on previous experiences.”
Making patients part of the discussion
Clinicians should have open discussions with patients about their past experiences and current anxieties about a gynecologic procedure, according to Dr. Bayer.
“Part of it is just creating a really safe environment of trust as a medical provider,” she said.
A study published in 2016 of more than 800 patients undergoing oocyte retrieval, which has clear protocols for pain management, found that previous negative gynecologic experiences were significantly correlated to greater amounts of pain reported during the procedure.
If pain isn’t properly managed, patients may avoid care in the future, putting them at risk for unplanned pregnancies, skipped cancer screenings, and complications from undiagnosed conditions and infections, Dr. Bayer added. Clinician offices will not always have access to all pain management options, so making referrals to another physician who has access to the appropriate technique may be the best thing for the patient, Dr. Bayer said.
Downplaying the experience
Informing a patient that she will feel only a little discomfort during a procedure – when a clinician doesn’t know how exactly the patient will react – can also result in distrust.
When a clinician says, “ ’It’s only going to be a little cramp, it’s only going to be a little pinch,’ we know extreme pain is a possibility, we’ve seen it,” Dr. Fenton said. “But if we choose to disregard that [possibility], it feels invalidating for patients.”
Failing to fully explain the possible pain scale can also directly interfere with the procedure at hand.
“My first concern is if they aren’t anticipating the amount of pain they are going to experience, they may move; For biopsies and IUD insertions, we need them to be still,” Dr. Wasson said. “If they are unable to tolerate the procedure, we’ve put them through pain and not been able to accomplish the primary goal.”
Managing both pain and what patients can expect is even more crucial for adolescent and teenage patients who are often having their first gynecologic experience.
“We’re framing what these experiences look like,” Dr. Fenton said. “That means there are opportunities for creating a space that builds trust and security for the patients moving forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
During a fellowship rotation in gynecology, Rebekah D. Fenton, MD, asked the attending physicians what pain management options they could offer patients for insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD). Their answer surprised her: None.
The research on the effectiveness of pain management techniques during the procedure were not strong enough to warrant providing potential relief.
But Dr. Fenton knew the attending physician was wrong: She’d received the drug lidocaine during a recent visit to her own ob.gyn. to get an IUD placed. The local anesthetic enabled her to avoid the experiences of many patients who often withstand debilitating cramping and pain during insertion, side effects that can last for hours after the procedure has ended.
By not teaching her how to administer pain treatment options such as lidocaine gel or injection, “they made the decision for me, whether I could give patients this option,” said Dr. Fenton, now an adolescent medicine specialist at Alivio Medical Center in Chicago.
As a result, patients undergoing IUD placements, biopsies, hysteroscopies, and pelvic exams are often subject to pain that could be mitigated.
Some research suggests simple numbing agents, including lidocaine, may induce less pain without the need for full anesthesia. But clinicians don’t always present these options.
During gynecologic procedures, the amount of pain a patient can expect is often downplayed by clinicians. Because every patient experiences the sensation differently, discussing options for pain management and the range of possible pain is paramount in building patient-clinician trust, and ultimately providing the best care for patients in the long run, according to Megan Wasson, DO, chair of the department of medical and surgical gynecology at Mayo Clinic Arizona in Phoenix.
“It comes down to shared decision-making so the patient is aware of the pain that should be expected and what avenue they want to go down,” Dr. Wasson said. “It’s not a one-size-fits-all.”
Lack of uniform protocols
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) has clear guidelines for pain management during pregnancy and delivery but not for many routine gynecologic procedures. Some experts say not offering options for pain management based on lack of efficacy evidence can undermine a patient’s experience.
ACOG does have recommendations for reducing dilation pain during a hysteroscopy, including providing intravaginal misoprostol and estrogen. The organization also recommends performing a vaginoscopy instead if possible because the procedure is typically less painful than is a hysteroscopy.
For an IUD placement, ACOG states that the procedure “may cause temporary discomfort” and recommends that patients take over-the-counter pain relief before a procedure. The most recent clinical bulletin on the topic, published in 2016, states routine misoprostol is not recommended for IUD placement, although it may be considered with difficult insertions for management of pain.
A clinical inquiry published in 2020 outlined the efficacy of several pain options that practitioners can weigh with patients. The inquiry cited a 2019 meta-analysis of 38 studies that found lidocaine-prilocaine cream to be the most effective option for pain management during IUD placement, reducing insertion pain by nearly 30%. The inquiry concluded that a combination of 600 mcg of misoprostol and 4% lidocaine gel may be effective, while lower dosages of both drugs were not effective. A 2018 clinical trial cited in the analysis found that though a 20-cc 1% lidocaine paracervical block on its own did not reduce pain, the block mixed with sodium bicarbonate reduced pain during IUD insertion by 22%.
Some doctors make the decision to not use lidocaine without offering it to patients first, according to Dr. Fenton. Instead, clinicians should discuss any potential drawbacks, such as pain from administering the numbing agent with a needle or the procedure taking extra time while the patient waits for the lidocaine to kick in.
“That always felt unfair, to make that decision for [the patient],” Dr. Fenton said.
Often clinicians won’t know how a patient will respond to a procedure: A 2014 secondary analysis of a clinical trial compared how patients rated their pain after an IUD procedure to the amount of pain physicians perceived the procedure to cause. They found that the average pain scores patients reported were nearly twice as high as clinician expectations were.
ACOG’s guideline states that the evidence backing paracervical blocks and lidocaine to IUD insertion pain is controversial. The American College of Physicians also cites “low-quality evidence” to support patient reports of pain and discomfort during pelvic exams. Some studies have found up to 60% of women report these negative experiences.
The varying evidence highlights the need for a personalized approach – one that includes patients – to pain management for routine gynecological procedures.
“Usually patients are pretty good predictors,” said Lisa Bayer, MD, MPH, associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Oregon Health & Science University in Portland. “They can anticipate what different things are going to feel like based on previous experiences.”
Making patients part of the discussion
Clinicians should have open discussions with patients about their past experiences and current anxieties about a gynecologic procedure, according to Dr. Bayer.
“Part of it is just creating a really safe environment of trust as a medical provider,” she said.
A study published in 2016 of more than 800 patients undergoing oocyte retrieval, which has clear protocols for pain management, found that previous negative gynecologic experiences were significantly correlated to greater amounts of pain reported during the procedure.
If pain isn’t properly managed, patients may avoid care in the future, putting them at risk for unplanned pregnancies, skipped cancer screenings, and complications from undiagnosed conditions and infections, Dr. Bayer added. Clinician offices will not always have access to all pain management options, so making referrals to another physician who has access to the appropriate technique may be the best thing for the patient, Dr. Bayer said.
Downplaying the experience
Informing a patient that she will feel only a little discomfort during a procedure – when a clinician doesn’t know how exactly the patient will react – can also result in distrust.
When a clinician says, “ ’It’s only going to be a little cramp, it’s only going to be a little pinch,’ we know extreme pain is a possibility, we’ve seen it,” Dr. Fenton said. “But if we choose to disregard that [possibility], it feels invalidating for patients.”
Failing to fully explain the possible pain scale can also directly interfere with the procedure at hand.
“My first concern is if they aren’t anticipating the amount of pain they are going to experience, they may move; For biopsies and IUD insertions, we need them to be still,” Dr. Wasson said. “If they are unable to tolerate the procedure, we’ve put them through pain and not been able to accomplish the primary goal.”
Managing both pain and what patients can expect is even more crucial for adolescent and teenage patients who are often having their first gynecologic experience.
“We’re framing what these experiences look like,” Dr. Fenton said. “That means there are opportunities for creating a space that builds trust and security for the patients moving forward.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Taking a new obesity drug and birth control pills? Be careful
For women who are obese, daily life is wrought with landmines. Whether it’s the challenges of air travel because plane seats are too small, the need to shield themselves from the world’s discriminating eyes, or the great lengths many will go to achieve better health and the promise of longevity, navigating life as an obese person requires a thick skin.
So, it’s no wonder so many are willing to pay more than $1,000 a month out of pocket to get their hands on drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro). The benefits of these drugs, which are part of a new class called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, include significant and rapid weight loss, blood sugar control, and improved life quality; they are unprecedented in a setting where surgery has long been considered the most effective long-term option.
On the flip side, the desire for rapid weight loss and better blood sugar control also comes with an unexpected cost. , making an unintended pregnancy more likely.
Neel Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said he has had several patients become pregnant without intending to.
“It was when Mounjaro came out on the market when we started using it,” he said of the drug the Food and Drug Administration approved for type 2 diabetes in 2022. “It [the warning] was in the product insert, but clinically speaking, I don’t know if it was at the top of providers’ minds when they were prescribing Mounjaro.”
When asked if he believed that we were going to be seeing a significant increase in so-called Mounjaro babies, Dr. Shah was sure in his response.
“Absolutely. We will because the sheer volume [of patients] will increase,” he said.
It’s all in the gut
One of the ways that drugs like Mounjaro work is by delaying the time that it takes for food to move from the stomach to the small intestine. Although data are still evolving, it is believed that this process – delayed gastric emptying – may affect the absorption of birth control pills.
Dr. Shah said another theory is that vomiting, which is a common side effect of these types of drugs, also affects the pills’ ability to prevent pregnancy.
And “there’s a prolonged period of ramping up the dose because of the GI side effects,” said Pinar Kodaman, MD, PhD, a reproductive endocrinologist and assistant professor of gynecology at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“Initially, at the lowest dose, there may not be a lot of potential effect on absorption and gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes more common, and it can cause diarrhea, which is another condition that can affect the absorption of any medication,” she said.
Unanticipated outcomes, extra prevention
Roughly 42% of women in the United States are obese, 40% of whom are between the ages of 20 and 39. Although these new drugs can improve fertility outcomes for women who are obese (especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS), only one – Mounjaro – currently carries a warning about birth control pill effectiveness on its label. Unfortunately, it appears that some doctors are unaware or not counseling patients about this risk, and the data are unclear about whether other drugs in this class, like Ozempic and Wegovy, have the same risks.
“To date, it hasn’t been a typical thing that we counsel about,” said Dr. Kodaman. “It’s all fairly new, but when we have patients on birth control pills, we do review other medications that they are on because some can affect efficacy, and it’s something to keep in mind.”
It’s also unclear if other forms of birth control – for example, birth control patches that deliver through the skin – might carry similar pregnancy risks. Dr. Shah said some of his patients who became pregnant without intending to were using these patches. This raises even more questions, since they deliver drugs through the skin directly into the bloodstream and not through the GI system.
What can women do to help ensure that they don’t become pregnant while using these drugs?
“I really think that if patients want to protect themselves from an unplanned pregnancy, that as soon as they start the GLP receptor agonists, it wouldn’t be a bad idea to use condoms, because the onset of action is pretty quick,” said Dr. Kodaman, noting also that “at the lowest dose there may not be a lot of potential effect on gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes much more common or can cause diarrhea.”
Dr. Shah said that in his practice he’s “been telling patients to add barrier contraception” 4 weeks before they start their first dose “and at any dose adjustment.”
Zoobia Chaudhry, an obesity medicine doctor and assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, recommends that “patients just make sure that the injection and medication that they take are at least 1 hour apart.”
“Most of the time, patients do take birth control before bedtime, so if the two are spaced, it should be OK,” she said.
Another option is for women to speak to their doctors about other contraceptive options like IUDs or implantable rods, where gastric absorption is not going to be an issue.
“There’s very little research on this class of drugs,” said Emily Goodstein, a 40-year-old small-business owner in Washington, who recently switched from Ozempic to Mounjaro. “Being a person who lives in a larger body is such a horrifying experience because of the way that the world discriminates against you.”
She appreciates the feeling of being proactive that these new drugs grant. It has “opened up a bunch of opportunities for me to be seen as a full individual by the medical establishment,” she said. “I was willing to take the risk, knowing that I would be on these drugs for the rest of my life.”
In addition to being what Dr. Goodstein refers to as a guinea pig, she said she made sure that her primary care doctor was aware that she was not trying or planning to become pregnant again. (She has a 3-year-old child.) Still, her doctor mentioned only the most common side effects linked to these drugs, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, and did not mention the risk of pregnancy.
“Folks are really not talking about the reproductive implications,” she said, referring to members of a Facebook group on these drugs that she belongs to.
Like patients themselves, many doctors are just beginning to get their arms around these agents. “Awareness, education, provider involvement, and having a multidisciplinary team could help patients achieve the goals that they set out for themselves,” said Dr. Shah.
Clear conversations are key.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For women who are obese, daily life is wrought with landmines. Whether it’s the challenges of air travel because plane seats are too small, the need to shield themselves from the world’s discriminating eyes, or the great lengths many will go to achieve better health and the promise of longevity, navigating life as an obese person requires a thick skin.
So, it’s no wonder so many are willing to pay more than $1,000 a month out of pocket to get their hands on drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro). The benefits of these drugs, which are part of a new class called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, include significant and rapid weight loss, blood sugar control, and improved life quality; they are unprecedented in a setting where surgery has long been considered the most effective long-term option.
On the flip side, the desire for rapid weight loss and better blood sugar control also comes with an unexpected cost. , making an unintended pregnancy more likely.
Neel Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said he has had several patients become pregnant without intending to.
“It was when Mounjaro came out on the market when we started using it,” he said of the drug the Food and Drug Administration approved for type 2 diabetes in 2022. “It [the warning] was in the product insert, but clinically speaking, I don’t know if it was at the top of providers’ minds when they were prescribing Mounjaro.”
When asked if he believed that we were going to be seeing a significant increase in so-called Mounjaro babies, Dr. Shah was sure in his response.
“Absolutely. We will because the sheer volume [of patients] will increase,” he said.
It’s all in the gut
One of the ways that drugs like Mounjaro work is by delaying the time that it takes for food to move from the stomach to the small intestine. Although data are still evolving, it is believed that this process – delayed gastric emptying – may affect the absorption of birth control pills.
Dr. Shah said another theory is that vomiting, which is a common side effect of these types of drugs, also affects the pills’ ability to prevent pregnancy.
And “there’s a prolonged period of ramping up the dose because of the GI side effects,” said Pinar Kodaman, MD, PhD, a reproductive endocrinologist and assistant professor of gynecology at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“Initially, at the lowest dose, there may not be a lot of potential effect on absorption and gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes more common, and it can cause diarrhea, which is another condition that can affect the absorption of any medication,” she said.
Unanticipated outcomes, extra prevention
Roughly 42% of women in the United States are obese, 40% of whom are between the ages of 20 and 39. Although these new drugs can improve fertility outcomes for women who are obese (especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS), only one – Mounjaro – currently carries a warning about birth control pill effectiveness on its label. Unfortunately, it appears that some doctors are unaware or not counseling patients about this risk, and the data are unclear about whether other drugs in this class, like Ozempic and Wegovy, have the same risks.
“To date, it hasn’t been a typical thing that we counsel about,” said Dr. Kodaman. “It’s all fairly new, but when we have patients on birth control pills, we do review other medications that they are on because some can affect efficacy, and it’s something to keep in mind.”
It’s also unclear if other forms of birth control – for example, birth control patches that deliver through the skin – might carry similar pregnancy risks. Dr. Shah said some of his patients who became pregnant without intending to were using these patches. This raises even more questions, since they deliver drugs through the skin directly into the bloodstream and not through the GI system.
What can women do to help ensure that they don’t become pregnant while using these drugs?
“I really think that if patients want to protect themselves from an unplanned pregnancy, that as soon as they start the GLP receptor agonists, it wouldn’t be a bad idea to use condoms, because the onset of action is pretty quick,” said Dr. Kodaman, noting also that “at the lowest dose there may not be a lot of potential effect on gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes much more common or can cause diarrhea.”
Dr. Shah said that in his practice he’s “been telling patients to add barrier contraception” 4 weeks before they start their first dose “and at any dose adjustment.”
Zoobia Chaudhry, an obesity medicine doctor and assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, recommends that “patients just make sure that the injection and medication that they take are at least 1 hour apart.”
“Most of the time, patients do take birth control before bedtime, so if the two are spaced, it should be OK,” she said.
Another option is for women to speak to their doctors about other contraceptive options like IUDs or implantable rods, where gastric absorption is not going to be an issue.
“There’s very little research on this class of drugs,” said Emily Goodstein, a 40-year-old small-business owner in Washington, who recently switched from Ozempic to Mounjaro. “Being a person who lives in a larger body is such a horrifying experience because of the way that the world discriminates against you.”
She appreciates the feeling of being proactive that these new drugs grant. It has “opened up a bunch of opportunities for me to be seen as a full individual by the medical establishment,” she said. “I was willing to take the risk, knowing that I would be on these drugs for the rest of my life.”
In addition to being what Dr. Goodstein refers to as a guinea pig, she said she made sure that her primary care doctor was aware that she was not trying or planning to become pregnant again. (She has a 3-year-old child.) Still, her doctor mentioned only the most common side effects linked to these drugs, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, and did not mention the risk of pregnancy.
“Folks are really not talking about the reproductive implications,” she said, referring to members of a Facebook group on these drugs that she belongs to.
Like patients themselves, many doctors are just beginning to get their arms around these agents. “Awareness, education, provider involvement, and having a multidisciplinary team could help patients achieve the goals that they set out for themselves,” said Dr. Shah.
Clear conversations are key.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For women who are obese, daily life is wrought with landmines. Whether it’s the challenges of air travel because plane seats are too small, the need to shield themselves from the world’s discriminating eyes, or the great lengths many will go to achieve better health and the promise of longevity, navigating life as an obese person requires a thick skin.
So, it’s no wonder so many are willing to pay more than $1,000 a month out of pocket to get their hands on drugs like semaglutide (Ozempic and Wegovy) or tirzepatide (Mounjaro). The benefits of these drugs, which are part of a new class called glucagonlike peptide–1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, include significant and rapid weight loss, blood sugar control, and improved life quality; they are unprecedented in a setting where surgery has long been considered the most effective long-term option.
On the flip side, the desire for rapid weight loss and better blood sugar control also comes with an unexpected cost. , making an unintended pregnancy more likely.
Neel Shah, MD, an endocrinologist and associate professor at the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, said he has had several patients become pregnant without intending to.
“It was when Mounjaro came out on the market when we started using it,” he said of the drug the Food and Drug Administration approved for type 2 diabetes in 2022. “It [the warning] was in the product insert, but clinically speaking, I don’t know if it was at the top of providers’ minds when they were prescribing Mounjaro.”
When asked if he believed that we were going to be seeing a significant increase in so-called Mounjaro babies, Dr. Shah was sure in his response.
“Absolutely. We will because the sheer volume [of patients] will increase,” he said.
It’s all in the gut
One of the ways that drugs like Mounjaro work is by delaying the time that it takes for food to move from the stomach to the small intestine. Although data are still evolving, it is believed that this process – delayed gastric emptying – may affect the absorption of birth control pills.
Dr. Shah said another theory is that vomiting, which is a common side effect of these types of drugs, also affects the pills’ ability to prevent pregnancy.
And “there’s a prolonged period of ramping up the dose because of the GI side effects,” said Pinar Kodaman, MD, PhD, a reproductive endocrinologist and assistant professor of gynecology at Yale University in New Haven, Conn.
“Initially, at the lowest dose, there may not be a lot of potential effect on absorption and gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes more common, and it can cause diarrhea, which is another condition that can affect the absorption of any medication,” she said.
Unanticipated outcomes, extra prevention
Roughly 42% of women in the United States are obese, 40% of whom are between the ages of 20 and 39. Although these new drugs can improve fertility outcomes for women who are obese (especially those with polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS), only one – Mounjaro – currently carries a warning about birth control pill effectiveness on its label. Unfortunately, it appears that some doctors are unaware or not counseling patients about this risk, and the data are unclear about whether other drugs in this class, like Ozempic and Wegovy, have the same risks.
“To date, it hasn’t been a typical thing that we counsel about,” said Dr. Kodaman. “It’s all fairly new, but when we have patients on birth control pills, we do review other medications that they are on because some can affect efficacy, and it’s something to keep in mind.”
It’s also unclear if other forms of birth control – for example, birth control patches that deliver through the skin – might carry similar pregnancy risks. Dr. Shah said some of his patients who became pregnant without intending to were using these patches. This raises even more questions, since they deliver drugs through the skin directly into the bloodstream and not through the GI system.
What can women do to help ensure that they don’t become pregnant while using these drugs?
“I really think that if patients want to protect themselves from an unplanned pregnancy, that as soon as they start the GLP receptor agonists, it wouldn’t be a bad idea to use condoms, because the onset of action is pretty quick,” said Dr. Kodaman, noting also that “at the lowest dose there may not be a lot of potential effect on gastric emptying. But as the dose goes up, it becomes much more common or can cause diarrhea.”
Dr. Shah said that in his practice he’s “been telling patients to add barrier contraception” 4 weeks before they start their first dose “and at any dose adjustment.”
Zoobia Chaudhry, an obesity medicine doctor and assistant professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, recommends that “patients just make sure that the injection and medication that they take are at least 1 hour apart.”
“Most of the time, patients do take birth control before bedtime, so if the two are spaced, it should be OK,” she said.
Another option is for women to speak to their doctors about other contraceptive options like IUDs or implantable rods, where gastric absorption is not going to be an issue.
“There’s very little research on this class of drugs,” said Emily Goodstein, a 40-year-old small-business owner in Washington, who recently switched from Ozempic to Mounjaro. “Being a person who lives in a larger body is such a horrifying experience because of the way that the world discriminates against you.”
She appreciates the feeling of being proactive that these new drugs grant. It has “opened up a bunch of opportunities for me to be seen as a full individual by the medical establishment,” she said. “I was willing to take the risk, knowing that I would be on these drugs for the rest of my life.”
In addition to being what Dr. Goodstein refers to as a guinea pig, she said she made sure that her primary care doctor was aware that she was not trying or planning to become pregnant again. (She has a 3-year-old child.) Still, her doctor mentioned only the most common side effects linked to these drugs, like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, and did not mention the risk of pregnancy.
“Folks are really not talking about the reproductive implications,” she said, referring to members of a Facebook group on these drugs that she belongs to.
Like patients themselves, many doctors are just beginning to get their arms around these agents. “Awareness, education, provider involvement, and having a multidisciplinary team could help patients achieve the goals that they set out for themselves,” said Dr. Shah.
Clear conversations are key.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
2023 Update on contraception
More US women are using IUDs than ever before. With more use comes the potential for complications and more requests related to non-contraceptive benefits. New information provides contemporary insight into rare IUD complications and the use of hormonal IUDs for treatment of HMB.
The first intrauterine device (IUD) to be approved in the United States, the Lippes Loop, became available in 1964. Sixty years later, more US women are using IUDs than ever before, and numbers are trending upward (FIGURE).1,2 Over the past year, contemporary information has become available to further inform IUD management when pregnancy occurs with an IUD in situ, as well as counseling about device breakage. Additionally, new data help clinicians expand which patients can use a levonorgestrel (LNG) 52-mg IUD for heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) treatment.
As the total absolute number of IUD users increases, so do the absolute numbers of rare outcomes, such as pregnancy among IUD users. These highly effective contraceptives have a failure rate within the first year after placement ranging from 0.1% for the LNG 52-mg IUD to 0.8% for the copper 380-mm2 IUD.3 Although the possibility for extrauterine gestation is higher when pregnancy occurs while a patient is using an IUD as compared with most other contraceptive methods, most pregnancies that occur with an IUD in situ are intrauterine.4
The high contraceptive efficacy of IUDs make pregnancy with a retained IUD rare; therefore, it is difficult to perform a study with a large enough population to evaluate management of pregnancy complicated by an IUD in situ. Clinical management recommendations for these situations are 20 years old and are supported by limited data from case reports and series with fewer than 200 patients.5,6
Intrauterine device breakage is another rare event that is poorly understood due to the low absolute number of cases. Information about breakage has similarly been limited to case reports and case series.7,8 This past year, contemporary data were published to provide more insight into both intrauterine pregnancy with an IUD in situ and IUD breakage.
Beyond contraception, hormonal IUDs have become a popular and evidence-based treatment option for patients with HMB. The initial LNG 52-mg IUD (Mirena) regulatory approval studies for HMB treatment included data limited to parous patients and users with a body mass index (BMI) less than 35 kg/m2.9 Since that time, no studies have explored these populations. Although current practice has commonly extended use to include patients with these characteristics, we have lacked outcome data. New phase 3 data on the LNG 52-mg IUD (Liletta) included a broader range of participants and provide evidence to support this practice.
Removing retained copper 380-mm2 IUDs improves pregnancy outcomes
Panchal VR, Rau AR, Mandelbaum RS, et al. Pregnancy with retained intrauterine device: national-level assessment of characteristics and outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023;5:101056. doi:10.1016/j.ajogmf.2023.101056
Karakuş SS, Karakuş R, Akalın EE, et al. Pregnancy outcomes with a copper 380 mm2 intrauterine device in place: a retrospective cohort study in Turkey, 2011-2021. Contraception. 2023;125:110090. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2023.110090
To update our understanding of outcomes of pregnancy with an IUD in situ, Panchal and colleagues performed a cross-sectional study using the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s National Inpatient Sample. This data set represents 85% of US hospital discharges. The population investigated included hospital deliveries from 2016 to 2020 with an ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision) code of retained IUD. Those without the code were assigned to the comparison non-retained IUD group.
The primary outcome studied was the incidence rate of retained IUD, patient and pregnancy characteristics, and delivery outcomes including but not limited to gestational age at delivery, placental abnormalities, intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, and hysterectomy.
Outcomes were worse with retained IUD, regardless of IUD removal status
The authors found that an IUD in situ was reported in 1 out of 8,307 pregnancies and was associated with PPROM, fetal malpresentation, IUFD, placental abnormalities including abruption, accreta spectrum, retained placenta, and need for manual removal (TABLE 1). About three-quarters (76.3%) of patients had a term delivery (≥37 weeks).
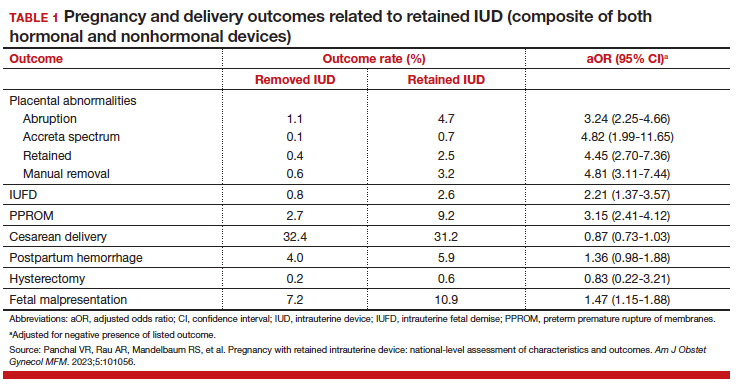
Retained IUD was associated with previable loss, defined as less than 22 weeks’ gestation (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 5.49; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.30–9.15) and periviable delivery, defined as 22 to 25 weeks’ gestation (aOR, 2.81; 95% CI, 1.63–4.85). Retained IUD was not associated with preterm delivery beyond 26 weeks’ gestation, cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, or hysterectomy.
Important limitations of this study are the lack of information on IUD type (copper vs hormonal) and the timing of removal or attempted removal in relation to measured pregnancy outcomes.
Continue to: Removal of copper IUD improves, but does not eliminate, poor pregnancy outcomes...
Removal of copper IUD improves, but does not eliminate, poor pregnancy outcomes
Karakus and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study of 233 patients in Turkey with pregnancies that occurred during copper 380-mm2 IUD use from 2011 to 2021. The authors reported that, at the time of first contact with the health system and diagnosis of retained IUD, 18.9% of the pregnancies were ectopic, 13.2% were first trimester losses, and 67.5% were ongoing pregnancies.
The authors assessed outcomes in patients with ongoing pregnancies based on whether or not the IUD was removed or retained. Outcomes included gestational age at delivery and adverse pregnancy outcomes, assessed as a composite of preterm delivery, PPROM, chorioamnionitis, placental abruption, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Of those with ongoing pregnancies, 13.3% chose to have an abortion, leaving 137 (86.7%) with continuing pregnancy. The IUD was able to be removed in 39.4% of the sample, with an average gestational age of 7 weeks at the time of removal.
Compared with those with a retained IUD, patients in the removal group had a lower rate of pregnancy loss (33.3% vs 61.4%; P<.001) and a lower rate of the composite adverse pregnancy outcomes (53.1% vs 27.8%; P=.03). TABLE 2 shows the approximate rate of ongoing pregnancy by gestational age in patients with retained and removed copper 380-mm2 IUDs. Notably, the largest change occurred periviably, with the proportion of patients with an ongoing pregnancy after 26 weeks reducing to about half for patients with a retained IUD as compared with patients with a removed IUD; this proportion of ongoing pregnancies held through the remainder of gestation.
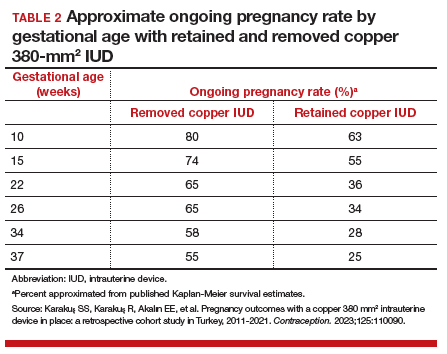
These studies confirm that a retained IUD is a rare outcome, occurring in about 1 in 8,000 pregnancies. Previous US national data from 2010 reported a similar incidence of 1 in 6,203 pregnancies (0.02%).10 Management and counseling depend on the patient’s desire to continue the pregnancy, gestational age, intrauterine IUD location, and ability to see the IUD strings. Contemporary data support management practices created from limited and outdated data, which include device removal (if able) and counseling those who desire to continue pregnancy about high-risk pregnancy complications. Those with a retained IUD should be counseled about increased risk of preterm or previable delivery, IUFD, and placental abnormalities (including accreta spectrum and retained placenta). Specifically, these contemporary data highlight that, beyond approximately 26 weeks’ gestation, the pregnancy loss rate is not different for those with a retained or removed IUD. Obstetric care providers should feel confident in using this more nuanced risk of extreme preterm delivery when counseling future patients. Implications for antepartum care and delivery timing with a retained IUD have not yet been defined.
Do national data reveal more breakage reports for copper 380-mm2 or LNG IUDs?
Latack KR, Nguyen BT. Trends in copper versus hormonal intrauterine device breakage reporting within the United States’ Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Contraception. 2023;118:109909. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2022.10.011
Latack and Nguyen reviewed postmarket surveillance data of IUD adverse events in the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) from 1998 to 2022. The FAERS is a voluntary, or passive, reporting system.
Study findings
Of the approximately 170,000 IUD-related adverse events reported to the agency during the 24-year timeframe, 25.4% were for copper IUDs and 74.6% were for hormonal IUDs. Slightly more than 4,000 reports were specific for device breakage, which the authors grouped into copper (copper 380-mm2)and hormonal (LNG 52 mg, 19.5 mg, and 13.5 mg) IUDs.
The copper 380-mm2 IUD was 6.19 times more likely to have a breakage report than hormonal IUDs (9.6% vs 1.7%; 95% CI, 5.87–6.53).
The overall proportion of IUD-related adverse events reported to the FDA was about 25% for copper and 75% for hormonal IUDs; this proportion is similar to sales figures, which show that about 15% of IUDs sold in the United States are copper and 85% are hormonal.11 However, the proportion of breakage events reported to the FDA is the inverse, with about 6 times more breakage reports with copper than with hormonal IUDs. Because these data come from a passive reporting system, the true incidence of IUD breakage cannot be assessed. However, these findings should remind clinicians to inform patients about this rare occurrence during counseling at the time of placement and, especially, when preparing for copper IUD removal. As the absolute number of IUD users increases, clinicians may be more likely to encounter this relatively rare event.
Management of IUD breakage is based on expert opinion, and recommendations are varied, ranging from observation to removal using an IUD hook, alligator forceps, manual vacuum aspiration, or hysteroscopy.7,10 Importantly, each individual patient situation will vary depending on the presence or absence of other symptoms and whether or not future pregnancy is desired.
Continue to: Data support the LNG 52-mg IUD for HMB in nulliparous and obese patients...
Data support the LNG 52-mg IUD for HMB in nulliparous and obese patients
Creinin MD, Barnhart KT, Gawron LM, et al. Heavy menstrual bleeding treatment with a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine device. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:971-978. doi:10.1097AOG.0000000000005137
Creinin and colleagues conducted a study for US regulatory product approval of the LNG 52-mg IUD (Liletta) for HMB. This multicenter phase 3 open-label clinical trial recruited nonpregnant participants aged 18 to 50 years with HMB at 29 clinical sites in the United States. No BMI cutoff was used.
Baseline menstrual flow data were obtained over 2 to 3 screening cycles by collection of menstrual products and quantification of blood loss using alkaline hematin measurement. Patients with 2 cycles with a blood loss exceeding 80 mL had an IUD placement, with similar flow evaluations during the third and sixth postplacement cycles.
Treatment success was defined as a reduction in blood loss by more than 50% as compared with baseline (during screening) and measured blood loss of less than 80 mL. The enrolled population (n=105) included 28% nulliparous users, with 49% and 28% of participants having a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher and higher than 35 kg/m2, respectively.
Treatment highly successful in reducing blood loss
Participants in this trial had a 93% and a 98% reduction in blood loss at the third and sixth cycles of use, respectively. Additionally, during the sixth cycle of use, 19% of users had no bleeding. Treatment success occurred in about 80% of participants overall and occurred regardless of parity or BMI.
To assess a subjective measure of success, participants were asked to evaluate their menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea severity, acceptability, and overall impact on quality of life at 3 time points: during prior typical menses, cycle 3, and cycle 6. At cycle 6, all participants reported significantly improved acceptability of bleeding and uterine pain and, importantly, decreased overall menstrual interference with the ability to complete daily activities (TABLE 3).
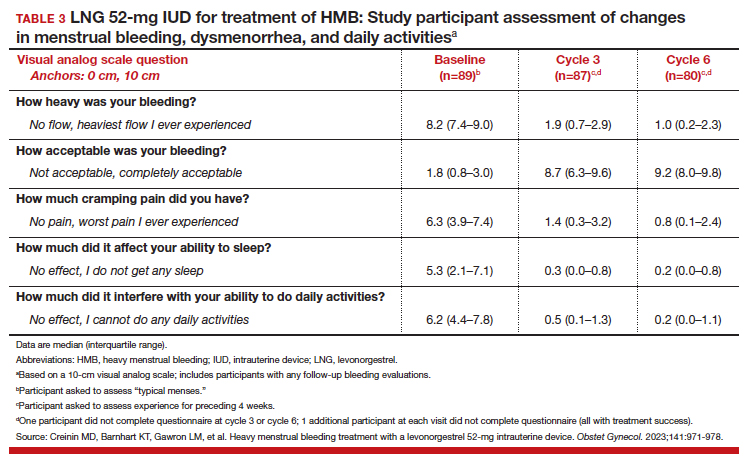
IUD expulsion and replacement rates
Although bleeding greatly decreased in all participants, 13% (n=14) discontinued before cycle 6 due to expulsion or IUD-related symptoms, with the majority citing bleeding irregularities. Expulsion occurred in 9% (n=5) of users, with the majority (2/3) occurring in the first 3 months of use and more commonly in obese and/or parous users. About half of participants with expulsion had the IUD replaced during the study. ●
Interestingly, both LNG 52-mg IUDs have been approved in most countries throughout the world for HMB treatment, and only in the United States was one of the products (Liletta) not approved until this past year. The FDA required more stringent trials than had been previously performed for approval outside of the United States. However, a benefit for clinicians is that this phase 3 study provided data in a contemporary US population. Clinicians can feel confident in counseling and offering the LNG 52-mg IUD as a first-line treatment option for patients with HMB, including those who have never been pregnant or have a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2.
Importantly, though, clinicians should be realistic with all patients that this treatment, although highly effective, is not successful for about 20% of patients by about 6 months of use. For those in whom the treatment is beneficial, the quality-of-life improvement is dramatic. Additionally, this study reminds us that expulsion risk in a population primarily using the IUD for HMB, especially if also obese and/or parous, is higher in the first 6 months of use than patients using the method for contraception. Expulsion occurs in 1.6% of contraception users through 6 months of use.12 These data highlight that IUD expulsion risk is not a fixed number, but instead is modified by patient characteristics. Patients should be counseled regarding the appropriate expulsion risk and that the IUD can be safely replaced should expulsion occur.
- Hubacher D, Kavanaugh M. Historical record-setting trends in IUD use in the United States. Contraception. 2018;98:467470. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2018.05.016
- Kavanaugh ML, Pliskin E. Use of contraception among reproductive-aged women in the United States, 2014 and 2016. F S Rep. 2020;1:83-93. doi:10.1016/j.xfre.2020.06.006
- Jensen JT, Creinin MD. Speroff & Darney’s Clinical Guide to Contraception. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2020:15.
- Jensen JT, Creinin MD. Speroff & Darney’s Clinical Guide to Contraception. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2020:185.
- Ozgu-Erdinc AS, Tasdemir UG, Uygur D, et al. Outcome of intrauterine pregnancies with intrauterine device in place and effects of device location on prognosis. Contraception. 2014;89:426-430. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.01.002
- Brahmi D, Steenland MW, Renner RM, et al. Pregnancy outcomes with an IUD in situ: a systematic review. Contraception. 2012;85:131-139. doi:10.1016/j.contraception . 2011.06.010
- Wilson S, Tan G, Baylson M, et al. Controversies in family planning: how to manage a fractured IUD. Contraception. 2013;88:599-603. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2013.07.007
- Fulkerson Schaeffer S, Gimovsky AC, Aly H, et al. Pregnancy and delivery with an intrauterine device in situ: outcomes in the National Inpatient Sample Database. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:798-803. doi:10.1080/14767058.2017.1 391783
- Mirena. Prescribing information. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Accessed August 22, 2023. https://www .mirena-us.com/pi
- Myo MG, Nguyen BT. Intrauterine device complications and their management. Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2023;12:88-95. doi.org/10.1007/s13669-023-00357-8
- National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). 2017-2019 National Survey of Family Growth. Public-Use Data File Documentation. CDC National Center for Health Statistics. Accessed August 28, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /nsfg/NSFG-2017-2019-UG-MainText-508.pdf
- Gilliam ML, Jensen JT, Eisenberg DL, et al. Relationship of parity and prior cesarean delivery to levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine system expulsion over 6 years. Contraception. 2021;103:444-449. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2021.02.013
More US women are using IUDs than ever before. With more use comes the potential for complications and more requests related to non-contraceptive benefits. New information provides contemporary insight into rare IUD complications and the use of hormonal IUDs for treatment of HMB.
The first intrauterine device (IUD) to be approved in the United States, the Lippes Loop, became available in 1964. Sixty years later, more US women are using IUDs than ever before, and numbers are trending upward (FIGURE).1,2 Over the past year, contemporary information has become available to further inform IUD management when pregnancy occurs with an IUD in situ, as well as counseling about device breakage. Additionally, new data help clinicians expand which patients can use a levonorgestrel (LNG) 52-mg IUD for heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) treatment.

As the total absolute number of IUD users increases, so do the absolute numbers of rare outcomes, such as pregnancy among IUD users. These highly effective contraceptives have a failure rate within the first year after placement ranging from 0.1% for the LNG 52-mg IUD to 0.8% for the copper 380-mm2 IUD.3 Although the possibility for extrauterine gestation is higher when pregnancy occurs while a patient is using an IUD as compared with most other contraceptive methods, most pregnancies that occur with an IUD in situ are intrauterine.4
The high contraceptive efficacy of IUDs make pregnancy with a retained IUD rare; therefore, it is difficult to perform a study with a large enough population to evaluate management of pregnancy complicated by an IUD in situ. Clinical management recommendations for these situations are 20 years old and are supported by limited data from case reports and series with fewer than 200 patients.5,6
Intrauterine device breakage is another rare event that is poorly understood due to the low absolute number of cases. Information about breakage has similarly been limited to case reports and case series.7,8 This past year, contemporary data were published to provide more insight into both intrauterine pregnancy with an IUD in situ and IUD breakage.
Beyond contraception, hormonal IUDs have become a popular and evidence-based treatment option for patients with HMB. The initial LNG 52-mg IUD (Mirena) regulatory approval studies for HMB treatment included data limited to parous patients and users with a body mass index (BMI) less than 35 kg/m2.9 Since that time, no studies have explored these populations. Although current practice has commonly extended use to include patients with these characteristics, we have lacked outcome data. New phase 3 data on the LNG 52-mg IUD (Liletta) included a broader range of participants and provide evidence to support this practice.
Removing retained copper 380-mm2 IUDs improves pregnancy outcomes
Panchal VR, Rau AR, Mandelbaum RS, et al. Pregnancy with retained intrauterine device: national-level assessment of characteristics and outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023;5:101056. doi:10.1016/j.ajogmf.2023.101056
Karakuş SS, Karakuş R, Akalın EE, et al. Pregnancy outcomes with a copper 380 mm2 intrauterine device in place: a retrospective cohort study in Turkey, 2011-2021. Contraception. 2023;125:110090. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2023.110090
To update our understanding of outcomes of pregnancy with an IUD in situ, Panchal and colleagues performed a cross-sectional study using the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s National Inpatient Sample. This data set represents 85% of US hospital discharges. The population investigated included hospital deliveries from 2016 to 2020 with an ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision) code of retained IUD. Those without the code were assigned to the comparison non-retained IUD group.
The primary outcome studied was the incidence rate of retained IUD, patient and pregnancy characteristics, and delivery outcomes including but not limited to gestational age at delivery, placental abnormalities, intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, and hysterectomy.
Outcomes were worse with retained IUD, regardless of IUD removal status
The authors found that an IUD in situ was reported in 1 out of 8,307 pregnancies and was associated with PPROM, fetal malpresentation, IUFD, placental abnormalities including abruption, accreta spectrum, retained placenta, and need for manual removal (TABLE 1). About three-quarters (76.3%) of patients had a term delivery (≥37 weeks).

Retained IUD was associated with previable loss, defined as less than 22 weeks’ gestation (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 5.49; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.30–9.15) and periviable delivery, defined as 22 to 25 weeks’ gestation (aOR, 2.81; 95% CI, 1.63–4.85). Retained IUD was not associated with preterm delivery beyond 26 weeks’ gestation, cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, or hysterectomy.
Important limitations of this study are the lack of information on IUD type (copper vs hormonal) and the timing of removal or attempted removal in relation to measured pregnancy outcomes.
Continue to: Removal of copper IUD improves, but does not eliminate, poor pregnancy outcomes...
Removal of copper IUD improves, but does not eliminate, poor pregnancy outcomes
Karakus and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study of 233 patients in Turkey with pregnancies that occurred during copper 380-mm2 IUD use from 2011 to 2021. The authors reported that, at the time of first contact with the health system and diagnosis of retained IUD, 18.9% of the pregnancies were ectopic, 13.2% were first trimester losses, and 67.5% were ongoing pregnancies.
The authors assessed outcomes in patients with ongoing pregnancies based on whether or not the IUD was removed or retained. Outcomes included gestational age at delivery and adverse pregnancy outcomes, assessed as a composite of preterm delivery, PPROM, chorioamnionitis, placental abruption, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Of those with ongoing pregnancies, 13.3% chose to have an abortion, leaving 137 (86.7%) with continuing pregnancy. The IUD was able to be removed in 39.4% of the sample, with an average gestational age of 7 weeks at the time of removal.
Compared with those with a retained IUD, patients in the removal group had a lower rate of pregnancy loss (33.3% vs 61.4%; P<.001) and a lower rate of the composite adverse pregnancy outcomes (53.1% vs 27.8%; P=.03). TABLE 2 shows the approximate rate of ongoing pregnancy by gestational age in patients with retained and removed copper 380-mm2 IUDs. Notably, the largest change occurred periviably, with the proportion of patients with an ongoing pregnancy after 26 weeks reducing to about half for patients with a retained IUD as compared with patients with a removed IUD; this proportion of ongoing pregnancies held through the remainder of gestation.

These studies confirm that a retained IUD is a rare outcome, occurring in about 1 in 8,000 pregnancies. Previous US national data from 2010 reported a similar incidence of 1 in 6,203 pregnancies (0.02%).10 Management and counseling depend on the patient’s desire to continue the pregnancy, gestational age, intrauterine IUD location, and ability to see the IUD strings. Contemporary data support management practices created from limited and outdated data, which include device removal (if able) and counseling those who desire to continue pregnancy about high-risk pregnancy complications. Those with a retained IUD should be counseled about increased risk of preterm or previable delivery, IUFD, and placental abnormalities (including accreta spectrum and retained placenta). Specifically, these contemporary data highlight that, beyond approximately 26 weeks’ gestation, the pregnancy loss rate is not different for those with a retained or removed IUD. Obstetric care providers should feel confident in using this more nuanced risk of extreme preterm delivery when counseling future patients. Implications for antepartum care and delivery timing with a retained IUD have not yet been defined.
Do national data reveal more breakage reports for copper 380-mm2 or LNG IUDs?
Latack KR, Nguyen BT. Trends in copper versus hormonal intrauterine device breakage reporting within the United States’ Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Contraception. 2023;118:109909. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2022.10.011
Latack and Nguyen reviewed postmarket surveillance data of IUD adverse events in the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) from 1998 to 2022. The FAERS is a voluntary, or passive, reporting system.
Study findings
Of the approximately 170,000 IUD-related adverse events reported to the agency during the 24-year timeframe, 25.4% were for copper IUDs and 74.6% were for hormonal IUDs. Slightly more than 4,000 reports were specific for device breakage, which the authors grouped into copper (copper 380-mm2)and hormonal (LNG 52 mg, 19.5 mg, and 13.5 mg) IUDs.
The copper 380-mm2 IUD was 6.19 times more likely to have a breakage report than hormonal IUDs (9.6% vs 1.7%; 95% CI, 5.87–6.53).
The overall proportion of IUD-related adverse events reported to the FDA was about 25% for copper and 75% for hormonal IUDs; this proportion is similar to sales figures, which show that about 15% of IUDs sold in the United States are copper and 85% are hormonal.11 However, the proportion of breakage events reported to the FDA is the inverse, with about 6 times more breakage reports with copper than with hormonal IUDs. Because these data come from a passive reporting system, the true incidence of IUD breakage cannot be assessed. However, these findings should remind clinicians to inform patients about this rare occurrence during counseling at the time of placement and, especially, when preparing for copper IUD removal. As the absolute number of IUD users increases, clinicians may be more likely to encounter this relatively rare event.
Management of IUD breakage is based on expert opinion, and recommendations are varied, ranging from observation to removal using an IUD hook, alligator forceps, manual vacuum aspiration, or hysteroscopy.7,10 Importantly, each individual patient situation will vary depending on the presence or absence of other symptoms and whether or not future pregnancy is desired.
Continue to: Data support the LNG 52-mg IUD for HMB in nulliparous and obese patients...
Data support the LNG 52-mg IUD for HMB in nulliparous and obese patients
Creinin MD, Barnhart KT, Gawron LM, et al. Heavy menstrual bleeding treatment with a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine device. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:971-978. doi:10.1097AOG.0000000000005137
Creinin and colleagues conducted a study for US regulatory product approval of the LNG 52-mg IUD (Liletta) for HMB. This multicenter phase 3 open-label clinical trial recruited nonpregnant participants aged 18 to 50 years with HMB at 29 clinical sites in the United States. No BMI cutoff was used.
Baseline menstrual flow data were obtained over 2 to 3 screening cycles by collection of menstrual products and quantification of blood loss using alkaline hematin measurement. Patients with 2 cycles with a blood loss exceeding 80 mL had an IUD placement, with similar flow evaluations during the third and sixth postplacement cycles.
Treatment success was defined as a reduction in blood loss by more than 50% as compared with baseline (during screening) and measured blood loss of less than 80 mL. The enrolled population (n=105) included 28% nulliparous users, with 49% and 28% of participants having a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher and higher than 35 kg/m2, respectively.
Treatment highly successful in reducing blood loss
Participants in this trial had a 93% and a 98% reduction in blood loss at the third and sixth cycles of use, respectively. Additionally, during the sixth cycle of use, 19% of users had no bleeding. Treatment success occurred in about 80% of participants overall and occurred regardless of parity or BMI.
To assess a subjective measure of success, participants were asked to evaluate their menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea severity, acceptability, and overall impact on quality of life at 3 time points: during prior typical menses, cycle 3, and cycle 6. At cycle 6, all participants reported significantly improved acceptability of bleeding and uterine pain and, importantly, decreased overall menstrual interference with the ability to complete daily activities (TABLE 3).

IUD expulsion and replacement rates
Although bleeding greatly decreased in all participants, 13% (n=14) discontinued before cycle 6 due to expulsion or IUD-related symptoms, with the majority citing bleeding irregularities. Expulsion occurred in 9% (n=5) of users, with the majority (2/3) occurring in the first 3 months of use and more commonly in obese and/or parous users. About half of participants with expulsion had the IUD replaced during the study. ●
Interestingly, both LNG 52-mg IUDs have been approved in most countries throughout the world for HMB treatment, and only in the United States was one of the products (Liletta) not approved until this past year. The FDA required more stringent trials than had been previously performed for approval outside of the United States. However, a benefit for clinicians is that this phase 3 study provided data in a contemporary US population. Clinicians can feel confident in counseling and offering the LNG 52-mg IUD as a first-line treatment option for patients with HMB, including those who have never been pregnant or have a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2.
Importantly, though, clinicians should be realistic with all patients that this treatment, although highly effective, is not successful for about 20% of patients by about 6 months of use. For those in whom the treatment is beneficial, the quality-of-life improvement is dramatic. Additionally, this study reminds us that expulsion risk in a population primarily using the IUD for HMB, especially if also obese and/or parous, is higher in the first 6 months of use than patients using the method for contraception. Expulsion occurs in 1.6% of contraception users through 6 months of use.12 These data highlight that IUD expulsion risk is not a fixed number, but instead is modified by patient characteristics. Patients should be counseled regarding the appropriate expulsion risk and that the IUD can be safely replaced should expulsion occur.
More US women are using IUDs than ever before. With more use comes the potential for complications and more requests related to non-contraceptive benefits. New information provides contemporary insight into rare IUD complications and the use of hormonal IUDs for treatment of HMB.
The first intrauterine device (IUD) to be approved in the United States, the Lippes Loop, became available in 1964. Sixty years later, more US women are using IUDs than ever before, and numbers are trending upward (FIGURE).1,2 Over the past year, contemporary information has become available to further inform IUD management when pregnancy occurs with an IUD in situ, as well as counseling about device breakage. Additionally, new data help clinicians expand which patients can use a levonorgestrel (LNG) 52-mg IUD for heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB) treatment.

As the total absolute number of IUD users increases, so do the absolute numbers of rare outcomes, such as pregnancy among IUD users. These highly effective contraceptives have a failure rate within the first year after placement ranging from 0.1% for the LNG 52-mg IUD to 0.8% for the copper 380-mm2 IUD.3 Although the possibility for extrauterine gestation is higher when pregnancy occurs while a patient is using an IUD as compared with most other contraceptive methods, most pregnancies that occur with an IUD in situ are intrauterine.4
The high contraceptive efficacy of IUDs make pregnancy with a retained IUD rare; therefore, it is difficult to perform a study with a large enough population to evaluate management of pregnancy complicated by an IUD in situ. Clinical management recommendations for these situations are 20 years old and are supported by limited data from case reports and series with fewer than 200 patients.5,6
Intrauterine device breakage is another rare event that is poorly understood due to the low absolute number of cases. Information about breakage has similarly been limited to case reports and case series.7,8 This past year, contemporary data were published to provide more insight into both intrauterine pregnancy with an IUD in situ and IUD breakage.
Beyond contraception, hormonal IUDs have become a popular and evidence-based treatment option for patients with HMB. The initial LNG 52-mg IUD (Mirena) regulatory approval studies for HMB treatment included data limited to parous patients and users with a body mass index (BMI) less than 35 kg/m2.9 Since that time, no studies have explored these populations. Although current practice has commonly extended use to include patients with these characteristics, we have lacked outcome data. New phase 3 data on the LNG 52-mg IUD (Liletta) included a broader range of participants and provide evidence to support this practice.
Removing retained copper 380-mm2 IUDs improves pregnancy outcomes
Panchal VR, Rau AR, Mandelbaum RS, et al. Pregnancy with retained intrauterine device: national-level assessment of characteristics and outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023;5:101056. doi:10.1016/j.ajogmf.2023.101056
Karakuş SS, Karakuş R, Akalın EE, et al. Pregnancy outcomes with a copper 380 mm2 intrauterine device in place: a retrospective cohort study in Turkey, 2011-2021. Contraception. 2023;125:110090. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2023.110090
To update our understanding of outcomes of pregnancy with an IUD in situ, Panchal and colleagues performed a cross-sectional study using the Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project’s National Inpatient Sample. This data set represents 85% of US hospital discharges. The population investigated included hospital deliveries from 2016 to 2020 with an ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision) code of retained IUD. Those without the code were assigned to the comparison non-retained IUD group.
The primary outcome studied was the incidence rate of retained IUD, patient and pregnancy characteristics, and delivery outcomes including but not limited to gestational age at delivery, placental abnormalities, intrauterine fetal demise (IUFD), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, and hysterectomy.
Outcomes were worse with retained IUD, regardless of IUD removal status
The authors found that an IUD in situ was reported in 1 out of 8,307 pregnancies and was associated with PPROM, fetal malpresentation, IUFD, placental abnormalities including abruption, accreta spectrum, retained placenta, and need for manual removal (TABLE 1). About three-quarters (76.3%) of patients had a term delivery (≥37 weeks).

Retained IUD was associated with previable loss, defined as less than 22 weeks’ gestation (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 5.49; 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.30–9.15) and periviable delivery, defined as 22 to 25 weeks’ gestation (aOR, 2.81; 95% CI, 1.63–4.85). Retained IUD was not associated with preterm delivery beyond 26 weeks’ gestation, cesarean delivery, postpartum hemorrhage, or hysterectomy.
Important limitations of this study are the lack of information on IUD type (copper vs hormonal) and the timing of removal or attempted removal in relation to measured pregnancy outcomes.
Continue to: Removal of copper IUD improves, but does not eliminate, poor pregnancy outcomes...
Removal of copper IUD improves, but does not eliminate, poor pregnancy outcomes
Karakus and colleagues conducted a retrospective cohort study of 233 patients in Turkey with pregnancies that occurred during copper 380-mm2 IUD use from 2011 to 2021. The authors reported that, at the time of first contact with the health system and diagnosis of retained IUD, 18.9% of the pregnancies were ectopic, 13.2% were first trimester losses, and 67.5% were ongoing pregnancies.
The authors assessed outcomes in patients with ongoing pregnancies based on whether or not the IUD was removed or retained. Outcomes included gestational age at delivery and adverse pregnancy outcomes, assessed as a composite of preterm delivery, PPROM, chorioamnionitis, placental abruption, and postpartum hemorrhage.
Of those with ongoing pregnancies, 13.3% chose to have an abortion, leaving 137 (86.7%) with continuing pregnancy. The IUD was able to be removed in 39.4% of the sample, with an average gestational age of 7 weeks at the time of removal.
Compared with those with a retained IUD, patients in the removal group had a lower rate of pregnancy loss (33.3% vs 61.4%; P<.001) and a lower rate of the composite adverse pregnancy outcomes (53.1% vs 27.8%; P=.03). TABLE 2 shows the approximate rate of ongoing pregnancy by gestational age in patients with retained and removed copper 380-mm2 IUDs. Notably, the largest change occurred periviably, with the proportion of patients with an ongoing pregnancy after 26 weeks reducing to about half for patients with a retained IUD as compared with patients with a removed IUD; this proportion of ongoing pregnancies held through the remainder of gestation.

These studies confirm that a retained IUD is a rare outcome, occurring in about 1 in 8,000 pregnancies. Previous US national data from 2010 reported a similar incidence of 1 in 6,203 pregnancies (0.02%).10 Management and counseling depend on the patient’s desire to continue the pregnancy, gestational age, intrauterine IUD location, and ability to see the IUD strings. Contemporary data support management practices created from limited and outdated data, which include device removal (if able) and counseling those who desire to continue pregnancy about high-risk pregnancy complications. Those with a retained IUD should be counseled about increased risk of preterm or previable delivery, IUFD, and placental abnormalities (including accreta spectrum and retained placenta). Specifically, these contemporary data highlight that, beyond approximately 26 weeks’ gestation, the pregnancy loss rate is not different for those with a retained or removed IUD. Obstetric care providers should feel confident in using this more nuanced risk of extreme preterm delivery when counseling future patients. Implications for antepartum care and delivery timing with a retained IUD have not yet been defined.
Do national data reveal more breakage reports for copper 380-mm2 or LNG IUDs?
Latack KR, Nguyen BT. Trends in copper versus hormonal intrauterine device breakage reporting within the United States’ Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System. Contraception. 2023;118:109909. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2022.10.011
Latack and Nguyen reviewed postmarket surveillance data of IUD adverse events in the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) from 1998 to 2022. The FAERS is a voluntary, or passive, reporting system.
Study findings
Of the approximately 170,000 IUD-related adverse events reported to the agency during the 24-year timeframe, 25.4% were for copper IUDs and 74.6% were for hormonal IUDs. Slightly more than 4,000 reports were specific for device breakage, which the authors grouped into copper (copper 380-mm2)and hormonal (LNG 52 mg, 19.5 mg, and 13.5 mg) IUDs.
The copper 380-mm2 IUD was 6.19 times more likely to have a breakage report than hormonal IUDs (9.6% vs 1.7%; 95% CI, 5.87–6.53).
The overall proportion of IUD-related adverse events reported to the FDA was about 25% for copper and 75% for hormonal IUDs; this proportion is similar to sales figures, which show that about 15% of IUDs sold in the United States are copper and 85% are hormonal.11 However, the proportion of breakage events reported to the FDA is the inverse, with about 6 times more breakage reports with copper than with hormonal IUDs. Because these data come from a passive reporting system, the true incidence of IUD breakage cannot be assessed. However, these findings should remind clinicians to inform patients about this rare occurrence during counseling at the time of placement and, especially, when preparing for copper IUD removal. As the absolute number of IUD users increases, clinicians may be more likely to encounter this relatively rare event.
Management of IUD breakage is based on expert opinion, and recommendations are varied, ranging from observation to removal using an IUD hook, alligator forceps, manual vacuum aspiration, or hysteroscopy.7,10 Importantly, each individual patient situation will vary depending on the presence or absence of other symptoms and whether or not future pregnancy is desired.
Continue to: Data support the LNG 52-mg IUD for HMB in nulliparous and obese patients...
Data support the LNG 52-mg IUD for HMB in nulliparous and obese patients
Creinin MD, Barnhart KT, Gawron LM, et al. Heavy menstrual bleeding treatment with a levonorgestrel 52-mg intrauterine device. Obstet Gynecol. 2023;141:971-978. doi:10.1097AOG.0000000000005137
Creinin and colleagues conducted a study for US regulatory product approval of the LNG 52-mg IUD (Liletta) for HMB. This multicenter phase 3 open-label clinical trial recruited nonpregnant participants aged 18 to 50 years with HMB at 29 clinical sites in the United States. No BMI cutoff was used.
Baseline menstrual flow data were obtained over 2 to 3 screening cycles by collection of menstrual products and quantification of blood loss using alkaline hematin measurement. Patients with 2 cycles with a blood loss exceeding 80 mL had an IUD placement, with similar flow evaluations during the third and sixth postplacement cycles.
Treatment success was defined as a reduction in blood loss by more than 50% as compared with baseline (during screening) and measured blood loss of less than 80 mL. The enrolled population (n=105) included 28% nulliparous users, with 49% and 28% of participants having a BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher and higher than 35 kg/m2, respectively.
Treatment highly successful in reducing blood loss
Participants in this trial had a 93% and a 98% reduction in blood loss at the third and sixth cycles of use, respectively. Additionally, during the sixth cycle of use, 19% of users had no bleeding. Treatment success occurred in about 80% of participants overall and occurred regardless of parity or BMI.
To assess a subjective measure of success, participants were asked to evaluate their menstrual bleeding and dysmenorrhea severity, acceptability, and overall impact on quality of life at 3 time points: during prior typical menses, cycle 3, and cycle 6. At cycle 6, all participants reported significantly improved acceptability of bleeding and uterine pain and, importantly, decreased overall menstrual interference with the ability to complete daily activities (TABLE 3).

IUD expulsion and replacement rates
Although bleeding greatly decreased in all participants, 13% (n=14) discontinued before cycle 6 due to expulsion or IUD-related symptoms, with the majority citing bleeding irregularities. Expulsion occurred in 9% (n=5) of users, with the majority (2/3) occurring in the first 3 months of use and more commonly in obese and/or parous users. About half of participants with expulsion had the IUD replaced during the study. ●
Interestingly, both LNG 52-mg IUDs have been approved in most countries throughout the world for HMB treatment, and only in the United States was one of the products (Liletta) not approved until this past year. The FDA required more stringent trials than had been previously performed for approval outside of the United States. However, a benefit for clinicians is that this phase 3 study provided data in a contemporary US population. Clinicians can feel confident in counseling and offering the LNG 52-mg IUD as a first-line treatment option for patients with HMB, including those who have never been pregnant or have a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2.
Importantly, though, clinicians should be realistic with all patients that this treatment, although highly effective, is not successful for about 20% of patients by about 6 months of use. For those in whom the treatment is beneficial, the quality-of-life improvement is dramatic. Additionally, this study reminds us that expulsion risk in a population primarily using the IUD for HMB, especially if also obese and/or parous, is higher in the first 6 months of use than patients using the method for contraception. Expulsion occurs in 1.6% of contraception users through 6 months of use.12 These data highlight that IUD expulsion risk is not a fixed number, but instead is modified by patient characteristics. Patients should be counseled regarding the appropriate expulsion risk and that the IUD can be safely replaced should expulsion occur.
- Hubacher D, Kavanaugh M. Historical record-setting trends in IUD use in the United States. Contraception. 2018;98:467470. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2018.05.016
- Kavanaugh ML, Pliskin E. Use of contraception among reproductive-aged women in the United States, 2014 and 2016. F S Rep. 2020;1:83-93. doi:10.1016/j.xfre.2020.06.006
- Jensen JT, Creinin MD. Speroff & Darney’s Clinical Guide to Contraception. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2020:15.
- Jensen JT, Creinin MD. Speroff & Darney’s Clinical Guide to Contraception. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2020:185.
- Ozgu-Erdinc AS, Tasdemir UG, Uygur D, et al. Outcome of intrauterine pregnancies with intrauterine device in place and effects of device location on prognosis. Contraception. 2014;89:426-430. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.01.002
- Brahmi D, Steenland MW, Renner RM, et al. Pregnancy outcomes with an IUD in situ: a systematic review. Contraception. 2012;85:131-139. doi:10.1016/j.contraception . 2011.06.010
- Wilson S, Tan G, Baylson M, et al. Controversies in family planning: how to manage a fractured IUD. Contraception. 2013;88:599-603. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2013.07.007
- Fulkerson Schaeffer S, Gimovsky AC, Aly H, et al. Pregnancy and delivery with an intrauterine device in situ: outcomes in the National Inpatient Sample Database. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:798-803. doi:10.1080/14767058.2017.1 391783
- Mirena. Prescribing information. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Accessed August 22, 2023. https://www .mirena-us.com/pi
- Myo MG, Nguyen BT. Intrauterine device complications and their management. Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2023;12:88-95. doi.org/10.1007/s13669-023-00357-8
- National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). 2017-2019 National Survey of Family Growth. Public-Use Data File Documentation. CDC National Center for Health Statistics. Accessed August 28, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /nsfg/NSFG-2017-2019-UG-MainText-508.pdf
- Gilliam ML, Jensen JT, Eisenberg DL, et al. Relationship of parity and prior cesarean delivery to levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine system expulsion over 6 years. Contraception. 2021;103:444-449. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2021.02.013
- Hubacher D, Kavanaugh M. Historical record-setting trends in IUD use in the United States. Contraception. 2018;98:467470. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2018.05.016
- Kavanaugh ML, Pliskin E. Use of contraception among reproductive-aged women in the United States, 2014 and 2016. F S Rep. 2020;1:83-93. doi:10.1016/j.xfre.2020.06.006
- Jensen JT, Creinin MD. Speroff & Darney’s Clinical Guide to Contraception. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2020:15.
- Jensen JT, Creinin MD. Speroff & Darney’s Clinical Guide to Contraception. 6th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2020:185.
- Ozgu-Erdinc AS, Tasdemir UG, Uygur D, et al. Outcome of intrauterine pregnancies with intrauterine device in place and effects of device location on prognosis. Contraception. 2014;89:426-430. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2014.01.002
- Brahmi D, Steenland MW, Renner RM, et al. Pregnancy outcomes with an IUD in situ: a systematic review. Contraception. 2012;85:131-139. doi:10.1016/j.contraception . 2011.06.010
- Wilson S, Tan G, Baylson M, et al. Controversies in family planning: how to manage a fractured IUD. Contraception. 2013;88:599-603. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2013.07.007
- Fulkerson Schaeffer S, Gimovsky AC, Aly H, et al. Pregnancy and delivery with an intrauterine device in situ: outcomes in the National Inpatient Sample Database. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019;32:798-803. doi:10.1080/14767058.2017.1 391783
- Mirena. Prescribing information. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Accessed August 22, 2023. https://www .mirena-us.com/pi
- Myo MG, Nguyen BT. Intrauterine device complications and their management. Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep. 2023;12:88-95. doi.org/10.1007/s13669-023-00357-8
- National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). 2017-2019 National Survey of Family Growth. Public-Use Data File Documentation. CDC National Center for Health Statistics. Accessed August 28, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data /nsfg/NSFG-2017-2019-UG-MainText-508.pdf
- Gilliam ML, Jensen JT, Eisenberg DL, et al. Relationship of parity and prior cesarean delivery to levonorgestrel 52 mg intrauterine system expulsion over 6 years. Contraception. 2021;103:444-449. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2021.02.013
Federal Health Care Data Trends 2023
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
In this issue:
- Limb Loss and Prostheses
- Neurology
- Cardiology
- Mental Health
- Diabetes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Respiratory illnesses
- Women's Health
- HPV and Related Cancers
Piroxicam boosts success of levonorgestrel for emergency contraception
Adding oral piroxicam to oral levonorgestrel significantly improved the efficacy of emergency contraception, based on data from 860 women.
Oral hormonal emergency contraception (EC) is the most widely used EC method worldwide, but the two currently available drugs, levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate (UPA), are not effective when given after ovulation, wrote Raymond Hang Wun Li, MD, of the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors may disrupt follicular rupture and prevent ovulation, but data on their use in combination with current oral ECs are lacking, the researchers said.
In a study published in The Lancet, the researchers randomized 430 women to receive a single oral dose of 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus 40 mg of the COX-2 inhibitor piroxicam or 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus a placebo. The study participants were women aged 18 years and older who requested EC within 72 hours of unprotected sex and who had regular menstrual cycles between 24 and 42 days long. The median age of the participants was 30 years; 97% were Chinese. The median time from intercourse to treatment was 18 hours for both groups.
The primary outcome was the percentage of pregnancies prevented, based on pregnancy status 1-2 weeks after treatment.
One pregnancy occurred in the piroxicam group, compared with seven pregnancies in the placebo group, which translated to a significant difference in the percentage of pregnancies prevented (94.7% vs. 63.4%, P < .0001).
No trend toward increased failure rates appeared based on the time elapsed between intercourse and EC use in either group, and no differences appeared in the return or delay of subsequent menstrual periods between the groups.
The most common adverse events (reported by more than 5% of participants in both groups) included fatigue or weakness, nausea, lower abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache.
The choice of piroxicam as the COX inhibitor in conjunction with levonorgestrel for the current study had several potential advantages, the researchers wrote in their discussion. These advantages include the widespread availability and long-acting characteristics of piroxicam, which is also true of levonorgestrel, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the generalizability to other settings and populations, the researchers noted. The efficacy of the levonorgestrel/piroxicam combination in women with a body mass index greater than 26 kg/m2 may be lower, but the current study population did not have enough women in this category to measure the potential effect, they said. The study also did not examine the effect of piroxicam in combination with ulipristal acetate.
However, the results are the first known to demonstrate the improved effectiveness of oral piroxicam coadministered with oral levonorgestrel for EC, they said.
“The strength of this recommendation and changes in clinical guidelines may be determined upon demonstration of reproducible results in further studies,” they added.
Pill combination shows potential and practicality
Oral emergency contraception on demand is an unmet need on a global level, Erica P. Cahill, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and division of family planning services at Stanford (Calif.) University, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Cahill noted the longer half-life of piroxicam compared with other COX-2 inhibitors, which made it a practical choice. Although the study was not powered to evaluate secondary outcomes, bleeding patterns consistent with use of EC pills were observed. Documentation of these patterns is worthwhile, Dr. Cahill said, “because people using emergency contraceptive pills might also be using fertility awareness methods and need to know when they can be certain they are not pregnant.”
Overall, the study supports the addition of 40 mg piroxicam to 1.5 mg levonorgestrel as emergency contraception, said Dr. Cahill. Future studies can build on the current findings by evaluating repeat dosing of the piroxicam/levonorgestrel combination and by evaluating the combination of COX-2 inhibitors and ulipristal acetate to prevent pregnancy, she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Cahill had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adding oral piroxicam to oral levonorgestrel significantly improved the efficacy of emergency contraception, based on data from 860 women.
Oral hormonal emergency contraception (EC) is the most widely used EC method worldwide, but the two currently available drugs, levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate (UPA), are not effective when given after ovulation, wrote Raymond Hang Wun Li, MD, of the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors may disrupt follicular rupture and prevent ovulation, but data on their use in combination with current oral ECs are lacking, the researchers said.
In a study published in The Lancet, the researchers randomized 430 women to receive a single oral dose of 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus 40 mg of the COX-2 inhibitor piroxicam or 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus a placebo. The study participants were women aged 18 years and older who requested EC within 72 hours of unprotected sex and who had regular menstrual cycles between 24 and 42 days long. The median age of the participants was 30 years; 97% were Chinese. The median time from intercourse to treatment was 18 hours for both groups.
The primary outcome was the percentage of pregnancies prevented, based on pregnancy status 1-2 weeks after treatment.
One pregnancy occurred in the piroxicam group, compared with seven pregnancies in the placebo group, which translated to a significant difference in the percentage of pregnancies prevented (94.7% vs. 63.4%, P < .0001).
No trend toward increased failure rates appeared based on the time elapsed between intercourse and EC use in either group, and no differences appeared in the return or delay of subsequent menstrual periods between the groups.
The most common adverse events (reported by more than 5% of participants in both groups) included fatigue or weakness, nausea, lower abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache.
The choice of piroxicam as the COX inhibitor in conjunction with levonorgestrel for the current study had several potential advantages, the researchers wrote in their discussion. These advantages include the widespread availability and long-acting characteristics of piroxicam, which is also true of levonorgestrel, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the generalizability to other settings and populations, the researchers noted. The efficacy of the levonorgestrel/piroxicam combination in women with a body mass index greater than 26 kg/m2 may be lower, but the current study population did not have enough women in this category to measure the potential effect, they said. The study also did not examine the effect of piroxicam in combination with ulipristal acetate.
However, the results are the first known to demonstrate the improved effectiveness of oral piroxicam coadministered with oral levonorgestrel for EC, they said.
“The strength of this recommendation and changes in clinical guidelines may be determined upon demonstration of reproducible results in further studies,” they added.
Pill combination shows potential and practicality
Oral emergency contraception on demand is an unmet need on a global level, Erica P. Cahill, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and division of family planning services at Stanford (Calif.) University, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Cahill noted the longer half-life of piroxicam compared with other COX-2 inhibitors, which made it a practical choice. Although the study was not powered to evaluate secondary outcomes, bleeding patterns consistent with use of EC pills were observed. Documentation of these patterns is worthwhile, Dr. Cahill said, “because people using emergency contraceptive pills might also be using fertility awareness methods and need to know when they can be certain they are not pregnant.”
Overall, the study supports the addition of 40 mg piroxicam to 1.5 mg levonorgestrel as emergency contraception, said Dr. Cahill. Future studies can build on the current findings by evaluating repeat dosing of the piroxicam/levonorgestrel combination and by evaluating the combination of COX-2 inhibitors and ulipristal acetate to prevent pregnancy, she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Cahill had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Adding oral piroxicam to oral levonorgestrel significantly improved the efficacy of emergency contraception, based on data from 860 women.
Oral hormonal emergency contraception (EC) is the most widely used EC method worldwide, but the two currently available drugs, levonorgestrel and ulipristal acetate (UPA), are not effective when given after ovulation, wrote Raymond Hang Wun Li, MD, of the University of Hong Kong, and colleagues. Previous studies suggest that cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors may disrupt follicular rupture and prevent ovulation, but data on their use in combination with current oral ECs are lacking, the researchers said.
In a study published in The Lancet, the researchers randomized 430 women to receive a single oral dose of 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus 40 mg of the COX-2 inhibitor piroxicam or 1.5 mg levonorgestrel plus a placebo. The study participants were women aged 18 years and older who requested EC within 72 hours of unprotected sex and who had regular menstrual cycles between 24 and 42 days long. The median age of the participants was 30 years; 97% were Chinese. The median time from intercourse to treatment was 18 hours for both groups.
The primary outcome was the percentage of pregnancies prevented, based on pregnancy status 1-2 weeks after treatment.
One pregnancy occurred in the piroxicam group, compared with seven pregnancies in the placebo group, which translated to a significant difference in the percentage of pregnancies prevented (94.7% vs. 63.4%, P < .0001).
No trend toward increased failure rates appeared based on the time elapsed between intercourse and EC use in either group, and no differences appeared in the return or delay of subsequent menstrual periods between the groups.
The most common adverse events (reported by more than 5% of participants in both groups) included fatigue or weakness, nausea, lower abdominal pain, dizziness, and headache.
The choice of piroxicam as the COX inhibitor in conjunction with levonorgestrel for the current study had several potential advantages, the researchers wrote in their discussion. These advantages include the widespread availability and long-acting characteristics of piroxicam, which is also true of levonorgestrel, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the generalizability to other settings and populations, the researchers noted. The efficacy of the levonorgestrel/piroxicam combination in women with a body mass index greater than 26 kg/m2 may be lower, but the current study population did not have enough women in this category to measure the potential effect, they said. The study also did not examine the effect of piroxicam in combination with ulipristal acetate.
However, the results are the first known to demonstrate the improved effectiveness of oral piroxicam coadministered with oral levonorgestrel for EC, they said.
“The strength of this recommendation and changes in clinical guidelines may be determined upon demonstration of reproducible results in further studies,” they added.
Pill combination shows potential and practicality
Oral emergency contraception on demand is an unmet need on a global level, Erica P. Cahill, MD, of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and division of family planning services at Stanford (Calif.) University, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Dr. Cahill noted the longer half-life of piroxicam compared with other COX-2 inhibitors, which made it a practical choice. Although the study was not powered to evaluate secondary outcomes, bleeding patterns consistent with use of EC pills were observed. Documentation of these patterns is worthwhile, Dr. Cahill said, “because people using emergency contraceptive pills might also be using fertility awareness methods and need to know when they can be certain they are not pregnant.”
Overall, the study supports the addition of 40 mg piroxicam to 1.5 mg levonorgestrel as emergency contraception, said Dr. Cahill. Future studies can build on the current findings by evaluating repeat dosing of the piroxicam/levonorgestrel combination and by evaluating the combination of COX-2 inhibitors and ulipristal acetate to prevent pregnancy, she said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers and Dr. Cahill had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE LANCET