User login
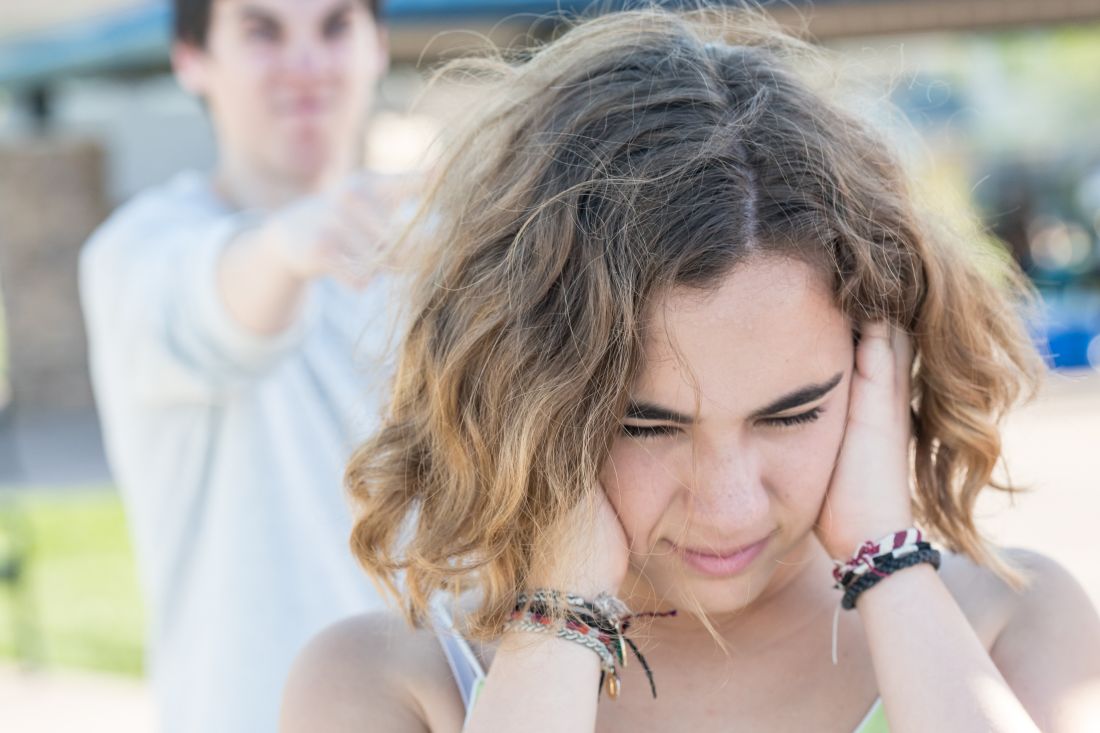
Universal adolescent education on healthy relationships needed
Sexually active adolescent girls face reproductive coercion (RC) and adolescent relationship abuse (ARA), but there seems to be no statistically significant demographic factors, so education should be universally provided, wrote Amber L. Hill, MSPH, and colleagues in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Ms. Hill of the University of Pittsburgh and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of data from a cross-sectional baseline survey that had been used in a cluster-randomized trial. The SHARP (School Health Center Healthy Adolescent Relationship Program) trial, investigated an educational intervention regarding healthy relationships. Their analysis included survey data for 550 sexually active girls aged 14-19 years who’d received services from any of eight student health centers across Northern California during the 2012-2013 school year.
The investigators explained that ARA includes physical, sexual, and emotional abuse among adolescents in a romantic relationship; they further described RC as a form of ARA that increases risks of unintended pregnancy, such as contraceptive sabotage, condom manipulation, and pregnancy coercion. RC was defined as a positive response on a 10-item validated measure, and ARA was defined by positive response to at least one of three items that had been derived from Conflict Tactics Scale 2 and the Sexual Experiences Survey.
Among all females in the analysis, 12% reported reproductive coercion, and 17% reported relationship abuse . Black and Hispanic girls were the most likely to report RC, each at 15%; white girls were the most likely to report ARA at 22%. However, none of the demographic differences evaluated in this analysis, including these, were statistically significant, the authors cautioned.
One of the limitations of this study is that its sample was limited to school health centers in Northern California so it may not be generalizable. Furthermore, its cross-sectional design limits causal inference.
“By highlighting the relevance of reproductive coercion in adolescence, this study substantiates the urgent need for developmentally appropriate interventions,” Ms. Hill and associates concluded.
The authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Grants from the National Institute of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health supported the study.
SOURCE: Hill AL et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134(2):351-9.
Sexually active adolescent girls face reproductive coercion (RC) and adolescent relationship abuse (ARA), but there seems to be no statistically significant demographic factors, so education should be universally provided, wrote Amber L. Hill, MSPH, and colleagues in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Ms. Hill of the University of Pittsburgh and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of data from a cross-sectional baseline survey that had been used in a cluster-randomized trial. The SHARP (School Health Center Healthy Adolescent Relationship Program) trial, investigated an educational intervention regarding healthy relationships. Their analysis included survey data for 550 sexually active girls aged 14-19 years who’d received services from any of eight student health centers across Northern California during the 2012-2013 school year.
The investigators explained that ARA includes physical, sexual, and emotional abuse among adolescents in a romantic relationship; they further described RC as a form of ARA that increases risks of unintended pregnancy, such as contraceptive sabotage, condom manipulation, and pregnancy coercion. RC was defined as a positive response on a 10-item validated measure, and ARA was defined by positive response to at least one of three items that had been derived from Conflict Tactics Scale 2 and the Sexual Experiences Survey.
Among all females in the analysis, 12% reported reproductive coercion, and 17% reported relationship abuse . Black and Hispanic girls were the most likely to report RC, each at 15%; white girls were the most likely to report ARA at 22%. However, none of the demographic differences evaluated in this analysis, including these, were statistically significant, the authors cautioned.
One of the limitations of this study is that its sample was limited to school health centers in Northern California so it may not be generalizable. Furthermore, its cross-sectional design limits causal inference.
“By highlighting the relevance of reproductive coercion in adolescence, this study substantiates the urgent need for developmentally appropriate interventions,” Ms. Hill and associates concluded.
The authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Grants from the National Institute of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health supported the study.
SOURCE: Hill AL et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134(2):351-9.
Sexually active adolescent girls face reproductive coercion (RC) and adolescent relationship abuse (ARA), but there seems to be no statistically significant demographic factors, so education should be universally provided, wrote Amber L. Hill, MSPH, and colleagues in Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Ms. Hill of the University of Pittsburgh and colleagues conducted a secondary analysis of data from a cross-sectional baseline survey that had been used in a cluster-randomized trial. The SHARP (School Health Center Healthy Adolescent Relationship Program) trial, investigated an educational intervention regarding healthy relationships. Their analysis included survey data for 550 sexually active girls aged 14-19 years who’d received services from any of eight student health centers across Northern California during the 2012-2013 school year.
The investigators explained that ARA includes physical, sexual, and emotional abuse among adolescents in a romantic relationship; they further described RC as a form of ARA that increases risks of unintended pregnancy, such as contraceptive sabotage, condom manipulation, and pregnancy coercion. RC was defined as a positive response on a 10-item validated measure, and ARA was defined by positive response to at least one of three items that had been derived from Conflict Tactics Scale 2 and the Sexual Experiences Survey.
Among all females in the analysis, 12% reported reproductive coercion, and 17% reported relationship abuse . Black and Hispanic girls were the most likely to report RC, each at 15%; white girls were the most likely to report ARA at 22%. However, none of the demographic differences evaluated in this analysis, including these, were statistically significant, the authors cautioned.
One of the limitations of this study is that its sample was limited to school health centers in Northern California so it may not be generalizable. Furthermore, its cross-sectional design limits causal inference.
“By highlighting the relevance of reproductive coercion in adolescence, this study substantiates the urgent need for developmentally appropriate interventions,” Ms. Hill and associates concluded.
The authors did not report any potential conflicts of interest. Grants from the National Institute of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, U.S. Department of Justice and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health supported the study.
SOURCE: Hill AL et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;134(2):351-9.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
Expert advice for immediate postpartum LARC insertion
Evidence-based education about long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) for women in the postpartum period can result in the increased continuation of and satisfaction with LARC.1 However, nearly 40% of women do not attend a postpartum visit.2 And up to 57% of women report having unprotected intercourse before the 6-week postpartum visit, which increases the risk of unplanned pregnancy.3 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) supports immediate postpartum LARC insertion as best practice,3 and clinicians providing care for women during the peripartum period can counsel women regarding informed contraceptive decisions and provide guidance regarding both short-acting contraception and LARC.1
Immediate postpartum LARC, using intrauterine devices (IUDs) in particular, has been used around the world for a long time, says Lisa Hofler, MD, MPH, MBA, Chief in the Division of Family Planning at the University of New Mexico School of Medicine in Albuquerque. “Much of our initial data came from other countries, but eventually people in the United States said, ‘This is a great option, why aren't we doing this?’" In addition, although women considering immediate postpartum LARC should be counseled about the theoretical risk of reduced duration of breastfeeding, the evidence overwhelmingly has not shown a negative effect on actual breastfeeding outcomes according to ACOG.3 OBG MANAGEMENT recently met up with Dr. Hofler to ask her which patients are ideal for postpartum LARC, how to troubleshoot common pitfalls, and how to implement the practice within one’s own institution.
OBG Management: Who do you consider to be the ideal patient for immediate postpartum LARC?
Lisa Hofler, MD: The great thing about immediate postpartum LARC (including IUDs and implants) is that any woman is an ideal candidate. We are simply talking about the timing of when a woman chooses to get an IUD or an implant after the birth of her child. There is no one perfect woman; it is the person who chooses the method and wants to use that method immediately after birth. When a woman chooses a LARC, she can be assured that after the birth of her child she will be protected against pregnancy. If she chooses an IUD as her LARC method, she will be comfortable at insertion because the cervix is already dilated when it is inserted.
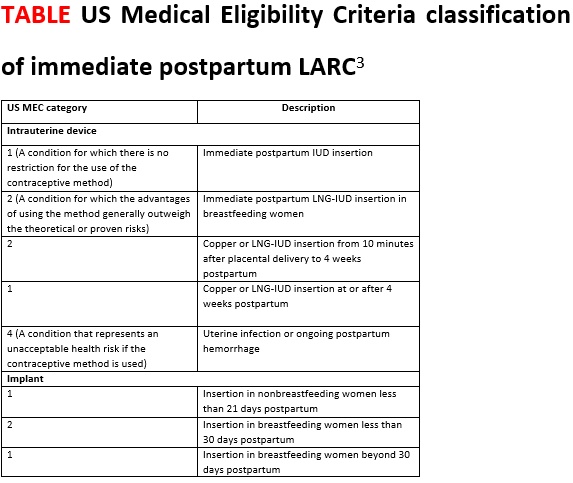
For the implant, the contraindications are the same as in the outpatient setting. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use covers many medical conditions and whether or not a person might be a candidate for different birth control methods.4 Those same considerations apply for the implant postpartum (TABLE).3
For the IUD, similarly, anyone who would not be a candidate for the IUD in the outpatient setting is not a candidate for immediate postpartum IUD. For instance, if the person has an intrauterine infection, you should not place an IUD. Also, if a patient is hemorrhaging and you are managing the hemorrhage (say she has retained placenta or membranes or she has uterine atony), you are not going to put an IUD in, as you need to attend to her bleeding.
OBG Management: What is your approach to counseling a patient for immediate postpartum LARC?
Dr. Hofler: The ideal time to counsel about postbirth contraception is in the prenatal period, when the patient is making decisions about what method she wants to use after the birth. Once she chooses her preferred method, address timing if appropriate. It is less ideal to talk to a woman about the option of immediate postpartum LARC when she comes to labor and delivery, especially if that is the first time she has heard about it. Certainly, the time to talk about postpartum LARC options is not immediately after the baby is born. Approaching your patient with, "What do you want for birth control? Do you want this IUD? I can put it in right now," can feel coercive. This approach does not put the woman in a position in which she has enough decision-making time or time to ask questions.
OBG Management: What problems do clinicians run into when placing an immediate postpartum IUD, and can you offer solutions?
Dr. Hofler: When placing an immediate postpartum IUD, people might run into a few problems. The first relates to preplacement counseling. Perhaps when making the plan for the postpartum IUD the clinician did not counsel the woman that there are certain conditions that could preclude IUD placement—such as intrauterine infection or postpartum hemorrhage. When dealing with those types of issues, a patient is not eligible for an IUD, and she should be mentally prepared for this type of situation. Let her know during the counseling before the birth that immediately postpartum is a great time and opportunity for effective contraception placement. Tell her that hopefully IUD placement will be possible but that occasionally it is not, and make a back-up plan in case the IUD cannot be placed immediately postpartum.
The second unique area for counseling with immediate postpartum IUDs is a slightly increased risk of expulsion of an IUD placed immediately postpartum compared with in the office. The risk of expulsion varies by type of delivery. For instance, cesarean delivery births have a lower expulsion rate than vaginal births. The expulsion rate seems to vary by type of IUD as well. Copper IUDs seem to have a slightly lower expulsion rate than hormonal IUDs. (See “Levonorgestrel vs copper IUD expulsion rates after immediate postpartum insertion.”) This consideration should be talked about ahead of time, too. Provider training in IUD placement does impact the likelihood of expulsion, and if you place the IUD at the fundus, it is less likely to expel. (See “Inserting the immediate postpartum IUD after vaginal and cesarean birth step by step.”)
A third issue that clinicians run into is actually the systems of care—making sure that the IUD or implant is available when you need it, making sure that documentation happens the way it should, and ensuring that the follow-up billing and revenue cycle happens so that the woman gets the device that she wants and the providers get paid for having provided it. These issues require a multidisciplinary team to work through in order to ensure that postpartum LARC placement is a sustainable process in the long run.
Often, when people think of immediate postpartum LARC they think of postplacental IUDs. However, an implant also is an option, and that too is immediate postpartum LARC. Placing an implant is often a lot easier to do after the birth than placing an IUD. As clinicians work toward bringing an immediate postpartum LARC program to their hospital system, starting with implants is a smart thing to do because clinicians do not have to learn or teach new clinical skills. Because of that, immediate postpartum implants are a good troubleshooting mechanism for opening up the conversation about immediate postpartum LARC at your institution.
OBG MANAGEMENT: What advice do you have for administrators or physicians looking to implement an immediate postpartum LARC program into a hospital setting?
Dr. Hofler: Probably the best single resource is the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Postpartum Contraception Access Initiative (PCAI). They have a dedicated website and offer a lot of support and resources that include site-specific training at the hospital or the institution; clinician training on implants and IUDs; and administrator training on some of the systems of care, the billing process, the stocking process, and pharmacy education. They also provide information on all the things that should be included beyond the clinical aspects. I strongly recommend looking at what they offer.
Also, because many hospitals say, "We love this idea. We would support immediate postpartum LARC, we just want to make sure we get paid," the ACOG LARC Program website includes state-specific guidance for how Medicaid pays for LARC devices. There is state-specific guidance about how the device payment can be separated from the global payment for delivery—specific things for each institution to do to get reimbursed.
A 2017 prospective cohort study was the first to directly compare expulsion rates of the levonorgestrel (LNG) intrauterine device (IUD) and the copper IUD placed postplacentally (within 10 minutes of placental delivery). The study investigators found that, among 96 women at 12 weeks, 38% of the LNG-IUD users and 20% of the copper IUD users experienced IUD expulsion (odds ratio, 2.55; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.99-6.55; P = .05). Women were aged 18 to 40 and had a singleton vaginal delivery at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestation.1 The two study groups were similar except that more copper IUD users were Hispanic (66% vs 38%) and fewer were primiparous (16% vs 31%). The study authors found the only independent predictor of device expulsion to be IUD type.
In a 2019 prospective cohort study, Hinz and colleagues compared the 6-month expulsion rate of IUDs inserted in the immediate postpartum period (within 10 to 15 minutes of placental delivery) after vaginal or cesarean delivery.2 Women were aged 18 to 45 years and selected a LNG 52-mg IUD (75 women) or copper IUD (58 women) for postpartum contraception. They completed a survey from weeks 0 to 5 and on weeks 12 and 24 postpartum regarding IUD expulsion, IUD removal, vaginal bleeding, and breastfeeding. A total of 58 women had a vaginal delivery, and 56 had a cesarean delivery.
At 6 months, the expulsion rates were similar in the two groups: 26.7% of the LNG IUDs expelled, compared with 20.5% of the copper IUDs (P = .38). The study groups were similar, point out the study investigators, except that the copper IUD users had a higher median parity (3 vs. 2; P = .03). In addition, the copper IUDs were inserted by more senior than junior residents (46.2% vs 22.7%, P = .02).
A 2018 systematic review pooled absolute rates of IUD expulsion and estimated adjusted relative risk (RR) for IUD type. A total of 48 studies (rated level I to II-3 of poor to good quality) were included in the analysis, and results indicated that the LNG-IUD was associated with a higher risk of expulsion at less than 4 weeks postpartum than the copper IUD (adjusted RR, 1.91; 95% CI, 1.50-2.43).3
References
1. Goldthwaite LM, Sheeder J, Hyer J, et al. Postplacental intrauterine device expulsion by 12 weeks: a prospective cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217:674.e1-674.e8.
2. Hinz EK, Murthy A, Wang B, Ryan N, Ades V. A prospective cohort study comparing expulsion after postplacental insertion: the levonorgestrel versus the copper intrauterine device. Contraception. May 17, 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2019.04.011.
3. Jatlaoui TC, Whiteman MK, Jeng G, et al. Intrauterine device expulsion after postpartum placement. Obstet Gynecol. 2018:895-905.
Technique for placing an IUD immediately after vaginal birth
1. Bring supplies for intrauterine device (IUD) insertion: the IUD, posterior blade of a speculum or retractor for posterior vagina, ring forceps, curved Kelly placenta forceps, and scissors.
2. Determine that the patient still wants the IUD and is still medically eligible for the IUD. Place the IUD as soon as possible following placenta delivery; in most studies IUD placement occurred within 10 minutes of the placenta. Any perineal lacerations should be repaired after IUD placement.
3. Break down the bed to facilitate placement. If the perineum or vagina is soiled with stool or meconium then consider povodine-iodine prep.
4. Place the posterior blade of the speculum into the vagina and grasp the anterior cervix with the ring forceps.
5. Set up the IUD for insertion: Change into new sterile gloves. Remove the IUD from the inserter. For levonorgestrel IUDs, cut the strings so that the length of the IUD and strings together is approximately 10 to 12 cm; copper IUDs do not need strings trimmed. Hold one arm of the IUD with the long Kelly placenta forceps so that the stem of the IUD is approximately parallel to the shaft of the forceps.
6. Insert the IUD: Guide the IUD into the lower uterine segment with the left hand on the cervix ring forceps and the right hand on the IUD forceps. After passing the IUD through the cervix, move the left hand to the abdomen and press the fundus posterior and caudad to straighten the endometrial canal and to feel the IUD at the fundus. With the right hand, guide the IUD to the fundus; this often entails dropping the hand significantly and guiding the IUD much more anteriorly than first expected.
7. Release the IUD with forceps wide open, sweeping the forceps to one side to avoid pulling the IUD out with the forceps. 8. Consider use of ultrasound guidance and ultrasound verification of fundal location, especially when first performing postplacental IUD placements.
8. Consider use of ultrasound guidance and ultrasound verification of fundal location, especially when first performing postplacental IUD placements.
Troubleshooting tips:
- If you are unable to visualize the anterior cervix, try to place the ring forceps by palpation.
- If you are unable to grasp the cervix with ring forceps by palpation, you may try to place the IUD manually. Hold the IUD between the first and second fingers of the right hand and place the IUD at the fundus. Release the IUD with the fingers wide open and remove the hand without removing the IUD.
Technique for placing an IUD immediately after cesarean birth
1. Determine that the patient still wants the IUD and is still medically eligible for the IUD. Place the IUD as soon as possible following placenta delivery; in most studies IUD placement occurred within 10 minutes of the placenta.
2. For levonorgestrel IUDs: Remove the IUD from the inserter. Cut the strings so that the length of the IUD and strings together is approximately 10 to 12 cm. Place the IUD at the fundus with a ring forceps and tuck the strings toward the cervix. It is not necessary to open the cervix or to place the strings through the cervix.
3. For copper IUDs: String trimming is not necessary. Place the IUD at the fundus with the IUD inserter or a ring forceps and tuck the strings toward the cervix. It is not necessary to open the cervix or to place the strings through the cervix.
4. Repair the hysterotomy as usual.
1. Dole DM, Martin J. What nurses need to know about immediate postpartum initiation of long-acting reversible contraception. Nurs Womens Health. 2017;21:186-195.
2. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 736: optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150.
3. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology, Long-Acting Reversible Contraception Work Group. Practice Bulletin no. 186: long-acting reversible contraception: implants and intrauterine devices. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:e251-e269.
4. Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-104.
Evidence-based education about long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) for women in the postpartum period can result in the increased continuation of and satisfaction with LARC.1 However, nearly 40% of women do not attend a postpartum visit.2 And up to 57% of women report having unprotected intercourse before the 6-week postpartum visit, which increases the risk of unplanned pregnancy.3 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) supports immediate postpartum LARC insertion as best practice,3 and clinicians providing care for women during the peripartum period can counsel women regarding informed contraceptive decisions and provide guidance regarding both short-acting contraception and LARC.1
Immediate postpartum LARC, using intrauterine devices (IUDs) in particular, has been used around the world for a long time, says Lisa Hofler, MD, MPH, MBA, Chief in the Division of Family Planning at the University of New Mexico School of Medicine in Albuquerque. “Much of our initial data came from other countries, but eventually people in the United States said, ‘This is a great option, why aren't we doing this?’" In addition, although women considering immediate postpartum LARC should be counseled about the theoretical risk of reduced duration of breastfeeding, the evidence overwhelmingly has not shown a negative effect on actual breastfeeding outcomes according to ACOG.3 OBG MANAGEMENT recently met up with Dr. Hofler to ask her which patients are ideal for postpartum LARC, how to troubleshoot common pitfalls, and how to implement the practice within one’s own institution.
OBG Management: Who do you consider to be the ideal patient for immediate postpartum LARC?
Lisa Hofler, MD: The great thing about immediate postpartum LARC (including IUDs and implants) is that any woman is an ideal candidate. We are simply talking about the timing of when a woman chooses to get an IUD or an implant after the birth of her child. There is no one perfect woman; it is the person who chooses the method and wants to use that method immediately after birth. When a woman chooses a LARC, she can be assured that after the birth of her child she will be protected against pregnancy. If she chooses an IUD as her LARC method, she will be comfortable at insertion because the cervix is already dilated when it is inserted.
For the implant, the contraindications are the same as in the outpatient setting. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use covers many medical conditions and whether or not a person might be a candidate for different birth control methods.4 Those same considerations apply for the implant postpartum (TABLE).3
For the IUD, similarly, anyone who would not be a candidate for the IUD in the outpatient setting is not a candidate for immediate postpartum IUD. For instance, if the person has an intrauterine infection, you should not place an IUD. Also, if a patient is hemorrhaging and you are managing the hemorrhage (say she has retained placenta or membranes or she has uterine atony), you are not going to put an IUD in, as you need to attend to her bleeding.

OBG Management: What is your approach to counseling a patient for immediate postpartum LARC?
Dr. Hofler: The ideal time to counsel about postbirth contraception is in the prenatal period, when the patient is making decisions about what method she wants to use after the birth. Once she chooses her preferred method, address timing if appropriate. It is less ideal to talk to a woman about the option of immediate postpartum LARC when she comes to labor and delivery, especially if that is the first time she has heard about it. Certainly, the time to talk about postpartum LARC options is not immediately after the baby is born. Approaching your patient with, "What do you want for birth control? Do you want this IUD? I can put it in right now," can feel coercive. This approach does not put the woman in a position in which she has enough decision-making time or time to ask questions.
OBG Management: What problems do clinicians run into when placing an immediate postpartum IUD, and can you offer solutions?
Dr. Hofler: When placing an immediate postpartum IUD, people might run into a few problems. The first relates to preplacement counseling. Perhaps when making the plan for the postpartum IUD the clinician did not counsel the woman that there are certain conditions that could preclude IUD placement—such as intrauterine infection or postpartum hemorrhage. When dealing with those types of issues, a patient is not eligible for an IUD, and she should be mentally prepared for this type of situation. Let her know during the counseling before the birth that immediately postpartum is a great time and opportunity for effective contraception placement. Tell her that hopefully IUD placement will be possible but that occasionally it is not, and make a back-up plan in case the IUD cannot be placed immediately postpartum.
The second unique area for counseling with immediate postpartum IUDs is a slightly increased risk of expulsion of an IUD placed immediately postpartum compared with in the office. The risk of expulsion varies by type of delivery. For instance, cesarean delivery births have a lower expulsion rate than vaginal births. The expulsion rate seems to vary by type of IUD as well. Copper IUDs seem to have a slightly lower expulsion rate than hormonal IUDs. (See “Levonorgestrel vs copper IUD expulsion rates after immediate postpartum insertion.”) This consideration should be talked about ahead of time, too. Provider training in IUD placement does impact the likelihood of expulsion, and if you place the IUD at the fundus, it is less likely to expel. (See “Inserting the immediate postpartum IUD after vaginal and cesarean birth step by step.”)
A third issue that clinicians run into is actually the systems of care—making sure that the IUD or implant is available when you need it, making sure that documentation happens the way it should, and ensuring that the follow-up billing and revenue cycle happens so that the woman gets the device that she wants and the providers get paid for having provided it. These issues require a multidisciplinary team to work through in order to ensure that postpartum LARC placement is a sustainable process in the long run.
Often, when people think of immediate postpartum LARC they think of postplacental IUDs. However, an implant also is an option, and that too is immediate postpartum LARC. Placing an implant is often a lot easier to do after the birth than placing an IUD. As clinicians work toward bringing an immediate postpartum LARC program to their hospital system, starting with implants is a smart thing to do because clinicians do not have to learn or teach new clinical skills. Because of that, immediate postpartum implants are a good troubleshooting mechanism for opening up the conversation about immediate postpartum LARC at your institution.
OBG MANAGEMENT: What advice do you have for administrators or physicians looking to implement an immediate postpartum LARC program into a hospital setting?
Dr. Hofler: Probably the best single resource is the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Postpartum Contraception Access Initiative (PCAI). They have a dedicated website and offer a lot of support and resources that include site-specific training at the hospital or the institution; clinician training on implants and IUDs; and administrator training on some of the systems of care, the billing process, the stocking process, and pharmacy education. They also provide information on all the things that should be included beyond the clinical aspects. I strongly recommend looking at what they offer.
Also, because many hospitals say, "We love this idea. We would support immediate postpartum LARC, we just want to make sure we get paid," the ACOG LARC Program website includes state-specific guidance for how Medicaid pays for LARC devices. There is state-specific guidance about how the device payment can be separated from the global payment for delivery—specific things for each institution to do to get reimbursed.
A 2017 prospective cohort study was the first to directly compare expulsion rates of the levonorgestrel (LNG) intrauterine device (IUD) and the copper IUD placed postplacentally (within 10 minutes of placental delivery). The study investigators found that, among 96 women at 12 weeks, 38% of the LNG-IUD users and 20% of the copper IUD users experienced IUD expulsion (odds ratio, 2.55; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.99-6.55; P = .05). Women were aged 18 to 40 and had a singleton vaginal delivery at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestation.1 The two study groups were similar except that more copper IUD users were Hispanic (66% vs 38%) and fewer were primiparous (16% vs 31%). The study authors found the only independent predictor of device expulsion to be IUD type.
In a 2019 prospective cohort study, Hinz and colleagues compared the 6-month expulsion rate of IUDs inserted in the immediate postpartum period (within 10 to 15 minutes of placental delivery) after vaginal or cesarean delivery.2 Women were aged 18 to 45 years and selected a LNG 52-mg IUD (75 women) or copper IUD (58 women) for postpartum contraception. They completed a survey from weeks 0 to 5 and on weeks 12 and 24 postpartum regarding IUD expulsion, IUD removal, vaginal bleeding, and breastfeeding. A total of 58 women had a vaginal delivery, and 56 had a cesarean delivery.
At 6 months, the expulsion rates were similar in the two groups: 26.7% of the LNG IUDs expelled, compared with 20.5% of the copper IUDs (P = .38). The study groups were similar, point out the study investigators, except that the copper IUD users had a higher median parity (3 vs. 2; P = .03). In addition, the copper IUDs were inserted by more senior than junior residents (46.2% vs 22.7%, P = .02).
A 2018 systematic review pooled absolute rates of IUD expulsion and estimated adjusted relative risk (RR) for IUD type. A total of 48 studies (rated level I to II-3 of poor to good quality) were included in the analysis, and results indicated that the LNG-IUD was associated with a higher risk of expulsion at less than 4 weeks postpartum than the copper IUD (adjusted RR, 1.91; 95% CI, 1.50-2.43).3
References
1. Goldthwaite LM, Sheeder J, Hyer J, et al. Postplacental intrauterine device expulsion by 12 weeks: a prospective cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217:674.e1-674.e8.
2. Hinz EK, Murthy A, Wang B, Ryan N, Ades V. A prospective cohort study comparing expulsion after postplacental insertion: the levonorgestrel versus the copper intrauterine device. Contraception. May 17, 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2019.04.011.
3. Jatlaoui TC, Whiteman MK, Jeng G, et al. Intrauterine device expulsion after postpartum placement. Obstet Gynecol. 2018:895-905.
Technique for placing an IUD immediately after vaginal birth
1. Bring supplies for intrauterine device (IUD) insertion: the IUD, posterior blade of a speculum or retractor for posterior vagina, ring forceps, curved Kelly placenta forceps, and scissors.
2. Determine that the patient still wants the IUD and is still medically eligible for the IUD. Place the IUD as soon as possible following placenta delivery; in most studies IUD placement occurred within 10 minutes of the placenta. Any perineal lacerations should be repaired after IUD placement.
3. Break down the bed to facilitate placement. If the perineum or vagina is soiled with stool or meconium then consider povodine-iodine prep.
4. Place the posterior blade of the speculum into the vagina and grasp the anterior cervix with the ring forceps.
5. Set up the IUD for insertion: Change into new sterile gloves. Remove the IUD from the inserter. For levonorgestrel IUDs, cut the strings so that the length of the IUD and strings together is approximately 10 to 12 cm; copper IUDs do not need strings trimmed. Hold one arm of the IUD with the long Kelly placenta forceps so that the stem of the IUD is approximately parallel to the shaft of the forceps.
6. Insert the IUD: Guide the IUD into the lower uterine segment with the left hand on the cervix ring forceps and the right hand on the IUD forceps. After passing the IUD through the cervix, move the left hand to the abdomen and press the fundus posterior and caudad to straighten the endometrial canal and to feel the IUD at the fundus. With the right hand, guide the IUD to the fundus; this often entails dropping the hand significantly and guiding the IUD much more anteriorly than first expected.
7. Release the IUD with forceps wide open, sweeping the forceps to one side to avoid pulling the IUD out with the forceps. 8. Consider use of ultrasound guidance and ultrasound verification of fundal location, especially when first performing postplacental IUD placements.
8. Consider use of ultrasound guidance and ultrasound verification of fundal location, especially when first performing postplacental IUD placements.
Troubleshooting tips:
- If you are unable to visualize the anterior cervix, try to place the ring forceps by palpation.
- If you are unable to grasp the cervix with ring forceps by palpation, you may try to place the IUD manually. Hold the IUD between the first and second fingers of the right hand and place the IUD at the fundus. Release the IUD with the fingers wide open and remove the hand without removing the IUD.
Technique for placing an IUD immediately after cesarean birth
1. Determine that the patient still wants the IUD and is still medically eligible for the IUD. Place the IUD as soon as possible following placenta delivery; in most studies IUD placement occurred within 10 minutes of the placenta.
2. For levonorgestrel IUDs: Remove the IUD from the inserter. Cut the strings so that the length of the IUD and strings together is approximately 10 to 12 cm. Place the IUD at the fundus with a ring forceps and tuck the strings toward the cervix. It is not necessary to open the cervix or to place the strings through the cervix.
3. For copper IUDs: String trimming is not necessary. Place the IUD at the fundus with the IUD inserter or a ring forceps and tuck the strings toward the cervix. It is not necessary to open the cervix or to place the strings through the cervix.
4. Repair the hysterotomy as usual.
Evidence-based education about long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) for women in the postpartum period can result in the increased continuation of and satisfaction with LARC.1 However, nearly 40% of women do not attend a postpartum visit.2 And up to 57% of women report having unprotected intercourse before the 6-week postpartum visit, which increases the risk of unplanned pregnancy.3 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) supports immediate postpartum LARC insertion as best practice,3 and clinicians providing care for women during the peripartum period can counsel women regarding informed contraceptive decisions and provide guidance regarding both short-acting contraception and LARC.1
Immediate postpartum LARC, using intrauterine devices (IUDs) in particular, has been used around the world for a long time, says Lisa Hofler, MD, MPH, MBA, Chief in the Division of Family Planning at the University of New Mexico School of Medicine in Albuquerque. “Much of our initial data came from other countries, but eventually people in the United States said, ‘This is a great option, why aren't we doing this?’" In addition, although women considering immediate postpartum LARC should be counseled about the theoretical risk of reduced duration of breastfeeding, the evidence overwhelmingly has not shown a negative effect on actual breastfeeding outcomes according to ACOG.3 OBG MANAGEMENT recently met up with Dr. Hofler to ask her which patients are ideal for postpartum LARC, how to troubleshoot common pitfalls, and how to implement the practice within one’s own institution.
OBG Management: Who do you consider to be the ideal patient for immediate postpartum LARC?
Lisa Hofler, MD: The great thing about immediate postpartum LARC (including IUDs and implants) is that any woman is an ideal candidate. We are simply talking about the timing of when a woman chooses to get an IUD or an implant after the birth of her child. There is no one perfect woman; it is the person who chooses the method and wants to use that method immediately after birth. When a woman chooses a LARC, she can be assured that after the birth of her child she will be protected against pregnancy. If she chooses an IUD as her LARC method, she will be comfortable at insertion because the cervix is already dilated when it is inserted.
For the implant, the contraindications are the same as in the outpatient setting. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use covers many medical conditions and whether or not a person might be a candidate for different birth control methods.4 Those same considerations apply for the implant postpartum (TABLE).3
For the IUD, similarly, anyone who would not be a candidate for the IUD in the outpatient setting is not a candidate for immediate postpartum IUD. For instance, if the person has an intrauterine infection, you should not place an IUD. Also, if a patient is hemorrhaging and you are managing the hemorrhage (say she has retained placenta or membranes or she has uterine atony), you are not going to put an IUD in, as you need to attend to her bleeding.

OBG Management: What is your approach to counseling a patient for immediate postpartum LARC?
Dr. Hofler: The ideal time to counsel about postbirth contraception is in the prenatal period, when the patient is making decisions about what method she wants to use after the birth. Once she chooses her preferred method, address timing if appropriate. It is less ideal to talk to a woman about the option of immediate postpartum LARC when she comes to labor and delivery, especially if that is the first time she has heard about it. Certainly, the time to talk about postpartum LARC options is not immediately after the baby is born. Approaching your patient with, "What do you want for birth control? Do you want this IUD? I can put it in right now," can feel coercive. This approach does not put the woman in a position in which she has enough decision-making time or time to ask questions.
OBG Management: What problems do clinicians run into when placing an immediate postpartum IUD, and can you offer solutions?
Dr. Hofler: When placing an immediate postpartum IUD, people might run into a few problems. The first relates to preplacement counseling. Perhaps when making the plan for the postpartum IUD the clinician did not counsel the woman that there are certain conditions that could preclude IUD placement—such as intrauterine infection or postpartum hemorrhage. When dealing with those types of issues, a patient is not eligible for an IUD, and she should be mentally prepared for this type of situation. Let her know during the counseling before the birth that immediately postpartum is a great time and opportunity for effective contraception placement. Tell her that hopefully IUD placement will be possible but that occasionally it is not, and make a back-up plan in case the IUD cannot be placed immediately postpartum.
The second unique area for counseling with immediate postpartum IUDs is a slightly increased risk of expulsion of an IUD placed immediately postpartum compared with in the office. The risk of expulsion varies by type of delivery. For instance, cesarean delivery births have a lower expulsion rate than vaginal births. The expulsion rate seems to vary by type of IUD as well. Copper IUDs seem to have a slightly lower expulsion rate than hormonal IUDs. (See “Levonorgestrel vs copper IUD expulsion rates after immediate postpartum insertion.”) This consideration should be talked about ahead of time, too. Provider training in IUD placement does impact the likelihood of expulsion, and if you place the IUD at the fundus, it is less likely to expel. (See “Inserting the immediate postpartum IUD after vaginal and cesarean birth step by step.”)
A third issue that clinicians run into is actually the systems of care—making sure that the IUD or implant is available when you need it, making sure that documentation happens the way it should, and ensuring that the follow-up billing and revenue cycle happens so that the woman gets the device that she wants and the providers get paid for having provided it. These issues require a multidisciplinary team to work through in order to ensure that postpartum LARC placement is a sustainable process in the long run.
Often, when people think of immediate postpartum LARC they think of postplacental IUDs. However, an implant also is an option, and that too is immediate postpartum LARC. Placing an implant is often a lot easier to do after the birth than placing an IUD. As clinicians work toward bringing an immediate postpartum LARC program to their hospital system, starting with implants is a smart thing to do because clinicians do not have to learn or teach new clinical skills. Because of that, immediate postpartum implants are a good troubleshooting mechanism for opening up the conversation about immediate postpartum LARC at your institution.
OBG MANAGEMENT: What advice do you have for administrators or physicians looking to implement an immediate postpartum LARC program into a hospital setting?
Dr. Hofler: Probably the best single resource is the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Postpartum Contraception Access Initiative (PCAI). They have a dedicated website and offer a lot of support and resources that include site-specific training at the hospital or the institution; clinician training on implants and IUDs; and administrator training on some of the systems of care, the billing process, the stocking process, and pharmacy education. They also provide information on all the things that should be included beyond the clinical aspects. I strongly recommend looking at what they offer.
Also, because many hospitals say, "We love this idea. We would support immediate postpartum LARC, we just want to make sure we get paid," the ACOG LARC Program website includes state-specific guidance for how Medicaid pays for LARC devices. There is state-specific guidance about how the device payment can be separated from the global payment for delivery—specific things for each institution to do to get reimbursed.
A 2017 prospective cohort study was the first to directly compare expulsion rates of the levonorgestrel (LNG) intrauterine device (IUD) and the copper IUD placed postplacentally (within 10 minutes of placental delivery). The study investigators found that, among 96 women at 12 weeks, 38% of the LNG-IUD users and 20% of the copper IUD users experienced IUD expulsion (odds ratio, 2.55; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.99-6.55; P = .05). Women were aged 18 to 40 and had a singleton vaginal delivery at ≥ 35 weeks’ gestation.1 The two study groups were similar except that more copper IUD users were Hispanic (66% vs 38%) and fewer were primiparous (16% vs 31%). The study authors found the only independent predictor of device expulsion to be IUD type.
In a 2019 prospective cohort study, Hinz and colleagues compared the 6-month expulsion rate of IUDs inserted in the immediate postpartum period (within 10 to 15 minutes of placental delivery) after vaginal or cesarean delivery.2 Women were aged 18 to 45 years and selected a LNG 52-mg IUD (75 women) or copper IUD (58 women) for postpartum contraception. They completed a survey from weeks 0 to 5 and on weeks 12 and 24 postpartum regarding IUD expulsion, IUD removal, vaginal bleeding, and breastfeeding. A total of 58 women had a vaginal delivery, and 56 had a cesarean delivery.
At 6 months, the expulsion rates were similar in the two groups: 26.7% of the LNG IUDs expelled, compared with 20.5% of the copper IUDs (P = .38). The study groups were similar, point out the study investigators, except that the copper IUD users had a higher median parity (3 vs. 2; P = .03). In addition, the copper IUDs were inserted by more senior than junior residents (46.2% vs 22.7%, P = .02).
A 2018 systematic review pooled absolute rates of IUD expulsion and estimated adjusted relative risk (RR) for IUD type. A total of 48 studies (rated level I to II-3 of poor to good quality) were included in the analysis, and results indicated that the LNG-IUD was associated with a higher risk of expulsion at less than 4 weeks postpartum than the copper IUD (adjusted RR, 1.91; 95% CI, 1.50-2.43).3
References
1. Goldthwaite LM, Sheeder J, Hyer J, et al. Postplacental intrauterine device expulsion by 12 weeks: a prospective cohort study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217:674.e1-674.e8.
2. Hinz EK, Murthy A, Wang B, Ryan N, Ades V. A prospective cohort study comparing expulsion after postplacental insertion: the levonorgestrel versus the copper intrauterine device. Contraception. May 17, 2019. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2019.04.011.
3. Jatlaoui TC, Whiteman MK, Jeng G, et al. Intrauterine device expulsion after postpartum placement. Obstet Gynecol. 2018:895-905.
Technique for placing an IUD immediately after vaginal birth
1. Bring supplies for intrauterine device (IUD) insertion: the IUD, posterior blade of a speculum or retractor for posterior vagina, ring forceps, curved Kelly placenta forceps, and scissors.
2. Determine that the patient still wants the IUD and is still medically eligible for the IUD. Place the IUD as soon as possible following placenta delivery; in most studies IUD placement occurred within 10 minutes of the placenta. Any perineal lacerations should be repaired after IUD placement.
3. Break down the bed to facilitate placement. If the perineum or vagina is soiled with stool or meconium then consider povodine-iodine prep.
4. Place the posterior blade of the speculum into the vagina and grasp the anterior cervix with the ring forceps.
5. Set up the IUD for insertion: Change into new sterile gloves. Remove the IUD from the inserter. For levonorgestrel IUDs, cut the strings so that the length of the IUD and strings together is approximately 10 to 12 cm; copper IUDs do not need strings trimmed. Hold one arm of the IUD with the long Kelly placenta forceps so that the stem of the IUD is approximately parallel to the shaft of the forceps.
6. Insert the IUD: Guide the IUD into the lower uterine segment with the left hand on the cervix ring forceps and the right hand on the IUD forceps. After passing the IUD through the cervix, move the left hand to the abdomen and press the fundus posterior and caudad to straighten the endometrial canal and to feel the IUD at the fundus. With the right hand, guide the IUD to the fundus; this often entails dropping the hand significantly and guiding the IUD much more anteriorly than first expected.
7. Release the IUD with forceps wide open, sweeping the forceps to one side to avoid pulling the IUD out with the forceps. 8. Consider use of ultrasound guidance and ultrasound verification of fundal location, especially when first performing postplacental IUD placements.
8. Consider use of ultrasound guidance and ultrasound verification of fundal location, especially when first performing postplacental IUD placements.
Troubleshooting tips:
- If you are unable to visualize the anterior cervix, try to place the ring forceps by palpation.
- If you are unable to grasp the cervix with ring forceps by palpation, you may try to place the IUD manually. Hold the IUD between the first and second fingers of the right hand and place the IUD at the fundus. Release the IUD with the fingers wide open and remove the hand without removing the IUD.
Technique for placing an IUD immediately after cesarean birth
1. Determine that the patient still wants the IUD and is still medically eligible for the IUD. Place the IUD as soon as possible following placenta delivery; in most studies IUD placement occurred within 10 minutes of the placenta.
2. For levonorgestrel IUDs: Remove the IUD from the inserter. Cut the strings so that the length of the IUD and strings together is approximately 10 to 12 cm. Place the IUD at the fundus with a ring forceps and tuck the strings toward the cervix. It is not necessary to open the cervix or to place the strings through the cervix.
3. For copper IUDs: String trimming is not necessary. Place the IUD at the fundus with the IUD inserter or a ring forceps and tuck the strings toward the cervix. It is not necessary to open the cervix or to place the strings through the cervix.
4. Repair the hysterotomy as usual.
1. Dole DM, Martin J. What nurses need to know about immediate postpartum initiation of long-acting reversible contraception. Nurs Womens Health. 2017;21:186-195.
2. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 736: optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150.
3. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology, Long-Acting Reversible Contraception Work Group. Practice Bulletin no. 186: long-acting reversible contraception: implants and intrauterine devices. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:e251-e269.
4. Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-104.
1. Dole DM, Martin J. What nurses need to know about immediate postpartum initiation of long-acting reversible contraception. Nurs Womens Health. 2017;21:186-195.
2. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Committee Opinion no. 736: optimizing postpartum care. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131:e140-e150.
3. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Practice Bulletins-Gynecology, Long-Acting Reversible Contraception Work Group. Practice Bulletin no. 186: long-acting reversible contraception: implants and intrauterine devices. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130:e251-e269.
4. Curtis KM, Tepper NK, Jatlaoui TC, et al. U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65:1-104.
Bilateral salpingectomy gains favor for sterilization
NASHVILLE, TENN. –
“[It is] probably the newest thing on the block ... this is becoming super widespread,” Eve Espey, MD, said of the procedure during a contraceptive update at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Although evidence directly supporting bilateral salpingectomy for sterilization is lacking, there are good reasons to consider it, she said.
For example, the procedure is likely more effective than tubal ligation with no increased risk for complications, and is probably more likely to cut ovarian cancer risk than is tubal ligation, explained Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
“So we don’t actually have good [randomized controlled trials] on effectiveness for [bilateral] salpingectomy, but it is most like a partial salpingectomy, which is highly effective, so there is reason to believe that it might be more effective,” she added. The downsides are that the procedure may take longer, it may impair ovarian blood supply, and long-term population-level data on outcomes are lacking.
ACOG said in a 2015 committee opinion that when counseling women, bilateral salpingectomy can be discussed and considered “a method that provides effective contraception,” but also stressed the need for randomized controlled trials to support any related reduction in ovarian cancer risk. That opinion (#620) was replaced in April 2019 by Committee Opinion #774, which addresses opportunistic salpingectomy for epithelial ovarian cancer prevention, and which states that “the risks and benefits of salpingectomy should be discussed with patients who desire permanent sterilization.”
“[The Society of Gynecologic Oncology] is much, much more emphatic,” Dr. Espey said, citing a 2013 Clinical Practice Statement calling for discussion and consideration of risk-reducing salpingectomy in lieu of tubal ligation for women at average risk of ovarian cancer (after childbearing).
Dr. Espey also noted that during a recent grand rounds on sterilization, about 90% of participants said they were doing bilateral salpingectomy in the setting of vaginal delivery. “So I think we’re going to see this coming not just with C-section, but also with vaginal delivery.”
Dr. Espey reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. –
“[It is] probably the newest thing on the block ... this is becoming super widespread,” Eve Espey, MD, said of the procedure during a contraceptive update at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Although evidence directly supporting bilateral salpingectomy for sterilization is lacking, there are good reasons to consider it, she said.
For example, the procedure is likely more effective than tubal ligation with no increased risk for complications, and is probably more likely to cut ovarian cancer risk than is tubal ligation, explained Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
“So we don’t actually have good [randomized controlled trials] on effectiveness for [bilateral] salpingectomy, but it is most like a partial salpingectomy, which is highly effective, so there is reason to believe that it might be more effective,” she added. The downsides are that the procedure may take longer, it may impair ovarian blood supply, and long-term population-level data on outcomes are lacking.
ACOG said in a 2015 committee opinion that when counseling women, bilateral salpingectomy can be discussed and considered “a method that provides effective contraception,” but also stressed the need for randomized controlled trials to support any related reduction in ovarian cancer risk. That opinion (#620) was replaced in April 2019 by Committee Opinion #774, which addresses opportunistic salpingectomy for epithelial ovarian cancer prevention, and which states that “the risks and benefits of salpingectomy should be discussed with patients who desire permanent sterilization.”
“[The Society of Gynecologic Oncology] is much, much more emphatic,” Dr. Espey said, citing a 2013 Clinical Practice Statement calling for discussion and consideration of risk-reducing salpingectomy in lieu of tubal ligation for women at average risk of ovarian cancer (after childbearing).
Dr. Espey also noted that during a recent grand rounds on sterilization, about 90% of participants said they were doing bilateral salpingectomy in the setting of vaginal delivery. “So I think we’re going to see this coming not just with C-section, but also with vaginal delivery.”
Dr. Espey reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. –
“[It is] probably the newest thing on the block ... this is becoming super widespread,” Eve Espey, MD, said of the procedure during a contraceptive update at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Although evidence directly supporting bilateral salpingectomy for sterilization is lacking, there are good reasons to consider it, she said.
For example, the procedure is likely more effective than tubal ligation with no increased risk for complications, and is probably more likely to cut ovarian cancer risk than is tubal ligation, explained Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque.
“So we don’t actually have good [randomized controlled trials] on effectiveness for [bilateral] salpingectomy, but it is most like a partial salpingectomy, which is highly effective, so there is reason to believe that it might be more effective,” she added. The downsides are that the procedure may take longer, it may impair ovarian blood supply, and long-term population-level data on outcomes are lacking.
ACOG said in a 2015 committee opinion that when counseling women, bilateral salpingectomy can be discussed and considered “a method that provides effective contraception,” but also stressed the need for randomized controlled trials to support any related reduction in ovarian cancer risk. That opinion (#620) was replaced in April 2019 by Committee Opinion #774, which addresses opportunistic salpingectomy for epithelial ovarian cancer prevention, and which states that “the risks and benefits of salpingectomy should be discussed with patients who desire permanent sterilization.”
“[The Society of Gynecologic Oncology] is much, much more emphatic,” Dr. Espey said, citing a 2013 Clinical Practice Statement calling for discussion and consideration of risk-reducing salpingectomy in lieu of tubal ligation for women at average risk of ovarian cancer (after childbearing).
Dr. Espey also noted that during a recent grand rounds on sterilization, about 90% of participants said they were doing bilateral salpingectomy in the setting of vaginal delivery. “So I think we’re going to see this coming not just with C-section, but also with vaginal delivery.”
Dr. Espey reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT COMMENTARY FROM ACOG 2019
Teen mothers using long-acting reversible contraception are least likely to use condoms
such as the birth control pill, vaginal ring, contraceptive patch, or injection, according to research in JAMA Pediatrics.
This highlights a need for education to lower the risk of sexually transmitted infections in this population.
“Our finding that less than 30% of sexually active teenage mothers using LARC or non-LARC hormonal methods also reported using condoms suggests the need for enhanced efforts to increase condom use among teenage mothers,” wrote Katherine Kortsmit, PhD, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
The researchers performed a cross-sectional analysis of contraceptive use among 5,480 new teenage mothers between 2012 and 2015 who were aged 19 years or younger in the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS). Participants were mainly first-time teenage mothers between ages 18 and 19 years (46% non-Hispanic white), current Medicaid users, and reported an unintended pregnancy. Dr. Kortsmit and colleagues monitored use of LARC and non-LARC hormonal methods, including condom use, among participants in PRAMS from 37 different sites.
Among teenage mothers in PRAM, 29% reported using condoms; 18% of mothers using LARC said they also used condoms, compared with 36% of mothers who used non-LARC hormonal methods (adjusted prevalence ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.41-0.60). Participants with IUDs were least likely to report using condoms (15%), compared with participants using implants (22%; aPR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.98), participants using the patch, ring, or injection (25%; aPR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.47-0.79), or the pill (47%; aPR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.25-0.40).
“These findings can be used to inform clinician counseling that sexually active teenage mothers have low uptake of condom use combined with more effective contraceptive methods and may need additional counseling on the importance of consistent and correct condom use for the prevention of STIs,” Dr. Kortsmit and associates wrote.
Limitations included the self-reported nature of the study, and lack of information on baseline condom use prior to pregnancy, relationship characteristics, and sexual partners during the postpartum period.
Education on contraceptive methods by clinicians is an important part of an adolescent’s contextualization of the benefits and risks of those methods, especially for women of color and marginalized groups, Andrea J. Hoopes, MD, MPH; and Gina S. Sucato, MD, MPH, wrote in an editorial related to the study by Kortsmit and colleagues.
In particular, these groups have higher rates of unplanned pregnancy, may have a history of being coerced to use contraception, and may be reluctant to discuss their sexual history or contraception use. “Many young women, including teenage mothers, remain at risk for coercion from partners, family members, and health care clinicians, so adopting a stance that ensures autonomy while eliciting unique developmental perspectives is paramount,” they said.
It is critically important to give women access to LARCs that are effective and easily used, and patients have a right to choose the contraception method that best fits their situation. It is through integrated programs, made available by Title X funding, that clinicians may be able to monitor their patients’ sexual, reproductive, and psychological health needs, and have conversations about the importance of contraception and prevention of sexually transmitted infections.
“Future studies should examine specific interventions aimed at promoting all adolescents’ motivations to remain safe and healthy by using condoms consistently and by seeking comprehensive sexual health care services, regardless of contraceptive method,” concluded Dr. Hoopes and Dr. Sucato, of the Adolescent Center at Kaiser Permanente Washington in Seattle. “In addition to receiving counseling about, and access to, condoms, adolescents need to develop the skills to negotiate condom use with partners.”
Dr. Kortsmit received support in the form of an appointment to the Research Participation Program at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through an interagency agreement. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Hoopes reported previous grant support from Bayer and the North American Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology. Dr. Sucato reported previous grant and other research support from Teva.
SOURCE: Kortsmit K et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1136; Hoopes AJ et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1133.
such as the birth control pill, vaginal ring, contraceptive patch, or injection, according to research in JAMA Pediatrics.
This highlights a need for education to lower the risk of sexually transmitted infections in this population.
“Our finding that less than 30% of sexually active teenage mothers using LARC or non-LARC hormonal methods also reported using condoms suggests the need for enhanced efforts to increase condom use among teenage mothers,” wrote Katherine Kortsmit, PhD, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
The researchers performed a cross-sectional analysis of contraceptive use among 5,480 new teenage mothers between 2012 and 2015 who were aged 19 years or younger in the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS). Participants were mainly first-time teenage mothers between ages 18 and 19 years (46% non-Hispanic white), current Medicaid users, and reported an unintended pregnancy. Dr. Kortsmit and colleagues monitored use of LARC and non-LARC hormonal methods, including condom use, among participants in PRAMS from 37 different sites.
Among teenage mothers in PRAM, 29% reported using condoms; 18% of mothers using LARC said they also used condoms, compared with 36% of mothers who used non-LARC hormonal methods (adjusted prevalence ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.41-0.60). Participants with IUDs were least likely to report using condoms (15%), compared with participants using implants (22%; aPR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.98), participants using the patch, ring, or injection (25%; aPR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.47-0.79), or the pill (47%; aPR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.25-0.40).
“These findings can be used to inform clinician counseling that sexually active teenage mothers have low uptake of condom use combined with more effective contraceptive methods and may need additional counseling on the importance of consistent and correct condom use for the prevention of STIs,” Dr. Kortsmit and associates wrote.
Limitations included the self-reported nature of the study, and lack of information on baseline condom use prior to pregnancy, relationship characteristics, and sexual partners during the postpartum period.
Education on contraceptive methods by clinicians is an important part of an adolescent’s contextualization of the benefits and risks of those methods, especially for women of color and marginalized groups, Andrea J. Hoopes, MD, MPH; and Gina S. Sucato, MD, MPH, wrote in an editorial related to the study by Kortsmit and colleagues.
In particular, these groups have higher rates of unplanned pregnancy, may have a history of being coerced to use contraception, and may be reluctant to discuss their sexual history or contraception use. “Many young women, including teenage mothers, remain at risk for coercion from partners, family members, and health care clinicians, so adopting a stance that ensures autonomy while eliciting unique developmental perspectives is paramount,” they said.
It is critically important to give women access to LARCs that are effective and easily used, and patients have a right to choose the contraception method that best fits their situation. It is through integrated programs, made available by Title X funding, that clinicians may be able to monitor their patients’ sexual, reproductive, and psychological health needs, and have conversations about the importance of contraception and prevention of sexually transmitted infections.
“Future studies should examine specific interventions aimed at promoting all adolescents’ motivations to remain safe and healthy by using condoms consistently and by seeking comprehensive sexual health care services, regardless of contraceptive method,” concluded Dr. Hoopes and Dr. Sucato, of the Adolescent Center at Kaiser Permanente Washington in Seattle. “In addition to receiving counseling about, and access to, condoms, adolescents need to develop the skills to negotiate condom use with partners.”
Dr. Kortsmit received support in the form of an appointment to the Research Participation Program at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through an interagency agreement. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Hoopes reported previous grant support from Bayer and the North American Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology. Dr. Sucato reported previous grant and other research support from Teva.
SOURCE: Kortsmit K et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1136; Hoopes AJ et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1133.
such as the birth control pill, vaginal ring, contraceptive patch, or injection, according to research in JAMA Pediatrics.
This highlights a need for education to lower the risk of sexually transmitted infections in this population.
“Our finding that less than 30% of sexually active teenage mothers using LARC or non-LARC hormonal methods also reported using condoms suggests the need for enhanced efforts to increase condom use among teenage mothers,” wrote Katherine Kortsmit, PhD, MPH, of the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues.
The researchers performed a cross-sectional analysis of contraceptive use among 5,480 new teenage mothers between 2012 and 2015 who were aged 19 years or younger in the Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System (PRAMS). Participants were mainly first-time teenage mothers between ages 18 and 19 years (46% non-Hispanic white), current Medicaid users, and reported an unintended pregnancy. Dr. Kortsmit and colleagues monitored use of LARC and non-LARC hormonal methods, including condom use, among participants in PRAMS from 37 different sites.
Among teenage mothers in PRAM, 29% reported using condoms; 18% of mothers using LARC said they also used condoms, compared with 36% of mothers who used non-LARC hormonal methods (adjusted prevalence ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.41-0.60). Participants with IUDs were least likely to report using condoms (15%), compared with participants using implants (22%; aPR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.51-0.98), participants using the patch, ring, or injection (25%; aPR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.47-0.79), or the pill (47%; aPR, 0.32; 95% CI, 0.25-0.40).
“These findings can be used to inform clinician counseling that sexually active teenage mothers have low uptake of condom use combined with more effective contraceptive methods and may need additional counseling on the importance of consistent and correct condom use for the prevention of STIs,” Dr. Kortsmit and associates wrote.
Limitations included the self-reported nature of the study, and lack of information on baseline condom use prior to pregnancy, relationship characteristics, and sexual partners during the postpartum period.
Education on contraceptive methods by clinicians is an important part of an adolescent’s contextualization of the benefits and risks of those methods, especially for women of color and marginalized groups, Andrea J. Hoopes, MD, MPH; and Gina S. Sucato, MD, MPH, wrote in an editorial related to the study by Kortsmit and colleagues.
In particular, these groups have higher rates of unplanned pregnancy, may have a history of being coerced to use contraception, and may be reluctant to discuss their sexual history or contraception use. “Many young women, including teenage mothers, remain at risk for coercion from partners, family members, and health care clinicians, so adopting a stance that ensures autonomy while eliciting unique developmental perspectives is paramount,” they said.
It is critically important to give women access to LARCs that are effective and easily used, and patients have a right to choose the contraception method that best fits their situation. It is through integrated programs, made available by Title X funding, that clinicians may be able to monitor their patients’ sexual, reproductive, and psychological health needs, and have conversations about the importance of contraception and prevention of sexually transmitted infections.
“Future studies should examine specific interventions aimed at promoting all adolescents’ motivations to remain safe and healthy by using condoms consistently and by seeking comprehensive sexual health care services, regardless of contraceptive method,” concluded Dr. Hoopes and Dr. Sucato, of the Adolescent Center at Kaiser Permanente Washington in Seattle. “In addition to receiving counseling about, and access to, condoms, adolescents need to develop the skills to negotiate condom use with partners.”
Dr. Kortsmit received support in the form of an appointment to the Research Participation Program at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through an interagency agreement. The other authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Hoopes reported previous grant support from Bayer and the North American Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology. Dr. Sucato reported previous grant and other research support from Teva.
SOURCE: Kortsmit K et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1136; Hoopes AJ et al. JAMA Pediatr. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2019.1133.
FROM JAMA PEDIATRICS
The Affordable Care Act, closing in on a decade
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) was enacted on March 23, 2010. Controversies, complaints, and detractors have and continue to abound. But the ACA’s landmark women’s health gains are unmistakable. Contraceptive coverage, maternity coverage, Medicaid coverage of low-income women, coverage for individuals with preexisting conditions, and gender-neutral premiums are now a part of the fabric of our society. For most.
Many physicians and patients—many lawmakers, too—do not remember the serious problems people had with their insurance companies before the ACA. Maternity coverage was usually a free-standing rider to an insurance policy, making it very expensive. Insurance plans did not have to, and often did not, cover contraceptives, and none did without copays or deductibles. Women were routinely denied coverage if they had ever had a cesarean delivery, had once been the victim of domestic violence, or had any one of many common conditions, like diabetes. The many exclusionary conditions are so common, in fact, that one study estimated that around 52 million adults in the United States (27% of those younger than age 65 years) have preexisting conditions that would potentially make them uninsurable without the ACA’s protections.1
Before the ACA, it also was common for women with insurance policies to find their coverage rescinded, often with no explanation, even though they paid their premiums every month. And women with serious medical conditions often saw their coverage ended midway through their course of treatment. That placed their ObGyns in a terrible situation, too.
The insurance industry as a whole was running rough-shod over its customers, and making a lot of money by creatively and routinely denying coverage and payment for care. People were often insured, but not covered. The ACA halted many of these practices, and required insurers to meet high medical loss ratios, guaranteeing that 80% of the premiums’ for individual and small market insurers (and 85% for large insurers) are returned to patients in care payments or even in checks. In fact, nearly $4 billion in premiums have been rebated to insured individuals over the last 7 years under the ACA.2
The commitment of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) to women’s health and to our members’ ability to provide the best care has centered on preserving the critical gains of the ACA for women, improving them when we can, and making sure politicians don’t turn back the clock on women’s health. We have been busy.
In this article, we will look at what has happened to these landmark gains and promises of improved women’s health, specifically preexisting condition protections and contraceptive coverage, under a new Administration. What happens when good health care policy and political enmity collide?

Preexisting coverage protections
The 1996 Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) defines a preexisting condition exclusionas a “limitation or exclusion of benefits relating to a condition based on the fact that the condition was present before the date of enrollment for the coverage, whether or not any medical advice, diagnosis, care, or treatment was recommended or received before that date.” HIPPA prohibited employer-sponsored health plans from discriminating against individuals through denying them coverage or charging them more based on their or their family members’ health problems. The ACA expanded protections to prohibit the insurance practice of denying coverage altogether to an individual with a preexisting condition.3
Continue to: Under Congress...
Under Congress
Republicans held the majority in both chambers of the 115th Congress (2017–2018), and hoped to use their majority status to get an ACA repeal bill to the Republican President’s desk for speedy enactment. It was not easy, and they were not successful. Four major bills—the American Health Care Act, the Better Care Reconciliation Act, the Health Care Freedom Act, and the Graham-Cassidy Amendment—never made it over the finish line, with some not even making it to a vote. The Health Care Freedom Act was voted down in the Senate 51-49 when Senator John McCain came back from brain surgery to cast his famous thumbs-down vote.4 These bills all would have repealed or hobbled guaranteed issue, community rating, and essential health benefits of the ACA. Of all the legislative attempts to undermine the ACA, only the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) was signed into law, repealing the ACA individual mandate.
Handling by the courts
The TCJA gave ACA opponents their opening in court. Twenty Republican state attorneys general and governors brought suit in February 2018 (Texas v Azar), arguing that because the ACA relies on the mandate, and the mandate has been repealed, the rest of the ACA also should be struck down. A federal district judge agreed, on December 15, 2018, declaring the entire ACA unconstitutional.5
That decision has been limited in its practical effect so far, and maybe it was not altogether unexpected. What was unexpected was that the US Department of Justice (DOJ) refused to defend a federal law, in this case, the ACA. In June 2018, the DOJ declined to defend the individual mandate, as well as guaranteed issue, community rating, the ban on preexisting condition exclusions, and discrimination based on health status in the ACA. The DOJ at that time, however, did not agree with the plaintiffs that without the mandate the entire ACA should be struck down. It said, “There is no reason why the ACA’s particular expansion of Medicaid hinges on the individual mandate.” Later, after the December 15 ruling, the DOJ changed its position and agreed with the judge, in a two-sentence letter to the court, that the ACA should be stricken altogether—shortly after which 3 career DOJ attorneys resigned.6
A legal expert observed: “The DOJ’s decision not to defend the ACA breaks with the Department’s long-standing bipartisan commitment to defend federal laws if reasonable arguments can be made in their defense. Decisions not to defend federal law are exceedingly rare. It seems even rarer to change the government’s position mid-appeal in such a high-profile lawsuit that risks disrupting the entire health care system and health insurance coverage for millions of Americans.”7
Regulatory tactics
What a policy maker cannot do by law, he or she can try to accomplish by regulation. The Administration is using 3 regulatory routes to undercut the ACA preexisting coverage protections and market stability.
Route 1: Short-Term Limited Duration (STLD) plans. These plans were created in the ACA to provide bridge coverage for up to 3 months for individuals in between health insurance plans. These plans do not have to comply with ACA patient protections, can deny coverage for preexisting conditions, and do not cover maternity care. In 2018, the Administration moved to allow these plans to be marketed broadly and renewed for up to 3 years. Because these plans provide less coverage and often come with high deductibles, they can be marketed with lower premiums, skimming off healthier younger people who do not expect to need much care, as well as lower-income families. This destabilizes the market and leaves people insured but not covered, exactly the situation before the ACA. Seven public health and medical groups sued to challenge the Administration’s STLD regulation; the lawsuit is presently pending.
Continue to: Route 2: Association Health Plans (AHPs)...
Route 2: Association Health Plans (AHPs). The Administration also has allowed the sale of AHPs, marketed to small employers and self-employed individuals. These plans also do not have to comply with ACA consumer protections. They often do not cover maternity care or other essential benefits, and can charge women higher premiums for the same insurance. This regulation, too, resulted in litigation and a federal judge enjoined the rule, but the case is now on appeal.
Route 3: ACA Section 1332 waivers. These waivers were created in the ACA to encourage state innovation to increase access to health coverage, under certain guardrails: states must ensure coverage is at least as comprehensive as the Essential Health Benefits; cost sharing protections must be at least as affordable as under the ACA; the plan must cover at least a comparable number of its residents; and the plan must not increase the federal deficit.
The Adminstration has come under fire for approving 1332 waiver plans that do not meet these guardrails, and allow insurers to exclude coverage for individuals with preexisting conditions, as well as skirt other important ACA patient protections. In response, Seema Verma, Administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, promised as recently as April 23, that the Administration will not allow any weakening of the ACA preexisting coverage guarantee.8 So far, however, we do not know what action this means, and not surprisingly, House Democrats, now in the majority, are waiting to see those assurances come true. Consistent polling shows that a large majority of Americans, across political parties, think preexisting coverage protections are very important.9
Already, the House passed HR986, to repeal the Administration’s changes to the 1332 waiver rules. The bill won only 4 Republican votes in the House and now waits a Senate vote.
The House is ready to vote on HR1010, which returns the STLD rules to the original ACA version. The Congressional Budget Office has determined that this bill will reduce the federal deficit by $8.9 billion over 10 years, in part by reestablishing a large risk pool. Lower ACA premiums would mean lower federal subsidies and small federal outlays.
Contraceptive coverage
Since 2012, the ACA has required non-grandfathered individual and group health plans to cover, with no copays or deductibles, women’s preventive services, as determined by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA). HRSA asked the National Academy of Medicine (the Institute of Medicine [IOM] at the time) to develop these coverage guidelines based on clinical and scientific relevance. The IOM relied heavily on ACOG’s testimony and women’s health guidelines. The guidelines are updated every 5 years, based on extensive review by the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative, led by ACOG. By law and regulation, covered services include:
- well-woman visits
- contraceptive methods and counseling, including all methods approved for women by the FDA
- breast and cervical cancer screening
- counseling for sexually transmitted infections
- counseling and screening for HIV
- screening for gestational diabetes
- breastfeeding support, supplies, and counseling
- screening and counseling for interpersonal and domestic violence.
Continue to: The previous administration offered a narrow exemption...
The previous administration offered a narrow exemption—an accommodation—for churches, religious orders, and integrated auxiliaries (organizations with financial support primarily from churches). That accommodation was expanded in the Supreme Court’s decision in Hobby Lobby, for closely held for-profit organizations that had religious objections to covering some or all contraceptives. Under the accommodation, the entity’s insurer or third-party administrator was responsible for providing contraceptive services to the entity’s plan participants and beneficiaries.
In October 2017, the Trump administration acted to greatly expand the ability of any employer, college or university, individual, or insurer to opt out of the ACA’s contraceptive coverage requirement. You will read more about this later.
ACOG’s business case for contraception
Early in the Trump Administration, the White House released a statement saying, “Ensuring affordable, accessible, and quality healthcare is critical to improving women’s health and ensuring that it fits their priorities at any stage of life.”10 ACOG could not agree more, and we encouraged the President to accomplish this important goal by protecting the landmark women’s health gains of the ACA. Our call to the President and the US Congress was: “Don’t turn back the clock on women’s health.”
We made a business case for continued contraceptive coverage:
Contraception reduces unintended pregnancies and saves federal dollars.
- Approximately 45% of US pregnancies are unintended.11
- No-copay coverage of contraception has contributed to a dramatic decline in the unintended pregnancy rate in the United States, now at a 30-year low.12
- When cost is not a barrier, women choose more effective forms of contraception, such as intrauterine devices and implants.13
- Unintended pregnancies cost approximately $12.5 billion in government expenditures in 2008.14
- Private health plans spend as much as $4.6 billion annually in costs related to unintended pregnancies.15
Contraception means healthier women and healthier families.
- Under the ACA, the uninsured rate among women ages 18 to 64 almost halved, decreasing from 19.3% to 10.8%.16
- More than 55 million women gained access to preventive services, including contraception, without a copay or a deductible.16
- Women with unintended pregnancies are more likely to delay prenatal care. Infants are at greater risk of birth defects, low birth weight, and poor mental and physical functioning in early childhood.17
Increased access to contraception helps families and improves economic security.
- Women saved $1.4 billion in out-of-pocket costs for contraception in 1 year.18
- Before the ACA, women were spending between 30% and 44% of their total out-of-pocket health costs just on birth control.19
- The ability to plan a pregnancy increases engagement of women in the workforce and improves economic stability for women and their families.20
Administration expands religious exemptions to contraception coverage
Still, on October 6, 2017, the Trump Administration moved to curtail women’s access to and coverage of contraception with the Religious Exemptions and Accommodations for Coverage of Certain Preventive Services under the Affordable Care Act and Moral Exemptions and Accommodations for Coverage of Certain Preventive Services Under the Affordable Care Act. In November 2018, the Administration published a revised rule, to take effect in January 2019.21 The rule immediately was taken to court by more than a dozen states and, 1 month later, was subject to an injunction by the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, blocking the rules from going into effect in those states.
Continue to: The rule vastly expands the Obama Administration’s religious accommodation...
The rule vastly expands the Obama Administration’s religious accommodation to include “nonprofit organizations, small businesses, and individuals that have nonreligious moral convictions opposing services covered by the contraceptive mandate.” The covered entities include21:
- churches, integrated auxiliaries, and religious orders with religious objections
- nonprofit organizations with religious or moral objections
- for-profit entities that are not publicly traded, with religious or moral objections
- for-profit entities that are publicly traded, with religious objections
- other nongovernmental employers with religious objections
- nongovernmental institutions of higher education with religious or moral objections
- individuals with religious or moral objections, with employer sponsored or individual market coverage, where the plan sponsor and/or issuer (as applicable) are willing to offer them a plan omitting contraceptive coverage to which they object
- issuers with religious or moral objections, to the extent they provide coverage to a plan sponsor or individual that is also exempt.
The Administration says women losing coverage can get contraceptives through Title X clinics or other government programs. Of course, many women losing coverage are employed, and earn above the low income (100% of the federal poverty level) eligibility requirement for Title X assistance. To address that, the Administration, through its proposed Title X regulations, broadens the definition of “low income” in that program to include women who lose their contraceptive coverage through the employer-base health insurance plan. This move further limits the ability of the Title X program to adequately care for already-qualified individuals.
The Administration’s rule also relied on major inaccuracies, which ACOG corrected.22 First, ACOG pointed out that, in fact, FDA-approved contraceptive methods are not abortifacients, countering the Administration’s contention that contraception is an abortifacient, and that contraceptives cause abortions or miscarriages. Every FDA-approved contraceptive acts before implantation, does not interfere with a pregnancy, and is not effective after a fertilized egg has implanted successfully in the uterus.23 No credible research supports the false statement that birth control causes miscarriages.24
Second, ACOG offered data proving that increased access to contraception is not associated with increased unsafe sexual behavior or increased sexual activity.25,26 The facts are that:
- The percentage of teens who are having sex has declined significantly, by 14% for female and 22% for male teenagers, over the past 25 years.27
- More women are using contraception the first time they have sex. Young women who do not use birth control at first sexual intercourse are twice as likely to become teen mothers.28
- Increased access to and use of contraception has contributed to a dramatic decline in rates of adolescent pregnancy.29
- School-based health centers that provide access to contraceptives are proven to increase use of contraceptives by already sexually active students, not to increase onset of sexual activity.30,31
Third, ACOG made clear the benefits to women’s health from contraception. ACOG asserted: As with any medication, certain types of contraception may be contraindicated for patients with certain medical conditions, including high blood pressure, lupus, or a history of breast cancer.32,33 For these and many other reasons, access to the full range of FDA-approved contraception, with no cost sharing or other barriers, is critical to women’s health. Regarding VTE, the risk among oral contraceptive users is very low. In fact, it is much lower than the risk of VTE during pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period.34
Continue to: Regarding breast cancer: there is no proven increased risk...
Regarding breast cancer: there is no proven increased risk of breast cancer among contraceptive users, particularly among those younger than age 40. For women older than 40, health care providers must consider both the risks of becoming pregnant at advanced reproductive age and the risks of continuing contraception use until menopause.35
ACOG has 2 clear messages for politicians
ACOG has remained steadfast in its opposition to the Administration’s proposals to block access to contraception. ACOG expressed its strong opposition to political interference in medical care, saying “Every woman, regardless of her insurer, employer, state of residence, or income, should have affordable, seamless access to the right form of contraception for her, free from interference from her employer or politicians.”22
ACOG’s voice has been joined by 5 other major medical associations—American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychiatric Association, American Academy of Pediatrics, and American Osteopathic Association—together representing more than 560,000 physicians and medical students, in urging the Administration to immediately withdraw its proposals. This broad coalition unequivocally stated36:
Contraception is an integral part of preventive care and a medical necessity for women during approximately 30 years of their lives. Access to no-copay contraception leads to healthier women and families. Changes to our healthcare system come with very high stakes – impacting tens of millions of our patients. Access to contraception allows women to achieve, lead and reach their full potentials, becoming key drivers of our Nation’s economic success. These rules would create a new standard whereby employers can deny their employees coverage, based on their own moral objections. This interferes in the personal health care decisions of our patients, and inappropriately inserts a patient’s employer into the physician-patient relationship. In addition, these rules open the door to moral exemptions for other essential health care, including vaccinations.
These are challenging days for women’s health policy and legislation federally, and in many states. ACOG has two clear messages for politicians: Don’t turn back the clock on women’s health, and stay out of our exam rooms.
- Claxton G, Cox C, Damico A, et al. Pre-existing conditions and medical underwriting in the individual insurance market prior to the ACA. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Published December 12, 2016. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Norris L. Billions in ACA rebates show 80/20 rule’s impact. HealthInsurance.org website. Published May 10, 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act: Preexisting condition exclusions, lifetime and annual limits, rescissions, and patient protections. Regulations.gov website. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Jost T. The Senate’s Health Care Freedom Act. Health Affairs website. Updated July 28, 2017. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Texas v Azar decision. American Medical Association website. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Keith K. DOJ, plaintiffs file in Texas v United States. Health Affairs website. Published May 2 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- John & Rusty Report. Trump Administration asks court to strike down entire ACA. March 26, 2019. https://jrreport.wordandbrown.com/2019/03/26/trump-administration-asks-court-to-strike-down-entire-aca/. Accessed June 29, 2019.
- Speech: Remarks by Administrator Seema Verma at the CMS National Forum on State Relief and Empowerment Waivers. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid website. Published April 23, 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Poll: The ACA’s pre-existing condition protections remain popular with the public, including republicans, as legal challenge looms this week. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Published September 5, 2018. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Statement from President Donald J. Trump on Women’s Health Week. White House website. Issued May 14, 2017. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Finer LB, Zolna MR. Declines in unintended pregnancy in the United States, 2008-2011. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:843-852.
- Insurance coverage of contraception. Guttmacher Institute website. Published August 2018. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Carlin CS, Fertig AR, Dowd BE. Affordable Care Act’s mandate eliminating contraceptive cost sharing influenced choices of women with employer coverage. Health Affairs. 2016;35:1608-1615.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Access to contraception. Committee Opinion No. 615. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:250–255.
- Canestaro W, et al. Implications of employer coverage of contraception: cost-effectiveness analysis of contraception coverage under an employer mandate. Contraception. 2017;95:77-89.
- Simmons A, et al. The Affordable Care Act: Promoting better health for women. Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation Issue Brief, Department of Health and Human Services. June 14, 2016. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Conde-Agudelo A, Rosas-Bermudez A, Kafury-Goeta AC. Birth spacing and risk of adverse perinatal outcomes: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2006;295:1809–1823.
- Becker NV, Polsky D. Women saw large decrease in out-of-pocket spending for contraceptives after ACA mandate removed cost sharing. Health Affairs. 2015;34:1204-1211. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Becker NV, Polsky D. Women saw large decrease in out-of-pocket spending for contraceptives after ACA mandate removed cost sharing. Health Affairs. 2015;34(7).
- Sonfield A, Hasstedt K, Kavanaugh ML, Anderson R. The social and economic benefits of women’s ability to determine whether and when to have children. New York, NY: Guttmacher Institute; 2013.
- Department of Health and Human Services. Fact sheet: Final rules on religious and moral exemptions and accommodation for coverage of certain preventive services under the Affordable Care Act. November 7, 2018. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Facts are important: Correcting the record on the Administration’s contraceptive coverage roll back rule. October 2017. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Brief for Physicians for Reproductive Health, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists et al. as Amici Curiae Supporting Respondents, Sebelius v. Hobby Lobby, 573 U.S. XXX. 2014. (No. 13-354).
- Early pregnancy loss. FAQ No. 90. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. August 2015.
- Kirby D. Emerging answers 2007: Research findings on programs to reduce teen pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases. Washington, DC: The National Campaign to Prevent Teen and Unplanned Pregnancy; 2009.
- Meyer JL, Gold MA, Haggerty CL. Advance provision of emergency contraception among adolescent and young adult women: a systematic review of literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2011;24:2-9.
- Martinez GM and Abma JC. Sexual activity, contraceptive use, and childbearing of teenagers aged 15–19 in the United States. NCHS Data Brief, 2015, No. 209. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2015.
- Martinez GM, Abma JC. Sexual activity, contraceptive use, and childbearing of teenagers aged 15-19 in the United States. NCHS Data Brief. July 2015. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Lindberg L, Santelli J, Desai S. Understanding the decline in adolescent fertility in the United States, 2007–2012. J Adolesc Health. 2016;59:577-583.
- Minguez M, Santelli JS, Gibson E, et al. Reproductive health impact of a school health center. J Adolesc Health. 2015;56:338-344.
- Knopf JA, Finnie RK, Peng Y, et al. Community Preventive Services Task Force. School-based health centers to advance health equity: a Community Guide systematic review. Am J Preventive Med. 2016;51:114-126.
- Progestin-only hormonal birth control: pill and injection. FAQ No. 86. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. July 2014.
- Combined hormonal birth control: pill, patch, and ring. FAQ No. 185. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. July 2014.
- Risk of venous thromboembolism among users of drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills. Committee Opinion No. 540. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No. RR-4):1–66.
- Letter to President Donald J. Trump. October 6, 2017. https://www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/advocacy/coverage/aca/LT-Group6-President-ContraceptionIFRs-100617.pdf. Accessed June 26, 2019.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) was enacted on March 23, 2010. Controversies, complaints, and detractors have and continue to abound. But the ACA’s landmark women’s health gains are unmistakable. Contraceptive coverage, maternity coverage, Medicaid coverage of low-income women, coverage for individuals with preexisting conditions, and gender-neutral premiums are now a part of the fabric of our society. For most.
Many physicians and patients—many lawmakers, too—do not remember the serious problems people had with their insurance companies before the ACA. Maternity coverage was usually a free-standing rider to an insurance policy, making it very expensive. Insurance plans did not have to, and often did not, cover contraceptives, and none did without copays or deductibles. Women were routinely denied coverage if they had ever had a cesarean delivery, had once been the victim of domestic violence, or had any one of many common conditions, like diabetes. The many exclusionary conditions are so common, in fact, that one study estimated that around 52 million adults in the United States (27% of those younger than age 65 years) have preexisting conditions that would potentially make them uninsurable without the ACA’s protections.1
Before the ACA, it also was common for women with insurance policies to find their coverage rescinded, often with no explanation, even though they paid their premiums every month. And women with serious medical conditions often saw their coverage ended midway through their course of treatment. That placed their ObGyns in a terrible situation, too.
The insurance industry as a whole was running rough-shod over its customers, and making a lot of money by creatively and routinely denying coverage and payment for care. People were often insured, but not covered. The ACA halted many of these practices, and required insurers to meet high medical loss ratios, guaranteeing that 80% of the premiums’ for individual and small market insurers (and 85% for large insurers) are returned to patients in care payments or even in checks. In fact, nearly $4 billion in premiums have been rebated to insured individuals over the last 7 years under the ACA.2
The commitment of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) to women’s health and to our members’ ability to provide the best care has centered on preserving the critical gains of the ACA for women, improving them when we can, and making sure politicians don’t turn back the clock on women’s health. We have been busy.
In this article, we will look at what has happened to these landmark gains and promises of improved women’s health, specifically preexisting condition protections and contraceptive coverage, under a new Administration. What happens when good health care policy and political enmity collide?

Preexisting coverage protections
The 1996 Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) defines a preexisting condition exclusionas a “limitation or exclusion of benefits relating to a condition based on the fact that the condition was present before the date of enrollment for the coverage, whether or not any medical advice, diagnosis, care, or treatment was recommended or received before that date.” HIPPA prohibited employer-sponsored health plans from discriminating against individuals through denying them coverage or charging them more based on their or their family members’ health problems. The ACA expanded protections to prohibit the insurance practice of denying coverage altogether to an individual with a preexisting condition.3
Continue to: Under Congress...
Under Congress
Republicans held the majority in both chambers of the 115th Congress (2017–2018), and hoped to use their majority status to get an ACA repeal bill to the Republican President’s desk for speedy enactment. It was not easy, and they were not successful. Four major bills—the American Health Care Act, the Better Care Reconciliation Act, the Health Care Freedom Act, and the Graham-Cassidy Amendment—never made it over the finish line, with some not even making it to a vote. The Health Care Freedom Act was voted down in the Senate 51-49 when Senator John McCain came back from brain surgery to cast his famous thumbs-down vote.4 These bills all would have repealed or hobbled guaranteed issue, community rating, and essential health benefits of the ACA. Of all the legislative attempts to undermine the ACA, only the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) was signed into law, repealing the ACA individual mandate.
Handling by the courts
The TCJA gave ACA opponents their opening in court. Twenty Republican state attorneys general and governors brought suit in February 2018 (Texas v Azar), arguing that because the ACA relies on the mandate, and the mandate has been repealed, the rest of the ACA also should be struck down. A federal district judge agreed, on December 15, 2018, declaring the entire ACA unconstitutional.5
That decision has been limited in its practical effect so far, and maybe it was not altogether unexpected. What was unexpected was that the US Department of Justice (DOJ) refused to defend a federal law, in this case, the ACA. In June 2018, the DOJ declined to defend the individual mandate, as well as guaranteed issue, community rating, the ban on preexisting condition exclusions, and discrimination based on health status in the ACA. The DOJ at that time, however, did not agree with the plaintiffs that without the mandate the entire ACA should be struck down. It said, “There is no reason why the ACA’s particular expansion of Medicaid hinges on the individual mandate.” Later, after the December 15 ruling, the DOJ changed its position and agreed with the judge, in a two-sentence letter to the court, that the ACA should be stricken altogether—shortly after which 3 career DOJ attorneys resigned.6
A legal expert observed: “The DOJ’s decision not to defend the ACA breaks with the Department’s long-standing bipartisan commitment to defend federal laws if reasonable arguments can be made in their defense. Decisions not to defend federal law are exceedingly rare. It seems even rarer to change the government’s position mid-appeal in such a high-profile lawsuit that risks disrupting the entire health care system and health insurance coverage for millions of Americans.”7
Regulatory tactics
What a policy maker cannot do by law, he or she can try to accomplish by regulation. The Administration is using 3 regulatory routes to undercut the ACA preexisting coverage protections and market stability.
Route 1: Short-Term Limited Duration (STLD) plans. These plans were created in the ACA to provide bridge coverage for up to 3 months for individuals in between health insurance plans. These plans do not have to comply with ACA patient protections, can deny coverage for preexisting conditions, and do not cover maternity care. In 2018, the Administration moved to allow these plans to be marketed broadly and renewed for up to 3 years. Because these plans provide less coverage and often come with high deductibles, they can be marketed with lower premiums, skimming off healthier younger people who do not expect to need much care, as well as lower-income families. This destabilizes the market and leaves people insured but not covered, exactly the situation before the ACA. Seven public health and medical groups sued to challenge the Administration’s STLD regulation; the lawsuit is presently pending.
Continue to: Route 2: Association Health Plans (AHPs)...
Route 2: Association Health Plans (AHPs). The Administration also has allowed the sale of AHPs, marketed to small employers and self-employed individuals. These plans also do not have to comply with ACA consumer protections. They often do not cover maternity care or other essential benefits, and can charge women higher premiums for the same insurance. This regulation, too, resulted in litigation and a federal judge enjoined the rule, but the case is now on appeal.
Route 3: ACA Section 1332 waivers. These waivers were created in the ACA to encourage state innovation to increase access to health coverage, under certain guardrails: states must ensure coverage is at least as comprehensive as the Essential Health Benefits; cost sharing protections must be at least as affordable as under the ACA; the plan must cover at least a comparable number of its residents; and the plan must not increase the federal deficit.
The Adminstration has come under fire for approving 1332 waiver plans that do not meet these guardrails, and allow insurers to exclude coverage for individuals with preexisting conditions, as well as skirt other important ACA patient protections. In response, Seema Verma, Administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, promised as recently as April 23, that the Administration will not allow any weakening of the ACA preexisting coverage guarantee.8 So far, however, we do not know what action this means, and not surprisingly, House Democrats, now in the majority, are waiting to see those assurances come true. Consistent polling shows that a large majority of Americans, across political parties, think preexisting coverage protections are very important.9
Already, the House passed HR986, to repeal the Administration’s changes to the 1332 waiver rules. The bill won only 4 Republican votes in the House and now waits a Senate vote.
The House is ready to vote on HR1010, which returns the STLD rules to the original ACA version. The Congressional Budget Office has determined that this bill will reduce the federal deficit by $8.9 billion over 10 years, in part by reestablishing a large risk pool. Lower ACA premiums would mean lower federal subsidies and small federal outlays.
Contraceptive coverage
Since 2012, the ACA has required non-grandfathered individual and group health plans to cover, with no copays or deductibles, women’s preventive services, as determined by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA). HRSA asked the National Academy of Medicine (the Institute of Medicine [IOM] at the time) to develop these coverage guidelines based on clinical and scientific relevance. The IOM relied heavily on ACOG’s testimony and women’s health guidelines. The guidelines are updated every 5 years, based on extensive review by the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative, led by ACOG. By law and regulation, covered services include:
- well-woman visits
- contraceptive methods and counseling, including all methods approved for women by the FDA
- breast and cervical cancer screening
- counseling for sexually transmitted infections
- counseling and screening for HIV
- screening for gestational diabetes
- breastfeeding support, supplies, and counseling
- screening and counseling for interpersonal and domestic violence.
Continue to: The previous administration offered a narrow exemption...
The previous administration offered a narrow exemption—an accommodation—for churches, religious orders, and integrated auxiliaries (organizations with financial support primarily from churches). That accommodation was expanded in the Supreme Court’s decision in Hobby Lobby, for closely held for-profit organizations that had religious objections to covering some or all contraceptives. Under the accommodation, the entity’s insurer or third-party administrator was responsible for providing contraceptive services to the entity’s plan participants and beneficiaries.
In October 2017, the Trump administration acted to greatly expand the ability of any employer, college or university, individual, or insurer to opt out of the ACA’s contraceptive coverage requirement. You will read more about this later.
ACOG’s business case for contraception
Early in the Trump Administration, the White House released a statement saying, “Ensuring affordable, accessible, and quality healthcare is critical to improving women’s health and ensuring that it fits their priorities at any stage of life.”10 ACOG could not agree more, and we encouraged the President to accomplish this important goal by protecting the landmark women’s health gains of the ACA. Our call to the President and the US Congress was: “Don’t turn back the clock on women’s health.”
We made a business case for continued contraceptive coverage:
Contraception reduces unintended pregnancies and saves federal dollars.
- Approximately 45% of US pregnancies are unintended.11
- No-copay coverage of contraception has contributed to a dramatic decline in the unintended pregnancy rate in the United States, now at a 30-year low.12
- When cost is not a barrier, women choose more effective forms of contraception, such as intrauterine devices and implants.13
- Unintended pregnancies cost approximately $12.5 billion in government expenditures in 2008.14
- Private health plans spend as much as $4.6 billion annually in costs related to unintended pregnancies.15
Contraception means healthier women and healthier families.
- Under the ACA, the uninsured rate among women ages 18 to 64 almost halved, decreasing from 19.3% to 10.8%.16
- More than 55 million women gained access to preventive services, including contraception, without a copay or a deductible.16
- Women with unintended pregnancies are more likely to delay prenatal care. Infants are at greater risk of birth defects, low birth weight, and poor mental and physical functioning in early childhood.17
Increased access to contraception helps families and improves economic security.
- Women saved $1.4 billion in out-of-pocket costs for contraception in 1 year.18
- Before the ACA, women were spending between 30% and 44% of their total out-of-pocket health costs just on birth control.19
- The ability to plan a pregnancy increases engagement of women in the workforce and improves economic stability for women and their families.20
Administration expands religious exemptions to contraception coverage
Still, on October 6, 2017, the Trump Administration moved to curtail women’s access to and coverage of contraception with the Religious Exemptions and Accommodations for Coverage of Certain Preventive Services under the Affordable Care Act and Moral Exemptions and Accommodations for Coverage of Certain Preventive Services Under the Affordable Care Act. In November 2018, the Administration published a revised rule, to take effect in January 2019.21 The rule immediately was taken to court by more than a dozen states and, 1 month later, was subject to an injunction by the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, blocking the rules from going into effect in those states.
Continue to: The rule vastly expands the Obama Administration’s religious accommodation...
The rule vastly expands the Obama Administration’s religious accommodation to include “nonprofit organizations, small businesses, and individuals that have nonreligious moral convictions opposing services covered by the contraceptive mandate.” The covered entities include21:
- churches, integrated auxiliaries, and religious orders with religious objections
- nonprofit organizations with religious or moral objections
- for-profit entities that are not publicly traded, with religious or moral objections
- for-profit entities that are publicly traded, with religious objections
- other nongovernmental employers with religious objections
- nongovernmental institutions of higher education with religious or moral objections
- individuals with religious or moral objections, with employer sponsored or individual market coverage, where the plan sponsor and/or issuer (as applicable) are willing to offer them a plan omitting contraceptive coverage to which they object
- issuers with religious or moral objections, to the extent they provide coverage to a plan sponsor or individual that is also exempt.
The Administration says women losing coverage can get contraceptives through Title X clinics or other government programs. Of course, many women losing coverage are employed, and earn above the low income (100% of the federal poverty level) eligibility requirement for Title X assistance. To address that, the Administration, through its proposed Title X regulations, broadens the definition of “low income” in that program to include women who lose their contraceptive coverage through the employer-base health insurance plan. This move further limits the ability of the Title X program to adequately care for already-qualified individuals.
The Administration’s rule also relied on major inaccuracies, which ACOG corrected.22 First, ACOG pointed out that, in fact, FDA-approved contraceptive methods are not abortifacients, countering the Administration’s contention that contraception is an abortifacient, and that contraceptives cause abortions or miscarriages. Every FDA-approved contraceptive acts before implantation, does not interfere with a pregnancy, and is not effective after a fertilized egg has implanted successfully in the uterus.23 No credible research supports the false statement that birth control causes miscarriages.24
Second, ACOG offered data proving that increased access to contraception is not associated with increased unsafe sexual behavior or increased sexual activity.25,26 The facts are that:
- The percentage of teens who are having sex has declined significantly, by 14% for female and 22% for male teenagers, over the past 25 years.27
- More women are using contraception the first time they have sex. Young women who do not use birth control at first sexual intercourse are twice as likely to become teen mothers.28
- Increased access to and use of contraception has contributed to a dramatic decline in rates of adolescent pregnancy.29
- School-based health centers that provide access to contraceptives are proven to increase use of contraceptives by already sexually active students, not to increase onset of sexual activity.30,31
Third, ACOG made clear the benefits to women’s health from contraception. ACOG asserted: As with any medication, certain types of contraception may be contraindicated for patients with certain medical conditions, including high blood pressure, lupus, or a history of breast cancer.32,33 For these and many other reasons, access to the full range of FDA-approved contraception, with no cost sharing or other barriers, is critical to women’s health. Regarding VTE, the risk among oral contraceptive users is very low. In fact, it is much lower than the risk of VTE during pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period.34
Continue to: Regarding breast cancer: there is no proven increased risk...
Regarding breast cancer: there is no proven increased risk of breast cancer among contraceptive users, particularly among those younger than age 40. For women older than 40, health care providers must consider both the risks of becoming pregnant at advanced reproductive age and the risks of continuing contraception use until menopause.35
ACOG has 2 clear messages for politicians
ACOG has remained steadfast in its opposition to the Administration’s proposals to block access to contraception. ACOG expressed its strong opposition to political interference in medical care, saying “Every woman, regardless of her insurer, employer, state of residence, or income, should have affordable, seamless access to the right form of contraception for her, free from interference from her employer or politicians.”22
ACOG’s voice has been joined by 5 other major medical associations—American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychiatric Association, American Academy of Pediatrics, and American Osteopathic Association—together representing more than 560,000 physicians and medical students, in urging the Administration to immediately withdraw its proposals. This broad coalition unequivocally stated36:
Contraception is an integral part of preventive care and a medical necessity for women during approximately 30 years of their lives. Access to no-copay contraception leads to healthier women and families. Changes to our healthcare system come with very high stakes – impacting tens of millions of our patients. Access to contraception allows women to achieve, lead and reach their full potentials, becoming key drivers of our Nation’s economic success. These rules would create a new standard whereby employers can deny their employees coverage, based on their own moral objections. This interferes in the personal health care decisions of our patients, and inappropriately inserts a patient’s employer into the physician-patient relationship. In addition, these rules open the door to moral exemptions for other essential health care, including vaccinations.
These are challenging days for women’s health policy and legislation federally, and in many states. ACOG has two clear messages for politicians: Don’t turn back the clock on women’s health, and stay out of our exam rooms.
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) was enacted on March 23, 2010. Controversies, complaints, and detractors have and continue to abound. But the ACA’s landmark women’s health gains are unmistakable. Contraceptive coverage, maternity coverage, Medicaid coverage of low-income women, coverage for individuals with preexisting conditions, and gender-neutral premiums are now a part of the fabric of our society. For most.
Many physicians and patients—many lawmakers, too—do not remember the serious problems people had with their insurance companies before the ACA. Maternity coverage was usually a free-standing rider to an insurance policy, making it very expensive. Insurance plans did not have to, and often did not, cover contraceptives, and none did without copays or deductibles. Women were routinely denied coverage if they had ever had a cesarean delivery, had once been the victim of domestic violence, or had any one of many common conditions, like diabetes. The many exclusionary conditions are so common, in fact, that one study estimated that around 52 million adults in the United States (27% of those younger than age 65 years) have preexisting conditions that would potentially make them uninsurable without the ACA’s protections.1
Before the ACA, it also was common for women with insurance policies to find their coverage rescinded, often with no explanation, even though they paid their premiums every month. And women with serious medical conditions often saw their coverage ended midway through their course of treatment. That placed their ObGyns in a terrible situation, too.
The insurance industry as a whole was running rough-shod over its customers, and making a lot of money by creatively and routinely denying coverage and payment for care. People were often insured, but not covered. The ACA halted many of these practices, and required insurers to meet high medical loss ratios, guaranteeing that 80% of the premiums’ for individual and small market insurers (and 85% for large insurers) are returned to patients in care payments or even in checks. In fact, nearly $4 billion in premiums have been rebated to insured individuals over the last 7 years under the ACA.2
The commitment of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) to women’s health and to our members’ ability to provide the best care has centered on preserving the critical gains of the ACA for women, improving them when we can, and making sure politicians don’t turn back the clock on women’s health. We have been busy.
In this article, we will look at what has happened to these landmark gains and promises of improved women’s health, specifically preexisting condition protections and contraceptive coverage, under a new Administration. What happens when good health care policy and political enmity collide?

Preexisting coverage protections
The 1996 Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) defines a preexisting condition exclusionas a “limitation or exclusion of benefits relating to a condition based on the fact that the condition was present before the date of enrollment for the coverage, whether or not any medical advice, diagnosis, care, or treatment was recommended or received before that date.” HIPPA prohibited employer-sponsored health plans from discriminating against individuals through denying them coverage or charging them more based on their or their family members’ health problems. The ACA expanded protections to prohibit the insurance practice of denying coverage altogether to an individual with a preexisting condition.3
Continue to: Under Congress...
Under Congress
Republicans held the majority in both chambers of the 115th Congress (2017–2018), and hoped to use their majority status to get an ACA repeal bill to the Republican President’s desk for speedy enactment. It was not easy, and they were not successful. Four major bills—the American Health Care Act, the Better Care Reconciliation Act, the Health Care Freedom Act, and the Graham-Cassidy Amendment—never made it over the finish line, with some not even making it to a vote. The Health Care Freedom Act was voted down in the Senate 51-49 when Senator John McCain came back from brain surgery to cast his famous thumbs-down vote.4 These bills all would have repealed or hobbled guaranteed issue, community rating, and essential health benefits of the ACA. Of all the legislative attempts to undermine the ACA, only the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) was signed into law, repealing the ACA individual mandate.
Handling by the courts
The TCJA gave ACA opponents their opening in court. Twenty Republican state attorneys general and governors brought suit in February 2018 (Texas v Azar), arguing that because the ACA relies on the mandate, and the mandate has been repealed, the rest of the ACA also should be struck down. A federal district judge agreed, on December 15, 2018, declaring the entire ACA unconstitutional.5
That decision has been limited in its practical effect so far, and maybe it was not altogether unexpected. What was unexpected was that the US Department of Justice (DOJ) refused to defend a federal law, in this case, the ACA. In June 2018, the DOJ declined to defend the individual mandate, as well as guaranteed issue, community rating, the ban on preexisting condition exclusions, and discrimination based on health status in the ACA. The DOJ at that time, however, did not agree with the plaintiffs that without the mandate the entire ACA should be struck down. It said, “There is no reason why the ACA’s particular expansion of Medicaid hinges on the individual mandate.” Later, after the December 15 ruling, the DOJ changed its position and agreed with the judge, in a two-sentence letter to the court, that the ACA should be stricken altogether—shortly after which 3 career DOJ attorneys resigned.6
A legal expert observed: “The DOJ’s decision not to defend the ACA breaks with the Department’s long-standing bipartisan commitment to defend federal laws if reasonable arguments can be made in their defense. Decisions not to defend federal law are exceedingly rare. It seems even rarer to change the government’s position mid-appeal in such a high-profile lawsuit that risks disrupting the entire health care system and health insurance coverage for millions of Americans.”7
Regulatory tactics
What a policy maker cannot do by law, he or she can try to accomplish by regulation. The Administration is using 3 regulatory routes to undercut the ACA preexisting coverage protections and market stability.
Route 1: Short-Term Limited Duration (STLD) plans. These plans were created in the ACA to provide bridge coverage for up to 3 months for individuals in between health insurance plans. These plans do not have to comply with ACA patient protections, can deny coverage for preexisting conditions, and do not cover maternity care. In 2018, the Administration moved to allow these plans to be marketed broadly and renewed for up to 3 years. Because these plans provide less coverage and often come with high deductibles, they can be marketed with lower premiums, skimming off healthier younger people who do not expect to need much care, as well as lower-income families. This destabilizes the market and leaves people insured but not covered, exactly the situation before the ACA. Seven public health and medical groups sued to challenge the Administration’s STLD regulation; the lawsuit is presently pending.
Continue to: Route 2: Association Health Plans (AHPs)...
Route 2: Association Health Plans (AHPs). The Administration also has allowed the sale of AHPs, marketed to small employers and self-employed individuals. These plans also do not have to comply with ACA consumer protections. They often do not cover maternity care or other essential benefits, and can charge women higher premiums for the same insurance. This regulation, too, resulted in litigation and a federal judge enjoined the rule, but the case is now on appeal.
Route 3: ACA Section 1332 waivers. These waivers were created in the ACA to encourage state innovation to increase access to health coverage, under certain guardrails: states must ensure coverage is at least as comprehensive as the Essential Health Benefits; cost sharing protections must be at least as affordable as under the ACA; the plan must cover at least a comparable number of its residents; and the plan must not increase the federal deficit.
The Adminstration has come under fire for approving 1332 waiver plans that do not meet these guardrails, and allow insurers to exclude coverage for individuals with preexisting conditions, as well as skirt other important ACA patient protections. In response, Seema Verma, Administrator of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, promised as recently as April 23, that the Administration will not allow any weakening of the ACA preexisting coverage guarantee.8 So far, however, we do not know what action this means, and not surprisingly, House Democrats, now in the majority, are waiting to see those assurances come true. Consistent polling shows that a large majority of Americans, across political parties, think preexisting coverage protections are very important.9
Already, the House passed HR986, to repeal the Administration’s changes to the 1332 waiver rules. The bill won only 4 Republican votes in the House and now waits a Senate vote.
The House is ready to vote on HR1010, which returns the STLD rules to the original ACA version. The Congressional Budget Office has determined that this bill will reduce the federal deficit by $8.9 billion over 10 years, in part by reestablishing a large risk pool. Lower ACA premiums would mean lower federal subsidies and small federal outlays.
Contraceptive coverage
Since 2012, the ACA has required non-grandfathered individual and group health plans to cover, with no copays or deductibles, women’s preventive services, as determined by the Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA). HRSA asked the National Academy of Medicine (the Institute of Medicine [IOM] at the time) to develop these coverage guidelines based on clinical and scientific relevance. The IOM relied heavily on ACOG’s testimony and women’s health guidelines. The guidelines are updated every 5 years, based on extensive review by the Women’s Preventive Services Initiative, led by ACOG. By law and regulation, covered services include:
- well-woman visits
- contraceptive methods and counseling, including all methods approved for women by the FDA
- breast and cervical cancer screening
- counseling for sexually transmitted infections
- counseling and screening for HIV
- screening for gestational diabetes
- breastfeeding support, supplies, and counseling
- screening and counseling for interpersonal and domestic violence.
Continue to: The previous administration offered a narrow exemption...
The previous administration offered a narrow exemption—an accommodation—for churches, religious orders, and integrated auxiliaries (organizations with financial support primarily from churches). That accommodation was expanded in the Supreme Court’s decision in Hobby Lobby, for closely held for-profit organizations that had religious objections to covering some or all contraceptives. Under the accommodation, the entity’s insurer or third-party administrator was responsible for providing contraceptive services to the entity’s plan participants and beneficiaries.
In October 2017, the Trump administration acted to greatly expand the ability of any employer, college or university, individual, or insurer to opt out of the ACA’s contraceptive coverage requirement. You will read more about this later.
ACOG’s business case for contraception
Early in the Trump Administration, the White House released a statement saying, “Ensuring affordable, accessible, and quality healthcare is critical to improving women’s health and ensuring that it fits their priorities at any stage of life.”10 ACOG could not agree more, and we encouraged the President to accomplish this important goal by protecting the landmark women’s health gains of the ACA. Our call to the President and the US Congress was: “Don’t turn back the clock on women’s health.”
We made a business case for continued contraceptive coverage:
Contraception reduces unintended pregnancies and saves federal dollars.
- Approximately 45% of US pregnancies are unintended.11
- No-copay coverage of contraception has contributed to a dramatic decline in the unintended pregnancy rate in the United States, now at a 30-year low.12
- When cost is not a barrier, women choose more effective forms of contraception, such as intrauterine devices and implants.13
- Unintended pregnancies cost approximately $12.5 billion in government expenditures in 2008.14
- Private health plans spend as much as $4.6 billion annually in costs related to unintended pregnancies.15
Contraception means healthier women and healthier families.
- Under the ACA, the uninsured rate among women ages 18 to 64 almost halved, decreasing from 19.3% to 10.8%.16
- More than 55 million women gained access to preventive services, including contraception, without a copay or a deductible.16
- Women with unintended pregnancies are more likely to delay prenatal care. Infants are at greater risk of birth defects, low birth weight, and poor mental and physical functioning in early childhood.17
Increased access to contraception helps families and improves economic security.
- Women saved $1.4 billion in out-of-pocket costs for contraception in 1 year.18
- Before the ACA, women were spending between 30% and 44% of their total out-of-pocket health costs just on birth control.19
- The ability to plan a pregnancy increases engagement of women in the workforce and improves economic stability for women and their families.20
Administration expands religious exemptions to contraception coverage
Still, on October 6, 2017, the Trump Administration moved to curtail women’s access to and coverage of contraception with the Religious Exemptions and Accommodations for Coverage of Certain Preventive Services under the Affordable Care Act and Moral Exemptions and Accommodations for Coverage of Certain Preventive Services Under the Affordable Care Act. In November 2018, the Administration published a revised rule, to take effect in January 2019.21 The rule immediately was taken to court by more than a dozen states and, 1 month later, was subject to an injunction by the US Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, blocking the rules from going into effect in those states.
Continue to: The rule vastly expands the Obama Administration’s religious accommodation...
The rule vastly expands the Obama Administration’s religious accommodation to include “nonprofit organizations, small businesses, and individuals that have nonreligious moral convictions opposing services covered by the contraceptive mandate.” The covered entities include21:
- churches, integrated auxiliaries, and religious orders with religious objections
- nonprofit organizations with religious or moral objections
- for-profit entities that are not publicly traded, with religious or moral objections
- for-profit entities that are publicly traded, with religious objections
- other nongovernmental employers with religious objections
- nongovernmental institutions of higher education with religious or moral objections
- individuals with religious or moral objections, with employer sponsored or individual market coverage, where the plan sponsor and/or issuer (as applicable) are willing to offer them a plan omitting contraceptive coverage to which they object
- issuers with religious or moral objections, to the extent they provide coverage to a plan sponsor or individual that is also exempt.
The Administration says women losing coverage can get contraceptives through Title X clinics or other government programs. Of course, many women losing coverage are employed, and earn above the low income (100% of the federal poverty level) eligibility requirement for Title X assistance. To address that, the Administration, through its proposed Title X regulations, broadens the definition of “low income” in that program to include women who lose their contraceptive coverage through the employer-base health insurance plan. This move further limits the ability of the Title X program to adequately care for already-qualified individuals.
The Administration’s rule also relied on major inaccuracies, which ACOG corrected.22 First, ACOG pointed out that, in fact, FDA-approved contraceptive methods are not abortifacients, countering the Administration’s contention that contraception is an abortifacient, and that contraceptives cause abortions or miscarriages. Every FDA-approved contraceptive acts before implantation, does not interfere with a pregnancy, and is not effective after a fertilized egg has implanted successfully in the uterus.23 No credible research supports the false statement that birth control causes miscarriages.24
Second, ACOG offered data proving that increased access to contraception is not associated with increased unsafe sexual behavior or increased sexual activity.25,26 The facts are that:
- The percentage of teens who are having sex has declined significantly, by 14% for female and 22% for male teenagers, over the past 25 years.27
- More women are using contraception the first time they have sex. Young women who do not use birth control at first sexual intercourse are twice as likely to become teen mothers.28
- Increased access to and use of contraception has contributed to a dramatic decline in rates of adolescent pregnancy.29
- School-based health centers that provide access to contraceptives are proven to increase use of contraceptives by already sexually active students, not to increase onset of sexual activity.30,31
Third, ACOG made clear the benefits to women’s health from contraception. ACOG asserted: As with any medication, certain types of contraception may be contraindicated for patients with certain medical conditions, including high blood pressure, lupus, or a history of breast cancer.32,33 For these and many other reasons, access to the full range of FDA-approved contraception, with no cost sharing or other barriers, is critical to women’s health. Regarding VTE, the risk among oral contraceptive users is very low. In fact, it is much lower than the risk of VTE during pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period.34
Continue to: Regarding breast cancer: there is no proven increased risk...
Regarding breast cancer: there is no proven increased risk of breast cancer among contraceptive users, particularly among those younger than age 40. For women older than 40, health care providers must consider both the risks of becoming pregnant at advanced reproductive age and the risks of continuing contraception use until menopause.35
ACOG has 2 clear messages for politicians
ACOG has remained steadfast in its opposition to the Administration’s proposals to block access to contraception. ACOG expressed its strong opposition to political interference in medical care, saying “Every woman, regardless of her insurer, employer, state of residence, or income, should have affordable, seamless access to the right form of contraception for her, free from interference from her employer or politicians.”22
ACOG’s voice has been joined by 5 other major medical associations—American Academy of Family Physicians, American Academy of Pediatrics, American Psychiatric Association, American Academy of Pediatrics, and American Osteopathic Association—together representing more than 560,000 physicians and medical students, in urging the Administration to immediately withdraw its proposals. This broad coalition unequivocally stated36:
Contraception is an integral part of preventive care and a medical necessity for women during approximately 30 years of their lives. Access to no-copay contraception leads to healthier women and families. Changes to our healthcare system come with very high stakes – impacting tens of millions of our patients. Access to contraception allows women to achieve, lead and reach their full potentials, becoming key drivers of our Nation’s economic success. These rules would create a new standard whereby employers can deny their employees coverage, based on their own moral objections. This interferes in the personal health care decisions of our patients, and inappropriately inserts a patient’s employer into the physician-patient relationship. In addition, these rules open the door to moral exemptions for other essential health care, including vaccinations.
These are challenging days for women’s health policy and legislation federally, and in many states. ACOG has two clear messages for politicians: Don’t turn back the clock on women’s health, and stay out of our exam rooms.
- Claxton G, Cox C, Damico A, et al. Pre-existing conditions and medical underwriting in the individual insurance market prior to the ACA. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Published December 12, 2016. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Norris L. Billions in ACA rebates show 80/20 rule’s impact. HealthInsurance.org website. Published May 10, 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act: Preexisting condition exclusions, lifetime and annual limits, rescissions, and patient protections. Regulations.gov website. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Jost T. The Senate’s Health Care Freedom Act. Health Affairs website. Updated July 28, 2017. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Texas v Azar decision. American Medical Association website. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Keith K. DOJ, plaintiffs file in Texas v United States. Health Affairs website. Published May 2 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- John & Rusty Report. Trump Administration asks court to strike down entire ACA. March 26, 2019. https://jrreport.wordandbrown.com/2019/03/26/trump-administration-asks-court-to-strike-down-entire-aca/. Accessed June 29, 2019.
- Speech: Remarks by Administrator Seema Verma at the CMS National Forum on State Relief and Empowerment Waivers. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid website. Published April 23, 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Poll: The ACA’s pre-existing condition protections remain popular with the public, including republicans, as legal challenge looms this week. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Published September 5, 2018. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Statement from President Donald J. Trump on Women’s Health Week. White House website. Issued May 14, 2017. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Finer LB, Zolna MR. Declines in unintended pregnancy in the United States, 2008-2011. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:843-852.
- Insurance coverage of contraception. Guttmacher Institute website. Published August 2018. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Carlin CS, Fertig AR, Dowd BE. Affordable Care Act’s mandate eliminating contraceptive cost sharing influenced choices of women with employer coverage. Health Affairs. 2016;35:1608-1615.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Access to contraception. Committee Opinion No. 615. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:250–255.
- Canestaro W, et al. Implications of employer coverage of contraception: cost-effectiveness analysis of contraception coverage under an employer mandate. Contraception. 2017;95:77-89.
- Simmons A, et al. The Affordable Care Act: Promoting better health for women. Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation Issue Brief, Department of Health and Human Services. June 14, 2016. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Conde-Agudelo A, Rosas-Bermudez A, Kafury-Goeta AC. Birth spacing and risk of adverse perinatal outcomes: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2006;295:1809–1823.
- Becker NV, Polsky D. Women saw large decrease in out-of-pocket spending for contraceptives after ACA mandate removed cost sharing. Health Affairs. 2015;34:1204-1211. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Becker NV, Polsky D. Women saw large decrease in out-of-pocket spending for contraceptives after ACA mandate removed cost sharing. Health Affairs. 2015;34(7).
- Sonfield A, Hasstedt K, Kavanaugh ML, Anderson R. The social and economic benefits of women’s ability to determine whether and when to have children. New York, NY: Guttmacher Institute; 2013.
- Department of Health and Human Services. Fact sheet: Final rules on religious and moral exemptions and accommodation for coverage of certain preventive services under the Affordable Care Act. November 7, 2018. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Facts are important: Correcting the record on the Administration’s contraceptive coverage roll back rule. October 2017. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Brief for Physicians for Reproductive Health, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists et al. as Amici Curiae Supporting Respondents, Sebelius v. Hobby Lobby, 573 U.S. XXX. 2014. (No. 13-354).
- Early pregnancy loss. FAQ No. 90. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. August 2015.
- Kirby D. Emerging answers 2007: Research findings on programs to reduce teen pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases. Washington, DC: The National Campaign to Prevent Teen and Unplanned Pregnancy; 2009.
- Meyer JL, Gold MA, Haggerty CL. Advance provision of emergency contraception among adolescent and young adult women: a systematic review of literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2011;24:2-9.
- Martinez GM and Abma JC. Sexual activity, contraceptive use, and childbearing of teenagers aged 15–19 in the United States. NCHS Data Brief, 2015, No. 209. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2015.
- Martinez GM, Abma JC. Sexual activity, contraceptive use, and childbearing of teenagers aged 15-19 in the United States. NCHS Data Brief. July 2015. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Lindberg L, Santelli J, Desai S. Understanding the decline in adolescent fertility in the United States, 2007–2012. J Adolesc Health. 2016;59:577-583.
- Minguez M, Santelli JS, Gibson E, et al. Reproductive health impact of a school health center. J Adolesc Health. 2015;56:338-344.
- Knopf JA, Finnie RK, Peng Y, et al. Community Preventive Services Task Force. School-based health centers to advance health equity: a Community Guide systematic review. Am J Preventive Med. 2016;51:114-126.
- Progestin-only hormonal birth control: pill and injection. FAQ No. 86. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. July 2014.
- Combined hormonal birth control: pill, patch, and ring. FAQ No. 185. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. July 2014.
- Risk of venous thromboembolism among users of drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills. Committee Opinion No. 540. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No. RR-4):1–66.
- Letter to President Donald J. Trump. October 6, 2017. https://www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/advocacy/coverage/aca/LT-Group6-President-ContraceptionIFRs-100617.pdf. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Claxton G, Cox C, Damico A, et al. Pre-existing conditions and medical underwriting in the individual insurance market prior to the ACA. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Published December 12, 2016. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Norris L. Billions in ACA rebates show 80/20 rule’s impact. HealthInsurance.org website. Published May 10, 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act: Preexisting condition exclusions, lifetime and annual limits, rescissions, and patient protections. Regulations.gov website. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Jost T. The Senate’s Health Care Freedom Act. Health Affairs website. Updated July 28, 2017. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Texas v Azar decision. American Medical Association website. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Keith K. DOJ, plaintiffs file in Texas v United States. Health Affairs website. Published May 2 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- John & Rusty Report. Trump Administration asks court to strike down entire ACA. March 26, 2019. https://jrreport.wordandbrown.com/2019/03/26/trump-administration-asks-court-to-strike-down-entire-aca/. Accessed June 29, 2019.
- Speech: Remarks by Administrator Seema Verma at the CMS National Forum on State Relief and Empowerment Waivers. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid website. Published April 23, 2019. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Poll: The ACA’s pre-existing condition protections remain popular with the public, including republicans, as legal challenge looms this week. Kaiser Family Foundation website. Published September 5, 2018. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Statement from President Donald J. Trump on Women’s Health Week. White House website. Issued May 14, 2017. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Finer LB, Zolna MR. Declines in unintended pregnancy in the United States, 2008-2011. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:843-852.
- Insurance coverage of contraception. Guttmacher Institute website. Published August 2018. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Carlin CS, Fertig AR, Dowd BE. Affordable Care Act’s mandate eliminating contraceptive cost sharing influenced choices of women with employer coverage. Health Affairs. 2016;35:1608-1615.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Access to contraception. Committee Opinion No. 615. Obstet Gynecol. 2015;125:250–255.
- Canestaro W, et al. Implications of employer coverage of contraception: cost-effectiveness analysis of contraception coverage under an employer mandate. Contraception. 2017;95:77-89.
- Simmons A, et al. The Affordable Care Act: Promoting better health for women. Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation Issue Brief, Department of Health and Human Services. June 14, 2016. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Conde-Agudelo A, Rosas-Bermudez A, Kafury-Goeta AC. Birth spacing and risk of adverse perinatal outcomes: a meta-analysis. JAMA. 2006;295:1809–1823.
- Becker NV, Polsky D. Women saw large decrease in out-of-pocket spending for contraceptives after ACA mandate removed cost sharing. Health Affairs. 2015;34:1204-1211. Accessed June 25, 2019.
- Becker NV, Polsky D. Women saw large decrease in out-of-pocket spending for contraceptives after ACA mandate removed cost sharing. Health Affairs. 2015;34(7).
- Sonfield A, Hasstedt K, Kavanaugh ML, Anderson R. The social and economic benefits of women’s ability to determine whether and when to have children. New York, NY: Guttmacher Institute; 2013.
- Department of Health and Human Services. Fact sheet: Final rules on religious and moral exemptions and accommodation for coverage of certain preventive services under the Affordable Care Act. November 7, 2018. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Facts are important: Correcting the record on the Administration’s contraceptive coverage roll back rule. October 2017. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Brief for Physicians for Reproductive Health, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists et al. as Amici Curiae Supporting Respondents, Sebelius v. Hobby Lobby, 573 U.S. XXX. 2014. (No. 13-354).
- Early pregnancy loss. FAQ No. 90. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. August 2015.
- Kirby D. Emerging answers 2007: Research findings on programs to reduce teen pregnancy and sexually transmitted diseases. Washington, DC: The National Campaign to Prevent Teen and Unplanned Pregnancy; 2009.
- Meyer JL, Gold MA, Haggerty CL. Advance provision of emergency contraception among adolescent and young adult women: a systematic review of literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2011;24:2-9.
- Martinez GM and Abma JC. Sexual activity, contraceptive use, and childbearing of teenagers aged 15–19 in the United States. NCHS Data Brief, 2015, No. 209. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2015.
- Martinez GM, Abma JC. Sexual activity, contraceptive use, and childbearing of teenagers aged 15-19 in the United States. NCHS Data Brief. July 2015. Accessed June 26, 2019.
- Lindberg L, Santelli J, Desai S. Understanding the decline in adolescent fertility in the United States, 2007–2012. J Adolesc Health. 2016;59:577-583.
- Minguez M, Santelli JS, Gibson E, et al. Reproductive health impact of a school health center. J Adolesc Health. 2015;56:338-344.
- Knopf JA, Finnie RK, Peng Y, et al. Community Preventive Services Task Force. School-based health centers to advance health equity: a Community Guide systematic review. Am J Preventive Med. 2016;51:114-126.
- Progestin-only hormonal birth control: pill and injection. FAQ No. 86. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. July 2014.
- Combined hormonal birth control: pill, patch, and ring. FAQ No. 185. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. July 2014.
- Risk of venous thromboembolism among users of drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills. Committee Opinion No. 540. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
- Curtis KM, Jatlaoui TC, Tepper NK, et al. U.S. Selected Practice Recommendations for Contraceptive Use, 2016. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2016;65(No. RR-4):1–66.
- Letter to President Donald J. Trump. October 6, 2017. https://www.aafp.org/dam/AAFP/documents/advocacy/coverage/aca/LT-Group6-President-ContraceptionIFRs-100617.pdf. Accessed June 26, 2019.
Dr. Eve Espey: Some good news in her 2019 contraceptive update
NASHVILLE, TENN. – There’s some good news on the contraception and reproductive health front, according to a recent update from Eve Espey, MD.
The unintended pregnancy rate in the United States, including among adolescents and young women, is declining, and the U.S. abortion rate is at its lowest level since Roe v. Wade, she said at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
A 2016 article based on 2008-2011 data showed that after hovering around 50% for nearly 3 decades, the unintended pregnancy rate dropped “for the first time in a very long period of time,” said Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics & gynecology, division of family planning at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque (N Engl J Med. 2016; 374[9]:843-52).
“It doesn’t look that impressive – it basically went down to 45%, but considering the scope and the number of women who are affected by unplanned pregnancy, this is actually a huge public health achievement,” she said. “And I think ... in the next cycles of the [Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s] National Survey of Family Growth ... we’ll hopefully continue to see this and potentially more [decline].”
As for abortion rates, an increase occurred following Roe v. Wade, but rates are now down to pre-Roe levels.
“One of the things that we know about the abortion rate is that the most important determinant ... is access to contraceptives,” Dr. Espey said, noting that both the abortion and unintended pregnancy rate declines are attributable to better and more consistent use of contraceptives, increased abstinence as teens are waiting longer to have sex, and the “meteoric rise in long-acting reversible contraceptive (LARC) use.”
Importantly, while improvements in public health have traditionally only impacted upper-class white women, a reduction is finally occurring in disparities with women of color, but those disparities still remain,” she added. “Just like we’re focusing so much on this relative to maternal mortality, the same kinds of disparities occur in access to reproductive health.”
Dr. Espey also provided updates on other aspects of contraception.
IUDs and other LARC methods
The use of LARCs increased from 2% of contraceptive types used by reproductive-aged women in 2002 to 12% in 2012. The majority of that change was in IUD use, with a small increase in implant use, she said, noting that the latest data from the 2015-2017 cycle of the National Survey of Family Growth shows that the rate is now up to 16%.
“The rise has been nothing that I ever imagined that I would see, certainly in my professional career,” she said.
The huge impact of LARCs on the unintended pregnancy rate is attributable to consistent effectiveness over time, compared with an increasing failure rate over time with short-acting contraceptive methods, she said, explaining that while the failure rate with oral contraceptives is about 8%-9% over the first 3 years, it increases to 53% at 8 years.
It’s a matter of looking at both “typical use” effectiveness and continuation rates: LARCs have continuation rates of about 75%-85%; Depot-Provera, for example, has a 25%-30% continuation rate at 1 year, she noted.
Dr. Espey also attributed the gains to improved access via the Affordable Care Act’s contraceptive mandate, which has been shown in numerous studies to have improved access and consistency of contraceptive use, but which is “currently being chipped away,” and to the federal Title X program that covers family planning care for low income women, including undocumented women.
“These two programs have made a huge impact for us, and I hope that we as ob.gyns. will continue to support them,” she said.
Reproductive justice
Despite their effectiveness, it is important to remember that LARC methods are not right for everyone, Dr. Espey said.
“It’s not all about effectiveness. Women have many reasons for accessing contraception, and our job is not to reduce unintended pregnancy. ... The idea really is that we empower women. ... We should really give choices and trust women to make the best choices for them,” she explained.
Barriers to IUD removal also should be eliminated, she noted, explaining that a woman who wants her IUD removed a month after insertion should have that option.
She said she has “changed her language,” from asking why a woman wants an $800 IUD removed after a month to asking whether she would like to hear about ways to make it better or if she is “just ready to have it removed.”
For those not interested in a discussion about birth control, she suggested providing information about the bedsider.org site.
“This is a great resource for patients,” she said, noting that it is available in both English and Spanish.
U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria and Selected Practice Recommendations on contraceptive use
The MEC contraceptive guidance, a regularly updated, evidence-based project of the CDC, provides “best practices” information on candidate selection, or the “who” of contraceptive selection (who is a candidate for a particular method), Dr. Espy said, noting that it’s a “handy resource” for in-office use.
The SPR is more of a “how-to” guide that provides specifics on contraceptive use, such as when a woman can rely on the pill for contraception after she starts taking it, or how a woman should be followed after IUD placement, she said.
A free CDC app provides access to both.
Emergency contraception
The best overall emergency contraceptive method is the copper IUD, but often it is less accessible than oral methods, of which ulipristal acetate (ella), is the best choice, Dr. Espy said.
“Ulipristal is kind of a best-kept secret. It’s a selective estrogen-receptor modulator – it actually works better and longer than Plan B (levonorgestrel). What’s great about Plan B is that you can get it over the counter, but ulipristal delays ovulation longer,” she explained.
Contraceptives and obesity
Oral contraceptive efficacy is “so much more about adherence,” than about weight, she said.
With respect to the contraceptive patch, limited evidence suggests that obesity may reduce effectiveness, but “it’s still way better than barrier methods,” and for the contraceptive ring, no evidence suggests that obesity affects efficacy, she said.
For emergency contraception, evidence suggests that ulipristal is more effective than Plan B in women with high body mass index.
OTC contraceptive access
Pharmacy and OTC access are a good idea, Dr. Espy said.
“ACOG now supports both, which is great, and there are now a number of states where women can access contraception through the pharmacy. There are a lot of barriers there as well, and really the answer is OTC access,” she said. “There is a pill right now that is seeking [Food and Drug Administration] approval; it will be a progestin-only pill – the first one to be available over the counter, so I think this is something that we’ll see in the next 5-10 years.”
Additional future directions
One technology in development is a longer-acting injectable, such as a 6- or 9-month Depot-type shot.
Biodegradable implants also are in development. “What a cool idea – it just disappears in your arm, no need to remove it,” Dr. Espey said, adding that nonsurgical permanent sterilization is another possible advance, which would be “a holy grail.”
As for male contraception?
“I’ve been saying for about 25 years that in 5 years we’ll have a male contraceptive, so I’m not going to say it anymore with any kind of time frame, but it’s possible,” she said.
Dr. Espey reported having no financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – There’s some good news on the contraception and reproductive health front, according to a recent update from Eve Espey, MD.
The unintended pregnancy rate in the United States, including among adolescents and young women, is declining, and the U.S. abortion rate is at its lowest level since Roe v. Wade, she said at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
A 2016 article based on 2008-2011 data showed that after hovering around 50% for nearly 3 decades, the unintended pregnancy rate dropped “for the first time in a very long period of time,” said Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics & gynecology, division of family planning at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque (N Engl J Med. 2016; 374[9]:843-52).
“It doesn’t look that impressive – it basically went down to 45%, but considering the scope and the number of women who are affected by unplanned pregnancy, this is actually a huge public health achievement,” she said. “And I think ... in the next cycles of the [Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s] National Survey of Family Growth ... we’ll hopefully continue to see this and potentially more [decline].”
As for abortion rates, an increase occurred following Roe v. Wade, but rates are now down to pre-Roe levels.
“One of the things that we know about the abortion rate is that the most important determinant ... is access to contraceptives,” Dr. Espey said, noting that both the abortion and unintended pregnancy rate declines are attributable to better and more consistent use of contraceptives, increased abstinence as teens are waiting longer to have sex, and the “meteoric rise in long-acting reversible contraceptive (LARC) use.”
Importantly, while improvements in public health have traditionally only impacted upper-class white women, a reduction is finally occurring in disparities with women of color, but those disparities still remain,” she added. “Just like we’re focusing so much on this relative to maternal mortality, the same kinds of disparities occur in access to reproductive health.”
Dr. Espey also provided updates on other aspects of contraception.
IUDs and other LARC methods
The use of LARCs increased from 2% of contraceptive types used by reproductive-aged women in 2002 to 12% in 2012. The majority of that change was in IUD use, with a small increase in implant use, she said, noting that the latest data from the 2015-2017 cycle of the National Survey of Family Growth shows that the rate is now up to 16%.
“The rise has been nothing that I ever imagined that I would see, certainly in my professional career,” she said.
The huge impact of LARCs on the unintended pregnancy rate is attributable to consistent effectiveness over time, compared with an increasing failure rate over time with short-acting contraceptive methods, she said, explaining that while the failure rate with oral contraceptives is about 8%-9% over the first 3 years, it increases to 53% at 8 years.
It’s a matter of looking at both “typical use” effectiveness and continuation rates: LARCs have continuation rates of about 75%-85%; Depot-Provera, for example, has a 25%-30% continuation rate at 1 year, she noted.
Dr. Espey also attributed the gains to improved access via the Affordable Care Act’s contraceptive mandate, which has been shown in numerous studies to have improved access and consistency of contraceptive use, but which is “currently being chipped away,” and to the federal Title X program that covers family planning care for low income women, including undocumented women.
“These two programs have made a huge impact for us, and I hope that we as ob.gyns. will continue to support them,” she said.
Reproductive justice
Despite their effectiveness, it is important to remember that LARC methods are not right for everyone, Dr. Espey said.
“It’s not all about effectiveness. Women have many reasons for accessing contraception, and our job is not to reduce unintended pregnancy. ... The idea really is that we empower women. ... We should really give choices and trust women to make the best choices for them,” she explained.
Barriers to IUD removal also should be eliminated, she noted, explaining that a woman who wants her IUD removed a month after insertion should have that option.
She said she has “changed her language,” from asking why a woman wants an $800 IUD removed after a month to asking whether she would like to hear about ways to make it better or if she is “just ready to have it removed.”
For those not interested in a discussion about birth control, she suggested providing information about the bedsider.org site.
“This is a great resource for patients,” she said, noting that it is available in both English and Spanish.
U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria and Selected Practice Recommendations on contraceptive use
The MEC contraceptive guidance, a regularly updated, evidence-based project of the CDC, provides “best practices” information on candidate selection, or the “who” of contraceptive selection (who is a candidate for a particular method), Dr. Espy said, noting that it’s a “handy resource” for in-office use.
The SPR is more of a “how-to” guide that provides specifics on contraceptive use, such as when a woman can rely on the pill for contraception after she starts taking it, or how a woman should be followed after IUD placement, she said.
A free CDC app provides access to both.
Emergency contraception
The best overall emergency contraceptive method is the copper IUD, but often it is less accessible than oral methods, of which ulipristal acetate (ella), is the best choice, Dr. Espy said.
“Ulipristal is kind of a best-kept secret. It’s a selective estrogen-receptor modulator – it actually works better and longer than Plan B (levonorgestrel). What’s great about Plan B is that you can get it over the counter, but ulipristal delays ovulation longer,” she explained.
Contraceptives and obesity
Oral contraceptive efficacy is “so much more about adherence,” than about weight, she said.
With respect to the contraceptive patch, limited evidence suggests that obesity may reduce effectiveness, but “it’s still way better than barrier methods,” and for the contraceptive ring, no evidence suggests that obesity affects efficacy, she said.
For emergency contraception, evidence suggests that ulipristal is more effective than Plan B in women with high body mass index.
OTC contraceptive access
Pharmacy and OTC access are a good idea, Dr. Espy said.
“ACOG now supports both, which is great, and there are now a number of states where women can access contraception through the pharmacy. There are a lot of barriers there as well, and really the answer is OTC access,” she said. “There is a pill right now that is seeking [Food and Drug Administration] approval; it will be a progestin-only pill – the first one to be available over the counter, so I think this is something that we’ll see in the next 5-10 years.”
Additional future directions
One technology in development is a longer-acting injectable, such as a 6- or 9-month Depot-type shot.
Biodegradable implants also are in development. “What a cool idea – it just disappears in your arm, no need to remove it,” Dr. Espey said, adding that nonsurgical permanent sterilization is another possible advance, which would be “a holy grail.”
As for male contraception?
“I’ve been saying for about 25 years that in 5 years we’ll have a male contraceptive, so I’m not going to say it anymore with any kind of time frame, but it’s possible,” she said.
Dr. Espey reported having no financial disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – There’s some good news on the contraception and reproductive health front, according to a recent update from Eve Espey, MD.
The unintended pregnancy rate in the United States, including among adolescents and young women, is declining, and the U.S. abortion rate is at its lowest level since Roe v. Wade, she said at the annual clinical and scientific meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
A 2016 article based on 2008-2011 data showed that after hovering around 50% for nearly 3 decades, the unintended pregnancy rate dropped “for the first time in a very long period of time,” said Dr. Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics & gynecology, division of family planning at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque (N Engl J Med. 2016; 374[9]:843-52).
“It doesn’t look that impressive – it basically went down to 45%, but considering the scope and the number of women who are affected by unplanned pregnancy, this is actually a huge public health achievement,” she said. “And I think ... in the next cycles of the [Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s] National Survey of Family Growth ... we’ll hopefully continue to see this and potentially more [decline].”
As for abortion rates, an increase occurred following Roe v. Wade, but rates are now down to pre-Roe levels.
“One of the things that we know about the abortion rate is that the most important determinant ... is access to contraceptives,” Dr. Espey said, noting that both the abortion and unintended pregnancy rate declines are attributable to better and more consistent use of contraceptives, increased abstinence as teens are waiting longer to have sex, and the “meteoric rise in long-acting reversible contraceptive (LARC) use.”
Importantly, while improvements in public health have traditionally only impacted upper-class white women, a reduction is finally occurring in disparities with women of color, but those disparities still remain,” she added. “Just like we’re focusing so much on this relative to maternal mortality, the same kinds of disparities occur in access to reproductive health.”
Dr. Espey also provided updates on other aspects of contraception.
IUDs and other LARC methods
The use of LARCs increased from 2% of contraceptive types used by reproductive-aged women in 2002 to 12% in 2012. The majority of that change was in IUD use, with a small increase in implant use, she said, noting that the latest data from the 2015-2017 cycle of the National Survey of Family Growth shows that the rate is now up to 16%.
“The rise has been nothing that I ever imagined that I would see, certainly in my professional career,” she said.
The huge impact of LARCs on the unintended pregnancy rate is attributable to consistent effectiveness over time, compared with an increasing failure rate over time with short-acting contraceptive methods, she said, explaining that while the failure rate with oral contraceptives is about 8%-9% over the first 3 years, it increases to 53% at 8 years.
It’s a matter of looking at both “typical use” effectiveness and continuation rates: LARCs have continuation rates of about 75%-85%; Depot-Provera, for example, has a 25%-30% continuation rate at 1 year, she noted.
Dr. Espey also attributed the gains to improved access via the Affordable Care Act’s contraceptive mandate, which has been shown in numerous studies to have improved access and consistency of contraceptive use, but which is “currently being chipped away,” and to the federal Title X program that covers family planning care for low income women, including undocumented women.
“These two programs have made a huge impact for us, and I hope that we as ob.gyns. will continue to support them,” she said.
Reproductive justice
Despite their effectiveness, it is important to remember that LARC methods are not right for everyone, Dr. Espey said.
“It’s not all about effectiveness. Women have many reasons for accessing contraception, and our job is not to reduce unintended pregnancy. ... The idea really is that we empower women. ... We should really give choices and trust women to make the best choices for them,” she explained.
Barriers to IUD removal also should be eliminated, she noted, explaining that a woman who wants her IUD removed a month after insertion should have that option.
She said she has “changed her language,” from asking why a woman wants an $800 IUD removed after a month to asking whether she would like to hear about ways to make it better or if she is “just ready to have it removed.”
For those not interested in a discussion about birth control, she suggested providing information about the bedsider.org site.
“This is a great resource for patients,” she said, noting that it is available in both English and Spanish.
U.S. Medical Eligibility Criteria and Selected Practice Recommendations on contraceptive use
The MEC contraceptive guidance, a regularly updated, evidence-based project of the CDC, provides “best practices” information on candidate selection, or the “who” of contraceptive selection (who is a candidate for a particular method), Dr. Espy said, noting that it’s a “handy resource” for in-office use.
The SPR is more of a “how-to” guide that provides specifics on contraceptive use, such as when a woman can rely on the pill for contraception after she starts taking it, or how a woman should be followed after IUD placement, she said.
A free CDC app provides access to both.
Emergency contraception
The best overall emergency contraceptive method is the copper IUD, but often it is less accessible than oral methods, of which ulipristal acetate (ella), is the best choice, Dr. Espy said.
“Ulipristal is kind of a best-kept secret. It’s a selective estrogen-receptor modulator – it actually works better and longer than Plan B (levonorgestrel). What’s great about Plan B is that you can get it over the counter, but ulipristal delays ovulation longer,” she explained.
Contraceptives and obesity
Oral contraceptive efficacy is “so much more about adherence,” than about weight, she said.
With respect to the contraceptive patch, limited evidence suggests that obesity may reduce effectiveness, but “it’s still way better than barrier methods,” and for the contraceptive ring, no evidence suggests that obesity affects efficacy, she said.
For emergency contraception, evidence suggests that ulipristal is more effective than Plan B in women with high body mass index.
OTC contraceptive access
Pharmacy and OTC access are a good idea, Dr. Espy said.
“ACOG now supports both, which is great, and there are now a number of states where women can access contraception through the pharmacy. There are a lot of barriers there as well, and really the answer is OTC access,” she said. “There is a pill right now that is seeking [Food and Drug Administration] approval; it will be a progestin-only pill – the first one to be available over the counter, so I think this is something that we’ll see in the next 5-10 years.”
Additional future directions
One technology in development is a longer-acting injectable, such as a 6- or 9-month Depot-type shot.
Biodegradable implants also are in development. “What a cool idea – it just disappears in your arm, no need to remove it,” Dr. Espey said, adding that nonsurgical permanent sterilization is another possible advance, which would be “a holy grail.”
As for male contraception?
“I’ve been saying for about 25 years that in 5 years we’ll have a male contraceptive, so I’m not going to say it anymore with any kind of time frame, but it’s possible,” she said.
Dr. Espey reported having no financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACOG 2019
LARC prolongs interpregnancy intervals but doesn’t cut preterm birth risk
NASHVILLE, TENN. – when used between a first and second pregnancy, results of a retrospective cohort study suggest.
Of 35,754 women who had a first and second live birth between 2005 and 2015 and who received non-emergent care within 10 years of the first birth, 3,083 (9%) had evidence of interpregnancy LARC exposure and were significantly less likely to have short interpregnancy intervals than were 32,671 with either non-LARC contraceptive use or no record of contraceptive-related care (P less than .0001), Sara E. Simonsen, PhD, reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Intervals in those with intrapartum LARC use were 12 months or less in 4% of women, 13-18 months in 8%, 19-24 months in 11%, and greater than 24 months in 13%.
However, preterm birth, which occurred in 7% of first births and 6% of second births, was not lower among those with LARC exposure vs. those with no contraceptive encounters after adjustment for interpregnancy interval and a number of demographic factors, including education, presence of father, mother’s age, Hispanic ethnicity, fetal anomalies, and preterm birth history (adjusted odds ratio, 1.13), said Dr. Simonsen, a certified nurse midwife at the University of Utah Hospital, Salt Lake City.
“Preterm birth, a live birth at less than 37 weeks’ gestation, is a major determinant of poor neonatal outcomes,” she and her colleagues wrote. “Short interpregnancy interval, defined as less than 18 months, is an important risk factor for preterm birth.”
Given the increasing number of U.S. women who use highly effective LARCs to space pregnancies, she and her colleagues performed a retrospective cohort study of electronic medical records from two large health systems and linked them with birth and fetal death records to explore the relationship between interpregnancy LARC and both interpregnancy interval and preterm birth in the subsequent pregnancy.
“We did find that women who used LARC between their pregnancies were less likely to have a short interpregnancy interval, but in adjusted models ... we found no association with intrapartum LARC use and preterm birth in the second birth,” Dr. Simonsen said during an e-poster presentation at the meeting.
In fact, preterm birth in the second birth was most strongly associated with a prior preterm birth – a finding consistent with the literature, she and her colleagues noted.
Although the findings are limited by the use of retrospective data not designed for research, the data came from a large population-based sample representing about 85% of Utah births, they said.
The findings suggest that while LARC use may not reduce preterm birth risk, it “may contribute favorably to outcomes to the extent that having optimal interpregnancy interval does,” they wrote.
“‘We feel that these findings support providers counseling women on the full range of contraception options in the postpartum and not pushing [intrauterine devices,]” Dr. Simonsen added.
The related topic of immediate postpartum LARC use was addressed by Eve Espey, MD, in a separate presentation at the meeting.
Dr .Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, reported that immediate postpartum insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD) is highly cost-effective despite an expulsion rate of between 10% and 30%. She also addressed the value of postpartum LARC for reducing rapid-repeat pregnancy rates.
Payment models for immediate postpartum LARC are “very cumbersome,” but at the university, a persistent effort over 4 years has led to success. Immediate postpartum LARC is offered to women with Medicaid coverage, and payment is received in about 97% of cases, she said, adding that efforts are underway to help other hospitals “troubleshoot the issues.”
The lack of private insurance coverage for immediate postpartum LARC remains a challenge, but Dr. Espey said she remains “super enthusiastic” about its use.
“I think it’s going to take another 5 years or so [for better coverage], and honestly I think what we really need is an inpatient LARC CPT code to make this happen,” she said, urging colleagues to advocate for that within their American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists sections when possible.
Dr. Simonsen and Dr. Espey reported having no relevant disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – when used between a first and second pregnancy, results of a retrospective cohort study suggest.
Of 35,754 women who had a first and second live birth between 2005 and 2015 and who received non-emergent care within 10 years of the first birth, 3,083 (9%) had evidence of interpregnancy LARC exposure and were significantly less likely to have short interpregnancy intervals than were 32,671 with either non-LARC contraceptive use or no record of contraceptive-related care (P less than .0001), Sara E. Simonsen, PhD, reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Intervals in those with intrapartum LARC use were 12 months or less in 4% of women, 13-18 months in 8%, 19-24 months in 11%, and greater than 24 months in 13%.
However, preterm birth, which occurred in 7% of first births and 6% of second births, was not lower among those with LARC exposure vs. those with no contraceptive encounters after adjustment for interpregnancy interval and a number of demographic factors, including education, presence of father, mother’s age, Hispanic ethnicity, fetal anomalies, and preterm birth history (adjusted odds ratio, 1.13), said Dr. Simonsen, a certified nurse midwife at the University of Utah Hospital, Salt Lake City.
“Preterm birth, a live birth at less than 37 weeks’ gestation, is a major determinant of poor neonatal outcomes,” she and her colleagues wrote. “Short interpregnancy interval, defined as less than 18 months, is an important risk factor for preterm birth.”
Given the increasing number of U.S. women who use highly effective LARCs to space pregnancies, she and her colleagues performed a retrospective cohort study of electronic medical records from two large health systems and linked them with birth and fetal death records to explore the relationship between interpregnancy LARC and both interpregnancy interval and preterm birth in the subsequent pregnancy.
“We did find that women who used LARC between their pregnancies were less likely to have a short interpregnancy interval, but in adjusted models ... we found no association with intrapartum LARC use and preterm birth in the second birth,” Dr. Simonsen said during an e-poster presentation at the meeting.
In fact, preterm birth in the second birth was most strongly associated with a prior preterm birth – a finding consistent with the literature, she and her colleagues noted.
Although the findings are limited by the use of retrospective data not designed for research, the data came from a large population-based sample representing about 85% of Utah births, they said.
The findings suggest that while LARC use may not reduce preterm birth risk, it “may contribute favorably to outcomes to the extent that having optimal interpregnancy interval does,” they wrote.
“‘We feel that these findings support providers counseling women on the full range of contraception options in the postpartum and not pushing [intrauterine devices,]” Dr. Simonsen added.
The related topic of immediate postpartum LARC use was addressed by Eve Espey, MD, in a separate presentation at the meeting.
Dr .Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, reported that immediate postpartum insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD) is highly cost-effective despite an expulsion rate of between 10% and 30%. She also addressed the value of postpartum LARC for reducing rapid-repeat pregnancy rates.
Payment models for immediate postpartum LARC are “very cumbersome,” but at the university, a persistent effort over 4 years has led to success. Immediate postpartum LARC is offered to women with Medicaid coverage, and payment is received in about 97% of cases, she said, adding that efforts are underway to help other hospitals “troubleshoot the issues.”
The lack of private insurance coverage for immediate postpartum LARC remains a challenge, but Dr. Espey said she remains “super enthusiastic” about its use.
“I think it’s going to take another 5 years or so [for better coverage], and honestly I think what we really need is an inpatient LARC CPT code to make this happen,” she said, urging colleagues to advocate for that within their American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists sections when possible.
Dr. Simonsen and Dr. Espey reported having no relevant disclosures.
NASHVILLE, TENN. – when used between a first and second pregnancy, results of a retrospective cohort study suggest.
Of 35,754 women who had a first and second live birth between 2005 and 2015 and who received non-emergent care within 10 years of the first birth, 3,083 (9%) had evidence of interpregnancy LARC exposure and were significantly less likely to have short interpregnancy intervals than were 32,671 with either non-LARC contraceptive use or no record of contraceptive-related care (P less than .0001), Sara E. Simonsen, PhD, reported in a poster at the annual meeting of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists.
Intervals in those with intrapartum LARC use were 12 months or less in 4% of women, 13-18 months in 8%, 19-24 months in 11%, and greater than 24 months in 13%.
However, preterm birth, which occurred in 7% of first births and 6% of second births, was not lower among those with LARC exposure vs. those with no contraceptive encounters after adjustment for interpregnancy interval and a number of demographic factors, including education, presence of father, mother’s age, Hispanic ethnicity, fetal anomalies, and preterm birth history (adjusted odds ratio, 1.13), said Dr. Simonsen, a certified nurse midwife at the University of Utah Hospital, Salt Lake City.
“Preterm birth, a live birth at less than 37 weeks’ gestation, is a major determinant of poor neonatal outcomes,” she and her colleagues wrote. “Short interpregnancy interval, defined as less than 18 months, is an important risk factor for preterm birth.”
Given the increasing number of U.S. women who use highly effective LARCs to space pregnancies, she and her colleagues performed a retrospective cohort study of electronic medical records from two large health systems and linked them with birth and fetal death records to explore the relationship between interpregnancy LARC and both interpregnancy interval and preterm birth in the subsequent pregnancy.
“We did find that women who used LARC between their pregnancies were less likely to have a short interpregnancy interval, but in adjusted models ... we found no association with intrapartum LARC use and preterm birth in the second birth,” Dr. Simonsen said during an e-poster presentation at the meeting.
In fact, preterm birth in the second birth was most strongly associated with a prior preterm birth – a finding consistent with the literature, she and her colleagues noted.
Although the findings are limited by the use of retrospective data not designed for research, the data came from a large population-based sample representing about 85% of Utah births, they said.
The findings suggest that while LARC use may not reduce preterm birth risk, it “may contribute favorably to outcomes to the extent that having optimal interpregnancy interval does,” they wrote.
“‘We feel that these findings support providers counseling women on the full range of contraception options in the postpartum and not pushing [intrauterine devices,]” Dr. Simonsen added.
The related topic of immediate postpartum LARC use was addressed by Eve Espey, MD, in a separate presentation at the meeting.
Dr .Espey, professor and chair of the department of obstetrics and gynecology and director of the family planning fellowship at the University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, reported that immediate postpartum insertion of an intrauterine device (IUD) is highly cost-effective despite an expulsion rate of between 10% and 30%. She also addressed the value of postpartum LARC for reducing rapid-repeat pregnancy rates.
Payment models for immediate postpartum LARC are “very cumbersome,” but at the university, a persistent effort over 4 years has led to success. Immediate postpartum LARC is offered to women with Medicaid coverage, and payment is received in about 97% of cases, she said, adding that efforts are underway to help other hospitals “troubleshoot the issues.”
The lack of private insurance coverage for immediate postpartum LARC remains a challenge, but Dr. Espey said she remains “super enthusiastic” about its use.
“I think it’s going to take another 5 years or so [for better coverage], and honestly I think what we really need is an inpatient LARC CPT code to make this happen,” she said, urging colleagues to advocate for that within their American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists sections when possible.
Dr. Simonsen and Dr. Espey reported having no relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM ACOG 2019
Ovarian reserve markers fall on isotretinoin, but rebound after stopping treatment
MILAN – according to data presented at the World Congress of Dermatology.
Although markers for ovarian reserve, including anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) serum levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count, were significantly lower during a period of isotretinoin use than at baseline, these values were were not significantly different from pretreatment levels by 1 month after stopping isotretinoin.
For patients taking isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day, AMH levels fell from a baseline level of 5.29 ng/mL to 4.16 ng/mL during treatment, but rebounded to 4.77 ng/mL 1 month after stopping treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), Tuğba Özkök Akbulut, MD, said during a late-breaking abstracts session.
For women taking isotretinoin 1 mg/kg/day, AMH levels went from 5.14 ng/mL at baseline to 4.24 ng/mL on treatment, to 4.65 ng/mL 1 month after treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), reported Dr. Akbulut a dermatologist at the Haseki Training Research Hospital, Istanbul.
Women on the higher dose of isotretinoin had a similar pattern of decline while on treatment and rebound after ceasing isotretinoin for ovarian volume and antral follicle count (P less than .001 for all values). These differences were not statistically significant for women taking 0.5 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin, except for right ovarian volume (P = 0.013).
Although values were numerically lower for many markers of ovarian reserve after ceasing treatment, compared with baseline figures, these differences were not statistically significantly different. Markers of ovarian reserve did not change significantly for a control group of women without acne.
Dr. Akbulut and her colleagues conducted this prospective case-control study of 42 women of reproductive age who sought dermatologist care for severe acne unresponsive to conservative therapy; 26 women who did not have acne constituted the control group. Smokers, patients with thyroid disease, and those with known polycystic ovary syndrome were excluded from participation.
The women with acne received oral isotretinoin dosed either at 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day, with treatment lasting 5-9 months. For each patient, treatment was stopped when the cumulative dose reached 120 mg/kg.
After an initial visit at which blood was collected from all participants to measure serum AMH levels, those receiving isotretinoin were seen every 4 weeks to check serum lipid and liver enzyme levels.
At the 3-month mark during the study period and 1 month after the end of completing isotretinoin treatment, or at the end of the study period for the control group, blood samples also were drawn for AMH levels.
To measure hormone levels, also blood was drawn between days 2 and 5 of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Participants received ultrasounds to measure antral follicle count and ovarian volume between days 2 and 5 of the menstrual cycle at the initial visit, at the 3-month visit, and at the final visit. Results were interpreted by a trained gynecologist.
Patients, who were mostly in their early 20s, had a mean body mass index of about 22 kg/m2. Hormone levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count did not differ among study arms at baseline.
“There are contradictory reports in the literature regarding the effect of retinoic acid on ovarian reserve,” noted Dr. Akbulut. Some preclinical studies found that retinoic acid increased fertility and ovarian reserve in rodents; however, some human studies had shown lower serum AMH concentrations in patients using isotretinoin.
This new demonstration of the reversibility of isotretinoin’s negative effect on ovarian reserve helps clarify a confused picture in the medical literature, said Dr. Akbulut. “The results of our study demonstrated that systemic isotretinoin had a reversible effect on ovarian reserve.”
Dr. Akbulut reported no outside sources of funding and that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
MILAN – according to data presented at the World Congress of Dermatology.
Although markers for ovarian reserve, including anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) serum levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count, were significantly lower during a period of isotretinoin use than at baseline, these values were were not significantly different from pretreatment levels by 1 month after stopping isotretinoin.
For patients taking isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day, AMH levels fell from a baseline level of 5.29 ng/mL to 4.16 ng/mL during treatment, but rebounded to 4.77 ng/mL 1 month after stopping treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), Tuğba Özkök Akbulut, MD, said during a late-breaking abstracts session.
For women taking isotretinoin 1 mg/kg/day, AMH levels went from 5.14 ng/mL at baseline to 4.24 ng/mL on treatment, to 4.65 ng/mL 1 month after treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), reported Dr. Akbulut a dermatologist at the Haseki Training Research Hospital, Istanbul.
Women on the higher dose of isotretinoin had a similar pattern of decline while on treatment and rebound after ceasing isotretinoin for ovarian volume and antral follicle count (P less than .001 for all values). These differences were not statistically significant for women taking 0.5 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin, except for right ovarian volume (P = 0.013).
Although values were numerically lower for many markers of ovarian reserve after ceasing treatment, compared with baseline figures, these differences were not statistically significantly different. Markers of ovarian reserve did not change significantly for a control group of women without acne.
Dr. Akbulut and her colleagues conducted this prospective case-control study of 42 women of reproductive age who sought dermatologist care for severe acne unresponsive to conservative therapy; 26 women who did not have acne constituted the control group. Smokers, patients with thyroid disease, and those with known polycystic ovary syndrome were excluded from participation.
The women with acne received oral isotretinoin dosed either at 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day, with treatment lasting 5-9 months. For each patient, treatment was stopped when the cumulative dose reached 120 mg/kg.
After an initial visit at which blood was collected from all participants to measure serum AMH levels, those receiving isotretinoin were seen every 4 weeks to check serum lipid and liver enzyme levels.
At the 3-month mark during the study period and 1 month after the end of completing isotretinoin treatment, or at the end of the study period for the control group, blood samples also were drawn for AMH levels.
To measure hormone levels, also blood was drawn between days 2 and 5 of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Participants received ultrasounds to measure antral follicle count and ovarian volume between days 2 and 5 of the menstrual cycle at the initial visit, at the 3-month visit, and at the final visit. Results were interpreted by a trained gynecologist.
Patients, who were mostly in their early 20s, had a mean body mass index of about 22 kg/m2. Hormone levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count did not differ among study arms at baseline.
“There are contradictory reports in the literature regarding the effect of retinoic acid on ovarian reserve,” noted Dr. Akbulut. Some preclinical studies found that retinoic acid increased fertility and ovarian reserve in rodents; however, some human studies had shown lower serum AMH concentrations in patients using isotretinoin.
This new demonstration of the reversibility of isotretinoin’s negative effect on ovarian reserve helps clarify a confused picture in the medical literature, said Dr. Akbulut. “The results of our study demonstrated that systemic isotretinoin had a reversible effect on ovarian reserve.”
Dr. Akbulut reported no outside sources of funding and that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
MILAN – according to data presented at the World Congress of Dermatology.
Although markers for ovarian reserve, including anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) serum levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count, were significantly lower during a period of isotretinoin use than at baseline, these values were were not significantly different from pretreatment levels by 1 month after stopping isotretinoin.
For patients taking isotretinoin at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day, AMH levels fell from a baseline level of 5.29 ng/mL to 4.16 ng/mL during treatment, but rebounded to 4.77 ng/mL 1 month after stopping treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), Tuğba Özkök Akbulut, MD, said during a late-breaking abstracts session.
For women taking isotretinoin 1 mg/kg/day, AMH levels went from 5.14 ng/mL at baseline to 4.24 ng/mL on treatment, to 4.65 ng/mL 1 month after treatment (P less than .001 for difference between baseline and on-drug values), reported Dr. Akbulut a dermatologist at the Haseki Training Research Hospital, Istanbul.
Women on the higher dose of isotretinoin had a similar pattern of decline while on treatment and rebound after ceasing isotretinoin for ovarian volume and antral follicle count (P less than .001 for all values). These differences were not statistically significant for women taking 0.5 mg/kg/day of isotretinoin, except for right ovarian volume (P = 0.013).
Although values were numerically lower for many markers of ovarian reserve after ceasing treatment, compared with baseline figures, these differences were not statistically significantly different. Markers of ovarian reserve did not change significantly for a control group of women without acne.
Dr. Akbulut and her colleagues conducted this prospective case-control study of 42 women of reproductive age who sought dermatologist care for severe acne unresponsive to conservative therapy; 26 women who did not have acne constituted the control group. Smokers, patients with thyroid disease, and those with known polycystic ovary syndrome were excluded from participation.
The women with acne received oral isotretinoin dosed either at 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg/day, with treatment lasting 5-9 months. For each patient, treatment was stopped when the cumulative dose reached 120 mg/kg.
After an initial visit at which blood was collected from all participants to measure serum AMH levels, those receiving isotretinoin were seen every 4 weeks to check serum lipid and liver enzyme levels.
At the 3-month mark during the study period and 1 month after the end of completing isotretinoin treatment, or at the end of the study period for the control group, blood samples also were drawn for AMH levels.
To measure hormone levels, also blood was drawn between days 2 and 5 of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Participants received ultrasounds to measure antral follicle count and ovarian volume between days 2 and 5 of the menstrual cycle at the initial visit, at the 3-month visit, and at the final visit. Results were interpreted by a trained gynecologist.
Patients, who were mostly in their early 20s, had a mean body mass index of about 22 kg/m2. Hormone levels, ovarian volume, and antral follicle count did not differ among study arms at baseline.
“There are contradictory reports in the literature regarding the effect of retinoic acid on ovarian reserve,” noted Dr. Akbulut. Some preclinical studies found that retinoic acid increased fertility and ovarian reserve in rodents; however, some human studies had shown lower serum AMH concentrations in patients using isotretinoin.
This new demonstration of the reversibility of isotretinoin’s negative effect on ovarian reserve helps clarify a confused picture in the medical literature, said Dr. Akbulut. “The results of our study demonstrated that systemic isotretinoin had a reversible effect on ovarian reserve.”
Dr. Akbulut reported no outside sources of funding and that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM WCD2019
Judge bars contraceptive mandate from being enforced
In a June 5, 2019, opinion, U.S. District Judge Reed O’Connor granted a permanent injunction on the contraceptive mandate, ruling that both the mandate and the accommodation process violate the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. The injunction applies to all individuals and employers – regardless of size or nonprofit status – that oppose contraceptive coverage based on religious beliefs.
In his ruling, Judge O’Connor said the contraceptive mandate substantially burdens the plaintiffs’ religious exercise.
“The point of the contraceptive mandate is to ensure all ACA-compliant insurance plans include cost-free coverage of all FDA [Food and Drug Administration]-approved contraceptive methods [and] the point of the individual mandate is to ensure individuals purchase ACA-compliant insurance plans,” Judge O’Conner wrote. “The result? The individual plaintiffs are forced out of either the health insurance market or their religious exercise. And by choosing to adhere to their religious beliefs, not only are the individual plaintiffs excluded from the insurance market, they are forced to violate federal law. That the contraceptive mandate systematically discriminates against the individual class by blocking members’ entrance into the marketplace – due to religious exercise – is a substantial burden of the highest order.”
The case, DeOtte v. Azar, started with an October 2018 legal challenge by several Texas residents and a business over having to comply with the Affordable Care Act mandate. The plaintiffs argued the requirement violates their religious freedom, and that the court should strike it down as unconstitutional. The current Justice Department has largely chosen not to defend the case, agreeing that forcing people and employers with religious objections to comply with the contraceptive mandate violates the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. In 2018, the department issued new rules expanding exemptions to the ACA’s contraceptive mandate on moral or religious grounds.
Legal challenges against the expanded exemptions continue through the courts. Judges in California and Pennsylvania have temporarily banned the rules from taking effect. Analysts say the final answer on the contraceptive mandate could come from the U.S. Supreme Court.
In a June 5, 2019, opinion, U.S. District Judge Reed O’Connor granted a permanent injunction on the contraceptive mandate, ruling that both the mandate and the accommodation process violate the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. The injunction applies to all individuals and employers – regardless of size or nonprofit status – that oppose contraceptive coverage based on religious beliefs.
In his ruling, Judge O’Connor said the contraceptive mandate substantially burdens the plaintiffs’ religious exercise.
“The point of the contraceptive mandate is to ensure all ACA-compliant insurance plans include cost-free coverage of all FDA [Food and Drug Administration]-approved contraceptive methods [and] the point of the individual mandate is to ensure individuals purchase ACA-compliant insurance plans,” Judge O’Conner wrote. “The result? The individual plaintiffs are forced out of either the health insurance market or their religious exercise. And by choosing to adhere to their religious beliefs, not only are the individual plaintiffs excluded from the insurance market, they are forced to violate federal law. That the contraceptive mandate systematically discriminates against the individual class by blocking members’ entrance into the marketplace – due to religious exercise – is a substantial burden of the highest order.”
The case, DeOtte v. Azar, started with an October 2018 legal challenge by several Texas residents and a business over having to comply with the Affordable Care Act mandate. The plaintiffs argued the requirement violates their religious freedom, and that the court should strike it down as unconstitutional. The current Justice Department has largely chosen not to defend the case, agreeing that forcing people and employers with religious objections to comply with the contraceptive mandate violates the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. In 2018, the department issued new rules expanding exemptions to the ACA’s contraceptive mandate on moral or religious grounds.
Legal challenges against the expanded exemptions continue through the courts. Judges in California and Pennsylvania have temporarily banned the rules from taking effect. Analysts say the final answer on the contraceptive mandate could come from the U.S. Supreme Court.
In a June 5, 2019, opinion, U.S. District Judge Reed O’Connor granted a permanent injunction on the contraceptive mandate, ruling that both the mandate and the accommodation process violate the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. The injunction applies to all individuals and employers – regardless of size or nonprofit status – that oppose contraceptive coverage based on religious beliefs.
In his ruling, Judge O’Connor said the contraceptive mandate substantially burdens the plaintiffs’ religious exercise.
“The point of the contraceptive mandate is to ensure all ACA-compliant insurance plans include cost-free coverage of all FDA [Food and Drug Administration]-approved contraceptive methods [and] the point of the individual mandate is to ensure individuals purchase ACA-compliant insurance plans,” Judge O’Conner wrote. “The result? The individual plaintiffs are forced out of either the health insurance market or their religious exercise. And by choosing to adhere to their religious beliefs, not only are the individual plaintiffs excluded from the insurance market, they are forced to violate federal law. That the contraceptive mandate systematically discriminates against the individual class by blocking members’ entrance into the marketplace – due to religious exercise – is a substantial burden of the highest order.”
The case, DeOtte v. Azar, started with an October 2018 legal challenge by several Texas residents and a business over having to comply with the Affordable Care Act mandate. The plaintiffs argued the requirement violates their religious freedom, and that the court should strike it down as unconstitutional. The current Justice Department has largely chosen not to defend the case, agreeing that forcing people and employers with religious objections to comply with the contraceptive mandate violates the Religious Freedom Restoration Act. In 2018, the department issued new rules expanding exemptions to the ACA’s contraceptive mandate on moral or religious grounds.
Legal challenges against the expanded exemptions continue through the courts. Judges in California and Pennsylvania have temporarily banned the rules from taking effect. Analysts say the final answer on the contraceptive mandate could come from the U.S. Supreme Court.
Postpartum LARC uptake increased with separate payment
The introduction of separate payment for the immediate postpartum implantation of long-acting reversible contraception was associated with increased use and a slow-down in the number of short-interval births in patients covered by South Carolina’s Medicaid program.
Immediate postpartum long-acting reversible contraception (IPP-LARC) is recommended to reduce the incidence of short pregnancy intervals – pregnancies within 6-24 months of each other. The global payment for hospital labor and delivery, however, may act as a disincentive to providing IPP-LARC, according to Maria W. Steenland of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and co-authors.
They looked at inpatient Medicaid claims data for 242,825 childbirth hospitalizations in South Carolina from 2010-2017; during that time the state Medicaid program began to provide an additional payment for IPP-LARC.
At the start of the study, just 0.07% of women received an IPP-LARC. After the change in reimbursement policy in March 2012, there was a steady 0.07 percentage point monthly increase in their use in adults and 0.1 percentage point increase per month in adolescents. In December 2017, 5.65% of adults and 10.48% of adolescents received an IPP-LARC (JAMA. 2019; doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.6854).
There was a corresponding, significant change in the trend of short-interval births among adolescents. Before the policy change, adolescent short-interval births had been increasing, but by March 2016 – 4 years after the payment change – the adolescent short-interval birth rate was 5.28 percentage points lower than what was expected had the increasing trend continued.
There was no significant change in the trend for short-interval births among adults.
“These findings suggest that IPP-LARC reimbursement could increase immediate postpartum contraceptive options and help adolescents avoid short-interval births,” the authors wrote, noting that as of February 2018, 36 other states’ Medicaid programs had began separately reimbursing for IPP-LARC.
They also raised the possibility that there may have been confounding due to other events that occurred at the same time as the policy changes.
The study was supported by the Eric M. Mindich Research Fund and one author was supported by National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Steenland M et al. JAMA 2019, DOI:10.1001/jama.2019.6854.
The introduction of separate payment for the immediate postpartum implantation of long-acting reversible contraception was associated with increased use and a slow-down in the number of short-interval births in patients covered by South Carolina’s Medicaid program.
Immediate postpartum long-acting reversible contraception (IPP-LARC) is recommended to reduce the incidence of short pregnancy intervals – pregnancies within 6-24 months of each other. The global payment for hospital labor and delivery, however, may act as a disincentive to providing IPP-LARC, according to Maria W. Steenland of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and co-authors.
They looked at inpatient Medicaid claims data for 242,825 childbirth hospitalizations in South Carolina from 2010-2017; during that time the state Medicaid program began to provide an additional payment for IPP-LARC.
At the start of the study, just 0.07% of women received an IPP-LARC. After the change in reimbursement policy in March 2012, there was a steady 0.07 percentage point monthly increase in their use in adults and 0.1 percentage point increase per month in adolescents. In December 2017, 5.65% of adults and 10.48% of adolescents received an IPP-LARC (JAMA. 2019; doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.6854).
There was a corresponding, significant change in the trend of short-interval births among adolescents. Before the policy change, adolescent short-interval births had been increasing, but by March 2016 – 4 years after the payment change – the adolescent short-interval birth rate was 5.28 percentage points lower than what was expected had the increasing trend continued.
There was no significant change in the trend for short-interval births among adults.
“These findings suggest that IPP-LARC reimbursement could increase immediate postpartum contraceptive options and help adolescents avoid short-interval births,” the authors wrote, noting that as of February 2018, 36 other states’ Medicaid programs had began separately reimbursing for IPP-LARC.
They also raised the possibility that there may have been confounding due to other events that occurred at the same time as the policy changes.
The study was supported by the Eric M. Mindich Research Fund and one author was supported by National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Steenland M et al. JAMA 2019, DOI:10.1001/jama.2019.6854.
The introduction of separate payment for the immediate postpartum implantation of long-acting reversible contraception was associated with increased use and a slow-down in the number of short-interval births in patients covered by South Carolina’s Medicaid program.
Immediate postpartum long-acting reversible contraception (IPP-LARC) is recommended to reduce the incidence of short pregnancy intervals – pregnancies within 6-24 months of each other. The global payment for hospital labor and delivery, however, may act as a disincentive to providing IPP-LARC, according to Maria W. Steenland of Brown University, Providence, R.I., and co-authors.
They looked at inpatient Medicaid claims data for 242,825 childbirth hospitalizations in South Carolina from 2010-2017; during that time the state Medicaid program began to provide an additional payment for IPP-LARC.
At the start of the study, just 0.07% of women received an IPP-LARC. After the change in reimbursement policy in March 2012, there was a steady 0.07 percentage point monthly increase in their use in adults and 0.1 percentage point increase per month in adolescents. In December 2017, 5.65% of adults and 10.48% of adolescents received an IPP-LARC (JAMA. 2019; doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.6854).
There was a corresponding, significant change in the trend of short-interval births among adolescents. Before the policy change, adolescent short-interval births had been increasing, but by March 2016 – 4 years after the payment change – the adolescent short-interval birth rate was 5.28 percentage points lower than what was expected had the increasing trend continued.
There was no significant change in the trend for short-interval births among adults.
“These findings suggest that IPP-LARC reimbursement could increase immediate postpartum contraceptive options and help adolescents avoid short-interval births,” the authors wrote, noting that as of February 2018, 36 other states’ Medicaid programs had began separately reimbursing for IPP-LARC.
They also raised the possibility that there may have been confounding due to other events that occurred at the same time as the policy changes.
The study was supported by the Eric M. Mindich Research Fund and one author was supported by National Institutes of Health. No conflicts of interest were declared.
SOURCE: Steenland M et al. JAMA 2019, DOI:10.1001/jama.2019.6854.
FROM JAMA