User login
MDedge latest news is breaking news from medical conferences, journals, guidelines, the FDA and CDC.
Journal Highlights: July-November 2025
Endoscopy
Barkun AN, et al. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Clinical Practice Guideline for the Endoscopic Management of Nonvariceal Nonpeptic Ulcer Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.04.041.
Kindel TL, et al. Multisociety Clinical Practice Guidance for the Safe Use of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Perioperative Period. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.10.003.
Roy A, et al. Endohepatology: Evolving Indications, Challenges, Unmet Needs and Opportunities. Gastro Hep Advances. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100838.
Esophagus
Wani S, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Surveillance of Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.09.012.
Reed CC, et al. Worsening Disease Severity as Measured by I-SEE Associates With Decreased Treatment Response to Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Sep. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.01.015.
Kagzi Y, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication for Post–Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease With Esophagitis: A Meta-Analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 Oct. doi:10.1016/j.tige.2025.250953.
Stomach
Staller K, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Management of Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.08.004.
Colon
Bergman D, et al. Cholecystectomy Is a Risk Factor for Microscopic Colitis: A Nationwide Population-based Matched Case Control Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.12.032.
Liver
Younossi ZM, et al. Global Consensus Recommendations for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.02.044.
Kabelitz MA, et al. Early Occurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy Following Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Insertion is Linked to Impaired Survival: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.01.024.
Brar G, et al. Association of Cirrhosis Etiology with Outcomes After TIPS: A National Cohort Study. Gastro Hep Advances. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100850.
IBD
Kucharzik T, et al. Role of Noninvasive Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Suspected and Established Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.002.
Griffiths BJ, et al. Hypercoagulation After Hospital Discharge in Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Sep. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.10.031.
Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction
Trindade IA, et al. Implications of Shame for Patient-Reported Outcomes in Bowel Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.030.
Salwen-Deremer JK, et al. A Practical Guide to Incorporating a Psychologist Into a Gastroenterology Practice. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.05.014.
Misc
Monahan K, et al. In Our Scope of Practice: Genetic Risk Assessment and Testing for Gastrointestinal Cancers and Polyposis in Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.001.
Dr. Trieu is assistant professor of medicine, interventional endoscopy, in the Division of Gastroenterology at Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, Missouri.
Endoscopy
Barkun AN, et al. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Clinical Practice Guideline for the Endoscopic Management of Nonvariceal Nonpeptic Ulcer Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.04.041.
Kindel TL, et al. Multisociety Clinical Practice Guidance for the Safe Use of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Perioperative Period. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.10.003.
Roy A, et al. Endohepatology: Evolving Indications, Challenges, Unmet Needs and Opportunities. Gastro Hep Advances. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100838.
Esophagus
Wani S, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Surveillance of Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.09.012.
Reed CC, et al. Worsening Disease Severity as Measured by I-SEE Associates With Decreased Treatment Response to Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Sep. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.01.015.
Kagzi Y, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication for Post–Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease With Esophagitis: A Meta-Analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 Oct. doi:10.1016/j.tige.2025.250953.
Stomach
Staller K, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Management of Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.08.004.
Colon
Bergman D, et al. Cholecystectomy Is a Risk Factor for Microscopic Colitis: A Nationwide Population-based Matched Case Control Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.12.032.
Liver
Younossi ZM, et al. Global Consensus Recommendations for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.02.044.
Kabelitz MA, et al. Early Occurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy Following Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Insertion is Linked to Impaired Survival: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.01.024.
Brar G, et al. Association of Cirrhosis Etiology with Outcomes After TIPS: A National Cohort Study. Gastro Hep Advances. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100850.
IBD
Kucharzik T, et al. Role of Noninvasive Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Suspected and Established Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.002.
Griffiths BJ, et al. Hypercoagulation After Hospital Discharge in Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Sep. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.10.031.
Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction
Trindade IA, et al. Implications of Shame for Patient-Reported Outcomes in Bowel Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.030.
Salwen-Deremer JK, et al. A Practical Guide to Incorporating a Psychologist Into a Gastroenterology Practice. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.05.014.
Misc
Monahan K, et al. In Our Scope of Practice: Genetic Risk Assessment and Testing for Gastrointestinal Cancers and Polyposis in Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.001.
Dr. Trieu is assistant professor of medicine, interventional endoscopy, in the Division of Gastroenterology at Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, Missouri.
Endoscopy
Barkun AN, et al. Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Clinical Practice Guideline for the Endoscopic Management of Nonvariceal Nonpeptic Ulcer Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.04.041.
Kindel TL, et al. Multisociety Clinical Practice Guidance for the Safe Use of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in the Perioperative Period. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.10.003.
Roy A, et al. Endohepatology: Evolving Indications, Challenges, Unmet Needs and Opportunities. Gastro Hep Advances. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100838.
Esophagus
Wani S, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Surveillance of Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.09.012.
Reed CC, et al. Worsening Disease Severity as Measured by I-SEE Associates With Decreased Treatment Response to Topical Steroids in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Sep. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.01.015.
Kagzi Y, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication for Post–Esophageal Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease With Esophagitis: A Meta-Analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2025 Oct. doi:10.1016/j.tige.2025.250953.
Stomach
Staller K, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on Management of Gastroparesis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.08.004.
Colon
Bergman D, et al. Cholecystectomy Is a Risk Factor for Microscopic Colitis: A Nationwide Population-based Matched Case Control Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.12.032.
Liver
Younossi ZM, et al. Global Consensus Recommendations for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology. 2025 Oct. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.02.044.
Kabelitz MA, et al. Early Occurrence of Hepatic Encephalopathy Following Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Insertion is Linked to Impaired Survival: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.01.024.
Brar G, et al. Association of Cirrhosis Etiology with Outcomes After TIPS: A National Cohort Study. Gastro Hep Advances. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2025.100850.
IBD
Kucharzik T, et al. Role of Noninvasive Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Suspected and Established Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.002.
Griffiths BJ, et al. Hypercoagulation After Hospital Discharge in Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis: A Prospective Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Sep. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2024.10.031.
Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction
Trindade IA, et al. Implications of Shame for Patient-Reported Outcomes in Bowel Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction. Gastroenterology. 2025 Aug. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.030.
Salwen-Deremer JK, et al. A Practical Guide to Incorporating a Psychologist Into a Gastroenterology Practice. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.05.014.
Misc
Monahan K, et al. In Our Scope of Practice: Genetic Risk Assessment and Testing for Gastrointestinal Cancers and Polyposis in Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology. 2025 Nov. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.06.001.
Dr. Trieu is assistant professor of medicine, interventional endoscopy, in the Division of Gastroenterology at Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, Missouri.
Office-Based Endoscopy Model Offers Way Forward for Outpatient GI
After decades of successful growth, the ambulatory surgery center (ASC) model may be turning a corner, opening up opportunity for office-based endoscopy models, according to a recent practice management editorial published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Although office endoscopy has been an option, it hasn’t always felt practical or financially viable in the past. However, the paradigm appears to be shifting as ASC-based revenue streams show signs of stress and fail to keep pace with inflation. As healthcare regulatory and economic environments continue to change, gastroenterologists need a new model to support equity, efficiency, and growth in gastrointestinal (GI) care delivery, the authors wrote.
“Through the course of my 40-year career, I’ve been hit with a lot of changes related to regulations, insurance, and the market. You can’t stay entrenched in your old ways. You have to remain pivotable and come up with new strategic positions,” said Lawrence Kosinski, MD, AGAF, lead author and founder of SonarMD and VOCnomics.
During his private practice career, Kosinski built one of the largest GI practices in Illinois, which had seven ASCs and is now part of one of the largest GI groups in the country. Across 30 years of experience with ASCs, Kosinski has watched the reimbursement for professional services decline, as well as for added revenue streams such as pathology and anesthesia.
Looking for a better solution, Kosinski served on the governing board for the American Gastroenterological Association as the councilor for development and growth. During the past 3 years, he has spoken with GI practices and worked with a national anesthesia company — Ambulatory Anesthesia Care — to better understand the office endoscopy setting.
“In the ’90s, all I wanted was to have an ASC because that was in vogue,” he said. “But if you look critically at what has happened to the business of outpatient endoscopy in the past 25 years, you’ll see that professional fees haven’t kept up, and trying to replace that lost revenue is a losing battle.”
Considering Financial Shifts
Since 2001, professional reimbursement for colonoscopies has fallen by more than 40% while ASC revenue has risen, decreasing the percentage of revenue from professional fees (from 34% to 23%) and increasing the facility component (from 44% to 60%), Kosinski and colleagues wrote.
When looking at profit, compression of professional service fees appears even greater, especially with surging costs of anesthesia care due to high demand and provider shortages. Beyond that, about a third of ASCs are owned at least partially by national entities, as of 2024, leading to even lower realization of profit.
“The profit margins have really been crushed, so what is a GI doc to do? Go where there is opportunity,” Kosinski said. “The difference between hospitals and ASCs has been compressed, so what about the office?”
The proposed 2026 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule includes a 14% increase in reimbursement for office-based procedures, including endoscopy, as well as a 7% decrease for facility-based procedures.
In several states — such as Illinois, Oregon, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin — health plans are introducing programs to promote the transition of outpatient endoscopy to office settings rather than hospital-based or ASC-based settings due to costs, the authors wrote.
“The decision to start offering office-based endoscopy services was an easy one for our practice, as it provides a way for us to provide patients convenient, easy-to-access endoscopy that is high quality yet much more affordable than hospital-based settings,” said Neil Gupta, MD, managing partner at Midwest Digestive Health & Nutrition in Des Plaines, Illinois.
The practice has used office-based endoscopy for nearly 2 years, Gupta said, performing about 5000 GI endoscopy procedures per year.
“As we all try to find better ways to provide high-quality but affordable care for patients, office-based endoscopy is a great way to help achieve those goals,” he said. “Healthcare professionals and patients should all be asking, ‘What type of site am I getting my GI endoscopy scheduled at — hospital, surgery center, or physician’s office?’”
Regaining Autonomy and Time
Beyond the financial dynamics, , Kosinski and colleagues wrote.
Looking ahead, office-based models can also provide the agility and infrastructure to compete in value-based care models, they wrote. In turn, value-based models can create relevance and resilience in a continually changing healthcare environment.
Without the involvement of ASC managers, investors, or health system partners, physicians retain control of scheduling, clinical protocols, financial decisions, and operational workflows, the authors wrote. This could create better alignment with personal preferences, clinical judgment, and patient needs, they noted.
“GI physicians should no longer feel trapped in a hospital setting where they lack independence and influence over decision-making,” said Rock Rockett, PhD, owner and principal consultant of Rockett Healthcare Strategies, which partners with GI groups nationwide to help with development, accreditation, and payer contracting for office endoscopy.
“GI physicians should also no longer feel trapped in a ‘bad marriage’ with partners in an ASC or partners in a practice who create a difficult work environment,” he said. “The viability of office endoscopy allows them to strike out on their own or set up a new partnership on more equitable terms that are attractive for them.”
Patient safety and quality also appear to be similar or better in office-based settings, based on benchmarking data analyzed so far. Hospital transfers were lower, falls were similar, and patient experience was positive, the authors wrote.
At the same time, Kosinski and colleagues noted the difficulty in shifting to office-based models. Most practices have committed to ASCs, for instance, and adding an office-based room can be challenging. Otherwise, practices already use their available office space and don’t have extra rooms available. In that case, an office endoscopy suite may be best suited for expansion sites, allowing practices to grow into new service areas, they wrote.
“You can’t fight the market. You have to focus on what the market wants and needs,” Kosinski said. “To do that, you have to be able to pivot and change direction, looking for new ways to change your mission. This could be an option to do that.”
Kosinski, Gupta, and Rockett declared having no conflicts of interest other than their current employments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
After decades of successful growth, the ambulatory surgery center (ASC) model may be turning a corner, opening up opportunity for office-based endoscopy models, according to a recent practice management editorial published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Although office endoscopy has been an option, it hasn’t always felt practical or financially viable in the past. However, the paradigm appears to be shifting as ASC-based revenue streams show signs of stress and fail to keep pace with inflation. As healthcare regulatory and economic environments continue to change, gastroenterologists need a new model to support equity, efficiency, and growth in gastrointestinal (GI) care delivery, the authors wrote.
“Through the course of my 40-year career, I’ve been hit with a lot of changes related to regulations, insurance, and the market. You can’t stay entrenched in your old ways. You have to remain pivotable and come up with new strategic positions,” said Lawrence Kosinski, MD, AGAF, lead author and founder of SonarMD and VOCnomics.
During his private practice career, Kosinski built one of the largest GI practices in Illinois, which had seven ASCs and is now part of one of the largest GI groups in the country. Across 30 years of experience with ASCs, Kosinski has watched the reimbursement for professional services decline, as well as for added revenue streams such as pathology and anesthesia.
Looking for a better solution, Kosinski served on the governing board for the American Gastroenterological Association as the councilor for development and growth. During the past 3 years, he has spoken with GI practices and worked with a national anesthesia company — Ambulatory Anesthesia Care — to better understand the office endoscopy setting.
“In the ’90s, all I wanted was to have an ASC because that was in vogue,” he said. “But if you look critically at what has happened to the business of outpatient endoscopy in the past 25 years, you’ll see that professional fees haven’t kept up, and trying to replace that lost revenue is a losing battle.”
Considering Financial Shifts
Since 2001, professional reimbursement for colonoscopies has fallen by more than 40% while ASC revenue has risen, decreasing the percentage of revenue from professional fees (from 34% to 23%) and increasing the facility component (from 44% to 60%), Kosinski and colleagues wrote.
When looking at profit, compression of professional service fees appears even greater, especially with surging costs of anesthesia care due to high demand and provider shortages. Beyond that, about a third of ASCs are owned at least partially by national entities, as of 2024, leading to even lower realization of profit.
“The profit margins have really been crushed, so what is a GI doc to do? Go where there is opportunity,” Kosinski said. “The difference between hospitals and ASCs has been compressed, so what about the office?”
The proposed 2026 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule includes a 14% increase in reimbursement for office-based procedures, including endoscopy, as well as a 7% decrease for facility-based procedures.
In several states — such as Illinois, Oregon, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin — health plans are introducing programs to promote the transition of outpatient endoscopy to office settings rather than hospital-based or ASC-based settings due to costs, the authors wrote.
“The decision to start offering office-based endoscopy services was an easy one for our practice, as it provides a way for us to provide patients convenient, easy-to-access endoscopy that is high quality yet much more affordable than hospital-based settings,” said Neil Gupta, MD, managing partner at Midwest Digestive Health & Nutrition in Des Plaines, Illinois.
The practice has used office-based endoscopy for nearly 2 years, Gupta said, performing about 5000 GI endoscopy procedures per year.
“As we all try to find better ways to provide high-quality but affordable care for patients, office-based endoscopy is a great way to help achieve those goals,” he said. “Healthcare professionals and patients should all be asking, ‘What type of site am I getting my GI endoscopy scheduled at — hospital, surgery center, or physician’s office?’”
Regaining Autonomy and Time
Beyond the financial dynamics, , Kosinski and colleagues wrote.
Looking ahead, office-based models can also provide the agility and infrastructure to compete in value-based care models, they wrote. In turn, value-based models can create relevance and resilience in a continually changing healthcare environment.
Without the involvement of ASC managers, investors, or health system partners, physicians retain control of scheduling, clinical protocols, financial decisions, and operational workflows, the authors wrote. This could create better alignment with personal preferences, clinical judgment, and patient needs, they noted.
“GI physicians should no longer feel trapped in a hospital setting where they lack independence and influence over decision-making,” said Rock Rockett, PhD, owner and principal consultant of Rockett Healthcare Strategies, which partners with GI groups nationwide to help with development, accreditation, and payer contracting for office endoscopy.
“GI physicians should also no longer feel trapped in a ‘bad marriage’ with partners in an ASC or partners in a practice who create a difficult work environment,” he said. “The viability of office endoscopy allows them to strike out on their own or set up a new partnership on more equitable terms that are attractive for them.”
Patient safety and quality also appear to be similar or better in office-based settings, based on benchmarking data analyzed so far. Hospital transfers were lower, falls were similar, and patient experience was positive, the authors wrote.
At the same time, Kosinski and colleagues noted the difficulty in shifting to office-based models. Most practices have committed to ASCs, for instance, and adding an office-based room can be challenging. Otherwise, practices already use their available office space and don’t have extra rooms available. In that case, an office endoscopy suite may be best suited for expansion sites, allowing practices to grow into new service areas, they wrote.
“You can’t fight the market. You have to focus on what the market wants and needs,” Kosinski said. “To do that, you have to be able to pivot and change direction, looking for new ways to change your mission. This could be an option to do that.”
Kosinski, Gupta, and Rockett declared having no conflicts of interest other than their current employments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
After decades of successful growth, the ambulatory surgery center (ASC) model may be turning a corner, opening up opportunity for office-based endoscopy models, according to a recent practice management editorial published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Although office endoscopy has been an option, it hasn’t always felt practical or financially viable in the past. However, the paradigm appears to be shifting as ASC-based revenue streams show signs of stress and fail to keep pace with inflation. As healthcare regulatory and economic environments continue to change, gastroenterologists need a new model to support equity, efficiency, and growth in gastrointestinal (GI) care delivery, the authors wrote.
“Through the course of my 40-year career, I’ve been hit with a lot of changes related to regulations, insurance, and the market. You can’t stay entrenched in your old ways. You have to remain pivotable and come up with new strategic positions,” said Lawrence Kosinski, MD, AGAF, lead author and founder of SonarMD and VOCnomics.
During his private practice career, Kosinski built one of the largest GI practices in Illinois, which had seven ASCs and is now part of one of the largest GI groups in the country. Across 30 years of experience with ASCs, Kosinski has watched the reimbursement for professional services decline, as well as for added revenue streams such as pathology and anesthesia.
Looking for a better solution, Kosinski served on the governing board for the American Gastroenterological Association as the councilor for development and growth. During the past 3 years, he has spoken with GI practices and worked with a national anesthesia company — Ambulatory Anesthesia Care — to better understand the office endoscopy setting.
“In the ’90s, all I wanted was to have an ASC because that was in vogue,” he said. “But if you look critically at what has happened to the business of outpatient endoscopy in the past 25 years, you’ll see that professional fees haven’t kept up, and trying to replace that lost revenue is a losing battle.”
Considering Financial Shifts
Since 2001, professional reimbursement for colonoscopies has fallen by more than 40% while ASC revenue has risen, decreasing the percentage of revenue from professional fees (from 34% to 23%) and increasing the facility component (from 44% to 60%), Kosinski and colleagues wrote.
When looking at profit, compression of professional service fees appears even greater, especially with surging costs of anesthesia care due to high demand and provider shortages. Beyond that, about a third of ASCs are owned at least partially by national entities, as of 2024, leading to even lower realization of profit.
“The profit margins have really been crushed, so what is a GI doc to do? Go where there is opportunity,” Kosinski said. “The difference between hospitals and ASCs has been compressed, so what about the office?”
The proposed 2026 Medicare Physician Fee Schedule includes a 14% increase in reimbursement for office-based procedures, including endoscopy, as well as a 7% decrease for facility-based procedures.
In several states — such as Illinois, Oregon, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin — health plans are introducing programs to promote the transition of outpatient endoscopy to office settings rather than hospital-based or ASC-based settings due to costs, the authors wrote.
“The decision to start offering office-based endoscopy services was an easy one for our practice, as it provides a way for us to provide patients convenient, easy-to-access endoscopy that is high quality yet much more affordable than hospital-based settings,” said Neil Gupta, MD, managing partner at Midwest Digestive Health & Nutrition in Des Plaines, Illinois.
The practice has used office-based endoscopy for nearly 2 years, Gupta said, performing about 5000 GI endoscopy procedures per year.
“As we all try to find better ways to provide high-quality but affordable care for patients, office-based endoscopy is a great way to help achieve those goals,” he said. “Healthcare professionals and patients should all be asking, ‘What type of site am I getting my GI endoscopy scheduled at — hospital, surgery center, or physician’s office?’”
Regaining Autonomy and Time
Beyond the financial dynamics, , Kosinski and colleagues wrote.
Looking ahead, office-based models can also provide the agility and infrastructure to compete in value-based care models, they wrote. In turn, value-based models can create relevance and resilience in a continually changing healthcare environment.
Without the involvement of ASC managers, investors, or health system partners, physicians retain control of scheduling, clinical protocols, financial decisions, and operational workflows, the authors wrote. This could create better alignment with personal preferences, clinical judgment, and patient needs, they noted.
“GI physicians should no longer feel trapped in a hospital setting where they lack independence and influence over decision-making,” said Rock Rockett, PhD, owner and principal consultant of Rockett Healthcare Strategies, which partners with GI groups nationwide to help with development, accreditation, and payer contracting for office endoscopy.
“GI physicians should also no longer feel trapped in a ‘bad marriage’ with partners in an ASC or partners in a practice who create a difficult work environment,” he said. “The viability of office endoscopy allows them to strike out on their own or set up a new partnership on more equitable terms that are attractive for them.”
Patient safety and quality also appear to be similar or better in office-based settings, based on benchmarking data analyzed so far. Hospital transfers were lower, falls were similar, and patient experience was positive, the authors wrote.
At the same time, Kosinski and colleagues noted the difficulty in shifting to office-based models. Most practices have committed to ASCs, for instance, and adding an office-based room can be challenging. Otherwise, practices already use their available office space and don’t have extra rooms available. In that case, an office endoscopy suite may be best suited for expansion sites, allowing practices to grow into new service areas, they wrote.
“You can’t fight the market. You have to focus on what the market wants and needs,” Kosinski said. “To do that, you have to be able to pivot and change direction, looking for new ways to change your mission. This could be an option to do that.”
Kosinski, Gupta, and Rockett declared having no conflicts of interest other than their current employments.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
New Drug Eases Side Effects of Weight-Loss Meds
, based on data from a phase 2 trial presented at the Obesity Society’s Obesity Week 2025 in Atlanta.
Previous research published in JAMA Network Open showed a nearly 65% discontinuation rate for three GLP-1s (liraglutide, semaglutide, or tirzepatide) among adults with overweight or obesity and without type 2 diabetes. Gastrointestinal (GI) side effects topped the list of reasons for dropping the medications.
Given the impact of nausea and vomiting on discontinuation, there is an unmet need for therapies to manage GI symptoms, said Kimberley Cummings, PhD, of Neurogastrx, Inc., in her presentation.
In the new study, Cummings and colleagues randomly assigned 90 adults aged 18-55 years with overweight or obesity (defined as a BMI ranging from 22.0 to 35.0) to receive a single subcutaneous dose of semaglutide (0.5 mg) plus 5 days of NG101 at 20 mg twice daily, or a placebo.
NG101 is a peripherally acting D2 antagonist designed to reduce nausea and vomiting associated with GLP-1 use, Cummings said. NG101 targets the nausea center of the brain but is peripherally restricted to prevent central nervous system side effects, she explained.
Compared with placebo, NG101 significantly reduced the incidence of nausea and vomiting by 40% and 67%, respectively. Use of NG101 also was associated with a significant reduction in the duration of nausea and vomiting; GI events lasting longer than 1 day were reported in 22% and 51% of the NG101 patients and placebo patients, respectively.
In addition, participants who received NG101 reported a 70% decrease in nausea severity from baseline.
Overall, patients in the NG101 group also reported significantly fewer adverse events than those in the placebo group (74 vs 135), suggesting an improved safety profile when semaglutide is administered in conjunction with NG101, the researchers noted. No serious adverse events related to the study drug were reported in either group.
The findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small sample size. Additional research is needed with other GLP-1 agonists in larger populations with longer follow-up periods, Cummings said. However, the results suggest that NG101 was safe and effectively improved side effects associated with GLP-1 agonists.
“We know there are receptors for GLP-1 in the area postrema (nausea center of the brain), and that NG101 works on this area to reduce nausea and vomiting, so the study findings were not unexpected,” said Jim O’Mara, president and CEO of Neurogastrx, in an interview.
The study was a single-dose study designed to show proof of concept, and future studies would involve treating patients going through the recommended titration schedule for their GLP-1s, O’Mara said. However, NG101 offers an opportunity to keep more patients on GLP-1 therapy and help them reach their long-term therapeutic goals, he said.
Decrease Side Effects for Weight-Loss Success
“GI side effects are often the rate-limiting step in implementing an effective medication that patients want to take but may not be able to tolerate,” Sean Wharton, MD, PharmD, medical director of the Wharton Medical Clinic for Weight and Diabetes Management, Burlington, Ontario, Canada, said in an interview. “If we can decrease side effects, these medications could improve patients’ lives,” said Wharton, who was not involved in the study.
The improvement after a single dose of NG101 in patients receiving a single dose of semaglutide was impressive and in keeping with the mechanism of the drug action, said Wharton. “I was not surprised by the result but pleased that this single dose was shown to reduce the overall incidence of nausea and vomiting, the duration of nausea, the severity of nausea as rated by the study participants compared to placebo,” he said.
Ultimately, the clinical implications for NG101 are improved patient tolerance for GLP-1s and the ability to titrate and stay on them long term, incurring greater cardiometabolic benefit, Wharton told GI & Hepatology News.
The current trial was limited to GLP1-1s on the market; newer medications may have fewer side effects, Wharton noted. “In clinical practice, patients often decrease the medication or titrate slower, and this could be the comparator,” he added.
The study was funded by Neurogastrx.
Wharton disclosed serving as a consultant for Neurogastrx but not as an investigator on the current study. He also reported having disclosed research on various GLP-1 medications.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, based on data from a phase 2 trial presented at the Obesity Society’s Obesity Week 2025 in Atlanta.
Previous research published in JAMA Network Open showed a nearly 65% discontinuation rate for three GLP-1s (liraglutide, semaglutide, or tirzepatide) among adults with overweight or obesity and without type 2 diabetes. Gastrointestinal (GI) side effects topped the list of reasons for dropping the medications.
Given the impact of nausea and vomiting on discontinuation, there is an unmet need for therapies to manage GI symptoms, said Kimberley Cummings, PhD, of Neurogastrx, Inc., in her presentation.
In the new study, Cummings and colleagues randomly assigned 90 adults aged 18-55 years with overweight or obesity (defined as a BMI ranging from 22.0 to 35.0) to receive a single subcutaneous dose of semaglutide (0.5 mg) plus 5 days of NG101 at 20 mg twice daily, or a placebo.
NG101 is a peripherally acting D2 antagonist designed to reduce nausea and vomiting associated with GLP-1 use, Cummings said. NG101 targets the nausea center of the brain but is peripherally restricted to prevent central nervous system side effects, she explained.
Compared with placebo, NG101 significantly reduced the incidence of nausea and vomiting by 40% and 67%, respectively. Use of NG101 also was associated with a significant reduction in the duration of nausea and vomiting; GI events lasting longer than 1 day were reported in 22% and 51% of the NG101 patients and placebo patients, respectively.
In addition, participants who received NG101 reported a 70% decrease in nausea severity from baseline.
Overall, patients in the NG101 group also reported significantly fewer adverse events than those in the placebo group (74 vs 135), suggesting an improved safety profile when semaglutide is administered in conjunction with NG101, the researchers noted. No serious adverse events related to the study drug were reported in either group.
The findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small sample size. Additional research is needed with other GLP-1 agonists in larger populations with longer follow-up periods, Cummings said. However, the results suggest that NG101 was safe and effectively improved side effects associated with GLP-1 agonists.
“We know there are receptors for GLP-1 in the area postrema (nausea center of the brain), and that NG101 works on this area to reduce nausea and vomiting, so the study findings were not unexpected,” said Jim O’Mara, president and CEO of Neurogastrx, in an interview.
The study was a single-dose study designed to show proof of concept, and future studies would involve treating patients going through the recommended titration schedule for their GLP-1s, O’Mara said. However, NG101 offers an opportunity to keep more patients on GLP-1 therapy and help them reach their long-term therapeutic goals, he said.
Decrease Side Effects for Weight-Loss Success
“GI side effects are often the rate-limiting step in implementing an effective medication that patients want to take but may not be able to tolerate,” Sean Wharton, MD, PharmD, medical director of the Wharton Medical Clinic for Weight and Diabetes Management, Burlington, Ontario, Canada, said in an interview. “If we can decrease side effects, these medications could improve patients’ lives,” said Wharton, who was not involved in the study.
The improvement after a single dose of NG101 in patients receiving a single dose of semaglutide was impressive and in keeping with the mechanism of the drug action, said Wharton. “I was not surprised by the result but pleased that this single dose was shown to reduce the overall incidence of nausea and vomiting, the duration of nausea, the severity of nausea as rated by the study participants compared to placebo,” he said.
Ultimately, the clinical implications for NG101 are improved patient tolerance for GLP-1s and the ability to titrate and stay on them long term, incurring greater cardiometabolic benefit, Wharton told GI & Hepatology News.
The current trial was limited to GLP1-1s on the market; newer medications may have fewer side effects, Wharton noted. “In clinical practice, patients often decrease the medication or titrate slower, and this could be the comparator,” he added.
The study was funded by Neurogastrx.
Wharton disclosed serving as a consultant for Neurogastrx but not as an investigator on the current study. He also reported having disclosed research on various GLP-1 medications.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, based on data from a phase 2 trial presented at the Obesity Society’s Obesity Week 2025 in Atlanta.
Previous research published in JAMA Network Open showed a nearly 65% discontinuation rate for three GLP-1s (liraglutide, semaglutide, or tirzepatide) among adults with overweight or obesity and without type 2 diabetes. Gastrointestinal (GI) side effects topped the list of reasons for dropping the medications.
Given the impact of nausea and vomiting on discontinuation, there is an unmet need for therapies to manage GI symptoms, said Kimberley Cummings, PhD, of Neurogastrx, Inc., in her presentation.
In the new study, Cummings and colleagues randomly assigned 90 adults aged 18-55 years with overweight or obesity (defined as a BMI ranging from 22.0 to 35.0) to receive a single subcutaneous dose of semaglutide (0.5 mg) plus 5 days of NG101 at 20 mg twice daily, or a placebo.
NG101 is a peripherally acting D2 antagonist designed to reduce nausea and vomiting associated with GLP-1 use, Cummings said. NG101 targets the nausea center of the brain but is peripherally restricted to prevent central nervous system side effects, she explained.
Compared with placebo, NG101 significantly reduced the incidence of nausea and vomiting by 40% and 67%, respectively. Use of NG101 also was associated with a significant reduction in the duration of nausea and vomiting; GI events lasting longer than 1 day were reported in 22% and 51% of the NG101 patients and placebo patients, respectively.
In addition, participants who received NG101 reported a 70% decrease in nausea severity from baseline.
Overall, patients in the NG101 group also reported significantly fewer adverse events than those in the placebo group (74 vs 135), suggesting an improved safety profile when semaglutide is administered in conjunction with NG101, the researchers noted. No serious adverse events related to the study drug were reported in either group.
The findings were limited by several factors including the relatively small sample size. Additional research is needed with other GLP-1 agonists in larger populations with longer follow-up periods, Cummings said. However, the results suggest that NG101 was safe and effectively improved side effects associated with GLP-1 agonists.
“We know there are receptors for GLP-1 in the area postrema (nausea center of the brain), and that NG101 works on this area to reduce nausea and vomiting, so the study findings were not unexpected,” said Jim O’Mara, president and CEO of Neurogastrx, in an interview.
The study was a single-dose study designed to show proof of concept, and future studies would involve treating patients going through the recommended titration schedule for their GLP-1s, O’Mara said. However, NG101 offers an opportunity to keep more patients on GLP-1 therapy and help them reach their long-term therapeutic goals, he said.
Decrease Side Effects for Weight-Loss Success
“GI side effects are often the rate-limiting step in implementing an effective medication that patients want to take but may not be able to tolerate,” Sean Wharton, MD, PharmD, medical director of the Wharton Medical Clinic for Weight and Diabetes Management, Burlington, Ontario, Canada, said in an interview. “If we can decrease side effects, these medications could improve patients’ lives,” said Wharton, who was not involved in the study.
The improvement after a single dose of NG101 in patients receiving a single dose of semaglutide was impressive and in keeping with the mechanism of the drug action, said Wharton. “I was not surprised by the result but pleased that this single dose was shown to reduce the overall incidence of nausea and vomiting, the duration of nausea, the severity of nausea as rated by the study participants compared to placebo,” he said.
Ultimately, the clinical implications for NG101 are improved patient tolerance for GLP-1s and the ability to titrate and stay on them long term, incurring greater cardiometabolic benefit, Wharton told GI & Hepatology News.
The current trial was limited to GLP1-1s on the market; newer medications may have fewer side effects, Wharton noted. “In clinical practice, patients often decrease the medication or titrate slower, and this could be the comparator,” he added.
The study was funded by Neurogastrx.
Wharton disclosed serving as a consultant for Neurogastrx but not as an investigator on the current study. He also reported having disclosed research on various GLP-1 medications.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Nailing Neoplastic Lesions in Barrett’s Esophagus
, said Prateek Sharma, MD, in a presentation on the management of BE at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
However, clinicians often make mistakes such as failing to remove debris such as saliva and bile from the esophagus prior to assessing a patient, said Sharma, professor of medicine and the Elaine Blaylock Endowed Professor at the University of Kansas School of Medicine and the Cancer Center, Kansas City, Kansas.
More than 90% of neoplasias in patients with BE are found on an index endoscopy or within 6 months, as shown by Sharma and his colleagues in a systematic review, which highlights the importance of a high-quality index endoscopy, he told meeting attendees.
To improve the index endoscopy, Sharma developed a new algorithm called “CLEAN.”
The algorithm is composed of five steps, he said, the first of which is Clear: clear the esophagus of debris, including saliva and bile. Adequate prep is essential to detecting clinically significant lesions in patients with BE, he explained. In a study published in 2024, Sharma and colleagues found adequate cleanliness of the upper gastrointestinal tract was associated with a significantly higher detection rate of clinically significant lesions.
The second step of the algorithm is Learn: pay attention to BE inspection time and learn slow withdrawal strategies.
It’s important not to shortchange inspection time, Sharma emphasized. He cited a previous study in which the percentage of patients with BE who had high-grade dysplasia or esophageal adenocarcinoma during a surveillance endoscopy was 15% with inspection times of 2 minutes or less but jumped to 69% with inspection times of 7 minutes or more.
The third step of CLEAN is Endoscope: conduct a high-definition white-light endoscopy, which should be coupled with the fourth step, Acquire: acquire education on BE-related neoplasia, to learn how to recognize neoplastic lesions, he stressed.
The final step of the algorithm is Neoplasia detection rate (NDR): follow a quality metric to measure NDR.
The algorithm emphasizes a comprehensive approach in conjunction with resection of visible lesions followed by ablation for complete eradication, Sharma told GI & Hepatology News.
After Identification: What’s Next?
If lesions are identified, the next step is resection and/or ablation, Sharma said.
“Resection is typically used for visible lesions, nodules, or masses, while ablation is used to treat the remaining underlying Barrett tissue,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “A combination of both is often necessary to fully treat advanced cases, such as when a nodule is resected and the surrounding area is subsequently ablated.”
“It’s important to understand why we need to resect,” he said.
“Resection removes the lesion” and “provides more accurate histopathology reading and staging of how deep the lesion is,” he explained. Options for resection of cancerous or precancerous lesions in patients with BE include endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
The treatment algorithm for BE continues to evolve, Sharma said in his presentation. Currently, evidence supports EMR for most cases, but ESD is based on factors including lesion size ≥ 25-30 mm and potential submucosal invasion, he said.
He cited a study of 1000 adults with early BE who were managed with EMR that showed a 96% curative response after 5 years. Similarly, a review of ESD for early BE neoplasia including 501 patients showed a 75% curative response rate overall and a 93% en bloc resection rate, he noted.
Ablation
In terms of ablation, radiofrequency ablation, hybrid argon plasma coagulation, and the multifocal cryoballoon procedure have shown significant effectiveness, Sharma said.
In a 2020 multicenter, prospective study of 120 adult patients with BE, 76% achieved complete eradication of dysplasia, and 72% achieved complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia. As for safety, data from nine European centers including 154 patients who underwent ablation after resection had an adverse event rate of 6%, said Sharma.
In the Clinic
“It is sometimes difficult to detect subtle nodularity and irregularity that would benefit more from resection therapy/EMR rather than ablation,” said Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, associate professor of medicine (digestive diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut.
“Lesions can be obscured by esophagitis, peristalsis, or the shape of the [gastroesophageal] GE junction,” he noted. Therefore, careful scope cleaning and inspection with high-definition white light and narrow band imaging are important, he said. “Using a cap on the scope to better distend or manipulate the gastroesophageal junction also helps identify obscured lesions,” he added.
“Any acronym or approach that reminds us to slow down, and examine carefully, is welcome,” Ketwaroo told GI & Hepatology News. The CLEAN algorithm provides a useful summary of some of the key steps all clinicians should incorporate into approaching BE and could be useful for teaching trainees, he added.
Sharma disclosed serving as a consultant for the Olympus Corporation and Exact Sciences and receiving grant support from Fujifilm, Erbe Medical, and Braintree Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, said Prateek Sharma, MD, in a presentation on the management of BE at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
However, clinicians often make mistakes such as failing to remove debris such as saliva and bile from the esophagus prior to assessing a patient, said Sharma, professor of medicine and the Elaine Blaylock Endowed Professor at the University of Kansas School of Medicine and the Cancer Center, Kansas City, Kansas.
More than 90% of neoplasias in patients with BE are found on an index endoscopy or within 6 months, as shown by Sharma and his colleagues in a systematic review, which highlights the importance of a high-quality index endoscopy, he told meeting attendees.
To improve the index endoscopy, Sharma developed a new algorithm called “CLEAN.”
The algorithm is composed of five steps, he said, the first of which is Clear: clear the esophagus of debris, including saliva and bile. Adequate prep is essential to detecting clinically significant lesions in patients with BE, he explained. In a study published in 2024, Sharma and colleagues found adequate cleanliness of the upper gastrointestinal tract was associated with a significantly higher detection rate of clinically significant lesions.
The second step of the algorithm is Learn: pay attention to BE inspection time and learn slow withdrawal strategies.
It’s important not to shortchange inspection time, Sharma emphasized. He cited a previous study in which the percentage of patients with BE who had high-grade dysplasia or esophageal adenocarcinoma during a surveillance endoscopy was 15% with inspection times of 2 minutes or less but jumped to 69% with inspection times of 7 minutes or more.
The third step of CLEAN is Endoscope: conduct a high-definition white-light endoscopy, which should be coupled with the fourth step, Acquire: acquire education on BE-related neoplasia, to learn how to recognize neoplastic lesions, he stressed.
The final step of the algorithm is Neoplasia detection rate (NDR): follow a quality metric to measure NDR.
The algorithm emphasizes a comprehensive approach in conjunction with resection of visible lesions followed by ablation for complete eradication, Sharma told GI & Hepatology News.
After Identification: What’s Next?
If lesions are identified, the next step is resection and/or ablation, Sharma said.
“Resection is typically used for visible lesions, nodules, or masses, while ablation is used to treat the remaining underlying Barrett tissue,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “A combination of both is often necessary to fully treat advanced cases, such as when a nodule is resected and the surrounding area is subsequently ablated.”
“It’s important to understand why we need to resect,” he said.
“Resection removes the lesion” and “provides more accurate histopathology reading and staging of how deep the lesion is,” he explained. Options for resection of cancerous or precancerous lesions in patients with BE include endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
The treatment algorithm for BE continues to evolve, Sharma said in his presentation. Currently, evidence supports EMR for most cases, but ESD is based on factors including lesion size ≥ 25-30 mm and potential submucosal invasion, he said.
He cited a study of 1000 adults with early BE who were managed with EMR that showed a 96% curative response after 5 years. Similarly, a review of ESD for early BE neoplasia including 501 patients showed a 75% curative response rate overall and a 93% en bloc resection rate, he noted.
Ablation
In terms of ablation, radiofrequency ablation, hybrid argon plasma coagulation, and the multifocal cryoballoon procedure have shown significant effectiveness, Sharma said.
In a 2020 multicenter, prospective study of 120 adult patients with BE, 76% achieved complete eradication of dysplasia, and 72% achieved complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia. As for safety, data from nine European centers including 154 patients who underwent ablation after resection had an adverse event rate of 6%, said Sharma.
In the Clinic
“It is sometimes difficult to detect subtle nodularity and irregularity that would benefit more from resection therapy/EMR rather than ablation,” said Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, associate professor of medicine (digestive diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut.
“Lesions can be obscured by esophagitis, peristalsis, or the shape of the [gastroesophageal] GE junction,” he noted. Therefore, careful scope cleaning and inspection with high-definition white light and narrow band imaging are important, he said. “Using a cap on the scope to better distend or manipulate the gastroesophageal junction also helps identify obscured lesions,” he added.
“Any acronym or approach that reminds us to slow down, and examine carefully, is welcome,” Ketwaroo told GI & Hepatology News. The CLEAN algorithm provides a useful summary of some of the key steps all clinicians should incorporate into approaching BE and could be useful for teaching trainees, he added.
Sharma disclosed serving as a consultant for the Olympus Corporation and Exact Sciences and receiving grant support from Fujifilm, Erbe Medical, and Braintree Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, said Prateek Sharma, MD, in a presentation on the management of BE at the American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) 2025 Annual Scientific Meeting.
However, clinicians often make mistakes such as failing to remove debris such as saliva and bile from the esophagus prior to assessing a patient, said Sharma, professor of medicine and the Elaine Blaylock Endowed Professor at the University of Kansas School of Medicine and the Cancer Center, Kansas City, Kansas.
More than 90% of neoplasias in patients with BE are found on an index endoscopy or within 6 months, as shown by Sharma and his colleagues in a systematic review, which highlights the importance of a high-quality index endoscopy, he told meeting attendees.
To improve the index endoscopy, Sharma developed a new algorithm called “CLEAN.”
The algorithm is composed of five steps, he said, the first of which is Clear: clear the esophagus of debris, including saliva and bile. Adequate prep is essential to detecting clinically significant lesions in patients with BE, he explained. In a study published in 2024, Sharma and colleagues found adequate cleanliness of the upper gastrointestinal tract was associated with a significantly higher detection rate of clinically significant lesions.
The second step of the algorithm is Learn: pay attention to BE inspection time and learn slow withdrawal strategies.
It’s important not to shortchange inspection time, Sharma emphasized. He cited a previous study in which the percentage of patients with BE who had high-grade dysplasia or esophageal adenocarcinoma during a surveillance endoscopy was 15% with inspection times of 2 minutes or less but jumped to 69% with inspection times of 7 minutes or more.
The third step of CLEAN is Endoscope: conduct a high-definition white-light endoscopy, which should be coupled with the fourth step, Acquire: acquire education on BE-related neoplasia, to learn how to recognize neoplastic lesions, he stressed.
The final step of the algorithm is Neoplasia detection rate (NDR): follow a quality metric to measure NDR.
The algorithm emphasizes a comprehensive approach in conjunction with resection of visible lesions followed by ablation for complete eradication, Sharma told GI & Hepatology News.
After Identification: What’s Next?
If lesions are identified, the next step is resection and/or ablation, Sharma said.
“Resection is typically used for visible lesions, nodules, or masses, while ablation is used to treat the remaining underlying Barrett tissue,” he told GI & Hepatology News. “A combination of both is often necessary to fully treat advanced cases, such as when a nodule is resected and the surrounding area is subsequently ablated.”
“It’s important to understand why we need to resect,” he said.
“Resection removes the lesion” and “provides more accurate histopathology reading and staging of how deep the lesion is,” he explained. Options for resection of cancerous or precancerous lesions in patients with BE include endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD).
The treatment algorithm for BE continues to evolve, Sharma said in his presentation. Currently, evidence supports EMR for most cases, but ESD is based on factors including lesion size ≥ 25-30 mm and potential submucosal invasion, he said.
He cited a study of 1000 adults with early BE who were managed with EMR that showed a 96% curative response after 5 years. Similarly, a review of ESD for early BE neoplasia including 501 patients showed a 75% curative response rate overall and a 93% en bloc resection rate, he noted.
Ablation
In terms of ablation, radiofrequency ablation, hybrid argon plasma coagulation, and the multifocal cryoballoon procedure have shown significant effectiveness, Sharma said.
In a 2020 multicenter, prospective study of 120 adult patients with BE, 76% achieved complete eradication of dysplasia, and 72% achieved complete eradication of intestinal metaplasia. As for safety, data from nine European centers including 154 patients who underwent ablation after resection had an adverse event rate of 6%, said Sharma.
In the Clinic
“It is sometimes difficult to detect subtle nodularity and irregularity that would benefit more from resection therapy/EMR rather than ablation,” said Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, associate professor of medicine (digestive diseases) at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut.
“Lesions can be obscured by esophagitis, peristalsis, or the shape of the [gastroesophageal] GE junction,” he noted. Therefore, careful scope cleaning and inspection with high-definition white light and narrow band imaging are important, he said. “Using a cap on the scope to better distend or manipulate the gastroesophageal junction also helps identify obscured lesions,” he added.
“Any acronym or approach that reminds us to slow down, and examine carefully, is welcome,” Ketwaroo told GI & Hepatology News. The CLEAN algorithm provides a useful summary of some of the key steps all clinicians should incorporate into approaching BE and could be useful for teaching trainees, he added.
Sharma disclosed serving as a consultant for the Olympus Corporation and Exact Sciences and receiving grant support from Fujifilm, Erbe Medical, and Braintree Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2025
Research Focuses on Mental Health Needs of Women Veterans
The more than 2 million women US veterans are the fastest-growing military population. While research into women veterans has traditionally lagged, more recently studies have begun to focus on their needs impacts of combat and service on women. These studies have found that women veterans preferred tailored solutions focused on women veterans.
A November 2025 study is one of the first to examine the impact of combat on women veterans. It found that those in combat roles had higher levels of depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), dissociation, and overall poorer health compared with civilians and noncombat women military personnel. Previous research had found that women veterans had higher rates of lifetime and past-year PTSD (13.4%) compared with female civilians (8.0%), male veterans (7.7%), and male civilians (3.4%). A 2020 US Department of Veterans (VA) study of 4,928,638 men and 448,455 women similarly found that women had nearly twice the rates of depression and anxiety compared with men.
For many veterans, mental health issues may develop or be exacerbated in their return to civilian life. That transition can be especially confusing and isolating for women veterans, according to a 2024 study: “They neither fit in the military due to gendered relations centered on masculinity, or civilian life where they are largely misunderstood as ‘veterans.’ This ‘no woman’s land’ is poorly understood.” Few programs for transitioning veterans have been found effective for women veterans because they’ve been developed for a largely male veteran population. That includes mental health support programs.
Some women may prefer women-only groups, and even that choice may be dependent on their background, service history, socioeconomic level, and other factors. They may feel more comfortable in women-only groups if they’ve experienced MST. Others who have served in combat may choose mixed-gender programs. One study found that some women benefited from being in a mixed-gender group because it enabled them to work on difficulties with men in a safe environment. Other research has found that women veterans with substance use disorders are reluctant to seek help alongside men in the same facilities.
Accessing care may be especially challenging for rural women veterans. However, separate facilities and women-only groups are not always available, particularly in rural areas where there may be very few women veterans. And even if they are available, rural women are often up against barriers that urban women do not face, such as having to travel long distances to get care. Clinicians also may be hard to find in rural areas. Some participants in a 2025 study were hampered not only by a lack of female practitioners, but practitioners who were well trained to understand and treat the unique needs of female veterans: “[It’s] incredibly difficult to find a mental health practitioner that understands a veteran’s unique experience as a woman,” a participant said.
The more than 2 million women US veterans are the fastest-growing military population. While research into women veterans has traditionally lagged, more recently studies have begun to focus on their needs impacts of combat and service on women. These studies have found that women veterans preferred tailored solutions focused on women veterans.
A November 2025 study is one of the first to examine the impact of combat on women veterans. It found that those in combat roles had higher levels of depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), dissociation, and overall poorer health compared with civilians and noncombat women military personnel. Previous research had found that women veterans had higher rates of lifetime and past-year PTSD (13.4%) compared with female civilians (8.0%), male veterans (7.7%), and male civilians (3.4%). A 2020 US Department of Veterans (VA) study of 4,928,638 men and 448,455 women similarly found that women had nearly twice the rates of depression and anxiety compared with men.
For many veterans, mental health issues may develop or be exacerbated in their return to civilian life. That transition can be especially confusing and isolating for women veterans, according to a 2024 study: “They neither fit in the military due to gendered relations centered on masculinity, or civilian life where they are largely misunderstood as ‘veterans.’ This ‘no woman’s land’ is poorly understood.” Few programs for transitioning veterans have been found effective for women veterans because they’ve been developed for a largely male veteran population. That includes mental health support programs.
Some women may prefer women-only groups, and even that choice may be dependent on their background, service history, socioeconomic level, and other factors. They may feel more comfortable in women-only groups if they’ve experienced MST. Others who have served in combat may choose mixed-gender programs. One study found that some women benefited from being in a mixed-gender group because it enabled them to work on difficulties with men in a safe environment. Other research has found that women veterans with substance use disorders are reluctant to seek help alongside men in the same facilities.
Accessing care may be especially challenging for rural women veterans. However, separate facilities and women-only groups are not always available, particularly in rural areas where there may be very few women veterans. And even if they are available, rural women are often up against barriers that urban women do not face, such as having to travel long distances to get care. Clinicians also may be hard to find in rural areas. Some participants in a 2025 study were hampered not only by a lack of female practitioners, but practitioners who were well trained to understand and treat the unique needs of female veterans: “[It’s] incredibly difficult to find a mental health practitioner that understands a veteran’s unique experience as a woman,” a participant said.
The more than 2 million women US veterans are the fastest-growing military population. While research into women veterans has traditionally lagged, more recently studies have begun to focus on their needs impacts of combat and service on women. These studies have found that women veterans preferred tailored solutions focused on women veterans.
A November 2025 study is one of the first to examine the impact of combat on women veterans. It found that those in combat roles had higher levels of depression, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), dissociation, and overall poorer health compared with civilians and noncombat women military personnel. Previous research had found that women veterans had higher rates of lifetime and past-year PTSD (13.4%) compared with female civilians (8.0%), male veterans (7.7%), and male civilians (3.4%). A 2020 US Department of Veterans (VA) study of 4,928,638 men and 448,455 women similarly found that women had nearly twice the rates of depression and anxiety compared with men.
For many veterans, mental health issues may develop or be exacerbated in their return to civilian life. That transition can be especially confusing and isolating for women veterans, according to a 2024 study: “They neither fit in the military due to gendered relations centered on masculinity, or civilian life where they are largely misunderstood as ‘veterans.’ This ‘no woman’s land’ is poorly understood.” Few programs for transitioning veterans have been found effective for women veterans because they’ve been developed for a largely male veteran population. That includes mental health support programs.
Some women may prefer women-only groups, and even that choice may be dependent on their background, service history, socioeconomic level, and other factors. They may feel more comfortable in women-only groups if they’ve experienced MST. Others who have served in combat may choose mixed-gender programs. One study found that some women benefited from being in a mixed-gender group because it enabled them to work on difficulties with men in a safe environment. Other research has found that women veterans with substance use disorders are reluctant to seek help alongside men in the same facilities.
Accessing care may be especially challenging for rural women veterans. However, separate facilities and women-only groups are not always available, particularly in rural areas where there may be very few women veterans. And even if they are available, rural women are often up against barriers that urban women do not face, such as having to travel long distances to get care. Clinicians also may be hard to find in rural areas. Some participants in a 2025 study were hampered not only by a lack of female practitioners, but practitioners who were well trained to understand and treat the unique needs of female veterans: “[It’s] incredibly difficult to find a mental health practitioner that understands a veteran’s unique experience as a woman,” a participant said.
Finding Your Voice in Advocacy
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
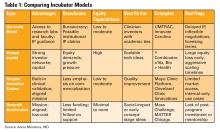
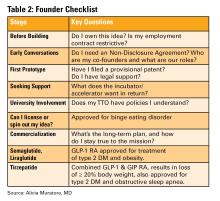
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Since moving to Missouri a little over 2 years ago, I got involved with the Missouri GI Society. They held their inaugural in-person meeting in September, and it was exciting to see and meet gastroenterologists and associates from all over the state. The meeting sparked conversations about challenges in practices and ways to improve patient care. It was incredibly inspiring to see the beginnings and bright future of a society motivated to mobilize change in the community. On a national scale, AGA Advocacy Day 2025 this fall was another example of how to make an impact for the field. I am grateful that local and national GI communities can be a platform for our voices.
In this issue’s “In Focus,” Dr. Colleen R. Kelly discusses the approach for weight management for the gastroenterologist, including how to discuss lifestyle modifications, anti-obesity medications, endoscopic therapies, and bariatric surgeries. In the “Short Clinical Review,” Dr. Ekta Gupta, Dr. Carol Burke, and Dr. Carole Macaron review available non-invasive blood and stool tests for colorectal cancer screening, including guidelines recommendations and evidence supporting each modality.
In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Mayada Ismail shares her personal journey in making the difficult decision of leaving her first job as an early career gastroenterologist, outlining the challenges and lessons learned along the way.
Dr. Alicia Muratore, Dr. Emily V. Wechsler, and Dr. Eric D. Shah provide a practical guide to tech and device development in the “Finance/Legal” section of this issue, outlining everything from intellectual property ownership to building the right team, and selecting the right incubator.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: screening colonoscopy for colorectal cancer was only first introduced in the mid-1990s with Medicare coverage for high-risk individuals starting in 1998, followed by coverage for average-risk patients in 2001.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
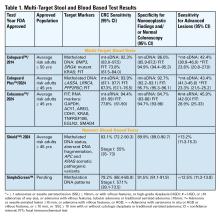
Non-Invasive Blood and Stool CRC Screening Tests: Available Modalities and Their Clinical Application
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) screening significantly reduces CRC incidence and mortality, but only 65% of eligible individuals report being up-to-date with screening.1 Colonoscopy is the most widely used opportunistic screening method in the United States and is associated with many barriers to uptake. Providing patients a choice of colonoscopy and/or stool-based tests, improves screening adherence in randomized controlled trials.2,3 Non-invasive screening options have expanded from stool occult blood and multi-target DNA tests, to multi-target stool RNA tests, and novel blood-based tests, the latter only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for patients who refuse colonoscopy and stool-based tests.
Stool Occult Blood Tests
Guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT) significantly reduces CRC mortality by 33%-35% when implemented on an annual or biennial basis.4,5 Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) has supplanted gFOBT with advantages including independence from dietary restriction and medication-related interference, use of antibodies specific to human globin, and the need for only a single stool sample.
The most common threshold for a positive FIT in the U.S. is ≥ 20 micrograms (μg) of hemoglobin per gram (g) of stool. FIT is approved by the FDA as a qualitative positive or negative result based on a threshold value.6 A meta-analysis summarized test characteristics of commercially available FITs at various detection thresholds.7 The CRC sensitivity and specificity was 75% and 95% for ≥ 20 ug hemoglobin/g stool, and 91% and 90% for 10 ug hemoglobin/g stool, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas ranged from 25% at 20 μg/g to 40% at a 10 μg/g. Programmatic use of FIT in adults ages ≥ 50 years at 20 ug/g of stool, in cohort and case control studies, has been shown to significantly reduce CRC mortality by 33%-40% and advanced stage CRC by 34%.8,9
Over 57,000 average-risk individuals ages 50–69 years were randomized to biennial FIT or one-time colonoscopy and followed for 10 years.10 CRC mortality and incidence was similar between the groups: 0.22% with FIT vs. 0.24% with colonoscopy and 1.13% with FIT vs. 1.22% with colonoscopy, respectively. Thus, confirming biennial FIT screening is non-inferior to one-time colonoscopy in important CRC-related outcomes.
Multi-Target Stool Tests
Two multitarget stool DNA tests (mt-sDNA) known as Cologuard™ and Cologuard Plus™ have been approved by the FDA. Both tests include a FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin per gram of stool) combined with DNA methylation markers. The test result is qualitative, reported as a positive or negative. Cologuard™ markers include methylated BMP3, NDRG4, and mutant KRAS while Cologuard Plus™ assesses methylated LASS4, LRRC4, and PPP2R5C. The respective mt-sDNA tests were studied in 9989 of 12,776 and 20,176 of 26,758 average-risk individuals undergoing colonoscopy and the results were compared to a commercially available FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool).11,12 In both trials, the sensitivity for CRC and advanced precancerous lesions was higher with the mt-sDNA tests compared to FIT but had a significantly lower specificity for advanced precancerous lesions versus FIT (see Table 1). An age-related decline in specificity was noted in both trials with mt-sDNA, a trend not observed with FIT. This reduction may be attributed to age-related DNA methylation.
Multi-Target Stool RNA Test
A multi-target stool RNA test (mt-sRNA) commercially available as ColoSense™ is FDA-approved. It combines FIT (at a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool) with RNA-based stool markers. The combined results of the RNA markers, FIT, and smoking status provide a qualitative single test result. In the trial, 8,920 adults aged ≥45 underwent the mt-sRNA test and FIT followed by colonoscopy (13). The mt-sRNA showed higher sensitivity for CRC than FIT (94.4% versus 77.8%) and advanced adenomas (45.9% versus 28.9%) but lower CRC specificity (84.7% vs 94.7%) (Table 1). Unlike mt-sDNA-based tests, mt-sRNA showed consistent performance across age groups, addressing concerns about age-related declines in specificity attributed to DNA methylation.
Blood-Based Tests
In 2014, the first blood-based (BBT) CRC screening test known as Epi proColon™ was FDA but not Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) approved for average-risk adults ≥50 years of age who are offered and refused other U.S Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) endorsed CRC screening tests. It is a qualitative test for detection of circulating methylated Septin 9 (mSeptin9). The accuracy of mSeptin9 to detect CRC was assessed in a subset of 7941 asymptomatic average risk adults undergoing screening colonoscopy.14 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC were 48% and 91.5%, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas was 11.2%. An increase in sensitivity to 63.9% and reduction in specificity to 88.4% for CRC was demonstrated in a sub-analysis of available samples where an additional (third) polymerase chain replicate was performed. Epi proColon™ is not currently reimbursed by Medicare and not endorsed in the latest USPSTF guidelines.
Technologic advancements have improved the detection of circulating tumor markers in the blood. The Shield™ BBT approved by the FDA in 2024 for average risk adults ≥ 45 years integrates three types of cfDNA data (epigenetic changes resulting in the aberrant methylation or fragmentation patterns, and genomic changes resulting in somatic mutations) into a positive or negative test result. In the trial, 22,877 average-risk, asymptomatic individuals ages 45–84 were enrolled and clinical validation was performed in 7,861 of the participants.15 The sensitivity for CRC was 83.1% which decreased to 55% for stage I tumors (see Table 1). CRC specificity was 89.6% and the sensitivity for advanced adenomas and large sessile serrated lesions was 13.2%.
Another BBT SimpleScreen™, which is not yet FDA-approved, analyzed circulating, cell-free DNA methylation patterns in 27,010 evaluable average-risk, asymptomatic adults ages 45–85 years undergoing screening colonoscopy.16 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC was 79.2% and 91.5%, respectively. Similar to Shield, the sensitivity for stage I CRC was low at 57.1%. The sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions, a secondary endpoint, was 12.5% which did not meet the prespecified study criteria.
Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
Modeling studies have evaluated novel noninvasive CRC screening tests compared to FIT and colonoscopy.17-20 One compared a hypothetical BBT performed every 3 years that meets the minimum CMS threshold CRC sensitivity and specificity of 74% and 90%, respectively, to other established CRC screening tests beginning at age 45.17 Every 3-year BBT reduced CRC incidence and mortality by 40% and 52%, respectively compared to no screening. However, the reductions were much lower than yearly FIT (72% and 76%, respectively), every 10 year colonoscopy (79% and 81%, respectively), and triennial mt-sDNA (68% and 73%, respectively). The BBT resulted in fewer quality-adjusted life-years per person compared to the alternatives.
Additionally, FIT, colonoscopy, and mt-sDNA were less costly and more effective. Advanced precancerous lesion detection was a key measure for a test’s effectiveness. BBT characteristics would require a CRC sensitivity and specificity of >90% and 90%, respectively, and 80% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions at a cost of ≤$120–$140 to be cost-effective compared to FIT at comparable participation rates.
Another analysis simulated colorectal neoplasia progression and compared clinical effectiveness and cost between annual FIT, every 3 year stool mt-sRNA, every 3 year stool mt-sDNA tests, every 3 year stool Shield™; these outcomes were compared to colonoscopy every 10 years and no screening in adults ≥ age 45 over different adherence rates.19 At real-world adherence rates of 60%, colonoscopy prevented most CRC cases and associated deaths. FIT was the most cost-effective strategy at all adherence levels. Between the multi-target stool tests and Shield™, mt-sRNA was the most cost-effective. Compared to FIT, mt-sRNA reduced CRC cases and deaths by 1% and 14%.
The third study evaluated CRC incidence and mortality, quality-adjusted life-years and costs with annual FIT, colonoscopy every 10 years, mt- sDNA tests, mt-sRNA test, and BBTs.20 The latest mt-sDNA (Colguard plus™) and mt-sRNA achieved benefits approaching FIT but the Shield™ test was substantially less effective. The authors hypothesized that if 15% of the population substituted Shield™ for current effective CRC screening strategies, an increase in CRC deaths would occur and require 9-10% of the unscreened population to uptake screening with Shield to avert the increases in CRC deaths due to the substitution effect.
Clinical Implications
The effectiveness of non-invasive screening strategies depends on their diagnostic performance, adherence, and ensuring a timely colonoscopy after a positive test. Two claims-based studies found 47.9% and 49% of patients underwent follow-up colonoscopy within 6 months of an abnormal stool or BBT CRC screening test, respectively.21-22
Conclusions
Non-invasive stool mt-sDNA and mt-sRNA have higher effectiveness than the new BBTs. BBTs can lead to increased CRC mortality if substituted for the FDA and CMS-approved, USPSTF-endorsed, CRC screening modalities. If future BBTs increase their sensitivity for CRC (including early-stage CRC) and advanced precancerous lesions and decrease their cost, they may prove to have similar cost-effectiveness to stool-based tests. Currently, BBTs are not a substitute for colonoscopy or other stool tests and should be offered to patients who refuse other CRC screening modalities. A personalized, risk-adapted approach, paired with improved adherence and follow-up are essential to optimize the population-level impact of CRC screening and ensure equitable, effective cancer prevention.
Dr. Gupta is based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. Dr. Burke and Dr. Macaron are based at the Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio. Dr. Gupta and Dr. Macaron declared no conflicts of interest in regard to this article. Dr. Burke declared research support from Emtora Biosciences. She is a current consultant for Lumabridge, and has been a consultant for Sebela and Almirall. She also disclosed support from Myriad, Genzyme, Ferring, Merck, Sharp and Dohme, Abbvie, Salix, and Natera.
References
1. Benavidez GA, Sedani AE, Felder TM, Asare M, Rogers CR. Rural-urban disparities and trends in cancer screening: an analysis of Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System data (2018-2022). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Nov 1;8(6):pkae113
2. Galoosian A, Dai H, Croymans D, et al. Population Health Colorectal Cancer Screening Strategies in Adults Aged 45 to 49 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2025 Aug 4:e2512049. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.12049. Epub ahead of print.
3. Pilonis ND, Bugajski M, Wieszczy P, et al. Participation in Competing Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Randomized Health Services Study (PICCOLINO Study). Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1097-1105.
4. Shaukat A, Mongin SJ, Geisser MS, et al. Long-term mortality after screening for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1106–1114.
5. Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jørgensen OD, Søndergaard O. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996 Nov 30;348(9040):1467-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)03430-7. PMID: 8942774.
6. Burke CA, Lieberman D, Feuerstein JD. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Approach to the Use of Noninvasive Colorectal Cancer Screening Options: Commentary. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):952-956. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.075. Epub 2022 Jan 28. PMID: 35094786.
7. Imperiale TF, Gruber RN Stump TE, et al. Performance characteristics of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer and advanced adenomatous polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2019; 170(5):319-329
8. Doubeni CA, Corley DA, Jensen CD, et al. Fecal Immunochemical Test Screening and Risk of Colorectal Cancer Death. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2423671. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.23671.
9. Chiu HM, Jen GH, Wang YW, et al. Long-term effectiveness of faecal immunochemical test screening for proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Gut. 2021 Dec;70(12):2321-2329. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322545. Epub 2021 Jan 25.
10. Castells A, Quintero E, Bujanda L, et al; COLONPREV study investigators. Effect of invitation to colonoscopy versus fecal immunochemical test screening on colorectal cancer mortality (COLONPREV): a pragmatic, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2025;405(10486):1231–1239
11. Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297
12. Imperiale TF, Porter K, Zella J, et al. Next-Generation Multitarget Stool DNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):984-993
13. Barnell EK, Wurtzler EM, La Rocca J, et al. Multitarget Stool RNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. JAMA. 2023 Nov 14;330(18):1760-1768.
14. Church TR, Wandell M, Lofton-Day C, et al. Prospective evaluation of methylated SEPT9 in plasma for detection of asymptomatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2014; 63:317–325.
15. Chung DC, Gray DM 2nd, Singh H, et al. A Cell-free DNA Blood-Based Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):973-983.
16. Shaukat A, Burke CA, Chan AT, et al. Clinical Validation of a Circulating Tumor DNA-Based Blood Test to Screen for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA. 2025 Jul 1;334(1):56-63.
17. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Weng Y, et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening with Blood-Based Biomarkers (Liquid Biopsy) vs Fecal Tests or Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jul;167(2):378-391.
18. van den Puttelaar R, Nascimento de Lima P, Knudsen AB, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening with a blood test that meets the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services coverage decision. Gastroenterology 2024;167:368–377.
19. Shaukat A, Levin TR, Liang PS. Cost-effectiveness of Novel Noninvasive Screening Tests for Colorectal Neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun 23:S1542-3565(25)00525-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.06.006. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40562290.
20. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Schoen RE, Dominitz JA, Lieberman D. Projected Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Novel Molecular Blood-Based or Stool-Based Screening Tests for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec;177(12):1610-1620.
20. Ciemins EL, Mohl JT, Moreno CA, Colangelo F, Smith RA, Barton M. Development of a Follow-Up Measure to Ensure Complete Screening for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e242693. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693.
21. Zaki TA, Zhang NJ, Forbes SP, Raymond VM, Das AK, May FP. Colonoscopic Follow-up After Abnormal Blood-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening Results. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul 21:S0016-5085(25)05775-0. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.019. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40744392.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) screening significantly reduces CRC incidence and mortality, but only 65% of eligible individuals report being up-to-date with screening.1 Colonoscopy is the most widely used opportunistic screening method in the United States and is associated with many barriers to uptake. Providing patients a choice of colonoscopy and/or stool-based tests, improves screening adherence in randomized controlled trials.2,3 Non-invasive screening options have expanded from stool occult blood and multi-target DNA tests, to multi-target stool RNA tests, and novel blood-based tests, the latter only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for patients who refuse colonoscopy and stool-based tests.
Stool Occult Blood Tests
Guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT) significantly reduces CRC mortality by 33%-35% when implemented on an annual or biennial basis.4,5 Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) has supplanted gFOBT with advantages including independence from dietary restriction and medication-related interference, use of antibodies specific to human globin, and the need for only a single stool sample.
The most common threshold for a positive FIT in the U.S. is ≥ 20 micrograms (μg) of hemoglobin per gram (g) of stool. FIT is approved by the FDA as a qualitative positive or negative result based on a threshold value.6 A meta-analysis summarized test characteristics of commercially available FITs at various detection thresholds.7 The CRC sensitivity and specificity was 75% and 95% for ≥ 20 ug hemoglobin/g stool, and 91% and 90% for 10 ug hemoglobin/g stool, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas ranged from 25% at 20 μg/g to 40% at a 10 μg/g. Programmatic use of FIT in adults ages ≥ 50 years at 20 ug/g of stool, in cohort and case control studies, has been shown to significantly reduce CRC mortality by 33%-40% and advanced stage CRC by 34%.8,9
Over 57,000 average-risk individuals ages 50–69 years were randomized to biennial FIT or one-time colonoscopy and followed for 10 years.10 CRC mortality and incidence was similar between the groups: 0.22% with FIT vs. 0.24% with colonoscopy and 1.13% with FIT vs. 1.22% with colonoscopy, respectively. Thus, confirming biennial FIT screening is non-inferior to one-time colonoscopy in important CRC-related outcomes.
Multi-Target Stool Tests
Two multitarget stool DNA tests (mt-sDNA) known as Cologuard™ and Cologuard Plus™ have been approved by the FDA. Both tests include a FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin per gram of stool) combined with DNA methylation markers. The test result is qualitative, reported as a positive or negative. Cologuard™ markers include methylated BMP3, NDRG4, and mutant KRAS while Cologuard Plus™ assesses methylated LASS4, LRRC4, and PPP2R5C. The respective mt-sDNA tests were studied in 9989 of 12,776 and 20,176 of 26,758 average-risk individuals undergoing colonoscopy and the results were compared to a commercially available FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool).11,12 In both trials, the sensitivity for CRC and advanced precancerous lesions was higher with the mt-sDNA tests compared to FIT but had a significantly lower specificity for advanced precancerous lesions versus FIT (see Table 1). An age-related decline in specificity was noted in both trials with mt-sDNA, a trend not observed with FIT. This reduction may be attributed to age-related DNA methylation.
Multi-Target Stool RNA Test
A multi-target stool RNA test (mt-sRNA) commercially available as ColoSense™ is FDA-approved. It combines FIT (at a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool) with RNA-based stool markers. The combined results of the RNA markers, FIT, and smoking status provide a qualitative single test result. In the trial, 8,920 adults aged ≥45 underwent the mt-sRNA test and FIT followed by colonoscopy (13). The mt-sRNA showed higher sensitivity for CRC than FIT (94.4% versus 77.8%) and advanced adenomas (45.9% versus 28.9%) but lower CRC specificity (84.7% vs 94.7%) (Table 1). Unlike mt-sDNA-based tests, mt-sRNA showed consistent performance across age groups, addressing concerns about age-related declines in specificity attributed to DNA methylation.
Blood-Based Tests
In 2014, the first blood-based (BBT) CRC screening test known as Epi proColon™ was FDA but not Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) approved for average-risk adults ≥50 years of age who are offered and refused other U.S Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) endorsed CRC screening tests. It is a qualitative test for detection of circulating methylated Septin 9 (mSeptin9). The accuracy of mSeptin9 to detect CRC was assessed in a subset of 7941 asymptomatic average risk adults undergoing screening colonoscopy.14 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC were 48% and 91.5%, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas was 11.2%. An increase in sensitivity to 63.9% and reduction in specificity to 88.4% for CRC was demonstrated in a sub-analysis of available samples where an additional (third) polymerase chain replicate was performed. Epi proColon™ is not currently reimbursed by Medicare and not endorsed in the latest USPSTF guidelines.
Technologic advancements have improved the detection of circulating tumor markers in the blood. The Shield™ BBT approved by the FDA in 2024 for average risk adults ≥ 45 years integrates three types of cfDNA data (epigenetic changes resulting in the aberrant methylation or fragmentation patterns, and genomic changes resulting in somatic mutations) into a positive or negative test result. In the trial, 22,877 average-risk, asymptomatic individuals ages 45–84 were enrolled and clinical validation was performed in 7,861 of the participants.15 The sensitivity for CRC was 83.1% which decreased to 55% for stage I tumors (see Table 1). CRC specificity was 89.6% and the sensitivity for advanced adenomas and large sessile serrated lesions was 13.2%.
Another BBT SimpleScreen™, which is not yet FDA-approved, analyzed circulating, cell-free DNA methylation patterns in 27,010 evaluable average-risk, asymptomatic adults ages 45–85 years undergoing screening colonoscopy.16 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC was 79.2% and 91.5%, respectively. Similar to Shield, the sensitivity for stage I CRC was low at 57.1%. The sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions, a secondary endpoint, was 12.5% which did not meet the prespecified study criteria.
Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
Modeling studies have evaluated novel noninvasive CRC screening tests compared to FIT and colonoscopy.17-20 One compared a hypothetical BBT performed every 3 years that meets the minimum CMS threshold CRC sensitivity and specificity of 74% and 90%, respectively, to other established CRC screening tests beginning at age 45.17 Every 3-year BBT reduced CRC incidence and mortality by 40% and 52%, respectively compared to no screening. However, the reductions were much lower than yearly FIT (72% and 76%, respectively), every 10 year colonoscopy (79% and 81%, respectively), and triennial mt-sDNA (68% and 73%, respectively). The BBT resulted in fewer quality-adjusted life-years per person compared to the alternatives.
Additionally, FIT, colonoscopy, and mt-sDNA were less costly and more effective. Advanced precancerous lesion detection was a key measure for a test’s effectiveness. BBT characteristics would require a CRC sensitivity and specificity of >90% and 90%, respectively, and 80% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions at a cost of ≤$120–$140 to be cost-effective compared to FIT at comparable participation rates.
Another analysis simulated colorectal neoplasia progression and compared clinical effectiveness and cost between annual FIT, every 3 year stool mt-sRNA, every 3 year stool mt-sDNA tests, every 3 year stool Shield™; these outcomes were compared to colonoscopy every 10 years and no screening in adults ≥ age 45 over different adherence rates.19 At real-world adherence rates of 60%, colonoscopy prevented most CRC cases and associated deaths. FIT was the most cost-effective strategy at all adherence levels. Between the multi-target stool tests and Shield™, mt-sRNA was the most cost-effective. Compared to FIT, mt-sRNA reduced CRC cases and deaths by 1% and 14%.
The third study evaluated CRC incidence and mortality, quality-adjusted life-years and costs with annual FIT, colonoscopy every 10 years, mt- sDNA tests, mt-sRNA test, and BBTs.20 The latest mt-sDNA (Colguard plus™) and mt-sRNA achieved benefits approaching FIT but the Shield™ test was substantially less effective. The authors hypothesized that if 15% of the population substituted Shield™ for current effective CRC screening strategies, an increase in CRC deaths would occur and require 9-10% of the unscreened population to uptake screening with Shield to avert the increases in CRC deaths due to the substitution effect.
Clinical Implications
The effectiveness of non-invasive screening strategies depends on their diagnostic performance, adherence, and ensuring a timely colonoscopy after a positive test. Two claims-based studies found 47.9% and 49% of patients underwent follow-up colonoscopy within 6 months of an abnormal stool or BBT CRC screening test, respectively.21-22
Conclusions
Non-invasive stool mt-sDNA and mt-sRNA have higher effectiveness than the new BBTs. BBTs can lead to increased CRC mortality if substituted for the FDA and CMS-approved, USPSTF-endorsed, CRC screening modalities. If future BBTs increase their sensitivity for CRC (including early-stage CRC) and advanced precancerous lesions and decrease their cost, they may prove to have similar cost-effectiveness to stool-based tests. Currently, BBTs are not a substitute for colonoscopy or other stool tests and should be offered to patients who refuse other CRC screening modalities. A personalized, risk-adapted approach, paired with improved adherence and follow-up are essential to optimize the population-level impact of CRC screening and ensure equitable, effective cancer prevention.
Dr. Gupta is based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. Dr. Burke and Dr. Macaron are based at the Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio. Dr. Gupta and Dr. Macaron declared no conflicts of interest in regard to this article. Dr. Burke declared research support from Emtora Biosciences. She is a current consultant for Lumabridge, and has been a consultant for Sebela and Almirall. She also disclosed support from Myriad, Genzyme, Ferring, Merck, Sharp and Dohme, Abbvie, Salix, and Natera.
References
1. Benavidez GA, Sedani AE, Felder TM, Asare M, Rogers CR. Rural-urban disparities and trends in cancer screening: an analysis of Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System data (2018-2022). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Nov 1;8(6):pkae113
2. Galoosian A, Dai H, Croymans D, et al. Population Health Colorectal Cancer Screening Strategies in Adults Aged 45 to 49 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2025 Aug 4:e2512049. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.12049. Epub ahead of print.
3. Pilonis ND, Bugajski M, Wieszczy P, et al. Participation in Competing Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Randomized Health Services Study (PICCOLINO Study). Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1097-1105.
4. Shaukat A, Mongin SJ, Geisser MS, et al. Long-term mortality after screening for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1106–1114.
5. Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jørgensen OD, Søndergaard O. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996 Nov 30;348(9040):1467-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)03430-7. PMID: 8942774.
6. Burke CA, Lieberman D, Feuerstein JD. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Approach to the Use of Noninvasive Colorectal Cancer Screening Options: Commentary. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):952-956. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.075. Epub 2022 Jan 28. PMID: 35094786.
7. Imperiale TF, Gruber RN Stump TE, et al. Performance characteristics of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer and advanced adenomatous polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2019; 170(5):319-329
8. Doubeni CA, Corley DA, Jensen CD, et al. Fecal Immunochemical Test Screening and Risk of Colorectal Cancer Death. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2423671. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.23671.
9. Chiu HM, Jen GH, Wang YW, et al. Long-term effectiveness of faecal immunochemical test screening for proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Gut. 2021 Dec;70(12):2321-2329. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322545. Epub 2021 Jan 25.
10. Castells A, Quintero E, Bujanda L, et al; COLONPREV study investigators. Effect of invitation to colonoscopy versus fecal immunochemical test screening on colorectal cancer mortality (COLONPREV): a pragmatic, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2025;405(10486):1231–1239
11. Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297
12. Imperiale TF, Porter K, Zella J, et al. Next-Generation Multitarget Stool DNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):984-993
13. Barnell EK, Wurtzler EM, La Rocca J, et al. Multitarget Stool RNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. JAMA. 2023 Nov 14;330(18):1760-1768.
14. Church TR, Wandell M, Lofton-Day C, et al. Prospective evaluation of methylated SEPT9 in plasma for detection of asymptomatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2014; 63:317–325.
15. Chung DC, Gray DM 2nd, Singh H, et al. A Cell-free DNA Blood-Based Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):973-983.
16. Shaukat A, Burke CA, Chan AT, et al. Clinical Validation of a Circulating Tumor DNA-Based Blood Test to Screen for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA. 2025 Jul 1;334(1):56-63.
17. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Weng Y, et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening with Blood-Based Biomarkers (Liquid Biopsy) vs Fecal Tests or Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jul;167(2):378-391.
18. van den Puttelaar R, Nascimento de Lima P, Knudsen AB, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening with a blood test that meets the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services coverage decision. Gastroenterology 2024;167:368–377.
19. Shaukat A, Levin TR, Liang PS. Cost-effectiveness of Novel Noninvasive Screening Tests for Colorectal Neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun 23:S1542-3565(25)00525-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.06.006. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40562290.
20. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Schoen RE, Dominitz JA, Lieberman D. Projected Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Novel Molecular Blood-Based or Stool-Based Screening Tests for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec;177(12):1610-1620.
20. Ciemins EL, Mohl JT, Moreno CA, Colangelo F, Smith RA, Barton M. Development of a Follow-Up Measure to Ensure Complete Screening for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e242693. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693.
21. Zaki TA, Zhang NJ, Forbes SP, Raymond VM, Das AK, May FP. Colonoscopic Follow-up After Abnormal Blood-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening Results. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul 21:S0016-5085(25)05775-0. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.019. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40744392.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) screening significantly reduces CRC incidence and mortality, but only 65% of eligible individuals report being up-to-date with screening.1 Colonoscopy is the most widely used opportunistic screening method in the United States and is associated with many barriers to uptake. Providing patients a choice of colonoscopy and/or stool-based tests, improves screening adherence in randomized controlled trials.2,3 Non-invasive screening options have expanded from stool occult blood and multi-target DNA tests, to multi-target stool RNA tests, and novel blood-based tests, the latter only U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved for patients who refuse colonoscopy and stool-based tests.
Stool Occult Blood Tests
Guaiac-based fecal occult blood testing (gFOBT) significantly reduces CRC mortality by 33%-35% when implemented on an annual or biennial basis.4,5 Fecal immunochemical testing (FIT) has supplanted gFOBT with advantages including independence from dietary restriction and medication-related interference, use of antibodies specific to human globin, and the need for only a single stool sample.
The most common threshold for a positive FIT in the U.S. is ≥ 20 micrograms (μg) of hemoglobin per gram (g) of stool. FIT is approved by the FDA as a qualitative positive or negative result based on a threshold value.6 A meta-analysis summarized test characteristics of commercially available FITs at various detection thresholds.7 The CRC sensitivity and specificity was 75% and 95% for ≥ 20 ug hemoglobin/g stool, and 91% and 90% for 10 ug hemoglobin/g stool, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas ranged from 25% at 20 μg/g to 40% at a 10 μg/g. Programmatic use of FIT in adults ages ≥ 50 years at 20 ug/g of stool, in cohort and case control studies, has been shown to significantly reduce CRC mortality by 33%-40% and advanced stage CRC by 34%.8,9
Over 57,000 average-risk individuals ages 50–69 years were randomized to biennial FIT or one-time colonoscopy and followed for 10 years.10 CRC mortality and incidence was similar between the groups: 0.22% with FIT vs. 0.24% with colonoscopy and 1.13% with FIT vs. 1.22% with colonoscopy, respectively. Thus, confirming biennial FIT screening is non-inferior to one-time colonoscopy in important CRC-related outcomes.
Multi-Target Stool Tests
Two multitarget stool DNA tests (mt-sDNA) known as Cologuard™ and Cologuard Plus™ have been approved by the FDA. Both tests include a FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin per gram of stool) combined with DNA methylation markers. The test result is qualitative, reported as a positive or negative. Cologuard™ markers include methylated BMP3, NDRG4, and mutant KRAS while Cologuard Plus™ assesses methylated LASS4, LRRC4, and PPP2R5C. The respective mt-sDNA tests were studied in 9989 of 12,776 and 20,176 of 26,758 average-risk individuals undergoing colonoscopy and the results were compared to a commercially available FIT (with a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool).11,12 In both trials, the sensitivity for CRC and advanced precancerous lesions was higher with the mt-sDNA tests compared to FIT but had a significantly lower specificity for advanced precancerous lesions versus FIT (see Table 1). An age-related decline in specificity was noted in both trials with mt-sDNA, a trend not observed with FIT. This reduction may be attributed to age-related DNA methylation.
Multi-Target Stool RNA Test
A multi-target stool RNA test (mt-sRNA) commercially available as ColoSense™ is FDA-approved. It combines FIT (at a positivity threshold of 20 μg hemoglobin/gram of stool) with RNA-based stool markers. The combined results of the RNA markers, FIT, and smoking status provide a qualitative single test result. In the trial, 8,920 adults aged ≥45 underwent the mt-sRNA test and FIT followed by colonoscopy (13). The mt-sRNA showed higher sensitivity for CRC than FIT (94.4% versus 77.8%) and advanced adenomas (45.9% versus 28.9%) but lower CRC specificity (84.7% vs 94.7%) (Table 1). Unlike mt-sDNA-based tests, mt-sRNA showed consistent performance across age groups, addressing concerns about age-related declines in specificity attributed to DNA methylation.
Blood-Based Tests
In 2014, the first blood-based (BBT) CRC screening test known as Epi proColon™ was FDA but not Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) approved for average-risk adults ≥50 years of age who are offered and refused other U.S Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) endorsed CRC screening tests. It is a qualitative test for detection of circulating methylated Septin 9 (mSeptin9). The accuracy of mSeptin9 to detect CRC was assessed in a subset of 7941 asymptomatic average risk adults undergoing screening colonoscopy.14 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC were 48% and 91.5%, respectively. The sensitivity for advanced adenomas was 11.2%. An increase in sensitivity to 63.9% and reduction in specificity to 88.4% for CRC was demonstrated in a sub-analysis of available samples where an additional (third) polymerase chain replicate was performed. Epi proColon™ is not currently reimbursed by Medicare and not endorsed in the latest USPSTF guidelines.
Technologic advancements have improved the detection of circulating tumor markers in the blood. The Shield™ BBT approved by the FDA in 2024 for average risk adults ≥ 45 years integrates three types of cfDNA data (epigenetic changes resulting in the aberrant methylation or fragmentation patterns, and genomic changes resulting in somatic mutations) into a positive or negative test result. In the trial, 22,877 average-risk, asymptomatic individuals ages 45–84 were enrolled and clinical validation was performed in 7,861 of the participants.15 The sensitivity for CRC was 83.1% which decreased to 55% for stage I tumors (see Table 1). CRC specificity was 89.6% and the sensitivity for advanced adenomas and large sessile serrated lesions was 13.2%.
Another BBT SimpleScreen™, which is not yet FDA-approved, analyzed circulating, cell-free DNA methylation patterns in 27,010 evaluable average-risk, asymptomatic adults ages 45–85 years undergoing screening colonoscopy.16 The sensitivity and specificity for CRC was 79.2% and 91.5%, respectively. Similar to Shield, the sensitivity for stage I CRC was low at 57.1%. The sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions, a secondary endpoint, was 12.5% which did not meet the prespecified study criteria.
Effectiveness and Cost Effectiveness
Modeling studies have evaluated novel noninvasive CRC screening tests compared to FIT and colonoscopy.17-20 One compared a hypothetical BBT performed every 3 years that meets the minimum CMS threshold CRC sensitivity and specificity of 74% and 90%, respectively, to other established CRC screening tests beginning at age 45.17 Every 3-year BBT reduced CRC incidence and mortality by 40% and 52%, respectively compared to no screening. However, the reductions were much lower than yearly FIT (72% and 76%, respectively), every 10 year colonoscopy (79% and 81%, respectively), and triennial mt-sDNA (68% and 73%, respectively). The BBT resulted in fewer quality-adjusted life-years per person compared to the alternatives.
Additionally, FIT, colonoscopy, and mt-sDNA were less costly and more effective. Advanced precancerous lesion detection was a key measure for a test’s effectiveness. BBT characteristics would require a CRC sensitivity and specificity of >90% and 90%, respectively, and 80% sensitivity for advanced precancerous lesions at a cost of ≤$120–$140 to be cost-effective compared to FIT at comparable participation rates.
Another analysis simulated colorectal neoplasia progression and compared clinical effectiveness and cost between annual FIT, every 3 year stool mt-sRNA, every 3 year stool mt-sDNA tests, every 3 year stool Shield™; these outcomes were compared to colonoscopy every 10 years and no screening in adults ≥ age 45 over different adherence rates.19 At real-world adherence rates of 60%, colonoscopy prevented most CRC cases and associated deaths. FIT was the most cost-effective strategy at all adherence levels. Between the multi-target stool tests and Shield™, mt-sRNA was the most cost-effective. Compared to FIT, mt-sRNA reduced CRC cases and deaths by 1% and 14%.
The third study evaluated CRC incidence and mortality, quality-adjusted life-years and costs with annual FIT, colonoscopy every 10 years, mt- sDNA tests, mt-sRNA test, and BBTs.20 The latest mt-sDNA (Colguard plus™) and mt-sRNA achieved benefits approaching FIT but the Shield™ test was substantially less effective. The authors hypothesized that if 15% of the population substituted Shield™ for current effective CRC screening strategies, an increase in CRC deaths would occur and require 9-10% of the unscreened population to uptake screening with Shield to avert the increases in CRC deaths due to the substitution effect.
Clinical Implications
The effectiveness of non-invasive screening strategies depends on their diagnostic performance, adherence, and ensuring a timely colonoscopy after a positive test. Two claims-based studies found 47.9% and 49% of patients underwent follow-up colonoscopy within 6 months of an abnormal stool or BBT CRC screening test, respectively.21-22
Conclusions
Non-invasive stool mt-sDNA and mt-sRNA have higher effectiveness than the new BBTs. BBTs can lead to increased CRC mortality if substituted for the FDA and CMS-approved, USPSTF-endorsed, CRC screening modalities. If future BBTs increase their sensitivity for CRC (including early-stage CRC) and advanced precancerous lesions and decrease their cost, they may prove to have similar cost-effectiveness to stool-based tests. Currently, BBTs are not a substitute for colonoscopy or other stool tests and should be offered to patients who refuse other CRC screening modalities. A personalized, risk-adapted approach, paired with improved adherence and follow-up are essential to optimize the population-level impact of CRC screening and ensure equitable, effective cancer prevention.
Dr. Gupta is based at the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore. Dr. Burke and Dr. Macaron are based at the Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, Ohio. Dr. Gupta and Dr. Macaron declared no conflicts of interest in regard to this article. Dr. Burke declared research support from Emtora Biosciences. She is a current consultant for Lumabridge, and has been a consultant for Sebela and Almirall. She also disclosed support from Myriad, Genzyme, Ferring, Merck, Sharp and Dohme, Abbvie, Salix, and Natera.
References
1. Benavidez GA, Sedani AE, Felder TM, Asare M, Rogers CR. Rural-urban disparities and trends in cancer screening: an analysis of Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System data (2018-2022). JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Nov 1;8(6):pkae113
2. Galoosian A, Dai H, Croymans D, et al. Population Health Colorectal Cancer Screening Strategies in Adults Aged 45 to 49 Years: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2025 Aug 4:e2512049. doi: 10.1001/jama.2025.12049. Epub ahead of print.
3. Pilonis ND, Bugajski M, Wieszczy P, et al. Participation in Competing Strategies for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Randomized Health Services Study (PICCOLINO Study). Gastroenterology. 2021 Mar;160(4):1097-1105.
4. Shaukat A, Mongin SJ, Geisser MS, et al. Long-term mortality after screening for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(12):1106–1114.
5. Kronborg O, Fenger C, Olsen J, Jørgensen OD, Søndergaard O. Randomised study of screening for colorectal cancer with faecal-occult-blood test. Lancet. 1996 Nov 30;348(9040):1467-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)03430-7. PMID: 8942774.
6. Burke CA, Lieberman D, Feuerstein JD. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Approach to the Use of Noninvasive Colorectal Cancer Screening Options: Commentary. Gastroenterology. 2022 Mar;162(3):952-956. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.075. Epub 2022 Jan 28. PMID: 35094786.
7. Imperiale TF, Gruber RN Stump TE, et al. Performance characteristics of fecal immunochemical tests for colorectal cancer and advanced adenomatous polyps: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2019; 170(5):319-329
8. Doubeni CA, Corley DA, Jensen CD, et al. Fecal Immunochemical Test Screening and Risk of Colorectal Cancer Death. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2423671. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.23671.
9. Chiu HM, Jen GH, Wang YW, et al. Long-term effectiveness of faecal immunochemical test screening for proximal and distal colorectal cancers. Gut. 2021 Dec;70(12):2321-2329. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322545. Epub 2021 Jan 25.
10. Castells A, Quintero E, Bujanda L, et al; COLONPREV study investigators. Effect of invitation to colonoscopy versus fecal immunochemical test screening on colorectal cancer mortality (COLONPREV): a pragmatic, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2025;405(10486):1231–1239
11. Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH, et al. Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(14):1287-1297
12. Imperiale TF, Porter K, Zella J, et al. Next-Generation Multitarget Stool DNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):984-993
13. Barnell EK, Wurtzler EM, La Rocca J, et al. Multitarget Stool RNA Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. JAMA. 2023 Nov 14;330(18):1760-1768.
14. Church TR, Wandell M, Lofton-Day C, et al. Prospective evaluation of methylated SEPT9 in plasma for detection of asymptomatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2014; 63:317–325.
15. Chung DC, Gray DM 2nd, Singh H, et al. A Cell-free DNA Blood-Based Test for Colorectal Cancer Screening. N Engl J Med. 2024 Mar 14;390(11):973-983.
16. Shaukat A, Burke CA, Chan AT, et al. Clinical Validation of a Circulating Tumor DNA-Based Blood Test to Screen for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA. 2025 Jul 1;334(1):56-63.
17. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Weng Y, et al. Comparative Effectiveness and Cost-Effectiveness of Colorectal Cancer Screening with Blood-Based Biomarkers (Liquid Biopsy) vs Fecal Tests or Colonoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jul;167(2):378-391.
18. van den Puttelaar R, Nascimento de Lima P, Knudsen AB, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening with a blood test that meets the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services coverage decision. Gastroenterology 2024;167:368–377.
19. Shaukat A, Levin TR, Liang PS. Cost-effectiveness of Novel Noninvasive Screening Tests for Colorectal Neoplasia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2025 Jun 23:S1542-3565(25)00525-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2025.06.006. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40562290.
20. Ladabaum U, Mannalithara A, Schoen RE, Dominitz JA, Lieberman D. Projected Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Novel Molecular Blood-Based or Stool-Based Screening Tests for Colorectal Cancer. Ann Intern Med. 2024 Dec;177(12):1610-1620.
20. Ciemins EL, Mohl JT, Moreno CA, Colangelo F, Smith RA, Barton M. Development of a Follow-Up Measure to Ensure Complete Screening for Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Mar 4;7(3):e242693. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.2693.
21. Zaki TA, Zhang NJ, Forbes SP, Raymond VM, Das AK, May FP. Colonoscopic Follow-up After Abnormal Blood-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening Results. Gastroenterology. 2025 Jul 21:S0016-5085(25)05775-0. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2025.07.019. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40744392.
Text vs Video Psychotherapy: Which Is Better for Depression?
Text vs Video Psychotherapy: Which Is Better for Depression?
TOPLINE:
Message-based psychotherapy (MBP), which uses asynchronous emails or texts, showed effectiveness comparable with that of video-based psychotherapy (VBP) for the treatment of depression on a commercial digital mental health platform, a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a pragmatic sequential multiple-assignment randomized clinical trial from 2022 to 2024 involving 850 adult patients with a diagnosis of depression (mean age, 34 years; 66% women; 60% White, 22% Black and 14% Hispanic).
- Patients were initially randomly assigned to receive weekly MBP (n = 423) or VBP (n = 427), with nonresponders randomly assigned at week 6 to receive combination therapy of MBP plus weekly or monthly VBP. All patients received treatment for up to 12 weeks.
- Primary outcomes included depression severity measured by the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), social functioning measured by the Quality of Life in Neurological Disorders 8-item tool, response to treatment (≥ 50% reduction in PHQ-9 total score or Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement score ≤ 2), and remissions (PHQ-9 score < 5).
- Secondary outcomes were treating disengagement, therapeutic alliance measured on the Working Alliance Inventory-Short Revised, quality of care in the past 4 weeks, and treatment satisfaction.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rates of response (47.5% and 47.2%, respectively) and remission (31.4% and 30.3%, respectively) were not significantly different at week 12 between the MBP and VBP groups or for nonresponders rerandomized to either group.
- There were also no significant differences in depression change scores between the MBP and VBP groups or for nonresponders rerandomized to either group.
- Treatment disengagement by week 5 was significantly higher in the VBP vs MBP group (21.3% vs 13.2%; P = .003); VBP responders had stronger initial therapeutic alliance at week 4 than MBP responders (P < .001).
- No significant differences were observed in the quality of care among those who responded only after the second randomization to MBP or VBP.
IN PRACTICE:
"Findings reinforced MBP as viable alternative to VBP. Broader insurance reimbursement for MBP could improve access to evidence-based care," the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Michael D. Pullmann, PhD, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online on October 30 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The absence of a waiting list or a no-treatment control group made it difficult to rule out regression to the mean as an explanation for improvements. Additionally, missing data may have affected the robustness of some findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. Several investigators reported having financial ties with various sources. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Message-based psychotherapy (MBP), which uses asynchronous emails or texts, showed effectiveness comparable with that of video-based psychotherapy (VBP) for the treatment of depression on a commercial digital mental health platform, a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a pragmatic sequential multiple-assignment randomized clinical trial from 2022 to 2024 involving 850 adult patients with a diagnosis of depression (mean age, 34 years; 66% women; 60% White, 22% Black and 14% Hispanic).
- Patients were initially randomly assigned to receive weekly MBP (n = 423) or VBP (n = 427), with nonresponders randomly assigned at week 6 to receive combination therapy of MBP plus weekly or monthly VBP. All patients received treatment for up to 12 weeks.
- Primary outcomes included depression severity measured by the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), social functioning measured by the Quality of Life in Neurological Disorders 8-item tool, response to treatment (≥ 50% reduction in PHQ-9 total score or Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement score ≤ 2), and remissions (PHQ-9 score < 5).
- Secondary outcomes were treating disengagement, therapeutic alliance measured on the Working Alliance Inventory-Short Revised, quality of care in the past 4 weeks, and treatment satisfaction.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rates of response (47.5% and 47.2%, respectively) and remission (31.4% and 30.3%, respectively) were not significantly different at week 12 between the MBP and VBP groups or for nonresponders rerandomized to either group.
- There were also no significant differences in depression change scores between the MBP and VBP groups or for nonresponders rerandomized to either group.
- Treatment disengagement by week 5 was significantly higher in the VBP vs MBP group (21.3% vs 13.2%; P = .003); VBP responders had stronger initial therapeutic alliance at week 4 than MBP responders (P < .001).
- No significant differences were observed in the quality of care among those who responded only after the second randomization to MBP or VBP.
IN PRACTICE:
"Findings reinforced MBP as viable alternative to VBP. Broader insurance reimbursement for MBP could improve access to evidence-based care," the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Michael D. Pullmann, PhD, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online on October 30 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The absence of a waiting list or a no-treatment control group made it difficult to rule out regression to the mean as an explanation for improvements. Additionally, missing data may have affected the robustness of some findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. Several investigators reported having financial ties with various sources. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Message-based psychotherapy (MBP), which uses asynchronous emails or texts, showed effectiveness comparable with that of video-based psychotherapy (VBP) for the treatment of depression on a commercial digital mental health platform, a new study showed.
METHODOLOGY:
- Investigators conducted a pragmatic sequential multiple-assignment randomized clinical trial from 2022 to 2024 involving 850 adult patients with a diagnosis of depression (mean age, 34 years; 66% women; 60% White, 22% Black and 14% Hispanic).
- Patients were initially randomly assigned to receive weekly MBP (n = 423) or VBP (n = 427), with nonresponders randomly assigned at week 6 to receive combination therapy of MBP plus weekly or monthly VBP. All patients received treatment for up to 12 weeks.
- Primary outcomes included depression severity measured by the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), social functioning measured by the Quality of Life in Neurological Disorders 8-item tool, response to treatment (≥ 50% reduction in PHQ-9 total score or Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement score ≤ 2), and remissions (PHQ-9 score < 5).
- Secondary outcomes were treating disengagement, therapeutic alliance measured on the Working Alliance Inventory-Short Revised, quality of care in the past 4 weeks, and treatment satisfaction.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rates of response (47.5% and 47.2%, respectively) and remission (31.4% and 30.3%, respectively) were not significantly different at week 12 between the MBP and VBP groups or for nonresponders rerandomized to either group.
- There were also no significant differences in depression change scores between the MBP and VBP groups or for nonresponders rerandomized to either group.
- Treatment disengagement by week 5 was significantly higher in the VBP vs MBP group (21.3% vs 13.2%; P = .003); VBP responders had stronger initial therapeutic alliance at week 4 than MBP responders (P < .001).
- No significant differences were observed in the quality of care among those who responded only after the second randomization to MBP or VBP.
IN PRACTICE:
"Findings reinforced MBP as viable alternative to VBP. Broader insurance reimbursement for MBP could improve access to evidence-based care," the investigators wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Michael D. Pullmann, PhD, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online on October 30 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The absence of a waiting list or a no-treatment control group made it difficult to rule out regression to the mean as an explanation for improvements. Additionally, missing data may have affected the robustness of some findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The research was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. Several investigators reported having financial ties with various sources. Details are provided in the original article.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Text vs Video Psychotherapy: Which Is Better for Depression?
Text vs Video Psychotherapy: Which Is Better for Depression?
GLP-1s May Improve Colon Cancer Outcomes
Treatment with a GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) may offer a survival advantage in patients with colon cancer and obesity.
In a real-world analysis of nearly 7000 patients with colon cancer, those taking a GLP-1 RA were less than half as likely to die within 5 years compared with those who weren’t on a GLP-1 drug.
The association between GLP-1 exposure and lower 5–year mortality in colon cancer was “robust” and appeared to be concentrated in patients with severe obesity (BMI ≥ 35), lead investigator Raphael E. Cuomo, PhD, with University of California San Diego, told this news organization.
The apparent protective effect “persisted after controlling for differences in disease severity and demographics, as well as differences in circulating carcinoembryonic antigen, a biomarker of disease aggressiveness,” Cuomo said.
The study was published online in Cancer Investigation.
Effects Beyond Glucose-Lowering
Colon cancer remains a major global cause of cancer-related deaths, and obesity is both a risk factor and a driver of worse outcomes.
Beyond regulating blood sugar, GLP-1 drugs reduce systemic inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss. Prior preclinical work has also suggested they may prevent cancer cell growth, trigger cancer cell death, and reshape the tumor microenvironment.
To investigate further, Cuomo analyzed electronic health records of 6871 patients diagnosed with primary colon cancer before 2019 — of which 103 had at least 1 documented prescription for a GLP-1 drug within 5 years of diagnosis.
Five–year mortality was significantly lower in GLP-1 RA users than in nonusers (15.5% vs 37.1%; P < .001). A significant reduction in 5–year mortality among GLP-1 RA users was evident in an unadjusted model (odds ratio [OR], 0.38; P < .001) and persisted in fully adjusted models (OR, 0.28; P < .001).
When stratified by BMI, the odds of 5-year mortality with GLP-1 use was reduced only in patients with Class II obesity (BMI ≥ 35: fully adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.051; P = .004). In this group, fully adjusted hazard ratios suggested markedly lower risk for death (HR, 0.07; P = .009).
Beyond mortality, GLP-1 users also experienced fewer late cardiovascular events and had fewer markers of advanced colon cancer progression in the final months of follow-up, “which suggests that GLP-1 drugs exert benefits through both oncologic and cardiometabolic pathways,” Cuomo told this news organization.
Intriguing and Promising — but Further Studies Needed
“To further study the potential of GLP-1 therapy as an adjunct to standard care in colon cancer, randomized trials should be conducted with stratification by BMI, diabetes status, and disease severity, with endpoints spanning overall and cancerspecific survival and major cardiovascular events,” Cuomo said.
“We also need prospective translational studies integrating dosing/timing, adherence, tumor genomics, and serial biomarkers (including ctDNA and metabolic panels) to elucidate mechanisms, assess the role of adiposity and insulin resistance, and identify the patient subgroups most likely to benefit,” he noted.
For now, GLP1 medications are an option in “eligible colon cancer patients with severe obesity or diabetes who meet standard metabolic indications,” Cuomo told this news organization.
Commenting on this study for this news organization, David Greenwald, MD, director of Clinical Gastroenterology and Endoscopy at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City, noted “other studies have showed a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer in the first place and then improved survival.”
Greenwald cited a recent study that found people with diabetes who took GLP-1 RAs had a 44% lower risk of developing colorectal cancer than those who took insulin, and a 25% lower risk than those who took metformin.
The effects of GLP-1s in colon cancer are “very intriguing and very promising but more research is needed to confirm whether this is really true and the mechanisms behind it,” said Greenwald.
In terms of the lowering risk of developing colorectal cancer, “probably first and foremost is that the drugs are really effective in promoting weight loss. And if you can reduce obesity in the population, you do all sorts of good things — reduce diabetes, reduce heart disease, and maybe reduce colorectal cancer,” Greenwald said.
This study had no specific funding. Cuomo and Greenwald had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with a GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) may offer a survival advantage in patients with colon cancer and obesity.
In a real-world analysis of nearly 7000 patients with colon cancer, those taking a GLP-1 RA were less than half as likely to die within 5 years compared with those who weren’t on a GLP-1 drug.
The association between GLP-1 exposure and lower 5–year mortality in colon cancer was “robust” and appeared to be concentrated in patients with severe obesity (BMI ≥ 35), lead investigator Raphael E. Cuomo, PhD, with University of California San Diego, told this news organization.
The apparent protective effect “persisted after controlling for differences in disease severity and demographics, as well as differences in circulating carcinoembryonic antigen, a biomarker of disease aggressiveness,” Cuomo said.
The study was published online in Cancer Investigation.
Effects Beyond Glucose-Lowering
Colon cancer remains a major global cause of cancer-related deaths, and obesity is both a risk factor and a driver of worse outcomes.
Beyond regulating blood sugar, GLP-1 drugs reduce systemic inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss. Prior preclinical work has also suggested they may prevent cancer cell growth, trigger cancer cell death, and reshape the tumor microenvironment.
To investigate further, Cuomo analyzed electronic health records of 6871 patients diagnosed with primary colon cancer before 2019 — of which 103 had at least 1 documented prescription for a GLP-1 drug within 5 years of diagnosis.
Five–year mortality was significantly lower in GLP-1 RA users than in nonusers (15.5% vs 37.1%; P < .001). A significant reduction in 5–year mortality among GLP-1 RA users was evident in an unadjusted model (odds ratio [OR], 0.38; P < .001) and persisted in fully adjusted models (OR, 0.28; P < .001).
When stratified by BMI, the odds of 5-year mortality with GLP-1 use was reduced only in patients with Class II obesity (BMI ≥ 35: fully adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.051; P = .004). In this group, fully adjusted hazard ratios suggested markedly lower risk for death (HR, 0.07; P = .009).
Beyond mortality, GLP-1 users also experienced fewer late cardiovascular events and had fewer markers of advanced colon cancer progression in the final months of follow-up, “which suggests that GLP-1 drugs exert benefits through both oncologic and cardiometabolic pathways,” Cuomo told this news organization.
Intriguing and Promising — but Further Studies Needed
“To further study the potential of GLP-1 therapy as an adjunct to standard care in colon cancer, randomized trials should be conducted with stratification by BMI, diabetes status, and disease severity, with endpoints spanning overall and cancerspecific survival and major cardiovascular events,” Cuomo said.
“We also need prospective translational studies integrating dosing/timing, adherence, tumor genomics, and serial biomarkers (including ctDNA and metabolic panels) to elucidate mechanisms, assess the role of adiposity and insulin resistance, and identify the patient subgroups most likely to benefit,” he noted.
For now, GLP1 medications are an option in “eligible colon cancer patients with severe obesity or diabetes who meet standard metabolic indications,” Cuomo told this news organization.
Commenting on this study for this news organization, David Greenwald, MD, director of Clinical Gastroenterology and Endoscopy at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City, noted “other studies have showed a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer in the first place and then improved survival.”
Greenwald cited a recent study that found people with diabetes who took GLP-1 RAs had a 44% lower risk of developing colorectal cancer than those who took insulin, and a 25% lower risk than those who took metformin.
The effects of GLP-1s in colon cancer are “very intriguing and very promising but more research is needed to confirm whether this is really true and the mechanisms behind it,” said Greenwald.
In terms of the lowering risk of developing colorectal cancer, “probably first and foremost is that the drugs are really effective in promoting weight loss. And if you can reduce obesity in the population, you do all sorts of good things — reduce diabetes, reduce heart disease, and maybe reduce colorectal cancer,” Greenwald said.
This study had no specific funding. Cuomo and Greenwald had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment with a GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) may offer a survival advantage in patients with colon cancer and obesity.
In a real-world analysis of nearly 7000 patients with colon cancer, those taking a GLP-1 RA were less than half as likely to die within 5 years compared with those who weren’t on a GLP-1 drug.
The association between GLP-1 exposure and lower 5–year mortality in colon cancer was “robust” and appeared to be concentrated in patients with severe obesity (BMI ≥ 35), lead investigator Raphael E. Cuomo, PhD, with University of California San Diego, told this news organization.
The apparent protective effect “persisted after controlling for differences in disease severity and demographics, as well as differences in circulating carcinoembryonic antigen, a biomarker of disease aggressiveness,” Cuomo said.
The study was published online in Cancer Investigation.
Effects Beyond Glucose-Lowering
Colon cancer remains a major global cause of cancer-related deaths, and obesity is both a risk factor and a driver of worse outcomes.
Beyond regulating blood sugar, GLP-1 drugs reduce systemic inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss. Prior preclinical work has also suggested they may prevent cancer cell growth, trigger cancer cell death, and reshape the tumor microenvironment.
To investigate further, Cuomo analyzed electronic health records of 6871 patients diagnosed with primary colon cancer before 2019 — of which 103 had at least 1 documented prescription for a GLP-1 drug within 5 years of diagnosis.
Five–year mortality was significantly lower in GLP-1 RA users than in nonusers (15.5% vs 37.1%; P < .001). A significant reduction in 5–year mortality among GLP-1 RA users was evident in an unadjusted model (odds ratio [OR], 0.38; P < .001) and persisted in fully adjusted models (OR, 0.28; P < .001).
When stratified by BMI, the odds of 5-year mortality with GLP-1 use was reduced only in patients with Class II obesity (BMI ≥ 35: fully adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.051; P = .004). In this group, fully adjusted hazard ratios suggested markedly lower risk for death (HR, 0.07; P = .009).
Beyond mortality, GLP-1 users also experienced fewer late cardiovascular events and had fewer markers of advanced colon cancer progression in the final months of follow-up, “which suggests that GLP-1 drugs exert benefits through both oncologic and cardiometabolic pathways,” Cuomo told this news organization.
Intriguing and Promising — but Further Studies Needed
“To further study the potential of GLP-1 therapy as an adjunct to standard care in colon cancer, randomized trials should be conducted with stratification by BMI, diabetes status, and disease severity, with endpoints spanning overall and cancerspecific survival and major cardiovascular events,” Cuomo said.
“We also need prospective translational studies integrating dosing/timing, adherence, tumor genomics, and serial biomarkers (including ctDNA and metabolic panels) to elucidate mechanisms, assess the role of adiposity and insulin resistance, and identify the patient subgroups most likely to benefit,” he noted.
For now, GLP1 medications are an option in “eligible colon cancer patients with severe obesity or diabetes who meet standard metabolic indications,” Cuomo told this news organization.
Commenting on this study for this news organization, David Greenwald, MD, director of Clinical Gastroenterology and Endoscopy at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City, noted “other studies have showed a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer in the first place and then improved survival.”
Greenwald cited a recent study that found people with diabetes who took GLP-1 RAs had a 44% lower risk of developing colorectal cancer than those who took insulin, and a 25% lower risk than those who took metformin.
The effects of GLP-1s in colon cancer are “very intriguing and very promising but more research is needed to confirm whether this is really true and the mechanisms behind it,” said Greenwald.
In terms of the lowering risk of developing colorectal cancer, “probably first and foremost is that the drugs are really effective in promoting weight loss. And if you can reduce obesity in the population, you do all sorts of good things — reduce diabetes, reduce heart disease, and maybe reduce colorectal cancer,” Greenwald said.
This study had no specific funding. Cuomo and Greenwald had no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CANCER INVESTIGATION
‘So You Have an Idea…’: A Practical Guide to Tech and Device Development for the Early Career GI
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.
You are in the middle of a busy clinic day and think, “there has to be a better way to do this.” Suddenly, a better way to do something becomes obvious. Maybe it’s a tool that simplifies documentation, a device that improves patient comfort, or an app that bridges a clinical gap. Many physicians, especially early career gastroenterologists, have ideas like this, but few know what to do next.
This article is for the curious innovator at the beginning of their clinical career. It offers practical, real-world guidance on developing a clinical product: whether that be hardware, software, or a hybrid. It outlines what questions to ask, who to consult, and how to protect your work, using personal insights and business principles learned through lived experience.
1. Understand Intellectual Property (IP): Know Its Value and Ownership
What is IP?
Intellectual property refers to your original creations: inventions, designs, software, and more. This is what you want to protect legally through patents, trademarks, or copyrights.
Who owns your idea?
This is the first and most important question to ask. If you are employed (especially by a hospital or academic center), your contract may already give your employer rights to any inventions you create, even those developed in your personal time.
What to ask:
- Does my employment contract include an “assignment of inventions” clause?
- Does the institution claim rights to anything developed with institutional resources?
- Are there moonlighting or external activity policies that affect this?
If you are developing an idea on your personal time, with your own resources, and outside your scope of clinical duties, it might still be considered “theirs” under some contracts. Early legal consultation is critical. A specialized IP attorney can help you understand what you own and how to protect it. This should be done early, ideally before you start building anything.
2. Lawyers Aren’t Optional: They’re Essential Early Partners
You do not need a full legal team, but you do need a lawyer early. An early consultation with an IP attorney can clarify your rights, guide your filing process (e.g. provisional patents), and help you avoid costly missteps.
Do this before sharing your idea publicly, including in academic presentations, pitch competitions, or even on social media. Public disclosure can start a clock ticking for application to protect your IP.
3. Build a Founding Team with Intent
Think of your startup team like a long-term relationship: you’re committing to build something together through uncertainty, tension, and change.
Strong early-stage teams often include:
- The Visionary – understands the clinical need and vision
- The Builder – engineer, developer, or designer
- The Doer – project manager or operations lead
Before forming a company, clearly define:
- Ownership (equity percentages)
- Roles and responsibilities
- Time commitments
- What happens if someone exits
Have these discussions early and document your agreements. Avoid informal “handshake” deals that can lead to serious disputes later.
4. You Don’t Need to Know Everything on Day One
You do not need to know how to write code, build a prototype, or get FDA clearance on day one. Successful innovators are humble learners. Use a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), a simple, functional version of your idea, to test assumptions and gather feedback. Iterate based on what you learn. Do not chase perfection; pursue progress. Consider using online accelerators like Y Combinator’s startup school or AGA’s Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
5. Incubators: Use them Strategically
Incubators can offer mentorship, seed funding, legal support, and technical resources, but they vary widely in value (see Table 1). Many may want equity, and not all offer when you truly need.
Ask Yourself:
- Do I need technical help, business mentorship, or just accountability?
- What does this incubator offer in terms of IP protection, exposure, and connections?
- Do I understand the equity trade-off?
- What services and funding do they provide?
- Do they take equity? How much and when?
- What’s their track record with similar ventures?
- Are their incentives aligned with your vision?
6. Academic Institutions: Partners or Pitfalls?
Universities can provide credibility, resources, and early funding through their tech transfer office (TTO).
Key Questions to Ask:
- Will my IP be managed by the TTO?
- How much say do I have in licensing decisions?
- Are there royalty-sharing agreements in place?
- Can I form a startup while employed here?
You may need to negotiate if you want to commercialize your idea independently.
7. Do it for Purpose, Not Payday
Most founders end up owning only a small percentage of their company by the time a product reaches the market. Do not expect to get rich. Do it because it solves a problem you care about. If it happens to come with a nice paycheck, then that is an added bonus.
Your clinical training and insight give you a unique edge. You already know what’s broken. Use that as your compass.
Conclusion
Innovation isn’t about brilliance, it’s about curiosity, structure, and tenacity (see Table 2). Start small. Protect your work. Choose the right partners. Most importantly, stay anchored in your mission to make GI care better.
Dr. Muratore is based at UNC Rex Digestive Health, Raleigh, North Carolina. She has no conflicts related to this article. Dr. Wechsler is based at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. She holds a patent assigned to Trustees of Dartmouth College. Dr. Shah is based at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan. He consults for Ardelyx, Laborie, Neuraxis, Salix, Sanofi, and Takeda and holds a patent with the Regents of the University of Michigan.