User login
MASH: Experts Offer Noninvasive Cutoffs for Prescribing Resmetirom
This guidance document allows clinicians to use a variety of NITs to start and monitor resmetirom therapy, precluding the need for a biopsy, lead author Mazen Noureddin, MD, of Houston Research Institute, Houston Methodist Hospital in Texas, and colleagues reported.
“The recent conditional approval by the [Food and Drug Administration] of resmetirom ... presents a much-anticipated therapeutic option for patients with noncirrhotic advanced MASH,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
However, the approval also “presents important challenges,” they noted, “including how to noninvasively identify patients with fibrosis stages 2-3, and how to exclude patients with more advanced disease who should not be treated until further data emerge on the use of resmetirom in this population.”
To help identify which patients should get this new intervention, Noureddin and colleagues considered benchmarks from published literature, and conducted a post hoc analysis of phase 3 MASTERO-NASH trial data. Trial enrollment required at least three cardiometabolic risk factors and a vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) prescreening within the past 3 months. The population included 888 patients with F2 or F3 disease.
Recommendations were split into three categories: treat with resmetirom, consider treating with resmetirom, and do not treat with resmetirom.
The recommendation to treat calls for a VCTE of 10-15 kPa, a magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of 3.3-4.2 kPa, or an Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score of 9.2-10.4, with the caveat that an ELF score below 9.8 requires a second NIT for confirmation. Alternatively, a positive composite score such as FibroScan–aspartate aminotransferase (FAST), MRI–AST (MAST), or MRE + Fibrosis-4 (MEFIB) may serve as grounds for treatment. For any of the previous, platelets must concurrently be at least 140 with no evidence of portal hypertension.
The recommendation to consider treatment depends upon a VCTE of 15.1-19.9 kPa, an MRE of 4.3-4.9 kPa, an ELF score of 10.5-11.3, or positive FAST, MAST, or MEFIB. Again, these require a concurrent platelet count of 140 and no portal hypertension.
Finally, patients should not be treated with resmetirom if they have a VCTE of 20 kPa or greater, an MRE of 5 kPa or greater, and an ELF score greater than 11.3.
Noureddin and colleagues also offered guidance on monitoring strategies, including follow-up at 3, 6, and 12 months.
At 3 months, the focus should be safety, including screening for drug-related liver injury and other adverse events that warrant cessation.
At 6 months, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels, VCTE, or MRI–proton density fat fraction (PDFF) tests can indicate early response, but treatment should generally continue regardless of results.
At 12 months, efficacy can be fully evaluated. ALT normalization, or improvement of more than 17 IU/L or more than 20%, along with a 30% or greater drop in VCTE, or at least 30% drop in liver fat on MRI-PDFF, serve as grounds for continuation.
Noureddin and colleagues noted that ALT improvement should be paired with corresponding improvements in imaging, such as a 30% reduction in MRI-PDFF. Even if ALT levels do not improve, a 30% or greater reduction in MRI-PDFF can still indicate a positive response; however, VCTE alone may not be sufficient to fully assess treatment response.
“Emerging data, particularly regarding the noninvasive assessment of treatment response, are likely to further modify patient selection, safety signals, and efficacy algorithms,” they concluded.This study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the John C. Martin Foundation, and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Shire, and others.
The approval of resmetirom as the first registered treatment for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) marks a historic moment. This expert panel recommendation document offers valuable guidance on patient selection for resmetirom treatment, monitoring responses, and managing potential side effects and drug-drug interactions. It also highlights the complexities of applying noninvasive tests for treatment initiation. Clinicians must identify MASH patients with significant or advanced fibrosis while avoiding those with cirrhosis and hepatic decompensation. Management will be simplified if the MAESTRO-OUTCOMES trial confirms that resmetirom is safe and effective for patients with compensated MASH cirrhosis.
The most reliable response biomarkers in the MAESTRO-NASH trial include reductions in MRI–proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) and serum alanine aminotransferase, despite MRI-PDFF being limited by cost and availability. Worsening liver stiffness measurement via vibration-controlled transient elastography is suggested as a stopping rule, although this is not supported by resmetirom trial data. Short-term increases in liver stiffness may yield false positives, so it is advisable to repeat or use alternative noninvasive tests before discontinuing treatment.
Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, MD, is Mok Hing Yiu Professor of Medicine at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, China. He reported his role as a consultant or advisory board member for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Echosens, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Inventiva, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sagimet Biosciences, TARGET PharmaSolutions, and Visirna; and a speaker for Abbott, AbbVie, Echosens, Gilead Sciences, Novo Nordisk, and Unilab. He has received a research grant from Gilead Sciences, and is the cofounder of Illuminatio Medical Technology.
The approval of resmetirom as the first registered treatment for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) marks a historic moment. This expert panel recommendation document offers valuable guidance on patient selection for resmetirom treatment, monitoring responses, and managing potential side effects and drug-drug interactions. It also highlights the complexities of applying noninvasive tests for treatment initiation. Clinicians must identify MASH patients with significant or advanced fibrosis while avoiding those with cirrhosis and hepatic decompensation. Management will be simplified if the MAESTRO-OUTCOMES trial confirms that resmetirom is safe and effective for patients with compensated MASH cirrhosis.
The most reliable response biomarkers in the MAESTRO-NASH trial include reductions in MRI–proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) and serum alanine aminotransferase, despite MRI-PDFF being limited by cost and availability. Worsening liver stiffness measurement via vibration-controlled transient elastography is suggested as a stopping rule, although this is not supported by resmetirom trial data. Short-term increases in liver stiffness may yield false positives, so it is advisable to repeat or use alternative noninvasive tests before discontinuing treatment.
Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, MD, is Mok Hing Yiu Professor of Medicine at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, China. He reported his role as a consultant or advisory board member for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Echosens, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Inventiva, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sagimet Biosciences, TARGET PharmaSolutions, and Visirna; and a speaker for Abbott, AbbVie, Echosens, Gilead Sciences, Novo Nordisk, and Unilab. He has received a research grant from Gilead Sciences, and is the cofounder of Illuminatio Medical Technology.
The approval of resmetirom as the first registered treatment for metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) marks a historic moment. This expert panel recommendation document offers valuable guidance on patient selection for resmetirom treatment, monitoring responses, and managing potential side effects and drug-drug interactions. It also highlights the complexities of applying noninvasive tests for treatment initiation. Clinicians must identify MASH patients with significant or advanced fibrosis while avoiding those with cirrhosis and hepatic decompensation. Management will be simplified if the MAESTRO-OUTCOMES trial confirms that resmetirom is safe and effective for patients with compensated MASH cirrhosis.
The most reliable response biomarkers in the MAESTRO-NASH trial include reductions in MRI–proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) and serum alanine aminotransferase, despite MRI-PDFF being limited by cost and availability. Worsening liver stiffness measurement via vibration-controlled transient elastography is suggested as a stopping rule, although this is not supported by resmetirom trial data. Short-term increases in liver stiffness may yield false positives, so it is advisable to repeat or use alternative noninvasive tests before discontinuing treatment.
Vincent Wai-Sun Wong, MD, is Mok Hing Yiu Professor of Medicine at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, China. He reported his role as a consultant or advisory board member for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Echosens, Eli Lilly, Gilead Sciences, Intercept, Inventiva, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sagimet Biosciences, TARGET PharmaSolutions, and Visirna; and a speaker for Abbott, AbbVie, Echosens, Gilead Sciences, Novo Nordisk, and Unilab. He has received a research grant from Gilead Sciences, and is the cofounder of Illuminatio Medical Technology.
This guidance document allows clinicians to use a variety of NITs to start and monitor resmetirom therapy, precluding the need for a biopsy, lead author Mazen Noureddin, MD, of Houston Research Institute, Houston Methodist Hospital in Texas, and colleagues reported.
“The recent conditional approval by the [Food and Drug Administration] of resmetirom ... presents a much-anticipated therapeutic option for patients with noncirrhotic advanced MASH,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
However, the approval also “presents important challenges,” they noted, “including how to noninvasively identify patients with fibrosis stages 2-3, and how to exclude patients with more advanced disease who should not be treated until further data emerge on the use of resmetirom in this population.”
To help identify which patients should get this new intervention, Noureddin and colleagues considered benchmarks from published literature, and conducted a post hoc analysis of phase 3 MASTERO-NASH trial data. Trial enrollment required at least three cardiometabolic risk factors and a vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) prescreening within the past 3 months. The population included 888 patients with F2 or F3 disease.
Recommendations were split into three categories: treat with resmetirom, consider treating with resmetirom, and do not treat with resmetirom.
The recommendation to treat calls for a VCTE of 10-15 kPa, a magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of 3.3-4.2 kPa, or an Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score of 9.2-10.4, with the caveat that an ELF score below 9.8 requires a second NIT for confirmation. Alternatively, a positive composite score such as FibroScan–aspartate aminotransferase (FAST), MRI–AST (MAST), or MRE + Fibrosis-4 (MEFIB) may serve as grounds for treatment. For any of the previous, platelets must concurrently be at least 140 with no evidence of portal hypertension.
The recommendation to consider treatment depends upon a VCTE of 15.1-19.9 kPa, an MRE of 4.3-4.9 kPa, an ELF score of 10.5-11.3, or positive FAST, MAST, or MEFIB. Again, these require a concurrent platelet count of 140 and no portal hypertension.
Finally, patients should not be treated with resmetirom if they have a VCTE of 20 kPa or greater, an MRE of 5 kPa or greater, and an ELF score greater than 11.3.
Noureddin and colleagues also offered guidance on monitoring strategies, including follow-up at 3, 6, and 12 months.
At 3 months, the focus should be safety, including screening for drug-related liver injury and other adverse events that warrant cessation.
At 6 months, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels, VCTE, or MRI–proton density fat fraction (PDFF) tests can indicate early response, but treatment should generally continue regardless of results.
At 12 months, efficacy can be fully evaluated. ALT normalization, or improvement of more than 17 IU/L or more than 20%, along with a 30% or greater drop in VCTE, or at least 30% drop in liver fat on MRI-PDFF, serve as grounds for continuation.
Noureddin and colleagues noted that ALT improvement should be paired with corresponding improvements in imaging, such as a 30% reduction in MRI-PDFF. Even if ALT levels do not improve, a 30% or greater reduction in MRI-PDFF can still indicate a positive response; however, VCTE alone may not be sufficient to fully assess treatment response.
“Emerging data, particularly regarding the noninvasive assessment of treatment response, are likely to further modify patient selection, safety signals, and efficacy algorithms,” they concluded.This study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the John C. Martin Foundation, and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Shire, and others.
This guidance document allows clinicians to use a variety of NITs to start and monitor resmetirom therapy, precluding the need for a biopsy, lead author Mazen Noureddin, MD, of Houston Research Institute, Houston Methodist Hospital in Texas, and colleagues reported.
“The recent conditional approval by the [Food and Drug Administration] of resmetirom ... presents a much-anticipated therapeutic option for patients with noncirrhotic advanced MASH,” the investigators wrote in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
However, the approval also “presents important challenges,” they noted, “including how to noninvasively identify patients with fibrosis stages 2-3, and how to exclude patients with more advanced disease who should not be treated until further data emerge on the use of resmetirom in this population.”
To help identify which patients should get this new intervention, Noureddin and colleagues considered benchmarks from published literature, and conducted a post hoc analysis of phase 3 MASTERO-NASH trial data. Trial enrollment required at least three cardiometabolic risk factors and a vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) prescreening within the past 3 months. The population included 888 patients with F2 or F3 disease.
Recommendations were split into three categories: treat with resmetirom, consider treating with resmetirom, and do not treat with resmetirom.
The recommendation to treat calls for a VCTE of 10-15 kPa, a magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) of 3.3-4.2 kPa, or an Enhanced Liver Fibrosis (ELF) score of 9.2-10.4, with the caveat that an ELF score below 9.8 requires a second NIT for confirmation. Alternatively, a positive composite score such as FibroScan–aspartate aminotransferase (FAST), MRI–AST (MAST), or MRE + Fibrosis-4 (MEFIB) may serve as grounds for treatment. For any of the previous, platelets must concurrently be at least 140 with no evidence of portal hypertension.
The recommendation to consider treatment depends upon a VCTE of 15.1-19.9 kPa, an MRE of 4.3-4.9 kPa, an ELF score of 10.5-11.3, or positive FAST, MAST, or MEFIB. Again, these require a concurrent platelet count of 140 and no portal hypertension.
Finally, patients should not be treated with resmetirom if they have a VCTE of 20 kPa or greater, an MRE of 5 kPa or greater, and an ELF score greater than 11.3.
Noureddin and colleagues also offered guidance on monitoring strategies, including follow-up at 3, 6, and 12 months.
At 3 months, the focus should be safety, including screening for drug-related liver injury and other adverse events that warrant cessation.
At 6 months, alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels, VCTE, or MRI–proton density fat fraction (PDFF) tests can indicate early response, but treatment should generally continue regardless of results.
At 12 months, efficacy can be fully evaluated. ALT normalization, or improvement of more than 17 IU/L or more than 20%, along with a 30% or greater drop in VCTE, or at least 30% drop in liver fat on MRI-PDFF, serve as grounds for continuation.
Noureddin and colleagues noted that ALT improvement should be paired with corresponding improvements in imaging, such as a 30% reduction in MRI-PDFF. Even if ALT levels do not improve, a 30% or greater reduction in MRI-PDFF can still indicate a positive response; however, VCTE alone may not be sufficient to fully assess treatment response.
“Emerging data, particularly regarding the noninvasive assessment of treatment response, are likely to further modify patient selection, safety signals, and efficacy algorithms,” they concluded.This study was supported by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, the John C. Martin Foundation, and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Shire, and others.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Can We Repurpose Obesity Drugs to Reverse Liver Disease?
Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) has become the most common liver disease worldwide, with a global prevalence of 32.4%. Its growth over the past three decades has occurred in tandem with increasing rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes — two cornerstones of MASLD.
Higher rates of MASLD and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) with fibrosis are present in adults with obesity and diabetes, noted Arun Sanyal, MD, professor and director of the Stravitz-Sanyal Institute for Liver Disease and Metabolic Health, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia.
The success surrounding the medications for obesity and type 2 diabetes, including glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), has sparked studies investigating whether they could also be an effective treatment for liver disease.
In particular, GLP-1 RAs help patients lose weight and/or control diabetes by mimicking the function of the gut hormone GLP-1, released in response to nutrient intake, and are able to increase insulin secretion and reduce glucagon secretion, delay gastric emptying, and reduce appetite and caloric intake.
The studies for MASLD are testing whether these functions will also work against liver disease, either directly or indirectly, through obesity and diabetes control. The early results are promising.
More Than One Risk Factor in Play
MASLD is defined by the presence of hepatic steatosis and at least one of five cardiometabolic risk factors: Overweight/obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia with either low-plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or high triglycerides, or treatment for these conditions.
It is a grim trajectory if the disease progresses to MASH, as the patient may accumulate hepatic fibrosis and go on to develop cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Typically, more than one risk factor is at play in MASLD, noted Adnan Said, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin.
“It most commonly occurs in the setting of weight gain and obesity, which are epidemics in the United States and worldwide, as well as the associated condition — metabolic syndrome — which goes along with obesity and includes type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and sleep apnea,” Said, a hepatology and gastroenterology professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, told this news organization.
The research surrounding MASLD is investigating GLP-1 RAs as single agents and in combination with other drugs.
Finding treatment is critical, as there is only one drug — resmetirom — approved for the treatment of MASH with moderate to advanced fibrosis. But because it’s not approved for earlier stages, a treatment gap exists. The drug also doesn’t produce weight loss, which is key to treating MASLD. And while GLP-1 RAs help patients with the weight loss that is critical to MASLD, they are only approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Single Agents
The GLP-1 RAs liraglutide and semaglutide, both approved for diabetes and weight loss, are being studied as single agents against liver disease, Said said.
“Their action in the setting of MASLD and MASH is primarily indirect, through systemic pathways, improving these conditions via weight loss, as well as by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing lipotoxicity,” he added.
One of the first trials of these agents for liver disease was in 2016. In that double-blind, randomized, 48-week clinical trial of liraglutide in patients with MASH and overweight, 39% of patients who received liraglutide had a resolution of MASH compared with only 9% of those who received placebo. Moreover, only 9% vs 36% of patients in the treatment vs placebo group had progression of fibrosis.
Since then, a 72-week phase 2 trial in patients with MASH, liver fibrosis (stages F1-F3), and overweight or obesity found that once-daily subcutaneous semaglutide (0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg) outperformed placebo on MASH resolution without worsening of fibrosis (36%-59% vs 17%) and on weight loss (5%-13% vs 1%), with the greatest benefits at the largest dose. However, neoplasms were reported in 15% of patients receiving semaglutide vs 8% of those receiving placebo.
A phase 1 trial involving patients with liver stiffness, steatosis, and overweight or obesity found significantly greater reductions in liver fat at 48 weeks with semaglutide vs placebo, as well as decreases in liver enzymes, body weight, and A1c. There was no significant difference in liver stiffness.
Furthermore, a meta-analysis of eight studies found that treatment with 24 weeks of semaglutide significantly improved liver enzymes, reduced liver stiffness, and improved metabolic parameters in patients with MASLD/MASH. The authors cautioned that gastrointestinal adverse effects “could be a major concern.”
Several studies have found other GLP-1 RAs, including exenatide and dulaglutide, have a beneficial impact on liver injury indices and liver steatosis.
A new retrospective observational study offers evidence that GLP-1 RAs may have a direct impact on MASLD, independent of weight loss. Among the 28% of patients with type 2 diabetes and MASLD who received a GLP-1 RA, there was a significant reduction not only in body mass index but also in A1c, liver enzymes, and controlled attenuation parameter scores. A beneficial impact on liver parameters was observed even in patients who didn’t lose weight. While there was no difference in liver stiffness measurement, the median 60-month follow-up time may not have been long enough to capture such changes.
Another study indicated that the apparent benefits of GLP-1 RAs, in this case semaglutide, may not extend to patients whose disease has progressed to cirrhosis.
Dual and Triple Mechanisms of Action
Newer agents with double or triple mechanisms of action appear to have a more direct effect on the liver.
“Dual agents may have an added effect by improving MASLD directly through adipose regulation and thermogenesis, thereby improving fibrosis,” Said said.
An example is tirzepatide, a GLP-1 RA and an agonist of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Like GLP-1, GIP is an incretin. When used together as co-agonists, GLP-1 and GIP have been shown to increase insulin and glucagonostatic response and may work synergistically.
A new phase 2 trial that randomly assigned patients with biopsy-confirmed MASH and moderate or severe fibrosis to receive either once-weekly subcutaneous tirzepatide at one of three doses (5, 10, or 15 mg) or placebo found that tirzepatide at each dosage outperformed placebo in resolution of MASH without worsening of fibrosis.
“These findings were encouraging,” Said said. “We’ll see if the results continue into phase 3 trials.”
The combination of GLP-1 RAs with glucagon (GCG) receptor agonists also has garnered interest.
In a phase 2 trial, adults with biopsy-confirmed MASH and fibrosis stages F1-F3 were randomly assigned to receive either one of three doses of the GLP-1/GCG RA survodutide (2.4, 4.8, or 6 mg) or placebo. Survodutide at each dose was found to be superior to placebo in improving MASH without the worsening of fibrosis, reducing liver fat content by at least 30%, and decreasing liver fibrosis by at least one stage, with the 4.8-mg dose showing the best performance for each measure. However, adverse events, including nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting, were more frequent with survodutide than with placebo.
Trials of triple-action agents (GLP-1/GIP/GCG RAs) are underway too.
The hope is the triple agonists could deliver greater reduction in hepatic fat in patients with MASLD, Sanyal said.
Sanyal further noted that a reduction in liver fat is important, citing a meta-analysis that showed ≥ 30% relative decline in liver fat is associated with higher odds of histologic response and MASH resolution.
Sanyal pointed to efocipegtrutide (HM15211), a GLP-1/GIP/GCG RA, which demonstrated significant liver fat reduction after 12 weeks in patients with MASLD in a phase 1b/2a randomized, placebo-controlled trial and is now in phase 2 development.
Another example is retatrutide (LY3437943), a once-weekly injectable, that was associated with up to a 24.2% reduction in body weight at 48 weeks, compared with 2.1% with placebo, in a phase 2 trial involving patients with obesity.
A sub-study assessed the mean relative change from baseline in liver fat at 24 weeks. These participants, who also had MASLD and ≥ 10% of liver fat content, were randomly assigned to receive either retatrutide in one of four doses (1, 4, 8, or 12 mg) or placebo for 48 weeks. All doses of retatrutide showed significantly greater reduction in liver fat content compared with placebo in weeks 24-48, with a mean relative liver fat reduction > 80% at the two higher doses. Moreover, ≥ 80% of participants on the higher retatrutide doses experienced ≥ 70% reduction in liver fat at 48 weeks, compared with 0% reduction in those on placebo, and hepatic steatosis resolved in > 85% of these participants.
This space “continues to evolve at a rapid rate,” Sanyal said. For example, oral dual-action agents are under development.
Obstacles and Warnings
Sanyal warned that GLP-1 RAs can cause nausea, so they have to be introduced at a low dose and slowly titrated upward. They should be used with caution in people with a history of multiple endocrine neoplasia. There is also a small but increased risk for gallstone formation and gallstone-induced pancreatitis with rapid weight loss.
GLP-1 RAs may increase the risk for suicidal ideation, with the authors of a recent study calling for “urgent clarification” regarding this possibility.
Following reports of suicidality submitted through its Adverse Events Reporting System, the FDA concluded that it could find no causal relationship between these agents and increased risk for suicidal ideation but also that it could not “definitively rule out that a small risk may exist” and would continue to investigate.
Access to GLP-1 RAs is an obstacle as well. Semaglutide continues to be on the FDA’s shortage list.
“This is improving, but there are still issues around getting approval from insurance companies,” Sanyal said.
Many patients discontinue use because of tolerability or access issues, which is problematic because most regain the weight they had lost while on the medication.
“Right now, we see GLP-1 RAs as a long-term therapeutic commitment, but there is a lot of research interest in figuring out if there’s a more modest benefit — almost an induction-remission maintenance approach to weight loss,” Sanyal said. These are “evolving trends,” and it’s unclear how they will unfold.
“As of now, you have to decide that if you’re putting your patient on these medications, they will have to take them on a long-term basis and include that consideration in your risk-benefit analysis, together with any concerns about adverse effects,” he said.
Sanyal reported consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk. Said received research support from Exact Sciences, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Mallinckrodt.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) has become the most common liver disease worldwide, with a global prevalence of 32.4%. Its growth over the past three decades has occurred in tandem with increasing rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes — two cornerstones of MASLD.
Higher rates of MASLD and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) with fibrosis are present in adults with obesity and diabetes, noted Arun Sanyal, MD, professor and director of the Stravitz-Sanyal Institute for Liver Disease and Metabolic Health, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia.
The success surrounding the medications for obesity and type 2 diabetes, including glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), has sparked studies investigating whether they could also be an effective treatment for liver disease.
In particular, GLP-1 RAs help patients lose weight and/or control diabetes by mimicking the function of the gut hormone GLP-1, released in response to nutrient intake, and are able to increase insulin secretion and reduce glucagon secretion, delay gastric emptying, and reduce appetite and caloric intake.
The studies for MASLD are testing whether these functions will also work against liver disease, either directly or indirectly, through obesity and diabetes control. The early results are promising.
More Than One Risk Factor in Play
MASLD is defined by the presence of hepatic steatosis and at least one of five cardiometabolic risk factors: Overweight/obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia with either low-plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or high triglycerides, or treatment for these conditions.
It is a grim trajectory if the disease progresses to MASH, as the patient may accumulate hepatic fibrosis and go on to develop cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Typically, more than one risk factor is at play in MASLD, noted Adnan Said, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin.
“It most commonly occurs in the setting of weight gain and obesity, which are epidemics in the United States and worldwide, as well as the associated condition — metabolic syndrome — which goes along with obesity and includes type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and sleep apnea,” Said, a hepatology and gastroenterology professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, told this news organization.
The research surrounding MASLD is investigating GLP-1 RAs as single agents and in combination with other drugs.
Finding treatment is critical, as there is only one drug — resmetirom — approved for the treatment of MASH with moderate to advanced fibrosis. But because it’s not approved for earlier stages, a treatment gap exists. The drug also doesn’t produce weight loss, which is key to treating MASLD. And while GLP-1 RAs help patients with the weight loss that is critical to MASLD, they are only approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Single Agents
The GLP-1 RAs liraglutide and semaglutide, both approved for diabetes and weight loss, are being studied as single agents against liver disease, Said said.
“Their action in the setting of MASLD and MASH is primarily indirect, through systemic pathways, improving these conditions via weight loss, as well as by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing lipotoxicity,” he added.
One of the first trials of these agents for liver disease was in 2016. In that double-blind, randomized, 48-week clinical trial of liraglutide in patients with MASH and overweight, 39% of patients who received liraglutide had a resolution of MASH compared with only 9% of those who received placebo. Moreover, only 9% vs 36% of patients in the treatment vs placebo group had progression of fibrosis.
Since then, a 72-week phase 2 trial in patients with MASH, liver fibrosis (stages F1-F3), and overweight or obesity found that once-daily subcutaneous semaglutide (0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg) outperformed placebo on MASH resolution without worsening of fibrosis (36%-59% vs 17%) and on weight loss (5%-13% vs 1%), with the greatest benefits at the largest dose. However, neoplasms were reported in 15% of patients receiving semaglutide vs 8% of those receiving placebo.
A phase 1 trial involving patients with liver stiffness, steatosis, and overweight or obesity found significantly greater reductions in liver fat at 48 weeks with semaglutide vs placebo, as well as decreases in liver enzymes, body weight, and A1c. There was no significant difference in liver stiffness.
Furthermore, a meta-analysis of eight studies found that treatment with 24 weeks of semaglutide significantly improved liver enzymes, reduced liver stiffness, and improved metabolic parameters in patients with MASLD/MASH. The authors cautioned that gastrointestinal adverse effects “could be a major concern.”
Several studies have found other GLP-1 RAs, including exenatide and dulaglutide, have a beneficial impact on liver injury indices and liver steatosis.
A new retrospective observational study offers evidence that GLP-1 RAs may have a direct impact on MASLD, independent of weight loss. Among the 28% of patients with type 2 diabetes and MASLD who received a GLP-1 RA, there was a significant reduction not only in body mass index but also in A1c, liver enzymes, and controlled attenuation parameter scores. A beneficial impact on liver parameters was observed even in patients who didn’t lose weight. While there was no difference in liver stiffness measurement, the median 60-month follow-up time may not have been long enough to capture such changes.
Another study indicated that the apparent benefits of GLP-1 RAs, in this case semaglutide, may not extend to patients whose disease has progressed to cirrhosis.
Dual and Triple Mechanisms of Action
Newer agents with double or triple mechanisms of action appear to have a more direct effect on the liver.
“Dual agents may have an added effect by improving MASLD directly through adipose regulation and thermogenesis, thereby improving fibrosis,” Said said.
An example is tirzepatide, a GLP-1 RA and an agonist of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Like GLP-1, GIP is an incretin. When used together as co-agonists, GLP-1 and GIP have been shown to increase insulin and glucagonostatic response and may work synergistically.
A new phase 2 trial that randomly assigned patients with biopsy-confirmed MASH and moderate or severe fibrosis to receive either once-weekly subcutaneous tirzepatide at one of three doses (5, 10, or 15 mg) or placebo found that tirzepatide at each dosage outperformed placebo in resolution of MASH without worsening of fibrosis.
“These findings were encouraging,” Said said. “We’ll see if the results continue into phase 3 trials.”
The combination of GLP-1 RAs with glucagon (GCG) receptor agonists also has garnered interest.
In a phase 2 trial, adults with biopsy-confirmed MASH and fibrosis stages F1-F3 were randomly assigned to receive either one of three doses of the GLP-1/GCG RA survodutide (2.4, 4.8, or 6 mg) or placebo. Survodutide at each dose was found to be superior to placebo in improving MASH without the worsening of fibrosis, reducing liver fat content by at least 30%, and decreasing liver fibrosis by at least one stage, with the 4.8-mg dose showing the best performance for each measure. However, adverse events, including nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting, were more frequent with survodutide than with placebo.
Trials of triple-action agents (GLP-1/GIP/GCG RAs) are underway too.
The hope is the triple agonists could deliver greater reduction in hepatic fat in patients with MASLD, Sanyal said.
Sanyal further noted that a reduction in liver fat is important, citing a meta-analysis that showed ≥ 30% relative decline in liver fat is associated with higher odds of histologic response and MASH resolution.
Sanyal pointed to efocipegtrutide (HM15211), a GLP-1/GIP/GCG RA, which demonstrated significant liver fat reduction after 12 weeks in patients with MASLD in a phase 1b/2a randomized, placebo-controlled trial and is now in phase 2 development.
Another example is retatrutide (LY3437943), a once-weekly injectable, that was associated with up to a 24.2% reduction in body weight at 48 weeks, compared with 2.1% with placebo, in a phase 2 trial involving patients with obesity.
A sub-study assessed the mean relative change from baseline in liver fat at 24 weeks. These participants, who also had MASLD and ≥ 10% of liver fat content, were randomly assigned to receive either retatrutide in one of four doses (1, 4, 8, or 12 mg) or placebo for 48 weeks. All doses of retatrutide showed significantly greater reduction in liver fat content compared with placebo in weeks 24-48, with a mean relative liver fat reduction > 80% at the two higher doses. Moreover, ≥ 80% of participants on the higher retatrutide doses experienced ≥ 70% reduction in liver fat at 48 weeks, compared with 0% reduction in those on placebo, and hepatic steatosis resolved in > 85% of these participants.
This space “continues to evolve at a rapid rate,” Sanyal said. For example, oral dual-action agents are under development.
Obstacles and Warnings
Sanyal warned that GLP-1 RAs can cause nausea, so they have to be introduced at a low dose and slowly titrated upward. They should be used with caution in people with a history of multiple endocrine neoplasia. There is also a small but increased risk for gallstone formation and gallstone-induced pancreatitis with rapid weight loss.
GLP-1 RAs may increase the risk for suicidal ideation, with the authors of a recent study calling for “urgent clarification” regarding this possibility.
Following reports of suicidality submitted through its Adverse Events Reporting System, the FDA concluded that it could find no causal relationship between these agents and increased risk for suicidal ideation but also that it could not “definitively rule out that a small risk may exist” and would continue to investigate.
Access to GLP-1 RAs is an obstacle as well. Semaglutide continues to be on the FDA’s shortage list.
“This is improving, but there are still issues around getting approval from insurance companies,” Sanyal said.
Many patients discontinue use because of tolerability or access issues, which is problematic because most regain the weight they had lost while on the medication.
“Right now, we see GLP-1 RAs as a long-term therapeutic commitment, but there is a lot of research interest in figuring out if there’s a more modest benefit — almost an induction-remission maintenance approach to weight loss,” Sanyal said. These are “evolving trends,” and it’s unclear how they will unfold.
“As of now, you have to decide that if you’re putting your patient on these medications, they will have to take them on a long-term basis and include that consideration in your risk-benefit analysis, together with any concerns about adverse effects,” he said.
Sanyal reported consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk. Said received research support from Exact Sciences, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Mallinckrodt.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) has become the most common liver disease worldwide, with a global prevalence of 32.4%. Its growth over the past three decades has occurred in tandem with increasing rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes — two cornerstones of MASLD.
Higher rates of MASLD and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis (MASH) with fibrosis are present in adults with obesity and diabetes, noted Arun Sanyal, MD, professor and director of the Stravitz-Sanyal Institute for Liver Disease and Metabolic Health, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia.
The success surrounding the medications for obesity and type 2 diabetes, including glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), has sparked studies investigating whether they could also be an effective treatment for liver disease.
In particular, GLP-1 RAs help patients lose weight and/or control diabetes by mimicking the function of the gut hormone GLP-1, released in response to nutrient intake, and are able to increase insulin secretion and reduce glucagon secretion, delay gastric emptying, and reduce appetite and caloric intake.
The studies for MASLD are testing whether these functions will also work against liver disease, either directly or indirectly, through obesity and diabetes control. The early results are promising.
More Than One Risk Factor in Play
MASLD is defined by the presence of hepatic steatosis and at least one of five cardiometabolic risk factors: Overweight/obesity, hypertension, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia with either low-plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or high triglycerides, or treatment for these conditions.
It is a grim trajectory if the disease progresses to MASH, as the patient may accumulate hepatic fibrosis and go on to develop cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Typically, more than one risk factor is at play in MASLD, noted Adnan Said, MD, chief of the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at the William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital, Madison, Wisconsin.
“It most commonly occurs in the setting of weight gain and obesity, which are epidemics in the United States and worldwide, as well as the associated condition — metabolic syndrome — which goes along with obesity and includes type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and sleep apnea,” Said, a hepatology and gastroenterology professor at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, told this news organization.
The research surrounding MASLD is investigating GLP-1 RAs as single agents and in combination with other drugs.
Finding treatment is critical, as there is only one drug — resmetirom — approved for the treatment of MASH with moderate to advanced fibrosis. But because it’s not approved for earlier stages, a treatment gap exists. The drug also doesn’t produce weight loss, which is key to treating MASLD. And while GLP-1 RAs help patients with the weight loss that is critical to MASLD, they are only approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Single Agents
The GLP-1 RAs liraglutide and semaglutide, both approved for diabetes and weight loss, are being studied as single agents against liver disease, Said said.
“Their action in the setting of MASLD and MASH is primarily indirect, through systemic pathways, improving these conditions via weight loss, as well as by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing lipotoxicity,” he added.
One of the first trials of these agents for liver disease was in 2016. In that double-blind, randomized, 48-week clinical trial of liraglutide in patients with MASH and overweight, 39% of patients who received liraglutide had a resolution of MASH compared with only 9% of those who received placebo. Moreover, only 9% vs 36% of patients in the treatment vs placebo group had progression of fibrosis.
Since then, a 72-week phase 2 trial in patients with MASH, liver fibrosis (stages F1-F3), and overweight or obesity found that once-daily subcutaneous semaglutide (0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg) outperformed placebo on MASH resolution without worsening of fibrosis (36%-59% vs 17%) and on weight loss (5%-13% vs 1%), with the greatest benefits at the largest dose. However, neoplasms were reported in 15% of patients receiving semaglutide vs 8% of those receiving placebo.
A phase 1 trial involving patients with liver stiffness, steatosis, and overweight or obesity found significantly greater reductions in liver fat at 48 weeks with semaglutide vs placebo, as well as decreases in liver enzymes, body weight, and A1c. There was no significant difference in liver stiffness.
Furthermore, a meta-analysis of eight studies found that treatment with 24 weeks of semaglutide significantly improved liver enzymes, reduced liver stiffness, and improved metabolic parameters in patients with MASLD/MASH. The authors cautioned that gastrointestinal adverse effects “could be a major concern.”
Several studies have found other GLP-1 RAs, including exenatide and dulaglutide, have a beneficial impact on liver injury indices and liver steatosis.
A new retrospective observational study offers evidence that GLP-1 RAs may have a direct impact on MASLD, independent of weight loss. Among the 28% of patients with type 2 diabetes and MASLD who received a GLP-1 RA, there was a significant reduction not only in body mass index but also in A1c, liver enzymes, and controlled attenuation parameter scores. A beneficial impact on liver parameters was observed even in patients who didn’t lose weight. While there was no difference in liver stiffness measurement, the median 60-month follow-up time may not have been long enough to capture such changes.
Another study indicated that the apparent benefits of GLP-1 RAs, in this case semaglutide, may not extend to patients whose disease has progressed to cirrhosis.
Dual and Triple Mechanisms of Action
Newer agents with double or triple mechanisms of action appear to have a more direct effect on the liver.
“Dual agents may have an added effect by improving MASLD directly through adipose regulation and thermogenesis, thereby improving fibrosis,” Said said.
An example is tirzepatide, a GLP-1 RA and an agonist of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Like GLP-1, GIP is an incretin. When used together as co-agonists, GLP-1 and GIP have been shown to increase insulin and glucagonostatic response and may work synergistically.
A new phase 2 trial that randomly assigned patients with biopsy-confirmed MASH and moderate or severe fibrosis to receive either once-weekly subcutaneous tirzepatide at one of three doses (5, 10, or 15 mg) or placebo found that tirzepatide at each dosage outperformed placebo in resolution of MASH without worsening of fibrosis.
“These findings were encouraging,” Said said. “We’ll see if the results continue into phase 3 trials.”
The combination of GLP-1 RAs with glucagon (GCG) receptor agonists also has garnered interest.
In a phase 2 trial, adults with biopsy-confirmed MASH and fibrosis stages F1-F3 were randomly assigned to receive either one of three doses of the GLP-1/GCG RA survodutide (2.4, 4.8, or 6 mg) or placebo. Survodutide at each dose was found to be superior to placebo in improving MASH without the worsening of fibrosis, reducing liver fat content by at least 30%, and decreasing liver fibrosis by at least one stage, with the 4.8-mg dose showing the best performance for each measure. However, adverse events, including nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting, were more frequent with survodutide than with placebo.
Trials of triple-action agents (GLP-1/GIP/GCG RAs) are underway too.
The hope is the triple agonists could deliver greater reduction in hepatic fat in patients with MASLD, Sanyal said.
Sanyal further noted that a reduction in liver fat is important, citing a meta-analysis that showed ≥ 30% relative decline in liver fat is associated with higher odds of histologic response and MASH resolution.
Sanyal pointed to efocipegtrutide (HM15211), a GLP-1/GIP/GCG RA, which demonstrated significant liver fat reduction after 12 weeks in patients with MASLD in a phase 1b/2a randomized, placebo-controlled trial and is now in phase 2 development.
Another example is retatrutide (LY3437943), a once-weekly injectable, that was associated with up to a 24.2% reduction in body weight at 48 weeks, compared with 2.1% with placebo, in a phase 2 trial involving patients with obesity.
A sub-study assessed the mean relative change from baseline in liver fat at 24 weeks. These participants, who also had MASLD and ≥ 10% of liver fat content, were randomly assigned to receive either retatrutide in one of four doses (1, 4, 8, or 12 mg) or placebo for 48 weeks. All doses of retatrutide showed significantly greater reduction in liver fat content compared with placebo in weeks 24-48, with a mean relative liver fat reduction > 80% at the two higher doses. Moreover, ≥ 80% of participants on the higher retatrutide doses experienced ≥ 70% reduction in liver fat at 48 weeks, compared with 0% reduction in those on placebo, and hepatic steatosis resolved in > 85% of these participants.
This space “continues to evolve at a rapid rate,” Sanyal said. For example, oral dual-action agents are under development.
Obstacles and Warnings
Sanyal warned that GLP-1 RAs can cause nausea, so they have to be introduced at a low dose and slowly titrated upward. They should be used with caution in people with a history of multiple endocrine neoplasia. There is also a small but increased risk for gallstone formation and gallstone-induced pancreatitis with rapid weight loss.
GLP-1 RAs may increase the risk for suicidal ideation, with the authors of a recent study calling for “urgent clarification” regarding this possibility.
Following reports of suicidality submitted through its Adverse Events Reporting System, the FDA concluded that it could find no causal relationship between these agents and increased risk for suicidal ideation but also that it could not “definitively rule out that a small risk may exist” and would continue to investigate.
Access to GLP-1 RAs is an obstacle as well. Semaglutide continues to be on the FDA’s shortage list.
“This is improving, but there are still issues around getting approval from insurance companies,” Sanyal said.
Many patients discontinue use because of tolerability or access issues, which is problematic because most regain the weight they had lost while on the medication.
“Right now, we see GLP-1 RAs as a long-term therapeutic commitment, but there is a lot of research interest in figuring out if there’s a more modest benefit — almost an induction-remission maintenance approach to weight loss,” Sanyal said. These are “evolving trends,” and it’s unclear how they will unfold.
“As of now, you have to decide that if you’re putting your patient on these medications, they will have to take them on a long-term basis and include that consideration in your risk-benefit analysis, together with any concerns about adverse effects,” he said.
Sanyal reported consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk. Said received research support from Exact Sciences, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Mallinckrodt.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lichenoid Drug Eruption Secondary to Apalutamide Treatment
To the Editor:
Lichenoid drug eruptions are lichen planus–like hypersensitivity reactions induced by medications. These reactions are rare but cause irritation to the skin, as extreme pruritus is common. One review of 300 consecutive cases of drug eruptions submitted to dermatopathology revealed that 12% of cases were classified as lichenoid drug reactions.1 Lichenoid dermatitis is characterized by extremely pruritic, scaly, eczematous or psoriasiform papules, often along the extensor surfaces and trunk.2 The pruritic nature of the rash can negatively impact quality of life. Treatment typically involves discontinuation of the offending medication, although complete resolution can take months, even after the drug is stopped. Although there have been some data suggesting that topical and/or oral corticosteroids can help with resolution, the rash can persist even with steroid treatment.2
The histopathologic findings of lichenoid drug eruptions show lichen planus–like changes such as hyperkeratosis, irregular acanthosis, and lichenoid interface dermatitis. Accordingly, idiopathic lichen planus is an important differential diagnosis for lichenoid drug eruptions; however, compared to idiopathic lichen planus, lichenoid drug eruptions are more likely to be associated with eosinophils and parakeratosis.1,3 In some cases, the histopathologic distinction between the 2 conditions is impossible, and clinical history needs to be considered to make a diagnosis.1 Drugs known to cause lichenoid drug reactions more commonly include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazides, gold, penicillamine, and antimalarials.2 Lichenoid drug eruptions also have been documented in patients taking the second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide, which is used for the treatment of prostate cancer.4 More recently, the newer second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist apalutamide has been implicated in several cases of lichenoid drug eruptions.5,6
We present a case of an apalutamide-induced lichenoid drug eruption that was resistant to dose reduction and required discontinuation of treatment due to the negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. Once the rash resolved, the patient transitioned to enzalutamide without any adverse events (AEs).
A 72-year-old man with a history of metastatic prostate cancer (stage IVB) presented to the dermatology clinic with a 4-month history of a dry itchy rash on the face, chest, back, and legs that had developed 2 to 3 months after oncology started him on apalutamide. The patient initially received apalutamide 240 mg/d, which was reduced by his oncologist 3 months later to 180 mg/d following the appearance of the rash. Then apalutamide was held as he awaited improvement of the rash.
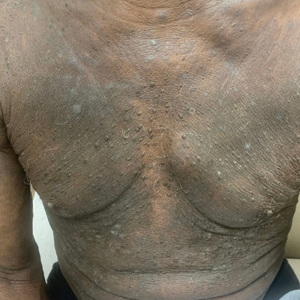
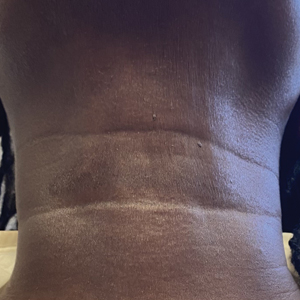
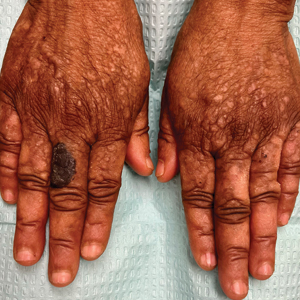
One week after the apalutamide was held, the patient presented to dermatology. He reported that he had tried over-the-counter ammonium lactate 12% lotion twice daily when the rash first developed without improvement. When the apalutamide was held, oncology prescribed mupirocin ointment 2% 3 times daily which yielded minimal relief. On physical examination, widespread lichenified papules and plaques were noted on the face, chest, back, and legs (Figure 1). Dermatology initially prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen of the upper back revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with numerous eosinophils compatible with a lichenoid hypersensitivity reaction (Figure 2). Considering the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of lichenoid drug eruption secondary to apalutamide treatment was made.
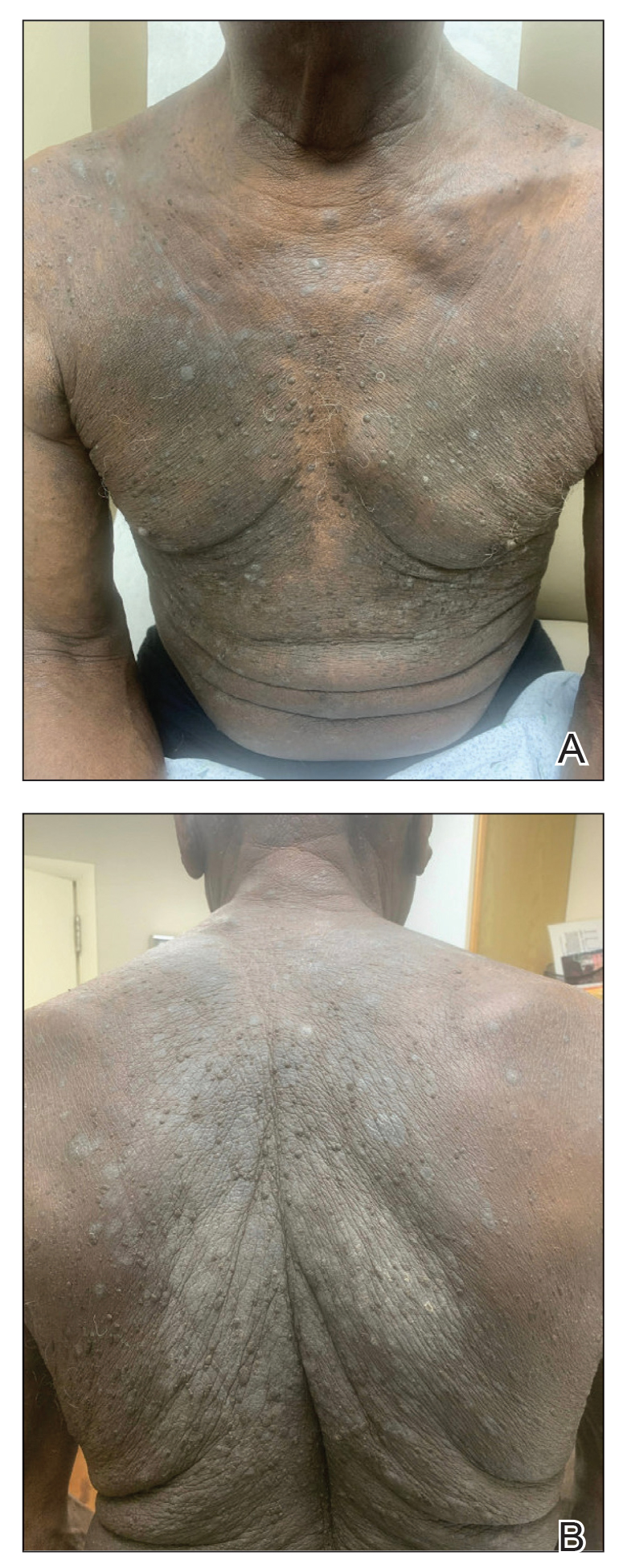
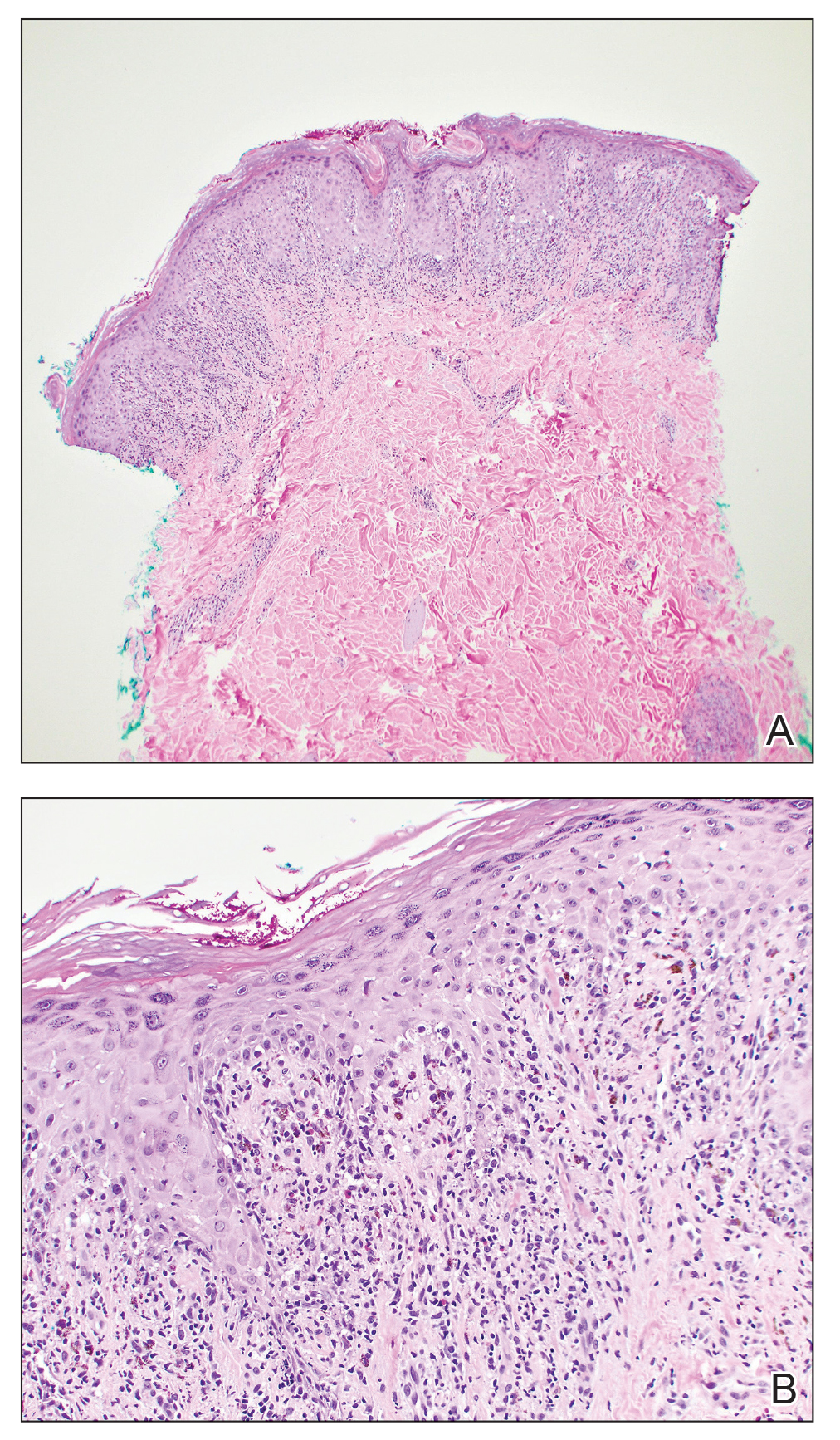
Two weeks after discontinuation of the medication, the rash improved, and the patient restarted apalutamide at a dosage of 120 mg/d; however, the rash re-emerged within 1 month and was resistant to the triamcinolone ointment 0.1%. Apalutamide was again discontinued, and oncology switched the patient to enzalutamide 160 mg/d in an effort to find a medication the patient could better tolerate. Two months after starting enzalutamide, the patient had resolution of the rash and no further dermatologic complications.
Apalutamide is a second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist used in the treatment of nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC).7 It stops the spread and growth of prostate cancer cells by several different mechanisms, including competitively binding androgen receptors, preventing 5α-dihydrotestosterone from binding to androgen receptors, blocking androgen receptor nuclear translocation, impairing co-activator recruitment, and restraining androgen receptor DNA binding.7 The SPARTAN and TITAN phase 3 clinical trials demonstrated increased overall survival and time to progression with apalutamide in both nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC. In both trials, the rash was shown to be an AE more commonly associated with apalutamide than placebo.8,9
Until recently, the characteristics of apalutamide-induced drug rashes have not been well described. One literature review reported 6 cases of cutaneous apalutamide-induced drug eruptions.5 Four (66.7%) of these eruptions were maculopapular rashes, only 2 of which were histologically classified as lichenoid in nature. The other 2 eruptions were classified as toxic epidermal necrosis.5 Another study of 303 patients with prostate cancer who were treated with apalutamide recorded the frequency and time to onset of dermatologic AEs.6 Seventy-one (23.4%) of the patients had dermatologic AEs, and of those, only 20 (28.2%) had AEs that resulted in interruptions in apalutamide therapy (with only 5 [25.0%] requiring medication discontinuation). Thirty-two (45.1%) patients were managed with topical or oral corticosteroids or dose modification. In this study, histopathology was examined in 8 cases (one of which had 2 biopsies for a total of 9 biopsies), 7 of which were consistent with lichenoid interface dermatitis.6
Lichenoid interface dermatitis is a rare manifestation of an apalutamide-induced drug eruption and also has been reported secondary to treatment with enzalutamide, another second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist.4 Enzalutamide was the first second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of prostate cancer. It originally was approved only for metastatic CRPC after docetaxel therapy in 2012, then later was expanded to metastatic and nonmetastatic CRPC in 2012 and 2018, respectively, as well as metastatic CSPC in 2019.7 Because enzalutamide is from the same medication class as apalutamide and has been on the market longer for the treatment of nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC, it is not surprising that similar drug eruptions now are being reported secondary to apalutamide use as well.
It is important for providers to consider lichenoid drug eruptions in the differential diagnosis of pruritic rashes in patients taking second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide or enzalutamide. Although dose reduction or treatment discontinuation have been the standard of care for patients with extremely pruritic lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to these medications, these are not ideal because they are important for cancer treatment. Interestingly, after our patient’s apalutamide-induced rash resolved and he was switched to enzalutamide, he did not develop any AEs. Based on our patient’s experience, physicians could consider switching their patients to another drug of the same class, as they may be able tolerate that medication. More research is needed to determine how commonly patients tolerate a different second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist after not tolerating another medication from the same class.
- Weyers W, Metze D. Histopathology of drug eruptions—general criteria, common patterns, and differential diagnosis. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011;1:33-47. doi:10.5826/dpc.0101a09
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruption, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Thompson DF, Skaehill PA. Drug-induced lichen planus. Pharmacotherapy. 1994;14:561-571.
- Khan S, Saizan AL, O’Brien K, et al. Diffuse hyperpigmented lichenoid drug eruption secondary to enzalutamide. Curr Probl Cancer Case Rep. 2022;5:100135. doi:10.1016/j.cpccr.2021.100135
- Katayama H, Saeki H, Osada S-I. Maculopapular drug eruption caused by apalutamide: case report and review of the literature. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89:550-554. doi:10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-503
- Pan A, Reingold RE, Zhao JL, et al. Dermatologic adverse events in prostate cancer patients treated with the androgen receptor inhibitor apalutamide. J Urol. 2022;207:1010-1019. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002425
- Rajaram P, Rivera A, Muthima K, et al. Second-generation androgen receptor antagonists as hormonal therapeutics for three forms of prostate cancer. Molecules. 2020;25:2448. doi:10.3390/molecules25102448
- Smith MR, Saad F, Chowdhury S, et al. Apalutamide treatment and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1408-1418. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1715546
- Chi KN, Agarwal N, Bjartell A, et al. Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensative prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:13-24. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903307
To the Editor:
Lichenoid drug eruptions are lichen planus–like hypersensitivity reactions induced by medications. These reactions are rare but cause irritation to the skin, as extreme pruritus is common. One review of 300 consecutive cases of drug eruptions submitted to dermatopathology revealed that 12% of cases were classified as lichenoid drug reactions.1 Lichenoid dermatitis is characterized by extremely pruritic, scaly, eczematous or psoriasiform papules, often along the extensor surfaces and trunk.2 The pruritic nature of the rash can negatively impact quality of life. Treatment typically involves discontinuation of the offending medication, although complete resolution can take months, even after the drug is stopped. Although there have been some data suggesting that topical and/or oral corticosteroids can help with resolution, the rash can persist even with steroid treatment.2
The histopathologic findings of lichenoid drug eruptions show lichen planus–like changes such as hyperkeratosis, irregular acanthosis, and lichenoid interface dermatitis. Accordingly, idiopathic lichen planus is an important differential diagnosis for lichenoid drug eruptions; however, compared to idiopathic lichen planus, lichenoid drug eruptions are more likely to be associated with eosinophils and parakeratosis.1,3 In some cases, the histopathologic distinction between the 2 conditions is impossible, and clinical history needs to be considered to make a diagnosis.1 Drugs known to cause lichenoid drug reactions more commonly include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazides, gold, penicillamine, and antimalarials.2 Lichenoid drug eruptions also have been documented in patients taking the second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide, which is used for the treatment of prostate cancer.4 More recently, the newer second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist apalutamide has been implicated in several cases of lichenoid drug eruptions.5,6
We present a case of an apalutamide-induced lichenoid drug eruption that was resistant to dose reduction and required discontinuation of treatment due to the negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. Once the rash resolved, the patient transitioned to enzalutamide without any adverse events (AEs).
A 72-year-old man with a history of metastatic prostate cancer (stage IVB) presented to the dermatology clinic with a 4-month history of a dry itchy rash on the face, chest, back, and legs that had developed 2 to 3 months after oncology started him on apalutamide. The patient initially received apalutamide 240 mg/d, which was reduced by his oncologist 3 months later to 180 mg/d following the appearance of the rash. Then apalutamide was held as he awaited improvement of the rash.
One week after the apalutamide was held, the patient presented to dermatology. He reported that he had tried over-the-counter ammonium lactate 12% lotion twice daily when the rash first developed without improvement. When the apalutamide was held, oncology prescribed mupirocin ointment 2% 3 times daily which yielded minimal relief. On physical examination, widespread lichenified papules and plaques were noted on the face, chest, back, and legs (Figure 1). Dermatology initially prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen of the upper back revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with numerous eosinophils compatible with a lichenoid hypersensitivity reaction (Figure 2). Considering the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of lichenoid drug eruption secondary to apalutamide treatment was made.


Two weeks after discontinuation of the medication, the rash improved, and the patient restarted apalutamide at a dosage of 120 mg/d; however, the rash re-emerged within 1 month and was resistant to the triamcinolone ointment 0.1%. Apalutamide was again discontinued, and oncology switched the patient to enzalutamide 160 mg/d in an effort to find a medication the patient could better tolerate. Two months after starting enzalutamide, the patient had resolution of the rash and no further dermatologic complications.
Apalutamide is a second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist used in the treatment of nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC).7 It stops the spread and growth of prostate cancer cells by several different mechanisms, including competitively binding androgen receptors, preventing 5α-dihydrotestosterone from binding to androgen receptors, blocking androgen receptor nuclear translocation, impairing co-activator recruitment, and restraining androgen receptor DNA binding.7 The SPARTAN and TITAN phase 3 clinical trials demonstrated increased overall survival and time to progression with apalutamide in both nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC. In both trials, the rash was shown to be an AE more commonly associated with apalutamide than placebo.8,9
Until recently, the characteristics of apalutamide-induced drug rashes have not been well described. One literature review reported 6 cases of cutaneous apalutamide-induced drug eruptions.5 Four (66.7%) of these eruptions were maculopapular rashes, only 2 of which were histologically classified as lichenoid in nature. The other 2 eruptions were classified as toxic epidermal necrosis.5 Another study of 303 patients with prostate cancer who were treated with apalutamide recorded the frequency and time to onset of dermatologic AEs.6 Seventy-one (23.4%) of the patients had dermatologic AEs, and of those, only 20 (28.2%) had AEs that resulted in interruptions in apalutamide therapy (with only 5 [25.0%] requiring medication discontinuation). Thirty-two (45.1%) patients were managed with topical or oral corticosteroids or dose modification. In this study, histopathology was examined in 8 cases (one of which had 2 biopsies for a total of 9 biopsies), 7 of which were consistent with lichenoid interface dermatitis.6
Lichenoid interface dermatitis is a rare manifestation of an apalutamide-induced drug eruption and also has been reported secondary to treatment with enzalutamide, another second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist.4 Enzalutamide was the first second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of prostate cancer. It originally was approved only for metastatic CRPC after docetaxel therapy in 2012, then later was expanded to metastatic and nonmetastatic CRPC in 2012 and 2018, respectively, as well as metastatic CSPC in 2019.7 Because enzalutamide is from the same medication class as apalutamide and has been on the market longer for the treatment of nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC, it is not surprising that similar drug eruptions now are being reported secondary to apalutamide use as well.
It is important for providers to consider lichenoid drug eruptions in the differential diagnosis of pruritic rashes in patients taking second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide or enzalutamide. Although dose reduction or treatment discontinuation have been the standard of care for patients with extremely pruritic lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to these medications, these are not ideal because they are important for cancer treatment. Interestingly, after our patient’s apalutamide-induced rash resolved and he was switched to enzalutamide, he did not develop any AEs. Based on our patient’s experience, physicians could consider switching their patients to another drug of the same class, as they may be able tolerate that medication. More research is needed to determine how commonly patients tolerate a different second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist after not tolerating another medication from the same class.
To the Editor:
Lichenoid drug eruptions are lichen planus–like hypersensitivity reactions induced by medications. These reactions are rare but cause irritation to the skin, as extreme pruritus is common. One review of 300 consecutive cases of drug eruptions submitted to dermatopathology revealed that 12% of cases were classified as lichenoid drug reactions.1 Lichenoid dermatitis is characterized by extremely pruritic, scaly, eczematous or psoriasiform papules, often along the extensor surfaces and trunk.2 The pruritic nature of the rash can negatively impact quality of life. Treatment typically involves discontinuation of the offending medication, although complete resolution can take months, even after the drug is stopped. Although there have been some data suggesting that topical and/or oral corticosteroids can help with resolution, the rash can persist even with steroid treatment.2
The histopathologic findings of lichenoid drug eruptions show lichen planus–like changes such as hyperkeratosis, irregular acanthosis, and lichenoid interface dermatitis. Accordingly, idiopathic lichen planus is an important differential diagnosis for lichenoid drug eruptions; however, compared to idiopathic lichen planus, lichenoid drug eruptions are more likely to be associated with eosinophils and parakeratosis.1,3 In some cases, the histopathologic distinction between the 2 conditions is impossible, and clinical history needs to be considered to make a diagnosis.1 Drugs known to cause lichenoid drug reactions more commonly include angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, beta blockers, thiazides, gold, penicillamine, and antimalarials.2 Lichenoid drug eruptions also have been documented in patients taking the second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist enzalutamide, which is used for the treatment of prostate cancer.4 More recently, the newer second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist apalutamide has been implicated in several cases of lichenoid drug eruptions.5,6
We present a case of an apalutamide-induced lichenoid drug eruption that was resistant to dose reduction and required discontinuation of treatment due to the negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. Once the rash resolved, the patient transitioned to enzalutamide without any adverse events (AEs).
A 72-year-old man with a history of metastatic prostate cancer (stage IVB) presented to the dermatology clinic with a 4-month history of a dry itchy rash on the face, chest, back, and legs that had developed 2 to 3 months after oncology started him on apalutamide. The patient initially received apalutamide 240 mg/d, which was reduced by his oncologist 3 months later to 180 mg/d following the appearance of the rash. Then apalutamide was held as he awaited improvement of the rash.
One week after the apalutamide was held, the patient presented to dermatology. He reported that he had tried over-the-counter ammonium lactate 12% lotion twice daily when the rash first developed without improvement. When the apalutamide was held, oncology prescribed mupirocin ointment 2% 3 times daily which yielded minimal relief. On physical examination, widespread lichenified papules and plaques were noted on the face, chest, back, and legs (Figure 1). Dermatology initially prescribed triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily. A 4-mm punch biopsy specimen of the upper back revealed a lichenoid interface dermatitis with numerous eosinophils compatible with a lichenoid hypersensitivity reaction (Figure 2). Considering the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of lichenoid drug eruption secondary to apalutamide treatment was made.


Two weeks after discontinuation of the medication, the rash improved, and the patient restarted apalutamide at a dosage of 120 mg/d; however, the rash re-emerged within 1 month and was resistant to the triamcinolone ointment 0.1%. Apalutamide was again discontinued, and oncology switched the patient to enzalutamide 160 mg/d in an effort to find a medication the patient could better tolerate. Two months after starting enzalutamide, the patient had resolution of the rash and no further dermatologic complications.
Apalutamide is a second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist used in the treatment of nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (CSPC).7 It stops the spread and growth of prostate cancer cells by several different mechanisms, including competitively binding androgen receptors, preventing 5α-dihydrotestosterone from binding to androgen receptors, blocking androgen receptor nuclear translocation, impairing co-activator recruitment, and restraining androgen receptor DNA binding.7 The SPARTAN and TITAN phase 3 clinical trials demonstrated increased overall survival and time to progression with apalutamide in both nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC. In both trials, the rash was shown to be an AE more commonly associated with apalutamide than placebo.8,9
Until recently, the characteristics of apalutamide-induced drug rashes have not been well described. One literature review reported 6 cases of cutaneous apalutamide-induced drug eruptions.5 Four (66.7%) of these eruptions were maculopapular rashes, only 2 of which were histologically classified as lichenoid in nature. The other 2 eruptions were classified as toxic epidermal necrosis.5 Another study of 303 patients with prostate cancer who were treated with apalutamide recorded the frequency and time to onset of dermatologic AEs.6 Seventy-one (23.4%) of the patients had dermatologic AEs, and of those, only 20 (28.2%) had AEs that resulted in interruptions in apalutamide therapy (with only 5 [25.0%] requiring medication discontinuation). Thirty-two (45.1%) patients were managed with topical or oral corticosteroids or dose modification. In this study, histopathology was examined in 8 cases (one of which had 2 biopsies for a total of 9 biopsies), 7 of which were consistent with lichenoid interface dermatitis.6
Lichenoid interface dermatitis is a rare manifestation of an apalutamide-induced drug eruption and also has been reported secondary to treatment with enzalutamide, another second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist.4 Enzalutamide was the first second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist approved for the treatment of prostate cancer. It originally was approved only for metastatic CRPC after docetaxel therapy in 2012, then later was expanded to metastatic and nonmetastatic CRPC in 2012 and 2018, respectively, as well as metastatic CSPC in 2019.7 Because enzalutamide is from the same medication class as apalutamide and has been on the market longer for the treatment of nonmetastatic CRPC and metastatic CSPC, it is not surprising that similar drug eruptions now are being reported secondary to apalutamide use as well.
It is important for providers to consider lichenoid drug eruptions in the differential diagnosis of pruritic rashes in patients taking second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide or enzalutamide. Although dose reduction or treatment discontinuation have been the standard of care for patients with extremely pruritic lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to these medications, these are not ideal because they are important for cancer treatment. Interestingly, after our patient’s apalutamide-induced rash resolved and he was switched to enzalutamide, he did not develop any AEs. Based on our patient’s experience, physicians could consider switching their patients to another drug of the same class, as they may be able tolerate that medication. More research is needed to determine how commonly patients tolerate a different second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist after not tolerating another medication from the same class.
- Weyers W, Metze D. Histopathology of drug eruptions—general criteria, common patterns, and differential diagnosis. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011;1:33-47. doi:10.5826/dpc.0101a09
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruption, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Thompson DF, Skaehill PA. Drug-induced lichen planus. Pharmacotherapy. 1994;14:561-571.
- Khan S, Saizan AL, O’Brien K, et al. Diffuse hyperpigmented lichenoid drug eruption secondary to enzalutamide. Curr Probl Cancer Case Rep. 2022;5:100135. doi:10.1016/j.cpccr.2021.100135
- Katayama H, Saeki H, Osada S-I. Maculopapular drug eruption caused by apalutamide: case report and review of the literature. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89:550-554. doi:10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-503
- Pan A, Reingold RE, Zhao JL, et al. Dermatologic adverse events in prostate cancer patients treated with the androgen receptor inhibitor apalutamide. J Urol. 2022;207:1010-1019. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002425
- Rajaram P, Rivera A, Muthima K, et al. Second-generation androgen receptor antagonists as hormonal therapeutics for three forms of prostate cancer. Molecules. 2020;25:2448. doi:10.3390/molecules25102448
- Smith MR, Saad F, Chowdhury S, et al. Apalutamide treatment and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1408-1418. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1715546
- Chi KN, Agarwal N, Bjartell A, et al. Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensative prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:13-24. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903307
- Weyers W, Metze D. Histopathology of drug eruptions—general criteria, common patterns, and differential diagnosis. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2011;1:33-47. doi:10.5826/dpc.0101a09
- Cheraghlou S, Levy LL. Fixed drug eruption, bullous drug eruptions, and lichenoid drug eruptions. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38:679-692. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.010
- Thompson DF, Skaehill PA. Drug-induced lichen planus. Pharmacotherapy. 1994;14:561-571.
- Khan S, Saizan AL, O’Brien K, et al. Diffuse hyperpigmented lichenoid drug eruption secondary to enzalutamide. Curr Probl Cancer Case Rep. 2022;5:100135. doi:10.1016/j.cpccr.2021.100135
- Katayama H, Saeki H, Osada S-I. Maculopapular drug eruption caused by apalutamide: case report and review of the literature. J Nippon Med Sch. 2022;89:550-554. doi:10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2022_89-503
- Pan A, Reingold RE, Zhao JL, et al. Dermatologic adverse events in prostate cancer patients treated with the androgen receptor inhibitor apalutamide. J Urol. 2022;207:1010-1019. doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000002425
- Rajaram P, Rivera A, Muthima K, et al. Second-generation androgen receptor antagonists as hormonal therapeutics for three forms of prostate cancer. Molecules. 2020;25:2448. doi:10.3390/molecules25102448
- Smith MR, Saad F, Chowdhury S, et al. Apalutamide treatment and metastasis-free survival in prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1408-1418. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1715546
- Chi KN, Agarwal N, Bjartell A, et al. Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensative prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:13-24. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1903307
Practice Points
- Although it is rare, patients can develop lichenoid drug eruptions secondary to treatment with second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonists such as apalutamide.
- If a patient develops a lichenoid drug eruption while taking a specific second-generation nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist, the entire class of medications should not be ruled out, as some patients can tolerate other drugs from that class.
Botulinum Toxin Injection for Treatment of Scleroderma-Related Anterior Neck Sclerosis
To the Editor:
Scleroderma is a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease that results in excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs throughout the body. On its own or in the setting of mixed connective tissue disease, scleroderma can result in systemic or localized symptoms that can limit patients’ functional capabilities, cause pain and discomfort, and reduce self-esteem—all negatively impacting patients’ quality of life.1,2 Neck sclerosis is a common manifestation of scleroderma. There is no curative treatment for scleroderma; thus, therapy is focused on slowing disease progression and improving quality of life. We present a case of neck sclerosis in a 44-year-old woman with scleroderma that was successfully treated with botulinum toxin (BTX) type A injection, resulting in improved skin laxity and appearance with high patient satisfaction. Our case demonstrates the potential positive effects of BTX treatment in patients with features of sclerosis or fibrosis, particularly in the neck region.
A 44-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for treatment of thickened neck skin with stiffness and tightness that had been present for months to years. She had a history of mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD)(positive anti-ribonucleoprotein, anti–Sjögren syndrome–related antigen, and anti-Smith antibodies) with features of scleroderma and polyarthritis. The patient currently was taking sulfasalazine for the polyarthritis; she previously had taken hydroxychloroquine but discontinued treatment due to ineffectiveness. She was not taking any topical or systemic medications for scleroderma. On physical examination, the skin on the anterior neck appeared thickened with shiny patches (Figure 1). Pinching the skin in the affected area demonstrated sclerosis with high tension.
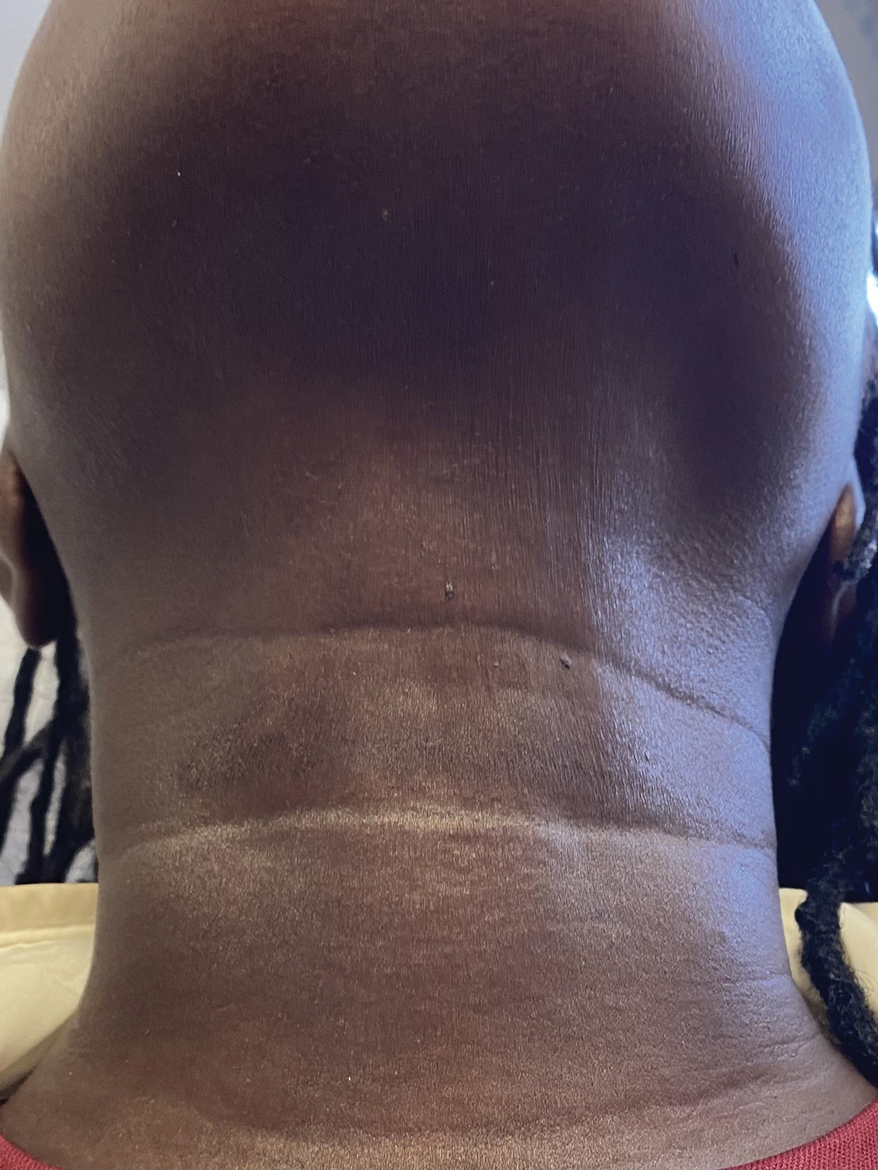
The dermatologist (J.J.) discussed potential treatment options to help relax the tension in the skin of the anterior neck, including BTX injections. After receiving counsel on adverse effects, alternative treatments, and postprocedural care, the patient decided to proceed with the procedure. The anterior neck was cleansed with an alcohol swab and 37 units (range, 25–50 units) of incobotulinumtoxinA (reconstituted using 2.5-mL bacteriostatic normal saline per 100 units) was injected transdermally using a 9-point injection technique, with each injection placed approximately 1 cm apart. The approximate treatment area included the space between the sternocleidomastoid anterior edges and below the hyoid bone up to the cricothyroid membrane (anatomic zone II).
When the patient returned for follow-up 3 weeks later, she reported considerable improvement in the stiffness and appearance of the skin on the anterior neck. On physical examination, the skin of the neck appeared softened, and improved laxity was seen on pinching the skin compared to the initial presentation (Figure 2). The patient expressed satisfaction with the results and denied any adverse events following the procedure.
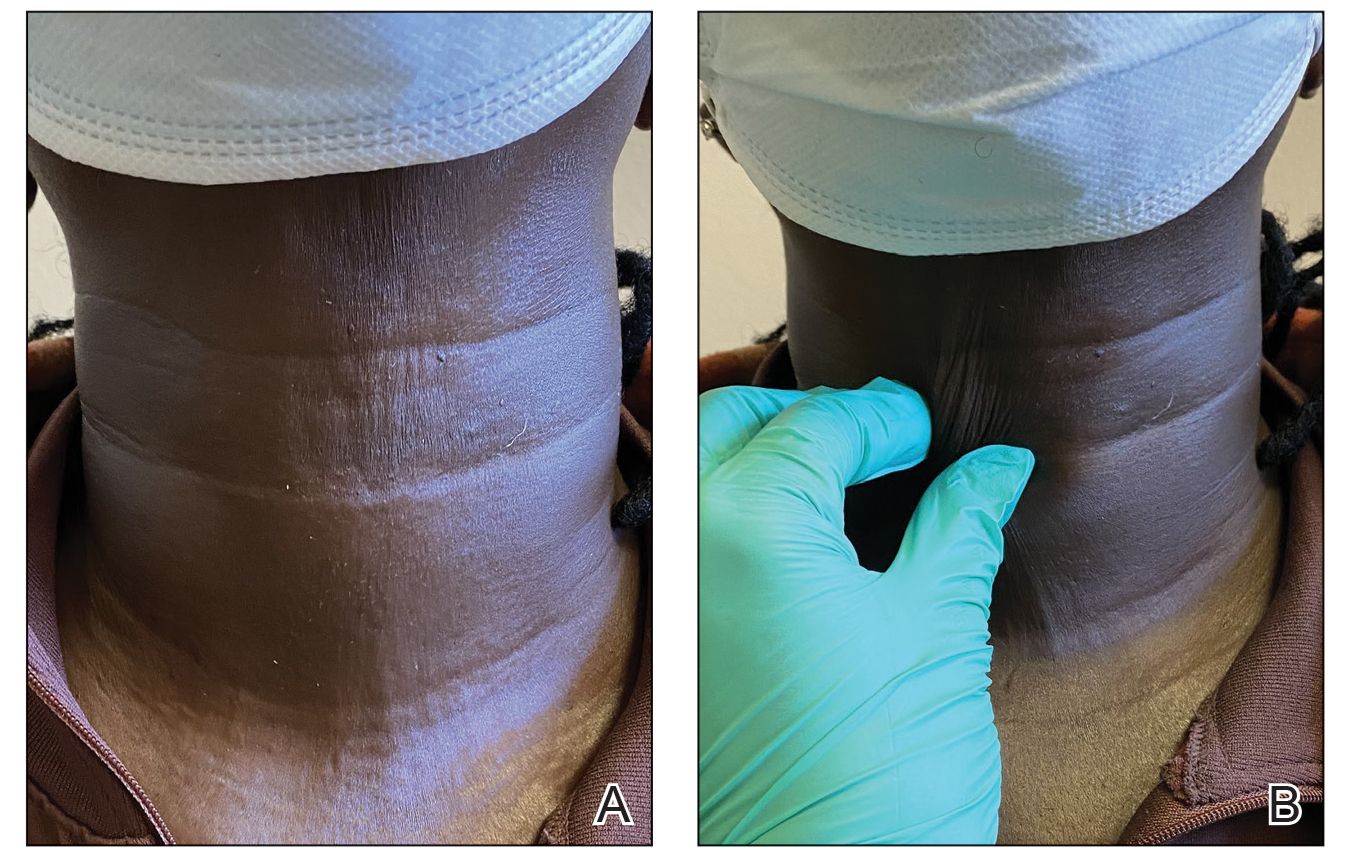
Mixed connective tissue disease manifests with a combination of features from various disorders—mainly lupus, scleroderma, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It is most prevalent in females and often is diagnosed in the third decade of life.3 It is associated with positive antinuclear antibodies and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) II alleles (HLA-DR4, HLA-DR1, and HLA-DR2). Raynaud phenomenon (RP), one of the most common skin manifestations in both scleroderma and MCTD, is present in 75% to 90% of patients with MCTD.3
Scleroderma is a chronic connective tissue disorder that results in excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs throughout the body.4 Although the etiology is unknown, scleroderma develops when overactivation of the immune system leads to CD4+ T-lymphocyte infiltration in the skin, along with the release of profibrotic interleukins and growth factors, resulting in fibrosis.4 Subtypes include localized scleroderma (morphea), limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (formerly known as CREST [calcinosis, RP, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia] syndrome), diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, and systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma.5 Scleroderma is associated with positive antinuclear antibodies and HLA II alleles (HLA-DR2 and HLA-DR5).
On its own or in the setting of MCTD, scleroderma can result in systemic or localized symptoms. Overall, the most common symptom is RP.5 Localized scleroderma and limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis manifest with symptoms of the skin and underlying tissues. Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis involves cutaneous and visceral symptoms, including lung, esophageal, and vascular involvement.6 Similar to MCTD, scleroderma is most prevalent in middle-aged females,7 though it occurs at a higher rate and with a more severe disease course in Black patients.8
A highly sensitive and specific test for scleroderma that can aid in diagnosis is the neck sign—tightening of the skin of the neck when the head extends.9,10 In one study, the neck sign was positive in more than 90% of patients with scleroderma and negative for control patients and those with primary RP.9 Thus, neck sclerosis is a common manifestation of scleroderma for which patients may seek treatment.
While there is no curative treatment for scleroderma, skin manifestations can be treated with mycophenolate mofetil or methotrexate.5 Systemic treatments may be recommended if the patient has additional symptoms, such as azathioprine for myositis/arthritis and cyclophosphamide for interstitial lung disease.5 However, it is important to note that these medications are associated with risk for gastrointestinal upset, mouth sores, fatigue, or other complications.
Botulinum toxin is a bacterial protein toxin and neuromodulator that inhibits neurotransmitter release by cleaving SNARE proteins at peripheral nerve terminal junctions.11 It has been used in a variety of dermatologic and nondermatologic conditions, including migraines, hyperhidrosis, contractures, scars, and overactive bladder. It also has been used in aesthetics for facial rejuvenation and minimization of wrinkle appearance. Dermatologists and rheumatologists have successfully used BTX to treat primary and secondary RP—the most common symptom of scleroderma—due to its vasodilatation properties.12 Although our patient did not have RP, use of BTX to treat other features of scleroderma, including en coup de sabre, thoracic outlet syndrome, dyspareunia, gastroparesis, pterygium inversum unguis, and dysphagia has been documented.13-18 An in vivo mouse study that examined the possible mechanism for BTX as a treatment in scleroderma found that BTX injections significantly decreased dermal thickness and inflammation in fibrosis (P<.05). An analysis of oxidative stress and mRNA expression showed that BTX may treat fibrosis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory cells, resulting in decreased apoptosis and oxidant-induced intracellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species.19 Another animal study demonstrated the positive effects of BTX treatment for fibrosis of the bladder in rats.20 In one case report, a female patient with scleroderma and facial fibrosis received perioral BTX injections for cosmetic purposes but also observed improvement in mouth constriction, demonstrating the potential efficacy of BTX for facial fibrosis.21
Our case demonstrates the potential positive effects of BTX treatment in patients with features of sclerosis or fibrosis, particularly in the neck region. We recommend assessing the efficacy of the initial BTX treatment after 2 to 3 weeks, with additional injections as needed to achieve the patient’s desired level of comfort and appearance at approximately 3-month intervals (aligning with the expected duration of efficacy of BTX).22 Our patient experienced considerable relief and high satisfaction with BTX treatment. Given the limitations of sclerosis treatments and the unwanted adverse-effect profile of systemic treatments, BTX injections may be a preferrable treatment option for cutaneous manifestations of scleroderma among patients. Future studies with larger patient populations and a control group are warranted to further explore the use of BTX for the dermatologic treatment of scleroderma.
- Lis-S´wie¸ty A, Skrzypek-Salamon A, Ranosz-Janicka I, et al. Health-related quality of life and its influencing factors in adult patients with localized scleroderma—a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18:133. doi:10.1186/s12955-020-01386-0
- Almeida C, Almeida I, Vasconcelos C. Quality of life in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14:1087-1096. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2015.07.012
- Ortega-Hernandez OD, Shoenfeld Y. Mixed connective tissue disease: an overview of clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012;26:61-72. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2012.01.009
- Rongioletti F, Ferreli C, Atzori L, et al. Scleroderma with an update about clinico-pathological correlation. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:208-215. doi:10.23736/S0392-0488.18.05922-9
- Fett N. Scleroderma: nomenclature, etiology, pathogenesis, prognosis, and treatments: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:432-437. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.010
- Careta MF, Romiti R. Localized scleroderma: clinical spectrum and therapeutic update. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:62-73. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152890
- Calderon LM, Pope JE. Scleroderma epidemiology update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2021;33:122-127. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000785
- Morgan ND, Gelber AC. African Americans and scleroderma: examining the root cause of the association. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71:1151-1153. doi:10.1002/acr.23860
- Barnett AJ. The “neck sign” in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32:209-211. doi:10.1002/anr.1780320215
- Barnett AJ, Miller M, Littlejohn GO. The diagnosis and classification of scleroderma (systemic sclerosis). Postgrad Med J. 1988;64:121-125. doi:10.1136/pgmj.64.748.121
- Rossetto O, Pirazzini M, Fabris F, et al. Botulinum neurotoxins: mechanism of action. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;263:35-47.doi:10.1007/164_2020_355
- Ennis D, Ahmad Z, Anderson MA, et al. Botulinum toxin in the management of primary and secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021;35:101684. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2021.101684
- Turkmani MG, Alnomair N. Enhancement of the aesthetic outcome of scleroderma en coup de sabre with botulinum toxin injection. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:579-581. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.03.023
- Le EN, Freischlag JA, Christo PJ, et al. Thoracic outlet syndrome secondary to localized scleroderma treated with botulinum toxin injection. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62:430-433. doi:10.1002/acr.20099
- Mousty E, Rathat G, Rouleau C, et al. Botulinum toxin type A for treatment of dyspareunia caused by localized scleroderma. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011;90:926-927. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0412.2011.01183.x
- Tang DM, Friedenberg FK. Gastroparesis: approach, diagnostic evaluation, and management. Dis Mon. 2011;57:74-101. doi:10.1016/j.disamonth.2010.12.007
- Katschinski M. [Diagnosis and treatment of esophageal motility disorders]. Ther Umsch. 2001;58:128-133. doi:10.1024/0040-5930.58.3.128
- Kim DJ, Odell ID. Improvement of pterygium inversum unguis and Raynaud phenomenon with interdigital botulinum toxin injections. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;26:79-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.06.009
- Baral H, Sekiguchi A, Uchiyama A, et al. Inhibition of skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis by botulinum toxin B via the suppression of oxidative stress. J Dermatol. 2021;48:1052-1061. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15888
- Jia C, Xing T, Shang Z, et al. Botulinum toxin A improves neurogenic bladder fibrosis by suppressing transforming growth factor β1 expression in rats. Transl Androl Urol. 2021;10:2000-2007. doi:10.21037/tau-21-62
- Hoverson K, Love T, Lam TK, et al. A novel treatment for limited mouth opening due to facial fibrosis: a case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:190-192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.07.006
- Kollewe K, Mohammadi B, Köhler S, et al. Blepharospasm: long-term treatment with either Botox®, Xeomin® or Dysport®. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015;122:427-431. doi:10.1007/s00702-014-1278-z
To the Editor:
Scleroderma is a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease that results in excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs throughout the body. On its own or in the setting of mixed connective tissue disease, scleroderma can result in systemic or localized symptoms that can limit patients’ functional capabilities, cause pain and discomfort, and reduce self-esteem—all negatively impacting patients’ quality of life.1,2 Neck sclerosis is a common manifestation of scleroderma. There is no curative treatment for scleroderma; thus, therapy is focused on slowing disease progression and improving quality of life. We present a case of neck sclerosis in a 44-year-old woman with scleroderma that was successfully treated with botulinum toxin (BTX) type A injection, resulting in improved skin laxity and appearance with high patient satisfaction. Our case demonstrates the potential positive effects of BTX treatment in patients with features of sclerosis or fibrosis, particularly in the neck region.
A 44-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for treatment of thickened neck skin with stiffness and tightness that had been present for months to years. She had a history of mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD)(positive anti-ribonucleoprotein, anti–Sjögren syndrome–related antigen, and anti-Smith antibodies) with features of scleroderma and polyarthritis. The patient currently was taking sulfasalazine for the polyarthritis; she previously had taken hydroxychloroquine but discontinued treatment due to ineffectiveness. She was not taking any topical or systemic medications for scleroderma. On physical examination, the skin on the anterior neck appeared thickened with shiny patches (Figure 1). Pinching the skin in the affected area demonstrated sclerosis with high tension.

The dermatologist (J.J.) discussed potential treatment options to help relax the tension in the skin of the anterior neck, including BTX injections. After receiving counsel on adverse effects, alternative treatments, and postprocedural care, the patient decided to proceed with the procedure. The anterior neck was cleansed with an alcohol swab and 37 units (range, 25–50 units) of incobotulinumtoxinA (reconstituted using 2.5-mL bacteriostatic normal saline per 100 units) was injected transdermally using a 9-point injection technique, with each injection placed approximately 1 cm apart. The approximate treatment area included the space between the sternocleidomastoid anterior edges and below the hyoid bone up to the cricothyroid membrane (anatomic zone II).
When the patient returned for follow-up 3 weeks later, she reported considerable improvement in the stiffness and appearance of the skin on the anterior neck. On physical examination, the skin of the neck appeared softened, and improved laxity was seen on pinching the skin compared to the initial presentation (Figure 2). The patient expressed satisfaction with the results and denied any adverse events following the procedure.

Mixed connective tissue disease manifests with a combination of features from various disorders—mainly lupus, scleroderma, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It is most prevalent in females and often is diagnosed in the third decade of life.3 It is associated with positive antinuclear antibodies and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) II alleles (HLA-DR4, HLA-DR1, and HLA-DR2). Raynaud phenomenon (RP), one of the most common skin manifestations in both scleroderma and MCTD, is present in 75% to 90% of patients with MCTD.3
Scleroderma is a chronic connective tissue disorder that results in excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs throughout the body.4 Although the etiology is unknown, scleroderma develops when overactivation of the immune system leads to CD4+ T-lymphocyte infiltration in the skin, along with the release of profibrotic interleukins and growth factors, resulting in fibrosis.4 Subtypes include localized scleroderma (morphea), limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (formerly known as CREST [calcinosis, RP, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia] syndrome), diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, and systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma.5 Scleroderma is associated with positive antinuclear antibodies and HLA II alleles (HLA-DR2 and HLA-DR5).
On its own or in the setting of MCTD, scleroderma can result in systemic or localized symptoms. Overall, the most common symptom is RP.5 Localized scleroderma and limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis manifest with symptoms of the skin and underlying tissues. Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis involves cutaneous and visceral symptoms, including lung, esophageal, and vascular involvement.6 Similar to MCTD, scleroderma is most prevalent in middle-aged females,7 though it occurs at a higher rate and with a more severe disease course in Black patients.8
A highly sensitive and specific test for scleroderma that can aid in diagnosis is the neck sign—tightening of the skin of the neck when the head extends.9,10 In one study, the neck sign was positive in more than 90% of patients with scleroderma and negative for control patients and those with primary RP.9 Thus, neck sclerosis is a common manifestation of scleroderma for which patients may seek treatment.
While there is no curative treatment for scleroderma, skin manifestations can be treated with mycophenolate mofetil or methotrexate.5 Systemic treatments may be recommended if the patient has additional symptoms, such as azathioprine for myositis/arthritis and cyclophosphamide for interstitial lung disease.5 However, it is important to note that these medications are associated with risk for gastrointestinal upset, mouth sores, fatigue, or other complications.
Botulinum toxin is a bacterial protein toxin and neuromodulator that inhibits neurotransmitter release by cleaving SNARE proteins at peripheral nerve terminal junctions.11 It has been used in a variety of dermatologic and nondermatologic conditions, including migraines, hyperhidrosis, contractures, scars, and overactive bladder. It also has been used in aesthetics for facial rejuvenation and minimization of wrinkle appearance. Dermatologists and rheumatologists have successfully used BTX to treat primary and secondary RP—the most common symptom of scleroderma—due to its vasodilatation properties.12 Although our patient did not have RP, use of BTX to treat other features of scleroderma, including en coup de sabre, thoracic outlet syndrome, dyspareunia, gastroparesis, pterygium inversum unguis, and dysphagia has been documented.13-18 An in vivo mouse study that examined the possible mechanism for BTX as a treatment in scleroderma found that BTX injections significantly decreased dermal thickness and inflammation in fibrosis (P<.05). An analysis of oxidative stress and mRNA expression showed that BTX may treat fibrosis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory cells, resulting in decreased apoptosis and oxidant-induced intracellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species.19 Another animal study demonstrated the positive effects of BTX treatment for fibrosis of the bladder in rats.20 In one case report, a female patient with scleroderma and facial fibrosis received perioral BTX injections for cosmetic purposes but also observed improvement in mouth constriction, demonstrating the potential efficacy of BTX for facial fibrosis.21
Our case demonstrates the potential positive effects of BTX treatment in patients with features of sclerosis or fibrosis, particularly in the neck region. We recommend assessing the efficacy of the initial BTX treatment after 2 to 3 weeks, with additional injections as needed to achieve the patient’s desired level of comfort and appearance at approximately 3-month intervals (aligning with the expected duration of efficacy of BTX).22 Our patient experienced considerable relief and high satisfaction with BTX treatment. Given the limitations of sclerosis treatments and the unwanted adverse-effect profile of systemic treatments, BTX injections may be a preferrable treatment option for cutaneous manifestations of scleroderma among patients. Future studies with larger patient populations and a control group are warranted to further explore the use of BTX for the dermatologic treatment of scleroderma.
To the Editor:
Scleroderma is a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease that results in excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs throughout the body. On its own or in the setting of mixed connective tissue disease, scleroderma can result in systemic or localized symptoms that can limit patients’ functional capabilities, cause pain and discomfort, and reduce self-esteem—all negatively impacting patients’ quality of life.1,2 Neck sclerosis is a common manifestation of scleroderma. There is no curative treatment for scleroderma; thus, therapy is focused on slowing disease progression and improving quality of life. We present a case of neck sclerosis in a 44-year-old woman with scleroderma that was successfully treated with botulinum toxin (BTX) type A injection, resulting in improved skin laxity and appearance with high patient satisfaction. Our case demonstrates the potential positive effects of BTX treatment in patients with features of sclerosis or fibrosis, particularly in the neck region.
A 44-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic for treatment of thickened neck skin with stiffness and tightness that had been present for months to years. She had a history of mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD)(positive anti-ribonucleoprotein, anti–Sjögren syndrome–related antigen, and anti-Smith antibodies) with features of scleroderma and polyarthritis. The patient currently was taking sulfasalazine for the polyarthritis; she previously had taken hydroxychloroquine but discontinued treatment due to ineffectiveness. She was not taking any topical or systemic medications for scleroderma. On physical examination, the skin on the anterior neck appeared thickened with shiny patches (Figure 1). Pinching the skin in the affected area demonstrated sclerosis with high tension.

The dermatologist (J.J.) discussed potential treatment options to help relax the tension in the skin of the anterior neck, including BTX injections. After receiving counsel on adverse effects, alternative treatments, and postprocedural care, the patient decided to proceed with the procedure. The anterior neck was cleansed with an alcohol swab and 37 units (range, 25–50 units) of incobotulinumtoxinA (reconstituted using 2.5-mL bacteriostatic normal saline per 100 units) was injected transdermally using a 9-point injection technique, with each injection placed approximately 1 cm apart. The approximate treatment area included the space between the sternocleidomastoid anterior edges and below the hyoid bone up to the cricothyroid membrane (anatomic zone II).
When the patient returned for follow-up 3 weeks later, she reported considerable improvement in the stiffness and appearance of the skin on the anterior neck. On physical examination, the skin of the neck appeared softened, and improved laxity was seen on pinching the skin compared to the initial presentation (Figure 2). The patient expressed satisfaction with the results and denied any adverse events following the procedure.

Mixed connective tissue disease manifests with a combination of features from various disorders—mainly lupus, scleroderma, polymyositis, and rheumatoid arthritis. It is most prevalent in females and often is diagnosed in the third decade of life.3 It is associated with positive antinuclear antibodies and human leukocyte antigen (HLA) II alleles (HLA-DR4, HLA-DR1, and HLA-DR2). Raynaud phenomenon (RP), one of the most common skin manifestations in both scleroderma and MCTD, is present in 75% to 90% of patients with MCTD.3
Scleroderma is a chronic connective tissue disorder that results in excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs throughout the body.4 Although the etiology is unknown, scleroderma develops when overactivation of the immune system leads to CD4+ T-lymphocyte infiltration in the skin, along with the release of profibrotic interleukins and growth factors, resulting in fibrosis.4 Subtypes include localized scleroderma (morphea), limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (formerly known as CREST [calcinosis, RP, esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly, and telangiectasia] syndrome), diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis, and systemic sclerosis sine scleroderma.5 Scleroderma is associated with positive antinuclear antibodies and HLA II alleles (HLA-DR2 and HLA-DR5).
On its own or in the setting of MCTD, scleroderma can result in systemic or localized symptoms. Overall, the most common symptom is RP.5 Localized scleroderma and limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis manifest with symptoms of the skin and underlying tissues. Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis involves cutaneous and visceral symptoms, including lung, esophageal, and vascular involvement.6 Similar to MCTD, scleroderma is most prevalent in middle-aged females,7 though it occurs at a higher rate and with a more severe disease course in Black patients.8
A highly sensitive and specific test for scleroderma that can aid in diagnosis is the neck sign—tightening of the skin of the neck when the head extends.9,10 In one study, the neck sign was positive in more than 90% of patients with scleroderma and negative for control patients and those with primary RP.9 Thus, neck sclerosis is a common manifestation of scleroderma for which patients may seek treatment.
While there is no curative treatment for scleroderma, skin manifestations can be treated with mycophenolate mofetil or methotrexate.5 Systemic treatments may be recommended if the patient has additional symptoms, such as azathioprine for myositis/arthritis and cyclophosphamide for interstitial lung disease.5 However, it is important to note that these medications are associated with risk for gastrointestinal upset, mouth sores, fatigue, or other complications.
Botulinum toxin is a bacterial protein toxin and neuromodulator that inhibits neurotransmitter release by cleaving SNARE proteins at peripheral nerve terminal junctions.11 It has been used in a variety of dermatologic and nondermatologic conditions, including migraines, hyperhidrosis, contractures, scars, and overactive bladder. It also has been used in aesthetics for facial rejuvenation and minimization of wrinkle appearance. Dermatologists and rheumatologists have successfully used BTX to treat primary and secondary RP—the most common symptom of scleroderma—due to its vasodilatation properties.12 Although our patient did not have RP, use of BTX to treat other features of scleroderma, including en coup de sabre, thoracic outlet syndrome, dyspareunia, gastroparesis, pterygium inversum unguis, and dysphagia has been documented.13-18 An in vivo mouse study that examined the possible mechanism for BTX as a treatment in scleroderma found that BTX injections significantly decreased dermal thickness and inflammation in fibrosis (P<.05). An analysis of oxidative stress and mRNA expression showed that BTX may treat fibrosis by suppressing oxidative stress and inflammatory cells, resulting in decreased apoptosis and oxidant-induced intracellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species.19 Another animal study demonstrated the positive effects of BTX treatment for fibrosis of the bladder in rats.20 In one case report, a female patient with scleroderma and facial fibrosis received perioral BTX injections for cosmetic purposes but also observed improvement in mouth constriction, demonstrating the potential efficacy of BTX for facial fibrosis.21
Our case demonstrates the potential positive effects of BTX treatment in patients with features of sclerosis or fibrosis, particularly in the neck region. We recommend assessing the efficacy of the initial BTX treatment after 2 to 3 weeks, with additional injections as needed to achieve the patient’s desired level of comfort and appearance at approximately 3-month intervals (aligning with the expected duration of efficacy of BTX).22 Our patient experienced considerable relief and high satisfaction with BTX treatment. Given the limitations of sclerosis treatments and the unwanted adverse-effect profile of systemic treatments, BTX injections may be a preferrable treatment option for cutaneous manifestations of scleroderma among patients. Future studies with larger patient populations and a control group are warranted to further explore the use of BTX for the dermatologic treatment of scleroderma.
- Lis-S´wie¸ty A, Skrzypek-Salamon A, Ranosz-Janicka I, et al. Health-related quality of life and its influencing factors in adult patients with localized scleroderma—a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18:133. doi:10.1186/s12955-020-01386-0
- Almeida C, Almeida I, Vasconcelos C. Quality of life in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14:1087-1096. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2015.07.012
- Ortega-Hernandez OD, Shoenfeld Y. Mixed connective tissue disease: an overview of clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012;26:61-72. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2012.01.009
- Rongioletti F, Ferreli C, Atzori L, et al. Scleroderma with an update about clinico-pathological correlation. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:208-215. doi:10.23736/S0392-0488.18.05922-9
- Fett N. Scleroderma: nomenclature, etiology, pathogenesis, prognosis, and treatments: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:432-437. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.010
- Careta MF, Romiti R. Localized scleroderma: clinical spectrum and therapeutic update. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:62-73. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152890
- Calderon LM, Pope JE. Scleroderma epidemiology update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2021;33:122-127. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000785
- Morgan ND, Gelber AC. African Americans and scleroderma: examining the root cause of the association. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71:1151-1153. doi:10.1002/acr.23860
- Barnett AJ. The “neck sign” in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32:209-211. doi:10.1002/anr.1780320215
- Barnett AJ, Miller M, Littlejohn GO. The diagnosis and classification of scleroderma (systemic sclerosis). Postgrad Med J. 1988;64:121-125. doi:10.1136/pgmj.64.748.121
- Rossetto O, Pirazzini M, Fabris F, et al. Botulinum neurotoxins: mechanism of action. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;263:35-47.doi:10.1007/164_2020_355
- Ennis D, Ahmad Z, Anderson MA, et al. Botulinum toxin in the management of primary and secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021;35:101684. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2021.101684
- Turkmani MG, Alnomair N. Enhancement of the aesthetic outcome of scleroderma en coup de sabre with botulinum toxin injection. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:579-581. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.03.023
- Le EN, Freischlag JA, Christo PJ, et al. Thoracic outlet syndrome secondary to localized scleroderma treated with botulinum toxin injection. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62:430-433. doi:10.1002/acr.20099
- Mousty E, Rathat G, Rouleau C, et al. Botulinum toxin type A for treatment of dyspareunia caused by localized scleroderma. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011;90:926-927. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0412.2011.01183.x
- Tang DM, Friedenberg FK. Gastroparesis: approach, diagnostic evaluation, and management. Dis Mon. 2011;57:74-101. doi:10.1016/j.disamonth.2010.12.007
- Katschinski M. [Diagnosis and treatment of esophageal motility disorders]. Ther Umsch. 2001;58:128-133. doi:10.1024/0040-5930.58.3.128
- Kim DJ, Odell ID. Improvement of pterygium inversum unguis and Raynaud phenomenon with interdigital botulinum toxin injections. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;26:79-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.06.009
- Baral H, Sekiguchi A, Uchiyama A, et al. Inhibition of skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis by botulinum toxin B via the suppression of oxidative stress. J Dermatol. 2021;48:1052-1061. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15888
- Jia C, Xing T, Shang Z, et al. Botulinum toxin A improves neurogenic bladder fibrosis by suppressing transforming growth factor β1 expression in rats. Transl Androl Urol. 2021;10:2000-2007. doi:10.21037/tau-21-62
- Hoverson K, Love T, Lam TK, et al. A novel treatment for limited mouth opening due to facial fibrosis: a case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:190-192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.07.006
- Kollewe K, Mohammadi B, Köhler S, et al. Blepharospasm: long-term treatment with either Botox®, Xeomin® or Dysport®. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015;122:427-431. doi:10.1007/s00702-014-1278-z
- Lis-S´wie¸ty A, Skrzypek-Salamon A, Ranosz-Janicka I, et al. Health-related quality of life and its influencing factors in adult patients with localized scleroderma—a cross-sectional study. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020;18:133. doi:10.1186/s12955-020-01386-0
- Almeida C, Almeida I, Vasconcelos C. Quality of life in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14:1087-1096. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2015.07.012
- Ortega-Hernandez OD, Shoenfeld Y. Mixed connective tissue disease: an overview of clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2012;26:61-72. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2012.01.009
- Rongioletti F, Ferreli C, Atzori L, et al. Scleroderma with an update about clinico-pathological correlation. G Ital Dermatol Venereol. 2018;153:208-215. doi:10.23736/S0392-0488.18.05922-9
- Fett N. Scleroderma: nomenclature, etiology, pathogenesis, prognosis, and treatments: facts and controversies. Clin Dermatol. 2013;31:432-437. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.010
- Careta MF, Romiti R. Localized scleroderma: clinical spectrum and therapeutic update. An Bras Dermatol. 2015;90:62-73. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20152890
- Calderon LM, Pope JE. Scleroderma epidemiology update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2021;33:122-127. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000785
- Morgan ND, Gelber AC. African Americans and scleroderma: examining the root cause of the association. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019;71:1151-1153. doi:10.1002/acr.23860
- Barnett AJ. The “neck sign” in scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32:209-211. doi:10.1002/anr.1780320215
- Barnett AJ, Miller M, Littlejohn GO. The diagnosis and classification of scleroderma (systemic sclerosis). Postgrad Med J. 1988;64:121-125. doi:10.1136/pgmj.64.748.121
- Rossetto O, Pirazzini M, Fabris F, et al. Botulinum neurotoxins: mechanism of action. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;263:35-47.doi:10.1007/164_2020_355
- Ennis D, Ahmad Z, Anderson MA, et al. Botulinum toxin in the management of primary and secondary Raynaud’s phenomenon. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021;35:101684. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2021.101684
- Turkmani MG, Alnomair N. Enhancement of the aesthetic outcome of scleroderma en coup de sabre with botulinum toxin injection. JAAD Case Rep. 2018;4:579-581. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2018.03.023
- Le EN, Freischlag JA, Christo PJ, et al. Thoracic outlet syndrome secondary to localized scleroderma treated with botulinum toxin injection. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2010;62:430-433. doi:10.1002/acr.20099
- Mousty E, Rathat G, Rouleau C, et al. Botulinum toxin type A for treatment of dyspareunia caused by localized scleroderma. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011;90:926-927. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0412.2011.01183.x
- Tang DM, Friedenberg FK. Gastroparesis: approach, diagnostic evaluation, and management. Dis Mon. 2011;57:74-101. doi:10.1016/j.disamonth.2010.12.007
- Katschinski M. [Diagnosis and treatment of esophageal motility disorders]. Ther Umsch. 2001;58:128-133. doi:10.1024/0040-5930.58.3.128
- Kim DJ, Odell ID. Improvement of pterygium inversum unguis and Raynaud phenomenon with interdigital botulinum toxin injections. JAAD Case Rep. 2022;26:79-81. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.06.009
- Baral H, Sekiguchi A, Uchiyama A, et al. Inhibition of skin fibrosis in systemic sclerosis by botulinum toxin B via the suppression of oxidative stress. J Dermatol. 2021;48:1052-1061. doi:10.1111/1346-8138.15888
- Jia C, Xing T, Shang Z, et al. Botulinum toxin A improves neurogenic bladder fibrosis by suppressing transforming growth factor β1 expression in rats. Transl Androl Urol. 2021;10:2000-2007. doi:10.21037/tau-21-62
- Hoverson K, Love T, Lam TK, et al. A novel treatment for limited mouth opening due to facial fibrosis: a case series. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018;78:190-192. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2017.07.006
- Kollewe K, Mohammadi B, Köhler S, et al. Blepharospasm: long-term treatment with either Botox®, Xeomin® or Dysport®. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015;122:427-431. doi:10.1007/s00702-014-1278-z
Practice Points
- Scleroderma is a chronic autoimmune connective tissue disease that results in excessive collagen deposition in the skin and other organs throughout the body.
- Although there is no curative treatment for scleroderma, there are options to slow disease progression and improve quality of life.
- Botulinum toxin injection may be a preferred treatment option in patients with features of sclerosis or fibrosis related to scleroderma, particularly in the neck region.
Anaphylaxis Treatment Uncertainty Persists for Patients and Professionals
Misinformation and outdated protocols contribute to the suboptimal management of anaphylaxis by patients and healthcare professionals, based on data from two new studies presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Annual Scientific Meeting.
Anaphylaxis can strike suddenly, and many patients and caregivers at risk do not know which symptoms to treat with epinephrine, said Joni Chow, DO, of Baylor College of Medicine, San Antonio, Texas, in her presentation at the meeting.
“Early identification of anaphylaxis and early intervention with epinephrine are critical for improving patient outcomes,” Chow said in an interview.
“Many allergic reactions occur in community settings, where written action plans serve to instruct patients and caregivers on how to recognize and respond to these emergencies,” she said. “Currently, anaphylaxis action plans are developed based on the consensus of healthcare professionals, with limited information available on the preferences of patients and caregivers,” she noted. However, even with action plans, many patients and families struggle to recognize and manage severe allergic reactions effectively, she added.
In response to this issue, Chow and colleagues created a survey designed to assess the understanding of anaphylaxis recognition and management by patients and caregivers and to identify their preferences regarding the elements included in the action plans.
In the study, Chow and colleagues surveyed 96 patients and caregivers in an allergy clinic waiting room. The majority (95%) of the patients were prescribed epinephrine. Although 73% said they were comfortable identifying signs of anaphylaxis, only 14% said they were likely to use epinephrine as a first-line treatment.
The most common reason given for avoiding epinephrine was uncertainty over which symptoms to treat (40.6%), followed by hesitancy to visit an emergency department (24%), hesitancy to call 911 (17.7%), uncertainty about how to use epinephrine auto-injectors (11.5%), and fear of needles (5.2%).
Although 85% of the respondents understood that antihistamine use does not prevent the need for epinephrine in cases of anaphylactic reactions, 23.7% said they would use an antihistamine as the first treatment in these cases.
For patients with rash and wheezing after a suspected allergen exposure, approximately two thirds (64.5%) of the respondents said they would inject epinephrine and 10.8% would drive to the emergency room before taking any action, Chow said in her presentation.
The relatively low impact of fear of needles was unexpected, as fear of needles is considered a significant deterrent to epinephrine use, Chow told this news organization. “However, our respondents were more inclined to acknowledge a reluctance to escalate to emergency response as the major barrier to treatment,” she said.
The survey also asked patients what features of an anaphylaxis action plan would be most helpful. A majority of respondents (93%) rated a section for the management of mild (non-anaphylactic) allergic reaction symptoms as somewhat or very important. Visual aids for injection of epinephrine and visuals of anaphylaxis symptoms also ranked as somewhat or very important for 87.6% and 81% of respondents, respectively.
The study highlights the importance of educating allergy patients on recognizing and treating anaphylaxis and demonstrates that visuals were preferred in this survey population, Chow said. “Most patients and caregivers from our surveyed population report knowing how to treat anaphylaxis, but many would not use epinephrine as the first treatment,” she noted.
“The study focused on a single community clinic, and it would be beneficial to gather feedback from patients and caregivers representing a wider variety of educational, cultural, social, and socioeconomic backgrounds,” Chow told this news organization. “Additionally, input from other stakeholders, such as school nurses, would enhance knowledge,” she said.
Clinical Anaphylaxis Protocols Fall Short
A second study presented at the meeting showed the need to improve anaphylaxis education for clinicians.
Discrepancies in anaphylaxis management include variations in the definition and treatment of the condition, according to Carly Gunderson, DO, of Memorial Healthcare System, Pembroke Pines, Florida, who presented the study at the meeting.
“So often, we see patients in our office with a history of symptoms that meet criteria for anaphylaxis, yet when they call 911 and emergency medical services (EMS) arrive, they never receive epinephrine,” Gunderson said in an interview. “They receive antihistamines, steroids, everything except epinephrine, which is incredibly concerning given that epinephrine is always the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis,” she said.
“Because EMS providers are often the first healthcare professionals to assess patients experiencing anaphylaxis, their ability to recognize and appropriately treat anaphylaxis is essential,” Gunderson emphasized.
Gunderson and colleagues analyzed data from 30 states with mandatory Advanced Cardiac Life Support protocols to identify gaps in recognizing anaphylaxis and areas for improvement in prehospital management.
Only 15 states (50%) included gastrointestinal symptoms in the definition of anaphylaxis, 40% included neurologic manifestations, and 47% used a two-organ system definition, Gunderson noted in her presentation.
All 30 state protocols recommended diphenhydramine and epinephrine for anaphylactic reactions, 90% recommended albuterol if respiratory symptoms were present, 73% recommended intravenous fluids, and 60% recommended steroids. All but one of the state protocols listed epinephrine as the first-line recommendation for anaphylaxis; 25 states allowed epinephrine autoinjectors and 17 provided autoinjectors.
“We were shocked by how many protocols didn’t include gastrointestinal (abdominal pain, vomiting) or neurologic (lethargy, altered mental status) manifestations, when these are common presenting symptoms of anaphylaxis,” Gunderson told this news organization.
“We were also disappointed by how many protocols continue to recommend outdated interventions such as first-generation antihistamines and corticosteroids in the treatment of anaphylaxis,” she said.
Although anaphylaxis management has come a long way, the current study suggests that there is clearly room for improvement in the education of healthcare providers on how to identify and treat anaphylaxis, said Gunderson. “Most people think of anaphylaxis as the typical ‘face swelling up, throat closing’ type of reaction, which it can be, but in reality, there are so many other ways that it can present,” she said. “Healthcare providers must be aware of all of these possible manifestations so that we can treat in a timely manner to improve outcomes,” she added.
Limitations of the study included the focus only on states with mandatory or model EMS protocols, Gunderson told this news organization. As for additional research, the most important next steps are practical ones, namely, identifying ways to realistically implement necessary protocol changes, she said.
Real-World Data Support Need for Education
Real-world studies are important to identify current practice and opportunities for improvement, S. Shahzad Mustafa, MD, lead physician in allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at Rochester Regional Health and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York, said in an interview.
“Management of anaphylaxis continues to evolve, and studies like these can help standardize evidence-based care across different medical settings, such as emergency medical services, urgent care, and emergency departments,” said Mustafa, who was not involved in either study.
The findings of the two studies were not unexpected, Mustafa said. “Heterogeneity in medical care is well recognized in numerous conditions, and anaphylaxis is no different. Patients and healthcare providers continue to have hesitation to use epinephrine and continue to overly rely on antihistamines and/or systemic steroids,” he noted.
For both studies, the takeaway message is that education is paramount to optimize anaphylaxis management, Mustafa told this news organization. “Education needs to focus on timely recognition of anaphylaxis, including atypical features such as gastrointestinal symptoms, and appropriate therapy with epinephrine,” he said.
Looking ahead, “research demonstrating differences in clinical outcomes with differing approaches to anaphylaxis may highlight the importance of early recognition and treatment with epinephrine,” said Mustafa. Management of anaphylaxis also lends itself to quality improvement studies, he added.
Neither of the studies received any outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Mustafa had no disclosures related to anaphylaxis but disclosed serving on the speakers’ bureau for Genentech, GSK, AstraZeneca, Regeneron/Sanofi, and CSL Behring and received grants from Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Misinformation and outdated protocols contribute to the suboptimal management of anaphylaxis by patients and healthcare professionals, based on data from two new studies presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Annual Scientific Meeting.
Anaphylaxis can strike suddenly, and many patients and caregivers at risk do not know which symptoms to treat with epinephrine, said Joni Chow, DO, of Baylor College of Medicine, San Antonio, Texas, in her presentation at the meeting.
“Early identification of anaphylaxis and early intervention with epinephrine are critical for improving patient outcomes,” Chow said in an interview.
“Many allergic reactions occur in community settings, where written action plans serve to instruct patients and caregivers on how to recognize and respond to these emergencies,” she said. “Currently, anaphylaxis action plans are developed based on the consensus of healthcare professionals, with limited information available on the preferences of patients and caregivers,” she noted. However, even with action plans, many patients and families struggle to recognize and manage severe allergic reactions effectively, she added.
In response to this issue, Chow and colleagues created a survey designed to assess the understanding of anaphylaxis recognition and management by patients and caregivers and to identify their preferences regarding the elements included in the action plans.
In the study, Chow and colleagues surveyed 96 patients and caregivers in an allergy clinic waiting room. The majority (95%) of the patients were prescribed epinephrine. Although 73% said they were comfortable identifying signs of anaphylaxis, only 14% said they were likely to use epinephrine as a first-line treatment.
The most common reason given for avoiding epinephrine was uncertainty over which symptoms to treat (40.6%), followed by hesitancy to visit an emergency department (24%), hesitancy to call 911 (17.7%), uncertainty about how to use epinephrine auto-injectors (11.5%), and fear of needles (5.2%).
Although 85% of the respondents understood that antihistamine use does not prevent the need for epinephrine in cases of anaphylactic reactions, 23.7% said they would use an antihistamine as the first treatment in these cases.
For patients with rash and wheezing after a suspected allergen exposure, approximately two thirds (64.5%) of the respondents said they would inject epinephrine and 10.8% would drive to the emergency room before taking any action, Chow said in her presentation.
The relatively low impact of fear of needles was unexpected, as fear of needles is considered a significant deterrent to epinephrine use, Chow told this news organization. “However, our respondents were more inclined to acknowledge a reluctance to escalate to emergency response as the major barrier to treatment,” she said.
The survey also asked patients what features of an anaphylaxis action plan would be most helpful. A majority of respondents (93%) rated a section for the management of mild (non-anaphylactic) allergic reaction symptoms as somewhat or very important. Visual aids for injection of epinephrine and visuals of anaphylaxis symptoms also ranked as somewhat or very important for 87.6% and 81% of respondents, respectively.
The study highlights the importance of educating allergy patients on recognizing and treating anaphylaxis and demonstrates that visuals were preferred in this survey population, Chow said. “Most patients and caregivers from our surveyed population report knowing how to treat anaphylaxis, but many would not use epinephrine as the first treatment,” she noted.
“The study focused on a single community clinic, and it would be beneficial to gather feedback from patients and caregivers representing a wider variety of educational, cultural, social, and socioeconomic backgrounds,” Chow told this news organization. “Additionally, input from other stakeholders, such as school nurses, would enhance knowledge,” she said.
Clinical Anaphylaxis Protocols Fall Short
A second study presented at the meeting showed the need to improve anaphylaxis education for clinicians.
Discrepancies in anaphylaxis management include variations in the definition and treatment of the condition, according to Carly Gunderson, DO, of Memorial Healthcare System, Pembroke Pines, Florida, who presented the study at the meeting.
“So often, we see patients in our office with a history of symptoms that meet criteria for anaphylaxis, yet when they call 911 and emergency medical services (EMS) arrive, they never receive epinephrine,” Gunderson said in an interview. “They receive antihistamines, steroids, everything except epinephrine, which is incredibly concerning given that epinephrine is always the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis,” she said.
“Because EMS providers are often the first healthcare professionals to assess patients experiencing anaphylaxis, their ability to recognize and appropriately treat anaphylaxis is essential,” Gunderson emphasized.
Gunderson and colleagues analyzed data from 30 states with mandatory Advanced Cardiac Life Support protocols to identify gaps in recognizing anaphylaxis and areas for improvement in prehospital management.
Only 15 states (50%) included gastrointestinal symptoms in the definition of anaphylaxis, 40% included neurologic manifestations, and 47% used a two-organ system definition, Gunderson noted in her presentation.
All 30 state protocols recommended diphenhydramine and epinephrine for anaphylactic reactions, 90% recommended albuterol if respiratory symptoms were present, 73% recommended intravenous fluids, and 60% recommended steroids. All but one of the state protocols listed epinephrine as the first-line recommendation for anaphylaxis; 25 states allowed epinephrine autoinjectors and 17 provided autoinjectors.
“We were shocked by how many protocols didn’t include gastrointestinal (abdominal pain, vomiting) or neurologic (lethargy, altered mental status) manifestations, when these are common presenting symptoms of anaphylaxis,” Gunderson told this news organization.
“We were also disappointed by how many protocols continue to recommend outdated interventions such as first-generation antihistamines and corticosteroids in the treatment of anaphylaxis,” she said.
Although anaphylaxis management has come a long way, the current study suggests that there is clearly room for improvement in the education of healthcare providers on how to identify and treat anaphylaxis, said Gunderson. “Most people think of anaphylaxis as the typical ‘face swelling up, throat closing’ type of reaction, which it can be, but in reality, there are so many other ways that it can present,” she said. “Healthcare providers must be aware of all of these possible manifestations so that we can treat in a timely manner to improve outcomes,” she added.
Limitations of the study included the focus only on states with mandatory or model EMS protocols, Gunderson told this news organization. As for additional research, the most important next steps are practical ones, namely, identifying ways to realistically implement necessary protocol changes, she said.
Real-World Data Support Need for Education
Real-world studies are important to identify current practice and opportunities for improvement, S. Shahzad Mustafa, MD, lead physician in allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at Rochester Regional Health and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York, said in an interview.
“Management of anaphylaxis continues to evolve, and studies like these can help standardize evidence-based care across different medical settings, such as emergency medical services, urgent care, and emergency departments,” said Mustafa, who was not involved in either study.
The findings of the two studies were not unexpected, Mustafa said. “Heterogeneity in medical care is well recognized in numerous conditions, and anaphylaxis is no different. Patients and healthcare providers continue to have hesitation to use epinephrine and continue to overly rely on antihistamines and/or systemic steroids,” he noted.
For both studies, the takeaway message is that education is paramount to optimize anaphylaxis management, Mustafa told this news organization. “Education needs to focus on timely recognition of anaphylaxis, including atypical features such as gastrointestinal symptoms, and appropriate therapy with epinephrine,” he said.
Looking ahead, “research demonstrating differences in clinical outcomes with differing approaches to anaphylaxis may highlight the importance of early recognition and treatment with epinephrine,” said Mustafa. Management of anaphylaxis also lends itself to quality improvement studies, he added.
Neither of the studies received any outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Mustafa had no disclosures related to anaphylaxis but disclosed serving on the speakers’ bureau for Genentech, GSK, AstraZeneca, Regeneron/Sanofi, and CSL Behring and received grants from Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Misinformation and outdated protocols contribute to the suboptimal management of anaphylaxis by patients and healthcare professionals, based on data from two new studies presented at the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology Annual Scientific Meeting.
Anaphylaxis can strike suddenly, and many patients and caregivers at risk do not know which symptoms to treat with epinephrine, said Joni Chow, DO, of Baylor College of Medicine, San Antonio, Texas, in her presentation at the meeting.
“Early identification of anaphylaxis and early intervention with epinephrine are critical for improving patient outcomes,” Chow said in an interview.
“Many allergic reactions occur in community settings, where written action plans serve to instruct patients and caregivers on how to recognize and respond to these emergencies,” she said. “Currently, anaphylaxis action plans are developed based on the consensus of healthcare professionals, with limited information available on the preferences of patients and caregivers,” she noted. However, even with action plans, many patients and families struggle to recognize and manage severe allergic reactions effectively, she added.
In response to this issue, Chow and colleagues created a survey designed to assess the understanding of anaphylaxis recognition and management by patients and caregivers and to identify their preferences regarding the elements included in the action plans.
In the study, Chow and colleagues surveyed 96 patients and caregivers in an allergy clinic waiting room. The majority (95%) of the patients were prescribed epinephrine. Although 73% said they were comfortable identifying signs of anaphylaxis, only 14% said they were likely to use epinephrine as a first-line treatment.
The most common reason given for avoiding epinephrine was uncertainty over which symptoms to treat (40.6%), followed by hesitancy to visit an emergency department (24%), hesitancy to call 911 (17.7%), uncertainty about how to use epinephrine auto-injectors (11.5%), and fear of needles (5.2%).
Although 85% of the respondents understood that antihistamine use does not prevent the need for epinephrine in cases of anaphylactic reactions, 23.7% said they would use an antihistamine as the first treatment in these cases.
For patients with rash and wheezing after a suspected allergen exposure, approximately two thirds (64.5%) of the respondents said they would inject epinephrine and 10.8% would drive to the emergency room before taking any action, Chow said in her presentation.
The relatively low impact of fear of needles was unexpected, as fear of needles is considered a significant deterrent to epinephrine use, Chow told this news organization. “However, our respondents were more inclined to acknowledge a reluctance to escalate to emergency response as the major barrier to treatment,” she said.
The survey also asked patients what features of an anaphylaxis action plan would be most helpful. A majority of respondents (93%) rated a section for the management of mild (non-anaphylactic) allergic reaction symptoms as somewhat or very important. Visual aids for injection of epinephrine and visuals of anaphylaxis symptoms also ranked as somewhat or very important for 87.6% and 81% of respondents, respectively.
The study highlights the importance of educating allergy patients on recognizing and treating anaphylaxis and demonstrates that visuals were preferred in this survey population, Chow said. “Most patients and caregivers from our surveyed population report knowing how to treat anaphylaxis, but many would not use epinephrine as the first treatment,” she noted.
“The study focused on a single community clinic, and it would be beneficial to gather feedback from patients and caregivers representing a wider variety of educational, cultural, social, and socioeconomic backgrounds,” Chow told this news organization. “Additionally, input from other stakeholders, such as school nurses, would enhance knowledge,” she said.
Clinical Anaphylaxis Protocols Fall Short
A second study presented at the meeting showed the need to improve anaphylaxis education for clinicians.
Discrepancies in anaphylaxis management include variations in the definition and treatment of the condition, according to Carly Gunderson, DO, of Memorial Healthcare System, Pembroke Pines, Florida, who presented the study at the meeting.
“So often, we see patients in our office with a history of symptoms that meet criteria for anaphylaxis, yet when they call 911 and emergency medical services (EMS) arrive, they never receive epinephrine,” Gunderson said in an interview. “They receive antihistamines, steroids, everything except epinephrine, which is incredibly concerning given that epinephrine is always the first-line treatment for anaphylaxis,” she said.
“Because EMS providers are often the first healthcare professionals to assess patients experiencing anaphylaxis, their ability to recognize and appropriately treat anaphylaxis is essential,” Gunderson emphasized.
Gunderson and colleagues analyzed data from 30 states with mandatory Advanced Cardiac Life Support protocols to identify gaps in recognizing anaphylaxis and areas for improvement in prehospital management.
Only 15 states (50%) included gastrointestinal symptoms in the definition of anaphylaxis, 40% included neurologic manifestations, and 47% used a two-organ system definition, Gunderson noted in her presentation.
All 30 state protocols recommended diphenhydramine and epinephrine for anaphylactic reactions, 90% recommended albuterol if respiratory symptoms were present, 73% recommended intravenous fluids, and 60% recommended steroids. All but one of the state protocols listed epinephrine as the first-line recommendation for anaphylaxis; 25 states allowed epinephrine autoinjectors and 17 provided autoinjectors.
“We were shocked by how many protocols didn’t include gastrointestinal (abdominal pain, vomiting) or neurologic (lethargy, altered mental status) manifestations, when these are common presenting symptoms of anaphylaxis,” Gunderson told this news organization.
“We were also disappointed by how many protocols continue to recommend outdated interventions such as first-generation antihistamines and corticosteroids in the treatment of anaphylaxis,” she said.
Although anaphylaxis management has come a long way, the current study suggests that there is clearly room for improvement in the education of healthcare providers on how to identify and treat anaphylaxis, said Gunderson. “Most people think of anaphylaxis as the typical ‘face swelling up, throat closing’ type of reaction, which it can be, but in reality, there are so many other ways that it can present,” she said. “Healthcare providers must be aware of all of these possible manifestations so that we can treat in a timely manner to improve outcomes,” she added.
Limitations of the study included the focus only on states with mandatory or model EMS protocols, Gunderson told this news organization. As for additional research, the most important next steps are practical ones, namely, identifying ways to realistically implement necessary protocol changes, she said.
Real-World Data Support Need for Education
Real-world studies are important to identify current practice and opportunities for improvement, S. Shahzad Mustafa, MD, lead physician in allergy, immunology, and rheumatology at Rochester Regional Health and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, New York, said in an interview.
“Management of anaphylaxis continues to evolve, and studies like these can help standardize evidence-based care across different medical settings, such as emergency medical services, urgent care, and emergency departments,” said Mustafa, who was not involved in either study.
The findings of the two studies were not unexpected, Mustafa said. “Heterogeneity in medical care is well recognized in numerous conditions, and anaphylaxis is no different. Patients and healthcare providers continue to have hesitation to use epinephrine and continue to overly rely on antihistamines and/or systemic steroids,” he noted.
For both studies, the takeaway message is that education is paramount to optimize anaphylaxis management, Mustafa told this news organization. “Education needs to focus on timely recognition of anaphylaxis, including atypical features such as gastrointestinal symptoms, and appropriate therapy with epinephrine,” he said.
Looking ahead, “research demonstrating differences in clinical outcomes with differing approaches to anaphylaxis may highlight the importance of early recognition and treatment with epinephrine,” said Mustafa. Management of anaphylaxis also lends itself to quality improvement studies, he added.
Neither of the studies received any outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Mustafa had no disclosures related to anaphylaxis but disclosed serving on the speakers’ bureau for Genentech, GSK, AstraZeneca, Regeneron/Sanofi, and CSL Behring and received grants from Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hyperkeratotic Papules and Black Macules on the Hands
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Hemorrhagic Darier Disease
Darier disease (DD), also known as keratosis follicularis, is a rare autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by mutations in the ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 2 gene (ATP2A2). This gene encodes the enzyme sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2, which results in abnormal calcium signaling in keratinocytes and leads to dyskeratosis.1 Darier disease commonly manifests in the second decade of life with hyperkeratotic papules coalescing into plaques, often accompanied by erosions and fissures that cause discomfort and pruritus. Darier disease also is associated with characteristic nail findings such as the classic candy cane nails and V-shaped nicking.
Acral hemorrhagic lesions are a rare manifestation of DD. Clinically, these lesions can manifest as hemorrhagic macules, papules, and/or vesicles, most commonly occurring following local trauma or retinoid use. Patients with these lesions are believed to have either specific mutations in the ATP2A2 gene that impair sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 function in the vascular endothelium or a mutation in the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase protein itself, leading to dysregulation of mitochondrial homeostasis from within the cell, provoking oxidative stress and causing detrimental effects on blood vessels.2 Patients with this variant can present with all the features of classic DD concomitantly, with varying symptom severity or distinct clinical features during separate episodic flares, or as the sole manifestation. Other nonclassical lesions of DD include acral keratoderma, giant comedones, keloidlike vegetations, and leucodermic macules (Figure).3
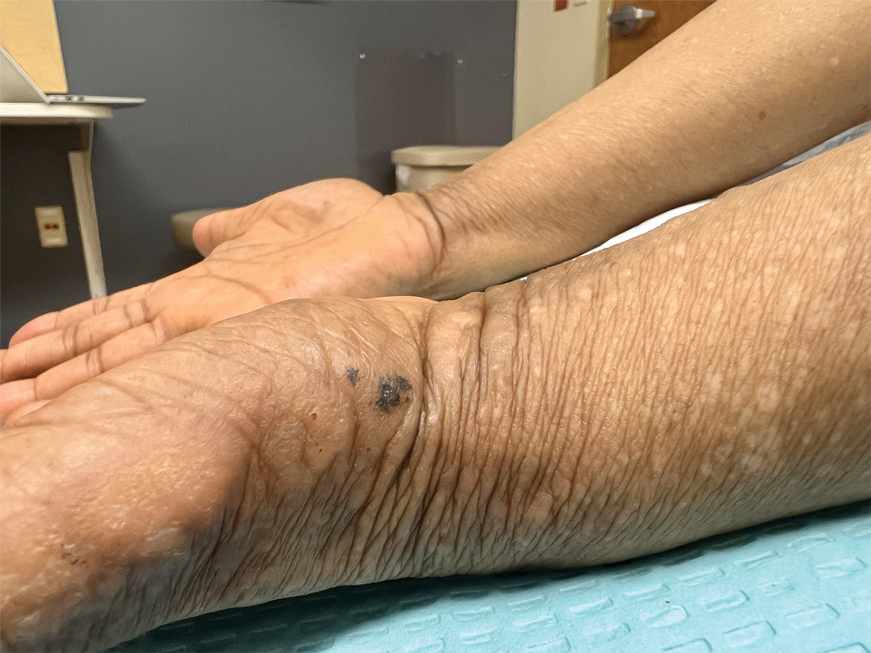
Acral hemorrhagic DD may appear either in isolation or in tandem with more traditional symptoms, necessitating consideration of other possible differential diagnoses such as acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf (AKV), porphyria cutanea tarda, bullous lichen planus (BLP), and hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus.
Sometimes regarded as a variant of DD, AKV is an autosomal- dominant genodermatosis characterized by flat or verrucous hyperkeratotic papules on the hands and feet. In AKV, the nails also may be affected, with changes including striations, subungual hyperkeratosis, and V-shaped nicking of the distal nails. Although our patient displayed features of AKV, it has not been associated with acral hemorrhagic macules, making this diagnosis less likely than DD.4
Porphyria cutanea tarda, a condition caused by decreased levels of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, also can cause skin manifestations such as blistering as well as increased skin fragility, predominantly in sun-exposed areas.5 Our patient’s lack of photosensitivity and absence of other common symptoms of this disorder, such as hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, made porphyria cutanea tarda less likely.
Bullous lichen planus is a rare subtype of lichen planus characterized by tense bullae arising from preexisting lichen planus lesions or appearing de novo, most commonly manifesting on the oral mucosa or the legs.6 The bullae associated with BLP can rupture and form ulcers—a symptom that could potentially be mistaken for hemorrhagic macules like the ones observed in our patient. However, BLP typically is characterized by erythematous, violaceous, polygonal papules commonly appearing on the oral mucosa and the legs with blisters developing near or on pre-existing lichen planus lesions. These are different from the hyperkeratotic papules and leucodermic macules seen in our patient, which aligned more closely with the clinical presentation of DD.
Hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus presents with white atrophic patches and plaques and hemorrhagic bullae, which may resemble the leucodermic macules and hemorrhagic macules of DD. However, hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus most commonly involves the genital area in postmenopausal women. Extragenital manifestations of lichen sclerosus, although less common, can occur and typically manifest on the thighs, buttocks, breasts, back, chest, axillae, shoulders, and wrists.7 Notably, these hemorrhagic lesions typically are surrounded by hypopigmented skin and display an atrophic appearance.
Management of DD can be challenging. General measures include sun protection, heat avoidance, and friction reduction. Retinoids are considered the first-line therapy for severe DD, as they help normalize keratinocyte differentiation and reduce keratotic scaling.8 Topical corticosteroids can help manage inflammation and reduce the risk for secondary infections. Our patient responded well to this treatment approach, with a notable reduction in the number and severity of the hyperkeratotic plaques and resolution of the acral hemorrhagic lesions.
- Savignac M, Edir A, Simon M, et al. Darier disease: a disease model of impaired calcium homeostasis in the skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1111-1117. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.12.006
- Hong E, Hu R, Posligua A, et al. Acral hemorrhagic Darier disease: a case report of a rare presentation and literature review. JAAD Case Rep. 2023;31:93-96. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.05.030
- Yeshurun A, Ziv M, Cohen-Barak E, et al. An update on the cutaneous manifestations of Darier disease. J Cutan Med Surg. 2021;25:498-503. doi:10.1177/1203475421999331
- Williams GM, Lincoln M. Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; May 1, 2023.
- Shah A, Bhatt H. Cutanea tarda porphyria. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; April 17, 2023.
- Liakopoulou A, Rallis E. Bullous lichen planus—a review. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2017;11:1-4. doi:10.3315/jdcr.2017.1239
- Arnold N, Manway M, Stephenson S, et al. Extragenital bullous lichen sclerosus on the anterior lower extremities: report of a case and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030
- Haber RN, Dib NG. Management of Darier disease: a review of the literature and update. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87:14-21. doi:10.25259/IJDVL_963_19 /qt8dn3p7kv.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Hemorrhagic Darier Disease
Darier disease (DD), also known as keratosis follicularis, is a rare autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by mutations in the ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 2 gene (ATP2A2). This gene encodes the enzyme sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2, which results in abnormal calcium signaling in keratinocytes and leads to dyskeratosis.1 Darier disease commonly manifests in the second decade of life with hyperkeratotic papules coalescing into plaques, often accompanied by erosions and fissures that cause discomfort and pruritus. Darier disease also is associated with characteristic nail findings such as the classic candy cane nails and V-shaped nicking.
Acral hemorrhagic lesions are a rare manifestation of DD. Clinically, these lesions can manifest as hemorrhagic macules, papules, and/or vesicles, most commonly occurring following local trauma or retinoid use. Patients with these lesions are believed to have either specific mutations in the ATP2A2 gene that impair sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 function in the vascular endothelium or a mutation in the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase protein itself, leading to dysregulation of mitochondrial homeostasis from within the cell, provoking oxidative stress and causing detrimental effects on blood vessels.2 Patients with this variant can present with all the features of classic DD concomitantly, with varying symptom severity or distinct clinical features during separate episodic flares, or as the sole manifestation. Other nonclassical lesions of DD include acral keratoderma, giant comedones, keloidlike vegetations, and leucodermic macules (Figure).3

Acral hemorrhagic DD may appear either in isolation or in tandem with more traditional symptoms, necessitating consideration of other possible differential diagnoses such as acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf (AKV), porphyria cutanea tarda, bullous lichen planus (BLP), and hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus.
Sometimes regarded as a variant of DD, AKV is an autosomal- dominant genodermatosis characterized by flat or verrucous hyperkeratotic papules on the hands and feet. In AKV, the nails also may be affected, with changes including striations, subungual hyperkeratosis, and V-shaped nicking of the distal nails. Although our patient displayed features of AKV, it has not been associated with acral hemorrhagic macules, making this diagnosis less likely than DD.4
Porphyria cutanea tarda, a condition caused by decreased levels of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, also can cause skin manifestations such as blistering as well as increased skin fragility, predominantly in sun-exposed areas.5 Our patient’s lack of photosensitivity and absence of other common symptoms of this disorder, such as hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, made porphyria cutanea tarda less likely.
Bullous lichen planus is a rare subtype of lichen planus characterized by tense bullae arising from preexisting lichen planus lesions or appearing de novo, most commonly manifesting on the oral mucosa or the legs.6 The bullae associated with BLP can rupture and form ulcers—a symptom that could potentially be mistaken for hemorrhagic macules like the ones observed in our patient. However, BLP typically is characterized by erythematous, violaceous, polygonal papules commonly appearing on the oral mucosa and the legs with blisters developing near or on pre-existing lichen planus lesions. These are different from the hyperkeratotic papules and leucodermic macules seen in our patient, which aligned more closely with the clinical presentation of DD.
Hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus presents with white atrophic patches and plaques and hemorrhagic bullae, which may resemble the leucodermic macules and hemorrhagic macules of DD. However, hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus most commonly involves the genital area in postmenopausal women. Extragenital manifestations of lichen sclerosus, although less common, can occur and typically manifest on the thighs, buttocks, breasts, back, chest, axillae, shoulders, and wrists.7 Notably, these hemorrhagic lesions typically are surrounded by hypopigmented skin and display an atrophic appearance.
Management of DD can be challenging. General measures include sun protection, heat avoidance, and friction reduction. Retinoids are considered the first-line therapy for severe DD, as they help normalize keratinocyte differentiation and reduce keratotic scaling.8 Topical corticosteroids can help manage inflammation and reduce the risk for secondary infections. Our patient responded well to this treatment approach, with a notable reduction in the number and severity of the hyperkeratotic plaques and resolution of the acral hemorrhagic lesions.
THE DIAGNOSIS: Acral Hemorrhagic Darier Disease
Darier disease (DD), also known as keratosis follicularis, is a rare autosomal-dominant genodermatosis caused by mutations in the ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 2 gene (ATP2A2). This gene encodes the enzyme sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2, which results in abnormal calcium signaling in keratinocytes and leads to dyskeratosis.1 Darier disease commonly manifests in the second decade of life with hyperkeratotic papules coalescing into plaques, often accompanied by erosions and fissures that cause discomfort and pruritus. Darier disease also is associated with characteristic nail findings such as the classic candy cane nails and V-shaped nicking.
Acral hemorrhagic lesions are a rare manifestation of DD. Clinically, these lesions can manifest as hemorrhagic macules, papules, and/or vesicles, most commonly occurring following local trauma or retinoid use. Patients with these lesions are believed to have either specific mutations in the ATP2A2 gene that impair sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 function in the vascular endothelium or a mutation in the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase protein itself, leading to dysregulation of mitochondrial homeostasis from within the cell, provoking oxidative stress and causing detrimental effects on blood vessels.2 Patients with this variant can present with all the features of classic DD concomitantly, with varying symptom severity or distinct clinical features during separate episodic flares, or as the sole manifestation. Other nonclassical lesions of DD include acral keratoderma, giant comedones, keloidlike vegetations, and leucodermic macules (Figure).3

Acral hemorrhagic DD may appear either in isolation or in tandem with more traditional symptoms, necessitating consideration of other possible differential diagnoses such as acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf (AKV), porphyria cutanea tarda, bullous lichen planus (BLP), and hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus.
Sometimes regarded as a variant of DD, AKV is an autosomal- dominant genodermatosis characterized by flat or verrucous hyperkeratotic papules on the hands and feet. In AKV, the nails also may be affected, with changes including striations, subungual hyperkeratosis, and V-shaped nicking of the distal nails. Although our patient displayed features of AKV, it has not been associated with acral hemorrhagic macules, making this diagnosis less likely than DD.4
Porphyria cutanea tarda, a condition caused by decreased levels of uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase, also can cause skin manifestations such as blistering as well as increased skin fragility, predominantly in sun-exposed areas.5 Our patient’s lack of photosensitivity and absence of other common symptoms of this disorder, such as hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation, made porphyria cutanea tarda less likely.
Bullous lichen planus is a rare subtype of lichen planus characterized by tense bullae arising from preexisting lichen planus lesions or appearing de novo, most commonly manifesting on the oral mucosa or the legs.6 The bullae associated with BLP can rupture and form ulcers—a symptom that could potentially be mistaken for hemorrhagic macules like the ones observed in our patient. However, BLP typically is characterized by erythematous, violaceous, polygonal papules commonly appearing on the oral mucosa and the legs with blisters developing near or on pre-existing lichen planus lesions. These are different from the hyperkeratotic papules and leucodermic macules seen in our patient, which aligned more closely with the clinical presentation of DD.
Hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus presents with white atrophic patches and plaques and hemorrhagic bullae, which may resemble the leucodermic macules and hemorrhagic macules of DD. However, hemorrhagic lichen sclerosus most commonly involves the genital area in postmenopausal women. Extragenital manifestations of lichen sclerosus, although less common, can occur and typically manifest on the thighs, buttocks, breasts, back, chest, axillae, shoulders, and wrists.7 Notably, these hemorrhagic lesions typically are surrounded by hypopigmented skin and display an atrophic appearance.
Management of DD can be challenging. General measures include sun protection, heat avoidance, and friction reduction. Retinoids are considered the first-line therapy for severe DD, as they help normalize keratinocyte differentiation and reduce keratotic scaling.8 Topical corticosteroids can help manage inflammation and reduce the risk for secondary infections. Our patient responded well to this treatment approach, with a notable reduction in the number and severity of the hyperkeratotic plaques and resolution of the acral hemorrhagic lesions.
- Savignac M, Edir A, Simon M, et al. Darier disease: a disease model of impaired calcium homeostasis in the skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1111-1117. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.12.006
- Hong E, Hu R, Posligua A, et al. Acral hemorrhagic Darier disease: a case report of a rare presentation and literature review. JAAD Case Rep. 2023;31:93-96. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.05.030
- Yeshurun A, Ziv M, Cohen-Barak E, et al. An update on the cutaneous manifestations of Darier disease. J Cutan Med Surg. 2021;25:498-503. doi:10.1177/1203475421999331
- Williams GM, Lincoln M. Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; May 1, 2023.
- Shah A, Bhatt H. Cutanea tarda porphyria. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; April 17, 2023.
- Liakopoulou A, Rallis E. Bullous lichen planus—a review. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2017;11:1-4. doi:10.3315/jdcr.2017.1239
- Arnold N, Manway M, Stephenson S, et al. Extragenital bullous lichen sclerosus on the anterior lower extremities: report of a case and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030
- Haber RN, Dib NG. Management of Darier disease: a review of the literature and update. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87:14-21. doi:10.25259/IJDVL_963_19 /qt8dn3p7kv.
- Savignac M, Edir A, Simon M, et al. Darier disease: a disease model of impaired calcium homeostasis in the skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813:1111-1117. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.12.006
- Hong E, Hu R, Posligua A, et al. Acral hemorrhagic Darier disease: a case report of a rare presentation and literature review. JAAD Case Rep. 2023;31:93-96. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.05.030
- Yeshurun A, Ziv M, Cohen-Barak E, et al. An update on the cutaneous manifestations of Darier disease. J Cutan Med Surg. 2021;25:498-503. doi:10.1177/1203475421999331
- Williams GM, Lincoln M. Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; May 1, 2023.
- Shah A, Bhatt H. Cutanea tarda porphyria. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; April 17, 2023.
- Liakopoulou A, Rallis E. Bullous lichen planus—a review. J Dermatol Case Rep. 2017;11:1-4. doi:10.3315/jdcr.2017.1239
- Arnold N, Manway M, Stephenson S, et al. Extragenital bullous lichen sclerosus on the anterior lower extremities: report of a case and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2017;23:13030
- Haber RN, Dib NG. Management of Darier disease: a review of the literature and update. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87:14-21. doi:10.25259/IJDVL_963_19 /qt8dn3p7kv.
An elderly woman with a long history of hyperkeratotic papules on the abdomen, forearms, dorsal hands, and skinfolds presented with new lesions on the dorsal hands that had developed over the preceding few months after a lapse in treatment with her previous dermatologist. Her medical history was otherwise unremarkable. Physical examination revealed hyperkeratotic papules, black hemorrhagic macules with jagged borders, and a thin hemorrhagic plaque on the dorsal hands. Nail findings were notable for alternating white and red longitudinal bands with nicking of the distal nail plates. She also had scattered leucodermic macules over the trunk, feet, arms, and legs, as well as numerous hyperkeratotic papules coalescing into plaques over the mons pubis and in the inguinal folds.
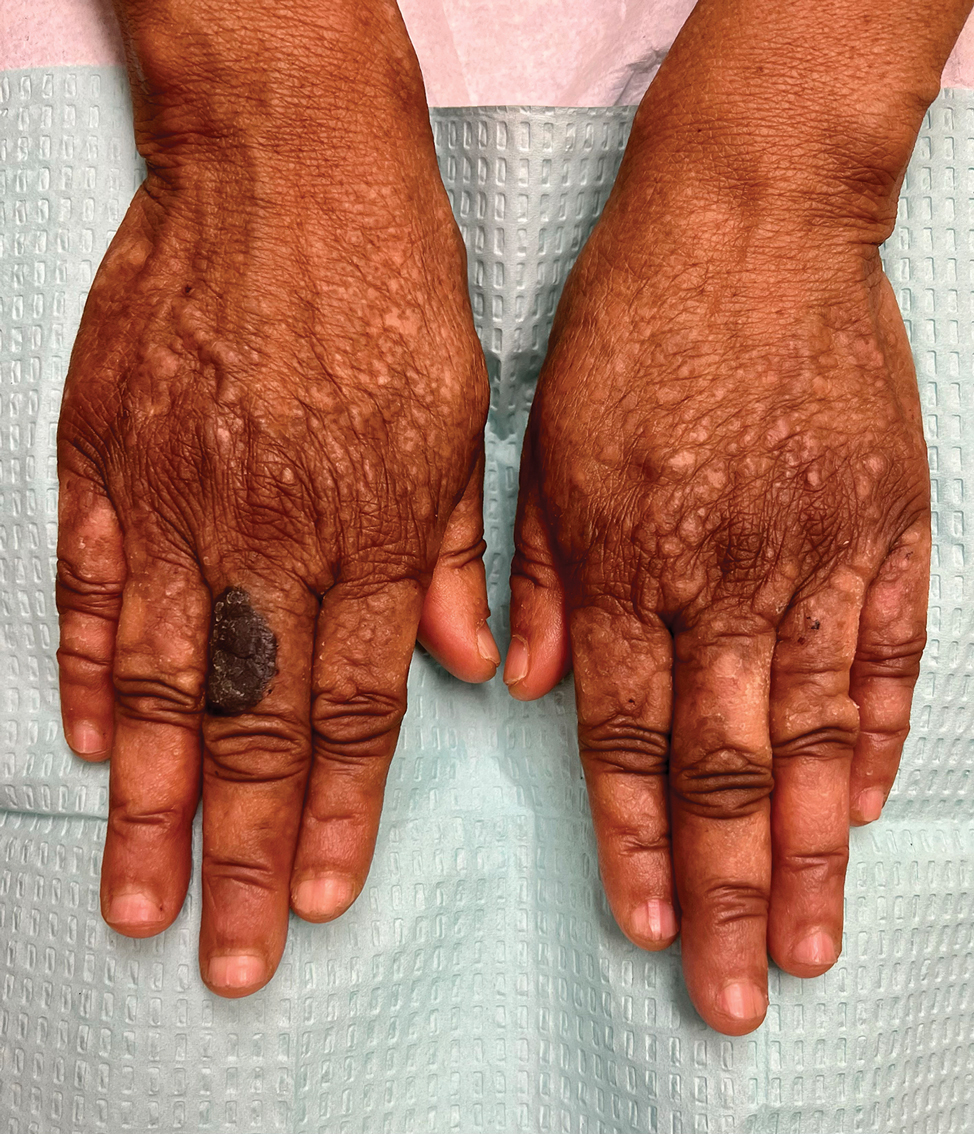
Gardasil 9 at 10 Years: Vaccine Protects Against Multiple Cancers
Vaccination against human papilloma virus (HPV), a group of more than 200 viruses infecting at least 50% of sexually active people over their lifetimes, has proved more than 90% effective for preventing several diseases caused by high-risk HPV types.
Gardasil 4: 2006
It started in 2006 with the approval of Human Papillomavirus Quadrivalent, types 6, 11, 16, and 18 (Gardasil 4). Merck’s vaccine began to lower rates of cervical cancer, a major global killer of women.
“It’s fair to say the vaccine has been an American and a global public health success story in reducing rates of cervical cancer,” Paula M. Cuccaro, PhD, assistant professor of health promotion and behavioral sciences at University of Texas School of Public Health, Houston, said in an interview.
How does a common virus trigger such a lethal gynecologic malignancy? “It knocks out two important cancer suppressor genes in cells,” explained Christina Annunziata,MD, PhD, a medical oncologist and senior vice president of extramural discovery science for the American Cancer Society. HPV oncoproteins are encoded by the E6 and E7 genes. As in other DNA tumor viruses, the E6 and E7 proteins functionally inactivate the tumor suppressor proteins p53 and pRB, respectively.
US Prevalence
Despite screening and vaccination, cervical cancer is still very much around. This year, 13,820 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed in the United States, and approximately 4360 women will die of it, according to the American Cancer Society. Even before the advent of Gardasil 4, incidence rates had already decreased by more than half from the mid-1970s to the mid-2000s, thanks largely to Pap smear screening programs for treatable premalignant lesions. “The US rate had dropped to about 20 per 100,000 women even before Gardasil 4,” said Annunziata. “After the introduction of the first vaccine, it decreased to 7 per 100,000, a decrease of about 30%, but it remains plateaued now at about the same level.”
Although the past decade has seen rates generally stabilize, there have been some changes in different age groups. In women ages 30-44, rates increased 1.7% each year from 2012 to 2019, while rates declined 11% each year for women ages 20-24— probably reflecting the impact of the first wave of prevention from Gardasil 4.
In one 2021 population-based study of US cancer registry data from 1999 to 2017, rates of both cervical squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma dropped. The largest declines occurred in females 15-20 years old, the age group most likely to be vaccinated against HPV but not typically screened, suggesting a vaccine-related effect.
Gardasil 9: 2014
With the 2014 approval of the vaccine’s second iteration, Gardasil 9, which replaced Gardasil 4 and targeted 9 HPV strains, immunization has taken broader aim. The strains covered by Gardasil 9 protect against oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers — as well as penile, anal, vulvar, and vaginal malignancies and premalignancies, and genital warts in both sexes ages 9-45.
It may be years, however, before the impact of the newer polyvalent formulation is felt. “While the first vaccine has been successful against the prevalent strains of HPV linked to cervical cancer, it’s a little early to call it for the newer vaccine since oropharyngeal cancers tend to develop later in older men,” Cuccaro said. “But the types of HPV linked to mouth and throat cancers and covered by the newer vaccines are much less prevalent in those who are vaccinated. The strains not covered in the vaccine you see are equally present in the vaccinated and non-vaccinated.”
Angela L. Myers, MD, MPH, division director of infectious diseases and medical director of the Center for Wellbeing at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Missouri, added, “Unlike for cervical cancer, there are no screening programs for oropharyngeal lesions, so you have to wait to see rates until actual cancer develops.”
A 2023 review reported that HPV vaccination reduced levels of oropharyngeal HPV positivity in men, strengthening the case for pangender immunization.
And in a recent phase 3 doubled-blind trial, GARDASIL 9 reduced the incidence of anogenital persistent infection caused by nine types of HPV compared with a placebo.
Increasing Uptake
The current public health aim is to have 80% of young people in the targeted age group vaccinated with two doses. Today, uptake among those 9-26 years old stands at about 78% of girls and 75% of boys for the first dose, said Annunziata. “But it’s only about 61% for the two doses in the current series, and we want to improve that.”
Some parents may still harbor fears that immunizing teens and tweens — both the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Cancer Society recommend immunization at age 9 — will open the door to precocious sexual activity.
“But overall, uptake in tweens and young teens has increased because the messaging has changed,” said Myers, with the rationale now focusing on cancer prevention not sexual-infection prophylaxis. “This is similar to the hepatitis B vaccine, which used to be given to young adults and is now given to newborns to prevent cancer.”
Cuccaro added that a proactive presentation by healthcare professionals has a significant effect on vaccine uptake and increases the odds of vaccination ninefold. “Providers should take a presumptive approach and avoid just offering the vaccine as an option. It should be included with regular childhood vaccinations,” she said. “And the advantage of starting early at age 9 is that you can spread the doses out across other regular childhood vaccinations, whereas if you start at age 11, you need to add the HPV vaccine to three other vaccines that are given at that time.”
After age 15, three doses are necessary. “Providers should stress to parents that it’s most effective when given before young people become sexually active and exposed to HPV,” Cuccaro said. And Myers stressed that despite the vaccine’s effectiveness, routine screening for cervical premalignancies is still important.
Despite increasing coverage, vaccination rates have some distance to go before the public health target of at least 80% uptake of the series in the targeted age group, Cuccaro cautioned.
On the global stage, barriers to immunization remain, but the World Health Organization has endorsed a campaign to eradicate cervical cancer through HPV vaccination. It has predicted that the 21st century may be the last to experience HPV-associated cancers, currently responsible for more than 300,000 annual deaths worldwide.
A Brief History of HPV Vaccines
- 1951. Cervical cancer patient Henrietta Lacks’ rapidly dividing cervical cells are collected by George Otto Gey at Johns Hopkins Hospital. They create the first immortal cell line (HeLa) used to study cancers and vaccines worldwide.
- 1976. Harald zur Hausen suggests that genital wart-associated HPV, not herpes simplex, is the probable cause of cervical cancer.
- 1983. HPV is confirmed as a cause of cancer.
- 1991. The first HPV vaccine is developed.
- 2002. Proof of principle and protective efficacy for the monovalent HPV 16 are shown.
- 2006. Merck’s Gardasil 4 (HPV 4) is FDA approved in girls ages 9-26 for protection against strains 6, 11, 16, and 18 — the cause of more than 70% of cervical cancer cases.
- 2009. Approval of Gardasil 4 is expanded to boys ages 9-26 for the prevention of genital warts.
- 2009. The FDA approves GlaxoSmithKline’s Cervarix (HPV 16 and 18) for girls and young women. The vaccine was withdrawn from the US market in 2016 following the success of Gardasil 9 but is used abroad for HPV cancer prevention.
- 2014. The 9-valent recombinant vaccine Gardasil 9 is FDA approved for protection against several low-risk, wart-causing HPV strains as well as the high-risk cancer strains targeted by HPV 4.
- 2018. The FDA expands approval to include females and males 27-45 years old.
- 2020. The FDA extends approval of Gardasil 9 to include prevention not only of cervical cancer but also, vaginal, vulvar, anal, oropharyngeal, and other head and neck cancers.
Annunziata, Cuccaro, and Myers had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccination against human papilloma virus (HPV), a group of more than 200 viruses infecting at least 50% of sexually active people over their lifetimes, has proved more than 90% effective for preventing several diseases caused by high-risk HPV types.
Gardasil 4: 2006
It started in 2006 with the approval of Human Papillomavirus Quadrivalent, types 6, 11, 16, and 18 (Gardasil 4). Merck’s vaccine began to lower rates of cervical cancer, a major global killer of women.
“It’s fair to say the vaccine has been an American and a global public health success story in reducing rates of cervical cancer,” Paula M. Cuccaro, PhD, assistant professor of health promotion and behavioral sciences at University of Texas School of Public Health, Houston, said in an interview.
How does a common virus trigger such a lethal gynecologic malignancy? “It knocks out two important cancer suppressor genes in cells,” explained Christina Annunziata,MD, PhD, a medical oncologist and senior vice president of extramural discovery science for the American Cancer Society. HPV oncoproteins are encoded by the E6 and E7 genes. As in other DNA tumor viruses, the E6 and E7 proteins functionally inactivate the tumor suppressor proteins p53 and pRB, respectively.
US Prevalence
Despite screening and vaccination, cervical cancer is still very much around. This year, 13,820 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed in the United States, and approximately 4360 women will die of it, according to the American Cancer Society. Even before the advent of Gardasil 4, incidence rates had already decreased by more than half from the mid-1970s to the mid-2000s, thanks largely to Pap smear screening programs for treatable premalignant lesions. “The US rate had dropped to about 20 per 100,000 women even before Gardasil 4,” said Annunziata. “After the introduction of the first vaccine, it decreased to 7 per 100,000, a decrease of about 30%, but it remains plateaued now at about the same level.”
Although the past decade has seen rates generally stabilize, there have been some changes in different age groups. In women ages 30-44, rates increased 1.7% each year from 2012 to 2019, while rates declined 11% each year for women ages 20-24— probably reflecting the impact of the first wave of prevention from Gardasil 4.
In one 2021 population-based study of US cancer registry data from 1999 to 2017, rates of both cervical squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma dropped. The largest declines occurred in females 15-20 years old, the age group most likely to be vaccinated against HPV but not typically screened, suggesting a vaccine-related effect.
Gardasil 9: 2014
With the 2014 approval of the vaccine’s second iteration, Gardasil 9, which replaced Gardasil 4 and targeted 9 HPV strains, immunization has taken broader aim. The strains covered by Gardasil 9 protect against oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers — as well as penile, anal, vulvar, and vaginal malignancies and premalignancies, and genital warts in both sexes ages 9-45.
It may be years, however, before the impact of the newer polyvalent formulation is felt. “While the first vaccine has been successful against the prevalent strains of HPV linked to cervical cancer, it’s a little early to call it for the newer vaccine since oropharyngeal cancers tend to develop later in older men,” Cuccaro said. “But the types of HPV linked to mouth and throat cancers and covered by the newer vaccines are much less prevalent in those who are vaccinated. The strains not covered in the vaccine you see are equally present in the vaccinated and non-vaccinated.”
Angela L. Myers, MD, MPH, division director of infectious diseases and medical director of the Center for Wellbeing at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Missouri, added, “Unlike for cervical cancer, there are no screening programs for oropharyngeal lesions, so you have to wait to see rates until actual cancer develops.”
A 2023 review reported that HPV vaccination reduced levels of oropharyngeal HPV positivity in men, strengthening the case for pangender immunization.
And in a recent phase 3 doubled-blind trial, GARDASIL 9 reduced the incidence of anogenital persistent infection caused by nine types of HPV compared with a placebo.
Increasing Uptake
The current public health aim is to have 80% of young people in the targeted age group vaccinated with two doses. Today, uptake among those 9-26 years old stands at about 78% of girls and 75% of boys for the first dose, said Annunziata. “But it’s only about 61% for the two doses in the current series, and we want to improve that.”
Some parents may still harbor fears that immunizing teens and tweens — both the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Cancer Society recommend immunization at age 9 — will open the door to precocious sexual activity.
“But overall, uptake in tweens and young teens has increased because the messaging has changed,” said Myers, with the rationale now focusing on cancer prevention not sexual-infection prophylaxis. “This is similar to the hepatitis B vaccine, which used to be given to young adults and is now given to newborns to prevent cancer.”
Cuccaro added that a proactive presentation by healthcare professionals has a significant effect on vaccine uptake and increases the odds of vaccination ninefold. “Providers should take a presumptive approach and avoid just offering the vaccine as an option. It should be included with regular childhood vaccinations,” she said. “And the advantage of starting early at age 9 is that you can spread the doses out across other regular childhood vaccinations, whereas if you start at age 11, you need to add the HPV vaccine to three other vaccines that are given at that time.”
After age 15, three doses are necessary. “Providers should stress to parents that it’s most effective when given before young people become sexually active and exposed to HPV,” Cuccaro said. And Myers stressed that despite the vaccine’s effectiveness, routine screening for cervical premalignancies is still important.
Despite increasing coverage, vaccination rates have some distance to go before the public health target of at least 80% uptake of the series in the targeted age group, Cuccaro cautioned.
On the global stage, barriers to immunization remain, but the World Health Organization has endorsed a campaign to eradicate cervical cancer through HPV vaccination. It has predicted that the 21st century may be the last to experience HPV-associated cancers, currently responsible for more than 300,000 annual deaths worldwide.
A Brief History of HPV Vaccines
- 1951. Cervical cancer patient Henrietta Lacks’ rapidly dividing cervical cells are collected by George Otto Gey at Johns Hopkins Hospital. They create the first immortal cell line (HeLa) used to study cancers and vaccines worldwide.
- 1976. Harald zur Hausen suggests that genital wart-associated HPV, not herpes simplex, is the probable cause of cervical cancer.
- 1983. HPV is confirmed as a cause of cancer.
- 1991. The first HPV vaccine is developed.
- 2002. Proof of principle and protective efficacy for the monovalent HPV 16 are shown.
- 2006. Merck’s Gardasil 4 (HPV 4) is FDA approved in girls ages 9-26 for protection against strains 6, 11, 16, and 18 — the cause of more than 70% of cervical cancer cases.
- 2009. Approval of Gardasil 4 is expanded to boys ages 9-26 for the prevention of genital warts.
- 2009. The FDA approves GlaxoSmithKline’s Cervarix (HPV 16 and 18) for girls and young women. The vaccine was withdrawn from the US market in 2016 following the success of Gardasil 9 but is used abroad for HPV cancer prevention.
- 2014. The 9-valent recombinant vaccine Gardasil 9 is FDA approved for protection against several low-risk, wart-causing HPV strains as well as the high-risk cancer strains targeted by HPV 4.
- 2018. The FDA expands approval to include females and males 27-45 years old.
- 2020. The FDA extends approval of Gardasil 9 to include prevention not only of cervical cancer but also, vaginal, vulvar, anal, oropharyngeal, and other head and neck cancers.
Annunziata, Cuccaro, and Myers had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Vaccination against human papilloma virus (HPV), a group of more than 200 viruses infecting at least 50% of sexually active people over their lifetimes, has proved more than 90% effective for preventing several diseases caused by high-risk HPV types.
Gardasil 4: 2006
It started in 2006 with the approval of Human Papillomavirus Quadrivalent, types 6, 11, 16, and 18 (Gardasil 4). Merck’s vaccine began to lower rates of cervical cancer, a major global killer of women.
“It’s fair to say the vaccine has been an American and a global public health success story in reducing rates of cervical cancer,” Paula M. Cuccaro, PhD, assistant professor of health promotion and behavioral sciences at University of Texas School of Public Health, Houston, said in an interview.
How does a common virus trigger such a lethal gynecologic malignancy? “It knocks out two important cancer suppressor genes in cells,” explained Christina Annunziata,MD, PhD, a medical oncologist and senior vice president of extramural discovery science for the American Cancer Society. HPV oncoproteins are encoded by the E6 and E7 genes. As in other DNA tumor viruses, the E6 and E7 proteins functionally inactivate the tumor suppressor proteins p53 and pRB, respectively.
US Prevalence
Despite screening and vaccination, cervical cancer is still very much around. This year, 13,820 new cases of invasive cervical cancer will be diagnosed in the United States, and approximately 4360 women will die of it, according to the American Cancer Society. Even before the advent of Gardasil 4, incidence rates had already decreased by more than half from the mid-1970s to the mid-2000s, thanks largely to Pap smear screening programs for treatable premalignant lesions. “The US rate had dropped to about 20 per 100,000 women even before Gardasil 4,” said Annunziata. “After the introduction of the first vaccine, it decreased to 7 per 100,000, a decrease of about 30%, but it remains plateaued now at about the same level.”
Although the past decade has seen rates generally stabilize, there have been some changes in different age groups. In women ages 30-44, rates increased 1.7% each year from 2012 to 2019, while rates declined 11% each year for women ages 20-24— probably reflecting the impact of the first wave of prevention from Gardasil 4.
In one 2021 population-based study of US cancer registry data from 1999 to 2017, rates of both cervical squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma dropped. The largest declines occurred in females 15-20 years old, the age group most likely to be vaccinated against HPV but not typically screened, suggesting a vaccine-related effect.
Gardasil 9: 2014
With the 2014 approval of the vaccine’s second iteration, Gardasil 9, which replaced Gardasil 4 and targeted 9 HPV strains, immunization has taken broader aim. The strains covered by Gardasil 9 protect against oropharyngeal and other head and neck cancers — as well as penile, anal, vulvar, and vaginal malignancies and premalignancies, and genital warts in both sexes ages 9-45.
It may be years, however, before the impact of the newer polyvalent formulation is felt. “While the first vaccine has been successful against the prevalent strains of HPV linked to cervical cancer, it’s a little early to call it for the newer vaccine since oropharyngeal cancers tend to develop later in older men,” Cuccaro said. “But the types of HPV linked to mouth and throat cancers and covered by the newer vaccines are much less prevalent in those who are vaccinated. The strains not covered in the vaccine you see are equally present in the vaccinated and non-vaccinated.”
Angela L. Myers, MD, MPH, division director of infectious diseases and medical director of the Center for Wellbeing at Children’s Mercy in Kansas City, Missouri, added, “Unlike for cervical cancer, there are no screening programs for oropharyngeal lesions, so you have to wait to see rates until actual cancer develops.”
A 2023 review reported that HPV vaccination reduced levels of oropharyngeal HPV positivity in men, strengthening the case for pangender immunization.
And in a recent phase 3 doubled-blind trial, GARDASIL 9 reduced the incidence of anogenital persistent infection caused by nine types of HPV compared with a placebo.
Increasing Uptake
The current public health aim is to have 80% of young people in the targeted age group vaccinated with two doses. Today, uptake among those 9-26 years old stands at about 78% of girls and 75% of boys for the first dose, said Annunziata. “But it’s only about 61% for the two doses in the current series, and we want to improve that.”
Some parents may still harbor fears that immunizing teens and tweens — both the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Cancer Society recommend immunization at age 9 — will open the door to precocious sexual activity.
“But overall, uptake in tweens and young teens has increased because the messaging has changed,” said Myers, with the rationale now focusing on cancer prevention not sexual-infection prophylaxis. “This is similar to the hepatitis B vaccine, which used to be given to young adults and is now given to newborns to prevent cancer.”
Cuccaro added that a proactive presentation by healthcare professionals has a significant effect on vaccine uptake and increases the odds of vaccination ninefold. “Providers should take a presumptive approach and avoid just offering the vaccine as an option. It should be included with regular childhood vaccinations,” she said. “And the advantage of starting early at age 9 is that you can spread the doses out across other regular childhood vaccinations, whereas if you start at age 11, you need to add the HPV vaccine to three other vaccines that are given at that time.”
After age 15, three doses are necessary. “Providers should stress to parents that it’s most effective when given before young people become sexually active and exposed to HPV,” Cuccaro said. And Myers stressed that despite the vaccine’s effectiveness, routine screening for cervical premalignancies is still important.
Despite increasing coverage, vaccination rates have some distance to go before the public health target of at least 80% uptake of the series in the targeted age group, Cuccaro cautioned.
On the global stage, barriers to immunization remain, but the World Health Organization has endorsed a campaign to eradicate cervical cancer through HPV vaccination. It has predicted that the 21st century may be the last to experience HPV-associated cancers, currently responsible for more than 300,000 annual deaths worldwide.
A Brief History of HPV Vaccines
- 1951. Cervical cancer patient Henrietta Lacks’ rapidly dividing cervical cells are collected by George Otto Gey at Johns Hopkins Hospital. They create the first immortal cell line (HeLa) used to study cancers and vaccines worldwide.
- 1976. Harald zur Hausen suggests that genital wart-associated HPV, not herpes simplex, is the probable cause of cervical cancer.
- 1983. HPV is confirmed as a cause of cancer.
- 1991. The first HPV vaccine is developed.
- 2002. Proof of principle and protective efficacy for the monovalent HPV 16 are shown.
- 2006. Merck’s Gardasil 4 (HPV 4) is FDA approved in girls ages 9-26 for protection against strains 6, 11, 16, and 18 — the cause of more than 70% of cervical cancer cases.
- 2009. Approval of Gardasil 4 is expanded to boys ages 9-26 for the prevention of genital warts.
- 2009. The FDA approves GlaxoSmithKline’s Cervarix (HPV 16 and 18) for girls and young women. The vaccine was withdrawn from the US market in 2016 following the success of Gardasil 9 but is used abroad for HPV cancer prevention.
- 2014. The 9-valent recombinant vaccine Gardasil 9 is FDA approved for protection against several low-risk, wart-causing HPV strains as well as the high-risk cancer strains targeted by HPV 4.
- 2018. The FDA expands approval to include females and males 27-45 years old.
- 2020. The FDA extends approval of Gardasil 9 to include prevention not only of cervical cancer but also, vaginal, vulvar, anal, oropharyngeal, and other head and neck cancers.
Annunziata, Cuccaro, and Myers had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Cannabis Use Linked to Brain Thinning in Adolescents
, research in mice and humans suggested.
The multilevel study demonstrated that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), an active substance in cannabis, causes shrinkage of dendritic arborization — the neurons’ network of antennae that play a critical role in communication between brain cells.
The connection between dendritic arborization and cortical thickness was hinted at in an earlier study by Tomáš Paus, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and addictology at the University of Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues, who found that cannabis use in early adolescence was associated with lower cortical thickness in boys with a high genetic risk for schizophrenia.
“We speculated at that time that the differences in cortical thickness might be related to differences in dendritic arborization, and our current study confirmed it,” Paus said.
That confirmation came in the mouse part of the study, when coauthor Graciela Piñeyro, MD, PhD, also of the University of Montreal, counted the dendritic branches of mice exposed to THC and compared the total with the number of dendritic branches in unexposed mice. “What surprised me was finding that THC in the mice was targeting the same type of cells and structures that Dr. Paus had predicted would be affected from the human studies,” she said. “Structurally, they were mostly the neurons that contribute to synapses in the cortex, and their branching was reduced.”
Paus explained that in humans, a decrease in input from the affected dendrites “makes it harder for the brain to learn new things, interact with people, cope with new situations, et cetera. In other words, it makes the brain more vulnerable to everything that can happen in a young person’s life.”
The study was published online on October 9 in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Of Mice, Men, and Cannabis
Although associations between cannabis use by teenagers and variations in brain maturation have been well studied, the cellular and molecular underpinnings of these associations were unclear, according to the authors.
To investigate further, they conducted this three-step study. First, they exposed adolescent male mice to THC or a synthetic cannabinoid (WIN 55,212-2) and assessed differentially expressed genes, spine numbers, and the extent of dendritic complexity in the frontal cortex of each mouse.
Next, using MRI, they examined differences in cortical thickness in 34 brain regions in 140 male adolescents who experimented with cannabis before age 16 years and 327 who did not.
Then, they again conducted experiments in mice and found that 13 THC-related genes correlated with variations in cortical thickness. Virtual histology revealed that these 13 genes were coexpressed with cell markers of astrocytes, microglia, and a type of pyramidal cell enriched in genes that regulate dendritic expression.
Similarly, the WIN-related genes correlated with differences in cortical thickness and showed coexpression patterns with the same three cell types.
Furthermore, the affected genes were also found in humans, particularly in the thinner cortical regions of the adolescents who experimented with cannabis.
By acting on microglia, THC seems to promote the removal of synapses and, eventually, the reduction of the dendritic tree in mice, Piñeyro explained. That’s important not only because a similar mechanism may be at work in humans but also because “we now might have a model to test different types of cannabis products to see which ones are producing the greatest effect on neurons and therefore greater removal of synapses through the microglia. This could be a way of testing drugs that are out in the street to see which would be the most or least dangerous to the synapses in the brain.”
‘Significant Implications’
Commenting on the study, Yasmin Hurd, PhD, Ward-Coleman chair of translational neuroscience at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and director of the Addiction Institute of Mount Sinai in New York City, said, “These findings are in line with previous results, so they are feasible. This study adds more depth by showing that cortical genes that were differentially altered by adolescent THC correlated with cannabis-related changes in cortical thickness based on human neuroimaging data.” Hurd did not participate in the research.
“The results emphasize that consumption of potent cannabis products during adolescence can impact cortical function, which has significant implications for decision-making and risky behavior as well. It also can increase vulnerability to psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.”
Although a mouse model is “not truly the same as the human condition, the fact that the animal model also showed evidence of the morphological changes indicative of reduced cortical thickness, [like] the humans, is strong,” she said.
Additional research could include women and assess potential sex differences, she added.
Ronald Ellis, MD, PhD, an investigator in the Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, said, “The findings are plausible and extend prior work showing evidence of increased risk for psychotic disorders later in life in adolescents who use cannabis.” Ellis did not participate in the research.
“Future studies should explore how these findings might vary across different demographic groups, which could provide a more inclusive understanding of how cannabis impacts the brain,” he said. “Additionally, longitudinal studies to track changes in the brain over time could help to establish causal relationships more robustly.
“The take-home message to clinicians at this point is to discuss cannabis use history carefully and confidentially with adolescent patients to better provide advice on its potential risks,” he concluded.
Paus added that he would tell patients, “If you’re going to use cannabis, don’t start early. If you have to, then do so in moderation. And if you have family history of mental illness, be very careful.”
No funding for the study was reported. Paus, Piñeyro, Hurd, and Ellis declared having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, research in mice and humans suggested.
The multilevel study demonstrated that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), an active substance in cannabis, causes shrinkage of dendritic arborization — the neurons’ network of antennae that play a critical role in communication between brain cells.
The connection between dendritic arborization and cortical thickness was hinted at in an earlier study by Tomáš Paus, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and addictology at the University of Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues, who found that cannabis use in early adolescence was associated with lower cortical thickness in boys with a high genetic risk for schizophrenia.
“We speculated at that time that the differences in cortical thickness might be related to differences in dendritic arborization, and our current study confirmed it,” Paus said.
That confirmation came in the mouse part of the study, when coauthor Graciela Piñeyro, MD, PhD, also of the University of Montreal, counted the dendritic branches of mice exposed to THC and compared the total with the number of dendritic branches in unexposed mice. “What surprised me was finding that THC in the mice was targeting the same type of cells and structures that Dr. Paus had predicted would be affected from the human studies,” she said. “Structurally, they were mostly the neurons that contribute to synapses in the cortex, and their branching was reduced.”
Paus explained that in humans, a decrease in input from the affected dendrites “makes it harder for the brain to learn new things, interact with people, cope with new situations, et cetera. In other words, it makes the brain more vulnerable to everything that can happen in a young person’s life.”
The study was published online on October 9 in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Of Mice, Men, and Cannabis
Although associations between cannabis use by teenagers and variations in brain maturation have been well studied, the cellular and molecular underpinnings of these associations were unclear, according to the authors.
To investigate further, they conducted this three-step study. First, they exposed adolescent male mice to THC or a synthetic cannabinoid (WIN 55,212-2) and assessed differentially expressed genes, spine numbers, and the extent of dendritic complexity in the frontal cortex of each mouse.
Next, using MRI, they examined differences in cortical thickness in 34 brain regions in 140 male adolescents who experimented with cannabis before age 16 years and 327 who did not.
Then, they again conducted experiments in mice and found that 13 THC-related genes correlated with variations in cortical thickness. Virtual histology revealed that these 13 genes were coexpressed with cell markers of astrocytes, microglia, and a type of pyramidal cell enriched in genes that regulate dendritic expression.
Similarly, the WIN-related genes correlated with differences in cortical thickness and showed coexpression patterns with the same three cell types.
Furthermore, the affected genes were also found in humans, particularly in the thinner cortical regions of the adolescents who experimented with cannabis.
By acting on microglia, THC seems to promote the removal of synapses and, eventually, the reduction of the dendritic tree in mice, Piñeyro explained. That’s important not only because a similar mechanism may be at work in humans but also because “we now might have a model to test different types of cannabis products to see which ones are producing the greatest effect on neurons and therefore greater removal of synapses through the microglia. This could be a way of testing drugs that are out in the street to see which would be the most or least dangerous to the synapses in the brain.”
‘Significant Implications’
Commenting on the study, Yasmin Hurd, PhD, Ward-Coleman chair of translational neuroscience at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and director of the Addiction Institute of Mount Sinai in New York City, said, “These findings are in line with previous results, so they are feasible. This study adds more depth by showing that cortical genes that were differentially altered by adolescent THC correlated with cannabis-related changes in cortical thickness based on human neuroimaging data.” Hurd did not participate in the research.
“The results emphasize that consumption of potent cannabis products during adolescence can impact cortical function, which has significant implications for decision-making and risky behavior as well. It also can increase vulnerability to psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.”
Although a mouse model is “not truly the same as the human condition, the fact that the animal model also showed evidence of the morphological changes indicative of reduced cortical thickness, [like] the humans, is strong,” she said.
Additional research could include women and assess potential sex differences, she added.
Ronald Ellis, MD, PhD, an investigator in the Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, said, “The findings are plausible and extend prior work showing evidence of increased risk for psychotic disorders later in life in adolescents who use cannabis.” Ellis did not participate in the research.
“Future studies should explore how these findings might vary across different demographic groups, which could provide a more inclusive understanding of how cannabis impacts the brain,” he said. “Additionally, longitudinal studies to track changes in the brain over time could help to establish causal relationships more robustly.
“The take-home message to clinicians at this point is to discuss cannabis use history carefully and confidentially with adolescent patients to better provide advice on its potential risks,” he concluded.
Paus added that he would tell patients, “If you’re going to use cannabis, don’t start early. If you have to, then do so in moderation. And if you have family history of mental illness, be very careful.”
No funding for the study was reported. Paus, Piñeyro, Hurd, and Ellis declared having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, research in mice and humans suggested.
The multilevel study demonstrated that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), an active substance in cannabis, causes shrinkage of dendritic arborization — the neurons’ network of antennae that play a critical role in communication between brain cells.
The connection between dendritic arborization and cortical thickness was hinted at in an earlier study by Tomáš Paus, MD, PhD, professor of psychiatry and addictology at the University of Montreal, Quebec, Canada, and colleagues, who found that cannabis use in early adolescence was associated with lower cortical thickness in boys with a high genetic risk for schizophrenia.
“We speculated at that time that the differences in cortical thickness might be related to differences in dendritic arborization, and our current study confirmed it,” Paus said.
That confirmation came in the mouse part of the study, when coauthor Graciela Piñeyro, MD, PhD, also of the University of Montreal, counted the dendritic branches of mice exposed to THC and compared the total with the number of dendritic branches in unexposed mice. “What surprised me was finding that THC in the mice was targeting the same type of cells and structures that Dr. Paus had predicted would be affected from the human studies,” she said. “Structurally, they were mostly the neurons that contribute to synapses in the cortex, and their branching was reduced.”
Paus explained that in humans, a decrease in input from the affected dendrites “makes it harder for the brain to learn new things, interact with people, cope with new situations, et cetera. In other words, it makes the brain more vulnerable to everything that can happen in a young person’s life.”
The study was published online on October 9 in the Journal of Neuroscience.
Of Mice, Men, and Cannabis
Although associations between cannabis use by teenagers and variations in brain maturation have been well studied, the cellular and molecular underpinnings of these associations were unclear, according to the authors.
To investigate further, they conducted this three-step study. First, they exposed adolescent male mice to THC or a synthetic cannabinoid (WIN 55,212-2) and assessed differentially expressed genes, spine numbers, and the extent of dendritic complexity in the frontal cortex of each mouse.
Next, using MRI, they examined differences in cortical thickness in 34 brain regions in 140 male adolescents who experimented with cannabis before age 16 years and 327 who did not.
Then, they again conducted experiments in mice and found that 13 THC-related genes correlated with variations in cortical thickness. Virtual histology revealed that these 13 genes were coexpressed with cell markers of astrocytes, microglia, and a type of pyramidal cell enriched in genes that regulate dendritic expression.
Similarly, the WIN-related genes correlated with differences in cortical thickness and showed coexpression patterns with the same three cell types.
Furthermore, the affected genes were also found in humans, particularly in the thinner cortical regions of the adolescents who experimented with cannabis.
By acting on microglia, THC seems to promote the removal of synapses and, eventually, the reduction of the dendritic tree in mice, Piñeyro explained. That’s important not only because a similar mechanism may be at work in humans but also because “we now might have a model to test different types of cannabis products to see which ones are producing the greatest effect on neurons and therefore greater removal of synapses through the microglia. This could be a way of testing drugs that are out in the street to see which would be the most or least dangerous to the synapses in the brain.”
‘Significant Implications’
Commenting on the study, Yasmin Hurd, PhD, Ward-Coleman chair of translational neuroscience at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and director of the Addiction Institute of Mount Sinai in New York City, said, “These findings are in line with previous results, so they are feasible. This study adds more depth by showing that cortical genes that were differentially altered by adolescent THC correlated with cannabis-related changes in cortical thickness based on human neuroimaging data.” Hurd did not participate in the research.
“The results emphasize that consumption of potent cannabis products during adolescence can impact cortical function, which has significant implications for decision-making and risky behavior as well. It also can increase vulnerability to psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia.”
Although a mouse model is “not truly the same as the human condition, the fact that the animal model also showed evidence of the morphological changes indicative of reduced cortical thickness, [like] the humans, is strong,” she said.
Additional research could include women and assess potential sex differences, she added.
Ronald Ellis, MD, PhD, an investigator in the Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, said, “The findings are plausible and extend prior work showing evidence of increased risk for psychotic disorders later in life in adolescents who use cannabis.” Ellis did not participate in the research.
“Future studies should explore how these findings might vary across different demographic groups, which could provide a more inclusive understanding of how cannabis impacts the brain,” he said. “Additionally, longitudinal studies to track changes in the brain over time could help to establish causal relationships more robustly.
“The take-home message to clinicians at this point is to discuss cannabis use history carefully and confidentially with adolescent patients to better provide advice on its potential risks,” he concluded.
Paus added that he would tell patients, “If you’re going to use cannabis, don’t start early. If you have to, then do so in moderation. And if you have family history of mental illness, be very careful.”
No funding for the study was reported. Paus, Piñeyro, Hurd, and Ellis declared having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF NEUROSCIENCE
Outpatient CAR T: Safe, Effective, Accessible
In one recent study, an industry-funded phase 2 trial, researchers found similar outcomes from outpatient and inpatient CAR T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma with lisocabtagene maraleucel (Breyanzi).
Another recent study reported that outpatient treatment of B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) had similar efficacy to inpatient treatment. Meanwhile, a 2023 review of CAR T-cell therapy in various settings found similar outcomes in outpatient and inpatient treatment.
“The future of CAR T-cell therapy lies in balancing safety with accessibility,” said Rayne Rouce, MD, a pediatric oncologist at Texas Children’s Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, in an interview. “Expanding CAR T-cell therapy beyond large medical centers is a critical next step.”
Great Outcomes, Low Access
Since 2017, the FDA has approved six CAR T-cell therapies, which target cancer by harnessing the power of a patient’s own T cells. As an Oregon Health & Sciences University/Knight Cancer Center website explains, T cells are removed from the patient’s body, “genetically modified to make the chimeric antigen receptor, or CAR, [which] protein binds to specific proteins on the surface of cancer cells.”
Modified cells are grown and then infused back into the body, where they “multiply and may be able to destroy all the cancer cells.”
As Rouce puts it, “CAR T-cells have revolutionized the treatment of relapsed or refractory blood cancers.” One or more of the therapies have been approved to treat types of lymphoblastic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
A 2023 review of clinical trial data reported complete response rates of 40%-54% in aggressive B-cell lymphoma, 67% in mantle cell lymphoma, and 69%-74% in indolent B cell lymphoma.
“Commercialization of CAR T-cell therapy brought hope that access would expand beyond the major academic medical centers with the highly specialized infrastructure and advanced laboratories required to manufacture and ultimately treat patients,” Rouce said. “However, it quickly became clear that patients who are underinsured or uninsured — or who live outside the network of the well-resourced institutions that house these therapies — are still unable to access these potentially life-saving therapies.”
A 2024 report estimated the cost of CAR T-cell therapy as $700,000-$1 million and said only a small percentage of those who could benefit from the treatment actually get it. For example, an estimated 10,000 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma alone could benefit from CAR T therapy annually, but a survey of 200 US healthcare centers in 2021 found that 1900 procedures were performed overall for all indications.
Distance to Treatment Is a Major Obstacle
Even if patients have insurance plans willing to cover CAR T-cell therapy, they may not be able get care. While more than 150 US centers are certified to administer the therapy, “distance to major medical centers with CAR T capabilities is a major obstacle,” Yuliya Linhares, MD, chief of lymphoma at Miami Cancer Institute in Miami, Florida, said in an interview.
“I have had patients who chose to not proceed with CAR T therapy due to inability to travel the distance to the medical center for pre-CAR T appointments and assessments and a lack of caretakers who are available to stay nearby,” Linhares said.
Indeed, the challenges facing patients in rural and underserved urban areas can be overwhelming, Hoda Badr, PhD, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, said in an interview.
“They must take time off work, arrange accommodations near treatment sites, and manage travel costs, all of which strain limited financial resources. The inability to afford these additional expenses can lead to delays in receiving care or patients forgoing the treatment altogether,” Badr said. She added that “the psychological and social burden of being away from family and community support systems during treatment can intensify the stress of an already difficult situation.”
A statistic tells the story of the urban/community divide. CAR T-cell therapy administration at academic centers after leukapheresis — the separation and collection of white blood cells — is reported to be at around 90%, while it’s only 47% in community-based practices that have to refer patients elsewhere, Linhares noted.
Researchers Explore CAR T-Cell Therapy in the Community
Linhares is lead author of the phase 2 trial that explored administration of lisocabtagene maraleucel in 82 patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. The findings were published Sept. 30 in Blood Advances.
The OUTREACH trial, funded by Juno/Bristol-Myers Squibb, treated patients in the third line and beyond at community medical centers (outpatient-monitored, 70%; inpatient-monitored, 30%). The trial didn’t require facilities to be certified by the Foundation for the Accreditation of Cellular Therapy (FACT); all had to be non-tertiary cancer centers that weren’t associated with a university. In order to administer therapy on the outpatient basis, the centers had to have phase 1 or hematopoietic stem cell transplant capabilities.
As Linhares explained, 72% of participating centers hadn’t provided CAR T-cell therapy before, and 44% did not have FACT accreditation. “About 32% of patients received CAR T at CAR T naive sites, while 70% of patients received CAR T as outpatients. Investigators had to decide whether patients qualified for the outpatient observation or had to be admitted for the inpatient observation,” she noted.
Community Outcomes Were Comparable to Major Trial
As for the results, grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred at a similar frequency among outpatients and inpatients at 74% and 76%, Linhares said. There were no grade 5 adverse events, and 25% of patients treated as outpatients were never hospitalized.
Response rates were similar to those in the major TRANSCEND trial with the objective response rates rate of 80% and complete response rates of 54%.
“Overall,” Linhares said, “our study demonstrated that with the availability of standard operating procedures, specially trained staff and a multidisciplinary team trained in CAR T toxicity management, inpatient and outpatient CAR T administration is feasible at specialized community medical centers.”
In 2023, another study examined patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma who were treated on an outpatient basis with tisagenlecleucel. Researchers reported that outpatient therapy was “feasible and associated with similar efficacy outcomes as inpatient treatment.”
And a 2023 systematic literature review identified 11 studies that reported outpatient vs inpatient outcomes in CAR T-cell therapy and found “comparable response rates (80-82% in outpatient and 72-80% in inpatient).” Costs were cheaper in the outpatient setting.
Research findings like these are good news, Baylor College of Medicine’s Badr said. “Outpatient administration could help to scale the availability of this therapy to a broader range of healthcare settings, including those serving underserved populations. Findings indicate promising safety profiles, which is encouraging for expanding access.”
Not Every Patient Can Tolerate Outpatient Care
Linhares noted that the patients who received outpatient care in the lisocabtagene maraleucel study were in better shape than those in the inpatient group. Those selected for inpatient care had “higher disease risk characteristics, including high grade B cell lymphoma histology, higher disease burden, and having received bridging therapy. This points to the fact that the investigators properly selected patients who were at a higher risk of complications for inpatient observation. Additionally, some patients stayed as inpatient due to social factors, which increases length of stay independently of disease characteristics.”
Specifically, reasons for inpatient monitoring were disease characteristics (48%) including tumor burden and risk of adverse events; psychosocial factors (32%) including lack of caregiver support or transportation; COVID-19 precautions (8%); pre-infusion adverse events (8%) of fever and vasovagal reaction; and principal investigator decision (4%) due to limited hospital experience with CAR T-cell therapy.
Texas Children’s Cancer Center’s Rouce said “certain patients, particularly those with higher risk for complications or those who require intensive monitoring, may not be suited for outpatient CAR T-cell therapy. This may be due to other comorbidities or baseline factors known to predispose to CAR T-related toxicities. However, evidence-based risk mitigation algorithms may still allow closely monitored outpatient treatment, with recognition that hospital admission for incipient side effects may be necessary.”
What’s Next for Access to Therapy?
Rouce noted that her institution, like many others, is offering CAR T-cell therapy on an outpatient basis. “Additionally, continued scientific innovation, such as immediately available, off-the-shelf cell therapies and inducible safety switches, will ultimately improve access,” she said.
Linhares noted a recent advance and highlighted research that’s now in progress. “CAR Ts now have an indication as a second-line therapy in relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma, and there are ongoing clinical trials that will potentially move CAR Ts into the first line,” she said. “Some trials are exploring allogeneic, readily available off-the-shelf CAR T for the treatment of minimal residual disease positive large B-cell lymphoma after completion of first-line therapy.”
These potential advances “are increasing the need for CAR T-capable medical centers,” Linhares noted. “More and more medical centers with expert hematology teams are becoming CAR T-certified, with more patients having access to CAR T.”
Still, she said, “I don’t think access is nearly as good as it should be. Many patients in rural areas are still unable to get this life-saving treatment. “However, “it is very possible that other novel targeted therapies, such as bispecific antibodies, will be used in place of CAR T in areas with poor CAR T access. Bispecific antibody efficacy in various B cell lymphoma histologies are being currently explored.”
Rouce discloses relationships with Novartis and Pfizer. Linhares reports ties with Kyowa Kirin, AbbVie, ADC, BeiGene, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Seagen, and TG. Badr has no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In one recent study, an industry-funded phase 2 trial, researchers found similar outcomes from outpatient and inpatient CAR T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma with lisocabtagene maraleucel (Breyanzi).
Another recent study reported that outpatient treatment of B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) had similar efficacy to inpatient treatment. Meanwhile, a 2023 review of CAR T-cell therapy in various settings found similar outcomes in outpatient and inpatient treatment.
“The future of CAR T-cell therapy lies in balancing safety with accessibility,” said Rayne Rouce, MD, a pediatric oncologist at Texas Children’s Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, in an interview. “Expanding CAR T-cell therapy beyond large medical centers is a critical next step.”
Great Outcomes, Low Access
Since 2017, the FDA has approved six CAR T-cell therapies, which target cancer by harnessing the power of a patient’s own T cells. As an Oregon Health & Sciences University/Knight Cancer Center website explains, T cells are removed from the patient’s body, “genetically modified to make the chimeric antigen receptor, or CAR, [which] protein binds to specific proteins on the surface of cancer cells.”
Modified cells are grown and then infused back into the body, where they “multiply and may be able to destroy all the cancer cells.”
As Rouce puts it, “CAR T-cells have revolutionized the treatment of relapsed or refractory blood cancers.” One or more of the therapies have been approved to treat types of lymphoblastic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
A 2023 review of clinical trial data reported complete response rates of 40%-54% in aggressive B-cell lymphoma, 67% in mantle cell lymphoma, and 69%-74% in indolent B cell lymphoma.
“Commercialization of CAR T-cell therapy brought hope that access would expand beyond the major academic medical centers with the highly specialized infrastructure and advanced laboratories required to manufacture and ultimately treat patients,” Rouce said. “However, it quickly became clear that patients who are underinsured or uninsured — or who live outside the network of the well-resourced institutions that house these therapies — are still unable to access these potentially life-saving therapies.”
A 2024 report estimated the cost of CAR T-cell therapy as $700,000-$1 million and said only a small percentage of those who could benefit from the treatment actually get it. For example, an estimated 10,000 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma alone could benefit from CAR T therapy annually, but a survey of 200 US healthcare centers in 2021 found that 1900 procedures were performed overall for all indications.
Distance to Treatment Is a Major Obstacle
Even if patients have insurance plans willing to cover CAR T-cell therapy, they may not be able get care. While more than 150 US centers are certified to administer the therapy, “distance to major medical centers with CAR T capabilities is a major obstacle,” Yuliya Linhares, MD, chief of lymphoma at Miami Cancer Institute in Miami, Florida, said in an interview.
“I have had patients who chose to not proceed with CAR T therapy due to inability to travel the distance to the medical center for pre-CAR T appointments and assessments and a lack of caretakers who are available to stay nearby,” Linhares said.
Indeed, the challenges facing patients in rural and underserved urban areas can be overwhelming, Hoda Badr, PhD, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, said in an interview.
“They must take time off work, arrange accommodations near treatment sites, and manage travel costs, all of which strain limited financial resources. The inability to afford these additional expenses can lead to delays in receiving care or patients forgoing the treatment altogether,” Badr said. She added that “the psychological and social burden of being away from family and community support systems during treatment can intensify the stress of an already difficult situation.”
A statistic tells the story of the urban/community divide. CAR T-cell therapy administration at academic centers after leukapheresis — the separation and collection of white blood cells — is reported to be at around 90%, while it’s only 47% in community-based practices that have to refer patients elsewhere, Linhares noted.
Researchers Explore CAR T-Cell Therapy in the Community
Linhares is lead author of the phase 2 trial that explored administration of lisocabtagene maraleucel in 82 patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. The findings were published Sept. 30 in Blood Advances.
The OUTREACH trial, funded by Juno/Bristol-Myers Squibb, treated patients in the third line and beyond at community medical centers (outpatient-monitored, 70%; inpatient-monitored, 30%). The trial didn’t require facilities to be certified by the Foundation for the Accreditation of Cellular Therapy (FACT); all had to be non-tertiary cancer centers that weren’t associated with a university. In order to administer therapy on the outpatient basis, the centers had to have phase 1 or hematopoietic stem cell transplant capabilities.
As Linhares explained, 72% of participating centers hadn’t provided CAR T-cell therapy before, and 44% did not have FACT accreditation. “About 32% of patients received CAR T at CAR T naive sites, while 70% of patients received CAR T as outpatients. Investigators had to decide whether patients qualified for the outpatient observation or had to be admitted for the inpatient observation,” she noted.
Community Outcomes Were Comparable to Major Trial
As for the results, grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred at a similar frequency among outpatients and inpatients at 74% and 76%, Linhares said. There were no grade 5 adverse events, and 25% of patients treated as outpatients were never hospitalized.
Response rates were similar to those in the major TRANSCEND trial with the objective response rates rate of 80% and complete response rates of 54%.
“Overall,” Linhares said, “our study demonstrated that with the availability of standard operating procedures, specially trained staff and a multidisciplinary team trained in CAR T toxicity management, inpatient and outpatient CAR T administration is feasible at specialized community medical centers.”
In 2023, another study examined patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma who were treated on an outpatient basis with tisagenlecleucel. Researchers reported that outpatient therapy was “feasible and associated with similar efficacy outcomes as inpatient treatment.”
And a 2023 systematic literature review identified 11 studies that reported outpatient vs inpatient outcomes in CAR T-cell therapy and found “comparable response rates (80-82% in outpatient and 72-80% in inpatient).” Costs were cheaper in the outpatient setting.
Research findings like these are good news, Baylor College of Medicine’s Badr said. “Outpatient administration could help to scale the availability of this therapy to a broader range of healthcare settings, including those serving underserved populations. Findings indicate promising safety profiles, which is encouraging for expanding access.”
Not Every Patient Can Tolerate Outpatient Care
Linhares noted that the patients who received outpatient care in the lisocabtagene maraleucel study were in better shape than those in the inpatient group. Those selected for inpatient care had “higher disease risk characteristics, including high grade B cell lymphoma histology, higher disease burden, and having received bridging therapy. This points to the fact that the investigators properly selected patients who were at a higher risk of complications for inpatient observation. Additionally, some patients stayed as inpatient due to social factors, which increases length of stay independently of disease characteristics.”
Specifically, reasons for inpatient monitoring were disease characteristics (48%) including tumor burden and risk of adverse events; psychosocial factors (32%) including lack of caregiver support or transportation; COVID-19 precautions (8%); pre-infusion adverse events (8%) of fever and vasovagal reaction; and principal investigator decision (4%) due to limited hospital experience with CAR T-cell therapy.
Texas Children’s Cancer Center’s Rouce said “certain patients, particularly those with higher risk for complications or those who require intensive monitoring, may not be suited for outpatient CAR T-cell therapy. This may be due to other comorbidities or baseline factors known to predispose to CAR T-related toxicities. However, evidence-based risk mitigation algorithms may still allow closely monitored outpatient treatment, with recognition that hospital admission for incipient side effects may be necessary.”
What’s Next for Access to Therapy?
Rouce noted that her institution, like many others, is offering CAR T-cell therapy on an outpatient basis. “Additionally, continued scientific innovation, such as immediately available, off-the-shelf cell therapies and inducible safety switches, will ultimately improve access,” she said.
Linhares noted a recent advance and highlighted research that’s now in progress. “CAR Ts now have an indication as a second-line therapy in relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma, and there are ongoing clinical trials that will potentially move CAR Ts into the first line,” she said. “Some trials are exploring allogeneic, readily available off-the-shelf CAR T for the treatment of minimal residual disease positive large B-cell lymphoma after completion of first-line therapy.”
These potential advances “are increasing the need for CAR T-capable medical centers,” Linhares noted. “More and more medical centers with expert hematology teams are becoming CAR T-certified, with more patients having access to CAR T.”
Still, she said, “I don’t think access is nearly as good as it should be. Many patients in rural areas are still unable to get this life-saving treatment. “However, “it is very possible that other novel targeted therapies, such as bispecific antibodies, will be used in place of CAR T in areas with poor CAR T access. Bispecific antibody efficacy in various B cell lymphoma histologies are being currently explored.”
Rouce discloses relationships with Novartis and Pfizer. Linhares reports ties with Kyowa Kirin, AbbVie, ADC, BeiGene, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Seagen, and TG. Badr has no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In one recent study, an industry-funded phase 2 trial, researchers found similar outcomes from outpatient and inpatient CAR T-cell therapy for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma with lisocabtagene maraleucel (Breyanzi).
Another recent study reported that outpatient treatment of B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) had similar efficacy to inpatient treatment. Meanwhile, a 2023 review of CAR T-cell therapy in various settings found similar outcomes in outpatient and inpatient treatment.
“The future of CAR T-cell therapy lies in balancing safety with accessibility,” said Rayne Rouce, MD, a pediatric oncologist at Texas Children’s Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, in an interview. “Expanding CAR T-cell therapy beyond large medical centers is a critical next step.”
Great Outcomes, Low Access
Since 2017, the FDA has approved six CAR T-cell therapies, which target cancer by harnessing the power of a patient’s own T cells. As an Oregon Health & Sciences University/Knight Cancer Center website explains, T cells are removed from the patient’s body, “genetically modified to make the chimeric antigen receptor, or CAR, [which] protein binds to specific proteins on the surface of cancer cells.”
Modified cells are grown and then infused back into the body, where they “multiply and may be able to destroy all the cancer cells.”
As Rouce puts it, “CAR T-cells have revolutionized the treatment of relapsed or refractory blood cancers.” One or more of the therapies have been approved to treat types of lymphoblastic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
A 2023 review of clinical trial data reported complete response rates of 40%-54% in aggressive B-cell lymphoma, 67% in mantle cell lymphoma, and 69%-74% in indolent B cell lymphoma.
“Commercialization of CAR T-cell therapy brought hope that access would expand beyond the major academic medical centers with the highly specialized infrastructure and advanced laboratories required to manufacture and ultimately treat patients,” Rouce said. “However, it quickly became clear that patients who are underinsured or uninsured — or who live outside the network of the well-resourced institutions that house these therapies — are still unable to access these potentially life-saving therapies.”
A 2024 report estimated the cost of CAR T-cell therapy as $700,000-$1 million and said only a small percentage of those who could benefit from the treatment actually get it. For example, an estimated 10,000 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma alone could benefit from CAR T therapy annually, but a survey of 200 US healthcare centers in 2021 found that 1900 procedures were performed overall for all indications.
Distance to Treatment Is a Major Obstacle
Even if patients have insurance plans willing to cover CAR T-cell therapy, they may not be able get care. While more than 150 US centers are certified to administer the therapy, “distance to major medical centers with CAR T capabilities is a major obstacle,” Yuliya Linhares, MD, chief of lymphoma at Miami Cancer Institute in Miami, Florida, said in an interview.
“I have had patients who chose to not proceed with CAR T therapy due to inability to travel the distance to the medical center for pre-CAR T appointments and assessments and a lack of caretakers who are available to stay nearby,” Linhares said.
Indeed, the challenges facing patients in rural and underserved urban areas can be overwhelming, Hoda Badr, PhD, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas, said in an interview.
“They must take time off work, arrange accommodations near treatment sites, and manage travel costs, all of which strain limited financial resources. The inability to afford these additional expenses can lead to delays in receiving care or patients forgoing the treatment altogether,” Badr said. She added that “the psychological and social burden of being away from family and community support systems during treatment can intensify the stress of an already difficult situation.”
A statistic tells the story of the urban/community divide. CAR T-cell therapy administration at academic centers after leukapheresis — the separation and collection of white blood cells — is reported to be at around 90%, while it’s only 47% in community-based practices that have to refer patients elsewhere, Linhares noted.
Researchers Explore CAR T-Cell Therapy in the Community
Linhares is lead author of the phase 2 trial that explored administration of lisocabtagene maraleucel in 82 patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma. The findings were published Sept. 30 in Blood Advances.
The OUTREACH trial, funded by Juno/Bristol-Myers Squibb, treated patients in the third line and beyond at community medical centers (outpatient-monitored, 70%; inpatient-monitored, 30%). The trial didn’t require facilities to be certified by the Foundation for the Accreditation of Cellular Therapy (FACT); all had to be non-tertiary cancer centers that weren’t associated with a university. In order to administer therapy on the outpatient basis, the centers had to have phase 1 or hematopoietic stem cell transplant capabilities.
As Linhares explained, 72% of participating centers hadn’t provided CAR T-cell therapy before, and 44% did not have FACT accreditation. “About 32% of patients received CAR T at CAR T naive sites, while 70% of patients received CAR T as outpatients. Investigators had to decide whether patients qualified for the outpatient observation or had to be admitted for the inpatient observation,” she noted.
Community Outcomes Were Comparable to Major Trial
As for the results, grade 3 or higher adverse events occurred at a similar frequency among outpatients and inpatients at 74% and 76%, Linhares said. There were no grade 5 adverse events, and 25% of patients treated as outpatients were never hospitalized.
Response rates were similar to those in the major TRANSCEND trial with the objective response rates rate of 80% and complete response rates of 54%.
“Overall,” Linhares said, “our study demonstrated that with the availability of standard operating procedures, specially trained staff and a multidisciplinary team trained in CAR T toxicity management, inpatient and outpatient CAR T administration is feasible at specialized community medical centers.”
In 2023, another study examined patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma who were treated on an outpatient basis with tisagenlecleucel. Researchers reported that outpatient therapy was “feasible and associated with similar efficacy outcomes as inpatient treatment.”
And a 2023 systematic literature review identified 11 studies that reported outpatient vs inpatient outcomes in CAR T-cell therapy and found “comparable response rates (80-82% in outpatient and 72-80% in inpatient).” Costs were cheaper in the outpatient setting.
Research findings like these are good news, Baylor College of Medicine’s Badr said. “Outpatient administration could help to scale the availability of this therapy to a broader range of healthcare settings, including those serving underserved populations. Findings indicate promising safety profiles, which is encouraging for expanding access.”
Not Every Patient Can Tolerate Outpatient Care
Linhares noted that the patients who received outpatient care in the lisocabtagene maraleucel study were in better shape than those in the inpatient group. Those selected for inpatient care had “higher disease risk characteristics, including high grade B cell lymphoma histology, higher disease burden, and having received bridging therapy. This points to the fact that the investigators properly selected patients who were at a higher risk of complications for inpatient observation. Additionally, some patients stayed as inpatient due to social factors, which increases length of stay independently of disease characteristics.”
Specifically, reasons for inpatient monitoring were disease characteristics (48%) including tumor burden and risk of adverse events; psychosocial factors (32%) including lack of caregiver support or transportation; COVID-19 precautions (8%); pre-infusion adverse events (8%) of fever and vasovagal reaction; and principal investigator decision (4%) due to limited hospital experience with CAR T-cell therapy.
Texas Children’s Cancer Center’s Rouce said “certain patients, particularly those with higher risk for complications or those who require intensive monitoring, may not be suited for outpatient CAR T-cell therapy. This may be due to other comorbidities or baseline factors known to predispose to CAR T-related toxicities. However, evidence-based risk mitigation algorithms may still allow closely monitored outpatient treatment, with recognition that hospital admission for incipient side effects may be necessary.”
What’s Next for Access to Therapy?
Rouce noted that her institution, like many others, is offering CAR T-cell therapy on an outpatient basis. “Additionally, continued scientific innovation, such as immediately available, off-the-shelf cell therapies and inducible safety switches, will ultimately improve access,” she said.
Linhares noted a recent advance and highlighted research that’s now in progress. “CAR Ts now have an indication as a second-line therapy in relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma, and there are ongoing clinical trials that will potentially move CAR Ts into the first line,” she said. “Some trials are exploring allogeneic, readily available off-the-shelf CAR T for the treatment of minimal residual disease positive large B-cell lymphoma after completion of first-line therapy.”
These potential advances “are increasing the need for CAR T-capable medical centers,” Linhares noted. “More and more medical centers with expert hematology teams are becoming CAR T-certified, with more patients having access to CAR T.”
Still, she said, “I don’t think access is nearly as good as it should be. Many patients in rural areas are still unable to get this life-saving treatment. “However, “it is very possible that other novel targeted therapies, such as bispecific antibodies, will be used in place of CAR T in areas with poor CAR T access. Bispecific antibody efficacy in various B cell lymphoma histologies are being currently explored.”
Rouce discloses relationships with Novartis and Pfizer. Linhares reports ties with Kyowa Kirin, AbbVie, ADC, BeiGene, Genentech, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Seagen, and TG. Badr has no disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ATA: Updates on Risk, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
The study, presented by Juan Brito Campana, MBBS, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, used Medicare records to perform a secondary analysis of 41,000 adults with type 2 diabetes and moderate cardiovascular risk who were new users of GLP-1 receptor agonists, compared to users of other diabetes medications.
“We took the innovative approach of applying the methodological rigor of a randomized clinical trial to the very large dataset of observational studies,” said Brito Campana.
The results showed a low absolute risk of thyroid cancer, with only 0.17% of patients in the GLP-1 group developing the disease. However, the data also showed a potential relative increase in risk during the first year of GLP-1 receptor agonist use.
“This is likely due to increased detection rather than true incidence, as the latency period for thyroid cancer development is typically longer,” Brito Campana said.
“We also note the limitations of the observational study design, including the short follow-up period and lack of detailed histological data. However, we believe the benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists likely outweigh the risk of thyroid cancer.”
Malignancy in Bethesda III and IV Thyroid Nodules
At the same ATA session, Sapir Nachum Goldberg, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, presented the results of a retrospective record review that examined the prevalence of malignancy in Bethesda III and IV thyroid nodules with negative Thyrogen Receptor Signaling (ThyroSeq) version 3 molecular testing results.
Goldberg reported that 87% of patients with ThyroSeq negative subtype results were managed nonoperatively. “Based on our data, the true prevalence of malignancy likely lies between our low and high estimates of 3% and 23%,” she said. “We believe that the prevalence of malignancy may be higher in real-world practice than validation studies.”
Additionally, nodules with “currently negative” or “negative but limited” ThyroSeq results had a higher prevalence of malignancy (7%), compared with those with a “negative” result (2%). Factors like immediate vs delayed surgery, nodule size, and ultrasound pattern did not significantly impact malignancy prevalence.
The study results also indicated that surveillance ultrasonography is not routinely performed in up to one-third of patients, Goldberg said.
She closed by suggesting that colleagues consider the negative subtype in clinical decision-making. For “negative but limited” nodules, repeat the fine needle aspiration and, for “negative” and “currently negative” nodules, consider ultrasound follow-up as per ATA guidelines for Bethesda II cytology, she said.
RET-Mutated Medullary Thyroid Cancer
For patients with RET-mutated medullary thyroid cancer, Julien Hadoux, MD, PhD, of Institut de Cancérologie Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, presented a combined analysis of the efficacy of the RET inhibitor selpercatinib from the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 and phase 3 LIBRETTO-531 trials.
This post hoc analysis used a combined cohort of 509 patients with RET-mutated advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer who had received selpercatinib in the two trials.
Hadoux reported that robust and durable responses were seen across all mutation groups, including M918T, extracellular cysteine, and an “other” group composed of various uncommon RET mutations. “The median [progression-free survival] PFS was not reached for either the M918T or extracellular groups and it was 51.4 months for the Other group,” he said.
“Selpercatinib showed superior median PFS vs control, regardless of the RET mutation. This analysis constitutes the largest catalog of RET mutations in medullary thyroid cancers treated with RET-specific inhibitors.”
TRK-Fusion Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Steven Waguespack, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, shared updated efficacy and safety data from three phase 1/2 pooled clinical trials of the tropomyosin kinase receptor (TRK) inhibitor larotrectinib in thyroid cancer. These data updated results initially published in 2022.
“Larotrectinib continues to demonstrate rapid and durable responses, extended survival, and offers a favorable safety profile in patients with TRK fusion differentiated thyroid cancer, with limited activity in anaplastic thyroid cancer,” Waguespack said.
“Additionally, in a subset of patients, we identified some acquired on-target NTRK mutations and off-target GNAS and TP53 mutations that may give further insight into mechanisms of resistance.”
The primary endpoint was the investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR); at 48 months, the ORR was 79% by independent review. The median PFS in patients with TRK fusion differentiated thyroid cancer was 44 months, while the median duration of response was 41 months. The 4-year overall survival rate was 86%.
Waguespack closed with a cautionary note to colleagues: “While circulating tumor DNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis can be used to test for NTRK gene fusions, negative results should be followed up with tissue-based NGS,” he said.
Brito Campana and Goldberg disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Hadoux reported receiving honoraria for speaker engagements, advisory roles, or funding for CME from Eli Lilly, AAA, IPSEN, Roche, Pharma Mar, and EISAI, and research grants from Novartis, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, presented by Juan Brito Campana, MBBS, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, used Medicare records to perform a secondary analysis of 41,000 adults with type 2 diabetes and moderate cardiovascular risk who were new users of GLP-1 receptor agonists, compared to users of other diabetes medications.
“We took the innovative approach of applying the methodological rigor of a randomized clinical trial to the very large dataset of observational studies,” said Brito Campana.
The results showed a low absolute risk of thyroid cancer, with only 0.17% of patients in the GLP-1 group developing the disease. However, the data also showed a potential relative increase in risk during the first year of GLP-1 receptor agonist use.
“This is likely due to increased detection rather than true incidence, as the latency period for thyroid cancer development is typically longer,” Brito Campana said.
“We also note the limitations of the observational study design, including the short follow-up period and lack of detailed histological data. However, we believe the benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists likely outweigh the risk of thyroid cancer.”
Malignancy in Bethesda III and IV Thyroid Nodules
At the same ATA session, Sapir Nachum Goldberg, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, presented the results of a retrospective record review that examined the prevalence of malignancy in Bethesda III and IV thyroid nodules with negative Thyrogen Receptor Signaling (ThyroSeq) version 3 molecular testing results.
Goldberg reported that 87% of patients with ThyroSeq negative subtype results were managed nonoperatively. “Based on our data, the true prevalence of malignancy likely lies between our low and high estimates of 3% and 23%,” she said. “We believe that the prevalence of malignancy may be higher in real-world practice than validation studies.”
Additionally, nodules with “currently negative” or “negative but limited” ThyroSeq results had a higher prevalence of malignancy (7%), compared with those with a “negative” result (2%). Factors like immediate vs delayed surgery, nodule size, and ultrasound pattern did not significantly impact malignancy prevalence.
The study results also indicated that surveillance ultrasonography is not routinely performed in up to one-third of patients, Goldberg said.
She closed by suggesting that colleagues consider the negative subtype in clinical decision-making. For “negative but limited” nodules, repeat the fine needle aspiration and, for “negative” and “currently negative” nodules, consider ultrasound follow-up as per ATA guidelines for Bethesda II cytology, she said.
RET-Mutated Medullary Thyroid Cancer
For patients with RET-mutated medullary thyroid cancer, Julien Hadoux, MD, PhD, of Institut de Cancérologie Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, presented a combined analysis of the efficacy of the RET inhibitor selpercatinib from the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 and phase 3 LIBRETTO-531 trials.
This post hoc analysis used a combined cohort of 509 patients with RET-mutated advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer who had received selpercatinib in the two trials.
Hadoux reported that robust and durable responses were seen across all mutation groups, including M918T, extracellular cysteine, and an “other” group composed of various uncommon RET mutations. “The median [progression-free survival] PFS was not reached for either the M918T or extracellular groups and it was 51.4 months for the Other group,” he said.
“Selpercatinib showed superior median PFS vs control, regardless of the RET mutation. This analysis constitutes the largest catalog of RET mutations in medullary thyroid cancers treated with RET-specific inhibitors.”
TRK-Fusion Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Steven Waguespack, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, shared updated efficacy and safety data from three phase 1/2 pooled clinical trials of the tropomyosin kinase receptor (TRK) inhibitor larotrectinib in thyroid cancer. These data updated results initially published in 2022.
“Larotrectinib continues to demonstrate rapid and durable responses, extended survival, and offers a favorable safety profile in patients with TRK fusion differentiated thyroid cancer, with limited activity in anaplastic thyroid cancer,” Waguespack said.
“Additionally, in a subset of patients, we identified some acquired on-target NTRK mutations and off-target GNAS and TP53 mutations that may give further insight into mechanisms of resistance.”
The primary endpoint was the investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR); at 48 months, the ORR was 79% by independent review. The median PFS in patients with TRK fusion differentiated thyroid cancer was 44 months, while the median duration of response was 41 months. The 4-year overall survival rate was 86%.
Waguespack closed with a cautionary note to colleagues: “While circulating tumor DNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis can be used to test for NTRK gene fusions, negative results should be followed up with tissue-based NGS,” he said.
Brito Campana and Goldberg disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Hadoux reported receiving honoraria for speaker engagements, advisory roles, or funding for CME from Eli Lilly, AAA, IPSEN, Roche, Pharma Mar, and EISAI, and research grants from Novartis, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The study, presented by Juan Brito Campana, MBBS, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, used Medicare records to perform a secondary analysis of 41,000 adults with type 2 diabetes and moderate cardiovascular risk who were new users of GLP-1 receptor agonists, compared to users of other diabetes medications.
“We took the innovative approach of applying the methodological rigor of a randomized clinical trial to the very large dataset of observational studies,” said Brito Campana.
The results showed a low absolute risk of thyroid cancer, with only 0.17% of patients in the GLP-1 group developing the disease. However, the data also showed a potential relative increase in risk during the first year of GLP-1 receptor agonist use.
“This is likely due to increased detection rather than true incidence, as the latency period for thyroid cancer development is typically longer,” Brito Campana said.
“We also note the limitations of the observational study design, including the short follow-up period and lack of detailed histological data. However, we believe the benefits of GLP-1 receptor agonists likely outweigh the risk of thyroid cancer.”
Malignancy in Bethesda III and IV Thyroid Nodules
At the same ATA session, Sapir Nachum Goldberg, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, presented the results of a retrospective record review that examined the prevalence of malignancy in Bethesda III and IV thyroid nodules with negative Thyrogen Receptor Signaling (ThyroSeq) version 3 molecular testing results.
Goldberg reported that 87% of patients with ThyroSeq negative subtype results were managed nonoperatively. “Based on our data, the true prevalence of malignancy likely lies between our low and high estimates of 3% and 23%,” she said. “We believe that the prevalence of malignancy may be higher in real-world practice than validation studies.”
Additionally, nodules with “currently negative” or “negative but limited” ThyroSeq results had a higher prevalence of malignancy (7%), compared with those with a “negative” result (2%). Factors like immediate vs delayed surgery, nodule size, and ultrasound pattern did not significantly impact malignancy prevalence.
The study results also indicated that surveillance ultrasonography is not routinely performed in up to one-third of patients, Goldberg said.
She closed by suggesting that colleagues consider the negative subtype in clinical decision-making. For “negative but limited” nodules, repeat the fine needle aspiration and, for “negative” and “currently negative” nodules, consider ultrasound follow-up as per ATA guidelines for Bethesda II cytology, she said.
RET-Mutated Medullary Thyroid Cancer
For patients with RET-mutated medullary thyroid cancer, Julien Hadoux, MD, PhD, of Institut de Cancérologie Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France, presented a combined analysis of the efficacy of the RET inhibitor selpercatinib from the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 and phase 3 LIBRETTO-531 trials.
This post hoc analysis used a combined cohort of 509 patients with RET-mutated advanced or metastatic medullary thyroid cancer who had received selpercatinib in the two trials.
Hadoux reported that robust and durable responses were seen across all mutation groups, including M918T, extracellular cysteine, and an “other” group composed of various uncommon RET mutations. “The median [progression-free survival] PFS was not reached for either the M918T or extracellular groups and it was 51.4 months for the Other group,” he said.
“Selpercatinib showed superior median PFS vs control, regardless of the RET mutation. This analysis constitutes the largest catalog of RET mutations in medullary thyroid cancers treated with RET-specific inhibitors.”
TRK-Fusion Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Steven Waguespack, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, shared updated efficacy and safety data from three phase 1/2 pooled clinical trials of the tropomyosin kinase receptor (TRK) inhibitor larotrectinib in thyroid cancer. These data updated results initially published in 2022.
“Larotrectinib continues to demonstrate rapid and durable responses, extended survival, and offers a favorable safety profile in patients with TRK fusion differentiated thyroid cancer, with limited activity in anaplastic thyroid cancer,” Waguespack said.
“Additionally, in a subset of patients, we identified some acquired on-target NTRK mutations and off-target GNAS and TP53 mutations that may give further insight into mechanisms of resistance.”
The primary endpoint was the investigator-assessed objective response rate (ORR); at 48 months, the ORR was 79% by independent review. The median PFS in patients with TRK fusion differentiated thyroid cancer was 44 months, while the median duration of response was 41 months. The 4-year overall survival rate was 86%.
Waguespack closed with a cautionary note to colleagues: “While circulating tumor DNA next-generation sequencing (NGS) analysis can be used to test for NTRK gene fusions, negative results should be followed up with tissue-based NGS,” he said.
Brito Campana and Goldberg disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Hadoux reported receiving honoraria for speaker engagements, advisory roles, or funding for CME from Eli Lilly, AAA, IPSEN, Roche, Pharma Mar, and EISAI, and research grants from Novartis, Sanofi, and Eli Lilly.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ATA 2024