User login
Exercise Plus GLP-1 RAs Upped Weight Loss, Bone Retention
TOPLINE:
People with obesity who exercise while taking glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; liraglutide) showed increased weight loss and preserved bone health, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients were placed on an initial diet that consisted of no more than 800 calories per day for 8 weeks. Those who lost at least 5% of their starting weight were then placed into a 1-year program.
- Participants included 195 adults aged between 18 and 65 years with obesity and no diabetes, 64% of whom were women.
- They were split into four groups of interventions: Exercise only (48 patients), liraglutide only (49 patients), a combination of both (49 participants), and placebo (49 participants), for a 1-year period.
- Patients received liraglutide or volume-matched placebo as daily injections starting at 0.6 mg/d with a weekly increase until 3 mg/d was reached; exercise entailed 30-minute sessions for 4 days a week.
- Researchers studied bone health at each patient’s hip, spine, and forearm after they lost weight, by measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall average change in weight loss over the course of 52 weeks was 7.03 kg in the placebo group, 11.19 kg in the exercise group, 13.74 kg in the liraglutide group, and 16.88 kg in the combination group.
- BMD did not change in the combination group in comparison to the placebo group at the hip (mean change, −0.006 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.017 to 0.004 g/cm2; P = .24) or spine (−0.010 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.025 to 0.005 g/cm2; P = .20).
- BMD of the spine in the liraglutide group decreased in comparison to the exercise group (mean change, −0.016 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.032 to −0.001 g/cm2; P = .04) and the placebo group, in addition to decreases in the hip.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results show that the combination of exercise and GLP-1 RA was the most effective weight loss strategy while preserving bone health,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simon Birk Kjær Jensen, PhD, of the Department of Biomedical Sciences and Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and published on June 25 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only included adults aged between 18 and 65 years without other chronic diseases and may not apply to patients who are older or have diabetes. The study sample was diverse but was conducted in Denmark, with a population of generally similar ancestry.
DISCLOSURES:
One study author reported serving on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, and Amgen, among others. Other authors reported various financial interests, including grants, personal fees, and salaries, from Amgen, Novo Nordisk, and Abbott Lab, among others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
People with obesity who exercise while taking glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; liraglutide) showed increased weight loss and preserved bone health, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients were placed on an initial diet that consisted of no more than 800 calories per day for 8 weeks. Those who lost at least 5% of their starting weight were then placed into a 1-year program.
- Participants included 195 adults aged between 18 and 65 years with obesity and no diabetes, 64% of whom were women.
- They were split into four groups of interventions: Exercise only (48 patients), liraglutide only (49 patients), a combination of both (49 participants), and placebo (49 participants), for a 1-year period.
- Patients received liraglutide or volume-matched placebo as daily injections starting at 0.6 mg/d with a weekly increase until 3 mg/d was reached; exercise entailed 30-minute sessions for 4 days a week.
- Researchers studied bone health at each patient’s hip, spine, and forearm after they lost weight, by measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall average change in weight loss over the course of 52 weeks was 7.03 kg in the placebo group, 11.19 kg in the exercise group, 13.74 kg in the liraglutide group, and 16.88 kg in the combination group.
- BMD did not change in the combination group in comparison to the placebo group at the hip (mean change, −0.006 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.017 to 0.004 g/cm2; P = .24) or spine (−0.010 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.025 to 0.005 g/cm2; P = .20).
- BMD of the spine in the liraglutide group decreased in comparison to the exercise group (mean change, −0.016 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.032 to −0.001 g/cm2; P = .04) and the placebo group, in addition to decreases in the hip.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results show that the combination of exercise and GLP-1 RA was the most effective weight loss strategy while preserving bone health,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simon Birk Kjær Jensen, PhD, of the Department of Biomedical Sciences and Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and published on June 25 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only included adults aged between 18 and 65 years without other chronic diseases and may not apply to patients who are older or have diabetes. The study sample was diverse but was conducted in Denmark, with a population of generally similar ancestry.
DISCLOSURES:
One study author reported serving on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, and Amgen, among others. Other authors reported various financial interests, including grants, personal fees, and salaries, from Amgen, Novo Nordisk, and Abbott Lab, among others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
People with obesity who exercise while taking glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs; liraglutide) showed increased weight loss and preserved bone health, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients were placed on an initial diet that consisted of no more than 800 calories per day for 8 weeks. Those who lost at least 5% of their starting weight were then placed into a 1-year program.
- Participants included 195 adults aged between 18 and 65 years with obesity and no diabetes, 64% of whom were women.
- They were split into four groups of interventions: Exercise only (48 patients), liraglutide only (49 patients), a combination of both (49 participants), and placebo (49 participants), for a 1-year period.
- Patients received liraglutide or volume-matched placebo as daily injections starting at 0.6 mg/d with a weekly increase until 3 mg/d was reached; exercise entailed 30-minute sessions for 4 days a week.
- Researchers studied bone health at each patient’s hip, spine, and forearm after they lost weight, by measuring bone mineral density (BMD).
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall average change in weight loss over the course of 52 weeks was 7.03 kg in the placebo group, 11.19 kg in the exercise group, 13.74 kg in the liraglutide group, and 16.88 kg in the combination group.
- BMD did not change in the combination group in comparison to the placebo group at the hip (mean change, −0.006 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.017 to 0.004 g/cm2; P = .24) or spine (−0.010 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.025 to 0.005 g/cm2; P = .20).
- BMD of the spine in the liraglutide group decreased in comparison to the exercise group (mean change, −0.016 g/cm2; 95% CI, −0.032 to −0.001 g/cm2; P = .04) and the placebo group, in addition to decreases in the hip.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results show that the combination of exercise and GLP-1 RA was the most effective weight loss strategy while preserving bone health,” study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Simon Birk Kjær Jensen, PhD, of the Department of Biomedical Sciences and Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark, and published on June 25 in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The study only included adults aged between 18 and 65 years without other chronic diseases and may not apply to patients who are older or have diabetes. The study sample was diverse but was conducted in Denmark, with a population of generally similar ancestry.
DISCLOSURES:
One study author reported serving on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, and Amgen, among others. Other authors reported various financial interests, including grants, personal fees, and salaries, from Amgen, Novo Nordisk, and Abbott Lab, among others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Semaglutide Reduce Inflammation?
LYON, FRANCE — The anti-obesity drug semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in the inflammatory marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP), even in patients who do not lose substantial amounts of weight with the drug, according to data from the SELECT clinical trial.
The research, presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society 2024, involved over 17,600 patients with overweight or obesity and had established cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with greater high-sensitivity CRP reduction in both treatment groups,” said study presenter Jorge Plutzky, MD, director of Preventive Cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, but “with increased high-sensitivity CRP reductions in those receiving semaglutide.”
The drug also “significantly reduced high-sensitivity CRP early,” he said, “prior to major weight loss and in those who did not lose significant amounts of weight.” The reductions reached approximately 12% at 4 weeks and around 20% at 8 weeks, when the weight loss “was still quite modest,” at 2% and 3% of body weight, respectively. Even among patients who achieved weight loss of less than 2% body weight, semaglutide was associated with a reduction in high-sensitivity CRP levels.
In the SELECT trial, semaglutide also resulted in a consistent reduction of around 20% vs placebo in major adverse cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
But Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, said in an interview that body weight “is probably the major driver” of CRP levels in the population, accounting for between 20% and 30% of the variation.
Dr. Sattar, who was not involved in the study, said that because drugs like semaglutide lower weight but also have anti-inflammatory effects, the question becomes: “Could the anti-inflammatory effects be part of the mechanisms by which these drugs affect the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events?”
Reducing Cardiovascular Events
The current analysis, however, cannot answer the question, he said. “All it tells us is about associations.”
“What we do know is semaglutide, predominantly by lowering weight, is lowering CRP levels and equally, we know that when you lose weight, you improve blood pressure, you improve lipids, and you reduce the risk of diabetes,” he said.
Dr. Sattar also took issue with the researchers’ conclusion that the high-sensitivity CRP reductions seen in SELECT occurred prior to major weight loss because the “pattern of CRP reduction and weight reduction is almost identical.”
Dr. Sattar also pointed out in a recent editorial that the drug appears to have a direct effect on blood vessels and the heart, which may lead to improvements in systemic inflammation. Consequently, he said, any assertion that semaglutide is genuinely anti-inflammatory is, at this stage, “speculation.”
Dr. Plutzky said that “systemic, chronic inflammation is implicated as a potential mechanism and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis and major adverse cardiovascular events, as well as obesity,” and high-sensitivity CRP levels are an “established biomarker of inflammation and have been shown to predict cardiovascular risk.”
However, the relationship between high-sensitivity CRP, responses to glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide, and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity “remains incompletely understood,” said Dr. Plutzky.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LYON, FRANCE — The anti-obesity drug semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in the inflammatory marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP), even in patients who do not lose substantial amounts of weight with the drug, according to data from the SELECT clinical trial.
The research, presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society 2024, involved over 17,600 patients with overweight or obesity and had established cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with greater high-sensitivity CRP reduction in both treatment groups,” said study presenter Jorge Plutzky, MD, director of Preventive Cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, but “with increased high-sensitivity CRP reductions in those receiving semaglutide.”
The drug also “significantly reduced high-sensitivity CRP early,” he said, “prior to major weight loss and in those who did not lose significant amounts of weight.” The reductions reached approximately 12% at 4 weeks and around 20% at 8 weeks, when the weight loss “was still quite modest,” at 2% and 3% of body weight, respectively. Even among patients who achieved weight loss of less than 2% body weight, semaglutide was associated with a reduction in high-sensitivity CRP levels.
In the SELECT trial, semaglutide also resulted in a consistent reduction of around 20% vs placebo in major adverse cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
But Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, said in an interview that body weight “is probably the major driver” of CRP levels in the population, accounting for between 20% and 30% of the variation.
Dr. Sattar, who was not involved in the study, said that because drugs like semaglutide lower weight but also have anti-inflammatory effects, the question becomes: “Could the anti-inflammatory effects be part of the mechanisms by which these drugs affect the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events?”
Reducing Cardiovascular Events
The current analysis, however, cannot answer the question, he said. “All it tells us is about associations.”
“What we do know is semaglutide, predominantly by lowering weight, is lowering CRP levels and equally, we know that when you lose weight, you improve blood pressure, you improve lipids, and you reduce the risk of diabetes,” he said.
Dr. Sattar also took issue with the researchers’ conclusion that the high-sensitivity CRP reductions seen in SELECT occurred prior to major weight loss because the “pattern of CRP reduction and weight reduction is almost identical.”
Dr. Sattar also pointed out in a recent editorial that the drug appears to have a direct effect on blood vessels and the heart, which may lead to improvements in systemic inflammation. Consequently, he said, any assertion that semaglutide is genuinely anti-inflammatory is, at this stage, “speculation.”
Dr. Plutzky said that “systemic, chronic inflammation is implicated as a potential mechanism and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis and major adverse cardiovascular events, as well as obesity,” and high-sensitivity CRP levels are an “established biomarker of inflammation and have been shown to predict cardiovascular risk.”
However, the relationship between high-sensitivity CRP, responses to glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide, and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity “remains incompletely understood,” said Dr. Plutzky.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
LYON, FRANCE — The anti-obesity drug semaglutide is associated with significant reductions in the inflammatory marker high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP), even in patients who do not lose substantial amounts of weight with the drug, according to data from the SELECT clinical trial.
The research, presented at the European Atherosclerosis Society 2024, involved over 17,600 patients with overweight or obesity and had established cardiovascular disease but not diabetes.
“Weight loss was associated with greater high-sensitivity CRP reduction in both treatment groups,” said study presenter Jorge Plutzky, MD, director of Preventive Cardiology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, but “with increased high-sensitivity CRP reductions in those receiving semaglutide.”
The drug also “significantly reduced high-sensitivity CRP early,” he said, “prior to major weight loss and in those who did not lose significant amounts of weight.” The reductions reached approximately 12% at 4 weeks and around 20% at 8 weeks, when the weight loss “was still quite modest,” at 2% and 3% of body weight, respectively. Even among patients who achieved weight loss of less than 2% body weight, semaglutide was associated with a reduction in high-sensitivity CRP levels.
In the SELECT trial, semaglutide also resulted in a consistent reduction of around 20% vs placebo in major adverse cardiovascular events such as cardiovascular mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke.
But Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, professor of cardiometabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, Scotland, said in an interview that body weight “is probably the major driver” of CRP levels in the population, accounting for between 20% and 30% of the variation.
Dr. Sattar, who was not involved in the study, said that because drugs like semaglutide lower weight but also have anti-inflammatory effects, the question becomes: “Could the anti-inflammatory effects be part of the mechanisms by which these drugs affect the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events?”
Reducing Cardiovascular Events
The current analysis, however, cannot answer the question, he said. “All it tells us is about associations.”
“What we do know is semaglutide, predominantly by lowering weight, is lowering CRP levels and equally, we know that when you lose weight, you improve blood pressure, you improve lipids, and you reduce the risk of diabetes,” he said.
Dr. Sattar also took issue with the researchers’ conclusion that the high-sensitivity CRP reductions seen in SELECT occurred prior to major weight loss because the “pattern of CRP reduction and weight reduction is almost identical.”
Dr. Sattar also pointed out in a recent editorial that the drug appears to have a direct effect on blood vessels and the heart, which may lead to improvements in systemic inflammation. Consequently, he said, any assertion that semaglutide is genuinely anti-inflammatory is, at this stage, “speculation.”
Dr. Plutzky said that “systemic, chronic inflammation is implicated as a potential mechanism and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis and major adverse cardiovascular events, as well as obesity,” and high-sensitivity CRP levels are an “established biomarker of inflammation and have been shown to predict cardiovascular risk.”
However, the relationship between high-sensitivity CRP, responses to glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists like semaglutide, and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity “remains incompletely understood,” said Dr. Plutzky.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnostic yield reporting of bronchoscopic peripheral pulmonary nodule biopsies: A call for standardization
THORACIC ONCOLOGY AND CHEST PROCEDURES NETWORK
Interventional Procedures Section
More than 1.5 million Americans are diagnosed with an incidental CT scan-detected lung nodule annually. Advanced bronchoscopy, as a diagnostic tool for evaluation of these nodules, has evolved rapidly, incorporating a range of techniques and tools beyond CT scan-guided biopsies to assess peripheral lesions. The primary goal is to provide patients with accurate benign or malignant diagnoses. However, accurately determining the effectiveness of innovative technologies in providing a diagnosis remains challenging, in part due to limitations in study design and outcome reporting, along with the scarcity of comparative and randomized controlled studies.1,2 Current literature shows significant variability in diagnostic yield definition, lacking generalizability.
To address this issue, an official research statement by the American Thoracic Society and CHEST defines the diagnostic yield as “the proportion of all individuals undergoing the diagnostic procedure under evaluation in whom a specific malignant or benign diagnosis is established.”3 To achieve this measure, the numerator includes all patients with lung nodules in whom the result of a diagnostic procedure establishes a specific benign or malignant diagnosis that is readily sufficient to inform patient care without additional diagnostic workup, and the denominator should include all patients in whom the procedure was attempted or performed. This standardized definition is crucial for ensuring consistency across studies, allowing for comparison or pooling of results, enhancing the reliability of diagnostic yield data, and informing clinical decisions.
The adoption of standardized outcome definitions is essential to critically evaluate modern, minimally invasive procedures for peripheral lung nodules diagnosis and to guide patient-centered care while minimizing the downstream effects of nondiagnostic biopsies. Clear, transparent, and consistent reporting will enable physicians to choose the most appropriate diagnostic tools, improve patient outcomes by reducing unnecessary procedures, and expedite accurate diagnoses. This initiative is a crucial first step toward creating high-quality studies that can inform technology implementation decisions and promote equitable health care.
References
1. Tanner NT, Yarmus L, Chen A, et al. Standard bronchoscopy with fluoroscopy vs thin bronchoscopy and radial endobronchial ultrasound for biopsy of pulmonary lesions: a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial. Chest. 2018;154(5):1035-1043.
2. Ost DE, Ernst A, Lei X, et al. Diagnostic yield and complications of bronchoscopy for peripheral lung lesions. Results of the AQuIRE Registry. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2016;193(1):68-77.
3. Gonzalez AV, Silvestri GA, Korevaar DA, et al. Assessment of advanced diagnostic bronchoscopy outcomes for peripheral lung lesions: a Delphi consensus definition of diagnostic yield and recommendations for patient-centered study designs. An official American Thoracic Society/American College of Chest Physicians research statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(6):634-646.
THORACIC ONCOLOGY AND CHEST PROCEDURES NETWORK
Interventional Procedures Section
More than 1.5 million Americans are diagnosed with an incidental CT scan-detected lung nodule annually. Advanced bronchoscopy, as a diagnostic tool for evaluation of these nodules, has evolved rapidly, incorporating a range of techniques and tools beyond CT scan-guided biopsies to assess peripheral lesions. The primary goal is to provide patients with accurate benign or malignant diagnoses. However, accurately determining the effectiveness of innovative technologies in providing a diagnosis remains challenging, in part due to limitations in study design and outcome reporting, along with the scarcity of comparative and randomized controlled studies.1,2 Current literature shows significant variability in diagnostic yield definition, lacking generalizability.
To address this issue, an official research statement by the American Thoracic Society and CHEST defines the diagnostic yield as “the proportion of all individuals undergoing the diagnostic procedure under evaluation in whom a specific malignant or benign diagnosis is established.”3 To achieve this measure, the numerator includes all patients with lung nodules in whom the result of a diagnostic procedure establishes a specific benign or malignant diagnosis that is readily sufficient to inform patient care without additional diagnostic workup, and the denominator should include all patients in whom the procedure was attempted or performed. This standardized definition is crucial for ensuring consistency across studies, allowing for comparison or pooling of results, enhancing the reliability of diagnostic yield data, and informing clinical decisions.
The adoption of standardized outcome definitions is essential to critically evaluate modern, minimally invasive procedures for peripheral lung nodules diagnosis and to guide patient-centered care while minimizing the downstream effects of nondiagnostic biopsies. Clear, transparent, and consistent reporting will enable physicians to choose the most appropriate diagnostic tools, improve patient outcomes by reducing unnecessary procedures, and expedite accurate diagnoses. This initiative is a crucial first step toward creating high-quality studies that can inform technology implementation decisions and promote equitable health care.
References
1. Tanner NT, Yarmus L, Chen A, et al. Standard bronchoscopy with fluoroscopy vs thin bronchoscopy and radial endobronchial ultrasound for biopsy of pulmonary lesions: a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial. Chest. 2018;154(5):1035-1043.
2. Ost DE, Ernst A, Lei X, et al. Diagnostic yield and complications of bronchoscopy for peripheral lung lesions. Results of the AQuIRE Registry. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2016;193(1):68-77.
3. Gonzalez AV, Silvestri GA, Korevaar DA, et al. Assessment of advanced diagnostic bronchoscopy outcomes for peripheral lung lesions: a Delphi consensus definition of diagnostic yield and recommendations for patient-centered study designs. An official American Thoracic Society/American College of Chest Physicians research statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(6):634-646.
THORACIC ONCOLOGY AND CHEST PROCEDURES NETWORK
Interventional Procedures Section
More than 1.5 million Americans are diagnosed with an incidental CT scan-detected lung nodule annually. Advanced bronchoscopy, as a diagnostic tool for evaluation of these nodules, has evolved rapidly, incorporating a range of techniques and tools beyond CT scan-guided biopsies to assess peripheral lesions. The primary goal is to provide patients with accurate benign or malignant diagnoses. However, accurately determining the effectiveness of innovative technologies in providing a diagnosis remains challenging, in part due to limitations in study design and outcome reporting, along with the scarcity of comparative and randomized controlled studies.1,2 Current literature shows significant variability in diagnostic yield definition, lacking generalizability.
To address this issue, an official research statement by the American Thoracic Society and CHEST defines the diagnostic yield as “the proportion of all individuals undergoing the diagnostic procedure under evaluation in whom a specific malignant or benign diagnosis is established.”3 To achieve this measure, the numerator includes all patients with lung nodules in whom the result of a diagnostic procedure establishes a specific benign or malignant diagnosis that is readily sufficient to inform patient care without additional diagnostic workup, and the denominator should include all patients in whom the procedure was attempted or performed. This standardized definition is crucial for ensuring consistency across studies, allowing for comparison or pooling of results, enhancing the reliability of diagnostic yield data, and informing clinical decisions.
The adoption of standardized outcome definitions is essential to critically evaluate modern, minimally invasive procedures for peripheral lung nodules diagnosis and to guide patient-centered care while minimizing the downstream effects of nondiagnostic biopsies. Clear, transparent, and consistent reporting will enable physicians to choose the most appropriate diagnostic tools, improve patient outcomes by reducing unnecessary procedures, and expedite accurate diagnoses. This initiative is a crucial first step toward creating high-quality studies that can inform technology implementation decisions and promote equitable health care.
References
1. Tanner NT, Yarmus L, Chen A, et al. Standard bronchoscopy with fluoroscopy vs thin bronchoscopy and radial endobronchial ultrasound for biopsy of pulmonary lesions: a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial. Chest. 2018;154(5):1035-1043.
2. Ost DE, Ernst A, Lei X, et al. Diagnostic yield and complications of bronchoscopy for peripheral lung lesions. Results of the AQuIRE Registry. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2016;193(1):68-77.
3. Gonzalez AV, Silvestri GA, Korevaar DA, et al. Assessment of advanced diagnostic bronchoscopy outcomes for peripheral lung lesions: a Delphi consensus definition of diagnostic yield and recommendations for patient-centered study designs. An official American Thoracic Society/American College of Chest Physicians research statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024;209(6):634-646.
Post–intensive care syndrome and insomnia
SLEEP MEDICINE NETWORK
Nonrespiratory Sleep Section
There has been a recent interest in post–intensive care syndrome (PICS), as an increasing number of patients are surviving critical illness. PICS is defined as “new onset or worsening of impairments in physical, cognitive, and/or mental health that arises after an ICU stay and persists beyond hospital discharge.1 We know that poor sleep is a common occurrence in the ICU, which can contribute to cognitive impairment and could be due to various risk factors, including age, individual comorbidities, reason for admission, and ICU interventions.2 Sleep impairment after hospital discharge is highly prevalent for up to 1 year after hospitalization.
The most common sleep impairment described after hospital discharge from the ICU is insomnia, which coexists with anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder.3 When patients are seen in a post-ICU clinic, a multimodal strategy is needed for the treatment of insomnia, which includes practicing good sleep hygiene, cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), and pharmacotherapy if indicated.
Since the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) 2021 clinical practice guideline on behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia, which made a strong recommendation for CBT-I, we continue to face barriers to incorporating CBT-I into our own clinical practice.4 This is due to limited access to CBT-I psychotherapists and patients’ lack of knowledge or treatment beliefs, among other reasons. However, there are numerous digital CBT-I platforms that patients can freely access from their mobile phone and are listed in the AASM article, “Digital cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia: Platforms and characteristics,” which can help with treatment of insomnia.
For patients who are seen in post-ICU clinics, the first step in treating insomnia is discussing good sleep hygiene, providing resources for CBT-I (digital or in person), and treating coexistent psychiatric conditions.
References
1. Rawal G, Yadav S, Kumar R. Post-intensive care syndrome: an overview. J Transl Int Med. 2017;5(2):90-92.
2. Zampieri FG, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(11):1558-1560.
3. Altman MT, Knauert MP, Pisani MA. Sleep disturbance after hospitalization and critical illness: a systematic review. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(9):1457-1468.
4. Edinger JD, Arnedt JT, Bertisch SM, et al. Behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia disorder in adults: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021;17(2):255-262.
SLEEP MEDICINE NETWORK
Nonrespiratory Sleep Section
There has been a recent interest in post–intensive care syndrome (PICS), as an increasing number of patients are surviving critical illness. PICS is defined as “new onset or worsening of impairments in physical, cognitive, and/or mental health that arises after an ICU stay and persists beyond hospital discharge.1 We know that poor sleep is a common occurrence in the ICU, which can contribute to cognitive impairment and could be due to various risk factors, including age, individual comorbidities, reason for admission, and ICU interventions.2 Sleep impairment after hospital discharge is highly prevalent for up to 1 year after hospitalization.
The most common sleep impairment described after hospital discharge from the ICU is insomnia, which coexists with anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder.3 When patients are seen in a post-ICU clinic, a multimodal strategy is needed for the treatment of insomnia, which includes practicing good sleep hygiene, cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), and pharmacotherapy if indicated.
Since the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) 2021 clinical practice guideline on behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia, which made a strong recommendation for CBT-I, we continue to face barriers to incorporating CBT-I into our own clinical practice.4 This is due to limited access to CBT-I psychotherapists and patients’ lack of knowledge or treatment beliefs, among other reasons. However, there are numerous digital CBT-I platforms that patients can freely access from their mobile phone and are listed in the AASM article, “Digital cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia: Platforms and characteristics,” which can help with treatment of insomnia.
For patients who are seen in post-ICU clinics, the first step in treating insomnia is discussing good sleep hygiene, providing resources for CBT-I (digital or in person), and treating coexistent psychiatric conditions.
References
1. Rawal G, Yadav S, Kumar R. Post-intensive care syndrome: an overview. J Transl Int Med. 2017;5(2):90-92.
2. Zampieri FG, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(11):1558-1560.
3. Altman MT, Knauert MP, Pisani MA. Sleep disturbance after hospitalization and critical illness: a systematic review. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(9):1457-1468.
4. Edinger JD, Arnedt JT, Bertisch SM, et al. Behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia disorder in adults: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021;17(2):255-262.
SLEEP MEDICINE NETWORK
Nonrespiratory Sleep Section
There has been a recent interest in post–intensive care syndrome (PICS), as an increasing number of patients are surviving critical illness. PICS is defined as “new onset or worsening of impairments in physical, cognitive, and/or mental health that arises after an ICU stay and persists beyond hospital discharge.1 We know that poor sleep is a common occurrence in the ICU, which can contribute to cognitive impairment and could be due to various risk factors, including age, individual comorbidities, reason for admission, and ICU interventions.2 Sleep impairment after hospital discharge is highly prevalent for up to 1 year after hospitalization.
The most common sleep impairment described after hospital discharge from the ICU is insomnia, which coexists with anxiety, depression, and posttraumatic stress disorder.3 When patients are seen in a post-ICU clinic, a multimodal strategy is needed for the treatment of insomnia, which includes practicing good sleep hygiene, cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I), and pharmacotherapy if indicated.
Since the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) 2021 clinical practice guideline on behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia, which made a strong recommendation for CBT-I, we continue to face barriers to incorporating CBT-I into our own clinical practice.4 This is due to limited access to CBT-I psychotherapists and patients’ lack of knowledge or treatment beliefs, among other reasons. However, there are numerous digital CBT-I platforms that patients can freely access from their mobile phone and are listed in the AASM article, “Digital cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia: Platforms and characteristics,” which can help with treatment of insomnia.
For patients who are seen in post-ICU clinics, the first step in treating insomnia is discussing good sleep hygiene, providing resources for CBT-I (digital or in person), and treating coexistent psychiatric conditions.
References
1. Rawal G, Yadav S, Kumar R. Post-intensive care syndrome: an overview. J Transl Int Med. 2017;5(2):90-92.
2. Zampieri FG, et al. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(11):1558-1560.
3. Altman MT, Knauert MP, Pisani MA. Sleep disturbance after hospitalization and critical illness: a systematic review. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017;14(9):1457-1468.
4. Edinger JD, Arnedt JT, Bertisch SM, et al. Behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia disorder in adults: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021;17(2):255-262.
Short telomere length and immunosuppression: Updates in nonidiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial lung disease
DIFFUSE LUNG DISEASE AND LUNG TRANSPLANT NETWORK
Interstitial Lung Disease Section
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are a diverse group of relentlessly progressive fibroinflammatory disorders. Pharmacotherapy includes antifibrotics and immunosuppressants as foundational strategies to mitigate loss of lung function. There has been a growing interest in telomere length and its response to immunosuppression in the ILD community.
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences that “cap” chromosomes and protect against chromosomal shortening during cell replication. Genetic and environmental factors can lead to premature shortening of telomeres. Once a critical length is reached, the cell enters senescence. Short telomere length has been linked to rapid progression, worse outcomes, and poor response to immunosuppressants in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Data in patients with non-IPF ILD (which is arguably more difficult to diagnose and manage) were lacking until a recent retrospective cohort study of patients from five centers across the US demonstrated that immunosuppressant exposure in patients with age-adjusted telomere length <10th percentile was associated with a reduced 2-year transplant-free survival in fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and unclassifiable ILD subgroups.1 This study was underpowered to detect associations in the connective tissue disease-ILD group. Interestingly, authors noted that immunosuppressant exposure was not associated with lung function decline in the short telomere group, suggesting that worse outcomes may be attributable to unmasking extrapulmonary manifestations of short telomeres, such as bone marrow failure and impaired adaptive immunity. Studies like these are essential to guide decision-making in the age of personalized medicine and underscore the necessity for prospective studies to validate these findings.
References
1. Zhang D, Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, et al. Telomere length and immunosuppression in non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300441.
DIFFUSE LUNG DISEASE AND LUNG TRANSPLANT NETWORK
Interstitial Lung Disease Section
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are a diverse group of relentlessly progressive fibroinflammatory disorders. Pharmacotherapy includes antifibrotics and immunosuppressants as foundational strategies to mitigate loss of lung function. There has been a growing interest in telomere length and its response to immunosuppression in the ILD community.
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences that “cap” chromosomes and protect against chromosomal shortening during cell replication. Genetic and environmental factors can lead to premature shortening of telomeres. Once a critical length is reached, the cell enters senescence. Short telomere length has been linked to rapid progression, worse outcomes, and poor response to immunosuppressants in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Data in patients with non-IPF ILD (which is arguably more difficult to diagnose and manage) were lacking until a recent retrospective cohort study of patients from five centers across the US demonstrated that immunosuppressant exposure in patients with age-adjusted telomere length <10th percentile was associated with a reduced 2-year transplant-free survival in fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and unclassifiable ILD subgroups.1 This study was underpowered to detect associations in the connective tissue disease-ILD group. Interestingly, authors noted that immunosuppressant exposure was not associated with lung function decline in the short telomere group, suggesting that worse outcomes may be attributable to unmasking extrapulmonary manifestations of short telomeres, such as bone marrow failure and impaired adaptive immunity. Studies like these are essential to guide decision-making in the age of personalized medicine and underscore the necessity for prospective studies to validate these findings.
References
1. Zhang D, Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, et al. Telomere length and immunosuppression in non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300441.
DIFFUSE LUNG DISEASE AND LUNG TRANSPLANT NETWORK
Interstitial Lung Disease Section
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are a diverse group of relentlessly progressive fibroinflammatory disorders. Pharmacotherapy includes antifibrotics and immunosuppressants as foundational strategies to mitigate loss of lung function. There has been a growing interest in telomere length and its response to immunosuppression in the ILD community.
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences that “cap” chromosomes and protect against chromosomal shortening during cell replication. Genetic and environmental factors can lead to premature shortening of telomeres. Once a critical length is reached, the cell enters senescence. Short telomere length has been linked to rapid progression, worse outcomes, and poor response to immunosuppressants in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).
Data in patients with non-IPF ILD (which is arguably more difficult to diagnose and manage) were lacking until a recent retrospective cohort study of patients from five centers across the US demonstrated that immunosuppressant exposure in patients with age-adjusted telomere length <10th percentile was associated with a reduced 2-year transplant-free survival in fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and unclassifiable ILD subgroups.1 This study was underpowered to detect associations in the connective tissue disease-ILD group. Interestingly, authors noted that immunosuppressant exposure was not associated with lung function decline in the short telomere group, suggesting that worse outcomes may be attributable to unmasking extrapulmonary manifestations of short telomeres, such as bone marrow failure and impaired adaptive immunity. Studies like these are essential to guide decision-making in the age of personalized medicine and underscore the necessity for prospective studies to validate these findings.
References
1. Zhang D, Adegunsoye A, Oldham JM, et al. Telomere length and immunosuppression in non-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2023;62(5):2300441.
Expanding recommendations for RSV vaccination
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Asthma and COPD Section
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has been increasingly recognized as a prevalent cause of lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) among adults in the United States. The risk of hospitalization and mortality from RSV-associated respiratory failure is higher in those with chronic lung disease. In adults aged 65 years or older, RSV has shown to cause up to 160,000 hospitalizations and 10,000 deaths annually.
RSV has been well established as a major cause of LRTI and morbidity among infants. Maternal vaccination with RSVPreF in patients who are pregnant is suggested between 32 0/7 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation if the date of delivery falls during RSV season to prevent severe illness in young infants in their first months of life. At present, there are no data supporting vaccine administration to patients who are pregnant delivering outside of the RSV season.
What about the rest of the patients? A phase 3b clinical trial to assess the safety and immunogenicity of the RSVPreF3 vaccine in individuals 18 to 49 years of age at increased risk for RSV LRTI, including those with chronic respiratory diseases, is currently underway with projected completion in April 2025 (clinical trials.gov; ID NCT06389487). Additional studies examining safety and immunogenicity combining RSV vaccines with PCV20, influenza, COVID, or Tdap vaccines are also underway. These outcomes will be significant for future recommendations to further lower the risk of developing LRTI, hospitalization, and death among patients less than the age of 60 with chronic lung diseases.
Resources
1. Melgar M, Britton A, Roper LE, et al. Use of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines in older adults: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(29):793-801.
2. Healthcare Providers: RSV Vaccination for Adults 60 Years of Age and Over. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated March 1, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/rsv/hcp/older-adults.html
3. Ault KA, Hughes BL, Riley LE. Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Updated December 11, 2023. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-advisory/articles/2023/09/maternal-respiratory-syncytial-virus-vaccination
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Asthma and COPD Section
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has been increasingly recognized as a prevalent cause of lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) among adults in the United States. The risk of hospitalization and mortality from RSV-associated respiratory failure is higher in those with chronic lung disease. In adults aged 65 years or older, RSV has shown to cause up to 160,000 hospitalizations and 10,000 deaths annually.
RSV has been well established as a major cause of LRTI and morbidity among infants. Maternal vaccination with RSVPreF in patients who are pregnant is suggested between 32 0/7 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation if the date of delivery falls during RSV season to prevent severe illness in young infants in their first months of life. At present, there are no data supporting vaccine administration to patients who are pregnant delivering outside of the RSV season.
What about the rest of the patients? A phase 3b clinical trial to assess the safety and immunogenicity of the RSVPreF3 vaccine in individuals 18 to 49 years of age at increased risk for RSV LRTI, including those with chronic respiratory diseases, is currently underway with projected completion in April 2025 (clinical trials.gov; ID NCT06389487). Additional studies examining safety and immunogenicity combining RSV vaccines with PCV20, influenza, COVID, or Tdap vaccines are also underway. These outcomes will be significant for future recommendations to further lower the risk of developing LRTI, hospitalization, and death among patients less than the age of 60 with chronic lung diseases.
Resources
1. Melgar M, Britton A, Roper LE, et al. Use of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines in older adults: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(29):793-801.
2. Healthcare Providers: RSV Vaccination for Adults 60 Years of Age and Over. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated March 1, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/rsv/hcp/older-adults.html
3. Ault KA, Hughes BL, Riley LE. Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Updated December 11, 2023. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-advisory/articles/2023/09/maternal-respiratory-syncytial-virus-vaccination
AIRWAYS DISORDERS NETWORK
Asthma and COPD Section
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) has been increasingly recognized as a prevalent cause of lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) among adults in the United States. The risk of hospitalization and mortality from RSV-associated respiratory failure is higher in those with chronic lung disease. In adults aged 65 years or older, RSV has shown to cause up to 160,000 hospitalizations and 10,000 deaths annually.
RSV has been well established as a major cause of LRTI and morbidity among infants. Maternal vaccination with RSVPreF in patients who are pregnant is suggested between 32 0/7 and 36 6/7 weeks of gestation if the date of delivery falls during RSV season to prevent severe illness in young infants in their first months of life. At present, there are no data supporting vaccine administration to patients who are pregnant delivering outside of the RSV season.
What about the rest of the patients? A phase 3b clinical trial to assess the safety and immunogenicity of the RSVPreF3 vaccine in individuals 18 to 49 years of age at increased risk for RSV LRTI, including those with chronic respiratory diseases, is currently underway with projected completion in April 2025 (clinical trials.gov; ID NCT06389487). Additional studies examining safety and immunogenicity combining RSV vaccines with PCV20, influenza, COVID, or Tdap vaccines are also underway. These outcomes will be significant for future recommendations to further lower the risk of developing LRTI, hospitalization, and death among patients less than the age of 60 with chronic lung diseases.
Resources
1. Melgar M, Britton A, Roper LE, et al. Use of respiratory syncytial virus vaccines in older adults: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices - United States, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(29):793-801.
2. Healthcare Providers: RSV Vaccination for Adults 60 Years of Age and Over. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated March 1, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vpd/rsv/hcp/older-adults.html
3. Ault KA, Hughes BL, Riley LE. Maternal Respiratory Syncytial Virus Vaccination. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Updated December 11, 2023. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-advisory/articles/2023/09/maternal-respiratory-syncytial-virus-vaccination
Bringing trainee wellness to the forefront
Researching the impact of reflection in medical training
Before the spread of COVID-19, and increasingly during the pandemic, Ilana Krumm, MD, noticed a burgeoning focus on wellness for trainees and how to combat burnout in the medical space.
But Dr. Krumm also noticed that most of the existing programs focused on the individual level, rather than the system level. The onus was on the trainees to manage their wellness and burnout.
“I wanted to look at something that could be instituted at a systems level as opposed to putting all the burden of this wellness on the resident, as someone who already has a huge burden of work, stress, and time constraints as they try to learn their discipline,” Dr. Krumm said. “Asking them to meditate on their own time seemed very impractical.”
Eager to research this idea, Dr. Krumm applied for the CHEST Research Grant in Medical Education.
“The fact that CHEST is willing to support medical education research is really important for all those trying to better the educational environment. Although there’s a movement toward more support for medical education research and more recognition of its value, I think the fact that CHEST has already done so has helped advance the field and the support for the field as a whole,” Dr. Krumm said.
“Having the support from a reputable institution like CHEST inherently gave the work that I was doing value,” Dr. Krumm said. “It gave folks an understanding that this research in medical education has importance.”
Dr. Krumm’s project focused on the monthly Reflection Rounds between the ICU, palliative care, and chaplaincy staff that were held at the Seattle VA Medical Center, where residents could discuss the challenges of caring for critically ill patients during a protected time. While similar interventions around death and dying have been shown to help residents reduce burnout in medical intensive care rotations, it was unknown which aspects of these sessions would be most effective.
Participant interviews were conducted before and after the residents’ monthly sessions to understand the impact these sessions had on wellness and burnout levels.
“With the grant funding from CHEST, our team was able to purchase the recording equipment, transcription, and software necessary to complete a thorough qualitative research project, which greatly accelerated the project timeline,” she said.
Through these interviews, Dr. Krumm’s team identified three key themes that shed light on the impact of Reflection Rounds.
1. Cultural precedent
Participants were encouraged to participate as little or as much as they wanted during the session. Despite some residents being less vocal during these discussions, every resident agreed that this type of session set an important cultural precedent in their program and acknowledged the value of a program that encouraged space for decompression and reflection.
2. Shared experiences
During this project, many residents experienced an increased sense of isolation, as COVID-19 precautions were stricter in the ICU. Having this protected time together allowed residents to discover their shared experiences and find comfort in them while feeling supported.
“A lot of residents commented that it was nice to know that others were going through this as well or that they were also finding this particular instance difficult,” Dr. Krumm said.
3. Ritual
At the opening of each hour-long session, participants were invited to light a candle and say aloud or think to themselves the name of a patient they had lost, had a hard time with, or cared for during their time in the ICU.
“Every single person pointed to that moment as meaningful and impactful,” Dr. Krumm said.
This ritual gave the residents time to center and have a common focus with their peers to think about patient stories that they were carrying with them.
“Maybe just incorporating a small moment like that, a point of reflection, could potentially have a big impact on the weight we carry as providers who care for [patients who are] critically ill,” Dr. Krumm said. “What I’ve learned from this project will make me a better leader in the ICU, not only in taking care of critically ill individuals but also in taking care of the team doing that work.”
Dr. Krumm credits the CHEST grant funding and subsequent research project with helping her join a highly competitive fellowship program at the University of California San Francisco, where she can continue to conduct research in the field of medical education.
“I am working closely with medical education faculty and peers to design new research studies and further establish myself in the field of medical education, leading to my ultimate goal of becoming a program director at a strong med-ed-focused program.”
This article was adapted from the Spring 2024 online issue of CHEST Advocates. For the full article—and to engage with the other content from this issue—visit chestnet.org/chest-advocates.
Support CHEST grants like this
Through clinical research grants, CHEST assists in acquiring vital data and clinically important results that can advance medical care. You can help support projects like this by making a gift to CHEST.
MAKE A GIFT » | LEARN ABOUT CHEST PHILANTHROPY »
Researching the impact of reflection in medical training
Researching the impact of reflection in medical training
Before the spread of COVID-19, and increasingly during the pandemic, Ilana Krumm, MD, noticed a burgeoning focus on wellness for trainees and how to combat burnout in the medical space.
But Dr. Krumm also noticed that most of the existing programs focused on the individual level, rather than the system level. The onus was on the trainees to manage their wellness and burnout.
“I wanted to look at something that could be instituted at a systems level as opposed to putting all the burden of this wellness on the resident, as someone who already has a huge burden of work, stress, and time constraints as they try to learn their discipline,” Dr. Krumm said. “Asking them to meditate on their own time seemed very impractical.”
Eager to research this idea, Dr. Krumm applied for the CHEST Research Grant in Medical Education.
“The fact that CHEST is willing to support medical education research is really important for all those trying to better the educational environment. Although there’s a movement toward more support for medical education research and more recognition of its value, I think the fact that CHEST has already done so has helped advance the field and the support for the field as a whole,” Dr. Krumm said.
“Having the support from a reputable institution like CHEST inherently gave the work that I was doing value,” Dr. Krumm said. “It gave folks an understanding that this research in medical education has importance.”
Dr. Krumm’s project focused on the monthly Reflection Rounds between the ICU, palliative care, and chaplaincy staff that were held at the Seattle VA Medical Center, where residents could discuss the challenges of caring for critically ill patients during a protected time. While similar interventions around death and dying have been shown to help residents reduce burnout in medical intensive care rotations, it was unknown which aspects of these sessions would be most effective.
Participant interviews were conducted before and after the residents’ monthly sessions to understand the impact these sessions had on wellness and burnout levels.
“With the grant funding from CHEST, our team was able to purchase the recording equipment, transcription, and software necessary to complete a thorough qualitative research project, which greatly accelerated the project timeline,” she said.
Through these interviews, Dr. Krumm’s team identified three key themes that shed light on the impact of Reflection Rounds.
1. Cultural precedent
Participants were encouraged to participate as little or as much as they wanted during the session. Despite some residents being less vocal during these discussions, every resident agreed that this type of session set an important cultural precedent in their program and acknowledged the value of a program that encouraged space for decompression and reflection.
2. Shared experiences
During this project, many residents experienced an increased sense of isolation, as COVID-19 precautions were stricter in the ICU. Having this protected time together allowed residents to discover their shared experiences and find comfort in them while feeling supported.
“A lot of residents commented that it was nice to know that others were going through this as well or that they were also finding this particular instance difficult,” Dr. Krumm said.
3. Ritual
At the opening of each hour-long session, participants were invited to light a candle and say aloud or think to themselves the name of a patient they had lost, had a hard time with, or cared for during their time in the ICU.
“Every single person pointed to that moment as meaningful and impactful,” Dr. Krumm said.
This ritual gave the residents time to center and have a common focus with their peers to think about patient stories that they were carrying with them.
“Maybe just incorporating a small moment like that, a point of reflection, could potentially have a big impact on the weight we carry as providers who care for [patients who are] critically ill,” Dr. Krumm said. “What I’ve learned from this project will make me a better leader in the ICU, not only in taking care of critically ill individuals but also in taking care of the team doing that work.”
Dr. Krumm credits the CHEST grant funding and subsequent research project with helping her join a highly competitive fellowship program at the University of California San Francisco, where she can continue to conduct research in the field of medical education.
“I am working closely with medical education faculty and peers to design new research studies and further establish myself in the field of medical education, leading to my ultimate goal of becoming a program director at a strong med-ed-focused program.”
This article was adapted from the Spring 2024 online issue of CHEST Advocates. For the full article—and to engage with the other content from this issue—visit chestnet.org/chest-advocates.
Support CHEST grants like this
Through clinical research grants, CHEST assists in acquiring vital data and clinically important results that can advance medical care. You can help support projects like this by making a gift to CHEST.
MAKE A GIFT » | LEARN ABOUT CHEST PHILANTHROPY »
Before the spread of COVID-19, and increasingly during the pandemic, Ilana Krumm, MD, noticed a burgeoning focus on wellness for trainees and how to combat burnout in the medical space.
But Dr. Krumm also noticed that most of the existing programs focused on the individual level, rather than the system level. The onus was on the trainees to manage their wellness and burnout.
“I wanted to look at something that could be instituted at a systems level as opposed to putting all the burden of this wellness on the resident, as someone who already has a huge burden of work, stress, and time constraints as they try to learn their discipline,” Dr. Krumm said. “Asking them to meditate on their own time seemed very impractical.”
Eager to research this idea, Dr. Krumm applied for the CHEST Research Grant in Medical Education.
“The fact that CHEST is willing to support medical education research is really important for all those trying to better the educational environment. Although there’s a movement toward more support for medical education research and more recognition of its value, I think the fact that CHEST has already done so has helped advance the field and the support for the field as a whole,” Dr. Krumm said.
“Having the support from a reputable institution like CHEST inherently gave the work that I was doing value,” Dr. Krumm said. “It gave folks an understanding that this research in medical education has importance.”
Dr. Krumm’s project focused on the monthly Reflection Rounds between the ICU, palliative care, and chaplaincy staff that were held at the Seattle VA Medical Center, where residents could discuss the challenges of caring for critically ill patients during a protected time. While similar interventions around death and dying have been shown to help residents reduce burnout in medical intensive care rotations, it was unknown which aspects of these sessions would be most effective.
Participant interviews were conducted before and after the residents’ monthly sessions to understand the impact these sessions had on wellness and burnout levels.
“With the grant funding from CHEST, our team was able to purchase the recording equipment, transcription, and software necessary to complete a thorough qualitative research project, which greatly accelerated the project timeline,” she said.
Through these interviews, Dr. Krumm’s team identified three key themes that shed light on the impact of Reflection Rounds.
1. Cultural precedent
Participants were encouraged to participate as little or as much as they wanted during the session. Despite some residents being less vocal during these discussions, every resident agreed that this type of session set an important cultural precedent in their program and acknowledged the value of a program that encouraged space for decompression and reflection.
2. Shared experiences
During this project, many residents experienced an increased sense of isolation, as COVID-19 precautions were stricter in the ICU. Having this protected time together allowed residents to discover their shared experiences and find comfort in them while feeling supported.
“A lot of residents commented that it was nice to know that others were going through this as well or that they were also finding this particular instance difficult,” Dr. Krumm said.
3. Ritual
At the opening of each hour-long session, participants were invited to light a candle and say aloud or think to themselves the name of a patient they had lost, had a hard time with, or cared for during their time in the ICU.
“Every single person pointed to that moment as meaningful and impactful,” Dr. Krumm said.
This ritual gave the residents time to center and have a common focus with their peers to think about patient stories that they were carrying with them.
“Maybe just incorporating a small moment like that, a point of reflection, could potentially have a big impact on the weight we carry as providers who care for [patients who are] critically ill,” Dr. Krumm said. “What I’ve learned from this project will make me a better leader in the ICU, not only in taking care of critically ill individuals but also in taking care of the team doing that work.”
Dr. Krumm credits the CHEST grant funding and subsequent research project with helping her join a highly competitive fellowship program at the University of California San Francisco, where she can continue to conduct research in the field of medical education.
“I am working closely with medical education faculty and peers to design new research studies and further establish myself in the field of medical education, leading to my ultimate goal of becoming a program director at a strong med-ed-focused program.”
This article was adapted from the Spring 2024 online issue of CHEST Advocates. For the full article—and to engage with the other content from this issue—visit chestnet.org/chest-advocates.
Support CHEST grants like this
Through clinical research grants, CHEST assists in acquiring vital data and clinically important results that can advance medical care. You can help support projects like this by making a gift to CHEST.
MAKE A GIFT » | LEARN ABOUT CHEST PHILANTHROPY »
Coding & billing: A look into G2211 for visit complexities
This add-on code is for new (99202-99205) and established (99212-99215) office visits. CMS created this add-on code to address the additional costs and resources associated with providing longitudinal care.
G2211 – Visit complexity inherent to evaluation and management (E/M) associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or a complex condition (Add-on code; list separately in addition to office/outpatient (O/O) E/M visit, new or established)
The documentation should demonstrate the intent and need for ongoing care. Otherwise, no additional documentation is required. CMS pays $16.04 for each service (wRVU = 0.33). It may be reported each time the patient is seen, and there is currently no limit to how often it may be used. Also, there is no additional copay requirement for patients.
Do’s and don’ts
Do report in the following situations when longitudinal care is provided:
- The provider has or intends to have a long-term, ongoing relationship with the patient (ie, G2211 can be used for a new patient visit)
- Audio/video virtual visits
- May be reported with Prolonged Care Services G2212
- When advanced practice providers or physician colleagues in the same specialty practice see the patient (ie, if you see the patient for an urgent visit, but the patient is usually followed by your partner, you can still use G2211)
- When working with graduate medical education trainees (along with the -GC modifier), and as long as the conditions described in the description of G2211 are met
Do NOT report in the following situations:
- If modifier -25 is appended to the E/M service when another service is provided on the same day (eg, pulmonary function tests, 6-minute walk tests, immunization)
- Audio-only virtual visits, hospital, skilled nursing facility, or long-term acute care hospital
- If the patient is not expected to return for ongoing care
- If the reason for longitudinal care does not include a “single, serious condition or a complex condition” (eg, annual visits for a stable 6 mm lung nodule)
CMS expects that this will be billed with 38% of all E/M services initially and potentially up to 54% over time. We feel this is reimbursement for the work being done to care for our patients with single, serious, or complex conditions. Both Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans are expected to reimburse for this service. Whether other payers will do the same is unclear, but it will become clear with time and further negotiation at the local level. In the meantime, members are encouraged to report this code for all appropriate patient encounters.
Questions and answers — G2211
Question: What private insurances cover G2211?
Answer: As of March 1, 2024, four national payers have confirmed coverage of G2211:
- Cigna (Medicare Advantage only),
- Humana (commercial and Medicare Advantage),
- United Healthcare (commercial and Medicare Advantage), and
- Aetna (Medicare Advantage).
Question: What needs to be documented for G2211?
Answer: CMS states, “You must document the reason for billing the office and outpatient (O/O) and evaluation and management (E/M). The visits themselves would need to be medically reasonable and necessary for the practitioner to report G2211. In addition, the documentation would need to illustrate medical necessity of the O/O E/M visit. We [CMS] haven’t required additional documentation.”
American Thoracic Society (ATS) and CHEST also recommend including a detailed assessment and plan for the visit, as well as any follow-up. The complexity of the visit should be clear in your documentation to support the medical necessity for reporting the G2211.
Question: How can a provider show that a new patient visit (99202-99205) is part of continuing care?
Answer: The treating practitioner should make sure their documentation supports their intent to provide ongoing care to the patient. Establishing such intent goes beyond a statement that the provider plans to provide ongoing care or schedule a follow-up visit. The circumstances of the visit should support the extra work involved in becoming the focal point of the patient’s care or providing ongoing care for a serious or complex condition.
Question: Dr. Red works at a primary care practice, is the focal point for a patient’s care, and has reported G2211. If Dr. Yellow, who is in the same specialty, or Mr. Green, a nurse practitioner, is covering for Dr. Red, and the patient comes in for a visit, can they report G2211 for that visit?
Answer: Yes. The same specialty/same provider rules would apply in this situation. But remember that Dr. Yellow’s or Mr. Green’s documentation for that encounter must support the code.
Question: Can a resident report G2211 under the primary care exemption?
Answer: Yes, according to CMS staff, so long as the service and the documentation meet all the requirements for the exemption and the visit complexity code. For example, the resident can only report low-level E/M codes, and the resident must be “the focal point for that person’s care.”
Question: Are there frequency limits for how often we can report G2211, either for a single patient in a given time period or by a provider or a practice?
Answer: Not at this time, but make sure your providers are following the rules for reporting the code. “There’s got to be documentation that suggests why the practitioner believes they are treating the patient on this long-standing, longitudinal trajectory, and we’ll be able to see how that interaction is happening,” senior CMS staff said. CMS staff further issued a subtle warning to providers by reminding them that CMS has a very strong integrity program. Your practice can avoid problems with thorough training, frequent chart review, and encouraging the team to ask questions until you feel that everyone is comfortable with the code.
Question: Are there any limits on the specialties that can report the code? Is it just for primary care providers?
Answer: No. Remember that a provider who is managing a single serious or complex condition can also report the code. But CMS expects the documentation to support the ongoing nature of the treatment. If a patient sees a provider as a one-off encounter, perhaps to manage an acute problem, that visit wouldn’t qualify. But if the provider clearly documents that they are actively managing the patient’s condition, the encounters could qualify.
Question: Will CMS issue a list of conditions that meet the code’s serious or complex condition requirement?
Answer: CMS has included the examples of HIV and sickle cell anemia in existing guidance, and it plans to issue a few more examples “that help folks understand what is expected.” However, it won’t be a complete list of every condition that might qualify.
Originally published in the May 2023 issue of the American Thoracic Society’s ATS Coding & Billing Quarterly. Republished with permission from the American Thoracic Society.
This add-on code is for new (99202-99205) and established (99212-99215) office visits. CMS created this add-on code to address the additional costs and resources associated with providing longitudinal care.
G2211 – Visit complexity inherent to evaluation and management (E/M) associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or a complex condition (Add-on code; list separately in addition to office/outpatient (O/O) E/M visit, new or established)
The documentation should demonstrate the intent and need for ongoing care. Otherwise, no additional documentation is required. CMS pays $16.04 for each service (wRVU = 0.33). It may be reported each time the patient is seen, and there is currently no limit to how often it may be used. Also, there is no additional copay requirement for patients.
Do’s and don’ts
Do report in the following situations when longitudinal care is provided:
- The provider has or intends to have a long-term, ongoing relationship with the patient (ie, G2211 can be used for a new patient visit)
- Audio/video virtual visits
- May be reported with Prolonged Care Services G2212
- When advanced practice providers or physician colleagues in the same specialty practice see the patient (ie, if you see the patient for an urgent visit, but the patient is usually followed by your partner, you can still use G2211)
- When working with graduate medical education trainees (along with the -GC modifier), and as long as the conditions described in the description of G2211 are met
Do NOT report in the following situations:
- If modifier -25 is appended to the E/M service when another service is provided on the same day (eg, pulmonary function tests, 6-minute walk tests, immunization)
- Audio-only virtual visits, hospital, skilled nursing facility, or long-term acute care hospital
- If the patient is not expected to return for ongoing care
- If the reason for longitudinal care does not include a “single, serious condition or a complex condition” (eg, annual visits for a stable 6 mm lung nodule)
CMS expects that this will be billed with 38% of all E/M services initially and potentially up to 54% over time. We feel this is reimbursement for the work being done to care for our patients with single, serious, or complex conditions. Both Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans are expected to reimburse for this service. Whether other payers will do the same is unclear, but it will become clear with time and further negotiation at the local level. In the meantime, members are encouraged to report this code for all appropriate patient encounters.
Questions and answers — G2211
Question: What private insurances cover G2211?
Answer: As of March 1, 2024, four national payers have confirmed coverage of G2211:
- Cigna (Medicare Advantage only),
- Humana (commercial and Medicare Advantage),
- United Healthcare (commercial and Medicare Advantage), and
- Aetna (Medicare Advantage).
Question: What needs to be documented for G2211?
Answer: CMS states, “You must document the reason for billing the office and outpatient (O/O) and evaluation and management (E/M). The visits themselves would need to be medically reasonable and necessary for the practitioner to report G2211. In addition, the documentation would need to illustrate medical necessity of the O/O E/M visit. We [CMS] haven’t required additional documentation.”
American Thoracic Society (ATS) and CHEST also recommend including a detailed assessment and plan for the visit, as well as any follow-up. The complexity of the visit should be clear in your documentation to support the medical necessity for reporting the G2211.
Question: How can a provider show that a new patient visit (99202-99205) is part of continuing care?
Answer: The treating practitioner should make sure their documentation supports their intent to provide ongoing care to the patient. Establishing such intent goes beyond a statement that the provider plans to provide ongoing care or schedule a follow-up visit. The circumstances of the visit should support the extra work involved in becoming the focal point of the patient’s care or providing ongoing care for a serious or complex condition.
Question: Dr. Red works at a primary care practice, is the focal point for a patient’s care, and has reported G2211. If Dr. Yellow, who is in the same specialty, or Mr. Green, a nurse practitioner, is covering for Dr. Red, and the patient comes in for a visit, can they report G2211 for that visit?
Answer: Yes. The same specialty/same provider rules would apply in this situation. But remember that Dr. Yellow’s or Mr. Green’s documentation for that encounter must support the code.
Question: Can a resident report G2211 under the primary care exemption?
Answer: Yes, according to CMS staff, so long as the service and the documentation meet all the requirements for the exemption and the visit complexity code. For example, the resident can only report low-level E/M codes, and the resident must be “the focal point for that person’s care.”
Question: Are there frequency limits for how often we can report G2211, either for a single patient in a given time period or by a provider or a practice?
Answer: Not at this time, but make sure your providers are following the rules for reporting the code. “There’s got to be documentation that suggests why the practitioner believes they are treating the patient on this long-standing, longitudinal trajectory, and we’ll be able to see how that interaction is happening,” senior CMS staff said. CMS staff further issued a subtle warning to providers by reminding them that CMS has a very strong integrity program. Your practice can avoid problems with thorough training, frequent chart review, and encouraging the team to ask questions until you feel that everyone is comfortable with the code.
Question: Are there any limits on the specialties that can report the code? Is it just for primary care providers?
Answer: No. Remember that a provider who is managing a single serious or complex condition can also report the code. But CMS expects the documentation to support the ongoing nature of the treatment. If a patient sees a provider as a one-off encounter, perhaps to manage an acute problem, that visit wouldn’t qualify. But if the provider clearly documents that they are actively managing the patient’s condition, the encounters could qualify.
Question: Will CMS issue a list of conditions that meet the code’s serious or complex condition requirement?
Answer: CMS has included the examples of HIV and sickle cell anemia in existing guidance, and it plans to issue a few more examples “that help folks understand what is expected.” However, it won’t be a complete list of every condition that might qualify.
Originally published in the May 2023 issue of the American Thoracic Society’s ATS Coding & Billing Quarterly. Republished with permission from the American Thoracic Society.
This add-on code is for new (99202-99205) and established (99212-99215) office visits. CMS created this add-on code to address the additional costs and resources associated with providing longitudinal care.
G2211 – Visit complexity inherent to evaluation and management (E/M) associated with medical care services that serve as the continuing focal point for all needed health care services and/or with medical care services that are part of ongoing care related to a patient’s single, serious condition, or a complex condition (Add-on code; list separately in addition to office/outpatient (O/O) E/M visit, new or established)
The documentation should demonstrate the intent and need for ongoing care. Otherwise, no additional documentation is required. CMS pays $16.04 for each service (wRVU = 0.33). It may be reported each time the patient is seen, and there is currently no limit to how often it may be used. Also, there is no additional copay requirement for patients.
Do’s and don’ts
Do report in the following situations when longitudinal care is provided:
- The provider has or intends to have a long-term, ongoing relationship with the patient (ie, G2211 can be used for a new patient visit)
- Audio/video virtual visits
- May be reported with Prolonged Care Services G2212
- When advanced practice providers or physician colleagues in the same specialty practice see the patient (ie, if you see the patient for an urgent visit, but the patient is usually followed by your partner, you can still use G2211)
- When working with graduate medical education trainees (along with the -GC modifier), and as long as the conditions described in the description of G2211 are met
Do NOT report in the following situations:
- If modifier -25 is appended to the E/M service when another service is provided on the same day (eg, pulmonary function tests, 6-minute walk tests, immunization)
- Audio-only virtual visits, hospital, skilled nursing facility, or long-term acute care hospital
- If the patient is not expected to return for ongoing care
- If the reason for longitudinal care does not include a “single, serious condition or a complex condition” (eg, annual visits for a stable 6 mm lung nodule)
CMS expects that this will be billed with 38% of all E/M services initially and potentially up to 54% over time. We feel this is reimbursement for the work being done to care for our patients with single, serious, or complex conditions. Both Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans are expected to reimburse for this service. Whether other payers will do the same is unclear, but it will become clear with time and further negotiation at the local level. In the meantime, members are encouraged to report this code for all appropriate patient encounters.
Questions and answers — G2211
Question: What private insurances cover G2211?
Answer: As of March 1, 2024, four national payers have confirmed coverage of G2211:
- Cigna (Medicare Advantage only),
- Humana (commercial and Medicare Advantage),
- United Healthcare (commercial and Medicare Advantage), and
- Aetna (Medicare Advantage).
Question: What needs to be documented for G2211?
Answer: CMS states, “You must document the reason for billing the office and outpatient (O/O) and evaluation and management (E/M). The visits themselves would need to be medically reasonable and necessary for the practitioner to report G2211. In addition, the documentation would need to illustrate medical necessity of the O/O E/M visit. We [CMS] haven’t required additional documentation.”
American Thoracic Society (ATS) and CHEST also recommend including a detailed assessment and plan for the visit, as well as any follow-up. The complexity of the visit should be clear in your documentation to support the medical necessity for reporting the G2211.
Question: How can a provider show that a new patient visit (99202-99205) is part of continuing care?
Answer: The treating practitioner should make sure their documentation supports their intent to provide ongoing care to the patient. Establishing such intent goes beyond a statement that the provider plans to provide ongoing care or schedule a follow-up visit. The circumstances of the visit should support the extra work involved in becoming the focal point of the patient’s care or providing ongoing care for a serious or complex condition.
Question: Dr. Red works at a primary care practice, is the focal point for a patient’s care, and has reported G2211. If Dr. Yellow, who is in the same specialty, or Mr. Green, a nurse practitioner, is covering for Dr. Red, and the patient comes in for a visit, can they report G2211 for that visit?
Answer: Yes. The same specialty/same provider rules would apply in this situation. But remember that Dr. Yellow’s or Mr. Green’s documentation for that encounter must support the code.
Question: Can a resident report G2211 under the primary care exemption?
Answer: Yes, according to CMS staff, so long as the service and the documentation meet all the requirements for the exemption and the visit complexity code. For example, the resident can only report low-level E/M codes, and the resident must be “the focal point for that person’s care.”
Question: Are there frequency limits for how often we can report G2211, either for a single patient in a given time period or by a provider or a practice?
Answer: Not at this time, but make sure your providers are following the rules for reporting the code. “There’s got to be documentation that suggests why the practitioner believes they are treating the patient on this long-standing, longitudinal trajectory, and we’ll be able to see how that interaction is happening,” senior CMS staff said. CMS staff further issued a subtle warning to providers by reminding them that CMS has a very strong integrity program. Your practice can avoid problems with thorough training, frequent chart review, and encouraging the team to ask questions until you feel that everyone is comfortable with the code.
Question: Are there any limits on the specialties that can report the code? Is it just for primary care providers?
Answer: No. Remember that a provider who is managing a single serious or complex condition can also report the code. But CMS expects the documentation to support the ongoing nature of the treatment. If a patient sees a provider as a one-off encounter, perhaps to manage an acute problem, that visit wouldn’t qualify. But if the provider clearly documents that they are actively managing the patient’s condition, the encounters could qualify.
Question: Will CMS issue a list of conditions that meet the code’s serious or complex condition requirement?
Answer: CMS has included the examples of HIV and sickle cell anemia in existing guidance, and it plans to issue a few more examples “that help folks understand what is expected.” However, it won’t be a complete list of every condition that might qualify.
Originally published in the May 2023 issue of the American Thoracic Society’s ATS Coding & Billing Quarterly. Republished with permission from the American Thoracic Society.
Top reads from the CHEST journal portfolio
Understanding RA with COPD, lung cancer prediction models, and chronic cardiac dysfunction
Journal CHEST®
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Increase the Risk of COPD?
By: Chiwook Chung, MD, and colleagues
Notably, individuals with seropositive RA exhibit a greater risk of COPD onset than those with seronegative RA. Although smoking history didn’t affect the relationship between RA and COPD, monitoring respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in patients with RA, especially patients who are seropositive, is crucial. These findings underscore the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between rheumatologists and pulmonologists to enhance early detection and management strategies for pulmonary complications in patients with RA.
– Commentary by Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician® Editorial Board
CHEST Pulmonary®
The Lung Cancer Prediction Model “Stress Test”
By: Brent E. Heideman, MD, and colleagues
Current lung cancer prediction models have limited utility in high-risk patients referred for diagnostic biopsy. In a study of 322 indeterminate pulmonary nodules, the Brock, Mayo Clinic, Herder, and Veterans Affairs models showed modest discrimination between benign and malignant nodules (AUCs 0.67-0.77). The models performed poorly for low-risk patients (negative predictive values 63%-71%) and suboptimally for high-risk patients (positive predictive values 73%-87%), suggesting referring physicians use additional clinical information not captured in these models to identify high-risk patients needing biopsy. New prediction models and biomarkers specifically developed and calibrated for high-risk populations are needed to better inform clinical decision-making. Incorporating interval imaging to assess changes in nodule characteristics could potentially improve model performance. Tailored risk assessment tools are crucial for optimizing management and reducing unnecessary invasive procedures in this challenging patient population.
– Commentary by Russell Miller, MD, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST Critical Care ®
Characterizing Cardiac Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis
By: Kevin Garrity, MBChB, and colleagues
While chronic cardiac dysfunction is one of the proposed mechanisms of long-term impairment post critical illness, its prevalence, mechanisms, and associations with disability following admission for sepsis are not well understood. Garrity and colleagues describe the Characterization of Cardiovascular Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis (CONDUCT-ICU) protocol, a prospective study including two ICUs in Scotland aimed to better define cardiovascular dysfunction in survivors of sepsis. Designed to enroll 69 patients, demographics, cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers, and echocardiograms will be obtained on ICU discharge with additional laboratory data, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and patient-reported outcome measures to be obtained at 6 to 10 weeks. This novel multimodal approach will provide understanding into the role of cardiovascular dysfunction following critical illness as well as offer mechanistic insights. The investigators hope to obtain operational and pilot data for larger future studies.
– Commentary by Eugene Yuriditsky, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
Understanding RA with COPD, lung cancer prediction models, and chronic cardiac dysfunction
Understanding RA with COPD, lung cancer prediction models, and chronic cardiac dysfunction
Journal CHEST®
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Increase the Risk of COPD?
By: Chiwook Chung, MD, and colleagues
Notably, individuals with seropositive RA exhibit a greater risk of COPD onset than those with seronegative RA. Although smoking history didn’t affect the relationship between RA and COPD, monitoring respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in patients with RA, especially patients who are seropositive, is crucial. These findings underscore the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between rheumatologists and pulmonologists to enhance early detection and management strategies for pulmonary complications in patients with RA.
– Commentary by Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician® Editorial Board
CHEST Pulmonary®
The Lung Cancer Prediction Model “Stress Test”
By: Brent E. Heideman, MD, and colleagues
Current lung cancer prediction models have limited utility in high-risk patients referred for diagnostic biopsy. In a study of 322 indeterminate pulmonary nodules, the Brock, Mayo Clinic, Herder, and Veterans Affairs models showed modest discrimination between benign and malignant nodules (AUCs 0.67-0.77). The models performed poorly for low-risk patients (negative predictive values 63%-71%) and suboptimally for high-risk patients (positive predictive values 73%-87%), suggesting referring physicians use additional clinical information not captured in these models to identify high-risk patients needing biopsy. New prediction models and biomarkers specifically developed and calibrated for high-risk populations are needed to better inform clinical decision-making. Incorporating interval imaging to assess changes in nodule characteristics could potentially improve model performance. Tailored risk assessment tools are crucial for optimizing management and reducing unnecessary invasive procedures in this challenging patient population.
– Commentary by Russell Miller, MD, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST Critical Care ®
Characterizing Cardiac Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis
By: Kevin Garrity, MBChB, and colleagues
While chronic cardiac dysfunction is one of the proposed mechanisms of long-term impairment post critical illness, its prevalence, mechanisms, and associations with disability following admission for sepsis are not well understood. Garrity and colleagues describe the Characterization of Cardiovascular Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis (CONDUCT-ICU) protocol, a prospective study including two ICUs in Scotland aimed to better define cardiovascular dysfunction in survivors of sepsis. Designed to enroll 69 patients, demographics, cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers, and echocardiograms will be obtained on ICU discharge with additional laboratory data, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and patient-reported outcome measures to be obtained at 6 to 10 weeks. This novel multimodal approach will provide understanding into the role of cardiovascular dysfunction following critical illness as well as offer mechanistic insights. The investigators hope to obtain operational and pilot data for larger future studies.
– Commentary by Eugene Yuriditsky, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
Journal CHEST®
Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Increase the Risk of COPD?
By: Chiwook Chung, MD, and colleagues
Notably, individuals with seropositive RA exhibit a greater risk of COPD onset than those with seronegative RA. Although smoking history didn’t affect the relationship between RA and COPD, monitoring respiratory symptoms and pulmonary function in patients with RA, especially patients who are seropositive, is crucial. These findings underscore the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration between rheumatologists and pulmonologists to enhance early detection and management strategies for pulmonary complications in patients with RA.
– Commentary by Corinne Young, MSN, FNP-C, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician® Editorial Board
CHEST Pulmonary®
The Lung Cancer Prediction Model “Stress Test”
By: Brent E. Heideman, MD, and colleagues
Current lung cancer prediction models have limited utility in high-risk patients referred for diagnostic biopsy. In a study of 322 indeterminate pulmonary nodules, the Brock, Mayo Clinic, Herder, and Veterans Affairs models showed modest discrimination between benign and malignant nodules (AUCs 0.67-0.77). The models performed poorly for low-risk patients (negative predictive values 63%-71%) and suboptimally for high-risk patients (positive predictive values 73%-87%), suggesting referring physicians use additional clinical information not captured in these models to identify high-risk patients needing biopsy. New prediction models and biomarkers specifically developed and calibrated for high-risk populations are needed to better inform clinical decision-making. Incorporating interval imaging to assess changes in nodule characteristics could potentially improve model performance. Tailored risk assessment tools are crucial for optimizing management and reducing unnecessary invasive procedures in this challenging patient population.
– Commentary by Russell Miller, MD, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
CHEST Critical Care ®
Characterizing Cardiac Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis
By: Kevin Garrity, MBChB, and colleagues
While chronic cardiac dysfunction is one of the proposed mechanisms of long-term impairment post critical illness, its prevalence, mechanisms, and associations with disability following admission for sepsis are not well understood. Garrity and colleagues describe the Characterization of Cardiovascular Function in ICU Survivors of Sepsis (CONDUCT-ICU) protocol, a prospective study including two ICUs in Scotland aimed to better define cardiovascular dysfunction in survivors of sepsis. Designed to enroll 69 patients, demographics, cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers, and echocardiograms will be obtained on ICU discharge with additional laboratory data, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging, and patient-reported outcome measures to be obtained at 6 to 10 weeks. This novel multimodal approach will provide understanding into the role of cardiovascular dysfunction following critical illness as well as offer mechanistic insights. The investigators hope to obtain operational and pilot data for larger future studies.
– Commentary by Eugene Yuriditsky, MD, FCCP, Member of the CHEST Physician Editorial Board
Use of albumin in critically ill patients
Intravenous albumin is a human-derived blood product studied widely in a variety of patient populations. Despite its frequent use in critical care, few high-quality studies have demonstrated improvements in patient-important outcomes. Compared with crystalloids, albumin increases the risk of fluid overload and bleeding and infections in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.1,2 In addition, albumin is costly, and its production is fraught with donor supply chain ethical concerns (the majority of albumin is derived from paid plasma donors).
Albumin use is highly variable between countries, hospitals, and even clinicians within the same specialty due to several factors, including the perception of minimal risk with albumin, concerns regarding insufficient short-term hemodynamic response to crystalloid, and lack of high-quality evidence to inform clinical practice. We will discuss when intensivists should consider albumin use (with prescription personalized to patient context) and when it should be avoided due to the concerns for patient harm.
An intensivist might consider albumin as a reasonable treatment option in patients with cirrhosis undergoing large volume paracentesis to prevent paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction, and in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), as data suggests use in this setting leads to a reduction in mortality.3 Clinicians should be aware that even for these widely accepted albumin indications, which are supported by published guidelines, the certainty of evidence is low, recommendations are weak (conditional), and, therefore, albumin should always be personalized to the patient based on volume of paracentesis fluid removed, prior history of hypotension after procedures, and degree of renal dysfunction.4
There are also several conditions for which an intensivist might consider albumin and for which albumin is commonly administered but lacks high-quality studies to support its use either as a frontline or rescue fluid therapy. One such condition is type 1 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for which albumin is widely used; however, there are no randomized controlled trials that have compared albumin with placebo. 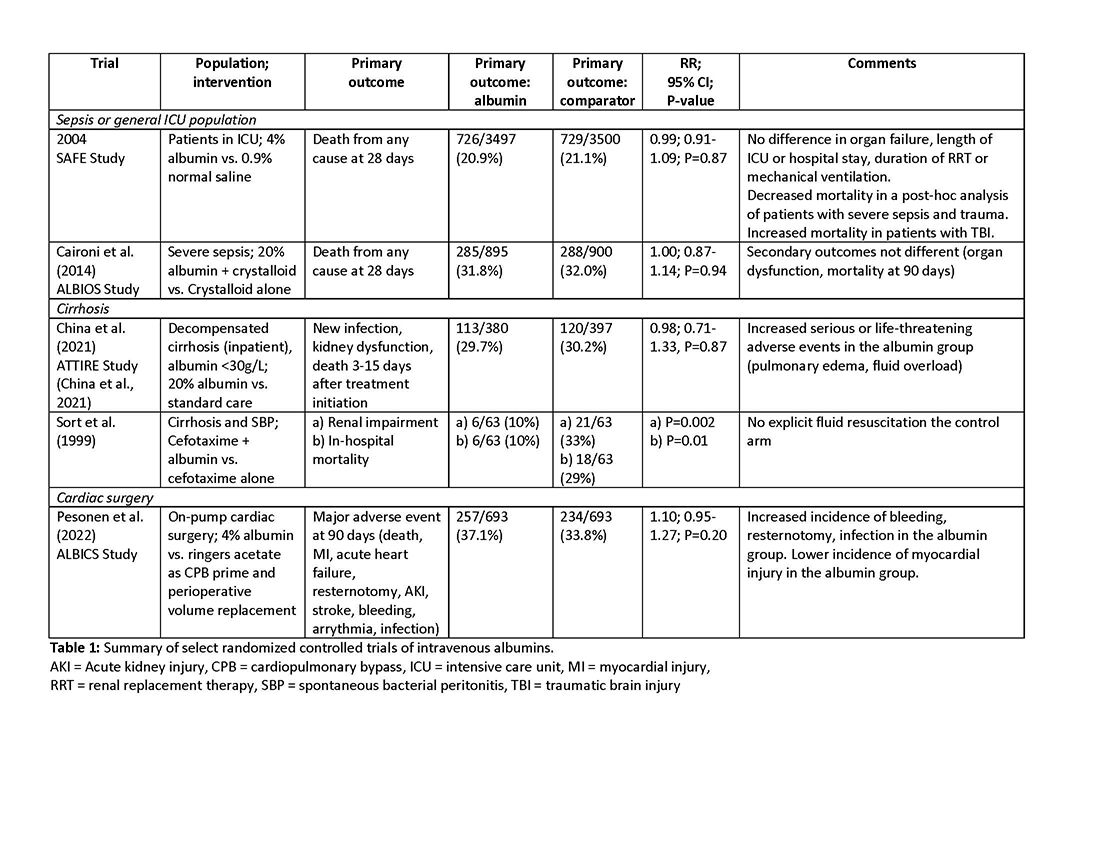
As with any intervention, the use of albumin is associated with risks. In patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery, the ALBICS study showed that albumin did not reduce the risk of major adverse events and, instead, increased risk of bleeding, resternotomy, and infection.2 The ATTIRE trial showed that in patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and serum albumin <30 g/L, albumin failed to reduce infection, renal impairment, or mortality while increasing life-threatening adverse events, including pulmonary edema and fluid overload.1 Similarly, in patients with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, albumin showed no benefit in reducing renal impairment or mortality, and its use was associated with higher rates of pulmonary edema.6 Lastly, critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) who received fluid resuscitation with albumin have been shown to experience higher mortality compared with saline.7 Thus, based on current evidence, intravenous albumin is not recommended for patients undergoing cardiac surgery (priming of the bypass circuit or volume replacement), patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia, patients hospitalized with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, and critically ill patients with TBI.4
Overall, intravenous albumin prescription in critical care patients requires a personalized approach informed by current best evidence and is not without potential harm. 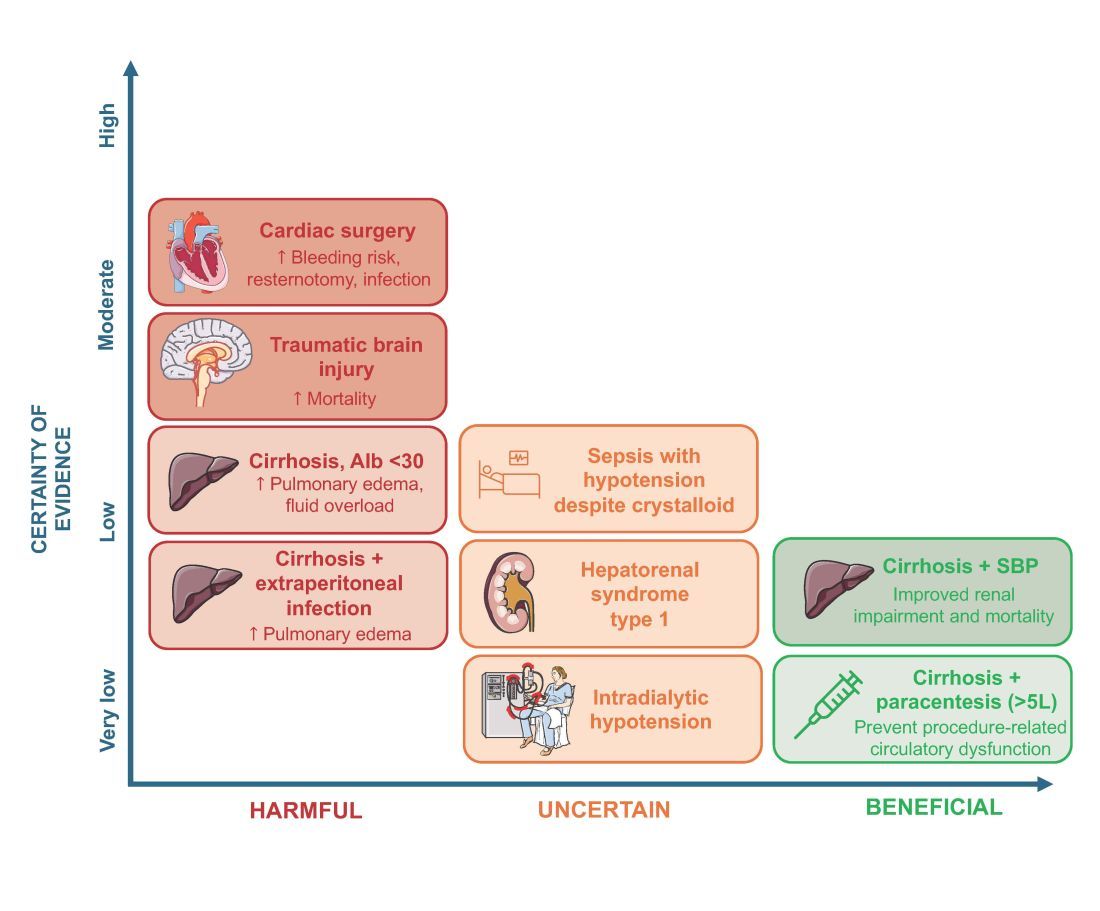
High-quality evidence is currently lacking in many clinical settings, and large randomized controlled trials are underway to provide further insights into the utility of albumin. These trials will address albumin use in the following: acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy (ALTER-AKI, NCT04705896), inpatients with community-acquired pneumonia (NCT04071041), high-risk cardiac surgery (ACTRN1261900135516703), and septic shock (NCT03869385).
Financial/nonfinancial disclosures
Nicole Relke: None. Mark Hewitt: None. Bram Rochwerg: None. Jeannie Callum: Research support from Canadian Blood Services and Octapharma.
References
1. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
2. Pesonen E, Vlasov H, Suojaranta R, et al. Effect of 4% albumin solution vs ringer acetate on major adverse events in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;328(3):251-258. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.10461
3. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. NEJM. 1999;341:403-409.
4. Callum J, Skubas NJ, Bathla A, et al. Use of intravenous albumin: a guideline from the international collaboration for transfusion medicine guidelines. Chest. 2024:S0012-3692(24)00285-X. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2024.02.049
5. Torp N. High doses of albumin increases mortality and complications in terlipressin treated patients with cirrhosis: insights from the ATTIRE trial. Paper presented at the AASLD; 2023; San Diego, CA. https://www.aasld.org/the-liver-meeting/high-doses-albumin-increases-mortality-and-complications-terlipressin-treated
6. Wong YJ, Qiu TY, Tam YC, Mohan BP, Gallegos-Orozco JF, Adler DG. Efficacy and safety of IV albumin for non-spontaneous bacterial peritonitis infection among patients with cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(10):1137-1142. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.047
7. Myburgh J, Cooper JD, Finfer S, et al. Saline or albumin for fluid resuscitation in patients with traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):874-884.
Intravenous albumin is a human-derived blood product studied widely in a variety of patient populations. Despite its frequent use in critical care, few high-quality studies have demonstrated improvements in patient-important outcomes. Compared with crystalloids, albumin increases the risk of fluid overload and bleeding and infections in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.1,2 In addition, albumin is costly, and its production is fraught with donor supply chain ethical concerns (the majority of albumin is derived from paid plasma donors).
Albumin use is highly variable between countries, hospitals, and even clinicians within the same specialty due to several factors, including the perception of minimal risk with albumin, concerns regarding insufficient short-term hemodynamic response to crystalloid, and lack of high-quality evidence to inform clinical practice. We will discuss when intensivists should consider albumin use (with prescription personalized to patient context) and when it should be avoided due to the concerns for patient harm.
An intensivist might consider albumin as a reasonable treatment option in patients with cirrhosis undergoing large volume paracentesis to prevent paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction, and in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), as data suggests use in this setting leads to a reduction in mortality.3 Clinicians should be aware that even for these widely accepted albumin indications, which are supported by published guidelines, the certainty of evidence is low, recommendations are weak (conditional), and, therefore, albumin should always be personalized to the patient based on volume of paracentesis fluid removed, prior history of hypotension after procedures, and degree of renal dysfunction.4
There are also several conditions for which an intensivist might consider albumin and for which albumin is commonly administered but lacks high-quality studies to support its use either as a frontline or rescue fluid therapy. One such condition is type 1 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for which albumin is widely used; however, there are no randomized controlled trials that have compared albumin with placebo. 
As with any intervention, the use of albumin is associated with risks. In patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery, the ALBICS study showed that albumin did not reduce the risk of major adverse events and, instead, increased risk of bleeding, resternotomy, and infection.2 The ATTIRE trial showed that in patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and serum albumin <30 g/L, albumin failed to reduce infection, renal impairment, or mortality while increasing life-threatening adverse events, including pulmonary edema and fluid overload.1 Similarly, in patients with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, albumin showed no benefit in reducing renal impairment or mortality, and its use was associated with higher rates of pulmonary edema.6 Lastly, critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) who received fluid resuscitation with albumin have been shown to experience higher mortality compared with saline.7 Thus, based on current evidence, intravenous albumin is not recommended for patients undergoing cardiac surgery (priming of the bypass circuit or volume replacement), patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia, patients hospitalized with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, and critically ill patients with TBI.4
Overall, intravenous albumin prescription in critical care patients requires a personalized approach informed by current best evidence and is not without potential harm. 
High-quality evidence is currently lacking in many clinical settings, and large randomized controlled trials are underway to provide further insights into the utility of albumin. These trials will address albumin use in the following: acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy (ALTER-AKI, NCT04705896), inpatients with community-acquired pneumonia (NCT04071041), high-risk cardiac surgery (ACTRN1261900135516703), and septic shock (NCT03869385).
Financial/nonfinancial disclosures
Nicole Relke: None. Mark Hewitt: None. Bram Rochwerg: None. Jeannie Callum: Research support from Canadian Blood Services and Octapharma.
References
1. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
2. Pesonen E, Vlasov H, Suojaranta R, et al. Effect of 4% albumin solution vs ringer acetate on major adverse events in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;328(3):251-258. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.10461
3. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. NEJM. 1999;341:403-409.
4. Callum J, Skubas NJ, Bathla A, et al. Use of intravenous albumin: a guideline from the international collaboration for transfusion medicine guidelines. Chest. 2024:S0012-3692(24)00285-X. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2024.02.049
5. Torp N. High doses of albumin increases mortality and complications in terlipressin treated patients with cirrhosis: insights from the ATTIRE trial. Paper presented at the AASLD; 2023; San Diego, CA. https://www.aasld.org/the-liver-meeting/high-doses-albumin-increases-mortality-and-complications-terlipressin-treated
6. Wong YJ, Qiu TY, Tam YC, Mohan BP, Gallegos-Orozco JF, Adler DG. Efficacy and safety of IV albumin for non-spontaneous bacterial peritonitis infection among patients with cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(10):1137-1142. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.047
7. Myburgh J, Cooper JD, Finfer S, et al. Saline or albumin for fluid resuscitation in patients with traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):874-884.
Intravenous albumin is a human-derived blood product studied widely in a variety of patient populations. Despite its frequent use in critical care, few high-quality studies have demonstrated improvements in patient-important outcomes. Compared with crystalloids, albumin increases the risk of fluid overload and bleeding and infections in patients undergoing cardiac surgery.1,2 In addition, albumin is costly, and its production is fraught with donor supply chain ethical concerns (the majority of albumin is derived from paid plasma donors).
Albumin use is highly variable between countries, hospitals, and even clinicians within the same specialty due to several factors, including the perception of minimal risk with albumin, concerns regarding insufficient short-term hemodynamic response to crystalloid, and lack of high-quality evidence to inform clinical practice. We will discuss when intensivists should consider albumin use (with prescription personalized to patient context) and when it should be avoided due to the concerns for patient harm.
An intensivist might consider albumin as a reasonable treatment option in patients with cirrhosis undergoing large volume paracentesis to prevent paracentesis-induced circulatory dysfunction, and in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP), as data suggests use in this setting leads to a reduction in mortality.3 Clinicians should be aware that even for these widely accepted albumin indications, which are supported by published guidelines, the certainty of evidence is low, recommendations are weak (conditional), and, therefore, albumin should always be personalized to the patient based on volume of paracentesis fluid removed, prior history of hypotension after procedures, and degree of renal dysfunction.4
There are also several conditions for which an intensivist might consider albumin and for which albumin is commonly administered but lacks high-quality studies to support its use either as a frontline or rescue fluid therapy. One such condition is type 1 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS), for which albumin is widely used; however, there are no randomized controlled trials that have compared albumin with placebo. 
As with any intervention, the use of albumin is associated with risks. In patients undergoing on-pump cardiac surgery, the ALBICS study showed that albumin did not reduce the risk of major adverse events and, instead, increased risk of bleeding, resternotomy, and infection.2 The ATTIRE trial showed that in patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and serum albumin <30 g/L, albumin failed to reduce infection, renal impairment, or mortality while increasing life-threatening adverse events, including pulmonary edema and fluid overload.1 Similarly, in patients with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, albumin showed no benefit in reducing renal impairment or mortality, and its use was associated with higher rates of pulmonary edema.6 Lastly, critically ill patients with traumatic brain injury (TBI) who received fluid resuscitation with albumin have been shown to experience higher mortality compared with saline.7 Thus, based on current evidence, intravenous albumin is not recommended for patients undergoing cardiac surgery (priming of the bypass circuit or volume replacement), patients hospitalized with decompensated cirrhosis and hypoalbuminemia, patients hospitalized with cirrhosis and extraperitoneal infections, and critically ill patients with TBI.4
Overall, intravenous albumin prescription in critical care patients requires a personalized approach informed by current best evidence and is not without potential harm. 
High-quality evidence is currently lacking in many clinical settings, and large randomized controlled trials are underway to provide further insights into the utility of albumin. These trials will address albumin use in the following: acute kidney injury requiring renal replacement therapy (ALTER-AKI, NCT04705896), inpatients with community-acquired pneumonia (NCT04071041), high-risk cardiac surgery (ACTRN1261900135516703), and septic shock (NCT03869385).
Financial/nonfinancial disclosures
Nicole Relke: None. Mark Hewitt: None. Bram Rochwerg: None. Jeannie Callum: Research support from Canadian Blood Services and Octapharma.
References
1. China L, Freemantle N, Forrest E, et al. A randomized trial of albumin infusions in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(9):808-817. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2022166
2. Pesonen E, Vlasov H, Suojaranta R, et al. Effect of 4% albumin solution vs ringer acetate on major adverse events in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;328(3):251-258. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.10461
3. Sort P, Navasa M, Arroyo V, et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. NEJM. 1999;341:403-409.
4. Callum J, Skubas NJ, Bathla A, et al. Use of intravenous albumin: a guideline from the international collaboration for transfusion medicine guidelines. Chest. 2024:S0012-3692(24)00285-X. doi:10.1016/j.chest.2024.02.049
5. Torp N. High doses of albumin increases mortality and complications in terlipressin treated patients with cirrhosis: insights from the ATTIRE trial. Paper presented at the AASLD; 2023; San Diego, CA. https://www.aasld.org/the-liver-meeting/high-doses-albumin-increases-mortality-and-complications-terlipressin-treated
6. Wong YJ, Qiu TY, Tam YC, Mohan BP, Gallegos-Orozco JF, Adler DG. Efficacy and safety of IV albumin for non-spontaneous bacterial peritonitis infection among patients with cirrhosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(10):1137-1142. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.05.047
7. Myburgh J, Cooper JD, Finfer S, et al. Saline or albumin for fluid resuscitation in patients with traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(9):874-884.






















