User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
The Next Frontier of Antibiotic Discovery: Inside Your Gut
Scientists at Stanford University and the University of Pennsylvania have discovered a new antibiotic candidate in a surprising place: the human gut.
In mice, the antibiotic — a peptide known as prevotellin-2 — showed antimicrobial potency on par with polymyxin B, an antibiotic medication used to treat multidrug-resistant infections. Meanwhile, the peptide mainly left commensal, or beneficial, bacteria alone. The study, published in Cell, also identified several other potent antibiotic peptides with the potential to combat antimicrobial-resistant infections.
The research is part of a larger quest to find new antibiotics that can fight drug-resistant infections, a critical public health threat with more than 2.8 million cases and 35,000 deaths annually in the United States. That quest is urgent, said study author César de la Fuente, PhD, professor of bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“The main pillars that have enabled us to almost double our lifespan in the last 100 years or so have been antibiotics, vaccines, and clean water,” said Dr. de la Fuente. “Imagine taking out one of those. I think it would be pretty dramatic.” (Dr. De la Fuente’s lab has become known for finding antibiotic candidates in unusual places, like ancient genetic information of Neanderthals and woolly mammoths.)
The first widely used antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered in 1928, when a physician studying Staphylococcus bacteria returned to his lab after summer break to find mold growing in one of his petri dishes. But many other antibiotics — like streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin — were discovered from soil bacteria, which produce variations of these substances to compete with other microorganisms.
By looking in the gut microbiome, the researchers hoped to identify peptides that the trillions of microbes use against each other in the fight for limited resources — ideally, peptides that wouldn’t broadly kill off the entire microbiome.
Kill the Bad, Spare the Good
Many traditional antibiotics are small molecules. This means they can wipe out the good bacteria in your body, and because each targets a specific bacterial function, bad bacteria can become resistant to them.
Peptide antibiotics, on the other hand, don’t diffuse into the whole body. If taken orally, they stay in the gut; if taken intravenously, they generally stay in the blood. And because of how they kill bacteria, targeting the membrane, they’re also less prone to bacterial resistance.
The microbiome is like a big reservoir of pathogens, said Ami Bhatt, MD, PhD, hematologist at Stanford University in California and one of the study’s authors. Because many antibiotics kill healthy gut bacteria, “what you have left over,” Dr. Bhatt said, “is this big open niche that gets filled up with multidrug-resistant organisms like E coli [Escherichia coli] or vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus.”
Dr. Bhatt has seen cancer patients undergo successful treatment only to die of a multidrug-resistant infection, because current antibiotics fail against those pathogens. “That’s like winning the battle to lose the war.”
By investigating the microbiome, “we wanted to see if we could identify antimicrobial peptides that might spare key members of our regular microbiome, so that we wouldn’t totally disrupt the microbiome the way we do when we use broad-spectrum, small molecule–based antibiotics,” Dr. Bhatt said.
The researchers used artificial intelligence to sift through 400,000 proteins to predict, based on known antibiotics, which peptide sequences might have antimicrobial properties. From the results, they chose 78 peptides to synthesize and test.
“The application of computational approaches combined with experimental validation is very powerful and exciting,” said Jennifer Geddes-McAlister, PhD, professor of cell biology at the University of Guelph in Ontario, Canada, who was not involved in the study. “The study is robust in its approach to microbiome sampling.”
The Long Journey from Lab to Clinic
More than half of the peptides the team tested effectively inhibited the growth of harmful bacteria, and prevotellin-2 (derived from the bacteria Prevotella copri)stood out as the most powerful.
“The study validates experimental data from the lab using animal models, which moves discoveries closer to the clinic,” said Dr. Geddes-McAlister. “Further testing with clinical trials is needed, but the potential for clinical application is promising.”
Unfortunately, that’s not likely to happen anytime soon, said Dr. de la Fuente. “There is not enough economic incentive” for companies to develop new antibiotics. Ten years is his most hopeful guess for when we might see prevotellin-2, or a similar antibiotic, complete clinical trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientists at Stanford University and the University of Pennsylvania have discovered a new antibiotic candidate in a surprising place: the human gut.
In mice, the antibiotic — a peptide known as prevotellin-2 — showed antimicrobial potency on par with polymyxin B, an antibiotic medication used to treat multidrug-resistant infections. Meanwhile, the peptide mainly left commensal, or beneficial, bacteria alone. The study, published in Cell, also identified several other potent antibiotic peptides with the potential to combat antimicrobial-resistant infections.
The research is part of a larger quest to find new antibiotics that can fight drug-resistant infections, a critical public health threat with more than 2.8 million cases and 35,000 deaths annually in the United States. That quest is urgent, said study author César de la Fuente, PhD, professor of bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“The main pillars that have enabled us to almost double our lifespan in the last 100 years or so have been antibiotics, vaccines, and clean water,” said Dr. de la Fuente. “Imagine taking out one of those. I think it would be pretty dramatic.” (Dr. De la Fuente’s lab has become known for finding antibiotic candidates in unusual places, like ancient genetic information of Neanderthals and woolly mammoths.)
The first widely used antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered in 1928, when a physician studying Staphylococcus bacteria returned to his lab after summer break to find mold growing in one of his petri dishes. But many other antibiotics — like streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin — were discovered from soil bacteria, which produce variations of these substances to compete with other microorganisms.
By looking in the gut microbiome, the researchers hoped to identify peptides that the trillions of microbes use against each other in the fight for limited resources — ideally, peptides that wouldn’t broadly kill off the entire microbiome.
Kill the Bad, Spare the Good
Many traditional antibiotics are small molecules. This means they can wipe out the good bacteria in your body, and because each targets a specific bacterial function, bad bacteria can become resistant to them.
Peptide antibiotics, on the other hand, don’t diffuse into the whole body. If taken orally, they stay in the gut; if taken intravenously, they generally stay in the blood. And because of how they kill bacteria, targeting the membrane, they’re also less prone to bacterial resistance.
The microbiome is like a big reservoir of pathogens, said Ami Bhatt, MD, PhD, hematologist at Stanford University in California and one of the study’s authors. Because many antibiotics kill healthy gut bacteria, “what you have left over,” Dr. Bhatt said, “is this big open niche that gets filled up with multidrug-resistant organisms like E coli [Escherichia coli] or vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus.”
Dr. Bhatt has seen cancer patients undergo successful treatment only to die of a multidrug-resistant infection, because current antibiotics fail against those pathogens. “That’s like winning the battle to lose the war.”
By investigating the microbiome, “we wanted to see if we could identify antimicrobial peptides that might spare key members of our regular microbiome, so that we wouldn’t totally disrupt the microbiome the way we do when we use broad-spectrum, small molecule–based antibiotics,” Dr. Bhatt said.
The researchers used artificial intelligence to sift through 400,000 proteins to predict, based on known antibiotics, which peptide sequences might have antimicrobial properties. From the results, they chose 78 peptides to synthesize and test.
“The application of computational approaches combined with experimental validation is very powerful and exciting,” said Jennifer Geddes-McAlister, PhD, professor of cell biology at the University of Guelph in Ontario, Canada, who was not involved in the study. “The study is robust in its approach to microbiome sampling.”
The Long Journey from Lab to Clinic
More than half of the peptides the team tested effectively inhibited the growth of harmful bacteria, and prevotellin-2 (derived from the bacteria Prevotella copri)stood out as the most powerful.
“The study validates experimental data from the lab using animal models, which moves discoveries closer to the clinic,” said Dr. Geddes-McAlister. “Further testing with clinical trials is needed, but the potential for clinical application is promising.”
Unfortunately, that’s not likely to happen anytime soon, said Dr. de la Fuente. “There is not enough economic incentive” for companies to develop new antibiotics. Ten years is his most hopeful guess for when we might see prevotellin-2, or a similar antibiotic, complete clinical trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Scientists at Stanford University and the University of Pennsylvania have discovered a new antibiotic candidate in a surprising place: the human gut.
In mice, the antibiotic — a peptide known as prevotellin-2 — showed antimicrobial potency on par with polymyxin B, an antibiotic medication used to treat multidrug-resistant infections. Meanwhile, the peptide mainly left commensal, or beneficial, bacteria alone. The study, published in Cell, also identified several other potent antibiotic peptides with the potential to combat antimicrobial-resistant infections.
The research is part of a larger quest to find new antibiotics that can fight drug-resistant infections, a critical public health threat with more than 2.8 million cases and 35,000 deaths annually in the United States. That quest is urgent, said study author César de la Fuente, PhD, professor of bioengineering at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“The main pillars that have enabled us to almost double our lifespan in the last 100 years or so have been antibiotics, vaccines, and clean water,” said Dr. de la Fuente. “Imagine taking out one of those. I think it would be pretty dramatic.” (Dr. De la Fuente’s lab has become known for finding antibiotic candidates in unusual places, like ancient genetic information of Neanderthals and woolly mammoths.)
The first widely used antibiotic, penicillin, was discovered in 1928, when a physician studying Staphylococcus bacteria returned to his lab after summer break to find mold growing in one of his petri dishes. But many other antibiotics — like streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin — were discovered from soil bacteria, which produce variations of these substances to compete with other microorganisms.
By looking in the gut microbiome, the researchers hoped to identify peptides that the trillions of microbes use against each other in the fight for limited resources — ideally, peptides that wouldn’t broadly kill off the entire microbiome.
Kill the Bad, Spare the Good
Many traditional antibiotics are small molecules. This means they can wipe out the good bacteria in your body, and because each targets a specific bacterial function, bad bacteria can become resistant to them.
Peptide antibiotics, on the other hand, don’t diffuse into the whole body. If taken orally, they stay in the gut; if taken intravenously, they generally stay in the blood. And because of how they kill bacteria, targeting the membrane, they’re also less prone to bacterial resistance.
The microbiome is like a big reservoir of pathogens, said Ami Bhatt, MD, PhD, hematologist at Stanford University in California and one of the study’s authors. Because many antibiotics kill healthy gut bacteria, “what you have left over,” Dr. Bhatt said, “is this big open niche that gets filled up with multidrug-resistant organisms like E coli [Escherichia coli] or vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus.”
Dr. Bhatt has seen cancer patients undergo successful treatment only to die of a multidrug-resistant infection, because current antibiotics fail against those pathogens. “That’s like winning the battle to lose the war.”
By investigating the microbiome, “we wanted to see if we could identify antimicrobial peptides that might spare key members of our regular microbiome, so that we wouldn’t totally disrupt the microbiome the way we do when we use broad-spectrum, small molecule–based antibiotics,” Dr. Bhatt said.
The researchers used artificial intelligence to sift through 400,000 proteins to predict, based on known antibiotics, which peptide sequences might have antimicrobial properties. From the results, they chose 78 peptides to synthesize and test.
“The application of computational approaches combined with experimental validation is very powerful and exciting,” said Jennifer Geddes-McAlister, PhD, professor of cell biology at the University of Guelph in Ontario, Canada, who was not involved in the study. “The study is robust in its approach to microbiome sampling.”
The Long Journey from Lab to Clinic
More than half of the peptides the team tested effectively inhibited the growth of harmful bacteria, and prevotellin-2 (derived from the bacteria Prevotella copri)stood out as the most powerful.
“The study validates experimental data from the lab using animal models, which moves discoveries closer to the clinic,” said Dr. Geddes-McAlister. “Further testing with clinical trials is needed, but the potential for clinical application is promising.”
Unfortunately, that’s not likely to happen anytime soon, said Dr. de la Fuente. “There is not enough economic incentive” for companies to develop new antibiotics. Ten years is his most hopeful guess for when we might see prevotellin-2, or a similar antibiotic, complete clinical trials.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CELL
Physicians Lament Over Reliance on Relative Value Units: Survey
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Most physicians oppose the way standardized relative value units (RVUs) are used to determine performance and compensation, according to Medscape’s 2024 Physicians and RVUs Report. About 6 in 10 survey respondents were unhappy with how RVUs affected them financially, while 7 in 10 said RVUs were poor measures of productivity.
The report analyzed 2024 survey data from 1005 practicing physicians who earn RVUs.
“I’m already mad that the medical field is controlled by health insurers and what they pay and authorize,” said an anesthesiologist in New York. “Then [that approach] is transferred to medical offices and hospitals, where physicians are paid by RVUs.”
Most physicians surveyed produced between 4000 and 8000 RVUs per year. Roughly one in six were high RVU generators, generating more than 10,000 annually.
In most cases, the metric influences earning potential — 42% of doctors surveyed said RVUs affect their salaries to some degree. One quarter said their salary was based entirely on RVUs. More than three fourths of physicians who received performance bonuses said they must meet RVU targets to do so.
“The current RVU system encourages unnecessary procedures, hurting patients,” said an orthopedic surgeon in Maine.
Nearly three fourths of practitioners surveyed said they occasionally to frequently felt pressure to take on more patients as a result of this system.
“I know numerous primary care doctors and specialists who have been forced to increase patient volume to meet RVU goals, and none is happy about it,” said Alok Patel, MD, a pediatric hospitalist with Stanford Hospital in Palo Alto, California. “Plus, patients are definitely not happy about being rushed.”
More than half of respondents said they occasionally or frequently felt compelled by their employer to use higher-level coding, which interferes with a physician’s ethical responsibility to the patient, said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a bioethicist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York City.
“Rather than rewarding excellence or good outcomes, you’re kind of rewarding procedures and volume,” said Dr. Caplan. “It’s more than pressure; it’s expected.”
Nearly 6 in 10 physicians said that the method for calculating reimbursements was unfair. Almost half said that they weren’t happy with how their workplace uses RVUs.
A few respondents said that their RVU model, which is often based on what Dr. Patel called an “overly complicated algorithm,” did not account for the time spent on tasks or the fact that some patients miss appointments. RVUs also rely on factors outside the control of a physician, such as location and patient volume, said one doctor.
The model can also lower the level of care patients receive, Dr. Patel said.
“I know primary care doctors who work in RVU-based systems and simply cannot take the necessary time — even if it’s 30-45 minutes — to thoroughly assess a patient, when the model forces them to take on 15-minute encounters.”
Finally, over half of clinicians said alternatives to the RVU system would be more effective, and 77% suggested including qualitative data. One respondent recommended incorporating time spent doing paperwork and communicating with patients, complexity of conditions, and medication management.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PrEP Prescription Pickups Vary With Prescriber Specialty
Preexposure prophylaxis prescription reversals and abandonments were lower for patients seen by primary care clinicians than by other non–infectious disease clinicians, based on data from approximately 37,000 individuals.
Although preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has been associated with a reduced risk of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection when used as prescribed, the association between PrEP prescription pickup and specialty of the prescribing clinician has not been examined, wrote Lorraine T. Dean, ScD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues.
“HIV PrEP is highly effective at preventing new HIV cases, and while use is on the rise, is still used much less than it should be by people who are at risk of HIV,” Dr. Dean said in an interview. “This study is helpful in pinpointing who is at risk for not picking up PrEP and in helping us think through how to reach them so that they can be better positioned to get PrEP,” she said.
In a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the researchers reviewed data for PrEP care. The study population included 37,003 patients aged 18 years and older who received new insurer-approved PrEP prescriptions between 2015 and 2019. Most of the patients (77%) ranged in age from 25 to 64 years; 88% were male.
Pharmacy claims data were matched with clinician data from the US National Plan and Provider Enumeration System.
Clinicians were divided into three groups: primary care providers (PCPs), infectious disease specialists (IDs), and other specialists (defined as any clinician prescribing PrEP but not classified as a PCP or an ID specialist). The main binary outcomes were prescription reversal (defined as when a patient failed to retrieve a prescription) and abandonment (defined as when a patient neglected to pick up a prescription for 1 year).
Overall, of 24,604 patients 67% received prescriptions from PCPs, 3,571 (10%) received prescriptions from ID specialists, and 8828 (24%) received prescriptions from other specialty clinicians.
The prevalence of reversals for patients seen by PCPs, ID specialists, and other specialty clinicians was 18%, 18%, and 25%, respectively. The prevalence of abandonments by clinician group was 12%, 12%, and 20%, respectively.
In a regression analysis, patients prescribed PrEP by ID specialists had 10% lower odds of reversals and 12% lower odds of abandonments compared to those seen by PCPs (odds ratio 0.90 and 0.88, respectively). However, patients seen by other clinicians (not primary care or ID) were 33% and 54% more likely to have reversals and abandonments, respectively, compared with those seen by PCPs.
Many patients at risk for HIV first see a PCP and then are referred to a specialist, such as an ID physician, Dr. Dean said. “The patients who take the time to then follow up with a specialist may be most motivated and able to follow through with the specialist’s request, in this case, accessing their PrEP prescription,” she said. In the current study, the researchers were most surprised by how many other specialty providers are involved in PrEP care, which is very positive given the effectiveness of the medication, she noted.
“Our results suggest that a wide range of prescribers, regardless of specialty, should be equipped to prescribe PrEP as well as offer PrEP counseling,” Dr. Dean said. A key takeaway for clinicians is that PrEP should have no cost for the majority of patients in the United States, she emphasized. The absence of cost expands the population who should be interested and able to access PrEP, she said. Therefore, providers should be prepared to recommend PrEP to eligible patients, and seek training or continuing medical education for themselves so they feel equipped to prescribe and counsel patients on PrEP, she said.
“One limitation of this work is that, while it can point to what is happening, it cannot tell us why the reversals are happening; what is the reason patients prescribed by certain providers are more or less likely to get their PrEP,” Dr. Dean explained. “We have tried to do interviews with patients to understand why this might be happening, but it’s hard to find people who aren’t showing up to do something, compared to finding people who are showing up to do something,” she said. Alternatively, researchers could interview providers to understand their perspective on why differences in prescription pickups occur across specialties, she said.
Looking ahead, “a national PrEP program that includes elements of required clinician training could be beneficial, and research on how a national PrEP program could be implemented and impact HIV rates would be helpful in considering this strategy of prevention,” said Dr. Dean.
Support All Prescribers to Increase PrEP Adherence
Differences in uptake of PrEP prescriptions may be explained by the different populations seen by various specialties, Meredith Green, MD, of Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and Lona Mody, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, wrote in an accompanying editorial. However, the key question is how to support all prescribers and promote initiation and adherence to PrEP, they said.
Considerations include whether people at risk for HIV prefer to discuss PrEP with a clinician they already know, vs. a new specialist, but many PCPs are not familiar with the latest PrEP guidelines, they said.
“Interventions that support PrEP provision by PCPs, especially since they prescribed the largest proportion of PrEP prescriptions, can accelerate the uptake of PrEP,” the editorialists wrote.
“Supporting a diverse clinician workforce reflective of communities most impacted by HIV will remain critical, as will acknowledging and addressing HIV stigma,” they said. Educational interventions, including online programs and specialist access for complex cases, would help as well, they said. The approval of additional PrEP agents since the current study was conducted make it even more important to support PrEP prescribers and promote treatment adherence for those at risk for HIV, Dr. Green and Dr. Mody emphasized.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dean had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Green disclosed grants from Gilead and royalties from Wolters Kluwer unrelated to the current study; she also disclosed serving on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Health Resources and Services Administration advisory committee on HIV, viral hepatitis, and sexually transmitted infection prevention and treatment. Dr. Mody disclosed grants from the US National Institute on Aging, Veterans Affairs, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NanoVibronix, and UpToDate unrelated to the current study.
Preexposure prophylaxis prescription reversals and abandonments were lower for patients seen by primary care clinicians than by other non–infectious disease clinicians, based on data from approximately 37,000 individuals.
Although preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has been associated with a reduced risk of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection when used as prescribed, the association between PrEP prescription pickup and specialty of the prescribing clinician has not been examined, wrote Lorraine T. Dean, ScD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues.
“HIV PrEP is highly effective at preventing new HIV cases, and while use is on the rise, is still used much less than it should be by people who are at risk of HIV,” Dr. Dean said in an interview. “This study is helpful in pinpointing who is at risk for not picking up PrEP and in helping us think through how to reach them so that they can be better positioned to get PrEP,” she said.
In a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the researchers reviewed data for PrEP care. The study population included 37,003 patients aged 18 years and older who received new insurer-approved PrEP prescriptions between 2015 and 2019. Most of the patients (77%) ranged in age from 25 to 64 years; 88% were male.
Pharmacy claims data were matched with clinician data from the US National Plan and Provider Enumeration System.
Clinicians were divided into three groups: primary care providers (PCPs), infectious disease specialists (IDs), and other specialists (defined as any clinician prescribing PrEP but not classified as a PCP or an ID specialist). The main binary outcomes were prescription reversal (defined as when a patient failed to retrieve a prescription) and abandonment (defined as when a patient neglected to pick up a prescription for 1 year).
Overall, of 24,604 patients 67% received prescriptions from PCPs, 3,571 (10%) received prescriptions from ID specialists, and 8828 (24%) received prescriptions from other specialty clinicians.
The prevalence of reversals for patients seen by PCPs, ID specialists, and other specialty clinicians was 18%, 18%, and 25%, respectively. The prevalence of abandonments by clinician group was 12%, 12%, and 20%, respectively.
In a regression analysis, patients prescribed PrEP by ID specialists had 10% lower odds of reversals and 12% lower odds of abandonments compared to those seen by PCPs (odds ratio 0.90 and 0.88, respectively). However, patients seen by other clinicians (not primary care or ID) were 33% and 54% more likely to have reversals and abandonments, respectively, compared with those seen by PCPs.
Many patients at risk for HIV first see a PCP and then are referred to a specialist, such as an ID physician, Dr. Dean said. “The patients who take the time to then follow up with a specialist may be most motivated and able to follow through with the specialist’s request, in this case, accessing their PrEP prescription,” she said. In the current study, the researchers were most surprised by how many other specialty providers are involved in PrEP care, which is very positive given the effectiveness of the medication, she noted.
“Our results suggest that a wide range of prescribers, regardless of specialty, should be equipped to prescribe PrEP as well as offer PrEP counseling,” Dr. Dean said. A key takeaway for clinicians is that PrEP should have no cost for the majority of patients in the United States, she emphasized. The absence of cost expands the population who should be interested and able to access PrEP, she said. Therefore, providers should be prepared to recommend PrEP to eligible patients, and seek training or continuing medical education for themselves so they feel equipped to prescribe and counsel patients on PrEP, she said.
“One limitation of this work is that, while it can point to what is happening, it cannot tell us why the reversals are happening; what is the reason patients prescribed by certain providers are more or less likely to get their PrEP,” Dr. Dean explained. “We have tried to do interviews with patients to understand why this might be happening, but it’s hard to find people who aren’t showing up to do something, compared to finding people who are showing up to do something,” she said. Alternatively, researchers could interview providers to understand their perspective on why differences in prescription pickups occur across specialties, she said.
Looking ahead, “a national PrEP program that includes elements of required clinician training could be beneficial, and research on how a national PrEP program could be implemented and impact HIV rates would be helpful in considering this strategy of prevention,” said Dr. Dean.
Support All Prescribers to Increase PrEP Adherence
Differences in uptake of PrEP prescriptions may be explained by the different populations seen by various specialties, Meredith Green, MD, of Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and Lona Mody, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, wrote in an accompanying editorial. However, the key question is how to support all prescribers and promote initiation and adherence to PrEP, they said.
Considerations include whether people at risk for HIV prefer to discuss PrEP with a clinician they already know, vs. a new specialist, but many PCPs are not familiar with the latest PrEP guidelines, they said.
“Interventions that support PrEP provision by PCPs, especially since they prescribed the largest proportion of PrEP prescriptions, can accelerate the uptake of PrEP,” the editorialists wrote.
“Supporting a diverse clinician workforce reflective of communities most impacted by HIV will remain critical, as will acknowledging and addressing HIV stigma,” they said. Educational interventions, including online programs and specialist access for complex cases, would help as well, they said. The approval of additional PrEP agents since the current study was conducted make it even more important to support PrEP prescribers and promote treatment adherence for those at risk for HIV, Dr. Green and Dr. Mody emphasized.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dean had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Green disclosed grants from Gilead and royalties from Wolters Kluwer unrelated to the current study; she also disclosed serving on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Health Resources and Services Administration advisory committee on HIV, viral hepatitis, and sexually transmitted infection prevention and treatment. Dr. Mody disclosed grants from the US National Institute on Aging, Veterans Affairs, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NanoVibronix, and UpToDate unrelated to the current study.
Preexposure prophylaxis prescription reversals and abandonments were lower for patients seen by primary care clinicians than by other non–infectious disease clinicians, based on data from approximately 37,000 individuals.
Although preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has been associated with a reduced risk of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection when used as prescribed, the association between PrEP prescription pickup and specialty of the prescribing clinician has not been examined, wrote Lorraine T. Dean, ScD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, Maryland, and colleagues.
“HIV PrEP is highly effective at preventing new HIV cases, and while use is on the rise, is still used much less than it should be by people who are at risk of HIV,” Dr. Dean said in an interview. “This study is helpful in pinpointing who is at risk for not picking up PrEP and in helping us think through how to reach them so that they can be better positioned to get PrEP,” she said.
In a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the researchers reviewed data for PrEP care. The study population included 37,003 patients aged 18 years and older who received new insurer-approved PrEP prescriptions between 2015 and 2019. Most of the patients (77%) ranged in age from 25 to 64 years; 88% were male.
Pharmacy claims data were matched with clinician data from the US National Plan and Provider Enumeration System.
Clinicians were divided into three groups: primary care providers (PCPs), infectious disease specialists (IDs), and other specialists (defined as any clinician prescribing PrEP but not classified as a PCP or an ID specialist). The main binary outcomes were prescription reversal (defined as when a patient failed to retrieve a prescription) and abandonment (defined as when a patient neglected to pick up a prescription for 1 year).
Overall, of 24,604 patients 67% received prescriptions from PCPs, 3,571 (10%) received prescriptions from ID specialists, and 8828 (24%) received prescriptions from other specialty clinicians.
The prevalence of reversals for patients seen by PCPs, ID specialists, and other specialty clinicians was 18%, 18%, and 25%, respectively. The prevalence of abandonments by clinician group was 12%, 12%, and 20%, respectively.
In a regression analysis, patients prescribed PrEP by ID specialists had 10% lower odds of reversals and 12% lower odds of abandonments compared to those seen by PCPs (odds ratio 0.90 and 0.88, respectively). However, patients seen by other clinicians (not primary care or ID) were 33% and 54% more likely to have reversals and abandonments, respectively, compared with those seen by PCPs.
Many patients at risk for HIV first see a PCP and then are referred to a specialist, such as an ID physician, Dr. Dean said. “The patients who take the time to then follow up with a specialist may be most motivated and able to follow through with the specialist’s request, in this case, accessing their PrEP prescription,” she said. In the current study, the researchers were most surprised by how many other specialty providers are involved in PrEP care, which is very positive given the effectiveness of the medication, she noted.
“Our results suggest that a wide range of prescribers, regardless of specialty, should be equipped to prescribe PrEP as well as offer PrEP counseling,” Dr. Dean said. A key takeaway for clinicians is that PrEP should have no cost for the majority of patients in the United States, she emphasized. The absence of cost expands the population who should be interested and able to access PrEP, she said. Therefore, providers should be prepared to recommend PrEP to eligible patients, and seek training or continuing medical education for themselves so they feel equipped to prescribe and counsel patients on PrEP, she said.
“One limitation of this work is that, while it can point to what is happening, it cannot tell us why the reversals are happening; what is the reason patients prescribed by certain providers are more or less likely to get their PrEP,” Dr. Dean explained. “We have tried to do interviews with patients to understand why this might be happening, but it’s hard to find people who aren’t showing up to do something, compared to finding people who are showing up to do something,” she said. Alternatively, researchers could interview providers to understand their perspective on why differences in prescription pickups occur across specialties, she said.
Looking ahead, “a national PrEP program that includes elements of required clinician training could be beneficial, and research on how a national PrEP program could be implemented and impact HIV rates would be helpful in considering this strategy of prevention,” said Dr. Dean.
Support All Prescribers to Increase PrEP Adherence
Differences in uptake of PrEP prescriptions may be explained by the different populations seen by various specialties, Meredith Green, MD, of Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, and Lona Mody, MD, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, wrote in an accompanying editorial. However, the key question is how to support all prescribers and promote initiation and adherence to PrEP, they said.
Considerations include whether people at risk for HIV prefer to discuss PrEP with a clinician they already know, vs. a new specialist, but many PCPs are not familiar with the latest PrEP guidelines, they said.
“Interventions that support PrEP provision by PCPs, especially since they prescribed the largest proportion of PrEP prescriptions, can accelerate the uptake of PrEP,” the editorialists wrote.
“Supporting a diverse clinician workforce reflective of communities most impacted by HIV will remain critical, as will acknowledging and addressing HIV stigma,” they said. Educational interventions, including online programs and specialist access for complex cases, would help as well, they said. The approval of additional PrEP agents since the current study was conducted make it even more important to support PrEP prescribers and promote treatment adherence for those at risk for HIV, Dr. Green and Dr. Mody emphasized.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dean had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Green disclosed grants from Gilead and royalties from Wolters Kluwer unrelated to the current study; she also disclosed serving on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Health Resources and Services Administration advisory committee on HIV, viral hepatitis, and sexually transmitted infection prevention and treatment. Dr. Mody disclosed grants from the US National Institute on Aging, Veterans Affairs, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, NanoVibronix, and UpToDate unrelated to the current study.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
Low HPV Vaccination in the United States Is a Public Health ‘Failure’
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss what I consider to be a very discouraging report and one that I believe we as an oncology society and, quite frankly, as a medical community need to deal with.
The manuscript I’m referring to is from the United States Department of Health and Human Services, titled, “Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Coverage in Children Ages 9-17 Years: United States, 2022.” This particular analysis looked at the coverage of both men and women — young boys and young girls, I would say — receiving at least one dose of the recommended human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination.
Since 2006, girls have been recommended to receive HPV vaccination; for boys, it’s been since 2011. Certainly, the time period that we’re considering falls within the recommendations based on overwhelmingly positive data. Now, today, still, the recommendation is for more than one vaccine. Obviously, there may be evidence in the future that a single vaccination may be acceptable or appropriate. But today, it’s more than one.
In this particular analysis, they were looking at just a single vaccination. The vaccines have targeted young individuals, both male and female children aged 11-12 years, but it’s certainly acceptable to look starting at age 9.
What is the bottom line? At least one dose of the HPV vaccination was given to 38.6% of children aged 9-17 years in 2022. We are talking about a cancer-preventive vaccine, which on the basis of population-based data in the United States, but also in other countries, is incredibly effective in preventing HPV-associated cancers. This not only includes cervical cancer, but also a large percentage of head and neck cancers.
For this vaccine, which is incredibly safe and incredibly effective, in this country, only 38.6% have received even a single dose. It is noted that the individuals with private insurance had a higher rate, at 41.5%, than individuals with no insurance, at only 20.7%.
In my opinion, this is clearly a failure of our public health establishment at all levels. My own focus has been in gynecologic cancers. I’ve seen young women with advanced cervical cancer, and this is a disease we can prevent. Yet, this is where we are.
For those of you who are interested in cancer prevention or public health, I think this is a very sobering statistic. It’s my plea and my hope that we can, as a society, somehow do something about it.
I thank you for listening. I would encourage you to think about this question if you’re in this area.
Dr. Markman, professor, Department of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix, disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss what I consider to be a very discouraging report and one that I believe we as an oncology society and, quite frankly, as a medical community need to deal with.
The manuscript I’m referring to is from the United States Department of Health and Human Services, titled, “Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Coverage in Children Ages 9-17 Years: United States, 2022.” This particular analysis looked at the coverage of both men and women — young boys and young girls, I would say — receiving at least one dose of the recommended human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination.
Since 2006, girls have been recommended to receive HPV vaccination; for boys, it’s been since 2011. Certainly, the time period that we’re considering falls within the recommendations based on overwhelmingly positive data. Now, today, still, the recommendation is for more than one vaccine. Obviously, there may be evidence in the future that a single vaccination may be acceptable or appropriate. But today, it’s more than one.
In this particular analysis, they were looking at just a single vaccination. The vaccines have targeted young individuals, both male and female children aged 11-12 years, but it’s certainly acceptable to look starting at age 9.
What is the bottom line? At least one dose of the HPV vaccination was given to 38.6% of children aged 9-17 years in 2022. We are talking about a cancer-preventive vaccine, which on the basis of population-based data in the United States, but also in other countries, is incredibly effective in preventing HPV-associated cancers. This not only includes cervical cancer, but also a large percentage of head and neck cancers.
For this vaccine, which is incredibly safe and incredibly effective, in this country, only 38.6% have received even a single dose. It is noted that the individuals with private insurance had a higher rate, at 41.5%, than individuals with no insurance, at only 20.7%.
In my opinion, this is clearly a failure of our public health establishment at all levels. My own focus has been in gynecologic cancers. I’ve seen young women with advanced cervical cancer, and this is a disease we can prevent. Yet, this is where we are.
For those of you who are interested in cancer prevention or public health, I think this is a very sobering statistic. It’s my plea and my hope that we can, as a society, somehow do something about it.
I thank you for listening. I would encourage you to think about this question if you’re in this area.
Dr. Markman, professor, Department of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix, disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
I would like to briefly discuss what I consider to be a very discouraging report and one that I believe we as an oncology society and, quite frankly, as a medical community need to deal with.
The manuscript I’m referring to is from the United States Department of Health and Human Services, titled, “Human Papillomavirus Vaccination Coverage in Children Ages 9-17 Years: United States, 2022.” This particular analysis looked at the coverage of both men and women — young boys and young girls, I would say — receiving at least one dose of the recommended human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination.
Since 2006, girls have been recommended to receive HPV vaccination; for boys, it’s been since 2011. Certainly, the time period that we’re considering falls within the recommendations based on overwhelmingly positive data. Now, today, still, the recommendation is for more than one vaccine. Obviously, there may be evidence in the future that a single vaccination may be acceptable or appropriate. But today, it’s more than one.
In this particular analysis, they were looking at just a single vaccination. The vaccines have targeted young individuals, both male and female children aged 11-12 years, but it’s certainly acceptable to look starting at age 9.
What is the bottom line? At least one dose of the HPV vaccination was given to 38.6% of children aged 9-17 years in 2022. We are talking about a cancer-preventive vaccine, which on the basis of population-based data in the United States, but also in other countries, is incredibly effective in preventing HPV-associated cancers. This not only includes cervical cancer, but also a large percentage of head and neck cancers.
For this vaccine, which is incredibly safe and incredibly effective, in this country, only 38.6% have received even a single dose. It is noted that the individuals with private insurance had a higher rate, at 41.5%, than individuals with no insurance, at only 20.7%.
In my opinion, this is clearly a failure of our public health establishment at all levels. My own focus has been in gynecologic cancers. I’ve seen young women with advanced cervical cancer, and this is a disease we can prevent. Yet, this is where we are.
For those of you who are interested in cancer prevention or public health, I think this is a very sobering statistic. It’s my plea and my hope that we can, as a society, somehow do something about it.
I thank you for listening. I would encourage you to think about this question if you’re in this area.
Dr. Markman, professor, Department of Medical Oncology and Therapeutics Research, City of Hope, Duarte, California, and president of Medicine & Science, City of Hope Atlanta, Chicago, and Phoenix, disclosed ties with GlaxoSmithKline and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Predicting RSV’s Role in the Upcoming Winter Respiratory Season
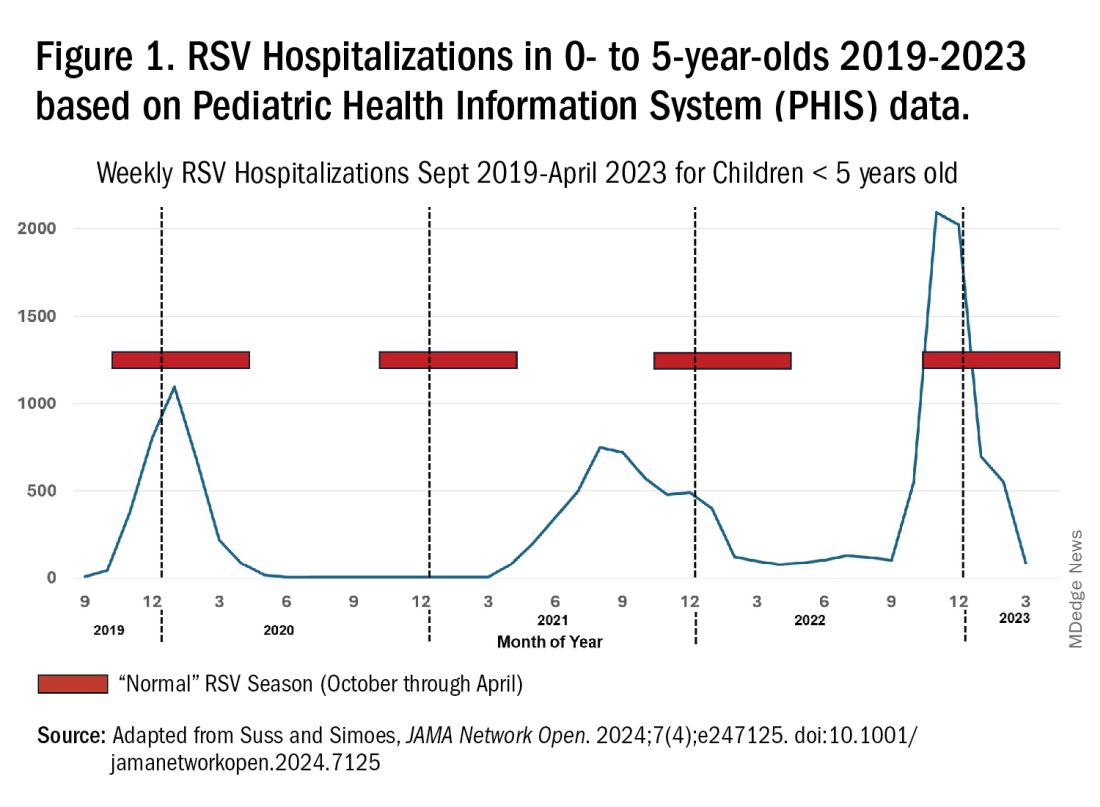
For children younger than 5 years old, RSV is the main drive — approximately 2,000,000 outpatient/ED visits and about 75,000 hospitalizations annually. RSV disease ranges from upper respiratory tract infections, eg, in older children and healthy adults, to more severe lower tract disease in young children and the elderly. Premature infants and high-risk groups are particularly prone to severe disease.1 Up to 300 pediatric RSV deaths occur yearly. “Normal” RSV seasons start in mid-November, peak in late December-January, and end after April. Note: More drawn out seasons occur in southern latitudes, eg Texas or Florida. But lately RSV seasons have been anything but normal.
2015-2016 to 2022-2023
RSV data from the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS), collected at over 49 US children’s hospitals during 2015 to early 2023, show how crazy RSV seasons have been lately.2 The involved months, intensity, and duration of four prepandemic seasons were pretty “normal” (Figure 1). The 2019-2020 season started normally, peaked in January 2020, and was slowing as expected by February. But when SARS-Cov-2 restrictions kicked in during mid-March, RSV detections tanked to almost nothing (ditto other respiratory viruses). A near 14-month RSV hiatus meant that the 2020-2021 RSV season never materialized. However, RSV was not done with us in 2021. It rebounded in May with weekly hospitalizations peaking in late July; this “rebound season” lasted 9 months, not dropping to baseline until February 2022 (Figure 1).
I guess we should have expected a post-pandemic “disturbance in the Force,” as Yoda once said; but I sure didn’t see a prolonged summer/fall/early winter RSV season coming. It was like two “normal” seasons mashed up into one late-but-long season. Not to be outdone, the 2022-2023 RSV season started early (September) and hospitalizations skyrocketed to peak in November at over twice the peak number from any year since 2015, overloading hospitals (influenza and SARS-Cov-2 seasons were co-circulating). The season terminated early though (March 2023).
Okay, so RSV seasonality/intensity were weird post pandemic, but was anything else different? Some 2021-2023 data suggest more RSV disease in older children, rather than the usual younger than 18 month-olds going through their first winter.3 More medically attended RSV in older ages (2-4 years of life) may have been due to the pandemic year without RSV circulation distorting herd immunity, ie older children remained RSV naive. Other data suggest the apparent increase was really just more frequent multiplex viral testing in older children triggered by SARS-CoV-2 co-circulation.4 More data are needed to decide.
CDC 2023-2024 RESP-NET data
The 2023-2024 winter surge (Figure 2), as measured by RESP-NET’s cumulative RSV,influenza and SARS-CoV-2 hospitalization rates for 0- to 5-year-olds,5 shows that all three viruses’ seasonal months were normal-ish: late October 2023 start, late December-early January peak, and mid-May 2024 return to baseline. RSV season was approximately 22% less severe by area-under-the-curve calculations compared with 2022-2023, but still worse than prepandemic years.6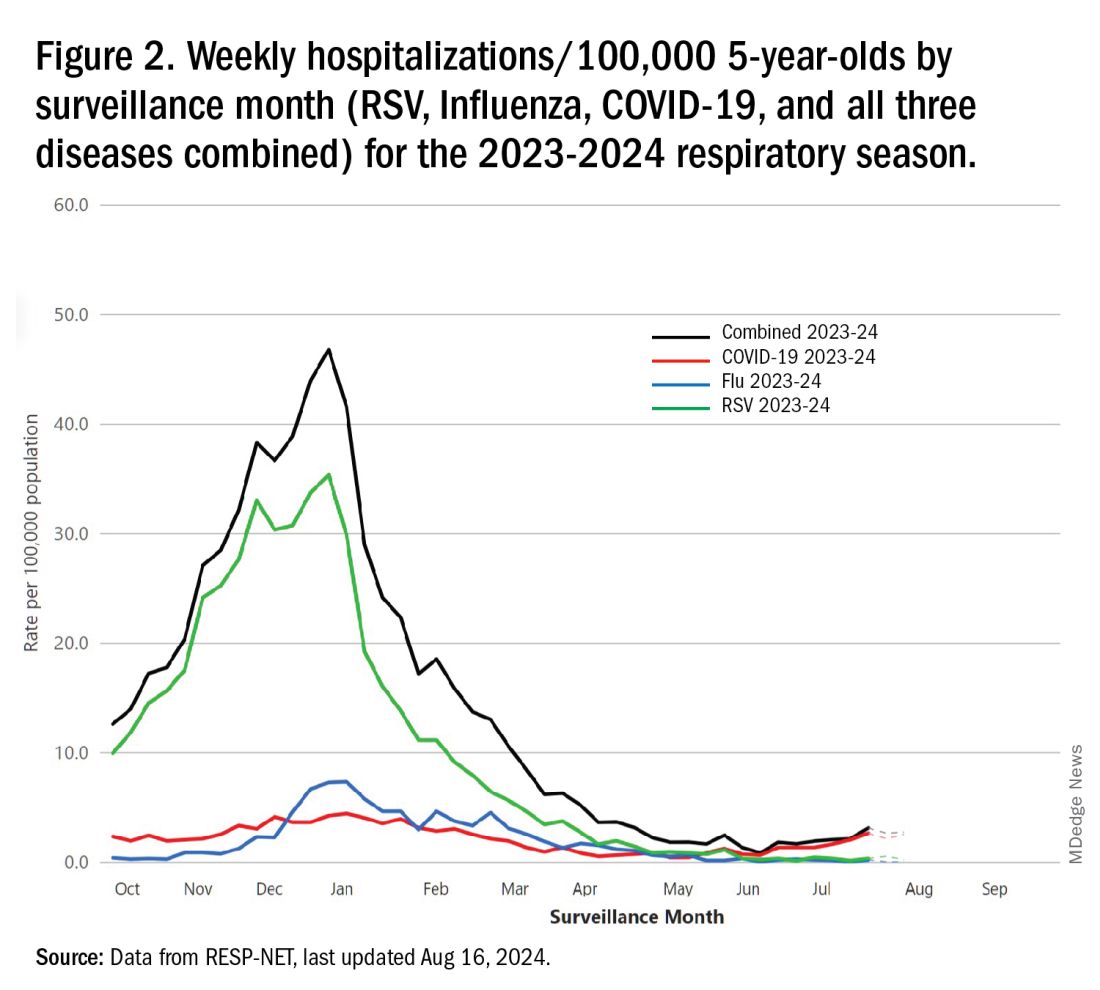
One wonders if the 2022-2023 RSV season might have been worse but for use of the limited supply of nirsevimab.7
Viral Parade
Now we ready ourselves for the 2024-2025 respiratory surge, wondering what nature has in store for us. Will the usual “respiratory virus parade” occur? Will rhinovirus and parainfluenza prevalence bump after a few weeks of schools being in session, adding to the now-usual summer/fall SARS-CoV-2 surge? Note: Twenty-seven states as of Aug. 16 had high SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater. Will RSV and influenza start sometime in October/November, peak in January (along with rising SARS-CoV2 activity), followed by a second parainfluenza bump as SARS-CoV-2, influenza, and RSV drop off in April/May? Further, will RSV and influenza seasons be more or less severe than the last 2 years?
Prediction
The overall 2024-2025 respiratory season will be less severe than the past 2 years and hopefully than recent prepandemic years. What is the blueprint for a milder season? First, herd immunity to non-RSV and non-influenza viruses (parainfluenza, rhinovirus, metapneumovirus, adenovirus) in older children should be normalized after 2 years back to usual social activity. So, I expect no mega-seasons from them. The emerging SARS-CoV-2 virus (LB.1) is immunologically close to its recent still-circulating ancestors (KP.2, KP.2.3, KP.3 and KP.3.1.1), so existing SARS-CoV2 herd immunity along with recommended booster vaccine uptake should keep the lid on SARS-CoV2.
Influenza Could Be the Bad News
Which type will dominate? Will a drift/shift occur or vaccine-mismatch reduce vaccine effectiveness? Can we get at least half the population influenza vaccinated, given the vaccine fatigue permeating the US population? The influenza season now underway in the Southern Hemisphere usually helps us predict our season. The Australian May-August 2024 experience (still on an upward trajectory for severity in mid-August) saw no drift/shift or vaccine mismatch. However, this 2024 season has been as severe as 2022 (their worst in a decade). That said, more than 95% has been type A (mostly H1N1 but H3N2 increased in July). So, if our overall 2024-2025 respiratory season is not milder, influenza is the most likely culprit. To reduce chances of influenza being the fly-in-the-ointment, we need to be particularly proactive with seasonal influenza vaccine which is back to the traditional trivalent formulation (one H1N1, one H3N2, and one B type).8 All of this could go out the window if avian influenza becomes more transmissible, but that seems unlikely at present.
Mild RSV Season?
RSV season should be blunted because of the increased use of both the remarkably effective CDC-recommended maternal RSV vaccine9 (one dose during pregnancy weeks 32 through 36, administered September through January) and of nirsevimab (up to 90% reduction in hospitalizations and ED visits).10 (See Figure 3.) 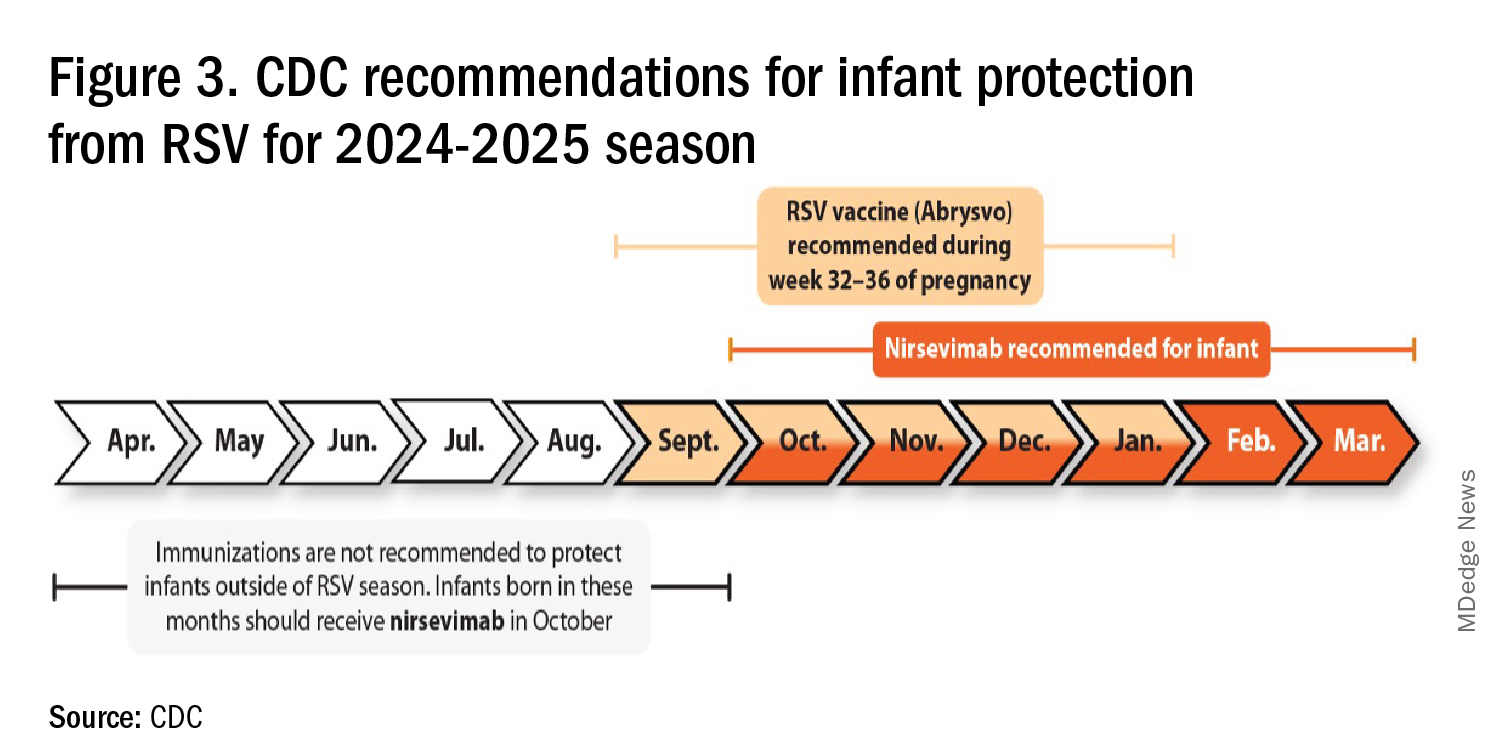
I also expect residual disease to occur mostly in younger than 18 month-olds (the “normal” aged population experiencing their first winter), who received no passive immunity (mother RSV unvaccinated and child did not receive nirsevimab). Some disease will still occur in high-risk infants/children. However, unlike active vaccination strategies, a competent immune system is not required to benefit from passive antibody, whether transplacental or directly administered.
Deep Thought
What if the traditional RSV seasonal hospitalization surge fails to materialize this season? It could happen. If we could get high acceptance/uptake of maternal vaccine and infant nirsevimab, RSV season could resemble the dramatic drop in rotavirus disease the second year after rotavirus vaccine introduction. We could be asking ourselves — “What happened to RSV?”
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. CDC. RSV in Infants and Young Children. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection (RSV). June 18, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/infants-young-children/index.html.
2. Suss RJ and Simões EAF. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospital-Based Burden of Disease in Children Younger Than 5 Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospital-Based Burden of Disease in Children Younger Than 5 Years, 2015-2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247125. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7125.
3. Winthrop ZA et al. Pediatric Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospitalizations and Respiratory Support After the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(6):e2416852. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16852.
4. Petros BA et al. Increased Pediatric RSV Case Counts Following the Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Are Attributable to Increased Testing. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 12:2024.02.06.24302387. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.06.24302387.
5. Rates of Laboratory-Confirmed RSV, COVID-19, and Flu Hospitalizations from the RESP-NET Surveillance Systems. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://data.cdc.gov/Public-Health-Surveillance/Rates-of-Laboratory-Confirmed-RSV-COVID-19-and-Flu/kvib-3txy/about_data.
6. CDC. Evaluating the 2023-2024 Respiratory Disease Season Outlook. CFA: Qualitative Assessments. August 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/cfa-qualitative-assessments/php/data-research/2023-2024-season-outlook-retro.html.
7. Health Alert Network (HAN). Limited Availability of Nirsevimab in the United States—Interim CDC Recommendations to Protect Infants from Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) during the 2023–2024 Respiratory Virus Season. October 23, 2023. https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2023/han00499.asp.
8. CDC. Information for the 2024-2025 Flu Season. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. March 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/season/faq-flu-season-2024-2025.htm.
9. Kampmann B et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N Engl J Med. 2023 Apr 20;388(16):1451-1464. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2216480.
10. Moline HL. Early Estimate of Nirsevimab Effectiveness for Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus–Associated Hospitalization Among Infants Entering Their First Respiratory Syncytial Virus Season — New Vaccine Surveillance Network, October 2023–February 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7309a4.
For children younger than 5 years old, RSV is the main drive — approximately 2,000,000 outpatient/ED visits and about 75,000 hospitalizations annually. RSV disease ranges from upper respiratory tract infections, eg, in older children and healthy adults, to more severe lower tract disease in young children and the elderly. Premature infants and high-risk groups are particularly prone to severe disease.1 Up to 300 pediatric RSV deaths occur yearly. “Normal” RSV seasons start in mid-November, peak in late December-January, and end after April. Note: More drawn out seasons occur in southern latitudes, eg Texas or Florida. But lately RSV seasons have been anything but normal.
2015-2016 to 2022-2023
RSV data from the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS), collected at over 49 US children’s hospitals during 2015 to early 2023, show how crazy RSV seasons have been lately.2 The involved months, intensity, and duration of four prepandemic seasons were pretty “normal” (Figure 1). The 2019-2020 season started normally, peaked in January 2020, and was slowing as expected by February. But when SARS-Cov-2 restrictions kicked in during mid-March, RSV detections tanked to almost nothing (ditto other respiratory viruses). A near 14-month RSV hiatus meant that the 2020-2021 RSV season never materialized. However, RSV was not done with us in 2021. It rebounded in May with weekly hospitalizations peaking in late July; this “rebound season” lasted 9 months, not dropping to baseline until February 2022 (Figure 1).
I guess we should have expected a post-pandemic “disturbance in the Force,” as Yoda once said; but I sure didn’t see a prolonged summer/fall/early winter RSV season coming. It was like two “normal” seasons mashed up into one late-but-long season. Not to be outdone, the 2022-2023 RSV season started early (September) and hospitalizations skyrocketed to peak in November at over twice the peak number from any year since 2015, overloading hospitals (influenza and SARS-Cov-2 seasons were co-circulating). The season terminated early though (March 2023).
Okay, so RSV seasonality/intensity were weird post pandemic, but was anything else different? Some 2021-2023 data suggest more RSV disease in older children, rather than the usual younger than 18 month-olds going through their first winter.3 More medically attended RSV in older ages (2-4 years of life) may have been due to the pandemic year without RSV circulation distorting herd immunity, ie older children remained RSV naive. Other data suggest the apparent increase was really just more frequent multiplex viral testing in older children triggered by SARS-CoV-2 co-circulation.4 More data are needed to decide.
CDC 2023-2024 RESP-NET data
The 2023-2024 winter surge (Figure 2), as measured by RESP-NET’s cumulative RSV,influenza and SARS-CoV-2 hospitalization rates for 0- to 5-year-olds,5 shows that all three viruses’ seasonal months were normal-ish: late October 2023 start, late December-early January peak, and mid-May 2024 return to baseline. RSV season was approximately 22% less severe by area-under-the-curve calculations compared with 2022-2023, but still worse than prepandemic years.6
One wonders if the 2022-2023 RSV season might have been worse but for use of the limited supply of nirsevimab.7
Viral Parade
Now we ready ourselves for the 2024-2025 respiratory surge, wondering what nature has in store for us. Will the usual “respiratory virus parade” occur? Will rhinovirus and parainfluenza prevalence bump after a few weeks of schools being in session, adding to the now-usual summer/fall SARS-CoV-2 surge? Note: Twenty-seven states as of Aug. 16 had high SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater. Will RSV and influenza start sometime in October/November, peak in January (along with rising SARS-CoV2 activity), followed by a second parainfluenza bump as SARS-CoV-2, influenza, and RSV drop off in April/May? Further, will RSV and influenza seasons be more or less severe than the last 2 years?
Prediction
The overall 2024-2025 respiratory season will be less severe than the past 2 years and hopefully than recent prepandemic years. What is the blueprint for a milder season? First, herd immunity to non-RSV and non-influenza viruses (parainfluenza, rhinovirus, metapneumovirus, adenovirus) in older children should be normalized after 2 years back to usual social activity. So, I expect no mega-seasons from them. The emerging SARS-CoV-2 virus (LB.1) is immunologically close to its recent still-circulating ancestors (KP.2, KP.2.3, KP.3 and KP.3.1.1), so existing SARS-CoV2 herd immunity along with recommended booster vaccine uptake should keep the lid on SARS-CoV2.
Influenza Could Be the Bad News
Which type will dominate? Will a drift/shift occur or vaccine-mismatch reduce vaccine effectiveness? Can we get at least half the population influenza vaccinated, given the vaccine fatigue permeating the US population? The influenza season now underway in the Southern Hemisphere usually helps us predict our season. The Australian May-August 2024 experience (still on an upward trajectory for severity in mid-August) saw no drift/shift or vaccine mismatch. However, this 2024 season has been as severe as 2022 (their worst in a decade). That said, more than 95% has been type A (mostly H1N1 but H3N2 increased in July). So, if our overall 2024-2025 respiratory season is not milder, influenza is the most likely culprit. To reduce chances of influenza being the fly-in-the-ointment, we need to be particularly proactive with seasonal influenza vaccine which is back to the traditional trivalent formulation (one H1N1, one H3N2, and one B type).8 All of this could go out the window if avian influenza becomes more transmissible, but that seems unlikely at present.
Mild RSV Season?
RSV season should be blunted because of the increased use of both the remarkably effective CDC-recommended maternal RSV vaccine9 (one dose during pregnancy weeks 32 through 36, administered September through January) and of nirsevimab (up to 90% reduction in hospitalizations and ED visits).10 (See Figure 3.) 
I also expect residual disease to occur mostly in younger than 18 month-olds (the “normal” aged population experiencing their first winter), who received no passive immunity (mother RSV unvaccinated and child did not receive nirsevimab). Some disease will still occur in high-risk infants/children. However, unlike active vaccination strategies, a competent immune system is not required to benefit from passive antibody, whether transplacental or directly administered.
Deep Thought
What if the traditional RSV seasonal hospitalization surge fails to materialize this season? It could happen. If we could get high acceptance/uptake of maternal vaccine and infant nirsevimab, RSV season could resemble the dramatic drop in rotavirus disease the second year after rotavirus vaccine introduction. We could be asking ourselves — “What happened to RSV?”
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. CDC. RSV in Infants and Young Children. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection (RSV). June 18, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/infants-young-children/index.html.
2. Suss RJ and Simões EAF. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospital-Based Burden of Disease in Children Younger Than 5 Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospital-Based Burden of Disease in Children Younger Than 5 Years, 2015-2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247125. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7125.
3. Winthrop ZA et al. Pediatric Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospitalizations and Respiratory Support After the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(6):e2416852. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16852.
4. Petros BA et al. Increased Pediatric RSV Case Counts Following the Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Are Attributable to Increased Testing. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 12:2024.02.06.24302387. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.06.24302387.
5. Rates of Laboratory-Confirmed RSV, COVID-19, and Flu Hospitalizations from the RESP-NET Surveillance Systems. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://data.cdc.gov/Public-Health-Surveillance/Rates-of-Laboratory-Confirmed-RSV-COVID-19-and-Flu/kvib-3txy/about_data.
6. CDC. Evaluating the 2023-2024 Respiratory Disease Season Outlook. CFA: Qualitative Assessments. August 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/cfa-qualitative-assessments/php/data-research/2023-2024-season-outlook-retro.html.
7. Health Alert Network (HAN). Limited Availability of Nirsevimab in the United States—Interim CDC Recommendations to Protect Infants from Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) during the 2023–2024 Respiratory Virus Season. October 23, 2023. https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2023/han00499.asp.
8. CDC. Information for the 2024-2025 Flu Season. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. March 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/season/faq-flu-season-2024-2025.htm.
9. Kampmann B et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N Engl J Med. 2023 Apr 20;388(16):1451-1464. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2216480.
10. Moline HL. Early Estimate of Nirsevimab Effectiveness for Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus–Associated Hospitalization Among Infants Entering Their First Respiratory Syncytial Virus Season — New Vaccine Surveillance Network, October 2023–February 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7309a4.
For children younger than 5 years old, RSV is the main drive — approximately 2,000,000 outpatient/ED visits and about 75,000 hospitalizations annually. RSV disease ranges from upper respiratory tract infections, eg, in older children and healthy adults, to more severe lower tract disease in young children and the elderly. Premature infants and high-risk groups are particularly prone to severe disease.1 Up to 300 pediatric RSV deaths occur yearly. “Normal” RSV seasons start in mid-November, peak in late December-January, and end after April. Note: More drawn out seasons occur in southern latitudes, eg Texas or Florida. But lately RSV seasons have been anything but normal.
2015-2016 to 2022-2023
RSV data from the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS), collected at over 49 US children’s hospitals during 2015 to early 2023, show how crazy RSV seasons have been lately.2 The involved months, intensity, and duration of four prepandemic seasons were pretty “normal” (Figure 1). The 2019-2020 season started normally, peaked in January 2020, and was slowing as expected by February. But when SARS-Cov-2 restrictions kicked in during mid-March, RSV detections tanked to almost nothing (ditto other respiratory viruses). A near 14-month RSV hiatus meant that the 2020-2021 RSV season never materialized. However, RSV was not done with us in 2021. It rebounded in May with weekly hospitalizations peaking in late July; this “rebound season” lasted 9 months, not dropping to baseline until February 2022 (Figure 1).
I guess we should have expected a post-pandemic “disturbance in the Force,” as Yoda once said; but I sure didn’t see a prolonged summer/fall/early winter RSV season coming. It was like two “normal” seasons mashed up into one late-but-long season. Not to be outdone, the 2022-2023 RSV season started early (September) and hospitalizations skyrocketed to peak in November at over twice the peak number from any year since 2015, overloading hospitals (influenza and SARS-Cov-2 seasons were co-circulating). The season terminated early though (March 2023).
Okay, so RSV seasonality/intensity were weird post pandemic, but was anything else different? Some 2021-2023 data suggest more RSV disease in older children, rather than the usual younger than 18 month-olds going through their first winter.3 More medically attended RSV in older ages (2-4 years of life) may have been due to the pandemic year without RSV circulation distorting herd immunity, ie older children remained RSV naive. Other data suggest the apparent increase was really just more frequent multiplex viral testing in older children triggered by SARS-CoV-2 co-circulation.4 More data are needed to decide.
CDC 2023-2024 RESP-NET data
The 2023-2024 winter surge (Figure 2), as measured by RESP-NET’s cumulative RSV,influenza and SARS-CoV-2 hospitalization rates for 0- to 5-year-olds,5 shows that all three viruses’ seasonal months were normal-ish: late October 2023 start, late December-early January peak, and mid-May 2024 return to baseline. RSV season was approximately 22% less severe by area-under-the-curve calculations compared with 2022-2023, but still worse than prepandemic years.6
One wonders if the 2022-2023 RSV season might have been worse but for use of the limited supply of nirsevimab.7
Viral Parade
Now we ready ourselves for the 2024-2025 respiratory surge, wondering what nature has in store for us. Will the usual “respiratory virus parade” occur? Will rhinovirus and parainfluenza prevalence bump after a few weeks of schools being in session, adding to the now-usual summer/fall SARS-CoV-2 surge? Note: Twenty-seven states as of Aug. 16 had high SARS-CoV-2 detection in wastewater. Will RSV and influenza start sometime in October/November, peak in January (along with rising SARS-CoV2 activity), followed by a second parainfluenza bump as SARS-CoV-2, influenza, and RSV drop off in April/May? Further, will RSV and influenza seasons be more or less severe than the last 2 years?
Prediction
The overall 2024-2025 respiratory season will be less severe than the past 2 years and hopefully than recent prepandemic years. What is the blueprint for a milder season? First, herd immunity to non-RSV and non-influenza viruses (parainfluenza, rhinovirus, metapneumovirus, adenovirus) in older children should be normalized after 2 years back to usual social activity. So, I expect no mega-seasons from them. The emerging SARS-CoV-2 virus (LB.1) is immunologically close to its recent still-circulating ancestors (KP.2, KP.2.3, KP.3 and KP.3.1.1), so existing SARS-CoV2 herd immunity along with recommended booster vaccine uptake should keep the lid on SARS-CoV2.
Influenza Could Be the Bad News
Which type will dominate? Will a drift/shift occur or vaccine-mismatch reduce vaccine effectiveness? Can we get at least half the population influenza vaccinated, given the vaccine fatigue permeating the US population? The influenza season now underway in the Southern Hemisphere usually helps us predict our season. The Australian May-August 2024 experience (still on an upward trajectory for severity in mid-August) saw no drift/shift or vaccine mismatch. However, this 2024 season has been as severe as 2022 (their worst in a decade). That said, more than 95% has been type A (mostly H1N1 but H3N2 increased in July). So, if our overall 2024-2025 respiratory season is not milder, influenza is the most likely culprit. To reduce chances of influenza being the fly-in-the-ointment, we need to be particularly proactive with seasonal influenza vaccine which is back to the traditional trivalent formulation (one H1N1, one H3N2, and one B type).8 All of this could go out the window if avian influenza becomes more transmissible, but that seems unlikely at present.
Mild RSV Season?
RSV season should be blunted because of the increased use of both the remarkably effective CDC-recommended maternal RSV vaccine9 (one dose during pregnancy weeks 32 through 36, administered September through January) and of nirsevimab (up to 90% reduction in hospitalizations and ED visits).10 (See Figure 3.) 
I also expect residual disease to occur mostly in younger than 18 month-olds (the “normal” aged population experiencing their first winter), who received no passive immunity (mother RSV unvaccinated and child did not receive nirsevimab). Some disease will still occur in high-risk infants/children. However, unlike active vaccination strategies, a competent immune system is not required to benefit from passive antibody, whether transplacental or directly administered.
Deep Thought
What if the traditional RSV seasonal hospitalization surge fails to materialize this season? It could happen. If we could get high acceptance/uptake of maternal vaccine and infant nirsevimab, RSV season could resemble the dramatic drop in rotavirus disease the second year after rotavirus vaccine introduction. We could be asking ourselves — “What happened to RSV?”
Dr. Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. CDC. RSV in Infants and Young Children. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection (RSV). June 18, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/rsv/infants-young-children/index.html.
2. Suss RJ and Simões EAF. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospital-Based Burden of Disease in Children Younger Than 5 Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospital-Based Burden of Disease in Children Younger Than 5 Years, 2015-2022. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(4):e247125. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.7125.
3. Winthrop ZA et al. Pediatric Respiratory Syncytial Virus Hospitalizations and Respiratory Support After the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2024;7(6):e2416852. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.16852.
4. Petros BA et al. Increased Pediatric RSV Case Counts Following the Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Are Attributable to Increased Testing. medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 12:2024.02.06.24302387. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.06.24302387.
5. Rates of Laboratory-Confirmed RSV, COVID-19, and Flu Hospitalizations from the RESP-NET Surveillance Systems. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://data.cdc.gov/Public-Health-Surveillance/Rates-of-Laboratory-Confirmed-RSV-COVID-19-and-Flu/kvib-3txy/about_data.
6. CDC. Evaluating the 2023-2024 Respiratory Disease Season Outlook. CFA: Qualitative Assessments. August 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/cfa-qualitative-assessments/php/data-research/2023-2024-season-outlook-retro.html.
7. Health Alert Network (HAN). Limited Availability of Nirsevimab in the United States—Interim CDC Recommendations to Protect Infants from Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) during the 2023–2024 Respiratory Virus Season. October 23, 2023. https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2023/han00499.asp.
8. CDC. Information for the 2024-2025 Flu Season. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. March 14, 2024. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/season/faq-flu-season-2024-2025.htm.
9. Kampmann B et al. Bivalent Prefusion F Vaccine in Pregnancy to Prevent RSV Illness in Infants. N Engl J Med. 2023 Apr 20;388(16):1451-1464. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2216480.
10. Moline HL. Early Estimate of Nirsevimab Effectiveness for Prevention of Respiratory Syncytial Virus–Associated Hospitalization Among Infants Entering Their First Respiratory Syncytial Virus Season — New Vaccine Surveillance Network, October 2023–February 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7309a4.
Doctors Are Seeking Professional Coaches More Often. Here’s Why
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When Andrea Austin, MD, an emergency medicine specialist, left the military in 2020, she knew the adjustment to civilian life and practice might be difficult. To help smooth the transition, she reached out to a physician mentor who also had a professional coaching certificate. After a conversation, Dr. Austin signed up for 6 months of career coaching.
It was time well spent, according to Dr. Austin, who today is a coach herself. “It was really the first time I had the ability to choose what I wanted to do, and that required a mindset shift,” she explains. “A big part of coaching is helping physicians discover their agency so that they can make the best career choices.”
Physicians have long lacked the coaching resources typically made available to corporate executives. But that’s changing. In today’s high-pressure environment, where doctors are burning out at a rapid pace, coaching can sometimes be an avenue to staying in the field, especially if that coach is a fellow physician who understands what you’re facing.
With a physician shortage that the Association of American Medical Colleges expects to hit 86,000 in the next decade or so, coaching could be a stone worth turning over. A 2024 report in JAMA Network Open found that coaching provided by physician peers led to a significant reduction in interpersonal disengagement and burnout.
“What I think is exciting about coaching is that it allows you to better understand yourself and know your strengths and weaknesses,” said Dr. Austin. “It might seem simple, but many ‘soft skills’ aren’t considered mainstream in medicine. Coaching allows us to understand them and ourselves better.”
Why Are Doctors Using Coaches?
Although it’s hard to put a number on how many physicians are turning to coaches, the number of coaches available for doctors is growing rapidly. The American Medical Women’s Association maintains a database of physician coaches. According to deputy director Jodi Godfrey, MS, RDN, the number of members who have added coaching to their skill set has tripled in the past 4 years. “Many cite burnout as the reason they sought coaching support, and then they decided to go on to get certified in coaching.”
The pandemic is one reason physician coaching has grown, said Elizabeth Esparaz, MD, an ophthalmologist and physician coach. “Since the pandemic, the word ‘burnout’ is thrown around a good deal.” And the causes are clear. “Doctors are facing longer hours, they must make split-second decisions, they’re multitasking, and they have less support staff.”
Among her coaching clients, Dr. Austin has noticed other common struggles: fears of litigation, time scarcity with patients, declining reimbursement that hasn’t kept up with inflation, and loss of autonomy because of the corporatization of healthcare.
Coaching, Dr. Esparaz believes, can be an antidote to many of these issues. “Coaches help doctors see their strengths and find better ways of applying them,” she said. “We help them move forward, and also see their blind spots.”
Clarity, Goals, and Making the Right Choices
Physician coaching comes in a variety of flavors — some one on one, and others in the form of group sessions. All, however, serve the purpose of helping physicians gain career clarity. “Sometimes clients realize their job may not be working for them, but that there are things they can do to change that without having to leave the field,” said Jattu Senesie, MD, a former ob.gyn. who is now a physician coach.
Dr. Esparaz works with doctors to establish SMART goals: specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time based. She gave the example of learning how to set boundaries. “If a physician is asked to create a presentation for work, I encourage them to ask for compensation or administrative time before committing to unpaid tasks.”
Another big issue: charting. It’s increasingly burdensome, and many doctors find it encroaching on their home lives. “If we can identify a problem like that, we can come up with a strategy for mitigating it,” Dr. Esparaz said. This might include setting a goal of getting 80% of charting completed immediately after the patient encounter on the busiest clinic day of the week. The client tests the experiment and then revisits it with the coach to discuss what worked and what didn’t, refining the process until it has freed up the physician’s home life.
The younger generation of doctors often struggles with career choices, too, because it’s the first time they are without structure, said Dr. Senesie. There’s med school and residency, which puts a framework around every move a doctor makes. But once they become attending physicians, the choices are endless. “Coaching can help them find a new structure and systems that will allow them to thrive.”
Although mentoring has been a well-embraced concept for decades, it “hits a wall,” at some point in terms of what it can offer, Dr. Austin said. That’s where coaching can take over. “There’s a point where a mentor cannot help someone self-actualize. As a coach, you don’t need to know everything about a doctor’s life, but you can help them learn to ask themselves the right questions to solve problems.”
Should You Stay or Should You Go?
Dr. Austin’s approach begins with the premise that healthcare today is challenging and dysfunctional — but doctors still have agency. She has worked with clients on the verge of leaving the field and helped them find their way back.
“They have a light bulb moment and open up to the idea that they have much to give still,” she said. “We take an inventory to help them better communicate their needs and make changes, and I help them connect to their values. Sometimes that exercise allows them to reframe their current work environment.”
Not every doctor who goes through coaching remains in the field. But “that’s the exception, not the rule,” Dr. Austin said. And that’s okay. “If that’s the outcome, coaching probably helped them get to that point faster, and with an informed decision.”
Dr. Senesie has been coaching for about a decade, and in that time, she’s seen a shift that goes beyond figuring out career goals. “Doctors are more aware of the need for well-being today. The pandemic made it impossible to ignore what doesn’t work for us. When I work with clients, we look for ways to make the job more tenable.”
According to Dr. Senesie, younger doctors are looking for that balance at the outset. “They want to be physicians, but they also want a life,” she said. “It’s a challenge for them because in addition to that mindset, they’re also coming out with more debt than older generations. They want out from underneath that.”
When It’s Time to Find a Physician Coach
Wondering whether coaching is right for you? Consider these symptoms:
- You need help setting boundaries at work.
- You feel like you’re sacrificing your own well-being for your job.
- You’re using maladaptive strategies to cope with the stress at work.
- You’ve reached a point where you are considering leaving the field.
If you’re interested in finding a physician coach, there are several places to begin your search, word of mouth being one of them. “Conferences and social media can also expose you to coaches,” suggested Dr. Esparaz. There are different methods and approaches to coaching. So, as you research, “make sure the coach you choose has techniques and a framework that fit what you’re after.”
Dr. Austin warned that it is an unregulated industry, so buyer beware. To ensure you’re getting an accredited physician coach, look for people who have obtained an International Coach Federation (ICF) accreditation. These coaches will hold an associate certified coach credential, which requires at least 60 hours of coaching-specific training approved by the ICF, in addition to other assessments and education.
Ensure that the coach you choose is within your budget. “There are some people charging astronomical rates out there,” Dr. Austin said. “If you’re burned out or struggling, it can be easy to reach for your credit card.”
Dr. Austin also cautioned doctors seeking a coach to avoid promises that sound too good to be true. Some coaching can have a gaslighting quality to it, she warned, “suggesting it can allow you to endure any environment.” But positive self-talk alone won’t cure an abusive or discriminatory situation. “If a client describes a toxic work environment,” the coach has an “ethical imperative” to help that person protect themselves.
A Side Gig or a New Career Path
After Dr. Austin’s experience with her coach, she made the choice to continue as an emergency physician part-time while starting her own coaching business. “It’s important for me personally to keep in touch with what’s happening on the ground, but I have no judgment for anyone who chooses to leave clinical practice to become a coach.”
When Dr. Senesie looks back on her own struggles as a clinician, she recognizes the state of burnout she was in 10 years ago. “I knew there was an issue, but I didn’t have the mindset to find a way to make it work,” she said. “I left the field when I was at my depths of burnout, which is generally not the best way to go about it.”
Guidance might have allowed her to take into account other avenues and helped her remain in the field, said Dr. Senesie. She has since learned that “there are many ways to practice medicine, and the way we’ve gone about it traditionally has worked for some, but not necessarily for everyone.”
There may be more possibilities than you think. By helping you assess your path and make meaningful changes, a physician coach might be the key to remaining in the field you love.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Whooping Cough Likely on Pace for a 5-Year High
Like many diseases, whooping cough reached record low levels during the early days of the COVID pandemic.
More than 10,000 cases of whooping cough have been reported in the United States so far this year, and weekly reports say cases have more than tripled 2023 levels as of June, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In 2023, there were 2815 cases reported during the entire year.
“The number of reported cases this year is close to what was seen at the same time in 2019, prior to the pandemic,” the CDC reported. There were 18,617 cases of whooping cough in 2019.
There were 259 cases reported nationwide for the week ending Aug. 3, with nearly half occurring in the mid-Atlantic region. Public health officials believe the resurgence of whooping cough is likely due to declining vaccination rates, mainly due to the missed vaccines during the height of the COVID pandemic. The diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccines (DTaP) have been given together since the 1940s, typically during infancy and again during early childhood. In 1941, there were more than 220,000 cases of whooping cough.
Whooping cough is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. The bacteria attach to tiny, hair-like extensions in the upper respiratory system called cilia, and toxins released by them damage the cilia and cause airways to swell. Early symptoms are similar to the common cold, but the condition eventually leads to coughing fits and a high-pitched “whoop” sound made when inhaling after a fit subsides. Coughing fits can be so severe that people can fracture a rib.
Vaccinated people may get a less severe illness, compared to unvaccinated people, the CDC says. Babies and children are particularly at risk for severe and even potentially deadly complications. About one in three babies under age 1 who get whooping cough will need to be hospitalized, and among those hospitalized babies, 1 in 100 die from complications.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Like many diseases, whooping cough reached record low levels during the early days of the COVID pandemic.
More than 10,000 cases of whooping cough have been reported in the United States so far this year, and weekly reports say cases have more than tripled 2023 levels as of June, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In 2023, there were 2815 cases reported during the entire year.
“The number of reported cases this year is close to what was seen at the same time in 2019, prior to the pandemic,” the CDC reported. There were 18,617 cases of whooping cough in 2019.
There were 259 cases reported nationwide for the week ending Aug. 3, with nearly half occurring in the mid-Atlantic region. Public health officials believe the resurgence of whooping cough is likely due to declining vaccination rates, mainly due to the missed vaccines during the height of the COVID pandemic. The diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccines (DTaP) have been given together since the 1940s, typically during infancy and again during early childhood. In 1941, there were more than 220,000 cases of whooping cough.
Whooping cough is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. The bacteria attach to tiny, hair-like extensions in the upper respiratory system called cilia, and toxins released by them damage the cilia and cause airways to swell. Early symptoms are similar to the common cold, but the condition eventually leads to coughing fits and a high-pitched “whoop” sound made when inhaling after a fit subsides. Coughing fits can be so severe that people can fracture a rib.
Vaccinated people may get a less severe illness, compared to unvaccinated people, the CDC says. Babies and children are particularly at risk for severe and even potentially deadly complications. About one in three babies under age 1 who get whooping cough will need to be hospitalized, and among those hospitalized babies, 1 in 100 die from complications.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
Like many diseases, whooping cough reached record low levels during the early days of the COVID pandemic.
More than 10,000 cases of whooping cough have been reported in the United States so far this year, and weekly reports say cases have more than tripled 2023 levels as of June, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). In 2023, there were 2815 cases reported during the entire year.
“The number of reported cases this year is close to what was seen at the same time in 2019, prior to the pandemic,” the CDC reported. There were 18,617 cases of whooping cough in 2019.
There were 259 cases reported nationwide for the week ending Aug. 3, with nearly half occurring in the mid-Atlantic region. Public health officials believe the resurgence of whooping cough is likely due to declining vaccination rates, mainly due to the missed vaccines during the height of the COVID pandemic. The diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccines (DTaP) have been given together since the 1940s, typically during infancy and again during early childhood. In 1941, there were more than 220,000 cases of whooping cough.
Whooping cough is caused by the bacteria Bordetella pertussis. The bacteria attach to tiny, hair-like extensions in the upper respiratory system called cilia, and toxins released by them damage the cilia and cause airways to swell. Early symptoms are similar to the common cold, but the condition eventually leads to coughing fits and a high-pitched “whoop” sound made when inhaling after a fit subsides. Coughing fits can be so severe that people can fracture a rib.
Vaccinated people may get a less severe illness, compared to unvaccinated people, the CDC says. Babies and children are particularly at risk for severe and even potentially deadly complications. About one in three babies under age 1 who get whooping cough will need to be hospitalized, and among those hospitalized babies, 1 in 100 die from complications.
A version of this article appeared on WebMD.com.
After Rapid Weight Loss, Monitor Antiobesity Drug Dosing
A patient who developed atrial fibrillation resulting from the failure to adjust the levothyroxine dose after rapid, significant weight loss while on the antiobesity drug tirzepatide (Zepbound) serves as a key reminder in managing patients experiencing rapid weight loss, either from antiobesity medications or any other means: Patients taking medications with weight-based dosing need to have their doses closely monitored.
“Failing to monitor and adjust dosing of these [and other] medications during a period of rapid weight loss may lead to supratherapeutic — even toxic — levels, as was seen in this [case],” underscore the authors of an editorial regarding the Teachable Moment case, published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Toxicities from excessive doses can have a range of detrimental effects. In terms of thyroid medicine, the failure to adjust levothyroxine treatment for hypothyroidism in cases of rapid weight loss can lead to thyrotoxicosis, and in older patients in particular, a resulting thyrotropin level < 0.1 mIU/L is associated with as much as a threefold increased risk for atrial fibrillation, as observed in the report.
Case Demonstrates Risks
The case involved a 62-year-old man with obesity, hypothyroidism, and type 1 diabetes who presented to the emergency department with palpitations, excessive sweating, confusion, fever, and hand tremors. Upon being diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, the patient was immediately treated.
His medical history revealed the underlying culprit: Six months earlier, the patient had started treatment with the gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/glucagon-like peptide (GLP) 1 dual agonist tirzepatide. As is typical with the drug, the patient’s weight quickly plummeted, dropping from a starting body mass index of 44.4 down to 31.2 after 6 months and a decrease in body weight from 132 kg to 93 kg (a loss of 39 kg [approximately 86 lb]).
When he was prescribed tirzepatide, 2.5 mg weekly, for obesity, the patient had been recommended to increase the dose every 4 weeks as tolerated and, importantly, to have a follow-up visit in a month. But because he lived in different states seasonally, the follow-up never occurred.
Upon his emergency department visit, the patient’s thyrotropin level had dropped from 1.9 mIU/L at the first visit 6 months earlier to 0.001 mIU/L (well within the atrial fibrillation risk range), and his free thyroxine level (fT4) was 7.26 ng/ dL — substantially outside of the normal range of about 0.9-1.7 ng/dL for adults.
“The patient had 4-times higher fT4 levels of the upper limit,” first author Kagan E. Karakus, MD, of the Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, told this news organization. “That is why he had experienced the adverse event of atrial fibrillation.”
Thyrotoxicosis Symptoms Can Be ‘Insidious,’ Levothyroxine Should Be Monitored
Although tirzepatide has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of type 1 diabetes, obesity is on the rise among patients with this disorder and recent research has shown a more than 10% reduction in body weight in 6 months and significant reductions in A1c with various doses.
Of note, in the current case, although the patient’s levothyroxine dose was not adjusted, his insulin dose was gradually self-decreased during his tirzepatide treatment to prevent hypoglycemia.
“If insulin treatment is excessive in diabetes, it causes hypoglycemia, [and] people with type 1 diabetes will recognize the signs of hypoglycemia related to excessive insulin earlier,” Dr. Karakus said.
If symptoms appear, patients can reduce their insulin doses on their own; however, the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis caused by excessive levothyroxine can be more insidious compared with hypoglycemia, he explained.
“Although patients can change their insulin doses, they cannot change the levothyroxine doses since it requires a blood test [thyroid-stimulating hormone; TSH] and a new prescription of the new dose.”
The key lesson is that “following levothyroxine treatment initiation or dose adjustment, 4-6 weeks is the optimal duration to recheck [the] thyrotropin level and adjust the dose as needed,” Dr. Karakus said.
Key Medications to Monitor
Other common outpatient medications that should be closely monitored in patients experiencing rapid weight loss, by any method, range from anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, and antituberculosis drugs to antibiotics and antifungals, the authors note.
Of note, medications with a narrow therapeutic index include phenytoin, warfarin, lithium carbonate, digoxin theophylline, tacrolimus, valproic acid, carbamazepine, and cyclosporine.
The failure to make necessary dose adjustments “is seen more often since the newer antiobesity drugs reduce a great amount of weight within months, almost as rapidly as bariatric surgery,” Dr. Karakus said.
“It is very important for physicians to be aware of the weight-based medications and narrow therapeutic index medications since their doses should be adjusted carefully, especially during weight loss,” he added.
Furthermore, “the patient should also know that weight reduction medication may cause adverse effects like nausea, vomiting and also may affect metabolism of other medications such that some medication doses should be adjusted regularly.”
In the editorial published with the study, Tyrone A. Johnson, MD, of the Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues note that the need for close monitoring is particularly important with older patients, who, in addition to having a higher likelihood of comorbidities, commonly have polypharmacy that could increase the potential for adverse effects.
Another key area concern is the emergence of direct-to-consumer avenues for GLP-1/GIP agonists for the many who either cannot afford or do not have access to the drugs, providing further opportunities for treatment without appropriate clinical oversight, they add.
Overall, the case “highlights the potential dangers underlying under-supervised prescribing of GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists and affirms the need for strong partnerships between patients and their clinicians during their use,” they wrote.
“These medications are best used in collaboration with continuity care teams, in context of a patient’s entire health, and in comprehensive risk-benefit assessment throughout the entire duration of treatment.”
A Caveat: Subclinical Levothyroxine Dosing
Commenting on the study, Matthew Ettleson, MD, a clinical instructor of medicine in the Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism, University of Chicago, noted the important caveat that patients with hypothyroidism are commonly on subclinical doses, with varying dose adjustment needs.
“The patient in the case was clearly on a replacement level dose. However, many patients are on low doses of levothyroxine (75 µg or lower) for subclinical hypothyroidism, and, in general, I think the risks are lower with patients with subclinical hypothyroidism on lower doses of levothyroxine,” he told this news organization.
Because of that, “frequent TSH monitoring may be excessive in this population,” he said. “I would hesitate to empirically lower the dose with weight loss, unless it was clear that the patient was unlikely to follow up.
“Checking TSH at a more frequent interval and adjusting the dose accordingly should be adequate to prevent situations like this case.”
Dr. Karakus, Dr. Ettleson, and the editorial authors had no relevant disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A patient who developed atrial fibrillation resulting from the failure to adjust the levothyroxine dose after rapid, significant weight loss while on the antiobesity drug tirzepatide (Zepbound) serves as a key reminder in managing patients experiencing rapid weight loss, either from antiobesity medications or any other means: Patients taking medications with weight-based dosing need to have their doses closely monitored.
“Failing to monitor and adjust dosing of these [and other] medications during a period of rapid weight loss may lead to supratherapeutic — even toxic — levels, as was seen in this [case],” underscore the authors of an editorial regarding the Teachable Moment case, published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Toxicities from excessive doses can have a range of detrimental effects. In terms of thyroid medicine, the failure to adjust levothyroxine treatment for hypothyroidism in cases of rapid weight loss can lead to thyrotoxicosis, and in older patients in particular, a resulting thyrotropin level < 0.1 mIU/L is associated with as much as a threefold increased risk for atrial fibrillation, as observed in the report.
Case Demonstrates Risks
The case involved a 62-year-old man with obesity, hypothyroidism, and type 1 diabetes who presented to the emergency department with palpitations, excessive sweating, confusion, fever, and hand tremors. Upon being diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, the patient was immediately treated.
His medical history revealed the underlying culprit: Six months earlier, the patient had started treatment with the gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/glucagon-like peptide (GLP) 1 dual agonist tirzepatide. As is typical with the drug, the patient’s weight quickly plummeted, dropping from a starting body mass index of 44.4 down to 31.2 after 6 months and a decrease in body weight from 132 kg to 93 kg (a loss of 39 kg [approximately 86 lb]).
When he was prescribed tirzepatide, 2.5 mg weekly, for obesity, the patient had been recommended to increase the dose every 4 weeks as tolerated and, importantly, to have a follow-up visit in a month. But because he lived in different states seasonally, the follow-up never occurred.
Upon his emergency department visit, the patient’s thyrotropin level had dropped from 1.9 mIU/L at the first visit 6 months earlier to 0.001 mIU/L (well within the atrial fibrillation risk range), and his free thyroxine level (fT4) was 7.26 ng/ dL — substantially outside of the normal range of about 0.9-1.7 ng/dL for adults.
“The patient had 4-times higher fT4 levels of the upper limit,” first author Kagan E. Karakus, MD, of the Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, told this news organization. “That is why he had experienced the adverse event of atrial fibrillation.”
Thyrotoxicosis Symptoms Can Be ‘Insidious,’ Levothyroxine Should Be Monitored
Although tirzepatide has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of type 1 diabetes, obesity is on the rise among patients with this disorder and recent research has shown a more than 10% reduction in body weight in 6 months and significant reductions in A1c with various doses.
Of note, in the current case, although the patient’s levothyroxine dose was not adjusted, his insulin dose was gradually self-decreased during his tirzepatide treatment to prevent hypoglycemia.
“If insulin treatment is excessive in diabetes, it causes hypoglycemia, [and] people with type 1 diabetes will recognize the signs of hypoglycemia related to excessive insulin earlier,” Dr. Karakus said.
If symptoms appear, patients can reduce their insulin doses on their own; however, the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis caused by excessive levothyroxine can be more insidious compared with hypoglycemia, he explained.
“Although patients can change their insulin doses, they cannot change the levothyroxine doses since it requires a blood test [thyroid-stimulating hormone; TSH] and a new prescription of the new dose.”
The key lesson is that “following levothyroxine treatment initiation or dose adjustment, 4-6 weeks is the optimal duration to recheck [the] thyrotropin level and adjust the dose as needed,” Dr. Karakus said.
Key Medications to Monitor
Other common outpatient medications that should be closely monitored in patients experiencing rapid weight loss, by any method, range from anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, and antituberculosis drugs to antibiotics and antifungals, the authors note.
Of note, medications with a narrow therapeutic index include phenytoin, warfarin, lithium carbonate, digoxin theophylline, tacrolimus, valproic acid, carbamazepine, and cyclosporine.
The failure to make necessary dose adjustments “is seen more often since the newer antiobesity drugs reduce a great amount of weight within months, almost as rapidly as bariatric surgery,” Dr. Karakus said.
“It is very important for physicians to be aware of the weight-based medications and narrow therapeutic index medications since their doses should be adjusted carefully, especially during weight loss,” he added.
Furthermore, “the patient should also know that weight reduction medication may cause adverse effects like nausea, vomiting and also may affect metabolism of other medications such that some medication doses should be adjusted regularly.”
In the editorial published with the study, Tyrone A. Johnson, MD, of the Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues note that the need for close monitoring is particularly important with older patients, who, in addition to having a higher likelihood of comorbidities, commonly have polypharmacy that could increase the potential for adverse effects.
Another key area concern is the emergence of direct-to-consumer avenues for GLP-1/GIP agonists for the many who either cannot afford or do not have access to the drugs, providing further opportunities for treatment without appropriate clinical oversight, they add.
Overall, the case “highlights the potential dangers underlying under-supervised prescribing of GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists and affirms the need for strong partnerships between patients and their clinicians during their use,” they wrote.
“These medications are best used in collaboration with continuity care teams, in context of a patient’s entire health, and in comprehensive risk-benefit assessment throughout the entire duration of treatment.”
A Caveat: Subclinical Levothyroxine Dosing
Commenting on the study, Matthew Ettleson, MD, a clinical instructor of medicine in the Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism, University of Chicago, noted the important caveat that patients with hypothyroidism are commonly on subclinical doses, with varying dose adjustment needs.
“The patient in the case was clearly on a replacement level dose. However, many patients are on low doses of levothyroxine (75 µg or lower) for subclinical hypothyroidism, and, in general, I think the risks are lower with patients with subclinical hypothyroidism on lower doses of levothyroxine,” he told this news organization.
Because of that, “frequent TSH monitoring may be excessive in this population,” he said. “I would hesitate to empirically lower the dose with weight loss, unless it was clear that the patient was unlikely to follow up.
“Checking TSH at a more frequent interval and adjusting the dose accordingly should be adequate to prevent situations like this case.”
Dr. Karakus, Dr. Ettleson, and the editorial authors had no relevant disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A patient who developed atrial fibrillation resulting from the failure to adjust the levothyroxine dose after rapid, significant weight loss while on the antiobesity drug tirzepatide (Zepbound) serves as a key reminder in managing patients experiencing rapid weight loss, either from antiobesity medications or any other means: Patients taking medications with weight-based dosing need to have their doses closely monitored.
“Failing to monitor and adjust dosing of these [and other] medications during a period of rapid weight loss may lead to supratherapeutic — even toxic — levels, as was seen in this [case],” underscore the authors of an editorial regarding the Teachable Moment case, published in JAMA Internal Medicine.
Toxicities from excessive doses can have a range of detrimental effects. In terms of thyroid medicine, the failure to adjust levothyroxine treatment for hypothyroidism in cases of rapid weight loss can lead to thyrotoxicosis, and in older patients in particular, a resulting thyrotropin level < 0.1 mIU/L is associated with as much as a threefold increased risk for atrial fibrillation, as observed in the report.
Case Demonstrates Risks
The case involved a 62-year-old man with obesity, hypothyroidism, and type 1 diabetes who presented to the emergency department with palpitations, excessive sweating, confusion, fever, and hand tremors. Upon being diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, the patient was immediately treated.
His medical history revealed the underlying culprit: Six months earlier, the patient had started treatment with the gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP)/glucagon-like peptide (GLP) 1 dual agonist tirzepatide. As is typical with the drug, the patient’s weight quickly plummeted, dropping from a starting body mass index of 44.4 down to 31.2 after 6 months and a decrease in body weight from 132 kg to 93 kg (a loss of 39 kg [approximately 86 lb]).
When he was prescribed tirzepatide, 2.5 mg weekly, for obesity, the patient had been recommended to increase the dose every 4 weeks as tolerated and, importantly, to have a follow-up visit in a month. But because he lived in different states seasonally, the follow-up never occurred.
Upon his emergency department visit, the patient’s thyrotropin level had dropped from 1.9 mIU/L at the first visit 6 months earlier to 0.001 mIU/L (well within the atrial fibrillation risk range), and his free thyroxine level (fT4) was 7.26 ng/ dL — substantially outside of the normal range of about 0.9-1.7 ng/dL for adults.
“The patient had 4-times higher fT4 levels of the upper limit,” first author Kagan E. Karakus, MD, of the Barbara Davis Center for Diabetes, University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Aurora, told this news organization. “That is why he had experienced the adverse event of atrial fibrillation.”
Thyrotoxicosis Symptoms Can Be ‘Insidious,’ Levothyroxine Should Be Monitored
Although tirzepatide has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of type 1 diabetes, obesity is on the rise among patients with this disorder and recent research has shown a more than 10% reduction in body weight in 6 months and significant reductions in A1c with various doses.
Of note, in the current case, although the patient’s levothyroxine dose was not adjusted, his insulin dose was gradually self-decreased during his tirzepatide treatment to prevent hypoglycemia.
“If insulin treatment is excessive in diabetes, it causes hypoglycemia, [and] people with type 1 diabetes will recognize the signs of hypoglycemia related to excessive insulin earlier,” Dr. Karakus said.
If symptoms appear, patients can reduce their insulin doses on their own; however, the symptoms of thyrotoxicosis caused by excessive levothyroxine can be more insidious compared with hypoglycemia, he explained.
“Although patients can change their insulin doses, they cannot change the levothyroxine doses since it requires a blood test [thyroid-stimulating hormone; TSH] and a new prescription of the new dose.”
The key lesson is that “following levothyroxine treatment initiation or dose adjustment, 4-6 weeks is the optimal duration to recheck [the] thyrotropin level and adjust the dose as needed,” Dr. Karakus said.
Key Medications to Monitor
Other common outpatient medications that should be closely monitored in patients experiencing rapid weight loss, by any method, range from anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, and antituberculosis drugs to antibiotics and antifungals, the authors note.
Of note, medications with a narrow therapeutic index include phenytoin, warfarin, lithium carbonate, digoxin theophylline, tacrolimus, valproic acid, carbamazepine, and cyclosporine.
The failure to make necessary dose adjustments “is seen more often since the newer antiobesity drugs reduce a great amount of weight within months, almost as rapidly as bariatric surgery,” Dr. Karakus said.
“It is very important for physicians to be aware of the weight-based medications and narrow therapeutic index medications since their doses should be adjusted carefully, especially during weight loss,” he added.
Furthermore, “the patient should also know that weight reduction medication may cause adverse effects like nausea, vomiting and also may affect metabolism of other medications such that some medication doses should be adjusted regularly.”
In the editorial published with the study, Tyrone A. Johnson, MD, of the Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, and colleagues note that the need for close monitoring is particularly important with older patients, who, in addition to having a higher likelihood of comorbidities, commonly have polypharmacy that could increase the potential for adverse effects.
Another key area concern is the emergence of direct-to-consumer avenues for GLP-1/GIP agonists for the many who either cannot afford or do not have access to the drugs, providing further opportunities for treatment without appropriate clinical oversight, they add.
Overall, the case “highlights the potential dangers underlying under-supervised prescribing of GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists and affirms the need for strong partnerships between patients and their clinicians during their use,” they wrote.
“These medications are best used in collaboration with continuity care teams, in context of a patient’s entire health, and in comprehensive risk-benefit assessment throughout the entire duration of treatment.”
A Caveat: Subclinical Levothyroxine Dosing
Commenting on the study, Matthew Ettleson, MD, a clinical instructor of medicine in the Section of Endocrinology, Diabetes, & Metabolism, University of Chicago, noted the important caveat that patients with hypothyroidism are commonly on subclinical doses, with varying dose adjustment needs.
“The patient in the case was clearly on a replacement level dose. However, many patients are on low doses of levothyroxine (75 µg or lower) for subclinical hypothyroidism, and, in general, I think the risks are lower with patients with subclinical hypothyroidism on lower doses of levothyroxine,” he told this news organization.
Because of that, “frequent TSH monitoring may be excessive in this population,” he said. “I would hesitate to empirically lower the dose with weight loss, unless it was clear that the patient was unlikely to follow up.
“Checking TSH at a more frequent interval and adjusting the dose accordingly should be adequate to prevent situations like this case.”
Dr. Karakus, Dr. Ettleson, and the editorial authors had no relevant disclosures to report.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FTC Interim Report on Pharmacy Middlemen Is First Step of Many Needed in Addressing Drug Costs, Access
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Rising consolidation among pharmacy benefit managers (PBMs) allows the companies to profit at the expense of patients and independent pharmacists. That’s the conclusion of a recent Federal Trade Commission (FTC) report on interim findings from the agency’s ongoing investigation of PBMs.
Lawmakers are increasingly scrutinizing the industry amid growing concern among physicians and consumers about how PBMs exploit their market dominance. The top six PBMs managed 94% of US drug claims in 2023, with the majority handled by the industry’s three giants: CVS Caremark, Cigna’s Express Scripts, and United Healthcare’s OptumRx.
PBMs manage prescription drug benefits for health insurers, Medicare Part D drug plans, and large employers. They act as middlemen between health insurers and pharmacies, developing formularies of covered drugs and promising savings from the discounts and rebates they negotiate with drugmakers.
The FTC’s interim report found that the giant PBMs often exercise significant control over what drugs are available and at what price and which pharmacies patients can use to access their prescribed medications. Consumers suffer as a result, the report concluded.
Madelaine A. Feldman, MD, vice president for advocacy and government affairs for the Coalition of State Rheumatology Organizations, shared her perspective on the FTC report in an email Q&A with this news organization. She is affiliated with The Rheumatology Group, based in Metairie, Louisiana.
Dr. Feldman has long tracked the PBM industry and appeared as a witness before influential government panels, including the House Energy and Commerce Committee. She has highlighted for lawmakers the challenges physicians face in helping patients get needed medicines.
For example, she shared cases of PBMs steering patients toward the more expensive of three widely used rheumatoid arthritis medicines that have a similar mechanism of action, the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, Dr. Feldman said.
One of the drugs cost roughly half of the other two — about $30,000 per year vs $65,000-$70,000. Yet only the two expensive drugs were included in the PBM formulary. As a result, the cheapest drug holds only a sliver of market share; the remainder is dominated by the two expensive products, she told the House Oversight and Accountability Committee in 2021.
This Q&A has been edited for length and clarity.
What would you want federal and state policymakers to do in response to the FTC’s report?
I think Congress needs to clearly delineate the differences between anticompetitive pharmacy issues, drug pricing issues, and their effect on formulary construction issues.
Lawmakers should demand more transparency and consider legislation that would remove perverse incentives that prompt PBMs to choose higher priced drugs for their formularies.
That may require other regulatory or legislative actions to ensure lower prices (not higher kickbacks) are incentivized. Ultimately, in order to gain true competition within the health insurance business, these oligopolies of multiple businesses need to be broken up. Anything less seems to be nibbling around the edges and allows the Big Three to continue their “whack-a mole” in circumventing piecemeal regulatory and legislative policies.
You’ve followed PBM practices closely for many years. Was there anything in this interim FTC report that surprised you?
Though not surprised, I am glad that it was released because it had been a year in investigation and there were many requests for some type of substantive report.
Two things that are missing that I feel are paramount are investigating how the three big PBMs are causing physical harm to patients as a result of the profit component in formulary construction and the profound financial impact of hidden PBM profit centers in self-insured employer health plans.
What we have seen over the years is the result of the perverse incentives for the PBMs to prefer the most profitable medications on their formularies.
They use utilization management tools such as step therapy, nonmedical switching, and exclusions to maintain their formularies’ profitability. These tools have been shown to delay and deny the proper care of patients, resulting in not just monetary but physical harm as well.
I would think the physical harm done to patients in manipulating the formularies should be addressed in this report as well and, in fact, may be the most important aspect of consumer protection of this issue.
In terms of the FTC’s mission to not “unduly burden” legitimate business, I would like to see the sector of self-insured employers addressed.
The report details how PBMs steer prescriptions to their affiliated pharmacies. The FTC says that can push smaller pharmacies out of the market, ultimately leading to higher costs and lower quality services for people. What’s your perspective?
Having more community pharmacies is better than having less. We are seeing more “pharmacy deserts” in rural areas as a result of many community pharmacies having to close.
The FTC voted 4-1 to allow staff to issue the interim report, with Commissioner Melissa Holyoak voting no. And some FTC commissioners seem divided on the usefulness of the report. Why?
Commissioner Holyoak states the “the Report leaves us without a better understanding of the competition concerns surrounding PBMs or how consumers are impacted by PBM practices.”
I do agree with her that the harm to patients’ medical status was not even addressed as far as I could tell in this report. There are multiple news articles and reports on the harms inflicted upon patients by the UM tools that drive the construction of ever changing formularies, all based on contracting with manufacturers that result in the highest profit for the PBM.
Holyoak also states, “Among other critical conclusions, the Report does not address the seemingly contradictory conclusions in the 2005 Report that PBMs, including vertically owned PBMs, generated cost savings for consumers.”
That may be true, but in 2005, the rise of PBMs was just beginning and the huge vertical and horizontal integration had yet to begin. Also, 2005 was still in the beginning of the biologic drug deluge, which did create competition to get on the formulary. Since then, PBMs have done nothing to control the rise in prices but instead, apparently have used the competition to get higher price concessions from manufacturers based on a percentage of the list price to line their pockets.
Commissioner Ferguson agreed with releasing the report but he had many issues with this report including the lack of PBM response.
I do agree with him that the FTC should have used some type of “force” to get the information they needed from the PBMs. The Big Three are known for obfuscation and delaying providing information to legislative and regulatory agencies.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ABIM Revokes Two Physicians’ Certifications Over Accusations of COVID Misinformation
The American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) has revoked certification for two physicians known for leading an organization that promotes ivermectin as a treatment for COVID-19.
Pierre Kory, MD, is no longer certified in critical care medicine, pulmonary disease, and internal medicine, according to the ABIM website. Paul Ellis Marik, MD, is no longer certified in critical care medicine or internal medicine.
Dr. Marik is the chief scientific officer and Dr. Kory is president emeritus of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, a group they founded in March 2020. and also offers treatments for Lyme disease.
Ivermectin was proven to not be of use in treating COVID. Studies purporting to show a benefit were later linked to errors, and some were found to have been based on potentially fraudulent research.
The ABIM declined to comment when asked by this news organization about its action. Its website indicates that “revoked” indicates “loss of certification due to disciplinary action for which ABIM has determined that the conduct underlying the sanction does not warrant a defined pathway for restoration of certification at the time of disciplinary sanction.”
In a statement emailed to this news organization, Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik said, “we believe this decision represents a dangerous shift away from the foundation principles of medical discourse and scientific debate that have historically been the bedrock of medical education associations.”
The FLCCC said in the statement that it, along with Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik, are “evaluating options to challenge these decisions.”
Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik said they were notified in May 2022 that they were facing a potential ABIM disciplinary action. An ABIM committee recommended the revocation in July 2023, saying the two men were spreading “false or inaccurate medical information,” according to FLCCC. Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik lost an appeal.
In a 2023 statement, Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik called the ABIM action an “attack on freedom of speech.”
“This isn’t a free speech question,” said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, the Drs. William F. and Virginia Connolly Mitty Professor of Bioethics at NYU Grossman School of Medicine’s Department of Population Health, New York City. “You do have the right to free speech, but you don’t have the right to practice outside of the standard of care boundaries,” he told this news organization.
The ABIM action “is the field standing up and saying, ‘These are the limits of what you can do,’” said Dr. Caplan. It means the profession is rejecting those “who are involved in things that harm patients or delay them getting accepted treatments,” he said. Caplan noted that a disciplinary action had been a long time in coming — 3 years since the first battles over ivermectin.
Wendy Parmet, JD, Matthews Distinguished University Professor of Law at Northeastern University School of Public Policy and Urban Affairs, Boston, said that misinformation spread by physicians is especially harmful because it comes with an air of credibility.
“We certainly want people to be able to dissent,” Ms. Parmet told this news organization. To engender trust, any sanctions by a professional board should be done in a deliberative process with a strong evidentiary base, she said.
“You want to leave sufficient room for discourse and discussion within the profession, and you don’t want the board to enforce a narrow, rigid orthodoxy,” she said. But in cases where people are “peddling information that is way outside the consensus” or are “profiting off of it, for the profession to take no action, that is, I think, detrimental also to the trust in the profession,” she said.
She was not surprised that Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik would fight to retain certification. “Board certification is an important, very worthwhile thing to have,” she said. “Losing it is not trivial.”
Dr. Kory, who is licensed in California, New York, and Wisconsin, “does not require this certification for his independent practice but is evaluating next steps with attorneys,” according to the statement from FLCCC.
Dr. Marik, whose Virginia medical license expired in 2022, “is no longer treating patients and has dedicated his time and efforts to the FLCCC Alliance,” the statement said.
Dr. Caplan served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position) and is a contributing author and advisor for this news organization. Ms. Parmet reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) has revoked certification for two physicians known for leading an organization that promotes ivermectin as a treatment for COVID-19.
Pierre Kory, MD, is no longer certified in critical care medicine, pulmonary disease, and internal medicine, according to the ABIM website. Paul Ellis Marik, MD, is no longer certified in critical care medicine or internal medicine.
Dr. Marik is the chief scientific officer and Dr. Kory is president emeritus of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, a group they founded in March 2020. and also offers treatments for Lyme disease.
Ivermectin was proven to not be of use in treating COVID. Studies purporting to show a benefit were later linked to errors, and some were found to have been based on potentially fraudulent research.
The ABIM declined to comment when asked by this news organization about its action. Its website indicates that “revoked” indicates “loss of certification due to disciplinary action for which ABIM has determined that the conduct underlying the sanction does not warrant a defined pathway for restoration of certification at the time of disciplinary sanction.”
In a statement emailed to this news organization, Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik said, “we believe this decision represents a dangerous shift away from the foundation principles of medical discourse and scientific debate that have historically been the bedrock of medical education associations.”
The FLCCC said in the statement that it, along with Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik, are “evaluating options to challenge these decisions.”
Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik said they were notified in May 2022 that they were facing a potential ABIM disciplinary action. An ABIM committee recommended the revocation in July 2023, saying the two men were spreading “false or inaccurate medical information,” according to FLCCC. Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik lost an appeal.
In a 2023 statement, Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik called the ABIM action an “attack on freedom of speech.”
“This isn’t a free speech question,” said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, the Drs. William F. and Virginia Connolly Mitty Professor of Bioethics at NYU Grossman School of Medicine’s Department of Population Health, New York City. “You do have the right to free speech, but you don’t have the right to practice outside of the standard of care boundaries,” he told this news organization.
The ABIM action “is the field standing up and saying, ‘These are the limits of what you can do,’” said Dr. Caplan. It means the profession is rejecting those “who are involved in things that harm patients or delay them getting accepted treatments,” he said. Caplan noted that a disciplinary action had been a long time in coming — 3 years since the first battles over ivermectin.
Wendy Parmet, JD, Matthews Distinguished University Professor of Law at Northeastern University School of Public Policy and Urban Affairs, Boston, said that misinformation spread by physicians is especially harmful because it comes with an air of credibility.
“We certainly want people to be able to dissent,” Ms. Parmet told this news organization. To engender trust, any sanctions by a professional board should be done in a deliberative process with a strong evidentiary base, she said.
“You want to leave sufficient room for discourse and discussion within the profession, and you don’t want the board to enforce a narrow, rigid orthodoxy,” she said. But in cases where people are “peddling information that is way outside the consensus” or are “profiting off of it, for the profession to take no action, that is, I think, detrimental also to the trust in the profession,” she said.
She was not surprised that Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik would fight to retain certification. “Board certification is an important, very worthwhile thing to have,” she said. “Losing it is not trivial.”
Dr. Kory, who is licensed in California, New York, and Wisconsin, “does not require this certification for his independent practice but is evaluating next steps with attorneys,” according to the statement from FLCCC.
Dr. Marik, whose Virginia medical license expired in 2022, “is no longer treating patients and has dedicated his time and efforts to the FLCCC Alliance,” the statement said.
Dr. Caplan served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position) and is a contributing author and advisor for this news organization. Ms. Parmet reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) has revoked certification for two physicians known for leading an organization that promotes ivermectin as a treatment for COVID-19.
Pierre Kory, MD, is no longer certified in critical care medicine, pulmonary disease, and internal medicine, according to the ABIM website. Paul Ellis Marik, MD, is no longer certified in critical care medicine or internal medicine.
Dr. Marik is the chief scientific officer and Dr. Kory is president emeritus of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance, a group they founded in March 2020. and also offers treatments for Lyme disease.
Ivermectin was proven to not be of use in treating COVID. Studies purporting to show a benefit were later linked to errors, and some were found to have been based on potentially fraudulent research.
The ABIM declined to comment when asked by this news organization about its action. Its website indicates that “revoked” indicates “loss of certification due to disciplinary action for which ABIM has determined that the conduct underlying the sanction does not warrant a defined pathway for restoration of certification at the time of disciplinary sanction.”
In a statement emailed to this news organization, Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik said, “we believe this decision represents a dangerous shift away from the foundation principles of medical discourse and scientific debate that have historically been the bedrock of medical education associations.”
The FLCCC said in the statement that it, along with Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik, are “evaluating options to challenge these decisions.”
Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik said they were notified in May 2022 that they were facing a potential ABIM disciplinary action. An ABIM committee recommended the revocation in July 2023, saying the two men were spreading “false or inaccurate medical information,” according to FLCCC. Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik lost an appeal.
In a 2023 statement, Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik called the ABIM action an “attack on freedom of speech.”
“This isn’t a free speech question,” said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, the Drs. William F. and Virginia Connolly Mitty Professor of Bioethics at NYU Grossman School of Medicine’s Department of Population Health, New York City. “You do have the right to free speech, but you don’t have the right to practice outside of the standard of care boundaries,” he told this news organization.
The ABIM action “is the field standing up and saying, ‘These are the limits of what you can do,’” said Dr. Caplan. It means the profession is rejecting those “who are involved in things that harm patients or delay them getting accepted treatments,” he said. Caplan noted that a disciplinary action had been a long time in coming — 3 years since the first battles over ivermectin.
Wendy Parmet, JD, Matthews Distinguished University Professor of Law at Northeastern University School of Public Policy and Urban Affairs, Boston, said that misinformation spread by physicians is especially harmful because it comes with an air of credibility.
“We certainly want people to be able to dissent,” Ms. Parmet told this news organization. To engender trust, any sanctions by a professional board should be done in a deliberative process with a strong evidentiary base, she said.
“You want to leave sufficient room for discourse and discussion within the profession, and you don’t want the board to enforce a narrow, rigid orthodoxy,” she said. But in cases where people are “peddling information that is way outside the consensus” or are “profiting off of it, for the profession to take no action, that is, I think, detrimental also to the trust in the profession,” she said.
She was not surprised that Dr. Kory and Dr. Marik would fight to retain certification. “Board certification is an important, very worthwhile thing to have,” she said. “Losing it is not trivial.”
Dr. Kory, who is licensed in California, New York, and Wisconsin, “does not require this certification for his independent practice but is evaluating next steps with attorneys,” according to the statement from FLCCC.
Dr. Marik, whose Virginia medical license expired in 2022, “is no longer treating patients and has dedicated his time and efforts to the FLCCC Alliance,” the statement said.
Dr. Caplan served as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for Johnson & Johnson’s Panel for Compassionate Drug Use (unpaid position) and is a contributing author and advisor for this news organization. Ms. Parmet reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.