User login
ID Practitioner is an independent news source that provides infectious disease specialists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the infectious disease specialist’s practice. Specialty focus topics include antimicrobial resistance, emerging infections, global ID, hepatitis, HIV, hospital-acquired infections, immunizations and vaccines, influenza, mycoses, pediatric infections, and STIs. Infectious Diseases News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
sofosbuvir
ritonavir with dasabuvir
discount
support path
program
ritonavir
greedy
ledipasvir
assistance
viekira pak
vpak
advocacy
needy
protest
abbvie
paritaprevir
ombitasvir
direct-acting antivirals
dasabuvir
gilead
fake-ovir
support
v pak
oasis
harvoni
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-medstat-latest-articles-articles-section')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-idp')]
Daily Recap: Higher risk of severe COVID-19 seen in pregnancy, primary care practices at risk
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Pregnant women at higher risk for severe COVID-19
Pregnant women may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness, according to a report published online June 26 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among reproductive-aged women (15-44 years) infected with SARS-CoV-2, pregnancy was associated with a greater likelihood of hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), and mechanical ventilation, but not death. Pregnant women were 5.4 times more likely to be hospitalized, 1.5 times more likely to be admitted to the ICU, and 1.7 times more likely to need mechanical ventilation, after adjustment for age, underlying conditions, and race/ethnicity.
CDC researchers said that preventing COVID-19 infection in pregnant women should be a priority and any potential barriers to compliance with preventive measures need to be removed.
“During pregnancy, women experience immunologic and physiologic changes that could increase their risk for more severe illness from respiratory infections,” they wrote. Read more.
Going out of business: Primary care practices at risk
In a recently published editorial, Tom Frieden, MD, MPH, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, argued that primary care is in deep trouble, its long-standing financial problems exacerbated by the fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. In an interview with Kenny Lin, MD, MPH, a family physician, Dr. Frieden discussed the future of primary care.
Here is a sample of Dr. Frieden’s observations:
“When I’ve looked around the United States, I’ve been extremely concerned about both the risk that primary care practitioners are subjected to in their everyday practice and the economic risk that we could lose many of our primary care practices around the country. It’s really striking to see that the number of visits has plummeted. Because of our payment structure, that means incomes have plummeted. We’re hearing about doctors’ offices getting boarded up and shuttering. As I write in the piece, it’s one thing for a theater or a restaurant or another important community entity to shut because of economic downturn, and these are real losses, but to lose their only primary care practice or one of the few in an area really is a matter of life and death for many communities.” Read more.
Surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests that placed a huge burden on first responders, according to a new analysis.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
Read more.
Fenfluramine approved for Dravet syndrome
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved fenfluramine (Fintepla, Zogenix) oral solution, a Schedule IV controlled substance, for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome in children age 2 years and older.
Dravet syndrome is a rare childhood-onset epilepsy characterized by frequent, drug-resistant convulsive seizures that may contribute to intellectual disability and impairments in motor control, behavior, and cognition, as well as an increased risk of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy.
Dravet syndrome takes a “tremendous toll on both patients and their families. Fintepla offers an additional effective treatment option for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome,” Billy Dunn, MD, director, Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Pregnant women at higher risk for severe COVID-19
Pregnant women may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness, according to a report published online June 26 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among reproductive-aged women (15-44 years) infected with SARS-CoV-2, pregnancy was associated with a greater likelihood of hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), and mechanical ventilation, but not death. Pregnant women were 5.4 times more likely to be hospitalized, 1.5 times more likely to be admitted to the ICU, and 1.7 times more likely to need mechanical ventilation, after adjustment for age, underlying conditions, and race/ethnicity.
CDC researchers said that preventing COVID-19 infection in pregnant women should be a priority and any potential barriers to compliance with preventive measures need to be removed.
“During pregnancy, women experience immunologic and physiologic changes that could increase their risk for more severe illness from respiratory infections,” they wrote. Read more.
Going out of business: Primary care practices at risk
In a recently published editorial, Tom Frieden, MD, MPH, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, argued that primary care is in deep trouble, its long-standing financial problems exacerbated by the fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. In an interview with Kenny Lin, MD, MPH, a family physician, Dr. Frieden discussed the future of primary care.
Here is a sample of Dr. Frieden’s observations:
“When I’ve looked around the United States, I’ve been extremely concerned about both the risk that primary care practitioners are subjected to in their everyday practice and the economic risk that we could lose many of our primary care practices around the country. It’s really striking to see that the number of visits has plummeted. Because of our payment structure, that means incomes have plummeted. We’re hearing about doctors’ offices getting boarded up and shuttering. As I write in the piece, it’s one thing for a theater or a restaurant or another important community entity to shut because of economic downturn, and these are real losses, but to lose their only primary care practice or one of the few in an area really is a matter of life and death for many communities.” Read more.
Surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests that placed a huge burden on first responders, according to a new analysis.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
Read more.
Fenfluramine approved for Dravet syndrome
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved fenfluramine (Fintepla, Zogenix) oral solution, a Schedule IV controlled substance, for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome in children age 2 years and older.
Dravet syndrome is a rare childhood-onset epilepsy characterized by frequent, drug-resistant convulsive seizures that may contribute to intellectual disability and impairments in motor control, behavior, and cognition, as well as an increased risk of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy.
Dravet syndrome takes a “tremendous toll on both patients and their families. Fintepla offers an additional effective treatment option for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome,” Billy Dunn, MD, director, Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
Pregnant women at higher risk for severe COVID-19
Pregnant women may be at increased risk for severe COVID-19 illness, according to a report published online June 26 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Among reproductive-aged women (15-44 years) infected with SARS-CoV-2, pregnancy was associated with a greater likelihood of hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), and mechanical ventilation, but not death. Pregnant women were 5.4 times more likely to be hospitalized, 1.5 times more likely to be admitted to the ICU, and 1.7 times more likely to need mechanical ventilation, after adjustment for age, underlying conditions, and race/ethnicity.
CDC researchers said that preventing COVID-19 infection in pregnant women should be a priority and any potential barriers to compliance with preventive measures need to be removed.
“During pregnancy, women experience immunologic and physiologic changes that could increase their risk for more severe illness from respiratory infections,” they wrote. Read more.
Going out of business: Primary care practices at risk
In a recently published editorial, Tom Frieden, MD, MPH, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, argued that primary care is in deep trouble, its long-standing financial problems exacerbated by the fallout from the COVID-19 pandemic. In an interview with Kenny Lin, MD, MPH, a family physician, Dr. Frieden discussed the future of primary care.
Here is a sample of Dr. Frieden’s observations:
“When I’ve looked around the United States, I’ve been extremely concerned about both the risk that primary care practitioners are subjected to in their everyday practice and the economic risk that we could lose many of our primary care practices around the country. It’s really striking to see that the number of visits has plummeted. Because of our payment structure, that means incomes have plummeted. We’re hearing about doctors’ offices getting boarded up and shuttering. As I write in the piece, it’s one thing for a theater or a restaurant or another important community entity to shut because of economic downturn, and these are real losses, but to lose their only primary care practice or one of the few in an area really is a matter of life and death for many communities.” Read more.
Surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests that placed a huge burden on first responders, according to a new analysis.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
Read more.
Fenfluramine approved for Dravet syndrome
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved fenfluramine (Fintepla, Zogenix) oral solution, a Schedule IV controlled substance, for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome in children age 2 years and older.
Dravet syndrome is a rare childhood-onset epilepsy characterized by frequent, drug-resistant convulsive seizures that may contribute to intellectual disability and impairments in motor control, behavior, and cognition, as well as an increased risk of sudden unexpected death in epilepsy.
Dravet syndrome takes a “tremendous toll on both patients and their families. Fintepla offers an additional effective treatment option for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome,” Billy Dunn, MD, director, Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said in a news release. Read more.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
COVID-19: ‘dramatic’ surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in NYC
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCAs) that placed a huge burden on first responders, a new analysis shows.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
New York City has the largest and busiest EMS system in the United States, serving a population of more than 8.4 million people and responding to more than 1.5 million calls every year.
To gauge the impact of COVID-19 on first responders, Dr. Prezant and colleagues analyzed data for adults with OHCA who received EMS resuscitation from March 1, when the first case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in the city, through April 25, when EMS call volume had receded to pre-COVID-19 levels.
Compared with the same period in 2019, the COVID-19 period had an excess of 2,653 patients with OHCA who underwent EMS resuscitation attempts (3,989 in 2020 vs. 1,336 in 2019, P < .001), an incidence rate triple that of 2019 (47.5 vs. 15.9 per 100,000).
On the worst day – Monday, April 6 – OHCAs peaked at 305 cases, an increase of nearly 10-fold compared with the same day in 2019.
Despite the surge in cases, the median response time of available EMS units to OHCAs increased by about 1 minute over 2019, a nonsignificant difference. Although the average time varied, median response time during the COVID-19 period was less than 3 minutes.
A more vulnerable group
Compared with 2019, patients suffering OHCA during the pandemic period were older (mean age 72 vs. 68 years), less likely to be white (20% white vs. 33%) and more likely to have hypertension (54% vs. 46%), diabetes (36% vs. 26%), physical limitations (57% vs. 48%) and cardiac rhythms that don’t respond to defibrillator shocks (92% vs. 81%).
Compared with 2019, the COVID-19 period had substantial reductions in return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) (18% vs. 35%; P < .001) and sustained ROSC (11% vs. 25%; P < .001). The case fatality rate was 90% in the COVID-19 period vs. 75% a year earlier.
“The tragedy of the COVID-19 pandemic is not just the number of patients infected, but the large increase in OHCAs and deaths,” Dr. Prezant and colleagues said.
Identifying patients with the greatest risk for OHCA and death during the COVID-19 pandemic “should allow for early, targeted interventions in the outpatient setting that could lead to reductions in out-of-hospital deaths,” they noted.
“Vulnerable patient populations need outreach, telephonic medicine, televideo medicine, home visits, not just temperature monitoring but home O2 saturation monitoring,” Dr. Prezant said in an interview. “Barriers need to be removed, not just for this pandemic but for the future – no matter what the trigger is.”
Unsung heroes
In an Editor’s Note in JAMA Cardiology, Robert O. Bonow, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues said the American people owe a debt of gratitude to first responders for their “heroic work” triaging, resuscitating, and transporting thousands of people affected by COVID-19.
“Although the typically bustling NYC streets remained eerily deserted, the characteristic cacophony of sounds of the ‘City that Never Sleeps’ was replaced by sirens wailing all hours of the night,” they wrote.
First responders to OHCAs in the COVID-19 era place themselves at extremely high risk, in some cases without optimal personal protective equipment, they pointed out. “Sadly,” many first responders have fallen ill to COVID-19 infection, they added.
As of June 1, 29 EMS workers and volunteers across the United States had died of COVID-19.
They are James Villecco, Gregory Hodge, Tony Thomas, Mike Field, John Redd, Idris Bey, Richard Seaberry, and Sal Mancuso of New York; Israel Tolentino, Reuven Maroth, Liana Sá, Kevin Leiva, Frank Molinari, Robert Weber, Robert Tarrant, Solomon Donald, Scott Geiger, John Farrarella, John Careccia, Bill Nauta, and David Pinto of New Jersey; Kevin Bundy, Robert Zerman, and Jeremy Emerich of Pennsylvania; Paul Cary of Colorado; Paul Novicki of Michigan; David Martin of Mississippi; Billy Birmingham of Missouri; and John “JP” Granger of South Carolina.
“We offer their families, friends, and colleagues our sincerest condolences and honor their memory with our highest respect and gratitude,” Dr. Bonow and colleagues wrote.
This study was supported by the City of New York and the Fire Department of the City of New York. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCAs) that placed a huge burden on first responders, a new analysis shows.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
New York City has the largest and busiest EMS system in the United States, serving a population of more than 8.4 million people and responding to more than 1.5 million calls every year.
To gauge the impact of COVID-19 on first responders, Dr. Prezant and colleagues analyzed data for adults with OHCA who received EMS resuscitation from March 1, when the first case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in the city, through April 25, when EMS call volume had receded to pre-COVID-19 levels.
Compared with the same period in 2019, the COVID-19 period had an excess of 2,653 patients with OHCA who underwent EMS resuscitation attempts (3,989 in 2020 vs. 1,336 in 2019, P < .001), an incidence rate triple that of 2019 (47.5 vs. 15.9 per 100,000).
On the worst day – Monday, April 6 – OHCAs peaked at 305 cases, an increase of nearly 10-fold compared with the same day in 2019.
Despite the surge in cases, the median response time of available EMS units to OHCAs increased by about 1 minute over 2019, a nonsignificant difference. Although the average time varied, median response time during the COVID-19 period was less than 3 minutes.
A more vulnerable group
Compared with 2019, patients suffering OHCA during the pandemic period were older (mean age 72 vs. 68 years), less likely to be white (20% white vs. 33%) and more likely to have hypertension (54% vs. 46%), diabetes (36% vs. 26%), physical limitations (57% vs. 48%) and cardiac rhythms that don’t respond to defibrillator shocks (92% vs. 81%).
Compared with 2019, the COVID-19 period had substantial reductions in return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) (18% vs. 35%; P < .001) and sustained ROSC (11% vs. 25%; P < .001). The case fatality rate was 90% in the COVID-19 period vs. 75% a year earlier.
“The tragedy of the COVID-19 pandemic is not just the number of patients infected, but the large increase in OHCAs and deaths,” Dr. Prezant and colleagues said.
Identifying patients with the greatest risk for OHCA and death during the COVID-19 pandemic “should allow for early, targeted interventions in the outpatient setting that could lead to reductions in out-of-hospital deaths,” they noted.
“Vulnerable patient populations need outreach, telephonic medicine, televideo medicine, home visits, not just temperature monitoring but home O2 saturation monitoring,” Dr. Prezant said in an interview. “Barriers need to be removed, not just for this pandemic but for the future – no matter what the trigger is.”
Unsung heroes
In an Editor’s Note in JAMA Cardiology, Robert O. Bonow, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues said the American people owe a debt of gratitude to first responders for their “heroic work” triaging, resuscitating, and transporting thousands of people affected by COVID-19.
“Although the typically bustling NYC streets remained eerily deserted, the characteristic cacophony of sounds of the ‘City that Never Sleeps’ was replaced by sirens wailing all hours of the night,” they wrote.
First responders to OHCAs in the COVID-19 era place themselves at extremely high risk, in some cases without optimal personal protective equipment, they pointed out. “Sadly,” many first responders have fallen ill to COVID-19 infection, they added.
As of June 1, 29 EMS workers and volunteers across the United States had died of COVID-19.
They are James Villecco, Gregory Hodge, Tony Thomas, Mike Field, John Redd, Idris Bey, Richard Seaberry, and Sal Mancuso of New York; Israel Tolentino, Reuven Maroth, Liana Sá, Kevin Leiva, Frank Molinari, Robert Weber, Robert Tarrant, Solomon Donald, Scott Geiger, John Farrarella, John Careccia, Bill Nauta, and David Pinto of New Jersey; Kevin Bundy, Robert Zerman, and Jeremy Emerich of Pennsylvania; Paul Cary of Colorado; Paul Novicki of Michigan; David Martin of Mississippi; Billy Birmingham of Missouri; and John “JP” Granger of South Carolina.
“We offer their families, friends, and colleagues our sincerest condolences and honor their memory with our highest respect and gratitude,” Dr. Bonow and colleagues wrote.
This study was supported by the City of New York and the Fire Department of the City of New York. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The COVID-19 pandemic in New York City led to a surge in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests (OHCAs) that placed a huge burden on first responders, a new analysis shows.
During the height of the pandemic in New York, there was a “dramatic increase in cardiopulmonary arrests, nearly all presented in non-shockable cardiac rhythms (> 90% fatality rate) and vulnerable patient populations were most affected,” David J. Prezant, MD, chief medical officer, Fire Department of New York (FDNY), said in an interview.
In a news release, Dr. Prezant noted that “relatively few, if any, patients were tested to confirm the presence of COVID-19,” making it impossible to distinguish between cardiac arrests as a result of COVID-19 and those that may have resulted from other health conditions.
“We also can’t rule out the possibility that some people may have died from delays in seeking or receiving treatment for non–COVID-19-related conditions. However, the dramatic increase in cardiac arrests compared to the same period in 2019 strongly indicates that the pandemic was directly or indirectly responsible for that surge in cardiac arrests and deaths,” said Dr. Prezant.
The study was published online June 19 in JAMA Cardiology.
New York City has the largest and busiest EMS system in the United States, serving a population of more than 8.4 million people and responding to more than 1.5 million calls every year.
To gauge the impact of COVID-19 on first responders, Dr. Prezant and colleagues analyzed data for adults with OHCA who received EMS resuscitation from March 1, when the first case of COVID-19 was diagnosed in the city, through April 25, when EMS call volume had receded to pre-COVID-19 levels.
Compared with the same period in 2019, the COVID-19 period had an excess of 2,653 patients with OHCA who underwent EMS resuscitation attempts (3,989 in 2020 vs. 1,336 in 2019, P < .001), an incidence rate triple that of 2019 (47.5 vs. 15.9 per 100,000).
On the worst day – Monday, April 6 – OHCAs peaked at 305 cases, an increase of nearly 10-fold compared with the same day in 2019.
Despite the surge in cases, the median response time of available EMS units to OHCAs increased by about 1 minute over 2019, a nonsignificant difference. Although the average time varied, median response time during the COVID-19 period was less than 3 minutes.
A more vulnerable group
Compared with 2019, patients suffering OHCA during the pandemic period were older (mean age 72 vs. 68 years), less likely to be white (20% white vs. 33%) and more likely to have hypertension (54% vs. 46%), diabetes (36% vs. 26%), physical limitations (57% vs. 48%) and cardiac rhythms that don’t respond to defibrillator shocks (92% vs. 81%).
Compared with 2019, the COVID-19 period had substantial reductions in return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) (18% vs. 35%; P < .001) and sustained ROSC (11% vs. 25%; P < .001). The case fatality rate was 90% in the COVID-19 period vs. 75% a year earlier.
“The tragedy of the COVID-19 pandemic is not just the number of patients infected, but the large increase in OHCAs and deaths,” Dr. Prezant and colleagues said.
Identifying patients with the greatest risk for OHCA and death during the COVID-19 pandemic “should allow for early, targeted interventions in the outpatient setting that could lead to reductions in out-of-hospital deaths,” they noted.
“Vulnerable patient populations need outreach, telephonic medicine, televideo medicine, home visits, not just temperature monitoring but home O2 saturation monitoring,” Dr. Prezant said in an interview. “Barriers need to be removed, not just for this pandemic but for the future – no matter what the trigger is.”
Unsung heroes
In an Editor’s Note in JAMA Cardiology, Robert O. Bonow, MD, Northwestern University, Chicago, and colleagues said the American people owe a debt of gratitude to first responders for their “heroic work” triaging, resuscitating, and transporting thousands of people affected by COVID-19.
“Although the typically bustling NYC streets remained eerily deserted, the characteristic cacophony of sounds of the ‘City that Never Sleeps’ was replaced by sirens wailing all hours of the night,” they wrote.
First responders to OHCAs in the COVID-19 era place themselves at extremely high risk, in some cases without optimal personal protective equipment, they pointed out. “Sadly,” many first responders have fallen ill to COVID-19 infection, they added.
As of June 1, 29 EMS workers and volunteers across the United States had died of COVID-19.
They are James Villecco, Gregory Hodge, Tony Thomas, Mike Field, John Redd, Idris Bey, Richard Seaberry, and Sal Mancuso of New York; Israel Tolentino, Reuven Maroth, Liana Sá, Kevin Leiva, Frank Molinari, Robert Weber, Robert Tarrant, Solomon Donald, Scott Geiger, John Farrarella, John Careccia, Bill Nauta, and David Pinto of New Jersey; Kevin Bundy, Robert Zerman, and Jeremy Emerich of Pennsylvania; Paul Cary of Colorado; Paul Novicki of Michigan; David Martin of Mississippi; Billy Birmingham of Missouri; and John “JP” Granger of South Carolina.
“We offer their families, friends, and colleagues our sincerest condolences and honor their memory with our highest respect and gratitude,” Dr. Bonow and colleagues wrote.
This study was supported by the City of New York and the Fire Department of the City of New York. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
ACIP approves flu vaccine recommendations for 2020-2021
– Fluzone high-dose quadrivalent, which replaces the trivalent Fluzone high-dose and Fluad quadrivalent (Seqirus), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
At a virtual meeting on June 24, the committee voted unanimously to approve the vaccine recommendations for annual influenza immunization of all individuals aged 6 months and older. They also voted to accept some guidance and language changes to the recommendations.
The past flu season was unique in its overlap with the emergence of the COVID-19 coronavirus, which likely contributed to a third peak in reported cases of influenza-like illness at approximately week 14 of last season, said Lisa Grohskopf, MD, of the CDC’s influenza division, who presented data on last year’s activity and the updates for next season.
The CDC estimates that 39,000,000-56,000,000 flu illnesses occurred in the United States from Oct. 1, 2019, to April 4, 2020, said Dr. Grohskopf. Estimates also suggest as many as 740,000 hospitalizations and 62,000 deaths related to the seasonal flu.
Preliminary results of vaccine effectiveness showed 39% overall for the 2019-2020 season, with more substantial protection against influenza B and lower protection against A/H1N1pmd09.
Vaccine safety data from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System and Vaccine Safety Datalink showed no new safety concerns for any flu vaccine types used last year, Dr. Grohskopf noted.
Based on this information, three components (A/H1N1pdm09, A/H3N2, and B/Victoria) have been updated for the 2020-2021 vaccines, said Dr. Grohskopf. The egg-based influenza vaccines will include hemagglutinin derived from an A/Guangdong-Maonan/SWL1536/2019(H1N1)pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/2671/2019(H3N2)–like virus and a B/Washington/02/2019 (Victoria lineage)–like virus, and (for quadrivalent vaccines) a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (Yamagata lineage)–like virus.
Nonegg vaccines will contain hemagglutinin derived from an A/Hawaii/70/2019 (H1N1)pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/45/2019 (H3N2)–like virus, a B/Washington/02/2019 (Victoria lineage)–like virus, and a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (Yamagata lineage)–like virus.
New guidance for next year’s flu season includes a change to the language in the contraindications and precautions table to simply read “Contraindications,” with more details in the text explaining package insert contraindications and ACIP recommendations, Dr. Grohskopf said. In addition, updated guidance clarifies that live-attenuated influenza vaccine quadravalents (LAIV4) should not be used in patients with cochlear implants, active cerebrospinal fluid leaks, and anatomical or functional asplenia, based on ACIP’s review of the latest evidence and the availability of alternative vaccines.
ACIP also updated guidance on the use of antivirals and LAIV4. Based on half-lives, language was added indicating that clinicians should assume interference if antivirals are given within certain intervals of LAIV4, Dr. Grohskopf explained. “Newer antivirals peramivir and baloxavir have longer half-lives than oseltamivir and zanamivir, and insufficient data are available on the use of LAIV4 in the setting of antiviral use.”
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
– Fluzone high-dose quadrivalent, which replaces the trivalent Fluzone high-dose and Fluad quadrivalent (Seqirus), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
At a virtual meeting on June 24, the committee voted unanimously to approve the vaccine recommendations for annual influenza immunization of all individuals aged 6 months and older. They also voted to accept some guidance and language changes to the recommendations.
The past flu season was unique in its overlap with the emergence of the COVID-19 coronavirus, which likely contributed to a third peak in reported cases of influenza-like illness at approximately week 14 of last season, said Lisa Grohskopf, MD, of the CDC’s influenza division, who presented data on last year’s activity and the updates for next season.
The CDC estimates that 39,000,000-56,000,000 flu illnesses occurred in the United States from Oct. 1, 2019, to April 4, 2020, said Dr. Grohskopf. Estimates also suggest as many as 740,000 hospitalizations and 62,000 deaths related to the seasonal flu.
Preliminary results of vaccine effectiveness showed 39% overall for the 2019-2020 season, with more substantial protection against influenza B and lower protection against A/H1N1pmd09.
Vaccine safety data from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System and Vaccine Safety Datalink showed no new safety concerns for any flu vaccine types used last year, Dr. Grohskopf noted.
Based on this information, three components (A/H1N1pdm09, A/H3N2, and B/Victoria) have been updated for the 2020-2021 vaccines, said Dr. Grohskopf. The egg-based influenza vaccines will include hemagglutinin derived from an A/Guangdong-Maonan/SWL1536/2019(H1N1)pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/2671/2019(H3N2)–like virus and a B/Washington/02/2019 (Victoria lineage)–like virus, and (for quadrivalent vaccines) a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (Yamagata lineage)–like virus.
Nonegg vaccines will contain hemagglutinin derived from an A/Hawaii/70/2019 (H1N1)pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/45/2019 (H3N2)–like virus, a B/Washington/02/2019 (Victoria lineage)–like virus, and a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (Yamagata lineage)–like virus.
New guidance for next year’s flu season includes a change to the language in the contraindications and precautions table to simply read “Contraindications,” with more details in the text explaining package insert contraindications and ACIP recommendations, Dr. Grohskopf said. In addition, updated guidance clarifies that live-attenuated influenza vaccine quadravalents (LAIV4) should not be used in patients with cochlear implants, active cerebrospinal fluid leaks, and anatomical or functional asplenia, based on ACIP’s review of the latest evidence and the availability of alternative vaccines.
ACIP also updated guidance on the use of antivirals and LAIV4. Based on half-lives, language was added indicating that clinicians should assume interference if antivirals are given within certain intervals of LAIV4, Dr. Grohskopf explained. “Newer antivirals peramivir and baloxavir have longer half-lives than oseltamivir and zanamivir, and insufficient data are available on the use of LAIV4 in the setting of antiviral use.”
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
– Fluzone high-dose quadrivalent, which replaces the trivalent Fluzone high-dose and Fluad quadrivalent (Seqirus), according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
At a virtual meeting on June 24, the committee voted unanimously to approve the vaccine recommendations for annual influenza immunization of all individuals aged 6 months and older. They also voted to accept some guidance and language changes to the recommendations.
The past flu season was unique in its overlap with the emergence of the COVID-19 coronavirus, which likely contributed to a third peak in reported cases of influenza-like illness at approximately week 14 of last season, said Lisa Grohskopf, MD, of the CDC’s influenza division, who presented data on last year’s activity and the updates for next season.
The CDC estimates that 39,000,000-56,000,000 flu illnesses occurred in the United States from Oct. 1, 2019, to April 4, 2020, said Dr. Grohskopf. Estimates also suggest as many as 740,000 hospitalizations and 62,000 deaths related to the seasonal flu.
Preliminary results of vaccine effectiveness showed 39% overall for the 2019-2020 season, with more substantial protection against influenza B and lower protection against A/H1N1pmd09.
Vaccine safety data from the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System and Vaccine Safety Datalink showed no new safety concerns for any flu vaccine types used last year, Dr. Grohskopf noted.
Based on this information, three components (A/H1N1pdm09, A/H3N2, and B/Victoria) have been updated for the 2020-2021 vaccines, said Dr. Grohskopf. The egg-based influenza vaccines will include hemagglutinin derived from an A/Guangdong-Maonan/SWL1536/2019(H1N1)pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/2671/2019(H3N2)–like virus and a B/Washington/02/2019 (Victoria lineage)–like virus, and (for quadrivalent vaccines) a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (Yamagata lineage)–like virus.
Nonegg vaccines will contain hemagglutinin derived from an A/Hawaii/70/2019 (H1N1)pdm09–like virus, an A/Hong Kong/45/2019 (H3N2)–like virus, a B/Washington/02/2019 (Victoria lineage)–like virus, and a B/Phuket/3073/2013 (Yamagata lineage)–like virus.
New guidance for next year’s flu season includes a change to the language in the contraindications and precautions table to simply read “Contraindications,” with more details in the text explaining package insert contraindications and ACIP recommendations, Dr. Grohskopf said. In addition, updated guidance clarifies that live-attenuated influenza vaccine quadravalents (LAIV4) should not be used in patients with cochlear implants, active cerebrospinal fluid leaks, and anatomical or functional asplenia, based on ACIP’s review of the latest evidence and the availability of alternative vaccines.
ACIP also updated guidance on the use of antivirals and LAIV4. Based on half-lives, language was added indicating that clinicians should assume interference if antivirals are given within certain intervals of LAIV4, Dr. Grohskopf explained. “Newer antivirals peramivir and baloxavir have longer half-lives than oseltamivir and zanamivir, and insufficient data are available on the use of LAIV4 in the setting of antiviral use.”
The ACIP members had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Daily Recap: Healthy lifestyle may stave off dementia; Tentative evidence on marijuana for migraine
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
First reported U.S. case of COVID-19 linked to Guillain-Barré syndrome
The first official U.S. case of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) associated with COVID-19 has been reported by neurologists from Allegheny General Hospital in Pittsburgh, further supporting a link between the virus and neurologic complications, including GBS.
Physicians in China reported the first case that initially presented as acute GBS. Subsequently, physicians in Italy reported five cases of GBS in association with COVID-19.
“This onset is similar to a case report of acute Zika virus infection with concurrent GBS suggesting a parainfectious complication,” first author Sandeep Rana, MD, and colleagues noted. Read more.
Five healthy lifestyle choices tied to dramatic cut in dementia risk
Combining four of five healthy lifestyle choices has been linked to up to a 60% reduced risk for Alzheimer’s dementia in new research that strengthens ties between healthy behaviors and lower dementia risk. “I hope this study will motivate people to engage in a healthy lifestyle by not smoking, being physically and cognitively active, and having a high-quality diet,” lead investigator Klodian Dhana, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
They defined a healthy lifestyle score on the basis of the following factors: not smoking; engaging in 150 min/wk or more of physical exercise; light to moderate alcohol consumption; consuming a high-quality Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay diet (upper 40%); and engaging in late-life cognitive activities.
“What needs to be determined is how early should we start ‘behaving.’ We should all aim to score four to five factors across our entire lifespan, but this is not always feasible. So, when is the time to behave? Also, what is the relative weight of each of these factors?” said Luca Giliberto, MD, PhD. Read more.
Marijuana for migraine? Some tentative evidence
Medical marijuana may have promise for managing headache pain, according to results from a small study conducted at the Jefferson Headache Center at Thomas Jefferson University. The researchers found general satisfaction with medical marijuana, more frequent use as an abortive medication rather than a preventative, and more than two-thirds using the inhaled form rather than oral.
“A lot of patients are interested in medical marijuana but don’t know how to integrate it into the therapy plan they already have – whether it should be just to treat bad headaches when they happen, or is it meant to be a preventive medicine they use every day? We have some data out there that it can be helpful, but not a lot of specific information to guide your recommendations,” said Jefferson headache fellow Claire Ceriani, MD, in an interview. Read more.
Inside Mercy’s mission to care for non-COVID patients in Los Angeles
When the hospital ship USNS Mercy departed San Diego’s Naval Station North Island on March 23, 2020, to support the Department of Defense efforts in Los Angeles during the coronavirus outbreak, Commander Erin Blevins remembers the crew’s excitement was palpable. “We normally do partnerships abroad and respond to tsunamis and earthquakes,” said Cdr. Blevins, MD, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist who served as director of medical services for the mission.
Between March 29 and May 15, about 1,071 medical personnel aboard the Mercy cared for 77 patients with an average age of 53 years who were referred from 11 Los Angeles area hospitals.
Care aboard the ship ranged from basic medical and surgical care to critical care and trauma. The most common procedures were cholecystectomies and orthopedic procedures, and the average length of stay was 4-5 days, according to Cdr. Blevins. Over the course of the mission, the medical professionals conducted 36 surgeries, 77 x-ray exams, 26 CT scans, and administered hundreds of ancillary studies ranging from routine labs to high-end x-rays and blood transfusion support. Special Feature.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
First reported U.S. case of COVID-19 linked to Guillain-Barré syndrome
The first official U.S. case of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) associated with COVID-19 has been reported by neurologists from Allegheny General Hospital in Pittsburgh, further supporting a link between the virus and neurologic complications, including GBS.
Physicians in China reported the first case that initially presented as acute GBS. Subsequently, physicians in Italy reported five cases of GBS in association with COVID-19.
“This onset is similar to a case report of acute Zika virus infection with concurrent GBS suggesting a parainfectious complication,” first author Sandeep Rana, MD, and colleagues noted. Read more.
Five healthy lifestyle choices tied to dramatic cut in dementia risk
Combining four of five healthy lifestyle choices has been linked to up to a 60% reduced risk for Alzheimer’s dementia in new research that strengthens ties between healthy behaviors and lower dementia risk. “I hope this study will motivate people to engage in a healthy lifestyle by not smoking, being physically and cognitively active, and having a high-quality diet,” lead investigator Klodian Dhana, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
They defined a healthy lifestyle score on the basis of the following factors: not smoking; engaging in 150 min/wk or more of physical exercise; light to moderate alcohol consumption; consuming a high-quality Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay diet (upper 40%); and engaging in late-life cognitive activities.
“What needs to be determined is how early should we start ‘behaving.’ We should all aim to score four to five factors across our entire lifespan, but this is not always feasible. So, when is the time to behave? Also, what is the relative weight of each of these factors?” said Luca Giliberto, MD, PhD. Read more.
Marijuana for migraine? Some tentative evidence
Medical marijuana may have promise for managing headache pain, according to results from a small study conducted at the Jefferson Headache Center at Thomas Jefferson University. The researchers found general satisfaction with medical marijuana, more frequent use as an abortive medication rather than a preventative, and more than two-thirds using the inhaled form rather than oral.
“A lot of patients are interested in medical marijuana but don’t know how to integrate it into the therapy plan they already have – whether it should be just to treat bad headaches when they happen, or is it meant to be a preventive medicine they use every day? We have some data out there that it can be helpful, but not a lot of specific information to guide your recommendations,” said Jefferson headache fellow Claire Ceriani, MD, in an interview. Read more.
Inside Mercy’s mission to care for non-COVID patients in Los Angeles
When the hospital ship USNS Mercy departed San Diego’s Naval Station North Island on March 23, 2020, to support the Department of Defense efforts in Los Angeles during the coronavirus outbreak, Commander Erin Blevins remembers the crew’s excitement was palpable. “We normally do partnerships abroad and respond to tsunamis and earthquakes,” said Cdr. Blevins, MD, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist who served as director of medical services for the mission.
Between March 29 and May 15, about 1,071 medical personnel aboard the Mercy cared for 77 patients with an average age of 53 years who were referred from 11 Los Angeles area hospitals.
Care aboard the ship ranged from basic medical and surgical care to critical care and trauma. The most common procedures were cholecystectomies and orthopedic procedures, and the average length of stay was 4-5 days, according to Cdr. Blevins. Over the course of the mission, the medical professionals conducted 36 surgeries, 77 x-ray exams, 26 CT scans, and administered hundreds of ancillary studies ranging from routine labs to high-end x-rays and blood transfusion support. Special Feature.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
Here are the stories our MDedge editors across specialties think you need to know about today:
First reported U.S. case of COVID-19 linked to Guillain-Barré syndrome
The first official U.S. case of Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) associated with COVID-19 has been reported by neurologists from Allegheny General Hospital in Pittsburgh, further supporting a link between the virus and neurologic complications, including GBS.
Physicians in China reported the first case that initially presented as acute GBS. Subsequently, physicians in Italy reported five cases of GBS in association with COVID-19.
“This onset is similar to a case report of acute Zika virus infection with concurrent GBS suggesting a parainfectious complication,” first author Sandeep Rana, MD, and colleagues noted. Read more.
Five healthy lifestyle choices tied to dramatic cut in dementia risk
Combining four of five healthy lifestyle choices has been linked to up to a 60% reduced risk for Alzheimer’s dementia in new research that strengthens ties between healthy behaviors and lower dementia risk. “I hope this study will motivate people to engage in a healthy lifestyle by not smoking, being physically and cognitively active, and having a high-quality diet,” lead investigator Klodian Dhana, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
They defined a healthy lifestyle score on the basis of the following factors: not smoking; engaging in 150 min/wk or more of physical exercise; light to moderate alcohol consumption; consuming a high-quality Mediterranean-DASH Diet Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay diet (upper 40%); and engaging in late-life cognitive activities.
“What needs to be determined is how early should we start ‘behaving.’ We should all aim to score four to five factors across our entire lifespan, but this is not always feasible. So, when is the time to behave? Also, what is the relative weight of each of these factors?” said Luca Giliberto, MD, PhD. Read more.
Marijuana for migraine? Some tentative evidence
Medical marijuana may have promise for managing headache pain, according to results from a small study conducted at the Jefferson Headache Center at Thomas Jefferson University. The researchers found general satisfaction with medical marijuana, more frequent use as an abortive medication rather than a preventative, and more than two-thirds using the inhaled form rather than oral.
“A lot of patients are interested in medical marijuana but don’t know how to integrate it into the therapy plan they already have – whether it should be just to treat bad headaches when they happen, or is it meant to be a preventive medicine they use every day? We have some data out there that it can be helpful, but not a lot of specific information to guide your recommendations,” said Jefferson headache fellow Claire Ceriani, MD, in an interview. Read more.
Inside Mercy’s mission to care for non-COVID patients in Los Angeles
When the hospital ship USNS Mercy departed San Diego’s Naval Station North Island on March 23, 2020, to support the Department of Defense efforts in Los Angeles during the coronavirus outbreak, Commander Erin Blevins remembers the crew’s excitement was palpable. “We normally do partnerships abroad and respond to tsunamis and earthquakes,” said Cdr. Blevins, MD, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist who served as director of medical services for the mission.
Between March 29 and May 15, about 1,071 medical personnel aboard the Mercy cared for 77 patients with an average age of 53 years who were referred from 11 Los Angeles area hospitals.
Care aboard the ship ranged from basic medical and surgical care to critical care and trauma. The most common procedures were cholecystectomies and orthopedic procedures, and the average length of stay was 4-5 days, according to Cdr. Blevins. Over the course of the mission, the medical professionals conducted 36 surgeries, 77 x-ray exams, 26 CT scans, and administered hundreds of ancillary studies ranging from routine labs to high-end x-rays and blood transfusion support. Special Feature.
For more on COVID-19, visit our Resource Center. All of our latest news is available on MDedge.com.
COVID-associated pancreatitis may disproportionately affect young, overweight men
Patients with COVID-19 develop a distinct subset of pancreatitis hallmarked by duodenal and periduodenal inflammation, according to a recent case series.
Although all five patients presented with multiple predictive markers of severe pancreatitis, the subsequent clinical pathway “was much more benign than anticipated,” reported lead author Peter Szatmary, MB, BChir, PhD, of the University of Liverpool (England) and colleagues. Still, they noted prolonged hospital stays because of persistent inflammation and poor diabetic control.
“As the global pandemic of SARS-CoV-2 continues, nuances of the disease it precipitates in humans continue to emerge,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. “[A] group from Wuhan reported a series of 9 patients with purported pancreatic injury in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection, but did not provide robust evidence for pancreatitis relying on mild hyperamylasemia alone.”
For the present series, Dr. Szatmary and colleagues restricted diagnosis of pancreatitis to international consensus guidelines, which require “abdominal pain consistent with pancreatitis, serum amylase/lipase greater than three times the upper limit of normal, and characteristic findings on cross-sectional imaging.”
From middle of March to late April, the investigators identified 35 patients with acute pancreatitis at Royal Liverpool (England) University Hospital, 25 of whom tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, which resulted in study exclusion. An additional five patients were excluded from the series as another etiology for pancreatitis was clearly present, such as gallstones.
“The remaining 5 patients, all with SARS-CoV-2, presented atypically yet homogenously with a distinct metabolic-pancreatitis phenotype,” the investigators wrote.
All five patients were obese or overweight young men with a median body mass index of 30 kg/m2 and age of 42 years. On presentation, all patients had elevated, but nondiagnostic, levels of amylase (median, 149 U/L). Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT revealed moderate to severe hepatic steatosis (less than 104 HU), which rapidly regressed within a week among patients who underwent repeat imaging.
“The pattern of pancreatic inflammation was similarly unusual in these patients,” the investigators wrote, going on to describe “mild pancreatic edema without significant pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis, with distinct duodenal/periduodenal inflammation involving the second and third part of the duodenum.”
According to Dr. Szatmary and colleagues, these findings were “accompanied by a profound systemic inflammatory response,” including 1-2 criteria for systemic inflammatory response syndrome that increased to 2-4 criteria within 48 hours. During hospitalization, patients also exhibited a “dramatic elevation” of C-reactive protein, from a median of 31 mg/L upon admission to 485 mg/L within 48 hours.
Although these markers predicted severe disease, all cases followed a clinical course similar to “a typical attack of moderate pancreatitis,” the investigators wrote.
All patients were treated with IV fluids, four out of five received broad-spectrum IV antibiotics for pneumonitis, three out of five received fibrate and/or insulin therapy, and two out of five received pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy. No patients required corticosteroids, organ support, or respiratory support beyond low-flow oxygen. Median hospital stay was 14 days.
“We ... propose the combination of male sex, abdominal pain, metabolic stress, and CT-findings of predominantly pancreatico-duodenal inflammation with steatosis represent a distinct subset of pancreatitis in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2,” the investigators wrote.
They suggested that the endocrine pancreas may be “particularly vulnerable to this infection,” citing prolonged hospital stays because of poor diabetic control.
“[T]ransient dyslipidemias and impaired glucose tolerance may be common in SARS-CoV-2 patients and warrant further investigation,” they concluded.
Oscar J. Hines, MD, chief of the division of general surgery at UCLA Medical Center and leader in the field of pancreatitis management, said that the case series has a limited impact.
“The findings are unlikely to change practice and only call attention for physicians to the possibility of pancreatitis in COVID-positive patients,” Dr. Hines said.
The investigators reported grants from NIHR, Wellcome Trust, Mylan, and others.
SOURCE: Szatmary P et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.069.
Patients with COVID-19 develop a distinct subset of pancreatitis hallmarked by duodenal and periduodenal inflammation, according to a recent case series.
Although all five patients presented with multiple predictive markers of severe pancreatitis, the subsequent clinical pathway “was much more benign than anticipated,” reported lead author Peter Szatmary, MB, BChir, PhD, of the University of Liverpool (England) and colleagues. Still, they noted prolonged hospital stays because of persistent inflammation and poor diabetic control.
“As the global pandemic of SARS-CoV-2 continues, nuances of the disease it precipitates in humans continue to emerge,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. “[A] group from Wuhan reported a series of 9 patients with purported pancreatic injury in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection, but did not provide robust evidence for pancreatitis relying on mild hyperamylasemia alone.”
For the present series, Dr. Szatmary and colleagues restricted diagnosis of pancreatitis to international consensus guidelines, which require “abdominal pain consistent with pancreatitis, serum amylase/lipase greater than three times the upper limit of normal, and characteristic findings on cross-sectional imaging.”
From middle of March to late April, the investigators identified 35 patients with acute pancreatitis at Royal Liverpool (England) University Hospital, 25 of whom tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, which resulted in study exclusion. An additional five patients were excluded from the series as another etiology for pancreatitis was clearly present, such as gallstones.
“The remaining 5 patients, all with SARS-CoV-2, presented atypically yet homogenously with a distinct metabolic-pancreatitis phenotype,” the investigators wrote.
All five patients were obese or overweight young men with a median body mass index of 30 kg/m2 and age of 42 years. On presentation, all patients had elevated, but nondiagnostic, levels of amylase (median, 149 U/L). Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT revealed moderate to severe hepatic steatosis (less than 104 HU), which rapidly regressed within a week among patients who underwent repeat imaging.
“The pattern of pancreatic inflammation was similarly unusual in these patients,” the investigators wrote, going on to describe “mild pancreatic edema without significant pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis, with distinct duodenal/periduodenal inflammation involving the second and third part of the duodenum.”
According to Dr. Szatmary and colleagues, these findings were “accompanied by a profound systemic inflammatory response,” including 1-2 criteria for systemic inflammatory response syndrome that increased to 2-4 criteria within 48 hours. During hospitalization, patients also exhibited a “dramatic elevation” of C-reactive protein, from a median of 31 mg/L upon admission to 485 mg/L within 48 hours.
Although these markers predicted severe disease, all cases followed a clinical course similar to “a typical attack of moderate pancreatitis,” the investigators wrote.
All patients were treated with IV fluids, four out of five received broad-spectrum IV antibiotics for pneumonitis, three out of five received fibrate and/or insulin therapy, and two out of five received pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy. No patients required corticosteroids, organ support, or respiratory support beyond low-flow oxygen. Median hospital stay was 14 days.
“We ... propose the combination of male sex, abdominal pain, metabolic stress, and CT-findings of predominantly pancreatico-duodenal inflammation with steatosis represent a distinct subset of pancreatitis in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2,” the investigators wrote.
They suggested that the endocrine pancreas may be “particularly vulnerable to this infection,” citing prolonged hospital stays because of poor diabetic control.
“[T]ransient dyslipidemias and impaired glucose tolerance may be common in SARS-CoV-2 patients and warrant further investigation,” they concluded.
Oscar J. Hines, MD, chief of the division of general surgery at UCLA Medical Center and leader in the field of pancreatitis management, said that the case series has a limited impact.
“The findings are unlikely to change practice and only call attention for physicians to the possibility of pancreatitis in COVID-positive patients,” Dr. Hines said.
The investigators reported grants from NIHR, Wellcome Trust, Mylan, and others.
SOURCE: Szatmary P et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.069.
Patients with COVID-19 develop a distinct subset of pancreatitis hallmarked by duodenal and periduodenal inflammation, according to a recent case series.
Although all five patients presented with multiple predictive markers of severe pancreatitis, the subsequent clinical pathway “was much more benign than anticipated,” reported lead author Peter Szatmary, MB, BChir, PhD, of the University of Liverpool (England) and colleagues. Still, they noted prolonged hospital stays because of persistent inflammation and poor diabetic control.
“As the global pandemic of SARS-CoV-2 continues, nuances of the disease it precipitates in humans continue to emerge,” the investigators wrote in Gastroenterology. “[A] group from Wuhan reported a series of 9 patients with purported pancreatic injury in the context of SARS-CoV-2 infection, but did not provide robust evidence for pancreatitis relying on mild hyperamylasemia alone.”
For the present series, Dr. Szatmary and colleagues restricted diagnosis of pancreatitis to international consensus guidelines, which require “abdominal pain consistent with pancreatitis, serum amylase/lipase greater than three times the upper limit of normal, and characteristic findings on cross-sectional imaging.”
From middle of March to late April, the investigators identified 35 patients with acute pancreatitis at Royal Liverpool (England) University Hospital, 25 of whom tested negative for SARS-CoV-2, which resulted in study exclusion. An additional five patients were excluded from the series as another etiology for pancreatitis was clearly present, such as gallstones.
“The remaining 5 patients, all with SARS-CoV-2, presented atypically yet homogenously with a distinct metabolic-pancreatitis phenotype,” the investigators wrote.
All five patients were obese or overweight young men with a median body mass index of 30 kg/m2 and age of 42 years. On presentation, all patients had elevated, but nondiagnostic, levels of amylase (median, 149 U/L). Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT revealed moderate to severe hepatic steatosis (less than 104 HU), which rapidly regressed within a week among patients who underwent repeat imaging.
“The pattern of pancreatic inflammation was similarly unusual in these patients,” the investigators wrote, going on to describe “mild pancreatic edema without significant pancreatic or peripancreatic necrosis, with distinct duodenal/periduodenal inflammation involving the second and third part of the duodenum.”
According to Dr. Szatmary and colleagues, these findings were “accompanied by a profound systemic inflammatory response,” including 1-2 criteria for systemic inflammatory response syndrome that increased to 2-4 criteria within 48 hours. During hospitalization, patients also exhibited a “dramatic elevation” of C-reactive protein, from a median of 31 mg/L upon admission to 485 mg/L within 48 hours.
Although these markers predicted severe disease, all cases followed a clinical course similar to “a typical attack of moderate pancreatitis,” the investigators wrote.
All patients were treated with IV fluids, four out of five received broad-spectrum IV antibiotics for pneumonitis, three out of five received fibrate and/or insulin therapy, and two out of five received pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy. No patients required corticosteroids, organ support, or respiratory support beyond low-flow oxygen. Median hospital stay was 14 days.
“We ... propose the combination of male sex, abdominal pain, metabolic stress, and CT-findings of predominantly pancreatico-duodenal inflammation with steatosis represent a distinct subset of pancreatitis in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2,” the investigators wrote.
They suggested that the endocrine pancreas may be “particularly vulnerable to this infection,” citing prolonged hospital stays because of poor diabetic control.
“[T]ransient dyslipidemias and impaired glucose tolerance may be common in SARS-CoV-2 patients and warrant further investigation,” they concluded.
Oscar J. Hines, MD, chief of the division of general surgery at UCLA Medical Center and leader in the field of pancreatitis management, said that the case series has a limited impact.
“The findings are unlikely to change practice and only call attention for physicians to the possibility of pancreatitis in COVID-positive patients,” Dr. Hines said.
The investigators reported grants from NIHR, Wellcome Trust, Mylan, and others.
SOURCE: Szatmary P et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jun 1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.069.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY
First reported U.S. case of COVID-19 linked to Guillain-Barré syndrome
further supporting a link between the virus and neurologic complications, including GBS.
Physicians in China reported the first case of COVID-19 that initially presented as acute GBS. The patient was a 61-year-old woman returning home from Wuhan during the pandemic.
Subsequently, physicians in Italy reported five cases of GBS in association with COVID-19.
The first U.S. case is described in the June issue of the Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease.
Like cases from China and Italy, the U.S. patient’s symptoms of GBS reportedly occurred within days of being infected with SARS-CoV-2. “This onset is similar to a case report of acute Zika virus infection with concurrent GBS suggesting a parainfectious complication,” first author Sandeep Rana, MD, and colleagues noted.
The 54-year-old man was transferred to Allegheny General Hospital after developing ascending limb weakness and numbness that followed symptoms of a respiratory infection. Two weeks earlier, he initially developed rhinorrhea, odynophagia, fevers, chills, and night sweats. The man reported that his wife had tested positive for COVID-19 and that his symptoms started soon after her illness. The man also tested positive for COVID-19.
His deficits were characterized by quadriparesis and areflexia, burning dysesthesias, mild ophthalmoparesis, and dysautonomia. He did not have the loss of smell and taste documented in other COVID-19 patients. He briefly required mechanical ventilation and was successfully weaned after receiving a course of intravenous immunoglobulin.
Compared with other cases reported in the literature, the unique clinical features in the U.S. case are urinary retention secondary to dysautonomia and ocular symptoms of diplopia. These highlight the variability in the clinical presentation of GBS associated with COVID-19, the researchers noted.
They added that, with the Pittsburgh patient, electrophysiological findings were typical of demyelinating polyneuropathy seen in patients with GBS. The case series from Italy suggests that axonal variants could be as common in COVID-19–associated GBS.
“Although the number of documented cases internationally is notably small to date, it’s not completely surprising that a COVID-19 diagnosis may lead to a patient developing GBS. The increase of inflammation and inflammatory cells caused by the infection may trigger an irregular immune response that leads to the hallmark symptoms of this neurological disorder,” Dr. Rana said in a news release.
“Since GBS can significantly affect the respiratory system and other vital organs being pushed into overdrive during a COVID-19 immune response, it will be critically important to further investigate and understand this potential connection,” he added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
further supporting a link between the virus and neurologic complications, including GBS.
Physicians in China reported the first case of COVID-19 that initially presented as acute GBS. The patient was a 61-year-old woman returning home from Wuhan during the pandemic.
Subsequently, physicians in Italy reported five cases of GBS in association with COVID-19.
The first U.S. case is described in the June issue of the Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease.
Like cases from China and Italy, the U.S. patient’s symptoms of GBS reportedly occurred within days of being infected with SARS-CoV-2. “This onset is similar to a case report of acute Zika virus infection with concurrent GBS suggesting a parainfectious complication,” first author Sandeep Rana, MD, and colleagues noted.
The 54-year-old man was transferred to Allegheny General Hospital after developing ascending limb weakness and numbness that followed symptoms of a respiratory infection. Two weeks earlier, he initially developed rhinorrhea, odynophagia, fevers, chills, and night sweats. The man reported that his wife had tested positive for COVID-19 and that his symptoms started soon after her illness. The man also tested positive for COVID-19.
His deficits were characterized by quadriparesis and areflexia, burning dysesthesias, mild ophthalmoparesis, and dysautonomia. He did not have the loss of smell and taste documented in other COVID-19 patients. He briefly required mechanical ventilation and was successfully weaned after receiving a course of intravenous immunoglobulin.
Compared with other cases reported in the literature, the unique clinical features in the U.S. case are urinary retention secondary to dysautonomia and ocular symptoms of diplopia. These highlight the variability in the clinical presentation of GBS associated with COVID-19, the researchers noted.
They added that, with the Pittsburgh patient, electrophysiological findings were typical of demyelinating polyneuropathy seen in patients with GBS. The case series from Italy suggests that axonal variants could be as common in COVID-19–associated GBS.
“Although the number of documented cases internationally is notably small to date, it’s not completely surprising that a COVID-19 diagnosis may lead to a patient developing GBS. The increase of inflammation and inflammatory cells caused by the infection may trigger an irregular immune response that leads to the hallmark symptoms of this neurological disorder,” Dr. Rana said in a news release.
“Since GBS can significantly affect the respiratory system and other vital organs being pushed into overdrive during a COVID-19 immune response, it will be critically important to further investigate and understand this potential connection,” he added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
further supporting a link between the virus and neurologic complications, including GBS.
Physicians in China reported the first case of COVID-19 that initially presented as acute GBS. The patient was a 61-year-old woman returning home from Wuhan during the pandemic.
Subsequently, physicians in Italy reported five cases of GBS in association with COVID-19.
The first U.S. case is described in the June issue of the Journal of Clinical Neuromuscular Disease.
Like cases from China and Italy, the U.S. patient’s symptoms of GBS reportedly occurred within days of being infected with SARS-CoV-2. “This onset is similar to a case report of acute Zika virus infection with concurrent GBS suggesting a parainfectious complication,” first author Sandeep Rana, MD, and colleagues noted.
The 54-year-old man was transferred to Allegheny General Hospital after developing ascending limb weakness and numbness that followed symptoms of a respiratory infection. Two weeks earlier, he initially developed rhinorrhea, odynophagia, fevers, chills, and night sweats. The man reported that his wife had tested positive for COVID-19 and that his symptoms started soon after her illness. The man also tested positive for COVID-19.
His deficits were characterized by quadriparesis and areflexia, burning dysesthesias, mild ophthalmoparesis, and dysautonomia. He did not have the loss of smell and taste documented in other COVID-19 patients. He briefly required mechanical ventilation and was successfully weaned after receiving a course of intravenous immunoglobulin.
Compared with other cases reported in the literature, the unique clinical features in the U.S. case are urinary retention secondary to dysautonomia and ocular symptoms of diplopia. These highlight the variability in the clinical presentation of GBS associated with COVID-19, the researchers noted.
They added that, with the Pittsburgh patient, electrophysiological findings were typical of demyelinating polyneuropathy seen in patients with GBS. The case series from Italy suggests that axonal variants could be as common in COVID-19–associated GBS.
“Although the number of documented cases internationally is notably small to date, it’s not completely surprising that a COVID-19 diagnosis may lead to a patient developing GBS. The increase of inflammation and inflammatory cells caused by the infection may trigger an irregular immune response that leads to the hallmark symptoms of this neurological disorder,” Dr. Rana said in a news release.
“Since GBS can significantly affect the respiratory system and other vital organs being pushed into overdrive during a COVID-19 immune response, it will be critically important to further investigate and understand this potential connection,” he added.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
What COVID-19 has taught us about senior care
Across the globe, there are marked differences in how countries responded to the COVID-19 outbreak, with varying degrees of success in limiting the spread of the virus. Some countries learned important lessons from previous outbreaks, including SARS and MERS, and put policies in place that contributed to lower infection and death rates from COVID-19 in these countries. Others struggled to respond appropriately to the outbreak.
The United States and most of the world was not affected significantly by SARS and MERS. Hence there is a need for different perspectives and observations on lessons that can be learned from this outbreak to help develop effective strategies and policies for the future. It also makes sense to focus intently on the demographic most affected by COVID-19 – the elderly.
Medical care, for the most part, is governed by protocols that clearly detail processes to be followed for the prevention and treatment of disease. Caring for older patients requires going above and beyond the protocols. That is one of the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic – a wake-up call for a more proactive approach for at-risk patients, in this case everyone over the age of 60 years.
In this context, it is important for medical outreach to continue with the senior population long after the pandemic has run its course. Many seniors, particularly those susceptible to other illnesses or exhibiting ongoing issues, would benefit from a consistent and preplanned pattern of contacts by medical professionals and agencies that work with the aging population. These proactive follow-ups can facilitate prevention and treatment and, at the same time, reduce costs that would otherwise increase when health care is reactive.
Lessons in infectious disease containment
As COVID-19 spread globally, there were contrasting responses from individual countries in their efforts to contain the disease. Unfortunately, Italy suffered from its decision to lock down only specific regions of the country initially. The leadership in Italy may have ignored the advice of medical experts and been caught off guard by the intensity of the spread of COVID-19. In fact, they might not have taken strict actions right away because they did not want their responses to be viewed as an overreaction to the disease.
The government decided to shut down areas where the infection rates were high (“red zones”) rather than implement restrictions nationally. This may have inadvertently increased the spread as Italians vacated those “red zones” for other areas of the country not yet affected by COVID-19. Italy’s decentralized health care system also played a part in the effects of the disease, with some regions demonstrating more success in slowing the reach of the disease. According to an article in the Harvard Business Review, the neighboring regions of Lombardy and Veneto applied similar approaches to social distancing and retail closures. Veneto was more proactive, and its response to the outbreak was multipronged, including putting a “strong emphasis on home diagnosis and care” and “specific efforts to monitor and protect health care and other essential workers.” These measures most likely contributed to a slowdown of the spread of the disease in Veneto’s health care facilities, which lessened the load on medical providers.1
Conversely, Taiwan implemented proactive measures swiftly after learning about COVID-19. Taiwan was impacted adversely by the SARS outbreak in 2003 and, afterward, revised their medical policies and procedures to respond quickly to future infectious disease crises. In the beginning, little was known about COVID-19 or how it spread. However, Taiwan’s swift public health response to COVID-19 included early travel restrictions, patient screening, and quarantining of symptomatic patients. The government emphasized education and created real-time digital updates and alerts sent to their citizens, as well as partnering with media to broadcast crucial proactive health information and quickly disproving false information related to COVID-19. They coordinated with organizations throughout the country to increase supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE).2
Although countries and even cities within a country differ in terms of population demographics, health resources, government policies, and cultural practices, initial success stories have some similarities, including the following:
- Early travel restrictions from countries with positive cases, with some circumstances requiring compulsory quarantine periods and testing before entry.
- Extensive testing and proactive tracing of symptomatic cases early. Contacts of people testing positive were also tested, irrespective of being symptomatic or asymptomatic. If testing kits were unavailable, the contacts were self-quarantined.
- Emphasis on avoiding overburdening hospitals by having the public health infrastructure to divert people exhibiting symptoms, including using public health hotlines to send patients to dedicated testing sites and drive-through testing, rather than have patients presenting to emergency rooms and hospitals. This approach protected medical staff from exposure and allowed the focus to remain on treating severe symptomatic patients.
The vastly different response to the COVID-19 outbreak in these two countries illuminates the need for better preparation in the United States. At the onset of this outbreak, emergency room medical professionals, hospitalists, and outpatient primary care providers did not know how to screen for or treat this virus. Additionally, there was limited information on the most effective contact protocols for medical professionals, patients, and visitors. Finally, the lack of PPE and COVID-19 test kits hindered the U.S. response. Once the country is on the road to recovery from COVID-19, it is imperative to set the groundwork to prepare for future outbreaks and create mechanisms to quickly identify vulnerable populations when outbreaks occur.
Senior care in future infectious disease outbreaks
How can medical providers translate lessons learned from this outbreak into improving the quality of care for seniors? The National Institute on Aging (NIA) maintains a website with information about healthy aging. Seniors and their caregivers can use this website to learn more about chronic diseases, lifestyle modifications, disease prevention, and mental health.
In times of a pandemic, this website provides consistent and accurate information and education. One recommendation for reaching the elderly population during future outbreaks is for NIA to develop and implement strategies to increase the use of the website, including adding more audio and visual interfaces and developing a mobile app. Other recommendations for improving the quality of care for seniors include the following:
1. Identify which populations may be most affected when future outbreaks occur.
2. Consider nontraditional platforms, including social media, for communicating with the general population and for medical providers worldwide to learn from each other about new diseases, including the signs, symptoms, and treatment plans. Some medical professionals created specific WhatsApp groups to communicate, and the World Health Organization sent updated information about COVID-19 to anyone who texted them via WhatsApp.3
3. Create a checklist of signs and symptoms related to current infectious diseases and assess every vulnerable patient.
4. Share these guidelines with medical facilities that treat these populations, such as senior care, assisted living and rehabilitation facilities, hospitals, and outpatient treatment centers. Teach the staff at these medical facilities how to screen patients for signs and symptoms of the disease.
5. Implement social isolation strategies, travel and visitor restrictions, and testing and screening as soon as possible at these medical facilities.
6. Recognize that these strategies may affect the psychological and emotional well-being of seniors, increasing their risk for depression and anxiety and negatively affecting their immunity and mental health. Additionally, the use of PPE, either by the medical providers or the patient, may cause anxiety in seniors and those with mild cognitive impairment.
7. Encourage these medical facilities to improve coping strategies with older patients, such as incorporating communication technology that helps seniors stay connected with their families, and participating in physical and mental exercise, as well as religious activities.
8. Ask these medical facilities to create isolation or quarantine rooms for infected seniors.
9. Work with family members to proactively report to medical professionals any symptoms noticed in their senior relatives. Educate seniors to report symptoms earlier.
10. Offer incentives for medical professionals to conduct on-site testing in primary care offices or senior care facilities instead of sending patients to hospital emergency rooms for evaluation. This will only be effective if there are enough test kits available.
11. Urge insurance companies and Medicare to allow additional medical visits for screening vulnerable populations. Encourage the use of telemedicine in place of in-office visits (preferably billed at the same rate as an in-office visit) where appropriate, especially with nonambulatory patients or those with transportation issues. Many insurance companies, including Medicare, approved COVID-19–related coverage of telemedicine in place of office visits to limit the spread of the disease.
12. Provide community health care and integration and better coordination of local, state, and national health care.
13. Hold regular epidemic and pandemic preparedness exercises in every hospital, nursing home, and assisted living facility.
Proactive health care outreach
It is easier to identify the signs and symptoms of already identified infectious diseases as opposed to a novel one like COVID-19. The United States faced a steep learning curve with COVID-19. Hospitalists and other medical professionals were not able to learn about COVID-19 in a journal. At first, they did not know how to screen patients coming into the ER, how to protect staff, or what the treatment plan was for this new disease. As a result, the medical system experienced disorder and confusion. Investing in community health care and better coordination of local, state, and national health care resources is a priority.
The senior citizen population appears to be most vulnerable to this virus and may be just as vulnerable in future outbreaks. Yet the insights gained from this pandemic can lead to a more comprehensive outreach to senior patients and increased screenings for comorbidities and future contagious diseases. An emphasis on proactive health care and outreach for seniors, with a focus on identifying and treating comorbid conditions, improves the medical care system overall and may prevent or slow future community outbreaks.
Dr. Kasarla is a hospitalist with APOGEE Physicians at Wise Surgical at Parkway in Fort Worth, Tex. He did his internal medicine residency at Mercy Hospital & Medical Center, Chicago. Readers can contact him at madhukarreddy.kasarla@apogeephysicians.com. Dr. Devireddy is a family physician at Positive Health Medical Center, Kingston, Jamaica. Contact him at drjaisheel@gmail.com.
References
1. Pisano GP et al. Lessons from Italy’s response to coronavirus. Harvard Business Review. 2020 Mar 27. https://hbr.org/2020/03/lessons-from-italys-response-to-coronavirus.
2. Tu C. Lessons from Taiwan’s experience with COVID-19. New Atlanticist. 2020 Apr 7. https://atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/lessons-from-taiwans-experience-with-covid-19/.
3. Newman LH. WhatsApp is at the center of coronavirus response. WIRED. 2020 Mar 20. https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-coronavirus-who-information-app/.
Across the globe, there are marked differences in how countries responded to the COVID-19 outbreak, with varying degrees of success in limiting the spread of the virus. Some countries learned important lessons from previous outbreaks, including SARS and MERS, and put policies in place that contributed to lower infection and death rates from COVID-19 in these countries. Others struggled to respond appropriately to the outbreak.
The United States and most of the world was not affected significantly by SARS and MERS. Hence there is a need for different perspectives and observations on lessons that can be learned from this outbreak to help develop effective strategies and policies for the future. It also makes sense to focus intently on the demographic most affected by COVID-19 – the elderly.
Medical care, for the most part, is governed by protocols that clearly detail processes to be followed for the prevention and treatment of disease. Caring for older patients requires going above and beyond the protocols. That is one of the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic – a wake-up call for a more proactive approach for at-risk patients, in this case everyone over the age of 60 years.
In this context, it is important for medical outreach to continue with the senior population long after the pandemic has run its course. Many seniors, particularly those susceptible to other illnesses or exhibiting ongoing issues, would benefit from a consistent and preplanned pattern of contacts by medical professionals and agencies that work with the aging population. These proactive follow-ups can facilitate prevention and treatment and, at the same time, reduce costs that would otherwise increase when health care is reactive.
Lessons in infectious disease containment
As COVID-19 spread globally, there were contrasting responses from individual countries in their efforts to contain the disease. Unfortunately, Italy suffered from its decision to lock down only specific regions of the country initially. The leadership in Italy may have ignored the advice of medical experts and been caught off guard by the intensity of the spread of COVID-19. In fact, they might not have taken strict actions right away because they did not want their responses to be viewed as an overreaction to the disease.
The government decided to shut down areas where the infection rates were high (“red zones”) rather than implement restrictions nationally. This may have inadvertently increased the spread as Italians vacated those “red zones” for other areas of the country not yet affected by COVID-19. Italy’s decentralized health care system also played a part in the effects of the disease, with some regions demonstrating more success in slowing the reach of the disease. According to an article in the Harvard Business Review, the neighboring regions of Lombardy and Veneto applied similar approaches to social distancing and retail closures. Veneto was more proactive, and its response to the outbreak was multipronged, including putting a “strong emphasis on home diagnosis and care” and “specific efforts to monitor and protect health care and other essential workers.” These measures most likely contributed to a slowdown of the spread of the disease in Veneto’s health care facilities, which lessened the load on medical providers.1
Conversely, Taiwan implemented proactive measures swiftly after learning about COVID-19. Taiwan was impacted adversely by the SARS outbreak in 2003 and, afterward, revised their medical policies and procedures to respond quickly to future infectious disease crises. In the beginning, little was known about COVID-19 or how it spread. However, Taiwan’s swift public health response to COVID-19 included early travel restrictions, patient screening, and quarantining of symptomatic patients. The government emphasized education and created real-time digital updates and alerts sent to their citizens, as well as partnering with media to broadcast crucial proactive health information and quickly disproving false information related to COVID-19. They coordinated with organizations throughout the country to increase supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE).2
Although countries and even cities within a country differ in terms of population demographics, health resources, government policies, and cultural practices, initial success stories have some similarities, including the following:
- Early travel restrictions from countries with positive cases, with some circumstances requiring compulsory quarantine periods and testing before entry.
- Extensive testing and proactive tracing of symptomatic cases early. Contacts of people testing positive were also tested, irrespective of being symptomatic or asymptomatic. If testing kits were unavailable, the contacts were self-quarantined.
- Emphasis on avoiding overburdening hospitals by having the public health infrastructure to divert people exhibiting symptoms, including using public health hotlines to send patients to dedicated testing sites and drive-through testing, rather than have patients presenting to emergency rooms and hospitals. This approach protected medical staff from exposure and allowed the focus to remain on treating severe symptomatic patients.
The vastly different response to the COVID-19 outbreak in these two countries illuminates the need for better preparation in the United States. At the onset of this outbreak, emergency room medical professionals, hospitalists, and outpatient primary care providers did not know how to screen for or treat this virus. Additionally, there was limited information on the most effective contact protocols for medical professionals, patients, and visitors. Finally, the lack of PPE and COVID-19 test kits hindered the U.S. response. Once the country is on the road to recovery from COVID-19, it is imperative to set the groundwork to prepare for future outbreaks and create mechanisms to quickly identify vulnerable populations when outbreaks occur.
Senior care in future infectious disease outbreaks
How can medical providers translate lessons learned from this outbreak into improving the quality of care for seniors? The National Institute on Aging (NIA) maintains a website with information about healthy aging. Seniors and their caregivers can use this website to learn more about chronic diseases, lifestyle modifications, disease prevention, and mental health.
In times of a pandemic, this website provides consistent and accurate information and education. One recommendation for reaching the elderly population during future outbreaks is for NIA to develop and implement strategies to increase the use of the website, including adding more audio and visual interfaces and developing a mobile app. Other recommendations for improving the quality of care for seniors include the following:
1. Identify which populations may be most affected when future outbreaks occur.
2. Consider nontraditional platforms, including social media, for communicating with the general population and for medical providers worldwide to learn from each other about new diseases, including the signs, symptoms, and treatment plans. Some medical professionals created specific WhatsApp groups to communicate, and the World Health Organization sent updated information about COVID-19 to anyone who texted them via WhatsApp.3
3. Create a checklist of signs and symptoms related to current infectious diseases and assess every vulnerable patient.
4. Share these guidelines with medical facilities that treat these populations, such as senior care, assisted living and rehabilitation facilities, hospitals, and outpatient treatment centers. Teach the staff at these medical facilities how to screen patients for signs and symptoms of the disease.
5. Implement social isolation strategies, travel and visitor restrictions, and testing and screening as soon as possible at these medical facilities.
6. Recognize that these strategies may affect the psychological and emotional well-being of seniors, increasing their risk for depression and anxiety and negatively affecting their immunity and mental health. Additionally, the use of PPE, either by the medical providers or the patient, may cause anxiety in seniors and those with mild cognitive impairment.
7. Encourage these medical facilities to improve coping strategies with older patients, such as incorporating communication technology that helps seniors stay connected with their families, and participating in physical and mental exercise, as well as religious activities.
8. Ask these medical facilities to create isolation or quarantine rooms for infected seniors.
9. Work with family members to proactively report to medical professionals any symptoms noticed in their senior relatives. Educate seniors to report symptoms earlier.
10. Offer incentives for medical professionals to conduct on-site testing in primary care offices or senior care facilities instead of sending patients to hospital emergency rooms for evaluation. This will only be effective if there are enough test kits available.
11. Urge insurance companies and Medicare to allow additional medical visits for screening vulnerable populations. Encourage the use of telemedicine in place of in-office visits (preferably billed at the same rate as an in-office visit) where appropriate, especially with nonambulatory patients or those with transportation issues. Many insurance companies, including Medicare, approved COVID-19–related coverage of telemedicine in place of office visits to limit the spread of the disease.
12. Provide community health care and integration and better coordination of local, state, and national health care.
13. Hold regular epidemic and pandemic preparedness exercises in every hospital, nursing home, and assisted living facility.
Proactive health care outreach
It is easier to identify the signs and symptoms of already identified infectious diseases as opposed to a novel one like COVID-19. The United States faced a steep learning curve with COVID-19. Hospitalists and other medical professionals were not able to learn about COVID-19 in a journal. At first, they did not know how to screen patients coming into the ER, how to protect staff, or what the treatment plan was for this new disease. As a result, the medical system experienced disorder and confusion. Investing in community health care and better coordination of local, state, and national health care resources is a priority.
The senior citizen population appears to be most vulnerable to this virus and may be just as vulnerable in future outbreaks. Yet the insights gained from this pandemic can lead to a more comprehensive outreach to senior patients and increased screenings for comorbidities and future contagious diseases. An emphasis on proactive health care and outreach for seniors, with a focus on identifying and treating comorbid conditions, improves the medical care system overall and may prevent or slow future community outbreaks.
Dr. Kasarla is a hospitalist with APOGEE Physicians at Wise Surgical at Parkway in Fort Worth, Tex. He did his internal medicine residency at Mercy Hospital & Medical Center, Chicago. Readers can contact him at madhukarreddy.kasarla@apogeephysicians.com. Dr. Devireddy is a family physician at Positive Health Medical Center, Kingston, Jamaica. Contact him at drjaisheel@gmail.com.
References
1. Pisano GP et al. Lessons from Italy’s response to coronavirus. Harvard Business Review. 2020 Mar 27. https://hbr.org/2020/03/lessons-from-italys-response-to-coronavirus.
2. Tu C. Lessons from Taiwan’s experience with COVID-19. New Atlanticist. 2020 Apr 7. https://atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/lessons-from-taiwans-experience-with-covid-19/.
3. Newman LH. WhatsApp is at the center of coronavirus response. WIRED. 2020 Mar 20. https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-coronavirus-who-information-app/.
Across the globe, there are marked differences in how countries responded to the COVID-19 outbreak, with varying degrees of success in limiting the spread of the virus. Some countries learned important lessons from previous outbreaks, including SARS and MERS, and put policies in place that contributed to lower infection and death rates from COVID-19 in these countries. Others struggled to respond appropriately to the outbreak.
The United States and most of the world was not affected significantly by SARS and MERS. Hence there is a need for different perspectives and observations on lessons that can be learned from this outbreak to help develop effective strategies and policies for the future. It also makes sense to focus intently on the demographic most affected by COVID-19 – the elderly.
Medical care, for the most part, is governed by protocols that clearly detail processes to be followed for the prevention and treatment of disease. Caring for older patients requires going above and beyond the protocols. That is one of the lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic – a wake-up call for a more proactive approach for at-risk patients, in this case everyone over the age of 60 years.
In this context, it is important for medical outreach to continue with the senior population long after the pandemic has run its course. Many seniors, particularly those susceptible to other illnesses or exhibiting ongoing issues, would benefit from a consistent and preplanned pattern of contacts by medical professionals and agencies that work with the aging population. These proactive follow-ups can facilitate prevention and treatment and, at the same time, reduce costs that would otherwise increase when health care is reactive.
Lessons in infectious disease containment
As COVID-19 spread globally, there were contrasting responses from individual countries in their efforts to contain the disease. Unfortunately, Italy suffered from its decision to lock down only specific regions of the country initially. The leadership in Italy may have ignored the advice of medical experts and been caught off guard by the intensity of the spread of COVID-19. In fact, they might not have taken strict actions right away because they did not want their responses to be viewed as an overreaction to the disease.
The government decided to shut down areas where the infection rates were high (“red zones”) rather than implement restrictions nationally. This may have inadvertently increased the spread as Italians vacated those “red zones” for other areas of the country not yet affected by COVID-19. Italy’s decentralized health care system also played a part in the effects of the disease, with some regions demonstrating more success in slowing the reach of the disease. According to an article in the Harvard Business Review, the neighboring regions of Lombardy and Veneto applied similar approaches to social distancing and retail closures. Veneto was more proactive, and its response to the outbreak was multipronged, including putting a “strong emphasis on home diagnosis and care” and “specific efforts to monitor and protect health care and other essential workers.” These measures most likely contributed to a slowdown of the spread of the disease in Veneto’s health care facilities, which lessened the load on medical providers.1
Conversely, Taiwan implemented proactive measures swiftly after learning about COVID-19. Taiwan was impacted adversely by the SARS outbreak in 2003 and, afterward, revised their medical policies and procedures to respond quickly to future infectious disease crises. In the beginning, little was known about COVID-19 or how it spread. However, Taiwan’s swift public health response to COVID-19 included early travel restrictions, patient screening, and quarantining of symptomatic patients. The government emphasized education and created real-time digital updates and alerts sent to their citizens, as well as partnering with media to broadcast crucial proactive health information and quickly disproving false information related to COVID-19. They coordinated with organizations throughout the country to increase supplies of personal protective equipment (PPE).2
Although countries and even cities within a country differ in terms of population demographics, health resources, government policies, and cultural practices, initial success stories have some similarities, including the following:
- Early travel restrictions from countries with positive cases, with some circumstances requiring compulsory quarantine periods and testing before entry.
- Extensive testing and proactive tracing of symptomatic cases early. Contacts of people testing positive were also tested, irrespective of being symptomatic or asymptomatic. If testing kits were unavailable, the contacts were self-quarantined.
- Emphasis on avoiding overburdening hospitals by having the public health infrastructure to divert people exhibiting symptoms, including using public health hotlines to send patients to dedicated testing sites and drive-through testing, rather than have patients presenting to emergency rooms and hospitals. This approach protected medical staff from exposure and allowed the focus to remain on treating severe symptomatic patients.
The vastly different response to the COVID-19 outbreak in these two countries illuminates the need for better preparation in the United States. At the onset of this outbreak, emergency room medical professionals, hospitalists, and outpatient primary care providers did not know how to screen for or treat this virus. Additionally, there was limited information on the most effective contact protocols for medical professionals, patients, and visitors. Finally, the lack of PPE and COVID-19 test kits hindered the U.S. response. Once the country is on the road to recovery from COVID-19, it is imperative to set the groundwork to prepare for future outbreaks and create mechanisms to quickly identify vulnerable populations when outbreaks occur.
Senior care in future infectious disease outbreaks
How can medical providers translate lessons learned from this outbreak into improving the quality of care for seniors? The National Institute on Aging (NIA) maintains a website with information about healthy aging. Seniors and their caregivers can use this website to learn more about chronic diseases, lifestyle modifications, disease prevention, and mental health.
In times of a pandemic, this website provides consistent and accurate information and education. One recommendation for reaching the elderly population during future outbreaks is for NIA to develop and implement strategies to increase the use of the website, including adding more audio and visual interfaces and developing a mobile app. Other recommendations for improving the quality of care for seniors include the following:
1. Identify which populations may be most affected when future outbreaks occur.
2. Consider nontraditional platforms, including social media, for communicating with the general population and for medical providers worldwide to learn from each other about new diseases, including the signs, symptoms, and treatment plans. Some medical professionals created specific WhatsApp groups to communicate, and the World Health Organization sent updated information about COVID-19 to anyone who texted them via WhatsApp.3
3. Create a checklist of signs and symptoms related to current infectious diseases and assess every vulnerable patient.
4. Share these guidelines with medical facilities that treat these populations, such as senior care, assisted living and rehabilitation facilities, hospitals, and outpatient treatment centers. Teach the staff at these medical facilities how to screen patients for signs and symptoms of the disease.
5. Implement social isolation strategies, travel and visitor restrictions, and testing and screening as soon as possible at these medical facilities.
6. Recognize that these strategies may affect the psychological and emotional well-being of seniors, increasing their risk for depression and anxiety and negatively affecting their immunity and mental health. Additionally, the use of PPE, either by the medical providers or the patient, may cause anxiety in seniors and those with mild cognitive impairment.
7. Encourage these medical facilities to improve coping strategies with older patients, such as incorporating communication technology that helps seniors stay connected with their families, and participating in physical and mental exercise, as well as religious activities.
8. Ask these medical facilities to create isolation or quarantine rooms for infected seniors.
9. Work with family members to proactively report to medical professionals any symptoms noticed in their senior relatives. Educate seniors to report symptoms earlier.
10. Offer incentives for medical professionals to conduct on-site testing in primary care offices or senior care facilities instead of sending patients to hospital emergency rooms for evaluation. This will only be effective if there are enough test kits available.
11. Urge insurance companies and Medicare to allow additional medical visits for screening vulnerable populations. Encourage the use of telemedicine in place of in-office visits (preferably billed at the same rate as an in-office visit) where appropriate, especially with nonambulatory patients or those with transportation issues. Many insurance companies, including Medicare, approved COVID-19–related coverage of telemedicine in place of office visits to limit the spread of the disease.
12. Provide community health care and integration and better coordination of local, state, and national health care.
13. Hold regular epidemic and pandemic preparedness exercises in every hospital, nursing home, and assisted living facility.
Proactive health care outreach
It is easier to identify the signs and symptoms of already identified infectious diseases as opposed to a novel one like COVID-19. The United States faced a steep learning curve with COVID-19. Hospitalists and other medical professionals were not able to learn about COVID-19 in a journal. At first, they did not know how to screen patients coming into the ER, how to protect staff, or what the treatment plan was for this new disease. As a result, the medical system experienced disorder and confusion. Investing in community health care and better coordination of local, state, and national health care resources is a priority.
The senior citizen population appears to be most vulnerable to this virus and may be just as vulnerable in future outbreaks. Yet the insights gained from this pandemic can lead to a more comprehensive outreach to senior patients and increased screenings for comorbidities and future contagious diseases. An emphasis on proactive health care and outreach for seniors, with a focus on identifying and treating comorbid conditions, improves the medical care system overall and may prevent or slow future community outbreaks.
Dr. Kasarla is a hospitalist with APOGEE Physicians at Wise Surgical at Parkway in Fort Worth, Tex. He did his internal medicine residency at Mercy Hospital & Medical Center, Chicago. Readers can contact him at madhukarreddy.kasarla@apogeephysicians.com. Dr. Devireddy is a family physician at Positive Health Medical Center, Kingston, Jamaica. Contact him at drjaisheel@gmail.com.
References
1. Pisano GP et al. Lessons from Italy’s response to coronavirus. Harvard Business Review. 2020 Mar 27. https://hbr.org/2020/03/lessons-from-italys-response-to-coronavirus.
2. Tu C. Lessons from Taiwan’s experience with COVID-19. New Atlanticist. 2020 Apr 7. https://atlanticcouncil.org/blogs/new-atlanticist/lessons-from-taiwans-experience-with-covid-19/.
3. Newman LH. WhatsApp is at the center of coronavirus response. WIRED. 2020 Mar 20. https://www.wired.com/story/whatsapp-coronavirus-who-information-app/.
Telehealth and medical liability
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the rapid uptake of telehealth nationwide in primary care and specialty practices. Over the last few months many practices have actually performed more telehealth visits than traditional in-person visits. The use of telehealth, which had been increasing slowly for the last few years, accelerated rapidly during the pandemic. Long term, telehealth has the potential to increase access to primary care and specialists, and make follow-up easier for many patients, changing how health care is delivered to millions of patients throughout the world.
Since telehealth will be a regular part of our practices from now on, it is important for clinicians to recognize how telehealth visits are viewed in a legal arena.
As is often the case with technological advances, the law needs time to adapt. Will a health care provider treating a patient using telemedicine be held to the same standard of care applicable to an in-person encounter? Stated differently, will consideration be given to the obvious limitations imposed by a telemedicine exam?
Standard of care in medical malpractice cases
The central question in most medical malpractice cases is whether the provider complied with the generally accepted standard of care when evaluating, diagnosing, or treating a patient. This standard typically takes into consideration the provider’s particular specialty as well as all the circumstances surrounding the encounter.1 Medical providers, not state legislators, usually define the standard of care for medical professionals. In malpractice cases, medical experts explain the applicable standard of care to the jury and guide its determination of whether, in the particular case, the standard of care was met. In this way, the law has long recognized that the medical profession itself is best suited to establish the appropriate standards of care under any particular set of circumstances. This standard of care is often referred to as the “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard of care.
Telemedicine standard of care
Despite the fact that the complex and often nebulous concept of standard of care has been traditionally left to the medical experts to define, state legislators and regulators throughout the nation have chosen to weigh in on this issue in the context of telemedicine. Most states with telemedicine regulations have followed the model policy adopted by the Federation of State Medical Boards in April 2014 which states that “[t]reatment and consultation recommendations made in an online setting … will be held to the same standards of appropriate practice as those in traditional (in-person) settings.”2 States that have adopted this model policy have effectively created a “legal fiction” requiring a jury to ignore the fact that the care was provided virtually by telemedicine technologies and instead assume that the physician treated the patient in person, i.e, applying an “in-person” standard of care. Hawaii appears to be the lone notable exception. Its telemedicine law recognizes that an in-person standard of care should not be applied if there was not a face-to-face visit.3
Proponents of the in-person telemedicine standard claim that it is necessary to ensure patient safety, thus justifying the “legal fiction.” Holding the provider to the in-person standard, it is argued, forces the physician to err on the side of caution and require an actual in-person encounter to ensure the advantages of sight, touch, and sense of things are fully available.4 This discourages the use of telemedicine and deprives the population of its many benefits.
Telemedicine can overcome geographical barriers, increase clinical support, improve health outcomes, reduce health care costs, encourage patient input, reduce travel, and foster continuity of care. The pandemic, which has significantly limited the ability of providers to see patients in person, only underscores the benefits of telemedicine.
The legislatively imposed in-person telemedicine standard of care should be replaced with the “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard in order to fairly judge physicians’ care and promote overall population health. The “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard has applied to physicians and other health care professionals outside of telemedicine for decades, and it has served the medical community and public well. It is unfortunate that legislators felt the need to weigh in and define a distinctly different standard of care for telemedicine than for the rest of medicine, as this may present unforeseen obstacles to the use of telemedicine.
The in-person telemedicine standard of care remains a significant barrier for long-term telemedicine. Eliminating this legal fiction has the potential to further expand physicians’ use of telemedicine and fulfill its promise of improving access to care and improving population health.
Mr. Horner (partner), Mr. Milewski (partner), and Mr. Gajer (associate) are attorneys with White and Williams. They specialize in defending health care providers in medical malpractice lawsuits and other health care–related matters. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community Medicine at the Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow Dr. Skolnik, and feel free to submit questions to him on Twitter: @neilskolnik. The authors have no financial conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Cowan v. Doering, 111 N.J. 451-62,.1988.
2. Model Policy For The Appropriate Use Of Telemedicine Technologies In The Practice Of Medicine. State Medical Boards Appropriate Regulation of Telemedicine. April 2014..
3. Haw. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 453-1.3(c).
4. Kaspar BJ. Iowa Law Review. 2014 Jan;99:839-59.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the rapid uptake of telehealth nationwide in primary care and specialty practices. Over the last few months many practices have actually performed more telehealth visits than traditional in-person visits. The use of telehealth, which had been increasing slowly for the last few years, accelerated rapidly during the pandemic. Long term, telehealth has the potential to increase access to primary care and specialists, and make follow-up easier for many patients, changing how health care is delivered to millions of patients throughout the world.
Since telehealth will be a regular part of our practices from now on, it is important for clinicians to recognize how telehealth visits are viewed in a legal arena.
As is often the case with technological advances, the law needs time to adapt. Will a health care provider treating a patient using telemedicine be held to the same standard of care applicable to an in-person encounter? Stated differently, will consideration be given to the obvious limitations imposed by a telemedicine exam?
Standard of care in medical malpractice cases
The central question in most medical malpractice cases is whether the provider complied with the generally accepted standard of care when evaluating, diagnosing, or treating a patient. This standard typically takes into consideration the provider’s particular specialty as well as all the circumstances surrounding the encounter.1 Medical providers, not state legislators, usually define the standard of care for medical professionals. In malpractice cases, medical experts explain the applicable standard of care to the jury and guide its determination of whether, in the particular case, the standard of care was met. In this way, the law has long recognized that the medical profession itself is best suited to establish the appropriate standards of care under any particular set of circumstances. This standard of care is often referred to as the “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard of care.
Telemedicine standard of care
Despite the fact that the complex and often nebulous concept of standard of care has been traditionally left to the medical experts to define, state legislators and regulators throughout the nation have chosen to weigh in on this issue in the context of telemedicine. Most states with telemedicine regulations have followed the model policy adopted by the Federation of State Medical Boards in April 2014 which states that “[t]reatment and consultation recommendations made in an online setting … will be held to the same standards of appropriate practice as those in traditional (in-person) settings.”2 States that have adopted this model policy have effectively created a “legal fiction” requiring a jury to ignore the fact that the care was provided virtually by telemedicine technologies and instead assume that the physician treated the patient in person, i.e, applying an “in-person” standard of care. Hawaii appears to be the lone notable exception. Its telemedicine law recognizes that an in-person standard of care should not be applied if there was not a face-to-face visit.3
Proponents of the in-person telemedicine standard claim that it is necessary to ensure patient safety, thus justifying the “legal fiction.” Holding the provider to the in-person standard, it is argued, forces the physician to err on the side of caution and require an actual in-person encounter to ensure the advantages of sight, touch, and sense of things are fully available.4 This discourages the use of telemedicine and deprives the population of its many benefits.
Telemedicine can overcome geographical barriers, increase clinical support, improve health outcomes, reduce health care costs, encourage patient input, reduce travel, and foster continuity of care. The pandemic, which has significantly limited the ability of providers to see patients in person, only underscores the benefits of telemedicine.
The legislatively imposed in-person telemedicine standard of care should be replaced with the “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard in order to fairly judge physicians’ care and promote overall population health. The “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard has applied to physicians and other health care professionals outside of telemedicine for decades, and it has served the medical community and public well. It is unfortunate that legislators felt the need to weigh in and define a distinctly different standard of care for telemedicine than for the rest of medicine, as this may present unforeseen obstacles to the use of telemedicine.
The in-person telemedicine standard of care remains a significant barrier for long-term telemedicine. Eliminating this legal fiction has the potential to further expand physicians’ use of telemedicine and fulfill its promise of improving access to care and improving population health.
Mr. Horner (partner), Mr. Milewski (partner), and Mr. Gajer (associate) are attorneys with White and Williams. They specialize in defending health care providers in medical malpractice lawsuits and other health care–related matters. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community Medicine at the Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow Dr. Skolnik, and feel free to submit questions to him on Twitter: @neilskolnik. The authors have no financial conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Cowan v. Doering, 111 N.J. 451-62,.1988.
2. Model Policy For The Appropriate Use Of Telemedicine Technologies In The Practice Of Medicine. State Medical Boards Appropriate Regulation of Telemedicine. April 2014..
3. Haw. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 453-1.3(c).
4. Kaspar BJ. Iowa Law Review. 2014 Jan;99:839-59.
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the rapid uptake of telehealth nationwide in primary care and specialty practices. Over the last few months many practices have actually performed more telehealth visits than traditional in-person visits. The use of telehealth, which had been increasing slowly for the last few years, accelerated rapidly during the pandemic. Long term, telehealth has the potential to increase access to primary care and specialists, and make follow-up easier for many patients, changing how health care is delivered to millions of patients throughout the world.
Since telehealth will be a regular part of our practices from now on, it is important for clinicians to recognize how telehealth visits are viewed in a legal arena.
As is often the case with technological advances, the law needs time to adapt. Will a health care provider treating a patient using telemedicine be held to the same standard of care applicable to an in-person encounter? Stated differently, will consideration be given to the obvious limitations imposed by a telemedicine exam?
Standard of care in medical malpractice cases
The central question in most medical malpractice cases is whether the provider complied with the generally accepted standard of care when evaluating, diagnosing, or treating a patient. This standard typically takes into consideration the provider’s particular specialty as well as all the circumstances surrounding the encounter.1 Medical providers, not state legislators, usually define the standard of care for medical professionals. In malpractice cases, medical experts explain the applicable standard of care to the jury and guide its determination of whether, in the particular case, the standard of care was met. In this way, the law has long recognized that the medical profession itself is best suited to establish the appropriate standards of care under any particular set of circumstances. This standard of care is often referred to as the “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard of care.
Telemedicine standard of care
Despite the fact that the complex and often nebulous concept of standard of care has been traditionally left to the medical experts to define, state legislators and regulators throughout the nation have chosen to weigh in on this issue in the context of telemedicine. Most states with telemedicine regulations have followed the model policy adopted by the Federation of State Medical Boards in April 2014 which states that “[t]reatment and consultation recommendations made in an online setting … will be held to the same standards of appropriate practice as those in traditional (in-person) settings.”2 States that have adopted this model policy have effectively created a “legal fiction” requiring a jury to ignore the fact that the care was provided virtually by telemedicine technologies and instead assume that the physician treated the patient in person, i.e, applying an “in-person” standard of care. Hawaii appears to be the lone notable exception. Its telemedicine law recognizes that an in-person standard of care should not be applied if there was not a face-to-face visit.3
Proponents of the in-person telemedicine standard claim that it is necessary to ensure patient safety, thus justifying the “legal fiction.” Holding the provider to the in-person standard, it is argued, forces the physician to err on the side of caution and require an actual in-person encounter to ensure the advantages of sight, touch, and sense of things are fully available.4 This discourages the use of telemedicine and deprives the population of its many benefits.
Telemedicine can overcome geographical barriers, increase clinical support, improve health outcomes, reduce health care costs, encourage patient input, reduce travel, and foster continuity of care. The pandemic, which has significantly limited the ability of providers to see patients in person, only underscores the benefits of telemedicine.
The legislatively imposed in-person telemedicine standard of care should be replaced with the “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard in order to fairly judge physicians’ care and promote overall population health. The “reasonable professional under the circumstances” standard has applied to physicians and other health care professionals outside of telemedicine for decades, and it has served the medical community and public well. It is unfortunate that legislators felt the need to weigh in and define a distinctly different standard of care for telemedicine than for the rest of medicine, as this may present unforeseen obstacles to the use of telemedicine.
The in-person telemedicine standard of care remains a significant barrier for long-term telemedicine. Eliminating this legal fiction has the potential to further expand physicians’ use of telemedicine and fulfill its promise of improving access to care and improving population health.
Mr. Horner (partner), Mr. Milewski (partner), and Mr. Gajer (associate) are attorneys with White and Williams. They specialize in defending health care providers in medical malpractice lawsuits and other health care–related matters. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community Medicine at the Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow Dr. Skolnik, and feel free to submit questions to him on Twitter: @neilskolnik. The authors have no financial conflicts related to the content of this piece.
References
1. Cowan v. Doering, 111 N.J. 451-62,.1988.
2. Model Policy For The Appropriate Use Of Telemedicine Technologies In The Practice Of Medicine. State Medical Boards Appropriate Regulation of Telemedicine. April 2014..
3. Haw. Rev. Stat. Ann. § 453-1.3(c).
4. Kaspar BJ. Iowa Law Review. 2014 Jan;99:839-59.
COVID-19: Medicare data show long hospital stays, disparities
according to a new analysis by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
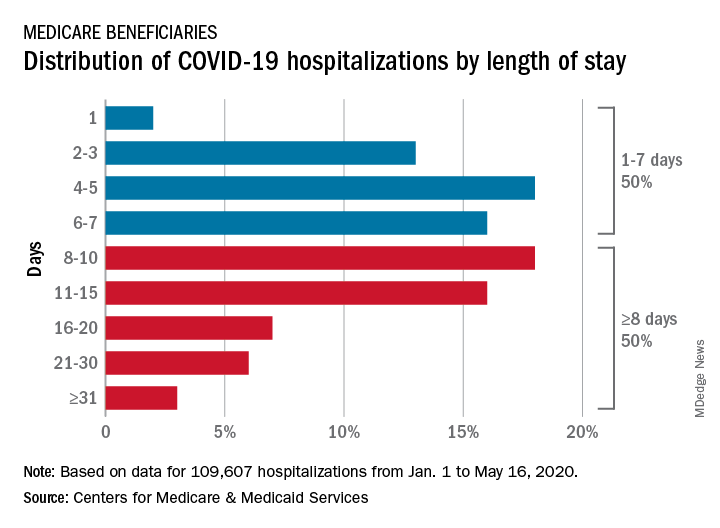
CMS encounter and claims data show almost 110,000 hospital stays for COVID-19 from Jan. 1 to May 16, 2020. Of the longer admissions, 18% were 8-10 days, 16% were 11-15 days, and another 16% were 16 days or longer, the CMS reported in a preliminary data snapshot released June 22.
The hospitalization rate for the Medicare population was 175 per 100,000 as of May 16, but the CMS data show a number of disparities involving race/ethnicity and other demographic characteristics were uncovered, such as the following:
- Black patients were hospitalized for COVID-19 at a much higher rate, at 465 per 100,000 beneficiaries, than were Hispanics (258), Asians (187), and whites (123).
- Residents of urban/suburban areas had a much higher hospitalization rate than did those living in rural areas: 205 versus 57 per 100,000.
- Beneficiaries enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid had 473 hospitalizations per 100,000, but the rate for those with Medicare only was 112.
“The disparities in the data reflect longstanding challenges facing minority communities and low-income older adults, many of whom face structural challenges to their health that go far beyond what is traditionally considered ‘medical,’ ” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a separate statement.
according to a new analysis by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

CMS encounter and claims data show almost 110,000 hospital stays for COVID-19 from Jan. 1 to May 16, 2020. Of the longer admissions, 18% were 8-10 days, 16% were 11-15 days, and another 16% were 16 days or longer, the CMS reported in a preliminary data snapshot released June 22.
The hospitalization rate for the Medicare population was 175 per 100,000 as of May 16, but the CMS data show a number of disparities involving race/ethnicity and other demographic characteristics were uncovered, such as the following:
- Black patients were hospitalized for COVID-19 at a much higher rate, at 465 per 100,000 beneficiaries, than were Hispanics (258), Asians (187), and whites (123).
- Residents of urban/suburban areas had a much higher hospitalization rate than did those living in rural areas: 205 versus 57 per 100,000.
- Beneficiaries enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid had 473 hospitalizations per 100,000, but the rate for those with Medicare only was 112.
“The disparities in the data reflect longstanding challenges facing minority communities and low-income older adults, many of whom face structural challenges to their health that go far beyond what is traditionally considered ‘medical,’ ” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a separate statement.
according to a new analysis by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

CMS encounter and claims data show almost 110,000 hospital stays for COVID-19 from Jan. 1 to May 16, 2020. Of the longer admissions, 18% were 8-10 days, 16% were 11-15 days, and another 16% were 16 days or longer, the CMS reported in a preliminary data snapshot released June 22.
The hospitalization rate for the Medicare population was 175 per 100,000 as of May 16, but the CMS data show a number of disparities involving race/ethnicity and other demographic characteristics were uncovered, such as the following:
- Black patients were hospitalized for COVID-19 at a much higher rate, at 465 per 100,000 beneficiaries, than were Hispanics (258), Asians (187), and whites (123).
- Residents of urban/suburban areas had a much higher hospitalization rate than did those living in rural areas: 205 versus 57 per 100,000.
- Beneficiaries enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid had 473 hospitalizations per 100,000, but the rate for those with Medicare only was 112.
“The disparities in the data reflect longstanding challenges facing minority communities and low-income older adults, many of whom face structural challenges to their health that go far beyond what is traditionally considered ‘medical,’ ” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a separate statement.
Inside Mercy’s mission to care for non-COVID patients in Los Angeles
When the hospital ship USNS Mercy departed San Diego’s Naval Station North Island on March 23, 2020, to support the Department of Defense efforts in Los Angeles during the coronavirus outbreak, Commander Erin Blevins remembers the crew’s excitement was palpable.
“We normally do partnerships abroad and respond to tsunamis and earthquakes,” said Cdr. Blevins, MD, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist who served as director of medical services for the mission. “This was a slight change in situation, but still disaster relief in the form of a pandemic. We switched our mindset to putting together the best experts for an infectious disease pandemic versus an earthquake disaster relief.”
A new mission
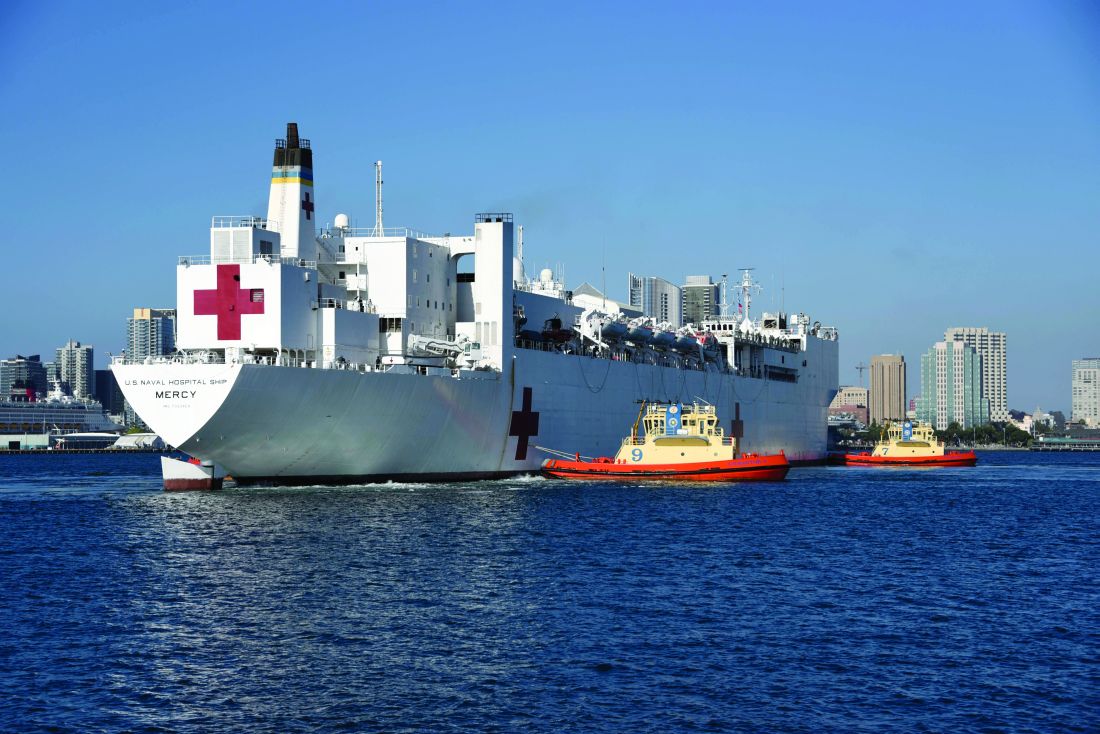
The 1,000-bed Mercy ship – a converted San Clemente–class oil tanker that was delivered in 1986 – spent nearly 50 days pier side in Los Angeles as a referral hospital for non–COVID-19 patients, so that clinicians at Los Angeles area hospitals could care for an anticipated surge of COVID-19 patients. “We went into it with expectations of, ‘We’ll treat as many patients as you need us to take,” Cdr. Blevins recalled. “I don’t even think Los Angeles [health officials] knew exactly where they were going to peak and what the need was going to be.”
Between March 29 and May 15, about 1,071 medical personnel aboard the Mercy cared for 77 patients with an average age of 53 years who were referred from 11 Los Angeles area hospitals. The physicians, nurses, and other medical support personnel were drawn from military treatment facilities across the country. “We had additional people join us as we scoped the mission to be more medically heavy and surgically light,” said Captain John Rotruck, MD, an anesthesiologist who is commanding officer of Mercy’s medical treatment facility. “We did adjust to make sure that we had the right staffing mix to meet the parameters that we were assigned. That was the crux of the change: a change in flavors of staffing to ensure that we focused on ICU and ward medical care as opposed to very heavy surgical care in support of a combat operation.”
About 10% of the team consisted of reservists who volunteered for the mission. “There’s no way you could have walked around the ship and known who was active duty and who was reservist,” said Capt. Rotruck, who was formerly chief of staff at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md. “They worked together so well, and I think that marriage of active duty who are used to working in a military medical treatment facility – in our case, a Navy medical treatment facility – together with our reservist physician colleagues who work in civilian facilities around the country, was beneficial. It was a synergistic relationship. I think both sides walked away learning quite a bit from each other.”
Start with screening
All crew members underwent a temperature check and completed a health screening questionnaire: once before departing their home of record and again before boarding Mercy. Based on those results, crew members and medical staff were screened for COVID-19 and tested as needed in order to minimize the risk of an outbreak aboard the ship.
Fewer than 1% of crew members developed COVID-19 or tested positive for the virus during the mission, according to Capt. Rotruck. Affected individuals were isolated and quarantined. “All staff have recovered and are doing well,” he said.
Mercy personnel worked with local health officials to ensure that all patients transferred to the ship tested negative for COVID-19. Physicians aboard the Mercy then worked directly with the patients’ civilian physician to ensure a safe and thorough turnover process before the patients were transferred.
From basic medical to trauma care
Care aboard the ship, which consists of open-bay medical wards, ranged from basic medical and surgical care to critical care and trauma. The most common procedures were cholecystectomies and orthopedic procedures, and the average length of stay was 4-5 days, according to Cdr. Blevins. Over the course of the mission, the medical professionals conducted 36 surgeries, 77 x-ray exams, 26 CT scans, and administered hundreds of ancillary studies ranging from routine labs to high-end x-rays and blood transfusion support.
“Within our ICU, we did have some end-of-life patients who ended up dying on our ship in comfort care,” Cdr. Blevins said. “Fortunately, we had a wonderful ICU team who had a great deal of experience with end-of-life care and were able to take care of these patients very comfortably and ensure good communication with family and loved ones during that time. In most instances we tried to make sure that people got to FaceTime or video chat with their loved one before they passed away.”
The Mercy, which includes 12 operating rooms, four x-ray units, and one CAT-scan unit, was not equipped to deliver pediatric or obstetrical care. Other unavailable services included psychiatry, oncology, cardiac and thoracic surgery, nuclear medicine, MRI, mammography, electrophysiology, cardiac catheterization, negative-pressure isolation, speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
Not your typical hospital experience
But for patients who did receive medical care aboard the Mercy – which made three 150-day deployments in recent years for the military-led humanitarian response known as Pacific Partnership in 2015, 2016, and 2018 – it was an experience that they are unlikely to forget.
“Every time a patient left the ship, our team on the ground surveyed them to see how their experience was and see what we could do to improve,” Cdr. Blevins said. “Across the board, they were all very appreciative of the medical care. We had a couple of veterans on board. They got [USNS Mercy] hats on their way out and seemed to very much enjoy a slightly different experience than they would get at a regular hospital.”
Capt. Rotruck added that the enthusiasm crew members had for supporting fellow Americans “really energized our team and really saturated that caring aspect of the people who interacted directly with patients,” he said. “It wasn’t just the physicians and nurses, but it was the staff delivering the food and coming to take blood samples and every other interaction that the patients had with our team. I think they really felt that enthusiasm for being there and supporting our neighbors in LA [Los Angeles].”
Crew life aboard the Mercy
Just as with any hospital on shore, personnel aboard the Mercy practiced preventive hygiene measures recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to help prevent the spread of COVID-19, such as wearing cloth face masks, spacing out tables in the dining hall, closing indoor gyms, and devising creative ways to stay physically fit. Popular options included jogging around the perimeter of the ship and practicing yoga and calisthenics on the deck, “making sure you were physically distanced appropriately, and when you were done, putting your mask back on,” Cdr. Blevins said. Others supplemented their workouts with a pull-up bar on the deck. “In addition, we have a series of ramps that run on the starboard side of the ship that we can use for patient movement with litters on wheels or patient beds,” Capt. Rotruck said. “The uphill portion of those ramps represents a good workout opportunity as well.”
Downtime in an era of physical distancing also afforded crew members the opportunity to call or FaceTime with loved ones, watch streamed TV shows and movies, and work on their own professional development. Some continued with coursework for online degree programs offered by colleges and universities they were enrolled in, while some enlisted personnel used the time to complete the Navy Enlisted Warfare Qualification Programs Instruction, which issues the basic overarching requirements for the qualification and designation of all enlisted warfare programs.
“As you can imagine, people spend a lot of time learning how the ship works and how it integrates into larger naval forces and so forth,” Capt. Rotruck said. “Not just our ship but also other ships: their weapons systems and defense mechanisms and navigation systems. We had people spending a significant amount of time working on that. We had people complete their Enlisted Surface Warfare qualification while we were on the mission.”
End of the mission
Mercy returned to its home base in San Diego on May 15, but about 60 medical personnel stayed behind in Los Angeles to support Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), state, and local health care professionals. Some worked at a site where clinicians provided care for COVID-19–positive patients who had been transferred from area skilled nursing facilities.
In addition, a team consisting of one nurse and five corpsmen “would go out to individual skilled nursing facilities and mainly conduct assessments and training, such as training in donning proper PPE [personal protective equipment] and determining what needs they had,” Capt. Rotruck said. “They met those needs if possible or [communicated with California officials] and let them know what the requirements were and what the needs were in that facility.” The assignment for those who stayed behind ended on May 31.
On the opposite coast, Mercy’s sister ship, USNS Comfort, arrived in New York Harbor from Norfolk, Va., on March 30 and spent 3½ weeks assisting area hospitals in the COVID-19 pandemic fight. A few days into the mission, Comfort’s internal spaces were reconfigured to create separate COVID-negative and COVID-positive sections. Medical teams aboard the ship cared for a total of 182 patients during the assignment.
Looking back on Mercy’s mission, Cdr. Blevins marveled at the sense of teamwork that unfolded. “We have quarterly training exercises with a core set of personnel, [and] we train getting ready for activation in 5 days,” she said. “All of that training kicks in and it comes to fruition in a mission like this. It was terrific to see a group of very disparate subject matter experts from all over the country come together with one purpose: which was to serve our own country during the pandemic.”
Capt. Rotruck pointed out that the experience enabled enlisted and nonenlisted physicians to maintain their skill sets during a time when military and civilian hospitals had stopped doing elective procedures and routine appointments. “The fact that those people were able to come on board the ship and continue to conduct their medical practice and maintain their skills and competencies in an environment that they weren’t quite used to is great,” he said. “Otherwise, some of those medical personnel would have been sitting idle, wherever they were from. This is the power of Navy medicine on behalf of our country.”
When the hospital ship USNS Mercy departed San Diego’s Naval Station North Island on March 23, 2020, to support the Department of Defense efforts in Los Angeles during the coronavirus outbreak, Commander Erin Blevins remembers the crew’s excitement was palpable.
“We normally do partnerships abroad and respond to tsunamis and earthquakes,” said Cdr. Blevins, MD, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist who served as director of medical services for the mission. “This was a slight change in situation, but still disaster relief in the form of a pandemic. We switched our mindset to putting together the best experts for an infectious disease pandemic versus an earthquake disaster relief.”
A new mission

The 1,000-bed Mercy ship – a converted San Clemente–class oil tanker that was delivered in 1986 – spent nearly 50 days pier side in Los Angeles as a referral hospital for non–COVID-19 patients, so that clinicians at Los Angeles area hospitals could care for an anticipated surge of COVID-19 patients. “We went into it with expectations of, ‘We’ll treat as many patients as you need us to take,” Cdr. Blevins recalled. “I don’t even think Los Angeles [health officials] knew exactly where they were going to peak and what the need was going to be.”
Between March 29 and May 15, about 1,071 medical personnel aboard the Mercy cared for 77 patients with an average age of 53 years who were referred from 11 Los Angeles area hospitals. The physicians, nurses, and other medical support personnel were drawn from military treatment facilities across the country. “We had additional people join us as we scoped the mission to be more medically heavy and surgically light,” said Captain John Rotruck, MD, an anesthesiologist who is commanding officer of Mercy’s medical treatment facility. “We did adjust to make sure that we had the right staffing mix to meet the parameters that we were assigned. That was the crux of the change: a change in flavors of staffing to ensure that we focused on ICU and ward medical care as opposed to very heavy surgical care in support of a combat operation.”
About 10% of the team consisted of reservists who volunteered for the mission. “There’s no way you could have walked around the ship and known who was active duty and who was reservist,” said Capt. Rotruck, who was formerly chief of staff at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md. “They worked together so well, and I think that marriage of active duty who are used to working in a military medical treatment facility – in our case, a Navy medical treatment facility – together with our reservist physician colleagues who work in civilian facilities around the country, was beneficial. It was a synergistic relationship. I think both sides walked away learning quite a bit from each other.”
Start with screening
All crew members underwent a temperature check and completed a health screening questionnaire: once before departing their home of record and again before boarding Mercy. Based on those results, crew members and medical staff were screened for COVID-19 and tested as needed in order to minimize the risk of an outbreak aboard the ship.
Fewer than 1% of crew members developed COVID-19 or tested positive for the virus during the mission, according to Capt. Rotruck. Affected individuals were isolated and quarantined. “All staff have recovered and are doing well,” he said.
Mercy personnel worked with local health officials to ensure that all patients transferred to the ship tested negative for COVID-19. Physicians aboard the Mercy then worked directly with the patients’ civilian physician to ensure a safe and thorough turnover process before the patients were transferred.
From basic medical to trauma care

Care aboard the ship, which consists of open-bay medical wards, ranged from basic medical and surgical care to critical care and trauma. The most common procedures were cholecystectomies and orthopedic procedures, and the average length of stay was 4-5 days, according to Cdr. Blevins. Over the course of the mission, the medical professionals conducted 36 surgeries, 77 x-ray exams, 26 CT scans, and administered hundreds of ancillary studies ranging from routine labs to high-end x-rays and blood transfusion support.
“Within our ICU, we did have some end-of-life patients who ended up dying on our ship in comfort care,” Cdr. Blevins said. “Fortunately, we had a wonderful ICU team who had a great deal of experience with end-of-life care and were able to take care of these patients very comfortably and ensure good communication with family and loved ones during that time. In most instances we tried to make sure that people got to FaceTime or video chat with their loved one before they passed away.”
The Mercy, which includes 12 operating rooms, four x-ray units, and one CAT-scan unit, was not equipped to deliver pediatric or obstetrical care. Other unavailable services included psychiatry, oncology, cardiac and thoracic surgery, nuclear medicine, MRI, mammography, electrophysiology, cardiac catheterization, negative-pressure isolation, speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
Not your typical hospital experience
But for patients who did receive medical care aboard the Mercy – which made three 150-day deployments in recent years for the military-led humanitarian response known as Pacific Partnership in 2015, 2016, and 2018 – it was an experience that they are unlikely to forget.
“Every time a patient left the ship, our team on the ground surveyed them to see how their experience was and see what we could do to improve,” Cdr. Blevins said. “Across the board, they were all very appreciative of the medical care. We had a couple of veterans on board. They got [USNS Mercy] hats on their way out and seemed to very much enjoy a slightly different experience than they would get at a regular hospital.”
Capt. Rotruck added that the enthusiasm crew members had for supporting fellow Americans “really energized our team and really saturated that caring aspect of the people who interacted directly with patients,” he said. “It wasn’t just the physicians and nurses, but it was the staff delivering the food and coming to take blood samples and every other interaction that the patients had with our team. I think they really felt that enthusiasm for being there and supporting our neighbors in LA [Los Angeles].”
Crew life aboard the Mercy
Just as with any hospital on shore, personnel aboard the Mercy practiced preventive hygiene measures recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to help prevent the spread of COVID-19, such as wearing cloth face masks, spacing out tables in the dining hall, closing indoor gyms, and devising creative ways to stay physically fit. Popular options included jogging around the perimeter of the ship and practicing yoga and calisthenics on the deck, “making sure you were physically distanced appropriately, and when you were done, putting your mask back on,” Cdr. Blevins said. Others supplemented their workouts with a pull-up bar on the deck. “In addition, we have a series of ramps that run on the starboard side of the ship that we can use for patient movement with litters on wheels or patient beds,” Capt. Rotruck said. “The uphill portion of those ramps represents a good workout opportunity as well.”
Downtime in an era of physical distancing also afforded crew members the opportunity to call or FaceTime with loved ones, watch streamed TV shows and movies, and work on their own professional development. Some continued with coursework for online degree programs offered by colleges and universities they were enrolled in, while some enlisted personnel used the time to complete the Navy Enlisted Warfare Qualification Programs Instruction, which issues the basic overarching requirements for the qualification and designation of all enlisted warfare programs.
“As you can imagine, people spend a lot of time learning how the ship works and how it integrates into larger naval forces and so forth,” Capt. Rotruck said. “Not just our ship but also other ships: their weapons systems and defense mechanisms and navigation systems. We had people spending a significant amount of time working on that. We had people complete their Enlisted Surface Warfare qualification while we were on the mission.”
End of the mission
Mercy returned to its home base in San Diego on May 15, but about 60 medical personnel stayed behind in Los Angeles to support Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), state, and local health care professionals. Some worked at a site where clinicians provided care for COVID-19–positive patients who had been transferred from area skilled nursing facilities.
In addition, a team consisting of one nurse and five corpsmen “would go out to individual skilled nursing facilities and mainly conduct assessments and training, such as training in donning proper PPE [personal protective equipment] and determining what needs they had,” Capt. Rotruck said. “They met those needs if possible or [communicated with California officials] and let them know what the requirements were and what the needs were in that facility.” The assignment for those who stayed behind ended on May 31.
On the opposite coast, Mercy’s sister ship, USNS Comfort, arrived in New York Harbor from Norfolk, Va., on March 30 and spent 3½ weeks assisting area hospitals in the COVID-19 pandemic fight. A few days into the mission, Comfort’s internal spaces were reconfigured to create separate COVID-negative and COVID-positive sections. Medical teams aboard the ship cared for a total of 182 patients during the assignment.
Looking back on Mercy’s mission, Cdr. Blevins marveled at the sense of teamwork that unfolded. “We have quarterly training exercises with a core set of personnel, [and] we train getting ready for activation in 5 days,” she said. “All of that training kicks in and it comes to fruition in a mission like this. It was terrific to see a group of very disparate subject matter experts from all over the country come together with one purpose: which was to serve our own country during the pandemic.”
Capt. Rotruck pointed out that the experience enabled enlisted and nonenlisted physicians to maintain their skill sets during a time when military and civilian hospitals had stopped doing elective procedures and routine appointments. “The fact that those people were able to come on board the ship and continue to conduct their medical practice and maintain their skills and competencies in an environment that they weren’t quite used to is great,” he said. “Otherwise, some of those medical personnel would have been sitting idle, wherever they were from. This is the power of Navy medicine on behalf of our country.”
When the hospital ship USNS Mercy departed San Diego’s Naval Station North Island on March 23, 2020, to support the Department of Defense efforts in Los Angeles during the coronavirus outbreak, Commander Erin Blevins remembers the crew’s excitement was palpable.
“We normally do partnerships abroad and respond to tsunamis and earthquakes,” said Cdr. Blevins, MD, a pediatric hematologist-oncologist who served as director of medical services for the mission. “This was a slight change in situation, but still disaster relief in the form of a pandemic. We switched our mindset to putting together the best experts for an infectious disease pandemic versus an earthquake disaster relief.”
A new mission

The 1,000-bed Mercy ship – a converted San Clemente–class oil tanker that was delivered in 1986 – spent nearly 50 days pier side in Los Angeles as a referral hospital for non–COVID-19 patients, so that clinicians at Los Angeles area hospitals could care for an anticipated surge of COVID-19 patients. “We went into it with expectations of, ‘We’ll treat as many patients as you need us to take,” Cdr. Blevins recalled. “I don’t even think Los Angeles [health officials] knew exactly where they were going to peak and what the need was going to be.”
Between March 29 and May 15, about 1,071 medical personnel aboard the Mercy cared for 77 patients with an average age of 53 years who were referred from 11 Los Angeles area hospitals. The physicians, nurses, and other medical support personnel were drawn from military treatment facilities across the country. “We had additional people join us as we scoped the mission to be more medically heavy and surgically light,” said Captain John Rotruck, MD, an anesthesiologist who is commanding officer of Mercy’s medical treatment facility. “We did adjust to make sure that we had the right staffing mix to meet the parameters that we were assigned. That was the crux of the change: a change in flavors of staffing to ensure that we focused on ICU and ward medical care as opposed to very heavy surgical care in support of a combat operation.”
About 10% of the team consisted of reservists who volunteered for the mission. “There’s no way you could have walked around the ship and known who was active duty and who was reservist,” said Capt. Rotruck, who was formerly chief of staff at Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, Md. “They worked together so well, and I think that marriage of active duty who are used to working in a military medical treatment facility – in our case, a Navy medical treatment facility – together with our reservist physician colleagues who work in civilian facilities around the country, was beneficial. It was a synergistic relationship. I think both sides walked away learning quite a bit from each other.”
Start with screening
All crew members underwent a temperature check and completed a health screening questionnaire: once before departing their home of record and again before boarding Mercy. Based on those results, crew members and medical staff were screened for COVID-19 and tested as needed in order to minimize the risk of an outbreak aboard the ship.
Fewer than 1% of crew members developed COVID-19 or tested positive for the virus during the mission, according to Capt. Rotruck. Affected individuals were isolated and quarantined. “All staff have recovered and are doing well,” he said.
Mercy personnel worked with local health officials to ensure that all patients transferred to the ship tested negative for COVID-19. Physicians aboard the Mercy then worked directly with the patients’ civilian physician to ensure a safe and thorough turnover process before the patients were transferred.
From basic medical to trauma care

Care aboard the ship, which consists of open-bay medical wards, ranged from basic medical and surgical care to critical care and trauma. The most common procedures were cholecystectomies and orthopedic procedures, and the average length of stay was 4-5 days, according to Cdr. Blevins. Over the course of the mission, the medical professionals conducted 36 surgeries, 77 x-ray exams, 26 CT scans, and administered hundreds of ancillary studies ranging from routine labs to high-end x-rays and blood transfusion support.
“Within our ICU, we did have some end-of-life patients who ended up dying on our ship in comfort care,” Cdr. Blevins said. “Fortunately, we had a wonderful ICU team who had a great deal of experience with end-of-life care and were able to take care of these patients very comfortably and ensure good communication with family and loved ones during that time. In most instances we tried to make sure that people got to FaceTime or video chat with their loved one before they passed away.”
The Mercy, which includes 12 operating rooms, four x-ray units, and one CAT-scan unit, was not equipped to deliver pediatric or obstetrical care. Other unavailable services included psychiatry, oncology, cardiac and thoracic surgery, nuclear medicine, MRI, mammography, electrophysiology, cardiac catheterization, negative-pressure isolation, speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
Not your typical hospital experience
But for patients who did receive medical care aboard the Mercy – which made three 150-day deployments in recent years for the military-led humanitarian response known as Pacific Partnership in 2015, 2016, and 2018 – it was an experience that they are unlikely to forget.
“Every time a patient left the ship, our team on the ground surveyed them to see how their experience was and see what we could do to improve,” Cdr. Blevins said. “Across the board, they were all very appreciative of the medical care. We had a couple of veterans on board. They got [USNS Mercy] hats on their way out and seemed to very much enjoy a slightly different experience than they would get at a regular hospital.”
Capt. Rotruck added that the enthusiasm crew members had for supporting fellow Americans “really energized our team and really saturated that caring aspect of the people who interacted directly with patients,” he said. “It wasn’t just the physicians and nurses, but it was the staff delivering the food and coming to take blood samples and every other interaction that the patients had with our team. I think they really felt that enthusiasm for being there and supporting our neighbors in LA [Los Angeles].”
Crew life aboard the Mercy
Just as with any hospital on shore, personnel aboard the Mercy practiced preventive hygiene measures recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to help prevent the spread of COVID-19, such as wearing cloth face masks, spacing out tables in the dining hall, closing indoor gyms, and devising creative ways to stay physically fit. Popular options included jogging around the perimeter of the ship and practicing yoga and calisthenics on the deck, “making sure you were physically distanced appropriately, and when you were done, putting your mask back on,” Cdr. Blevins said. Others supplemented their workouts with a pull-up bar on the deck. “In addition, we have a series of ramps that run on the starboard side of the ship that we can use for patient movement with litters on wheels or patient beds,” Capt. Rotruck said. “The uphill portion of those ramps represents a good workout opportunity as well.”
Downtime in an era of physical distancing also afforded crew members the opportunity to call or FaceTime with loved ones, watch streamed TV shows and movies, and work on their own professional development. Some continued with coursework for online degree programs offered by colleges and universities they were enrolled in, while some enlisted personnel used the time to complete the Navy Enlisted Warfare Qualification Programs Instruction, which issues the basic overarching requirements for the qualification and designation of all enlisted warfare programs.
“As you can imagine, people spend a lot of time learning how the ship works and how it integrates into larger naval forces and so forth,” Capt. Rotruck said. “Not just our ship but also other ships: their weapons systems and defense mechanisms and navigation systems. We had people spending a significant amount of time working on that. We had people complete their Enlisted Surface Warfare qualification while we were on the mission.”
End of the mission
Mercy returned to its home base in San Diego on May 15, but about 60 medical personnel stayed behind in Los Angeles to support Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), state, and local health care professionals. Some worked at a site where clinicians provided care for COVID-19–positive patients who had been transferred from area skilled nursing facilities.
In addition, a team consisting of one nurse and five corpsmen “would go out to individual skilled nursing facilities and mainly conduct assessments and training, such as training in donning proper PPE [personal protective equipment] and determining what needs they had,” Capt. Rotruck said. “They met those needs if possible or [communicated with California officials] and let them know what the requirements were and what the needs were in that facility.” The assignment for those who stayed behind ended on May 31.
On the opposite coast, Mercy’s sister ship, USNS Comfort, arrived in New York Harbor from Norfolk, Va., on March 30 and spent 3½ weeks assisting area hospitals in the COVID-19 pandemic fight. A few days into the mission, Comfort’s internal spaces were reconfigured to create separate COVID-negative and COVID-positive sections. Medical teams aboard the ship cared for a total of 182 patients during the assignment.
Looking back on Mercy’s mission, Cdr. Blevins marveled at the sense of teamwork that unfolded. “We have quarterly training exercises with a core set of personnel, [and] we train getting ready for activation in 5 days,” she said. “All of that training kicks in and it comes to fruition in a mission like this. It was terrific to see a group of very disparate subject matter experts from all over the country come together with one purpose: which was to serve our own country during the pandemic.”
Capt. Rotruck pointed out that the experience enabled enlisted and nonenlisted physicians to maintain their skill sets during a time when military and civilian hospitals had stopped doing elective procedures and routine appointments. “The fact that those people were able to come on board the ship and continue to conduct their medical practice and maintain their skills and competencies in an environment that they weren’t quite used to is great,” he said. “Otherwise, some of those medical personnel would have been sitting idle, wherever they were from. This is the power of Navy medicine on behalf of our country.”










