User login
according to a new analysis by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
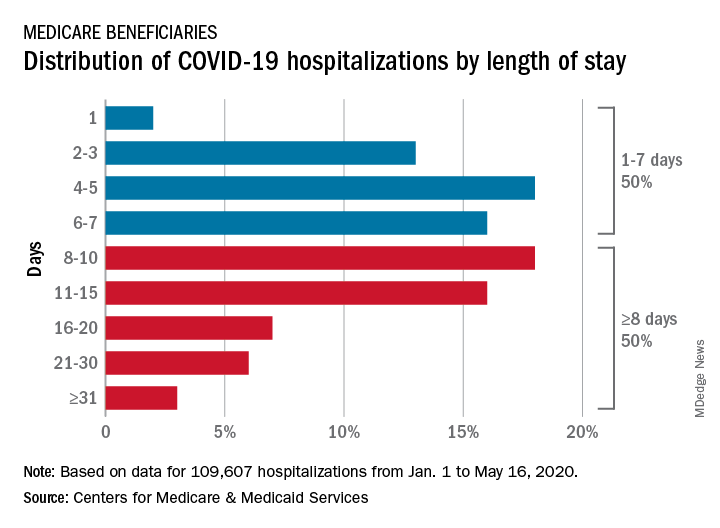
CMS encounter and claims data show almost 110,000 hospital stays for COVID-19 from Jan. 1 to May 16, 2020. Of the longer admissions, 18% were 8-10 days, 16% were 11-15 days, and another 16% were 16 days or longer, the CMS reported in a preliminary data snapshot released June 22.
The hospitalization rate for the Medicare population was 175 per 100,000 as of May 16, but the CMS data show a number of disparities involving race/ethnicity and other demographic characteristics were uncovered, such as the following:
- Black patients were hospitalized for COVID-19 at a much higher rate, at 465 per 100,000 beneficiaries, than were Hispanics (258), Asians (187), and whites (123).
- Residents of urban/suburban areas had a much higher hospitalization rate than did those living in rural areas: 205 versus 57 per 100,000.
- Beneficiaries enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid had 473 hospitalizations per 100,000, but the rate for those with Medicare only was 112.
“The disparities in the data reflect longstanding challenges facing minority communities and low-income older adults, many of whom face structural challenges to their health that go far beyond what is traditionally considered ‘medical,’ ” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a separate statement.
according to a new analysis by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

CMS encounter and claims data show almost 110,000 hospital stays for COVID-19 from Jan. 1 to May 16, 2020. Of the longer admissions, 18% were 8-10 days, 16% were 11-15 days, and another 16% were 16 days or longer, the CMS reported in a preliminary data snapshot released June 22.
The hospitalization rate for the Medicare population was 175 per 100,000 as of May 16, but the CMS data show a number of disparities involving race/ethnicity and other demographic characteristics were uncovered, such as the following:
- Black patients were hospitalized for COVID-19 at a much higher rate, at 465 per 100,000 beneficiaries, than were Hispanics (258), Asians (187), and whites (123).
- Residents of urban/suburban areas had a much higher hospitalization rate than did those living in rural areas: 205 versus 57 per 100,000.
- Beneficiaries enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid had 473 hospitalizations per 100,000, but the rate for those with Medicare only was 112.
“The disparities in the data reflect longstanding challenges facing minority communities and low-income older adults, many of whom face structural challenges to their health that go far beyond what is traditionally considered ‘medical,’ ” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a separate statement.
according to a new analysis by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

CMS encounter and claims data show almost 110,000 hospital stays for COVID-19 from Jan. 1 to May 16, 2020. Of the longer admissions, 18% were 8-10 days, 16% were 11-15 days, and another 16% were 16 days or longer, the CMS reported in a preliminary data snapshot released June 22.
The hospitalization rate for the Medicare population was 175 per 100,000 as of May 16, but the CMS data show a number of disparities involving race/ethnicity and other demographic characteristics were uncovered, such as the following:
- Black patients were hospitalized for COVID-19 at a much higher rate, at 465 per 100,000 beneficiaries, than were Hispanics (258), Asians (187), and whites (123).
- Residents of urban/suburban areas had a much higher hospitalization rate than did those living in rural areas: 205 versus 57 per 100,000.
- Beneficiaries enrolled in both Medicare and Medicaid had 473 hospitalizations per 100,000, but the rate for those with Medicare only was 112.
“The disparities in the data reflect longstanding challenges facing minority communities and low-income older adults, many of whom face structural challenges to their health that go far beyond what is traditionally considered ‘medical,’ ” CMS Administrator Seema Verma said in a separate statement.