User login
Richard Franki is the associate editor who writes and creates graphs. He started with the company in 1987, when it was known as the International Medical News Group. In his years as a journalist, Richard has worked for Cap Cities/ABC, Disney, Harcourt, Elsevier, Quadrant, Frontline, and Internet Brands. In the 1990s, he was a contributor to the ill-fated Indications column, predecessor of Livin' on the MDedge.
Study shifts burden of IgG4-related disease to women
The incidence and prevalence of IgG4-related disease each rose considerably from 2015 to 2019 in the United States, and the risk of death in those with the immune-mediated condition is about 2.5 times higher than those who are not affected, based on an analysis of claims data from commercially insured adults.
The first population-based study of IgG4-RD incidence, prevalence, and mortality establishes “key benchmarks for informing the diagnosis and management of patients” with a condition “that causes fibrosing inflammatory lesions at nearly any anatomic site,” and wasn’t initially described until 2001, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and associates said in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The increases in incidence and prevalence likely reflected increased disease awareness, they suggested. Overall U.S. incidence was 1.2 per 100,000 person-years for the 5-year period of 2015-2019, rising 86% from 0.78 per 100,000 person-years to 1.45 in 2018 before dropping to 1.39 in 2019. The change in prevalence was even greater, increasing 122% from 2.41 per 100,000 persons in 2015 to 5.34 per 100,000 in 2019, the investigators said.
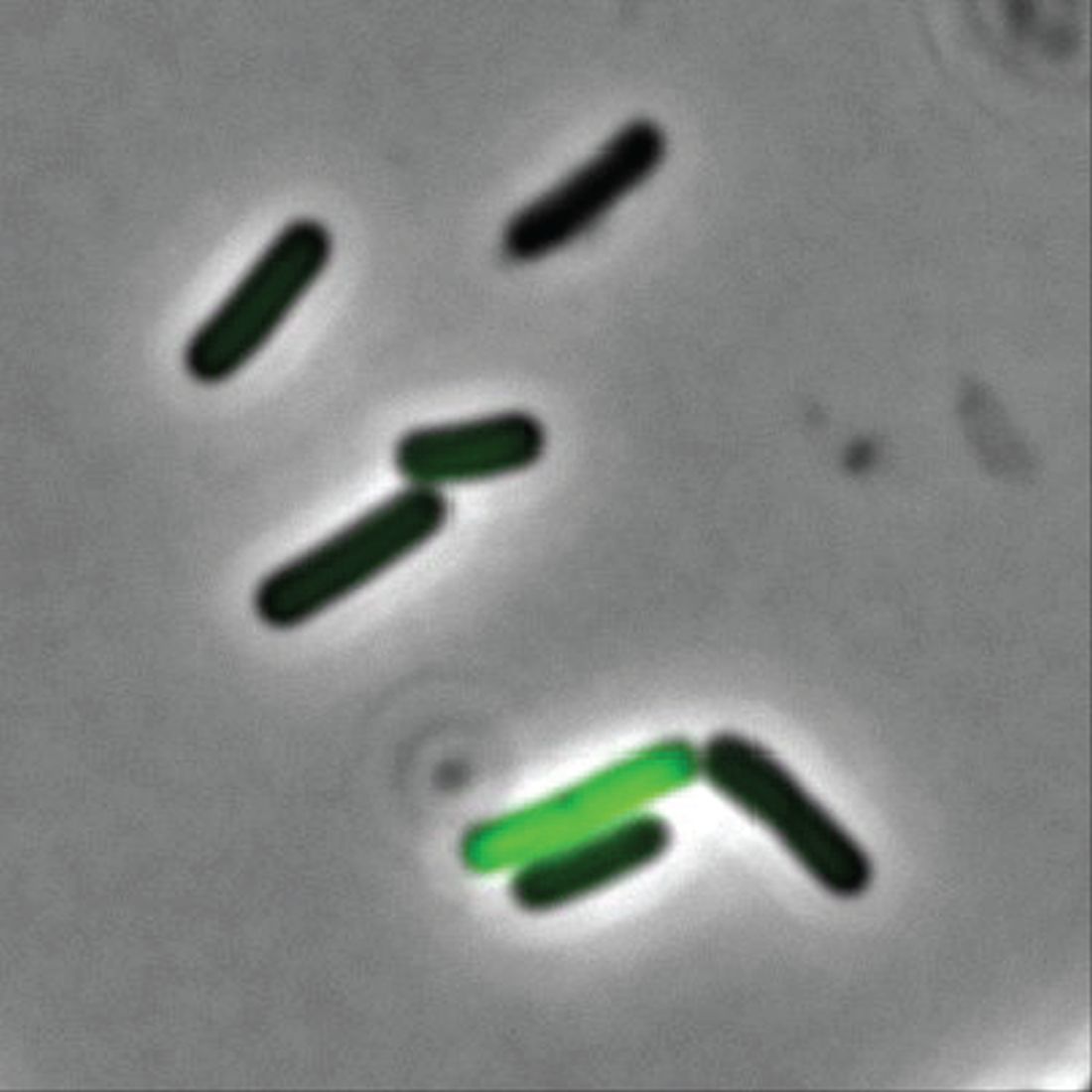
Previous studies had indicated that the majority of patients with IgG4-RD were male, but the current study, using Optum’s Clinformatics Data Mart, which includes commercial health plan and Medicare Advantage members in all 50 states, showed that both incidence and prevalence (see graph) were higher among women, noted Dr. Wallace of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and associates. They identified 524 patients (57.6% female) in the database who met the criteria for IgG4-RD from Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2019.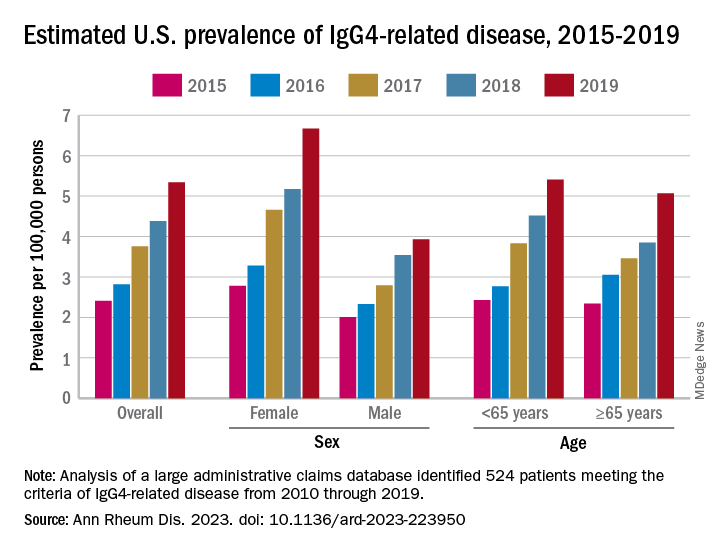
Incidence over the course of the study “was similar in patients identified as Asian or White but lower in those identified as Black or Hispanic,” they noted, adding that “the prevalence of IgG4-RD during this period reflected similar trends.” A jump in prevalence from 2018 to 2019, however, left White patients with a much higher rate (6.13 per 100,000 persons) than Asian patients (4.54 per 100,000), Black patients (3.42), and Hispanic patients (3.02).
For the mortality analysis, 516 patients with IgG4-RD were age-, sex-, and race-matched with 5,160 patients without IgG4-RD. Mortality was 3.42 and 1.46 per 100 person-years, respectively, over the 5.5 years of follow-up, so IgG4-RD was associated with a 2.5-fold higher risk of death. “The association of IgG4-RD with a higher risk of death was observed across the age spectrum and among both male and female patients,” the researchers said.
“Clinicians across specialties should be aware of IgG4-RD given the incidence, prevalence, and excess risk of death associated with this condition. ... Additional studies are urgently needed to define optimal management strategies to improve survival,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant to Massachusetts General Hospital from Sanofi, and Dr. Wallace received funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. He has received research support and consulting fees from several companies, and four coinvestigators are employees of Sanofi.
The incidence and prevalence of IgG4-related disease each rose considerably from 2015 to 2019 in the United States, and the risk of death in those with the immune-mediated condition is about 2.5 times higher than those who are not affected, based on an analysis of claims data from commercially insured adults.
The first population-based study of IgG4-RD incidence, prevalence, and mortality establishes “key benchmarks for informing the diagnosis and management of patients” with a condition “that causes fibrosing inflammatory lesions at nearly any anatomic site,” and wasn’t initially described until 2001, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and associates said in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The increases in incidence and prevalence likely reflected increased disease awareness, they suggested. Overall U.S. incidence was 1.2 per 100,000 person-years for the 5-year period of 2015-2019, rising 86% from 0.78 per 100,000 person-years to 1.45 in 2018 before dropping to 1.39 in 2019. The change in prevalence was even greater, increasing 122% from 2.41 per 100,000 persons in 2015 to 5.34 per 100,000 in 2019, the investigators said.
Previous studies had indicated that the majority of patients with IgG4-RD were male, but the current study, using Optum’s Clinformatics Data Mart, which includes commercial health plan and Medicare Advantage members in all 50 states, showed that both incidence and prevalence (see graph) were higher among women, noted Dr. Wallace of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and associates. They identified 524 patients (57.6% female) in the database who met the criteria for IgG4-RD from Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2019.
Incidence over the course of the study “was similar in patients identified as Asian or White but lower in those identified as Black or Hispanic,” they noted, adding that “the prevalence of IgG4-RD during this period reflected similar trends.” A jump in prevalence from 2018 to 2019, however, left White patients with a much higher rate (6.13 per 100,000 persons) than Asian patients (4.54 per 100,000), Black patients (3.42), and Hispanic patients (3.02).
For the mortality analysis, 516 patients with IgG4-RD were age-, sex-, and race-matched with 5,160 patients without IgG4-RD. Mortality was 3.42 and 1.46 per 100 person-years, respectively, over the 5.5 years of follow-up, so IgG4-RD was associated with a 2.5-fold higher risk of death. “The association of IgG4-RD with a higher risk of death was observed across the age spectrum and among both male and female patients,” the researchers said.
“Clinicians across specialties should be aware of IgG4-RD given the incidence, prevalence, and excess risk of death associated with this condition. ... Additional studies are urgently needed to define optimal management strategies to improve survival,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant to Massachusetts General Hospital from Sanofi, and Dr. Wallace received funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. He has received research support and consulting fees from several companies, and four coinvestigators are employees of Sanofi.
The incidence and prevalence of IgG4-related disease each rose considerably from 2015 to 2019 in the United States, and the risk of death in those with the immune-mediated condition is about 2.5 times higher than those who are not affected, based on an analysis of claims data from commercially insured adults.
The first population-based study of IgG4-RD incidence, prevalence, and mortality establishes “key benchmarks for informing the diagnosis and management of patients” with a condition “that causes fibrosing inflammatory lesions at nearly any anatomic site,” and wasn’t initially described until 2001, Zachary S. Wallace, MD, and associates said in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
The increases in incidence and prevalence likely reflected increased disease awareness, they suggested. Overall U.S. incidence was 1.2 per 100,000 person-years for the 5-year period of 2015-2019, rising 86% from 0.78 per 100,000 person-years to 1.45 in 2018 before dropping to 1.39 in 2019. The change in prevalence was even greater, increasing 122% from 2.41 per 100,000 persons in 2015 to 5.34 per 100,000 in 2019, the investigators said.
Previous studies had indicated that the majority of patients with IgG4-RD were male, but the current study, using Optum’s Clinformatics Data Mart, which includes commercial health plan and Medicare Advantage members in all 50 states, showed that both incidence and prevalence (see graph) were higher among women, noted Dr. Wallace of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and associates. They identified 524 patients (57.6% female) in the database who met the criteria for IgG4-RD from Jan. 1, 2010, to Dec. 31, 2019.
Incidence over the course of the study “was similar in patients identified as Asian or White but lower in those identified as Black or Hispanic,” they noted, adding that “the prevalence of IgG4-RD during this period reflected similar trends.” A jump in prevalence from 2018 to 2019, however, left White patients with a much higher rate (6.13 per 100,000 persons) than Asian patients (4.54 per 100,000), Black patients (3.42), and Hispanic patients (3.02).
For the mortality analysis, 516 patients with IgG4-RD were age-, sex-, and race-matched with 5,160 patients without IgG4-RD. Mortality was 3.42 and 1.46 per 100 person-years, respectively, over the 5.5 years of follow-up, so IgG4-RD was associated with a 2.5-fold higher risk of death. “The association of IgG4-RD with a higher risk of death was observed across the age spectrum and among both male and female patients,” the researchers said.
“Clinicians across specialties should be aware of IgG4-RD given the incidence, prevalence, and excess risk of death associated with this condition. ... Additional studies are urgently needed to define optimal management strategies to improve survival,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant to Massachusetts General Hospital from Sanofi, and Dr. Wallace received funding from the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, and the Rheumatology Research Foundation. He has received research support and consulting fees from several companies, and four coinvestigators are employees of Sanofi.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Medical-level empathy? Yup, ChatGPT can fake that
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
Caution: Robotic uprisings in the rearview mirror are closer than they appear
ChatGPT. If you’ve been even in the proximity of the Internet lately, you may have heard of it. It’s quite an incredible piece of technology, an artificial intelligence that really could up-end a lot of industries. And lest doctors believe they’re safe from robotic replacement, consider this: ChatGPT took a test commonly used as a study resource by ophthalmologists and scored a 46%. Obviously, that’s not a passing grade. Job safe, right?
A month later, the researchers tried again. This time, ChatGPT got a 58%. Still not passing, and ChatGPT did especially poorly on ophthalmology specialty questions (it got 80% of general medicine questions right), but still, the jump in quality after just a month is ... concerning. It’s not like an AI will forget things. That score can only go up, and it’ll go up faster than you think.
“Sure, the robot is smart,” the doctors out there are thinking, “but how can an AI compete with human compassion, understanding, and bedside manner?”
And they’d be right. When it comes to bedside manner, there’s no competition between man and bot. ChatGPT is already winning.
In another study, researchers sampled nearly 200 questions from the subreddit r/AskDocs, which received verified physician responses. The researchers fed ChatGPT the questions – without the doctor’s answer – and a panel of health care professionals evaluated both the human doctor and ChatGPT in terms of quality and empathy.
Perhaps not surprisingly, the robot did better when it came to quality, providing a high-quality response 79% of the time, versus 22% for the human. But empathy? It was a bloodbath. ChatGPT provided an empathetic or very empathetic response 45% of the time, while humans could only do so 4.6% of the time. So much for bedside manner.
The researchers were suspiciously quick to note that ChatGPT isn’t a legitimate replacement for physicians, but could represent a tool to better provide care for patients. But let’s be honest, given ChatGPT’s quick advancement, how long before some intrepid stockholder says: “Hey, instead of paying doctors, why don’t we just use the free robot instead?” We give it a week. Or 11 minutes.
This week, on ‘As the sperm turns’
We’ve got a lot of spermy ground to cover, so let’s get right to it, starting with the small and working our way up.
We’re all pretty familiar with the basic structure of a sperm cell, yes? Bulbous head that contains all the important genetic information and a tail-like flagellum to propel it to its ultimate destination. Not much to work with there, you’d think, but what if Mother Nature, who clearly has a robust sense of humor, had something else in mind?
We present exhibit A, Paramormyorps kingsleyae, also known as the electric elephantfish, which happens to be the only known vertebrate species with tailless sperm. Sounds crazy to us, too, but Jason Gallant, PhD, of
Michigan State University, Lansing, has a theory: “A general notion in biology is that sperm are cheap, and eggs are expensive – but these fish may be telling us that sperm are more expensive than we might think. They could be saving energy by cutting back on sperm tails.”
He and his team think that finding the gene that turns off development of the flagellum in the elephant fish could benefit humans, specifically those with a genetic disorder called primary ciliary dyskinesia, whose lack of normally functioning cilia and flagella leads to chronic respiratory infection, abnormally positioned organs, fluid on the brain, and infertility.
And that – with “that” being infertility – brings us to exhibit B, a 41-year-old Dutch man named Jonathan Meijer who clearly has too much time on his hands.
A court in the Netherlands recently ordered him, and not for the first time, to stop donating sperm to fertility clinics after it was discovered that he had fathered between 500 and 600 children around the world. He had been banned from donating to Dutch clinics in 2017, at which point he had already fathered 100 children, but managed a workaround by donating internationally and online, sometimes using another name.
The judge ordered Mr. Meijer to contact all of the clinics abroad and ask them to destroy any of his sperm they still had in stock and threatened to fine him over $100,000 for each future violation.
Okay, so here’s the thing. We have been, um, let’s call it ... warned, about the evils of tastelessness in journalism, so we’re going to do what Mr. Meijer should have done and abstain. And we can last for longer than 11 minutes.
The realm of lost luggage and lost sleep
It may be convenient to live near an airport if you’re a frequent flyer, but it really doesn’t help your sleep numbers.
The first look at how such a common sound affects sleep duration showed that people exposed to even 45 decibels of airplane noise were less likely to get the 7-9 hours of sleep needed for healthy functioning, investigators said in Environmental Health Perspectives.
How loud is 45 dB exactly? A normal conversation is about 50 dB, while a whisper is 30 dB, to give you an idea. Airplane noise at 45 dB? You might not even notice it amongst the other noises in daily life.
The researchers looked at data from about 35,000 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study who live around 90 major U.S. airports. They examined plane noise every 5 years between 1995 and 2005, focusing on estimates of nighttime and daytime levels. Short sleep was most common among the nurses who lived on the West Coast, near major cargo airports or large bodies of water, and also among those who reported no hearing loss.
The investigators noted, however, that there was no consistent association between airplane noise and quality of sleep and stopped short of making any policy recommendations. Still, sleep is a very important, yet slept-on (pun intended) factor for our overall health, so it’s good to know if anything has the potential to cause disruption.
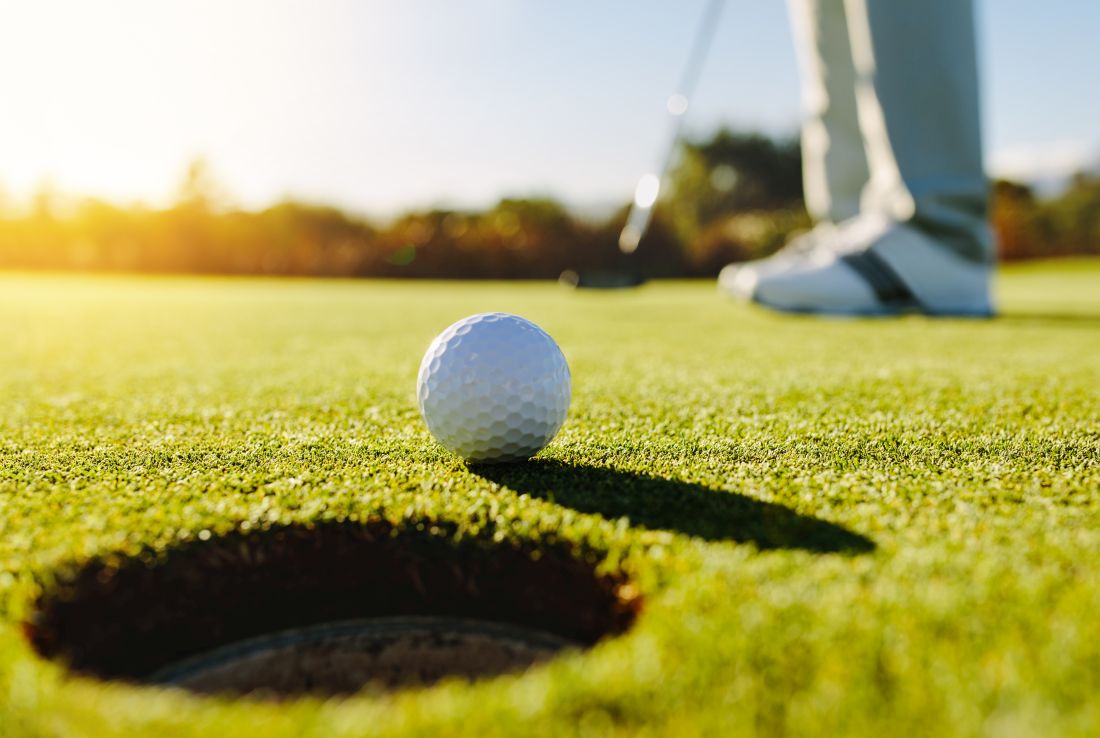
Drive, chip, and putt your way to osteoarthritis relief
Taking a swing against arthritis
Osteoarthritis is a tough disease to manage. Exercise helps ease the stiffness and pain of the joints, but at the same time, the disease makes it difficult to do that beneficial exercise. Even a relatively simple activity like jogging can hurt more than it helps. If only there were a low-impact exercise that was incredibly popular among the generally older population who are likely to have arthritis.
We love a good golf study here at LOTME, and a group of Australian and U.K. researchers have provided. Osteoarthritis affects 2 million people in the land down under, making it the most common source of disability there. In that population, only 64% reported their physical health to be good, very good, or excellent. Among the 459 golfers with OA that the study authors surveyed, however, the percentage reporting good health rose to more than 90%.
A similar story emerged when they looked at mental health. Nearly a quarter of nongolfers with OA reported high or very high levels of psychological distress, compared with just 8% of golfers. This pattern of improved physical and mental health remained when the researchers looked at the general, non-OA population.
This isn’t the first time golf’s been connected with improved health, and previous studies have shown golf to reduce the risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity, among other things. Just walking one 18-hole round significantly exceeds the CDC’s recommended 150 minutes of physical activity per week. Go out multiple times a week – leaving the cart and beer at home, American golfers – and you’ll be fit for a lifetime.
The golfers on our staff, however, are still waiting for those mental health benefits to kick in. Because when we’re adding up our scorecard after that string of four double bogeys to end the round, we’re most definitely thinking: “Yes, this sport is reducing my psychological distress. I am having fun right now.”
Battle of the sexes’ intestines
There are, we’re sure you’ve noticed, some differences between males and females. Females, for one thing, have longer small intestines than males. Everybody knows that, right? You didn’t know? Really? … Really?
Well, then, we’re guessing you haven’t read “Hidden diversity: Comparative functional morphology of humans and other species” by Erin A. McKenney, PhD, of North Carolina State University, Raleigh, and associates, which just appeared in PeerJ. We couldn’t put it down, even in the shower – a real page-turner/scroller. (It’s a great way to clean a phone, for those who also like to scroll, text, or talk on the toilet.)
The researchers got out their rulers, calipers, and string and took many measurements of the digestive systems of 45 human cadavers (21 female and 24 male), which were compared with data from 10 rats, 10 pigs, and 10 bullfrogs, which had been collected (the measurements, not the animals) by undergraduate students enrolled in a comparative anatomy laboratory course at the university.
There was little intestinal-length variation among the four-legged subjects, but when it comes to humans, females have “consistently and significantly longer small intestines than males,” the investigators noted.
The women’s small intestines, almost 14 feet long on average, were about a foot longer than the men’s, which suggests that women are better able to extract nutrients from food and “supports the canalization hypothesis, which posits that women are better able to survive during periods of stress,” coauthor Amanda Hale said in a written statement from the school. The way to a man’s heart may be through his stomach, but the way to a woman’s heart is through her duodenum, it seems.
Fascinating stuff, to be sure, but the thing that really caught our eye in the PeerJ article was the authors’ suggestion “that organs behave independently of one another, both within and across species.” Organs behaving independently? A somewhat ominous concept, no doubt, but it does explain a lot of the sounds we hear coming from our guts, which can get pretty frightening, especially on chili night.
Dog walking is dangerous business
Yes, you did read that right. A lot of strange things can send you to the emergency department. Go ahead and add dog walking onto that list.
Investigators from Johns Hopkins University estimate that over 422,000 adults presented to U.S. emergency departments with leash-dependent dog walking-related injuries between 2001 and 2020.
With almost 53% of U.S. households owning at least one dog in 2021-2022 in the wake of the COVID pet boom, this kind of occurrence is becoming more common than you think. The annual number of dog-walking injuries more than quadrupled from 7,300 to 32,000 over the course of the study, and the researchers link that spike to the promotion of dog walking for fitness, along with the boost of ownership itself.
The most common injuries listed in the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System database were finger fracture, traumatic brain injury, and shoulder sprain or strain. These mostly involved falls from being pulled, tripped, or tangled up in the leash while walking. For those aged 65 years and older, traumatic brain injury and hip fracture were the most common.
Women were 50% more likely to sustain a fracture than were men, and dog owners aged 65 and older were three times as likely to fall, twice as likely to get a fracture, and 60% more likely to have brain injury than were younger people. Now, that’s not to say younger people don’t also get hurt. After all, dogs aren’t ageists. The researchers have that data but it’s coming out later.
Meanwhile, the pitfalls involved with just trying to get our daily steps in while letting Muffin do her business have us on the lookout for random squirrels.
Taking a swing against arthritis
Osteoarthritis is a tough disease to manage. Exercise helps ease the stiffness and pain of the joints, but at the same time, the disease makes it difficult to do that beneficial exercise. Even a relatively simple activity like jogging can hurt more than it helps. If only there were a low-impact exercise that was incredibly popular among the generally older population who are likely to have arthritis.
We love a good golf study here at LOTME, and a group of Australian and U.K. researchers have provided. Osteoarthritis affects 2 million people in the land down under, making it the most common source of disability there. In that population, only 64% reported their physical health to be good, very good, or excellent. Among the 459 golfers with OA that the study authors surveyed, however, the percentage reporting good health rose to more than 90%.
A similar story emerged when they looked at mental health. Nearly a quarter of nongolfers with OA reported high or very high levels of psychological distress, compared with just 8% of golfers. This pattern of improved physical and mental health remained when the researchers looked at the general, non-OA population.
This isn’t the first time golf’s been connected with improved health, and previous studies have shown golf to reduce the risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity, among other things. Just walking one 18-hole round significantly exceeds the CDC’s recommended 150 minutes of physical activity per week. Go out multiple times a week – leaving the cart and beer at home, American golfers – and you’ll be fit for a lifetime.
The golfers on our staff, however, are still waiting for those mental health benefits to kick in. Because when we’re adding up our scorecard after that string of four double bogeys to end the round, we’re most definitely thinking: “Yes, this sport is reducing my psychological distress. I am having fun right now.”
Battle of the sexes’ intestines
There are, we’re sure you’ve noticed, some differences between males and females. Females, for one thing, have longer small intestines than males. Everybody knows that, right? You didn’t know? Really? … Really?
Well, then, we’re guessing you haven’t read “Hidden diversity: Comparative functional morphology of humans and other species” by Erin A. McKenney, PhD, of North Carolina State University, Raleigh, and associates, which just appeared in PeerJ. We couldn’t put it down, even in the shower – a real page-turner/scroller. (It’s a great way to clean a phone, for those who also like to scroll, text, or talk on the toilet.)
The researchers got out their rulers, calipers, and string and took many measurements of the digestive systems of 45 human cadavers (21 female and 24 male), which were compared with data from 10 rats, 10 pigs, and 10 bullfrogs, which had been collected (the measurements, not the animals) by undergraduate students enrolled in a comparative anatomy laboratory course at the university.
There was little intestinal-length variation among the four-legged subjects, but when it comes to humans, females have “consistently and significantly longer small intestines than males,” the investigators noted.
The women’s small intestines, almost 14 feet long on average, were about a foot longer than the men’s, which suggests that women are better able to extract nutrients from food and “supports the canalization hypothesis, which posits that women are better able to survive during periods of stress,” coauthor Amanda Hale said in a written statement from the school. The way to a man’s heart may be through his stomach, but the way to a woman’s heart is through her duodenum, it seems.
Fascinating stuff, to be sure, but the thing that really caught our eye in the PeerJ article was the authors’ suggestion “that organs behave independently of one another, both within and across species.” Organs behaving independently? A somewhat ominous concept, no doubt, but it does explain a lot of the sounds we hear coming from our guts, which can get pretty frightening, especially on chili night.
Dog walking is dangerous business
Yes, you did read that right. A lot of strange things can send you to the emergency department. Go ahead and add dog walking onto that list.
Investigators from Johns Hopkins University estimate that over 422,000 adults presented to U.S. emergency departments with leash-dependent dog walking-related injuries between 2001 and 2020.
With almost 53% of U.S. households owning at least one dog in 2021-2022 in the wake of the COVID pet boom, this kind of occurrence is becoming more common than you think. The annual number of dog-walking injuries more than quadrupled from 7,300 to 32,000 over the course of the study, and the researchers link that spike to the promotion of dog walking for fitness, along with the boost of ownership itself.
The most common injuries listed in the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System database were finger fracture, traumatic brain injury, and shoulder sprain or strain. These mostly involved falls from being pulled, tripped, or tangled up in the leash while walking. For those aged 65 years and older, traumatic brain injury and hip fracture were the most common.
Women were 50% more likely to sustain a fracture than were men, and dog owners aged 65 and older were three times as likely to fall, twice as likely to get a fracture, and 60% more likely to have brain injury than were younger people. Now, that’s not to say younger people don’t also get hurt. After all, dogs aren’t ageists. The researchers have that data but it’s coming out later.
Meanwhile, the pitfalls involved with just trying to get our daily steps in while letting Muffin do her business have us on the lookout for random squirrels.
Taking a swing against arthritis
Osteoarthritis is a tough disease to manage. Exercise helps ease the stiffness and pain of the joints, but at the same time, the disease makes it difficult to do that beneficial exercise. Even a relatively simple activity like jogging can hurt more than it helps. If only there were a low-impact exercise that was incredibly popular among the generally older population who are likely to have arthritis.
We love a good golf study here at LOTME, and a group of Australian and U.K. researchers have provided. Osteoarthritis affects 2 million people in the land down under, making it the most common source of disability there. In that population, only 64% reported their physical health to be good, very good, or excellent. Among the 459 golfers with OA that the study authors surveyed, however, the percentage reporting good health rose to more than 90%.
A similar story emerged when they looked at mental health. Nearly a quarter of nongolfers with OA reported high or very high levels of psychological distress, compared with just 8% of golfers. This pattern of improved physical and mental health remained when the researchers looked at the general, non-OA population.
This isn’t the first time golf’s been connected with improved health, and previous studies have shown golf to reduce the risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity, among other things. Just walking one 18-hole round significantly exceeds the CDC’s recommended 150 minutes of physical activity per week. Go out multiple times a week – leaving the cart and beer at home, American golfers – and you’ll be fit for a lifetime.
The golfers on our staff, however, are still waiting for those mental health benefits to kick in. Because when we’re adding up our scorecard after that string of four double bogeys to end the round, we’re most definitely thinking: “Yes, this sport is reducing my psychological distress. I am having fun right now.”
Battle of the sexes’ intestines
There are, we’re sure you’ve noticed, some differences between males and females. Females, for one thing, have longer small intestines than males. Everybody knows that, right? You didn’t know? Really? … Really?
Well, then, we’re guessing you haven’t read “Hidden diversity: Comparative functional morphology of humans and other species” by Erin A. McKenney, PhD, of North Carolina State University, Raleigh, and associates, which just appeared in PeerJ. We couldn’t put it down, even in the shower – a real page-turner/scroller. (It’s a great way to clean a phone, for those who also like to scroll, text, or talk on the toilet.)
The researchers got out their rulers, calipers, and string and took many measurements of the digestive systems of 45 human cadavers (21 female and 24 male), which were compared with data from 10 rats, 10 pigs, and 10 bullfrogs, which had been collected (the measurements, not the animals) by undergraduate students enrolled in a comparative anatomy laboratory course at the university.
There was little intestinal-length variation among the four-legged subjects, but when it comes to humans, females have “consistently and significantly longer small intestines than males,” the investigators noted.
The women’s small intestines, almost 14 feet long on average, were about a foot longer than the men’s, which suggests that women are better able to extract nutrients from food and “supports the canalization hypothesis, which posits that women are better able to survive during periods of stress,” coauthor Amanda Hale said in a written statement from the school. The way to a man’s heart may be through his stomach, but the way to a woman’s heart is through her duodenum, it seems.
Fascinating stuff, to be sure, but the thing that really caught our eye in the PeerJ article was the authors’ suggestion “that organs behave independently of one another, both within and across species.” Organs behaving independently? A somewhat ominous concept, no doubt, but it does explain a lot of the sounds we hear coming from our guts, which can get pretty frightening, especially on chili night.
Dog walking is dangerous business
Yes, you did read that right. A lot of strange things can send you to the emergency department. Go ahead and add dog walking onto that list.
Investigators from Johns Hopkins University estimate that over 422,000 adults presented to U.S. emergency departments with leash-dependent dog walking-related injuries between 2001 and 2020.
With almost 53% of U.S. households owning at least one dog in 2021-2022 in the wake of the COVID pet boom, this kind of occurrence is becoming more common than you think. The annual number of dog-walking injuries more than quadrupled from 7,300 to 32,000 over the course of the study, and the researchers link that spike to the promotion of dog walking for fitness, along with the boost of ownership itself.
The most common injuries listed in the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System database were finger fracture, traumatic brain injury, and shoulder sprain or strain. These mostly involved falls from being pulled, tripped, or tangled up in the leash while walking. For those aged 65 years and older, traumatic brain injury and hip fracture were the most common.
Women were 50% more likely to sustain a fracture than were men, and dog owners aged 65 and older were three times as likely to fall, twice as likely to get a fracture, and 60% more likely to have brain injury than were younger people. Now, that’s not to say younger people don’t also get hurt. After all, dogs aren’t ageists. The researchers have that data but it’s coming out later.
Meanwhile, the pitfalls involved with just trying to get our daily steps in while letting Muffin do her business have us on the lookout for random squirrels.
Poor representation of patients with darker skin phototypes in laser and light device studies
, according to a systematic review of the literature, the authors reported.
“While there broadly appears to be skin of color representation [in such studies], a more granular understanding of the data shows a large discrepancy in representation between ‘lighter’ and ‘darker’ skin of color patients,” Priya Manjaly and associates wrote in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.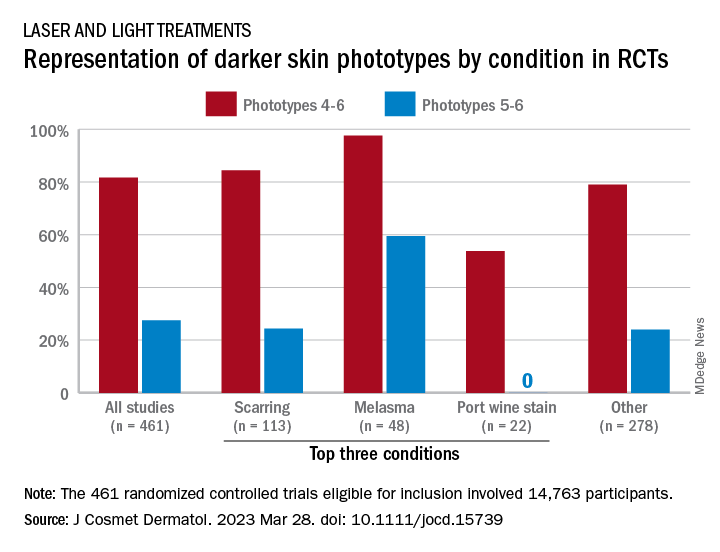
Among the 461 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) eligible for inclusion, most (81.7%) included participants with skin phototypes 4-6, which is considered skin of color. When only phototypes 5 and 6 were included, however, representation in studies involving laser and light devices was only 27.5%, said Ms. Manjaly, a research fellow in the department of dermatology at Boston University, and associates.
“This trend of excluding darker skin phototypes persisted when the results were stratified by condition, laser of study, study location, journal type, and funding source,” the investigators noted.
RCTs of laser/light devices for scarring, the most common dermatologic condition represented, included phototypes 5 and 6 in 24.4% of studies, compared with 84.4% for phototypes 4-6. The gap was smaller for melasma, but not for port wine stains. Among the devices examined, RCTs of diode lasers and intense pulsed light had the smallest gaps between inclusion of the two groups of phototypes, while pulsed-dye laser studies had the largest, they reported.
Stratification by journal showed the largest gap in studies published by Lasers in Medical Science and the smallest gap coming from Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. Funding was not specified for the majority of the eligible device RCTs, but those funded by industry had the smallest discrepancy between types 5-6 and types 4-6 and those supported by foundations/nonprofits the largest, Ms. Manjaly and associates said.
“With projections estimating that more than 50% of the U.S. population is set to identify as Hispanic or nonwhite by 2045 ... the lack of information has important consequences for clinical practice, as clinicians are unable to counsel patients on the efficacy and possible complications of various devices in patient with skin of color,” they wrote.
The investigators did not declare any conflicts of interest or funding sources.
, according to a systematic review of the literature, the authors reported.
“While there broadly appears to be skin of color representation [in such studies], a more granular understanding of the data shows a large discrepancy in representation between ‘lighter’ and ‘darker’ skin of color patients,” Priya Manjaly and associates wrote in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Among the 461 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) eligible for inclusion, most (81.7%) included participants with skin phototypes 4-6, which is considered skin of color. When only phototypes 5 and 6 were included, however, representation in studies involving laser and light devices was only 27.5%, said Ms. Manjaly, a research fellow in the department of dermatology at Boston University, and associates.
“This trend of excluding darker skin phototypes persisted when the results were stratified by condition, laser of study, study location, journal type, and funding source,” the investigators noted.
RCTs of laser/light devices for scarring, the most common dermatologic condition represented, included phototypes 5 and 6 in 24.4% of studies, compared with 84.4% for phototypes 4-6. The gap was smaller for melasma, but not for port wine stains. Among the devices examined, RCTs of diode lasers and intense pulsed light had the smallest gaps between inclusion of the two groups of phototypes, while pulsed-dye laser studies had the largest, they reported.
Stratification by journal showed the largest gap in studies published by Lasers in Medical Science and the smallest gap coming from Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. Funding was not specified for the majority of the eligible device RCTs, but those funded by industry had the smallest discrepancy between types 5-6 and types 4-6 and those supported by foundations/nonprofits the largest, Ms. Manjaly and associates said.
“With projections estimating that more than 50% of the U.S. population is set to identify as Hispanic or nonwhite by 2045 ... the lack of information has important consequences for clinical practice, as clinicians are unable to counsel patients on the efficacy and possible complications of various devices in patient with skin of color,” they wrote.
The investigators did not declare any conflicts of interest or funding sources.
, according to a systematic review of the literature, the authors reported.
“While there broadly appears to be skin of color representation [in such studies], a more granular understanding of the data shows a large discrepancy in representation between ‘lighter’ and ‘darker’ skin of color patients,” Priya Manjaly and associates wrote in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.
Among the 461 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) eligible for inclusion, most (81.7%) included participants with skin phototypes 4-6, which is considered skin of color. When only phototypes 5 and 6 were included, however, representation in studies involving laser and light devices was only 27.5%, said Ms. Manjaly, a research fellow in the department of dermatology at Boston University, and associates.
“This trend of excluding darker skin phototypes persisted when the results were stratified by condition, laser of study, study location, journal type, and funding source,” the investigators noted.
RCTs of laser/light devices for scarring, the most common dermatologic condition represented, included phototypes 5 and 6 in 24.4% of studies, compared with 84.4% for phototypes 4-6. The gap was smaller for melasma, but not for port wine stains. Among the devices examined, RCTs of diode lasers and intense pulsed light had the smallest gaps between inclusion of the two groups of phototypes, while pulsed-dye laser studies had the largest, they reported.
Stratification by journal showed the largest gap in studies published by Lasers in Medical Science and the smallest gap coming from Lasers in Surgery and Medicine. Funding was not specified for the majority of the eligible device RCTs, but those funded by industry had the smallest discrepancy between types 5-6 and types 4-6 and those supported by foundations/nonprofits the largest, Ms. Manjaly and associates said.
“With projections estimating that more than 50% of the U.S. population is set to identify as Hispanic or nonwhite by 2045 ... the lack of information has important consequences for clinical practice, as clinicians are unable to counsel patients on the efficacy and possible complications of various devices in patient with skin of color,” they wrote.
The investigators did not declare any conflicts of interest or funding sources.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF COSMETIC DERMATOLOGY
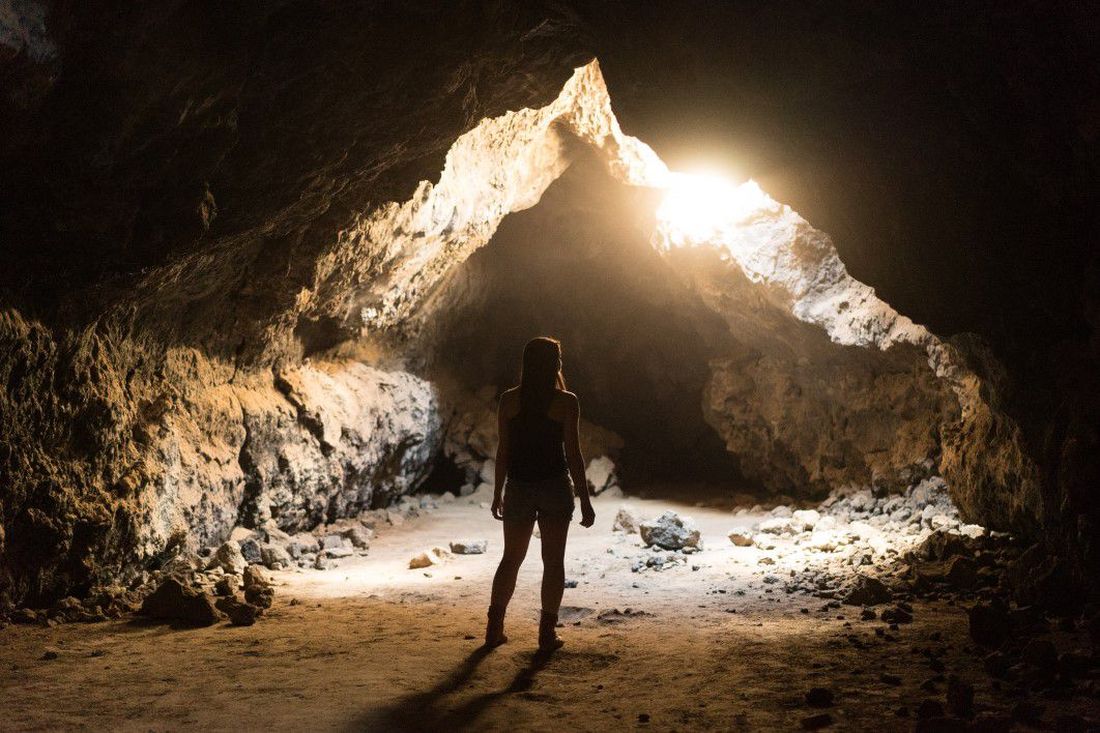
Living the introvert’s dream: Alone for 500 days, but never lonely
Beating the allegory of the cave
When Beatriz Flamini spoke with reporters on April 14, she knew nothing of the previous 18 months. The Russian invasion of Ukraine? Nope. The death of Queen Elizabeth? Also no. But before you make fun of her, she has an excuse. She’s been living under a rock.
As part of an experiment to test how social isolation and disorientation affect a person’s mind, sense of time, and sleeping patterns, Ms. Flamini lived in a 70-meter-deep cave in southern Spain for 500 days, starting in November 2021. Alone. No outside communication with the outside world in any way, though she was constantly monitored by a team of researchers. She also had multiple cameras filming her for an upcoming documentary.
This is a massive step up from the previous record for time spent underground for science: A team of 15 spent 50 days underground in 2021 to similar study of isolation and how it affected circadian rhythms. It’s also almost certainly a world record for time spent underground.
All that time alone certainly sounds like some sort of medieval torture, but Ms. Flamini had access to food, water, and a library of books. Which she made liberal use of, reading at least 60 books during her stay. She also had a panic button in case the isolation became too much or an emergency developed, but she never considered using it.
She lost track of time after 2 months, flies invaded the cave on occasion, and maintaining coherence was occasionally a struggle, but she kept things together very well. In fact, she didn’t even want to leave when her team came for her. She wasn’t even finished with her 61st book.
When she spoke with gathered reporters after the ordeal, words were obviously difficult to come by for her, having not spoken in nearly 18 months, but her mind was clearly still sharp and she had a very important question for everyone gathered around her.
Who’s buying the beer?
We approve of this request.
Staphylococcus and the speed of evolution
Bacteria, we know, are tough little buggers that are hard to see and even harder to get rid of. So hard, actually, that human bodies eventually gave up on the task and decided to just incorporate them into our organ systems. But why are bacteria so hard to eliminate?
Two words: rapid evolution. How rapid? For the first time, scientists have directly observed adaptive evolution by Staphylococcus aureus in a single person’s skin microbiome. That’s how rapid.
For their study, the researchers collected samples from the nostrils, backs of knees, insides of elbows, and forearms of 23 children with eczema. They eventually cultured almost 1,500 unique colonies of S. aureus cells from those samples and sequenced the cells’ genomes.
All that sampling and culturing and sequencing showed that it was rare for a new S. aureus strain to come in and replace the existing strain. “Despite the stability at the lineage level, we see a lot of dynamics at the whole genome level, where new mutations are constantly arising in these bacteria and then spreading throughout the entire body,” Tami D. Lieberman, PhD, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, said in a written statement from MIT.
One frequent mutation involved a gene called capD, which encodes an enzyme necessary for synthesizing the capsular polysaccharide – a coating that protects S. aureus from recognition by immune cells. In one patient, four different mutations of capD arose independently in different samples before one variant became dominant and spread over the entire microbiome, MIT reported.
The mutation, which actually results in the loss of the polysaccharide capsule, may allow cells to grow faster than those without the mutation because they have more fuel to power their own growth, the researchers suggested. It’s also possible that loss of the capsule allows S. aureus cells to stick to the skin better because proteins that allow them to adhere to the skin are more exposed.
Dr. Lieberman and her associates hope that these variant-containing cells could be a new target for eczema treatments, but we’re never optimistic when it comes to bacteria. That’s because some of us are old enough to remember evolutionary biologist Stephen Jay Gould, who wrote in his book “Full House”: “Our planet has always been in the ‘Age of Bacteria,’ ever since the first fossils – bacteria, of course – were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are – and always have been – the dominant forms of life on Earth.”
In the distant future, long after humans have left the scene, the bacteria will be laughing at the last rats and cockroaches scurrying across the landscape. Wanna bet?
The height of genetic prediction
Genetics are practically a DNA Scrabble bag. Traits like eye color and hair texture are chosen in the same fashion, based on what gets pulled from our own genetic bag of letters, but what about height? Researchers may now have a way to predict adult height and make it more than just an educated guess.
How? By looking at the genes in our growth plates. The cartilage on the ends of our bones hardens as we age, eventually deciding an individual’s stature. In a recently published study, a research team looked at 600 million cartilage cells linked to maturation and cell growth in mice. Because everything starts with rodents.
After that search identified 145 genes linked to growth plate maturation and formation of the bones, they compared the mouse genes with data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of human height to look for hotspots where the height genes exist in human DNA.
The results showed which genes play a role in deciding height, and the GWAS data also suggested that genetic changes affecting cartilage cell maturation may strongly influence adult height, said the investigators, who hope that earlier interventions can improve outcomes in patients with conditions such as skeletal dysplasia.
So, yeah, you may want to be a little taller or shorter, but the outcome of that particular Scrabble game was determined when your parents, you know, dropped the letters in the bag.
Beating the allegory of the cave
When Beatriz Flamini spoke with reporters on April 14, she knew nothing of the previous 18 months. The Russian invasion of Ukraine? Nope. The death of Queen Elizabeth? Also no. But before you make fun of her, she has an excuse. She’s been living under a rock.
As part of an experiment to test how social isolation and disorientation affect a person’s mind, sense of time, and sleeping patterns, Ms. Flamini lived in a 70-meter-deep cave in southern Spain for 500 days, starting in November 2021. Alone. No outside communication with the outside world in any way, though she was constantly monitored by a team of researchers. She also had multiple cameras filming her for an upcoming documentary.
This is a massive step up from the previous record for time spent underground for science: A team of 15 spent 50 days underground in 2021 to similar study of isolation and how it affected circadian rhythms. It’s also almost certainly a world record for time spent underground.
All that time alone certainly sounds like some sort of medieval torture, but Ms. Flamini had access to food, water, and a library of books. Which she made liberal use of, reading at least 60 books during her stay. She also had a panic button in case the isolation became too much or an emergency developed, but she never considered using it.
She lost track of time after 2 months, flies invaded the cave on occasion, and maintaining coherence was occasionally a struggle, but she kept things together very well. In fact, she didn’t even want to leave when her team came for her. She wasn’t even finished with her 61st book.
When she spoke with gathered reporters after the ordeal, words were obviously difficult to come by for her, having not spoken in nearly 18 months, but her mind was clearly still sharp and she had a very important question for everyone gathered around her.
Who’s buying the beer?
We approve of this request.
Staphylococcus and the speed of evolution
Bacteria, we know, are tough little buggers that are hard to see and even harder to get rid of. So hard, actually, that human bodies eventually gave up on the task and decided to just incorporate them into our organ systems. But why are bacteria so hard to eliminate?
Two words: rapid evolution. How rapid? For the first time, scientists have directly observed adaptive evolution by Staphylococcus aureus in a single person’s skin microbiome. That’s how rapid.
For their study, the researchers collected samples from the nostrils, backs of knees, insides of elbows, and forearms of 23 children with eczema. They eventually cultured almost 1,500 unique colonies of S. aureus cells from those samples and sequenced the cells’ genomes.
All that sampling and culturing and sequencing showed that it was rare for a new S. aureus strain to come in and replace the existing strain. “Despite the stability at the lineage level, we see a lot of dynamics at the whole genome level, where new mutations are constantly arising in these bacteria and then spreading throughout the entire body,” Tami D. Lieberman, PhD, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, said in a written statement from MIT.
One frequent mutation involved a gene called capD, which encodes an enzyme necessary for synthesizing the capsular polysaccharide – a coating that protects S. aureus from recognition by immune cells. In one patient, four different mutations of capD arose independently in different samples before one variant became dominant and spread over the entire microbiome, MIT reported.
The mutation, which actually results in the loss of the polysaccharide capsule, may allow cells to grow faster than those without the mutation because they have more fuel to power their own growth, the researchers suggested. It’s also possible that loss of the capsule allows S. aureus cells to stick to the skin better because proteins that allow them to adhere to the skin are more exposed.
Dr. Lieberman and her associates hope that these variant-containing cells could be a new target for eczema treatments, but we’re never optimistic when it comes to bacteria. That’s because some of us are old enough to remember evolutionary biologist Stephen Jay Gould, who wrote in his book “Full House”: “Our planet has always been in the ‘Age of Bacteria,’ ever since the first fossils – bacteria, of course – were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are – and always have been – the dominant forms of life on Earth.”
In the distant future, long after humans have left the scene, the bacteria will be laughing at the last rats and cockroaches scurrying across the landscape. Wanna bet?
The height of genetic prediction
Genetics are practically a DNA Scrabble bag. Traits like eye color and hair texture are chosen in the same fashion, based on what gets pulled from our own genetic bag of letters, but what about height? Researchers may now have a way to predict adult height and make it more than just an educated guess.
How? By looking at the genes in our growth plates. The cartilage on the ends of our bones hardens as we age, eventually deciding an individual’s stature. In a recently published study, a research team looked at 600 million cartilage cells linked to maturation and cell growth in mice. Because everything starts with rodents.
After that search identified 145 genes linked to growth plate maturation and formation of the bones, they compared the mouse genes with data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of human height to look for hotspots where the height genes exist in human DNA.
The results showed which genes play a role in deciding height, and the GWAS data also suggested that genetic changes affecting cartilage cell maturation may strongly influence adult height, said the investigators, who hope that earlier interventions can improve outcomes in patients with conditions such as skeletal dysplasia.
So, yeah, you may want to be a little taller or shorter, but the outcome of that particular Scrabble game was determined when your parents, you know, dropped the letters in the bag.
Beating the allegory of the cave
When Beatriz Flamini spoke with reporters on April 14, she knew nothing of the previous 18 months. The Russian invasion of Ukraine? Nope. The death of Queen Elizabeth? Also no. But before you make fun of her, she has an excuse. She’s been living under a rock.
As part of an experiment to test how social isolation and disorientation affect a person’s mind, sense of time, and sleeping patterns, Ms. Flamini lived in a 70-meter-deep cave in southern Spain for 500 days, starting in November 2021. Alone. No outside communication with the outside world in any way, though she was constantly monitored by a team of researchers. She also had multiple cameras filming her for an upcoming documentary.
This is a massive step up from the previous record for time spent underground for science: A team of 15 spent 50 days underground in 2021 to similar study of isolation and how it affected circadian rhythms. It’s also almost certainly a world record for time spent underground.
All that time alone certainly sounds like some sort of medieval torture, but Ms. Flamini had access to food, water, and a library of books. Which she made liberal use of, reading at least 60 books during her stay. She also had a panic button in case the isolation became too much or an emergency developed, but she never considered using it.
She lost track of time after 2 months, flies invaded the cave on occasion, and maintaining coherence was occasionally a struggle, but she kept things together very well. In fact, she didn’t even want to leave when her team came for her. She wasn’t even finished with her 61st book.
When she spoke with gathered reporters after the ordeal, words were obviously difficult to come by for her, having not spoken in nearly 18 months, but her mind was clearly still sharp and she had a very important question for everyone gathered around her.
Who’s buying the beer?
We approve of this request.
Staphylococcus and the speed of evolution
Bacteria, we know, are tough little buggers that are hard to see and even harder to get rid of. So hard, actually, that human bodies eventually gave up on the task and decided to just incorporate them into our organ systems. But why are bacteria so hard to eliminate?
Two words: rapid evolution. How rapid? For the first time, scientists have directly observed adaptive evolution by Staphylococcus aureus in a single person’s skin microbiome. That’s how rapid.
For their study, the researchers collected samples from the nostrils, backs of knees, insides of elbows, and forearms of 23 children with eczema. They eventually cultured almost 1,500 unique colonies of S. aureus cells from those samples and sequenced the cells’ genomes.
All that sampling and culturing and sequencing showed that it was rare for a new S. aureus strain to come in and replace the existing strain. “Despite the stability at the lineage level, we see a lot of dynamics at the whole genome level, where new mutations are constantly arising in these bacteria and then spreading throughout the entire body,” Tami D. Lieberman, PhD, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, said in a written statement from MIT.
One frequent mutation involved a gene called capD, which encodes an enzyme necessary for synthesizing the capsular polysaccharide – a coating that protects S. aureus from recognition by immune cells. In one patient, four different mutations of capD arose independently in different samples before one variant became dominant and spread over the entire microbiome, MIT reported.
The mutation, which actually results in the loss of the polysaccharide capsule, may allow cells to grow faster than those without the mutation because they have more fuel to power their own growth, the researchers suggested. It’s also possible that loss of the capsule allows S. aureus cells to stick to the skin better because proteins that allow them to adhere to the skin are more exposed.
Dr. Lieberman and her associates hope that these variant-containing cells could be a new target for eczema treatments, but we’re never optimistic when it comes to bacteria. That’s because some of us are old enough to remember evolutionary biologist Stephen Jay Gould, who wrote in his book “Full House”: “Our planet has always been in the ‘Age of Bacteria,’ ever since the first fossils – bacteria, of course – were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are – and always have been – the dominant forms of life on Earth.”
In the distant future, long after humans have left the scene, the bacteria will be laughing at the last rats and cockroaches scurrying across the landscape. Wanna bet?
The height of genetic prediction
Genetics are practically a DNA Scrabble bag. Traits like eye color and hair texture are chosen in the same fashion, based on what gets pulled from our own genetic bag of letters, but what about height? Researchers may now have a way to predict adult height and make it more than just an educated guess.
How? By looking at the genes in our growth plates. The cartilage on the ends of our bones hardens as we age, eventually deciding an individual’s stature. In a recently published study, a research team looked at 600 million cartilage cells linked to maturation and cell growth in mice. Because everything starts with rodents.
After that search identified 145 genes linked to growth plate maturation and formation of the bones, they compared the mouse genes with data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of human height to look for hotspots where the height genes exist in human DNA.
The results showed which genes play a role in deciding height, and the GWAS data also suggested that genetic changes affecting cartilage cell maturation may strongly influence adult height, said the investigators, who hope that earlier interventions can improve outcomes in patients with conditions such as skeletal dysplasia.
So, yeah, you may want to be a little taller or shorter, but the outcome of that particular Scrabble game was determined when your parents, you know, dropped the letters in the bag.
Previously unknown viral families hide in the darnedest places
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
You and me and baby makes 10,003
If you were a virus hunter, looking for your next big virus discovery, where would you go? The wholesale seafood market in Wuhan? A gathering of unmasked anti-vaxxers in the heartland of America? The frozen snot fields of northwest Siberia?
How about babies? Well, it’s too late now, because that’s what Dennis Sandris Nielsen, PhD, of the University of Copenhagen, and his associates did, and they hit the mother lode. Actually, it was more like the infant load, if we’re being honest here.
“We found an exceptional number of unknown viruses in the faeces of these babies,” Dr. Nielsen said in a written statement from the university. (The study was published in Nature Microbiology, so we get the English spelling of feces.)
The investigators mapped the gut “viromes” of 647 healthy Danish 1-year-old children over the course of 5 years and found 10,000 species of viruses distributed across 248 different viral families, of which only 16 were already known. Incredible stuff, but then things took a turn for the cute. “The researchers named the remaining 232 unknown viral families after the children whose diapers made the study possible. As a result, new viral families include names like Sylvesterviridae, Rigmorviridae and Tristanviridae,” the university said.
About 90% of the viruses found in the feces are bacterial viruses, aka bacteriophages, which have bacteria as their hosts and don’t attack the children’s cells, so they don’t cause disease. The other 10%, however, are eukaryotic: They use human cells as hosts, so they can be either friend or foe. “It is thought-provoking that all children run around with 10-20 of these virus types that infect human cells. So, there is a constant viral infection taking place, which apparently doesn’t make them sick,” Dr. Nielsen said.
Doesn’t make them sick? Riiiight. The thought that this gives rise to now? People love babies. Everyone wants to pick up the baby. Now we know why. Because the viruses want us to! Well, those cute little faces aren’t fooling us anymore. No more babies for us. Everyone should stay away from babies and their evil little eukaryotic viruses. STOP THE BABIES!
[Editor’s note: After a short timeout, we explained to the staff that the human species actually needs babies for its survival. They calmed down, picked up their crayons, and quietly went back to work.]
Fooled them. Stop the babies!
At least someone out there appreciates hospital food
Life in Alaska is not for the meek. It’s dark half the year. Summer is 3 weeks in July. And somehow, there’s a moose in line ahead of you at the doctor’s office. To make matters worse, it’s arguing about insurance. “What do you mean, you’ve heard the Moo Cross Moo Shield joke before?”
One might expect that Providence Alaska Health Park, located near downtown Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska by a massive margin, might be safe from ungulate invasion. Nope. In recent days, a young moose has taken to hanging around Providence campus, and it just could not find anything to eat. Remember, it may be early April, but this is Alaska. It’s still winter there. The ground’s still covered in snow.
Eventually, the gears in our young moose friend’s mind turned and it settled on a course of action: “Hey, those are some nice-looking plants behind that door over there. …” And that’s how Providence Alaska Health ended up with a moose munching on decorative potted plants in the hospital lobby.
Funnily enough, the moose didn’t even make a big scene. It just walked through the automatic doors and started chowing down. Security only found out because a tenant called them. Naturally though, once security made the announcement that a massive wild animal had been spotted in the building, the lobby was evacuated. … What do you mean, half the hospital came around to see it? Apparently, even though Alaskans have to fight moose herds on their daily commute, a lot of people wanted to see our moose friend do its thing.
“That’s crazy,” a woman in scrubs said in a video as she snapped a photo with her phone.
“This is the best. Like, what’s the code for this?” asked another bystander.
Despite security’s best efforts to shoo the moose out with barricades and offers of tasty branches, our furry friend left of its own volition, presumably irritated that his breakfast had become a spectator sport. But it didn’t go far. It hung around the front drive for a while, then went around the back of the building for a nap. What has four hooves and still doesn’t give a crap? Bob Moose-o! How you doing?
That click sounded stressed
How can people tell that you’re stressed? Maybe you get irritable and a little snappy. Some people have an inability to concentrate or focus. Eating that muffin when you weren’t really hungry could be a sign you’re not relaxed.
Did you know that your computer can be an indicator of your stress levels?
We tend to be working when we’re using computers, right? That can be a stressor in itself. Well, some researchers at ETH Zürich decided to have a look at the situation. Surprisingly, at least to us, one in three Swiss employees experience workplace stress, which makes us wonder what the percentage is in this country.
The Swiss researchers developed a model that tells how stressed someone is just by the way they use their computer mouse or type. The results of their study showed that those who were stressed clicked and tapped differently than participants who were more relaxed.
Stressed people click “more often and less precisely and cover longer distances on the screen,” while the relaxed take “shorter, more direct routes to reach their destination and take more time doing so,” study author Mara Nägelin explained in a written statement from ETH (Eidgenössische Technische Hochschule, or Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) Zürich.
Ever find when you’re frustrated and in a rush you end up making more mistakes? Same deal. Coauthor Jasmine Kerr noted that “increased levels of stress negatively impact our brain’s ability to process information.” Which totally is going to affect how we move.
Hopefully, these results can give insight to companies on how stressed their employees are and the effect it has on their work performance, eventually leading to, guess what, more research on how to alleviate workplace stress in general, which can benefit us all.
So if you find yourself in the office working on your computer like it’s a game of Perfection and time is running out, take a beat. Maybe try a stress-relieving breathing technique. Nonstressed people, according to the study, take fewer and longer pauses on their computers. Perfection on the job may mean relaxing first.
Lack of food for thought: Starve a bacterium, feed an infection
A whole new, tiny level of hangry
Ever been so hungry that everything just got on your nerves? Maybe you feel a little snappy right now? Like you’ll just lash out unless you get something to eat? Been there. And so have bacteria.
New research shows that some bacteria go into a full-on Hulk smash if they’re not getting the nutrients they need by releasing toxins into the body. Sounds like a bacterial temper tantrum.
Even though two cells may be genetically identical, they don’t always behave the same in a bacterial community. Some do their job and stay in line, but some evil twins rage out and make people sick by releasing toxins into the environment, Adam Rosenthal, PhD, of the University of North Carolina and his colleagues discovered.
To figure out why some cells were all business as usual while others were not, the investigators looked at Clostridium perfringens, a bacterium found in the intestines of humans and other vertebrates. When the C. perfringens cells were fed a little acetate to munch on, the hangry cells calmed down faster than a kid with a bag of fruit snacks, reducing toxin levels. Some cells even disappeared, falling in line with their model-citizen counterparts.
So what does this really mean? More research, duh. Now that we know nutrients play a role in toxicity, it may open the door to finding a way to fight against antibiotic resistance in humans and reduce antibiotic use in the food industry.
So think to yourself. Are you bothered for no reason? Getting a little testy with your friends and coworkers? Maybe you just haven’t eaten in a while. You’re literally not alone. Even a single-cell organism can behave based on its hunger levels.
Now go have a snack. Your bacteria are getting restless.
The very hangry iguana?
Imagine yourself on a warm, sunny tropical beach. You are enjoying a piece of cake as you take in the slow beat of the waves lapping against the shore. Life is as good as it could be.
Then you feel a presence nearby. Hostility. Hunger. A set of feral, covetous eyes in the nearby jungle. A reptilian beast stalks you, and its all-encompassing sweet tooth desires your cake.
Wait, hold on, what?
As an unfortunate 3-year-old on vacation in Costa Rica found out, there’s at least one iguana in the world out there with a taste for sugar (better than a taste for blood, we suppose).
While out on the beach, the lizard darted out of nowhere, bit the girl on the back of the hand, and stole her cake. Still not the worst party guest ever. The child was taken to a local clinic, where the wound was cleaned and a 5-day antibiotic treatment (lizards carry salmonella) was provided. Things seemed fine, and the girl returned home without incident.
But of course, that’s not the end of the story. Five months later, the girl’s parents noticed a red bump at the wound site. Over the next 3 months, the surrounding skin grew red and painful. A trip to the hospital in California revealed that she had a ganglion cyst and a discharge of pus. Turns out our cake-obsessed lizard friend did give the little girl a gift: the first known human case of Mycobacterium marinum infection following an iguana bite on record.
M. marinum, which causes a disease similar to tuberculosis, typically infects fish but can infect humans if skin wounds are exposed to contaminated water. It’s also resistant to most antibiotics, which is why the first round didn’t clear up the infection. A second round of more-potent antibiotics seems to be working well.
So, to sum up, this poor child got bitten by a lizard, had her cake stolen, and contracted a rare illness in exchange. For a 3-year-old, that’s gotta be in the top-10 worst days ever. Unless, of course, we’re actually living in the Marvel universe (sorry, multiverse at this point). Then we’re totally going to see the emergence of the new superhero Iguana Girl in 15 years or so. Keep your eyes open.
No allergies? Let them give up cake
Allergy season is already here – starting earlier every year, it seems – and many people are not happy about it. So unhappy, actually, that there’s a list of things they would be willing to give up for a year to get rid of their of allergies, according to a survey conducted by OnePoll on behalf of Flonase.
Nearly 40% of 2,000 respondents with allergies would go a year without eating cake or chocolate or playing video games in exchange for allergy-free status, the survey results show. Almost as many would forgo coffee (38%) or pizza (37%) for a year, while 36% would stay off social media and 31% would take a pay cut or give up their smartphones, the Independent reported.
More than half of the allergic Americans – 54%, to be exact – who were polled this past winter – Feb. 24 to March 1, to be exact – consider allergy symptoms to be the most frustrating part of the spring. Annoying things that were less frustrating to the group included mosquitoes (41%), filing tax returns (38%), and daylight savings time (37%).
The Trump arraignment circus, of course, occurred too late to make the list, as did the big “We’re going back to the office! No wait, we’re closing the office forever!” email extravaganza and emotional roller coaster. That second one, however, did not get nearly as much media coverage.
A whole new, tiny level of hangry
Ever been so hungry that everything just got on your nerves? Maybe you feel a little snappy right now? Like you’ll just lash out unless you get something to eat? Been there. And so have bacteria.
New research shows that some bacteria go into a full-on Hulk smash if they’re not getting the nutrients they need by releasing toxins into the body. Sounds like a bacterial temper tantrum.
Even though two cells may be genetically identical, they don’t always behave the same in a bacterial community. Some do their job and stay in line, but some evil twins rage out and make people sick by releasing toxins into the environment, Adam Rosenthal, PhD, of the University of North Carolina and his colleagues discovered.
To figure out why some cells were all business as usual while others were not, the investigators looked at Clostridium perfringens, a bacterium found in the intestines of humans and other vertebrates. When the C. perfringens cells were fed a little acetate to munch on, the hangry cells calmed down faster than a kid with a bag of fruit snacks, reducing toxin levels. Some cells even disappeared, falling in line with their model-citizen counterparts.
So what does this really mean? More research, duh. Now that we know nutrients play a role in toxicity, it may open the door to finding a way to fight against antibiotic resistance in humans and reduce antibiotic use in the food industry.
So think to yourself. Are you bothered for no reason? Getting a little testy with your friends and coworkers? Maybe you just haven’t eaten in a while. You’re literally not alone. Even a single-cell organism can behave based on its hunger levels.
Now go have a snack. Your bacteria are getting restless.
The very hangry iguana?
Imagine yourself on a warm, sunny tropical beach. You are enjoying a piece of cake as you take in the slow beat of the waves lapping against the shore. Life is as good as it could be.
Then you feel a presence nearby. Hostility. Hunger. A set of feral, covetous eyes in the nearby jungle. A reptilian beast stalks you, and its all-encompassing sweet tooth desires your cake.
Wait, hold on, what?
As an unfortunate 3-year-old on vacation in Costa Rica found out, there’s at least one iguana in the world out there with a taste for sugar (better than a taste for blood, we suppose).
While out on the beach, the lizard darted out of nowhere, bit the girl on the back of the hand, and stole her cake. Still not the worst party guest ever. The child was taken to a local clinic, where the wound was cleaned and a 5-day antibiotic treatment (lizards carry salmonella) was provided. Things seemed fine, and the girl returned home without incident.
But of course, that’s not the end of the story. Five months later, the girl’s parents noticed a red bump at the wound site. Over the next 3 months, the surrounding skin grew red and painful. A trip to the hospital in California revealed that she had a ganglion cyst and a discharge of pus. Turns out our cake-obsessed lizard friend did give the little girl a gift: the first known human case of Mycobacterium marinum infection following an iguana bite on record.
M. marinum, which causes a disease similar to tuberculosis, typically infects fish but can infect humans if skin wounds are exposed to contaminated water. It’s also resistant to most antibiotics, which is why the first round didn’t clear up the infection. A second round of more-potent antibiotics seems to be working well.
So, to sum up, this poor child got bitten by a lizard, had her cake stolen, and contracted a rare illness in exchange. For a 3-year-old, that’s gotta be in the top-10 worst days ever. Unless, of course, we’re actually living in the Marvel universe (sorry, multiverse at this point). Then we’re totally going to see the emergence of the new superhero Iguana Girl in 15 years or so. Keep your eyes open.
No allergies? Let them give up cake
Allergy season is already here – starting earlier every year, it seems – and many people are not happy about it. So unhappy, actually, that there’s a list of things they would be willing to give up for a year to get rid of their of allergies, according to a survey conducted by OnePoll on behalf of Flonase.
Nearly 40% of 2,000 respondents with allergies would go a year without eating cake or chocolate or playing video games in exchange for allergy-free status, the survey results show. Almost as many would forgo coffee (38%) or pizza (37%) for a year, while 36% would stay off social media and 31% would take a pay cut or give up their smartphones, the Independent reported.
More than half of the allergic Americans – 54%, to be exact – who were polled this past winter – Feb. 24 to March 1, to be exact – consider allergy symptoms to be the most frustrating part of the spring. Annoying things that were less frustrating to the group included mosquitoes (41%), filing tax returns (38%), and daylight savings time (37%).
The Trump arraignment circus, of course, occurred too late to make the list, as did the big “We’re going back to the office! No wait, we’re closing the office forever!” email extravaganza and emotional roller coaster. That second one, however, did not get nearly as much media coverage.
A whole new, tiny level of hangry
Ever been so hungry that everything just got on your nerves? Maybe you feel a little snappy right now? Like you’ll just lash out unless you get something to eat? Been there. And so have bacteria.
New research shows that some bacteria go into a full-on Hulk smash if they’re not getting the nutrients they need by releasing toxins into the body. Sounds like a bacterial temper tantrum.
Even though two cells may be genetically identical, they don’t always behave the same in a bacterial community. Some do their job and stay in line, but some evil twins rage out and make people sick by releasing toxins into the environment, Adam Rosenthal, PhD, of the University of North Carolina and his colleagues discovered.
To figure out why some cells were all business as usual while others were not, the investigators looked at Clostridium perfringens, a bacterium found in the intestines of humans and other vertebrates. When the C. perfringens cells were fed a little acetate to munch on, the hangry cells calmed down faster than a kid with a bag of fruit snacks, reducing toxin levels. Some cells even disappeared, falling in line with their model-citizen counterparts.
So what does this really mean? More research, duh. Now that we know nutrients play a role in toxicity, it may open the door to finding a way to fight against antibiotic resistance in humans and reduce antibiotic use in the food industry.
So think to yourself. Are you bothered for no reason? Getting a little testy with your friends and coworkers? Maybe you just haven’t eaten in a while. You’re literally not alone. Even a single-cell organism can behave based on its hunger levels.
Now go have a snack. Your bacteria are getting restless.
The very hangry iguana?
Imagine yourself on a warm, sunny tropical beach. You are enjoying a piece of cake as you take in the slow beat of the waves lapping against the shore. Life is as good as it could be.
Then you feel a presence nearby. Hostility. Hunger. A set of feral, covetous eyes in the nearby jungle. A reptilian beast stalks you, and its all-encompassing sweet tooth desires your cake.
Wait, hold on, what?
As an unfortunate 3-year-old on vacation in Costa Rica found out, there’s at least one iguana in the world out there with a taste for sugar (better than a taste for blood, we suppose).
While out on the beach, the lizard darted out of nowhere, bit the girl on the back of the hand, and stole her cake. Still not the worst party guest ever. The child was taken to a local clinic, where the wound was cleaned and a 5-day antibiotic treatment (lizards carry salmonella) was provided. Things seemed fine, and the girl returned home without incident.
But of course, that’s not the end of the story. Five months later, the girl’s parents noticed a red bump at the wound site. Over the next 3 months, the surrounding skin grew red and painful. A trip to the hospital in California revealed that she had a ganglion cyst and a discharge of pus. Turns out our cake-obsessed lizard friend did give the little girl a gift: the first known human case of Mycobacterium marinum infection following an iguana bite on record.
M. marinum, which causes a disease similar to tuberculosis, typically infects fish but can infect humans if skin wounds are exposed to contaminated water. It’s also resistant to most antibiotics, which is why the first round didn’t clear up the infection. A second round of more-potent antibiotics seems to be working well.
So, to sum up, this poor child got bitten by a lizard, had her cake stolen, and contracted a rare illness in exchange. For a 3-year-old, that’s gotta be in the top-10 worst days ever. Unless, of course, we’re actually living in the Marvel universe (sorry, multiverse at this point). Then we’re totally going to see the emergence of the new superhero Iguana Girl in 15 years or so. Keep your eyes open.
No allergies? Let them give up cake
Allergy season is already here – starting earlier every year, it seems – and many people are not happy about it. So unhappy, actually, that there’s a list of things they would be willing to give up for a year to get rid of their of allergies, according to a survey conducted by OnePoll on behalf of Flonase.
Nearly 40% of 2,000 respondents with allergies would go a year without eating cake or chocolate or playing video games in exchange for allergy-free status, the survey results show. Almost as many would forgo coffee (38%) or pizza (37%) for a year, while 36% would stay off social media and 31% would take a pay cut or give up their smartphones, the Independent reported.
More than half of the allergic Americans – 54%, to be exact – who were polled this past winter – Feb. 24 to March 1, to be exact – consider allergy symptoms to be the most frustrating part of the spring. Annoying things that were less frustrating to the group included mosquitoes (41%), filing tax returns (38%), and daylight savings time (37%).
The Trump arraignment circus, of course, occurred too late to make the list, as did the big “We’re going back to the office! No wait, we’re closing the office forever!” email extravaganza and emotional roller coaster. That second one, however, did not get nearly as much media coverage.
Analysis identifies gaps in CV risk screening of patients with psoriasis
Just , according to an analysis of 10 years of national survey data.
From 2007 to 2016, national screening rates for four CV risk factors at 14.8 million psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers were 11% (body-mass index), 7.4% (blood pressure), 2.9% (cholesterol), and 1.7% (glucose). Data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey showed that at least one of the four factors was screened at 16% of dermatology visits, said William B. Song, BS, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and associates.
The main focus of their study, however, was regional differences. “CV risk factor screening by dermatology providers for patients with psoriasis is low across all regions of the United States and lowest in the South, the region that experiences the highest CVD burden in the United States,” they wrote in a letter to the editor.
Compared with the South, the adjusted odds of any CV screening were 0.98 in the West, 1.25 in the Northeast, and 1.92 in the Midwest. Blood pressure screening was significantly higher in all three regions, compared with the South, while BMI screening was actually lower in the West (0.74), the investigators reported. Odds ratios were not available for cholesterol and glucose screening because of sample size limitations.
The regional variation in screening rates “is not explained by patient demographics or disease severity,” they noted, adding that 2.8 million visits with BP screening would have been added over the 10-year study period “if providers in the South screened patients with psoriasis for high blood pressure at the same rate as providers in the Northeast.”
Guidelines published in 2019 by the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation – which were cowritten by Joel M. Gelfand, MD, senior author of the current study – noted that dermatologists “play an important role in evidence-based screening of CV risk factors in patients with psoriasis,” the investigators wrote. But the regional variations suggest “that some regions experience barriers to appropriate screening or challenges in adhering to guidelines for managing psoriasis and CV risk.”
While the lack of data from after 2016 is one of the study limitations, they added, “continued efforts to develop effective interventions to improve CV screening and care for people with psoriasis in all regions of the U.S. are needed to more effectively address the burden of CV disease experienced by people with psoriasis.”
The study was partly funded by the National Psoriasis Foundation. Three of the seven investigators disclosed earnings from private companies in the form of consultant fees, research support, and honoraria. Dr. Gelfand is a deputy editor for the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Just , according to an analysis of 10 years of national survey data.
From 2007 to 2016, national screening rates for four CV risk factors at 14.8 million psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers were 11% (body-mass index), 7.4% (blood pressure), 2.9% (cholesterol), and 1.7% (glucose). Data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey showed that at least one of the four factors was screened at 16% of dermatology visits, said William B. Song, BS, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and associates.
The main focus of their study, however, was regional differences. “CV risk factor screening by dermatology providers for patients with psoriasis is low across all regions of the United States and lowest in the South, the region that experiences the highest CVD burden in the United States,” they wrote in a letter to the editor.
Compared with the South, the adjusted odds of any CV screening were 0.98 in the West, 1.25 in the Northeast, and 1.92 in the Midwest. Blood pressure screening was significantly higher in all three regions, compared with the South, while BMI screening was actually lower in the West (0.74), the investigators reported. Odds ratios were not available for cholesterol and glucose screening because of sample size limitations.
The regional variation in screening rates “is not explained by patient demographics or disease severity,” they noted, adding that 2.8 million visits with BP screening would have been added over the 10-year study period “if providers in the South screened patients with psoriasis for high blood pressure at the same rate as providers in the Northeast.”
Guidelines published in 2019 by the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation – which were cowritten by Joel M. Gelfand, MD, senior author of the current study – noted that dermatologists “play an important role in evidence-based screening of CV risk factors in patients with psoriasis,” the investigators wrote. But the regional variations suggest “that some regions experience barriers to appropriate screening or challenges in adhering to guidelines for managing psoriasis and CV risk.”
While the lack of data from after 2016 is one of the study limitations, they added, “continued efforts to develop effective interventions to improve CV screening and care for people with psoriasis in all regions of the U.S. are needed to more effectively address the burden of CV disease experienced by people with psoriasis.”
The study was partly funded by the National Psoriasis Foundation. Three of the seven investigators disclosed earnings from private companies in the form of consultant fees, research support, and honoraria. Dr. Gelfand is a deputy editor for the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
Just , according to an analysis of 10 years of national survey data.
From 2007 to 2016, national screening rates for four CV risk factors at 14.8 million psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers were 11% (body-mass index), 7.4% (blood pressure), 2.9% (cholesterol), and 1.7% (glucose). Data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey showed that at least one of the four factors was screened at 16% of dermatology visits, said William B. Song, BS, of the department of dermatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and associates.
The main focus of their study, however, was regional differences. “CV risk factor screening by dermatology providers for patients with psoriasis is low across all regions of the United States and lowest in the South, the region that experiences the highest CVD burden in the United States,” they wrote in a letter to the editor.
Compared with the South, the adjusted odds of any CV screening were 0.98 in the West, 1.25 in the Northeast, and 1.92 in the Midwest. Blood pressure screening was significantly higher in all three regions, compared with the South, while BMI screening was actually lower in the West (0.74), the investigators reported. Odds ratios were not available for cholesterol and glucose screening because of sample size limitations.
The regional variation in screening rates “is not explained by patient demographics or disease severity,” they noted, adding that 2.8 million visits with BP screening would have been added over the 10-year study period “if providers in the South screened patients with psoriasis for high blood pressure at the same rate as providers in the Northeast.”
Guidelines published in 2019 by the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation – which were cowritten by Joel M. Gelfand, MD, senior author of the current study – noted that dermatologists “play an important role in evidence-based screening of CV risk factors in patients with psoriasis,” the investigators wrote. But the regional variations suggest “that some regions experience barriers to appropriate screening or challenges in adhering to guidelines for managing psoriasis and CV risk.”
While the lack of data from after 2016 is one of the study limitations, they added, “continued efforts to develop effective interventions to improve CV screening and care for people with psoriasis in all regions of the U.S. are needed to more effectively address the burden of CV disease experienced by people with psoriasis.”
The study was partly funded by the National Psoriasis Foundation. Three of the seven investigators disclosed earnings from private companies in the form of consultant fees, research support, and honoraria. Dr. Gelfand is a deputy editor for the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INVESTIGATIVE DERMATOLOGY
Sweaty treatment for social anxiety could pass the sniff test
Getting sweet on sweat
Are you the sort of person who struggles in social situations? Have the past 3 years been a secret respite from the terror and exhaustion of meeting new people? We understand your plight. People kind of suck. And you don’t have to look far to be reminded of it.
Unfortunately, on occasion we all have to interact with other human beings. If you suffer from social anxiety, this is not a fun thing to do. But new research indicates that there may be a way to alleviate the stress for those with social anxiety: armpits.
Specifically, sweat from the armpits of other people. Yes, this means a group of scientists gathered up some volunteers and collected their armpit sweat while the volunteers watched a variety of movies (horror, comedy, romance, etc.). Our condolences to the poor unpaid interns tasked with gathering the sweat.
Once they had their precious new medicine, the researchers took a group of women and administered a round of mindfulness therapy. Some of the participants then received the various sweats, while the rest were forced to smell only clean air. (The horror!) Lo and behold, the sweat groups had their anxiety scores reduced by about 40% after their therapy, compared with just 17% in the control group.
The researchers also found that the source of the sweat didn’t matter. Their study subjects responded the same to sweat excreted during a scary movie as they did to sweat from a comedy, a result that surprised the researchers. They suggested chemosignals in the sweat may affect the treatment response and advised further research. Which means more sweat collection! They plan on testing emotionally neutral movies next time, and if we can make a humble suggestion, they also should try the sweatiest movies.
Before the Food and Drug Administration can approve armpit sweat as a treatment for social anxiety, we have some advice for those shut-in introverts out there. Next time you have to interact with rabid extroverts, instead of shaking their hands, walk up to them and take a deep whiff of their armpits. Establish dominance. Someone will feel awkward, and science has proved it won’t be you.
The puff that vaccinates
Ever been shot with a Nerf gun or hit with a foam pool tube? More annoying than painful, right? If we asked if you’d rather get pelted with one of those than receive a traditional vaccine injection, you would choose the former. Maybe someday you actually will.
During the boredom of the early pandemic lockdown, Jeremiah Gassensmith, PhD, of the department of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Texas, Dallas, ordered a compressed gas–powered jet injection system to fool around with at home. Hey, who didn’t? Anyway, when it was time to go back to the lab he handed it over to one of his grad students, Yalini Wijesundara, and asked her to see what could be done with it.
In her tinkering she found that the jet injector could deliver metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that can hold a bunch of different materials, like proteins and nucleic acids, through the skin.
Thus the “MOF-Jet” was born!
Jet injectors are nothing new, but they hurt. The MOF-Jet, however, is practically painless and cheaper than the gene guns that veterinarians use to inject biological cargo attached to the surface of a metal microparticle.
Changing the carrier gas also changes the time needed to break down the MOF and thus alters delivery of the drug inside. “If you shoot it with carbon dioxide, it will release its cargo faster within cells; if you use regular air, it will take 4 or 5 days,” Ms. Wijesundara explained in a written statement. That means the same drug could be released over different timescales without changing its formulation.
While testing on onion cells and mice, Ms. Wijesundara noted that it was as easy as “pointing and shooting” to distribute the puff of gas into the cells. A saving grace to those with needle anxiety. Not that we would know anything about needle anxiety.
More testing needs to be done before bringing this technology to human use, obviously, but we’re looking forward to saying goodbye to that dreaded prick and hello to a puff.
Your hippocampus is showing
Brain anatomy is one of the many, many things that’s not really our thing, but we do know a cool picture when we see one. Case in point: The image just below, which happens to be a full-scale, single-cell resolution model of the CA1 region of the hippocampus that “replicates the structure and architecture of the area, along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons,” according to a statement from the Human Brain Project.
“We have performed a data mining operation on high resolution images of the human hippocampus, obtained from the BigBrain database. The position of individual neurons has been derived from a detailed analysis of these images,” said senior author Michele Migliore, PhD, of the Italian National Research Council’s Institute of Biophysics in Palermo.
Yes, he did say BigBrain database. BigBrain is – we checked and it’s definitely not this – a 3D model of a brain that was sectioned into 7,404 slices just 20 micrometers thick and then scanned by MRI. Digital reconstruction of those slices was done by supercomputer and the results are now available for analysis.
Dr. Migliore and his associates developed an image-processing algorithm to obtain neuronal positioning distribution and an algorithm to generate neuronal connectivity by approximating the shapes of dendrites and axons. (Our brains are starting to hurt just trying to write this.) “Some fit into narrow cones, others have a broad complex extension that can be approximated by dedicated geometrical volumes, and the connectivity to nearby neurons changes accordingly,” explained lead author Daniela Gandolfi of the University of Modena (Italy) and Reggio Emilia.
The investigators have made their dataset and the extraction methodology available on the EBRAINS platform and through the Human Brain Project and are moving on to other brain regions. And then, once everyone can find their way in and around the old gray matter, it should bring an end to conversations like this, which no doubt occur between male and female neuroscientists every day:
“Arnold, I think we’re lost.”
“Don’t worry, Bev, I know where I’m going.”
“Stop and ask this lady for directions.”
“I said I can find it.”
“Just ask her.”
“Fine. Excuse me, ma’am, can you tell us how to get to the corpora quadrigemina from here?
Getting sweet on sweat
Are you the sort of person who struggles in social situations? Have the past 3 years been a secret respite from the terror and exhaustion of meeting new people? We understand your plight. People kind of suck. And you don’t have to look far to be reminded of it.
Unfortunately, on occasion we all have to interact with other human beings. If you suffer from social anxiety, this is not a fun thing to do. But new research indicates that there may be a way to alleviate the stress for those with social anxiety: armpits.
Specifically, sweat from the armpits of other people. Yes, this means a group of scientists gathered up some volunteers and collected their armpit sweat while the volunteers watched a variety of movies (horror, comedy, romance, etc.). Our condolences to the poor unpaid interns tasked with gathering the sweat.
Once they had their precious new medicine, the researchers took a group of women and administered a round of mindfulness therapy. Some of the participants then received the various sweats, while the rest were forced to smell only clean air. (The horror!) Lo and behold, the sweat groups had their anxiety scores reduced by about 40% after their therapy, compared with just 17% in the control group.
The researchers also found that the source of the sweat didn’t matter. Their study subjects responded the same to sweat excreted during a scary movie as they did to sweat from a comedy, a result that surprised the researchers. They suggested chemosignals in the sweat may affect the treatment response and advised further research. Which means more sweat collection! They plan on testing emotionally neutral movies next time, and if we can make a humble suggestion, they also should try the sweatiest movies.
Before the Food and Drug Administration can approve armpit sweat as a treatment for social anxiety, we have some advice for those shut-in introverts out there. Next time you have to interact with rabid extroverts, instead of shaking their hands, walk up to them and take a deep whiff of their armpits. Establish dominance. Someone will feel awkward, and science has proved it won’t be you.
The puff that vaccinates
Ever been shot with a Nerf gun or hit with a foam pool tube? More annoying than painful, right? If we asked if you’d rather get pelted with one of those than receive a traditional vaccine injection, you would choose the former. Maybe someday you actually will.
During the boredom of the early pandemic lockdown, Jeremiah Gassensmith, PhD, of the department of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Texas, Dallas, ordered a compressed gas–powered jet injection system to fool around with at home. Hey, who didn’t? Anyway, when it was time to go back to the lab he handed it over to one of his grad students, Yalini Wijesundara, and asked her to see what could be done with it.
In her tinkering she found that the jet injector could deliver metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that can hold a bunch of different materials, like proteins and nucleic acids, through the skin.
Thus the “MOF-Jet” was born!
Jet injectors are nothing new, but they hurt. The MOF-Jet, however, is practically painless and cheaper than the gene guns that veterinarians use to inject biological cargo attached to the surface of a metal microparticle.
Changing the carrier gas also changes the time needed to break down the MOF and thus alters delivery of the drug inside. “If you shoot it with carbon dioxide, it will release its cargo faster within cells; if you use regular air, it will take 4 or 5 days,” Ms. Wijesundara explained in a written statement. That means the same drug could be released over different timescales without changing its formulation.
While testing on onion cells and mice, Ms. Wijesundara noted that it was as easy as “pointing and shooting” to distribute the puff of gas into the cells. A saving grace to those with needle anxiety. Not that we would know anything about needle anxiety.
More testing needs to be done before bringing this technology to human use, obviously, but we’re looking forward to saying goodbye to that dreaded prick and hello to a puff.
Your hippocampus is showing
Brain anatomy is one of the many, many things that’s not really our thing, but we do know a cool picture when we see one. Case in point: The image just below, which happens to be a full-scale, single-cell resolution model of the CA1 region of the hippocampus that “replicates the structure and architecture of the area, along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons,” according to a statement from the Human Brain Project.
“We have performed a data mining operation on high resolution images of the human hippocampus, obtained from the BigBrain database. The position of individual neurons has been derived from a detailed analysis of these images,” said senior author Michele Migliore, PhD, of the Italian National Research Council’s Institute of Biophysics in Palermo.
Yes, he did say BigBrain database. BigBrain is – we checked and it’s definitely not this – a 3D model of a brain that was sectioned into 7,404 slices just 20 micrometers thick and then scanned by MRI. Digital reconstruction of those slices was done by supercomputer and the results are now available for analysis.
Dr. Migliore and his associates developed an image-processing algorithm to obtain neuronal positioning distribution and an algorithm to generate neuronal connectivity by approximating the shapes of dendrites and axons. (Our brains are starting to hurt just trying to write this.) “Some fit into narrow cones, others have a broad complex extension that can be approximated by dedicated geometrical volumes, and the connectivity to nearby neurons changes accordingly,” explained lead author Daniela Gandolfi of the University of Modena (Italy) and Reggio Emilia.
The investigators have made their dataset and the extraction methodology available on the EBRAINS platform and through the Human Brain Project and are moving on to other brain regions. And then, once everyone can find their way in and around the old gray matter, it should bring an end to conversations like this, which no doubt occur between male and female neuroscientists every day:
“Arnold, I think we’re lost.”
“Don’t worry, Bev, I know where I’m going.”
“Stop and ask this lady for directions.”
“I said I can find it.”
“Just ask her.”
“Fine. Excuse me, ma’am, can you tell us how to get to the corpora quadrigemina from here?
Getting sweet on sweat
Are you the sort of person who struggles in social situations? Have the past 3 years been a secret respite from the terror and exhaustion of meeting new people? We understand your plight. People kind of suck. And you don’t have to look far to be reminded of it.
Unfortunately, on occasion we all have to interact with other human beings. If you suffer from social anxiety, this is not a fun thing to do. But new research indicates that there may be a way to alleviate the stress for those with social anxiety: armpits.
Specifically, sweat from the armpits of other people. Yes, this means a group of scientists gathered up some volunteers and collected their armpit sweat while the volunteers watched a variety of movies (horror, comedy, romance, etc.). Our condolences to the poor unpaid interns tasked with gathering the sweat.
Once they had their precious new medicine, the researchers took a group of women and administered a round of mindfulness therapy. Some of the participants then received the various sweats, while the rest were forced to smell only clean air. (The horror!) Lo and behold, the sweat groups had their anxiety scores reduced by about 40% after their therapy, compared with just 17% in the control group.
The researchers also found that the source of the sweat didn’t matter. Their study subjects responded the same to sweat excreted during a scary movie as they did to sweat from a comedy, a result that surprised the researchers. They suggested chemosignals in the sweat may affect the treatment response and advised further research. Which means more sweat collection! They plan on testing emotionally neutral movies next time, and if we can make a humble suggestion, they also should try the sweatiest movies.
Before the Food and Drug Administration can approve armpit sweat as a treatment for social anxiety, we have some advice for those shut-in introverts out there. Next time you have to interact with rabid extroverts, instead of shaking their hands, walk up to them and take a deep whiff of their armpits. Establish dominance. Someone will feel awkward, and science has proved it won’t be you.
The puff that vaccinates
Ever been shot with a Nerf gun or hit with a foam pool tube? More annoying than painful, right? If we asked if you’d rather get pelted with one of those than receive a traditional vaccine injection, you would choose the former. Maybe someday you actually will.
During the boredom of the early pandemic lockdown, Jeremiah Gassensmith, PhD, of the department of chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Texas, Dallas, ordered a compressed gas–powered jet injection system to fool around with at home. Hey, who didn’t? Anyway, when it was time to go back to the lab he handed it over to one of his grad students, Yalini Wijesundara, and asked her to see what could be done with it.
In her tinkering she found that the jet injector could deliver metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) that can hold a bunch of different materials, like proteins and nucleic acids, through the skin.
Thus the “MOF-Jet” was born!
Jet injectors are nothing new, but they hurt. The MOF-Jet, however, is practically painless and cheaper than the gene guns that veterinarians use to inject biological cargo attached to the surface of a metal microparticle.
Changing the carrier gas also changes the time needed to break down the MOF and thus alters delivery of the drug inside. “If you shoot it with carbon dioxide, it will release its cargo faster within cells; if you use regular air, it will take 4 or 5 days,” Ms. Wijesundara explained in a written statement. That means the same drug could be released over different timescales without changing its formulation.
While testing on onion cells and mice, Ms. Wijesundara noted that it was as easy as “pointing and shooting” to distribute the puff of gas into the cells. A saving grace to those with needle anxiety. Not that we would know anything about needle anxiety.
More testing needs to be done before bringing this technology to human use, obviously, but we’re looking forward to saying goodbye to that dreaded prick and hello to a puff.
Your hippocampus is showing
Brain anatomy is one of the many, many things that’s not really our thing, but we do know a cool picture when we see one. Case in point: The image just below, which happens to be a full-scale, single-cell resolution model of the CA1 region of the hippocampus that “replicates the structure and architecture of the area, along with the position and relative connectivity of the neurons,” according to a statement from the Human Brain Project.
“We have performed a data mining operation on high resolution images of the human hippocampus, obtained from the BigBrain database. The position of individual neurons has been derived from a detailed analysis of these images,” said senior author Michele Migliore, PhD, of the Italian National Research Council’s Institute of Biophysics in Palermo.
Yes, he did say BigBrain database. BigBrain is – we checked and it’s definitely not this – a 3D model of a brain that was sectioned into 7,404 slices just 20 micrometers thick and then scanned by MRI. Digital reconstruction of those slices was done by supercomputer and the results are now available for analysis.
Dr. Migliore and his associates developed an image-processing algorithm to obtain neuronal positioning distribution and an algorithm to generate neuronal connectivity by approximating the shapes of dendrites and axons. (Our brains are starting to hurt just trying to write this.) “Some fit into narrow cones, others have a broad complex extension that can be approximated by dedicated geometrical volumes, and the connectivity to nearby neurons changes accordingly,” explained lead author Daniela Gandolfi of the University of Modena (Italy) and Reggio Emilia.
The investigators have made their dataset and the extraction methodology available on the EBRAINS platform and through the Human Brain Project and are moving on to other brain regions. And then, once everyone can find their way in and around the old gray matter, it should bring an end to conversations like this, which no doubt occur between male and female neuroscientists every day:
“Arnold, I think we’re lost.”
“Don’t worry, Bev, I know where I’m going.”
“Stop and ask this lady for directions.”
“I said I can find it.”
“Just ask her.”
“Fine. Excuse me, ma’am, can you tell us how to get to the corpora quadrigemina from here?
The air up there: Oxygen could be a bit overrated
Into thin, but healthy, air
Human civilization has essentially been built on proximity to water. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, and India were all intimately connected to either rivers or the ocean. Even today, with all our technology, about a third of Earth’s 8 billion people live within 100 vertical meters of sea level, and the median person lives at an elevation of just 200 meters.
All things considered, one might imagine life is pretty tough for the 2 million people living at an elevation of 4,500 meters (nearly 15,000 feet). Not too many Wal-Marts or McDonalds up there. Oh, and not much air either. And for most of us not named Spongebob, air is good.
Or is it? That’s the question posed by a new study. After all, the researchers said, people living at high altitudes, where the air has only 11% effective oxygen instead of the 21% we have at low altitude, have significantly lower rates of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and heart diseases. Maybe breathing isn’t all it’s cracked up to be.
To find out, the researchers placed a group of mice in environments with either 11% oxygen or 8% oxygen. This netted them a bunch of very tired mice. Hey, sudden altitude gain doesn’t go too well for us either, but after 3 weeks, all the mice in the hypoxic environments had regained their normal movement and were behaving as any mouse would.
While the critters seemed normal on the outside, a closer examination found the truth. Their metabolism had been permanently altered, and their blood sugar and weight went down and never bounced back up. Further examination through PET scans showed that the hypoxic mice’s organs showed an increase in glucose metabolism and that brown fat and skeletal muscles reduced the amount of sugar they used.
This goes against the prevailing assumption about hypoxic conditions, the researchers said, since it was previously theorized that the body simply burned more glucose in response to having less oxygen. And while that’s true, our organs also conspicuously use less glucose. Currently, many athletes use hypoxic environments to train, but these new data suggest that people with metabolic disorders also would see benefits from living in low-oxygen environments.
Do you know what this means? All we have to do to stop diabetes is take civilization and push it somewhere else. This can’t possibly end badly.
Sleep survey: The restless majority
Newsflash! This just in: Nobody is sleeping well.
When we go to bed, our goal is to get rest, right? Sorry America, but you’re falling short. In a recent survey conducted by OnePoll for Purple Mattress, almost two-thirds of the 2,011 participants considered themselves restless sleepers.
Not surprised. So what’s keeping us up?
Snoring partners (20%) and anxiety (26%) made the list, but the award for top complaint goes to body pain. Back pain was most prevalent, reported by 36% of respondents, followed by neck pain (33%) and shoulder pain (24%). No wonder, then, that only 10% of the group reported feeling well rested when they woke up.
Do you ever blame your tiredness on sleeping funny? Well, we all kind of sleep funny, and yet we’re still not sleeping well.
The largest proportion of people like to sleep on their side (48%), compared with 18% on their back and 17% on their stomach. The main reasons to choose certain positions were to ease soreness or sleep better, both at 28%. The largest share of participants (47%) reported sleeping in a “yearner” position, while 40% lay on their stomachs in the “free faller” position, and 39% reported using the “soldier” position.
Regardless of the method people use to get to sleep or the position they’re in, the goal is always the same. We’re all just trying to figure out what’s the right one for us.
Seen a UFO recently? Don’t blame COVID
First of all, because we know you’re going to be thinking it in a minute, no, we did not make this up. With COVID-19 still hanging around, there’s no need for fabrication on our part.
The pandemic, clearly, has caused humans to do some strange things over the last 3 years, but what about some of the more, shall we say … eccentric behavior that people were already exhibiting before COVID found its way into our lives?
If, like R. Chase Cockrell, PhD, of the University of Vermont and associates at the Center for UFO Studies, you were wondering if the pandemic affected UFO reporting, then wonder no more. After all, with all that extra time being spent outdoors back in 2020 and all the additional anxiety, surely somebody must have seen something.
The investigators started with the basics by analyzing data from the National UFO Reporting Center and the Mutual UFO Network. Sightings did increase by about 600 in each database during 2020, compared with 2018 and 2019, but not because of the pandemic.
That’s right, we can’t pin this one on our good friend SARS-CoV-2. Further analysis showed that the launches of SpaceX Starlink satellites – sometimes as many as 60 at a time – probably caused the increase in UFO sightings, which means that our favorite billionaire, Elon Musk, is to blame. Yup, the genial Mr. Muskellunge did something that even a global pandemic couldn’t, and yet we vaccinate for COVID.
Next week on tenuous connections: A new study links the 2020 presidential election to increased emergency department visits for external hemorrhoids.
See? That’s fabrication. We made that up.
This article was updated 5/15/23.
Into thin, but healthy, air
Human civilization has essentially been built on proximity to water. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, and India were all intimately connected to either rivers or the ocean. Even today, with all our technology, about a third of Earth’s 8 billion people live within 100 vertical meters of sea level, and the median person lives at an elevation of just 200 meters.
All things considered, one might imagine life is pretty tough for the 2 million people living at an elevation of 4,500 meters (nearly 15,000 feet). Not too many Wal-Marts or McDonalds up there. Oh, and not much air either. And for most of us not named Spongebob, air is good.
Or is it? That’s the question posed by a new study. After all, the researchers said, people living at high altitudes, where the air has only 11% effective oxygen instead of the 21% we have at low altitude, have significantly lower rates of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and heart diseases. Maybe breathing isn’t all it’s cracked up to be.
To find out, the researchers placed a group of mice in environments with either 11% oxygen or 8% oxygen. This netted them a bunch of very tired mice. Hey, sudden altitude gain doesn’t go too well for us either, but after 3 weeks, all the mice in the hypoxic environments had regained their normal movement and were behaving as any mouse would.
While the critters seemed normal on the outside, a closer examination found the truth. Their metabolism had been permanently altered, and their blood sugar and weight went down and never bounced back up. Further examination through PET scans showed that the hypoxic mice’s organs showed an increase in glucose metabolism and that brown fat and skeletal muscles reduced the amount of sugar they used.
This goes against the prevailing assumption about hypoxic conditions, the researchers said, since it was previously theorized that the body simply burned more glucose in response to having less oxygen. And while that’s true, our organs also conspicuously use less glucose. Currently, many athletes use hypoxic environments to train, but these new data suggest that people with metabolic disorders also would see benefits from living in low-oxygen environments.
Do you know what this means? All we have to do to stop diabetes is take civilization and push it somewhere else. This can’t possibly end badly.
Sleep survey: The restless majority
Newsflash! This just in: Nobody is sleeping well.
When we go to bed, our goal is to get rest, right? Sorry America, but you’re falling short. In a recent survey conducted by OnePoll for Purple Mattress, almost two-thirds of the 2,011 participants considered themselves restless sleepers.
Not surprised. So what’s keeping us up?
Snoring partners (20%) and anxiety (26%) made the list, but the award for top complaint goes to body pain. Back pain was most prevalent, reported by 36% of respondents, followed by neck pain (33%) and shoulder pain (24%). No wonder, then, that only 10% of the group reported feeling well rested when they woke up.
Do you ever blame your tiredness on sleeping funny? Well, we all kind of sleep funny, and yet we’re still not sleeping well.
The largest proportion of people like to sleep on their side (48%), compared with 18% on their back and 17% on their stomach. The main reasons to choose certain positions were to ease soreness or sleep better, both at 28%. The largest share of participants (47%) reported sleeping in a “yearner” position, while 40% lay on their stomachs in the “free faller” position, and 39% reported using the “soldier” position.
Regardless of the method people use to get to sleep or the position they’re in, the goal is always the same. We’re all just trying to figure out what’s the right one for us.
Seen a UFO recently? Don’t blame COVID
First of all, because we know you’re going to be thinking it in a minute, no, we did not make this up. With COVID-19 still hanging around, there’s no need for fabrication on our part.
The pandemic, clearly, has caused humans to do some strange things over the last 3 years, but what about some of the more, shall we say … eccentric behavior that people were already exhibiting before COVID found its way into our lives?
If, like R. Chase Cockrell, PhD, of the University of Vermont and associates at the Center for UFO Studies, you were wondering if the pandemic affected UFO reporting, then wonder no more. After all, with all that extra time being spent outdoors back in 2020 and all the additional anxiety, surely somebody must have seen something.
The investigators started with the basics by analyzing data from the National UFO Reporting Center and the Mutual UFO Network. Sightings did increase by about 600 in each database during 2020, compared with 2018 and 2019, but not because of the pandemic.
That’s right, we can’t pin this one on our good friend SARS-CoV-2. Further analysis showed that the launches of SpaceX Starlink satellites – sometimes as many as 60 at a time – probably caused the increase in UFO sightings, which means that our favorite billionaire, Elon Musk, is to blame. Yup, the genial Mr. Muskellunge did something that even a global pandemic couldn’t, and yet we vaccinate for COVID.
Next week on tenuous connections: A new study links the 2020 presidential election to increased emergency department visits for external hemorrhoids.
See? That’s fabrication. We made that up.
This article was updated 5/15/23.
Into thin, but healthy, air
Human civilization has essentially been built on proximity to water. Ancient civilizations in Mesopotamia, Egypt, Greece, China, and India were all intimately connected to either rivers or the ocean. Even today, with all our technology, about a third of Earth’s 8 billion people live within 100 vertical meters of sea level, and the median person lives at an elevation of just 200 meters.
All things considered, one might imagine life is pretty tough for the 2 million people living at an elevation of 4,500 meters (nearly 15,000 feet). Not too many Wal-Marts or McDonalds up there. Oh, and not much air either. And for most of us not named Spongebob, air is good.
Or is it? That’s the question posed by a new study. After all, the researchers said, people living at high altitudes, where the air has only 11% effective oxygen instead of the 21% we have at low altitude, have significantly lower rates of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and heart diseases. Maybe breathing isn’t all it’s cracked up to be.
To find out, the researchers placed a group of mice in environments with either 11% oxygen or 8% oxygen. This netted them a bunch of very tired mice. Hey, sudden altitude gain doesn’t go too well for us either, but after 3 weeks, all the mice in the hypoxic environments had regained their normal movement and were behaving as any mouse would.
While the critters seemed normal on the outside, a closer examination found the truth. Their metabolism had been permanently altered, and their blood sugar and weight went down and never bounced back up. Further examination through PET scans showed that the hypoxic mice’s organs showed an increase in glucose metabolism and that brown fat and skeletal muscles reduced the amount of sugar they used.
This goes against the prevailing assumption about hypoxic conditions, the researchers said, since it was previously theorized that the body simply burned more glucose in response to having less oxygen. And while that’s true, our organs also conspicuously use less glucose. Currently, many athletes use hypoxic environments to train, but these new data suggest that people with metabolic disorders also would see benefits from living in low-oxygen environments.
Do you know what this means? All we have to do to stop diabetes is take civilization and push it somewhere else. This can’t possibly end badly.
Sleep survey: The restless majority
Newsflash! This just in: Nobody is sleeping well.
When we go to bed, our goal is to get rest, right? Sorry America, but you’re falling short. In a recent survey conducted by OnePoll for Purple Mattress, almost two-thirds of the 2,011 participants considered themselves restless sleepers.
Not surprised. So what’s keeping us up?
Snoring partners (20%) and anxiety (26%) made the list, but the award for top complaint goes to body pain. Back pain was most prevalent, reported by 36% of respondents, followed by neck pain (33%) and shoulder pain (24%). No wonder, then, that only 10% of the group reported feeling well rested when they woke up.
Do you ever blame your tiredness on sleeping funny? Well, we all kind of sleep funny, and yet we’re still not sleeping well.
The largest proportion of people like to sleep on their side (48%), compared with 18% on their back and 17% on their stomach. The main reasons to choose certain positions were to ease soreness or sleep better, both at 28%. The largest share of participants (47%) reported sleeping in a “yearner” position, while 40% lay on their stomachs in the “free faller” position, and 39% reported using the “soldier” position.
Regardless of the method people use to get to sleep or the position they’re in, the goal is always the same. We’re all just trying to figure out what’s the right one for us.
Seen a UFO recently? Don’t blame COVID
First of all, because we know you’re going to be thinking it in a minute, no, we did not make this up. With COVID-19 still hanging around, there’s no need for fabrication on our part.
The pandemic, clearly, has caused humans to do some strange things over the last 3 years, but what about some of the more, shall we say … eccentric behavior that people were already exhibiting before COVID found its way into our lives?
If, like R. Chase Cockrell, PhD, of the University of Vermont and associates at the Center for UFO Studies, you were wondering if the pandemic affected UFO reporting, then wonder no more. After all, with all that extra time being spent outdoors back in 2020 and all the additional anxiety, surely somebody must have seen something.
The investigators started with the basics by analyzing data from the National UFO Reporting Center and the Mutual UFO Network. Sightings did increase by about 600 in each database during 2020, compared with 2018 and 2019, but not because of the pandemic.
That’s right, we can’t pin this one on our good friend SARS-CoV-2. Further analysis showed that the launches of SpaceX Starlink satellites – sometimes as many as 60 at a time – probably caused the increase in UFO sightings, which means that our favorite billionaire, Elon Musk, is to blame. Yup, the genial Mr. Muskellunge did something that even a global pandemic couldn’t, and yet we vaccinate for COVID.
Next week on tenuous connections: A new study links the 2020 presidential election to increased emergency department visits for external hemorrhoids.
See? That’s fabrication. We made that up.
This article was updated 5/15/23.