User login
COVID-19 CRISIS: We must care for ourselves as we care for others
“I do not shrink from this responsibility, I welcome it.” —John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto. Family physicians’ place on the front line of medicine is more important now than it has ever been.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said, “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers—family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses—who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call—and take care of ourselves—in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So, too, must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in 3 domains: physical, mental, and social.
Physical. With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
Continue to: Mentally...
Mentally we need the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
Social distancing doesn’t have to mean emotional isolation; technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, co-workers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on, amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant; someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, or plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946, after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms—to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
1. Brockell G. During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely. The Washington Post. March 12, 2020. 2. Frankl VE. Man’s Search for Meaning. Boston, MA: Beacon Press; 2006.
“I do not shrink from this responsibility, I welcome it.” —John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto. Family physicians’ place on the front line of medicine is more important now than it has ever been.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said, “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers—family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses—who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call—and take care of ourselves—in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So, too, must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in 3 domains: physical, mental, and social.
Physical. With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
Continue to: Mentally...
Mentally we need the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
Social distancing doesn’t have to mean emotional isolation; technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, co-workers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on, amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant; someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, or plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946, after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms—to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
“I do not shrink from this responsibility, I welcome it.” —John F. Kennedy, inaugural address
COVID-19 has changed our world. Social distancing is now the norm and flattening the curve is our motto. Family physicians’ place on the front line of medicine is more important now than it has ever been.
In the Pennsylvania community in which we work, the first person to don protective gear and sample patients for viral testing in a rapidly organized COVID-19 testing site was John Russell, MD, a family physician. When I asked him about his experience, Dr. Russell said, “No one became a fireman to get cats out of trees ... it was to fight fires. As doctors, this is the same idea ... this is a chance to help fight the fires in our community.”
And, of course, it is primary care providers—family physicians, internists, pediatricians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, and nurses—who day in and day out are putting aside their own fears, while dealing with those of their family, to come to work with a sense of purpose and courage.
The military uses the term “operational tempo” to describe the speed and intensity of actions relative to the speed and intensity of unfolding events in the operational environment. Family physicians are being asked to work at an increased speed in unfamiliar terrain as our environments change by the hour. The challenge is to answer the call—and take care of ourselves—in unprecedented ways. We often use anticipatory guidance with our patients to help prepare them for the challenges they will face. So, too, must we anticipate the things we will need to be attentive to in the coming months in order to sustain the effort that will be required of us.
With this in mind, we would be wise to consider developing plans in 3 domains: physical, mental, and social.
Physical. With gyms closed and restaurants limiting their offerings to take-out, this is an opportune time to create an exercise regimen at home and experiment with healthy meal options. YouTube videos abound for workouts of every length. And of course, you can simply take a daily walk, go for a run, or take a bike ride. Similarly, good choices can be made with take-out and the foods we prepare at home.
Continue to: Mentally...
Mentally we need the discipline to take breaks, delegate when necessary, and use downtime to clear our minds. Need another option? Consider meditation. Google “best meditation apps” and take your pick.
Social distancing doesn’t have to mean emotional isolation; technology allows us to connect with others through messaging and face-to-face video. We need to remember to regularly check in with those we care about; few things in life are as affirming as the connections with those who are close to us: family, co-workers, and patients.
Out of crisis comes opportunity. Should we be quarantined, we can remind ourselves that Sir Isaac Newton, while in quarantine during the bubonic plague, laid the foundation for classical physics, composed theories on light and optics, and penned his first draft of the law of gravity.1
Life carries on, amidst the pandemic. Even though the current focus is on the COVID-19 crisis, our many needs, joys, and challenges as human beings remain. Today, someone will find out she is pregnant; someone else will be diagnosed with cancer, or plan a wedding, or attend the funeral of a loved one. We, as family physicians, have the training to lead with courage and empathy. We have the expertise gained through years of helping patients though diverse physical and emotional challenges.
We will continue to listen to our patients’ stories, diagnose and treat their diseases, and take steps to bring a sense of calm to the chaos around us. We need to be mindful of our own mindset, because we have a choice. As the psychologist Victor Frankl said in 1946, after being liberated from the concentration camps, “Everything can be taken from a man but one thing: the last of the human freedoms—to choose one’s attitude in any given set of circumstances, to choose one’s own way.”2
1. Brockell G. During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely. The Washington Post. March 12, 2020. 2. Frankl VE. Man’s Search for Meaning. Boston, MA: Beacon Press; 2006.
1. Brockell G. During a pandemic, Isaac Newton had to work from home, too. He used the time wisely. The Washington Post. March 12, 2020. 2. Frankl VE. Man’s Search for Meaning. Boston, MA: Beacon Press; 2006.
The power and promise of person-generated health data (Part II)
In Part I of our discussion we introduced the concept of person-generated health data (PGHD), defined as wellness and/or health-related data created, recorded, or gathered by individuals.
Such rich, longitudinal information is now being used in combination with traditional clinical information to predict, diagnose, and formulate treatment plans for diseases, as well as understand the safety and effectiveness of medical interventions.
Identifying a disease early
One novel example of digital technologies being used for early identification of disease was a promising 2019 study by Eli Lilly (in collaboration with Apple and Evidation Health) called the Lilly Exploratory Digital Assessment Study.
In this study, the feasibility of using PGHD for identifying physiological and behavioral signatures of cognitive impairment was examined for the purpose of seeking new methods to detect mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in a timely and cost-effective manner. The study enrolled 31 study participants with cognitive impairment and 82 without cognitive impairment. It used consumer-grade sensor technologies (the iPhone, Apple Watch, iPad, and Beddit sleep monitor) to continuously and unobtrusively collect data. Among the information the researchers collected were interaction with the phone keyboard, accelerometer data from the Apple Watch, volume of messages sent/received, and sleep cycles.1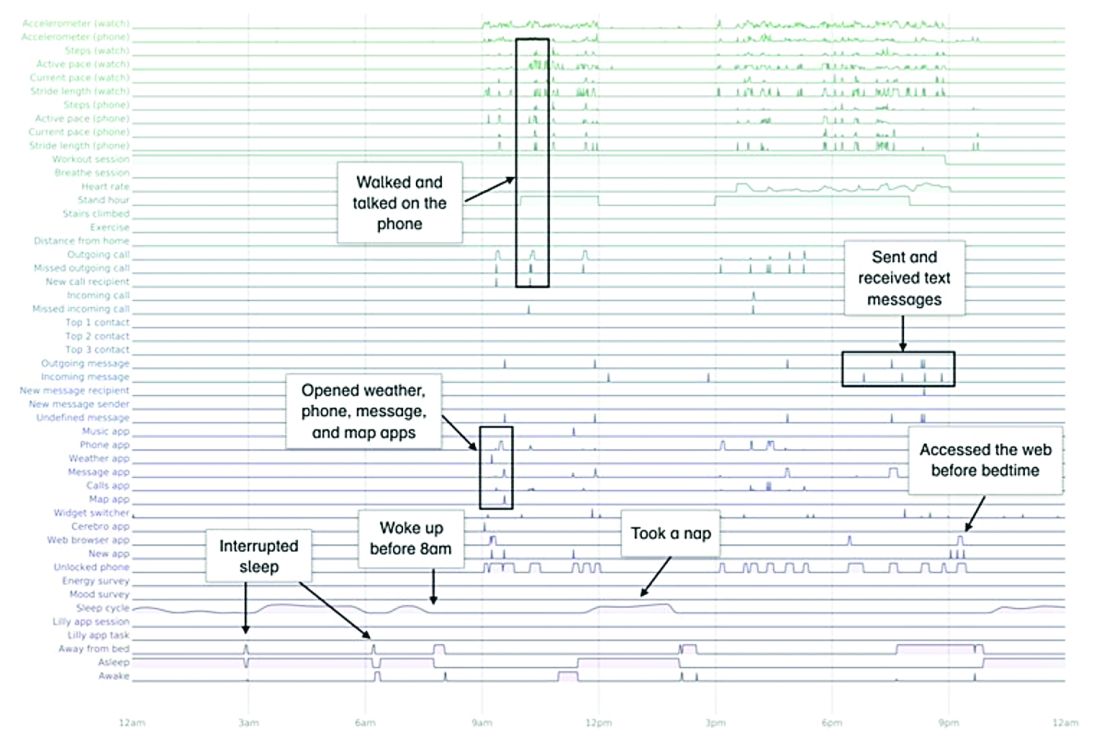
A total of 16 terabytes of data were collected over the course of 12 weeks. Data were organized into a behaviorgram (See Figure 1) that gives a holistic picture of a day in a patient’s life. A machine learning model was used to distinguish between behaviorgrams of symptomatic versus healthy controls, identifying typing speed, circadian rhythm shifts, and reliance on helper apps, among other things, as differentiating cognitively impaired from healthy controls. These behaviorgrams may someday serve as “fingerprints” of different diseases, with specific diseases displaying predictable patterns. In the near future, digital measures like the ones investigated in this study are likely to be used to help clinicians predict and diagnose disease, as well as to better understand disease progression and treatment response.
Leading to better health outcomes
The potential of PGHD to detect diseases early and lead to better health outcomes is being investigated in the Heartline study, a collaboration between Johnson & Johnson and Apple, which is supported by Evidation.2
This study aims to enroll 150,000 adults age 65 years and over to analyze the impact of Apple Watch–based early detection of irregular heart rhythms consistent with atrial fibrillation (AFib). The researchers’ hypothesis is that jointly detecting atrial fibrillation early and providing cardiovascular health programs to new AFib patients, will lead to patients being treated by a medical provider for AFib that otherwise would not have been detected. This, in turn, would lead to these AFib patients decreasing their risks of stroke and other serious cardiovascular events, including death, the study authors speculated.
Presenting new challenges
While PGHD has the potential to help people, it also presents new challenges. It is highly sensitive and personal – it can be as identifying as DNA.3
The vast amount of data that PGHD can collect from interaction with consumer wearable devices poses serious privacy risks if done improperly. To address those risks, companies like Evidation have built in protections. Evidation has an app, Achievement, that has enlisted a connected population of more than 3.5 million members who earn rewards for performing health-related actions, as tracked by wearables devices and apps. Through the Achievement app (See Figure 2.), members are provided opportunities to join research studies. As part of these studies, data collected from sensors and apps is used by permission of the member so that it is clear how their data are contributing to specific research questions or use cases.
This is a collaborative model of data collection built upon trust and permission and is substantially different than the collection of data from electronic health records (EHRs) – which is typically aggregated, deidentified, and commercialized, often without the patients’ knowledge or consent. Stringent protections, explicit permission, and transparency are absolutely imperative until privacy frameworks for data outside of HIPAA regulation catches up and protects patients from discrimination and unintended uses of their data.
Large connected cohorts can help advance our understanding of public health. In one study run on Achievement during the 2017-2018 flu season, a survey was sent to the Achievement population every week asking about symptoms of influenza-like illness and requesting permission to access historical data from their wearable around the influenza-like illness event.4 With the data, it was possible to analyze patterns of activity, sleep, and resting heart rate change around flu events. Resting heart rate, in particular, is shown to increase during fever and at the population level. In fact, through the use of PGHD, it is possible to use the fraction of people with resting heart rate above their usual baseline as a proxy to quantify the number of infected people in a region.5 This resting heart rate–informed flu surveillance method, if refined to increased accuracy, can work in near real time. This means it may be able detect influenza outbreaks days earlier than current epidemiological methods.
Health data generated by connected populations are in the early stages of development. It is clear that it will yield novel insights into health and disease. Only time will tell if it will be able to help clinicians and patients better predict, diagnose, and formulate treatment plans for disease.
Neil Skolnik, M.D. is a professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, and associate director of the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington Jefferson Health. Luca Foschini PhD, is co-founder & chief data scientist at Evidation Health. Bray Patrick-Lake, MFS, is a patient thought leader and director of strategic partnerships at Evidation Health.
References
1. Chen R et al. Developing measures of cognitive impairment in the real world from consumer-grade multimodal sensor streams. KDD ’19. August 4–8, 2019 Aug 4-8.
2. The Heartline Study. https://www.heartline.com.
3. Foschini L. Privacy of Wearable and Sensors Data (or, the Lack Thereof?). Data Driven Investor, Medium. 2019.
4. Bradshaw B et al. Influenza surveillance using wearable mobile health devices. Online J Public Health Inform. 2019;11(1):e249.
5. Radin JM et al. Harnessing wearable device data to improve state-level real-time surveillance of influenza-like illness in the USA: a population-based study. Lancet Digital Health. 2020. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30222-5.
In Part I of our discussion we introduced the concept of person-generated health data (PGHD), defined as wellness and/or health-related data created, recorded, or gathered by individuals.
Such rich, longitudinal information is now being used in combination with traditional clinical information to predict, diagnose, and formulate treatment plans for diseases, as well as understand the safety and effectiveness of medical interventions.
Identifying a disease early
One novel example of digital technologies being used for early identification of disease was a promising 2019 study by Eli Lilly (in collaboration with Apple and Evidation Health) called the Lilly Exploratory Digital Assessment Study.
In this study, the feasibility of using PGHD for identifying physiological and behavioral signatures of cognitive impairment was examined for the purpose of seeking new methods to detect mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in a timely and cost-effective manner. The study enrolled 31 study participants with cognitive impairment and 82 without cognitive impairment. It used consumer-grade sensor technologies (the iPhone, Apple Watch, iPad, and Beddit sleep monitor) to continuously and unobtrusively collect data. Among the information the researchers collected were interaction with the phone keyboard, accelerometer data from the Apple Watch, volume of messages sent/received, and sleep cycles.1
A total of 16 terabytes of data were collected over the course of 12 weeks. Data were organized into a behaviorgram (See Figure 1) that gives a holistic picture of a day in a patient’s life. A machine learning model was used to distinguish between behaviorgrams of symptomatic versus healthy controls, identifying typing speed, circadian rhythm shifts, and reliance on helper apps, among other things, as differentiating cognitively impaired from healthy controls. These behaviorgrams may someday serve as “fingerprints” of different diseases, with specific diseases displaying predictable patterns. In the near future, digital measures like the ones investigated in this study are likely to be used to help clinicians predict and diagnose disease, as well as to better understand disease progression and treatment response.
Leading to better health outcomes
The potential of PGHD to detect diseases early and lead to better health outcomes is being investigated in the Heartline study, a collaboration between Johnson & Johnson and Apple, which is supported by Evidation.2
This study aims to enroll 150,000 adults age 65 years and over to analyze the impact of Apple Watch–based early detection of irregular heart rhythms consistent with atrial fibrillation (AFib). The researchers’ hypothesis is that jointly detecting atrial fibrillation early and providing cardiovascular health programs to new AFib patients, will lead to patients being treated by a medical provider for AFib that otherwise would not have been detected. This, in turn, would lead to these AFib patients decreasing their risks of stroke and other serious cardiovascular events, including death, the study authors speculated.
Presenting new challenges
While PGHD has the potential to help people, it also presents new challenges. It is highly sensitive and personal – it can be as identifying as DNA.3
The vast amount of data that PGHD can collect from interaction with consumer wearable devices poses serious privacy risks if done improperly. To address those risks, companies like Evidation have built in protections. Evidation has an app, Achievement, that has enlisted a connected population of more than 3.5 million members who earn rewards for performing health-related actions, as tracked by wearables devices and apps. Through the Achievement app (See Figure 2.), members are provided opportunities to join research studies. As part of these studies, data collected from sensors and apps is used by permission of the member so that it is clear how their data are contributing to specific research questions or use cases.
This is a collaborative model of data collection built upon trust and permission and is substantially different than the collection of data from electronic health records (EHRs) – which is typically aggregated, deidentified, and commercialized, often without the patients’ knowledge or consent. Stringent protections, explicit permission, and transparency are absolutely imperative until privacy frameworks for data outside of HIPAA regulation catches up and protects patients from discrimination and unintended uses of their data.
Large connected cohorts can help advance our understanding of public health. In one study run on Achievement during the 2017-2018 flu season, a survey was sent to the Achievement population every week asking about symptoms of influenza-like illness and requesting permission to access historical data from their wearable around the influenza-like illness event.4 With the data, it was possible to analyze patterns of activity, sleep, and resting heart rate change around flu events. Resting heart rate, in particular, is shown to increase during fever and at the population level. In fact, through the use of PGHD, it is possible to use the fraction of people with resting heart rate above their usual baseline as a proxy to quantify the number of infected people in a region.5 This resting heart rate–informed flu surveillance method, if refined to increased accuracy, can work in near real time. This means it may be able detect influenza outbreaks days earlier than current epidemiological methods.
Health data generated by connected populations are in the early stages of development. It is clear that it will yield novel insights into health and disease. Only time will tell if it will be able to help clinicians and patients better predict, diagnose, and formulate treatment plans for disease.
Neil Skolnik, M.D. is a professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, and associate director of the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington Jefferson Health. Luca Foschini PhD, is co-founder & chief data scientist at Evidation Health. Bray Patrick-Lake, MFS, is a patient thought leader and director of strategic partnerships at Evidation Health.
References
1. Chen R et al. Developing measures of cognitive impairment in the real world from consumer-grade multimodal sensor streams. KDD ’19. August 4–8, 2019 Aug 4-8.
2. The Heartline Study. https://www.heartline.com.
3. Foschini L. Privacy of Wearable and Sensors Data (or, the Lack Thereof?). Data Driven Investor, Medium. 2019.
4. Bradshaw B et al. Influenza surveillance using wearable mobile health devices. Online J Public Health Inform. 2019;11(1):e249.
5. Radin JM et al. Harnessing wearable device data to improve state-level real-time surveillance of influenza-like illness in the USA: a population-based study. Lancet Digital Health. 2020. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30222-5.
In Part I of our discussion we introduced the concept of person-generated health data (PGHD), defined as wellness and/or health-related data created, recorded, or gathered by individuals.
Such rich, longitudinal information is now being used in combination with traditional clinical information to predict, diagnose, and formulate treatment plans for diseases, as well as understand the safety and effectiveness of medical interventions.
Identifying a disease early
One novel example of digital technologies being used for early identification of disease was a promising 2019 study by Eli Lilly (in collaboration with Apple and Evidation Health) called the Lilly Exploratory Digital Assessment Study.
In this study, the feasibility of using PGHD for identifying physiological and behavioral signatures of cognitive impairment was examined for the purpose of seeking new methods to detect mild cognitive impairment (MCI) in a timely and cost-effective manner. The study enrolled 31 study participants with cognitive impairment and 82 without cognitive impairment. It used consumer-grade sensor technologies (the iPhone, Apple Watch, iPad, and Beddit sleep monitor) to continuously and unobtrusively collect data. Among the information the researchers collected were interaction with the phone keyboard, accelerometer data from the Apple Watch, volume of messages sent/received, and sleep cycles.1
A total of 16 terabytes of data were collected over the course of 12 weeks. Data were organized into a behaviorgram (See Figure 1) that gives a holistic picture of a day in a patient’s life. A machine learning model was used to distinguish between behaviorgrams of symptomatic versus healthy controls, identifying typing speed, circadian rhythm shifts, and reliance on helper apps, among other things, as differentiating cognitively impaired from healthy controls. These behaviorgrams may someday serve as “fingerprints” of different diseases, with specific diseases displaying predictable patterns. In the near future, digital measures like the ones investigated in this study are likely to be used to help clinicians predict and diagnose disease, as well as to better understand disease progression and treatment response.
Leading to better health outcomes
The potential of PGHD to detect diseases early and lead to better health outcomes is being investigated in the Heartline study, a collaboration between Johnson & Johnson and Apple, which is supported by Evidation.2
This study aims to enroll 150,000 adults age 65 years and over to analyze the impact of Apple Watch–based early detection of irregular heart rhythms consistent with atrial fibrillation (AFib). The researchers’ hypothesis is that jointly detecting atrial fibrillation early and providing cardiovascular health programs to new AFib patients, will lead to patients being treated by a medical provider for AFib that otherwise would not have been detected. This, in turn, would lead to these AFib patients decreasing their risks of stroke and other serious cardiovascular events, including death, the study authors speculated.
Presenting new challenges
While PGHD has the potential to help people, it also presents new challenges. It is highly sensitive and personal – it can be as identifying as DNA.3
The vast amount of data that PGHD can collect from interaction with consumer wearable devices poses serious privacy risks if done improperly. To address those risks, companies like Evidation have built in protections. Evidation has an app, Achievement, that has enlisted a connected population of more than 3.5 million members who earn rewards for performing health-related actions, as tracked by wearables devices and apps. Through the Achievement app (See Figure 2.), members are provided opportunities to join research studies. As part of these studies, data collected from sensors and apps is used by permission of the member so that it is clear how their data are contributing to specific research questions or use cases.
This is a collaborative model of data collection built upon trust and permission and is substantially different than the collection of data from electronic health records (EHRs) – which is typically aggregated, deidentified, and commercialized, often without the patients’ knowledge or consent. Stringent protections, explicit permission, and transparency are absolutely imperative until privacy frameworks for data outside of HIPAA regulation catches up and protects patients from discrimination and unintended uses of their data.
Large connected cohorts can help advance our understanding of public health. In one study run on Achievement during the 2017-2018 flu season, a survey was sent to the Achievement population every week asking about symptoms of influenza-like illness and requesting permission to access historical data from their wearable around the influenza-like illness event.4 With the data, it was possible to analyze patterns of activity, sleep, and resting heart rate change around flu events. Resting heart rate, in particular, is shown to increase during fever and at the population level. In fact, through the use of PGHD, it is possible to use the fraction of people with resting heart rate above their usual baseline as a proxy to quantify the number of infected people in a region.5 This resting heart rate–informed flu surveillance method, if refined to increased accuracy, can work in near real time. This means it may be able detect influenza outbreaks days earlier than current epidemiological methods.
Health data generated by connected populations are in the early stages of development. It is clear that it will yield novel insights into health and disease. Only time will tell if it will be able to help clinicians and patients better predict, diagnose, and formulate treatment plans for disease.
Neil Skolnik, M.D. is a professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, and associate director of the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington Jefferson Health. Luca Foschini PhD, is co-founder & chief data scientist at Evidation Health. Bray Patrick-Lake, MFS, is a patient thought leader and director of strategic partnerships at Evidation Health.
References
1. Chen R et al. Developing measures of cognitive impairment in the real world from consumer-grade multimodal sensor streams. KDD ’19. August 4–8, 2019 Aug 4-8.
2. The Heartline Study. https://www.heartline.com.
3. Foschini L. Privacy of Wearable and Sensors Data (or, the Lack Thereof?). Data Driven Investor, Medium. 2019.
4. Bradshaw B et al. Influenza surveillance using wearable mobile health devices. Online J Public Health Inform. 2019;11(1):e249.
5. Radin JM et al. Harnessing wearable device data to improve state-level real-time surveillance of influenza-like illness in the USA: a population-based study. Lancet Digital Health. 2020. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30222-5.
Clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects hair follicles, with predilection for intertriginous sites. The prevalence of HS ranges from 0.1% to 2%, with HS significantly affecting the quality of life for patients, with both physical and emotional consequences.
Guidelines from the U.S. and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations provide a summary of management and treatment for patients.
Grading
Hurley staging is recommended to determine therapies. Stage I is classified by recurrent nodules and abscesses with minimal scars. Stage II is classified by one or a limited number of sinuses and/or scarring within a body region. Stage III is classified by multiple or extensive sinuses and/or scarring. The Dermatology Life Quality Index and pain visual analog scale scores can be used in addition to the Hurley staging for management.
Diagnostic testing/comorbidities screening
There is limited evidence for microbiological testing for HS because skin flora is the main bacteria cultured. Patients should be screened for smoking use, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, depression/anxiety, follicular occlusion tetrad, and squamous cell carcinoma. Some studies have suggested an association between the severity of HS and smoking; therefore, smoking cessation is recommended. Patients should also be counseled on weight loss.
Zinc supplementation (90 mg daily) may be helpful. However, there is insufficient evidence for recommendations to avoid diary, brewer’s yeast, friction, deodorant, depilation, or shaving. There is also insufficient data to support vitamin D supplementation.
Topical/intralesional therapies
Expert opinion supports the use of chlorhexidine, benzoyl peroxide, or zinc pyrithione. A keratolytic and antiseptic cream such as resorcinol 15% cream may be used but can cause contact dermatitis. Topical clindamycin may decrease pustules formation, but it can increase resistance to Staphylococcus aureus. Triamcinolone intravlesional injections may decrease inflamed HS lesions in the short term.
Systemic antibiotics
Systemic antibiotics have been used for decades to treat HS. Tetracyclines for a 12-week course or long-term maintenance can be used in mild to moderate HS. Clindamycin and rifampin combination can be used as second-line therapy for mild to moderate HS. Moxifloxacin, metronidazole, and rifampin combination can also be considered second-line treatment for moderate to severe disease. Dapsone can be used in patients with Hurley stage I or II for maintenance therapy. Ertapenem IV can be used as a rescue or as bridge therapy for severe disease.
The duration of antibiotics and frequency of use depends on each patient and resistance.
Hormonal agents and retinoids
Although androgens may influence HS, evidence for hormonal agents is limited. Hormonal agents, such as ethinyl estradiol and spironolactone, can be considered for females with mild to moderate HS. Retinoids may be considered as a second- or third-line agent, especially in patients with severe acne and HS.
Immunosuppressants and biologics
Immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and azathioprine provide limited benefit; therefore, they are not recommended. Colchicine with minocycline may provide slight benefit in refractory mild to moderate HS. Cyclosporine may be considered in recalcitrant, severe HS. Systemic corticosteroids can be used short term for acute flares or long term for severe HS.
Biologic therapy is becoming more common and the choice of therapy for moderate to severe HS. Adalimumab is currently the only Food and Drug Administration–approved tumor necrosis factor–inhibitor treatment for HS. Other biologics – including infliximab, anakinra, and ustekinumab – may be effective for HS, but optimal dosing needs to be determined.
Pain management
While there are no studies about pain in HS, acute pain management should include topical analgesics and oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anticonvulsants such as pregabalin or gabapentin may help with neuropathic pain, and opioids can be considered if there is no improvement with first-line agents.
Surgical management
Recurrent nodules and tunnels can be deroofed or excised. Acute abscesses may be relieved by incision and drainage. Extensive lesions may require wide local scalpel excision, carbon dioxide laser excision, or electrosurgical excision. Surgery alone does not affect the biology of HS; therefore, surgical interventions should be reserved for disease that is not managed by medical therapy.
The bottom line
HS is a chronic inflammatory condition with complex medical management and surgical treatment options. Hurley staging I-III can be used to grade severity and determine therapy. Management of pain, tobacco cessation, weight loss, and mental health are important aspects of HS. Zinc supplementation (90 mg daily) may be helpful. Experts opinion supports the use of chlorhexidine, benzoyl peroxide or zinc pyrithione.
Acute lesions may be managed with short-term oral or intralesional corticosteroids, as well as deroofing or incision and drainage. Moderate-to-severe HS may be managed with systemic antibiotics or biologics and surgical therapy. Adalimumab is the only FDA-approved biologic for treatment of HS.
Dr. Chuong is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
References
Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. Part I: Diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jul;81(1):76-90.
Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication form the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. Part II: Topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jul;81(1):91-101.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects hair follicles, with predilection for intertriginous sites. The prevalence of HS ranges from 0.1% to 2%, with HS significantly affecting the quality of life for patients, with both physical and emotional consequences.
Guidelines from the U.S. and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations provide a summary of management and treatment for patients.
Grading
Hurley staging is recommended to determine therapies. Stage I is classified by recurrent nodules and abscesses with minimal scars. Stage II is classified by one or a limited number of sinuses and/or scarring within a body region. Stage III is classified by multiple or extensive sinuses and/or scarring. The Dermatology Life Quality Index and pain visual analog scale scores can be used in addition to the Hurley staging for management.
Diagnostic testing/comorbidities screening
There is limited evidence for microbiological testing for HS because skin flora is the main bacteria cultured. Patients should be screened for smoking use, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, depression/anxiety, follicular occlusion tetrad, and squamous cell carcinoma. Some studies have suggested an association between the severity of HS and smoking; therefore, smoking cessation is recommended. Patients should also be counseled on weight loss.
Zinc supplementation (90 mg daily) may be helpful. However, there is insufficient evidence for recommendations to avoid diary, brewer’s yeast, friction, deodorant, depilation, or shaving. There is also insufficient data to support vitamin D supplementation.
Topical/intralesional therapies
Expert opinion supports the use of chlorhexidine, benzoyl peroxide, or zinc pyrithione. A keratolytic and antiseptic cream such as resorcinol 15% cream may be used but can cause contact dermatitis. Topical clindamycin may decrease pustules formation, but it can increase resistance to Staphylococcus aureus. Triamcinolone intravlesional injections may decrease inflamed HS lesions in the short term.
Systemic antibiotics
Systemic antibiotics have been used for decades to treat HS. Tetracyclines for a 12-week course or long-term maintenance can be used in mild to moderate HS. Clindamycin and rifampin combination can be used as second-line therapy for mild to moderate HS. Moxifloxacin, metronidazole, and rifampin combination can also be considered second-line treatment for moderate to severe disease. Dapsone can be used in patients with Hurley stage I or II for maintenance therapy. Ertapenem IV can be used as a rescue or as bridge therapy for severe disease.
The duration of antibiotics and frequency of use depends on each patient and resistance.
Hormonal agents and retinoids
Although androgens may influence HS, evidence for hormonal agents is limited. Hormonal agents, such as ethinyl estradiol and spironolactone, can be considered for females with mild to moderate HS. Retinoids may be considered as a second- or third-line agent, especially in patients with severe acne and HS.
Immunosuppressants and biologics
Immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and azathioprine provide limited benefit; therefore, they are not recommended. Colchicine with minocycline may provide slight benefit in refractory mild to moderate HS. Cyclosporine may be considered in recalcitrant, severe HS. Systemic corticosteroids can be used short term for acute flares or long term for severe HS.
Biologic therapy is becoming more common and the choice of therapy for moderate to severe HS. Adalimumab is currently the only Food and Drug Administration–approved tumor necrosis factor–inhibitor treatment for HS. Other biologics – including infliximab, anakinra, and ustekinumab – may be effective for HS, but optimal dosing needs to be determined.
Pain management
While there are no studies about pain in HS, acute pain management should include topical analgesics and oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anticonvulsants such as pregabalin or gabapentin may help with neuropathic pain, and opioids can be considered if there is no improvement with first-line agents.
Surgical management
Recurrent nodules and tunnels can be deroofed or excised. Acute abscesses may be relieved by incision and drainage. Extensive lesions may require wide local scalpel excision, carbon dioxide laser excision, or electrosurgical excision. Surgery alone does not affect the biology of HS; therefore, surgical interventions should be reserved for disease that is not managed by medical therapy.
The bottom line
HS is a chronic inflammatory condition with complex medical management and surgical treatment options. Hurley staging I-III can be used to grade severity and determine therapy. Management of pain, tobacco cessation, weight loss, and mental health are important aspects of HS. Zinc supplementation (90 mg daily) may be helpful. Experts opinion supports the use of chlorhexidine, benzoyl peroxide or zinc pyrithione.
Acute lesions may be managed with short-term oral or intralesional corticosteroids, as well as deroofing or incision and drainage. Moderate-to-severe HS may be managed with systemic antibiotics or biologics and surgical therapy. Adalimumab is the only FDA-approved biologic for treatment of HS.
Dr. Chuong is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
References
Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. Part I: Diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jul;81(1):76-90.
Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication form the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. Part II: Topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jul;81(1):91-101.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that affects hair follicles, with predilection for intertriginous sites. The prevalence of HS ranges from 0.1% to 2%, with HS significantly affecting the quality of life for patients, with both physical and emotional consequences.
Guidelines from the U.S. and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations provide a summary of management and treatment for patients.
Grading
Hurley staging is recommended to determine therapies. Stage I is classified by recurrent nodules and abscesses with minimal scars. Stage II is classified by one or a limited number of sinuses and/or scarring within a body region. Stage III is classified by multiple or extensive sinuses and/or scarring. The Dermatology Life Quality Index and pain visual analog scale scores can be used in addition to the Hurley staging for management.
Diagnostic testing/comorbidities screening
There is limited evidence for microbiological testing for HS because skin flora is the main bacteria cultured. Patients should be screened for smoking use, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, depression/anxiety, follicular occlusion tetrad, and squamous cell carcinoma. Some studies have suggested an association between the severity of HS and smoking; therefore, smoking cessation is recommended. Patients should also be counseled on weight loss.
Zinc supplementation (90 mg daily) may be helpful. However, there is insufficient evidence for recommendations to avoid diary, brewer’s yeast, friction, deodorant, depilation, or shaving. There is also insufficient data to support vitamin D supplementation.
Topical/intralesional therapies
Expert opinion supports the use of chlorhexidine, benzoyl peroxide, or zinc pyrithione. A keratolytic and antiseptic cream such as resorcinol 15% cream may be used but can cause contact dermatitis. Topical clindamycin may decrease pustules formation, but it can increase resistance to Staphylococcus aureus. Triamcinolone intravlesional injections may decrease inflamed HS lesions in the short term.
Systemic antibiotics
Systemic antibiotics have been used for decades to treat HS. Tetracyclines for a 12-week course or long-term maintenance can be used in mild to moderate HS. Clindamycin and rifampin combination can be used as second-line therapy for mild to moderate HS. Moxifloxacin, metronidazole, and rifampin combination can also be considered second-line treatment for moderate to severe disease. Dapsone can be used in patients with Hurley stage I or II for maintenance therapy. Ertapenem IV can be used as a rescue or as bridge therapy for severe disease.
The duration of antibiotics and frequency of use depends on each patient and resistance.
Hormonal agents and retinoids
Although androgens may influence HS, evidence for hormonal agents is limited. Hormonal agents, such as ethinyl estradiol and spironolactone, can be considered for females with mild to moderate HS. Retinoids may be considered as a second- or third-line agent, especially in patients with severe acne and HS.
Immunosuppressants and biologics
Immunosuppressants such as methotrexate and azathioprine provide limited benefit; therefore, they are not recommended. Colchicine with minocycline may provide slight benefit in refractory mild to moderate HS. Cyclosporine may be considered in recalcitrant, severe HS. Systemic corticosteroids can be used short term for acute flares or long term for severe HS.
Biologic therapy is becoming more common and the choice of therapy for moderate to severe HS. Adalimumab is currently the only Food and Drug Administration–approved tumor necrosis factor–inhibitor treatment for HS. Other biologics – including infliximab, anakinra, and ustekinumab – may be effective for HS, but optimal dosing needs to be determined.
Pain management
While there are no studies about pain in HS, acute pain management should include topical analgesics and oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Anticonvulsants such as pregabalin or gabapentin may help with neuropathic pain, and opioids can be considered if there is no improvement with first-line agents.
Surgical management
Recurrent nodules and tunnels can be deroofed or excised. Acute abscesses may be relieved by incision and drainage. Extensive lesions may require wide local scalpel excision, carbon dioxide laser excision, or electrosurgical excision. Surgery alone does not affect the biology of HS; therefore, surgical interventions should be reserved for disease that is not managed by medical therapy.
The bottom line
HS is a chronic inflammatory condition with complex medical management and surgical treatment options. Hurley staging I-III can be used to grade severity and determine therapy. Management of pain, tobacco cessation, weight loss, and mental health are important aspects of HS. Zinc supplementation (90 mg daily) may be helpful. Experts opinion supports the use of chlorhexidine, benzoyl peroxide or zinc pyrithione.
Acute lesions may be managed with short-term oral or intralesional corticosteroids, as well as deroofing or incision and drainage. Moderate-to-severe HS may be managed with systemic antibiotics or biologics and surgical therapy. Adalimumab is the only FDA-approved biologic for treatment of HS.
Dr. Chuong is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
References
Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication from the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. Part I: Diagnosis, evaluation, and the use of complementary and procedural management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jul;81(1):76-90.
Alikhan A, Sayed C, Alavi A, et al. North American clinical management guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa: A publication form the United States and Canadian Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundations. Part II: Topical, intralesional, and systemic medical management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jul;81(1):91-101.
Are patient portals living up to the hype? Ask your mother-in-law!
While preparing to write this technology column, I received a great deal of insight from the unlikeliest of sources: my mother-in-law.
Now don’t get me wrong – she’s a truly lovely, intelligent, and capable woman. I have sought her advice often on many things and have always been impressed by her wisdom and pragmatism, but I’ve just never thought of asking her for her opinion on medicine or technology, as I considered her knowledge of both subjects to be limited.
This occasion changed my opinion. In fact, I believe that, as health care IT becomes more complex, people like my mother-in-law may be exactly who we should be looking to for answers.
A few weeks ago, my mother-in-law and I were discussing her recent trip to the doctor. When she mentioned some lab tests, I suggested that we log in to her patient portal to view the results. This elicited several questions and a declaration of frustration.
“Which portal?” she asked. “I have so many and can’t keep all of the websites and passwords straight! Why can’t all of my doctors use the same portal, and why do they all have different password requirements?”
As she spoke these words, I was immediately struck with an unfortunate reality of EHRs: We have done a brilliant job creating state-of-the-art digital castles and have filled them with the data needed to revolutionize care and improve population health – but we haven’t given our patients the keys to get inside.
We must ask ourselves if, in trying to construct fortresses of information around our patients, we have lost sight of the individuals in the center. I believe that we can answer this question and improve the benefits of patient portals, but we all must agree to a few simple steps to streamline the experience for everyone.
Make it easy
A study recently published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine surveyed several hospitals on their usage of patient portals. After determining whether or not the institutions had such portals, the authors then investigated to find out what, if any, guidance was provided to patients about how to use them.
Their findings are frustrating, though not surprising. While 89% of hospitals had some form of patient portal, only 65% of those “had links that were easily found, defined as links accessible within two clicks from the home page.”
Furthermore, even in cases where portals were easily found, good instructions on how to use them were missing. Those instructions that did exist centered on rules and restrictions and laying out “terms and conditions” and informing patients on “what not to do,” rather than explaining how to make the most of the experience.
According to the authors, “this focus on curtailing behavior, and the hurdles placed on finding and understanding guidance, suggest that some hospitals may be prioritizing reducing liability over improving the patient experience with portals.”
If we want our patients to use them, portals must be easy to access and intuitive to use. They also must provide value.
Make it meaningful
Patient portals have proliferated exponentially over the last 10 years, thanks to government incentive programs. One such program, known as “meaningful use,” is primarily responsible for this, as it made implementation of a patient portal one of its core requirements.
Sadly, in spite of its oft-reviled name, the meaningful use program never defined patient-friendly standards of usability for patient portals. As a result, current portals just aren’t very good. Patients like my mother-in-law find them to be too numerous, too unfriendly to use, and too limited, so they are not being used to their full potential.
In fact, many institutions may choose not to enable all of the available features in order to limit technical issues and reduce the burden on providers. In the study referenced above, only 63% of portals offered the ability for patients to communicate directly with their physicians, and only 43% offered the ability to refill prescriptions.
When enabled, these functions improve patient engagement and efficiency. Without them, patients are less likely to log on, and physicians are forced to rely on less-efficient telephone calls or traditional letters to communicate results to their patients.
Put the patient, not the portal, at the center
History has all but forgotten the attempts by tech giants such as Google and Microsoft to create personal health records. While these initially seemed like a wonderful concept, they sadly proved to be a total flop. Some patients embraced the idea, but security concerns and the lack of buy-in from EHR vendors significantly limited their uptake.
They may simply have been ahead of their time.
A decade later, wearable technology and telemedicine are ushering in a new era of patient-centric care. Individuals have been embracing a greater share of the responsibility for their own personal health information, yet most EHRs lack the ability to easily incorporate data acquired outside physicians’ offices.
It’s time for EHR vendors to go all in and change that. Instead of enslaving patients to the tyranny of fragmented health records, they should prioritize the creation of a robust, standardized, and portable health record that travels with the patient, not the other way around.
Have any other ideas on how to improve patient engagement? We’d love to hear about them and share them in a future column.
If you want to contribute but don’t have any ideas, we have a suggestion: Ask your mother-in-law. You may be surprised at what you learn!
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health.
Reference
Lee JL et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-05528-z.
While preparing to write this technology column, I received a great deal of insight from the unlikeliest of sources: my mother-in-law.
Now don’t get me wrong – she’s a truly lovely, intelligent, and capable woman. I have sought her advice often on many things and have always been impressed by her wisdom and pragmatism, but I’ve just never thought of asking her for her opinion on medicine or technology, as I considered her knowledge of both subjects to be limited.
This occasion changed my opinion. In fact, I believe that, as health care IT becomes more complex, people like my mother-in-law may be exactly who we should be looking to for answers.
A few weeks ago, my mother-in-law and I were discussing her recent trip to the doctor. When she mentioned some lab tests, I suggested that we log in to her patient portal to view the results. This elicited several questions and a declaration of frustration.
“Which portal?” she asked. “I have so many and can’t keep all of the websites and passwords straight! Why can’t all of my doctors use the same portal, and why do they all have different password requirements?”
As she spoke these words, I was immediately struck with an unfortunate reality of EHRs: We have done a brilliant job creating state-of-the-art digital castles and have filled them with the data needed to revolutionize care and improve population health – but we haven’t given our patients the keys to get inside.
We must ask ourselves if, in trying to construct fortresses of information around our patients, we have lost sight of the individuals in the center. I believe that we can answer this question and improve the benefits of patient portals, but we all must agree to a few simple steps to streamline the experience for everyone.
Make it easy
A study recently published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine surveyed several hospitals on their usage of patient portals. After determining whether or not the institutions had such portals, the authors then investigated to find out what, if any, guidance was provided to patients about how to use them.
Their findings are frustrating, though not surprising. While 89% of hospitals had some form of patient portal, only 65% of those “had links that were easily found, defined as links accessible within two clicks from the home page.”
Furthermore, even in cases where portals were easily found, good instructions on how to use them were missing. Those instructions that did exist centered on rules and restrictions and laying out “terms and conditions” and informing patients on “what not to do,” rather than explaining how to make the most of the experience.
According to the authors, “this focus on curtailing behavior, and the hurdles placed on finding and understanding guidance, suggest that some hospitals may be prioritizing reducing liability over improving the patient experience with portals.”
If we want our patients to use them, portals must be easy to access and intuitive to use. They also must provide value.
Make it meaningful
Patient portals have proliferated exponentially over the last 10 years, thanks to government incentive programs. One such program, known as “meaningful use,” is primarily responsible for this, as it made implementation of a patient portal one of its core requirements.
Sadly, in spite of its oft-reviled name, the meaningful use program never defined patient-friendly standards of usability for patient portals. As a result, current portals just aren’t very good. Patients like my mother-in-law find them to be too numerous, too unfriendly to use, and too limited, so they are not being used to their full potential.
In fact, many institutions may choose not to enable all of the available features in order to limit technical issues and reduce the burden on providers. In the study referenced above, only 63% of portals offered the ability for patients to communicate directly with their physicians, and only 43% offered the ability to refill prescriptions.
When enabled, these functions improve patient engagement and efficiency. Without them, patients are less likely to log on, and physicians are forced to rely on less-efficient telephone calls or traditional letters to communicate results to their patients.
Put the patient, not the portal, at the center
History has all but forgotten the attempts by tech giants such as Google and Microsoft to create personal health records. While these initially seemed like a wonderful concept, they sadly proved to be a total flop. Some patients embraced the idea, but security concerns and the lack of buy-in from EHR vendors significantly limited their uptake.
They may simply have been ahead of their time.
A decade later, wearable technology and telemedicine are ushering in a new era of patient-centric care. Individuals have been embracing a greater share of the responsibility for their own personal health information, yet most EHRs lack the ability to easily incorporate data acquired outside physicians’ offices.
It’s time for EHR vendors to go all in and change that. Instead of enslaving patients to the tyranny of fragmented health records, they should prioritize the creation of a robust, standardized, and portable health record that travels with the patient, not the other way around.
Have any other ideas on how to improve patient engagement? We’d love to hear about them and share them in a future column.
If you want to contribute but don’t have any ideas, we have a suggestion: Ask your mother-in-law. You may be surprised at what you learn!
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health.
Reference
Lee JL et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-05528-z.
While preparing to write this technology column, I received a great deal of insight from the unlikeliest of sources: my mother-in-law.
Now don’t get me wrong – she’s a truly lovely, intelligent, and capable woman. I have sought her advice often on many things and have always been impressed by her wisdom and pragmatism, but I’ve just never thought of asking her for her opinion on medicine or technology, as I considered her knowledge of both subjects to be limited.
This occasion changed my opinion. In fact, I believe that, as health care IT becomes more complex, people like my mother-in-law may be exactly who we should be looking to for answers.
A few weeks ago, my mother-in-law and I were discussing her recent trip to the doctor. When she mentioned some lab tests, I suggested that we log in to her patient portal to view the results. This elicited several questions and a declaration of frustration.
“Which portal?” she asked. “I have so many and can’t keep all of the websites and passwords straight! Why can’t all of my doctors use the same portal, and why do they all have different password requirements?”
As she spoke these words, I was immediately struck with an unfortunate reality of EHRs: We have done a brilliant job creating state-of-the-art digital castles and have filled them with the data needed to revolutionize care and improve population health – but we haven’t given our patients the keys to get inside.
We must ask ourselves if, in trying to construct fortresses of information around our patients, we have lost sight of the individuals in the center. I believe that we can answer this question and improve the benefits of patient portals, but we all must agree to a few simple steps to streamline the experience for everyone.
Make it easy
A study recently published in the Journal of General Internal Medicine surveyed several hospitals on their usage of patient portals. After determining whether or not the institutions had such portals, the authors then investigated to find out what, if any, guidance was provided to patients about how to use them.
Their findings are frustrating, though not surprising. While 89% of hospitals had some form of patient portal, only 65% of those “had links that were easily found, defined as links accessible within two clicks from the home page.”
Furthermore, even in cases where portals were easily found, good instructions on how to use them were missing. Those instructions that did exist centered on rules and restrictions and laying out “terms and conditions” and informing patients on “what not to do,” rather than explaining how to make the most of the experience.
According to the authors, “this focus on curtailing behavior, and the hurdles placed on finding and understanding guidance, suggest that some hospitals may be prioritizing reducing liability over improving the patient experience with portals.”
If we want our patients to use them, portals must be easy to access and intuitive to use. They also must provide value.
Make it meaningful
Patient portals have proliferated exponentially over the last 10 years, thanks to government incentive programs. One such program, known as “meaningful use,” is primarily responsible for this, as it made implementation of a patient portal one of its core requirements.
Sadly, in spite of its oft-reviled name, the meaningful use program never defined patient-friendly standards of usability for patient portals. As a result, current portals just aren’t very good. Patients like my mother-in-law find them to be too numerous, too unfriendly to use, and too limited, so they are not being used to their full potential.
In fact, many institutions may choose not to enable all of the available features in order to limit technical issues and reduce the burden on providers. In the study referenced above, only 63% of portals offered the ability for patients to communicate directly with their physicians, and only 43% offered the ability to refill prescriptions.
When enabled, these functions improve patient engagement and efficiency. Without them, patients are less likely to log on, and physicians are forced to rely on less-efficient telephone calls or traditional letters to communicate results to their patients.
Put the patient, not the portal, at the center
History has all but forgotten the attempts by tech giants such as Google and Microsoft to create personal health records. While these initially seemed like a wonderful concept, they sadly proved to be a total flop. Some patients embraced the idea, but security concerns and the lack of buy-in from EHR vendors significantly limited their uptake.
They may simply have been ahead of their time.
A decade later, wearable technology and telemedicine are ushering in a new era of patient-centric care. Individuals have been embracing a greater share of the responsibility for their own personal health information, yet most EHRs lack the ability to easily incorporate data acquired outside physicians’ offices.
It’s time for EHR vendors to go all in and change that. Instead of enslaving patients to the tyranny of fragmented health records, they should prioritize the creation of a robust, standardized, and portable health record that travels with the patient, not the other way around.
Have any other ideas on how to improve patient engagement? We’d love to hear about them and share them in a future column.
If you want to contribute but don’t have any ideas, we have a suggestion: Ask your mother-in-law. You may be surprised at what you learn!
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Follow him on twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health.
Reference
Lee JL et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-05528-z.
USPSTF recommendations on screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm
The prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) is decreasing, thought to be caused by a decrease in smoking. But the risk of death if one ruptures is as high as 81%. So, screening is still an important part of preventive medicine.
When the abdominal aorta enlarges to greater than 3.0 cm, it is considered an aneurysm. Risk factors that can lead to an enlarged aorta include older age, male sex, smoking, history of AAA in a first-degree relative, hypertension, history of other aneurysms, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerosis, and hypercholesterolemia.
History of AAA in a first-degree relative puts patients at double the risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Interestingly, diabetes has been associated with a reduced risk of AAA. People of African American, Asian, and Hispanic descent have a reduced risk of AAA.
Screening
Screening is performed using abdominal duplex ultrasound. It has high sensitivity (94%-100%) and specificity (98%-100%), is low cost, and has low risk to the patient. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force breaks its screening recommendations into four categories:
1. Men aged 65-75 years who have ever smoked (at least 100 cigarettes in their lifetime): One-time screening (grade B, moderate net benefit).
2. Men aged 65-75 years who have never smoked: Selectively offer screening (grade C, small net benefit). “To determine whether this service is appropriate, patients and clinicians should consider the patient’s medical history, family history, other risk factors, and personal values.”
3. Women without a smoking history or family history of AAA: Do not perform screening (grade D, recommendation against the service).
4. Women aged 65-75 years who have a smoking history or family history of AAA: There is insufficient evidence on whether or not to screen for AAA (grade I, insufficient evidence).
To assess screening and treatment of AAAs, the USPSTF looked at four randomized, controlled trials largely focused on men older than 65 years. With the combined data, they found 246 men would need to be screened to prevent 1 AAA rupture, and 305 men would need to be screened to prevent 1 death from AAA.
The USPSTF does note that, while the risk of death is lower for elective AAA repair than ruptured AAA, there is still increased risk with elective surgery. In addition, increased screening and detection increases the rate of elective surgery. Overdiagnosis and overtreatment could represent a harm.
Treatment
Surgical repair of AAA in men depends on the size of the aneurysm and rate of growth.
For men, surgical repair is standard when the AAA reaches 5.5 cm or if the AAA is growing faster than 1.0 cm per year and is larger than 4.0 cm. For women, surgical repair is often recommended between 5.0 cm and 5.4 cm in size.
Surgical repair is not recommended for AAAs that are less than 5.0 cm because the annual risk of rupture is 0%-1% below 5.0 cm. The risk increases to 11% for aneurysms that are 5.0-5.9 cm in size.
There are two methods of surgical repair: endovascular aneurysm repair and open repair. Recommendations for the surveillance of AAA between 3.0 cm and 5.5 cm is regular ultrasound surveillance, with the interval becoming shorter as the aneurysm size becomes larger. Exact intervals differ from one guideline group to another.
Screening and treatment in women
While it is true that AAAs in women are more likely to rupture at smaller sizes than AAAs in men, the AAAs that rupture in women are more likely to rupture at an older age than AAAs rupture in men.
The prevalence of AAAs in women is thought to be one-sixth of the prevalence of men. In addition, women had a higher 30-day mortality after surgical repair. They also had higher rates of complications for elective surgical repair of AAAs.
For these reasons, it is unclear that the benefits of AAA screening and treatment in women outweigh the risks, and the USPSTF cannot come to a conclusive recommendation for women who have ever smoked or women who have a family history of AAA.
The USPSTF is able to state definitively that they do not recommend screening in women with no smoking history or family history of AAA.
Bottom line
The USPSTF recommends screening men aged 65-75 years who have ever smoked and selectively screening men aged 65-75 years with no smoking history. The USPSTF recommends against screening women aged 65-75 years who have never smoked and have no family history of AAA. There is insufficient evidence to either recommend for or against screening women aged 65-75 years who have smoked or have a family history of AAA.
Reference
Owens DK et al. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2211-18.
Dr. Sprogell is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health.
The prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) is decreasing, thought to be caused by a decrease in smoking. But the risk of death if one ruptures is as high as 81%. So, screening is still an important part of preventive medicine.
When the abdominal aorta enlarges to greater than 3.0 cm, it is considered an aneurysm. Risk factors that can lead to an enlarged aorta include older age, male sex, smoking, history of AAA in a first-degree relative, hypertension, history of other aneurysms, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerosis, and hypercholesterolemia.
History of AAA in a first-degree relative puts patients at double the risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Interestingly, diabetes has been associated with a reduced risk of AAA. People of African American, Asian, and Hispanic descent have a reduced risk of AAA.
Screening
Screening is performed using abdominal duplex ultrasound. It has high sensitivity (94%-100%) and specificity (98%-100%), is low cost, and has low risk to the patient. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force breaks its screening recommendations into four categories:
1. Men aged 65-75 years who have ever smoked (at least 100 cigarettes in their lifetime): One-time screening (grade B, moderate net benefit).
2. Men aged 65-75 years who have never smoked: Selectively offer screening (grade C, small net benefit). “To determine whether this service is appropriate, patients and clinicians should consider the patient’s medical history, family history, other risk factors, and personal values.”
3. Women without a smoking history or family history of AAA: Do not perform screening (grade D, recommendation against the service).
4. Women aged 65-75 years who have a smoking history or family history of AAA: There is insufficient evidence on whether or not to screen for AAA (grade I, insufficient evidence).
To assess screening and treatment of AAAs, the USPSTF looked at four randomized, controlled trials largely focused on men older than 65 years. With the combined data, they found 246 men would need to be screened to prevent 1 AAA rupture, and 305 men would need to be screened to prevent 1 death from AAA.
The USPSTF does note that, while the risk of death is lower for elective AAA repair than ruptured AAA, there is still increased risk with elective surgery. In addition, increased screening and detection increases the rate of elective surgery. Overdiagnosis and overtreatment could represent a harm.
Treatment
Surgical repair of AAA in men depends on the size of the aneurysm and rate of growth.
For men, surgical repair is standard when the AAA reaches 5.5 cm or if the AAA is growing faster than 1.0 cm per year and is larger than 4.0 cm. For women, surgical repair is often recommended between 5.0 cm and 5.4 cm in size.
Surgical repair is not recommended for AAAs that are less than 5.0 cm because the annual risk of rupture is 0%-1% below 5.0 cm. The risk increases to 11% for aneurysms that are 5.0-5.9 cm in size.
There are two methods of surgical repair: endovascular aneurysm repair and open repair. Recommendations for the surveillance of AAA between 3.0 cm and 5.5 cm is regular ultrasound surveillance, with the interval becoming shorter as the aneurysm size becomes larger. Exact intervals differ from one guideline group to another.
Screening and treatment in women
While it is true that AAAs in women are more likely to rupture at smaller sizes than AAAs in men, the AAAs that rupture in women are more likely to rupture at an older age than AAAs rupture in men.
The prevalence of AAAs in women is thought to be one-sixth of the prevalence of men. In addition, women had a higher 30-day mortality after surgical repair. They also had higher rates of complications for elective surgical repair of AAAs.
For these reasons, it is unclear that the benefits of AAA screening and treatment in women outweigh the risks, and the USPSTF cannot come to a conclusive recommendation for women who have ever smoked or women who have a family history of AAA.
The USPSTF is able to state definitively that they do not recommend screening in women with no smoking history or family history of AAA.
Bottom line
The USPSTF recommends screening men aged 65-75 years who have ever smoked and selectively screening men aged 65-75 years with no smoking history. The USPSTF recommends against screening women aged 65-75 years who have never smoked and have no family history of AAA. There is insufficient evidence to either recommend for or against screening women aged 65-75 years who have smoked or have a family history of AAA.
Reference
Owens DK et al. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2211-18.
Dr. Sprogell is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health.
The prevalence of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) is decreasing, thought to be caused by a decrease in smoking. But the risk of death if one ruptures is as high as 81%. So, screening is still an important part of preventive medicine.
When the abdominal aorta enlarges to greater than 3.0 cm, it is considered an aneurysm. Risk factors that can lead to an enlarged aorta include older age, male sex, smoking, history of AAA in a first-degree relative, hypertension, history of other aneurysms, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerosis, and hypercholesterolemia.
History of AAA in a first-degree relative puts patients at double the risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Interestingly, diabetes has been associated with a reduced risk of AAA. People of African American, Asian, and Hispanic descent have a reduced risk of AAA.
Screening
Screening is performed using abdominal duplex ultrasound. It has high sensitivity (94%-100%) and specificity (98%-100%), is low cost, and has low risk to the patient. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force breaks its screening recommendations into four categories:
1. Men aged 65-75 years who have ever smoked (at least 100 cigarettes in their lifetime): One-time screening (grade B, moderate net benefit).
2. Men aged 65-75 years who have never smoked: Selectively offer screening (grade C, small net benefit). “To determine whether this service is appropriate, patients and clinicians should consider the patient’s medical history, family history, other risk factors, and personal values.”
3. Women without a smoking history or family history of AAA: Do not perform screening (grade D, recommendation against the service).
4. Women aged 65-75 years who have a smoking history or family history of AAA: There is insufficient evidence on whether or not to screen for AAA (grade I, insufficient evidence).
To assess screening and treatment of AAAs, the USPSTF looked at four randomized, controlled trials largely focused on men older than 65 years. With the combined data, they found 246 men would need to be screened to prevent 1 AAA rupture, and 305 men would need to be screened to prevent 1 death from AAA.
The USPSTF does note that, while the risk of death is lower for elective AAA repair than ruptured AAA, there is still increased risk with elective surgery. In addition, increased screening and detection increases the rate of elective surgery. Overdiagnosis and overtreatment could represent a harm.
Treatment
Surgical repair of AAA in men depends on the size of the aneurysm and rate of growth.
For men, surgical repair is standard when the AAA reaches 5.5 cm or if the AAA is growing faster than 1.0 cm per year and is larger than 4.0 cm. For women, surgical repair is often recommended between 5.0 cm and 5.4 cm in size.
Surgical repair is not recommended for AAAs that are less than 5.0 cm because the annual risk of rupture is 0%-1% below 5.0 cm. The risk increases to 11% for aneurysms that are 5.0-5.9 cm in size.
There are two methods of surgical repair: endovascular aneurysm repair and open repair. Recommendations for the surveillance of AAA between 3.0 cm and 5.5 cm is regular ultrasound surveillance, with the interval becoming shorter as the aneurysm size becomes larger. Exact intervals differ from one guideline group to another.
Screening and treatment in women
While it is true that AAAs in women are more likely to rupture at smaller sizes than AAAs in men, the AAAs that rupture in women are more likely to rupture at an older age than AAAs rupture in men.
The prevalence of AAAs in women is thought to be one-sixth of the prevalence of men. In addition, women had a higher 30-day mortality after surgical repair. They also had higher rates of complications for elective surgical repair of AAAs.
For these reasons, it is unclear that the benefits of AAA screening and treatment in women outweigh the risks, and the USPSTF cannot come to a conclusive recommendation for women who have ever smoked or women who have a family history of AAA.
The USPSTF is able to state definitively that they do not recommend screening in women with no smoking history or family history of AAA.
Bottom line
The USPSTF recommends screening men aged 65-75 years who have ever smoked and selectively screening men aged 65-75 years with no smoking history. The USPSTF recommends against screening women aged 65-75 years who have never smoked and have no family history of AAA. There is insufficient evidence to either recommend for or against screening women aged 65-75 years who have smoked or have a family history of AAA.
Reference
Owens DK et al. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2019 Dec 10;322(22):2211-18.
Dr. Sprogell is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Hospital–Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Philadelphia, and associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Hospital–Jefferson Health.
The power and promise of person-generated health data – part 1
The time shared during clinical encounters provides small peeks into patients’ lives that get documented as episodic snapshots in electronic health records. But there is little information about how patients are doing outside of the office. With increasing emphasis on filling out mandatory parts of the EHR, there is less time available for in-depth, in-office conversations and phone follow-ups.
At the same time, it has become clear that it is not just the medicines we prescribe that affect our patients’ lives. Their behaviors outside of the office – being physically active, eating well, getting a good night’s rest, and adhering to medications – also impact their health outcomes.
The explosion of technology and personal data in our increasingly connected world provides powerful new sources of health and behavior information that generate new understanding of patients’ lives in their everyday settings.
The ubiquity and remarkable technological progress of personal computing devices – including wearables, smartphones, and tablets – along with the multitude of sensor modalities embedded within these devices, has enabled us to establish a continuous connection with people who want to share information about their behavior and daily life.
Such rich, longitudinal information, known as person-generated health data (PGHD), can be searched for physiological and behavioral signatures that can be used in combination with traditional clinical information to predict, diagnose, and treat disease. It can also be used to understand the safety and effectiveness of medical interventions.
PGHD is defined as wellness and/or health-related data created, recorded, or gathered by individuals. It reflects events and interactions that occur during an person’s everyday life. Systematically gathering this information and organizing it to better understand patients’ approach to their health or their unique experience living with disease provides meaningful insights that complement the data traditionally collected as part of clinical trials or periodic office visits.
PGHD can produce a rich picture of a person’s health or symptom burden with disease. It allows the opportunity to measure the real human burden of a patient’s disease and how it changes over time, with an opportunity to detect changes in symptoms in real time.
PGHD can also enable participation in health research.
An example would be the work of Evidation Health in San Mateo, Calif. Evidation provides a platform to run research studies utilizing technology and systems to measure health in everyday life. Its app, Achievement, collects continuous behavior-related data from smartphones, wearables, connected devices, and apps. That provides opportunities for participants to join research studies that develop novel measures designed to quantify health outcomes in a way that more accurately reflects an individual’s day-to-day activities and experience. All data collected are at the direction of and with the permission of the individual.
“Achievers” are given points for taking health-related actions such as tracking steps or their sleep, which convert to cash that can be kept or donated to their favorite charities. Achievement’s 3.5 million diverse participants also receive offers to join research studies. This paradigm shift dramatically expands access to research to increase diversity, shortens the time to first data through rapid recruitment, and enhances retention rates by making it easier to engage. To date, more than 1 million users have chosen to participate in research studies. The technology is bringing new data and insights to health research; it supports important questions about quality of life, medical products’ real-world effectiveness, and the development of hyperpersonalized health care services.
This new type of data is transforming medical research by creating real-world studies of unprecedented size, such as the Apple Heart Study – a virtual study with more than 400,000 enrolled participants – which was designed to test the accuracy of Apple Watches in safely identifying atrial fibrillation. The FDA has cleared two features on the Apple Watch: the device’s ability to detect and notify the user of an irregular heart rhythm, and the ability to take a single-lead EKG feature that can provide a rhythm strip for a clinician to review.
The FDA clearance letters specify that the apps are “not intended to replace traditional methods of diagnosis or treatment.” They provide extra information, and that information might be helpful – but the apps won’t replace a doctor’s visit. It remains to be seen how these data will be used, but they have the potential to identify atrial fibrillation early, leading to treatment that may prevent devastating strokes.
Another example of home-generated health data is a tool that has obtained FDA clearance as a diagnostic device with insurance reimbursement: WatchPAT, a portable sleep apnea diagnostic device. WatchPAT is worn like a simple wristwatch, with no need for belts, wires, or nasal cannulas.
Over time, in-home tests like these that are of minimal inconvenience to the patient and reflect a real-world experience may eclipse traditional sleep studies that require patients to spend the night in a clinic while attached to wires and monitors.
Health data generated by connected populations will yield novel insights that may help us better predict, diagnose, and treat disease. These are examples of innovations that can extend clinicians’ abilities to remotely monitor or diagnose health conditions, and we can expect that more will continue to be integrated into the clinical and research settings in the near future.
In part 2 of this series, we will discuss novel digital measures and studies utilizing PGHD to impact population health.
Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, family medicine residency program, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Foschini is cofounder and chief data scientist at Evidation Health in San Mateo, Calif. Bray Patrick-Lake is a patient thought leader and director, strategic partnerships, at Evidation Health.
References
Determining real-world data’s fitness for use and the role of reliability, September 2019. Duke-Margolis Center for Health Policy.
N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 14;381(20):1909-17.
The time shared during clinical encounters provides small peeks into patients’ lives that get documented as episodic snapshots in electronic health records. But there is little information about how patients are doing outside of the office. With increasing emphasis on filling out mandatory parts of the EHR, there is less time available for in-depth, in-office conversations and phone follow-ups.
At the same time, it has become clear that it is not just the medicines we prescribe that affect our patients’ lives. Their behaviors outside of the office – being physically active, eating well, getting a good night’s rest, and adhering to medications – also impact their health outcomes.
The explosion of technology and personal data in our increasingly connected world provides powerful new sources of health and behavior information that generate new understanding of patients’ lives in their everyday settings.
The ubiquity and remarkable technological progress of personal computing devices – including wearables, smartphones, and tablets – along with the multitude of sensor modalities embedded within these devices, has enabled us to establish a continuous connection with people who want to share information about their behavior and daily life.
Such rich, longitudinal information, known as person-generated health data (PGHD), can be searched for physiological and behavioral signatures that can be used in combination with traditional clinical information to predict, diagnose, and treat disease. It can also be used to understand the safety and effectiveness of medical interventions.
PGHD is defined as wellness and/or health-related data created, recorded, or gathered by individuals. It reflects events and interactions that occur during an person’s everyday life. Systematically gathering this information and organizing it to better understand patients’ approach to their health or their unique experience living with disease provides meaningful insights that complement the data traditionally collected as part of clinical trials or periodic office visits.
PGHD can produce a rich picture of a person’s health or symptom burden with disease. It allows the opportunity to measure the real human burden of a patient’s disease and how it changes over time, with an opportunity to detect changes in symptoms in real time.
PGHD can also enable participation in health research.
An example would be the work of Evidation Health in San Mateo, Calif. Evidation provides a platform to run research studies utilizing technology and systems to measure health in everyday life. Its app, Achievement, collects continuous behavior-related data from smartphones, wearables, connected devices, and apps. That provides opportunities for participants to join research studies that develop novel measures designed to quantify health outcomes in a way that more accurately reflects an individual’s day-to-day activities and experience. All data collected are at the direction of and with the permission of the individual.
“Achievers” are given points for taking health-related actions such as tracking steps or their sleep, which convert to cash that can be kept or donated to their favorite charities. Achievement’s 3.5 million diverse participants also receive offers to join research studies. This paradigm shift dramatically expands access to research to increase diversity, shortens the time to first data through rapid recruitment, and enhances retention rates by making it easier to engage. To date, more than 1 million users have chosen to participate in research studies. The technology is bringing new data and insights to health research; it supports important questions about quality of life, medical products’ real-world effectiveness, and the development of hyperpersonalized health care services.
This new type of data is transforming medical research by creating real-world studies of unprecedented size, such as the Apple Heart Study – a virtual study with more than 400,000 enrolled participants – which was designed to test the accuracy of Apple Watches in safely identifying atrial fibrillation. The FDA has cleared two features on the Apple Watch: the device’s ability to detect and notify the user of an irregular heart rhythm, and the ability to take a single-lead EKG feature that can provide a rhythm strip for a clinician to review.
The FDA clearance letters specify that the apps are “not intended to replace traditional methods of diagnosis or treatment.” They provide extra information, and that information might be helpful – but the apps won’t replace a doctor’s visit. It remains to be seen how these data will be used, but they have the potential to identify atrial fibrillation early, leading to treatment that may prevent devastating strokes.
Another example of home-generated health data is a tool that has obtained FDA clearance as a diagnostic device with insurance reimbursement: WatchPAT, a portable sleep apnea diagnostic device. WatchPAT is worn like a simple wristwatch, with no need for belts, wires, or nasal cannulas.
Over time, in-home tests like these that are of minimal inconvenience to the patient and reflect a real-world experience may eclipse traditional sleep studies that require patients to spend the night in a clinic while attached to wires and monitors.
Health data generated by connected populations will yield novel insights that may help us better predict, diagnose, and treat disease. These are examples of innovations that can extend clinicians’ abilities to remotely monitor or diagnose health conditions, and we can expect that more will continue to be integrated into the clinical and research settings in the near future.
In part 2 of this series, we will discuss novel digital measures and studies utilizing PGHD to impact population health.
Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, family medicine residency program, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Foschini is cofounder and chief data scientist at Evidation Health in San Mateo, Calif. Bray Patrick-Lake is a patient thought leader and director, strategic partnerships, at Evidation Health.
References
Determining real-world data’s fitness for use and the role of reliability, September 2019. Duke-Margolis Center for Health Policy.
N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 14;381(20):1909-17.
The time shared during clinical encounters provides small peeks into patients’ lives that get documented as episodic snapshots in electronic health records. But there is little information about how patients are doing outside of the office. With increasing emphasis on filling out mandatory parts of the EHR, there is less time available for in-depth, in-office conversations and phone follow-ups.
At the same time, it has become clear that it is not just the medicines we prescribe that affect our patients’ lives. Their behaviors outside of the office – being physically active, eating well, getting a good night’s rest, and adhering to medications – also impact their health outcomes.
The explosion of technology and personal data in our increasingly connected world provides powerful new sources of health and behavior information that generate new understanding of patients’ lives in their everyday settings.
The ubiquity and remarkable technological progress of personal computing devices – including wearables, smartphones, and tablets – along with the multitude of sensor modalities embedded within these devices, has enabled us to establish a continuous connection with people who want to share information about their behavior and daily life.
Such rich, longitudinal information, known as person-generated health data (PGHD), can be searched for physiological and behavioral signatures that can be used in combination with traditional clinical information to predict, diagnose, and treat disease. It can also be used to understand the safety and effectiveness of medical interventions.
PGHD is defined as wellness and/or health-related data created, recorded, or gathered by individuals. It reflects events and interactions that occur during an person’s everyday life. Systematically gathering this information and organizing it to better understand patients’ approach to their health or their unique experience living with disease provides meaningful insights that complement the data traditionally collected as part of clinical trials or periodic office visits.
PGHD can produce a rich picture of a person’s health or symptom burden with disease. It allows the opportunity to measure the real human burden of a patient’s disease and how it changes over time, with an opportunity to detect changes in symptoms in real time.
PGHD can also enable participation in health research.
An example would be the work of Evidation Health in San Mateo, Calif. Evidation provides a platform to run research studies utilizing technology and systems to measure health in everyday life. Its app, Achievement, collects continuous behavior-related data from smartphones, wearables, connected devices, and apps. That provides opportunities for participants to join research studies that develop novel measures designed to quantify health outcomes in a way that more accurately reflects an individual’s day-to-day activities and experience. All data collected are at the direction of and with the permission of the individual.
“Achievers” are given points for taking health-related actions such as tracking steps or their sleep, which convert to cash that can be kept or donated to their favorite charities. Achievement’s 3.5 million diverse participants also receive offers to join research studies. This paradigm shift dramatically expands access to research to increase diversity, shortens the time to first data through rapid recruitment, and enhances retention rates by making it easier to engage. To date, more than 1 million users have chosen to participate in research studies. The technology is bringing new data and insights to health research; it supports important questions about quality of life, medical products’ real-world effectiveness, and the development of hyperpersonalized health care services.
This new type of data is transforming medical research by creating real-world studies of unprecedented size, such as the Apple Heart Study – a virtual study with more than 400,000 enrolled participants – which was designed to test the accuracy of Apple Watches in safely identifying atrial fibrillation. The FDA has cleared two features on the Apple Watch: the device’s ability to detect and notify the user of an irregular heart rhythm, and the ability to take a single-lead EKG feature that can provide a rhythm strip for a clinician to review.
The FDA clearance letters specify that the apps are “not intended to replace traditional methods of diagnosis or treatment.” They provide extra information, and that information might be helpful – but the apps won’t replace a doctor’s visit. It remains to be seen how these data will be used, but they have the potential to identify atrial fibrillation early, leading to treatment that may prevent devastating strokes.
Another example of home-generated health data is a tool that has obtained FDA clearance as a diagnostic device with insurance reimbursement: WatchPAT, a portable sleep apnea diagnostic device. WatchPAT is worn like a simple wristwatch, with no need for belts, wires, or nasal cannulas.
Over time, in-home tests like these that are of minimal inconvenience to the patient and reflect a real-world experience may eclipse traditional sleep studies that require patients to spend the night in a clinic while attached to wires and monitors.
Health data generated by connected populations will yield novel insights that may help us better predict, diagnose, and treat disease. These are examples of innovations that can extend clinicians’ abilities to remotely monitor or diagnose health conditions, and we can expect that more will continue to be integrated into the clinical and research settings in the near future.
In part 2 of this series, we will discuss novel digital measures and studies utilizing PGHD to impact population health.
Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Sidney Kimmel Medical College, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, and associate director, family medicine residency program, Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Foschini is cofounder and chief data scientist at Evidation Health in San Mateo, Calif. Bray Patrick-Lake is a patient thought leader and director, strategic partnerships, at Evidation Health.
References
Determining real-world data’s fitness for use and the role of reliability, September 2019. Duke-Margolis Center for Health Policy.
N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 14;381(20):1909-17.
Is there a (robotic) doctor in the house?
In the 2012 movie “Robot and Frank,” an aging ex-jewel thief named Frank receives a robotic home assistant from his well-meaning son. Frank lives alone and suffers from dementia, and his son hopes that the friendly electronic companion will help keep his father safe, assisting him with housework and improving his cognitive health. Frank initially rejects the idea but changes his mind when he realizes the robot’s talents aren’t limited to domestic chores. He begins teaching the robot new skills, and an unlikely partnership develops. With Frank’s penchant for pilfering and the robot’s digital dexterity, the two of them pull off a multimillion-dollar jewelry heist – and Frank’s outlook improves in ways his son never dreamed possible!
“Robot and Frank” takes place “in the near future,” and while we don’t yet have robotic home companions as capable as the one in the movie, we need not look very far to realize that robotics and artificial intelligence may revolutionize the delivery of health care.
With an aging population and an industry shift toward value-based care, new research has focused on novel ways of avoiding hospitalization and reducing hospital readmission. We have seen a resurgence of home visits and the development of telemedicine and remote monitoring.
To stay healthy, patients need to be safe in their home environment and at a minimum need to be able to navigate their activities of daily living. Research published last year by Washington University’s Center for Advanced Studies in Adaptive Systems (CASAS) describes a technology that aims to help patients in their own homes.
The Robot Activity Support system, or RAS, interacts with intelligent sensors in a home environment “to detect and assist with activity errors that may occur in everyday settings.”1 If sensors in the home indicate that a person is experiencing difficulty completing a certain task such as taking a medication or finding a bathroom, a robot can navigate to the person in need and show an instructional video, or lead the patient to the next step in the process.
Another manufacturer is taking a ‘softer’ approach to activity support in the elderly. Toymaker Hasbro has developed a line of robotic cats that provide companionship and comfort. While currently limited to tactile stimulation and simple responses, the manufacturer is working in collaboration with researchers at Brown University to add artificial intelligence capabilities. The goal of the program – Project ARIES (Affordable Robotic Intelligence for Elderly Support) – is to give the cats useful skills such as being able to provide medication and safety reminders while keeping their price point accessible to all.
Other organizations are attempting to take the robotic home health aide idea to the next level. “RUDY,” a robotic companion developed by INF Robotics, is capable of much more than just educating patients and leading them around the house. About the size of small child and wearing a huge smile, Rudy can detect falls, ensure medication adherence, provide social interaction, and even offer remote patient monitoring. According to the manufacturer, it uses natural language processing, machine learning, and a smart social interface to “facilitate trusting relationships between RUDY and older adults.” The idea is to promote acceptance from patients and offer peace of mind to their loved ones. This can be particularly valuable in assisting those with dementia, as a heavy emphasis is placed on socialization and maintaining cognitive stimulation.
Instead of developing novel artificial intelligence platforms, many groups are attempting to leverage existing technologies to assist patients in their homes. One such technology is Amazon’s Echo smart speakers, which became more attractive to health care providers on April 4 of this year with the launch of the Alexa Healthcare Skills Kit. This is Amazon’s HIPAA-compliant application programming interface (API) that allows developers to create ‘skills’ (apps for Echo devices) that can securely handle protected health information.
At launch, Amazon announced six partner organizations who have already written skills for patients. One organization, Boston Children’s Hospital, developed a skill called My Children’s Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS). According to John Brownstein, the hospital’s Chief Innovation Officer, it “allows patients and caregivers to easily share recovery progress with their care team post surgery ... it is just one example of how voice technology can extend the care and support of our patients beyond the four walls of the hospital.”
Some companies, such as HealthTap, have been working on artificial intelligence to build a platform to allow physicians and patients to interact online. HealthTap is leveraging the wisdom of those interactions to power a deep learning system called Dr. A.I. Available for Alexa and mobile devices, it attempts to assess patients’ symptoms and provide personalized medical explanations and health recommendations. In the developer’s own words: “Dr. A.I. engages with you in an empathetic conversation about your symptoms and overall health ... then gives you appropriate doctor-recommended insights as well as the best possible courses of action you can take on the road to feeling good.”
Some physicians may find this movement troubling, but we believe it represents an early glimpse of what is to come. with no shortage of companies stepping up to meet the demand. While it’s doubtful the robots they create can be easily reprogrammed to steal jewelry, it won’t stop them from trying to steal our jobs. We as physicians will need to continue to hone our skills in compassion and empathy to provide something a computer never can: true care for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow him on twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Reference
1. Robot-enabled support of daily activities in smart home environments. Cogn Syst Res. 2019 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.10.032.
In the 2012 movie “Robot and Frank,” an aging ex-jewel thief named Frank receives a robotic home assistant from his well-meaning son. Frank lives alone and suffers from dementia, and his son hopes that the friendly electronic companion will help keep his father safe, assisting him with housework and improving his cognitive health. Frank initially rejects the idea but changes his mind when he realizes the robot’s talents aren’t limited to domestic chores. He begins teaching the robot new skills, and an unlikely partnership develops. With Frank’s penchant for pilfering and the robot’s digital dexterity, the two of them pull off a multimillion-dollar jewelry heist – and Frank’s outlook improves in ways his son never dreamed possible!
“Robot and Frank” takes place “in the near future,” and while we don’t yet have robotic home companions as capable as the one in the movie, we need not look very far to realize that robotics and artificial intelligence may revolutionize the delivery of health care.
With an aging population and an industry shift toward value-based care, new research has focused on novel ways of avoiding hospitalization and reducing hospital readmission. We have seen a resurgence of home visits and the development of telemedicine and remote monitoring.
To stay healthy, patients need to be safe in their home environment and at a minimum need to be able to navigate their activities of daily living. Research published last year by Washington University’s Center for Advanced Studies in Adaptive Systems (CASAS) describes a technology that aims to help patients in their own homes.
The Robot Activity Support system, or RAS, interacts with intelligent sensors in a home environment “to detect and assist with activity errors that may occur in everyday settings.”1 If sensors in the home indicate that a person is experiencing difficulty completing a certain task such as taking a medication or finding a bathroom, a robot can navigate to the person in need and show an instructional video, or lead the patient to the next step in the process.
Another manufacturer is taking a ‘softer’ approach to activity support in the elderly. Toymaker Hasbro has developed a line of robotic cats that provide companionship and comfort. While currently limited to tactile stimulation and simple responses, the manufacturer is working in collaboration with researchers at Brown University to add artificial intelligence capabilities. The goal of the program – Project ARIES (Affordable Robotic Intelligence for Elderly Support) – is to give the cats useful skills such as being able to provide medication and safety reminders while keeping their price point accessible to all.
Other organizations are attempting to take the robotic home health aide idea to the next level. “RUDY,” a robotic companion developed by INF Robotics, is capable of much more than just educating patients and leading them around the house. About the size of small child and wearing a huge smile, Rudy can detect falls, ensure medication adherence, provide social interaction, and even offer remote patient monitoring. According to the manufacturer, it uses natural language processing, machine learning, and a smart social interface to “facilitate trusting relationships between RUDY and older adults.” The idea is to promote acceptance from patients and offer peace of mind to their loved ones. This can be particularly valuable in assisting those with dementia, as a heavy emphasis is placed on socialization and maintaining cognitive stimulation.
Instead of developing novel artificial intelligence platforms, many groups are attempting to leverage existing technologies to assist patients in their homes. One such technology is Amazon’s Echo smart speakers, which became more attractive to health care providers on April 4 of this year with the launch of the Alexa Healthcare Skills Kit. This is Amazon’s HIPAA-compliant application programming interface (API) that allows developers to create ‘skills’ (apps for Echo devices) that can securely handle protected health information.
At launch, Amazon announced six partner organizations who have already written skills for patients. One organization, Boston Children’s Hospital, developed a skill called My Children’s Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS). According to John Brownstein, the hospital’s Chief Innovation Officer, it “allows patients and caregivers to easily share recovery progress with their care team post surgery ... it is just one example of how voice technology can extend the care and support of our patients beyond the four walls of the hospital.”
Some companies, such as HealthTap, have been working on artificial intelligence to build a platform to allow physicians and patients to interact online. HealthTap is leveraging the wisdom of those interactions to power a deep learning system called Dr. A.I. Available for Alexa and mobile devices, it attempts to assess patients’ symptoms and provide personalized medical explanations and health recommendations. In the developer’s own words: “Dr. A.I. engages with you in an empathetic conversation about your symptoms and overall health ... then gives you appropriate doctor-recommended insights as well as the best possible courses of action you can take on the road to feeling good.”
Some physicians may find this movement troubling, but we believe it represents an early glimpse of what is to come. with no shortage of companies stepping up to meet the demand. While it’s doubtful the robots they create can be easily reprogrammed to steal jewelry, it won’t stop them from trying to steal our jobs. We as physicians will need to continue to hone our skills in compassion and empathy to provide something a computer never can: true care for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow him on twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Reference
1. Robot-enabled support of daily activities in smart home environments. Cogn Syst Res. 2019 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.10.032.
In the 2012 movie “Robot and Frank,” an aging ex-jewel thief named Frank receives a robotic home assistant from his well-meaning son. Frank lives alone and suffers from dementia, and his son hopes that the friendly electronic companion will help keep his father safe, assisting him with housework and improving his cognitive health. Frank initially rejects the idea but changes his mind when he realizes the robot’s talents aren’t limited to domestic chores. He begins teaching the robot new skills, and an unlikely partnership develops. With Frank’s penchant for pilfering and the robot’s digital dexterity, the two of them pull off a multimillion-dollar jewelry heist – and Frank’s outlook improves in ways his son never dreamed possible!
“Robot and Frank” takes place “in the near future,” and while we don’t yet have robotic home companions as capable as the one in the movie, we need not look very far to realize that robotics and artificial intelligence may revolutionize the delivery of health care.
With an aging population and an industry shift toward value-based care, new research has focused on novel ways of avoiding hospitalization and reducing hospital readmission. We have seen a resurgence of home visits and the development of telemedicine and remote monitoring.
To stay healthy, patients need to be safe in their home environment and at a minimum need to be able to navigate their activities of daily living. Research published last year by Washington University’s Center for Advanced Studies in Adaptive Systems (CASAS) describes a technology that aims to help patients in their own homes.
The Robot Activity Support system, or RAS, interacts with intelligent sensors in a home environment “to detect and assist with activity errors that may occur in everyday settings.”1 If sensors in the home indicate that a person is experiencing difficulty completing a certain task such as taking a medication or finding a bathroom, a robot can navigate to the person in need and show an instructional video, or lead the patient to the next step in the process.
Another manufacturer is taking a ‘softer’ approach to activity support in the elderly. Toymaker Hasbro has developed a line of robotic cats that provide companionship and comfort. While currently limited to tactile stimulation and simple responses, the manufacturer is working in collaboration with researchers at Brown University to add artificial intelligence capabilities. The goal of the program – Project ARIES (Affordable Robotic Intelligence for Elderly Support) – is to give the cats useful skills such as being able to provide medication and safety reminders while keeping their price point accessible to all.
Other organizations are attempting to take the robotic home health aide idea to the next level. “RUDY,” a robotic companion developed by INF Robotics, is capable of much more than just educating patients and leading them around the house. About the size of small child and wearing a huge smile, Rudy can detect falls, ensure medication adherence, provide social interaction, and even offer remote patient monitoring. According to the manufacturer, it uses natural language processing, machine learning, and a smart social interface to “facilitate trusting relationships between RUDY and older adults.” The idea is to promote acceptance from patients and offer peace of mind to their loved ones. This can be particularly valuable in assisting those with dementia, as a heavy emphasis is placed on socialization and maintaining cognitive stimulation.
Instead of developing novel artificial intelligence platforms, many groups are attempting to leverage existing technologies to assist patients in their homes. One such technology is Amazon’s Echo smart speakers, which became more attractive to health care providers on April 4 of this year with the launch of the Alexa Healthcare Skills Kit. This is Amazon’s HIPAA-compliant application programming interface (API) that allows developers to create ‘skills’ (apps for Echo devices) that can securely handle protected health information.
At launch, Amazon announced six partner organizations who have already written skills for patients. One organization, Boston Children’s Hospital, developed a skill called My Children’s Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS). According to John Brownstein, the hospital’s Chief Innovation Officer, it “allows patients and caregivers to easily share recovery progress with their care team post surgery ... it is just one example of how voice technology can extend the care and support of our patients beyond the four walls of the hospital.”
Some companies, such as HealthTap, have been working on artificial intelligence to build a platform to allow physicians and patients to interact online. HealthTap is leveraging the wisdom of those interactions to power a deep learning system called Dr. A.I. Available for Alexa and mobile devices, it attempts to assess patients’ symptoms and provide personalized medical explanations and health recommendations. In the developer’s own words: “Dr. A.I. engages with you in an empathetic conversation about your symptoms and overall health ... then gives you appropriate doctor-recommended insights as well as the best possible courses of action you can take on the road to feeling good.”
Some physicians may find this movement troubling, but we believe it represents an early glimpse of what is to come. with no shortage of companies stepping up to meet the demand. While it’s doubtful the robots they create can be easily reprogrammed to steal jewelry, it won’t stop them from trying to steal our jobs. We as physicians will need to continue to hone our skills in compassion and empathy to provide something a computer never can: true care for our patients.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow him on twitter (@doctornotte). Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Reference
1. Robot-enabled support of daily activities in smart home environments. Cogn Syst Res. 2019 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsys.2018.10.032.
Guideline: Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia
A new guideline has been published to update the 2007 guidelines for the management of adults with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
The practice guideline was jointly written by an ad hoc committee of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. CAP refers to a pneumonia infection that was acquired by a patient in his or her community. Decisions about which antibiotics to use to treat this kind of infection are based on risk factors for resistant organisms and the severity of illness.
Pathogens
Traditionally, CAP is caused by common bacterial pathogens that include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Legionella species, Chlamydia pneumonia, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Risk factors for multidrug resistant pathogens such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa include previous infection with MRSA or P. aeruginosa, recent hospitalization, and requiring parenteral antibiotics in the last 90 days.
Defining severe community-acquired pneumonia
The health care–associated pneumonia, or HCAP, classification should no longer be used to determine empiric treatment. The recommendations for which antibiotics to use are linked to the severity of illness. Previously the site of treatment drove antibiotic selection, but since decision about the site of care can be affected by many considerations, the guidelines recommend using the CAP severity criteria. Severe CAP includes either one major or at least three minor criteria.
Major criteria are:
- Septic shock requiring vasopressors.
- Respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation.
Minor criteria are:
- Respiratory rate greater than or equal to 30 breaths/min.
- Ratio of arterial O2 partial pressure to fractional inspired O2 less than or equal to 250.
- Multilobar infiltrates.
- Confusion/disorientation.
- Uremia (blood urea nitrogen level greater than or equal to 20 mg/dL).
- Leukopenia (white blood cell count less than 4,000 cells/mcL).
- Thrombocytopenia (platelet count less than 100,000 mcL)
- Hypothermia (core temperature less than 36º C).
- Hypotension requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation.
Management and diagnostic testing
Clinicians should use the Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) and clinical judgment to guide the site of treatment for patients. Gram stain, sputum, and blood culture should not be routinely obtained in an outpatient setting. Legionella antigen should not be routinely obtained unless indicated by epidemiological factors. During influenza season, a rapid influenza assay, preferably a nucleic acid amplification test, should be obtained to help guide treatment.
For patients with severe CAP or risk factors for MRSA or P. aeruginosa, gram stain and culture and Legionella antigen should be obtained to manage antibiotic choices. Also, blood cultures should be obtained for these patients.
Empiric antibiotic therapy should be initiated based on clinical judgment and radiographic confirmation of CAP. Serum procalcitonin should not be used to assess initiation of antibiotic therapy.
Empiric antibiotic therapy
Healthy adults without comorbidities should be treated with monotherapy of either:
- Amoxicillin 1 g three times daily.
- OR doxycycline 100 mg twice daily.
- OR a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg on first day then 250 mg daily or clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily or clarithromycin extended release 1,000 mg daily) only in areas with pneumococcal resistance to macrolides less than 25%.
Adults with comorbidities such as chronic heart, lung, liver, or renal disease; diabetes mellitus; alcoholism; malignancy; or asplenia should be treated with:
- Amoxicillin/clavulanate 500 mg/125 mg three times daily, or amoxicillin/ clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg twice daily, or 2,000 mg/125 mg twice daily, or a cephalosporin (cefpodoxime 200 mg twice daily or cefuroxime 500 mg twice daily); and a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg on first day then 250 mg daily, clarithromycin [500 mg twice daily or extended release 1,000 mg once daily]), or doxycycline 100 mg twice daily. (Some experts recommend that the first dose of doxycycline should be 200 mg.)
- OR monotherapy with respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin 750 mg daily, moxifloxacin 400 mg daily, or gemifloxacin 320 mg daily).
Inpatient pneumonia that is not severe, without risk factors for resistant organisms should be treated with:
- Beta-lactam (ampicillin 1 sulbactam 1.5-3 g every 6 h, cefotaxime 1-2 g every 8 h, ceftriaxone 1-2 g daily, or ceftaroline 600 mg every 12 h) and a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg daily or clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily).
- OR monotherapy with a respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin 750 mg daily, moxifloxacin 400 mg daily).
If there is a contraindication for the use of both a macrolide and a fluoroquinolone, then doxycycline can be used instead.
Severe inpatient pneumonia without risk factors for resistant organisms should be treated with combination therapy of either (agents and doses the same as above):
- Beta-lactam and macrolide.
- OR fluoroquinolone and beta-lactam.
It is recommended to not routinely add anaerobic coverage for suspected aspiration pneumonia unless lung abscess or empyema is suspected. Clinicians should identify risk factors for MRSA or P. aeruginosa before adding additional agents.
Duration of antibiotic therapy is determined by the patient achieving clinical stability with no less than 5 days of antibiotics. In adults with symptom resolution within 5-7 days, no additional follow-up chest imaging is recommended. If patients test positive for influenza, then anti-influenza treatment such as oseltamivir should be used in addition to antibiotics regardless of length of influenza symptoms before presentation.
The bottom line
CAP treatment should be based on severity of illness and risk factors for resistant organisms. Blood and sputum cultures are recommended only for patients with severe pneumonia. There have been important changes in the recommendations for antibiotic treatment of CAP, with high-dose amoxicillin recommended for most patients with CAP who are treated as outpatients. Patients who exhibit clinical stability should be treated for at least 5 days and do not require follow up imaging studies.
For a podcast of this guideline, go to iTunes and download the Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline podcast.
Reference
Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):e45-e67.
Tina Chuong, DO, is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
A new guideline has been published to update the 2007 guidelines for the management of adults with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
The practice guideline was jointly written by an ad hoc committee of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. CAP refers to a pneumonia infection that was acquired by a patient in his or her community. Decisions about which antibiotics to use to treat this kind of infection are based on risk factors for resistant organisms and the severity of illness.
Pathogens
Traditionally, CAP is caused by common bacterial pathogens that include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Legionella species, Chlamydia pneumonia, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Risk factors for multidrug resistant pathogens such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa include previous infection with MRSA or P. aeruginosa, recent hospitalization, and requiring parenteral antibiotics in the last 90 days.
Defining severe community-acquired pneumonia
The health care–associated pneumonia, or HCAP, classification should no longer be used to determine empiric treatment. The recommendations for which antibiotics to use are linked to the severity of illness. Previously the site of treatment drove antibiotic selection, but since decision about the site of care can be affected by many considerations, the guidelines recommend using the CAP severity criteria. Severe CAP includes either one major or at least three minor criteria.
Major criteria are:
- Septic shock requiring vasopressors.
- Respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation.
Minor criteria are:
- Respiratory rate greater than or equal to 30 breaths/min.
- Ratio of arterial O2 partial pressure to fractional inspired O2 less than or equal to 250.
- Multilobar infiltrates.
- Confusion/disorientation.
- Uremia (blood urea nitrogen level greater than or equal to 20 mg/dL).
- Leukopenia (white blood cell count less than 4,000 cells/mcL).
- Thrombocytopenia (platelet count less than 100,000 mcL)
- Hypothermia (core temperature less than 36º C).
- Hypotension requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation.
Management and diagnostic testing
Clinicians should use the Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) and clinical judgment to guide the site of treatment for patients. Gram stain, sputum, and blood culture should not be routinely obtained in an outpatient setting. Legionella antigen should not be routinely obtained unless indicated by epidemiological factors. During influenza season, a rapid influenza assay, preferably a nucleic acid amplification test, should be obtained to help guide treatment.
For patients with severe CAP or risk factors for MRSA or P. aeruginosa, gram stain and culture and Legionella antigen should be obtained to manage antibiotic choices. Also, blood cultures should be obtained for these patients.
Empiric antibiotic therapy should be initiated based on clinical judgment and radiographic confirmation of CAP. Serum procalcitonin should not be used to assess initiation of antibiotic therapy.
Empiric antibiotic therapy
Healthy adults without comorbidities should be treated with monotherapy of either:
- Amoxicillin 1 g three times daily.
- OR doxycycline 100 mg twice daily.
- OR a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg on first day then 250 mg daily or clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily or clarithromycin extended release 1,000 mg daily) only in areas with pneumococcal resistance to macrolides less than 25%.
Adults with comorbidities such as chronic heart, lung, liver, or renal disease; diabetes mellitus; alcoholism; malignancy; or asplenia should be treated with:
- Amoxicillin/clavulanate 500 mg/125 mg three times daily, or amoxicillin/ clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg twice daily, or 2,000 mg/125 mg twice daily, or a cephalosporin (cefpodoxime 200 mg twice daily or cefuroxime 500 mg twice daily); and a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg on first day then 250 mg daily, clarithromycin [500 mg twice daily or extended release 1,000 mg once daily]), or doxycycline 100 mg twice daily. (Some experts recommend that the first dose of doxycycline should be 200 mg.)
- OR monotherapy with respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin 750 mg daily, moxifloxacin 400 mg daily, or gemifloxacin 320 mg daily).
Inpatient pneumonia that is not severe, without risk factors for resistant organisms should be treated with:
- Beta-lactam (ampicillin 1 sulbactam 1.5-3 g every 6 h, cefotaxime 1-2 g every 8 h, ceftriaxone 1-2 g daily, or ceftaroline 600 mg every 12 h) and a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg daily or clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily).
- OR monotherapy with a respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin 750 mg daily, moxifloxacin 400 mg daily).
If there is a contraindication for the use of both a macrolide and a fluoroquinolone, then doxycycline can be used instead.
Severe inpatient pneumonia without risk factors for resistant organisms should be treated with combination therapy of either (agents and doses the same as above):
- Beta-lactam and macrolide.
- OR fluoroquinolone and beta-lactam.
It is recommended to not routinely add anaerobic coverage for suspected aspiration pneumonia unless lung abscess or empyema is suspected. Clinicians should identify risk factors for MRSA or P. aeruginosa before adding additional agents.
Duration of antibiotic therapy is determined by the patient achieving clinical stability with no less than 5 days of antibiotics. In adults with symptom resolution within 5-7 days, no additional follow-up chest imaging is recommended. If patients test positive for influenza, then anti-influenza treatment such as oseltamivir should be used in addition to antibiotics regardless of length of influenza symptoms before presentation.
The bottom line
CAP treatment should be based on severity of illness and risk factors for resistant organisms. Blood and sputum cultures are recommended only for patients with severe pneumonia. There have been important changes in the recommendations for antibiotic treatment of CAP, with high-dose amoxicillin recommended for most patients with CAP who are treated as outpatients. Patients who exhibit clinical stability should be treated for at least 5 days and do not require follow up imaging studies.
For a podcast of this guideline, go to iTunes and download the Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline podcast.
Reference
Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):e45-e67.
Tina Chuong, DO, is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
A new guideline has been published to update the 2007 guidelines for the management of adults with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP).
The practice guideline was jointly written by an ad hoc committee of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. CAP refers to a pneumonia infection that was acquired by a patient in his or her community. Decisions about which antibiotics to use to treat this kind of infection are based on risk factors for resistant organisms and the severity of illness.
Pathogens
Traditionally, CAP is caused by common bacterial pathogens that include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Legionella species, Chlamydia pneumonia, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Risk factors for multidrug resistant pathogens such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa include previous infection with MRSA or P. aeruginosa, recent hospitalization, and requiring parenteral antibiotics in the last 90 days.
Defining severe community-acquired pneumonia
The health care–associated pneumonia, or HCAP, classification should no longer be used to determine empiric treatment. The recommendations for which antibiotics to use are linked to the severity of illness. Previously the site of treatment drove antibiotic selection, but since decision about the site of care can be affected by many considerations, the guidelines recommend using the CAP severity criteria. Severe CAP includes either one major or at least three minor criteria.
Major criteria are:
- Septic shock requiring vasopressors.
- Respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation.
Minor criteria are:
- Respiratory rate greater than or equal to 30 breaths/min.
- Ratio of arterial O2 partial pressure to fractional inspired O2 less than or equal to 250.
- Multilobar infiltrates.
- Confusion/disorientation.
- Uremia (blood urea nitrogen level greater than or equal to 20 mg/dL).
- Leukopenia (white blood cell count less than 4,000 cells/mcL).
- Thrombocytopenia (platelet count less than 100,000 mcL)
- Hypothermia (core temperature less than 36º C).
- Hypotension requiring aggressive fluid resuscitation.
Management and diagnostic testing
Clinicians should use the Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) and clinical judgment to guide the site of treatment for patients. Gram stain, sputum, and blood culture should not be routinely obtained in an outpatient setting. Legionella antigen should not be routinely obtained unless indicated by epidemiological factors. During influenza season, a rapid influenza assay, preferably a nucleic acid amplification test, should be obtained to help guide treatment.
For patients with severe CAP or risk factors for MRSA or P. aeruginosa, gram stain and culture and Legionella antigen should be obtained to manage antibiotic choices. Also, blood cultures should be obtained for these patients.
Empiric antibiotic therapy should be initiated based on clinical judgment and radiographic confirmation of CAP. Serum procalcitonin should not be used to assess initiation of antibiotic therapy.
Empiric antibiotic therapy
Healthy adults without comorbidities should be treated with monotherapy of either:
- Amoxicillin 1 g three times daily.
- OR doxycycline 100 mg twice daily.
- OR a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg on first day then 250 mg daily or clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily or clarithromycin extended release 1,000 mg daily) only in areas with pneumococcal resistance to macrolides less than 25%.
Adults with comorbidities such as chronic heart, lung, liver, or renal disease; diabetes mellitus; alcoholism; malignancy; or asplenia should be treated with:
- Amoxicillin/clavulanate 500 mg/125 mg three times daily, or amoxicillin/ clavulanate 875 mg/125 mg twice daily, or 2,000 mg/125 mg twice daily, or a cephalosporin (cefpodoxime 200 mg twice daily or cefuroxime 500 mg twice daily); and a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg on first day then 250 mg daily, clarithromycin [500 mg twice daily or extended release 1,000 mg once daily]), or doxycycline 100 mg twice daily. (Some experts recommend that the first dose of doxycycline should be 200 mg.)
- OR monotherapy with respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin 750 mg daily, moxifloxacin 400 mg daily, or gemifloxacin 320 mg daily).
Inpatient pneumonia that is not severe, without risk factors for resistant organisms should be treated with:
- Beta-lactam (ampicillin 1 sulbactam 1.5-3 g every 6 h, cefotaxime 1-2 g every 8 h, ceftriaxone 1-2 g daily, or ceftaroline 600 mg every 12 h) and a macrolide (azithromycin 500 mg daily or clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily).
- OR monotherapy with a respiratory fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin 750 mg daily, moxifloxacin 400 mg daily).
If there is a contraindication for the use of both a macrolide and a fluoroquinolone, then doxycycline can be used instead.
Severe inpatient pneumonia without risk factors for resistant organisms should be treated with combination therapy of either (agents and doses the same as above):
- Beta-lactam and macrolide.
- OR fluoroquinolone and beta-lactam.
It is recommended to not routinely add anaerobic coverage for suspected aspiration pneumonia unless lung abscess or empyema is suspected. Clinicians should identify risk factors for MRSA or P. aeruginosa before adding additional agents.
Duration of antibiotic therapy is determined by the patient achieving clinical stability with no less than 5 days of antibiotics. In adults with symptom resolution within 5-7 days, no additional follow-up chest imaging is recommended. If patients test positive for influenza, then anti-influenza treatment such as oseltamivir should be used in addition to antibiotics regardless of length of influenza symptoms before presentation.
The bottom line
CAP treatment should be based on severity of illness and risk factors for resistant organisms. Blood and sputum cultures are recommended only for patients with severe pneumonia. There have been important changes in the recommendations for antibiotic treatment of CAP, with high-dose amoxicillin recommended for most patients with CAP who are treated as outpatients. Patients who exhibit clinical stability should be treated for at least 5 days and do not require follow up imaging studies.
For a podcast of this guideline, go to iTunes and download the Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline podcast.
Reference
Metlay JP, Waterer GW, Long AC, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Oct 1;200(7):e45-e67.
Tina Chuong, DO, is a second-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
USPSTF recommendations on risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for BRCA-related cancer
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.
A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.

A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.

A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
A cigarette in one hand and a Fitbit on the other
A cardiologist friend of mine told me a story about one of his patients. The man had recently been in to see him for an office visit. He had quite a scare needing two stents after an episode of prolonged chest pain and, during the office visit, apparently had said that he had “found religion” and was going to change his ways. He showed off the Fitbit that he had gotten and shared his excitement about using a new app to track his diet on his smart phone. His blood pressure was a little elevated, so my friend added a third antihypertensive in an effort to get his blood pressure under control. He referred the patient back to his primary care physician to address his elevated hemoglobin A1c.
My friend saw the patient again a couple of weeks later – this time at the mall. As he was driving through the parking lot, he noticed his patient sitting on a bench outside the entrance. He also noticed a cigarette in his patient’s right hand and saw the Fitbit still on his wrist. Now, it’s not that there is anything wrong with wearing a Fitbit, but …
My friend is an incredibly respectful person, and very nice. He decided not to say hello and risk embarrassing his patient, so he walked to a different door far from the bench and went inside. Nonetheless, the image bothered him. It bothered him enough to repeat the story to me 2 weeks later. It bothers me too.
The other day I was talking to a healthy young nurse with whom I work. She has been trying to get into shape, and her goal is to get to the gym 5 days a week after work. She read on a popular website that she should use a heart rate monitor to keep track of her training and that, if her heart rate is too slow, she should run faster and, if her heart rate is too fast, she should slow down. She was discouraged the other day, however, because her watch indicated that her pulse was going up to 170 while she was running hard, and she had heard that could be dangerous for her heart.
When she doesn’t push hard, though, she told me that her heart rate often plateaus at about 110, sometimes 115. She has been finding it difficult to achieve her calculated target heart rate of 120-160 beats per minute. She is frustrated and was going to skip her workout that evening. I explained to her that she should stop checking her pulse and just run – if she felt she was running too slow she could run faster.
With everything that we have learned about science and technology, the reality is that we are still people, with all our weaknesses and strengths. We often set goals with ambivalence, then rush forward hoping that a technological solution will move us in the direction we think we want to move. Unfortunately, owning a Fitbit will not make us more fit, and checking our pulse every five minutes while working out will not lead to a better exercise session. With the availability of so much technology for tracking our daily exercise, vital signs, and various other measures of health, we need to be more careful than ever to determine specifically what it is that we are trying to accomplish with the use of our technology.
When it comes to good health, it is the fundamentals that matter, and achieving the fundamentals requires being mindful and making repeated efforts to master them. For almost all adults, the most important habits to develop are still related to diet and exercise. Consuming the right diet and exercising adequately requires that the correct choices be made each and every day, all day long. Technology can help but will not do it for us. We need to be thoughtful about how we use technology and explicit about how we expect it to help. After a reasonable amount of time, we should evaluate to see if it is working for us. If it is, then we should continue to use it. If it is not, then we should stop using it or make a different change, like performing a new type of exercise.
Our goal should be to have intelligent empathic integration of technological and behavioral techniques to achieve an optimal health outcome. Putting running shoes by the bed at night is a great thing to do to encourage us to run in the morning. Choosing motivational music can help us get the energy and enthusiasm to go for that run (our favorites include the Rocky theme song and “I Didn’t Come this Far to Only Come this Far”). A visual reminder over the refrigerator can “nudge” us to make good choices as we open the door.
For those who want to learn more about how to integrate behavioral management into their advice for patients we highly recommend reading “Switch: How to Change Things When Change Is Hard” by Chip Heath and “Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness” by Richard Thaler. We have always been, and remain, excited about the promise of technology to help us accomplish our goals. That said, we told the nurse to stop checking her pulse, to put on some music, and to appreciate the leaves on the trees this autumn while she was running. As for the gentleman outside the mall, well …
We are interested in your thoughts. Please email us at fpnews@mdedge.com.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter @doctornotte. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
A cardiologist friend of mine told me a story about one of his patients. The man had recently been in to see him for an office visit. He had quite a scare needing two stents after an episode of prolonged chest pain and, during the office visit, apparently had said that he had “found religion” and was going to change his ways. He showed off the Fitbit that he had gotten and shared his excitement about using a new app to track his diet on his smart phone. His blood pressure was a little elevated, so my friend added a third antihypertensive in an effort to get his blood pressure under control. He referred the patient back to his primary care physician to address his elevated hemoglobin A1c.
My friend saw the patient again a couple of weeks later – this time at the mall. As he was driving through the parking lot, he noticed his patient sitting on a bench outside the entrance. He also noticed a cigarette in his patient’s right hand and saw the Fitbit still on his wrist. Now, it’s not that there is anything wrong with wearing a Fitbit, but …
My friend is an incredibly respectful person, and very nice. He decided not to say hello and risk embarrassing his patient, so he walked to a different door far from the bench and went inside. Nonetheless, the image bothered him. It bothered him enough to repeat the story to me 2 weeks later. It bothers me too.
The other day I was talking to a healthy young nurse with whom I work. She has been trying to get into shape, and her goal is to get to the gym 5 days a week after work. She read on a popular website that she should use a heart rate monitor to keep track of her training and that, if her heart rate is too slow, she should run faster and, if her heart rate is too fast, she should slow down. She was discouraged the other day, however, because her watch indicated that her pulse was going up to 170 while she was running hard, and she had heard that could be dangerous for her heart.
When she doesn’t push hard, though, she told me that her heart rate often plateaus at about 110, sometimes 115. She has been finding it difficult to achieve her calculated target heart rate of 120-160 beats per minute. She is frustrated and was going to skip her workout that evening. I explained to her that she should stop checking her pulse and just run – if she felt she was running too slow she could run faster.
With everything that we have learned about science and technology, the reality is that we are still people, with all our weaknesses and strengths. We often set goals with ambivalence, then rush forward hoping that a technological solution will move us in the direction we think we want to move. Unfortunately, owning a Fitbit will not make us more fit, and checking our pulse every five minutes while working out will not lead to a better exercise session. With the availability of so much technology for tracking our daily exercise, vital signs, and various other measures of health, we need to be more careful than ever to determine specifically what it is that we are trying to accomplish with the use of our technology.
When it comes to good health, it is the fundamentals that matter, and achieving the fundamentals requires being mindful and making repeated efforts to master them. For almost all adults, the most important habits to develop are still related to diet and exercise. Consuming the right diet and exercising adequately requires that the correct choices be made each and every day, all day long. Technology can help but will not do it for us. We need to be thoughtful about how we use technology and explicit about how we expect it to help. After a reasonable amount of time, we should evaluate to see if it is working for us. If it is, then we should continue to use it. If it is not, then we should stop using it or make a different change, like performing a new type of exercise.
Our goal should be to have intelligent empathic integration of technological and behavioral techniques to achieve an optimal health outcome. Putting running shoes by the bed at night is a great thing to do to encourage us to run in the morning. Choosing motivational music can help us get the energy and enthusiasm to go for that run (our favorites include the Rocky theme song and “I Didn’t Come this Far to Only Come this Far”). A visual reminder over the refrigerator can “nudge” us to make good choices as we open the door.
For those who want to learn more about how to integrate behavioral management into their advice for patients we highly recommend reading “Switch: How to Change Things When Change Is Hard” by Chip Heath and “Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness” by Richard Thaler. We have always been, and remain, excited about the promise of technology to help us accomplish our goals. That said, we told the nurse to stop checking her pulse, to put on some music, and to appreciate the leaves on the trees this autumn while she was running. As for the gentleman outside the mall, well …
We are interested in your thoughts. Please email us at fpnews@mdedge.com.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter @doctornotte. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
A cardiologist friend of mine told me a story about one of his patients. The man had recently been in to see him for an office visit. He had quite a scare needing two stents after an episode of prolonged chest pain and, during the office visit, apparently had said that he had “found religion” and was going to change his ways. He showed off the Fitbit that he had gotten and shared his excitement about using a new app to track his diet on his smart phone. His blood pressure was a little elevated, so my friend added a third antihypertensive in an effort to get his blood pressure under control. He referred the patient back to his primary care physician to address his elevated hemoglobin A1c.
My friend saw the patient again a couple of weeks later – this time at the mall. As he was driving through the parking lot, he noticed his patient sitting on a bench outside the entrance. He also noticed a cigarette in his patient’s right hand and saw the Fitbit still on his wrist. Now, it’s not that there is anything wrong with wearing a Fitbit, but …
My friend is an incredibly respectful person, and very nice. He decided not to say hello and risk embarrassing his patient, so he walked to a different door far from the bench and went inside. Nonetheless, the image bothered him. It bothered him enough to repeat the story to me 2 weeks later. It bothers me too.
The other day I was talking to a healthy young nurse with whom I work. She has been trying to get into shape, and her goal is to get to the gym 5 days a week after work. She read on a popular website that she should use a heart rate monitor to keep track of her training and that, if her heart rate is too slow, she should run faster and, if her heart rate is too fast, she should slow down. She was discouraged the other day, however, because her watch indicated that her pulse was going up to 170 while she was running hard, and she had heard that could be dangerous for her heart.
When she doesn’t push hard, though, she told me that her heart rate often plateaus at about 110, sometimes 115. She has been finding it difficult to achieve her calculated target heart rate of 120-160 beats per minute. She is frustrated and was going to skip her workout that evening. I explained to her that she should stop checking her pulse and just run – if she felt she was running too slow she could run faster.
With everything that we have learned about science and technology, the reality is that we are still people, with all our weaknesses and strengths. We often set goals with ambivalence, then rush forward hoping that a technological solution will move us in the direction we think we want to move. Unfortunately, owning a Fitbit will not make us more fit, and checking our pulse every five minutes while working out will not lead to a better exercise session. With the availability of so much technology for tracking our daily exercise, vital signs, and various other measures of health, we need to be more careful than ever to determine specifically what it is that we are trying to accomplish with the use of our technology.
When it comes to good health, it is the fundamentals that matter, and achieving the fundamentals requires being mindful and making repeated efforts to master them. For almost all adults, the most important habits to develop are still related to diet and exercise. Consuming the right diet and exercising adequately requires that the correct choices be made each and every day, all day long. Technology can help but will not do it for us. We need to be thoughtful about how we use technology and explicit about how we expect it to help. After a reasonable amount of time, we should evaluate to see if it is working for us. If it is, then we should continue to use it. If it is not, then we should stop using it or make a different change, like performing a new type of exercise.
Our goal should be to have intelligent empathic integration of technological and behavioral techniques to achieve an optimal health outcome. Putting running shoes by the bed at night is a great thing to do to encourage us to run in the morning. Choosing motivational music can help us get the energy and enthusiasm to go for that run (our favorites include the Rocky theme song and “I Didn’t Come this Far to Only Come this Far”). A visual reminder over the refrigerator can “nudge” us to make good choices as we open the door.
For those who want to learn more about how to integrate behavioral management into their advice for patients we highly recommend reading “Switch: How to Change Things When Change Is Hard” by Chip Heath and “Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness” by Richard Thaler. We have always been, and remain, excited about the promise of technology to help us accomplish our goals. That said, we told the nurse to stop checking her pulse, to put on some music, and to appreciate the leaves on the trees this autumn while she was running. As for the gentleman outside the mall, well …
We are interested in your thoughts. Please email us at fpnews@mdedge.com.
Dr. Notte is a family physician and associate chief medical information officer for Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Follow him on Twitter @doctornotte. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.