User login
CDC signs off on RSV vaccine for older adults
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has given a green light to two new vaccines to protect against respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, in older adults.
CDC Director Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH, agreed with and endorsed the recommendations made earlier by CDC advisors that people age 60 and over may get one of two new vaccines for RSV. Decisions should be made based on discussions with one’s health care provider about whether the vaccine is right for them, the federal health agency said.
The new vaccines, the first licensed in the United States to protect against the respiratory illness, are expected to be available this fall.
On June 21, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), an independent panel, stopped short of recommending the vaccines for everyone age 65 and above, which was the original question the committee was to consider. The experts amended that question, changing it to whether the panel should recommend the vaccine for those 65 and above if the person and their doctor agreed. The committee voted 9 to 5 in favor.
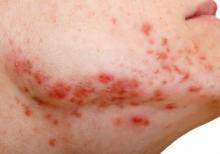
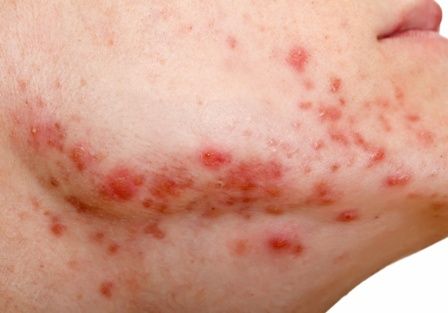
RSV vaccines
RSV leads to 6,000 to 10,000 deaths a year in the United States among those age 65 and older and 60,000 to 160,000 hospitalizations in that group. Seniors and infants are among the most vulnerable to the lower respiratory infection, marked by runny nose, wheezing, sneezing, decreased appetite, and fever.
The FDA in May approved two vaccines — GSK’s Arexvy and Pfizer’s Abrysvo — for adults age 60 and above.
The vote recommending shared decision-making about the vaccine, instead of a routine vaccination recommended for all, “is a weaker recommendation,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville and medical director of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases. Dr. Schaffner is a non-voting member of ACIP. He attended the meeting.
He said the experts voiced concern about a number of issues, including what some saw as a lack of sufficient data from trials on the most vulnerable groups, such as nursing home residents.
Experts also wanted more information about the duration of protection and exactly when a second dose might be needed. At the meeting, a GSK official said its vaccine was 84.6% effective after one and a half seasons, down from 94.1% after one season. A Pfizer official said its vaccine decreased the risk of RSV with three or more symptoms by 78.6% after a season and a half, down from 88.9% after one season.
The panel also wanted more data on whether the RSV vaccines could be administered at the same time as other vaccines recommended for adults.
Both companies gave a range of cost estimates. Pfizer expects its vaccine to cost $180 to $270 but said it could not guarantee that range. GSK said it expects a price of $200 to $295. Under the Inflation Reduction Act, recommended vaccines are covered under Medicare for those with Part D plans, which 51 million of 65 million Medicare patients have. Commercial insurance is likely to cover the vaccines if the CDC recommends them.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
This article was updated 7/5/23.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has given a green light to two new vaccines to protect against respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, in older adults.
CDC Director Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH, agreed with and endorsed the recommendations made earlier by CDC advisors that people age 60 and over may get one of two new vaccines for RSV. Decisions should be made based on discussions with one’s health care provider about whether the vaccine is right for them, the federal health agency said.
The new vaccines, the first licensed in the United States to protect against the respiratory illness, are expected to be available this fall.
On June 21, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), an independent panel, stopped short of recommending the vaccines for everyone age 65 and above, which was the original question the committee was to consider. The experts amended that question, changing it to whether the panel should recommend the vaccine for those 65 and above if the person and their doctor agreed. The committee voted 9 to 5 in favor.
RSV vaccines
RSV leads to 6,000 to 10,000 deaths a year in the United States among those age 65 and older and 60,000 to 160,000 hospitalizations in that group. Seniors and infants are among the most vulnerable to the lower respiratory infection, marked by runny nose, wheezing, sneezing, decreased appetite, and fever.
The FDA in May approved two vaccines — GSK’s Arexvy and Pfizer’s Abrysvo — for adults age 60 and above.
The vote recommending shared decision-making about the vaccine, instead of a routine vaccination recommended for all, “is a weaker recommendation,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville and medical director of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases. Dr. Schaffner is a non-voting member of ACIP. He attended the meeting.
He said the experts voiced concern about a number of issues, including what some saw as a lack of sufficient data from trials on the most vulnerable groups, such as nursing home residents.
Experts also wanted more information about the duration of protection and exactly when a second dose might be needed. At the meeting, a GSK official said its vaccine was 84.6% effective after one and a half seasons, down from 94.1% after one season. A Pfizer official said its vaccine decreased the risk of RSV with three or more symptoms by 78.6% after a season and a half, down from 88.9% after one season.
The panel also wanted more data on whether the RSV vaccines could be administered at the same time as other vaccines recommended for adults.
Both companies gave a range of cost estimates. Pfizer expects its vaccine to cost $180 to $270 but said it could not guarantee that range. GSK said it expects a price of $200 to $295. Under the Inflation Reduction Act, recommended vaccines are covered under Medicare for those with Part D plans, which 51 million of 65 million Medicare patients have. Commercial insurance is likely to cover the vaccines if the CDC recommends them.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
This article was updated 7/5/23.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has given a green light to two new vaccines to protect against respiratory syncytial virus, or RSV, in older adults.
CDC Director Rochelle P. Walensky, MD, MPH, agreed with and endorsed the recommendations made earlier by CDC advisors that people age 60 and over may get one of two new vaccines for RSV. Decisions should be made based on discussions with one’s health care provider about whether the vaccine is right for them, the federal health agency said.
The new vaccines, the first licensed in the United States to protect against the respiratory illness, are expected to be available this fall.
On June 21, the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), an independent panel, stopped short of recommending the vaccines for everyone age 65 and above, which was the original question the committee was to consider. The experts amended that question, changing it to whether the panel should recommend the vaccine for those 65 and above if the person and their doctor agreed. The committee voted 9 to 5 in favor.
RSV vaccines
RSV leads to 6,000 to 10,000 deaths a year in the United States among those age 65 and older and 60,000 to 160,000 hospitalizations in that group. Seniors and infants are among the most vulnerable to the lower respiratory infection, marked by runny nose, wheezing, sneezing, decreased appetite, and fever.
The FDA in May approved two vaccines — GSK’s Arexvy and Pfizer’s Abrysvo — for adults age 60 and above.
The vote recommending shared decision-making about the vaccine, instead of a routine vaccination recommended for all, “is a weaker recommendation,” said William Schaffner, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville and medical director of the National Foundation for Infectious Diseases. Dr. Schaffner is a non-voting member of ACIP. He attended the meeting.
He said the experts voiced concern about a number of issues, including what some saw as a lack of sufficient data from trials on the most vulnerable groups, such as nursing home residents.
Experts also wanted more information about the duration of protection and exactly when a second dose might be needed. At the meeting, a GSK official said its vaccine was 84.6% effective after one and a half seasons, down from 94.1% after one season. A Pfizer official said its vaccine decreased the risk of RSV with three or more symptoms by 78.6% after a season and a half, down from 88.9% after one season.
The panel also wanted more data on whether the RSV vaccines could be administered at the same time as other vaccines recommended for adults.
Both companies gave a range of cost estimates. Pfizer expects its vaccine to cost $180 to $270 but said it could not guarantee that range. GSK said it expects a price of $200 to $295. Under the Inflation Reduction Act, recommended vaccines are covered under Medicare for those with Part D plans, which 51 million of 65 million Medicare patients have. Commercial insurance is likely to cover the vaccines if the CDC recommends them.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
This article was updated 7/5/23.
Anxiety, your brain, and long COVID: What the research says
Having anxiety and depression before a COVID infection increases the risk of developing long COVID, researchers have found.
Those with long COVID who develop anxiety and depression after an infection may have brain shrinkage in areas that regulate memory, emotion, and other functions as well as disruption of brain connectivity.
While many questions remain about these intertwined relationships, the associations aren’t a complete surprise. Experts already know that depression and anxiety are associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction, perhaps helping to explain the link between these mental health conditions, the risk of long COVID, and the changes in the brain.
Brain changes accompanying a COVID infection have concerned researchers since earlier in the pandemic, when U.K. Biobank researchers found brain atrophy, loss of grey matter, and decline in cognition in those infected with COVID, compared with those not infected.
Common conditions
The ramifications of the research linking anxiety, depression, and long COVID are far-reaching. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 12.5% of U.S. adults have regular feelings of anxiety (as well as nervousness and worry), and the latest Gallup Poll found that nearly 18% of adults currently have or are being treated for depression.
As of May 8, 10% of infected adults in the United States have long COVID, according to the CDC, and among U.S. adults ever infected, 27% have reported long COVID. Long COVID has been defined by the CDC as symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, and cough that persist longer than 4 weeks and by the World Health Organization as symptoms persisting for 3 months or more.
Here’s a roundup of what the research shows about mental health and long COVID risk – along with other research finding that paying attention to health habits may reduce that risk.
Pre-existing depression, anxiety, and long COVID risk
A history of mental health issues – including depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, and loneliness – raises the risk of long COVID if infection occurs, Harvard researchers have found.
The researchers evaluated data from three large, ongoing studies including nearly 55,000 participants to determine the effects of high levels of psychological distress before a COVID infection.
“Our study was purely survey based,” said Siwen Wang, MD, the study’s lead author and a research fellow at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
At the start of the survey in April 2020, none of the participants reported a current or previous COVID infection. They answered surveys about psychological distress at the start of the study, at 6 monthly time points, then quarterly until November 2021.
Over the follow up, 3,193 people reported a positive COVID test and 43% of those, or 1,403, developed long COVID. That number may seem high, but 38% of the 55,000 were active health care workers. On the final questionnaire, they reported whether their symptoms persisted for 4 weeks or longer and thus had long COVID by the standard CDC definition.
Dr. Wang’s team then looked at the infected participants’ psychological status. Anxiety raised the risk of long COVID by 42%, depression by 32%, worry about COVID by 37%, perceived stress, 46%, and loneliness, 32%.
COVID patients with a history of depression or anxiety are also more likely than others to report trouble with cognition in the weeks after a COVID infection and to develop brain fog and long COVID, UCLA researchers found. They evaluated 766 people with a confirmed COVID infection; 36% said their thinking was affected within 4 weeks of the infection. Those with anxiety and depression were more likely to report those difficulties.
Long COVID, then anxiety, depression, brain changes
Even mild cases of COVID infection can lead to long COVID and brain changes in those who suffer anxiety or depression after the infection, according to Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, assistant professor of neurology at the University of Campinas in Sao Paulo. She has researched long COVID’s effects on the brain, even as she is coping with being a long COVID patient.
In one of her studies, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, she found brain changes in people with anxiety, depression, and COVID but not in those infected who did not have either mental health issue. She evaluated 254 people, median age 41, after about 82 days from their positive PCR test for COVID. Everyone completed a standard questionnaire for depression (the Beck Depression Inventory) and another for anxiety (the Beck Anxiety Inventory). She further divided them into two groups – the 102 with symptoms and the 152 who had no symptoms of either depression or anxiety.
Brain scans showed those with COVID who also had anxiety and depression had shrinkage in the limbic area of the brain (which helps process emotion and memory), while those infected who didn’t have anxiety or depression did not. The researchers then scanned the brains of 148 healthy people without COVID and found no shrinkage.
The atrophy, Dr. Yasuda said, “is not something you can see with your eyes. It was only detected with computer analysis. Visualization on an MRI is normal.”
The number of people in this study with mental health issues was surprisingly high, Dr. Yasuda said. “It was intriguing for us that we noticed many individuals have both symptoms, anxiety and depression. We were not expecting it at that proportion.”
The researchers found a pattern of change not only in brain structure but in brain communication. They found those changes by using specialized software to analyze brain networks in some of the participants. Those with anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of 12 networks tested. The participants without mental health symptoms showed changes in just five networks. These changes are enough to lead to problems with thinking skills and memory, Dr. Yasuda said.
Explaining the links
Several ideas have been proposed to explain the link between psychological distress and long COVID risk, Dr. Wang said. “The first and most mainstream mechanism for long COVID is chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation. Several mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, are associated with inflammation and dysfunction and that might be the link between depression, anxiety, and long COVID.”
Another less mainstream hypothesis, she said, is that “those with long COVID have more autoantibodies and they are more likely to have blood clotting issues. These have also been found in people with anxiety, depression, or other psychological distress.”
Other researchers are looking more broadly at how COVID infections affect the brain. When German researchers evaluated the brain and other body parts of 20 patients who died from non-COVID causes but had documented COVID infections, they found that 12 had accumulations of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the brain tissue as well as the skull and meninges, the membranes that line the skull and spinal cord. Healthy controls did not.
The findings suggest the persistence of the spike protein may contribute to the long-term neurologic symptoms of long COVID and may also lead to understanding of the molecular mechanisms as well as therapies for long COVID, the researchers said in their preprint report, which has not yet been peer reviewed.
In another recent study, researchers from Germany performed neuroimaging and neuropsychological assessments of 223 people who were not vaccinated and recovered from mild to moderate COVID infections, comparing them with 223 matched healthy controls who had the same testing. In those infected, they found alterations in the cerebral white matter but no worse cognitive function in the first year after recovering. They conclude that the infection triggers a prolonged neuroinflammatory response.
Can the brain changes reverse? “We don’t have an answer right now, but we are working on that,” Dr. Yasuda said. For now, she speculates about the return of brain volume: “I think for most it will. But I think we need to treat the symptoms. We can’t disregard the symptoms of long COVID. People are suffering a lot, and this suffering is causing some brain damage.”
Lifestyle habits and risk of long COVID
Meanwhile, healthy lifestyle habits in those infected can reduce the risk of long COVID, research by Dr. Wang and colleagues found. They followed nearly 2,000 women with a positive COVID test over 19 months. Of these, 44%, or 871, developed long COVID. Compared with women who followed none of the healthy lifestyle habits evaluated, those with five to six of the habits had a 49% lower risk of long COVID.
The habits included: a healthy body mass index (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), never smoking, at least 150 minutes weekly of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake (5-15 grams a day), high diet quality, and good sleep (7-9 hours nightly).
Long-term solutions
Dr. Yasuda hopes that mental health care – of those infected and those not – will be taken more seriously. In a commentary on her own long COVID experience, she wrote, in part: “I fear for the numerous survivors of COVID-19 who do not have access to medical attention for their post-COVID symptoms. ... The mental health system needs to become prepared to receive survivors with different neuropsychiatric symptoms, including anxiety and depression.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Having anxiety and depression before a COVID infection increases the risk of developing long COVID, researchers have found.
Those with long COVID who develop anxiety and depression after an infection may have brain shrinkage in areas that regulate memory, emotion, and other functions as well as disruption of brain connectivity.
While many questions remain about these intertwined relationships, the associations aren’t a complete surprise. Experts already know that depression and anxiety are associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction, perhaps helping to explain the link between these mental health conditions, the risk of long COVID, and the changes in the brain.
Brain changes accompanying a COVID infection have concerned researchers since earlier in the pandemic, when U.K. Biobank researchers found brain atrophy, loss of grey matter, and decline in cognition in those infected with COVID, compared with those not infected.
Common conditions
The ramifications of the research linking anxiety, depression, and long COVID are far-reaching. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 12.5% of U.S. adults have regular feelings of anxiety (as well as nervousness and worry), and the latest Gallup Poll found that nearly 18% of adults currently have or are being treated for depression.
As of May 8, 10% of infected adults in the United States have long COVID, according to the CDC, and among U.S. adults ever infected, 27% have reported long COVID. Long COVID has been defined by the CDC as symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, and cough that persist longer than 4 weeks and by the World Health Organization as symptoms persisting for 3 months or more.
Here’s a roundup of what the research shows about mental health and long COVID risk – along with other research finding that paying attention to health habits may reduce that risk.
Pre-existing depression, anxiety, and long COVID risk
A history of mental health issues – including depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, and loneliness – raises the risk of long COVID if infection occurs, Harvard researchers have found.
The researchers evaluated data from three large, ongoing studies including nearly 55,000 participants to determine the effects of high levels of psychological distress before a COVID infection.
“Our study was purely survey based,” said Siwen Wang, MD, the study’s lead author and a research fellow at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
At the start of the survey in April 2020, none of the participants reported a current or previous COVID infection. They answered surveys about psychological distress at the start of the study, at 6 monthly time points, then quarterly until November 2021.
Over the follow up, 3,193 people reported a positive COVID test and 43% of those, or 1,403, developed long COVID. That number may seem high, but 38% of the 55,000 were active health care workers. On the final questionnaire, they reported whether their symptoms persisted for 4 weeks or longer and thus had long COVID by the standard CDC definition.
Dr. Wang’s team then looked at the infected participants’ psychological status. Anxiety raised the risk of long COVID by 42%, depression by 32%, worry about COVID by 37%, perceived stress, 46%, and loneliness, 32%.
COVID patients with a history of depression or anxiety are also more likely than others to report trouble with cognition in the weeks after a COVID infection and to develop brain fog and long COVID, UCLA researchers found. They evaluated 766 people with a confirmed COVID infection; 36% said their thinking was affected within 4 weeks of the infection. Those with anxiety and depression were more likely to report those difficulties.
Long COVID, then anxiety, depression, brain changes
Even mild cases of COVID infection can lead to long COVID and brain changes in those who suffer anxiety or depression after the infection, according to Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, assistant professor of neurology at the University of Campinas in Sao Paulo. She has researched long COVID’s effects on the brain, even as she is coping with being a long COVID patient.
In one of her studies, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, she found brain changes in people with anxiety, depression, and COVID but not in those infected who did not have either mental health issue. She evaluated 254 people, median age 41, after about 82 days from their positive PCR test for COVID. Everyone completed a standard questionnaire for depression (the Beck Depression Inventory) and another for anxiety (the Beck Anxiety Inventory). She further divided them into two groups – the 102 with symptoms and the 152 who had no symptoms of either depression or anxiety.
Brain scans showed those with COVID who also had anxiety and depression had shrinkage in the limbic area of the brain (which helps process emotion and memory), while those infected who didn’t have anxiety or depression did not. The researchers then scanned the brains of 148 healthy people without COVID and found no shrinkage.
The atrophy, Dr. Yasuda said, “is not something you can see with your eyes. It was only detected with computer analysis. Visualization on an MRI is normal.”
The number of people in this study with mental health issues was surprisingly high, Dr. Yasuda said. “It was intriguing for us that we noticed many individuals have both symptoms, anxiety and depression. We were not expecting it at that proportion.”
The researchers found a pattern of change not only in brain structure but in brain communication. They found those changes by using specialized software to analyze brain networks in some of the participants. Those with anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of 12 networks tested. The participants without mental health symptoms showed changes in just five networks. These changes are enough to lead to problems with thinking skills and memory, Dr. Yasuda said.
Explaining the links
Several ideas have been proposed to explain the link between psychological distress and long COVID risk, Dr. Wang said. “The first and most mainstream mechanism for long COVID is chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation. Several mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, are associated with inflammation and dysfunction and that might be the link between depression, anxiety, and long COVID.”
Another less mainstream hypothesis, she said, is that “those with long COVID have more autoantibodies and they are more likely to have blood clotting issues. These have also been found in people with anxiety, depression, or other psychological distress.”
Other researchers are looking more broadly at how COVID infections affect the brain. When German researchers evaluated the brain and other body parts of 20 patients who died from non-COVID causes but had documented COVID infections, they found that 12 had accumulations of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the brain tissue as well as the skull and meninges, the membranes that line the skull and spinal cord. Healthy controls did not.
The findings suggest the persistence of the spike protein may contribute to the long-term neurologic symptoms of long COVID and may also lead to understanding of the molecular mechanisms as well as therapies for long COVID, the researchers said in their preprint report, which has not yet been peer reviewed.
In another recent study, researchers from Germany performed neuroimaging and neuropsychological assessments of 223 people who were not vaccinated and recovered from mild to moderate COVID infections, comparing them with 223 matched healthy controls who had the same testing. In those infected, they found alterations in the cerebral white matter but no worse cognitive function in the first year after recovering. They conclude that the infection triggers a prolonged neuroinflammatory response.
Can the brain changes reverse? “We don’t have an answer right now, but we are working on that,” Dr. Yasuda said. For now, she speculates about the return of brain volume: “I think for most it will. But I think we need to treat the symptoms. We can’t disregard the symptoms of long COVID. People are suffering a lot, and this suffering is causing some brain damage.”
Lifestyle habits and risk of long COVID
Meanwhile, healthy lifestyle habits in those infected can reduce the risk of long COVID, research by Dr. Wang and colleagues found. They followed nearly 2,000 women with a positive COVID test over 19 months. Of these, 44%, or 871, developed long COVID. Compared with women who followed none of the healthy lifestyle habits evaluated, those with five to six of the habits had a 49% lower risk of long COVID.
The habits included: a healthy body mass index (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), never smoking, at least 150 minutes weekly of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake (5-15 grams a day), high diet quality, and good sleep (7-9 hours nightly).
Long-term solutions
Dr. Yasuda hopes that mental health care – of those infected and those not – will be taken more seriously. In a commentary on her own long COVID experience, she wrote, in part: “I fear for the numerous survivors of COVID-19 who do not have access to medical attention for their post-COVID symptoms. ... The mental health system needs to become prepared to receive survivors with different neuropsychiatric symptoms, including anxiety and depression.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Having anxiety and depression before a COVID infection increases the risk of developing long COVID, researchers have found.
Those with long COVID who develop anxiety and depression after an infection may have brain shrinkage in areas that regulate memory, emotion, and other functions as well as disruption of brain connectivity.
While many questions remain about these intertwined relationships, the associations aren’t a complete surprise. Experts already know that depression and anxiety are associated with inflammation and immune dysfunction, perhaps helping to explain the link between these mental health conditions, the risk of long COVID, and the changes in the brain.
Brain changes accompanying a COVID infection have concerned researchers since earlier in the pandemic, when U.K. Biobank researchers found brain atrophy, loss of grey matter, and decline in cognition in those infected with COVID, compared with those not infected.
Common conditions
The ramifications of the research linking anxiety, depression, and long COVID are far-reaching. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 12.5% of U.S. adults have regular feelings of anxiety (as well as nervousness and worry), and the latest Gallup Poll found that nearly 18% of adults currently have or are being treated for depression.
As of May 8, 10% of infected adults in the United States have long COVID, according to the CDC, and among U.S. adults ever infected, 27% have reported long COVID. Long COVID has been defined by the CDC as symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, and cough that persist longer than 4 weeks and by the World Health Organization as symptoms persisting for 3 months or more.
Here’s a roundup of what the research shows about mental health and long COVID risk – along with other research finding that paying attention to health habits may reduce that risk.
Pre-existing depression, anxiety, and long COVID risk
A history of mental health issues – including depression, anxiety, worry, perceived stress, and loneliness – raises the risk of long COVID if infection occurs, Harvard researchers have found.
The researchers evaluated data from three large, ongoing studies including nearly 55,000 participants to determine the effects of high levels of psychological distress before a COVID infection.
“Our study was purely survey based,” said Siwen Wang, MD, the study’s lead author and a research fellow at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
At the start of the survey in April 2020, none of the participants reported a current or previous COVID infection. They answered surveys about psychological distress at the start of the study, at 6 monthly time points, then quarterly until November 2021.
Over the follow up, 3,193 people reported a positive COVID test and 43% of those, or 1,403, developed long COVID. That number may seem high, but 38% of the 55,000 were active health care workers. On the final questionnaire, they reported whether their symptoms persisted for 4 weeks or longer and thus had long COVID by the standard CDC definition.
Dr. Wang’s team then looked at the infected participants’ psychological status. Anxiety raised the risk of long COVID by 42%, depression by 32%, worry about COVID by 37%, perceived stress, 46%, and loneliness, 32%.
COVID patients with a history of depression or anxiety are also more likely than others to report trouble with cognition in the weeks after a COVID infection and to develop brain fog and long COVID, UCLA researchers found. They evaluated 766 people with a confirmed COVID infection; 36% said their thinking was affected within 4 weeks of the infection. Those with anxiety and depression were more likely to report those difficulties.
Long COVID, then anxiety, depression, brain changes
Even mild cases of COVID infection can lead to long COVID and brain changes in those who suffer anxiety or depression after the infection, according to Clarissa Yasuda, MD, PhD, assistant professor of neurology at the University of Campinas in Sao Paulo. She has researched long COVID’s effects on the brain, even as she is coping with being a long COVID patient.
In one of her studies, presented at the 2023 annual meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, she found brain changes in people with anxiety, depression, and COVID but not in those infected who did not have either mental health issue. She evaluated 254 people, median age 41, after about 82 days from their positive PCR test for COVID. Everyone completed a standard questionnaire for depression (the Beck Depression Inventory) and another for anxiety (the Beck Anxiety Inventory). She further divided them into two groups – the 102 with symptoms and the 152 who had no symptoms of either depression or anxiety.
Brain scans showed those with COVID who also had anxiety and depression had shrinkage in the limbic area of the brain (which helps process emotion and memory), while those infected who didn’t have anxiety or depression did not. The researchers then scanned the brains of 148 healthy people without COVID and found no shrinkage.
The atrophy, Dr. Yasuda said, “is not something you can see with your eyes. It was only detected with computer analysis. Visualization on an MRI is normal.”
The number of people in this study with mental health issues was surprisingly high, Dr. Yasuda said. “It was intriguing for us that we noticed many individuals have both symptoms, anxiety and depression. We were not expecting it at that proportion.”
The researchers found a pattern of change not only in brain structure but in brain communication. They found those changes by using specialized software to analyze brain networks in some of the participants. Those with anxiety and depression had widespread functional changes in each of 12 networks tested. The participants without mental health symptoms showed changes in just five networks. These changes are enough to lead to problems with thinking skills and memory, Dr. Yasuda said.
Explaining the links
Several ideas have been proposed to explain the link between psychological distress and long COVID risk, Dr. Wang said. “The first and most mainstream mechanism for long COVID is chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation. Several mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, are associated with inflammation and dysfunction and that might be the link between depression, anxiety, and long COVID.”
Another less mainstream hypothesis, she said, is that “those with long COVID have more autoantibodies and they are more likely to have blood clotting issues. These have also been found in people with anxiety, depression, or other psychological distress.”
Other researchers are looking more broadly at how COVID infections affect the brain. When German researchers evaluated the brain and other body parts of 20 patients who died from non-COVID causes but had documented COVID infections, they found that 12 had accumulations of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the brain tissue as well as the skull and meninges, the membranes that line the skull and spinal cord. Healthy controls did not.
The findings suggest the persistence of the spike protein may contribute to the long-term neurologic symptoms of long COVID and may also lead to understanding of the molecular mechanisms as well as therapies for long COVID, the researchers said in their preprint report, which has not yet been peer reviewed.
In another recent study, researchers from Germany performed neuroimaging and neuropsychological assessments of 223 people who were not vaccinated and recovered from mild to moderate COVID infections, comparing them with 223 matched healthy controls who had the same testing. In those infected, they found alterations in the cerebral white matter but no worse cognitive function in the first year after recovering. They conclude that the infection triggers a prolonged neuroinflammatory response.
Can the brain changes reverse? “We don’t have an answer right now, but we are working on that,” Dr. Yasuda said. For now, she speculates about the return of brain volume: “I think for most it will. But I think we need to treat the symptoms. We can’t disregard the symptoms of long COVID. People are suffering a lot, and this suffering is causing some brain damage.”
Lifestyle habits and risk of long COVID
Meanwhile, healthy lifestyle habits in those infected can reduce the risk of long COVID, research by Dr. Wang and colleagues found. They followed nearly 2,000 women with a positive COVID test over 19 months. Of these, 44%, or 871, developed long COVID. Compared with women who followed none of the healthy lifestyle habits evaluated, those with five to six of the habits had a 49% lower risk of long COVID.
The habits included: a healthy body mass index (18.5-24.9 kg/m2), never smoking, at least 150 minutes weekly of moderate to vigorous physical activity, moderate alcohol intake (5-15 grams a day), high diet quality, and good sleep (7-9 hours nightly).
Long-term solutions
Dr. Yasuda hopes that mental health care – of those infected and those not – will be taken more seriously. In a commentary on her own long COVID experience, she wrote, in part: “I fear for the numerous survivors of COVID-19 who do not have access to medical attention for their post-COVID symptoms. ... The mental health system needs to become prepared to receive survivors with different neuropsychiatric symptoms, including anxiety and depression.”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Preventing breaks and falls in older adults
LONG BEACH, CALIF. – Ms. S had recently arrived home after a stay at a skilled nursing facility to recover from a hip fracture resulting from osteoporosis. For many patients, follow-up care would have included a DEXA scan or a prescription for a bisphosphonate from a primary care clinician not trained in geriatrics.
But the 85-year-old received care that went further and that is considered best practice for the management of geriatric fractures: A physical therapist visited her after discharge and provided education on the importance of maintaining mobility. Ms. S also underwent assessment for fall risk and gait balance, and a team of multidisciplinary clinicians managed other factors, from postural hypotension to footwear and foot problems.
Sonja Rosen, MD, professor of medicine and chief of geriatric medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, talked about Ms. S as part of a panel discussion on applying the “Geriatric 5Ms” for patients with osteoporosis at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
“You have to figure out why they are falling and help them not fall again,” Dr. Rosen said.
Approximately 10 million Americans have osteoporosis, and another 44 million have low bone density. One in two women and up to one in four men will experience a bone fracture as a result of osteoporosis, according to the Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation.
, which involves considering the care preferences and goals for health care outcomes of individuals.
Ms. S eventually visited a geriatrician through the Cedars-Sinai Geriatric Fracture Program, which has been shown to lower costs and shorten hospital stays. In the program, she was advised to use a walker. Initially, she saw the aid as a hindrance – she felt she should be able to walk without it, like before. But with education, she learned that it is impossible to predict falls and that the walking aid could reduce her risk of a stumble.
Dr. Rosen said clinicians should address any vision problems, prescriptions for psychotropic drugs,which can affect balance, and heart rate and rhythm abnormalities, and they should suggest modifications to the home environment, such as installing grab bars in showers and removing rugs that can easily be tripped over.
The program at Cedars-Sinai, like similar initiatives, offers a team with resources that some clinicians may not have access to, such as a care coordinator and bone-health coach. But health care providers can utilize aspects, such as making referrals to community exercise classes.
Dr. Rosen and her colleagues studied the effects of such exercise programs and found that the programs lessen loneliness and social isolation. Fear of falling decreased in 75% of participants, “which is so key to these postfracture patients in getting back out into the world and engaging in their prior level of functional status,” Dr. Rosen said.
The second ‘M’: Medication management
The second “M,” medications, can help clinicians sequence osteoporosis drugs, depending on patient characteristics and scenarios.
Cathleen Colon-Emeric, MD, MHS, chief of geriatrics at Duke University, in Durham, N.C., dived into the case history of Ms. S, who had hypertension and insomnia in addition to osteoporosis.
First-line treatment for Ms. S – and for most patients – was an oral bisphosphonate, Dr. Colon-Emeric said. Compared with placebo, the drugs decrease the risk of overall osteoporotic fractures by nearly 40% (odds ratio, 0.62). But the medications are linked to injury of the esophageal mucosa. This risk is decreased when a patient stays upright for 30 minutes after taking oral bisphosphonates. Dr. Colon-Emeric displayed a slide of a woman receiving a pedicure at a nail salon.
“The picture of the pedicure is to share the wonderful idea I got from one skilled nursing facility I was working with, who makes sure they do safe administration to prevent esophagitis in their patients by having them all go to a spa day, where they all sit up and get their nails done while they wait their 30 minutes [after taking the pill] sitting up safely,” Dr. Colon-Emeric said.
This strategy drew applause from the audience.
Dr. Colon-Emeric advised that clinicians use judgment in the interpretation of results from the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX). Incorporating race into estimates of fracture risk has pros and cons. While there are racial and ethnic differences in average bone density, the data for race calibrations to estimate risk are dated, she said. Clinicians should compare FRAX estimates with and without race input to help patients understand a range of risks.
Some patients may be reluctant to begin taking osteoporosis drugs because of misinformation originating from inaccurate news reports or anecdotes from friends. Dr. Colon-Emeric advised clinicians to remind patients that one in five who experience a fracture will have another injury in the following 2 years.
“A major osteoporotic fracture is akin to a heart attack; it has a very similar 1-year mortality rate and a very similar rate of a subsequent secondary event,” Dr. Colon-Emeric said. “We have a class of medications that decrease both those risks by nearly a third.”
Shared decision-making can help patients understand the risks and benefits of treatment, she said.
“People are really scared about the side effects,” Michelle Keller, PhD, MPH, a research scientist at Cedars-Sinai who attended the session, said. “The idea that a “bone attack” is like a heart attack gets the message across.”
Mind and multicomplexity
Medical complexity of a patient must be considered when making decisions on treatment, according to Joshua Niznik, PharmD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine in the Center for Aging and Health at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“Medical complexity is an acknowledgment of the entire person, the burden of their multiple chronic conditions, advanced illnesses, and also their biopsychosocial needs and how those together might augment treatment selection and decision-making,” Dr. Niznik said.
Studies by Dr. Niznik and others have shown that swallowing difficulties, severe dementia, and being older than 90 are linked with a lower likelihood of receiving treatment for osteoporosis.
But therapies for fracture prevention, especially bisphosphonates, appear to be at least as effective for adults with medical complexity as they are for people without such conditions, Dr. Niznik said. Physicians must consider the potential treatment burden and the likelihood of benefit, he said.
Dr. Niznik’s research has shown a lack of strong evidence on how clinicians can manage patients in nursing homes. In some cases, deprescribing is reasonable, such as for patients who have undergone treatment for several years and whose life expectancy is less than 2 years.
“In the absence of any of those, if they are not already treated for osteoporosis, it makes sense to initiate treatment at that time,” Dr. Niznik said.
Matters most: Patient input
Clinicians need to educate patients on how long they must undergo a treatment before they experience benefits, according to Sarah D. Berry, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, in Boston.
A meta-analysis of studies that included more than 20,000 women who were randomly assigned to receive bisphosphonate or placebo found that one nonvertebral fracture was avoided during a 12-month period for every 100 persons treated. One hip fracture was avoided during a 20-month period for every 200 patients treated.
“In general, in persons with a 2-year life expectancy, time to benefit favors bisphosphonate use,” Dr. Berry said. “Anabolics may have an even quicker time to benefit.”
Dr. Berry said a shared a decision-making model can help clinicians facilitate discussions that help patients prioritize goals and compare options while considering results, benefits, and harms. And she offered a final tip: Use tools with absolute risk reduction to convey risks and benefits, as the relative risk calculations overestimate how effective treatment will be.
Dr. Rosen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Colon-Emeric has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and VA Health Services Research and Development Funding; has served as endpoint adjudication chair for UCB Pharma; and has received royalties from Wolters Kluwer. Dr. Niznik has received funding from the National Institute of Aging and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Berry has received funding from the NIH and royalties from Wolters Kluwer.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
LONG BEACH, CALIF. – Ms. S had recently arrived home after a stay at a skilled nursing facility to recover from a hip fracture resulting from osteoporosis. For many patients, follow-up care would have included a DEXA scan or a prescription for a bisphosphonate from a primary care clinician not trained in geriatrics.
But the 85-year-old received care that went further and that is considered best practice for the management of geriatric fractures: A physical therapist visited her after discharge and provided education on the importance of maintaining mobility. Ms. S also underwent assessment for fall risk and gait balance, and a team of multidisciplinary clinicians managed other factors, from postural hypotension to footwear and foot problems.
Sonja Rosen, MD, professor of medicine and chief of geriatric medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, talked about Ms. S as part of a panel discussion on applying the “Geriatric 5Ms” for patients with osteoporosis at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
“You have to figure out why they are falling and help them not fall again,” Dr. Rosen said.
Approximately 10 million Americans have osteoporosis, and another 44 million have low bone density. One in two women and up to one in four men will experience a bone fracture as a result of osteoporosis, according to the Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation.
, which involves considering the care preferences and goals for health care outcomes of individuals.
Ms. S eventually visited a geriatrician through the Cedars-Sinai Geriatric Fracture Program, which has been shown to lower costs and shorten hospital stays. In the program, she was advised to use a walker. Initially, she saw the aid as a hindrance – she felt she should be able to walk without it, like before. But with education, she learned that it is impossible to predict falls and that the walking aid could reduce her risk of a stumble.
Dr. Rosen said clinicians should address any vision problems, prescriptions for psychotropic drugs,which can affect balance, and heart rate and rhythm abnormalities, and they should suggest modifications to the home environment, such as installing grab bars in showers and removing rugs that can easily be tripped over.
The program at Cedars-Sinai, like similar initiatives, offers a team with resources that some clinicians may not have access to, such as a care coordinator and bone-health coach. But health care providers can utilize aspects, such as making referrals to community exercise classes.
Dr. Rosen and her colleagues studied the effects of such exercise programs and found that the programs lessen loneliness and social isolation. Fear of falling decreased in 75% of participants, “which is so key to these postfracture patients in getting back out into the world and engaging in their prior level of functional status,” Dr. Rosen said.
The second ‘M’: Medication management
The second “M,” medications, can help clinicians sequence osteoporosis drugs, depending on patient characteristics and scenarios.
Cathleen Colon-Emeric, MD, MHS, chief of geriatrics at Duke University, in Durham, N.C., dived into the case history of Ms. S, who had hypertension and insomnia in addition to osteoporosis.
First-line treatment for Ms. S – and for most patients – was an oral bisphosphonate, Dr. Colon-Emeric said. Compared with placebo, the drugs decrease the risk of overall osteoporotic fractures by nearly 40% (odds ratio, 0.62). But the medications are linked to injury of the esophageal mucosa. This risk is decreased when a patient stays upright for 30 minutes after taking oral bisphosphonates. Dr. Colon-Emeric displayed a slide of a woman receiving a pedicure at a nail salon.
“The picture of the pedicure is to share the wonderful idea I got from one skilled nursing facility I was working with, who makes sure they do safe administration to prevent esophagitis in their patients by having them all go to a spa day, where they all sit up and get their nails done while they wait their 30 minutes [after taking the pill] sitting up safely,” Dr. Colon-Emeric said.
This strategy drew applause from the audience.
Dr. Colon-Emeric advised that clinicians use judgment in the interpretation of results from the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX). Incorporating race into estimates of fracture risk has pros and cons. While there are racial and ethnic differences in average bone density, the data for race calibrations to estimate risk are dated, she said. Clinicians should compare FRAX estimates with and without race input to help patients understand a range of risks.
Some patients may be reluctant to begin taking osteoporosis drugs because of misinformation originating from inaccurate news reports or anecdotes from friends. Dr. Colon-Emeric advised clinicians to remind patients that one in five who experience a fracture will have another injury in the following 2 years.
“A major osteoporotic fracture is akin to a heart attack; it has a very similar 1-year mortality rate and a very similar rate of a subsequent secondary event,” Dr. Colon-Emeric said. “We have a class of medications that decrease both those risks by nearly a third.”
Shared decision-making can help patients understand the risks and benefits of treatment, she said.
“People are really scared about the side effects,” Michelle Keller, PhD, MPH, a research scientist at Cedars-Sinai who attended the session, said. “The idea that a “bone attack” is like a heart attack gets the message across.”
Mind and multicomplexity
Medical complexity of a patient must be considered when making decisions on treatment, according to Joshua Niznik, PharmD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine in the Center for Aging and Health at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“Medical complexity is an acknowledgment of the entire person, the burden of their multiple chronic conditions, advanced illnesses, and also their biopsychosocial needs and how those together might augment treatment selection and decision-making,” Dr. Niznik said.
Studies by Dr. Niznik and others have shown that swallowing difficulties, severe dementia, and being older than 90 are linked with a lower likelihood of receiving treatment for osteoporosis.
But therapies for fracture prevention, especially bisphosphonates, appear to be at least as effective for adults with medical complexity as they are for people without such conditions, Dr. Niznik said. Physicians must consider the potential treatment burden and the likelihood of benefit, he said.
Dr. Niznik’s research has shown a lack of strong evidence on how clinicians can manage patients in nursing homes. In some cases, deprescribing is reasonable, such as for patients who have undergone treatment for several years and whose life expectancy is less than 2 years.
“In the absence of any of those, if they are not already treated for osteoporosis, it makes sense to initiate treatment at that time,” Dr. Niznik said.
Matters most: Patient input
Clinicians need to educate patients on how long they must undergo a treatment before they experience benefits, according to Sarah D. Berry, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, in Boston.
A meta-analysis of studies that included more than 20,000 women who were randomly assigned to receive bisphosphonate or placebo found that one nonvertebral fracture was avoided during a 12-month period for every 100 persons treated. One hip fracture was avoided during a 20-month period for every 200 patients treated.
“In general, in persons with a 2-year life expectancy, time to benefit favors bisphosphonate use,” Dr. Berry said. “Anabolics may have an even quicker time to benefit.”
Dr. Berry said a shared a decision-making model can help clinicians facilitate discussions that help patients prioritize goals and compare options while considering results, benefits, and harms. And she offered a final tip: Use tools with absolute risk reduction to convey risks and benefits, as the relative risk calculations overestimate how effective treatment will be.
Dr. Rosen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Colon-Emeric has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and VA Health Services Research and Development Funding; has served as endpoint adjudication chair for UCB Pharma; and has received royalties from Wolters Kluwer. Dr. Niznik has received funding from the National Institute of Aging and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Berry has received funding from the NIH and royalties from Wolters Kluwer.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
LONG BEACH, CALIF. – Ms. S had recently arrived home after a stay at a skilled nursing facility to recover from a hip fracture resulting from osteoporosis. For many patients, follow-up care would have included a DEXA scan or a prescription for a bisphosphonate from a primary care clinician not trained in geriatrics.
But the 85-year-old received care that went further and that is considered best practice for the management of geriatric fractures: A physical therapist visited her after discharge and provided education on the importance of maintaining mobility. Ms. S also underwent assessment for fall risk and gait balance, and a team of multidisciplinary clinicians managed other factors, from postural hypotension to footwear and foot problems.
Sonja Rosen, MD, professor of medicine and chief of geriatric medicine at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, talked about Ms. S as part of a panel discussion on applying the “Geriatric 5Ms” for patients with osteoporosis at the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society.
“You have to figure out why they are falling and help them not fall again,” Dr. Rosen said.
Approximately 10 million Americans have osteoporosis, and another 44 million have low bone density. One in two women and up to one in four men will experience a bone fracture as a result of osteoporosis, according to the Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation.
, which involves considering the care preferences and goals for health care outcomes of individuals.
Ms. S eventually visited a geriatrician through the Cedars-Sinai Geriatric Fracture Program, which has been shown to lower costs and shorten hospital stays. In the program, she was advised to use a walker. Initially, she saw the aid as a hindrance – she felt she should be able to walk without it, like before. But with education, she learned that it is impossible to predict falls and that the walking aid could reduce her risk of a stumble.
Dr. Rosen said clinicians should address any vision problems, prescriptions for psychotropic drugs,which can affect balance, and heart rate and rhythm abnormalities, and they should suggest modifications to the home environment, such as installing grab bars in showers and removing rugs that can easily be tripped over.
The program at Cedars-Sinai, like similar initiatives, offers a team with resources that some clinicians may not have access to, such as a care coordinator and bone-health coach. But health care providers can utilize aspects, such as making referrals to community exercise classes.
Dr. Rosen and her colleagues studied the effects of such exercise programs and found that the programs lessen loneliness and social isolation. Fear of falling decreased in 75% of participants, “which is so key to these postfracture patients in getting back out into the world and engaging in their prior level of functional status,” Dr. Rosen said.
The second ‘M’: Medication management
The second “M,” medications, can help clinicians sequence osteoporosis drugs, depending on patient characteristics and scenarios.
Cathleen Colon-Emeric, MD, MHS, chief of geriatrics at Duke University, in Durham, N.C., dived into the case history of Ms. S, who had hypertension and insomnia in addition to osteoporosis.
First-line treatment for Ms. S – and for most patients – was an oral bisphosphonate, Dr. Colon-Emeric said. Compared with placebo, the drugs decrease the risk of overall osteoporotic fractures by nearly 40% (odds ratio, 0.62). But the medications are linked to injury of the esophageal mucosa. This risk is decreased when a patient stays upright for 30 minutes after taking oral bisphosphonates. Dr. Colon-Emeric displayed a slide of a woman receiving a pedicure at a nail salon.
“The picture of the pedicure is to share the wonderful idea I got from one skilled nursing facility I was working with, who makes sure they do safe administration to prevent esophagitis in their patients by having them all go to a spa day, where they all sit up and get their nails done while they wait their 30 minutes [after taking the pill] sitting up safely,” Dr. Colon-Emeric said.
This strategy drew applause from the audience.
Dr. Colon-Emeric advised that clinicians use judgment in the interpretation of results from the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX). Incorporating race into estimates of fracture risk has pros and cons. While there are racial and ethnic differences in average bone density, the data for race calibrations to estimate risk are dated, she said. Clinicians should compare FRAX estimates with and without race input to help patients understand a range of risks.
Some patients may be reluctant to begin taking osteoporosis drugs because of misinformation originating from inaccurate news reports or anecdotes from friends. Dr. Colon-Emeric advised clinicians to remind patients that one in five who experience a fracture will have another injury in the following 2 years.
“A major osteoporotic fracture is akin to a heart attack; it has a very similar 1-year mortality rate and a very similar rate of a subsequent secondary event,” Dr. Colon-Emeric said. “We have a class of medications that decrease both those risks by nearly a third.”
Shared decision-making can help patients understand the risks and benefits of treatment, she said.
“People are really scared about the side effects,” Michelle Keller, PhD, MPH, a research scientist at Cedars-Sinai who attended the session, said. “The idea that a “bone attack” is like a heart attack gets the message across.”
Mind and multicomplexity
Medical complexity of a patient must be considered when making decisions on treatment, according to Joshua Niznik, PharmD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine in the Center for Aging and Health at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“Medical complexity is an acknowledgment of the entire person, the burden of their multiple chronic conditions, advanced illnesses, and also their biopsychosocial needs and how those together might augment treatment selection and decision-making,” Dr. Niznik said.
Studies by Dr. Niznik and others have shown that swallowing difficulties, severe dementia, and being older than 90 are linked with a lower likelihood of receiving treatment for osteoporosis.
But therapies for fracture prevention, especially bisphosphonates, appear to be at least as effective for adults with medical complexity as they are for people without such conditions, Dr. Niznik said. Physicians must consider the potential treatment burden and the likelihood of benefit, he said.
Dr. Niznik’s research has shown a lack of strong evidence on how clinicians can manage patients in nursing homes. In some cases, deprescribing is reasonable, such as for patients who have undergone treatment for several years and whose life expectancy is less than 2 years.
“In the absence of any of those, if they are not already treated for osteoporosis, it makes sense to initiate treatment at that time,” Dr. Niznik said.
Matters most: Patient input
Clinicians need to educate patients on how long they must undergo a treatment before they experience benefits, according to Sarah D. Berry, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, in Boston.
A meta-analysis of studies that included more than 20,000 women who were randomly assigned to receive bisphosphonate or placebo found that one nonvertebral fracture was avoided during a 12-month period for every 100 persons treated. One hip fracture was avoided during a 20-month period for every 200 patients treated.
“In general, in persons with a 2-year life expectancy, time to benefit favors bisphosphonate use,” Dr. Berry said. “Anabolics may have an even quicker time to benefit.”
Dr. Berry said a shared a decision-making model can help clinicians facilitate discussions that help patients prioritize goals and compare options while considering results, benefits, and harms. And she offered a final tip: Use tools with absolute risk reduction to convey risks and benefits, as the relative risk calculations overestimate how effective treatment will be.
Dr. Rosen has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Colon-Emeric has received grants from the National Institutes of Health and VA Health Services Research and Development Funding; has served as endpoint adjudication chair for UCB Pharma; and has received royalties from Wolters Kluwer. Dr. Niznik has received funding from the National Institute of Aging and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Dr. Berry has received funding from the NIH and royalties from Wolters Kluwer.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AGS 2023
High cholesterol in seniors: Use statins for primary prevention?
LONG BEACH, CALIF. – For years, clinicians have debated whether prescribing statins to patients older than 75 for the prevention of cardiovascular events is appropriate.
In 2022, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded that scientific evidence was insufficient to assess the balance between the benefits and harms of the therapy for this older population.
At a session of the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society, experts laid out new preliminary recommendations of the AGS and the National Lipid Association on assessing risk and deciding on treatment.
The group concluded that LDL cholesterol levels are associated with incident arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), that the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score can be a valuable measure, and that statins may be reasonable to prescribe, even given the risks that have been linked to statins, such as that for muscle pain. Final recommendations are expected by fall 2023.
“This is still a work in progress,” said Daniel E. Forman, MD, professor of medicine and chair of geriatric cardiology at the University of Pittsburgh.
The AGS-NLA panel concluded that, for those aged 75 or older without established ASCVD, LDL cholesterol is associated with incident ASCVD, the only recommendation to be given a class I (strong) rating; others were classed as moderate or weak.
Dr. Forman reviewed the evidence for lowering LDL cholesterol to decrease ASCVD, citing a 2018 study that concluded, “Reverse causation may contribute to the association of lower TC with higher mortality in nonrandomized studies.”
However, research overall shows that, as LDL cholesterol levels increase, patients are more likely to experience a heart event.
Dr. Forman noted that the utility of equations for assessing 5- or 10-year risk of ASCVD is uncertain. However, he said, traditional risk factors, such as family history and ethnicity, still have value.
Assessing risk “has been enriched in the past few years by the introduction of the coronary artery calcium [CAC] score,” he said.
Lower scores predict lower rates of CVD events, Forman said. The AGS-NLA recommends measuring CAC if clinical uncertainty exists about the value of statins.
“It’s reasonable to measure CAC and to withhold statins when the CAC is zero,” Dr. Forman said. “When the CAC score is zero ... the risk of having a cardiovascular event is really next to nil. Patients are happy to know they have a CAC of zero.”
Likewise, patients appreciate knowing whether their score is high, which would indicate increased risk. He said the CAC score is underused by geriatric physicians.
The group also determined, after reviewing the research, that starting treatment is reasonable for patients with an LDL cholesterol level of 70-189 if they have no life-limiting illness and their life expectancy is over 5 years.
Other preliminary recommendations include the use of statins for those aged 75 and older, irrespective of risk for statin-associated muscle symptoms, type 2 diabetes, or impaired cognition. These associations are often weak, Dr. Forman added.
Focusing on person-centered decisions
Ariel Green, MD, MPH, PhD, associate professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said statin therapy “should be individualized” to weigh benefits, noncardiac risks, and other considerations.
Clinicians can incorporate life expectancy into prevention decisions using tools such as ePrognosis, from the University of California, San Francisco, Dr. Green said.
If life expectancy is greater than the time to benefit, statin therapy may help. Dr. Green cited research that showed that 2.5 years of statin therapy was needed to prevent one major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) per 100 patients in a population aged 50-75. Other data show reductions in MACE for those older than 75, but overall, the data are limited in this population.
The proposed recommendation is to use tools such as life tables that include comorbid conditions and functional status to guide clinical decisions.
“Another aspect of assessing net benefits of statin therapy is to consider competing health risks,” Dr. Green said.
The group recommends considering using competing risk-adjusted CVD models, though these are not widely used.
The group also recommends integrating screenings for frailty (Clinical Frailty Scale), dementia (Mini-Cog), and functional status (Vulnerable Elders Scale–13) into assessments.
“The presence of these syndromes should prompt elicitation of patient values and preferences related to prevention and medication use,” Dr. Green said.
Clinicians can use decision aids, but these are not always practical, owing to obstacles such as patients’ cognitive problems, Dr. Green said.
“Another approach is asking people to prioritize a set of universal health outcomes that apply across health conditions, such as maintaining independence, staying alive, reducing, or eliminating symptoms and focusing on comfort,” Dr. Green said.
She addressed the evidence about deprescribing statins, with a focus on those with a life expectancy of less than a year. Researchers have found an increase in quality of life and no increases in cardiovascular events or death when statins were deprescribed.
A welcome framework
Cory Krueger, MD, an internal medicine and geriatric physician in Cornville, Ariz., who attended the talk, said he welcomed the presentation, in which preliminary recommendations were explained.
“This has been a controversial area in geriatrics,” Dr. Krueger said. “At least this gave me a framework for discussing this with my patients in a reasonable way.”
Dr. Forman and Dr. Krueger disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Green receives funding from the National Institute of Aging and Impact Collaboratory.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONG BEACH, CALIF. – For years, clinicians have debated whether prescribing statins to patients older than 75 for the prevention of cardiovascular events is appropriate.
In 2022, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded that scientific evidence was insufficient to assess the balance between the benefits and harms of the therapy for this older population.
At a session of the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society, experts laid out new preliminary recommendations of the AGS and the National Lipid Association on assessing risk and deciding on treatment.
The group concluded that LDL cholesterol levels are associated with incident arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), that the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score can be a valuable measure, and that statins may be reasonable to prescribe, even given the risks that have been linked to statins, such as that for muscle pain. Final recommendations are expected by fall 2023.
“This is still a work in progress,” said Daniel E. Forman, MD, professor of medicine and chair of geriatric cardiology at the University of Pittsburgh.
The AGS-NLA panel concluded that, for those aged 75 or older without established ASCVD, LDL cholesterol is associated with incident ASCVD, the only recommendation to be given a class I (strong) rating; others were classed as moderate or weak.
Dr. Forman reviewed the evidence for lowering LDL cholesterol to decrease ASCVD, citing a 2018 study that concluded, “Reverse causation may contribute to the association of lower TC with higher mortality in nonrandomized studies.”
However, research overall shows that, as LDL cholesterol levels increase, patients are more likely to experience a heart event.
Dr. Forman noted that the utility of equations for assessing 5- or 10-year risk of ASCVD is uncertain. However, he said, traditional risk factors, such as family history and ethnicity, still have value.
Assessing risk “has been enriched in the past few years by the introduction of the coronary artery calcium [CAC] score,” he said.
Lower scores predict lower rates of CVD events, Forman said. The AGS-NLA recommends measuring CAC if clinical uncertainty exists about the value of statins.
“It’s reasonable to measure CAC and to withhold statins when the CAC is zero,” Dr. Forman said. “When the CAC score is zero ... the risk of having a cardiovascular event is really next to nil. Patients are happy to know they have a CAC of zero.”
Likewise, patients appreciate knowing whether their score is high, which would indicate increased risk. He said the CAC score is underused by geriatric physicians.
The group also determined, after reviewing the research, that starting treatment is reasonable for patients with an LDL cholesterol level of 70-189 if they have no life-limiting illness and their life expectancy is over 5 years.
Other preliminary recommendations include the use of statins for those aged 75 and older, irrespective of risk for statin-associated muscle symptoms, type 2 diabetes, or impaired cognition. These associations are often weak, Dr. Forman added.
Focusing on person-centered decisions
Ariel Green, MD, MPH, PhD, associate professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said statin therapy “should be individualized” to weigh benefits, noncardiac risks, and other considerations.
Clinicians can incorporate life expectancy into prevention decisions using tools such as ePrognosis, from the University of California, San Francisco, Dr. Green said.
If life expectancy is greater than the time to benefit, statin therapy may help. Dr. Green cited research that showed that 2.5 years of statin therapy was needed to prevent one major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) per 100 patients in a population aged 50-75. Other data show reductions in MACE for those older than 75, but overall, the data are limited in this population.
The proposed recommendation is to use tools such as life tables that include comorbid conditions and functional status to guide clinical decisions.
“Another aspect of assessing net benefits of statin therapy is to consider competing health risks,” Dr. Green said.
The group recommends considering using competing risk-adjusted CVD models, though these are not widely used.
The group also recommends integrating screenings for frailty (Clinical Frailty Scale), dementia (Mini-Cog), and functional status (Vulnerable Elders Scale–13) into assessments.
“The presence of these syndromes should prompt elicitation of patient values and preferences related to prevention and medication use,” Dr. Green said.
Clinicians can use decision aids, but these are not always practical, owing to obstacles such as patients’ cognitive problems, Dr. Green said.
“Another approach is asking people to prioritize a set of universal health outcomes that apply across health conditions, such as maintaining independence, staying alive, reducing, or eliminating symptoms and focusing on comfort,” Dr. Green said.
She addressed the evidence about deprescribing statins, with a focus on those with a life expectancy of less than a year. Researchers have found an increase in quality of life and no increases in cardiovascular events or death when statins were deprescribed.
A welcome framework
Cory Krueger, MD, an internal medicine and geriatric physician in Cornville, Ariz., who attended the talk, said he welcomed the presentation, in which preliminary recommendations were explained.
“This has been a controversial area in geriatrics,” Dr. Krueger said. “At least this gave me a framework for discussing this with my patients in a reasonable way.”
Dr. Forman and Dr. Krueger disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Green receives funding from the National Institute of Aging and Impact Collaboratory.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LONG BEACH, CALIF. – For years, clinicians have debated whether prescribing statins to patients older than 75 for the prevention of cardiovascular events is appropriate.
In 2022, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force concluded that scientific evidence was insufficient to assess the balance between the benefits and harms of the therapy for this older population.
At a session of the annual meeting of the American Geriatrics Society, experts laid out new preliminary recommendations of the AGS and the National Lipid Association on assessing risk and deciding on treatment.
The group concluded that LDL cholesterol levels are associated with incident arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), that the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score can be a valuable measure, and that statins may be reasonable to prescribe, even given the risks that have been linked to statins, such as that for muscle pain. Final recommendations are expected by fall 2023.
“This is still a work in progress,” said Daniel E. Forman, MD, professor of medicine and chair of geriatric cardiology at the University of Pittsburgh.
The AGS-NLA panel concluded that, for those aged 75 or older without established ASCVD, LDL cholesterol is associated with incident ASCVD, the only recommendation to be given a class I (strong) rating; others were classed as moderate or weak.
Dr. Forman reviewed the evidence for lowering LDL cholesterol to decrease ASCVD, citing a 2018 study that concluded, “Reverse causation may contribute to the association of lower TC with higher mortality in nonrandomized studies.”
However, research overall shows that, as LDL cholesterol levels increase, patients are more likely to experience a heart event.
Dr. Forman noted that the utility of equations for assessing 5- or 10-year risk of ASCVD is uncertain. However, he said, traditional risk factors, such as family history and ethnicity, still have value.
Assessing risk “has been enriched in the past few years by the introduction of the coronary artery calcium [CAC] score,” he said.
Lower scores predict lower rates of CVD events, Forman said. The AGS-NLA recommends measuring CAC if clinical uncertainty exists about the value of statins.
“It’s reasonable to measure CAC and to withhold statins when the CAC is zero,” Dr. Forman said. “When the CAC score is zero ... the risk of having a cardiovascular event is really next to nil. Patients are happy to know they have a CAC of zero.”
Likewise, patients appreciate knowing whether their score is high, which would indicate increased risk. He said the CAC score is underused by geriatric physicians.
The group also determined, after reviewing the research, that starting treatment is reasonable for patients with an LDL cholesterol level of 70-189 if they have no life-limiting illness and their life expectancy is over 5 years.
Other preliminary recommendations include the use of statins for those aged 75 and older, irrespective of risk for statin-associated muscle symptoms, type 2 diabetes, or impaired cognition. These associations are often weak, Dr. Forman added.
Focusing on person-centered decisions
Ariel Green, MD, MPH, PhD, associate professor of medicine at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said statin therapy “should be individualized” to weigh benefits, noncardiac risks, and other considerations.
Clinicians can incorporate life expectancy into prevention decisions using tools such as ePrognosis, from the University of California, San Francisco, Dr. Green said.
If life expectancy is greater than the time to benefit, statin therapy may help. Dr. Green cited research that showed that 2.5 years of statin therapy was needed to prevent one major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) per 100 patients in a population aged 50-75. Other data show reductions in MACE for those older than 75, but overall, the data are limited in this population.
The proposed recommendation is to use tools such as life tables that include comorbid conditions and functional status to guide clinical decisions.
“Another aspect of assessing net benefits of statin therapy is to consider competing health risks,” Dr. Green said.
The group recommends considering using competing risk-adjusted CVD models, though these are not widely used.
The group also recommends integrating screenings for frailty (Clinical Frailty Scale), dementia (Mini-Cog), and functional status (Vulnerable Elders Scale–13) into assessments.
“The presence of these syndromes should prompt elicitation of patient values and preferences related to prevention and medication use,” Dr. Green said.
Clinicians can use decision aids, but these are not always practical, owing to obstacles such as patients’ cognitive problems, Dr. Green said.
“Another approach is asking people to prioritize a set of universal health outcomes that apply across health conditions, such as maintaining independence, staying alive, reducing, or eliminating symptoms and focusing on comfort,” Dr. Green said.
She addressed the evidence about deprescribing statins, with a focus on those with a life expectancy of less than a year. Researchers have found an increase in quality of life and no increases in cardiovascular events or death when statins were deprescribed.
A welcome framework
Cory Krueger, MD, an internal medicine and geriatric physician in Cornville, Ariz., who attended the talk, said he welcomed the presentation, in which preliminary recommendations were explained.
“This has been a controversial area in geriatrics,” Dr. Krueger said. “At least this gave me a framework for discussing this with my patients in a reasonable way.”
Dr. Forman and Dr. Krueger disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Green receives funding from the National Institute of Aging and Impact Collaboratory.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT AGS 2023
As COVID tracking wanes, are we letting our guard down too soon?
The 30-second commercial, part of the government’s We Can Do This campaign, shows everyday people going about their lives, then reminds them that, “because COVID is still out there and so are you,” it might be time to update your vaccine.
Many data tracking sources, both federal and others, are no longer reporting, as often, the number of COVID cases, hospitalizations, and deaths.
The Department of Health & Human Services in February stopped updating its public COVID data site, instead directing all queries to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which itself has been updating only weekly instead of daily since 2022.
Nongovernmental sources, such as John Hopkins University, stopped reporting pandemic data in March, The New York Times also ended its COVID data-gathering project in March, stating that “the comprehensive real-time reporting that The Times has prioritized is no longer possible.” It will rely on reporting weekly CDC data moving forward.
Along with the tracking sites, masking and social distancing mandates have mostly disappeared. President Joe Biden signed a bipartisan bill on April 10 that ended the national emergency for COVID. While some programs will stay in place for now, such as free vaccines, treatments, and tests, that too will go away when the federal public health emergency expires on May 11. The HHS already has issued its transition roadmap.
Many Americans, meanwhile, are still on the fence about the pandemic. A Gallup poll from March shows that about half of the American public say it’s over, and about half disagree.
Are we closing up shop on COVID-19 too soon, or is it time? Not surprisingly, experts don’t agree. Some say the pandemic is now endemic – which broadly means the virus and its patterns are predictable and steady in designated regions – and that it’s critical to catch up on health needs neglected during the pandemic, such as screenings and other vaccinations
But others don’t think it’s reached that stage yet, saying that we are letting our guard down too soon and we can’t be blind to the possibility of another strong variant – or pandemic – emerging. Surveillance must continue, not decline, and be improved.
Time to move on?
In its transition roadmap released in February, the HHS notes that daily COVID reported cases are down over 90%, compared with the peak of the Omicron surge at the end of January 2022; deaths have declined by over 80%; and new hospitalizations caused by COVID have dropped by nearly 80%.
It is time to move on, said Ali Mokdad, PhD, a professor and chief strategy officer of population health at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“Many people were delaying a lot of medical care, because they were afraid” during COVID’s height, he said, explaining that elective surgeries were postponed, prenatal care went down, as did screenings for blood pressure and diabetes.
His institute was tracking COVID projections every week but stopped in December.
As for emerging variants, “we haven’t seen a variant that scares us since Omicron” in November 2021, said Dr. Mokdad, who agrees that COVID is endemic now. The subvariants that followed it are very similar, and the current vaccines are working.
“We can move on, but we cannot drop the ball on keeping an eye on the genetic sequencing of the virus,” he said. That will enable quick identification of new variants.
If a worrisome new variant does surface, Dr. Mokdad said, certain locations and resources will be able to gear up quickly, while others won’t be as fast, but overall the United States is in a much better position now.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, also believes the pandemic phase is behind us
“This can’t be an emergency in perpetuity,” he said “Just because something is not a pandemic [anymore] does not mean that all activities related to it cease.”
COVID is highly unlikely to overwhelm hospitals again, and that was the main reason for the emergency declaration, he said.
“It’s not all or none – collapsing COVID-related [monitoring] activities into the routine monitoring that is done for other infectious disease should be seen as an achievement in taming the virus,” he said.
Not endemic yet
Closing up shop too early could mean we are blindsided, said Rajendram Rajnarayanan, PhD, an assistant dean of research and associate professor at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University in Jonesboro.
Already, he said, large labs have closed or scaled down as testing demand has declined, and many centers that offered community testing have also closed. Plus, home test results are often not reported.
Continued monitoring is key, he said. “You have to maintain a base level of sequencing for new variants,” he said. “Right now, the variant that is ‘top dog’ in the world is XBB.1.16.”
That’s an Omicron subvariant that the World Health Organization is currently keeping its eye on, according to a media briefing on March 29. There are about 800 sequences of it from 22 countries, mostly India, and it’s been in circulation a few months.
Dr. Rajnarayanan said he’s not overly worried about this variant, but surveillance must continue. His own breakdown of XBB.1.16 found the subvariant in 27 countries, including the United States, as of April 10.
Ideally, Dr. Rajnarayanan would suggest four areas to keep focusing on, moving forward:
- Active, random surveillance for new variants, especially in hot spots.
- Hospital surveillance and surveillance of long-term care, especially in congregate settings where people can more easily spread the virus.
- Travelers’ surveillance, now at , according to the CDC.
- Surveillance of animals such as mink and deer, because these animals can not only pick up the virus, but the virus can mutate in the animals, which could then transmit it back to people.
With less testing, baseline surveillance for new variants has declined. The other three surveillance areas need improvement, too, he said, as the reporting is often delayed.
Continued surveillance is crucial, agreed Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, an epidemiologist and data scientist who publishes a newsletter, Your Local Epidemiologist, updating developments in COVID and other pressing health issues.
“It’s a bit ironic to have a date for the end of a public health emergency; viruses don’t care about calendars,” said Dr. Jetelina, who is also director of population health analytics for the Meadows Mental Health Policy Institute. “COVID-19 is still going to be here, it’s still going to mutate,” and still cause grief for those affected. “I’m most concerned about our ability to track the virus. It’s not clear what surveillance we will still have in the states and around the globe.”
It’s a bit ironic to have a date for the end of a public health emergency; viruses don’t care about calendars.
For surveillance, she calls wastewater monitoring “the lowest-hanging fruit.” That’s because it “is not based on bias testing and has the potential to help with other outbreaks, too.” Hospitalization data is also essential, she said, as that information is the basis for public health decisions on updated vaccines and other protective measures.
While Dr. Jetelina is hopeful that COVID will someday be universally viewed as endemic, with predictable seasonal patterns, “I don’t think we are there yet. We still need to approach this virus with humility; that’s at least what I will continue to do.”
Dr. Rajnarayanan agreed that the pandemic has not yet reached endemic phase, though the situation is much improved. “Our vaccines are still protecting us from severe disease and hospitalization, and [the antiviral drug] Paxlovid is a great tool that works.”
Keeping tabs
While some data tracking has been eliminated, not all has, or will be. The CDC, as mentioned, continues to post cases, deaths, and a daily average of new hospital admissions weekly. The WHO’s dashboard tracks deaths, cases, and vaccine doses globally.
In March, the WHO updated its working definitions and tracking system for SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants of interest, with goals of evaluating the sublineages independently and to classify new variants more clearly when that’s needed.
Still, WHO is considering ending its declaration of COVID as a public health emergency of international concern sometime in 2023.
Some public companies are staying vigilant. The drugstore chain Walgreens said it plans to maintain its COVID-19 Index, which launched in January 2022.
“Data regarding spread of variants is important to our understanding of viral transmission and, as new variants emerge, it will be critical to continue to track this information quickly to predict which communities are most at risk,” Anita Patel, PharmD, vice president of pharmacy services development for Walgreens, said in a statement.
The data also reinforces the importance of vaccinations and testing in helping to stop the spread of COVID-19, she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The 30-second commercial, part of the government’s We Can Do This campaign, shows everyday people going about their lives, then reminds them that, “because COVID is still out there and so are you,” it might be time to update your vaccine.
Many data tracking sources, both federal and others, are no longer reporting, as often, the number of COVID cases, hospitalizations, and deaths.
The Department of Health & Human Services in February stopped updating its public COVID data site, instead directing all queries to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which itself has been updating only weekly instead of daily since 2022.
Nongovernmental sources, such as John Hopkins University, stopped reporting pandemic data in March, The New York Times also ended its COVID data-gathering project in March, stating that “the comprehensive real-time reporting that The Times has prioritized is no longer possible.” It will rely on reporting weekly CDC data moving forward.
Along with the tracking sites, masking and social distancing mandates have mostly disappeared. President Joe Biden signed a bipartisan bill on April 10 that ended the national emergency for COVID. While some programs will stay in place for now, such as free vaccines, treatments, and tests, that too will go away when the federal public health emergency expires on May 11. The HHS already has issued its transition roadmap.
Many Americans, meanwhile, are still on the fence about the pandemic. A Gallup poll from March shows that about half of the American public say it’s over, and about half disagree.
Are we closing up shop on COVID-19 too soon, or is it time? Not surprisingly, experts don’t agree. Some say the pandemic is now endemic – which broadly means the virus and its patterns are predictable and steady in designated regions – and that it’s critical to catch up on health needs neglected during the pandemic, such as screenings and other vaccinations
But others don’t think it’s reached that stage yet, saying that we are letting our guard down too soon and we can’t be blind to the possibility of another strong variant – or pandemic – emerging. Surveillance must continue, not decline, and be improved.
Time to move on?
In its transition roadmap released in February, the HHS notes that daily COVID reported cases are down over 90%, compared with the peak of the Omicron surge at the end of January 2022; deaths have declined by over 80%; and new hospitalizations caused by COVID have dropped by nearly 80%.
It is time to move on, said Ali Mokdad, PhD, a professor and chief strategy officer of population health at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“Many people were delaying a lot of medical care, because they were afraid” during COVID’s height, he said, explaining that elective surgeries were postponed, prenatal care went down, as did screenings for blood pressure and diabetes.
His institute was tracking COVID projections every week but stopped in December.
As for emerging variants, “we haven’t seen a variant that scares us since Omicron” in November 2021, said Dr. Mokdad, who agrees that COVID is endemic now. The subvariants that followed it are very similar, and the current vaccines are working.
“We can move on, but we cannot drop the ball on keeping an eye on the genetic sequencing of the virus,” he said. That will enable quick identification of new variants.
If a worrisome new variant does surface, Dr. Mokdad said, certain locations and resources will be able to gear up quickly, while others won’t be as fast, but overall the United States is in a much better position now.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, also believes the pandemic phase is behind us
“This can’t be an emergency in perpetuity,” he said “Just because something is not a pandemic [anymore] does not mean that all activities related to it cease.”
COVID is highly unlikely to overwhelm hospitals again, and that was the main reason for the emergency declaration, he said.
“It’s not all or none – collapsing COVID-related [monitoring] activities into the routine monitoring that is done for other infectious disease should be seen as an achievement in taming the virus,” he said.
Not endemic yet
Closing up shop too early could mean we are blindsided, said Rajendram Rajnarayanan, PhD, an assistant dean of research and associate professor at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University in Jonesboro.
Already, he said, large labs have closed or scaled down as testing demand has declined, and many centers that offered community testing have also closed. Plus, home test results are often not reported.
Continued monitoring is key, he said. “You have to maintain a base level of sequencing for new variants,” he said. “Right now, the variant that is ‘top dog’ in the world is XBB.1.16.”
That’s an Omicron subvariant that the World Health Organization is currently keeping its eye on, according to a media briefing on March 29. There are about 800 sequences of it from 22 countries, mostly India, and it’s been in circulation a few months.
Dr. Rajnarayanan said he’s not overly worried about this variant, but surveillance must continue. His own breakdown of XBB.1.16 found the subvariant in 27 countries, including the United States, as of April 10.
Ideally, Dr. Rajnarayanan would suggest four areas to keep focusing on, moving forward:
- Active, random surveillance for new variants, especially in hot spots.
- Hospital surveillance and surveillance of long-term care, especially in congregate settings where people can more easily spread the virus.
- Travelers’ surveillance, now at , according to the CDC.
- Surveillance of animals such as mink and deer, because these animals can not only pick up the virus, but the virus can mutate in the animals, which could then transmit it back to people.
With less testing, baseline surveillance for new variants has declined. The other three surveillance areas need improvement, too, he said, as the reporting is often delayed.
Continued surveillance is crucial, agreed Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, an epidemiologist and data scientist who publishes a newsletter, Your Local Epidemiologist, updating developments in COVID and other pressing health issues.
“It’s a bit ironic to have a date for the end of a public health emergency; viruses don’t care about calendars,” said Dr. Jetelina, who is also director of population health analytics for the Meadows Mental Health Policy Institute. “COVID-19 is still going to be here, it’s still going to mutate,” and still cause grief for those affected. “I’m most concerned about our ability to track the virus. It’s not clear what surveillance we will still have in the states and around the globe.”
It’s a bit ironic to have a date for the end of a public health emergency; viruses don’t care about calendars.
For surveillance, she calls wastewater monitoring “the lowest-hanging fruit.” That’s because it “is not based on bias testing and has the potential to help with other outbreaks, too.” Hospitalization data is also essential, she said, as that information is the basis for public health decisions on updated vaccines and other protective measures.
While Dr. Jetelina is hopeful that COVID will someday be universally viewed as endemic, with predictable seasonal patterns, “I don’t think we are there yet. We still need to approach this virus with humility; that’s at least what I will continue to do.”
Dr. Rajnarayanan agreed that the pandemic has not yet reached endemic phase, though the situation is much improved. “Our vaccines are still protecting us from severe disease and hospitalization, and [the antiviral drug] Paxlovid is a great tool that works.”
Keeping tabs
While some data tracking has been eliminated, not all has, or will be. The CDC, as mentioned, continues to post cases, deaths, and a daily average of new hospital admissions weekly. The WHO’s dashboard tracks deaths, cases, and vaccine doses globally.
In March, the WHO updated its working definitions and tracking system for SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants of interest, with goals of evaluating the sublineages independently and to classify new variants more clearly when that’s needed.
Still, WHO is considering ending its declaration of COVID as a public health emergency of international concern sometime in 2023.
Some public companies are staying vigilant. The drugstore chain Walgreens said it plans to maintain its COVID-19 Index, which launched in January 2022.
“Data regarding spread of variants is important to our understanding of viral transmission and, as new variants emerge, it will be critical to continue to track this information quickly to predict which communities are most at risk,” Anita Patel, PharmD, vice president of pharmacy services development for Walgreens, said in a statement.
The data also reinforces the importance of vaccinations and testing in helping to stop the spread of COVID-19, she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The 30-second commercial, part of the government’s We Can Do This campaign, shows everyday people going about their lives, then reminds them that, “because COVID is still out there and so are you,” it might be time to update your vaccine.
Many data tracking sources, both federal and others, are no longer reporting, as often, the number of COVID cases, hospitalizations, and deaths.
The Department of Health & Human Services in February stopped updating its public COVID data site, instead directing all queries to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which itself has been updating only weekly instead of daily since 2022.
Nongovernmental sources, such as John Hopkins University, stopped reporting pandemic data in March, The New York Times also ended its COVID data-gathering project in March, stating that “the comprehensive real-time reporting that The Times has prioritized is no longer possible.” It will rely on reporting weekly CDC data moving forward.
Along with the tracking sites, masking and social distancing mandates have mostly disappeared. President Joe Biden signed a bipartisan bill on April 10 that ended the national emergency for COVID. While some programs will stay in place for now, such as free vaccines, treatments, and tests, that too will go away when the federal public health emergency expires on May 11. The HHS already has issued its transition roadmap.
Many Americans, meanwhile, are still on the fence about the pandemic. A Gallup poll from March shows that about half of the American public say it’s over, and about half disagree.
Are we closing up shop on COVID-19 too soon, or is it time? Not surprisingly, experts don’t agree. Some say the pandemic is now endemic – which broadly means the virus and its patterns are predictable and steady in designated regions – and that it’s critical to catch up on health needs neglected during the pandemic, such as screenings and other vaccinations
But others don’t think it’s reached that stage yet, saying that we are letting our guard down too soon and we can’t be blind to the possibility of another strong variant – or pandemic – emerging. Surveillance must continue, not decline, and be improved.
Time to move on?
In its transition roadmap released in February, the HHS notes that daily COVID reported cases are down over 90%, compared with the peak of the Omicron surge at the end of January 2022; deaths have declined by over 80%; and new hospitalizations caused by COVID have dropped by nearly 80%.
It is time to move on, said Ali Mokdad, PhD, a professor and chief strategy officer of population health at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington, Seattle.
“Many people were delaying a lot of medical care, because they were afraid” during COVID’s height, he said, explaining that elective surgeries were postponed, prenatal care went down, as did screenings for blood pressure and diabetes.
His institute was tracking COVID projections every week but stopped in December.
As for emerging variants, “we haven’t seen a variant that scares us since Omicron” in November 2021, said Dr. Mokdad, who agrees that COVID is endemic now. The subvariants that followed it are very similar, and the current vaccines are working.
“We can move on, but we cannot drop the ball on keeping an eye on the genetic sequencing of the virus,” he said. That will enable quick identification of new variants.
If a worrisome new variant does surface, Dr. Mokdad said, certain locations and resources will be able to gear up quickly, while others won’t be as fast, but overall the United States is in a much better position now.
Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, also believes the pandemic phase is behind us
“This can’t be an emergency in perpetuity,” he said “Just because something is not a pandemic [anymore] does not mean that all activities related to it cease.”
COVID is highly unlikely to overwhelm hospitals again, and that was the main reason for the emergency declaration, he said.
“It’s not all or none – collapsing COVID-related [monitoring] activities into the routine monitoring that is done for other infectious disease should be seen as an achievement in taming the virus,” he said.
Not endemic yet
Closing up shop too early could mean we are blindsided, said Rajendram Rajnarayanan, PhD, an assistant dean of research and associate professor at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine at Arkansas State University in Jonesboro.
Already, he said, large labs have closed or scaled down as testing demand has declined, and many centers that offered community testing have also closed. Plus, home test results are often not reported.
Continued monitoring is key, he said. “You have to maintain a base level of sequencing for new variants,” he said. “Right now, the variant that is ‘top dog’ in the world is XBB.1.16.”
That’s an Omicron subvariant that the World Health Organization is currently keeping its eye on, according to a media briefing on March 29. There are about 800 sequences of it from 22 countries, mostly India, and it’s been in circulation a few months.
Dr. Rajnarayanan said he’s not overly worried about this variant, but surveillance must continue. His own breakdown of XBB.1.16 found the subvariant in 27 countries, including the United States, as of April 10.
Ideally, Dr. Rajnarayanan would suggest four areas to keep focusing on, moving forward:
- Active, random surveillance for new variants, especially in hot spots.
- Hospital surveillance and surveillance of long-term care, especially in congregate settings where people can more easily spread the virus.
- Travelers’ surveillance, now at , according to the CDC.
- Surveillance of animals such as mink and deer, because these animals can not only pick up the virus, but the virus can mutate in the animals, which could then transmit it back to people.
With less testing, baseline surveillance for new variants has declined. The other three surveillance areas need improvement, too, he said, as the reporting is often delayed.
Continued surveillance is crucial, agreed Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, an epidemiologist and data scientist who publishes a newsletter, Your Local Epidemiologist, updating developments in COVID and other pressing health issues.
“It’s a bit ironic to have a date for the end of a public health emergency; viruses don’t care about calendars,” said Dr. Jetelina, who is also director of population health analytics for the Meadows Mental Health Policy Institute. “COVID-19 is still going to be here, it’s still going to mutate,” and still cause grief for those affected. “I’m most concerned about our ability to track the virus. It’s not clear what surveillance we will still have in the states and around the globe.”
It’s a bit ironic to have a date for the end of a public health emergency; viruses don’t care about calendars.
For surveillance, she calls wastewater monitoring “the lowest-hanging fruit.” That’s because it “is not based on bias testing and has the potential to help with other outbreaks, too.” Hospitalization data is also essential, she said, as that information is the basis for public health decisions on updated vaccines and other protective measures.
While Dr. Jetelina is hopeful that COVID will someday be universally viewed as endemic, with predictable seasonal patterns, “I don’t think we are there yet. We still need to approach this virus with humility; that’s at least what I will continue to do.”
Dr. Rajnarayanan agreed that the pandemic has not yet reached endemic phase, though the situation is much improved. “Our vaccines are still protecting us from severe disease and hospitalization, and [the antiviral drug] Paxlovid is a great tool that works.”
Keeping tabs
While some data tracking has been eliminated, not all has, or will be. The CDC, as mentioned, continues to post cases, deaths, and a daily average of new hospital admissions weekly. The WHO’s dashboard tracks deaths, cases, and vaccine doses globally.
In March, the WHO updated its working definitions and tracking system for SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and variants of interest, with goals of evaluating the sublineages independently and to classify new variants more clearly when that’s needed.
Still, WHO is considering ending its declaration of COVID as a public health emergency of international concern sometime in 2023.
Some public companies are staying vigilant. The drugstore chain Walgreens said it plans to maintain its COVID-19 Index, which launched in January 2022.
“Data regarding spread of variants is important to our understanding of viral transmission and, as new variants emerge, it will be critical to continue to track this information quickly to predict which communities are most at risk,” Anita Patel, PharmD, vice president of pharmacy services development for Walgreens, said in a statement.
The data also reinforces the importance of vaccinations and testing in helping to stop the spread of COVID-19, she said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
NOVIDs: Do some have the genes to dodge COVID?
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a field service representative for a slot machine company, Ryan Alexander, 37, of Louisville, Ky., spends his working hours in casinos, covering a large territory including Norfolk, Va., Indianapolis, and Charlotte. Social distancing in the casinos is not the norm. Despite all this up-close contact with people, he said he is still COVID-free, 3 years into the pandemic.
There was one nervous night when his temperature rose to 101° F, and he figured the virus had caught up with him. “I took a test and was fine,” he said, relieved that the result was negative. The fever disappeared, and he was back to normal soon. “Maybe it was just an exhausting day.”
Mr. Alexander is one of those people who have managed – or at least think they have managed – to avoid getting COVID-19.
He is, some say, a NOVID. While some scientists cringe at the term, it’s caught on to describe these virus super-dodgers. Online entrepreneurs offer NOVID-19 T-shirts, masks, and stickers, in case these super-healthy or super-lucky folks want to publicize their good luck. On Twitter, NOVIDs share stories of how they’ve done it.
How many NOVIDs?
As of March 16, according to the CDC, almost 104 million cases of COVID – about one-third of the U.S. population – have been reported, but many cases are known to go unreported. About half of American adults surveyed said they have had COVID, according to a December report by the COVID States Project, a multiuniversity effort to supply pandemic data.
As the numbers settle over time, though, it becomes clearer that some in the U.S. have apparently managed to avoid the virus.
But some scientists bristle at the term NOVIDs. They prefer the term “resisters,” according to Elena Hsieh, MD, associate professor of pediatrics and immunology at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora. Currently, she said, there is much more information on who is more susceptible to contracting severe COVID than who is resistant.
Dr. Hsieh is one of the regional coordinators for the COVID Human Genetic Effort, an international consortium of more than 250 researchers and doctors dedicated to discovering the genetic and immunological bases of the forms of SARS-CoV-2 infection. These researchers and others are looking for explanations for why some people get severe COVID while others seem resistant despite repeated exposure.
Resistance research
In determining explanations for resistance to infection, “the needle in the haystack that we are looking for is a change in the genetic code that would allow for you to avoid entry of the virus into the cell,” Dr. Hsieh said. “That is what being resistant to infection is.”
Part of the reason it’s so difficult to study resistance is defining a resister, she said. While many people consider themselves among that group because they’re been exposed multiple times – even with close family members infected and sick, yet they still felt fine – that doesn’t necessarily make them a resister, she said.
Those people could have been infected but remained without symptoms. “Resistance means the virus was inside you, it was near your cell and it did not infect your cell,” Dr. Hsieh said.
“I don’t think we know a lot so far,” Dr. Hsieh said about resisters. “I do believe that, just like there are genetic defects that make someone more susceptible, there are likely to be genetic defects that make somebody less susceptible.’’
“To identify genetic variants that are protective is a really challenging thing to do,” agreed Peter K. Gregersen, MD, professor of genetics at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research at Northwell Health in Manhasset, N.Y. Dr. Gregersen is also a regional coordinator for the COVID Human Genetic Effort.
He suspects the number found to be truly resistant to COVID – versus dodging it so far – is going to be very small or not found at all.
“It may exist for COVID or it may not,” he said. Some people may simply have what he calls a robust immune response in the upper part of the throat, perhaps killing off the virus quickly as soon as it enters, so they don’t get a positive test.
Genetic resistance has been found for other diseases, such as HIV.
“For HIV, scientists have been able to identify a specific gene that codes for a protein that can prevent individuals from getting infected,” said Sabrina Assoumou, MD, MPH, professor of medicine at Boston University, who researches HIV.
However, she said, “we haven’t yet found a similar gene or protein that can prevent people from getting infected with SARS-CoV-2.”
What has been found “is that some people might have a mutation in a gene that encodes for what’s called human leukocyte antigen (HLA),” Dr. Assoumou said. HLA, a molecule found on the surface of most cells, has a crucial role in the immune response to foreign substances. “A mutation in HLA can make people less likely to have symptoms if they get infected. Individuals still get infected, but they are less likely to have symptoms.”
Other research has found that those with food allergies are also less likely to be infected. The researchers have speculated that the inflammation characteristic of allergic conditions may reduce levels of a protein called the ACE2 receptor on the surface of airway cells. The SARS-CoV-2 virus uses the receptor to enter the cells, so if levels are low, that could reduce the ability of the virus to infect people.
The COVID Human Genetic Effort continues to search for participants, both those who were admitted to a hospital or repeatedly seen at a hospital because of COVID, as well as those who did not get infected, even after “intense and repeated” exposure.
The number of people likely to be resistant is much smaller, Dr. Hsieh said, than the number of people susceptible to severe disease.
The testing ... or lack thereof factor
The timing of testing and a person’s “infection profile” may be factors in people incorrectly declaring themselves NOVIDs, said Anne Wyllie, PhD, a research scientist in epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Conn., and a codeveloper of a saliva PCR test for COVID.
“Infection profiles can vary between individuals,” she said. For some, the infection may start in the lower respiratory tract, others in the higher respiratory tract. “Depending on where the virus takes up residence, that can affect test results.”
Then there’s the following-instructions factor. “It’s very likely that due to tests not being done at the right time, with the right sample, or not repeated if there is ongoing evidence of symptoms, that there are individuals out there who believe they are NOVIDs but just missed catching their infection at the window of opportunity.” Dr. Wyllie said.
Susceptibility research
“The part we have proven is the genetic defect that would make you more susceptible to having severe disease,” Dr. Hsieh said.
Many published papers report that inherited and/or autoimmune deficiencies of type I interferon immunity, important for combating viral infections and modulating the immune response, can be a significant cause of life-threatening COVID pneumonia.
More recently, researchers, including Jean-Laurent Casanova, MD, PhD, professor at Rockefeller University, New York, and cofounder of the COVID Human Genome Effort, reported that deficiencies in a gene that plays a role in built-in immunity (the early response), and a gene involved in signaling within the immune cells, impair interferon production and may be the basis of severe COVID pneumonia.
NOVIDs’ habits run the gamut
As scientists continue their research, the NOVIDs have their own ideas about why they’ve dodged the pandemic bullet, and they have a variety of approaches to handling the pandemic now.
Ryan Alexander, the field rep who travels to casinos, is up to date on his vaccinations and has gotten all the recommended COVID shots. “I was wearing a mask when told to wear masks,” he said.
He still observes the social distance habit but lives life. “I’ve been to three or four concerts in the past couple of years.”
And does he worry his number will eventually be up? “Not at this point, no,” he said.
Joe Asher, 46, said he has not gotten COVID despite being in contact with about 100 people a day, on average. He works as a bartender at an Evansville, Ind., brewery.
“On a Friday night, we can get 500 people,” he said. “I feel like almost everyone at the brewery got it. There’s no way I wasn’t exposed to it all the time.”
However, he said, his coworkers who did get sick were very cautious about not infecting others, partly to help protect a coworker’s family with newborn twins, so that may have helped him stay uninfected, too.
Mr. Asher said he’s in good physical shape, and he’s worked around the public for a long time, so figures maybe that has strengthened his immune system. He’s always been careful about handwashing and said he’s perhaps a bit more conscious of germs than others might be.
Roselyn Mena, 68, a retired teacher in Richmond, Calif., about 16 miles northeast of San Francisco, said she’s managed to avoid the virus even though her husband, Jesus Mena, got infected, as did her two adult children. Now, she remains vigilant about wearing a mask. She tries not to eat inside at restaurants. “I’m super careful,” she said.
Besides her teacher training, Ms. Mena had training as a medical assistant and learned a lot about sanitizing methods. She gets an annual flu shot, washes her hands often, and uses hand sanitizer.
When she shops, she will ask salespeople not wearing masks to please mask. “Only one refused, and she got someone else [to wait on her].”
One reason she is always careful about hygiene, Ms. Mena said, is that “when I get a cold, I get really sick. It last and lasts.” Now, she does worry she might still get it, she said, with the prospect of getting long COVID driving that worry.
In the beginning of the pandemic, Rhonda Fleming, 68, of Los Angeles, lived in a “COVID bubble,” interacting with just a few close family members. As cases went down, she enlarged the bubble. Her two grown daughters got infected, but her granddaughter did not.
She has been vigilant about masking, she said, “and I do still mask in public places.” She has a mask wardrobe, including basic black as well as glittery masks for dressier occasions. “I always carry a mask because inevitably, a cougher surrounds me.”
Now, she will bypass restaurants if she doesn’t feel comfortable with the environment, choosing ones with good air flow. When she flew to Mexico recently, she masked on the plane.
At this point, she said she doesn’t worry about getting infected but remains careful.
Recently, two friends, who have been as diligent as she has about precautions, got infected, “and they don’t know how they got it.”
Bragging rights?
Until researchers separate out the true resisters from those who claim to be, some NOVIDs are simply quietly grateful for their luck, while others mention their COVID-free status to anyone who asks or who will listen, and are proud of it.
And what about those who wear a “NOVID” T-shirt?
“I would think they have a need to convey to the world they are different, perhaps special, because they beat COVID,” said Richard B. Joelson, a New York–based doctor of social work, a psychotherapist, and the author of Help Me! A Psychotherapist’s Tried-and-True Techniques for a Happier Relationship with Yourself and the People You Love. “They didn’t beat COVID, they just didn’t get it.”
Or they may be relieved they didn’t get sick, he said, because they feel defeated when they do. So “it’s a source of pride.” It might be the same people who tell anyone who will listen they never need a doctor or take no medicines, he said.
Even though science may prove many NOVIDs are inaccurate when they call themselves resisters, Dr. Hsieh understands the temptation to talk about it. “It’s kind of cool to think you are supernatural,” she said. “It’s much more attractive than being susceptible. It’s a lot sexier.” ■
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can California solve its ob.gyn. shortage?
Three patients were waiting in a queue for their telemedicine visit. Four others were in exam rooms, waiting for their appointments. Another patient was on the phone, requesting a prescription renewal.
On a sunny Wednesday afternoon in February, David Ahdoot, MD, FACOG, an ob.gyn. in Burbank, Calif., about 10 miles north of downtown Los Angeles, knows he’ll be working late.
“Normally, we would be closed on Wednesday afternoon,” he said. That time would ordinarily be used to schedule surgeries, make dictation, and perform other tasks. But those were the old days, before the COVID-19 pandemic, before the ob.gyn. shortage got even worse, and before many of the other obstacles that make his practice more burdensome worsened.
Those Wednesday afternoon tasks must be done another time. “There are too many patients to see in the office,” said Dr. Ahdoot, who’s also an assistant clinical professor at UCLA. Because of the shortage of primary care physicians, he has taken on new patients, although he said he would like to focus on his existing ones.
Many of those existing patients have been coming to Dr. Ahdoot for years. “I love my job,” he said, and it shows.
His patient reviews online include the usual grumblings about waiting time and being rushed, but many, especially those from new parents, praise him as caring, compassionate, exceptional – the kind of doctor women trust to deliver their first baby and their next ones, then guide them through menopause and other issues.
The shortage of ob.gyns. in California, as elsewhere, is real, as Dr. Ahdoot’s day-to-day attests. The implications are in evidence well beyond his higher patient loads. Lately, Dr. Ahdoot said, the calls from headhunters seeking to fill positions for locum tenens have increased from twice a month to three times a day. Despite his love for his practice, he admits he thinks about stepping away. He is 56, 8 years short of the average retirement age for ob.gyns. nationally, according to a 2018 report.
Projected shortages
The shortage of primary care doctors, including ob.gyns., is nationwide. Dr. Ahdoot is one of many faces behind the statistics. According to a 2021 update from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, the number of ob.gyns. nationwide is expected to decrease 7% between 2018 and 2030, from 50,850 to 47,490. Meanwhile, demand is headed in the other direction – it is projected to rise 4%, from 50,850 to 52,660 ob.gyns. needed. The need for nurse-midwives, nurse-practitioners, and physician assistants who provide women’s health care is also expected to exceed the supply in coming years.
Some areas are harder hit. The Northeast is expected to have enough maternal health care providers to meet the current average level of care nationally but the West, Midwest, and South will not, according to HHS.
California will likely need an additional 4,700 primary care clinicians by 2025, according to projections by the HealthForce Center at the University of California, San Francisco.
Solutions in sight?
Efforts are increasing to make it easier or more appealing for ob.gyns. to practice, or remain in practice, in California. Some existing programs have received funding, while new initiatives to improve the situation are launching.
Some of these efforts and programs will be viewed as a model by some other states, said Janet Coffman, PhD, associate professor at UC San Francisco and a health policy expert who is familiar with new programs and established ones.
“I would say that California offers an example of a multifaceted approach to addressing the shortage of reproductive health providers in general and abortion providers in particular.”
The state has not sat idly in the face of dire predictions of shortfalls in the number of ob.gyns. Over the past decade, Dr. Coffman said, the legislature has “substantially” boosted funding for grants to support ob.gyn. residency programs through CalMedForce and the Song-Brown Healthcare Workforce Training Program. The result: an 18% increase in the number of residents entering the field over the past decade.
“These programs have also substantially increased funding for family medicine residency programs, which are important because family physicians are trained to provide preventive reproductive health services and manage low-risk deliveries,” she added. “Funding for midwifery, nurse midwifery, and nurse practitioner education has been more modest, which I find disappointing because they are qualified to provide many reproductive health services and are more likely to care for underserved populations.”
Other new programs and legislation are focused on expanding the scope of practice for nonphysician health care providers who care for women. Many of these measures are meant to ensure continued access to abortion services not just for California residents, who are guaranteed that right in the state constitution, but for the influx of women expected from states that limited or prohibited abortion after the overturn of Roe v. Wade.
Gavin Newsom, the state’s Democratic governor, has promoted California as a safe haven for women seeking abortions. In September, Gov. Newsom’s reelection campaign rented billboards in six states that have restrictive abortion laws with messages directing women to a website informing them “abortion is legal and protected in California.” The website includes a search function for women looking for providers – representing a further potential strain on the already stressed pool of clinicians. Each year, an estimated 8,000 to 16,100 more people are expected to travel to California for abortions, according to projections made in 2022 by the UCLA Center on Reproductive Health, Law, and Policy.
The questions are, will the efforts be enough to stall or reverse the shortage, and will the efforts to expand other health care providers’ scope of practice be met with cooperation or resistance by MDs?
Just launched: California reproductive health service corps
Brand new, as of January 2023, is the California Reproductive Health Service Corps, created by a bill Gov. Newsom signed into law last September. The program operates within the Department of Health Care Access and Information. Rajeena Victoria Bisla, a spokesperson for assemblywoman Cottie Petrie-Norris (D-Irvine), who authored the bill, said: “The Corps will be responsible for recruiting, training, and retaining a diverse workforce of health care professionals who will be part of reproductive health care teams assigned to work in underserved areas.”
The teams will include MDs as well as licensed midwives, nurses, physician’s assistants, doulas, and medical assistants. They will provide abortion care, contraception, perinatal care, gynecology services, and gender-affirming care, among other needs, Ms. Bisla said.
The California Medical Association’s philanthropic arm, Physicians for a Healthy California (PHC), has two programs that aim to grow and diversify the physician workforce and invest in the state’s underserved areas, according to Lupe Alonzo-Diaz, CEO and president of PHC.
CalMedForce gives annual grants to fund new residency positions at graduate medical education (GME) programs throughout the state. The goal, Ms. Alonzo-Diaz said, is to expand the physician training pool. Funds were generated by Proposition 56, which was passed in 2016. The legislation generates tax on tobacco products. To date, GME programs have received more than $112 million to retain and expand primary care GME programs.
A second program, CalHealthCares, also funded by Proposition 56, offers a loan repayment program of up to $300,000 for physicians who meet certain criteria. “We are incentivizing young physicians and dentists to practice in Medi-Cal communities,” Ms. Alonzo-Diaz said, referring to the state’s Medicaid program. Clinicians must have graduated within the past 5 years (since Jan. 1, 2018) or will be graduating from a residency or fellowship program no later than June 30, 2023. Dentists applying for the practice support grant must have graduated from dental school or residency program within the past 15 years (since Jan. 1, 2008).
In exchange for the loan repayment, the health care providers are asked to commit to 5 years of service in the underserved community. So far, about 800 providers are part of the program, she said. According to Ms. Alonzo-Diaz, the average educational debt for health care providers in California is $315,000 to $350,000. That is as much as $100,000 above the national average.
What else is needed? Shannan Velayas, a spokesperson for the California Medical Association, said the state should invest in the Medi-Cal system to improve “meaningful access” to health care services and to expand loan repayment and residency programs like CalHealthCares and CalMedForce.
“Workforce shortages are not a reason to sacrifice quality of care or compromise patient safety but do warrant additional investment to increase access to medical providers working within their scope of practice,” Ms. Velayas said.
Widening scopes
Efforts are also underway to expand the scope of practice for nurse-practitioners, certified nurse-midwives, and physician assistants. Triggering these efforts has been the fallout and expected consequences of the overturning of Roe v. Wade, removing the federal right to abortion care.
Effective January 2023, trained and qualified nurse-practitioners and certified nurse-midwives in California can perform first-trimester abortions without a doctor’s supervision. Toni Atkins (D-San Diego), now president pro tempore of the California State Senate, authored the bill, SB1375. The measure builds on a 2013 law she spearheaded that allowed certain advanced-practice providers to perform first-trimester abortions with physician supervision.
On Feb. 13, Ms. Atkins introduced SB385, which gives physician assistants the same ability to become qualified in abortion care.
Ms. Atkins expressed confidence that teamwork would prevail in the efforts to have enough providers in the state. “One of the biggest lessons I learned working at a women’s health clinic [prior to her assuming her legislative positions] is that providers put their patients above all else, whether they are doctors, registered nurses, nurse practitioners, certified nurse-midwives, or physician assistants,” she said. “Everyone is on the same team when it comes to breaking down barriers and ensuring all Californians get the care they need without delay.”
Will other states follow suit? “This is pure speculation, but I believe states in which the political leadership supports abortion rights may see the California Reproductive Service Corps and the changes to scope-of-practice laws that allow specially trained CNMs, NPs, and PAs to provide abortions as a model for preserving access to abortion in their states,” Dr. Coffman said.
However, she said, “other states are less likely to view CalMedForce and CalHealthCares as models, because other states have had similar programs for many years, and some have historically invested larger shares of state budget resources into these programs, especially some rural states.”
Reports from the trenches
Laurie Love, DNP, RN, is a family nurse practitioner in Valencia and a clinical instructor and lecturer at the UCLA School of Nursing. When a patient becomes pregnant, she refers her to one of four local ob.gyns.
The working relationships she has with them, she said, “are extremely collaborative. There is no animosity or lack of respect because I don’t have an MD behind my name.”
One of those doctors is Dr. Ahdoot, who said he welcomes the expansion of scope of practice for non-MD health care providers. Some of his colleagues, he said, have tried to fight it, but many have come to the point of welcoming the help. “The consensus is you can’t practice without a nurse practitioner anymore,” Dr. Ahdoot told this news organization.
Expanding the scope of practice for other clinicians helps everyone, including patients, he said. He thinks about how the shortage affects them. “For patients, there is frustration,” he said. He said he often hears women saying they can’t schedule a pap smear for 3 months, or they can’t get a return call from their doctor.
Nalo Hamilton, PhD, an ob.gyn. nurse practitioner and associate professor at UCLA, said the physicians she interacts with support the expanded scope of practice. “Many are confused about details, about what it means and how it will impact them,” she said. “Those who understand it, yes, they agree with it. Doctors will simply have more health care providers who are able to do independent practice.” And she makes another point clear: “We won’t replace ob.gyns.”
None of the persons quoted in this story have disclosed any relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Three patients were waiting in a queue for their telemedicine visit. Four others were in exam rooms, waiting for their appointments. Another patient was on the phone, requesting a prescription renewal.
On a sunny Wednesday afternoon in February, David Ahdoot, MD, FACOG, an ob.gyn. in Burbank, Calif., about 10 miles north of downtown Los Angeles, knows he’ll be working late.
“Normally, we would be closed on Wednesday afternoon,” he said. That time would ordinarily be used to schedule surgeries, make dictation, and perform other tasks. But those were the old days, before the COVID-19 pandemic, before the ob.gyn. shortage got even worse, and before many of the other obstacles that make his practice more burdensome worsened.
Those Wednesday afternoon tasks must be done another time. “There are too many patients to see in the office,” said Dr. Ahdoot, who’s also an assistant clinical professor at UCLA. Because of the shortage of primary care physicians, he has taken on new patients, although he said he would like to focus on his existing ones.
Many of those existing patients have been coming to Dr. Ahdoot for years. “I love my job,” he said, and it shows.
His patient reviews online include the usual grumblings about waiting time and being rushed, but many, especially those from new parents, praise him as caring, compassionate, exceptional – the kind of doctor women trust to deliver their first baby and their next ones, then guide them through menopause and other issues.
The shortage of ob.gyns. in California, as elsewhere, is real, as Dr. Ahdoot’s day-to-day attests. The implications are in evidence well beyond his higher patient loads. Lately, Dr. Ahdoot said, the calls from headhunters seeking to fill positions for locum tenens have increased from twice a month to three times a day. Despite his love for his practice, he admits he thinks about stepping away. He is 56, 8 years short of the average retirement age for ob.gyns. nationally, according to a 2018 report.
Projected shortages
The shortage of primary care doctors, including ob.gyns., is nationwide. Dr. Ahdoot is one of many faces behind the statistics. According to a 2021 update from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, the number of ob.gyns. nationwide is expected to decrease 7% between 2018 and 2030, from 50,850 to 47,490. Meanwhile, demand is headed in the other direction – it is projected to rise 4%, from 50,850 to 52,660 ob.gyns. needed. The need for nurse-midwives, nurse-practitioners, and physician assistants who provide women’s health care is also expected to exceed the supply in coming years.
Some areas are harder hit. The Northeast is expected to have enough maternal health care providers to meet the current average level of care nationally but the West, Midwest, and South will not, according to HHS.
California will likely need an additional 4,700 primary care clinicians by 2025, according to projections by the HealthForce Center at the University of California, San Francisco.
Solutions in sight?
Efforts are increasing to make it easier or more appealing for ob.gyns. to practice, or remain in practice, in California. Some existing programs have received funding, while new initiatives to improve the situation are launching.
Some of these efforts and programs will be viewed as a model by some other states, said Janet Coffman, PhD, associate professor at UC San Francisco and a health policy expert who is familiar with new programs and established ones.
“I would say that California offers an example of a multifaceted approach to addressing the shortage of reproductive health providers in general and abortion providers in particular.”
The state has not sat idly in the face of dire predictions of shortfalls in the number of ob.gyns. Over the past decade, Dr. Coffman said, the legislature has “substantially” boosted funding for grants to support ob.gyn. residency programs through CalMedForce and the Song-Brown Healthcare Workforce Training Program. The result: an 18% increase in the number of residents entering the field over the past decade.
“These programs have also substantially increased funding for family medicine residency programs, which are important because family physicians are trained to provide preventive reproductive health services and manage low-risk deliveries,” she added. “Funding for midwifery, nurse midwifery, and nurse practitioner education has been more modest, which I find disappointing because they are qualified to provide many reproductive health services and are more likely to care for underserved populations.”
Other new programs and legislation are focused on expanding the scope of practice for nonphysician health care providers who care for women. Many of these measures are meant to ensure continued access to abortion services not just for California residents, who are guaranteed that right in the state constitution, but for the influx of women expected from states that limited or prohibited abortion after the overturn of Roe v. Wade.
Gavin Newsom, the state’s Democratic governor, has promoted California as a safe haven for women seeking abortions. In September, Gov. Newsom’s reelection campaign rented billboards in six states that have restrictive abortion laws with messages directing women to a website informing them “abortion is legal and protected in California.” The website includes a search function for women looking for providers – representing a further potential strain on the already stressed pool of clinicians. Each year, an estimated 8,000 to 16,100 more people are expected to travel to California for abortions, according to projections made in 2022 by the UCLA Center on Reproductive Health, Law, and Policy.
The questions are, will the efforts be enough to stall or reverse the shortage, and will the efforts to expand other health care providers’ scope of practice be met with cooperation or resistance by MDs?
Just launched: California reproductive health service corps
Brand new, as of January 2023, is the California Reproductive Health Service Corps, created by a bill Gov. Newsom signed into law last September. The program operates within the Department of Health Care Access and Information. Rajeena Victoria Bisla, a spokesperson for assemblywoman Cottie Petrie-Norris (D-Irvine), who authored the bill, said: “The Corps will be responsible for recruiting, training, and retaining a diverse workforce of health care professionals who will be part of reproductive health care teams assigned to work in underserved areas.”
The teams will include MDs as well as licensed midwives, nurses, physician’s assistants, doulas, and medical assistants. They will provide abortion care, contraception, perinatal care, gynecology services, and gender-affirming care, among other needs, Ms. Bisla said.
The California Medical Association’s philanthropic arm, Physicians for a Healthy California (PHC), has two programs that aim to grow and diversify the physician workforce and invest in the state’s underserved areas, according to Lupe Alonzo-Diaz, CEO and president of PHC.
CalMedForce gives annual grants to fund new residency positions at graduate medical education (GME) programs throughout the state. The goal, Ms. Alonzo-Diaz said, is to expand the physician training pool. Funds were generated by Proposition 56, which was passed in 2016. The legislation generates tax on tobacco products. To date, GME programs have received more than $112 million to retain and expand primary care GME programs.
A second program, CalHealthCares, also funded by Proposition 56, offers a loan repayment program of up to $300,000 for physicians who meet certain criteria. “We are incentivizing young physicians and dentists to practice in Medi-Cal communities,” Ms. Alonzo-Diaz said, referring to the state’s Medicaid program. Clinicians must have graduated within the past 5 years (since Jan. 1, 2018) or will be graduating from a residency or fellowship program no later than June 30, 2023. Dentists applying for the practice support grant must have graduated from dental school or residency program within the past 15 years (since Jan. 1, 2008).
In exchange for the loan repayment, the health care providers are asked to commit to 5 years of service in the underserved community. So far, about 800 providers are part of the program, she said. According to Ms. Alonzo-Diaz, the average educational debt for health care providers in California is $315,000 to $350,000. That is as much as $100,000 above the national average.
What else is needed? Shannan Velayas, a spokesperson for the California Medical Association, said the state should invest in the Medi-Cal system to improve “meaningful access” to health care services and to expand loan repayment and residency programs like CalHealthCares and CalMedForce.
“Workforce shortages are not a reason to sacrifice quality of care or compromise patient safety but do warrant additional investment to increase access to medical providers working within their scope of practice,” Ms. Velayas said.
Widening scopes
Efforts are also underway to expand the scope of practice for nurse-practitioners, certified nurse-midwives, and physician assistants. Triggering these efforts has been the fallout and expected consequences of the overturning of Roe v. Wade, removing the federal right to abortion care.
Effective January 2023, trained and qualified nurse-practitioners and certified nurse-midwives in California can perform first-trimester abortions without a doctor’s supervision. Toni Atkins (D-San Diego), now president pro tempore of the California State Senate, authored the bill, SB1375. The measure builds on a 2013 law she spearheaded that allowed certain advanced-practice providers to perform first-trimester abortions with physician supervision.
On Feb. 13, Ms. Atkins introduced SB385, which gives physician assistants the same ability to become qualified in abortion care.
Ms. Atkins expressed confidence that teamwork would prevail in the efforts to have enough providers in the state. “One of the biggest lessons I learned working at a women’s health clinic [prior to her assuming her legislative positions] is that providers put their patients above all else, whether they are doctors, registered nurses, nurse practitioners, certified nurse-midwives, or physician assistants,” she said. “Everyone is on the same team when it comes to breaking down barriers and ensuring all Californians get the care they need without delay.”
Will other states follow suit? “This is pure speculation, but I believe states in which the political leadership supports abortion rights may see the California Reproductive Service Corps and the changes to scope-of-practice laws that allow specially trained CNMs, NPs, and PAs to provide abortions as a model for preserving access to abortion in their states,” Dr. Coffman said.
However, she said, “other states are less likely to view CalMedForce and CalHealthCares as models, because other states have had similar programs for many years, and some have historically invested larger shares of state budget resources into these programs, especially some rural states.”
Reports from the trenches
Laurie Love, DNP, RN, is a family nurse practitioner in Valencia and a clinical instructor and lecturer at the UCLA School of Nursing. When a patient becomes pregnant, she refers her to one of four local ob.gyns.
The working relationships she has with them, she said, “are extremely collaborative. There is no animosity or lack of respect because I don’t have an MD behind my name.”
One of those doctors is Dr. Ahdoot, who said he welcomes the expansion of scope of practice for non-MD health care providers. Some of his colleagues, he said, have tried to fight it, but many have come to the point of welcoming the help. “The consensus is you can’t practice without a nurse practitioner anymore,” Dr. Ahdoot told this news organization.
Expanding the scope of practice for other clinicians helps everyone, including patients, he said. He thinks about how the shortage affects them. “For patients, there is frustration,” he said. He said he often hears women saying they can’t schedule a pap smear for 3 months, or they can’t get a return call from their doctor.
Nalo Hamilton, PhD, an ob.gyn. nurse practitioner and associate professor at UCLA, said the physicians she interacts with support the expanded scope of practice. “Many are confused about details, about what it means and how it will impact them,” she said. “Those who understand it, yes, they agree with it. Doctors will simply have more health care providers who are able to do independent practice.” And she makes another point clear: “We won’t replace ob.gyns.”
None of the persons quoted in this story have disclosed any relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Three patients were waiting in a queue for their telemedicine visit. Four others were in exam rooms, waiting for their appointments. Another patient was on the phone, requesting a prescription renewal.
On a sunny Wednesday afternoon in February, David Ahdoot, MD, FACOG, an ob.gyn. in Burbank, Calif., about 10 miles north of downtown Los Angeles, knows he’ll be working late.
“Normally, we would be closed on Wednesday afternoon,” he said. That time would ordinarily be used to schedule surgeries, make dictation, and perform other tasks. But those were the old days, before the COVID-19 pandemic, before the ob.gyn. shortage got even worse, and before many of the other obstacles that make his practice more burdensome worsened.
Those Wednesday afternoon tasks must be done another time. “There are too many patients to see in the office,” said Dr. Ahdoot, who’s also an assistant clinical professor at UCLA. Because of the shortage of primary care physicians, he has taken on new patients, although he said he would like to focus on his existing ones.
Many of those existing patients have been coming to Dr. Ahdoot for years. “I love my job,” he said, and it shows.
His patient reviews online include the usual grumblings about waiting time and being rushed, but many, especially those from new parents, praise him as caring, compassionate, exceptional – the kind of doctor women trust to deliver their first baby and their next ones, then guide them through menopause and other issues.
The shortage of ob.gyns. in California, as elsewhere, is real, as Dr. Ahdoot’s day-to-day attests. The implications are in evidence well beyond his higher patient loads. Lately, Dr. Ahdoot said, the calls from headhunters seeking to fill positions for locum tenens have increased from twice a month to three times a day. Despite his love for his practice, he admits he thinks about stepping away. He is 56, 8 years short of the average retirement age for ob.gyns. nationally, according to a 2018 report.
Projected shortages
The shortage of primary care doctors, including ob.gyns., is nationwide. Dr. Ahdoot is one of many faces behind the statistics. According to a 2021 update from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, the number of ob.gyns. nationwide is expected to decrease 7% between 2018 and 2030, from 50,850 to 47,490. Meanwhile, demand is headed in the other direction – it is projected to rise 4%, from 50,850 to 52,660 ob.gyns. needed. The need for nurse-midwives, nurse-practitioners, and physician assistants who provide women’s health care is also expected to exceed the supply in coming years.
Some areas are harder hit. The Northeast is expected to have enough maternal health care providers to meet the current average level of care nationally but the West, Midwest, and South will not, according to HHS.
California will likely need an additional 4,700 primary care clinicians by 2025, according to projections by the HealthForce Center at the University of California, San Francisco.
Solutions in sight?
Efforts are increasing to make it easier or more appealing for ob.gyns. to practice, or remain in practice, in California. Some existing programs have received funding, while new initiatives to improve the situation are launching.
Some of these efforts and programs will be viewed as a model by some other states, said Janet Coffman, PhD, associate professor at UC San Francisco and a health policy expert who is familiar with new programs and established ones.
“I would say that California offers an example of a multifaceted approach to addressing the shortage of reproductive health providers in general and abortion providers in particular.”
The state has not sat idly in the face of dire predictions of shortfalls in the number of ob.gyns. Over the past decade, Dr. Coffman said, the legislature has “substantially” boosted funding for grants to support ob.gyn. residency programs through CalMedForce and the Song-Brown Healthcare Workforce Training Program. The result: an 18% increase in the number of residents entering the field over the past decade.
“These programs have also substantially increased funding for family medicine residency programs, which are important because family physicians are trained to provide preventive reproductive health services and manage low-risk deliveries,” she added. “Funding for midwifery, nurse midwifery, and nurse practitioner education has been more modest, which I find disappointing because they are qualified to provide many reproductive health services and are more likely to care for underserved populations.”
Other new programs and legislation are focused on expanding the scope of practice for nonphysician health care providers who care for women. Many of these measures are meant to ensure continued access to abortion services not just for California residents, who are guaranteed that right in the state constitution, but for the influx of women expected from states that limited or prohibited abortion after the overturn of Roe v. Wade.
Gavin Newsom, the state’s Democratic governor, has promoted California as a safe haven for women seeking abortions. In September, Gov. Newsom’s reelection campaign rented billboards in six states that have restrictive abortion laws with messages directing women to a website informing them “abortion is legal and protected in California.” The website includes a search function for women looking for providers – representing a further potential strain on the already stressed pool of clinicians. Each year, an estimated 8,000 to 16,100 more people are expected to travel to California for abortions, according to projections made in 2022 by the UCLA Center on Reproductive Health, Law, and Policy.
The questions are, will the efforts be enough to stall or reverse the shortage, and will the efforts to expand other health care providers’ scope of practice be met with cooperation or resistance by MDs?
Just launched: California reproductive health service corps
Brand new, as of January 2023, is the California Reproductive Health Service Corps, created by a bill Gov. Newsom signed into law last September. The program operates within the Department of Health Care Access and Information. Rajeena Victoria Bisla, a spokesperson for assemblywoman Cottie Petrie-Norris (D-Irvine), who authored the bill, said: “The Corps will be responsible for recruiting, training, and retaining a diverse workforce of health care professionals who will be part of reproductive health care teams assigned to work in underserved areas.”
The teams will include MDs as well as licensed midwives, nurses, physician’s assistants, doulas, and medical assistants. They will provide abortion care, contraception, perinatal care, gynecology services, and gender-affirming care, among other needs, Ms. Bisla said.
The California Medical Association’s philanthropic arm, Physicians for a Healthy California (PHC), has two programs that aim to grow and diversify the physician workforce and invest in the state’s underserved areas, according to Lupe Alonzo-Diaz, CEO and president of PHC.
CalMedForce gives annual grants to fund new residency positions at graduate medical education (GME) programs throughout the state. The goal, Ms. Alonzo-Diaz said, is to expand the physician training pool. Funds were generated by Proposition 56, which was passed in 2016. The legislation generates tax on tobacco products. To date, GME programs have received more than $112 million to retain and expand primary care GME programs.
A second program, CalHealthCares, also funded by Proposition 56, offers a loan repayment program of up to $300,000 for physicians who meet certain criteria. “We are incentivizing young physicians and dentists to practice in Medi-Cal communities,” Ms. Alonzo-Diaz said, referring to the state’s Medicaid program. Clinicians must have graduated within the past 5 years (since Jan. 1, 2018) or will be graduating from a residency or fellowship program no later than June 30, 2023. Dentists applying for the practice support grant must have graduated from dental school or residency program within the past 15 years (since Jan. 1, 2008).
In exchange for the loan repayment, the health care providers are asked to commit to 5 years of service in the underserved community. So far, about 800 providers are part of the program, she said. According to Ms. Alonzo-Diaz, the average educational debt for health care providers in California is $315,000 to $350,000. That is as much as $100,000 above the national average.
What else is needed? Shannan Velayas, a spokesperson for the California Medical Association, said the state should invest in the Medi-Cal system to improve “meaningful access” to health care services and to expand loan repayment and residency programs like CalHealthCares and CalMedForce.
“Workforce shortages are not a reason to sacrifice quality of care or compromise patient safety but do warrant additional investment to increase access to medical providers working within their scope of practice,” Ms. Velayas said.
Widening scopes
Efforts are also underway to expand the scope of practice for nurse-practitioners, certified nurse-midwives, and physician assistants. Triggering these efforts has been the fallout and expected consequences of the overturning of Roe v. Wade, removing the federal right to abortion care.
Effective January 2023, trained and qualified nurse-practitioners and certified nurse-midwives in California can perform first-trimester abortions without a doctor’s supervision. Toni Atkins (D-San Diego), now president pro tempore of the California State Senate, authored the bill, SB1375. The measure builds on a 2013 law she spearheaded that allowed certain advanced-practice providers to perform first-trimester abortions with physician supervision.
On Feb. 13, Ms. Atkins introduced SB385, which gives physician assistants the same ability to become qualified in abortion care.
Ms. Atkins expressed confidence that teamwork would prevail in the efforts to have enough providers in the state. “One of the biggest lessons I learned working at a women’s health clinic [prior to her assuming her legislative positions] is that providers put their patients above all else, whether they are doctors, registered nurses, nurse practitioners, certified nurse-midwives, or physician assistants,” she said. “Everyone is on the same team when it comes to breaking down barriers and ensuring all Californians get the care they need without delay.”
Will other states follow suit? “This is pure speculation, but I believe states in which the political leadership supports abortion rights may see the California Reproductive Service Corps and the changes to scope-of-practice laws that allow specially trained CNMs, NPs, and PAs to provide abortions as a model for preserving access to abortion in their states,” Dr. Coffman said.
However, she said, “other states are less likely to view CalMedForce and CalHealthCares as models, because other states have had similar programs for many years, and some have historically invested larger shares of state budget resources into these programs, especially some rural states.”
Reports from the trenches
Laurie Love, DNP, RN, is a family nurse practitioner in Valencia and a clinical instructor and lecturer at the UCLA School of Nursing. When a patient becomes pregnant, she refers her to one of four local ob.gyns.
The working relationships she has with them, she said, “are extremely collaborative. There is no animosity or lack of respect because I don’t have an MD behind my name.”
One of those doctors is Dr. Ahdoot, who said he welcomes the expansion of scope of practice for non-MD health care providers. Some of his colleagues, he said, have tried to fight it, but many have come to the point of welcoming the help. “The consensus is you can’t practice without a nurse practitioner anymore,” Dr. Ahdoot told this news organization.
Expanding the scope of practice for other clinicians helps everyone, including patients, he said. He thinks about how the shortage affects them. “For patients, there is frustration,” he said. He said he often hears women saying they can’t schedule a pap smear for 3 months, or they can’t get a return call from their doctor.
Nalo Hamilton, PhD, an ob.gyn. nurse practitioner and associate professor at UCLA, said the physicians she interacts with support the expanded scope of practice. “Many are confused about details, about what it means and how it will impact them,” she said. “Those who understand it, yes, they agree with it. Doctors will simply have more health care providers who are able to do independent practice.” And she makes another point clear: “We won’t replace ob.gyns.”
None of the persons quoted in this story have disclosed any relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Embattled iPLEDGE program: Changes ahead?
In December 2021, major changes took effect in the iPLEDGE program, the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program for managing the risks of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity and preventing exposure during pregnancy. Now, more modifications may be coming to the acne drug’s safety program.
The risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) requirements. The aim, according to the FDA meeting announcement, is “to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of isotretinoin oral capsules for patients.”
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane. Its former brand name was Accutane.
Problems began to surface days after a new, gender-neutral approach to the risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, 2021. That program had been approved earlier by the FDA.
However, the problems that were encountered were a result of glitches in changes in the platform that had been planned, and were not related to the gender-neutral changes. The iPLEDGE program had transitioned to the new platform, and the rollout was far from smooth. Dermatologists, pharmacists, patients, parents of patients, and others were frustrated and angry that they could not access the new platform and obtain the medication promptly. Reaching the help line to sort out problems was another exercise in frustration. Wait times while on hold were unbearably long, or problems were not resolved over the phone.
(The new gender-neutral approach, which advocates said was needed to preserve inclusiveness of their patients, including transgender patients, places potential patients into two categories: those who can become pregnant, and those who cannot. Previously, there were three categories into which patients were classified: females who have reproductive potential, females who do not have reproductive potential, and males.)
Before pharmacists can fill a prescription for isotretinoin, a medical provider must confirm a patient’s negative pregnancy test and inform a patient with reproductive potential of the risks of the medication.
In January 2022, to deal with the chaotic launch and subsequent problems, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve the problems reported by clinicians, pharmacists, and patients.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association formed an iPLEDGE work group to address the issues and suggest solutions. It has made several requests of and suggestions for the IPMG, which manages the program, according to Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Penn State Hershey (Pa.) Medical Center, and a member of the work group.
“We are asking them to eliminate the monthly attestation for patients who can’t get pregnant and to review and modify restrictive and punitive waiting and lockout periods for all patients,” she told this news organization.
As of February 2023, most of the platform glitches had been smoothed out, Dr. Zaenglein said. Still, “improvements to the design of the website could improve the user interface,” she added.
The FDA has established a docket for the public to submit comments before the meeting. The docket number is FDA-2022-N-3071. The electronic filing system will accept comments until 11:59 p.m. Eastern time on March 27. Background material and a link to the live webcast of the panel meeting will be available to the public no later than 2 days before the meeting and will be posted on the FDA web page or at the time of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In December 2021, major changes took effect in the iPLEDGE program, the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program for managing the risks of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity and preventing exposure during pregnancy. Now, more modifications may be coming to the acne drug’s safety program.
The risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) requirements. The aim, according to the FDA meeting announcement, is “to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of isotretinoin oral capsules for patients.”
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane. Its former brand name was Accutane.
Problems began to surface days after a new, gender-neutral approach to the risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, 2021. That program had been approved earlier by the FDA.
However, the problems that were encountered were a result of glitches in changes in the platform that had been planned, and were not related to the gender-neutral changes. The iPLEDGE program had transitioned to the new platform, and the rollout was far from smooth. Dermatologists, pharmacists, patients, parents of patients, and others were frustrated and angry that they could not access the new platform and obtain the medication promptly. Reaching the help line to sort out problems was another exercise in frustration. Wait times while on hold were unbearably long, or problems were not resolved over the phone.
(The new gender-neutral approach, which advocates said was needed to preserve inclusiveness of their patients, including transgender patients, places potential patients into two categories: those who can become pregnant, and those who cannot. Previously, there were three categories into which patients were classified: females who have reproductive potential, females who do not have reproductive potential, and males.)
Before pharmacists can fill a prescription for isotretinoin, a medical provider must confirm a patient’s negative pregnancy test and inform a patient with reproductive potential of the risks of the medication.
In January 2022, to deal with the chaotic launch and subsequent problems, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve the problems reported by clinicians, pharmacists, and patients.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association formed an iPLEDGE work group to address the issues and suggest solutions. It has made several requests of and suggestions for the IPMG, which manages the program, according to Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Penn State Hershey (Pa.) Medical Center, and a member of the work group.
“We are asking them to eliminate the monthly attestation for patients who can’t get pregnant and to review and modify restrictive and punitive waiting and lockout periods for all patients,” she told this news organization.
As of February 2023, most of the platform glitches had been smoothed out, Dr. Zaenglein said. Still, “improvements to the design of the website could improve the user interface,” she added.
The FDA has established a docket for the public to submit comments before the meeting. The docket number is FDA-2022-N-3071. The electronic filing system will accept comments until 11:59 p.m. Eastern time on March 27. Background material and a link to the live webcast of the panel meeting will be available to the public no later than 2 days before the meeting and will be posted on the FDA web page or at the time of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In December 2021, major changes took effect in the iPLEDGE program, the Food and Drug Administration–required safety program for managing the risks of isotretinoin’s teratogenicity and preventing exposure during pregnancy. Now, more modifications may be coming to the acne drug’s safety program.
The risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) requirements. The aim, according to the FDA meeting announcement, is “to minimize burden on patients, pharmacies, and prescribers while maintaining safe use of isotretinoin oral capsules for patients.”
Isotretinoin is marketed as Absorica, Absorica LD, Claravis, Amnesteem, Myorisan, and Zenatane. Its former brand name was Accutane.
Problems began to surface days after a new, gender-neutral approach to the risk mitigation program was launched on Dec. 13, 2021. That program had been approved earlier by the FDA.
However, the problems that were encountered were a result of glitches in changes in the platform that had been planned, and were not related to the gender-neutral changes. The iPLEDGE program had transitioned to the new platform, and the rollout was far from smooth. Dermatologists, pharmacists, patients, parents of patients, and others were frustrated and angry that they could not access the new platform and obtain the medication promptly. Reaching the help line to sort out problems was another exercise in frustration. Wait times while on hold were unbearably long, or problems were not resolved over the phone.
(The new gender-neutral approach, which advocates said was needed to preserve inclusiveness of their patients, including transgender patients, places potential patients into two categories: those who can become pregnant, and those who cannot. Previously, there were three categories into which patients were classified: females who have reproductive potential, females who do not have reproductive potential, and males.)
Before pharmacists can fill a prescription for isotretinoin, a medical provider must confirm a patient’s negative pregnancy test and inform a patient with reproductive potential of the risks of the medication.
In January 2022, to deal with the chaotic launch and subsequent problems, the FDA said it would continue to meet with the Isotretinoin Products Manufacturers Group (IPMG) to resolve the problems reported by clinicians, pharmacists, and patients.
The American Academy of Dermatology Association formed an iPLEDGE work group to address the issues and suggest solutions. It has made several requests of and suggestions for the IPMG, which manages the program, according to Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at Penn State Hershey (Pa.) Medical Center, and a member of the work group.
“We are asking them to eliminate the monthly attestation for patients who can’t get pregnant and to review and modify restrictive and punitive waiting and lockout periods for all patients,” she told this news organization.
As of February 2023, most of the platform glitches had been smoothed out, Dr. Zaenglein said. Still, “improvements to the design of the website could improve the user interface,” she added.
The FDA has established a docket for the public to submit comments before the meeting. The docket number is FDA-2022-N-3071. The electronic filing system will accept comments until 11:59 p.m. Eastern time on March 27. Background material and a link to the live webcast of the panel meeting will be available to the public no later than 2 days before the meeting and will be posted on the FDA web page or at the time of the meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is it time for yet another COVID booster? It’s complicated
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
For some people who have received a two-dose primary series and all the recommended boosters, that could mean a sixth shot since COVID-19 vaccines became available. But is even that enough (or too much)?
At this point, no one knows for sure, but new guidance may be on the docket.
On Jan. 26, the FDA’s Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee is meeting. On the agenda is discussion about plans for future vaccinations for COVID-19.The committee, made up of external advisers, evaluates data on vaccines and other products for the agency.
According to the FDA announcement, after the meeting, “the FDA will consider whether to recommend adjustments to the current authorizations and approvals, and the FDA will consider the most efficient and transparent process to use for selection of strains for inclusion in the primary and booster vaccines.”
From there, the CDC will take up the issue and decide on recommendations.
The issue is important, as more than 550 Americans a day are still dying from COVID-19, as of the week ending Jan. 13, the CDC reported. That’s up from 346 a day for the week ending Dec. 28.
Yet, uptake of the newest vaccine, the bivalent booster, has been slow. As of Jan. 11, just 15.9% of the population 5 years and up has gotten it; for those most vulnerable to COVID19 – those 65 and up – the number is just 39%.
COVID vaccines, 2023 and beyond
Meanwhile, infectious disease experts have widely differing views on what the vaccination landscape of 2023 and beyond should look like. Among the areas of disagreement are how effective the bivalent vaccine is, which people most need another shot, and what type of vaccine is best.
“I think we probably will need another booster,” says Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, dean of the National School of Tropical Medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, and codirector of the Center for Vaccine Development at Texas Children’s Hospital in Houston. “The question is, what is it going to be? Is it going to be the same bivalent that we just got, or will it be a new bivalent or even a trivalent?”
The trivalent booster, he suggested, might include something more protective against XBB.1.5.
The bivalent booster gives “broadened immunity” that is improved from the original booster shots, says Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape, WebMD’s sister site for health professionals.
In his publication Ground Truths, Dr. Topol on Jan. 11 explained how new data caused him to reverse his previously skeptical view of how the FDA authorized the bivalent vaccine in September without data on how it affected humans at the time.
Paul Offit, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center and a professor of pediatrics at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is a member of the FDA advisory committee for vaccines. He still takes a dimmer view of more bivalent booster vaccines, at least as a blanket recommendation.
While he acknowledges that boosters can help some groups – such as older adults, people with multiple health conditions, and those with compromised immune systems – he opposes a recommendation that’s population-wide.
“People who fall into those three groups do benefit,” he says, “but the recommendation is everyone over 6 months get the bivalent, and what I’m asking is, ‘Where is the data that a healthy 12-year-old boy needs a booster to stay out of the hospital?’ ”
Evolving research
“We are trying to understand how to stay one step ahead rather than several steps behind [the virus],“ says Michael Osterholm, PhD, director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
Among the key questions: How well can a vaccine work against a single subvariant, when no one can say for sure what the next predominant subvariant will be?
Much more research has become available recently about the bivalent vaccine and its effectiveness, Dr. Osterholm says. “The bivalent vaccine is working as well as we could have expected,” he says, especially in high-risk people and in those over age 65. “The challenge we have is, what does that mean going forward?”
In his review, Dr. Topol concludes: “There is now more than ample, highly consistent evidence via lab studies and clinical outcomes to support the bivalent’s benefit over the original booster.”
Among other evidence, he looked at eight studies, including four that used a live virus as part of the research. Six of the eight studies showed the bivalent booster is more effective against the BA.5 variant, compared with the original booster shots. Two others showed no real difference.
“The four live virus studies offer consistent evidence of broadened immunity for the BA.5 vaccine that is improved over the original booster shots,” Dr. Topol wrote. The evidence also found the bivalent antibody response superior against XBB, he wrote.
Dr. Topol also cited CDC data that supports the benefits of the bivalent shot on hospitalization in older adults. During November, hospitalization of adults 65 and above was 2.5 times higher for those vaccinated who did not get the booster, compared to those who got the updated bivalent booster.
Boosters do matter, Dr. Offit says. “But not for all.” In a perspective published Jan. 11 in the New England Journal of Medicine – the same issue that published the two studies finding few differences between the original and bivalent – Dr. Offit wrote that boosting is best reserved for vulnerable groups.
Chasing the variants with a bivalent vaccine, he says, “has not panned out. There remains no evidence that a bivalent vaccine is any better than what we had. Please, show me the data that one is better than the other.”
Dr. Offit believes the goal should not be to prevent all symptomatic infections in healthy, young people by boosting them “with vaccines containing mRNA from strains that might disappear a few months later.”
The CDC needs to parse the data by subgroups, Dr. Offit says. “The critical question is, ‘Who gets hospitalized and who is dying? Who are they?’ ”
That data should take into account age, ethnicity, vaccine history, and other factors, Dr. Offit says, because right now, there is no great data to say, “OK, everyone gets a boost.”
Future vaccine costs
Another debate – for not only current boosters but future ones, too – centers on cost. Without congressional action to fund more vaccines, vaccine makers have suggested their prices may reach $130 a dose, compared with the average $20-per-dose cost the federal government pays now, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation report.
The government has spent more than $30 billion on COVID-19 vaccines, including the bivalent, to provide them free of charge.
The suggested price increase infuriated many. On Jan. 10, Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.), incoming chair of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, sent a letter to Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel, urging him to reconsider and refrain from any price increase.
“The huge increase in price that you have proposed will have a significantly negative impact on the budgets of Medicaid, Medicare and other government programs that will continue covering the vaccine without cost-sharing for patients.”
He pointed out, too, the $19 billion in profits Moderna has made over the past 2 years.
While most people with health insurance would likely still get the vaccines and booster for free, according to the Kaiser analysis, will a higher price discourage people from keeping up with recommended vaccinations, including a possible new booster?
“I think so, yes,” Dr. Hotez says, noting that vaccine reluctance is high as it is, even with free vaccinations and easy access.
“The government is balking at paying for the boosters,” he says. “I think it’s very tone deaf from the pharmaceutical companies [to increase the price]. Given all the help they’ve gotten from the American people, I think they should not be gouging at this point.”
He noted that the federal government provided not just money to the companies for the vaccines, but a “glide path” through the FDA for the vaccine approvals.
Are new, variant-specific boosters coming?
Are Moderna, Pfizer-BioNTech, and others developing more variant-specific vaccines, boosters, or other advances?
Novavax, approved in July 2022 as a primary series and in some cases as a booster, is “also developing an Omicron-containing bivalent vaccine at the direction of public health agencies,” says spokesperson Alison Chartan.
Pfizer responded: “When and if we have something to share we will let you know.”
Moderna did not respond.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
What’s next for COVID? Here’s what to know
As holiday celebrations wind down in the United States, COVID is on the rise.
Will there be another winter surge? If so, can we minimize it? How big a role might the boosters play in that? Are more mandates coming, along with a return to closed offices and businesses? Read on for a look at the latest info.
Cases, hospitalizations, deaths
As of Dec. 27, the latest statistics, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports more than 487,000 weekly cases, compared to about 265,000 for the week ending Oct. 12. On average, 4,938 people were admitted to the hospital daily from Dec. 19 to 25, down about 6% from the 5,257 admitted daily the week before.
Deaths totaled 2,952 weekly as of Dec. 21, up from 2,699 on Dec. 14.
“What’s sobering overall is still seeing about 400 deaths a day in the U.S.,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor of medicine and infectious disease specialist at the University of California, San Francisco. “It’s still very high.”
As of Dec. 17, the variants predominating are BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and XBB. Experts said they are paying close attention to XBB, which is increasing quickly in the Northeast.
Predicting a winter surge
Experts tracking the pandemic agree there will be a surge.
“We are in the midst of it now,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape (MDedge’s sister site). “It’s not nearly like what we’ve had in Omicron or other waves; it’s not as severe. But it’s being particularly felt by seniors.”
One bit of good news: “Outside of that group it doesn’t look like – so far – it is going to be as bad a wave [as in the past],” Dr. Topol said.
Predicting the extent of the post-holiday surge “is the billion-dollar question right now,” said Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, a San Diego epidemiologist and author of the newsletter Your Local Epidemiologist.
“Much of these waves are not being driven by subvariants of concern but rather behavior,” she said.
People are opening up their social networks to gather for celebrations and family time. That’s unique to this winter, she said.
“I think our numbers will continue to go up, but certainly not like 2021 or 2020,” Dr. Chin-Hong said.
Others point out that the surge doesn’t involve just COVID.
“We are expecting a Christmas surge and we are concerned it might be a triple surge,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., referring to the rising cases of flu and RSV (respiratory syncytial virus).
Dr. Jetelina shares that concern, worrying that those illnesses may be what overwhelms hospital capacity.
Another wild card is the situation in China. With the easing of China’s “zero COVID” policies, cases there are rising dramatically. Some models are predicting up to 1 million COVID deaths could occur in China in 2023. (The United States is now requiring travelers from China to show a negative COVID test before entering. Italy and Japan have taken similar measures.)
“The suffering that is going to occur in China is not good news at all,” Dr. Topol said. “We are going to be seeing that for many weeks if not months ahead.”
Theoretically, uncontained spread such as what is expected there could generate a whole new family of variants, he said. But “the main hit is going to be in China,” he predicted. “But it’s hard to project with accuracy.”
“China is 20% of the global population, so we can’t ignore it,” Dr. Jetelina said. “The question is, what’s the probability of a subvariant of concern coming from China? I think the probability is pretty low, but the possibility is there.”
What happens with cases in China may “throw a wrench” in the transition from pandemic to endemic, Dr. Chin-Hong said. But even if the rising cases in China do result in a new variant, “there’s so much T cell and B cell immunity [here], your average person is still not going to get seriously ill, even if the variant looks really scary.”
Minimizing the damage
Experts echo the same advice on stemming the surge, especially for adults who are 65 or older: Get the bivalent booster, and get it now.
“The same with the influenza vaccine,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Both the booster vaccine and the flu vaccine have been underused this year, he said. “It’s part of the general vaccine fatigue.”
The low uptake of the booster vaccine is concerning, Dr. Topol said, especially among adults aged 65 and older, the age group most vulnerable to severe disease. Just 35.7% of U.S. adults 65 and older have gotten the booster, according to the CDC. Dr. Topol calls that a tragedy.
Younger people have not taken to the booster, either. Overall, only 14.1% of people aged 5 and up have gotten an updated booster dose, according to the CDC.
Recent studies find value in the boosters. One study looked only at adults age 65 or older, finding that the bivalent booster reduced the risk of hospitalization by 84% compared to someone not vaccinated, and 73% compared to someone who had received only the monovalent vaccine. Another study of adults found those who had gotten the bivalent were less likely to need COVID-related emergency room care or urgent care.
In a Dec. 21 report in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers took plasma samples from people who had gotten either one or two monovalent boosters or the bivalent to determine how well they worked against the circulating Omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.5, BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, and XBB. The bivalent worked better than the monovalent against all the Omicron subvariants, but especially against BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, and XBB.
Rapid testing can help minimize transmission. On Dec. 15, the Biden administration announced its Winter Preparedness Plan, urging Americans to test before and after travel as well as indoor visiting with vulnerable individuals, providing another round of free at-home tests, continuing to make community testing available and continuing to provide vaccines.
Besides the general precautions, Dr. Schaffner suggested: “Look at yourself. Who are you? If you are older than 65, or have underlying illness or are immunocompromised, or are pregnant, please put your mask back on. And think about social distancing. It might be time to worship at home and stream a movie,” instead of going to the theaters, he said.
Back to mandates?
On Dec. 9, the New York City Commissioner of Health and Mental Hygiene urged a return to masking indoors, saying people “should” mask up, including in schools, stores, offices, and when in crowded outdoor settings.
On the same date, the County of Los Angeles Public Health urged a return to masking for everyone aged 2 and older when indoors, including at schools, in transit, or in work sites when around others.
While the CDC order requiring masks on public transportation is no longer in effect, the agency continues to recommend that those using public transportation do so.
But some are taking that further. In Philadelphia, for example, School Superintendent Tony B. Watlington Sr., EdD, announced before the winter break that indoor masking would be required for all students and staff for the first 2 weeks of school return, through Jan. 13, citing guidance from the Philadelphia Department of Public Health.
Universal masking in schools does reduce COVID transmission, as a study published in late November suggests. After Massachusetts dropped the statewide universal masking policy in public schools in February 2022, researchers compared the incidence of COVID in 70 school districts there that dropped the mandate with two school districts that kept it. In the 15 weeks after the policy was rescinded, the lifting of the mandate was linked with an additional 44.9 cases of COVID per 1,000 students and staff. That corresponded to an estimated 11,901 cases and to nearly 30% of the cases in all districts during that time.
That said, experts see mandates as the exception rather than the rule, at least for now, citing public backlash against mandates to mask or follow other restrictions.
“Mandating, we know, it shuts people off,” Dr. Topol said. “It’s unenforceable. If you have a very strong recommendation, that’s probably as good as you’re going to be able to do right now.”
There may be communities where mandates go over better than others, Dr. Schaffner said, such as communities where people have confidence in their public health authorities.
Glimmers of hope
Despite uncertainties, experts offered some not-so-dismal perspectives as well.
“I think our numbers will continue to go up, but certainly not like 2021 or 2020,” Dr. Chin-Hong said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As holiday celebrations wind down in the United States, COVID is on the rise.
Will there be another winter surge? If so, can we minimize it? How big a role might the boosters play in that? Are more mandates coming, along with a return to closed offices and businesses? Read on for a look at the latest info.
Cases, hospitalizations, deaths
As of Dec. 27, the latest statistics, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports more than 487,000 weekly cases, compared to about 265,000 for the week ending Oct. 12. On average, 4,938 people were admitted to the hospital daily from Dec. 19 to 25, down about 6% from the 5,257 admitted daily the week before.
Deaths totaled 2,952 weekly as of Dec. 21, up from 2,699 on Dec. 14.
“What’s sobering overall is still seeing about 400 deaths a day in the U.S.,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor of medicine and infectious disease specialist at the University of California, San Francisco. “It’s still very high.”
As of Dec. 17, the variants predominating are BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and XBB. Experts said they are paying close attention to XBB, which is increasing quickly in the Northeast.
Predicting a winter surge
Experts tracking the pandemic agree there will be a surge.
“We are in the midst of it now,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape (MDedge’s sister site). “It’s not nearly like what we’ve had in Omicron or other waves; it’s not as severe. But it’s being particularly felt by seniors.”
One bit of good news: “Outside of that group it doesn’t look like – so far – it is going to be as bad a wave [as in the past],” Dr. Topol said.
Predicting the extent of the post-holiday surge “is the billion-dollar question right now,” said Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, a San Diego epidemiologist and author of the newsletter Your Local Epidemiologist.
“Much of these waves are not being driven by subvariants of concern but rather behavior,” she said.
People are opening up their social networks to gather for celebrations and family time. That’s unique to this winter, she said.
“I think our numbers will continue to go up, but certainly not like 2021 or 2020,” Dr. Chin-Hong said.
Others point out that the surge doesn’t involve just COVID.
“We are expecting a Christmas surge and we are concerned it might be a triple surge,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., referring to the rising cases of flu and RSV (respiratory syncytial virus).
Dr. Jetelina shares that concern, worrying that those illnesses may be what overwhelms hospital capacity.
Another wild card is the situation in China. With the easing of China’s “zero COVID” policies, cases there are rising dramatically. Some models are predicting up to 1 million COVID deaths could occur in China in 2023. (The United States is now requiring travelers from China to show a negative COVID test before entering. Italy and Japan have taken similar measures.)
“The suffering that is going to occur in China is not good news at all,” Dr. Topol said. “We are going to be seeing that for many weeks if not months ahead.”
Theoretically, uncontained spread such as what is expected there could generate a whole new family of variants, he said. But “the main hit is going to be in China,” he predicted. “But it’s hard to project with accuracy.”
“China is 20% of the global population, so we can’t ignore it,” Dr. Jetelina said. “The question is, what’s the probability of a subvariant of concern coming from China? I think the probability is pretty low, but the possibility is there.”
What happens with cases in China may “throw a wrench” in the transition from pandemic to endemic, Dr. Chin-Hong said. But even if the rising cases in China do result in a new variant, “there’s so much T cell and B cell immunity [here], your average person is still not going to get seriously ill, even if the variant looks really scary.”
Minimizing the damage
Experts echo the same advice on stemming the surge, especially for adults who are 65 or older: Get the bivalent booster, and get it now.
“The same with the influenza vaccine,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Both the booster vaccine and the flu vaccine have been underused this year, he said. “It’s part of the general vaccine fatigue.”
The low uptake of the booster vaccine is concerning, Dr. Topol said, especially among adults aged 65 and older, the age group most vulnerable to severe disease. Just 35.7% of U.S. adults 65 and older have gotten the booster, according to the CDC. Dr. Topol calls that a tragedy.
Younger people have not taken to the booster, either. Overall, only 14.1% of people aged 5 and up have gotten an updated booster dose, according to the CDC.
Recent studies find value in the boosters. One study looked only at adults age 65 or older, finding that the bivalent booster reduced the risk of hospitalization by 84% compared to someone not vaccinated, and 73% compared to someone who had received only the monovalent vaccine. Another study of adults found those who had gotten the bivalent were less likely to need COVID-related emergency room care or urgent care.
In a Dec. 21 report in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers took plasma samples from people who had gotten either one or two monovalent boosters or the bivalent to determine how well they worked against the circulating Omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.5, BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, and XBB. The bivalent worked better than the monovalent against all the Omicron subvariants, but especially against BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, and XBB.
Rapid testing can help minimize transmission. On Dec. 15, the Biden administration announced its Winter Preparedness Plan, urging Americans to test before and after travel as well as indoor visiting with vulnerable individuals, providing another round of free at-home tests, continuing to make community testing available and continuing to provide vaccines.
Besides the general precautions, Dr. Schaffner suggested: “Look at yourself. Who are you? If you are older than 65, or have underlying illness or are immunocompromised, or are pregnant, please put your mask back on. And think about social distancing. It might be time to worship at home and stream a movie,” instead of going to the theaters, he said.
Back to mandates?
On Dec. 9, the New York City Commissioner of Health and Mental Hygiene urged a return to masking indoors, saying people “should” mask up, including in schools, stores, offices, and when in crowded outdoor settings.
On the same date, the County of Los Angeles Public Health urged a return to masking for everyone aged 2 and older when indoors, including at schools, in transit, or in work sites when around others.
While the CDC order requiring masks on public transportation is no longer in effect, the agency continues to recommend that those using public transportation do so.
But some are taking that further. In Philadelphia, for example, School Superintendent Tony B. Watlington Sr., EdD, announced before the winter break that indoor masking would be required for all students and staff for the first 2 weeks of school return, through Jan. 13, citing guidance from the Philadelphia Department of Public Health.
Universal masking in schools does reduce COVID transmission, as a study published in late November suggests. After Massachusetts dropped the statewide universal masking policy in public schools in February 2022, researchers compared the incidence of COVID in 70 school districts there that dropped the mandate with two school districts that kept it. In the 15 weeks after the policy was rescinded, the lifting of the mandate was linked with an additional 44.9 cases of COVID per 1,000 students and staff. That corresponded to an estimated 11,901 cases and to nearly 30% of the cases in all districts during that time.
That said, experts see mandates as the exception rather than the rule, at least for now, citing public backlash against mandates to mask or follow other restrictions.
“Mandating, we know, it shuts people off,” Dr. Topol said. “It’s unenforceable. If you have a very strong recommendation, that’s probably as good as you’re going to be able to do right now.”
There may be communities where mandates go over better than others, Dr. Schaffner said, such as communities where people have confidence in their public health authorities.
Glimmers of hope
Despite uncertainties, experts offered some not-so-dismal perspectives as well.
“I think our numbers will continue to go up, but certainly not like 2021 or 2020,” Dr. Chin-Hong said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As holiday celebrations wind down in the United States, COVID is on the rise.
Will there be another winter surge? If so, can we minimize it? How big a role might the boosters play in that? Are more mandates coming, along with a return to closed offices and businesses? Read on for a look at the latest info.
Cases, hospitalizations, deaths
As of Dec. 27, the latest statistics, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports more than 487,000 weekly cases, compared to about 265,000 for the week ending Oct. 12. On average, 4,938 people were admitted to the hospital daily from Dec. 19 to 25, down about 6% from the 5,257 admitted daily the week before.
Deaths totaled 2,952 weekly as of Dec. 21, up from 2,699 on Dec. 14.
“What’s sobering overall is still seeing about 400 deaths a day in the U.S.,” said Peter Chin-Hong, MD, professor of medicine and infectious disease specialist at the University of California, San Francisco. “It’s still very high.”
As of Dec. 17, the variants predominating are BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and XBB. Experts said they are paying close attention to XBB, which is increasing quickly in the Northeast.
Predicting a winter surge
Experts tracking the pandemic agree there will be a surge.
“We are in the midst of it now,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape (MDedge’s sister site). “It’s not nearly like what we’ve had in Omicron or other waves; it’s not as severe. But it’s being particularly felt by seniors.”
One bit of good news: “Outside of that group it doesn’t look like – so far – it is going to be as bad a wave [as in the past],” Dr. Topol said.
Predicting the extent of the post-holiday surge “is the billion-dollar question right now,” said Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, a San Diego epidemiologist and author of the newsletter Your Local Epidemiologist.
“Much of these waves are not being driven by subvariants of concern but rather behavior,” she said.
People are opening up their social networks to gather for celebrations and family time. That’s unique to this winter, she said.
“I think our numbers will continue to go up, but certainly not like 2021 or 2020,” Dr. Chin-Hong said.
Others point out that the surge doesn’t involve just COVID.
“We are expecting a Christmas surge and we are concerned it might be a triple surge,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., referring to the rising cases of flu and RSV (respiratory syncytial virus).
Dr. Jetelina shares that concern, worrying that those illnesses may be what overwhelms hospital capacity.
Another wild card is the situation in China. With the easing of China’s “zero COVID” policies, cases there are rising dramatically. Some models are predicting up to 1 million COVID deaths could occur in China in 2023. (The United States is now requiring travelers from China to show a negative COVID test before entering. Italy and Japan have taken similar measures.)
“The suffering that is going to occur in China is not good news at all,” Dr. Topol said. “We are going to be seeing that for many weeks if not months ahead.”
Theoretically, uncontained spread such as what is expected there could generate a whole new family of variants, he said. But “the main hit is going to be in China,” he predicted. “But it’s hard to project with accuracy.”
“China is 20% of the global population, so we can’t ignore it,” Dr. Jetelina said. “The question is, what’s the probability of a subvariant of concern coming from China? I think the probability is pretty low, but the possibility is there.”
What happens with cases in China may “throw a wrench” in the transition from pandemic to endemic, Dr. Chin-Hong said. But even if the rising cases in China do result in a new variant, “there’s so much T cell and B cell immunity [here], your average person is still not going to get seriously ill, even if the variant looks really scary.”
Minimizing the damage
Experts echo the same advice on stemming the surge, especially for adults who are 65 or older: Get the bivalent booster, and get it now.
“The same with the influenza vaccine,” Dr. Schaffner said.
Both the booster vaccine and the flu vaccine have been underused this year, he said. “It’s part of the general vaccine fatigue.”
The low uptake of the booster vaccine is concerning, Dr. Topol said, especially among adults aged 65 and older, the age group most vulnerable to severe disease. Just 35.7% of U.S. adults 65 and older have gotten the booster, according to the CDC. Dr. Topol calls that a tragedy.
Younger people have not taken to the booster, either. Overall, only 14.1% of people aged 5 and up have gotten an updated booster dose, according to the CDC.
Recent studies find value in the boosters. One study looked only at adults age 65 or older, finding that the bivalent booster reduced the risk of hospitalization by 84% compared to someone not vaccinated, and 73% compared to someone who had received only the monovalent vaccine. Another study of adults found those who had gotten the bivalent were less likely to need COVID-related emergency room care or urgent care.
In a Dec. 21 report in the New England Journal of Medicine, researchers took plasma samples from people who had gotten either one or two monovalent boosters or the bivalent to determine how well they worked against the circulating Omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.5, BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, and XBB. The bivalent worked better than the monovalent against all the Omicron subvariants, but especially against BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, and XBB.
Rapid testing can help minimize transmission. On Dec. 15, the Biden administration announced its Winter Preparedness Plan, urging Americans to test before and after travel as well as indoor visiting with vulnerable individuals, providing another round of free at-home tests, continuing to make community testing available and continuing to provide vaccines.
Besides the general precautions, Dr. Schaffner suggested: “Look at yourself. Who are you? If you are older than 65, or have underlying illness or are immunocompromised, or are pregnant, please put your mask back on. And think about social distancing. It might be time to worship at home and stream a movie,” instead of going to the theaters, he said.
Back to mandates?
On Dec. 9, the New York City Commissioner of Health and Mental Hygiene urged a return to masking indoors, saying people “should” mask up, including in schools, stores, offices, and when in crowded outdoor settings.
On the same date, the County of Los Angeles Public Health urged a return to masking for everyone aged 2 and older when indoors, including at schools, in transit, or in work sites when around others.
While the CDC order requiring masks on public transportation is no longer in effect, the agency continues to recommend that those using public transportation do so.
But some are taking that further. In Philadelphia, for example, School Superintendent Tony B. Watlington Sr., EdD, announced before the winter break that indoor masking would be required for all students and staff for the first 2 weeks of school return, through Jan. 13, citing guidance from the Philadelphia Department of Public Health.
Universal masking in schools does reduce COVID transmission, as a study published in late November suggests. After Massachusetts dropped the statewide universal masking policy in public schools in February 2022, researchers compared the incidence of COVID in 70 school districts there that dropped the mandate with two school districts that kept it. In the 15 weeks after the policy was rescinded, the lifting of the mandate was linked with an additional 44.9 cases of COVID per 1,000 students and staff. That corresponded to an estimated 11,901 cases and to nearly 30% of the cases in all districts during that time.
That said, experts see mandates as the exception rather than the rule, at least for now, citing public backlash against mandates to mask or follow other restrictions.
“Mandating, we know, it shuts people off,” Dr. Topol said. “It’s unenforceable. If you have a very strong recommendation, that’s probably as good as you’re going to be able to do right now.”
There may be communities where mandates go over better than others, Dr. Schaffner said, such as communities where people have confidence in their public health authorities.
Glimmers of hope
Despite uncertainties, experts offered some not-so-dismal perspectives as well.
“I think our numbers will continue to go up, but certainly not like 2021 or 2020,” Dr. Chin-Hong said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.