User login
Single chest x-ray could predict 10-year CVD risk
who presented the results of their deep-learning model at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America.
Current American College of Cardiologists and American Heart Association guidelines recommend estimating 10-year risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) to determine whether a patient should receive statins to help prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Statins are recommended for patients with a 10-year risk of 7.5% or higher, the authors noted.
The current ASCVD risk score is determined with nine factors: age, sex, race, systolic blood pressure, hypertension treatment, smoking, type 2 diabetes, and a lipid panel.
Not all data points available in EHR
But not all of those data points may be available through the electronic health record, “which makes novel and easier approaches for population-wide screening desirable,” said lead researcher Jakob Weiss, MD, a radiologist affiliated with the Cardiovascular Imaging Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital and the AI in medicine program at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Chest x-ray images, on the other hand, are commonly available. The images carry rich information beyond diagnostic data but have not been used in this type of prediction model because AI models have been lacking, Dr. Weiss said.
The researchers trained a deep-learning model with single chest x-rays only.
They used 147,497 chest x-rays from 40,643 participants in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer (PLCO) Screening Trial, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial designed and sponsored by the National Cancer Institute.
Dr. Weiss acknowledged that the population used to train the model was heavily White and that should be a consideration in validating the model.
They compared their model’s ability to predict 10-year ASCVD risk with the standard ACC/AHA model.
“Based on a single chest radiograph image, deep learning can predict the risk of future cardiovascular events independent of cardiovascular risk factors and with similar performance to the established and guideline-recommended ASCVD risk score,” Dr. Weiss said.
Tested against independent group
They tested the model against an independent group of 11,430 outpatients (average age, 60 years; 42.9% male) who underwent a routine outpatient chest x-ray at Mass General Brigham and were potentially eligible to receive statins.
Of those 11,430 patients, 1,096 (9.6%) had a major adverse cardiac event over the median follow-up of 10.3 years.
There was a significant association of CXR-CVD risk and MACE among patients eligible to receive statins, the researchers found (hazard ratio, 2.03; 95% confidence interval, 1.81-2.30; P < .001), which remained significant after adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors (adjusted HR, 1.63; 95% CI, 1.43-1.86; P < .001).
Some of the variables were missing in the standard model, but in a subgroup of 2,401 patients, all the variables were available.
They calculated ASCVD risk in that subgroup using the standard model and the CXR model and found that the performance was similar (c-statistic, 0.64 vs. 0.65; P = .48) to the ASCVD risk score (aHR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.20-2.09; P = .001).
Ritu R. Gill MD, MPH, associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School in Boston, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that “the predictive algorithm is promising and potentially translatable and could enhance the annual medical checkup in a select population.
“The algorithm was developed using the PLCO cohort with radiographs, which are likely subjects in the lung cancer screening arm,” she said. “This cohort would be at high risk of cardiovascular diseases, as smoking is a known risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, and therefore the results are expected.
“The algorithm needs to be validated in an independent database with inclusion of subjects with younger age groups and adjusted for gender and racial diversity,” Gill said.
David Cho, MD, a cardiologist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who also was not part of the study, said in an interview that “this work is a great example of AI being able to detect clinically relevant outcomes with a widely used and low-cost screening test.
“The volume of data needed to train these models is already out there,” Dr. Cho said. “It just needs to be mined.”
He noted that this tool, if validated in randomized trials, could help determine risk among patients living in places where access to specialized cardiac care is limited.
Dr. Weiss and Dr. Cho disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gill has received research support from Cannon Inc and consultant fees from Imbio and WorldCare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
who presented the results of their deep-learning model at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America.
Current American College of Cardiologists and American Heart Association guidelines recommend estimating 10-year risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) to determine whether a patient should receive statins to help prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Statins are recommended for patients with a 10-year risk of 7.5% or higher, the authors noted.
The current ASCVD risk score is determined with nine factors: age, sex, race, systolic blood pressure, hypertension treatment, smoking, type 2 diabetes, and a lipid panel.
Not all data points available in EHR
But not all of those data points may be available through the electronic health record, “which makes novel and easier approaches for population-wide screening desirable,” said lead researcher Jakob Weiss, MD, a radiologist affiliated with the Cardiovascular Imaging Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital and the AI in medicine program at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Chest x-ray images, on the other hand, are commonly available. The images carry rich information beyond diagnostic data but have not been used in this type of prediction model because AI models have been lacking, Dr. Weiss said.
The researchers trained a deep-learning model with single chest x-rays only.
They used 147,497 chest x-rays from 40,643 participants in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer (PLCO) Screening Trial, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial designed and sponsored by the National Cancer Institute.
Dr. Weiss acknowledged that the population used to train the model was heavily White and that should be a consideration in validating the model.
They compared their model’s ability to predict 10-year ASCVD risk with the standard ACC/AHA model.
“Based on a single chest radiograph image, deep learning can predict the risk of future cardiovascular events independent of cardiovascular risk factors and with similar performance to the established and guideline-recommended ASCVD risk score,” Dr. Weiss said.
Tested against independent group
They tested the model against an independent group of 11,430 outpatients (average age, 60 years; 42.9% male) who underwent a routine outpatient chest x-ray at Mass General Brigham and were potentially eligible to receive statins.
Of those 11,430 patients, 1,096 (9.6%) had a major adverse cardiac event over the median follow-up of 10.3 years.
There was a significant association of CXR-CVD risk and MACE among patients eligible to receive statins, the researchers found (hazard ratio, 2.03; 95% confidence interval, 1.81-2.30; P < .001), which remained significant after adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors (adjusted HR, 1.63; 95% CI, 1.43-1.86; P < .001).
Some of the variables were missing in the standard model, but in a subgroup of 2,401 patients, all the variables were available.
They calculated ASCVD risk in that subgroup using the standard model and the CXR model and found that the performance was similar (c-statistic, 0.64 vs. 0.65; P = .48) to the ASCVD risk score (aHR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.20-2.09; P = .001).
Ritu R. Gill MD, MPH, associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School in Boston, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that “the predictive algorithm is promising and potentially translatable and could enhance the annual medical checkup in a select population.
“The algorithm was developed using the PLCO cohort with radiographs, which are likely subjects in the lung cancer screening arm,” she said. “This cohort would be at high risk of cardiovascular diseases, as smoking is a known risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, and therefore the results are expected.
“The algorithm needs to be validated in an independent database with inclusion of subjects with younger age groups and adjusted for gender and racial diversity,” Gill said.
David Cho, MD, a cardiologist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who also was not part of the study, said in an interview that “this work is a great example of AI being able to detect clinically relevant outcomes with a widely used and low-cost screening test.
“The volume of data needed to train these models is already out there,” Dr. Cho said. “It just needs to be mined.”
He noted that this tool, if validated in randomized trials, could help determine risk among patients living in places where access to specialized cardiac care is limited.
Dr. Weiss and Dr. Cho disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gill has received research support from Cannon Inc and consultant fees from Imbio and WorldCare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
who presented the results of their deep-learning model at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America.
Current American College of Cardiologists and American Heart Association guidelines recommend estimating 10-year risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) to determine whether a patient should receive statins to help prevent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Statins are recommended for patients with a 10-year risk of 7.5% or higher, the authors noted.
The current ASCVD risk score is determined with nine factors: age, sex, race, systolic blood pressure, hypertension treatment, smoking, type 2 diabetes, and a lipid panel.
Not all data points available in EHR
But not all of those data points may be available through the electronic health record, “which makes novel and easier approaches for population-wide screening desirable,” said lead researcher Jakob Weiss, MD, a radiologist affiliated with the Cardiovascular Imaging Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital and the AI in medicine program at the Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Chest x-ray images, on the other hand, are commonly available. The images carry rich information beyond diagnostic data but have not been used in this type of prediction model because AI models have been lacking, Dr. Weiss said.
The researchers trained a deep-learning model with single chest x-rays only.
They used 147,497 chest x-rays from 40,643 participants in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer (PLCO) Screening Trial, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial designed and sponsored by the National Cancer Institute.
Dr. Weiss acknowledged that the population used to train the model was heavily White and that should be a consideration in validating the model.
They compared their model’s ability to predict 10-year ASCVD risk with the standard ACC/AHA model.
“Based on a single chest radiograph image, deep learning can predict the risk of future cardiovascular events independent of cardiovascular risk factors and with similar performance to the established and guideline-recommended ASCVD risk score,” Dr. Weiss said.
Tested against independent group
They tested the model against an independent group of 11,430 outpatients (average age, 60 years; 42.9% male) who underwent a routine outpatient chest x-ray at Mass General Brigham and were potentially eligible to receive statins.
Of those 11,430 patients, 1,096 (9.6%) had a major adverse cardiac event over the median follow-up of 10.3 years.
There was a significant association of CXR-CVD risk and MACE among patients eligible to receive statins, the researchers found (hazard ratio, 2.03; 95% confidence interval, 1.81-2.30; P < .001), which remained significant after adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors (adjusted HR, 1.63; 95% CI, 1.43-1.86; P < .001).
Some of the variables were missing in the standard model, but in a subgroup of 2,401 patients, all the variables were available.
They calculated ASCVD risk in that subgroup using the standard model and the CXR model and found that the performance was similar (c-statistic, 0.64 vs. 0.65; P = .48) to the ASCVD risk score (aHR, 1.58; 95% CI, 1.20-2.09; P = .001).
Ritu R. Gill MD, MPH, associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School in Boston, who was not part of the study, said in an interview that “the predictive algorithm is promising and potentially translatable and could enhance the annual medical checkup in a select population.
“The algorithm was developed using the PLCO cohort with radiographs, which are likely subjects in the lung cancer screening arm,” she said. “This cohort would be at high risk of cardiovascular diseases, as smoking is a known risk factor for atherosclerotic disease, and therefore the results are expected.
“The algorithm needs to be validated in an independent database with inclusion of subjects with younger age groups and adjusted for gender and racial diversity,” Gill said.
David Cho, MD, a cardiologist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who also was not part of the study, said in an interview that “this work is a great example of AI being able to detect clinically relevant outcomes with a widely used and low-cost screening test.
“The volume of data needed to train these models is already out there,” Dr. Cho said. “It just needs to be mined.”
He noted that this tool, if validated in randomized trials, could help determine risk among patients living in places where access to specialized cardiac care is limited.
Dr. Weiss and Dr. Cho disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gill has received research support from Cannon Inc and consultant fees from Imbio and WorldCare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT RSNA 2022
Advancing health equity in neurology is essential to patient care
Black and Latinx older adults are up to three times as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than non-Latinx White adults and tend to experience onset at a younger age with more severe symptoms, according to Monica Rivera-Mindt, PhD, a professor of psychology at Fordham University and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Looking ahead, that means by 2030, nearly 40% of the 8.4 million Americans affected by Alzheimer’s disease will be Black and/or Latinx, she said. These facts were among the stark disparities in health care outcomes Dr. Rivera-Mindt discussed in her presentation on brain health equity at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Dr. Rivera-Mindt’s presentation opened the ANA’s plenary session on health disparities and inequities. The plenary, “Advancing Neurologic Equity: Challenges and Paths Forward,” did not simply enumerate racial and ethnic disparities that exist with various neurological conditions. Rather it went beyond the discussion of what disparities exist into understanding the roots of them as well as tips, tools, and resources that can aid clinicians in addressing or ameliorating them.
Roy Hamilton, MD, an associate professor of neurology and physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “If clinicians are unaware of these disparities or don’t have any sense of how to start to address or think about them, then they’re really missing out on an important component of their education as persons who take care of patients with brain disorders.”
Dr. Hamilton, who organized the plenary, noted that awareness of these disparities is crucial to comprehensively caring for patients.
Missed opportunities
“We’re talking about disadvantages that are structural and large scale, but those disadvantages play themselves out in the individual encounter,” Dr. Hamilton said. “When physicians see patients, they have to treat the whole patient in front of them,” which means being aware of the risks and factors that could affect a patient’s clinical presentation. “Being aware of disparities has practical impacts on physician judgment,” he said.
For example, recent research in multiple sclerosis (MS) has highlighted how clinicians may be missing diagnosis of this condition in non-White populations because the condition has been regarded for so long as a “White person’s” disease, Dr. Hamilton said. In non-White patients exhibiting MS symptoms, then, clinicians may have been less likely to consider MS as a possibility, thereby delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Those patterns may partly explain why the mortality rate for MS is greater in Black patients, who also show more rapid neurodegeneration than White patients with MS, Lilyana Amezcua, MD, an associate professor of neurology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, reported in the plenary’s second presentation.
Transgender issues
The third session, presented by Nicole Rosendale, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the San Francisco General Hospital neurology inpatient services, examined disparities in neurology within the LGBTQ+ community through representative case studies and then offered specific ways that neurologists could make their practices more inclusive and equitable for sexual and gender minorities.
Her first case study was a 52-year-old man who presented with new-onset seizures, right hemiparesis, and aphasia. A brain biopsy consistent with adenocarcinoma eventually led his physician to discover he had metastatic breast cancer. It turned out the man was transgender and, despite a family history of breast cancer, hadn’t been advised to get breast cancer screenings.
“Breast cancer was not initially on the differential as no one had identified that the patient was transmasculine,” Dr. Rosendale said. A major challenge to providing care to transgender patients is a dearth of data on risks and screening recommendations. Another barrier is low knowledge of LGBTQ+ health among neurologists, Dr. Rosendale said while sharing findings from her 2019 study on the topic and calling for more research in LGBTQ+ populations.
Dr. Rosendale’s second case study dealt with a nonbinary patient who suffered from debilitating headaches for decades, first because they lacked access to health insurance and then because negative experiences with providers dissuaded them from seeking care. In data from the Center for American Progress she shared, 8% of LGB respondents and 22% of transgender respondents said they had avoided or delayed care because of fear of discrimination or mistreatment.
“So it’s not only access but also what experiences people are having when they go in and whether they’re actually even getting access to care or being taken care of,” Dr. Rosendale said. Other findings from the CAP found that:
- 8% of LGB patients and 29% of transgender patients reported having a clinician refuse to see them.
- 6% of LGB patients and 12% of transgender patients reported that a clinician refused to give them health care.
- 9% of LGB patients and 21% of transgender patients experienced harsh or abusive language during a health care experience.
- 7% of LGB patients and nearly a third (29%) of transgender patients experienced unwanted physical contact, such as fondling or sexual assault.
Reducing the disparities
Adys Mendizabal, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Institute of Society and Genetics at the University of California, Los Angeles, who attended the presentation, was grateful to see how the various lectures enriched the discussion beyond stating the fact of racial/ethnic disparities and dug into the nuances on how to think about and address these disparities. She particularly appreciated discussion about the need to go out of the way to recruit diverse patient populations for clinical trials while also providing them care.
“It is definitely complicated, but it’s not impossible for an individual neurologist or an individual department to do something to reduce some of the disparities,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It starts with just knowing that they exist and being aware of some of the things that may be impacting care for a particular patient.”
Tools to counter disparity
In the final presentation, Amy Kind, MD, PhD, the associate dean for social health sciences and programs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, rounded out the discussion by exploring social determinants of health and their influence on outcomes.
“Social determinants impact brain health, and brain health is not distributed equally,” Dr. Kind told attendees. “We have known this for decades, yet disparities persist.”
Dr. Kind described the “exposome,” a “measure of all the exposures of an individual in a lifetime and how those exposures relate to health,” according to the CDC, and then introduced a tool clinicians can use to better understand social determinants of health in specific geographic areas. The Neighborhood Atlas, which Dr. Kind described in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018, measures 17 social determinants across small population-sensitive areas and provides an area deprivation index. A high area deprivation index is linked to a range of negative outcomes, including reshopitalization, later diagnoses, less comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, increased risk of postsurgical complications, and decreased life expectancy.
“One of the things that really stood out to me about Dr. Kind’s discussion of the use of the area deprivation index was the fact that understanding and quantifying these kinds of risks and exposures is the vehicle for creating the kinds of social changes, including policy changes, that will actually lead to addressing and mitigating some of these lifelong risks and exposures,” Dr. Hamilton said. “It is implausible to think that a specific group of people would be genetically more susceptible to basically every disease that we know,” he added. “It makes much more sense to think that groups of individuals have been subjected systematically to conditions that impair health in a variety of ways.”
Not just race, ethnicity, sex, and gender
Following the four presentations from researchers in health inequities was an Emerging Scholar presentation in which Jay B. Lusk, an MD/MBA candidate at Duke University, Durham, N.C., shared new research findings on the role of neighborhood disadvantage in predicting mortality from coma, stroke, and other neurologic conditions. His findings revealed that living in a neighborhood with greater deprivation substantially increased risk of mortality even after accounting for individual wealth and demographics.
Maria Eugenia Diaz-Ortiz, PhD, of the department of neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said she found the five presentations to be an excellent introduction to people like herself who are in the earlier stages of learning about health equity research.
“I think they introduced various important concepts and frameworks and provided tools for people who don’t know about them,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “Then they asked important questions and provided some solutions to them.”
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz also appreciated seemingly minor but actually important details in how the speakers presented themselves, such as Dr. Rivera-Mindt opening with a land acknowledgment and her disclosures of “positionality.” The former recognized the traditional Native American custodians of the land on which she lives and works, and the latter revealed details about her as an individual – such as being the Afro-Latinx daughter of immigrants yet being cisgender, able-bodied, and U.S.-born – that show where she falls on the axis of adversity and axis of privilege.
Implications for research
The biggest takeaway for Dr. Diaz-Ortiz, however, came from the first Q&A session when someone asked how to increase underrepresented populations in dementia research. Dr. Rivera-Mindt described her experience engaging these communities by employing “community-based participatory research practices, which involves making yourself a part of the community and making the community active participants in the research,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “It’s an evidence-based approach that has been shown to increase participation in research not only in her work but in the work of others.”
Preaching to the choir
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz was pleased overall with the plenary but disappointed in its placement at the end of the meeting, when attendance is always lower as attendees head home.
“The people who stayed were people who already know and recognize the value of health equity work, so I think that was a missed opportunity where the session could have been included on day one or two to boost attendance and also to educate like a broader group of neurologists,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said in an interview.
Dr. Mendizabal felt similarly, appreciating the plenary but noting it was “definitely overdue” and that it should not be the last session. Instead, sessions on health equity should be as easy as possible to attend to bring in larger audiences. “Perhaps having that session on a Saturday or Sunday would have a higher likelihood of greater attendance than on a Tuesday,” she said. That said, Dr. Mendizabal also noticed that greater attention to health care disparities was woven into many other sessions throughout the conference, which is “the best way of addressing health equity instead of trying to just designate a session,” she said.
Dr. Mendizabal hopes that plenaries like this one and the weaving of health equity issues into presentations throughout neurology conferences continue.
“After the racial reckoning in 2020, there was a big impetus and a big wave of energy in addressing health disparities in the field, and I hope that that momentum is not starting to wane,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It’s important because not talking about is not going to make this issue go away.”
Dr. Hamilton agreed that it is important that the conversation continue and that physicians recognize the importance of understanding health care disparities and determinants of health, regardless of where they fall on the political spectrum or whether they choose to get involved in policy or advocacy.
“Irrespective of whether you think race or ethnicity or socioeconomic status are political issues or not, it is the case that you’re obligated to have an objective understanding of the factors that contribute to your patient’s health and as points of intervention,” Dr. Hamilton said. “So even if you don’t want to sit down and jot off that email to your senator, you still have to take these factors into account when you’re treating the person who’s sitting right in front of you, and that’s not political. That’s the promise of being a physician.”
Dr. Amezcua has received personal compensation for consulting, speaking, or serving on steering committees or advisory boards for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genentech, and EMD Serono, and she has received research support from Biogen Idec and Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation. Dr. Kind reported support from the Alzheimer’s Association. Dr. Diaz-Ortiz is coinventor of a provisional patent submitted by the University of Pennsylvania that relates to a potential therapeutic in Parkinson’s disease. Mr. Lusk reported fellowship support from American Heart Association and travel support from the American Neurological Association. No other speakers or sources had relevant disclosures.
Black and Latinx older adults are up to three times as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than non-Latinx White adults and tend to experience onset at a younger age with more severe symptoms, according to Monica Rivera-Mindt, PhD, a professor of psychology at Fordham University and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Looking ahead, that means by 2030, nearly 40% of the 8.4 million Americans affected by Alzheimer’s disease will be Black and/or Latinx, she said. These facts were among the stark disparities in health care outcomes Dr. Rivera-Mindt discussed in her presentation on brain health equity at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Dr. Rivera-Mindt’s presentation opened the ANA’s plenary session on health disparities and inequities. The plenary, “Advancing Neurologic Equity: Challenges and Paths Forward,” did not simply enumerate racial and ethnic disparities that exist with various neurological conditions. Rather it went beyond the discussion of what disparities exist into understanding the roots of them as well as tips, tools, and resources that can aid clinicians in addressing or ameliorating them.
Roy Hamilton, MD, an associate professor of neurology and physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “If clinicians are unaware of these disparities or don’t have any sense of how to start to address or think about them, then they’re really missing out on an important component of their education as persons who take care of patients with brain disorders.”
Dr. Hamilton, who organized the plenary, noted that awareness of these disparities is crucial to comprehensively caring for patients.
Missed opportunities
“We’re talking about disadvantages that are structural and large scale, but those disadvantages play themselves out in the individual encounter,” Dr. Hamilton said. “When physicians see patients, they have to treat the whole patient in front of them,” which means being aware of the risks and factors that could affect a patient’s clinical presentation. “Being aware of disparities has practical impacts on physician judgment,” he said.
For example, recent research in multiple sclerosis (MS) has highlighted how clinicians may be missing diagnosis of this condition in non-White populations because the condition has been regarded for so long as a “White person’s” disease, Dr. Hamilton said. In non-White patients exhibiting MS symptoms, then, clinicians may have been less likely to consider MS as a possibility, thereby delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Those patterns may partly explain why the mortality rate for MS is greater in Black patients, who also show more rapid neurodegeneration than White patients with MS, Lilyana Amezcua, MD, an associate professor of neurology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, reported in the plenary’s second presentation.
Transgender issues
The third session, presented by Nicole Rosendale, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the San Francisco General Hospital neurology inpatient services, examined disparities in neurology within the LGBTQ+ community through representative case studies and then offered specific ways that neurologists could make their practices more inclusive and equitable for sexual and gender minorities.
Her first case study was a 52-year-old man who presented with new-onset seizures, right hemiparesis, and aphasia. A brain biopsy consistent with adenocarcinoma eventually led his physician to discover he had metastatic breast cancer. It turned out the man was transgender and, despite a family history of breast cancer, hadn’t been advised to get breast cancer screenings.
“Breast cancer was not initially on the differential as no one had identified that the patient was transmasculine,” Dr. Rosendale said. A major challenge to providing care to transgender patients is a dearth of data on risks and screening recommendations. Another barrier is low knowledge of LGBTQ+ health among neurologists, Dr. Rosendale said while sharing findings from her 2019 study on the topic and calling for more research in LGBTQ+ populations.
Dr. Rosendale’s second case study dealt with a nonbinary patient who suffered from debilitating headaches for decades, first because they lacked access to health insurance and then because negative experiences with providers dissuaded them from seeking care. In data from the Center for American Progress she shared, 8% of LGB respondents and 22% of transgender respondents said they had avoided or delayed care because of fear of discrimination or mistreatment.
“So it’s not only access but also what experiences people are having when they go in and whether they’re actually even getting access to care or being taken care of,” Dr. Rosendale said. Other findings from the CAP found that:
- 8% of LGB patients and 29% of transgender patients reported having a clinician refuse to see them.
- 6% of LGB patients and 12% of transgender patients reported that a clinician refused to give them health care.
- 9% of LGB patients and 21% of transgender patients experienced harsh or abusive language during a health care experience.
- 7% of LGB patients and nearly a third (29%) of transgender patients experienced unwanted physical contact, such as fondling or sexual assault.
Reducing the disparities
Adys Mendizabal, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Institute of Society and Genetics at the University of California, Los Angeles, who attended the presentation, was grateful to see how the various lectures enriched the discussion beyond stating the fact of racial/ethnic disparities and dug into the nuances on how to think about and address these disparities. She particularly appreciated discussion about the need to go out of the way to recruit diverse patient populations for clinical trials while also providing them care.
“It is definitely complicated, but it’s not impossible for an individual neurologist or an individual department to do something to reduce some of the disparities,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It starts with just knowing that they exist and being aware of some of the things that may be impacting care for a particular patient.”
Tools to counter disparity
In the final presentation, Amy Kind, MD, PhD, the associate dean for social health sciences and programs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, rounded out the discussion by exploring social determinants of health and their influence on outcomes.
“Social determinants impact brain health, and brain health is not distributed equally,” Dr. Kind told attendees. “We have known this for decades, yet disparities persist.”
Dr. Kind described the “exposome,” a “measure of all the exposures of an individual in a lifetime and how those exposures relate to health,” according to the CDC, and then introduced a tool clinicians can use to better understand social determinants of health in specific geographic areas. The Neighborhood Atlas, which Dr. Kind described in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018, measures 17 social determinants across small population-sensitive areas and provides an area deprivation index. A high area deprivation index is linked to a range of negative outcomes, including reshopitalization, later diagnoses, less comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, increased risk of postsurgical complications, and decreased life expectancy.
“One of the things that really stood out to me about Dr. Kind’s discussion of the use of the area deprivation index was the fact that understanding and quantifying these kinds of risks and exposures is the vehicle for creating the kinds of social changes, including policy changes, that will actually lead to addressing and mitigating some of these lifelong risks and exposures,” Dr. Hamilton said. “It is implausible to think that a specific group of people would be genetically more susceptible to basically every disease that we know,” he added. “It makes much more sense to think that groups of individuals have been subjected systematically to conditions that impair health in a variety of ways.”
Not just race, ethnicity, sex, and gender
Following the four presentations from researchers in health inequities was an Emerging Scholar presentation in which Jay B. Lusk, an MD/MBA candidate at Duke University, Durham, N.C., shared new research findings on the role of neighborhood disadvantage in predicting mortality from coma, stroke, and other neurologic conditions. His findings revealed that living in a neighborhood with greater deprivation substantially increased risk of mortality even after accounting for individual wealth and demographics.
Maria Eugenia Diaz-Ortiz, PhD, of the department of neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said she found the five presentations to be an excellent introduction to people like herself who are in the earlier stages of learning about health equity research.
“I think they introduced various important concepts and frameworks and provided tools for people who don’t know about them,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “Then they asked important questions and provided some solutions to them.”
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz also appreciated seemingly minor but actually important details in how the speakers presented themselves, such as Dr. Rivera-Mindt opening with a land acknowledgment and her disclosures of “positionality.” The former recognized the traditional Native American custodians of the land on which she lives and works, and the latter revealed details about her as an individual – such as being the Afro-Latinx daughter of immigrants yet being cisgender, able-bodied, and U.S.-born – that show where she falls on the axis of adversity and axis of privilege.
Implications for research
The biggest takeaway for Dr. Diaz-Ortiz, however, came from the first Q&A session when someone asked how to increase underrepresented populations in dementia research. Dr. Rivera-Mindt described her experience engaging these communities by employing “community-based participatory research practices, which involves making yourself a part of the community and making the community active participants in the research,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “It’s an evidence-based approach that has been shown to increase participation in research not only in her work but in the work of others.”
Preaching to the choir
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz was pleased overall with the plenary but disappointed in its placement at the end of the meeting, when attendance is always lower as attendees head home.
“The people who stayed were people who already know and recognize the value of health equity work, so I think that was a missed opportunity where the session could have been included on day one or two to boost attendance and also to educate like a broader group of neurologists,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said in an interview.
Dr. Mendizabal felt similarly, appreciating the plenary but noting it was “definitely overdue” and that it should not be the last session. Instead, sessions on health equity should be as easy as possible to attend to bring in larger audiences. “Perhaps having that session on a Saturday or Sunday would have a higher likelihood of greater attendance than on a Tuesday,” she said. That said, Dr. Mendizabal also noticed that greater attention to health care disparities was woven into many other sessions throughout the conference, which is “the best way of addressing health equity instead of trying to just designate a session,” she said.
Dr. Mendizabal hopes that plenaries like this one and the weaving of health equity issues into presentations throughout neurology conferences continue.
“After the racial reckoning in 2020, there was a big impetus and a big wave of energy in addressing health disparities in the field, and I hope that that momentum is not starting to wane,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It’s important because not talking about is not going to make this issue go away.”
Dr. Hamilton agreed that it is important that the conversation continue and that physicians recognize the importance of understanding health care disparities and determinants of health, regardless of where they fall on the political spectrum or whether they choose to get involved in policy or advocacy.
“Irrespective of whether you think race or ethnicity or socioeconomic status are political issues or not, it is the case that you’re obligated to have an objective understanding of the factors that contribute to your patient’s health and as points of intervention,” Dr. Hamilton said. “So even if you don’t want to sit down and jot off that email to your senator, you still have to take these factors into account when you’re treating the person who’s sitting right in front of you, and that’s not political. That’s the promise of being a physician.”
Dr. Amezcua has received personal compensation for consulting, speaking, or serving on steering committees or advisory boards for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genentech, and EMD Serono, and she has received research support from Biogen Idec and Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation. Dr. Kind reported support from the Alzheimer’s Association. Dr. Diaz-Ortiz is coinventor of a provisional patent submitted by the University of Pennsylvania that relates to a potential therapeutic in Parkinson’s disease. Mr. Lusk reported fellowship support from American Heart Association and travel support from the American Neurological Association. No other speakers or sources had relevant disclosures.
Black and Latinx older adults are up to three times as likely to develop Alzheimer’s disease than non-Latinx White adults and tend to experience onset at a younger age with more severe symptoms, according to Monica Rivera-Mindt, PhD, a professor of psychology at Fordham University and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. Looking ahead, that means by 2030, nearly 40% of the 8.4 million Americans affected by Alzheimer’s disease will be Black and/or Latinx, she said. These facts were among the stark disparities in health care outcomes Dr. Rivera-Mindt discussed in her presentation on brain health equity at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Neurological Association.
Dr. Rivera-Mindt’s presentation opened the ANA’s plenary session on health disparities and inequities. The plenary, “Advancing Neurologic Equity: Challenges and Paths Forward,” did not simply enumerate racial and ethnic disparities that exist with various neurological conditions. Rather it went beyond the discussion of what disparities exist into understanding the roots of them as well as tips, tools, and resources that can aid clinicians in addressing or ameliorating them.
Roy Hamilton, MD, an associate professor of neurology and physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said. “If clinicians are unaware of these disparities or don’t have any sense of how to start to address or think about them, then they’re really missing out on an important component of their education as persons who take care of patients with brain disorders.”
Dr. Hamilton, who organized the plenary, noted that awareness of these disparities is crucial to comprehensively caring for patients.
Missed opportunities
“We’re talking about disadvantages that are structural and large scale, but those disadvantages play themselves out in the individual encounter,” Dr. Hamilton said. “When physicians see patients, they have to treat the whole patient in front of them,” which means being aware of the risks and factors that could affect a patient’s clinical presentation. “Being aware of disparities has practical impacts on physician judgment,” he said.
For example, recent research in multiple sclerosis (MS) has highlighted how clinicians may be missing diagnosis of this condition in non-White populations because the condition has been regarded for so long as a “White person’s” disease, Dr. Hamilton said. In non-White patients exhibiting MS symptoms, then, clinicians may have been less likely to consider MS as a possibility, thereby delaying diagnosis and treatment.
Those patterns may partly explain why the mortality rate for MS is greater in Black patients, who also show more rapid neurodegeneration than White patients with MS, Lilyana Amezcua, MD, an associate professor of neurology at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, reported in the plenary’s second presentation.
Transgender issues
The third session, presented by Nicole Rosendale, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the San Francisco General Hospital neurology inpatient services, examined disparities in neurology within the LGBTQ+ community through representative case studies and then offered specific ways that neurologists could make their practices more inclusive and equitable for sexual and gender minorities.
Her first case study was a 52-year-old man who presented with new-onset seizures, right hemiparesis, and aphasia. A brain biopsy consistent with adenocarcinoma eventually led his physician to discover he had metastatic breast cancer. It turned out the man was transgender and, despite a family history of breast cancer, hadn’t been advised to get breast cancer screenings.
“Breast cancer was not initially on the differential as no one had identified that the patient was transmasculine,” Dr. Rosendale said. A major challenge to providing care to transgender patients is a dearth of data on risks and screening recommendations. Another barrier is low knowledge of LGBTQ+ health among neurologists, Dr. Rosendale said while sharing findings from her 2019 study on the topic and calling for more research in LGBTQ+ populations.
Dr. Rosendale’s second case study dealt with a nonbinary patient who suffered from debilitating headaches for decades, first because they lacked access to health insurance and then because negative experiences with providers dissuaded them from seeking care. In data from the Center for American Progress she shared, 8% of LGB respondents and 22% of transgender respondents said they had avoided or delayed care because of fear of discrimination or mistreatment.
“So it’s not only access but also what experiences people are having when they go in and whether they’re actually even getting access to care or being taken care of,” Dr. Rosendale said. Other findings from the CAP found that:
- 8% of LGB patients and 29% of transgender patients reported having a clinician refuse to see them.
- 6% of LGB patients and 12% of transgender patients reported that a clinician refused to give them health care.
- 9% of LGB patients and 21% of transgender patients experienced harsh or abusive language during a health care experience.
- 7% of LGB patients and nearly a third (29%) of transgender patients experienced unwanted physical contact, such as fondling or sexual assault.
Reducing the disparities
Adys Mendizabal, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the Institute of Society and Genetics at the University of California, Los Angeles, who attended the presentation, was grateful to see how the various lectures enriched the discussion beyond stating the fact of racial/ethnic disparities and dug into the nuances on how to think about and address these disparities. She particularly appreciated discussion about the need to go out of the way to recruit diverse patient populations for clinical trials while also providing them care.
“It is definitely complicated, but it’s not impossible for an individual neurologist or an individual department to do something to reduce some of the disparities,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It starts with just knowing that they exist and being aware of some of the things that may be impacting care for a particular patient.”
Tools to counter disparity
In the final presentation, Amy Kind, MD, PhD, the associate dean for social health sciences and programs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, rounded out the discussion by exploring social determinants of health and their influence on outcomes.
“Social determinants impact brain health, and brain health is not distributed equally,” Dr. Kind told attendees. “We have known this for decades, yet disparities persist.”
Dr. Kind described the “exposome,” a “measure of all the exposures of an individual in a lifetime and how those exposures relate to health,” according to the CDC, and then introduced a tool clinicians can use to better understand social determinants of health in specific geographic areas. The Neighborhood Atlas, which Dr. Kind described in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2018, measures 17 social determinants across small population-sensitive areas and provides an area deprivation index. A high area deprivation index is linked to a range of negative outcomes, including reshopitalization, later diagnoses, less comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, increased risk of postsurgical complications, and decreased life expectancy.
“One of the things that really stood out to me about Dr. Kind’s discussion of the use of the area deprivation index was the fact that understanding and quantifying these kinds of risks and exposures is the vehicle for creating the kinds of social changes, including policy changes, that will actually lead to addressing and mitigating some of these lifelong risks and exposures,” Dr. Hamilton said. “It is implausible to think that a specific group of people would be genetically more susceptible to basically every disease that we know,” he added. “It makes much more sense to think that groups of individuals have been subjected systematically to conditions that impair health in a variety of ways.”
Not just race, ethnicity, sex, and gender
Following the four presentations from researchers in health inequities was an Emerging Scholar presentation in which Jay B. Lusk, an MD/MBA candidate at Duke University, Durham, N.C., shared new research findings on the role of neighborhood disadvantage in predicting mortality from coma, stroke, and other neurologic conditions. His findings revealed that living in a neighborhood with greater deprivation substantially increased risk of mortality even after accounting for individual wealth and demographics.
Maria Eugenia Diaz-Ortiz, PhD, of the department of neurology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said she found the five presentations to be an excellent introduction to people like herself who are in the earlier stages of learning about health equity research.
“I think they introduced various important concepts and frameworks and provided tools for people who don’t know about them,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “Then they asked important questions and provided some solutions to them.”
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz also appreciated seemingly minor but actually important details in how the speakers presented themselves, such as Dr. Rivera-Mindt opening with a land acknowledgment and her disclosures of “positionality.” The former recognized the traditional Native American custodians of the land on which she lives and works, and the latter revealed details about her as an individual – such as being the Afro-Latinx daughter of immigrants yet being cisgender, able-bodied, and U.S.-born – that show where she falls on the axis of adversity and axis of privilege.
Implications for research
The biggest takeaway for Dr. Diaz-Ortiz, however, came from the first Q&A session when someone asked how to increase underrepresented populations in dementia research. Dr. Rivera-Mindt described her experience engaging these communities by employing “community-based participatory research practices, which involves making yourself a part of the community and making the community active participants in the research,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said. “It’s an evidence-based approach that has been shown to increase participation in research not only in her work but in the work of others.”
Preaching to the choir
Dr. Diaz-Ortiz was pleased overall with the plenary but disappointed in its placement at the end of the meeting, when attendance is always lower as attendees head home.
“The people who stayed were people who already know and recognize the value of health equity work, so I think that was a missed opportunity where the session could have been included on day one or two to boost attendance and also to educate like a broader group of neurologists,” Dr. Diaz-Ortiz said in an interview.
Dr. Mendizabal felt similarly, appreciating the plenary but noting it was “definitely overdue” and that it should not be the last session. Instead, sessions on health equity should be as easy as possible to attend to bring in larger audiences. “Perhaps having that session on a Saturday or Sunday would have a higher likelihood of greater attendance than on a Tuesday,” she said. That said, Dr. Mendizabal also noticed that greater attention to health care disparities was woven into many other sessions throughout the conference, which is “the best way of addressing health equity instead of trying to just designate a session,” she said.
Dr. Mendizabal hopes that plenaries like this one and the weaving of health equity issues into presentations throughout neurology conferences continue.
“After the racial reckoning in 2020, there was a big impetus and a big wave of energy in addressing health disparities in the field, and I hope that that momentum is not starting to wane,” Dr. Mendizabal said. “It’s important because not talking about is not going to make this issue go away.”
Dr. Hamilton agreed that it is important that the conversation continue and that physicians recognize the importance of understanding health care disparities and determinants of health, regardless of where they fall on the political spectrum or whether they choose to get involved in policy or advocacy.
“Irrespective of whether you think race or ethnicity or socioeconomic status are political issues or not, it is the case that you’re obligated to have an objective understanding of the factors that contribute to your patient’s health and as points of intervention,” Dr. Hamilton said. “So even if you don’t want to sit down and jot off that email to your senator, you still have to take these factors into account when you’re treating the person who’s sitting right in front of you, and that’s not political. That’s the promise of being a physician.”
Dr. Amezcua has received personal compensation for consulting, speaking, or serving on steering committees or advisory boards for Biogen Idec, Novartis, Genentech, and EMD Serono, and she has received research support from Biogen Idec and Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation. Dr. Kind reported support from the Alzheimer’s Association. Dr. Diaz-Ortiz is coinventor of a provisional patent submitted by the University of Pennsylvania that relates to a potential therapeutic in Parkinson’s disease. Mr. Lusk reported fellowship support from American Heart Association and travel support from the American Neurological Association. No other speakers or sources had relevant disclosures.
FROM ANA 2022
Persistent asthma linked to higher carotid plaque burden
Persistent asthma is associated with increased carotid plaque burden and higher levels of inflammation, putting these patients at risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) events, new research suggests.
Using data from the MESA study, investigators analyzed more than 5,000 individuals, comparing carotid plaque and inflammatory markers in those with and without asthma.
They found that carotid plaque was present in half of participants without asthma and half of those with intermittent asthma but in close to 70% of participants with persistent asthma.
.
“The take-home message is that the current study, paired with prior studies, highlights that individuals with more significant forms of asthma may be at higher cardiovascular risk and makes it imperative to address modifiable risk factors among patients with asthma,” lead author Matthew Tattersall, DO, MS, assistant professor of cardiovascular medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, told this news organization.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Limited data
Asthma and ASCVD are “highly prevalent inflammatory diseases,” the authors write. Carotid artery plaque detected by B-mode ultrasound “represents advanced, typically subclinical atherosclerosis that is a strong independent predictor of incident ASCVD events,” with inflammation playing a “key role” in precipitating these events, they note.
Serum inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and IL-6 are associated with increased ASCVD events, and in asthma, CRP and other inflammatory biomarkers are elevated and tend to further increase during exacerbations.
Currently, there are limited data looking at the associations of asthma, asthma severity, and atherosclerotic plaque burden, they note, so the researchers turned to the MESA study – a multiethnic population of individuals free of prevalent ASCVD at baseline. They hypothesized that persistent asthma would be associated with higher carotid plaque presence and burden.
They also wanted to explore “whether these associations would be attenuated after adjustment for baseline inflammatory biomarkers.”
Dr. Tattersall said the current study “links our previous work studying the manifestations of asthma,” in which he and his colleagues demonstrated increased cardiovascular events among MESA participants with persistent asthma, as well as late-onset asthma participants in the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. His group also showed that early arterial injury occurs in adolescents with asthma.
However, there are also few data looking at the association with carotid plaque, “a late manifestation of arterial injury and a strong predictor of future cardiovascular events and asthma,” Dr. Tattersall added.
He and his group therefore “wanted to explore the entire spectrum of arterial injury, from the initial increase in the carotid media thickness to plaque formation to cardiovascular events.”
To do so, they studied participants in MESA, a study of close to 7,000 adults that began in the year 2000 and continues to follow participants today. At the time of enrollment, all were free from CVD.
The current analysis looked at 5,029 MESA participants (mean age 61.6 years, 53% female, 26% Black, 23% Hispanic, 12% Asian), comparing those with persistent asthma, defined as “asthma requiring use of controller medications,” intermittent asthma, defined as “asthma without controller medications,” and no asthma.
Participants underwent B-mode carotid ultrasound to detect carotid plaques, with a total plaque score (TPS) ranging from 0-12. The researchers used multivariable regression modeling to evaluate the association of asthma subtype and carotid plaque burden.
Interpret cautiously
Participants with persistent asthma were more likely to be female, have higher body mass index (BMI), and higher high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, compared with those without asthma.
Participants with persistent asthma had the highest burden of carotid plaque (P ≤ .003 for comparison of proportions and .002 for comparison of means).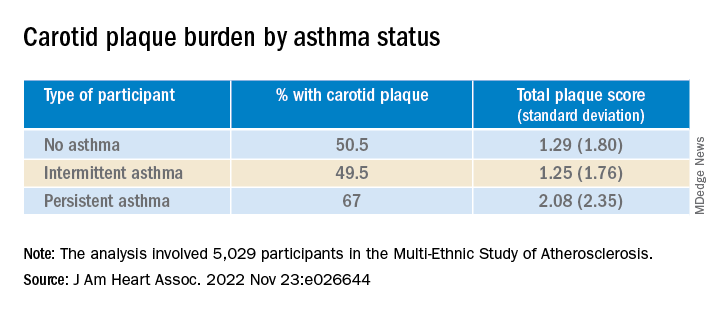
Moreover, participants with persistent asthma also had the highest systemic inflammatory marker levels – both CRP and IL-6 – compared with those without asthma. While participants with intermittent asthma also had higher average CRP, compared with those without asthma, their IL-6 levels were comparable.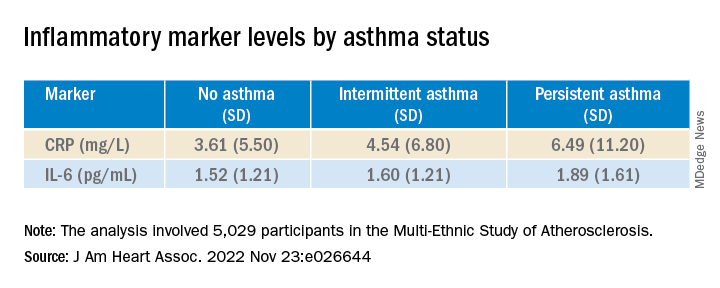
In unadjusted models, persistent asthma was associated with higher odds of carotid plaque presence (odds ratio, 1.97; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.95) – an association that persisted even in models that adjusted for biologic confounders (both P < .01). There also was an association between persistent asthma and higher carotid TPS (P < .001).
In further adjusted models, IL-6 was independently associated with presence of carotid plaque (P = .0001 per 1-SD increment of 1.53), as well as TPS (P < .001). CRP was “slightly associated” with carotid TPS (P = .04) but not carotid plaque presence (P = .07).
There was no attenuation after the researchers evaluated the associations of asthma subtype and carotid plaque presence or TPS and fully adjusted for baseline IL-6 or CRP (P = .02 and P = .01, respectively).
“Since this study is observational, we cannot confirm causation, but the study adds to the growing literature exploring the systemic effects of asthma,” Dr. Tattersall commented.
“Our initial hypothesis was that it was driven by inflammation, as both asthma and CVD are inflammatory conditions,” he continued. “We did adjust for inflammatory biomarkers in this analysis, but there was no change in the association.”
Nevertheless, Dr. Tattersall and colleagues are “cautious in the interpretation,” since the inflammatory biomarkers “were only collected at one point, and these measures can be dynamic, thus adjustment may not tell the whole story.”
Heightened awareness
Robert Brook, MD, professor and director of cardiovascular disease prevention, Wayne State University, Detroit, said the “main contribution of this study is the novel demonstration of a significant association between persistent (but not intermittent) asthma with carotid atherosclerosis in the MESA cohort, a large multi-ethnic population.”
These findings “support the biological plausibility of the growing epidemiological evidence that asthma independently increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality,” added Dr. Brook, who was not involved with the study.
“The main take-home message for clinicians is that, just like in COPD (which is well-established), asthma is often a systemic condition in that the inflammation and disease process can impact the whole body,” he said.
“Health care providers should have a heightened awareness of the potentially increased cardiovascular risk of their patients with asthma and pay special attention to controlling their heart disease risk factors (for example, hyperlipidemia, hypertension),” Dr. Brook stated.
Dr. Tattersall was supported by an American Heart Association Career Development Award. The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Research Resources. Dr. Tattersall and co-authors and Dr. Brook declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Persistent asthma is associated with increased carotid plaque burden and higher levels of inflammation, putting these patients at risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) events, new research suggests.
Using data from the MESA study, investigators analyzed more than 5,000 individuals, comparing carotid plaque and inflammatory markers in those with and without asthma.
They found that carotid plaque was present in half of participants without asthma and half of those with intermittent asthma but in close to 70% of participants with persistent asthma.
.
“The take-home message is that the current study, paired with prior studies, highlights that individuals with more significant forms of asthma may be at higher cardiovascular risk and makes it imperative to address modifiable risk factors among patients with asthma,” lead author Matthew Tattersall, DO, MS, assistant professor of cardiovascular medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, told this news organization.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Limited data
Asthma and ASCVD are “highly prevalent inflammatory diseases,” the authors write. Carotid artery plaque detected by B-mode ultrasound “represents advanced, typically subclinical atherosclerosis that is a strong independent predictor of incident ASCVD events,” with inflammation playing a “key role” in precipitating these events, they note.
Serum inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and IL-6 are associated with increased ASCVD events, and in asthma, CRP and other inflammatory biomarkers are elevated and tend to further increase during exacerbations.
Currently, there are limited data looking at the associations of asthma, asthma severity, and atherosclerotic plaque burden, they note, so the researchers turned to the MESA study – a multiethnic population of individuals free of prevalent ASCVD at baseline. They hypothesized that persistent asthma would be associated with higher carotid plaque presence and burden.
They also wanted to explore “whether these associations would be attenuated after adjustment for baseline inflammatory biomarkers.”
Dr. Tattersall said the current study “links our previous work studying the manifestations of asthma,” in which he and his colleagues demonstrated increased cardiovascular events among MESA participants with persistent asthma, as well as late-onset asthma participants in the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. His group also showed that early arterial injury occurs in adolescents with asthma.
However, there are also few data looking at the association with carotid plaque, “a late manifestation of arterial injury and a strong predictor of future cardiovascular events and asthma,” Dr. Tattersall added.
He and his group therefore “wanted to explore the entire spectrum of arterial injury, from the initial increase in the carotid media thickness to plaque formation to cardiovascular events.”
To do so, they studied participants in MESA, a study of close to 7,000 adults that began in the year 2000 and continues to follow participants today. At the time of enrollment, all were free from CVD.
The current analysis looked at 5,029 MESA participants (mean age 61.6 years, 53% female, 26% Black, 23% Hispanic, 12% Asian), comparing those with persistent asthma, defined as “asthma requiring use of controller medications,” intermittent asthma, defined as “asthma without controller medications,” and no asthma.
Participants underwent B-mode carotid ultrasound to detect carotid plaques, with a total plaque score (TPS) ranging from 0-12. The researchers used multivariable regression modeling to evaluate the association of asthma subtype and carotid plaque burden.
Interpret cautiously
Participants with persistent asthma were more likely to be female, have higher body mass index (BMI), and higher high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, compared with those without asthma.
Participants with persistent asthma had the highest burden of carotid plaque (P ≤ .003 for comparison of proportions and .002 for comparison of means).
Moreover, participants with persistent asthma also had the highest systemic inflammatory marker levels – both CRP and IL-6 – compared with those without asthma. While participants with intermittent asthma also had higher average CRP, compared with those without asthma, their IL-6 levels were comparable.
In unadjusted models, persistent asthma was associated with higher odds of carotid plaque presence (odds ratio, 1.97; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.95) – an association that persisted even in models that adjusted for biologic confounders (both P < .01). There also was an association between persistent asthma and higher carotid TPS (P < .001).
In further adjusted models, IL-6 was independently associated with presence of carotid plaque (P = .0001 per 1-SD increment of 1.53), as well as TPS (P < .001). CRP was “slightly associated” with carotid TPS (P = .04) but not carotid plaque presence (P = .07).
There was no attenuation after the researchers evaluated the associations of asthma subtype and carotid plaque presence or TPS and fully adjusted for baseline IL-6 or CRP (P = .02 and P = .01, respectively).
“Since this study is observational, we cannot confirm causation, but the study adds to the growing literature exploring the systemic effects of asthma,” Dr. Tattersall commented.
“Our initial hypothesis was that it was driven by inflammation, as both asthma and CVD are inflammatory conditions,” he continued. “We did adjust for inflammatory biomarkers in this analysis, but there was no change in the association.”
Nevertheless, Dr. Tattersall and colleagues are “cautious in the interpretation,” since the inflammatory biomarkers “were only collected at one point, and these measures can be dynamic, thus adjustment may not tell the whole story.”
Heightened awareness
Robert Brook, MD, professor and director of cardiovascular disease prevention, Wayne State University, Detroit, said the “main contribution of this study is the novel demonstration of a significant association between persistent (but not intermittent) asthma with carotid atherosclerosis in the MESA cohort, a large multi-ethnic population.”
These findings “support the biological plausibility of the growing epidemiological evidence that asthma independently increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality,” added Dr. Brook, who was not involved with the study.
“The main take-home message for clinicians is that, just like in COPD (which is well-established), asthma is often a systemic condition in that the inflammation and disease process can impact the whole body,” he said.
“Health care providers should have a heightened awareness of the potentially increased cardiovascular risk of their patients with asthma and pay special attention to controlling their heart disease risk factors (for example, hyperlipidemia, hypertension),” Dr. Brook stated.
Dr. Tattersall was supported by an American Heart Association Career Development Award. The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Research Resources. Dr. Tattersall and co-authors and Dr. Brook declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Persistent asthma is associated with increased carotid plaque burden and higher levels of inflammation, putting these patients at risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) events, new research suggests.
Using data from the MESA study, investigators analyzed more than 5,000 individuals, comparing carotid plaque and inflammatory markers in those with and without asthma.
They found that carotid plaque was present in half of participants without asthma and half of those with intermittent asthma but in close to 70% of participants with persistent asthma.
.
“The take-home message is that the current study, paired with prior studies, highlights that individuals with more significant forms of asthma may be at higher cardiovascular risk and makes it imperative to address modifiable risk factors among patients with asthma,” lead author Matthew Tattersall, DO, MS, assistant professor of cardiovascular medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, told this news organization.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Limited data
Asthma and ASCVD are “highly prevalent inflammatory diseases,” the authors write. Carotid artery plaque detected by B-mode ultrasound “represents advanced, typically subclinical atherosclerosis that is a strong independent predictor of incident ASCVD events,” with inflammation playing a “key role” in precipitating these events, they note.
Serum inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and IL-6 are associated with increased ASCVD events, and in asthma, CRP and other inflammatory biomarkers are elevated and tend to further increase during exacerbations.
Currently, there are limited data looking at the associations of asthma, asthma severity, and atherosclerotic plaque burden, they note, so the researchers turned to the MESA study – a multiethnic population of individuals free of prevalent ASCVD at baseline. They hypothesized that persistent asthma would be associated with higher carotid plaque presence and burden.
They also wanted to explore “whether these associations would be attenuated after adjustment for baseline inflammatory biomarkers.”
Dr. Tattersall said the current study “links our previous work studying the manifestations of asthma,” in which he and his colleagues demonstrated increased cardiovascular events among MESA participants with persistent asthma, as well as late-onset asthma participants in the Wisconsin Sleep Cohort. His group also showed that early arterial injury occurs in adolescents with asthma.
However, there are also few data looking at the association with carotid plaque, “a late manifestation of arterial injury and a strong predictor of future cardiovascular events and asthma,” Dr. Tattersall added.
He and his group therefore “wanted to explore the entire spectrum of arterial injury, from the initial increase in the carotid media thickness to plaque formation to cardiovascular events.”
To do so, they studied participants in MESA, a study of close to 7,000 adults that began in the year 2000 and continues to follow participants today. At the time of enrollment, all were free from CVD.
The current analysis looked at 5,029 MESA participants (mean age 61.6 years, 53% female, 26% Black, 23% Hispanic, 12% Asian), comparing those with persistent asthma, defined as “asthma requiring use of controller medications,” intermittent asthma, defined as “asthma without controller medications,” and no asthma.
Participants underwent B-mode carotid ultrasound to detect carotid plaques, with a total plaque score (TPS) ranging from 0-12. The researchers used multivariable regression modeling to evaluate the association of asthma subtype and carotid plaque burden.
Interpret cautiously
Participants with persistent asthma were more likely to be female, have higher body mass index (BMI), and higher high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels, compared with those without asthma.
Participants with persistent asthma had the highest burden of carotid plaque (P ≤ .003 for comparison of proportions and .002 for comparison of means).
Moreover, participants with persistent asthma also had the highest systemic inflammatory marker levels – both CRP and IL-6 – compared with those without asthma. While participants with intermittent asthma also had higher average CRP, compared with those without asthma, their IL-6 levels were comparable.
In unadjusted models, persistent asthma was associated with higher odds of carotid plaque presence (odds ratio, 1.97; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.95) – an association that persisted even in models that adjusted for biologic confounders (both P < .01). There also was an association between persistent asthma and higher carotid TPS (P < .001).
In further adjusted models, IL-6 was independently associated with presence of carotid plaque (P = .0001 per 1-SD increment of 1.53), as well as TPS (P < .001). CRP was “slightly associated” with carotid TPS (P = .04) but not carotid plaque presence (P = .07).
There was no attenuation after the researchers evaluated the associations of asthma subtype and carotid plaque presence or TPS and fully adjusted for baseline IL-6 or CRP (P = .02 and P = .01, respectively).
“Since this study is observational, we cannot confirm causation, but the study adds to the growing literature exploring the systemic effects of asthma,” Dr. Tattersall commented.
“Our initial hypothesis was that it was driven by inflammation, as both asthma and CVD are inflammatory conditions,” he continued. “We did adjust for inflammatory biomarkers in this analysis, but there was no change in the association.”
Nevertheless, Dr. Tattersall and colleagues are “cautious in the interpretation,” since the inflammatory biomarkers “were only collected at one point, and these measures can be dynamic, thus adjustment may not tell the whole story.”
Heightened awareness
Robert Brook, MD, professor and director of cardiovascular disease prevention, Wayne State University, Detroit, said the “main contribution of this study is the novel demonstration of a significant association between persistent (but not intermittent) asthma with carotid atherosclerosis in the MESA cohort, a large multi-ethnic population.”
These findings “support the biological plausibility of the growing epidemiological evidence that asthma independently increases the risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality,” added Dr. Brook, who was not involved with the study.
“The main take-home message for clinicians is that, just like in COPD (which is well-established), asthma is often a systemic condition in that the inflammation and disease process can impact the whole body,” he said.
“Health care providers should have a heightened awareness of the potentially increased cardiovascular risk of their patients with asthma and pay special attention to controlling their heart disease risk factors (for example, hyperlipidemia, hypertension),” Dr. Brook stated.
Dr. Tattersall was supported by an American Heart Association Career Development Award. The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the National Center for Research Resources. Dr. Tattersall and co-authors and Dr. Brook declare no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mortality after acute stroke worsened by accompanying acute AFib
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study covered in this summary was published on ResearchSquare.com as a preprint and has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Key takeaway
Why this matters
- A comprehensive understanding of the relationship between acute AF and risk for acute ischemic stroke and prognosis will help improve management and treatment of patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Study design
- The retrospective study included patients with acute ischemic stroke within the prior 24 hours; 12-lead electrocardiogram in the emergency department; and hospitalization and treatment at the hospital stroke center.
- The cohort of 706 patients admitted to a single center in Shanghai, China, from December 2019 to December 2021, included 142 with episodes of acute AF and 564 without such episodes.
- Patients with acute ischemic stroke and acute AF – including AF of new onset, paroxysmal, persistent, or permanent with symptoms such as palpitations or dizziness attributed to rapid ventricular rates – were identified.
- Neurological deficits were assessed using the 7-day National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale/Score (NIHSS). Patients with a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 were considered to have moderate to severe stroke.
- Associations between acute AF onset and the severity of early neurological deficits were assessed and related to all-cause mortality within 30 days of the stroke.
Key results
- Patients with acute AF were older than those without acute AF (80.3 years vs. 71.0 years; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS scores averaged 16.09 for the stroke patients with acute AF and 8.65 for those without acute AF (P < .001).
- Significantly more patients with acute AF than without acute AF had a 7-day NIHSS score of at least 16 (45.1% vs. 14.4%; P < .001).
- More patients with than without acute AF underwent transcatheter thrombectomy (44.4% vs. 24.5%; P < .001) or received thrombolytic therapy (31.6% vs. 19.7%; P = .005).
- Patients aged 73 years or older showed baseline NIHSS score and acute AF as independent risk factors for early neurological deficits in stroke patients admitted to the emergency department.
- Mortality at 30 days was significantly higher in patients with acute AF than in those without acute AF (30.3% vs. 10.1%; P < .001).
- Baseline NIHSS had an adjusted odds ratio for 30-day mortality of 1.18 (95% confidence interval, 1.15-1.22; P < .001).
- Other independent predictors included acute AF (1.87 [95% CI, 1.09-3.19; P = .022]) and age 73 or older (2.00 [95% CI, 1.18-3.37; P = .01]).
Limitations
- The study was retrospective and didn’t have access to some potentially relevant data, such as duration of AF.
- The single-center study with limited generalizability does not necessarily represent the broad population of stroke patients in China or elsewhere.
Disclosures
- This study was supported by the Cardiovascular Multidisciplinary Integrated Research Fund and Construction of Shanghai Municipal Health Commission.
- The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
This is a summary of a preprint research study, “Acute Atrial Fibrillation During Onset of Stroke Indicates Higher Probability of Post-Stroke Death Outcomes,” written by Yongxia Li, from the Shanghai Sixth People’s Hospital, and colleagues, on ResearchSquare.com. This study has not yet been peer reviewed. The full text of the study can be found on ResearchSquare.com.A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical school culinary medicine programs grow despite limited funding
The way he sees it, the stakes couldn’t be higher. He believes doctors need to see food as medicine to be able to stem the tide of chronic disease.
About 6 in 10 adults in the United States live with chronic diseases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, costing $4.1 trillion in annual health care costs. Adult obesity rates are rising, as are obesity-related conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
To turn the tide, Dr. Marvasti created a culinary medicine program in 2020 in collaboration with the University of Arizona Cooperative Extension and local chefs.
Dr. Marvasti, who is board certified in family medicine, graduated from the University of Arizona, Phoenix, where he serves as the director of the medical school’s Culinary Medicine Program.
The program offers an elective course for third- and fourth-year medical students, which introduces the evidence-based field of culinary medicine. Dr Marvasti’s goal is for the course to teach students how to use this science and the joy of cooking to improve long-term health outcomes for their patients.
As part of Dr. Marvasti’s program, students learn cooking fundamentals through chef demonstrations and hands-on practice – to teach students how food can be used to prevent and treat many chronic diseases.
One of the dishes students learn to make includes a quinoa salad made with cucumber, onion, bell peppers, corn, cherry tomatoes, beans, garlic, olive oil, and lemon juice. Another recipe includes a healthier take on dessert: Dark chocolate mousse made with three large, ripe avocados, dark chocolate powder, three tablespoons of agave or maple, coconut cream, nondairy milk, salt, and vanilla. Dr. Marvasti and his team are set to build out the existing program to develop additional resources for medically underserved and rural communities in Arizona, according to a statement from the university. These plans will be funded by a $750,000 grant from Novo Nordisk.
“We’re going to develop an open education curriculum to share, so it’s open access to everyone,” said Dr. Marvasti, who is also director of Public Health, Prevention and Health Promotion and an associate professor at the university. “It can be adaptable at the undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate level.”
Dr. Marvasti and his colleagues at the University of Arizona aren’t alone. In fact, culinary medicine programs are sprouting some serious legs.
Culinary medicine programs catch on
Jaclyn Albin, MD, CCMS, an associate professor in the departments of internal medicine and pediatrics at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, conducted a scoping review of the literature on culinary medicine programs for medical students.* Her purpose was to learn how the programs were structured and how they assessed student knowledge and attitudes regarding nutrition counseling for patients.
Dr. Albin and her colleagues performed an initial literature search between June 1 and Aug. 1, 2020, of papers published between Jan. 1, 2012, and Aug. 1, 2020 – excluding some newer programs such as the one at the University of Arizona. The results of their research were published in Academic Medicine.
Ultimately, the authors identified and examined 34 programs offering medical student–focused culinary medicine courses.
Program instructors typically included a team of physicians, dietitians, chefs, and other professionals, the study found.
Most program participants exclusively taught medical students, though the training years of participants varied among programs, and they included first-, second-, third-, and fourth-year students. Some programs allowed students from outside their respective medical school to participate in the trainings.
As for the formats of the program, most included cohorts of 10-20 students attending multiple 2- to 3-hour sessions over the course of several months. The University of Alabama at Birmingham offers one of the longest courses, which spans 4-5 months, according to the paper. In contrast, the University of Rochester (N.Y.) program offers only a 1-day lab divided into four sessions, with each session lasting about 2 hours.
The culinary medicine programs’ course sessions tended to include a 10- to 30-minute didactic session involving videos, research articles, culinary theories, and other lectures, a 60- to 90-minute hands-on cooking session, and a 30-minute discussion around nutrition, culture, and patient care.
Most programs used pre- and post-program surveys to evaluate outcomes, though results varied between programs, according to the study. While each program evaluation had different metrics, the surveys generally revealed students felt more confident discussing dietary interventions with patients and in their own cooking skills following completion.
Course correction
Most of those programs are unfunded or minimally funded, Dr. Albin said.
Her own program, which is immensely popular with medical students, is one she teaches on a volunteer basis.
“I do this for free, in the evenings, because I believe in it,” she said.
Medical school education real estate is limited, so convincing medical schools to add something to the curriculum is difficult, Dr. Albin noted.
But it’s worth it, she said, because nutrition is the underpinning of so many diseases.
“Food is the top risk factor for early death in the U.S.,” Dr. Albin said. “I like to say that five times in a row. People have not digested it.”
During her culinary medicine courses, she also asks her medical students: “Who is comfortable in the kitchen?” Some sheepishly raise their hands, she said. Some don’t. Many don’t know anything about cooking.
Then she teaches students about healthy food and how to make it. As part of her program, medical students are given a pantry starter kit with olive oil and a variety of spices to take home and use.
Some recipes Dr. Albin teaches includes mango chili shrimp salad with lime vinaigrette, eggplant sliders, yellow vegetable curry, and strawberry banana chia pudding.
“If you figure out how to do it for your own busy, everyday life, you are now empowered to tell someone else about it,” she said.
A dietitian’s involvement
Milette Siler, RD, LD, CCMS, works with Dr. Albin to educate medical students and patients about food as medicine. A significant chunk of her job involves teaching future doctors what dietitians do.
When the class starts, many students don’t know two of the five basic things dietitians do, Ms. Siler said. By the end of the class, all students know what a dietitian does.
That’s important as students go on to become doctors.
“For us to remove barriers to care, we have to acknowledge most patients’ entry into health care is their physician,” she said. “The dietitian is often a referral. Doctors need to know enough to do no harm.”
Clinicians are often siloed, she said, and the key to better serving patients is partnership, transparency, and relationships. “I think everybody is at a point where everyone is saying what we’re doing isn’t working,” she said. “The American public deserves better, physicians deserve better, and clinicians deserve better.”
Popular with students
While the old guard has been slow to embrace the shift, her students have helped drive the growth of the culinary medicine field, Dr. Albin said.
“They are not settling for the inadequacy that somehow the rest of us did,” she continued. “I’m so hopeful for the future of the health system. We have a generation of people who will not stand for neglecting the most vital elements.”
Lyndon Bui, a second-year medical student at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, is an example of one of these people.
As a member of a culinary medicine interest group on campus, he said, he has learned a lot about the importance of diet for long-term health. This has given him confidence to talk about food and nutrition.
His group does cooking demos at the Phoenix Farmers Market using food from various local vendors. They usually make a salad from local greens and cook seasonal veggies in a stir fry, he said.
They’ve previously made salad with microgreens – young seedlings of edible vegetables and herbs – and pomegranate seeds with a honey mustard vinaigrette, eggplant or cucumber, and hummus on pita bread, as well as almond butter and honey sandwiches, according to the university.
The group also talks with people in the community, answers questions, and learns about community needs.
Mr. Bui’s participation in this group has helped him cultivate a passion for community outreach that he wants to incorporate into his career.
“I feel like I have the knowledge to provide better advice to patients,” he said. “Knowing all these things about food, I feel more comfortable talking about it and more inclined to refer to a dietitian when maybe I wouldn’t have before.”
Family physician applauds culinary medicine programs
When Angie Neison, MD, CCMS, went to medical school, she was surprised there wasn’t more education on nutrition.
In fact, on average, physicians receive less than 20 hours of nutrition education, according to the University of Arizona.
Now 15 years into her career as a family physician, Dr. Neison says nutrition is a huge part of her practice. She spends time working to bust myths about nutrition for her patients – including that healthy food is boring and bland, that making it is time consuming, and that healthy food is expensive. She also spends time teaching aspects of culinary medicine to her colleagues – many of whom are well into their careers – so they can better serve their patients.
It’s worth it to spend time learning about nutrition, she said, whether that’s as a medical student in a culinary medicine program or a practicing physician taking additional courses.
Nutrition education in medical school hasn’t been a priority, she said, maybe because there is so much to learn, or maybe because there is no money to be made in prevention.
“If doctors learn it, they are able to better guide patients,” she said.
Correction, 11/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Albin's institution.
The way he sees it, the stakes couldn’t be higher. He believes doctors need to see food as medicine to be able to stem the tide of chronic disease.
About 6 in 10 adults in the United States live with chronic diseases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, costing $4.1 trillion in annual health care costs. Adult obesity rates are rising, as are obesity-related conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
To turn the tide, Dr. Marvasti created a culinary medicine program in 2020 in collaboration with the University of Arizona Cooperative Extension and local chefs.
Dr. Marvasti, who is board certified in family medicine, graduated from the University of Arizona, Phoenix, where he serves as the director of the medical school’s Culinary Medicine Program.
The program offers an elective course for third- and fourth-year medical students, which introduces the evidence-based field of culinary medicine. Dr Marvasti’s goal is for the course to teach students how to use this science and the joy of cooking to improve long-term health outcomes for their patients.
As part of Dr. Marvasti’s program, students learn cooking fundamentals through chef demonstrations and hands-on practice – to teach students how food can be used to prevent and treat many chronic diseases.
One of the dishes students learn to make includes a quinoa salad made with cucumber, onion, bell peppers, corn, cherry tomatoes, beans, garlic, olive oil, and lemon juice. Another recipe includes a healthier take on dessert: Dark chocolate mousse made with three large, ripe avocados, dark chocolate powder, three tablespoons of agave or maple, coconut cream, nondairy milk, salt, and vanilla. Dr. Marvasti and his team are set to build out the existing program to develop additional resources for medically underserved and rural communities in Arizona, according to a statement from the university. These plans will be funded by a $750,000 grant from Novo Nordisk.
“We’re going to develop an open education curriculum to share, so it’s open access to everyone,” said Dr. Marvasti, who is also director of Public Health, Prevention and Health Promotion and an associate professor at the university. “It can be adaptable at the undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate level.”
Dr. Marvasti and his colleagues at the University of Arizona aren’t alone. In fact, culinary medicine programs are sprouting some serious legs.
Culinary medicine programs catch on
Jaclyn Albin, MD, CCMS, an associate professor in the departments of internal medicine and pediatrics at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, conducted a scoping review of the literature on culinary medicine programs for medical students.* Her purpose was to learn how the programs were structured and how they assessed student knowledge and attitudes regarding nutrition counseling for patients.
Dr. Albin and her colleagues performed an initial literature search between June 1 and Aug. 1, 2020, of papers published between Jan. 1, 2012, and Aug. 1, 2020 – excluding some newer programs such as the one at the University of Arizona. The results of their research were published in Academic Medicine.
Ultimately, the authors identified and examined 34 programs offering medical student–focused culinary medicine courses.
Program instructors typically included a team of physicians, dietitians, chefs, and other professionals, the study found.
Most program participants exclusively taught medical students, though the training years of participants varied among programs, and they included first-, second-, third-, and fourth-year students. Some programs allowed students from outside their respective medical school to participate in the trainings.
As for the formats of the program, most included cohorts of 10-20 students attending multiple 2- to 3-hour sessions over the course of several months. The University of Alabama at Birmingham offers one of the longest courses, which spans 4-5 months, according to the paper. In contrast, the University of Rochester (N.Y.) program offers only a 1-day lab divided into four sessions, with each session lasting about 2 hours.
The culinary medicine programs’ course sessions tended to include a 10- to 30-minute didactic session involving videos, research articles, culinary theories, and other lectures, a 60- to 90-minute hands-on cooking session, and a 30-minute discussion around nutrition, culture, and patient care.
Most programs used pre- and post-program surveys to evaluate outcomes, though results varied between programs, according to the study. While each program evaluation had different metrics, the surveys generally revealed students felt more confident discussing dietary interventions with patients and in their own cooking skills following completion.
Course correction
Most of those programs are unfunded or minimally funded, Dr. Albin said.
Her own program, which is immensely popular with medical students, is one she teaches on a volunteer basis.
“I do this for free, in the evenings, because I believe in it,” she said.
Medical school education real estate is limited, so convincing medical schools to add something to the curriculum is difficult, Dr. Albin noted.
But it’s worth it, she said, because nutrition is the underpinning of so many diseases.
“Food is the top risk factor for early death in the U.S.,” Dr. Albin said. “I like to say that five times in a row. People have not digested it.”
During her culinary medicine courses, she also asks her medical students: “Who is comfortable in the kitchen?” Some sheepishly raise their hands, she said. Some don’t. Many don’t know anything about cooking.
Then she teaches students about healthy food and how to make it. As part of her program, medical students are given a pantry starter kit with olive oil and a variety of spices to take home and use.
Some recipes Dr. Albin teaches includes mango chili shrimp salad with lime vinaigrette, eggplant sliders, yellow vegetable curry, and strawberry banana chia pudding.
“If you figure out how to do it for your own busy, everyday life, you are now empowered to tell someone else about it,” she said.
A dietitian’s involvement
Milette Siler, RD, LD, CCMS, works with Dr. Albin to educate medical students and patients about food as medicine. A significant chunk of her job involves teaching future doctors what dietitians do.
When the class starts, many students don’t know two of the five basic things dietitians do, Ms. Siler said. By the end of the class, all students know what a dietitian does.
That’s important as students go on to become doctors.
“For us to remove barriers to care, we have to acknowledge most patients’ entry into health care is their physician,” she said. “The dietitian is often a referral. Doctors need to know enough to do no harm.”
Clinicians are often siloed, she said, and the key to better serving patients is partnership, transparency, and relationships. “I think everybody is at a point where everyone is saying what we’re doing isn’t working,” she said. “The American public deserves better, physicians deserve better, and clinicians deserve better.”
Popular with students
While the old guard has been slow to embrace the shift, her students have helped drive the growth of the culinary medicine field, Dr. Albin said.
“They are not settling for the inadequacy that somehow the rest of us did,” she continued. “I’m so hopeful for the future of the health system. We have a generation of people who will not stand for neglecting the most vital elements.”
Lyndon Bui, a second-year medical student at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, is an example of one of these people.
As a member of a culinary medicine interest group on campus, he said, he has learned a lot about the importance of diet for long-term health. This has given him confidence to talk about food and nutrition.
His group does cooking demos at the Phoenix Farmers Market using food from various local vendors. They usually make a salad from local greens and cook seasonal veggies in a stir fry, he said.
They’ve previously made salad with microgreens – young seedlings of edible vegetables and herbs – and pomegranate seeds with a honey mustard vinaigrette, eggplant or cucumber, and hummus on pita bread, as well as almond butter and honey sandwiches, according to the university.
The group also talks with people in the community, answers questions, and learns about community needs.
Mr. Bui’s participation in this group has helped him cultivate a passion for community outreach that he wants to incorporate into his career.
“I feel like I have the knowledge to provide better advice to patients,” he said. “Knowing all these things about food, I feel more comfortable talking about it and more inclined to refer to a dietitian when maybe I wouldn’t have before.”
Family physician applauds culinary medicine programs
When Angie Neison, MD, CCMS, went to medical school, she was surprised there wasn’t more education on nutrition.
In fact, on average, physicians receive less than 20 hours of nutrition education, according to the University of Arizona.
Now 15 years into her career as a family physician, Dr. Neison says nutrition is a huge part of her practice. She spends time working to bust myths about nutrition for her patients – including that healthy food is boring and bland, that making it is time consuming, and that healthy food is expensive. She also spends time teaching aspects of culinary medicine to her colleagues – many of whom are well into their careers – so they can better serve their patients.
It’s worth it to spend time learning about nutrition, she said, whether that’s as a medical student in a culinary medicine program or a practicing physician taking additional courses.
Nutrition education in medical school hasn’t been a priority, she said, maybe because there is so much to learn, or maybe because there is no money to be made in prevention.
“If doctors learn it, they are able to better guide patients,” she said.
Correction, 11/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Albin's institution.
The way he sees it, the stakes couldn’t be higher. He believes doctors need to see food as medicine to be able to stem the tide of chronic disease.
About 6 in 10 adults in the United States live with chronic diseases, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, costing $4.1 trillion in annual health care costs. Adult obesity rates are rising, as are obesity-related conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
To turn the tide, Dr. Marvasti created a culinary medicine program in 2020 in collaboration with the University of Arizona Cooperative Extension and local chefs.
Dr. Marvasti, who is board certified in family medicine, graduated from the University of Arizona, Phoenix, where he serves as the director of the medical school’s Culinary Medicine Program.
The program offers an elective course for third- and fourth-year medical students, which introduces the evidence-based field of culinary medicine. Dr Marvasti’s goal is for the course to teach students how to use this science and the joy of cooking to improve long-term health outcomes for their patients.
As part of Dr. Marvasti’s program, students learn cooking fundamentals through chef demonstrations and hands-on practice – to teach students how food can be used to prevent and treat many chronic diseases.
One of the dishes students learn to make includes a quinoa salad made with cucumber, onion, bell peppers, corn, cherry tomatoes, beans, garlic, olive oil, and lemon juice. Another recipe includes a healthier take on dessert: Dark chocolate mousse made with three large, ripe avocados, dark chocolate powder, three tablespoons of agave or maple, coconut cream, nondairy milk, salt, and vanilla. Dr. Marvasti and his team are set to build out the existing program to develop additional resources for medically underserved and rural communities in Arizona, according to a statement from the university. These plans will be funded by a $750,000 grant from Novo Nordisk.
“We’re going to develop an open education curriculum to share, so it’s open access to everyone,” said Dr. Marvasti, who is also director of Public Health, Prevention and Health Promotion and an associate professor at the university. “It can be adaptable at the undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate level.”
Dr. Marvasti and his colleagues at the University of Arizona aren’t alone. In fact, culinary medicine programs are sprouting some serious legs.
Culinary medicine programs catch on
Jaclyn Albin, MD, CCMS, an associate professor in the departments of internal medicine and pediatrics at UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, conducted a scoping review of the literature on culinary medicine programs for medical students.* Her purpose was to learn how the programs were structured and how they assessed student knowledge and attitudes regarding nutrition counseling for patients.
Dr. Albin and her colleagues performed an initial literature search between June 1 and Aug. 1, 2020, of papers published between Jan. 1, 2012, and Aug. 1, 2020 – excluding some newer programs such as the one at the University of Arizona. The results of their research were published in Academic Medicine.
Ultimately, the authors identified and examined 34 programs offering medical student–focused culinary medicine courses.
Program instructors typically included a team of physicians, dietitians, chefs, and other professionals, the study found.
Most program participants exclusively taught medical students, though the training years of participants varied among programs, and they included first-, second-, third-, and fourth-year students. Some programs allowed students from outside their respective medical school to participate in the trainings.
As for the formats of the program, most included cohorts of 10-20 students attending multiple 2- to 3-hour sessions over the course of several months. The University of Alabama at Birmingham offers one of the longest courses, which spans 4-5 months, according to the paper. In contrast, the University of Rochester (N.Y.) program offers only a 1-day lab divided into four sessions, with each session lasting about 2 hours.
The culinary medicine programs’ course sessions tended to include a 10- to 30-minute didactic session involving videos, research articles, culinary theories, and other lectures, a 60- to 90-minute hands-on cooking session, and a 30-minute discussion around nutrition, culture, and patient care.
Most programs used pre- and post-program surveys to evaluate outcomes, though results varied between programs, according to the study. While each program evaluation had different metrics, the surveys generally revealed students felt more confident discussing dietary interventions with patients and in their own cooking skills following completion.
Course correction
Most of those programs are unfunded or minimally funded, Dr. Albin said.
Her own program, which is immensely popular with medical students, is one she teaches on a volunteer basis.
“I do this for free, in the evenings, because I believe in it,” she said.
Medical school education real estate is limited, so convincing medical schools to add something to the curriculum is difficult, Dr. Albin noted.
But it’s worth it, she said, because nutrition is the underpinning of so many diseases.
“Food is the top risk factor for early death in the U.S.,” Dr. Albin said. “I like to say that five times in a row. People have not digested it.”
During her culinary medicine courses, she also asks her medical students: “Who is comfortable in the kitchen?” Some sheepishly raise their hands, she said. Some don’t. Many don’t know anything about cooking.
Then she teaches students about healthy food and how to make it. As part of her program, medical students are given a pantry starter kit with olive oil and a variety of spices to take home and use.
Some recipes Dr. Albin teaches includes mango chili shrimp salad with lime vinaigrette, eggplant sliders, yellow vegetable curry, and strawberry banana chia pudding.
“If you figure out how to do it for your own busy, everyday life, you are now empowered to tell someone else about it,” she said.
A dietitian’s involvement
Milette Siler, RD, LD, CCMS, works with Dr. Albin to educate medical students and patients about food as medicine. A significant chunk of her job involves teaching future doctors what dietitians do.
When the class starts, many students don’t know two of the five basic things dietitians do, Ms. Siler said. By the end of the class, all students know what a dietitian does.
That’s important as students go on to become doctors.
“For us to remove barriers to care, we have to acknowledge most patients’ entry into health care is their physician,” she said. “The dietitian is often a referral. Doctors need to know enough to do no harm.”
Clinicians are often siloed, she said, and the key to better serving patients is partnership, transparency, and relationships. “I think everybody is at a point where everyone is saying what we’re doing isn’t working,” she said. “The American public deserves better, physicians deserve better, and clinicians deserve better.”
Popular with students
While the old guard has been slow to embrace the shift, her students have helped drive the growth of the culinary medicine field, Dr. Albin said.
“They are not settling for the inadequacy that somehow the rest of us did,” she continued. “I’m so hopeful for the future of the health system. We have a generation of people who will not stand for neglecting the most vital elements.”
Lyndon Bui, a second-year medical student at the University of Arizona, Phoenix, is an example of one of these people.
As a member of a culinary medicine interest group on campus, he said, he has learned a lot about the importance of diet for long-term health. This has given him confidence to talk about food and nutrition.
His group does cooking demos at the Phoenix Farmers Market using food from various local vendors. They usually make a salad from local greens and cook seasonal veggies in a stir fry, he said.
They’ve previously made salad with microgreens – young seedlings of edible vegetables and herbs – and pomegranate seeds with a honey mustard vinaigrette, eggplant or cucumber, and hummus on pita bread, as well as almond butter and honey sandwiches, according to the university.
The group also talks with people in the community, answers questions, and learns about community needs.
Mr. Bui’s participation in this group has helped him cultivate a passion for community outreach that he wants to incorporate into his career.
“I feel like I have the knowledge to provide better advice to patients,” he said. “Knowing all these things about food, I feel more comfortable talking about it and more inclined to refer to a dietitian when maybe I wouldn’t have before.”
Family physician applauds culinary medicine programs
When Angie Neison, MD, CCMS, went to medical school, she was surprised there wasn’t more education on nutrition.
In fact, on average, physicians receive less than 20 hours of nutrition education, according to the University of Arizona.
Now 15 years into her career as a family physician, Dr. Neison says nutrition is a huge part of her practice. She spends time working to bust myths about nutrition for her patients – including that healthy food is boring and bland, that making it is time consuming, and that healthy food is expensive. She also spends time teaching aspects of culinary medicine to her colleagues – many of whom are well into their careers – so they can better serve their patients.
It’s worth it to spend time learning about nutrition, she said, whether that’s as a medical student in a culinary medicine program or a practicing physician taking additional courses.
Nutrition education in medical school hasn’t been a priority, she said, maybe because there is so much to learn, or maybe because there is no money to be made in prevention.
“If doctors learn it, they are able to better guide patients,” she said.
Correction, 11/29/22: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Albin's institution.
FROM ACADEMIC MEDICINE
Flu vaccination associated with reduced stroke risk
The risk of stroke was about 23% lower in the 6 months following a flu shot, regardless of the patient’s age, sex, or underlying health conditions.
“There is an established link between upper respiratory infection and both heart attack and stroke. This has been very salient in the past few years throughout the COVID-19 pandemic,” study author Jessalyn Holodinsky, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist and postdoctoral fellow in clinical neurosciences at the University of Calgary (Alta.) told this news organization.
“It is also known that the flu shot can reduce risk of heart attack and hospitalization for those with heart disease,” she said. “Given both of these [observations], we thought it prudent to study whether there is a link between vaccination for influenza and stroke.”
The study was published in the Lancet Public Health.
Large effect size
The investigators analyzed administrative data from 2009 through 2018 from the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan, which covers all residents of Alberta. The province provides free seasonal influenza vaccines to residents under the insurance plan.
The research team looked for stroke events such as acute ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attack. They then analyzed the risk of stroke events among those with or without a flu shot in the previous 6 months. They accounted for multiple factors, including age, sex, income, location, and factors related to stroke risk, such as anticoagulant use, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Among the 4.1 million adults included in the researchers’ analysis, about 1.8 million (43%) received at least one vaccination during the study period. Nearly 97,000 people received a flu vaccine in each year they were in the study, including 29,288 who received a shot in all 10 flu seasons included in the study.
About 38,000 stroke events were recorded, including about 34,000 (90%) first stroke events. Among the 10% of strokes that were recurrent events, the maximum number of stroke events in one person was nine.
Overall, patients who received at least one influenza vaccine were more likely to be older, be women, and have higher rates of comorbidities. The vaccinated group had a slightly higher proportion of people who lived in urban areas, but the income levels were similar between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups.
The crude incidence of stroke was higher among people who had ever received an influenza vaccination, at 1.25%, compared with 0.52% among those who hadn’t been vaccinated. However, after adjusting for age, sex, underlying conditions, and socioeconomic status, recent flu vaccination (that is, in the previous 6 months) was associated with a 23% reduced risk of stroke.
The significant reduction in risk applied to all stroke types, particularly acute ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, influenza vaccination was associated with a reduced risk across all ages and risk profiles, except patients without hypertension.
“What we were most surprised by was the sheer magnitude of the effect and that it existed across different adult age groups, for both sexes, and for those with and without risk factors for stroke,” said Dr. Holodinsky.
Vaccination was associated with a larger reduction in stroke risk in men than in women, perhaps because unvaccinated men had a significantly higher baseline risk for stroke than unvaccinated women, the study authors write.
Promoting cardiovascular health
In addition, vaccination was associated with a greater relative reduction in stroke risk in younger age groups, lower income groups, and those with diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and anticoagulant use.
Among 2.4 million people observed for the entire study period, vaccination protection increased with the number of vaccines received. People who were vaccinated serially each year had a significantly lower risk of stroke than those who received one shot.
Dr. Holodinsky and colleagues are conducting additional research into influenza vaccination, including stroke risk in children. They’re also investigating whether the reduced risk applies to other vaccinations for respiratory illnesses, such as COVID-19 and pneumonia.
“We hope that this added effect of vaccination encourages more adults to receive the flu shot,” she said. “One day, vaccinations might be considered a key pillar of cardiovascular health, along with diet, exercise, control of hypertension and high cholesterol, and smoking cessation.”
Future research should also investigate the reasons why adults – particularly people at high risk with underlying conditions – don’t receive recommended influenza vaccines, the study authors wrote.
‘Call to action’
Bahar Behrouzi, an MD-PhD candidate focused on clinical epidemiology at the Institute of Health Policy, Management, and Evaluation, University of Toronto, said: “There are a variety of observational studies around the world that show that flu vaccine uptake is low among the general population and high-risk persons. In studying these questions, our hope is that we can continue to build confidence in viral respiratory vaccines like the influenza vaccine by continuing to generate rigorous evidence with the latest data.”
Ms. Behrouzi, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched influenza vaccination and cardiovascular risk. She and her colleagues have found that flu vaccines were associated with a 34% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including a 45% reduced risk among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
“The broader public health message is for people to advocate for themselves and get the seasonal flu vaccine, especially if they are part of an at-risk group,” she said. “In our studies, we have positioned this message as a call to action not only for the public, but also for health care professionals – particularly specialists such as cardiologists or neurologists – to encourage or remind them to engage in conversation about the broad benefits of vaccination beyond just preventing or reducing the severity of flu infection.”
The study was conducted without outside funding. Dr. Holodinsky and Ms. Behrouzi have reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of stroke was about 23% lower in the 6 months following a flu shot, regardless of the patient’s age, sex, or underlying health conditions.
“There is an established link between upper respiratory infection and both heart attack and stroke. This has been very salient in the past few years throughout the COVID-19 pandemic,” study author Jessalyn Holodinsky, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist and postdoctoral fellow in clinical neurosciences at the University of Calgary (Alta.) told this news organization.
“It is also known that the flu shot can reduce risk of heart attack and hospitalization for those with heart disease,” she said. “Given both of these [observations], we thought it prudent to study whether there is a link between vaccination for influenza and stroke.”
The study was published in the Lancet Public Health.
Large effect size
The investigators analyzed administrative data from 2009 through 2018 from the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan, which covers all residents of Alberta. The province provides free seasonal influenza vaccines to residents under the insurance plan.
The research team looked for stroke events such as acute ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attack. They then analyzed the risk of stroke events among those with or without a flu shot in the previous 6 months. They accounted for multiple factors, including age, sex, income, location, and factors related to stroke risk, such as anticoagulant use, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Among the 4.1 million adults included in the researchers’ analysis, about 1.8 million (43%) received at least one vaccination during the study period. Nearly 97,000 people received a flu vaccine in each year they were in the study, including 29,288 who received a shot in all 10 flu seasons included in the study.
About 38,000 stroke events were recorded, including about 34,000 (90%) first stroke events. Among the 10% of strokes that were recurrent events, the maximum number of stroke events in one person was nine.
Overall, patients who received at least one influenza vaccine were more likely to be older, be women, and have higher rates of comorbidities. The vaccinated group had a slightly higher proportion of people who lived in urban areas, but the income levels were similar between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups.
The crude incidence of stroke was higher among people who had ever received an influenza vaccination, at 1.25%, compared with 0.52% among those who hadn’t been vaccinated. However, after adjusting for age, sex, underlying conditions, and socioeconomic status, recent flu vaccination (that is, in the previous 6 months) was associated with a 23% reduced risk of stroke.
The significant reduction in risk applied to all stroke types, particularly acute ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, influenza vaccination was associated with a reduced risk across all ages and risk profiles, except patients without hypertension.
“What we were most surprised by was the sheer magnitude of the effect and that it existed across different adult age groups, for both sexes, and for those with and without risk factors for stroke,” said Dr. Holodinsky.
Vaccination was associated with a larger reduction in stroke risk in men than in women, perhaps because unvaccinated men had a significantly higher baseline risk for stroke than unvaccinated women, the study authors write.
Promoting cardiovascular health
In addition, vaccination was associated with a greater relative reduction in stroke risk in younger age groups, lower income groups, and those with diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and anticoagulant use.
Among 2.4 million people observed for the entire study period, vaccination protection increased with the number of vaccines received. People who were vaccinated serially each year had a significantly lower risk of stroke than those who received one shot.
Dr. Holodinsky and colleagues are conducting additional research into influenza vaccination, including stroke risk in children. They’re also investigating whether the reduced risk applies to other vaccinations for respiratory illnesses, such as COVID-19 and pneumonia.
“We hope that this added effect of vaccination encourages more adults to receive the flu shot,” she said. “One day, vaccinations might be considered a key pillar of cardiovascular health, along with diet, exercise, control of hypertension and high cholesterol, and smoking cessation.”
Future research should also investigate the reasons why adults – particularly people at high risk with underlying conditions – don’t receive recommended influenza vaccines, the study authors wrote.
‘Call to action’
Bahar Behrouzi, an MD-PhD candidate focused on clinical epidemiology at the Institute of Health Policy, Management, and Evaluation, University of Toronto, said: “There are a variety of observational studies around the world that show that flu vaccine uptake is low among the general population and high-risk persons. In studying these questions, our hope is that we can continue to build confidence in viral respiratory vaccines like the influenza vaccine by continuing to generate rigorous evidence with the latest data.”
Ms. Behrouzi, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched influenza vaccination and cardiovascular risk. She and her colleagues have found that flu vaccines were associated with a 34% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including a 45% reduced risk among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
“The broader public health message is for people to advocate for themselves and get the seasonal flu vaccine, especially if they are part of an at-risk group,” she said. “In our studies, we have positioned this message as a call to action not only for the public, but also for health care professionals – particularly specialists such as cardiologists or neurologists – to encourage or remind them to engage in conversation about the broad benefits of vaccination beyond just preventing or reducing the severity of flu infection.”
The study was conducted without outside funding. Dr. Holodinsky and Ms. Behrouzi have reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of stroke was about 23% lower in the 6 months following a flu shot, regardless of the patient’s age, sex, or underlying health conditions.
“There is an established link between upper respiratory infection and both heart attack and stroke. This has been very salient in the past few years throughout the COVID-19 pandemic,” study author Jessalyn Holodinsky, PhD, a stroke epidemiologist and postdoctoral fellow in clinical neurosciences at the University of Calgary (Alta.) told this news organization.
“It is also known that the flu shot can reduce risk of heart attack and hospitalization for those with heart disease,” she said. “Given both of these [observations], we thought it prudent to study whether there is a link between vaccination for influenza and stroke.”
The study was published in the Lancet Public Health.
Large effect size
The investigators analyzed administrative data from 2009 through 2018 from the Alberta Health Care Insurance Plan, which covers all residents of Alberta. The province provides free seasonal influenza vaccines to residents under the insurance plan.
The research team looked for stroke events such as acute ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and transient ischemic attack. They then analyzed the risk of stroke events among those with or without a flu shot in the previous 6 months. They accounted for multiple factors, including age, sex, income, location, and factors related to stroke risk, such as anticoagulant use, atrial fibrillation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Among the 4.1 million adults included in the researchers’ analysis, about 1.8 million (43%) received at least one vaccination during the study period. Nearly 97,000 people received a flu vaccine in each year they were in the study, including 29,288 who received a shot in all 10 flu seasons included in the study.
About 38,000 stroke events were recorded, including about 34,000 (90%) first stroke events. Among the 10% of strokes that were recurrent events, the maximum number of stroke events in one person was nine.
Overall, patients who received at least one influenza vaccine were more likely to be older, be women, and have higher rates of comorbidities. The vaccinated group had a slightly higher proportion of people who lived in urban areas, but the income levels were similar between the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups.
The crude incidence of stroke was higher among people who had ever received an influenza vaccination, at 1.25%, compared with 0.52% among those who hadn’t been vaccinated. However, after adjusting for age, sex, underlying conditions, and socioeconomic status, recent flu vaccination (that is, in the previous 6 months) was associated with a 23% reduced risk of stroke.
The significant reduction in risk applied to all stroke types, particularly acute ischemic stroke and intracerebral hemorrhage. In addition, influenza vaccination was associated with a reduced risk across all ages and risk profiles, except patients without hypertension.
“What we were most surprised by was the sheer magnitude of the effect and that it existed across different adult age groups, for both sexes, and for those with and without risk factors for stroke,” said Dr. Holodinsky.
Vaccination was associated with a larger reduction in stroke risk in men than in women, perhaps because unvaccinated men had a significantly higher baseline risk for stroke than unvaccinated women, the study authors write.
Promoting cardiovascular health
In addition, vaccination was associated with a greater relative reduction in stroke risk in younger age groups, lower income groups, and those with diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and anticoagulant use.
Among 2.4 million people observed for the entire study period, vaccination protection increased with the number of vaccines received. People who were vaccinated serially each year had a significantly lower risk of stroke than those who received one shot.
Dr. Holodinsky and colleagues are conducting additional research into influenza vaccination, including stroke risk in children. They’re also investigating whether the reduced risk applies to other vaccinations for respiratory illnesses, such as COVID-19 and pneumonia.
“We hope that this added effect of vaccination encourages more adults to receive the flu shot,” she said. “One day, vaccinations might be considered a key pillar of cardiovascular health, along with diet, exercise, control of hypertension and high cholesterol, and smoking cessation.”
Future research should also investigate the reasons why adults – particularly people at high risk with underlying conditions – don’t receive recommended influenza vaccines, the study authors wrote.
‘Call to action’
Bahar Behrouzi, an MD-PhD candidate focused on clinical epidemiology at the Institute of Health Policy, Management, and Evaluation, University of Toronto, said: “There are a variety of observational studies around the world that show that flu vaccine uptake is low among the general population and high-risk persons. In studying these questions, our hope is that we can continue to build confidence in viral respiratory vaccines like the influenza vaccine by continuing to generate rigorous evidence with the latest data.”
Ms. Behrouzi, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched influenza vaccination and cardiovascular risk. She and her colleagues have found that flu vaccines were associated with a 34% lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including a 45% reduced risk among patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
“The broader public health message is for people to advocate for themselves and get the seasonal flu vaccine, especially if they are part of an at-risk group,” she said. “In our studies, we have positioned this message as a call to action not only for the public, but also for health care professionals – particularly specialists such as cardiologists or neurologists – to encourage or remind them to engage in conversation about the broad benefits of vaccination beyond just preventing or reducing the severity of flu infection.”
The study was conducted without outside funding. Dr. Holodinsky and Ms. Behrouzi have reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM LANCET PUBLIC HEALTH
No benefit of rivaroxaban in COVID outpatients: PREVENT-HD
A new U.S. randomized trial has failed to show benefit of a 35-day course of oral anticoagulation with rivaroxaban for the prevention of thrombotic events in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19.
The PREVENT-HD trial was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions by Gregory Piazza, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“With the caveat that the trial was underpowered to provide a definitive conclusion, these data do not support routine antithrombotic prophylaxis in nonhospitalized patients with symptomatic COVID-19,” Dr. Piazza concluded.
PREVENT-HD is the largest randomized study to look at anticoagulation in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients and joins a long list of smaller trials that have also shown no benefit with this approach.
However, anticoagulation is recommended in patients who are hospitalized with COVID-19.
Dr. Piazza noted that the issue of anticoagulation in COVID-19 has focused mainly on hospitalized patients, but most COVID-19 cases are treated as outpatients, who are also suspected to be at risk for venous and arterial thrombotic events, especially if they have additional risk factors. Histopathological evidence also suggests that at least part of the deterioration in lung function leading to hospitalization may be attributable to in situ pulmonary artery thrombosis.
The PREVENT-HD trial explored the question of whether early initiation of thromboprophylaxis dosing of rivaroxaban in higher-risk outpatients with COVID-19 may lower the incidence of venous and arterial thrombotic events, reduce in situ pulmonary thrombosis and the worsening of pulmonary function that may lead to hospitalization, and reduce all-cause mortality.
The trial included 1,284 outpatients with a positive test for COVID-19 and who were within 14 days of symptom onset. They also had to have at least one of the following additional risk factors: age over 60 years; prior history of venous thromboembolism (VTE), thrombophilia, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, cardiovascular disease or ischemic stroke, cancer, diabetes, heart failure, obesity (body mass index ≥ 35 kg/m2) or D-dimer > upper limit of normal. Around 35% of the study population had two or more of these risk factors.
Patients were randomized to rivaroxaban 10 mg daily for 35 days or placebo.
The primary efficacy endpoint was time to first occurrence of a composite of symptomatic VTE, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acute limb ischemia, non–central nervous system systemic embolization, all-cause hospitalization, and all-cause mortality up to day 35.
The primary safety endpoint was time to first occurrence of International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis (ISTH) critical-site and fatal bleeding.
A modified intention-to-treat analysis (all participants taking at least one dose of study intervention) was also planned.
The trial was stopped early in April this year because of a lower than expected event incidence (3.2%), compared with the planned rate (8.5%), giving a very low likelihood of being able to achieve the required number of events.
Dr. Piazza said reasons contributing to the low event rate included a falling COVID-19 death and hospitalization rate nationwide, and increased use of effective vaccines.
Results of the main intention-to-treat analysis (in 1,284 patients) showed no significant difference in the primary efficacy composite endpoint, which occurred in 3.4% of the rivaroxaban group versus 3.0% of the placebo group.
In the modified intention-to-treat analysis (which included 1,197 patients who actually took at least one dose of the study medication) there was shift in the directionality of the point estimate (rivaroxaban 2.0% vs. placebo 2.7%), which Dr. Piazza said was related to a higher number of patients hospitalized before receiving study drug in the rivaroxaban group. However, the difference was still nonsignificant.
The first major secondary outcome of symptomatic VTE, arterial thrombotic events, and all-cause mortality occurred in 0.3% of rivaroxaban patients versus 1.1% of placebo patients, but this difference did not reach statistical significance.
However, a post hoc exploratory analysis did show a significant reduction in the outcome of symptomatic VTE and arterial thrombotic events.
In terms of safety, there were no fatal critical-site bleeding events, and there was no difference in ISTH major bleeding, which occurred in one patient in the rivaroxaban group versus no patients in the placebo group.
There was, however, a significant increase in nonmajor clinically relevant bleeding with rivaroxaban, which occurred in nine patients (1.5%) versus one patient (0.2%) in the placebo group.
Trivial bleeding was also increased in the rivaroxaban group, occurring in 17 patients (2.8%) versus 5 patients (0.8%) in the placebo group.
Discussant for the study, Renato Lopes, MD, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., noted that the relationship between COVID-19 and thrombosis has been an important issue since the beginning of the pandemic, with many proposed mechanisms to explain the COVID-19–associated coagulopathy, which is a major cause of death and disability.
While observational data at the beginning of the pandemic suggested patients with COVID-19 might benefit from anticoagulation, looking at all the different randomized trials that have tested anticoagulation in COVID-19 outpatients, there is no treatment effect on the various different primary outcomes in those studies and also no effect on all-cause mortality, Dr. Lopes said.
He pointed out that PREVENT-HD was stopped prematurely with only about one-third of the planned number of patients enrolled, “just like every other outpatient COVID-19 trial.”
He also drew attention to the low rates of vaccination in the trial population, which does not reflect the current vaccination rate in the United States, and said the different direction of the results between the main intention-to-treat and modified intention-to-treat analyses deserve further investigation.
However, Dr. Lopes concluded, “The results of this trial, in line with the body of evidence in this field, do not support the routine use of any antithrombotic therapy for outpatients with COVID-19.”
The PREVENT-HD trial was sponsored by Janssen. Dr. Piazza has reported receiving research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, Bayer, Janssen, Alexion, Amgen, and Boston Scientific, and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, Boston Scientific, Janssen, NAMSA, Prairie Education and Research Cooperative, Boston Clinical Research Institute, and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new U.S. randomized trial has failed to show benefit of a 35-day course of oral anticoagulation with rivaroxaban for the prevention of thrombotic events in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19.
The PREVENT-HD trial was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions by Gregory Piazza, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“With the caveat that the trial was underpowered to provide a definitive conclusion, these data do not support routine antithrombotic prophylaxis in nonhospitalized patients with symptomatic COVID-19,” Dr. Piazza concluded.
PREVENT-HD is the largest randomized study to look at anticoagulation in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients and joins a long list of smaller trials that have also shown no benefit with this approach.
However, anticoagulation is recommended in patients who are hospitalized with COVID-19.
Dr. Piazza noted that the issue of anticoagulation in COVID-19 has focused mainly on hospitalized patients, but most COVID-19 cases are treated as outpatients, who are also suspected to be at risk for venous and arterial thrombotic events, especially if they have additional risk factors. Histopathological evidence also suggests that at least part of the deterioration in lung function leading to hospitalization may be attributable to in situ pulmonary artery thrombosis.
The PREVENT-HD trial explored the question of whether early initiation of thromboprophylaxis dosing of rivaroxaban in higher-risk outpatients with COVID-19 may lower the incidence of venous and arterial thrombotic events, reduce in situ pulmonary thrombosis and the worsening of pulmonary function that may lead to hospitalization, and reduce all-cause mortality.
The trial included 1,284 outpatients with a positive test for COVID-19 and who were within 14 days of symptom onset. They also had to have at least one of the following additional risk factors: age over 60 years; prior history of venous thromboembolism (VTE), thrombophilia, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, cardiovascular disease or ischemic stroke, cancer, diabetes, heart failure, obesity (body mass index ≥ 35 kg/m2) or D-dimer > upper limit of normal. Around 35% of the study population had two or more of these risk factors.
Patients were randomized to rivaroxaban 10 mg daily for 35 days or placebo.
The primary efficacy endpoint was time to first occurrence of a composite of symptomatic VTE, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acute limb ischemia, non–central nervous system systemic embolization, all-cause hospitalization, and all-cause mortality up to day 35.
The primary safety endpoint was time to first occurrence of International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis (ISTH) critical-site and fatal bleeding.
A modified intention-to-treat analysis (all participants taking at least one dose of study intervention) was also planned.
The trial was stopped early in April this year because of a lower than expected event incidence (3.2%), compared with the planned rate (8.5%), giving a very low likelihood of being able to achieve the required number of events.
Dr. Piazza said reasons contributing to the low event rate included a falling COVID-19 death and hospitalization rate nationwide, and increased use of effective vaccines.
Results of the main intention-to-treat analysis (in 1,284 patients) showed no significant difference in the primary efficacy composite endpoint, which occurred in 3.4% of the rivaroxaban group versus 3.0% of the placebo group.
In the modified intention-to-treat analysis (which included 1,197 patients who actually took at least one dose of the study medication) there was shift in the directionality of the point estimate (rivaroxaban 2.0% vs. placebo 2.7%), which Dr. Piazza said was related to a higher number of patients hospitalized before receiving study drug in the rivaroxaban group. However, the difference was still nonsignificant.
The first major secondary outcome of symptomatic VTE, arterial thrombotic events, and all-cause mortality occurred in 0.3% of rivaroxaban patients versus 1.1% of placebo patients, but this difference did not reach statistical significance.
However, a post hoc exploratory analysis did show a significant reduction in the outcome of symptomatic VTE and arterial thrombotic events.
In terms of safety, there were no fatal critical-site bleeding events, and there was no difference in ISTH major bleeding, which occurred in one patient in the rivaroxaban group versus no patients in the placebo group.
There was, however, a significant increase in nonmajor clinically relevant bleeding with rivaroxaban, which occurred in nine patients (1.5%) versus one patient (0.2%) in the placebo group.
Trivial bleeding was also increased in the rivaroxaban group, occurring in 17 patients (2.8%) versus 5 patients (0.8%) in the placebo group.
Discussant for the study, Renato Lopes, MD, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., noted that the relationship between COVID-19 and thrombosis has been an important issue since the beginning of the pandemic, with many proposed mechanisms to explain the COVID-19–associated coagulopathy, which is a major cause of death and disability.
While observational data at the beginning of the pandemic suggested patients with COVID-19 might benefit from anticoagulation, looking at all the different randomized trials that have tested anticoagulation in COVID-19 outpatients, there is no treatment effect on the various different primary outcomes in those studies and also no effect on all-cause mortality, Dr. Lopes said.
He pointed out that PREVENT-HD was stopped prematurely with only about one-third of the planned number of patients enrolled, “just like every other outpatient COVID-19 trial.”
He also drew attention to the low rates of vaccination in the trial population, which does not reflect the current vaccination rate in the United States, and said the different direction of the results between the main intention-to-treat and modified intention-to-treat analyses deserve further investigation.
However, Dr. Lopes concluded, “The results of this trial, in line with the body of evidence in this field, do not support the routine use of any antithrombotic therapy for outpatients with COVID-19.”
The PREVENT-HD trial was sponsored by Janssen. Dr. Piazza has reported receiving research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, Bayer, Janssen, Alexion, Amgen, and Boston Scientific, and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, Boston Scientific, Janssen, NAMSA, Prairie Education and Research Cooperative, Boston Clinical Research Institute, and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new U.S. randomized trial has failed to show benefit of a 35-day course of oral anticoagulation with rivaroxaban for the prevention of thrombotic events in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19.
The PREVENT-HD trial was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions by Gregory Piazza, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
“With the caveat that the trial was underpowered to provide a definitive conclusion, these data do not support routine antithrombotic prophylaxis in nonhospitalized patients with symptomatic COVID-19,” Dr. Piazza concluded.
PREVENT-HD is the largest randomized study to look at anticoagulation in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients and joins a long list of smaller trials that have also shown no benefit with this approach.
However, anticoagulation is recommended in patients who are hospitalized with COVID-19.
Dr. Piazza noted that the issue of anticoagulation in COVID-19 has focused mainly on hospitalized patients, but most COVID-19 cases are treated as outpatients, who are also suspected to be at risk for venous and arterial thrombotic events, especially if they have additional risk factors. Histopathological evidence also suggests that at least part of the deterioration in lung function leading to hospitalization may be attributable to in situ pulmonary artery thrombosis.
The PREVENT-HD trial explored the question of whether early initiation of thromboprophylaxis dosing of rivaroxaban in higher-risk outpatients with COVID-19 may lower the incidence of venous and arterial thrombotic events, reduce in situ pulmonary thrombosis and the worsening of pulmonary function that may lead to hospitalization, and reduce all-cause mortality.
The trial included 1,284 outpatients with a positive test for COVID-19 and who were within 14 days of symptom onset. They also had to have at least one of the following additional risk factors: age over 60 years; prior history of venous thromboembolism (VTE), thrombophilia, coronary artery disease, peripheral artery disease, cardiovascular disease or ischemic stroke, cancer, diabetes, heart failure, obesity (body mass index ≥ 35 kg/m2) or D-dimer > upper limit of normal. Around 35% of the study population had two or more of these risk factors.
Patients were randomized to rivaroxaban 10 mg daily for 35 days or placebo.
The primary efficacy endpoint was time to first occurrence of a composite of symptomatic VTE, myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, acute limb ischemia, non–central nervous system systemic embolization, all-cause hospitalization, and all-cause mortality up to day 35.
The primary safety endpoint was time to first occurrence of International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis (ISTH) critical-site and fatal bleeding.
A modified intention-to-treat analysis (all participants taking at least one dose of study intervention) was also planned.
The trial was stopped early in April this year because of a lower than expected event incidence (3.2%), compared with the planned rate (8.5%), giving a very low likelihood of being able to achieve the required number of events.
Dr. Piazza said reasons contributing to the low event rate included a falling COVID-19 death and hospitalization rate nationwide, and increased use of effective vaccines.
Results of the main intention-to-treat analysis (in 1,284 patients) showed no significant difference in the primary efficacy composite endpoint, which occurred in 3.4% of the rivaroxaban group versus 3.0% of the placebo group.
In the modified intention-to-treat analysis (which included 1,197 patients who actually took at least one dose of the study medication) there was shift in the directionality of the point estimate (rivaroxaban 2.0% vs. placebo 2.7%), which Dr. Piazza said was related to a higher number of patients hospitalized before receiving study drug in the rivaroxaban group. However, the difference was still nonsignificant.
The first major secondary outcome of symptomatic VTE, arterial thrombotic events, and all-cause mortality occurred in 0.3% of rivaroxaban patients versus 1.1% of placebo patients, but this difference did not reach statistical significance.
However, a post hoc exploratory analysis did show a significant reduction in the outcome of symptomatic VTE and arterial thrombotic events.
In terms of safety, there were no fatal critical-site bleeding events, and there was no difference in ISTH major bleeding, which occurred in one patient in the rivaroxaban group versus no patients in the placebo group.
There was, however, a significant increase in nonmajor clinically relevant bleeding with rivaroxaban, which occurred in nine patients (1.5%) versus one patient (0.2%) in the placebo group.
Trivial bleeding was also increased in the rivaroxaban group, occurring in 17 patients (2.8%) versus 5 patients (0.8%) in the placebo group.
Discussant for the study, Renato Lopes, MD, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., noted that the relationship between COVID-19 and thrombosis has been an important issue since the beginning of the pandemic, with many proposed mechanisms to explain the COVID-19–associated coagulopathy, which is a major cause of death and disability.
While observational data at the beginning of the pandemic suggested patients with COVID-19 might benefit from anticoagulation, looking at all the different randomized trials that have tested anticoagulation in COVID-19 outpatients, there is no treatment effect on the various different primary outcomes in those studies and also no effect on all-cause mortality, Dr. Lopes said.
He pointed out that PREVENT-HD was stopped prematurely with only about one-third of the planned number of patients enrolled, “just like every other outpatient COVID-19 trial.”
He also drew attention to the low rates of vaccination in the trial population, which does not reflect the current vaccination rate in the United States, and said the different direction of the results between the main intention-to-treat and modified intention-to-treat analyses deserve further investigation.
However, Dr. Lopes concluded, “The results of this trial, in line with the body of evidence in this field, do not support the routine use of any antithrombotic therapy for outpatients with COVID-19.”
The PREVENT-HD trial was sponsored by Janssen. Dr. Piazza has reported receiving research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, Bayer, Janssen, Alexion, Amgen, and Boston Scientific, and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, Boston Scientific, Janssen, NAMSA, Prairie Education and Research Cooperative, Boston Clinical Research Institute, and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2022
Stroke risk rises with years of drinking in young adults
“The rate of stroke among young adults has been increasing over the last few decades, and stroke in young adults causes death and serious disability,” study coauthor Eue-Keun Choi, MD, PhD, of Seoul National University, Republic of Korea, said in a statement.
“If we could prevent stroke in young adults by reducing alcohol consumption, that could potentially have a substantial impact on the health of individuals and the overall burden of stroke on society,” Dr. Choi added.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Compounding effects
Using data from a Korean national health database, the researchers identified roughly 1.5 million adults aged 20-39 years (mean age 29.5 years, 72% male) who had four consecutive annual health examinations during which they were asked about their alcohol use.
During a median follow-up of roughly 6 years, 3,153 individuals suffered a stroke.
After multivariate adjustment accounting for other factors that could affect the risk for stroke, such as hypertension, smoking, and body mass index, the risk of stroke increased steadily with the number of years of moderate to heavy drinking, defined as 105 grams or more of alcohol per week.
Compared with light drinkers or teetotalers, stroke risk increased 19% with 2 years of moderate to heavy drinking and 22% and 23%, respectively, for 3 and 4 years of moderate or heaving drinking.
The positive dose-response relationship was chiefly driven by increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke; with 2, 3 and 4 years of moderate to heavy drinking, hemorrhagic stroke risk increased 30%, 42% and 36%, respectively, relative to light/no drinking.
“Since more than 90% of the burden of stroke overall can be attributed to potentially modifiable risk factors, including alcohol consumption, and since stroke in young adults severely impacts both the individual and society by limiting their activities during their most productive years, reducing alcohol consumption should be emphasized in young adults with heavy drinking habits as part of any strategy to prevent stroke,” Dr. Choi said.
A limitation of the study is that only Korean people were included, so the results may not apply to people of other races and ethnicities, they noted. In addition, people filled out questionnaires about their alcohol consumption, which may introduce recall bias.
Consistent evidence
“For decades, the evidence was suggestive that a moderate amount of alcohol daily is actually beneficial – one to two drinks in men and one drink in women – at reducing major vascular outcomes,” Pierre Fayad, MD, professor, department of neurological sciences, and director of the Nebraska Stroke Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, said in commenting on the research.
Yet, over the past few years, some research has found no evidence of benefit with moderate alcohol intake. There is, however, “consistent evidence” that shows a detrimental effect of excessive alcohol, particularly binge drinking, especially in young adults, Dr. Fayad said.
This study, he said, “adds to the known detrimental effects of excessive alcohol intake, in increasing the risk of stroke, particularly in young adults.
“The bottom line: Young adults who usually have a low risk of stroke increase their risk significantly by heavy alcohol drinking, and Koreans are equally at risk as other populations,” Dr. Fayad said.
The study was supported by the Korea Medical Device Development Fund and the Korea National Research Foundation. Dr. Choi and Dr. Fayad report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The rate of stroke among young adults has been increasing over the last few decades, and stroke in young adults causes death and serious disability,” study coauthor Eue-Keun Choi, MD, PhD, of Seoul National University, Republic of Korea, said in a statement.
“If we could prevent stroke in young adults by reducing alcohol consumption, that could potentially have a substantial impact on the health of individuals and the overall burden of stroke on society,” Dr. Choi added.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Compounding effects
Using data from a Korean national health database, the researchers identified roughly 1.5 million adults aged 20-39 years (mean age 29.5 years, 72% male) who had four consecutive annual health examinations during which they were asked about their alcohol use.
During a median follow-up of roughly 6 years, 3,153 individuals suffered a stroke.
After multivariate adjustment accounting for other factors that could affect the risk for stroke, such as hypertension, smoking, and body mass index, the risk of stroke increased steadily with the number of years of moderate to heavy drinking, defined as 105 grams or more of alcohol per week.
Compared with light drinkers or teetotalers, stroke risk increased 19% with 2 years of moderate to heavy drinking and 22% and 23%, respectively, for 3 and 4 years of moderate or heaving drinking.
The positive dose-response relationship was chiefly driven by increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke; with 2, 3 and 4 years of moderate to heavy drinking, hemorrhagic stroke risk increased 30%, 42% and 36%, respectively, relative to light/no drinking.
“Since more than 90% of the burden of stroke overall can be attributed to potentially modifiable risk factors, including alcohol consumption, and since stroke in young adults severely impacts both the individual and society by limiting their activities during their most productive years, reducing alcohol consumption should be emphasized in young adults with heavy drinking habits as part of any strategy to prevent stroke,” Dr. Choi said.
A limitation of the study is that only Korean people were included, so the results may not apply to people of other races and ethnicities, they noted. In addition, people filled out questionnaires about their alcohol consumption, which may introduce recall bias.
Consistent evidence
“For decades, the evidence was suggestive that a moderate amount of alcohol daily is actually beneficial – one to two drinks in men and one drink in women – at reducing major vascular outcomes,” Pierre Fayad, MD, professor, department of neurological sciences, and director of the Nebraska Stroke Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, said in commenting on the research.
Yet, over the past few years, some research has found no evidence of benefit with moderate alcohol intake. There is, however, “consistent evidence” that shows a detrimental effect of excessive alcohol, particularly binge drinking, especially in young adults, Dr. Fayad said.
This study, he said, “adds to the known detrimental effects of excessive alcohol intake, in increasing the risk of stroke, particularly in young adults.
“The bottom line: Young adults who usually have a low risk of stroke increase their risk significantly by heavy alcohol drinking, and Koreans are equally at risk as other populations,” Dr. Fayad said.
The study was supported by the Korea Medical Device Development Fund and the Korea National Research Foundation. Dr. Choi and Dr. Fayad report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“The rate of stroke among young adults has been increasing over the last few decades, and stroke in young adults causes death and serious disability,” study coauthor Eue-Keun Choi, MD, PhD, of Seoul National University, Republic of Korea, said in a statement.
“If we could prevent stroke in young adults by reducing alcohol consumption, that could potentially have a substantial impact on the health of individuals and the overall burden of stroke on society,” Dr. Choi added.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Compounding effects
Using data from a Korean national health database, the researchers identified roughly 1.5 million adults aged 20-39 years (mean age 29.5 years, 72% male) who had four consecutive annual health examinations during which they were asked about their alcohol use.
During a median follow-up of roughly 6 years, 3,153 individuals suffered a stroke.
After multivariate adjustment accounting for other factors that could affect the risk for stroke, such as hypertension, smoking, and body mass index, the risk of stroke increased steadily with the number of years of moderate to heavy drinking, defined as 105 grams or more of alcohol per week.
Compared with light drinkers or teetotalers, stroke risk increased 19% with 2 years of moderate to heavy drinking and 22% and 23%, respectively, for 3 and 4 years of moderate or heaving drinking.
The positive dose-response relationship was chiefly driven by increased risk of hemorrhagic stroke; with 2, 3 and 4 years of moderate to heavy drinking, hemorrhagic stroke risk increased 30%, 42% and 36%, respectively, relative to light/no drinking.
“Since more than 90% of the burden of stroke overall can be attributed to potentially modifiable risk factors, including alcohol consumption, and since stroke in young adults severely impacts both the individual and society by limiting their activities during their most productive years, reducing alcohol consumption should be emphasized in young adults with heavy drinking habits as part of any strategy to prevent stroke,” Dr. Choi said.
A limitation of the study is that only Korean people were included, so the results may not apply to people of other races and ethnicities, they noted. In addition, people filled out questionnaires about their alcohol consumption, which may introduce recall bias.
Consistent evidence
“For decades, the evidence was suggestive that a moderate amount of alcohol daily is actually beneficial – one to two drinks in men and one drink in women – at reducing major vascular outcomes,” Pierre Fayad, MD, professor, department of neurological sciences, and director of the Nebraska Stroke Center, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, said in commenting on the research.
Yet, over the past few years, some research has found no evidence of benefit with moderate alcohol intake. There is, however, “consistent evidence” that shows a detrimental effect of excessive alcohol, particularly binge drinking, especially in young adults, Dr. Fayad said.
This study, he said, “adds to the known detrimental effects of excessive alcohol intake, in increasing the risk of stroke, particularly in young adults.
“The bottom line: Young adults who usually have a low risk of stroke increase their risk significantly by heavy alcohol drinking, and Koreans are equally at risk as other populations,” Dr. Fayad said.
The study was supported by the Korea Medical Device Development Fund and the Korea National Research Foundation. Dr. Choi and Dr. Fayad report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Combo thrombolytic approach fails to reduce ICH in stroke
A study evaluating a new approach using a combination of two thrombolytics designed to reduce bleeding risk in patients with acute ischemic stroke has not shown any benefit on the primary outcome of all intracranial hemorrhage (ICH).
However, there were some encouraging findings including a trend towards a reduction in symptomatic ICH, researchers report, and the combination approach did not show any depletion of fibrinogen levels, which suggests a potential lower bleeding risk.
“Although the main results of this study are neutral, we are encouraged that the combination approach with a low dose of alteplase followed by the new mutant pro-urokinase product looked as effective as full-dose alteplase alone, and there were some promising signs signaling a potential lower bleeding risk,” senior investigator, Diederik Dippel, MD, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, told this news organization.
The DUMAS study (Dual Thrombolytic Therapy With Mutant Pro-Urokinase and Low Dose Alteplase for Ischemic Stroke) was presented at the World Stroke Congress in Singapore by study coauthor Nadinda van der Ende, MD, also from Erasmus University Medical Center.
She pointed out that thrombolysis with intravenous alteplase increases the likelihood of a good outcome in acute ischemic stroke but can cause symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, which can be associated with death and major disability.
Mutant pro-urokinase is a new thrombolytic agent, in development by Thrombolytic Science, Cambridge, Mass., formed by changing one amino acid in pro-urokinase to make it more stable. It is more fibrin specific than alteplase and therefore believed to have a lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Fibrin is formed as the last step in the clotting process, and the precursor of fibrin in the blood is fibrinogen, Dr. van der Ende noted. Alteplase depletes fibrinogen, contributing to its increased bleeding risk, but mutant pro-urokinase is not believed to affect fibrinogen.
“Mutant pro-urokinase does not bind to intact fibrin. It only binds to fibrin that has already been primed by alteplase,” she explained.
The hypothesis behind the current study is that giving a small dose of alteplase will break down fibrin in the clot enough to expose the binding sites for mutant pro-urokinase, which can then be given to continue to lyse the clot.
As alteplase has a short half-life, it disappears quickly, and new fibrin is not affected. As mutant pro-urokinase can only lyse fibrin that is primed with alteplase, new hemostatic clots should stay intact. Animal studies have shown less bleeding from distant sites with this approach, Dr. van der Ende said.
The primary analysis of the phase 2 DUMAS study included 238 patients with mild ischemic stroke (median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale [NIHSS] score 3) who met the standard criteria for IV alteplase.
They were randomized to alteplase alone at the regular dose of 0.9 mg/kg (max 90 mg) with a 10% bolus and the remaining given over 60 minutes; or to a combination of a 5-mg bolus of IV alteplase followed by mutant pro-urokinase at a dose of 40 mg given over 60 minutes.
The primary outcome was the rate of all intracranial hemorrhage (symptomatic and asymptomatic) detected by neuroimaging.
This occurred in 14% of patients in the full-dose alteplase group vs. 13% of patients in the combined alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group, a nonsignificant difference: adjusted odds ratio, 0.99 (95% confidence interval, 0.46-2.14).
Secondary outcomes showed no significant differences in NIHSS scores at 24 hours or 5-7 days; functional outcome as measured by a shift analysis of the Modified Rankin Scale (mRS); final infarct volume; or perfusion deficit.
However, blood fibrinogen levels were not depleted and significantly higher in the alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group than in the full-dose alteplase alone group.
In terms of safety, symptomatic ICH occurred in three patients in the alteplase group (3%) and in none (0%) in the combined alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group; death occurred in 4% vs. 2% patients respectively; and major extracranial hemorrhage occurred in 1% in both groups.
Dr. Van der Ende concluded that the study showed an overall low rate of ICH; a combination of alteplase and mutant pro-urokinase was not superior to alteplase alone in reducing ICH rates in this population of patients with minor stroke; and mutant pro-urokinase appeared to be safe and, unlike alteplase, did not show any reduction in fibrinogen levels.
“We think the lack of an effect on fibrinogen with this new combination of a small alteplase bolus followed by mutant pro-urokinase infusion is promising,” Dr. Dippel commented. “The fact that there was no symptomatic ICH with the combination treatment is also encouraging. Although the primary endpoint of this trial was neutral, we still believe this is a very interesting approach, with the potential for reduced bleeding, compared with alteplase alone, but we need larger numbers to see an effect on outcomes.”
Dr. Dippel also pointed out that the study included only patients with minor stroke who were not eligible for endovascular therapy, and these patients have a low risk of a poor outcome and a low bleeding risk.
They are hoping to do another study in patients with more severe stroke, who have a higher bleeding risk and would have more to gain from this combination approach.
Because many patients with severe stroke now have immediate thrombectomy if they present to a comprehensive stroke center, a trial in severe stroke patients would have to be done in primary stroke centers, so if the patents are referred to thrombectomy, the thrombolytic would have a chance to work, Dr. Dippel added.
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Stefan Kiechl, MD, Medical University of Innsbruck (Austria), who is cochair of the World Stroke Congress scientific committee, said, “Alteplase is not fibrin specific, and also causes a degeneration of fibrinogen, which results in ‘fibrinogen depletion coagulopathy.’ It is assumed that 20%-40% of intracerebral bleeding after thrombolysis with alteplase is caused by this problem. DUMAS tests the combination of a substantially reduced alteplase [5 mg] dose plus mutant pro-urokinase to avoid this problem.”
The new thrombolysis protocol, however, did not result in a lower bleeding risk, compared to the comparator alteplase,” he added. “The main limitation of this study is that mainly patients with minor strokes were included. Patients with moderate and severe strokes, who have a substantial risk of bleeding, were not adequately addressed.”
The DUMAS trial was funded by an unrestricted grant from Thrombolytic Science, paid to the institution. Dr. Van der Ende and Dr. Dippel report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study evaluating a new approach using a combination of two thrombolytics designed to reduce bleeding risk in patients with acute ischemic stroke has not shown any benefit on the primary outcome of all intracranial hemorrhage (ICH).
However, there were some encouraging findings including a trend towards a reduction in symptomatic ICH, researchers report, and the combination approach did not show any depletion of fibrinogen levels, which suggests a potential lower bleeding risk.
“Although the main results of this study are neutral, we are encouraged that the combination approach with a low dose of alteplase followed by the new mutant pro-urokinase product looked as effective as full-dose alteplase alone, and there were some promising signs signaling a potential lower bleeding risk,” senior investigator, Diederik Dippel, MD, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, told this news organization.
The DUMAS study (Dual Thrombolytic Therapy With Mutant Pro-Urokinase and Low Dose Alteplase for Ischemic Stroke) was presented at the World Stroke Congress in Singapore by study coauthor Nadinda van der Ende, MD, also from Erasmus University Medical Center.
She pointed out that thrombolysis with intravenous alteplase increases the likelihood of a good outcome in acute ischemic stroke but can cause symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, which can be associated with death and major disability.
Mutant pro-urokinase is a new thrombolytic agent, in development by Thrombolytic Science, Cambridge, Mass., formed by changing one amino acid in pro-urokinase to make it more stable. It is more fibrin specific than alteplase and therefore believed to have a lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Fibrin is formed as the last step in the clotting process, and the precursor of fibrin in the blood is fibrinogen, Dr. van der Ende noted. Alteplase depletes fibrinogen, contributing to its increased bleeding risk, but mutant pro-urokinase is not believed to affect fibrinogen.
“Mutant pro-urokinase does not bind to intact fibrin. It only binds to fibrin that has already been primed by alteplase,” she explained.
The hypothesis behind the current study is that giving a small dose of alteplase will break down fibrin in the clot enough to expose the binding sites for mutant pro-urokinase, which can then be given to continue to lyse the clot.
As alteplase has a short half-life, it disappears quickly, and new fibrin is not affected. As mutant pro-urokinase can only lyse fibrin that is primed with alteplase, new hemostatic clots should stay intact. Animal studies have shown less bleeding from distant sites with this approach, Dr. van der Ende said.
The primary analysis of the phase 2 DUMAS study included 238 patients with mild ischemic stroke (median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale [NIHSS] score 3) who met the standard criteria for IV alteplase.
They were randomized to alteplase alone at the regular dose of 0.9 mg/kg (max 90 mg) with a 10% bolus and the remaining given over 60 minutes; or to a combination of a 5-mg bolus of IV alteplase followed by mutant pro-urokinase at a dose of 40 mg given over 60 minutes.
The primary outcome was the rate of all intracranial hemorrhage (symptomatic and asymptomatic) detected by neuroimaging.
This occurred in 14% of patients in the full-dose alteplase group vs. 13% of patients in the combined alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group, a nonsignificant difference: adjusted odds ratio, 0.99 (95% confidence interval, 0.46-2.14).
Secondary outcomes showed no significant differences in NIHSS scores at 24 hours or 5-7 days; functional outcome as measured by a shift analysis of the Modified Rankin Scale (mRS); final infarct volume; or perfusion deficit.
However, blood fibrinogen levels were not depleted and significantly higher in the alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group than in the full-dose alteplase alone group.
In terms of safety, symptomatic ICH occurred in three patients in the alteplase group (3%) and in none (0%) in the combined alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group; death occurred in 4% vs. 2% patients respectively; and major extracranial hemorrhage occurred in 1% in both groups.
Dr. Van der Ende concluded that the study showed an overall low rate of ICH; a combination of alteplase and mutant pro-urokinase was not superior to alteplase alone in reducing ICH rates in this population of patients with minor stroke; and mutant pro-urokinase appeared to be safe and, unlike alteplase, did not show any reduction in fibrinogen levels.
“We think the lack of an effect on fibrinogen with this new combination of a small alteplase bolus followed by mutant pro-urokinase infusion is promising,” Dr. Dippel commented. “The fact that there was no symptomatic ICH with the combination treatment is also encouraging. Although the primary endpoint of this trial was neutral, we still believe this is a very interesting approach, with the potential for reduced bleeding, compared with alteplase alone, but we need larger numbers to see an effect on outcomes.”
Dr. Dippel also pointed out that the study included only patients with minor stroke who were not eligible for endovascular therapy, and these patients have a low risk of a poor outcome and a low bleeding risk.
They are hoping to do another study in patients with more severe stroke, who have a higher bleeding risk and would have more to gain from this combination approach.
Because many patients with severe stroke now have immediate thrombectomy if they present to a comprehensive stroke center, a trial in severe stroke patients would have to be done in primary stroke centers, so if the patents are referred to thrombectomy, the thrombolytic would have a chance to work, Dr. Dippel added.
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Stefan Kiechl, MD, Medical University of Innsbruck (Austria), who is cochair of the World Stroke Congress scientific committee, said, “Alteplase is not fibrin specific, and also causes a degeneration of fibrinogen, which results in ‘fibrinogen depletion coagulopathy.’ It is assumed that 20%-40% of intracerebral bleeding after thrombolysis with alteplase is caused by this problem. DUMAS tests the combination of a substantially reduced alteplase [5 mg] dose plus mutant pro-urokinase to avoid this problem.”
The new thrombolysis protocol, however, did not result in a lower bleeding risk, compared to the comparator alteplase,” he added. “The main limitation of this study is that mainly patients with minor strokes were included. Patients with moderate and severe strokes, who have a substantial risk of bleeding, were not adequately addressed.”
The DUMAS trial was funded by an unrestricted grant from Thrombolytic Science, paid to the institution. Dr. Van der Ende and Dr. Dippel report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A study evaluating a new approach using a combination of two thrombolytics designed to reduce bleeding risk in patients with acute ischemic stroke has not shown any benefit on the primary outcome of all intracranial hemorrhage (ICH).
However, there were some encouraging findings including a trend towards a reduction in symptomatic ICH, researchers report, and the combination approach did not show any depletion of fibrinogen levels, which suggests a potential lower bleeding risk.
“Although the main results of this study are neutral, we are encouraged that the combination approach with a low dose of alteplase followed by the new mutant pro-urokinase product looked as effective as full-dose alteplase alone, and there were some promising signs signaling a potential lower bleeding risk,” senior investigator, Diederik Dippel, MD, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, told this news organization.
The DUMAS study (Dual Thrombolytic Therapy With Mutant Pro-Urokinase and Low Dose Alteplase for Ischemic Stroke) was presented at the World Stroke Congress in Singapore by study coauthor Nadinda van der Ende, MD, also from Erasmus University Medical Center.
She pointed out that thrombolysis with intravenous alteplase increases the likelihood of a good outcome in acute ischemic stroke but can cause symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, which can be associated with death and major disability.
Mutant pro-urokinase is a new thrombolytic agent, in development by Thrombolytic Science, Cambridge, Mass., formed by changing one amino acid in pro-urokinase to make it more stable. It is more fibrin specific than alteplase and therefore believed to have a lower risk of intracranial hemorrhage.
Fibrin is formed as the last step in the clotting process, and the precursor of fibrin in the blood is fibrinogen, Dr. van der Ende noted. Alteplase depletes fibrinogen, contributing to its increased bleeding risk, but mutant pro-urokinase is not believed to affect fibrinogen.
“Mutant pro-urokinase does not bind to intact fibrin. It only binds to fibrin that has already been primed by alteplase,” she explained.
The hypothesis behind the current study is that giving a small dose of alteplase will break down fibrin in the clot enough to expose the binding sites for mutant pro-urokinase, which can then be given to continue to lyse the clot.
As alteplase has a short half-life, it disappears quickly, and new fibrin is not affected. As mutant pro-urokinase can only lyse fibrin that is primed with alteplase, new hemostatic clots should stay intact. Animal studies have shown less bleeding from distant sites with this approach, Dr. van der Ende said.
The primary analysis of the phase 2 DUMAS study included 238 patients with mild ischemic stroke (median National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale [NIHSS] score 3) who met the standard criteria for IV alteplase.
They were randomized to alteplase alone at the regular dose of 0.9 mg/kg (max 90 mg) with a 10% bolus and the remaining given over 60 minutes; or to a combination of a 5-mg bolus of IV alteplase followed by mutant pro-urokinase at a dose of 40 mg given over 60 minutes.
The primary outcome was the rate of all intracranial hemorrhage (symptomatic and asymptomatic) detected by neuroimaging.
This occurred in 14% of patients in the full-dose alteplase group vs. 13% of patients in the combined alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group, a nonsignificant difference: adjusted odds ratio, 0.99 (95% confidence interval, 0.46-2.14).
Secondary outcomes showed no significant differences in NIHSS scores at 24 hours or 5-7 days; functional outcome as measured by a shift analysis of the Modified Rankin Scale (mRS); final infarct volume; or perfusion deficit.
However, blood fibrinogen levels were not depleted and significantly higher in the alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group than in the full-dose alteplase alone group.
In terms of safety, symptomatic ICH occurred in three patients in the alteplase group (3%) and in none (0%) in the combined alteplase/mutant pro-urokinase group; death occurred in 4% vs. 2% patients respectively; and major extracranial hemorrhage occurred in 1% in both groups.
Dr. Van der Ende concluded that the study showed an overall low rate of ICH; a combination of alteplase and mutant pro-urokinase was not superior to alteplase alone in reducing ICH rates in this population of patients with minor stroke; and mutant pro-urokinase appeared to be safe and, unlike alteplase, did not show any reduction in fibrinogen levels.
“We think the lack of an effect on fibrinogen with this new combination of a small alteplase bolus followed by mutant pro-urokinase infusion is promising,” Dr. Dippel commented. “The fact that there was no symptomatic ICH with the combination treatment is also encouraging. Although the primary endpoint of this trial was neutral, we still believe this is a very interesting approach, with the potential for reduced bleeding, compared with alteplase alone, but we need larger numbers to see an effect on outcomes.”
Dr. Dippel also pointed out that the study included only patients with minor stroke who were not eligible for endovascular therapy, and these patients have a low risk of a poor outcome and a low bleeding risk.
They are hoping to do another study in patients with more severe stroke, who have a higher bleeding risk and would have more to gain from this combination approach.
Because many patients with severe stroke now have immediate thrombectomy if they present to a comprehensive stroke center, a trial in severe stroke patients would have to be done in primary stroke centers, so if the patents are referred to thrombectomy, the thrombolytic would have a chance to work, Dr. Dippel added.
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Stefan Kiechl, MD, Medical University of Innsbruck (Austria), who is cochair of the World Stroke Congress scientific committee, said, “Alteplase is not fibrin specific, and also causes a degeneration of fibrinogen, which results in ‘fibrinogen depletion coagulopathy.’ It is assumed that 20%-40% of intracerebral bleeding after thrombolysis with alteplase is caused by this problem. DUMAS tests the combination of a substantially reduced alteplase [5 mg] dose plus mutant pro-urokinase to avoid this problem.”
The new thrombolysis protocol, however, did not result in a lower bleeding risk, compared to the comparator alteplase,” he added. “The main limitation of this study is that mainly patients with minor strokes were included. Patients with moderate and severe strokes, who have a substantial risk of bleeding, were not adequately addressed.”
The DUMAS trial was funded by an unrestricted grant from Thrombolytic Science, paid to the institution. Dr. Van der Ende and Dr. Dippel report no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM WSC 2022
Kidney function may help docs pick antiplatelet mix after stroke
Renal function should be considered when determining whether to pick ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin as the antiplatelet therapy for patients with minor stroke, according to new research.
The study, which was conducted in 202 centers in China and published in Annals of Internal Medicine, indicates that when patients had normal kidney function, ticagrelor-aspirin, compared with clopidogrel-aspirin, substantially reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days of follow-up.
However, this effect was not seen in patients with mildly, moderately or severely decreased kidney function.
Rates of severe or moderate bleeding did not differ substantially between the two treatments.
Results gleaned from CHANCE-2 data
The researchers, led by Anxin Wang, PhD, from Capital Medical University in Beijing, conducted a post hoc analysis of the CHANCE-2 (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events-II) trial.
The trial included 6,378 patients who carried cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) loss-of-function (LOF) alleles who had experienced a minor stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Patients received either ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin, and their renal function was measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate. The authors listed as a limitation that no data were available on the presence of albuminuria or proteinuria.
The researchers investigated what effect renal function had on the efficacy and safety of the therapies.
Differences in the therapies
Clopidogrel-aspirin is often recommended for preventing stroke. It can reduce thrombotic risk in patients with impaired kidney function, the authors noted. Ticagrelor can provide greater, faster, and more consistent P2Y12 inhibition than clopidogrel, and evidence shows it is effective in preventing stroke recurrence, particularly in people carrying CYP2C19 LOF alleles.
When people have reduced kidney function, clopidogrel may be harder to clear than ticagrelor and there may be increased plasma concentrations, so function is important to consider when choosing an antiplatelet therapy, the authors wrote.
Choice may come down to cost
Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, associate professor of vascular and cardiovascular medicine at University of Michigan Medicine in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that there has been momentum toward ticagrelor as a more potent choice than clopidogrel not just in populations with minor stroke but for people with MI and coronary stents.
He said he found the results surprising and was intrigued that this paper suggests looking more skeptically at ticagrelor when kidney function is impaired.
Still, the choice may also come down to what the patient can afford at the pharmacy, he said.
“The reality is many patients still get clopidogrel either because that’s what their physicians have been prescribing for well over a decade or because of cost issues, and clopidogrel, for many patients, can be less expensive,” Dr. Barnes noted.
He said he would like to see more study in different populations as the prevalence of people carrying CYP2C19 allele differs by race and results might be different in a non-Asian population. That allele is thought to affect how clopidogrel is metabolized.
Study should spur more research
Nada El Husseini, MD, associate professor of neurology and Duke Telestroke Medical Director at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said the study is hypothesis generating, but shouldn’t be thought of as the last word on the subject.
She pointed out some additional limitations of the study, including that it was a post hoc analysis. She explained that the question researchers asked in this study – about effect of kidney function on the safety and efficacy of the therapies – was not the focus of the original CHANCE-2 study, and, as such, the post hoc study may have been underpowered to answer the renal function question.
The authors acknowledged that limitation, noting that “the proportion of patients with severely decreased renal function was low.”
Among 6,378 patients, 4,050 (63.5%) had normal kidney function, 2,010 (31.5%) had mildly decreased function, and 318 (5.0%) had moderately to severely decreased function.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, the Chinese Stroke Association, the National Science and Technology Major Project and the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program). Salubris Pharmaceuticals contributed ticagrelor and, clopidogrel at no cost and with no restrictions. Dr. Wang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Barnes and Dr. El Husseini reported no relevant financial relationships.
Renal function should be considered when determining whether to pick ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin as the antiplatelet therapy for patients with minor stroke, according to new research.
The study, which was conducted in 202 centers in China and published in Annals of Internal Medicine, indicates that when patients had normal kidney function, ticagrelor-aspirin, compared with clopidogrel-aspirin, substantially reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days of follow-up.
However, this effect was not seen in patients with mildly, moderately or severely decreased kidney function.
Rates of severe or moderate bleeding did not differ substantially between the two treatments.
Results gleaned from CHANCE-2 data
The researchers, led by Anxin Wang, PhD, from Capital Medical University in Beijing, conducted a post hoc analysis of the CHANCE-2 (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events-II) trial.
The trial included 6,378 patients who carried cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) loss-of-function (LOF) alleles who had experienced a minor stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Patients received either ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin, and their renal function was measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate. The authors listed as a limitation that no data were available on the presence of albuminuria or proteinuria.
The researchers investigated what effect renal function had on the efficacy and safety of the therapies.
Differences in the therapies
Clopidogrel-aspirin is often recommended for preventing stroke. It can reduce thrombotic risk in patients with impaired kidney function, the authors noted. Ticagrelor can provide greater, faster, and more consistent P2Y12 inhibition than clopidogrel, and evidence shows it is effective in preventing stroke recurrence, particularly in people carrying CYP2C19 LOF alleles.
When people have reduced kidney function, clopidogrel may be harder to clear than ticagrelor and there may be increased plasma concentrations, so function is important to consider when choosing an antiplatelet therapy, the authors wrote.
Choice may come down to cost
Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, associate professor of vascular and cardiovascular medicine at University of Michigan Medicine in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that there has been momentum toward ticagrelor as a more potent choice than clopidogrel not just in populations with minor stroke but for people with MI and coronary stents.
He said he found the results surprising and was intrigued that this paper suggests looking more skeptically at ticagrelor when kidney function is impaired.
Still, the choice may also come down to what the patient can afford at the pharmacy, he said.
“The reality is many patients still get clopidogrel either because that’s what their physicians have been prescribing for well over a decade or because of cost issues, and clopidogrel, for many patients, can be less expensive,” Dr. Barnes noted.
He said he would like to see more study in different populations as the prevalence of people carrying CYP2C19 allele differs by race and results might be different in a non-Asian population. That allele is thought to affect how clopidogrel is metabolized.
Study should spur more research
Nada El Husseini, MD, associate professor of neurology and Duke Telestroke Medical Director at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said the study is hypothesis generating, but shouldn’t be thought of as the last word on the subject.
She pointed out some additional limitations of the study, including that it was a post hoc analysis. She explained that the question researchers asked in this study – about effect of kidney function on the safety and efficacy of the therapies – was not the focus of the original CHANCE-2 study, and, as such, the post hoc study may have been underpowered to answer the renal function question.
The authors acknowledged that limitation, noting that “the proportion of patients with severely decreased renal function was low.”
Among 6,378 patients, 4,050 (63.5%) had normal kidney function, 2,010 (31.5%) had mildly decreased function, and 318 (5.0%) had moderately to severely decreased function.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, the Chinese Stroke Association, the National Science and Technology Major Project and the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program). Salubris Pharmaceuticals contributed ticagrelor and, clopidogrel at no cost and with no restrictions. Dr. Wang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Barnes and Dr. El Husseini reported no relevant financial relationships.
Renal function should be considered when determining whether to pick ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin as the antiplatelet therapy for patients with minor stroke, according to new research.
The study, which was conducted in 202 centers in China and published in Annals of Internal Medicine, indicates that when patients had normal kidney function, ticagrelor-aspirin, compared with clopidogrel-aspirin, substantially reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days of follow-up.
However, this effect was not seen in patients with mildly, moderately or severely decreased kidney function.
Rates of severe or moderate bleeding did not differ substantially between the two treatments.
Results gleaned from CHANCE-2 data
The researchers, led by Anxin Wang, PhD, from Capital Medical University in Beijing, conducted a post hoc analysis of the CHANCE-2 (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events-II) trial.
The trial included 6,378 patients who carried cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) loss-of-function (LOF) alleles who had experienced a minor stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Patients received either ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin, and their renal function was measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate. The authors listed as a limitation that no data were available on the presence of albuminuria or proteinuria.
The researchers investigated what effect renal function had on the efficacy and safety of the therapies.
Differences in the therapies
Clopidogrel-aspirin is often recommended for preventing stroke. It can reduce thrombotic risk in patients with impaired kidney function, the authors noted. Ticagrelor can provide greater, faster, and more consistent P2Y12 inhibition than clopidogrel, and evidence shows it is effective in preventing stroke recurrence, particularly in people carrying CYP2C19 LOF alleles.
When people have reduced kidney function, clopidogrel may be harder to clear than ticagrelor and there may be increased plasma concentrations, so function is important to consider when choosing an antiplatelet therapy, the authors wrote.
Choice may come down to cost
Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, associate professor of vascular and cardiovascular medicine at University of Michigan Medicine in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that there has been momentum toward ticagrelor as a more potent choice than clopidogrel not just in populations with minor stroke but for people with MI and coronary stents.
He said he found the results surprising and was intrigued that this paper suggests looking more skeptically at ticagrelor when kidney function is impaired.
Still, the choice may also come down to what the patient can afford at the pharmacy, he said.
“The reality is many patients still get clopidogrel either because that’s what their physicians have been prescribing for well over a decade or because of cost issues, and clopidogrel, for many patients, can be less expensive,” Dr. Barnes noted.
He said he would like to see more study in different populations as the prevalence of people carrying CYP2C19 allele differs by race and results might be different in a non-Asian population. That allele is thought to affect how clopidogrel is metabolized.
Study should spur more research
Nada El Husseini, MD, associate professor of neurology and Duke Telestroke Medical Director at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said the study is hypothesis generating, but shouldn’t be thought of as the last word on the subject.
She pointed out some additional limitations of the study, including that it was a post hoc analysis. She explained that the question researchers asked in this study – about effect of kidney function on the safety and efficacy of the therapies – was not the focus of the original CHANCE-2 study, and, as such, the post hoc study may have been underpowered to answer the renal function question.
The authors acknowledged that limitation, noting that “the proportion of patients with severely decreased renal function was low.”
Among 6,378 patients, 4,050 (63.5%) had normal kidney function, 2,010 (31.5%) had mildly decreased function, and 318 (5.0%) had moderately to severely decreased function.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, the Chinese Stroke Association, the National Science and Technology Major Project and the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program). Salubris Pharmaceuticals contributed ticagrelor and, clopidogrel at no cost and with no restrictions. Dr. Wang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Barnes and Dr. El Husseini reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE







