User login
One in Ten Chronic Pain Patients May Develop Opioid Use Disorder
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Nearly 10% of patients with chronic pain treated with opioids develop opioid use disorder, whereas 30% show signs and symptoms of dependence, highlighting the need for monitoring and alternative pain management strategies.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis using MEDLINE, Embase, and PsycINFO databases from inception to January 27, 2021.
- The studies analyzed were predominantly from the United States (n = 115) as well as high-income countries such as the United Kingdom (n = 5), France (n = 3), Spain (n = 4), Germany (n = 4), and Australia (n = 2).
- A total of 148 studies from various settings with over 4.3 million participants were included, focusing on patients aged ≥ 12 years with chronic non-cancer pain of ≥ 3 months duration, treated with opioid analgesics.
- Problematic opioid use was categorized into four categories: dependence and opioid use disorder, signs and symptoms of dependence and opioid use disorder, aberrant behavior, and at risk for dependence and opioid use disorder.
TAKEAWAY:
- The pooled prevalence of dependence and opioid use disorder was 9.3% (95% CI, 5.7%-14.8%), with significant heterogeneity across studies.
- Signs and symptoms of dependence were observed in 29.6% (95% CI, 22.1%-38.3%) of patients, indicating a high prevalence of problematic opioid use.
- Aberrant behavior was reported in 22% (95% CI, 17.4%-27.3%) of patients, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and intervention.
- The prevalence of patients at risk of developing dependence was 12.4% (95% CI, 4.3%-30.7%), suggesting the importance of early identification and prevention strategies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Clinicians and policymakers need a more accurate estimate of the prevalence of problematic opioid use in pain patients so that they can gauge the true extent of the problem, change prescribing guidance if necessary, and develop and implement effective interventions to manage the problem,” Kyla H. Thomas, PhD, the lead author, noted in a press release. Knowing the size of the problem is a necessary step to managing it, she added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dr. Thomas, Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol in England. It was published online, in Addiction.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s high heterogeneity across included studies suggests caution in interpreting the findings. The reliance on self-reported data and varying definitions of problematic opioid use may affect the accuracy of prevalence estimates. Most studies were conducted in high-income countries, limiting the generalizability to other settings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR). Dr. Thomas reported receiving financial support from the NIHR for this study.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is SNRI Treatment of Fibromyalgia Working? Look at Sleep Patterns
Not a morning person? For patients with fibromyalgia, the answer to that question could be a clue about their treatment response with a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), suggested a new cross-sectional study published in Rheumatology International.
Compared with patients who had 30% or more pain relief after 8 or more weeks on an SNRI (duloxetine, venlafaxine, or milnacipran), those with less pain relief reported rougher mornings and worse sleep overall. Morningness, morning affect, diurnal dysrhythmia, anytime wakeability, overall sleep quality, subjective sleep quality and disturbances, sleep medication use, and daytime dysfunction were all predictors of nonresponse to SNRI treatment.
“The observed chronobiological characteristics of patients resistant to SNRI treatment are important because they can be targeted with adjunctive circadian interventions, ie, morning light therapy, in order to normalize circadian rhythms and improve sleep, and in effect, overcome the resistance to treatment and alleviate [the] patient’s pain,” said study author Anna Julia Krupa, MD, a psychiatrist and research assistant in the Department of Affective Disorders at Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland.
Fibromyalgia symptoms like sleep disturbance, low mood, fatigue, stiffness, cognitive impairment, and anxiety are often interlinked in positive feedback loops, meaning that the presence of one symptom (ie, sleep problems or depression) exacerbates the other (ie, pain or anxiety), Dr. Krupa said. While SNRIs can reduce pain, anxiety, and depression, they don’t directly improve sleep. Sometimes, pain relief smooths out minor sleep problems, but not always.
“Therefore, if circadian rhythm disruptions and sleep problems are significant, they may constitute a factor which limits SNRI effects on pain in people with fibromyalgia,” Dr. Krupa said.
With 60 patients with fibromyalgia (30 responsive to treatment and 30 nonresponsive to treatment) and 30 healthy controls, this was a small study, noted Daniel G. Arkfeld, MD, DDS, a rheumatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. However, “sleep is probably one of the most difficult things in fibromyalgia, and it definitely needs to be targeted.”
Decades of research suggest that important neurochemicals, like growth hormone, are released in deep sleep. “We know that sleep disturbances and time frame and release of neurochemicals [are] all super important in fibromyalgia,” he said.
Side effects of medication could be another factor at play here. As with any drug, the side effects of SNRIs vary widely from person to person, but palpitations, tremulousness, and insomnia are common, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, internal medicine/rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain & Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“SNRIs are often ‘activating’ because of the increase in norepinephrine,” Dr. Clauw said. “This is often helpful for symptoms such as fatigue and memory problems — but could worsen sleep.”
That’s why he always recommends that patients take an SNRI in the morning, not at night. Try that and the following tips to help patients with fibromyalgia sleep better and feel better, too.
Start with the basics. It’s worth reminding patients about the tried-and-true tips like going to bed and waking up at the same time every day and keeping your bedroom quiet and dark. “Patients should first try ‘sleep hygiene’ strategies,” said Dr. Clauw. “If that doesn’t help then cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia can be very helpful.”
A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that CBT for insomnia helped patients with fibromyalgia improve sleep quality, pain, anxiety, and depression compared with nonpharmacologic treatments. And if that doesn’t help? “If need be, they can try nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, eg, tricyclics or gabapentinoids taken at bedtime,” said Dr. Clauw.
Help them fall in love with exercise. A personalized approach to exercise can help patients with fibromyalgia feel better, suggested a study review in Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. Exercise can also help reset the circadian clock. Morning activity helps night owls get on an earlier schedule, suggested a study review published in Physical Activity and Nutrition.
Consider yoga, tai chi, or qigong. A study review published in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism suggested mind-body and combined exercises help improve sleep for people with fibromyalgia, while aerobic or strength training alone does not. One explanation is that mind-body exercises might do more than other types to tamp down sympathetic-excitatory overactivation in fibromyalgia, the researchers said. Use this handy guide from the European Pain Federation to help you start the exercise conversation.
Talk about sleep alongside other aspects of fibromyalgia. Psychoeducation for fibromyalgia often includes information about the distinction between acute and chronic pain, the nature of fibromyalgia syndrome, disease-contributing factors, safe and effective treatments, symptoms and characteristics, and coping strategies, according to a study review in the journal Behavioral Sciences. “As a psychiatrist and someone who often consults patients with fibromyalgia, I would also add the information about links between pain and mood, anxiety as well as sleep,” said Dr. Krupa.
Try morning light. Use light to shift circadian rhythms, suggested Dr. Krupa. People who struggle in the morning might benefit from 30-60 minutes of morning light therapy immediately after waking using a 10,000-lux light box or light glasses, as suggested by a study review from the University of Michigan.
Help them get off the night shift. “Fibromyalgia patients probably shouldn’t work the night shift and throw their circadian rhythm off,” said Dr. Arkfeld. Depending on a patient’s work and financial circumstances, a job change might not be possible, but consider writing a note to the patient’s employer asking them to switch the patient to the day shift. Dr. Arkfeld said this approach has worked for some of his patients.
Refer them for a sleep study. Many patients with fibromyalgia have obstructive sleep apnea or other sleep disorders that require additional intervention. “Sleep studies are important to kind of define the actual sleep problem that’s occurring as well, whether it’s the stage for interruption of sleep or sleep apnea or wakefulness,” said Dr. Arkfeld.
The study was funded by Jagiellonian University Medical College. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Not a morning person? For patients with fibromyalgia, the answer to that question could be a clue about their treatment response with a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), suggested a new cross-sectional study published in Rheumatology International.
Compared with patients who had 30% or more pain relief after 8 or more weeks on an SNRI (duloxetine, venlafaxine, or milnacipran), those with less pain relief reported rougher mornings and worse sleep overall. Morningness, morning affect, diurnal dysrhythmia, anytime wakeability, overall sleep quality, subjective sleep quality and disturbances, sleep medication use, and daytime dysfunction were all predictors of nonresponse to SNRI treatment.
“The observed chronobiological characteristics of patients resistant to SNRI treatment are important because they can be targeted with adjunctive circadian interventions, ie, morning light therapy, in order to normalize circadian rhythms and improve sleep, and in effect, overcome the resistance to treatment and alleviate [the] patient’s pain,” said study author Anna Julia Krupa, MD, a psychiatrist and research assistant in the Department of Affective Disorders at Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland.
Fibromyalgia symptoms like sleep disturbance, low mood, fatigue, stiffness, cognitive impairment, and anxiety are often interlinked in positive feedback loops, meaning that the presence of one symptom (ie, sleep problems or depression) exacerbates the other (ie, pain or anxiety), Dr. Krupa said. While SNRIs can reduce pain, anxiety, and depression, they don’t directly improve sleep. Sometimes, pain relief smooths out minor sleep problems, but not always.
“Therefore, if circadian rhythm disruptions and sleep problems are significant, they may constitute a factor which limits SNRI effects on pain in people with fibromyalgia,” Dr. Krupa said.
With 60 patients with fibromyalgia (30 responsive to treatment and 30 nonresponsive to treatment) and 30 healthy controls, this was a small study, noted Daniel G. Arkfeld, MD, DDS, a rheumatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. However, “sleep is probably one of the most difficult things in fibromyalgia, and it definitely needs to be targeted.”
Decades of research suggest that important neurochemicals, like growth hormone, are released in deep sleep. “We know that sleep disturbances and time frame and release of neurochemicals [are] all super important in fibromyalgia,” he said.
Side effects of medication could be another factor at play here. As with any drug, the side effects of SNRIs vary widely from person to person, but palpitations, tremulousness, and insomnia are common, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, internal medicine/rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain & Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“SNRIs are often ‘activating’ because of the increase in norepinephrine,” Dr. Clauw said. “This is often helpful for symptoms such as fatigue and memory problems — but could worsen sleep.”
That’s why he always recommends that patients take an SNRI in the morning, not at night. Try that and the following tips to help patients with fibromyalgia sleep better and feel better, too.
Start with the basics. It’s worth reminding patients about the tried-and-true tips like going to bed and waking up at the same time every day and keeping your bedroom quiet and dark. “Patients should first try ‘sleep hygiene’ strategies,” said Dr. Clauw. “If that doesn’t help then cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia can be very helpful.”
A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that CBT for insomnia helped patients with fibromyalgia improve sleep quality, pain, anxiety, and depression compared with nonpharmacologic treatments. And if that doesn’t help? “If need be, they can try nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, eg, tricyclics or gabapentinoids taken at bedtime,” said Dr. Clauw.
Help them fall in love with exercise. A personalized approach to exercise can help patients with fibromyalgia feel better, suggested a study review in Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. Exercise can also help reset the circadian clock. Morning activity helps night owls get on an earlier schedule, suggested a study review published in Physical Activity and Nutrition.
Consider yoga, tai chi, or qigong. A study review published in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism suggested mind-body and combined exercises help improve sleep for people with fibromyalgia, while aerobic or strength training alone does not. One explanation is that mind-body exercises might do more than other types to tamp down sympathetic-excitatory overactivation in fibromyalgia, the researchers said. Use this handy guide from the European Pain Federation to help you start the exercise conversation.
Talk about sleep alongside other aspects of fibromyalgia. Psychoeducation for fibromyalgia often includes information about the distinction between acute and chronic pain, the nature of fibromyalgia syndrome, disease-contributing factors, safe and effective treatments, symptoms and characteristics, and coping strategies, according to a study review in the journal Behavioral Sciences. “As a psychiatrist and someone who often consults patients with fibromyalgia, I would also add the information about links between pain and mood, anxiety as well as sleep,” said Dr. Krupa.
Try morning light. Use light to shift circadian rhythms, suggested Dr. Krupa. People who struggle in the morning might benefit from 30-60 minutes of morning light therapy immediately after waking using a 10,000-lux light box or light glasses, as suggested by a study review from the University of Michigan.
Help them get off the night shift. “Fibromyalgia patients probably shouldn’t work the night shift and throw their circadian rhythm off,” said Dr. Arkfeld. Depending on a patient’s work and financial circumstances, a job change might not be possible, but consider writing a note to the patient’s employer asking them to switch the patient to the day shift. Dr. Arkfeld said this approach has worked for some of his patients.
Refer them for a sleep study. Many patients with fibromyalgia have obstructive sleep apnea or other sleep disorders that require additional intervention. “Sleep studies are important to kind of define the actual sleep problem that’s occurring as well, whether it’s the stage for interruption of sleep or sleep apnea or wakefulness,” said Dr. Arkfeld.
The study was funded by Jagiellonian University Medical College. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Not a morning person? For patients with fibromyalgia, the answer to that question could be a clue about their treatment response with a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), suggested a new cross-sectional study published in Rheumatology International.
Compared with patients who had 30% or more pain relief after 8 or more weeks on an SNRI (duloxetine, venlafaxine, or milnacipran), those with less pain relief reported rougher mornings and worse sleep overall. Morningness, morning affect, diurnal dysrhythmia, anytime wakeability, overall sleep quality, subjective sleep quality and disturbances, sleep medication use, and daytime dysfunction were all predictors of nonresponse to SNRI treatment.
“The observed chronobiological characteristics of patients resistant to SNRI treatment are important because they can be targeted with adjunctive circadian interventions, ie, morning light therapy, in order to normalize circadian rhythms and improve sleep, and in effect, overcome the resistance to treatment and alleviate [the] patient’s pain,” said study author Anna Julia Krupa, MD, a psychiatrist and research assistant in the Department of Affective Disorders at Jagiellonian University Medical College, Kraków, Poland.
Fibromyalgia symptoms like sleep disturbance, low mood, fatigue, stiffness, cognitive impairment, and anxiety are often interlinked in positive feedback loops, meaning that the presence of one symptom (ie, sleep problems or depression) exacerbates the other (ie, pain or anxiety), Dr. Krupa said. While SNRIs can reduce pain, anxiety, and depression, they don’t directly improve sleep. Sometimes, pain relief smooths out minor sleep problems, but not always.
“Therefore, if circadian rhythm disruptions and sleep problems are significant, they may constitute a factor which limits SNRI effects on pain in people with fibromyalgia,” Dr. Krupa said.
With 60 patients with fibromyalgia (30 responsive to treatment and 30 nonresponsive to treatment) and 30 healthy controls, this was a small study, noted Daniel G. Arkfeld, MD, DDS, a rheumatologist and associate professor of clinical medicine at Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, Los Angeles. However, “sleep is probably one of the most difficult things in fibromyalgia, and it definitely needs to be targeted.”
Decades of research suggest that important neurochemicals, like growth hormone, are released in deep sleep. “We know that sleep disturbances and time frame and release of neurochemicals [are] all super important in fibromyalgia,” he said.
Side effects of medication could be another factor at play here. As with any drug, the side effects of SNRIs vary widely from person to person, but palpitations, tremulousness, and insomnia are common, said Daniel J. Clauw, MD, professor of anesthesiology, internal medicine/rheumatology, and psychiatry and director of the Chronic Pain & Fatigue Research Center at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
“SNRIs are often ‘activating’ because of the increase in norepinephrine,” Dr. Clauw said. “This is often helpful for symptoms such as fatigue and memory problems — but could worsen sleep.”
That’s why he always recommends that patients take an SNRI in the morning, not at night. Try that and the following tips to help patients with fibromyalgia sleep better and feel better, too.
Start with the basics. It’s worth reminding patients about the tried-and-true tips like going to bed and waking up at the same time every day and keeping your bedroom quiet and dark. “Patients should first try ‘sleep hygiene’ strategies,” said Dr. Clauw. “If that doesn’t help then cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia can be very helpful.”
A systematic review and meta-analysis showed that CBT for insomnia helped patients with fibromyalgia improve sleep quality, pain, anxiety, and depression compared with nonpharmacologic treatments. And if that doesn’t help? “If need be, they can try nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic drugs, eg, tricyclics or gabapentinoids taken at bedtime,” said Dr. Clauw.
Help them fall in love with exercise. A personalized approach to exercise can help patients with fibromyalgia feel better, suggested a study review in Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology. Exercise can also help reset the circadian clock. Morning activity helps night owls get on an earlier schedule, suggested a study review published in Physical Activity and Nutrition.
Consider yoga, tai chi, or qigong. A study review published in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism suggested mind-body and combined exercises help improve sleep for people with fibromyalgia, while aerobic or strength training alone does not. One explanation is that mind-body exercises might do more than other types to tamp down sympathetic-excitatory overactivation in fibromyalgia, the researchers said. Use this handy guide from the European Pain Federation to help you start the exercise conversation.
Talk about sleep alongside other aspects of fibromyalgia. Psychoeducation for fibromyalgia often includes information about the distinction between acute and chronic pain, the nature of fibromyalgia syndrome, disease-contributing factors, safe and effective treatments, symptoms and characteristics, and coping strategies, according to a study review in the journal Behavioral Sciences. “As a psychiatrist and someone who often consults patients with fibromyalgia, I would also add the information about links between pain and mood, anxiety as well as sleep,” said Dr. Krupa.
Try morning light. Use light to shift circadian rhythms, suggested Dr. Krupa. People who struggle in the morning might benefit from 30-60 minutes of morning light therapy immediately after waking using a 10,000-lux light box or light glasses, as suggested by a study review from the University of Michigan.
Help them get off the night shift. “Fibromyalgia patients probably shouldn’t work the night shift and throw their circadian rhythm off,” said Dr. Arkfeld. Depending on a patient’s work and financial circumstances, a job change might not be possible, but consider writing a note to the patient’s employer asking them to switch the patient to the day shift. Dr. Arkfeld said this approach has worked for some of his patients.
Refer them for a sleep study. Many patients with fibromyalgia have obstructive sleep apnea or other sleep disorders that require additional intervention. “Sleep studies are important to kind of define the actual sleep problem that’s occurring as well, whether it’s the stage for interruption of sleep or sleep apnea or wakefulness,” said Dr. Arkfeld.
The study was funded by Jagiellonian University Medical College. The authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM RHEUMATOLOGY INTERNATIONAL
Light Therapy, Phototherapy, Photobiomodulation: New Ways to Heal With Light
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A surprising therapy is showing promise for chronic pain, vision loss, and muscle recovery, among other conditions.
It’s not a pill, an injection, or surgery.
It’s light.
Yes, light. The thing that appears when you open the curtains, flip a switch, or strike a match.
Light illuminates our world and helps us see. Early human trials suggest it may help us heal in new ways as well.
“Phototherapy is still in its infancy,” said Mohab Ibrahim, MD, PhD, a professor of anesthesiology at the University of Arizona, Tucson, who studies the effects of light on chronic pain. “There are so many questions, a lot of things we do not understand yet. But that’s where it gets interesting. What we can conclude is that different colors of light can influence different biological functions.”
This growing field goes by several names. Light therapy. Phototherapy. Photobiomodulation.
It leverages known effects of light on human health — such as skin exposure to ultraviolet light producing vitamin D or blue light’s power to regulate human body clocks — to take light as medicine in surprising new directions.
New Science, Old Idea
The science is young, but the concept of using light to restore health is thousands of years old.
Hippocrates prescribed sunbathing to patients at his medical center on the Greek island of Kos in 400 BC. Florence Nightingale promoted sunshine, along with fresh air, as prerequisites for recovery in hospitals during the Civil War. A Danish doctor, Niels Finsen, won the Nobel Prize in 1903 for developing ultraviolet lamps to treat a tuberculosis-related skin condition. And worried parents of the 1930s sat their babies in front of mercury arc lamps, bought at the drugstore, to discourage rickets.
Today, light therapy is widely used in medicine for newborn jaundice, psoriasis, and seasonal affective disorder and in light-activated treatments for cancers of the esophagus and lungs, as well as for actinic keratosis, a skin condition that can lead to cancer.
But researchers are finding that light may be capable of far more, particularly in conditions with few treatment options or where available drugs have unwanted side effects.
How Red Light Could Restore Vision
When 100 midlife and older adults, aged 53-91, with the dry form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD) were treated with an experimental red-light therapy or a sham therapy, the light treatment group showed signs of improved vision, as measured on a standard eye chart.
Volunteers received the therapy three times a week for 3-5 weeks, every 4 months for 2 years. By the study’s end, 67% of those treated with light could read an additional five letters on the chart, and 20% could read 10 or more. About 7% developed geographic atrophy — the most advanced, vision-threatening stage of dry AMD — compared with 24% in the sham group.
The study, called LIGHTSITE III, was conducted at 10 ophthalmology centers across the United States. The device they used — the Valeda Light Delivery System from medical device company LumiThera — is available in Europe and now being reviewed by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Exposure to red light at the wavelengths used in the study likely revitalizes failing mitochondria — the power plants inside cells — so they produce more energy, the researchers say.
“This is the first therapy for dry AMD that’s actually shown a benefit in improving vision,” said study coauthor Richard Rosen, MD, chair of ophthalmology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and chief of Retinal Services at the New York Eye and Ear Infirmary in New York City. “Supplements called AREDS can reduce progression, and in wet AMD we can improve vision loss with injections. But in dry AMD, none of the treatments studied in the past have improved it.”
AMD develops when the eyes can’t break down natural by-products, which glom together as clumps of protein called drusen. Drusen can lodge under the retina, eventually damaging tissue.
“Retinal epithelial cells, a single layer of cells that cares for the photoreceptors in the eyes, are there for life,” Dr. Rosen said. “They have a tremendous capacity to repair themselves, but things [such as aging and smoking] get in the way.”
“I’m proposing,” Dr. Rosen said, “that by boosting energy levels in cells [with red light], we’re improving normal repair mechanisms.”
Lab studies support this idea.
In a 2017 mouse study from the University College London Institute of Ophthalmology in England, retinal function improved by 25% in old mice exposed to red light. And a 2019 study from the Ophthalmological Research Foundation, Oviedo, Spain, found that exposure to blue light harmed the mitochondria in retina cells, while red light somewhat counteracted the losses.
If cleared by the FDA — which the company anticipated could happen in 2024 — LumiThera’s light delivery device will likely be most useful in the beginning stages of dry AMD, Dr. Rosen said. “I think treatment of early dry AMD will be huge.”
Eventually, light therapy may also be valuable in treating or managing glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy.
For now, Dr. Rosen recommended that clinicians and consumers with AMD skip over-the-counter (OTC) red-light therapy devices currently on the market.
“We don’t know what kind of light the devices produce,” he said. “The wavelengths can vary. The eyes are delicate. Experimenting on your own may be hazardous to your vision.”
Green Light for Pain Relief
On his way to the pharmacy to pick up pain relievers for a headache, Dr. Ibrahim passed Gene C. Reid Park in Tucson. Recalling how his brother eased headaches by sitting in his backyard, Dr. Ibrahim pulled over.
“Reid Park is probably one of the greenest areas of Tucson,” said Dr. Ibrahim, who also serves as medical director of the Comprehensive Center for Pain & Addiction at Banner-University Medical Center Phoenix in Arizona. “I spent a half hour or 40 minutes there, and my headache felt better.”
Being outdoors in a green space may be soothing for lots of reasons, like the quiet or the fresh air. But there’s also sunlight reflected off and shining through greenery. The experience inspired Dr. Ibrahim to take a closer look at the effects of green light on chronic pain.
In his 2021 study of 29 people with migraines, participants reported that, after daily exposure to green light for 10 weeks, the number of days per month when they had headaches fell from 7.9 to 2.4 for those who had episodic migraines and from 22.3 to 9.4 for those with chronic migraines. In another 2021 study, 21 people with fibromyalgia who had green light therapy for 10 weeks said their average, self-reported pain intensity fell from 8.4 to 4.9 on a 10-point scale used at the University of Arizona’s pain clinic.
Volunteers in both studies got their light therapy at home, switching on green LED lights while they listened to music, read a book, relaxed, or exercised for 1 or 2 hours daily. The lights were within their field of vision, but they did not look directly at them.
Dr. Ibrahim now has funding from the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to find out why green light alters pain perception.
“What we know is that the visual system is connected to certain areas of the brain that also modulate pain,” he said. “We are trying to understand the connection.”
Padma Gulur, MD, a professor of anesthesiology and population health and director of Pain Management Strategy and Opioid Surveillance at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, saw similar results in a 2023 study of 45 people with fibromyalgia. But instead of using a light source, volunteers wore glasses with clear, green, or blue lenses for 4 hours a day.
After 2 weeks, 33% in the green lens group reduced their use of opioids by 10% or more, compared with 11% in the blue lens group and 8% who wore clear lenses. Previous studies have found green light affects levels of the feel-good brain chemical serotonin and stimulates the body’s own opioid system, the authors noted.
“Green light helps your body control and reduce pain,” Dr. Gulur said. It “seems to help with pain relief by affecting the body’s natural pain management system. This effect appears to play a crucial role in antinociception — reducing the sensation of pain; antiallodynia — preventing normal, nonpainful stimuli from causing pain; and antihyperalgesia — reducing heightened sensitivity to pain.”
Light therapy could help pain patients reduce their dose of opioids or even forgo the drugs altogether, Dr. Gulur said. “It is our hope this will become a useful adjuvant therapy to manage pain.”
In the University of Arizona studies, some patients on green-light therapy stopped their medications completely. Even if they didn’t, other benefits appeared. “They had improved quality of life, decreased depression and anxiety, and improved sleep,” Dr. Ibrahim said.
But not just any green light or green-tinted glasses will work, both researchers said. “We have found there are specific frequencies of green light that give this benefit,” Dr. Gulur said. “OTC products may not be helpful for that reason.”
While Dr. Ibrahim said it could be possible for healthcare practitioners and consumers to consult his studies and put together an inexpensive green-light device at home while carefully following the protocol participants used in the studies , it would first be a good idea for patients to talk with their family doctor or a pain specialist.
“A headache is not always just a headache,” Dr. Ibrahim said. “It could be some other abnormality that needs diagnosis and treatment. If you have long-lasting pain or pain that’s getting worse, it’s always better to discuss it with your physician.”
Helping Muscles Recover With Red Light
Intense exercise — whether it’s a sprint at the end of a morning run, an extra set of biceps curls, or a weekend of all-day DIY home improvement projects — can temporarily damage muscle, causing soreness, inflammation, and even swelling. Phototherapy with red and near-infrared light is widely used by sports trainers, physical therapists, and athletes to aid in recovery. It may even work better than a trendy plunge in an ice bath, according to a 2019 Texas State University review.
But how does it work? Jamie Ghigiarelli, PhD, professor of Allied Health & Kinesiology at Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York, looked closely at signs of inflammation and muscle damage in 12 athletes to find out.
Study participants overtaxed their muscles with rounds of chin-ups, high-speed sprints, and repeated bench presses. Afterward, they relaxed in a full-body red-light therapy bed or in a similar bed without lights.
The results, published in 2020, showed that blood levels of creatine kinase — an enzyme that’s elevated by muscle damage — were 18% lower 1-3 days after exercising for the light-bed group than for the control group.
“Photobiomodulation seems to help with muscle recovery,” Dr. Ghigiarelli said.
Red light at wavelengths from 650 to 820 nm can enter muscle cells, where it is absorbed by mitochondria and boosts their energy production, he said. At the time of his research, some exercise science researchers and athletes thought using light therapy before an event might also increase athletic performance, but according to Dr. Ghigiarelli, that use has not panned out.
Handheld red light and near-infrared light devices for muscle recovery are widely available, but it’s important to do your homework before buying one.
“You want to choose a device with the right energy production — the right wavelength of light, the right power — to be safe and effective,” he said.
For details, he recommends consulting a 2019 paper in The Brazilian Journal of Physical Therapy called “Clinical and scientific recommendations for the use of photobiomodulation therapy in exercise performance enhancement and post-exercise recovery: Current evidence and future directions.”
The paper, from the Laboratory of Phototherapy and Innovative Technologies in Health at the Universidade Nove de Julho in Sao Paulo, Brazil, recommends that for small muscle groups like the biceps or triceps, use red-light lasers or LED devices with a wavelength of 640 nm for red light or 950 nm for infrared light, at a power of 50-200 mW per diode for single-probe device types, at a dose of 20-60 J, given 5-10 minutes after exercise.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
AHS White Paper Guides Treatment of Posttraumatic Headache in Youth
The guidance document, the first of its kind, covers risk factors for prolonged recovery, along with pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic management strategies, and supports an emphasis on multidisciplinary care, lead author Carlyn Patterson Gentile, MD, PhD, attending physician in the Division of Neurology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in Pennsylvania, and colleagues reported.
“There are no guidelines to inform the management of posttraumatic headache in youth, but multiple studies have been conducted over the past 2 decades,” the authors wrote in Headache. “This white paper aims to provide a thorough review of the current literature, identify gaps in knowledge, and provide a road map for [posttraumatic headache] management in youth based on available evidence and expert opinion.”
Clarity for an Underrecognized Issue
According to Russell Lonser, MD, professor and chair of neurological surgery at Ohio State University, Columbus, the white paper is important because it offers concrete guidance for health care providers who may be less familiar with posttraumatic headache in youth.
“It brings together all of the previous literature ... in a very well-written way,” Dr. Lonser said in an interview. “More than anything, it could reassure [providers] that they shouldn’t be hunting down potentially magical cures, and reassure them in symptomatic management.”
Meeryo C. Choe, MD, associate clinical professor of pediatric neurology at UCLA Health in Calabasas, California, said the paper also helps shine a light on what may be a more common condition than the public suspects.
“While the media focuses on the effects of concussion in professional sports athletes, the biggest population of athletes is in our youth population,” Dr. Choe said in a written comment. “Almost 25 million children participate in sports throughout the country, and yet we lack guidelines on how to treat posttraumatic headache which can often develop into persistent postconcussive symptoms.”
This white paper, she noted, builds on Dr. Gentile’s 2021 systematic review, introduces new management recommendations, and aligns with the latest consensus statement from the Concussion in Sport Group.
Risk Factors
The white paper first emphasizes the importance of early identification of youth at high risk for prolonged recovery from posttraumatic headache. Risk factors include female sex, adolescent age, a high number of acute symptoms following the initial injury, and social determinants of health.
“I agree that it is important to identify these patients early to improve the recovery trajectory,” Dr. Choe said.
Identifying these individuals quickly allows for timely intervention with both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies, Dr. Gentile and colleagues noted, potentially mitigating persistent symptoms. Clinicians are encouraged to perform thorough initial assessments to identify these risk factors and initiate early, personalized management plans.
Initial Management of Acute Posttraumatic Headache
For the initial management of acute posttraumatic headache, the white paper recommends a scheduled dosing regimen of simple analgesics. Ibuprofen at a dosage of 10 mg/kg every 6-8 hours (up to a maximum of 600 mg per dose) combined with acetaminophen has shown the best evidence for efficacy. Provided the patient is clinically stable, this regimen should be initiated within 48 hours of the injury and maintained with scheduled dosing for 3-10 days.
If effective, these medications can subsequently be used on an as-needed basis. Careful usage of analgesics is crucial, the white paper cautions, as overadministration can lead to medication-overuse headaches, complicating the recovery process.
Secondary Treatment Options
In cases where first-line oral medications are ineffective, the AHS white paper outlines several secondary treatment options. These include acute intravenous therapies such as ketorolac, dopamine receptor antagonists, and intravenous fluids. Nerve blocks and oral corticosteroid bridges may also be considered.
The white paper stresses the importance of individualized treatment plans that consider the specific needs and responses of each patient, noting that the evidence supporting these approaches is primarily derived from retrospective studies and case reports.
“Patient preferences should be factored in,” said Sean Rose, MD, pediatric neurologist and codirector of the Complex Concussion Clinic at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio.
Supplements and Preventive Measures
For adolescents and young adults at high risk of prolonged posttraumatic headache, the white paper suggests the use of riboflavin and magnesium supplements. Small randomized clinical trials suggest that these supplements may aid in speeding recovery when administered for 1-2 weeks within 48 hours of injury.
If significant headache persists after 2 weeks, a regimen of riboflavin 400 mg daily and magnesium 400-500 mg nightly can be trialed for 6-8 weeks, in line with recommendations for migraine prevention. Additionally, melatonin at a dose of 3-5 mg nightly for an 8-week course may be considered for patients experiencing comorbid sleep disturbances.
Targeted Preventative Therapy
The white paper emphasizes the importance of targeting preventative therapy to the primary headache phenotype.
For instance, patients presenting with a migraine phenotype, or those with a personal or family history of migraines, may be most likely to respond to medications proven effective in migraine prevention, such as amitriptyline, topiramate, and propranolol.
“Most research evidence [for treating posttraumatic headache in youth] is still based on the treatment of migraine,” Dr. Rose pointed out in a written comment.
Dr. Gentile and colleagues recommend initiating preventive therapies 4-6 weeks post injury if headaches are not improving, occur more than 1-2 days per week, or significantly impact daily functioning.
Specialist Referrals and Physical Activity
Referral to a headache specialist is advised for patients who do not respond to first-line acute and preventive therapies. Specialists can offer advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options, the authors noted, ensuring a comprehensive approach to managing posttraumatic headache.
The white paper also recommends noncontact, sub–symptom threshold aerobic physical activity and activities of daily living after an initial 24-48 hour period of symptom-limited cognitive and physical rest. Engaging in these activities may promote faster recovery and help patients gradually return to their normal routines.
“This has been a shift in the concussion treatment approach over the last decade, and is one of the most important interventions we can recommend as physicians,” Dr. Choe noted. “This is where pediatricians and emergency department physicians seeing children acutely can really make a difference in the recovery trajectory for a child after a concussion. ‘Cocoon therapy’ has been proven not only to not work, but be detrimental to recovery.”
Nonpharmacologic Interventions
Based on clinical assessment, nonpharmacologic interventions may also be considered, according to the white paper. These interventions include cervico-vestibular therapy, which addresses neck and balance issues, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helps manage the psychological aspects of chronic headache. Dr. Gentile and colleagues highlighted the potential benefits of a collaborative care model that incorporates these nonpharmacologic interventions alongside pharmacologic treatments, providing a holistic approach to posttraumatic headache management.
“Persisting headaches after concussion are often driven by multiple factors,” Dr. Rose said. “Multidisciplinary concussion clinics can offer multiple treatment approaches such as behavioral, physical therapy, exercise, and medication options.”
Unmet Needs
The white paper concludes by calling for high-quality prospective cohort studies and placebo-controlled, randomized, controlled trials to further advance the understanding and treatment of posttraumatic headache in children.
Dr. Lonser, Dr. Choe, and Dr. Rose all agreed.
“More focused treatment trials are needed to gauge efficacy in children with headache after concussion,” Dr. Rose said.
Specifically, Dr. Gentile and colleagues underscored the need to standardize data collection via common elements, which could improve the ability to compare results across studies and develop more effective treatments. In addition, research into the underlying pathophysiology of posttraumatic headache is crucial for identifying new therapeutic targets and clinical and biological markers that can personalize patient care.
They also stressed the importance of exploring the impact of health disparities and social determinants on posttraumatic headache outcomes, aiming to develop interventions that are equitable and accessible to all patient populations.The white paper was approved by the AHS, and supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke K23 NS124986. The authors disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Amgen, and others. The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
The guidance document, the first of its kind, covers risk factors for prolonged recovery, along with pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic management strategies, and supports an emphasis on multidisciplinary care, lead author Carlyn Patterson Gentile, MD, PhD, attending physician in the Division of Neurology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in Pennsylvania, and colleagues reported.
“There are no guidelines to inform the management of posttraumatic headache in youth, but multiple studies have been conducted over the past 2 decades,” the authors wrote in Headache. “This white paper aims to provide a thorough review of the current literature, identify gaps in knowledge, and provide a road map for [posttraumatic headache] management in youth based on available evidence and expert opinion.”
Clarity for an Underrecognized Issue
According to Russell Lonser, MD, professor and chair of neurological surgery at Ohio State University, Columbus, the white paper is important because it offers concrete guidance for health care providers who may be less familiar with posttraumatic headache in youth.
“It brings together all of the previous literature ... in a very well-written way,” Dr. Lonser said in an interview. “More than anything, it could reassure [providers] that they shouldn’t be hunting down potentially magical cures, and reassure them in symptomatic management.”
Meeryo C. Choe, MD, associate clinical professor of pediatric neurology at UCLA Health in Calabasas, California, said the paper also helps shine a light on what may be a more common condition than the public suspects.
“While the media focuses on the effects of concussion in professional sports athletes, the biggest population of athletes is in our youth population,” Dr. Choe said in a written comment. “Almost 25 million children participate in sports throughout the country, and yet we lack guidelines on how to treat posttraumatic headache which can often develop into persistent postconcussive symptoms.”
This white paper, she noted, builds on Dr. Gentile’s 2021 systematic review, introduces new management recommendations, and aligns with the latest consensus statement from the Concussion in Sport Group.
Risk Factors
The white paper first emphasizes the importance of early identification of youth at high risk for prolonged recovery from posttraumatic headache. Risk factors include female sex, adolescent age, a high number of acute symptoms following the initial injury, and social determinants of health.
“I agree that it is important to identify these patients early to improve the recovery trajectory,” Dr. Choe said.
Identifying these individuals quickly allows for timely intervention with both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies, Dr. Gentile and colleagues noted, potentially mitigating persistent symptoms. Clinicians are encouraged to perform thorough initial assessments to identify these risk factors and initiate early, personalized management plans.
Initial Management of Acute Posttraumatic Headache
For the initial management of acute posttraumatic headache, the white paper recommends a scheduled dosing regimen of simple analgesics. Ibuprofen at a dosage of 10 mg/kg every 6-8 hours (up to a maximum of 600 mg per dose) combined with acetaminophen has shown the best evidence for efficacy. Provided the patient is clinically stable, this regimen should be initiated within 48 hours of the injury and maintained with scheduled dosing for 3-10 days.
If effective, these medications can subsequently be used on an as-needed basis. Careful usage of analgesics is crucial, the white paper cautions, as overadministration can lead to medication-overuse headaches, complicating the recovery process.
Secondary Treatment Options
In cases where first-line oral medications are ineffective, the AHS white paper outlines several secondary treatment options. These include acute intravenous therapies such as ketorolac, dopamine receptor antagonists, and intravenous fluids. Nerve blocks and oral corticosteroid bridges may also be considered.
The white paper stresses the importance of individualized treatment plans that consider the specific needs and responses of each patient, noting that the evidence supporting these approaches is primarily derived from retrospective studies and case reports.
“Patient preferences should be factored in,” said Sean Rose, MD, pediatric neurologist and codirector of the Complex Concussion Clinic at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio.
Supplements and Preventive Measures
For adolescents and young adults at high risk of prolonged posttraumatic headache, the white paper suggests the use of riboflavin and magnesium supplements. Small randomized clinical trials suggest that these supplements may aid in speeding recovery when administered for 1-2 weeks within 48 hours of injury.
If significant headache persists after 2 weeks, a regimen of riboflavin 400 mg daily and magnesium 400-500 mg nightly can be trialed for 6-8 weeks, in line with recommendations for migraine prevention. Additionally, melatonin at a dose of 3-5 mg nightly for an 8-week course may be considered for patients experiencing comorbid sleep disturbances.
Targeted Preventative Therapy
The white paper emphasizes the importance of targeting preventative therapy to the primary headache phenotype.
For instance, patients presenting with a migraine phenotype, or those with a personal or family history of migraines, may be most likely to respond to medications proven effective in migraine prevention, such as amitriptyline, topiramate, and propranolol.
“Most research evidence [for treating posttraumatic headache in youth] is still based on the treatment of migraine,” Dr. Rose pointed out in a written comment.
Dr. Gentile and colleagues recommend initiating preventive therapies 4-6 weeks post injury if headaches are not improving, occur more than 1-2 days per week, or significantly impact daily functioning.
Specialist Referrals and Physical Activity
Referral to a headache specialist is advised for patients who do not respond to first-line acute and preventive therapies. Specialists can offer advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options, the authors noted, ensuring a comprehensive approach to managing posttraumatic headache.
The white paper also recommends noncontact, sub–symptom threshold aerobic physical activity and activities of daily living after an initial 24-48 hour period of symptom-limited cognitive and physical rest. Engaging in these activities may promote faster recovery and help patients gradually return to their normal routines.
“This has been a shift in the concussion treatment approach over the last decade, and is one of the most important interventions we can recommend as physicians,” Dr. Choe noted. “This is where pediatricians and emergency department physicians seeing children acutely can really make a difference in the recovery trajectory for a child after a concussion. ‘Cocoon therapy’ has been proven not only to not work, but be detrimental to recovery.”
Nonpharmacologic Interventions
Based on clinical assessment, nonpharmacologic interventions may also be considered, according to the white paper. These interventions include cervico-vestibular therapy, which addresses neck and balance issues, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helps manage the psychological aspects of chronic headache. Dr. Gentile and colleagues highlighted the potential benefits of a collaborative care model that incorporates these nonpharmacologic interventions alongside pharmacologic treatments, providing a holistic approach to posttraumatic headache management.
“Persisting headaches after concussion are often driven by multiple factors,” Dr. Rose said. “Multidisciplinary concussion clinics can offer multiple treatment approaches such as behavioral, physical therapy, exercise, and medication options.”
Unmet Needs
The white paper concludes by calling for high-quality prospective cohort studies and placebo-controlled, randomized, controlled trials to further advance the understanding and treatment of posttraumatic headache in children.
Dr. Lonser, Dr. Choe, and Dr. Rose all agreed.
“More focused treatment trials are needed to gauge efficacy in children with headache after concussion,” Dr. Rose said.
Specifically, Dr. Gentile and colleagues underscored the need to standardize data collection via common elements, which could improve the ability to compare results across studies and develop more effective treatments. In addition, research into the underlying pathophysiology of posttraumatic headache is crucial for identifying new therapeutic targets and clinical and biological markers that can personalize patient care.
They also stressed the importance of exploring the impact of health disparities and social determinants on posttraumatic headache outcomes, aiming to develop interventions that are equitable and accessible to all patient populations.The white paper was approved by the AHS, and supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke K23 NS124986. The authors disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Amgen, and others. The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
The guidance document, the first of its kind, covers risk factors for prolonged recovery, along with pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic management strategies, and supports an emphasis on multidisciplinary care, lead author Carlyn Patterson Gentile, MD, PhD, attending physician in the Division of Neurology at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia in Pennsylvania, and colleagues reported.
“There are no guidelines to inform the management of posttraumatic headache in youth, but multiple studies have been conducted over the past 2 decades,” the authors wrote in Headache. “This white paper aims to provide a thorough review of the current literature, identify gaps in knowledge, and provide a road map for [posttraumatic headache] management in youth based on available evidence and expert opinion.”
Clarity for an Underrecognized Issue
According to Russell Lonser, MD, professor and chair of neurological surgery at Ohio State University, Columbus, the white paper is important because it offers concrete guidance for health care providers who may be less familiar with posttraumatic headache in youth.
“It brings together all of the previous literature ... in a very well-written way,” Dr. Lonser said in an interview. “More than anything, it could reassure [providers] that they shouldn’t be hunting down potentially magical cures, and reassure them in symptomatic management.”
Meeryo C. Choe, MD, associate clinical professor of pediatric neurology at UCLA Health in Calabasas, California, said the paper also helps shine a light on what may be a more common condition than the public suspects.
“While the media focuses on the effects of concussion in professional sports athletes, the biggest population of athletes is in our youth population,” Dr. Choe said in a written comment. “Almost 25 million children participate in sports throughout the country, and yet we lack guidelines on how to treat posttraumatic headache which can often develop into persistent postconcussive symptoms.”
This white paper, she noted, builds on Dr. Gentile’s 2021 systematic review, introduces new management recommendations, and aligns with the latest consensus statement from the Concussion in Sport Group.
Risk Factors
The white paper first emphasizes the importance of early identification of youth at high risk for prolonged recovery from posttraumatic headache. Risk factors include female sex, adolescent age, a high number of acute symptoms following the initial injury, and social determinants of health.
“I agree that it is important to identify these patients early to improve the recovery trajectory,” Dr. Choe said.
Identifying these individuals quickly allows for timely intervention with both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies, Dr. Gentile and colleagues noted, potentially mitigating persistent symptoms. Clinicians are encouraged to perform thorough initial assessments to identify these risk factors and initiate early, personalized management plans.
Initial Management of Acute Posttraumatic Headache
For the initial management of acute posttraumatic headache, the white paper recommends a scheduled dosing regimen of simple analgesics. Ibuprofen at a dosage of 10 mg/kg every 6-8 hours (up to a maximum of 600 mg per dose) combined with acetaminophen has shown the best evidence for efficacy. Provided the patient is clinically stable, this regimen should be initiated within 48 hours of the injury and maintained with scheduled dosing for 3-10 days.
If effective, these medications can subsequently be used on an as-needed basis. Careful usage of analgesics is crucial, the white paper cautions, as overadministration can lead to medication-overuse headaches, complicating the recovery process.
Secondary Treatment Options
In cases where first-line oral medications are ineffective, the AHS white paper outlines several secondary treatment options. These include acute intravenous therapies such as ketorolac, dopamine receptor antagonists, and intravenous fluids. Nerve blocks and oral corticosteroid bridges may also be considered.
The white paper stresses the importance of individualized treatment plans that consider the specific needs and responses of each patient, noting that the evidence supporting these approaches is primarily derived from retrospective studies and case reports.
“Patient preferences should be factored in,” said Sean Rose, MD, pediatric neurologist and codirector of the Complex Concussion Clinic at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio.
Supplements and Preventive Measures
For adolescents and young adults at high risk of prolonged posttraumatic headache, the white paper suggests the use of riboflavin and magnesium supplements. Small randomized clinical trials suggest that these supplements may aid in speeding recovery when administered for 1-2 weeks within 48 hours of injury.
If significant headache persists after 2 weeks, a regimen of riboflavin 400 mg daily and magnesium 400-500 mg nightly can be trialed for 6-8 weeks, in line with recommendations for migraine prevention. Additionally, melatonin at a dose of 3-5 mg nightly for an 8-week course may be considered for patients experiencing comorbid sleep disturbances.
Targeted Preventative Therapy
The white paper emphasizes the importance of targeting preventative therapy to the primary headache phenotype.
For instance, patients presenting with a migraine phenotype, or those with a personal or family history of migraines, may be most likely to respond to medications proven effective in migraine prevention, such as amitriptyline, topiramate, and propranolol.
“Most research evidence [for treating posttraumatic headache in youth] is still based on the treatment of migraine,” Dr. Rose pointed out in a written comment.
Dr. Gentile and colleagues recommend initiating preventive therapies 4-6 weeks post injury if headaches are not improving, occur more than 1-2 days per week, or significantly impact daily functioning.
Specialist Referrals and Physical Activity
Referral to a headache specialist is advised for patients who do not respond to first-line acute and preventive therapies. Specialists can offer advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options, the authors noted, ensuring a comprehensive approach to managing posttraumatic headache.
The white paper also recommends noncontact, sub–symptom threshold aerobic physical activity and activities of daily living after an initial 24-48 hour period of symptom-limited cognitive and physical rest. Engaging in these activities may promote faster recovery and help patients gradually return to their normal routines.
“This has been a shift in the concussion treatment approach over the last decade, and is one of the most important interventions we can recommend as physicians,” Dr. Choe noted. “This is where pediatricians and emergency department physicians seeing children acutely can really make a difference in the recovery trajectory for a child after a concussion. ‘Cocoon therapy’ has been proven not only to not work, but be detrimental to recovery.”
Nonpharmacologic Interventions
Based on clinical assessment, nonpharmacologic interventions may also be considered, according to the white paper. These interventions include cervico-vestibular therapy, which addresses neck and balance issues, and cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helps manage the psychological aspects of chronic headache. Dr. Gentile and colleagues highlighted the potential benefits of a collaborative care model that incorporates these nonpharmacologic interventions alongside pharmacologic treatments, providing a holistic approach to posttraumatic headache management.
“Persisting headaches after concussion are often driven by multiple factors,” Dr. Rose said. “Multidisciplinary concussion clinics can offer multiple treatment approaches such as behavioral, physical therapy, exercise, and medication options.”
Unmet Needs
The white paper concludes by calling for high-quality prospective cohort studies and placebo-controlled, randomized, controlled trials to further advance the understanding and treatment of posttraumatic headache in children.
Dr. Lonser, Dr. Choe, and Dr. Rose all agreed.
“More focused treatment trials are needed to gauge efficacy in children with headache after concussion,” Dr. Rose said.
Specifically, Dr. Gentile and colleagues underscored the need to standardize data collection via common elements, which could improve the ability to compare results across studies and develop more effective treatments. In addition, research into the underlying pathophysiology of posttraumatic headache is crucial for identifying new therapeutic targets and clinical and biological markers that can personalize patient care.
They also stressed the importance of exploring the impact of health disparities and social determinants on posttraumatic headache outcomes, aiming to develop interventions that are equitable and accessible to all patient populations.The white paper was approved by the AHS, and supported by the National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke K23 NS124986. The authors disclosed relationships with Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Amgen, and others. The interviewees disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM HEADACHE
New First-Line Therapies for Migraine Prevention
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 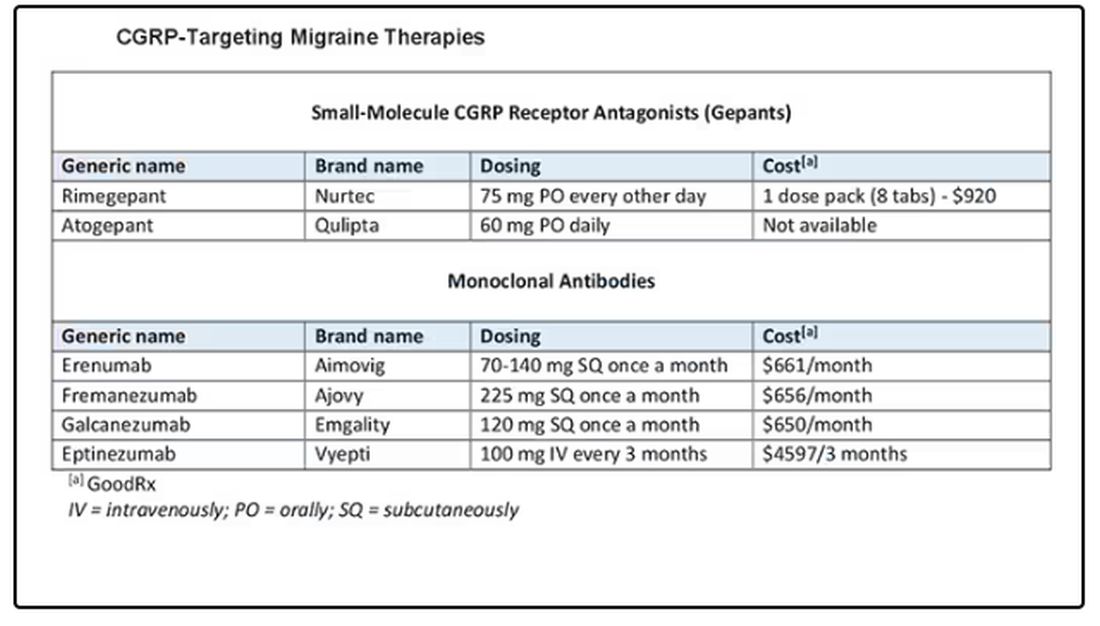
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Today I am going to talk about the position statement from the American Headache Society (AHS) “Calcitonin gene-related peptide [CGRP]–targeting therapies are a first-line option for the prevention of migraine”. This update is of critical importance because about three fourths of people with migraine get their care from a primary care clinician, not from a neurologist or a headache specialist. CGRP-targeting therapies have transformed migraine care at the specialty level, but many in primary care are not yet familiar with this class of medicines. Until this new statement was released, CGRPs were not viewed as first-line agents for migraine. That has now changed.
Two main types of therapy for people with migraine headache are: (1) acute or abortive therapy (when a headache develops, it is treated), and (2) preventive therapy. Preventive therapy is typically used when the patient has headaches on 4 or more days per month. Preventive therapy is aimed at reducing the frequency and severity of headaches. About 40% of patients with migraine qualify for preventive therapy, but only a minority are receiving it.
The armamentarium for preventive therapy of migraines had not changed in a long time — until now. First-line preventive therapy has traditionally consisted of three classes of agents: beta-blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, and topiramate. These medicines were developed for different therapeutic purposes, yet they work for migraines. These drugs may have off-target effects that can make them difficult to tolerate.
Based on new evidence, candesartan — an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) — is now also a first-line drug for migraine. This is good news, because ARBs are a drug class that we have a lot of experience with, are easy to use, and could be an excellent choice for people with concomitant hypertension or chronic kidney disease. The serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (venlafaxine and duloxetine) are also considered first-line agents for migraine treatment.
In the AHS’s new position statement, the two main drug classes are small-molecule CGRP receptor antagonists and monoclonal antibodies.
The role of the neuropeptide CGRP in migraine was originally discovered after finding that blood levels of CGRP were elevated during migraine attacks. This led to the discovery of agents that blocked CGRP, initially for acute treatment of migraine, and then for preventive therapy. Multiple clinical studies show the CGRP targeting therapies to be as or even more effective than traditional first-line agents at decreasing the number of migraine days per month.
The efficacy and safety of these agents have been demonstrated in both randomized trials and in real-world studies. Other important positive endpoints include fewer days of migraine, reduced acute medication use, and improvements in many quality-of-life outcomes. Studies also have shown that CGRP-targeting therapies are well tolerated and safe, with very few serious adverse events.
Furthermore, studies have shown the CGRP targeting therapies are effective in individuals who have failed multiple other first-line therapies. They fit now both as first-line agents and as agents that can be used in difficult-to-treat patients as well as in patients who struggle with acute medication overuse, which is often very challenging.
To quote from the AHS statement,
Side effects are uncommon and can include hypertension, constipation, and Raynaud phenomenon.
The position statement is strong and is based on a lot of evidence and clinical experience. CGRP-targeting therapies are now first-line agents for the prevention of migraine headache. We should learn more about and begin to feel comfortable using this class of agents because they stand to benefit our patients greatly. I’d suggest looking at the table below and picking one new agent to become familiar with so that you can add that agent to your toolbox. 
Dr. Skolnik, professor, Department of Family Medicine, Sidney Kimmel Medical College of Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and associate director, Department of Family Medicine, Abington Jefferson Health, Abington, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with AstraZeneca, Teva, Eli Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, Sanofi, Sanofi Pasteur, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Bayer, and Teva.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How Clinicians Can Help Patients Navigate Psychedelics/Microdosing
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Peter Grinspoon, MD, has some advice for clinicians when patients ask questions about microdosing of psychedelics: Keep the lines of communication open — and don’t be judgmental.
“If you’re dismissive or critical or sound like you’re judging them, then the patients just clam up,” said Dr. Grinspoon, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and a primary care physician at Massachusetts General Hospital, both in Boston.
Psychedelic drugs are still illegal in the majority of states despite the growth of public interest in and use of these substances. That growth is evidenced by a flurry of workshops, reports, law enforcement seizures, and pressure by Congressional members for the Food and Drug Administration to approve new psychedelic drugs, just in the past year.
A recent study in JAMA Health Forum showed a nearly 14-fold increase in Google searches — from 7.9 to 105.6 per 10 million nationwide — for the term “microdosing” and related wording, between 2015 and 2023.
Two states — Oregon and Colorado — have decriminalized certain psychedelic drugs and are in various stages of establishing regulations and centers for prospective clients. Almost two dozen localities, like Ann Arbor, Michigan, have decriminalized psychedelic drugs. A handful of states have active legislation to decriminalize use, while others have bills that never made it out of committee.
But no definitive studies have reported that microdosing produces positive mental effects at a higher rate than placebo, according to Dr. Grinspoon. So
“We’re in this renaissance where everybody is idealizing these medications, as opposed to 20 years ago when we were in the war on drugs and everybody was dismissing them,” Dr. Grinspoon said. “The truth is somewhere in between.”
The Science
Microdosing is defined as taking doses of 1/5 to 1/20 of the conventional recreational amount, which might include a dried psilocybin mushroom, lysergic acid diethylamide, or 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. But even that much may be neither effective nor safe.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should tell patients that psychedelics may cause harm, although the drugs are relatively nontoxic and are not addictive. An illegally obtained psilocybin could cause negative reactions, especially if the drug has been adulterated with other substances and if the actual dose is higher than what was indicated by the seller.
He noted that people have different reactions to psychedelics, just as they have to prescription medications. He cited one example of a woman who microdosed and could not sleep for 2 weeks afterward. Only recently have randomized, double-blinded studies begun on benefits and harms.
Researchers have also begun investigating whether long-term microdosing of psilocybin could lead to valvular heart disease (VHD), said Kevin Yang, MD, a psychiatry resident at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine. A recent review of evidence concluded that microdosing various psychedelics over a period of months can lead to drug-induced VHD.
“It’s extremely important to emphasize with patients that not only do we not know if it works or not, we also don’t really know how safe it is,” Dr. Yang said.
Dr. Yang also said clinicians should consider referring patients to a mental health professional, and especially those that may have expertise in psychedelic therapies.
One of those experts is Rachel Yehuda, PhD, director of the Center for Psychedelic Psychotherapy and Trauma Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York City. She said therapists should be able to assess the patient’s perceived need for microdosing and “invite reflections about why current approaches are falling short.”
“I would also not actively discourage it either but remain curious until both of you have a better understanding of the reasons for seeking this out and potential alternative strategies for obtaining more therapeutic benefits,” she said. “I think it is really important to study the effects of both micro- and macrodosing of psychedelics but not move in advance of the data.”
Navigating Legality
Recent ballot measures in Oregon and Colorado directed the states to develop regulated and licensed psilocybin-assisted therapy centers for legal “trips.” Oregon’s first center was opened in 2023, and Colorado is now developing its own licensing model.
According to the Oregon Health Authority, the centers are not medical facilities, and prescription or referral from a medical professional is not required.
The Oregon Academy of Family Physicians (OAFP) has yet to release guidance to clinicians on how to talk to their patients about these drugs or potential interest in visiting a licensed therapy center.
However, Betsy Boyd-Flynn, executive director of OAFP, said the organization is working on continuing medical education for what the average family physician needs to know if a patient asks about use.
“We suspect that many of our members have interest and want to learn more,” she said.
Dr. Grinspoon said clinicians should talk with patients about legality during these conversations.
“The big question I get is: ‘I really want to try microdosing, but how do I obtain the mushrooms?’ ” he said. “You can’t really as a physician tell them to do anything illegal. So you tell them to be safe, be careful, and to use their judgment.”
Patients who want to pursue microdosing who do not live in Oregon have two legal and safe options, Dr. Grinspoon said: Enroll in a clinical study or find a facility in a state or country — such as Oregon or Jamaica — that offers microdosing with psilocybin.
Clinicians also should warn their patients that the consequences of obtaining illicit psilocybin could exacerbate the mental health stresses they are seeking to alleviate.
“It’s going to get worse if they get tangled up with law enforcement or take something that’s contaminated and they get real sick,” he said.
Lisa Gillespie contributed reporting to this story. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Early Knee Osteoarthritis: Exercise Therapy’s Golden Window
TOPLINE:
People with knee osteoarthritis and symptoms for less than 1 year benefit more from exercise therapy than do those with longer symptom duration, especially when long-term outcomes are considered.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted an individual participant data meta-analysis using data from the OA Trial Bank, including 1769 participants (mean age, 65.1 years; 66% women) with knee osteoarthritis from 10 randomized controlled trials.
- The participants were categorized on the basis of their symptom duration: ≤ 1 year, > 1 and ≤ 2 years, and > 2 years.
- This study included an exercise therapy group comprising land- and water-based therapeutic exercise interventions and a control group comprising no exercise or sham treatment.
- The primary outcomes were self-reported pain and physical function, standardized to a 0-100 scale, at short-term (closest to 3 months) and long-term (closest to 12 months) follow-ups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall pain and physical function associated with osteoarthritis improved in the exercise therapy group at both short- and long-term follow-ups compared with in the control group.
- Exercise therapy led to a greater improvement in short-term (mean difference [MD], −3.57; P = .028) and long-term (MD, −8.33; P < .001) pain among participants with a symptom duration ≤ 1 year vs > 1 year.
- Similarly, those with a symptom duration ≤ 2 years vs > 2 years who underwent exercise therapy showed greater benefits in terms of short-term (P = .001) and long-term (P < .001) pain.
- Exercise therapy improved long-term physical function in those with a symptom duration ≤ 1 year vs > 1 year (MD, −5.46; P = .005) and ≤ 2 years vs > 2 years (MD, −4.56; P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Exercise should be encouraged as early as possible once symptoms emerge in the disease process to take advantage of its effects in potentially [slowing] disease progression within the suggested ‘window of opportunity,’ ” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Marienke van Middelkoop, PhD, Erasmus MC Medical University, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. It was published online in Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.
LIMITATIONS:
The dataset of most studies included in the meta-analysis lacked information on the radiographic severity of osteoarthritis. The relatively short follow-up time hindered interpreting the impact of exercise on the long-term progression of osteoarthritis. The reliance on patient recall for recording symptom duration may have led to misclassification.
DISCLOSURES:
The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development supported this study. Three authors received funding from the Dutch Arthritis Society for the program grant Center of Excellence “OA prevention and early treatment – OA Pearl.” One author declared receiving royalties for the UpToDate knee osteoarthritis clinical guidelines.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
People with knee osteoarthritis and symptoms for less than 1 year benefit more from exercise therapy than do those with longer symptom duration, especially when long-term outcomes are considered.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted an individual participant data meta-analysis using data from the OA Trial Bank, including 1769 participants (mean age, 65.1 years; 66% women) with knee osteoarthritis from 10 randomized controlled trials.
- The participants were categorized on the basis of their symptom duration: ≤ 1 year, > 1 and ≤ 2 years, and > 2 years.
- This study included an exercise therapy group comprising land- and water-based therapeutic exercise interventions and a control group comprising no exercise or sham treatment.
- The primary outcomes were self-reported pain and physical function, standardized to a 0-100 scale, at short-term (closest to 3 months) and long-term (closest to 12 months) follow-ups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall pain and physical function associated with osteoarthritis improved in the exercise therapy group at both short- and long-term follow-ups compared with in the control group.
- Exercise therapy led to a greater improvement in short-term (mean difference [MD], −3.57; P = .028) and long-term (MD, −8.33; P < .001) pain among participants with a symptom duration ≤ 1 year vs > 1 year.
- Similarly, those with a symptom duration ≤ 2 years vs > 2 years who underwent exercise therapy showed greater benefits in terms of short-term (P = .001) and long-term (P < .001) pain.
- Exercise therapy improved long-term physical function in those with a symptom duration ≤ 1 year vs > 1 year (MD, −5.46; P = .005) and ≤ 2 years vs > 2 years (MD, −4.56; P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Exercise should be encouraged as early as possible once symptoms emerge in the disease process to take advantage of its effects in potentially [slowing] disease progression within the suggested ‘window of opportunity,’ ” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Marienke van Middelkoop, PhD, Erasmus MC Medical University, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. It was published online in Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.
LIMITATIONS:
The dataset of most studies included in the meta-analysis lacked information on the radiographic severity of osteoarthritis. The relatively short follow-up time hindered interpreting the impact of exercise on the long-term progression of osteoarthritis. The reliance on patient recall for recording symptom duration may have led to misclassification.
DISCLOSURES:
The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development supported this study. Three authors received funding from the Dutch Arthritis Society for the program grant Center of Excellence “OA prevention and early treatment – OA Pearl.” One author declared receiving royalties for the UpToDate knee osteoarthritis clinical guidelines.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
People with knee osteoarthritis and symptoms for less than 1 year benefit more from exercise therapy than do those with longer symptom duration, especially when long-term outcomes are considered.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted an individual participant data meta-analysis using data from the OA Trial Bank, including 1769 participants (mean age, 65.1 years; 66% women) with knee osteoarthritis from 10 randomized controlled trials.
- The participants were categorized on the basis of their symptom duration: ≤ 1 year, > 1 and ≤ 2 years, and > 2 years.
- This study included an exercise therapy group comprising land- and water-based therapeutic exercise interventions and a control group comprising no exercise or sham treatment.
- The primary outcomes were self-reported pain and physical function, standardized to a 0-100 scale, at short-term (closest to 3 months) and long-term (closest to 12 months) follow-ups.
TAKEAWAY:
- The overall pain and physical function associated with osteoarthritis improved in the exercise therapy group at both short- and long-term follow-ups compared with in the control group.
- Exercise therapy led to a greater improvement in short-term (mean difference [MD], −3.57; P = .028) and long-term (MD, −8.33; P < .001) pain among participants with a symptom duration ≤ 1 year vs > 1 year.
- Similarly, those with a symptom duration ≤ 2 years vs > 2 years who underwent exercise therapy showed greater benefits in terms of short-term (P = .001) and long-term (P < .001) pain.
- Exercise therapy improved long-term physical function in those with a symptom duration ≤ 1 year vs > 1 year (MD, −5.46; P = .005) and ≤ 2 years vs > 2 years (MD, −4.56; P = .001).
IN PRACTICE:
“Exercise should be encouraged as early as possible once symptoms emerge in the disease process to take advantage of its effects in potentially [slowing] disease progression within the suggested ‘window of opportunity,’ ” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Marienke van Middelkoop, PhD, Erasmus MC Medical University, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. It was published online in Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.
LIMITATIONS:
The dataset of most studies included in the meta-analysis lacked information on the radiographic severity of osteoarthritis. The relatively short follow-up time hindered interpreting the impact of exercise on the long-term progression of osteoarthritis. The reliance on patient recall for recording symptom duration may have led to misclassification.
DISCLOSURES:
The Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development supported this study. Three authors received funding from the Dutch Arthritis Society for the program grant Center of Excellence “OA prevention and early treatment – OA Pearl.” One author declared receiving royalties for the UpToDate knee osteoarthritis clinical guidelines.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baseline Bone Pain Predicts Survival in Metastatic Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Prostate cancer often metastasizes to the bones, leading to pain and a reduced quality of life. While the relationship between bone pain and overall survival in metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer is well-documented, its impact in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer is less clear.
- Researchers conducted a post hoc secondary analysis using data from the SWOG-1216 phase 3 randomized clinical trial, which included 1279 men diagnosed with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer from 248 centers across the United States. Patients had received androgen deprivation therapy either with orteronel or bicalutamide.
- Among the 1197 patients (median age, 67.6 years) with data on bone pain included in the secondary analysis, 301 (23.5%) reported bone pain at baseline.
- The primary outcome was overall survival; secondary outcomes included progression-free survival and prostate-specific antigen response.
TAKEAWAY:
- The median overall survival for patients with baseline bone pain was 3.9 years compared with not reached (95% CI, 6.6 years to not reached) for those without bone pain at a median follow-up of 4 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.66; P < .001).
- Similarly, patients with bone pain had a shorter progression-free survival vs those without bone pain (median, 1.3 years vs 3.7 years; aHR, 1.46; P < .001).
- The complete prostate-specific antigen response rate at 7 months was also lower for patients with baseline bone pain (46.3% vs 66.3%; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
Patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer “with baseline bone pain had worse survival outcomes than those without baseline bone pain,” the authors wrote. “These results highlight the need to consider bone pain in prognostic modeling, treatment selection, patient monitoring, and follow-up and suggest prioritizing these patients for clinical trials and immediate systemic treatment initiation.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Georges Gebrael, MD, Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The post hoc design may introduce bias. Orteronel failed to receive regulatory approval, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. In addition, the study did not account for synchronous vs metachronous disease status, a known established prognostic factor.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute and Millennium Pharmaceuticals (Takeda Oncology Company). Several authors declared ties with various sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Prostate cancer often metastasizes to the bones, leading to pain and a reduced quality of life. While the relationship between bone pain and overall survival in metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer is well-documented, its impact in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer is less clear.
- Researchers conducted a post hoc secondary analysis using data from the SWOG-1216 phase 3 randomized clinical trial, which included 1279 men diagnosed with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer from 248 centers across the United States. Patients had received androgen deprivation therapy either with orteronel or bicalutamide.
- Among the 1197 patients (median age, 67.6 years) with data on bone pain included in the secondary analysis, 301 (23.5%) reported bone pain at baseline.
- The primary outcome was overall survival; secondary outcomes included progression-free survival and prostate-specific antigen response.
TAKEAWAY:
- The median overall survival for patients with baseline bone pain was 3.9 years compared with not reached (95% CI, 6.6 years to not reached) for those without bone pain at a median follow-up of 4 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.66; P < .001).
- Similarly, patients with bone pain had a shorter progression-free survival vs those without bone pain (median, 1.3 years vs 3.7 years; aHR, 1.46; P < .001).
- The complete prostate-specific antigen response rate at 7 months was also lower for patients with baseline bone pain (46.3% vs 66.3%; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
Patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer “with baseline bone pain had worse survival outcomes than those without baseline bone pain,” the authors wrote. “These results highlight the need to consider bone pain in prognostic modeling, treatment selection, patient monitoring, and follow-up and suggest prioritizing these patients for clinical trials and immediate systemic treatment initiation.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Georges Gebrael, MD, Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The post hoc design may introduce bias. Orteronel failed to receive regulatory approval, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. In addition, the study did not account for synchronous vs metachronous disease status, a known established prognostic factor.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute and Millennium Pharmaceuticals (Takeda Oncology Company). Several authors declared ties with various sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Prostate cancer often metastasizes to the bones, leading to pain and a reduced quality of life. While the relationship between bone pain and overall survival in metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer is well-documented, its impact in metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer is less clear.
- Researchers conducted a post hoc secondary analysis using data from the SWOG-1216 phase 3 randomized clinical trial, which included 1279 men diagnosed with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer from 248 centers across the United States. Patients had received androgen deprivation therapy either with orteronel or bicalutamide.
- Among the 1197 patients (median age, 67.6 years) with data on bone pain included in the secondary analysis, 301 (23.5%) reported bone pain at baseline.
- The primary outcome was overall survival; secondary outcomes included progression-free survival and prostate-specific antigen response.
TAKEAWAY:
- The median overall survival for patients with baseline bone pain was 3.9 years compared with not reached (95% CI, 6.6 years to not reached) for those without bone pain at a median follow-up of 4 years (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.66; P < .001).
- Similarly, patients with bone pain had a shorter progression-free survival vs those without bone pain (median, 1.3 years vs 3.7 years; aHR, 1.46; P < .001).
- The complete prostate-specific antigen response rate at 7 months was also lower for patients with baseline bone pain (46.3% vs 66.3%; P < .001).
IN PRACTICE:
Patients with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer “with baseline bone pain had worse survival outcomes than those without baseline bone pain,” the authors wrote. “These results highlight the need to consider bone pain in prognostic modeling, treatment selection, patient monitoring, and follow-up and suggest prioritizing these patients for clinical trials and immediate systemic treatment initiation.”
SOURCE:
The study, led by Georges Gebrael, MD, Huntsman Cancer Institute at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, Utah, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The post hoc design may introduce bias. Orteronel failed to receive regulatory approval, which may affect the generalizability of the findings. In addition, the study did not account for synchronous vs metachronous disease status, a known established prognostic factor.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute and Millennium Pharmaceuticals (Takeda Oncology Company). Several authors declared ties with various sources.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Atogepant May Prevent Rebound Headache From Medication Overuse in Chronic Migraine
The oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist atogepant is effective in preventing rebound headache related to medication overuse in patients with chronic migraine (CM), new research suggested.
Results of a subgroup analysis of a phase 3, 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed up to a 62% reduction in the proportion of atogepant-treated participants who met acute medication overuse criteria.
“Based on our findings, treatment with atogepant may potentially decrease the risk of developing rebound headache by reducing the use of pain medications,” principal investigator Peter Goadsby, MD, PhD, of King’s College London, London, England, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Effective Prevention Needed
Acute treatments for migraine can mitigate symptoms and reduce disability but can also be ineffective and even result in increased dosing and overuse of these medications, the investigators noted.
Acute medication overuse is defined as “taking simple analgesics for ≥ 15 days per month or taking triptans, ergots, opioids, or combinations of medications for ≥ 10 days per month.”
“There is a high prevalence of pain medication overuse among people with migraine as they try to manage what are often debilitating symptoms,” Dr. Goadsby said. “However, medication overuse can lead to more headaches, called rebound headaches, so more effective preventive treatments are needed.”
Atogepant was developed for migraine prevention in adults. It had been studied in the phase 3 PROGRESS trial, which showed it significantly reduced monthly migraine days (MMDs) compared with placebo during the 12-week trial.
The new subgroup analysis of the study focused specifically on the efficacy and safety of atogepant vs placebo in participants with CM with, and without, medication overuse.
Participants (mean age, 42.1 years; 87.6% women) were randomized to receive either atogepant 30 mg twice daily (n = 253), atogepant 60 mg once daily (n = 256), or placebo (n = 240), with baseline demographics and clinical characteristics similar across all treatment arms. A total of 66.2% met baseline acute medication overuse criteria.
Participants were asked to record migraine and headache experiences in an electronic diary.
‘Effective and Safe’
Participants in both atogepant groups experienced fewer monthly headache days (MHDs) than those in the placebo group, with a least squares mean difference (LSMD) of −2.7 (95% confidence interval [CI], −4.0 to −1.4) in the atogepant 30 mg twice daily group and −1.9 (95% CI, −3.2 to −0.6) in the atogepant 60 mg once daily group.
MHDs were also reduced in both treatment groups, with LSMDs of −2.8 (95% CI, −4.0 to −1.5) and −2.1 (95% CI, −3.3 to −0.8), respectively. Mean acute medication use days were lower in both the treatment groups, with LSMDs of −2.8 (95% CI, −4.1 to −1.6) and −2.6 (95% CI, −3.9 to −1.3), respectively.
A higher proportion of participants achieved a ≥ 50% reduction in MMDs with atogepant 30 mg twice daily (odds ratio [OR], 2.5; 95% CI, 1.5-4.0) and atogepant 60 mg once daily (OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-3.7).
Notably, the researchers found a 52.1%-61.9% reduction in the proportion of atogepant-treated participants meeting acute medication overuse criteria during the study period vs 38.3% in the placebo group.
Similar results were observed in the subgroup without acute medication overuse.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were reported by 55.8% of participants treated with atogepant 30 mg twice daily, 66.1% with atogepant 60 mg once daily, and 48.5% with placebo in the acute medication overuse subgroup, with similar reports in the non-overuse subgroup.
A limitation cited by the authors was that participants’ self-report of migraines and headaches via electronic diaries might have been inaccurate.
Nevertheless, they concluded that the results showed atogepant to be an “effective and safe” preventive treatment for patients with CM with, and without, acute medication overuse.
AbbVie funded this study and participated in the study design, research, analysis, data collection, interpretation of data, reviewing, and approval of the publication. No honoraria or payments were made for authorship. Dr. Goadsby received personal fees from AbbVie during the conduct of the study, and over the last 36 months, he received a research grant from Celgene; personal fees from Aeon Biopharma, Amgen, CoolTechLLC, Dr. Reddy’s, Eli Lilly and Company, Epalex, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Praxis, Sanofi, Satsuma, ShiraTronics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Tremeau; personal fees for advice through Gerson Lehrman Group, Guidepoint, SAI Med Partners, and Vector Metric; fees for educational materials from CME Outfitters; and publishing royalties or fees from Massachusetts Medical Society, Oxford University Press, UpToDate, and Wolters Kluwer. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist atogepant is effective in preventing rebound headache related to medication overuse in patients with chronic migraine (CM), new research suggested.
Results of a subgroup analysis of a phase 3, 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed up to a 62% reduction in the proportion of atogepant-treated participants who met acute medication overuse criteria.
“Based on our findings, treatment with atogepant may potentially decrease the risk of developing rebound headache by reducing the use of pain medications,” principal investigator Peter Goadsby, MD, PhD, of King’s College London, London, England, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Effective Prevention Needed
Acute treatments for migraine can mitigate symptoms and reduce disability but can also be ineffective and even result in increased dosing and overuse of these medications, the investigators noted.
Acute medication overuse is defined as “taking simple analgesics for ≥ 15 days per month or taking triptans, ergots, opioids, or combinations of medications for ≥ 10 days per month.”
“There is a high prevalence of pain medication overuse among people with migraine as they try to manage what are often debilitating symptoms,” Dr. Goadsby said. “However, medication overuse can lead to more headaches, called rebound headaches, so more effective preventive treatments are needed.”
Atogepant was developed for migraine prevention in adults. It had been studied in the phase 3 PROGRESS trial, which showed it significantly reduced monthly migraine days (MMDs) compared with placebo during the 12-week trial.
The new subgroup analysis of the study focused specifically on the efficacy and safety of atogepant vs placebo in participants with CM with, and without, medication overuse.
Participants (mean age, 42.1 years; 87.6% women) were randomized to receive either atogepant 30 mg twice daily (n = 253), atogepant 60 mg once daily (n = 256), or placebo (n = 240), with baseline demographics and clinical characteristics similar across all treatment arms. A total of 66.2% met baseline acute medication overuse criteria.
Participants were asked to record migraine and headache experiences in an electronic diary.
‘Effective and Safe’
Participants in both atogepant groups experienced fewer monthly headache days (MHDs) than those in the placebo group, with a least squares mean difference (LSMD) of −2.7 (95% confidence interval [CI], −4.0 to −1.4) in the atogepant 30 mg twice daily group and −1.9 (95% CI, −3.2 to −0.6) in the atogepant 60 mg once daily group.
MHDs were also reduced in both treatment groups, with LSMDs of −2.8 (95% CI, −4.0 to −1.5) and −2.1 (95% CI, −3.3 to −0.8), respectively. Mean acute medication use days were lower in both the treatment groups, with LSMDs of −2.8 (95% CI, −4.1 to −1.6) and −2.6 (95% CI, −3.9 to −1.3), respectively.
A higher proportion of participants achieved a ≥ 50% reduction in MMDs with atogepant 30 mg twice daily (odds ratio [OR], 2.5; 95% CI, 1.5-4.0) and atogepant 60 mg once daily (OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-3.7).
Notably, the researchers found a 52.1%-61.9% reduction in the proportion of atogepant-treated participants meeting acute medication overuse criteria during the study period vs 38.3% in the placebo group.
Similar results were observed in the subgroup without acute medication overuse.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were reported by 55.8% of participants treated with atogepant 30 mg twice daily, 66.1% with atogepant 60 mg once daily, and 48.5% with placebo in the acute medication overuse subgroup, with similar reports in the non-overuse subgroup.
A limitation cited by the authors was that participants’ self-report of migraines and headaches via electronic diaries might have been inaccurate.
Nevertheless, they concluded that the results showed atogepant to be an “effective and safe” preventive treatment for patients with CM with, and without, acute medication overuse.
AbbVie funded this study and participated in the study design, research, analysis, data collection, interpretation of data, reviewing, and approval of the publication. No honoraria or payments were made for authorship. Dr. Goadsby received personal fees from AbbVie during the conduct of the study, and over the last 36 months, he received a research grant from Celgene; personal fees from Aeon Biopharma, Amgen, CoolTechLLC, Dr. Reddy’s, Eli Lilly and Company, Epalex, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Praxis, Sanofi, Satsuma, ShiraTronics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Tremeau; personal fees for advice through Gerson Lehrman Group, Guidepoint, SAI Med Partners, and Vector Metric; fees for educational materials from CME Outfitters; and publishing royalties or fees from Massachusetts Medical Society, Oxford University Press, UpToDate, and Wolters Kluwer. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The oral calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor antagonist atogepant is effective in preventing rebound headache related to medication overuse in patients with chronic migraine (CM), new research suggested.
Results of a subgroup analysis of a phase 3, 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial showed up to a 62% reduction in the proportion of atogepant-treated participants who met acute medication overuse criteria.
“Based on our findings, treatment with atogepant may potentially decrease the risk of developing rebound headache by reducing the use of pain medications,” principal investigator Peter Goadsby, MD, PhD, of King’s College London, London, England, said in a news release.
The study was published online in Neurology.
Effective Prevention Needed
Acute treatments for migraine can mitigate symptoms and reduce disability but can also be ineffective and even result in increased dosing and overuse of these medications, the investigators noted.
Acute medication overuse is defined as “taking simple analgesics for ≥ 15 days per month or taking triptans, ergots, opioids, or combinations of medications for ≥ 10 days per month.”
“There is a high prevalence of pain medication overuse among people with migraine as they try to manage what are often debilitating symptoms,” Dr. Goadsby said. “However, medication overuse can lead to more headaches, called rebound headaches, so more effective preventive treatments are needed.”
Atogepant was developed for migraine prevention in adults. It had been studied in the phase 3 PROGRESS trial, which showed it significantly reduced monthly migraine days (MMDs) compared with placebo during the 12-week trial.
The new subgroup analysis of the study focused specifically on the efficacy and safety of atogepant vs placebo in participants with CM with, and without, medication overuse.
Participants (mean age, 42.1 years; 87.6% women) were randomized to receive either atogepant 30 mg twice daily (n = 253), atogepant 60 mg once daily (n = 256), or placebo (n = 240), with baseline demographics and clinical characteristics similar across all treatment arms. A total of 66.2% met baseline acute medication overuse criteria.
Participants were asked to record migraine and headache experiences in an electronic diary.
‘Effective and Safe’
Participants in both atogepant groups experienced fewer monthly headache days (MHDs) than those in the placebo group, with a least squares mean difference (LSMD) of −2.7 (95% confidence interval [CI], −4.0 to −1.4) in the atogepant 30 mg twice daily group and −1.9 (95% CI, −3.2 to −0.6) in the atogepant 60 mg once daily group.
MHDs were also reduced in both treatment groups, with LSMDs of −2.8 (95% CI, −4.0 to −1.5) and −2.1 (95% CI, −3.3 to −0.8), respectively. Mean acute medication use days were lower in both the treatment groups, with LSMDs of −2.8 (95% CI, −4.1 to −1.6) and −2.6 (95% CI, −3.9 to −1.3), respectively.
A higher proportion of participants achieved a ≥ 50% reduction in MMDs with atogepant 30 mg twice daily (odds ratio [OR], 2.5; 95% CI, 1.5-4.0) and atogepant 60 mg once daily (OR, 2.3; 95% CI, 1.4-3.7).
Notably, the researchers found a 52.1%-61.9% reduction in the proportion of atogepant-treated participants meeting acute medication overuse criteria during the study period vs 38.3% in the placebo group.
Similar results were observed in the subgroup without acute medication overuse.
Treatment-emergent adverse events were reported by 55.8% of participants treated with atogepant 30 mg twice daily, 66.1% with atogepant 60 mg once daily, and 48.5% with placebo in the acute medication overuse subgroup, with similar reports in the non-overuse subgroup.
A limitation cited by the authors was that participants’ self-report of migraines and headaches via electronic diaries might have been inaccurate.
Nevertheless, they concluded that the results showed atogepant to be an “effective and safe” preventive treatment for patients with CM with, and without, acute medication overuse.
AbbVie funded this study and participated in the study design, research, analysis, data collection, interpretation of data, reviewing, and approval of the publication. No honoraria or payments were made for authorship. Dr. Goadsby received personal fees from AbbVie during the conduct of the study, and over the last 36 months, he received a research grant from Celgene; personal fees from Aeon Biopharma, Amgen, CoolTechLLC, Dr. Reddy’s, Eli Lilly and Company, Epalex, Lundbeck, Novartis, Pfizer, Praxis, Sanofi, Satsuma, ShiraTronics, Teva Pharmaceuticals, and Tremeau; personal fees for advice through Gerson Lehrman Group, Guidepoint, SAI Med Partners, and Vector Metric; fees for educational materials from CME Outfitters; and publishing royalties or fees from Massachusetts Medical Society, Oxford University Press, UpToDate, and Wolters Kluwer. The other authors’ disclosures are listed on the original paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
New ACOG Guidance Advises Clinicians on Cannabis Use for Gynecologic Pain
An increasing proportion of people are using cannabis products for pain, including that associated with gynecologic conditions, according to new guidance from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The organization published its first guidance in July on the use of cannabis products for gynecologic pain.
“Many of our patients are using these products and many of our members are getting questions from their patients asking whether they should be using them,” Kimberly Gecsi, MD, a professor of ob.gyn. at Medical College of Wisconsin and Froedtert Health in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and one of the document’s coauthors, said in an interview.* “We want ACOG members to walk away with some understanding that their patients are using these products, what the different products are, and the current state of the science so they can guide their patients about the potential advantages as well as the potential risks.”
Use of cannabis in the past month in the United States rose 38.2% between 2015 and 2019, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Other research using data from that survey found that US use of cannabis for medicinal purposes more than doubled, from 1.2% to 2.5% between 2013-2014 and 2019-2020, and use in states where it was legalized increased fourfold. Though little data exist on its use for gynecologic pain, at least one peer-reviewed online survey found that 61% of those who had never used it and 90% of those who had ever used it were willing to consider its use for gynecologic pain.
In assessing the current evidence, the researchers excluded studies looking at use of cannabis to manage symptoms related to cancer, obstetrics, or gynecologic malignancy. Of the remaining evidence, however, “there just isn’t enough data on gynecologic pain to really have tipped the scale toward a recommendation,” Dr. Gecsi said.
The consensus recommendations therefore state that current data are not sufficient to recommend or discourage use of cannabis products to treat pain linked to gynecologic conditions. Yet the potential for benefit suggests that “if they are already using these products, there’s no need to discourage them, especially if the patients feel they are getting some benefit from them,” Dr. Gecsi said.
The guidance also highlights the importance of clinicians being aware that their patients may be using these products and being prepared to discuss with them the limited data available as well as the theoretical benefits and potential negative effects for adult patients. In adolescent patients, however, the increased risk of negative cognitive effects and psychotic conditions currently appears to outweigh the theoretical benefits. Use of cannabis products in teens should therefore not be recommended until more data is available on the short-term and long-term effects of its use on adolescent brain development, the authors wrote.
Josephine Urbina, MD, MAS, an assistant professor of ob.gyn. and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, said that the guidance confirms what most ob.gyns. suspected regarding the lack of data to support or refute the use of cannabis.
“Patients usually see cannabis as a last resort to control their pain,” Dr. Urbina added. “It seems that this decision to start using cannabis isn’t one that’s taken lightly, and they’re usually at their wits’ end. Some patients use cannabis as an adjunct so that they don’t have to rely on stronger pain medications like opioids, which we all know have a proven track record for being addicting.”
The ACOG guidance notes limited survey data suggesting that cannabis may help reduce patients’ use of opioids for pain relief, though there’s not enough data to confirm this potential benefit. The authors also highlight the limited data suggesting that PEA-transpolydatin may be effective for relieving pain related to primary dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, and chronic pelvic pain, but, again, there’s not yet enough data to formally recommend its use.
Current treatments for pain from gynecologic conditions depend on the cause of the pain, Dr. Gecsi said. One of the more common causes of pain, for example, is endometriosis, which can be treated with medications, including hormonal ones, or with surgery.
Other first-line treatments for pain, can include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and, for more complex cases, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants. “Nonpharmacological treatments like physical therapy, acupuncture, cognitive-behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, can also be beneficial,” Dr. Urbina added.
The new guidance also attempts to clarify the confusing legal landscape associated with cannabis use. In addition to the patchwork of state laws, federal distinctions in cannabis legality have been shifting in recent years. The 2018 Farm Bill defined any product with 0.3% or less tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) as hemp, which is now legal and commercially available in all states. That change introduced a wide range of topical and edible cannabidiol products to the market, even in states where marijuana is otherwise still illegal.
Products with a THC concentration greater than 0.3%, however, remain classified as a Schedule I drug, though the Justice Department proposed a rule in May to change that classification to Schedule III, which includes drugs such as ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone, and Tylenol with codeine. The guidance also includes a box of definitions for different types of cannabis products and differences in bioavailability, time to onset of effects, and duration of effects for different routes of exposure.
Kiran Kavipurapu, DO, JD, MPH, an assistant clinical professor and ob.gyn. residency program director at the University of California, Los Angeles, said the increasing availability and legalization of cannabis has meant that more patients are coming to their doctors’ offices having already tried it for medicinal purposes.
“Cannabis use discussions are often initiated by patients who are either inquiring about its benefits or because they have already tried it and want a physician to weigh in,” Dr. Kavipurapu said in an interview. “Over the past 5 years or so, this has become an increasingly common topic along with discussion of herbal or naturopathic remedies to supplement treatment of gynecologic conditions.”
Yet stigma about its use can lead patients to feel hesitant about bringing it up, Dr. Kavipurapu added. “I think it is necessary for clinicians to create a safe environment for patients to discuss their use of any and all therapies or supplements so their physician can assess for potential drug interactions or other harmful effects,” he said.
Dr. Gecsi agreed that this need to reassure patients was an important aspect of ACOG’s new guidance. Clinicians “should make sure that they strive to always foster a relationship with their patients where their patients can feel safe sharing their use and other things going on in their lives without feeling like they’re going to get in trouble,. Our job is not to put our patients at risk for any kind of legal or criminal problems.”
Meanwhile, the legal restrictions on cannabis remain a substantial barrier to the additional research that’s needed to make more informed recommendations about its use to patients, Dr. Gecsi said. But the inadequate amount of research goes beyond the challenges of studying cannabis in particular, Dr. Urbina noted.
“The paucity of research in women’s health, particularly in the realm of sexual and reproductive health care, underscores the urgent need to prioritize this topic in order to ensure comprehensive and equitable healthcare for women,” Dr. Urbina said. Underrepresentation of women’s health issues in clinical studies has led to knowledge gaps and “suboptimal treatment options for conditions unique to or more prevalent among women,” and it’s another reason for the lack of robust data on cannabis use for gynecologic-related pain.
“Prioritizing research in women’s health is essential to developing effective interventions, understanding gender-specific responses to treatments, and addressing the complex interplay of biological, social, and psychological factors affecting women’s well-being,” Dr. Urbina said. “Furthermore, advancing reproductive health research supports women’s reproductive autonomy, empowering them with the knowledge and resources to make informed decisions about their bodies and lives. By investing in robust, inclusive research, we can close existing gaps, improve health outcomes, and promote gender equity in healthcare — something that has been long overdue in this country.”
The guidance did not use external funding. Dr. Gecsi, Dr. Urbina, and Dr. Kavipurapu had no disclosures.
*This story was corrected on July 25, 2024.
An increasing proportion of people are using cannabis products for pain, including that associated with gynecologic conditions, according to new guidance from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The organization published its first guidance in July on the use of cannabis products for gynecologic pain.
“Many of our patients are using these products and many of our members are getting questions from their patients asking whether they should be using them,” Kimberly Gecsi, MD, a professor of ob.gyn. at Medical College of Wisconsin and Froedtert Health in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and one of the document’s coauthors, said in an interview.* “We want ACOG members to walk away with some understanding that their patients are using these products, what the different products are, and the current state of the science so they can guide their patients about the potential advantages as well as the potential risks.”
Use of cannabis in the past month in the United States rose 38.2% between 2015 and 2019, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Other research using data from that survey found that US use of cannabis for medicinal purposes more than doubled, from 1.2% to 2.5% between 2013-2014 and 2019-2020, and use in states where it was legalized increased fourfold. Though little data exist on its use for gynecologic pain, at least one peer-reviewed online survey found that 61% of those who had never used it and 90% of those who had ever used it were willing to consider its use for gynecologic pain.
In assessing the current evidence, the researchers excluded studies looking at use of cannabis to manage symptoms related to cancer, obstetrics, or gynecologic malignancy. Of the remaining evidence, however, “there just isn’t enough data on gynecologic pain to really have tipped the scale toward a recommendation,” Dr. Gecsi said.
The consensus recommendations therefore state that current data are not sufficient to recommend or discourage use of cannabis products to treat pain linked to gynecologic conditions. Yet the potential for benefit suggests that “if they are already using these products, there’s no need to discourage them, especially if the patients feel they are getting some benefit from them,” Dr. Gecsi said.
The guidance also highlights the importance of clinicians being aware that their patients may be using these products and being prepared to discuss with them the limited data available as well as the theoretical benefits and potential negative effects for adult patients. In adolescent patients, however, the increased risk of negative cognitive effects and psychotic conditions currently appears to outweigh the theoretical benefits. Use of cannabis products in teens should therefore not be recommended until more data is available on the short-term and long-term effects of its use on adolescent brain development, the authors wrote.
Josephine Urbina, MD, MAS, an assistant professor of ob.gyn. and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, said that the guidance confirms what most ob.gyns. suspected regarding the lack of data to support or refute the use of cannabis.
“Patients usually see cannabis as a last resort to control their pain,” Dr. Urbina added. “It seems that this decision to start using cannabis isn’t one that’s taken lightly, and they’re usually at their wits’ end. Some patients use cannabis as an adjunct so that they don’t have to rely on stronger pain medications like opioids, which we all know have a proven track record for being addicting.”
The ACOG guidance notes limited survey data suggesting that cannabis may help reduce patients’ use of opioids for pain relief, though there’s not enough data to confirm this potential benefit. The authors also highlight the limited data suggesting that PEA-transpolydatin may be effective for relieving pain related to primary dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, and chronic pelvic pain, but, again, there’s not yet enough data to formally recommend its use.
Current treatments for pain from gynecologic conditions depend on the cause of the pain, Dr. Gecsi said. One of the more common causes of pain, for example, is endometriosis, which can be treated with medications, including hormonal ones, or with surgery.
Other first-line treatments for pain, can include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and, for more complex cases, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants. “Nonpharmacological treatments like physical therapy, acupuncture, cognitive-behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, can also be beneficial,” Dr. Urbina added.
The new guidance also attempts to clarify the confusing legal landscape associated with cannabis use. In addition to the patchwork of state laws, federal distinctions in cannabis legality have been shifting in recent years. The 2018 Farm Bill defined any product with 0.3% or less tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) as hemp, which is now legal and commercially available in all states. That change introduced a wide range of topical and edible cannabidiol products to the market, even in states where marijuana is otherwise still illegal.
Products with a THC concentration greater than 0.3%, however, remain classified as a Schedule I drug, though the Justice Department proposed a rule in May to change that classification to Schedule III, which includes drugs such as ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone, and Tylenol with codeine. The guidance also includes a box of definitions for different types of cannabis products and differences in bioavailability, time to onset of effects, and duration of effects for different routes of exposure.
Kiran Kavipurapu, DO, JD, MPH, an assistant clinical professor and ob.gyn. residency program director at the University of California, Los Angeles, said the increasing availability and legalization of cannabis has meant that more patients are coming to their doctors’ offices having already tried it for medicinal purposes.
“Cannabis use discussions are often initiated by patients who are either inquiring about its benefits or because they have already tried it and want a physician to weigh in,” Dr. Kavipurapu said in an interview. “Over the past 5 years or so, this has become an increasingly common topic along with discussion of herbal or naturopathic remedies to supplement treatment of gynecologic conditions.”
Yet stigma about its use can lead patients to feel hesitant about bringing it up, Dr. Kavipurapu added. “I think it is necessary for clinicians to create a safe environment for patients to discuss their use of any and all therapies or supplements so their physician can assess for potential drug interactions or other harmful effects,” he said.
Dr. Gecsi agreed that this need to reassure patients was an important aspect of ACOG’s new guidance. Clinicians “should make sure that they strive to always foster a relationship with their patients where their patients can feel safe sharing their use and other things going on in their lives without feeling like they’re going to get in trouble,. Our job is not to put our patients at risk for any kind of legal or criminal problems.”
Meanwhile, the legal restrictions on cannabis remain a substantial barrier to the additional research that’s needed to make more informed recommendations about its use to patients, Dr. Gecsi said. But the inadequate amount of research goes beyond the challenges of studying cannabis in particular, Dr. Urbina noted.
“The paucity of research in women’s health, particularly in the realm of sexual and reproductive health care, underscores the urgent need to prioritize this topic in order to ensure comprehensive and equitable healthcare for women,” Dr. Urbina said. Underrepresentation of women’s health issues in clinical studies has led to knowledge gaps and “suboptimal treatment options for conditions unique to or more prevalent among women,” and it’s another reason for the lack of robust data on cannabis use for gynecologic-related pain.
“Prioritizing research in women’s health is essential to developing effective interventions, understanding gender-specific responses to treatments, and addressing the complex interplay of biological, social, and psychological factors affecting women’s well-being,” Dr. Urbina said. “Furthermore, advancing reproductive health research supports women’s reproductive autonomy, empowering them with the knowledge and resources to make informed decisions about their bodies and lives. By investing in robust, inclusive research, we can close existing gaps, improve health outcomes, and promote gender equity in healthcare — something that has been long overdue in this country.”
The guidance did not use external funding. Dr. Gecsi, Dr. Urbina, and Dr. Kavipurapu had no disclosures.
*This story was corrected on July 25, 2024.
An increasing proportion of people are using cannabis products for pain, including that associated with gynecologic conditions, according to new guidance from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. The organization published its first guidance in July on the use of cannabis products for gynecologic pain.
“Many of our patients are using these products and many of our members are getting questions from their patients asking whether they should be using them,” Kimberly Gecsi, MD, a professor of ob.gyn. at Medical College of Wisconsin and Froedtert Health in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, and one of the document’s coauthors, said in an interview.* “We want ACOG members to walk away with some understanding that their patients are using these products, what the different products are, and the current state of the science so they can guide their patients about the potential advantages as well as the potential risks.”
Use of cannabis in the past month in the United States rose 38.2% between 2015 and 2019, according to the National Survey on Drug Use and Health. Other research using data from that survey found that US use of cannabis for medicinal purposes more than doubled, from 1.2% to 2.5% between 2013-2014 and 2019-2020, and use in states where it was legalized increased fourfold. Though little data exist on its use for gynecologic pain, at least one peer-reviewed online survey found that 61% of those who had never used it and 90% of those who had ever used it were willing to consider its use for gynecologic pain.
In assessing the current evidence, the researchers excluded studies looking at use of cannabis to manage symptoms related to cancer, obstetrics, or gynecologic malignancy. Of the remaining evidence, however, “there just isn’t enough data on gynecologic pain to really have tipped the scale toward a recommendation,” Dr. Gecsi said.
The consensus recommendations therefore state that current data are not sufficient to recommend or discourage use of cannabis products to treat pain linked to gynecologic conditions. Yet the potential for benefit suggests that “if they are already using these products, there’s no need to discourage them, especially if the patients feel they are getting some benefit from them,” Dr. Gecsi said.
The guidance also highlights the importance of clinicians being aware that their patients may be using these products and being prepared to discuss with them the limited data available as well as the theoretical benefits and potential negative effects for adult patients. In adolescent patients, however, the increased risk of negative cognitive effects and psychotic conditions currently appears to outweigh the theoretical benefits. Use of cannabis products in teens should therefore not be recommended until more data is available on the short-term and long-term effects of its use on adolescent brain development, the authors wrote.
Josephine Urbina, MD, MAS, an assistant professor of ob.gyn. and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Francisco, said that the guidance confirms what most ob.gyns. suspected regarding the lack of data to support or refute the use of cannabis.
“Patients usually see cannabis as a last resort to control their pain,” Dr. Urbina added. “It seems that this decision to start using cannabis isn’t one that’s taken lightly, and they’re usually at their wits’ end. Some patients use cannabis as an adjunct so that they don’t have to rely on stronger pain medications like opioids, which we all know have a proven track record for being addicting.”
The ACOG guidance notes limited survey data suggesting that cannabis may help reduce patients’ use of opioids for pain relief, though there’s not enough data to confirm this potential benefit. The authors also highlight the limited data suggesting that PEA-transpolydatin may be effective for relieving pain related to primary dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, and chronic pelvic pain, but, again, there’s not yet enough data to formally recommend its use.
Current treatments for pain from gynecologic conditions depend on the cause of the pain, Dr. Gecsi said. One of the more common causes of pain, for example, is endometriosis, which can be treated with medications, including hormonal ones, or with surgery.
Other first-line treatments for pain, can include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and, for more complex cases, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants. “Nonpharmacological treatments like physical therapy, acupuncture, cognitive-behavioral therapy and lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, can also be beneficial,” Dr. Urbina added.
The new guidance also attempts to clarify the confusing legal landscape associated with cannabis use. In addition to the patchwork of state laws, federal distinctions in cannabis legality have been shifting in recent years. The 2018 Farm Bill defined any product with 0.3% or less tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) as hemp, which is now legal and commercially available in all states. That change introduced a wide range of topical and edible cannabidiol products to the market, even in states where marijuana is otherwise still illegal.
Products with a THC concentration greater than 0.3%, however, remain classified as a Schedule I drug, though the Justice Department proposed a rule in May to change that classification to Schedule III, which includes drugs such as ketamine, anabolic steroids, testosterone, and Tylenol with codeine. The guidance also includes a box of definitions for different types of cannabis products and differences in bioavailability, time to onset of effects, and duration of effects for different routes of exposure.
Kiran Kavipurapu, DO, JD, MPH, an assistant clinical professor and ob.gyn. residency program director at the University of California, Los Angeles, said the increasing availability and legalization of cannabis has meant that more patients are coming to their doctors’ offices having already tried it for medicinal purposes.
“Cannabis use discussions are often initiated by patients who are either inquiring about its benefits or because they have already tried it and want a physician to weigh in,” Dr. Kavipurapu said in an interview. “Over the past 5 years or so, this has become an increasingly common topic along with discussion of herbal or naturopathic remedies to supplement treatment of gynecologic conditions.”
Yet stigma about its use can lead patients to feel hesitant about bringing it up, Dr. Kavipurapu added. “I think it is necessary for clinicians to create a safe environment for patients to discuss their use of any and all therapies or supplements so their physician can assess for potential drug interactions or other harmful effects,” he said.
Dr. Gecsi agreed that this need to reassure patients was an important aspect of ACOG’s new guidance. Clinicians “should make sure that they strive to always foster a relationship with their patients where their patients can feel safe sharing their use and other things going on in their lives without feeling like they’re going to get in trouble,. Our job is not to put our patients at risk for any kind of legal or criminal problems.”
Meanwhile, the legal restrictions on cannabis remain a substantial barrier to the additional research that’s needed to make more informed recommendations about its use to patients, Dr. Gecsi said. But the inadequate amount of research goes beyond the challenges of studying cannabis in particular, Dr. Urbina noted.
“The paucity of research in women’s health, particularly in the realm of sexual and reproductive health care, underscores the urgent need to prioritize this topic in order to ensure comprehensive and equitable healthcare for women,” Dr. Urbina said. Underrepresentation of women’s health issues in clinical studies has led to knowledge gaps and “suboptimal treatment options for conditions unique to or more prevalent among women,” and it’s another reason for the lack of robust data on cannabis use for gynecologic-related pain.
“Prioritizing research in women’s health is essential to developing effective interventions, understanding gender-specific responses to treatments, and addressing the complex interplay of biological, social, and psychological factors affecting women’s well-being,” Dr. Urbina said. “Furthermore, advancing reproductive health research supports women’s reproductive autonomy, empowering them with the knowledge and resources to make informed decisions about their bodies and lives. By investing in robust, inclusive research, we can close existing gaps, improve health outcomes, and promote gender equity in healthcare — something that has been long overdue in this country.”
The guidance did not use external funding. Dr. Gecsi, Dr. Urbina, and Dr. Kavipurapu had no disclosures.
*This story was corrected on July 25, 2024.





