User login
Smoking, hypoglycemia, kidney function tied to vision loss in type 2 diabetes
according to new findings published in the Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.
“Smoking cessation strategies and optimal cardiometabolic risk factor management, including blood glucose lowering regimens that minimize hypoglycemia, appear important in preventing the loss of vision associated with type 2 diabetes,” wrote Jocelyn J. Drinkwater of the University of Western Australia, Perth, and coauthors, noting that all three noted risk factors were “potentially modifiable.”
To investigate the impact of type 2 diabetes and associated risk factors on vision, the researchers recruited 1,732 participants for the Fremantle Diabetes Study Phase II, of whom 1,551 patients had type 2 diabetes and underwent face-to-face and visual acuity assessments at baseline and at 2 and 4 years. Visual acuity was measured via the Bailey Lovie chart at a distance of 3 m in a well-lit room. Normal or near-normal vision was classified as a visual acuity of equal to or less than 6/19; visual impairment, a visual acuity of greater than 6/19 and equal to or less than 6/48; and blindness, a visual acuity of greater than 6/48. A change in vision was classified as a difference in visual acuity of more than 10 letters from baseline measurement.
Of the initial 1,551 participants, 31 were excluded because of missing baseline data for visual acuity. The remaining group comprised 52.2% men, the mean age was 65.6 years, and the median diabetes duration was 8.5 years (interquartile range, 2.9-15.8). At baseline, the prevalence of visual impairment was 1.8% (28 patients), and prevalence of blindness was 0.7% (11 patients), so those 39 patients were also excluded from further analysis.
After 4 years, 599 patients (39%) were excluded because of attrition or missing data; among them, 138 (23%) died before the follow-up.
The remaining 882 participants (58%) had their visual acuity measured. Among these patients, 62.2% were men, with a mean age of 65.1 years and an initial median diabetes duration of 7 years (IQR, 2.0-15.0). Their cumulative incidence of visual impairment was 0.9% (eight patients), and no patients with normal or near-normal vision had developed blindness. Cumulative incidence of vision loss was 2.9% (26), and 1.9% (17) had improved visual acuity.
After multivariable logistic regression to determine predictors for vision loss, the researchers found that participants who smoked at baseline were more than three times more likely to lose their vision (odds ratio, 3.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-8.76; P = .026). Although smoking was noted as a “well-recognized risk factor for ocular disease,” the authors added that ex-smokers did not have significantly higher odds of vision loss, compared with nonsmokers, suggesting that the “ocular damage caused by smoking may not be permanent.”
Participants who had suffered a severe hypoglycemic event before the study were five times more likely to lose their vision (OR, 5.59; 95% CI, 1.32-23.61; P = .019). The authors emphasized that severe hypoglycemia can worsen existing ischemic tissue damage or contribute to a long duration of poorly controlled diabetes, each of which could “increase the risk of ocular complications leading to impaired vision.”
The final notable risk factor was compromised kidney function, which is identified as a urinary albumin-creatinine ratio (uACR). The authors noted that the uACR has been associated with other ocular pathologies, such as retinopathy and macular edema, and that uACR may be a “surrogate marker of a variety of ocular diseases with shared risk factors, such as poor metabolic control, which have implications for vision.”
In regard to the possible limitations of the study, they authors noted that they had not used the “gold standard” Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study chart to assess visual acuity. In addition, although they had details on retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma status, they did not also consider less common ophthalmic conditions. Finally, as a survivor cohort, they acknowledged that they may have “underestimated the cumulative incidence” of vision issues in the participants.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Drinkwater JJ et al. J Diabetes Complications. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107560.
according to new findings published in the Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.
“Smoking cessation strategies and optimal cardiometabolic risk factor management, including blood glucose lowering regimens that minimize hypoglycemia, appear important in preventing the loss of vision associated with type 2 diabetes,” wrote Jocelyn J. Drinkwater of the University of Western Australia, Perth, and coauthors, noting that all three noted risk factors were “potentially modifiable.”
To investigate the impact of type 2 diabetes and associated risk factors on vision, the researchers recruited 1,732 participants for the Fremantle Diabetes Study Phase II, of whom 1,551 patients had type 2 diabetes and underwent face-to-face and visual acuity assessments at baseline and at 2 and 4 years. Visual acuity was measured via the Bailey Lovie chart at a distance of 3 m in a well-lit room. Normal or near-normal vision was classified as a visual acuity of equal to or less than 6/19; visual impairment, a visual acuity of greater than 6/19 and equal to or less than 6/48; and blindness, a visual acuity of greater than 6/48. A change in vision was classified as a difference in visual acuity of more than 10 letters from baseline measurement.
Of the initial 1,551 participants, 31 were excluded because of missing baseline data for visual acuity. The remaining group comprised 52.2% men, the mean age was 65.6 years, and the median diabetes duration was 8.5 years (interquartile range, 2.9-15.8). At baseline, the prevalence of visual impairment was 1.8% (28 patients), and prevalence of blindness was 0.7% (11 patients), so those 39 patients were also excluded from further analysis.
After 4 years, 599 patients (39%) were excluded because of attrition or missing data; among them, 138 (23%) died before the follow-up.
The remaining 882 participants (58%) had their visual acuity measured. Among these patients, 62.2% were men, with a mean age of 65.1 years and an initial median diabetes duration of 7 years (IQR, 2.0-15.0). Their cumulative incidence of visual impairment was 0.9% (eight patients), and no patients with normal or near-normal vision had developed blindness. Cumulative incidence of vision loss was 2.9% (26), and 1.9% (17) had improved visual acuity.
After multivariable logistic regression to determine predictors for vision loss, the researchers found that participants who smoked at baseline were more than three times more likely to lose their vision (odds ratio, 3.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-8.76; P = .026). Although smoking was noted as a “well-recognized risk factor for ocular disease,” the authors added that ex-smokers did not have significantly higher odds of vision loss, compared with nonsmokers, suggesting that the “ocular damage caused by smoking may not be permanent.”
Participants who had suffered a severe hypoglycemic event before the study were five times more likely to lose their vision (OR, 5.59; 95% CI, 1.32-23.61; P = .019). The authors emphasized that severe hypoglycemia can worsen existing ischemic tissue damage or contribute to a long duration of poorly controlled diabetes, each of which could “increase the risk of ocular complications leading to impaired vision.”
The final notable risk factor was compromised kidney function, which is identified as a urinary albumin-creatinine ratio (uACR). The authors noted that the uACR has been associated with other ocular pathologies, such as retinopathy and macular edema, and that uACR may be a “surrogate marker of a variety of ocular diseases with shared risk factors, such as poor metabolic control, which have implications for vision.”
In regard to the possible limitations of the study, they authors noted that they had not used the “gold standard” Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study chart to assess visual acuity. In addition, although they had details on retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma status, they did not also consider less common ophthalmic conditions. Finally, as a survivor cohort, they acknowledged that they may have “underestimated the cumulative incidence” of vision issues in the participants.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Drinkwater JJ et al. J Diabetes Complications. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107560.
according to new findings published in the Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.
“Smoking cessation strategies and optimal cardiometabolic risk factor management, including blood glucose lowering regimens that minimize hypoglycemia, appear important in preventing the loss of vision associated with type 2 diabetes,” wrote Jocelyn J. Drinkwater of the University of Western Australia, Perth, and coauthors, noting that all three noted risk factors were “potentially modifiable.”
To investigate the impact of type 2 diabetes and associated risk factors on vision, the researchers recruited 1,732 participants for the Fremantle Diabetes Study Phase II, of whom 1,551 patients had type 2 diabetes and underwent face-to-face and visual acuity assessments at baseline and at 2 and 4 years. Visual acuity was measured via the Bailey Lovie chart at a distance of 3 m in a well-lit room. Normal or near-normal vision was classified as a visual acuity of equal to or less than 6/19; visual impairment, a visual acuity of greater than 6/19 and equal to or less than 6/48; and blindness, a visual acuity of greater than 6/48. A change in vision was classified as a difference in visual acuity of more than 10 letters from baseline measurement.
Of the initial 1,551 participants, 31 were excluded because of missing baseline data for visual acuity. The remaining group comprised 52.2% men, the mean age was 65.6 years, and the median diabetes duration was 8.5 years (interquartile range, 2.9-15.8). At baseline, the prevalence of visual impairment was 1.8% (28 patients), and prevalence of blindness was 0.7% (11 patients), so those 39 patients were also excluded from further analysis.
After 4 years, 599 patients (39%) were excluded because of attrition or missing data; among them, 138 (23%) died before the follow-up.
The remaining 882 participants (58%) had their visual acuity measured. Among these patients, 62.2% were men, with a mean age of 65.1 years and an initial median diabetes duration of 7 years (IQR, 2.0-15.0). Their cumulative incidence of visual impairment was 0.9% (eight patients), and no patients with normal or near-normal vision had developed blindness. Cumulative incidence of vision loss was 2.9% (26), and 1.9% (17) had improved visual acuity.
After multivariable logistic regression to determine predictors for vision loss, the researchers found that participants who smoked at baseline were more than three times more likely to lose their vision (odds ratio, 3.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.15-8.76; P = .026). Although smoking was noted as a “well-recognized risk factor for ocular disease,” the authors added that ex-smokers did not have significantly higher odds of vision loss, compared with nonsmokers, suggesting that the “ocular damage caused by smoking may not be permanent.”
Participants who had suffered a severe hypoglycemic event before the study were five times more likely to lose their vision (OR, 5.59; 95% CI, 1.32-23.61; P = .019). The authors emphasized that severe hypoglycemia can worsen existing ischemic tissue damage or contribute to a long duration of poorly controlled diabetes, each of which could “increase the risk of ocular complications leading to impaired vision.”
The final notable risk factor was compromised kidney function, which is identified as a urinary albumin-creatinine ratio (uACR). The authors noted that the uACR has been associated with other ocular pathologies, such as retinopathy and macular edema, and that uACR may be a “surrogate marker of a variety of ocular diseases with shared risk factors, such as poor metabolic control, which have implications for vision.”
In regard to the possible limitations of the study, they authors noted that they had not used the “gold standard” Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study chart to assess visual acuity. In addition, although they had details on retinopathy, cataracts, and glaucoma status, they did not also consider less common ophthalmic conditions. Finally, as a survivor cohort, they acknowledged that they may have “underestimated the cumulative incidence” of vision issues in the participants.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Drinkwater JJ et al. J Diabetes Complications. 2020 Feb 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107560.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF DIABETES AND ITS COMPLICATIONS
Stillbirth linked to end-stage renal disease
and they were also at greater risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to findings published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Peter M Barrett, MB, of the University College Cork (Ireland), and colleagues conducted a population-based cohort study using data from the Swedish Medical Birth Register, National Patient Register, and the Swedish Renal Register to identify women who had live births and stillbirths. They then used anonymized unique personal identification numbers to cross-reference the registries.
From a full cohort of nearly 2 million women who gave birth during 1973-2012, and during a median follow-up of 20.7 years, 13,032 women experienced stillbirth, which, until 2008, was defined as fetal death after 28 weeks’ gestation, and after 2008, as occurring after 22 weeks. Women were excluded if they had any diagnosis of renal disease before their first pregnancy, as well as for a history of cardiovascular disease, chronic hypertension, diabetes, and certain other conditions at baseline.
Overall, 18,017 women developed CKD, and 1,283 developed ESRD. The fully adjusted model showed adjusted hazard ratios of 1.26 for CKD (95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.45) and 2.25 for ESRD (95% CI, 1.55-3.25) in women who had experienced stillbirth, compared with those who had not experienced stillbirth.
The researchers reported that associations between stillbirth and renal disease existed independently of underlying medical and obstetric comorbidities, such as congenital malformations, being small for gestational age, and preeclampsia, and that when those comorbidities were excluded, “the associations between stillbirth and maternal renal disease were strengthened (CKD: aHR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.13-1.57; and ESRD: aHR, 2.95; 95% CI, 1.86-4.68).”
In addition, they noted that there was no significant association between stillbirth and either CKD or ESRD in women who had prepregnancy medical comorbidities (CKD: aHR, 1.13; 95% CI 0.73-1.75; and ESRD: aHR 1.49; 95% CI, 0.78-2.85).
“Further research is required to better understand the underlying pathophysiology of this association and to determine whether affected women would benefit from closer surveillance and follow-up for future hypertension and renal disease,” the authors concluded.
The work was performed within the Irish Clinical Academic Training Programme and was funded by grants from several organizations. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Barret PM et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb 26. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.02.031.
and they were also at greater risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to findings published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Peter M Barrett, MB, of the University College Cork (Ireland), and colleagues conducted a population-based cohort study using data from the Swedish Medical Birth Register, National Patient Register, and the Swedish Renal Register to identify women who had live births and stillbirths. They then used anonymized unique personal identification numbers to cross-reference the registries.
From a full cohort of nearly 2 million women who gave birth during 1973-2012, and during a median follow-up of 20.7 years, 13,032 women experienced stillbirth, which, until 2008, was defined as fetal death after 28 weeks’ gestation, and after 2008, as occurring after 22 weeks. Women were excluded if they had any diagnosis of renal disease before their first pregnancy, as well as for a history of cardiovascular disease, chronic hypertension, diabetes, and certain other conditions at baseline.
Overall, 18,017 women developed CKD, and 1,283 developed ESRD. The fully adjusted model showed adjusted hazard ratios of 1.26 for CKD (95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.45) and 2.25 for ESRD (95% CI, 1.55-3.25) in women who had experienced stillbirth, compared with those who had not experienced stillbirth.
The researchers reported that associations between stillbirth and renal disease existed independently of underlying medical and obstetric comorbidities, such as congenital malformations, being small for gestational age, and preeclampsia, and that when those comorbidities were excluded, “the associations between stillbirth and maternal renal disease were strengthened (CKD: aHR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.13-1.57; and ESRD: aHR, 2.95; 95% CI, 1.86-4.68).”
In addition, they noted that there was no significant association between stillbirth and either CKD or ESRD in women who had prepregnancy medical comorbidities (CKD: aHR, 1.13; 95% CI 0.73-1.75; and ESRD: aHR 1.49; 95% CI, 0.78-2.85).
“Further research is required to better understand the underlying pathophysiology of this association and to determine whether affected women would benefit from closer surveillance and follow-up for future hypertension and renal disease,” the authors concluded.
The work was performed within the Irish Clinical Academic Training Programme and was funded by grants from several organizations. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Barret PM et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb 26. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.02.031.
and they were also at greater risk for chronic kidney disease (CKD), according to findings published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology.
Peter M Barrett, MB, of the University College Cork (Ireland), and colleagues conducted a population-based cohort study using data from the Swedish Medical Birth Register, National Patient Register, and the Swedish Renal Register to identify women who had live births and stillbirths. They then used anonymized unique personal identification numbers to cross-reference the registries.
From a full cohort of nearly 2 million women who gave birth during 1973-2012, and during a median follow-up of 20.7 years, 13,032 women experienced stillbirth, which, until 2008, was defined as fetal death after 28 weeks’ gestation, and after 2008, as occurring after 22 weeks. Women were excluded if they had any diagnosis of renal disease before their first pregnancy, as well as for a history of cardiovascular disease, chronic hypertension, diabetes, and certain other conditions at baseline.
Overall, 18,017 women developed CKD, and 1,283 developed ESRD. The fully adjusted model showed adjusted hazard ratios of 1.26 for CKD (95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.45) and 2.25 for ESRD (95% CI, 1.55-3.25) in women who had experienced stillbirth, compared with those who had not experienced stillbirth.
The researchers reported that associations between stillbirth and renal disease existed independently of underlying medical and obstetric comorbidities, such as congenital malformations, being small for gestational age, and preeclampsia, and that when those comorbidities were excluded, “the associations between stillbirth and maternal renal disease were strengthened (CKD: aHR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.13-1.57; and ESRD: aHR, 2.95; 95% CI, 1.86-4.68).”
In addition, they noted that there was no significant association between stillbirth and either CKD or ESRD in women who had prepregnancy medical comorbidities (CKD: aHR, 1.13; 95% CI 0.73-1.75; and ESRD: aHR 1.49; 95% CI, 0.78-2.85).
“Further research is required to better understand the underlying pathophysiology of this association and to determine whether affected women would benefit from closer surveillance and follow-up for future hypertension and renal disease,” the authors concluded.
The work was performed within the Irish Clinical Academic Training Programme and was funded by grants from several organizations. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Barret PM et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Feb 26. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.02.031.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY
RA magnifies fragility fracture risk in ESRD
MAUI, HAWAII – Comorbid rheumatoid arthritis is a force multiplier for fragility fracture risk in patients with end-stage renal disease, Renée Peterkin-McCalman, MD, reported at the 2020 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“Patients with RA and ESRD are at substantially increased risk of osteoporotic fragility fractures compared to the overall population of ESRD patients. So fracture prevention prior to initiation of dialysis should be a focus of care in patients with RA,” said Dr. Peterkin-McCalman, a rheumatology fellow at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta.
She presented a retrospective cohort study of 10,706 adults who initiated hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis for ESRD during 2005-2008, including 1,040 who also had RA. All subjects were drawn from the United States Renal Data System. The impetus for the study, Dr. Peterkin-McCalman explained in an interview, was that although prior studies have established that RA and ESRD are independent risk factors for osteoporotic fractures, the interplay between the two was previously unknown.
The risk of incident osteoporotic fractures during the first 3 years after going on renal dialysis was 14.7% in patients with ESRD only, vaulting to 25.6% in those with comorbid RA. Individuals with both RA and ESRD were at an adjusted 1.83-fold increased overall risk for new fragility fractures and at 1.85-fold increased risk for hip fracture, compared to those without RA.
Far and away the strongest risk factor for incident osteoporotic fractures in the group with RA plus ESRD was a history of a fracture sustained within 5 years prior to initiation of dialysis, with an associated 11.5-fold increased fracture risk overall and an 8.2-fold increased risk of hip fracture.
“The reason that’s important is we don’t really have any medications to reduce fracture risk once you get to ESRD. Of course, we have bisphosphonates and Prolia (denosumab) and things like that, but that’s in patients with milder CKD [chronic kidney disease] or no renal disease at all. So the goal is to identify the patients early who are at higher risk so that we can protect those bones before they get to ESRD and we have nothing left to treat them with,” she said.
In addition to a history of prevalent fracture prior to starting ESRD, the other risk factors for fracture in patients with ESRD and comorbid RA Dr. Peterkin-McCalman identified in her study included age greater than 50 years at the start of dialysis and female gender, which was associated with a twofold greater fracture risk than in men. Black patients with ESRD and RA were 64% less likely than whites to experience an incident fragility fracture. And the fracture risk was higher in patients on hemodialysis than with peritoneal dialysis.
Her study was supported by the Medical College of Georgia and a research grant from Dialysis Clinic Inc.
SOURCE: Peterkin-McCalman R et al. RWCS 2020.
MAUI, HAWAII – Comorbid rheumatoid arthritis is a force multiplier for fragility fracture risk in patients with end-stage renal disease, Renée Peterkin-McCalman, MD, reported at the 2020 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“Patients with RA and ESRD are at substantially increased risk of osteoporotic fragility fractures compared to the overall population of ESRD patients. So fracture prevention prior to initiation of dialysis should be a focus of care in patients with RA,” said Dr. Peterkin-McCalman, a rheumatology fellow at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta.
She presented a retrospective cohort study of 10,706 adults who initiated hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis for ESRD during 2005-2008, including 1,040 who also had RA. All subjects were drawn from the United States Renal Data System. The impetus for the study, Dr. Peterkin-McCalman explained in an interview, was that although prior studies have established that RA and ESRD are independent risk factors for osteoporotic fractures, the interplay between the two was previously unknown.
The risk of incident osteoporotic fractures during the first 3 years after going on renal dialysis was 14.7% in patients with ESRD only, vaulting to 25.6% in those with comorbid RA. Individuals with both RA and ESRD were at an adjusted 1.83-fold increased overall risk for new fragility fractures and at 1.85-fold increased risk for hip fracture, compared to those without RA.
Far and away the strongest risk factor for incident osteoporotic fractures in the group with RA plus ESRD was a history of a fracture sustained within 5 years prior to initiation of dialysis, with an associated 11.5-fold increased fracture risk overall and an 8.2-fold increased risk of hip fracture.
“The reason that’s important is we don’t really have any medications to reduce fracture risk once you get to ESRD. Of course, we have bisphosphonates and Prolia (denosumab) and things like that, but that’s in patients with milder CKD [chronic kidney disease] or no renal disease at all. So the goal is to identify the patients early who are at higher risk so that we can protect those bones before they get to ESRD and we have nothing left to treat them with,” she said.
In addition to a history of prevalent fracture prior to starting ESRD, the other risk factors for fracture in patients with ESRD and comorbid RA Dr. Peterkin-McCalman identified in her study included age greater than 50 years at the start of dialysis and female gender, which was associated with a twofold greater fracture risk than in men. Black patients with ESRD and RA were 64% less likely than whites to experience an incident fragility fracture. And the fracture risk was higher in patients on hemodialysis than with peritoneal dialysis.
Her study was supported by the Medical College of Georgia and a research grant from Dialysis Clinic Inc.
SOURCE: Peterkin-McCalman R et al. RWCS 2020.
MAUI, HAWAII – Comorbid rheumatoid arthritis is a force multiplier for fragility fracture risk in patients with end-stage renal disease, Renée Peterkin-McCalman, MD, reported at the 2020 Rheumatology Winter Clinical Symposium.
“Patients with RA and ESRD are at substantially increased risk of osteoporotic fragility fractures compared to the overall population of ESRD patients. So fracture prevention prior to initiation of dialysis should be a focus of care in patients with RA,” said Dr. Peterkin-McCalman, a rheumatology fellow at the Medical College of Georgia, Augusta.
She presented a retrospective cohort study of 10,706 adults who initiated hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis for ESRD during 2005-2008, including 1,040 who also had RA. All subjects were drawn from the United States Renal Data System. The impetus for the study, Dr. Peterkin-McCalman explained in an interview, was that although prior studies have established that RA and ESRD are independent risk factors for osteoporotic fractures, the interplay between the two was previously unknown.
The risk of incident osteoporotic fractures during the first 3 years after going on renal dialysis was 14.7% in patients with ESRD only, vaulting to 25.6% in those with comorbid RA. Individuals with both RA and ESRD were at an adjusted 1.83-fold increased overall risk for new fragility fractures and at 1.85-fold increased risk for hip fracture, compared to those without RA.
Far and away the strongest risk factor for incident osteoporotic fractures in the group with RA plus ESRD was a history of a fracture sustained within 5 years prior to initiation of dialysis, with an associated 11.5-fold increased fracture risk overall and an 8.2-fold increased risk of hip fracture.
“The reason that’s important is we don’t really have any medications to reduce fracture risk once you get to ESRD. Of course, we have bisphosphonates and Prolia (denosumab) and things like that, but that’s in patients with milder CKD [chronic kidney disease] or no renal disease at all. So the goal is to identify the patients early who are at higher risk so that we can protect those bones before they get to ESRD and we have nothing left to treat them with,” she said.
In addition to a history of prevalent fracture prior to starting ESRD, the other risk factors for fracture in patients with ESRD and comorbid RA Dr. Peterkin-McCalman identified in her study included age greater than 50 years at the start of dialysis and female gender, which was associated with a twofold greater fracture risk than in men. Black patients with ESRD and RA were 64% less likely than whites to experience an incident fragility fracture. And the fracture risk was higher in patients on hemodialysis than with peritoneal dialysis.
Her study was supported by the Medical College of Georgia and a research grant from Dialysis Clinic Inc.
SOURCE: Peterkin-McCalman R et al. RWCS 2020.
REPORTING FROM RWCS 2020
When Should I Refer My CKD Patient to Nephrology?
Q) When should I refer patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to a nephrology specialist?
Nephrology specialists can be of particular assistance to primary care providers in treating patients who are at different stages of CKD.1 Nephrologists can help determine the etiology of CKD, recommend specific disease-related therapy, suggest treatments to delay disease progression in patients who have not responded to conventional therapies, recognize and treat for disease-related complications, and plan for renal replacement therapy.1
Indications for referral vary across guidelines but there is one commonality: Patients with a severely decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of < 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 require prompt referral to a nephrologist for comanaged care.1-4 Patients with CKD who have an eGFR at or below this threshold are likely at an advanced stage of disease and are therefore at greater risk for progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), which requires dialysis.1 Research shows that late referral to nephrology is associated with significantly higher rates of mortality within the first 90 days of dialysis.5 Furthermore, the Renal Physicians Association Clinical Practice Guideline states that patients with advanced CKD (stages 4 and 5) have a greater predisposition for quick progression to ESRD with multiple comorbid conditions and poor outcomes.6
Clinical outcomes can improve when referrals are made before patients with CKD register a low eGFR—but the appropriate threshold (or when to refer patients with a higher eGFR) is less clear.1 Based in part on practice guidelines,2,3,6,7 referral to a nephrologist or clinician with expertise in CKD should be considered for patients with CKD who meet 1 or more of the following criteria:
- Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio > 300 mg/g (34 mg/mmoL), including nephrotic syndrome
- Hematuria that is not secondary to urologic conditions
- Inability to identify a presumed cause of CKD
- eGFR decline of > 30% in less than 4 months without an obvious explanation
- Difficult-to-manage complications, such as anemia requiring erythropoietin therapy or abnormalities of bone and mineral metabolism requiring phosphorus binders or vitamin D preparations
- Serum potassium > 5.5 mEq/L
- Difficult-to-manage drug complications
- Age < 18 y
- Resistant hypertension
- Recurrent or extensive nephrolithiasis
- Confirmed or presumed hereditary kidney disease (eg, polycystic kidney disease, Alport syndrome, or autosomal dominant interstitial kidney disease).1,2,4,7
These criteria can aid clinicians in deciding when a preemptive referral is needed to prevent advanced CKD stages and ESRD in their patients. Also, because patients with CKD can be at high risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes, referral to cardiology (eg, for patients with complicated cardiovascular disease) should be considered.1–YTM
Yolanda Thompson-Martin, DNP, RN, ANP-C, FNKF
University Health Physicians/Truman Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri
1. Levey AS, Inker LA. Definition and staging of chronic kidney disease in adults. UpToDate. www.uptodate.com/contents/definition-and-staging-of-chronic-kidney-disease-in-adults. Accessed January 29, 2020.
2. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J of Kidney Dis. 2002;39(suppl 1):S1-S266.
3. Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI). K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines on hypertension and antihypertensive agents in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(suppl 1):11-13.
4. Luxton G; Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. The CARI Guidelines. Timing of referral of chronic kidney disease patients to nephrology services (adult). Nephrology (Carlton). 2010;15(suppl 1):S2-S11.
5. Jungers P, Massy Z, Nguyen-Khoa T, et al. Longer duration of predialysis nephrological care is associated with improved long-term survival of dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(12):2357-2364.
6. WK Bolton. Renal Physicians Association Clinical Practice Guidelines: appropriate patient preparation for renal replacement therapy: guide line number 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(5):1406-1410.
7. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guidelines for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013;3(suppl):1-150.
Q) When should I refer patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to a nephrology specialist?
Nephrology specialists can be of particular assistance to primary care providers in treating patients who are at different stages of CKD.1 Nephrologists can help determine the etiology of CKD, recommend specific disease-related therapy, suggest treatments to delay disease progression in patients who have not responded to conventional therapies, recognize and treat for disease-related complications, and plan for renal replacement therapy.1
Indications for referral vary across guidelines but there is one commonality: Patients with a severely decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of < 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 require prompt referral to a nephrologist for comanaged care.1-4 Patients with CKD who have an eGFR at or below this threshold are likely at an advanced stage of disease and are therefore at greater risk for progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), which requires dialysis.1 Research shows that late referral to nephrology is associated with significantly higher rates of mortality within the first 90 days of dialysis.5 Furthermore, the Renal Physicians Association Clinical Practice Guideline states that patients with advanced CKD (stages 4 and 5) have a greater predisposition for quick progression to ESRD with multiple comorbid conditions and poor outcomes.6
Clinical outcomes can improve when referrals are made before patients with CKD register a low eGFR—but the appropriate threshold (or when to refer patients with a higher eGFR) is less clear.1 Based in part on practice guidelines,2,3,6,7 referral to a nephrologist or clinician with expertise in CKD should be considered for patients with CKD who meet 1 or more of the following criteria:
- Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio > 300 mg/g (34 mg/mmoL), including nephrotic syndrome
- Hematuria that is not secondary to urologic conditions
- Inability to identify a presumed cause of CKD
- eGFR decline of > 30% in less than 4 months without an obvious explanation
- Difficult-to-manage complications, such as anemia requiring erythropoietin therapy or abnormalities of bone and mineral metabolism requiring phosphorus binders or vitamin D preparations
- Serum potassium > 5.5 mEq/L
- Difficult-to-manage drug complications
- Age < 18 y
- Resistant hypertension
- Recurrent or extensive nephrolithiasis
- Confirmed or presumed hereditary kidney disease (eg, polycystic kidney disease, Alport syndrome, or autosomal dominant interstitial kidney disease).1,2,4,7
These criteria can aid clinicians in deciding when a preemptive referral is needed to prevent advanced CKD stages and ESRD in their patients. Also, because patients with CKD can be at high risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes, referral to cardiology (eg, for patients with complicated cardiovascular disease) should be considered.1–YTM
Yolanda Thompson-Martin, DNP, RN, ANP-C, FNKF
University Health Physicians/Truman Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri
Q) When should I refer patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to a nephrology specialist?
Nephrology specialists can be of particular assistance to primary care providers in treating patients who are at different stages of CKD.1 Nephrologists can help determine the etiology of CKD, recommend specific disease-related therapy, suggest treatments to delay disease progression in patients who have not responded to conventional therapies, recognize and treat for disease-related complications, and plan for renal replacement therapy.1
Indications for referral vary across guidelines but there is one commonality: Patients with a severely decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of < 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 require prompt referral to a nephrologist for comanaged care.1-4 Patients with CKD who have an eGFR at or below this threshold are likely at an advanced stage of disease and are therefore at greater risk for progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD), which requires dialysis.1 Research shows that late referral to nephrology is associated with significantly higher rates of mortality within the first 90 days of dialysis.5 Furthermore, the Renal Physicians Association Clinical Practice Guideline states that patients with advanced CKD (stages 4 and 5) have a greater predisposition for quick progression to ESRD with multiple comorbid conditions and poor outcomes.6
Clinical outcomes can improve when referrals are made before patients with CKD register a low eGFR—but the appropriate threshold (or when to refer patients with a higher eGFR) is less clear.1 Based in part on practice guidelines,2,3,6,7 referral to a nephrologist or clinician with expertise in CKD should be considered for patients with CKD who meet 1 or more of the following criteria:
- Urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio > 300 mg/g (34 mg/mmoL), including nephrotic syndrome
- Hematuria that is not secondary to urologic conditions
- Inability to identify a presumed cause of CKD
- eGFR decline of > 30% in less than 4 months without an obvious explanation
- Difficult-to-manage complications, such as anemia requiring erythropoietin therapy or abnormalities of bone and mineral metabolism requiring phosphorus binders or vitamin D preparations
- Serum potassium > 5.5 mEq/L
- Difficult-to-manage drug complications
- Age < 18 y
- Resistant hypertension
- Recurrent or extensive nephrolithiasis
- Confirmed or presumed hereditary kidney disease (eg, polycystic kidney disease, Alport syndrome, or autosomal dominant interstitial kidney disease).1,2,4,7
These criteria can aid clinicians in deciding when a preemptive referral is needed to prevent advanced CKD stages and ESRD in their patients. Also, because patients with CKD can be at high risk for adverse cardiovascular outcomes, referral to cardiology (eg, for patients with complicated cardiovascular disease) should be considered.1–YTM
Yolanda Thompson-Martin, DNP, RN, ANP-C, FNKF
University Health Physicians/Truman Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri
1. Levey AS, Inker LA. Definition and staging of chronic kidney disease in adults. UpToDate. www.uptodate.com/contents/definition-and-staging-of-chronic-kidney-disease-in-adults. Accessed January 29, 2020.
2. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J of Kidney Dis. 2002;39(suppl 1):S1-S266.
3. Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI). K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines on hypertension and antihypertensive agents in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(suppl 1):11-13.
4. Luxton G; Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. The CARI Guidelines. Timing of referral of chronic kidney disease patients to nephrology services (adult). Nephrology (Carlton). 2010;15(suppl 1):S2-S11.
5. Jungers P, Massy Z, Nguyen-Khoa T, et al. Longer duration of predialysis nephrological care is associated with improved long-term survival of dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(12):2357-2364.
6. WK Bolton. Renal Physicians Association Clinical Practice Guidelines: appropriate patient preparation for renal replacement therapy: guide line number 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(5):1406-1410.
7. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guidelines for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013;3(suppl):1-150.
1. Levey AS, Inker LA. Definition and staging of chronic kidney disease in adults. UpToDate. www.uptodate.com/contents/definition-and-staging-of-chronic-kidney-disease-in-adults. Accessed January 29, 2020.
2. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification and stratification. Am J of Kidney Dis. 2002;39(suppl 1):S1-S266.
3. Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (K/DOQI). K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines on hypertension and antihypertensive agents in chronic kidney disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;43(suppl 1):11-13.
4. Luxton G; Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. The CARI Guidelines. Timing of referral of chronic kidney disease patients to nephrology services (adult). Nephrology (Carlton). 2010;15(suppl 1):S2-S11.
5. Jungers P, Massy Z, Nguyen-Khoa T, et al. Longer duration of predialysis nephrological care is associated with improved long-term survival of dialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2001;16(12):2357-2364.
6. WK Bolton. Renal Physicians Association Clinical Practice Guidelines: appropriate patient preparation for renal replacement therapy: guide line number 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14(5):1406-1410.
7. Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guidelines for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013;3(suppl):1-150.
Improving Nephropathy Screening in Appalachian Patients With Diabetes Using Practice-Wide Outreach
From West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV.
Abstract
Objective: To describe the strategies a family medicine clinic in Appalachia utilized to increase nephropathy screening rates as well as to explore the factors predictive of nephropathy screening in patients with diabetes.
Design: This quality improvement project targeted the points in the care process when patients are lost to follow-up for nephropathy screening.
Setting and participants: Patients with diabetes cared for by a primary care provider (PCP) at an academic family medicine practice in Appalachia from January 2018 to November 2018.
Interventions: Bulk orders for albumin-to-creatinine (ACR) testing and urine collection during clinic visit, enhanced patient communication through bulk communication reminders and individual patient outreach, and education of clinic providers.
Measurements: Demographic data and monthly nephropathy screening rates.
Results: The nephropathy screening rate increased by 6.2% during the project. Older patients living closer to the clinic who visited their PCP 3 or more times per year were the most likely to be screened.
Conclusion: Combining team-based interventions with quality control monitoring can significantly improve compliance with recommended nephropathy treatment and screening in rural patients with diabetes at a family medicine clinic.
Keywords: rural; kidney disease; albumin-to-creatinine ratio; electronic health record.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), an estimated 30.3 million people in the United States—about 9.4% of the population—have been diagnosed with diabetes.1 Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States, and it contributes to other leading causes of death: heart disease and stroke.1 Diabetes also is related to high morbidity risk and is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease.1 The total cost of diagnosed diabetes was estimated at $327 billion in direct medical costs and reduced productivity.2
Residents of Appalachia bear a disproportionate burden of diabetes and other related negative health outcomes; these outcomes are influenced by a number of factors, including socioeconomic status, poverty, rurality, and health care access. Rates of chronic disease, such as diabetes, are most pronounced in Appalachia’s most economically distressed counties.3-5 In 2011, the CDC labeled a 644-county area the “diabetes belt,” which included most of Appalachia.6 As a result of this elevated prevalence of diabetes in Appalachia as compared to the rest of the country, complications directly associated with diabetes are more commonly observed in Appalachian residents. One of the most damaging complications is diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic nephropathy results from damage to the microvasculature of the kidney due to inadequately controlled blood glucose. This, in turn, leads to decreased renal function, eventually leading to clinically significant renal disease. The long-term complications associated with nephropathy can include many comorbid conditions, the most serious of which are progression to end-stage renal disease, dialysis requirement, and early mortality. Diabetic nephropathy affects approximately 40% of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.7,8
One way to prevent complications of diabetic nephropathy, in addition to good glycemic control in patients with diabetes, is early and regular screening. Currently, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends yearly screening for diabetic nephropathy in the form of a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) for patients 18 to 75 years of age.2 This screening to detect diabetic nephropathy is recognized as a marker of quality care by many public and private insurance agencies and medical specialty associations, such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Many patients with diabetes are cared for by primary care providers (PCP), and these PCP appointments provide an opportune time to screen and appropriately treat nephropathy. Screening opportunities are often missed, however, due to time constraints and competing health priorities. There are also a number of other factors specific to the Appalachian region that reduce the likelihood of screening for diabetic nephropathy, such as a lack of health insurance, the need to travel long distances to see a PCP, work and household responsibilities, low levels of education and health literacy, and a mistrust of outsiders regarding personal matters, including health.9-11 While nephropathy can have a detrimental impact on patients across populations, it is of particular concern for a state located in the heart of Appalachia, such as West Virginia.
Given the disproportionate burden of diabetes in this region and the potentially severe consequences of undetected nephropathy, clinicians from an academic family medicine clinic in West Virginia undertook a quality improvement project to increase the rate of nephropathy screening and treatment among patients with diabetes. This article describes the intervention strategies the team utilized to increase nephropathy screening and treatment in patients 18 to 75 years of age who met quality measures for nephropathy screening or treatment in the previous 12 months and explores the factors most predictive of nephropathy screening in Appalachian patients in this age group. It also reports the challenges and opportunities encountered and offers suggestions for other providers and clinics attempting to increase their nephropathy screening rates.
Methods
Setting and Study Population
The study population included patients ages 18 to 75 years under the care of providers in an academic family medicine practice in West Virginia who had been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. The study focused on those patients overdue for diabetic nephropathy screening (ie, had not been screened in previous 12 months). The project began in January 2018 with a screening rate of 83.8%. The goal of this project was to increase this compliance metric by at least 5%. The project protocol was submitted to the West Virginia University Institutional Review Board, and, because it is a quality improvement project, permission was given to proceed without a board review.
Interventions
The team identified and implemented several interventions intended to reduce screening barriers and increase the screening rate.
Bulk orders for ACR and urine collection during clinic visits. Prior to initiation of this project, it was left to individual clinic providers to order nephropathy screening for patients with diabetes during a clinic visit; after receiving the order for “random urine microalbumin/creatinine ratio,” patients then had to travel to a lab to provide a urine sample. For this project and moving forward, the team changed to the procedure of initiating bulk ACR orders and collecting urine samples during clinic visits from all patients ages 18 to 75 years who have diabetes.
Bulk communication reminders. Since many patients with diabetes may not have realized they were overdue for nephropathy screening, the team began sending out bulk communication reminders through either the institution’s electronic health record (EHR; MyChart) or postal service–delivered physical letters (according to patient communication preferences) to remind patients that they were due for screening and to encourage them to schedule an appointment or keep a previously scheduled appointment with their PCP.
Individual patient outreach. A team of pharmacy students led by a licensed pharmacist in the family medicine clinic contacted patients overdue for screening even after bulk communication reminders went out. The students telephoned patients 2 to 3 months following the bulk communication. The students obtained an updated list of patients with diabetes ages 18 to 75 years from an EHR quality report. They began by prescreening the patients on the overdue list for potential candidacy for an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Screening for candidacy included evaluation of recent blood pressure readings, electrolytes (ie, basic metabolic panel), and ACR. If the students determined a patient was a candidate, they presented the patient to the preceptor for verification and then reached out to the provider with a recommendation. If the provider agreed, the student contacted the patient by telephone for medication counseling and education. The remaining patients determined not to be candidates for ACE inhibitors or ARBs were contacted by the pharmacy students by telephone to remind them that laboratory work was pending. Up to 3 phone call attempts were made before patients were determined to be unreachable. Students left voice mails with generic reminders if a patient could not be reached. If a patient answered, the student provided a reminder but also reviewed indications for lab work, the reason why the provider wished for follow-up, and updated lab hours. Students also followed up with the results of the work-up, as appropriate. During this outreach process, the student team encountered a number of patients who had moved or changed to a PCP outside of the family medicine clinic. In these cases, the EHR was updated and those patients were removed from the list of patients altogether.
Education of clinic providers. Clinic providers were educated during faculty and resident meetings and didactic learning sessions on identifying patients within the EHR who are due for nephropathy screening. They also received instruction on how to update the EHR to reflect completed screenings.
Data Analysis
All analyses in this study were conducted using SAS (version 9.4, 2013, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC). Descriptive analyses were conducted to summarize basic patient demographic information. To compare patients screened within the previous 12 months to those patients overdue for screening, 2-sample t-tests were used to examine differences in patients’ age, HbA1c, ACR, and creatinine level and the distance (in miles) between the patient’s home and the clinic. Chi-square analyses were used to examine the relationship between whether a patient was recently screened for nephropathy and the patient’s insurance, number of patient visits in the previous 12 months, and provider level. Logistic regression analyses were conducted to control for covariates and to explore which factors were most predictive of nephropathy screening. All tests were 2-tailed, and P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient Characteristics
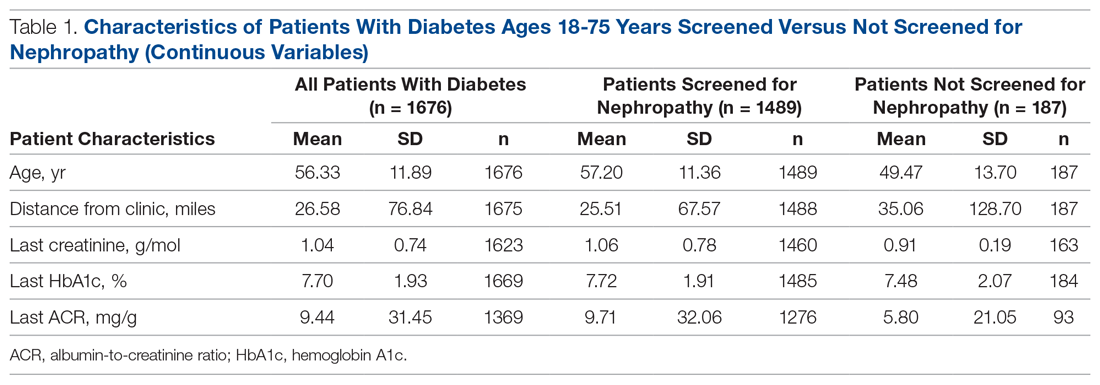
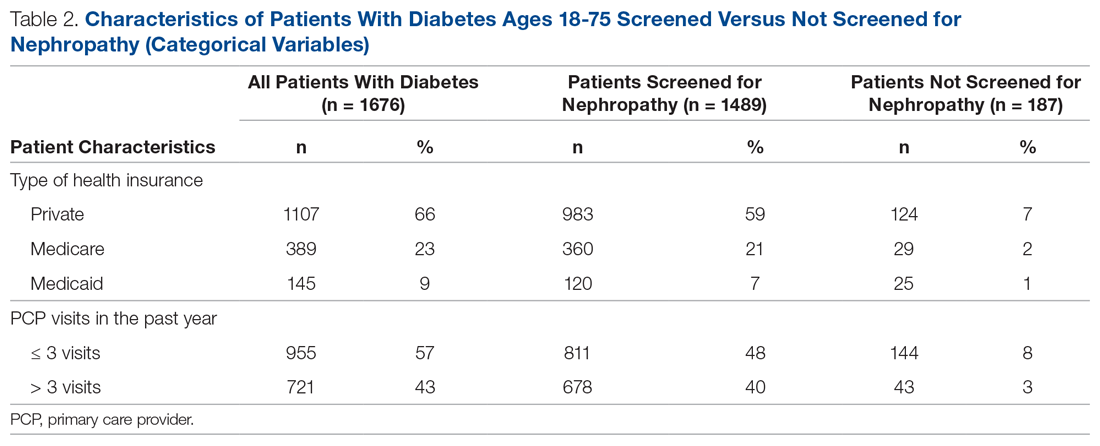
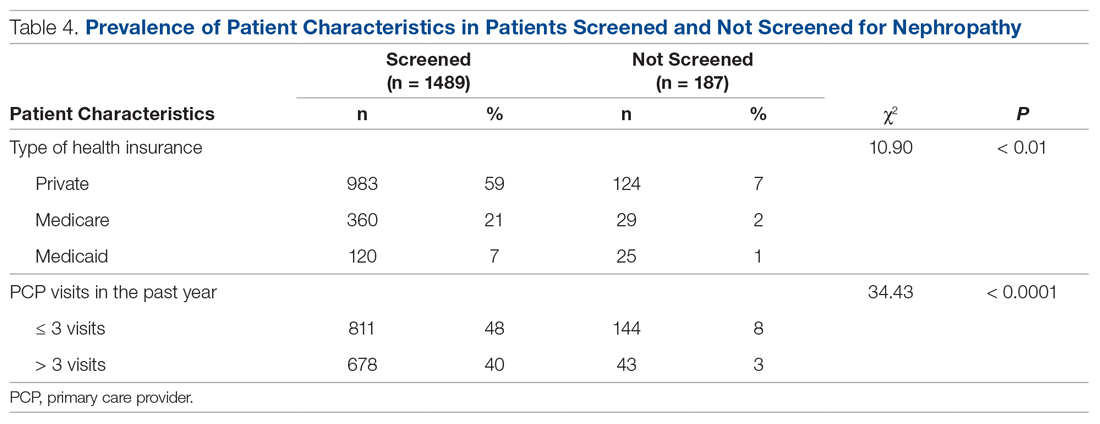
There were 1676 family medicine clinic patients with diabetes between 18 and 75 years of age (Table 1 and Table 2). Of the total sample, 1489 (88.8%) had completed screening for nephropathy in the 12 months prior to evaluation, and 67.5%, 23.7%, and 8.8% of patients had private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid, respectively.
The mean (SD) age of the patients was 56.3 (11.9) years. The mean distance between the patient’s home and the clinic was 26.6 (76.8) miles. The mean number of visits was 3.6 (2.9) per year, and 43.0% of the patientvisited the clinic more than 3 times in a year. The mean values for HbA1c (%), creatinine (g/mol), and ACR (mg/g) were 7.7 (1.9), 1.0 (0.7), and 9.4 (31.4), respectively.
Screening of Patients for Nephropathy
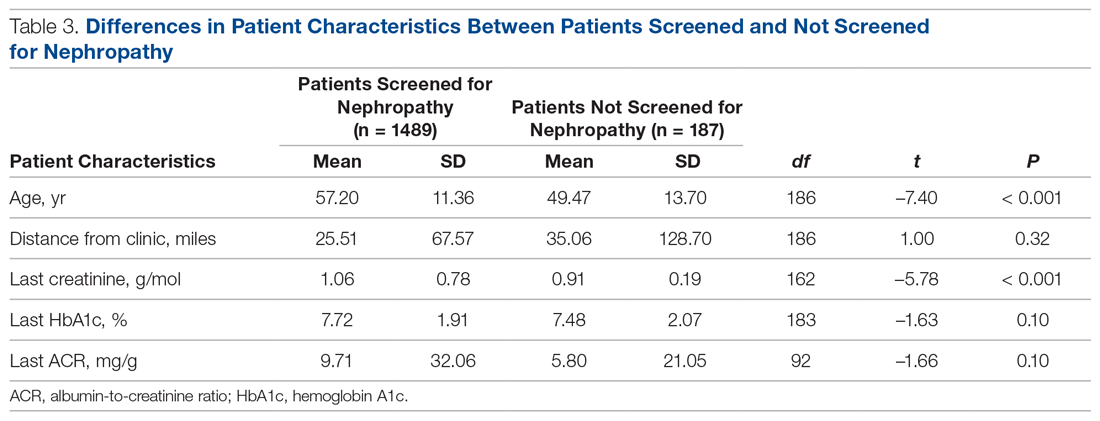
Patients with Medicare and private insurance were more likely to have completed the nephropathy screening than those with Medicaid (92.5% versus 88.8% versus 82.8%, P = 0.004; Table 3 and Table 4).
Changes in Screening Rate
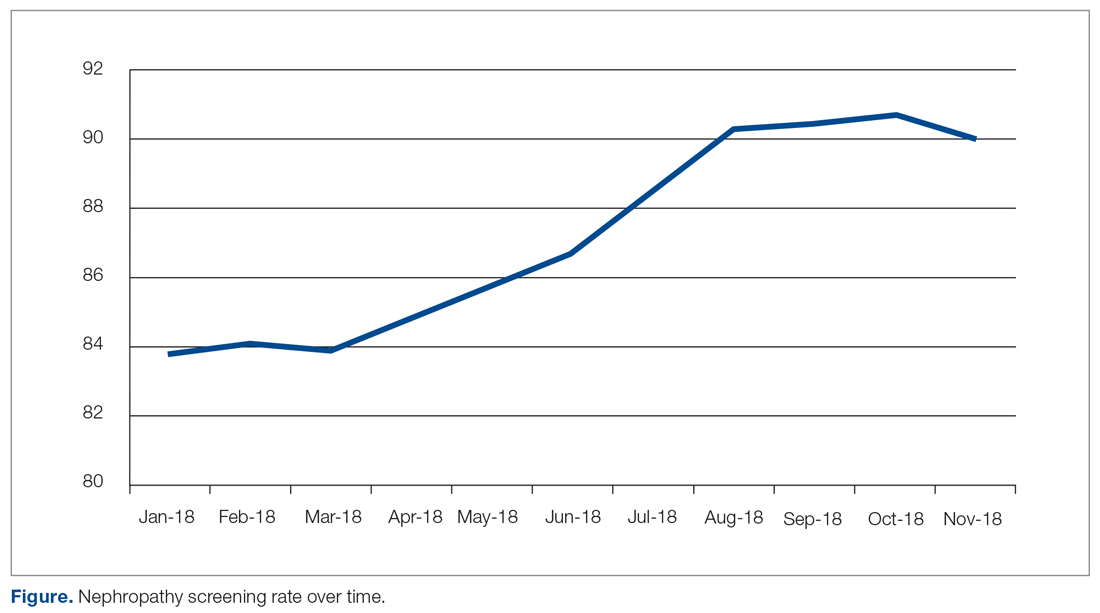
The practice-wide screening rate was 83.8% at the start of this project in January 2018. The screening rate steadily increased throughout 2018, reaching 90.3% in August 2018, and then leveled off around 90% when the project was concluded at the end of November 2018 (Figure). As an added benefit of the increased screening rates, a number of patients were initiated on an ACE inhibitor or ARB based on the team’s screening efforts.
Predictors of Nephropathy Screening
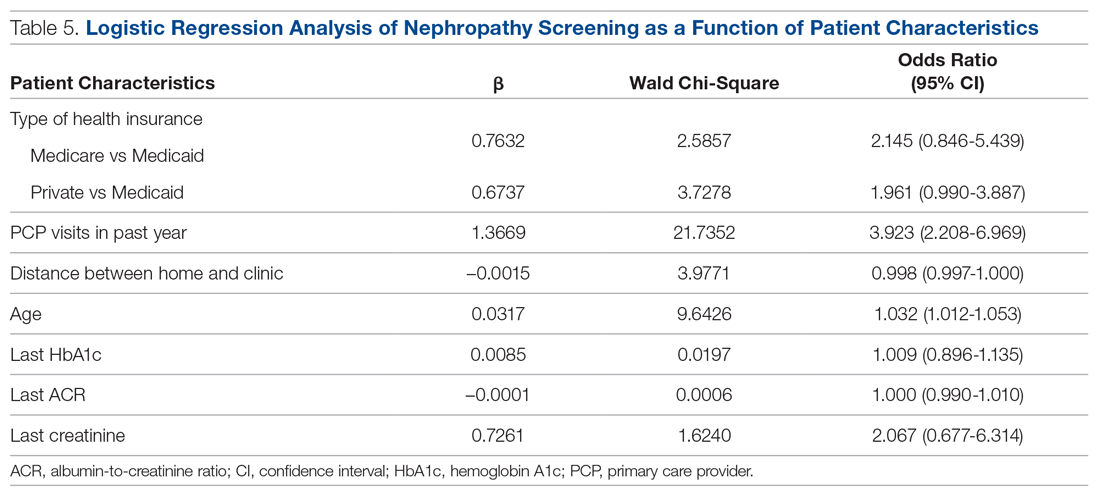
A logistic regression analysis was conducted with nephropathy screening (screened or not screened) as the outcome and 7 patient characteristics as predictors: type of insurance (private, Medicare, or Medicaid), PCP visits in the past 12 months (≤ 3 or > 3), distance in miles of the patient’s residence from the clinic, age, last HbA1c value, last ACR value, and last creatinine value. A test of the full model with all 7 predictors was statistically significant (χ2 (8) = 57.77, P < 0.001). Table 5 shows regression coefficients, Wald statistics, and 95% confidence intervals for odds ratios for each of the 7 predictors. According to the Wald criterion, 3 patient characteristics were significant predictors of nephropathy screening: age, distance between the patient’s home and clinic, and number of PCP visits in the past 12 months. After adjusting for the covariates, there were still significant associations between the nephropathy screening status and age ( χ2(1) = 9.64, P < 0.01); distance between the patient’s home and the clinic (χ2(1) = 3.98, P < 0.05); and the number of PCP visits in the previous year (χ2(1) = 21.74, P < 0.001). With each 1-year increment in age, the odds of completing the nephropathy screening increased by 3.2%. With each 1-mile increase in the distance between the patient’s home and clinic, the odds of completing the nephropathy screening decreased by 0.2%. Patients who visited the clinic more than 3 times in a year were 3.9 times (95% confidence interval, 2.2-7.0) more likely to complete the nephropathy screening than their counterparts who visited fewer than 3 times per year.
In summary, older patients living within about 164 miles of the clinic (ie, within 1 standard deviation from the average miles between patient’s homes and the clinic) who visited their PCP 3 or more times per year were the most likely to be screened.
Discussion
Diabetic nephropathy is a critical issue facing family medicine providers and patients. The morbidity and mortality costs are significant, as diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. While the ADA recommends annual ACR screening in patients with diabetes and prescription of ACE inhibitors or ARBs in patients who qualify, many patients do not receive these interventions, despite following up with a provider.12-15 There is no current literature that indicates the compliance rates in the rural setting. Due to health disparities in the rural setting noted in the literature, it could be hypothesized that these individuals are at high risk of not meeting these screening and treatment recommendations.16,17 Limited access to care and resources, gaps in insurance coverage, and lower health literacy are a few barriers identified in the rural population that may influence whether these measures are met.17
Considering the disease burden of diabetes and its related complications, including nephropathy, consistent screening is necessary to reduce diabetes-related burdens and cost, while also increasing the quality of life for patients with diabetes. All parties must be involved to ensure appropriate compliance and treatment. Our institution’s implementation of quality improvement strategies has key implications for nephropathy screening and treatment efforts in rural settings.
An additional step of having a health care provider (other than the PCP) screen all patients who are not meeting the standard allows for identification of gaps in care. In our quality improvement workflow, the clinical pharmacist screened all patients for candidacy for ACE inhibitor/ARB therapy. While only a small percentage of patients qualified, many of these patients had previously been on therapy and were discontinued for an unknown reason or were stopped due to an acute condition (eg, acute kidney injury) and never restarted after recovery. Other patients required additional education that therapy would be utilized for nephroprotection versus blood pressure management (secondary to an elevated ACR). This highlights the importance of transitions of care and ongoing, intensive education, not only during initial diagnosis but also throughout the disease-state progression.
Utilization of EHRs and telephone outreach are additional aspects of care that can be provided. Our improved rates of compliance with these care interventions parallel findings from previous studies.15,18 Optimization of an institution’s EHR can aid in standardization of care, workflow management, and communication with patients, as well as alert nursing or support staff of screening needs. Techniques such as best practice reminders, patient chart messages, and nursing-entered physician alerts on daily schedules have been shown to increase rates of compliance with nephropathy standards. These findings underscore an additional opportunity for nursing and support staff to be better integrated into care.
Despite the success of this quality improvement initiative, there remain some limitations. The processes we used in this project may not be applicable to every institution and may have limited external validity. Primarily, while these processes may be implemented at some sites, without additional support staff (ie, extra nursing staff, pharmacists) and students to aid in patient outreach, success may be limited due to provider time constraints. Additionally, our workflow process demonstrates significant incorporation of an EHR system for patient outreach. Institutions and/or clinics that heavily rely on paper charts and paper outreach may face barriers with bulk orders (eg, ACR) and messages, interventions that streamlined our population health management. Finally, this project focuses on only 1 aspect of population health management for patients with diabetes. While nephropathy is a critical aspect of caring for individuals with diabetes, this patient outreach does not address retinopathy screening, HbA1c control, or vaccination rates, which are other components of care.
Conclusion
Although this evaluation does not provide insight into why patients were not treated or screened, it demonstrates processes to improve compliance in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Rural health care facilities require an ongoing program of change and evaluation, with the aim to improve the provision of services, increase screening, and encourage team member involvement in health promotion. This study demonstrates that combining team-based interventions with quality control monitoring can significantly improve compliance with recommended nephropathy screening and treatment in rural patients with diabetes at a family medicine clinic.
Corresponding author: Amie M. Ashcraft, West Virginia University, Department of Family Medicine, 1 Medical Center Drive, Box 9152, Morgantown, WV 26506; amashcraft@hsc.wvu.edu.
Financial disclosures: None.
Acknowledgment: The authors thank the faculty, residents, nurses, and clinic staff for their hard work and dedication to this effort: Umama Sadia, Michelle Prestoza, Richard Dattola, Greg Doyle, Dana King, Mike Maroon, Kendra Under, Judy Siebert, Christine Snyder, Rachel Burge, Meagan Gribble, Lisa Metts, Kelsey Samek, Sarah Deavers, Amber Kitzmiller, Angela Lamp, Tina Waldeck, and Andrea Sukeruksa.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National diabetes statistics report. Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. Atlanta, GA: CDC; 2017www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf. Accessed December 20, 2020.
2. American Diabetes Association (ADA). Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2017. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:917-928.
3. Wood L. Trends in national and regional economic distress, 1960-2000. Washington, DC: Appalachian Regional Commission; 2005.
4. Barker L, Crespo R, Gerzoff RB, et al. Residence in a distressed county in Appalachia as a risk factor for diabetes, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2006-2007. Prev Chronic Dis. 2010;7:A104.
5. Barker L, Kirtland KA, Gregg E, et al. Geographic distribution of diagnosed diabetes in the United States: A diabetes belt. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40:434-439.
6. Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, et al. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:164-176.
7. United States Renal Data System (USRDS). Annual data report. Ann Arbor, MI: USRDS; 2018. www.usrds.org/2018/view/Default.aspx. Accessed December 20, 2020.
8. Halverson JA, Bichak G. Underlying socioeconomic factors influencing health disparities in the Appalachian region. Washington, DC: Appalachian Regional Commission; 2008.
9. Shell R, Tudiver F. Barriers to cancer screening by rural Appalachian primary care providers. J Rural Health. 2004;20:368-373.
10. Hatcher J, Dignan MB, Schoenberg N. How do rural health care providers and patients view barriers to colorectal cancer screening? Insights from Appalachian Kentucky. Nurs Clin North Am. 2011;46:181-192.
11. Scott S, McSpirit S. The suspicious, untrusting hillbilly in political-economic contexts: Stereotypes and social trust in the Appalachian coalfields. Pract Anthropol. 2014;36:42-46.
12. Kirkman MS, Williams SR, Caffrey HH, Marrero DG. Impact of a program to improve adherence to diabetes guidelines by primary care physicians. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1946-1951.
13. Byun SH, Ma SH, Jun JK, et al. Screening for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with diabetes: A nationwide survey in Korea. PLoS One. 2013;8:e62991.
14. Flood D, Garcia P, Douglas K, et al. Screening for chronic kidney disease in a community-based diabetes cohort in rural Guatemala: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e019778.
15. Anabtawi A, Mathew LM. Improving compliance with screening of diabetic patients for microalbuminuria in primary care practice. ISRN Endocrinology. 2013:893913.
16. Tonks SA, Makwana S, Salanitro AH, et al. Quality of diabetes mellitus care by rural primary care physicians. J Rural Health. 2012;28:364-371.
17. Douthit N, Kiv S, Dwolatzky T, Biswas S. Exposing some important barriers to health care access in the rural USA. Public Health. 2015;129:611-620.
18. Weber V, Bloom F, Pierdon S, Wood C. Employing the electronic health record to improve diabetes care: a multifaceted intervention in an integrated delivery system. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23:379-382.
From West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV.
Abstract
Objective: To describe the strategies a family medicine clinic in Appalachia utilized to increase nephropathy screening rates as well as to explore the factors predictive of nephropathy screening in patients with diabetes.
Design: This quality improvement project targeted the points in the care process when patients are lost to follow-up for nephropathy screening.
Setting and participants: Patients with diabetes cared for by a primary care provider (PCP) at an academic family medicine practice in Appalachia from January 2018 to November 2018.
Interventions: Bulk orders for albumin-to-creatinine (ACR) testing and urine collection during clinic visit, enhanced patient communication through bulk communication reminders and individual patient outreach, and education of clinic providers.
Measurements: Demographic data and monthly nephropathy screening rates.
Results: The nephropathy screening rate increased by 6.2% during the project. Older patients living closer to the clinic who visited their PCP 3 or more times per year were the most likely to be screened.
Conclusion: Combining team-based interventions with quality control monitoring can significantly improve compliance with recommended nephropathy treatment and screening in rural patients with diabetes at a family medicine clinic.
Keywords: rural; kidney disease; albumin-to-creatinine ratio; electronic health record.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), an estimated 30.3 million people in the United States—about 9.4% of the population—have been diagnosed with diabetes.1 Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States, and it contributes to other leading causes of death: heart disease and stroke.1 Diabetes also is related to high morbidity risk and is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease.1 The total cost of diagnosed diabetes was estimated at $327 billion in direct medical costs and reduced productivity.2
Residents of Appalachia bear a disproportionate burden of diabetes and other related negative health outcomes; these outcomes are influenced by a number of factors, including socioeconomic status, poverty, rurality, and health care access. Rates of chronic disease, such as diabetes, are most pronounced in Appalachia’s most economically distressed counties.3-5 In 2011, the CDC labeled a 644-county area the “diabetes belt,” which included most of Appalachia.6 As a result of this elevated prevalence of diabetes in Appalachia as compared to the rest of the country, complications directly associated with diabetes are more commonly observed in Appalachian residents. One of the most damaging complications is diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic nephropathy results from damage to the microvasculature of the kidney due to inadequately controlled blood glucose. This, in turn, leads to decreased renal function, eventually leading to clinically significant renal disease. The long-term complications associated with nephropathy can include many comorbid conditions, the most serious of which are progression to end-stage renal disease, dialysis requirement, and early mortality. Diabetic nephropathy affects approximately 40% of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.7,8
One way to prevent complications of diabetic nephropathy, in addition to good glycemic control in patients with diabetes, is early and regular screening. Currently, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends yearly screening for diabetic nephropathy in the form of a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) for patients 18 to 75 years of age.2 This screening to detect diabetic nephropathy is recognized as a marker of quality care by many public and private insurance agencies and medical specialty associations, such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Many patients with diabetes are cared for by primary care providers (PCP), and these PCP appointments provide an opportune time to screen and appropriately treat nephropathy. Screening opportunities are often missed, however, due to time constraints and competing health priorities. There are also a number of other factors specific to the Appalachian region that reduce the likelihood of screening for diabetic nephropathy, such as a lack of health insurance, the need to travel long distances to see a PCP, work and household responsibilities, low levels of education and health literacy, and a mistrust of outsiders regarding personal matters, including health.9-11 While nephropathy can have a detrimental impact on patients across populations, it is of particular concern for a state located in the heart of Appalachia, such as West Virginia.
Given the disproportionate burden of diabetes in this region and the potentially severe consequences of undetected nephropathy, clinicians from an academic family medicine clinic in West Virginia undertook a quality improvement project to increase the rate of nephropathy screening and treatment among patients with diabetes. This article describes the intervention strategies the team utilized to increase nephropathy screening and treatment in patients 18 to 75 years of age who met quality measures for nephropathy screening or treatment in the previous 12 months and explores the factors most predictive of nephropathy screening in Appalachian patients in this age group. It also reports the challenges and opportunities encountered and offers suggestions for other providers and clinics attempting to increase their nephropathy screening rates.
Methods
Setting and Study Population
The study population included patients ages 18 to 75 years under the care of providers in an academic family medicine practice in West Virginia who had been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. The study focused on those patients overdue for diabetic nephropathy screening (ie, had not been screened in previous 12 months). The project began in January 2018 with a screening rate of 83.8%. The goal of this project was to increase this compliance metric by at least 5%. The project protocol was submitted to the West Virginia University Institutional Review Board, and, because it is a quality improvement project, permission was given to proceed without a board review.
Interventions
The team identified and implemented several interventions intended to reduce screening barriers and increase the screening rate.
Bulk orders for ACR and urine collection during clinic visits. Prior to initiation of this project, it was left to individual clinic providers to order nephropathy screening for patients with diabetes during a clinic visit; after receiving the order for “random urine microalbumin/creatinine ratio,” patients then had to travel to a lab to provide a urine sample. For this project and moving forward, the team changed to the procedure of initiating bulk ACR orders and collecting urine samples during clinic visits from all patients ages 18 to 75 years who have diabetes.
Bulk communication reminders. Since many patients with diabetes may not have realized they were overdue for nephropathy screening, the team began sending out bulk communication reminders through either the institution’s electronic health record (EHR; MyChart) or postal service–delivered physical letters (according to patient communication preferences) to remind patients that they were due for screening and to encourage them to schedule an appointment or keep a previously scheduled appointment with their PCP.
Individual patient outreach. A team of pharmacy students led by a licensed pharmacist in the family medicine clinic contacted patients overdue for screening even after bulk communication reminders went out. The students telephoned patients 2 to 3 months following the bulk communication. The students obtained an updated list of patients with diabetes ages 18 to 75 years from an EHR quality report. They began by prescreening the patients on the overdue list for potential candidacy for an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Screening for candidacy included evaluation of recent blood pressure readings, electrolytes (ie, basic metabolic panel), and ACR. If the students determined a patient was a candidate, they presented the patient to the preceptor for verification and then reached out to the provider with a recommendation. If the provider agreed, the student contacted the patient by telephone for medication counseling and education. The remaining patients determined not to be candidates for ACE inhibitors or ARBs were contacted by the pharmacy students by telephone to remind them that laboratory work was pending. Up to 3 phone call attempts were made before patients were determined to be unreachable. Students left voice mails with generic reminders if a patient could not be reached. If a patient answered, the student provided a reminder but also reviewed indications for lab work, the reason why the provider wished for follow-up, and updated lab hours. Students also followed up with the results of the work-up, as appropriate. During this outreach process, the student team encountered a number of patients who had moved or changed to a PCP outside of the family medicine clinic. In these cases, the EHR was updated and those patients were removed from the list of patients altogether.
Education of clinic providers. Clinic providers were educated during faculty and resident meetings and didactic learning sessions on identifying patients within the EHR who are due for nephropathy screening. They also received instruction on how to update the EHR to reflect completed screenings.
Data Analysis
All analyses in this study were conducted using SAS (version 9.4, 2013, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC). Descriptive analyses were conducted to summarize basic patient demographic information. To compare patients screened within the previous 12 months to those patients overdue for screening, 2-sample t-tests were used to examine differences in patients’ age, HbA1c, ACR, and creatinine level and the distance (in miles) between the patient’s home and the clinic. Chi-square analyses were used to examine the relationship between whether a patient was recently screened for nephropathy and the patient’s insurance, number of patient visits in the previous 12 months, and provider level. Logistic regression analyses were conducted to control for covariates and to explore which factors were most predictive of nephropathy screening. All tests were 2-tailed, and P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient Characteristics
There were 1676 family medicine clinic patients with diabetes between 18 and 75 years of age (Table 1 and Table 2). Of the total sample, 1489 (88.8%) had completed screening for nephropathy in the 12 months prior to evaluation, and 67.5%, 23.7%, and 8.8% of patients had private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid, respectively.
The mean (SD) age of the patients was 56.3 (11.9) years. The mean distance between the patient’s home and the clinic was 26.6 (76.8) miles. The mean number of visits was 3.6 (2.9) per year, and 43.0% of the patientvisited the clinic more than 3 times in a year. The mean values for HbA1c (%), creatinine (g/mol), and ACR (mg/g) were 7.7 (1.9), 1.0 (0.7), and 9.4 (31.4), respectively.
Screening of Patients for Nephropathy
Patients with Medicare and private insurance were more likely to have completed the nephropathy screening than those with Medicaid (92.5% versus 88.8% versus 82.8%, P = 0.004; Table 3 and Table 4).
Changes in Screening Rate
The practice-wide screening rate was 83.8% at the start of this project in January 2018. The screening rate steadily increased throughout 2018, reaching 90.3% in August 2018, and then leveled off around 90% when the project was concluded at the end of November 2018 (Figure). As an added benefit of the increased screening rates, a number of patients were initiated on an ACE inhibitor or ARB based on the team’s screening efforts.
Predictors of Nephropathy Screening
A logistic regression analysis was conducted with nephropathy screening (screened or not screened) as the outcome and 7 patient characteristics as predictors: type of insurance (private, Medicare, or Medicaid), PCP visits in the past 12 months (≤ 3 or > 3), distance in miles of the patient’s residence from the clinic, age, last HbA1c value, last ACR value, and last creatinine value. A test of the full model with all 7 predictors was statistically significant (χ2 (8) = 57.77, P < 0.001). Table 5 shows regression coefficients, Wald statistics, and 95% confidence intervals for odds ratios for each of the 7 predictors. According to the Wald criterion, 3 patient characteristics were significant predictors of nephropathy screening: age, distance between the patient’s home and clinic, and number of PCP visits in the past 12 months. After adjusting for the covariates, there were still significant associations between the nephropathy screening status and age ( χ2(1) = 9.64, P < 0.01); distance between the patient’s home and the clinic (χ2(1) = 3.98, P < 0.05); and the number of PCP visits in the previous year (χ2(1) = 21.74, P < 0.001). With each 1-year increment in age, the odds of completing the nephropathy screening increased by 3.2%. With each 1-mile increase in the distance between the patient’s home and clinic, the odds of completing the nephropathy screening decreased by 0.2%. Patients who visited the clinic more than 3 times in a year were 3.9 times (95% confidence interval, 2.2-7.0) more likely to complete the nephropathy screening than their counterparts who visited fewer than 3 times per year.
In summary, older patients living within about 164 miles of the clinic (ie, within 1 standard deviation from the average miles between patient’s homes and the clinic) who visited their PCP 3 or more times per year were the most likely to be screened.
Discussion
Diabetic nephropathy is a critical issue facing family medicine providers and patients. The morbidity and mortality costs are significant, as diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. While the ADA recommends annual ACR screening in patients with diabetes and prescription of ACE inhibitors or ARBs in patients who qualify, many patients do not receive these interventions, despite following up with a provider.12-15 There is no current literature that indicates the compliance rates in the rural setting. Due to health disparities in the rural setting noted in the literature, it could be hypothesized that these individuals are at high risk of not meeting these screening and treatment recommendations.16,17 Limited access to care and resources, gaps in insurance coverage, and lower health literacy are a few barriers identified in the rural population that may influence whether these measures are met.17
Considering the disease burden of diabetes and its related complications, including nephropathy, consistent screening is necessary to reduce diabetes-related burdens and cost, while also increasing the quality of life for patients with diabetes. All parties must be involved to ensure appropriate compliance and treatment. Our institution’s implementation of quality improvement strategies has key implications for nephropathy screening and treatment efforts in rural settings.
An additional step of having a health care provider (other than the PCP) screen all patients who are not meeting the standard allows for identification of gaps in care. In our quality improvement workflow, the clinical pharmacist screened all patients for candidacy for ACE inhibitor/ARB therapy. While only a small percentage of patients qualified, many of these patients had previously been on therapy and were discontinued for an unknown reason or were stopped due to an acute condition (eg, acute kidney injury) and never restarted after recovery. Other patients required additional education that therapy would be utilized for nephroprotection versus blood pressure management (secondary to an elevated ACR). This highlights the importance of transitions of care and ongoing, intensive education, not only during initial diagnosis but also throughout the disease-state progression.
Utilization of EHRs and telephone outreach are additional aspects of care that can be provided. Our improved rates of compliance with these care interventions parallel findings from previous studies.15,18 Optimization of an institution’s EHR can aid in standardization of care, workflow management, and communication with patients, as well as alert nursing or support staff of screening needs. Techniques such as best practice reminders, patient chart messages, and nursing-entered physician alerts on daily schedules have been shown to increase rates of compliance with nephropathy standards. These findings underscore an additional opportunity for nursing and support staff to be better integrated into care.
Despite the success of this quality improvement initiative, there remain some limitations. The processes we used in this project may not be applicable to every institution and may have limited external validity. Primarily, while these processes may be implemented at some sites, without additional support staff (ie, extra nursing staff, pharmacists) and students to aid in patient outreach, success may be limited due to provider time constraints. Additionally, our workflow process demonstrates significant incorporation of an EHR system for patient outreach. Institutions and/or clinics that heavily rely on paper charts and paper outreach may face barriers with bulk orders (eg, ACR) and messages, interventions that streamlined our population health management. Finally, this project focuses on only 1 aspect of population health management for patients with diabetes. While nephropathy is a critical aspect of caring for individuals with diabetes, this patient outreach does not address retinopathy screening, HbA1c control, or vaccination rates, which are other components of care.
Conclusion
Although this evaluation does not provide insight into why patients were not treated or screened, it demonstrates processes to improve compliance in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Rural health care facilities require an ongoing program of change and evaluation, with the aim to improve the provision of services, increase screening, and encourage team member involvement in health promotion. This study demonstrates that combining team-based interventions with quality control monitoring can significantly improve compliance with recommended nephropathy screening and treatment in rural patients with diabetes at a family medicine clinic.
Corresponding author: Amie M. Ashcraft, West Virginia University, Department of Family Medicine, 1 Medical Center Drive, Box 9152, Morgantown, WV 26506; amashcraft@hsc.wvu.edu.
Financial disclosures: None.
Acknowledgment: The authors thank the faculty, residents, nurses, and clinic staff for their hard work and dedication to this effort: Umama Sadia, Michelle Prestoza, Richard Dattola, Greg Doyle, Dana King, Mike Maroon, Kendra Under, Judy Siebert, Christine Snyder, Rachel Burge, Meagan Gribble, Lisa Metts, Kelsey Samek, Sarah Deavers, Amber Kitzmiller, Angela Lamp, Tina Waldeck, and Andrea Sukeruksa.
From West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV.
Abstract
Objective: To describe the strategies a family medicine clinic in Appalachia utilized to increase nephropathy screening rates as well as to explore the factors predictive of nephropathy screening in patients with diabetes.
Design: This quality improvement project targeted the points in the care process when patients are lost to follow-up for nephropathy screening.
Setting and participants: Patients with diabetes cared for by a primary care provider (PCP) at an academic family medicine practice in Appalachia from January 2018 to November 2018.
Interventions: Bulk orders for albumin-to-creatinine (ACR) testing and urine collection during clinic visit, enhanced patient communication through bulk communication reminders and individual patient outreach, and education of clinic providers.
Measurements: Demographic data and monthly nephropathy screening rates.
Results: The nephropathy screening rate increased by 6.2% during the project. Older patients living closer to the clinic who visited their PCP 3 or more times per year were the most likely to be screened.
Conclusion: Combining team-based interventions with quality control monitoring can significantly improve compliance with recommended nephropathy treatment and screening in rural patients with diabetes at a family medicine clinic.
Keywords: rural; kidney disease; albumin-to-creatinine ratio; electronic health record.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), an estimated 30.3 million people in the United States—about 9.4% of the population—have been diagnosed with diabetes.1 Diabetes is the seventh leading cause of death in the United States, and it contributes to other leading causes of death: heart disease and stroke.1 Diabetes also is related to high morbidity risk and is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease.1 The total cost of diagnosed diabetes was estimated at $327 billion in direct medical costs and reduced productivity.2
Residents of Appalachia bear a disproportionate burden of diabetes and other related negative health outcomes; these outcomes are influenced by a number of factors, including socioeconomic status, poverty, rurality, and health care access. Rates of chronic disease, such as diabetes, are most pronounced in Appalachia’s most economically distressed counties.3-5 In 2011, the CDC labeled a 644-county area the “diabetes belt,” which included most of Appalachia.6 As a result of this elevated prevalence of diabetes in Appalachia as compared to the rest of the country, complications directly associated with diabetes are more commonly observed in Appalachian residents. One of the most damaging complications is diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic nephropathy results from damage to the microvasculature of the kidney due to inadequately controlled blood glucose. This, in turn, leads to decreased renal function, eventually leading to clinically significant renal disease. The long-term complications associated with nephropathy can include many comorbid conditions, the most serious of which are progression to end-stage renal disease, dialysis requirement, and early mortality. Diabetic nephropathy affects approximately 40% of patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.7,8
One way to prevent complications of diabetic nephropathy, in addition to good glycemic control in patients with diabetes, is early and regular screening. Currently, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends yearly screening for diabetic nephropathy in the form of a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) for patients 18 to 75 years of age.2 This screening to detect diabetic nephropathy is recognized as a marker of quality care by many public and private insurance agencies and medical specialty associations, such as the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Many patients with diabetes are cared for by primary care providers (PCP), and these PCP appointments provide an opportune time to screen and appropriately treat nephropathy. Screening opportunities are often missed, however, due to time constraints and competing health priorities. There are also a number of other factors specific to the Appalachian region that reduce the likelihood of screening for diabetic nephropathy, such as a lack of health insurance, the need to travel long distances to see a PCP, work and household responsibilities, low levels of education and health literacy, and a mistrust of outsiders regarding personal matters, including health.9-11 While nephropathy can have a detrimental impact on patients across populations, it is of particular concern for a state located in the heart of Appalachia, such as West Virginia.
Given the disproportionate burden of diabetes in this region and the potentially severe consequences of undetected nephropathy, clinicians from an academic family medicine clinic in West Virginia undertook a quality improvement project to increase the rate of nephropathy screening and treatment among patients with diabetes. This article describes the intervention strategies the team utilized to increase nephropathy screening and treatment in patients 18 to 75 years of age who met quality measures for nephropathy screening or treatment in the previous 12 months and explores the factors most predictive of nephropathy screening in Appalachian patients in this age group. It also reports the challenges and opportunities encountered and offers suggestions for other providers and clinics attempting to increase their nephropathy screening rates.
Methods
Setting and Study Population
The study population included patients ages 18 to 75 years under the care of providers in an academic family medicine practice in West Virginia who had been diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. The study focused on those patients overdue for diabetic nephropathy screening (ie, had not been screened in previous 12 months). The project began in January 2018 with a screening rate of 83.8%. The goal of this project was to increase this compliance metric by at least 5%. The project protocol was submitted to the West Virginia University Institutional Review Board, and, because it is a quality improvement project, permission was given to proceed without a board review.
Interventions
The team identified and implemented several interventions intended to reduce screening barriers and increase the screening rate.
Bulk orders for ACR and urine collection during clinic visits. Prior to initiation of this project, it was left to individual clinic providers to order nephropathy screening for patients with diabetes during a clinic visit; after receiving the order for “random urine microalbumin/creatinine ratio,” patients then had to travel to a lab to provide a urine sample. For this project and moving forward, the team changed to the procedure of initiating bulk ACR orders and collecting urine samples during clinic visits from all patients ages 18 to 75 years who have diabetes.
Bulk communication reminders. Since many patients with diabetes may not have realized they were overdue for nephropathy screening, the team began sending out bulk communication reminders through either the institution’s electronic health record (EHR; MyChart) or postal service–delivered physical letters (according to patient communication preferences) to remind patients that they were due for screening and to encourage them to schedule an appointment or keep a previously scheduled appointment with their PCP.
Individual patient outreach. A team of pharmacy students led by a licensed pharmacist in the family medicine clinic contacted patients overdue for screening even after bulk communication reminders went out. The students telephoned patients 2 to 3 months following the bulk communication. The students obtained an updated list of patients with diabetes ages 18 to 75 years from an EHR quality report. They began by prescreening the patients on the overdue list for potential candidacy for an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). Screening for candidacy included evaluation of recent blood pressure readings, electrolytes (ie, basic metabolic panel), and ACR. If the students determined a patient was a candidate, they presented the patient to the preceptor for verification and then reached out to the provider with a recommendation. If the provider agreed, the student contacted the patient by telephone for medication counseling and education. The remaining patients determined not to be candidates for ACE inhibitors or ARBs were contacted by the pharmacy students by telephone to remind them that laboratory work was pending. Up to 3 phone call attempts were made before patients were determined to be unreachable. Students left voice mails with generic reminders if a patient could not be reached. If a patient answered, the student provided a reminder but also reviewed indications for lab work, the reason why the provider wished for follow-up, and updated lab hours. Students also followed up with the results of the work-up, as appropriate. During this outreach process, the student team encountered a number of patients who had moved or changed to a PCP outside of the family medicine clinic. In these cases, the EHR was updated and those patients were removed from the list of patients altogether.
Education of clinic providers. Clinic providers were educated during faculty and resident meetings and didactic learning sessions on identifying patients within the EHR who are due for nephropathy screening. They also received instruction on how to update the EHR to reflect completed screenings.
Data Analysis
All analyses in this study were conducted using SAS (version 9.4, 2013, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC). Descriptive analyses were conducted to summarize basic patient demographic information. To compare patients screened within the previous 12 months to those patients overdue for screening, 2-sample t-tests were used to examine differences in patients’ age, HbA1c, ACR, and creatinine level and the distance (in miles) between the patient’s home and the clinic. Chi-square analyses were used to examine the relationship between whether a patient was recently screened for nephropathy and the patient’s insurance, number of patient visits in the previous 12 months, and provider level. Logistic regression analyses were conducted to control for covariates and to explore which factors were most predictive of nephropathy screening. All tests were 2-tailed, and P values less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient Characteristics
There were 1676 family medicine clinic patients with diabetes between 18 and 75 years of age (Table 1 and Table 2). Of the total sample, 1489 (88.8%) had completed screening for nephropathy in the 12 months prior to evaluation, and 67.5%, 23.7%, and 8.8% of patients had private insurance, Medicare, and Medicaid, respectively.
The mean (SD) age of the patients was 56.3 (11.9) years. The mean distance between the patient’s home and the clinic was 26.6 (76.8) miles. The mean number of visits was 3.6 (2.9) per year, and 43.0% of the patientvisited the clinic more than 3 times in a year. The mean values for HbA1c (%), creatinine (g/mol), and ACR (mg/g) were 7.7 (1.9), 1.0 (0.7), and 9.4 (31.4), respectively.
Screening of Patients for Nephropathy
Patients with Medicare and private insurance were more likely to have completed the nephropathy screening than those with Medicaid (92.5% versus 88.8% versus 82.8%, P = 0.004; Table 3 and Table 4).
Changes in Screening Rate
The practice-wide screening rate was 83.8% at the start of this project in January 2018. The screening rate steadily increased throughout 2018, reaching 90.3% in August 2018, and then leveled off around 90% when the project was concluded at the end of November 2018 (Figure). As an added benefit of the increased screening rates, a number of patients were initiated on an ACE inhibitor or ARB based on the team’s screening efforts.
Predictors of Nephropathy Screening
A logistic regression analysis was conducted with nephropathy screening (screened or not screened) as the outcome and 7 patient characteristics as predictors: type of insurance (private, Medicare, or Medicaid), PCP visits in the past 12 months (≤ 3 or > 3), distance in miles of the patient’s residence from the clinic, age, last HbA1c value, last ACR value, and last creatinine value. A test of the full model with all 7 predictors was statistically significant (χ2 (8) = 57.77, P < 0.001). Table 5 shows regression coefficients, Wald statistics, and 95% confidence intervals for odds ratios for each of the 7 predictors. According to the Wald criterion, 3 patient characteristics were significant predictors of nephropathy screening: age, distance between the patient’s home and clinic, and number of PCP visits in the past 12 months. After adjusting for the covariates, there were still significant associations between the nephropathy screening status and age ( χ2(1) = 9.64, P < 0.01); distance between the patient’s home and the clinic (χ2(1) = 3.98, P < 0.05); and the number of PCP visits in the previous year (χ2(1) = 21.74, P < 0.001). With each 1-year increment in age, the odds of completing the nephropathy screening increased by 3.2%. With each 1-mile increase in the distance between the patient’s home and clinic, the odds of completing the nephropathy screening decreased by 0.2%. Patients who visited the clinic more than 3 times in a year were 3.9 times (95% confidence interval, 2.2-7.0) more likely to complete the nephropathy screening than their counterparts who visited fewer than 3 times per year.
In summary, older patients living within about 164 miles of the clinic (ie, within 1 standard deviation from the average miles between patient’s homes and the clinic) who visited their PCP 3 or more times per year were the most likely to be screened.
Discussion
Diabetic nephropathy is a critical issue facing family medicine providers and patients. The morbidity and mortality costs are significant, as diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease. While the ADA recommends annual ACR screening in patients with diabetes and prescription of ACE inhibitors or ARBs in patients who qualify, many patients do not receive these interventions, despite following up with a provider.12-15 There is no current literature that indicates the compliance rates in the rural setting. Due to health disparities in the rural setting noted in the literature, it could be hypothesized that these individuals are at high risk of not meeting these screening and treatment recommendations.16,17 Limited access to care and resources, gaps in insurance coverage, and lower health literacy are a few barriers identified in the rural population that may influence whether these measures are met.17
Considering the disease burden of diabetes and its related complications, including nephropathy, consistent screening is necessary to reduce diabetes-related burdens and cost, while also increasing the quality of life for patients with diabetes. All parties must be involved to ensure appropriate compliance and treatment. Our institution’s implementation of quality improvement strategies has key implications for nephropathy screening and treatment efforts in rural settings.
An additional step of having a health care provider (other than the PCP) screen all patients who are not meeting the standard allows for identification of gaps in care. In our quality improvement workflow, the clinical pharmacist screened all patients for candidacy for ACE inhibitor/ARB therapy. While only a small percentage of patients qualified, many of these patients had previously been on therapy and were discontinued for an unknown reason or were stopped due to an acute condition (eg, acute kidney injury) and never restarted after recovery. Other patients required additional education that therapy would be utilized for nephroprotection versus blood pressure management (secondary to an elevated ACR). This highlights the importance of transitions of care and ongoing, intensive education, not only during initial diagnosis but also throughout the disease-state progression.
Utilization of EHRs and telephone outreach are additional aspects of care that can be provided. Our improved rates of compliance with these care interventions parallel findings from previous studies.15,18 Optimization of an institution’s EHR can aid in standardization of care, workflow management, and communication with patients, as well as alert nursing or support staff of screening needs. Techniques such as best practice reminders, patient chart messages, and nursing-entered physician alerts on daily schedules have been shown to increase rates of compliance with nephropathy standards. These findings underscore an additional opportunity for nursing and support staff to be better integrated into care.
Despite the success of this quality improvement initiative, there remain some limitations. The processes we used in this project may not be applicable to every institution and may have limited external validity. Primarily, while these processes may be implemented at some sites, without additional support staff (ie, extra nursing staff, pharmacists) and students to aid in patient outreach, success may be limited due to provider time constraints. Additionally, our workflow process demonstrates significant incorporation of an EHR system for patient outreach. Institutions and/or clinics that heavily rely on paper charts and paper outreach may face barriers with bulk orders (eg, ACR) and messages, interventions that streamlined our population health management. Finally, this project focuses on only 1 aspect of population health management for patients with diabetes. While nephropathy is a critical aspect of caring for individuals with diabetes, this patient outreach does not address retinopathy screening, HbA1c control, or vaccination rates, which are other components of care.
Conclusion
Although this evaluation does not provide insight into why patients were not treated or screened, it demonstrates processes to improve compliance in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Rural health care facilities require an ongoing program of change and evaluation, with the aim to improve the provision of services, increase screening, and encourage team member involvement in health promotion. This study demonstrates that combining team-based interventions with quality control monitoring can significantly improve compliance with recommended nephropathy screening and treatment in rural patients with diabetes at a family medicine clinic.
Corresponding author: Amie M. Ashcraft, West Virginia University, Department of Family Medicine, 1 Medical Center Drive, Box 9152, Morgantown, WV 26506; amashcraft@hsc.wvu.edu.
Financial disclosures: None.
Acknowledgment: The authors thank the faculty, residents, nurses, and clinic staff for their hard work and dedication to this effort: Umama Sadia, Michelle Prestoza, Richard Dattola, Greg Doyle, Dana King, Mike Maroon, Kendra Under, Judy Siebert, Christine Snyder, Rachel Burge, Meagan Gribble, Lisa Metts, Kelsey Samek, Sarah Deavers, Amber Kitzmiller, Angela Lamp, Tina Waldeck, and Andrea Sukeruksa.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National diabetes statistics report. Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. Atlanta, GA: CDC; 2017www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf. Accessed December 20, 2020.
2. American Diabetes Association (ADA). Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2017. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:917-928.
3. Wood L. Trends in national and regional economic distress, 1960-2000. Washington, DC: Appalachian Regional Commission; 2005.
4. Barker L, Crespo R, Gerzoff RB, et al. Residence in a distressed county in Appalachia as a risk factor for diabetes, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2006-2007. Prev Chronic Dis. 2010;7:A104.
5. Barker L, Kirtland KA, Gregg E, et al. Geographic distribution of diagnosed diabetes in the United States: A diabetes belt. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40:434-439.
6. Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, et al. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:164-176.
7. United States Renal Data System (USRDS). Annual data report. Ann Arbor, MI: USRDS; 2018. www.usrds.org/2018/view/Default.aspx. Accessed December 20, 2020.
8. Halverson JA, Bichak G. Underlying socioeconomic factors influencing health disparities in the Appalachian region. Washington, DC: Appalachian Regional Commission; 2008.
9. Shell R, Tudiver F. Barriers to cancer screening by rural Appalachian primary care providers. J Rural Health. 2004;20:368-373.
10. Hatcher J, Dignan MB, Schoenberg N. How do rural health care providers and patients view barriers to colorectal cancer screening? Insights from Appalachian Kentucky. Nurs Clin North Am. 2011;46:181-192.
11. Scott S, McSpirit S. The suspicious, untrusting hillbilly in political-economic contexts: Stereotypes and social trust in the Appalachian coalfields. Pract Anthropol. 2014;36:42-46.
12. Kirkman MS, Williams SR, Caffrey HH, Marrero DG. Impact of a program to improve adherence to diabetes guidelines by primary care physicians. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1946-1951.
13. Byun SH, Ma SH, Jun JK, et al. Screening for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with diabetes: A nationwide survey in Korea. PLoS One. 2013;8:e62991.
14. Flood D, Garcia P, Douglas K, et al. Screening for chronic kidney disease in a community-based diabetes cohort in rural Guatemala: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e019778.
15. Anabtawi A, Mathew LM. Improving compliance with screening of diabetic patients for microalbuminuria in primary care practice. ISRN Endocrinology. 2013:893913.
16. Tonks SA, Makwana S, Salanitro AH, et al. Quality of diabetes mellitus care by rural primary care physicians. J Rural Health. 2012;28:364-371.
17. Douthit N, Kiv S, Dwolatzky T, Biswas S. Exposing some important barriers to health care access in the rural USA. Public Health. 2015;129:611-620.
18. Weber V, Bloom F, Pierdon S, Wood C. Employing the electronic health record to improve diabetes care: a multifaceted intervention in an integrated delivery system. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23:379-382.
1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). National diabetes statistics report. Estimates of diabetes and its burden in the United States. Atlanta, GA: CDC; 2017www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-statistics-report.pdf. Accessed December 20, 2020.
2. American Diabetes Association (ADA). Economic costs of diabetes in the U.S. in 2017. Diabetes Care. 2018;41:917-928.
3. Wood L. Trends in national and regional economic distress, 1960-2000. Washington, DC: Appalachian Regional Commission; 2005.
4. Barker L, Crespo R, Gerzoff RB, et al. Residence in a distressed county in Appalachia as a risk factor for diabetes, Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2006-2007. Prev Chronic Dis. 2010;7:A104.
5. Barker L, Kirtland KA, Gregg E, et al. Geographic distribution of diagnosed diabetes in the United States: A diabetes belt. Am J Prev Med. 2011;40:434-439.
6. Gross JL, de Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP, et al. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:164-176.
7. United States Renal Data System (USRDS). Annual data report. Ann Arbor, MI: USRDS; 2018. www.usrds.org/2018/view/Default.aspx. Accessed December 20, 2020.
8. Halverson JA, Bichak G. Underlying socioeconomic factors influencing health disparities in the Appalachian region. Washington, DC: Appalachian Regional Commission; 2008.
9. Shell R, Tudiver F. Barriers to cancer screening by rural Appalachian primary care providers. J Rural Health. 2004;20:368-373.
10. Hatcher J, Dignan MB, Schoenberg N. How do rural health care providers and patients view barriers to colorectal cancer screening? Insights from Appalachian Kentucky. Nurs Clin North Am. 2011;46:181-192.
11. Scott S, McSpirit S. The suspicious, untrusting hillbilly in political-economic contexts: Stereotypes and social trust in the Appalachian coalfields. Pract Anthropol. 2014;36:42-46.
12. Kirkman MS, Williams SR, Caffrey HH, Marrero DG. Impact of a program to improve adherence to diabetes guidelines by primary care physicians. Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1946-1951.
13. Byun SH, Ma SH, Jun JK, et al. Screening for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy in patients with diabetes: A nationwide survey in Korea. PLoS One. 2013;8:e62991.
14. Flood D, Garcia P, Douglas K, et al. Screening for chronic kidney disease in a community-based diabetes cohort in rural Guatemala: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2018;8:e019778.
15. Anabtawi A, Mathew LM. Improving compliance with screening of diabetic patients for microalbuminuria in primary care practice. ISRN Endocrinology. 2013:893913.
16. Tonks SA, Makwana S, Salanitro AH, et al. Quality of diabetes mellitus care by rural primary care physicians. J Rural Health. 2012;28:364-371.
17. Douthit N, Kiv S, Dwolatzky T, Biswas S. Exposing some important barriers to health care access in the rural USA. Public Health. 2015;129:611-620.
18. Weber V, Bloom F, Pierdon S, Wood C. Employing the electronic health record to improve diabetes care: a multifaceted intervention in an integrated delivery system. J Gen Intern Med. 2008;23:379-382.
Children with resistant UTIs unexpectedly may respond to discordant antibiotics
Children with urinary tract infections (UTIs) may improve clinically, and pyuria may resolve, during empiric treatment with an antibiotic that turns out to be discordant, according a retrospective study in Pediatrics.
“The low rate of care escalation and high rate of clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics suggests that, for most patients, it would be reasonable to continue current empiric antibiotic practices until urine culture sensitivities return,” said first author Marie E. Wang, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
The researchers examined the initial clinical response and escalation of care for 316 children with UTIs who received therapy to which the infecting isolate was not susceptible. The study included patients who had infections that were resistant to third-generation cephalosporins – that is, urinalysis found that the infections were not susceptible to ceftriaxone or cefotaxime in vitro. Before the resistant organisms were identified, however, the patients were started on discordant antibiotics.
Escalation of care was uncommon
The patients had a median age of 2.4 years, and 78% were girls. Approximately 90% were started on a cephalosporin, and about 65% received a first-generation cephalosporin. Patients presented during 2012-2017 to one of five children’s hospitals or to a large managed care organization with 10 hospitals in the United States. The investigators defined care escalation as a visit to the emergency department, hospitalization, or transfer to the ICU.
In all, seven patients (2%) had escalation of care on discordant antibiotics. Four children visited an emergency department without hospitalization, and three children were hospitalized because of persistent symptoms.
Among 230 cases for which the researchers had data about clinical response at a median follow-up of 3 days, 84% “had overall clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics,” the authors said.
For 22 children who had repeat urine testing while on discordant antibiotics, 53% had resolution of pyuria, and 32% had improvement of pyuria, whereas 16% did not have improvement. Of the three patients without improvement, one had no change, and two had worsening.
Of 17 patients who had a repeat urine culture on discordant therapy, 65% had a negative repeat culture, and 18% grew the same pathogen with a decreased colony count. Two patients had a colony count that remained unchanged, and one patient had an increased colony count.
Small studies outside the United States have reported similar results, the researchers noted. Spontaneous resolution of UTIs or antibiotics reaching a sufficient concentration in the urine and renal parenchyma to achieve a clinical response are possible explanations for the findings, they wrote.
“Few children required escalation of care and most experienced initial clinical improvement,” noted Dr. Wang and colleagues. “Furthermore, in the small group of children that underwent repeat urine testing while on discordant therapy, most had resolution or improvement in pyuria and sterilization of their urine cultures. Our findings suggest that Additionally, given that these patients initially received what would generally be considered inadequate treatment, our findings may provide some insight into the natural history of UTIs and/or trigger further investigation into the relationship between in vitro urine culture susceptibilities and in vivo clinical response to treatment.”
‘Caution is needed’
The study “highlights an intriguing observation about children with UTIs unexpectedly responding to discordant antibiotic therapy,” Tej K. Mattoo, MD, and Basim I. Asmar, MD, wrote in an accompanying commentary.(doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3512). Dr. Mattoo and Dr. Asmar, a pediatric nephrologist and a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, respectively, at Wayne State University and affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Michigan, both in Detroit.
In an inpatient setting, it may be easy for physicians to reassess patients “once urine culture results reveal resistance to the treating antibiotic,” they noted. In an ambulatory setting, however, “it is likely that some patients will receive a full course of an antibiotic that does not have in vitro activity against the urinary pathogen.”
Physicians have a responsibility to use antibiotics judiciously, they said. Widely accepted principles include avoiding repeated courses of antibiotics, diagnosing UTIs appropriately, and not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria.
The study had no external funding. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang ME et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jan 17. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1608.
This article was updated 2/4/2020.
Children with urinary tract infections (UTIs) may improve clinically, and pyuria may resolve, during empiric treatment with an antibiotic that turns out to be discordant, according a retrospective study in Pediatrics.
“The low rate of care escalation and high rate of clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics suggests that, for most patients, it would be reasonable to continue current empiric antibiotic practices until urine culture sensitivities return,” said first author Marie E. Wang, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
The researchers examined the initial clinical response and escalation of care for 316 children with UTIs who received therapy to which the infecting isolate was not susceptible. The study included patients who had infections that were resistant to third-generation cephalosporins – that is, urinalysis found that the infections were not susceptible to ceftriaxone or cefotaxime in vitro. Before the resistant organisms were identified, however, the patients were started on discordant antibiotics.
Escalation of care was uncommon
The patients had a median age of 2.4 years, and 78% were girls. Approximately 90% were started on a cephalosporin, and about 65% received a first-generation cephalosporin. Patients presented during 2012-2017 to one of five children’s hospitals or to a large managed care organization with 10 hospitals in the United States. The investigators defined care escalation as a visit to the emergency department, hospitalization, or transfer to the ICU.
In all, seven patients (2%) had escalation of care on discordant antibiotics. Four children visited an emergency department without hospitalization, and three children were hospitalized because of persistent symptoms.
Among 230 cases for which the researchers had data about clinical response at a median follow-up of 3 days, 84% “had overall clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics,” the authors said.
For 22 children who had repeat urine testing while on discordant antibiotics, 53% had resolution of pyuria, and 32% had improvement of pyuria, whereas 16% did not have improvement. Of the three patients without improvement, one had no change, and two had worsening.
Of 17 patients who had a repeat urine culture on discordant therapy, 65% had a negative repeat culture, and 18% grew the same pathogen with a decreased colony count. Two patients had a colony count that remained unchanged, and one patient had an increased colony count.
Small studies outside the United States have reported similar results, the researchers noted. Spontaneous resolution of UTIs or antibiotics reaching a sufficient concentration in the urine and renal parenchyma to achieve a clinical response are possible explanations for the findings, they wrote.
“Few children required escalation of care and most experienced initial clinical improvement,” noted Dr. Wang and colleagues. “Furthermore, in the small group of children that underwent repeat urine testing while on discordant therapy, most had resolution or improvement in pyuria and sterilization of their urine cultures. Our findings suggest that Additionally, given that these patients initially received what would generally be considered inadequate treatment, our findings may provide some insight into the natural history of UTIs and/or trigger further investigation into the relationship between in vitro urine culture susceptibilities and in vivo clinical response to treatment.”
‘Caution is needed’
The study “highlights an intriguing observation about children with UTIs unexpectedly responding to discordant antibiotic therapy,” Tej K. Mattoo, MD, and Basim I. Asmar, MD, wrote in an accompanying commentary.(doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3512). Dr. Mattoo and Dr. Asmar, a pediatric nephrologist and a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, respectively, at Wayne State University and affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Michigan, both in Detroit.
In an inpatient setting, it may be easy for physicians to reassess patients “once urine culture results reveal resistance to the treating antibiotic,” they noted. In an ambulatory setting, however, “it is likely that some patients will receive a full course of an antibiotic that does not have in vitro activity against the urinary pathogen.”
Physicians have a responsibility to use antibiotics judiciously, they said. Widely accepted principles include avoiding repeated courses of antibiotics, diagnosing UTIs appropriately, and not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria.
The study had no external funding. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang ME et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jan 17. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1608.
This article was updated 2/4/2020.
Children with urinary tract infections (UTIs) may improve clinically, and pyuria may resolve, during empiric treatment with an antibiotic that turns out to be discordant, according a retrospective study in Pediatrics.
“The low rate of care escalation and high rate of clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics suggests that, for most patients, it would be reasonable to continue current empiric antibiotic practices until urine culture sensitivities return,” said first author Marie E. Wang, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Stanford (Calif.) University, and colleagues.
The researchers examined the initial clinical response and escalation of care for 316 children with UTIs who received therapy to which the infecting isolate was not susceptible. The study included patients who had infections that were resistant to third-generation cephalosporins – that is, urinalysis found that the infections were not susceptible to ceftriaxone or cefotaxime in vitro. Before the resistant organisms were identified, however, the patients were started on discordant antibiotics.
Escalation of care was uncommon
The patients had a median age of 2.4 years, and 78% were girls. Approximately 90% were started on a cephalosporin, and about 65% received a first-generation cephalosporin. Patients presented during 2012-2017 to one of five children’s hospitals or to a large managed care organization with 10 hospitals in the United States. The investigators defined care escalation as a visit to the emergency department, hospitalization, or transfer to the ICU.
In all, seven patients (2%) had escalation of care on discordant antibiotics. Four children visited an emergency department without hospitalization, and three children were hospitalized because of persistent symptoms.
Among 230 cases for which the researchers had data about clinical response at a median follow-up of 3 days, 84% “had overall clinical improvement while on discordant antibiotics,” the authors said.
For 22 children who had repeat urine testing while on discordant antibiotics, 53% had resolution of pyuria, and 32% had improvement of pyuria, whereas 16% did not have improvement. Of the three patients without improvement, one had no change, and two had worsening.
Of 17 patients who had a repeat urine culture on discordant therapy, 65% had a negative repeat culture, and 18% grew the same pathogen with a decreased colony count. Two patients had a colony count that remained unchanged, and one patient had an increased colony count.
Small studies outside the United States have reported similar results, the researchers noted. Spontaneous resolution of UTIs or antibiotics reaching a sufficient concentration in the urine and renal parenchyma to achieve a clinical response are possible explanations for the findings, they wrote.
“Few children required escalation of care and most experienced initial clinical improvement,” noted Dr. Wang and colleagues. “Furthermore, in the small group of children that underwent repeat urine testing while on discordant therapy, most had resolution or improvement in pyuria and sterilization of their urine cultures. Our findings suggest that Additionally, given that these patients initially received what would generally be considered inadequate treatment, our findings may provide some insight into the natural history of UTIs and/or trigger further investigation into the relationship between in vitro urine culture susceptibilities and in vivo clinical response to treatment.”
‘Caution is needed’
The study “highlights an intriguing observation about children with UTIs unexpectedly responding to discordant antibiotic therapy,” Tej K. Mattoo, MD, and Basim I. Asmar, MD, wrote in an accompanying commentary.(doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-3512). Dr. Mattoo and Dr. Asmar, a pediatric nephrologist and a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, respectively, at Wayne State University and affiliated with Children’s Hospital of Michigan, both in Detroit.
In an inpatient setting, it may be easy for physicians to reassess patients “once urine culture results reveal resistance to the treating antibiotic,” they noted. In an ambulatory setting, however, “it is likely that some patients will receive a full course of an antibiotic that does not have in vitro activity against the urinary pathogen.”
Physicians have a responsibility to use antibiotics judiciously, they said. Widely accepted principles include avoiding repeated courses of antibiotics, diagnosing UTIs appropriately, and not treating asymptomatic bacteriuria.
The study had no external funding. The authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Wang ME et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Jan 17. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1608.
This article was updated 2/4/2020.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Low RAAS inhibitor dosing linked to MACE risk
Suboptimal dosing of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors to reduce the risk of hyperkalemia could increase the risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or heart failure.
Researchers reported the outcomes of an observational study that explored the real-world associations between RAAS inhibitor dose, hyperkalemia, and clinical outcomes.
RAAS inhibitors – such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists – are known to reduce potassium excretion and therefore increase the risk of high potassium levels.
Dr. Cecilia Linde, from the Karolinska University Hospital and Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, and coauthors wrote that management of serum potassium levels often requires reducing the dosage of RAAS inhibitors or stopping them altogether. However, this is also associated with risks in patients with heart failure or CKD.
In this study, researchers looked at data from 100,572 people with nondialysis CKD and 13,113 with new-onset heart failure who were prescribed RAAS inhibitors during 2006-2015.
Overall, 58% of patients with CKD and 63% of patients with heart failure spent the majority of follow-up on prescribed optimal doses of RAAS inhibitors – defined as at least 50% of the guidelines-recommended dose.
Patients with hyperkalemia were more likely to have down-titrations or discontinue their RAAS inhibitors, and this increased with increasing hyperkalemia severity.
The study found consistently lower mortality rates among patients who spent most of their follow-up time on at least 50% of the guideline-recommended dose of RAAS inhibitors.
In patients with CKD, mortality rates were 7.2 deaths per 1,000 patient-years in those taking at least 50% of the recommended dose, compared with 57.7 deaths per 1,000 patient-years for those on suboptimal doses. The rates of MACE were 73 and 130 per 1,000 patient-years, respectively.
The differences were even more pronounced in patients with heart failure. Those taking at least 50% of the recommended dose had mortality rates of 12.5 per 1000 patient-years, compared with 141.7 among those on suboptimal doses. The rates of MACE were 148.5 and 290.4, respectively.
“The results highlight the potential negative impact of suboptimal RAASi dosing, indicate the generalizability of [European Society of Cardiology–recommended] RAASi doses in HF to CKD patients, and emphasize the need for strategies that allow patients to be maintained on appropriate therapy, avoiding RAASi dose modification or discontinuation,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. One author was an employee and stockholder of AstraZeneca, and five authors declared funding and support from the pharmaceutical sector, including AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Linde C et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012655.
Suboptimal dosing of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors to reduce the risk of hyperkalemia could increase the risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or heart failure.
Researchers reported the outcomes of an observational study that explored the real-world associations between RAAS inhibitor dose, hyperkalemia, and clinical outcomes.
RAAS inhibitors – such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists – are known to reduce potassium excretion and therefore increase the risk of high potassium levels.
Dr. Cecilia Linde, from the Karolinska University Hospital and Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, and coauthors wrote that management of serum potassium levels often requires reducing the dosage of RAAS inhibitors or stopping them altogether. However, this is also associated with risks in patients with heart failure or CKD.
In this study, researchers looked at data from 100,572 people with nondialysis CKD and 13,113 with new-onset heart failure who were prescribed RAAS inhibitors during 2006-2015.
Overall, 58% of patients with CKD and 63% of patients with heart failure spent the majority of follow-up on prescribed optimal doses of RAAS inhibitors – defined as at least 50% of the guidelines-recommended dose.
Patients with hyperkalemia were more likely to have down-titrations or discontinue their RAAS inhibitors, and this increased with increasing hyperkalemia severity.
The study found consistently lower mortality rates among patients who spent most of their follow-up time on at least 50% of the guideline-recommended dose of RAAS inhibitors.
In patients with CKD, mortality rates were 7.2 deaths per 1,000 patient-years in those taking at least 50% of the recommended dose, compared with 57.7 deaths per 1,000 patient-years for those on suboptimal doses. The rates of MACE were 73 and 130 per 1,000 patient-years, respectively.
The differences were even more pronounced in patients with heart failure. Those taking at least 50% of the recommended dose had mortality rates of 12.5 per 1000 patient-years, compared with 141.7 among those on suboptimal doses. The rates of MACE were 148.5 and 290.4, respectively.
“The results highlight the potential negative impact of suboptimal RAASi dosing, indicate the generalizability of [European Society of Cardiology–recommended] RAASi doses in HF to CKD patients, and emphasize the need for strategies that allow patients to be maintained on appropriate therapy, avoiding RAASi dose modification or discontinuation,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. One author was an employee and stockholder of AstraZeneca, and five authors declared funding and support from the pharmaceutical sector, including AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Linde C et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012655.
Suboptimal dosing of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors to reduce the risk of hyperkalemia could increase the risk of major adverse cardiac events (MACE) and all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or heart failure.
Researchers reported the outcomes of an observational study that explored the real-world associations between RAAS inhibitor dose, hyperkalemia, and clinical outcomes.
RAAS inhibitors – such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists – are known to reduce potassium excretion and therefore increase the risk of high potassium levels.
Dr. Cecilia Linde, from the Karolinska University Hospital and Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, and coauthors wrote that management of serum potassium levels often requires reducing the dosage of RAAS inhibitors or stopping them altogether. However, this is also associated with risks in patients with heart failure or CKD.
In this study, researchers looked at data from 100,572 people with nondialysis CKD and 13,113 with new-onset heart failure who were prescribed RAAS inhibitors during 2006-2015.
Overall, 58% of patients with CKD and 63% of patients with heart failure spent the majority of follow-up on prescribed optimal doses of RAAS inhibitors – defined as at least 50% of the guidelines-recommended dose.
Patients with hyperkalemia were more likely to have down-titrations or discontinue their RAAS inhibitors, and this increased with increasing hyperkalemia severity.
The study found consistently lower mortality rates among patients who spent most of their follow-up time on at least 50% of the guideline-recommended dose of RAAS inhibitors.
In patients with CKD, mortality rates were 7.2 deaths per 1,000 patient-years in those taking at least 50% of the recommended dose, compared with 57.7 deaths per 1,000 patient-years for those on suboptimal doses. The rates of MACE were 73 and 130 per 1,000 patient-years, respectively.
The differences were even more pronounced in patients with heart failure. Those taking at least 50% of the recommended dose had mortality rates of 12.5 per 1000 patient-years, compared with 141.7 among those on suboptimal doses. The rates of MACE were 148.5 and 290.4, respectively.
“The results highlight the potential negative impact of suboptimal RAASi dosing, indicate the generalizability of [European Society of Cardiology–recommended] RAASi doses in HF to CKD patients, and emphasize the need for strategies that allow patients to be maintained on appropriate therapy, avoiding RAASi dose modification or discontinuation,” the authors wrote.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. One author was an employee and stockholder of AstraZeneca, and five authors declared funding and support from the pharmaceutical sector, including AstraZeneca.
SOURCE: Linde C et al. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012655.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Cardioprotective Effect of Metformin in Patients with Decreased Renal Function
Study Overview
Objective. To assess whether metformin use is associated with lower risk of fatal or nonfatal major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) as compared to sulfonylurea use among diabetic patients with reduced kidney function.
Design. Retrospective cohort study of US Veterans receiving care within the Veterans Health Administration, with data supplemented by linkage to Medicare, Medicaid, and National Death Index data from 2001 through 2016.
Setting and participants. A retrospective cohort of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patients, aged 18 years and older. Pharmacy data included medication, date filled, days supplied, and number of pills dispensed. For Medicare and Medicaid patients, enrollees’ claims files and prescription (Part D) data were obtained. In addition, dates and cause of death were obtained from vital status and the National Death Index files.
Patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes were identified by selecting new users of metformin, glipizide, glyburide, or glimepiride. These patients were followed longitudinally and the date of cohort entry and start of follow-up was the day of reaching a reduced kidney function threshold, defined as either an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 60 mL/m
Main outcome measures. Primary outcome was the composite of MACE including hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or date of cardiovascular death. The secondary outcome excluded TIA as part of the composite MACE event because not all patients who sustain a TIA are admitted to the hospital.
Main results. From January 1, 2002 through December 30, 2015, 67,749 new metformin users and 28,976 new sulfonylurea users who persisted with treatment were identified. After using propensity score-weighted matching, 24,679 metformin users and 24,799 sulfonylurea users entered the final analysis. Cohort patients were 98% male and 81.8% white. Metformin users were younger than sulfonylurea users, with a median age of 61 years versus 71 years, respectively.
For the main outcome, there were 1048 composite MACE events among metformin patients with reduced kidney function and 1394 MACE events among sulfonylurea patients, yielding 23.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 21.7-24.4) versus 29.2 (95% CI, 27.7-30.7) events per 1000 person-years of use, respectively, after propensity score-weighting. After covariate adjustment, the cause-specific adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for MACE was 0.80 (95% CI, 0.75-0.86) among metformin users compared with sulfonylurea users. The adjusted incidence rate difference was 5.8 (95% CI, 4.1-7.3) fewer events per 1000-person years for metformin compared with sulfonylurea users. Results were also consistent for each component of the primary outcome, including cardiovascular hospitalizations (aHR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.80-0.95) and cardiovascular deaths (aHR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.63-0.78).
Analysis of secondary outcomes, which included AMI, stroke, and cardiovascular death and excluded TIA, demonstrated similar results, with a cause-specific aHR of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.72-0.84) among metformin users compared with sulfonylurea users. The adjusted incidence rate difference was 5.9 (95% CI, 4.3-7.6) fewer events per 1000-person years for metformin compared with sulfonylurea users.
Conclusion. For patients with diabetes and reduced kidney function, treatment with metformin monotherapy, as compared with a sulfonylurea, was associated with a lower risk of MACE.
Commentary
There are approximately 30 million US adults with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes (T2DM), of whom 20% also have impaired kidney function or chronic kidney disease (CKD).1 Metformin hydrochloride has remained the preferred first-line treatment for T2DM based on safety and effectiveness, as well as low cost.2 Metformin is eliminated by the kidneys and can accumulate as eGFR declines. Based on the negative clinical experience, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a safety warning restricting metformin for patients with serum creatinine levels of 1.5 mg/dL or greater for men or 1.4 mg/dL or greater for women. The FDA recommended against starting metformin therapy in patients with CKD with eGFR between 30 and 45 mL/min/1.73 m2, although patients already taking metformin can continue with caution in that setting.1,3
There are several limitations in conducting observational studies comparing metformin to other glucose-lowering medications. First, metformin trials typically excluded patients with CKD due to the FDA warnings. Second, there is usually a time-lag bias in which patients who initiate glucose-lowering medications other than metformin are at a later stage of disease. Third, there is often an allocation bias, as there are substantial differences in baseline characteristics between metformin and sulfonylurea monotherapy users, with metformin users usually being younger and healthier.4
In this retrospective cohort study by Roumie et al, the authors used propensity score–weighted matching to reduce the impacts on time-lag and allocation bias. However, several major limitations remained in this study. First, the study design excluded those who began diabetes treatment after the onset of reduced kidney function; therefore, this study cannot be generalized to patients who already have reduced eGFR at the time of metformin initiation. Second, cohort entry and the start of follow-up was either an elevated serum creatinine or reduced eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. The cohort may have included some patients with an acute kidney injury event, rather than progression to CKD, who recovered from their acute kidney injury. Third, the study population was mostly elderly white men; together with the lack of dose analysis, this study may not be generalizable to other populations.
Applications for Clinical Practice
The current study demonstrated that metformin use, as compared to sulfonylureas, has a lower risk of fatal or nonfatal major adverse cardiovascular events among patients with reduced kidney function. When clinicians are managing hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes, it is important to keep in mind that all medications have adverse effects. There are now 11 drug classes for treating diabetes, in addition to multiple insulin options, and the challenge for clinicians is to present clear information to guide patients using shared decision making, based on each patient’s clinical circumstances and preferences, to achieve individualized glycemic target ranges.
–Ka Ming Gordon Ngai, MD, MPH
1. Geiss LS, Kirtland K, Lin J, et al. Changes in diagnosed diabetes, obesity, and physical inactivity prevalence in US counties, 2004-2012. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173428.
2. Good CB, Pogach LM. Should metformin be first-line therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease? JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:911-912.
3. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA revises warnings regarding use of the diabetes medicine metformin in certain patients with reduced kidney function. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/UCM494140.pdf. Accessed September 30, 2019.
4. Wexler DJ. Sulfonylureas and cardiovascular safety the final verdict? JAMA. 2019;322:1147-1149.
Study Overview
Objective. To assess whether metformin use is associated with lower risk of fatal or nonfatal major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) as compared to sulfonylurea use among diabetic patients with reduced kidney function.
Design. Retrospective cohort study of US Veterans receiving care within the Veterans Health Administration, with data supplemented by linkage to Medicare, Medicaid, and National Death Index data from 2001 through 2016.
Setting and participants. A retrospective cohort of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patients, aged 18 years and older. Pharmacy data included medication, date filled, days supplied, and number of pills dispensed. For Medicare and Medicaid patients, enrollees’ claims files and prescription (Part D) data were obtained. In addition, dates and cause of death were obtained from vital status and the National Death Index files.
Patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes were identified by selecting new users of metformin, glipizide, glyburide, or glimepiride. These patients were followed longitudinally and the date of cohort entry and start of follow-up was the day of reaching a reduced kidney function threshold, defined as either an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 60 mL/m
Main outcome measures. Primary outcome was the composite of MACE including hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or date of cardiovascular death. The secondary outcome excluded TIA as part of the composite MACE event because not all patients who sustain a TIA are admitted to the hospital.
Main results. From January 1, 2002 through December 30, 2015, 67,749 new metformin users and 28,976 new sulfonylurea users who persisted with treatment were identified. After using propensity score-weighted matching, 24,679 metformin users and 24,799 sulfonylurea users entered the final analysis. Cohort patients were 98% male and 81.8% white. Metformin users were younger than sulfonylurea users, with a median age of 61 years versus 71 years, respectively.
For the main outcome, there were 1048 composite MACE events among metformin patients with reduced kidney function and 1394 MACE events among sulfonylurea patients, yielding 23.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 21.7-24.4) versus 29.2 (95% CI, 27.7-30.7) events per 1000 person-years of use, respectively, after propensity score-weighting. After covariate adjustment, the cause-specific adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for MACE was 0.80 (95% CI, 0.75-0.86) among metformin users compared with sulfonylurea users. The adjusted incidence rate difference was 5.8 (95% CI, 4.1-7.3) fewer events per 1000-person years for metformin compared with sulfonylurea users. Results were also consistent for each component of the primary outcome, including cardiovascular hospitalizations (aHR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.80-0.95) and cardiovascular deaths (aHR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.63-0.78).
Analysis of secondary outcomes, which included AMI, stroke, and cardiovascular death and excluded TIA, demonstrated similar results, with a cause-specific aHR of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.72-0.84) among metformin users compared with sulfonylurea users. The adjusted incidence rate difference was 5.9 (95% CI, 4.3-7.6) fewer events per 1000-person years for metformin compared with sulfonylurea users.
Conclusion. For patients with diabetes and reduced kidney function, treatment with metformin monotherapy, as compared with a sulfonylurea, was associated with a lower risk of MACE.
Commentary
There are approximately 30 million US adults with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes (T2DM), of whom 20% also have impaired kidney function or chronic kidney disease (CKD).1 Metformin hydrochloride has remained the preferred first-line treatment for T2DM based on safety and effectiveness, as well as low cost.2 Metformin is eliminated by the kidneys and can accumulate as eGFR declines. Based on the negative clinical experience, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a safety warning restricting metformin for patients with serum creatinine levels of 1.5 mg/dL or greater for men or 1.4 mg/dL or greater for women. The FDA recommended against starting metformin therapy in patients with CKD with eGFR between 30 and 45 mL/min/1.73 m2, although patients already taking metformin can continue with caution in that setting.1,3
There are several limitations in conducting observational studies comparing metformin to other glucose-lowering medications. First, metformin trials typically excluded patients with CKD due to the FDA warnings. Second, there is usually a time-lag bias in which patients who initiate glucose-lowering medications other than metformin are at a later stage of disease. Third, there is often an allocation bias, as there are substantial differences in baseline characteristics between metformin and sulfonylurea monotherapy users, with metformin users usually being younger and healthier.4
In this retrospective cohort study by Roumie et al, the authors used propensity score–weighted matching to reduce the impacts on time-lag and allocation bias. However, several major limitations remained in this study. First, the study design excluded those who began diabetes treatment after the onset of reduced kidney function; therefore, this study cannot be generalized to patients who already have reduced eGFR at the time of metformin initiation. Second, cohort entry and the start of follow-up was either an elevated serum creatinine or reduced eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. The cohort may have included some patients with an acute kidney injury event, rather than progression to CKD, who recovered from their acute kidney injury. Third, the study population was mostly elderly white men; together with the lack of dose analysis, this study may not be generalizable to other populations.
Applications for Clinical Practice
The current study demonstrated that metformin use, as compared to sulfonylureas, has a lower risk of fatal or nonfatal major adverse cardiovascular events among patients with reduced kidney function. When clinicians are managing hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes, it is important to keep in mind that all medications have adverse effects. There are now 11 drug classes for treating diabetes, in addition to multiple insulin options, and the challenge for clinicians is to present clear information to guide patients using shared decision making, based on each patient’s clinical circumstances and preferences, to achieve individualized glycemic target ranges.
–Ka Ming Gordon Ngai, MD, MPH
Study Overview
Objective. To assess whether metformin use is associated with lower risk of fatal or nonfatal major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) as compared to sulfonylurea use among diabetic patients with reduced kidney function.
Design. Retrospective cohort study of US Veterans receiving care within the Veterans Health Administration, with data supplemented by linkage to Medicare, Medicaid, and National Death Index data from 2001 through 2016.
Setting and participants. A retrospective cohort of Veterans Health Administration (VHA) patients, aged 18 years and older. Pharmacy data included medication, date filled, days supplied, and number of pills dispensed. For Medicare and Medicaid patients, enrollees’ claims files and prescription (Part D) data were obtained. In addition, dates and cause of death were obtained from vital status and the National Death Index files.
Patients with new-onset type 2 diabetes were identified by selecting new users of metformin, glipizide, glyburide, or glimepiride. These patients were followed longitudinally and the date of cohort entry and start of follow-up was the day of reaching a reduced kidney function threshold, defined as either an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 60 mL/m
Main outcome measures. Primary outcome was the composite of MACE including hospitalization for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or date of cardiovascular death. The secondary outcome excluded TIA as part of the composite MACE event because not all patients who sustain a TIA are admitted to the hospital.
Main results. From January 1, 2002 through December 30, 2015, 67,749 new metformin users and 28,976 new sulfonylurea users who persisted with treatment were identified. After using propensity score-weighted matching, 24,679 metformin users and 24,799 sulfonylurea users entered the final analysis. Cohort patients were 98% male and 81.8% white. Metformin users were younger than sulfonylurea users, with a median age of 61 years versus 71 years, respectively.
For the main outcome, there were 1048 composite MACE events among metformin patients with reduced kidney function and 1394 MACE events among sulfonylurea patients, yielding 23.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 21.7-24.4) versus 29.2 (95% CI, 27.7-30.7) events per 1000 person-years of use, respectively, after propensity score-weighting. After covariate adjustment, the cause-specific adjusted hazard ratio (aHR) for MACE was 0.80 (95% CI, 0.75-0.86) among metformin users compared with sulfonylurea users. The adjusted incidence rate difference was 5.8 (95% CI, 4.1-7.3) fewer events per 1000-person years for metformin compared with sulfonylurea users. Results were also consistent for each component of the primary outcome, including cardiovascular hospitalizations (aHR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.80-0.95) and cardiovascular deaths (aHR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.63-0.78).
Analysis of secondary outcomes, which included AMI, stroke, and cardiovascular death and excluded TIA, demonstrated similar results, with a cause-specific aHR of 0.78 (95% CI, 0.72-0.84) among metformin users compared with sulfonylurea users. The adjusted incidence rate difference was 5.9 (95% CI, 4.3-7.6) fewer events per 1000-person years for metformin compared with sulfonylurea users.
Conclusion. For patients with diabetes and reduced kidney function, treatment with metformin monotherapy, as compared with a sulfonylurea, was associated with a lower risk of MACE.
Commentary
There are approximately 30 million US adults with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes (T2DM), of whom 20% also have impaired kidney function or chronic kidney disease (CKD).1 Metformin hydrochloride has remained the preferred first-line treatment for T2DM based on safety and effectiveness, as well as low cost.2 Metformin is eliminated by the kidneys and can accumulate as eGFR declines. Based on the negative clinical experience, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a safety warning restricting metformin for patients with serum creatinine levels of 1.5 mg/dL or greater for men or 1.4 mg/dL or greater for women. The FDA recommended against starting metformin therapy in patients with CKD with eGFR between 30 and 45 mL/min/1.73 m2, although patients already taking metformin can continue with caution in that setting.1,3
There are several limitations in conducting observational studies comparing metformin to other glucose-lowering medications. First, metformin trials typically excluded patients with CKD due to the FDA warnings. Second, there is usually a time-lag bias in which patients who initiate glucose-lowering medications other than metformin are at a later stage of disease. Third, there is often an allocation bias, as there are substantial differences in baseline characteristics between metformin and sulfonylurea monotherapy users, with metformin users usually being younger and healthier.4
In this retrospective cohort study by Roumie et al, the authors used propensity score–weighted matching to reduce the impacts on time-lag and allocation bias. However, several major limitations remained in this study. First, the study design excluded those who began diabetes treatment after the onset of reduced kidney function; therefore, this study cannot be generalized to patients who already have reduced eGFR at the time of metformin initiation. Second, cohort entry and the start of follow-up was either an elevated serum creatinine or reduced eGFR less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. The cohort may have included some patients with an acute kidney injury event, rather than progression to CKD, who recovered from their acute kidney injury. Third, the study population was mostly elderly white men; together with the lack of dose analysis, this study may not be generalizable to other populations.
Applications for Clinical Practice
The current study demonstrated that metformin use, as compared to sulfonylureas, has a lower risk of fatal or nonfatal major adverse cardiovascular events among patients with reduced kidney function. When clinicians are managing hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes, it is important to keep in mind that all medications have adverse effects. There are now 11 drug classes for treating diabetes, in addition to multiple insulin options, and the challenge for clinicians is to present clear information to guide patients using shared decision making, based on each patient’s clinical circumstances and preferences, to achieve individualized glycemic target ranges.
–Ka Ming Gordon Ngai, MD, MPH
1. Geiss LS, Kirtland K, Lin J, et al. Changes in diagnosed diabetes, obesity, and physical inactivity prevalence in US counties, 2004-2012. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173428.
2. Good CB, Pogach LM. Should metformin be first-line therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease? JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:911-912.
3. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA revises warnings regarding use of the diabetes medicine metformin in certain patients with reduced kidney function. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/UCM494140.pdf. Accessed September 30, 2019.
4. Wexler DJ. Sulfonylureas and cardiovascular safety the final verdict? JAMA. 2019;322:1147-1149.
1. Geiss LS, Kirtland K, Lin J, et al. Changes in diagnosed diabetes, obesity, and physical inactivity prevalence in US counties, 2004-2012. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173428.
2. Good CB, Pogach LM. Should metformin be first-line therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease? JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178:911-912.
3. US Food and Drug Administration. FDA revises warnings regarding use of the diabetes medicine metformin in certain patients with reduced kidney function. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/DrugSafety/UCM494140.pdf. Accessed September 30, 2019.
4. Wexler DJ. Sulfonylureas and cardiovascular safety the final verdict? JAMA. 2019;322:1147-1149.
ISCHEMIA-CKD: No benefit for coronary revascularization in advanced CKD with stable angina
PHILADELPHIA – Coronary revascularization in patients with stage 4 or 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) and stable ischemic heart disease accomplishes nothing constructive, according to clear-cut results of the landmark ISCHEMIA-CKD trial.
In this multinational randomized trial including 777 stable patients with advanced CKD and moderate or severe myocardial ischemia on noninvasive testing, an early invasive strategy didn’t reduce the risks of death or ischemic events, didn’t provide any significant improvement in quality of life metrics, and resulted in an increased risk of stroke, Sripal Bangalore, MD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“ said Dr. Bangalore, professor of medicine and director of complex coronary intervention at New York University.
This was easily the largest-ever trial of an invasive versus conservative coronary artery disease management strategy in this challenging population. For example, in the COURAGE trial of optimal medical therapy with or without percutaneous coronary intervention for stable coronary disease (N Engl J Med. 2007 Apr 12;356[15]:1503-16), only 16 of the 2,287 participants had an estimated glomerular filtration rate below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Of note, the participating study sites received special training aimed at minimizing the risk of acute kidney injury after cardiac catheterization in this at-risk population. The training included utilization of a customized left ventricular end diastolic volume–based hydration protocol, guidance on how to perform percutaneous coronary intervention with little or no contrast material, and encouragement of a heart/kidney team approach involving a cardiologist, nephrologist, and cardiovascular surgeon. This training really paid off, with roughly a 7% incidence of acute kidney injury after catheterization.
“The expected rate in such patients would be 30%-60%,” according to Dr. Bangalore.
The primary endpoint in ISCHEMIA-CKD was the rates of death or MI during 3 years of prospective follow-up. This occurred in 36.7% of patients randomized to optimal medical therapy alone and 36.4% of those randomized to an early invasive strategy. Similarly, the major secondary endpoint, comprising death, MI, and hospitalization for unstable angina, heart failure, or resuscitated cardiac arrest, was also a virtual dead heat, occurring in about 39% of subjects. More than 27% of study participants had died by the 3-year mark regardless of how their coronary disease was managed.
The adjusted risk of stroke was 3.76-fold higher in the invasive strategy group; however, the most strokes were not procedurally related, and the explanation for the significantly increased risk in the invasively managed group remains unknown, the cardiologist said.
John A. Spertus, MD, who led the quality of life assessment in ISCHEMIA-CKD and in the 5,129-patient parent ISCHEMIA (International Study of Comparative Health Effectiveness with Medical and Invasive Approaches), also presented at the AHA scientific sessions. He reported that, unlike in the parent study, there was no hint of a meaningful long-term quality of life benefit for revascularization plus optimal medical therapy, compared with that of optimal medical therapy alone, in ISCHEMIA-CKD.
“We have greater than 93% confidence that there is more of a quality of life effect in patients without advanced CKD than in patients with advanced CKD,” said Dr. Spertus, director of health outcomes research at the Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and professor of medicine at the University of Missouri, Kansas City.
Discussant Glenn L. Levine, MD, hailed ISCHEMIA-CKD as “a monumental achievement,” an ambitious, well-powered study with essentially no loss of follow-up during up to 4 years. It helps fill an utter void in the AHA/American College of Cardiology guidelines, which to date offer no recommendations at all regarding revascularization in patients with CKD because of a lack of evidence. And he considers ISCHEMIA-CKD to be unequivocally practice changing and guideline changing.
“Based on the results of ISCHEMIA-CKD, I will generally not go searching for ischemia and [coronary artery disease] in most severe and end-stage CKD patients, absent marked or unacceptable angina, and will treat them with medical therapy alone,” declared Dr. Levine, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and director of the cardiac care unit at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, both in Houston.
He offered a few caveats. Excluded from participation in ISCHEMIA-CKD were patients with acute coronary syndrome, significant heart failure, or unacceptable angina despite optimal medical therapy at baseline, so the study results don’t apply to them. Also, the acute kidney injury rate after intervention was eye-catchingly low.
Dr. Bangalore discussed the ISCHEMIA-CKD trial and outcomes in a video interview with Medscape’s Tricia Ward.
“It seems unlikely that all centers routinely do and will exactly follow the very careful measures to limit contrast and minimize contrast nephropathy used in this study,” Dr. Levine commented.
ISCHEMIA-CKD, like its parent ISCHEMIA trial, was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Bangalore reported having no relevant financial interests. Dr. Spertus holds the copyright for the Seattle Angina Questionnaire, which was used for quality of life measurement in the trials. Dr. Levine disclosed that he has no relations with industry or conflicts of interest.
PHILADELPHIA – Coronary revascularization in patients with stage 4 or 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) and stable ischemic heart disease accomplishes nothing constructive, according to clear-cut results of the landmark ISCHEMIA-CKD trial.
In this multinational randomized trial including 777 stable patients with advanced CKD and moderate or severe myocardial ischemia on noninvasive testing, an early invasive strategy didn’t reduce the risks of death or ischemic events, didn’t provide any significant improvement in quality of life metrics, and resulted in an increased risk of stroke, Sripal Bangalore, MD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“ said Dr. Bangalore, professor of medicine and director of complex coronary intervention at New York University.
This was easily the largest-ever trial of an invasive versus conservative coronary artery disease management strategy in this challenging population. For example, in the COURAGE trial of optimal medical therapy with or without percutaneous coronary intervention for stable coronary disease (N Engl J Med. 2007 Apr 12;356[15]:1503-16), only 16 of the 2,287 participants had an estimated glomerular filtration rate below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Of note, the participating study sites received special training aimed at minimizing the risk of acute kidney injury after cardiac catheterization in this at-risk population. The training included utilization of a customized left ventricular end diastolic volume–based hydration protocol, guidance on how to perform percutaneous coronary intervention with little or no contrast material, and encouragement of a heart/kidney team approach involving a cardiologist, nephrologist, and cardiovascular surgeon. This training really paid off, with roughly a 7% incidence of acute kidney injury after catheterization.
“The expected rate in such patients would be 30%-60%,” according to Dr. Bangalore.
The primary endpoint in ISCHEMIA-CKD was the rates of death or MI during 3 years of prospective follow-up. This occurred in 36.7% of patients randomized to optimal medical therapy alone and 36.4% of those randomized to an early invasive strategy. Similarly, the major secondary endpoint, comprising death, MI, and hospitalization for unstable angina, heart failure, or resuscitated cardiac arrest, was also a virtual dead heat, occurring in about 39% of subjects. More than 27% of study participants had died by the 3-year mark regardless of how their coronary disease was managed.
The adjusted risk of stroke was 3.76-fold higher in the invasive strategy group; however, the most strokes were not procedurally related, and the explanation for the significantly increased risk in the invasively managed group remains unknown, the cardiologist said.
John A. Spertus, MD, who led the quality of life assessment in ISCHEMIA-CKD and in the 5,129-patient parent ISCHEMIA (International Study of Comparative Health Effectiveness with Medical and Invasive Approaches), also presented at the AHA scientific sessions. He reported that, unlike in the parent study, there was no hint of a meaningful long-term quality of life benefit for revascularization plus optimal medical therapy, compared with that of optimal medical therapy alone, in ISCHEMIA-CKD.
“We have greater than 93% confidence that there is more of a quality of life effect in patients without advanced CKD than in patients with advanced CKD,” said Dr. Spertus, director of health outcomes research at the Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and professor of medicine at the University of Missouri, Kansas City.
Discussant Glenn L. Levine, MD, hailed ISCHEMIA-CKD as “a monumental achievement,” an ambitious, well-powered study with essentially no loss of follow-up during up to 4 years. It helps fill an utter void in the AHA/American College of Cardiology guidelines, which to date offer no recommendations at all regarding revascularization in patients with CKD because of a lack of evidence. And he considers ISCHEMIA-CKD to be unequivocally practice changing and guideline changing.
“Based on the results of ISCHEMIA-CKD, I will generally not go searching for ischemia and [coronary artery disease] in most severe and end-stage CKD patients, absent marked or unacceptable angina, and will treat them with medical therapy alone,” declared Dr. Levine, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and director of the cardiac care unit at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, both in Houston.
He offered a few caveats. Excluded from participation in ISCHEMIA-CKD were patients with acute coronary syndrome, significant heart failure, or unacceptable angina despite optimal medical therapy at baseline, so the study results don’t apply to them. Also, the acute kidney injury rate after intervention was eye-catchingly low.
Dr. Bangalore discussed the ISCHEMIA-CKD trial and outcomes in a video interview with Medscape’s Tricia Ward.
“It seems unlikely that all centers routinely do and will exactly follow the very careful measures to limit contrast and minimize contrast nephropathy used in this study,” Dr. Levine commented.
ISCHEMIA-CKD, like its parent ISCHEMIA trial, was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Bangalore reported having no relevant financial interests. Dr. Spertus holds the copyright for the Seattle Angina Questionnaire, which was used for quality of life measurement in the trials. Dr. Levine disclosed that he has no relations with industry or conflicts of interest.
PHILADELPHIA – Coronary revascularization in patients with stage 4 or 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) and stable ischemic heart disease accomplishes nothing constructive, according to clear-cut results of the landmark ISCHEMIA-CKD trial.
In this multinational randomized trial including 777 stable patients with advanced CKD and moderate or severe myocardial ischemia on noninvasive testing, an early invasive strategy didn’t reduce the risks of death or ischemic events, didn’t provide any significant improvement in quality of life metrics, and resulted in an increased risk of stroke, Sripal Bangalore, MD, reported at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“ said Dr. Bangalore, professor of medicine and director of complex coronary intervention at New York University.
This was easily the largest-ever trial of an invasive versus conservative coronary artery disease management strategy in this challenging population. For example, in the COURAGE trial of optimal medical therapy with or without percutaneous coronary intervention for stable coronary disease (N Engl J Med. 2007 Apr 12;356[15]:1503-16), only 16 of the 2,287 participants had an estimated glomerular filtration rate below 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Of note, the participating study sites received special training aimed at minimizing the risk of acute kidney injury after cardiac catheterization in this at-risk population. The training included utilization of a customized left ventricular end diastolic volume–based hydration protocol, guidance on how to perform percutaneous coronary intervention with little or no contrast material, and encouragement of a heart/kidney team approach involving a cardiologist, nephrologist, and cardiovascular surgeon. This training really paid off, with roughly a 7% incidence of acute kidney injury after catheterization.
“The expected rate in such patients would be 30%-60%,” according to Dr. Bangalore.
The primary endpoint in ISCHEMIA-CKD was the rates of death or MI during 3 years of prospective follow-up. This occurred in 36.7% of patients randomized to optimal medical therapy alone and 36.4% of those randomized to an early invasive strategy. Similarly, the major secondary endpoint, comprising death, MI, and hospitalization for unstable angina, heart failure, or resuscitated cardiac arrest, was also a virtual dead heat, occurring in about 39% of subjects. More than 27% of study participants had died by the 3-year mark regardless of how their coronary disease was managed.
The adjusted risk of stroke was 3.76-fold higher in the invasive strategy group; however, the most strokes were not procedurally related, and the explanation for the significantly increased risk in the invasively managed group remains unknown, the cardiologist said.
John A. Spertus, MD, who led the quality of life assessment in ISCHEMIA-CKD and in the 5,129-patient parent ISCHEMIA (International Study of Comparative Health Effectiveness with Medical and Invasive Approaches), also presented at the AHA scientific sessions. He reported that, unlike in the parent study, there was no hint of a meaningful long-term quality of life benefit for revascularization plus optimal medical therapy, compared with that of optimal medical therapy alone, in ISCHEMIA-CKD.
“We have greater than 93% confidence that there is more of a quality of life effect in patients without advanced CKD than in patients with advanced CKD,” said Dr. Spertus, director of health outcomes research at the Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute and professor of medicine at the University of Missouri, Kansas City.
Discussant Glenn L. Levine, MD, hailed ISCHEMIA-CKD as “a monumental achievement,” an ambitious, well-powered study with essentially no loss of follow-up during up to 4 years. It helps fill an utter void in the AHA/American College of Cardiology guidelines, which to date offer no recommendations at all regarding revascularization in patients with CKD because of a lack of evidence. And he considers ISCHEMIA-CKD to be unequivocally practice changing and guideline changing.
“Based on the results of ISCHEMIA-CKD, I will generally not go searching for ischemia and [coronary artery disease] in most severe and end-stage CKD patients, absent marked or unacceptable angina, and will treat them with medical therapy alone,” declared Dr. Levine, professor of medicine at Baylor College of Medicine and director of the cardiac care unit at the Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center, both in Houston.
He offered a few caveats. Excluded from participation in ISCHEMIA-CKD were patients with acute coronary syndrome, significant heart failure, or unacceptable angina despite optimal medical therapy at baseline, so the study results don’t apply to them. Also, the acute kidney injury rate after intervention was eye-catchingly low.
Dr. Bangalore discussed the ISCHEMIA-CKD trial and outcomes in a video interview with Medscape’s Tricia Ward.
“It seems unlikely that all centers routinely do and will exactly follow the very careful measures to limit contrast and minimize contrast nephropathy used in this study,” Dr. Levine commented.
ISCHEMIA-CKD, like its parent ISCHEMIA trial, was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Bangalore reported having no relevant financial interests. Dr. Spertus holds the copyright for the Seattle Angina Questionnaire, which was used for quality of life measurement in the trials. Dr. Levine disclosed that he has no relations with industry or conflicts of interest.
REPORTING FROM AHA 2019
Novel antibody looks promising in lupus nephritis
WASHINGTON – A novel antibody, obinutuzumab, enhances renal responses in patients with lupus nephritis, through more complete B-cell depletion, compared with standard immunotherapy, and is well tolerated, according to results from the phase 2 NOBILITY trial.
“We know from our previous trials with anti–B-cell antibodies that results were mixed and we felt that these variable results were possibly due to variability in B-cell depletion with a type 1 anti-CD20 antibody such as rituximab,” Brad Rovin, MD, director, division of nephrology, Ohio State University in Columbus, told a press briefing here at Kidney Week 2019: American Society of Nephrology annual meeting.
“So we hypothesized that if we could deplete B cells more efficiently and completely, we would achieve better results. At week 52, 35% of patients in the obinutuzumab-treated group achieved a complete renal response, compared to 23% in the standard-of-care arm.”
And by week 76, the difference between obinutuzumab and the standard of care was actually larger at 40% vs. 18%, respectively, “and this was statistically significant at a P value of .01,” added Dr. Rovin, who presented the full findings of the study at the conference.
Obinutuzumab, a highly engineered anti-CD20 antibody, is already approved under the brand name Gazyva for use in certain leukemias and lymphomas. The NOBILITY study was funded by Genentech-Roche, and Dr. Rovin reported being a consultant for the company.
Asked by Medscape Medical News to comment on the study, Duvuru Geetha, MBBS, noted that with standard-of-care mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus corticosteroids, “the remissions rates we achieve [for lupus nephritis] are still not great,” ranging from 30% to 50%, depending on the patient population.
“This is why there is a need for alternative agents,” added Dr. Geetha, who is an associate professor of medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
With obinutuzumab, “the data look very promising because there is a much more profound and sustained effect on B-cell depletion and the renal response rate is much higher [than with MMF and corticosteroids],” she noted.
Dr. Geetha added, however, that she presumes patients were all premedicated with prophylactic agents to prevent infectious events, as they are when treated with rituximab.
“I think what is definitely different about this drug is that it induces direct cell death more efficiently than rituximab and that is probably what’s accounting for the higher efficacy seen with it,” said Dr. Geetha, who disclosed having received honoraria from Genentech a number of years ago.
“So yes, I believe the results are clinically meaningful,” she concluded.
NOBILITY study design
The NOBILITY trial randomized 125 patients with Class III or IV lupus nephritis to either obinutuzumab plus MMF and corticosteroids, or to MMF plus corticosteroids alone, for a treatment interval of 104 weeks.
Patients in the obinutuzumab group received two infusions of the highly engineered anti-CD20 antibody at week 0 and week 2 and another two infusions at 6 months.
“The primary endpoint was complete renal response at week 52,” the authors wrote, “while key secondary endpoints included overall renal response and modified complete renal response.”
Both at week 52 and week 76, more patients in the obinutuzumab group achieved an overall renal response as well as a modified complete renal response, compared with those treated with immunosuppression alone.
“If you look at the complete renal response over time, you can see that the curves separate after about 6 months but the placebo group starts to decline as you go further out, whereas the obinutuzumab group continues to separate, so my prediction is that we are going to see this trend continue because of the mechanism of action of obinutuzumab,” Dr. Rovin explained.
Phase 3 trials to start early 2020
All of the serologies relevant to lupus and lupus nephritis “including C3 and C4 improved while antidoubled stranded DNA levels declined, as did the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, although the decline was more rapid and more profound in the obinutuzumab-treated patients,” Dr. Rovin said.
Importantly as well, despite the profound B-cell depletion produced by obinutuzumab, “the adverse event profile of this drug was very similar to the placebo group,” he stressed.
As expected, rates of infusion reactions were slightly higher in the experimental group than the immunosuppression alone group, but rates of serious adverse events were the same between groups, as were adverse infectious events, he noted.
Investigators have now initiated a global phase 3 trial, scheduled to start in early 2020, to evaluate the same treatment protocol in a larger group of patients.
Kidney Week 2019. Abstract #FR-OR136. Presented Nov. 8, 2019.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – A novel antibody, obinutuzumab, enhances renal responses in patients with lupus nephritis, through more complete B-cell depletion, compared with standard immunotherapy, and is well tolerated, according to results from the phase 2 NOBILITY trial.
“We know from our previous trials with anti–B-cell antibodies that results were mixed and we felt that these variable results were possibly due to variability in B-cell depletion with a type 1 anti-CD20 antibody such as rituximab,” Brad Rovin, MD, director, division of nephrology, Ohio State University in Columbus, told a press briefing here at Kidney Week 2019: American Society of Nephrology annual meeting.
“So we hypothesized that if we could deplete B cells more efficiently and completely, we would achieve better results. At week 52, 35% of patients in the obinutuzumab-treated group achieved a complete renal response, compared to 23% in the standard-of-care arm.”
And by week 76, the difference between obinutuzumab and the standard of care was actually larger at 40% vs. 18%, respectively, “and this was statistically significant at a P value of .01,” added Dr. Rovin, who presented the full findings of the study at the conference.
Obinutuzumab, a highly engineered anti-CD20 antibody, is already approved under the brand name Gazyva for use in certain leukemias and lymphomas. The NOBILITY study was funded by Genentech-Roche, and Dr. Rovin reported being a consultant for the company.
Asked by Medscape Medical News to comment on the study, Duvuru Geetha, MBBS, noted that with standard-of-care mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus corticosteroids, “the remissions rates we achieve [for lupus nephritis] are still not great,” ranging from 30% to 50%, depending on the patient population.
“This is why there is a need for alternative agents,” added Dr. Geetha, who is an associate professor of medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
With obinutuzumab, “the data look very promising because there is a much more profound and sustained effect on B-cell depletion and the renal response rate is much higher [than with MMF and corticosteroids],” she noted.
Dr. Geetha added, however, that she presumes patients were all premedicated with prophylactic agents to prevent infectious events, as they are when treated with rituximab.
“I think what is definitely different about this drug is that it induces direct cell death more efficiently than rituximab and that is probably what’s accounting for the higher efficacy seen with it,” said Dr. Geetha, who disclosed having received honoraria from Genentech a number of years ago.
“So yes, I believe the results are clinically meaningful,” she concluded.
NOBILITY study design
The NOBILITY trial randomized 125 patients with Class III or IV lupus nephritis to either obinutuzumab plus MMF and corticosteroids, or to MMF plus corticosteroids alone, for a treatment interval of 104 weeks.
Patients in the obinutuzumab group received two infusions of the highly engineered anti-CD20 antibody at week 0 and week 2 and another two infusions at 6 months.
“The primary endpoint was complete renal response at week 52,” the authors wrote, “while key secondary endpoints included overall renal response and modified complete renal response.”
Both at week 52 and week 76, more patients in the obinutuzumab group achieved an overall renal response as well as a modified complete renal response, compared with those treated with immunosuppression alone.
“If you look at the complete renal response over time, you can see that the curves separate after about 6 months but the placebo group starts to decline as you go further out, whereas the obinutuzumab group continues to separate, so my prediction is that we are going to see this trend continue because of the mechanism of action of obinutuzumab,” Dr. Rovin explained.
Phase 3 trials to start early 2020
All of the serologies relevant to lupus and lupus nephritis “including C3 and C4 improved while antidoubled stranded DNA levels declined, as did the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, although the decline was more rapid and more profound in the obinutuzumab-treated patients,” Dr. Rovin said.
Importantly as well, despite the profound B-cell depletion produced by obinutuzumab, “the adverse event profile of this drug was very similar to the placebo group,” he stressed.
As expected, rates of infusion reactions were slightly higher in the experimental group than the immunosuppression alone group, but rates of serious adverse events were the same between groups, as were adverse infectious events, he noted.
Investigators have now initiated a global phase 3 trial, scheduled to start in early 2020, to evaluate the same treatment protocol in a larger group of patients.
Kidney Week 2019. Abstract #FR-OR136. Presented Nov. 8, 2019.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON – A novel antibody, obinutuzumab, enhances renal responses in patients with lupus nephritis, through more complete B-cell depletion, compared with standard immunotherapy, and is well tolerated, according to results from the phase 2 NOBILITY trial.
“We know from our previous trials with anti–B-cell antibodies that results were mixed and we felt that these variable results were possibly due to variability in B-cell depletion with a type 1 anti-CD20 antibody such as rituximab,” Brad Rovin, MD, director, division of nephrology, Ohio State University in Columbus, told a press briefing here at Kidney Week 2019: American Society of Nephrology annual meeting.
“So we hypothesized that if we could deplete B cells more efficiently and completely, we would achieve better results. At week 52, 35% of patients in the obinutuzumab-treated group achieved a complete renal response, compared to 23% in the standard-of-care arm.”
And by week 76, the difference between obinutuzumab and the standard of care was actually larger at 40% vs. 18%, respectively, “and this was statistically significant at a P value of .01,” added Dr. Rovin, who presented the full findings of the study at the conference.
Obinutuzumab, a highly engineered anti-CD20 antibody, is already approved under the brand name Gazyva for use in certain leukemias and lymphomas. The NOBILITY study was funded by Genentech-Roche, and Dr. Rovin reported being a consultant for the company.
Asked by Medscape Medical News to comment on the study, Duvuru Geetha, MBBS, noted that with standard-of-care mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) plus corticosteroids, “the remissions rates we achieve [for lupus nephritis] are still not great,” ranging from 30% to 50%, depending on the patient population.
“This is why there is a need for alternative agents,” added Dr. Geetha, who is an associate professor of medicine, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
With obinutuzumab, “the data look very promising because there is a much more profound and sustained effect on B-cell depletion and the renal response rate is much higher [than with MMF and corticosteroids],” she noted.
Dr. Geetha added, however, that she presumes patients were all premedicated with prophylactic agents to prevent infectious events, as they are when treated with rituximab.
“I think what is definitely different about this drug is that it induces direct cell death more efficiently than rituximab and that is probably what’s accounting for the higher efficacy seen with it,” said Dr. Geetha, who disclosed having received honoraria from Genentech a number of years ago.
“So yes, I believe the results are clinically meaningful,” she concluded.
NOBILITY study design
The NOBILITY trial randomized 125 patients with Class III or IV lupus nephritis to either obinutuzumab plus MMF and corticosteroids, or to MMF plus corticosteroids alone, for a treatment interval of 104 weeks.
Patients in the obinutuzumab group received two infusions of the highly engineered anti-CD20 antibody at week 0 and week 2 and another two infusions at 6 months.
“The primary endpoint was complete renal response at week 52,” the authors wrote, “while key secondary endpoints included overall renal response and modified complete renal response.”
Both at week 52 and week 76, more patients in the obinutuzumab group achieved an overall renal response as well as a modified complete renal response, compared with those treated with immunosuppression alone.
“If you look at the complete renal response over time, you can see that the curves separate after about 6 months but the placebo group starts to decline as you go further out, whereas the obinutuzumab group continues to separate, so my prediction is that we are going to see this trend continue because of the mechanism of action of obinutuzumab,” Dr. Rovin explained.
Phase 3 trials to start early 2020
All of the serologies relevant to lupus and lupus nephritis “including C3 and C4 improved while antidoubled stranded DNA levels declined, as did the urine protein-to-creatinine ratio, although the decline was more rapid and more profound in the obinutuzumab-treated patients,” Dr. Rovin said.
Importantly as well, despite the profound B-cell depletion produced by obinutuzumab, “the adverse event profile of this drug was very similar to the placebo group,” he stressed.
As expected, rates of infusion reactions were slightly higher in the experimental group than the immunosuppression alone group, but rates of serious adverse events were the same between groups, as were adverse infectious events, he noted.
Investigators have now initiated a global phase 3 trial, scheduled to start in early 2020, to evaluate the same treatment protocol in a larger group of patients.
Kidney Week 2019. Abstract #FR-OR136. Presented Nov. 8, 2019.
This story first appeared on Medscape.com.