User login
Promising new antibiotic emerges for treating UTIs
A new antibiotic for urinary tract infections is heading toward government approval.
It would be the first new treatment in 20 years for UTIs, which affect more than half of women at least sometime in their lives, according to data compiled by the Department of Health and Human Services.
Called Gepotidacin, the antibiotic’s trial has halted enrollment early due to excellent effectiveness and safety results thus far, drugmaker GSK announced in a press release Nov. 3. GSK will seek approval and peer-reviewed publication early next year.
There is a need for new antibiotics such as this because of increasing antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance to bacteria has become so prevalent that the World Health Organization recently began publishing a list of bacteria that pose the greatest public health threats.
“It’s definitely a big deal,” Cindy Liu, MD, MPH, PhD, of the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at George Washington University, told CNN.
However, antibiotics are not a particularly profitable type of drug, The Wall Street Journal reported. The newspaper noted that they need to be used sparingly to limit resistance, and the cheapest option is usually prescribed. Some small companies that make antibiotics have even gone bankrupt recently, the Journal noted.
The U.S. government has invested in GSK’s development of Gepotidacin. The company predicts the drug could be a “blockbuster” and earn more than $1 billion due to UTI resistance to other drugs, the Journal reported.
“I think it will be really interesting and important to the field to see both how the drug companies sort of market this product and sort of how it does,” Dr. Liu said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new antibiotic for urinary tract infections is heading toward government approval.
It would be the first new treatment in 20 years for UTIs, which affect more than half of women at least sometime in their lives, according to data compiled by the Department of Health and Human Services.
Called Gepotidacin, the antibiotic’s trial has halted enrollment early due to excellent effectiveness and safety results thus far, drugmaker GSK announced in a press release Nov. 3. GSK will seek approval and peer-reviewed publication early next year.
There is a need for new antibiotics such as this because of increasing antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance to bacteria has become so prevalent that the World Health Organization recently began publishing a list of bacteria that pose the greatest public health threats.
“It’s definitely a big deal,” Cindy Liu, MD, MPH, PhD, of the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at George Washington University, told CNN.
However, antibiotics are not a particularly profitable type of drug, The Wall Street Journal reported. The newspaper noted that they need to be used sparingly to limit resistance, and the cheapest option is usually prescribed. Some small companies that make antibiotics have even gone bankrupt recently, the Journal noted.
The U.S. government has invested in GSK’s development of Gepotidacin. The company predicts the drug could be a “blockbuster” and earn more than $1 billion due to UTI resistance to other drugs, the Journal reported.
“I think it will be really interesting and important to the field to see both how the drug companies sort of market this product and sort of how it does,” Dr. Liu said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new antibiotic for urinary tract infections is heading toward government approval.
It would be the first new treatment in 20 years for UTIs, which affect more than half of women at least sometime in their lives, according to data compiled by the Department of Health and Human Services.
Called Gepotidacin, the antibiotic’s trial has halted enrollment early due to excellent effectiveness and safety results thus far, drugmaker GSK announced in a press release Nov. 3. GSK will seek approval and peer-reviewed publication early next year.
There is a need for new antibiotics such as this because of increasing antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic resistance to bacteria has become so prevalent that the World Health Organization recently began publishing a list of bacteria that pose the greatest public health threats.
“It’s definitely a big deal,” Cindy Liu, MD, MPH, PhD, of the Antibiotic Resistance Action Center at George Washington University, told CNN.
However, antibiotics are not a particularly profitable type of drug, The Wall Street Journal reported. The newspaper noted that they need to be used sparingly to limit resistance, and the cheapest option is usually prescribed. Some small companies that make antibiotics have even gone bankrupt recently, the Journal noted.
The U.S. government has invested in GSK’s development of Gepotidacin. The company predicts the drug could be a “blockbuster” and earn more than $1 billion due to UTI resistance to other drugs, the Journal reported.
“I think it will be really interesting and important to the field to see both how the drug companies sort of market this product and sort of how it does,” Dr. Liu said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study sheds new light on RAS inhibitors’ role for advanced CKD
ORLANDO – Treatment with a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor is widely accepted as standard practice for slowing progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), but data have been inconsistent as to whether there is benefit to continuing RAS inhibition when patients develop advanced CKD, defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Now, in STOP ACEi, a new multicenter, randomized trial of 411 patients, , for 3 years.
People who continued RAS inhibitor treatment did not develop a significant or clinically relevant decrease in eGFR, the study’s primary outcome, both overall as well as in several prespecified subgroups compared with those who discontinued treatment, said Sunil Bhandari, MBChB, PhD, and associates, who presented the research in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
“I hope these results will reassure clinicians to continue ACE inhibitors or ARBs” in patients with advanced CKD, “with their known beneficial cardiovascular effects,” Dr. Bhandari said in an interview.
The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Similar eGFR levels after 3 years
While it’s clear that in patients with mild or moderate CKD, treatment with a RAS inhibitor, which includes angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), reduces blood pressure, slows decline in eGFR, reduces proteinuria, and delays progression to advanced CKD, there has been little evidence that the use of RAS inhibitors benefits patients with advanced CKD.
Data from previous trials have been inconsistent regarding whether the use of RAS inhibitors is nephroprotective in patients with advanced CKD, say Dr. Bhandari, a nephrologist and professor at Hull York Medical School, Hull, England, and colleagues.
“Current guidelines do not provide specific advice on whether to continue or stop ACE inhibitors or ARBs for advanced chronic kidney disease,” they also note.
And so they decided to assess whether discontinuation of ACE inhibitors/ARBs could slow progression of CKD in patients with advanced CKD.
Three years after 206 study participants stopped RAS inhibitor treatment, the least-squares mean eGFR was 12.6 mL/min per 1.73m2 in the discontinuation group and 13.3 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in the 205 patients in the continuation group, a difference that was not significant.
In addition to the primary outcome, 62% of patients who stopped RAS inhibitor treatment and 56% of those who continued developed end-stage kidney disease or required renal-replacement therapy, which translated into an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.28 for this outcome among those who discontinued compared with those who continued, which was just short of significance (95% CI, 0.99-1.65).
The two study groups also showed no significant differences in the 3-year incidence of hospitalization for any reason, cardiovascular events, or deaths. The two groups also showed no meaningful differences in various domains of quality of life and no differences in serious adverse effects.
Participants had an eGFR less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2
The study ran at 39 United Kingdom centers in 2014-2019. Investigators enrolled adults with an eGFR of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 who were not on dialysis and had not received a kidney transplant. In addition, all enrolled patients had to have an annual drop in eGFR of more than 2 mL/min per 1.73 m2 during the prior 2 years and had to have been on treatment with at least one RAS inhibitor for more than 6 months.
The randomization protocol insured balanced distribution of subjects between the two study arms by age, eGFR, presence of diabetes, and level of proteinuria, among other factors. The study design also mandated that participants maintain a blood pressure of no more than 140/85 mm Hg.
Those who discontinued RAS-inhibitor treatment could receive any guideline-recommended antihypertensive agent that was not a RAS inhibitor, although adding a RAS inhibitor was permitted as a last treatment resort.
People in the maintenance group could receive whichever additional antihypertensive agents their treating clinicians deemed necessary for maintaining the target blood pressure.
The enrolled population was a median age of 63 years old and 68% were men. Their average eGFR at baseline was 18 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and 118 (29%) had an eGFR of less than 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2. Their median level of proteinuria was 115 mg/mmol (about 1,018 mg/g). Diabetes was prevalent in 37%, and 58% of participants were taking at least three antihypertensive medications at entry.
Among the study’s limitations, the researchers cited the open-label design, which may have affected clinical care and the tally of subjective endpoints, including quality of life and exercise capacity. Also, because the study enrolled people who were on a RAS inhibitor at the time of randomization, it did not include anyone who had already discontinued these agents.
Continue RAS inhibitors in advanced CKD for best outcomes
Dr. Bhandari and colleagues note that in a large observational trial published in January 2021, Swedish researchers found an increase in the incidence of major cardiovascular events and death among patients with advanced CKD who had discontinued RAS inhibitors.
But they observe, “Our trial did not have sufficient power to investigate the effect of the discontinuation of RAS inhibitors on cardiovascular events or mortality. However, because our findings are consistent with a lack of advantage for such discontinuation with respect to kidney function, there is little rationale to conduct a larger randomized trial to investigate cardiovascular safety.”
“Our findings do not support the hypothesis that the discontinuation of RAS inhibitors in patients with advanced and progressive chronic kidney disease would improve kidney function, quality of life, or exercise capacity.”
“The results of this trial will inform future clinical practice worldwide and guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
STOP ACEi received no commercial funding. Dr. Bhandari has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO – Treatment with a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor is widely accepted as standard practice for slowing progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), but data have been inconsistent as to whether there is benefit to continuing RAS inhibition when patients develop advanced CKD, defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Now, in STOP ACEi, a new multicenter, randomized trial of 411 patients, , for 3 years.
People who continued RAS inhibitor treatment did not develop a significant or clinically relevant decrease in eGFR, the study’s primary outcome, both overall as well as in several prespecified subgroups compared with those who discontinued treatment, said Sunil Bhandari, MBChB, PhD, and associates, who presented the research in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
“I hope these results will reassure clinicians to continue ACE inhibitors or ARBs” in patients with advanced CKD, “with their known beneficial cardiovascular effects,” Dr. Bhandari said in an interview.
The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Similar eGFR levels after 3 years
While it’s clear that in patients with mild or moderate CKD, treatment with a RAS inhibitor, which includes angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), reduces blood pressure, slows decline in eGFR, reduces proteinuria, and delays progression to advanced CKD, there has been little evidence that the use of RAS inhibitors benefits patients with advanced CKD.
Data from previous trials have been inconsistent regarding whether the use of RAS inhibitors is nephroprotective in patients with advanced CKD, say Dr. Bhandari, a nephrologist and professor at Hull York Medical School, Hull, England, and colleagues.
“Current guidelines do not provide specific advice on whether to continue or stop ACE inhibitors or ARBs for advanced chronic kidney disease,” they also note.
And so they decided to assess whether discontinuation of ACE inhibitors/ARBs could slow progression of CKD in patients with advanced CKD.
Three years after 206 study participants stopped RAS inhibitor treatment, the least-squares mean eGFR was 12.6 mL/min per 1.73m2 in the discontinuation group and 13.3 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in the 205 patients in the continuation group, a difference that was not significant.
In addition to the primary outcome, 62% of patients who stopped RAS inhibitor treatment and 56% of those who continued developed end-stage kidney disease or required renal-replacement therapy, which translated into an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.28 for this outcome among those who discontinued compared with those who continued, which was just short of significance (95% CI, 0.99-1.65).
The two study groups also showed no significant differences in the 3-year incidence of hospitalization for any reason, cardiovascular events, or deaths. The two groups also showed no meaningful differences in various domains of quality of life and no differences in serious adverse effects.
Participants had an eGFR less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2
The study ran at 39 United Kingdom centers in 2014-2019. Investigators enrolled adults with an eGFR of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 who were not on dialysis and had not received a kidney transplant. In addition, all enrolled patients had to have an annual drop in eGFR of more than 2 mL/min per 1.73 m2 during the prior 2 years and had to have been on treatment with at least one RAS inhibitor for more than 6 months.
The randomization protocol insured balanced distribution of subjects between the two study arms by age, eGFR, presence of diabetes, and level of proteinuria, among other factors. The study design also mandated that participants maintain a blood pressure of no more than 140/85 mm Hg.
Those who discontinued RAS-inhibitor treatment could receive any guideline-recommended antihypertensive agent that was not a RAS inhibitor, although adding a RAS inhibitor was permitted as a last treatment resort.
People in the maintenance group could receive whichever additional antihypertensive agents their treating clinicians deemed necessary for maintaining the target blood pressure.
The enrolled population was a median age of 63 years old and 68% were men. Their average eGFR at baseline was 18 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and 118 (29%) had an eGFR of less than 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2. Their median level of proteinuria was 115 mg/mmol (about 1,018 mg/g). Diabetes was prevalent in 37%, and 58% of participants were taking at least three antihypertensive medications at entry.
Among the study’s limitations, the researchers cited the open-label design, which may have affected clinical care and the tally of subjective endpoints, including quality of life and exercise capacity. Also, because the study enrolled people who were on a RAS inhibitor at the time of randomization, it did not include anyone who had already discontinued these agents.
Continue RAS inhibitors in advanced CKD for best outcomes
Dr. Bhandari and colleagues note that in a large observational trial published in January 2021, Swedish researchers found an increase in the incidence of major cardiovascular events and death among patients with advanced CKD who had discontinued RAS inhibitors.
But they observe, “Our trial did not have sufficient power to investigate the effect of the discontinuation of RAS inhibitors on cardiovascular events or mortality. However, because our findings are consistent with a lack of advantage for such discontinuation with respect to kidney function, there is little rationale to conduct a larger randomized trial to investigate cardiovascular safety.”
“Our findings do not support the hypothesis that the discontinuation of RAS inhibitors in patients with advanced and progressive chronic kidney disease would improve kidney function, quality of life, or exercise capacity.”
“The results of this trial will inform future clinical practice worldwide and guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
STOP ACEi received no commercial funding. Dr. Bhandari has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO – Treatment with a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor is widely accepted as standard practice for slowing progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), but data have been inconsistent as to whether there is benefit to continuing RAS inhibition when patients develop advanced CKD, defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
Now, in STOP ACEi, a new multicenter, randomized trial of 411 patients, , for 3 years.
People who continued RAS inhibitor treatment did not develop a significant or clinically relevant decrease in eGFR, the study’s primary outcome, both overall as well as in several prespecified subgroups compared with those who discontinued treatment, said Sunil Bhandari, MBChB, PhD, and associates, who presented the research in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
“I hope these results will reassure clinicians to continue ACE inhibitors or ARBs” in patients with advanced CKD, “with their known beneficial cardiovascular effects,” Dr. Bhandari said in an interview.
The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Similar eGFR levels after 3 years
While it’s clear that in patients with mild or moderate CKD, treatment with a RAS inhibitor, which includes angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), reduces blood pressure, slows decline in eGFR, reduces proteinuria, and delays progression to advanced CKD, there has been little evidence that the use of RAS inhibitors benefits patients with advanced CKD.
Data from previous trials have been inconsistent regarding whether the use of RAS inhibitors is nephroprotective in patients with advanced CKD, say Dr. Bhandari, a nephrologist and professor at Hull York Medical School, Hull, England, and colleagues.
“Current guidelines do not provide specific advice on whether to continue or stop ACE inhibitors or ARBs for advanced chronic kidney disease,” they also note.
And so they decided to assess whether discontinuation of ACE inhibitors/ARBs could slow progression of CKD in patients with advanced CKD.
Three years after 206 study participants stopped RAS inhibitor treatment, the least-squares mean eGFR was 12.6 mL/min per 1.73m2 in the discontinuation group and 13.3 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in the 205 patients in the continuation group, a difference that was not significant.
In addition to the primary outcome, 62% of patients who stopped RAS inhibitor treatment and 56% of those who continued developed end-stage kidney disease or required renal-replacement therapy, which translated into an adjusted hazard ratio of 1.28 for this outcome among those who discontinued compared with those who continued, which was just short of significance (95% CI, 0.99-1.65).
The two study groups also showed no significant differences in the 3-year incidence of hospitalization for any reason, cardiovascular events, or deaths. The two groups also showed no meaningful differences in various domains of quality of life and no differences in serious adverse effects.
Participants had an eGFR less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2
The study ran at 39 United Kingdom centers in 2014-2019. Investigators enrolled adults with an eGFR of less than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2 who were not on dialysis and had not received a kidney transplant. In addition, all enrolled patients had to have an annual drop in eGFR of more than 2 mL/min per 1.73 m2 during the prior 2 years and had to have been on treatment with at least one RAS inhibitor for more than 6 months.
The randomization protocol insured balanced distribution of subjects between the two study arms by age, eGFR, presence of diabetes, and level of proteinuria, among other factors. The study design also mandated that participants maintain a blood pressure of no more than 140/85 mm Hg.
Those who discontinued RAS-inhibitor treatment could receive any guideline-recommended antihypertensive agent that was not a RAS inhibitor, although adding a RAS inhibitor was permitted as a last treatment resort.
People in the maintenance group could receive whichever additional antihypertensive agents their treating clinicians deemed necessary for maintaining the target blood pressure.
The enrolled population was a median age of 63 years old and 68% were men. Their average eGFR at baseline was 18 mL/min per 1.73 m2, and 118 (29%) had an eGFR of less than 15 mL/min per 1.73 m2. Their median level of proteinuria was 115 mg/mmol (about 1,018 mg/g). Diabetes was prevalent in 37%, and 58% of participants were taking at least three antihypertensive medications at entry.
Among the study’s limitations, the researchers cited the open-label design, which may have affected clinical care and the tally of subjective endpoints, including quality of life and exercise capacity. Also, because the study enrolled people who were on a RAS inhibitor at the time of randomization, it did not include anyone who had already discontinued these agents.
Continue RAS inhibitors in advanced CKD for best outcomes
Dr. Bhandari and colleagues note that in a large observational trial published in January 2021, Swedish researchers found an increase in the incidence of major cardiovascular events and death among patients with advanced CKD who had discontinued RAS inhibitors.
But they observe, “Our trial did not have sufficient power to investigate the effect of the discontinuation of RAS inhibitors on cardiovascular events or mortality. However, because our findings are consistent with a lack of advantage for such discontinuation with respect to kidney function, there is little rationale to conduct a larger randomized trial to investigate cardiovascular safety.”
“Our findings do not support the hypothesis that the discontinuation of RAS inhibitors in patients with advanced and progressive chronic kidney disease would improve kidney function, quality of life, or exercise capacity.”
“The results of this trial will inform future clinical practice worldwide and guideline recommendations,” they conclude.
STOP ACEi received no commercial funding. Dr. Bhandari has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT KIDNEY WEEK 2022
Moving the needle: SGLT2 inhibitor role for isolated kidney disease
ORLANDO – in a pivotal trial with more than 6,600 patients.
This confirms the efficacy for this population that was previously seen with dapagliflozin, another agent from the same class, in the DAPA-CKD trial.
In the new trial, EMPA-Kidney, treatment with empagliflozin 10 mg daily for a median of 2.0 years led to a significant 28% relative risk reduction in the primary combined endpoint in comparison with placebo, William G. Herrington, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In 2020, a different team of researchers running DAPA-CKD reported that during a median of 2.4 years, treatment of 4,304 patients with dapagliflozin 10 mg daily resulted in a significant 39% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo for an identical combined primary endpoint. Enrollment criteria for the DAPA-CKD trial were mostly similar to that of the current trial.
‘Remarkably similar’ findings
Results from EMPA-Kidney and DAPA-CKD are “remarkably similar,” said Dr. Herrington during a press briefing at the meeting.
He also noted that when the EMPA-Kidney study began – before results from DAPA-CKD were known – “we never imagined such a large effect” on important endpoints in people with CKD.
In addition to cardiovascular death, the combined primary endpoint included the incidence of renal death, incident end-stage kidney disease, a sustained decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate to less than 10 mL/min per 1.73m2, or a sustained decrease in eGFR of at least 40% from baseline.
Having similar evidence from both trials “will hopefully provide people with the confidence to start to use SGLT2 inhibitors as standard care in people with CKD” who match enrollment criteria of the two trials, added Dr. Herrington, a nephrologist at the University of Oxford (England).
The analyses he reported also showed that empagliflozin had similar efficacy for the primary endpoint regardless of whether patients had type 2 diabetes at the time of enrollment and regardless of their eGFR at entry.
To enter EMPA-Kidney, people needed to have either an eGFR of 20-44 mL/min per 1.73m2 with no minimum level of albuminuria or an eGFR of 45-89 mL/min per 1.73m2 with a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of at least 200 mg/g.
In contrast, to enroll in DAPA-CKD, patients had to have a UACR of at least 200 mg/g. This means that for the first time, EMPA-Kidney produced data on the relationship between albuminuria severity and the impact of treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor in the enrolled population.
A signal of greater efficacy with higher UACR
A total of 6,609 patients underwent randomization in EMPA-Kidney. During a median of 2.0 years of follow-up, the primary endpoint – progression of kidney disease or death from cardiovascular causes – occurred in 432 of 3,304 patients (13.1%) in the empagliflozin group and in 558 of 3,305 patients (16.9%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.72; P < .001).
The results “suggested that the effects [of empagliflozin] are greater in patients with higher levels of albuminuria, with statistically significant heterogeneity between this subgroup and those with a UACR of less than 200 mg/g (P = .02),” Dr. Herrington said.
Of the study population, 54% had no evidence of diabetes at enrollment.
Having data from a second large trial of an SGLT2 inhibitor that included people with isolated CKD who did not have diabetes or heart failure “will start to move the needle” on using this class of drugs in these types of patients, commented F. Perry Wilson, MD, a nephrologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
On the basis of the DAPA-CKD results, in April 2021 the Food and Drug Administration expanded dapagliflozin’s indications to include CKD, yet, “a lot of nephrologists consider SGLT2 inhibitors to be agents for people with diabetes or heart failure, and they defer prescribing them to endocrinologists and cardiologists,” Dr. Wilson said in an interview.
‘Flozinators’ rising
But Pascale H. Lane, MD, a pediatric nephrologist at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, commented that many nephrologists she knows have been prescribing dapagliflozin “widely” to their patients with CKD.
“I know many adult nephrologists who use it almost universally now,” Dr. Lane said. “They call themselves ‘flozinators.’ ”
EMPA-Kidney was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that along with Lilly markets empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Herrington, Dr. Wilson, and Dr. Lane disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO – in a pivotal trial with more than 6,600 patients.
This confirms the efficacy for this population that was previously seen with dapagliflozin, another agent from the same class, in the DAPA-CKD trial.
In the new trial, EMPA-Kidney, treatment with empagliflozin 10 mg daily for a median of 2.0 years led to a significant 28% relative risk reduction in the primary combined endpoint in comparison with placebo, William G. Herrington, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In 2020, a different team of researchers running DAPA-CKD reported that during a median of 2.4 years, treatment of 4,304 patients with dapagliflozin 10 mg daily resulted in a significant 39% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo for an identical combined primary endpoint. Enrollment criteria for the DAPA-CKD trial were mostly similar to that of the current trial.
‘Remarkably similar’ findings
Results from EMPA-Kidney and DAPA-CKD are “remarkably similar,” said Dr. Herrington during a press briefing at the meeting.
He also noted that when the EMPA-Kidney study began – before results from DAPA-CKD were known – “we never imagined such a large effect” on important endpoints in people with CKD.
In addition to cardiovascular death, the combined primary endpoint included the incidence of renal death, incident end-stage kidney disease, a sustained decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate to less than 10 mL/min per 1.73m2, or a sustained decrease in eGFR of at least 40% from baseline.
Having similar evidence from both trials “will hopefully provide people with the confidence to start to use SGLT2 inhibitors as standard care in people with CKD” who match enrollment criteria of the two trials, added Dr. Herrington, a nephrologist at the University of Oxford (England).
The analyses he reported also showed that empagliflozin had similar efficacy for the primary endpoint regardless of whether patients had type 2 diabetes at the time of enrollment and regardless of their eGFR at entry.
To enter EMPA-Kidney, people needed to have either an eGFR of 20-44 mL/min per 1.73m2 with no minimum level of albuminuria or an eGFR of 45-89 mL/min per 1.73m2 with a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of at least 200 mg/g.
In contrast, to enroll in DAPA-CKD, patients had to have a UACR of at least 200 mg/g. This means that for the first time, EMPA-Kidney produced data on the relationship between albuminuria severity and the impact of treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor in the enrolled population.
A signal of greater efficacy with higher UACR
A total of 6,609 patients underwent randomization in EMPA-Kidney. During a median of 2.0 years of follow-up, the primary endpoint – progression of kidney disease or death from cardiovascular causes – occurred in 432 of 3,304 patients (13.1%) in the empagliflozin group and in 558 of 3,305 patients (16.9%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.72; P < .001).
The results “suggested that the effects [of empagliflozin] are greater in patients with higher levels of albuminuria, with statistically significant heterogeneity between this subgroup and those with a UACR of less than 200 mg/g (P = .02),” Dr. Herrington said.
Of the study population, 54% had no evidence of diabetes at enrollment.
Having data from a second large trial of an SGLT2 inhibitor that included people with isolated CKD who did not have diabetes or heart failure “will start to move the needle” on using this class of drugs in these types of patients, commented F. Perry Wilson, MD, a nephrologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
On the basis of the DAPA-CKD results, in April 2021 the Food and Drug Administration expanded dapagliflozin’s indications to include CKD, yet, “a lot of nephrologists consider SGLT2 inhibitors to be agents for people with diabetes or heart failure, and they defer prescribing them to endocrinologists and cardiologists,” Dr. Wilson said in an interview.
‘Flozinators’ rising
But Pascale H. Lane, MD, a pediatric nephrologist at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, commented that many nephrologists she knows have been prescribing dapagliflozin “widely” to their patients with CKD.
“I know many adult nephrologists who use it almost universally now,” Dr. Lane said. “They call themselves ‘flozinators.’ ”
EMPA-Kidney was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that along with Lilly markets empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Herrington, Dr. Wilson, and Dr. Lane disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO – in a pivotal trial with more than 6,600 patients.
This confirms the efficacy for this population that was previously seen with dapagliflozin, another agent from the same class, in the DAPA-CKD trial.
In the new trial, EMPA-Kidney, treatment with empagliflozin 10 mg daily for a median of 2.0 years led to a significant 28% relative risk reduction in the primary combined endpoint in comparison with placebo, William G. Herrington, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Nephrology.
The results were simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
In 2020, a different team of researchers running DAPA-CKD reported that during a median of 2.4 years, treatment of 4,304 patients with dapagliflozin 10 mg daily resulted in a significant 39% relative risk reduction, compared with placebo for an identical combined primary endpoint. Enrollment criteria for the DAPA-CKD trial were mostly similar to that of the current trial.
‘Remarkably similar’ findings
Results from EMPA-Kidney and DAPA-CKD are “remarkably similar,” said Dr. Herrington during a press briefing at the meeting.
He also noted that when the EMPA-Kidney study began – before results from DAPA-CKD were known – “we never imagined such a large effect” on important endpoints in people with CKD.
In addition to cardiovascular death, the combined primary endpoint included the incidence of renal death, incident end-stage kidney disease, a sustained decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate to less than 10 mL/min per 1.73m2, or a sustained decrease in eGFR of at least 40% from baseline.
Having similar evidence from both trials “will hopefully provide people with the confidence to start to use SGLT2 inhibitors as standard care in people with CKD” who match enrollment criteria of the two trials, added Dr. Herrington, a nephrologist at the University of Oxford (England).
The analyses he reported also showed that empagliflozin had similar efficacy for the primary endpoint regardless of whether patients had type 2 diabetes at the time of enrollment and regardless of their eGFR at entry.
To enter EMPA-Kidney, people needed to have either an eGFR of 20-44 mL/min per 1.73m2 with no minimum level of albuminuria or an eGFR of 45-89 mL/min per 1.73m2 with a urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR) of at least 200 mg/g.
In contrast, to enroll in DAPA-CKD, patients had to have a UACR of at least 200 mg/g. This means that for the first time, EMPA-Kidney produced data on the relationship between albuminuria severity and the impact of treatment with an SGLT2 inhibitor in the enrolled population.
A signal of greater efficacy with higher UACR
A total of 6,609 patients underwent randomization in EMPA-Kidney. During a median of 2.0 years of follow-up, the primary endpoint – progression of kidney disease or death from cardiovascular causes – occurred in 432 of 3,304 patients (13.1%) in the empagliflozin group and in 558 of 3,305 patients (16.9%) in the placebo group (hazard ratio, 0.72; P < .001).
The results “suggested that the effects [of empagliflozin] are greater in patients with higher levels of albuminuria, with statistically significant heterogeneity between this subgroup and those with a UACR of less than 200 mg/g (P = .02),” Dr. Herrington said.
Of the study population, 54% had no evidence of diabetes at enrollment.
Having data from a second large trial of an SGLT2 inhibitor that included people with isolated CKD who did not have diabetes or heart failure “will start to move the needle” on using this class of drugs in these types of patients, commented F. Perry Wilson, MD, a nephrologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
On the basis of the DAPA-CKD results, in April 2021 the Food and Drug Administration expanded dapagliflozin’s indications to include CKD, yet, “a lot of nephrologists consider SGLT2 inhibitors to be agents for people with diabetes or heart failure, and they defer prescribing them to endocrinologists and cardiologists,” Dr. Wilson said in an interview.
‘Flozinators’ rising
But Pascale H. Lane, MD, a pediatric nephrologist at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, commented that many nephrologists she knows have been prescribing dapagliflozin “widely” to their patients with CKD.
“I know many adult nephrologists who use it almost universally now,” Dr. Lane said. “They call themselves ‘flozinators.’ ”
EMPA-Kidney was sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim, the company that along with Lilly markets empagliflozin (Jardiance). Dr. Herrington, Dr. Wilson, and Dr. Lane disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT KIDNEY WEEK 2022
Kidney function may help docs pick antiplatelet mix after stroke
Renal function should be considered when determining whether to pick ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin as the antiplatelet therapy for patients with minor stroke, according to new research.
The study, which was conducted in 202 centers in China and published in Annals of Internal Medicine, indicates that when patients had normal kidney function, ticagrelor-aspirin, compared with clopidogrel-aspirin, substantially reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days of follow-up.
However, this effect was not seen in patients with mildly, moderately or severely decreased kidney function.
Rates of severe or moderate bleeding did not differ substantially between the two treatments.
Results gleaned from CHANCE-2 data
The researchers, led by Anxin Wang, PhD, from Capital Medical University in Beijing, conducted a post hoc analysis of the CHANCE-2 (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events-II) trial.
The trial included 6,378 patients who carried cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) loss-of-function (LOF) alleles who had experienced a minor stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Patients received either ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin, and their renal function was measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate. The authors listed as a limitation that no data were available on the presence of albuminuria or proteinuria.
The researchers investigated what effect renal function had on the efficacy and safety of the therapies.
Differences in the therapies
Clopidogrel-aspirin is often recommended for preventing stroke. It can reduce thrombotic risk in patients with impaired kidney function, the authors noted. Ticagrelor can provide greater, faster, and more consistent P2Y12 inhibition than clopidogrel, and evidence shows it is effective in preventing stroke recurrence, particularly in people carrying CYP2C19 LOF alleles.
When people have reduced kidney function, clopidogrel may be harder to clear than ticagrelor and there may be increased plasma concentrations, so function is important to consider when choosing an antiplatelet therapy, the authors wrote.
Choice may come down to cost
Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, associate professor of vascular and cardiovascular medicine at University of Michigan Medicine in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that there has been momentum toward ticagrelor as a more potent choice than clopidogrel not just in populations with minor stroke but for people with MI and coronary stents.
He said he found the results surprising and was intrigued that this paper suggests looking more skeptically at ticagrelor when kidney function is impaired.
Still, the choice may also come down to what the patient can afford at the pharmacy, he said.
“The reality is many patients still get clopidogrel either because that’s what their physicians have been prescribing for well over a decade or because of cost issues, and clopidogrel, for many patients, can be less expensive,” Dr. Barnes noted.
He said he would like to see more study in different populations as the prevalence of people carrying CYP2C19 allele differs by race and results might be different in a non-Asian population. That allele is thought to affect how clopidogrel is metabolized.
Study should spur more research
Nada El Husseini, MD, associate professor of neurology and Duke Telestroke Medical Director at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said the study is hypothesis generating, but shouldn’t be thought of as the last word on the subject.
She pointed out some additional limitations of the study, including that it was a post hoc analysis. She explained that the question researchers asked in this study – about effect of kidney function on the safety and efficacy of the therapies – was not the focus of the original CHANCE-2 study, and, as such, the post hoc study may have been underpowered to answer the renal function question.
The authors acknowledged that limitation, noting that “the proportion of patients with severely decreased renal function was low.”
Among 6,378 patients, 4,050 (63.5%) had normal kidney function, 2,010 (31.5%) had mildly decreased function, and 318 (5.0%) had moderately to severely decreased function.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, the Chinese Stroke Association, the National Science and Technology Major Project and the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program). Salubris Pharmaceuticals contributed ticagrelor and, clopidogrel at no cost and with no restrictions. Dr. Wang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Barnes and Dr. El Husseini reported no relevant financial relationships.
Renal function should be considered when determining whether to pick ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin as the antiplatelet therapy for patients with minor stroke, according to new research.
The study, which was conducted in 202 centers in China and published in Annals of Internal Medicine, indicates that when patients had normal kidney function, ticagrelor-aspirin, compared with clopidogrel-aspirin, substantially reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days of follow-up.
However, this effect was not seen in patients with mildly, moderately or severely decreased kidney function.
Rates of severe or moderate bleeding did not differ substantially between the two treatments.
Results gleaned from CHANCE-2 data
The researchers, led by Anxin Wang, PhD, from Capital Medical University in Beijing, conducted a post hoc analysis of the CHANCE-2 (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events-II) trial.
The trial included 6,378 patients who carried cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) loss-of-function (LOF) alleles who had experienced a minor stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Patients received either ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin, and their renal function was measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate. The authors listed as a limitation that no data were available on the presence of albuminuria or proteinuria.
The researchers investigated what effect renal function had on the efficacy and safety of the therapies.
Differences in the therapies
Clopidogrel-aspirin is often recommended for preventing stroke. It can reduce thrombotic risk in patients with impaired kidney function, the authors noted. Ticagrelor can provide greater, faster, and more consistent P2Y12 inhibition than clopidogrel, and evidence shows it is effective in preventing stroke recurrence, particularly in people carrying CYP2C19 LOF alleles.
When people have reduced kidney function, clopidogrel may be harder to clear than ticagrelor and there may be increased plasma concentrations, so function is important to consider when choosing an antiplatelet therapy, the authors wrote.
Choice may come down to cost
Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, associate professor of vascular and cardiovascular medicine at University of Michigan Medicine in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that there has been momentum toward ticagrelor as a more potent choice than clopidogrel not just in populations with minor stroke but for people with MI and coronary stents.
He said he found the results surprising and was intrigued that this paper suggests looking more skeptically at ticagrelor when kidney function is impaired.
Still, the choice may also come down to what the patient can afford at the pharmacy, he said.
“The reality is many patients still get clopidogrel either because that’s what their physicians have been prescribing for well over a decade or because of cost issues, and clopidogrel, for many patients, can be less expensive,” Dr. Barnes noted.
He said he would like to see more study in different populations as the prevalence of people carrying CYP2C19 allele differs by race and results might be different in a non-Asian population. That allele is thought to affect how clopidogrel is metabolized.
Study should spur more research
Nada El Husseini, MD, associate professor of neurology and Duke Telestroke Medical Director at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said the study is hypothesis generating, but shouldn’t be thought of as the last word on the subject.
She pointed out some additional limitations of the study, including that it was a post hoc analysis. She explained that the question researchers asked in this study – about effect of kidney function on the safety and efficacy of the therapies – was not the focus of the original CHANCE-2 study, and, as such, the post hoc study may have been underpowered to answer the renal function question.
The authors acknowledged that limitation, noting that “the proportion of patients with severely decreased renal function was low.”
Among 6,378 patients, 4,050 (63.5%) had normal kidney function, 2,010 (31.5%) had mildly decreased function, and 318 (5.0%) had moderately to severely decreased function.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, the Chinese Stroke Association, the National Science and Technology Major Project and the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program). Salubris Pharmaceuticals contributed ticagrelor and, clopidogrel at no cost and with no restrictions. Dr. Wang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Barnes and Dr. El Husseini reported no relevant financial relationships.
Renal function should be considered when determining whether to pick ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin as the antiplatelet therapy for patients with minor stroke, according to new research.
The study, which was conducted in 202 centers in China and published in Annals of Internal Medicine, indicates that when patients had normal kidney function, ticagrelor-aspirin, compared with clopidogrel-aspirin, substantially reduced the risk for recurrent stroke within 90 days of follow-up.
However, this effect was not seen in patients with mildly, moderately or severely decreased kidney function.
Rates of severe or moderate bleeding did not differ substantially between the two treatments.
Results gleaned from CHANCE-2 data
The researchers, led by Anxin Wang, PhD, from Capital Medical University in Beijing, conducted a post hoc analysis of the CHANCE-2 (Clopidogrel in High-Risk Patients with Acute Nondisabling Cerebrovascular Events-II) trial.
The trial included 6,378 patients who carried cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) loss-of-function (LOF) alleles who had experienced a minor stroke or transient ischemic attack.
Patients received either ticagrelor-aspirin or clopidogrel-aspirin, and their renal function was measured by estimated glomerular filtration rate. The authors listed as a limitation that no data were available on the presence of albuminuria or proteinuria.
The researchers investigated what effect renal function had on the efficacy and safety of the therapies.
Differences in the therapies
Clopidogrel-aspirin is often recommended for preventing stroke. It can reduce thrombotic risk in patients with impaired kidney function, the authors noted. Ticagrelor can provide greater, faster, and more consistent P2Y12 inhibition than clopidogrel, and evidence shows it is effective in preventing stroke recurrence, particularly in people carrying CYP2C19 LOF alleles.
When people have reduced kidney function, clopidogrel may be harder to clear than ticagrelor and there may be increased plasma concentrations, so function is important to consider when choosing an antiplatelet therapy, the authors wrote.
Choice may come down to cost
Geoffrey Barnes, MD, MSc, associate professor of vascular and cardiovascular medicine at University of Michigan Medicine in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that there has been momentum toward ticagrelor as a more potent choice than clopidogrel not just in populations with minor stroke but for people with MI and coronary stents.
He said he found the results surprising and was intrigued that this paper suggests looking more skeptically at ticagrelor when kidney function is impaired.
Still, the choice may also come down to what the patient can afford at the pharmacy, he said.
“The reality is many patients still get clopidogrel either because that’s what their physicians have been prescribing for well over a decade or because of cost issues, and clopidogrel, for many patients, can be less expensive,” Dr. Barnes noted.
He said he would like to see more study in different populations as the prevalence of people carrying CYP2C19 allele differs by race and results might be different in a non-Asian population. That allele is thought to affect how clopidogrel is metabolized.
Study should spur more research
Nada El Husseini, MD, associate professor of neurology and Duke Telestroke Medical Director at Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., said the study is hypothesis generating, but shouldn’t be thought of as the last word on the subject.
She pointed out some additional limitations of the study, including that it was a post hoc analysis. She explained that the question researchers asked in this study – about effect of kidney function on the safety and efficacy of the therapies – was not the focus of the original CHANCE-2 study, and, as such, the post hoc study may have been underpowered to answer the renal function question.
The authors acknowledged that limitation, noting that “the proportion of patients with severely decreased renal function was low.”
Among 6,378 patients, 4,050 (63.5%) had normal kidney function, 2,010 (31.5%) had mildly decreased function, and 318 (5.0%) had moderately to severely decreased function.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, the Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Commission, the Chinese Stroke Association, the National Science and Technology Major Project and the Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Incubating Program). Salubris Pharmaceuticals contributed ticagrelor and, clopidogrel at no cost and with no restrictions. Dr. Wang reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Barnes and Dr. El Husseini reported no relevant financial relationships.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Terlipressin decreases need for renal replacement therapy in liver transplant recipients
In a subgroup of patients with hepatorenal syndrome type 1 (HRS) who received a liver transplant, terlipressin treatment appears to reduce the need for renal replacement therapy (RRT) through 12 months of follow-up, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Among transplant recipients, overall 12-month survival was 11% higher for those treated with terlipressin compared with placebo, said K. Rajender Reddy, MD, director of hepatology and medical director of liver transplantation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“Hepatorenal syndrome type 1 is a potentially reversible form of acute kidney injury that occurs in the setting of end-stage liver disease,” he said.
Liver transplantation, which eliminates end-stage liver disease, is the only definitive treatment for HRS. However, renal replacement therapy is common and associated with poor clinical outcomes and low patient survival rates in both the pretransplant and posttransplant settings, he noted.
Terlipressin, an injectable synthetic vasopressin analogue, restores renal blood flow and reverses HRS in 20%-40% of patients, Dr. Reddy said. In September, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved terlipressin (Terlivaz) for patients with HRS type 1. The label has a boxed warning for serious or fatal respiratory failure.
The safety and efficacy were assessed in the phase 3 CONFIRM trial, which Dr. Reddy and colleagues previously published. The randomized, placebo-controlled study demonstrated that terlipressin reversed HRS and reduced the need for RRT through day 30. The reversal of HRS with terlipressin did not improve 90-day survival as compared with placebo, which researchers attributed to a higher death rate within 90 days after the first dose despite improved kidney function.
A closer look at the liver transplant patients
In the subgroup analysis of the CONFIRM study, Dr. Reddy and colleagues analyzed the clinical outcomes through 12 months of follow-up in patients with HRS who received a liver transplant. They looked at the incidence of verified HRS reversal, HRS reversal, need for RRT, and overall survival.
Verified HRS reversal was defined as two consecutive serum creatinine measurements of 1.5 mg/dL or less at least 2 hours apart up to day 14 and survival without RRT for at least 10 days. HRS reversal was defined as a serum creatinine level of 1.5 mg/dL or less while on treatment. In addition, the need for RRT and overall survival were assessed at days 30, 60, 90, 180, and 365.
RRT was defined as any procedure that replaced nonendocrine kidney function, including continuous hemofiltration and hemodialysis, intermittent hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, ultrafiltration, or other dialysis and filtration techniques.
In the CONFIRM study, 199 patients with HRS were treated with terlipressin plus albumin, and 101 patients were treated with placebo plus albumin for up to 14 days. In the terlipressin group, 46 patients received liver transplants within the first 2 months of the study, as did 29 in the placebo group. Two patients in the terlipressin group and one in the placebo group received a simultaneous liver-kidney transplant.
Meaningful clinical outcomes
In the 12-month follow-up subgroup analysis, verified HRS reversal was statistically comparable between the groups, with a 30% decrease in the terlipressin group and 17% decrease in the placebo group, Dr. Reddy reported.
HRS reversal was higher in the terlipressin group, at 37%, as compared with 14% in the placebo group.
The pretransplant need for RRT was lower in the terlipressin group, at 30%, as compared with 62% in the placebo group. The posttransplant need for RRT remained numerically lower in the terlipressin group at all time points and was significantly lower at day 180 and day 365.
Overall survival for transplant recipients in the terlipressin group was 94%, as compared with 83% in the placebo group. Posttreatment adverse events and severe adverse events were similar between the groups.
“Collectively, these data indicate that terlipressin treatment in patients with HRS led to better long-term clinical outcomes in those who received a liver transplant,” Dr. Reddy said.
The study was funded by Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, which manufactures terlipressin. One author is an employee of Mallinckrodt, and the other authors have served in an advisory role or received grant support from Mallinckrodt. The authors also disclosed consultant roles and research support from several other pharmaceutical companies.
In a subgroup of patients with hepatorenal syndrome type 1 (HRS) who received a liver transplant, terlipressin treatment appears to reduce the need for renal replacement therapy (RRT) through 12 months of follow-up, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Among transplant recipients, overall 12-month survival was 11% higher for those treated with terlipressin compared with placebo, said K. Rajender Reddy, MD, director of hepatology and medical director of liver transplantation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“Hepatorenal syndrome type 1 is a potentially reversible form of acute kidney injury that occurs in the setting of end-stage liver disease,” he said.
Liver transplantation, which eliminates end-stage liver disease, is the only definitive treatment for HRS. However, renal replacement therapy is common and associated with poor clinical outcomes and low patient survival rates in both the pretransplant and posttransplant settings, he noted.
Terlipressin, an injectable synthetic vasopressin analogue, restores renal blood flow and reverses HRS in 20%-40% of patients, Dr. Reddy said. In September, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved terlipressin (Terlivaz) for patients with HRS type 1. The label has a boxed warning for serious or fatal respiratory failure.
The safety and efficacy were assessed in the phase 3 CONFIRM trial, which Dr. Reddy and colleagues previously published. The randomized, placebo-controlled study demonstrated that terlipressin reversed HRS and reduced the need for RRT through day 30. The reversal of HRS with terlipressin did not improve 90-day survival as compared with placebo, which researchers attributed to a higher death rate within 90 days after the first dose despite improved kidney function.
A closer look at the liver transplant patients
In the subgroup analysis of the CONFIRM study, Dr. Reddy and colleagues analyzed the clinical outcomes through 12 months of follow-up in patients with HRS who received a liver transplant. They looked at the incidence of verified HRS reversal, HRS reversal, need for RRT, and overall survival.
Verified HRS reversal was defined as two consecutive serum creatinine measurements of 1.5 mg/dL or less at least 2 hours apart up to day 14 and survival without RRT for at least 10 days. HRS reversal was defined as a serum creatinine level of 1.5 mg/dL or less while on treatment. In addition, the need for RRT and overall survival were assessed at days 30, 60, 90, 180, and 365.
RRT was defined as any procedure that replaced nonendocrine kidney function, including continuous hemofiltration and hemodialysis, intermittent hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, ultrafiltration, or other dialysis and filtration techniques.
In the CONFIRM study, 199 patients with HRS were treated with terlipressin plus albumin, and 101 patients were treated with placebo plus albumin for up to 14 days. In the terlipressin group, 46 patients received liver transplants within the first 2 months of the study, as did 29 in the placebo group. Two patients in the terlipressin group and one in the placebo group received a simultaneous liver-kidney transplant.
Meaningful clinical outcomes
In the 12-month follow-up subgroup analysis, verified HRS reversal was statistically comparable between the groups, with a 30% decrease in the terlipressin group and 17% decrease in the placebo group, Dr. Reddy reported.
HRS reversal was higher in the terlipressin group, at 37%, as compared with 14% in the placebo group.
The pretransplant need for RRT was lower in the terlipressin group, at 30%, as compared with 62% in the placebo group. The posttransplant need for RRT remained numerically lower in the terlipressin group at all time points and was significantly lower at day 180 and day 365.
Overall survival for transplant recipients in the terlipressin group was 94%, as compared with 83% in the placebo group. Posttreatment adverse events and severe adverse events were similar between the groups.
“Collectively, these data indicate that terlipressin treatment in patients with HRS led to better long-term clinical outcomes in those who received a liver transplant,” Dr. Reddy said.
The study was funded by Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, which manufactures terlipressin. One author is an employee of Mallinckrodt, and the other authors have served in an advisory role or received grant support from Mallinckrodt. The authors also disclosed consultant roles and research support from several other pharmaceutical companies.
In a subgroup of patients with hepatorenal syndrome type 1 (HRS) who received a liver transplant, terlipressin treatment appears to reduce the need for renal replacement therapy (RRT) through 12 months of follow-up, according to a study presented at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Among transplant recipients, overall 12-month survival was 11% higher for those treated with terlipressin compared with placebo, said K. Rajender Reddy, MD, director of hepatology and medical director of liver transplantation at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
“Hepatorenal syndrome type 1 is a potentially reversible form of acute kidney injury that occurs in the setting of end-stage liver disease,” he said.
Liver transplantation, which eliminates end-stage liver disease, is the only definitive treatment for HRS. However, renal replacement therapy is common and associated with poor clinical outcomes and low patient survival rates in both the pretransplant and posttransplant settings, he noted.
Terlipressin, an injectable synthetic vasopressin analogue, restores renal blood flow and reverses HRS in 20%-40% of patients, Dr. Reddy said. In September, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved terlipressin (Terlivaz) for patients with HRS type 1. The label has a boxed warning for serious or fatal respiratory failure.
The safety and efficacy were assessed in the phase 3 CONFIRM trial, which Dr. Reddy and colleagues previously published. The randomized, placebo-controlled study demonstrated that terlipressin reversed HRS and reduced the need for RRT through day 30. The reversal of HRS with terlipressin did not improve 90-day survival as compared with placebo, which researchers attributed to a higher death rate within 90 days after the first dose despite improved kidney function.
A closer look at the liver transplant patients
In the subgroup analysis of the CONFIRM study, Dr. Reddy and colleagues analyzed the clinical outcomes through 12 months of follow-up in patients with HRS who received a liver transplant. They looked at the incidence of verified HRS reversal, HRS reversal, need for RRT, and overall survival.
Verified HRS reversal was defined as two consecutive serum creatinine measurements of 1.5 mg/dL or less at least 2 hours apart up to day 14 and survival without RRT for at least 10 days. HRS reversal was defined as a serum creatinine level of 1.5 mg/dL or less while on treatment. In addition, the need for RRT and overall survival were assessed at days 30, 60, 90, 180, and 365.
RRT was defined as any procedure that replaced nonendocrine kidney function, including continuous hemofiltration and hemodialysis, intermittent hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, ultrafiltration, or other dialysis and filtration techniques.
In the CONFIRM study, 199 patients with HRS were treated with terlipressin plus albumin, and 101 patients were treated with placebo plus albumin for up to 14 days. In the terlipressin group, 46 patients received liver transplants within the first 2 months of the study, as did 29 in the placebo group. Two patients in the terlipressin group and one in the placebo group received a simultaneous liver-kidney transplant.
Meaningful clinical outcomes
In the 12-month follow-up subgroup analysis, verified HRS reversal was statistically comparable between the groups, with a 30% decrease in the terlipressin group and 17% decrease in the placebo group, Dr. Reddy reported.
HRS reversal was higher in the terlipressin group, at 37%, as compared with 14% in the placebo group.
The pretransplant need for RRT was lower in the terlipressin group, at 30%, as compared with 62% in the placebo group. The posttransplant need for RRT remained numerically lower in the terlipressin group at all time points and was significantly lower at day 180 and day 365.
Overall survival for transplant recipients in the terlipressin group was 94%, as compared with 83% in the placebo group. Posttreatment adverse events and severe adverse events were similar between the groups.
“Collectively, these data indicate that terlipressin treatment in patients with HRS led to better long-term clinical outcomes in those who received a liver transplant,” Dr. Reddy said.
The study was funded by Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals, which manufactures terlipressin. One author is an employee of Mallinckrodt, and the other authors have served in an advisory role or received grant support from Mallinckrodt. The authors also disclosed consultant roles and research support from several other pharmaceutical companies.
FROM ACG 2022
Goodbye ‘diabetes insipidus’, hello ‘AVP-D’ and ‘AVP-R’
An international group representing leading endocrinology associations has recommended that the name “diabetes insipidus” – which in some cases has led to harm – be changed to eliminate confusion with “diabetes mellitus” and to reflect the former condition’s pathophysiology.
The new proposed names are arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D) for central (also called “cranial”) etiologies and arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R) for nephrogenic (kidney) etiologies.
“What we’re proposing is to rename the disease according to the pathophysiology that defines it,” statement co-author Joseph G. Verbalis, MD, professor of medicine and chief of endocrinology and metabolism at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The statement advises that henceforth the new names be used in manuscripts and the medical literature while keeping the old names in parentheses during a transition period, as in “AVP-deficiency (cranial diabetes insipidus)” and “AVP-resistance (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus).”
The condition formerly known as diabetes insipidus is relatively rare, occurring in about 1 person per 10-15,000 population. It is caused by either deficient production or resistance in the kidney to the hormone AVP, normally produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary gland. AVP, also called antidiuretic hormone, regulates the body’s water level and urine production by the kidney.
Both etiologies lead to extreme thirst and excessive production of urine. Common causes of the deficiency include head trauma or brain tumor, while resistance in the kidney is often congenital. It is currently treated with a synthetic form of AVP called desmopressin and fluid replacement.
What’s in a name?
The proposal to change the name by the Working Group for Renaming Diabetes Insipidus is endorsed by The Endocrine Society, European Society of Endocrinology, Pituitary Society, Society for Endocrinology, European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology, Endocrine Society of Australia, Brazilian Endocrine Society, and Japanese Endocrine Society and is under review by several other societies. It was published as a position statement in several of those society’s journals, with more to follow.
Historically, the word “diabetes,” a Greek word meaning “siphon,” was used in the 1st and 2nd century BC to describe excess flow of urine. The Latin word “mellitus” or “honey” was added in the late 17th century to describe the sweetness of the urine in the dysglycemic condition.
A century later, the Latin word “insipidus,” meaning insipid or tasteless, was coined to distinguish between the two types of polyuria, the position statement details.
In the late 19th to early 20th century, the vasopressor and antidiuretic actions of posterior pituitary extracts were discovered and used to treat people with both the central and nephrogenic etiologies, which were also recognized around that time, yet the name “diabetes insipidus” has persisted.
“From a historical perspective, the name is perfectly appropriate. At the time it was identified, and it was realized that it was different from diabetes mellitus, that was a perfectly appropriate terminology based on what was known in the late 19th century – but not now. It has persisted through the years simply because in medicine there’s a lot of inertia for change ... It’s just always been called that. If there’s not a compelling reason to change a name, generally there’s no move to change it,” Dr. Verbalis observed.
‘Dramatic cases of patient mismanagement’ due to name confusion
Unfortunately, the urgency for the change arose from tragedy. In 2009, a 22-year-old man was admitted to the orthopedics department of a London teaching hospital for a hip replacement. Despite his known panhypopituitarism and diabetes insipidus, the nurses continually checked his blood glucose but didn’t give him desmopressin or sufficient fluids. Laboratory testing showed normal glucose, but his serum sodium was 149 mmol/L. The morning after his operation, he had a fatal cardiac arrest with a serum sodium of 169 mmol/L.
“The nurses thought he had diabetes mellitus ... So that was death due to failure to recognize that diabetes insipidus is not diabetes mellitus,” Dr. Verbalis said. “If he had been admitted to endocrinology, this wouldn’t have happened. But he was admitted to orthopedics. Non-endocrinologists are not so aware of diabetes insipidus, because it is a rare disease.”
In 2016, National Health Service England issued a patient safety alert about the “risk of severe harm or death when desmopressin is omitted or delayed in patients with cranial diabetes insipidus,” citing at least four incidents within the prior 7 years where omission of desmopressin had resulted in severe dehydration and death, with another 76 cases of omission or delay that were acted on before the patients became critically ill.
Further impetus for the name change came from the results of an anonymous web-based survey of 1,034 adult and pediatric patients with central diabetes insipidus conducted between August 2021 and February 2022. Overall, 80% reported encountering situations in which their condition had been confused with diabetes mellitus by health care professionals, and 85% supported renaming the disease.
There was some divergence in opinion as to what the new name(s) should be, but clear agreement that the term “diabetes” should not be part of it.
“We’ve only become recently aware that there are dramatic cases of patient mismanagement due to the confusion caused by the word ‘diabetes.’ We think patients should have a voice. If a legitimate patient survey says over 80% think this name should be changed, then I think we as endocrinologists need to pay attention to that,” Dr. Verbalis said.
But while endocrinologists are the ones who see these patients the most often, Dr. Verbalis said a main aim of the position statement “is really to change the mindset of non-endocrinologist doctors and nurses and other health care professionals that this is not diabetes mellitus. It’s a totally different disease. And if we give it a totally different name, then I think they will better recognize that.”
As to how long Dr. Verbalis thinks it will take for the new names to catch on, he pointed out that it’s taken about a decade for the rheumatology field to fully adopt the name “granulomatosis with polyangiitis” as a replacement for “Wegener’s granulomatosis” after the eponymous physician’s Nazi ties were revealed.
“So we’re not anticipating that this is going to change terminology tomorrow. It’s a long process. We just wanted to get the process started,” he said.
Dr. Verbalis has reported consulting for Otsuka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An international group representing leading endocrinology associations has recommended that the name “diabetes insipidus” – which in some cases has led to harm – be changed to eliminate confusion with “diabetes mellitus” and to reflect the former condition’s pathophysiology.
The new proposed names are arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D) for central (also called “cranial”) etiologies and arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R) for nephrogenic (kidney) etiologies.
“What we’re proposing is to rename the disease according to the pathophysiology that defines it,” statement co-author Joseph G. Verbalis, MD, professor of medicine and chief of endocrinology and metabolism at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The statement advises that henceforth the new names be used in manuscripts and the medical literature while keeping the old names in parentheses during a transition period, as in “AVP-deficiency (cranial diabetes insipidus)” and “AVP-resistance (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus).”
The condition formerly known as diabetes insipidus is relatively rare, occurring in about 1 person per 10-15,000 population. It is caused by either deficient production or resistance in the kidney to the hormone AVP, normally produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary gland. AVP, also called antidiuretic hormone, regulates the body’s water level and urine production by the kidney.
Both etiologies lead to extreme thirst and excessive production of urine. Common causes of the deficiency include head trauma or brain tumor, while resistance in the kidney is often congenital. It is currently treated with a synthetic form of AVP called desmopressin and fluid replacement.
What’s in a name?
The proposal to change the name by the Working Group for Renaming Diabetes Insipidus is endorsed by The Endocrine Society, European Society of Endocrinology, Pituitary Society, Society for Endocrinology, European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology, Endocrine Society of Australia, Brazilian Endocrine Society, and Japanese Endocrine Society and is under review by several other societies. It was published as a position statement in several of those society’s journals, with more to follow.
Historically, the word “diabetes,” a Greek word meaning “siphon,” was used in the 1st and 2nd century BC to describe excess flow of urine. The Latin word “mellitus” or “honey” was added in the late 17th century to describe the sweetness of the urine in the dysglycemic condition.
A century later, the Latin word “insipidus,” meaning insipid or tasteless, was coined to distinguish between the two types of polyuria, the position statement details.
In the late 19th to early 20th century, the vasopressor and antidiuretic actions of posterior pituitary extracts were discovered and used to treat people with both the central and nephrogenic etiologies, which were also recognized around that time, yet the name “diabetes insipidus” has persisted.
“From a historical perspective, the name is perfectly appropriate. At the time it was identified, and it was realized that it was different from diabetes mellitus, that was a perfectly appropriate terminology based on what was known in the late 19th century – but not now. It has persisted through the years simply because in medicine there’s a lot of inertia for change ... It’s just always been called that. If there’s not a compelling reason to change a name, generally there’s no move to change it,” Dr. Verbalis observed.
‘Dramatic cases of patient mismanagement’ due to name confusion
Unfortunately, the urgency for the change arose from tragedy. In 2009, a 22-year-old man was admitted to the orthopedics department of a London teaching hospital for a hip replacement. Despite his known panhypopituitarism and diabetes insipidus, the nurses continually checked his blood glucose but didn’t give him desmopressin or sufficient fluids. Laboratory testing showed normal glucose, but his serum sodium was 149 mmol/L. The morning after his operation, he had a fatal cardiac arrest with a serum sodium of 169 mmol/L.
“The nurses thought he had diabetes mellitus ... So that was death due to failure to recognize that diabetes insipidus is not diabetes mellitus,” Dr. Verbalis said. “If he had been admitted to endocrinology, this wouldn’t have happened. But he was admitted to orthopedics. Non-endocrinologists are not so aware of diabetes insipidus, because it is a rare disease.”
In 2016, National Health Service England issued a patient safety alert about the “risk of severe harm or death when desmopressin is omitted or delayed in patients with cranial diabetes insipidus,” citing at least four incidents within the prior 7 years where omission of desmopressin had resulted in severe dehydration and death, with another 76 cases of omission or delay that were acted on before the patients became critically ill.
Further impetus for the name change came from the results of an anonymous web-based survey of 1,034 adult and pediatric patients with central diabetes insipidus conducted between August 2021 and February 2022. Overall, 80% reported encountering situations in which their condition had been confused with diabetes mellitus by health care professionals, and 85% supported renaming the disease.
There was some divergence in opinion as to what the new name(s) should be, but clear agreement that the term “diabetes” should not be part of it.
“We’ve only become recently aware that there are dramatic cases of patient mismanagement due to the confusion caused by the word ‘diabetes.’ We think patients should have a voice. If a legitimate patient survey says over 80% think this name should be changed, then I think we as endocrinologists need to pay attention to that,” Dr. Verbalis said.
But while endocrinologists are the ones who see these patients the most often, Dr. Verbalis said a main aim of the position statement “is really to change the mindset of non-endocrinologist doctors and nurses and other health care professionals that this is not diabetes mellitus. It’s a totally different disease. And if we give it a totally different name, then I think they will better recognize that.”
As to how long Dr. Verbalis thinks it will take for the new names to catch on, he pointed out that it’s taken about a decade for the rheumatology field to fully adopt the name “granulomatosis with polyangiitis” as a replacement for “Wegener’s granulomatosis” after the eponymous physician’s Nazi ties were revealed.
“So we’re not anticipating that this is going to change terminology tomorrow. It’s a long process. We just wanted to get the process started,” he said.
Dr. Verbalis has reported consulting for Otsuka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An international group representing leading endocrinology associations has recommended that the name “diabetes insipidus” – which in some cases has led to harm – be changed to eliminate confusion with “diabetes mellitus” and to reflect the former condition’s pathophysiology.
The new proposed names are arginine vasopressin deficiency (AVP-D) for central (also called “cranial”) etiologies and arginine vasopressin resistance (AVP-R) for nephrogenic (kidney) etiologies.
“What we’re proposing is to rename the disease according to the pathophysiology that defines it,” statement co-author Joseph G. Verbalis, MD, professor of medicine and chief of endocrinology and metabolism at Georgetown University Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization.
The statement advises that henceforth the new names be used in manuscripts and the medical literature while keeping the old names in parentheses during a transition period, as in “AVP-deficiency (cranial diabetes insipidus)” and “AVP-resistance (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus).”
The condition formerly known as diabetes insipidus is relatively rare, occurring in about 1 person per 10-15,000 population. It is caused by either deficient production or resistance in the kidney to the hormone AVP, normally produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the pituitary gland. AVP, also called antidiuretic hormone, regulates the body’s water level and urine production by the kidney.
Both etiologies lead to extreme thirst and excessive production of urine. Common causes of the deficiency include head trauma or brain tumor, while resistance in the kidney is often congenital. It is currently treated with a synthetic form of AVP called desmopressin and fluid replacement.
What’s in a name?
The proposal to change the name by the Working Group for Renaming Diabetes Insipidus is endorsed by The Endocrine Society, European Society of Endocrinology, Pituitary Society, Society for Endocrinology, European Society for Paediatric Endocrinology, Endocrine Society of Australia, Brazilian Endocrine Society, and Japanese Endocrine Society and is under review by several other societies. It was published as a position statement in several of those society’s journals, with more to follow.
Historically, the word “diabetes,” a Greek word meaning “siphon,” was used in the 1st and 2nd century BC to describe excess flow of urine. The Latin word “mellitus” or “honey” was added in the late 17th century to describe the sweetness of the urine in the dysglycemic condition.
A century later, the Latin word “insipidus,” meaning insipid or tasteless, was coined to distinguish between the two types of polyuria, the position statement details.
In the late 19th to early 20th century, the vasopressor and antidiuretic actions of posterior pituitary extracts were discovered and used to treat people with both the central and nephrogenic etiologies, which were also recognized around that time, yet the name “diabetes insipidus” has persisted.
“From a historical perspective, the name is perfectly appropriate. At the time it was identified, and it was realized that it was different from diabetes mellitus, that was a perfectly appropriate terminology based on what was known in the late 19th century – but not now. It has persisted through the years simply because in medicine there’s a lot of inertia for change ... It’s just always been called that. If there’s not a compelling reason to change a name, generally there’s no move to change it,” Dr. Verbalis observed.
‘Dramatic cases of patient mismanagement’ due to name confusion
Unfortunately, the urgency for the change arose from tragedy. In 2009, a 22-year-old man was admitted to the orthopedics department of a London teaching hospital for a hip replacement. Despite his known panhypopituitarism and diabetes insipidus, the nurses continually checked his blood glucose but didn’t give him desmopressin or sufficient fluids. Laboratory testing showed normal glucose, but his serum sodium was 149 mmol/L. The morning after his operation, he had a fatal cardiac arrest with a serum sodium of 169 mmol/L.
“The nurses thought he had diabetes mellitus ... So that was death due to failure to recognize that diabetes insipidus is not diabetes mellitus,” Dr. Verbalis said. “If he had been admitted to endocrinology, this wouldn’t have happened. But he was admitted to orthopedics. Non-endocrinologists are not so aware of diabetes insipidus, because it is a rare disease.”
In 2016, National Health Service England issued a patient safety alert about the “risk of severe harm or death when desmopressin is omitted or delayed in patients with cranial diabetes insipidus,” citing at least four incidents within the prior 7 years where omission of desmopressin had resulted in severe dehydration and death, with another 76 cases of omission or delay that were acted on before the patients became critically ill.
Further impetus for the name change came from the results of an anonymous web-based survey of 1,034 adult and pediatric patients with central diabetes insipidus conducted between August 2021 and February 2022. Overall, 80% reported encountering situations in which their condition had been confused with diabetes mellitus by health care professionals, and 85% supported renaming the disease.
There was some divergence in opinion as to what the new name(s) should be, but clear agreement that the term “diabetes” should not be part of it.
“We’ve only become recently aware that there are dramatic cases of patient mismanagement due to the confusion caused by the word ‘diabetes.’ We think patients should have a voice. If a legitimate patient survey says over 80% think this name should be changed, then I think we as endocrinologists need to pay attention to that,” Dr. Verbalis said.
But while endocrinologists are the ones who see these patients the most often, Dr. Verbalis said a main aim of the position statement “is really to change the mindset of non-endocrinologist doctors and nurses and other health care professionals that this is not diabetes mellitus. It’s a totally different disease. And if we give it a totally different name, then I think they will better recognize that.”
As to how long Dr. Verbalis thinks it will take for the new names to catch on, he pointed out that it’s taken about a decade for the rheumatology field to fully adopt the name “granulomatosis with polyangiitis” as a replacement for “Wegener’s granulomatosis” after the eponymous physician’s Nazi ties were revealed.
“So we’re not anticipating that this is going to change terminology tomorrow. It’s a long process. We just wanted to get the process started,” he said.
Dr. Verbalis has reported consulting for Otsuka.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Islet transplants in type 1 diabetes durable up to 8 years
Transplantation of cadaveric pancreatic islet cells resulted in graft survival and function with acceptable safety for up to 8 years in selected individuals with type 1 diabetes, new research finds.
The study is a long-term follow-up of two phase 3 pivotal trials from the Clinical Islet Transplantation Consortium of a purified human pancreatic islet cell product for treating people with type 1 diabetes.
One trial involved islet transplantation in 48 people who experienced severe hypoglycemia and hypoglycemic unawareness, and the other trial included 24 people who also experienced those complications and were already receiving immunosuppression following kidney transplant. The trials, both registered with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), met their primary efficacy and safety endpoints at 2- and 3-year timepoints.
The follow-up data have now been published in Diabetes Care by Michael Rickels, MD, and colleagues.
The procedure involved infusion through the hepatic portal vein of one or more purified human pancreatic islet products under standardized immunosuppression using methods that Dr. Rickels and colleagues have been developing since 2004. The approach involves multiple modalities to protect the islets prior to transplantation.
Among the 34 islet-alone and eight islet-after–kidney transplant recipients who entered the extended follow-up, durable graft survival allowing for achievement of glycemic targets occurred without severe hypoglycemia or adverse effects from immunosuppression.
The primary outcome, actuarial survival of graft islet function, was 56% at the maximum follow-up of 8.3 years for the islet-only transplantation group and 49% at 7.3 years for the islet-after–kidney transplantation group (P = .004).
The findings suggest that “in the long run, islet transplantation has efficacy, including among those who have had kidney transplants ... Most type 1 diabetes patients are improved tremendously with current insulin delivery systems ... but for those having the most difficulty controlling their blood sugar – and those whose diabetes has already been complicated by needing a kidney transplant – the outcomes we saw in this study are what we’ve been hoping to achieve for more than 20 years,” said Dr. Rickels in a statement from his institution, the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
In the initial trials at day 75 after the initial transplant, 87.5% of the islet-alone and 71% of the islet-after–kidney transplant group achieved hemoglobin A1c under 7%, and 85% and 54%, respectively, achieved A1c at or under 6.5%. At the end of maximal follow-up, 49% of islet-only transplant recipients maintained A1c under 7%, although none had A1c at or under 6.5%. For the islet-after–kidney transplant group, these proportions were 35% and 17%, respectively (P = .0017 for A1c under 7.0% and P < .0001 for A1c ≤ 6.5%, respectively, between the groups).
There were 12 severe hypoglycemic episodes in five patients (three islet-alone and two islet-after–kidney transplant group) during the initial trials, but no additional episodes occurred in either group during long-term follow-up.
Overall, 53 individuals – 37 in the islet-alone and 16 in the islet-after–kidney transplant group – or 74% of the total, achieved a period of insulin independence with A1c under 7%, ranging from 36 to 481 days. The range of time to achieving insulin independence reflects individuals who received one, two, or three islet infusions.
The fact that most patients achieved insulin independence following just one (n = 20) or two (n = 30) infusions and only three patients required three infusions was notable, Dr. Rickels said.
“Currently, around the world, there’s an expectation of two to three donor pancreases being needed. Here, it’s one, maybe two. It’s a much more efficient protocol and opens up access for more islet transplantation as a hoped-for alternative to pancreas transplants.”
Of those who achieved insulin independence, 30 (57%) remained insulin-independent throughout follow-up (20 of 37 islet-alone and 10 of 16 islet-after–kidney transplant patients), with no difference in duration of insulin independence between the groups.
There were no deaths during post-transplant follow-up. Rates of serious adverse events were 0.31 and 0.43 per patient-year for the islet-after–kidney and islet-alone transplant groups, respectively. Of a total of 104 serious adverse events, 65 occurred during the initial trials and had been previously reported. Of the additional 39 serious adverse events that occurred during long-term follow-up, 11 were possibly due to immunosuppression and 27 were deemed unrelated to the procedures.
According to Dr. Rickels, “These are the most seriously affected patients, and you’d be expecting to see some hospitalizations in a population managed on immunosuppression therapy ... It’s important to note that none of the adverse events were related to the actual islet product. Also, kidney function remained stable during long-term follow-up in both cohorts, in fact, improving in those who had kidney transplants.”
Overall, he said, “This is a much less invasive procedure that opens itself up to significantly fewer complications than what many of these patients would otherwise require, a pancreas transplant, which involves major abdominal surgery.”
The investigators plan to submit these data as part of a biologic license application (BLA) to the FDA.
The research was supported by grants from JDRF, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Rickels has reported receiving consulting fees from Sernova and Vertex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplantation of cadaveric pancreatic islet cells resulted in graft survival and function with acceptable safety for up to 8 years in selected individuals with type 1 diabetes, new research finds.
The study is a long-term follow-up of two phase 3 pivotal trials from the Clinical Islet Transplantation Consortium of a purified human pancreatic islet cell product for treating people with type 1 diabetes.
One trial involved islet transplantation in 48 people who experienced severe hypoglycemia and hypoglycemic unawareness, and the other trial included 24 people who also experienced those complications and were already receiving immunosuppression following kidney transplant. The trials, both registered with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), met their primary efficacy and safety endpoints at 2- and 3-year timepoints.
The follow-up data have now been published in Diabetes Care by Michael Rickels, MD, and colleagues.
The procedure involved infusion through the hepatic portal vein of one or more purified human pancreatic islet products under standardized immunosuppression using methods that Dr. Rickels and colleagues have been developing since 2004. The approach involves multiple modalities to protect the islets prior to transplantation.
Among the 34 islet-alone and eight islet-after–kidney transplant recipients who entered the extended follow-up, durable graft survival allowing for achievement of glycemic targets occurred without severe hypoglycemia or adverse effects from immunosuppression.
The primary outcome, actuarial survival of graft islet function, was 56% at the maximum follow-up of 8.3 years for the islet-only transplantation group and 49% at 7.3 years for the islet-after–kidney transplantation group (P = .004).
The findings suggest that “in the long run, islet transplantation has efficacy, including among those who have had kidney transplants ... Most type 1 diabetes patients are improved tremendously with current insulin delivery systems ... but for those having the most difficulty controlling their blood sugar – and those whose diabetes has already been complicated by needing a kidney transplant – the outcomes we saw in this study are what we’ve been hoping to achieve for more than 20 years,” said Dr. Rickels in a statement from his institution, the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
In the initial trials at day 75 after the initial transplant, 87.5% of the islet-alone and 71% of the islet-after–kidney transplant group achieved hemoglobin A1c under 7%, and 85% and 54%, respectively, achieved A1c at or under 6.5%. At the end of maximal follow-up, 49% of islet-only transplant recipients maintained A1c under 7%, although none had A1c at or under 6.5%. For the islet-after–kidney transplant group, these proportions were 35% and 17%, respectively (P = .0017 for A1c under 7.0% and P < .0001 for A1c ≤ 6.5%, respectively, between the groups).
There were 12 severe hypoglycemic episodes in five patients (three islet-alone and two islet-after–kidney transplant group) during the initial trials, but no additional episodes occurred in either group during long-term follow-up.
Overall, 53 individuals – 37 in the islet-alone and 16 in the islet-after–kidney transplant group – or 74% of the total, achieved a period of insulin independence with A1c under 7%, ranging from 36 to 481 days. The range of time to achieving insulin independence reflects individuals who received one, two, or three islet infusions.
The fact that most patients achieved insulin independence following just one (n = 20) or two (n = 30) infusions and only three patients required three infusions was notable, Dr. Rickels said.
“Currently, around the world, there’s an expectation of two to three donor pancreases being needed. Here, it’s one, maybe two. It’s a much more efficient protocol and opens up access for more islet transplantation as a hoped-for alternative to pancreas transplants.”
Of those who achieved insulin independence, 30 (57%) remained insulin-independent throughout follow-up (20 of 37 islet-alone and 10 of 16 islet-after–kidney transplant patients), with no difference in duration of insulin independence between the groups.
There were no deaths during post-transplant follow-up. Rates of serious adverse events were 0.31 and 0.43 per patient-year for the islet-after–kidney and islet-alone transplant groups, respectively. Of a total of 104 serious adverse events, 65 occurred during the initial trials and had been previously reported. Of the additional 39 serious adverse events that occurred during long-term follow-up, 11 were possibly due to immunosuppression and 27 were deemed unrelated to the procedures.
According to Dr. Rickels, “These are the most seriously affected patients, and you’d be expecting to see some hospitalizations in a population managed on immunosuppression therapy ... It’s important to note that none of the adverse events were related to the actual islet product. Also, kidney function remained stable during long-term follow-up in both cohorts, in fact, improving in those who had kidney transplants.”
Overall, he said, “This is a much less invasive procedure that opens itself up to significantly fewer complications than what many of these patients would otherwise require, a pancreas transplant, which involves major abdominal surgery.”
The investigators plan to submit these data as part of a biologic license application (BLA) to the FDA.
The research was supported by grants from JDRF, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Rickels has reported receiving consulting fees from Sernova and Vertex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transplantation of cadaveric pancreatic islet cells resulted in graft survival and function with acceptable safety for up to 8 years in selected individuals with type 1 diabetes, new research finds.
The study is a long-term follow-up of two phase 3 pivotal trials from the Clinical Islet Transplantation Consortium of a purified human pancreatic islet cell product for treating people with type 1 diabetes.
One trial involved islet transplantation in 48 people who experienced severe hypoglycemia and hypoglycemic unawareness, and the other trial included 24 people who also experienced those complications and were already receiving immunosuppression following kidney transplant. The trials, both registered with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), met their primary efficacy and safety endpoints at 2- and 3-year timepoints.
The follow-up data have now been published in Diabetes Care by Michael Rickels, MD, and colleagues.
The procedure involved infusion through the hepatic portal vein of one or more purified human pancreatic islet products under standardized immunosuppression using methods that Dr. Rickels and colleagues have been developing since 2004. The approach involves multiple modalities to protect the islets prior to transplantation.
Among the 34 islet-alone and eight islet-after–kidney transplant recipients who entered the extended follow-up, durable graft survival allowing for achievement of glycemic targets occurred without severe hypoglycemia or adverse effects from immunosuppression.
The primary outcome, actuarial survival of graft islet function, was 56% at the maximum follow-up of 8.3 years for the islet-only transplantation group and 49% at 7.3 years for the islet-after–kidney transplantation group (P = .004).
The findings suggest that “in the long run, islet transplantation has efficacy, including among those who have had kidney transplants ... Most type 1 diabetes patients are improved tremendously with current insulin delivery systems ... but for those having the most difficulty controlling their blood sugar – and those whose diabetes has already been complicated by needing a kidney transplant – the outcomes we saw in this study are what we’ve been hoping to achieve for more than 20 years,” said Dr. Rickels in a statement from his institution, the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
In the initial trials at day 75 after the initial transplant, 87.5% of the islet-alone and 71% of the islet-after–kidney transplant group achieved hemoglobin A1c under 7%, and 85% and 54%, respectively, achieved A1c at or under 6.5%. At the end of maximal follow-up, 49% of islet-only transplant recipients maintained A1c under 7%, although none had A1c at or under 6.5%. For the islet-after–kidney transplant group, these proportions were 35% and 17%, respectively (P = .0017 for A1c under 7.0% and P < .0001 for A1c ≤ 6.5%, respectively, between the groups).
There were 12 severe hypoglycemic episodes in five patients (three islet-alone and two islet-after–kidney transplant group) during the initial trials, but no additional episodes occurred in either group during long-term follow-up.
Overall, 53 individuals – 37 in the islet-alone and 16 in the islet-after–kidney transplant group – or 74% of the total, achieved a period of insulin independence with A1c under 7%, ranging from 36 to 481 days. The range of time to achieving insulin independence reflects individuals who received one, two, or three islet infusions.
The fact that most patients achieved insulin independence following just one (n = 20) or two (n = 30) infusions and only three patients required three infusions was notable, Dr. Rickels said.
“Currently, around the world, there’s an expectation of two to three donor pancreases being needed. Here, it’s one, maybe two. It’s a much more efficient protocol and opens up access for more islet transplantation as a hoped-for alternative to pancreas transplants.”
Of those who achieved insulin independence, 30 (57%) remained insulin-independent throughout follow-up (20 of 37 islet-alone and 10 of 16 islet-after–kidney transplant patients), with no difference in duration of insulin independence between the groups.
There were no deaths during post-transplant follow-up. Rates of serious adverse events were 0.31 and 0.43 per patient-year for the islet-after–kidney and islet-alone transplant groups, respectively. Of a total of 104 serious adverse events, 65 occurred during the initial trials and had been previously reported. Of the additional 39 serious adverse events that occurred during long-term follow-up, 11 were possibly due to immunosuppression and 27 were deemed unrelated to the procedures.
According to Dr. Rickels, “These are the most seriously affected patients, and you’d be expecting to see some hospitalizations in a population managed on immunosuppression therapy ... It’s important to note that none of the adverse events were related to the actual islet product. Also, kidney function remained stable during long-term follow-up in both cohorts, in fact, improving in those who had kidney transplants.”
Overall, he said, “This is a much less invasive procedure that opens itself up to significantly fewer complications than what many of these patients would otherwise require, a pancreas transplant, which involves major abdominal surgery.”
The investigators plan to submit these data as part of a biologic license application (BLA) to the FDA.
The research was supported by grants from JDRF, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Rickels has reported receiving consulting fees from Sernova and Vertex Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM DIABETES CARE
‘Too good to be true’? Ultrasound safely treats kidney stones
Treatment with transcutaneous, focused ultrasound safely led to the repositioning and rupture of a majority of stones in the ureter when tested in 29 people at two U.S. centers in the first human feasibility study of the technology.*
potentially relieving pain and facilitating passage in awake patients,” write M. Kennedy Hall, MD, an emergency medicine physician at the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and co-authors in a report published in the Journal of Urology.
“This is the first human trial in awake subjects” of this method for nonsurgically facilitating ureteral stone clearance, and the results of limited patient discomfort and stone motion in 66% of treated patients seem “almost too good to be true,” comments Karen L. Stern, MD, a urologist at the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, in an accompanying editorial.
However, Dr. Stern notes two study limitations. First, to correctly target the focused ultrasound clinicians first need to visualize a stone with ultrasound. However, “most urologists are not experienced in ultrasound,” a limitation that could mean the treatment may be more likely performed by emergency physicians or radiologists in the future.
Second, the study had no control patients, and Dr. Stern cautions that the clinical significance of BWL cannot be definitively assessed without a randomized trial that directly compares the new method with either spontaneous stone passage or medical expulsion therapy.
“The authors showed a distal ureteral stone passage [rate] of 81%, but those stones passed within days, not minutes, of the procedure, and that rate is not too far off published data on spontaneous passage,” Dr. Stern notes in her editorial.*
Despite these caveats, Dr. Stern calls the potential for BWL “immense.”
Ultrasound for 10 minutes or less
The study enrolled adults who presented to the University of Washington emergency department or endo-urology clinic with a proximal or distal ureteral stone. Twenty-nine awake, unanesthetized patients in whom clinicians had an unobstructed view of a stone in the focal zone received ultrasound treatment performed by trained personnel.
Treatment involved ultrasound bursts of up to 3 seconds for stone propulsion and 30 seconds at a time for BWL. Total ultrasound exposure could not exceed 10 minutes, and no patient underwent more than one treatment. Sixteen patients received treatment for propulsion only, and 13 received both propulsion and BWL treatments.
The primary outcome was stone motion, which occurred in 19 of the 29 patients (66%). A prespecified secondary outcome was passage of the stone in the 26 patients with distal stones. Among the 21 patients with at least 14 days of follow-up, passage occurred in 18 (86%) after an average of 3.9 days following treatment. The researchers also confirmed stone fragmentation in five of the 13 patients (38%) who received BWL treatment.
The researchers infer that ultrasound treatment facilitated stone passage by stone propulsion, fragmentation, and peristalsis.
Mathew D. Sorensen, MD, a study co-investigator, likened the effect of ultrasound on the stones to a leaf blower on garden debris.
“Essentially, we use the acoustic energy of ultrasound, which gets focused on the stone and creates movement, like a blower,” said Dr. Sorensen, a urologist at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “A push of energy lasts a second or two, sort of a sweeping movement to try to get fragments to move out of what’s usually the bottom of the kidney, toward the exit. Because the energy moves in one way, away from the probe, it’s sort of like playing pool,” he explained.
All 29 treated patients in the current study tolerated the procedure, and none experienced unanticipated events. No patients needed to visit the emergency department or an intervention because of the treatment, and there were no observed ureter injuries.
Pain scores dropped significantly, procedure is ‘nearly painless’
Assessment of pain scores by each patient before and after treatment showed overall significant decreases in both mean and median scores, with 10 patients reporting decreased pain and two reporting increased pain.
When discomfort occurred during the procedure it was described by patients as either similar to a pinprick or as a referred sensation to pass urine and the stone. These effects occurred during 18 of 820 (2%) total propulsive bursts of ultrasound administered.
“It’s nearly painless, and you can do it while the patient is awake, and without sedation, which is critical,” said Dr. Hall in a statement from the University of Washington School of Medicine. He envisions eventually performing the procedure in a clinic or emergency department setting.
All three patients with a proximal stone and three patients with a distal stone who did not pass their stone after treatment underwent surgical stone removal.
The researchers acknowledge that a lack of a control group was a study limitation. They cite a historical, spontaneous stone passage rate of 54% included in a 2016 guideline from the American Urological Association and based on a meta-analysis of 27 studies with 1,205 total patients.
The study was funded by the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration, which is interested in having a technology available to treat ureteral stones that may develop during prolonged space travel.
The study received no commercial funding. Four of the study’s 23 authors, including Dr. Sorensen, are consultants to and hold equity in SonoMotion, a company that has licensed the tested technology from the University of Washington for commercial development. The report did not identify a specific manufacturer of the ultrasound equipment used for treatment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*Correction, 10/21/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the location of the stones. They were in the ureter.
Treatment with transcutaneous, focused ultrasound safely led to the repositioning and rupture of a majority of stones in the ureter when tested in 29 people at two U.S. centers in the first human feasibility study of the technology.*
potentially relieving pain and facilitating passage in awake patients,” write M. Kennedy Hall, MD, an emergency medicine physician at the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and co-authors in a report published in the Journal of Urology.
“This is the first human trial in awake subjects” of this method for nonsurgically facilitating ureteral stone clearance, and the results of limited patient discomfort and stone motion in 66% of treated patients seem “almost too good to be true,” comments Karen L. Stern, MD, a urologist at the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, in an accompanying editorial.
However, Dr. Stern notes two study limitations. First, to correctly target the focused ultrasound clinicians first need to visualize a stone with ultrasound. However, “most urologists are not experienced in ultrasound,” a limitation that could mean the treatment may be more likely performed by emergency physicians or radiologists in the future.
Second, the study had no control patients, and Dr. Stern cautions that the clinical significance of BWL cannot be definitively assessed without a randomized trial that directly compares the new method with either spontaneous stone passage or medical expulsion therapy.
“The authors showed a distal ureteral stone passage [rate] of 81%, but those stones passed within days, not minutes, of the procedure, and that rate is not too far off published data on spontaneous passage,” Dr. Stern notes in her editorial.*
Despite these caveats, Dr. Stern calls the potential for BWL “immense.”
Ultrasound for 10 minutes or less
The study enrolled adults who presented to the University of Washington emergency department or endo-urology clinic with a proximal or distal ureteral stone. Twenty-nine awake, unanesthetized patients in whom clinicians had an unobstructed view of a stone in the focal zone received ultrasound treatment performed by trained personnel.
Treatment involved ultrasound bursts of up to 3 seconds for stone propulsion and 30 seconds at a time for BWL. Total ultrasound exposure could not exceed 10 minutes, and no patient underwent more than one treatment. Sixteen patients received treatment for propulsion only, and 13 received both propulsion and BWL treatments.
The primary outcome was stone motion, which occurred in 19 of the 29 patients (66%). A prespecified secondary outcome was passage of the stone in the 26 patients with distal stones. Among the 21 patients with at least 14 days of follow-up, passage occurred in 18 (86%) after an average of 3.9 days following treatment. The researchers also confirmed stone fragmentation in five of the 13 patients (38%) who received BWL treatment.
The researchers infer that ultrasound treatment facilitated stone passage by stone propulsion, fragmentation, and peristalsis.
Mathew D. Sorensen, MD, a study co-investigator, likened the effect of ultrasound on the stones to a leaf blower on garden debris.
“Essentially, we use the acoustic energy of ultrasound, which gets focused on the stone and creates movement, like a blower,” said Dr. Sorensen, a urologist at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “A push of energy lasts a second or two, sort of a sweeping movement to try to get fragments to move out of what’s usually the bottom of the kidney, toward the exit. Because the energy moves in one way, away from the probe, it’s sort of like playing pool,” he explained.
All 29 treated patients in the current study tolerated the procedure, and none experienced unanticipated events. No patients needed to visit the emergency department or an intervention because of the treatment, and there were no observed ureter injuries.
Pain scores dropped significantly, procedure is ‘nearly painless’
Assessment of pain scores by each patient before and after treatment showed overall significant decreases in both mean and median scores, with 10 patients reporting decreased pain and two reporting increased pain.
When discomfort occurred during the procedure it was described by patients as either similar to a pinprick or as a referred sensation to pass urine and the stone. These effects occurred during 18 of 820 (2%) total propulsive bursts of ultrasound administered.
“It’s nearly painless, and you can do it while the patient is awake, and without sedation, which is critical,” said Dr. Hall in a statement from the University of Washington School of Medicine. He envisions eventually performing the procedure in a clinic or emergency department setting.
All three patients with a proximal stone and three patients with a distal stone who did not pass their stone after treatment underwent surgical stone removal.
The researchers acknowledge that a lack of a control group was a study limitation. They cite a historical, spontaneous stone passage rate of 54% included in a 2016 guideline from the American Urological Association and based on a meta-analysis of 27 studies with 1,205 total patients.
The study was funded by the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration, which is interested in having a technology available to treat ureteral stones that may develop during prolonged space travel.
The study received no commercial funding. Four of the study’s 23 authors, including Dr. Sorensen, are consultants to and hold equity in SonoMotion, a company that has licensed the tested technology from the University of Washington for commercial development. The report did not identify a specific manufacturer of the ultrasound equipment used for treatment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*Correction, 10/21/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the location of the stones. They were in the ureter.
Treatment with transcutaneous, focused ultrasound safely led to the repositioning and rupture of a majority of stones in the ureter when tested in 29 people at two U.S. centers in the first human feasibility study of the technology.*
potentially relieving pain and facilitating passage in awake patients,” write M. Kennedy Hall, MD, an emergency medicine physician at the University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, and co-authors in a report published in the Journal of Urology.
“This is the first human trial in awake subjects” of this method for nonsurgically facilitating ureteral stone clearance, and the results of limited patient discomfort and stone motion in 66% of treated patients seem “almost too good to be true,” comments Karen L. Stern, MD, a urologist at the Mayo Clinic, Phoenix, in an accompanying editorial.
However, Dr. Stern notes two study limitations. First, to correctly target the focused ultrasound clinicians first need to visualize a stone with ultrasound. However, “most urologists are not experienced in ultrasound,” a limitation that could mean the treatment may be more likely performed by emergency physicians or radiologists in the future.
Second, the study had no control patients, and Dr. Stern cautions that the clinical significance of BWL cannot be definitively assessed without a randomized trial that directly compares the new method with either spontaneous stone passage or medical expulsion therapy.
“The authors showed a distal ureteral stone passage [rate] of 81%, but those stones passed within days, not minutes, of the procedure, and that rate is not too far off published data on spontaneous passage,” Dr. Stern notes in her editorial.*
Despite these caveats, Dr. Stern calls the potential for BWL “immense.”
Ultrasound for 10 minutes or less
The study enrolled adults who presented to the University of Washington emergency department or endo-urology clinic with a proximal or distal ureteral stone. Twenty-nine awake, unanesthetized patients in whom clinicians had an unobstructed view of a stone in the focal zone received ultrasound treatment performed by trained personnel.
Treatment involved ultrasound bursts of up to 3 seconds for stone propulsion and 30 seconds at a time for BWL. Total ultrasound exposure could not exceed 10 minutes, and no patient underwent more than one treatment. Sixteen patients received treatment for propulsion only, and 13 received both propulsion and BWL treatments.
The primary outcome was stone motion, which occurred in 19 of the 29 patients (66%). A prespecified secondary outcome was passage of the stone in the 26 patients with distal stones. Among the 21 patients with at least 14 days of follow-up, passage occurred in 18 (86%) after an average of 3.9 days following treatment. The researchers also confirmed stone fragmentation in five of the 13 patients (38%) who received BWL treatment.
The researchers infer that ultrasound treatment facilitated stone passage by stone propulsion, fragmentation, and peristalsis.
Mathew D. Sorensen, MD, a study co-investigator, likened the effect of ultrasound on the stones to a leaf blower on garden debris.
“Essentially, we use the acoustic energy of ultrasound, which gets focused on the stone and creates movement, like a blower,” said Dr. Sorensen, a urologist at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “A push of energy lasts a second or two, sort of a sweeping movement to try to get fragments to move out of what’s usually the bottom of the kidney, toward the exit. Because the energy moves in one way, away from the probe, it’s sort of like playing pool,” he explained.
All 29 treated patients in the current study tolerated the procedure, and none experienced unanticipated events. No patients needed to visit the emergency department or an intervention because of the treatment, and there were no observed ureter injuries.
Pain scores dropped significantly, procedure is ‘nearly painless’
Assessment of pain scores by each patient before and after treatment showed overall significant decreases in both mean and median scores, with 10 patients reporting decreased pain and two reporting increased pain.
When discomfort occurred during the procedure it was described by patients as either similar to a pinprick or as a referred sensation to pass urine and the stone. These effects occurred during 18 of 820 (2%) total propulsive bursts of ultrasound administered.
“It’s nearly painless, and you can do it while the patient is awake, and without sedation, which is critical,” said Dr. Hall in a statement from the University of Washington School of Medicine. He envisions eventually performing the procedure in a clinic or emergency department setting.
All three patients with a proximal stone and three patients with a distal stone who did not pass their stone after treatment underwent surgical stone removal.
The researchers acknowledge that a lack of a control group was a study limitation. They cite a historical, spontaneous stone passage rate of 54% included in a 2016 guideline from the American Urological Association and based on a meta-analysis of 27 studies with 1,205 total patients.
The study was funded by the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration, which is interested in having a technology available to treat ureteral stones that may develop during prolonged space travel.
The study received no commercial funding. Four of the study’s 23 authors, including Dr. Sorensen, are consultants to and hold equity in SonoMotion, a company that has licensed the tested technology from the University of Washington for commercial development. The report did not identify a specific manufacturer of the ultrasound equipment used for treatment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
*Correction, 10/21/22: An earlier version of this article misstated the location of the stones. They were in the ureter.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY
Finerenone benefits T2D across spectrum of renal function
Treatment with finerenone produced roughly similar reductions in heart failure–related outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) across the spectrum of kidney function, compared with placebo, including those who had albuminuria but a preserved estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), in a post hoc analysis of pooled data from more than 13,000 people.
The findings, from the two pivotal trials for the agent, “reinforce the importance of routine eGFR and UACR [urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio] screening” in people with type 2 diabetes to identify new candidates for treatment with finerenone (Kerendia), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, and coauthors said in a report published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Among the 13,026 patients in the two combined trials, 40% had a preserved eGFR of greater than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 despite also having albuminuria with a UACR of at least 30 mg/g, showing how often this combination occurs. But many clinicians “do not follow the guidelines” and fail to measure the UACR in these patients in routine practice, noted Dr. Filippatos at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology in August.
“We now have something to do for these patients,” treat them with finerenone, said Dr. Filippatos, professor and director of heart failure at the Attikon University Hospital, Athens.
The availability of finerenone following its U.S. approval in 2021 means clinicians “must get used to measuring UACR” in people with type 2 diabetes even when their eGFR is normal, especially people with type 2 diabetes plus high cardiovascular disease risk, he said.
The Food and Drug Administration approved finerenone, a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, for treating people with type 2 diabetes and CKD in July 2021, but its uptake has been slow, experts say. In a talk in September 2022 during the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, Jennifer B. Green, MD, estimated that U.S. uptake of finerenone for appropriate people with type 2 diabetes had not advanced beyond 10%.
A recent review also noted that uptake of screening for elevated UACR in U.S. patients with type 2 diabetes was in the range of 10%-40% during 2017-2019, a “shockingly low rate,” said Dr. Green, a professor and diabetes specialist at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
A new reason to screen for albuminuria
“It’s an extremely important message,” Johann Bauersachs, MD, commented in an interview. Results from “many studies have shown that albuminuria is an excellent additional marker for cardiovascular disease risk. But measurement of albuminuria is not widely done, despite guidelines that recommend annual albuminuria testing in people with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Bauersachs, professor and head of the department of cardiology at Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
“Even before there was finerenone, there were reasons to measure UACR, but I hope adding finerenone will help, and more clinicians will incorporate UACR into their routine practice,” said Dr. Bauersachs, who was not involved with the finerenone studies.
The analyses reported by Dr. Filippatos and coauthors used data from two related trials of finerenone, FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD, combined by prespecified design into a single dataset, FIDELITY, with a total of 13,026 participants eligible for analysis and followed for a median of 3 years. All had type 2 diabetes and CKD based on having a UACR of at least 30 mg/g. Their eGFR levels could run as high as 74 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in FIDELIO-DKD, and as high as 90 mL/min/1.73m2 in FIGARO-DKD. The two trials excluded people with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and those with a serum potassium greater than 4.8 mmol/L.
In the FIDELITY dataset treatment with finerenone led to a significant 17% reduction in the combined incidence of cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for heart failure relative to those who received placebo. This relative risk reduction was not affected by either eGFR or UACR values at baseline, the new analysis showed.
The analysis also demonstrated a nonsignificant trend toward greater reductions in heart failure–related outcomes among study participants who began with an eGFR in the normal range of at least 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The researchers also found a nonsignificant trend to a greater reduction in heart failure–related events among those with a UACR of less than 300 mg/g.
Finerenone favors patients with less advanced CKD
In short “the magnitude of the treatment benefit tended to favor patients with less advanced CKD,” concluded the researchers, suggesting that “earlier intervention [with finerenone] in the CKD course is likely to provide the greatest long-term benefit on heart failure–related outcomes.” This led them to further infer “the importance of not only routine assessing eGFR, but also perhaps more importantly, routinely screening for UACR to facilitate early diagnosis and early intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes.”
Findings from FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD led to recent guideline additions for finerenone by several medical groups. In August 2022, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists released an update to its guideline for managing people with diabetes that recommended treating people with type 2 diabetes with finerenone when they have a UACR of at least 30 mg/g if they are already treated with a maximum-tolerated dose of a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor, have a normal serum potassium level, and have an eGFR of at least 25 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The identical recommendation also appeared in a Consensus Report from the American Diabetes Association and KDIGO, an international organization promoting evidence-based management of patients with CKD.
“Finerenone provides a very important contribution because it improves prognosis even in very well managed patients” with type 2 diabetes, commented Lars Rydén, MD, professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, as designated discussant for the report by Dr. Filippatos at the ESC congress.
The findings from the FIDELITY analysis are “trustworthy, and clinically important,” Dr. Rydén said. When left untreated, diabetic kidney disease “reduces life expectancy by an average of 16 years.”
The finerenone trials were sponsored by Bayer, which markets finerenone (Kerendia). Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from Bayer as well as from Amgen, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Green has financial ties to Bayer as well as to Anji, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim/Lilly, Hawthorne Effect/Omada, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi/Lexicon, and Valo. Dr. Bauersachs has been a consultant to Bayer as well as to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardior, Cervia, CVRx, Novartis, Pfizer, and Vifor, and he has received research funding from Abiomed. Dr. Rydén has financial ties to Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk.
Treatment with finerenone produced roughly similar reductions in heart failure–related outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) across the spectrum of kidney function, compared with placebo, including those who had albuminuria but a preserved estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), in a post hoc analysis of pooled data from more than 13,000 people.
The findings, from the two pivotal trials for the agent, “reinforce the importance of routine eGFR and UACR [urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio] screening” in people with type 2 diabetes to identify new candidates for treatment with finerenone (Kerendia), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, and coauthors said in a report published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Among the 13,026 patients in the two combined trials, 40% had a preserved eGFR of greater than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 despite also having albuminuria with a UACR of at least 30 mg/g, showing how often this combination occurs. But many clinicians “do not follow the guidelines” and fail to measure the UACR in these patients in routine practice, noted Dr. Filippatos at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology in August.
“We now have something to do for these patients,” treat them with finerenone, said Dr. Filippatos, professor and director of heart failure at the Attikon University Hospital, Athens.
The availability of finerenone following its U.S. approval in 2021 means clinicians “must get used to measuring UACR” in people with type 2 diabetes even when their eGFR is normal, especially people with type 2 diabetes plus high cardiovascular disease risk, he said.
The Food and Drug Administration approved finerenone, a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, for treating people with type 2 diabetes and CKD in July 2021, but its uptake has been slow, experts say. In a talk in September 2022 during the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, Jennifer B. Green, MD, estimated that U.S. uptake of finerenone for appropriate people with type 2 diabetes had not advanced beyond 10%.
A recent review also noted that uptake of screening for elevated UACR in U.S. patients with type 2 diabetes was in the range of 10%-40% during 2017-2019, a “shockingly low rate,” said Dr. Green, a professor and diabetes specialist at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
A new reason to screen for albuminuria
“It’s an extremely important message,” Johann Bauersachs, MD, commented in an interview. Results from “many studies have shown that albuminuria is an excellent additional marker for cardiovascular disease risk. But measurement of albuminuria is not widely done, despite guidelines that recommend annual albuminuria testing in people with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Bauersachs, professor and head of the department of cardiology at Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
“Even before there was finerenone, there were reasons to measure UACR, but I hope adding finerenone will help, and more clinicians will incorporate UACR into their routine practice,” said Dr. Bauersachs, who was not involved with the finerenone studies.
The analyses reported by Dr. Filippatos and coauthors used data from two related trials of finerenone, FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD, combined by prespecified design into a single dataset, FIDELITY, with a total of 13,026 participants eligible for analysis and followed for a median of 3 years. All had type 2 diabetes and CKD based on having a UACR of at least 30 mg/g. Their eGFR levels could run as high as 74 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in FIDELIO-DKD, and as high as 90 mL/min/1.73m2 in FIGARO-DKD. The two trials excluded people with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and those with a serum potassium greater than 4.8 mmol/L.
In the FIDELITY dataset treatment with finerenone led to a significant 17% reduction in the combined incidence of cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for heart failure relative to those who received placebo. This relative risk reduction was not affected by either eGFR or UACR values at baseline, the new analysis showed.
The analysis also demonstrated a nonsignificant trend toward greater reductions in heart failure–related outcomes among study participants who began with an eGFR in the normal range of at least 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The researchers also found a nonsignificant trend to a greater reduction in heart failure–related events among those with a UACR of less than 300 mg/g.
Finerenone favors patients with less advanced CKD
In short “the magnitude of the treatment benefit tended to favor patients with less advanced CKD,” concluded the researchers, suggesting that “earlier intervention [with finerenone] in the CKD course is likely to provide the greatest long-term benefit on heart failure–related outcomes.” This led them to further infer “the importance of not only routine assessing eGFR, but also perhaps more importantly, routinely screening for UACR to facilitate early diagnosis and early intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes.”
Findings from FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD led to recent guideline additions for finerenone by several medical groups. In August 2022, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists released an update to its guideline for managing people with diabetes that recommended treating people with type 2 diabetes with finerenone when they have a UACR of at least 30 mg/g if they are already treated with a maximum-tolerated dose of a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor, have a normal serum potassium level, and have an eGFR of at least 25 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The identical recommendation also appeared in a Consensus Report from the American Diabetes Association and KDIGO, an international organization promoting evidence-based management of patients with CKD.
“Finerenone provides a very important contribution because it improves prognosis even in very well managed patients” with type 2 diabetes, commented Lars Rydén, MD, professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, as designated discussant for the report by Dr. Filippatos at the ESC congress.
The findings from the FIDELITY analysis are “trustworthy, and clinically important,” Dr. Rydén said. When left untreated, diabetic kidney disease “reduces life expectancy by an average of 16 years.”
The finerenone trials were sponsored by Bayer, which markets finerenone (Kerendia). Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from Bayer as well as from Amgen, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Green has financial ties to Bayer as well as to Anji, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim/Lilly, Hawthorne Effect/Omada, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi/Lexicon, and Valo. Dr. Bauersachs has been a consultant to Bayer as well as to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardior, Cervia, CVRx, Novartis, Pfizer, and Vifor, and he has received research funding from Abiomed. Dr. Rydén has financial ties to Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk.
Treatment with finerenone produced roughly similar reductions in heart failure–related outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD) across the spectrum of kidney function, compared with placebo, including those who had albuminuria but a preserved estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), in a post hoc analysis of pooled data from more than 13,000 people.
The findings, from the two pivotal trials for the agent, “reinforce the importance of routine eGFR and UACR [urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio] screening” in people with type 2 diabetes to identify new candidates for treatment with finerenone (Kerendia), Gerasimos Filippatos, MD, and coauthors said in a report published online in JACC: Heart Failure.
Among the 13,026 patients in the two combined trials, 40% had a preserved eGFR of greater than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 despite also having albuminuria with a UACR of at least 30 mg/g, showing how often this combination occurs. But many clinicians “do not follow the guidelines” and fail to measure the UACR in these patients in routine practice, noted Dr. Filippatos at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology in August.
“We now have something to do for these patients,” treat them with finerenone, said Dr. Filippatos, professor and director of heart failure at the Attikon University Hospital, Athens.
The availability of finerenone following its U.S. approval in 2021 means clinicians “must get used to measuring UACR” in people with type 2 diabetes even when their eGFR is normal, especially people with type 2 diabetes plus high cardiovascular disease risk, he said.
The Food and Drug Administration approved finerenone, a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, for treating people with type 2 diabetes and CKD in July 2021, but its uptake has been slow, experts say. In a talk in September 2022 during the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, Jennifer B. Green, MD, estimated that U.S. uptake of finerenone for appropriate people with type 2 diabetes had not advanced beyond 10%.
A recent review also noted that uptake of screening for elevated UACR in U.S. patients with type 2 diabetes was in the range of 10%-40% during 2017-2019, a “shockingly low rate,” said Dr. Green, a professor and diabetes specialist at Duke University, Durham, N.C.
A new reason to screen for albuminuria
“It’s an extremely important message,” Johann Bauersachs, MD, commented in an interview. Results from “many studies have shown that albuminuria is an excellent additional marker for cardiovascular disease risk. But measurement of albuminuria is not widely done, despite guidelines that recommend annual albuminuria testing in people with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Bauersachs, professor and head of the department of cardiology at Hannover (Germany) Medical School.
“Even before there was finerenone, there were reasons to measure UACR, but I hope adding finerenone will help, and more clinicians will incorporate UACR into their routine practice,” said Dr. Bauersachs, who was not involved with the finerenone studies.
The analyses reported by Dr. Filippatos and coauthors used data from two related trials of finerenone, FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD, combined by prespecified design into a single dataset, FIDELITY, with a total of 13,026 participants eligible for analysis and followed for a median of 3 years. All had type 2 diabetes and CKD based on having a UACR of at least 30 mg/g. Their eGFR levels could run as high as 74 mL/min per 1.73 m2 in FIDELIO-DKD, and as high as 90 mL/min/1.73m2 in FIGARO-DKD. The two trials excluded people with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, and those with a serum potassium greater than 4.8 mmol/L.
In the FIDELITY dataset treatment with finerenone led to a significant 17% reduction in the combined incidence of cardiovascular death or first hospitalization for heart failure relative to those who received placebo. This relative risk reduction was not affected by either eGFR or UACR values at baseline, the new analysis showed.
The analysis also demonstrated a nonsignificant trend toward greater reductions in heart failure–related outcomes among study participants who began with an eGFR in the normal range of at least 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The researchers also found a nonsignificant trend to a greater reduction in heart failure–related events among those with a UACR of less than 300 mg/g.
Finerenone favors patients with less advanced CKD
In short “the magnitude of the treatment benefit tended to favor patients with less advanced CKD,” concluded the researchers, suggesting that “earlier intervention [with finerenone] in the CKD course is likely to provide the greatest long-term benefit on heart failure–related outcomes.” This led them to further infer “the importance of not only routine assessing eGFR, but also perhaps more importantly, routinely screening for UACR to facilitate early diagnosis and early intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes.”
Findings from FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD led to recent guideline additions for finerenone by several medical groups. In August 2022, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists released an update to its guideline for managing people with diabetes that recommended treating people with type 2 diabetes with finerenone when they have a UACR of at least 30 mg/g if they are already treated with a maximum-tolerated dose of a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor, have a normal serum potassium level, and have an eGFR of at least 25 mL/min per 1.73 m2. The identical recommendation also appeared in a Consensus Report from the American Diabetes Association and KDIGO, an international organization promoting evidence-based management of patients with CKD.
“Finerenone provides a very important contribution because it improves prognosis even in very well managed patients” with type 2 diabetes, commented Lars Rydén, MD, professor of cardiology at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, as designated discussant for the report by Dr. Filippatos at the ESC congress.
The findings from the FIDELITY analysis are “trustworthy, and clinically important,” Dr. Rydén said. When left untreated, diabetic kidney disease “reduces life expectancy by an average of 16 years.”
The finerenone trials were sponsored by Bayer, which markets finerenone (Kerendia). Dr. Filippatos has received lecture fees from Bayer as well as from Amgen, Medtronic, Novartis, Servier, and Vifor. Dr. Green has financial ties to Bayer as well as to Anji, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim/Lilly, Hawthorne Effect/Omada, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi/Lexicon, and Valo. Dr. Bauersachs has been a consultant to Bayer as well as to Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardior, Cervia, CVRx, Novartis, Pfizer, and Vifor, and he has received research funding from Abiomed. Dr. Rydén has financial ties to Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk.
FROM JACC: HEART FAILURE
Ultrasonic renal denervation passes 2-month test in uncontrolled HTN: RADIANCE II
Systolic blood pressure went down safely and consistently 2 months after renal denervation achieved by ultrasound ablation in patients with uncontrolled, mild to moderate hypertension (HTN) in a key sham-controlled test of the balloon-equipped catheter.
The BP reductions were significant almost regardless of how they were measured – at home, in the office, during the day, at night, or over 24 hours – and weren’t dependent on baseline BP levels.
The 224-patient RADIANCE II Pivotal Study follows two earlier successful sham-controlled trials that used the same renal denervation catheter in other types of patients with HTN. They were RADIANCE-HTN SOLO, which entered patients with mild to moderate HTN not taking medication, and RADIANCE-HTN TRIO, which included patients with HTN despite fixed-dose, single-pill, triple-antihypertensive therapy.
The consistent results of all three trials suggest that the ultrasound renal denervation (uRDN) technique “lowers blood pressure across the spectrum of hypertension,” concluded co–principal investigator Ajay J. Kirtane, MD, SM, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York–Presbyterian Hospital, when presenting RADIANCE II at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
RADIANCE II, the largest of the three studies, met its prespecified primary efficacy endpoint of change in daytime ambulatory systolic BP at 2 months by showing a significant 6.3–mm Hg greater reduction in the uRDN group, compared with the sham-control group. There were no major adverse events at 30 days in either group.
The trial was similarly successful for the secondary endpoints of change in systolic BP measured in various other settings, including over 24 hours. Reductions after uRDN averaged 5-7 mm Hg greater than in the control group.
Sparse top-line results of the RADIANCE II pivotal trial were announced in July by the study’s sponsor, ReCor Medical.
Dr. Kirtane stressed in an interview that uRDN and likely any form of HTN renal denervation therapy is not a substitute for standard management. “This is really for patients in whom you’ve made best efforts to do the traditional things – lifestyle modification, medications, all of that – and yet they’re still uncontrolled.” At that point, assuming denervation therapy is available in practice, “it would be something to potentially consider.”
As a panelist after Dr. Kirtane’s formal presentation of RADIANCE II at the conference, Naomi D. Fisher, MD, who was a RADIANCE-HTN TRIO investigator, described how the treatment’s perceived intended patient population evolved over time.
“We all began with the idea that we were going to treat patients with resistant hypertension, that was going to be the first target. We have learned that those patients are far fewer than we thought,” said Dr. Fisher, who directs the hypertension service at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Initial estimates were that such patients with the resistant form, “meaning they require more than three drugs to control their blood pressure,” would represent 15%-20% of patients with HTN.
“We learned from our TRIO data that if you give these patients one single combined pill, lo and behold, many of them become controlled,” she said. “There is so much nonadherence out there in the world, about 50% of our patients aren’t taking their pills. It’s a hard and true fact.”
Exclude patients who aren’t adherent and “our true resistance population becomes minuscule. So, I don’t think that’s going to be the main population” for renal denervation therapy.
More likely, she said, it would be “patients who are uncontrolled and unable to take their medications. So that is going to include nonadherence, intolerance. It’s a very large category of patients. And the priorities can be stacked in favor of those who have higher cardiovascular risk.”
RADIANCE II can show the persistence of uRDN’s BP-lowering effect only out to 2 months so far, but the effect’s durability based on the RADIANCE program’s combined experience appears to be at least 2 years, Dr. Kirtane said in an interview.
“The RADIANCE II pivotal trial is a powerful, well-designed study attesting to the efficacy of renal denervation in BP lowering,” Franz H. Messerli, MD, Swiss Cardiovascular Center, University Hospital Bern, said in an interview.
The trial “shows the well-known unpredictability of antihypertensive response. We cannot predict who responds to renal denervation and who does not, and who even has a paradoxical increase in BP,” Dr. Messerli, an international hypertension expert not associated with the trial, said in an interview.
“As long as we cannot predict the antihypertensive response to renal denervation therapy, potential synergism/antagonism with drug therapy remains an educated guess,” he said.
“Hypertension is a disease that lasts years and decades. As impressive as RADIANCE II’s 2-month snapshot is, I look forward to similar or better BP data 12 and 24 months after renal denervation,” Dr. Messerli added.
RADIANCE II entered patients with mild to moderate uncontrolled HTN, that is, a systolic BP at least 140/90 mm Hg and less than 180/120 mm Hg, who were receiving no more than two antihypertensive medications. They could have no history of cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events or uncontrolled diabetes, and their estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) had to be at least 40 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
After a 4-week drug washout period, patients who were clinically stable with an ambulatory BP of at least 135/85 mm Hg and less than 170/105 mm Hg underwent CT and renal angiography. Then, the 224 patients still anatomically eligible for the procedure were randomly assigned 2:1 to uRDN or a sham-control procedure: 150 and 74 patients, respectively.
At 2 months, daytime ambulatory systolic BP on average fell 7.9 mm Hg in the uRDN group and 1.8 mm Hg in the sham-control group, for a drop that was steeper by 6.3 mm Hg (P < .0001) after uRDN.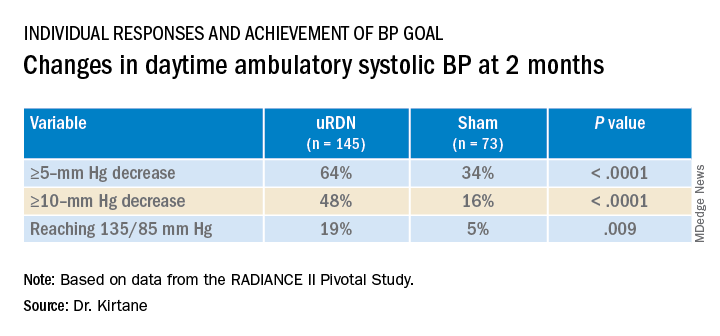
Also in the uRDN group, there was a 6.2–mm Hg larger decrease in 24-hour ambulatory systolic BP (P < .0001), a 5.8–mm Hg greater decline in nighttime ambulatory systolic BP (P < .0004), a 7.6–mm Hg steeper drop in mean home systolic BP (P < .0001), and 5.4 mm Hg more of a decrease in office-based systolic BP (P = .0035).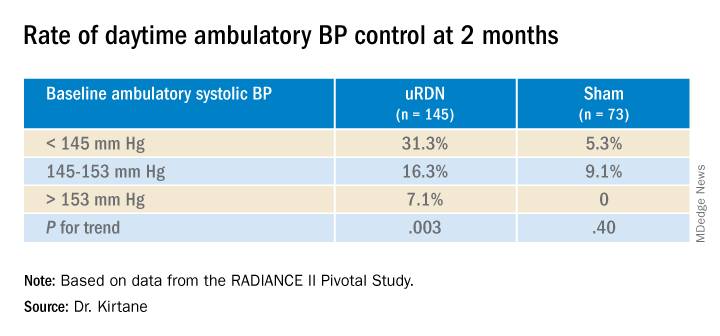
No significant differences were seen in subgroup analyses by sex, age, higher versus lower baseline systolic pressures, high versus low baseline eGFR, degree of abdominal obesity, U.S. versus European site, or whether patients entered before or during the COVID pandemic
Regulators have been accepting change in systolic BP as a surrogate for clinical endpoints in trials of antihypertensive therapy, whether pharmacologic or interventional, under consideration for approval. “That’s why safety endpoints are important to investigate” in these clinical trials, especially for invasive therapies like renal denervation, Dr. Kirtane observed.
That said, “in the longer-term follow-ups of the renal denervation therapies that are out there, including this one, there does not appear to be an appreciable decline in glomerular filtration rate, or any adverse safety signals that we see to date,” Dr. Kirtane said in an interview. “But we know that these are low-frequency events, so we have to be very vigilant, and we can’t get complacent about it.”
In RADIANCE II, there were zero adverse events within 30 days in both groups; the endpoint included death, new myocardial infarction, renal artery complications requiring invasive intervention, and hospitalization for major cardiovascular or hemodynamic-related events. Nor were there instances of new-onset renal artery stenosis greater than 70% documented by imaging at 6 months.
The ReCor uRDN catheter uses ultrasound energy to disrupt renal nerve signaling, a technology thought to deliver safer “burns,” compared with other renal denervation catheter technologies. It features an axially stabilizing balloon that transmits ultrasound energy – two to three sonications, each lasting 7 seconds, Dr. Kirtane said – outward through the arterial wall. The design is intended to ensure consistently circumferential ablation. Circulating saline within the balloon, Kirtane noted, directly cools the adjacent vessel wall to help it avoid thermal damage.
Dr. Kirtane reported receiving institutional funding from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Amgen, CSI, Philips, ReCor Medical, Neurotronic, Biotronik, Chiesi, Bolt Medical, Magenta Medical, Canon, SoniVie, Shockwave Medical, and Merck; consulting for IMDS; and receiving travel and meal expenses from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, CSI, Siemens, Philips, ReCor Medical, Chiesi, OpSens, Zoll, and Regeneron. Dr. Fisher disclosed receiving honoraria or fees for consulting or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Medtronic, ReCor Medical, and Aktiia and receiving grant support or holding research contracts for Recor Medical and Aktiia. Dr. Messerli disclosed receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Menarini, Krka, and Ipca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Systolic blood pressure went down safely and consistently 2 months after renal denervation achieved by ultrasound ablation in patients with uncontrolled, mild to moderate hypertension (HTN) in a key sham-controlled test of the balloon-equipped catheter.
The BP reductions were significant almost regardless of how they were measured – at home, in the office, during the day, at night, or over 24 hours – and weren’t dependent on baseline BP levels.
The 224-patient RADIANCE II Pivotal Study follows two earlier successful sham-controlled trials that used the same renal denervation catheter in other types of patients with HTN. They were RADIANCE-HTN SOLO, which entered patients with mild to moderate HTN not taking medication, and RADIANCE-HTN TRIO, which included patients with HTN despite fixed-dose, single-pill, triple-antihypertensive therapy.
The consistent results of all three trials suggest that the ultrasound renal denervation (uRDN) technique “lowers blood pressure across the spectrum of hypertension,” concluded co–principal investigator Ajay J. Kirtane, MD, SM, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York–Presbyterian Hospital, when presenting RADIANCE II at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
RADIANCE II, the largest of the three studies, met its prespecified primary efficacy endpoint of change in daytime ambulatory systolic BP at 2 months by showing a significant 6.3–mm Hg greater reduction in the uRDN group, compared with the sham-control group. There were no major adverse events at 30 days in either group.
The trial was similarly successful for the secondary endpoints of change in systolic BP measured in various other settings, including over 24 hours. Reductions after uRDN averaged 5-7 mm Hg greater than in the control group.
Sparse top-line results of the RADIANCE II pivotal trial were announced in July by the study’s sponsor, ReCor Medical.
Dr. Kirtane stressed in an interview that uRDN and likely any form of HTN renal denervation therapy is not a substitute for standard management. “This is really for patients in whom you’ve made best efforts to do the traditional things – lifestyle modification, medications, all of that – and yet they’re still uncontrolled.” At that point, assuming denervation therapy is available in practice, “it would be something to potentially consider.”
As a panelist after Dr. Kirtane’s formal presentation of RADIANCE II at the conference, Naomi D. Fisher, MD, who was a RADIANCE-HTN TRIO investigator, described how the treatment’s perceived intended patient population evolved over time.
“We all began with the idea that we were going to treat patients with resistant hypertension, that was going to be the first target. We have learned that those patients are far fewer than we thought,” said Dr. Fisher, who directs the hypertension service at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Initial estimates were that such patients with the resistant form, “meaning they require more than three drugs to control their blood pressure,” would represent 15%-20% of patients with HTN.
“We learned from our TRIO data that if you give these patients one single combined pill, lo and behold, many of them become controlled,” she said. “There is so much nonadherence out there in the world, about 50% of our patients aren’t taking their pills. It’s a hard and true fact.”
Exclude patients who aren’t adherent and “our true resistance population becomes minuscule. So, I don’t think that’s going to be the main population” for renal denervation therapy.
More likely, she said, it would be “patients who are uncontrolled and unable to take their medications. So that is going to include nonadherence, intolerance. It’s a very large category of patients. And the priorities can be stacked in favor of those who have higher cardiovascular risk.”
RADIANCE II can show the persistence of uRDN’s BP-lowering effect only out to 2 months so far, but the effect’s durability based on the RADIANCE program’s combined experience appears to be at least 2 years, Dr. Kirtane said in an interview.
“The RADIANCE II pivotal trial is a powerful, well-designed study attesting to the efficacy of renal denervation in BP lowering,” Franz H. Messerli, MD, Swiss Cardiovascular Center, University Hospital Bern, said in an interview.
The trial “shows the well-known unpredictability of antihypertensive response. We cannot predict who responds to renal denervation and who does not, and who even has a paradoxical increase in BP,” Dr. Messerli, an international hypertension expert not associated with the trial, said in an interview.
“As long as we cannot predict the antihypertensive response to renal denervation therapy, potential synergism/antagonism with drug therapy remains an educated guess,” he said.
“Hypertension is a disease that lasts years and decades. As impressive as RADIANCE II’s 2-month snapshot is, I look forward to similar or better BP data 12 and 24 months after renal denervation,” Dr. Messerli added.
RADIANCE II entered patients with mild to moderate uncontrolled HTN, that is, a systolic BP at least 140/90 mm Hg and less than 180/120 mm Hg, who were receiving no more than two antihypertensive medications. They could have no history of cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events or uncontrolled diabetes, and their estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) had to be at least 40 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
After a 4-week drug washout period, patients who were clinically stable with an ambulatory BP of at least 135/85 mm Hg and less than 170/105 mm Hg underwent CT and renal angiography. Then, the 224 patients still anatomically eligible for the procedure were randomly assigned 2:1 to uRDN or a sham-control procedure: 150 and 74 patients, respectively.
At 2 months, daytime ambulatory systolic BP on average fell 7.9 mm Hg in the uRDN group and 1.8 mm Hg in the sham-control group, for a drop that was steeper by 6.3 mm Hg (P < .0001) after uRDN.
Also in the uRDN group, there was a 6.2–mm Hg larger decrease in 24-hour ambulatory systolic BP (P < .0001), a 5.8–mm Hg greater decline in nighttime ambulatory systolic BP (P < .0004), a 7.6–mm Hg steeper drop in mean home systolic BP (P < .0001), and 5.4 mm Hg more of a decrease in office-based systolic BP (P = .0035).
No significant differences were seen in subgroup analyses by sex, age, higher versus lower baseline systolic pressures, high versus low baseline eGFR, degree of abdominal obesity, U.S. versus European site, or whether patients entered before or during the COVID pandemic
Regulators have been accepting change in systolic BP as a surrogate for clinical endpoints in trials of antihypertensive therapy, whether pharmacologic or interventional, under consideration for approval. “That’s why safety endpoints are important to investigate” in these clinical trials, especially for invasive therapies like renal denervation, Dr. Kirtane observed.
That said, “in the longer-term follow-ups of the renal denervation therapies that are out there, including this one, there does not appear to be an appreciable decline in glomerular filtration rate, or any adverse safety signals that we see to date,” Dr. Kirtane said in an interview. “But we know that these are low-frequency events, so we have to be very vigilant, and we can’t get complacent about it.”
In RADIANCE II, there were zero adverse events within 30 days in both groups; the endpoint included death, new myocardial infarction, renal artery complications requiring invasive intervention, and hospitalization for major cardiovascular or hemodynamic-related events. Nor were there instances of new-onset renal artery stenosis greater than 70% documented by imaging at 6 months.
The ReCor uRDN catheter uses ultrasound energy to disrupt renal nerve signaling, a technology thought to deliver safer “burns,” compared with other renal denervation catheter technologies. It features an axially stabilizing balloon that transmits ultrasound energy – two to three sonications, each lasting 7 seconds, Dr. Kirtane said – outward through the arterial wall. The design is intended to ensure consistently circumferential ablation. Circulating saline within the balloon, Kirtane noted, directly cools the adjacent vessel wall to help it avoid thermal damage.
Dr. Kirtane reported receiving institutional funding from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Amgen, CSI, Philips, ReCor Medical, Neurotronic, Biotronik, Chiesi, Bolt Medical, Magenta Medical, Canon, SoniVie, Shockwave Medical, and Merck; consulting for IMDS; and receiving travel and meal expenses from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, CSI, Siemens, Philips, ReCor Medical, Chiesi, OpSens, Zoll, and Regeneron. Dr. Fisher disclosed receiving honoraria or fees for consulting or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Medtronic, ReCor Medical, and Aktiia and receiving grant support or holding research contracts for Recor Medical and Aktiia. Dr. Messerli disclosed receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Menarini, Krka, and Ipca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Systolic blood pressure went down safely and consistently 2 months after renal denervation achieved by ultrasound ablation in patients with uncontrolled, mild to moderate hypertension (HTN) in a key sham-controlled test of the balloon-equipped catheter.
The BP reductions were significant almost regardless of how they were measured – at home, in the office, during the day, at night, or over 24 hours – and weren’t dependent on baseline BP levels.
The 224-patient RADIANCE II Pivotal Study follows two earlier successful sham-controlled trials that used the same renal denervation catheter in other types of patients with HTN. They were RADIANCE-HTN SOLO, which entered patients with mild to moderate HTN not taking medication, and RADIANCE-HTN TRIO, which included patients with HTN despite fixed-dose, single-pill, triple-antihypertensive therapy.
The consistent results of all three trials suggest that the ultrasound renal denervation (uRDN) technique “lowers blood pressure across the spectrum of hypertension,” concluded co–principal investigator Ajay J. Kirtane, MD, SM, Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York–Presbyterian Hospital, when presenting RADIANCE II at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
RADIANCE II, the largest of the three studies, met its prespecified primary efficacy endpoint of change in daytime ambulatory systolic BP at 2 months by showing a significant 6.3–mm Hg greater reduction in the uRDN group, compared with the sham-control group. There were no major adverse events at 30 days in either group.
The trial was similarly successful for the secondary endpoints of change in systolic BP measured in various other settings, including over 24 hours. Reductions after uRDN averaged 5-7 mm Hg greater than in the control group.
Sparse top-line results of the RADIANCE II pivotal trial were announced in July by the study’s sponsor, ReCor Medical.
Dr. Kirtane stressed in an interview that uRDN and likely any form of HTN renal denervation therapy is not a substitute for standard management. “This is really for patients in whom you’ve made best efforts to do the traditional things – lifestyle modification, medications, all of that – and yet they’re still uncontrolled.” At that point, assuming denervation therapy is available in practice, “it would be something to potentially consider.”
As a panelist after Dr. Kirtane’s formal presentation of RADIANCE II at the conference, Naomi D. Fisher, MD, who was a RADIANCE-HTN TRIO investigator, described how the treatment’s perceived intended patient population evolved over time.
“We all began with the idea that we were going to treat patients with resistant hypertension, that was going to be the first target. We have learned that those patients are far fewer than we thought,” said Dr. Fisher, who directs the hypertension service at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston.
Initial estimates were that such patients with the resistant form, “meaning they require more than three drugs to control their blood pressure,” would represent 15%-20% of patients with HTN.
“We learned from our TRIO data that if you give these patients one single combined pill, lo and behold, many of them become controlled,” she said. “There is so much nonadherence out there in the world, about 50% of our patients aren’t taking their pills. It’s a hard and true fact.”
Exclude patients who aren’t adherent and “our true resistance population becomes minuscule. So, I don’t think that’s going to be the main population” for renal denervation therapy.
More likely, she said, it would be “patients who are uncontrolled and unable to take their medications. So that is going to include nonadherence, intolerance. It’s a very large category of patients. And the priorities can be stacked in favor of those who have higher cardiovascular risk.”
RADIANCE II can show the persistence of uRDN’s BP-lowering effect only out to 2 months so far, but the effect’s durability based on the RADIANCE program’s combined experience appears to be at least 2 years, Dr. Kirtane said in an interview.
“The RADIANCE II pivotal trial is a powerful, well-designed study attesting to the efficacy of renal denervation in BP lowering,” Franz H. Messerli, MD, Swiss Cardiovascular Center, University Hospital Bern, said in an interview.
The trial “shows the well-known unpredictability of antihypertensive response. We cannot predict who responds to renal denervation and who does not, and who even has a paradoxical increase in BP,” Dr. Messerli, an international hypertension expert not associated with the trial, said in an interview.
“As long as we cannot predict the antihypertensive response to renal denervation therapy, potential synergism/antagonism with drug therapy remains an educated guess,” he said.
“Hypertension is a disease that lasts years and decades. As impressive as RADIANCE II’s 2-month snapshot is, I look forward to similar or better BP data 12 and 24 months after renal denervation,” Dr. Messerli added.
RADIANCE II entered patients with mild to moderate uncontrolled HTN, that is, a systolic BP at least 140/90 mm Hg and less than 180/120 mm Hg, who were receiving no more than two antihypertensive medications. They could have no history of cardiovascular or cerebrovascular events or uncontrolled diabetes, and their estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) had to be at least 40 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
After a 4-week drug washout period, patients who were clinically stable with an ambulatory BP of at least 135/85 mm Hg and less than 170/105 mm Hg underwent CT and renal angiography. Then, the 224 patients still anatomically eligible for the procedure were randomly assigned 2:1 to uRDN or a sham-control procedure: 150 and 74 patients, respectively.
At 2 months, daytime ambulatory systolic BP on average fell 7.9 mm Hg in the uRDN group and 1.8 mm Hg in the sham-control group, for a drop that was steeper by 6.3 mm Hg (P < .0001) after uRDN.
Also in the uRDN group, there was a 6.2–mm Hg larger decrease in 24-hour ambulatory systolic BP (P < .0001), a 5.8–mm Hg greater decline in nighttime ambulatory systolic BP (P < .0004), a 7.6–mm Hg steeper drop in mean home systolic BP (P < .0001), and 5.4 mm Hg more of a decrease in office-based systolic BP (P = .0035).
No significant differences were seen in subgroup analyses by sex, age, higher versus lower baseline systolic pressures, high versus low baseline eGFR, degree of abdominal obesity, U.S. versus European site, or whether patients entered before or during the COVID pandemic
Regulators have been accepting change in systolic BP as a surrogate for clinical endpoints in trials of antihypertensive therapy, whether pharmacologic or interventional, under consideration for approval. “That’s why safety endpoints are important to investigate” in these clinical trials, especially for invasive therapies like renal denervation, Dr. Kirtane observed.
That said, “in the longer-term follow-ups of the renal denervation therapies that are out there, including this one, there does not appear to be an appreciable decline in glomerular filtration rate, or any adverse safety signals that we see to date,” Dr. Kirtane said in an interview. “But we know that these are low-frequency events, so we have to be very vigilant, and we can’t get complacent about it.”
In RADIANCE II, there were zero adverse events within 30 days in both groups; the endpoint included death, new myocardial infarction, renal artery complications requiring invasive intervention, and hospitalization for major cardiovascular or hemodynamic-related events. Nor were there instances of new-onset renal artery stenosis greater than 70% documented by imaging at 6 months.
The ReCor uRDN catheter uses ultrasound energy to disrupt renal nerve signaling, a technology thought to deliver safer “burns,” compared with other renal denervation catheter technologies. It features an axially stabilizing balloon that transmits ultrasound energy – two to three sonications, each lasting 7 seconds, Dr. Kirtane said – outward through the arterial wall. The design is intended to ensure consistently circumferential ablation. Circulating saline within the balloon, Kirtane noted, directly cools the adjacent vessel wall to help it avoid thermal damage.
Dr. Kirtane reported receiving institutional funding from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, Amgen, CSI, Philips, ReCor Medical, Neurotronic, Biotronik, Chiesi, Bolt Medical, Magenta Medical, Canon, SoniVie, Shockwave Medical, and Merck; consulting for IMDS; and receiving travel and meal expenses from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott Vascular, CSI, Siemens, Philips, ReCor Medical, Chiesi, OpSens, Zoll, and Regeneron. Dr. Fisher disclosed receiving honoraria or fees for consulting or serving on a speaker’s bureau for Medtronic, ReCor Medical, and Aktiia and receiving grant support or holding research contracts for Recor Medical and Aktiia. Dr. Messerli disclosed receiving honoraria from Medtronic, Menarini, Krka, and Ipca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM TCT 2022






