User login
COVID-19 linked to rise in suicide-related ED visits among youth
After a steep decline in the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, youth with suicidal thoughts and behaviors visiting an emergency department (ED) resurged with an overrepresentation among girls and children without a prior psychiatric history, according to a cross-sectional study conducted at Kaiser Permanente Northern California.
The latest findings, published in JAMA Psychiatry, are highly consistent with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data published a few months earlier in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that looked at these trends among young people aged 12-25 before and during the pandemic. In addition, the new data suggest that prevention efforts might be particularly helpful for these young people and their families.
“As suicide-related encounters have made up more ED volume during the pandemic, increasing ED-based interventions, staff trained in addressing emergency mental health needs, and aftercare resources may also be valuable in addressing the needs of this population,” wrote Kathryn K. Erickson-Ridout, MD, PhD, first author of the more recent study and an adjunct investigator with the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research, Oakland, Calif.
“While these results suggest many of our youth are coping well through the pandemic, we need to be vigilant as health care workers,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Ridout and associates evaluated suicide-related ED visits among children aged 5-17 years presenting to EDs in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system. Four periods in 2020 were compared with the same four periods in 2019.
In the first period, March through May 2020, the incidence rate ratio (IRR) of suicide-related ED visits among children and adolescents fell more than 40% (IRR, 0.53; P < .001) relative to the same months in 2019. This is consistent with a broader decline in other types of ED visits during the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the periods of June through August and September to Dec. 15, suicide-related ED visits increased, reaching prepandemic levels overall but with differences between genders. In girls, an increase in the first period reached significance (IRR, 1.19; P = .04) and then climbed even higher in the second (hazard ratio, 1.22; P < .001).
Youth present with no prior psychiatric history
Among boys, the increase relative to 2019 in the first period was modest and nonsignificant (IRR, 1.05; P = .26) In the second period, suicide-related ED visits fell and the difference relative to the same period in 2019 reached statistical significance (IRR, 0.81; P = .02).
Other characteristics of suicide-related ED visits during the pandemic were also different from those observed in 2019. One was an increase in visits from youth with no prior history of mental health or suicide-related outpatient visits.
“This finding may suggest that a youth’s first presentation to the ED for suicidal thoughts and behaviors differed during the pandemic, compared to prior to the pandemic,” Dr. Erickson-Ridout explained. “Mental health comorbidities first diagnosed at the ED encounter may suggest an increased complexity at first presentation.”
These data are remarkably similar to ED visits for suicide attempts that were reported by the CDC several months earlier. The CDC data were drawn from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program, which captures data from 71% of the EDs in the United States.
Measured from March 29 to April 25, 2020, ED visits for a suicide attempt declined by more than 25% in both girls and boys, but by early May, those visits were already starting to return to prepandemic levels, particularly among girls, according to the CDC report. When evaluated from July 26 through Aug. 22, 2020, the mean weekly ED visits for suspected suicide attempts had increased 26.2% among girls but only 10.8% among boys, compared with the same period in 2019.
‘More severe distress’ found among girls
In the most recent period evaluated, starting Feb. 21, 2021, and extending to March 20, , compared with the same period in 2019. For boys, the increase was 3.7%.
Higher rates of suicide attempts among girls have been reported by others independent of the COVID-19 pandemic, but the CDC investigators led by Ellen Yard, PhD, a researcher in the CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health, Chamblee, Ga., reported that others have also found greater suicide ideation and attempts by girls during the pandemic.
Neither study was designed to isolate the reason or reasons for an increase in suicide-related ED visits overall or among girls specifically, but Dr. Yard and her coinvestigators speculated that social distancing and isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic might be affecting girls more.
The faster increase in suicide attempts among girls compared with boys “speaks to the importance of upstream prevention to prevent this group from becoming suicidal in the first place as well as improving suicide care both during and after ED visits,” said Dr. Yard, who was interviewed about this research.
For clinicians, she recommended “scaling up adoption of evidence-based best practice.” She cited two such resources from the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention (NAASP). One resource is the Best Practices in Care Transitions for Individuals with Suicide Risk: Inpatient Care to Outpatient Care; the other is called Recommended Standard Care. Both are available online for free from the NAASP.
Dr. Erickson-Ridout and Dr. Yard reported no potential conflicts of interest.
After a steep decline in the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, youth with suicidal thoughts and behaviors visiting an emergency department (ED) resurged with an overrepresentation among girls and children without a prior psychiatric history, according to a cross-sectional study conducted at Kaiser Permanente Northern California.
The latest findings, published in JAMA Psychiatry, are highly consistent with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data published a few months earlier in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that looked at these trends among young people aged 12-25 before and during the pandemic. In addition, the new data suggest that prevention efforts might be particularly helpful for these young people and their families.
“As suicide-related encounters have made up more ED volume during the pandemic, increasing ED-based interventions, staff trained in addressing emergency mental health needs, and aftercare resources may also be valuable in addressing the needs of this population,” wrote Kathryn K. Erickson-Ridout, MD, PhD, first author of the more recent study and an adjunct investigator with the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research, Oakland, Calif.
“While these results suggest many of our youth are coping well through the pandemic, we need to be vigilant as health care workers,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Ridout and associates evaluated suicide-related ED visits among children aged 5-17 years presenting to EDs in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system. Four periods in 2020 were compared with the same four periods in 2019.
In the first period, March through May 2020, the incidence rate ratio (IRR) of suicide-related ED visits among children and adolescents fell more than 40% (IRR, 0.53; P < .001) relative to the same months in 2019. This is consistent with a broader decline in other types of ED visits during the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the periods of June through August and September to Dec. 15, suicide-related ED visits increased, reaching prepandemic levels overall but with differences between genders. In girls, an increase in the first period reached significance (IRR, 1.19; P = .04) and then climbed even higher in the second (hazard ratio, 1.22; P < .001).
Youth present with no prior psychiatric history
Among boys, the increase relative to 2019 in the first period was modest and nonsignificant (IRR, 1.05; P = .26) In the second period, suicide-related ED visits fell and the difference relative to the same period in 2019 reached statistical significance (IRR, 0.81; P = .02).
Other characteristics of suicide-related ED visits during the pandemic were also different from those observed in 2019. One was an increase in visits from youth with no prior history of mental health or suicide-related outpatient visits.
“This finding may suggest that a youth’s first presentation to the ED for suicidal thoughts and behaviors differed during the pandemic, compared to prior to the pandemic,” Dr. Erickson-Ridout explained. “Mental health comorbidities first diagnosed at the ED encounter may suggest an increased complexity at first presentation.”
These data are remarkably similar to ED visits for suicide attempts that were reported by the CDC several months earlier. The CDC data were drawn from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program, which captures data from 71% of the EDs in the United States.
Measured from March 29 to April 25, 2020, ED visits for a suicide attempt declined by more than 25% in both girls and boys, but by early May, those visits were already starting to return to prepandemic levels, particularly among girls, according to the CDC report. When evaluated from July 26 through Aug. 22, 2020, the mean weekly ED visits for suspected suicide attempts had increased 26.2% among girls but only 10.8% among boys, compared with the same period in 2019.
‘More severe distress’ found among girls
In the most recent period evaluated, starting Feb. 21, 2021, and extending to March 20, , compared with the same period in 2019. For boys, the increase was 3.7%.
Higher rates of suicide attempts among girls have been reported by others independent of the COVID-19 pandemic, but the CDC investigators led by Ellen Yard, PhD, a researcher in the CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health, Chamblee, Ga., reported that others have also found greater suicide ideation and attempts by girls during the pandemic.
Neither study was designed to isolate the reason or reasons for an increase in suicide-related ED visits overall or among girls specifically, but Dr. Yard and her coinvestigators speculated that social distancing and isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic might be affecting girls more.
The faster increase in suicide attempts among girls compared with boys “speaks to the importance of upstream prevention to prevent this group from becoming suicidal in the first place as well as improving suicide care both during and after ED visits,” said Dr. Yard, who was interviewed about this research.
For clinicians, she recommended “scaling up adoption of evidence-based best practice.” She cited two such resources from the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention (NAASP). One resource is the Best Practices in Care Transitions for Individuals with Suicide Risk: Inpatient Care to Outpatient Care; the other is called Recommended Standard Care. Both are available online for free from the NAASP.
Dr. Erickson-Ridout and Dr. Yard reported no potential conflicts of interest.
After a steep decline in the first months of the COVID-19 pandemic, youth with suicidal thoughts and behaviors visiting an emergency department (ED) resurged with an overrepresentation among girls and children without a prior psychiatric history, according to a cross-sectional study conducted at Kaiser Permanente Northern California.
The latest findings, published in JAMA Psychiatry, are highly consistent with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data published a few months earlier in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report that looked at these trends among young people aged 12-25 before and during the pandemic. In addition, the new data suggest that prevention efforts might be particularly helpful for these young people and their families.
“As suicide-related encounters have made up more ED volume during the pandemic, increasing ED-based interventions, staff trained in addressing emergency mental health needs, and aftercare resources may also be valuable in addressing the needs of this population,” wrote Kathryn K. Erickson-Ridout, MD, PhD, first author of the more recent study and an adjunct investigator with the Kaiser Permanente Division of Research, Oakland, Calif.
“While these results suggest many of our youth are coping well through the pandemic, we need to be vigilant as health care workers,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Ridout and associates evaluated suicide-related ED visits among children aged 5-17 years presenting to EDs in the Kaiser Permanente Northern California system. Four periods in 2020 were compared with the same four periods in 2019.
In the first period, March through May 2020, the incidence rate ratio (IRR) of suicide-related ED visits among children and adolescents fell more than 40% (IRR, 0.53; P < .001) relative to the same months in 2019. This is consistent with a broader decline in other types of ED visits during the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In the periods of June through August and September to Dec. 15, suicide-related ED visits increased, reaching prepandemic levels overall but with differences between genders. In girls, an increase in the first period reached significance (IRR, 1.19; P = .04) and then climbed even higher in the second (hazard ratio, 1.22; P < .001).
Youth present with no prior psychiatric history
Among boys, the increase relative to 2019 in the first period was modest and nonsignificant (IRR, 1.05; P = .26) In the second period, suicide-related ED visits fell and the difference relative to the same period in 2019 reached statistical significance (IRR, 0.81; P = .02).
Other characteristics of suicide-related ED visits during the pandemic were also different from those observed in 2019. One was an increase in visits from youth with no prior history of mental health or suicide-related outpatient visits.
“This finding may suggest that a youth’s first presentation to the ED for suicidal thoughts and behaviors differed during the pandemic, compared to prior to the pandemic,” Dr. Erickson-Ridout explained. “Mental health comorbidities first diagnosed at the ED encounter may suggest an increased complexity at first presentation.”
These data are remarkably similar to ED visits for suicide attempts that were reported by the CDC several months earlier. The CDC data were drawn from the National Syndromic Surveillance Program, which captures data from 71% of the EDs in the United States.
Measured from March 29 to April 25, 2020, ED visits for a suicide attempt declined by more than 25% in both girls and boys, but by early May, those visits were already starting to return to prepandemic levels, particularly among girls, according to the CDC report. When evaluated from July 26 through Aug. 22, 2020, the mean weekly ED visits for suspected suicide attempts had increased 26.2% among girls but only 10.8% among boys, compared with the same period in 2019.
‘More severe distress’ found among girls
In the most recent period evaluated, starting Feb. 21, 2021, and extending to March 20, , compared with the same period in 2019. For boys, the increase was 3.7%.
Higher rates of suicide attempts among girls have been reported by others independent of the COVID-19 pandemic, but the CDC investigators led by Ellen Yard, PhD, a researcher in the CDC’s National Center for Environmental Health, Chamblee, Ga., reported that others have also found greater suicide ideation and attempts by girls during the pandemic.
Neither study was designed to isolate the reason or reasons for an increase in suicide-related ED visits overall or among girls specifically, but Dr. Yard and her coinvestigators speculated that social distancing and isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic might be affecting girls more.
The faster increase in suicide attempts among girls compared with boys “speaks to the importance of upstream prevention to prevent this group from becoming suicidal in the first place as well as improving suicide care both during and after ED visits,” said Dr. Yard, who was interviewed about this research.
For clinicians, she recommended “scaling up adoption of evidence-based best practice.” She cited two such resources from the National Action Alliance for Suicide Prevention (NAASP). One resource is the Best Practices in Care Transitions for Individuals with Suicide Risk: Inpatient Care to Outpatient Care; the other is called Recommended Standard Care. Both are available online for free from the NAASP.
Dr. Erickson-Ridout and Dr. Yard reported no potential conflicts of interest.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
FDA inaction on hair loss drug’s suicide, depression, erectile dysfunction risk sparks lawsuit
Consumer advocacy group 4 years ago.
The September 2017 petition requested that the FDA take the popular hair-loss drug (1 mg finasteride, Propecia) off the market because of evidence of serious risk of patient injury, including depression and suicidal ideation.
As an alternative, PFSF requested that the FDA require the drug’s manufacturers revise the safety information on the labeling and add boxed warnings to disclose the potential for side effects, another of which is erectile dysfunction.
Public Citizen points to a recent analysis of the VigiBase global database, which tracks adverse effects from global pharmacovigilance agencies, lists 356 reports of suicidality and 2,926 reports of psychological adverse events in finasteride users. Yet, 4 years after submitting the petition, the FDA has neither granted nor denied it.
The lawsuit claims that FDA has acted unlawfully in failing to act on PFSF’s petition, and further cites “88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use” per data from the VigiBase database.
“On the same day that PFSF submitted the petition, FDA’s docket management division acknowledged receipt and assigned the petition a docket number,” Michael Kirkpatrick, the Public Citizen attorney serving as lead counsel for PFSF, told this news organization.
Yet, to date, “there has been no substantive response to the petition. The lawsuit filed today seeks to force FDA to issue a decision on PFSF’s petition,” Mr. Kirkpatrick said.
“The FDA needs to act in a timely way to protect the public from the risks associated with use of Propecia. The FDA’s failure to act exposes consumers to potentially life-threatening harm,” he added in a statement.
The complaint filed today by Public Citizen in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia is available online.
This news organization reached out to the FDA for comment but did not receive a response by press time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumer advocacy group 4 years ago.
The September 2017 petition requested that the FDA take the popular hair-loss drug (1 mg finasteride, Propecia) off the market because of evidence of serious risk of patient injury, including depression and suicidal ideation.
As an alternative, PFSF requested that the FDA require the drug’s manufacturers revise the safety information on the labeling and add boxed warnings to disclose the potential for side effects, another of which is erectile dysfunction.
Public Citizen points to a recent analysis of the VigiBase global database, which tracks adverse effects from global pharmacovigilance agencies, lists 356 reports of suicidality and 2,926 reports of psychological adverse events in finasteride users. Yet, 4 years after submitting the petition, the FDA has neither granted nor denied it.
The lawsuit claims that FDA has acted unlawfully in failing to act on PFSF’s petition, and further cites “88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use” per data from the VigiBase database.
“On the same day that PFSF submitted the petition, FDA’s docket management division acknowledged receipt and assigned the petition a docket number,” Michael Kirkpatrick, the Public Citizen attorney serving as lead counsel for PFSF, told this news organization.
Yet, to date, “there has been no substantive response to the petition. The lawsuit filed today seeks to force FDA to issue a decision on PFSF’s petition,” Mr. Kirkpatrick said.
“The FDA needs to act in a timely way to protect the public from the risks associated with use of Propecia. The FDA’s failure to act exposes consumers to potentially life-threatening harm,” he added in a statement.
The complaint filed today by Public Citizen in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia is available online.
This news organization reached out to the FDA for comment but did not receive a response by press time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Consumer advocacy group 4 years ago.
The September 2017 petition requested that the FDA take the popular hair-loss drug (1 mg finasteride, Propecia) off the market because of evidence of serious risk of patient injury, including depression and suicidal ideation.
As an alternative, PFSF requested that the FDA require the drug’s manufacturers revise the safety information on the labeling and add boxed warnings to disclose the potential for side effects, another of which is erectile dysfunction.
Public Citizen points to a recent analysis of the VigiBase global database, which tracks adverse effects from global pharmacovigilance agencies, lists 356 reports of suicidality and 2,926 reports of psychological adverse events in finasteride users. Yet, 4 years after submitting the petition, the FDA has neither granted nor denied it.
The lawsuit claims that FDA has acted unlawfully in failing to act on PFSF’s petition, and further cites “88 cases of completed suicide associated with finasteride use” per data from the VigiBase database.
“On the same day that PFSF submitted the petition, FDA’s docket management division acknowledged receipt and assigned the petition a docket number,” Michael Kirkpatrick, the Public Citizen attorney serving as lead counsel for PFSF, told this news organization.
Yet, to date, “there has been no substantive response to the petition. The lawsuit filed today seeks to force FDA to issue a decision on PFSF’s petition,” Mr. Kirkpatrick said.
“The FDA needs to act in a timely way to protect the public from the risks associated with use of Propecia. The FDA’s failure to act exposes consumers to potentially life-threatening harm,” he added in a statement.
The complaint filed today by Public Citizen in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia is available online.
This news organization reached out to the FDA for comment but did not receive a response by press time.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 continues to complicate children’s mental health care
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to impact child and adolescent mental health, and clinicians are learning as they go to develop strategies that address the challenges of providing both medical and mental health care to young patients, including those who test positive for COVID-19, according to Hani Talebi, PhD, director of pediatric psychology, and Jorge Ganem, MD, FAAP, director of pediatric hospital medicine, both of the University of Texas at Austin and Dell Children’s Medical Center.
In a presentation at the 2021 virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine conference, Dr. Talebi and Dr. Ganem shared their experiences in identifying the impact of the pandemic on mental health services in a freestanding hospital, and synthesizing inpatient mental health care and medical care outside of a dedicated mental health unit.
Mental health is a significant pediatric issue; approximately one in five children have a diagnosable mental or behavioral health problem, but nearly two-thirds get little or no help, Dr. Talebi said. “COVID-19 has only exacerbated these mental health challenges,” he said.
He noted that beginning in April 2020, the proportion of children’s mental health-related emergency department visits increased and remained elevated through the spring, summer, and fall of 2020, as families fearful of COVID-19 avoided regular hospital visits.
Data suggest that up to 50% of all adolescent psychiatric crises that led to inpatient admissions were related in some way to COVID-19, Dr. Talebi said. In addition, “individuals with a recent diagnosis of a mental health disorder are at increased risk for COVID-19 infection,” and the risk is even higher among women and African Americans, he said.
The past year significantly impacted the mental wellbeing of parents and children, Dr. Talebi said. He cited a June 2020 study in Pediatrics in which 27% of parents reported worsening mental health for themselves, and 14% reported worsening behavioral health for their children. Ongoing issues including food insecurity, loss of regular child care, and an overall “very disorienting experience in the day-to-day” compromised the mental health of families, Dr. Talebi emphasized. Children isolated at home were not meeting developmental milestones that organically occur when socializing with peers, parents didn’t know how to handle some of their children’s issues without support from schools, and many people were struggling with other preexisting health conditions, he said.
This confluence of factors helped drive a surge in emergency department visits, meaning longer wait times and concerns about meeting urgent medical and mental health needs while maintaining safety, he added.
Parents and children waited longer to seek care, and community hospitals such as Dell Children’s Medical Center were faced with children in the emergency department with crisis-level mental health issues, along with children already waiting in the ED to address medical emergencies. All these patients had to be tested for COVID-19 and managed accordingly, Dr. Talebi noted.
Dr. Talebi emphasized the need for clinically robust care of the children who were in isolation for 10 days on the medical unit, waiting to test negative. New protocols were created for social workers to conduct daily safety checks, and to develop regular schedules for screening, “so they are having an experience on the medical floors similar to what they would have in a mental health unit,” he said.
Dr. Ganem reflected on the logistical challenges of managing mental health care while observing COVID-19 safety protocols. “COVID-19 added a new wrinkle of isolation,” he said. As institutional guidelines on testing and isolation evolved, negative COVID-19 tests were required for admission to the mental health units both in the hospital and throughout the region. Patients who tested positive had to be quarantined for 10 days, at which time they could be admitted to a mental health unit if necessary, he said.
Dr. Ganem shared details of some strategies adopted by Dell Children’s. He explained that the COVID-19 psychiatry patient workflow started with an ED evaluation, followed by medical clearance and consideration for admission.
“There was significant coordination between the social worker in the emergency department and the psychiatry social worker,” he said.
Key elements of the treatment plan for children with positive COVID-19 tests included an “interprofessional huddle” to coordinate the plan of care, goals for admission, and goals for safety, Dr. Ganem said.
Patients who required admission were expected to have an initial length of stay of 72 hours, and those who tested positive for COVID-19 were admitted to a medical unit with COVID-19 isolation, he said.
Once a patient is admitted, an RN activates a suicide prevention pathway, and an interprofessional team meets to determine what patients need for safe and effective discharge, said Dr. Ganem. He cited the SAFE-T protocol (Suicide Assessment Five-step Evaluation and Triage) as one of the tools used to determine safe discharge criteria. Considerations on the SAFE-T list include family support, an established outpatient therapist and psychiatrist, no suicide attempts prior to the current admission, or a low lethality attempt, and access to partial hospitalization or intensive outpatient programs.
Patients who could not be discharged because of suicidality or inadequate support or concerns about safety at home were considered for inpatient admission. Patients with COVID-19–positive tests who had continued need for inpatient mental health services could be transferred to an inpatient mental health unit after a 10-day quarantine.
Overall, “this has been a continuum of lessons learned, with some things we know now that we didn’t know in April or May of 2020,” Dr. Ganem said. Early in the pandemic, the focus was on minimizing risk, securing personal protective equipment, and determining who provided services in a patient’s room. “We developed new paradigms on the fly,” he said, including the use of virtual visits, which included securing and cleaning devices, as well as learning how to use them in this setting,” he said.
More recently, the emphasis has been on providing services to patients before they need to visit the hospital, rather than automatically admitting any patients with suicidal ideation and a positive COVID-19 test, Dr. Ganem said.
Dr. Talebi and Dr. Ganem had no financial conflicts to disclose. The conference was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to impact child and adolescent mental health, and clinicians are learning as they go to develop strategies that address the challenges of providing both medical and mental health care to young patients, including those who test positive for COVID-19, according to Hani Talebi, PhD, director of pediatric psychology, and Jorge Ganem, MD, FAAP, director of pediatric hospital medicine, both of the University of Texas at Austin and Dell Children’s Medical Center.
In a presentation at the 2021 virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine conference, Dr. Talebi and Dr. Ganem shared their experiences in identifying the impact of the pandemic on mental health services in a freestanding hospital, and synthesizing inpatient mental health care and medical care outside of a dedicated mental health unit.
Mental health is a significant pediatric issue; approximately one in five children have a diagnosable mental or behavioral health problem, but nearly two-thirds get little or no help, Dr. Talebi said. “COVID-19 has only exacerbated these mental health challenges,” he said.
He noted that beginning in April 2020, the proportion of children’s mental health-related emergency department visits increased and remained elevated through the spring, summer, and fall of 2020, as families fearful of COVID-19 avoided regular hospital visits.
Data suggest that up to 50% of all adolescent psychiatric crises that led to inpatient admissions were related in some way to COVID-19, Dr. Talebi said. In addition, “individuals with a recent diagnosis of a mental health disorder are at increased risk for COVID-19 infection,” and the risk is even higher among women and African Americans, he said.
The past year significantly impacted the mental wellbeing of parents and children, Dr. Talebi said. He cited a June 2020 study in Pediatrics in which 27% of parents reported worsening mental health for themselves, and 14% reported worsening behavioral health for their children. Ongoing issues including food insecurity, loss of regular child care, and an overall “very disorienting experience in the day-to-day” compromised the mental health of families, Dr. Talebi emphasized. Children isolated at home were not meeting developmental milestones that organically occur when socializing with peers, parents didn’t know how to handle some of their children’s issues without support from schools, and many people were struggling with other preexisting health conditions, he said.
This confluence of factors helped drive a surge in emergency department visits, meaning longer wait times and concerns about meeting urgent medical and mental health needs while maintaining safety, he added.
Parents and children waited longer to seek care, and community hospitals such as Dell Children’s Medical Center were faced with children in the emergency department with crisis-level mental health issues, along with children already waiting in the ED to address medical emergencies. All these patients had to be tested for COVID-19 and managed accordingly, Dr. Talebi noted.
Dr. Talebi emphasized the need for clinically robust care of the children who were in isolation for 10 days on the medical unit, waiting to test negative. New protocols were created for social workers to conduct daily safety checks, and to develop regular schedules for screening, “so they are having an experience on the medical floors similar to what they would have in a mental health unit,” he said.
Dr. Ganem reflected on the logistical challenges of managing mental health care while observing COVID-19 safety protocols. “COVID-19 added a new wrinkle of isolation,” he said. As institutional guidelines on testing and isolation evolved, negative COVID-19 tests were required for admission to the mental health units both in the hospital and throughout the region. Patients who tested positive had to be quarantined for 10 days, at which time they could be admitted to a mental health unit if necessary, he said.
Dr. Ganem shared details of some strategies adopted by Dell Children’s. He explained that the COVID-19 psychiatry patient workflow started with an ED evaluation, followed by medical clearance and consideration for admission.
“There was significant coordination between the social worker in the emergency department and the psychiatry social worker,” he said.
Key elements of the treatment plan for children with positive COVID-19 tests included an “interprofessional huddle” to coordinate the plan of care, goals for admission, and goals for safety, Dr. Ganem said.
Patients who required admission were expected to have an initial length of stay of 72 hours, and those who tested positive for COVID-19 were admitted to a medical unit with COVID-19 isolation, he said.
Once a patient is admitted, an RN activates a suicide prevention pathway, and an interprofessional team meets to determine what patients need for safe and effective discharge, said Dr. Ganem. He cited the SAFE-T protocol (Suicide Assessment Five-step Evaluation and Triage) as one of the tools used to determine safe discharge criteria. Considerations on the SAFE-T list include family support, an established outpatient therapist and psychiatrist, no suicide attempts prior to the current admission, or a low lethality attempt, and access to partial hospitalization or intensive outpatient programs.
Patients who could not be discharged because of suicidality or inadequate support or concerns about safety at home were considered for inpatient admission. Patients with COVID-19–positive tests who had continued need for inpatient mental health services could be transferred to an inpatient mental health unit after a 10-day quarantine.
Overall, “this has been a continuum of lessons learned, with some things we know now that we didn’t know in April or May of 2020,” Dr. Ganem said. Early in the pandemic, the focus was on minimizing risk, securing personal protective equipment, and determining who provided services in a patient’s room. “We developed new paradigms on the fly,” he said, including the use of virtual visits, which included securing and cleaning devices, as well as learning how to use them in this setting,” he said.
More recently, the emphasis has been on providing services to patients before they need to visit the hospital, rather than automatically admitting any patients with suicidal ideation and a positive COVID-19 test, Dr. Ganem said.
Dr. Talebi and Dr. Ganem had no financial conflicts to disclose. The conference was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
The COVID-19 pandemic continues to impact child and adolescent mental health, and clinicians are learning as they go to develop strategies that address the challenges of providing both medical and mental health care to young patients, including those who test positive for COVID-19, according to Hani Talebi, PhD, director of pediatric psychology, and Jorge Ganem, MD, FAAP, director of pediatric hospital medicine, both of the University of Texas at Austin and Dell Children’s Medical Center.
In a presentation at the 2021 virtual Pediatric Hospital Medicine conference, Dr. Talebi and Dr. Ganem shared their experiences in identifying the impact of the pandemic on mental health services in a freestanding hospital, and synthesizing inpatient mental health care and medical care outside of a dedicated mental health unit.
Mental health is a significant pediatric issue; approximately one in five children have a diagnosable mental or behavioral health problem, but nearly two-thirds get little or no help, Dr. Talebi said. “COVID-19 has only exacerbated these mental health challenges,” he said.
He noted that beginning in April 2020, the proportion of children’s mental health-related emergency department visits increased and remained elevated through the spring, summer, and fall of 2020, as families fearful of COVID-19 avoided regular hospital visits.
Data suggest that up to 50% of all adolescent psychiatric crises that led to inpatient admissions were related in some way to COVID-19, Dr. Talebi said. In addition, “individuals with a recent diagnosis of a mental health disorder are at increased risk for COVID-19 infection,” and the risk is even higher among women and African Americans, he said.
The past year significantly impacted the mental wellbeing of parents and children, Dr. Talebi said. He cited a June 2020 study in Pediatrics in which 27% of parents reported worsening mental health for themselves, and 14% reported worsening behavioral health for their children. Ongoing issues including food insecurity, loss of regular child care, and an overall “very disorienting experience in the day-to-day” compromised the mental health of families, Dr. Talebi emphasized. Children isolated at home were not meeting developmental milestones that organically occur when socializing with peers, parents didn’t know how to handle some of their children’s issues without support from schools, and many people were struggling with other preexisting health conditions, he said.
This confluence of factors helped drive a surge in emergency department visits, meaning longer wait times and concerns about meeting urgent medical and mental health needs while maintaining safety, he added.
Parents and children waited longer to seek care, and community hospitals such as Dell Children’s Medical Center were faced with children in the emergency department with crisis-level mental health issues, along with children already waiting in the ED to address medical emergencies. All these patients had to be tested for COVID-19 and managed accordingly, Dr. Talebi noted.
Dr. Talebi emphasized the need for clinically robust care of the children who were in isolation for 10 days on the medical unit, waiting to test negative. New protocols were created for social workers to conduct daily safety checks, and to develop regular schedules for screening, “so they are having an experience on the medical floors similar to what they would have in a mental health unit,” he said.
Dr. Ganem reflected on the logistical challenges of managing mental health care while observing COVID-19 safety protocols. “COVID-19 added a new wrinkle of isolation,” he said. As institutional guidelines on testing and isolation evolved, negative COVID-19 tests were required for admission to the mental health units both in the hospital and throughout the region. Patients who tested positive had to be quarantined for 10 days, at which time they could be admitted to a mental health unit if necessary, he said.
Dr. Ganem shared details of some strategies adopted by Dell Children’s. He explained that the COVID-19 psychiatry patient workflow started with an ED evaluation, followed by medical clearance and consideration for admission.
“There was significant coordination between the social worker in the emergency department and the psychiatry social worker,” he said.
Key elements of the treatment plan for children with positive COVID-19 tests included an “interprofessional huddle” to coordinate the plan of care, goals for admission, and goals for safety, Dr. Ganem said.
Patients who required admission were expected to have an initial length of stay of 72 hours, and those who tested positive for COVID-19 were admitted to a medical unit with COVID-19 isolation, he said.
Once a patient is admitted, an RN activates a suicide prevention pathway, and an interprofessional team meets to determine what patients need for safe and effective discharge, said Dr. Ganem. He cited the SAFE-T protocol (Suicide Assessment Five-step Evaluation and Triage) as one of the tools used to determine safe discharge criteria. Considerations on the SAFE-T list include family support, an established outpatient therapist and psychiatrist, no suicide attempts prior to the current admission, or a low lethality attempt, and access to partial hospitalization or intensive outpatient programs.
Patients who could not be discharged because of suicidality or inadequate support or concerns about safety at home were considered for inpatient admission. Patients with COVID-19–positive tests who had continued need for inpatient mental health services could be transferred to an inpatient mental health unit after a 10-day quarantine.
Overall, “this has been a continuum of lessons learned, with some things we know now that we didn’t know in April or May of 2020,” Dr. Ganem said. Early in the pandemic, the focus was on minimizing risk, securing personal protective equipment, and determining who provided services in a patient’s room. “We developed new paradigms on the fly,” he said, including the use of virtual visits, which included securing and cleaning devices, as well as learning how to use them in this setting,” he said.
More recently, the emphasis has been on providing services to patients before they need to visit the hospital, rather than automatically admitting any patients with suicidal ideation and a positive COVID-19 test, Dr. Ganem said.
Dr. Talebi and Dr. Ganem had no financial conflicts to disclose. The conference was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
FROM PHM 2021
The trauma and healing of 9/11 echo in COVID-19
The scope and magnitude of the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon were unprecedented in U.S. history. It was arguably the most serious trauma to beset Americans on U.S. soil. The 20th anniversary of 9/11 will take place during another crisis, not only in American history but also in world history – the COVID-19 pandemic.
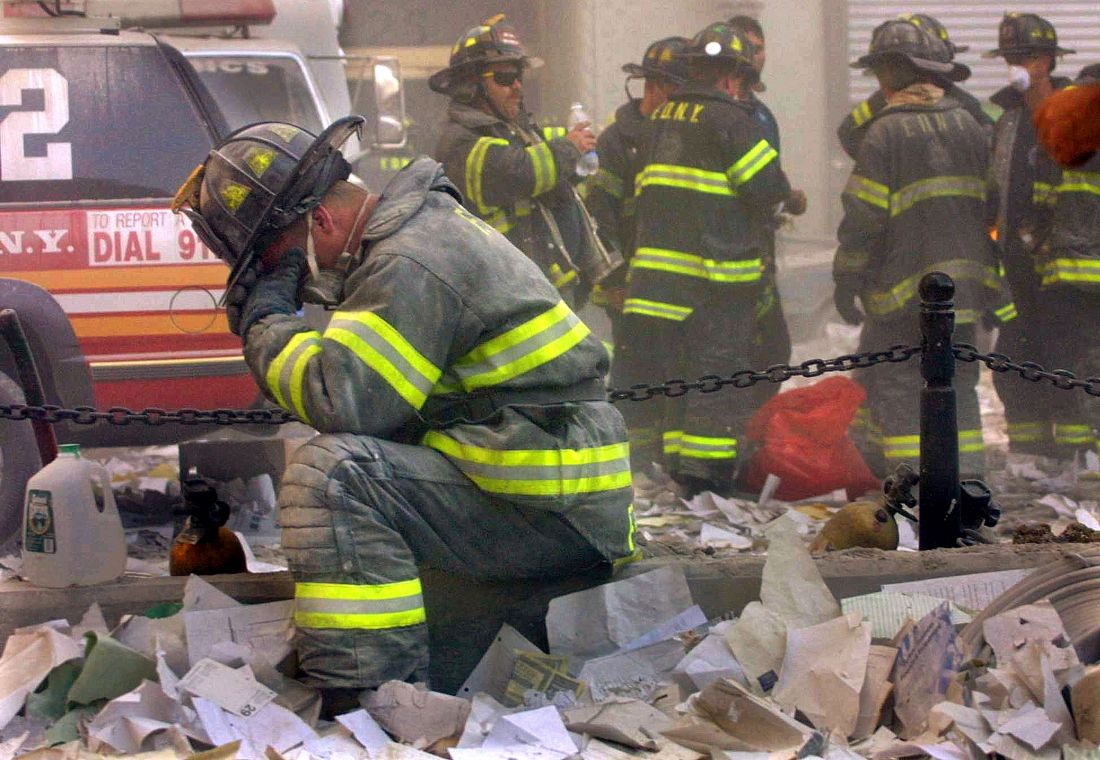

“As different as these two events are, there are obvious points of comparison,” Jonathan DePierro, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Both were unprecedented life-threatening situations, presenting threats to individuals’ lives and profoundly traumatizing not only society as a whole but also first responders.”
Dr. DePierro, who is also the clinical director of the Center for Stress, Resilience, and Personal Growth at Mount Sinai, thinks there are many lessons to be learned from the mental health response to 9/11 that can inform our understanding of and response to the mental health needs of today’s first responders in the COVID-19 crisis, particularly health care professionals.
“Every one of our hospitals became a ‘ground zero’ early during the pandemic, and we see the numbers rising again and hospitals again overwhelmed, so he said.
Placing trauma within a new framework
According to Priscilla Dass-Brailsford, EdD, MPH, professor of psychology, department of psychiatry, Georgetown University, Washington, Sept. 11, 2001, “placed trauma within a new framework.”
“Prior to 9/11, crisis protocols and how to manage stress in the aftermath of violent events were uncommon,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford, a clinical psychologist with expertise in trauma who also chairs a clinical psychology program for the Chicago School of Professional Psychology, said in an interview.
As a first responder, she was involved in early interventions for survivors of 9/11. On Sept. 11, 2001, she had just resigned her position as coordinator of the community crisis response team – the first of its kind in the United States – through the Victims of Violence Program in Cambridge, in Cambridge, Mass.
The program responded to communities in which there were high rates of drive-by shootings and similar acts of violence. Because of her crisis experience, Dr. Dass-Brailsford was asked to conduct debriefings in Boston in the area where the 9/11 terrorists had stayed prior to boarding the planes that were used in the terrorist attacks. She subsequently went to New York City to conduct similar psychological debriefings with affected communities.
“What we’ve learned is that we had no crisis protocol on how to manage the stress in the aftermath of such a violent event, no standard operating procedures. There were very few people trained in crisis and trauma response at that time. Partially spurred by 9/11, trauma training programs became more prolific,” she said. Dr. Dass-Brailsford developed a trauma certification program at Lesley University in Cambridge, Mass., where she began to teach after 9/11. “I saw the importance of having clinicians trained to respond in a crisis, because responding to a crisis is very different from conducting regular mental health interventions.”
Short- and long-term interventions
Dr. DePierro said that Mount Sinai has a 20-year history of responding to the physical and mental health needs of 9/11 responders.
“We saw a number of first responders experiencing clinical depression, anxiety, a lot of worry, symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, and an increase in alcohol and/or substance use,” he recounted. In some, these responses were immediate; in others, the onset of symptoms was more gradual. Some responders had acute reactions that lasted for several months to a year, whereas for others, the reactions were prolonged, and they remained “chronically distressed long after the immediate exposure to the event,” he said.
Recent studies have shown that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, health care professionals and many essential workers have experienced similar symptoms, Dr. DePierro noted.
Mental health care professionals who provided interventions for workers involved in recovery and cleanup at the World Trade Center have highlighted the need for long-term monitoring of people on the front lines during the COVID-19 pandemic – especially health care workers, other essential personnel (for example, delivery, postal, and grocery store workers) and surviving family members. “Health monitoring and treatment efforts for 9/11 survivors and responders were put into place soon after the attacks and continue to this day,” using funding provided through the James Zadroga Act, Dr. DePierro said.
“Without similarly unified health registry and treatment services, many individuals – especially from underserved groups – will likely experience chronic mental health consequences and will be unable to access high-quality health care services,” he stated.
‘Psychological first aid’
“Although many people who go through a crisis – whether as a result of terrorism, such as 9/11, or a medical crisis, such as the current pandemic, or a natural disaster, such as Hurricane Katrina – experience PTSD, it’s important to note that not everyone who goes through a crisis and is traumatized will go on to develop PTSD,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford emphasized.
“To me, 9/11 placed psychological first aid on the map. Even if you are not a clinician, you can be trained to provide psychological first aid by becoming familiar with people’s reactions to trauma and how you can support them through it,” she continued.
For example, if a coworker is agitated or “seems to be having a meltdown, you can be there by offering support and getting them the appropriate help.” Research has suggested that having social support before and after a traumatic event can be helpful in determining vulnerability to the development of PTSD and in modulating the impact of the trauma.
Psychological first aid is helpful as an interim measure. “If you see a coworker holding their head in their hands all day and staring at the screen, identifying whether the person might be having a dissociative episode is critical. Providing some support is important, but if more intensive professional support is needed, determining that and making a referral becomes key,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford stated.
Dr. DePierro added: “One of the most important messages that I want health care workers to know from my years of working with 9/11 survivors is that feeling distressed after a traumatic event is very common, but with effective care, one doesn’t necessarily need to be in treatment for years.”
Danielle Ofri, MD, PhD, clinical professor, department of medicine, New York University, agreed. “It is important to continue keeping tabs on each other and remaining sensitive to the collateral struggles of our colleagues. Some have children who are struggling in school, others have parents who have lost a job. Continuing to check in on others and offer support is critical going forward,” she said in an interview.
Cohesiveness and volunteerism
One of the most powerful antidotes to long-term traumatization is a sense of community cohesiveness. This was the case following 9/11, and it is the case during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Dr. Ofri, an internist at Bellevue Hospital in New York.
“There was an enormous mobilization. Bellevue is a city hospital with a level 1 trauma center, and we expected to be swamped, so the whole hospital shifted into gear,” said Dr. Ofri. “What would have been terrifying seemed tolerable because we felt that we were in it together. We discharged the inpatients to make beds available. Within hours, we had converted clinics into emergency departments and ICUs. We worked seamlessly, and the crisis brought us together ... but then, of course, no patients showed up.”
She described her relationship with her colleagues as “feeling almost like a family, especially during the pandemic, when so many others were in lockdown and feeling isolated and useless.”
She and her colleagues saw each other daily. Although the content of their tasks and responsibilities changed and people were redeployed to other areas, “our workday didn’t really change. It would have been overwhelming if we hadn’t had our daily meetings to regroup and assess where we were. Each day, everything we had learned or implemented the day before – treatment protocols, testing protocols, our understanding of how the virus was communicated – would change and need to be reevaluated. Those morning meetings were critical to staying centered. It felt as though we were building a plane and flying it at the same time, which felt both scary and heady. Luckily, it took place within the fraternity of a committed and caring group.”
Dr. Ofri recounted that, after 9/11, as well as during the pandemic, “professionals kept jumping in from the sidelines to volunteer. Within hours of the collapse of the towers, the ED had filled with staff. People came out of retirement and out from vacation and out of the woodwork. It was very heartening.”
Even more inspiring, “all the departmental barriers seemed to break down. People were willing to step out of their ordinary roles and check their egos at the door. Seasoned physicians were willing to function as medical interns.”
This generosity of time and spirit “helped keep us going,” she said.
Dr. DePierro agreed. “One of the things I’ve seen on medical floors is that COVID actually brought some units together, increasing their cohesion and mutual support and increasing the bonds between people.” These intensified bonds “increased the resilience of everyone involved.”
Commitment to the community
Dr. Ofri recalls families gathering at the hospital after 9/11, watching posters of missing people going up all over the hospital as well as on mailboxes and lampposts. Because the center for missing people was located right next door to Bellevue, there were long lines of families coming in to register. The chief medical office was there, and a huge tent was built to accommodate the families. The tent took up the entire block. “We felt a lot of ownership, because families were coming here,” she said.
The street remained closed even as the days, weeks, and years stretched on, and the tent remained. It was used as a reflection area for families. During the pandemic, that area was used for refrigerated trucks that served as temporary morgues.
“Both logistically and emotionally, we had a feeling during the pandemic of, ‘We’ve been here before, we’ll do it again and be there for the community,’ ” Dr. Ofri said.
She noted that the sense of commitment to the community carried her and fellow clinicians through the toughest parts of 9/11 and of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“People look to the medical system as a lodestar. ‘Where’s my family member? What should I do? Should I be tested? Vaccinated?’ We were there to be a steady presence for the community physically, psychologically, emotionally, and medically, which helped center us as well,” Dr. Ofri said. “If we didn’t have that, we might have all given in to existential panic.”
She added: “Although we had to work twice as hard, often amid great personal risk, we had the good fortune of having a sense of purpose, something to contribute, plus the community of colleagues we cared about and trusted with our lives.”
Crisis and personal growth
Dr. DePierro said that participants who went through 9/11 have been coming to Mount Sinai’s World Trade Center Health Program for care for nearly two decades. “Many are doing quite well, despite the emotional trauma and the dust and toxin exposure, which has given us a window into what makes people resilient.”
Social and community support are key factors in resilience. Another is recognizing opportunities for personal or professional growth during the crisis, according to Dr. DePierro.
During the pandemic, hospital staff were redeployed to departments where they didn’t typically work. They worked with new colleagues and used skills in patient care that they hadn’t needed for years or even decades. “Although this was stressful and distressing, quite a number said they came through with more medical knowledge than before and that they had forged relationships in the trenches that have been lasting and have become important to them,” he reported.
He noted that, during both crises, for first responders and health care practitioners, religious or spiritual faith was a source of resilience. “During the peak of the pandemic, chaplains provided an exorbitant amount of staff support as clinicians turned to the chaplain to help make sense of what they were going through and connect to something greater than themselves.” Similarly, during 9/11, police and fire department chaplains “played a huge role in supporting the first responders,” Dr. DePierro said.
He said that Mount Sinai holds resilience workshops “where we focus on these topics and teach health care workers how to build resilience in their lives, heal day-to-day stressors, and even grow from the experience.”
Dr. Ofri, who is the founder and editor-in-chief of the Bellevue Literary Review, added that the arts played an important role in bolstering resilience and providing a creative outlet for clinicians after 9/11 and again during the pandemic.
The publication is celebrating its twentieth anniversary – its first issue went to press in September 2001. The cover contained an acknowledgment of 9/11.
Dr. Ofri said that a gala event had been planned for Oct. 7, 2001, to celebrate the inaugural issue of the publication. She assumed no one would show up, given that the United States had invaded Afghanistan only hours earlier. To her surprise, over a hundred people attended, “which made me realize the role of the arts during trauma. People were seeking to come together and hear poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction.”
Dr. Ofri has been “impressed by the amount of incredible creative writing of all sorts that has been submitted [to the publication] during the pandemic, an unexpected flowering of the arts.”
Unique challenges, unique opportunities
All three experts pointed to several noteworthy differences between the experiences of first responders following 9/11 and those of today’s health care professionals during the pandemic.
“What happened on Sept. 11 was one discrete event, and although it obviously led to years of recovering body parts and cleaning up Ground Zero, and on a national level it led to a war, it nevertheless was a single event,” Dr. DePierro observed. By contrast, the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, and for health care practitioners, “it’s by no means over. Again and again, they are being thrown back into battle, dealing with fatigue, weariness, and loss of life.”
Moreover, “it is my understanding that immediately following 9/11, there was a general coming together in our country, but it’s obvious that today, there’s a great deal of fractiousness, contention, disagreement, and disunity in our country when it comes to COVID-19,” Dr. DePierro continued.
“This takes a great toll, particularly on health care workers who are dealing with COVID-19 on a daily basis and experience a disconnect between what they see on their floors and ICUs of the hospital, experiencing loss of life they’ve likely never encountered in their careers, and what people are saying when they downplay the seriousness of COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Ofri agreed. “The fragmentation of our country and the failure of leadership at the highest level to provide even the basics, such as PPE [personal protective equipment] for health care professionals, left us baffled, profoundly hurt, and angry.”
A positive difference between the COVID-19 pandemic and the aftermath of 9/11 is the development of sophisticated technology that allows interventions for traumatized individuals – both health care professionals and the general public – through telehealth, Dr. DePierro pointed out.
“I would say that these resources and technologies are a silver lining and should continue to be expanded on,” he said. “Now, busy health care workers can access all manner of supportive services, including teletherapy, right from home or between shifts.”
Another “silver lining” is that the pandemic has shone a spotlight on an issue that predated the pandemic – the mental health of health care professionals. Opening a discussion about this has reduced stigma and hopefully has paved the way for improved treatments and for providing resources.
Dr. Dass-Brailsford added that “it is important, going forward, for all of us to be trauma informed, to know how trauma and trauma-related stress unfolds in both other people and yourself, and to know what coping skills can be used to avoid crises from developing – a task that extends across all types of disasters.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The scope and magnitude of the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon were unprecedented in U.S. history. It was arguably the most serious trauma to beset Americans on U.S. soil. The 20th anniversary of 9/11 will take place during another crisis, not only in American history but also in world history – the COVID-19 pandemic.

“As different as these two events are, there are obvious points of comparison,” Jonathan DePierro, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Both were unprecedented life-threatening situations, presenting threats to individuals’ lives and profoundly traumatizing not only society as a whole but also first responders.”
Dr. DePierro, who is also the clinical director of the Center for Stress, Resilience, and Personal Growth at Mount Sinai, thinks there are many lessons to be learned from the mental health response to 9/11 that can inform our understanding of and response to the mental health needs of today’s first responders in the COVID-19 crisis, particularly health care professionals.
“Every one of our hospitals became a ‘ground zero’ early during the pandemic, and we see the numbers rising again and hospitals again overwhelmed, so he said.
Placing trauma within a new framework
According to Priscilla Dass-Brailsford, EdD, MPH, professor of psychology, department of psychiatry, Georgetown University, Washington, Sept. 11, 2001, “placed trauma within a new framework.”
“Prior to 9/11, crisis protocols and how to manage stress in the aftermath of violent events were uncommon,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford, a clinical psychologist with expertise in trauma who also chairs a clinical psychology program for the Chicago School of Professional Psychology, said in an interview.
As a first responder, she was involved in early interventions for survivors of 9/11. On Sept. 11, 2001, she had just resigned her position as coordinator of the community crisis response team – the first of its kind in the United States – through the Victims of Violence Program in Cambridge, in Cambridge, Mass.
The program responded to communities in which there were high rates of drive-by shootings and similar acts of violence. Because of her crisis experience, Dr. Dass-Brailsford was asked to conduct debriefings in Boston in the area where the 9/11 terrorists had stayed prior to boarding the planes that were used in the terrorist attacks. She subsequently went to New York City to conduct similar psychological debriefings with affected communities.
“What we’ve learned is that we had no crisis protocol on how to manage the stress in the aftermath of such a violent event, no standard operating procedures. There were very few people trained in crisis and trauma response at that time. Partially spurred by 9/11, trauma training programs became more prolific,” she said. Dr. Dass-Brailsford developed a trauma certification program at Lesley University in Cambridge, Mass., where she began to teach after 9/11. “I saw the importance of having clinicians trained to respond in a crisis, because responding to a crisis is very different from conducting regular mental health interventions.”
Short- and long-term interventions
Dr. DePierro said that Mount Sinai has a 20-year history of responding to the physical and mental health needs of 9/11 responders.
“We saw a number of first responders experiencing clinical depression, anxiety, a lot of worry, symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, and an increase in alcohol and/or substance use,” he recounted. In some, these responses were immediate; in others, the onset of symptoms was more gradual. Some responders had acute reactions that lasted for several months to a year, whereas for others, the reactions were prolonged, and they remained “chronically distressed long after the immediate exposure to the event,” he said.
Recent studies have shown that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, health care professionals and many essential workers have experienced similar symptoms, Dr. DePierro noted.
Mental health care professionals who provided interventions for workers involved in recovery and cleanup at the World Trade Center have highlighted the need for long-term monitoring of people on the front lines during the COVID-19 pandemic – especially health care workers, other essential personnel (for example, delivery, postal, and grocery store workers) and surviving family members. “Health monitoring and treatment efforts for 9/11 survivors and responders were put into place soon after the attacks and continue to this day,” using funding provided through the James Zadroga Act, Dr. DePierro said.
“Without similarly unified health registry and treatment services, many individuals – especially from underserved groups – will likely experience chronic mental health consequences and will be unable to access high-quality health care services,” he stated.
‘Psychological first aid’
“Although many people who go through a crisis – whether as a result of terrorism, such as 9/11, or a medical crisis, such as the current pandemic, or a natural disaster, such as Hurricane Katrina – experience PTSD, it’s important to note that not everyone who goes through a crisis and is traumatized will go on to develop PTSD,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford emphasized.
“To me, 9/11 placed psychological first aid on the map. Even if you are not a clinician, you can be trained to provide psychological first aid by becoming familiar with people’s reactions to trauma and how you can support them through it,” she continued.
For example, if a coworker is agitated or “seems to be having a meltdown, you can be there by offering support and getting them the appropriate help.” Research has suggested that having social support before and after a traumatic event can be helpful in determining vulnerability to the development of PTSD and in modulating the impact of the trauma.
Psychological first aid is helpful as an interim measure. “If you see a coworker holding their head in their hands all day and staring at the screen, identifying whether the person might be having a dissociative episode is critical. Providing some support is important, but if more intensive professional support is needed, determining that and making a referral becomes key,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford stated.
Dr. DePierro added: “One of the most important messages that I want health care workers to know from my years of working with 9/11 survivors is that feeling distressed after a traumatic event is very common, but with effective care, one doesn’t necessarily need to be in treatment for years.”
Danielle Ofri, MD, PhD, clinical professor, department of medicine, New York University, agreed. “It is important to continue keeping tabs on each other and remaining sensitive to the collateral struggles of our colleagues. Some have children who are struggling in school, others have parents who have lost a job. Continuing to check in on others and offer support is critical going forward,” she said in an interview.
Cohesiveness and volunteerism
One of the most powerful antidotes to long-term traumatization is a sense of community cohesiveness. This was the case following 9/11, and it is the case during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Dr. Ofri, an internist at Bellevue Hospital in New York.
“There was an enormous mobilization. Bellevue is a city hospital with a level 1 trauma center, and we expected to be swamped, so the whole hospital shifted into gear,” said Dr. Ofri. “What would have been terrifying seemed tolerable because we felt that we were in it together. We discharged the inpatients to make beds available. Within hours, we had converted clinics into emergency departments and ICUs. We worked seamlessly, and the crisis brought us together ... but then, of course, no patients showed up.”
She described her relationship with her colleagues as “feeling almost like a family, especially during the pandemic, when so many others were in lockdown and feeling isolated and useless.”
She and her colleagues saw each other daily. Although the content of their tasks and responsibilities changed and people were redeployed to other areas, “our workday didn’t really change. It would have been overwhelming if we hadn’t had our daily meetings to regroup and assess where we were. Each day, everything we had learned or implemented the day before – treatment protocols, testing protocols, our understanding of how the virus was communicated – would change and need to be reevaluated. Those morning meetings were critical to staying centered. It felt as though we were building a plane and flying it at the same time, which felt both scary and heady. Luckily, it took place within the fraternity of a committed and caring group.”
Dr. Ofri recounted that, after 9/11, as well as during the pandemic, “professionals kept jumping in from the sidelines to volunteer. Within hours of the collapse of the towers, the ED had filled with staff. People came out of retirement and out from vacation and out of the woodwork. It was very heartening.”
Even more inspiring, “all the departmental barriers seemed to break down. People were willing to step out of their ordinary roles and check their egos at the door. Seasoned physicians were willing to function as medical interns.”
This generosity of time and spirit “helped keep us going,” she said.
Dr. DePierro agreed. “One of the things I’ve seen on medical floors is that COVID actually brought some units together, increasing their cohesion and mutual support and increasing the bonds between people.” These intensified bonds “increased the resilience of everyone involved.”
Commitment to the community
Dr. Ofri recalls families gathering at the hospital after 9/11, watching posters of missing people going up all over the hospital as well as on mailboxes and lampposts. Because the center for missing people was located right next door to Bellevue, there were long lines of families coming in to register. The chief medical office was there, and a huge tent was built to accommodate the families. The tent took up the entire block. “We felt a lot of ownership, because families were coming here,” she said.
The street remained closed even as the days, weeks, and years stretched on, and the tent remained. It was used as a reflection area for families. During the pandemic, that area was used for refrigerated trucks that served as temporary morgues.
“Both logistically and emotionally, we had a feeling during the pandemic of, ‘We’ve been here before, we’ll do it again and be there for the community,’ ” Dr. Ofri said.
She noted that the sense of commitment to the community carried her and fellow clinicians through the toughest parts of 9/11 and of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“People look to the medical system as a lodestar. ‘Where’s my family member? What should I do? Should I be tested? Vaccinated?’ We were there to be a steady presence for the community physically, psychologically, emotionally, and medically, which helped center us as well,” Dr. Ofri said. “If we didn’t have that, we might have all given in to existential panic.”
She added: “Although we had to work twice as hard, often amid great personal risk, we had the good fortune of having a sense of purpose, something to contribute, plus the community of colleagues we cared about and trusted with our lives.”
Crisis and personal growth
Dr. DePierro said that participants who went through 9/11 have been coming to Mount Sinai’s World Trade Center Health Program for care for nearly two decades. “Many are doing quite well, despite the emotional trauma and the dust and toxin exposure, which has given us a window into what makes people resilient.”
Social and community support are key factors in resilience. Another is recognizing opportunities for personal or professional growth during the crisis, according to Dr. DePierro.
During the pandemic, hospital staff were redeployed to departments where they didn’t typically work. They worked with new colleagues and used skills in patient care that they hadn’t needed for years or even decades. “Although this was stressful and distressing, quite a number said they came through with more medical knowledge than before and that they had forged relationships in the trenches that have been lasting and have become important to them,” he reported.
He noted that, during both crises, for first responders and health care practitioners, religious or spiritual faith was a source of resilience. “During the peak of the pandemic, chaplains provided an exorbitant amount of staff support as clinicians turned to the chaplain to help make sense of what they were going through and connect to something greater than themselves.” Similarly, during 9/11, police and fire department chaplains “played a huge role in supporting the first responders,” Dr. DePierro said.
He said that Mount Sinai holds resilience workshops “where we focus on these topics and teach health care workers how to build resilience in their lives, heal day-to-day stressors, and even grow from the experience.”
Dr. Ofri, who is the founder and editor-in-chief of the Bellevue Literary Review, added that the arts played an important role in bolstering resilience and providing a creative outlet for clinicians after 9/11 and again during the pandemic.
The publication is celebrating its twentieth anniversary – its first issue went to press in September 2001. The cover contained an acknowledgment of 9/11.
Dr. Ofri said that a gala event had been planned for Oct. 7, 2001, to celebrate the inaugural issue of the publication. She assumed no one would show up, given that the United States had invaded Afghanistan only hours earlier. To her surprise, over a hundred people attended, “which made me realize the role of the arts during trauma. People were seeking to come together and hear poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction.”
Dr. Ofri has been “impressed by the amount of incredible creative writing of all sorts that has been submitted [to the publication] during the pandemic, an unexpected flowering of the arts.”
Unique challenges, unique opportunities
All three experts pointed to several noteworthy differences between the experiences of first responders following 9/11 and those of today’s health care professionals during the pandemic.
“What happened on Sept. 11 was one discrete event, and although it obviously led to years of recovering body parts and cleaning up Ground Zero, and on a national level it led to a war, it nevertheless was a single event,” Dr. DePierro observed. By contrast, the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, and for health care practitioners, “it’s by no means over. Again and again, they are being thrown back into battle, dealing with fatigue, weariness, and loss of life.”
Moreover, “it is my understanding that immediately following 9/11, there was a general coming together in our country, but it’s obvious that today, there’s a great deal of fractiousness, contention, disagreement, and disunity in our country when it comes to COVID-19,” Dr. DePierro continued.
“This takes a great toll, particularly on health care workers who are dealing with COVID-19 on a daily basis and experience a disconnect between what they see on their floors and ICUs of the hospital, experiencing loss of life they’ve likely never encountered in their careers, and what people are saying when they downplay the seriousness of COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Ofri agreed. “The fragmentation of our country and the failure of leadership at the highest level to provide even the basics, such as PPE [personal protective equipment] for health care professionals, left us baffled, profoundly hurt, and angry.”
A positive difference between the COVID-19 pandemic and the aftermath of 9/11 is the development of sophisticated technology that allows interventions for traumatized individuals – both health care professionals and the general public – through telehealth, Dr. DePierro pointed out.
“I would say that these resources and technologies are a silver lining and should continue to be expanded on,” he said. “Now, busy health care workers can access all manner of supportive services, including teletherapy, right from home or between shifts.”
Another “silver lining” is that the pandemic has shone a spotlight on an issue that predated the pandemic – the mental health of health care professionals. Opening a discussion about this has reduced stigma and hopefully has paved the way for improved treatments and for providing resources.
Dr. Dass-Brailsford added that “it is important, going forward, for all of us to be trauma informed, to know how trauma and trauma-related stress unfolds in both other people and yourself, and to know what coping skills can be used to avoid crises from developing – a task that extends across all types of disasters.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The scope and magnitude of the Sept. 11, 2001, attacks on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon were unprecedented in U.S. history. It was arguably the most serious trauma to beset Americans on U.S. soil. The 20th anniversary of 9/11 will take place during another crisis, not only in American history but also in world history – the COVID-19 pandemic.

“As different as these two events are, there are obvious points of comparison,” Jonathan DePierro, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said in an interview. “Both were unprecedented life-threatening situations, presenting threats to individuals’ lives and profoundly traumatizing not only society as a whole but also first responders.”
Dr. DePierro, who is also the clinical director of the Center for Stress, Resilience, and Personal Growth at Mount Sinai, thinks there are many lessons to be learned from the mental health response to 9/11 that can inform our understanding of and response to the mental health needs of today’s first responders in the COVID-19 crisis, particularly health care professionals.
“Every one of our hospitals became a ‘ground zero’ early during the pandemic, and we see the numbers rising again and hospitals again overwhelmed, so he said.
Placing trauma within a new framework
According to Priscilla Dass-Brailsford, EdD, MPH, professor of psychology, department of psychiatry, Georgetown University, Washington, Sept. 11, 2001, “placed trauma within a new framework.”
“Prior to 9/11, crisis protocols and how to manage stress in the aftermath of violent events were uncommon,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford, a clinical psychologist with expertise in trauma who also chairs a clinical psychology program for the Chicago School of Professional Psychology, said in an interview.
As a first responder, she was involved in early interventions for survivors of 9/11. On Sept. 11, 2001, she had just resigned her position as coordinator of the community crisis response team – the first of its kind in the United States – through the Victims of Violence Program in Cambridge, in Cambridge, Mass.
The program responded to communities in which there were high rates of drive-by shootings and similar acts of violence. Because of her crisis experience, Dr. Dass-Brailsford was asked to conduct debriefings in Boston in the area where the 9/11 terrorists had stayed prior to boarding the planes that were used in the terrorist attacks. She subsequently went to New York City to conduct similar psychological debriefings with affected communities.
“What we’ve learned is that we had no crisis protocol on how to manage the stress in the aftermath of such a violent event, no standard operating procedures. There were very few people trained in crisis and trauma response at that time. Partially spurred by 9/11, trauma training programs became more prolific,” she said. Dr. Dass-Brailsford developed a trauma certification program at Lesley University in Cambridge, Mass., where she began to teach after 9/11. “I saw the importance of having clinicians trained to respond in a crisis, because responding to a crisis is very different from conducting regular mental health interventions.”
Short- and long-term interventions
Dr. DePierro said that Mount Sinai has a 20-year history of responding to the physical and mental health needs of 9/11 responders.
“We saw a number of first responders experiencing clinical depression, anxiety, a lot of worry, symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, and an increase in alcohol and/or substance use,” he recounted. In some, these responses were immediate; in others, the onset of symptoms was more gradual. Some responders had acute reactions that lasted for several months to a year, whereas for others, the reactions were prolonged, and they remained “chronically distressed long after the immediate exposure to the event,” he said.
Recent studies have shown that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, health care professionals and many essential workers have experienced similar symptoms, Dr. DePierro noted.
Mental health care professionals who provided interventions for workers involved in recovery and cleanup at the World Trade Center have highlighted the need for long-term monitoring of people on the front lines during the COVID-19 pandemic – especially health care workers, other essential personnel (for example, delivery, postal, and grocery store workers) and surviving family members. “Health monitoring and treatment efforts for 9/11 survivors and responders were put into place soon after the attacks and continue to this day,” using funding provided through the James Zadroga Act, Dr. DePierro said.
“Without similarly unified health registry and treatment services, many individuals – especially from underserved groups – will likely experience chronic mental health consequences and will be unable to access high-quality health care services,” he stated.
‘Psychological first aid’
“Although many people who go through a crisis – whether as a result of terrorism, such as 9/11, or a medical crisis, such as the current pandemic, or a natural disaster, such as Hurricane Katrina – experience PTSD, it’s important to note that not everyone who goes through a crisis and is traumatized will go on to develop PTSD,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford emphasized.
“To me, 9/11 placed psychological first aid on the map. Even if you are not a clinician, you can be trained to provide psychological first aid by becoming familiar with people’s reactions to trauma and how you can support them through it,” she continued.
For example, if a coworker is agitated or “seems to be having a meltdown, you can be there by offering support and getting them the appropriate help.” Research has suggested that having social support before and after a traumatic event can be helpful in determining vulnerability to the development of PTSD and in modulating the impact of the trauma.
Psychological first aid is helpful as an interim measure. “If you see a coworker holding their head in their hands all day and staring at the screen, identifying whether the person might be having a dissociative episode is critical. Providing some support is important, but if more intensive professional support is needed, determining that and making a referral becomes key,” Dr. Dass-Brailsford stated.
Dr. DePierro added: “One of the most important messages that I want health care workers to know from my years of working with 9/11 survivors is that feeling distressed after a traumatic event is very common, but with effective care, one doesn’t necessarily need to be in treatment for years.”
Danielle Ofri, MD, PhD, clinical professor, department of medicine, New York University, agreed. “It is important to continue keeping tabs on each other and remaining sensitive to the collateral struggles of our colleagues. Some have children who are struggling in school, others have parents who have lost a job. Continuing to check in on others and offer support is critical going forward,” she said in an interview.
Cohesiveness and volunteerism
One of the most powerful antidotes to long-term traumatization is a sense of community cohesiveness. This was the case following 9/11, and it is the case during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to Dr. Ofri, an internist at Bellevue Hospital in New York.
“There was an enormous mobilization. Bellevue is a city hospital with a level 1 trauma center, and we expected to be swamped, so the whole hospital shifted into gear,” said Dr. Ofri. “What would have been terrifying seemed tolerable because we felt that we were in it together. We discharged the inpatients to make beds available. Within hours, we had converted clinics into emergency departments and ICUs. We worked seamlessly, and the crisis brought us together ... but then, of course, no patients showed up.”
She described her relationship with her colleagues as “feeling almost like a family, especially during the pandemic, when so many others were in lockdown and feeling isolated and useless.”
She and her colleagues saw each other daily. Although the content of their tasks and responsibilities changed and people were redeployed to other areas, “our workday didn’t really change. It would have been overwhelming if we hadn’t had our daily meetings to regroup and assess where we were. Each day, everything we had learned or implemented the day before – treatment protocols, testing protocols, our understanding of how the virus was communicated – would change and need to be reevaluated. Those morning meetings were critical to staying centered. It felt as though we were building a plane and flying it at the same time, which felt both scary and heady. Luckily, it took place within the fraternity of a committed and caring group.”
Dr. Ofri recounted that, after 9/11, as well as during the pandemic, “professionals kept jumping in from the sidelines to volunteer. Within hours of the collapse of the towers, the ED had filled with staff. People came out of retirement and out from vacation and out of the woodwork. It was very heartening.”
Even more inspiring, “all the departmental barriers seemed to break down. People were willing to step out of their ordinary roles and check their egos at the door. Seasoned physicians were willing to function as medical interns.”
This generosity of time and spirit “helped keep us going,” she said.
Dr. DePierro agreed. “One of the things I’ve seen on medical floors is that COVID actually brought some units together, increasing their cohesion and mutual support and increasing the bonds between people.” These intensified bonds “increased the resilience of everyone involved.”
Commitment to the community
Dr. Ofri recalls families gathering at the hospital after 9/11, watching posters of missing people going up all over the hospital as well as on mailboxes and lampposts. Because the center for missing people was located right next door to Bellevue, there were long lines of families coming in to register. The chief medical office was there, and a huge tent was built to accommodate the families. The tent took up the entire block. “We felt a lot of ownership, because families were coming here,” she said.
The street remained closed even as the days, weeks, and years stretched on, and the tent remained. It was used as a reflection area for families. During the pandemic, that area was used for refrigerated trucks that served as temporary morgues.
“Both logistically and emotionally, we had a feeling during the pandemic of, ‘We’ve been here before, we’ll do it again and be there for the community,’ ” Dr. Ofri said.
She noted that the sense of commitment to the community carried her and fellow clinicians through the toughest parts of 9/11 and of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“People look to the medical system as a lodestar. ‘Where’s my family member? What should I do? Should I be tested? Vaccinated?’ We were there to be a steady presence for the community physically, psychologically, emotionally, and medically, which helped center us as well,” Dr. Ofri said. “If we didn’t have that, we might have all given in to existential panic.”
She added: “Although we had to work twice as hard, often amid great personal risk, we had the good fortune of having a sense of purpose, something to contribute, plus the community of colleagues we cared about and trusted with our lives.”
Crisis and personal growth
Dr. DePierro said that participants who went through 9/11 have been coming to Mount Sinai’s World Trade Center Health Program for care for nearly two decades. “Many are doing quite well, despite the emotional trauma and the dust and toxin exposure, which has given us a window into what makes people resilient.”
Social and community support are key factors in resilience. Another is recognizing opportunities for personal or professional growth during the crisis, according to Dr. DePierro.
During the pandemic, hospital staff were redeployed to departments where they didn’t typically work. They worked with new colleagues and used skills in patient care that they hadn’t needed for years or even decades. “Although this was stressful and distressing, quite a number said they came through with more medical knowledge than before and that they had forged relationships in the trenches that have been lasting and have become important to them,” he reported.
He noted that, during both crises, for first responders and health care practitioners, religious or spiritual faith was a source of resilience. “During the peak of the pandemic, chaplains provided an exorbitant amount of staff support as clinicians turned to the chaplain to help make sense of what they were going through and connect to something greater than themselves.” Similarly, during 9/11, police and fire department chaplains “played a huge role in supporting the first responders,” Dr. DePierro said.
He said that Mount Sinai holds resilience workshops “where we focus on these topics and teach health care workers how to build resilience in their lives, heal day-to-day stressors, and even grow from the experience.”
Dr. Ofri, who is the founder and editor-in-chief of the Bellevue Literary Review, added that the arts played an important role in bolstering resilience and providing a creative outlet for clinicians after 9/11 and again during the pandemic.
The publication is celebrating its twentieth anniversary – its first issue went to press in September 2001. The cover contained an acknowledgment of 9/11.
Dr. Ofri said that a gala event had been planned for Oct. 7, 2001, to celebrate the inaugural issue of the publication. She assumed no one would show up, given that the United States had invaded Afghanistan only hours earlier. To her surprise, over a hundred people attended, “which made me realize the role of the arts during trauma. People were seeking to come together and hear poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction.”
Dr. Ofri has been “impressed by the amount of incredible creative writing of all sorts that has been submitted [to the publication] during the pandemic, an unexpected flowering of the arts.”
Unique challenges, unique opportunities
All three experts pointed to several noteworthy differences between the experiences of first responders following 9/11 and those of today’s health care professionals during the pandemic.
“What happened on Sept. 11 was one discrete event, and although it obviously led to years of recovering body parts and cleaning up Ground Zero, and on a national level it led to a war, it nevertheless was a single event,” Dr. DePierro observed. By contrast, the COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing, and for health care practitioners, “it’s by no means over. Again and again, they are being thrown back into battle, dealing with fatigue, weariness, and loss of life.”
Moreover, “it is my understanding that immediately following 9/11, there was a general coming together in our country, but it’s obvious that today, there’s a great deal of fractiousness, contention, disagreement, and disunity in our country when it comes to COVID-19,” Dr. DePierro continued.
“This takes a great toll, particularly on health care workers who are dealing with COVID-19 on a daily basis and experience a disconnect between what they see on their floors and ICUs of the hospital, experiencing loss of life they’ve likely never encountered in their careers, and what people are saying when they downplay the seriousness of COVID-19,” he said.
Dr. Ofri agreed. “The fragmentation of our country and the failure of leadership at the highest level to provide even the basics, such as PPE [personal protective equipment] for health care professionals, left us baffled, profoundly hurt, and angry.”
A positive difference between the COVID-19 pandemic and the aftermath of 9/11 is the development of sophisticated technology that allows interventions for traumatized individuals – both health care professionals and the general public – through telehealth, Dr. DePierro pointed out.
“I would say that these resources and technologies are a silver lining and should continue to be expanded on,” he said. “Now, busy health care workers can access all manner of supportive services, including teletherapy, right from home or between shifts.”
Another “silver lining” is that the pandemic has shone a spotlight on an issue that predated the pandemic – the mental health of health care professionals. Opening a discussion about this has reduced stigma and hopefully has paved the way for improved treatments and for providing resources.
Dr. Dass-Brailsford added that “it is important, going forward, for all of us to be trauma informed, to know how trauma and trauma-related stress unfolds in both other people and yourself, and to know what coping skills can be used to avoid crises from developing – a task that extends across all types of disasters.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Innovative’ equine therapy helps overcome PTSD symptoms
Equine therapy, which involves interactions with horses in a controlled environment, reduces fear and other symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.

Results from a study of about 60 military veterans who underwent weekly sessions of horse-assisted therapy showed “marked reductions” in clinician-rated and self-reported symptoms of PTSD and depression up to 3 months post treatment.
“What we’re doing here with horses is helping people overcome something very specific to PTSD,” coinvestigator Yuval Neria, PhD, professor of clinical medical psychology and director of the PTSD treatment and research program, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
“It offers the opportunity to overcome fear, to facilitate self-efficacy, to facilitate trust in yourself, to understand your feelings, and perhaps to change them over time, he said.
In addition, veterans loved the experience, Dr. Neria reported. He noted that many patients with PTSD have trouble with traditional treatments and are eager to try something “creative and new.”
The findings were published online Aug. 31, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Building bonds
PTSD affects an estimated 10%-30% of U.S. military personnel. These rates are higher than in the general population because veterans may experience increased trauma through combat, injury, and sexual assault, the investigators noted.
Previous research has suggested that horse-human interactions can build bonds that foster behavioral changes. These powerful animals provide instantaneous feedback, allowing patients to develop emotional awareness.
“Horses are very sensitive to whatever we communicate with them, whether it’s fear or anger or stress,” said Dr. Neria.
Equine-assisted therapy is increasingly being used for various mental and physical conditions. Launching an open-label study to examine this type of treatment for PTSD “was an opportunity to look at something very, very different,” Dr. Neria said.
“This is not psychotherapy, it’s not medication, and it’s not neural stimulation,” he added.
The study included 63 veterans with PTSD (mean age, 50 years; 37% women). Of these, 47 were receiving psychotherapy alone, pharmacotherapy alone, or both. In addition, 48 had at least one comorbid disorder. All were divided into 16 groups of three to five participants each.
The program consisted of eight 90-minute weekly sessions conducted at a large equestrian center. Sessions were coled by a mental health professional and an equine specialist who guided participants in horse communication and behavior.
Early sessions focused on acquainting patients with the horses, grooming exercises, and learning “leading,” which involved directing a horse with a rope or wand. During subsequent sessions, patients became more comfortable with managing the horses in individual and teamwork exercises.
The horses were specifically chosen for their temperament and had no history of aggression. A horse wrangler attended sessions to further ensure safety.
Few dropouts
The study included four assessment points: pretreatment, midpoint, post treatment, and 3-month follow-up.
All 63 participants completed baseline assessments. Only five patients (7.9%) discontinued the program.
“We didn’t see dropouts at the rate we usually see in evidence-based therapies for PTSD, which is remarkable and suggests that people really loved it,” said Dr. Neria.
The primary outcome was the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale–5 (CAPS-5), a structured interview that evaluates intrusive memories, social avoidance, and other symptoms based on DSM-5 criteria.
In the intent-to-treat analysis, mean CAPS-5 scores decreased from 38.6 at baseline to 26.9 post treatment. In addition, 29 (46.0%) and 23 (36.5%) participants scored below the PTSD diagnostic threshold of 25 at posttreatment and follow-up, respectively.
Notably, 50.8% of the study population had a clinically significant change, defined as 30% or greater decrease in CAPS-5 score, at post treatment; 54.0% had a significant change at follow-up.
Mean scores on the self-reported 20-item PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 questionnaire decreased from 50.7 at baseline to 34.6 at study termination.
Depression symptoms, measured by the clinician-rated Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the self-reported Beck Depression Inventory–II, also improved.
Structural, functional change
The results did not differ by age, gender, or type of trauma. Dr. Neria noted that many women in the study had suffered sexual abuse or assault, suggesting that the intervention might be appropriate for PTSD outside the military.
“I’m very keen on moving this along into a civilian population,” he said.
The study did not examine potential mechanisms of action. where the treatment took place, the investigators noted.
However, Dr. Neria thinks there is another potential explanation – real changes in the brain.
Neuroimaging of a subsample of 20 participants before and after the intervention showed a significant increase in caudate functional connectivity and a reduction in gray matter density of the thalamus and the caudate.
“We see a big change both structurally and functionally,” with the results pointing to an impact on the reward network of the brain, said Dr. Neria.
“This suggests that pleasure was perhaps the main mechanism of action,” which corresponds with patient reports of really enjoying the experience, he added.
Dr. Neria noted that equine therapy is different from bonding with a loyal dog. Interacting with a large and powerful animal may give veterans a sense of accomplishment and self-worth, which can be tremendously therapeutic.
Next step in therapy?
Commenting on the research, retired Col. Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chair of psychiatry, MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, called equine therapy “innovative” in PTSD.
“I see this as the next step in finding acceptable therapies that people like to do,” she said.
Some patients have an aversion to talk therapy because it makes them relive their trauma; and many dislike the side effects of medications, which can include erectile dysfunction, said Dr. Ritchie, who was not involved with the research.
“So something like this that they can enjoy, have a sense of mastery, can bond with an animal, I think is wonderful,” she said.
Dr. Ritchie noted that working with animals offers “a kind of biofeedback” that may calm anxieties, help maintain control, and “is very nonjudgmental.”
However, she pointed out that equine therapy is not new. For example, horses have been used previously to treat patients with a variety of disabilities, including autism.
Dr. Ritchie thought it was “very wise” that study participants just learned to control the horses and didn’t actually ride them, because that could be a frightening experience.
Nonetheless, she noted equine therapy “is not going to be accessible for everybody.”
In addition, Dr. Ritchie was surprised that the investigators didn’t mention more of the quite extensive research that has been conducted on dog therapy in patients with PTSD.
Dr. Neria and Ritchie disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Equine therapy, which involves interactions with horses in a controlled environment, reduces fear and other symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.

Results from a study of about 60 military veterans who underwent weekly sessions of horse-assisted therapy showed “marked reductions” in clinician-rated and self-reported symptoms of PTSD and depression up to 3 months post treatment.
“What we’re doing here with horses is helping people overcome something very specific to PTSD,” coinvestigator Yuval Neria, PhD, professor of clinical medical psychology and director of the PTSD treatment and research program, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
“It offers the opportunity to overcome fear, to facilitate self-efficacy, to facilitate trust in yourself, to understand your feelings, and perhaps to change them over time, he said.
In addition, veterans loved the experience, Dr. Neria reported. He noted that many patients with PTSD have trouble with traditional treatments and are eager to try something “creative and new.”
The findings were published online Aug. 31, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Building bonds
PTSD affects an estimated 10%-30% of U.S. military personnel. These rates are higher than in the general population because veterans may experience increased trauma through combat, injury, and sexual assault, the investigators noted.
Previous research has suggested that horse-human interactions can build bonds that foster behavioral changes. These powerful animals provide instantaneous feedback, allowing patients to develop emotional awareness.
“Horses are very sensitive to whatever we communicate with them, whether it’s fear or anger or stress,” said Dr. Neria.
Equine-assisted therapy is increasingly being used for various mental and physical conditions. Launching an open-label study to examine this type of treatment for PTSD “was an opportunity to look at something very, very different,” Dr. Neria said.
“This is not psychotherapy, it’s not medication, and it’s not neural stimulation,” he added.
The study included 63 veterans with PTSD (mean age, 50 years; 37% women). Of these, 47 were receiving psychotherapy alone, pharmacotherapy alone, or both. In addition, 48 had at least one comorbid disorder. All were divided into 16 groups of three to five participants each.
The program consisted of eight 90-minute weekly sessions conducted at a large equestrian center. Sessions were coled by a mental health professional and an equine specialist who guided participants in horse communication and behavior.
Early sessions focused on acquainting patients with the horses, grooming exercises, and learning “leading,” which involved directing a horse with a rope or wand. During subsequent sessions, patients became more comfortable with managing the horses in individual and teamwork exercises.
The horses were specifically chosen for their temperament and had no history of aggression. A horse wrangler attended sessions to further ensure safety.
Few dropouts
The study included four assessment points: pretreatment, midpoint, post treatment, and 3-month follow-up.
All 63 participants completed baseline assessments. Only five patients (7.9%) discontinued the program.
“We didn’t see dropouts at the rate we usually see in evidence-based therapies for PTSD, which is remarkable and suggests that people really loved it,” said Dr. Neria.
The primary outcome was the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale–5 (CAPS-5), a structured interview that evaluates intrusive memories, social avoidance, and other symptoms based on DSM-5 criteria.
In the intent-to-treat analysis, mean CAPS-5 scores decreased from 38.6 at baseline to 26.9 post treatment. In addition, 29 (46.0%) and 23 (36.5%) participants scored below the PTSD diagnostic threshold of 25 at posttreatment and follow-up, respectively.
Notably, 50.8% of the study population had a clinically significant change, defined as 30% or greater decrease in CAPS-5 score, at post treatment; 54.0% had a significant change at follow-up.
Mean scores on the self-reported 20-item PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 questionnaire decreased from 50.7 at baseline to 34.6 at study termination.
Depression symptoms, measured by the clinician-rated Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the self-reported Beck Depression Inventory–II, also improved.
Structural, functional change
The results did not differ by age, gender, or type of trauma. Dr. Neria noted that many women in the study had suffered sexual abuse or assault, suggesting that the intervention might be appropriate for PTSD outside the military.
“I’m very keen on moving this along into a civilian population,” he said.
The study did not examine potential mechanisms of action. where the treatment took place, the investigators noted.
However, Dr. Neria thinks there is another potential explanation – real changes in the brain.
Neuroimaging of a subsample of 20 participants before and after the intervention showed a significant increase in caudate functional connectivity and a reduction in gray matter density of the thalamus and the caudate.
“We see a big change both structurally and functionally,” with the results pointing to an impact on the reward network of the brain, said Dr. Neria.
“This suggests that pleasure was perhaps the main mechanism of action,” which corresponds with patient reports of really enjoying the experience, he added.
Dr. Neria noted that equine therapy is different from bonding with a loyal dog. Interacting with a large and powerful animal may give veterans a sense of accomplishment and self-worth, which can be tremendously therapeutic.
Next step in therapy?
Commenting on the research, retired Col. Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chair of psychiatry, MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, called equine therapy “innovative” in PTSD.
“I see this as the next step in finding acceptable therapies that people like to do,” she said.
Some patients have an aversion to talk therapy because it makes them relive their trauma; and many dislike the side effects of medications, which can include erectile dysfunction, said Dr. Ritchie, who was not involved with the research.
“So something like this that they can enjoy, have a sense of mastery, can bond with an animal, I think is wonderful,” she said.
Dr. Ritchie noted that working with animals offers “a kind of biofeedback” that may calm anxieties, help maintain control, and “is very nonjudgmental.”
However, she pointed out that equine therapy is not new. For example, horses have been used previously to treat patients with a variety of disabilities, including autism.
Dr. Ritchie thought it was “very wise” that study participants just learned to control the horses and didn’t actually ride them, because that could be a frightening experience.
Nonetheless, she noted equine therapy “is not going to be accessible for everybody.”
In addition, Dr. Ritchie was surprised that the investigators didn’t mention more of the quite extensive research that has been conducted on dog therapy in patients with PTSD.
Dr. Neria and Ritchie disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Equine therapy, which involves interactions with horses in a controlled environment, reduces fear and other symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, new research suggests.

Results from a study of about 60 military veterans who underwent weekly sessions of horse-assisted therapy showed “marked reductions” in clinician-rated and self-reported symptoms of PTSD and depression up to 3 months post treatment.
“What we’re doing here with horses is helping people overcome something very specific to PTSD,” coinvestigator Yuval Neria, PhD, professor of clinical medical psychology and director of the PTSD treatment and research program, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, said in an interview.
“It offers the opportunity to overcome fear, to facilitate self-efficacy, to facilitate trust in yourself, to understand your feelings, and perhaps to change them over time, he said.
In addition, veterans loved the experience, Dr. Neria reported. He noted that many patients with PTSD have trouble with traditional treatments and are eager to try something “creative and new.”
The findings were published online Aug. 31, 2021, in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Building bonds
PTSD affects an estimated 10%-30% of U.S. military personnel. These rates are higher than in the general population because veterans may experience increased trauma through combat, injury, and sexual assault, the investigators noted.
Previous research has suggested that horse-human interactions can build bonds that foster behavioral changes. These powerful animals provide instantaneous feedback, allowing patients to develop emotional awareness.
“Horses are very sensitive to whatever we communicate with them, whether it’s fear or anger or stress,” said Dr. Neria.
Equine-assisted therapy is increasingly being used for various mental and physical conditions. Launching an open-label study to examine this type of treatment for PTSD “was an opportunity to look at something very, very different,” Dr. Neria said.
“This is not psychotherapy, it’s not medication, and it’s not neural stimulation,” he added.
The study included 63 veterans with PTSD (mean age, 50 years; 37% women). Of these, 47 were receiving psychotherapy alone, pharmacotherapy alone, or both. In addition, 48 had at least one comorbid disorder. All were divided into 16 groups of three to five participants each.
The program consisted of eight 90-minute weekly sessions conducted at a large equestrian center. Sessions were coled by a mental health professional and an equine specialist who guided participants in horse communication and behavior.
Early sessions focused on acquainting patients with the horses, grooming exercises, and learning “leading,” which involved directing a horse with a rope or wand. During subsequent sessions, patients became more comfortable with managing the horses in individual and teamwork exercises.
The horses were specifically chosen for their temperament and had no history of aggression. A horse wrangler attended sessions to further ensure safety.
Few dropouts
The study included four assessment points: pretreatment, midpoint, post treatment, and 3-month follow-up.
All 63 participants completed baseline assessments. Only five patients (7.9%) discontinued the program.
“We didn’t see dropouts at the rate we usually see in evidence-based therapies for PTSD, which is remarkable and suggests that people really loved it,” said Dr. Neria.
The primary outcome was the Clinician-Administered PTSD Scale–5 (CAPS-5), a structured interview that evaluates intrusive memories, social avoidance, and other symptoms based on DSM-5 criteria.
In the intent-to-treat analysis, mean CAPS-5 scores decreased from 38.6 at baseline to 26.9 post treatment. In addition, 29 (46.0%) and 23 (36.5%) participants scored below the PTSD diagnostic threshold of 25 at posttreatment and follow-up, respectively.
Notably, 50.8% of the study population had a clinically significant change, defined as 30% or greater decrease in CAPS-5 score, at post treatment; 54.0% had a significant change at follow-up.
Mean scores on the self-reported 20-item PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 questionnaire decreased from 50.7 at baseline to 34.6 at study termination.
Depression symptoms, measured by the clinician-rated Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the self-reported Beck Depression Inventory–II, also improved.
Structural, functional change
The results did not differ by age, gender, or type of trauma. Dr. Neria noted that many women in the study had suffered sexual abuse or assault, suggesting that the intervention might be appropriate for PTSD outside the military.
“I’m very keen on moving this along into a civilian population,” he said.
The study did not examine potential mechanisms of action. where the treatment took place, the investigators noted.
However, Dr. Neria thinks there is another potential explanation – real changes in the brain.
Neuroimaging of a subsample of 20 participants before and after the intervention showed a significant increase in caudate functional connectivity and a reduction in gray matter density of the thalamus and the caudate.
“We see a big change both structurally and functionally,” with the results pointing to an impact on the reward network of the brain, said Dr. Neria.
“This suggests that pleasure was perhaps the main mechanism of action,” which corresponds with patient reports of really enjoying the experience, he added.
Dr. Neria noted that equine therapy is different from bonding with a loyal dog. Interacting with a large and powerful animal may give veterans a sense of accomplishment and self-worth, which can be tremendously therapeutic.
Next step in therapy?
Commenting on the research, retired Col. Elspeth Cameron Ritchie, MD, chair of psychiatry, MedStar Washington Hospital Center, Washington, called equine therapy “innovative” in PTSD.
“I see this as the next step in finding acceptable therapies that people like to do,” she said.
Some patients have an aversion to talk therapy because it makes them relive their trauma; and many dislike the side effects of medications, which can include erectile dysfunction, said Dr. Ritchie, who was not involved with the research.
“So something like this that they can enjoy, have a sense of mastery, can bond with an animal, I think is wonderful,” she said.
Dr. Ritchie noted that working with animals offers “a kind of biofeedback” that may calm anxieties, help maintain control, and “is very nonjudgmental.”
However, she pointed out that equine therapy is not new. For example, horses have been used previously to treat patients with a variety of disabilities, including autism.
Dr. Ritchie thought it was “very wise” that study participants just learned to control the horses and didn’t actually ride them, because that could be a frightening experience.
Nonetheless, she noted equine therapy “is not going to be accessible for everybody.”
In addition, Dr. Ritchie was surprised that the investigators didn’t mention more of the quite extensive research that has been conducted on dog therapy in patients with PTSD.
Dr. Neria and Ritchie disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Teleintegrated versus telereferral care for complex psychiatric disorders
Two models for treating patients with complex psychiatric disorders in primary care are equally effective, new research suggests.
Results from a pragmatic, randomized comparative effectiveness study involving more than 1,000 patients showed that both integrated telepsychiatry collaborative care (TCC) and telepsychiatry/telepsychology enhanced referral (TER) provided “significantly and substantially” improved clinical outcomes, researchers noted.
However, the referral model required substantially more mental health specialist time than does the integrated model.
Therefore, ,” lead author John Fortney, PhD, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization.
The findings were published online Aug. 25 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Clinically meaningful improvement
The Study to Promote Innovation in Rural Integrated Telepsychiatry (SPIRIT) trial included 1,004 adults with untreated posttraumatic stress disorder and/or bipolar disorder. The participants were from 24 primary care clinics in rural and underserved areas in which there were no on-site psychiatrists or psychologists.
In SPIRIT, 508 patients were randomly allocated to TCC, and 496 were assigned to TER.
With TCC, an on-site behavioral health care manager and an off-site telepsychiatrist consultant support the primary care clinician in prescribing medications. With TER, an off-site telepsychiatrist prescribes medication, and an off-site telepsychologist delivers therapy.
The primary outcome was mental health functioning at 12 months, as measured by the Veterans RAND 12-item Health Survey Mental Component Summary (MCS) score. MSC scores range from 0 to 100.
Baseline MCS scores for the study participants were two standard deviations below the national average. The mean MCS scores were 39.7 and 41.2 in the TCC and TER groups, respectively.
There was no significant difference between TCC and TER in 12-month MCS score (beta = 1.0; 95% confidence interval, –0.8 to 2.8; P = .28). In addition, no significant differences in treatment effects were identified.
Patients in both groups experienced “large and clinically meaningful” improvements in MCS scores from baseline to 12 months (Cohen d = 0.81 and 0.90 for TCC and TER, respectively), the researchers report.
‘Bit of a surprise’
The comparative effectiveness of both models in this study was “a bit of a surprise,” Dr. Fortney noted.
“We hypothesized that TCC would have better outcomes than TER because we thought patients would be more likely to engage in treatment,” he said.
In collaborative care, the familiar primary care practitioner is the prescriber. The local care manager’s job is to keep patients engaged in care, said Dr. Fortney.
“However, because the medical school telemental health providers were privileged and credentialed to practice in the primary care clinic, the referral process to the telepsychiatrist and telepsychologist was much more successful than it usually is. So engagement was the same in both groups, and thus outcomes were equally as good,” Dr. Fortney said.
He noted that the referral model is used more than the collaborative care model “because it is similar to the more traditional approach to managing complex psychiatric disorders. I would say this is true both before and after COVID-19, but more so after.”
From a health care system perspective, “clinical leadership should implement whichever approach is most sustainable,” the investigators concluded.
Good news for clinics
Commenting on the study, Adam C. Powell, PhD, president of Payer+Provider Syndicate, said the “similar efficacy” of teleintegrated care and telereferral care for delivering behavioral health services in primary care is “good news for clinics,” because it suggests that clinicians may pick between the two modes of delivery and achieve similar outcomes.
“The resources available within a clinic may determine which of these approaches is most viable. The teleintegrated care approach requires the clinic to have more extensive resources locally,” Dr. Powell noted.
However, he pointed out that the study did not report relative costs of the two approaches, which may also be a factor in determining which one clinics choose to implement.
“Overall, the study shows that advances in telemedicine are making it possible for patients to access telepsychiatry and to achieve improvements in their mental health. Given the lack of access that many patients face, telepsychiatry offers one potential solution,” Dr. Powell concluded.
The SPIRIT study was funded by a grant from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Fortney and Dr. Powell have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two models for treating patients with complex psychiatric disorders in primary care are equally effective, new research suggests.
Results from a pragmatic, randomized comparative effectiveness study involving more than 1,000 patients showed that both integrated telepsychiatry collaborative care (TCC) and telepsychiatry/telepsychology enhanced referral (TER) provided “significantly and substantially” improved clinical outcomes, researchers noted.
However, the referral model required substantially more mental health specialist time than does the integrated model.
Therefore, ,” lead author John Fortney, PhD, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization.
The findings were published online Aug. 25 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Clinically meaningful improvement
The Study to Promote Innovation in Rural Integrated Telepsychiatry (SPIRIT) trial included 1,004 adults with untreated posttraumatic stress disorder and/or bipolar disorder. The participants were from 24 primary care clinics in rural and underserved areas in which there were no on-site psychiatrists or psychologists.
In SPIRIT, 508 patients were randomly allocated to TCC, and 496 were assigned to TER.
With TCC, an on-site behavioral health care manager and an off-site telepsychiatrist consultant support the primary care clinician in prescribing medications. With TER, an off-site telepsychiatrist prescribes medication, and an off-site telepsychologist delivers therapy.
The primary outcome was mental health functioning at 12 months, as measured by the Veterans RAND 12-item Health Survey Mental Component Summary (MCS) score. MSC scores range from 0 to 100.
Baseline MCS scores for the study participants were two standard deviations below the national average. The mean MCS scores were 39.7 and 41.2 in the TCC and TER groups, respectively.
There was no significant difference between TCC and TER in 12-month MCS score (beta = 1.0; 95% confidence interval, –0.8 to 2.8; P = .28). In addition, no significant differences in treatment effects were identified.
Patients in both groups experienced “large and clinically meaningful” improvements in MCS scores from baseline to 12 months (Cohen d = 0.81 and 0.90 for TCC and TER, respectively), the researchers report.
‘Bit of a surprise’
The comparative effectiveness of both models in this study was “a bit of a surprise,” Dr. Fortney noted.
“We hypothesized that TCC would have better outcomes than TER because we thought patients would be more likely to engage in treatment,” he said.
In collaborative care, the familiar primary care practitioner is the prescriber. The local care manager’s job is to keep patients engaged in care, said Dr. Fortney.
“However, because the medical school telemental health providers were privileged and credentialed to practice in the primary care clinic, the referral process to the telepsychiatrist and telepsychologist was much more successful than it usually is. So engagement was the same in both groups, and thus outcomes were equally as good,” Dr. Fortney said.
He noted that the referral model is used more than the collaborative care model “because it is similar to the more traditional approach to managing complex psychiatric disorders. I would say this is true both before and after COVID-19, but more so after.”
From a health care system perspective, “clinical leadership should implement whichever approach is most sustainable,” the investigators concluded.
Good news for clinics
Commenting on the study, Adam C. Powell, PhD, president of Payer+Provider Syndicate, said the “similar efficacy” of teleintegrated care and telereferral care for delivering behavioral health services in primary care is “good news for clinics,” because it suggests that clinicians may pick between the two modes of delivery and achieve similar outcomes.
“The resources available within a clinic may determine which of these approaches is most viable. The teleintegrated care approach requires the clinic to have more extensive resources locally,” Dr. Powell noted.
However, he pointed out that the study did not report relative costs of the two approaches, which may also be a factor in determining which one clinics choose to implement.
“Overall, the study shows that advances in telemedicine are making it possible for patients to access telepsychiatry and to achieve improvements in their mental health. Given the lack of access that many patients face, telepsychiatry offers one potential solution,” Dr. Powell concluded.
The SPIRIT study was funded by a grant from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Fortney and Dr. Powell have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two models for treating patients with complex psychiatric disorders in primary care are equally effective, new research suggests.
Results from a pragmatic, randomized comparative effectiveness study involving more than 1,000 patients showed that both integrated telepsychiatry collaborative care (TCC) and telepsychiatry/telepsychology enhanced referral (TER) provided “significantly and substantially” improved clinical outcomes, researchers noted.
However, the referral model required substantially more mental health specialist time than does the integrated model.
Therefore, ,” lead author John Fortney, PhD, department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, told this news organization.
The findings were published online Aug. 25 in JAMA Psychiatry.
Clinically meaningful improvement
The Study to Promote Innovation in Rural Integrated Telepsychiatry (SPIRIT) trial included 1,004 adults with untreated posttraumatic stress disorder and/or bipolar disorder. The participants were from 24 primary care clinics in rural and underserved areas in which there were no on-site psychiatrists or psychologists.
In SPIRIT, 508 patients were randomly allocated to TCC, and 496 were assigned to TER.
With TCC, an on-site behavioral health care manager and an off-site telepsychiatrist consultant support the primary care clinician in prescribing medications. With TER, an off-site telepsychiatrist prescribes medication, and an off-site telepsychologist delivers therapy.
The primary outcome was mental health functioning at 12 months, as measured by the Veterans RAND 12-item Health Survey Mental Component Summary (MCS) score. MSC scores range from 0 to 100.
Baseline MCS scores for the study participants were two standard deviations below the national average. The mean MCS scores were 39.7 and 41.2 in the TCC and TER groups, respectively.
There was no significant difference between TCC and TER in 12-month MCS score (beta = 1.0; 95% confidence interval, –0.8 to 2.8; P = .28). In addition, no significant differences in treatment effects were identified.
Patients in both groups experienced “large and clinically meaningful” improvements in MCS scores from baseline to 12 months (Cohen d = 0.81 and 0.90 for TCC and TER, respectively), the researchers report.
‘Bit of a surprise’
The comparative effectiveness of both models in this study was “a bit of a surprise,” Dr. Fortney noted.
“We hypothesized that TCC would have better outcomes than TER because we thought patients would be more likely to engage in treatment,” he said.
In collaborative care, the familiar primary care practitioner is the prescriber. The local care manager’s job is to keep patients engaged in care, said Dr. Fortney.
“However, because the medical school telemental health providers were privileged and credentialed to practice in the primary care clinic, the referral process to the telepsychiatrist and telepsychologist was much more successful than it usually is. So engagement was the same in both groups, and thus outcomes were equally as good,” Dr. Fortney said.
He noted that the referral model is used more than the collaborative care model “because it is similar to the more traditional approach to managing complex psychiatric disorders. I would say this is true both before and after COVID-19, but more so after.”
From a health care system perspective, “clinical leadership should implement whichever approach is most sustainable,” the investigators concluded.
Good news for clinics
Commenting on the study, Adam C. Powell, PhD, president of Payer+Provider Syndicate, said the “similar efficacy” of teleintegrated care and telereferral care for delivering behavioral health services in primary care is “good news for clinics,” because it suggests that clinicians may pick between the two modes of delivery and achieve similar outcomes.
“The resources available within a clinic may determine which of these approaches is most viable. The teleintegrated care approach requires the clinic to have more extensive resources locally,” Dr. Powell noted.
However, he pointed out that the study did not report relative costs of the two approaches, which may also be a factor in determining which one clinics choose to implement.
“Overall, the study shows that advances in telemedicine are making it possible for patients to access telepsychiatry and to achieve improvements in their mental health. Given the lack of access that many patients face, telepsychiatry offers one potential solution,” Dr. Powell concluded.
The SPIRIT study was funded by a grant from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute. Dr. Fortney and Dr. Powell have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves first twice-yearly antipsychotic for schizophrenia
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved a 6-month injection form of the long-acting atypical antipsychotic paliperidone palmitate (Invega Hafyera, Janssen Pharmaceuticals) for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults, the company has announced.
This marks the “first-and-only twice-yearly injectable” approved for treating schizophrenia, the company added in a press release.
Before transitioning to the 6-month form, patients must be adequately treated for a minimum of 4 months with the company’s 1-month formulation of paliperidone (Invega Sustenna), or with the 3-month version (Invega Trinza) for at least one 3-month injection cycle.
The FDA approved the twice-yearly formulation on the basis of results from a 12-month, randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study that enrolled 702 adults with schizophrenia from 20 countries.
“The phase 3 trial results provide compelling evidence that 6-month paliperidone palmitate offers longer-term symptom control with the fewest doses per year, which may support greater patient adherence,” Gustavo Alva, MD, medical director at ATP Clinical Research, Costa Mesa, Calif., and 6-month paliperidone palmitate clinical trial investigator, said in the release.
Noninferiority results
In the phase 3 trial, the twice-yearly version of the drug proved noninferior to the 3-month version on the primary endpoint of time to first relapse at the end of 12 months, with 92.5% and 95% of patients, respectively, relapse-free at 12 months.
Relapse was defined as psychiatric hospitalization, increase in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score, increase in individual PANSS item scores, self-injury, violent behavior, or suicidal/homicidal ideation.
The safety profile observed in the trial was in line with prior studies of the 1-month and 3-month versions, with no new safety signals, the researchers note.
The most common adverse reactions affecting at least 5% of participants in the clinical trial receiving twice-year paliperidone were upper respiratory tract infection (12%), injection site reaction (11%), weight gain (9%), headache (7%), and parkinsonism (5%).
Relapse is common in adults with schizophrenia, often because of missed doses of medication, the company said in the news release.
, while research continues to demonstrate that stronger medication adherence means better patient outcomes,” Dr. Alva said.
Recently updated evidence-based guidelines from the American Psychiatric Association recommend consideration of long-acting injectables for appropriate adults living with schizophrenia.
“Long-acting injectable treatments offer a number of advantages, compared to oral medication for schizophrenia, including relief from needing to remember to take medication daily, lower discontinuation rates, and sustained treatment over longer periods,” Bill Martin, PhD, with Janssen Research & Development, said in the release.
“Today’s approval enables us to rethink how we manage this chronic disease by offering patients and caregivers the potential for a life less defined by schizophrenia medication,” Dr. Martin added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved a 6-month injection form of the long-acting atypical antipsychotic paliperidone palmitate (Invega Hafyera, Janssen Pharmaceuticals) for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults, the company has announced.
This marks the “first-and-only twice-yearly injectable” approved for treating schizophrenia, the company added in a press release.
Before transitioning to the 6-month form, patients must be adequately treated for a minimum of 4 months with the company’s 1-month formulation of paliperidone (Invega Sustenna), or with the 3-month version (Invega Trinza) for at least one 3-month injection cycle.
The FDA approved the twice-yearly formulation on the basis of results from a 12-month, randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study that enrolled 702 adults with schizophrenia from 20 countries.
“The phase 3 trial results provide compelling evidence that 6-month paliperidone palmitate offers longer-term symptom control with the fewest doses per year, which may support greater patient adherence,” Gustavo Alva, MD, medical director at ATP Clinical Research, Costa Mesa, Calif., and 6-month paliperidone palmitate clinical trial investigator, said in the release.
Noninferiority results
In the phase 3 trial, the twice-yearly version of the drug proved noninferior to the 3-month version on the primary endpoint of time to first relapse at the end of 12 months, with 92.5% and 95% of patients, respectively, relapse-free at 12 months.
Relapse was defined as psychiatric hospitalization, increase in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score, increase in individual PANSS item scores, self-injury, violent behavior, or suicidal/homicidal ideation.
The safety profile observed in the trial was in line with prior studies of the 1-month and 3-month versions, with no new safety signals, the researchers note.
The most common adverse reactions affecting at least 5% of participants in the clinical trial receiving twice-year paliperidone were upper respiratory tract infection (12%), injection site reaction (11%), weight gain (9%), headache (7%), and parkinsonism (5%).
Relapse is common in adults with schizophrenia, often because of missed doses of medication, the company said in the news release.
, while research continues to demonstrate that stronger medication adherence means better patient outcomes,” Dr. Alva said.
Recently updated evidence-based guidelines from the American Psychiatric Association recommend consideration of long-acting injectables for appropriate adults living with schizophrenia.
“Long-acting injectable treatments offer a number of advantages, compared to oral medication for schizophrenia, including relief from needing to remember to take medication daily, lower discontinuation rates, and sustained treatment over longer periods,” Bill Martin, PhD, with Janssen Research & Development, said in the release.
“Today’s approval enables us to rethink how we manage this chronic disease by offering patients and caregivers the potential for a life less defined by schizophrenia medication,” Dr. Martin added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved a 6-month injection form of the long-acting atypical antipsychotic paliperidone palmitate (Invega Hafyera, Janssen Pharmaceuticals) for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults, the company has announced.
This marks the “first-and-only twice-yearly injectable” approved for treating schizophrenia, the company added in a press release.
Before transitioning to the 6-month form, patients must be adequately treated for a minimum of 4 months with the company’s 1-month formulation of paliperidone (Invega Sustenna), or with the 3-month version (Invega Trinza) for at least one 3-month injection cycle.
The FDA approved the twice-yearly formulation on the basis of results from a 12-month, randomized, double-blind, phase 3 study that enrolled 702 adults with schizophrenia from 20 countries.
“The phase 3 trial results provide compelling evidence that 6-month paliperidone palmitate offers longer-term symptom control with the fewest doses per year, which may support greater patient adherence,” Gustavo Alva, MD, medical director at ATP Clinical Research, Costa Mesa, Calif., and 6-month paliperidone palmitate clinical trial investigator, said in the release.
Noninferiority results
In the phase 3 trial, the twice-yearly version of the drug proved noninferior to the 3-month version on the primary endpoint of time to first relapse at the end of 12 months, with 92.5% and 95% of patients, respectively, relapse-free at 12 months.
Relapse was defined as psychiatric hospitalization, increase in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score, increase in individual PANSS item scores, self-injury, violent behavior, or suicidal/homicidal ideation.
The safety profile observed in the trial was in line with prior studies of the 1-month and 3-month versions, with no new safety signals, the researchers note.
The most common adverse reactions affecting at least 5% of participants in the clinical trial receiving twice-year paliperidone were upper respiratory tract infection (12%), injection site reaction (11%), weight gain (9%), headache (7%), and parkinsonism (5%).
Relapse is common in adults with schizophrenia, often because of missed doses of medication, the company said in the news release.
, while research continues to demonstrate that stronger medication adherence means better patient outcomes,” Dr. Alva said.
Recently updated evidence-based guidelines from the American Psychiatric Association recommend consideration of long-acting injectables for appropriate adults living with schizophrenia.
“Long-acting injectable treatments offer a number of advantages, compared to oral medication for schizophrenia, including relief from needing to remember to take medication daily, lower discontinuation rates, and sustained treatment over longer periods,” Bill Martin, PhD, with Janssen Research & Development, said in the release.
“Today’s approval enables us to rethink how we manage this chronic disease by offering patients and caregivers the potential for a life less defined by schizophrenia medication,” Dr. Martin added.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Neuropsychiatry affects pediatric OCD treatment
Treatment of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) has evolved in recent years, with more attention given to some of the neuropsychiatric underpinnings of the condition and how they can affect treatment response.
At the Focus on Neuropsychiatry 2021 meeting, Jeffrey Strawn, MD, outlined some of the neuropsychiatry affecting disease and potential mechanisms to help control obsessions and behaviors, and how they may fit with some therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Strawn discussed the psychological construct of cognitive control, which can provide patients an “out” from the cycle of obsession/fear/worry and compulsion/avoidance. In the face of distress, compulsion and avoidance lead to relief, which reinforces the obsession/fear/worry; this in turn leads to more distress.
“We have an escape door for this circuit” in the form of cognitive control, said Dr. Strawn, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Cognitive control is linked to insight, which can in turn increase adaptive behaviors that help the patient resist the compulsion. Patients won’t eliminate distress, but they can be helped to make it more tolerable. Therapists can then help them move toward goal-directed thoughts and behaviors. Cognitive control is associated with several neural networks, but Dr. Strawn focused on two: the frontoparietal network, associated with top-down regulation; and the cingular-opercular network. Both of these are engaged during cognitive control processes, and play a role inhibitory control and error monitoring.
Dr. Strawn discussed a recent study that explored the neurofunctional basis of treatment. It compared the effects of a stress management therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in children and adults with OCD at 6 and 12 weeks. The study found similar symptom reductions in both adults and adolescents in both intervention groups.
Before initiating treatment, the researchers conducted functional MRI scans of participants while conducting an incentive flanker task, which reveals brain activity in response to cognitive control and reward processing.
A larger therapeutic response was found in the CBT group among patients who had a larger pretreatment activation within the right temporal lobe and rostral anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive control, as well as those with more activation within the medial prefrontal, orbitofrontal, lateral prefrontal, and amygdala regions during reward processing. On the other hand, within the stress management therapy group, treatment responses were better among those who had lower pretreatment activation among overlapping regions.
“There was a difference in terms of the neurofunctional predictors of treatment response. One of the key regions is the medial prefrontal cortex as well as the rostral anterior cingulate,” said Dr. Strawn, at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
On the neuropharmacology side, numerous medications have been approved for OCD. Dr. Strawn highlighted some studies to illustrate general OCD treatment concepts. That included the 2004 Pediatric OCD Treatment Study, which was one of the only trials to compare placebo with an SSRI, CBT, and the combination of SSRI and CBT. It showed the best results with combination therapy, and the difference appeared early in the treatment course.
That study had aggressive dosing, which led to some issues with sertraline tolerability. Dr. Strawn showed results of a study at his institution which showed that the drug levels of pediatric patients treated with sertraline depended on CYP2C19 metabolism, which affects overall exposure and peak dose concentration. In pediatric populations, some SSRIs clear more slowly and can have high peak concentrations. SSRIs have more side effects than serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in both anxiety disorders and OCD. A key difference between the two is that SSRI treatment is associated with greater frequency of activation, which is difficult to define, but includes restlessness and agitation and insomnia in the beginning stages of treatment.
SSRIs also lead to improvement early in the course of treatment, which was shown in a meta-analysis of nine trials. However, the same study showed that clomipramine is associated with a faster and greater magnitude of improvement, compared with SSRIs, even when the latter are dosed aggressively.
Clomipramine is a potent inhibitor of both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. It is recommended to monitor clomipramine levels in pediatric OCD patients, and Dr. Strawn suggested that monitoring should include both the parent drug and its primary metabolite, norclomipramine. At a given dose, there can be a great deal of variation in drug level. The clomipramine/norclomipramine ratio can provide information about the patient’s metabolic state, as well as drug adherence.
Dr. Strawn noted that peak levels occur around 1-3 hours after the dose, “and we really do want at least a 12-hour trough level.” EKGs should be performed at baseline and after any titration of clomipramine dose.
He also discussed pediatric OCD patients with OCD and tics. About one-third of Tourette syndrome patients experience OCD at some point. Tics often improve, whereas OCD more often persists. Tics that co-occur with OCD are associated with a lesser response to SSRI treatment, but not CBT treatment. Similarly, patients with hoarding tendencies are about one-third less likely to respond to SSRIs, CBT, or combination therapy.
Dr. Strawn discussed the concept of accommodation, in which family members cope with a patient’s behavior by altering routines to minimize distress and impairment. This may take the form of facilitating rituals, providing reassurance about a patient’s fears, acquiescing to demands, reducing the child’s day-to-day responsibilities, or helping the child complete tasks. Such actions are well intentioned, but they undermine cognitive control, negatively reinforce symptom engagement, and are associated with functional impairment. Reassurance is the most important behavior, occurring in more than half of patients, and it’s measurable. Parental involvement with rituals is also a concern. “This is associated with higher levels of child OCD severity, as well as parental psychopathology, and lower family cohesion. So
New developments in neurobiology and neuropsychology have changed the view of exposure. The old model emphasized the child’s fear rating as an index of corrective learning. The idea was that habituation would decrease anxiety and distress from future exposures. The new model revolves around inhibitory learning theory, which focuses on the variability of distress and aims to increase tolerance of distress. Another goal is to develop new, non-threat associations.
Finally, Dr. Strawn pointed out predictors of poor outcomes in pediatric OCD, including factors such as compulsion severity, oppositional behavior, frequent handwashing, functional impairment, lack of insight, externalizing symptoms, and possibly hoarding. Problematic family characteristics include higher levels of accommodation, parental anxiety, low family cohesion, and high levels of conflict. “The last three really represent a very concerning triad of family behaviors that may necessitate specific family work in order to facilitate the recovery of the pediatric patient,” Dr. Strawn said.
During the question-and-answer session after the talk, Dr. Strawn was asked whether there might be an inflammatory component to OCD, and whether pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus (PANDAS) might be a prodromal condition. He noted that some studies have shown a relationship, but results have been mixed, with lots of heterogeneity within the studied populations. To be suspicious that a patient had OCD resulting from PANDAS would require a high threshold, including an acute onset of symptoms. “This is a situation also where I would tend to involve consultation with some other specialties, including neurology. And obviously there would be follow-up in terms of the general workup,” he said.
Dr. Strawn has received research funding from Allergan, Otsuka, and Myriad Genetics. He has consulted for Myriad Genetics, and is a speaker for CMEology and the Neuroscience Education Institute.
Treatment of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) has evolved in recent years, with more attention given to some of the neuropsychiatric underpinnings of the condition and how they can affect treatment response.
At the Focus on Neuropsychiatry 2021 meeting, Jeffrey Strawn, MD, outlined some of the neuropsychiatry affecting disease and potential mechanisms to help control obsessions and behaviors, and how they may fit with some therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Strawn discussed the psychological construct of cognitive control, which can provide patients an “out” from the cycle of obsession/fear/worry and compulsion/avoidance. In the face of distress, compulsion and avoidance lead to relief, which reinforces the obsession/fear/worry; this in turn leads to more distress.
“We have an escape door for this circuit” in the form of cognitive control, said Dr. Strawn, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Cognitive control is linked to insight, which can in turn increase adaptive behaviors that help the patient resist the compulsion. Patients won’t eliminate distress, but they can be helped to make it more tolerable. Therapists can then help them move toward goal-directed thoughts and behaviors. Cognitive control is associated with several neural networks, but Dr. Strawn focused on two: the frontoparietal network, associated with top-down regulation; and the cingular-opercular network. Both of these are engaged during cognitive control processes, and play a role inhibitory control and error monitoring.
Dr. Strawn discussed a recent study that explored the neurofunctional basis of treatment. It compared the effects of a stress management therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in children and adults with OCD at 6 and 12 weeks. The study found similar symptom reductions in both adults and adolescents in both intervention groups.
Before initiating treatment, the researchers conducted functional MRI scans of participants while conducting an incentive flanker task, which reveals brain activity in response to cognitive control and reward processing.
A larger therapeutic response was found in the CBT group among patients who had a larger pretreatment activation within the right temporal lobe and rostral anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive control, as well as those with more activation within the medial prefrontal, orbitofrontal, lateral prefrontal, and amygdala regions during reward processing. On the other hand, within the stress management therapy group, treatment responses were better among those who had lower pretreatment activation among overlapping regions.
“There was a difference in terms of the neurofunctional predictors of treatment response. One of the key regions is the medial prefrontal cortex as well as the rostral anterior cingulate,” said Dr. Strawn, at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
On the neuropharmacology side, numerous medications have been approved for OCD. Dr. Strawn highlighted some studies to illustrate general OCD treatment concepts. That included the 2004 Pediatric OCD Treatment Study, which was one of the only trials to compare placebo with an SSRI, CBT, and the combination of SSRI and CBT. It showed the best results with combination therapy, and the difference appeared early in the treatment course.
That study had aggressive dosing, which led to some issues with sertraline tolerability. Dr. Strawn showed results of a study at his institution which showed that the drug levels of pediatric patients treated with sertraline depended on CYP2C19 metabolism, which affects overall exposure and peak dose concentration. In pediatric populations, some SSRIs clear more slowly and can have high peak concentrations. SSRIs have more side effects than serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in both anxiety disorders and OCD. A key difference between the two is that SSRI treatment is associated with greater frequency of activation, which is difficult to define, but includes restlessness and agitation and insomnia in the beginning stages of treatment.
SSRIs also lead to improvement early in the course of treatment, which was shown in a meta-analysis of nine trials. However, the same study showed that clomipramine is associated with a faster and greater magnitude of improvement, compared with SSRIs, even when the latter are dosed aggressively.
Clomipramine is a potent inhibitor of both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. It is recommended to monitor clomipramine levels in pediatric OCD patients, and Dr. Strawn suggested that monitoring should include both the parent drug and its primary metabolite, norclomipramine. At a given dose, there can be a great deal of variation in drug level. The clomipramine/norclomipramine ratio can provide information about the patient’s metabolic state, as well as drug adherence.
Dr. Strawn noted that peak levels occur around 1-3 hours after the dose, “and we really do want at least a 12-hour trough level.” EKGs should be performed at baseline and after any titration of clomipramine dose.
He also discussed pediatric OCD patients with OCD and tics. About one-third of Tourette syndrome patients experience OCD at some point. Tics often improve, whereas OCD more often persists. Tics that co-occur with OCD are associated with a lesser response to SSRI treatment, but not CBT treatment. Similarly, patients with hoarding tendencies are about one-third less likely to respond to SSRIs, CBT, or combination therapy.
Dr. Strawn discussed the concept of accommodation, in which family members cope with a patient’s behavior by altering routines to minimize distress and impairment. This may take the form of facilitating rituals, providing reassurance about a patient’s fears, acquiescing to demands, reducing the child’s day-to-day responsibilities, or helping the child complete tasks. Such actions are well intentioned, but they undermine cognitive control, negatively reinforce symptom engagement, and are associated with functional impairment. Reassurance is the most important behavior, occurring in more than half of patients, and it’s measurable. Parental involvement with rituals is also a concern. “This is associated with higher levels of child OCD severity, as well as parental psychopathology, and lower family cohesion. So
New developments in neurobiology and neuropsychology have changed the view of exposure. The old model emphasized the child’s fear rating as an index of corrective learning. The idea was that habituation would decrease anxiety and distress from future exposures. The new model revolves around inhibitory learning theory, which focuses on the variability of distress and aims to increase tolerance of distress. Another goal is to develop new, non-threat associations.
Finally, Dr. Strawn pointed out predictors of poor outcomes in pediatric OCD, including factors such as compulsion severity, oppositional behavior, frequent handwashing, functional impairment, lack of insight, externalizing symptoms, and possibly hoarding. Problematic family characteristics include higher levels of accommodation, parental anxiety, low family cohesion, and high levels of conflict. “The last three really represent a very concerning triad of family behaviors that may necessitate specific family work in order to facilitate the recovery of the pediatric patient,” Dr. Strawn said.
During the question-and-answer session after the talk, Dr. Strawn was asked whether there might be an inflammatory component to OCD, and whether pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus (PANDAS) might be a prodromal condition. He noted that some studies have shown a relationship, but results have been mixed, with lots of heterogeneity within the studied populations. To be suspicious that a patient had OCD resulting from PANDAS would require a high threshold, including an acute onset of symptoms. “This is a situation also where I would tend to involve consultation with some other specialties, including neurology. And obviously there would be follow-up in terms of the general workup,” he said.
Dr. Strawn has received research funding from Allergan, Otsuka, and Myriad Genetics. He has consulted for Myriad Genetics, and is a speaker for CMEology and the Neuroscience Education Institute.
Treatment of pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) has evolved in recent years, with more attention given to some of the neuropsychiatric underpinnings of the condition and how they can affect treatment response.
At the Focus on Neuropsychiatry 2021 meeting, Jeffrey Strawn, MD, outlined some of the neuropsychiatry affecting disease and potential mechanisms to help control obsessions and behaviors, and how they may fit with some therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Strawn discussed the psychological construct of cognitive control, which can provide patients an “out” from the cycle of obsession/fear/worry and compulsion/avoidance. In the face of distress, compulsion and avoidance lead to relief, which reinforces the obsession/fear/worry; this in turn leads to more distress.
“We have an escape door for this circuit” in the form of cognitive control, said Dr. Strawn, who is an associate professor of pediatrics at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center.
Cognitive control is linked to insight, which can in turn increase adaptive behaviors that help the patient resist the compulsion. Patients won’t eliminate distress, but they can be helped to make it more tolerable. Therapists can then help them move toward goal-directed thoughts and behaviors. Cognitive control is associated with several neural networks, but Dr. Strawn focused on two: the frontoparietal network, associated with top-down regulation; and the cingular-opercular network. Both of these are engaged during cognitive control processes, and play a role inhibitory control and error monitoring.
Dr. Strawn discussed a recent study that explored the neurofunctional basis of treatment. It compared the effects of a stress management therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in children and adults with OCD at 6 and 12 weeks. The study found similar symptom reductions in both adults and adolescents in both intervention groups.
Before initiating treatment, the researchers conducted functional MRI scans of participants while conducting an incentive flanker task, which reveals brain activity in response to cognitive control and reward processing.
A larger therapeutic response was found in the CBT group among patients who had a larger pretreatment activation within the right temporal lobe and rostral anterior cingulate cortex during cognitive control, as well as those with more activation within the medial prefrontal, orbitofrontal, lateral prefrontal, and amygdala regions during reward processing. On the other hand, within the stress management therapy group, treatment responses were better among those who had lower pretreatment activation among overlapping regions.
“There was a difference in terms of the neurofunctional predictors of treatment response. One of the key regions is the medial prefrontal cortex as well as the rostral anterior cingulate,” said Dr. Strawn, at the meeting presented by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
On the neuropharmacology side, numerous medications have been approved for OCD. Dr. Strawn highlighted some studies to illustrate general OCD treatment concepts. That included the 2004 Pediatric OCD Treatment Study, which was one of the only trials to compare placebo with an SSRI, CBT, and the combination of SSRI and CBT. It showed the best results with combination therapy, and the difference appeared early in the treatment course.
That study had aggressive dosing, which led to some issues with sertraline tolerability. Dr. Strawn showed results of a study at his institution which showed that the drug levels of pediatric patients treated with sertraline depended on CYP2C19 metabolism, which affects overall exposure and peak dose concentration. In pediatric populations, some SSRIs clear more slowly and can have high peak concentrations. SSRIs have more side effects than serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors in both anxiety disorders and OCD. A key difference between the two is that SSRI treatment is associated with greater frequency of activation, which is difficult to define, but includes restlessness and agitation and insomnia in the beginning stages of treatment.
SSRIs also lead to improvement early in the course of treatment, which was shown in a meta-analysis of nine trials. However, the same study showed that clomipramine is associated with a faster and greater magnitude of improvement, compared with SSRIs, even when the latter are dosed aggressively.
Clomipramine is a potent inhibitor of both serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake. It is recommended to monitor clomipramine levels in pediatric OCD patients, and Dr. Strawn suggested that monitoring should include both the parent drug and its primary metabolite, norclomipramine. At a given dose, there can be a great deal of variation in drug level. The clomipramine/norclomipramine ratio can provide information about the patient’s metabolic state, as well as drug adherence.
Dr. Strawn noted that peak levels occur around 1-3 hours after the dose, “and we really do want at least a 12-hour trough level.” EKGs should be performed at baseline and after any titration of clomipramine dose.
He also discussed pediatric OCD patients with OCD and tics. About one-third of Tourette syndrome patients experience OCD at some point. Tics often improve, whereas OCD more often persists. Tics that co-occur with OCD are associated with a lesser response to SSRI treatment, but not CBT treatment. Similarly, patients with hoarding tendencies are about one-third less likely to respond to SSRIs, CBT, or combination therapy.
Dr. Strawn discussed the concept of accommodation, in which family members cope with a patient’s behavior by altering routines to minimize distress and impairment. This may take the form of facilitating rituals, providing reassurance about a patient’s fears, acquiescing to demands, reducing the child’s day-to-day responsibilities, or helping the child complete tasks. Such actions are well intentioned, but they undermine cognitive control, negatively reinforce symptom engagement, and are associated with functional impairment. Reassurance is the most important behavior, occurring in more than half of patients, and it’s measurable. Parental involvement with rituals is also a concern. “This is associated with higher levels of child OCD severity, as well as parental psychopathology, and lower family cohesion. So
New developments in neurobiology and neuropsychology have changed the view of exposure. The old model emphasized the child’s fear rating as an index of corrective learning. The idea was that habituation would decrease anxiety and distress from future exposures. The new model revolves around inhibitory learning theory, which focuses on the variability of distress and aims to increase tolerance of distress. Another goal is to develop new, non-threat associations.
Finally, Dr. Strawn pointed out predictors of poor outcomes in pediatric OCD, including factors such as compulsion severity, oppositional behavior, frequent handwashing, functional impairment, lack of insight, externalizing symptoms, and possibly hoarding. Problematic family characteristics include higher levels of accommodation, parental anxiety, low family cohesion, and high levels of conflict. “The last three really represent a very concerning triad of family behaviors that may necessitate specific family work in order to facilitate the recovery of the pediatric patient,” Dr. Strawn said.
During the question-and-answer session after the talk, Dr. Strawn was asked whether there might be an inflammatory component to OCD, and whether pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcus (PANDAS) might be a prodromal condition. He noted that some studies have shown a relationship, but results have been mixed, with lots of heterogeneity within the studied populations. To be suspicious that a patient had OCD resulting from PANDAS would require a high threshold, including an acute onset of symptoms. “This is a situation also where I would tend to involve consultation with some other specialties, including neurology. And obviously there would be follow-up in terms of the general workup,” he said.
Dr. Strawn has received research funding from Allergan, Otsuka, and Myriad Genetics. He has consulted for Myriad Genetics, and is a speaker for CMEology and the Neuroscience Education Institute.
FROM FOCUS ON NEUROPSYCHIATRY 2021
EDs saw more benzodiazepine overdoses, but fewer patients overall, in 2020
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
In a year when emergency department visits dropped by almost 18%, visits for benzodiazepine overdoses did the opposite, according to a report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

The actual increase in the number of overdose visits for benzodiazepine overdoses was quite small – from 15,547 in 2019 to 15,830 in 2020 (1.8%) – but the 11 million fewer ED visits magnified its effect, Stephen Liu, PhD, and associates said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The rate of benzodiazepine overdose visits to all visits increased by 23.7% from 2019 (24.22 per 100,000 ED visits) to 2020 (29.97 per 100,000), with the larger share going to those involving opioids, which were up by 34.4%, compared with overdose visits not involving opioids (21.0%), the investigators said, based on data reported by 32 states and the District of Columbia to the CDC’s Drug Overdose Surveillance and Epidemiology system. All of the rate changes are statistically significant.
The number of overdose visits without opioid coinvolvement actually dropped, from 2019 (12,276) to 2020 (12,218), but not by enough to offset the decline in total visits, noted Dr. Liu, of the CDC’s National Center for Injury Prevention and Control and associates.
The number of deaths from benzodiazepine overdose, on the other hand, did not drop in 2020. Those data, coming from 23 states participating in the CDC’s State Unintentional Drug Overdose Reporting System, were available only for the first half of the year.
In those 6 months, The first quarter of 2020 also showed an increase, but exact numbers were not provided in the report. Overdose deaths rose by 22% for prescription forms of benzodiazepine and 520% for illicit forms in Q2 of 2020, compared with 2019, the researchers said.
Almost all of the benzodiazepine deaths (93%) in the first half of 2020 also involved opioids, mostly in the form of illicitly manufactured fentanyls (67% of all deaths). Between Q2 of 2019 and Q2 of 2020, involvement of illicit fentanyls in benzodiazepine overdose deaths increased from almost 57% to 71%, Dr. Liu and associates reported.
“Despite progress in reducing coprescribing [of opioids and benzodiazepines] before 2019, this study suggests a reversal in the decline in benzodiazepine deaths from 2017 to 2019, driven in part by increasing involvement of [illicitly manufactured fentanyls] in benzodiazepine deaths and influxes of illicit benzodiazepines,” they wrote.
FROM MMWR
Number of global deaths by suicide increased over 30 years
The overall global number of deaths by suicide increased by almost 20,000 during the past 30 years, new research shows.
The increase occurred despite a significant decrease in age-specific suicide rates from 1990 through 2019, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
Population growth, population aging, and changes in population age structure may explain the increase in number of suicide deaths, the investigators note.
“As suicide rates are highest among the elderly (70 years or above) for both genders in almost all regions of the world, the rapidly aging population globally will pose huge challenges for the reduction in the number of suicide deaths in the future,” write the researchers, led by Paul Siu Fai Yip, PhD, of the HKJC Center for Suicide Research and Prevention, University of Hong Kong, China.
The findings were published online Aug. 16 in Injury Prevention.
Global public health concern
Around the world, approximately 800,000 individuals die by suicide each year, while many others attempt suicide. Yet suicide has not received the same level of attention as other global public health concerns, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, the investigators write.
They examined data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 to assess how demographic and epidemiologic factors contributed to the number of suicide deaths during the past 30 years.
The researchers also analyzed relationships between population growth, population age structure, income level, and gender- and age-specific suicide rates.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 includes information from 204 countries about 369 diseases and injuries by age and gender. The dataset also includes population estimates for each year by location, age group, and gender.
In their analysis, the investigators looked at changes in suicide rates and the number of suicide deaths from 1990 to 2019 by gender and age group in the four income level regions defined by the World Bank. These categories include low-income, lower-middle–income, upper-middle–income, and high-income regions.
Number of deaths versus suicide rates
The number of deaths was 738,799 in 1990 and 758,696 in 2019.
The largest increase in deaths occurred in the lower-middle–income region, where the number of suicide deaths increased by 72,550 (from 232,340 to 304,890).
Population growth (300,942; 1,512.5%) was the major contributor to the overall increase in total number of suicide deaths. The second largest contributor was population age structure (189,512; 952.4%).
However, the effects of these factors were offset to a large extent by the effect of reduction in overall suicide rates (−470,556; −2,364.9%).
Interestingly, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 population decreased from 13.8 in 1990 to 9.8 in 2019.
The upper-middle–income region had the largest decline (−6.25 per 100,000), and the high-income region had the smallest decline (−1.77 per 100,000). Suicide rates also decreased in lower-middle–income (−2.51 per 100,000) and low-income regions (−1.96 per 100,000).
Reasons for the declines across all regions “have yet to be determined,” write the investigators. International efforts coordinated by the United Nations and World Health Organization likely contributed to these declines, they add.
‘Imbalance of resources’
The overall reduction in suicide rate of −4.01 per 100,000 “was mainly due” to reduction in age-specific suicide rates (−6.09; 152%), the researchers report.
This effect was partly offset, however, by the effect of the changing population age structure (2.08; −52%). In the high-income–level region, for example, the reduction in age-specific suicide rate (−3.83; 216.3%) was greater than the increase resulting from the change in population age structure (2.06; −116.3%).
“The overall contribution of population age structure mainly came from the 45-64 (565.2%) and 65+ (528.7%) age groups,” the investigators write. “This effect was observed in middle-income– as well as high-income–level regions, reflecting the global effect of population aging.”
They add that world populations will “experience pronounced and historically unprecedented aging in the coming decades” because of increasing life expectancy and declining fertility.
Men, but not women, had a notable increase in total number of suicide deaths. The significant effect of male population growth (177,128; 890.2% vs. 123,814; 622.3% for women) and male population age structure (120,186; 604.0% vs. 69,325; 348.4%) were the main factors that explained this increase, the investigators note.
However, from 1990 to 2019, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 men decreased from 16.6 to 13.5 (–3.09). The decline in overall suicide rate was even greater for women, from 11.0 to 6.1 (–4.91).
This finding was particularly notable in the upper-middle–income region (–8.12 women vs. –4.37 men per 100,000).
“This study highlighted the considerable imbalance of the resources in carrying out suicide prevention work, especially in low-income and middle-income countries,” the investigators write.
“It is time to revisit this situation to ensure that sufficient resources can be redeployed globally to meet the future challenges,” they add.
The study was funded by a Humanities and Social Sciences Prestigious Fellowship, which Dr. Yip received. He declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The overall global number of deaths by suicide increased by almost 20,000 during the past 30 years, new research shows.
The increase occurred despite a significant decrease in age-specific suicide rates from 1990 through 2019, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
Population growth, population aging, and changes in population age structure may explain the increase in number of suicide deaths, the investigators note.
“As suicide rates are highest among the elderly (70 years or above) for both genders in almost all regions of the world, the rapidly aging population globally will pose huge challenges for the reduction in the number of suicide deaths in the future,” write the researchers, led by Paul Siu Fai Yip, PhD, of the HKJC Center for Suicide Research and Prevention, University of Hong Kong, China.
The findings were published online Aug. 16 in Injury Prevention.
Global public health concern
Around the world, approximately 800,000 individuals die by suicide each year, while many others attempt suicide. Yet suicide has not received the same level of attention as other global public health concerns, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, the investigators write.
They examined data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 to assess how demographic and epidemiologic factors contributed to the number of suicide deaths during the past 30 years.
The researchers also analyzed relationships between population growth, population age structure, income level, and gender- and age-specific suicide rates.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 includes information from 204 countries about 369 diseases and injuries by age and gender. The dataset also includes population estimates for each year by location, age group, and gender.
In their analysis, the investigators looked at changes in suicide rates and the number of suicide deaths from 1990 to 2019 by gender and age group in the four income level regions defined by the World Bank. These categories include low-income, lower-middle–income, upper-middle–income, and high-income regions.
Number of deaths versus suicide rates
The number of deaths was 738,799 in 1990 and 758,696 in 2019.
The largest increase in deaths occurred in the lower-middle–income region, where the number of suicide deaths increased by 72,550 (from 232,340 to 304,890).
Population growth (300,942; 1,512.5%) was the major contributor to the overall increase in total number of suicide deaths. The second largest contributor was population age structure (189,512; 952.4%).
However, the effects of these factors were offset to a large extent by the effect of reduction in overall suicide rates (−470,556; −2,364.9%).
Interestingly, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 population decreased from 13.8 in 1990 to 9.8 in 2019.
The upper-middle–income region had the largest decline (−6.25 per 100,000), and the high-income region had the smallest decline (−1.77 per 100,000). Suicide rates also decreased in lower-middle–income (−2.51 per 100,000) and low-income regions (−1.96 per 100,000).
Reasons for the declines across all regions “have yet to be determined,” write the investigators. International efforts coordinated by the United Nations and World Health Organization likely contributed to these declines, they add.
‘Imbalance of resources’
The overall reduction in suicide rate of −4.01 per 100,000 “was mainly due” to reduction in age-specific suicide rates (−6.09; 152%), the researchers report.
This effect was partly offset, however, by the effect of the changing population age structure (2.08; −52%). In the high-income–level region, for example, the reduction in age-specific suicide rate (−3.83; 216.3%) was greater than the increase resulting from the change in population age structure (2.06; −116.3%).
“The overall contribution of population age structure mainly came from the 45-64 (565.2%) and 65+ (528.7%) age groups,” the investigators write. “This effect was observed in middle-income– as well as high-income–level regions, reflecting the global effect of population aging.”
They add that world populations will “experience pronounced and historically unprecedented aging in the coming decades” because of increasing life expectancy and declining fertility.
Men, but not women, had a notable increase in total number of suicide deaths. The significant effect of male population growth (177,128; 890.2% vs. 123,814; 622.3% for women) and male population age structure (120,186; 604.0% vs. 69,325; 348.4%) were the main factors that explained this increase, the investigators note.
However, from 1990 to 2019, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 men decreased from 16.6 to 13.5 (–3.09). The decline in overall suicide rate was even greater for women, from 11.0 to 6.1 (–4.91).
This finding was particularly notable in the upper-middle–income region (–8.12 women vs. –4.37 men per 100,000).
“This study highlighted the considerable imbalance of the resources in carrying out suicide prevention work, especially in low-income and middle-income countries,” the investigators write.
“It is time to revisit this situation to ensure that sufficient resources can be redeployed globally to meet the future challenges,” they add.
The study was funded by a Humanities and Social Sciences Prestigious Fellowship, which Dr. Yip received. He declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The overall global number of deaths by suicide increased by almost 20,000 during the past 30 years, new research shows.
The increase occurred despite a significant decrease in age-specific suicide rates from 1990 through 2019, according to data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.
Population growth, population aging, and changes in population age structure may explain the increase in number of suicide deaths, the investigators note.
“As suicide rates are highest among the elderly (70 years or above) for both genders in almost all regions of the world, the rapidly aging population globally will pose huge challenges for the reduction in the number of suicide deaths in the future,” write the researchers, led by Paul Siu Fai Yip, PhD, of the HKJC Center for Suicide Research and Prevention, University of Hong Kong, China.
The findings were published online Aug. 16 in Injury Prevention.
Global public health concern
Around the world, approximately 800,000 individuals die by suicide each year, while many others attempt suicide. Yet suicide has not received the same level of attention as other global public health concerns, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, the investigators write.
They examined data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 to assess how demographic and epidemiologic factors contributed to the number of suicide deaths during the past 30 years.
The researchers also analyzed relationships between population growth, population age structure, income level, and gender- and age-specific suicide rates.
The Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 includes information from 204 countries about 369 diseases and injuries by age and gender. The dataset also includes population estimates for each year by location, age group, and gender.
In their analysis, the investigators looked at changes in suicide rates and the number of suicide deaths from 1990 to 2019 by gender and age group in the four income level regions defined by the World Bank. These categories include low-income, lower-middle–income, upper-middle–income, and high-income regions.
Number of deaths versus suicide rates
The number of deaths was 738,799 in 1990 and 758,696 in 2019.
The largest increase in deaths occurred in the lower-middle–income region, where the number of suicide deaths increased by 72,550 (from 232,340 to 304,890).
Population growth (300,942; 1,512.5%) was the major contributor to the overall increase in total number of suicide deaths. The second largest contributor was population age structure (189,512; 952.4%).
However, the effects of these factors were offset to a large extent by the effect of reduction in overall suicide rates (−470,556; −2,364.9%).
Interestingly, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 population decreased from 13.8 in 1990 to 9.8 in 2019.
The upper-middle–income region had the largest decline (−6.25 per 100,000), and the high-income region had the smallest decline (−1.77 per 100,000). Suicide rates also decreased in lower-middle–income (−2.51 per 100,000) and low-income regions (−1.96 per 100,000).
Reasons for the declines across all regions “have yet to be determined,” write the investigators. International efforts coordinated by the United Nations and World Health Organization likely contributed to these declines, they add.
‘Imbalance of resources’
The overall reduction in suicide rate of −4.01 per 100,000 “was mainly due” to reduction in age-specific suicide rates (−6.09; 152%), the researchers report.
This effect was partly offset, however, by the effect of the changing population age structure (2.08; −52%). In the high-income–level region, for example, the reduction in age-specific suicide rate (−3.83; 216.3%) was greater than the increase resulting from the change in population age structure (2.06; −116.3%).
“The overall contribution of population age structure mainly came from the 45-64 (565.2%) and 65+ (528.7%) age groups,” the investigators write. “This effect was observed in middle-income– as well as high-income–level regions, reflecting the global effect of population aging.”
They add that world populations will “experience pronounced and historically unprecedented aging in the coming decades” because of increasing life expectancy and declining fertility.
Men, but not women, had a notable increase in total number of suicide deaths. The significant effect of male population growth (177,128; 890.2% vs. 123,814; 622.3% for women) and male population age structure (120,186; 604.0% vs. 69,325; 348.4%) were the main factors that explained this increase, the investigators note.
However, from 1990 to 2019, the overall suicide rate per 100,000 men decreased from 16.6 to 13.5 (–3.09). The decline in overall suicide rate was even greater for women, from 11.0 to 6.1 (–4.91).
This finding was particularly notable in the upper-middle–income region (–8.12 women vs. –4.37 men per 100,000).
“This study highlighted the considerable imbalance of the resources in carrying out suicide prevention work, especially in low-income and middle-income countries,” the investigators write.
“It is time to revisit this situation to ensure that sufficient resources can be redeployed globally to meet the future challenges,” they add.
The study was funded by a Humanities and Social Sciences Prestigious Fellowship, which Dr. Yip received. He declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.











