User login
Universal testing for Lp(a): What are we waiting for?
It soon became clear that Lp(a) was associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), but whether an elevated blood level was a biomarker or a causal factor proved difficult to determine. Studies of inheritance patterns confirmed that blood levels were primarily genetically determined and largely resistant to lifestyle and pharmacologic intervention. It seemed senseless to test for something that was deemed “unmodifiable,” so untreatable. That label stuck for decades.
Fortunately, a resurgent interest in molecular pathophysiology this past decade has clarified Lp(a)’s unique contribution to atherothrombotic disease and calcific aortic stenosis. While there remains much to be learned about this complex, highly atherogenic molecule and its role in cardiac disease, it seems shortsighted not to take the simple step of identifying who carries this risk. Why are we not testing everyone for an extremely common and potent risk factor for the most lethal disease on the planet?
Epidemiologic studies project a stunning number of people in the United States to be at increased risk for Lp(a)-mediated coronary and cerebrovascular events. Because the LPA gene which codes for the apo(a) component of the Lp(a) molecule is fully expressed at age 2, this is a truly lifelong risk factor for a projected 64 million individuals with blood levels (> 60 mg/dL) high enough to double their risk for ASCVD. Because risk increases linearly, this includes 16 million, like me, with levels > 116 mg/dL, who are at four times the risk for ASCVD as those with normal levels (< 30 mg/dL).
Because Lp(a) level remains relatively constant throughout life, a single blood test would help stratify the risk it confers on millions of people who, under current U.S. guidelines, would never be tested. Until Lp(a) is integrated into its algorithms, the commonly used ASCVD Risk Calculator will substantially underestimate risk in 20% of the population.
A potential barrier to universal testing is that the ideal method to measure Lp(a) has yet to be determined. Lp(a) comprises an apoB particle bonded to an apo(a) particle. Apo(a) is complex and has a number of isoforms that can result in large heterogeneity in apo(a) size between, as well as within, individuals. This contributes to controversy about the ideal assay and whether Lp(a) levels should be expressed as mass (mg/dL) or number of particles (nmols/L). This should not, however, deter universal testing.
One-time cost, lifetime benefit?
Absent universal testing, it’s impossible to estimate the economic toll that Lp(a) exacts, but it’s surely an extraordinary number, particularly because the highest-risk individuals are prone to recurrent, nonfatal vascular events. The substantial price tag for my personal decade of Lp(a)-induced vascular havoc included four percutaneous coronary interventions with rapid stent restenosis, an eventual bypass surgery, and an aborted left hemispheric stroke, requiring an urgent carotid endarterectomy.
As a frame of reference, U.S. expenditures related to ASCVD are estimated to be $351 billion annually. If everyone in the United States over the age of 18 were tested for Lp(a) at a cost of $100 per person, this would be a $21 billion expenditure. This nonrecurring expense would identify the 20% – or almost 42 million individuals – at high risk for ASCVD, a number of whom would have already had vascular events. This one-time cost would be a foundational step in securing year-after-year savings from enhanced ASCVD prevention and reduction in recurrent vascular events.
Such savings would be significantly enhanced if and when targeted, effective Lp(a) treatments become available, but it seems shortsighted to make this the linchpin for universal testing. It’s noteworthy that Canadian and European guidelines already endorse one-time testing for all.
The confirmation of Lp(a)’s causal role in ASCVD remains underappreciated by medical providers across all specialties. Much of the elegant Lp(a)-related science of the past decade has yet to translate to the clinical world. What better way to rectify this than by identifying those with high Lp(a)? Since the advent of the statin era, “good” and “bad” cholesterol values are common conversational fare, in part because virtually every adult has had not one, but many lipid panels. Universal Lp(a) testing would spotlight this pervasive and important risk factor that was referred to as the “horrible” cholesterol in a recent review.
U.S. guidelines need updating
To foster this, U.S. guidelines, which influence every aspect of care, including testing, prevention, treatment, reimbursement, and medical legal issues, need to be simplified. The discussion of Lp(a) testing in the 2018 U.S. guidelines on cholesterol management is already obsolete. The contingencies on when testing is “reasonable” or “may be reasonable” are dated and cumbersome. In contrast, a recommendation to test everyone once, perhaps in adolescence, would be a useful, forward-looking strategy.
To date, trials of an antisense oligonucleotide and a small interfering RNA molecule targeting hepatic LPA messenger RNA have confirmed that plasma Lp(a) levels can be significantly and safely lowered. If the ongoing Lp(a) HORIZON and OCEAN(a) phase 3 trials have positive outcomes in patients with known ASCVD, this would spawn a host of clinical trials to explore the possibilities of these therapies in primary prevention as well. These will require tens of thousands of enrollees, and universal testing would expand the pool of potential participants.
The majority of at-risk individuals identified through universal testing would be candidates for primary prevention. This large, currently unidentified cohort should have all coexisting risk factors assessed and managed; lowering elevated LDL cholesterol early and aggressively is paramount. Recent data from the United Kingdom suggest that attainment of specific LDL cholesterol levels may offset the risk for vascular events in those with high Lp(a) levels.
Of note, this was the advice given to the small fraction of high-risk individuals like me, who had their Lp(a) level tested long before its ominous implications were understood. This recommendation was informed mostly by common sense. For any number of reasons, the same might be said for universal testing.
Dr. Leahy, a retired cardiologist in San Diego, has an abiding professional and personal interest in Lp(a), which has been responsible for a number of cardiovascular events in his own life over the past 2 decades. He was a participant in the phase 2 clinical trial of the Lp(a)-lowering antisense oligonucleotide being studied in the Lp(a) HORIZON trial, funded by Novartis, and is currently undergoing apheresis treatment. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
It soon became clear that Lp(a) was associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), but whether an elevated blood level was a biomarker or a causal factor proved difficult to determine. Studies of inheritance patterns confirmed that blood levels were primarily genetically determined and largely resistant to lifestyle and pharmacologic intervention. It seemed senseless to test for something that was deemed “unmodifiable,” so untreatable. That label stuck for decades.
Fortunately, a resurgent interest in molecular pathophysiology this past decade has clarified Lp(a)’s unique contribution to atherothrombotic disease and calcific aortic stenosis. While there remains much to be learned about this complex, highly atherogenic molecule and its role in cardiac disease, it seems shortsighted not to take the simple step of identifying who carries this risk. Why are we not testing everyone for an extremely common and potent risk factor for the most lethal disease on the planet?
Epidemiologic studies project a stunning number of people in the United States to be at increased risk for Lp(a)-mediated coronary and cerebrovascular events. Because the LPA gene which codes for the apo(a) component of the Lp(a) molecule is fully expressed at age 2, this is a truly lifelong risk factor for a projected 64 million individuals with blood levels (> 60 mg/dL) high enough to double their risk for ASCVD. Because risk increases linearly, this includes 16 million, like me, with levels > 116 mg/dL, who are at four times the risk for ASCVD as those with normal levels (< 30 mg/dL).
Because Lp(a) level remains relatively constant throughout life, a single blood test would help stratify the risk it confers on millions of people who, under current U.S. guidelines, would never be tested. Until Lp(a) is integrated into its algorithms, the commonly used ASCVD Risk Calculator will substantially underestimate risk in 20% of the population.
A potential barrier to universal testing is that the ideal method to measure Lp(a) has yet to be determined. Lp(a) comprises an apoB particle bonded to an apo(a) particle. Apo(a) is complex and has a number of isoforms that can result in large heterogeneity in apo(a) size between, as well as within, individuals. This contributes to controversy about the ideal assay and whether Lp(a) levels should be expressed as mass (mg/dL) or number of particles (nmols/L). This should not, however, deter universal testing.
One-time cost, lifetime benefit?
Absent universal testing, it’s impossible to estimate the economic toll that Lp(a) exacts, but it’s surely an extraordinary number, particularly because the highest-risk individuals are prone to recurrent, nonfatal vascular events. The substantial price tag for my personal decade of Lp(a)-induced vascular havoc included four percutaneous coronary interventions with rapid stent restenosis, an eventual bypass surgery, and an aborted left hemispheric stroke, requiring an urgent carotid endarterectomy.
As a frame of reference, U.S. expenditures related to ASCVD are estimated to be $351 billion annually. If everyone in the United States over the age of 18 were tested for Lp(a) at a cost of $100 per person, this would be a $21 billion expenditure. This nonrecurring expense would identify the 20% – or almost 42 million individuals – at high risk for ASCVD, a number of whom would have already had vascular events. This one-time cost would be a foundational step in securing year-after-year savings from enhanced ASCVD prevention and reduction in recurrent vascular events.
Such savings would be significantly enhanced if and when targeted, effective Lp(a) treatments become available, but it seems shortsighted to make this the linchpin for universal testing. It’s noteworthy that Canadian and European guidelines already endorse one-time testing for all.
The confirmation of Lp(a)’s causal role in ASCVD remains underappreciated by medical providers across all specialties. Much of the elegant Lp(a)-related science of the past decade has yet to translate to the clinical world. What better way to rectify this than by identifying those with high Lp(a)? Since the advent of the statin era, “good” and “bad” cholesterol values are common conversational fare, in part because virtually every adult has had not one, but many lipid panels. Universal Lp(a) testing would spotlight this pervasive and important risk factor that was referred to as the “horrible” cholesterol in a recent review.
U.S. guidelines need updating
To foster this, U.S. guidelines, which influence every aspect of care, including testing, prevention, treatment, reimbursement, and medical legal issues, need to be simplified. The discussion of Lp(a) testing in the 2018 U.S. guidelines on cholesterol management is already obsolete. The contingencies on when testing is “reasonable” or “may be reasonable” are dated and cumbersome. In contrast, a recommendation to test everyone once, perhaps in adolescence, would be a useful, forward-looking strategy.
To date, trials of an antisense oligonucleotide and a small interfering RNA molecule targeting hepatic LPA messenger RNA have confirmed that plasma Lp(a) levels can be significantly and safely lowered. If the ongoing Lp(a) HORIZON and OCEAN(a) phase 3 trials have positive outcomes in patients with known ASCVD, this would spawn a host of clinical trials to explore the possibilities of these therapies in primary prevention as well. These will require tens of thousands of enrollees, and universal testing would expand the pool of potential participants.
The majority of at-risk individuals identified through universal testing would be candidates for primary prevention. This large, currently unidentified cohort should have all coexisting risk factors assessed and managed; lowering elevated LDL cholesterol early and aggressively is paramount. Recent data from the United Kingdom suggest that attainment of specific LDL cholesterol levels may offset the risk for vascular events in those with high Lp(a) levels.
Of note, this was the advice given to the small fraction of high-risk individuals like me, who had their Lp(a) level tested long before its ominous implications were understood. This recommendation was informed mostly by common sense. For any number of reasons, the same might be said for universal testing.
Dr. Leahy, a retired cardiologist in San Diego, has an abiding professional and personal interest in Lp(a), which has been responsible for a number of cardiovascular events in his own life over the past 2 decades. He was a participant in the phase 2 clinical trial of the Lp(a)-lowering antisense oligonucleotide being studied in the Lp(a) HORIZON trial, funded by Novartis, and is currently undergoing apheresis treatment. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
It soon became clear that Lp(a) was associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), but whether an elevated blood level was a biomarker or a causal factor proved difficult to determine. Studies of inheritance patterns confirmed that blood levels were primarily genetically determined and largely resistant to lifestyle and pharmacologic intervention. It seemed senseless to test for something that was deemed “unmodifiable,” so untreatable. That label stuck for decades.
Fortunately, a resurgent interest in molecular pathophysiology this past decade has clarified Lp(a)’s unique contribution to atherothrombotic disease and calcific aortic stenosis. While there remains much to be learned about this complex, highly atherogenic molecule and its role in cardiac disease, it seems shortsighted not to take the simple step of identifying who carries this risk. Why are we not testing everyone for an extremely common and potent risk factor for the most lethal disease on the planet?
Epidemiologic studies project a stunning number of people in the United States to be at increased risk for Lp(a)-mediated coronary and cerebrovascular events. Because the LPA gene which codes for the apo(a) component of the Lp(a) molecule is fully expressed at age 2, this is a truly lifelong risk factor for a projected 64 million individuals with blood levels (> 60 mg/dL) high enough to double their risk for ASCVD. Because risk increases linearly, this includes 16 million, like me, with levels > 116 mg/dL, who are at four times the risk for ASCVD as those with normal levels (< 30 mg/dL).
Because Lp(a) level remains relatively constant throughout life, a single blood test would help stratify the risk it confers on millions of people who, under current U.S. guidelines, would never be tested. Until Lp(a) is integrated into its algorithms, the commonly used ASCVD Risk Calculator will substantially underestimate risk in 20% of the population.
A potential barrier to universal testing is that the ideal method to measure Lp(a) has yet to be determined. Lp(a) comprises an apoB particle bonded to an apo(a) particle. Apo(a) is complex and has a number of isoforms that can result in large heterogeneity in apo(a) size between, as well as within, individuals. This contributes to controversy about the ideal assay and whether Lp(a) levels should be expressed as mass (mg/dL) or number of particles (nmols/L). This should not, however, deter universal testing.
One-time cost, lifetime benefit?
Absent universal testing, it’s impossible to estimate the economic toll that Lp(a) exacts, but it’s surely an extraordinary number, particularly because the highest-risk individuals are prone to recurrent, nonfatal vascular events. The substantial price tag for my personal decade of Lp(a)-induced vascular havoc included four percutaneous coronary interventions with rapid stent restenosis, an eventual bypass surgery, and an aborted left hemispheric stroke, requiring an urgent carotid endarterectomy.
As a frame of reference, U.S. expenditures related to ASCVD are estimated to be $351 billion annually. If everyone in the United States over the age of 18 were tested for Lp(a) at a cost of $100 per person, this would be a $21 billion expenditure. This nonrecurring expense would identify the 20% – or almost 42 million individuals – at high risk for ASCVD, a number of whom would have already had vascular events. This one-time cost would be a foundational step in securing year-after-year savings from enhanced ASCVD prevention and reduction in recurrent vascular events.
Such savings would be significantly enhanced if and when targeted, effective Lp(a) treatments become available, but it seems shortsighted to make this the linchpin for universal testing. It’s noteworthy that Canadian and European guidelines already endorse one-time testing for all.
The confirmation of Lp(a)’s causal role in ASCVD remains underappreciated by medical providers across all specialties. Much of the elegant Lp(a)-related science of the past decade has yet to translate to the clinical world. What better way to rectify this than by identifying those with high Lp(a)? Since the advent of the statin era, “good” and “bad” cholesterol values are common conversational fare, in part because virtually every adult has had not one, but many lipid panels. Universal Lp(a) testing would spotlight this pervasive and important risk factor that was referred to as the “horrible” cholesterol in a recent review.
U.S. guidelines need updating
To foster this, U.S. guidelines, which influence every aspect of care, including testing, prevention, treatment, reimbursement, and medical legal issues, need to be simplified. The discussion of Lp(a) testing in the 2018 U.S. guidelines on cholesterol management is already obsolete. The contingencies on when testing is “reasonable” or “may be reasonable” are dated and cumbersome. In contrast, a recommendation to test everyone once, perhaps in adolescence, would be a useful, forward-looking strategy.
To date, trials of an antisense oligonucleotide and a small interfering RNA molecule targeting hepatic LPA messenger RNA have confirmed that plasma Lp(a) levels can be significantly and safely lowered. If the ongoing Lp(a) HORIZON and OCEAN(a) phase 3 trials have positive outcomes in patients with known ASCVD, this would spawn a host of clinical trials to explore the possibilities of these therapies in primary prevention as well. These will require tens of thousands of enrollees, and universal testing would expand the pool of potential participants.
The majority of at-risk individuals identified through universal testing would be candidates for primary prevention. This large, currently unidentified cohort should have all coexisting risk factors assessed and managed; lowering elevated LDL cholesterol early and aggressively is paramount. Recent data from the United Kingdom suggest that attainment of specific LDL cholesterol levels may offset the risk for vascular events in those with high Lp(a) levels.
Of note, this was the advice given to the small fraction of high-risk individuals like me, who had their Lp(a) level tested long before its ominous implications were understood. This recommendation was informed mostly by common sense. For any number of reasons, the same might be said for universal testing.
Dr. Leahy, a retired cardiologist in San Diego, has an abiding professional and personal interest in Lp(a), which has been responsible for a number of cardiovascular events in his own life over the past 2 decades. He was a participant in the phase 2 clinical trial of the Lp(a)-lowering antisense oligonucleotide being studied in the Lp(a) HORIZON trial, funded by Novartis, and is currently undergoing apheresis treatment. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CV deaths jumped in 2020, reflecting pandemic toll
Cardiovascular-related deaths increased dramatically in 2020, marking the largest single-year increase since 2015 and surpassing the previous record from 2003, according to the American Heart Association’s 2023 Statistical Update.
During the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the largest increases in cardiovascular disease (CVD) deaths were seen among Asian, Black, and Hispanic people.
“We thought we had been improving as a country with respect to CVD deaths over the past few decades,” Connie Tsao, MD, chair of the AHA Statistical Update writing committee, told this news organization.
Since 2020, however, those trends have changed. Dr. Tsao, a staff cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, noted the firsthand experience that many clinicians had in seeing the shift.
“We observed this sharp rise in age-adjusted CVD deaths, which corresponds to the COVID-19 pandemic,” she said. “Those of us health care providers knew from the overfull hospitals and ICUs that clearly COVID took a toll, particularly in those with cardiovascular risk factors.”
The AHA Statistical Update was published online in the journal Circulation.
Data on deaths
Each year, the American Heart Association and National Institutes of Health report the latest statistics related to heart disease, stroke, and cardiovascular risk factors. The 2023 update includes additional information about pandemic-related data.
Overall, the number of people who died from cardiovascular disease increased during the first year of the pandemic, rising from 876,613 in 2019 to 928,741 in 2020. This topped the previous high of 910,000 in 2003.
In addition, the age-adjusted mortality rate increased for the first time in several years, Dr. Tsao said, by a “fairly substantial” 4.6%. The age-adjusted mortality rate incorporates the variability in the aging population from year to year, accounting for higher death rates among older people.
“Even though our total number of deaths has been slowly increasing over the past decade, we have seen a decline each year in our age-adjusted rates – until 2020,” she said. “I think that is very indicative of what has been going on within our country – and the world – in light of people of all ages being impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, especially before vaccines were available to slow the spread.”
The largest increases in CVD-related deaths occurred among Asian, Black, and Hispanic people, who were most heavily affected during the first year of the pandemic.
“People from communities of color were among those most highly impacted, especially early on, often due to a disproportionate burden of cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension and obesity,” Michelle Albert, MD, MPH, president of AHA and a professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, said in a statement.
Dr. Albert, who is also the director of UCSF’s Center for the Study of Adversity and Cardiovascular Disease, does research on health equity and noted the disparities seen in the 2020 numbers. “Additionally, there are socioeconomic considerations, as well as the ongoing impact of structural racism on multiple factors, including limiting the ability to access quality health care,” she said.
Additional considerations
In a special commentary, the Statistical Update writing committee pointed to the need to track data for other underrepresented communities, including LGBTQ people and those living in rural or urban areas. The authors outlined several ways to better understand the effects of identity and social determinants of health, as well as strategies to reduce cardiovascular-related disparities.
“This year’s writing group made a concerted effort to gather information on specific social factors related to health risk and outcomes, including sexual orientation, gender identity, urbanization, and socioeconomic position,” Dr. Tsao said. “However, the data are lacking because these communities are grossly underrepresented in clinical and epidemiological research.”
For the next several years, the AHA Statistical Update will likely include more insights about the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as ongoing disparities.
“For sure, we will be continuing to see the effects of the pandemic for years to come,” Dr. Tsao said. “Recognition of the disparities in outcomes among vulnerable groups should be a call to action among health care providers and researchers, administration, and policy leaders to investigate the reasons and make changes to reverse these trends.”
The statistical update was prepared by a volunteer writing group on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular-related deaths increased dramatically in 2020, marking the largest single-year increase since 2015 and surpassing the previous record from 2003, according to the American Heart Association’s 2023 Statistical Update.
During the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the largest increases in cardiovascular disease (CVD) deaths were seen among Asian, Black, and Hispanic people.
“We thought we had been improving as a country with respect to CVD deaths over the past few decades,” Connie Tsao, MD, chair of the AHA Statistical Update writing committee, told this news organization.
Since 2020, however, those trends have changed. Dr. Tsao, a staff cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, noted the firsthand experience that many clinicians had in seeing the shift.
“We observed this sharp rise in age-adjusted CVD deaths, which corresponds to the COVID-19 pandemic,” she said. “Those of us health care providers knew from the overfull hospitals and ICUs that clearly COVID took a toll, particularly in those with cardiovascular risk factors.”
The AHA Statistical Update was published online in the journal Circulation.
Data on deaths
Each year, the American Heart Association and National Institutes of Health report the latest statistics related to heart disease, stroke, and cardiovascular risk factors. The 2023 update includes additional information about pandemic-related data.
Overall, the number of people who died from cardiovascular disease increased during the first year of the pandemic, rising from 876,613 in 2019 to 928,741 in 2020. This topped the previous high of 910,000 in 2003.
In addition, the age-adjusted mortality rate increased for the first time in several years, Dr. Tsao said, by a “fairly substantial” 4.6%. The age-adjusted mortality rate incorporates the variability in the aging population from year to year, accounting for higher death rates among older people.
“Even though our total number of deaths has been slowly increasing over the past decade, we have seen a decline each year in our age-adjusted rates – until 2020,” she said. “I think that is very indicative of what has been going on within our country – and the world – in light of people of all ages being impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, especially before vaccines were available to slow the spread.”
The largest increases in CVD-related deaths occurred among Asian, Black, and Hispanic people, who were most heavily affected during the first year of the pandemic.
“People from communities of color were among those most highly impacted, especially early on, often due to a disproportionate burden of cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension and obesity,” Michelle Albert, MD, MPH, president of AHA and a professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, said in a statement.
Dr. Albert, who is also the director of UCSF’s Center for the Study of Adversity and Cardiovascular Disease, does research on health equity and noted the disparities seen in the 2020 numbers. “Additionally, there are socioeconomic considerations, as well as the ongoing impact of structural racism on multiple factors, including limiting the ability to access quality health care,” she said.
Additional considerations
In a special commentary, the Statistical Update writing committee pointed to the need to track data for other underrepresented communities, including LGBTQ people and those living in rural or urban areas. The authors outlined several ways to better understand the effects of identity and social determinants of health, as well as strategies to reduce cardiovascular-related disparities.
“This year’s writing group made a concerted effort to gather information on specific social factors related to health risk and outcomes, including sexual orientation, gender identity, urbanization, and socioeconomic position,” Dr. Tsao said. “However, the data are lacking because these communities are grossly underrepresented in clinical and epidemiological research.”
For the next several years, the AHA Statistical Update will likely include more insights about the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as ongoing disparities.
“For sure, we will be continuing to see the effects of the pandemic for years to come,” Dr. Tsao said. “Recognition of the disparities in outcomes among vulnerable groups should be a call to action among health care providers and researchers, administration, and policy leaders to investigate the reasons and make changes to reverse these trends.”
The statistical update was prepared by a volunteer writing group on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiovascular-related deaths increased dramatically in 2020, marking the largest single-year increase since 2015 and surpassing the previous record from 2003, according to the American Heart Association’s 2023 Statistical Update.
During the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the largest increases in cardiovascular disease (CVD) deaths were seen among Asian, Black, and Hispanic people.
“We thought we had been improving as a country with respect to CVD deaths over the past few decades,” Connie Tsao, MD, chair of the AHA Statistical Update writing committee, told this news organization.
Since 2020, however, those trends have changed. Dr. Tsao, a staff cardiologist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, noted the firsthand experience that many clinicians had in seeing the shift.
“We observed this sharp rise in age-adjusted CVD deaths, which corresponds to the COVID-19 pandemic,” she said. “Those of us health care providers knew from the overfull hospitals and ICUs that clearly COVID took a toll, particularly in those with cardiovascular risk factors.”
The AHA Statistical Update was published online in the journal Circulation.
Data on deaths
Each year, the American Heart Association and National Institutes of Health report the latest statistics related to heart disease, stroke, and cardiovascular risk factors. The 2023 update includes additional information about pandemic-related data.
Overall, the number of people who died from cardiovascular disease increased during the first year of the pandemic, rising from 876,613 in 2019 to 928,741 in 2020. This topped the previous high of 910,000 in 2003.
In addition, the age-adjusted mortality rate increased for the first time in several years, Dr. Tsao said, by a “fairly substantial” 4.6%. The age-adjusted mortality rate incorporates the variability in the aging population from year to year, accounting for higher death rates among older people.
“Even though our total number of deaths has been slowly increasing over the past decade, we have seen a decline each year in our age-adjusted rates – until 2020,” she said. “I think that is very indicative of what has been going on within our country – and the world – in light of people of all ages being impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, especially before vaccines were available to slow the spread.”
The largest increases in CVD-related deaths occurred among Asian, Black, and Hispanic people, who were most heavily affected during the first year of the pandemic.
“People from communities of color were among those most highly impacted, especially early on, often due to a disproportionate burden of cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension and obesity,” Michelle Albert, MD, MPH, president of AHA and a professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, said in a statement.
Dr. Albert, who is also the director of UCSF’s Center for the Study of Adversity and Cardiovascular Disease, does research on health equity and noted the disparities seen in the 2020 numbers. “Additionally, there are socioeconomic considerations, as well as the ongoing impact of structural racism on multiple factors, including limiting the ability to access quality health care,” she said.
Additional considerations
In a special commentary, the Statistical Update writing committee pointed to the need to track data for other underrepresented communities, including LGBTQ people and those living in rural or urban areas. The authors outlined several ways to better understand the effects of identity and social determinants of health, as well as strategies to reduce cardiovascular-related disparities.
“This year’s writing group made a concerted effort to gather information on specific social factors related to health risk and outcomes, including sexual orientation, gender identity, urbanization, and socioeconomic position,” Dr. Tsao said. “However, the data are lacking because these communities are grossly underrepresented in clinical and epidemiological research.”
For the next several years, the AHA Statistical Update will likely include more insights about the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, as well as ongoing disparities.
“For sure, we will be continuing to see the effects of the pandemic for years to come,” Dr. Tsao said. “Recognition of the disparities in outcomes among vulnerable groups should be a call to action among health care providers and researchers, administration, and policy leaders to investigate the reasons and make changes to reverse these trends.”
The statistical update was prepared by a volunteer writing group on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
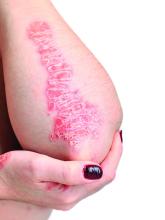
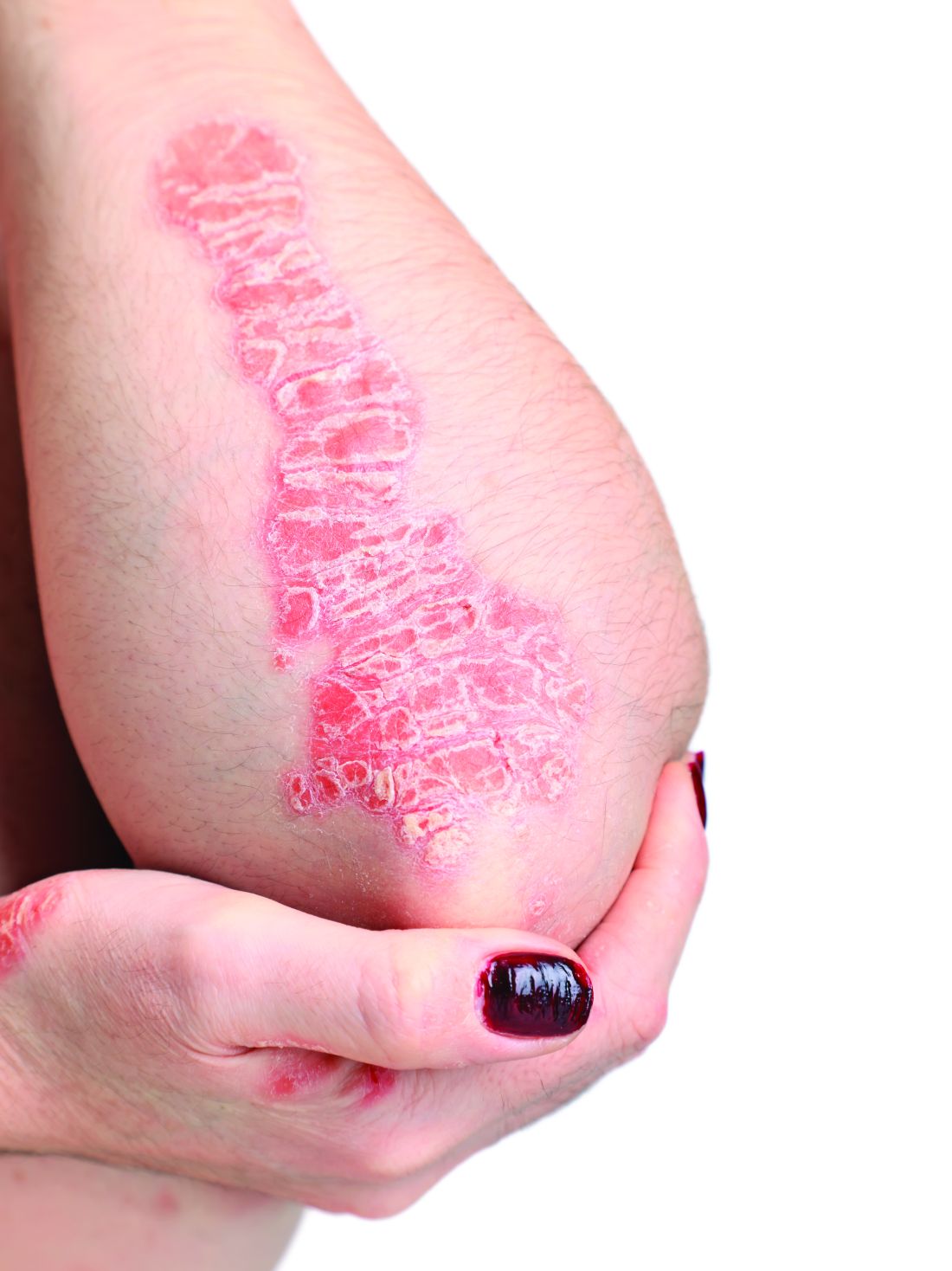
Elevated PCSK9 levels associated with psoriasis suggest new treatment target
A Mendelian randomization study employing data from nearly 300,000 individuals has linked elevated levels of the PCSK9 enzyme with an increased risk of psoriasis, suggesting it might be targetable as an intervention.
. Conversely, psoriasis risk did not appear to be affected when LDL-C was reduced by other pathways of lipid control.
This study “suggests that PCSK9 inhibition is causally associated with reduced risk of psoriasis,” reported a team of investigators led by Sizheng Steven Zhao, MD, PhD, of the division of musculoskeletal and dermatological sciences, University of Manchester (England). “Existing PCSK9 inhibitors hold potential as therapeutic targets for prevention, and possibly treatment, of psoriasis, although further clinical studies are needed,” they concluded.
In an interview, Dr. Zhao also noted that it will be interesting to look at psoriasis susceptibility in post hoc analyses of large randomized controlled trials of PCSK9 inhibitors for cardiovascular disease.
“Genetically proxied” inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, which is targeted by statins, and NPC1L1 which is targeted by ezetimibe, “were not associated with psoriasis risk,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
Abnormal lipid metabolism is sufficiently common among people with psoriasis that screening in patients with moderate to severe disease is recommended in 2019 psoriasis guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation. However, the link between these diseases is unclear. This study was launched to explore genetically proxied relationships between psoriasis and LDL-C reductions as well as specific treatments for elevated LDL-C.
Mendelian randomizations were applied to deidentified data from two sources, a UK biobank and FinnGen, a Finnish-based project for identifying genotype-to-phenotype correlations. Genetic proxies for these variables were established on the basis of genomewide association studies on large population samples.
Ultimately, 34 genetic variants were selected to proxy for lipid lowering by PCSK9, 19 were selected to proxy for HMG-CoA reductase, and 9 for NPC1L1. In the Mendelian analyses performed on the two sources, genetically proxied PCSK9 inhibition was associated with about a 30% reduction in the odds ratio of psoriasis (OR, 0.69; P = .003). There were no robust associations with proxies for reductions in either HMG-CoA reductase or NPC1L1.
In sensitivity analyses, there was no evidence of bias from pleiotropy or genetic confounding, according to Dr. Zhao and his coauthors, who noted that the relationship between reductions in PCSK9 and reduced risk of psoriasis appeared to be independent of change in circulating LDL-C.
Given the prior evidence implicating the PCSK9 enzyme in psoriasis risk, “this is an exciting study that really highlights the importance of studying and targeting lipid metabolism in psoriasis for a few reasons,” according to Michael S. Garshick, MD, a researcher, cardiologist, and director of the cardio-rheumatology program, New York University Langone Health.
An investigator who has participated in several studies evaluating the relationship between cardiovascular risk and psoriasis, Dr. Garshick said there is increasing interest in PCSK9 as a biomarker or even a mediator of inflammation independent of blood lipid levels.
“In psoriasis regarding PCSK9, we and others have shown PCSK9 is elevated in psoriatic lesion skin, and studies are starting to investigate the unique lipidomic profile in psoriasis,” Dr. Garshick said in an interview. The study he led that showed elevated PCSK9 levels in psoriatic skin was published in 2021 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
While the Mendelian randomization provides only “an inference” that PCSK9 plays a role in mediating risk of psoriasis, Dr. Zhao and coauthors cited numerous studies linking elevated PCSK9 to psoriasis pathophysiology. This not only includes the elevated PCSK9 expression in psoriatic plaques as shown by Dr. Garshick and others but several sets of experimental evidence linking PCSK9 to inflammatory pathways, including upregulation of interleukin-17 and stimulation of macrophage activation.
While Dr. Zhao and coauthors suggested that clinical trials are now needed to test the potential of PCSK9 inhibitors to modify the risk of psoriasis, Dr. Garshick indicated that there are numerous variables to unravel in the relationship between elevated lipids, PCSK9, and psoriasis.
“In our own studies, we did see a statistical correlation between circulating PCSK9 and psoriasis severity,” Dr. Garshick said. But he added, “I think we are just beginning to understand the functions of circulating (extrahepatic) PCSK9 independent of lipid metabolism.”
While he is intrigued by the evidence that PCSK9 is linked to systemic inflammation, he pointed out that several medications used to treat dyslipidemias, such as statins, are associated with an anti-inflammatory effect.
This study “further emphasizes the need to conduct clinical trials treating dyslipidemia in psoriasis, including the targeting of PCSK9, whether it is with statins with lipid lowering and potential pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties or PCSK9 inhibition,” he said. If positive, “both would be exciting.“
From a cardiologist’s point of view, there is an upside for including patients with psoriasis in lipid-lowering trials even if the effect on psoriasis is modest. Either way, “you still get the lipid-lowering benefit, which is important for reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Garshick said.
Dr. Zhao reported financial relationships with UCB, although UCB did not provide funding for this study. One author reported grants from Versus Arthritis and the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre during the study, grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Pfizer, and personal fees from Chugai Roche outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was supported by grants from Versus Arthritis and the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Garshick reported financial relationships with AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics.
A Mendelian randomization study employing data from nearly 300,000 individuals has linked elevated levels of the PCSK9 enzyme with an increased risk of psoriasis, suggesting it might be targetable as an intervention.
. Conversely, psoriasis risk did not appear to be affected when LDL-C was reduced by other pathways of lipid control.
This study “suggests that PCSK9 inhibition is causally associated with reduced risk of psoriasis,” reported a team of investigators led by Sizheng Steven Zhao, MD, PhD, of the division of musculoskeletal and dermatological sciences, University of Manchester (England). “Existing PCSK9 inhibitors hold potential as therapeutic targets for prevention, and possibly treatment, of psoriasis, although further clinical studies are needed,” they concluded.
In an interview, Dr. Zhao also noted that it will be interesting to look at psoriasis susceptibility in post hoc analyses of large randomized controlled trials of PCSK9 inhibitors for cardiovascular disease.
“Genetically proxied” inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, which is targeted by statins, and NPC1L1 which is targeted by ezetimibe, “were not associated with psoriasis risk,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
Abnormal lipid metabolism is sufficiently common among people with psoriasis that screening in patients with moderate to severe disease is recommended in 2019 psoriasis guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation. However, the link between these diseases is unclear. This study was launched to explore genetically proxied relationships between psoriasis and LDL-C reductions as well as specific treatments for elevated LDL-C.
Mendelian randomizations were applied to deidentified data from two sources, a UK biobank and FinnGen, a Finnish-based project for identifying genotype-to-phenotype correlations. Genetic proxies for these variables were established on the basis of genomewide association studies on large population samples.
Ultimately, 34 genetic variants were selected to proxy for lipid lowering by PCSK9, 19 were selected to proxy for HMG-CoA reductase, and 9 for NPC1L1. In the Mendelian analyses performed on the two sources, genetically proxied PCSK9 inhibition was associated with about a 30% reduction in the odds ratio of psoriasis (OR, 0.69; P = .003). There were no robust associations with proxies for reductions in either HMG-CoA reductase or NPC1L1.
In sensitivity analyses, there was no evidence of bias from pleiotropy or genetic confounding, according to Dr. Zhao and his coauthors, who noted that the relationship between reductions in PCSK9 and reduced risk of psoriasis appeared to be independent of change in circulating LDL-C.
Given the prior evidence implicating the PCSK9 enzyme in psoriasis risk, “this is an exciting study that really highlights the importance of studying and targeting lipid metabolism in psoriasis for a few reasons,” according to Michael S. Garshick, MD, a researcher, cardiologist, and director of the cardio-rheumatology program, New York University Langone Health.
An investigator who has participated in several studies evaluating the relationship between cardiovascular risk and psoriasis, Dr. Garshick said there is increasing interest in PCSK9 as a biomarker or even a mediator of inflammation independent of blood lipid levels.
“In psoriasis regarding PCSK9, we and others have shown PCSK9 is elevated in psoriatic lesion skin, and studies are starting to investigate the unique lipidomic profile in psoriasis,” Dr. Garshick said in an interview. The study he led that showed elevated PCSK9 levels in psoriatic skin was published in 2021 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
While the Mendelian randomization provides only “an inference” that PCSK9 plays a role in mediating risk of psoriasis, Dr. Zhao and coauthors cited numerous studies linking elevated PCSK9 to psoriasis pathophysiology. This not only includes the elevated PCSK9 expression in psoriatic plaques as shown by Dr. Garshick and others but several sets of experimental evidence linking PCSK9 to inflammatory pathways, including upregulation of interleukin-17 and stimulation of macrophage activation.
While Dr. Zhao and coauthors suggested that clinical trials are now needed to test the potential of PCSK9 inhibitors to modify the risk of psoriasis, Dr. Garshick indicated that there are numerous variables to unravel in the relationship between elevated lipids, PCSK9, and psoriasis.
“In our own studies, we did see a statistical correlation between circulating PCSK9 and psoriasis severity,” Dr. Garshick said. But he added, “I think we are just beginning to understand the functions of circulating (extrahepatic) PCSK9 independent of lipid metabolism.”
While he is intrigued by the evidence that PCSK9 is linked to systemic inflammation, he pointed out that several medications used to treat dyslipidemias, such as statins, are associated with an anti-inflammatory effect.
This study “further emphasizes the need to conduct clinical trials treating dyslipidemia in psoriasis, including the targeting of PCSK9, whether it is with statins with lipid lowering and potential pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties or PCSK9 inhibition,” he said. If positive, “both would be exciting.“
From a cardiologist’s point of view, there is an upside for including patients with psoriasis in lipid-lowering trials even if the effect on psoriasis is modest. Either way, “you still get the lipid-lowering benefit, which is important for reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Garshick said.
Dr. Zhao reported financial relationships with UCB, although UCB did not provide funding for this study. One author reported grants from Versus Arthritis and the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre during the study, grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Pfizer, and personal fees from Chugai Roche outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was supported by grants from Versus Arthritis and the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Garshick reported financial relationships with AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics.
A Mendelian randomization study employing data from nearly 300,000 individuals has linked elevated levels of the PCSK9 enzyme with an increased risk of psoriasis, suggesting it might be targetable as an intervention.
. Conversely, psoriasis risk did not appear to be affected when LDL-C was reduced by other pathways of lipid control.
This study “suggests that PCSK9 inhibition is causally associated with reduced risk of psoriasis,” reported a team of investigators led by Sizheng Steven Zhao, MD, PhD, of the division of musculoskeletal and dermatological sciences, University of Manchester (England). “Existing PCSK9 inhibitors hold potential as therapeutic targets for prevention, and possibly treatment, of psoriasis, although further clinical studies are needed,” they concluded.
In an interview, Dr. Zhao also noted that it will be interesting to look at psoriasis susceptibility in post hoc analyses of large randomized controlled trials of PCSK9 inhibitors for cardiovascular disease.
“Genetically proxied” inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, which is targeted by statins, and NPC1L1 which is targeted by ezetimibe, “were not associated with psoriasis risk,” the investigators reported in the study, published in JAMA Dermatology.
Abnormal lipid metabolism is sufficiently common among people with psoriasis that screening in patients with moderate to severe disease is recommended in 2019 psoriasis guidelines from the American Academy of Dermatology and the National Psoriasis Foundation. However, the link between these diseases is unclear. This study was launched to explore genetically proxied relationships between psoriasis and LDL-C reductions as well as specific treatments for elevated LDL-C.
Mendelian randomizations were applied to deidentified data from two sources, a UK biobank and FinnGen, a Finnish-based project for identifying genotype-to-phenotype correlations. Genetic proxies for these variables were established on the basis of genomewide association studies on large population samples.
Ultimately, 34 genetic variants were selected to proxy for lipid lowering by PCSK9, 19 were selected to proxy for HMG-CoA reductase, and 9 for NPC1L1. In the Mendelian analyses performed on the two sources, genetically proxied PCSK9 inhibition was associated with about a 30% reduction in the odds ratio of psoriasis (OR, 0.69; P = .003). There were no robust associations with proxies for reductions in either HMG-CoA reductase or NPC1L1.
In sensitivity analyses, there was no evidence of bias from pleiotropy or genetic confounding, according to Dr. Zhao and his coauthors, who noted that the relationship between reductions in PCSK9 and reduced risk of psoriasis appeared to be independent of change in circulating LDL-C.
Given the prior evidence implicating the PCSK9 enzyme in psoriasis risk, “this is an exciting study that really highlights the importance of studying and targeting lipid metabolism in psoriasis for a few reasons,” according to Michael S. Garshick, MD, a researcher, cardiologist, and director of the cardio-rheumatology program, New York University Langone Health.
An investigator who has participated in several studies evaluating the relationship between cardiovascular risk and psoriasis, Dr. Garshick said there is increasing interest in PCSK9 as a biomarker or even a mediator of inflammation independent of blood lipid levels.
“In psoriasis regarding PCSK9, we and others have shown PCSK9 is elevated in psoriatic lesion skin, and studies are starting to investigate the unique lipidomic profile in psoriasis,” Dr. Garshick said in an interview. The study he led that showed elevated PCSK9 levels in psoriatic skin was published in 2021 in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology.
While the Mendelian randomization provides only “an inference” that PCSK9 plays a role in mediating risk of psoriasis, Dr. Zhao and coauthors cited numerous studies linking elevated PCSK9 to psoriasis pathophysiology. This not only includes the elevated PCSK9 expression in psoriatic plaques as shown by Dr. Garshick and others but several sets of experimental evidence linking PCSK9 to inflammatory pathways, including upregulation of interleukin-17 and stimulation of macrophage activation.
While Dr. Zhao and coauthors suggested that clinical trials are now needed to test the potential of PCSK9 inhibitors to modify the risk of psoriasis, Dr. Garshick indicated that there are numerous variables to unravel in the relationship between elevated lipids, PCSK9, and psoriasis.
“In our own studies, we did see a statistical correlation between circulating PCSK9 and psoriasis severity,” Dr. Garshick said. But he added, “I think we are just beginning to understand the functions of circulating (extrahepatic) PCSK9 independent of lipid metabolism.”
While he is intrigued by the evidence that PCSK9 is linked to systemic inflammation, he pointed out that several medications used to treat dyslipidemias, such as statins, are associated with an anti-inflammatory effect.
This study “further emphasizes the need to conduct clinical trials treating dyslipidemia in psoriasis, including the targeting of PCSK9, whether it is with statins with lipid lowering and potential pleiotropic anti-inflammatory properties or PCSK9 inhibition,” he said. If positive, “both would be exciting.“
From a cardiologist’s point of view, there is an upside for including patients with psoriasis in lipid-lowering trials even if the effect on psoriasis is modest. Either way, “you still get the lipid-lowering benefit, which is important for reducing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Garshick said.
Dr. Zhao reported financial relationships with UCB, although UCB did not provide funding for this study. One author reported grants from Versus Arthritis and the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre during the study, grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Galapagos, and Pfizer, and personal fees from Chugai Roche outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. The study was supported by grants from Versus Arthritis and the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. Dr. Garshick reported financial relationships with AbbVie and Horizon Therapeutics.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
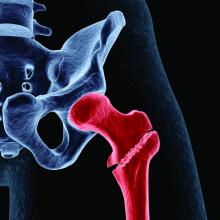
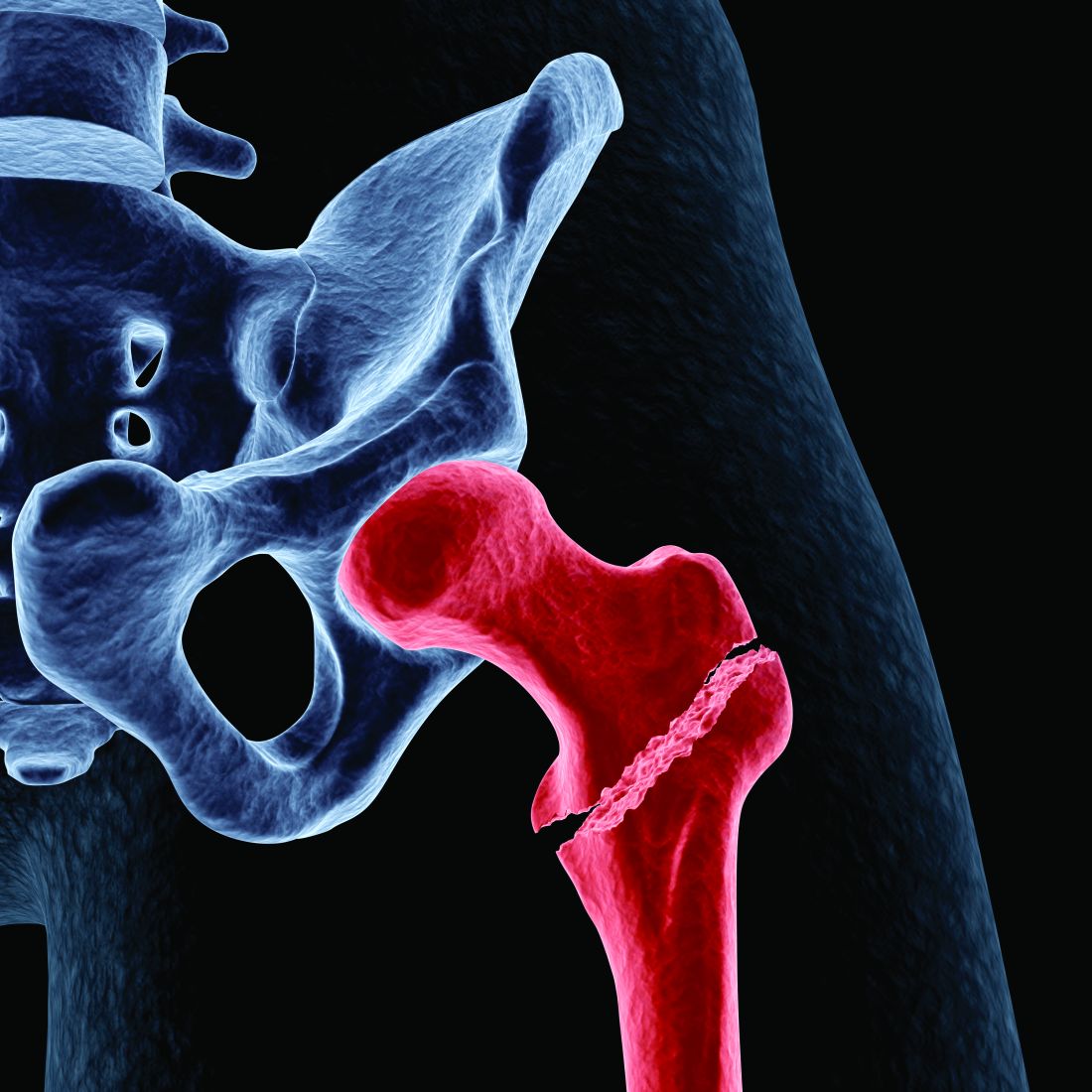
High HDL-C levels linked to increased fracture risk
High levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in older adults are associated with a higher risk of sustaining a fracture than lower HDL-C levels, a new study suggests.
“Two animal studies showing that HDL-C reduces bone mineral density by reducing osteoblast number and function provide a plausible explanation for why high HDL-C may increase the risk of fractures,” Monira Hussain, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Monash University in Melbourne, told this news organization. “So, it was not surprising when our analyses provided evidence that amongst those in the highest quintile of HDL-C (> 74 mg/dL), there was a [33%] increased risk of fractures.”
After adjustment, one standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fracture during a 4-year follow-up.
Based on this and other studies, Dr. Hussain said, “I believe that the finding of a very high HDL-C [should] alert clinicians to a higher risk of mortality, fractures, and possibly other threats to their patient’s health.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Independent risk factor
For this report, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) clinical trial and the ASPREE-Fracture substudy.
ASPREE was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled primary prevention trial of aspirin. Participants were 16,703 community-dwelling Australians and 2,411 individuals from the United States with a mean age of 75 and without evident cardiovascular disease, dementia, physical disability, or life-limiting chronic illness.
The ASPREE-Fracture substudy collected data on fractures reported post randomization from the Australian participants. Fractures were confirmed by imaging and adjudicated by an expert panel and included both traumatic and minimal trauma fractures.
Of the 16,262 participants who had a plasma HDL-C measurement at baseline (55% women), 1,659 (10.2%) experienced at least one fracture over a median of 4 years. This included 711 minimal trauma fractures (for example, falls from standing height) and 948 other trauma fractures, mainly falls on stairs, ladders, or stools.
Higher rates of fractures occurred in the highest quintile of HDL-C level where the mean level was 89 mg/dL. At baseline, participants in that quintile had a lower BMI, a high prevalence of current/former smoking and current alcohol use, 12 years or longer of school, more physical activity, and higher use of antiosteoporosis medication. They also had less chronic kidney disease, diabetes, prefrailty/frailty, or treatment with lipid-lowering drugs.
In a fully adjusted model, each standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fractures (hazard ratio, 1.14). When analyzed in quintiles, compared with participants in Q1, those in Q5 had a 33% higher risk for fracture (HR, 1.33).
Prevalence rates were similar between the sexes. The increase in fracture risk appeared to be independent of traditional risk factors for fractures, including age, sex, physical activity, alcohol use, frailty, BMI, smoking status, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, use of lipid-lowering or antiosteoporosis drugs, and education, the authors note.
The results persisted in sensitivity analyses in restricted subgroups of interest and in stratified analyses – including, for example, only minimal fractures; participants not taking antiosteoporosis drugs or statins; never smokers; nondrinkers; and those engaging in minimal physical activity (walking less than 30 minutes per day).
No association was observed between non–HDL-C levels and fractures.
The authors conclude that the study “provides robust evidence that higher levels of HDL-C are associated with incident fractures in both male and female individuals, independent of conventional risk factors.”
Clinically useful?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Marilyn Tan, MD, clinic chief of the Endocrine Clinic and clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said, “I certainly would not recommend anyone do anything to actively lower their HDL levels. HDL levels are largely determined by genetics, diet, and lifestyle, with some effects from certain medications/supplements. Studies have demonstrated that moderately higher HDL levels may be protective for atherosclerosis.”
In the current study, she said, “Causation has not been proven, and importantly there is no evidence that reducing HDL levels reduces fracture risk. Also, this association between raised HDL levels and fracture risk has not been demonstrated consistently in other studies.”
Furthermore, she noted, the preclinical trials on which the authors based their hypothesis – that is, an association between HDL and a reduction in the number and function of osteoblasts – “has not been demonstrated widely in human subjects.”
“We have a large armamentarium of FDA-approved treatments for osteoporosis that have been clinically proven to reduce fracture risk very significantly, and these are the tools [in addition to lifestyle changes] we should use to reduce fracture risk,” Dr. Tan concluded.
John Wilkins, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and Anand Rohatgi, MD, MSCS, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, also point out some limitations of the study in a related editorial.
They note the inclusion of predominantly healthy adults with a mean age of 75, a population that could yield different findings from middle-aged cohorts with chronic illnesses, as well as a lack of clarity regarding the possible role of alcohol intake among the study participants.
Furthermore, the editorialists write, although significant associations were shown in this study, “models were not adjusted for detailed measures of exercise/activity, triglycerides, or any other lipids, including other HDL compositional measures such as HDL-P or ApoA-I levels. There was no assessment of whether HDL-C improved discrimination, reclassification, or any other validated measures of risk prediction performance.
“Taken together,” they conclude, “this study alone leaves several unanswered questions as to whether high HDL-C could be a useful biomarker to detect fracture risk.”
No commercial funding was disclosed. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
High levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in older adults are associated with a higher risk of sustaining a fracture than lower HDL-C levels, a new study suggests.
“Two animal studies showing that HDL-C reduces bone mineral density by reducing osteoblast number and function provide a plausible explanation for why high HDL-C may increase the risk of fractures,” Monira Hussain, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Monash University in Melbourne, told this news organization. “So, it was not surprising when our analyses provided evidence that amongst those in the highest quintile of HDL-C (> 74 mg/dL), there was a [33%] increased risk of fractures.”
After adjustment, one standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fracture during a 4-year follow-up.
Based on this and other studies, Dr. Hussain said, “I believe that the finding of a very high HDL-C [should] alert clinicians to a higher risk of mortality, fractures, and possibly other threats to their patient’s health.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Independent risk factor
For this report, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) clinical trial and the ASPREE-Fracture substudy.
ASPREE was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled primary prevention trial of aspirin. Participants were 16,703 community-dwelling Australians and 2,411 individuals from the United States with a mean age of 75 and without evident cardiovascular disease, dementia, physical disability, or life-limiting chronic illness.
The ASPREE-Fracture substudy collected data on fractures reported post randomization from the Australian participants. Fractures were confirmed by imaging and adjudicated by an expert panel and included both traumatic and minimal trauma fractures.
Of the 16,262 participants who had a plasma HDL-C measurement at baseline (55% women), 1,659 (10.2%) experienced at least one fracture over a median of 4 years. This included 711 minimal trauma fractures (for example, falls from standing height) and 948 other trauma fractures, mainly falls on stairs, ladders, or stools.
Higher rates of fractures occurred in the highest quintile of HDL-C level where the mean level was 89 mg/dL. At baseline, participants in that quintile had a lower BMI, a high prevalence of current/former smoking and current alcohol use, 12 years or longer of school, more physical activity, and higher use of antiosteoporosis medication. They also had less chronic kidney disease, diabetes, prefrailty/frailty, or treatment with lipid-lowering drugs.
In a fully adjusted model, each standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fractures (hazard ratio, 1.14). When analyzed in quintiles, compared with participants in Q1, those in Q5 had a 33% higher risk for fracture (HR, 1.33).
Prevalence rates were similar between the sexes. The increase in fracture risk appeared to be independent of traditional risk factors for fractures, including age, sex, physical activity, alcohol use, frailty, BMI, smoking status, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, use of lipid-lowering or antiosteoporosis drugs, and education, the authors note.
The results persisted in sensitivity analyses in restricted subgroups of interest and in stratified analyses – including, for example, only minimal fractures; participants not taking antiosteoporosis drugs or statins; never smokers; nondrinkers; and those engaging in minimal physical activity (walking less than 30 minutes per day).
No association was observed between non–HDL-C levels and fractures.
The authors conclude that the study “provides robust evidence that higher levels of HDL-C are associated with incident fractures in both male and female individuals, independent of conventional risk factors.”
Clinically useful?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Marilyn Tan, MD, clinic chief of the Endocrine Clinic and clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said, “I certainly would not recommend anyone do anything to actively lower their HDL levels. HDL levels are largely determined by genetics, diet, and lifestyle, with some effects from certain medications/supplements. Studies have demonstrated that moderately higher HDL levels may be protective for atherosclerosis.”
In the current study, she said, “Causation has not been proven, and importantly there is no evidence that reducing HDL levels reduces fracture risk. Also, this association between raised HDL levels and fracture risk has not been demonstrated consistently in other studies.”
Furthermore, she noted, the preclinical trials on which the authors based their hypothesis – that is, an association between HDL and a reduction in the number and function of osteoblasts – “has not been demonstrated widely in human subjects.”
“We have a large armamentarium of FDA-approved treatments for osteoporosis that have been clinically proven to reduce fracture risk very significantly, and these are the tools [in addition to lifestyle changes] we should use to reduce fracture risk,” Dr. Tan concluded.
John Wilkins, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and Anand Rohatgi, MD, MSCS, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, also point out some limitations of the study in a related editorial.
They note the inclusion of predominantly healthy adults with a mean age of 75, a population that could yield different findings from middle-aged cohorts with chronic illnesses, as well as a lack of clarity regarding the possible role of alcohol intake among the study participants.
Furthermore, the editorialists write, although significant associations were shown in this study, “models were not adjusted for detailed measures of exercise/activity, triglycerides, or any other lipids, including other HDL compositional measures such as HDL-P or ApoA-I levels. There was no assessment of whether HDL-C improved discrimination, reclassification, or any other validated measures of risk prediction performance.
“Taken together,” they conclude, “this study alone leaves several unanswered questions as to whether high HDL-C could be a useful biomarker to detect fracture risk.”
No commercial funding was disclosed. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
High levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in older adults are associated with a higher risk of sustaining a fracture than lower HDL-C levels, a new study suggests.
“Two animal studies showing that HDL-C reduces bone mineral density by reducing osteoblast number and function provide a plausible explanation for why high HDL-C may increase the risk of fractures,” Monira Hussain, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Monash University in Melbourne, told this news organization. “So, it was not surprising when our analyses provided evidence that amongst those in the highest quintile of HDL-C (> 74 mg/dL), there was a [33%] increased risk of fractures.”
After adjustment, one standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fracture during a 4-year follow-up.
Based on this and other studies, Dr. Hussain said, “I believe that the finding of a very high HDL-C [should] alert clinicians to a higher risk of mortality, fractures, and possibly other threats to their patient’s health.”
The study was published online in JAMA Cardiology.
Independent risk factor
For this report, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of data from the Aspirin in Reducing Events in the Elderly (ASPREE) clinical trial and the ASPREE-Fracture substudy.
ASPREE was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled primary prevention trial of aspirin. Participants were 16,703 community-dwelling Australians and 2,411 individuals from the United States with a mean age of 75 and without evident cardiovascular disease, dementia, physical disability, or life-limiting chronic illness.
The ASPREE-Fracture substudy collected data on fractures reported post randomization from the Australian participants. Fractures were confirmed by imaging and adjudicated by an expert panel and included both traumatic and minimal trauma fractures.
Of the 16,262 participants who had a plasma HDL-C measurement at baseline (55% women), 1,659 (10.2%) experienced at least one fracture over a median of 4 years. This included 711 minimal trauma fractures (for example, falls from standing height) and 948 other trauma fractures, mainly falls on stairs, ladders, or stools.
Higher rates of fractures occurred in the highest quintile of HDL-C level where the mean level was 89 mg/dL. At baseline, participants in that quintile had a lower BMI, a high prevalence of current/former smoking and current alcohol use, 12 years or longer of school, more physical activity, and higher use of antiosteoporosis medication. They also had less chronic kidney disease, diabetes, prefrailty/frailty, or treatment with lipid-lowering drugs.
In a fully adjusted model, each standard deviation increment in HDL-C level was associated with a 14% higher risk of fractures (hazard ratio, 1.14). When analyzed in quintiles, compared with participants in Q1, those in Q5 had a 33% higher risk for fracture (HR, 1.33).
Prevalence rates were similar between the sexes. The increase in fracture risk appeared to be independent of traditional risk factors for fractures, including age, sex, physical activity, alcohol use, frailty, BMI, smoking status, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, use of lipid-lowering or antiosteoporosis drugs, and education, the authors note.
The results persisted in sensitivity analyses in restricted subgroups of interest and in stratified analyses – including, for example, only minimal fractures; participants not taking antiosteoporosis drugs or statins; never smokers; nondrinkers; and those engaging in minimal physical activity (walking less than 30 minutes per day).
No association was observed between non–HDL-C levels and fractures.
The authors conclude that the study “provides robust evidence that higher levels of HDL-C are associated with incident fractures in both male and female individuals, independent of conventional risk factors.”
Clinically useful?
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Marilyn Tan, MD, clinic chief of the Endocrine Clinic and clinical associate professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, said, “I certainly would not recommend anyone do anything to actively lower their HDL levels. HDL levels are largely determined by genetics, diet, and lifestyle, with some effects from certain medications/supplements. Studies have demonstrated that moderately higher HDL levels may be protective for atherosclerosis.”
In the current study, she said, “Causation has not been proven, and importantly there is no evidence that reducing HDL levels reduces fracture risk. Also, this association between raised HDL levels and fracture risk has not been demonstrated consistently in other studies.”
Furthermore, she noted, the preclinical trials on which the authors based their hypothesis – that is, an association between HDL and a reduction in the number and function of osteoblasts – “has not been demonstrated widely in human subjects.”
“We have a large armamentarium of FDA-approved treatments for osteoporosis that have been clinically proven to reduce fracture risk very significantly, and these are the tools [in addition to lifestyle changes] we should use to reduce fracture risk,” Dr. Tan concluded.
John Wilkins, MD, of Northwestern University, Chicago, and Anand Rohatgi, MD, MSCS, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, also point out some limitations of the study in a related editorial.
They note the inclusion of predominantly healthy adults with a mean age of 75, a population that could yield different findings from middle-aged cohorts with chronic illnesses, as well as a lack of clarity regarding the possible role of alcohol intake among the study participants.
Furthermore, the editorialists write, although significant associations were shown in this study, “models were not adjusted for detailed measures of exercise/activity, triglycerides, or any other lipids, including other HDL compositional measures such as HDL-P or ApoA-I levels. There was no assessment of whether HDL-C improved discrimination, reclassification, or any other validated measures of risk prediction performance.
“Taken together,” they conclude, “this study alone leaves several unanswered questions as to whether high HDL-C could be a useful biomarker to detect fracture risk.”
No commercial funding was disclosed. The authors report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
PCSK9 inhibitors for severe COVID? Pilot trial signals of benefit
PCSK9 inhibitors may best be known for their powerful LDL-lowering effects but are less appreciated as anti-inflammatory agents with potential beyond cardiovascular health.
In a small pilot trial, for example, patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 who received a single injection of PCSK9 inhibitor became less sick and more likely to survive than those given a placebo. Their 30-day risk of death or intubation fell significantly, as did their levels of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 (IL-6).
Indeed, survival gains in the PCSK9-inhibitor group were greatest among patients with higher baseline concentrations of IL-6. Although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, it suggests the drugs’ efficacy in COVID-19 tracks with intensity of inflammation, proposes a report published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Therefore, “PCSK9 inhibition may represent a novel therapeutic pathway in addition to currently recommended therapeutic approaches for severe COVID-19,” conclude the authors, led by Eliano P. Navarese, MD, PhD, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland.
PCSK9 inhibitors as anti-inflammatories
Although the study was small and only hypothesis-generating, the fact that outcomes for actively treated patients were proportional to baseline IL-6 levels “strongly suggests that PCSK9 inhibition can directly modulate inflammation in COVID-19,” argues an editorial accompanying the report.
and likely sheds light on “mechanisms through which PCSK9 inhibition dually modulates lipoprotein metabolism and inflammation,” write Sascha N. Goonewardena, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Robert S. Rosenson, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
The results are consistent with prior evidence that the drugs are anti-inflammatory at least partly because of their interference with inflammatory pathways triggered by PCSK9 and mediated by IL-6, as described by Dr. Navarese and colleagues.
Indeed, they write, PCSK9 inhibitors may improve COVID outcomes mostly through mechanisms unrelated to LDL-receptor expression, “including direct inhibition of PCSK9-triggered inflammation.”
If true, the authors observe, it might explain “why the positive findings of the present study have not been consistently observed in trials involving other lipid-lowering agents, such as statins.” Those drugs are well-known to decrease levels of the inflammatory biomarker C-reactive protein.
In patients with stable coronary disease, in whom inflammation is typically tracked by measuring CRP, “the PCSK9 inhibitors have not been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect,” Dr. Rosenson further explained.
But the current study’s patients with acute, severe COVID-19, a “profound inflammatory insult” with upregulation of IL-6, were “a good population” for evaluating the drugs’ potential anti-inflammatory effects, Dr. Rosenson said in an interview. The results “are quite enticing but require corroboration in a larger trial.”
A single injection
The IMPACT-SIRIO 5 trial entered 60 adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19 and elevated IL-6 at four centers in Poland. Patients with other known active infections were excluded.
They were randomly assigned double-blind to receive a 140 mg injection of evolocumab (Repatha) or placebo. The 2 groups were similar with respect to demographics, body-mass index, time since symptom onset, and treatments for managing COVID-19 and its complications.
Rates of death or need for intubation at 30 days, the primary endpoint, were 23.3% in the PCSK9-inhibitor group and 53.3% for controls, a risk difference of 30% (95% confidence interval –53.4% to –6.6%). The median durations of oxygen therapy were significantly different at 13 days and 20 days, respectively, the report states.
Serum IL-6 levels fell further over 30 days in the PCSK9-inhibitor group (–56% vs. –21% among controls). A drop by more than 90% was seen in 60% of patients in the PCSK9-inhibitor group and in 27% of controls.
The average hospital stay was shorter for those getting the PCSK9 inhibitor, compared with placebo, 16 days versus 22 days, and their 30-day mortality was numerically lower, 16% versus 33.3%.
Patients’ baseline IL-6 levels above the median, the report states, had a lower mortality on the PCSK9 inhibitor versus placebo (risk difference –37.5%; 95% CI –68.2% to –6.70%).
A larger trial to corroborate these results would potentially enter similar patients hospitalized with COVID-19 with reproducible evidence of an ongoing cytokine storm, such as elevated levels of IL-6, who would be assigned to either a PCSK9 inhibitor or placebo, Dr. Rosenson proposed.
Although the current primary endpoint that combines mortality and intubation was “reasonable” for a small pilot trial, he said, if the researchers embark on a larger study, “they’ll want to look at those events separately.”
Dr. Navarese discloses receiving speaker and consultancy fees from Amgen, Sanofi-Regeneron, Bayer; and grants from Abbott. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Rosenson discloses receiving research funding to his institution from Amgen, Arrowhead, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Regeneron; consulting fees from Amgen, Arrowhead, CRISPR Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Lipigon, Novartis, Precision Biosciences, Regeneron, Ultragenyx, and Verve; speaking fees from Amgen, Kowa, and Regeneron; and royalties from Wolters Kluwer; and owning stock in MediMergent. Dr. Goonewardena reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCSK9 inhibitors may best be known for their powerful LDL-lowering effects but are less appreciated as anti-inflammatory agents with potential beyond cardiovascular health.
In a small pilot trial, for example, patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 who received a single injection of PCSK9 inhibitor became less sick and more likely to survive than those given a placebo. Their 30-day risk of death or intubation fell significantly, as did their levels of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 (IL-6).
Indeed, survival gains in the PCSK9-inhibitor group were greatest among patients with higher baseline concentrations of IL-6. Although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, it suggests the drugs’ efficacy in COVID-19 tracks with intensity of inflammation, proposes a report published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Therefore, “PCSK9 inhibition may represent a novel therapeutic pathway in addition to currently recommended therapeutic approaches for severe COVID-19,” conclude the authors, led by Eliano P. Navarese, MD, PhD, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland.
PCSK9 inhibitors as anti-inflammatories
Although the study was small and only hypothesis-generating, the fact that outcomes for actively treated patients were proportional to baseline IL-6 levels “strongly suggests that PCSK9 inhibition can directly modulate inflammation in COVID-19,” argues an editorial accompanying the report.
and likely sheds light on “mechanisms through which PCSK9 inhibition dually modulates lipoprotein metabolism and inflammation,” write Sascha N. Goonewardena, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Robert S. Rosenson, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
The results are consistent with prior evidence that the drugs are anti-inflammatory at least partly because of their interference with inflammatory pathways triggered by PCSK9 and mediated by IL-6, as described by Dr. Navarese and colleagues.
Indeed, they write, PCSK9 inhibitors may improve COVID outcomes mostly through mechanisms unrelated to LDL-receptor expression, “including direct inhibition of PCSK9-triggered inflammation.”
If true, the authors observe, it might explain “why the positive findings of the present study have not been consistently observed in trials involving other lipid-lowering agents, such as statins.” Those drugs are well-known to decrease levels of the inflammatory biomarker C-reactive protein.
In patients with stable coronary disease, in whom inflammation is typically tracked by measuring CRP, “the PCSK9 inhibitors have not been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect,” Dr. Rosenson further explained.
But the current study’s patients with acute, severe COVID-19, a “profound inflammatory insult” with upregulation of IL-6, were “a good population” for evaluating the drugs’ potential anti-inflammatory effects, Dr. Rosenson said in an interview. The results “are quite enticing but require corroboration in a larger trial.”
A single injection
The IMPACT-SIRIO 5 trial entered 60 adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19 and elevated IL-6 at four centers in Poland. Patients with other known active infections were excluded.
They were randomly assigned double-blind to receive a 140 mg injection of evolocumab (Repatha) or placebo. The 2 groups were similar with respect to demographics, body-mass index, time since symptom onset, and treatments for managing COVID-19 and its complications.
Rates of death or need for intubation at 30 days, the primary endpoint, were 23.3% in the PCSK9-inhibitor group and 53.3% for controls, a risk difference of 30% (95% confidence interval –53.4% to –6.6%). The median durations of oxygen therapy were significantly different at 13 days and 20 days, respectively, the report states.
Serum IL-6 levels fell further over 30 days in the PCSK9-inhibitor group (–56% vs. –21% among controls). A drop by more than 90% was seen in 60% of patients in the PCSK9-inhibitor group and in 27% of controls.
The average hospital stay was shorter for those getting the PCSK9 inhibitor, compared with placebo, 16 days versus 22 days, and their 30-day mortality was numerically lower, 16% versus 33.3%.
Patients’ baseline IL-6 levels above the median, the report states, had a lower mortality on the PCSK9 inhibitor versus placebo (risk difference –37.5%; 95% CI –68.2% to –6.70%).
A larger trial to corroborate these results would potentially enter similar patients hospitalized with COVID-19 with reproducible evidence of an ongoing cytokine storm, such as elevated levels of IL-6, who would be assigned to either a PCSK9 inhibitor or placebo, Dr. Rosenson proposed.
Although the current primary endpoint that combines mortality and intubation was “reasonable” for a small pilot trial, he said, if the researchers embark on a larger study, “they’ll want to look at those events separately.”
Dr. Navarese discloses receiving speaker and consultancy fees from Amgen, Sanofi-Regeneron, Bayer; and grants from Abbott. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Rosenson discloses receiving research funding to his institution from Amgen, Arrowhead, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Regeneron; consulting fees from Amgen, Arrowhead, CRISPR Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Lipigon, Novartis, Precision Biosciences, Regeneron, Ultragenyx, and Verve; speaking fees from Amgen, Kowa, and Regeneron; and royalties from Wolters Kluwer; and owning stock in MediMergent. Dr. Goonewardena reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCSK9 inhibitors may best be known for their powerful LDL-lowering effects but are less appreciated as anti-inflammatory agents with potential beyond cardiovascular health.
In a small pilot trial, for example, patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 who received a single injection of PCSK9 inhibitor became less sick and more likely to survive than those given a placebo. Their 30-day risk of death or intubation fell significantly, as did their levels of the inflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 (IL-6).
Indeed, survival gains in the PCSK9-inhibitor group were greatest among patients with higher baseline concentrations of IL-6. Although the trial wasn’t powered for clinical outcomes, it suggests the drugs’ efficacy in COVID-19 tracks with intensity of inflammation, proposes a report published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Therefore, “PCSK9 inhibition may represent a novel therapeutic pathway in addition to currently recommended therapeutic approaches for severe COVID-19,” conclude the authors, led by Eliano P. Navarese, MD, PhD, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Bydgoszcz, Poland.
PCSK9 inhibitors as anti-inflammatories
Although the study was small and only hypothesis-generating, the fact that outcomes for actively treated patients were proportional to baseline IL-6 levels “strongly suggests that PCSK9 inhibition can directly modulate inflammation in COVID-19,” argues an editorial accompanying the report.
and likely sheds light on “mechanisms through which PCSK9 inhibition dually modulates lipoprotein metabolism and inflammation,” write Sascha N. Goonewardena, MD, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Robert S. Rosenson, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
The results are consistent with prior evidence that the drugs are anti-inflammatory at least partly because of their interference with inflammatory pathways triggered by PCSK9 and mediated by IL-6, as described by Dr. Navarese and colleagues.
Indeed, they write, PCSK9 inhibitors may improve COVID outcomes mostly through mechanisms unrelated to LDL-receptor expression, “including direct inhibition of PCSK9-triggered inflammation.”
If true, the authors observe, it might explain “why the positive findings of the present study have not been consistently observed in trials involving other lipid-lowering agents, such as statins.” Those drugs are well-known to decrease levels of the inflammatory biomarker C-reactive protein.
In patients with stable coronary disease, in whom inflammation is typically tracked by measuring CRP, “the PCSK9 inhibitors have not been shown to have an anti-inflammatory effect,” Dr. Rosenson further explained.
But the current study’s patients with acute, severe COVID-19, a “profound inflammatory insult” with upregulation of IL-6, were “a good population” for evaluating the drugs’ potential anti-inflammatory effects, Dr. Rosenson said in an interview. The results “are quite enticing but require corroboration in a larger trial.”
A single injection
The IMPACT-SIRIO 5 trial entered 60 adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19 and elevated IL-6 at four centers in Poland. Patients with other known active infections were excluded.
They were randomly assigned double-blind to receive a 140 mg injection of evolocumab (Repatha) or placebo. The 2 groups were similar with respect to demographics, body-mass index, time since symptom onset, and treatments for managing COVID-19 and its complications.
Rates of death or need for intubation at 30 days, the primary endpoint, were 23.3% in the PCSK9-inhibitor group and 53.3% for controls, a risk difference of 30% (95% confidence interval –53.4% to –6.6%). The median durations of oxygen therapy were significantly different at 13 days and 20 days, respectively, the report states.
Serum IL-6 levels fell further over 30 days in the PCSK9-inhibitor group (–56% vs. –21% among controls). A drop by more than 90% was seen in 60% of patients in the PCSK9-inhibitor group and in 27% of controls.
The average hospital stay was shorter for those getting the PCSK9 inhibitor, compared with placebo, 16 days versus 22 days, and their 30-day mortality was numerically lower, 16% versus 33.3%.
Patients’ baseline IL-6 levels above the median, the report states, had a lower mortality on the PCSK9 inhibitor versus placebo (risk difference –37.5%; 95% CI –68.2% to –6.70%).
A larger trial to corroborate these results would potentially enter similar patients hospitalized with COVID-19 with reproducible evidence of an ongoing cytokine storm, such as elevated levels of IL-6, who would be assigned to either a PCSK9 inhibitor or placebo, Dr. Rosenson proposed.
Although the current primary endpoint that combines mortality and intubation was “reasonable” for a small pilot trial, he said, if the researchers embark on a larger study, “they’ll want to look at those events separately.”
Dr. Navarese discloses receiving speaker and consultancy fees from Amgen, Sanofi-Regeneron, Bayer; and grants from Abbott. Disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Rosenson discloses receiving research funding to his institution from Amgen, Arrowhead, Eli Lilly, Novartis, and Regeneron; consulting fees from Amgen, Arrowhead, CRISPR Therapeutics, Eli Lilly, Lipigon, Novartis, Precision Biosciences, Regeneron, Ultragenyx, and Verve; speaking fees from Amgen, Kowa, and Regeneron; and royalties from Wolters Kluwer; and owning stock in MediMergent. Dr. Goonewardena reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Size of meals, not timing, linked to weight loss
The number of daily meals, but not the timing between first and last daily meals, was significantly associated with weight changes over a 6-year period, in a prospective study of more than 500 adults.
Some studies suggest that timing food intake – through time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting – can promote weight loss, but these strategies have yielded similar weight loss to eating throughout the day in randomized trials, and population-based studies of meal intervals and weight changes are needed, Di Zhao, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Obesity is an epidemic,” corresponding author Wendy Bennett, MD, also of Johns Hopkins University, said in an interview. “We are interested in identifying ways to prevent weight gain over time and reduce obesity risk, since telling people to ‘just eat less’ doesn’t always work.”
In a study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, the researchers recruited 1,017 adults who were patients at one of three health systems; of these, complete data were available for 547 individuals.
The participants downloaded an app called Daily24 to record the timing of their meals and sleep for at least 1 day. The researchers used electronic medical records to obtain information on weight and comorbidities of the participants for up to 10 years before study enrollment through 10 months after enrollment.
The mean age of the participants was 51.1 years, 78% were women, and 78% were White; the mean body mass index was 30.8 kg/m2.
The mean interval from first to last meal was 11.5 hours, and this was not associated with change in weight. The mean times from waking up to the first meal and the time from the last meal to sleeping were 1.6 hours and 4.0 hours, respectively, and these were not associated with weight changes over the follow-up period, the researchers wrote. Sleep duration (mean of 7.5 hours) also was not associated with weight change over time.
However, the total daily number of large and medium-sized meals was associated with weight gain over time, while those who reported more smaller meals showed weight loss. A daily increase of one large, medium, or small meal was associated with an average annual weight change of 0.69 kg, 0.97 kg, and –0.30 kg, respectively.
Benefits of time-restricted eating remain unclear
“Animal studies have shown benefits for time restricted feeding, but there are still questions about whether or not it helps prevent weight gain or promotes weight loss in humans,” Dr. Bennett said in an interview.
As for the current study findings, “we were not surprised; humans are more complicated than animals, and we have complicated behaviors, especially with eating,” she said.
“We showed that windows of eating (eating for longer periods of time or less in a day) was not associated with weight change over time among patients from three health systems,” said Dr. Bennett. “The main implication is that restricting your window of eating, such as eating over less time, or having more fasting time, may not reduce weight gain over time, while eating fewer large meals is associated with less weight gain over time.”
The findings were limited by several factors including the exclusion of many younger and less educated individuals, the short follow-up period, and lack of information on weight loss intention at baseline, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the inability to evaluate time-restricted eating or fasting, and the inclusion of individuals currently seeking care, which may limit generalizability.
However, the results were strengthened by the repeated measures of weight, detailed information on obesity risk factors, and real-time assessment of eating behaviors. The results do not support time-restricted eating as a long-term weight-loss strategy, and more studies are needed with a longer follow-up period, the researchers concluded.
However, there may be a role for time restricted eating as a method of total calorie control, Dr. Bennett said.
“Other studies do show that people might be able to use time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting to help them reduce their caloric intake and thus lose weight, so it can still be a helpful weight loss tool for some people who can adhere to it,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the American Heart Association to Johns Hopkins University. Dr. Bennett had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The number of daily meals, but not the timing between first and last daily meals, was significantly associated with weight changes over a 6-year period, in a prospective study of more than 500 adults.
Some studies suggest that timing food intake – through time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting – can promote weight loss, but these strategies have yielded similar weight loss to eating throughout the day in randomized trials, and population-based studies of meal intervals and weight changes are needed, Di Zhao, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Obesity is an epidemic,” corresponding author Wendy Bennett, MD, also of Johns Hopkins University, said in an interview. “We are interested in identifying ways to prevent weight gain over time and reduce obesity risk, since telling people to ‘just eat less’ doesn’t always work.”
In a study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, the researchers recruited 1,017 adults who were patients at one of three health systems; of these, complete data were available for 547 individuals.
The participants downloaded an app called Daily24 to record the timing of their meals and sleep for at least 1 day. The researchers used electronic medical records to obtain information on weight and comorbidities of the participants for up to 10 years before study enrollment through 10 months after enrollment.
The mean age of the participants was 51.1 years, 78% were women, and 78% were White; the mean body mass index was 30.8 kg/m2.
The mean interval from first to last meal was 11.5 hours, and this was not associated with change in weight. The mean times from waking up to the first meal and the time from the last meal to sleeping were 1.6 hours and 4.0 hours, respectively, and these were not associated with weight changes over the follow-up period, the researchers wrote. Sleep duration (mean of 7.5 hours) also was not associated with weight change over time.
However, the total daily number of large and medium-sized meals was associated with weight gain over time, while those who reported more smaller meals showed weight loss. A daily increase of one large, medium, or small meal was associated with an average annual weight change of 0.69 kg, 0.97 kg, and –0.30 kg, respectively.
Benefits of time-restricted eating remain unclear
“Animal studies have shown benefits for time restricted feeding, but there are still questions about whether or not it helps prevent weight gain or promotes weight loss in humans,” Dr. Bennett said in an interview.
As for the current study findings, “we were not surprised; humans are more complicated than animals, and we have complicated behaviors, especially with eating,” she said.
“We showed that windows of eating (eating for longer periods of time or less in a day) was not associated with weight change over time among patients from three health systems,” said Dr. Bennett. “The main implication is that restricting your window of eating, such as eating over less time, or having more fasting time, may not reduce weight gain over time, while eating fewer large meals is associated with less weight gain over time.”
The findings were limited by several factors including the exclusion of many younger and less educated individuals, the short follow-up period, and lack of information on weight loss intention at baseline, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the inability to evaluate time-restricted eating or fasting, and the inclusion of individuals currently seeking care, which may limit generalizability.
However, the results were strengthened by the repeated measures of weight, detailed information on obesity risk factors, and real-time assessment of eating behaviors. The results do not support time-restricted eating as a long-term weight-loss strategy, and more studies are needed with a longer follow-up period, the researchers concluded.
However, there may be a role for time restricted eating as a method of total calorie control, Dr. Bennett said.
“Other studies do show that people might be able to use time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting to help them reduce their caloric intake and thus lose weight, so it can still be a helpful weight loss tool for some people who can adhere to it,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the American Heart Association to Johns Hopkins University. Dr. Bennett had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The number of daily meals, but not the timing between first and last daily meals, was significantly associated with weight changes over a 6-year period, in a prospective study of more than 500 adults.
Some studies suggest that timing food intake – through time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting – can promote weight loss, but these strategies have yielded similar weight loss to eating throughout the day in randomized trials, and population-based studies of meal intervals and weight changes are needed, Di Zhao, PhD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote.
“Obesity is an epidemic,” corresponding author Wendy Bennett, MD, also of Johns Hopkins University, said in an interview. “We are interested in identifying ways to prevent weight gain over time and reduce obesity risk, since telling people to ‘just eat less’ doesn’t always work.”
In a study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association, the researchers recruited 1,017 adults who were patients at one of three health systems; of these, complete data were available for 547 individuals.
The participants downloaded an app called Daily24 to record the timing of their meals and sleep for at least 1 day. The researchers used electronic medical records to obtain information on weight and comorbidities of the participants for up to 10 years before study enrollment through 10 months after enrollment.
The mean age of the participants was 51.1 years, 78% were women, and 78% were White; the mean body mass index was 30.8 kg/m2.
The mean interval from first to last meal was 11.5 hours, and this was not associated with change in weight. The mean times from waking up to the first meal and the time from the last meal to sleeping were 1.6 hours and 4.0 hours, respectively, and these were not associated with weight changes over the follow-up period, the researchers wrote. Sleep duration (mean of 7.5 hours) also was not associated with weight change over time.
However, the total daily number of large and medium-sized meals was associated with weight gain over time, while those who reported more smaller meals showed weight loss. A daily increase of one large, medium, or small meal was associated with an average annual weight change of 0.69 kg, 0.97 kg, and –0.30 kg, respectively.
Benefits of time-restricted eating remain unclear
“Animal studies have shown benefits for time restricted feeding, but there are still questions about whether or not it helps prevent weight gain or promotes weight loss in humans,” Dr. Bennett said in an interview.
As for the current study findings, “we were not surprised; humans are more complicated than animals, and we have complicated behaviors, especially with eating,” she said.
“We showed that windows of eating (eating for longer periods of time or less in a day) was not associated with weight change over time among patients from three health systems,” said Dr. Bennett. “The main implication is that restricting your window of eating, such as eating over less time, or having more fasting time, may not reduce weight gain over time, while eating fewer large meals is associated with less weight gain over time.”
The findings were limited by several factors including the exclusion of many younger and less educated individuals, the short follow-up period, and lack of information on weight loss intention at baseline, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the inability to evaluate time-restricted eating or fasting, and the inclusion of individuals currently seeking care, which may limit generalizability.
However, the results were strengthened by the repeated measures of weight, detailed information on obesity risk factors, and real-time assessment of eating behaviors. The results do not support time-restricted eating as a long-term weight-loss strategy, and more studies are needed with a longer follow-up period, the researchers concluded.
However, there may be a role for time restricted eating as a method of total calorie control, Dr. Bennett said.
“Other studies do show that people might be able to use time-restricted eating or intermittent fasting to help them reduce their caloric intake and thus lose weight, so it can still be a helpful weight loss tool for some people who can adhere to it,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the American Heart Association to Johns Hopkins University. Dr. Bennett had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN HEART ASSOCIATION
Evolocumab’s LDL lowering surpassed inclisiran’s in ORION-3
Patients who received an injection of inclisiran (Leqvio), a small interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, every 6 months for as long as 4 years safely maintained about a 45% reduction from baseline in their level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in an open-label extension study with 382 patients.
In addition to providing the longest reported treatment experience with inclisiran, which received Food and Drug Administration marketing approval a little over a year ago, the results also suggest with the most definitive evidence to date that inclisiran is less effective for lowering LDL-C, compared with a class of medications that reduce LDL-C by a related but distinct mechanism: antibodies that directly inhibit activity of the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) enzyme, a drug class that includes alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha). Inclisiran cuts PCSK9 activity by blocking this enzyme’s gene transcription in liver cells thereby interfering with PCSK9 production.
Results from this study, the ORION-3 trial, provide “the first prospective long-term evaluation of the durability and safety of an siRNA-based therapy to provide clinically meaningful reductions in LDL cholesterol with a convenient dosing schedule,” wrote Kausik K. Ray, MD, and coauthors in a report in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The findings “provide assurance that siRNA-based therapies are safe and have the potential to provide a convenient approach to managing” LDL-C, wrote Dr. Ray, a cardiologist and professor of public health at Imperial College London, and his associates.
Evolocumab surpasses inclisiran in crossover cohort
The new data from ORION-3 study included findings from 92 patients first treated with evolocumab injections every 2 weeks for a year, an intervention that lowered their LDL-C levels by an average of about 60%, compared with their pretreatment level. ORION-3’s study design then crossed these patients to treatment with injections of inclisiran twice a year during 3 further years of follow-up, during which their average LDL levels reset to a roughly 45% drop from baseline, a potentially clinically meaningful difference, commented Robert S. Rosenson, MD, a lipid management specialist who was not involved in the ORION-3 study.
“This is the first evidence that compared the two classes” within a single study, thereby avoiding a problematic cross-study comparison. “That’s why the data are important. They underscore that the monoclonal antibodies are more effective for lowering LDL-C,” compared with inclisiran, said Dr. Rosenson, professor and director of cardiometabolic disorders at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
The findings “confirm in a trial that the PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies are indeed more potent,” he said in an interview.
But Dr. Rosenson acknowledged that, while this analysis used data on patients treated with evolocumab and then switched to inclisiran collected prospectively in a single study, it has the limitation of involving a comparison that was not prespecified. The primary goal of the evolocumab-to-inclisiran switch included in ORION-3 was to assess the ease, safety, and efficacy of a switch to inclisiran from treatment with a PCSK9 antibody and was not intended to compare the two drug classes.
The roughly 15% absolute difference in LDL-C lowering between the two tested drug classes can have substantial clinical implications for patients who start treatment with highly elevated levels of LDL-C, more than 190 mg/dL, because they have heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, are unable to take a statin because of intolerance, or both. The difference in LDL-C reduction with an antibody or with inclisiran could mean the difference between whether or not a patient like this achieves their LDL-C goal level, Dr. Rosenson explained.
Inclisiran’s upside
On the other hand, inclisiran has a couple of important advantages. First, its mechanism of action means that effective treatment involves one injection every 6 months following a patient’s first two injections at onset and after 90 days, with all injections administered in a clinician’s office. In contrast, both of the monoclonal antibodies require injections every other week, a schedule that depends on patient self-injections using prefilled syringes obtained from a pharmacy.
Twice-a-year dosing by a clinician can be a major attraction because it helps ensure treatment compliance, aids patients with physical or psychological limitations to self-injection, reduces the pill burden for patients who require multiple medications, and facilitates frequent travelers who would otherwise need to carry syringes with them on trips, Dr. Rosenson noted.
The second big advantage of office-based administration of inclisiran for U.S. Medicare patients is that the treatment is billed under a patient’s part B coverage, usually resulting in easier coverage and a significantly lower patient co-pay, compared with Medicare’s coverage for a pharmacy-dispensed agent, which is covered under Medicare part D. “Part B coverage is financially more doable” for most Medicare patients, said Dr. Rosenson.
The administration schedule for inclisiran as well as its superior Medicare coverage makes the agent “transformative” for LDL-C lowering in patients for whom treatment delivery, frequency, and payment are issues, he said.
Inclisiran uptake modest after FDA approval
Despite these pluses, uptake of inclisiran has been modest since it received U.S. marketing approval in December 2021. In its most recent quarterly financial filing, in October 2022, Novartis reported total worldwide income from inclisiran (Leqvio) of $70 million during the first 9 months of 2022, although a Novartis spokesperson noted that the company has seen “positive trends in uptake” over the course of 2022. Inclisiran is labeled as an “adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for the treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional lowering” of LDL-C.
During 2022, inclisiran uptake lagged because of the usual problems that slow the introduction of new drugs and new drug classes, especially ones that require dosing by a clinician. Months were spent waiting for billing codes to roll out, for clinical staffs to incorporate inclisiran injections into their routines, and for commercial insurers to get up to speed on their coverage, Dr. Rosenson said.
Also, a key step for widespread uptake of a new medication for improving cardiovascular disease outcomes – results from phase 3 studies that document safety and efficacy for these outcomes – remains several years off. The ORION-4 trial and the VICTORION-2P trial, each assessing the impact of inclisiran on cardiovascular disease events in roughly 15,000 people, will need about another 3-4 years before their results become available.
Professional medical societies that issue cardiovascular-disease management guidelines “prefer agents with proven benefits in phase 3 trials,” Dr. Rosenson noted.
Hence, the most recent update to U.S. LDL-C–management guidelines, released in the second half of 2022 by the American College of Cardiology as an Expert Consensus Decision Pathway, said this about the current role for inclisiran: “At the present time, a PCSK9 monoclonal antibody is preferred as the initial PCSK9 inhibitor of choice in view of its demonstrated safety, efficacy, and benefits for cardiovascular outcomes in the FOURIER [for evolocumab] and ODYSSEY Outcomes [for alirocumab] trials. The ORION-4 and VICTORION-2P cardiovascular outcomes trials with inclisiran are currently underway, and their completion is anticipated in 2026 and 2027, respectively. In view of the twice-yearly dosing regimen, inclisiran may be considered in patients with demonstrated poor adherence to PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies. Patients with adverse effects from both PSCK9 monoclonal antibodies or those who may be unable to self-inject may also be considered for therapy with inclisiran.”
ORION-3 extended the ORION-1 trial
The ORION-1 study was a phase 2 placebo-controlled, dose-ranging safety and efficacy assessment of inclisiran that gave patients two injections of the drug, at day zero and 90 days, and followed them for an additional 120 days (210 days total follow-up duration), and in some cases for as long as 360 days total. Of the 370 patients who received inclisiran in ORION-1, 290 agreed to continue inclisiran in the open-label extension, ORION-3. ORION-1 also included 127 patients randomized to initial placebo treatment, and 92 of these patients agreed to continue in ORION-3 and became the patients initially treated with evolocumab injections every other week for 1 year followed by initiation of an inclisiran regimen.
The primary outcome of ORION-3 was the change in LDL-C from baseline (the ORION-1 baseline) after 210 days of receiving inclisiran in ORION-3 (or a total of roughly 570 days after the start of ORION-1). The primary endpoint showed that, at day 210 of ORION-3 the average reduction in LDL-C from the original baseline level was 47.5%.
But a “more important” outcome, said Dr. Ray when he first reported the ORION-3 results during the American Heart Association scientific sessions in Chicago in November 2022, was that, overall, during 4 years on inclisiran this cohort showed an average cut in LDL-C from baseline of about 45% that consistently remained at this level throughout the 4 years of treatment.
“This provides us with an idea of what happens with chronic inclisiran dosing,” Dr. Ray explained. “There was no loss of biological efficacy, and we achieved these clinically meaningful, time-averaged reductions with a good safety profile. The great thing is that when patients get their injections [every 6 months] you see a consistent LDL-C reduction. A twice-annual injection is an opportunity to redesign” the way patients receive preventive cardiology care and treatment to lower LDL-C, Dr Ray said.
ORION-1 was sponsored by The Medicines Company. ORION-3 was sponsored by Novartis (which acquired The Medicines Company). Dr. Ray has received consulting fees, personal fees, and research grants from Novartis, as well as consulting fees and research grants from Amgen, the company that markets evolocumab (Repatha), and research grants from Regeneron, the company that markets alirocumab (Praluent). He has also received consulting fee, personal fees, and research grants from numerous other companies. Dr. Rosenson has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Amgen, Novartis, and Regeneron, and he has received speaking fees from Amgen and Regeneron, and has ties to several other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was updated on 1/26/2023.
Patients who received an injection of inclisiran (Leqvio), a small interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, every 6 months for as long as 4 years safely maintained about a 45% reduction from baseline in their level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in an open-label extension study with 382 patients.
In addition to providing the longest reported treatment experience with inclisiran, which received Food and Drug Administration marketing approval a little over a year ago, the results also suggest with the most definitive evidence to date that inclisiran is less effective for lowering LDL-C, compared with a class of medications that reduce LDL-C by a related but distinct mechanism: antibodies that directly inhibit activity of the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) enzyme, a drug class that includes alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha). Inclisiran cuts PCSK9 activity by blocking this enzyme’s gene transcription in liver cells thereby interfering with PCSK9 production.
Results from this study, the ORION-3 trial, provide “the first prospective long-term evaluation of the durability and safety of an siRNA-based therapy to provide clinically meaningful reductions in LDL cholesterol with a convenient dosing schedule,” wrote Kausik K. Ray, MD, and coauthors in a report in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The findings “provide assurance that siRNA-based therapies are safe and have the potential to provide a convenient approach to managing” LDL-C, wrote Dr. Ray, a cardiologist and professor of public health at Imperial College London, and his associates.
Evolocumab surpasses inclisiran in crossover cohort
The new data from ORION-3 study included findings from 92 patients first treated with evolocumab injections every 2 weeks for a year, an intervention that lowered their LDL-C levels by an average of about 60%, compared with their pretreatment level. ORION-3’s study design then crossed these patients to treatment with injections of inclisiran twice a year during 3 further years of follow-up, during which their average LDL levels reset to a roughly 45% drop from baseline, a potentially clinically meaningful difference, commented Robert S. Rosenson, MD, a lipid management specialist who was not involved in the ORION-3 study.
“This is the first evidence that compared the two classes” within a single study, thereby avoiding a problematic cross-study comparison. “That’s why the data are important. They underscore that the monoclonal antibodies are more effective for lowering LDL-C,” compared with inclisiran, said Dr. Rosenson, professor and director of cardiometabolic disorders at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
The findings “confirm in a trial that the PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies are indeed more potent,” he said in an interview.
But Dr. Rosenson acknowledged that, while this analysis used data on patients treated with evolocumab and then switched to inclisiran collected prospectively in a single study, it has the limitation of involving a comparison that was not prespecified. The primary goal of the evolocumab-to-inclisiran switch included in ORION-3 was to assess the ease, safety, and efficacy of a switch to inclisiran from treatment with a PCSK9 antibody and was not intended to compare the two drug classes.
The roughly 15% absolute difference in LDL-C lowering between the two tested drug classes can have substantial clinical implications for patients who start treatment with highly elevated levels of LDL-C, more than 190 mg/dL, because they have heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, are unable to take a statin because of intolerance, or both. The difference in LDL-C reduction with an antibody or with inclisiran could mean the difference between whether or not a patient like this achieves their LDL-C goal level, Dr. Rosenson explained.
Inclisiran’s upside
On the other hand, inclisiran has a couple of important advantages. First, its mechanism of action means that effective treatment involves one injection every 6 months following a patient’s first two injections at onset and after 90 days, with all injections administered in a clinician’s office. In contrast, both of the monoclonal antibodies require injections every other week, a schedule that depends on patient self-injections using prefilled syringes obtained from a pharmacy.
Twice-a-year dosing by a clinician can be a major attraction because it helps ensure treatment compliance, aids patients with physical or psychological limitations to self-injection, reduces the pill burden for patients who require multiple medications, and facilitates frequent travelers who would otherwise need to carry syringes with them on trips, Dr. Rosenson noted.
The second big advantage of office-based administration of inclisiran for U.S. Medicare patients is that the treatment is billed under a patient’s part B coverage, usually resulting in easier coverage and a significantly lower patient co-pay, compared with Medicare’s coverage for a pharmacy-dispensed agent, which is covered under Medicare part D. “Part B coverage is financially more doable” for most Medicare patients, said Dr. Rosenson.
The administration schedule for inclisiran as well as its superior Medicare coverage makes the agent “transformative” for LDL-C lowering in patients for whom treatment delivery, frequency, and payment are issues, he said.
Inclisiran uptake modest after FDA approval
Despite these pluses, uptake of inclisiran has been modest since it received U.S. marketing approval in December 2021. In its most recent quarterly financial filing, in October 2022, Novartis reported total worldwide income from inclisiran (Leqvio) of $70 million during the first 9 months of 2022, although a Novartis spokesperson noted that the company has seen “positive trends in uptake” over the course of 2022. Inclisiran is labeled as an “adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for the treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional lowering” of LDL-C.
During 2022, inclisiran uptake lagged because of the usual problems that slow the introduction of new drugs and new drug classes, especially ones that require dosing by a clinician. Months were spent waiting for billing codes to roll out, for clinical staffs to incorporate inclisiran injections into their routines, and for commercial insurers to get up to speed on their coverage, Dr. Rosenson said.
Also, a key step for widespread uptake of a new medication for improving cardiovascular disease outcomes – results from phase 3 studies that document safety and efficacy for these outcomes – remains several years off. The ORION-4 trial and the VICTORION-2P trial, each assessing the impact of inclisiran on cardiovascular disease events in roughly 15,000 people, will need about another 3-4 years before their results become available.
Professional medical societies that issue cardiovascular-disease management guidelines “prefer agents with proven benefits in phase 3 trials,” Dr. Rosenson noted.
Hence, the most recent update to U.S. LDL-C–management guidelines, released in the second half of 2022 by the American College of Cardiology as an Expert Consensus Decision Pathway, said this about the current role for inclisiran: “At the present time, a PCSK9 monoclonal antibody is preferred as the initial PCSK9 inhibitor of choice in view of its demonstrated safety, efficacy, and benefits for cardiovascular outcomes in the FOURIER [for evolocumab] and ODYSSEY Outcomes [for alirocumab] trials. The ORION-4 and VICTORION-2P cardiovascular outcomes trials with inclisiran are currently underway, and their completion is anticipated in 2026 and 2027, respectively. In view of the twice-yearly dosing regimen, inclisiran may be considered in patients with demonstrated poor adherence to PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies. Patients with adverse effects from both PSCK9 monoclonal antibodies or those who may be unable to self-inject may also be considered for therapy with inclisiran.”
ORION-3 extended the ORION-1 trial
The ORION-1 study was a phase 2 placebo-controlled, dose-ranging safety and efficacy assessment of inclisiran that gave patients two injections of the drug, at day zero and 90 days, and followed them for an additional 120 days (210 days total follow-up duration), and in some cases for as long as 360 days total. Of the 370 patients who received inclisiran in ORION-1, 290 agreed to continue inclisiran in the open-label extension, ORION-3. ORION-1 also included 127 patients randomized to initial placebo treatment, and 92 of these patients agreed to continue in ORION-3 and became the patients initially treated with evolocumab injections every other week for 1 year followed by initiation of an inclisiran regimen.
The primary outcome of ORION-3 was the change in LDL-C from baseline (the ORION-1 baseline) after 210 days of receiving inclisiran in ORION-3 (or a total of roughly 570 days after the start of ORION-1). The primary endpoint showed that, at day 210 of ORION-3 the average reduction in LDL-C from the original baseline level was 47.5%.
But a “more important” outcome, said Dr. Ray when he first reported the ORION-3 results during the American Heart Association scientific sessions in Chicago in November 2022, was that, overall, during 4 years on inclisiran this cohort showed an average cut in LDL-C from baseline of about 45% that consistently remained at this level throughout the 4 years of treatment.
“This provides us with an idea of what happens with chronic inclisiran dosing,” Dr. Ray explained. “There was no loss of biological efficacy, and we achieved these clinically meaningful, time-averaged reductions with a good safety profile. The great thing is that when patients get their injections [every 6 months] you see a consistent LDL-C reduction. A twice-annual injection is an opportunity to redesign” the way patients receive preventive cardiology care and treatment to lower LDL-C, Dr Ray said.
ORION-1 was sponsored by The Medicines Company. ORION-3 was sponsored by Novartis (which acquired The Medicines Company). Dr. Ray has received consulting fees, personal fees, and research grants from Novartis, as well as consulting fees and research grants from Amgen, the company that markets evolocumab (Repatha), and research grants from Regeneron, the company that markets alirocumab (Praluent). He has also received consulting fee, personal fees, and research grants from numerous other companies. Dr. Rosenson has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Amgen, Novartis, and Regeneron, and he has received speaking fees from Amgen and Regeneron, and has ties to several other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was updated on 1/26/2023.
Patients who received an injection of inclisiran (Leqvio), a small interfering RNA (siRNA) agent, every 6 months for as long as 4 years safely maintained about a 45% reduction from baseline in their level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in an open-label extension study with 382 patients.
In addition to providing the longest reported treatment experience with inclisiran, which received Food and Drug Administration marketing approval a little over a year ago, the results also suggest with the most definitive evidence to date that inclisiran is less effective for lowering LDL-C, compared with a class of medications that reduce LDL-C by a related but distinct mechanism: antibodies that directly inhibit activity of the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) enzyme, a drug class that includes alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha). Inclisiran cuts PCSK9 activity by blocking this enzyme’s gene transcription in liver cells thereby interfering with PCSK9 production.
Results from this study, the ORION-3 trial, provide “the first prospective long-term evaluation of the durability and safety of an siRNA-based therapy to provide clinically meaningful reductions in LDL cholesterol with a convenient dosing schedule,” wrote Kausik K. Ray, MD, and coauthors in a report in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
The findings “provide assurance that siRNA-based therapies are safe and have the potential to provide a convenient approach to managing” LDL-C, wrote Dr. Ray, a cardiologist and professor of public health at Imperial College London, and his associates.
Evolocumab surpasses inclisiran in crossover cohort
The new data from ORION-3 study included findings from 92 patients first treated with evolocumab injections every 2 weeks for a year, an intervention that lowered their LDL-C levels by an average of about 60%, compared with their pretreatment level. ORION-3’s study design then crossed these patients to treatment with injections of inclisiran twice a year during 3 further years of follow-up, during which their average LDL levels reset to a roughly 45% drop from baseline, a potentially clinically meaningful difference, commented Robert S. Rosenson, MD, a lipid management specialist who was not involved in the ORION-3 study.
“This is the first evidence that compared the two classes” within a single study, thereby avoiding a problematic cross-study comparison. “That’s why the data are important. They underscore that the monoclonal antibodies are more effective for lowering LDL-C,” compared with inclisiran, said Dr. Rosenson, professor and director of cardiometabolic disorders at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York.
The findings “confirm in a trial that the PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies are indeed more potent,” he said in an interview.
But Dr. Rosenson acknowledged that, while this analysis used data on patients treated with evolocumab and then switched to inclisiran collected prospectively in a single study, it has the limitation of involving a comparison that was not prespecified. The primary goal of the evolocumab-to-inclisiran switch included in ORION-3 was to assess the ease, safety, and efficacy of a switch to inclisiran from treatment with a PCSK9 antibody and was not intended to compare the two drug classes.
The roughly 15% absolute difference in LDL-C lowering between the two tested drug classes can have substantial clinical implications for patients who start treatment with highly elevated levels of LDL-C, more than 190 mg/dL, because they have heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, are unable to take a statin because of intolerance, or both. The difference in LDL-C reduction with an antibody or with inclisiran could mean the difference between whether or not a patient like this achieves their LDL-C goal level, Dr. Rosenson explained.
Inclisiran’s upside
On the other hand, inclisiran has a couple of important advantages. First, its mechanism of action means that effective treatment involves one injection every 6 months following a patient’s first two injections at onset and after 90 days, with all injections administered in a clinician’s office. In contrast, both of the monoclonal antibodies require injections every other week, a schedule that depends on patient self-injections using prefilled syringes obtained from a pharmacy.
Twice-a-year dosing by a clinician can be a major attraction because it helps ensure treatment compliance, aids patients with physical or psychological limitations to self-injection, reduces the pill burden for patients who require multiple medications, and facilitates frequent travelers who would otherwise need to carry syringes with them on trips, Dr. Rosenson noted.
The second big advantage of office-based administration of inclisiran for U.S. Medicare patients is that the treatment is billed under a patient’s part B coverage, usually resulting in easier coverage and a significantly lower patient co-pay, compared with Medicare’s coverage for a pharmacy-dispensed agent, which is covered under Medicare part D. “Part B coverage is financially more doable” for most Medicare patients, said Dr. Rosenson.
The administration schedule for inclisiran as well as its superior Medicare coverage makes the agent “transformative” for LDL-C lowering in patients for whom treatment delivery, frequency, and payment are issues, he said.
Inclisiran uptake modest after FDA approval
Despite these pluses, uptake of inclisiran has been modest since it received U.S. marketing approval in December 2021. In its most recent quarterly financial filing, in October 2022, Novartis reported total worldwide income from inclisiran (Leqvio) of $70 million during the first 9 months of 2022, although a Novartis spokesperson noted that the company has seen “positive trends in uptake” over the course of 2022. Inclisiran is labeled as an “adjunct to diet and maximally tolerated statin therapy for the treatment of adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or clinical atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease who require additional lowering” of LDL-C.
During 2022, inclisiran uptake lagged because of the usual problems that slow the introduction of new drugs and new drug classes, especially ones that require dosing by a clinician. Months were spent waiting for billing codes to roll out, for clinical staffs to incorporate inclisiran injections into their routines, and for commercial insurers to get up to speed on their coverage, Dr. Rosenson said.
Also, a key step for widespread uptake of a new medication for improving cardiovascular disease outcomes – results from phase 3 studies that document safety and efficacy for these outcomes – remains several years off. The ORION-4 trial and the VICTORION-2P trial, each assessing the impact of inclisiran on cardiovascular disease events in roughly 15,000 people, will need about another 3-4 years before their results become available.
Professional medical societies that issue cardiovascular-disease management guidelines “prefer agents with proven benefits in phase 3 trials,” Dr. Rosenson noted.
Hence, the most recent update to U.S. LDL-C–management guidelines, released in the second half of 2022 by the American College of Cardiology as an Expert Consensus Decision Pathway, said this about the current role for inclisiran: “At the present time, a PCSK9 monoclonal antibody is preferred as the initial PCSK9 inhibitor of choice in view of its demonstrated safety, efficacy, and benefits for cardiovascular outcomes in the FOURIER [for evolocumab] and ODYSSEY Outcomes [for alirocumab] trials. The ORION-4 and VICTORION-2P cardiovascular outcomes trials with inclisiran are currently underway, and their completion is anticipated in 2026 and 2027, respectively. In view of the twice-yearly dosing regimen, inclisiran may be considered in patients with demonstrated poor adherence to PCSK9 monoclonal antibodies. Patients with adverse effects from both PSCK9 monoclonal antibodies or those who may be unable to self-inject may also be considered for therapy with inclisiran.”
ORION-3 extended the ORION-1 trial
The ORION-1 study was a phase 2 placebo-controlled, dose-ranging safety and efficacy assessment of inclisiran that gave patients two injections of the drug, at day zero and 90 days, and followed them for an additional 120 days (210 days total follow-up duration), and in some cases for as long as 360 days total. Of the 370 patients who received inclisiran in ORION-1, 290 agreed to continue inclisiran in the open-label extension, ORION-3. ORION-1 also included 127 patients randomized to initial placebo treatment, and 92 of these patients agreed to continue in ORION-3 and became the patients initially treated with evolocumab injections every other week for 1 year followed by initiation of an inclisiran regimen.
The primary outcome of ORION-3 was the change in LDL-C from baseline (the ORION-1 baseline) after 210 days of receiving inclisiran in ORION-3 (or a total of roughly 570 days after the start of ORION-1). The primary endpoint showed that, at day 210 of ORION-3 the average reduction in LDL-C from the original baseline level was 47.5%.
But a “more important” outcome, said Dr. Ray when he first reported the ORION-3 results during the American Heart Association scientific sessions in Chicago in November 2022, was that, overall, during 4 years on inclisiran this cohort showed an average cut in LDL-C from baseline of about 45% that consistently remained at this level throughout the 4 years of treatment.
“This provides us with an idea of what happens with chronic inclisiran dosing,” Dr. Ray explained. “There was no loss of biological efficacy, and we achieved these clinically meaningful, time-averaged reductions with a good safety profile. The great thing is that when patients get their injections [every 6 months] you see a consistent LDL-C reduction. A twice-annual injection is an opportunity to redesign” the way patients receive preventive cardiology care and treatment to lower LDL-C, Dr Ray said.
ORION-1 was sponsored by The Medicines Company. ORION-3 was sponsored by Novartis (which acquired The Medicines Company). Dr. Ray has received consulting fees, personal fees, and research grants from Novartis, as well as consulting fees and research grants from Amgen, the company that markets evolocumab (Repatha), and research grants from Regeneron, the company that markets alirocumab (Praluent). He has also received consulting fee, personal fees, and research grants from numerous other companies. Dr. Rosenson has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Amgen, Novartis, and Regeneron, and he has received speaking fees from Amgen and Regeneron, and has ties to several other pharmaceutical companies.
This article was updated on 1/26/2023.
FROM THE LANCET DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY
Components of coffee other than caffeine linked to reduced NAFLD severity
Increased intake of both regular and decaffeinated coffee was significantly associated with a reduced severity of NAFLD in the study, published in Nutrients. The study participants included 156 overweight adults, most of whom had type 2 diabetes.
A confluence of factors including diet and lifestyle changes and increased obesity have contributed to a rise in type 2 diabetes and of NAFLD, Margarida Coelho, of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra (Portugal), and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies support an association between coffee and protection against NAFLD, but the roles of the caffeine and noncaffeine components of coffee have not been examined, corresponding author John Griffith Jones, PhD, also of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra, said in an interview.
“There have been previous studies indicating a link between coffee intake and NAFLD amelioration, but these were entirely based on self-reporting questionnaire data, but the main limitation of this approach is that it does not provide any information on which components of coffee confer the beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “The development of new analytical techniques allowing reliable profiling of coffee metabolites in urine allowed this limitation to be addressed.”
Dr. Jones and associates examined the relationship between consumption of regular and decaffeinated coffee on the fatty liver index (FLI), a validated predictor of NAFLD. They measured coffee intake of 156 overweight adults, 135 of whom had type 2 diabetes. The study population included 76 women and 80 men with a mean age of 59 years and a mean body mass index of 29 kg/m2.
The participants reported coffee intake via questionnaires, and 98 participants (all with type 2 diabetes) also provided urine samples for measurement of caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites (the products of the body breaking down coffee). NAFLD was assessed using the FLI and a scanning measure of fibrosis.
Overall, no associations appeared between self-reported coffee intake and NAFLD measures. However, urine caffeine metabolite levels were significantly higher among individuals with no liver fibrosis, compared with those with fibrosis, and noncaffeine metabolites showed a significant negative association with FLI measures.
In a multiple regression analysis of 89 individuals with type 2 diabetes, both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites were negatively associated with FLI, which suggests less severe NAFLD, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the findings suggest that other noncaffeine coffee components such as polyphenols may reduce the risk of fibrosis by reducing oxidative stress on the liver, they said.
Benefits beyond caffeine
“The main surprise of the study was that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites had beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “We had anticipated caffeine, based on its well-known effects on inhibiting liver fibrosis, but the effects of other components were less well described.”
Clinicians can encourage their patients with type 2 diabetes who drink coffee to continue to do so within a normal range (up to three to four cups per day) including decaffeinated coffee; however, “they should be strongly encouraged to drink coffee without added fats and sugars, otherwise the protective benefits [against more severe NAFLD] will not be realized,” Dr. Jones said.
Additional research is needed to extend the analysis to include more coffee compounds, especially those truly unique to coffee, since caffeine can be found in many other foods and beverages, Dr. Jones added.
Limitations include 24-hour time frame
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 24-hour urine sample, which may not represent an individual’s habitual coffee consumption, the researchers noted. The urine metabolites measured also may be derived from foods and beverages other than coffee. In addition, the assessment of NAFLD was based on serum markers and ultrasound/elastography, which are less precise than liver biopsy and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
However, the study is the first known to use urine data to examine coffee’s protective effect against NAFLD and suggests that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites are associated with less severe disease, they concluded.
Findings intriguing but not ready for prime time
“The bottom line is that we have a major epidemic of NAFLD in the United States,” Victor L. Roberts, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. NAFLD has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, and will become one of the leading causes of cirrhosis – surpassing infections as the main driver of end-stage liver disease.
“In this country, the epidemic of obesity compounds the problem, and risks for NAFLD include obesity and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Roberts.
The concept of coffee as beneficial is not new, but data suggest that the effects vary with insulin resistance, he said. If liver disease is advanced, coffee and its components may not have much benefit, but early on, it might have a role.
The likely mechanism of action for the benefits of coffee on the reduction in liver fibrosis is through a complex set of metabolic steps that interrupt the promotion of collagen production and reduce liver stiffness, said Dr. Roberts.
The current study authors were up front about the limitations, mainly the use of self-reports, although including the urine collection provided more scientific data, he said. More studies are needed in other populations, but the findings are interesting enough to merit additional research.
The take-home message for primary care, however, is that drinking coffee – regular or decaf – does not replace standard of care, Dr. Roberts emphasized.
“If a patient is a coffee drinker and they have NAFLD or are at risk, they could be encouraged to continue drinking coffee,” in reasonable amounts, said Dr. Roberts. “Anywhere from 1-3 cups a day is unlikely to be a problem, and there is some hope and interest in this area,” but the findings of the current study “should not be taken as gospel or advocacy as a solution for people with NAFLD.”
Instead, clinicians should focus on the standard of care for management of patients at risk for NAFLD, promoting lifestyle changes such as weight loss, diet, and exercise (challenging as that may be), and prescribing appropriate medications, he said.
The study was supported by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee, and the researchers received funding from the ISIC to conduct the study. Dr. Roberts had no financial conflicts to disclose, but he serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Increased intake of both regular and decaffeinated coffee was significantly associated with a reduced severity of NAFLD in the study, published in Nutrients. The study participants included 156 overweight adults, most of whom had type 2 diabetes.
A confluence of factors including diet and lifestyle changes and increased obesity have contributed to a rise in type 2 diabetes and of NAFLD, Margarida Coelho, of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra (Portugal), and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies support an association between coffee and protection against NAFLD, but the roles of the caffeine and noncaffeine components of coffee have not been examined, corresponding author John Griffith Jones, PhD, also of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra, said in an interview.
“There have been previous studies indicating a link between coffee intake and NAFLD amelioration, but these were entirely based on self-reporting questionnaire data, but the main limitation of this approach is that it does not provide any information on which components of coffee confer the beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “The development of new analytical techniques allowing reliable profiling of coffee metabolites in urine allowed this limitation to be addressed.”
Dr. Jones and associates examined the relationship between consumption of regular and decaffeinated coffee on the fatty liver index (FLI), a validated predictor of NAFLD. They measured coffee intake of 156 overweight adults, 135 of whom had type 2 diabetes. The study population included 76 women and 80 men with a mean age of 59 years and a mean body mass index of 29 kg/m2.
The participants reported coffee intake via questionnaires, and 98 participants (all with type 2 diabetes) also provided urine samples for measurement of caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites (the products of the body breaking down coffee). NAFLD was assessed using the FLI and a scanning measure of fibrosis.
Overall, no associations appeared between self-reported coffee intake and NAFLD measures. However, urine caffeine metabolite levels were significantly higher among individuals with no liver fibrosis, compared with those with fibrosis, and noncaffeine metabolites showed a significant negative association with FLI measures.
In a multiple regression analysis of 89 individuals with type 2 diabetes, both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites were negatively associated with FLI, which suggests less severe NAFLD, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the findings suggest that other noncaffeine coffee components such as polyphenols may reduce the risk of fibrosis by reducing oxidative stress on the liver, they said.
Benefits beyond caffeine
“The main surprise of the study was that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites had beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “We had anticipated caffeine, based on its well-known effects on inhibiting liver fibrosis, but the effects of other components were less well described.”
Clinicians can encourage their patients with type 2 diabetes who drink coffee to continue to do so within a normal range (up to three to four cups per day) including decaffeinated coffee; however, “they should be strongly encouraged to drink coffee without added fats and sugars, otherwise the protective benefits [against more severe NAFLD] will not be realized,” Dr. Jones said.
Additional research is needed to extend the analysis to include more coffee compounds, especially those truly unique to coffee, since caffeine can be found in many other foods and beverages, Dr. Jones added.
Limitations include 24-hour time frame
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 24-hour urine sample, which may not represent an individual’s habitual coffee consumption, the researchers noted. The urine metabolites measured also may be derived from foods and beverages other than coffee. In addition, the assessment of NAFLD was based on serum markers and ultrasound/elastography, which are less precise than liver biopsy and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
However, the study is the first known to use urine data to examine coffee’s protective effect against NAFLD and suggests that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites are associated with less severe disease, they concluded.
Findings intriguing but not ready for prime time
“The bottom line is that we have a major epidemic of NAFLD in the United States,” Victor L. Roberts, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. NAFLD has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, and will become one of the leading causes of cirrhosis – surpassing infections as the main driver of end-stage liver disease.
“In this country, the epidemic of obesity compounds the problem, and risks for NAFLD include obesity and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Roberts.
The concept of coffee as beneficial is not new, but data suggest that the effects vary with insulin resistance, he said. If liver disease is advanced, coffee and its components may not have much benefit, but early on, it might have a role.
The likely mechanism of action for the benefits of coffee on the reduction in liver fibrosis is through a complex set of metabolic steps that interrupt the promotion of collagen production and reduce liver stiffness, said Dr. Roberts.
The current study authors were up front about the limitations, mainly the use of self-reports, although including the urine collection provided more scientific data, he said. More studies are needed in other populations, but the findings are interesting enough to merit additional research.
The take-home message for primary care, however, is that drinking coffee – regular or decaf – does not replace standard of care, Dr. Roberts emphasized.
“If a patient is a coffee drinker and they have NAFLD or are at risk, they could be encouraged to continue drinking coffee,” in reasonable amounts, said Dr. Roberts. “Anywhere from 1-3 cups a day is unlikely to be a problem, and there is some hope and interest in this area,” but the findings of the current study “should not be taken as gospel or advocacy as a solution for people with NAFLD.”
Instead, clinicians should focus on the standard of care for management of patients at risk for NAFLD, promoting lifestyle changes such as weight loss, diet, and exercise (challenging as that may be), and prescribing appropriate medications, he said.
The study was supported by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee, and the researchers received funding from the ISIC to conduct the study. Dr. Roberts had no financial conflicts to disclose, but he serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Increased intake of both regular and decaffeinated coffee was significantly associated with a reduced severity of NAFLD in the study, published in Nutrients. The study participants included 156 overweight adults, most of whom had type 2 diabetes.
A confluence of factors including diet and lifestyle changes and increased obesity have contributed to a rise in type 2 diabetes and of NAFLD, Margarida Coelho, of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra (Portugal), and colleagues wrote.
Previous studies support an association between coffee and protection against NAFLD, but the roles of the caffeine and noncaffeine components of coffee have not been examined, corresponding author John Griffith Jones, PhD, also of the Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology at the University of Coimbra, said in an interview.
“There have been previous studies indicating a link between coffee intake and NAFLD amelioration, but these were entirely based on self-reporting questionnaire data, but the main limitation of this approach is that it does not provide any information on which components of coffee confer the beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “The development of new analytical techniques allowing reliable profiling of coffee metabolites in urine allowed this limitation to be addressed.”
Dr. Jones and associates examined the relationship between consumption of regular and decaffeinated coffee on the fatty liver index (FLI), a validated predictor of NAFLD. They measured coffee intake of 156 overweight adults, 135 of whom had type 2 diabetes. The study population included 76 women and 80 men with a mean age of 59 years and a mean body mass index of 29 kg/m2.
The participants reported coffee intake via questionnaires, and 98 participants (all with type 2 diabetes) also provided urine samples for measurement of caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites (the products of the body breaking down coffee). NAFLD was assessed using the FLI and a scanning measure of fibrosis.
Overall, no associations appeared between self-reported coffee intake and NAFLD measures. However, urine caffeine metabolite levels were significantly higher among individuals with no liver fibrosis, compared with those with fibrosis, and noncaffeine metabolites showed a significant negative association with FLI measures.
In a multiple regression analysis of 89 individuals with type 2 diabetes, both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites were negatively associated with FLI, which suggests less severe NAFLD, the researchers noted.
Although the mechanism of action remains unclear, the findings suggest that other noncaffeine coffee components such as polyphenols may reduce the risk of fibrosis by reducing oxidative stress on the liver, they said.
Benefits beyond caffeine
“The main surprise of the study was that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites had beneficial effects,” Dr. Jones said. “We had anticipated caffeine, based on its well-known effects on inhibiting liver fibrosis, but the effects of other components were less well described.”
Clinicians can encourage their patients with type 2 diabetes who drink coffee to continue to do so within a normal range (up to three to four cups per day) including decaffeinated coffee; however, “they should be strongly encouraged to drink coffee without added fats and sugars, otherwise the protective benefits [against more severe NAFLD] will not be realized,” Dr. Jones said.
Additional research is needed to extend the analysis to include more coffee compounds, especially those truly unique to coffee, since caffeine can be found in many other foods and beverages, Dr. Jones added.
Limitations include 24-hour time frame
The findings were limited by several factors, including the use of 24-hour urine sample, which may not represent an individual’s habitual coffee consumption, the researchers noted. The urine metabolites measured also may be derived from foods and beverages other than coffee. In addition, the assessment of NAFLD was based on serum markers and ultrasound/elastography, which are less precise than liver biopsy and magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
However, the study is the first known to use urine data to examine coffee’s protective effect against NAFLD and suggests that both caffeine and noncaffeine metabolites are associated with less severe disease, they concluded.
Findings intriguing but not ready for prime time
“The bottom line is that we have a major epidemic of NAFLD in the United States,” Victor L. Roberts, MD, professor of internal medicine at the University of Central Florida, Orlando, said in an interview. NAFLD has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease worldwide, and will become one of the leading causes of cirrhosis – surpassing infections as the main driver of end-stage liver disease.
“In this country, the epidemic of obesity compounds the problem, and risks for NAFLD include obesity and type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Roberts.
The concept of coffee as beneficial is not new, but data suggest that the effects vary with insulin resistance, he said. If liver disease is advanced, coffee and its components may not have much benefit, but early on, it might have a role.
The likely mechanism of action for the benefits of coffee on the reduction in liver fibrosis is through a complex set of metabolic steps that interrupt the promotion of collagen production and reduce liver stiffness, said Dr. Roberts.
The current study authors were up front about the limitations, mainly the use of self-reports, although including the urine collection provided more scientific data, he said. More studies are needed in other populations, but the findings are interesting enough to merit additional research.
The take-home message for primary care, however, is that drinking coffee – regular or decaf – does not replace standard of care, Dr. Roberts emphasized.
“If a patient is a coffee drinker and they have NAFLD or are at risk, they could be encouraged to continue drinking coffee,” in reasonable amounts, said Dr. Roberts. “Anywhere from 1-3 cups a day is unlikely to be a problem, and there is some hope and interest in this area,” but the findings of the current study “should not be taken as gospel or advocacy as a solution for people with NAFLD.”
Instead, clinicians should focus on the standard of care for management of patients at risk for NAFLD, promoting lifestyle changes such as weight loss, diet, and exercise (challenging as that may be), and prescribing appropriate medications, he said.
The study was supported by the Institute for Scientific Information on Coffee, and the researchers received funding from the ISIC to conduct the study. Dr. Roberts had no financial conflicts to disclose, but he serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
FROM NUTRIENTS
Does EPA lower CV risk? REDUCE-IT revisited
The prescription product (Vascepa), consisting of a “highly purified” form of the omega-3 acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), was heralded in 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22) as ushering in “the dawn of a new era” in cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention that “should definitely change practice going forward,” according to REDUCE-IT’s lead author Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, formerly of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and now director of the Mount Sinai Heart Center in New York.
However, skeptics questioned why the results differed from most previous trials of fish oil that showed no benefit. Was it caused by the high dose of EPA: 4 g/daily versus 1 g daily in earlier trials with fish oil capsules? Was it the different formulation of purified EPA versus more common combinations of EPA plus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)? Or, as suggested by Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of Cleveland Clinic’s Heart and Vascular Institute and others, was it caused by the negative effects of the mineral oil placebo, given the significant increases in LDL cholesterol and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) seen in the control group?
‘Not all omega-3s created equal’
Dr. Bhatt recently said in an interview: “I think there’s confusion in the field. It’s a challenge when just one drug in a class looks good and everything else in that class looks bad. That in itself can breed some skepticism. Also, not everyone always embraces advances. Some people have other reasons to impugn datasets; for example, it could be because they are running competing trials with competing drugs.”
REDUCE-IT enrolled more than 8,000 patients at high CV risk despite statin treatment, and randomly assigned them to 2 g of EPA twice daily or the mineral oil placebo. Although the results showed a 25% reduction in the rate of CV events in the EPA group, there was also an increased risk of atrial fibrillation among those taking EPA after a median of 4.9 years follow-up.
Dr. Bhatt noted that Amarin, which manufactures Vascepa, is essentially a one-drug company, and its stock price is dependent on the product. When the trial results were released, he said, “there were people in the investor world that wanted the stock price to go up or wanted it to go down, and they were alternately hyping or disparaging the data in both cases, sometimes inappropriately and excessively, which created noise around the science.”
The fact is, he said, “not all omega-3 fatty acids are created equal. There are differences between supplements and prescription medicines, and within the prescription medicines, differences between pure EPA and the mixtures of EPA and DHA.”
Dr. Bhatt added that other trials also showed positive results. He pointed to the JELIS trial, published in 2007, which showed a 19% reduction in major adverse CV events with a 1.8-g daily EPA dose.
More recently, RESPECT-EPA was presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Heart Association. That study had methodological issues and was underpowered, but it did suggest a possible benefit of EPA in reducing CV events in patients with chronic coronary artery disease who were taking statins. “Looking at the totality of evidence, I think it’s quite clear there’s CV benefit,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Placebo effects?
Concerns about the mineral oil placebo cast doubt on that benefit. Table 4 of the supplement accompanying REDUCE-IT’s publication in the New England Journal of Medicine shows significant increases of non–HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and hsCRP in the control group.
Jane Armitage, MBBS, a professor of clinical trials and epidemiology, clinical trial service unit at Oxford University (England), said in an interview: “I was surprised by the backlash and at the time felt that it was unlikely that the mineral oil was the problem. But the size of benefit was still out of kilter.”
“Two further pieces of evidence have influenced my thoughts since then,” she said. One is the lack of effect of high doses of fish oils in the STRENGTH trial. STRENGTH tested 4 g of omega-3 oil containing a mixture of EPA and DHA and found no benefit in statin-treated, high-risk patients.
“The amount of EPA [was] substantially less than given in REDUCE-IT,” Armitage said, “but it seems to me that in a similar hypertriglyceridemic population, if the effect were due to the EPA, you would have seen some impact in STRENGTH – and none was seen.”
“The other piece of evidence is in a paper by Paul Ridker, MD, et al. on the changes in biomarkers during REDUCE-IT,” she said. “Several inflammatory biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis rose during the study among those allocated mineral oil, but remained largely unchanged in the EPA group. This is in contrast to what is seen with these biomarkers in other large trials, where no changes were seen in the placebo groups, and once again raises the possibility that the apparent benefits of EPA may be related to hazard from the mineral oil.”
Still room for benefit?
Based largely on the results of REDUCE-IT, Vascepa is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration as an adjunctive therapy to lower the risk for CV events among adults with elevated triglyceride levels (≥ 150 mg/dL). Patients must also have either established CVD or diabetes and two or more additional CV risk factors and are advised to continue physical activity and maintain a healthy diet.
Dr. Nissen, the principal author of the STRENGTH trial, said in an interview, “REDUCE-IT is an outlier. Other trials of omega-3 fatty acids, some of them very large, showed no benefits, and a meta-analysis of nearly 78,000 patients showed no beneficial effects. In this context,” he said, “the large ‘benefit’ observed in REDUCE-IT doesn’t make any sense.”
Dr. Nissen noted that a secondary analysis of STRENGTH further showed that higher plasma EPA levels did not reduce CV outcomes. He also highlighted the elevated risk of atrial fibrillation with EPA. “We need to see another study comparing EPA to a neutral comparator such as corn oil, which had no significant effect on lipid or inflammatory biomarkers in STRENGTH,” he said. “Without such a trial, the results of REDUCE-IT cannot be accepted as definitive.”
Dr. Ridker, the lead author of the REDUCE-IT substudy that found biomarker changes with the mineral oil placebo, said in an interview: “Is it possible that EPA is an outstanding drug? Absolutely, and I continue to think it useful for our very high-risk, secondary-prevention patients when we are running out of options.”
“But,” said Dr. Ridker, who is a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s, “the reality ... is that ongoing uncertainties need resolution.” Like Dr. Nissen, he thinks the best way to resolve these uncertainties is through a second trial using a fully neutral comparator. “I am hopeful that the U.S. National Institutes of Health will see fit to undertake such an endeavor, perhaps with support from industry partners.”
Although Dr. Armitage is no longer in clinical practice, when asked how she might use EPA, she said it might be reasonable for patients who meet the prescribing criteria and remain high risk after all other risk factors have been addressed. She added that, although EPA is approved in the United Kingdom, she doesn’t think it is being widely prescribed.
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, a professor in the Sections of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research at Baylor College of Medicine who has published articles about REDUCE-IT and on the eligibility and cost of EPA in the Veterans Affairs system, said in an interview: “In my personal opinion, clinicians [should] first optimize diet and lifestyle and work on secondary causes, as they play a very big role in hypertriglyceridemia.” He also recommended optimizing LDL-C levels because of “consistent data showing that LDL [cholesterol] control leads to significant reduction in atherosclerotic CVD events.”
“Once these two steps are taken and triglycerides still remain elevated,” he said, “then adding EPA in patients with established atherosclerotic CVD or those with diabetes plus other CV risk factors may be a reasonable option to further lower residual atherosclerotic CVD risk.”
Clinical inertia?
Dr. Bhatt acknowledged that, despite the benefit of EPA in the context of REDUCE-IT, “a few issues stand in the way of prescribing, particularly in the U.S.”
Vascepa’s manufacturer Amarin lost a patent challenge in the United States, enabling the relatively early introduction of multiple generics. “They’ve lost interest in the U.S. because there are three generics.”
“The sad truth is, if there isn’t a drug rep saying, ‘hey, look at this new data,’ there’s clinical inertia,” said Dr. Bhatt. He believes that the lack of marketing will hurt awareness among physicians and “ultimately hurt patients because they won’t get the drug.”
Cost is also an issue, Dr. Bhatt affirmed. Vascepa has significant out-of-pocket costs for many patients, as do some of the generics. Currently, the branded product costs about $300 per month without insurance, according to drugs.com; prices for generics vary widely, running anywhere from $82 to $200 or more.
Despite these challenges, he noted that many guidelines around the world have already changed to reflect the data, including the American Diabetes Association and the U.S. National Lipid Association.
Will there be another trial of EPA with a neutral placebo? Dr. Bhatt believes it’s not going to happen. “The company that funded REDUCE-IT is struggling just to stay alive, and another investigator-funded trial like RESPECT EPA would probably be underpowered and not move the needle much.”
Dr. Virani agreed that while it would be best to test EPA against a fully inert placebo, “whether there is enough appetite to fund such a large trial remains a big question.”
Meanwhile, Dr. Bhatt said, “EPA is not for everybody, but for the high-risk patients who meet the stringent inclusion criteria of REDUCE-IT, I think clinicians should at least consider use of EPA in a way consistent with the U.S. FDA label, the Canadian label, and the label in parts of Europe where the drug is being introduced.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prescription product (Vascepa), consisting of a “highly purified” form of the omega-3 acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), was heralded in 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22) as ushering in “the dawn of a new era” in cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention that “should definitely change practice going forward,” according to REDUCE-IT’s lead author Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, formerly of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and now director of the Mount Sinai Heart Center in New York.
However, skeptics questioned why the results differed from most previous trials of fish oil that showed no benefit. Was it caused by the high dose of EPA: 4 g/daily versus 1 g daily in earlier trials with fish oil capsules? Was it the different formulation of purified EPA versus more common combinations of EPA plus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)? Or, as suggested by Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of Cleveland Clinic’s Heart and Vascular Institute and others, was it caused by the negative effects of the mineral oil placebo, given the significant increases in LDL cholesterol and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) seen in the control group?
‘Not all omega-3s created equal’
Dr. Bhatt recently said in an interview: “I think there’s confusion in the field. It’s a challenge when just one drug in a class looks good and everything else in that class looks bad. That in itself can breed some skepticism. Also, not everyone always embraces advances. Some people have other reasons to impugn datasets; for example, it could be because they are running competing trials with competing drugs.”
REDUCE-IT enrolled more than 8,000 patients at high CV risk despite statin treatment, and randomly assigned them to 2 g of EPA twice daily or the mineral oil placebo. Although the results showed a 25% reduction in the rate of CV events in the EPA group, there was also an increased risk of atrial fibrillation among those taking EPA after a median of 4.9 years follow-up.
Dr. Bhatt noted that Amarin, which manufactures Vascepa, is essentially a one-drug company, and its stock price is dependent on the product. When the trial results were released, he said, “there were people in the investor world that wanted the stock price to go up or wanted it to go down, and they were alternately hyping or disparaging the data in both cases, sometimes inappropriately and excessively, which created noise around the science.”
The fact is, he said, “not all omega-3 fatty acids are created equal. There are differences between supplements and prescription medicines, and within the prescription medicines, differences between pure EPA and the mixtures of EPA and DHA.”
Dr. Bhatt added that other trials also showed positive results. He pointed to the JELIS trial, published in 2007, which showed a 19% reduction in major adverse CV events with a 1.8-g daily EPA dose.
More recently, RESPECT-EPA was presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Heart Association. That study had methodological issues and was underpowered, but it did suggest a possible benefit of EPA in reducing CV events in patients with chronic coronary artery disease who were taking statins. “Looking at the totality of evidence, I think it’s quite clear there’s CV benefit,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Placebo effects?
Concerns about the mineral oil placebo cast doubt on that benefit. Table 4 of the supplement accompanying REDUCE-IT’s publication in the New England Journal of Medicine shows significant increases of non–HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and hsCRP in the control group.
Jane Armitage, MBBS, a professor of clinical trials and epidemiology, clinical trial service unit at Oxford University (England), said in an interview: “I was surprised by the backlash and at the time felt that it was unlikely that the mineral oil was the problem. But the size of benefit was still out of kilter.”
“Two further pieces of evidence have influenced my thoughts since then,” she said. One is the lack of effect of high doses of fish oils in the STRENGTH trial. STRENGTH tested 4 g of omega-3 oil containing a mixture of EPA and DHA and found no benefit in statin-treated, high-risk patients.
“The amount of EPA [was] substantially less than given in REDUCE-IT,” Armitage said, “but it seems to me that in a similar hypertriglyceridemic population, if the effect were due to the EPA, you would have seen some impact in STRENGTH – and none was seen.”
“The other piece of evidence is in a paper by Paul Ridker, MD, et al. on the changes in biomarkers during REDUCE-IT,” she said. “Several inflammatory biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis rose during the study among those allocated mineral oil, but remained largely unchanged in the EPA group. This is in contrast to what is seen with these biomarkers in other large trials, where no changes were seen in the placebo groups, and once again raises the possibility that the apparent benefits of EPA may be related to hazard from the mineral oil.”
Still room for benefit?
Based largely on the results of REDUCE-IT, Vascepa is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration as an adjunctive therapy to lower the risk for CV events among adults with elevated triglyceride levels (≥ 150 mg/dL). Patients must also have either established CVD or diabetes and two or more additional CV risk factors and are advised to continue physical activity and maintain a healthy diet.
Dr. Nissen, the principal author of the STRENGTH trial, said in an interview, “REDUCE-IT is an outlier. Other trials of omega-3 fatty acids, some of them very large, showed no benefits, and a meta-analysis of nearly 78,000 patients showed no beneficial effects. In this context,” he said, “the large ‘benefit’ observed in REDUCE-IT doesn’t make any sense.”
Dr. Nissen noted that a secondary analysis of STRENGTH further showed that higher plasma EPA levels did not reduce CV outcomes. He also highlighted the elevated risk of atrial fibrillation with EPA. “We need to see another study comparing EPA to a neutral comparator such as corn oil, which had no significant effect on lipid or inflammatory biomarkers in STRENGTH,” he said. “Without such a trial, the results of REDUCE-IT cannot be accepted as definitive.”
Dr. Ridker, the lead author of the REDUCE-IT substudy that found biomarker changes with the mineral oil placebo, said in an interview: “Is it possible that EPA is an outstanding drug? Absolutely, and I continue to think it useful for our very high-risk, secondary-prevention patients when we are running out of options.”
“But,” said Dr. Ridker, who is a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s, “the reality ... is that ongoing uncertainties need resolution.” Like Dr. Nissen, he thinks the best way to resolve these uncertainties is through a second trial using a fully neutral comparator. “I am hopeful that the U.S. National Institutes of Health will see fit to undertake such an endeavor, perhaps with support from industry partners.”
Although Dr. Armitage is no longer in clinical practice, when asked how she might use EPA, she said it might be reasonable for patients who meet the prescribing criteria and remain high risk after all other risk factors have been addressed. She added that, although EPA is approved in the United Kingdom, she doesn’t think it is being widely prescribed.
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, a professor in the Sections of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research at Baylor College of Medicine who has published articles about REDUCE-IT and on the eligibility and cost of EPA in the Veterans Affairs system, said in an interview: “In my personal opinion, clinicians [should] first optimize diet and lifestyle and work on secondary causes, as they play a very big role in hypertriglyceridemia.” He also recommended optimizing LDL-C levels because of “consistent data showing that LDL [cholesterol] control leads to significant reduction in atherosclerotic CVD events.”
“Once these two steps are taken and triglycerides still remain elevated,” he said, “then adding EPA in patients with established atherosclerotic CVD or those with diabetes plus other CV risk factors may be a reasonable option to further lower residual atherosclerotic CVD risk.”
Clinical inertia?
Dr. Bhatt acknowledged that, despite the benefit of EPA in the context of REDUCE-IT, “a few issues stand in the way of prescribing, particularly in the U.S.”
Vascepa’s manufacturer Amarin lost a patent challenge in the United States, enabling the relatively early introduction of multiple generics. “They’ve lost interest in the U.S. because there are three generics.”
“The sad truth is, if there isn’t a drug rep saying, ‘hey, look at this new data,’ there’s clinical inertia,” said Dr. Bhatt. He believes that the lack of marketing will hurt awareness among physicians and “ultimately hurt patients because they won’t get the drug.”
Cost is also an issue, Dr. Bhatt affirmed. Vascepa has significant out-of-pocket costs for many patients, as do some of the generics. Currently, the branded product costs about $300 per month without insurance, according to drugs.com; prices for generics vary widely, running anywhere from $82 to $200 or more.
Despite these challenges, he noted that many guidelines around the world have already changed to reflect the data, including the American Diabetes Association and the U.S. National Lipid Association.
Will there be another trial of EPA with a neutral placebo? Dr. Bhatt believes it’s not going to happen. “The company that funded REDUCE-IT is struggling just to stay alive, and another investigator-funded trial like RESPECT EPA would probably be underpowered and not move the needle much.”
Dr. Virani agreed that while it would be best to test EPA against a fully inert placebo, “whether there is enough appetite to fund such a large trial remains a big question.”
Meanwhile, Dr. Bhatt said, “EPA is not for everybody, but for the high-risk patients who meet the stringent inclusion criteria of REDUCE-IT, I think clinicians should at least consider use of EPA in a way consistent with the U.S. FDA label, the Canadian label, and the label in parts of Europe where the drug is being introduced.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The prescription product (Vascepa), consisting of a “highly purified” form of the omega-3 acid eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), was heralded in 2018 (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:11-22) as ushering in “the dawn of a new era” in cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention that “should definitely change practice going forward,” according to REDUCE-IT’s lead author Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, formerly of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston and now director of the Mount Sinai Heart Center in New York.
However, skeptics questioned why the results differed from most previous trials of fish oil that showed no benefit. Was it caused by the high dose of EPA: 4 g/daily versus 1 g daily in earlier trials with fish oil capsules? Was it the different formulation of purified EPA versus more common combinations of EPA plus docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)? Or, as suggested by Steven Nissen, MD, chief academic officer of Cleveland Clinic’s Heart and Vascular Institute and others, was it caused by the negative effects of the mineral oil placebo, given the significant increases in LDL cholesterol and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) seen in the control group?
‘Not all omega-3s created equal’
Dr. Bhatt recently said in an interview: “I think there’s confusion in the field. It’s a challenge when just one drug in a class looks good and everything else in that class looks bad. That in itself can breed some skepticism. Also, not everyone always embraces advances. Some people have other reasons to impugn datasets; for example, it could be because they are running competing trials with competing drugs.”
REDUCE-IT enrolled more than 8,000 patients at high CV risk despite statin treatment, and randomly assigned them to 2 g of EPA twice daily or the mineral oil placebo. Although the results showed a 25% reduction in the rate of CV events in the EPA group, there was also an increased risk of atrial fibrillation among those taking EPA after a median of 4.9 years follow-up.
Dr. Bhatt noted that Amarin, which manufactures Vascepa, is essentially a one-drug company, and its stock price is dependent on the product. When the trial results were released, he said, “there were people in the investor world that wanted the stock price to go up or wanted it to go down, and they were alternately hyping or disparaging the data in both cases, sometimes inappropriately and excessively, which created noise around the science.”
The fact is, he said, “not all omega-3 fatty acids are created equal. There are differences between supplements and prescription medicines, and within the prescription medicines, differences between pure EPA and the mixtures of EPA and DHA.”
Dr. Bhatt added that other trials also showed positive results. He pointed to the JELIS trial, published in 2007, which showed a 19% reduction in major adverse CV events with a 1.8-g daily EPA dose.
More recently, RESPECT-EPA was presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Heart Association. That study had methodological issues and was underpowered, but it did suggest a possible benefit of EPA in reducing CV events in patients with chronic coronary artery disease who were taking statins. “Looking at the totality of evidence, I think it’s quite clear there’s CV benefit,” Dr. Bhatt said.
Placebo effects?
Concerns about the mineral oil placebo cast doubt on that benefit. Table 4 of the supplement accompanying REDUCE-IT’s publication in the New England Journal of Medicine shows significant increases of non–HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and hsCRP in the control group.
Jane Armitage, MBBS, a professor of clinical trials and epidemiology, clinical trial service unit at Oxford University (England), said in an interview: “I was surprised by the backlash and at the time felt that it was unlikely that the mineral oil was the problem. But the size of benefit was still out of kilter.”
“Two further pieces of evidence have influenced my thoughts since then,” she said. One is the lack of effect of high doses of fish oils in the STRENGTH trial. STRENGTH tested 4 g of omega-3 oil containing a mixture of EPA and DHA and found no benefit in statin-treated, high-risk patients.
“The amount of EPA [was] substantially less than given in REDUCE-IT,” Armitage said, “but it seems to me that in a similar hypertriglyceridemic population, if the effect were due to the EPA, you would have seen some impact in STRENGTH – and none was seen.”
“The other piece of evidence is in a paper by Paul Ridker, MD, et al. on the changes in biomarkers during REDUCE-IT,” she said. “Several inflammatory biomarkers associated with atherosclerosis rose during the study among those allocated mineral oil, but remained largely unchanged in the EPA group. This is in contrast to what is seen with these biomarkers in other large trials, where no changes were seen in the placebo groups, and once again raises the possibility that the apparent benefits of EPA may be related to hazard from the mineral oil.”
Still room for benefit?
Based largely on the results of REDUCE-IT, Vascepa is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration as an adjunctive therapy to lower the risk for CV events among adults with elevated triglyceride levels (≥ 150 mg/dL). Patients must also have either established CVD or diabetes and two or more additional CV risk factors and are advised to continue physical activity and maintain a healthy diet.
Dr. Nissen, the principal author of the STRENGTH trial, said in an interview, “REDUCE-IT is an outlier. Other trials of omega-3 fatty acids, some of them very large, showed no benefits, and a meta-analysis of nearly 78,000 patients showed no beneficial effects. In this context,” he said, “the large ‘benefit’ observed in REDUCE-IT doesn’t make any sense.”
Dr. Nissen noted that a secondary analysis of STRENGTH further showed that higher plasma EPA levels did not reduce CV outcomes. He also highlighted the elevated risk of atrial fibrillation with EPA. “We need to see another study comparing EPA to a neutral comparator such as corn oil, which had no significant effect on lipid or inflammatory biomarkers in STRENGTH,” he said. “Without such a trial, the results of REDUCE-IT cannot be accepted as definitive.”
Dr. Ridker, the lead author of the REDUCE-IT substudy that found biomarker changes with the mineral oil placebo, said in an interview: “Is it possible that EPA is an outstanding drug? Absolutely, and I continue to think it useful for our very high-risk, secondary-prevention patients when we are running out of options.”
“But,” said Dr. Ridker, who is a professor at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and director of the Center for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention at Brigham and Women’s, “the reality ... is that ongoing uncertainties need resolution.” Like Dr. Nissen, he thinks the best way to resolve these uncertainties is through a second trial using a fully neutral comparator. “I am hopeful that the U.S. National Institutes of Health will see fit to undertake such an endeavor, perhaps with support from industry partners.”
Although Dr. Armitage is no longer in clinical practice, when asked how she might use EPA, she said it might be reasonable for patients who meet the prescribing criteria and remain high risk after all other risk factors have been addressed. She added that, although EPA is approved in the United Kingdom, she doesn’t think it is being widely prescribed.
Salim S. Virani, MD, PhD, a professor in the Sections of Cardiology and Cardiovascular Research at Baylor College of Medicine who has published articles about REDUCE-IT and on the eligibility and cost of EPA in the Veterans Affairs system, said in an interview: “In my personal opinion, clinicians [should] first optimize diet and lifestyle and work on secondary causes, as they play a very big role in hypertriglyceridemia.” He also recommended optimizing LDL-C levels because of “consistent data showing that LDL [cholesterol] control leads to significant reduction in atherosclerotic CVD events.”
“Once these two steps are taken and triglycerides still remain elevated,” he said, “then adding EPA in patients with established atherosclerotic CVD or those with diabetes plus other CV risk factors may be a reasonable option to further lower residual atherosclerotic CVD risk.”
Clinical inertia?
Dr. Bhatt acknowledged that, despite the benefit of EPA in the context of REDUCE-IT, “a few issues stand in the way of prescribing, particularly in the U.S.”
Vascepa’s manufacturer Amarin lost a patent challenge in the United States, enabling the relatively early introduction of multiple generics. “They’ve lost interest in the U.S. because there are three generics.”
“The sad truth is, if there isn’t a drug rep saying, ‘hey, look at this new data,’ there’s clinical inertia,” said Dr. Bhatt. He believes that the lack of marketing will hurt awareness among physicians and “ultimately hurt patients because they won’t get the drug.”
Cost is also an issue, Dr. Bhatt affirmed. Vascepa has significant out-of-pocket costs for many patients, as do some of the generics. Currently, the branded product costs about $300 per month without insurance, according to drugs.com; prices for generics vary widely, running anywhere from $82 to $200 or more.
Despite these challenges, he noted that many guidelines around the world have already changed to reflect the data, including the American Diabetes Association and the U.S. National Lipid Association.
Will there be another trial of EPA with a neutral placebo? Dr. Bhatt believes it’s not going to happen. “The company that funded REDUCE-IT is struggling just to stay alive, and another investigator-funded trial like RESPECT EPA would probably be underpowered and not move the needle much.”
Dr. Virani agreed that while it would be best to test EPA against a fully inert placebo, “whether there is enough appetite to fund such a large trial remains a big question.”
Meanwhile, Dr. Bhatt said, “EPA is not for everybody, but for the high-risk patients who meet the stringent inclusion criteria of REDUCE-IT, I think clinicians should at least consider use of EPA in a way consistent with the U.S. FDA label, the Canadian label, and the label in parts of Europe where the drug is being introduced.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PPI use in type 2 diabetes links with cardiovascular events
Among people with type 2 diabetes who self-reported regularly using a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events as well as all-cause death was significantly increased in a study of more than 19,000 people with type 2 diabetes in a prospective U.K. database.
During median follow-up of about 11 years, regular use of a PPI by people with type 2 diabetes was significantly linked with a 27% relative increase in the incidence of coronary artery disease, compared with nonuse of a PPI, after full adjustment for potential confounding variables.
The results also show PPI use was significantly linked after full adjustment with a 34% relative increase in MI, a 35% relative increase in heart failure, and a 30% relative increase in all-cause death, say a team of Chinese researchers in a recent report in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
PPIs are a medication class widely used in both over-the-counter and prescription formulations to reduce acid production in the stomach and to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and other acid-related disorders. The PPI class includes such widely used agents as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and omeprazole (Prilosec).
The analyses in this report, which used data collected in the UK Biobank, are “rigorous,” and the findings of “a modest elevation of CVD risk are consistent with a growing number of observational studies in populations with and without diabetes,” commented Mary R. Rooney, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who focuses on diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Prior observational reports
For example, a report from a prospective, observational study of more than 4300 U.S. residents published in 2021 that Dr. Rooney coauthored documented that cumulative PPI exposure for more than 5 years was significantly linked with a twofold increase in the rate of CVD events, compared with people who did not use a PPI. (This analysis did not examine a possible effect of diabetes status.)
And in a separate prospective, observational study of more than 1,000 Australians with type 2 diabetes, initiation of PPI treatment was significantly linked with a 3.6-fold increased incidence of CVD events, compared with PPI nonuse.
However, Dr. Rooney cautioned that the role of PPI use in raising CVD events “is still an unresolved question. It is too soon to tell if PPI use in people with diabetes should trigger additional caution.” Findings are needed from prospective, randomized trials to determine more definitively whether PPIs play a causal role in the incidence of CVD events, she said in an interview.
U.S. practice often results in unwarranted prolongation of PPI treatment, said the authors of an editorial that accompanied the 2021 report by Dr. Rooney and coauthors.
Long-term PPI use threatens harm
“The practice of initiating stress ulcer prophylaxis [by administering a PPI] in critical care is common,” wrote the authors of the 2021 editorial, Nitin Malik, MD, and William S. Weintraub, MD. “Although it is data driven and well intentioned, the possibility of causing harm – if it is continued on a long-term basis after resolution of the acute illness – is palpable.”
The new analyses using UK Biobank data included 19,229 adults with type 2 diabetes and no preexisting coronary artery disease, MI, heart failure, or stroke. The cohort included 15,954 people (83%) who did not report using a PPI and 3,275 who currently used PPIs regularly. Study limitations include self-report as the only verification of PPI use and lack of information on type of PPI, dose size, or use duration.
The findings remained consistent in several sensitivity analyses, including a propensity score–matched analysis and after further adjustment for use of histamine2 receptor antagonists, a drug class with indications similar to those for PPIs.
The authors of the report speculated that mechanisms that might link PPI use and increased CVD and mortality risk could include changes to the gut microbiota and possible interactions between PPIs and antiplatelet agents.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Rooney disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among people with type 2 diabetes who self-reported regularly using a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events as well as all-cause death was significantly increased in a study of more than 19,000 people with type 2 diabetes in a prospective U.K. database.
During median follow-up of about 11 years, regular use of a PPI by people with type 2 diabetes was significantly linked with a 27% relative increase in the incidence of coronary artery disease, compared with nonuse of a PPI, after full adjustment for potential confounding variables.
The results also show PPI use was significantly linked after full adjustment with a 34% relative increase in MI, a 35% relative increase in heart failure, and a 30% relative increase in all-cause death, say a team of Chinese researchers in a recent report in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
PPIs are a medication class widely used in both over-the-counter and prescription formulations to reduce acid production in the stomach and to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and other acid-related disorders. The PPI class includes such widely used agents as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and omeprazole (Prilosec).
The analyses in this report, which used data collected in the UK Biobank, are “rigorous,” and the findings of “a modest elevation of CVD risk are consistent with a growing number of observational studies in populations with and without diabetes,” commented Mary R. Rooney, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who focuses on diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Prior observational reports
For example, a report from a prospective, observational study of more than 4300 U.S. residents published in 2021 that Dr. Rooney coauthored documented that cumulative PPI exposure for more than 5 years was significantly linked with a twofold increase in the rate of CVD events, compared with people who did not use a PPI. (This analysis did not examine a possible effect of diabetes status.)
And in a separate prospective, observational study of more than 1,000 Australians with type 2 diabetes, initiation of PPI treatment was significantly linked with a 3.6-fold increased incidence of CVD events, compared with PPI nonuse.
However, Dr. Rooney cautioned that the role of PPI use in raising CVD events “is still an unresolved question. It is too soon to tell if PPI use in people with diabetes should trigger additional caution.” Findings are needed from prospective, randomized trials to determine more definitively whether PPIs play a causal role in the incidence of CVD events, she said in an interview.
U.S. practice often results in unwarranted prolongation of PPI treatment, said the authors of an editorial that accompanied the 2021 report by Dr. Rooney and coauthors.
Long-term PPI use threatens harm
“The practice of initiating stress ulcer prophylaxis [by administering a PPI] in critical care is common,” wrote the authors of the 2021 editorial, Nitin Malik, MD, and William S. Weintraub, MD. “Although it is data driven and well intentioned, the possibility of causing harm – if it is continued on a long-term basis after resolution of the acute illness – is palpable.”
The new analyses using UK Biobank data included 19,229 adults with type 2 diabetes and no preexisting coronary artery disease, MI, heart failure, or stroke. The cohort included 15,954 people (83%) who did not report using a PPI and 3,275 who currently used PPIs regularly. Study limitations include self-report as the only verification of PPI use and lack of information on type of PPI, dose size, or use duration.
The findings remained consistent in several sensitivity analyses, including a propensity score–matched analysis and after further adjustment for use of histamine2 receptor antagonists, a drug class with indications similar to those for PPIs.
The authors of the report speculated that mechanisms that might link PPI use and increased CVD and mortality risk could include changes to the gut microbiota and possible interactions between PPIs and antiplatelet agents.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Rooney disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among people with type 2 diabetes who self-reported regularly using a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) events as well as all-cause death was significantly increased in a study of more than 19,000 people with type 2 diabetes in a prospective U.K. database.
During median follow-up of about 11 years, regular use of a PPI by people with type 2 diabetes was significantly linked with a 27% relative increase in the incidence of coronary artery disease, compared with nonuse of a PPI, after full adjustment for potential confounding variables.
The results also show PPI use was significantly linked after full adjustment with a 34% relative increase in MI, a 35% relative increase in heart failure, and a 30% relative increase in all-cause death, say a team of Chinese researchers in a recent report in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
PPIs are a medication class widely used in both over-the-counter and prescription formulations to reduce acid production in the stomach and to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease and other acid-related disorders. The PPI class includes such widely used agents as esomeprazole (Nexium), lansoprazole (Prevacid), and omeprazole (Prilosec).
The analyses in this report, which used data collected in the UK Biobank, are “rigorous,” and the findings of “a modest elevation of CVD risk are consistent with a growing number of observational studies in populations with and without diabetes,” commented Mary R. Rooney, PhD, an epidemiologist at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, who focuses on diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Prior observational reports
For example, a report from a prospective, observational study of more than 4300 U.S. residents published in 2021 that Dr. Rooney coauthored documented that cumulative PPI exposure for more than 5 years was significantly linked with a twofold increase in the rate of CVD events, compared with people who did not use a PPI. (This analysis did not examine a possible effect of diabetes status.)
And in a separate prospective, observational study of more than 1,000 Australians with type 2 diabetes, initiation of PPI treatment was significantly linked with a 3.6-fold increased incidence of CVD events, compared with PPI nonuse.
However, Dr. Rooney cautioned that the role of PPI use in raising CVD events “is still an unresolved question. It is too soon to tell if PPI use in people with diabetes should trigger additional caution.” Findings are needed from prospective, randomized trials to determine more definitively whether PPIs play a causal role in the incidence of CVD events, she said in an interview.
U.S. practice often results in unwarranted prolongation of PPI treatment, said the authors of an editorial that accompanied the 2021 report by Dr. Rooney and coauthors.
Long-term PPI use threatens harm
“The practice of initiating stress ulcer prophylaxis [by administering a PPI] in critical care is common,” wrote the authors of the 2021 editorial, Nitin Malik, MD, and William S. Weintraub, MD. “Although it is data driven and well intentioned, the possibility of causing harm – if it is continued on a long-term basis after resolution of the acute illness – is palpable.”
The new analyses using UK Biobank data included 19,229 adults with type 2 diabetes and no preexisting coronary artery disease, MI, heart failure, or stroke. The cohort included 15,954 people (83%) who did not report using a PPI and 3,275 who currently used PPIs regularly. Study limitations include self-report as the only verification of PPI use and lack of information on type of PPI, dose size, or use duration.
The findings remained consistent in several sensitivity analyses, including a propensity score–matched analysis and after further adjustment for use of histamine2 receptor antagonists, a drug class with indications similar to those for PPIs.
The authors of the report speculated that mechanisms that might link PPI use and increased CVD and mortality risk could include changes to the gut microbiota and possible interactions between PPIs and antiplatelet agents.
The study received no commercial funding. The authors and Dr. Rooney disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM