User login
The Genitals Are a Window Into Health: Sex as a Vital Sign
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: I’m Dr. Rachel Rubin, a urologist and sexual medicine specialist in the Washington, DC, area. And I am so thrilled because my co-fellow, the brilliant and famous Dr. Ashley Winter, a board-certified urologist and a certified menopause practitioner, who sees patients in our practice from Los Angeles, is joining us today to talk about sex as a vital sign.
Ashley Winter, MD: To have the best sexual function, you need many different systems to work. You need your hormones to be in the right place. You need your blood vessels to dilate when you want them to. You need your nerves to connect to your genitalia to make them responsive. The way people say, “The eyes are the window into the soul” — well, the genitals are the window into the cardiovascular system, the peripheral nervous system, and the hormonal system. It’s so dynamic. Patients can understand how this reflects their health. We just need healthcare providers to hammer home how those things connect.
Rubin: If you’re a primary care doctor seeing a patient and you want to educate them on diabetes or high blood pressure, how can you “ ‘sell it with ‘sex”? How can you use sex to educate them about these important medical conditions?
Winter: I hate using it as a fear tactic, but sometimes you have to. Time and again, I’ve seen men with severe profound erectile dysfunction at a young age, with chronically uncontrolled diabetes.
Diabetes can impair the peripheral nerves, resulting in peripheral neuropathy. The same way that it can affect the fingers and toes, diabetes can affect the penis, even before those other areas. Diabetes can also lead to other conditions such as low testosterone, which also affects the function of the penis.
I’m being brutally honest when I tell patients that diabetes control is critical to having a wonderful sexspan — the duration of your life where you’re able to be sexually active and have great sex and do it in the way that you want.
Chronic conditions such as high cholesterol or hypertension can affect your ability to become erect or aroused whether you have a penis or a vulva, and even your ability to have an orgasm.
Rubin: None of my doctors has ever asked me about these issues. But we have to bring them up with patients because they›re not going to bring them up to us. I always say in the review of systems, we shouldn›t just ask, “Do you have any sexual problems?” (which nobody ever does) and move past the question about men, women or both. We should be asking, “Do you have any issues with libido? Do you want to talk about it? Any issues with erection, arousal, orgasm, or sexual pain?”
When you can talk about those things, you can treat the patient from a whole physiologic perspective. For example, how does their sciatica affect their sexual pain? How does their antidepressant cause a delayed orgasm? How does their low testosterone level affect their energy level, their libido, and their desire?
We see so much shame and guilt in sexual health, to the extent that patients feel broken. We can help them understand the anatomy and physiology and explain that they aren’t broken. Instead, it’s “You need this medicine for your crippling anxiety, and that’s why your orgasm is delayed, and so can we augment it or add or subtract something to help you with it.”
Winter: In a primary care setting, where we are considering the patient›s overall health, we strive for medication compliance, but a huge part of medication noncompliance is sexual side effects, whether it›s antidepressants, beta-blockers, birth control, or this new world of GLP-1 agonists.
Rubin: I would add breast cancer treatments. Many patients go off their anastrozole or their tamoxifen because of the sexual side effects.
Winter: This is where we get to the crux of this discussion about sex being a vital sign — something you need to check routinely. We need to become comfortable with it, because then we are unlocking the ability to treat every patient like a whole person, give them better outcomes, improve their compliance, and have a really powerful tool for education.
Rubin: We have a growing toolbox for all genders when it comes to sexual health. We have FDA- approved medications for low libido in women. We use testosterone in men in an evidence-based way to safely improve libido. We use medications to help with the genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Orgasm is a challenging one, but we have devices that can help with those reflexes. And working with people who specialize in sexual pain can be extremely helpful for patients.
Dr. Winter, having practiced in different settings, what would you tell the primary care doctors who don’t want to talk about libido or who minimize sexual complaints because they don’t know how to navigate them?
Winter: I do not envy the challenge of being a primary care provider in the healthcare world we are living in. I think it is the hardest job. The ultimate takeaway is to just normalize the conversation and be able to validate what is happening. Have a few basic tools, and then have referrals. It›s not that you have to have all the time in the world or you have to treat every condition, but you have to start the conversation, be comfortable with it, and then get patients hooked up with the right resources.
Rubin: Every doctor of every kind can connect with patients and try to understand what they care about. What are their goals? What do they want for their families, for their relationships, for their quality of life? And how can we work collaboratively as a team to help them with those things?
Sex is a huge part of people’s lives. If we don’t ask about it; if we don’t look into it; and if we don’t admit that our physiology, our medications, and our surgeries can affect sexual health and functioning, how can we improve people’s lives? We can do so much as a team when we consider sex as a true vital sign.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, DC, has disclosed ties with Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: I’m Dr. Rachel Rubin, a urologist and sexual medicine specialist in the Washington, DC, area. And I am so thrilled because my co-fellow, the brilliant and famous Dr. Ashley Winter, a board-certified urologist and a certified menopause practitioner, who sees patients in our practice from Los Angeles, is joining us today to talk about sex as a vital sign.
Ashley Winter, MD: To have the best sexual function, you need many different systems to work. You need your hormones to be in the right place. You need your blood vessels to dilate when you want them to. You need your nerves to connect to your genitalia to make them responsive. The way people say, “The eyes are the window into the soul” — well, the genitals are the window into the cardiovascular system, the peripheral nervous system, and the hormonal system. It’s so dynamic. Patients can understand how this reflects their health. We just need healthcare providers to hammer home how those things connect.
Rubin: If you’re a primary care doctor seeing a patient and you want to educate them on diabetes or high blood pressure, how can you “ ‘sell it with ‘sex”? How can you use sex to educate them about these important medical conditions?
Winter: I hate using it as a fear tactic, but sometimes you have to. Time and again, I’ve seen men with severe profound erectile dysfunction at a young age, with chronically uncontrolled diabetes.
Diabetes can impair the peripheral nerves, resulting in peripheral neuropathy. The same way that it can affect the fingers and toes, diabetes can affect the penis, even before those other areas. Diabetes can also lead to other conditions such as low testosterone, which also affects the function of the penis.
I’m being brutally honest when I tell patients that diabetes control is critical to having a wonderful sexspan — the duration of your life where you’re able to be sexually active and have great sex and do it in the way that you want.
Chronic conditions such as high cholesterol or hypertension can affect your ability to become erect or aroused whether you have a penis or a vulva, and even your ability to have an orgasm.
Rubin: None of my doctors has ever asked me about these issues. But we have to bring them up with patients because they›re not going to bring them up to us. I always say in the review of systems, we shouldn›t just ask, “Do you have any sexual problems?” (which nobody ever does) and move past the question about men, women or both. We should be asking, “Do you have any issues with libido? Do you want to talk about it? Any issues with erection, arousal, orgasm, or sexual pain?”
When you can talk about those things, you can treat the patient from a whole physiologic perspective. For example, how does their sciatica affect their sexual pain? How does their antidepressant cause a delayed orgasm? How does their low testosterone level affect their energy level, their libido, and their desire?
We see so much shame and guilt in sexual health, to the extent that patients feel broken. We can help them understand the anatomy and physiology and explain that they aren’t broken. Instead, it’s “You need this medicine for your crippling anxiety, and that’s why your orgasm is delayed, and so can we augment it or add or subtract something to help you with it.”
Winter: In a primary care setting, where we are considering the patient›s overall health, we strive for medication compliance, but a huge part of medication noncompliance is sexual side effects, whether it›s antidepressants, beta-blockers, birth control, or this new world of GLP-1 agonists.
Rubin: I would add breast cancer treatments. Many patients go off their anastrozole or their tamoxifen because of the sexual side effects.
Winter: This is where we get to the crux of this discussion about sex being a vital sign — something you need to check routinely. We need to become comfortable with it, because then we are unlocking the ability to treat every patient like a whole person, give them better outcomes, improve their compliance, and have a really powerful tool for education.
Rubin: We have a growing toolbox for all genders when it comes to sexual health. We have FDA- approved medications for low libido in women. We use testosterone in men in an evidence-based way to safely improve libido. We use medications to help with the genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Orgasm is a challenging one, but we have devices that can help with those reflexes. And working with people who specialize in sexual pain can be extremely helpful for patients.
Dr. Winter, having practiced in different settings, what would you tell the primary care doctors who don’t want to talk about libido or who minimize sexual complaints because they don’t know how to navigate them?
Winter: I do not envy the challenge of being a primary care provider in the healthcare world we are living in. I think it is the hardest job. The ultimate takeaway is to just normalize the conversation and be able to validate what is happening. Have a few basic tools, and then have referrals. It›s not that you have to have all the time in the world or you have to treat every condition, but you have to start the conversation, be comfortable with it, and then get patients hooked up with the right resources.
Rubin: Every doctor of every kind can connect with patients and try to understand what they care about. What are their goals? What do they want for their families, for their relationships, for their quality of life? And how can we work collaboratively as a team to help them with those things?
Sex is a huge part of people’s lives. If we don’t ask about it; if we don’t look into it; and if we don’t admit that our physiology, our medications, and our surgeries can affect sexual health and functioning, how can we improve people’s lives? We can do so much as a team when we consider sex as a true vital sign.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, DC, has disclosed ties with Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Rachel S. Rubin, MD: I’m Dr. Rachel Rubin, a urologist and sexual medicine specialist in the Washington, DC, area. And I am so thrilled because my co-fellow, the brilliant and famous Dr. Ashley Winter, a board-certified urologist and a certified menopause practitioner, who sees patients in our practice from Los Angeles, is joining us today to talk about sex as a vital sign.
Ashley Winter, MD: To have the best sexual function, you need many different systems to work. You need your hormones to be in the right place. You need your blood vessels to dilate when you want them to. You need your nerves to connect to your genitalia to make them responsive. The way people say, “The eyes are the window into the soul” — well, the genitals are the window into the cardiovascular system, the peripheral nervous system, and the hormonal system. It’s so dynamic. Patients can understand how this reflects their health. We just need healthcare providers to hammer home how those things connect.
Rubin: If you’re a primary care doctor seeing a patient and you want to educate them on diabetes or high blood pressure, how can you “ ‘sell it with ‘sex”? How can you use sex to educate them about these important medical conditions?
Winter: I hate using it as a fear tactic, but sometimes you have to. Time and again, I’ve seen men with severe profound erectile dysfunction at a young age, with chronically uncontrolled diabetes.
Diabetes can impair the peripheral nerves, resulting in peripheral neuropathy. The same way that it can affect the fingers and toes, diabetes can affect the penis, even before those other areas. Diabetes can also lead to other conditions such as low testosterone, which also affects the function of the penis.
I’m being brutally honest when I tell patients that diabetes control is critical to having a wonderful sexspan — the duration of your life where you’re able to be sexually active and have great sex and do it in the way that you want.
Chronic conditions such as high cholesterol or hypertension can affect your ability to become erect or aroused whether you have a penis or a vulva, and even your ability to have an orgasm.
Rubin: None of my doctors has ever asked me about these issues. But we have to bring them up with patients because they›re not going to bring them up to us. I always say in the review of systems, we shouldn›t just ask, “Do you have any sexual problems?” (which nobody ever does) and move past the question about men, women or both. We should be asking, “Do you have any issues with libido? Do you want to talk about it? Any issues with erection, arousal, orgasm, or sexual pain?”
When you can talk about those things, you can treat the patient from a whole physiologic perspective. For example, how does their sciatica affect their sexual pain? How does their antidepressant cause a delayed orgasm? How does their low testosterone level affect their energy level, their libido, and their desire?
We see so much shame and guilt in sexual health, to the extent that patients feel broken. We can help them understand the anatomy and physiology and explain that they aren’t broken. Instead, it’s “You need this medicine for your crippling anxiety, and that’s why your orgasm is delayed, and so can we augment it or add or subtract something to help you with it.”
Winter: In a primary care setting, where we are considering the patient›s overall health, we strive for medication compliance, but a huge part of medication noncompliance is sexual side effects, whether it›s antidepressants, beta-blockers, birth control, or this new world of GLP-1 agonists.
Rubin: I would add breast cancer treatments. Many patients go off their anastrozole or their tamoxifen because of the sexual side effects.
Winter: This is where we get to the crux of this discussion about sex being a vital sign — something you need to check routinely. We need to become comfortable with it, because then we are unlocking the ability to treat every patient like a whole person, give them better outcomes, improve their compliance, and have a really powerful tool for education.
Rubin: We have a growing toolbox for all genders when it comes to sexual health. We have FDA- approved medications for low libido in women. We use testosterone in men in an evidence-based way to safely improve libido. We use medications to help with the genitourinary syndrome of menopause. Orgasm is a challenging one, but we have devices that can help with those reflexes. And working with people who specialize in sexual pain can be extremely helpful for patients.
Dr. Winter, having practiced in different settings, what would you tell the primary care doctors who don’t want to talk about libido or who minimize sexual complaints because they don’t know how to navigate them?
Winter: I do not envy the challenge of being a primary care provider in the healthcare world we are living in. I think it is the hardest job. The ultimate takeaway is to just normalize the conversation and be able to validate what is happening. Have a few basic tools, and then have referrals. It›s not that you have to have all the time in the world or you have to treat every condition, but you have to start the conversation, be comfortable with it, and then get patients hooked up with the right resources.
Rubin: Every doctor of every kind can connect with patients and try to understand what they care about. What are their goals? What do they want for their families, for their relationships, for their quality of life? And how can we work collaboratively as a team to help them with those things?
Sex is a huge part of people’s lives. If we don’t ask about it; if we don’t look into it; and if we don’t admit that our physiology, our medications, and our surgeries can affect sexual health and functioning, how can we improve people’s lives? We can do so much as a team when we consider sex as a true vital sign.
Dr. Rubin, Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Urology, Georgetown University, Washington, DC, has disclosed ties with Maternal Medical, Absorption Pharmaceuticals, GlaxoSmithKline, and Endo.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCOS Linked to Hypertensive Blood Pressure in Teens
TOPLINE:
Adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have an increased risk for hypertension, according to a new study which underscores the importance of blood pressure surveillance in this population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective cohort study examined the association between PCOS and hypertension in adolescent girls within a diverse community-based US healthcare population.
- The researchers analyzed data from 224,418 adolescent girls (mean age at index visit, 14.9 years; 15.8% classified as having obesity) who had a well-child visit between 2013 and 2019, during which their systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured.
- Blood pressure in the hypertensive range was classified using the 2017 American Academy of Pediatrics Practice Guideline, with thresholds of 130/80 mm Hg or greater.
TAKEAWAY:
- The proportion of adolescent girls with high blood pressure was significantly greater among those with PCOS than among those without the condition (18.2% vs 7.1%; P < .001).
- Adolescent girls with PCOS had a 25% higher risk for hypertension than those without the disorder (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.42).
- Similarly, adolescent girls with obesity and PCOS had a 23% higher risk for high blood pressure than those without PCOS (aOR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.06-1.42).
IN PRACTICE:
“The high prevalence of [hypertension] associated with PCOS emphasizes the key role of early [blood pressure] monitoring in this high-risk group,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sherry Zhang, MD, Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, Oakland, California, and was published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study relied on coded diagnoses of PCOS from clinical settings, which may have led to detection and referral biases. The findings may not be generalizable to an unselected population in which adolescent girls are systematically screened for both PCOS and hypertension.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Conditions Research Section and the Biostatistical Consulting Unit at the Division of Research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California and by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Program. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have an increased risk for hypertension, according to a new study which underscores the importance of blood pressure surveillance in this population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective cohort study examined the association between PCOS and hypertension in adolescent girls within a diverse community-based US healthcare population.
- The researchers analyzed data from 224,418 adolescent girls (mean age at index visit, 14.9 years; 15.8% classified as having obesity) who had a well-child visit between 2013 and 2019, during which their systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured.
- Blood pressure in the hypertensive range was classified using the 2017 American Academy of Pediatrics Practice Guideline, with thresholds of 130/80 mm Hg or greater.
TAKEAWAY:
- The proportion of adolescent girls with high blood pressure was significantly greater among those with PCOS than among those without the condition (18.2% vs 7.1%; P < .001).
- Adolescent girls with PCOS had a 25% higher risk for hypertension than those without the disorder (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.42).
- Similarly, adolescent girls with obesity and PCOS had a 23% higher risk for high blood pressure than those without PCOS (aOR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.06-1.42).
IN PRACTICE:
“The high prevalence of [hypertension] associated with PCOS emphasizes the key role of early [blood pressure] monitoring in this high-risk group,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sherry Zhang, MD, Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, Oakland, California, and was published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study relied on coded diagnoses of PCOS from clinical settings, which may have led to detection and referral biases. The findings may not be generalizable to an unselected population in which adolescent girls are systematically screened for both PCOS and hypertension.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Conditions Research Section and the Biostatistical Consulting Unit at the Division of Research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California and by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Program. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Adolescent girls with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have an increased risk for hypertension, according to a new study which underscores the importance of blood pressure surveillance in this population.
METHODOLOGY:
- The retrospective cohort study examined the association between PCOS and hypertension in adolescent girls within a diverse community-based US healthcare population.
- The researchers analyzed data from 224,418 adolescent girls (mean age at index visit, 14.9 years; 15.8% classified as having obesity) who had a well-child visit between 2013 and 2019, during which their systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure were measured.
- Blood pressure in the hypertensive range was classified using the 2017 American Academy of Pediatrics Practice Guideline, with thresholds of 130/80 mm Hg or greater.
TAKEAWAY:
- The proportion of adolescent girls with high blood pressure was significantly greater among those with PCOS than among those without the condition (18.2% vs 7.1%; P < .001).
- Adolescent girls with PCOS had a 25% higher risk for hypertension than those without the disorder (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 1.25; 95% CI, 1.10-1.42).
- Similarly, adolescent girls with obesity and PCOS had a 23% higher risk for high blood pressure than those without PCOS (aOR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.06-1.42).
IN PRACTICE:
“The high prevalence of [hypertension] associated with PCOS emphasizes the key role of early [blood pressure] monitoring in this high-risk group,” the authors of the study wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Sherry Zhang, MD, Kaiser Permanente Oakland Medical Center, Oakland, California, and was published online in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
LIMITATIONS:
The study relied on coded diagnoses of PCOS from clinical settings, which may have led to detection and referral biases. The findings may not be generalizable to an unselected population in which adolescent girls are systematically screened for both PCOS and hypertension.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Conditions Research Section and the Biostatistical Consulting Unit at the Division of Research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California and by the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Community Health Program. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Higher Doses of Vitamin D3 Do Not Reduce Cardiac Biomarkers in Older Adults
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly reduce cardiac biomarkers in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels. The STURDY trial found no significant differences in high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) between low- and high-dose groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 688 participants aged 70 years or older with low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels (10-29 ng/mL) were included in the STURDY trial.
- Participants were randomized to receive one of four doses of vitamin D3 supplementation: 200, 1000, 2000, or 4000 IU/d, with 200 IU/d as the reference dose.
- Cardiac biomarkers, including hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP, were measured at baseline, 3 months, 12 months, and 24 months.
- The trial was conducted at two community-based research institutions in the United States between July 2015 and March 2019.
- The effects of vitamin D3 dose on biomarkers were assessed via mixed-effects tobit models, with participants followed up to 24 months or until study termination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly affect hs-cTnI levels compared with the low-dose group (1.6% difference; 95% CI, −5.3 to 8.9).
- No significant differences were observed in NT-proBNP levels between the high-dose and low-dose groups (−1.8% difference; 95% CI, −9.3 to 6.3).
- Both hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP levels increased in both low- and high-dose groups over time, with hs-cTnI increasing by 5.2% and 7.0%, respectively, and NT-proBNP increasing by 11.3% and 9.3%, respectively.
- The findings suggest that higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation do not reduce markers of subclinical cardiovascular disease in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“We can speculate that the systemic effects of vitamin D deficiency are more profound among the very old, and there may be an inverse relationship between supplementation and inflammation. It is also possible that serum vitamin D level is a risk marker but not a risk factor for CVD risk and related underlying mechanisms,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Katharine W. Rainer, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s community-based population may limit the generalizability of the findings to populations at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, the baseline cardiac biomarkers were lower than those in some high-risk populations, which may affect the precision of the assay performance. The study may not have had adequate power for cross-sectional and subgroup analyses. Both groups received some vitamin D3 supplementation, making it difficult to determine the impact of lower-dose supplementation vs no supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the Mid-Atlantic Nutrition Obesity Research Center, and the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research. Rainer disclosed receiving grants from these organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly reduce cardiac biomarkers in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels. The STURDY trial found no significant differences in high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) between low- and high-dose groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 688 participants aged 70 years or older with low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels (10-29 ng/mL) were included in the STURDY trial.
- Participants were randomized to receive one of four doses of vitamin D3 supplementation: 200, 1000, 2000, or 4000 IU/d, with 200 IU/d as the reference dose.
- Cardiac biomarkers, including hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP, were measured at baseline, 3 months, 12 months, and 24 months.
- The trial was conducted at two community-based research institutions in the United States between July 2015 and March 2019.
- The effects of vitamin D3 dose on biomarkers were assessed via mixed-effects tobit models, with participants followed up to 24 months or until study termination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly affect hs-cTnI levels compared with the low-dose group (1.6% difference; 95% CI, −5.3 to 8.9).
- No significant differences were observed in NT-proBNP levels between the high-dose and low-dose groups (−1.8% difference; 95% CI, −9.3 to 6.3).
- Both hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP levels increased in both low- and high-dose groups over time, with hs-cTnI increasing by 5.2% and 7.0%, respectively, and NT-proBNP increasing by 11.3% and 9.3%, respectively.
- The findings suggest that higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation do not reduce markers of subclinical cardiovascular disease in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“We can speculate that the systemic effects of vitamin D deficiency are more profound among the very old, and there may be an inverse relationship between supplementation and inflammation. It is also possible that serum vitamin D level is a risk marker but not a risk factor for CVD risk and related underlying mechanisms,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Katharine W. Rainer, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s community-based population may limit the generalizability of the findings to populations at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, the baseline cardiac biomarkers were lower than those in some high-risk populations, which may affect the precision of the assay performance. The study may not have had adequate power for cross-sectional and subgroup analyses. Both groups received some vitamin D3 supplementation, making it difficult to determine the impact of lower-dose supplementation vs no supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the Mid-Atlantic Nutrition Obesity Research Center, and the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research. Rainer disclosed receiving grants from these organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly reduce cardiac biomarkers in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels. The STURDY trial found no significant differences in high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I (hs-cTnI) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) between low- and high-dose groups.
METHODOLOGY:
- A total of 688 participants aged 70 years or older with low serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels (10-29 ng/mL) were included in the STURDY trial.
- Participants were randomized to receive one of four doses of vitamin D3 supplementation: 200, 1000, 2000, or 4000 IU/d, with 200 IU/d as the reference dose.
- Cardiac biomarkers, including hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP, were measured at baseline, 3 months, 12 months, and 24 months.
- The trial was conducted at two community-based research institutions in the United States between July 2015 and March 2019.
- The effects of vitamin D3 dose on biomarkers were assessed via mixed-effects tobit models, with participants followed up to 24 months or until study termination.
TAKEAWAY:
- Higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation did not significantly affect hs-cTnI levels compared with the low-dose group (1.6% difference; 95% CI, −5.3 to 8.9).
- No significant differences were observed in NT-proBNP levels between the high-dose and low-dose groups (−1.8% difference; 95% CI, −9.3 to 6.3).
- Both hs-cTnI and NT-proBNP levels increased in both low- and high-dose groups over time, with hs-cTnI increasing by 5.2% and 7.0%, respectively, and NT-proBNP increasing by 11.3% and 9.3%, respectively.
- The findings suggest that higher doses of vitamin D3 supplementation do not reduce markers of subclinical cardiovascular disease in older adults with low serum vitamin D levels.
IN PRACTICE:
“We can speculate that the systemic effects of vitamin D deficiency are more profound among the very old, and there may be an inverse relationship between supplementation and inflammation. It is also possible that serum vitamin D level is a risk marker but not a risk factor for CVD risk and related underlying mechanisms,” wrote the authors of the study.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Katharine W. Rainer, MD, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s community-based population may limit the generalizability of the findings to populations at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, the baseline cardiac biomarkers were lower than those in some high-risk populations, which may affect the precision of the assay performance. The study may not have had adequate power for cross-sectional and subgroup analyses. Both groups received some vitamin D3 supplementation, making it difficult to determine the impact of lower-dose supplementation vs no supplementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute on Aging, the Office of Dietary Supplements, the Mid-Atlantic Nutrition Obesity Research Center, and the Johns Hopkins Institute for Clinical and Translational Research. Rainer disclosed receiving grants from these organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Type 2 Diabetes: Insulin-Free for 24 Months After Novel Endoscopic Procedure
TOPLINE:
VIENNA, AUSTRIA —
METHODOLOGY:
- ReCET technology, manufactured by Endogenex, uses a specialized catheter that ablates the duodenal mucosa with electroporation, enhancing sensitivity to endogenous insulin.
- In the first-in-human study, a total of 14 participants (aged 28-75 years; body mass index, 24-40) underwent the ReCET procedure. They then followed a 2-week isocaloric liquid diet, after which they were initiated on semaglutide and gradually titrated up to 1 mg/wk.
- Patients were followed for a total of 24 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 14 participants, 12 (86%) no longer required insulin at the 6- and 12-month follow-ups.
- At the 24-month follow-up, 11 patients were still insulin-free while maintaining A1c levels below 7.5%. (One patient withdrew consent at 18 months.)
- Semaglutide at the maximum dose was well-tolerated by 93% of participants. One patient experienced nausea that limited titration to the maximum dose. There were no serious adverse events to the ReCET procedure.
- Researchers have started the EMINENT-2 trial that will compare the use of ReCET with a sham procedure. All patients will still receive semaglutide.
IN PRACTICE:
- “These findings are very encouraging, suggesting that ReCET is a safe and feasible procedure that, when combined with semaglutide, can effectively eliminate the need for insulin therapy,” said the study’s lead author.
- It’s a novel way of treating type 2 diabetes using a single endoscopic procedure instead of repeated insulin injections, Busch explained. “But we do need to consider whether repeat treatment will be necessary because I don’t believe this will be forever.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Celine Busch, MBBS, a PhD candidate in gastroenterology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and was presented (abstract OP049) at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024 in Vienna, Austria, on October 14, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included the small sample size, uncontrolled nature, and bias due to combination therapy.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received an unrestricted research grant from Endogenex. No other relevant disclosures were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
VIENNA, AUSTRIA —
METHODOLOGY:
- ReCET technology, manufactured by Endogenex, uses a specialized catheter that ablates the duodenal mucosa with electroporation, enhancing sensitivity to endogenous insulin.
- In the first-in-human study, a total of 14 participants (aged 28-75 years; body mass index, 24-40) underwent the ReCET procedure. They then followed a 2-week isocaloric liquid diet, after which they were initiated on semaglutide and gradually titrated up to 1 mg/wk.
- Patients were followed for a total of 24 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 14 participants, 12 (86%) no longer required insulin at the 6- and 12-month follow-ups.
- At the 24-month follow-up, 11 patients were still insulin-free while maintaining A1c levels below 7.5%. (One patient withdrew consent at 18 months.)
- Semaglutide at the maximum dose was well-tolerated by 93% of participants. One patient experienced nausea that limited titration to the maximum dose. There were no serious adverse events to the ReCET procedure.
- Researchers have started the EMINENT-2 trial that will compare the use of ReCET with a sham procedure. All patients will still receive semaglutide.
IN PRACTICE:
- “These findings are very encouraging, suggesting that ReCET is a safe and feasible procedure that, when combined with semaglutide, can effectively eliminate the need for insulin therapy,” said the study’s lead author.
- It’s a novel way of treating type 2 diabetes using a single endoscopic procedure instead of repeated insulin injections, Busch explained. “But we do need to consider whether repeat treatment will be necessary because I don’t believe this will be forever.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Celine Busch, MBBS, a PhD candidate in gastroenterology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and was presented (abstract OP049) at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024 in Vienna, Austria, on October 14, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included the small sample size, uncontrolled nature, and bias due to combination therapy.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received an unrestricted research grant from Endogenex. No other relevant disclosures were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
VIENNA, AUSTRIA —
METHODOLOGY:
- ReCET technology, manufactured by Endogenex, uses a specialized catheter that ablates the duodenal mucosa with electroporation, enhancing sensitivity to endogenous insulin.
- In the first-in-human study, a total of 14 participants (aged 28-75 years; body mass index, 24-40) underwent the ReCET procedure. They then followed a 2-week isocaloric liquid diet, after which they were initiated on semaglutide and gradually titrated up to 1 mg/wk.
- Patients were followed for a total of 24 months.
TAKEAWAY:
- Of the 14 participants, 12 (86%) no longer required insulin at the 6- and 12-month follow-ups.
- At the 24-month follow-up, 11 patients were still insulin-free while maintaining A1c levels below 7.5%. (One patient withdrew consent at 18 months.)
- Semaglutide at the maximum dose was well-tolerated by 93% of participants. One patient experienced nausea that limited titration to the maximum dose. There were no serious adverse events to the ReCET procedure.
- Researchers have started the EMINENT-2 trial that will compare the use of ReCET with a sham procedure. All patients will still receive semaglutide.
IN PRACTICE:
- “These findings are very encouraging, suggesting that ReCET is a safe and feasible procedure that, when combined with semaglutide, can effectively eliminate the need for insulin therapy,” said the study’s lead author.
- It’s a novel way of treating type 2 diabetes using a single endoscopic procedure instead of repeated insulin injections, Busch explained. “But we do need to consider whether repeat treatment will be necessary because I don’t believe this will be forever.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Celine Busch, MBBS, a PhD candidate in gastroenterology at Amsterdam University Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, and was presented (abstract OP049) at the United European Gastroenterology (UEG) Week 2024 in Vienna, Austria, on October 14, 2024.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included the small sample size, uncontrolled nature, and bias due to combination therapy.
DISCLOSURES:
This study received an unrestricted research grant from Endogenex. No other relevant disclosures were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CGM With Geriatric Care Simplifies T1D Management in Seniors
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of CGM use enhanced by geriatric principles in adults aged ≥ 65 years with T1D and at least two episodes of hypoglycemia (blood glucose level, < 70 mg/dL for ≥ 20 minutes over 2 weeks), who were either CGM-naive or CGM users prior to the study.
- Participants were randomly assigned to an intervention group using CGM with geriatric principles (ie, adjusting goals based on overall health and simplifying regimens based on CGM patterns and clinical characteristics) or a control group receiving usual care by their endocrinologist.
- The primary outcome was the change in duration of hypoglycemia from baseline to 6 months.
- A cost-effectiveness analysis was also performed for the intervention using a healthcare sector perspective, considering the cost of CGM devices and the cost of medical staff time.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers included 131 participants (mean age, 71 years), of whom 68 were in the intervention group (35 CGM-naive) and 63 in the control group (23 CGM-naive).
- The intervention group showed a median reduction of 2.6% in the duration of hypoglycemia vs a 0.3% reduction in the control group (median difference, −2.3%; P < .001).
- This reduction was observed in both CGM users (median difference, −1.2%) and CGM-naive participants (median difference, −2.8%) in the intervention group.
- No significant difference in A1c levels was observed between the intervention and control groups, indicating that CGM enhanced with geriatric principles did not worsen glycemic control.
- The intervention was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $71,623 per quality-adjusted life-year and was cost-effective for CGM-naive participants but at a lower level owing to the high cost of the CGM device.
IN PRACTICE:
“Personalization of goals and simplification of complex regimens can be combined with CGM use to improve management of type 1 diabetes in older adults,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Medha N. Munshi, MD, Joslin Diabetes Center, Boston. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included a relatively small sample size and an ethnically homogeneous and highly educated cohort, which may have limited the generalizability of its findings. Additionally, the study did not measure adherence to individual simplification strategies, which may have hindered the quantification of behavioral changes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Two authors declared serving as consultants for pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of CGM use enhanced by geriatric principles in adults aged ≥ 65 years with T1D and at least two episodes of hypoglycemia (blood glucose level, < 70 mg/dL for ≥ 20 minutes over 2 weeks), who were either CGM-naive or CGM users prior to the study.
- Participants were randomly assigned to an intervention group using CGM with geriatric principles (ie, adjusting goals based on overall health and simplifying regimens based on CGM patterns and clinical characteristics) or a control group receiving usual care by their endocrinologist.
- The primary outcome was the change in duration of hypoglycemia from baseline to 6 months.
- A cost-effectiveness analysis was also performed for the intervention using a healthcare sector perspective, considering the cost of CGM devices and the cost of medical staff time.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers included 131 participants (mean age, 71 years), of whom 68 were in the intervention group (35 CGM-naive) and 63 in the control group (23 CGM-naive).
- The intervention group showed a median reduction of 2.6% in the duration of hypoglycemia vs a 0.3% reduction in the control group (median difference, −2.3%; P < .001).
- This reduction was observed in both CGM users (median difference, −1.2%) and CGM-naive participants (median difference, −2.8%) in the intervention group.
- No significant difference in A1c levels was observed between the intervention and control groups, indicating that CGM enhanced with geriatric principles did not worsen glycemic control.
- The intervention was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $71,623 per quality-adjusted life-year and was cost-effective for CGM-naive participants but at a lower level owing to the high cost of the CGM device.
IN PRACTICE:
“Personalization of goals and simplification of complex regimens can be combined with CGM use to improve management of type 1 diabetes in older adults,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Medha N. Munshi, MD, Joslin Diabetes Center, Boston. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included a relatively small sample size and an ethnically homogeneous and highly educated cohort, which may have limited the generalizability of its findings. Additionally, the study did not measure adherence to individual simplification strategies, which may have hindered the quantification of behavioral changes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Two authors declared serving as consultants for pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers evaluated the effectiveness of CGM use enhanced by geriatric principles in adults aged ≥ 65 years with T1D and at least two episodes of hypoglycemia (blood glucose level, < 70 mg/dL for ≥ 20 minutes over 2 weeks), who were either CGM-naive or CGM users prior to the study.
- Participants were randomly assigned to an intervention group using CGM with geriatric principles (ie, adjusting goals based on overall health and simplifying regimens based on CGM patterns and clinical characteristics) or a control group receiving usual care by their endocrinologist.
- The primary outcome was the change in duration of hypoglycemia from baseline to 6 months.
- A cost-effectiveness analysis was also performed for the intervention using a healthcare sector perspective, considering the cost of CGM devices and the cost of medical staff time.
TAKEAWAY:
- Researchers included 131 participants (mean age, 71 years), of whom 68 were in the intervention group (35 CGM-naive) and 63 in the control group (23 CGM-naive).
- The intervention group showed a median reduction of 2.6% in the duration of hypoglycemia vs a 0.3% reduction in the control group (median difference, −2.3%; P < .001).
- This reduction was observed in both CGM users (median difference, −1.2%) and CGM-naive participants (median difference, −2.8%) in the intervention group.
- No significant difference in A1c levels was observed between the intervention and control groups, indicating that CGM enhanced with geriatric principles did not worsen glycemic control.
- The intervention was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of $71,623 per quality-adjusted life-year and was cost-effective for CGM-naive participants but at a lower level owing to the high cost of the CGM device.
IN PRACTICE:
“Personalization of goals and simplification of complex regimens can be combined with CGM use to improve management of type 1 diabetes in older adults,” the study authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Medha N. Munshi, MD, Joslin Diabetes Center, Boston. It was published online in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
The study included a relatively small sample size and an ethnically homogeneous and highly educated cohort, which may have limited the generalizability of its findings. Additionally, the study did not measure adherence to individual simplification strategies, which may have hindered the quantification of behavioral changes.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. Two authors declared serving as consultants for pharmaceutical companies.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How to Treat Cancer While Preserving Fertility
Thanks to the continuously improving treatment options for cancer, the number of cancer survivors is increasing, and a large proportion of survivors is confronted with the long-term effects of cancer treatment. Especially for young patients, the question of the impact of therapy on fertility arises.
Dose adjustment or modification of the treatment regimen can achieve a lot. But experts at the congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 noted that knowledge about newer treatment options like immunotherapies is still insufficient.
Therapy Selection
The question of preserving fertility must be considered when deciding on the appropriate treatment, said Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, medical oncology consultant at the University of Genoa in Genoa, Italy. “Preserving fertility is also an aim of cancer therapy,” he said.
Lambertini, who is also a member of the ESMO Guideline Group on fertility preservation in cancer patients, referred to the 2020 ESMO guidelines, which list the gonadotoxicity of a substance depending on the treatment regimen and the patient’s age.
Isabelle Demeestere, MD, PhD, director of the research lab for human reproduction at the Erasmus Hospital of the Free University of Brussels in Brussels, Belgium, pointed out the limitations of general guidelines. “Therapies change over time, and a classification must be updated regularly.”
Knowledge gaps related to well-known therapies and many novel options persist. “For many FDA-approved medications, there are either no fertility data or only preclinical data available,” she added.
Chemotherapies and Immunotherapies
Chemotherapies with alkylating or platinum-containing substances are known for their effects on oocytes, follicle maturation, and spermatogenesis, said Demeestere.
Chemotherapy is gonadotoxic and leads to a temporary decrease in sperm quality or temporary azoospermia in men.
These effects, however, can lead to permanent azoospermia and endocrine disorders, depending on the dose, duration, or combination with radiation, said Demeestere.
Cryopreservation of sperm should always be performed before starting treatment. For high-risk patients who are prepubertal, samples of testicular tissue are taken.
In women, chemotherapy affects primordial follicles and follicle maturation through DNA damage. This process results in severe or temporary amenorrhea, a temporary or permanent decrease in egg reserve, and ultimately premature egg insufficiency.
Novel immunotherapies also influence fertility, presumably through interactions of the immune system with the reproductive organs. But insufficient data are available, according to Lambertini, who emphasized that “these data are urgently needed, especially for young patients with cancer.”
In a mouse model, immune checkpoint inhibitors affected ovarian function, and the inflammatory reaction in humans can affect fertility. No long-term data are available for women yet, however, explained Demeestere. The effects of other therapeutics such as PARP, CDK4/6, or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, as well as monoclonal antibodies like trastuzumab, are only seen sporadically.
In the PENELOPE-B phase 3 study, the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib did not affect ovarian function, even though the cyclin-dependent kinases play an important role in mitotic arrest, said Demeestere.
Adjusting the Regimen
In a PET-guided approach, Demeestere’s research team investigated the effects of dose reduction or adjustment of the treatment regimen of procarbazine and cyclophosphamide on the fertility of patients younger than 45 years with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma.
By regularly controlling tumor growth with PET, the treatment could be adjusted so that the effect on egg reserve or spermatogenesis was significantly reduced and loss of fertility could be prevented.
During the 5-year follow-up period, the ovarian function of participating women was assessed by the serum concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) to evaluate egg reserve. In men, testicular function was assessed at the beginning of the study. At the end of treatment, sperm analysis and FSH and testosterone levels were checked.
Demeestere and colleagues demonstrated that dose reduction or altering the treatment regimen for patients who responded early to treatment (determined by PET-guided monitoring) reduced the risk for gonadotoxicity from 46% to 14.5%. That is, the risk was reduced by more than half.
FSH and AMH correlated with the patient’s age and the dose of the alkylating agent. In men, sperm parameters recovered after dose or agent adjustment compared with the unchanged treatment regimen.
Newer results from the PHERGain study in women with early human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer also provided hope, according to Demeestere. Under PET-guided control, chemotherapy could be reduced.
More Data Needed
The new treatment options pose a challenge to preserving fertility during cancer treatment, said Demeestere.
For new targeted therapies, uniform recommendations cannot be issued because of the lack of data and varying treatment durations. Still, the new therapies are safer than chemotherapy.
The need to collect data on fertility and long-term effects in cancer survivors in clinical studies is also reflected in the literature, according to Demeestere. “There are more review articles on this topic than clinical studies.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to the continuously improving treatment options for cancer, the number of cancer survivors is increasing, and a large proportion of survivors is confronted with the long-term effects of cancer treatment. Especially for young patients, the question of the impact of therapy on fertility arises.
Dose adjustment or modification of the treatment regimen can achieve a lot. But experts at the congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 noted that knowledge about newer treatment options like immunotherapies is still insufficient.
Therapy Selection
The question of preserving fertility must be considered when deciding on the appropriate treatment, said Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, medical oncology consultant at the University of Genoa in Genoa, Italy. “Preserving fertility is also an aim of cancer therapy,” he said.
Lambertini, who is also a member of the ESMO Guideline Group on fertility preservation in cancer patients, referred to the 2020 ESMO guidelines, which list the gonadotoxicity of a substance depending on the treatment regimen and the patient’s age.
Isabelle Demeestere, MD, PhD, director of the research lab for human reproduction at the Erasmus Hospital of the Free University of Brussels in Brussels, Belgium, pointed out the limitations of general guidelines. “Therapies change over time, and a classification must be updated regularly.”
Knowledge gaps related to well-known therapies and many novel options persist. “For many FDA-approved medications, there are either no fertility data or only preclinical data available,” she added.
Chemotherapies and Immunotherapies
Chemotherapies with alkylating or platinum-containing substances are known for their effects on oocytes, follicle maturation, and spermatogenesis, said Demeestere.
Chemotherapy is gonadotoxic and leads to a temporary decrease in sperm quality or temporary azoospermia in men.
These effects, however, can lead to permanent azoospermia and endocrine disorders, depending on the dose, duration, or combination with radiation, said Demeestere.
Cryopreservation of sperm should always be performed before starting treatment. For high-risk patients who are prepubertal, samples of testicular tissue are taken.
In women, chemotherapy affects primordial follicles and follicle maturation through DNA damage. This process results in severe or temporary amenorrhea, a temporary or permanent decrease in egg reserve, and ultimately premature egg insufficiency.
Novel immunotherapies also influence fertility, presumably through interactions of the immune system with the reproductive organs. But insufficient data are available, according to Lambertini, who emphasized that “these data are urgently needed, especially for young patients with cancer.”
In a mouse model, immune checkpoint inhibitors affected ovarian function, and the inflammatory reaction in humans can affect fertility. No long-term data are available for women yet, however, explained Demeestere. The effects of other therapeutics such as PARP, CDK4/6, or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, as well as monoclonal antibodies like trastuzumab, are only seen sporadically.
In the PENELOPE-B phase 3 study, the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib did not affect ovarian function, even though the cyclin-dependent kinases play an important role in mitotic arrest, said Demeestere.
Adjusting the Regimen
In a PET-guided approach, Demeestere’s research team investigated the effects of dose reduction or adjustment of the treatment regimen of procarbazine and cyclophosphamide on the fertility of patients younger than 45 years with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma.
By regularly controlling tumor growth with PET, the treatment could be adjusted so that the effect on egg reserve or spermatogenesis was significantly reduced and loss of fertility could be prevented.
During the 5-year follow-up period, the ovarian function of participating women was assessed by the serum concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) to evaluate egg reserve. In men, testicular function was assessed at the beginning of the study. At the end of treatment, sperm analysis and FSH and testosterone levels were checked.
Demeestere and colleagues demonstrated that dose reduction or altering the treatment regimen for patients who responded early to treatment (determined by PET-guided monitoring) reduced the risk for gonadotoxicity from 46% to 14.5%. That is, the risk was reduced by more than half.
FSH and AMH correlated with the patient’s age and the dose of the alkylating agent. In men, sperm parameters recovered after dose or agent adjustment compared with the unchanged treatment regimen.
Newer results from the PHERGain study in women with early human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer also provided hope, according to Demeestere. Under PET-guided control, chemotherapy could be reduced.
More Data Needed
The new treatment options pose a challenge to preserving fertility during cancer treatment, said Demeestere.
For new targeted therapies, uniform recommendations cannot be issued because of the lack of data and varying treatment durations. Still, the new therapies are safer than chemotherapy.
The need to collect data on fertility and long-term effects in cancer survivors in clinical studies is also reflected in the literature, according to Demeestere. “There are more review articles on this topic than clinical studies.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to the continuously improving treatment options for cancer, the number of cancer survivors is increasing, and a large proportion of survivors is confronted with the long-term effects of cancer treatment. Especially for young patients, the question of the impact of therapy on fertility arises.
Dose adjustment or modification of the treatment regimen can achieve a lot. But experts at the congress of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 noted that knowledge about newer treatment options like immunotherapies is still insufficient.
Therapy Selection
The question of preserving fertility must be considered when deciding on the appropriate treatment, said Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, medical oncology consultant at the University of Genoa in Genoa, Italy. “Preserving fertility is also an aim of cancer therapy,” he said.
Lambertini, who is also a member of the ESMO Guideline Group on fertility preservation in cancer patients, referred to the 2020 ESMO guidelines, which list the gonadotoxicity of a substance depending on the treatment regimen and the patient’s age.
Isabelle Demeestere, MD, PhD, director of the research lab for human reproduction at the Erasmus Hospital of the Free University of Brussels in Brussels, Belgium, pointed out the limitations of general guidelines. “Therapies change over time, and a classification must be updated regularly.”
Knowledge gaps related to well-known therapies and many novel options persist. “For many FDA-approved medications, there are either no fertility data or only preclinical data available,” she added.
Chemotherapies and Immunotherapies
Chemotherapies with alkylating or platinum-containing substances are known for their effects on oocytes, follicle maturation, and spermatogenesis, said Demeestere.
Chemotherapy is gonadotoxic and leads to a temporary decrease in sperm quality or temporary azoospermia in men.
These effects, however, can lead to permanent azoospermia and endocrine disorders, depending on the dose, duration, or combination with radiation, said Demeestere.
Cryopreservation of sperm should always be performed before starting treatment. For high-risk patients who are prepubertal, samples of testicular tissue are taken.
In women, chemotherapy affects primordial follicles and follicle maturation through DNA damage. This process results in severe or temporary amenorrhea, a temporary or permanent decrease in egg reserve, and ultimately premature egg insufficiency.
Novel immunotherapies also influence fertility, presumably through interactions of the immune system with the reproductive organs. But insufficient data are available, according to Lambertini, who emphasized that “these data are urgently needed, especially for young patients with cancer.”
In a mouse model, immune checkpoint inhibitors affected ovarian function, and the inflammatory reaction in humans can affect fertility. No long-term data are available for women yet, however, explained Demeestere. The effects of other therapeutics such as PARP, CDK4/6, or tyrosine kinase inhibitors, as well as monoclonal antibodies like trastuzumab, are only seen sporadically.
In the PENELOPE-B phase 3 study, the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib did not affect ovarian function, even though the cyclin-dependent kinases play an important role in mitotic arrest, said Demeestere.
Adjusting the Regimen
In a PET-guided approach, Demeestere’s research team investigated the effects of dose reduction or adjustment of the treatment regimen of procarbazine and cyclophosphamide on the fertility of patients younger than 45 years with advanced Hodgkin lymphoma.
By regularly controlling tumor growth with PET, the treatment could be adjusted so that the effect on egg reserve or spermatogenesis was significantly reduced and loss of fertility could be prevented.
During the 5-year follow-up period, the ovarian function of participating women was assessed by the serum concentration of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol, and anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) to evaluate egg reserve. In men, testicular function was assessed at the beginning of the study. At the end of treatment, sperm analysis and FSH and testosterone levels were checked.
Demeestere and colleagues demonstrated that dose reduction or altering the treatment regimen for patients who responded early to treatment (determined by PET-guided monitoring) reduced the risk for gonadotoxicity from 46% to 14.5%. That is, the risk was reduced by more than half.
FSH and AMH correlated with the patient’s age and the dose of the alkylating agent. In men, sperm parameters recovered after dose or agent adjustment compared with the unchanged treatment regimen.
Newer results from the PHERGain study in women with early human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive breast cancer also provided hope, according to Demeestere. Under PET-guided control, chemotherapy could be reduced.
More Data Needed
The new treatment options pose a challenge to preserving fertility during cancer treatment, said Demeestere.
For new targeted therapies, uniform recommendations cannot be issued because of the lack of data and varying treatment durations. Still, the new therapies are safer than chemotherapy.
The need to collect data on fertility and long-term effects in cancer survivors in clinical studies is also reflected in the literature, according to Demeestere. “There are more review articles on this topic than clinical studies.”
This story was translated from the Medscape German edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Tirzepatide Shortage Resolved? FDA Says Yes, Compounders No
The agency wrote in a clarification aimed at compounders that Lilly said it can meet the “present and projected national demand” and that compounders are restricted from making the products.
Nevertheless, patients and prescribers may still see “intermittent localized supply disruptions as the products move through the supply chain,” the FDA noted.
The Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) responded swiftly, alerting its members and the public to the resolved shortage and stating that compounders “must immediately cease preparing and dispensing compounded copies” of the two drugs.
However, APC CEO Scott Brunner added it often takes a long time for FDA-approved versions of the drug to become widely available to wholesalers, hospitals, and clinics. Even after Lilly announced greater availability for the drugs, including in a new vial format for low doses, “for most pharmacies, they’re lucky to get two or three boxes of Zepbound a day from their wholesaler — for a patient waiting list that can number in the hundreds.”
“We have already heard this morning from APC members that they are unable to fill orders for their patients,” he said.
Furthermore, he contended, “I suspect plenty of patients taking compounded tirzepatide are going to be caught flat-footed by this. They are being cut off cold turkey, their prescription no longer fillable. They’ll need to get in to see their provider to get a new prescription, and that will take some time. It’s possible that so many patients presently taking compounded GLP-1s [glucagon-like peptide 1] will be eventually switched to the FDA-approved versions — if they can afford them, of course — that it will push tirzepatide injection back into shortage.”
Commenting on the shortage resolution, endocrinologist Beverly Tchang, MD, DABOM, an assistant professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City told this news organization, “we are not yet experiencing relief from the shortages, but I hope this resolves at least one barrier to access for our patients.”
“I don’t think it will create confusion,” she said. “Fortunately or unfortunately, patients and clinicians are adept by now with therapeutic transitions because we’ve been forced to do so whenever insurance withdraws coverage or a shortage recurs or a coupon expires. It’s obviously not ideal but patients are motivated and clinicians don’t give up.”
This news organization has previously reported on the impact of the shortages and how endocrinologists and obesity medicine specialists were handling them, in light of concerns about compounding pharmacies that may or may not be well founded.
Dr. Tchang declared that she is an adviser to Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency wrote in a clarification aimed at compounders that Lilly said it can meet the “present and projected national demand” and that compounders are restricted from making the products.
Nevertheless, patients and prescribers may still see “intermittent localized supply disruptions as the products move through the supply chain,” the FDA noted.
The Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) responded swiftly, alerting its members and the public to the resolved shortage and stating that compounders “must immediately cease preparing and dispensing compounded copies” of the two drugs.
However, APC CEO Scott Brunner added it often takes a long time for FDA-approved versions of the drug to become widely available to wholesalers, hospitals, and clinics. Even after Lilly announced greater availability for the drugs, including in a new vial format for low doses, “for most pharmacies, they’re lucky to get two or three boxes of Zepbound a day from their wholesaler — for a patient waiting list that can number in the hundreds.”
“We have already heard this morning from APC members that they are unable to fill orders for their patients,” he said.
Furthermore, he contended, “I suspect plenty of patients taking compounded tirzepatide are going to be caught flat-footed by this. They are being cut off cold turkey, their prescription no longer fillable. They’ll need to get in to see their provider to get a new prescription, and that will take some time. It’s possible that so many patients presently taking compounded GLP-1s [glucagon-like peptide 1] will be eventually switched to the FDA-approved versions — if they can afford them, of course — that it will push tirzepatide injection back into shortage.”
Commenting on the shortage resolution, endocrinologist Beverly Tchang, MD, DABOM, an assistant professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City told this news organization, “we are not yet experiencing relief from the shortages, but I hope this resolves at least one barrier to access for our patients.”
“I don’t think it will create confusion,” she said. “Fortunately or unfortunately, patients and clinicians are adept by now with therapeutic transitions because we’ve been forced to do so whenever insurance withdraws coverage or a shortage recurs or a coupon expires. It’s obviously not ideal but patients are motivated and clinicians don’t give up.”
This news organization has previously reported on the impact of the shortages and how endocrinologists and obesity medicine specialists were handling them, in light of concerns about compounding pharmacies that may or may not be well founded.
Dr. Tchang declared that she is an adviser to Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The agency wrote in a clarification aimed at compounders that Lilly said it can meet the “present and projected national demand” and that compounders are restricted from making the products.
Nevertheless, patients and prescribers may still see “intermittent localized supply disruptions as the products move through the supply chain,” the FDA noted.
The Alliance for Pharmacy Compounding (APC) responded swiftly, alerting its members and the public to the resolved shortage and stating that compounders “must immediately cease preparing and dispensing compounded copies” of the two drugs.
However, APC CEO Scott Brunner added it often takes a long time for FDA-approved versions of the drug to become widely available to wholesalers, hospitals, and clinics. Even after Lilly announced greater availability for the drugs, including in a new vial format for low doses, “for most pharmacies, they’re lucky to get two or three boxes of Zepbound a day from their wholesaler — for a patient waiting list that can number in the hundreds.”
“We have already heard this morning from APC members that they are unable to fill orders for their patients,” he said.
Furthermore, he contended, “I suspect plenty of patients taking compounded tirzepatide are going to be caught flat-footed by this. They are being cut off cold turkey, their prescription no longer fillable. They’ll need to get in to see their provider to get a new prescription, and that will take some time. It’s possible that so many patients presently taking compounded GLP-1s [glucagon-like peptide 1] will be eventually switched to the FDA-approved versions — if they can afford them, of course — that it will push tirzepatide injection back into shortage.”
Commenting on the shortage resolution, endocrinologist Beverly Tchang, MD, DABOM, an assistant professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine in New York City told this news organization, “we are not yet experiencing relief from the shortages, but I hope this resolves at least one barrier to access for our patients.”
“I don’t think it will create confusion,” she said. “Fortunately or unfortunately, patients and clinicians are adept by now with therapeutic transitions because we’ve been forced to do so whenever insurance withdraws coverage or a shortage recurs or a coupon expires. It’s obviously not ideal but patients are motivated and clinicians don’t give up.”
This news organization has previously reported on the impact of the shortages and how endocrinologists and obesity medicine specialists were handling them, in light of concerns about compounding pharmacies that may or may not be well founded.
Dr. Tchang declared that she is an adviser to Novo Nordisk.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Time-Restricted Eating Is Not a Metabolic Magic Bullet
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
One out of three American adults — about 100 million people in this country — have the metabolic syndrome. I’m showing you the official criteria here, but essentially this is a syndrome of insulin resistance and visceral adiposity that predisposes us to a host of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and even dementia.
The metabolic syndrome is, fundamentally, a lifestyle disease. There is a direct line between our dietary habits and the wide availability of carbohydrate-rich, highly processed foods, and the rise in the syndrome in the population.
A saying I learned from one of my epidemiology teachers comes to mind: “Lifestyle diseases require lifestyle reinterventions.” But you know what? I’m not so sure anymore.
I’ve been around long enough to see multiple dietary fads come and go with varying efficacy. I grew up in the low-fat era, probably the most detrimental time to our national health as food manufacturers started replacing fats with carbohydrates, driving much of the problem we’re faced with today.
But I was also around for the Atkins diet and the low-carb craze — a healthier approach, all things being equal. And I’ve seen variants of these: the paleo diet (essentially a low-carb, high-protein diet based on minimally processed foods) and the Mediterranean diet, which sought to replace some percentage of fats with healthier fats.
And, of course, there is time-restricted eating.
Time-restricted eating, a variant of intermittent fasting, has the advantage of being very simple. No cookbooks, no recipes. Eat what you want — but limit it to certain hours in the day, ideally a window of less than 10 hours, such as 8 a.m. to 6 p.m.
When it comes to weight loss, the diets that work tend to work because they reduce calorie intake. I know, people will get angry about this, but thermodynamics is not just a good idea, it’s the law.
But weight loss is not the only reason we need to eat healthier. What we eat can impact our health in multiple ways; certain foods lead to more atherosclerosis, more inflammation, increased strain on the kidney and liver, and can affect our glucose homeostasis.
So I was really interested when I saw this article, “Time-Restricted Eating in Adults With Metabolic Syndrome,” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine October 1, which examined the effect of time-restricted eating on the metabolic syndrome itself. Could this lifestyle intervention cure this lifestyle disease?
In the study, 108 individuals, all of whom had the metabolic syndrome but not full-blown diabetes, were randomized to usual care — basically, nutrition education — vs time-restricted eating. In that group, participants were instructed to reduce their window of eating by at least 4 hours to achieve an 8- to 10-hour eating window. The groups were followed for 3 months.
Now, before we get to the results, it’s important to remember that the success of a lifestyle intervention trial is quite dependent on how well people adhere to the lifestyle intervention. Time-restricted eating is not as easy as taking a pill once a day.
The researchers had participants log their consumption using a smartphone app to confirm whether they were adhering to that restricted eating window.
Broadly speaking, they did. At baseline, both groups had an eating window of about 14 hours a day — think 7 a.m. to 9 p.m. The intervention group reduced that to just under 10 hours, with 10% of days falling outside of the target window.
Lifestyle change achieved, the primary outcome was the change in hemoglobin A1c at 3 months. A1c integrates the serum glucose over time and is thus a good indicator of the success of the intervention in terms of insulin resistance. But the effect was, honestly, disappointing.
Technically, the time-restricted-eating group had a greater A1c change than the control group — by 0.1 percentage points. On average, they went from a baseline A1c of 5.87 to a 3-month A1c of 5.75.
Other metabolic syndrome markers were equally lackluster: no difference in fasting glucose, mean glucose, or fasting insulin.
There was some weight change. The control group, which got that dietary education, lost 1.5% of body weight over the 3 months. The time-restricted-eating group lost 3.3% — about 7 pounds, which is reasonable.
With that weight loss came statistically significant, albeit modest improvements in BMI, body fat percentage, and LDL cholesterol.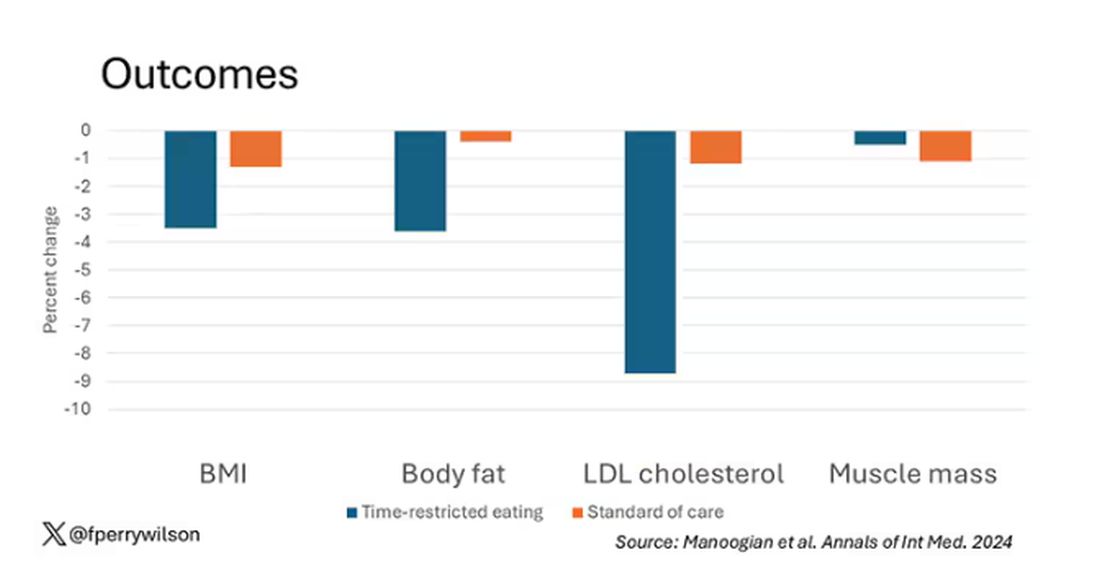
Of interest, despite the larger weight loss in the intermittent-fasting group, there was no difference in muscle mass loss, which is encouraging.
Taken together, we can say that, yes, it seems like time-restricted eating can help people lose some weight. This is essentially due to the fact that people eat fewer calories when they do time-restricted eating, as you can see here.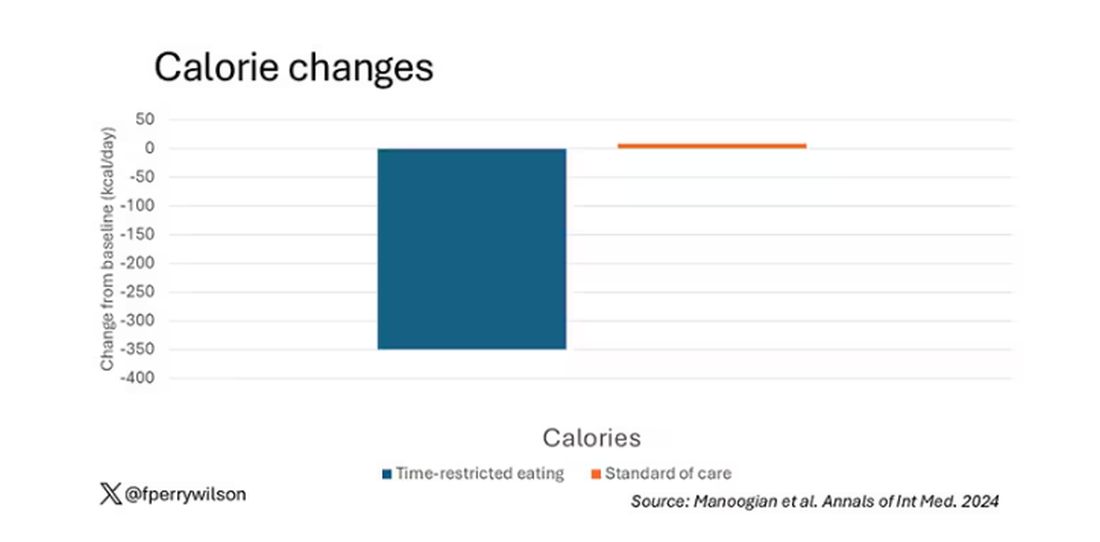
But, in the end, this trial examined whether this relatively straightforward lifestyle intervention would move the needle in terms of metabolic syndrome, and the data are not very compelling for that.
This graph shows how many of those five factors for metabolic syndrome the individuals in this trial had from the start to the end. You see that, over the 3 months, seven people in the time-restricted-eating group moved from having three criteria to two or one — being “cured” of metabolic syndrome, if you will. Nine people in the standard group were cured by that definition. Remember, they had to have at least three to have the syndrome and thus be eligible for the trial. 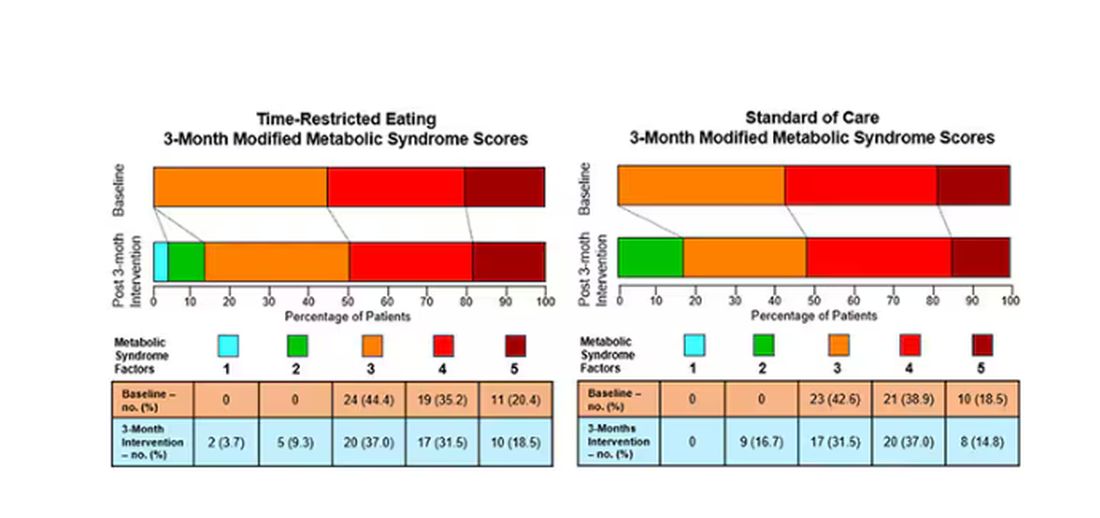
So If it just leads to weight loss by forcing people to consume less calories, then we need to acknowledge that we probably have better methods to achieve this same end. Ten years ago, I would have said that lifestyle change is the only way to end the epidemic of the metabolic syndrome in this country. Today, well, we live in a world of GLP-1 weight loss drugs. It is simply a different world now. Yes, they are expensive. Yes, they have side effects. But we need to evaluate them against the comparison. And so far, lifestyle changes alone are really no comparison.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
One out of three American adults — about 100 million people in this country — have the metabolic syndrome. I’m showing you the official criteria here, but essentially this is a syndrome of insulin resistance and visceral adiposity that predisposes us to a host of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and even dementia.
The metabolic syndrome is, fundamentally, a lifestyle disease. There is a direct line between our dietary habits and the wide availability of carbohydrate-rich, highly processed foods, and the rise in the syndrome in the population.
A saying I learned from one of my epidemiology teachers comes to mind: “Lifestyle diseases require lifestyle reinterventions.” But you know what? I’m not so sure anymore.
I’ve been around long enough to see multiple dietary fads come and go with varying efficacy. I grew up in the low-fat era, probably the most detrimental time to our national health as food manufacturers started replacing fats with carbohydrates, driving much of the problem we’re faced with today.
But I was also around for the Atkins diet and the low-carb craze — a healthier approach, all things being equal. And I’ve seen variants of these: the paleo diet (essentially a low-carb, high-protein diet based on minimally processed foods) and the Mediterranean diet, which sought to replace some percentage of fats with healthier fats.
And, of course, there is time-restricted eating.
Time-restricted eating, a variant of intermittent fasting, has the advantage of being very simple. No cookbooks, no recipes. Eat what you want — but limit it to certain hours in the day, ideally a window of less than 10 hours, such as 8 a.m. to 6 p.m.
When it comes to weight loss, the diets that work tend to work because they reduce calorie intake. I know, people will get angry about this, but thermodynamics is not just a good idea, it’s the law.
But weight loss is not the only reason we need to eat healthier. What we eat can impact our health in multiple ways; certain foods lead to more atherosclerosis, more inflammation, increased strain on the kidney and liver, and can affect our glucose homeostasis.
So I was really interested when I saw this article, “Time-Restricted Eating in Adults With Metabolic Syndrome,” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine October 1, which examined the effect of time-restricted eating on the metabolic syndrome itself. Could this lifestyle intervention cure this lifestyle disease?
In the study, 108 individuals, all of whom had the metabolic syndrome but not full-blown diabetes, were randomized to usual care — basically, nutrition education — vs time-restricted eating. In that group, participants were instructed to reduce their window of eating by at least 4 hours to achieve an 8- to 10-hour eating window. The groups were followed for 3 months.
Now, before we get to the results, it’s important to remember that the success of a lifestyle intervention trial is quite dependent on how well people adhere to the lifestyle intervention. Time-restricted eating is not as easy as taking a pill once a day.
The researchers had participants log their consumption using a smartphone app to confirm whether they were adhering to that restricted eating window.
Broadly speaking, they did. At baseline, both groups had an eating window of about 14 hours a day — think 7 a.m. to 9 p.m. The intervention group reduced that to just under 10 hours, with 10% of days falling outside of the target window.
Lifestyle change achieved, the primary outcome was the change in hemoglobin A1c at 3 months. A1c integrates the serum glucose over time and is thus a good indicator of the success of the intervention in terms of insulin resistance. But the effect was, honestly, disappointing.
Technically, the time-restricted-eating group had a greater A1c change than the control group — by 0.1 percentage points. On average, they went from a baseline A1c of 5.87 to a 3-month A1c of 5.75.
Other metabolic syndrome markers were equally lackluster: no difference in fasting glucose, mean glucose, or fasting insulin.
There was some weight change. The control group, which got that dietary education, lost 1.5% of body weight over the 3 months. The time-restricted-eating group lost 3.3% — about 7 pounds, which is reasonable.
With that weight loss came statistically significant, albeit modest improvements in BMI, body fat percentage, and LDL cholesterol.
Of interest, despite the larger weight loss in the intermittent-fasting group, there was no difference in muscle mass loss, which is encouraging.
Taken together, we can say that, yes, it seems like time-restricted eating can help people lose some weight. This is essentially due to the fact that people eat fewer calories when they do time-restricted eating, as you can see here.
But, in the end, this trial examined whether this relatively straightforward lifestyle intervention would move the needle in terms of metabolic syndrome, and the data are not very compelling for that.
This graph shows how many of those five factors for metabolic syndrome the individuals in this trial had from the start to the end. You see that, over the 3 months, seven people in the time-restricted-eating group moved from having three criteria to two or one — being “cured” of metabolic syndrome, if you will. Nine people in the standard group were cured by that definition. Remember, they had to have at least three to have the syndrome and thus be eligible for the trial. 
So If it just leads to weight loss by forcing people to consume less calories, then we need to acknowledge that we probably have better methods to achieve this same end. Ten years ago, I would have said that lifestyle change is the only way to end the epidemic of the metabolic syndrome in this country. Today, well, we live in a world of GLP-1 weight loss drugs. It is simply a different world now. Yes, they are expensive. Yes, they have side effects. But we need to evaluate them against the comparison. And so far, lifestyle changes alone are really no comparison.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
One out of three American adults — about 100 million people in this country — have the metabolic syndrome. I’m showing you the official criteria here, but essentially this is a syndrome of insulin resistance and visceral adiposity that predisposes us to a host of chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and even dementia.
The metabolic syndrome is, fundamentally, a lifestyle disease. There is a direct line between our dietary habits and the wide availability of carbohydrate-rich, highly processed foods, and the rise in the syndrome in the population.
A saying I learned from one of my epidemiology teachers comes to mind: “Lifestyle diseases require lifestyle reinterventions.” But you know what? I’m not so sure anymore.
I’ve been around long enough to see multiple dietary fads come and go with varying efficacy. I grew up in the low-fat era, probably the most detrimental time to our national health as food manufacturers started replacing fats with carbohydrates, driving much of the problem we’re faced with today.
But I was also around for the Atkins diet and the low-carb craze — a healthier approach, all things being equal. And I’ve seen variants of these: the paleo diet (essentially a low-carb, high-protein diet based on minimally processed foods) and the Mediterranean diet, which sought to replace some percentage of fats with healthier fats.
And, of course, there is time-restricted eating.
Time-restricted eating, a variant of intermittent fasting, has the advantage of being very simple. No cookbooks, no recipes. Eat what you want — but limit it to certain hours in the day, ideally a window of less than 10 hours, such as 8 a.m. to 6 p.m.
When it comes to weight loss, the diets that work tend to work because they reduce calorie intake. I know, people will get angry about this, but thermodynamics is not just a good idea, it’s the law.
But weight loss is not the only reason we need to eat healthier. What we eat can impact our health in multiple ways; certain foods lead to more atherosclerosis, more inflammation, increased strain on the kidney and liver, and can affect our glucose homeostasis.
So I was really interested when I saw this article, “Time-Restricted Eating in Adults With Metabolic Syndrome,” appearing in Annals of Internal Medicine October 1, which examined the effect of time-restricted eating on the metabolic syndrome itself. Could this lifestyle intervention cure this lifestyle disease?
In the study, 108 individuals, all of whom had the metabolic syndrome but not full-blown diabetes, were randomized to usual care — basically, nutrition education — vs time-restricted eating. In that group, participants were instructed to reduce their window of eating by at least 4 hours to achieve an 8- to 10-hour eating window. The groups were followed for 3 months.
Now, before we get to the results, it’s important to remember that the success of a lifestyle intervention trial is quite dependent on how well people adhere to the lifestyle intervention. Time-restricted eating is not as easy as taking a pill once a day.
The researchers had participants log their consumption using a smartphone app to confirm whether they were adhering to that restricted eating window.
Broadly speaking, they did. At baseline, both groups had an eating window of about 14 hours a day — think 7 a.m. to 9 p.m. The intervention group reduced that to just under 10 hours, with 10% of days falling outside of the target window.
Lifestyle change achieved, the primary outcome was the change in hemoglobin A1c at 3 months. A1c integrates the serum glucose over time and is thus a good indicator of the success of the intervention in terms of insulin resistance. But the effect was, honestly, disappointing.
Technically, the time-restricted-eating group had a greater A1c change than the control group — by 0.1 percentage points. On average, they went from a baseline A1c of 5.87 to a 3-month A1c of 5.75.
Other metabolic syndrome markers were equally lackluster: no difference in fasting glucose, mean glucose, or fasting insulin.
There was some weight change. The control group, which got that dietary education, lost 1.5% of body weight over the 3 months. The time-restricted-eating group lost 3.3% — about 7 pounds, which is reasonable.
With that weight loss came statistically significant, albeit modest improvements in BMI, body fat percentage, and LDL cholesterol.
Of interest, despite the larger weight loss in the intermittent-fasting group, there was no difference in muscle mass loss, which is encouraging.
Taken together, we can say that, yes, it seems like time-restricted eating can help people lose some weight. This is essentially due to the fact that people eat fewer calories when they do time-restricted eating, as you can see here.
But, in the end, this trial examined whether this relatively straightforward lifestyle intervention would move the needle in terms of metabolic syndrome, and the data are not very compelling for that.
This graph shows how many of those five factors for metabolic syndrome the individuals in this trial had from the start to the end. You see that, over the 3 months, seven people in the time-restricted-eating group moved from having three criteria to two or one — being “cured” of metabolic syndrome, if you will. Nine people in the standard group were cured by that definition. Remember, they had to have at least three to have the syndrome and thus be eligible for the trial. 
So If it just leads to weight loss by forcing people to consume less calories, then we need to acknowledge that we probably have better methods to achieve this same end. Ten years ago, I would have said that lifestyle change is the only way to end the epidemic of the metabolic syndrome in this country. Today, well, we live in a world of GLP-1 weight loss drugs. It is simply a different world now. Yes, they are expensive. Yes, they have side effects. But we need to evaluate them against the comparison. And so far, lifestyle changes alone are really no comparison.
Dr. Wilson is associate professor of medicine and public health and director of the Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator at Yale University, New Haven, Conn. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Detecting Type 2 Diabetes Through Voice: How Does It Work?
An international study, Colive Voice, presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 conference, shows that These results “open up possibilities for developing a first-line, noninvasive, and rapid screening tool for T2D, feasible with just a few seconds of voice recording on a smartphone or during consultations,” explained the study’s principal investigator Guy Fagherazzi, PhD, a diabetes epidemiologist at the Luxembourg Institute of Health, in an interview with this news organization.
How did the idea of detecting diabetes through voice come about?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we began analyzing voice recordings from patients with chronic diseases. We wanted to find solutions to assess people’s health remotely, without physical contact. We quickly realized that this approach could be extended to other diseases. Because my main research focus has always been diabetes, I looked into how voice characteristics might correlate with diabetes. Previous studies had indicated that patients with diabetes have distinct voices compared with the general population, and this insight formed the starting point.
What mechanism could explain why patients with T2D have different voice characteristics?
It’s challenging to pinpoint a single factor that would explain why patients with T2D have different voices from those without diabetes. Several factors are involved.
Some biological mechanisms, especially those affecting the vascular system, influence symptoms in people with metabolic diseases such as diabetes. For example, people with T2D have more frequent cardiorespiratory fatigue. Obesity and overweight are also key factors, as these conditions can slightly alter vocal parameters compared with people of normal weight. Hypertension, common in patients with T2D, adds to the complexity.
Neurologic complications can affect the nerves and muscles involved in voice production, particularly the vocal cords.
Therefore, respiratory fatigue, neuropathies, and other conditions such as dehydration and gastric acid reflux, which are more common in patients with diabetes, can contribute to differences in voice.
These differences might not be noticeable to the human ear. That’s why we often don’t notice the link between voice and diabetes. However, technological advancements in signal processing and artificial intelligence allow us to extract a large amount of information from these subtle variations. By analyzing these small differences, we can detect diabetes with a reasonable degree of accuracy.
In your study, you mention that voice tone can indicate diabetic status. Could you elaborate?
Yes, voice tone can be affected, though it’s a complex, multidimensional phenomenon.
Patients who have had diabetes for 5-10 years, or longer, tend to have a rougher voice than those without diabetes of the same age and gender. In our study, we were able to extract many voice characteristics from the raw audio signal, which is why it’s difficult to isolate one specific factor that stands out.
Is there a difference in voice changes between patients with well-managed diabetes and those whose disease is uncontrolled?
The roughness of the voice tends to increase with the duration of diabetes. It’s more noticeable in people with poorly controlled diabetes. Our hypothesis, based on the results we presented at the EASD conference, is that fluctuations in blood sugar levels, both hypo- and hyperglycemia, may cause short-term changes in the voice. There are also many subtle, rapid changes that could potentially be detected, though we haven’t confirmed this yet. We’re currently conducting additional studies to explore this.
Why did you ask participants to read a passage from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
We used a highly standardized approach. Participants completed several recordings, including holding the sound “Aaaaaa” for as long as possible in one breath. They also read a passage, which helps us better distinguish between patients with and those without diabetes. This method works slightly better than other sounds typically used for analyzing diseases. We chose this particular text in the participant’s native language because it’s neutral and doesn’t trigger emotional fluctuations. Because Colive Voice is an international, multilingual study, we use official translations in various languages.
Your research focuses on T2D. Do you plan to study type 1 diabetes (T1D) as well?
We believe that individuals with T1D also exhibit voice changes over time. However, our current focus is on T2D because our goal is to develop large-scale screening methods. T1D, typically diagnosed in childhood, requires different screening approaches. For now, our research mainly involves adults.
Were there any gender differences in the accuracy of your voice analysis?
Yes, voice studies generally show that women have different vocal signatures from men, partly owing to hormonal fluctuations that affect pitch and tone. Detecting differences between healthy individuals and those with diabetes can sometimes be more challenging in women, depending on the condition. In our study, we achieved about 70% accuracy for women compared with 75% for men.
The EASD results focused on a US-based population. When can we expect data from France?
We started with the US because we could quickly gather a large number of patients. Now, we’re expanding to global and language-specific analyses. French data are certainly a priority, and we’re working on it. We encourage people to participate — it takes only 20 minutes and contributes to innovative research on noninvasive diabetes detection. Participants can sign up at www.colivevoice.org
Dr. Fagherazzi heads the Deep Digital Phenotyping laboratory and the Department of Precision Health at the Luxembourg Institute of Health. His research focuses on integrating new technologies and digital data into diabetes research. He has declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An international study, Colive Voice, presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 conference, shows that These results “open up possibilities for developing a first-line, noninvasive, and rapid screening tool for T2D, feasible with just a few seconds of voice recording on a smartphone or during consultations,” explained the study’s principal investigator Guy Fagherazzi, PhD, a diabetes epidemiologist at the Luxembourg Institute of Health, in an interview with this news organization.
How did the idea of detecting diabetes through voice come about?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we began analyzing voice recordings from patients with chronic diseases. We wanted to find solutions to assess people’s health remotely, without physical contact. We quickly realized that this approach could be extended to other diseases. Because my main research focus has always been diabetes, I looked into how voice characteristics might correlate with diabetes. Previous studies had indicated that patients with diabetes have distinct voices compared with the general population, and this insight formed the starting point.
What mechanism could explain why patients with T2D have different voice characteristics?
It’s challenging to pinpoint a single factor that would explain why patients with T2D have different voices from those without diabetes. Several factors are involved.
Some biological mechanisms, especially those affecting the vascular system, influence symptoms in people with metabolic diseases such as diabetes. For example, people with T2D have more frequent cardiorespiratory fatigue. Obesity and overweight are also key factors, as these conditions can slightly alter vocal parameters compared with people of normal weight. Hypertension, common in patients with T2D, adds to the complexity.
Neurologic complications can affect the nerves and muscles involved in voice production, particularly the vocal cords.
Therefore, respiratory fatigue, neuropathies, and other conditions such as dehydration and gastric acid reflux, which are more common in patients with diabetes, can contribute to differences in voice.
These differences might not be noticeable to the human ear. That’s why we often don’t notice the link between voice and diabetes. However, technological advancements in signal processing and artificial intelligence allow us to extract a large amount of information from these subtle variations. By analyzing these small differences, we can detect diabetes with a reasonable degree of accuracy.
In your study, you mention that voice tone can indicate diabetic status. Could you elaborate?
Yes, voice tone can be affected, though it’s a complex, multidimensional phenomenon.
Patients who have had diabetes for 5-10 years, or longer, tend to have a rougher voice than those without diabetes of the same age and gender. In our study, we were able to extract many voice characteristics from the raw audio signal, which is why it’s difficult to isolate one specific factor that stands out.
Is there a difference in voice changes between patients with well-managed diabetes and those whose disease is uncontrolled?
The roughness of the voice tends to increase with the duration of diabetes. It’s more noticeable in people with poorly controlled diabetes. Our hypothesis, based on the results we presented at the EASD conference, is that fluctuations in blood sugar levels, both hypo- and hyperglycemia, may cause short-term changes in the voice. There are also many subtle, rapid changes that could potentially be detected, though we haven’t confirmed this yet. We’re currently conducting additional studies to explore this.
Why did you ask participants to read a passage from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
We used a highly standardized approach. Participants completed several recordings, including holding the sound “Aaaaaa” for as long as possible in one breath. They also read a passage, which helps us better distinguish between patients with and those without diabetes. This method works slightly better than other sounds typically used for analyzing diseases. We chose this particular text in the participant’s native language because it’s neutral and doesn’t trigger emotional fluctuations. Because Colive Voice is an international, multilingual study, we use official translations in various languages.
Your research focuses on T2D. Do you plan to study type 1 diabetes (T1D) as well?
We believe that individuals with T1D also exhibit voice changes over time. However, our current focus is on T2D because our goal is to develop large-scale screening methods. T1D, typically diagnosed in childhood, requires different screening approaches. For now, our research mainly involves adults.
Were there any gender differences in the accuracy of your voice analysis?
Yes, voice studies generally show that women have different vocal signatures from men, partly owing to hormonal fluctuations that affect pitch and tone. Detecting differences between healthy individuals and those with diabetes can sometimes be more challenging in women, depending on the condition. In our study, we achieved about 70% accuracy for women compared with 75% for men.
The EASD results focused on a US-based population. When can we expect data from France?
We started with the US because we could quickly gather a large number of patients. Now, we’re expanding to global and language-specific analyses. French data are certainly a priority, and we’re working on it. We encourage people to participate — it takes only 20 minutes and contributes to innovative research on noninvasive diabetes detection. Participants can sign up at www.colivevoice.org
Dr. Fagherazzi heads the Deep Digital Phenotyping laboratory and the Department of Precision Health at the Luxembourg Institute of Health. His research focuses on integrating new technologies and digital data into diabetes research. He has declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
An international study, Colive Voice, presented at the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) 2024 conference, shows that These results “open up possibilities for developing a first-line, noninvasive, and rapid screening tool for T2D, feasible with just a few seconds of voice recording on a smartphone or during consultations,” explained the study’s principal investigator Guy Fagherazzi, PhD, a diabetes epidemiologist at the Luxembourg Institute of Health, in an interview with this news organization.
How did the idea of detecting diabetes through voice come about?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, we began analyzing voice recordings from patients with chronic diseases. We wanted to find solutions to assess people’s health remotely, without physical contact. We quickly realized that this approach could be extended to other diseases. Because my main research focus has always been diabetes, I looked into how voice characteristics might correlate with diabetes. Previous studies had indicated that patients with diabetes have distinct voices compared with the general population, and this insight formed the starting point.
What mechanism could explain why patients with T2D have different voice characteristics?
It’s challenging to pinpoint a single factor that would explain why patients with T2D have different voices from those without diabetes. Several factors are involved.
Some biological mechanisms, especially those affecting the vascular system, influence symptoms in people with metabolic diseases such as diabetes. For example, people with T2D have more frequent cardiorespiratory fatigue. Obesity and overweight are also key factors, as these conditions can slightly alter vocal parameters compared with people of normal weight. Hypertension, common in patients with T2D, adds to the complexity.
Neurologic complications can affect the nerves and muscles involved in voice production, particularly the vocal cords.
Therefore, respiratory fatigue, neuropathies, and other conditions such as dehydration and gastric acid reflux, which are more common in patients with diabetes, can contribute to differences in voice.
These differences might not be noticeable to the human ear. That’s why we often don’t notice the link between voice and diabetes. However, technological advancements in signal processing and artificial intelligence allow us to extract a large amount of information from these subtle variations. By analyzing these small differences, we can detect diabetes with a reasonable degree of accuracy.
In your study, you mention that voice tone can indicate diabetic status. Could you elaborate?
Yes, voice tone can be affected, though it’s a complex, multidimensional phenomenon.
Patients who have had diabetes for 5-10 years, or longer, tend to have a rougher voice than those without diabetes of the same age and gender. In our study, we were able to extract many voice characteristics from the raw audio signal, which is why it’s difficult to isolate one specific factor that stands out.
Is there a difference in voice changes between patients with well-managed diabetes and those whose disease is uncontrolled?
The roughness of the voice tends to increase with the duration of diabetes. It’s more noticeable in people with poorly controlled diabetes. Our hypothesis, based on the results we presented at the EASD conference, is that fluctuations in blood sugar levels, both hypo- and hyperglycemia, may cause short-term changes in the voice. There are also many subtle, rapid changes that could potentially be detected, though we haven’t confirmed this yet. We’re currently conducting additional studies to explore this.
Why did you ask participants to read a passage from the Universal Declaration of Human Rights?
We used a highly standardized approach. Participants completed several recordings, including holding the sound “Aaaaaa” for as long as possible in one breath. They also read a passage, which helps us better distinguish between patients with and those without diabetes. This method works slightly better than other sounds typically used for analyzing diseases. We chose this particular text in the participant’s native language because it’s neutral and doesn’t trigger emotional fluctuations. Because Colive Voice is an international, multilingual study, we use official translations in various languages.
Your research focuses on T2D. Do you plan to study type 1 diabetes (T1D) as well?
We believe that individuals with T1D also exhibit voice changes over time. However, our current focus is on T2D because our goal is to develop large-scale screening methods. T1D, typically diagnosed in childhood, requires different screening approaches. For now, our research mainly involves adults.
Were there any gender differences in the accuracy of your voice analysis?
Yes, voice studies generally show that women have different vocal signatures from men, partly owing to hormonal fluctuations that affect pitch and tone. Detecting differences between healthy individuals and those with diabetes can sometimes be more challenging in women, depending on the condition. In our study, we achieved about 70% accuracy for women compared with 75% for men.
The EASD results focused on a US-based population. When can we expect data from France?
We started with the US because we could quickly gather a large number of patients. Now, we’re expanding to global and language-specific analyses. French data are certainly a priority, and we’re working on it. We encourage people to participate — it takes only 20 minutes and contributes to innovative research on noninvasive diabetes detection. Participants can sign up at www.colivevoice.org
Dr. Fagherazzi heads the Deep Digital Phenotyping laboratory and the Department of Precision Health at the Luxembourg Institute of Health. His research focuses on integrating new technologies and digital data into diabetes research. He has declared no relevant financial relationships.
This story was translated from the Medscape French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2024
Cannabis Use Rising in Diabetes: What Do Endos Need to Know?
A recent US prevalence study estimated that 9% adults with diabetes used cannabis in the last month, a 33.7% increase between 2021 and 2022. Nearly half (48.9%) of users were younger than 50 years.
Cannabis use is also increasing sharply among those aged 65 years or older, many of whom have diabetes and other chronic conditions. In this demographic, the perceived risk surrounding regular cannabis use has dropped significantly, even as the data tell another story — that they are particularly at risk from emergency department visits for cannabis poisoning.
As legalization continues and cannabis products proliferate, endocrinologists will likely face more patients of all ages seeking advice about its use. Yet with few evidence-based resources to turn to, endocrinologists advising patients in this area are mostly left fending for themselves.
Evidence ‘Limited’
“The evidence on cannabis is limited mainly because of its scheduling in the United States,” Jay Shubrook, DO, a professor and diabetologist at College of Osteopathic Medicine, Touro University California, in Vallejo, California, told this news organization.
“It was declared to be a schedule I drug in the 1970s, which meant it was ‘dangerous’ and ‘had no medical benefit.’ This made it hard to access and study in human trials.”
That will likely change soon. On May 16, 2024, the US Department of Justice submitted a proposal to move marijuana from a schedule I to a schedule III drug under the Controlled Substances Act, emphasizing its accepted medical use. If approved, the door will open to more investigators seeking to study the effects of cannabis.
Yet, even in Canada, where recreational use has been legal since 2018 and cannabis is sold widely with government support, there are little hard data to guide practice. In 2019, Diabetes Canada issued a position statement on recreational cannabis use in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). It sought to evaluate the effects of cannabis on metabolic factors and diabetes complications, as well as self-management behaviors in those aged 13 years or older.
The authors noted that five of the six studies upon which the statement was based did not consider or report the routes of cannabis administration, which have differing risks. In addition, their recommendations were based on grade D evidence and consensus.
What Patients Are Taking
Cannabis — also known as marijuana, weed, pot, or bud — refers to the dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. The plant contains more than 100 compounds, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the euphoric “high,” and other active compounds, including cannabidiol (CBD), which by itself is not mind-altering.
Cannabis can be ingested in several ways. It can be smoked (ie, joints, blunts, pipes, and water pipes), ingested in edible form (mixed or infused into foods), and inhaled using electronic vaporizing devices (ie, e-cigarettes or vape pens).
Compounds in cannabis can also be extracted to make oils and concentrates that can be vaped or inhaled. Smoking oils, concentrates, and extracts from the cannabis plant, known as “dabbing,” are on the rise in the United States.
There are no validated or standard dosage recommendations for cannabis strains and formulations, THC/CBD ratios, or modes of administration. Therefore, the Canadian Pharmacists Association prepared a guide for finding a safe and effective dose for medical purposes. GoodRx, a website with information on prescription drug prices, says that larger doses of THC pose greater risks, noting that the potency of cannabis has increased from 4% in 1995 to about 14% in 2019.
Potential Risks and Benefits: Canadian and US Perspectives
Health and safety risks vary with each of the different ways of using cannabis for individuals with and without diabetes, depending on a host of patient- and product-specific factors.
In a recent article proposing a “THC unit” for Canada’s legal cannabis market, researchers reported that consumers lack familiarity with THC levels, don’t know what constitutes a “low” or “high” THC amount, have trouble dosing, overconsume, and commonly experience adverse health events from cannabis use.
A recent study suggested that most clinicians are similarly uninformed, with “a lack of knowledge of beneficial effects, adverse effects, and of how to advise patients,” even for medical cannabis.
Diabetes Canada takes a stab at summarizing what’s known with respect to cannabis and diabetes, stating that:
“Research on recreational cannabis use suggests it may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors. The safety of recreational cannabis use has not been demonstrated, whereas regular cannabis use is associated with worsening glycemic control, more diabetes-related complications, and poorer self-care behaviors, such as adequate glucose monitoring, adherence to medications, and compliance with dietary and physical activity recommendations for people living with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.”
The American Diabetes Association’s information on cannabis consists of a patient-oriented article on CBD oil. The article stated:
“There’s a lot of hype surrounding CBD oil and diabetes. There is no noticeable effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers continue to study the effects of CBD on diabetes in animal studies.”
It concludes that:
“Although many claims continue to be made about CBD oil, there is little evidence of any benefit. It’s certainly not an alternative to traditional diabetes management. The safety of CBD is also unknown — it may have dangerous side effects that we won’t know about unless further research is done.”
A Roundup of Recent Studies
A smattering of recent studies have touched on various aspects of cannabis consumption and diabetes.
Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and co-director of CUChange at the University of Colorado Boulder, has been evaluating cannabis use in young adults (ages 21-40 years) in the SONIC study. Dr. Bryan reported at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions that cannabis users were more likely to have a lower body mass index and less likely to develop T2D. Furthermore, chronic cannabis users were less likely to have measures of inflammation and no loss of insulin sensitivity.
Another study by Dr. Bryan’s group found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
Similarly positive results were found in a 15-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of THC/CBD spray for neuropathic pain among treatment-resistant patients. The investigators reported that “clinically important improvements” were seen in pain, sleep quality, and subjective impressions of pain. Another small study of inhaled cannabis in treatment-refractory patients found a dose-dependent reduction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain.
Findings from a 9-year longitudinal study of approximately 18,000 Swedish men and women suggested no association between cannabis and subsequent T2D development after controlling for age, although these authors also called for longer follow-up and more detailed information about cannabis use to make “more robust” conclusions.
On the other side of the spectrum, a “rapid” review of recreational cannabis use in people with T1D and T2D found that recreational cannabis use may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors and may increase risks for peripheral arterial occlusion, myocardial infarction, and renal disease. However, the authors cautioned that more robust research is needed to confirm the potential impact of cannabis on diabetes.
How to Advise Patients
When Dr. Shubrook was working with patients with diabetes in his family medicine practice in Ohio, cannabis wasn’t legal.
“’Don’t ask, don’t tell’ was the way we handled it then,” he said.
By contrast, in California, where he’s currently located, “it’s pretty well accepted and legal, and patients volunteer information about use, even if it’s recreational,” he said. “Realizing this was something we could talk about was really eye-opening to me.”
Talking to patients about cannabis use is a “20-minute conversation that details what they’re doing,” he said. He proceeds by asking questions: Are you using for recreational or medicinal purposes? What do you take? What do you take it for? Does it work?
“People will tell you,” Dr. Shubrook said. “They know exactly what it works or doesn’t work for and how it affects their glucose control, which in most cases is only minimally.”
He tells patients he would prefer they don’t inhale cannabis, given the risks posed to the lungs.
“Edibles may have a slower onset of effect, but depending on what they’re adding it to, glucose might be affected,” he noted. “And I have seen that chronic use can lead to hyperemesis syndrome.”
Overall, he said, “Take the time to talk to your patients about cannabis — it will allow them to be honest with you, and you can improve the specificity and safety of its use. If cannabis is legal in your state, encourage people to go to legal dispensaries, which will reduce the risk of it being laced with another drug that could increase the danger of use.”
A recent US prevalence study found that people with diabetes who use cannabis likely engage in other substance and psychoactive substance use, including tobacco use, binge drinking, and misuse of opioids and stimulants.
“Use of these additional substances could further exacerbate the health risks associated with diabetes and also emphasizes the importance of addressing polysubstance use among adults with diabetes,” the study’s author Benjamin H. Han, MD, Division of Geriatrics, Gerontology and Palliative Care, Department of Medicine, US San Diego School of Medicine in La Jolla, California, told this news organization.
“We were surprised at how strong the associations were, especially with use of substances that can increase cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Han added. “And given the strong association we found between cannabis use and use of other psychoactive substances in diabetes, clinicians must screen all their patients for psychoactive substance use.”
Diabetes Canada’s position paper states that despite the limited evidence, “there were sufficient data to begin developing recommendations for type 1 and type 2 diabetes about education, counseling, and management related to recreational cannabis use.”
Their recommendations include the following:
- Healthcare professionals should engage their patients in discussions about substance use on a regular basis, with a nonjudgmental approach.
- The use of recreational cannabis is not recommended for adolescents and adults with diabetes.
- People with T1D should avoid recreational cannabis use because of the increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- For adults with T1D or T2D who intend to use cannabis recreationally, individualized assessment and counseling should be offered to inform them of the general risks of cannabis, with a focus on harm reduction and reduction of the risk for potential adverse effects on diabetes management and complications.
- People with T1D or T2D should be offered education on and encouraged to read public information available through resources from various Canadian health authorities about the general risks of cannabis use to reduce the risk for nondiabetes-related adverse effects of cannabis consumption.
Of note, in 2018, the Canadian government produced an exhaustive compendium of information on cannabis for healthcare professionals that includes information relevant to managing patients with diabetes.
Dr. Shubrook and Dr. Han reported no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent US prevalence study estimated that 9% adults with diabetes used cannabis in the last month, a 33.7% increase between 2021 and 2022. Nearly half (48.9%) of users were younger than 50 years.
Cannabis use is also increasing sharply among those aged 65 years or older, many of whom have diabetes and other chronic conditions. In this demographic, the perceived risk surrounding regular cannabis use has dropped significantly, even as the data tell another story — that they are particularly at risk from emergency department visits for cannabis poisoning.
As legalization continues and cannabis products proliferate, endocrinologists will likely face more patients of all ages seeking advice about its use. Yet with few evidence-based resources to turn to, endocrinologists advising patients in this area are mostly left fending for themselves.
Evidence ‘Limited’
“The evidence on cannabis is limited mainly because of its scheduling in the United States,” Jay Shubrook, DO, a professor and diabetologist at College of Osteopathic Medicine, Touro University California, in Vallejo, California, told this news organization.
“It was declared to be a schedule I drug in the 1970s, which meant it was ‘dangerous’ and ‘had no medical benefit.’ This made it hard to access and study in human trials.”
That will likely change soon. On May 16, 2024, the US Department of Justice submitted a proposal to move marijuana from a schedule I to a schedule III drug under the Controlled Substances Act, emphasizing its accepted medical use. If approved, the door will open to more investigators seeking to study the effects of cannabis.
Yet, even in Canada, where recreational use has been legal since 2018 and cannabis is sold widely with government support, there are little hard data to guide practice. In 2019, Diabetes Canada issued a position statement on recreational cannabis use in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). It sought to evaluate the effects of cannabis on metabolic factors and diabetes complications, as well as self-management behaviors in those aged 13 years or older.
The authors noted that five of the six studies upon which the statement was based did not consider or report the routes of cannabis administration, which have differing risks. In addition, their recommendations were based on grade D evidence and consensus.
What Patients Are Taking
Cannabis — also known as marijuana, weed, pot, or bud — refers to the dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. The plant contains more than 100 compounds, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the euphoric “high,” and other active compounds, including cannabidiol (CBD), which by itself is not mind-altering.
Cannabis can be ingested in several ways. It can be smoked (ie, joints, blunts, pipes, and water pipes), ingested in edible form (mixed or infused into foods), and inhaled using electronic vaporizing devices (ie, e-cigarettes or vape pens).
Compounds in cannabis can also be extracted to make oils and concentrates that can be vaped or inhaled. Smoking oils, concentrates, and extracts from the cannabis plant, known as “dabbing,” are on the rise in the United States.
There are no validated or standard dosage recommendations for cannabis strains and formulations, THC/CBD ratios, or modes of administration. Therefore, the Canadian Pharmacists Association prepared a guide for finding a safe and effective dose for medical purposes. GoodRx, a website with information on prescription drug prices, says that larger doses of THC pose greater risks, noting that the potency of cannabis has increased from 4% in 1995 to about 14% in 2019.
Potential Risks and Benefits: Canadian and US Perspectives
Health and safety risks vary with each of the different ways of using cannabis for individuals with and without diabetes, depending on a host of patient- and product-specific factors.
In a recent article proposing a “THC unit” for Canada’s legal cannabis market, researchers reported that consumers lack familiarity with THC levels, don’t know what constitutes a “low” or “high” THC amount, have trouble dosing, overconsume, and commonly experience adverse health events from cannabis use.
A recent study suggested that most clinicians are similarly uninformed, with “a lack of knowledge of beneficial effects, adverse effects, and of how to advise patients,” even for medical cannabis.
Diabetes Canada takes a stab at summarizing what’s known with respect to cannabis and diabetes, stating that:
“Research on recreational cannabis use suggests it may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors. The safety of recreational cannabis use has not been demonstrated, whereas regular cannabis use is associated with worsening glycemic control, more diabetes-related complications, and poorer self-care behaviors, such as adequate glucose monitoring, adherence to medications, and compliance with dietary and physical activity recommendations for people living with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.”
The American Diabetes Association’s information on cannabis consists of a patient-oriented article on CBD oil. The article stated:
“There’s a lot of hype surrounding CBD oil and diabetes. There is no noticeable effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers continue to study the effects of CBD on diabetes in animal studies.”
It concludes that:
“Although many claims continue to be made about CBD oil, there is little evidence of any benefit. It’s certainly not an alternative to traditional diabetes management. The safety of CBD is also unknown — it may have dangerous side effects that we won’t know about unless further research is done.”
A Roundup of Recent Studies
A smattering of recent studies have touched on various aspects of cannabis consumption and diabetes.
Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and co-director of CUChange at the University of Colorado Boulder, has been evaluating cannabis use in young adults (ages 21-40 years) in the SONIC study. Dr. Bryan reported at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions that cannabis users were more likely to have a lower body mass index and less likely to develop T2D. Furthermore, chronic cannabis users were less likely to have measures of inflammation and no loss of insulin sensitivity.
Another study by Dr. Bryan’s group found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
Similarly positive results were found in a 15-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of THC/CBD spray for neuropathic pain among treatment-resistant patients. The investigators reported that “clinically important improvements” were seen in pain, sleep quality, and subjective impressions of pain. Another small study of inhaled cannabis in treatment-refractory patients found a dose-dependent reduction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain.
Findings from a 9-year longitudinal study of approximately 18,000 Swedish men and women suggested no association between cannabis and subsequent T2D development after controlling for age, although these authors also called for longer follow-up and more detailed information about cannabis use to make “more robust” conclusions.
On the other side of the spectrum, a “rapid” review of recreational cannabis use in people with T1D and T2D found that recreational cannabis use may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors and may increase risks for peripheral arterial occlusion, myocardial infarction, and renal disease. However, the authors cautioned that more robust research is needed to confirm the potential impact of cannabis on diabetes.
How to Advise Patients
When Dr. Shubrook was working with patients with diabetes in his family medicine practice in Ohio, cannabis wasn’t legal.
“’Don’t ask, don’t tell’ was the way we handled it then,” he said.
By contrast, in California, where he’s currently located, “it’s pretty well accepted and legal, and patients volunteer information about use, even if it’s recreational,” he said. “Realizing this was something we could talk about was really eye-opening to me.”
Talking to patients about cannabis use is a “20-minute conversation that details what they’re doing,” he said. He proceeds by asking questions: Are you using for recreational or medicinal purposes? What do you take? What do you take it for? Does it work?
“People will tell you,” Dr. Shubrook said. “They know exactly what it works or doesn’t work for and how it affects their glucose control, which in most cases is only minimally.”
He tells patients he would prefer they don’t inhale cannabis, given the risks posed to the lungs.
“Edibles may have a slower onset of effect, but depending on what they’re adding it to, glucose might be affected,” he noted. “And I have seen that chronic use can lead to hyperemesis syndrome.”
Overall, he said, “Take the time to talk to your patients about cannabis — it will allow them to be honest with you, and you can improve the specificity and safety of its use. If cannabis is legal in your state, encourage people to go to legal dispensaries, which will reduce the risk of it being laced with another drug that could increase the danger of use.”
A recent US prevalence study found that people with diabetes who use cannabis likely engage in other substance and psychoactive substance use, including tobacco use, binge drinking, and misuse of opioids and stimulants.
“Use of these additional substances could further exacerbate the health risks associated with diabetes and also emphasizes the importance of addressing polysubstance use among adults with diabetes,” the study’s author Benjamin H. Han, MD, Division of Geriatrics, Gerontology and Palliative Care, Department of Medicine, US San Diego School of Medicine in La Jolla, California, told this news organization.
“We were surprised at how strong the associations were, especially with use of substances that can increase cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Han added. “And given the strong association we found between cannabis use and use of other psychoactive substances in diabetes, clinicians must screen all their patients for psychoactive substance use.”
Diabetes Canada’s position paper states that despite the limited evidence, “there were sufficient data to begin developing recommendations for type 1 and type 2 diabetes about education, counseling, and management related to recreational cannabis use.”
Their recommendations include the following:
- Healthcare professionals should engage their patients in discussions about substance use on a regular basis, with a nonjudgmental approach.
- The use of recreational cannabis is not recommended for adolescents and adults with diabetes.
- People with T1D should avoid recreational cannabis use because of the increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- For adults with T1D or T2D who intend to use cannabis recreationally, individualized assessment and counseling should be offered to inform them of the general risks of cannabis, with a focus on harm reduction and reduction of the risk for potential adverse effects on diabetes management and complications.
- People with T1D or T2D should be offered education on and encouraged to read public information available through resources from various Canadian health authorities about the general risks of cannabis use to reduce the risk for nondiabetes-related adverse effects of cannabis consumption.
Of note, in 2018, the Canadian government produced an exhaustive compendium of information on cannabis for healthcare professionals that includes information relevant to managing patients with diabetes.
Dr. Shubrook and Dr. Han reported no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent US prevalence study estimated that 9% adults with diabetes used cannabis in the last month, a 33.7% increase between 2021 and 2022. Nearly half (48.9%) of users were younger than 50 years.
Cannabis use is also increasing sharply among those aged 65 years or older, many of whom have diabetes and other chronic conditions. In this demographic, the perceived risk surrounding regular cannabis use has dropped significantly, even as the data tell another story — that they are particularly at risk from emergency department visits for cannabis poisoning.
As legalization continues and cannabis products proliferate, endocrinologists will likely face more patients of all ages seeking advice about its use. Yet with few evidence-based resources to turn to, endocrinologists advising patients in this area are mostly left fending for themselves.
Evidence ‘Limited’
“The evidence on cannabis is limited mainly because of its scheduling in the United States,” Jay Shubrook, DO, a professor and diabetologist at College of Osteopathic Medicine, Touro University California, in Vallejo, California, told this news organization.
“It was declared to be a schedule I drug in the 1970s, which meant it was ‘dangerous’ and ‘had no medical benefit.’ This made it hard to access and study in human trials.”
That will likely change soon. On May 16, 2024, the US Department of Justice submitted a proposal to move marijuana from a schedule I to a schedule III drug under the Controlled Substances Act, emphasizing its accepted medical use. If approved, the door will open to more investigators seeking to study the effects of cannabis.
Yet, even in Canada, where recreational use has been legal since 2018 and cannabis is sold widely with government support, there are little hard data to guide practice. In 2019, Diabetes Canada issued a position statement on recreational cannabis use in people with type 1 diabetes (T1D) and type 2 diabetes (T2D). It sought to evaluate the effects of cannabis on metabolic factors and diabetes complications, as well as self-management behaviors in those aged 13 years or older.
The authors noted that five of the six studies upon which the statement was based did not consider or report the routes of cannabis administration, which have differing risks. In addition, their recommendations were based on grade D evidence and consensus.
What Patients Are Taking
Cannabis — also known as marijuana, weed, pot, or bud — refers to the dried flowers, leaves, stems, and seeds of the cannabis plant. The plant contains more than 100 compounds, including tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is responsible for the euphoric “high,” and other active compounds, including cannabidiol (CBD), which by itself is not mind-altering.
Cannabis can be ingested in several ways. It can be smoked (ie, joints, blunts, pipes, and water pipes), ingested in edible form (mixed or infused into foods), and inhaled using electronic vaporizing devices (ie, e-cigarettes or vape pens).
Compounds in cannabis can also be extracted to make oils and concentrates that can be vaped or inhaled. Smoking oils, concentrates, and extracts from the cannabis plant, known as “dabbing,” are on the rise in the United States.
There are no validated or standard dosage recommendations for cannabis strains and formulations, THC/CBD ratios, or modes of administration. Therefore, the Canadian Pharmacists Association prepared a guide for finding a safe and effective dose for medical purposes. GoodRx, a website with information on prescription drug prices, says that larger doses of THC pose greater risks, noting that the potency of cannabis has increased from 4% in 1995 to about 14% in 2019.
Potential Risks and Benefits: Canadian and US Perspectives
Health and safety risks vary with each of the different ways of using cannabis for individuals with and without diabetes, depending on a host of patient- and product-specific factors.
In a recent article proposing a “THC unit” for Canada’s legal cannabis market, researchers reported that consumers lack familiarity with THC levels, don’t know what constitutes a “low” or “high” THC amount, have trouble dosing, overconsume, and commonly experience adverse health events from cannabis use.
A recent study suggested that most clinicians are similarly uninformed, with “a lack of knowledge of beneficial effects, adverse effects, and of how to advise patients,” even for medical cannabis.
Diabetes Canada takes a stab at summarizing what’s known with respect to cannabis and diabetes, stating that:
“Research on recreational cannabis use suggests it may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors. The safety of recreational cannabis use has not been demonstrated, whereas regular cannabis use is associated with worsening glycemic control, more diabetes-related complications, and poorer self-care behaviors, such as adequate glucose monitoring, adherence to medications, and compliance with dietary and physical activity recommendations for people living with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.”
The American Diabetes Association’s information on cannabis consists of a patient-oriented article on CBD oil. The article stated:
“There’s a lot of hype surrounding CBD oil and diabetes. There is no noticeable effect on blood glucose (blood sugar) or insulin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. Researchers continue to study the effects of CBD on diabetes in animal studies.”
It concludes that:
“Although many claims continue to be made about CBD oil, there is little evidence of any benefit. It’s certainly not an alternative to traditional diabetes management. The safety of CBD is also unknown — it may have dangerous side effects that we won’t know about unless further research is done.”
A Roundup of Recent Studies
A smattering of recent studies have touched on various aspects of cannabis consumption and diabetes.
Angela Bryan, PhD, professor and co-director of CUChange at the University of Colorado Boulder, has been evaluating cannabis use in young adults (ages 21-40 years) in the SONIC study. Dr. Bryan reported at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 84th Scientific Sessions that cannabis users were more likely to have a lower body mass index and less likely to develop T2D. Furthermore, chronic cannabis users were less likely to have measures of inflammation and no loss of insulin sensitivity.
Another study by Dr. Bryan’s group found that CBD-dominant forms of cannabis were associated with acute tension reduction, which might lead to longer-term reductions in anxiety. Bryan said the findings could be relevant in the context of diabetes distress.
Similarly positive results were found in a 15-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study of THC/CBD spray for neuropathic pain among treatment-resistant patients. The investigators reported that “clinically important improvements” were seen in pain, sleep quality, and subjective impressions of pain. Another small study of inhaled cannabis in treatment-refractory patients found a dose-dependent reduction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain.
Findings from a 9-year longitudinal study of approximately 18,000 Swedish men and women suggested no association between cannabis and subsequent T2D development after controlling for age, although these authors also called for longer follow-up and more detailed information about cannabis use to make “more robust” conclusions.
On the other side of the spectrum, a “rapid” review of recreational cannabis use in people with T1D and T2D found that recreational cannabis use may negatively impact diabetes metabolic factors and self-management behaviors and may increase risks for peripheral arterial occlusion, myocardial infarction, and renal disease. However, the authors cautioned that more robust research is needed to confirm the potential impact of cannabis on diabetes.
How to Advise Patients
When Dr. Shubrook was working with patients with diabetes in his family medicine practice in Ohio, cannabis wasn’t legal.
“’Don’t ask, don’t tell’ was the way we handled it then,” he said.
By contrast, in California, where he’s currently located, “it’s pretty well accepted and legal, and patients volunteer information about use, even if it’s recreational,” he said. “Realizing this was something we could talk about was really eye-opening to me.”
Talking to patients about cannabis use is a “20-minute conversation that details what they’re doing,” he said. He proceeds by asking questions: Are you using for recreational or medicinal purposes? What do you take? What do you take it for? Does it work?
“People will tell you,” Dr. Shubrook said. “They know exactly what it works or doesn’t work for and how it affects their glucose control, which in most cases is only minimally.”
He tells patients he would prefer they don’t inhale cannabis, given the risks posed to the lungs.
“Edibles may have a slower onset of effect, but depending on what they’re adding it to, glucose might be affected,” he noted. “And I have seen that chronic use can lead to hyperemesis syndrome.”
Overall, he said, “Take the time to talk to your patients about cannabis — it will allow them to be honest with you, and you can improve the specificity and safety of its use. If cannabis is legal in your state, encourage people to go to legal dispensaries, which will reduce the risk of it being laced with another drug that could increase the danger of use.”
A recent US prevalence study found that people with diabetes who use cannabis likely engage in other substance and psychoactive substance use, including tobacco use, binge drinking, and misuse of opioids and stimulants.
“Use of these additional substances could further exacerbate the health risks associated with diabetes and also emphasizes the importance of addressing polysubstance use among adults with diabetes,” the study’s author Benjamin H. Han, MD, Division of Geriatrics, Gerontology and Palliative Care, Department of Medicine, US San Diego School of Medicine in La Jolla, California, told this news organization.
“We were surprised at how strong the associations were, especially with use of substances that can increase cardiovascular risk,” Dr. Han added. “And given the strong association we found between cannabis use and use of other psychoactive substances in diabetes, clinicians must screen all their patients for psychoactive substance use.”
Diabetes Canada’s position paper states that despite the limited evidence, “there were sufficient data to begin developing recommendations for type 1 and type 2 diabetes about education, counseling, and management related to recreational cannabis use.”
Their recommendations include the following:
- Healthcare professionals should engage their patients in discussions about substance use on a regular basis, with a nonjudgmental approach.
- The use of recreational cannabis is not recommended for adolescents and adults with diabetes.
- People with T1D should avoid recreational cannabis use because of the increased risk for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- For adults with T1D or T2D who intend to use cannabis recreationally, individualized assessment and counseling should be offered to inform them of the general risks of cannabis, with a focus on harm reduction and reduction of the risk for potential adverse effects on diabetes management and complications.
- People with T1D or T2D should be offered education on and encouraged to read public information available through resources from various Canadian health authorities about the general risks of cannabis use to reduce the risk for nondiabetes-related adverse effects of cannabis consumption.
Of note, in 2018, the Canadian government produced an exhaustive compendium of information on cannabis for healthcare professionals that includes information relevant to managing patients with diabetes.
Dr. Shubrook and Dr. Han reported no competing interests.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.

