User login
The Need for a Multidisciplinary Approach for Successful High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
The Need for a Multidisciplinary Approach for Successful High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in the general population.1 The incidence of PE has been reported to range from 39 to 115 per 100,000 persons per year and has remained stable.2 Although mortality rates have declined, they remain high.3 The clinical presentation is nonspecific, making diagnosis and management challenging. A crucial and difficult aspect in the management of patients with PE is weighing the risks vs benefits of treatment, including thrombolytic therapy and other invasive procedures, which carry inherent risks. These factors have led to the development of PE response teams (PERTs) in some hospitals to implement effective multidisciplinary protocols that facilitate prompt diagnosis, management, and follow-up.4
CASE PRESENTATIONS
Case 1
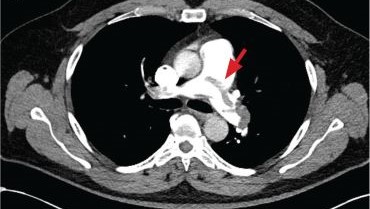
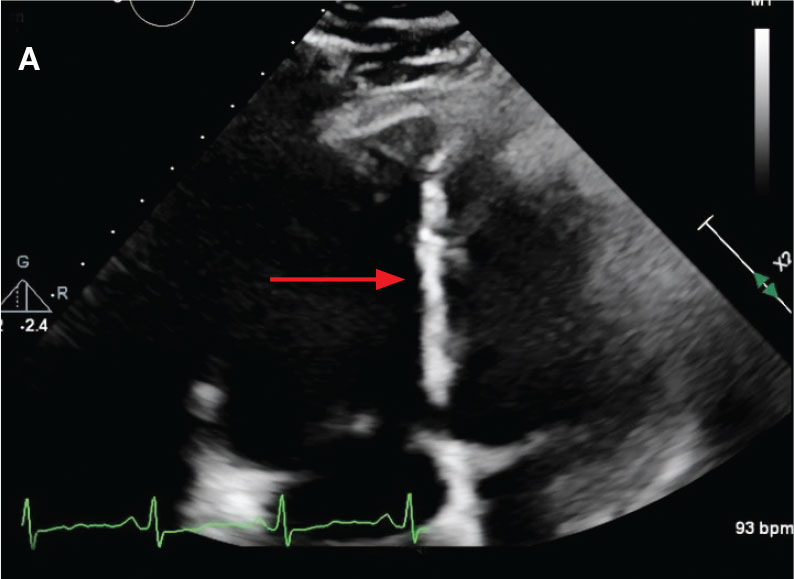
New onset seizures and cardiac arrest in the treatment of saddle PE. A 54-year-old male who worked as a draftsman and truck driver with a history of hypertension and nephrolithiasis presented to the emergency department (ED) with progressive shortness of breath for 2 weeks. On the morning of ED presentation the patient experienced an episode of severe shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and chest pressure. He reported no other symptoms such as palpitations, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, or extremity pain or swelling. He reported no recent travel, immunization, falls, or surgery. Upon evaluation, the patient was found to be in no acute distress, with stable vital signs and laboratory results except for 2 elevated results: > 20 μg/mL D-dimer (reference range, < 0.5 μg/mL) and N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP) level, 3455 pg/mL (reference range, < 125 pg/mL for patients aged < 75 years). Electrocardiogram showed T-wave inversions in leads V2 to V4. Imaging revealed a saddle PE and left popliteal deep venous thrombosis (Figure 1). The patient received an anticoagulation loading dose and was started on heparin drip upon admission to the medical intensive care unit (MICU) for further management and monitoring. The Interventional Radiology Service recommended full anticoagulation with consideration of reperfusion therapies if deterioration developed.
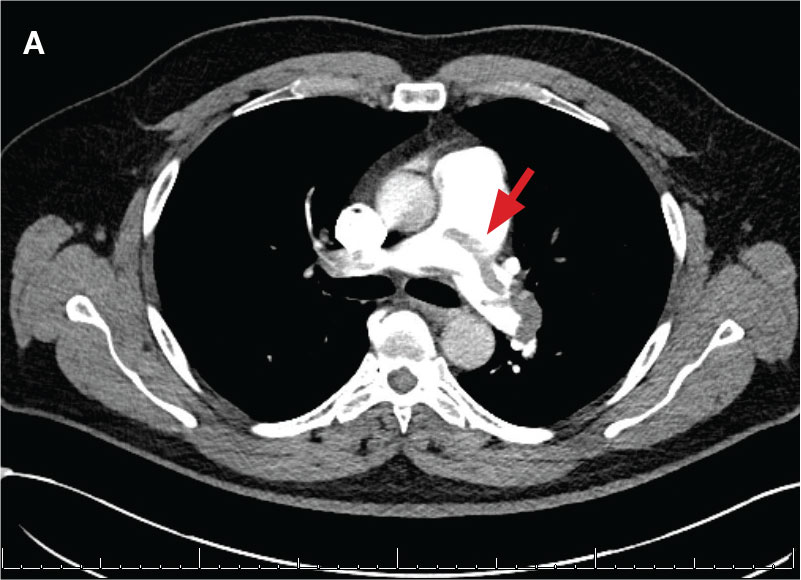
indicated by arrows in the pulmonary trunk extending to the left pulmonary artery (A),
and obliterating right pulmonary artery and branches of left pulmonary artery (B).
indicated by arrows in the pulmonary trunk extending to the left pulmonary artery (A),
and obliterating right pulmonary artery and branches of left pulmonary artery (B).
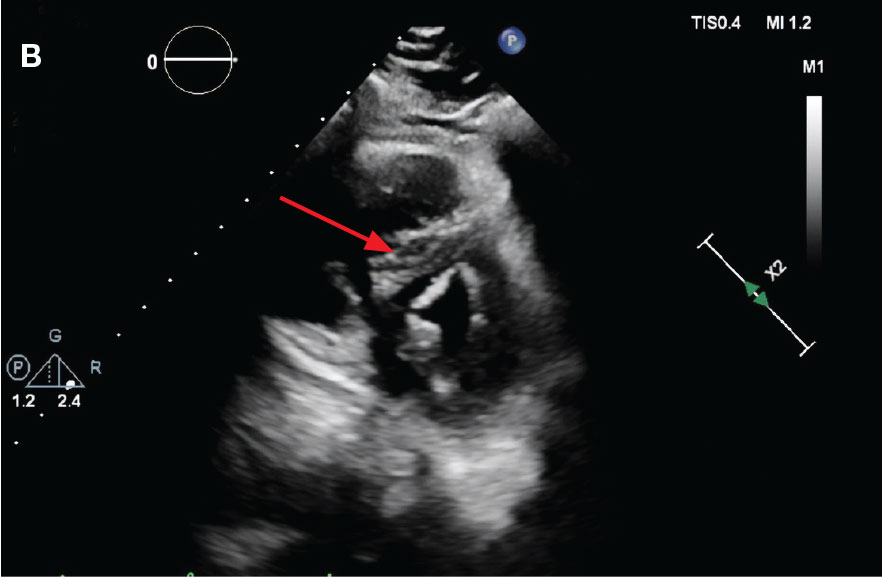
While in the MICU, point-of-care ultrasound findings were confirmed with official echocardiogram by the cardiology service, which demonstrated a preserved ejection fraction of 60% to 65%, a D-shaped left ventricle with septal wall hypokinesis secondary to right heart strain (Figure 2), a markedly elevated right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) of 73 mm Hg, and a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) of 38 mm Hg. The patient’s blood pressure progressively decreased, heart rate increased, and he required increased oxygen supplementation. The case was discussed with the Pharmacy Service, and since the patient had no contraindications to thrombolytic therapy, the appropriate dosage was calculated and 100 mg intravenous (IV) tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) was administered over 2 hours.
flattening and deviation to left in direction (A) and septal deviation to left with
formation of D-sign (B).
flattening and deviation to left in direction (A) and septal deviation to left with
formation of D-sign (B).
About 40 minutes into tPA infusion, the patient suddenly experienced marked shortness of breath, diaphoresis, and anxiety with seizure-like involuntary movements; as a result, the infusion was stopped. He also had episodes of posturing, mental status decline, and briefly going in and out of consciousness, which lasted about 3 minutes before he lost consciousness and pulse. High-quality advanced cardiac life support was initiated, followed by endotracheal intubation. Despite a secured airway and return of spontaneous circulation, the patient remained hypotensive and continued to have seizure-like activity.
The patient was administered a total of 8 mg of lorazepam, sedated with propofol, initiated at 5 μg/kg/min, titrated to stop seizure activity at 15μg/kg/min, and later maintained at 10 μg/kg/min, for a RASS of -1, and started on norepinephrine 0.1 μg/kg/min for acute stabilization. Head computed tomography without contrast showed no acute intracranial pathology as etiology of seizures. Seizure etiology differential at this time was broad; however, hypoxemia due to PE and medication adverse effects were strongly suspected.
The patient’s condition improved, and vasopressor therapy was tapered off the next day. Four days later, the patient was weaned from mechanical ventilation and transferred to the step-down unit. Echocardiogram obtained 48 hours after tPA infusion showed essentially normal left ventricular function (60%-65%), a RVSP of 17 mm Hg and mPAP of 13 mm Hg. The patient’s ProBNP levels markedly decreased to 137 pg/mL. Postextubation, the neurologic examination was at baseline. The Neurology Service recommended temporary treatment with levetiracetam, 1000 mg every 12 hours, and the Hematology Service recommended transitioning to direct oral anticoagulation with follow-up. The patient presented significant clinical and respiratory improvement and was referred for home-based physical rehabilitation as recommended by the physical medicine and rehabilitation service before being discharged.
Case 2
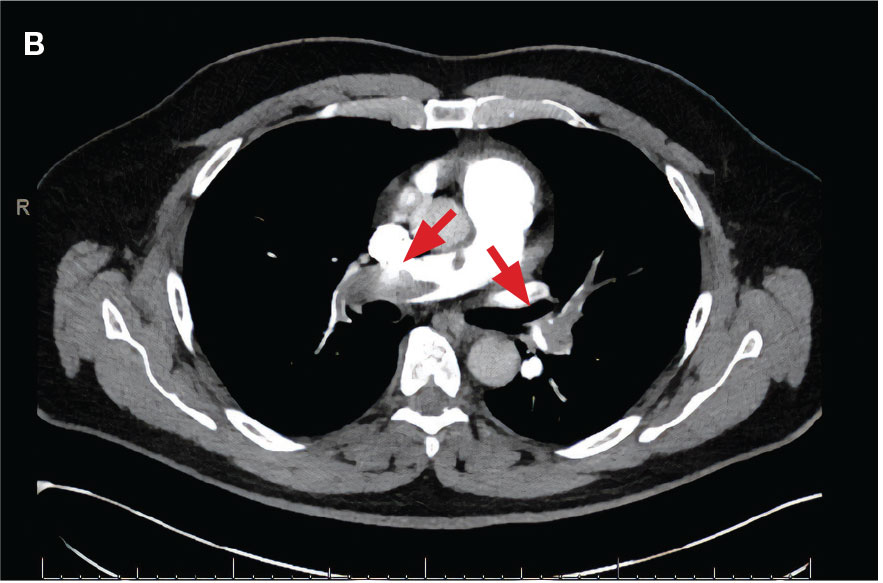
Localized tPA infusion for bilateral PEs via infusion catheters. A 91-year-old male with no history of smoking and a medical history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, prostate cancer (> 20 years postradiotherapy) and severe osteoarthritis was receiving treatment in the medical ward for medication-induced liver injury secondary to an antibiotic for a urinary tract infection. During the night the patient developed hypotension (86/46 mm Hg), shortness of breath, tachypnea, desaturation, nonradiating retrosternal chest pain, and tachycardia. The hypotension resolved after a 500-mL 0.9 normal saline bolus, and hypoxemia improved with supplemental oxygen via Venturi mask. Chest computed tomography angiography was performed immediately and revealed extensive bilateral acute PE, located most proximally in the right main pulmonary artery (PA) and on the left in the proximal lobar branches, with associated right heart strain. The patient was started on IV heparin with a bolus of 5000 units (80 u/kg) followed by a drip with a partial thromboplastin time goal of 62-103 seconds and transferred to MICU.
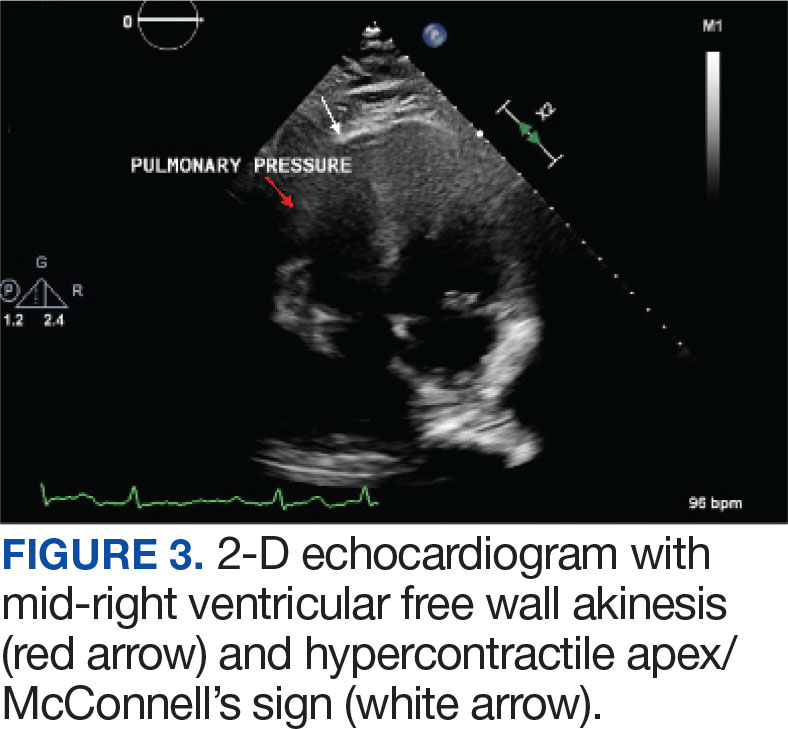
Laboratory findings were notable for proBNP that increased from 115 pg/mL to 4470 pg/mL (reference range, < 450 pg/mL for patients aged 75 years) and elevated troponin levels at 218 ng/L to 295 ng/L (reference range, < 22 ng/L), exhibiting chemical evidence of right heart strain. Initial echocardiogram showed mid-right ventricular free wall akinesis with a hypercontractile apex, suggestive of PE (McConnell’s sign) (Figure 3). Interventional Radiology Service was consulted and recommended tPA infusion given that the patient had bilateral PEs and stable blood pressure.
Pulmonary angiogram showed elevated pressures in the right PA of 64/21 mm Hg and the left PA pressures of 63/20 mm Hg. Mechanical disruption of the larger right lower PA thrombus was achieved via a pigtail catheter followed by bilateral catheter bolus infusions of 2 mg tPA (alteplase) and a continuous tPA infusion 0.5 mg/h for 24 hours, in conjunction with a heparin infusion.
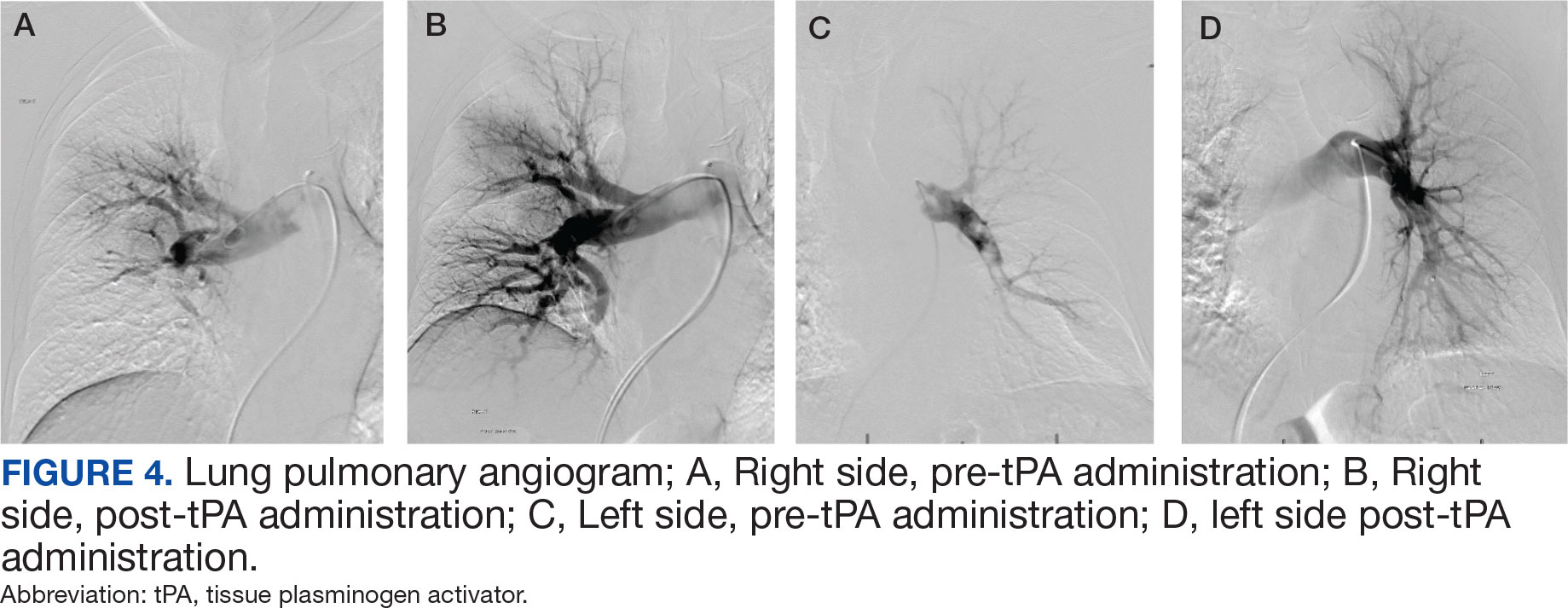
After 24 hours of tPA infusion, the catheters were removed, with posttreatment pulmonary angiography demonstrating right and left PA pressures of 42/15 mm Hg and 40/16 mm Hg, respectively. Pre- and postlocalized tPA infusion treatment images are provided for visual comparison (Figure 4). An echocardiogram performed after tPA infusion showed no signs of pulmonary hypertension. The Hematology Service provided recommendations regarding anticoagulation, and after completion of tPA infusion, the patient was transitioned to an unfractioned heparin infusion and subsequently to direct oral anticoagulation prior to transfer back to the medical ward, hemodynamically stable and asymptomatic.
DISCUSSION
PE management can be a straightforward decision when the patient meets criteria for hemodynamic instability, or with small PE burden. In contrast, management can be more challenging in intermediate-risk (submassive) PE when patients remain hemodynamically stable but show signs of cardiopulmonary stress, such as right heart strain, elevated troponins, or increased proBNP levels.2 In these situations, case-by- case evaluation is warranted. A PERT can assess the most beneficial treatment approach by considering factors such as right ventricular dysfunction, hemodynamic status, clot burden, and clinical deterioration despite appropriate anticoagulation. The evidence supporting the benefits these organized teams can provide is growing. These case reports emphasize the need for a multidisciplinary and systematic approach in these complex cases, especially in the management of intermediate-risk PE patients.
Currently, the Veterans Affairs Caribbean Healthcare System does not have an organized PERT, although a multidisciplinary approach was applied in the management of these patients. A systematic, structured team could have decreased time to interventions and alleviated the burden of physician decision-making. Having such a team would streamline the diagnostic pathway for patients presenting from a ward or emergency department with suspected PE.
We present 2 cases of patients found to have a high clot burden from PEs. The patients were initially hemodynamically stable (intermediate-risk PE), but later required systemic or localized thrombolysis due to hemodynamic deterioration despite adequate anticoagulation. Despite similar diagnoses and etiologies, these patients were successfully managed using different approaches, yielding positive outcomes. This reflects the complexity and variability in diagnosing and managing intermediate-risk PE in patients with different comorbidities and clot burden effects. In Case 1, our multidisciplinary approach was obtained via consults to selected services such as interventional radiology, cardiology, and direct involvement of pharmacy. An organized PERT conceivably would have allowed quicker discussions among these services, including hematology, to provide recommendations and collaborative support upon the patient’s arrival to the ED. Additionally, with a PERT team, a systematic approach to these patients could have allowed for an earlier official echocardiogram report for evaluation of right heart strain and develop an adequate therapeutic plan in a timely manner.
In Case 2, consultation with the Interventional Radiology Service yielded a better therapeutic plan, utilizing localized tPA infusion for this older adult patient with increased risk of bleeding with systemic tPA infusion. Having a PERT presents an opportunity to optimize PE management through early recognition, diagnosis, and treatment by institutional consensus from an interdisciplinary team.5,6 These response teams may improve outcomes and prognosis for patients with PE, especially where diagnosis and management is not clear.
The definite etiology of seizure activity in the first case pre- and postcardiac arrest, in the context of no acute intracranial process, remains unknown. Reports have emerged about postreperfusion seizures in acute ischemic stroke, as well as cases of seizures masquerading as PE as the primary presentation. 7,8 However, there were no reports of patients developing seizures post tPA infusion for the treatment of PE. This report may shed light into possible complications secondary to tPA infusion, raising awareness among physicians and encouraging further investigation into its possible etiologies.
CONCLUSIONS
Management of PE can be challenging in patients that meet criteria for intermediate risk. PERTs are a tool that allow for a multidisciplinary, standardized and systematic approach with a diagnostic and treatment algorithm that conceivably would result in a better consensus and therapeutic approach.
- Thompson BT, Kabrhel C. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of acute pulmonary embolism in adults. UpToDate. Wolters Kluwer. Updated December 4, 2023. Accessed February 26, 2025. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/epidemiology-and-pathogenesis-of-acute-pulmonary-embolism-in-adults
- Kulka HC, Zeller A, Fornaro J, Wuillemin WA, Konstantinides S, Christ M. Acute pulmonary embolism– its diagnosis and treatment from a multidisciplinary viewpoint. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021;118(37):618-628. doi:10.3238/arztebl.m2021.0226
- Zghouzi M, Mwansa H, Shore S, et al. Sex, racial, and geographic disparities in pulmonary embolism-related mortality nationwide. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(11):1571-1577. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202302-091OC
- Channick RN. The pulmonary embolism response team: why and how? Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;42(2):212-217. doi:10.1055/s-0041-1722963
- Rosovsky R, Zhao K, Sista A, Rivera-Lebron B, Kabrhel C. Pulmonary embolism response teams: purpose, evidence for efficacy, and future research directions. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019;3(3):315-330. doi:10.1002/rth2.12216
- Glazier JJ, Patiño-Velasquez S, Oviedo C. The pulmonary embolism response team: rationale, operation, and outcomes. Int J Angiol. 2022;31(3):198-202. doi:10.1055/s-0042-1750328
- Lekoubou A, Fox J, Ssentongo P. Incidence and association of reperfusion therapies with poststroke seizures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2020;51(9):2715-2723.doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119. 028899
- Alemany M, Nuñez A, Falip M, et al. Acute symptomatic seizures and epilepsy after mechanical thrombectomy. A prospective long-term follow-up study. Seizure. 2021;89:5-9. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2021.04.011
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in the general population.1 The incidence of PE has been reported to range from 39 to 115 per 100,000 persons per year and has remained stable.2 Although mortality rates have declined, they remain high.3 The clinical presentation is nonspecific, making diagnosis and management challenging. A crucial and difficult aspect in the management of patients with PE is weighing the risks vs benefits of treatment, including thrombolytic therapy and other invasive procedures, which carry inherent risks. These factors have led to the development of PE response teams (PERTs) in some hospitals to implement effective multidisciplinary protocols that facilitate prompt diagnosis, management, and follow-up.4
CASE PRESENTATIONS
Case 1
New onset seizures and cardiac arrest in the treatment of saddle PE. A 54-year-old male who worked as a draftsman and truck driver with a history of hypertension and nephrolithiasis presented to the emergency department (ED) with progressive shortness of breath for 2 weeks. On the morning of ED presentation the patient experienced an episode of severe shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and chest pressure. He reported no other symptoms such as palpitations, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, or extremity pain or swelling. He reported no recent travel, immunization, falls, or surgery. Upon evaluation, the patient was found to be in no acute distress, with stable vital signs and laboratory results except for 2 elevated results: > 20 μg/mL D-dimer (reference range, < 0.5 μg/mL) and N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP) level, 3455 pg/mL (reference range, < 125 pg/mL for patients aged < 75 years). Electrocardiogram showed T-wave inversions in leads V2 to V4. Imaging revealed a saddle PE and left popliteal deep venous thrombosis (Figure 1). The patient received an anticoagulation loading dose and was started on heparin drip upon admission to the medical intensive care unit (MICU) for further management and monitoring. The Interventional Radiology Service recommended full anticoagulation with consideration of reperfusion therapies if deterioration developed.

indicated by arrows in the pulmonary trunk extending to the left pulmonary artery (A),
and obliterating right pulmonary artery and branches of left pulmonary artery (B).

indicated by arrows in the pulmonary trunk extending to the left pulmonary artery (A),
and obliterating right pulmonary artery and branches of left pulmonary artery (B).
While in the MICU, point-of-care ultrasound findings were confirmed with official echocardiogram by the cardiology service, which demonstrated a preserved ejection fraction of 60% to 65%, a D-shaped left ventricle with septal wall hypokinesis secondary to right heart strain (Figure 2), a markedly elevated right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) of 73 mm Hg, and a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) of 38 mm Hg. The patient’s blood pressure progressively decreased, heart rate increased, and he required increased oxygen supplementation. The case was discussed with the Pharmacy Service, and since the patient had no contraindications to thrombolytic therapy, the appropriate dosage was calculated and 100 mg intravenous (IV) tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) was administered over 2 hours.

flattening and deviation to left in direction (A) and septal deviation to left with
formation of D-sign (B).

flattening and deviation to left in direction (A) and septal deviation to left with
formation of D-sign (B).
About 40 minutes into tPA infusion, the patient suddenly experienced marked shortness of breath, diaphoresis, and anxiety with seizure-like involuntary movements; as a result, the infusion was stopped. He also had episodes of posturing, mental status decline, and briefly going in and out of consciousness, which lasted about 3 minutes before he lost consciousness and pulse. High-quality advanced cardiac life support was initiated, followed by endotracheal intubation. Despite a secured airway and return of spontaneous circulation, the patient remained hypotensive and continued to have seizure-like activity.
The patient was administered a total of 8 mg of lorazepam, sedated with propofol, initiated at 5 μg/kg/min, titrated to stop seizure activity at 15μg/kg/min, and later maintained at 10 μg/kg/min, for a RASS of -1, and started on norepinephrine 0.1 μg/kg/min for acute stabilization. Head computed tomography without contrast showed no acute intracranial pathology as etiology of seizures. Seizure etiology differential at this time was broad; however, hypoxemia due to PE and medication adverse effects were strongly suspected.
The patient’s condition improved, and vasopressor therapy was tapered off the next day. Four days later, the patient was weaned from mechanical ventilation and transferred to the step-down unit. Echocardiogram obtained 48 hours after tPA infusion showed essentially normal left ventricular function (60%-65%), a RVSP of 17 mm Hg and mPAP of 13 mm Hg. The patient’s ProBNP levels markedly decreased to 137 pg/mL. Postextubation, the neurologic examination was at baseline. The Neurology Service recommended temporary treatment with levetiracetam, 1000 mg every 12 hours, and the Hematology Service recommended transitioning to direct oral anticoagulation with follow-up. The patient presented significant clinical and respiratory improvement and was referred for home-based physical rehabilitation as recommended by the physical medicine and rehabilitation service before being discharged.
Case 2
Localized tPA infusion for bilateral PEs via infusion catheters. A 91-year-old male with no history of smoking and a medical history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, prostate cancer (> 20 years postradiotherapy) and severe osteoarthritis was receiving treatment in the medical ward for medication-induced liver injury secondary to an antibiotic for a urinary tract infection. During the night the patient developed hypotension (86/46 mm Hg), shortness of breath, tachypnea, desaturation, nonradiating retrosternal chest pain, and tachycardia. The hypotension resolved after a 500-mL 0.9 normal saline bolus, and hypoxemia improved with supplemental oxygen via Venturi mask. Chest computed tomography angiography was performed immediately and revealed extensive bilateral acute PE, located most proximally in the right main pulmonary artery (PA) and on the left in the proximal lobar branches, with associated right heart strain. The patient was started on IV heparin with a bolus of 5000 units (80 u/kg) followed by a drip with a partial thromboplastin time goal of 62-103 seconds and transferred to MICU.
Laboratory findings were notable for proBNP that increased from 115 pg/mL to 4470 pg/mL (reference range, < 450 pg/mL for patients aged 75 years) and elevated troponin levels at 218 ng/L to 295 ng/L (reference range, < 22 ng/L), exhibiting chemical evidence of right heart strain. Initial echocardiogram showed mid-right ventricular free wall akinesis with a hypercontractile apex, suggestive of PE (McConnell’s sign) (Figure 3). Interventional Radiology Service was consulted and recommended tPA infusion given that the patient had bilateral PEs and stable blood pressure.

Pulmonary angiogram showed elevated pressures in the right PA of 64/21 mm Hg and the left PA pressures of 63/20 mm Hg. Mechanical disruption of the larger right lower PA thrombus was achieved via a pigtail catheter followed by bilateral catheter bolus infusions of 2 mg tPA (alteplase) and a continuous tPA infusion 0.5 mg/h for 24 hours, in conjunction with a heparin infusion.
After 24 hours of tPA infusion, the catheters were removed, with posttreatment pulmonary angiography demonstrating right and left PA pressures of 42/15 mm Hg and 40/16 mm Hg, respectively. Pre- and postlocalized tPA infusion treatment images are provided for visual comparison (Figure 4). An echocardiogram performed after tPA infusion showed no signs of pulmonary hypertension. The Hematology Service provided recommendations regarding anticoagulation, and after completion of tPA infusion, the patient was transitioned to an unfractioned heparin infusion and subsequently to direct oral anticoagulation prior to transfer back to the medical ward, hemodynamically stable and asymptomatic.

DISCUSSION
PE management can be a straightforward decision when the patient meets criteria for hemodynamic instability, or with small PE burden. In contrast, management can be more challenging in intermediate-risk (submassive) PE when patients remain hemodynamically stable but show signs of cardiopulmonary stress, such as right heart strain, elevated troponins, or increased proBNP levels.2 In these situations, case-by- case evaluation is warranted. A PERT can assess the most beneficial treatment approach by considering factors such as right ventricular dysfunction, hemodynamic status, clot burden, and clinical deterioration despite appropriate anticoagulation. The evidence supporting the benefits these organized teams can provide is growing. These case reports emphasize the need for a multidisciplinary and systematic approach in these complex cases, especially in the management of intermediate-risk PE patients.
Currently, the Veterans Affairs Caribbean Healthcare System does not have an organized PERT, although a multidisciplinary approach was applied in the management of these patients. A systematic, structured team could have decreased time to interventions and alleviated the burden of physician decision-making. Having such a team would streamline the diagnostic pathway for patients presenting from a ward or emergency department with suspected PE.
We present 2 cases of patients found to have a high clot burden from PEs. The patients were initially hemodynamically stable (intermediate-risk PE), but later required systemic or localized thrombolysis due to hemodynamic deterioration despite adequate anticoagulation. Despite similar diagnoses and etiologies, these patients were successfully managed using different approaches, yielding positive outcomes. This reflects the complexity and variability in diagnosing and managing intermediate-risk PE in patients with different comorbidities and clot burden effects. In Case 1, our multidisciplinary approach was obtained via consults to selected services such as interventional radiology, cardiology, and direct involvement of pharmacy. An organized PERT conceivably would have allowed quicker discussions among these services, including hematology, to provide recommendations and collaborative support upon the patient’s arrival to the ED. Additionally, with a PERT team, a systematic approach to these patients could have allowed for an earlier official echocardiogram report for evaluation of right heart strain and develop an adequate therapeutic plan in a timely manner.
In Case 2, consultation with the Interventional Radiology Service yielded a better therapeutic plan, utilizing localized tPA infusion for this older adult patient with increased risk of bleeding with systemic tPA infusion. Having a PERT presents an opportunity to optimize PE management through early recognition, diagnosis, and treatment by institutional consensus from an interdisciplinary team.5,6 These response teams may improve outcomes and prognosis for patients with PE, especially where diagnosis and management is not clear.
The definite etiology of seizure activity in the first case pre- and postcardiac arrest, in the context of no acute intracranial process, remains unknown. Reports have emerged about postreperfusion seizures in acute ischemic stroke, as well as cases of seizures masquerading as PE as the primary presentation. 7,8 However, there were no reports of patients developing seizures post tPA infusion for the treatment of PE. This report may shed light into possible complications secondary to tPA infusion, raising awareness among physicians and encouraging further investigation into its possible etiologies.
CONCLUSIONS
Management of PE can be challenging in patients that meet criteria for intermediate risk. PERTs are a tool that allow for a multidisciplinary, standardized and systematic approach with a diagnostic and treatment algorithm that conceivably would result in a better consensus and therapeutic approach.
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common cause of morbidity and mortality in the general population.1 The incidence of PE has been reported to range from 39 to 115 per 100,000 persons per year and has remained stable.2 Although mortality rates have declined, they remain high.3 The clinical presentation is nonspecific, making diagnosis and management challenging. A crucial and difficult aspect in the management of patients with PE is weighing the risks vs benefits of treatment, including thrombolytic therapy and other invasive procedures, which carry inherent risks. These factors have led to the development of PE response teams (PERTs) in some hospitals to implement effective multidisciplinary protocols that facilitate prompt diagnosis, management, and follow-up.4
CASE PRESENTATIONS
Case 1
New onset seizures and cardiac arrest in the treatment of saddle PE. A 54-year-old male who worked as a draftsman and truck driver with a history of hypertension and nephrolithiasis presented to the emergency department (ED) with progressive shortness of breath for 2 weeks. On the morning of ED presentation the patient experienced an episode of severe shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and chest pressure. He reported no other symptoms such as palpitations, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, or extremity pain or swelling. He reported no recent travel, immunization, falls, or surgery. Upon evaluation, the patient was found to be in no acute distress, with stable vital signs and laboratory results except for 2 elevated results: > 20 μg/mL D-dimer (reference range, < 0.5 μg/mL) and N-terminal prohormone brain natriuretic peptide (proBNP) level, 3455 pg/mL (reference range, < 125 pg/mL for patients aged < 75 years). Electrocardiogram showed T-wave inversions in leads V2 to V4. Imaging revealed a saddle PE and left popliteal deep venous thrombosis (Figure 1). The patient received an anticoagulation loading dose and was started on heparin drip upon admission to the medical intensive care unit (MICU) for further management and monitoring. The Interventional Radiology Service recommended full anticoagulation with consideration of reperfusion therapies if deterioration developed.

indicated by arrows in the pulmonary trunk extending to the left pulmonary artery (A),
and obliterating right pulmonary artery and branches of left pulmonary artery (B).

indicated by arrows in the pulmonary trunk extending to the left pulmonary artery (A),
and obliterating right pulmonary artery and branches of left pulmonary artery (B).
While in the MICU, point-of-care ultrasound findings were confirmed with official echocardiogram by the cardiology service, which demonstrated a preserved ejection fraction of 60% to 65%, a D-shaped left ventricle with septal wall hypokinesis secondary to right heart strain (Figure 2), a markedly elevated right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) of 73 mm Hg, and a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) of 38 mm Hg. The patient’s blood pressure progressively decreased, heart rate increased, and he required increased oxygen supplementation. The case was discussed with the Pharmacy Service, and since the patient had no contraindications to thrombolytic therapy, the appropriate dosage was calculated and 100 mg intravenous (IV) tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) was administered over 2 hours.

flattening and deviation to left in direction (A) and septal deviation to left with
formation of D-sign (B).

flattening and deviation to left in direction (A) and septal deviation to left with
formation of D-sign (B).
About 40 minutes into tPA infusion, the patient suddenly experienced marked shortness of breath, diaphoresis, and anxiety with seizure-like involuntary movements; as a result, the infusion was stopped. He also had episodes of posturing, mental status decline, and briefly going in and out of consciousness, which lasted about 3 minutes before he lost consciousness and pulse. High-quality advanced cardiac life support was initiated, followed by endotracheal intubation. Despite a secured airway and return of spontaneous circulation, the patient remained hypotensive and continued to have seizure-like activity.
The patient was administered a total of 8 mg of lorazepam, sedated with propofol, initiated at 5 μg/kg/min, titrated to stop seizure activity at 15μg/kg/min, and later maintained at 10 μg/kg/min, for a RASS of -1, and started on norepinephrine 0.1 μg/kg/min for acute stabilization. Head computed tomography without contrast showed no acute intracranial pathology as etiology of seizures. Seizure etiology differential at this time was broad; however, hypoxemia due to PE and medication adverse effects were strongly suspected.
The patient’s condition improved, and vasopressor therapy was tapered off the next day. Four days later, the patient was weaned from mechanical ventilation and transferred to the step-down unit. Echocardiogram obtained 48 hours after tPA infusion showed essentially normal left ventricular function (60%-65%), a RVSP of 17 mm Hg and mPAP of 13 mm Hg. The patient’s ProBNP levels markedly decreased to 137 pg/mL. Postextubation, the neurologic examination was at baseline. The Neurology Service recommended temporary treatment with levetiracetam, 1000 mg every 12 hours, and the Hematology Service recommended transitioning to direct oral anticoagulation with follow-up. The patient presented significant clinical and respiratory improvement and was referred for home-based physical rehabilitation as recommended by the physical medicine and rehabilitation service before being discharged.
Case 2
Localized tPA infusion for bilateral PEs via infusion catheters. A 91-year-old male with no history of smoking and a medical history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, prostate cancer (> 20 years postradiotherapy) and severe osteoarthritis was receiving treatment in the medical ward for medication-induced liver injury secondary to an antibiotic for a urinary tract infection. During the night the patient developed hypotension (86/46 mm Hg), shortness of breath, tachypnea, desaturation, nonradiating retrosternal chest pain, and tachycardia. The hypotension resolved after a 500-mL 0.9 normal saline bolus, and hypoxemia improved with supplemental oxygen via Venturi mask. Chest computed tomography angiography was performed immediately and revealed extensive bilateral acute PE, located most proximally in the right main pulmonary artery (PA) and on the left in the proximal lobar branches, with associated right heart strain. The patient was started on IV heparin with a bolus of 5000 units (80 u/kg) followed by a drip with a partial thromboplastin time goal of 62-103 seconds and transferred to MICU.
Laboratory findings were notable for proBNP that increased from 115 pg/mL to 4470 pg/mL (reference range, < 450 pg/mL for patients aged 75 years) and elevated troponin levels at 218 ng/L to 295 ng/L (reference range, < 22 ng/L), exhibiting chemical evidence of right heart strain. Initial echocardiogram showed mid-right ventricular free wall akinesis with a hypercontractile apex, suggestive of PE (McConnell’s sign) (Figure 3). Interventional Radiology Service was consulted and recommended tPA infusion given that the patient had bilateral PEs and stable blood pressure.

Pulmonary angiogram showed elevated pressures in the right PA of 64/21 mm Hg and the left PA pressures of 63/20 mm Hg. Mechanical disruption of the larger right lower PA thrombus was achieved via a pigtail catheter followed by bilateral catheter bolus infusions of 2 mg tPA (alteplase) and a continuous tPA infusion 0.5 mg/h for 24 hours, in conjunction with a heparin infusion.
After 24 hours of tPA infusion, the catheters were removed, with posttreatment pulmonary angiography demonstrating right and left PA pressures of 42/15 mm Hg and 40/16 mm Hg, respectively. Pre- and postlocalized tPA infusion treatment images are provided for visual comparison (Figure 4). An echocardiogram performed after tPA infusion showed no signs of pulmonary hypertension. The Hematology Service provided recommendations regarding anticoagulation, and after completion of tPA infusion, the patient was transitioned to an unfractioned heparin infusion and subsequently to direct oral anticoagulation prior to transfer back to the medical ward, hemodynamically stable and asymptomatic.

DISCUSSION
PE management can be a straightforward decision when the patient meets criteria for hemodynamic instability, or with small PE burden. In contrast, management can be more challenging in intermediate-risk (submassive) PE when patients remain hemodynamically stable but show signs of cardiopulmonary stress, such as right heart strain, elevated troponins, or increased proBNP levels.2 In these situations, case-by- case evaluation is warranted. A PERT can assess the most beneficial treatment approach by considering factors such as right ventricular dysfunction, hemodynamic status, clot burden, and clinical deterioration despite appropriate anticoagulation. The evidence supporting the benefits these organized teams can provide is growing. These case reports emphasize the need for a multidisciplinary and systematic approach in these complex cases, especially in the management of intermediate-risk PE patients.
Currently, the Veterans Affairs Caribbean Healthcare System does not have an organized PERT, although a multidisciplinary approach was applied in the management of these patients. A systematic, structured team could have decreased time to interventions and alleviated the burden of physician decision-making. Having such a team would streamline the diagnostic pathway for patients presenting from a ward or emergency department with suspected PE.
We present 2 cases of patients found to have a high clot burden from PEs. The patients were initially hemodynamically stable (intermediate-risk PE), but later required systemic or localized thrombolysis due to hemodynamic deterioration despite adequate anticoagulation. Despite similar diagnoses and etiologies, these patients were successfully managed using different approaches, yielding positive outcomes. This reflects the complexity and variability in diagnosing and managing intermediate-risk PE in patients with different comorbidities and clot burden effects. In Case 1, our multidisciplinary approach was obtained via consults to selected services such as interventional radiology, cardiology, and direct involvement of pharmacy. An organized PERT conceivably would have allowed quicker discussions among these services, including hematology, to provide recommendations and collaborative support upon the patient’s arrival to the ED. Additionally, with a PERT team, a systematic approach to these patients could have allowed for an earlier official echocardiogram report for evaluation of right heart strain and develop an adequate therapeutic plan in a timely manner.
In Case 2, consultation with the Interventional Radiology Service yielded a better therapeutic plan, utilizing localized tPA infusion for this older adult patient with increased risk of bleeding with systemic tPA infusion. Having a PERT presents an opportunity to optimize PE management through early recognition, diagnosis, and treatment by institutional consensus from an interdisciplinary team.5,6 These response teams may improve outcomes and prognosis for patients with PE, especially where diagnosis and management is not clear.
The definite etiology of seizure activity in the first case pre- and postcardiac arrest, in the context of no acute intracranial process, remains unknown. Reports have emerged about postreperfusion seizures in acute ischemic stroke, as well as cases of seizures masquerading as PE as the primary presentation. 7,8 However, there were no reports of patients developing seizures post tPA infusion for the treatment of PE. This report may shed light into possible complications secondary to tPA infusion, raising awareness among physicians and encouraging further investigation into its possible etiologies.
CONCLUSIONS
Management of PE can be challenging in patients that meet criteria for intermediate risk. PERTs are a tool that allow for a multidisciplinary, standardized and systematic approach with a diagnostic and treatment algorithm that conceivably would result in a better consensus and therapeutic approach.
- Thompson BT, Kabrhel C. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of acute pulmonary embolism in adults. UpToDate. Wolters Kluwer. Updated December 4, 2023. Accessed February 26, 2025. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/epidemiology-and-pathogenesis-of-acute-pulmonary-embolism-in-adults
- Kulka HC, Zeller A, Fornaro J, Wuillemin WA, Konstantinides S, Christ M. Acute pulmonary embolism– its diagnosis and treatment from a multidisciplinary viewpoint. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021;118(37):618-628. doi:10.3238/arztebl.m2021.0226
- Zghouzi M, Mwansa H, Shore S, et al. Sex, racial, and geographic disparities in pulmonary embolism-related mortality nationwide. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(11):1571-1577. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202302-091OC
- Channick RN. The pulmonary embolism response team: why and how? Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;42(2):212-217. doi:10.1055/s-0041-1722963
- Rosovsky R, Zhao K, Sista A, Rivera-Lebron B, Kabrhel C. Pulmonary embolism response teams: purpose, evidence for efficacy, and future research directions. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019;3(3):315-330. doi:10.1002/rth2.12216
- Glazier JJ, Patiño-Velasquez S, Oviedo C. The pulmonary embolism response team: rationale, operation, and outcomes. Int J Angiol. 2022;31(3):198-202. doi:10.1055/s-0042-1750328
- Lekoubou A, Fox J, Ssentongo P. Incidence and association of reperfusion therapies with poststroke seizures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2020;51(9):2715-2723.doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119. 028899
- Alemany M, Nuñez A, Falip M, et al. Acute symptomatic seizures and epilepsy after mechanical thrombectomy. A prospective long-term follow-up study. Seizure. 2021;89:5-9. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2021.04.011
- Thompson BT, Kabrhel C. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of acute pulmonary embolism in adults. UpToDate. Wolters Kluwer. Updated December 4, 2023. Accessed February 26, 2025. https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/epidemiology-and-pathogenesis-of-acute-pulmonary-embolism-in-adults
- Kulka HC, Zeller A, Fornaro J, Wuillemin WA, Konstantinides S, Christ M. Acute pulmonary embolism– its diagnosis and treatment from a multidisciplinary viewpoint. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021;118(37):618-628. doi:10.3238/arztebl.m2021.0226
- Zghouzi M, Mwansa H, Shore S, et al. Sex, racial, and geographic disparities in pulmonary embolism-related mortality nationwide. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023;20(11):1571-1577. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202302-091OC
- Channick RN. The pulmonary embolism response team: why and how? Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;42(2):212-217. doi:10.1055/s-0041-1722963
- Rosovsky R, Zhao K, Sista A, Rivera-Lebron B, Kabrhel C. Pulmonary embolism response teams: purpose, evidence for efficacy, and future research directions. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019;3(3):315-330. doi:10.1002/rth2.12216
- Glazier JJ, Patiño-Velasquez S, Oviedo C. The pulmonary embolism response team: rationale, operation, and outcomes. Int J Angiol. 2022;31(3):198-202. doi:10.1055/s-0042-1750328
- Lekoubou A, Fox J, Ssentongo P. Incidence and association of reperfusion therapies with poststroke seizures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke. 2020;51(9):2715-2723.doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.119. 028899
- Alemany M, Nuñez A, Falip M, et al. Acute symptomatic seizures and epilepsy after mechanical thrombectomy. A prospective long-term follow-up study. Seizure. 2021;89:5-9. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2021.04.011
The Need for a Multidisciplinary Approach for Successful High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
The Need for a Multidisciplinary Approach for Successful High-Risk Pulmonary Embolism Treatment
‘Door-to-Thrombectomy’ Time for Acute PE Linked to Better Outcomes
In the article "‘Door-to-thrombectomy ’ time linked to better acute PE outcomes" in the November 2024 issue of CHEST Physician, Dr. Patel was quoted as stating, "Mechanical thrombectomy in the FLASH registry showed mortality benefit," and, "There's a mortality benefit in any case whether the patient is high risk or intermediate-high." Dr. Patel was referring to the FLASH registry as a whole and not to the registry data study described in this article. CHEST Physician regrets the error and any confusion this may have caused.
BOSTON —
Among nearly 800 patients with acute PE whose data are recorded in the FlowTriever All-Comer Registry for Patient Safety and Hemodynamics (FLASH), a prospective multicenter registry of individuals treated with mechanical thrombectomy using the FlowTriever system (Inari Medical), shorter time from admission to mechanical thrombectomy was associated with significantly greater reductions in intraprocedural mean and systolic pulmonary artery pressures (PAP), greater reductions in the right ventricular/left ventricular (RV/LV) ratio, and longer 6-minute walk times at 6 months, reported Krunal H. Patel, MD, a pulmonary and critical care fellow at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Hospital in Philadelphia.
“Mechanical thrombectomy in the FLASH registry showed a mortality benefit. I think as time progresses and mechanical thrombectomy becomes more popular, we’re just going to need to figure out what is the ideal time for intervention,” he said during an oral abstract session at the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) 2024 Annual Meeting.
“There’s mortality benefit in any case whether the patient is high-risk or intermediate-high. This is a thought-provoking retrospective analysis that says that early intervention is probably better than doing it late, but regardless, the FLASH registry trial showed that early thrombectomy or thrombectomy in general shows positive mortality benefit,” Patel said in an interview.
He likened the challenge for pulmonary and critical care specialists to that of interventional cardiologists, who have determined that the ideal window for starting percutaneous coronary interventions is within 90 minutes of the patient’s arrival at the facility.
“I think we have to get our ‘door-to-balloon’ time for PE care,” he said.
Study Details
Patel and colleague Parth M. Rali, MD, FCCP, associate professor of thoracic medicine at Temple, conducted a retrospective review of data on 787 US patients in the FLASH registry for whom time to mechanical thrombectomy data were available. They stratified the patients into short and long time to mechanical thrombectomy groups, with “short” defined as ≤ 12 hours of presentation and “long” as > 12 hours.
They found that the median time to thrombectomy was 19.68 hours. In all, 242 patients (31%) were treated within the short window, and the remaining 545 patients (69%) were treated after at least 12 hours had passed.
Comparing clinical characteristics between the groups, the investigators noted that significantly more patients in the short time group vs long time group were categorized as high-risk (11.2% vs 6.2%; P = .0026). This difference is likely due to the need for greater urgency among high-risk patients, Patel said.
Patients in the short time group also had significantly higher baseline RV/LV ratios and lactate levels, but baseline dyspnea scores and pre-procedure median and systolic PAP were similar between the groups.
The mean time to thrombectomy was 6.08 hours in the short time group vs 34.04 hours in the long time group. Their respective median times were 6.01 and 24.73 hours.
The procedural time was similar between the groups, at 45 and 42 minutes, respectively.
The location of the treated thrombus was central only in 35.1% and 26.5% patients in the short and long time groups, respectively. Lobar-only thrombi were treated in 7.9% and 14.3%, respectively, and both central and lobar thrombi were treated in 57.0% and 59.2%, respectively.
Both 48-hour and 30-day all-cause mortality rates were similar between the groups (0.4%/0.2% and 0.5%/1.0%).
Patients in the short time group had slightly but significantly longer post-procedure hospital and intensive care unit stays, but 30-day readmission rates — whether for PE- or non-PE–related causes — were similar.
Where the differences between the groups really showed, however, were PAP reductions over baseline, with decline in median pressures of −8.7 mm Hg in the short group vs −7.2 mm Hg in the long group (P = .0008), and drops in systolic PAP of −14.4 vs −12.1 mm Hg, respectively (P = .0011).
In addition, reductions in RV/LV ratios from baseline were also significantly greater among patients whose thrombectomies had been expedited at the 48-hour, 30-day, and 6-month follow-up periods.
At 6 months, patients who had received mechanical thrombectomy within 12 hours also had significantly longer 6-minute walk distances (442.2 vs 390.5 m; P = .0032).
Low Thrombolysis Rate
Following his presentation, session co-moderator Galina Glazman-Kuczaj, MD, from the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Albany Med Health System, Albany, New York, asked Patel what percentage of patients, if any, had received thrombolytic therapy before the thrombectomy procedure.
He noted that only 1% or 2% patients in the FLASH registry received thrombolysis.
In an interview, Glazman-Kuczaj said that “it was reassuring for [Patel] to report that it was only a small population of patients who got thrombolysis beforehand in either group because you would expect that maybe people in the group that took longer to have a thrombectomy got some thrombolysis beforehand and that perhaps they were more stable, but it seems like thrombectomy was the first-line treatment in both groups.”
The FLASH Registry is funded by Inari Medical. Patel and Glazman-Kuczaj reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In the article "‘Door-to-thrombectomy ’ time linked to better acute PE outcomes" in the November 2024 issue of CHEST Physician, Dr. Patel was quoted as stating, "Mechanical thrombectomy in the FLASH registry showed mortality benefit," and, "There's a mortality benefit in any case whether the patient is high risk or intermediate-high." Dr. Patel was referring to the FLASH registry as a whole and not to the registry data study described in this article. CHEST Physician regrets the error and any confusion this may have caused.
BOSTON —
Among nearly 800 patients with acute PE whose data are recorded in the FlowTriever All-Comer Registry for Patient Safety and Hemodynamics (FLASH), a prospective multicenter registry of individuals treated with mechanical thrombectomy using the FlowTriever system (Inari Medical), shorter time from admission to mechanical thrombectomy was associated with significantly greater reductions in intraprocedural mean and systolic pulmonary artery pressures (PAP), greater reductions in the right ventricular/left ventricular (RV/LV) ratio, and longer 6-minute walk times at 6 months, reported Krunal H. Patel, MD, a pulmonary and critical care fellow at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Hospital in Philadelphia.
“Mechanical thrombectomy in the FLASH registry showed a mortality benefit. I think as time progresses and mechanical thrombectomy becomes more popular, we’re just going to need to figure out what is the ideal time for intervention,” he said during an oral abstract session at the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) 2024 Annual Meeting.
“There’s mortality benefit in any case whether the patient is high-risk or intermediate-high. This is a thought-provoking retrospective analysis that says that early intervention is probably better than doing it late, but regardless, the FLASH registry trial showed that early thrombectomy or thrombectomy in general shows positive mortality benefit,” Patel said in an interview.
He likened the challenge for pulmonary and critical care specialists to that of interventional cardiologists, who have determined that the ideal window for starting percutaneous coronary interventions is within 90 minutes of the patient’s arrival at the facility.
“I think we have to get our ‘door-to-balloon’ time for PE care,” he said.
Study Details
Patel and colleague Parth M. Rali, MD, FCCP, associate professor of thoracic medicine at Temple, conducted a retrospective review of data on 787 US patients in the FLASH registry for whom time to mechanical thrombectomy data were available. They stratified the patients into short and long time to mechanical thrombectomy groups, with “short” defined as ≤ 12 hours of presentation and “long” as > 12 hours.
They found that the median time to thrombectomy was 19.68 hours. In all, 242 patients (31%) were treated within the short window, and the remaining 545 patients (69%) were treated after at least 12 hours had passed.
Comparing clinical characteristics between the groups, the investigators noted that significantly more patients in the short time group vs long time group were categorized as high-risk (11.2% vs 6.2%; P = .0026). This difference is likely due to the need for greater urgency among high-risk patients, Patel said.
Patients in the short time group also had significantly higher baseline RV/LV ratios and lactate levels, but baseline dyspnea scores and pre-procedure median and systolic PAP were similar between the groups.
The mean time to thrombectomy was 6.08 hours in the short time group vs 34.04 hours in the long time group. Their respective median times were 6.01 and 24.73 hours.
The procedural time was similar between the groups, at 45 and 42 minutes, respectively.
The location of the treated thrombus was central only in 35.1% and 26.5% patients in the short and long time groups, respectively. Lobar-only thrombi were treated in 7.9% and 14.3%, respectively, and both central and lobar thrombi were treated in 57.0% and 59.2%, respectively.
Both 48-hour and 30-day all-cause mortality rates were similar between the groups (0.4%/0.2% and 0.5%/1.0%).
Patients in the short time group had slightly but significantly longer post-procedure hospital and intensive care unit stays, but 30-day readmission rates — whether for PE- or non-PE–related causes — were similar.
Where the differences between the groups really showed, however, were PAP reductions over baseline, with decline in median pressures of −8.7 mm Hg in the short group vs −7.2 mm Hg in the long group (P = .0008), and drops in systolic PAP of −14.4 vs −12.1 mm Hg, respectively (P = .0011).
In addition, reductions in RV/LV ratios from baseline were also significantly greater among patients whose thrombectomies had been expedited at the 48-hour, 30-day, and 6-month follow-up periods.
At 6 months, patients who had received mechanical thrombectomy within 12 hours also had significantly longer 6-minute walk distances (442.2 vs 390.5 m; P = .0032).
Low Thrombolysis Rate
Following his presentation, session co-moderator Galina Glazman-Kuczaj, MD, from the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Albany Med Health System, Albany, New York, asked Patel what percentage of patients, if any, had received thrombolytic therapy before the thrombectomy procedure.
He noted that only 1% or 2% patients in the FLASH registry received thrombolysis.
In an interview, Glazman-Kuczaj said that “it was reassuring for [Patel] to report that it was only a small population of patients who got thrombolysis beforehand in either group because you would expect that maybe people in the group that took longer to have a thrombectomy got some thrombolysis beforehand and that perhaps they were more stable, but it seems like thrombectomy was the first-line treatment in both groups.”
The FLASH Registry is funded by Inari Medical. Patel and Glazman-Kuczaj reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In the article "‘Door-to-thrombectomy ’ time linked to better acute PE outcomes" in the November 2024 issue of CHEST Physician, Dr. Patel was quoted as stating, "Mechanical thrombectomy in the FLASH registry showed mortality benefit," and, "There's a mortality benefit in any case whether the patient is high risk or intermediate-high." Dr. Patel was referring to the FLASH registry as a whole and not to the registry data study described in this article. CHEST Physician regrets the error and any confusion this may have caused.
BOSTON —
Among nearly 800 patients with acute PE whose data are recorded in the FlowTriever All-Comer Registry for Patient Safety and Hemodynamics (FLASH), a prospective multicenter registry of individuals treated with mechanical thrombectomy using the FlowTriever system (Inari Medical), shorter time from admission to mechanical thrombectomy was associated with significantly greater reductions in intraprocedural mean and systolic pulmonary artery pressures (PAP), greater reductions in the right ventricular/left ventricular (RV/LV) ratio, and longer 6-minute walk times at 6 months, reported Krunal H. Patel, MD, a pulmonary and critical care fellow at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Hospital in Philadelphia.
“Mechanical thrombectomy in the FLASH registry showed a mortality benefit. I think as time progresses and mechanical thrombectomy becomes more popular, we’re just going to need to figure out what is the ideal time for intervention,” he said during an oral abstract session at the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) 2024 Annual Meeting.
“There’s mortality benefit in any case whether the patient is high-risk or intermediate-high. This is a thought-provoking retrospective analysis that says that early intervention is probably better than doing it late, but regardless, the FLASH registry trial showed that early thrombectomy or thrombectomy in general shows positive mortality benefit,” Patel said in an interview.
He likened the challenge for pulmonary and critical care specialists to that of interventional cardiologists, who have determined that the ideal window for starting percutaneous coronary interventions is within 90 minutes of the patient’s arrival at the facility.
“I think we have to get our ‘door-to-balloon’ time for PE care,” he said.
Study Details
Patel and colleague Parth M. Rali, MD, FCCP, associate professor of thoracic medicine at Temple, conducted a retrospective review of data on 787 US patients in the FLASH registry for whom time to mechanical thrombectomy data were available. They stratified the patients into short and long time to mechanical thrombectomy groups, with “short” defined as ≤ 12 hours of presentation and “long” as > 12 hours.
They found that the median time to thrombectomy was 19.68 hours. In all, 242 patients (31%) were treated within the short window, and the remaining 545 patients (69%) were treated after at least 12 hours had passed.
Comparing clinical characteristics between the groups, the investigators noted that significantly more patients in the short time group vs long time group were categorized as high-risk (11.2% vs 6.2%; P = .0026). This difference is likely due to the need for greater urgency among high-risk patients, Patel said.
Patients in the short time group also had significantly higher baseline RV/LV ratios and lactate levels, but baseline dyspnea scores and pre-procedure median and systolic PAP were similar between the groups.
The mean time to thrombectomy was 6.08 hours in the short time group vs 34.04 hours in the long time group. Their respective median times were 6.01 and 24.73 hours.
The procedural time was similar between the groups, at 45 and 42 minutes, respectively.
The location of the treated thrombus was central only in 35.1% and 26.5% patients in the short and long time groups, respectively. Lobar-only thrombi were treated in 7.9% and 14.3%, respectively, and both central and lobar thrombi were treated in 57.0% and 59.2%, respectively.
Both 48-hour and 30-day all-cause mortality rates were similar between the groups (0.4%/0.2% and 0.5%/1.0%).
Patients in the short time group had slightly but significantly longer post-procedure hospital and intensive care unit stays, but 30-day readmission rates — whether for PE- or non-PE–related causes — were similar.
Where the differences between the groups really showed, however, were PAP reductions over baseline, with decline in median pressures of −8.7 mm Hg in the short group vs −7.2 mm Hg in the long group (P = .0008), and drops in systolic PAP of −14.4 vs −12.1 mm Hg, respectively (P = .0011).
In addition, reductions in RV/LV ratios from baseline were also significantly greater among patients whose thrombectomies had been expedited at the 48-hour, 30-day, and 6-month follow-up periods.
At 6 months, patients who had received mechanical thrombectomy within 12 hours also had significantly longer 6-minute walk distances (442.2 vs 390.5 m; P = .0032).
Low Thrombolysis Rate
Following his presentation, session co-moderator Galina Glazman-Kuczaj, MD, from the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at Albany Med Health System, Albany, New York, asked Patel what percentage of patients, if any, had received thrombolytic therapy before the thrombectomy procedure.
He noted that only 1% or 2% patients in the FLASH registry received thrombolysis.
In an interview, Glazman-Kuczaj said that “it was reassuring for [Patel] to report that it was only a small population of patients who got thrombolysis beforehand in either group because you would expect that maybe people in the group that took longer to have a thrombectomy got some thrombolysis beforehand and that perhaps they were more stable, but it seems like thrombectomy was the first-line treatment in both groups.”
The FLASH Registry is funded by Inari Medical. Patel and Glazman-Kuczaj reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CHEST 2024
Factors linked with increased VTE risk in COVID outpatients
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
Though VTE risk is well studied and significant in those hospitalized with COVID, little is known about the risk in the outpatient setting, said the authors of the new research published online in JAMA Network Open.
The study was conducted at two integrated health care delivery systems in northern and southern California. Data were gathered from the Kaiser Permanente Virtual Data Warehouse and electronic health records.
Nearly 400,000 patients studied
Researchers, led by Margaret Fang, MD, with the division of hospital medicine, University of California, San Francisco, identified 398,530 outpatients with COVID-19 from Jan. 1, 2020, through Jan. 31, 2021.
VTE risk was low overall for ambulatory COVID patients.
“It is a reassuring study,” Dr. Fang said in an interview.
The researchers found that the risk is highest in the first 30 days after COVID-19 diagnosis (unadjusted rate, 0.58; 95% confidence interval, 0.51-0.67 per 100 person-years vs. 0.09; 95% CI, 0.08-0.11 per 100 person-years after 30 days).
Factors linked with high VTE risk
They also found that several factors were linked with a higher risk of blood clots in the study population, including being at least 55 years old; being male; having a history of blood clots or thrombophilia; and a body mass index (BMI) of at least 30 kg/m2.
The authors write, “These findings may help identify subsets of patients with COVID-19 who could benefit from VTE preventive strategies and more intensive short-term surveillance.”
Are routine anticoagulants justified?
Previously, randomized clinical trials have found that hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 may benefit from therapeutically dosed heparin anticoagulants but that therapeutic anticoagulation had no net benefit – and perhaps could even harm – patients who were critically ill with COVID.
“[M]uch less is known about the optimal thromboprophylaxis strategy for people with milder presentations of COVID-19 who do not require hospitalization,” they write.
Mild COVID VTE risk similar to general population
The authors note that rates of blood clots linked with COVID-19 are not much higher than the average blood clot rate in the general population, which is about 0.1-0.2 per 100 person-years.
Therefore, the results don’t justify routine administration of anticoagulation given the costs, inconvenience, and bleeding risks, they acknowledge.
Dr. Fang told this publication that it’s hard to know what to tell patients, given the overall low VTE risk. She said their study wasn’t designed to advise when to give prophylaxis.
Physicians should inform patients of their higher risk
“We should tell our patients who fall into these risk categories that blood clot is a concern after the development of COVID, especially in those first 30 days. And some people might benefit from increased surveillance,” Dr. Fang said.
”I think this study would support ongoing studies that look at whether selected patients benefit from VTE prophylaxis, for example low-dose anticoagulants,” she said.
Dr. Fang said the subgroup factors they found increased risk of blood clots for all patients, not just COVID-19 patients. It’s not clear why factors such as being male may increase blood clot risk, though that is consistent with previous literature, but higher risk with higher BMI might be related to a combination of inflammation or decreased mobility, she said.
Unanswered questions
Robert H. Hopkins Jr., MD, says the study helps answer a couple of important questions – that the VTE risk in nonhospitalized COVID-19 patients is low and when and for which patients risk may be highest.
However, there are several unanswered questions that argue against routine initiation of anticoagulants, notes the professor of internal medicine and pediatrics chief, division of general internal medicine, at University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, Little Rock.
One is the change in the COVID variant landscape.
“We do not know whether rates of VTE are same or lower or higher with current circulating variants,” Dr. Hopkins said.
The authors acknowledge this as a limitation. Study data predate Omicron and subvariants, which appear to lower clinical severity, so it’s unclear whether VTE risk is different in this Omicron era.
Dr. Hopkins added another unknown: “We do not know whether vaccination affects rates of VTE in ambulatory breakthrough infection.”
Dr. Hopkins and the authors also note the lack of a control group in the study, to better compare risk.
Coauthor Dr. Prasad reports consultant fees from EpiExcellence LLC outside the submitted work. Coauthor Dr. Go reports grants paid to the division of research, Kaiser Permanente Northern California, from CSL Behring, Novartis, Bristol Meyers Squibb/Pfizer Alliance, and Janssen outside the submitted work.
The research was funded through Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute.
Dr. Hopkins reports no relevant financial relationships.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Must-read acute care medicine articles from 2022
When 2022 began, we started seeing some light at the end of the COVID-19 tunnel. Vaccines were widely available, and even with new variants of the virus still occasionally emerging, the rates of severe morbidity and mortality appeared to be decreasing.
Expectedly, journals appeared to start moving more toward mainstream topics and publications rather than what seemed like a major focus on COVID-19 publications. The resulting literature was fantastic.
Several of those topics were discussed in a prior Emergency Medicine Viewpoint from this news organization, and many more of the research advances of 2022 will be discussed in the near future. However, in this Viewpoint, I would like to present my annual review of my three “must-read” articles of the past year.
As in past years, I am choosing reviews of the literature rather than original research articles (which, all too often, become outdated or debunked within a few years). I choose these articles in the hopes that readers will not simply settle for my brief reviews of the key points but instead will feel compelled to download and read the entire articles. These publications address common conditions and quandaries we face in the daily practice of emergency medicine and are practice-changing.
Myocardial dysfunction after cardiac arrest: Tips and pitfalls
The management of post–cardiac arrest patients remains a hot topic in the resuscitation literature as we continue to understand that the immediate post-arrest period is critical to patient outcome.
Ortuno and colleagues reviewed the current literature on post-arrest care and wrote an outstanding summary of how to optimally care for these patients. More specifically, they focused on post-arrest patients who demonstrate continued shock, or “post–cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction” (PCAMD).
They propose three mechanisms for the pathogenesis of PCAMD: ischemia reperfusion phenomenon, systemic inflammatory response, and increased catecholamine release
I will skip through the details of the pathophysiology that they describe in the article, but I certainly do recommend that everyone review their descriptions.
Management of these patients begins with a good hemodynamic assessment, which includes clinical markers of perfusion (blood pressure, capillary refill), ECG, and point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS). If the initial assessment reveals an obvious cause of the cardiac arrest (e.g., massive pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, pericardial tamponade), then the underlying cause should be treated expeditiously.
In the absence of an obvious treatable cause of the shock, the fluid status and cardiac function should be addressed with POCUS. If the patient is hypovolemic, intravenous fluids should be administered. If the fluid status is adequate, POCUS should be used to estimate the patient’s ventricular function. If the ventricle appears to be hyperdynamic with good contractility, shock should be treated with norepinephrine. On the other hand, if the ventricle is hypodynamic, dobutamine should be substituted for norepinephrine or, more often, added to norepinephrine.
The above represents a simplified summary of the critical points, but the authors do delve into further detail and also discuss some other options for therapies, including steroids, coronary revascularization, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and so on. The review is very thoughtful, thorough, and definitely worth a full read.
Top myths of diagnosis and management of infectious diseases in hospital medicine
Most, if not all of us in medicine, have heard the saying that 50% of what we learn in medical school (or residency) will turn out to be wrong. I certainly believe in this concept and consequently, like many of you, I enjoy reading about myths and misconceptions that we have been taught. With that in mind, I have to say that I love this article because it seems to have been written specifically to address what I was taught!
This author group, consisting mostly of clinical PharmDs who are experts in antibiotic use, provide us with an evidence-based discussion of myths and pitfalls in how antibiotics are often used in current clinical practice. The authors review their top 10 myths involving the use of antibiotics in treating infections in the hospital setting. A few of these relate more to the inpatient setting, but here are my favorite emergency department (ED)–related myths that they address:
- “Antibiotics do no harm.” The authors address the risk-benefit of antibiotics based on assumed vs. confirmed infections, including a brief discussion of adverse drug effects.
- “Antibiotic durations of 7, 14, or 21 days are typically necessary.” The authors address appropriate duration of antibiotic use and the fact that unnecessarily long durations of use can lead to resistance. They also provide reassurance that some infections can be treated with quite short durations of antibiotics.
- “If one drug is good, two (or more!) is better.” The use of multiple antibiotics, often with overlapping bacterial coverage, is rampant in medicine and further increases the risk for adverse drug effects and resistance.
- “Oral antibiotics are not as good as intravenous antibiotics for hospitalized patients.” This is definitely a myth that I learned. I recall being taught by many senior physicians that anyone sick enough for admission should be treated with intravenous antibiotics. As it turns out, absorption and effectiveness of most oral antibiotics is just as good as intravenous antibiotics, and the oral formulations are often safer.
- “A history of a penicillin allergy means the patient can never receive a beta-lactam antibiotic.” This is a myth that was debunked quite a few years ago, but it seems that many clinicians still need a reminder.
The authors included five more myths that are worth the read. This is an article that needs to be disseminated among all hospital clinicians.
Guidelines for low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the emergency department
The Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) recently initiated a program focused on creating evidence-based approaches to challenging chief complaints and presentations in the emergency department (ED). In 2021, they published an approach to managing patients with recurrent, low-risk chest pain in the ED. This past year, they published their second guideline, focused on the management of patients with low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the ED.
Recurrent low-risk abdominal pain is a common and vexing presentation to EDs around the world, and there is little prior published guidance. Do all of these patients need repeat imaging? How do we manage their pain? Are there nonabdominal conditions that should be considered?
Broder and colleagues did a fantastic review of the current literature and, on behalf of SAEM, have provided a rational approach to optimal management of these patients. The four major questions they addressed, with brief summaries of their recommendations, are:
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive a repeat CT abdomen-pelvis (CTAP) after a negative CTAP within the past 12 months? This is a typical question that we all ponder when managing these patients. Unfortunately, the writing group found insufficient evidence to definitively identify populations in whom CTAP was recommended vs could be safely withheld. It is a bit disappointing that there is no definite answer to the question. On the other hand, it is reassuring to know that the world’s best evidence essentially says that it is perfectly appropriate to use your own good clinical judgment.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain with a negative CTAP receive additional imaging with abdominal ultrasound? In this case, the writing group found enough evidence, though low-level, to suggest against routine ultrasound in the absence of concern specifically for pelvic or hepatobiliary pathology. Like most tests, ultrasound is best used when there are specific concerns rather than being used in an undifferentiated fashion.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive screening for depression/anxiety? The writing group found enough evidence, though low-level again, to suggest that screening for depression and/or anxiety be performed during the ED evaluation. This could lead to successful therapy for the abdominal pain.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive nonopioid and/or nonpharmacologic analgesics? The writing group found little evidence to suggest for or against these analgesics, but they made a consensus recommendation suggesting an opioid-minimizing strategy for pain control.
Although the final recommendations of the writing group were not definitive or based on the strongest level of evidence, I find it helpful to have this guidance, nevertheless, on behalf of a major national organization. I also find it helpful to know that even with the best evidence available, optimal patient care will often boil down to physician experience and gestalt. I should also add that the overall article is chock-full of pearls and helpful information that will further inform the readers’ decisions, and so the full version is definitely worth the read.
In summary
There you have it – my three favorite practice-changing articles of 2022. Although I have tried to provide key points here, the full discussions of those key points in the published articles will provide a great deal more education than I can offer in this brief write-up, and so I strongly encourage everyone to read the full versions. Please be sure to include in the comments section your own pick for favorite or must-read articles from the past year.
Amal Mattu, MD, is a professor, vice chair of education, and codirector of the emergency cardiology fellowship in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 2022 began, we started seeing some light at the end of the COVID-19 tunnel. Vaccines were widely available, and even with new variants of the virus still occasionally emerging, the rates of severe morbidity and mortality appeared to be decreasing.
Expectedly, journals appeared to start moving more toward mainstream topics and publications rather than what seemed like a major focus on COVID-19 publications. The resulting literature was fantastic.
Several of those topics were discussed in a prior Emergency Medicine Viewpoint from this news organization, and many more of the research advances of 2022 will be discussed in the near future. However, in this Viewpoint, I would like to present my annual review of my three “must-read” articles of the past year.
As in past years, I am choosing reviews of the literature rather than original research articles (which, all too often, become outdated or debunked within a few years). I choose these articles in the hopes that readers will not simply settle for my brief reviews of the key points but instead will feel compelled to download and read the entire articles. These publications address common conditions and quandaries we face in the daily practice of emergency medicine and are practice-changing.
Myocardial dysfunction after cardiac arrest: Tips and pitfalls
The management of post–cardiac arrest patients remains a hot topic in the resuscitation literature as we continue to understand that the immediate post-arrest period is critical to patient outcome.
Ortuno and colleagues reviewed the current literature on post-arrest care and wrote an outstanding summary of how to optimally care for these patients. More specifically, they focused on post-arrest patients who demonstrate continued shock, or “post–cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction” (PCAMD).
They propose three mechanisms for the pathogenesis of PCAMD: ischemia reperfusion phenomenon, systemic inflammatory response, and increased catecholamine release
I will skip through the details of the pathophysiology that they describe in the article, but I certainly do recommend that everyone review their descriptions.
Management of these patients begins with a good hemodynamic assessment, which includes clinical markers of perfusion (blood pressure, capillary refill), ECG, and point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS). If the initial assessment reveals an obvious cause of the cardiac arrest (e.g., massive pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, pericardial tamponade), then the underlying cause should be treated expeditiously.
In the absence of an obvious treatable cause of the shock, the fluid status and cardiac function should be addressed with POCUS. If the patient is hypovolemic, intravenous fluids should be administered. If the fluid status is adequate, POCUS should be used to estimate the patient’s ventricular function. If the ventricle appears to be hyperdynamic with good contractility, shock should be treated with norepinephrine. On the other hand, if the ventricle is hypodynamic, dobutamine should be substituted for norepinephrine or, more often, added to norepinephrine.
The above represents a simplified summary of the critical points, but the authors do delve into further detail and also discuss some other options for therapies, including steroids, coronary revascularization, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and so on. The review is very thoughtful, thorough, and definitely worth a full read.
Top myths of diagnosis and management of infectious diseases in hospital medicine
Most, if not all of us in medicine, have heard the saying that 50% of what we learn in medical school (or residency) will turn out to be wrong. I certainly believe in this concept and consequently, like many of you, I enjoy reading about myths and misconceptions that we have been taught. With that in mind, I have to say that I love this article because it seems to have been written specifically to address what I was taught!
This author group, consisting mostly of clinical PharmDs who are experts in antibiotic use, provide us with an evidence-based discussion of myths and pitfalls in how antibiotics are often used in current clinical practice. The authors review their top 10 myths involving the use of antibiotics in treating infections in the hospital setting. A few of these relate more to the inpatient setting, but here are my favorite emergency department (ED)–related myths that they address:
- “Antibiotics do no harm.” The authors address the risk-benefit of antibiotics based on assumed vs. confirmed infections, including a brief discussion of adverse drug effects.
- “Antibiotic durations of 7, 14, or 21 days are typically necessary.” The authors address appropriate duration of antibiotic use and the fact that unnecessarily long durations of use can lead to resistance. They also provide reassurance that some infections can be treated with quite short durations of antibiotics.
- “If one drug is good, two (or more!) is better.” The use of multiple antibiotics, often with overlapping bacterial coverage, is rampant in medicine and further increases the risk for adverse drug effects and resistance.
- “Oral antibiotics are not as good as intravenous antibiotics for hospitalized patients.” This is definitely a myth that I learned. I recall being taught by many senior physicians that anyone sick enough for admission should be treated with intravenous antibiotics. As it turns out, absorption and effectiveness of most oral antibiotics is just as good as intravenous antibiotics, and the oral formulations are often safer.
- “A history of a penicillin allergy means the patient can never receive a beta-lactam antibiotic.” This is a myth that was debunked quite a few years ago, but it seems that many clinicians still need a reminder.
The authors included five more myths that are worth the read. This is an article that needs to be disseminated among all hospital clinicians.
Guidelines for low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the emergency department
The Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) recently initiated a program focused on creating evidence-based approaches to challenging chief complaints and presentations in the emergency department (ED). In 2021, they published an approach to managing patients with recurrent, low-risk chest pain in the ED. This past year, they published their second guideline, focused on the management of patients with low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the ED.
Recurrent low-risk abdominal pain is a common and vexing presentation to EDs around the world, and there is little prior published guidance. Do all of these patients need repeat imaging? How do we manage their pain? Are there nonabdominal conditions that should be considered?
Broder and colleagues did a fantastic review of the current literature and, on behalf of SAEM, have provided a rational approach to optimal management of these patients. The four major questions they addressed, with brief summaries of their recommendations, are:
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive a repeat CT abdomen-pelvis (CTAP) after a negative CTAP within the past 12 months? This is a typical question that we all ponder when managing these patients. Unfortunately, the writing group found insufficient evidence to definitively identify populations in whom CTAP was recommended vs could be safely withheld. It is a bit disappointing that there is no definite answer to the question. On the other hand, it is reassuring to know that the world’s best evidence essentially says that it is perfectly appropriate to use your own good clinical judgment.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain with a negative CTAP receive additional imaging with abdominal ultrasound? In this case, the writing group found enough evidence, though low-level, to suggest against routine ultrasound in the absence of concern specifically for pelvic or hepatobiliary pathology. Like most tests, ultrasound is best used when there are specific concerns rather than being used in an undifferentiated fashion.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive screening for depression/anxiety? The writing group found enough evidence, though low-level again, to suggest that screening for depression and/or anxiety be performed during the ED evaluation. This could lead to successful therapy for the abdominal pain.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive nonopioid and/or nonpharmacologic analgesics? The writing group found little evidence to suggest for or against these analgesics, but they made a consensus recommendation suggesting an opioid-minimizing strategy for pain control.
Although the final recommendations of the writing group were not definitive or based on the strongest level of evidence, I find it helpful to have this guidance, nevertheless, on behalf of a major national organization. I also find it helpful to know that even with the best evidence available, optimal patient care will often boil down to physician experience and gestalt. I should also add that the overall article is chock-full of pearls and helpful information that will further inform the readers’ decisions, and so the full version is definitely worth the read.
In summary
There you have it – my three favorite practice-changing articles of 2022. Although I have tried to provide key points here, the full discussions of those key points in the published articles will provide a great deal more education than I can offer in this brief write-up, and so I strongly encourage everyone to read the full versions. Please be sure to include in the comments section your own pick for favorite or must-read articles from the past year.
Amal Mattu, MD, is a professor, vice chair of education, and codirector of the emergency cardiology fellowship in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When 2022 began, we started seeing some light at the end of the COVID-19 tunnel. Vaccines were widely available, and even with new variants of the virus still occasionally emerging, the rates of severe morbidity and mortality appeared to be decreasing.
Expectedly, journals appeared to start moving more toward mainstream topics and publications rather than what seemed like a major focus on COVID-19 publications. The resulting literature was fantastic.
Several of those topics were discussed in a prior Emergency Medicine Viewpoint from this news organization, and many more of the research advances of 2022 will be discussed in the near future. However, in this Viewpoint, I would like to present my annual review of my three “must-read” articles of the past year.
As in past years, I am choosing reviews of the literature rather than original research articles (which, all too often, become outdated or debunked within a few years). I choose these articles in the hopes that readers will not simply settle for my brief reviews of the key points but instead will feel compelled to download and read the entire articles. These publications address common conditions and quandaries we face in the daily practice of emergency medicine and are practice-changing.
Myocardial dysfunction after cardiac arrest: Tips and pitfalls
The management of post–cardiac arrest patients remains a hot topic in the resuscitation literature as we continue to understand that the immediate post-arrest period is critical to patient outcome.
Ortuno and colleagues reviewed the current literature on post-arrest care and wrote an outstanding summary of how to optimally care for these patients. More specifically, they focused on post-arrest patients who demonstrate continued shock, or “post–cardiac arrest myocardial dysfunction” (PCAMD).
They propose three mechanisms for the pathogenesis of PCAMD: ischemia reperfusion phenomenon, systemic inflammatory response, and increased catecholamine release
I will skip through the details of the pathophysiology that they describe in the article, but I certainly do recommend that everyone review their descriptions.
Management of these patients begins with a good hemodynamic assessment, which includes clinical markers of perfusion (blood pressure, capillary refill), ECG, and point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS). If the initial assessment reveals an obvious cause of the cardiac arrest (e.g., massive pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, pericardial tamponade), then the underlying cause should be treated expeditiously.
In the absence of an obvious treatable cause of the shock, the fluid status and cardiac function should be addressed with POCUS. If the patient is hypovolemic, intravenous fluids should be administered. If the fluid status is adequate, POCUS should be used to estimate the patient’s ventricular function. If the ventricle appears to be hyperdynamic with good contractility, shock should be treated with norepinephrine. On the other hand, if the ventricle is hypodynamic, dobutamine should be substituted for norepinephrine or, more often, added to norepinephrine.
The above represents a simplified summary of the critical points, but the authors do delve into further detail and also discuss some other options for therapies, including steroids, coronary revascularization, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and so on. The review is very thoughtful, thorough, and definitely worth a full read.
Top myths of diagnosis and management of infectious diseases in hospital medicine
Most, if not all of us in medicine, have heard the saying that 50% of what we learn in medical school (or residency) will turn out to be wrong. I certainly believe in this concept and consequently, like many of you, I enjoy reading about myths and misconceptions that we have been taught. With that in mind, I have to say that I love this article because it seems to have been written specifically to address what I was taught!
This author group, consisting mostly of clinical PharmDs who are experts in antibiotic use, provide us with an evidence-based discussion of myths and pitfalls in how antibiotics are often used in current clinical practice. The authors review their top 10 myths involving the use of antibiotics in treating infections in the hospital setting. A few of these relate more to the inpatient setting, but here are my favorite emergency department (ED)–related myths that they address:
- “Antibiotics do no harm.” The authors address the risk-benefit of antibiotics based on assumed vs. confirmed infections, including a brief discussion of adverse drug effects.
- “Antibiotic durations of 7, 14, or 21 days are typically necessary.” The authors address appropriate duration of antibiotic use and the fact that unnecessarily long durations of use can lead to resistance. They also provide reassurance that some infections can be treated with quite short durations of antibiotics.
- “If one drug is good, two (or more!) is better.” The use of multiple antibiotics, often with overlapping bacterial coverage, is rampant in medicine and further increases the risk for adverse drug effects and resistance.
- “Oral antibiotics are not as good as intravenous antibiotics for hospitalized patients.” This is definitely a myth that I learned. I recall being taught by many senior physicians that anyone sick enough for admission should be treated with intravenous antibiotics. As it turns out, absorption and effectiveness of most oral antibiotics is just as good as intravenous antibiotics, and the oral formulations are often safer.
- “A history of a penicillin allergy means the patient can never receive a beta-lactam antibiotic.” This is a myth that was debunked quite a few years ago, but it seems that many clinicians still need a reminder.
The authors included five more myths that are worth the read. This is an article that needs to be disseminated among all hospital clinicians.
Guidelines for low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the emergency department
The Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM) recently initiated a program focused on creating evidence-based approaches to challenging chief complaints and presentations in the emergency department (ED). In 2021, they published an approach to managing patients with recurrent, low-risk chest pain in the ED. This past year, they published their second guideline, focused on the management of patients with low-risk, recurrent abdominal pain in the ED.
Recurrent low-risk abdominal pain is a common and vexing presentation to EDs around the world, and there is little prior published guidance. Do all of these patients need repeat imaging? How do we manage their pain? Are there nonabdominal conditions that should be considered?
Broder and colleagues did a fantastic review of the current literature and, on behalf of SAEM, have provided a rational approach to optimal management of these patients. The four major questions they addressed, with brief summaries of their recommendations, are:
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive a repeat CT abdomen-pelvis (CTAP) after a negative CTAP within the past 12 months? This is a typical question that we all ponder when managing these patients. Unfortunately, the writing group found insufficient evidence to definitively identify populations in whom CTAP was recommended vs could be safely withheld. It is a bit disappointing that there is no definite answer to the question. On the other hand, it is reassuring to know that the world’s best evidence essentially says that it is perfectly appropriate to use your own good clinical judgment.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain with a negative CTAP receive additional imaging with abdominal ultrasound? In this case, the writing group found enough evidence, though low-level, to suggest against routine ultrasound in the absence of concern specifically for pelvic or hepatobiliary pathology. Like most tests, ultrasound is best used when there are specific concerns rather than being used in an undifferentiated fashion.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive screening for depression/anxiety? The writing group found enough evidence, though low-level again, to suggest that screening for depression and/or anxiety be performed during the ED evaluation. This could lead to successful therapy for the abdominal pain.
- Should adult ED patients with low-risk, recurrent, and previously undifferentiated abdominal pain receive nonopioid and/or nonpharmacologic analgesics? The writing group found little evidence to suggest for or against these analgesics, but they made a consensus recommendation suggesting an opioid-minimizing strategy for pain control.
Although the final recommendations of the writing group were not definitive or based on the strongest level of evidence, I find it helpful to have this guidance, nevertheless, on behalf of a major national organization. I also find it helpful to know that even with the best evidence available, optimal patient care will often boil down to physician experience and gestalt. I should also add that the overall article is chock-full of pearls and helpful information that will further inform the readers’ decisions, and so the full version is definitely worth the read.
In summary
There you have it – my three favorite practice-changing articles of 2022. Although I have tried to provide key points here, the full discussions of those key points in the published articles will provide a great deal more education than I can offer in this brief write-up, and so I strongly encourage everyone to read the full versions. Please be sure to include in the comments section your own pick for favorite or must-read articles from the past year.
Amal Mattu, MD, is a professor, vice chair of education, and codirector of the emergency cardiology fellowship in the department of emergency medicine at the University of Maryland, Baltimore. She reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Know the right resuscitation for right-sided heart failure
Amado Alejandro Baez, MD, said in a presentation at the 2022 scientific assembly of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The patient arrived on day 20 after a radical cystoprostatectomy. He had driven 4 hours from another city for a urology follow-up visit. On arrival, he developed respiratory distress symptoms and presented to the emergency department, said Dr. Baez, professor of emergency medicine and epidemiology at the Medical College of Georgia/Augusta University and triple-board certified in EMS, emergency medicine, and critical care.
The patient developed a massive pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure). An electrocardiogram showed an S1Q3T3, demonstrating the distinctive nature of right ventricular failure, said Dr. Baez.
Research has demonstrated the differences in physiology between the right and left ventricles, he said.
Dr. Baez highlighted some of the features of right ventricle (RV) failure and how to manage it. Notably, the RV is thinner and less resilient. “RV failure patients may fall off the Starling curve,” in contrast to patients with isolated left ventricle (LV) failure.
RV pressure overload is associated with a range of conditions, such as pericardial disease, pulmonary embolism, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. When combined with RV overload, patients may develop intracardiac shunting or coronary heart disease, Dr. Baez said. Decreased contractility associated with RV failure can result from sepsis, right ventricular myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and arrhythmia.
Dr. Baez cited the 2018 scientific statement from the American Heart Association on the evaluation and management of right-sided heart failure. The authors of the statement noted that the complicated geometry of the right heart makes functional assessment a challenge. They wrote that various hemodynamic and biochemical markers can help guide clinical assessment and therapeutic decision-making.
Increased RV afterload drives multiple factors that can ultimately lead to cardiogenic shock and death, said Dr. Baez. These factors include decreased RV oxygen delivery, decreased RV coronary perfusion, decreased systemic blood pressure, and low carbon monoxide levels. RV afterload also leads to decreased RV contractility, an increase in RV oxygen demand, and tension in the RV wall, and it may contribute to tricuspid valve insufficiency, neurohormonal activation, and RV ischemia.
Treatment strategies involve improving symptoms and stopping disease progression, said Baez. In its scientific statement, the AHA recommends steps for assessing RV and LV function so as to identify RV failure as soon as possible, he said. After excluding pericardial disease, the AHA advises diagnosis and treatment of etiology-specific causes, such as right ventricular MI, pulmonary embolism, and sepsis. For arrhythmias, it recommends maintaining sinus rhythm when possible and considering a pacemaker to maintain atrioventricular synchrony and to avoid excessive bradycardia.
In its statement, the AHA also recommends optimizing preload with right arterial pressure/central venous pressure of 8-12 mm Hg, said Dr. Baez. Preload optimization combined with afterload reduction and improved contractility are hallmarks of care for patients with RV failure.
Avoiding systemic hypotension can prevent sequelae, such as myocardial ischemia and further hypotension, he said.
Optimization of fluid status is another key to managing RV failure, said Dr. Baez. Right heart coronary perfusion pressure can be protected by maintaining mean arterial pressure, and consideration should be given to reducing the RV afterload. Other strategies include inotropic medications and rhythm stabilization.
In general, for RV failure patients, “correct hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis and avoid intubation when possible,” he said. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be an option, depending on how many mechanical ventilator settings need to be adjusted.
In a study by Dr. Baez and colleagues published in Critical Care Medicine, the authors presented a Bayesian probability model for plasma lactate and severity of illness in cases of acute pulmonary embolism. “This Bayesian model demonstrated that the combination of shock index and lactate yield superior diagnostic gains than those compare to the sPESI and lactate,” Dr. Baez said.
The care model needs to be specific to the etiology, he added. Volume management in congested pulmonary hypertension involves a “squeeze and diurese” strategy.
According to the Internet Book of Critical Care, for patients with mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 60 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) of 25 mm Hg, renal perfusion pressure of 25 mm Hg, and no urine output, a vasopressor should be added to treatment, Dr. Baez said. In cases in which the MAP 75 mm Hg, the CVP is 25 mm Hg, the renal perfusion pressure is 50 mm Hg, and the patient has good urine output, vasopressors should be continued and fluid should be removed through use of a diuretic. For patients with a MAP of 75 mm Hg, a CVP of 12 mm Hg, and renal perfusion pressure of 63 mm Hg who have good urine output, the diuretic and the vasopressor should be discontinued.
Dr. Baez also reviewed several clinical studies of the utility of acute mechanical circulatory support systems for RV failure.
In two small studies involving a heart pump and a right ventricular assistive device, the 30-day survival rate was approximately 72%-73%. A study of 179 patients involving ECMO showed an in-hospital mortality rate of 38.6%, he said.
Overall, “prompt diagnosis, hemodynamic support, and initiation of specific treatment” are the foundations of managing RV failure, he concluded.
Dr. Baez disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Amado Alejandro Baez, MD, said in a presentation at the 2022 scientific assembly of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The patient arrived on day 20 after a radical cystoprostatectomy. He had driven 4 hours from another city for a urology follow-up visit. On arrival, he developed respiratory distress symptoms and presented to the emergency department, said Dr. Baez, professor of emergency medicine and epidemiology at the Medical College of Georgia/Augusta University and triple-board certified in EMS, emergency medicine, and critical care.
The patient developed a massive pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure). An electrocardiogram showed an S1Q3T3, demonstrating the distinctive nature of right ventricular failure, said Dr. Baez.
Research has demonstrated the differences in physiology between the right and left ventricles, he said.
Dr. Baez highlighted some of the features of right ventricle (RV) failure and how to manage it. Notably, the RV is thinner and less resilient. “RV failure patients may fall off the Starling curve,” in contrast to patients with isolated left ventricle (LV) failure.
RV pressure overload is associated with a range of conditions, such as pericardial disease, pulmonary embolism, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. When combined with RV overload, patients may develop intracardiac shunting or coronary heart disease, Dr. Baez said. Decreased contractility associated with RV failure can result from sepsis, right ventricular myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and arrhythmia.
Dr. Baez cited the 2018 scientific statement from the American Heart Association on the evaluation and management of right-sided heart failure. The authors of the statement noted that the complicated geometry of the right heart makes functional assessment a challenge. They wrote that various hemodynamic and biochemical markers can help guide clinical assessment and therapeutic decision-making.
Increased RV afterload drives multiple factors that can ultimately lead to cardiogenic shock and death, said Dr. Baez. These factors include decreased RV oxygen delivery, decreased RV coronary perfusion, decreased systemic blood pressure, and low carbon monoxide levels. RV afterload also leads to decreased RV contractility, an increase in RV oxygen demand, and tension in the RV wall, and it may contribute to tricuspid valve insufficiency, neurohormonal activation, and RV ischemia.
Treatment strategies involve improving symptoms and stopping disease progression, said Baez. In its scientific statement, the AHA recommends steps for assessing RV and LV function so as to identify RV failure as soon as possible, he said. After excluding pericardial disease, the AHA advises diagnosis and treatment of etiology-specific causes, such as right ventricular MI, pulmonary embolism, and sepsis. For arrhythmias, it recommends maintaining sinus rhythm when possible and considering a pacemaker to maintain atrioventricular synchrony and to avoid excessive bradycardia.
In its statement, the AHA also recommends optimizing preload with right arterial pressure/central venous pressure of 8-12 mm Hg, said Dr. Baez. Preload optimization combined with afterload reduction and improved contractility are hallmarks of care for patients with RV failure.
Avoiding systemic hypotension can prevent sequelae, such as myocardial ischemia and further hypotension, he said.
Optimization of fluid status is another key to managing RV failure, said Dr. Baez. Right heart coronary perfusion pressure can be protected by maintaining mean arterial pressure, and consideration should be given to reducing the RV afterload. Other strategies include inotropic medications and rhythm stabilization.
In general, for RV failure patients, “correct hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis and avoid intubation when possible,” he said. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be an option, depending on how many mechanical ventilator settings need to be adjusted.
In a study by Dr. Baez and colleagues published in Critical Care Medicine, the authors presented a Bayesian probability model for plasma lactate and severity of illness in cases of acute pulmonary embolism. “This Bayesian model demonstrated that the combination of shock index and lactate yield superior diagnostic gains than those compare to the sPESI and lactate,” Dr. Baez said.
The care model needs to be specific to the etiology, he added. Volume management in congested pulmonary hypertension involves a “squeeze and diurese” strategy.
According to the Internet Book of Critical Care, for patients with mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 60 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) of 25 mm Hg, renal perfusion pressure of 25 mm Hg, and no urine output, a vasopressor should be added to treatment, Dr. Baez said. In cases in which the MAP 75 mm Hg, the CVP is 25 mm Hg, the renal perfusion pressure is 50 mm Hg, and the patient has good urine output, vasopressors should be continued and fluid should be removed through use of a diuretic. For patients with a MAP of 75 mm Hg, a CVP of 12 mm Hg, and renal perfusion pressure of 63 mm Hg who have good urine output, the diuretic and the vasopressor should be discontinued.
Dr. Baez also reviewed several clinical studies of the utility of acute mechanical circulatory support systems for RV failure.
In two small studies involving a heart pump and a right ventricular assistive device, the 30-day survival rate was approximately 72%-73%. A study of 179 patients involving ECMO showed an in-hospital mortality rate of 38.6%, he said.
Overall, “prompt diagnosis, hemodynamic support, and initiation of specific treatment” are the foundations of managing RV failure, he concluded.
Dr. Baez disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Amado Alejandro Baez, MD, said in a presentation at the 2022 scientific assembly of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The patient arrived on day 20 after a radical cystoprostatectomy. He had driven 4 hours from another city for a urology follow-up visit. On arrival, he developed respiratory distress symptoms and presented to the emergency department, said Dr. Baez, professor of emergency medicine and epidemiology at the Medical College of Georgia/Augusta University and triple-board certified in EMS, emergency medicine, and critical care.
The patient developed a massive pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure). An electrocardiogram showed an S1Q3T3, demonstrating the distinctive nature of right ventricular failure, said Dr. Baez.
Research has demonstrated the differences in physiology between the right and left ventricles, he said.
Dr. Baez highlighted some of the features of right ventricle (RV) failure and how to manage it. Notably, the RV is thinner and less resilient. “RV failure patients may fall off the Starling curve,” in contrast to patients with isolated left ventricle (LV) failure.
RV pressure overload is associated with a range of conditions, such as pericardial disease, pulmonary embolism, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary arterial hypertension. When combined with RV overload, patients may develop intracardiac shunting or coronary heart disease, Dr. Baez said. Decreased contractility associated with RV failure can result from sepsis, right ventricular myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and arrhythmia.
Dr. Baez cited the 2018 scientific statement from the American Heart Association on the evaluation and management of right-sided heart failure. The authors of the statement noted that the complicated geometry of the right heart makes functional assessment a challenge. They wrote that various hemodynamic and biochemical markers can help guide clinical assessment and therapeutic decision-making.
Increased RV afterload drives multiple factors that can ultimately lead to cardiogenic shock and death, said Dr. Baez. These factors include decreased RV oxygen delivery, decreased RV coronary perfusion, decreased systemic blood pressure, and low carbon monoxide levels. RV afterload also leads to decreased RV contractility, an increase in RV oxygen demand, and tension in the RV wall, and it may contribute to tricuspid valve insufficiency, neurohormonal activation, and RV ischemia.
Treatment strategies involve improving symptoms and stopping disease progression, said Baez. In its scientific statement, the AHA recommends steps for assessing RV and LV function so as to identify RV failure as soon as possible, he said. After excluding pericardial disease, the AHA advises diagnosis and treatment of etiology-specific causes, such as right ventricular MI, pulmonary embolism, and sepsis. For arrhythmias, it recommends maintaining sinus rhythm when possible and considering a pacemaker to maintain atrioventricular synchrony and to avoid excessive bradycardia.
In its statement, the AHA also recommends optimizing preload with right arterial pressure/central venous pressure of 8-12 mm Hg, said Dr. Baez. Preload optimization combined with afterload reduction and improved contractility are hallmarks of care for patients with RV failure.
Avoiding systemic hypotension can prevent sequelae, such as myocardial ischemia and further hypotension, he said.
Optimization of fluid status is another key to managing RV failure, said Dr. Baez. Right heart coronary perfusion pressure can be protected by maintaining mean arterial pressure, and consideration should be given to reducing the RV afterload. Other strategies include inotropic medications and rhythm stabilization.
In general, for RV failure patients, “correct hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis and avoid intubation when possible,” he said. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be an option, depending on how many mechanical ventilator settings need to be adjusted.
In a study by Dr. Baez and colleagues published in Critical Care Medicine, the authors presented a Bayesian probability model for plasma lactate and severity of illness in cases of acute pulmonary embolism. “This Bayesian model demonstrated that the combination of shock index and lactate yield superior diagnostic gains than those compare to the sPESI and lactate,” Dr. Baez said.
The care model needs to be specific to the etiology, he added. Volume management in congested pulmonary hypertension involves a “squeeze and diurese” strategy.
According to the Internet Book of Critical Care, for patients with mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 60 mm Hg, central venous pressure (CVP) of 25 mm Hg, renal perfusion pressure of 25 mm Hg, and no urine output, a vasopressor should be added to treatment, Dr. Baez said. In cases in which the MAP 75 mm Hg, the CVP is 25 mm Hg, the renal perfusion pressure is 50 mm Hg, and the patient has good urine output, vasopressors should be continued and fluid should be removed through use of a diuretic. For patients with a MAP of 75 mm Hg, a CVP of 12 mm Hg, and renal perfusion pressure of 63 mm Hg who have good urine output, the diuretic and the vasopressor should be discontinued.
Dr. Baez also reviewed several clinical studies of the utility of acute mechanical circulatory support systems for RV failure.
In two small studies involving a heart pump and a right ventricular assistive device, the 30-day survival rate was approximately 72%-73%. A study of 179 patients involving ECMO showed an in-hospital mortality rate of 38.6%, he said.
Overall, “prompt diagnosis, hemodynamic support, and initiation of specific treatment” are the foundations of managing RV failure, he concluded.
Dr. Baez disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACEP 2022
New ASH guideline: VTE prophylaxis after major surgery
ORLANDO – The latest American Society of Hematology guideline on venous thromboembolism (VTE) tackles 30 key questions regarding prophylaxis in hospitalized patients undergoing surgery, according to the chair of the guideline panel, who highlighted 9 of those questions during a special session at the society’s annual meeting.
The clinical practice guideline, published just about a week before the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, focuses mainly on pharmacologic prophylaxis in specific surgical settings, said David R. Anderson, MD, dean of the faculty of medicine of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S.
“Our guidelines focused upon clinically important symptomatic outcomes, with less emphasis being placed on asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis detected by screening tests,” Dr. Anderson said.
At the special education session, Dr. Anderson highlighted several specific recommendations on prophylaxis in surgical patients.
Pharmacologic prophylaxis is not recommended for patients experiencing major trauma deemed to be at high risk of bleeding. Its use does reduce risk of symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) by about 10 events per 1,000 patients treated; however, Dr. Anderson said, the panel’s opinion was that this benefit was outweighed by increased risk of major bleeding, at 24 events per 1,000 patients treated.
“We do recommend, however that this risk of bleeding must be reevaluated over the course of recovery of patients, and this may change the decision around this intervention over time,” Dr. Anderson told attendees at the special session.
That’s because pharmacologic prophylaxis is recommended in surgical patients at low to moderate risk of bleeding. In this scenario, the incremental risk of major bleeding (14 events per 1,000 patients treated) is outweighed by the benefit of the reduction of symptomatic VTE events, according to Dr. Anderson.
When pharmacologic prophylaxis is used, the panel recommends combined prophylaxis – mechanical prophylaxis in addition to pharmacologic prophylaxis – especially in those patients at high or very high risk of VTE. Evidence shows that the combination approach significantly reduces risk of PE, and strongly suggests it may also reduce risk of symptomatic proximal DVT, Dr. Anderson said.
In surgical patients not receiving pharmacologic prophylaxis, mechanical prophylaxis is recommended over no mechanical prophylaxis, he added. Moreover, in those patients receiving mechanical prophylaxis, the ASH panel recommends use of intermittent compression devices over graduated compression stockings.
The panel comes out against prophylactic inferior vena cava (IVC) filter insertion in the guidelines. Dr. Anderson said that the “small reduction” in PE risk seen in observational studies is outweighed by increased risk of DVT, and a resulting trend for increased mortality, associated with insertion of the devices.
“We did not consider other risks of IVC filters such as filter embolization or perforation, which again would be complications that would support our recommendation against routine use of these devices in patients undergoing major surgery,” he said.
In terms of the type of pharmacologic prophylaxis to use, the panel said low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin would be reasonable choices in this setting. Available data do not demonstrate any significant differences between these choices for major clinical outcomes, Dr. Anderson added.
The guideline also addresses duration of pharmacologic prophylaxis, stating that extended prophylaxis – of at least 3 weeks – is favored over short-term prophylaxis, or up to 2 weeks of treatment. The extended approach significantly reduces risk of symptomatic PE and proximal DVT, though most of the supporting data come from studies of major joint arthroplasty and major general surgical procedures for patients with cancer. “We need more studies in other clinical areas to examine this particular question,” Dr. Anderson said.
The guideline on prophylaxis in surgical patients was published in Blood Advances (2019 Dec 3;3[23]:3898-944). Six other ASH VTE guidelines, all published in 2018, covered prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, VTE in pregnancy, optimal anticoagulation, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and pediatric considerations. The guidelines are available on the ASH website.
Dr. Anderson reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – The latest American Society of Hematology guideline on venous thromboembolism (VTE) tackles 30 key questions regarding prophylaxis in hospitalized patients undergoing surgery, according to the chair of the guideline panel, who highlighted 9 of those questions during a special session at the society’s annual meeting.
The clinical practice guideline, published just about a week before the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, focuses mainly on pharmacologic prophylaxis in specific surgical settings, said David R. Anderson, MD, dean of the faculty of medicine of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S.
“Our guidelines focused upon clinically important symptomatic outcomes, with less emphasis being placed on asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis detected by screening tests,” Dr. Anderson said.
At the special education session, Dr. Anderson highlighted several specific recommendations on prophylaxis in surgical patients.
Pharmacologic prophylaxis is not recommended for patients experiencing major trauma deemed to be at high risk of bleeding. Its use does reduce risk of symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) by about 10 events per 1,000 patients treated; however, Dr. Anderson said, the panel’s opinion was that this benefit was outweighed by increased risk of major bleeding, at 24 events per 1,000 patients treated.
“We do recommend, however that this risk of bleeding must be reevaluated over the course of recovery of patients, and this may change the decision around this intervention over time,” Dr. Anderson told attendees at the special session.
That’s because pharmacologic prophylaxis is recommended in surgical patients at low to moderate risk of bleeding. In this scenario, the incremental risk of major bleeding (14 events per 1,000 patients treated) is outweighed by the benefit of the reduction of symptomatic VTE events, according to Dr. Anderson.
When pharmacologic prophylaxis is used, the panel recommends combined prophylaxis – mechanical prophylaxis in addition to pharmacologic prophylaxis – especially in those patients at high or very high risk of VTE. Evidence shows that the combination approach significantly reduces risk of PE, and strongly suggests it may also reduce risk of symptomatic proximal DVT, Dr. Anderson said.
In surgical patients not receiving pharmacologic prophylaxis, mechanical prophylaxis is recommended over no mechanical prophylaxis, he added. Moreover, in those patients receiving mechanical prophylaxis, the ASH panel recommends use of intermittent compression devices over graduated compression stockings.
The panel comes out against prophylactic inferior vena cava (IVC) filter insertion in the guidelines. Dr. Anderson said that the “small reduction” in PE risk seen in observational studies is outweighed by increased risk of DVT, and a resulting trend for increased mortality, associated with insertion of the devices.
“We did not consider other risks of IVC filters such as filter embolization or perforation, which again would be complications that would support our recommendation against routine use of these devices in patients undergoing major surgery,” he said.
In terms of the type of pharmacologic prophylaxis to use, the panel said low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin would be reasonable choices in this setting. Available data do not demonstrate any significant differences between these choices for major clinical outcomes, Dr. Anderson added.
The guideline also addresses duration of pharmacologic prophylaxis, stating that extended prophylaxis – of at least 3 weeks – is favored over short-term prophylaxis, or up to 2 weeks of treatment. The extended approach significantly reduces risk of symptomatic PE and proximal DVT, though most of the supporting data come from studies of major joint arthroplasty and major general surgical procedures for patients with cancer. “We need more studies in other clinical areas to examine this particular question,” Dr. Anderson said.
The guideline on prophylaxis in surgical patients was published in Blood Advances (2019 Dec 3;3[23]:3898-944). Six other ASH VTE guidelines, all published in 2018, covered prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, VTE in pregnancy, optimal anticoagulation, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and pediatric considerations. The guidelines are available on the ASH website.
Dr. Anderson reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – The latest American Society of Hematology guideline on venous thromboembolism (VTE) tackles 30 key questions regarding prophylaxis in hospitalized patients undergoing surgery, according to the chair of the guideline panel, who highlighted 9 of those questions during a special session at the society’s annual meeting.
The clinical practice guideline, published just about a week before the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, focuses mainly on pharmacologic prophylaxis in specific surgical settings, said David R. Anderson, MD, dean of the faculty of medicine of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S.
“Our guidelines focused upon clinically important symptomatic outcomes, with less emphasis being placed on asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis detected by screening tests,” Dr. Anderson said.
At the special education session, Dr. Anderson highlighted several specific recommendations on prophylaxis in surgical patients.
Pharmacologic prophylaxis is not recommended for patients experiencing major trauma deemed to be at high risk of bleeding. Its use does reduce risk of symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) by about 10 events per 1,000 patients treated; however, Dr. Anderson said, the panel’s opinion was that this benefit was outweighed by increased risk of major bleeding, at 24 events per 1,000 patients treated.
“We do recommend, however that this risk of bleeding must be reevaluated over the course of recovery of patients, and this may change the decision around this intervention over time,” Dr. Anderson told attendees at the special session.
That’s because pharmacologic prophylaxis is recommended in surgical patients at low to moderate risk of bleeding. In this scenario, the incremental risk of major bleeding (14 events per 1,000 patients treated) is outweighed by the benefit of the reduction of symptomatic VTE events, according to Dr. Anderson.
When pharmacologic prophylaxis is used, the panel recommends combined prophylaxis – mechanical prophylaxis in addition to pharmacologic prophylaxis – especially in those patients at high or very high risk of VTE. Evidence shows that the combination approach significantly reduces risk of PE, and strongly suggests it may also reduce risk of symptomatic proximal DVT, Dr. Anderson said.
In surgical patients not receiving pharmacologic prophylaxis, mechanical prophylaxis is recommended over no mechanical prophylaxis, he added. Moreover, in those patients receiving mechanical prophylaxis, the ASH panel recommends use of intermittent compression devices over graduated compression stockings.
The panel comes out against prophylactic inferior vena cava (IVC) filter insertion in the guidelines. Dr. Anderson said that the “small reduction” in PE risk seen in observational studies is outweighed by increased risk of DVT, and a resulting trend for increased mortality, associated with insertion of the devices.
“We did not consider other risks of IVC filters such as filter embolization or perforation, which again would be complications that would support our recommendation against routine use of these devices in patients undergoing major surgery,” he said.
In terms of the type of pharmacologic prophylaxis to use, the panel said low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin would be reasonable choices in this setting. Available data do not demonstrate any significant differences between these choices for major clinical outcomes, Dr. Anderson added.
The guideline also addresses duration of pharmacologic prophylaxis, stating that extended prophylaxis – of at least 3 weeks – is favored over short-term prophylaxis, or up to 2 weeks of treatment. The extended approach significantly reduces risk of symptomatic PE and proximal DVT, though most of the supporting data come from studies of major joint arthroplasty and major general surgical procedures for patients with cancer. “We need more studies in other clinical areas to examine this particular question,” Dr. Anderson said.
The guideline on prophylaxis in surgical patients was published in Blood Advances (2019 Dec 3;3[23]:3898-944). Six other ASH VTE guidelines, all published in 2018, covered prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, VTE in pregnancy, optimal anticoagulation, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and pediatric considerations. The guidelines are available on the ASH website.
Dr. Anderson reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASH 2019
Pulmonary embolism treatment teams adopted widely for complex disease
NEW YORK – Seven years after the formation of the first pulmonary embolism response team (PERT), more than 100 institutions have joined the PERT Consortium, which was created to guide care and research for this thrombotic complication, according to a status report at a symposium on vascular and endovascular issues sponsored by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
“Why are PERTs needed? Pulmonary embolism patients are like snowflakes. No two are the same,” explained Richard Channick, MD, director of the pulmonary vascular disease program, University of California, Los Angeles.
Patient variability is an issue because algorithms for pulmonary embolism (PE) often differ at the point of diagnosis, such as the emergency department or intensive are unit, according to Dr. Channick, who was present when the first PERT was created in 2012 at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston. In addition, treatment algorithms can seem complex at a time when patients are deteriorating quickly.
“The treatment algorithms always say consider this or consider that, and then you get a recommendation with a 2B grade of evidence. So what do you do?” Dr. Channick asked, “This has really been crying for an organized approach.”
PERTs were created to fill this need. In most centers, PERTs are organized to respond to a diagnosis of PE wherever it occurs in the hospital. The goal is rapid activation of a team of experts who can reach a single consensus recommendation.
At MGH and UCLA, a similar relatively simple scheme has been created to guide physicians on how to activate the PERT and which situations make this appropriate.
“A big part of the PERT value has been our ability to conduct a real-time virtual consultation where we leverage online technology to look at images together in order to agree on a strategy,” Dr. Channick explained.
Although frequently asked what specialists are needed for an effective PERT, Dr. Channick said it depends on institutional structures, the types of specialists available, and, in some cases, the specific characteristics of the patient. In many situations, a pulmonary vascular specialist and an interventional radiologist might be sufficient. In others, team members might include some combination of an interventional cardiologist, a cardiac surgeon, and a hematologist.
It is also appropriate to include clinicians likely to participate in care following acute treatment of the PE. “One of the most critical values to PERT is the ability to systematically follow patients” after the PE is treated, Dr. Channick said.
So far, there are no data to confirm patients managed with PERT achieve better outcomes than those who are not. Reductions in mortality, length of stay, and costs are reasonably anticipated and might eventually be demonstrated, but Dr. Channick said that PERTs already have value.
“I think the efficiency of care is important,”he said. He called PERT a “one-stop shopping” approach to ensuring that multiple strategies are considered systematically.
There are many anecdotal examples of the benefits of shared decision-making for PE treatment. In one, a pulmonary specialist in a PERT team narrowly averted a planned thrombolysis in a patient diagnosed with PE who was actually found to have severe pulmonary fibrosis, according to Dr. Channick.
Not least important, the shared decision-making of a PERT could relieve the burden of difficult choices in complex situations. Bad outcomes in PE can be unavoidable even with optimal therapy.
“To me personally, a very important benefit of being part of a PERT is the feeling that we are all in it together,” Dr. Channick said. “Patients can go from being pretty stable to being dead very quickly.”
The PERT Consortium has sponsored an annual meeting on PE since 2015. It also maintains an ongoing registry for PE data from member institutions. These data are expected to have increasing value for comparing the impact of patient characteristics, treatment strategies, and other variables on outcomes.
For clinicians who are uncertain whether the PE incidence at their institution justifies a PERT, Dr. Channick had some advice. “If you build it, they will clot,” he said, meaning that due to the frequency of PE, a PERT will generally have plenty of work once created.
SOURCE: VEITHSYMPOSIUM
NEW YORK – Seven years after the formation of the first pulmonary embolism response team (PERT), more than 100 institutions have joined the PERT Consortium, which was created to guide care and research for this thrombotic complication, according to a status report at a symposium on vascular and endovascular issues sponsored by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
“Why are PERTs needed? Pulmonary embolism patients are like snowflakes. No two are the same,” explained Richard Channick, MD, director of the pulmonary vascular disease program, University of California, Los Angeles.
Patient variability is an issue because algorithms for pulmonary embolism (PE) often differ at the point of diagnosis, such as the emergency department or intensive are unit, according to Dr. Channick, who was present when the first PERT was created in 2012 at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston. In addition, treatment algorithms can seem complex at a time when patients are deteriorating quickly.
“The treatment algorithms always say consider this or consider that, and then you get a recommendation with a 2B grade of evidence. So what do you do?” Dr. Channick asked, “This has really been crying for an organized approach.”
PERTs were created to fill this need. In most centers, PERTs are organized to respond to a diagnosis of PE wherever it occurs in the hospital. The goal is rapid activation of a team of experts who can reach a single consensus recommendation.
At MGH and UCLA, a similar relatively simple scheme has been created to guide physicians on how to activate the PERT and which situations make this appropriate.
“A big part of the PERT value has been our ability to conduct a real-time virtual consultation where we leverage online technology to look at images together in order to agree on a strategy,” Dr. Channick explained.
Although frequently asked what specialists are needed for an effective PERT, Dr. Channick said it depends on institutional structures, the types of specialists available, and, in some cases, the specific characteristics of the patient. In many situations, a pulmonary vascular specialist and an interventional radiologist might be sufficient. In others, team members might include some combination of an interventional cardiologist, a cardiac surgeon, and a hematologist.
It is also appropriate to include clinicians likely to participate in care following acute treatment of the PE. “One of the most critical values to PERT is the ability to systematically follow patients” after the PE is treated, Dr. Channick said.
So far, there are no data to confirm patients managed with PERT achieve better outcomes than those who are not. Reductions in mortality, length of stay, and costs are reasonably anticipated and might eventually be demonstrated, but Dr. Channick said that PERTs already have value.
“I think the efficiency of care is important,”he said. He called PERT a “one-stop shopping” approach to ensuring that multiple strategies are considered systematically.
There are many anecdotal examples of the benefits of shared decision-making for PE treatment. In one, a pulmonary specialist in a PERT team narrowly averted a planned thrombolysis in a patient diagnosed with PE who was actually found to have severe pulmonary fibrosis, according to Dr. Channick.
Not least important, the shared decision-making of a PERT could relieve the burden of difficult choices in complex situations. Bad outcomes in PE can be unavoidable even with optimal therapy.
“To me personally, a very important benefit of being part of a PERT is the feeling that we are all in it together,” Dr. Channick said. “Patients can go from being pretty stable to being dead very quickly.”
The PERT Consortium has sponsored an annual meeting on PE since 2015. It also maintains an ongoing registry for PE data from member institutions. These data are expected to have increasing value for comparing the impact of patient characteristics, treatment strategies, and other variables on outcomes.
For clinicians who are uncertain whether the PE incidence at their institution justifies a PERT, Dr. Channick had some advice. “If you build it, they will clot,” he said, meaning that due to the frequency of PE, a PERT will generally have plenty of work once created.
SOURCE: VEITHSYMPOSIUM
NEW YORK – Seven years after the formation of the first pulmonary embolism response team (PERT), more than 100 institutions have joined the PERT Consortium, which was created to guide care and research for this thrombotic complication, according to a status report at a symposium on vascular and endovascular issues sponsored by the Cleveland Clinic Foundation.
“Why are PERTs needed? Pulmonary embolism patients are like snowflakes. No two are the same,” explained Richard Channick, MD, director of the pulmonary vascular disease program, University of California, Los Angeles.
Patient variability is an issue because algorithms for pulmonary embolism (PE) often differ at the point of diagnosis, such as the emergency department or intensive are unit, according to Dr. Channick, who was present when the first PERT was created in 2012 at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston. In addition, treatment algorithms can seem complex at a time when patients are deteriorating quickly.
“The treatment algorithms always say consider this or consider that, and then you get a recommendation with a 2B grade of evidence. So what do you do?” Dr. Channick asked, “This has really been crying for an organized approach.”
PERTs were created to fill this need. In most centers, PERTs are organized to respond to a diagnosis of PE wherever it occurs in the hospital. The goal is rapid activation of a team of experts who can reach a single consensus recommendation.
At MGH and UCLA, a similar relatively simple scheme has been created to guide physicians on how to activate the PERT and which situations make this appropriate.
“A big part of the PERT value has been our ability to conduct a real-time virtual consultation where we leverage online technology to look at images together in order to agree on a strategy,” Dr. Channick explained.
Although frequently asked what specialists are needed for an effective PERT, Dr. Channick said it depends on institutional structures, the types of specialists available, and, in some cases, the specific characteristics of the patient. In many situations, a pulmonary vascular specialist and an interventional radiologist might be sufficient. In others, team members might include some combination of an interventional cardiologist, a cardiac surgeon, and a hematologist.
It is also appropriate to include clinicians likely to participate in care following acute treatment of the PE. “One of the most critical values to PERT is the ability to systematically follow patients” after the PE is treated, Dr. Channick said.
So far, there are no data to confirm patients managed with PERT achieve better outcomes than those who are not. Reductions in mortality, length of stay, and costs are reasonably anticipated and might eventually be demonstrated, but Dr. Channick said that PERTs already have value.
“I think the efficiency of care is important,”he said. He called PERT a “one-stop shopping” approach to ensuring that multiple strategies are considered systematically.
There are many anecdotal examples of the benefits of shared decision-making for PE treatment. In one, a pulmonary specialist in a PERT team narrowly averted a planned thrombolysis in a patient diagnosed with PE who was actually found to have severe pulmonary fibrosis, according to Dr. Channick.
Not least important, the shared decision-making of a PERT could relieve the burden of difficult choices in complex situations. Bad outcomes in PE can be unavoidable even with optimal therapy.
“To me personally, a very important benefit of being part of a PERT is the feeling that we are all in it together,” Dr. Channick said. “Patients can go from being pretty stable to being dead very quickly.”
The PERT Consortium has sponsored an annual meeting on PE since 2015. It also maintains an ongoing registry for PE data from member institutions. These data are expected to have increasing value for comparing the impact of patient characteristics, treatment strategies, and other variables on outcomes.
For clinicians who are uncertain whether the PE incidence at their institution justifies a PERT, Dr. Channick had some advice. “If you build it, they will clot,” he said, meaning that due to the frequency of PE, a PERT will generally have plenty of work once created.
SOURCE: VEITHSYMPOSIUM
REPORTING FROM THE VEITHSYMPOSIUM
Thromboembolic events more likely among CIDP patients with CVAD
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) who receive intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) appear to have an increased risk of thromboembolic events if it is administered with a central venous access device (CVAD) when compared against those without a CVAD, according to a recent study.
Although CVADs can reliably deliver IVIg, they also represent an established risk factor for thromboembolic events, Ami Patel, PhD, a senior epidemiologist at CSL Behring, and colleagues noted on their poster at the annual meeting of the American Association for Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine.
The results suggest a need for physicians to be vigilant about patients’ potential risk factors for thromboembolic events, Dr. Patel said in an interview. Further research is planned, however, because the current study did not control for other risk factors or explore other possible confounding, she said.
Dr. Patel and her associates analyzed U.S. claims data (IBM/Truven MarketScan) from 2006 to 2018 and included all patients with a CIDP diagnosis claim and a postdiagnosis code for IVIg. A code for CVAD up to 2 months before CIDP diagnosis without removal before IVIg treatment ended determined those with CVAD exposure, and thromboembolic events included any codes related to arterial, venous, or vascular prostheses.
The researchers then compared patients in a case-control fashion, matching each one with a CVAD to five patients of similar demographics without a CVAD. Characteristics used for matching included medical insurance type, prescription data availability, sex, age, geographic region, and years enrolled in the database.
Among 7,447 patients with at least one IVIg claim, 11.8% (n = 882) had CVAD exposure and 88.2% (n = 6,565) did not. Of those without a CVAD, 3,642 patients were matched to patients with CVAD. A quarter (25.4%) of patients with a CVAD had a thromboembolic event, compared with 11.2% of matched patients without CVADs (P less than .0001).
In the year leading up to IVIg therapy, 16.9% of those with a CVAD and 10.9% of matched patients without one had a previous thromboembolic event (P less than .0001). Patients with a CVAD also had significantly higher rates of hypertension (51.9% vs. 45.0% with placebo; P less than .001) and anticoagulation therapy (7.0% vs. 5.2% with placebo; P less than .05). Differences between the groups were not significant for diabetes (26.9% vs. 24.2%) and hyperlipidemia (19.1% vs. 17.8%).
Occlusion and stenosis of the carotid artery was the most common arterial thromboembolic outcome, occurring in 5.3% of those with a CVAD and in 2.8% of those without a CVAD. The most common venous thromboembolic event was acute venous embolism and thrombosis of lower-extremity deep vessels, which occurred in 7% of those with a CVAD and in 1.8% of those without.
The researchers also compared inpatient admissions and emergency department visits among those with and without a CVAD; both rates were higher in patients with a CVAD. Visits to the emergency department occurred at a rate of 0.14 events per month for those with a CVAD (2.01 distinct months with a claim) and 0.09 events per month for those without a CVAD (0.65 distinct months with a claim). Patients with a CVAD had 1.44 months with an inpatient admissions claim, in comparison with 0.41 months among matched patients without a CVAD. Inpatient admission frequency per month was 0.14 for those with a CVAD and 0.08 for those without.
The research was funded by CSL Behring. Dr. Patel and two of the other five authors are employees of CSL Behring.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. AANEM 2019, Abstract 94.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) who receive intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) appear to have an increased risk of thromboembolic events if it is administered with a central venous access device (CVAD) when compared against those without a CVAD, according to a recent study.
Although CVADs can reliably deliver IVIg, they also represent an established risk factor for thromboembolic events, Ami Patel, PhD, a senior epidemiologist at CSL Behring, and colleagues noted on their poster at the annual meeting of the American Association for Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine.
The results suggest a need for physicians to be vigilant about patients’ potential risk factors for thromboembolic events, Dr. Patel said in an interview. Further research is planned, however, because the current study did not control for other risk factors or explore other possible confounding, she said.
Dr. Patel and her associates analyzed U.S. claims data (IBM/Truven MarketScan) from 2006 to 2018 and included all patients with a CIDP diagnosis claim and a postdiagnosis code for IVIg. A code for CVAD up to 2 months before CIDP diagnosis without removal before IVIg treatment ended determined those with CVAD exposure, and thromboembolic events included any codes related to arterial, venous, or vascular prostheses.
The researchers then compared patients in a case-control fashion, matching each one with a CVAD to five patients of similar demographics without a CVAD. Characteristics used for matching included medical insurance type, prescription data availability, sex, age, geographic region, and years enrolled in the database.
Among 7,447 patients with at least one IVIg claim, 11.8% (n = 882) had CVAD exposure and 88.2% (n = 6,565) did not. Of those without a CVAD, 3,642 patients were matched to patients with CVAD. A quarter (25.4%) of patients with a CVAD had a thromboembolic event, compared with 11.2% of matched patients without CVADs (P less than .0001).
In the year leading up to IVIg therapy, 16.9% of those with a CVAD and 10.9% of matched patients without one had a previous thromboembolic event (P less than .0001). Patients with a CVAD also had significantly higher rates of hypertension (51.9% vs. 45.0% with placebo; P less than .001) and anticoagulation therapy (7.0% vs. 5.2% with placebo; P less than .05). Differences between the groups were not significant for diabetes (26.9% vs. 24.2%) and hyperlipidemia (19.1% vs. 17.8%).
Occlusion and stenosis of the carotid artery was the most common arterial thromboembolic outcome, occurring in 5.3% of those with a CVAD and in 2.8% of those without a CVAD. The most common venous thromboembolic event was acute venous embolism and thrombosis of lower-extremity deep vessels, which occurred in 7% of those with a CVAD and in 1.8% of those without.
The researchers also compared inpatient admissions and emergency department visits among those with and without a CVAD; both rates were higher in patients with a CVAD. Visits to the emergency department occurred at a rate of 0.14 events per month for those with a CVAD (2.01 distinct months with a claim) and 0.09 events per month for those without a CVAD (0.65 distinct months with a claim). Patients with a CVAD had 1.44 months with an inpatient admissions claim, in comparison with 0.41 months among matched patients without a CVAD. Inpatient admission frequency per month was 0.14 for those with a CVAD and 0.08 for those without.
The research was funded by CSL Behring. Dr. Patel and two of the other five authors are employees of CSL Behring.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. AANEM 2019, Abstract 94.
AUSTIN, TEX. – Patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) who receive intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) appear to have an increased risk of thromboembolic events if it is administered with a central venous access device (CVAD) when compared against those without a CVAD, according to a recent study.
Although CVADs can reliably deliver IVIg, they also represent an established risk factor for thromboembolic events, Ami Patel, PhD, a senior epidemiologist at CSL Behring, and colleagues noted on their poster at the annual meeting of the American Association for Neuromuscular and Electrodiagnostic Medicine.
The results suggest a need for physicians to be vigilant about patients’ potential risk factors for thromboembolic events, Dr. Patel said in an interview. Further research is planned, however, because the current study did not control for other risk factors or explore other possible confounding, she said.
Dr. Patel and her associates analyzed U.S. claims data (IBM/Truven MarketScan) from 2006 to 2018 and included all patients with a CIDP diagnosis claim and a postdiagnosis code for IVIg. A code for CVAD up to 2 months before CIDP diagnosis without removal before IVIg treatment ended determined those with CVAD exposure, and thromboembolic events included any codes related to arterial, venous, or vascular prostheses.
The researchers then compared patients in a case-control fashion, matching each one with a CVAD to five patients of similar demographics without a CVAD. Characteristics used for matching included medical insurance type, prescription data availability, sex, age, geographic region, and years enrolled in the database.
Among 7,447 patients with at least one IVIg claim, 11.8% (n = 882) had CVAD exposure and 88.2% (n = 6,565) did not. Of those without a CVAD, 3,642 patients were matched to patients with CVAD. A quarter (25.4%) of patients with a CVAD had a thromboembolic event, compared with 11.2% of matched patients without CVADs (P less than .0001).
In the year leading up to IVIg therapy, 16.9% of those with a CVAD and 10.9% of matched patients without one had a previous thromboembolic event (P less than .0001). Patients with a CVAD also had significantly higher rates of hypertension (51.9% vs. 45.0% with placebo; P less than .001) and anticoagulation therapy (7.0% vs. 5.2% with placebo; P less than .05). Differences between the groups were not significant for diabetes (26.9% vs. 24.2%) and hyperlipidemia (19.1% vs. 17.8%).
Occlusion and stenosis of the carotid artery was the most common arterial thromboembolic outcome, occurring in 5.3% of those with a CVAD and in 2.8% of those without a CVAD. The most common venous thromboembolic event was acute venous embolism and thrombosis of lower-extremity deep vessels, which occurred in 7% of those with a CVAD and in 1.8% of those without.
The researchers also compared inpatient admissions and emergency department visits among those with and without a CVAD; both rates were higher in patients with a CVAD. Visits to the emergency department occurred at a rate of 0.14 events per month for those with a CVAD (2.01 distinct months with a claim) and 0.09 events per month for those without a CVAD (0.65 distinct months with a claim). Patients with a CVAD had 1.44 months with an inpatient admissions claim, in comparison with 0.41 months among matched patients without a CVAD. Inpatient admission frequency per month was 0.14 for those with a CVAD and 0.08 for those without.
The research was funded by CSL Behring. Dr. Patel and two of the other five authors are employees of CSL Behring.
SOURCE: Patel A et al. AANEM 2019, Abstract 94.
REPORTING FROM AANEM 2019
FDA approves rivaroxaban for VTE prevention in hospitalized, acutely ill patients
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in hospitalized, acutely ill patients at risk for thromboembolic complications who do not have a high bleeding risk, according to a release from Janssen.
FDA approval for the new indication is based on results from the phase 3 MAGELLAN and MARINER trials, which included more than 20,000 hospitalized, acutely ill patients. In MAGELLAN, rivaroxaban demonstrated noninferiority to enoxaparin, a low-molecular-weight heparin, in short-term usage, and it was superior over the long term, compared with short-term enoxaparin followed by placebo.
While VTE and VTE-related deaths were not reduced in MARINER, compared with placebo, patients who received rivaroxaban did see a significantly reduction in symptomatic VTE with a favorable safety profile.
According to the indication, rivaroxaban can be administered to patients during hospitalization and can be continued after discharge for 31-39 days. The safety profile in MAGELLAN and MARINER was consistent with that already seen, with the most common adverse event being bleeding.
The new indication is the eighth for rivaroxaban, the most of any direct oral anticoagulant; six of these are specifically for the treatment, prevention, and reduction in the risk of VTE recurrence.
“With this new approval, Xarelto as an oral-only option now has the potential to change how acutely ill medical patients are managed for the prevention of blood clots, both in the hospital and for an extended period after discharge,” said Alex C. Spyropoulos, MD, of Northwell Health at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, and a member of the steering committee of the MAGELLAN trial.
Find the full press release on the Janssen website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in hospitalized, acutely ill patients at risk for thromboembolic complications who do not have a high bleeding risk, according to a release from Janssen.
FDA approval for the new indication is based on results from the phase 3 MAGELLAN and MARINER trials, which included more than 20,000 hospitalized, acutely ill patients. In MAGELLAN, rivaroxaban demonstrated noninferiority to enoxaparin, a low-molecular-weight heparin, in short-term usage, and it was superior over the long term, compared with short-term enoxaparin followed by placebo.
While VTE and VTE-related deaths were not reduced in MARINER, compared with placebo, patients who received rivaroxaban did see a significantly reduction in symptomatic VTE with a favorable safety profile.
According to the indication, rivaroxaban can be administered to patients during hospitalization and can be continued after discharge for 31-39 days. The safety profile in MAGELLAN and MARINER was consistent with that already seen, with the most common adverse event being bleeding.
The new indication is the eighth for rivaroxaban, the most of any direct oral anticoagulant; six of these are specifically for the treatment, prevention, and reduction in the risk of VTE recurrence.
“With this new approval, Xarelto as an oral-only option now has the potential to change how acutely ill medical patients are managed for the prevention of blood clots, both in the hospital and for an extended period after discharge,” said Alex C. Spyropoulos, MD, of Northwell Health at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, and a member of the steering committee of the MAGELLAN trial.
Find the full press release on the Janssen website.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rivaroxaban (Xarelto) for the prevention of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in hospitalized, acutely ill patients at risk for thromboembolic complications who do not have a high bleeding risk, according to a release from Janssen.
FDA approval for the new indication is based on results from the phase 3 MAGELLAN and MARINER trials, which included more than 20,000 hospitalized, acutely ill patients. In MAGELLAN, rivaroxaban demonstrated noninferiority to enoxaparin, a low-molecular-weight heparin, in short-term usage, and it was superior over the long term, compared with short-term enoxaparin followed by placebo.
While VTE and VTE-related deaths were not reduced in MARINER, compared with placebo, patients who received rivaroxaban did see a significantly reduction in symptomatic VTE with a favorable safety profile.
According to the indication, rivaroxaban can be administered to patients during hospitalization and can be continued after discharge for 31-39 days. The safety profile in MAGELLAN and MARINER was consistent with that already seen, with the most common adverse event being bleeding.
The new indication is the eighth for rivaroxaban, the most of any direct oral anticoagulant; six of these are specifically for the treatment, prevention, and reduction in the risk of VTE recurrence.
“With this new approval, Xarelto as an oral-only option now has the potential to change how acutely ill medical patients are managed for the prevention of blood clots, both in the hospital and for an extended period after discharge,” said Alex C. Spyropoulos, MD, of Northwell Health at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, and a member of the steering committee of the MAGELLAN trial.
Find the full press release on the Janssen website.
Older IBD patients are most at risk of postdischarge VTE
Hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are most likely to be readmitted for venous thromboembolism (VTE) within 60 days of discharge, according to a new study that analyzed 5 years of U.S. readmissions data.
“Given increased thrombotic risk postdischarge, as well as overall safety of VTE prophylaxis, extending prophylaxis for those at highest risk may have significant benefits,” wrote Adam S. Faye, MD, of Columbia University, and coauthors. The study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
To determine which IBD patients would be most in need of postdischarge VTE prophylaxis, as well as when to administer it, the researchers analyzed 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD). They found a total of 872,122 index admissions for IBD patients; 4% of those patients had a prior VTE. Of the index admissions, 1,160 led to a VTE readmission within 90 days. Readmitted patients had a relatively equal proportion of ulcerative colitis (n = 522) and Crohn’s disease (n = 638).
More than 90% of VTE readmissions occurred within 60 days of discharge; the risk was highest over the first 10 days and then decreased in each ensuing 10-day period until a slight increase at the 81- to 90-day period. All patients over age 30 had higher rates of readmission than those of patients under age 18, with the highest risk in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 years (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01). Women were at lower risk (RR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.92, P less than .01). Higher risks of readmission were also associated with being on Medicare (RR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.23-1.58, P less than .01) compared with being on private insurance and being cared for at a large hospital (RR 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52, P = .02) compared with a small hospital.
The highest risk of VTE readmission was associated with a prior history of VTE (RR 2.89; 95% CI, 2.40-3.48, P less than .01), having two or more comorbidities (RR 2.57; 95% CI, 2.11-3.12, P less than .01) and having a Clostridioides difficile infection as of index admission (RR 1.90; 95% CI, 1.51-2.38, P less than .01). In addition, increased risk was associated with being discharged to a nursing or care facility (RR 1.85; 95% CI, 1.56-2.20, P less than .01) or home with health services (RR 2.05; 95% CI, 1.78-2.38, P less than .01) compared with a routine discharge.
In their multivariable analysis, similar factors such as a history of VTE (adjusted RR 2.41; 95% CI, 1.99-2.90, P less than .01), two or more comorbidities (aRR 1.78; 95% CI, 1.44-2.20, P less than .01) and C. difficile infection (aRR 1.47; 95% CI, 1.17-1.85, P less than.01) continued to be associated with higher risk of VTE readmission.
Though they emphasized that the use of NRD data offered the impressive ability to “review over 15 million discharges across the U.S. annually,” Dr. Faye and coauthors acknowledged that their study did have limitations. These included the inability to verify via chart review the study’s outcomes and covariates. In addition, they were unable to assess potential contributing risk factors such as medication use, use of VTE prophylaxis during hospitalization, disease severity, and family history. Finally, though unlikely, they admitted the possibility that patients could be counted more than once if they were readmitted with a VTE each year of the study.
The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
SOURCE: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.
Hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are most likely to be readmitted for venous thromboembolism (VTE) within 60 days of discharge, according to a new study that analyzed 5 years of U.S. readmissions data.
“Given increased thrombotic risk postdischarge, as well as overall safety of VTE prophylaxis, extending prophylaxis for those at highest risk may have significant benefits,” wrote Adam S. Faye, MD, of Columbia University, and coauthors. The study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
To determine which IBD patients would be most in need of postdischarge VTE prophylaxis, as well as when to administer it, the researchers analyzed 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD). They found a total of 872,122 index admissions for IBD patients; 4% of those patients had a prior VTE. Of the index admissions, 1,160 led to a VTE readmission within 90 days. Readmitted patients had a relatively equal proportion of ulcerative colitis (n = 522) and Crohn’s disease (n = 638).
More than 90% of VTE readmissions occurred within 60 days of discharge; the risk was highest over the first 10 days and then decreased in each ensuing 10-day period until a slight increase at the 81- to 90-day period. All patients over age 30 had higher rates of readmission than those of patients under age 18, with the highest risk in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 years (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01). Women were at lower risk (RR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.92, P less than .01). Higher risks of readmission were also associated with being on Medicare (RR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.23-1.58, P less than .01) compared with being on private insurance and being cared for at a large hospital (RR 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52, P = .02) compared with a small hospital.
The highest risk of VTE readmission was associated with a prior history of VTE (RR 2.89; 95% CI, 2.40-3.48, P less than .01), having two or more comorbidities (RR 2.57; 95% CI, 2.11-3.12, P less than .01) and having a Clostridioides difficile infection as of index admission (RR 1.90; 95% CI, 1.51-2.38, P less than .01). In addition, increased risk was associated with being discharged to a nursing or care facility (RR 1.85; 95% CI, 1.56-2.20, P less than .01) or home with health services (RR 2.05; 95% CI, 1.78-2.38, P less than .01) compared with a routine discharge.
In their multivariable analysis, similar factors such as a history of VTE (adjusted RR 2.41; 95% CI, 1.99-2.90, P less than .01), two or more comorbidities (aRR 1.78; 95% CI, 1.44-2.20, P less than .01) and C. difficile infection (aRR 1.47; 95% CI, 1.17-1.85, P less than.01) continued to be associated with higher risk of VTE readmission.
Though they emphasized that the use of NRD data offered the impressive ability to “review over 15 million discharges across the U.S. annually,” Dr. Faye and coauthors acknowledged that their study did have limitations. These included the inability to verify via chart review the study’s outcomes and covariates. In addition, they were unable to assess potential contributing risk factors such as medication use, use of VTE prophylaxis during hospitalization, disease severity, and family history. Finally, though unlikely, they admitted the possibility that patients could be counted more than once if they were readmitted with a VTE each year of the study.
The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
SOURCE: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.
Hospitalized patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are most likely to be readmitted for venous thromboembolism (VTE) within 60 days of discharge, according to a new study that analyzed 5 years of U.S. readmissions data.
“Given increased thrombotic risk postdischarge, as well as overall safety of VTE prophylaxis, extending prophylaxis for those at highest risk may have significant benefits,” wrote Adam S. Faye, MD, of Columbia University, and coauthors. The study was published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
To determine which IBD patients would be most in need of postdischarge VTE prophylaxis, as well as when to administer it, the researchers analyzed 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database (NRD). They found a total of 872,122 index admissions for IBD patients; 4% of those patients had a prior VTE. Of the index admissions, 1,160 led to a VTE readmission within 90 days. Readmitted patients had a relatively equal proportion of ulcerative colitis (n = 522) and Crohn’s disease (n = 638).
More than 90% of VTE readmissions occurred within 60 days of discharge; the risk was highest over the first 10 days and then decreased in each ensuing 10-day period until a slight increase at the 81- to 90-day period. All patients over age 30 had higher rates of readmission than those of patients under age 18, with the highest risk in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 years (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01). Women were at lower risk (RR 0.82; 95% CI, 0.73-0.92, P less than .01). Higher risks of readmission were also associated with being on Medicare (RR 1.39; 95% CI, 1.23-1.58, P less than .01) compared with being on private insurance and being cared for at a large hospital (RR 1.26; 95% CI, 1.04-1.52, P = .02) compared with a small hospital.
The highest risk of VTE readmission was associated with a prior history of VTE (RR 2.89; 95% CI, 2.40-3.48, P less than .01), having two or more comorbidities (RR 2.57; 95% CI, 2.11-3.12, P less than .01) and having a Clostridioides difficile infection as of index admission (RR 1.90; 95% CI, 1.51-2.38, P less than .01). In addition, increased risk was associated with being discharged to a nursing or care facility (RR 1.85; 95% CI, 1.56-2.20, P less than .01) or home with health services (RR 2.05; 95% CI, 1.78-2.38, P less than .01) compared with a routine discharge.
In their multivariable analysis, similar factors such as a history of VTE (adjusted RR 2.41; 95% CI, 1.99-2.90, P less than .01), two or more comorbidities (aRR 1.78; 95% CI, 1.44-2.20, P less than .01) and C. difficile infection (aRR 1.47; 95% CI, 1.17-1.85, P less than.01) continued to be associated with higher risk of VTE readmission.
Though they emphasized that the use of NRD data offered the impressive ability to “review over 15 million discharges across the U.S. annually,” Dr. Faye and coauthors acknowledged that their study did have limitations. These included the inability to verify via chart review the study’s outcomes and covariates. In addition, they were unable to assess potential contributing risk factors such as medication use, use of VTE prophylaxis during hospitalization, disease severity, and family history. Finally, though unlikely, they admitted the possibility that patients could be counted more than once if they were readmitted with a VTE each year of the study.
The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
SOURCE: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Readmission for VTE in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases most often occurs within 60 days of discharge.
Major finding: The highest readmission risk was in patients between the ages of 66 and 80 (risk ratio 4.04; 95% confidence interval, 2.54-6.44, P less than .01).
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of 1,160 IBD patients who had VTE readmissions via 2010-2014 data from the Nationwide Readmissions Database.
Disclosures: The authors reported being supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health and various pharmaceutical companies, as well as receiving honoraria and serving as consultants.
Source: Faye AS et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 July 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.028.