User login
Expected spike in acute flaccid myelitis did not occur in 2020
suggested researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is an uncommon but serious complication of some viral infections, including West Nile virus and nonpolio enteroviruses. It is “characterized by sudden onset of limb weakness and lesions in the gray matter of the spinal cord,” they said, and more than 90% of cases occur in young children.
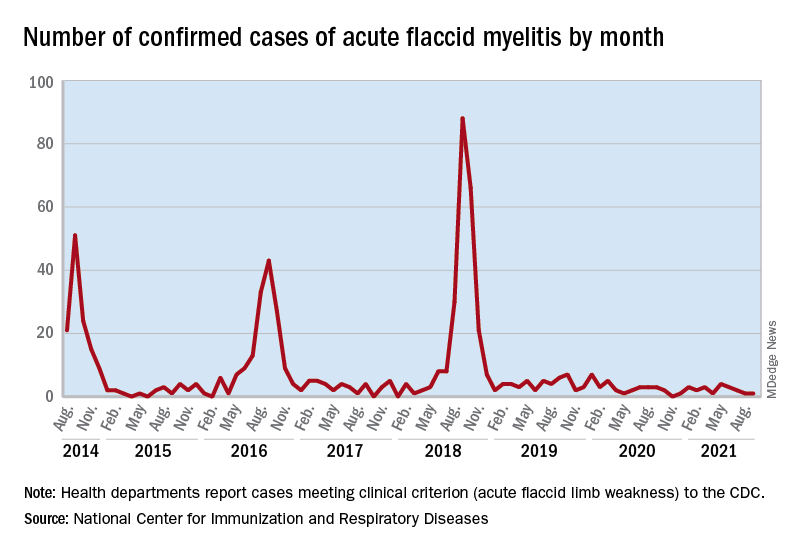
Cases of AFM, which can lead to respiratory insufficiency and permanent paralysis, spiked during the late summer and early fall in 2014, 2016, and 2018 and were expected to do so again in 2020, Sarah Kidd, MD, and associates at the division of viral diseases at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Monthly peaks in those previous years – each occurring in September – reached 51 cases in 2014, 43 cases in 2016, and 88 cases in 2018, but in 2020 there was only 1 case reported in September, with a high of 4 coming in May, CDC data show. The total number of cases for 2020 (32) was, in fact, lower than in 2019, when 47 were reported.
The investigators’ main objective was to see if there were any differences between the 2018 and 2019-2020 cases. Reports from state health departments to the CDC showed that, in 2019-2020, “patients were older; more likely to have lower limb involvement; and less likely to have upper limb involvement, prodromal illness, [cerebrospinal fluid] pleocytosis, or specimens that tested positive for EV [enterovirus]-D68” than patients from 2018, Dr. Kidd and associates said.
Mask wearing and reduced in-school attendance may have decreased circulation of EV-D68 – the enterovirus type most often detected in the stool and respiratory specimens of AFM patients – as was seen with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, in 2020. Previous studies have suggested that EV-D68 drives the increases in cases during peak years, the researchers noted.
The absence of such an increase “in 2020 reflects a deviation from the previously observed biennial pattern, and it is unclear when the next increase in AFM should be expected. Clinicians should continue to maintain vigilance and suspect AFM in any child with acute flaccid limb weakness, particularly in the setting of recent febrile or respiratory illness,” they wrote.
suggested researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is an uncommon but serious complication of some viral infections, including West Nile virus and nonpolio enteroviruses. It is “characterized by sudden onset of limb weakness and lesions in the gray matter of the spinal cord,” they said, and more than 90% of cases occur in young children.
Cases of AFM, which can lead to respiratory insufficiency and permanent paralysis, spiked during the late summer and early fall in 2014, 2016, and 2018 and were expected to do so again in 2020, Sarah Kidd, MD, and associates at the division of viral diseases at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Monthly peaks in those previous years – each occurring in September – reached 51 cases in 2014, 43 cases in 2016, and 88 cases in 2018, but in 2020 there was only 1 case reported in September, with a high of 4 coming in May, CDC data show. The total number of cases for 2020 (32) was, in fact, lower than in 2019, when 47 were reported.
The investigators’ main objective was to see if there were any differences between the 2018 and 2019-2020 cases. Reports from state health departments to the CDC showed that, in 2019-2020, “patients were older; more likely to have lower limb involvement; and less likely to have upper limb involvement, prodromal illness, [cerebrospinal fluid] pleocytosis, or specimens that tested positive for EV [enterovirus]-D68” than patients from 2018, Dr. Kidd and associates said.
Mask wearing and reduced in-school attendance may have decreased circulation of EV-D68 – the enterovirus type most often detected in the stool and respiratory specimens of AFM patients – as was seen with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, in 2020. Previous studies have suggested that EV-D68 drives the increases in cases during peak years, the researchers noted.
The absence of such an increase “in 2020 reflects a deviation from the previously observed biennial pattern, and it is unclear when the next increase in AFM should be expected. Clinicians should continue to maintain vigilance and suspect AFM in any child with acute flaccid limb weakness, particularly in the setting of recent febrile or respiratory illness,” they wrote.
suggested researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.

Acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) is an uncommon but serious complication of some viral infections, including West Nile virus and nonpolio enteroviruses. It is “characterized by sudden onset of limb weakness and lesions in the gray matter of the spinal cord,” they said, and more than 90% of cases occur in young children.
Cases of AFM, which can lead to respiratory insufficiency and permanent paralysis, spiked during the late summer and early fall in 2014, 2016, and 2018 and were expected to do so again in 2020, Sarah Kidd, MD, and associates at the division of viral diseases at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Monthly peaks in those previous years – each occurring in September – reached 51 cases in 2014, 43 cases in 2016, and 88 cases in 2018, but in 2020 there was only 1 case reported in September, with a high of 4 coming in May, CDC data show. The total number of cases for 2020 (32) was, in fact, lower than in 2019, when 47 were reported.
The investigators’ main objective was to see if there were any differences between the 2018 and 2019-2020 cases. Reports from state health departments to the CDC showed that, in 2019-2020, “patients were older; more likely to have lower limb involvement; and less likely to have upper limb involvement, prodromal illness, [cerebrospinal fluid] pleocytosis, or specimens that tested positive for EV [enterovirus]-D68” than patients from 2018, Dr. Kidd and associates said.
Mask wearing and reduced in-school attendance may have decreased circulation of EV-D68 – the enterovirus type most often detected in the stool and respiratory specimens of AFM patients – as was seen with other respiratory viruses, such as influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, in 2020. Previous studies have suggested that EV-D68 drives the increases in cases during peak years, the researchers noted.
The absence of such an increase “in 2020 reflects a deviation from the previously observed biennial pattern, and it is unclear when the next increase in AFM should be expected. Clinicians should continue to maintain vigilance and suspect AFM in any child with acute flaccid limb weakness, particularly in the setting of recent febrile or respiratory illness,” they wrote.
FROM MMWR
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: COVID-19 November 2021
Similarly, Lin et al report the results of an international study of adults from 99 countries, which utilized longitudinal mobile based surveys to examine risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The mobile surveys captured baseline characteristics and behaviors of participants, and data was reported out for the study period of March to October 2020 (before vaccines were available). Adjusting for demographics, education level, a proxy for occupational risk, as well as medical comorbidities, authors found that greater number of non-household contacts, attending events with 10 or more individuals and restaurant visits predicted higher risk of SARS-CoV-2. Alternatively, older age was associated with lower risk, likely because of the protective behaviors undertaken by many in the older age group.
Lastly, the RECoVERED Study (Wynberg, at al), based in Netherlands, followed recently diagnosed laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 patients for a year, initially with three in person visits (where disease severity was determined based on vital signs and level of care needed) within the first month of illness and then monthly online surveys. Authors utilized a survey examining severity of 18 symptoms based on the World Health Organization Case Report Form. Authors found 86.7% of those with initial severe disease [95% confidence interval {CI} = 76.5–92.7%]), 63.8% of those moderate disease 63.8% [95% CI = 54.8–71.5%], and 30.7% of those with mild disease [95% CI = 21.1–40.9%] had at least one persistent symptom at 12 weeks. Fatigue was the most common symptom reported at 12 weeks overall, but among those with moderate and severe disease, dyspnea and myalgia also persisted frequently. After one years of follow up, about one-fifth still had one persistent symptom. Over half of those with initial severe disease reported symptom persistence (52.5% [95% CI = 38.0–65.1%]). In a multivariable Cox proportional hazard model, female sex and higher BMI were associated with slower recovery. One limitation of the study was that was no control group recruited.
Similarly, Lin et al report the results of an international study of adults from 99 countries, which utilized longitudinal mobile based surveys to examine risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The mobile surveys captured baseline characteristics and behaviors of participants, and data was reported out for the study period of March to October 2020 (before vaccines were available). Adjusting for demographics, education level, a proxy for occupational risk, as well as medical comorbidities, authors found that greater number of non-household contacts, attending events with 10 or more individuals and restaurant visits predicted higher risk of SARS-CoV-2. Alternatively, older age was associated with lower risk, likely because of the protective behaviors undertaken by many in the older age group.
Lastly, the RECoVERED Study (Wynberg, at al), based in Netherlands, followed recently diagnosed laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 patients for a year, initially with three in person visits (where disease severity was determined based on vital signs and level of care needed) within the first month of illness and then monthly online surveys. Authors utilized a survey examining severity of 18 symptoms based on the World Health Organization Case Report Form. Authors found 86.7% of those with initial severe disease [95% confidence interval {CI} = 76.5–92.7%]), 63.8% of those moderate disease 63.8% [95% CI = 54.8–71.5%], and 30.7% of those with mild disease [95% CI = 21.1–40.9%] had at least one persistent symptom at 12 weeks. Fatigue was the most common symptom reported at 12 weeks overall, but among those with moderate and severe disease, dyspnea and myalgia also persisted frequently. After one years of follow up, about one-fifth still had one persistent symptom. Over half of those with initial severe disease reported symptom persistence (52.5% [95% CI = 38.0–65.1%]). In a multivariable Cox proportional hazard model, female sex and higher BMI were associated with slower recovery. One limitation of the study was that was no control group recruited.
Similarly, Lin et al report the results of an international study of adults from 99 countries, which utilized longitudinal mobile based surveys to examine risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. The mobile surveys captured baseline characteristics and behaviors of participants, and data was reported out for the study period of March to October 2020 (before vaccines were available). Adjusting for demographics, education level, a proxy for occupational risk, as well as medical comorbidities, authors found that greater number of non-household contacts, attending events with 10 or more individuals and restaurant visits predicted higher risk of SARS-CoV-2. Alternatively, older age was associated with lower risk, likely because of the protective behaviors undertaken by many in the older age group.
Lastly, the RECoVERED Study (Wynberg, at al), based in Netherlands, followed recently diagnosed laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 patients for a year, initially with three in person visits (where disease severity was determined based on vital signs and level of care needed) within the first month of illness and then monthly online surveys. Authors utilized a survey examining severity of 18 symptoms based on the World Health Organization Case Report Form. Authors found 86.7% of those with initial severe disease [95% confidence interval {CI} = 76.5–92.7%]), 63.8% of those moderate disease 63.8% [95% CI = 54.8–71.5%], and 30.7% of those with mild disease [95% CI = 21.1–40.9%] had at least one persistent symptom at 12 weeks. Fatigue was the most common symptom reported at 12 weeks overall, but among those with moderate and severe disease, dyspnea and myalgia also persisted frequently. After one years of follow up, about one-fifth still had one persistent symptom. Over half of those with initial severe disease reported symptom persistence (52.5% [95% CI = 38.0–65.1%]). In a multivariable Cox proportional hazard model, female sex and higher BMI were associated with slower recovery. One limitation of the study was that was no control group recruited.
Chatbots can improve mental health in vulnerable populations
In this modern age of health care where telemedicine rules, conversational agents (CAs) that use text messaging systems are becoming a major mode of communication.
Many people are familiar with voice-enabled agents, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Now, and Microsoft’s Cortana. However, CAs come in different forms of complexity, ranging from a short message service–based texting platform to an embodied conversational agent (ECA).
ECAs allow participants to interact with a physical or graphical figure that simulates a person in appearance, behavior, and dialect. These are essentially virtual humans, or avatars, who talk with participants. By taking greater advantage of these automated agents, some have projected there may be $11 billion in combined cost savings across a variety of business sectors by 2023.1 The health care field is one sector in which CAs can play an important role. Because of their accessibility, CAs have the potential to improve mental health by combating health care inequities and stigma, encouraging disclosure from participants, and serving as companions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
CAs provide accessible health care for rural, low socioeconomic status (SES), and minority communities in a variety of advantageous ways. For example, one study found that long-term use of a text-based agent that combines motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can support smoking cessation in adolescents of low SES.2
CAs can help vulnerable participants advocate for themselves and proactively maintain their mental health through access to health care resources. In specific cases, these agents equalize health care treatment for different populations. Even though some participants live in secluded areas or are blocked by barriers, these text-based agents can still provide self-help intervention for them at any time on an individual basis, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Furthermore, they serve as highly cost-effective mental health promotion tools for large populations, some of which might not otherwise be reached by mental health care.
In combating mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety, studies have found that CAs are great treatment tools. For example, participants in an experimental group who received a self-help program based on CBT from a text-based CA named Woebot experienced significantly reduced depression symptoms when compared to the control group of participants, who received only information from a self-help electronic book.3 As a result, CAs might prove successful in treating younger populations who find online tools more feasible and accessible. Often, this population self-identifies depressive and anxiety symptoms without consulting a health care professional. Thus, this tool would prove useful to those who are bothered by the stigma of seeing a mental health professional.
Virtual human–based CAs also encourage participants to disclose more information in a nonjudgmental manner, especially among people with diseases with stigma. CAs use neutral languages, which may be helpful when dealing with stigmatized issues such as HIV, family planning, and abortion care because this heightens confidentiality and privacy. When participants believe that the agent does not “judge” or evaluate their capabilities, this elicits more sensitive information from them. For example, one study found that military service members who believed that they were interacting with a computer rather than a human operator reported lower fear of self-disclosure, displayed more sadness, and were rated by observers as more willing to disclose posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms.4 Additional findings show that participants prefer CAs when topics are highly sensitive and more likely to evoke negative self-admissions.
In what we hope will soon be a post–COVID-19 landscape of medicine, CAs are fast being used on the front lines of health care technology. Empathetic CAs can combat adverse effects of social exclusion during these pressing times. Etsuko Ishii, a researcher affiliated with the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and associates demonstrated that a virtual CA was as effective as a COVID-19 companion because it uses natural language processing (NLP) and nonverbal facial expressions to give users the feeling that they are being treated with empathy.5 While minimizing the number of in-person interactions that could potentially spread COVID-19, these agents promote virtual companionship that mirrors natural conversations and provide emotional support with psychological safety as participants express their pent-up thoughts. Not only do these agents help recover mood quickly, but they also have the power to overcome geographic barriers, be constantly available, and alleviate the high demand for mental health care. As a result, CAs have the potential to facilitate better communication and sustain social interactions within the isolated environment the pandemic has created.
CAs can predict, detect, and determine treatment solutions for mental health conditions based on behavioral insights. These agents’ natural language processing also allows them to be powerful therapeutic agents that can serve different communities, particularly for populations with limited access to medical resources. As the use of CAs becomes more integrated into telemedicine, their utility will continue to grow as their proven versatility in many situations expands the boundaries of health care technology.
Ms. Wong, a medical student at New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, conducts research related to mental health care services. She disclosed writing a telemental health software platform called Orchid. Dr. Vo, a board-certified psychiatrist, is the medical director of telehealth for the department of child and adolescent psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. She is a faculty member of the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. Dr. Vo conducts digital health research focused on using automation and artificial intelligence for suicide risk screening and connecting patients to mental health care services. She disclosed serving as cofounder of Orchid.
References
1. Chatbots: Vendor opportunities & market forecasts 2020-2024. Juniper Research, 2020.
2. Simon P et al. On using chatbots to promote smoking cessation among adolescents of low socioeconomic status, Artificial Intelligence and Work: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2019 Fall Symposium, 2019.
3. Fitzpatrick KK et al. JMIR Mental Health. 2017;4(2):e19.
4. Lucas GM et al. Front Robot AI. 2017 Oct 12. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2017.00051.
5. Ishii E et al. ERICA: An empathetic android companion for COVID-19 quarantine. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.02325.
In this modern age of health care where telemedicine rules, conversational agents (CAs) that use text messaging systems are becoming a major mode of communication.
Many people are familiar with voice-enabled agents, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Now, and Microsoft’s Cortana. However, CAs come in different forms of complexity, ranging from a short message service–based texting platform to an embodied conversational agent (ECA).
ECAs allow participants to interact with a physical or graphical figure that simulates a person in appearance, behavior, and dialect. These are essentially virtual humans, or avatars, who talk with participants. By taking greater advantage of these automated agents, some have projected there may be $11 billion in combined cost savings across a variety of business sectors by 2023.1 The health care field is one sector in which CAs can play an important role. Because of their accessibility, CAs have the potential to improve mental health by combating health care inequities and stigma, encouraging disclosure from participants, and serving as companions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
CAs provide accessible health care for rural, low socioeconomic status (SES), and minority communities in a variety of advantageous ways. For example, one study found that long-term use of a text-based agent that combines motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can support smoking cessation in adolescents of low SES.2
CAs can help vulnerable participants advocate for themselves and proactively maintain their mental health through access to health care resources. In specific cases, these agents equalize health care treatment for different populations. Even though some participants live in secluded areas or are blocked by barriers, these text-based agents can still provide self-help intervention for them at any time on an individual basis, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Furthermore, they serve as highly cost-effective mental health promotion tools for large populations, some of which might not otherwise be reached by mental health care.
In combating mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety, studies have found that CAs are great treatment tools. For example, participants in an experimental group who received a self-help program based on CBT from a text-based CA named Woebot experienced significantly reduced depression symptoms when compared to the control group of participants, who received only information from a self-help electronic book.3 As a result, CAs might prove successful in treating younger populations who find online tools more feasible and accessible. Often, this population self-identifies depressive and anxiety symptoms without consulting a health care professional. Thus, this tool would prove useful to those who are bothered by the stigma of seeing a mental health professional.
Virtual human–based CAs also encourage participants to disclose more information in a nonjudgmental manner, especially among people with diseases with stigma. CAs use neutral languages, which may be helpful when dealing with stigmatized issues such as HIV, family planning, and abortion care because this heightens confidentiality and privacy. When participants believe that the agent does not “judge” or evaluate their capabilities, this elicits more sensitive information from them. For example, one study found that military service members who believed that they were interacting with a computer rather than a human operator reported lower fear of self-disclosure, displayed more sadness, and were rated by observers as more willing to disclose posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms.4 Additional findings show that participants prefer CAs when topics are highly sensitive and more likely to evoke negative self-admissions.
In what we hope will soon be a post–COVID-19 landscape of medicine, CAs are fast being used on the front lines of health care technology. Empathetic CAs can combat adverse effects of social exclusion during these pressing times. Etsuko Ishii, a researcher affiliated with the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and associates demonstrated that a virtual CA was as effective as a COVID-19 companion because it uses natural language processing (NLP) and nonverbal facial expressions to give users the feeling that they are being treated with empathy.5 While minimizing the number of in-person interactions that could potentially spread COVID-19, these agents promote virtual companionship that mirrors natural conversations and provide emotional support with psychological safety as participants express their pent-up thoughts. Not only do these agents help recover mood quickly, but they also have the power to overcome geographic barriers, be constantly available, and alleviate the high demand for mental health care. As a result, CAs have the potential to facilitate better communication and sustain social interactions within the isolated environment the pandemic has created.
CAs can predict, detect, and determine treatment solutions for mental health conditions based on behavioral insights. These agents’ natural language processing also allows them to be powerful therapeutic agents that can serve different communities, particularly for populations with limited access to medical resources. As the use of CAs becomes more integrated into telemedicine, their utility will continue to grow as their proven versatility in many situations expands the boundaries of health care technology.
Ms. Wong, a medical student at New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, conducts research related to mental health care services. She disclosed writing a telemental health software platform called Orchid. Dr. Vo, a board-certified psychiatrist, is the medical director of telehealth for the department of child and adolescent psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. She is a faculty member of the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. Dr. Vo conducts digital health research focused on using automation and artificial intelligence for suicide risk screening and connecting patients to mental health care services. She disclosed serving as cofounder of Orchid.
References
1. Chatbots: Vendor opportunities & market forecasts 2020-2024. Juniper Research, 2020.
2. Simon P et al. On using chatbots to promote smoking cessation among adolescents of low socioeconomic status, Artificial Intelligence and Work: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2019 Fall Symposium, 2019.
3. Fitzpatrick KK et al. JMIR Mental Health. 2017;4(2):e19.
4. Lucas GM et al. Front Robot AI. 2017 Oct 12. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2017.00051.
5. Ishii E et al. ERICA: An empathetic android companion for COVID-19 quarantine. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.02325.
In this modern age of health care where telemedicine rules, conversational agents (CAs) that use text messaging systems are becoming a major mode of communication.
Many people are familiar with voice-enabled agents, such as Apple’s Siri, Google Now, and Microsoft’s Cortana. However, CAs come in different forms of complexity, ranging from a short message service–based texting platform to an embodied conversational agent (ECA).
ECAs allow participants to interact with a physical or graphical figure that simulates a person in appearance, behavior, and dialect. These are essentially virtual humans, or avatars, who talk with participants. By taking greater advantage of these automated agents, some have projected there may be $11 billion in combined cost savings across a variety of business sectors by 2023.1 The health care field is one sector in which CAs can play an important role. Because of their accessibility, CAs have the potential to improve mental health by combating health care inequities and stigma, encouraging disclosure from participants, and serving as companions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
CAs provide accessible health care for rural, low socioeconomic status (SES), and minority communities in a variety of advantageous ways. For example, one study found that long-term use of a text-based agent that combines motivational interviewing and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can support smoking cessation in adolescents of low SES.2
CAs can help vulnerable participants advocate for themselves and proactively maintain their mental health through access to health care resources. In specific cases, these agents equalize health care treatment for different populations. Even though some participants live in secluded areas or are blocked by barriers, these text-based agents can still provide self-help intervention for them at any time on an individual basis, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. Furthermore, they serve as highly cost-effective mental health promotion tools for large populations, some of which might not otherwise be reached by mental health care.
In combating mental illnesses such as depression and anxiety, studies have found that CAs are great treatment tools. For example, participants in an experimental group who received a self-help program based on CBT from a text-based CA named Woebot experienced significantly reduced depression symptoms when compared to the control group of participants, who received only information from a self-help electronic book.3 As a result, CAs might prove successful in treating younger populations who find online tools more feasible and accessible. Often, this population self-identifies depressive and anxiety symptoms without consulting a health care professional. Thus, this tool would prove useful to those who are bothered by the stigma of seeing a mental health professional.
Virtual human–based CAs also encourage participants to disclose more information in a nonjudgmental manner, especially among people with diseases with stigma. CAs use neutral languages, which may be helpful when dealing with stigmatized issues such as HIV, family planning, and abortion care because this heightens confidentiality and privacy. When participants believe that the agent does not “judge” or evaluate their capabilities, this elicits more sensitive information from them. For example, one study found that military service members who believed that they were interacting with a computer rather than a human operator reported lower fear of self-disclosure, displayed more sadness, and were rated by observers as more willing to disclose posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms.4 Additional findings show that participants prefer CAs when topics are highly sensitive and more likely to evoke negative self-admissions.
In what we hope will soon be a post–COVID-19 landscape of medicine, CAs are fast being used on the front lines of health care technology. Empathetic CAs can combat adverse effects of social exclusion during these pressing times. Etsuko Ishii, a researcher affiliated with the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and associates demonstrated that a virtual CA was as effective as a COVID-19 companion because it uses natural language processing (NLP) and nonverbal facial expressions to give users the feeling that they are being treated with empathy.5 While minimizing the number of in-person interactions that could potentially spread COVID-19, these agents promote virtual companionship that mirrors natural conversations and provide emotional support with psychological safety as participants express their pent-up thoughts. Not only do these agents help recover mood quickly, but they also have the power to overcome geographic barriers, be constantly available, and alleviate the high demand for mental health care. As a result, CAs have the potential to facilitate better communication and sustain social interactions within the isolated environment the pandemic has created.
CAs can predict, detect, and determine treatment solutions for mental health conditions based on behavioral insights. These agents’ natural language processing also allows them to be powerful therapeutic agents that can serve different communities, particularly for populations with limited access to medical resources. As the use of CAs becomes more integrated into telemedicine, their utility will continue to grow as their proven versatility in many situations expands the boundaries of health care technology.
Ms. Wong, a medical student at New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine in Old Westbury, conducts research related to mental health care services. She disclosed writing a telemental health software platform called Orchid. Dr. Vo, a board-certified psychiatrist, is the medical director of telehealth for the department of child and adolescent psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia. She is a faculty member of the University of Pennsylvania, also in Philadelphia. Dr. Vo conducts digital health research focused on using automation and artificial intelligence for suicide risk screening and connecting patients to mental health care services. She disclosed serving as cofounder of Orchid.
References
1. Chatbots: Vendor opportunities & market forecasts 2020-2024. Juniper Research, 2020.
2. Simon P et al. On using chatbots to promote smoking cessation among adolescents of low socioeconomic status, Artificial Intelligence and Work: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) 2019 Fall Symposium, 2019.
3. Fitzpatrick KK et al. JMIR Mental Health. 2017;4(2):e19.
4. Lucas GM et al. Front Robot AI. 2017 Oct 12. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2017.00051.
5. Ishii E et al. ERICA: An empathetic android companion for COVID-19 quarantine. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.02325.
Immune response detected in most IBD patients after COVID vaccines
Most patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) develop a humoral immune response after completing an mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine series, according to data from almost 800 patients.
Anti–receptor binding domain IgG antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2 were detectable in 95% of patients, with “generally similar” results across vaccine type, age group, and medication class, apart from corticosteroid users, who had an 86% antibody detection rate, reported lead author Kimberly N. Weaver, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and colleagues.
“Patients with IBD on immunosuppressive medications have the potential for attenuated response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination,” Dr. Weaver said at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
In support of this possibility, Dr. Weaver cited two recent trials from earlier in 2021: one demonstrated blunted antibody responses in IBD patients taking infliximab, while the other showed that full vaccination was less effective at preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with IBD than nonimmunosuppressed individuals.
To better characterize antibody responses after receiving an mRNA vaccination series, Dr. Weaver and colleagues launched the PREVENT-COVID trial, including the present dataset of 787 patients with IBD older than 12 years, all of whom provided serum samples 8 weeks after completing an mRNA vaccine series. Patients with positive nucleocapsid antibody (indicating prior infection), and/or those who reported prior COVID-19 infection, were excluded. Most patients were White (95%) and female (73%), with an average age of 48 years. Slightly more patients received the BNT162b2 vaccine than the mRNA-1273 vaccine (58% vs. 42%).
At 8 weeks, 752 out of 787 patients had detectable antibodies (95%). Antibody rates were highest among patients receiving vedolizumab monotherapy (n = 83; 99%) or ustekinumab monotherapy (n = 102; 99%), followed by mercaptopurine, azathioprine, or methotrexate monotherapy (n = 67; 97%); anti–tumor necrosis factor monotherapy (n = 270; 96%); mesalamine, sulfasalazine, or budesonide monotherapy or no medication (n = 143; 95%); and finally anti-TNF/immunosuppressive combination therapy (n = 75; 86%). Median and mean antibody titers were lowest for anti-TNF combination therapy and highest for vedolizumab.
Thirty-five patients taking corticosteroids had an antibody detection rate of 85.7% (95% CI, 70.6-93.7), compared with 95.9% (95% CI, 94.2-97.1) among nonsteroid users. In contrast, antibody detection rates were not significantly affected by age or vaccine type.
“Reassuringly, most IBD medications do not prevent an initial antibody response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, and this is unlike other classes of immune suppression such as B-cell depletion therapy,” Dr. Weaver concluded. “Additional data are forthcoming on a larger subset of participants in the PREVENT-COVID study which will allow for analysis of factors associated with humoral immune response and potential optimization of immunization strategies.” She described a dataset of about 500 IBD patients in which booster vaccines overcame poor antibody responses to the initial vaccine series.
‘The data we need’
Serre-yu Wong, MD, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, agreed that the findings should offer some reassurance to patients with IBD and their care providers.
“At the end of the day we have really nice seroconversion rates for the IBD population,” Dr. Wong said.
In April 2021, Dr. Wong and the ICARUS-IBD Working Group published a similar report of 48 patients with IBD receiving biologic therapies, among whom the seroconversion rate was 100%.
“A lot of the early data, including ours, are on infusion medications, and that’s sort of a practical thing because those were the only patients we could get samples from, but [Dr. Weaver and colleagues] were able to get samples from patients not on medications, on oral medications, and on other injection medications that people can take at home, and these are really the data we need for all of our other IBD patients,” Dr. Wong said.
Dr. Wong highlighted that both trials showed some IBD patients generating “very, very high” titers, many of them above the threshold needed for donating convalescent plasma for COVID-19 treatment; still, exact titer levels needed to protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection remain unclear.
“This is going to require longitudinal studies,” Dr. Wong said. “We can’t answer that perfectly right now. We don’t know the magic level of antibodies. I don’t know if you need a titer of 1:100 or 1:1,000.”
Although postvaccination antibody testing is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Dr. Wong said that “many patients” check their titers anyway, leading to anxiety if antibodies are low or undetectable.
“I know that it’s very disconcerting sometimes when you don’t see an antibody response, and this is one of the hardest things to try to explain to patients,” Dr. Wong said. “[It’s necessary] to have a frank discussion about the fact that we don’t know the magic level of antibodies, and that there are also other parts of the immune system that we haven’t tested with antibodies. We haven’t tested the T-cell response, and we do know you can have a T-cell response even if you don’t have a B-cell response.”
Dr. Wong suggested that more work is needed to determine the impact of the IBD disease process on susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, and the rates of antibody responses for the various other vaccines being used around the world.
The PREVENT-COVID study was supported by the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, Genentech, and others. Dr. Wong reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was updated Oct. 28, 2021.
Most patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) develop a humoral immune response after completing an mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine series, according to data from almost 800 patients.
Anti–receptor binding domain IgG antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2 were detectable in 95% of patients, with “generally similar” results across vaccine type, age group, and medication class, apart from corticosteroid users, who had an 86% antibody detection rate, reported lead author Kimberly N. Weaver, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and colleagues.
“Patients with IBD on immunosuppressive medications have the potential for attenuated response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination,” Dr. Weaver said at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
In support of this possibility, Dr. Weaver cited two recent trials from earlier in 2021: one demonstrated blunted antibody responses in IBD patients taking infliximab, while the other showed that full vaccination was less effective at preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with IBD than nonimmunosuppressed individuals.
To better characterize antibody responses after receiving an mRNA vaccination series, Dr. Weaver and colleagues launched the PREVENT-COVID trial, including the present dataset of 787 patients with IBD older than 12 years, all of whom provided serum samples 8 weeks after completing an mRNA vaccine series. Patients with positive nucleocapsid antibody (indicating prior infection), and/or those who reported prior COVID-19 infection, were excluded. Most patients were White (95%) and female (73%), with an average age of 48 years. Slightly more patients received the BNT162b2 vaccine than the mRNA-1273 vaccine (58% vs. 42%).
At 8 weeks, 752 out of 787 patients had detectable antibodies (95%). Antibody rates were highest among patients receiving vedolizumab monotherapy (n = 83; 99%) or ustekinumab monotherapy (n = 102; 99%), followed by mercaptopurine, azathioprine, or methotrexate monotherapy (n = 67; 97%); anti–tumor necrosis factor monotherapy (n = 270; 96%); mesalamine, sulfasalazine, or budesonide monotherapy or no medication (n = 143; 95%); and finally anti-TNF/immunosuppressive combination therapy (n = 75; 86%). Median and mean antibody titers were lowest for anti-TNF combination therapy and highest for vedolizumab.
Thirty-five patients taking corticosteroids had an antibody detection rate of 85.7% (95% CI, 70.6-93.7), compared with 95.9% (95% CI, 94.2-97.1) among nonsteroid users. In contrast, antibody detection rates were not significantly affected by age or vaccine type.
“Reassuringly, most IBD medications do not prevent an initial antibody response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, and this is unlike other classes of immune suppression such as B-cell depletion therapy,” Dr. Weaver concluded. “Additional data are forthcoming on a larger subset of participants in the PREVENT-COVID study which will allow for analysis of factors associated with humoral immune response and potential optimization of immunization strategies.” She described a dataset of about 500 IBD patients in which booster vaccines overcame poor antibody responses to the initial vaccine series.
‘The data we need’
Serre-yu Wong, MD, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, agreed that the findings should offer some reassurance to patients with IBD and their care providers.
“At the end of the day we have really nice seroconversion rates for the IBD population,” Dr. Wong said.
In April 2021, Dr. Wong and the ICARUS-IBD Working Group published a similar report of 48 patients with IBD receiving biologic therapies, among whom the seroconversion rate was 100%.
“A lot of the early data, including ours, are on infusion medications, and that’s sort of a practical thing because those were the only patients we could get samples from, but [Dr. Weaver and colleagues] were able to get samples from patients not on medications, on oral medications, and on other injection medications that people can take at home, and these are really the data we need for all of our other IBD patients,” Dr. Wong said.
Dr. Wong highlighted that both trials showed some IBD patients generating “very, very high” titers, many of them above the threshold needed for donating convalescent plasma for COVID-19 treatment; still, exact titer levels needed to protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection remain unclear.
“This is going to require longitudinal studies,” Dr. Wong said. “We can’t answer that perfectly right now. We don’t know the magic level of antibodies. I don’t know if you need a titer of 1:100 or 1:1,000.”
Although postvaccination antibody testing is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Dr. Wong said that “many patients” check their titers anyway, leading to anxiety if antibodies are low or undetectable.
“I know that it’s very disconcerting sometimes when you don’t see an antibody response, and this is one of the hardest things to try to explain to patients,” Dr. Wong said. “[It’s necessary] to have a frank discussion about the fact that we don’t know the magic level of antibodies, and that there are also other parts of the immune system that we haven’t tested with antibodies. We haven’t tested the T-cell response, and we do know you can have a T-cell response even if you don’t have a B-cell response.”
Dr. Wong suggested that more work is needed to determine the impact of the IBD disease process on susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, and the rates of antibody responses for the various other vaccines being used around the world.
The PREVENT-COVID study was supported by the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, Genentech, and others. Dr. Wong reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was updated Oct. 28, 2021.
Most patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) develop a humoral immune response after completing an mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine series, according to data from almost 800 patients.
Anti–receptor binding domain IgG antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2 were detectable in 95% of patients, with “generally similar” results across vaccine type, age group, and medication class, apart from corticosteroid users, who had an 86% antibody detection rate, reported lead author Kimberly N. Weaver, MD, of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and colleagues.
“Patients with IBD on immunosuppressive medications have the potential for attenuated response to the SARS-CoV-2 vaccination,” Dr. Weaver said at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
In support of this possibility, Dr. Weaver cited two recent trials from earlier in 2021: one demonstrated blunted antibody responses in IBD patients taking infliximab, while the other showed that full vaccination was less effective at preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with IBD than nonimmunosuppressed individuals.
To better characterize antibody responses after receiving an mRNA vaccination series, Dr. Weaver and colleagues launched the PREVENT-COVID trial, including the present dataset of 787 patients with IBD older than 12 years, all of whom provided serum samples 8 weeks after completing an mRNA vaccine series. Patients with positive nucleocapsid antibody (indicating prior infection), and/or those who reported prior COVID-19 infection, were excluded. Most patients were White (95%) and female (73%), with an average age of 48 years. Slightly more patients received the BNT162b2 vaccine than the mRNA-1273 vaccine (58% vs. 42%).
At 8 weeks, 752 out of 787 patients had detectable antibodies (95%). Antibody rates were highest among patients receiving vedolizumab monotherapy (n = 83; 99%) or ustekinumab monotherapy (n = 102; 99%), followed by mercaptopurine, azathioprine, or methotrexate monotherapy (n = 67; 97%); anti–tumor necrosis factor monotherapy (n = 270; 96%); mesalamine, sulfasalazine, or budesonide monotherapy or no medication (n = 143; 95%); and finally anti-TNF/immunosuppressive combination therapy (n = 75; 86%). Median and mean antibody titers were lowest for anti-TNF combination therapy and highest for vedolizumab.
Thirty-five patients taking corticosteroids had an antibody detection rate of 85.7% (95% CI, 70.6-93.7), compared with 95.9% (95% CI, 94.2-97.1) among nonsteroid users. In contrast, antibody detection rates were not significantly affected by age or vaccine type.
“Reassuringly, most IBD medications do not prevent an initial antibody response after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, and this is unlike other classes of immune suppression such as B-cell depletion therapy,” Dr. Weaver concluded. “Additional data are forthcoming on a larger subset of participants in the PREVENT-COVID study which will allow for analysis of factors associated with humoral immune response and potential optimization of immunization strategies.” She described a dataset of about 500 IBD patients in which booster vaccines overcame poor antibody responses to the initial vaccine series.
‘The data we need’
Serre-yu Wong, MD, PhD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, agreed that the findings should offer some reassurance to patients with IBD and their care providers.
“At the end of the day we have really nice seroconversion rates for the IBD population,” Dr. Wong said.
In April 2021, Dr. Wong and the ICARUS-IBD Working Group published a similar report of 48 patients with IBD receiving biologic therapies, among whom the seroconversion rate was 100%.
“A lot of the early data, including ours, are on infusion medications, and that’s sort of a practical thing because those were the only patients we could get samples from, but [Dr. Weaver and colleagues] were able to get samples from patients not on medications, on oral medications, and on other injection medications that people can take at home, and these are really the data we need for all of our other IBD patients,” Dr. Wong said.
Dr. Wong highlighted that both trials showed some IBD patients generating “very, very high” titers, many of them above the threshold needed for donating convalescent plasma for COVID-19 treatment; still, exact titer levels needed to protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection remain unclear.
“This is going to require longitudinal studies,” Dr. Wong said. “We can’t answer that perfectly right now. We don’t know the magic level of antibodies. I don’t know if you need a titer of 1:100 or 1:1,000.”
Although postvaccination antibody testing is not recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Dr. Wong said that “many patients” check their titers anyway, leading to anxiety if antibodies are low or undetectable.
“I know that it’s very disconcerting sometimes when you don’t see an antibody response, and this is one of the hardest things to try to explain to patients,” Dr. Wong said. “[It’s necessary] to have a frank discussion about the fact that we don’t know the magic level of antibodies, and that there are also other parts of the immune system that we haven’t tested with antibodies. We haven’t tested the T-cell response, and we do know you can have a T-cell response even if you don’t have a B-cell response.”
Dr. Wong suggested that more work is needed to determine the impact of the IBD disease process on susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, and the rates of antibody responses for the various other vaccines being used around the world.
The PREVENT-COVID study was supported by the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. The investigators disclosed additional relationships with AbbVie, Johnson & Johnson, Genentech, and others. Dr. Wong reported no relevant conflicts of interest.
This article was updated Oct. 28, 2021.
AT ACG 2021
Unvaccinated pregnant women have more severe COVID
An increasing number of people who are unvaccinated and pregnant are being hospitalized for COVID-19, report investigators who saw hospital admissions double in a single year.
“With the surge, we had expected to begin treating patients who developed severe or critical illness again in pregnancy,” says Emily Adhikari, MD, from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “But we did not expect the level of respiratory illness that we began to see in our patients. That was a surprise and an alarming finding that we felt was really important to get out there.”
The researchers followed more than 1,500 pregnant women diagnosed with COVID-19 who received care from Parkland Health and Hospital System in Dallas County, one of the nation’s busiest for deliveries. After the emergence of the Delta variant, the number of pregnant women hospitalized with COVID-19 more than doubled over the previous year.
And 82 pregnant women went on to develop severe or critical COVID, they report in their study, published online in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. All but 1 of these patients were unvaccinated, 10 needed a ventilator, and two died.
The proportion of cases that were critical was about 5% in 2020. However, in April 2021, even though the number of total cases remained low, the number of severe illnesses started to rise. After the Delta variant became dominant, both the number and severity of cases increased, and after August 2021, more than 25% of pregnant people diagnosed with COVID-19 required hospitalization.
Hospitalizations Double
“We need to focus and really act urgently to recommend vaccination in pregnancy because that is the primary prevention tool that we have,” says Dr. Adhikari. “We do not have a proven cure for this illness, and that is important to know.”
These findings, which focus on a vulnerable population, are especially important given the elevated prevalence of COVID-19 in pregnant people of lower economic status, said Lissette Tanner, MD, MPH, from Emory University in Atlanta, who was not involved with the study.
“There are higher rates of hospitalization and death among Black, Hispanic, and Native American communities,” she reported. “It is essential to know how the virus is affecting those most affected and often most disadvantaged to deal with the pandemic.”
Vaccination rates are low in this population; just 19.2% of pregnant women receive at least one dose during pregnancy, according to the CDC. But pregnancy confers a higher risk for severe COVID-19 illness and for adverse outcomes, such as preterm birth and stillbirth.
Of the 665 people in the study cohort who were pregnant or had given birth when the vaccines were available, only 21.4% received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
Given the increased risk for COVID-19 during pregnancy, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the CDC recommend vaccination for people who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or trying to get pregnant.
According to ACOG, pregnant women who are fully vaccinated can follow the same guidelines as everyone else who is fully vaccinated; however, to prevent breakthrough infections, they might want to continue wearing a mask. ACOG also recommends that those not fully vaccinated follow physical-distancing guidelines and limit contact with people as much as possible to avoid infection.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
An increasing number of people who are unvaccinated and pregnant are being hospitalized for COVID-19, report investigators who saw hospital admissions double in a single year.
“With the surge, we had expected to begin treating patients who developed severe or critical illness again in pregnancy,” says Emily Adhikari, MD, from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “But we did not expect the level of respiratory illness that we began to see in our patients. That was a surprise and an alarming finding that we felt was really important to get out there.”
The researchers followed more than 1,500 pregnant women diagnosed with COVID-19 who received care from Parkland Health and Hospital System in Dallas County, one of the nation’s busiest for deliveries. After the emergence of the Delta variant, the number of pregnant women hospitalized with COVID-19 more than doubled over the previous year.
And 82 pregnant women went on to develop severe or critical COVID, they report in their study, published online in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. All but 1 of these patients were unvaccinated, 10 needed a ventilator, and two died.
The proportion of cases that were critical was about 5% in 2020. However, in April 2021, even though the number of total cases remained low, the number of severe illnesses started to rise. After the Delta variant became dominant, both the number and severity of cases increased, and after August 2021, more than 25% of pregnant people diagnosed with COVID-19 required hospitalization.
Hospitalizations Double
“We need to focus and really act urgently to recommend vaccination in pregnancy because that is the primary prevention tool that we have,” says Dr. Adhikari. “We do not have a proven cure for this illness, and that is important to know.”
These findings, which focus on a vulnerable population, are especially important given the elevated prevalence of COVID-19 in pregnant people of lower economic status, said Lissette Tanner, MD, MPH, from Emory University in Atlanta, who was not involved with the study.
“There are higher rates of hospitalization and death among Black, Hispanic, and Native American communities,” she reported. “It is essential to know how the virus is affecting those most affected and often most disadvantaged to deal with the pandemic.”
Vaccination rates are low in this population; just 19.2% of pregnant women receive at least one dose during pregnancy, according to the CDC. But pregnancy confers a higher risk for severe COVID-19 illness and for adverse outcomes, such as preterm birth and stillbirth.
Of the 665 people in the study cohort who were pregnant or had given birth when the vaccines were available, only 21.4% received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
Given the increased risk for COVID-19 during pregnancy, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the CDC recommend vaccination for people who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or trying to get pregnant.
According to ACOG, pregnant women who are fully vaccinated can follow the same guidelines as everyone else who is fully vaccinated; however, to prevent breakthrough infections, they might want to continue wearing a mask. ACOG also recommends that those not fully vaccinated follow physical-distancing guidelines and limit contact with people as much as possible to avoid infection.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
An increasing number of people who are unvaccinated and pregnant are being hospitalized for COVID-19, report investigators who saw hospital admissions double in a single year.
“With the surge, we had expected to begin treating patients who developed severe or critical illness again in pregnancy,” says Emily Adhikari, MD, from the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas. “But we did not expect the level of respiratory illness that we began to see in our patients. That was a surprise and an alarming finding that we felt was really important to get out there.”
The researchers followed more than 1,500 pregnant women diagnosed with COVID-19 who received care from Parkland Health and Hospital System in Dallas County, one of the nation’s busiest for deliveries. After the emergence of the Delta variant, the number of pregnant women hospitalized with COVID-19 more than doubled over the previous year.
And 82 pregnant women went on to develop severe or critical COVID, they report in their study, published online in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. All but 1 of these patients were unvaccinated, 10 needed a ventilator, and two died.
The proportion of cases that were critical was about 5% in 2020. However, in April 2021, even though the number of total cases remained low, the number of severe illnesses started to rise. After the Delta variant became dominant, both the number and severity of cases increased, and after August 2021, more than 25% of pregnant people diagnosed with COVID-19 required hospitalization.
Hospitalizations Double
“We need to focus and really act urgently to recommend vaccination in pregnancy because that is the primary prevention tool that we have,” says Dr. Adhikari. “We do not have a proven cure for this illness, and that is important to know.”
These findings, which focus on a vulnerable population, are especially important given the elevated prevalence of COVID-19 in pregnant people of lower economic status, said Lissette Tanner, MD, MPH, from Emory University in Atlanta, who was not involved with the study.
“There are higher rates of hospitalization and death among Black, Hispanic, and Native American communities,” she reported. “It is essential to know how the virus is affecting those most affected and often most disadvantaged to deal with the pandemic.”
Vaccination rates are low in this population; just 19.2% of pregnant women receive at least one dose during pregnancy, according to the CDC. But pregnancy confers a higher risk for severe COVID-19 illness and for adverse outcomes, such as preterm birth and stillbirth.
Of the 665 people in the study cohort who were pregnant or had given birth when the vaccines were available, only 21.4% received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine.
Given the increased risk for COVID-19 during pregnancy, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the CDC recommend vaccination for people who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or trying to get pregnant.
According to ACOG, pregnant women who are fully vaccinated can follow the same guidelines as everyone else who is fully vaccinated; however, to prevent breakthrough infections, they might want to continue wearing a mask. ACOG also recommends that those not fully vaccinated follow physical-distancing guidelines and limit contact with people as much as possible to avoid infection.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
My experience as a family medicine resident in 2021
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19-era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time,” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic, Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today, you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician.
Dr. Persampiere is a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at victoria.persampiere@jefferson.edu or via fpnews@mdedge.com.
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19-era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time,” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic, Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today, you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician.
Dr. Persampiere is a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at victoria.persampiere@jefferson.edu or via fpnews@mdedge.com.
I did not get a medical school graduation; I was one of the many thousands of newly graduated students who simply left their 4th-year rotation sites one chilly day in March 2020 and just never went back. My medical school education didn’t end with me walking triumphantly across the stage – a first-generation college student finally achieving the greatest dream in her life. Instead, it ended with a Zoom “graduation” and a cross-country move from Georgia to Pennsylvania amidst the greatest pandemic in recent memory. To say my impostor syndrome was bad would be an understatement.
Residency in the COVID-19-era
The joy and the draw to family medicine for me has always been the broad scope of conditions that we see and treat. From day 1, however, much of my residency has been devoted to one very small subset of patients – those with COVID-19. At one point, our hospital was so strained that our family medicine program had to run a second inpatient service alongside our usual five-resident service team just to provide care to everybody. Patients were in the hallways. The ER was packed to the gills. We were sleepless, terrified, unvaccinated, and desperate to help our patients survive a disease that was incompletely understood, with very few tools in our toolbox to combat it.
I distinctly remember sitting in the workroom with a coresident of mine, our faces seemingly permanently lined from wearing N95s all shift, and saying to him, “I worry I will be a bad family medicine physician. I worry I haven’t seen enough, other than COVID.” It was midway through my intern year; the days were short, so I was driving to and from the hospital in chilly darkness. My patients, like many around the country, were doing poorly. Vaccines seemed like a promise too good to be true. Worst of all: Those of us who were interns, who had no triumphant podium moment to end our medical school education, were suffering with an intense sense of impostor syndrome which was strengthened by every “there is nothing else we can offer your loved one at this time,” conversation we had. My apprehension about not having seen a wider breadth of medicine during my training is a sentiment still widely shared by COVID-era residents.
Luckily, my coresident was supportive.
“We’re going to be great family medicine physicians,” he said. “We’re learning the hard stuff – the bread and butter of FM – up-front. You’ll see.”
In some ways, I think he was right. Clinical skills, empathy, humility, and forging strong relationships are at the center of every family medicine physician’s heart; my generation has had to learn these skills early and under pressure. Sometimes, there are no answers. Sometimes, the best thing a family doctor can do for a patient is to hear them, understand them, and hold their hand.
‘We watched Cinderella together’
Shortly after that conversation with my coresident, I had a particular case which moved me. This gentleman with intellectual disability and COVID had been declining steadily since his admission to the hospital. He was isolated from everybody he knew and loved, but it did not dampen his spirits. He was cheerful to every person who entered his room, clad in their shrouds of PPE, which more often than not felt more like mourning garb than protective wear. I remember very little about this patient’s clinical picture – the COVID, the superimposed pneumonia, the repeated intubations. What I do remember is he loved the Disney classic, Cinderella. I knew this because I developed a very close relationship with his family during the course of his hospitalization. Amidst the torrential onslaught of patients, I made sure to call families every day – not because I wanted to, but because my mentors and attendings and coresidents had all drilled into me from day 1 that we are family medicine, and a large part of our role is to advocate for our patients, and to communicate with their loved ones. So I called. I learned a lot about him; his likes, his dislikes, his close bond with his siblings, and of course his lifelong love for Cinderella. On the last week of my ICU rotation, my patient passed peacefully. His nurse and I were bedside. We held his hand. We told him his family loved him. We watched Cinderella together on an iPad encased in protective plastic.
My next rotation was an outpatient one and it looked more like the “bread and butter” of family medicine. But as I whisked in and out of patient rooms, attending to patients with diabetes, with depression, with pain, I could not stop thinking about my hospitalized patients who my coresidents had assumed care of. Each exam room I entered, I rather morbidly thought “this patient could be next on our hospital service.” Without realizing it, I made more of an effort to get to know each patient holistically. I learned who they were as people. I found myself writing small, medically low-yield details in the chart: “Margaret loves to sing in her church choir;” “Katherine is a self-published author.”
I learned from my attendings. As I sat at the precepting table with them, observing their conversations about patients, their collective decades of experience were apparent.
“I’ve been seeing this patient every few weeks since I was a resident,” said one of my attendings.
“I don’t even see my parents that often,” I thought.
The depth of her relationship with, understanding of, and compassion for this patient struck me deeply. This was why I went into family medicine. My attending knew her patients; they were not faceless unknowns in a hospital gown to her. She would have known to play Cinderella for them in the end.
This is a unique time for trainees. We have been challenged, terrified, overwhelmed, and heartbroken. But at no point have we been isolated. We’ve had the generations of doctors before us to lead the way, to teach us the “hard stuff.” We’ve had senior residents to lean on, who have taken us aside and told us, “I can do the goals-of-care talk today, you need a break.” While the plague seems to have passed over our hospital for now, it has left behind a class of family medicine residents who are proud to carry on our specialty’s long tradition of compassionate, empathetic, lifelong care. “We care for all life stages, from cradle to grave,” says every family medicine physician.
My class, for better or for worse, has cared more often for patients in the twilight of their lives, and while it has been hard, I believe it has made us all better doctors. Now, when I hold a newborn in my arms for a well-child check, I am exceptionally grateful – for the opportunities I have been given, for new beginnings amidst so much sadness, and for the great privilege of being a family medicine physician.
Dr. Persampiere is a 2nd-year resident in the family medicine residency program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. You can contact her directly at victoria.persampiere@jefferson.edu or via fpnews@mdedge.com.
Post-COVID-19 syndrome for a year after illness is common
Key clinical point: Persistence of COVID-19-related symptoms for 1 year after the onset of illness is common, even in some individuals with initial mild disease.
Major finding: Overall, 40.7% of participants continued to report 1 or more COVID-19-related symptoms at 12 months after illness onset. 16.4%, 49.5%, and 52.5% of patients with mild, moderate, and severe/critical COVID-19 had 1 or more COVID-19-related symptoms at 12 months after illness onset
Study details: The data come from a Dutch prospective cohort study (RECoVERED) involving 342 patients with COVID-19.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMw) and the Public Health Service of Amsterdam. A Boyd received a grant from ANRS and participated in the Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for ZonMw for another study. G de Bree served as a paid member of the scientific advisory board of ExeVir. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Wynberg E et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 2. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab759.
Key clinical point: Persistence of COVID-19-related symptoms for 1 year after the onset of illness is common, even in some individuals with initial mild disease.
Major finding: Overall, 40.7% of participants continued to report 1 or more COVID-19-related symptoms at 12 months after illness onset. 16.4%, 49.5%, and 52.5% of patients with mild, moderate, and severe/critical COVID-19 had 1 or more COVID-19-related symptoms at 12 months after illness onset
Study details: The data come from a Dutch prospective cohort study (RECoVERED) involving 342 patients with COVID-19.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMw) and the Public Health Service of Amsterdam. A Boyd received a grant from ANRS and participated in the Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for ZonMw for another study. G de Bree served as a paid member of the scientific advisory board of ExeVir. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Wynberg E et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 2. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab759.
Key clinical point: Persistence of COVID-19-related symptoms for 1 year after the onset of illness is common, even in some individuals with initial mild disease.
Major finding: Overall, 40.7% of participants continued to report 1 or more COVID-19-related symptoms at 12 months after illness onset. 16.4%, 49.5%, and 52.5% of patients with mild, moderate, and severe/critical COVID-19 had 1 or more COVID-19-related symptoms at 12 months after illness onset
Study details: The data come from a Dutch prospective cohort study (RECoVERED) involving 342 patients with COVID-19.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMw) and the Public Health Service of Amsterdam. A Boyd received a grant from ANRS and participated in the Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for ZonMw for another study. G de Bree served as a paid member of the scientific advisory board of ExeVir. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Wynberg E et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 2. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab759.
COVID-19: CPAP has no advantage over conventional oxygen therapy
Key clinical point: Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy in patients with severe COVID-19 who are not likely to benefit from invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) does not confer a survival advantage over oxygen alone.
Major finding: The overall 30-day mortality rate was 75.6% in the oxygen group vs 77.7% in the CPAP group (Pearson’s Chi-square, P = .8).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective multicentre cohort study involving 479 patients with COVID-19 ineligible for IMV from 7 UK hospitals. Patients given CPAP were compared with those receiving oxygen therapy.
Disclosures: L Pearmain is supported by the Medical Research Council, and TW Felton is supported by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. AB reported relationships with Fisher and Paykel and Sanofi Genzyme. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Bradley P et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2021 Sep 8. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101122.
Key clinical point: Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy in patients with severe COVID-19 who are not likely to benefit from invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) does not confer a survival advantage over oxygen alone.
Major finding: The overall 30-day mortality rate was 75.6% in the oxygen group vs 77.7% in the CPAP group (Pearson’s Chi-square, P = .8).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective multicentre cohort study involving 479 patients with COVID-19 ineligible for IMV from 7 UK hospitals. Patients given CPAP were compared with those receiving oxygen therapy.
Disclosures: L Pearmain is supported by the Medical Research Council, and TW Felton is supported by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. AB reported relationships with Fisher and Paykel and Sanofi Genzyme. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Bradley P et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2021 Sep 8. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101122.
Key clinical point: Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy in patients with severe COVID-19 who are not likely to benefit from invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) does not confer a survival advantage over oxygen alone.
Major finding: The overall 30-day mortality rate was 75.6% in the oxygen group vs 77.7% in the CPAP group (Pearson’s Chi-square, P = .8).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective multicentre cohort study involving 479 patients with COVID-19 ineligible for IMV from 7 UK hospitals. Patients given CPAP were compared with those receiving oxygen therapy.
Disclosures: L Pearmain is supported by the Medical Research Council, and TW Felton is supported by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. AB reported relationships with Fisher and Paykel and Sanofi Genzyme. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Bradley P et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2021 Sep 8. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101122.
Does smoking influence COVID-19 outcomes?
Key clinical point: Smokers have a significantly higher risk for COVID-19 related hospital admission and mortality than nonsmokers.
Major finding: Current smokers had an 80% higher risk for hospitalization than never-smokers (odds ratio, 1.80; 95% confidence interval, 1.26-2.29). Smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day had a 6.11-fold higher risk of dying from COVID-19 than never-smokers.
Study details: The data come from an observational study of 421,469 individuals from the UK Biobank.
Disclosures: The study was supported by individual grants to several authors. PS Tan, CAC Coupland, MR Munafò, J Hippisley-Cox, and A von Ende reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Clift AK et al. Thorax. 2021 Sep 27. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217080.
Key clinical point: Smokers have a significantly higher risk for COVID-19 related hospital admission and mortality than nonsmokers.
Major finding: Current smokers had an 80% higher risk for hospitalization than never-smokers (odds ratio, 1.80; 95% confidence interval, 1.26-2.29). Smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day had a 6.11-fold higher risk of dying from COVID-19 than never-smokers.
Study details: The data come from an observational study of 421,469 individuals from the UK Biobank.
Disclosures: The study was supported by individual grants to several authors. PS Tan, CAC Coupland, MR Munafò, J Hippisley-Cox, and A von Ende reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Clift AK et al. Thorax. 2021 Sep 27. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217080.
Key clinical point: Smokers have a significantly higher risk for COVID-19 related hospital admission and mortality than nonsmokers.
Major finding: Current smokers had an 80% higher risk for hospitalization than never-smokers (odds ratio, 1.80; 95% confidence interval, 1.26-2.29). Smokers who smoked more than 20 cigarettes a day had a 6.11-fold higher risk of dying from COVID-19 than never-smokers.
Study details: The data come from an observational study of 421,469 individuals from the UK Biobank.
Disclosures: The study was supported by individual grants to several authors. PS Tan, CAC Coupland, MR Munafò, J Hippisley-Cox, and A von Ende reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Clift AK et al. Thorax. 2021 Sep 27. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-217080.
Anti-CD20-treated multiple sclerosis patients show robust response to COVID-19 vaccines
Key clinical point: Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) receiving anti-CD20 (aCD20) treatment demonstrate a robust T-cell response to an mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
Major finding: Thirty days following the second dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, 89% of patients with MS had antispike antibodies, and 50% had mounted anti-receptor-binding domain responses.
Study details: A study assessed antibody and T-cell responses in 20 patients with MS receiving aCD20 treatment and 10 healthy controls.
Disclosures: The study was supported by individual grants to several authors. SE Hensley, EJ Wherry, A Sette, ET Luning Prak, D Jacobs, and A Bar-Or reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Apostolidis SA et al. Nat Med. 2021 Sep 14. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01507-2.
Key clinical point: Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) receiving anti-CD20 (aCD20) treatment demonstrate a robust T-cell response to an mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
Major finding: Thirty days following the second dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, 89% of patients with MS had antispike antibodies, and 50% had mounted anti-receptor-binding domain responses.
Study details: A study assessed antibody and T-cell responses in 20 patients with MS receiving aCD20 treatment and 10 healthy controls.
Disclosures: The study was supported by individual grants to several authors. SE Hensley, EJ Wherry, A Sette, ET Luning Prak, D Jacobs, and A Bar-Or reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Apostolidis SA et al. Nat Med. 2021 Sep 14. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01507-2.
Key clinical point: Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) receiving anti-CD20 (aCD20) treatment demonstrate a robust T-cell response to an mRNA COVID-19 vaccines.
Major finding: Thirty days following the second dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine, 89% of patients with MS had antispike antibodies, and 50% had mounted anti-receptor-binding domain responses.
Study details: A study assessed antibody and T-cell responses in 20 patients with MS receiving aCD20 treatment and 10 healthy controls.
Disclosures: The study was supported by individual grants to several authors. SE Hensley, EJ Wherry, A Sette, ET Luning Prak, D Jacobs, and A Bar-Or reported relationships with pharmaceutical companies and/or research organizations. The remaining authors declared no conflict of interests.
Source: Apostolidis SA et al. Nat Med. 2021 Sep 14. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01507-2.