User login
Treating lung cancer in COVID-19 times: Update from experts
Lung cancer experts in Europe issued highly considered recommendations for the management of lung cancer during the COVID-19 crisis, the main intention of which is to minimize the risk of patients getting infected by SARS-CoV-2 while in hospital receiving treatment.
The recommendations were published online April 3 in ESMO Open.
“We know that having cancer increases the risk of dying of COVID-19, although not necessarily the risk of getting the virus, and we also know that having lung cancer could increase the risk of pulmonary complications from SARS-CoV-2,” lead author Alfredo Addeo, MD, University Hospital of Geneva, Switzerland, told Medscape Medical News.
“But patients who are often in the hospital have a higher risk of catching the virus. So this paper is not about not giving necessary treatment, it’s about treating patients the best you can based on the area where you live and the resources you have and keeping patients away from the hospital as much as possible,” he added.
“The main message is, try to personalize the care you deliver,” Addeo said. “Rather than remain rigid about how you’ve been treating patients thus far, try to think outside the box and find a way to minimize the risk of infection, and, if you have to limit treatment, discuss the pros and cons of your treatment plan with the patient and make sure the message is given clearly.”
How much benefit?
The first general concept to keep in mind is: How likely is a patient to benefit from treatment?
“All regimens with a survival benefit should be maintained and prioritised whenever possible,” Addeo and colleagues observe. The other co-authors of the paper are Giuseppe Banna, MD, Ospedale Cannizzaro, Catania, Italy; Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro, MD, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland; and Alex Friedlaender, MD, University Hospital of Geneva.
For non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced resectable disease and sequential/concurrent chemotherapy/radiation therapy for patients with stage III lung cancer – provided they have adequate respiratory function – should be started when possible and should not be stopped without justification, the authors point out.
This is also true for first-line therapy in patients with metastatic disease. Treatment should also not be stopped without good reason among patients already receiving maintenance immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
For small cell lung cancer (SCLC), both first-line treatment for extensive-stage disease as well as concurrent chemotherapy/radiotherapy for patients with limited-stage disease should be started when possible, again provided they have adequate respiratory function.
Palliative or stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) delivered outside the lung should also be initiated when possible in SCLC patients.
The authors caution, however, that if palliative or SBRT outside the lung requires multiple visits to the hospital, treatment to the lung should be limited to cases with compression of airways or bleeding.
Oncologists should also try to start radiotherapy on day 1 of chemotherapy because then only 2 cycles will be needed; if radiotherapy is started with cycle 2 or is given sequentially, 3 cycles of treatment will be required.
“Fractions of SBRT could be reduced, depending on organ at risk (8 fractions to 5 or 3) while palliative RT [given] as a single fraction or two (8-10 Gy or 17 Gy, respectively) should be used where possible,” the authors observe.
Concurrent chemotherapy with radiotherapy for limited-stage disease should not be stopped without justification and nor should first-line treatment for metastatic SCLC, the authors continue.
Again, however, patients must have adequate respiratory function to receive or continue with concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy, they add.
For patients with stage III NSCLC, concurrent chemotherapy plus radiotherapy may be considered and given preferentially or not.
Similarly, oral rather than intravenous chemotherapy may be preferred for elderly NSCLC patients or for those with an ECOG performance status of 2 as well as for SCLC patients.
Delaying surgery
As a general principle, the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy instead of adjuvant therapy following surgery can delay the need for immediate surgery. If surgery can be delayed, “the risk of a patient catching the virus several months from now might be less,” Addeo noted. Thus, treating patients upfront with chemotherapy is one tactic to consider in appropriate patients.
For NSCLC patients at high risk for COVID-19, adjuvant chemotherapy should be discussed and potentially withheld, the authors observe.
NSCLC patients at high risk for COVID-19 include those with comorbidities, such as cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, as well as patients who are 70 years of age and older.
Immunotherapy should also be discussed and possibly delayed for stage III NSCLC patients following concurrent chemotherapy and radiation, they add.
Maintenance pemetrexed also may be withheld for NSCLC patients, and intervals of immunotherapy may be prolonged (e.g., nivolumab every 4 weeks and pembrolizumab every 6 weeks).
Intervals of immunotherapy should be similarly prolonged for SCLC patients, they continue.
“Shorter duration of chemotherapy (e.g., four cycles of chemotherapy instead of six) should be discussed with patients and maintenance chemotherapy can be withheld,” the authors note.
Furthermore, “given the pandemic, it is highly likely that metastatic cancer patients will be less likely to be intubated or to be heavily ventilated compared to patients without any comorbidity,” Addeo explained.
“So we have to acknowledge that metastatic lung cancer patients will be at higher risk of dying due to severe pulmonary COVID-19 complications,” he added.
Therefore, third and further lines of chemotherapy in both NSCLC and SCLC patients at significant COVID-19 risk should not be initiated without having a good reason to do so.
“Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is still a matter of debate [in SCLC patients],” Addeo noted. “So the reasonable alternative is to do surveillance MRI, and, in 6 or 8 months, we can probably offer PCI more safely at that point,” he suggested, adding that radiation therapy to the brain should only be considered if a patient develops brain metastases.
The authors also suggest that thoracic consolidation radiotherapy for extensive stage SCLC should not be initiated unless there is good reason to do so.
Patients with family members or caregivers who have tested positive for COVID-19 should themselves be tested before or during any cancer treatment.
If patients themselves then test positive and are asymptomatic, “28 days of delay should be considered before (re)starting the treatment,” the authors advise.
However, two negative tests done 1 week apart should be carried out before starting or restarting treatment, they note.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lung cancer experts in Europe issued highly considered recommendations for the management of lung cancer during the COVID-19 crisis, the main intention of which is to minimize the risk of patients getting infected by SARS-CoV-2 while in hospital receiving treatment.
The recommendations were published online April 3 in ESMO Open.
“We know that having cancer increases the risk of dying of COVID-19, although not necessarily the risk of getting the virus, and we also know that having lung cancer could increase the risk of pulmonary complications from SARS-CoV-2,” lead author Alfredo Addeo, MD, University Hospital of Geneva, Switzerland, told Medscape Medical News.
“But patients who are often in the hospital have a higher risk of catching the virus. So this paper is not about not giving necessary treatment, it’s about treating patients the best you can based on the area where you live and the resources you have and keeping patients away from the hospital as much as possible,” he added.
“The main message is, try to personalize the care you deliver,” Addeo said. “Rather than remain rigid about how you’ve been treating patients thus far, try to think outside the box and find a way to minimize the risk of infection, and, if you have to limit treatment, discuss the pros and cons of your treatment plan with the patient and make sure the message is given clearly.”
How much benefit?
The first general concept to keep in mind is: How likely is a patient to benefit from treatment?
“All regimens with a survival benefit should be maintained and prioritised whenever possible,” Addeo and colleagues observe. The other co-authors of the paper are Giuseppe Banna, MD, Ospedale Cannizzaro, Catania, Italy; Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro, MD, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland; and Alex Friedlaender, MD, University Hospital of Geneva.
For non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced resectable disease and sequential/concurrent chemotherapy/radiation therapy for patients with stage III lung cancer – provided they have adequate respiratory function – should be started when possible and should not be stopped without justification, the authors point out.
This is also true for first-line therapy in patients with metastatic disease. Treatment should also not be stopped without good reason among patients already receiving maintenance immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
For small cell lung cancer (SCLC), both first-line treatment for extensive-stage disease as well as concurrent chemotherapy/radiotherapy for patients with limited-stage disease should be started when possible, again provided they have adequate respiratory function.
Palliative or stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) delivered outside the lung should also be initiated when possible in SCLC patients.
The authors caution, however, that if palliative or SBRT outside the lung requires multiple visits to the hospital, treatment to the lung should be limited to cases with compression of airways or bleeding.
Oncologists should also try to start radiotherapy on day 1 of chemotherapy because then only 2 cycles will be needed; if radiotherapy is started with cycle 2 or is given sequentially, 3 cycles of treatment will be required.
“Fractions of SBRT could be reduced, depending on organ at risk (8 fractions to 5 or 3) while palliative RT [given] as a single fraction or two (8-10 Gy or 17 Gy, respectively) should be used where possible,” the authors observe.
Concurrent chemotherapy with radiotherapy for limited-stage disease should not be stopped without justification and nor should first-line treatment for metastatic SCLC, the authors continue.
Again, however, patients must have adequate respiratory function to receive or continue with concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy, they add.
For patients with stage III NSCLC, concurrent chemotherapy plus radiotherapy may be considered and given preferentially or not.
Similarly, oral rather than intravenous chemotherapy may be preferred for elderly NSCLC patients or for those with an ECOG performance status of 2 as well as for SCLC patients.
Delaying surgery
As a general principle, the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy instead of adjuvant therapy following surgery can delay the need for immediate surgery. If surgery can be delayed, “the risk of a patient catching the virus several months from now might be less,” Addeo noted. Thus, treating patients upfront with chemotherapy is one tactic to consider in appropriate patients.
For NSCLC patients at high risk for COVID-19, adjuvant chemotherapy should be discussed and potentially withheld, the authors observe.
NSCLC patients at high risk for COVID-19 include those with comorbidities, such as cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, as well as patients who are 70 years of age and older.
Immunotherapy should also be discussed and possibly delayed for stage III NSCLC patients following concurrent chemotherapy and radiation, they add.
Maintenance pemetrexed also may be withheld for NSCLC patients, and intervals of immunotherapy may be prolonged (e.g., nivolumab every 4 weeks and pembrolizumab every 6 weeks).
Intervals of immunotherapy should be similarly prolonged for SCLC patients, they continue.
“Shorter duration of chemotherapy (e.g., four cycles of chemotherapy instead of six) should be discussed with patients and maintenance chemotherapy can be withheld,” the authors note.
Furthermore, “given the pandemic, it is highly likely that metastatic cancer patients will be less likely to be intubated or to be heavily ventilated compared to patients without any comorbidity,” Addeo explained.
“So we have to acknowledge that metastatic lung cancer patients will be at higher risk of dying due to severe pulmonary COVID-19 complications,” he added.
Therefore, third and further lines of chemotherapy in both NSCLC and SCLC patients at significant COVID-19 risk should not be initiated without having a good reason to do so.
“Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is still a matter of debate [in SCLC patients],” Addeo noted. “So the reasonable alternative is to do surveillance MRI, and, in 6 or 8 months, we can probably offer PCI more safely at that point,” he suggested, adding that radiation therapy to the brain should only be considered if a patient develops brain metastases.
The authors also suggest that thoracic consolidation radiotherapy for extensive stage SCLC should not be initiated unless there is good reason to do so.
Patients with family members or caregivers who have tested positive for COVID-19 should themselves be tested before or during any cancer treatment.
If patients themselves then test positive and are asymptomatic, “28 days of delay should be considered before (re)starting the treatment,” the authors advise.
However, two negative tests done 1 week apart should be carried out before starting or restarting treatment, they note.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lung cancer experts in Europe issued highly considered recommendations for the management of lung cancer during the COVID-19 crisis, the main intention of which is to minimize the risk of patients getting infected by SARS-CoV-2 while in hospital receiving treatment.
The recommendations were published online April 3 in ESMO Open.
“We know that having cancer increases the risk of dying of COVID-19, although not necessarily the risk of getting the virus, and we also know that having lung cancer could increase the risk of pulmonary complications from SARS-CoV-2,” lead author Alfredo Addeo, MD, University Hospital of Geneva, Switzerland, told Medscape Medical News.
“But patients who are often in the hospital have a higher risk of catching the virus. So this paper is not about not giving necessary treatment, it’s about treating patients the best you can based on the area where you live and the resources you have and keeping patients away from the hospital as much as possible,” he added.
“The main message is, try to personalize the care you deliver,” Addeo said. “Rather than remain rigid about how you’ve been treating patients thus far, try to think outside the box and find a way to minimize the risk of infection, and, if you have to limit treatment, discuss the pros and cons of your treatment plan with the patient and make sure the message is given clearly.”
How much benefit?
The first general concept to keep in mind is: How likely is a patient to benefit from treatment?
“All regimens with a survival benefit should be maintained and prioritised whenever possible,” Addeo and colleagues observe. The other co-authors of the paper are Giuseppe Banna, MD, Ospedale Cannizzaro, Catania, Italy; Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro, MD, University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland; and Alex Friedlaender, MD, University Hospital of Geneva.
For non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced resectable disease and sequential/concurrent chemotherapy/radiation therapy for patients with stage III lung cancer – provided they have adequate respiratory function – should be started when possible and should not be stopped without justification, the authors point out.
This is also true for first-line therapy in patients with metastatic disease. Treatment should also not be stopped without good reason among patients already receiving maintenance immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy.
For small cell lung cancer (SCLC), both first-line treatment for extensive-stage disease as well as concurrent chemotherapy/radiotherapy for patients with limited-stage disease should be started when possible, again provided they have adequate respiratory function.
Palliative or stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) delivered outside the lung should also be initiated when possible in SCLC patients.
The authors caution, however, that if palliative or SBRT outside the lung requires multiple visits to the hospital, treatment to the lung should be limited to cases with compression of airways or bleeding.
Oncologists should also try to start radiotherapy on day 1 of chemotherapy because then only 2 cycles will be needed; if radiotherapy is started with cycle 2 or is given sequentially, 3 cycles of treatment will be required.
“Fractions of SBRT could be reduced, depending on organ at risk (8 fractions to 5 or 3) while palliative RT [given] as a single fraction or two (8-10 Gy or 17 Gy, respectively) should be used where possible,” the authors observe.
Concurrent chemotherapy with radiotherapy for limited-stage disease should not be stopped without justification and nor should first-line treatment for metastatic SCLC, the authors continue.
Again, however, patients must have adequate respiratory function to receive or continue with concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy, they add.
For patients with stage III NSCLC, concurrent chemotherapy plus radiotherapy may be considered and given preferentially or not.
Similarly, oral rather than intravenous chemotherapy may be preferred for elderly NSCLC patients or for those with an ECOG performance status of 2 as well as for SCLC patients.
Delaying surgery
As a general principle, the use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy instead of adjuvant therapy following surgery can delay the need for immediate surgery. If surgery can be delayed, “the risk of a patient catching the virus several months from now might be less,” Addeo noted. Thus, treating patients upfront with chemotherapy is one tactic to consider in appropriate patients.
For NSCLC patients at high risk for COVID-19, adjuvant chemotherapy should be discussed and potentially withheld, the authors observe.
NSCLC patients at high risk for COVID-19 include those with comorbidities, such as cardiovascular or pulmonary disease, as well as patients who are 70 years of age and older.
Immunotherapy should also be discussed and possibly delayed for stage III NSCLC patients following concurrent chemotherapy and radiation, they add.
Maintenance pemetrexed also may be withheld for NSCLC patients, and intervals of immunotherapy may be prolonged (e.g., nivolumab every 4 weeks and pembrolizumab every 6 weeks).
Intervals of immunotherapy should be similarly prolonged for SCLC patients, they continue.
“Shorter duration of chemotherapy (e.g., four cycles of chemotherapy instead of six) should be discussed with patients and maintenance chemotherapy can be withheld,” the authors note.
Furthermore, “given the pandemic, it is highly likely that metastatic cancer patients will be less likely to be intubated or to be heavily ventilated compared to patients without any comorbidity,” Addeo explained.
“So we have to acknowledge that metastatic lung cancer patients will be at higher risk of dying due to severe pulmonary COVID-19 complications,” he added.
Therefore, third and further lines of chemotherapy in both NSCLC and SCLC patients at significant COVID-19 risk should not be initiated without having a good reason to do so.
“Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) is still a matter of debate [in SCLC patients],” Addeo noted. “So the reasonable alternative is to do surveillance MRI, and, in 6 or 8 months, we can probably offer PCI more safely at that point,” he suggested, adding that radiation therapy to the brain should only be considered if a patient develops brain metastases.
The authors also suggest that thoracic consolidation radiotherapy for extensive stage SCLC should not be initiated unless there is good reason to do so.
Patients with family members or caregivers who have tested positive for COVID-19 should themselves be tested before or during any cancer treatment.
If patients themselves then test positive and are asymptomatic, “28 days of delay should be considered before (re)starting the treatment,” the authors advise.
However, two negative tests done 1 week apart should be carried out before starting or restarting treatment, they note.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Conducting cancer trials amid the COVID-19 pandemic
More than three-quarters of cancer clinical research programs have experienced operational changes during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey conducted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers (ACCC) during a recent webinar.
The webinar included insights into how some cancer research programs have adapted to the pandemic, a review of guidance for conducting cancer trials during this time, and a discussion of how the cancer research landscape may be affected by COVID-19 going forward.
The webinar was led by Randall A. Oyer, MD, president of the ACCC and medical director of the oncology program at Penn Medicine Lancaster General Health in Pennsylvania.
The impact of COVID-19 on cancer research
Dr. Oyer observed that planning and implementation for COVID-19–related illness at U.S. health care institutions has had a predictable effect of limiting patient access and staff availability for nonessential services.
Coronavirus-related exposure and/or illness has relegated cancer research to a lower-level priority. As a result, ACCC institutions have made adjustments in their cancer research programs, including moving clinical research coordinators off-campus and deploying them in clinical areas.
New clinical trials have not been opened. In some cases, new accruals have been halted, particularly for registry, prevention, and symptom control trials.
Standards that have changed and those that have not
Guidance documents for conducting clinical trials during the pandemic have been developed by the Food and Drug Administration, the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Central Institutional Review Board, and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Extramural Research. Industry sponsors and parent institutions of research programs have also disseminated guidance.
Among other topics, guidance documents have addressed:
- How COVID-19-related protocol deviations will be judged at monitoring visits and audits
- Missed office visits and endpoint evaluations
- Providing investigational oral medications to patients via mail and potential issues of medication unavailability
- Processes for patients to have interim visits with providers at external institutions, including providers who may not be personally engaged in or credentialed for the research trial
- Potential delays in submitting protocol amendments for institutional review board (IRB) review
- Recommendations for patients confirmed or suspected of having a coronavirus infection.
Dr. Oyer emphasized that patient safety must remain the highest priority for patient management, on or off study. He advised continuing investigational therapy when potential benefit from treatment is anticipated and identifying alternative methods to face-to-face visits for monitoring and access to treatment.
Dr. Oyer urged programs to:
- Maintain good clinical practice standards
- Consult with sponsors and IRBs when questions arise but implement changes that affect patient safety prior to IRB review if necessary
- Document all deviations and COVID-19 related adaptations in a log or spreadsheet in anticipation of future questions from sponsors, monitors, and other entities.
New questions and considerations
In the short-term, Dr. Oyer predicts fewer available trials and a decreased rate of accrual to existing studies. This may result in delays in trial completion and the possibility of redesign for some trials.
He predicts the emergence of COVID-19-focused research questions, including those assessing the course of coronavirus infection in various malignant settings and the impact of cancer-directed treatments and supportive care interventions (e.g., treatment for graft-versus-host disease) on response to COVID-19.
To facilitate developing a clinically and research-relevant database, Dr. Oyer stressed the importance of documentation in the research record, reporting infections as serious adverse events. Documentation should specify whether the infection was confirmed or suspected coronavirus or related to another organism.
In general, when coronavirus infection is strongly suspected, Dr. Oyer said investigational treatments should be interrupted, but study-specific criteria will be forthcoming on that issue.
Looking to the future
For patients with advanced cancers, clinical trials provide an important option for hope and clinical benefit. Disrupting the conduct of clinical trials could endanger the lives of participants and delay the emergence of promising treatments and diagnostic tests.
When the coronavirus pandemic recedes, advancing knowledge and treatments for cancer will demand renewed commitment across the oncology care community.
Going forward, Dr. Oyer advised that clinical research staff protect their own health and the safety of trial participants. He encouraged programs to work with sponsors and IRBs to solve logistical problems and clarify individual issues.
He was optimistic that resumption of more normal conduct of studies will enable the successful completion of ongoing trials, enhanced by the creative solutions that were devised during the crisis and by additional prospective, clinically annotated, carefully recorded data from academic and community research sites.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
More than three-quarters of cancer clinical research programs have experienced operational changes during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey conducted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers (ACCC) during a recent webinar.
The webinar included insights into how some cancer research programs have adapted to the pandemic, a review of guidance for conducting cancer trials during this time, and a discussion of how the cancer research landscape may be affected by COVID-19 going forward.
The webinar was led by Randall A. Oyer, MD, president of the ACCC and medical director of the oncology program at Penn Medicine Lancaster General Health in Pennsylvania.
The impact of COVID-19 on cancer research
Dr. Oyer observed that planning and implementation for COVID-19–related illness at U.S. health care institutions has had a predictable effect of limiting patient access and staff availability for nonessential services.
Coronavirus-related exposure and/or illness has relegated cancer research to a lower-level priority. As a result, ACCC institutions have made adjustments in their cancer research programs, including moving clinical research coordinators off-campus and deploying them in clinical areas.
New clinical trials have not been opened. In some cases, new accruals have been halted, particularly for registry, prevention, and symptom control trials.
Standards that have changed and those that have not
Guidance documents for conducting clinical trials during the pandemic have been developed by the Food and Drug Administration, the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Central Institutional Review Board, and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Extramural Research. Industry sponsors and parent institutions of research programs have also disseminated guidance.
Among other topics, guidance documents have addressed:
- How COVID-19-related protocol deviations will be judged at monitoring visits and audits
- Missed office visits and endpoint evaluations
- Providing investigational oral medications to patients via mail and potential issues of medication unavailability
- Processes for patients to have interim visits with providers at external institutions, including providers who may not be personally engaged in or credentialed for the research trial
- Potential delays in submitting protocol amendments for institutional review board (IRB) review
- Recommendations for patients confirmed or suspected of having a coronavirus infection.
Dr. Oyer emphasized that patient safety must remain the highest priority for patient management, on or off study. He advised continuing investigational therapy when potential benefit from treatment is anticipated and identifying alternative methods to face-to-face visits for monitoring and access to treatment.
Dr. Oyer urged programs to:
- Maintain good clinical practice standards
- Consult with sponsors and IRBs when questions arise but implement changes that affect patient safety prior to IRB review if necessary
- Document all deviations and COVID-19 related adaptations in a log or spreadsheet in anticipation of future questions from sponsors, monitors, and other entities.
New questions and considerations
In the short-term, Dr. Oyer predicts fewer available trials and a decreased rate of accrual to existing studies. This may result in delays in trial completion and the possibility of redesign for some trials.
He predicts the emergence of COVID-19-focused research questions, including those assessing the course of coronavirus infection in various malignant settings and the impact of cancer-directed treatments and supportive care interventions (e.g., treatment for graft-versus-host disease) on response to COVID-19.
To facilitate developing a clinically and research-relevant database, Dr. Oyer stressed the importance of documentation in the research record, reporting infections as serious adverse events. Documentation should specify whether the infection was confirmed or suspected coronavirus or related to another organism.
In general, when coronavirus infection is strongly suspected, Dr. Oyer said investigational treatments should be interrupted, but study-specific criteria will be forthcoming on that issue.
Looking to the future
For patients with advanced cancers, clinical trials provide an important option for hope and clinical benefit. Disrupting the conduct of clinical trials could endanger the lives of participants and delay the emergence of promising treatments and diagnostic tests.
When the coronavirus pandemic recedes, advancing knowledge and treatments for cancer will demand renewed commitment across the oncology care community.
Going forward, Dr. Oyer advised that clinical research staff protect their own health and the safety of trial participants. He encouraged programs to work with sponsors and IRBs to solve logistical problems and clarify individual issues.
He was optimistic that resumption of more normal conduct of studies will enable the successful completion of ongoing trials, enhanced by the creative solutions that were devised during the crisis and by additional prospective, clinically annotated, carefully recorded data from academic and community research sites.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
More than three-quarters of cancer clinical research programs have experienced operational changes during the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a survey conducted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers (ACCC) during a recent webinar.
The webinar included insights into how some cancer research programs have adapted to the pandemic, a review of guidance for conducting cancer trials during this time, and a discussion of how the cancer research landscape may be affected by COVID-19 going forward.
The webinar was led by Randall A. Oyer, MD, president of the ACCC and medical director of the oncology program at Penn Medicine Lancaster General Health in Pennsylvania.
The impact of COVID-19 on cancer research
Dr. Oyer observed that planning and implementation for COVID-19–related illness at U.S. health care institutions has had a predictable effect of limiting patient access and staff availability for nonessential services.
Coronavirus-related exposure and/or illness has relegated cancer research to a lower-level priority. As a result, ACCC institutions have made adjustments in their cancer research programs, including moving clinical research coordinators off-campus and deploying them in clinical areas.
New clinical trials have not been opened. In some cases, new accruals have been halted, particularly for registry, prevention, and symptom control trials.
Standards that have changed and those that have not
Guidance documents for conducting clinical trials during the pandemic have been developed by the Food and Drug Administration, the National Cancer Institute’s Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program and Central Institutional Review Board, and the National Institutes of Health’s Office of Extramural Research. Industry sponsors and parent institutions of research programs have also disseminated guidance.
Among other topics, guidance documents have addressed:
- How COVID-19-related protocol deviations will be judged at monitoring visits and audits
- Missed office visits and endpoint evaluations
- Providing investigational oral medications to patients via mail and potential issues of medication unavailability
- Processes for patients to have interim visits with providers at external institutions, including providers who may not be personally engaged in or credentialed for the research trial
- Potential delays in submitting protocol amendments for institutional review board (IRB) review
- Recommendations for patients confirmed or suspected of having a coronavirus infection.
Dr. Oyer emphasized that patient safety must remain the highest priority for patient management, on or off study. He advised continuing investigational therapy when potential benefit from treatment is anticipated and identifying alternative methods to face-to-face visits for monitoring and access to treatment.
Dr. Oyer urged programs to:
- Maintain good clinical practice standards
- Consult with sponsors and IRBs when questions arise but implement changes that affect patient safety prior to IRB review if necessary
- Document all deviations and COVID-19 related adaptations in a log or spreadsheet in anticipation of future questions from sponsors, monitors, and other entities.
New questions and considerations
In the short-term, Dr. Oyer predicts fewer available trials and a decreased rate of accrual to existing studies. This may result in delays in trial completion and the possibility of redesign for some trials.
He predicts the emergence of COVID-19-focused research questions, including those assessing the course of coronavirus infection in various malignant settings and the impact of cancer-directed treatments and supportive care interventions (e.g., treatment for graft-versus-host disease) on response to COVID-19.
To facilitate developing a clinically and research-relevant database, Dr. Oyer stressed the importance of documentation in the research record, reporting infections as serious adverse events. Documentation should specify whether the infection was confirmed or suspected coronavirus or related to another organism.
In general, when coronavirus infection is strongly suspected, Dr. Oyer said investigational treatments should be interrupted, but study-specific criteria will be forthcoming on that issue.
Looking to the future
For patients with advanced cancers, clinical trials provide an important option for hope and clinical benefit. Disrupting the conduct of clinical trials could endanger the lives of participants and delay the emergence of promising treatments and diagnostic tests.
When the coronavirus pandemic recedes, advancing knowledge and treatments for cancer will demand renewed commitment across the oncology care community.
Going forward, Dr. Oyer advised that clinical research staff protect their own health and the safety of trial participants. He encouraged programs to work with sponsors and IRBs to solve logistical problems and clarify individual issues.
He was optimistic that resumption of more normal conduct of studies will enable the successful completion of ongoing trials, enhanced by the creative solutions that were devised during the crisis and by additional prospective, clinically annotated, carefully recorded data from academic and community research sites.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
NCCN panel: Defer nonurgent skin cancer care during pandemic
Amid the except when metastatic nodes are threatening vital structures or neoadjuvant therapy is not possible or has already failed, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network said in a new document about managing melanoma during the pandemic.
“The NCCN Melanoma Panel does not consider neoadjuvant therapy as a superior option to surgery followed by systemic adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma, but available data suggest this is a reasonable resource-conserving option during the COVID-19 outbreak,” according to the panel. Surgery should be performed 8-9 weeks after initiation, said the group, an alliance of physicians from 30 U.S. cancer centers.
Echoing pandemic advice from other medical fields, the group’s melanoma recommendations focused on deferring nonurgent care until after the pandemic passes, and in the meantime limiting patient contact with the medical system and preserving hospital resources by, for instance, using telemedicine and opting for treatment regimens that require fewer trips to the clinic.
In a separate document on nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), the group said that, with the exception of Merkel cell carcinoma, excisions for NMSC – including basal and squamous cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and rare tumors – should also generally be postponed during the pandemic.
The exception is if there is a risk of metastases within 3 months, but “such estimations of risks ... should be weighed against risks of the patient contracting COVID-19 infection or asymptomatically transmitting COVID-19 to health care workers,” the panel said.
Along the same lines, adjuvant therapy after surgical clearance of localized NMSC “should generally not be undertaken given the multiple visits required,” except for more extensive disease.
For primary cutaneous melanoma , “most time-to-treat studies show no adverse patient outcomes following a 90-day treatment delay, even for thicker [cutaneous melanoma],” the group said, so it recommended delaying wide excisions for melanoma in situ, lesions no thicker than 1 mm (T1) so long as the biopsy removed most of the lesion, and invasive melanomas of any depth if the biopsy had clear margins or only peripheral transection of the in situ component. They said sentinel lymph node biopsy can also be delayed for up to 3 months.
Resections for metastatic stage III-IV disease should also be put on hold unless the patient is symptomatic; systemic treatments should instead be continued. However, “given hospital-intensive resources, the use of talimogene laherparepvec for cutaneous/nodal/in-transit metastasis should be cautiously considered and, if possible, deferred until the COVID-19 crisis abates. A single dose of palliative radiation therapy may be useful for larger/symptomatic metastasis, as appropriate,” the group said.
If resection is still a go, the group noted that adjuvant therapy “has not been shown to improve melanoma-specific survival and should be deferred during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with [a less than] 50% chance of disease relapse.” Dabrafenib/trametinib is the evidence-based choice if adjuvant treatment is opted for, but “alternative BRAF/MEK inhibitor regimens (encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib) may be substituted if drug supply is limited” by the pandemic, the group said.
For stage IV melanoma, “single-agent anti-PD-1 [programmed cell death 1] is recommended over combination ipilimumab/nivolumab at present” because there’s less inflammation and possible exacerbation of COVID-19, less need for steroids to counter adverse events, and less need for follow up to check for toxicities.
The group said evidence supports that 400 mg pembrolizumab administered intravenously every 6 weeks would likely be as effective as 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks and would help keep people out of the hospital.
However, for stage IV melanoma with brain metastasis, there’s a strong rate of response to ipilimumab/nivolumab, so it may still be an option. In that case, “a regimen of ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four infusions, with subsequent consideration for nivolumab monotherapy, is associated with lower rates of immune-mediated toxicity,” compared with standard dosing.
Regarding potential drug shortages, the group noted that encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib combinations can be substituted for dabrafenib/trametinib for adjuvant therapy, and single-agent BRAF inhibitors can be used in the event of MEK inhibitor shortages.
In hospice, the group said oral temozolomide is the preferred option for palliative chemotherapy since it would limit resource utilization and contact with the medical system.
Amid the except when metastatic nodes are threatening vital structures or neoadjuvant therapy is not possible or has already failed, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network said in a new document about managing melanoma during the pandemic.
“The NCCN Melanoma Panel does not consider neoadjuvant therapy as a superior option to surgery followed by systemic adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma, but available data suggest this is a reasonable resource-conserving option during the COVID-19 outbreak,” according to the panel. Surgery should be performed 8-9 weeks after initiation, said the group, an alliance of physicians from 30 U.S. cancer centers.
Echoing pandemic advice from other medical fields, the group’s melanoma recommendations focused on deferring nonurgent care until after the pandemic passes, and in the meantime limiting patient contact with the medical system and preserving hospital resources by, for instance, using telemedicine and opting for treatment regimens that require fewer trips to the clinic.
In a separate document on nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), the group said that, with the exception of Merkel cell carcinoma, excisions for NMSC – including basal and squamous cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and rare tumors – should also generally be postponed during the pandemic.
The exception is if there is a risk of metastases within 3 months, but “such estimations of risks ... should be weighed against risks of the patient contracting COVID-19 infection or asymptomatically transmitting COVID-19 to health care workers,” the panel said.
Along the same lines, adjuvant therapy after surgical clearance of localized NMSC “should generally not be undertaken given the multiple visits required,” except for more extensive disease.
For primary cutaneous melanoma , “most time-to-treat studies show no adverse patient outcomes following a 90-day treatment delay, even for thicker [cutaneous melanoma],” the group said, so it recommended delaying wide excisions for melanoma in situ, lesions no thicker than 1 mm (T1) so long as the biopsy removed most of the lesion, and invasive melanomas of any depth if the biopsy had clear margins or only peripheral transection of the in situ component. They said sentinel lymph node biopsy can also be delayed for up to 3 months.
Resections for metastatic stage III-IV disease should also be put on hold unless the patient is symptomatic; systemic treatments should instead be continued. However, “given hospital-intensive resources, the use of talimogene laherparepvec for cutaneous/nodal/in-transit metastasis should be cautiously considered and, if possible, deferred until the COVID-19 crisis abates. A single dose of palliative radiation therapy may be useful for larger/symptomatic metastasis, as appropriate,” the group said.
If resection is still a go, the group noted that adjuvant therapy “has not been shown to improve melanoma-specific survival and should be deferred during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with [a less than] 50% chance of disease relapse.” Dabrafenib/trametinib is the evidence-based choice if adjuvant treatment is opted for, but “alternative BRAF/MEK inhibitor regimens (encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib) may be substituted if drug supply is limited” by the pandemic, the group said.
For stage IV melanoma, “single-agent anti-PD-1 [programmed cell death 1] is recommended over combination ipilimumab/nivolumab at present” because there’s less inflammation and possible exacerbation of COVID-19, less need for steroids to counter adverse events, and less need for follow up to check for toxicities.
The group said evidence supports that 400 mg pembrolizumab administered intravenously every 6 weeks would likely be as effective as 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks and would help keep people out of the hospital.
However, for stage IV melanoma with brain metastasis, there’s a strong rate of response to ipilimumab/nivolumab, so it may still be an option. In that case, “a regimen of ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four infusions, with subsequent consideration for nivolumab monotherapy, is associated with lower rates of immune-mediated toxicity,” compared with standard dosing.
Regarding potential drug shortages, the group noted that encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib combinations can be substituted for dabrafenib/trametinib for adjuvant therapy, and single-agent BRAF inhibitors can be used in the event of MEK inhibitor shortages.
In hospice, the group said oral temozolomide is the preferred option for palliative chemotherapy since it would limit resource utilization and contact with the medical system.
Amid the except when metastatic nodes are threatening vital structures or neoadjuvant therapy is not possible or has already failed, the National Comprehensive Cancer Network said in a new document about managing melanoma during the pandemic.
“The NCCN Melanoma Panel does not consider neoadjuvant therapy as a superior option to surgery followed by systemic adjuvant therapy for stage III melanoma, but available data suggest this is a reasonable resource-conserving option during the COVID-19 outbreak,” according to the panel. Surgery should be performed 8-9 weeks after initiation, said the group, an alliance of physicians from 30 U.S. cancer centers.
Echoing pandemic advice from other medical fields, the group’s melanoma recommendations focused on deferring nonurgent care until after the pandemic passes, and in the meantime limiting patient contact with the medical system and preserving hospital resources by, for instance, using telemedicine and opting for treatment regimens that require fewer trips to the clinic.
In a separate document on nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), the group said that, with the exception of Merkel cell carcinoma, excisions for NMSC – including basal and squamous cell carcinoma, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, and rare tumors – should also generally be postponed during the pandemic.
The exception is if there is a risk of metastases within 3 months, but “such estimations of risks ... should be weighed against risks of the patient contracting COVID-19 infection or asymptomatically transmitting COVID-19 to health care workers,” the panel said.
Along the same lines, adjuvant therapy after surgical clearance of localized NMSC “should generally not be undertaken given the multiple visits required,” except for more extensive disease.
For primary cutaneous melanoma , “most time-to-treat studies show no adverse patient outcomes following a 90-day treatment delay, even for thicker [cutaneous melanoma],” the group said, so it recommended delaying wide excisions for melanoma in situ, lesions no thicker than 1 mm (T1) so long as the biopsy removed most of the lesion, and invasive melanomas of any depth if the biopsy had clear margins or only peripheral transection of the in situ component. They said sentinel lymph node biopsy can also be delayed for up to 3 months.
Resections for metastatic stage III-IV disease should also be put on hold unless the patient is symptomatic; systemic treatments should instead be continued. However, “given hospital-intensive resources, the use of talimogene laherparepvec for cutaneous/nodal/in-transit metastasis should be cautiously considered and, if possible, deferred until the COVID-19 crisis abates. A single dose of palliative radiation therapy may be useful for larger/symptomatic metastasis, as appropriate,” the group said.
If resection is still a go, the group noted that adjuvant therapy “has not been shown to improve melanoma-specific survival and should be deferred during the COVID-19 pandemic for patients with [a less than] 50% chance of disease relapse.” Dabrafenib/trametinib is the evidence-based choice if adjuvant treatment is opted for, but “alternative BRAF/MEK inhibitor regimens (encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib) may be substituted if drug supply is limited” by the pandemic, the group said.
For stage IV melanoma, “single-agent anti-PD-1 [programmed cell death 1] is recommended over combination ipilimumab/nivolumab at present” because there’s less inflammation and possible exacerbation of COVID-19, less need for steroids to counter adverse events, and less need for follow up to check for toxicities.
The group said evidence supports that 400 mg pembrolizumab administered intravenously every 6 weeks would likely be as effective as 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks and would help keep people out of the hospital.
However, for stage IV melanoma with brain metastasis, there’s a strong rate of response to ipilimumab/nivolumab, so it may still be an option. In that case, “a regimen of ipilimumab 1 mg/kg and nivolumab 3 mg/kg every 3 weeks for four infusions, with subsequent consideration for nivolumab monotherapy, is associated with lower rates of immune-mediated toxicity,” compared with standard dosing.
Regarding potential drug shortages, the group noted that encorafenib/binimetinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib combinations can be substituted for dabrafenib/trametinib for adjuvant therapy, and single-agent BRAF inhibitors can be used in the event of MEK inhibitor shortages.
In hospice, the group said oral temozolomide is the preferred option for palliative chemotherapy since it would limit resource utilization and contact with the medical system.
Guidelines for radiotherapy in prostate cancer during the pandemic
The framework involves using remote visits via telemedicine, avoiding radiotherapy in applicable cases, deferring radiotherapy as appropriate, and shortening the fractionation schedule of treatment based on safety and efficacy parameters.
Nicholas G. Zaorsky, MD, of Penn State Cancer Institute in Hershey, Pennsylvania, and colleagues described the framework and recommendations in Advances in Radiation Oncology.
The authors systematically reviewed the body of literature for evidence pertaining to the safe use of telemedicine, avoidance or deferral of radiotherapy, and optimal use of androgen deprivation therapy for patients with prostate cancer. The team also reviewed best practices for patients undergoing radiotherapy based on disease risk.
Based on their findings, Dr. Zaorsky and colleagues recommended that, during the pandemic, all consultations and return visits become telehealth visits. “Very few prostate cancer patients require an in-person visit during a pandemic,” the authors wrote.
Lower-risk disease
Dr. Zaorsky and colleagues recommended avoiding radiotherapy in patients with very-low-, low-, and favorable intermediate-risk disease. The authors said data suggest that, in general, treatment can be safely deferred in these patients “until after pandemic-related restrictions have been lifted.” However, this recommendation presumes the pandemic will wane over the next 12 months.
“I reassure my patients with very-low- and low-risk prostate cancer that the preferred, evidence-based treatment for patients in these categories is active surveillance,” said study author Amar U. Kishan, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
“If surveillance is an option, then delaying treatment must be reasonable [during the pandemic],” he added. “For favorable intermediate-risk disease, I [review] the data supporting this approach and discuss that short delays are very unlikely to compromise outcomes.”
Higher-risk disease
The authors recommended deferral of radiotherapy for 4-6 months in patients with higher-risk disease, which includes those with unfavorable intermediate-risk, high-risk, very-high-risk, clinical node-positive, oligometastatic, and low-volume M1 disease, as well as patients who have undergone prostatectomy.
The authors noted that in-person consultations and return visits should be converted to “timely remote telehealth visits” for these patients. After these patients have started treatment, androgen deprivation therapy “can allow for further deferral of radiotherapy as necessary based on the nature of the ongoing epidemic.”
In cases where radiotherapy cannot be deferred safely, “the shortest fractionation schedule should be adopted that has evidence of safety and efficacy,” the authors wrote.
They acknowledged that these recommendations are only applicable to patients not infected with COVID-19. In cases of suspected or confirmed COVID-19, local institutional policies and practices should be followed.
The authors further explained that, due to the rapidly evolving nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, state and federal guidelines should be followed when made available.
The authors reported having no conflicts of interest. No funding sources were reported.
SOURCE: Zaorsky NG et al. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020 Apr 1. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2020.03.010.
The framework involves using remote visits via telemedicine, avoiding radiotherapy in applicable cases, deferring radiotherapy as appropriate, and shortening the fractionation schedule of treatment based on safety and efficacy parameters.
Nicholas G. Zaorsky, MD, of Penn State Cancer Institute in Hershey, Pennsylvania, and colleagues described the framework and recommendations in Advances in Radiation Oncology.
The authors systematically reviewed the body of literature for evidence pertaining to the safe use of telemedicine, avoidance or deferral of radiotherapy, and optimal use of androgen deprivation therapy for patients with prostate cancer. The team also reviewed best practices for patients undergoing radiotherapy based on disease risk.
Based on their findings, Dr. Zaorsky and colleagues recommended that, during the pandemic, all consultations and return visits become telehealth visits. “Very few prostate cancer patients require an in-person visit during a pandemic,” the authors wrote.
Lower-risk disease
Dr. Zaorsky and colleagues recommended avoiding radiotherapy in patients with very-low-, low-, and favorable intermediate-risk disease. The authors said data suggest that, in general, treatment can be safely deferred in these patients “until after pandemic-related restrictions have been lifted.” However, this recommendation presumes the pandemic will wane over the next 12 months.
“I reassure my patients with very-low- and low-risk prostate cancer that the preferred, evidence-based treatment for patients in these categories is active surveillance,” said study author Amar U. Kishan, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
“If surveillance is an option, then delaying treatment must be reasonable [during the pandemic],” he added. “For favorable intermediate-risk disease, I [review] the data supporting this approach and discuss that short delays are very unlikely to compromise outcomes.”
Higher-risk disease
The authors recommended deferral of radiotherapy for 4-6 months in patients with higher-risk disease, which includes those with unfavorable intermediate-risk, high-risk, very-high-risk, clinical node-positive, oligometastatic, and low-volume M1 disease, as well as patients who have undergone prostatectomy.
The authors noted that in-person consultations and return visits should be converted to “timely remote telehealth visits” for these patients. After these patients have started treatment, androgen deprivation therapy “can allow for further deferral of radiotherapy as necessary based on the nature of the ongoing epidemic.”
In cases where radiotherapy cannot be deferred safely, “the shortest fractionation schedule should be adopted that has evidence of safety and efficacy,” the authors wrote.
They acknowledged that these recommendations are only applicable to patients not infected with COVID-19. In cases of suspected or confirmed COVID-19, local institutional policies and practices should be followed.
The authors further explained that, due to the rapidly evolving nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, state and federal guidelines should be followed when made available.
The authors reported having no conflicts of interest. No funding sources were reported.
SOURCE: Zaorsky NG et al. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020 Apr 1. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2020.03.010.
The framework involves using remote visits via telemedicine, avoiding radiotherapy in applicable cases, deferring radiotherapy as appropriate, and shortening the fractionation schedule of treatment based on safety and efficacy parameters.
Nicholas G. Zaorsky, MD, of Penn State Cancer Institute in Hershey, Pennsylvania, and colleagues described the framework and recommendations in Advances in Radiation Oncology.
The authors systematically reviewed the body of literature for evidence pertaining to the safe use of telemedicine, avoidance or deferral of radiotherapy, and optimal use of androgen deprivation therapy for patients with prostate cancer. The team also reviewed best practices for patients undergoing radiotherapy based on disease risk.
Based on their findings, Dr. Zaorsky and colleagues recommended that, during the pandemic, all consultations and return visits become telehealth visits. “Very few prostate cancer patients require an in-person visit during a pandemic,” the authors wrote.
Lower-risk disease
Dr. Zaorsky and colleagues recommended avoiding radiotherapy in patients with very-low-, low-, and favorable intermediate-risk disease. The authors said data suggest that, in general, treatment can be safely deferred in these patients “until after pandemic-related restrictions have been lifted.” However, this recommendation presumes the pandemic will wane over the next 12 months.
“I reassure my patients with very-low- and low-risk prostate cancer that the preferred, evidence-based treatment for patients in these categories is active surveillance,” said study author Amar U. Kishan, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
“If surveillance is an option, then delaying treatment must be reasonable [during the pandemic],” he added. “For favorable intermediate-risk disease, I [review] the data supporting this approach and discuss that short delays are very unlikely to compromise outcomes.”
Higher-risk disease
The authors recommended deferral of radiotherapy for 4-6 months in patients with higher-risk disease, which includes those with unfavorable intermediate-risk, high-risk, very-high-risk, clinical node-positive, oligometastatic, and low-volume M1 disease, as well as patients who have undergone prostatectomy.
The authors noted that in-person consultations and return visits should be converted to “timely remote telehealth visits” for these patients. After these patients have started treatment, androgen deprivation therapy “can allow for further deferral of radiotherapy as necessary based on the nature of the ongoing epidemic.”
In cases where radiotherapy cannot be deferred safely, “the shortest fractionation schedule should be adopted that has evidence of safety and efficacy,” the authors wrote.
They acknowledged that these recommendations are only applicable to patients not infected with COVID-19. In cases of suspected or confirmed COVID-19, local institutional policies and practices should be followed.
The authors further explained that, due to the rapidly evolving nature of the COVID-19 pandemic, state and federal guidelines should be followed when made available.
The authors reported having no conflicts of interest. No funding sources were reported.
SOURCE: Zaorsky NG et al. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2020 Apr 1. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2020.03.010.
FROM ADVANCES IN RADIATION ONCOLOGY
‘Brutal’ plan to restrict palliative radiation during pandemic
A major comprehensive cancer center at the epicenter of the New York City COVID-19 storm is preparing to scale back palliative radiation therapy (RT), anticipating a focus on only oncologic emergencies.
“We’re not there yet, but we’re anticipating when the time comes in the next few weeks that we will have a system in place so we are able to handle it,” Jonathan Yang, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York City, told Medscape Medical News.
Yang and an expert panel of colleagues reviewed high-impact evidence, prior systematic reviews, and national guidelines to compile a set of recommendations for triage and shortened palliative rRT at their center, should the need arise.
The recommendations on palliative radiotherapy for oncologic emergencies in the setting of COVID-19 appear in a preprint version in Advances in Radiation Oncology, released by the American Society of Radiation Oncology.
Yang says the recommendations are a careful balance between the risk of COVID-19 exposure of staff and patients with the potential morbidity of delaying treatment.
“Everyone is conscious of decisions about whether patients need treatment now or can wait,” he told Medscape Medical News. “It’s a juggling act every single day, but by having this guideline in place, when we face the situation where we do have to make decisions, is helpful.”
The document aims to enable swift decisions based on best practice, including a three-tiered system prioritizing only “clinically urgent cases, in which delaying treatment would result in compromised outcomes or serious morbidity.”
“It’s brutal, that’s the only word for it. Not that I disagree with it,” commented Padraig Warde, MB BCh, professor, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Toronto, and radiation oncologist, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Like many places, Toronto is not yet experiencing the COVID-19 burden of New York City, but Warde says the MSKCC guideline is useful for everyone. “Other centers should review it and see how they could deal with resource limitations,” he said. “It’s sobering and sad, but if you don’t have the staff to treat all patients, which particular patients do you choose to treat?”
In a nutshell, the MSKCC recommendations defines Tier 1 patients as having oncologic emergencies that require palliative RT, including “cord compression, symptomatic brain metastases requiring whole-brain radiotherapy, life-threatening tumor bleeding, and malignant airway obstruction.”
According to the decision-making guideline, patients in Tiers 2 and 3 would have their palliative RT delayed. This would include Tier 2 patients whose needs are not classified as emergencies, but who have either symptomatic disease for which RT is usually the standard of care or asymptomatic disease for which RT is recommended “to prevent imminent functional deficits.” Tier 3 would be symptomatic or asymptomatic patients for whom RT is “one of the effective treatment options.”
“Rationing is always very difficult because as physicians you always want to do everything you can for your patients but we really have to strike the balance on when to do what, said Yang. The plan that he authored anticipates both reduced availability of radiation therapists as well as aggressive attempts to limit patients’ infection exposure.
“If a patient’s radiation is being considered for delay due to COVID-19, other means are utilized to achieve the goal of palliation in the interim, and in addition to the tier system, this decision is also made on a case-by-case basis with departmental discussion on the risks and benefits,” he explained.
“There are layers of checks and balances for these decisions...Obviously for oncologic emergencies, radiation will be implemented. However for less urgent situations, bringing them into the hospital when there are other ways to achieve the same goal, potential risk of exposure to COVID-19 is higher than the benefit we would be able to provide.”
The document also recommends shorter courses of RT when radiation is deemed appropriate.
“We have good evidence showing shorter courses of radiation can effectively treat the goal of palliation compared to longer courses of radiation,” he explained. “Going through this pandemic actually forces radiation oncologists in the United States to put that evidence into practice. It’s not suboptimal care in the sense that we are achieving the same goal — palliation. This paper is to remind people there are equally effective courses of palliation we can be using.”
“[There’s] nothing like a crisis to get people to do the right thing,” commented Louis Potters, MD, professor and chair of radiation medicine at the Feinstein Institutes, the research arm of Northwell Health, New York’s largest healthcare provider.
Northwell Health has been at the epicenter of the New York outbreak of COVID-19. Potters writes on an ASTRO blog that, as of March 26, Northwell Health “has diagnosed 4399 positive COVID-19 patients, which is about 20% of New York state and 1.2% of all cases in the world. All cancer surgery was discontinued as of March 20 and all of our 23 hospitals are seeing COVID-19 admissions, and ICU care became the primary focus of the entire system. As of today, we have reserved one floor in two hospitals for non-COVID care such as trauma. That’s it.”
Before the crisis, radiation medicine at Northwell consisted of eight separate locations treating on average 280 EBRT cases a day, not including SBRT/SRS and brachytherapy cases. “That of course was 3 weeks ago,” he notes.
Commenting on the recommendations from the MSKCC group, Potters told Medscape Medical News that the primary goal “was to document what are acceptable alternatives for accelerated care.”
“Ironically, these guidelines represent best practices with evidence that — in a non–COVID-19 world — make sense for the majority of patients requiring palliative radiotherapy,” he said.
Potters said there has been hesitance to transition to shorter radiation treatments for several reasons.
“Historically, palliative radiotherapy has been delivered over 2 to 4 weeks with good results. And, as is typical in medicine, the transition to shorter course care is slowed by financial incentives to protract care,” he explained.
“In a value-based future where payment is based on outcomes, this transition to shorter care will evolve very quickly. But given the current COVID-19 crisis, and the risk to patients and staff, the incentive for shorter treatment courses has been thrust upon us and the MSKCC outline helps to define how to do this safely and with evidence-based expected efficacy.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A major comprehensive cancer center at the epicenter of the New York City COVID-19 storm is preparing to scale back palliative radiation therapy (RT), anticipating a focus on only oncologic emergencies.
“We’re not there yet, but we’re anticipating when the time comes in the next few weeks that we will have a system in place so we are able to handle it,” Jonathan Yang, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York City, told Medscape Medical News.
Yang and an expert panel of colleagues reviewed high-impact evidence, prior systematic reviews, and national guidelines to compile a set of recommendations for triage and shortened palliative rRT at their center, should the need arise.
The recommendations on palliative radiotherapy for oncologic emergencies in the setting of COVID-19 appear in a preprint version in Advances in Radiation Oncology, released by the American Society of Radiation Oncology.
Yang says the recommendations are a careful balance between the risk of COVID-19 exposure of staff and patients with the potential morbidity of delaying treatment.
“Everyone is conscious of decisions about whether patients need treatment now or can wait,” he told Medscape Medical News. “It’s a juggling act every single day, but by having this guideline in place, when we face the situation where we do have to make decisions, is helpful.”
The document aims to enable swift decisions based on best practice, including a three-tiered system prioritizing only “clinically urgent cases, in which delaying treatment would result in compromised outcomes or serious morbidity.”
“It’s brutal, that’s the only word for it. Not that I disagree with it,” commented Padraig Warde, MB BCh, professor, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Toronto, and radiation oncologist, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Like many places, Toronto is not yet experiencing the COVID-19 burden of New York City, but Warde says the MSKCC guideline is useful for everyone. “Other centers should review it and see how they could deal with resource limitations,” he said. “It’s sobering and sad, but if you don’t have the staff to treat all patients, which particular patients do you choose to treat?”
In a nutshell, the MSKCC recommendations defines Tier 1 patients as having oncologic emergencies that require palliative RT, including “cord compression, symptomatic brain metastases requiring whole-brain radiotherapy, life-threatening tumor bleeding, and malignant airway obstruction.”
According to the decision-making guideline, patients in Tiers 2 and 3 would have their palliative RT delayed. This would include Tier 2 patients whose needs are not classified as emergencies, but who have either symptomatic disease for which RT is usually the standard of care or asymptomatic disease for which RT is recommended “to prevent imminent functional deficits.” Tier 3 would be symptomatic or asymptomatic patients for whom RT is “one of the effective treatment options.”
“Rationing is always very difficult because as physicians you always want to do everything you can for your patients but we really have to strike the balance on when to do what, said Yang. The plan that he authored anticipates both reduced availability of radiation therapists as well as aggressive attempts to limit patients’ infection exposure.
“If a patient’s radiation is being considered for delay due to COVID-19, other means are utilized to achieve the goal of palliation in the interim, and in addition to the tier system, this decision is also made on a case-by-case basis with departmental discussion on the risks and benefits,” he explained.
“There are layers of checks and balances for these decisions...Obviously for oncologic emergencies, radiation will be implemented. However for less urgent situations, bringing them into the hospital when there are other ways to achieve the same goal, potential risk of exposure to COVID-19 is higher than the benefit we would be able to provide.”
The document also recommends shorter courses of RT when radiation is deemed appropriate.
“We have good evidence showing shorter courses of radiation can effectively treat the goal of palliation compared to longer courses of radiation,” he explained. “Going through this pandemic actually forces radiation oncologists in the United States to put that evidence into practice. It’s not suboptimal care in the sense that we are achieving the same goal — palliation. This paper is to remind people there are equally effective courses of palliation we can be using.”
“[There’s] nothing like a crisis to get people to do the right thing,” commented Louis Potters, MD, professor and chair of radiation medicine at the Feinstein Institutes, the research arm of Northwell Health, New York’s largest healthcare provider.
Northwell Health has been at the epicenter of the New York outbreak of COVID-19. Potters writes on an ASTRO blog that, as of March 26, Northwell Health “has diagnosed 4399 positive COVID-19 patients, which is about 20% of New York state and 1.2% of all cases in the world. All cancer surgery was discontinued as of March 20 and all of our 23 hospitals are seeing COVID-19 admissions, and ICU care became the primary focus of the entire system. As of today, we have reserved one floor in two hospitals for non-COVID care such as trauma. That’s it.”
Before the crisis, radiation medicine at Northwell consisted of eight separate locations treating on average 280 EBRT cases a day, not including SBRT/SRS and brachytherapy cases. “That of course was 3 weeks ago,” he notes.
Commenting on the recommendations from the MSKCC group, Potters told Medscape Medical News that the primary goal “was to document what are acceptable alternatives for accelerated care.”
“Ironically, these guidelines represent best practices with evidence that — in a non–COVID-19 world — make sense for the majority of patients requiring palliative radiotherapy,” he said.
Potters said there has been hesitance to transition to shorter radiation treatments for several reasons.
“Historically, palliative radiotherapy has been delivered over 2 to 4 weeks with good results. And, as is typical in medicine, the transition to shorter course care is slowed by financial incentives to protract care,” he explained.
“In a value-based future where payment is based on outcomes, this transition to shorter care will evolve very quickly. But given the current COVID-19 crisis, and the risk to patients and staff, the incentive for shorter treatment courses has been thrust upon us and the MSKCC outline helps to define how to do this safely and with evidence-based expected efficacy.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A major comprehensive cancer center at the epicenter of the New York City COVID-19 storm is preparing to scale back palliative radiation therapy (RT), anticipating a focus on only oncologic emergencies.
“We’re not there yet, but we’re anticipating when the time comes in the next few weeks that we will have a system in place so we are able to handle it,” Jonathan Yang, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York City, told Medscape Medical News.
Yang and an expert panel of colleagues reviewed high-impact evidence, prior systematic reviews, and national guidelines to compile a set of recommendations for triage and shortened palliative rRT at their center, should the need arise.
The recommendations on palliative radiotherapy for oncologic emergencies in the setting of COVID-19 appear in a preprint version in Advances in Radiation Oncology, released by the American Society of Radiation Oncology.
Yang says the recommendations are a careful balance between the risk of COVID-19 exposure of staff and patients with the potential morbidity of delaying treatment.
“Everyone is conscious of decisions about whether patients need treatment now or can wait,” he told Medscape Medical News. “It’s a juggling act every single day, but by having this guideline in place, when we face the situation where we do have to make decisions, is helpful.”
The document aims to enable swift decisions based on best practice, including a three-tiered system prioritizing only “clinically urgent cases, in which delaying treatment would result in compromised outcomes or serious morbidity.”
“It’s brutal, that’s the only word for it. Not that I disagree with it,” commented Padraig Warde, MB BCh, professor, Department of Radiation Oncology, University of Toronto, and radiation oncologist, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Like many places, Toronto is not yet experiencing the COVID-19 burden of New York City, but Warde says the MSKCC guideline is useful for everyone. “Other centers should review it and see how they could deal with resource limitations,” he said. “It’s sobering and sad, but if you don’t have the staff to treat all patients, which particular patients do you choose to treat?”
In a nutshell, the MSKCC recommendations defines Tier 1 patients as having oncologic emergencies that require palliative RT, including “cord compression, symptomatic brain metastases requiring whole-brain radiotherapy, life-threatening tumor bleeding, and malignant airway obstruction.”
According to the decision-making guideline, patients in Tiers 2 and 3 would have their palliative RT delayed. This would include Tier 2 patients whose needs are not classified as emergencies, but who have either symptomatic disease for which RT is usually the standard of care or asymptomatic disease for which RT is recommended “to prevent imminent functional deficits.” Tier 3 would be symptomatic or asymptomatic patients for whom RT is “one of the effective treatment options.”
“Rationing is always very difficult because as physicians you always want to do everything you can for your patients but we really have to strike the balance on when to do what, said Yang. The plan that he authored anticipates both reduced availability of radiation therapists as well as aggressive attempts to limit patients’ infection exposure.
“If a patient’s radiation is being considered for delay due to COVID-19, other means are utilized to achieve the goal of palliation in the interim, and in addition to the tier system, this decision is also made on a case-by-case basis with departmental discussion on the risks and benefits,” he explained.
“There are layers of checks and balances for these decisions...Obviously for oncologic emergencies, radiation will be implemented. However for less urgent situations, bringing them into the hospital when there are other ways to achieve the same goal, potential risk of exposure to COVID-19 is higher than the benefit we would be able to provide.”
The document also recommends shorter courses of RT when radiation is deemed appropriate.
“We have good evidence showing shorter courses of radiation can effectively treat the goal of palliation compared to longer courses of radiation,” he explained. “Going through this pandemic actually forces radiation oncologists in the United States to put that evidence into practice. It’s not suboptimal care in the sense that we are achieving the same goal — palliation. This paper is to remind people there are equally effective courses of palliation we can be using.”
“[There’s] nothing like a crisis to get people to do the right thing,” commented Louis Potters, MD, professor and chair of radiation medicine at the Feinstein Institutes, the research arm of Northwell Health, New York’s largest healthcare provider.
Northwell Health has been at the epicenter of the New York outbreak of COVID-19. Potters writes on an ASTRO blog that, as of March 26, Northwell Health “has diagnosed 4399 positive COVID-19 patients, which is about 20% of New York state and 1.2% of all cases in the world. All cancer surgery was discontinued as of March 20 and all of our 23 hospitals are seeing COVID-19 admissions, and ICU care became the primary focus of the entire system. As of today, we have reserved one floor in two hospitals for non-COVID care such as trauma. That’s it.”
Before the crisis, radiation medicine at Northwell consisted of eight separate locations treating on average 280 EBRT cases a day, not including SBRT/SRS and brachytherapy cases. “That of course was 3 weeks ago,” he notes.
Commenting on the recommendations from the MSKCC group, Potters told Medscape Medical News that the primary goal “was to document what are acceptable alternatives for accelerated care.”
“Ironically, these guidelines represent best practices with evidence that — in a non–COVID-19 world — make sense for the majority of patients requiring palliative radiotherapy,” he said.
Potters said there has been hesitance to transition to shorter radiation treatments for several reasons.
“Historically, palliative radiotherapy has been delivered over 2 to 4 weeks with good results. And, as is typical in medicine, the transition to shorter course care is slowed by financial incentives to protract care,” he explained.
“In a value-based future where payment is based on outcomes, this transition to shorter care will evolve very quickly. But given the current COVID-19 crisis, and the risk to patients and staff, the incentive for shorter treatment courses has been thrust upon us and the MSKCC outline helps to define how to do this safely and with evidence-based expected efficacy.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
First report of MM patient successfully treated for COVID-19 with tocilizumab
Recent research has shown that severe cases of COVID-19 show an excessive immune response and a strong cytokine storm, which may include high levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Following up on that research, investigators from China reported the first case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma (MM) who was successfully treated with the humanized anti–IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab (an off-label use in the United States). The exceptional case report was published online in Blood Advances, an American Society of Hematology journal.
A 60-year-old man working in Wuhan, China, developed chest tightness without fever and cough on Feb. 1, 2020, and was admitted immediately after computed tomography (CT) imaging of his chest showed multiple ground-glass opacities and pneumatocele located in both subpleural spaces. He received 400 mg of moxifloxacin IV daily for 3 days while swab specimens were collected and tested by real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction. A positive result for SARS-CoV-2 infection was received 3 days later. The patient was subsequently given 200-mg umifenovir (Arbidol) tablets orally, three times daily, for antiviral treatment.
The patient had a history of symptomatic MM, which was diagnosed in 2015. The patient received two cycles of induction chemotherapy consisting of bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone, and his symptoms completely disappeared. After that, he received thalidomide for maintenance.
Chest CT imaging on hospital day 8 showed that the bilateral, multiple ground-glass opacities from the first scan remained, and laboratory investigations revealed a high level of serum IL-6. On hospital day 9, the patient was given a single, one-time dose of 8 mg/kg tocilizumab, administered by IV. On hospital day 12, his chest tightness disappeared. “After tocilizumab administration, the IL-6 level decreased gradually over the following 10 days (from 121.59 to 20.81 pg/mL), then increased rapidly to the peak (317.38 pg/mL), and then decreased to a low level (117.10 pg/mL). The transient rebounding of the IL-6 level to the peak does not mean COVID-19 relapse: Instead, this might be attributed to the recovery of the normal T cells,” the authors wrote.
On hospital day 19, the patient’s chest CT scan showed that the range of ground-glass opacities had obviously decreased, and he was declared cured and discharged from the hospital. The patient had no symptoms of MM, and related laboratory findings were all in normal ranges, according to the researchers.
“This case is the first to prove that tocilizumab is effective in the treatment of COVID-19 in MM with obvious clinical recovery; however, randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of tocilizumab,” the researchers concluded.
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhang X et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(7):1307-10.
Recent research has shown that severe cases of COVID-19 show an excessive immune response and a strong cytokine storm, which may include high levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Following up on that research, investigators from China reported the first case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma (MM) who was successfully treated with the humanized anti–IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab (an off-label use in the United States). The exceptional case report was published online in Blood Advances, an American Society of Hematology journal.
A 60-year-old man working in Wuhan, China, developed chest tightness without fever and cough on Feb. 1, 2020, and was admitted immediately after computed tomography (CT) imaging of his chest showed multiple ground-glass opacities and pneumatocele located in both subpleural spaces. He received 400 mg of moxifloxacin IV daily for 3 days while swab specimens were collected and tested by real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction. A positive result for SARS-CoV-2 infection was received 3 days later. The patient was subsequently given 200-mg umifenovir (Arbidol) tablets orally, three times daily, for antiviral treatment.
The patient had a history of symptomatic MM, which was diagnosed in 2015. The patient received two cycles of induction chemotherapy consisting of bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone, and his symptoms completely disappeared. After that, he received thalidomide for maintenance.
Chest CT imaging on hospital day 8 showed that the bilateral, multiple ground-glass opacities from the first scan remained, and laboratory investigations revealed a high level of serum IL-6. On hospital day 9, the patient was given a single, one-time dose of 8 mg/kg tocilizumab, administered by IV. On hospital day 12, his chest tightness disappeared. “After tocilizumab administration, the IL-6 level decreased gradually over the following 10 days (from 121.59 to 20.81 pg/mL), then increased rapidly to the peak (317.38 pg/mL), and then decreased to a low level (117.10 pg/mL). The transient rebounding of the IL-6 level to the peak does not mean COVID-19 relapse: Instead, this might be attributed to the recovery of the normal T cells,” the authors wrote.
On hospital day 19, the patient’s chest CT scan showed that the range of ground-glass opacities had obviously decreased, and he was declared cured and discharged from the hospital. The patient had no symptoms of MM, and related laboratory findings were all in normal ranges, according to the researchers.
“This case is the first to prove that tocilizumab is effective in the treatment of COVID-19 in MM with obvious clinical recovery; however, randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of tocilizumab,” the researchers concluded.
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhang X et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(7):1307-10.
Recent research has shown that severe cases of COVID-19 show an excessive immune response and a strong cytokine storm, which may include high levels of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GSF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Following up on that research, investigators from China reported the first case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma (MM) who was successfully treated with the humanized anti–IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab (an off-label use in the United States). The exceptional case report was published online in Blood Advances, an American Society of Hematology journal.
A 60-year-old man working in Wuhan, China, developed chest tightness without fever and cough on Feb. 1, 2020, and was admitted immediately after computed tomography (CT) imaging of his chest showed multiple ground-glass opacities and pneumatocele located in both subpleural spaces. He received 400 mg of moxifloxacin IV daily for 3 days while swab specimens were collected and tested by real-time reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction. A positive result for SARS-CoV-2 infection was received 3 days later. The patient was subsequently given 200-mg umifenovir (Arbidol) tablets orally, three times daily, for antiviral treatment.
The patient had a history of symptomatic MM, which was diagnosed in 2015. The patient received two cycles of induction chemotherapy consisting of bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone, and his symptoms completely disappeared. After that, he received thalidomide for maintenance.
Chest CT imaging on hospital day 8 showed that the bilateral, multiple ground-glass opacities from the first scan remained, and laboratory investigations revealed a high level of serum IL-6. On hospital day 9, the patient was given a single, one-time dose of 8 mg/kg tocilizumab, administered by IV. On hospital day 12, his chest tightness disappeared. “After tocilizumab administration, the IL-6 level decreased gradually over the following 10 days (from 121.59 to 20.81 pg/mL), then increased rapidly to the peak (317.38 pg/mL), and then decreased to a low level (117.10 pg/mL). The transient rebounding of the IL-6 level to the peak does not mean COVID-19 relapse: Instead, this might be attributed to the recovery of the normal T cells,” the authors wrote.
On hospital day 19, the patient’s chest CT scan showed that the range of ground-glass opacities had obviously decreased, and he was declared cured and discharged from the hospital. The patient had no symptoms of MM, and related laboratory findings were all in normal ranges, according to the researchers.
“This case is the first to prove that tocilizumab is effective in the treatment of COVID-19 in MM with obvious clinical recovery; however, randomized controlled trials are needed to determine the safety and efficacy of tocilizumab,” the researchers concluded.
The authors declared that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zhang X et al. Blood Adv. 2020;4(7):1307-10.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES
Rethink urologic cancer treatment in the era of COVID-19
according to an editorial set to be published in European Urology.
“Regimens with a clear survival advantage should be prioritized, with curative treatments remaining mandatory,” wrote Silke Gillessen Sommer, MD, of Istituto Oncologico della Svizzera Italiana in Bellizona, Switzerland, and Thomas Powles, MD, of Barts Cancer Institute in London.
However, it may be appropriate to stop or delay therapies with modest or unproven survival benefits. “Delaying the start of therapy ... is an appropriate measure for many of the therapies in urology cancer,” they wrote.
Timely recommendations for oncologists
The COVID-19 pandemic is limiting resources for cancer, noted Zachery Reichert, MD, PhD, a urological oncologist and assistant professor at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who was asked for his thoughts about the editorial.
Oncologists and oncology nurses are being shifted to care for COVID-19 patients, space once devoted to cancer care is being repurposed for the pandemic, and personal protective equipment needed to prepare chemotherapies is in short supply.
Meanwhile, cancer patients are at increased risk of dying from the virus (Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:335-7), so there’s a need to minimize their contact with the health care system to protect them from nosocomial infection, and a need to keep their immune system as strong as possible to fight it off.
To help cancer patients fight off infection and keep them out of the hospital, the editorialists recommended growth factors and prophylactic antibiotics after chemotherapy, palliative therapies at doses that avoid febrile neutropenia, discontinuing steroids or at least reducing their doses, and avoiding bisphosphonates if they involve potential COVID-19 exposure in medical facilities.
The advice in the editorial mirrors many of the discussions going on right now at the University of Michigan, Dr. Reichert said, and perhaps other oncology services across the United States.
It will come down to how severe the pandemic becomes locally, but he said it seems likely “a lot of us are going to be wearing a different hat for a while.”
Patients who have symptoms from a growing tumor will likely take precedence at the university, but treatment might be postponed until after COVID-19 peaks if tumors don’t affect quality of life. Also, bladder cancer surgery will probably remain urgent “because the longer you wait, the worse the outcomes,” but perhaps not prostate and kidney cancer surgery, where delay is safer, Dr. Reichert said.
Prostate/renal cancers and germ cell tumors
The editorialists noted that oral androgen receptor therapy should be preferred over chemotherapy for prostate cancer. Dr. Reichert explained that’s because androgen blockade is effective, requires less contact with health care providers, and doesn’t suppress the immune system or tie up hospital resources as much as chemotherapy. “In the world we are in right now, oral pills are a better choice,” he said.
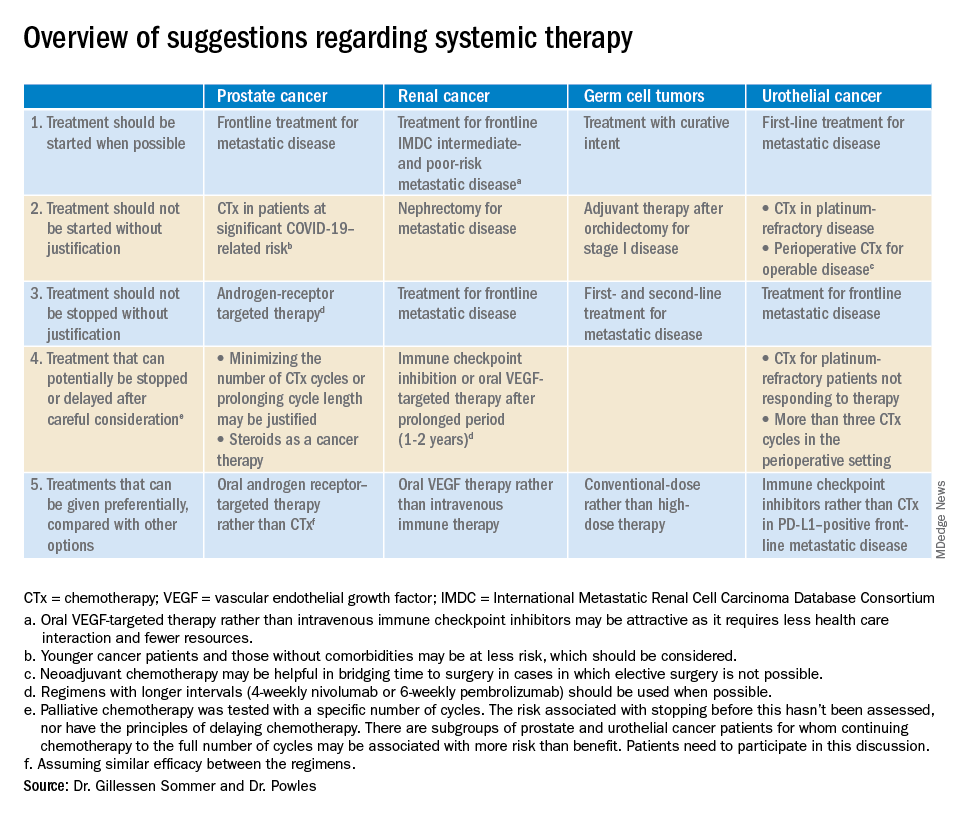
The editorialists recommended against both nephrectomy for metastatic renal cancer and adjuvant therapy after orchidectomy for stage 1 germ cell tumors for similar reasons, and also because there’s minimal evidence of benefit.
Dr. Powles and Dr. Gillessen Sommer suggested considering a break from immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and oral vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) for renal cancer patients who have been on them a year or two. It’s something that would be considered even under normal circumstances, Dr. Reichert explained, but it’s more urgent now to keep people out of the hospital. VEGFs should also be prioritized over ICIs; they have similar efficacy in renal cancer, but VEGFs are a pill.
They also called for oncologists to favor conventional-dose treatments for germ cell tumors over high-dose treatments, meaning bone marrow transplants or high-intensity chemotherapy. Amid a pandemic, the preference is for options “that don’t require a hospital bed,” Dr. Reichert said.
Urothelial cancer
Dr. Powles and Dr. Gillessen Sommer suggested not starting or continuing second-line chemotherapies in urothelial cancer patients refractory to first-line platinum-based therapies. The chance they will respond to second-line options is low, perhaps around 10%. That might have been enough before the pandemic, but it’s less justified amid resource shortages and the risk of COVID-19 in the infusion suite, Dr. Reichert explained.
Along the same lines, they also suggested reconsidering perioperative chemotherapy for urothelial cancer, and, if it’s still a go, recommended against going past three cycles, as the benefits in both scenarios are likely marginal. However, if COVID-19 cancels surgeries, neoadjuvant therapy might be the right – and only – call, according to the editorialists.
They recommended prioritizing ICIs over chemotherapy in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer who are positive for programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). PD-L1–positive patients have a good chance of responding, and ICIs don’t suppress the immune system.
“Chemotherapy still has a slightly higher percent response, but right now, this is a better choice for” PD-L1-positive patients, Dr. Reichert said.
Dr. Gillessen Sommer and Dr. Powles disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, and numerous other companies. Dr. Reichert has no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Gillessen Sommer S, Powles T. “Advice regarding systemic therapy in patients with urological cancers during the COVID-19 pandemic.” Eur Urol. https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/pb/assets/raw/Health%20Advance/journals/eururo/EURUROL-D-20-00382-1585928967060.pdf.
according to an editorial set to be published in European Urology.
“Regimens with a clear survival advantage should be prioritized, with curative treatments remaining mandatory,” wrote Silke Gillessen Sommer, MD, of Istituto Oncologico della Svizzera Italiana in Bellizona, Switzerland, and Thomas Powles, MD, of Barts Cancer Institute in London.
However, it may be appropriate to stop or delay therapies with modest or unproven survival benefits. “Delaying the start of therapy ... is an appropriate measure for many of the therapies in urology cancer,” they wrote.
Timely recommendations for oncologists
The COVID-19 pandemic is limiting resources for cancer, noted Zachery Reichert, MD, PhD, a urological oncologist and assistant professor at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who was asked for his thoughts about the editorial.
Oncologists and oncology nurses are being shifted to care for COVID-19 patients, space once devoted to cancer care is being repurposed for the pandemic, and personal protective equipment needed to prepare chemotherapies is in short supply.
Meanwhile, cancer patients are at increased risk of dying from the virus (Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:335-7), so there’s a need to minimize their contact with the health care system to protect them from nosocomial infection, and a need to keep their immune system as strong as possible to fight it off.
To help cancer patients fight off infection and keep them out of the hospital, the editorialists recommended growth factors and prophylactic antibiotics after chemotherapy, palliative therapies at doses that avoid febrile neutropenia, discontinuing steroids or at least reducing their doses, and avoiding bisphosphonates if they involve potential COVID-19 exposure in medical facilities.
The advice in the editorial mirrors many of the discussions going on right now at the University of Michigan, Dr. Reichert said, and perhaps other oncology services across the United States.
It will come down to how severe the pandemic becomes locally, but he said it seems likely “a lot of us are going to be wearing a different hat for a while.”
Patients who have symptoms from a growing tumor will likely take precedence at the university, but treatment might be postponed until after COVID-19 peaks if tumors don’t affect quality of life. Also, bladder cancer surgery will probably remain urgent “because the longer you wait, the worse the outcomes,” but perhaps not prostate and kidney cancer surgery, where delay is safer, Dr. Reichert said.
Prostate/renal cancers and germ cell tumors
The editorialists noted that oral androgen receptor therapy should be preferred over chemotherapy for prostate cancer. Dr. Reichert explained that’s because androgen blockade is effective, requires less contact with health care providers, and doesn’t suppress the immune system or tie up hospital resources as much as chemotherapy. “In the world we are in right now, oral pills are a better choice,” he said.

The editorialists recommended against both nephrectomy for metastatic renal cancer and adjuvant therapy after orchidectomy for stage 1 germ cell tumors for similar reasons, and also because there’s minimal evidence of benefit.
Dr. Powles and Dr. Gillessen Sommer suggested considering a break from immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and oral vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) for renal cancer patients who have been on them a year or two. It’s something that would be considered even under normal circumstances, Dr. Reichert explained, but it’s more urgent now to keep people out of the hospital. VEGFs should also be prioritized over ICIs; they have similar efficacy in renal cancer, but VEGFs are a pill.
They also called for oncologists to favor conventional-dose treatments for germ cell tumors over high-dose treatments, meaning bone marrow transplants or high-intensity chemotherapy. Amid a pandemic, the preference is for options “that don’t require a hospital bed,” Dr. Reichert said.
Urothelial cancer
Dr. Powles and Dr. Gillessen Sommer suggested not starting or continuing second-line chemotherapies in urothelial cancer patients refractory to first-line platinum-based therapies. The chance they will respond to second-line options is low, perhaps around 10%. That might have been enough before the pandemic, but it’s less justified amid resource shortages and the risk of COVID-19 in the infusion suite, Dr. Reichert explained.
Along the same lines, they also suggested reconsidering perioperative chemotherapy for urothelial cancer, and, if it’s still a go, recommended against going past three cycles, as the benefits in both scenarios are likely marginal. However, if COVID-19 cancels surgeries, neoadjuvant therapy might be the right – and only – call, according to the editorialists.
They recommended prioritizing ICIs over chemotherapy in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer who are positive for programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). PD-L1–positive patients have a good chance of responding, and ICIs don’t suppress the immune system.
“Chemotherapy still has a slightly higher percent response, but right now, this is a better choice for” PD-L1-positive patients, Dr. Reichert said.
Dr. Gillessen Sommer and Dr. Powles disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, and numerous other companies. Dr. Reichert has no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Gillessen Sommer S, Powles T. “Advice regarding systemic therapy in patients with urological cancers during the COVID-19 pandemic.” Eur Urol. https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/pb/assets/raw/Health%20Advance/journals/eururo/EURUROL-D-20-00382-1585928967060.pdf.
according to an editorial set to be published in European Urology.
“Regimens with a clear survival advantage should be prioritized, with curative treatments remaining mandatory,” wrote Silke Gillessen Sommer, MD, of Istituto Oncologico della Svizzera Italiana in Bellizona, Switzerland, and Thomas Powles, MD, of Barts Cancer Institute in London.
However, it may be appropriate to stop or delay therapies with modest or unproven survival benefits. “Delaying the start of therapy ... is an appropriate measure for many of the therapies in urology cancer,” they wrote.
Timely recommendations for oncologists
The COVID-19 pandemic is limiting resources for cancer, noted Zachery Reichert, MD, PhD, a urological oncologist and assistant professor at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who was asked for his thoughts about the editorial.
Oncologists and oncology nurses are being shifted to care for COVID-19 patients, space once devoted to cancer care is being repurposed for the pandemic, and personal protective equipment needed to prepare chemotherapies is in short supply.
Meanwhile, cancer patients are at increased risk of dying from the virus (Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:335-7), so there’s a need to minimize their contact with the health care system to protect them from nosocomial infection, and a need to keep their immune system as strong as possible to fight it off.
To help cancer patients fight off infection and keep them out of the hospital, the editorialists recommended growth factors and prophylactic antibiotics after chemotherapy, palliative therapies at doses that avoid febrile neutropenia, discontinuing steroids or at least reducing their doses, and avoiding bisphosphonates if they involve potential COVID-19 exposure in medical facilities.
The advice in the editorial mirrors many of the discussions going on right now at the University of Michigan, Dr. Reichert said, and perhaps other oncology services across the United States.
It will come down to how severe the pandemic becomes locally, but he said it seems likely “a lot of us are going to be wearing a different hat for a while.”
Patients who have symptoms from a growing tumor will likely take precedence at the university, but treatment might be postponed until after COVID-19 peaks if tumors don’t affect quality of life. Also, bladder cancer surgery will probably remain urgent “because the longer you wait, the worse the outcomes,” but perhaps not prostate and kidney cancer surgery, where delay is safer, Dr. Reichert said.
Prostate/renal cancers and germ cell tumors
The editorialists noted that oral androgen receptor therapy should be preferred over chemotherapy for prostate cancer. Dr. Reichert explained that’s because androgen blockade is effective, requires less contact with health care providers, and doesn’t suppress the immune system or tie up hospital resources as much as chemotherapy. “In the world we are in right now, oral pills are a better choice,” he said.

The editorialists recommended against both nephrectomy for metastatic renal cancer and adjuvant therapy after orchidectomy for stage 1 germ cell tumors for similar reasons, and also because there’s minimal evidence of benefit.
Dr. Powles and Dr. Gillessen Sommer suggested considering a break from immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and oral vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) for renal cancer patients who have been on them a year or two. It’s something that would be considered even under normal circumstances, Dr. Reichert explained, but it’s more urgent now to keep people out of the hospital. VEGFs should also be prioritized over ICIs; they have similar efficacy in renal cancer, but VEGFs are a pill.
They also called for oncologists to favor conventional-dose treatments for germ cell tumors over high-dose treatments, meaning bone marrow transplants or high-intensity chemotherapy. Amid a pandemic, the preference is for options “that don’t require a hospital bed,” Dr. Reichert said.
Urothelial cancer
Dr. Powles and Dr. Gillessen Sommer suggested not starting or continuing second-line chemotherapies in urothelial cancer patients refractory to first-line platinum-based therapies. The chance they will respond to second-line options is low, perhaps around 10%. That might have been enough before the pandemic, but it’s less justified amid resource shortages and the risk of COVID-19 in the infusion suite, Dr. Reichert explained.
Along the same lines, they also suggested reconsidering perioperative chemotherapy for urothelial cancer, and, if it’s still a go, recommended against going past three cycles, as the benefits in both scenarios are likely marginal. However, if COVID-19 cancels surgeries, neoadjuvant therapy might be the right – and only – call, according to the editorialists.
They recommended prioritizing ICIs over chemotherapy in patients with metastatic urothelial cancer who are positive for programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1). PD-L1–positive patients have a good chance of responding, and ICIs don’t suppress the immune system.
“Chemotherapy still has a slightly higher percent response, but right now, this is a better choice for” PD-L1-positive patients, Dr. Reichert said.
Dr. Gillessen Sommer and Dr. Powles disclosed ties to Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, and numerous other companies. Dr. Reichert has no relevant disclosures.
SOURCE: Gillessen Sommer S, Powles T. “Advice regarding systemic therapy in patients with urological cancers during the COVID-19 pandemic.” Eur Urol. https://els-jbs-prod-cdn.jbs.elsevierhealth.com/pb/assets/raw/Health%20Advance/journals/eururo/EURUROL-D-20-00382-1585928967060.pdf.
FROM EUROPEAN UROLOGY
Case study shows CLL may mask COVID-19 infection
Characteristics of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia can mask COVID-19 infection, creating a risk for patients, practitioners, and the community, according to a case study published in the Lancet Haematology.
A 39-year-old man with a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) presented at a clinic in Wenzhou, China, with symptoms of fever, sore throat, productive cough, and dyspnea, according to the authors. COVID-19 infection was not initially suspected, as his whole blood cell and lymphocyte counts were high, the CLL masked a potential infection, and the patient claimed he had no suspect recent travel history.
However, a CT chest scan showed bilateral ground-glass opacities and a small amount of fluid in the patient’s left pleural cavity, leading the attending physician to suspect COVID-19. Testing was ordered and the real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay result was positive. The patient was immediately transferred to the isolation ward for management and confirmed COVID-19 infection.
Subsequently, the patient admitted travel to the COVID-19 epicenter in Wuhan province, although it was 25 days prior, indicating a longer period of incubation than generally believed, according to the authors. The patient survived treatment and was eventually discharged.
“Clinical and biochemical data of COVID-19 might be partly masked by coexisting chronic lymphocytic leukemia; better diagnostic strategies (i.e., superior CT differential techniques such as radiomics) could be used for diagnosis,” the researchers concluded, speculating that the apparently longer-than-normal COVID-19 incubation period might be the result of the patient’s compromised immune system.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jin X-H et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(4):E351-2.
Characteristics of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia can mask COVID-19 infection, creating a risk for patients, practitioners, and the community, according to a case study published in the Lancet Haematology.
A 39-year-old man with a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) presented at a clinic in Wenzhou, China, with symptoms of fever, sore throat, productive cough, and dyspnea, according to the authors. COVID-19 infection was not initially suspected, as his whole blood cell and lymphocyte counts were high, the CLL masked a potential infection, and the patient claimed he had no suspect recent travel history.
However, a CT chest scan showed bilateral ground-glass opacities and a small amount of fluid in the patient’s left pleural cavity, leading the attending physician to suspect COVID-19. Testing was ordered and the real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay result was positive. The patient was immediately transferred to the isolation ward for management and confirmed COVID-19 infection.
Subsequently, the patient admitted travel to the COVID-19 epicenter in Wuhan province, although it was 25 days prior, indicating a longer period of incubation than generally believed, according to the authors. The patient survived treatment and was eventually discharged.
“Clinical and biochemical data of COVID-19 might be partly masked by coexisting chronic lymphocytic leukemia; better diagnostic strategies (i.e., superior CT differential techniques such as radiomics) could be used for diagnosis,” the researchers concluded, speculating that the apparently longer-than-normal COVID-19 incubation period might be the result of the patient’s compromised immune system.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jin X-H et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(4):E351-2.
Characteristics of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia can mask COVID-19 infection, creating a risk for patients, practitioners, and the community, according to a case study published in the Lancet Haematology.
A 39-year-old man with a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) presented at a clinic in Wenzhou, China, with symptoms of fever, sore throat, productive cough, and dyspnea, according to the authors. COVID-19 infection was not initially suspected, as his whole blood cell and lymphocyte counts were high, the CLL masked a potential infection, and the patient claimed he had no suspect recent travel history.
However, a CT chest scan showed bilateral ground-glass opacities and a small amount of fluid in the patient’s left pleural cavity, leading the attending physician to suspect COVID-19. Testing was ordered and the real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction assay result was positive. The patient was immediately transferred to the isolation ward for management and confirmed COVID-19 infection.
Subsequently, the patient admitted travel to the COVID-19 epicenter in Wuhan province, although it was 25 days prior, indicating a longer period of incubation than generally believed, according to the authors. The patient survived treatment and was eventually discharged.
“Clinical and biochemical data of COVID-19 might be partly masked by coexisting chronic lymphocytic leukemia; better diagnostic strategies (i.e., superior CT differential techniques such as radiomics) could be used for diagnosis,” the researchers concluded, speculating that the apparently longer-than-normal COVID-19 incubation period might be the result of the patient’s compromised immune system.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jin X-H et al. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(4):E351-2.
FROM THE LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Advice from the front lines: How cancer centers can cope with COVID-19
according to the medical director of a cancer care alliance in the first U.S. epicenter of the coronavirus outbreak.
Jennie R. Crews, MD, the medical director of the Seattle Cancer Care Alliance (SCCA), discussed the SCCA experience and offered advice for other cancer centers in a webinar hosted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers.
Dr. Crews highlighted the SCCA’s use of algorithms to predict which patients can be managed via telehealth and which require face-to-face visits, human resource issues that arose at SCCA, screening and testing procedures, and the importance of communication with patients, caregivers, and staff.
Communication
Dr. Crews stressed the value of clear, regular, and internally consistent staff communication in a variety of formats. SCCA sends daily email blasts to their personnel regarding policies and procedures, which are archived on the SCCA intranet site.
SCCA also holds weekly town hall meetings at which leaders respond to staff questions regarding practical matters they have encountered and future plans. Providers’ up-to-the-minute familiarity with policies and procedures enables all team members to uniformly and clearly communicate to patients and caregivers.
Dr. Crews emphasized the value of consistency and “over-communication” in projecting confidence and preparedness to patients and caregivers during an unsettling time. SCCA has developed fact sheets, posted current information on the SCCA website, and provided education during doorway screenings.
Screening and testing
All SCCA staff members are screened daily at the practice entrance so they have personal experience with the process utilized for patients. Because symptoms associated with coronavirus infection may overlap with cancer treatment–related complaints, SCCA clinicians have expanded the typical coronavirus screening questionnaire for patients on cancer treatment.
Patients with ambiguous symptoms are masked, taken to a physically separate area of the SCCA clinics, and screened further by an advanced practice provider. The patients are then triaged to either the clinic for treatment or to the emergency department for further triage and care.
Although testing processes and procedures have been modified, Dr. Crews advised codifying those policies and procedures, including notification of results and follow-up for both patients and staff. Dr. Crews also stressed the importance of clearly articulated return-to-work policies for staff who have potential exposure and/or positive test results.
At the University of Washington’s virology laboratory, they have a test turnaround time of less than 12 hours.
Planning ahead
Dr. Crews highlighted the importance of community-based surge planning, utilizing predictive models to assess inpatient capacity requirements and potential repurposing of providers.
The SCCA is prepared to close selected community sites and shift personnel to other locations if personnel needs cannot be met because of illness or quarantine. Contingency plans include specialized pharmacy services for patients requiring chemotherapy.
The SCCA has not yet experienced shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE). However, Dr. Crews said staff require detailed education regarding the use of PPE in order to safeguard the supply while providing maximal staff protection.
Helping the helpers
During the pandemic, SCCA has dealt with a variety of challenging human resource issues, including:
- Extending sick time beyond what was previously “stored” in staff members’ earned time off.
- Childcare during an extended hiatus in school and daycare schedules.
- Programs to maintain and/or restore employee wellness (including staff-centered support services, spiritual care, mindfulness exercises, and town halls).
Dr. Crews also discussed recruitment of community resources to provide meals for staff from local restaurants with restricted hours and transportation resources for staff and patients, as visitors are restricted (currently one per patient).
Managing care
Dr. Crews noted that the University of Washington had a foundational structure for a telehealth program prior to the pandemic. Their telehealth committee enabled SCCA to scale up the service quickly with their academic partners, including training modules for and certification of providers, outfitting off-site personnel with dedicated lines and hardware, and provision of personal Zoom accounts.
SCCA also devised algorithms for determining when face-to-face visits, remote management, or deferred visits are appropriate in various scenarios. The algorithms were developed by disease-specialized teams.
As a general rule, routine chemotherapy and radiation are administered on schedule. On-treatment and follow-up office visits are conducted via telehealth if possible. In some cases, initiation of chemotherapy and radiation has been delayed, and screening services have been suspended.
In response to questions about palliative care during the pandemic, Dr. Crews said SCCA has encouraged their patients to complete, review, or update their advance directives. The SCCA has not had the need to resuscitate a coronavirus-infected outpatient but has instituted policies for utilizing full PPE on any patient requiring resuscitation.
In her closing remarks, Dr. Crews stressed that the response to COVID-19 in Washington state has required an intense collaboration among colleagues, the community, and government leaders, as the actions required extended far beyond medical decision makers alone.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
according to the medical director of a cancer care alliance in the first U.S. epicenter of the coronavirus outbreak.
Jennie R. Crews, MD, the medical director of the Seattle Cancer Care Alliance (SCCA), discussed the SCCA experience and offered advice for other cancer centers in a webinar hosted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers.
Dr. Crews highlighted the SCCA’s use of algorithms to predict which patients can be managed via telehealth and which require face-to-face visits, human resource issues that arose at SCCA, screening and testing procedures, and the importance of communication with patients, caregivers, and staff.
Communication
Dr. Crews stressed the value of clear, regular, and internally consistent staff communication in a variety of formats. SCCA sends daily email blasts to their personnel regarding policies and procedures, which are archived on the SCCA intranet site.
SCCA also holds weekly town hall meetings at which leaders respond to staff questions regarding practical matters they have encountered and future plans. Providers’ up-to-the-minute familiarity with policies and procedures enables all team members to uniformly and clearly communicate to patients and caregivers.
Dr. Crews emphasized the value of consistency and “over-communication” in projecting confidence and preparedness to patients and caregivers during an unsettling time. SCCA has developed fact sheets, posted current information on the SCCA website, and provided education during doorway screenings.
Screening and testing
All SCCA staff members are screened daily at the practice entrance so they have personal experience with the process utilized for patients. Because symptoms associated with coronavirus infection may overlap with cancer treatment–related complaints, SCCA clinicians have expanded the typical coronavirus screening questionnaire for patients on cancer treatment.
Patients with ambiguous symptoms are masked, taken to a physically separate area of the SCCA clinics, and screened further by an advanced practice provider. The patients are then triaged to either the clinic for treatment or to the emergency department for further triage and care.
Although testing processes and procedures have been modified, Dr. Crews advised codifying those policies and procedures, including notification of results and follow-up for both patients and staff. Dr. Crews also stressed the importance of clearly articulated return-to-work policies for staff who have potential exposure and/or positive test results.
At the University of Washington’s virology laboratory, they have a test turnaround time of less than 12 hours.
Planning ahead
Dr. Crews highlighted the importance of community-based surge planning, utilizing predictive models to assess inpatient capacity requirements and potential repurposing of providers.
The SCCA is prepared to close selected community sites and shift personnel to other locations if personnel needs cannot be met because of illness or quarantine. Contingency plans include specialized pharmacy services for patients requiring chemotherapy.
The SCCA has not yet experienced shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE). However, Dr. Crews said staff require detailed education regarding the use of PPE in order to safeguard the supply while providing maximal staff protection.
Helping the helpers
During the pandemic, SCCA has dealt with a variety of challenging human resource issues, including:
- Extending sick time beyond what was previously “stored” in staff members’ earned time off.
- Childcare during an extended hiatus in school and daycare schedules.
- Programs to maintain and/or restore employee wellness (including staff-centered support services, spiritual care, mindfulness exercises, and town halls).
Dr. Crews also discussed recruitment of community resources to provide meals for staff from local restaurants with restricted hours and transportation resources for staff and patients, as visitors are restricted (currently one per patient).
Managing care
Dr. Crews noted that the University of Washington had a foundational structure for a telehealth program prior to the pandemic. Their telehealth committee enabled SCCA to scale up the service quickly with their academic partners, including training modules for and certification of providers, outfitting off-site personnel with dedicated lines and hardware, and provision of personal Zoom accounts.
SCCA also devised algorithms for determining when face-to-face visits, remote management, or deferred visits are appropriate in various scenarios. The algorithms were developed by disease-specialized teams.
As a general rule, routine chemotherapy and radiation are administered on schedule. On-treatment and follow-up office visits are conducted via telehealth if possible. In some cases, initiation of chemotherapy and radiation has been delayed, and screening services have been suspended.
In response to questions about palliative care during the pandemic, Dr. Crews said SCCA has encouraged their patients to complete, review, or update their advance directives. The SCCA has not had the need to resuscitate a coronavirus-infected outpatient but has instituted policies for utilizing full PPE on any patient requiring resuscitation.
In her closing remarks, Dr. Crews stressed that the response to COVID-19 in Washington state has required an intense collaboration among colleagues, the community, and government leaders, as the actions required extended far beyond medical decision makers alone.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
according to the medical director of a cancer care alliance in the first U.S. epicenter of the coronavirus outbreak.
Jennie R. Crews, MD, the medical director of the Seattle Cancer Care Alliance (SCCA), discussed the SCCA experience and offered advice for other cancer centers in a webinar hosted by the Association of Community Cancer Centers.
Dr. Crews highlighted the SCCA’s use of algorithms to predict which patients can be managed via telehealth and which require face-to-face visits, human resource issues that arose at SCCA, screening and testing procedures, and the importance of communication with patients, caregivers, and staff.
Communication
Dr. Crews stressed the value of clear, regular, and internally consistent staff communication in a variety of formats. SCCA sends daily email blasts to their personnel regarding policies and procedures, which are archived on the SCCA intranet site.
SCCA also holds weekly town hall meetings at which leaders respond to staff questions regarding practical matters they have encountered and future plans. Providers’ up-to-the-minute familiarity with policies and procedures enables all team members to uniformly and clearly communicate to patients and caregivers.
Dr. Crews emphasized the value of consistency and “over-communication” in projecting confidence and preparedness to patients and caregivers during an unsettling time. SCCA has developed fact sheets, posted current information on the SCCA website, and provided education during doorway screenings.
Screening and testing
All SCCA staff members are screened daily at the practice entrance so they have personal experience with the process utilized for patients. Because symptoms associated with coronavirus infection may overlap with cancer treatment–related complaints, SCCA clinicians have expanded the typical coronavirus screening questionnaire for patients on cancer treatment.
Patients with ambiguous symptoms are masked, taken to a physically separate area of the SCCA clinics, and screened further by an advanced practice provider. The patients are then triaged to either the clinic for treatment or to the emergency department for further triage and care.
Although testing processes and procedures have been modified, Dr. Crews advised codifying those policies and procedures, including notification of results and follow-up for both patients and staff. Dr. Crews also stressed the importance of clearly articulated return-to-work policies for staff who have potential exposure and/or positive test results.
At the University of Washington’s virology laboratory, they have a test turnaround time of less than 12 hours.
Planning ahead
Dr. Crews highlighted the importance of community-based surge planning, utilizing predictive models to assess inpatient capacity requirements and potential repurposing of providers.
The SCCA is prepared to close selected community sites and shift personnel to other locations if personnel needs cannot be met because of illness or quarantine. Contingency plans include specialized pharmacy services for patients requiring chemotherapy.
The SCCA has not yet experienced shortages of personal protective equipment (PPE). However, Dr. Crews said staff require detailed education regarding the use of PPE in order to safeguard the supply while providing maximal staff protection.
Helping the helpers
During the pandemic, SCCA has dealt with a variety of challenging human resource issues, including:
- Extending sick time beyond what was previously “stored” in staff members’ earned time off.
- Childcare during an extended hiatus in school and daycare schedules.
- Programs to maintain and/or restore employee wellness (including staff-centered support services, spiritual care, mindfulness exercises, and town halls).
Dr. Crews also discussed recruitment of community resources to provide meals for staff from local restaurants with restricted hours and transportation resources for staff and patients, as visitors are restricted (currently one per patient).
Managing care
Dr. Crews noted that the University of Washington had a foundational structure for a telehealth program prior to the pandemic. Their telehealth committee enabled SCCA to scale up the service quickly with their academic partners, including training modules for and certification of providers, outfitting off-site personnel with dedicated lines and hardware, and provision of personal Zoom accounts.
SCCA also devised algorithms for determining when face-to-face visits, remote management, or deferred visits are appropriate in various scenarios. The algorithms were developed by disease-specialized teams.
As a general rule, routine chemotherapy and radiation are administered on schedule. On-treatment and follow-up office visits are conducted via telehealth if possible. In some cases, initiation of chemotherapy and radiation has been delayed, and screening services have been suspended.
In response to questions about palliative care during the pandemic, Dr. Crews said SCCA has encouraged their patients to complete, review, or update their advance directives. The SCCA has not had the need to resuscitate a coronavirus-infected outpatient but has instituted policies for utilizing full PPE on any patient requiring resuscitation.
In her closing remarks, Dr. Crews stressed that the response to COVID-19 in Washington state has required an intense collaboration among colleagues, the community, and government leaders, as the actions required extended far beyond medical decision makers alone.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
No staff COVID-19 diagnoses after plan at Chinese cancer center
Short-term results
No staff members or patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 after “strict protective measures” for screening and managing patients were implemented at the National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Beijing, according to a report published online April 1 in JAMA Oncology.
However, the time period for the analysis, which included nearly 3000 patients, was short — only about 3 weeks (February 12 to March 3). Also, Beijing is more than 1100 kilometers from Wuhan, the center of the Chinese outbreak of COVID-19.
The Beijing cancer hospital implemented a multipronged safety plan in February in order to “avoid COVID-19 related nosocomial cross-infection between patients and medical staff,” explain the authors, led by medical oncologist Zhijie Wang, MD.
Notably, “all of the measures taken in China are actively being implemented and used in major oncology centers in the United States,” Robert Carlson, MD, chief executive officer, National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), told Medscape Medical News.
John Greene, MD, section chief, Infectious Disease and Tropical Medicine, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Florida, pointed out that the Chinese safety plan, which is full of “good measures,” is being largely used at his center. However, he observed that one tool — doing a temperature check at the hospital front door — is not well supported by most of the literature. “It gives good optics and looks like you are doing the most you possibly can, but scientifically it may not be as effective [as other screening measures],” he said.
The Chinese plan consists of four broad elements
First, the above-mentioned on-site temperature tests are performed at the entrances of the hospital, outpatient clinic, and wards. Contact and travel histories related to the Wuhan epidemic area are also established and recorded.
Second, an outpatient appointment scheduling system allows both online scheduling and on-site registration. Online consultation channels are open daily, featuring instruction on medication taking and cancer-related symptom management. These “substantially reduced the flow of people in the hospital,” write the authors. On-site patients must wear a mask and have their own disinfectant.
Third, for patients with cancer preparing to be admitted to hospital, symptoms associated with COVID-19, such as fever and cough, are recorded. Mandatory blood tests and CT scans of the lungs are performed. COVID-19 virus nucleic acid tests are performed for patients with suspected pneumonia on imaging.
Fourth, some anticancer drugs conventionally administered by infusion have been changed to oral administration, such as etoposide and vinorelbine. For adjuvant or maintenance chemotherapy, the infusion intervals were appropriately prolonged depending on patients’ conditions.
Eight out of 2,900 patients had imaging suspicious for infection
The Chinese authors report that a total of 2,944 patients with cancer were seen for clinic consultation and treatment in the wards (2795 outpatients and 149 inpatients).
Patients with cancer are believed to have a higher probability of severe illness and increased mortality compared with the healthy population once infected with COVID-19, point out the authors.
Under the new “strict screening strategy,” 27 patients showed radiologic manifestations of inflammatory changes or multiple-site exudative pneumonia in the lungs, including eight suspected of having COVID-19 infection. “Fortunately, negative results from nucleic acid testing ultimately excluded COVID-19 infection in all these patients,” the authors report.
However, two of these patients “presented with recovered pneumonia after symptomatic treatment.” Commenting on this finding, Moffitt’s Greene said that may mean these two patients were tested and found to be positive but were early in the infection and not yet shedding the virus, or they were infected after the initial negative result.
Greene said his center has implemented some measures not mentioned in the Chinese plan. For example, the Florida center no longer allows inpatient visitation. Also, one third of staff now work from home, resulting in less social interaction. Social distancing in meetings, the cafeteria, and hallways is being observed “aggressively,” and most meetings are now on Zoom, he said.
Moffitt has not been hard hit with COVID-19 and is at level one preparedness, the lowest rung. The center has performed 60 tests to date, with only one positive for the virus (< 2%), Greene told Medscape Medical News.
Currently, in the larger Tampa Bay community setting, about 12% of tests are positive.
The low percentage found among the Moffitt patients “tells you that a lot of cancer patients have fever and respiratory symptoms due to other viruses and, more importantly, other reasons, whether it’s their immunotherapy or chemotherapy or their cancer,” said Greene.
NCCN’s Carlson said the publication of the Chinese data was a good sign in terms of international science.
“This is a strong example of how the global oncology community rapidly shares information and experience whenever it makes a difference in patient care,” he commented.
The authors, as well as Carlson and Greene, have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Short-term results
Short-term results
No staff members or patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 after “strict protective measures” for screening and managing patients were implemented at the National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Beijing, according to a report published online April 1 in JAMA Oncology.
However, the time period for the analysis, which included nearly 3000 patients, was short — only about 3 weeks (February 12 to March 3). Also, Beijing is more than 1100 kilometers from Wuhan, the center of the Chinese outbreak of COVID-19.
The Beijing cancer hospital implemented a multipronged safety plan in February in order to “avoid COVID-19 related nosocomial cross-infection between patients and medical staff,” explain the authors, led by medical oncologist Zhijie Wang, MD.
Notably, “all of the measures taken in China are actively being implemented and used in major oncology centers in the United States,” Robert Carlson, MD, chief executive officer, National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), told Medscape Medical News.
John Greene, MD, section chief, Infectious Disease and Tropical Medicine, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Florida, pointed out that the Chinese safety plan, which is full of “good measures,” is being largely used at his center. However, he observed that one tool — doing a temperature check at the hospital front door — is not well supported by most of the literature. “It gives good optics and looks like you are doing the most you possibly can, but scientifically it may not be as effective [as other screening measures],” he said.
The Chinese plan consists of four broad elements
First, the above-mentioned on-site temperature tests are performed at the entrances of the hospital, outpatient clinic, and wards. Contact and travel histories related to the Wuhan epidemic area are also established and recorded.
Second, an outpatient appointment scheduling system allows both online scheduling and on-site registration. Online consultation channels are open daily, featuring instruction on medication taking and cancer-related symptom management. These “substantially reduced the flow of people in the hospital,” write the authors. On-site patients must wear a mask and have their own disinfectant.
Third, for patients with cancer preparing to be admitted to hospital, symptoms associated with COVID-19, such as fever and cough, are recorded. Mandatory blood tests and CT scans of the lungs are performed. COVID-19 virus nucleic acid tests are performed for patients with suspected pneumonia on imaging.
Fourth, some anticancer drugs conventionally administered by infusion have been changed to oral administration, such as etoposide and vinorelbine. For adjuvant or maintenance chemotherapy, the infusion intervals were appropriately prolonged depending on patients’ conditions.
Eight out of 2,900 patients had imaging suspicious for infection
The Chinese authors report that a total of 2,944 patients with cancer were seen for clinic consultation and treatment in the wards (2795 outpatients and 149 inpatients).
Patients with cancer are believed to have a higher probability of severe illness and increased mortality compared with the healthy population once infected with COVID-19, point out the authors.
Under the new “strict screening strategy,” 27 patients showed radiologic manifestations of inflammatory changes or multiple-site exudative pneumonia in the lungs, including eight suspected of having COVID-19 infection. “Fortunately, negative results from nucleic acid testing ultimately excluded COVID-19 infection in all these patients,” the authors report.
However, two of these patients “presented with recovered pneumonia after symptomatic treatment.” Commenting on this finding, Moffitt’s Greene said that may mean these two patients were tested and found to be positive but were early in the infection and not yet shedding the virus, or they were infected after the initial negative result.
Greene said his center has implemented some measures not mentioned in the Chinese plan. For example, the Florida center no longer allows inpatient visitation. Also, one third of staff now work from home, resulting in less social interaction. Social distancing in meetings, the cafeteria, and hallways is being observed “aggressively,” and most meetings are now on Zoom, he said.
Moffitt has not been hard hit with COVID-19 and is at level one preparedness, the lowest rung. The center has performed 60 tests to date, with only one positive for the virus (< 2%), Greene told Medscape Medical News.
Currently, in the larger Tampa Bay community setting, about 12% of tests are positive.
The low percentage found among the Moffitt patients “tells you that a lot of cancer patients have fever and respiratory symptoms due to other viruses and, more importantly, other reasons, whether it’s their immunotherapy or chemotherapy or their cancer,” said Greene.
NCCN’s Carlson said the publication of the Chinese data was a good sign in terms of international science.
“This is a strong example of how the global oncology community rapidly shares information and experience whenever it makes a difference in patient care,” he commented.
The authors, as well as Carlson and Greene, have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No staff members or patients were diagnosed with COVID-19 after “strict protective measures” for screening and managing patients were implemented at the National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in Beijing, according to a report published online April 1 in JAMA Oncology.
However, the time period for the analysis, which included nearly 3000 patients, was short — only about 3 weeks (February 12 to March 3). Also, Beijing is more than 1100 kilometers from Wuhan, the center of the Chinese outbreak of COVID-19.
The Beijing cancer hospital implemented a multipronged safety plan in February in order to “avoid COVID-19 related nosocomial cross-infection between patients and medical staff,” explain the authors, led by medical oncologist Zhijie Wang, MD.
Notably, “all of the measures taken in China are actively being implemented and used in major oncology centers in the United States,” Robert Carlson, MD, chief executive officer, National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN), told Medscape Medical News.
John Greene, MD, section chief, Infectious Disease and Tropical Medicine, Moffitt Cancer Center, Tampa, Florida, pointed out that the Chinese safety plan, which is full of “good measures,” is being largely used at his center. However, he observed that one tool — doing a temperature check at the hospital front door — is not well supported by most of the literature. “It gives good optics and looks like you are doing the most you possibly can, but scientifically it may not be as effective [as other screening measures],” he said.
The Chinese plan consists of four broad elements
First, the above-mentioned on-site temperature tests are performed at the entrances of the hospital, outpatient clinic, and wards. Contact and travel histories related to the Wuhan epidemic area are also established and recorded.
Second, an outpatient appointment scheduling system allows both online scheduling and on-site registration. Online consultation channels are open daily, featuring instruction on medication taking and cancer-related symptom management. These “substantially reduced the flow of people in the hospital,” write the authors. On-site patients must wear a mask and have their own disinfectant.
Third, for patients with cancer preparing to be admitted to hospital, symptoms associated with COVID-19, such as fever and cough, are recorded. Mandatory blood tests and CT scans of the lungs are performed. COVID-19 virus nucleic acid tests are performed for patients with suspected pneumonia on imaging.
Fourth, some anticancer drugs conventionally administered by infusion have been changed to oral administration, such as etoposide and vinorelbine. For adjuvant or maintenance chemotherapy, the infusion intervals were appropriately prolonged depending on patients’ conditions.
Eight out of 2,900 patients had imaging suspicious for infection
The Chinese authors report that a total of 2,944 patients with cancer were seen for clinic consultation and treatment in the wards (2795 outpatients and 149 inpatients).
Patients with cancer are believed to have a higher probability of severe illness and increased mortality compared with the healthy population once infected with COVID-19, point out the authors.
Under the new “strict screening strategy,” 27 patients showed radiologic manifestations of inflammatory changes or multiple-site exudative pneumonia in the lungs, including eight suspected of having COVID-19 infection. “Fortunately, negative results from nucleic acid testing ultimately excluded COVID-19 infection in all these patients,” the authors report.
However, two of these patients “presented with recovered pneumonia after symptomatic treatment.” Commenting on this finding, Moffitt’s Greene said that may mean these two patients were tested and found to be positive but were early in the infection and not yet shedding the virus, or they were infected after the initial negative result.
Greene said his center has implemented some measures not mentioned in the Chinese plan. For example, the Florida center no longer allows inpatient visitation. Also, one third of staff now work from home, resulting in less social interaction. Social distancing in meetings, the cafeteria, and hallways is being observed “aggressively,” and most meetings are now on Zoom, he said.
Moffitt has not been hard hit with COVID-19 and is at level one preparedness, the lowest rung. The center has performed 60 tests to date, with only one positive for the virus (< 2%), Greene told Medscape Medical News.
Currently, in the larger Tampa Bay community setting, about 12% of tests are positive.
The low percentage found among the Moffitt patients “tells you that a lot of cancer patients have fever and respiratory symptoms due to other viruses and, more importantly, other reasons, whether it’s their immunotherapy or chemotherapy or their cancer,” said Greene.
NCCN’s Carlson said the publication of the Chinese data was a good sign in terms of international science.
“This is a strong example of how the global oncology community rapidly shares information and experience whenever it makes a difference in patient care,” he commented.
The authors, as well as Carlson and Greene, have reported no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.