User login
The Aftermath of Kennedy vs. Braidwood
In our June issue, I highlighted the potentially seismic clinical implications of the U.S. Supreme Court’s then-pending decision in the Kennedy vs. Braidwood Management, Inc., case. That ruling, recently released at the conclusion of the Court’s term, ultimately affirmed the Affordable Care Act’s mandate requiring insurers to cover certain preventive services, including colorectal cancer screening tests, without cost-sharing.
In doing so, however, the court determined that members of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), which recommends these services, are “inferior officers” appropriately appointed by the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS), rather than needing Senate confirmation. Thus, the decision reinforced the HHS Secretary’s authority to oversee and potentially influence USPSTF recommendations in the future. While the decision represented a victory in upholding a key provision of the ACA, it also signaled a potential threat to the scientific independence of the body charged with making those preventive care recommendations in a scientifically rigorous, unbiased manner.
As anticipated, the HHS Secretary responded to the Supreme Court’s ruling by abruptly canceling the USPSTF’s scheduled July meeting. This decision, coupled with his recent disbanding of the entire 17-member Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — the group responsible for shaping evidence-based vaccine policy — has raised serious concerns across the healthcare field. On July 9th, AGA joined a coalition of 104 health organizations in submitting a letter to the Chair and Ranking Members of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions and the House Committee on Energy and Commerce, urging them to protect the integrity of the USPSTF.
The fight to protect science-based health policy is far from over — effective advocacy necessitates that clinicians use their professional platforms to push back against the politicization of science – not only for the integrity of the medical profession, but for the health and future of the patients we serve.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
In our June issue, I highlighted the potentially seismic clinical implications of the U.S. Supreme Court’s then-pending decision in the Kennedy vs. Braidwood Management, Inc., case. That ruling, recently released at the conclusion of the Court’s term, ultimately affirmed the Affordable Care Act’s mandate requiring insurers to cover certain preventive services, including colorectal cancer screening tests, without cost-sharing.
In doing so, however, the court determined that members of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), which recommends these services, are “inferior officers” appropriately appointed by the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS), rather than needing Senate confirmation. Thus, the decision reinforced the HHS Secretary’s authority to oversee and potentially influence USPSTF recommendations in the future. While the decision represented a victory in upholding a key provision of the ACA, it also signaled a potential threat to the scientific independence of the body charged with making those preventive care recommendations in a scientifically rigorous, unbiased manner.
As anticipated, the HHS Secretary responded to the Supreme Court’s ruling by abruptly canceling the USPSTF’s scheduled July meeting. This decision, coupled with his recent disbanding of the entire 17-member Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — the group responsible for shaping evidence-based vaccine policy — has raised serious concerns across the healthcare field. On July 9th, AGA joined a coalition of 104 health organizations in submitting a letter to the Chair and Ranking Members of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions and the House Committee on Energy and Commerce, urging them to protect the integrity of the USPSTF.
The fight to protect science-based health policy is far from over — effective advocacy necessitates that clinicians use their professional platforms to push back against the politicization of science – not only for the integrity of the medical profession, but for the health and future of the patients we serve.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
In our June issue, I highlighted the potentially seismic clinical implications of the U.S. Supreme Court’s then-pending decision in the Kennedy vs. Braidwood Management, Inc., case. That ruling, recently released at the conclusion of the Court’s term, ultimately affirmed the Affordable Care Act’s mandate requiring insurers to cover certain preventive services, including colorectal cancer screening tests, without cost-sharing.
In doing so, however, the court determined that members of the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), which recommends these services, are “inferior officers” appropriately appointed by the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS), rather than needing Senate confirmation. Thus, the decision reinforced the HHS Secretary’s authority to oversee and potentially influence USPSTF recommendations in the future. While the decision represented a victory in upholding a key provision of the ACA, it also signaled a potential threat to the scientific independence of the body charged with making those preventive care recommendations in a scientifically rigorous, unbiased manner.
As anticipated, the HHS Secretary responded to the Supreme Court’s ruling by abruptly canceling the USPSTF’s scheduled July meeting. This decision, coupled with his recent disbanding of the entire 17-member Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices — the group responsible for shaping evidence-based vaccine policy — has raised serious concerns across the healthcare field. On July 9th, AGA joined a coalition of 104 health organizations in submitting a letter to the Chair and Ranking Members of the Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions and the House Committee on Energy and Commerce, urging them to protect the integrity of the USPSTF.
The fight to protect science-based health policy is far from over — effective advocacy necessitates that clinicians use their professional platforms to push back against the politicization of science – not only for the integrity of the medical profession, but for the health and future of the patients we serve.
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
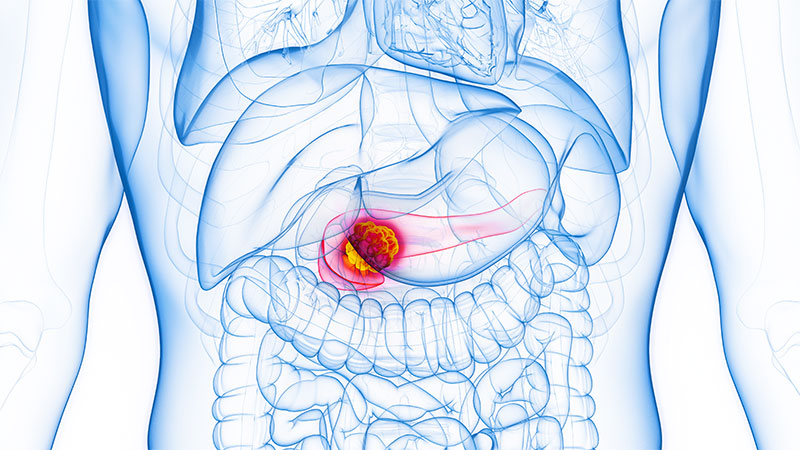
Metastases-Directed Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: More Questions Than Answers
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Dr Maurie Markman, from City of Hope. I’d like to discuss what I consider to be an absolutely fascinating paper, and one that I will say has very interesting results but raises many more questions than it answers. I think that was the intent of the authors.
The paper is entitled, “Addition of metastasis-directed therapy to systemic therapy for oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase 2 trial,” published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
You might ask what metastasis-directed therapy in pancreatic cancer means. Have we really made much of an impact on pancreatic cancer? In fact, in my earlier years of training, if somebody came up with the idea, or suggested as part of a trial or treatment of an individual patient, that they would focus on metastases in pancreas cancer, you might say they’re crazy, or you might say: “Yeah, but they probably don’t know anything about the disease and its natural history.”
Now, fast forward several decades. Even with the recognized, modest advances in systemic therapy, what we see are tremendous, really remarkable advances in innovations in radiation therapy. Of course, this includes not only the use of radiation itself but also the imaging technology that is used to direct the radiation therapy. These advances have permitted asking the questions that are addressed in the current study.
Again, this study is fascinating. They randomized a very small number. Again, it’s a randomized phase 2 study. It’s really more of a proof of principle here. They randomized 41 patients with five or fewer metastatic lesions — with oligometastatic disease, they could have numerous lesions — to undergo what they’ve described as comprehensive metastases-directed therapy.
Most of this was external beam radiation therapy and stereotactic radiation therapy, but there were some localized radiation implants as well, plus chemotherapy. This was comprehensive metastases-directed therapy to each of these sites plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone.
What was shown in this trial? The progression-free survival (PFS) in the metastases-directed therapy group was 10.3 months vs 2.5 months in the group of patients who received chemotherapy only, with a hazard ratio of 0.43 and statistical significance.
Remember, this was a very small study, but we see more than a tripling in the PFS. There was no difference in overall survival, which is not at all surprising because it was a very small sample size.
Very importantly — and essential to doing this trial ethically — a crossover was permitted at the time of progression, meaning that if a patient received chemotherapy only and progressed, they could potentially get stereotactic radiation to sites of metastatic disease. They might have also benefited from that kind of strategy to the metastasis-[therapy] so that overall survival in the small population may not be different. Again, there was a tripling of the time to disease progression.
Clearly, a larger study will be required to be more definitive. We would need more centers involved and maybe some modification in the study design in this trial because of any issues that the investigators may have identified. Of course, overall survival would be a fair endpoint to look at, but again, crossover would be essential, and that might influence an ultimate outcome. PFS is a very valid endpoint.
The only other point to mention is, with these results — and as I mentioned, advances in radiation and imaging — is it reasonable to potentially consider this type of approach for individual patients as a component of aggressive standard of care? Of course, this would be with very adequate informed consent from patients, because we don’t know what the impact will be.
With the limited morbidity associated with the radiation, for an individual patient with pancreatic cancer who has an adequate performance status and limited metastases, if we give them chemotherapy and also directed radiation, is it reasonable to consider that as an appropriate treatment option outside the setting of a clinical trial?
I think this is a very valid question that needs to be addressed. In my opinion, the answer in some settings should be yes, but that needs to be discussed much more widely than simply in this randomized phase 2 trial.
Thank you for your attention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Dr Maurie Markman, from City of Hope. I’d like to discuss what I consider to be an absolutely fascinating paper, and one that I will say has very interesting results but raises many more questions than it answers. I think that was the intent of the authors.
The paper is entitled, “Addition of metastasis-directed therapy to systemic therapy for oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase 2 trial,” published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
You might ask what metastasis-directed therapy in pancreatic cancer means. Have we really made much of an impact on pancreatic cancer? In fact, in my earlier years of training, if somebody came up with the idea, or suggested as part of a trial or treatment of an individual patient, that they would focus on metastases in pancreas cancer, you might say they’re crazy, or you might say: “Yeah, but they probably don’t know anything about the disease and its natural history.”
Now, fast forward several decades. Even with the recognized, modest advances in systemic therapy, what we see are tremendous, really remarkable advances in innovations in radiation therapy. Of course, this includes not only the use of radiation itself but also the imaging technology that is used to direct the radiation therapy. These advances have permitted asking the questions that are addressed in the current study.
Again, this study is fascinating. They randomized a very small number. Again, it’s a randomized phase 2 study. It’s really more of a proof of principle here. They randomized 41 patients with five or fewer metastatic lesions — with oligometastatic disease, they could have numerous lesions — to undergo what they’ve described as comprehensive metastases-directed therapy.
Most of this was external beam radiation therapy and stereotactic radiation therapy, but there were some localized radiation implants as well, plus chemotherapy. This was comprehensive metastases-directed therapy to each of these sites plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone.
What was shown in this trial? The progression-free survival (PFS) in the metastases-directed therapy group was 10.3 months vs 2.5 months in the group of patients who received chemotherapy only, with a hazard ratio of 0.43 and statistical significance.
Remember, this was a very small study, but we see more than a tripling in the PFS. There was no difference in overall survival, which is not at all surprising because it was a very small sample size.
Very importantly — and essential to doing this trial ethically — a crossover was permitted at the time of progression, meaning that if a patient received chemotherapy only and progressed, they could potentially get stereotactic radiation to sites of metastatic disease. They might have also benefited from that kind of strategy to the metastasis-[therapy] so that overall survival in the small population may not be different. Again, there was a tripling of the time to disease progression.
Clearly, a larger study will be required to be more definitive. We would need more centers involved and maybe some modification in the study design in this trial because of any issues that the investigators may have identified. Of course, overall survival would be a fair endpoint to look at, but again, crossover would be essential, and that might influence an ultimate outcome. PFS is a very valid endpoint.
The only other point to mention is, with these results — and as I mentioned, advances in radiation and imaging — is it reasonable to potentially consider this type of approach for individual patients as a component of aggressive standard of care? Of course, this would be with very adequate informed consent from patients, because we don’t know what the impact will be.
With the limited morbidity associated with the radiation, for an individual patient with pancreatic cancer who has an adequate performance status and limited metastases, if we give them chemotherapy and also directed radiation, is it reasonable to consider that as an appropriate treatment option outside the setting of a clinical trial?
I think this is a very valid question that needs to be addressed. In my opinion, the answer in some settings should be yes, but that needs to be discussed much more widely than simply in this randomized phase 2 trial.
Thank you for your attention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Hello. I’m Dr Maurie Markman, from City of Hope. I’d like to discuss what I consider to be an absolutely fascinating paper, and one that I will say has very interesting results but raises many more questions than it answers. I think that was the intent of the authors.
The paper is entitled, “Addition of metastasis-directed therapy to systemic therapy for oligometastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (EXTEND): a multicenter, randomized phase 2 trial,” published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
You might ask what metastasis-directed therapy in pancreatic cancer means. Have we really made much of an impact on pancreatic cancer? In fact, in my earlier years of training, if somebody came up with the idea, or suggested as part of a trial or treatment of an individual patient, that they would focus on metastases in pancreas cancer, you might say they’re crazy, or you might say: “Yeah, but they probably don’t know anything about the disease and its natural history.”
Now, fast forward several decades. Even with the recognized, modest advances in systemic therapy, what we see are tremendous, really remarkable advances in innovations in radiation therapy. Of course, this includes not only the use of radiation itself but also the imaging technology that is used to direct the radiation therapy. These advances have permitted asking the questions that are addressed in the current study.
Again, this study is fascinating. They randomized a very small number. Again, it’s a randomized phase 2 study. It’s really more of a proof of principle here. They randomized 41 patients with five or fewer metastatic lesions — with oligometastatic disease, they could have numerous lesions — to undergo what they’ve described as comprehensive metastases-directed therapy.
Most of this was external beam radiation therapy and stereotactic radiation therapy, but there were some localized radiation implants as well, plus chemotherapy. This was comprehensive metastases-directed therapy to each of these sites plus chemotherapy vs chemotherapy alone.
What was shown in this trial? The progression-free survival (PFS) in the metastases-directed therapy group was 10.3 months vs 2.5 months in the group of patients who received chemotherapy only, with a hazard ratio of 0.43 and statistical significance.
Remember, this was a very small study, but we see more than a tripling in the PFS. There was no difference in overall survival, which is not at all surprising because it was a very small sample size.
Very importantly — and essential to doing this trial ethically — a crossover was permitted at the time of progression, meaning that if a patient received chemotherapy only and progressed, they could potentially get stereotactic radiation to sites of metastatic disease. They might have also benefited from that kind of strategy to the metastasis-[therapy] so that overall survival in the small population may not be different. Again, there was a tripling of the time to disease progression.
Clearly, a larger study will be required to be more definitive. We would need more centers involved and maybe some modification in the study design in this trial because of any issues that the investigators may have identified. Of course, overall survival would be a fair endpoint to look at, but again, crossover would be essential, and that might influence an ultimate outcome. PFS is a very valid endpoint.
The only other point to mention is, with these results — and as I mentioned, advances in radiation and imaging — is it reasonable to potentially consider this type of approach for individual patients as a component of aggressive standard of care? Of course, this would be with very adequate informed consent from patients, because we don’t know what the impact will be.
With the limited morbidity associated with the radiation, for an individual patient with pancreatic cancer who has an adequate performance status and limited metastases, if we give them chemotherapy and also directed radiation, is it reasonable to consider that as an appropriate treatment option outside the setting of a clinical trial?
I think this is a very valid question that needs to be addressed. In my opinion, the answer in some settings should be yes, but that needs to be discussed much more widely than simply in this randomized phase 2 trial.
Thank you for your attention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Can We Successfully Adapt to Changes in Direction and Support for Acne?
Can We Successfully Adapt to Changes in Direction and Support for Acne?
How did I develop a strong interest in acne and rosacea? Interest on a personal level was with me throughout my adolescence and post-teen years as I suffered with very severe facial acne from ages 13 through 23 (1967-1977). I was sometimes called “pizza face” in high school, and biweekly trips to a dermatology office that always had a packed waiting room were of little help that I could appreciate visibly. Six straight years of extractions, intralesional injections, draining of fluctuant cysts, UVC light treatments, oral tetracycline, irritating topical formulations of benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin, and topical sulfacetamide-sulfur products resulted in minimal improvement. However, maybe all of this did something to what was happening underneath the skin surface, as I have no residual acne scars. I do recall vividly that I walked the halls in high school and college consistently affected by a very red face from the topical agents and smelling like rotten eggs from the topical sulfur application. I fortunately handled it well emotionally and socially, for which I am very thankful. Many people affected with acne do not.
In dermatology, I have always had a strong interest in pathophysiology and therapeutics, rooted I am sure in my background as a pharmacist. Although I was always interested in acne therapy, I was fully captivated by a presentation given by Dr. Jim Leyden many years ago at a small meeting in Myrtle Beach, South Carolina. He brought the subject of acne to life in a way that more than grabbed my complete attention and ignited an interest in learning everything I could about it. Over time, I was fortunate enough to work alongside Dr. Leyden and many other household names in acne at meetings and publications to further education on one of the most common disease states seen in ambulatory dermatology practices worldwide. The rest is history, leading to almost 4 decades of work in acne on many levels in dermatology, all being efforts that I am grateful for.
What I have observed to date is that we have had few revolutionary advances in acne therapy, the major one being oral isotretinoin, which was first brought to market in 1982. We are still utilizing many of the same therapeutic agents that I used back when I was treated for acne. A few new topical compounds have emerged, such as dapsone and clascoterone, and a narrow-spectrum tetracycline agent, sarecycline, also was developed. These agents do represent important advances with some specific benefits. There have been many major improvements in drug delivery formulations, including several vehicle technologies that allow augmented skin tolerability, increased efficacy, and improved stability, allowing for combination therapy products containing 2 or 3 active ingredients. A recent example is the first triple-combination topical acne therapy with excellent supporting data on speed of onset, efficacy, and safety.1
Technological advances also have aided in the development of modified- or extended-release formulations of oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline and minocycline, which allow for reduced adverse effects and lower daily dosages. Lidose formulations of isotretinoin have circumvented the need for concurrent ingestion of a high-fat meal to facilitate its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract (as required with conventional formulations). Many hours also have been spent on delivery devices and vehicles such as pumps, foams, and aqueous-based gels. Let us not forget the efforts and myriad products directed at skin care, cosmeceuticals, and physical devices (lasers and lights) for acne. Regardless of the above, we have not seen the monumental therapeutic and research revolution for acne that we have experienced more recently with biologic agents, Janus kinase inhibitors, and other modes of action for many common disease states such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hidradenitis suppurativa, prurigo nodularis, and chronic spontaneous urticaria.
Unfortunately, the slow development of advances in treatments for acne has been compounded further by the widespread availability of generic equivalents of most topical and oral therapies along with several over-the- counter topical medications. The expanded skin care and cosmeceutical product world has further diluted the perceived value of topical prescription therapies for acne. The marked difficulty in achieving and sustaining total clearance of acne, with the exception of many individuals treated with oral isotretinoin, results in many patients searching for other options, often through sources beyond dermatology practices (eg, the internet). While some of these sources may provide valid suggestions, they often are not truly substantiated by valid clinical research and are not formally regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration.
All of the above, in addition to the barriers to medication coverage put in place by third-party organizations such as pharmacy benefit managers, have contributed to the extreme slowdown in the development of new prescription therapies for acne. What this leads me to believe is that until there is a true meeting of the minds of all stakeholders on policies that facilitate access to both established and newly available acne therapies, there will be an enduring diminished incentive to support the development of newer acne treatments that will continue to spiral progressively downward. Some research on acne will always continue, such as the search for an acne vaccine and cutaneous microbiome alterations that are in progress.2,3 However, I do not see much happening in the foreseeable future. I am not inherently a pessimist or a “prophet of doom,” so I sincerely hope I am wrong.
- Stein Gold L, Baldwin H, Kircik LH, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose clindamycin phosphate 1.2%, benzoyl peroxide 3.1%, and adapalene 0.15% gel for moderate-to-severe acne: a randomized phase II study of the first triple-combination drug. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:93-104. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00650-3
- Keshari S, Kumar M, Balasubramaniam A, et al. Prospects of acne vaccines targeting secreted virulence factors of Cutibacterium acnes. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019;18:433-437. doi:10.1080/14760584
- Dreno B, Dekio I, Baldwin H, et al. Acne microbiome: from phyla to phylotypes. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:657- 664. doi:10.1111/jdv.19540 .2019.1593830
How did I develop a strong interest in acne and rosacea? Interest on a personal level was with me throughout my adolescence and post-teen years as I suffered with very severe facial acne from ages 13 through 23 (1967-1977). I was sometimes called “pizza face” in high school, and biweekly trips to a dermatology office that always had a packed waiting room were of little help that I could appreciate visibly. Six straight years of extractions, intralesional injections, draining of fluctuant cysts, UVC light treatments, oral tetracycline, irritating topical formulations of benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin, and topical sulfacetamide-sulfur products resulted in minimal improvement. However, maybe all of this did something to what was happening underneath the skin surface, as I have no residual acne scars. I do recall vividly that I walked the halls in high school and college consistently affected by a very red face from the topical agents and smelling like rotten eggs from the topical sulfur application. I fortunately handled it well emotionally and socially, for which I am very thankful. Many people affected with acne do not.
In dermatology, I have always had a strong interest in pathophysiology and therapeutics, rooted I am sure in my background as a pharmacist. Although I was always interested in acne therapy, I was fully captivated by a presentation given by Dr. Jim Leyden many years ago at a small meeting in Myrtle Beach, South Carolina. He brought the subject of acne to life in a way that more than grabbed my complete attention and ignited an interest in learning everything I could about it. Over time, I was fortunate enough to work alongside Dr. Leyden and many other household names in acne at meetings and publications to further education on one of the most common disease states seen in ambulatory dermatology practices worldwide. The rest is history, leading to almost 4 decades of work in acne on many levels in dermatology, all being efforts that I am grateful for.
What I have observed to date is that we have had few revolutionary advances in acne therapy, the major one being oral isotretinoin, which was first brought to market in 1982. We are still utilizing many of the same therapeutic agents that I used back when I was treated for acne. A few new topical compounds have emerged, such as dapsone and clascoterone, and a narrow-spectrum tetracycline agent, sarecycline, also was developed. These agents do represent important advances with some specific benefits. There have been many major improvements in drug delivery formulations, including several vehicle technologies that allow augmented skin tolerability, increased efficacy, and improved stability, allowing for combination therapy products containing 2 or 3 active ingredients. A recent example is the first triple-combination topical acne therapy with excellent supporting data on speed of onset, efficacy, and safety.1
Technological advances also have aided in the development of modified- or extended-release formulations of oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline and minocycline, which allow for reduced adverse effects and lower daily dosages. Lidose formulations of isotretinoin have circumvented the need for concurrent ingestion of a high-fat meal to facilitate its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract (as required with conventional formulations). Many hours also have been spent on delivery devices and vehicles such as pumps, foams, and aqueous-based gels. Let us not forget the efforts and myriad products directed at skin care, cosmeceuticals, and physical devices (lasers and lights) for acne. Regardless of the above, we have not seen the monumental therapeutic and research revolution for acne that we have experienced more recently with biologic agents, Janus kinase inhibitors, and other modes of action for many common disease states such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hidradenitis suppurativa, prurigo nodularis, and chronic spontaneous urticaria.
Unfortunately, the slow development of advances in treatments for acne has been compounded further by the widespread availability of generic equivalents of most topical and oral therapies along with several over-the- counter topical medications. The expanded skin care and cosmeceutical product world has further diluted the perceived value of topical prescription therapies for acne. The marked difficulty in achieving and sustaining total clearance of acne, with the exception of many individuals treated with oral isotretinoin, results in many patients searching for other options, often through sources beyond dermatology practices (eg, the internet). While some of these sources may provide valid suggestions, they often are not truly substantiated by valid clinical research and are not formally regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration.
All of the above, in addition to the barriers to medication coverage put in place by third-party organizations such as pharmacy benefit managers, have contributed to the extreme slowdown in the development of new prescription therapies for acne. What this leads me to believe is that until there is a true meeting of the minds of all stakeholders on policies that facilitate access to both established and newly available acne therapies, there will be an enduring diminished incentive to support the development of newer acne treatments that will continue to spiral progressively downward. Some research on acne will always continue, such as the search for an acne vaccine and cutaneous microbiome alterations that are in progress.2,3 However, I do not see much happening in the foreseeable future. I am not inherently a pessimist or a “prophet of doom,” so I sincerely hope I am wrong.
How did I develop a strong interest in acne and rosacea? Interest on a personal level was with me throughout my adolescence and post-teen years as I suffered with very severe facial acne from ages 13 through 23 (1967-1977). I was sometimes called “pizza face” in high school, and biweekly trips to a dermatology office that always had a packed waiting room were of little help that I could appreciate visibly. Six straight years of extractions, intralesional injections, draining of fluctuant cysts, UVC light treatments, oral tetracycline, irritating topical formulations of benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin, and topical sulfacetamide-sulfur products resulted in minimal improvement. However, maybe all of this did something to what was happening underneath the skin surface, as I have no residual acne scars. I do recall vividly that I walked the halls in high school and college consistently affected by a very red face from the topical agents and smelling like rotten eggs from the topical sulfur application. I fortunately handled it well emotionally and socially, for which I am very thankful. Many people affected with acne do not.
In dermatology, I have always had a strong interest in pathophysiology and therapeutics, rooted I am sure in my background as a pharmacist. Although I was always interested in acne therapy, I was fully captivated by a presentation given by Dr. Jim Leyden many years ago at a small meeting in Myrtle Beach, South Carolina. He brought the subject of acne to life in a way that more than grabbed my complete attention and ignited an interest in learning everything I could about it. Over time, I was fortunate enough to work alongside Dr. Leyden and many other household names in acne at meetings and publications to further education on one of the most common disease states seen in ambulatory dermatology practices worldwide. The rest is history, leading to almost 4 decades of work in acne on many levels in dermatology, all being efforts that I am grateful for.
What I have observed to date is that we have had few revolutionary advances in acne therapy, the major one being oral isotretinoin, which was first brought to market in 1982. We are still utilizing many of the same therapeutic agents that I used back when I was treated for acne. A few new topical compounds have emerged, such as dapsone and clascoterone, and a narrow-spectrum tetracycline agent, sarecycline, also was developed. These agents do represent important advances with some specific benefits. There have been many major improvements in drug delivery formulations, including several vehicle technologies that allow augmented skin tolerability, increased efficacy, and improved stability, allowing for combination therapy products containing 2 or 3 active ingredients. A recent example is the first triple-combination topical acne therapy with excellent supporting data on speed of onset, efficacy, and safety.1
Technological advances also have aided in the development of modified- or extended-release formulations of oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline and minocycline, which allow for reduced adverse effects and lower daily dosages. Lidose formulations of isotretinoin have circumvented the need for concurrent ingestion of a high-fat meal to facilitate its absorption in the gastrointestinal tract (as required with conventional formulations). Many hours also have been spent on delivery devices and vehicles such as pumps, foams, and aqueous-based gels. Let us not forget the efforts and myriad products directed at skin care, cosmeceuticals, and physical devices (lasers and lights) for acne. Regardless of the above, we have not seen the monumental therapeutic and research revolution for acne that we have experienced more recently with biologic agents, Janus kinase inhibitors, and other modes of action for many common disease states such as atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, hidradenitis suppurativa, prurigo nodularis, and chronic spontaneous urticaria.
Unfortunately, the slow development of advances in treatments for acne has been compounded further by the widespread availability of generic equivalents of most topical and oral therapies along with several over-the- counter topical medications. The expanded skin care and cosmeceutical product world has further diluted the perceived value of topical prescription therapies for acne. The marked difficulty in achieving and sustaining total clearance of acne, with the exception of many individuals treated with oral isotretinoin, results in many patients searching for other options, often through sources beyond dermatology practices (eg, the internet). While some of these sources may provide valid suggestions, they often are not truly substantiated by valid clinical research and are not formally regulated by the US Food and Drug Administration.
All of the above, in addition to the barriers to medication coverage put in place by third-party organizations such as pharmacy benefit managers, have contributed to the extreme slowdown in the development of new prescription therapies for acne. What this leads me to believe is that until there is a true meeting of the minds of all stakeholders on policies that facilitate access to both established and newly available acne therapies, there will be an enduring diminished incentive to support the development of newer acne treatments that will continue to spiral progressively downward. Some research on acne will always continue, such as the search for an acne vaccine and cutaneous microbiome alterations that are in progress.2,3 However, I do not see much happening in the foreseeable future. I am not inherently a pessimist or a “prophet of doom,” so I sincerely hope I am wrong.
- Stein Gold L, Baldwin H, Kircik LH, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose clindamycin phosphate 1.2%, benzoyl peroxide 3.1%, and adapalene 0.15% gel for moderate-to-severe acne: a randomized phase II study of the first triple-combination drug. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:93-104. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00650-3
- Keshari S, Kumar M, Balasubramaniam A, et al. Prospects of acne vaccines targeting secreted virulence factors of Cutibacterium acnes. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019;18:433-437. doi:10.1080/14760584
- Dreno B, Dekio I, Baldwin H, et al. Acne microbiome: from phyla to phylotypes. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:657- 664. doi:10.1111/jdv.19540 .2019.1593830
- Stein Gold L, Baldwin H, Kircik LH, et al. Efficacy and safety of a fixed-dose clindamycin phosphate 1.2%, benzoyl peroxide 3.1%, and adapalene 0.15% gel for moderate-to-severe acne: a randomized phase II study of the first triple-combination drug. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2022;23:93-104. doi:10.1007/s40257-021-00650-3
- Keshari S, Kumar M, Balasubramaniam A, et al. Prospects of acne vaccines targeting secreted virulence factors of Cutibacterium acnes. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2019;18:433-437. doi:10.1080/14760584
- Dreno B, Dekio I, Baldwin H, et al. Acne microbiome: from phyla to phylotypes. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2024;38:657- 664. doi:10.1111/jdv.19540 .2019.1593830
Can We Successfully Adapt to Changes in Direction and Support for Acne?
Can We Successfully Adapt to Changes in Direction and Support for Acne?
Experiencing DDW as an Early Career GI
Dear Friends,
Like many readers, I just returned from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) in San Diego, California. For the first time in my early career, my experience was not just overwhelming and exhausting. Before, I wanted to do everything – lectures, posters, meetings with friends, prospective research collaborators, and more! This year, I acknowledged that instead of spreading myself thin and not fully engaging, I made a focused daily schedule mixed with productivity and social events, selecting only what was most important to me at this time in my career. This time, after DDW, instead of giving in to my inner introvert and holing myself in my house for a week to recover, I am invigorated by what I learned and the people I met. I can’t wait to see what’s to come next year!
In this issue’s “In Focus”, Dr. Evan Dellon describes his diagnostic approach, including a clear history, endoscopic evaluation with biopsy, and ruling out other causes of esophageal eosinophilia. He emphasizes that treatment should target both inflammation and fibrostenosis and reviews the guidelines and evidence behind first-line treatments, surveillance, and long-term maintenance.
In the second of a two-part series in the “Short Clinical Review” section, Dr. Christopher Vélez, Dr. Rosa L. Yu, and Dr. Jennifer Dimino discuss care for patients with disorders of brain-gut interaction from historically marginalized communities. They highlight ways to improve care for these patients in day-to-day clinical practice.
The transition from trainee to a practicing gastroenterologist may bring with it responsibilities of giving feedback to trainees and/or colleagues to improve. In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Michelle Baliss and Dr. Christine Hachem give practical tips on how best to deliver feedback, with a focus on creating time, building rapport, bidirectional communication, and more.
Lastly, in the “Finance/Legal” section, John S. Gardner, a financial advisor, guides trainees and early career gastroenterologists through estate planning – why it’s important, how to do it effectively, and long-term benefits to starting early.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: the first case of eosinophilic esophagitis was only first described in 1978 and became a distinct entity in the early 1990s.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Like many readers, I just returned from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) in San Diego, California. For the first time in my early career, my experience was not just overwhelming and exhausting. Before, I wanted to do everything – lectures, posters, meetings with friends, prospective research collaborators, and more! This year, I acknowledged that instead of spreading myself thin and not fully engaging, I made a focused daily schedule mixed with productivity and social events, selecting only what was most important to me at this time in my career. This time, after DDW, instead of giving in to my inner introvert and holing myself in my house for a week to recover, I am invigorated by what I learned and the people I met. I can’t wait to see what’s to come next year!
In this issue’s “In Focus”, Dr. Evan Dellon describes his diagnostic approach, including a clear history, endoscopic evaluation with biopsy, and ruling out other causes of esophageal eosinophilia. He emphasizes that treatment should target both inflammation and fibrostenosis and reviews the guidelines and evidence behind first-line treatments, surveillance, and long-term maintenance.
In the second of a two-part series in the “Short Clinical Review” section, Dr. Christopher Vélez, Dr. Rosa L. Yu, and Dr. Jennifer Dimino discuss care for patients with disorders of brain-gut interaction from historically marginalized communities. They highlight ways to improve care for these patients in day-to-day clinical practice.
The transition from trainee to a practicing gastroenterologist may bring with it responsibilities of giving feedback to trainees and/or colleagues to improve. In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Michelle Baliss and Dr. Christine Hachem give practical tips on how best to deliver feedback, with a focus on creating time, building rapport, bidirectional communication, and more.
Lastly, in the “Finance/Legal” section, John S. Gardner, a financial advisor, guides trainees and early career gastroenterologists through estate planning – why it’s important, how to do it effectively, and long-term benefits to starting early.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: the first case of eosinophilic esophagitis was only first described in 1978 and became a distinct entity in the early 1990s.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Dear Friends,
Like many readers, I just returned from Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) in San Diego, California. For the first time in my early career, my experience was not just overwhelming and exhausting. Before, I wanted to do everything – lectures, posters, meetings with friends, prospective research collaborators, and more! This year, I acknowledged that instead of spreading myself thin and not fully engaging, I made a focused daily schedule mixed with productivity and social events, selecting only what was most important to me at this time in my career. This time, after DDW, instead of giving in to my inner introvert and holing myself in my house for a week to recover, I am invigorated by what I learned and the people I met. I can’t wait to see what’s to come next year!
In this issue’s “In Focus”, Dr. Evan Dellon describes his diagnostic approach, including a clear history, endoscopic evaluation with biopsy, and ruling out other causes of esophageal eosinophilia. He emphasizes that treatment should target both inflammation and fibrostenosis and reviews the guidelines and evidence behind first-line treatments, surveillance, and long-term maintenance.
In the second of a two-part series in the “Short Clinical Review” section, Dr. Christopher Vélez, Dr. Rosa L. Yu, and Dr. Jennifer Dimino discuss care for patients with disorders of brain-gut interaction from historically marginalized communities. They highlight ways to improve care for these patients in day-to-day clinical practice.
The transition from trainee to a practicing gastroenterologist may bring with it responsibilities of giving feedback to trainees and/or colleagues to improve. In the “Early Career” section, Dr. Michelle Baliss and Dr. Christine Hachem give practical tips on how best to deliver feedback, with a focus on creating time, building rapport, bidirectional communication, and more.
Lastly, in the “Finance/Legal” section, John S. Gardner, a financial advisor, guides trainees and early career gastroenterologists through estate planning – why it’s important, how to do it effectively, and long-term benefits to starting early.
If you are interested in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (tjudy@wustl.edu) or Danielle Kiefer (dkiefer@gastro.org), Communications/Managing Editor of TNG.
Until next time, I leave you with a historical fun fact because we would not be where we are now without appreciating where we were: the first case of eosinophilic esophagitis was only first described in 1978 and became a distinct entity in the early 1990s.
Yours truly,
Judy A. Trieu, MD, MPH
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant Professor of Medicine
Interventional Endoscopy, Division of Gastroenterology
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
Practical Tips on Delivering Feedback to Trainees and Colleagues
Feedback is the purposeful practice of offering constructive, goal-directed input rooted in the power of observation and behavioral assessment. Healthcare inherently fosters a broad range of interactions among people with unique insights, and feedback can naturally emerge from this milieu. In medical training, feedback is an indispensable element that personalizes the learning process and drives the professional development of physicians through all career stages.
If delivered effectively, feedback can strengthen the relationship between the evaluator and recipient, promote self-reflection, and enhance motivation. As such, it has the potential to impact us and those we serve for a lifetime. Feedback has been invaluable to our growth as clinicians and has been embedded into our roles as educators. However, Here, we provide some “tried and true” practical tips on delivering feedback to trainees and co-workers and on navigating potential barriers based on lessons learned.
Barriers to Effective Feedback
- Time: Feedback is predicated on observation over time and consideration of repetitive processes rather than isolated events. Perhaps the most challenging factor faced by both parties is that of time constraints, leading to limited ability to engage and build rapport.
- Fear: Hesitancy by evaluators to provide feedback in fear of negative impacts on the recipient’s morale or rapport can lead them to shy away from personalized corrective feedback strategies and choose to rely on written evaluations or generic advice.
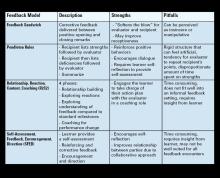
- Varying approaches: Feedback strategies have evolved from unidirectional, critique-based, hierarchical practices that emphasize the evaluator’s skills to models that prioritize the recipient’s goals and participation (see Table 1). Traditionally employed feedback models such as the “Feedback Sandwich” or the “Pendleton Rules” are criticized because of a lack of proven benefit on performance, recipient goal prioritization, and open communication.1,2 Studies showing incongruent perceptions of feedback adequacy between trainees and faculty further support the need for recipient-focused strategies.3 Recognition of the foundational role of the reciprocal learner-teacher alliance in feedback integration inspired newer feedback models, such as the “R2C2” and the “Self-Assessment, Feedback, Encouragement, Direction.”4,5
But which way is best? With increasing abundance and complexity of feedback frameworks, selecting an approach can feel overwhelming and impractical. A generic “one-size-fits-all” strategy or avoidance of feedback altogether can be detrimental. Structured feedback models can also lead to rigid, inauthentic interactions. Below, we suggest a more practical approach through our tips that unifies the common themes of various feedback models and embeds them into daily practice habits while leaving room for personalization.
Our Practical Feedback Tips
Tip 1: Set the scene: Create a positive feedback culture
Proactively creating a culture in which feedback is embedded and encouraged is perhaps the most important step. Priming both parties for feedback clarifies intent, increases receptiveness, and paves the way for growth and open communication. It also prevents the misinterpretation of unexpected feedback as an expression of disapproval. To do this, start by regularly stating your intentions at the start of every experience. Explicitly expressing your vision for mutual learning, bidirectional feedback, and growth in your respective roles attaches a positive intention to feedback. Providing a reminder that we are all works in progress and acknowledging this on a regular basis sets the stage for structured growth opportunities.
Scheduling future feedback encounters from the start maintains accountability and prevents feedback from being perceived as the consequence of a particular behavior. The number and timing of feedback sessions can be customized to the duration of the working relationship, generally allowing enough time for a second interaction (at the end of each week, halfway point, etc.).
Tip 2: Build rapport
Increasing clinical workloads and pressure to teach in time-constrained settings often results in insufficient time to engage in conversation and trust building. However, a foundational relationship is an essential precursor to meaningful feedback. Ramani et al. state that “relationships, not recipes, are more likely to promote feedback that has an impact on learner performance and ultimately patient care.”6 Building this rapport can begin by dedicating a few minutes (before/during rounds, between cases) to exchange information about career interests, hobbies, favorite restaurants, etc. This “small talk” is the beginning of a two-way exchange that ultimately develops into more meaningful exchanges.
In our experience, this simple step is impactful and fulfilling to both parties. This is also a good time for shared vulnerability by talking about what you are currently working on or have worked on at their stage to affirm that feedback is a continuous part of professional development and not a reflection of how far they are from competence at a given point in time.
Tip 3: Consider Timing, assess readiness, and preschedule sessions
Lack of attention to timing can hinder feedback acceptance. We suggest adhering to delivering positive feedback publicly and corrective feedback privately (“Praise in public, perfect in private”). This reinforces positive behaviors, increases motivation, and minimizes demoralization. Prolonged delays between the observed behavior and feedback can decrease its relevance. Conversely, delivering feedback too soon after an emotionally charged experience can be perceived as blame. Pre-designated times for feedback can minimize the guesswork and maintain your accountability for giving feedback without inadvertently linking it to one particular behavior. If the recipient does not appear to be in a state to receive feedback at the predesignated time, you can pivot to a “check-in” session to show support and strengthen rapport.
Tip 4: Customize to the learner and set shared goals
Diversity in backgrounds, perspectives, and personalities can impact how people perceive their own performances and experience feedback. Given the profound impact of sociocultural factors on feedback assimilation, maintaining the recipient and their goals at the core of performance evaluations is key to feedback acceptance.
A. Trainees
We suggest starting by introducing the idea of feedback as a partnership and something you feel privileged to do to help them achieve mutual goals. It helps to ask them to use the first day to get oriented with the experience, general expectations, challenges they expect to encounter, and their feedback goals. Tailoring your feedback to their goals creates a sense of shared purpose which increases motivation. Encouraging them to develop their own strategies allows them to play an active role in their growth. Giving them the opportunity to share their perceived strengths and deficiencies provides you with valuable information regarding their insight and ability to self-evaluate. This can help you predict their readiness for your feedback and to tailor your approach when there is a mismatch.
Examples:
- Medical student: Start with “What do you think you are doing well?” and “What do you think you need to work on?” Build on their response with encouragement and empathy. This helps make them more deliberate with what they work on because being a medical student can be overwhelming and can feel as though they have everything to work on.
- Resident/Fellow: By this point, trainees usually have an increased awareness of their strengths and deficiencies. Your questions can then be more specific, giving them autonomy over their learning, such as “What are some of the things you are working on that you want me to give you feedback on this week?” This makes them more aware, intentional, and receptive to your feedback because it is framed as something that they sought out.
B. Colleagues/Staff
Unlike the training environment in which feedback is built-in, giving feedback to co-workers requires you to establish a feedback-conducive environment and to develop a more in-depth understanding of coworkers’ personalities. Similar strategies can be applied, such as proactively setting the scene for open communication, scheduling check-ins, demonstrating receptiveness to feedback, and investing in trust-building.
Longer working relationships allow for strong foundational connections that make feedback less threatening. Personality assessment testing like Myers-Briggs Type Indicator or DiSC Assessment can aid in tailoring feedback to different individuals.7,8 An analytical thinker may appreciate direct, data-driven feedback. Relationship-oriented individuals might respond better to softer, encouragement-based approaches. Always maintain shared goals at the center of your interactions and consider collaborative opportunities such as quality improvement projects. This can improve your working relationship in a constructive way without casting blame.
Tip 5: Work on delivery: Bidirectional communication and body language
Non-verbal cues can have a profound impact on how your feedback is interpreted and on the recipient’s comfort to engage in conversation. Sitting down, making eye contact, nodding, and avoiding closed-off body posture can project support and feel less judgmental. Creating a safe and non-distracted environment with privacy can make them feel valued. Use motivating, respectful language focused on directly observed behaviors rather than personal attributes or second-hand reports.
Remember that focusing on repetitive patterns is likely more helpful than isolated incidents. Validate their hard work and give them a global idea of where they stand before diving into individual behaviors. Encourage their participation and empower them to suggest changes they plan to implement. Conclude by having them summarize their action plan to give them ownership and to verify that your feedback was interpreted as you intended. Thank them for being a part of the process, as it does take a partnership for feedback to be effective.
Tip 6: Be open to feedback
Demonstrating your willingness to accept and act on feedback reinforces a positive culture where feedback is normalized and valued. After an unintended outcome, initiate a two-way conversation and ask their input on anything they wish you would have done differently. This reaffirms your commitment to maintaining culture that does not revolve around one-sided critiques. Frequently soliciting feedback about your feedback skills can also guide you to adapt your approach and to recognize any ineffective feedback practices.
Tip 7: When things don’t go as planned
Receiving feedback, no matter how thoughtfully it is delivered, can be an emotionally-charged experience ending in hurt feelings. This happens because of misinterpretation of feedback as an indicator of inadequacy, heightened awareness of underlying insecurities, sociocultural or personal circumstances, frustration with oneself, needing additional guidance, or being caught off-guard by the assessment.
The evaluator should always acknowledge the recipient’s feelings, show compassion, and allow time for processing. When they are ready to talk, it is important to help reframe the recipients’ mindsets to recognize that feedback is not personal or defining and is not a “one and done” reflection of whether they have “made it.” Instead, it is a continual process that we benefit from through all career stages. Again, shared vulnerability can help to normalize feedback and maintain open dialogue. Setting an opportunity for a future check-in can reinforce support and lead to a more productive conversation after they have had time to process.
Conclusion
Effective feedback delivery is an invaluable skill that can result in meaningful goal-directed changes while strengthening professional relationships. Given the complexity of feedback interactions and the many factors that influence its acceptance, no single approach is suitable for all recipients and frequent adaptation of the approach is essential.
In our experience, adhering to these general overarching feedback principles (see Figure 1) has allowed us to have more successful interactions with trainees and colleagues.
Dr. Baliss is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. Dr. Hachem is director of the Division of Gastroenterology and Digestive Health at Intermountain Medical, Sandy, Utah. Both authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Parkes J, et al. Feedback sandwiches affect perceptions but not performance. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013 Aug. doi:10.1007/s10459-012-9377-9.
2. van de Ridder JMM and Wijnen-Meijer M. Pendleton’s Rules: A Mini Review of a Feedback Method. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2023 May. doi: 10.34297/AJBSR.2023.19.002542.
3. Sender Liberman A, et al. Surgery residents and attending surgeons have different perceptions of feedback. Med Teach. 2005 Aug. doi: 10.1080/0142590500129183.
4. Sargeant J, et al. R2C2 in Action: Testing an Evidence-Based Model to Facilitate Feedback and Coaching in Residency. J Grad Med Educ. 2017 Apr. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00398.1.
5. Liakos W, et al. Frameworks for Effective Feedback in Health Professions Education. Acad Med. 2023 May. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004884.
6. Ramani S, et al. Feedback Redefined: Principles and Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 May. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04874-2.
7. Woods RA and Hill PB. Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2022 Sept. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554596/
8. Slowikowski MK. Using the DISC behavioral instrument to guide leadership and communication. AORN J. 2005 Nov. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)60276-7.
Feedback is the purposeful practice of offering constructive, goal-directed input rooted in the power of observation and behavioral assessment. Healthcare inherently fosters a broad range of interactions among people with unique insights, and feedback can naturally emerge from this milieu. In medical training, feedback is an indispensable element that personalizes the learning process and drives the professional development of physicians through all career stages.
If delivered effectively, feedback can strengthen the relationship between the evaluator and recipient, promote self-reflection, and enhance motivation. As such, it has the potential to impact us and those we serve for a lifetime. Feedback has been invaluable to our growth as clinicians and has been embedded into our roles as educators. However, Here, we provide some “tried and true” practical tips on delivering feedback to trainees and co-workers and on navigating potential barriers based on lessons learned.
Barriers to Effective Feedback
- Time: Feedback is predicated on observation over time and consideration of repetitive processes rather than isolated events. Perhaps the most challenging factor faced by both parties is that of time constraints, leading to limited ability to engage and build rapport.
- Fear: Hesitancy by evaluators to provide feedback in fear of negative impacts on the recipient’s morale or rapport can lead them to shy away from personalized corrective feedback strategies and choose to rely on written evaluations or generic advice.
- Varying approaches: Feedback strategies have evolved from unidirectional, critique-based, hierarchical practices that emphasize the evaluator’s skills to models that prioritize the recipient’s goals and participation (see Table 1). Traditionally employed feedback models such as the “Feedback Sandwich” or the “Pendleton Rules” are criticized because of a lack of proven benefit on performance, recipient goal prioritization, and open communication.1,2 Studies showing incongruent perceptions of feedback adequacy between trainees and faculty further support the need for recipient-focused strategies.3 Recognition of the foundational role of the reciprocal learner-teacher alliance in feedback integration inspired newer feedback models, such as the “R2C2” and the “Self-Assessment, Feedback, Encouragement, Direction.”4,5
But which way is best? With increasing abundance and complexity of feedback frameworks, selecting an approach can feel overwhelming and impractical. A generic “one-size-fits-all” strategy or avoidance of feedback altogether can be detrimental. Structured feedback models can also lead to rigid, inauthentic interactions. Below, we suggest a more practical approach through our tips that unifies the common themes of various feedback models and embeds them into daily practice habits while leaving room for personalization.
Our Practical Feedback Tips
Tip 1: Set the scene: Create a positive feedback culture
Proactively creating a culture in which feedback is embedded and encouraged is perhaps the most important step. Priming both parties for feedback clarifies intent, increases receptiveness, and paves the way for growth and open communication. It also prevents the misinterpretation of unexpected feedback as an expression of disapproval. To do this, start by regularly stating your intentions at the start of every experience. Explicitly expressing your vision for mutual learning, bidirectional feedback, and growth in your respective roles attaches a positive intention to feedback. Providing a reminder that we are all works in progress and acknowledging this on a regular basis sets the stage for structured growth opportunities.
Scheduling future feedback encounters from the start maintains accountability and prevents feedback from being perceived as the consequence of a particular behavior. The number and timing of feedback sessions can be customized to the duration of the working relationship, generally allowing enough time for a second interaction (at the end of each week, halfway point, etc.).
Tip 2: Build rapport
Increasing clinical workloads and pressure to teach in time-constrained settings often results in insufficient time to engage in conversation and trust building. However, a foundational relationship is an essential precursor to meaningful feedback. Ramani et al. state that “relationships, not recipes, are more likely to promote feedback that has an impact on learner performance and ultimately patient care.”6 Building this rapport can begin by dedicating a few minutes (before/during rounds, between cases) to exchange information about career interests, hobbies, favorite restaurants, etc. This “small talk” is the beginning of a two-way exchange that ultimately develops into more meaningful exchanges.
In our experience, this simple step is impactful and fulfilling to both parties. This is also a good time for shared vulnerability by talking about what you are currently working on or have worked on at their stage to affirm that feedback is a continuous part of professional development and not a reflection of how far they are from competence at a given point in time.
Tip 3: Consider Timing, assess readiness, and preschedule sessions
Lack of attention to timing can hinder feedback acceptance. We suggest adhering to delivering positive feedback publicly and corrective feedback privately (“Praise in public, perfect in private”). This reinforces positive behaviors, increases motivation, and minimizes demoralization. Prolonged delays between the observed behavior and feedback can decrease its relevance. Conversely, delivering feedback too soon after an emotionally charged experience can be perceived as blame. Pre-designated times for feedback can minimize the guesswork and maintain your accountability for giving feedback without inadvertently linking it to one particular behavior. If the recipient does not appear to be in a state to receive feedback at the predesignated time, you can pivot to a “check-in” session to show support and strengthen rapport.
Tip 4: Customize to the learner and set shared goals
Diversity in backgrounds, perspectives, and personalities can impact how people perceive their own performances and experience feedback. Given the profound impact of sociocultural factors on feedback assimilation, maintaining the recipient and their goals at the core of performance evaluations is key to feedback acceptance.
A. Trainees
We suggest starting by introducing the idea of feedback as a partnership and something you feel privileged to do to help them achieve mutual goals. It helps to ask them to use the first day to get oriented with the experience, general expectations, challenges they expect to encounter, and their feedback goals. Tailoring your feedback to their goals creates a sense of shared purpose which increases motivation. Encouraging them to develop their own strategies allows them to play an active role in their growth. Giving them the opportunity to share their perceived strengths and deficiencies provides you with valuable information regarding their insight and ability to self-evaluate. This can help you predict their readiness for your feedback and to tailor your approach when there is a mismatch.
Examples:
- Medical student: Start with “What do you think you are doing well?” and “What do you think you need to work on?” Build on their response with encouragement and empathy. This helps make them more deliberate with what they work on because being a medical student can be overwhelming and can feel as though they have everything to work on.
- Resident/Fellow: By this point, trainees usually have an increased awareness of their strengths and deficiencies. Your questions can then be more specific, giving them autonomy over their learning, such as “What are some of the things you are working on that you want me to give you feedback on this week?” This makes them more aware, intentional, and receptive to your feedback because it is framed as something that they sought out.
B. Colleagues/Staff
Unlike the training environment in which feedback is built-in, giving feedback to co-workers requires you to establish a feedback-conducive environment and to develop a more in-depth understanding of coworkers’ personalities. Similar strategies can be applied, such as proactively setting the scene for open communication, scheduling check-ins, demonstrating receptiveness to feedback, and investing in trust-building.
Longer working relationships allow for strong foundational connections that make feedback less threatening. Personality assessment testing like Myers-Briggs Type Indicator or DiSC Assessment can aid in tailoring feedback to different individuals.7,8 An analytical thinker may appreciate direct, data-driven feedback. Relationship-oriented individuals might respond better to softer, encouragement-based approaches. Always maintain shared goals at the center of your interactions and consider collaborative opportunities such as quality improvement projects. This can improve your working relationship in a constructive way without casting blame.
Tip 5: Work on delivery: Bidirectional communication and body language
Non-verbal cues can have a profound impact on how your feedback is interpreted and on the recipient’s comfort to engage in conversation. Sitting down, making eye contact, nodding, and avoiding closed-off body posture can project support and feel less judgmental. Creating a safe and non-distracted environment with privacy can make them feel valued. Use motivating, respectful language focused on directly observed behaviors rather than personal attributes or second-hand reports.
Remember that focusing on repetitive patterns is likely more helpful than isolated incidents. Validate their hard work and give them a global idea of where they stand before diving into individual behaviors. Encourage their participation and empower them to suggest changes they plan to implement. Conclude by having them summarize their action plan to give them ownership and to verify that your feedback was interpreted as you intended. Thank them for being a part of the process, as it does take a partnership for feedback to be effective.
Tip 6: Be open to feedback
Demonstrating your willingness to accept and act on feedback reinforces a positive culture where feedback is normalized and valued. After an unintended outcome, initiate a two-way conversation and ask their input on anything they wish you would have done differently. This reaffirms your commitment to maintaining culture that does not revolve around one-sided critiques. Frequently soliciting feedback about your feedback skills can also guide you to adapt your approach and to recognize any ineffective feedback practices.
Tip 7: When things don’t go as planned
Receiving feedback, no matter how thoughtfully it is delivered, can be an emotionally-charged experience ending in hurt feelings. This happens because of misinterpretation of feedback as an indicator of inadequacy, heightened awareness of underlying insecurities, sociocultural or personal circumstances, frustration with oneself, needing additional guidance, or being caught off-guard by the assessment.
The evaluator should always acknowledge the recipient’s feelings, show compassion, and allow time for processing. When they are ready to talk, it is important to help reframe the recipients’ mindsets to recognize that feedback is not personal or defining and is not a “one and done” reflection of whether they have “made it.” Instead, it is a continual process that we benefit from through all career stages. Again, shared vulnerability can help to normalize feedback and maintain open dialogue. Setting an opportunity for a future check-in can reinforce support and lead to a more productive conversation after they have had time to process.
Conclusion
Effective feedback delivery is an invaluable skill that can result in meaningful goal-directed changes while strengthening professional relationships. Given the complexity of feedback interactions and the many factors that influence its acceptance, no single approach is suitable for all recipients and frequent adaptation of the approach is essential.
In our experience, adhering to these general overarching feedback principles (see Figure 1) has allowed us to have more successful interactions with trainees and colleagues.
Dr. Baliss is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. Dr. Hachem is director of the Division of Gastroenterology and Digestive Health at Intermountain Medical, Sandy, Utah. Both authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Parkes J, et al. Feedback sandwiches affect perceptions but not performance. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013 Aug. doi:10.1007/s10459-012-9377-9.
2. van de Ridder JMM and Wijnen-Meijer M. Pendleton’s Rules: A Mini Review of a Feedback Method. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2023 May. doi: 10.34297/AJBSR.2023.19.002542.
3. Sender Liberman A, et al. Surgery residents and attending surgeons have different perceptions of feedback. Med Teach. 2005 Aug. doi: 10.1080/0142590500129183.
4. Sargeant J, et al. R2C2 in Action: Testing an Evidence-Based Model to Facilitate Feedback and Coaching in Residency. J Grad Med Educ. 2017 Apr. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00398.1.
5. Liakos W, et al. Frameworks for Effective Feedback in Health Professions Education. Acad Med. 2023 May. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004884.
6. Ramani S, et al. Feedback Redefined: Principles and Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 May. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04874-2.
7. Woods RA and Hill PB. Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2022 Sept. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554596/
8. Slowikowski MK. Using the DISC behavioral instrument to guide leadership and communication. AORN J. 2005 Nov. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)60276-7.
Feedback is the purposeful practice of offering constructive, goal-directed input rooted in the power of observation and behavioral assessment. Healthcare inherently fosters a broad range of interactions among people with unique insights, and feedback can naturally emerge from this milieu. In medical training, feedback is an indispensable element that personalizes the learning process and drives the professional development of physicians through all career stages.
If delivered effectively, feedback can strengthen the relationship between the evaluator and recipient, promote self-reflection, and enhance motivation. As such, it has the potential to impact us and those we serve for a lifetime. Feedback has been invaluable to our growth as clinicians and has been embedded into our roles as educators. However, Here, we provide some “tried and true” practical tips on delivering feedback to trainees and co-workers and on navigating potential barriers based on lessons learned.
Barriers to Effective Feedback
- Time: Feedback is predicated on observation over time and consideration of repetitive processes rather than isolated events. Perhaps the most challenging factor faced by both parties is that of time constraints, leading to limited ability to engage and build rapport.
- Fear: Hesitancy by evaluators to provide feedback in fear of negative impacts on the recipient’s morale or rapport can lead them to shy away from personalized corrective feedback strategies and choose to rely on written evaluations or generic advice.
- Varying approaches: Feedback strategies have evolved from unidirectional, critique-based, hierarchical practices that emphasize the evaluator’s skills to models that prioritize the recipient’s goals and participation (see Table 1). Traditionally employed feedback models such as the “Feedback Sandwich” or the “Pendleton Rules” are criticized because of a lack of proven benefit on performance, recipient goal prioritization, and open communication.1,2 Studies showing incongruent perceptions of feedback adequacy between trainees and faculty further support the need for recipient-focused strategies.3 Recognition of the foundational role of the reciprocal learner-teacher alliance in feedback integration inspired newer feedback models, such as the “R2C2” and the “Self-Assessment, Feedback, Encouragement, Direction.”4,5
But which way is best? With increasing abundance and complexity of feedback frameworks, selecting an approach can feel overwhelming and impractical. A generic “one-size-fits-all” strategy or avoidance of feedback altogether can be detrimental. Structured feedback models can also lead to rigid, inauthentic interactions. Below, we suggest a more practical approach through our tips that unifies the common themes of various feedback models and embeds them into daily practice habits while leaving room for personalization.
Our Practical Feedback Tips
Tip 1: Set the scene: Create a positive feedback culture
Proactively creating a culture in which feedback is embedded and encouraged is perhaps the most important step. Priming both parties for feedback clarifies intent, increases receptiveness, and paves the way for growth and open communication. It also prevents the misinterpretation of unexpected feedback as an expression of disapproval. To do this, start by regularly stating your intentions at the start of every experience. Explicitly expressing your vision for mutual learning, bidirectional feedback, and growth in your respective roles attaches a positive intention to feedback. Providing a reminder that we are all works in progress and acknowledging this on a regular basis sets the stage for structured growth opportunities.
Scheduling future feedback encounters from the start maintains accountability and prevents feedback from being perceived as the consequence of a particular behavior. The number and timing of feedback sessions can be customized to the duration of the working relationship, generally allowing enough time for a second interaction (at the end of each week, halfway point, etc.).
Tip 2: Build rapport
Increasing clinical workloads and pressure to teach in time-constrained settings often results in insufficient time to engage in conversation and trust building. However, a foundational relationship is an essential precursor to meaningful feedback. Ramani et al. state that “relationships, not recipes, are more likely to promote feedback that has an impact on learner performance and ultimately patient care.”6 Building this rapport can begin by dedicating a few minutes (before/during rounds, between cases) to exchange information about career interests, hobbies, favorite restaurants, etc. This “small talk” is the beginning of a two-way exchange that ultimately develops into more meaningful exchanges.
In our experience, this simple step is impactful and fulfilling to both parties. This is also a good time for shared vulnerability by talking about what you are currently working on or have worked on at their stage to affirm that feedback is a continuous part of professional development and not a reflection of how far they are from competence at a given point in time.
Tip 3: Consider Timing, assess readiness, and preschedule sessions
Lack of attention to timing can hinder feedback acceptance. We suggest adhering to delivering positive feedback publicly and corrective feedback privately (“Praise in public, perfect in private”). This reinforces positive behaviors, increases motivation, and minimizes demoralization. Prolonged delays between the observed behavior and feedback can decrease its relevance. Conversely, delivering feedback too soon after an emotionally charged experience can be perceived as blame. Pre-designated times for feedback can minimize the guesswork and maintain your accountability for giving feedback without inadvertently linking it to one particular behavior. If the recipient does not appear to be in a state to receive feedback at the predesignated time, you can pivot to a “check-in” session to show support and strengthen rapport.
Tip 4: Customize to the learner and set shared goals
Diversity in backgrounds, perspectives, and personalities can impact how people perceive their own performances and experience feedback. Given the profound impact of sociocultural factors on feedback assimilation, maintaining the recipient and their goals at the core of performance evaluations is key to feedback acceptance.
A. Trainees
We suggest starting by introducing the idea of feedback as a partnership and something you feel privileged to do to help them achieve mutual goals. It helps to ask them to use the first day to get oriented with the experience, general expectations, challenges they expect to encounter, and their feedback goals. Tailoring your feedback to their goals creates a sense of shared purpose which increases motivation. Encouraging them to develop their own strategies allows them to play an active role in their growth. Giving them the opportunity to share their perceived strengths and deficiencies provides you with valuable information regarding their insight and ability to self-evaluate. This can help you predict their readiness for your feedback and to tailor your approach when there is a mismatch.
Examples:
- Medical student: Start with “What do you think you are doing well?” and “What do you think you need to work on?” Build on their response with encouragement and empathy. This helps make them more deliberate with what they work on because being a medical student can be overwhelming and can feel as though they have everything to work on.
- Resident/Fellow: By this point, trainees usually have an increased awareness of their strengths and deficiencies. Your questions can then be more specific, giving them autonomy over their learning, such as “What are some of the things you are working on that you want me to give you feedback on this week?” This makes them more aware, intentional, and receptive to your feedback because it is framed as something that they sought out.
B. Colleagues/Staff
Unlike the training environment in which feedback is built-in, giving feedback to co-workers requires you to establish a feedback-conducive environment and to develop a more in-depth understanding of coworkers’ personalities. Similar strategies can be applied, such as proactively setting the scene for open communication, scheduling check-ins, demonstrating receptiveness to feedback, and investing in trust-building.
Longer working relationships allow for strong foundational connections that make feedback less threatening. Personality assessment testing like Myers-Briggs Type Indicator or DiSC Assessment can aid in tailoring feedback to different individuals.7,8 An analytical thinker may appreciate direct, data-driven feedback. Relationship-oriented individuals might respond better to softer, encouragement-based approaches. Always maintain shared goals at the center of your interactions and consider collaborative opportunities such as quality improvement projects. This can improve your working relationship in a constructive way without casting blame.
Tip 5: Work on delivery: Bidirectional communication and body language
Non-verbal cues can have a profound impact on how your feedback is interpreted and on the recipient’s comfort to engage in conversation. Sitting down, making eye contact, nodding, and avoiding closed-off body posture can project support and feel less judgmental. Creating a safe and non-distracted environment with privacy can make them feel valued. Use motivating, respectful language focused on directly observed behaviors rather than personal attributes or second-hand reports.
Remember that focusing on repetitive patterns is likely more helpful than isolated incidents. Validate their hard work and give them a global idea of where they stand before diving into individual behaviors. Encourage their participation and empower them to suggest changes they plan to implement. Conclude by having them summarize their action plan to give them ownership and to verify that your feedback was interpreted as you intended. Thank them for being a part of the process, as it does take a partnership for feedback to be effective.
Tip 6: Be open to feedback
Demonstrating your willingness to accept and act on feedback reinforces a positive culture where feedback is normalized and valued. After an unintended outcome, initiate a two-way conversation and ask their input on anything they wish you would have done differently. This reaffirms your commitment to maintaining culture that does not revolve around one-sided critiques. Frequently soliciting feedback about your feedback skills can also guide you to adapt your approach and to recognize any ineffective feedback practices.
Tip 7: When things don’t go as planned
Receiving feedback, no matter how thoughtfully it is delivered, can be an emotionally-charged experience ending in hurt feelings. This happens because of misinterpretation of feedback as an indicator of inadequacy, heightened awareness of underlying insecurities, sociocultural or personal circumstances, frustration with oneself, needing additional guidance, or being caught off-guard by the assessment.
The evaluator should always acknowledge the recipient’s feelings, show compassion, and allow time for processing. When they are ready to talk, it is important to help reframe the recipients’ mindsets to recognize that feedback is not personal or defining and is not a “one and done” reflection of whether they have “made it.” Instead, it is a continual process that we benefit from through all career stages. Again, shared vulnerability can help to normalize feedback and maintain open dialogue. Setting an opportunity for a future check-in can reinforce support and lead to a more productive conversation after they have had time to process.
Conclusion
Effective feedback delivery is an invaluable skill that can result in meaningful goal-directed changes while strengthening professional relationships. Given the complexity of feedback interactions and the many factors that influence its acceptance, no single approach is suitable for all recipients and frequent adaptation of the approach is essential.
In our experience, adhering to these general overarching feedback principles (see Figure 1) has allowed us to have more successful interactions with trainees and colleagues.
Dr. Baliss is based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri. Dr. Hachem is director of the Division of Gastroenterology and Digestive Health at Intermountain Medical, Sandy, Utah. Both authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
1. Parkes J, et al. Feedback sandwiches affect perceptions but not performance. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2013 Aug. doi:10.1007/s10459-012-9377-9.
2. van de Ridder JMM and Wijnen-Meijer M. Pendleton’s Rules: A Mini Review of a Feedback Method. Am J Biomed Sci & Res. 2023 May. doi: 10.34297/AJBSR.2023.19.002542.
3. Sender Liberman A, et al. Surgery residents and attending surgeons have different perceptions of feedback. Med Teach. 2005 Aug. doi: 10.1080/0142590500129183.
4. Sargeant J, et al. R2C2 in Action: Testing an Evidence-Based Model to Facilitate Feedback and Coaching in Residency. J Grad Med Educ. 2017 Apr. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00398.1.
5. Liakos W, et al. Frameworks for Effective Feedback in Health Professions Education. Acad Med. 2023 May. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000004884.
6. Ramani S, et al. Feedback Redefined: Principles and Practice. J Gen Intern Med. 2019 May. doi: 10.1007/s11606-019-04874-2.
7. Woods RA and Hill PB. Myers-Briggs Type Indicator. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. 2022 Sept. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554596/
8. Slowikowski MK. Using the DISC behavioral instrument to guide leadership and communication. AORN J. 2005 Nov. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2092(06)60276-7.
Vital Partners in GI Care
Demand for specialized GI care has skyrocketed in recent years, eclipsing the supply of gastroenterologists and impairing patient access to high-quality GI care, particularly in rural and other underserved areas. In this environment,
Across specialties, APPs are estimated to constitute roughly a third of the US clinical workforce, and demand is only growing. A June 2024 MGMA Stat poll found that 63% of medical groups planned to add new APP roles in the next year. As the GI APP workforce grows, so too will demand for advanced training tailored to the APP role.
AGA has invested heavily in professional development opportunities for NPs and PAs, in recognition of their vital role in providing high-quality GI care. The newly formed AGA NPPA Task Force, co-chaired by Abigail Meyers (who we featured in GIHN’s April issue) and Kimberly Kearns, works closely with the Education and Training Committee to develop education programs to meet the specific needs of NPs and PAs, and advocate for more APP involvement in AGA programming. One example of this is AGA’s 2025 Principles of GI for the NP and PA course, which will be held in Chicago in early August – I encourage you to spread the word and support your APP colleagues in getting involved in these important initiatives as our vital partners in GI care delivery.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we present the exciting results of the BOSS trial, showing no survival difference between regular and at need surveillance for Barrett’s esophagus, suggesting that at need endoscopy may be a safe alternative for low-risk patients. Continuing our coverage of potentially practice-changing research from DDW, we highlight another recent RCT challenging the use of papillary sphincterotomy as a treatment for pancreas divisum.
In our July Member Spotlight, Eric Shah, MD, MBA (University of Michigan), a past AGA Research Scholar Award recipient, highlights how this critical research support aided him in his journey to develop a now FDA-approved point-of care screening tool used to evaluate patients with chronic constipation for pelvic floor dysfunction during a routine clinic visit. In our quarterly Perspectives column, Dr. David Wan (a GI hospitalist) and Dr. Zeyed Metwalli (an interventional radiologist) discuss best practices in management of lower GI bleeding. We hope you have a restful summer!
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Demand for specialized GI care has skyrocketed in recent years, eclipsing the supply of gastroenterologists and impairing patient access to high-quality GI care, particularly in rural and other underserved areas. In this environment,
Across specialties, APPs are estimated to constitute roughly a third of the US clinical workforce, and demand is only growing. A June 2024 MGMA Stat poll found that 63% of medical groups planned to add new APP roles in the next year. As the GI APP workforce grows, so too will demand for advanced training tailored to the APP role.
AGA has invested heavily in professional development opportunities for NPs and PAs, in recognition of their vital role in providing high-quality GI care. The newly formed AGA NPPA Task Force, co-chaired by Abigail Meyers (who we featured in GIHN’s April issue) and Kimberly Kearns, works closely with the Education and Training Committee to develop education programs to meet the specific needs of NPs and PAs, and advocate for more APP involvement in AGA programming. One example of this is AGA’s 2025 Principles of GI for the NP and PA course, which will be held in Chicago in early August – I encourage you to spread the word and support your APP colleagues in getting involved in these important initiatives as our vital partners in GI care delivery.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we present the exciting results of the BOSS trial, showing no survival difference between regular and at need surveillance for Barrett’s esophagus, suggesting that at need endoscopy may be a safe alternative for low-risk patients. Continuing our coverage of potentially practice-changing research from DDW, we highlight another recent RCT challenging the use of papillary sphincterotomy as a treatment for pancreas divisum.
In our July Member Spotlight, Eric Shah, MD, MBA (University of Michigan), a past AGA Research Scholar Award recipient, highlights how this critical research support aided him in his journey to develop a now FDA-approved point-of care screening tool used to evaluate patients with chronic constipation for pelvic floor dysfunction during a routine clinic visit. In our quarterly Perspectives column, Dr. David Wan (a GI hospitalist) and Dr. Zeyed Metwalli (an interventional radiologist) discuss best practices in management of lower GI bleeding. We hope you have a restful summer!
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
Demand for specialized GI care has skyrocketed in recent years, eclipsing the supply of gastroenterologists and impairing patient access to high-quality GI care, particularly in rural and other underserved areas. In this environment,
Across specialties, APPs are estimated to constitute roughly a third of the US clinical workforce, and demand is only growing. A June 2024 MGMA Stat poll found that 63% of medical groups planned to add new APP roles in the next year. As the GI APP workforce grows, so too will demand for advanced training tailored to the APP role.
AGA has invested heavily in professional development opportunities for NPs and PAs, in recognition of their vital role in providing high-quality GI care. The newly formed AGA NPPA Task Force, co-chaired by Abigail Meyers (who we featured in GIHN’s April issue) and Kimberly Kearns, works closely with the Education and Training Committee to develop education programs to meet the specific needs of NPs and PAs, and advocate for more APP involvement in AGA programming. One example of this is AGA’s 2025 Principles of GI for the NP and PA course, which will be held in Chicago in early August – I encourage you to spread the word and support your APP colleagues in getting involved in these important initiatives as our vital partners in GI care delivery.
In this month’s issue of GIHN, we present the exciting results of the BOSS trial, showing no survival difference between regular and at need surveillance for Barrett’s esophagus, suggesting that at need endoscopy may be a safe alternative for low-risk patients. Continuing our coverage of potentially practice-changing research from DDW, we highlight another recent RCT challenging the use of papillary sphincterotomy as a treatment for pancreas divisum.
In our July Member Spotlight, Eric Shah, MD, MBA (University of Michigan), a past AGA Research Scholar Award recipient, highlights how this critical research support aided him in his journey to develop a now FDA-approved point-of care screening tool used to evaluate patients with chronic constipation for pelvic floor dysfunction during a routine clinic visit. In our quarterly Perspectives column, Dr. David Wan (a GI hospitalist) and Dr. Zeyed Metwalli (an interventional radiologist) discuss best practices in management of lower GI bleeding. We hope you have a restful summer!
Megan A. Adams, MD, JD, MSc
Editor in Chief
The Essential Guide to Estate Planning for Physicians: Securing Your Legacy and Protecting Your Wealth
As a physician, you’ve spent years building a career that not only provides financial security for your family but also allows you to make a meaningful impact in your community. However, without a comprehensive estate plan in place, much of what you’ve worked so hard to build may not be preserved according to your wishes.
Many physicians delay estate planning, assuming it’s something to consider later in life. However, the most successful estate plans are those that are established early and evolve over time. Proper planning ensures that your assets are protected, your loved ones are provided for, and your legacy is preserved in the most tax-efficient and legally-sound manner possible.1
This article explores why estate planning is particularly crucial for physicians, the key elements of a strong estate plan, and how beginning early can create long-term financial advantages.
Why Estate Planning Matters for Physicians
Physicians are in a unique financial position compared to many other professionals. With high earning potential, specialized assets, and significant liability exposure, their estate planning needs differ from those of the average individual. A well-structured estate plan not only facilitates the smooth transfer of wealth but also protects assets from excessive taxation, legal complications, and potential risks such as malpractice claims.
1. High Net-Worth Considerations
Physicians often accumulate substantial wealth over time. Without a clear estate plan, your estate could face excessive taxation, with a large portion of your assets potentially going to the government rather than your heirs. Estate taxes, probate costs, and legal fees can significantly erode your legacy if not properly planned for.
2. Asset Protection from Liability Risks
Unlike most professionals, physicians are at a higher risk of litigation. A comprehensive estate plan can incorporate asset protection strategies, such as irrevocable trusts, family limited partnerships, or liability insurance, to shield your wealth from lawsuits or creditor claims.
3. Family and Generational Wealth Planning
Many physicians prioritize ensuring their family’s financial stability. Whether you want to provide for your spouse, children, or even charitable causes, estate planning allows you to dictate how your wealth is distributed. Establishing trusts for your children or grandchildren can help manage how and when they receive their inheritance, preventing mismanagement and ensuring financial responsibility.
4. Business and Practice Continuity
If you own a medical practice, succession planning should be part of your estate plan. Without clear directives, the future of your practice may be uncertain in the event of your passing or incapacitation. A well-drafted estate plan provides a roadmap for ownership transition, ensuring continuity for patients, employees, and business partners.
Key Elements of an Effective Estate Plan
Every estate plan should be customized based on your financial situation, goals, and family dynamics. However, certain fundamental components apply to nearly all high-net-worth individuals, including physicians.
1. Revocable Living Trusts
A revocable living trust allows you to manage your assets during your lifetime while providing a clear path for distribution after your passing. Unlike a will, a trust helps your estate avoid probate, ensuring a smoother and more private transition of wealth. You maintain control over your assets while also establishing clear rules for distribution, particularly useful if you have minor children or complex family structures.2
2. Irrevocable Trusts for Asset Protection
For physicians concerned about lawsuits or estate tax exposure, irrevocable trusts can offer robust asset protection. Since assets placed in these trusts are no longer legally owned by you, they are shielded from creditors and legal claims while also reducing your taxable estate.2
3. Powers of Attorney and Healthcare Directives
Estate planning isn’t just about what happens after your passing—it’s also about protecting you and your family if you become incapacitated. A durable power of attorney allows a trusted individual to manage your financial affairs, while a healthcare directive ensures your medical decisions align with your wishes.3
4. Life Insurance Planning
Life insurance is an essential estate planning tool for physicians, providing liquidity to cover estate taxes, debts, or income replacement for your family. A properly structured life insurance trust can help ensure that policy proceeds remain outside of your taxable estate while being efficiently distributed according to your wishes.4
5. Business Succession Planning
If you own a medical practice, a well-designed succession plan can ensure that your business continues to operate smoothly in your absence. This may involve buy-sell agreements, key-person insurance, or identifying a successor to take over your role.5
The Long-Term Benefits of Early Estate Planning
Estate planning is not a one-time event—it’s a process that should evolve with your career, financial growth, and family dynamics. The earlier you begin, the more control you have over your financial future. Here’s why starting early is a strategic advantage:
1. Maximizing Tax Efficiency
Many estate planning strategies, such as gifting assets or establishing irrevocable trusts, are most effective when implemented over time. By spreading out wealth transfers and taking advantage of annual gift exclusions, you can significantly reduce estate tax liability while maintaining financial security.
2. Adjusting for Life Changes
Your financial situation and family needs will change over the years. Marriages, births, career advancements, and new investments all impact your estate planning needs. By starting early, you can make gradual adjustments rather than facing an overwhelming restructuring later in life.1
3. Ensuring Asset Protection Strategies Are in Place
Many asset protection strategies require time to be effective. For instance, certain types of trusts must be in place for a number of years before they fully shield assets from legal claims. Delaying planning could leave your wealth unnecessarily exposed.
4. Creating a Legacy Beyond Wealth
Estate planning is not just about finances—it’s about legacy. Whether you want to support a charitable cause, endow a scholarship, or establish a foundation, early planning gives you the ability to shape your long-term impact.
5. Adapt to Ever Changing Legislation
Estate planning needs to be adaptable. The federal government can change the estate tax exemption at any time; this was even a topic of the last election cycle. Early planning allows you to implement necessary changes throughout your life to minimize estate taxes. At present, unless new policy is enacted, the exemption per individual will reduce by half in 2026 (see Figure 1).
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Today
The complexity of physician finances—ranging from high income and significant assets to legal risks—makes individualized estate planning an absolute necessity.
By taking proactive steps today, you can maximize tax efficiency, safeguard your assets, and ensure your wishes are carried out without unnecessary delays or legal battles. Working with a financial advisor and estate planning attorney who understands the unique needs of physicians can help you craft a plan that aligns with your goals and evolves as your career progresses.
Mr. Gardner is a financial advisor at Lifetime Financial Growth, LLC, in Columbus, Ohio, one of the largest privately held wealth management firms in the country. John has had a passion for finance since his early years in college when his tennis coach introduced him. He also has a passion for helping physicians, as his wife is a gastroenterologist at Ohio State University. He reports no relevant disclosures relevant to this article. If you have additional questions, please contact John at 740-403-4891 or john_s_gardner@glic.com.
References
1. The Law Offices of Diron Rutty, LLC. https://www.dironruttyllc.com/reasons-to-start-estate-planning-early/.
2. Physician Side Gigs. https://www.physiciansidegigs.com/estateplanning.
3. Afshar, A & MacBeth, S. https://www.schwabe.com/publication/estate-planning-for-physicians-why-its-important-and-how-to-get-started/. December 2024.
4. Skeeles, JC. https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/ep-1. July 2012.
5. Rosenfeld, J. Physician estate planning guide. Medical Economics. 2022 Nov. https://www.medicaleconomics.com/view/physician-estate-planning-guide.
As a physician, you’ve spent years building a career that not only provides financial security for your family but also allows you to make a meaningful impact in your community. However, without a comprehensive estate plan in place, much of what you’ve worked so hard to build may not be preserved according to your wishes.
Many physicians delay estate planning, assuming it’s something to consider later in life. However, the most successful estate plans are those that are established early and evolve over time. Proper planning ensures that your assets are protected, your loved ones are provided for, and your legacy is preserved in the most tax-efficient and legally-sound manner possible.1
This article explores why estate planning is particularly crucial for physicians, the key elements of a strong estate plan, and how beginning early can create long-term financial advantages.
Why Estate Planning Matters for Physicians
Physicians are in a unique financial position compared to many other professionals. With high earning potential, specialized assets, and significant liability exposure, their estate planning needs differ from those of the average individual. A well-structured estate plan not only facilitates the smooth transfer of wealth but also protects assets from excessive taxation, legal complications, and potential risks such as malpractice claims.
1. High Net-Worth Considerations
Physicians often accumulate substantial wealth over time. Without a clear estate plan, your estate could face excessive taxation, with a large portion of your assets potentially going to the government rather than your heirs. Estate taxes, probate costs, and legal fees can significantly erode your legacy if not properly planned for.
2. Asset Protection from Liability Risks
Unlike most professionals, physicians are at a higher risk of litigation. A comprehensive estate plan can incorporate asset protection strategies, such as irrevocable trusts, family limited partnerships, or liability insurance, to shield your wealth from lawsuits or creditor claims.
3. Family and Generational Wealth Planning
Many physicians prioritize ensuring their family’s financial stability. Whether you want to provide for your spouse, children, or even charitable causes, estate planning allows you to dictate how your wealth is distributed. Establishing trusts for your children or grandchildren can help manage how and when they receive their inheritance, preventing mismanagement and ensuring financial responsibility.
4. Business and Practice Continuity
If you own a medical practice, succession planning should be part of your estate plan. Without clear directives, the future of your practice may be uncertain in the event of your passing or incapacitation. A well-drafted estate plan provides a roadmap for ownership transition, ensuring continuity for patients, employees, and business partners.
Key Elements of an Effective Estate Plan
Every estate plan should be customized based on your financial situation, goals, and family dynamics. However, certain fundamental components apply to nearly all high-net-worth individuals, including physicians.
1. Revocable Living Trusts
A revocable living trust allows you to manage your assets during your lifetime while providing a clear path for distribution after your passing. Unlike a will, a trust helps your estate avoid probate, ensuring a smoother and more private transition of wealth. You maintain control over your assets while also establishing clear rules for distribution, particularly useful if you have minor children or complex family structures.2
2. Irrevocable Trusts for Asset Protection
For physicians concerned about lawsuits or estate tax exposure, irrevocable trusts can offer robust asset protection. Since assets placed in these trusts are no longer legally owned by you, they are shielded from creditors and legal claims while also reducing your taxable estate.2
3. Powers of Attorney and Healthcare Directives
Estate planning isn’t just about what happens after your passing—it’s also about protecting you and your family if you become incapacitated. A durable power of attorney allows a trusted individual to manage your financial affairs, while a healthcare directive ensures your medical decisions align with your wishes.3
4. Life Insurance Planning
Life insurance is an essential estate planning tool for physicians, providing liquidity to cover estate taxes, debts, or income replacement for your family. A properly structured life insurance trust can help ensure that policy proceeds remain outside of your taxable estate while being efficiently distributed according to your wishes.4
5. Business Succession Planning
If you own a medical practice, a well-designed succession plan can ensure that your business continues to operate smoothly in your absence. This may involve buy-sell agreements, key-person insurance, or identifying a successor to take over your role.5
The Long-Term Benefits of Early Estate Planning
Estate planning is not a one-time event—it’s a process that should evolve with your career, financial growth, and family dynamics. The earlier you begin, the more control you have over your financial future. Here’s why starting early is a strategic advantage:
1. Maximizing Tax Efficiency
Many estate planning strategies, such as gifting assets or establishing irrevocable trusts, are most effective when implemented over time. By spreading out wealth transfers and taking advantage of annual gift exclusions, you can significantly reduce estate tax liability while maintaining financial security.
2. Adjusting for Life Changes
Your financial situation and family needs will change over the years. Marriages, births, career advancements, and new investments all impact your estate planning needs. By starting early, you can make gradual adjustments rather than facing an overwhelming restructuring later in life.1
3. Ensuring Asset Protection Strategies Are in Place
Many asset protection strategies require time to be effective. For instance, certain types of trusts must be in place for a number of years before they fully shield assets from legal claims. Delaying planning could leave your wealth unnecessarily exposed.
4. Creating a Legacy Beyond Wealth
Estate planning is not just about finances—it’s about legacy. Whether you want to support a charitable cause, endow a scholarship, or establish a foundation, early planning gives you the ability to shape your long-term impact.
5. Adapt to Ever Changing Legislation
Estate planning needs to be adaptable. The federal government can change the estate tax exemption at any time; this was even a topic of the last election cycle. Early planning allows you to implement necessary changes throughout your life to minimize estate taxes. At present, unless new policy is enacted, the exemption per individual will reduce by half in 2026 (see Figure 1).
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Today
The complexity of physician finances—ranging from high income and significant assets to legal risks—makes individualized estate planning an absolute necessity.
By taking proactive steps today, you can maximize tax efficiency, safeguard your assets, and ensure your wishes are carried out without unnecessary delays or legal battles. Working with a financial advisor and estate planning attorney who understands the unique needs of physicians can help you craft a plan that aligns with your goals and evolves as your career progresses.
Mr. Gardner is a financial advisor at Lifetime Financial Growth, LLC, in Columbus, Ohio, one of the largest privately held wealth management firms in the country. John has had a passion for finance since his early years in college when his tennis coach introduced him. He also has a passion for helping physicians, as his wife is a gastroenterologist at Ohio State University. He reports no relevant disclosures relevant to this article. If you have additional questions, please contact John at 740-403-4891 or john_s_gardner@glic.com.
References
1. The Law Offices of Diron Rutty, LLC. https://www.dironruttyllc.com/reasons-to-start-estate-planning-early/.
2. Physician Side Gigs. https://www.physiciansidegigs.com/estateplanning.
3. Afshar, A & MacBeth, S. https://www.schwabe.com/publication/estate-planning-for-physicians-why-its-important-and-how-to-get-started/. December 2024.
4. Skeeles, JC. https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/ep-1. July 2012.
5. Rosenfeld, J. Physician estate planning guide. Medical Economics. 2022 Nov. https://www.medicaleconomics.com/view/physician-estate-planning-guide.
As a physician, you’ve spent years building a career that not only provides financial security for your family but also allows you to make a meaningful impact in your community. However, without a comprehensive estate plan in place, much of what you’ve worked so hard to build may not be preserved according to your wishes.
Many physicians delay estate planning, assuming it’s something to consider later in life. However, the most successful estate plans are those that are established early and evolve over time. Proper planning ensures that your assets are protected, your loved ones are provided for, and your legacy is preserved in the most tax-efficient and legally-sound manner possible.1
This article explores why estate planning is particularly crucial for physicians, the key elements of a strong estate plan, and how beginning early can create long-term financial advantages.
Why Estate Planning Matters for Physicians
Physicians are in a unique financial position compared to many other professionals. With high earning potential, specialized assets, and significant liability exposure, their estate planning needs differ from those of the average individual. A well-structured estate plan not only facilitates the smooth transfer of wealth but also protects assets from excessive taxation, legal complications, and potential risks such as malpractice claims.
1. High Net-Worth Considerations
Physicians often accumulate substantial wealth over time. Without a clear estate plan, your estate could face excessive taxation, with a large portion of your assets potentially going to the government rather than your heirs. Estate taxes, probate costs, and legal fees can significantly erode your legacy if not properly planned for.
2. Asset Protection from Liability Risks
Unlike most professionals, physicians are at a higher risk of litigation. A comprehensive estate plan can incorporate asset protection strategies, such as irrevocable trusts, family limited partnerships, or liability insurance, to shield your wealth from lawsuits or creditor claims.
3. Family and Generational Wealth Planning
Many physicians prioritize ensuring their family’s financial stability. Whether you want to provide for your spouse, children, or even charitable causes, estate planning allows you to dictate how your wealth is distributed. Establishing trusts for your children or grandchildren can help manage how and when they receive their inheritance, preventing mismanagement and ensuring financial responsibility.
4. Business and Practice Continuity
If you own a medical practice, succession planning should be part of your estate plan. Without clear directives, the future of your practice may be uncertain in the event of your passing or incapacitation. A well-drafted estate plan provides a roadmap for ownership transition, ensuring continuity for patients, employees, and business partners.
Key Elements of an Effective Estate Plan
Every estate plan should be customized based on your financial situation, goals, and family dynamics. However, certain fundamental components apply to nearly all high-net-worth individuals, including physicians.
1. Revocable Living Trusts
A revocable living trust allows you to manage your assets during your lifetime while providing a clear path for distribution after your passing. Unlike a will, a trust helps your estate avoid probate, ensuring a smoother and more private transition of wealth. You maintain control over your assets while also establishing clear rules for distribution, particularly useful if you have minor children or complex family structures.2
2. Irrevocable Trusts for Asset Protection
For physicians concerned about lawsuits or estate tax exposure, irrevocable trusts can offer robust asset protection. Since assets placed in these trusts are no longer legally owned by you, they are shielded from creditors and legal claims while also reducing your taxable estate.2
3. Powers of Attorney and Healthcare Directives
Estate planning isn’t just about what happens after your passing—it’s also about protecting you and your family if you become incapacitated. A durable power of attorney allows a trusted individual to manage your financial affairs, while a healthcare directive ensures your medical decisions align with your wishes.3
4. Life Insurance Planning
Life insurance is an essential estate planning tool for physicians, providing liquidity to cover estate taxes, debts, or income replacement for your family. A properly structured life insurance trust can help ensure that policy proceeds remain outside of your taxable estate while being efficiently distributed according to your wishes.4
5. Business Succession Planning
If you own a medical practice, a well-designed succession plan can ensure that your business continues to operate smoothly in your absence. This may involve buy-sell agreements, key-person insurance, or identifying a successor to take over your role.5
The Long-Term Benefits of Early Estate Planning
Estate planning is not a one-time event—it’s a process that should evolve with your career, financial growth, and family dynamics. The earlier you begin, the more control you have over your financial future. Here’s why starting early is a strategic advantage:
1. Maximizing Tax Efficiency
Many estate planning strategies, such as gifting assets or establishing irrevocable trusts, are most effective when implemented over time. By spreading out wealth transfers and taking advantage of annual gift exclusions, you can significantly reduce estate tax liability while maintaining financial security.
2. Adjusting for Life Changes
Your financial situation and family needs will change over the years. Marriages, births, career advancements, and new investments all impact your estate planning needs. By starting early, you can make gradual adjustments rather than facing an overwhelming restructuring later in life.1
3. Ensuring Asset Protection Strategies Are in Place
Many asset protection strategies require time to be effective. For instance, certain types of trusts must be in place for a number of years before they fully shield assets from legal claims. Delaying planning could leave your wealth unnecessarily exposed.
4. Creating a Legacy Beyond Wealth
Estate planning is not just about finances—it’s about legacy. Whether you want to support a charitable cause, endow a scholarship, or establish a foundation, early planning gives you the ability to shape your long-term impact.
5. Adapt to Ever Changing Legislation
Estate planning needs to be adaptable. The federal government can change the estate tax exemption at any time; this was even a topic of the last election cycle. Early planning allows you to implement necessary changes throughout your life to minimize estate taxes. At present, unless new policy is enacted, the exemption per individual will reduce by half in 2026 (see Figure 1).
Final Thoughts: Taking Action Today
The complexity of physician finances—ranging from high income and significant assets to legal risks—makes individualized estate planning an absolute necessity.
By taking proactive steps today, you can maximize tax efficiency, safeguard your assets, and ensure your wishes are carried out without unnecessary delays or legal battles. Working with a financial advisor and estate planning attorney who understands the unique needs of physicians can help you craft a plan that aligns with your goals and evolves as your career progresses.
Mr. Gardner is a financial advisor at Lifetime Financial Growth, LLC, in Columbus, Ohio, one of the largest privately held wealth management firms in the country. John has had a passion for finance since his early years in college when his tennis coach introduced him. He also has a passion for helping physicians, as his wife is a gastroenterologist at Ohio State University. He reports no relevant disclosures relevant to this article. If you have additional questions, please contact John at 740-403-4891 or john_s_gardner@glic.com.
References
1. The Law Offices of Diron Rutty, LLC. https://www.dironruttyllc.com/reasons-to-start-estate-planning-early/.
2. Physician Side Gigs. https://www.physiciansidegigs.com/estateplanning.
3. Afshar, A & MacBeth, S. https://www.schwabe.com/publication/estate-planning-for-physicians-why-its-important-and-how-to-get-started/. December 2024.
4. Skeeles, JC. https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/ep-1. July 2012.
5. Rosenfeld, J. Physician estate planning guide. Medical Economics. 2022 Nov. https://www.medicaleconomics.com/view/physician-estate-planning-guide.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Two Perspectives
Dear colleagues,
: What is the role and optimal timing of colonoscopy? How can we best utilize radiologic studies like CTA or tagged RBC scans? How should we manage patients with recurrent or intermittent bleeding that defies localization?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. David Wan, Dr. Fredella Lee, and Dr. Zeyad Metwalli offer their expert insights on these difficult questions. Dr. Wan, drawing on over 15 years of experience as a GI hospitalist, shares – along with his coauthor Dr. Lee – a pragmatic approach to LGIB based on clinical patterns, evolving data, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Dr. Metwalli provides the interventional radiologist’s perspective, highlighting how angiographic techniques can complement GI management and introducing novel IR strategies for patients with recurrent or elusive bleeding.
We hope their perspectives will offer valuable guidance for your practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Management of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeds: GI Perspective
BY FREDELLA LEE, MD; DAVID WAN, MD
Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) presents unique challenges. Much of this stems from the natural history of diverticular bleeding, the most common etiology of LGIB.
First, while bleeding can be severe, most will spontaneously stop. Second, despite our best efforts with imaging or colonoscopy, finding an intervenable lesion is rare. Third, LGIB has significant rates of rebleeding that are unpredictable.
While serving as a GI hospitalist for 15 years and after managing over 300 cases of LGIB, I often find myself frustrated and colonoscopy feels futile. So how can we rationally approach these patients? We will focus on three clinical questions to develop a framework for LGIB management.
- What is the role and timing for a colonoscopy?
- How do we best utilize radiologic tests?
- How can we prevent recurrent LGIB?
The Role of Colonoscopy
Traditionally, colonoscopy within 24 hours of presentation was recommended. This was based on retrospective cohort data showing higher endoscopic intervention rates and better clinical outcomes. However, this protocol requires patients to drink a significant volume of bowel preparation over a few hours (often requiring an NGT) to achieve clear rectal effluent. Moreover, one needs to mobilize a team (i.e., nurse, technician, anesthesiologist, and gastroenterologist), and find an appropriate location to scope (i.e., ED, ICU, or OR), Understandably, this is challenging, especially overnight. When the therapeutic yield is relatively low, this approach quickly loses enthusiasm.
Importantly, meta-analyses of the randomized controlled trials, have shown that urgent colonoscopies (<24 hours upon presentation), compared to elective colonoscopies (>24 hours upon presentation), do not improve clinical outcomes such as re-bleeding rates, transfusion requirements, mortality, or length of stay. In these studies, the endoscopic intervention rates were 17-34%, however, observational data shows rates of only 8%. In our practice, we will use a clear cap attachment device and water jet irrigation to increase the odds of detecting an active source of bleeding. Colonoscopy has a diagnostic yield of 95% – despite its low therapeutic yield; and while diverticular bleeds constitute up to 64% of cases, one does not want to miss colorectal cancer or other diagnoses. Regardless, there is generally no urgency to perform a colonoscopy. To quote a colleague, Dr. Elizabeth Ross, “there is no such thing as door-to-butt time.”
The Role of Radiology
Given the limits of colonoscopy, can radiographic tests such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) or tagged red blood cell (RBC) scan be helpful? Multiple studies have suggested using CTA as the initial diagnostic test. The advantages of CTAs are:
- Fast, readily available, and does not require a bowel preparation
- If negative, CTAs portend a good prognosis and make it highly unlikely to detect active extravasation on visceral angiography
- If positive, can localize the source of bleed and increase the success of intervention
Whether a positive CTA should be followed with a colonoscopy or visceral angiography remains unclear. Studies show that positive CTAs increase the detection rate of stigmata of recent hemorrhage on colonoscopy. Positive CTAs can also identify a target for embolization by interventional radiology (IR). Though an important caveat is that the success rate of embolization is highest when performed within 90 minutes of a positive CTA. This highlights that if you have IR availability, it is critical to have clear communication, a well-defined protocol, and collaboration among disciplines (i.e., ED, medical team, GI, and IR).
At our institution, we have implemented a CTA-guided protocol for severe LGIB. Those with positive CTAs are referred immediately to IR for embolization. If the embolization is unsuccessful or CTA is negative, the patient will be planned for a non-urgent inpatient colonoscopy. However, our unpublished data and other studies have shown that the overall CTA positivity rates are only between 16-22%. Moreover, one randomized controlled trial comparing CTA versus colonoscopy as an initial test did not show any meaningful difference in clinical outcomes. Thus, the benefit of CTA and the best approach to positive CTAs remains in question.
Lastly, people often ask about the utility of RBC nuclear scans. While they can detect bleeds at a slower rate (as low as 0.1 mL/min) compared to CTA (at least 0.4 mL/min), there are many limitations. RBC scans take time, are not available 24-7, and cannot precisely localize the site of bleeding. Therefore, we rarely recommend them for LGIB.
Approach to Recurrent Diverticular Bleeding
Unfortunately, diverticular bleeding recurs in the hospital 14% of the time and up to 25% at 5 years. When this occurs, is it worthwhile to repeat another colonoscopy or CTA?
Given the lack of clear data, we have adopted a shared decision-making framework with patients. Oftentimes, these patients are older and have significant co-morbidities, and undergoing bowel preparation, anesthesia, and colonoscopy is not trivial. If the patient is stable and prior work-up has excluded pertinent alternative diagnoses other than diverticular bleeding, then we tell patients the chance of finding an intervenable lesion is low and opt for conservative management. Meanwhile, if the patient has persistent, hemodynamically significant bleeding, we recommend a CTA based on the rationale discussed previously.
The most important clinical decision may not be about scoping or obtaining a CTA – it is medication management. If they are taking NSAIDs, they should be discontinued. If antiplatelet or anticoagulation agents were held, they should be restarted promptly in individuals with significant thrombotic risk given studies showing that while rebleeding rates may increase, overall mortality decreases.
In summary, managing LGIB and altering its natural history with either endoscopic or radiographic means is challenging. More studies are needed to guide the optimal approach. Reassuringly, most bleeding self-resolves and patients have good clinical outcomes.
Dr. Lee is a resident physician at New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY. Dr. Wan is associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, N.Y. They declare no conflicts of interest.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: An Interventional Radiologist’s Perspective
BY ZEYAD METWALLI, MD, FSIR
When colonoscopy fails to localize and/or stop lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), catheter angiography has been commonly employed as a tool for both diagnosis and treatment of bleeding with embolization. Nuclear medicine or CT imaging studies can serve as useful adjuncts for confirming active bleeding and localizing the site of bleeding prior to angiography, particularly if this information is not provided by colonoscopy. Provocative mesenteric angiography has also become increasingly popular as a troubleshooting technique in patients with initially negative angiography.
Localization of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Radionuclide technetium-99m-lableled red blood cell scintigraphy (RBCS), also known as tagged RBC scintigraphy, has been in use since the early 1980s for investigation of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. RBCS has a high sensitivity for detection of active bleeding with a theoretical ability to detect bleeding at rates as low as 0.04-0.2 mL/minute.
Imaging protocols vary but should include dynamic images, which may aid in localization of bleeding. The relatively long half-life of the tracer used for imaging allows for delayed imaging 12 to 24 hours after injection. This can be useful to confirm active bleeding, particularly when bleeding is intermittent and is not visible on initial images.
With the advent of computed tomography angiography (CTA), which continues to increase in speed, imaging quality and availability, the use of RBCS for evaluation of LGIB has declined. CTA is quicker to perform than RBCS and allows for detection of bleeding as well as accurate anatomic localization, which can guide interventions.
CTA provides a more comprehensive anatomic evaluation, which can aid in the diagnosis of a wide variety of intra-abdominal issues. Conversely, CTA may be less sensitive than RBCS for detection of slower acute bleeding, detecting bleeding at rates of 0.1-1 mL/min. In addition, intermittent bleeding which has temporarily stopped at the time of CTA may evade detection.
Lastly, CTA may not be appropriate in patients with impaired renal function due to risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with acute kidney injury, which commonly afflicts hospitalized patients with LGIB. Prophylaxis with normal saline hydration should be employed aggressively in patients with impaired renal function, particularly when eGFR is less than 30 mL/minute. Iodinated contrast should be used judiciously in these patients.
In clinical practice, CTA and RBCS have a similar ability to confirm the presence or absence of clinically significant active gastrointestinal bleeding. Given the greater ability to rapidly localize the bleeding site with CTA, this is generally preferred over RBCS unless there is a contraindication to performing CTA, such as severe contrast allergy or high risk for development of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Role of Catheter Angiography and Embolization
Mesenteric angiography is a well-established technique for both detection and treatment of LGIB. Hemodynamic instability and need for packed RBC transfusion increases the likelihood of positive angiography. Limitations include reduced sensitivity for detection of bleeding slower than 0.5-1 mL/minute as well as the intermittent nature of LGIB, which will often resolve spontaneously. Angiography is variably successful in the literature with a diagnostic yield between 40-80%, which encompasses the rate of success in my own practice.
Once bleeding is identified, microcatheter placement within the feeding vessel as close as possible to the site of bleeding is important to ensure treatment efficacy and to limit risk of complications such as non-target embolization and bowel ischemia. Once the feeding vessel is selected with a microcatheter, embolization can be accomplished with a wide variety of tools including metallic coils, liquid embolic agents, and particles. In the treatment of LGIB, liquid embolic agents (e.g., n-butyl cyanoacrylate or NBCA, ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, etc.) and particles should be used judiciously as distal penetration increases the risk of bowel ischemia and procedure-related morbidity. For this reason, metallic coils are often preferred in the treatment of LGIB.
Although the source of bleeding is variable and may include diverticulosis, recent polypectomy, ulcer, tumor or angiodysplasia, the techniques employed are similar. Accurate and distal microcatheter selection is a key driver for successful embolization and minimizing the risk of bowel ischemia. Small intestinal bleeds can be challenging to treat due to the redundant supply of the arterial arcades supplying small bowel and may require occlusion of several branches to achieve hemostasis. This approach must be balanced with the risk of developing ischemia after embolization. Angiodysplasia, a less frequently encountered culprit of LGIB, may also be managed with selective embolization with many reports of successful treatment with liquid embolic agents such as NBCA mixed with ethiodized oil.
Provocative Mesenteric Angiography for Occult Bleeding
When initial angiography in a patient with suspected active LGIB is negative, provocative angiography can be considered to uncover an intermittent bleed. This may be particularly helpful in a patient where active bleeding is confirmed on a prior diagnostic test.
The approach to provocative mesenteric angiography varies by center, and a variety of agents have been used to provoke bleeding including heparin, vasodilators (i.e., nitroglycerin, verapamil, etc.) and thrombolytics (i.e., tPA), often in combination. Thrombolytics can be administered directly into the territory of interest (i.e., superior mesenteric or inferior mesenteric artery) while heparin may be administered systemically or directly into the catheterized artery. Reported success rates for provoking angiographically visible bleeding vary, but most larger series report a 40-50% success rate. The newly detected bleeding can then be treated with either embolization or surgery. A surgeon should be involved and available when provocative angiography is planned should bleeding fail to be controlled by embolization.
In summary, when colonoscopy fails to identify or control lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), imaging techniques such as RBCS and CTA play a crucial role in localizing active bleeding. While RBCS is highly sensitive, especially for intermittent or slow bleeding, CTA offers faster, more detailed anatomical information and is typically preferred unless contraindicated by renal issues or contrast allergies. Catheter-based mesenteric angiography is a well-established method for both diagnosing and treating LGIB, often using metallic coils to minimize complications like bowel ischemia. In cases where initial angiography is negative, provocative angiography – using agents like heparin or thrombolytics – may help unmask intermittent bleeding, allowing for targeted embolization or surgical intervention.
Dr. Metwalli is associate professor in the Department of Interventional Radiology, Division of Diagnostic Imaging, at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
: What is the role and optimal timing of colonoscopy? How can we best utilize radiologic studies like CTA or tagged RBC scans? How should we manage patients with recurrent or intermittent bleeding that defies localization?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. David Wan, Dr. Fredella Lee, and Dr. Zeyad Metwalli offer their expert insights on these difficult questions. Dr. Wan, drawing on over 15 years of experience as a GI hospitalist, shares – along with his coauthor Dr. Lee – a pragmatic approach to LGIB based on clinical patterns, evolving data, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Dr. Metwalli provides the interventional radiologist’s perspective, highlighting how angiographic techniques can complement GI management and introducing novel IR strategies for patients with recurrent or elusive bleeding.
We hope their perspectives will offer valuable guidance for your practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Management of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeds: GI Perspective
BY FREDELLA LEE, MD; DAVID WAN, MD
Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) presents unique challenges. Much of this stems from the natural history of diverticular bleeding, the most common etiology of LGIB.
First, while bleeding can be severe, most will spontaneously stop. Second, despite our best efforts with imaging or colonoscopy, finding an intervenable lesion is rare. Third, LGIB has significant rates of rebleeding that are unpredictable.
While serving as a GI hospitalist for 15 years and after managing over 300 cases of LGIB, I often find myself frustrated and colonoscopy feels futile. So how can we rationally approach these patients? We will focus on three clinical questions to develop a framework for LGIB management.
- What is the role and timing for a colonoscopy?
- How do we best utilize radiologic tests?
- How can we prevent recurrent LGIB?
The Role of Colonoscopy
Traditionally, colonoscopy within 24 hours of presentation was recommended. This was based on retrospective cohort data showing higher endoscopic intervention rates and better clinical outcomes. However, this protocol requires patients to drink a significant volume of bowel preparation over a few hours (often requiring an NGT) to achieve clear rectal effluent. Moreover, one needs to mobilize a team (i.e., nurse, technician, anesthesiologist, and gastroenterologist), and find an appropriate location to scope (i.e., ED, ICU, or OR), Understandably, this is challenging, especially overnight. When the therapeutic yield is relatively low, this approach quickly loses enthusiasm.
Importantly, meta-analyses of the randomized controlled trials, have shown that urgent colonoscopies (<24 hours upon presentation), compared to elective colonoscopies (>24 hours upon presentation), do not improve clinical outcomes such as re-bleeding rates, transfusion requirements, mortality, or length of stay. In these studies, the endoscopic intervention rates were 17-34%, however, observational data shows rates of only 8%. In our practice, we will use a clear cap attachment device and water jet irrigation to increase the odds of detecting an active source of bleeding. Colonoscopy has a diagnostic yield of 95% – despite its low therapeutic yield; and while diverticular bleeds constitute up to 64% of cases, one does not want to miss colorectal cancer or other diagnoses. Regardless, there is generally no urgency to perform a colonoscopy. To quote a colleague, Dr. Elizabeth Ross, “there is no such thing as door-to-butt time.”
The Role of Radiology
Given the limits of colonoscopy, can radiographic tests such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) or tagged red blood cell (RBC) scan be helpful? Multiple studies have suggested using CTA as the initial diagnostic test. The advantages of CTAs are:
- Fast, readily available, and does not require a bowel preparation
- If negative, CTAs portend a good prognosis and make it highly unlikely to detect active extravasation on visceral angiography
- If positive, can localize the source of bleed and increase the success of intervention
Whether a positive CTA should be followed with a colonoscopy or visceral angiography remains unclear. Studies show that positive CTAs increase the detection rate of stigmata of recent hemorrhage on colonoscopy. Positive CTAs can also identify a target for embolization by interventional radiology (IR). Though an important caveat is that the success rate of embolization is highest when performed within 90 minutes of a positive CTA. This highlights that if you have IR availability, it is critical to have clear communication, a well-defined protocol, and collaboration among disciplines (i.e., ED, medical team, GI, and IR).
At our institution, we have implemented a CTA-guided protocol for severe LGIB. Those with positive CTAs are referred immediately to IR for embolization. If the embolization is unsuccessful or CTA is negative, the patient will be planned for a non-urgent inpatient colonoscopy. However, our unpublished data and other studies have shown that the overall CTA positivity rates are only between 16-22%. Moreover, one randomized controlled trial comparing CTA versus colonoscopy as an initial test did not show any meaningful difference in clinical outcomes. Thus, the benefit of CTA and the best approach to positive CTAs remains in question.
Lastly, people often ask about the utility of RBC nuclear scans. While they can detect bleeds at a slower rate (as low as 0.1 mL/min) compared to CTA (at least 0.4 mL/min), there are many limitations. RBC scans take time, are not available 24-7, and cannot precisely localize the site of bleeding. Therefore, we rarely recommend them for LGIB.
Approach to Recurrent Diverticular Bleeding
Unfortunately, diverticular bleeding recurs in the hospital 14% of the time and up to 25% at 5 years. When this occurs, is it worthwhile to repeat another colonoscopy or CTA?
Given the lack of clear data, we have adopted a shared decision-making framework with patients. Oftentimes, these patients are older and have significant co-morbidities, and undergoing bowel preparation, anesthesia, and colonoscopy is not trivial. If the patient is stable and prior work-up has excluded pertinent alternative diagnoses other than diverticular bleeding, then we tell patients the chance of finding an intervenable lesion is low and opt for conservative management. Meanwhile, if the patient has persistent, hemodynamically significant bleeding, we recommend a CTA based on the rationale discussed previously.
The most important clinical decision may not be about scoping or obtaining a CTA – it is medication management. If they are taking NSAIDs, they should be discontinued. If antiplatelet or anticoagulation agents were held, they should be restarted promptly in individuals with significant thrombotic risk given studies showing that while rebleeding rates may increase, overall mortality decreases.
In summary, managing LGIB and altering its natural history with either endoscopic or radiographic means is challenging. More studies are needed to guide the optimal approach. Reassuringly, most bleeding self-resolves and patients have good clinical outcomes.
Dr. Lee is a resident physician at New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY. Dr. Wan is associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, N.Y. They declare no conflicts of interest.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: An Interventional Radiologist’s Perspective
BY ZEYAD METWALLI, MD, FSIR
When colonoscopy fails to localize and/or stop lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), catheter angiography has been commonly employed as a tool for both diagnosis and treatment of bleeding with embolization. Nuclear medicine or CT imaging studies can serve as useful adjuncts for confirming active bleeding and localizing the site of bleeding prior to angiography, particularly if this information is not provided by colonoscopy. Provocative mesenteric angiography has also become increasingly popular as a troubleshooting technique in patients with initially negative angiography.
Localization of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Radionuclide technetium-99m-lableled red blood cell scintigraphy (RBCS), also known as tagged RBC scintigraphy, has been in use since the early 1980s for investigation of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. RBCS has a high sensitivity for detection of active bleeding with a theoretical ability to detect bleeding at rates as low as 0.04-0.2 mL/minute.
Imaging protocols vary but should include dynamic images, which may aid in localization of bleeding. The relatively long half-life of the tracer used for imaging allows for delayed imaging 12 to 24 hours after injection. This can be useful to confirm active bleeding, particularly when bleeding is intermittent and is not visible on initial images.
With the advent of computed tomography angiography (CTA), which continues to increase in speed, imaging quality and availability, the use of RBCS for evaluation of LGIB has declined. CTA is quicker to perform than RBCS and allows for detection of bleeding as well as accurate anatomic localization, which can guide interventions.
CTA provides a more comprehensive anatomic evaluation, which can aid in the diagnosis of a wide variety of intra-abdominal issues. Conversely, CTA may be less sensitive than RBCS for detection of slower acute bleeding, detecting bleeding at rates of 0.1-1 mL/min. In addition, intermittent bleeding which has temporarily stopped at the time of CTA may evade detection.
Lastly, CTA may not be appropriate in patients with impaired renal function due to risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with acute kidney injury, which commonly afflicts hospitalized patients with LGIB. Prophylaxis with normal saline hydration should be employed aggressively in patients with impaired renal function, particularly when eGFR is less than 30 mL/minute. Iodinated contrast should be used judiciously in these patients.
In clinical practice, CTA and RBCS have a similar ability to confirm the presence or absence of clinically significant active gastrointestinal bleeding. Given the greater ability to rapidly localize the bleeding site with CTA, this is generally preferred over RBCS unless there is a contraindication to performing CTA, such as severe contrast allergy or high risk for development of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Role of Catheter Angiography and Embolization
Mesenteric angiography is a well-established technique for both detection and treatment of LGIB. Hemodynamic instability and need for packed RBC transfusion increases the likelihood of positive angiography. Limitations include reduced sensitivity for detection of bleeding slower than 0.5-1 mL/minute as well as the intermittent nature of LGIB, which will often resolve spontaneously. Angiography is variably successful in the literature with a diagnostic yield between 40-80%, which encompasses the rate of success in my own practice.
Once bleeding is identified, microcatheter placement within the feeding vessel as close as possible to the site of bleeding is important to ensure treatment efficacy and to limit risk of complications such as non-target embolization and bowel ischemia. Once the feeding vessel is selected with a microcatheter, embolization can be accomplished with a wide variety of tools including metallic coils, liquid embolic agents, and particles. In the treatment of LGIB, liquid embolic agents (e.g., n-butyl cyanoacrylate or NBCA, ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, etc.) and particles should be used judiciously as distal penetration increases the risk of bowel ischemia and procedure-related morbidity. For this reason, metallic coils are often preferred in the treatment of LGIB.
Although the source of bleeding is variable and may include diverticulosis, recent polypectomy, ulcer, tumor or angiodysplasia, the techniques employed are similar. Accurate and distal microcatheter selection is a key driver for successful embolization and minimizing the risk of bowel ischemia. Small intestinal bleeds can be challenging to treat due to the redundant supply of the arterial arcades supplying small bowel and may require occlusion of several branches to achieve hemostasis. This approach must be balanced with the risk of developing ischemia after embolization. Angiodysplasia, a less frequently encountered culprit of LGIB, may also be managed with selective embolization with many reports of successful treatment with liquid embolic agents such as NBCA mixed with ethiodized oil.
Provocative Mesenteric Angiography for Occult Bleeding
When initial angiography in a patient with suspected active LGIB is negative, provocative angiography can be considered to uncover an intermittent bleed. This may be particularly helpful in a patient where active bleeding is confirmed on a prior diagnostic test.
The approach to provocative mesenteric angiography varies by center, and a variety of agents have been used to provoke bleeding including heparin, vasodilators (i.e., nitroglycerin, verapamil, etc.) and thrombolytics (i.e., tPA), often in combination. Thrombolytics can be administered directly into the territory of interest (i.e., superior mesenteric or inferior mesenteric artery) while heparin may be administered systemically or directly into the catheterized artery. Reported success rates for provoking angiographically visible bleeding vary, but most larger series report a 40-50% success rate. The newly detected bleeding can then be treated with either embolization or surgery. A surgeon should be involved and available when provocative angiography is planned should bleeding fail to be controlled by embolization.
In summary, when colonoscopy fails to identify or control lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), imaging techniques such as RBCS and CTA play a crucial role in localizing active bleeding. While RBCS is highly sensitive, especially for intermittent or slow bleeding, CTA offers faster, more detailed anatomical information and is typically preferred unless contraindicated by renal issues or contrast allergies. Catheter-based mesenteric angiography is a well-established method for both diagnosing and treating LGIB, often using metallic coils to minimize complications like bowel ischemia. In cases where initial angiography is negative, provocative angiography – using agents like heparin or thrombolytics – may help unmask intermittent bleeding, allowing for targeted embolization or surgical intervention.
Dr. Metwalli is associate professor in the Department of Interventional Radiology, Division of Diagnostic Imaging, at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Dear colleagues,
: What is the role and optimal timing of colonoscopy? How can we best utilize radiologic studies like CTA or tagged RBC scans? How should we manage patients with recurrent or intermittent bleeding that defies localization?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. David Wan, Dr. Fredella Lee, and Dr. Zeyad Metwalli offer their expert insights on these difficult questions. Dr. Wan, drawing on over 15 years of experience as a GI hospitalist, shares – along with his coauthor Dr. Lee – a pragmatic approach to LGIB based on clinical patterns, evolving data, and multidisciplinary collaboration. Dr. Metwalli provides the interventional radiologist’s perspective, highlighting how angiographic techniques can complement GI management and introducing novel IR strategies for patients with recurrent or elusive bleeding.
We hope their perspectives will offer valuable guidance for your practice. Join the conversation on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
Management of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeds: GI Perspective
BY FREDELLA LEE, MD; DAVID WAN, MD
Acute lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB) presents unique challenges. Much of this stems from the natural history of diverticular bleeding, the most common etiology of LGIB.
First, while bleeding can be severe, most will spontaneously stop. Second, despite our best efforts with imaging or colonoscopy, finding an intervenable lesion is rare. Third, LGIB has significant rates of rebleeding that are unpredictable.
While serving as a GI hospitalist for 15 years and after managing over 300 cases of LGIB, I often find myself frustrated and colonoscopy feels futile. So how can we rationally approach these patients? We will focus on three clinical questions to develop a framework for LGIB management.
- What is the role and timing for a colonoscopy?
- How do we best utilize radiologic tests?
- How can we prevent recurrent LGIB?
The Role of Colonoscopy
Traditionally, colonoscopy within 24 hours of presentation was recommended. This was based on retrospective cohort data showing higher endoscopic intervention rates and better clinical outcomes. However, this protocol requires patients to drink a significant volume of bowel preparation over a few hours (often requiring an NGT) to achieve clear rectal effluent. Moreover, one needs to mobilize a team (i.e., nurse, technician, anesthesiologist, and gastroenterologist), and find an appropriate location to scope (i.e., ED, ICU, or OR), Understandably, this is challenging, especially overnight. When the therapeutic yield is relatively low, this approach quickly loses enthusiasm.
Importantly, meta-analyses of the randomized controlled trials, have shown that urgent colonoscopies (<24 hours upon presentation), compared to elective colonoscopies (>24 hours upon presentation), do not improve clinical outcomes such as re-bleeding rates, transfusion requirements, mortality, or length of stay. In these studies, the endoscopic intervention rates were 17-34%, however, observational data shows rates of only 8%. In our practice, we will use a clear cap attachment device and water jet irrigation to increase the odds of detecting an active source of bleeding. Colonoscopy has a diagnostic yield of 95% – despite its low therapeutic yield; and while diverticular bleeds constitute up to 64% of cases, one does not want to miss colorectal cancer or other diagnoses. Regardless, there is generally no urgency to perform a colonoscopy. To quote a colleague, Dr. Elizabeth Ross, “there is no such thing as door-to-butt time.”
The Role of Radiology
Given the limits of colonoscopy, can radiographic tests such as computed tomography angiography (CTA) or tagged red blood cell (RBC) scan be helpful? Multiple studies have suggested using CTA as the initial diagnostic test. The advantages of CTAs are:
- Fast, readily available, and does not require a bowel preparation
- If negative, CTAs portend a good prognosis and make it highly unlikely to detect active extravasation on visceral angiography
- If positive, can localize the source of bleed and increase the success of intervention
Whether a positive CTA should be followed with a colonoscopy or visceral angiography remains unclear. Studies show that positive CTAs increase the detection rate of stigmata of recent hemorrhage on colonoscopy. Positive CTAs can also identify a target for embolization by interventional radiology (IR). Though an important caveat is that the success rate of embolization is highest when performed within 90 minutes of a positive CTA. This highlights that if you have IR availability, it is critical to have clear communication, a well-defined protocol, and collaboration among disciplines (i.e., ED, medical team, GI, and IR).
At our institution, we have implemented a CTA-guided protocol for severe LGIB. Those with positive CTAs are referred immediately to IR for embolization. If the embolization is unsuccessful or CTA is negative, the patient will be planned for a non-urgent inpatient colonoscopy. However, our unpublished data and other studies have shown that the overall CTA positivity rates are only between 16-22%. Moreover, one randomized controlled trial comparing CTA versus colonoscopy as an initial test did not show any meaningful difference in clinical outcomes. Thus, the benefit of CTA and the best approach to positive CTAs remains in question.
Lastly, people often ask about the utility of RBC nuclear scans. While they can detect bleeds at a slower rate (as low as 0.1 mL/min) compared to CTA (at least 0.4 mL/min), there are many limitations. RBC scans take time, are not available 24-7, and cannot precisely localize the site of bleeding. Therefore, we rarely recommend them for LGIB.
Approach to Recurrent Diverticular Bleeding
Unfortunately, diverticular bleeding recurs in the hospital 14% of the time and up to 25% at 5 years. When this occurs, is it worthwhile to repeat another colonoscopy or CTA?
Given the lack of clear data, we have adopted a shared decision-making framework with patients. Oftentimes, these patients are older and have significant co-morbidities, and undergoing bowel preparation, anesthesia, and colonoscopy is not trivial. If the patient is stable and prior work-up has excluded pertinent alternative diagnoses other than diverticular bleeding, then we tell patients the chance of finding an intervenable lesion is low and opt for conservative management. Meanwhile, if the patient has persistent, hemodynamically significant bleeding, we recommend a CTA based on the rationale discussed previously.
The most important clinical decision may not be about scoping or obtaining a CTA – it is medication management. If they are taking NSAIDs, they should be discontinued. If antiplatelet or anticoagulation agents were held, they should be restarted promptly in individuals with significant thrombotic risk given studies showing that while rebleeding rates may increase, overall mortality decreases.
In summary, managing LGIB and altering its natural history with either endoscopic or radiographic means is challenging. More studies are needed to guide the optimal approach. Reassuringly, most bleeding self-resolves and patients have good clinical outcomes.
Dr. Lee is a resident physician at New York Presbyterian Weill Cornell Medical Center, New York, NY. Dr. Wan is associate professor of clinical medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, N.Y. They declare no conflicts of interest.
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding: An Interventional Radiologist’s Perspective
BY ZEYAD METWALLI, MD, FSIR
When colonoscopy fails to localize and/or stop lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), catheter angiography has been commonly employed as a tool for both diagnosis and treatment of bleeding with embolization. Nuclear medicine or CT imaging studies can serve as useful adjuncts for confirming active bleeding and localizing the site of bleeding prior to angiography, particularly if this information is not provided by colonoscopy. Provocative mesenteric angiography has also become increasingly popular as a troubleshooting technique in patients with initially negative angiography.
Localization of Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Radionuclide technetium-99m-lableled red blood cell scintigraphy (RBCS), also known as tagged RBC scintigraphy, has been in use since the early 1980s for investigation of acute gastrointestinal bleeding. RBCS has a high sensitivity for detection of active bleeding with a theoretical ability to detect bleeding at rates as low as 0.04-0.2 mL/minute.
Imaging protocols vary but should include dynamic images, which may aid in localization of bleeding. The relatively long half-life of the tracer used for imaging allows for delayed imaging 12 to 24 hours after injection. This can be useful to confirm active bleeding, particularly when bleeding is intermittent and is not visible on initial images.
With the advent of computed tomography angiography (CTA), which continues to increase in speed, imaging quality and availability, the use of RBCS for evaluation of LGIB has declined. CTA is quicker to perform than RBCS and allows for detection of bleeding as well as accurate anatomic localization, which can guide interventions.
CTA provides a more comprehensive anatomic evaluation, which can aid in the diagnosis of a wide variety of intra-abdominal issues. Conversely, CTA may be less sensitive than RBCS for detection of slower acute bleeding, detecting bleeding at rates of 0.1-1 mL/min. In addition, intermittent bleeding which has temporarily stopped at the time of CTA may evade detection.
Lastly, CTA may not be appropriate in patients with impaired renal function due to risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, particularly in patients with acute kidney injury, which commonly afflicts hospitalized patients with LGIB. Prophylaxis with normal saline hydration should be employed aggressively in patients with impaired renal function, particularly when eGFR is less than 30 mL/minute. Iodinated contrast should be used judiciously in these patients.
In clinical practice, CTA and RBCS have a similar ability to confirm the presence or absence of clinically significant active gastrointestinal bleeding. Given the greater ability to rapidly localize the bleeding site with CTA, this is generally preferred over RBCS unless there is a contraindication to performing CTA, such as severe contrast allergy or high risk for development of contrast-induced nephropathy.
Role of Catheter Angiography and Embolization
Mesenteric angiography is a well-established technique for both detection and treatment of LGIB. Hemodynamic instability and need for packed RBC transfusion increases the likelihood of positive angiography. Limitations include reduced sensitivity for detection of bleeding slower than 0.5-1 mL/minute as well as the intermittent nature of LGIB, which will often resolve spontaneously. Angiography is variably successful in the literature with a diagnostic yield between 40-80%, which encompasses the rate of success in my own practice.
Once bleeding is identified, microcatheter placement within the feeding vessel as close as possible to the site of bleeding is important to ensure treatment efficacy and to limit risk of complications such as non-target embolization and bowel ischemia. Once the feeding vessel is selected with a microcatheter, embolization can be accomplished with a wide variety of tools including metallic coils, liquid embolic agents, and particles. In the treatment of LGIB, liquid embolic agents (e.g., n-butyl cyanoacrylate or NBCA, ethylene vinyl alcohol copolymer, etc.) and particles should be used judiciously as distal penetration increases the risk of bowel ischemia and procedure-related morbidity. For this reason, metallic coils are often preferred in the treatment of LGIB.
Although the source of bleeding is variable and may include diverticulosis, recent polypectomy, ulcer, tumor or angiodysplasia, the techniques employed are similar. Accurate and distal microcatheter selection is a key driver for successful embolization and minimizing the risk of bowel ischemia. Small intestinal bleeds can be challenging to treat due to the redundant supply of the arterial arcades supplying small bowel and may require occlusion of several branches to achieve hemostasis. This approach must be balanced with the risk of developing ischemia after embolization. Angiodysplasia, a less frequently encountered culprit of LGIB, may also be managed with selective embolization with many reports of successful treatment with liquid embolic agents such as NBCA mixed with ethiodized oil.
Provocative Mesenteric Angiography for Occult Bleeding
When initial angiography in a patient with suspected active LGIB is negative, provocative angiography can be considered to uncover an intermittent bleed. This may be particularly helpful in a patient where active bleeding is confirmed on a prior diagnostic test.
The approach to provocative mesenteric angiography varies by center, and a variety of agents have been used to provoke bleeding including heparin, vasodilators (i.e., nitroglycerin, verapamil, etc.) and thrombolytics (i.e., tPA), often in combination. Thrombolytics can be administered directly into the territory of interest (i.e., superior mesenteric or inferior mesenteric artery) while heparin may be administered systemically or directly into the catheterized artery. Reported success rates for provoking angiographically visible bleeding vary, but most larger series report a 40-50% success rate. The newly detected bleeding can then be treated with either embolization or surgery. A surgeon should be involved and available when provocative angiography is planned should bleeding fail to be controlled by embolization.
In summary, when colonoscopy fails to identify or control lower gastrointestinal bleeding (LGIB), imaging techniques such as RBCS and CTA play a crucial role in localizing active bleeding. While RBCS is highly sensitive, especially for intermittent or slow bleeding, CTA offers faster, more detailed anatomical information and is typically preferred unless contraindicated by renal issues or contrast allergies. Catheter-based mesenteric angiography is a well-established method for both diagnosing and treating LGIB, often using metallic coils to minimize complications like bowel ischemia. In cases where initial angiography is negative, provocative angiography – using agents like heparin or thrombolytics – may help unmask intermittent bleeding, allowing for targeted embolization or surgical intervention.
Dr. Metwalli is associate professor in the Department of Interventional Radiology, Division of Diagnostic Imaging, at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas. He declares no conflicts of interest.
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
There is a shortage of pediatric dermatologists in the United States, with fewer than 2% of practicing dermatologists specializing in pediatrics.1 Pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate by pediatricians but also is the third most challenging specialty to access, with an average appointment wait time of 92 days.2,3 Another factor leading to increased appointment wait times is the specificity of care required for pediatric patients. Frequently, pediatric patients evaluated by a general dermatologist will be referred to their pediatric dermatology colleagues. As medical students, we were introduced to the field of pediatric dermatology through different avenues—personal experience, research mentorship, or a clinical rotation in medical school. We found ourselves curious about the discrepancy between the supply of and demand for pediatric dermatologists and wondered what could be done to increase awareness of this subspecialty among medical students. We believe this workforce shortage can be ameliorated by improving early exposure to pediatric dermatology. In this article, we explore the existing framework surrounding pediatric dermatology in medical education and offer feasible recommendations and solutions to realistically combat this problem.
Pediatric dermatologists are essential to the greater dermatology community. Pediatric dermatologists receive advanced training in complex pediatric skin conditions that often is lacking in general dermatology residency. A large percentage of pediatric dermatology patients seen in academic medical centers have already been seen by general dermatologists who subsequently referred them to specialty care. In one study, 9.6% (10/108) of practicing pediatric dermatologists noted that their referrals were from general dermatologists.4 In another study, 42% (19/45) of referrals to a multidisciplinary pediatric dermatology-genetics were from general dermatologists.5 Given the shortage of pediatric dermatologists, these referrals undoubtedly overwhelm the system, and the results of these studies underscore the reality that general dermatologists do not necessarily feel adequately trained in complex pediatric conditions, creating an intrinsic need for pediatric dermatologists.
Admani et al6 reported that early mentorship was the single most important factor to 84% (91/109) of survey respondents who pursued pediatric dermatology. Forty percent (40/100) of survey respondents chose their specialty of pediatric dermatology during pediatrics residency, 34% (34/100) during medical school, 17% (17/100) during dermatology residency, and 5% (5/100) during internship, indicating that medical school is a crucial time for recruitment.6 It has been noted in the literature that more medical students matched to dermatology residency from schools with dermatology clerkships built into the curriculum than from schools without dedicated dermatology rotations, suggesting that early clinical exposure to dermatology fields has a predictable influence in matching.7 Currently, only about 10% (15/155) of allopathic medical schools in the United States offer a formal elective in pediatric dermatology via the Association of American Medical College’s Visiting Student Learning Opportunities program.8 When this information was cross-referenced with the most recently matched pediatric dermatology fellowship class (2023-2024), provided by the Fellowship Directors Chair of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, we found that 17% (4/24) of the matched fellows attended one of these 15 medical schools. We also found that the 2023-2024 pediatric dermatology fellowship class had 12 unmatched spots out of 36 total positions nationwide (33%), highlighting a gap in pediatric dermatology care and placing further strain on an already underserved subspecialty. These data suggest that, while dermatologists may decide to pursue pediatric dermatology fellowships during residency, there is an opportunity to foster interest during medical school training and improve the fellowship match rate.
Several medical schools in the United States incorporate pediatric dermatology into their curricula, including lectures in preclinical courses and career panels to pediatric dermatology electives in the third and fourth years. These institutions can serve as models for other medical schools. Within preclinical content, we recommend creating a designated dermatology unit that can incorporate common pediatric dermatology pathologies also seen by general practitioners, such as common childhood rashes, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Rare pediatric diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa, tuberous sclerosis, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome also may be included in the unit. If schools are not able to offer a stand-alone dermatology preclinical course, this content can be added to the immunology, musculoskeletal, infectious diseases, or genetics courses to account for the multisystemic effects of some of these conditions. Ideally, schools would offer elective exposure to pediatric dermatology during the clinical years of medical school to increase knowledge of the field; for example, pediatric dermatology materials could be included in core clerkships, as much of this content is applicable to the general pediatrics rotation. In particular, a lecture on common rashes in pediatric patients could be given before starting the core pediatric rotation. Additionally, problem-based pediatric dermatology cases could be implemented during the core pediatrics rotation. If students are offered an independent dermatology clinical elective, the already formatted 2- and 4-week basic dermatology courses designed by the American Academy of Dermatology could serve as suggested teaching guides or as self-teaching resources that could complement the dermatology rotation.9,10 Pediatric topics (eg, pediatric cutaneous fungal infections) are included within the American Academy of Dermatology basic dermatology curriculum.8,9
Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities could further broaden the pediatric dermatology knowledge base of medical students. Within medical school dermatology interest groups, there is an opportunity to have a pediatric dermatology lead to help coordinate lecture series and journal club sessions for interested students. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance have created programs to support students, and we encourage schools to raise awareness of these organizations as well as conference and grant opportunities. These initiatives foster meaningful mentor-mentee relationships, and more medical students may be interested if they are aware of these support networks.
There also may be opportunities to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants. Programs such as the newly implemented pediatric dermatology track at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University allow medical students who are interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology to have a more focused and linear training path.11,12 Due to the inherent competition in matching into dermatology, we surmise that many students with interest in pediatric dermatology are lost to pediatric residencies. Given the large percentage of pediatric residents who ultimately develop an interest in pediatric dermatology, holding a spot for pediatric dermatology applicants—akin to the combined medical-dermatology spots—may be an avenue to increase the pool of pediatric dermatology fellows.1,6 Another avenue is to encourage the development of first-year pediatric internship tracks that lead directly into dermatology residency, such as newly established programs at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University.11,12
As a group of both aspiring and practicing pediatric dermatologists, we have identified opportunities for formalized education in and early exposure to this subspecialty during medical training instead of leaving the discovery of the field to chance. The gaps in medical education that we have identified have already led us to present potential curricular changes to the medical education committee at our home institution. We hope to inspire the development of strong pediatric dermatology education at the medical school level.
While the solution to the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage is complex and multifaceted, there is a unique opportunity to target medical students through mentorship, access to education, and clinical experiences. We recommend that medical schools implement these educational methods and track the efficacy of these interventions to quantify the predicted association between an increased workforce and early exposure to pediatric dermatology. Addressing a lack of exposure to the field and increasing support of students pursuing pediatric dermatology can help to alleviate the shortage at the earliest point in training.
- Prindaville B, Antaya RJ, Siegfried EC. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12. doi:10.1111/pde.12362
- Wright TS. Update on the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage. Cutis. 2021;108:237-238. doi:10.12788/cutis.0379
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. ediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897. doi:10.1111/pde.13943
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. A survey to assess perceived differences in referral pathways to board-certified pediatric dermatologists. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:e314-e315. doi:10.1111/pde.12703
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.62095
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim SS, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-5.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.10.004
- Ogidi P, Ahmed F, Cahn BA, et al. Medical schools as gatekeepers: a survey and analysis of factors predicting dermatology residency placement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:490-492. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.09.027
- Visiting Student Learning Opportunities (VSLO). Accessed May 30, 2025. https://students-residents.aamc.org/visiting-student-learning-opportunities/visiting-student-learning-opportunities-vslo
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (2-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Listing/Basic-Dermatology-Curriculum-2-Week-Rotation-5395
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (4-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Public/Catalog/Details.aspx?id=YPssTVIbBO3Zb%2bOuf%2fM7Kg%3d%3d&returnurl=%2fUsers%2fUserOnlineCourse.aspx%3fLearningActivityID%3dYPssTVIbBO3Zb%252bOuf%252fM7Kg%253d%253d
- Penn Medicine Dermatology Residency Training Program. Residency tracks. Accessed May 12, 2025. https://dermatology.upenn.edu/residents/residency-tracks/
- Pediatric Dermatology Residency Track at NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Pediatric Track. Accessed May 30, 2025. https://med.nyu.edu/departments-institutes/dermatology/education/residency/pediatric-track
There is a shortage of pediatric dermatologists in the United States, with fewer than 2% of practicing dermatologists specializing in pediatrics.1 Pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate by pediatricians but also is the third most challenging specialty to access, with an average appointment wait time of 92 days.2,3 Another factor leading to increased appointment wait times is the specificity of care required for pediatric patients. Frequently, pediatric patients evaluated by a general dermatologist will be referred to their pediatric dermatology colleagues. As medical students, we were introduced to the field of pediatric dermatology through different avenues—personal experience, research mentorship, or a clinical rotation in medical school. We found ourselves curious about the discrepancy between the supply of and demand for pediatric dermatologists and wondered what could be done to increase awareness of this subspecialty among medical students. We believe this workforce shortage can be ameliorated by improving early exposure to pediatric dermatology. In this article, we explore the existing framework surrounding pediatric dermatology in medical education and offer feasible recommendations and solutions to realistically combat this problem.
Pediatric dermatologists are essential to the greater dermatology community. Pediatric dermatologists receive advanced training in complex pediatric skin conditions that often is lacking in general dermatology residency. A large percentage of pediatric dermatology patients seen in academic medical centers have already been seen by general dermatologists who subsequently referred them to specialty care. In one study, 9.6% (10/108) of practicing pediatric dermatologists noted that their referrals were from general dermatologists.4 In another study, 42% (19/45) of referrals to a multidisciplinary pediatric dermatology-genetics were from general dermatologists.5 Given the shortage of pediatric dermatologists, these referrals undoubtedly overwhelm the system, and the results of these studies underscore the reality that general dermatologists do not necessarily feel adequately trained in complex pediatric conditions, creating an intrinsic need for pediatric dermatologists.
Admani et al6 reported that early mentorship was the single most important factor to 84% (91/109) of survey respondents who pursued pediatric dermatology. Forty percent (40/100) of survey respondents chose their specialty of pediatric dermatology during pediatrics residency, 34% (34/100) during medical school, 17% (17/100) during dermatology residency, and 5% (5/100) during internship, indicating that medical school is a crucial time for recruitment.6 It has been noted in the literature that more medical students matched to dermatology residency from schools with dermatology clerkships built into the curriculum than from schools without dedicated dermatology rotations, suggesting that early clinical exposure to dermatology fields has a predictable influence in matching.7 Currently, only about 10% (15/155) of allopathic medical schools in the United States offer a formal elective in pediatric dermatology via the Association of American Medical College’s Visiting Student Learning Opportunities program.8 When this information was cross-referenced with the most recently matched pediatric dermatology fellowship class (2023-2024), provided by the Fellowship Directors Chair of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, we found that 17% (4/24) of the matched fellows attended one of these 15 medical schools. We also found that the 2023-2024 pediatric dermatology fellowship class had 12 unmatched spots out of 36 total positions nationwide (33%), highlighting a gap in pediatric dermatology care and placing further strain on an already underserved subspecialty. These data suggest that, while dermatologists may decide to pursue pediatric dermatology fellowships during residency, there is an opportunity to foster interest during medical school training and improve the fellowship match rate.
Several medical schools in the United States incorporate pediatric dermatology into their curricula, including lectures in preclinical courses and career panels to pediatric dermatology electives in the third and fourth years. These institutions can serve as models for other medical schools. Within preclinical content, we recommend creating a designated dermatology unit that can incorporate common pediatric dermatology pathologies also seen by general practitioners, such as common childhood rashes, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Rare pediatric diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa, tuberous sclerosis, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome also may be included in the unit. If schools are not able to offer a stand-alone dermatology preclinical course, this content can be added to the immunology, musculoskeletal, infectious diseases, or genetics courses to account for the multisystemic effects of some of these conditions. Ideally, schools would offer elective exposure to pediatric dermatology during the clinical years of medical school to increase knowledge of the field; for example, pediatric dermatology materials could be included in core clerkships, as much of this content is applicable to the general pediatrics rotation. In particular, a lecture on common rashes in pediatric patients could be given before starting the core pediatric rotation. Additionally, problem-based pediatric dermatology cases could be implemented during the core pediatrics rotation. If students are offered an independent dermatology clinical elective, the already formatted 2- and 4-week basic dermatology courses designed by the American Academy of Dermatology could serve as suggested teaching guides or as self-teaching resources that could complement the dermatology rotation.9,10 Pediatric topics (eg, pediatric cutaneous fungal infections) are included within the American Academy of Dermatology basic dermatology curriculum.8,9
Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities could further broaden the pediatric dermatology knowledge base of medical students. Within medical school dermatology interest groups, there is an opportunity to have a pediatric dermatology lead to help coordinate lecture series and journal club sessions for interested students. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance have created programs to support students, and we encourage schools to raise awareness of these organizations as well as conference and grant opportunities. These initiatives foster meaningful mentor-mentee relationships, and more medical students may be interested if they are aware of these support networks.
There also may be opportunities to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants. Programs such as the newly implemented pediatric dermatology track at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University allow medical students who are interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology to have a more focused and linear training path.11,12 Due to the inherent competition in matching into dermatology, we surmise that many students with interest in pediatric dermatology are lost to pediatric residencies. Given the large percentage of pediatric residents who ultimately develop an interest in pediatric dermatology, holding a spot for pediatric dermatology applicants—akin to the combined medical-dermatology spots—may be an avenue to increase the pool of pediatric dermatology fellows.1,6 Another avenue is to encourage the development of first-year pediatric internship tracks that lead directly into dermatology residency, such as newly established programs at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University.11,12
As a group of both aspiring and practicing pediatric dermatologists, we have identified opportunities for formalized education in and early exposure to this subspecialty during medical training instead of leaving the discovery of the field to chance. The gaps in medical education that we have identified have already led us to present potential curricular changes to the medical education committee at our home institution. We hope to inspire the development of strong pediatric dermatology education at the medical school level.
While the solution to the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage is complex and multifaceted, there is a unique opportunity to target medical students through mentorship, access to education, and clinical experiences. We recommend that medical schools implement these educational methods and track the efficacy of these interventions to quantify the predicted association between an increased workforce and early exposure to pediatric dermatology. Addressing a lack of exposure to the field and increasing support of students pursuing pediatric dermatology can help to alleviate the shortage at the earliest point in training.
There is a shortage of pediatric dermatologists in the United States, with fewer than 2% of practicing dermatologists specializing in pediatrics.1 Pediatric dermatology has the third highest referral rate by pediatricians but also is the third most challenging specialty to access, with an average appointment wait time of 92 days.2,3 Another factor leading to increased appointment wait times is the specificity of care required for pediatric patients. Frequently, pediatric patients evaluated by a general dermatologist will be referred to their pediatric dermatology colleagues. As medical students, we were introduced to the field of pediatric dermatology through different avenues—personal experience, research mentorship, or a clinical rotation in medical school. We found ourselves curious about the discrepancy between the supply of and demand for pediatric dermatologists and wondered what could be done to increase awareness of this subspecialty among medical students. We believe this workforce shortage can be ameliorated by improving early exposure to pediatric dermatology. In this article, we explore the existing framework surrounding pediatric dermatology in medical education and offer feasible recommendations and solutions to realistically combat this problem.
Pediatric dermatologists are essential to the greater dermatology community. Pediatric dermatologists receive advanced training in complex pediatric skin conditions that often is lacking in general dermatology residency. A large percentage of pediatric dermatology patients seen in academic medical centers have already been seen by general dermatologists who subsequently referred them to specialty care. In one study, 9.6% (10/108) of practicing pediatric dermatologists noted that their referrals were from general dermatologists.4 In another study, 42% (19/45) of referrals to a multidisciplinary pediatric dermatology-genetics were from general dermatologists.5 Given the shortage of pediatric dermatologists, these referrals undoubtedly overwhelm the system, and the results of these studies underscore the reality that general dermatologists do not necessarily feel adequately trained in complex pediatric conditions, creating an intrinsic need for pediatric dermatologists.
Admani et al6 reported that early mentorship was the single most important factor to 84% (91/109) of survey respondents who pursued pediatric dermatology. Forty percent (40/100) of survey respondents chose their specialty of pediatric dermatology during pediatrics residency, 34% (34/100) during medical school, 17% (17/100) during dermatology residency, and 5% (5/100) during internship, indicating that medical school is a crucial time for recruitment.6 It has been noted in the literature that more medical students matched to dermatology residency from schools with dermatology clerkships built into the curriculum than from schools without dedicated dermatology rotations, suggesting that early clinical exposure to dermatology fields has a predictable influence in matching.7 Currently, only about 10% (15/155) of allopathic medical schools in the United States offer a formal elective in pediatric dermatology via the Association of American Medical College’s Visiting Student Learning Opportunities program.8 When this information was cross-referenced with the most recently matched pediatric dermatology fellowship class (2023-2024), provided by the Fellowship Directors Chair of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, we found that 17% (4/24) of the matched fellows attended one of these 15 medical schools. We also found that the 2023-2024 pediatric dermatology fellowship class had 12 unmatched spots out of 36 total positions nationwide (33%), highlighting a gap in pediatric dermatology care and placing further strain on an already underserved subspecialty. These data suggest that, while dermatologists may decide to pursue pediatric dermatology fellowships during residency, there is an opportunity to foster interest during medical school training and improve the fellowship match rate.
Several medical schools in the United States incorporate pediatric dermatology into their curricula, including lectures in preclinical courses and career panels to pediatric dermatology electives in the third and fourth years. These institutions can serve as models for other medical schools. Within preclinical content, we recommend creating a designated dermatology unit that can incorporate common pediatric dermatology pathologies also seen by general practitioners, such as common childhood rashes, atopic dermatitis, alopecia areata, seborrheic dermatitis, and acne. Rare pediatric diseases such as epidermolysis bullosa, tuberous sclerosis, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome also may be included in the unit. If schools are not able to offer a stand-alone dermatology preclinical course, this content can be added to the immunology, musculoskeletal, infectious diseases, or genetics courses to account for the multisystemic effects of some of these conditions. Ideally, schools would offer elective exposure to pediatric dermatology during the clinical years of medical school to increase knowledge of the field; for example, pediatric dermatology materials could be included in core clerkships, as much of this content is applicable to the general pediatrics rotation. In particular, a lecture on common rashes in pediatric patients could be given before starting the core pediatric rotation. Additionally, problem-based pediatric dermatology cases could be implemented during the core pediatrics rotation. If students are offered an independent dermatology clinical elective, the already formatted 2- and 4-week basic dermatology courses designed by the American Academy of Dermatology could serve as suggested teaching guides or as self-teaching resources that could complement the dermatology rotation.9,10 Pediatric topics (eg, pediatric cutaneous fungal infections) are included within the American Academy of Dermatology basic dermatology curriculum.8,9
Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities could further broaden the pediatric dermatology knowledge base of medical students. Within medical school dermatology interest groups, there is an opportunity to have a pediatric dermatology lead to help coordinate lecture series and journal club sessions for interested students. The Society for Pediatric Dermatology and the Pediatric Dermatology Research Alliance have created programs to support students, and we encourage schools to raise awareness of these organizations as well as conference and grant opportunities. These initiatives foster meaningful mentor-mentee relationships, and more medical students may be interested if they are aware of these support networks.
There also may be opportunities to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants. Programs such as the newly implemented pediatric dermatology track at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University allow medical students who are interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology to have a more focused and linear training path.11,12 Due to the inherent competition in matching into dermatology, we surmise that many students with interest in pediatric dermatology are lost to pediatric residencies. Given the large percentage of pediatric residents who ultimately develop an interest in pediatric dermatology, holding a spot for pediatric dermatology applicants—akin to the combined medical-dermatology spots—may be an avenue to increase the pool of pediatric dermatology fellows.1,6 Another avenue is to encourage the development of first-year pediatric internship tracks that lead directly into dermatology residency, such as newly established programs at the University of Pennsylvania and New York University.11,12
As a group of both aspiring and practicing pediatric dermatologists, we have identified opportunities for formalized education in and early exposure to this subspecialty during medical training instead of leaving the discovery of the field to chance. The gaps in medical education that we have identified have already led us to present potential curricular changes to the medical education committee at our home institution. We hope to inspire the development of strong pediatric dermatology education at the medical school level.
While the solution to the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage is complex and multifaceted, there is a unique opportunity to target medical students through mentorship, access to education, and clinical experiences. We recommend that medical schools implement these educational methods and track the efficacy of these interventions to quantify the predicted association between an increased workforce and early exposure to pediatric dermatology. Addressing a lack of exposure to the field and increasing support of students pursuing pediatric dermatology can help to alleviate the shortage at the earliest point in training.
- Prindaville B, Antaya RJ, Siegfried EC. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12. doi:10.1111/pde.12362
- Wright TS. Update on the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage. Cutis. 2021;108:237-238. doi:10.12788/cutis.0379
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. ediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897. doi:10.1111/pde.13943
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. A survey to assess perceived differences in referral pathways to board-certified pediatric dermatologists. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:e314-e315. doi:10.1111/pde.12703
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.62095
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim SS, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-5.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.10.004
- Ogidi P, Ahmed F, Cahn BA, et al. Medical schools as gatekeepers: a survey and analysis of factors predicting dermatology residency placement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:490-492. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.09.027
- Visiting Student Learning Opportunities (VSLO). Accessed May 30, 2025. https://students-residents.aamc.org/visiting-student-learning-opportunities/visiting-student-learning-opportunities-vslo
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (2-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Listing/Basic-Dermatology-Curriculum-2-Week-Rotation-5395
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (4-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Public/Catalog/Details.aspx?id=YPssTVIbBO3Zb%2bOuf%2fM7Kg%3d%3d&returnurl=%2fUsers%2fUserOnlineCourse.aspx%3fLearningActivityID%3dYPssTVIbBO3Zb%252bOuf%252fM7Kg%253d%253d
- Penn Medicine Dermatology Residency Training Program. Residency tracks. Accessed May 12, 2025. https://dermatology.upenn.edu/residents/residency-tracks/
- Pediatric Dermatology Residency Track at NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Pediatric Track. Accessed May 30, 2025. https://med.nyu.edu/departments-institutes/dermatology/education/residency/pediatric-track
- Prindaville B, Antaya RJ, Siegfried EC. Pediatric dermatology: past, present, and future. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:1-12. doi:10.1111/pde.12362
- Wright TS. Update on the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage. Cutis. 2021;108:237-238. doi:10.12788/cutis.0379
- Stephens MR, Murthy AS, McMahon PJ. Wait times, health care touchpoints, and nonattendance in an academic pediatric dermatology clinic. ediatr Dermatol. 2019;36:893-897. doi:10.1111/pde.13943
- Fogel AL, Teng JM. A survey to assess perceived differences in referral pathways to board-certified pediatric dermatologists. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015;32:e314-e315. doi:10.1111/pde.12703
- Parker JC, Rangu S, Grand KL, et al. Genetic skin disorders: the value of a multidisciplinary clinic. Am J Med Genet A. 2021;185:1159-1167. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.62095
- Admani S, Caufield M, Kim SS, et al. Understanding the pediatric dermatology workforce shortage: mentoring matters. J Pediatr. 2014;164:372-5.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.10.004
- Ogidi P, Ahmed F, Cahn BA, et al. Medical schools as gatekeepers: a survey and analysis of factors predicting dermatology residency placement. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;86:490-492. doi:10.1016 /j.jaad.2021.09.027
- Visiting Student Learning Opportunities (VSLO). Accessed May 30, 2025. https://students-residents.aamc.org/visiting-student-learning-opportunities/visiting-student-learning-opportunities-vslo
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (2-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Listing/Basic-Dermatology-Curriculum-2-Week-Rotation-5395
- American Academy of Dermatology Association. AAD Learning Center. Basic dermatology curriculum (4-week rotation). Accessed May 12, 2025. https://learning.aad.org/Public/Catalog/Details.aspx?id=YPssTVIbBO3Zb%2bOuf%2fM7Kg%3d%3d&returnurl=%2fUsers%2fUserOnlineCourse.aspx%3fLearningActivityID%3dYPssTVIbBO3Zb%252bOuf%252fM7Kg%253d%253d
- Penn Medicine Dermatology Residency Training Program. Residency tracks. Accessed May 12, 2025. https://dermatology.upenn.edu/residents/residency-tracks/
- Pediatric Dermatology Residency Track at NYU Grossman School of Medicine. Pediatric Track. Accessed May 30, 2025. https://med.nyu.edu/departments-institutes/dermatology/education/residency/pediatric-track
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
Workforce Shortage of Pediatric Dermatologists: A Medical Student’s Perspective
PRACTICE POINTS
- Addressing a lack of exposure to pediatric dermatology in medical school and increasing support for students who are interested in the field can help alleviate the shortage of physicians at the earliest point in training.
- Increasing access to pediatric dermatology resources, such as lecture series and mentorship opportunities, could further broaden the medical student knowledge base.
- There is an opportunity to create residency tracks that increase the number of dermatology residency applicants who are medical students interested in pursuing pediatric dermatology.
What About Stolen Valor is Actually Illegal?
What About Stolen Valor is Actually Illegal?
Memorial Day is the most solemn of all American military commemorations. It is the day when we honor those who sacrificed their lives so that their fellow citizens could flourish in freedom. At 3 PM, a grateful nation is called to observe 2 minutes of silence in remembrance of the heroes who died in battle or of the wounds they sustained in combat. Communities across the country will carry out ceremonies, lining national cemeteries with flags, holding patriotic parades, and conducting spiritual observances.1
Sadly, almost as long as there has been a United States, there has been a parallel practice dishonoring the uniform and deceiving veterans and the public alike known as stolen valor. Stolen valor is a persistent, yet strange, psychological behavior: individuals who never served in the US Armed Forces claim they have done heroic deeds for which they often sustained serious injuries in the line of duty and almost always won medals for their heroism.2 This editorial will trace the US legal history of stolen valor cases to provide the background for next month’s editorial examining its clinical and ethical aspects.
While many cases of stolen valor do not receive media attention, the experience of Sarah Cavanaugh, a former VA social worker who claimed to be a marine veteran who served in Iraq and Afghanistan, was the subject of the Deep Cover podcast series.3 Cavanaugh had claimed that an improvised explosive device blew up her Humvee, crushing her hip. Still she somehow was able to help her fellow Marines and earned the Bronze Star among other decorations for her heroism. That was not the only lie Cavanaugh told: she also told her friends and wife that she had advanced lung cancer due to burn pit exposure. In line with the best-worst of those who have stolen valor, her mastery of manipulation enabled her to become the commander of a local Veterans of Foreign Wars post. Using stolen identities and fraudulent documents, Cavanaugh was able to purloin veteran benefits, donated leave from other VA employees and money, and stole goods and services from various charitable organizations whose mission was to help wounded veterans and those struggling to adjust to civilian life. Before law enforcement unraveled her sordid tale, she misappropriated hundreds of thousands of dollars in VA benefits and donations and exploited dozens of generous veterans and compassionate civilians.4
Cavanaugh’s story was so sordidly compelling that I kept saying out loud to myself (and my spouse), “This has to be illegal.” The truth about stolen valor law is far more ambivalent and frustrating than I had anticipated or wanted. The first insult to my sense of justice was that lying about military service is not in itself illegal: you can pad your military resume with unearned decorations or impress a future partner or employer with your combat exploits without much fear of legal repercussions. The legal history of attempting to make stealing valor a crime has almost as many twists and turns as the fallacious narratives of military imposters and illustrates the uniquely American experiment in balancing freedom and fairness.
The Stolen Valor Act of 2005 made it a federal misdemeanor to wear, manufacture, or sell military decorations, or medals (Cavanaugh bought her medals online) without legal authorization. It also made it a crime to falsely represent oneself as having been the recipient of a decoration, medical, or service badge that Congress or the Armed Forces authorized. There were even stiffer penalties if the medal was a Silver Star, Distinguished Service Cross, US Air Force or US Navy Cross, or Purple Heart. Punishments include fines and imprisonment. The stated legislative purpose was to prohibit fraud that devalued military awards and the dignity of those who legitimately earned them.5
Next comes a distinctly American reaction to the initial Congressional attempt to protect the legacy of those who served—a lawsuit. Xavier Alvarez was an official on a California district water board claimed to be a 25-year veteran of the US Marine Corps wounded in combat and received the Congressional Medal of Honor. The Federal Bureau of Investigation exposed the lie and instead of the nation’s highest honor, Alvarez was the first to be convicted under the Stolen Valor Act of 2005. Alvarez appealed the decision, ironically claiming the law violated his free speech rights. The case landed in the Supreme Court, which ruled that the Stolen Valor Act did indeed violate the Free Speech Clause of the First Amendment. The majority opinion found the Act as passed was too encompassing of all speech and needed to target only cases in which false statements resulted in actual harm.6
The Stolen Valor Act of 2013 amends the criminal code regarding fraudulent claims about military service to include those who don’t only lie but also profit from it, as Cavanaugh did. The revised act specifically focuses on individuals who claim to have earned military honors for the intended purpose of obtaining money, property, or any other tangible benefit.7
Despite the complicated nature of Stolen Valor Law, it did prevail in Cavanaugh’s case. A US District Court Judge in Rhode Island found her guilty of stolen valor in all its permutations, along with identity theft of other veterans’ military and medical records and fraud in obtaining benefits and services intended for real veterans. Cavanaugh was sentenced to 70 months in federal prison, 3 years of supervised release, ordered to pay $284,796.82 in restitution, and to restore 261 hours of donated leave to the federal government, charitable organizations, and good Samaritans she duped and swindled.8
The revised law under which Cavanaugh was punished lasted 10 years until another classically American ethical concern—privacy—motivated additional legislative effort. A 2023/2024 US House of Representatives proposal to amend the Stolen Valor Act would have strengthened the privacy protections afforded military records. It would have required the information to only be accessed with the permission of the individual who served or their family or through a Freedom of Information Act request. This would make the kind of journalistic and law enforcement investigations that eventually caught Cavanaugh in her lies far more laborious for false valor hunters while at the same time preventing unscrupulous inquiries into service members’ personal information. Advocates for free speech and defenders of military honor are both lobbying Congress; as of this writing the legislation has not been passed.9
As we close part 1 of this review of stolen valor, we return to Memorial Day. This day provides the somber recognition that without the brave men and women of integrity who died in defense of a democracy that promotes the political activity of its citizens, we would not even be able to have this debate over justice, freedom, and truth.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. The difference between Veterans Day and Memorial Day. October 30, 2023. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://news.va.gov/125549/difference-between-veterans-day-memorial-day/
- Home of Heroes. Stolen valor. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://homeofheroes.com/stolen-valor
- Halpern J. Deep cover: the truth about Sarah. May 2025. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.pushkin.fm/podcasts/deep-cover
- Stillwell B. The latest season of the ‘deep cover’ podcast dives into one of the biggest stolen valor cases ever. Military. com. May 22, 2025. Accessed May 27, 2025. https:// www.military.com/off-duty/2025/05/22/latest-season-of-deep-cover-podcast-dives-one-of-biggest-stolen-valor-cases-ever.html
- The Stolen Valor Act of 2005. Pub L No: 109-437. 120 Stat 3266
- Alvarez v United States. 567 US 2012.
- The Stolen Valor Act of 2013. 18 USC § 704(b)
- US Attorney’s Office, District of Rhode Island. Rhode Island woman sentenced to federal prison for falsifying military service; false use of military medals; identify theft, and fraudulently collecting more than $250,000, in veteran benefits and charitable contributions. March 14, 2023. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.justice.gov/usao-ri/pr/rhode-island-woman-sentenced-federal-prison-falsifying-military-service-false-use
- Armed Forces Benefit Association. Stolen Valor Act: all you need to know. February 21, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.afba.com/military-life/active-duty-and-veterans/stolen-valor-act-all-you-need-to-know/
Memorial Day is the most solemn of all American military commemorations. It is the day when we honor those who sacrificed their lives so that their fellow citizens could flourish in freedom. At 3 PM, a grateful nation is called to observe 2 minutes of silence in remembrance of the heroes who died in battle or of the wounds they sustained in combat. Communities across the country will carry out ceremonies, lining national cemeteries with flags, holding patriotic parades, and conducting spiritual observances.1
Sadly, almost as long as there has been a United States, there has been a parallel practice dishonoring the uniform and deceiving veterans and the public alike known as stolen valor. Stolen valor is a persistent, yet strange, psychological behavior: individuals who never served in the US Armed Forces claim they have done heroic deeds for which they often sustained serious injuries in the line of duty and almost always won medals for their heroism.2 This editorial will trace the US legal history of stolen valor cases to provide the background for next month’s editorial examining its clinical and ethical aspects.
While many cases of stolen valor do not receive media attention, the experience of Sarah Cavanaugh, a former VA social worker who claimed to be a marine veteran who served in Iraq and Afghanistan, was the subject of the Deep Cover podcast series.3 Cavanaugh had claimed that an improvised explosive device blew up her Humvee, crushing her hip. Still she somehow was able to help her fellow Marines and earned the Bronze Star among other decorations for her heroism. That was not the only lie Cavanaugh told: she also told her friends and wife that she had advanced lung cancer due to burn pit exposure. In line with the best-worst of those who have stolen valor, her mastery of manipulation enabled her to become the commander of a local Veterans of Foreign Wars post. Using stolen identities and fraudulent documents, Cavanaugh was able to purloin veteran benefits, donated leave from other VA employees and money, and stole goods and services from various charitable organizations whose mission was to help wounded veterans and those struggling to adjust to civilian life. Before law enforcement unraveled her sordid tale, she misappropriated hundreds of thousands of dollars in VA benefits and donations and exploited dozens of generous veterans and compassionate civilians.4
Cavanaugh’s story was so sordidly compelling that I kept saying out loud to myself (and my spouse), “This has to be illegal.” The truth about stolen valor law is far more ambivalent and frustrating than I had anticipated or wanted. The first insult to my sense of justice was that lying about military service is not in itself illegal: you can pad your military resume with unearned decorations or impress a future partner or employer with your combat exploits without much fear of legal repercussions. The legal history of attempting to make stealing valor a crime has almost as many twists and turns as the fallacious narratives of military imposters and illustrates the uniquely American experiment in balancing freedom and fairness.
The Stolen Valor Act of 2005 made it a federal misdemeanor to wear, manufacture, or sell military decorations, or medals (Cavanaugh bought her medals online) without legal authorization. It also made it a crime to falsely represent oneself as having been the recipient of a decoration, medical, or service badge that Congress or the Armed Forces authorized. There were even stiffer penalties if the medal was a Silver Star, Distinguished Service Cross, US Air Force or US Navy Cross, or Purple Heart. Punishments include fines and imprisonment. The stated legislative purpose was to prohibit fraud that devalued military awards and the dignity of those who legitimately earned them.5
Next comes a distinctly American reaction to the initial Congressional attempt to protect the legacy of those who served—a lawsuit. Xavier Alvarez was an official on a California district water board claimed to be a 25-year veteran of the US Marine Corps wounded in combat and received the Congressional Medal of Honor. The Federal Bureau of Investigation exposed the lie and instead of the nation’s highest honor, Alvarez was the first to be convicted under the Stolen Valor Act of 2005. Alvarez appealed the decision, ironically claiming the law violated his free speech rights. The case landed in the Supreme Court, which ruled that the Stolen Valor Act did indeed violate the Free Speech Clause of the First Amendment. The majority opinion found the Act as passed was too encompassing of all speech and needed to target only cases in which false statements resulted in actual harm.6
The Stolen Valor Act of 2013 amends the criminal code regarding fraudulent claims about military service to include those who don’t only lie but also profit from it, as Cavanaugh did. The revised act specifically focuses on individuals who claim to have earned military honors for the intended purpose of obtaining money, property, or any other tangible benefit.7
Despite the complicated nature of Stolen Valor Law, it did prevail in Cavanaugh’s case. A US District Court Judge in Rhode Island found her guilty of stolen valor in all its permutations, along with identity theft of other veterans’ military and medical records and fraud in obtaining benefits and services intended for real veterans. Cavanaugh was sentenced to 70 months in federal prison, 3 years of supervised release, ordered to pay $284,796.82 in restitution, and to restore 261 hours of donated leave to the federal government, charitable organizations, and good Samaritans she duped and swindled.8
The revised law under which Cavanaugh was punished lasted 10 years until another classically American ethical concern—privacy—motivated additional legislative effort. A 2023/2024 US House of Representatives proposal to amend the Stolen Valor Act would have strengthened the privacy protections afforded military records. It would have required the information to only be accessed with the permission of the individual who served or their family or through a Freedom of Information Act request. This would make the kind of journalistic and law enforcement investigations that eventually caught Cavanaugh in her lies far more laborious for false valor hunters while at the same time preventing unscrupulous inquiries into service members’ personal information. Advocates for free speech and defenders of military honor are both lobbying Congress; as of this writing the legislation has not been passed.9
As we close part 1 of this review of stolen valor, we return to Memorial Day. This day provides the somber recognition that without the brave men and women of integrity who died in defense of a democracy that promotes the political activity of its citizens, we would not even be able to have this debate over justice, freedom, and truth.
Memorial Day is the most solemn of all American military commemorations. It is the day when we honor those who sacrificed their lives so that their fellow citizens could flourish in freedom. At 3 PM, a grateful nation is called to observe 2 minutes of silence in remembrance of the heroes who died in battle or of the wounds they sustained in combat. Communities across the country will carry out ceremonies, lining national cemeteries with flags, holding patriotic parades, and conducting spiritual observances.1
Sadly, almost as long as there has been a United States, there has been a parallel practice dishonoring the uniform and deceiving veterans and the public alike known as stolen valor. Stolen valor is a persistent, yet strange, psychological behavior: individuals who never served in the US Armed Forces claim they have done heroic deeds for which they often sustained serious injuries in the line of duty and almost always won medals for their heroism.2 This editorial will trace the US legal history of stolen valor cases to provide the background for next month’s editorial examining its clinical and ethical aspects.
While many cases of stolen valor do not receive media attention, the experience of Sarah Cavanaugh, a former VA social worker who claimed to be a marine veteran who served in Iraq and Afghanistan, was the subject of the Deep Cover podcast series.3 Cavanaugh had claimed that an improvised explosive device blew up her Humvee, crushing her hip. Still she somehow was able to help her fellow Marines and earned the Bronze Star among other decorations for her heroism. That was not the only lie Cavanaugh told: she also told her friends and wife that she had advanced lung cancer due to burn pit exposure. In line with the best-worst of those who have stolen valor, her mastery of manipulation enabled her to become the commander of a local Veterans of Foreign Wars post. Using stolen identities and fraudulent documents, Cavanaugh was able to purloin veteran benefits, donated leave from other VA employees and money, and stole goods and services from various charitable organizations whose mission was to help wounded veterans and those struggling to adjust to civilian life. Before law enforcement unraveled her sordid tale, she misappropriated hundreds of thousands of dollars in VA benefits and donations and exploited dozens of generous veterans and compassionate civilians.4
Cavanaugh’s story was so sordidly compelling that I kept saying out loud to myself (and my spouse), “This has to be illegal.” The truth about stolen valor law is far more ambivalent and frustrating than I had anticipated or wanted. The first insult to my sense of justice was that lying about military service is not in itself illegal: you can pad your military resume with unearned decorations or impress a future partner or employer with your combat exploits without much fear of legal repercussions. The legal history of attempting to make stealing valor a crime has almost as many twists and turns as the fallacious narratives of military imposters and illustrates the uniquely American experiment in balancing freedom and fairness.
The Stolen Valor Act of 2005 made it a federal misdemeanor to wear, manufacture, or sell military decorations, or medals (Cavanaugh bought her medals online) without legal authorization. It also made it a crime to falsely represent oneself as having been the recipient of a decoration, medical, or service badge that Congress or the Armed Forces authorized. There were even stiffer penalties if the medal was a Silver Star, Distinguished Service Cross, US Air Force or US Navy Cross, or Purple Heart. Punishments include fines and imprisonment. The stated legislative purpose was to prohibit fraud that devalued military awards and the dignity of those who legitimately earned them.5
Next comes a distinctly American reaction to the initial Congressional attempt to protect the legacy of those who served—a lawsuit. Xavier Alvarez was an official on a California district water board claimed to be a 25-year veteran of the US Marine Corps wounded in combat and received the Congressional Medal of Honor. The Federal Bureau of Investigation exposed the lie and instead of the nation’s highest honor, Alvarez was the first to be convicted under the Stolen Valor Act of 2005. Alvarez appealed the decision, ironically claiming the law violated his free speech rights. The case landed in the Supreme Court, which ruled that the Stolen Valor Act did indeed violate the Free Speech Clause of the First Amendment. The majority opinion found the Act as passed was too encompassing of all speech and needed to target only cases in which false statements resulted in actual harm.6
The Stolen Valor Act of 2013 amends the criminal code regarding fraudulent claims about military service to include those who don’t only lie but also profit from it, as Cavanaugh did. The revised act specifically focuses on individuals who claim to have earned military honors for the intended purpose of obtaining money, property, or any other tangible benefit.7
Despite the complicated nature of Stolen Valor Law, it did prevail in Cavanaugh’s case. A US District Court Judge in Rhode Island found her guilty of stolen valor in all its permutations, along with identity theft of other veterans’ military and medical records and fraud in obtaining benefits and services intended for real veterans. Cavanaugh was sentenced to 70 months in federal prison, 3 years of supervised release, ordered to pay $284,796.82 in restitution, and to restore 261 hours of donated leave to the federal government, charitable organizations, and good Samaritans she duped and swindled.8
The revised law under which Cavanaugh was punished lasted 10 years until another classically American ethical concern—privacy—motivated additional legislative effort. A 2023/2024 US House of Representatives proposal to amend the Stolen Valor Act would have strengthened the privacy protections afforded military records. It would have required the information to only be accessed with the permission of the individual who served or their family or through a Freedom of Information Act request. This would make the kind of journalistic and law enforcement investigations that eventually caught Cavanaugh in her lies far more laborious for false valor hunters while at the same time preventing unscrupulous inquiries into service members’ personal information. Advocates for free speech and defenders of military honor are both lobbying Congress; as of this writing the legislation has not been passed.9
As we close part 1 of this review of stolen valor, we return to Memorial Day. This day provides the somber recognition that without the brave men and women of integrity who died in defense of a democracy that promotes the political activity of its citizens, we would not even be able to have this debate over justice, freedom, and truth.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. The difference between Veterans Day and Memorial Day. October 30, 2023. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://news.va.gov/125549/difference-between-veterans-day-memorial-day/
- Home of Heroes. Stolen valor. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://homeofheroes.com/stolen-valor
- Halpern J. Deep cover: the truth about Sarah. May 2025. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.pushkin.fm/podcasts/deep-cover
- Stillwell B. The latest season of the ‘deep cover’ podcast dives into one of the biggest stolen valor cases ever. Military. com. May 22, 2025. Accessed May 27, 2025. https:// www.military.com/off-duty/2025/05/22/latest-season-of-deep-cover-podcast-dives-one-of-biggest-stolen-valor-cases-ever.html
- The Stolen Valor Act of 2005. Pub L No: 109-437. 120 Stat 3266
- Alvarez v United States. 567 US 2012.
- The Stolen Valor Act of 2013. 18 USC § 704(b)
- US Attorney’s Office, District of Rhode Island. Rhode Island woman sentenced to federal prison for falsifying military service; false use of military medals; identify theft, and fraudulently collecting more than $250,000, in veteran benefits and charitable contributions. March 14, 2023. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.justice.gov/usao-ri/pr/rhode-island-woman-sentenced-federal-prison-falsifying-military-service-false-use
- Armed Forces Benefit Association. Stolen Valor Act: all you need to know. February 21, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.afba.com/military-life/active-duty-and-veterans/stolen-valor-act-all-you-need-to-know/
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. The difference between Veterans Day and Memorial Day. October 30, 2023. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://news.va.gov/125549/difference-between-veterans-day-memorial-day/
- Home of Heroes. Stolen valor. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://homeofheroes.com/stolen-valor
- Halpern J. Deep cover: the truth about Sarah. May 2025. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.pushkin.fm/podcasts/deep-cover
- Stillwell B. The latest season of the ‘deep cover’ podcast dives into one of the biggest stolen valor cases ever. Military. com. May 22, 2025. Accessed May 27, 2025. https:// www.military.com/off-duty/2025/05/22/latest-season-of-deep-cover-podcast-dives-one-of-biggest-stolen-valor-cases-ever.html
- The Stolen Valor Act of 2005. Pub L No: 109-437. 120 Stat 3266
- Alvarez v United States. 567 US 2012.
- The Stolen Valor Act of 2013. 18 USC § 704(b)
- US Attorney’s Office, District of Rhode Island. Rhode Island woman sentenced to federal prison for falsifying military service; false use of military medals; identify theft, and fraudulently collecting more than $250,000, in veteran benefits and charitable contributions. March 14, 2023. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.justice.gov/usao-ri/pr/rhode-island-woman-sentenced-federal-prison-falsifying-military-service-false-use
- Armed Forces Benefit Association. Stolen Valor Act: all you need to know. February 21, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2025. https://www.afba.com/military-life/active-duty-and-veterans/stolen-valor-act-all-you-need-to-know/
What About Stolen Valor is Actually Illegal?
What About Stolen Valor is Actually Illegal?