User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis Diagnosis
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
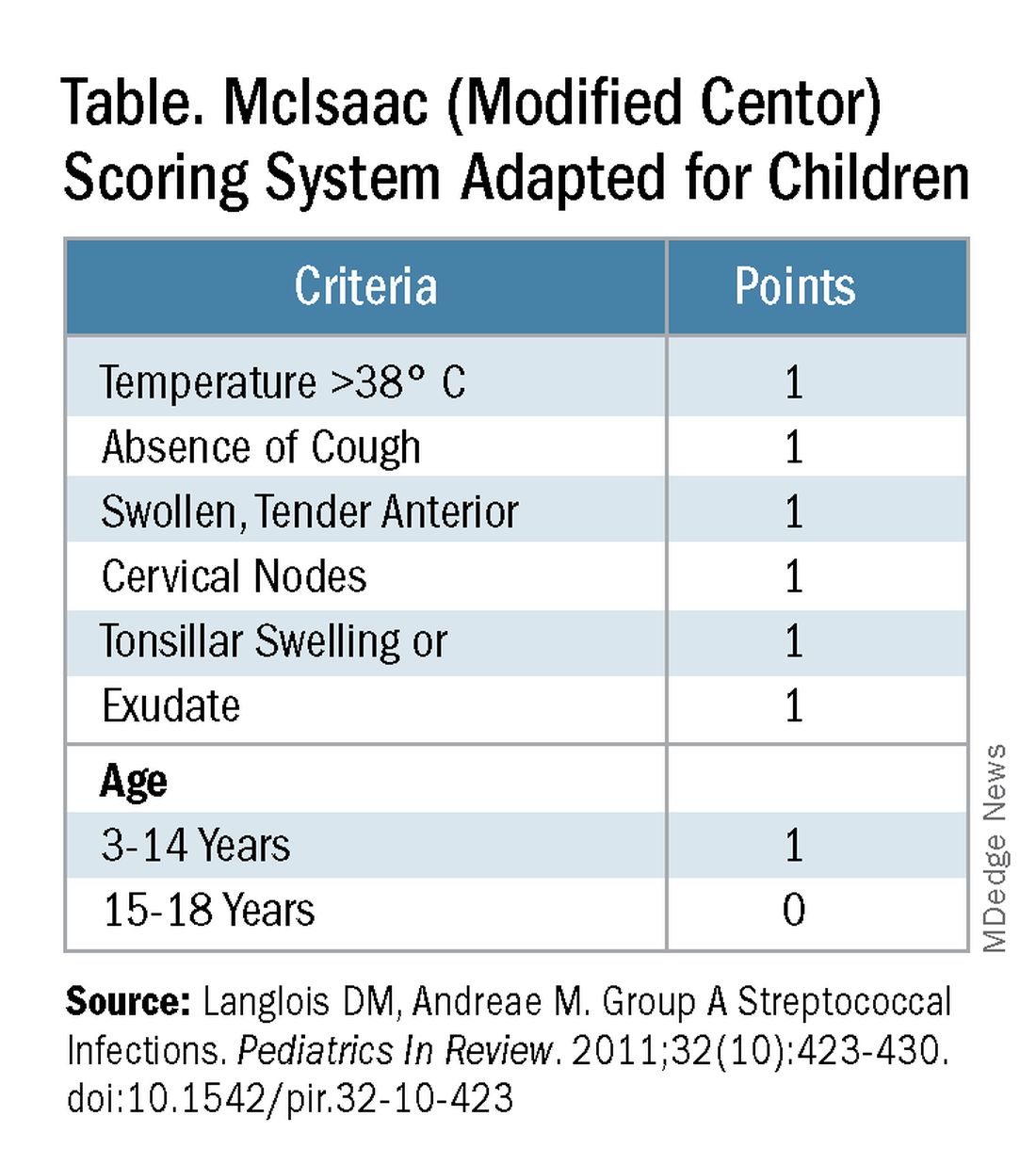
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)
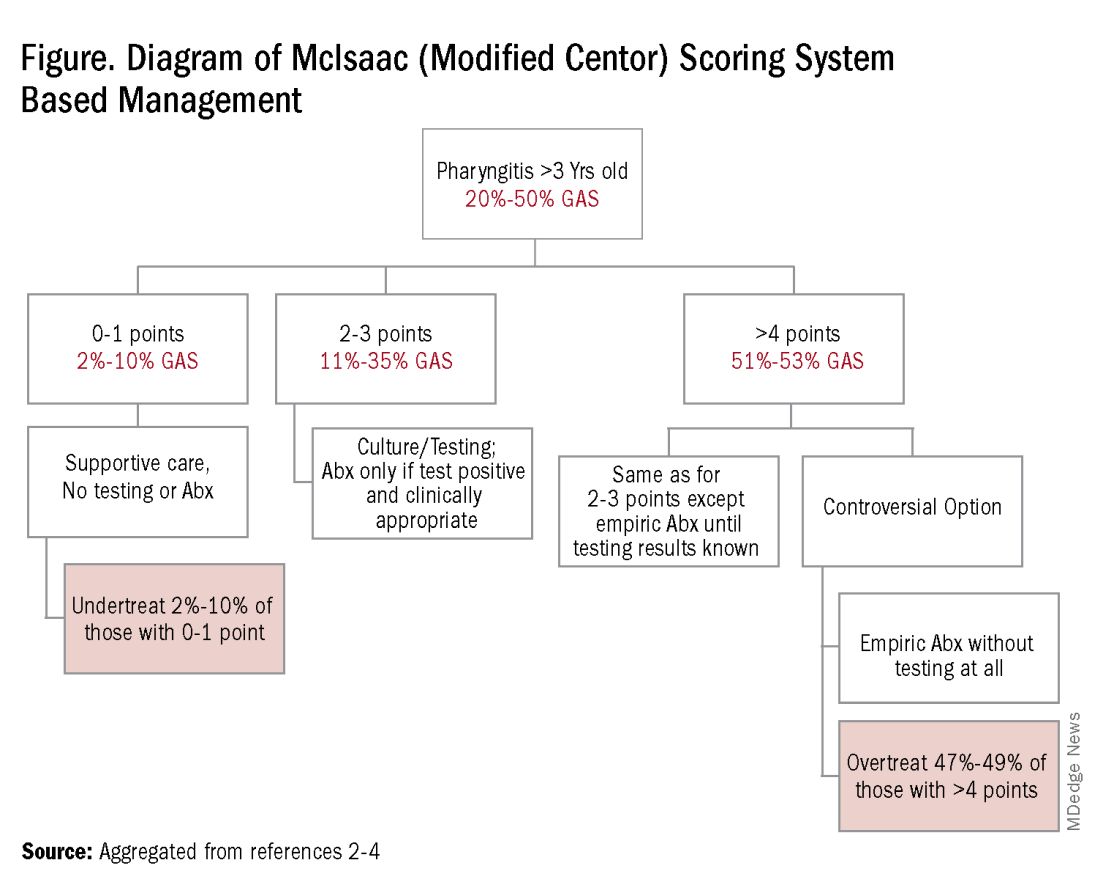
However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)
Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)

However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)

Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
It’s wintertime, peak season for GAS pharyngitis, and you’d think that this far into the 21st century we would have a foolproof process for diagnosing which among the many patients with pharyngitis have true GAS pharyngitis. Thinking back to the 1980s, we have come a long way from simple throat cultures for detecting GAS, e.g., numerous point of care (POC) Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), waved rapid antigen detection tests (RADT), and numerous highly sensitive molecular assays, e.g. nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT). But if you think the issues surrounding management of GAS pharyngitis have been solved by these newer tests, think again.
Several good reviews1-3 are excellent resources for those wishing a refresher on GAS diagnosis/management issues. They present nitty gritty details on comparative advantages/disadvantages of the many testing options while reminding us of the nuts and bolts of GAS pharyngitis. The following are a few nuggets from these articles.
Properly collected throat specimen. A quality throat specimen involves swabbing both tonsillar pillars plus posterior pharynx without touching tongue or inner cheeks. Two swab collections increase sensitivity by almost 10% compared with a single swab. Transport media is preferred if samples will not be cultured within 24 hours. Caveat: RADT testing of a transport media-diluted sample lowers sensitivity compared with direct swab use.
Reliable GAS detection. Commercially available tests in 2025 are well studied. Culture is considered a gold standard for detecting clinically relevant GAS by CDC.4 Culture has good sensitivity (estimated 80%-90% varying among studies and by quality of specimens) and 99% specificity but requires 16-24 hours for results. RADT solves the time-delay issues and has near 100% specificity but sensitivity used to be as low as 65%, hence the 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America guideline recommendation for backup throat culture for negative tests.5 However, current RADT have sensitivities in the 85%-90% range.3,4 So a positive RADT reliably and quickly indicates GAS antigens are present. NAAT have the highest combined sensitivity and specificity, near 100% for each, and a positive reliably indicates GAS nucleic acids are present.
So why not simply always use NAAT? First, it’s a “be careful what you wish for” scenario. NAAT can, and do, detect dead remnants and colonizing GAS way more than culture.2,3 So NAAT are overly sensitive, adding an extra layer of interpretation difficulty, ie, as many as 20% of positive NAAT detections may be carriers or dead GAS. Second, NAAT often requires special instrumentation and kits are more expensive. That said, reimbursement is often higher for NAAT.
Choice based on accuracy in detecting GAS. If time delays were not a problem, culture would still seem the answer. If more rapid detection is needed, either RADT with culture back up or NAAT could be the answer. That said, consider that in the real world, throat cultures are less sensitive and RADT are less specific than indicated by some published data.6 So, the ideal answer, it seems, would be NAAT GAS detection coupled with a confirmatory biomarker of GAS infection. Such innate immune biomarkers may be on the horizon.3
But first, pretest screening. In 2025 what do we do with a positive result? Do we prescribe antibiotics? Do we think the detected GAS bacteria/antigens/nucleic acids represent the cause of the pharyngitis? Or did we just detect dead GAS or even a carrier, while a virus is the true cause? Challenges for this decision include most pharyngitis (up to 70%) being due to viruses, not GAS, plus up to 20% of GAS detections even by less sensitive culture or RADT can be carriers, plus an added 10%-20% of RADT and NAAT detections are dead GAS. Thus, with indiscriminate testing of all pharyngitis patients, the number of truly positive GAS detections that are actually “false positives” (GAS in some form is present but not causing pharyngitis) may be almost as high as for those representing true GAS pharyngitis.
Some tool is needed to minimize testing patients who are likely to have viral pharyngitis to reduce test-positive/GAS-pharyngitis-negative scenarios. Pretest patient screening therefore is critical to increase the positive predictive value of positive GAS testing results. The history and physical can be helpful. In the simplest form of pretest screening, eliminate those younger than 3 years old* or those with viral type sign/symptoms, eg conjunctivitis, cough, coryza.7 This could cut “false” positives by as much as a half. More complete validated scoring systems are also available but remain imperfect. The most published is the McIsaac score (modified Centor score).3-5,8 (See Table and Figure.)

However, even with this validated scoring system, misdiagnoses and some antibiotic misuse will likely occur, particularly if the controversial option to treat a patient with a score above 4 without testing is used. For example, a 2004 study in patients older than 3 years old revealed that 45% with a score above 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis. (McIsaac et al.) A 2012 study showed similar potential overdiagnosis from using the score without testing (45% with > 4 points did not have GAS pharyngitis). Of note, clinical scores of below 2 comprised up to 10% and would be neither tested nor treated. (Figure.)

Best clinical judgment. Regardless of the chosen test, we still need to interpret positive results, ie, use best clinical judgment. We know that even with pretest screening some positives tests will represent carriers or nonviable GAS. Yet true GAS pharyngitis needs antibiotic treatment to minimize nonpyogenic and pyogenic complications, plus reduce contagion/transmission risk and days of illness. Thus, we are forced to use best clinical judgment when considering if what could be GAS pharyngitis, particularly exudative pharyngitis, could actually be due to EBV, adenovirus, or gonococcus, each of which can mimic GAS findings. Differentiating these requires discussion beyond the scope of this article, but clues are often found in the history, the patient’s age, associated symptoms and distribution of tonsillopharyngeal exudate. Likewise Group C and G streptococcal pharyngitis can mimic GAS. Note: A comprehensive throat culture can identify these streptococci but requires a special order and likely a call to the laboratory.
Summary: The age-old problem persists, ie, differentiating the minority (~30%) of pharyngitis cases needing antibiotics from the majority that do not. We all wish to promptly treat true GAS pharyngitis; however our current tools remain imperfect. That said, we should strive to correctly diagnose/manage as many patients with pharyngitis as possible. I, for one, can’t wait until we get a validated biomarker that confirms GAS as the culprit in pharyngitis episodes. In the meantime, most providers likely have clinic or hospital approved pathways for managing GAS pharyngitis, many of which are at least in part based on data from sources for this discussion. If not, a firm foundation for creating one can be found in sources among the reference list below. Finally, if you think such pathways somehow interfere with patient flow, consider that a busy multi-provider private practice successfully integrated pretest screening and a pathway while maintaining patient flow and improving antibiotic stewardship.7
*Focal pharyngotonsillar GAS infection is rare in children younger than 3 years old, when GAS nasal passage infection may manifest as streptococcosis.9
Dr Harrison is professor of pediatrics and pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, Missouri. He has no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
References
1. Bannerjee D, Selvarangan RS. The Evolution of Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis Testing. Association for Diagnostics and Laboratory Medicine, 2018, Sep 1.
2. Cohen JF et al. Group A Streptococcus Pharyngitis in Children: New Perspectives on Rapid Diagnostic Testing and Antimicrobial Stewardship. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2024 Apr 24;13(4):250-256. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piae0223.
3. Boyanton Jr BL et al. Current Laboratory and Point-of-Care Pharyngitis Diagnostic Testing and Knowledge Gaps. J Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 23;230(Suppl 3):S182–S189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiae415.
4. Group A Strep Infection. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2024, Mar 1.
5. Shulman ST et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis: 2012 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis. 2012 Nov 15;55(10):e86-102. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis629.
6. Rao A et al. Diagnosis and Antibiotic Treatment of Group A Streptococcal Pharyngitis in Children in a Primary Care Setting: Impact of Point-of-Care Polymerase Chain Reaction. BMC Pediatr. 2019 Jan 16;19(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1393-y.
7. Norton LE et al. Improving Guideline-Based Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing: A Quality Improvement Initiative. Pediatrics. 2018 Jul;142(1):e20172033. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-2033.
8. MD+ Calc website. Centor Score (Modified/McIsaac) for Strep Pharyngitis.
9. Langlois DM, Andreae M. Group A Streptococcal Infections. Pediatr Rev. 2011 Oct;32(10):423-9; quiz 430. doi: 10.1542/pir.32-10-423.
Crying Tolerance
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Most of the papers I review merely validate a relationship that most of us, including the investigators, have already assumed based on common sense. However, every now and then I encounter a study whose findings clearly don’t support the researchers’ initial thesis. The most recent example of this unexpected finding is a paper designed to determine whether the sound of a crying infant would have an effect on a parent’s ability to accurately mix formula.
After a cursory reading of the investigators’ plan, most of us would have assumed from our own difficulties trying to accomplish something while our infant is crying that the crying would have a negative effect on our accuracy. Especially if it was a task that required careful measurement. However, when I skipped ahead to read the paper’s conclusion I was surprised that the investigators could found no significant negative relationship.
The explanation for this counterintuitive finding became readily apparent when I read the details of the study’s design more carefully. The investigators had chosen to use a generic recording of an infant crying, not the parent’s child nor even a live generic child on site.
No one enjoys listening to a child cry. It is certainly not a pleasant sound to the human ear. We seem to be hardwired to find it irritating. But, listening to our own child cry raises an entirely different suite of emotions, particularly if the child is close enough for us to intervene.
I’m not sure exactly what made the investigators choose a generic recording, but I suspect it was less expensive. Otherwise it would have required that the parents agree to subjecting their child to some stimulus that would have predictably induced the child to cry. Fortunately, the investigators were able to regroup in the wake of this lack of common sense in their experimental design and realized that, while their data failed to show a negative association with crying, it did provide an important message. Formula mixing errors, some with potentially harmful consequences, are far too common. In a commentary accompanying this paper, a pediatrician not involved in the study observes that, in our efforts to promote breastfeeding, we have given short shrift to teaching parents about accurate and safe formula preparation.
But, let’s return to the crying piece. Why is it so difficult for parents to tolerate their own crying infant? Common sense should tell us that we know our infant is helpless. The little child is totally reliant on us to for nutrition and protection from the ever-present environmental threats to its health and safety in the environment. In short, whether we are parents, daycare providers, or the mother’s boyfriend who has been left in charge, we are totally responsible for the life of that infant, at times a heavy burden.
That example of biologic variability is just one of the reasons why so many families find it difficult to set limits and follow through with consequences. When I have written about and spoken to parents in the office about discipline, I am happy if I can convince both parents to be on the same page (literally sometimes) in how they respond to their crying child.
Helping an infant learn to put itself to sleep is usually the first challenge that requires some agreement between parents on how long they can tolerate crying. Although allowing the infant to cry itself to sleep may be the best and most efficient strategy, it isn’t going to work when two parents and/or caregivers have widely different cry tolerances. In some situations these discrepancies can be managed by having the less tolerant parent temporarily move himself/herself to a location out of earshot. Something often easier said than accomplished.
At the heart of the solution is an acceptance by both parents that differing cry intolerances are not unusual and don’t imply that one partner is a better parent. As advisors we also must accept this reality and help the family find some other solution. Nothing is gained by allowing a disagreement between parents to make an already uncomfortable situation any worse.
While we don’t give out merit badges for it, being able to tolerate one’s own child crying for brief periods of time is a gift that can be helpful in certain situations. It is not a skill listed in the curriculum of most parenting classes, but learning more about what prompts babies to cry can be very helpful. This educational approach is exemplified by a Pediatrics Patient Page in a recent issue of JAMA Pediatrics. It’s rarely hunger and most often is sleep deprivation. It’s rarely the result of an undiscovered injury or medical condition, but may be a response to an overstimulating environment.
For those of us who are advisers, one of our responsibilities is to be alert to those few individuals whose intolerance to crying is so great that they are likely to injure the child or its mother to stop the crying. The simple question at an early well-child visit should be something like “How is everyone in the house when the child starts crying” might save a life. The stereotypic example is the young boyfriend of the mother, who may suspect that he is not the biologic father. However, any parent who is feeling insecure because of a financial situation, poor physical or mental health, or fatigue may lash out to achieve quiet. Crying is one of the realities of infancy. It is our job to help parents cope with it safely.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
Online CBT for Patients with AD: Self-Guided vs. Clinician-Guided Intervention Compared
TOPLINE:
A brief on the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-blind randomized clinical noninferiority trial at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden, enrolling 168 adults with AD (mean age, 39 years; 84.5% women) from November 2022 to April 2023.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either a 12-week self-guided online CBT intervention (n = 86) without clinician support or a comprehensive 12-week clinician-guided online CBT program (n = 82).
- The primary outcome was the change in POEM score from baseline; reduction of 4 or more points was considered a response, and the predefined noninferiority margin was 3 points.
TAKEAWAY:
- The clinician-guided group improved by 4.20 points on POEM, while the self-guided group improved by 4.60 points, with an estimated mean difference in change of 0.36 points, which was below noninferiority margin.
- Clinicians spent a mean of 36 minutes on treatment guidance and an additional 14 minutes on assessments in the clinician-guided group, whereas they spent only 15.8 minutes on assessments in the self-guided group.
- Both groups demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life, sleep, depressive mood, pruritus, and stress, with no serious adverse events being reported.
- Completion rates were higher in the self-guided group with 81% of participants completing five or more modules, compared with 67% in the clinician-guided group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, the findings support a self-guided intervention as a noninferior and cost-effective alternative to a previously evaluated clinician-guided treatment,” the authors wrote. “Because psychological interventions are rare in dermatological care, this study is an important step toward implementation of CBT for people with AD. The effectiveness of CBT interventions in primary and dermatological specialist care should be investigated.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dorian Kern, PhD, Division of Psychology, Karolinska Institutet, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
High data loss for secondary measurements could affect interpretation of these results. The study relied solely on self-reported measures. The predominance of women participants and the Swedish-language requirement may have limited participation from migrant populations, which could hinder the broader implementation of the study’s findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Kern reported receiving grants from the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs during the conduct of the study. Other authors also reported authorships and royalties, personal fees, grants, or held stocks in DahliaQomit.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A brief on the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-blind randomized clinical noninferiority trial at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden, enrolling 168 adults with AD (mean age, 39 years; 84.5% women) from November 2022 to April 2023.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either a 12-week self-guided online CBT intervention (n = 86) without clinician support or a comprehensive 12-week clinician-guided online CBT program (n = 82).
- The primary outcome was the change in POEM score from baseline; reduction of 4 or more points was considered a response, and the predefined noninferiority margin was 3 points.
TAKEAWAY:
- The clinician-guided group improved by 4.20 points on POEM, while the self-guided group improved by 4.60 points, with an estimated mean difference in change of 0.36 points, which was below noninferiority margin.
- Clinicians spent a mean of 36 minutes on treatment guidance and an additional 14 minutes on assessments in the clinician-guided group, whereas they spent only 15.8 minutes on assessments in the self-guided group.
- Both groups demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life, sleep, depressive mood, pruritus, and stress, with no serious adverse events being reported.
- Completion rates were higher in the self-guided group with 81% of participants completing five or more modules, compared with 67% in the clinician-guided group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, the findings support a self-guided intervention as a noninferior and cost-effective alternative to a previously evaluated clinician-guided treatment,” the authors wrote. “Because psychological interventions are rare in dermatological care, this study is an important step toward implementation of CBT for people with AD. The effectiveness of CBT interventions in primary and dermatological specialist care should be investigated.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dorian Kern, PhD, Division of Psychology, Karolinska Institutet, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
High data loss for secondary measurements could affect interpretation of these results. The study relied solely on self-reported measures. The predominance of women participants and the Swedish-language requirement may have limited participation from migrant populations, which could hinder the broader implementation of the study’s findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Kern reported receiving grants from the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs during the conduct of the study. Other authors also reported authorships and royalties, personal fees, grants, or held stocks in DahliaQomit.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A brief on the Patient-Oriented Eczema Measure (POEM).
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers conducted a single-blind randomized clinical noninferiority trial at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm, Sweden, enrolling 168 adults with AD (mean age, 39 years; 84.5% women) from November 2022 to April 2023.
- Participants were randomly assigned to either a 12-week self-guided online CBT intervention (n = 86) without clinician support or a comprehensive 12-week clinician-guided online CBT program (n = 82).
- The primary outcome was the change in POEM score from baseline; reduction of 4 or more points was considered a response, and the predefined noninferiority margin was 3 points.
TAKEAWAY:
- The clinician-guided group improved by 4.20 points on POEM, while the self-guided group improved by 4.60 points, with an estimated mean difference in change of 0.36 points, which was below noninferiority margin.
- Clinicians spent a mean of 36 minutes on treatment guidance and an additional 14 minutes on assessments in the clinician-guided group, whereas they spent only 15.8 minutes on assessments in the self-guided group.
- Both groups demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life, sleep, depressive mood, pruritus, and stress, with no serious adverse events being reported.
- Completion rates were higher in the self-guided group with 81% of participants completing five or more modules, compared with 67% in the clinician-guided group.
IN PRACTICE:
“Overall, the findings support a self-guided intervention as a noninferior and cost-effective alternative to a previously evaluated clinician-guided treatment,” the authors wrote. “Because psychological interventions are rare in dermatological care, this study is an important step toward implementation of CBT for people with AD. The effectiveness of CBT interventions in primary and dermatological specialist care should be investigated.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Dorian Kern, PhD, Division of Psychology, Karolinska Institutet, and was published online in JAMA Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
High data loss for secondary measurements could affect interpretation of these results. The study relied solely on self-reported measures. The predominance of women participants and the Swedish-language requirement may have limited participation from migrant populations, which could hinder the broader implementation of the study’s findings.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Kern reported receiving grants from the Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs during the conduct of the study. Other authors also reported authorships and royalties, personal fees, grants, or held stocks in DahliaQomit.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Central Line Skin Reactions in Children: Survey Addresses Treatment Protocols in Use
TOPLINE:
A and reported varying management approaches.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers developed and administered a 14-item Qualtrics survey to 107 dermatologists providing pediatric inpatient care through the Society for Pediatric Dermatology’s Inpatient Dermatology Section and Section Chief email lists.
- A total of 35 dermatologists (33%) from multiple institutions responded to the survey; most respondents (94%) specialized in pediatric dermatology.
- Researchers assessed management of CLD-associated adverse skin reactions.
TAKEAWAY:
- All respondents reported receiving CLD-related consults, but 66% indicated there was no personal or institutional standardized approach for managing CLD-associated skin reactions.
- Respondents said most reactions were in children aged 1-12 years (19 or 76% of 25 respondents) compared with those aged < 1 year (3 or 12% of 25 respondents).
- Management strategies included switching to alternative products, applying topical corticosteroids, and performing patch testing for allergies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insights derived from this study, including variation in clinician familiarity with reaction patterns, underscore the necessity of a standardized protocol for classifying and managing cutaneous CLD reactions in pediatric patients,” the authors wrote. “Further investigation is needed to better characterize CLD-associated allergic CD [contact dermatitis], irritant CD, and skin infections, as well as at-risk populations, to better inform clinical approaches,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Carly Mulinda, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, and was published online on December 16 in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors noted variable respondent awareness of institutional CLD and potential recency bias as key limitations of the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Study funding source was not declared. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A and reported varying management approaches.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers developed and administered a 14-item Qualtrics survey to 107 dermatologists providing pediatric inpatient care through the Society for Pediatric Dermatology’s Inpatient Dermatology Section and Section Chief email lists.
- A total of 35 dermatologists (33%) from multiple institutions responded to the survey; most respondents (94%) specialized in pediatric dermatology.
- Researchers assessed management of CLD-associated adverse skin reactions.
TAKEAWAY:
- All respondents reported receiving CLD-related consults, but 66% indicated there was no personal or institutional standardized approach for managing CLD-associated skin reactions.
- Respondents said most reactions were in children aged 1-12 years (19 or 76% of 25 respondents) compared with those aged < 1 year (3 or 12% of 25 respondents).
- Management strategies included switching to alternative products, applying topical corticosteroids, and performing patch testing for allergies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insights derived from this study, including variation in clinician familiarity with reaction patterns, underscore the necessity of a standardized protocol for classifying and managing cutaneous CLD reactions in pediatric patients,” the authors wrote. “Further investigation is needed to better characterize CLD-associated allergic CD [contact dermatitis], irritant CD, and skin infections, as well as at-risk populations, to better inform clinical approaches,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Carly Mulinda, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, and was published online on December 16 in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors noted variable respondent awareness of institutional CLD and potential recency bias as key limitations of the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Study funding source was not declared. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A and reported varying management approaches.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers developed and administered a 14-item Qualtrics survey to 107 dermatologists providing pediatric inpatient care through the Society for Pediatric Dermatology’s Inpatient Dermatology Section and Section Chief email lists.
- A total of 35 dermatologists (33%) from multiple institutions responded to the survey; most respondents (94%) specialized in pediatric dermatology.
- Researchers assessed management of CLD-associated adverse skin reactions.
TAKEAWAY:
- All respondents reported receiving CLD-related consults, but 66% indicated there was no personal or institutional standardized approach for managing CLD-associated skin reactions.
- Respondents said most reactions were in children aged 1-12 years (19 or 76% of 25 respondents) compared with those aged < 1 year (3 or 12% of 25 respondents).
- Management strategies included switching to alternative products, applying topical corticosteroids, and performing patch testing for allergies.
IN PRACTICE:
“Insights derived from this study, including variation in clinician familiarity with reaction patterns, underscore the necessity of a standardized protocol for classifying and managing cutaneous CLD reactions in pediatric patients,” the authors wrote. “Further investigation is needed to better characterize CLD-associated allergic CD [contact dermatitis], irritant CD, and skin infections, as well as at-risk populations, to better inform clinical approaches,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Carly Mulinda, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, and was published online on December 16 in Pediatric Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
The authors noted variable respondent awareness of institutional CLD and potential recency bias as key limitations of the study.
DISCLOSURES:
Study funding source was not declared. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Brain Changes in Youth Who Use Substances: Cause or Effect?
A widely accepted assumption in the addiction field is that neuroanatomical changes observed in young people who use alcohol or other substances are largely the consequence of exposure to these substances.
But a new study suggests that neuroanatomical features in children, including greater whole brain and cortical volumes, are evident before exposure to any substances.
The investigators, led by Alex P. Miller, PhD, assistant professor, Department of Psychiatry, Indiana University, Indianapolis, noted that the findings add to a growing body of work that suggests
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Neuroanatomy a Predisposing Risk Factor?
Earlier research showed that substance use is associated with lower gray matter volume, thinner cortex, and less white matter integrity. While it has been widely thought that these changes were induced by the use of alcohol or illicit drugs, recent longitudinal and genetic studies suggest that the neuroanatomical changes may also be predisposing risk factors for substance use.
To better understand the issue, investigators analyzed data on 9804 children (mean baseline age, 9.9 years; 53% men; 76% White) at 22 US sites enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study that’s examining brain and behavioral development from middle childhood to young adulthood.
The researchers collected information on the use of alcohol, nicotine, cannabis, and other illicit substances from in-person interviews at baseline and years 1, 2, and 3, as well as interim phone interviews at 6, 18, and 30 months. MRI scans provided extensive brain structural data, including global and regional cortical volume, thickness, surface area, sulcal depth, and subcortical volume.
Of the total, 3460 participants (35%) initiated substance use before age 15, with 90% reporting alcohol use initiation. There was considerable overlap between initiation of alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis.
The researchers tested whether baseline neuroanatomical variability was associated with any substance use initiation before or up to 3 years following initial neuroimaging scans. Study covariates included baseline age, sex, pubertal status, familial relationship (eg, sibling or twin), and prenatal substance exposures. Researchers didn’t control for sociodemographic characteristics as these could influence associations.
Significant Brain Differences
Compared with no substance use initiation, any substance use initiation was associated with larger global neuroanatomical indices, including whole brain (beta = 0.05; P = 2.80 × 10–8), total intracranial (beta = 0.04; P = 3.49 × 10−6), cortical (beta = 0.05; P = 4.31 × 10–8), and subcortical volumes (beta = 0.05; P = 4.39 × 10–8), as well as greater total cortical surface area (beta = 0.04; P = 6.05 × 10–7).
The direction of associations between cortical thickness and substance use initiation was regionally specific; any substance use initiation was characterized by thinner cortex in all frontal regions (eg, rostral middle frontal gyrus, beta = −0.03; P = 6.99 × 10–6), but thicker cortex in all other lobes. It was also associated with larger regional brain volumes, deeper regional sulci, and differences in regional cortical surface area.
The authors noted total cortical thickness peaks at age 1.7 years and steadily declines throughout life. By contrast, subcortical volumes peak at 14.4 years of age and generally remain stable before steep later life declines.
Secondary analyses compared initiation of the three most commonly used substances in early adolescence (alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis) with no substance use.
Findings for alcohol largely mirrored those for any substance use. However, the study uncovered additional significant associations, including greater left lateral occipital volume and bilateral para-hippocampal gyri cortical thickness and less bilateral superior frontal gyri cortical thickness.
Nicotine use was associated with lower right superior frontal gyrus volume and deeper left lateral orbitofrontal cortex sulci. And cannabis use was associated with thinner left precentral gyrus and lower right inferior parietal gyrus and right caudate volumes.
The authors noted results for nicotine and cannabis may not have had adequate statistical power, and small effects suggest these findings aren’t clinically informative for individuals. However, they wrote, “They do inform and challenge current theoretical models of addiction.”
Associations Precede Substance Use
A post hoc analysis further challenges current models of addiction. When researchers looked only at the 1203 youth who initiated substance use after the baseline neuroimaging session, they found most associations preceded substance use.
“That regional associations may precede substance use initiation, including less cortical thickness in the right rostral middle frontal gyrus, challenges predominant interpretations that these associations arise largely due to neurotoxic consequences of exposure and increases the plausibility that these features may, at least partially, reflect markers of predispositional risk,” wrote the authors.
A study limitation was that unmeasured confounders and undetected systemic differences in missing data may have influenced associations. Sociodemographic, environmental, and genetic variables that were not included as covariates are likely associated with both neuroanatomical variability and substance use initiation and may moderate associations between them, said the authors.
The ABCD Study provides “a robust and large database of longitudinal data” that goes beyond previous neuroimaging research “to understand the bidirectional relationship between brain structure and substance use,” Miller said in a press release.
“The hope is that these types of studies, in conjunction with other data on environmental exposures and genetic risk, could help change how we think about the development of substance use disorders and inform more accurate models of addiction moving forward,” Miller said.
Reevaluating Causal Assumptions
In an accompanying editorial, Felix Pichardo, MA, and Sylia Wilson, PhD, from the Institute of Child Development, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, suggested that it may be time to “reevaluate the causal assumptions that underlie brain disease models of addiction” and the mechanisms by which it develops, persists, and becomes harmful.
Neurotoxic effects of substances are central to current brain disease models of addiction, wrote Pichardo and Wilson. “Substance exposure is thought to affect cortical and subcortical regions that support interrelated systems, resulting in desensitization of reward-related processing, increased stress that prompts cravings, negative emotions when cravings are unsated, and weakening of cognitive control abilities that leads to repeated returns to use.”
The editorial writers praised the ABCD Study for its large sample size for providing a level of precision, statistical accuracy, and ability to identify both larger and smaller effects, which are critical for addiction research.
Unlike most addiction research that relies on cross-sectional designs, the current study used longitudinal assessments, which is another of its strengths, they noted.
“Longitudinal study designs like in the ABCD Study are fundamental for establishing temporal ordering across constructs, which is important because establishing temporal precedence is a key step in determining causal links and underlying mechanisms.”
The inclusion of several genetically informative components, such as the family study design, nested twin subsamples, and DNA collection, “allows researchers to extend beyond temporal precedence toward increased causal inference and identification of mechanisms,” they added.
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health. The study authors and editorial writers had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A widely accepted assumption in the addiction field is that neuroanatomical changes observed in young people who use alcohol or other substances are largely the consequence of exposure to these substances.
But a new study suggests that neuroanatomical features in children, including greater whole brain and cortical volumes, are evident before exposure to any substances.
The investigators, led by Alex P. Miller, PhD, assistant professor, Department of Psychiatry, Indiana University, Indianapolis, noted that the findings add to a growing body of work that suggests
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Neuroanatomy a Predisposing Risk Factor?
Earlier research showed that substance use is associated with lower gray matter volume, thinner cortex, and less white matter integrity. While it has been widely thought that these changes were induced by the use of alcohol or illicit drugs, recent longitudinal and genetic studies suggest that the neuroanatomical changes may also be predisposing risk factors for substance use.
To better understand the issue, investigators analyzed data on 9804 children (mean baseline age, 9.9 years; 53% men; 76% White) at 22 US sites enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study that’s examining brain and behavioral development from middle childhood to young adulthood.
The researchers collected information on the use of alcohol, nicotine, cannabis, and other illicit substances from in-person interviews at baseline and years 1, 2, and 3, as well as interim phone interviews at 6, 18, and 30 months. MRI scans provided extensive brain structural data, including global and regional cortical volume, thickness, surface area, sulcal depth, and subcortical volume.
Of the total, 3460 participants (35%) initiated substance use before age 15, with 90% reporting alcohol use initiation. There was considerable overlap between initiation of alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis.
The researchers tested whether baseline neuroanatomical variability was associated with any substance use initiation before or up to 3 years following initial neuroimaging scans. Study covariates included baseline age, sex, pubertal status, familial relationship (eg, sibling or twin), and prenatal substance exposures. Researchers didn’t control for sociodemographic characteristics as these could influence associations.
Significant Brain Differences
Compared with no substance use initiation, any substance use initiation was associated with larger global neuroanatomical indices, including whole brain (beta = 0.05; P = 2.80 × 10–8), total intracranial (beta = 0.04; P = 3.49 × 10−6), cortical (beta = 0.05; P = 4.31 × 10–8), and subcortical volumes (beta = 0.05; P = 4.39 × 10–8), as well as greater total cortical surface area (beta = 0.04; P = 6.05 × 10–7).
The direction of associations between cortical thickness and substance use initiation was regionally specific; any substance use initiation was characterized by thinner cortex in all frontal regions (eg, rostral middle frontal gyrus, beta = −0.03; P = 6.99 × 10–6), but thicker cortex in all other lobes. It was also associated with larger regional brain volumes, deeper regional sulci, and differences in regional cortical surface area.
The authors noted total cortical thickness peaks at age 1.7 years and steadily declines throughout life. By contrast, subcortical volumes peak at 14.4 years of age and generally remain stable before steep later life declines.
Secondary analyses compared initiation of the three most commonly used substances in early adolescence (alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis) with no substance use.
Findings for alcohol largely mirrored those for any substance use. However, the study uncovered additional significant associations, including greater left lateral occipital volume and bilateral para-hippocampal gyri cortical thickness and less bilateral superior frontal gyri cortical thickness.
Nicotine use was associated with lower right superior frontal gyrus volume and deeper left lateral orbitofrontal cortex sulci. And cannabis use was associated with thinner left precentral gyrus and lower right inferior parietal gyrus and right caudate volumes.
The authors noted results for nicotine and cannabis may not have had adequate statistical power, and small effects suggest these findings aren’t clinically informative for individuals. However, they wrote, “They do inform and challenge current theoretical models of addiction.”
Associations Precede Substance Use
A post hoc analysis further challenges current models of addiction. When researchers looked only at the 1203 youth who initiated substance use after the baseline neuroimaging session, they found most associations preceded substance use.
“That regional associations may precede substance use initiation, including less cortical thickness in the right rostral middle frontal gyrus, challenges predominant interpretations that these associations arise largely due to neurotoxic consequences of exposure and increases the plausibility that these features may, at least partially, reflect markers of predispositional risk,” wrote the authors.
A study limitation was that unmeasured confounders and undetected systemic differences in missing data may have influenced associations. Sociodemographic, environmental, and genetic variables that were not included as covariates are likely associated with both neuroanatomical variability and substance use initiation and may moderate associations between them, said the authors.
The ABCD Study provides “a robust and large database of longitudinal data” that goes beyond previous neuroimaging research “to understand the bidirectional relationship between brain structure and substance use,” Miller said in a press release.
“The hope is that these types of studies, in conjunction with other data on environmental exposures and genetic risk, could help change how we think about the development of substance use disorders and inform more accurate models of addiction moving forward,” Miller said.
Reevaluating Causal Assumptions
In an accompanying editorial, Felix Pichardo, MA, and Sylia Wilson, PhD, from the Institute of Child Development, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, suggested that it may be time to “reevaluate the causal assumptions that underlie brain disease models of addiction” and the mechanisms by which it develops, persists, and becomes harmful.
Neurotoxic effects of substances are central to current brain disease models of addiction, wrote Pichardo and Wilson. “Substance exposure is thought to affect cortical and subcortical regions that support interrelated systems, resulting in desensitization of reward-related processing, increased stress that prompts cravings, negative emotions when cravings are unsated, and weakening of cognitive control abilities that leads to repeated returns to use.”
The editorial writers praised the ABCD Study for its large sample size for providing a level of precision, statistical accuracy, and ability to identify both larger and smaller effects, which are critical for addiction research.
Unlike most addiction research that relies on cross-sectional designs, the current study used longitudinal assessments, which is another of its strengths, they noted.
“Longitudinal study designs like in the ABCD Study are fundamental for establishing temporal ordering across constructs, which is important because establishing temporal precedence is a key step in determining causal links and underlying mechanisms.”
The inclusion of several genetically informative components, such as the family study design, nested twin subsamples, and DNA collection, “allows researchers to extend beyond temporal precedence toward increased causal inference and identification of mechanisms,” they added.
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health. The study authors and editorial writers had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A widely accepted assumption in the addiction field is that neuroanatomical changes observed in young people who use alcohol or other substances are largely the consequence of exposure to these substances.
But a new study suggests that neuroanatomical features in children, including greater whole brain and cortical volumes, are evident before exposure to any substances.
The investigators, led by Alex P. Miller, PhD, assistant professor, Department of Psychiatry, Indiana University, Indianapolis, noted that the findings add to a growing body of work that suggests
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Neuroanatomy a Predisposing Risk Factor?
Earlier research showed that substance use is associated with lower gray matter volume, thinner cortex, and less white matter integrity. While it has been widely thought that these changes were induced by the use of alcohol or illicit drugs, recent longitudinal and genetic studies suggest that the neuroanatomical changes may also be predisposing risk factors for substance use.
To better understand the issue, investigators analyzed data on 9804 children (mean baseline age, 9.9 years; 53% men; 76% White) at 22 US sites enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study that’s examining brain and behavioral development from middle childhood to young adulthood.
The researchers collected information on the use of alcohol, nicotine, cannabis, and other illicit substances from in-person interviews at baseline and years 1, 2, and 3, as well as interim phone interviews at 6, 18, and 30 months. MRI scans provided extensive brain structural data, including global and regional cortical volume, thickness, surface area, sulcal depth, and subcortical volume.
Of the total, 3460 participants (35%) initiated substance use before age 15, with 90% reporting alcohol use initiation. There was considerable overlap between initiation of alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis.
The researchers tested whether baseline neuroanatomical variability was associated with any substance use initiation before or up to 3 years following initial neuroimaging scans. Study covariates included baseline age, sex, pubertal status, familial relationship (eg, sibling or twin), and prenatal substance exposures. Researchers didn’t control for sociodemographic characteristics as these could influence associations.
Significant Brain Differences
Compared with no substance use initiation, any substance use initiation was associated with larger global neuroanatomical indices, including whole brain (beta = 0.05; P = 2.80 × 10–8), total intracranial (beta = 0.04; P = 3.49 × 10−6), cortical (beta = 0.05; P = 4.31 × 10–8), and subcortical volumes (beta = 0.05; P = 4.39 × 10–8), as well as greater total cortical surface area (beta = 0.04; P = 6.05 × 10–7).
The direction of associations between cortical thickness and substance use initiation was regionally specific; any substance use initiation was characterized by thinner cortex in all frontal regions (eg, rostral middle frontal gyrus, beta = −0.03; P = 6.99 × 10–6), but thicker cortex in all other lobes. It was also associated with larger regional brain volumes, deeper regional sulci, and differences in regional cortical surface area.
The authors noted total cortical thickness peaks at age 1.7 years and steadily declines throughout life. By contrast, subcortical volumes peak at 14.4 years of age and generally remain stable before steep later life declines.
Secondary analyses compared initiation of the three most commonly used substances in early adolescence (alcohol, nicotine, and cannabis) with no substance use.
Findings for alcohol largely mirrored those for any substance use. However, the study uncovered additional significant associations, including greater left lateral occipital volume and bilateral para-hippocampal gyri cortical thickness and less bilateral superior frontal gyri cortical thickness.
Nicotine use was associated with lower right superior frontal gyrus volume and deeper left lateral orbitofrontal cortex sulci. And cannabis use was associated with thinner left precentral gyrus and lower right inferior parietal gyrus and right caudate volumes.
The authors noted results for nicotine and cannabis may not have had adequate statistical power, and small effects suggest these findings aren’t clinically informative for individuals. However, they wrote, “They do inform and challenge current theoretical models of addiction.”
Associations Precede Substance Use
A post hoc analysis further challenges current models of addiction. When researchers looked only at the 1203 youth who initiated substance use after the baseline neuroimaging session, they found most associations preceded substance use.
“That regional associations may precede substance use initiation, including less cortical thickness in the right rostral middle frontal gyrus, challenges predominant interpretations that these associations arise largely due to neurotoxic consequences of exposure and increases the plausibility that these features may, at least partially, reflect markers of predispositional risk,” wrote the authors.
A study limitation was that unmeasured confounders and undetected systemic differences in missing data may have influenced associations. Sociodemographic, environmental, and genetic variables that were not included as covariates are likely associated with both neuroanatomical variability and substance use initiation and may moderate associations between them, said the authors.
The ABCD Study provides “a robust and large database of longitudinal data” that goes beyond previous neuroimaging research “to understand the bidirectional relationship between brain structure and substance use,” Miller said in a press release.
“The hope is that these types of studies, in conjunction with other data on environmental exposures and genetic risk, could help change how we think about the development of substance use disorders and inform more accurate models of addiction moving forward,” Miller said.
Reevaluating Causal Assumptions
In an accompanying editorial, Felix Pichardo, MA, and Sylia Wilson, PhD, from the Institute of Child Development, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, suggested that it may be time to “reevaluate the causal assumptions that underlie brain disease models of addiction” and the mechanisms by which it develops, persists, and becomes harmful.
Neurotoxic effects of substances are central to current brain disease models of addiction, wrote Pichardo and Wilson. “Substance exposure is thought to affect cortical and subcortical regions that support interrelated systems, resulting in desensitization of reward-related processing, increased stress that prompts cravings, negative emotions when cravings are unsated, and weakening of cognitive control abilities that leads to repeated returns to use.”
The editorial writers praised the ABCD Study for its large sample size for providing a level of precision, statistical accuracy, and ability to identify both larger and smaller effects, which are critical for addiction research.
Unlike most addiction research that relies on cross-sectional designs, the current study used longitudinal assessments, which is another of its strengths, they noted.
“Longitudinal study designs like in the ABCD Study are fundamental for establishing temporal ordering across constructs, which is important because establishing temporal precedence is a key step in determining causal links and underlying mechanisms.”
The inclusion of several genetically informative components, such as the family study design, nested twin subsamples, and DNA collection, “allows researchers to extend beyond temporal precedence toward increased causal inference and identification of mechanisms,” they added.
The study received support from the National Institutes of Health. The study authors and editorial writers had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Medical Education and Firearm-Related Deaths
For the third straight year, firearms killed more children and teens than any other cause, including motor vehicle crashes and cancer. The population-wide toll taken by guns is equally as discouraging. Finally, this elephant in the room is getting some attention from the medical community, but the voices asking for change have most recently been coming from medical students who feel that gun violence deserves to be given a larger role in their education. It’s unclear why this plea is coming from the younger end of the medical community. It may be that, unlike most of their older instructors, these 18- to 25-year-olds have grown up under the growing threat of school shootings and become uncomfortably accustomed to active shooter drills.
Should We Look to Medical School for Answers?
But, does the medical community need to take gun violence more seriously than the rest of the population? What should our response look like? To answer those questions we need to take several steps back to view the bigger picture.
Is the medical community more responsible for this current situation than any other segment of the population? Do physicians bear any more culpability than publishers who sell gun-related magazines? Since its inception pediatrics has taken on the role of advocate for children and their health and well-being. But, is there more we can and should do other than turn up the volume on our advocacy?
While still taking the longer view, let’s ask ourselves what the role of medical school should be. Not just with respect to gun violence but in producing physicians and healthcare providers. We are approaching a crisis in primary care as it loses appeal with physicians at both ends of the age continuum. It could be because it pays poorly — certainly in relation to the cost of medical school — or because the awareness that if done well primary care requires a commitment that is difficult to square with many individuals’ lifestyle expectations.
Is the traditional medical school the right place to be training primary care providers? Medical school is currently aimed at broad and deep exposure. The student will be exposed to the all the diseases to which he or she might be seeing anywhere in the world and at the same time will have learned the mechanisms down to the cellular level that lies behind that pathology. Does a primary care pediatrician practicing in a small city or suburbia need that depth of training? He or she might benefit from some breadth. But maybe it should be focused on socioeconomic and geographic population the doctor is likely to see. This is particularly true for gun-related deaths.
Returning our attention to gun violence and its relation to healthcare, let’s ask ourselves what role the traditional medical school should play. Should it be a breeding ground for gun control advocates? When physicians speak people tend to listen but our effectiveness on issues such as immunizations and gun control has not been what many have hoped for. The supply of guns available to the public in this country is staggering and certainly contributes to gun-related injuries and death. However, I’m afraid that making a significant dent in that supply, given our political history and current climate, is an issue whose ship has sailed.
On the other hand, as gun advocates are often quoted as saying, “it’s not guns that kill, it’s people.” We don’t need to go into to the fallacy of this argument, but it gives us a starting point from which a medical school might focus its efforts on addressing the fallout from gun violence. A curriculum that begins with a presentation of the grizzly statistics and moves on to research about gun-related mental health issues and the social environments that breed violence makes good sense. Recanting the depressing history of how our society got to this place, in which guns outnumber people, should be part of the undergraduate curriculum.
Addressing the specifics of gun safety and suicide prevention in general with families and individuals would be more appropriate during clinical specialty training.
How big a chunk of the curriculum should be committed to gun violence and its fallout? Some of the call for change seems to be suggesting a semester-long course. However, we must accept the reality that instructional time in medical school is a finite asset. Although gunshots are the leading cause of death in children, how effective will even the most cleverly crafted curriculum be in moving the needle on the embarrassing data?
Given what is known about the problem, a day, or at most a week would be sufficient in class time. This could include personal presentations by victims or family members. I’m sure there are some who would see that as insufficient. But I see it as realistic. For the large urban schools, observing an evening shift in the trauma unit of an ER could be a potent addition.
Beyond this, a commitment by the school to host seminars and workshops devoted to gun violence could be an important component. It might also be helpful for a school or training program to promote the habit of whenever an instructor is introducing a potentially fatal disease to the students for the first time, he or she would begin with “To put this in perspective, you should remember that xxx thousand children die of gunshot wounds every year.”
Unfortunately, like obesity, gun-related deaths and injuries are the result of our society’s failure to muster the political will to act in our best interest as a nation. The medical community is left to clean up the collateral damage. There is always more that we could do, but we must be thoughtful in how we invest our energies in the effort.
Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
For the third straight year, firearms killed more children and teens than any other cause, including motor vehicle crashes and cancer. The population-wide toll taken by guns is equally as discouraging. Finally, this elephant in the room is getting some attention from the medical community, but the voices asking for change have most recently been coming from medical students who feel that gun violence deserves to be given a larger role in their education. It’s unclear why this plea is coming from the younger end of the medical community. It may be that, unlike most of their older instructors, these 18- to 25-year-olds have grown up under the growing threat of school shootings and become uncomfortably accustomed to active shooter drills.
Should We Look to Medical School for Answers?
But, does the medical community need to take gun violence more seriously than the rest of the population? What should our response look like? To answer those questions we need to take several steps back to view the bigger picture.
Is the medical community more responsible for this current situation than any other segment of the population? Do physicians bear any more culpability than publishers who sell gun-related magazines? Since its inception pediatrics has taken on the role of advocate for children and their health and well-being. But, is there more we can and should do other than turn up the volume on our advocacy?
While still taking the longer view, let’s ask ourselves what the role of medical school should be. Not just with respect to gun violence but in producing physicians and healthcare providers. We are approaching a crisis in primary care as it loses appeal with physicians at both ends of the age continuum. It could be because it pays poorly — certainly in relation to the cost of medical school — or because the awareness that if done well primary care requires a commitment that is difficult to square with many individuals’ lifestyle expectations.
Is the traditional medical school the right place to be training primary care providers? Medical school is currently aimed at broad and deep exposure. The student will be exposed to the all the diseases to which he or she might be seeing anywhere in the world and at the same time will have learned the mechanisms down to the cellular level that lies behind that pathology. Does a primary care pediatrician practicing in a small city or suburbia need that depth of training? He or she might benefit from some breadth. But maybe it should be focused on socioeconomic and geographic population the doctor is likely to see. This is particularly true for gun-related deaths.
Returning our attention to gun violence and its relation to healthcare, let’s ask ourselves what role the traditional medical school should play. Should it be a breeding ground for gun control advocates? When physicians speak people tend to listen but our effectiveness on issues such as immunizations and gun control has not been what many have hoped for. The supply of guns available to the public in this country is staggering and certainly contributes to gun-related injuries and death. However, I’m afraid that making a significant dent in that supply, given our political history and current climate, is an issue whose ship has sailed.
On the other hand, as gun advocates are often quoted as saying, “it’s not guns that kill, it’s people.” We don’t need to go into to the fallacy of this argument, but it gives us a starting point from which a medical school might focus its efforts on addressing the fallout from gun violence. A curriculum that begins with a presentation of the grizzly statistics and moves on to research about gun-related mental health issues and the social environments that breed violence makes good sense. Recanting the depressing history of how our society got to this place, in which guns outnumber people, should be part of the undergraduate curriculum.
Addressing the specifics of gun safety and suicide prevention in general with families and individuals would be more appropriate during clinical specialty training.
How big a chunk of the curriculum should be committed to gun violence and its fallout? Some of the call for change seems to be suggesting a semester-long course. However, we must accept the reality that instructional time in medical school is a finite asset. Although gunshots are the leading cause of death in children, how effective will even the most cleverly crafted curriculum be in moving the needle on the embarrassing data?
Given what is known about the problem, a day, or at most a week would be sufficient in class time. This could include personal presentations by victims or family members. I’m sure there are some who would see that as insufficient. But I see it as realistic. For the large urban schools, observing an evening shift in the trauma unit of an ER could be a potent addition.
Beyond this, a commitment by the school to host seminars and workshops devoted to gun violence could be an important component. It might also be helpful for a school or training program to promote the habit of whenever an instructor is introducing a potentially fatal disease to the students for the first time, he or she would begin with “To put this in perspective, you should remember that xxx thousand children die of gunshot wounds every year.”
Unfortunately, like obesity, gun-related deaths and injuries are the result of our society’s failure to muster the political will to act in our best interest as a nation. The medical community is left to clean up the collateral damage. There is always more that we could do, but we must be thoughtful in how we invest our energies in the effort.
Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
For the third straight year, firearms killed more children and teens than any other cause, including motor vehicle crashes and cancer. The population-wide toll taken by guns is equally as discouraging. Finally, this elephant in the room is getting some attention from the medical community, but the voices asking for change have most recently been coming from medical students who feel that gun violence deserves to be given a larger role in their education. It’s unclear why this plea is coming from the younger end of the medical community. It may be that, unlike most of their older instructors, these 18- to 25-year-olds have grown up under the growing threat of school shootings and become uncomfortably accustomed to active shooter drills.
Should We Look to Medical School for Answers?
But, does the medical community need to take gun violence more seriously than the rest of the population? What should our response look like? To answer those questions we need to take several steps back to view the bigger picture.
Is the medical community more responsible for this current situation than any other segment of the population? Do physicians bear any more culpability than publishers who sell gun-related magazines? Since its inception pediatrics has taken on the role of advocate for children and their health and well-being. But, is there more we can and should do other than turn up the volume on our advocacy?
While still taking the longer view, let’s ask ourselves what the role of medical school should be. Not just with respect to gun violence but in producing physicians and healthcare providers. We are approaching a crisis in primary care as it loses appeal with physicians at both ends of the age continuum. It could be because it pays poorly — certainly in relation to the cost of medical school — or because the awareness that if done well primary care requires a commitment that is difficult to square with many individuals’ lifestyle expectations.
Is the traditional medical school the right place to be training primary care providers? Medical school is currently aimed at broad and deep exposure. The student will be exposed to the all the diseases to which he or she might be seeing anywhere in the world and at the same time will have learned the mechanisms down to the cellular level that lies behind that pathology. Does a primary care pediatrician practicing in a small city or suburbia need that depth of training? He or she might benefit from some breadth. But maybe it should be focused on socioeconomic and geographic population the doctor is likely to see. This is particularly true for gun-related deaths.
Returning our attention to gun violence and its relation to healthcare, let’s ask ourselves what role the traditional medical school should play. Should it be a breeding ground for gun control advocates? When physicians speak people tend to listen but our effectiveness on issues such as immunizations and gun control has not been what many have hoped for. The supply of guns available to the public in this country is staggering and certainly contributes to gun-related injuries and death. However, I’m afraid that making a significant dent in that supply, given our political history and current climate, is an issue whose ship has sailed.
On the other hand, as gun advocates are often quoted as saying, “it’s not guns that kill, it’s people.” We don’t need to go into to the fallacy of this argument, but it gives us a starting point from which a medical school might focus its efforts on addressing the fallout from gun violence. A curriculum that begins with a presentation of the grizzly statistics and moves on to research about gun-related mental health issues and the social environments that breed violence makes good sense. Recanting the depressing history of how our society got to this place, in which guns outnumber people, should be part of the undergraduate curriculum.
Addressing the specifics of gun safety and suicide prevention in general with families and individuals would be more appropriate during clinical specialty training.
How big a chunk of the curriculum should be committed to gun violence and its fallout? Some of the call for change seems to be suggesting a semester-long course. However, we must accept the reality that instructional time in medical school is a finite asset. Although gunshots are the leading cause of death in children, how effective will even the most cleverly crafted curriculum be in moving the needle on the embarrassing data?
Given what is known about the problem, a day, or at most a week would be sufficient in class time. This could include personal presentations by victims or family members. I’m sure there are some who would see that as insufficient. But I see it as realistic. For the large urban schools, observing an evening shift in the trauma unit of an ER could be a potent addition.
Beyond this, a commitment by the school to host seminars and workshops devoted to gun violence could be an important component. It might also be helpful for a school or training program to promote the habit of whenever an instructor is introducing a potentially fatal disease to the students for the first time, he or she would begin with “To put this in perspective, you should remember that xxx thousand children die of gunshot wounds every year.”
Unfortunately, like obesity, gun-related deaths and injuries are the result of our society’s failure to muster the political will to act in our best interest as a nation. The medical community is left to clean up the collateral damage. There is always more that we could do, but we must be thoughtful in how we invest our energies in the effort.
Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at pdnews@mdedge.com.
AI Shows Early Promise in Detecting Infantile Spasms
LOS ANGELES — according to a new study.
Infants with the condition can have poor outcomes with even small delays in diagnosis and ensuing treatment, potentially leading to intellectual disability, autism, and worse epilepsy. “It’s super important to start the treatment early, but oftentimes, these symptoms are just misrecognized by primary care or ER physicians. It takes a long time to diagnose,” said Gadi Miron, MD, who presented the study at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
What Is This? What Should I Do?
Parents who observe unusual behavior often seek advice from friends and family members and receive false reassurance that such behavior isn’t unusual. Even physicians may contribute if they are unaware of infantile spasms, which is a rare disorder. “And then again, they get false reassurance, and because of that false reassurance, you get a diagnostic delay,” said Shaun Hussain, MD, who was asked to comment on the study.
The timing and frequency of infantile spasms create challenges for diagnosis. They only last about 1 second, and they tend to cluster in the morning. By the time a caregiver brings an infant to a healthcare provider, they may have trouble describing the behavior. “Parents are struggling to describe what they saw, and it often just does not resonate, or doesn’t make the healthcare provider think about infantile spasms,” said Hussain.
The idea to employ AI came from looking at videos of infants on YouTube and the realization that many patients upload them in an effort to seek advice. “So many parents upload these videos and ask in the comments, ‘What is this? What should I do? Can somebody help me?’ said Miron, who is a neurologist and researcher at Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany.
AI and Video Can Aid Diagnosis
The researchers built a model that they trained to recognize epileptic spasms using openly available YouTube videos, including 141 infants, 991 recorded seizures, and 597 non-seizure video segments, along with a non-seizure cohort of 127 infants with an accompanying 1385 video segments.
Each video segment was reviewed by two specialists, and they had to agree for it to be counted as an epileptic spasm.
The model detected epileptic seizures with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96. It had a sensitivity of 82%, specificity of 90%, and accuracy of 85% when applied to the training set.
The researchers then tested it against three validation sets. In the first, a smartphone-based set retrieved from TikTok of 26 infants with 70 epileptic spasms and 31 non-seizure 5-second video segments, the model had an AUC of 0.98, a sensitivity of 89%, a specificity of 100%, and an accuracy of 92%.
A second smartphone-based set of 67 infants, drawn from YouTube, showed a false detection rate of 0.75% (five detections out of 666 video segments). A third dataset collected from in-hospital EEG monitoring of 21 infants without seizures revealed a false-positive rate of 3.4% (365 of 10,860 video segments).
The group is now developing an app that will allow parents to upload videos that can be analyzed using the model. Physicians can then view the video and determine if there is suspicion of a seizure.
Miron also believes that this approach could find use in other types of seizures and populations, including older children and adults. “We have actually built some models for detection of seizures for videos in adults as well. Looking more towards the future, I’m sure AI will be used to analyze videos of other neurological disorders with motor symptoms [such as] movement disorders and gait,” he said.
Encouraging Early Research
Hussain, who is a professor of pediatrics at UCLA Health, lauded the work generally but emphasized that it is still in the early stage. “Their comparison was a relatively easy one. They’re just comparing normal versus infantile spasms, and they’re looking at the seizure versus normal behavior. Usually, the distinction is much harder in that there are kids who are having behaviors that are maybe other types of seizures, which is much harder to distinguish from infantile spasms, in contrast to just normal behaviors. The other mimic of infantile spasms is things like infant heartburn. Those kids will often have some posturing, and they often will be in pain. They might cry. That’s something that infantile spasms will often generate, so that’s why there’s a lot of confusion between those two,” said Hussain.
He noted that there have been efforts to raise awareness of infantile spasms among physicians and the general public, but that hasn’t reduced the increased detection.
Another Resource
In fact, parents with suspicions often go to social media sites like YouTube and a Facebook group dedicated to infantile spasms. “You can Google infantile spasms, and you’ll see examples of weird behaviors, and then you’ll look in the comments, and you’ll see this commenter said: ‘These could be infantile spasms. You should go to a children’s hospital. Don’t leave until you get an EEG to make sure that these are not seizures. There’s all kinds of great advice there, and it really shouldn’t be the situation where to get the best care, you need to go on YouTube,’ ” said Hussain.
Miron and Hussain had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — according to a new study.
Infants with the condition can have poor outcomes with even small delays in diagnosis and ensuing treatment, potentially leading to intellectual disability, autism, and worse epilepsy. “It’s super important to start the treatment early, but oftentimes, these symptoms are just misrecognized by primary care or ER physicians. It takes a long time to diagnose,” said Gadi Miron, MD, who presented the study at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
What Is This? What Should I Do?
Parents who observe unusual behavior often seek advice from friends and family members and receive false reassurance that such behavior isn’t unusual. Even physicians may contribute if they are unaware of infantile spasms, which is a rare disorder. “And then again, they get false reassurance, and because of that false reassurance, you get a diagnostic delay,” said Shaun Hussain, MD, who was asked to comment on the study.
The timing and frequency of infantile spasms create challenges for diagnosis. They only last about 1 second, and they tend to cluster in the morning. By the time a caregiver brings an infant to a healthcare provider, they may have trouble describing the behavior. “Parents are struggling to describe what they saw, and it often just does not resonate, or doesn’t make the healthcare provider think about infantile spasms,” said Hussain.
The idea to employ AI came from looking at videos of infants on YouTube and the realization that many patients upload them in an effort to seek advice. “So many parents upload these videos and ask in the comments, ‘What is this? What should I do? Can somebody help me?’ said Miron, who is a neurologist and researcher at Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany.
AI and Video Can Aid Diagnosis
The researchers built a model that they trained to recognize epileptic spasms using openly available YouTube videos, including 141 infants, 991 recorded seizures, and 597 non-seizure video segments, along with a non-seizure cohort of 127 infants with an accompanying 1385 video segments.
Each video segment was reviewed by two specialists, and they had to agree for it to be counted as an epileptic spasm.
The model detected epileptic seizures with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96. It had a sensitivity of 82%, specificity of 90%, and accuracy of 85% when applied to the training set.
The researchers then tested it against three validation sets. In the first, a smartphone-based set retrieved from TikTok of 26 infants with 70 epileptic spasms and 31 non-seizure 5-second video segments, the model had an AUC of 0.98, a sensitivity of 89%, a specificity of 100%, and an accuracy of 92%.
A second smartphone-based set of 67 infants, drawn from YouTube, showed a false detection rate of 0.75% (five detections out of 666 video segments). A third dataset collected from in-hospital EEG monitoring of 21 infants without seizures revealed a false-positive rate of 3.4% (365 of 10,860 video segments).
The group is now developing an app that will allow parents to upload videos that can be analyzed using the model. Physicians can then view the video and determine if there is suspicion of a seizure.
Miron also believes that this approach could find use in other types of seizures and populations, including older children and adults. “We have actually built some models for detection of seizures for videos in adults as well. Looking more towards the future, I’m sure AI will be used to analyze videos of other neurological disorders with motor symptoms [such as] movement disorders and gait,” he said.
Encouraging Early Research
Hussain, who is a professor of pediatrics at UCLA Health, lauded the work generally but emphasized that it is still in the early stage. “Their comparison was a relatively easy one. They’re just comparing normal versus infantile spasms, and they’re looking at the seizure versus normal behavior. Usually, the distinction is much harder in that there are kids who are having behaviors that are maybe other types of seizures, which is much harder to distinguish from infantile spasms, in contrast to just normal behaviors. The other mimic of infantile spasms is things like infant heartburn. Those kids will often have some posturing, and they often will be in pain. They might cry. That’s something that infantile spasms will often generate, so that’s why there’s a lot of confusion between those two,” said Hussain.
He noted that there have been efforts to raise awareness of infantile spasms among physicians and the general public, but that hasn’t reduced the increased detection.
Another Resource
In fact, parents with suspicions often go to social media sites like YouTube and a Facebook group dedicated to infantile spasms. “You can Google infantile spasms, and you’ll see examples of weird behaviors, and then you’ll look in the comments, and you’ll see this commenter said: ‘These could be infantile spasms. You should go to a children’s hospital. Don’t leave until you get an EEG to make sure that these are not seizures. There’s all kinds of great advice there, and it really shouldn’t be the situation where to get the best care, you need to go on YouTube,’ ” said Hussain.
Miron and Hussain had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
LOS ANGELES — according to a new study.
Infants with the condition can have poor outcomes with even small delays in diagnosis and ensuing treatment, potentially leading to intellectual disability, autism, and worse epilepsy. “It’s super important to start the treatment early, but oftentimes, these symptoms are just misrecognized by primary care or ER physicians. It takes a long time to diagnose,” said Gadi Miron, MD, who presented the study at the American Epilepsy Society (AES) 78th Annual Meeting 2024.
What Is This? What Should I Do?
Parents who observe unusual behavior often seek advice from friends and family members and receive false reassurance that such behavior isn’t unusual. Even physicians may contribute if they are unaware of infantile spasms, which is a rare disorder. “And then again, they get false reassurance, and because of that false reassurance, you get a diagnostic delay,” said Shaun Hussain, MD, who was asked to comment on the study.
The timing and frequency of infantile spasms create challenges for diagnosis. They only last about 1 second, and they tend to cluster in the morning. By the time a caregiver brings an infant to a healthcare provider, they may have trouble describing the behavior. “Parents are struggling to describe what they saw, and it often just does not resonate, or doesn’t make the healthcare provider think about infantile spasms,” said Hussain.
The idea to employ AI came from looking at videos of infants on YouTube and the realization that many patients upload them in an effort to seek advice. “So many parents upload these videos and ask in the comments, ‘What is this? What should I do? Can somebody help me?’ said Miron, who is a neurologist and researcher at Charité — Universitätsmedizin Berlin in Germany.
AI and Video Can Aid Diagnosis
The researchers built a model that they trained to recognize epileptic spasms using openly available YouTube videos, including 141 infants, 991 recorded seizures, and 597 non-seizure video segments, along with a non-seizure cohort of 127 infants with an accompanying 1385 video segments.
Each video segment was reviewed by two specialists, and they had to agree for it to be counted as an epileptic spasm.
The model detected epileptic seizures with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96. It had a sensitivity of 82%, specificity of 90%, and accuracy of 85% when applied to the training set.
The researchers then tested it against three validation sets. In the first, a smartphone-based set retrieved from TikTok of 26 infants with 70 epileptic spasms and 31 non-seizure 5-second video segments, the model had an AUC of 0.98, a sensitivity of 89%, a specificity of 100%, and an accuracy of 92%.
A second smartphone-based set of 67 infants, drawn from YouTube, showed a false detection rate of 0.75% (five detections out of 666 video segments). A third dataset collected from in-hospital EEG monitoring of 21 infants without seizures revealed a false-positive rate of 3.4% (365 of 10,860 video segments).
The group is now developing an app that will allow parents to upload videos that can be analyzed using the model. Physicians can then view the video and determine if there is suspicion of a seizure.
Miron also believes that this approach could find use in other types of seizures and populations, including older children and adults. “We have actually built some models for detection of seizures for videos in adults as well. Looking more towards the future, I’m sure AI will be used to analyze videos of other neurological disorders with motor symptoms [such as] movement disorders and gait,” he said.
Encouraging Early Research
Hussain, who is a professor of pediatrics at UCLA Health, lauded the work generally but emphasized that it is still in the early stage. “Their comparison was a relatively easy one. They’re just comparing normal versus infantile spasms, and they’re looking at the seizure versus normal behavior. Usually, the distinction is much harder in that there are kids who are having behaviors that are maybe other types of seizures, which is much harder to distinguish from infantile spasms, in contrast to just normal behaviors. The other mimic of infantile spasms is things like infant heartburn. Those kids will often have some posturing, and they often will be in pain. They might cry. That’s something that infantile spasms will often generate, so that’s why there’s a lot of confusion between those two,” said Hussain.
He noted that there have been efforts to raise awareness of infantile spasms among physicians and the general public, but that hasn’t reduced the increased detection.
Another Resource
In fact, parents with suspicions often go to social media sites like YouTube and a Facebook group dedicated to infantile spasms. “You can Google infantile spasms, and you’ll see examples of weird behaviors, and then you’ll look in the comments, and you’ll see this commenter said: ‘These could be infantile spasms. You should go to a children’s hospital. Don’t leave until you get an EEG to make sure that these are not seizures. There’s all kinds of great advice there, and it really shouldn’t be the situation where to get the best care, you need to go on YouTube,’ ” said Hussain.
Miron and Hussain had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AES 2024
Stem Cell Transplant Effective for Children With Arthritis
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Retrospective cohort study of 13 children with refractory systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis–related lung disease (sJIA-LD) who had allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
- Children whose median age was 9 years at transplantation underwent HSCT at nine hospitals in the United States and Europe between January 2018 and October 2022, with a median follow-up of 16 months.
- Outcomes included transplant-related complications, pulmonary outcomes (eg, oxygen dependence and chest CT findings), and overall outcomes (eg, complete response, partial response, and death).
TAKEAWAY:
- Five patients developed acute graft vs host disease of varying grades, but none experienced chronic disease.
- All nine surviving patients achieved a complete response at the last follow-up, with no sJIA characteristics or need for immunosuppressive therapy or supplemental oxygen.
- Four patients died from complications including cytomegalovirus pneumonitis (n = 2), intracranial hemorrhage (n = 1), and progressive sJIA-LD (n = 1).
- Of six patients who underwent posttransplant chest CT, three had improved lung health, two had stable lung disease, and one experienced worsening lung disease, ultimately resulting in death.
IN PRACTICE:
“Allogeneic HSCT should be considered for treatment-refractory sJIA-LD,” the authors wrote.
“Efforts are being pursued for earlier recognition of patients with sJIA-LD at risk of adverse reactions to biologics. Early detection should help to avoid repeated treatments that are less effective and possibly deleterious and consider therapeutic approaches (eg, anti–[interleukin]-18 or [interferon]-delta–targeted treatments) that might act as a bridge therapy to control disease activity before HSCT,” wrote the author of an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
Michael G. Matt, MD, and Daniel Drozdov, MD, led the study, which was published online on December 20, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included sampling bias and heterogeneity in clinical follow-up. The small sample size made it difficult to identify variables affecting survival and the achievement of a complete response. Additionally, many patients had relatively short follow-up periods.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health. Several authors reported receiving advisory board fees, consulting fees, honoraria, grant funds, and stocks and shares from various research institutes and pharmaceutical organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Retrospective cohort study of 13 children with refractory systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis–related lung disease (sJIA-LD) who had allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
- Children whose median age was 9 years at transplantation underwent HSCT at nine hospitals in the United States and Europe between January 2018 and October 2022, with a median follow-up of 16 months.
- Outcomes included transplant-related complications, pulmonary outcomes (eg, oxygen dependence and chest CT findings), and overall outcomes (eg, complete response, partial response, and death).
TAKEAWAY:
- Five patients developed acute graft vs host disease of varying grades, but none experienced chronic disease.
- All nine surviving patients achieved a complete response at the last follow-up, with no sJIA characteristics or need for immunosuppressive therapy or supplemental oxygen.
- Four patients died from complications including cytomegalovirus pneumonitis (n = 2), intracranial hemorrhage (n = 1), and progressive sJIA-LD (n = 1).
- Of six patients who underwent posttransplant chest CT, three had improved lung health, two had stable lung disease, and one experienced worsening lung disease, ultimately resulting in death.
IN PRACTICE:
“Allogeneic HSCT should be considered for treatment-refractory sJIA-LD,” the authors wrote.
“Efforts are being pursued for earlier recognition of patients with sJIA-LD at risk of adverse reactions to biologics. Early detection should help to avoid repeated treatments that are less effective and possibly deleterious and consider therapeutic approaches (eg, anti–[interleukin]-18 or [interferon]-delta–targeted treatments) that might act as a bridge therapy to control disease activity before HSCT,” wrote the author of an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
Michael G. Matt, MD, and Daniel Drozdov, MD, led the study, which was published online on December 20, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included sampling bias and heterogeneity in clinical follow-up. The small sample size made it difficult to identify variables affecting survival and the achievement of a complete response. Additionally, many patients had relatively short follow-up periods.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health. Several authors reported receiving advisory board fees, consulting fees, honoraria, grant funds, and stocks and shares from various research institutes and pharmaceutical organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Retrospective cohort study of 13 children with refractory systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis–related lung disease (sJIA-LD) who had allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT).
- Children whose median age was 9 years at transplantation underwent HSCT at nine hospitals in the United States and Europe between January 2018 and October 2022, with a median follow-up of 16 months.
- Outcomes included transplant-related complications, pulmonary outcomes (eg, oxygen dependence and chest CT findings), and overall outcomes (eg, complete response, partial response, and death).
TAKEAWAY:
- Five patients developed acute graft vs host disease of varying grades, but none experienced chronic disease.
- All nine surviving patients achieved a complete response at the last follow-up, with no sJIA characteristics or need for immunosuppressive therapy or supplemental oxygen.
- Four patients died from complications including cytomegalovirus pneumonitis (n = 2), intracranial hemorrhage (n = 1), and progressive sJIA-LD (n = 1).
- Of six patients who underwent posttransplant chest CT, three had improved lung health, two had stable lung disease, and one experienced worsening lung disease, ultimately resulting in death.
IN PRACTICE:
“Allogeneic HSCT should be considered for treatment-refractory sJIA-LD,” the authors wrote.
“Efforts are being pursued for earlier recognition of patients with sJIA-LD at risk of adverse reactions to biologics. Early detection should help to avoid repeated treatments that are less effective and possibly deleterious and consider therapeutic approaches (eg, anti–[interleukin]-18 or [interferon]-delta–targeted treatments) that might act as a bridge therapy to control disease activity before HSCT,” wrote the author of an accompanying editorial.
SOURCE:
Michael G. Matt, MD, and Daniel Drozdov, MD, led the study, which was published online on December 20, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Limitations included sampling bias and heterogeneity in clinical follow-up. The small sample size made it difficult to identify variables affecting survival and the achievement of a complete response. Additionally, many patients had relatively short follow-up periods.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, National Institutes of Health. Several authors reported receiving advisory board fees, consulting fees, honoraria, grant funds, and stocks and shares from various research institutes and pharmaceutical organizations.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Axolotl Salamander Holds Potential for Cosmeceuticals, Wound Healing
For over 200 years, researchers have been captivated by axolotl salamanders (Ambystoma mexicanum) and their remarkable regenerative abilities, seeking to uncover secrets that could revolutionize regenerative medicine, including the scarless healing of wounds.
“The axolotl salamander is the most studied animal ever in science for its neotenic ability to regenerate,” Jill S. Waibel, MD, dermatologist and researcher in Miami, Florida, said in an interview. Neotenic tissue retains a juvenile or immature state throughout an organism’s life. In the case of the axolotl, “it can regenerate limbs, part of its heart, even its brain.”
A 2019 review of several studies on the regenerative abilities of axolotls highlights the importance of gene activity in controlling its skin regeneration. Specifically, growth factors such as fibroblast growth factors, transforming growth factor beta, and Wnt play a key role in guiding how the creature’s skin cells behave during healing and regrowth. The immune response , particularly the actions of macrophages and neutrophils, is also crucial in the early stages of regeneration, as these cells clear away dead tissue and kickstart the healing process.
without harming the animal. In axolotls, Waibel explained, damaged neotenic tissue “still thinks it’s in fetal mode, so if it injures its muscle, bone, nerves, collagen, or skin, everything will redevelop. After a few months in utero, that process stops in humans, but it never stops in the axolotl. The axolotl has scarless healing and immunity because of antimicrobial properties found in the neotenic tissue.”
RegenX scientists have developed a proprietary decellularization process that renders the urodele collagen extract safe and effective for use in humans. “We then harnessed a reservoir of bioactive peptides, which are small proteins that come from the axolotl, but they don’t contain any RNA or DNA that could confer the risk of any diseases or cancer,” she added.
According to Waibel, who is also subsection chief of dermatology at Baptist Hospital and past medical director of the Miami Cancer Institute’s Multidisciplinary Skin Cancer Clinic, genetic analysis of the axolotl revealed genes that have not been seen in humans. The urodele collagen extract also has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. “It decreases TNF [tumor necrosis factor] and IL [interleukin]–23 and stimulates regenerative pathways like FETUB (Fetuin-B), which is a gene involved in tissue regeneration,” she said. “We’re exploring these for some products.”
Institutional Review Board–approved human clinical trials at three US sites are nearly complete for evaluating an antiaging hydrating daily serum, an antiaging serum for damaged skin, and a restorative serum to be applied following cosmetic procedures, all containing the extract. The product furthest along is a “super gel” that contains properties of the urodele collagen extract.
In a proof-of-concept study using a third-degree burn model in two pigs, Waibel and colleagues at the University of Miami, found that 3 days after the injury was induced, application of the gel led to 92% reepithelialization of the pig’s skin, compared with only 54% in untreated skin.
Shortly after this study was conducted, a burn patient was referred to Waibel — 4 years after he was struck by lightning while fishing on a boat in Mississippi, an accident that resulted in the loss of his right arm and both legs. During a telemedicine consultation, Waibel noticed open ulcers on his chest. “What are those from?” she asked. “They’re from my accident 4 years ago,” he replied.
After the man flew to Miami for an in-person evaluation, Waibel treated his ulcers with a fractional laser to debride the wound, then applied the gel as part of a proof-of-concept approach, testing its potential in a real-world patient setting. Within 3 weeks, the long-standing ulcerated area had healed completely, marking the first time a human was treated with the super gel.
Looking ahead, the million-dollar question, Waibel noted, is how much healing can be achieved in humans with formulations of axolotl-derived technology. “For example, can we help a spinal cord injury patient? That sounds like a science fiction movie, but there are proteins in genes in this animal that we have turned off that potentially can be turned on in a human,” she said. “It’s very exciting.”
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, director of Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and current president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, who was asked to comment on this work, said that the use of urodele collagen extract derived from axolotl tissue “is an exciting innovation, especially given its unique properties like scarless healing and antimicrobial activity.”
While the results from preclinical and proof-of-concept studies are promising, “a key limitation lies in understanding the extent to which these findings will translate to human applications,” Ortiz said. “Overall, this research contributes significantly to the fields of regenerative medicine and dermatology, offering hope for more effective treatments in the future.”
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, who was also asked to provide her insights on the topic, said that, if researchers could replicate the axolotl salamander’s ability to regenerate its own limbs and organs, “medicine would be transformed. Rather than transplant another person’s organ with lifelong immunosuppression, a regenerative treatment could program a patient’s own body to create a needed organ.
“On a simpler level,” she continued, “regenerating skin and its underlying structures could hasten wound healing and potentially even treat hair loss. This is not a pipe dream, as Waibel has successfully treated severe ulcers using a super gel containing urodele collagen extract. Urodele collagen is type XII collagen, important in the salamander’s capacity to heal and regenerate.”
Waibel disclosed that she is a scientific adviser to RegenX and is a member of the company’s board of directors. Ortiz and Ko reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For over 200 years, researchers have been captivated by axolotl salamanders (Ambystoma mexicanum) and their remarkable regenerative abilities, seeking to uncover secrets that could revolutionize regenerative medicine, including the scarless healing of wounds.
“The axolotl salamander is the most studied animal ever in science for its neotenic ability to regenerate,” Jill S. Waibel, MD, dermatologist and researcher in Miami, Florida, said in an interview. Neotenic tissue retains a juvenile or immature state throughout an organism’s life. In the case of the axolotl, “it can regenerate limbs, part of its heart, even its brain.”
A 2019 review of several studies on the regenerative abilities of axolotls highlights the importance of gene activity in controlling its skin regeneration. Specifically, growth factors such as fibroblast growth factors, transforming growth factor beta, and Wnt play a key role in guiding how the creature’s skin cells behave during healing and regrowth. The immune response , particularly the actions of macrophages and neutrophils, is also crucial in the early stages of regeneration, as these cells clear away dead tissue and kickstart the healing process.
without harming the animal. In axolotls, Waibel explained, damaged neotenic tissue “still thinks it’s in fetal mode, so if it injures its muscle, bone, nerves, collagen, or skin, everything will redevelop. After a few months in utero, that process stops in humans, but it never stops in the axolotl. The axolotl has scarless healing and immunity because of antimicrobial properties found in the neotenic tissue.”
RegenX scientists have developed a proprietary decellularization process that renders the urodele collagen extract safe and effective for use in humans. “We then harnessed a reservoir of bioactive peptides, which are small proteins that come from the axolotl, but they don’t contain any RNA or DNA that could confer the risk of any diseases or cancer,” she added.
According to Waibel, who is also subsection chief of dermatology at Baptist Hospital and past medical director of the Miami Cancer Institute’s Multidisciplinary Skin Cancer Clinic, genetic analysis of the axolotl revealed genes that have not been seen in humans. The urodele collagen extract also has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. “It decreases TNF [tumor necrosis factor] and IL [interleukin]–23 and stimulates regenerative pathways like FETUB (Fetuin-B), which is a gene involved in tissue regeneration,” she said. “We’re exploring these for some products.”
Institutional Review Board–approved human clinical trials at three US sites are nearly complete for evaluating an antiaging hydrating daily serum, an antiaging serum for damaged skin, and a restorative serum to be applied following cosmetic procedures, all containing the extract. The product furthest along is a “super gel” that contains properties of the urodele collagen extract.
In a proof-of-concept study using a third-degree burn model in two pigs, Waibel and colleagues at the University of Miami, found that 3 days after the injury was induced, application of the gel led to 92% reepithelialization of the pig’s skin, compared with only 54% in untreated skin.
Shortly after this study was conducted, a burn patient was referred to Waibel — 4 years after he was struck by lightning while fishing on a boat in Mississippi, an accident that resulted in the loss of his right arm and both legs. During a telemedicine consultation, Waibel noticed open ulcers on his chest. “What are those from?” she asked. “They’re from my accident 4 years ago,” he replied.
After the man flew to Miami for an in-person evaluation, Waibel treated his ulcers with a fractional laser to debride the wound, then applied the gel as part of a proof-of-concept approach, testing its potential in a real-world patient setting. Within 3 weeks, the long-standing ulcerated area had healed completely, marking the first time a human was treated with the super gel.
Looking ahead, the million-dollar question, Waibel noted, is how much healing can be achieved in humans with formulations of axolotl-derived technology. “For example, can we help a spinal cord injury patient? That sounds like a science fiction movie, but there are proteins in genes in this animal that we have turned off that potentially can be turned on in a human,” she said. “It’s very exciting.”
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, director of Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and current president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, who was asked to comment on this work, said that the use of urodele collagen extract derived from axolotl tissue “is an exciting innovation, especially given its unique properties like scarless healing and antimicrobial activity.”
While the results from preclinical and proof-of-concept studies are promising, “a key limitation lies in understanding the extent to which these findings will translate to human applications,” Ortiz said. “Overall, this research contributes significantly to the fields of regenerative medicine and dermatology, offering hope for more effective treatments in the future.”
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, who was also asked to provide her insights on the topic, said that, if researchers could replicate the axolotl salamander’s ability to regenerate its own limbs and organs, “medicine would be transformed. Rather than transplant another person’s organ with lifelong immunosuppression, a regenerative treatment could program a patient’s own body to create a needed organ.
“On a simpler level,” she continued, “regenerating skin and its underlying structures could hasten wound healing and potentially even treat hair loss. This is not a pipe dream, as Waibel has successfully treated severe ulcers using a super gel containing urodele collagen extract. Urodele collagen is type XII collagen, important in the salamander’s capacity to heal and regenerate.”
Waibel disclosed that she is a scientific adviser to RegenX and is a member of the company’s board of directors. Ortiz and Ko reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For over 200 years, researchers have been captivated by axolotl salamanders (Ambystoma mexicanum) and their remarkable regenerative abilities, seeking to uncover secrets that could revolutionize regenerative medicine, including the scarless healing of wounds.
“The axolotl salamander is the most studied animal ever in science for its neotenic ability to regenerate,” Jill S. Waibel, MD, dermatologist and researcher in Miami, Florida, said in an interview. Neotenic tissue retains a juvenile or immature state throughout an organism’s life. In the case of the axolotl, “it can regenerate limbs, part of its heart, even its brain.”
A 2019 review of several studies on the regenerative abilities of axolotls highlights the importance of gene activity in controlling its skin regeneration. Specifically, growth factors such as fibroblast growth factors, transforming growth factor beta, and Wnt play a key role in guiding how the creature’s skin cells behave during healing and regrowth. The immune response , particularly the actions of macrophages and neutrophils, is also crucial in the early stages of regeneration, as these cells clear away dead tissue and kickstart the healing process.
without harming the animal. In axolotls, Waibel explained, damaged neotenic tissue “still thinks it’s in fetal mode, so if it injures its muscle, bone, nerves, collagen, or skin, everything will redevelop. After a few months in utero, that process stops in humans, but it never stops in the axolotl. The axolotl has scarless healing and immunity because of antimicrobial properties found in the neotenic tissue.”
RegenX scientists have developed a proprietary decellularization process that renders the urodele collagen extract safe and effective for use in humans. “We then harnessed a reservoir of bioactive peptides, which are small proteins that come from the axolotl, but they don’t contain any RNA or DNA that could confer the risk of any diseases or cancer,” she added.
According to Waibel, who is also subsection chief of dermatology at Baptist Hospital and past medical director of the Miami Cancer Institute’s Multidisciplinary Skin Cancer Clinic, genetic analysis of the axolotl revealed genes that have not been seen in humans. The urodele collagen extract also has anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. “It decreases TNF [tumor necrosis factor] and IL [interleukin]–23 and stimulates regenerative pathways like FETUB (Fetuin-B), which is a gene involved in tissue regeneration,” she said. “We’re exploring these for some products.”
Institutional Review Board–approved human clinical trials at three US sites are nearly complete for evaluating an antiaging hydrating daily serum, an antiaging serum for damaged skin, and a restorative serum to be applied following cosmetic procedures, all containing the extract. The product furthest along is a “super gel” that contains properties of the urodele collagen extract.
In a proof-of-concept study using a third-degree burn model in two pigs, Waibel and colleagues at the University of Miami, found that 3 days after the injury was induced, application of the gel led to 92% reepithelialization of the pig’s skin, compared with only 54% in untreated skin.
Shortly after this study was conducted, a burn patient was referred to Waibel — 4 years after he was struck by lightning while fishing on a boat in Mississippi, an accident that resulted in the loss of his right arm and both legs. During a telemedicine consultation, Waibel noticed open ulcers on his chest. “What are those from?” she asked. “They’re from my accident 4 years ago,” he replied.
After the man flew to Miami for an in-person evaluation, Waibel treated his ulcers with a fractional laser to debride the wound, then applied the gel as part of a proof-of-concept approach, testing its potential in a real-world patient setting. Within 3 weeks, the long-standing ulcerated area had healed completely, marking the first time a human was treated with the super gel.
Looking ahead, the million-dollar question, Waibel noted, is how much healing can be achieved in humans with formulations of axolotl-derived technology. “For example, can we help a spinal cord injury patient? That sounds like a science fiction movie, but there are proteins in genes in this animal that we have turned off that potentially can be turned on in a human,” she said. “It’s very exciting.”
Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, director of Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, and current president of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery, who was asked to comment on this work, said that the use of urodele collagen extract derived from axolotl tissue “is an exciting innovation, especially given its unique properties like scarless healing and antimicrobial activity.”
While the results from preclinical and proof-of-concept studies are promising, “a key limitation lies in understanding the extent to which these findings will translate to human applications,” Ortiz said. “Overall, this research contributes significantly to the fields of regenerative medicine and dermatology, offering hope for more effective treatments in the future.”
Christine Ko, MD, professor of dermatology and pathology at Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, who was also asked to provide her insights on the topic, said that, if researchers could replicate the axolotl salamander’s ability to regenerate its own limbs and organs, “medicine would be transformed. Rather than transplant another person’s organ with lifelong immunosuppression, a regenerative treatment could program a patient’s own body to create a needed organ.
“On a simpler level,” she continued, “regenerating skin and its underlying structures could hasten wound healing and potentially even treat hair loss. This is not a pipe dream, as Waibel has successfully treated severe ulcers using a super gel containing urodele collagen extract. Urodele collagen is type XII collagen, important in the salamander’s capacity to heal and regenerate.”
Waibel disclosed that she is a scientific adviser to RegenX and is a member of the company’s board of directors. Ortiz and Ko reported having no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Should the FDA Reconsider Boxed Warnings for Antidepressants?
Paradoxically, and for almost as long, evidence suggests these warnings may have led to fewer depression diagnoses, reduced prescriptions, and, ultimately, higher suicide rates.
With mounting evidence of these negative unintended consequences, some clinicians and researchers are urging the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to consider revising — or even eliminating — boxed warnings on these medications.
The latest report challenging the utility of the 2005 warnings was particularly sobering. Published in October in Health Affairs, the systematic review of studies from 2003 to 2022 showed a 20%-40% decline in physician visits for depression, a 20%-50% decline in antidepressant use, and an abrupt increase in psychotropic drug poisonings and suicides — all after the warnings were added.
“FDA officials should review the totality of evidence and err on the side of caution in acknowledging possible harms of the antidepressant warnings,” lead author Stephen Soumerai, ScD, professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, Massachusetts and colleagues wrote. They called on the FDA to replace the boxed warnings with a routine warning in labeling.
While good prospective data on the risks and benefits of antidepressants in youth were limited when the boxed warnings were instituted, there is more information now, said Jeffrey Strawn, MD, professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine in Ohio. Strawn, whose research on the topic has been cited frequently over the years, said the new evidence suggests it is time for the FDA to reevaluate the warnings.
“I don’t think that they’ve been useful. They’ve actually been harmful,” Strawn told this news organization. “These boxed warnings have decreased physicians’ and other clinicians’ comfort and tendency to prescribe.”
Decline in Diagnoses
The FDA issued its first warning about the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior in children in 2003. After an advisory panel weighed the evidence, the agency added a boxed warning in 2005 to all antidepressants for children younger than 18 years. The warning was expanded in 2007 to include young adults through age 24.
Data suggesting that the warnings have had unintended effects can be found going back to just after they were issued. For instance, in 2009, after rising for years, the rate of new pediatric depression diagnoses fell precipitously after the warning was added, with primary care physicians diagnosing 44% fewer cases.
In 2014, citing evidence of fewer diagnoses and rising psychotropic drug poisonings, Weill Cornell Medicine Professor Richard A. Friedman, MD, called on the FDA in a perspective to remove the boxed warnings.
Strawn and colleagues reported in an often-cited 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that, in nine trials involving 1673 patients and six medications, antidepressants were superior to placebo, with no increased risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior.
He has also studied adverse effects of the medications, reporting in Pharmacotherapy that suicidality risk might be more likely with some medications, such as paroxetine and venlafaxine, and that it could be influenced by baseline suicidality, among many other factors. A Swedish register study found that risk was highest the month before starting a medication, Strawn and colleagues wrote.
Dara Sakolsky, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and associate medical director, Services for Teens at Risk at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, told this news organization that, because of “these negative unintended consequences,” the FDA should lower the temperature by putting the warnings in labeling.
“It makes sense based on the data that we have at hand now,” said Sakolsky.
The Dangers of Untreated Depression
Even with this new information, lingering concerns about earlier studies that pointed to increased suicidality risk may discourage prescribing by primary care physicians and pediatricians, and that worries researchers and psychiatrists.
“My concern is that the risk for suicide and suicidal behavior may be higher in untreated depression than the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors from antidepressants,” Jeffrey Bridge, PhD, director of the Center for Suicide Prevention and Research at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, told this news organization.
Bridge is the lead author of a much-cited 2007 meta-analysis in JAMA that showed that the benefits of antidepressants in children and adolescents appeared to be greater than the risks for suicidality. “The concern about antidepressants must be considered in the context of possible benefit,” wrote Bridge, who also is professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and behavioral health at Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Depression and suicide are a scourge for those younger than 25 years. A 2021 literature review noted that the prevalence of depression — which has been increasing for all Americans — has risen more among adolescents than adults. Depression is “strongly associated with suicide,” the authors wrote.
In 2021, the National Institute of Mental Health reported suicide was the second leading cause of death among 10- to 14-year-olds and the third leading cause of death among those aged 15-24 years.
Suicide kills more kids aged between 10 and 24 years than cancer and all other illnesses combined, John Campo, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and vice president of psychiatric services at Kennedy Krieger Institute, told this news organization.
Meanwhile, he added, the medications work and clinicians balance risk and benefit in prescribing.
The landmark 2007 Treatment for Adolescents with Depression Study showed that fluoxetine, especially in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), was significantly better than placebo. Since that time, legions of trials have shown the drugs’ effectiveness.
The most effective treatment for teen depression is a combination of CBT and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, said Sakolsky.
“We know that the evidence for that is pretty good,” she said. “On the flip side, we know the risk of having an adverse outcome is pretty low.”
Sakolsky tells patients and families that perhaps 1 in 146 will have a suicidal thought or behavior. “That’s pretty rare when we know how effective these medicines are.”
Strawn said he always notes that no suicides took place in the trials that led to the warning and stresses that he closely monitors patients. “While the more recent prospective data are reassuring,” the suicidality risk “is something that we still talk about,” he said. He also discusses how some antidepressants seem to increase risk more than others.
For Campo, the discussion is based on his reading of the evidence, not the presence of the FDA warning.
“Based on what we know, I still think it’s fair to proceed with the idea that there is a small, but real risk,” he said. However, “at the same time, the medications might be exceptionally helpful for some kids.”
‘What Do We Do Now?’
When the FDA issued its warning in 2005, the agency said it identified the risk for suicidality in a combined analysis of short-term placebo-controlled trials of nine antidepressants. It ultimately included 24 trials involving more than 4400 patients. The risk was highest in the first few months. The average risk for those taking antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. There were no suicides in these trials, however.
The trials relied on spontaneous reports of adverse events, not predetermined measures, Campo said. Even so, that 2% difference is “nothing to sneeze at,” he noted.
Bridge’s meta-analysis showed a smaller difference — closer to 0.7%. “But it was still statistically significant,” Campo said. “I have trouble ignoring that.”
The unintended consequences of the warning can’t be studied in a randomized controlled trial. Studies have shown an association but not a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the warning and a decline in treatment and rise in suicides.
But the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressants has been studied prospectively. Some older studies found a significant risk, while more recent trials have not.
While the Health Affairs analysis “certainly makes a strong case,” it is observational data, Campo said.
“The question is, what do we do now in retrospect? Do you say, ‘Never mind. We don’t need the black box warning anymore?’ ” he said. “That would require a pretty careful look.”
The Health Affairs paper “makes me think that there are other areas of research that that need to be completed and done and updated, and then there should be an assessment, a reevaluation from the FDA,” said Bridge. A new meta-analysis “would be very informative,” he said.
What’s Next?
When asked about the Health Affairs paper and whether the agency would review the warnings, an FDA spokesperson told this news organization that the agency “does not comment on specific studies but evaluates them as part of the body of evidence to further our understanding about a particular issue and assist in our mission to protect public health.”
Sakolsky said the data clearly point to the damage that the warning has done over the past 2 decades, but that things might be improving. Studies conducted more recently might not have captured some changes in practice.
For instance, she noted, in 2022, the US Preventive Services Task Force recommended screening for major depressive disorder in adolescents aged 12-18 years. In turn, she has seen more patients in her office who were referred by pediatricians who had conducted the screening, said Sakolsky.
Strawn said the time for pontificating is long past due. “We’re withholding medications and other treatments that could potentially be effective for disorders that, in and of themselves, are associated with a significant increase in the risk of suicide.”
After the FDA instituted the warning, “we were all very nervous,” about the potential fallout, said Campo, adding that a part of him wishes that the warnings had been “more mundane and less dramatic.”
Despite the unintended consequences, “it’s going to be hard to put the genie back in the bottle,” he said.
Campo and Sakolsky reported no relevant financial relationships. Strawn disclosed that his institution has received research funding from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and AbbVie. Bridge reported that he received grant support from the National Institute of Mental Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and PCORI; is a scientific adviser to Clarigent Health; and is on the Scientific Council of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paradoxically, and for almost as long, evidence suggests these warnings may have led to fewer depression diagnoses, reduced prescriptions, and, ultimately, higher suicide rates.
With mounting evidence of these negative unintended consequences, some clinicians and researchers are urging the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to consider revising — or even eliminating — boxed warnings on these medications.
The latest report challenging the utility of the 2005 warnings was particularly sobering. Published in October in Health Affairs, the systematic review of studies from 2003 to 2022 showed a 20%-40% decline in physician visits for depression, a 20%-50% decline in antidepressant use, and an abrupt increase in psychotropic drug poisonings and suicides — all after the warnings were added.
“FDA officials should review the totality of evidence and err on the side of caution in acknowledging possible harms of the antidepressant warnings,” lead author Stephen Soumerai, ScD, professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, Massachusetts and colleagues wrote. They called on the FDA to replace the boxed warnings with a routine warning in labeling.
While good prospective data on the risks and benefits of antidepressants in youth were limited when the boxed warnings were instituted, there is more information now, said Jeffrey Strawn, MD, professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine in Ohio. Strawn, whose research on the topic has been cited frequently over the years, said the new evidence suggests it is time for the FDA to reevaluate the warnings.
“I don’t think that they’ve been useful. They’ve actually been harmful,” Strawn told this news organization. “These boxed warnings have decreased physicians’ and other clinicians’ comfort and tendency to prescribe.”
Decline in Diagnoses
The FDA issued its first warning about the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior in children in 2003. After an advisory panel weighed the evidence, the agency added a boxed warning in 2005 to all antidepressants for children younger than 18 years. The warning was expanded in 2007 to include young adults through age 24.
Data suggesting that the warnings have had unintended effects can be found going back to just after they were issued. For instance, in 2009, after rising for years, the rate of new pediatric depression diagnoses fell precipitously after the warning was added, with primary care physicians diagnosing 44% fewer cases.
In 2014, citing evidence of fewer diagnoses and rising psychotropic drug poisonings, Weill Cornell Medicine Professor Richard A. Friedman, MD, called on the FDA in a perspective to remove the boxed warnings.
Strawn and colleagues reported in an often-cited 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that, in nine trials involving 1673 patients and six medications, antidepressants were superior to placebo, with no increased risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior.
He has also studied adverse effects of the medications, reporting in Pharmacotherapy that suicidality risk might be more likely with some medications, such as paroxetine and venlafaxine, and that it could be influenced by baseline suicidality, among many other factors. A Swedish register study found that risk was highest the month before starting a medication, Strawn and colleagues wrote.
Dara Sakolsky, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and associate medical director, Services for Teens at Risk at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, told this news organization that, because of “these negative unintended consequences,” the FDA should lower the temperature by putting the warnings in labeling.
“It makes sense based on the data that we have at hand now,” said Sakolsky.
The Dangers of Untreated Depression
Even with this new information, lingering concerns about earlier studies that pointed to increased suicidality risk may discourage prescribing by primary care physicians and pediatricians, and that worries researchers and psychiatrists.
“My concern is that the risk for suicide and suicidal behavior may be higher in untreated depression than the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors from antidepressants,” Jeffrey Bridge, PhD, director of the Center for Suicide Prevention and Research at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, told this news organization.
Bridge is the lead author of a much-cited 2007 meta-analysis in JAMA that showed that the benefits of antidepressants in children and adolescents appeared to be greater than the risks for suicidality. “The concern about antidepressants must be considered in the context of possible benefit,” wrote Bridge, who also is professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and behavioral health at Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Depression and suicide are a scourge for those younger than 25 years. A 2021 literature review noted that the prevalence of depression — which has been increasing for all Americans — has risen more among adolescents than adults. Depression is “strongly associated with suicide,” the authors wrote.
In 2021, the National Institute of Mental Health reported suicide was the second leading cause of death among 10- to 14-year-olds and the third leading cause of death among those aged 15-24 years.
Suicide kills more kids aged between 10 and 24 years than cancer and all other illnesses combined, John Campo, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and vice president of psychiatric services at Kennedy Krieger Institute, told this news organization.
Meanwhile, he added, the medications work and clinicians balance risk and benefit in prescribing.
The landmark 2007 Treatment for Adolescents with Depression Study showed that fluoxetine, especially in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), was significantly better than placebo. Since that time, legions of trials have shown the drugs’ effectiveness.
The most effective treatment for teen depression is a combination of CBT and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, said Sakolsky.
“We know that the evidence for that is pretty good,” she said. “On the flip side, we know the risk of having an adverse outcome is pretty low.”
Sakolsky tells patients and families that perhaps 1 in 146 will have a suicidal thought or behavior. “That’s pretty rare when we know how effective these medicines are.”
Strawn said he always notes that no suicides took place in the trials that led to the warning and stresses that he closely monitors patients. “While the more recent prospective data are reassuring,” the suicidality risk “is something that we still talk about,” he said. He also discusses how some antidepressants seem to increase risk more than others.
For Campo, the discussion is based on his reading of the evidence, not the presence of the FDA warning.
“Based on what we know, I still think it’s fair to proceed with the idea that there is a small, but real risk,” he said. However, “at the same time, the medications might be exceptionally helpful for some kids.”
‘What Do We Do Now?’
When the FDA issued its warning in 2005, the agency said it identified the risk for suicidality in a combined analysis of short-term placebo-controlled trials of nine antidepressants. It ultimately included 24 trials involving more than 4400 patients. The risk was highest in the first few months. The average risk for those taking antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. There were no suicides in these trials, however.
The trials relied on spontaneous reports of adverse events, not predetermined measures, Campo said. Even so, that 2% difference is “nothing to sneeze at,” he noted.
Bridge’s meta-analysis showed a smaller difference — closer to 0.7%. “But it was still statistically significant,” Campo said. “I have trouble ignoring that.”
The unintended consequences of the warning can’t be studied in a randomized controlled trial. Studies have shown an association but not a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the warning and a decline in treatment and rise in suicides.
But the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressants has been studied prospectively. Some older studies found a significant risk, while more recent trials have not.
While the Health Affairs analysis “certainly makes a strong case,” it is observational data, Campo said.
“The question is, what do we do now in retrospect? Do you say, ‘Never mind. We don’t need the black box warning anymore?’ ” he said. “That would require a pretty careful look.”
The Health Affairs paper “makes me think that there are other areas of research that that need to be completed and done and updated, and then there should be an assessment, a reevaluation from the FDA,” said Bridge. A new meta-analysis “would be very informative,” he said.
What’s Next?
When asked about the Health Affairs paper and whether the agency would review the warnings, an FDA spokesperson told this news organization that the agency “does not comment on specific studies but evaluates them as part of the body of evidence to further our understanding about a particular issue and assist in our mission to protect public health.”
Sakolsky said the data clearly point to the damage that the warning has done over the past 2 decades, but that things might be improving. Studies conducted more recently might not have captured some changes in practice.
For instance, she noted, in 2022, the US Preventive Services Task Force recommended screening for major depressive disorder in adolescents aged 12-18 years. In turn, she has seen more patients in her office who were referred by pediatricians who had conducted the screening, said Sakolsky.
Strawn said the time for pontificating is long past due. “We’re withholding medications and other treatments that could potentially be effective for disorders that, in and of themselves, are associated with a significant increase in the risk of suicide.”
After the FDA instituted the warning, “we were all very nervous,” about the potential fallout, said Campo, adding that a part of him wishes that the warnings had been “more mundane and less dramatic.”
Despite the unintended consequences, “it’s going to be hard to put the genie back in the bottle,” he said.
Campo and Sakolsky reported no relevant financial relationships. Strawn disclosed that his institution has received research funding from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and AbbVie. Bridge reported that he received grant support from the National Institute of Mental Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and PCORI; is a scientific adviser to Clarigent Health; and is on the Scientific Council of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paradoxically, and for almost as long, evidence suggests these warnings may have led to fewer depression diagnoses, reduced prescriptions, and, ultimately, higher suicide rates.
With mounting evidence of these negative unintended consequences, some clinicians and researchers are urging the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to consider revising — or even eliminating — boxed warnings on these medications.
The latest report challenging the utility of the 2005 warnings was particularly sobering. Published in October in Health Affairs, the systematic review of studies from 2003 to 2022 showed a 20%-40% decline in physician visits for depression, a 20%-50% decline in antidepressant use, and an abrupt increase in psychotropic drug poisonings and suicides — all after the warnings were added.
“FDA officials should review the totality of evidence and err on the side of caution in acknowledging possible harms of the antidepressant warnings,” lead author Stephen Soumerai, ScD, professor of population medicine at Harvard Medical School at Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute, Boston, Massachusetts and colleagues wrote. They called on the FDA to replace the boxed warnings with a routine warning in labeling.
While good prospective data on the risks and benefits of antidepressants in youth were limited when the boxed warnings were instituted, there is more information now, said Jeffrey Strawn, MD, professor of psychiatry and pediatrics at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine in Ohio. Strawn, whose research on the topic has been cited frequently over the years, said the new evidence suggests it is time for the FDA to reevaluate the warnings.
“I don’t think that they’ve been useful. They’ve actually been harmful,” Strawn told this news organization. “These boxed warnings have decreased physicians’ and other clinicians’ comfort and tendency to prescribe.”
Decline in Diagnoses
The FDA issued its first warning about the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior in children in 2003. After an advisory panel weighed the evidence, the agency added a boxed warning in 2005 to all antidepressants for children younger than 18 years. The warning was expanded in 2007 to include young adults through age 24.
Data suggesting that the warnings have had unintended effects can be found going back to just after they were issued. For instance, in 2009, after rising for years, the rate of new pediatric depression diagnoses fell precipitously after the warning was added, with primary care physicians diagnosing 44% fewer cases.
In 2014, citing evidence of fewer diagnoses and rising psychotropic drug poisonings, Weill Cornell Medicine Professor Richard A. Friedman, MD, called on the FDA in a perspective to remove the boxed warnings.
Strawn and colleagues reported in an often-cited 2014 systematic review and meta-analysis that, in nine trials involving 1673 patients and six medications, antidepressants were superior to placebo, with no increased risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior.
He has also studied adverse effects of the medications, reporting in Pharmacotherapy that suicidality risk might be more likely with some medications, such as paroxetine and venlafaxine, and that it could be influenced by baseline suicidality, among many other factors. A Swedish register study found that risk was highest the month before starting a medication, Strawn and colleagues wrote.
Dara Sakolsky, MD, PhD, associate professor of psychiatry and associate medical director, Services for Teens at Risk at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, Pennsylvania, told this news organization that, because of “these negative unintended consequences,” the FDA should lower the temperature by putting the warnings in labeling.
“It makes sense based on the data that we have at hand now,” said Sakolsky.
The Dangers of Untreated Depression
Even with this new information, lingering concerns about earlier studies that pointed to increased suicidality risk may discourage prescribing by primary care physicians and pediatricians, and that worries researchers and psychiatrists.
“My concern is that the risk for suicide and suicidal behavior may be higher in untreated depression than the risk of suicidal thoughts or behaviors from antidepressants,” Jeffrey Bridge, PhD, director of the Center for Suicide Prevention and Research at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio, told this news organization.
Bridge is the lead author of a much-cited 2007 meta-analysis in JAMA that showed that the benefits of antidepressants in children and adolescents appeared to be greater than the risks for suicidality. “The concern about antidepressants must be considered in the context of possible benefit,” wrote Bridge, who also is professor of pediatrics, psychiatry, and behavioral health at Ohio State University College of Medicine, Columbus.
Depression and suicide are a scourge for those younger than 25 years. A 2021 literature review noted that the prevalence of depression — which has been increasing for all Americans — has risen more among adolescents than adults. Depression is “strongly associated with suicide,” the authors wrote.
In 2021, the National Institute of Mental Health reported suicide was the second leading cause of death among 10- to 14-year-olds and the third leading cause of death among those aged 15-24 years.
Suicide kills more kids aged between 10 and 24 years than cancer and all other illnesses combined, John Campo, MD, director of child and adolescent psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and vice president of psychiatric services at Kennedy Krieger Institute, told this news organization.
Meanwhile, he added, the medications work and clinicians balance risk and benefit in prescribing.
The landmark 2007 Treatment for Adolescents with Depression Study showed that fluoxetine, especially in combination with cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), was significantly better than placebo. Since that time, legions of trials have shown the drugs’ effectiveness.
The most effective treatment for teen depression is a combination of CBT and a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, said Sakolsky.
“We know that the evidence for that is pretty good,” she said. “On the flip side, we know the risk of having an adverse outcome is pretty low.”
Sakolsky tells patients and families that perhaps 1 in 146 will have a suicidal thought or behavior. “That’s pretty rare when we know how effective these medicines are.”
Strawn said he always notes that no suicides took place in the trials that led to the warning and stresses that he closely monitors patients. “While the more recent prospective data are reassuring,” the suicidality risk “is something that we still talk about,” he said. He also discusses how some antidepressants seem to increase risk more than others.
For Campo, the discussion is based on his reading of the evidence, not the presence of the FDA warning.
“Based on what we know, I still think it’s fair to proceed with the idea that there is a small, but real risk,” he said. However, “at the same time, the medications might be exceptionally helpful for some kids.”
‘What Do We Do Now?’
When the FDA issued its warning in 2005, the agency said it identified the risk for suicidality in a combined analysis of short-term placebo-controlled trials of nine antidepressants. It ultimately included 24 trials involving more than 4400 patients. The risk was highest in the first few months. The average risk for those taking antidepressants was 4%, twice the placebo risk of 2%. There were no suicides in these trials, however.
The trials relied on spontaneous reports of adverse events, not predetermined measures, Campo said. Even so, that 2% difference is “nothing to sneeze at,” he noted.
Bridge’s meta-analysis showed a smaller difference — closer to 0.7%. “But it was still statistically significant,” Campo said. “I have trouble ignoring that.”
The unintended consequences of the warning can’t be studied in a randomized controlled trial. Studies have shown an association but not a direct cause-and-effect relationship between the warning and a decline in treatment and rise in suicides.
But the potential for suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressants has been studied prospectively. Some older studies found a significant risk, while more recent trials have not.
While the Health Affairs analysis “certainly makes a strong case,” it is observational data, Campo said.
“The question is, what do we do now in retrospect? Do you say, ‘Never mind. We don’t need the black box warning anymore?’ ” he said. “That would require a pretty careful look.”
The Health Affairs paper “makes me think that there are other areas of research that that need to be completed and done and updated, and then there should be an assessment, a reevaluation from the FDA,” said Bridge. A new meta-analysis “would be very informative,” he said.
What’s Next?
When asked about the Health Affairs paper and whether the agency would review the warnings, an FDA spokesperson told this news organization that the agency “does not comment on specific studies but evaluates them as part of the body of evidence to further our understanding about a particular issue and assist in our mission to protect public health.”
Sakolsky said the data clearly point to the damage that the warning has done over the past 2 decades, but that things might be improving. Studies conducted more recently might not have captured some changes in practice.
For instance, she noted, in 2022, the US Preventive Services Task Force recommended screening for major depressive disorder in adolescents aged 12-18 years. In turn, she has seen more patients in her office who were referred by pediatricians who had conducted the screening, said Sakolsky.
Strawn said the time for pontificating is long past due. “We’re withholding medications and other treatments that could potentially be effective for disorders that, in and of themselves, are associated with a significant increase in the risk of suicide.”
After the FDA instituted the warning, “we were all very nervous,” about the potential fallout, said Campo, adding that a part of him wishes that the warnings had been “more mundane and less dramatic.”
Despite the unintended consequences, “it’s going to be hard to put the genie back in the bottle,” he said.
Campo and Sakolsky reported no relevant financial relationships. Strawn disclosed that his institution has received research funding from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI), and AbbVie. Bridge reported that he received grant support from the National Institute of Mental Health, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and PCORI; is a scientific adviser to Clarigent Health; and is on the Scientific Council of the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.




