User login
Sports Injuries of the Hip in Primary Care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.
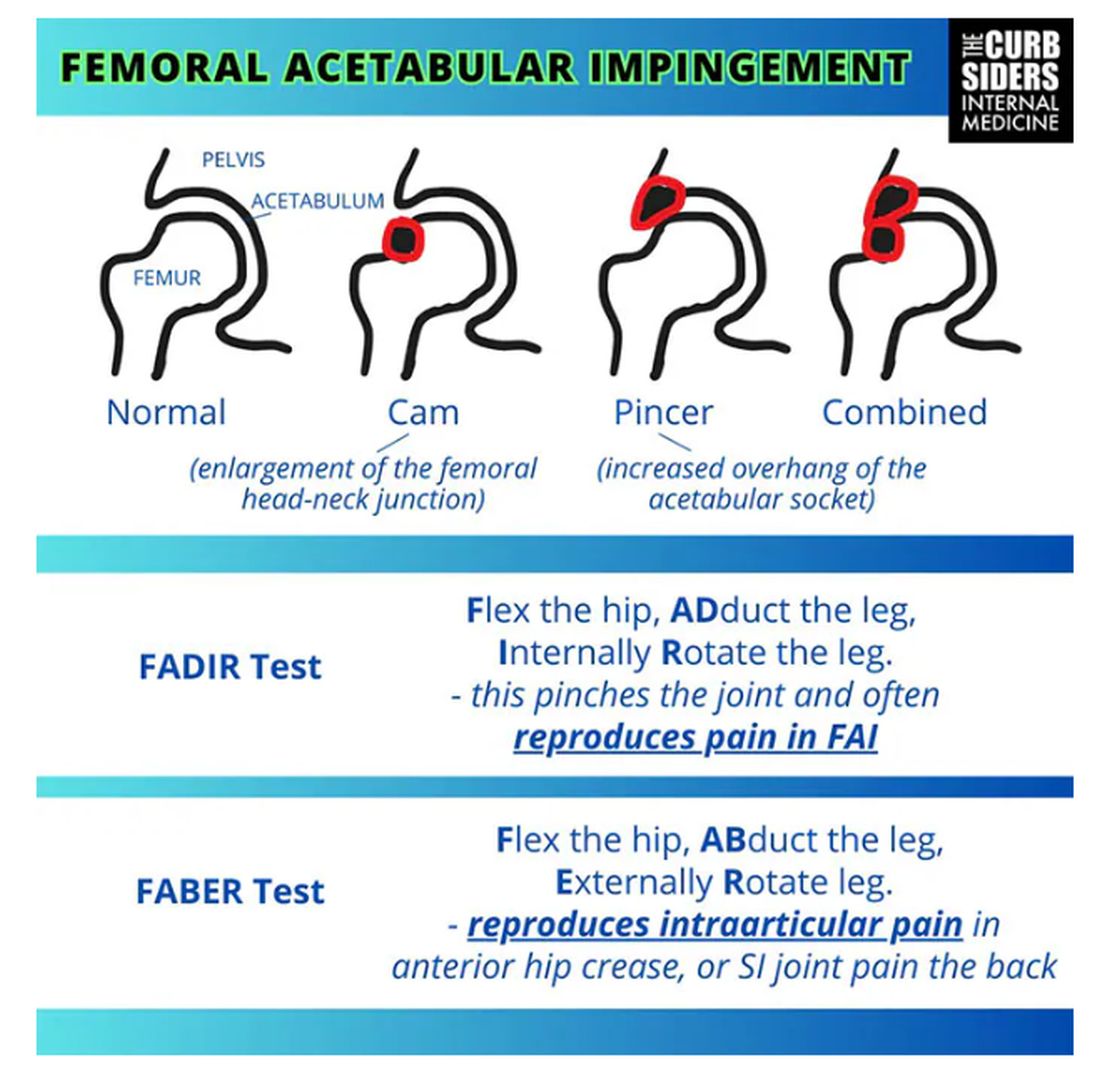
Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.
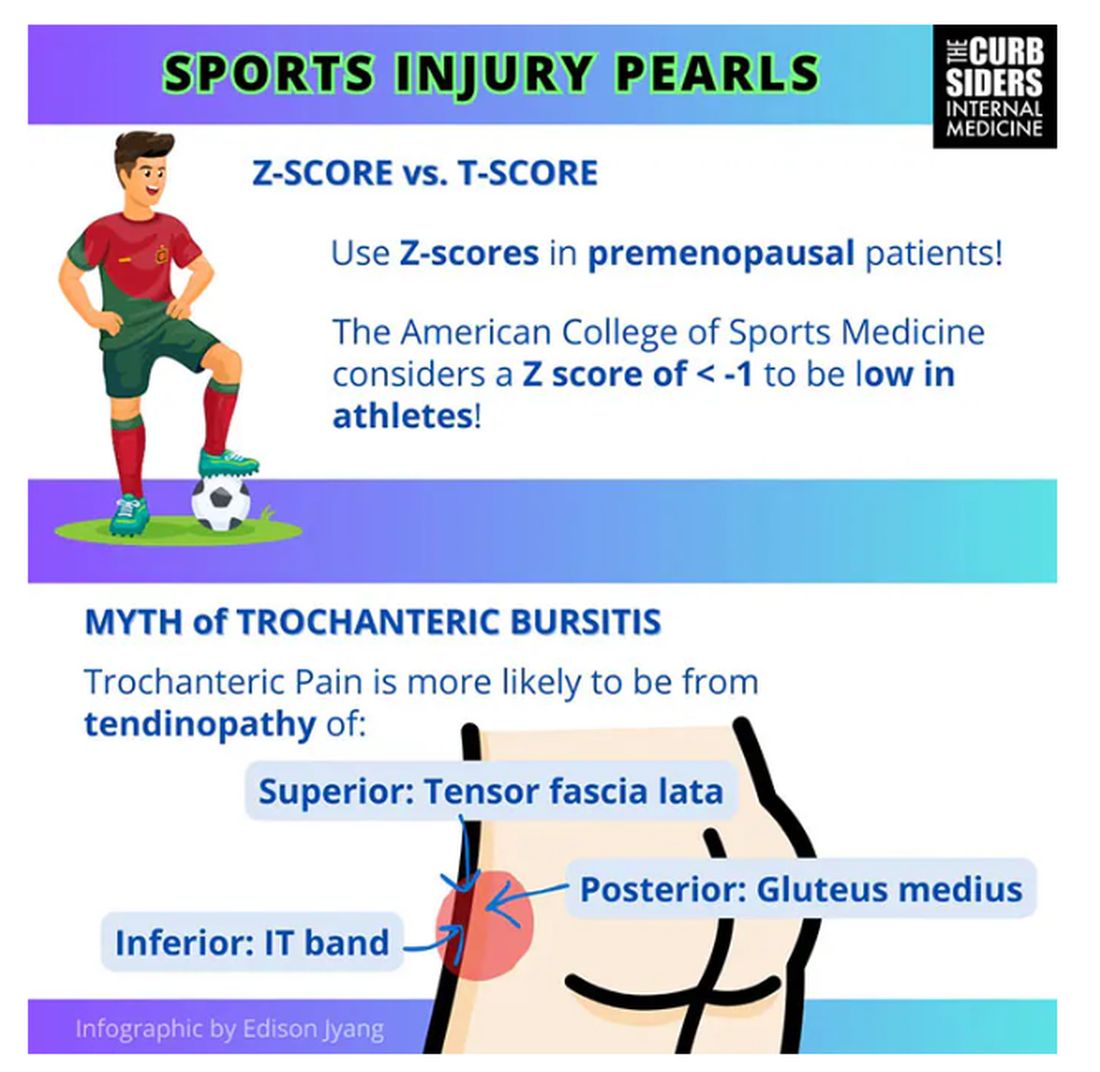
Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, how are you feeling about sports injuries?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m feeling great, Matt.
Watto: You had a sports injury of the hip. Maybe that’s an overshare, Paul, but we talked about it on a podcast with Dr Carlin Senter (part 1 and part 2).
Williams: I think I’ve shared more than my hip injury, for sure.
Watto: Whenever a patient presented with hip pain, I used to pray it was trochanteric bursitis, which now I know is not really the right thing to think about. Intra-articular hip pain presents as anterior hip pain, usually in the crease of the hip. Depending on the patient’s age and history, the differential for that type of pain includes iliopsoas tendonitis, FAI syndrome, a labral tear, a bone stress injury of the femoral neck, or osteoarthritis.
So, what exactly is FAI and how might we diagnose it?
Williams: FAI is what the cool kids call femoral acetabular impingement, and it’s exactly what it sounds like.

Something is pinching or impinging upon the joint itself and preventing full range of motion. This is a ball-and-socket joint, so it should have tremendous range of motion, able to move in all planes. If it’s impinged, then pain will occur with certain movements. There’s a cam type, which is characterized by enlargement of the femoral head neck junction, or a pincer type, which has more to do with overhang of the acetabulum, and it can also be mixed. In any case, impingement upon the patient’s full range of motion results in pain.
You evaluate this with a couple of tests — the FABER and the FADIR.
The FABER is flexion, abduction, and external rotation, and the FADIR is flexion, adduction, and internal rotation. If you elicit anterior pain with either of those tests, it’s probably one of the intra-articular pathologies, although it is hard to know for sure which one it is because these tests are fairly sensitive but not very specific.
Watto: You can get x-rays to help with the diagnosis. You would order two views of the hip: an AP of the pelvis, which is just a straight-on shot to look for arthritis or fracture. Is there a healthy joint line there? The second is the Dunn view, in which the hip is flexed 90 degrees and abducted about 20 degrees. You are looking for fracture or impingement. You can diagnose FAI based on that view, and you might be able to diagnose a hip stress injury or osteoarthritis.
Unfortunately, you’re not going to see a labral tear, but Dr Senter said that both FAI and labral tears are treated the same way, with physical therapy. Patients with FAI who aren’t getting better might end up going for surgery, so at some point I would refer them to orthopedic surgery. But I feel much more comfortable now diagnosing these conditions with these tests.
Let’s talk a little bit about trochanteric pain syndrome. I used to think it was all bursitis. Why is that not correct?
Williams: It’s nice of you to feign ignorance for the purpose of education. It used to be thought of as bursitis, but these days we know it is probably more likely a tendinopathy.

Trochanteric pain syndrome was formerly known as trochanteric bursitis, but the bursa is not typically involved. Trochanteric pain syndrome is a tendinopathy of the surrounding structures: the gluteus medius, the iliotibial band, and the tensor fascia latae. The way these structures relate looks a bit like the face of a clock, as you can see on the infographic. In general, you manage this condition the same way you do with bursitis — physical therapy. You can also give corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy is probably more durable in terms of pain relief and functionality, but in the short term, corticosteroids might provide some degree of analgesia as well.
Watto: The last thing we wanted to mention is bone stress injury, which can occur in high-mileage runners (20 miles or more per week). Patients with bone stress injury need to rest, usually non‒weight bearing, for a period of time.

Treatment of a bone stress fracture depends on which side it’s on (top or bottom). If it’s on the top of the femoral neck (the tension side), it has to be fixed. If it’s on the compression side (the bottom side of the femoral neck), it might be able to be managed conservatively, but many patients are going to need surgery. This is a big deal. But it’s a spectrum; in some cases the bone is merely irritated and unhappy, without a break in the cortex. Those patients might not need surgery.
In patients with a fracture of the femoral neck — especially younger, healthier patients — you should think about getting a bone density test and screening for relative energy deficiency in sport. This used to be called the female athlete triad, which includes disrupted menstrual cycles, being underweight, and fracture. We should be screening patients, asking them in a nonjudgmental way about their relationship with food, to make sure they are getting an appropriate number of calories.
They are actually in an energy deficit. They’re not eating enough to maintain a healthy body with so much activity.
Williams: If you’re interested in this topic, you should refer to the full podcast with Dr Senter which is chock-full of helpful information.
Dr Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
How to Avoid Freaking Out About Kidney Function
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
We had a great discussion with Kidney Boy, Dr Joel Topf, everyone’s favorite nephrologist, and he taught us how to manage blood pressure in chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Paul N. Williams, MD: Dr Topf focuses more on albuminuria than we are used to doing. It’s probably one of the most important prognostic indicators of how a patient is going to do from a renal standpoint.
Historically, I’ve tended to focus on the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and the lower that number gets, the more I sweat, but albuminuria is probably equally, if not more, important as a way of prognosticating whether a patient is going to progress to dialysis or transplant. He directed us towards this nifty little calculator, kidneyfailurerisk.com, where you plug in the patient’s age, eGFR, and degree of albuminuria, and it spits out their risk of progressing to hemodialysis or renal transplantation over the next 5 years. It’s a nice way to concretely explain to patients their risk for progression.
Instead of telling the patient, “You are high risk,” Dr Topf will say, “Your risk is 6% of needing dialysis in the next 5 years.” You can even use these thresholds to gauge when to refer a patient. If someone has a 5-year risk between 3% and 5% or higher, that patient should probably be seeing a nephrologist.
If their 2-year risk is greater than 20%, that patient probably should be evaluated for transplantation. This gives us have more concrete numbers to work with rather than just saying, “Your kidneys aren’t working as well as we would like and you should see a kidney doctor.” Patients have a better sense of how serious things might be.
Watto: It’s just easier for them to understand. Dr Topf made the point that we used to have a heat map based on the stage of CKD that would tell you how high a patient’s risk was compared with other people. But patients don’t really understand relative risk, so Dr Topf tells them their absolute risk for ending up on dialysis over the next 2-5 years.
Patients come in and they are worried because they looked at their lab results and see that their creatinine level is red, or their eGFR is low. They think, It says I have stage 3a CKD.
We should probably have the stages of CKD start at stage 3, which should be called stage 1 so it doesn’t sound as bad. Patients think they are halfway to dialysis; they are already at stage 3 and didn’t even know their kidneys were a problem.
Dr Topf said that cystatin C (something I only recently started ordering) can be obtained, and sometimes you can recategorize the patient, especially those with an eGFR between 45 and 60. The cystatin C can predict their renal function better than the creatinine-based equations. If you are using the creatinine equation, he recommends using the 2021 equations.
Another nice thing about cystatin C is that it isn’t tripped up in younger patients with a lot of muscle mass. You just have to watch out for inflammation, which can throw the test off. For example, when a patient is in the intensive care unit, it’s probably not that helpful, but for your outpatients, cystatin C works well.
Williams: I’ve been using it a fair amount in my patients with more muscle mass. And some patients have been taking creatine as a supplement, and that can alter the numbers as well. This is a nice way to get them out of CKD stage 2 or 3 and back where they belong, with normal healthy functioning kidneys.
Watto: Now, Paul, if we find a patient with more advanced CKD — let’s say stage 4, whether by cystatin C or serum creatinine, and their eGFR is less than 30 — should we start peeling off the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitor or the angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)? Those drugs can raise potassium. What should we do here?
Williams: That’s the temptation, Matt, and I feel like that was the old orthodoxy, back in residency. It didn’t take much for us to start taking off ACE inhibitors or ARBs once the kidney function started to drop, but it turns out you may be doing more harm than good.
Some data have shown that if you peel off those medications, you actually increase mortality and cardiovascular risk. So, in general, if you can keep them going, the patient will be better off. Hang onto the ACE inhibitors or ARBs as long as you are able to, because they confer a fair amount of benefit.
Watto: As long as the potassium isn’t in red on your lab’s range. It might go up to 5.2 or 5.4, but as long as it’s stable, that should be OK. You probably wouldn’t initiate an ACE inhibitor or ARB or spironolactone with a potassium level above 5, but if it’s below 5 when you start and it goes up slightly after you start the drug, that could be acceptable.
Another thing we talked about was when a patient progresses to CKD and ends up on dialysis, how helpful are those intradialysis blood pressures in predicting cardiovascular outcomes?
Williams: For someone who’s performing the dialysis, probably really helpful. In the outpatient setting to predict cardiovascular risk, probably less so. Dr Topf makes the point that the readings are done either shortly after or right when the patient is about to have a large-bore catheter inserted into their arm. And then they have liters of fluid drained out of them. So those numbers are going to have huge amounts of variability. You would not base the patient’s blood pressure treatment solely on those numbers. But regardless of what the numbers are, or even regardless of your office numbers, hopefully you’re working with a nephrologist to make sure that you’re actually in concert and not fighting each other with the blood pressure medications.
Watto: Dr Topf said that a lot of the hypertension in dialysis is because of too much volume. If you can get the volume down, you might be able to peel off blood pressure medications instead of adding more. But some patients have issues with cramping; it’s uncomfortable and not everyone tolerates it.
I was really surprised to learn that beta blockers, specifically atenolol, have some evidence of improving cardiovascular outcomes in patients on dialysis. Dr Topf speculated that this was because they are largely dying of cardiovascular disease, so maybe that’s why, but that’s one of the places, the only places I can think of aside from thyroid disease, where atenolol really shines.
If you want to hear this fantastic episode and all the great pearls, then click on this link.
Matthew F. Watto, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams, MD, has disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
The Most Common Chronic Liver Disease in the World
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, what is MASLD?
Paul N. Williams, MD:
Watto: We talked about a really stripped-down way of testing people for MASLD. If we see mildly elevated liver enzymes, what should we be testing, and how does alcohol factor in?
Williams: Before you can make a definitive diagnosis of MASLD, you need to rule out other causes of liver inflammation — things that would cause a patient’s transaminases to increase. Alcohol is synergistic with everything that can harm the liver.
A great place to start is to gauge someone’s alcohol intake to make sure it isn’t causing hepatic inflammation. The phosphatidyl ethanol level is a serologic test to determine chronic, heavy alcohol use. It’s a new kid on the block. I’ve seen it mostly ordered by hepatologists. It is a way of determining whether someone has had fairly consistent alcohol use up to 4 weeks after the fact. The cutoff for a positive test is 20 ng/mL.
Dr Tapper frames the test this way. He isn’t using the test to catch someone in a lie about their alcohol use. He tells patients that he orders this test for all patients with liver inflammation, because alcohol is a common cause. The test helps him better understand the factors that might be affecting the patient’s liver function.
If the test comes back positive, you can have a conversation about that, and if it’s not positive, you move on to the next possible cause. Other fairly common causes of liver inflammation are relatively easy to address.
Watto: Instead of ordering ceruloplasmin or alpha-1 antitrypsin tests, for example, the first thing Dr Tapper recommends is checking for hepatitis B and C. We can cure hepatitis C. We can’t cure hepatitis B, but it’s important to know if the patient has it. Primary care physicians should be comfortable ordering these tests.
Really high ALT levels (eg, in the 200s) don’t usually happen from steatotic liver disease. In those cases, we would send an expanded panel that might include tests for autoimmune hepatitis-ANA, anti–smooth muscle antibody, and IgG levels. Otherwise, most of these patients don’t need much more testing.
What is a FIB4 score and how does that factor in?
Williams: The FIB4 score estimates the degree of fibrosis based on the ALT and AST levels, platelet count, and the patient’s age. These data are plugged into a formula. If the FIB4 score is low (meaning not much fibrosis is present), you can stop there and do your counseling about lifestyle changes and address the reversible factors.
If the FIB4 score is above a certain threshold (1.3 in young adults and 2.0 in older adults), you need to find a more concrete way to determine the degree of fibrosis, typically through imaging.
Elastography can be done either with ultrasound or MRI. Ultrasound is typically ordered, but Dr Tapper recommends doing MRI on patients with a BMI > 40. Those patients are probably better served by doing MRI to determine the degree of liver fibrosis.
Watto: Patients with low FIB4 scores probably don’t need elastography but those with high FIB4 scores do. For the interpretation of ultrasound-based elastography results, Dr Tapper gave us the “rule of 5s”.
Elastography results are reported in kilopascal (kPa) units. A finding of 5 kPa or less is normal. Forty percent of those with a result of 10 kPa might have advanced liver disease. Above 15 kPa, the likelihood of cirrhosis is high, becoming very likely at 25 kPa. Finally, with a result of > 25 kPa, portal hypertension is likely, and you might need to have a conversation about starting the patient on medicine to prevent variceal bleeding.
We are moving toward more noninvasive testing and avoiding biopsies. We have cutoff values for MRI-based elastography as well. Both of these tests can help stage the liver.
What can we tell people about diet?
Williams: Weight loss is helpful. You can reverse fibrosis with weight loss. You can truly help your liver and bring it closer to its healthy baseline with weight loss. A loss of 7.5% body weight can reduce steatohepatitis, and with around 10% of body weight loss, you can actually resolve fibrosis, which is remarkable.
We all know that weight loss can be very therapeutic for many conditions. It’s just very hard to achieve. As primary care doctors, we should use what we have in our armamentarium to achieve that goal. Often, that will include certain medications.
Watto: I like giving patients the 10% number because if they weigh 220 pounds, they need to lose 22 pounds. If they weigh 300 pounds, it’s 30 pounds. Most people who weigh 300 pounds think they need to lose 100 pounds to have any sort of health benefit, but it’s much less than that. So, I do find that helpful.
But now a new drug has been approved. It’s a thyroid memetic called resmetirom. It was from the MAESTRO-NASH trial. Without weight loss, it helped to reverse fibrosis.
This is going to be used more and more in the future. It’s still being worked out exactly where the place is for that drug, so much so that Dr Tapper, as a liver expert, hadn’t even had the chance to prescribe it yet. Of course, it was very recently approved.
Dr. Tapper is one of our most celebrated guests, so check out the full podcast here.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, what is MASLD?
Paul N. Williams, MD:
Watto: We talked about a really stripped-down way of testing people for MASLD. If we see mildly elevated liver enzymes, what should we be testing, and how does alcohol factor in?
Williams: Before you can make a definitive diagnosis of MASLD, you need to rule out other causes of liver inflammation — things that would cause a patient’s transaminases to increase. Alcohol is synergistic with everything that can harm the liver.
A great place to start is to gauge someone’s alcohol intake to make sure it isn’t causing hepatic inflammation. The phosphatidyl ethanol level is a serologic test to determine chronic, heavy alcohol use. It’s a new kid on the block. I’ve seen it mostly ordered by hepatologists. It is a way of determining whether someone has had fairly consistent alcohol use up to 4 weeks after the fact. The cutoff for a positive test is 20 ng/mL.
Dr Tapper frames the test this way. He isn’t using the test to catch someone in a lie about their alcohol use. He tells patients that he orders this test for all patients with liver inflammation, because alcohol is a common cause. The test helps him better understand the factors that might be affecting the patient’s liver function.
If the test comes back positive, you can have a conversation about that, and if it’s not positive, you move on to the next possible cause. Other fairly common causes of liver inflammation are relatively easy to address.
Watto: Instead of ordering ceruloplasmin or alpha-1 antitrypsin tests, for example, the first thing Dr Tapper recommends is checking for hepatitis B and C. We can cure hepatitis C. We can’t cure hepatitis B, but it’s important to know if the patient has it. Primary care physicians should be comfortable ordering these tests.
Really high ALT levels (eg, in the 200s) don’t usually happen from steatotic liver disease. In those cases, we would send an expanded panel that might include tests for autoimmune hepatitis-ANA, anti–smooth muscle antibody, and IgG levels. Otherwise, most of these patients don’t need much more testing.
What is a FIB4 score and how does that factor in?
Williams: The FIB4 score estimates the degree of fibrosis based on the ALT and AST levels, platelet count, and the patient’s age. These data are plugged into a formula. If the FIB4 score is low (meaning not much fibrosis is present), you can stop there and do your counseling about lifestyle changes and address the reversible factors.
If the FIB4 score is above a certain threshold (1.3 in young adults and 2.0 in older adults), you need to find a more concrete way to determine the degree of fibrosis, typically through imaging.
Elastography can be done either with ultrasound or MRI. Ultrasound is typically ordered, but Dr Tapper recommends doing MRI on patients with a BMI > 40. Those patients are probably better served by doing MRI to determine the degree of liver fibrosis.
Watto: Patients with low FIB4 scores probably don’t need elastography but those with high FIB4 scores do. For the interpretation of ultrasound-based elastography results, Dr Tapper gave us the “rule of 5s”.
Elastography results are reported in kilopascal (kPa) units. A finding of 5 kPa or less is normal. Forty percent of those with a result of 10 kPa might have advanced liver disease. Above 15 kPa, the likelihood of cirrhosis is high, becoming very likely at 25 kPa. Finally, with a result of > 25 kPa, portal hypertension is likely, and you might need to have a conversation about starting the patient on medicine to prevent variceal bleeding.
We are moving toward more noninvasive testing and avoiding biopsies. We have cutoff values for MRI-based elastography as well. Both of these tests can help stage the liver.
What can we tell people about diet?
Williams: Weight loss is helpful. You can reverse fibrosis with weight loss. You can truly help your liver and bring it closer to its healthy baseline with weight loss. A loss of 7.5% body weight can reduce steatohepatitis, and with around 10% of body weight loss, you can actually resolve fibrosis, which is remarkable.
We all know that weight loss can be very therapeutic for many conditions. It’s just very hard to achieve. As primary care doctors, we should use what we have in our armamentarium to achieve that goal. Often, that will include certain medications.
Watto: I like giving patients the 10% number because if they weigh 220 pounds, they need to lose 22 pounds. If they weigh 300 pounds, it’s 30 pounds. Most people who weigh 300 pounds think they need to lose 100 pounds to have any sort of health benefit, but it’s much less than that. So, I do find that helpful.
But now a new drug has been approved. It’s a thyroid memetic called resmetirom. It was from the MAESTRO-NASH trial. Without weight loss, it helped to reverse fibrosis.
This is going to be used more and more in the future. It’s still being worked out exactly where the place is for that drug, so much so that Dr Tapper, as a liver expert, hadn’t even had the chance to prescribe it yet. Of course, it was very recently approved.
Dr. Tapper is one of our most celebrated guests, so check out the full podcast here.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, what is MASLD?
Paul N. Williams, MD:
Watto: We talked about a really stripped-down way of testing people for MASLD. If we see mildly elevated liver enzymes, what should we be testing, and how does alcohol factor in?
Williams: Before you can make a definitive diagnosis of MASLD, you need to rule out other causes of liver inflammation — things that would cause a patient’s transaminases to increase. Alcohol is synergistic with everything that can harm the liver.
A great place to start is to gauge someone’s alcohol intake to make sure it isn’t causing hepatic inflammation. The phosphatidyl ethanol level is a serologic test to determine chronic, heavy alcohol use. It’s a new kid on the block. I’ve seen it mostly ordered by hepatologists. It is a way of determining whether someone has had fairly consistent alcohol use up to 4 weeks after the fact. The cutoff for a positive test is 20 ng/mL.
Dr Tapper frames the test this way. He isn’t using the test to catch someone in a lie about their alcohol use. He tells patients that he orders this test for all patients with liver inflammation, because alcohol is a common cause. The test helps him better understand the factors that might be affecting the patient’s liver function.
If the test comes back positive, you can have a conversation about that, and if it’s not positive, you move on to the next possible cause. Other fairly common causes of liver inflammation are relatively easy to address.
Watto: Instead of ordering ceruloplasmin or alpha-1 antitrypsin tests, for example, the first thing Dr Tapper recommends is checking for hepatitis B and C. We can cure hepatitis C. We can’t cure hepatitis B, but it’s important to know if the patient has it. Primary care physicians should be comfortable ordering these tests.
Really high ALT levels (eg, in the 200s) don’t usually happen from steatotic liver disease. In those cases, we would send an expanded panel that might include tests for autoimmune hepatitis-ANA, anti–smooth muscle antibody, and IgG levels. Otherwise, most of these patients don’t need much more testing.
What is a FIB4 score and how does that factor in?
Williams: The FIB4 score estimates the degree of fibrosis based on the ALT and AST levels, platelet count, and the patient’s age. These data are plugged into a formula. If the FIB4 score is low (meaning not much fibrosis is present), you can stop there and do your counseling about lifestyle changes and address the reversible factors.
If the FIB4 score is above a certain threshold (1.3 in young adults and 2.0 in older adults), you need to find a more concrete way to determine the degree of fibrosis, typically through imaging.
Elastography can be done either with ultrasound or MRI. Ultrasound is typically ordered, but Dr Tapper recommends doing MRI on patients with a BMI > 40. Those patients are probably better served by doing MRI to determine the degree of liver fibrosis.
Watto: Patients with low FIB4 scores probably don’t need elastography but those with high FIB4 scores do. For the interpretation of ultrasound-based elastography results, Dr Tapper gave us the “rule of 5s”.
Elastography results are reported in kilopascal (kPa) units. A finding of 5 kPa or less is normal. Forty percent of those with a result of 10 kPa might have advanced liver disease. Above 15 kPa, the likelihood of cirrhosis is high, becoming very likely at 25 kPa. Finally, with a result of > 25 kPa, portal hypertension is likely, and you might need to have a conversation about starting the patient on medicine to prevent variceal bleeding.
We are moving toward more noninvasive testing and avoiding biopsies. We have cutoff values for MRI-based elastography as well. Both of these tests can help stage the liver.
What can we tell people about diet?
Williams: Weight loss is helpful. You can reverse fibrosis with weight loss. You can truly help your liver and bring it closer to its healthy baseline with weight loss. A loss of 7.5% body weight can reduce steatohepatitis, and with around 10% of body weight loss, you can actually resolve fibrosis, which is remarkable.
We all know that weight loss can be very therapeutic for many conditions. It’s just very hard to achieve. As primary care doctors, we should use what we have in our armamentarium to achieve that goal. Often, that will include certain medications.
Watto: I like giving patients the 10% number because if they weigh 220 pounds, they need to lose 22 pounds. If they weigh 300 pounds, it’s 30 pounds. Most people who weigh 300 pounds think they need to lose 100 pounds to have any sort of health benefit, but it’s much less than that. So, I do find that helpful.
But now a new drug has been approved. It’s a thyroid memetic called resmetirom. It was from the MAESTRO-NASH trial. Without weight loss, it helped to reverse fibrosis.
This is going to be used more and more in the future. It’s still being worked out exactly where the place is for that drug, so much so that Dr Tapper, as a liver expert, hadn’t even had the chance to prescribe it yet. Of course, it was very recently approved.
Dr. Tapper is one of our most celebrated guests, so check out the full podcast here.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Just Call It ‘Chronic Rhinitis’ and Reach for These Treatments
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about rhinitis?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m excited. It’s always the season to talk about rhinitis.
Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast, Rhinitis and Environmental Allergies with Dr. Olajumoke Fadugba from Penn Medicine. She’s an allergist and immunologist. One of her pet peeves is when people just call everything “allergic rhinitis” because we should be calling it “chronic rhinitis,” if it’s chronic. That’s an umbrella term, and there are many buckets underneath it that people could fall into.
When you’re taking a history, you have to figure out whether it’s perennial (meaning it happens year round) because certain things can cause that. Cat dander is around all the time, so people with cats might have sinus symptoms all year. Dust mites are another one, and it’s pretty hard to avoid those. Those are some perennial allergens.
Then there is allergic vs nonallergic rhinitis, which is something I hadn’t really put too much thought into.
Williams: I didn’t realize exactly how nuanced it got. Nonallergic rhinitis can still be seasonal because changes in temperature and humidity can trigger the rhinitis. And it matters what medications you use for what.
Watto: Here are some ways you can try to figure out if rhinitis is allergic or nonallergic. Ask the patient if they have itchy eyes and are sneezing a lot. That can be more of an allergic rhinitis, but both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis have the congestion, the rhinorrhea, so you can’t figure it out based on that alone.
Dr. Fadugba said that one clue that it might be nonallergic rhinitis is the age of onset. If the symptoms are later in onset (older age), then 30%-40% of rhinitis is nonallergic. If the patient has never had allergies and now all of a sudden they have new chronic sinus symptoms, it’s probably nonallergic rhinitis. It’s a diagnosis of exclusion.
I guess they need allergy testing?
Williams: If you want to make a definitive diagnosis, you need to rule it out. I suspect that you might be able to get away with some empirical treatment. If they get better, you can feel like a winner because getting booked in for allergy testing can be a little bit of a challenge.
Watto: The main treatment difference is that the oral antihistamines do not really seem to work for nonallergic rhinitis, but they can help with allergic rhinitis. Weirdly, the nasal antihistamines and nasal steroids do seem to work for both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis.
I don’t understand the mechanism there, but if you think someone might have nonallergic rhinitis, I wouldn’t go with the oral antihistamines as your first-line treatment. I would go with a nasal spray; you pretty much can’t go wrong with either an antihistamine or a steroid nasal spray.
Williams: We typically start with the nasal sprays. That’s kind of first-line for almost everybody, allergic or nonallergic. You’re probably going to start with an intranasal steroid, and then it’s kind of dealer’s choice what the patient can tolerate and afford. Sometimes you can get them covered by insurance, at least in my experience.
I will say that this is one of the medications — like nicotine patches and other things — where we as doctors don’t really counsel patients on how to use it appropriately. So with our expert, we revisited the idea of the patient pointing the nasal spray laterally, toward their ear basically, and not spraying toward their brain. There should not be a slurping sound afterward, because “if you taste it, you waste it,” as the allergists and immunologists say. It’s supposed to sit up there and not be swallowed immediately.
If your patient is sensitive to the floral flavor of some of the fluticasones (which I don’t mind so much as a user myself), then you can try mometasone or the other formulations. They are all roughly equivalent.
Speaking of medications, which medications can cause rhinitis? Any meds we commonly use in primary care?
Williams: Apparently the combined hormonal oral contraceptives can do it. Also the phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors. Drugs that cause vasodilation can also do it. Some of the antihypertensives. I’ve seen beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors listed specifically, and some of the medications for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). So there are a couple of medications that you can think about as a potential cause of rhinitis, although my suspicion is not going to be as high as for some of the other causes.
Watto: We mentioned medication treatments for patients who are really bothered by rhinorrhea, and maybe they are already on a steroid or an antihistamine.
You can try nasal ipratropium for people that have really prominent rhinorrhea. Dr. Fadugba said that can work well, and it’s usually taken three or four times a day. I’ve had good success prescribing it for my patients. Another one that I have never prescribed, but that Dr. Fadugba said is available over the counter, is intranasal cromolyn — a mast cell stabilizer. She said it can be beneficial.
Let’s say I had a cat allergy and I was going to visit Paul. I could use the intranasal cromolyn ahead of time to reduce rhinitis when I’m around the cats.
Paul, what about montelukast? I never know what to do with that one.
Williams: I’ve seen it prescribed as a last-ditch attempt to fix chronic rhinitis. Dr. Fadugba said she only ever prescribes it for patients who have rhinitis symptoms and asthma and never just for chronic rhinitis because it doesn’t work. And also, there have been some new black-box warnings from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). So unless there’s a solid indication for it, montelukast is not something you should just prescribe to try to see if it will work. That’s probably not the right approach for this.
But if the patient has challenging control asthma, and as a component, challenging nasal symptoms as well, it might be a reasonable medication to try.
Watto: And finally, Paul, how does climate change possibly have anything to do with rhinitis?
Williams: I feel like I’m just seeing more and more of the stuff every year. I don’t know if I’m more sensitive to it or because I’m having more symptoms myself, but it turns out the prevalence actually is going up.
We’re seeing more of it in part because it’s getting hotter outside, which is in turn worsening the production of allergens and increasing the allergen exposure and the severity of the symptoms that go along with it. More people are having more severe disease because the world is changing as a result of the stuff that we do. So fix that. But also be mindful and expect to see even more of these problems as you move forward in your careers.
Watto: Dr. Fadugba gave us so many great tips. You can listen to the full podcast episode here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about rhinitis?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m excited. It’s always the season to talk about rhinitis.
Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast, Rhinitis and Environmental Allergies with Dr. Olajumoke Fadugba from Penn Medicine. She’s an allergist and immunologist. One of her pet peeves is when people just call everything “allergic rhinitis” because we should be calling it “chronic rhinitis,” if it’s chronic. That’s an umbrella term, and there are many buckets underneath it that people could fall into.
When you’re taking a history, you have to figure out whether it’s perennial (meaning it happens year round) because certain things can cause that. Cat dander is around all the time, so people with cats might have sinus symptoms all year. Dust mites are another one, and it’s pretty hard to avoid those. Those are some perennial allergens.
Then there is allergic vs nonallergic rhinitis, which is something I hadn’t really put too much thought into.
Williams: I didn’t realize exactly how nuanced it got. Nonallergic rhinitis can still be seasonal because changes in temperature and humidity can trigger the rhinitis. And it matters what medications you use for what.
Watto: Here are some ways you can try to figure out if rhinitis is allergic or nonallergic. Ask the patient if they have itchy eyes and are sneezing a lot. That can be more of an allergic rhinitis, but both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis have the congestion, the rhinorrhea, so you can’t figure it out based on that alone.
Dr. Fadugba said that one clue that it might be nonallergic rhinitis is the age of onset. If the symptoms are later in onset (older age), then 30%-40% of rhinitis is nonallergic. If the patient has never had allergies and now all of a sudden they have new chronic sinus symptoms, it’s probably nonallergic rhinitis. It’s a diagnosis of exclusion.
I guess they need allergy testing?
Williams: If you want to make a definitive diagnosis, you need to rule it out. I suspect that you might be able to get away with some empirical treatment. If they get better, you can feel like a winner because getting booked in for allergy testing can be a little bit of a challenge.
Watto: The main treatment difference is that the oral antihistamines do not really seem to work for nonallergic rhinitis, but they can help with allergic rhinitis. Weirdly, the nasal antihistamines and nasal steroids do seem to work for both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis.
I don’t understand the mechanism there, but if you think someone might have nonallergic rhinitis, I wouldn’t go with the oral antihistamines as your first-line treatment. I would go with a nasal spray; you pretty much can’t go wrong with either an antihistamine or a steroid nasal spray.
Williams: We typically start with the nasal sprays. That’s kind of first-line for almost everybody, allergic or nonallergic. You’re probably going to start with an intranasal steroid, and then it’s kind of dealer’s choice what the patient can tolerate and afford. Sometimes you can get them covered by insurance, at least in my experience.
I will say that this is one of the medications — like nicotine patches and other things — where we as doctors don’t really counsel patients on how to use it appropriately. So with our expert, we revisited the idea of the patient pointing the nasal spray laterally, toward their ear basically, and not spraying toward their brain. There should not be a slurping sound afterward, because “if you taste it, you waste it,” as the allergists and immunologists say. It’s supposed to sit up there and not be swallowed immediately.
If your patient is sensitive to the floral flavor of some of the fluticasones (which I don’t mind so much as a user myself), then you can try mometasone or the other formulations. They are all roughly equivalent.
Speaking of medications, which medications can cause rhinitis? Any meds we commonly use in primary care?
Williams: Apparently the combined hormonal oral contraceptives can do it. Also the phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors. Drugs that cause vasodilation can also do it. Some of the antihypertensives. I’ve seen beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors listed specifically, and some of the medications for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). So there are a couple of medications that you can think about as a potential cause of rhinitis, although my suspicion is not going to be as high as for some of the other causes.
Watto: We mentioned medication treatments for patients who are really bothered by rhinorrhea, and maybe they are already on a steroid or an antihistamine.
You can try nasal ipratropium for people that have really prominent rhinorrhea. Dr. Fadugba said that can work well, and it’s usually taken three or four times a day. I’ve had good success prescribing it for my patients. Another one that I have never prescribed, but that Dr. Fadugba said is available over the counter, is intranasal cromolyn — a mast cell stabilizer. She said it can be beneficial.
Let’s say I had a cat allergy and I was going to visit Paul. I could use the intranasal cromolyn ahead of time to reduce rhinitis when I’m around the cats.
Paul, what about montelukast? I never know what to do with that one.
Williams: I’ve seen it prescribed as a last-ditch attempt to fix chronic rhinitis. Dr. Fadugba said she only ever prescribes it for patients who have rhinitis symptoms and asthma and never just for chronic rhinitis because it doesn’t work. And also, there have been some new black-box warnings from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). So unless there’s a solid indication for it, montelukast is not something you should just prescribe to try to see if it will work. That’s probably not the right approach for this.
But if the patient has challenging control asthma, and as a component, challenging nasal symptoms as well, it might be a reasonable medication to try.
Watto: And finally, Paul, how does climate change possibly have anything to do with rhinitis?
Williams: I feel like I’m just seeing more and more of the stuff every year. I don’t know if I’m more sensitive to it or because I’m having more symptoms myself, but it turns out the prevalence actually is going up.
We’re seeing more of it in part because it’s getting hotter outside, which is in turn worsening the production of allergens and increasing the allergen exposure and the severity of the symptoms that go along with it. More people are having more severe disease because the world is changing as a result of the stuff that we do. So fix that. But also be mindful and expect to see even more of these problems as you move forward in your careers.
Watto: Dr. Fadugba gave us so many great tips. You can listen to the full podcast episode here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about rhinitis?
Paul N. Williams, MD: I’m excited. It’s always the season to talk about rhinitis.
Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast, Rhinitis and Environmental Allergies with Dr. Olajumoke Fadugba from Penn Medicine. She’s an allergist and immunologist. One of her pet peeves is when people just call everything “allergic rhinitis” because we should be calling it “chronic rhinitis,” if it’s chronic. That’s an umbrella term, and there are many buckets underneath it that people could fall into.
When you’re taking a history, you have to figure out whether it’s perennial (meaning it happens year round) because certain things can cause that. Cat dander is around all the time, so people with cats might have sinus symptoms all year. Dust mites are another one, and it’s pretty hard to avoid those. Those are some perennial allergens.
Then there is allergic vs nonallergic rhinitis, which is something I hadn’t really put too much thought into.
Williams: I didn’t realize exactly how nuanced it got. Nonallergic rhinitis can still be seasonal because changes in temperature and humidity can trigger the rhinitis. And it matters what medications you use for what.
Watto: Here are some ways you can try to figure out if rhinitis is allergic or nonallergic. Ask the patient if they have itchy eyes and are sneezing a lot. That can be more of an allergic rhinitis, but both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis have the congestion, the rhinorrhea, so you can’t figure it out based on that alone.
Dr. Fadugba said that one clue that it might be nonallergic rhinitis is the age of onset. If the symptoms are later in onset (older age), then 30%-40% of rhinitis is nonallergic. If the patient has never had allergies and now all of a sudden they have new chronic sinus symptoms, it’s probably nonallergic rhinitis. It’s a diagnosis of exclusion.
I guess they need allergy testing?
Williams: If you want to make a definitive diagnosis, you need to rule it out. I suspect that you might be able to get away with some empirical treatment. If they get better, you can feel like a winner because getting booked in for allergy testing can be a little bit of a challenge.
Watto: The main treatment difference is that the oral antihistamines do not really seem to work for nonallergic rhinitis, but they can help with allergic rhinitis. Weirdly, the nasal antihistamines and nasal steroids do seem to work for both allergic and nonallergic rhinitis.
I don’t understand the mechanism there, but if you think someone might have nonallergic rhinitis, I wouldn’t go with the oral antihistamines as your first-line treatment. I would go with a nasal spray; you pretty much can’t go wrong with either an antihistamine or a steroid nasal spray.
Williams: We typically start with the nasal sprays. That’s kind of first-line for almost everybody, allergic or nonallergic. You’re probably going to start with an intranasal steroid, and then it’s kind of dealer’s choice what the patient can tolerate and afford. Sometimes you can get them covered by insurance, at least in my experience.
I will say that this is one of the medications — like nicotine patches and other things — where we as doctors don’t really counsel patients on how to use it appropriately. So with our expert, we revisited the idea of the patient pointing the nasal spray laterally, toward their ear basically, and not spraying toward their brain. There should not be a slurping sound afterward, because “if you taste it, you waste it,” as the allergists and immunologists say. It’s supposed to sit up there and not be swallowed immediately.
If your patient is sensitive to the floral flavor of some of the fluticasones (which I don’t mind so much as a user myself), then you can try mometasone or the other formulations. They are all roughly equivalent.
Speaking of medications, which medications can cause rhinitis? Any meds we commonly use in primary care?
Williams: Apparently the combined hormonal oral contraceptives can do it. Also the phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors. Drugs that cause vasodilation can also do it. Some of the antihypertensives. I’ve seen beta-blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors listed specifically, and some of the medications for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). So there are a couple of medications that you can think about as a potential cause of rhinitis, although my suspicion is not going to be as high as for some of the other causes.
Watto: We mentioned medication treatments for patients who are really bothered by rhinorrhea, and maybe they are already on a steroid or an antihistamine.
You can try nasal ipratropium for people that have really prominent rhinorrhea. Dr. Fadugba said that can work well, and it’s usually taken three or four times a day. I’ve had good success prescribing it for my patients. Another one that I have never prescribed, but that Dr. Fadugba said is available over the counter, is intranasal cromolyn — a mast cell stabilizer. She said it can be beneficial.
Let’s say I had a cat allergy and I was going to visit Paul. I could use the intranasal cromolyn ahead of time to reduce rhinitis when I’m around the cats.
Paul, what about montelukast? I never know what to do with that one.
Williams: I’ve seen it prescribed as a last-ditch attempt to fix chronic rhinitis. Dr. Fadugba said she only ever prescribes it for patients who have rhinitis symptoms and asthma and never just for chronic rhinitis because it doesn’t work. And also, there have been some new black-box warnings from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). So unless there’s a solid indication for it, montelukast is not something you should just prescribe to try to see if it will work. That’s probably not the right approach for this.
But if the patient has challenging control asthma, and as a component, challenging nasal symptoms as well, it might be a reasonable medication to try.
Watto: And finally, Paul, how does climate change possibly have anything to do with rhinitis?
Williams: I feel like I’m just seeing more and more of the stuff every year. I don’t know if I’m more sensitive to it or because I’m having more symptoms myself, but it turns out the prevalence actually is going up.
We’re seeing more of it in part because it’s getting hotter outside, which is in turn worsening the production of allergens and increasing the allergen exposure and the severity of the symptoms that go along with it. More people are having more severe disease because the world is changing as a result of the stuff that we do. So fix that. But also be mindful and expect to see even more of these problems as you move forward in your careers.
Watto: Dr. Fadugba gave us so many great tips. You can listen to the full podcast episode here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, disclosed ties with The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stones, Bones, Groans, and Moans: Could This Be Primary Hyperparathyroidism?
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Paul, we’re going to talk about our primary hyperparathyroidism podcast with Dr. Lindsay Kuo. It’s a topic that I feel much more clear on now.
Now, Paul, in primary care, you see a lot of calcium that is just slightly high. Can we just blame that on thiazide diuretics?
Paul N. Williams, MD: It’s a place to start. As you’re starting to think about the possible etiologies, primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy are the two that roll right off the tongue, but it is worth going back to the patient’s medication list and making sure you’re not missing something.
Thiazides famously cause hypercalcemia, but in some of the reading I did for this episode, they may just uncover it a little bit early. Patients who are on thiazides who become hypercalcemic seem to go on to develop primary hyperthyroidism anyway. So I don’t think you can solely blame the thiazide.
Another medication that can be causative is lithium. So a good place to look first after you’ve repeated the labs and confirmed hypercalcemia is the patient’s medication list.
Dr. Watto: We’ve talked before about the basic workup for hypercalcemia, and determining whether it’s PTH dependent or PTH independent. On the podcast, we talk more about the full workup, but I wanted to talk about the classic symptoms. Our expert made the point that we don’t see them as much anymore, although we do see kidney stones. People used to present very late in the disease because they weren’t having labs done routinely.
The classic symptoms include osteoporosis and bone tumors. People can get nephrocalcinosis and kidney stones. I hadn’t really thought of it this way because we’re used to diagnosing it early now. Do you feel the same?
Dr. Williams: As labs have started routinely reporting calcium levels, this is more and more often how it’s picked up. The other aspect is that as we are screening for and finding osteoporosis, part of the workup almost always involves getting a parathyroid hormone and a calcium level. We’re seeing these lab abnormalities before we’re seeing symptoms, which is good.
But it also makes things more diagnostically thorny.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Lindsay Kuo made the point that when she sees patients before and after surgery, she’s aware of these nonclassic symptoms — the stones, bones, groans, and the psychiatric overtones that can be anything from fatigue or irritability to dysphoria.
Some people have a generalized weakness that’s very nonspecific. Dr. Kuo said that sometimes these symptoms will disappear after surgery. The patients may just have gotten used to them, or they thought these symptoms were caused by something else, but after surgery they went away.
There are these nonclassic symptoms that are harder to pin down. I was surprised by that.
Dr. Williams: She mentioned polydipsia and polyuria, which have been reported in other studies. It seems like it can be anything. You have to take a good history, but none of those things in and of themselves is an indication for operating unless the patient has the classic renal or bone manifestations.
Dr. Watto: The other thing we talked about is a normal calcium level in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism, or the finding of a PTH level in the normal range but with a high calcium level that is inappropriate. Can you talk a little bit about those two situations?
Dr. Williams: They’re hard to say but kind of easy to manage because you treat them the same way as someone who has elevated calcium and PTH levels.
The normocalcemic patient is something we might stumble across with osteoporosis screening. Initially the calcium level is elevated, so you repeat it and it’s normal but with an elevated PTH level. You’re like, shoot. Now what?
It turns out that most endocrine surgeons say that the indications for surgery for the classic form of primary hyperparathyroidism apply to these patients as well, and it probably helps with the bone outcomes, which is one of the things they follow most closely. If you have hypercalcemia, you should have a suppressed PTH level, the so-called normohormonal hyperparathyroidism, which is not normal at all. So even if the PTH is in the normal range, it’s still relatively elevated compared with what it should be. That situation is treated in the same way as the classic elevated PTH and elevated calcium levels.
Dr. Watto: If the calcium is abnormal and the PTH is not quite what you’d expect it to be, you can always ask your friendly neighborhood endocrinologist to help you figure out whether the patient really has one of these conditions. You have to make sure that they don’t have a simple secondary cause like a low vitamin D level. In that case, you fix the vitamin D and then recheck the numbers to see if they’ve normalized. But I have found a bunch of these edge cases in which it has been helpful to confer with an endocrinologist, especially before you send someone to a surgeon to take out their parathyroid gland.
This was a really fantastic conversation. If you want to hear the full podcast episode, click here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders, and has received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Paul, we’re going to talk about our primary hyperparathyroidism podcast with Dr. Lindsay Kuo. It’s a topic that I feel much more clear on now.
Now, Paul, in primary care, you see a lot of calcium that is just slightly high. Can we just blame that on thiazide diuretics?
Paul N. Williams, MD: It’s a place to start. As you’re starting to think about the possible etiologies, primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy are the two that roll right off the tongue, but it is worth going back to the patient’s medication list and making sure you’re not missing something.
Thiazides famously cause hypercalcemia, but in some of the reading I did for this episode, they may just uncover it a little bit early. Patients who are on thiazides who become hypercalcemic seem to go on to develop primary hyperthyroidism anyway. So I don’t think you can solely blame the thiazide.
Another medication that can be causative is lithium. So a good place to look first after you’ve repeated the labs and confirmed hypercalcemia is the patient’s medication list.
Dr. Watto: We’ve talked before about the basic workup for hypercalcemia, and determining whether it’s PTH dependent or PTH independent. On the podcast, we talk more about the full workup, but I wanted to talk about the classic symptoms. Our expert made the point that we don’t see them as much anymore, although we do see kidney stones. People used to present very late in the disease because they weren’t having labs done routinely.
The classic symptoms include osteoporosis and bone tumors. People can get nephrocalcinosis and kidney stones. I hadn’t really thought of it this way because we’re used to diagnosing it early now. Do you feel the same?
Dr. Williams: As labs have started routinely reporting calcium levels, this is more and more often how it’s picked up. The other aspect is that as we are screening for and finding osteoporosis, part of the workup almost always involves getting a parathyroid hormone and a calcium level. We’re seeing these lab abnormalities before we’re seeing symptoms, which is good.
But it also makes things more diagnostically thorny.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Lindsay Kuo made the point that when she sees patients before and after surgery, she’s aware of these nonclassic symptoms — the stones, bones, groans, and the psychiatric overtones that can be anything from fatigue or irritability to dysphoria.
Some people have a generalized weakness that’s very nonspecific. Dr. Kuo said that sometimes these symptoms will disappear after surgery. The patients may just have gotten used to them, or they thought these symptoms were caused by something else, but after surgery they went away.
There are these nonclassic symptoms that are harder to pin down. I was surprised by that.
Dr. Williams: She mentioned polydipsia and polyuria, which have been reported in other studies. It seems like it can be anything. You have to take a good history, but none of those things in and of themselves is an indication for operating unless the patient has the classic renal or bone manifestations.
Dr. Watto: The other thing we talked about is a normal calcium level in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism, or the finding of a PTH level in the normal range but with a high calcium level that is inappropriate. Can you talk a little bit about those two situations?
Dr. Williams: They’re hard to say but kind of easy to manage because you treat them the same way as someone who has elevated calcium and PTH levels.
The normocalcemic patient is something we might stumble across with osteoporosis screening. Initially the calcium level is elevated, so you repeat it and it’s normal but with an elevated PTH level. You’re like, shoot. Now what?
It turns out that most endocrine surgeons say that the indications for surgery for the classic form of primary hyperparathyroidism apply to these patients as well, and it probably helps with the bone outcomes, which is one of the things they follow most closely. If you have hypercalcemia, you should have a suppressed PTH level, the so-called normohormonal hyperparathyroidism, which is not normal at all. So even if the PTH is in the normal range, it’s still relatively elevated compared with what it should be. That situation is treated in the same way as the classic elevated PTH and elevated calcium levels.
Dr. Watto: If the calcium is abnormal and the PTH is not quite what you’d expect it to be, you can always ask your friendly neighborhood endocrinologist to help you figure out whether the patient really has one of these conditions. You have to make sure that they don’t have a simple secondary cause like a low vitamin D level. In that case, you fix the vitamin D and then recheck the numbers to see if they’ve normalized. But I have found a bunch of these edge cases in which it has been helpful to confer with an endocrinologist, especially before you send someone to a surgeon to take out their parathyroid gland.
This was a really fantastic conversation. If you want to hear the full podcast episode, click here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders, and has received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Paul, we’re going to talk about our primary hyperparathyroidism podcast with Dr. Lindsay Kuo. It’s a topic that I feel much more clear on now.
Now, Paul, in primary care, you see a lot of calcium that is just slightly high. Can we just blame that on thiazide diuretics?
Paul N. Williams, MD: It’s a place to start. As you’re starting to think about the possible etiologies, primary hyperparathyroidism and malignancy are the two that roll right off the tongue, but it is worth going back to the patient’s medication list and making sure you’re not missing something.
Thiazides famously cause hypercalcemia, but in some of the reading I did for this episode, they may just uncover it a little bit early. Patients who are on thiazides who become hypercalcemic seem to go on to develop primary hyperthyroidism anyway. So I don’t think you can solely blame the thiazide.
Another medication that can be causative is lithium. So a good place to look first after you’ve repeated the labs and confirmed hypercalcemia is the patient’s medication list.
Dr. Watto: We’ve talked before about the basic workup for hypercalcemia, and determining whether it’s PTH dependent or PTH independent. On the podcast, we talk more about the full workup, but I wanted to talk about the classic symptoms. Our expert made the point that we don’t see them as much anymore, although we do see kidney stones. People used to present very late in the disease because they weren’t having labs done routinely.
The classic symptoms include osteoporosis and bone tumors. People can get nephrocalcinosis and kidney stones. I hadn’t really thought of it this way because we’re used to diagnosing it early now. Do you feel the same?
Dr. Williams: As labs have started routinely reporting calcium levels, this is more and more often how it’s picked up. The other aspect is that as we are screening for and finding osteoporosis, part of the workup almost always involves getting a parathyroid hormone and a calcium level. We’re seeing these lab abnormalities before we’re seeing symptoms, which is good.
But it also makes things more diagnostically thorny.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Lindsay Kuo made the point that when she sees patients before and after surgery, she’s aware of these nonclassic symptoms — the stones, bones, groans, and the psychiatric overtones that can be anything from fatigue or irritability to dysphoria.
Some people have a generalized weakness that’s very nonspecific. Dr. Kuo said that sometimes these symptoms will disappear after surgery. The patients may just have gotten used to them, or they thought these symptoms were caused by something else, but after surgery they went away.
There are these nonclassic symptoms that are harder to pin down. I was surprised by that.
Dr. Williams: She mentioned polydipsia and polyuria, which have been reported in other studies. It seems like it can be anything. You have to take a good history, but none of those things in and of themselves is an indication for operating unless the patient has the classic renal or bone manifestations.
Dr. Watto: The other thing we talked about is a normal calcium level in a patient with primary hyperparathyroidism, or the finding of a PTH level in the normal range but with a high calcium level that is inappropriate. Can you talk a little bit about those two situations?
Dr. Williams: They’re hard to say but kind of easy to manage because you treat them the same way as someone who has elevated calcium and PTH levels.
The normocalcemic patient is something we might stumble across with osteoporosis screening. Initially the calcium level is elevated, so you repeat it and it’s normal but with an elevated PTH level. You’re like, shoot. Now what?
It turns out that most endocrine surgeons say that the indications for surgery for the classic form of primary hyperparathyroidism apply to these patients as well, and it probably helps with the bone outcomes, which is one of the things they follow most closely. If you have hypercalcemia, you should have a suppressed PTH level, the so-called normohormonal hyperparathyroidism, which is not normal at all. So even if the PTH is in the normal range, it’s still relatively elevated compared with what it should be. That situation is treated in the same way as the classic elevated PTH and elevated calcium levels.
Dr. Watto: If the calcium is abnormal and the PTH is not quite what you’d expect it to be, you can always ask your friendly neighborhood endocrinologist to help you figure out whether the patient really has one of these conditions. You have to make sure that they don’t have a simple secondary cause like a low vitamin D level. In that case, you fix the vitamin D and then recheck the numbers to see if they’ve normalized. But I have found a bunch of these edge cases in which it has been helpful to confer with an endocrinologist, especially before you send someone to a surgeon to take out their parathyroid gland.
This was a really fantastic conversation. If you want to hear the full podcast episode, click here.
Dr. Watto, Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, served as a director, officer, partner, employee, adviser, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders, and has received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic Neck Pain: A Primary Care Approach
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome to The Curbsiders. I’m here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. We’re going to be talking about the evaluation of chronic neck pain, which is a really common complaint in primary care. So, Paul, what are the three buckets of neck pain?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Well, as our listeners probably know, neck pain is extraordinarily common. There are three big buckets. There is mechanical neck pain, which is sort of the bread-and-butter “my neck just hurts” — probably the one you’re going to see most commonly in the office. We’ll get into that in just a second.
The second bucket is cervical radiculopathy. We see a little bit more neurologic symptoms as part of the presentation. They may have weakness. They may have pain.
The third type of neck pain is cervical myelopathy, which is the one that probably warrants more aggressive follow-up and evaluation, and potentially even management. And that is typically your older patients in nontraumatic cases, who have bony impingement on the central spinal cord, often with upper motor neuron signs, and it can ultimately be very devastating. It’s almost a spectrum of presentations to worry about in terms of severity and outcomes.
We’ll start with the mechanical neck pain. It’s the one that we see the most commonly in the primary care office. We’ve all dealt with this. This is the patient who’s got localized neck pain that doesn’t really radiate anywhere; it kind of sits in the middle of the neck. In fact, if you actually poke back there where the patient says “ouch,” you’re probably in the right ballpark. The etiology and pathophysiology, weirdly, are still not super well-defined, but it’s probably mostly myofascial in etiology. And as such, it often gets better no matter what you do. It will probably get better with time.
You are not going to have neurologic deficits with this type of neck pain. There’s not going to be weakness, or radiation down the arm, or upper motor neuron signs. No one is mentioning the urinary symptoms with this. You can treat it with NSAIDs and physical therapy, which may be necessary if it persists. Massage can sometimes be helpful, but basically you’re just kind of supporting the patients through their own natural healing process. Physical therapy might help with the ergonomics and help make sure that they position themselves and move in a way that does not exacerbate the underlying structures. That is probably the one that we see the most and in some ways is probably the easiest to manage.
Dr. Watto: This is the one that we generally should be least worried about. But cervical radiculopathy, which is the second bucket, is not as severe as cervical myelopathy, so it’s kind of in between the two. Cervical radiculopathy is basically the patient who has neck pain that’s going down one arm or the other, usually not both arms because that would be weird for them to have symmetric radiculopathy. It’s a nerve being pinched somewhere, usually more on one side than the other.
The good news for patients is that the natural history is that it’s going to get better over time, almost no matter what we do. I almost think of this akin to sciatica. Usually sciatica and cervical radiculopathy do not have any motor weakness along with them. It’s really just the pain and maybe a little bit of mild sensory symptoms. So, you can reassure the patient that this usually goes away. Our guest said he sometimes gives gabapentin for this. That’s not my practice. I would be more likely to refer to physical therapy or try some NSAIDs if they’re really having trouble functioning or maybe some muscle relaxants. But they aren’t going to need to go to surgery.
What about cervical myelopathy, Paul? Do those patients need surgery?
Dr. Williams: Yes. The idea with cervical myelopathy is to keep it from progressing. It typically occurs in older patients. It’s like arthritis — a sort of bony buildup that compresses on the spinal cord itself. These patients will often have neck pain but not always. It’s also associated with impairments in motor function and other neurologic deficits. So, the patients may report that they have difficulty buttoning their buttons or managing fine-motor skills. They may have radicular symptoms down their arms. They may have an abnormal physical examination. They may have weakness on exam, but they’ll have a positive Hoffmann’s test where you flick the middle finger and look for flexion of the first finger and the thumb. They may have abnormal tandem gait, or patellar or Achilles hyperreflexia. Their neuro exam will not be normal much of the time, and in later cases because it’s upper motor neuron disease, they may even report urinary symptoms like urinary hesitancy or just a feeling of general unsteadiness of the gait, even though we’re at the cervical level. If you suspect myelopathy — and the trick is to think about it and recognize it when you see it — then you should send them for an MRI. If it persists or they have rapid regression, you get the MRI and refer them to neurosurgery. It’s not necessarily a neurosurgical emergency, but things should move along fairly briskly once you’ve actually identified it.
Dr. Watto: Dr. Mikula made the point that if someone comes to you in a wheelchair, they are probably not going to regain the ability to walk. You’re really trying to prevent progression. If they are already severely disabled, they’re probably not going to get totally back to full functioning, even with surgery. You’re just trying to prevent things from getting worse. That’s the main reason to identify this and get the patient to surgery.
We covered a lot more about neck pain. This was a very superficial review of what we talked about with Dr. Anthony Mikula. Click here to listen to the full podcast.
Matthew F. Watto is clinical assistant professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania, and internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Paul N. Williams is associate professor of clinical medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine, and staff physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for The Curbsiders; received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from The Curbsiders.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Management of Anxiety in Primary Care
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about anxiety?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Always. It’s one of my favorite topics.
Dr. Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast on anxiety — Dr. Jessi Gold, who gave us a lot of practical tips. The way she talks to her patients about anxiety is really useful. When patients say “my anxiety” or “I feel anxious,” she considers that a symptom. Anxiety can be a diagnosis or a symptom. You need to clarify what they mean when they refer to their anxiety and dig into how it affects their life.
We asked her about the Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)-7 score. Like most of the experts we’ve talked to, she’s internalized that, so she doesn’t need to rely on a questionnaire. But I still rely on a questionnaire when I’m taking a history for anxiety.
We also asked her how she explains anxiety to patients. I don’t know about you, Paul, but I’ve never really thought about explaining to patients why they have anxiety.
Dr. Williams: I’ve done my best to try to normalize it, but I haven’t actually talked to patients about the evolutionary advantage of anxiety.
Dr. Watto: She frames it to patients this way: As we were evolving, it was somewhat of an advantage to be hypervigilant, to have some anxiety and a healthy amount of fear so that you weren’t killed or eaten. But now, in the modern world, anxiety isn’t playing to our advantage. Anxiety is not making them safer; it’s making their lives worse. She explains to patients that she’s trying to help them overcome that.
In terms of pharmacotherapy for anxiety, I always think about SSRIs as one of the first steps. Why not use an SNRI as first-line treatment?
Dr. Williams: I was glad we had this conversation because I feel, for whatever reason, a bit more comfortable treating depression than anxiety. In any case, Dr. Gold reaches for the SSRI first, in part because getting off an SNRI (for example, to switch to something else) can be absolutely miserable. The discontinuation effects can be severe enough to have to bridge some patients with a benzodiazepine to get them fully off the SNRI. So, an SNRI is not the first drug you should necessarily reach for.
She thinks about using an SNRI if she has tried a couple of SSRIs that have been ineffective, or if the patient has a comorbid condition that might also benefit from the SNRI in the same way that you might use a tricyclic antidepressant in the patient with both migraines and anxiety. An SNRI might be a good medication to consider in the patient with neuropathic pain and anxiety but rarely as a first-line treatment, because if it doesn’t work out, getting the patient off that medication can be a challenge.
Dr. Watto: She mentioned venlafaxine as being especially difficult to get people off of. I’ve heard that bupropion should never be used in anxiety, and if you give it, you are a terrible doctor. What did we learn about that?
Dr. Williams: It’s a drug I’ve hesitated to prescribe to patients with anxiety or even comorbid anxiety. I’m a little bit nervous for someone who has depression and anxiety to prescribe bupropion because it can be activating and make things worse. But Dr. Gold says that she has seen bupropion work for some patients so she will consider it, especially for patients who don’t want to gain weight, or for whom sexual side effects would be bothersome. So, it’s not always the wrong answer. In her expert opinion, you can try it and see how the patient responds, using shared decision-making and letting the patient know that they may not tolerate it as well as other medications.
Dr. Watto: She sees a lot of younger people — students, working professionals — who do not want to gain weight, and that’s understandable. She will tell patients, “We can try bupropion, but if you get more anxious, we might not be able to continue it. We might have to use one of the first-line agents instead.”
Dr. Williams: We talked about mirtazapine as well. She tells patients they are going to gain weight with it. You have to have that conversation with the patient to see whether that is something they are willing to tolerate. If so, mirtazapine might be worth a try, but you have to be upfront about the potential side effects and know what the medications you’re prescribing will do to patients.
Dr. Watto: We asked her about benzodiazepines. For as-needed medication for people who are experiencing panic or anxiety attacks, she prescribes propranolol 10-20 mg twice a day as needed, which is a low dose. In primary care, we use higher doses for migraine prophylaxis.
She uses propranolol because for some patients, it’s the physical symptoms of anxiety that are bothering them. She can calm down the physical symptoms with that and get by without needing to use a benzodiazepine.
But what about thoughts that make people anxious? Can we change people’s thoughts with medication?
Dr. Williams: Dr. Gold made the point that we can medicate away insomnia, for the most part. We can medicate away the physical symptoms of anxiety, which can be really bothersome. But we can’t medicate away thoughts and thought patterns. You can make patients feel better with medications, but you may not be able to get rid of the persistent bothersome thoughts. That’s where cognitive-behavioral therapy can be especially helpful. Most of these patients would benefit from therapy.
Dr. Watto: I completely agree with that. We talked about so many great things with Dr. Gold, but we can’t recap all of it here. Please click on this link to hear the full podcast episode.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He disclosed receiving income from The Curbsiders. The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about anxiety?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Always. It’s one of my favorite topics.
Dr. Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast on anxiety — Dr. Jessi Gold, who gave us a lot of practical tips. The way she talks to her patients about anxiety is really useful. When patients say “my anxiety” or “I feel anxious,” she considers that a symptom. Anxiety can be a diagnosis or a symptom. You need to clarify what they mean when they refer to their anxiety and dig into how it affects their life.
We asked her about the Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)-7 score. Like most of the experts we’ve talked to, she’s internalized that, so she doesn’t need to rely on a questionnaire. But I still rely on a questionnaire when I’m taking a history for anxiety.
We also asked her how she explains anxiety to patients. I don’t know about you, Paul, but I’ve never really thought about explaining to patients why they have anxiety.
Dr. Williams: I’ve done my best to try to normalize it, but I haven’t actually talked to patients about the evolutionary advantage of anxiety.
Dr. Watto: She frames it to patients this way: As we were evolving, it was somewhat of an advantage to be hypervigilant, to have some anxiety and a healthy amount of fear so that you weren’t killed or eaten. But now, in the modern world, anxiety isn’t playing to our advantage. Anxiety is not making them safer; it’s making their lives worse. She explains to patients that she’s trying to help them overcome that.
In terms of pharmacotherapy for anxiety, I always think about SSRIs as one of the first steps. Why not use an SNRI as first-line treatment?
Dr. Williams: I was glad we had this conversation because I feel, for whatever reason, a bit more comfortable treating depression than anxiety. In any case, Dr. Gold reaches for the SSRI first, in part because getting off an SNRI (for example, to switch to something else) can be absolutely miserable. The discontinuation effects can be severe enough to have to bridge some patients with a benzodiazepine to get them fully off the SNRI. So, an SNRI is not the first drug you should necessarily reach for.
She thinks about using an SNRI if she has tried a couple of SSRIs that have been ineffective, or if the patient has a comorbid condition that might also benefit from the SNRI in the same way that you might use a tricyclic antidepressant in the patient with both migraines and anxiety. An SNRI might be a good medication to consider in the patient with neuropathic pain and anxiety but rarely as a first-line treatment, because if it doesn’t work out, getting the patient off that medication can be a challenge.
Dr. Watto: She mentioned venlafaxine as being especially difficult to get people off of. I’ve heard that bupropion should never be used in anxiety, and if you give it, you are a terrible doctor. What did we learn about that?
Dr. Williams: It’s a drug I’ve hesitated to prescribe to patients with anxiety or even comorbid anxiety. I’m a little bit nervous for someone who has depression and anxiety to prescribe bupropion because it can be activating and make things worse. But Dr. Gold says that she has seen bupropion work for some patients so she will consider it, especially for patients who don’t want to gain weight, or for whom sexual side effects would be bothersome. So, it’s not always the wrong answer. In her expert opinion, you can try it and see how the patient responds, using shared decision-making and letting the patient know that they may not tolerate it as well as other medications.
Dr. Watto: She sees a lot of younger people — students, working professionals — who do not want to gain weight, and that’s understandable. She will tell patients, “We can try bupropion, but if you get more anxious, we might not be able to continue it. We might have to use one of the first-line agents instead.”
Dr. Williams: We talked about mirtazapine as well. She tells patients they are going to gain weight with it. You have to have that conversation with the patient to see whether that is something they are willing to tolerate. If so, mirtazapine might be worth a try, but you have to be upfront about the potential side effects and know what the medications you’re prescribing will do to patients.
Dr. Watto: We asked her about benzodiazepines. For as-needed medication for people who are experiencing panic or anxiety attacks, she prescribes propranolol 10-20 mg twice a day as needed, which is a low dose. In primary care, we use higher doses for migraine prophylaxis.
She uses propranolol because for some patients, it’s the physical symptoms of anxiety that are bothering them. She can calm down the physical symptoms with that and get by without needing to use a benzodiazepine.
But what about thoughts that make people anxious? Can we change people’s thoughts with medication?
Dr. Williams: Dr. Gold made the point that we can medicate away insomnia, for the most part. We can medicate away the physical symptoms of anxiety, which can be really bothersome. But we can’t medicate away thoughts and thought patterns. You can make patients feel better with medications, but you may not be able to get rid of the persistent bothersome thoughts. That’s where cognitive-behavioral therapy can be especially helpful. Most of these patients would benefit from therapy.
Dr. Watto: I completely agree with that. We talked about so many great things with Dr. Gold, but we can’t recap all of it here. Please click on this link to hear the full podcast episode.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He disclosed receiving income from The Curbsiders. The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Frank Watto, here with my great friend and America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about anxiety?
Paul N. Williams, MD: Always. It’s one of my favorite topics.
Dr. Watto: We had a great guest for this podcast on anxiety — Dr. Jessi Gold, who gave us a lot of practical tips. The way she talks to her patients about anxiety is really useful. When patients say “my anxiety” or “I feel anxious,” she considers that a symptom. Anxiety can be a diagnosis or a symptom. You need to clarify what they mean when they refer to their anxiety and dig into how it affects their life.
We asked her about the Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)-7 score. Like most of the experts we’ve talked to, she’s internalized that, so she doesn’t need to rely on a questionnaire. But I still rely on a questionnaire when I’m taking a history for anxiety.
We also asked her how she explains anxiety to patients. I don’t know about you, Paul, but I’ve never really thought about explaining to patients why they have anxiety.
Dr. Williams: I’ve done my best to try to normalize it, but I haven’t actually talked to patients about the evolutionary advantage of anxiety.
Dr. Watto: She frames it to patients this way: As we were evolving, it was somewhat of an advantage to be hypervigilant, to have some anxiety and a healthy amount of fear so that you weren’t killed or eaten. But now, in the modern world, anxiety isn’t playing to our advantage. Anxiety is not making them safer; it’s making their lives worse. She explains to patients that she’s trying to help them overcome that.
In terms of pharmacotherapy for anxiety, I always think about SSRIs as one of the first steps. Why not use an SNRI as first-line treatment?
Dr. Williams: I was glad we had this conversation because I feel, for whatever reason, a bit more comfortable treating depression than anxiety. In any case, Dr. Gold reaches for the SSRI first, in part because getting off an SNRI (for example, to switch to something else) can be absolutely miserable. The discontinuation effects can be severe enough to have to bridge some patients with a benzodiazepine to get them fully off the SNRI. So, an SNRI is not the first drug you should necessarily reach for.
She thinks about using an SNRI if she has tried a couple of SSRIs that have been ineffective, or if the patient has a comorbid condition that might also benefit from the SNRI in the same way that you might use a tricyclic antidepressant in the patient with both migraines and anxiety. An SNRI might be a good medication to consider in the patient with neuropathic pain and anxiety but rarely as a first-line treatment, because if it doesn’t work out, getting the patient off that medication can be a challenge.
Dr. Watto: She mentioned venlafaxine as being especially difficult to get people off of. I’ve heard that bupropion should never be used in anxiety, and if you give it, you are a terrible doctor. What did we learn about that?
Dr. Williams: It’s a drug I’ve hesitated to prescribe to patients with anxiety or even comorbid anxiety. I’m a little bit nervous for someone who has depression and anxiety to prescribe bupropion because it can be activating and make things worse. But Dr. Gold says that she has seen bupropion work for some patients so she will consider it, especially for patients who don’t want to gain weight, or for whom sexual side effects would be bothersome. So, it’s not always the wrong answer. In her expert opinion, you can try it and see how the patient responds, using shared decision-making and letting the patient know that they may not tolerate it as well as other medications.
Dr. Watto: She sees a lot of younger people — students, working professionals — who do not want to gain weight, and that’s understandable. She will tell patients, “We can try bupropion, but if you get more anxious, we might not be able to continue it. We might have to use one of the first-line agents instead.”
Dr. Williams: We talked about mirtazapine as well. She tells patients they are going to gain weight with it. You have to have that conversation with the patient to see whether that is something they are willing to tolerate. If so, mirtazapine might be worth a try, but you have to be upfront about the potential side effects and know what the medications you’re prescribing will do to patients.
Dr. Watto: We asked her about benzodiazepines. For as-needed medication for people who are experiencing panic or anxiety attacks, she prescribes propranolol 10-20 mg twice a day as needed, which is a low dose. In primary care, we use higher doses for migraine prophylaxis.
She uses propranolol because for some patients, it’s the physical symptoms of anxiety that are bothering them. She can calm down the physical symptoms with that and get by without needing to use a benzodiazepine.
But what about thoughts that make people anxious? Can we change people’s thoughts with medication?
Dr. Williams: Dr. Gold made the point that we can medicate away insomnia, for the most part. We can medicate away the physical symptoms of anxiety, which can be really bothersome. But we can’t medicate away thoughts and thought patterns. You can make patients feel better with medications, but you may not be able to get rid of the persistent bothersome thoughts. That’s where cognitive-behavioral therapy can be especially helpful. Most of these patients would benefit from therapy.
Dr. Watto: I completely agree with that. We talked about so many great things with Dr. Gold, but we can’t recap all of it here. Please click on this link to hear the full podcast episode.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at University of Pennsylvania; Internist, Department of Medicine, Hospital Medicine Section, Pennsylvania Hospital, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Lewis Katz School of Medicine; Staff Physician, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple Internal Medicine Associates, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He disclosed receiving income from The Curbsiders. The Curbsiders is an internal medicine podcast, in which three board-certified internists interview experts on clinically important topics. In a collaboration with Medscape, the Curbsiders share clinical pearls and practice-changing knowledge from selected podcasts.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Diagnosing Adrenal Insufficiency: The ‘Quick and Dirty’ Method
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about some adrenal insufficiency? We had a great conversation with Dr. Atil Kargi, and I’d like you to start us off.
Paul N. Williams, MD: How about thinking about it? It’s a good place to start.
That’s one of the ways this episode changed my approach a little bit. I never really thought about the fact that . It’s such a protean sort of nonspecific presentation. But if you have someone with chronic malaise and poor appetite and maybe unexplained weight loss, and your GI workup is not really leading you anywhere, it’s probably worth thinking about adrenal insufficiency. Even though primary adrenal insufficiency is pretty rare — we’re talking cases per millions — secondary adrenal insufficiency is actually fairly common. It’s probably worth thinking about and testing for more often than I have in the past. So for me, it’s having a lower threshold to start looking for it.
Dr. Watto: When it’s adrenal crisis, you probably think about it, but then it’s too late. Ideally, you would think about it before that happens. But the symptoms can be quite vague. The mineralocorticoid symptoms, like salt cravings, dizziness, near syncope, muscle cramps, might make me think of it because they sound more like something endocrine is going on. But if it’s just a little weight loss, a little fatigue, or a little nausea, that’s everybody.
Dr. Williams: Right. If a patient came to me saying, “I’m craving salt,” that might hasten the workup a little bit, but that’s not the typical presentation.
Dr. Watto: If you are going to check a cortisol level, you should really check it in the morning, between 7 AM and 9 AM. If you check it too early, it might not have peaked yet, so you might get a level that looks low. But if you had checked an hour or 2 later, it might have been above a threshold, and then you would know you could rule out the diagnosis. The cutoffs depend on your source: < 3-5 µg/dL that early in the morning is pretty much diagnostic of adrenal insufficiency. If it’s > 15 µg/dL, that’s a pretty robust cortisol and the patient probably doesn’t have adrenal insufficiency. But if the level is between 5 µg/dL and 15 µg/dL, you’re in a gray zone, and that’s where you might think about doing a stimulation (stim) test.
Dr. Kargi gave us a quick and dirty version of the stim test. Paul, have you had a chance to try this yet?
Dr. Williams: I have not. Have you? I’m sure you’ve been just waiting for the chance.
Dr. Watto: I would love to do this. I don›t know whether I›m set up to do it in the office right now. But this is an aspirational goal for my practice, and I›m sure some physicians are set up in their office already to do it. You can give either intramuscular or subcutaneous cosyntropin 250 µg. You don›t even have to get a baseline cortisol level right before the injection. Let›s say the patient›s previous cortisol level was between 5 µg/dL and 15 µg/dL, so you weren›t sure about the diagnosis. You bring them back to the office one day, give them a shot of cosyntropin, and then 30-60 minutes later, have a random cortisol drawn. If it›s > 19 µg/dL, you›ve ruled out adrenal insufficiency. If it›s anything else, send them to an endocrinologist to sort it out. You might be able to make the diagnosis yourself doing that.
Any treatment pearls to leave the audience with?
Dr. Williams: I hope endocrinologists don›t take issue with this. I say this with respect and admiration, but it feels kind of vibe-based to me. Without a lab value to guide treatment, you are dependent on the patient telling you how they feel much of the time. You have to let their symptoms guide you. It is probably worth noting that because hydrocortisone has a relatively short half-life, within hours, in fact, you typically have to do twice-daily dosing, sometimes even three times daily dosing to get patients to where they feel okay. It sounds like there›s a fair amount of trial and error and some adjustments that you have to make depending on what›s going on with the patient at any given time. You land somewhere between a dose of 15-30 mg per day, but there will be some variability, even within an individual patient, depending on what›s going on with them from a physiologic standpoint.
Dr. Watto: They are going to take one dose in the morning and then a second dose in the afternoon, but they don’t want them to take it too late in the evening because it could cause insomnia, and you want to try to mimic physiologic levels as much as you can. Two thirds of the daily dose is given early in the morning and then another third of the daily dose later in the day if you are prescribing two times daily dosing.
And Dr. Kargi had a low threshold for doubling the dose. If the patient has a cold, double the dose for 2 or 3 days. With a high fever, triple the dose for a few days. If they are going for surgery, they are probably going to be getting some intravenous hydrocortisone while they’re in the hospital.
We really turned over like every stone we could possibly think of on this podcast. There were so many great pearls that we don’t have time to go through them all here. But we talked about steroid tapers and a lot more. You can check it out here.
Dr. Watto has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Williams has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: The CurbsidersReceived income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about some adrenal insufficiency? We had a great conversation with Dr. Atil Kargi, and I’d like you to start us off.
Paul N. Williams, MD: How about thinking about it? It’s a good place to start.
That’s one of the ways this episode changed my approach a little bit. I never really thought about the fact that . It’s such a protean sort of nonspecific presentation. But if you have someone with chronic malaise and poor appetite and maybe unexplained weight loss, and your GI workup is not really leading you anywhere, it’s probably worth thinking about adrenal insufficiency. Even though primary adrenal insufficiency is pretty rare — we’re talking cases per millions — secondary adrenal insufficiency is actually fairly common. It’s probably worth thinking about and testing for more often than I have in the past. So for me, it’s having a lower threshold to start looking for it.
Dr. Watto: When it’s adrenal crisis, you probably think about it, but then it’s too late. Ideally, you would think about it before that happens. But the symptoms can be quite vague. The mineralocorticoid symptoms, like salt cravings, dizziness, near syncope, muscle cramps, might make me think of it because they sound more like something endocrine is going on. But if it’s just a little weight loss, a little fatigue, or a little nausea, that’s everybody.
Dr. Williams: Right. If a patient came to me saying, “I’m craving salt,” that might hasten the workup a little bit, but that’s not the typical presentation.
Dr. Watto: If you are going to check a cortisol level, you should really check it in the morning, between 7 AM and 9 AM. If you check it too early, it might not have peaked yet, so you might get a level that looks low. But if you had checked an hour or 2 later, it might have been above a threshold, and then you would know you could rule out the diagnosis. The cutoffs depend on your source: < 3-5 µg/dL that early in the morning is pretty much diagnostic of adrenal insufficiency. If it’s > 15 µg/dL, that’s a pretty robust cortisol and the patient probably doesn’t have adrenal insufficiency. But if the level is between 5 µg/dL and 15 µg/dL, you’re in a gray zone, and that’s where you might think about doing a stimulation (stim) test.
Dr. Kargi gave us a quick and dirty version of the stim test. Paul, have you had a chance to try this yet?
Dr. Williams: I have not. Have you? I’m sure you’ve been just waiting for the chance.
Dr. Watto: I would love to do this. I don›t know whether I›m set up to do it in the office right now. But this is an aspirational goal for my practice, and I›m sure some physicians are set up in their office already to do it. You can give either intramuscular or subcutaneous cosyntropin 250 µg. You don›t even have to get a baseline cortisol level right before the injection. Let›s say the patient›s previous cortisol level was between 5 µg/dL and 15 µg/dL, so you weren›t sure about the diagnosis. You bring them back to the office one day, give them a shot of cosyntropin, and then 30-60 minutes later, have a random cortisol drawn. If it›s > 19 µg/dL, you›ve ruled out adrenal insufficiency. If it›s anything else, send them to an endocrinologist to sort it out. You might be able to make the diagnosis yourself doing that.
Any treatment pearls to leave the audience with?
Dr. Williams: I hope endocrinologists don›t take issue with this. I say this with respect and admiration, but it feels kind of vibe-based to me. Without a lab value to guide treatment, you are dependent on the patient telling you how they feel much of the time. You have to let their symptoms guide you. It is probably worth noting that because hydrocortisone has a relatively short half-life, within hours, in fact, you typically have to do twice-daily dosing, sometimes even three times daily dosing to get patients to where they feel okay. It sounds like there›s a fair amount of trial and error and some adjustments that you have to make depending on what›s going on with the patient at any given time. You land somewhere between a dose of 15-30 mg per day, but there will be some variability, even within an individual patient, depending on what›s going on with them from a physiologic standpoint.
Dr. Watto: They are going to take one dose in the morning and then a second dose in the afternoon, but they don’t want them to take it too late in the evening because it could cause insomnia, and you want to try to mimic physiologic levels as much as you can. Two thirds of the daily dose is given early in the morning and then another third of the daily dose later in the day if you are prescribing two times daily dosing.
And Dr. Kargi had a low threshold for doubling the dose. If the patient has a cold, double the dose for 2 or 3 days. With a high fever, triple the dose for a few days. If they are going for surgery, they are probably going to be getting some intravenous hydrocortisone while they’re in the hospital.
We really turned over like every stone we could possibly think of on this podcast. There were so many great pearls that we don’t have time to go through them all here. But we talked about steroid tapers and a lot more. You can check it out here.
Dr. Watto has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Williams has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: The CurbsidersReceived income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. I’m Dr. Matthew Watto, here with America’s primary care physician, Dr. Paul Nelson Williams. Paul, are you ready to talk about some adrenal insufficiency? We had a great conversation with Dr. Atil Kargi, and I’d like you to start us off.
Paul N. Williams, MD: How about thinking about it? It’s a good place to start.
That’s one of the ways this episode changed my approach a little bit. I never really thought about the fact that . It’s such a protean sort of nonspecific presentation. But if you have someone with chronic malaise and poor appetite and maybe unexplained weight loss, and your GI workup is not really leading you anywhere, it’s probably worth thinking about adrenal insufficiency. Even though primary adrenal insufficiency is pretty rare — we’re talking cases per millions — secondary adrenal insufficiency is actually fairly common. It’s probably worth thinking about and testing for more often than I have in the past. So for me, it’s having a lower threshold to start looking for it.
Dr. Watto: When it’s adrenal crisis, you probably think about it, but then it’s too late. Ideally, you would think about it before that happens. But the symptoms can be quite vague. The mineralocorticoid symptoms, like salt cravings, dizziness, near syncope, muscle cramps, might make me think of it because they sound more like something endocrine is going on. But if it’s just a little weight loss, a little fatigue, or a little nausea, that’s everybody.
Dr. Williams: Right. If a patient came to me saying, “I’m craving salt,” that might hasten the workup a little bit, but that’s not the typical presentation.
Dr. Watto: If you are going to check a cortisol level, you should really check it in the morning, between 7 AM and 9 AM. If you check it too early, it might not have peaked yet, so you might get a level that looks low. But if you had checked an hour or 2 later, it might have been above a threshold, and then you would know you could rule out the diagnosis. The cutoffs depend on your source: < 3-5 µg/dL that early in the morning is pretty much diagnostic of adrenal insufficiency. If it’s > 15 µg/dL, that’s a pretty robust cortisol and the patient probably doesn’t have adrenal insufficiency. But if the level is between 5 µg/dL and 15 µg/dL, you’re in a gray zone, and that’s where you might think about doing a stimulation (stim) test.
Dr. Kargi gave us a quick and dirty version of the stim test. Paul, have you had a chance to try this yet?
Dr. Williams: I have not. Have you? I’m sure you’ve been just waiting for the chance.
Dr. Watto: I would love to do this. I don›t know whether I›m set up to do it in the office right now. But this is an aspirational goal for my practice, and I›m sure some physicians are set up in their office already to do it. You can give either intramuscular or subcutaneous cosyntropin 250 µg. You don›t even have to get a baseline cortisol level right before the injection. Let›s say the patient›s previous cortisol level was between 5 µg/dL and 15 µg/dL, so you weren›t sure about the diagnosis. You bring them back to the office one day, give them a shot of cosyntropin, and then 30-60 minutes later, have a random cortisol drawn. If it›s > 19 µg/dL, you›ve ruled out adrenal insufficiency. If it›s anything else, send them to an endocrinologist to sort it out. You might be able to make the diagnosis yourself doing that.
Any treatment pearls to leave the audience with?
Dr. Williams: I hope endocrinologists don›t take issue with this. I say this with respect and admiration, but it feels kind of vibe-based to me. Without a lab value to guide treatment, you are dependent on the patient telling you how they feel much of the time. You have to let their symptoms guide you. It is probably worth noting that because hydrocortisone has a relatively short half-life, within hours, in fact, you typically have to do twice-daily dosing, sometimes even three times daily dosing to get patients to where they feel okay. It sounds like there›s a fair amount of trial and error and some adjustments that you have to make depending on what›s going on with the patient at any given time. You land somewhere between a dose of 15-30 mg per day, but there will be some variability, even within an individual patient, depending on what›s going on with them from a physiologic standpoint.
Dr. Watto: They are going to take one dose in the morning and then a second dose in the afternoon, but they don’t want them to take it too late in the evening because it could cause insomnia, and you want to try to mimic physiologic levels as much as you can. Two thirds of the daily dose is given early in the morning and then another third of the daily dose later in the day if you are prescribing two times daily dosing.
And Dr. Kargi had a low threshold for doubling the dose. If the patient has a cold, double the dose for 2 or 3 days. With a high fever, triple the dose for a few days. If they are going for surgery, they are probably going to be getting some intravenous hydrocortisone while they’re in the hospital.
We really turned over like every stone we could possibly think of on this podcast. There were so many great pearls that we don’t have time to go through them all here. But we talked about steroid tapers and a lot more. You can check it out here.
Dr. Watto has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Dr. Williams has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: The CurbsidersReceived income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: The Curbsiders.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Picking up the premotor symptoms of Parkinson’s
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. We had a great discussion on Parkinson’s Disease for Primary Care with Dr. Albert Hung. Paul, this was something that really made me nervous. I didn’t have a lot of comfort with it. But he taught us a lot of tips about how to recognize Parkinson’s.
I hadn’t been as aware of the premotor symptoms: constipation, hyposmia (loss of sense of smell), and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. If patients have those early on and they aren’t explained by other things (especially the REM sleep behavior disorder), you should really key in because those patients are at risk of developing Parkinson’s years down the line. Those symptoms could present first, which just kind of blew my mind.
What tips do you have about how to recognize Parkinson’s? Do you want to talk about the physical exam?
Paul N. Williams, MD: You know I love the physical exam stuff, so I’m happy to talk about that.
You were deeply upset that cogwheel rigidity was not pathognomonic for Parkinson’s, but you made the point – and our guest agreed – that asymmetry tends to be the key here. And I really appreciated the point about reemergent tremor. This is this idea of a resting tremor. If someone has more parkinsonian features, you might see an intention tremor with essential tremor. If they reach out, it might seem steady at first, but if they hold long enough, then the tremor may kind of reemerge. I thought that was a neat distinction.
And this idea of cogwheel rigidity is a combination of some of the cardinal features of Parkinson’s – it’s a little bit of tremor and a little bit of rigidity too. There’s a baseline increase in tone, and then the tremor is superimposed on top of that. When you’re feeling cogwheeling, that’s actually what you’re feeling on examination. Parkinson’s, with all of its physical exam findings has always fascinated me.
Dr. Watto: He also told us about some red flags.
With classic idiopathic parkinsonism, there’s asymmetric involvement of the tremor. So red flags include a symmetric tremor, which might be something other than idiopathic parkinsonism. He also mentioned that one of the reasons you may want to get imaging (which is not always necessary if someone has a classic presentation), is if you see lower body–predominant symptoms of parkinsonism. These patients have rigidity or slowness of movement in their legs, but their upper bodies are not affected. They don’t have masked facies or the tremor in their hands. You might get an MRI in that case because that could be presentation of vascular dementia or vascular disease in the brain or even normal pressure hydrocephalus, which is a treatable condition. That would be one reason to get imaging.
What if the patient was exposed to a drug like a dopamine antagonist? They will get better in a couple of days, right?
Dr. Williams: This was a really fascinating point because we typically think if a patient’s symptoms are related to a drug exposure – in this case, drug-induced parkinsonism – we can just stop the medication and the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days as the drug leaves the system. But as it turns out, it might take much longer. A mistake that Dr Hung often sees is that the clinician stops the possibly offending agent, but when they don’t see an immediate relief of symptoms, they assume the drug wasn’t causing them. You really have to give the patient a fair shot off the medication to experience recovery because those symptoms can last weeks or even months after the drug is discontinued.
Dr. Watto: Dr Hung looks at the patient’s problem list and asks whether is there any reason this patient might have been exposed to one of these medications?
We’re not going to get too much into specific Parkinson’s treatment, but I was glad to hear that exercise actually improves mobility and may even have some neuroprotective effects. He mentioned ongoing trials looking at that. We always love an excuse to tell patients that they should be moving around more and being physically active.
Dr. Williams: That was one of the more shocking things I learned, that exercise might actually be good for you. That will deeply inform my practice. Many of the treatments that we use for Parkinson’s only address symptoms. They don’t address progression or fix anything, but exercise can help with that.
Dr. Watto: Paul, the last question I wanted to ask you is about our role in primary care. Patients with Parkinson’s have autonomic symptoms. They have neurocognitive symptoms. What is our role in that as primary care physicians?
Dr. Williams: Myriad symptoms can accompany Parkinson’s, and we have experience with most of them. We should all feel fairly comfortable dealing with constipation, which can be a very bothersome symptom. And we can use our full arsenal for symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and even apathy – the anhedonia, which apparently can be the predominant feature. We do have the tools to address these problems.
This might be a situation where we might reach for bupropion or a tricyclic antidepressant, which might not be your initial choice for a patient with a possibly annoying mood disorder. But for someone with Parkinson’s disease, this actually may be very helpful. We know how to manage a lot of the symptoms that come along with Parkinson’s that are not just the motor symptoms, and we should take ownership of those things.
Dr. Watto: You can hear the rest of this podcast here. This has been another episode of The Curbsiders bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole. Until next time, I’ve been Dr Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is a clinical assistant professor, department of medicine, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, at Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither Dr. Watto nor Dr. Williams reported any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. We had a great discussion on Parkinson’s Disease for Primary Care with Dr. Albert Hung. Paul, this was something that really made me nervous. I didn’t have a lot of comfort with it. But he taught us a lot of tips about how to recognize Parkinson’s.
I hadn’t been as aware of the premotor symptoms: constipation, hyposmia (loss of sense of smell), and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. If patients have those early on and they aren’t explained by other things (especially the REM sleep behavior disorder), you should really key in because those patients are at risk of developing Parkinson’s years down the line. Those symptoms could present first, which just kind of blew my mind.
What tips do you have about how to recognize Parkinson’s? Do you want to talk about the physical exam?
Paul N. Williams, MD: You know I love the physical exam stuff, so I’m happy to talk about that.
You were deeply upset that cogwheel rigidity was not pathognomonic for Parkinson’s, but you made the point – and our guest agreed – that asymmetry tends to be the key here. And I really appreciated the point about reemergent tremor. This is this idea of a resting tremor. If someone has more parkinsonian features, you might see an intention tremor with essential tremor. If they reach out, it might seem steady at first, but if they hold long enough, then the tremor may kind of reemerge. I thought that was a neat distinction.
And this idea of cogwheel rigidity is a combination of some of the cardinal features of Parkinson’s – it’s a little bit of tremor and a little bit of rigidity too. There’s a baseline increase in tone, and then the tremor is superimposed on top of that. When you’re feeling cogwheeling, that’s actually what you’re feeling on examination. Parkinson’s, with all of its physical exam findings has always fascinated me.
Dr. Watto: He also told us about some red flags.
With classic idiopathic parkinsonism, there’s asymmetric involvement of the tremor. So red flags include a symmetric tremor, which might be something other than idiopathic parkinsonism. He also mentioned that one of the reasons you may want to get imaging (which is not always necessary if someone has a classic presentation), is if you see lower body–predominant symptoms of parkinsonism. These patients have rigidity or slowness of movement in their legs, but their upper bodies are not affected. They don’t have masked facies or the tremor in their hands. You might get an MRI in that case because that could be presentation of vascular dementia or vascular disease in the brain or even normal pressure hydrocephalus, which is a treatable condition. That would be one reason to get imaging.
What if the patient was exposed to a drug like a dopamine antagonist? They will get better in a couple of days, right?
Dr. Williams: This was a really fascinating point because we typically think if a patient’s symptoms are related to a drug exposure – in this case, drug-induced parkinsonism – we can just stop the medication and the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days as the drug leaves the system. But as it turns out, it might take much longer. A mistake that Dr Hung often sees is that the clinician stops the possibly offending agent, but when they don’t see an immediate relief of symptoms, they assume the drug wasn’t causing them. You really have to give the patient a fair shot off the medication to experience recovery because those symptoms can last weeks or even months after the drug is discontinued.
Dr. Watto: Dr Hung looks at the patient’s problem list and asks whether is there any reason this patient might have been exposed to one of these medications?
We’re not going to get too much into specific Parkinson’s treatment, but I was glad to hear that exercise actually improves mobility and may even have some neuroprotective effects. He mentioned ongoing trials looking at that. We always love an excuse to tell patients that they should be moving around more and being physically active.
Dr. Williams: That was one of the more shocking things I learned, that exercise might actually be good for you. That will deeply inform my practice. Many of the treatments that we use for Parkinson’s only address symptoms. They don’t address progression or fix anything, but exercise can help with that.
Dr. Watto: Paul, the last question I wanted to ask you is about our role in primary care. Patients with Parkinson’s have autonomic symptoms. They have neurocognitive symptoms. What is our role in that as primary care physicians?
Dr. Williams: Myriad symptoms can accompany Parkinson’s, and we have experience with most of them. We should all feel fairly comfortable dealing with constipation, which can be a very bothersome symptom. And we can use our full arsenal for symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and even apathy – the anhedonia, which apparently can be the predominant feature. We do have the tools to address these problems.
This might be a situation where we might reach for bupropion or a tricyclic antidepressant, which might not be your initial choice for a patient with a possibly annoying mood disorder. But for someone with Parkinson’s disease, this actually may be very helpful. We know how to manage a lot of the symptoms that come along with Parkinson’s that are not just the motor symptoms, and we should take ownership of those things.
Dr. Watto: You can hear the rest of this podcast here. This has been another episode of The Curbsiders bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole. Until next time, I’ve been Dr Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is a clinical assistant professor, department of medicine, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, at Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither Dr. Watto nor Dr. Williams reported any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. We had a great discussion on Parkinson’s Disease for Primary Care with Dr. Albert Hung. Paul, this was something that really made me nervous. I didn’t have a lot of comfort with it. But he taught us a lot of tips about how to recognize Parkinson’s.
I hadn’t been as aware of the premotor symptoms: constipation, hyposmia (loss of sense of smell), and rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. If patients have those early on and they aren’t explained by other things (especially the REM sleep behavior disorder), you should really key in because those patients are at risk of developing Parkinson’s years down the line. Those symptoms could present first, which just kind of blew my mind.
What tips do you have about how to recognize Parkinson’s? Do you want to talk about the physical exam?
Paul N. Williams, MD: You know I love the physical exam stuff, so I’m happy to talk about that.
You were deeply upset that cogwheel rigidity was not pathognomonic for Parkinson’s, but you made the point – and our guest agreed – that asymmetry tends to be the key here. And I really appreciated the point about reemergent tremor. This is this idea of a resting tremor. If someone has more parkinsonian features, you might see an intention tremor with essential tremor. If they reach out, it might seem steady at first, but if they hold long enough, then the tremor may kind of reemerge. I thought that was a neat distinction.
And this idea of cogwheel rigidity is a combination of some of the cardinal features of Parkinson’s – it’s a little bit of tremor and a little bit of rigidity too. There’s a baseline increase in tone, and then the tremor is superimposed on top of that. When you’re feeling cogwheeling, that’s actually what you’re feeling on examination. Parkinson’s, with all of its physical exam findings has always fascinated me.
Dr. Watto: He also told us about some red flags.
With classic idiopathic parkinsonism, there’s asymmetric involvement of the tremor. So red flags include a symmetric tremor, which might be something other than idiopathic parkinsonism. He also mentioned that one of the reasons you may want to get imaging (which is not always necessary if someone has a classic presentation), is if you see lower body–predominant symptoms of parkinsonism. These patients have rigidity or slowness of movement in their legs, but their upper bodies are not affected. They don’t have masked facies or the tremor in their hands. You might get an MRI in that case because that could be presentation of vascular dementia or vascular disease in the brain or even normal pressure hydrocephalus, which is a treatable condition. That would be one reason to get imaging.
What if the patient was exposed to a drug like a dopamine antagonist? They will get better in a couple of days, right?
Dr. Williams: This was a really fascinating point because we typically think if a patient’s symptoms are related to a drug exposure – in this case, drug-induced parkinsonism – we can just stop the medication and the symptoms will disappear in a couple of days as the drug leaves the system. But as it turns out, it might take much longer. A mistake that Dr Hung often sees is that the clinician stops the possibly offending agent, but when they don’t see an immediate relief of symptoms, they assume the drug wasn’t causing them. You really have to give the patient a fair shot off the medication to experience recovery because those symptoms can last weeks or even months after the drug is discontinued.
Dr. Watto: Dr Hung looks at the patient’s problem list and asks whether is there any reason this patient might have been exposed to one of these medications?
We’re not going to get too much into specific Parkinson’s treatment, but I was glad to hear that exercise actually improves mobility and may even have some neuroprotective effects. He mentioned ongoing trials looking at that. We always love an excuse to tell patients that they should be moving around more and being physically active.
Dr. Williams: That was one of the more shocking things I learned, that exercise might actually be good for you. That will deeply inform my practice. Many of the treatments that we use for Parkinson’s only address symptoms. They don’t address progression or fix anything, but exercise can help with that.
Dr. Watto: Paul, the last question I wanted to ask you is about our role in primary care. Patients with Parkinson’s have autonomic symptoms. They have neurocognitive symptoms. What is our role in that as primary care physicians?
Dr. Williams: Myriad symptoms can accompany Parkinson’s, and we have experience with most of them. We should all feel fairly comfortable dealing with constipation, which can be a very bothersome symptom. And we can use our full arsenal for symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and even apathy – the anhedonia, which apparently can be the predominant feature. We do have the tools to address these problems.
This might be a situation where we might reach for bupropion or a tricyclic antidepressant, which might not be your initial choice for a patient with a possibly annoying mood disorder. But for someone with Parkinson’s disease, this actually may be very helpful. We know how to manage a lot of the symptoms that come along with Parkinson’s that are not just the motor symptoms, and we should take ownership of those things.
Dr. Watto: You can hear the rest of this podcast here. This has been another episode of The Curbsiders bringing you a little knowledge food for your brain hole. Until next time, I’ve been Dr Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is a clinical assistant professor, department of medicine, at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, at Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither Dr. Watto nor Dr. Williams reported any relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Back pain: Red flags and when to image
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. On tonight’s episode, we are going to be talking about back pain. I’ll use one of my famous teaching techniques: If the patient has any kind of back pain, they should just not move. Right?
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right, Matt – we should recommend bedrest until they get better for anyone who has any back pain? No. For back pain, early activity and exercise are great. Patients are often concerned that physical therapy will make their pain worse, so they don’t exercise. This misunderstanding is not surprising. They believe that if they are experiencing pain, it’s facilitating more damage, which is not necessarily the case. It will get better, and a little bit of anticipatory guidance goes a long way in terms of managing patient expectations related to early mobilization, early exercise, and physical therapy.
Dr. Watto: Absolutely. One of the goals of treatment is symptom relief to the extent that we’re able to achieve. We’re not expecting the pain to go to zero. That just doesn’t happen, especially if someone’s on a medication long term. Another goal is return to function. We want them sleeping. We want them to be able to tolerate movement.
We have medications – NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, which are actually tranquilizers. But most therapy for back pain doesn’t involve medications. It involves active movement, so we have to find movement that the patient enjoys doing. Passive treatments, things being done to patients, just don’t work as well.
Dr. Williams: We should be clear – we’re talking primarily about chronic back pain here. For acute back pain, we actually have some decent medications, but acute back pain tends to improve no matter what you do. We don’t have much to offer pharmacologically for chronic low back pain. The best modalities usually involve physical activity of some kind.
Dr. Watto: Let’s discuss the evaluation of back pain. Something that always comes up: Should we order imaging, and is there a right time to get it? Dr. Baraki was very clear about when to do imaging. Two big buckets of patients might need imaging.
First, a patient who has a serious underlying condition and you’re using imaging to try to diagnose it; or in a chronic setting, a patient who needs surgery, and imaging is part of the presurgical evaluation. We talked about red flags.
The red flags are major trauma, where we have reason to believe there might be something going on – if we strongly suspect infection, or the patient is injecting drugs. If the patient has a history of cancer, we would be worried that they might have a recurrence. Those are some of the main red flags. With a patient who has osteoporosis or is on chronic steroids, you might even be able to get by with plain films instead of an MRI to look for fracture.
The other thing I wanted to ask you about is, when should we get imaging? Are there any pitfalls we need to worry about?
Dr. Williams: I always like podcasts I’m not on because I enjoy listening to them much more. Dr. Baraki talked about the very specific language that is used in radiology reports, such as spondylitis, spondylolysis, and multilevel degenerative disease. They sound bad, but if they are just reframed as age-related degenerative changes, that sounds so much more benign. When discussing with patients, we should avoid medical jargon and say that we saw some changes that we would expect for someone of your age. That sounds so much better than saying we saw multilevel degenerative disease, which sounds like an alarming pathology if you’re not a physician. Without being inaccurate, we should frame the discussion such that we aren’t providing a very specific diagnosis, because that is rarely the case with chronic low back pain. Typically, many things are going on and you may never identify a single unifying diagnosis, which doesn’t tend to help anyway.
Dr. Watto: There’s evidence showing that if the radiology report uses clinical terminology that both clinician and patient think of as less serious, they are less likely to proceed to more invasive treatments. Calling an episode of back pain a “lumbar strain” helps the patient understand that this is a pretty common thing. Almost everyone is going to have an episode of back pain at some point in their life, and almost all of them will get better. Most of the time there’s no serious underlying condition.
This was a great discussion with Dr. Baraki. Click on Back Pain Update with Dr Austin Baraki to hear the full discussion. Until next time, I’ve been Dr. Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. On tonight’s episode, we are going to be talking about back pain. I’ll use one of my famous teaching techniques: If the patient has any kind of back pain, they should just not move. Right?
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right, Matt – we should recommend bedrest until they get better for anyone who has any back pain? No. For back pain, early activity and exercise are great. Patients are often concerned that physical therapy will make their pain worse, so they don’t exercise. This misunderstanding is not surprising. They believe that if they are experiencing pain, it’s facilitating more damage, which is not necessarily the case. It will get better, and a little bit of anticipatory guidance goes a long way in terms of managing patient expectations related to early mobilization, early exercise, and physical therapy.
Dr. Watto: Absolutely. One of the goals of treatment is symptom relief to the extent that we’re able to achieve. We’re not expecting the pain to go to zero. That just doesn’t happen, especially if someone’s on a medication long term. Another goal is return to function. We want them sleeping. We want them to be able to tolerate movement.
We have medications – NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, which are actually tranquilizers. But most therapy for back pain doesn’t involve medications. It involves active movement, so we have to find movement that the patient enjoys doing. Passive treatments, things being done to patients, just don’t work as well.
Dr. Williams: We should be clear – we’re talking primarily about chronic back pain here. For acute back pain, we actually have some decent medications, but acute back pain tends to improve no matter what you do. We don’t have much to offer pharmacologically for chronic low back pain. The best modalities usually involve physical activity of some kind.
Dr. Watto: Let’s discuss the evaluation of back pain. Something that always comes up: Should we order imaging, and is there a right time to get it? Dr. Baraki was very clear about when to do imaging. Two big buckets of patients might need imaging.
First, a patient who has a serious underlying condition and you’re using imaging to try to diagnose it; or in a chronic setting, a patient who needs surgery, and imaging is part of the presurgical evaluation. We talked about red flags.
The red flags are major trauma, where we have reason to believe there might be something going on – if we strongly suspect infection, or the patient is injecting drugs. If the patient has a history of cancer, we would be worried that they might have a recurrence. Those are some of the main red flags. With a patient who has osteoporosis or is on chronic steroids, you might even be able to get by with plain films instead of an MRI to look for fracture.
The other thing I wanted to ask you about is, when should we get imaging? Are there any pitfalls we need to worry about?
Dr. Williams: I always like podcasts I’m not on because I enjoy listening to them much more. Dr. Baraki talked about the very specific language that is used in radiology reports, such as spondylitis, spondylolysis, and multilevel degenerative disease. They sound bad, but if they are just reframed as age-related degenerative changes, that sounds so much more benign. When discussing with patients, we should avoid medical jargon and say that we saw some changes that we would expect for someone of your age. That sounds so much better than saying we saw multilevel degenerative disease, which sounds like an alarming pathology if you’re not a physician. Without being inaccurate, we should frame the discussion such that we aren’t providing a very specific diagnosis, because that is rarely the case with chronic low back pain. Typically, many things are going on and you may never identify a single unifying diagnosis, which doesn’t tend to help anyway.
Dr. Watto: There’s evidence showing that if the radiology report uses clinical terminology that both clinician and patient think of as less serious, they are less likely to proceed to more invasive treatments. Calling an episode of back pain a “lumbar strain” helps the patient understand that this is a pretty common thing. Almost everyone is going to have an episode of back pain at some point in their life, and almost all of them will get better. Most of the time there’s no serious underlying condition.
This was a great discussion with Dr. Baraki. Click on Back Pain Update with Dr Austin Baraki to hear the full discussion. Until next time, I’ve been Dr. Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Matthew F. Watto, MD: Welcome back to The Curbsiders. On tonight’s episode, we are going to be talking about back pain. I’ll use one of my famous teaching techniques: If the patient has any kind of back pain, they should just not move. Right?
Paul N. Williams, MD: That’s right, Matt – we should recommend bedrest until they get better for anyone who has any back pain? No. For back pain, early activity and exercise are great. Patients are often concerned that physical therapy will make their pain worse, so they don’t exercise. This misunderstanding is not surprising. They believe that if they are experiencing pain, it’s facilitating more damage, which is not necessarily the case. It will get better, and a little bit of anticipatory guidance goes a long way in terms of managing patient expectations related to early mobilization, early exercise, and physical therapy.
Dr. Watto: Absolutely. One of the goals of treatment is symptom relief to the extent that we’re able to achieve. We’re not expecting the pain to go to zero. That just doesn’t happen, especially if someone’s on a medication long term. Another goal is return to function. We want them sleeping. We want them to be able to tolerate movement.
We have medications – NSAIDs and muscle relaxants, which are actually tranquilizers. But most therapy for back pain doesn’t involve medications. It involves active movement, so we have to find movement that the patient enjoys doing. Passive treatments, things being done to patients, just don’t work as well.
Dr. Williams: We should be clear – we’re talking primarily about chronic back pain here. For acute back pain, we actually have some decent medications, but acute back pain tends to improve no matter what you do. We don’t have much to offer pharmacologically for chronic low back pain. The best modalities usually involve physical activity of some kind.
Dr. Watto: Let’s discuss the evaluation of back pain. Something that always comes up: Should we order imaging, and is there a right time to get it? Dr. Baraki was very clear about when to do imaging. Two big buckets of patients might need imaging.
First, a patient who has a serious underlying condition and you’re using imaging to try to diagnose it; or in a chronic setting, a patient who needs surgery, and imaging is part of the presurgical evaluation. We talked about red flags.
The red flags are major trauma, where we have reason to believe there might be something going on – if we strongly suspect infection, or the patient is injecting drugs. If the patient has a history of cancer, we would be worried that they might have a recurrence. Those are some of the main red flags. With a patient who has osteoporosis or is on chronic steroids, you might even be able to get by with plain films instead of an MRI to look for fracture.
The other thing I wanted to ask you about is, when should we get imaging? Are there any pitfalls we need to worry about?
Dr. Williams: I always like podcasts I’m not on because I enjoy listening to them much more. Dr. Baraki talked about the very specific language that is used in radiology reports, such as spondylitis, spondylolysis, and multilevel degenerative disease. They sound bad, but if they are just reframed as age-related degenerative changes, that sounds so much more benign. When discussing with patients, we should avoid medical jargon and say that we saw some changes that we would expect for someone of your age. That sounds so much better than saying we saw multilevel degenerative disease, which sounds like an alarming pathology if you’re not a physician. Without being inaccurate, we should frame the discussion such that we aren’t providing a very specific diagnosis, because that is rarely the case with chronic low back pain. Typically, many things are going on and you may never identify a single unifying diagnosis, which doesn’t tend to help anyway.
Dr. Watto: There’s evidence showing that if the radiology report uses clinical terminology that both clinician and patient think of as less serious, they are less likely to proceed to more invasive treatments. Calling an episode of back pain a “lumbar strain” helps the patient understand that this is a pretty common thing. Almost everyone is going to have an episode of back pain at some point in their life, and almost all of them will get better. Most of the time there’s no serious underlying condition.
This was a great discussion with Dr. Baraki. Click on Back Pain Update with Dr Austin Baraki to hear the full discussion. Until next time, I’ve been Dr. Matthew Frank Watto.
Dr. Williams: And I’m Dr. Paul Nelson Williams.
Dr. Watto is Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Williams is Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, Department of General Internal Medicine, Temple University, Philadelphia. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.