User login
Pediatric study characterizes recurrent PSC
BOSTON – Children who have recurrence of primary sclerosing cholangitis after liver transplant tend to be younger and have more rapidly progressive disease, based on an international retrospective analysis.
Within 5 years of transplant, the probability of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) recurrence in pediatric patients is 26%, reported lead author Mercedes Martinez, MD, of Columbia University, New York, and colleagues.
“The aim of our study was to identify risk factors for primary sclerosing cholangitis recurrence following transplant,” Dr. Martinez said during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. This may be the largest pediatric study evaluating recurrent PSC to date, she added.
The investigators drew data from 35 centers around the world via the Pediatric PSC Consortium database. Recurrence was defined by cholestatic biochemistry with nonanastomotic biliary strictures and beading of bile ducts on cholangiography. Recurrences caused by hepatic artery thrombosis or chronic rejection were excluded, as were any cases that recurred within 6 months of transplant.
The final analysis included 149 patients with a median age at diagnosis and liver transplant of 12 years and 15.4 years, respectively. Of these, 31 patients had recurrence after a median of 3.3 years. A closer look at the data showed that recurrence was linked with younger median age at time of transplant (13.2 vs. 16.2 years). In cases of recurrence, PSC was generally more aggressive prior to transplant, with a shorter interval between diagnosis and transplant (1.6 vs. 4.1 years), higher total bilirubin (7.8 vs. 3.8 mg/dL), and higher ALT (118 vs. 62 U/L). Furthermore, almost half of the patients (45%) who had recurrence also had pretransplant autoimmune hepatitis overlap, compared with approximately one-quarter of the patients (27%) who did not have recurrence, although this trend was not statistically significant (P = .06).
Recurrent PSC was also associated with poorer outcomes; almost half of those with recurrence (48%) were relisted for liver transplant, developed portal hypertension, or died within 2 years of diagnosis. Mean rejection rates were higher in recurrent versus nonrecurrent cases (3 vs. 1); recurrent cases also had shorter time until rejection (3 vs. 6 months) and greater prevalence of rejection that was refractory to steroids (23% vs. 12%). Moreover, a significantly greater proportion of patients with recurrence had Epstein-Barr viremia (41% vs. 21%).
Dr. Martinez noted that ongoing therapy involving mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition was associated with lower rates of recurrence and suggested that this deserves further investigation; however, owing to small population size, she urged a cautious interpretation of this finding.
“We have to do prospective research,” Dr. Martinez said, emphasizing that tissue immunophenotyping was needed, as a better understanding of underlying immune processes and disease subtypes may open doors to more effective therapies.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Gilead, Merck, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Martinez M et al. The Liver Meeting 2019, Abstract 44.
BOSTON – Children who have recurrence of primary sclerosing cholangitis after liver transplant tend to be younger and have more rapidly progressive disease, based on an international retrospective analysis.
Within 5 years of transplant, the probability of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) recurrence in pediatric patients is 26%, reported lead author Mercedes Martinez, MD, of Columbia University, New York, and colleagues.
“The aim of our study was to identify risk factors for primary sclerosing cholangitis recurrence following transplant,” Dr. Martinez said during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. This may be the largest pediatric study evaluating recurrent PSC to date, she added.
The investigators drew data from 35 centers around the world via the Pediatric PSC Consortium database. Recurrence was defined by cholestatic biochemistry with nonanastomotic biliary strictures and beading of bile ducts on cholangiography. Recurrences caused by hepatic artery thrombosis or chronic rejection were excluded, as were any cases that recurred within 6 months of transplant.
The final analysis included 149 patients with a median age at diagnosis and liver transplant of 12 years and 15.4 years, respectively. Of these, 31 patients had recurrence after a median of 3.3 years. A closer look at the data showed that recurrence was linked with younger median age at time of transplant (13.2 vs. 16.2 years). In cases of recurrence, PSC was generally more aggressive prior to transplant, with a shorter interval between diagnosis and transplant (1.6 vs. 4.1 years), higher total bilirubin (7.8 vs. 3.8 mg/dL), and higher ALT (118 vs. 62 U/L). Furthermore, almost half of the patients (45%) who had recurrence also had pretransplant autoimmune hepatitis overlap, compared with approximately one-quarter of the patients (27%) who did not have recurrence, although this trend was not statistically significant (P = .06).
Recurrent PSC was also associated with poorer outcomes; almost half of those with recurrence (48%) were relisted for liver transplant, developed portal hypertension, or died within 2 years of diagnosis. Mean rejection rates were higher in recurrent versus nonrecurrent cases (3 vs. 1); recurrent cases also had shorter time until rejection (3 vs. 6 months) and greater prevalence of rejection that was refractory to steroids (23% vs. 12%). Moreover, a significantly greater proportion of patients with recurrence had Epstein-Barr viremia (41% vs. 21%).
Dr. Martinez noted that ongoing therapy involving mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition was associated with lower rates of recurrence and suggested that this deserves further investigation; however, owing to small population size, she urged a cautious interpretation of this finding.
“We have to do prospective research,” Dr. Martinez said, emphasizing that tissue immunophenotyping was needed, as a better understanding of underlying immune processes and disease subtypes may open doors to more effective therapies.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Gilead, Merck, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Martinez M et al. The Liver Meeting 2019, Abstract 44.
BOSTON – Children who have recurrence of primary sclerosing cholangitis after liver transplant tend to be younger and have more rapidly progressive disease, based on an international retrospective analysis.
Within 5 years of transplant, the probability of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) recurrence in pediatric patients is 26%, reported lead author Mercedes Martinez, MD, of Columbia University, New York, and colleagues.
“The aim of our study was to identify risk factors for primary sclerosing cholangitis recurrence following transplant,” Dr. Martinez said during a presentation at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. This may be the largest pediatric study evaluating recurrent PSC to date, she added.
The investigators drew data from 35 centers around the world via the Pediatric PSC Consortium database. Recurrence was defined by cholestatic biochemistry with nonanastomotic biliary strictures and beading of bile ducts on cholangiography. Recurrences caused by hepatic artery thrombosis or chronic rejection were excluded, as were any cases that recurred within 6 months of transplant.
The final analysis included 149 patients with a median age at diagnosis and liver transplant of 12 years and 15.4 years, respectively. Of these, 31 patients had recurrence after a median of 3.3 years. A closer look at the data showed that recurrence was linked with younger median age at time of transplant (13.2 vs. 16.2 years). In cases of recurrence, PSC was generally more aggressive prior to transplant, with a shorter interval between diagnosis and transplant (1.6 vs. 4.1 years), higher total bilirubin (7.8 vs. 3.8 mg/dL), and higher ALT (118 vs. 62 U/L). Furthermore, almost half of the patients (45%) who had recurrence also had pretransplant autoimmune hepatitis overlap, compared with approximately one-quarter of the patients (27%) who did not have recurrence, although this trend was not statistically significant (P = .06).
Recurrent PSC was also associated with poorer outcomes; almost half of those with recurrence (48%) were relisted for liver transplant, developed portal hypertension, or died within 2 years of diagnosis. Mean rejection rates were higher in recurrent versus nonrecurrent cases (3 vs. 1); recurrent cases also had shorter time until rejection (3 vs. 6 months) and greater prevalence of rejection that was refractory to steroids (23% vs. 12%). Moreover, a significantly greater proportion of patients with recurrence had Epstein-Barr viremia (41% vs. 21%).
Dr. Martinez noted that ongoing therapy involving mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition was associated with lower rates of recurrence and suggested that this deserves further investigation; however, owing to small population size, she urged a cautious interpretation of this finding.
“We have to do prospective research,” Dr. Martinez said, emphasizing that tissue immunophenotyping was needed, as a better understanding of underlying immune processes and disease subtypes may open doors to more effective therapies.
The investigators disclosed relationships with Gilead, Merck, Novartis, and others.
SOURCE: Martinez M et al. The Liver Meeting 2019, Abstract 44.
REPORTING FROM THE LIVER MEETING 2019
Teen survives double lung transplant after vaping injury
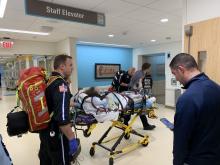
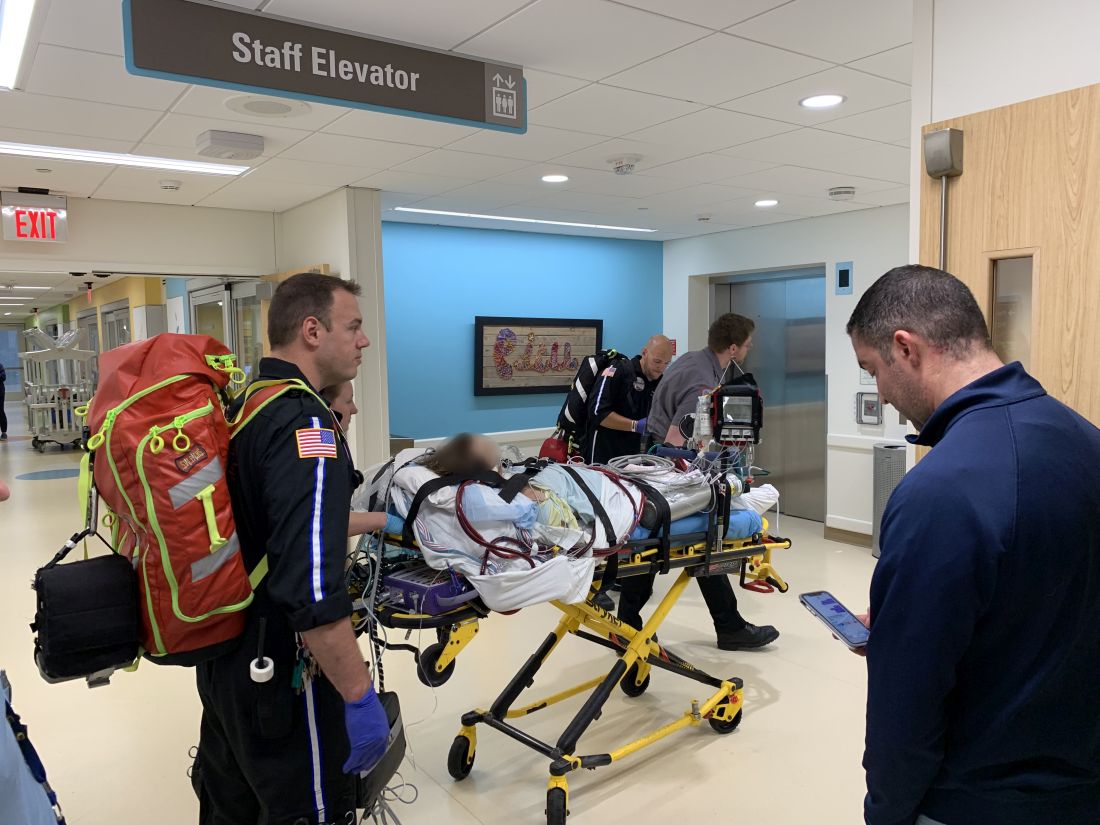
A Michigan teenager, described as an athlete and otherwise healthy, has survived a double lung transplant following lung damage attributed to vaping.
“On the 15th of October, the transplant team performed what we believe is the first double lung transplant done in the nation for a vaping-injury victim, who is a teenager,” Hassan Nemeh, MD, cardiothoracic surgeon with the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, said during a Nov. 12, 2019, press conference to discuss the surgery.
“What I saw in his lungs is nothing that I have ever seen before and I have been doing lung transplants for 20 years,” Dr. Nemeh said. “There was an enormous amount of inflammation and scarring, in addition to multiple spots of dead tissue. The lung itself was so firm and scarred, we had to deliver it out of the chest. This is an evil that I haven’t faced before.”
He noted that the patient, now 17 years old but 16 when the surgical procedure occurred, is doing well in his recovery, and although the patient and the family are not yet ready to be identified, the health system made the decision to tell the story of the surgery as a cautionary tale.
“The reason we wanted to bring this case to public attention is because of the epidemic of e-cigarettes and vaping-induced lung injury that we are witnessing in the country,” including more than 2,000 cases of injury and 39 deaths that have been confirmed from lung failure related to e-cigarettes and vaping that have been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, he said.
“Our teenage patient would have faced certain death if it weren’t for the lung transplant happening,” Dr. Nemeh said, adding that, while vaping and e-cigarettes are being presented as a benign habit, there are potentially very deadly consequences that Henry Ford Hospital System wanted to highlight. He described the patient’s lungs as essentially being nonfunctional with very little air being able to be passed into them, with the destruction to his native lung from pneumonia and dead tissue almost completely covering his lungs.
This story began with a morning call on Oct. 1 from the Children’s Hospital of Michigan alerting the Henry Ford Health System that they had a patient on life support because of complete lung failure who was not showing signs of healing and asking if the Henry Ford Health System could possibly handle a lung transplant for this patient.
Dr. Nemeh said that the patient was on a nontransportable extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machine at Children’s. Dr. Nemeh and the team at Henry Ford determined that the situation for the patient was so dire that they put a portable ECMO machine into the trunk of Dr. Nemeh’s car and delivered it to Children’s in order to facilitate the transfer of the patient for transplantation surgery.
Victor Coba, MD, a critical care specialist and medical director of the ECMO program at Henry Ford, said: “We evaluated the irreversible lung damage that had occurred associated with vaping. Working closely with the lung transplant team and noting that his lungs would not recover, we worked to get him on the lung transplant list.”
Lisa Allenspach, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the lung transplant program at Henry Ford, reiterated the need for caution when it comes to vaping and e-cigarette use.
“Vaping-related injuries are all too common these days and, actually, our adolescents are faced with a crisis,” she said. “I believe we are just beginning to see the tip of the iceberg. Making sure that our teens understand the danger of vaping is of paramount importance.”
She did not disclose specific details about the teen’s use of vaping/e-cigarette products, so it is unknown whether the injury was caused by standard off-the-shelf products or if it was related to vaping cartridges containing tetrahydrocannabinol.
“We are here today to beg the public to pay special attention to the steps that were taken in this case,” said Nicholas Yeldo, MD, anesthesiology and critical care specialist with Henry Ford. “Without the heroic measures that were taken in this case, this young patient would have died. There is no doubt about it. ... This was not just an unlucky one. This is happening way, way too much.”
Dr. Allenspach was positive that the young patient could live a long life, noting that there are those who have received lung transplants have survived for 15-20 years and second transplants are possible.
A Michigan teenager, described as an athlete and otherwise healthy, has survived a double lung transplant following lung damage attributed to vaping.
“On the 15th of October, the transplant team performed what we believe is the first double lung transplant done in the nation for a vaping-injury victim, who is a teenager,” Hassan Nemeh, MD, cardiothoracic surgeon with the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, said during a Nov. 12, 2019, press conference to discuss the surgery.
“What I saw in his lungs is nothing that I have ever seen before and I have been doing lung transplants for 20 years,” Dr. Nemeh said. “There was an enormous amount of inflammation and scarring, in addition to multiple spots of dead tissue. The lung itself was so firm and scarred, we had to deliver it out of the chest. This is an evil that I haven’t faced before.”
He noted that the patient, now 17 years old but 16 when the surgical procedure occurred, is doing well in his recovery, and although the patient and the family are not yet ready to be identified, the health system made the decision to tell the story of the surgery as a cautionary tale.
“The reason we wanted to bring this case to public attention is because of the epidemic of e-cigarettes and vaping-induced lung injury that we are witnessing in the country,” including more than 2,000 cases of injury and 39 deaths that have been confirmed from lung failure related to e-cigarettes and vaping that have been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, he said.
“Our teenage patient would have faced certain death if it weren’t for the lung transplant happening,” Dr. Nemeh said, adding that, while vaping and e-cigarettes are being presented as a benign habit, there are potentially very deadly consequences that Henry Ford Hospital System wanted to highlight. He described the patient’s lungs as essentially being nonfunctional with very little air being able to be passed into them, with the destruction to his native lung from pneumonia and dead tissue almost completely covering his lungs.
This story began with a morning call on Oct. 1 from the Children’s Hospital of Michigan alerting the Henry Ford Health System that they had a patient on life support because of complete lung failure who was not showing signs of healing and asking if the Henry Ford Health System could possibly handle a lung transplant for this patient.
Dr. Nemeh said that the patient was on a nontransportable extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machine at Children’s. Dr. Nemeh and the team at Henry Ford determined that the situation for the patient was so dire that they put a portable ECMO machine into the trunk of Dr. Nemeh’s car and delivered it to Children’s in order to facilitate the transfer of the patient for transplantation surgery.
Victor Coba, MD, a critical care specialist and medical director of the ECMO program at Henry Ford, said: “We evaluated the irreversible lung damage that had occurred associated with vaping. Working closely with the lung transplant team and noting that his lungs would not recover, we worked to get him on the lung transplant list.”
Lisa Allenspach, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the lung transplant program at Henry Ford, reiterated the need for caution when it comes to vaping and e-cigarette use.
“Vaping-related injuries are all too common these days and, actually, our adolescents are faced with a crisis,” she said. “I believe we are just beginning to see the tip of the iceberg. Making sure that our teens understand the danger of vaping is of paramount importance.”
She did not disclose specific details about the teen’s use of vaping/e-cigarette products, so it is unknown whether the injury was caused by standard off-the-shelf products or if it was related to vaping cartridges containing tetrahydrocannabinol.
“We are here today to beg the public to pay special attention to the steps that were taken in this case,” said Nicholas Yeldo, MD, anesthesiology and critical care specialist with Henry Ford. “Without the heroic measures that were taken in this case, this young patient would have died. There is no doubt about it. ... This was not just an unlucky one. This is happening way, way too much.”
Dr. Allenspach was positive that the young patient could live a long life, noting that there are those who have received lung transplants have survived for 15-20 years and second transplants are possible.
A Michigan teenager, described as an athlete and otherwise healthy, has survived a double lung transplant following lung damage attributed to vaping.
“On the 15th of October, the transplant team performed what we believe is the first double lung transplant done in the nation for a vaping-injury victim, who is a teenager,” Hassan Nemeh, MD, cardiothoracic surgeon with the Henry Ford Health System in Detroit, said during a Nov. 12, 2019, press conference to discuss the surgery.
“What I saw in his lungs is nothing that I have ever seen before and I have been doing lung transplants for 20 years,” Dr. Nemeh said. “There was an enormous amount of inflammation and scarring, in addition to multiple spots of dead tissue. The lung itself was so firm and scarred, we had to deliver it out of the chest. This is an evil that I haven’t faced before.”
He noted that the patient, now 17 years old but 16 when the surgical procedure occurred, is doing well in his recovery, and although the patient and the family are not yet ready to be identified, the health system made the decision to tell the story of the surgery as a cautionary tale.
“The reason we wanted to bring this case to public attention is because of the epidemic of e-cigarettes and vaping-induced lung injury that we are witnessing in the country,” including more than 2,000 cases of injury and 39 deaths that have been confirmed from lung failure related to e-cigarettes and vaping that have been reported to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, he said.
“Our teenage patient would have faced certain death if it weren’t for the lung transplant happening,” Dr. Nemeh said, adding that, while vaping and e-cigarettes are being presented as a benign habit, there are potentially very deadly consequences that Henry Ford Hospital System wanted to highlight. He described the patient’s lungs as essentially being nonfunctional with very little air being able to be passed into them, with the destruction to his native lung from pneumonia and dead tissue almost completely covering his lungs.
This story began with a morning call on Oct. 1 from the Children’s Hospital of Michigan alerting the Henry Ford Health System that they had a patient on life support because of complete lung failure who was not showing signs of healing and asking if the Henry Ford Health System could possibly handle a lung transplant for this patient.
Dr. Nemeh said that the patient was on a nontransportable extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) machine at Children’s. Dr. Nemeh and the team at Henry Ford determined that the situation for the patient was so dire that they put a portable ECMO machine into the trunk of Dr. Nemeh’s car and delivered it to Children’s in order to facilitate the transfer of the patient for transplantation surgery.
Victor Coba, MD, a critical care specialist and medical director of the ECMO program at Henry Ford, said: “We evaluated the irreversible lung damage that had occurred associated with vaping. Working closely with the lung transplant team and noting that his lungs would not recover, we worked to get him on the lung transplant list.”
Lisa Allenspach, MD, pulmonologist and medical director of the lung transplant program at Henry Ford, reiterated the need for caution when it comes to vaping and e-cigarette use.
“Vaping-related injuries are all too common these days and, actually, our adolescents are faced with a crisis,” she said. “I believe we are just beginning to see the tip of the iceberg. Making sure that our teens understand the danger of vaping is of paramount importance.”
She did not disclose specific details about the teen’s use of vaping/e-cigarette products, so it is unknown whether the injury was caused by standard off-the-shelf products or if it was related to vaping cartridges containing tetrahydrocannabinol.
“We are here today to beg the public to pay special attention to the steps that were taken in this case,” said Nicholas Yeldo, MD, anesthesiology and critical care specialist with Henry Ford. “Without the heroic measures that were taken in this case, this young patient would have died. There is no doubt about it. ... This was not just an unlucky one. This is happening way, way too much.”
Dr. Allenspach was positive that the young patient could live a long life, noting that there are those who have received lung transplants have survived for 15-20 years and second transplants are possible.
Short-course DAA therapy may prevent hepatitis transmission in transplant patients
BOSTON – A short course of results of a recent study show.
The regimen, given right before transplantation and for 7 days afterward, reduced the cost of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy and allowed patients to complete hepatitis C virus (HCV) therapy before hospital discharge, according to authors of the study, which was presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
If confirmed in subsequent studies, this regimen could become the standard of care for donor-positive, recipient-negative transplantation, said lead study author Jordan J. Feld, MD, R. Phelan Chair in translational liver disease research at the University of Toronto and research director at the Toronto Centre for Liver Disease.
“Transplant recipients are understandably nervous about accepting organs from people with HCV infection,” said Dr. Feld in a press release. “This very short therapy allows them to leave hospital free of HCV, which is a huge benefit. Not only is it cheaper and likely safer, but the patients really prefer not having to worry about HCV with all of the other challenges after a transplant.”
Results of this study come at a time when the proportion of overdose death organ donors is on the rise, from just 1% in 2000 to 15% in 2016, according to Dr. Feld. Overdose deaths account for the largest percentage of HCV-infected donors, most of whom are young and often otherwise healthy, he added.
Recipients of HCV-infected organs can be cured after transplant as a number of studies have previously shown. However, preventing transmission would be better than cure, Dr. Feld said, in part because of issues with drug-drug interactions, potential for relapse, and issues with procuring the drugs after transplant.
Accordingly, Dr. Feld and colleagues sought to evaluate “preemptive” treatment with DAA therapy combined with ezetimibe, which they said has been shown to inhibit HCV entry blockers. The recipients, who were listed for heart, lung, kidney, or kidney-pancreas transplant, were given glecaprevir/pibrentasvir plus ezetimibe starting 6-12 hours prior to transplantation, and then daily for 7 days.
The median age was 36 years for the 16 donors reported, and 61 years for the 25 recipients. Most recipients (12 patients) had a lung transplant, while 8 had a heart transplant, 4 had a kidney transplant, and 1 had a kidney-pancreas transplant.
There were no virologic failures, according to the investigators, with sustained virologic response (SVR) after 6 weeks in 7 patients, and SVR after 12 weeks in the remaining 18. Three recipients did have detectable HCV RNA, though all cleared and had SVR at 6 weeks in one case, and SVR at 12 weeks in the other two, according to the investigators’ report.
Of 22 serious adverse events noted in the study, 1 was considered treatment related, according to the report, and there were 2 deaths among lung transplant patients, caused by sepsis in 1 case to sepsis and subarachnoid hemorrhage in another.
It’s not clear whether ezetimibe is needed in this short-duration regimen, but in any case, it is well tolerated and inexpensive, and so there is “minimal downside” to include it, Dr. Feld and coinvestigators wrote in their report.
Dr. Feld reported disclosures related to Abbvie, Abbott, Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, and Roche.
SOURCE: Feld JJ et al. The Liver Meeting 2019, Abstract 38.
BOSTON – A short course of results of a recent study show.
The regimen, given right before transplantation and for 7 days afterward, reduced the cost of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy and allowed patients to complete hepatitis C virus (HCV) therapy before hospital discharge, according to authors of the study, which was presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
If confirmed in subsequent studies, this regimen could become the standard of care for donor-positive, recipient-negative transplantation, said lead study author Jordan J. Feld, MD, R. Phelan Chair in translational liver disease research at the University of Toronto and research director at the Toronto Centre for Liver Disease.
“Transplant recipients are understandably nervous about accepting organs from people with HCV infection,” said Dr. Feld in a press release. “This very short therapy allows them to leave hospital free of HCV, which is a huge benefit. Not only is it cheaper and likely safer, but the patients really prefer not having to worry about HCV with all of the other challenges after a transplant.”
Results of this study come at a time when the proportion of overdose death organ donors is on the rise, from just 1% in 2000 to 15% in 2016, according to Dr. Feld. Overdose deaths account for the largest percentage of HCV-infected donors, most of whom are young and often otherwise healthy, he added.
Recipients of HCV-infected organs can be cured after transplant as a number of studies have previously shown. However, preventing transmission would be better than cure, Dr. Feld said, in part because of issues with drug-drug interactions, potential for relapse, and issues with procuring the drugs after transplant.
Accordingly, Dr. Feld and colleagues sought to evaluate “preemptive” treatment with DAA therapy combined with ezetimibe, which they said has been shown to inhibit HCV entry blockers. The recipients, who were listed for heart, lung, kidney, or kidney-pancreas transplant, were given glecaprevir/pibrentasvir plus ezetimibe starting 6-12 hours prior to transplantation, and then daily for 7 days.
The median age was 36 years for the 16 donors reported, and 61 years for the 25 recipients. Most recipients (12 patients) had a lung transplant, while 8 had a heart transplant, 4 had a kidney transplant, and 1 had a kidney-pancreas transplant.
There were no virologic failures, according to the investigators, with sustained virologic response (SVR) after 6 weeks in 7 patients, and SVR after 12 weeks in the remaining 18. Three recipients did have detectable HCV RNA, though all cleared and had SVR at 6 weeks in one case, and SVR at 12 weeks in the other two, according to the investigators’ report.
Of 22 serious adverse events noted in the study, 1 was considered treatment related, according to the report, and there were 2 deaths among lung transplant patients, caused by sepsis in 1 case to sepsis and subarachnoid hemorrhage in another.
It’s not clear whether ezetimibe is needed in this short-duration regimen, but in any case, it is well tolerated and inexpensive, and so there is “minimal downside” to include it, Dr. Feld and coinvestigators wrote in their report.
Dr. Feld reported disclosures related to Abbvie, Abbott, Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, and Roche.
SOURCE: Feld JJ et al. The Liver Meeting 2019, Abstract 38.
BOSTON – A short course of results of a recent study show.
The regimen, given right before transplantation and for 7 days afterward, reduced the cost of direct-acting antiviral (DAA) therapy and allowed patients to complete hepatitis C virus (HCV) therapy before hospital discharge, according to authors of the study, which was presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
If confirmed in subsequent studies, this regimen could become the standard of care for donor-positive, recipient-negative transplantation, said lead study author Jordan J. Feld, MD, R. Phelan Chair in translational liver disease research at the University of Toronto and research director at the Toronto Centre for Liver Disease.
“Transplant recipients are understandably nervous about accepting organs from people with HCV infection,” said Dr. Feld in a press release. “This very short therapy allows them to leave hospital free of HCV, which is a huge benefit. Not only is it cheaper and likely safer, but the patients really prefer not having to worry about HCV with all of the other challenges after a transplant.”
Results of this study come at a time when the proportion of overdose death organ donors is on the rise, from just 1% in 2000 to 15% in 2016, according to Dr. Feld. Overdose deaths account for the largest percentage of HCV-infected donors, most of whom are young and often otherwise healthy, he added.
Recipients of HCV-infected organs can be cured after transplant as a number of studies have previously shown. However, preventing transmission would be better than cure, Dr. Feld said, in part because of issues with drug-drug interactions, potential for relapse, and issues with procuring the drugs after transplant.
Accordingly, Dr. Feld and colleagues sought to evaluate “preemptive” treatment with DAA therapy combined with ezetimibe, which they said has been shown to inhibit HCV entry blockers. The recipients, who were listed for heart, lung, kidney, or kidney-pancreas transplant, were given glecaprevir/pibrentasvir plus ezetimibe starting 6-12 hours prior to transplantation, and then daily for 7 days.
The median age was 36 years for the 16 donors reported, and 61 years for the 25 recipients. Most recipients (12 patients) had a lung transplant, while 8 had a heart transplant, 4 had a kidney transplant, and 1 had a kidney-pancreas transplant.
There were no virologic failures, according to the investigators, with sustained virologic response (SVR) after 6 weeks in 7 patients, and SVR after 12 weeks in the remaining 18. Three recipients did have detectable HCV RNA, though all cleared and had SVR at 6 weeks in one case, and SVR at 12 weeks in the other two, according to the investigators’ report.
Of 22 serious adverse events noted in the study, 1 was considered treatment related, according to the report, and there were 2 deaths among lung transplant patients, caused by sepsis in 1 case to sepsis and subarachnoid hemorrhage in another.
It’s not clear whether ezetimibe is needed in this short-duration regimen, but in any case, it is well tolerated and inexpensive, and so there is “minimal downside” to include it, Dr. Feld and coinvestigators wrote in their report.
Dr. Feld reported disclosures related to Abbvie, Abbott, Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Gilead, Janssen, Merck, and Roche.
SOURCE: Feld JJ et al. The Liver Meeting 2019, Abstract 38.
REPORTING FROM THE LIVER MEETING 2019
First NCCN guideline on hematopoietic cell transplantation focuses on GVHD
Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) are the central focus of the first National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guideline on hematopoietic cell transplantation.
The guideline presents detailed recommendations for the evaluation of hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients, and an extensive section on the diagnosis and workup of GVHD, including information on staging and grading of acute GVHD, grading of chronic GVHD, treatment response criteria, and suggested systemic therapies for steroid-refractory disease.
“We wanted to both build on the commonly used approach to stage and treat graft-versus-host disease, and make sure that this information is readily available for physicians-in-training and young physicians who are learning about transplants,” said guideline committee chair Ayman Saad, MB BCh, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute in Columbus, Ohio.
In an interview, Dr. Saad emphasized that an important goal of the guidelines is to encourage general oncologists to recognize early signs of GVHD and refer potential candidates to transplant centers for further evaluation.
“We also urge oncologists who may be caring for patients after HCT to familiarize themselves with the varied manifestations of GVHD – a very common and significant posttransplant complication – and to consult with transplant providers to optimize their ongoing care. The guidelines explain how to diagnose and treat this condition in order to achieve the best possible outcomes,” guideline panel member Alison W. Loren, MD, director of blood and marrow transplantation at Abraham Cancer Center, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a statement.
The guideline includes links to other NCCN guidelines for diseases where HCT is a common therapeutic option, including leukemias, myeloid malignancies, lymphomas, central nervous system cancers, and testicular cancer.
The HCT guideline includes:
- Pretransplant recipient evaluation with recommendations for clinical assessment and imaging.
- Diagnosis and workup of GVHD, with separate algorithms for suspected acute or chronic GVHD.
- Specific interventions for management of acute GVHD with corticosteroids or other systemic agents.
- Chronic GVHD diagnosis by organ site and symptoms, with a severity scoring system.
- Chronic GVHD steroid response definitions and criteria.
- Suggested systemic agents for steroid-refractory GVHD.
One feature that is unusual for an NCCN guideline document is a page of photographs to assist clinicians in diagnosing range-of-motion abnormalities in the shoulder, elbow, hand, and ankle of patients with suspected or confirmed GVHD. Dr. Saad said that future iterations of the guideline will include additional photos to help clinicians develop a visual repertoire of potential GVHD signs.
Future versions will also include a discussion section and more comprehensive information on other common complications following HCT transplant, as well as management of posttransplant relapse.
Ideally, the guideline will help clinicians document and justify clinical decisions surrounding HCT and GVHD management in discussions with third-party payers, Dr. Saad said.
“Sometimes we struggle with payers when we want to use a certain modality to treat GVHD, and they respond ‘that’s not approved,’ or ‘that’s not a common indication,’ et cetera,” he said. “What we’re trying to put here are the commonly used therapies that most, but not all, experts agree on, and we can use this to negotiate with payers.”
He also emphasized that the guideline is meant to be instructive rather than prescriptive and is not meant to hinder innovations that may emerge from clinical trials.
“We would appreciate any feedback from non-NCCN centers as well as experts at NCCN centers, and we’ll be more than happy to address any concerns or criticisms they have,” he said.
Dr. Saad reported financial relationships with Actinium and Incysus Biomedical. Dr. Loren has previously reported having no disclosures.
Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) are the central focus of the first National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guideline on hematopoietic cell transplantation.
The guideline presents detailed recommendations for the evaluation of hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients, and an extensive section on the diagnosis and workup of GVHD, including information on staging and grading of acute GVHD, grading of chronic GVHD, treatment response criteria, and suggested systemic therapies for steroid-refractory disease.
“We wanted to both build on the commonly used approach to stage and treat graft-versus-host disease, and make sure that this information is readily available for physicians-in-training and young physicians who are learning about transplants,” said guideline committee chair Ayman Saad, MB BCh, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute in Columbus, Ohio.
In an interview, Dr. Saad emphasized that an important goal of the guidelines is to encourage general oncologists to recognize early signs of GVHD and refer potential candidates to transplant centers for further evaluation.
“We also urge oncologists who may be caring for patients after HCT to familiarize themselves with the varied manifestations of GVHD – a very common and significant posttransplant complication – and to consult with transplant providers to optimize their ongoing care. The guidelines explain how to diagnose and treat this condition in order to achieve the best possible outcomes,” guideline panel member Alison W. Loren, MD, director of blood and marrow transplantation at Abraham Cancer Center, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a statement.
The guideline includes links to other NCCN guidelines for diseases where HCT is a common therapeutic option, including leukemias, myeloid malignancies, lymphomas, central nervous system cancers, and testicular cancer.
The HCT guideline includes:
- Pretransplant recipient evaluation with recommendations for clinical assessment and imaging.
- Diagnosis and workup of GVHD, with separate algorithms for suspected acute or chronic GVHD.
- Specific interventions for management of acute GVHD with corticosteroids or other systemic agents.
- Chronic GVHD diagnosis by organ site and symptoms, with a severity scoring system.
- Chronic GVHD steroid response definitions and criteria.
- Suggested systemic agents for steroid-refractory GVHD.
One feature that is unusual for an NCCN guideline document is a page of photographs to assist clinicians in diagnosing range-of-motion abnormalities in the shoulder, elbow, hand, and ankle of patients with suspected or confirmed GVHD. Dr. Saad said that future iterations of the guideline will include additional photos to help clinicians develop a visual repertoire of potential GVHD signs.
Future versions will also include a discussion section and more comprehensive information on other common complications following HCT transplant, as well as management of posttransplant relapse.
Ideally, the guideline will help clinicians document and justify clinical decisions surrounding HCT and GVHD management in discussions with third-party payers, Dr. Saad said.
“Sometimes we struggle with payers when we want to use a certain modality to treat GVHD, and they respond ‘that’s not approved,’ or ‘that’s not a common indication,’ et cetera,” he said. “What we’re trying to put here are the commonly used therapies that most, but not all, experts agree on, and we can use this to negotiate with payers.”
He also emphasized that the guideline is meant to be instructive rather than prescriptive and is not meant to hinder innovations that may emerge from clinical trials.
“We would appreciate any feedback from non-NCCN centers as well as experts at NCCN centers, and we’ll be more than happy to address any concerns or criticisms they have,” he said.
Dr. Saad reported financial relationships with Actinium and Incysus Biomedical. Dr. Loren has previously reported having no disclosures.
Recommendations for the diagnosis and management of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) are the central focus of the first National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guideline on hematopoietic cell transplantation.
The guideline presents detailed recommendations for the evaluation of hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipients, and an extensive section on the diagnosis and workup of GVHD, including information on staging and grading of acute GVHD, grading of chronic GVHD, treatment response criteria, and suggested systemic therapies for steroid-refractory disease.
“We wanted to both build on the commonly used approach to stage and treat graft-versus-host disease, and make sure that this information is readily available for physicians-in-training and young physicians who are learning about transplants,” said guideline committee chair Ayman Saad, MB BCh, of The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center, James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute in Columbus, Ohio.
In an interview, Dr. Saad emphasized that an important goal of the guidelines is to encourage general oncologists to recognize early signs of GVHD and refer potential candidates to transplant centers for further evaluation.
“We also urge oncologists who may be caring for patients after HCT to familiarize themselves with the varied manifestations of GVHD – a very common and significant posttransplant complication – and to consult with transplant providers to optimize their ongoing care. The guidelines explain how to diagnose and treat this condition in order to achieve the best possible outcomes,” guideline panel member Alison W. Loren, MD, director of blood and marrow transplantation at Abraham Cancer Center, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said in a statement.
The guideline includes links to other NCCN guidelines for diseases where HCT is a common therapeutic option, including leukemias, myeloid malignancies, lymphomas, central nervous system cancers, and testicular cancer.
The HCT guideline includes:
- Pretransplant recipient evaluation with recommendations for clinical assessment and imaging.
- Diagnosis and workup of GVHD, with separate algorithms for suspected acute or chronic GVHD.
- Specific interventions for management of acute GVHD with corticosteroids or other systemic agents.
- Chronic GVHD diagnosis by organ site and symptoms, with a severity scoring system.
- Chronic GVHD steroid response definitions and criteria.
- Suggested systemic agents for steroid-refractory GVHD.
One feature that is unusual for an NCCN guideline document is a page of photographs to assist clinicians in diagnosing range-of-motion abnormalities in the shoulder, elbow, hand, and ankle of patients with suspected or confirmed GVHD. Dr. Saad said that future iterations of the guideline will include additional photos to help clinicians develop a visual repertoire of potential GVHD signs.
Future versions will also include a discussion section and more comprehensive information on other common complications following HCT transplant, as well as management of posttransplant relapse.
Ideally, the guideline will help clinicians document and justify clinical decisions surrounding HCT and GVHD management in discussions with third-party payers, Dr. Saad said.
“Sometimes we struggle with payers when we want to use a certain modality to treat GVHD, and they respond ‘that’s not approved,’ or ‘that’s not a common indication,’ et cetera,” he said. “What we’re trying to put here are the commonly used therapies that most, but not all, experts agree on, and we can use this to negotiate with payers.”
He also emphasized that the guideline is meant to be instructive rather than prescriptive and is not meant to hinder innovations that may emerge from clinical trials.
“We would appreciate any feedback from non-NCCN centers as well as experts at NCCN centers, and we’ll be more than happy to address any concerns or criticisms they have,” he said.
Dr. Saad reported financial relationships with Actinium and Incysus Biomedical. Dr. Loren has previously reported having no disclosures.
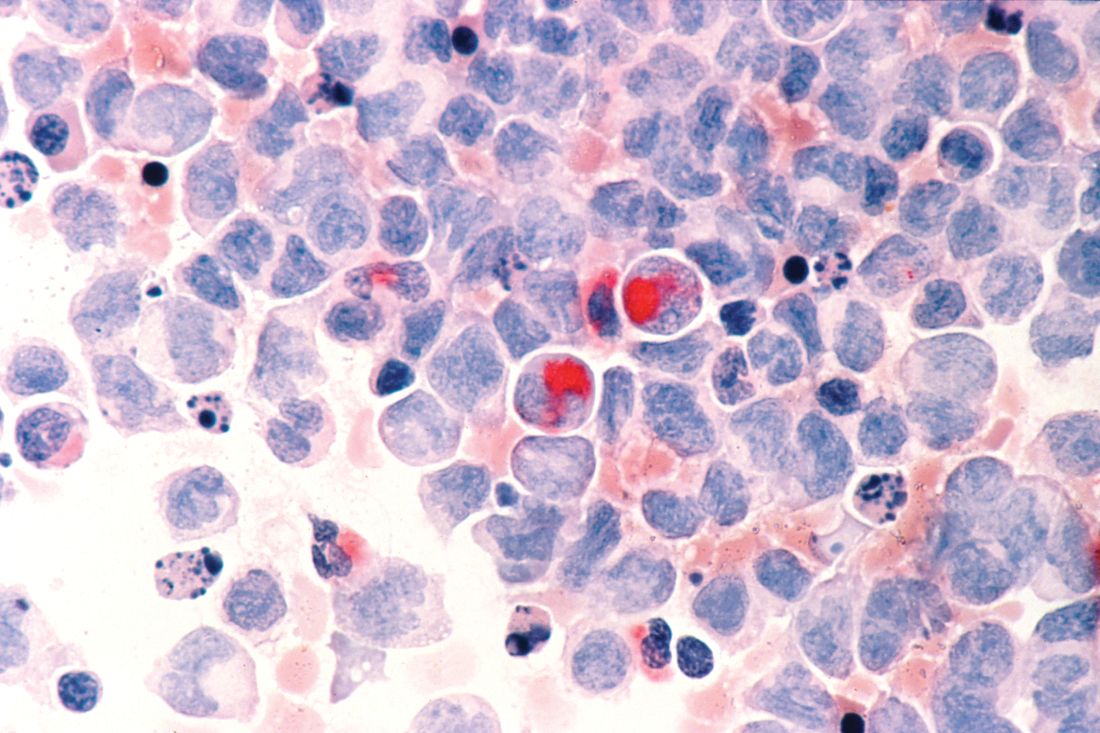
Hematopoietic cell transplant offers realistic cure in secondary AML
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
yielding significantly better survival outcomes, according to findings from an observational study.
Although secondary AML has been identified as an independent predictor of poor prognosis, it is not included in current risk classifications that provide the basis of deciding when to perform HCT.
Christer Nilsson, MD, of Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, and colleagues, used two nationwide Swedish registries – the Swedish AML Registry and the Swedish Cancer Registry – to characterize how often HCT is performed in these patients and to evaluate its impact in a real-world setting. The registries include all patients with AML diagnosed between 1997 and 2013.
Their findings are in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
The analysis included 3,337 adult patients with AML who were intensively treated and did not have acute promyelocytic leukemia. More than three-quarters of the patients had de novo AML and the remainder had secondary AML that was either therapy related or developed after an antecedent myeloid disease. In total, 100 patients with secondary AML underwent HCT while in first complete remission.
In terms of crude survival at 5 years after diagnosis, patients with secondary AML who did not undergo HCT did very poorly. The survival rate was 0% in those with AML preceded by myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN-AML), 2% in patients with AML preceded by myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS-AML), and 4% in patients with therapy-related AML (t-AML). In contrast, the 5-year overall survival in patients who underwent HCT at any time point or disease stage was 32% for patients with MPN-AML, 18% for patients with MDS-AML, and 25% for patients t-AML.
These crude survival figures suggest that “HCT is the sole realistic curable treatment option for [secondary] AML,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers also performed a propensity score matching analysis of HCT versus chemotherapy consolidation in patients with secondary AML who had been in first complete remission for more than 90 days. The model matched 45 patients who underwent HCT with 66 patients treated with chemotherapy consolidation. The projected 5-year overall survival was 48% in the HCT group, compared with 20% in the consolidation group (P = .01). Similarly, 5-year relapse-free survival was also higher in the HCT group, compared with the consolidation group (43% vs. 21%, P = .02).
“Ideally, the role of transplantation in [secondary] AML should be evaluated in a prospective randomized trial, minimizing the risk of any bias,” the researchers wrote. “However, such a trial is lacking and most likely will never be performed.”
The researchers concluded that HCT should be considered for all patients with secondary AML who are eligible and fit for transplantation.
The study was supported by the Swedish Cancer Foundation, Swedish Research Council, Stockholm County Council, Gothenberg Medical Society, and Assar Gabrielsson Foundation. The researchers reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Nilson C et al. Biol Blood Marrow Tranplant. 2019;25:1770-8.
FROM BIOLOGY OF BLOOD AND MARROW TRANSPLANTATION
Race mismatch may affect survival in lung transplant setting
NEW ORLEANS – Race compatibility is a factor that can affect survival and needs to be considered when matching lung transplant candidates to potential donors, results from a large retrospective analysis suggest.
Specifically, whites had significantly worse survival when receiving lungs from African American donors in this registry analysis, according to study investigator Alexis Kofi Okoh, MD.
By contrast, donor-to-recipient race compatibility (DRRC) did not affect posttransplant survival among African American or Hispanic patients, said Dr. Okoh, who is with the lung transplant division at the Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
While race mismatch has been shown to affect outcomes in kidney, heart, and liver transplant settings, the data for DRRC in lung transplant prior to this analysis generally has been limited to small, single-center studies, according to Dr. Okoh.
“If you do have the option, [race compatibility] should highly be considered, because it clearly has an impact on outcomes,” Dr. Okoh said in an interview here at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Considering the race of both donor and recipient is especially important now that the lung transplant population is becoming more ethnically diverse, he added.
The study was based on an analysis of 19,504 lung transplant recipients in the prospectively maintained United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database during 2006-2018. In that cohort, 16,485 recipients were white, 1,787 were African American, and 1,232 were Hispanic.
Race-matched donor organs were used in two-thirds (66.2%) of white recipients, about one-quarter (26.8%) of African American recipients, and one-third (33.0%) of Hispanic recipients.
Overall, survival post–lung transplant was significantly poorer among recipients who did not receive a race-matched organ in Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, Dr. Okoh said, though, that this effect was diminished after they adjusted for patient baseline characteristics (P = 0.2809).
For African American recipients, the unadjusted and adjusted survival estimates were no different regardless of donor race, and likewise, there were no apparent survival differences between Hispanic recipients who received race matched or mismatched organs.
Survival among white recipients, however, was significantly affected by race of the recipient, with decreased survival estimates noted even after adjustment for patient characteristics, according to Dr. Okoh’s presentation.
Results of regression analysis showed that white recipient/African American donor was the only race mismatch to significantly affect survival, Dr. Okoh said in the interview.
The posttransplant survival hazard ratios (and 95% confidence intervals) reported by Dr. Okoh with a no race mismatch serving as reference were 1.15 (1.08-1.23) for whites with African American donors, and 1.09 (1.01-1.18) for whites with Hispanic donors.
Dr. Okoh and coinvestigators reported no relevant conflicts in relation to their study.
SOURCE: Okoh A et al. CHEST 2019. Abstract, doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.220.
NEW ORLEANS – Race compatibility is a factor that can affect survival and needs to be considered when matching lung transplant candidates to potential donors, results from a large retrospective analysis suggest.
Specifically, whites had significantly worse survival when receiving lungs from African American donors in this registry analysis, according to study investigator Alexis Kofi Okoh, MD.
By contrast, donor-to-recipient race compatibility (DRRC) did not affect posttransplant survival among African American or Hispanic patients, said Dr. Okoh, who is with the lung transplant division at the Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
While race mismatch has been shown to affect outcomes in kidney, heart, and liver transplant settings, the data for DRRC in lung transplant prior to this analysis generally has been limited to small, single-center studies, according to Dr. Okoh.
“If you do have the option, [race compatibility] should highly be considered, because it clearly has an impact on outcomes,” Dr. Okoh said in an interview here at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Considering the race of both donor and recipient is especially important now that the lung transplant population is becoming more ethnically diverse, he added.
The study was based on an analysis of 19,504 lung transplant recipients in the prospectively maintained United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database during 2006-2018. In that cohort, 16,485 recipients were white, 1,787 were African American, and 1,232 were Hispanic.
Race-matched donor organs were used in two-thirds (66.2%) of white recipients, about one-quarter (26.8%) of African American recipients, and one-third (33.0%) of Hispanic recipients.
Overall, survival post–lung transplant was significantly poorer among recipients who did not receive a race-matched organ in Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, Dr. Okoh said, though, that this effect was diminished after they adjusted for patient baseline characteristics (P = 0.2809).
For African American recipients, the unadjusted and adjusted survival estimates were no different regardless of donor race, and likewise, there were no apparent survival differences between Hispanic recipients who received race matched or mismatched organs.
Survival among white recipients, however, was significantly affected by race of the recipient, with decreased survival estimates noted even after adjustment for patient characteristics, according to Dr. Okoh’s presentation.
Results of regression analysis showed that white recipient/African American donor was the only race mismatch to significantly affect survival, Dr. Okoh said in the interview.
The posttransplant survival hazard ratios (and 95% confidence intervals) reported by Dr. Okoh with a no race mismatch serving as reference were 1.15 (1.08-1.23) for whites with African American donors, and 1.09 (1.01-1.18) for whites with Hispanic donors.
Dr. Okoh and coinvestigators reported no relevant conflicts in relation to their study.
SOURCE: Okoh A et al. CHEST 2019. Abstract, doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.220.
NEW ORLEANS – Race compatibility is a factor that can affect survival and needs to be considered when matching lung transplant candidates to potential donors, results from a large retrospective analysis suggest.
Specifically, whites had significantly worse survival when receiving lungs from African American donors in this registry analysis, according to study investigator Alexis Kofi Okoh, MD.
By contrast, donor-to-recipient race compatibility (DRRC) did not affect posttransplant survival among African American or Hispanic patients, said Dr. Okoh, who is with the lung transplant division at the Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, N.J.
While race mismatch has been shown to affect outcomes in kidney, heart, and liver transplant settings, the data for DRRC in lung transplant prior to this analysis generally has been limited to small, single-center studies, according to Dr. Okoh.
“If you do have the option, [race compatibility] should highly be considered, because it clearly has an impact on outcomes,” Dr. Okoh said in an interview here at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Considering the race of both donor and recipient is especially important now that the lung transplant population is becoming more ethnically diverse, he added.
The study was based on an analysis of 19,504 lung transplant recipients in the prospectively maintained United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database during 2006-2018. In that cohort, 16,485 recipients were white, 1,787 were African American, and 1,232 were Hispanic.
Race-matched donor organs were used in two-thirds (66.2%) of white recipients, about one-quarter (26.8%) of African American recipients, and one-third (33.0%) of Hispanic recipients.
Overall, survival post–lung transplant was significantly poorer among recipients who did not receive a race-matched organ in Kaplan-Meier survival estimates, Dr. Okoh said, though, that this effect was diminished after they adjusted for patient baseline characteristics (P = 0.2809).
For African American recipients, the unadjusted and adjusted survival estimates were no different regardless of donor race, and likewise, there were no apparent survival differences between Hispanic recipients who received race matched or mismatched organs.
Survival among white recipients, however, was significantly affected by race of the recipient, with decreased survival estimates noted even after adjustment for patient characteristics, according to Dr. Okoh’s presentation.
Results of regression analysis showed that white recipient/African American donor was the only race mismatch to significantly affect survival, Dr. Okoh said in the interview.
The posttransplant survival hazard ratios (and 95% confidence intervals) reported by Dr. Okoh with a no race mismatch serving as reference were 1.15 (1.08-1.23) for whites with African American donors, and 1.09 (1.01-1.18) for whites with Hispanic donors.
Dr. Okoh and coinvestigators reported no relevant conflicts in relation to their study.
SOURCE: Okoh A et al. CHEST 2019. Abstract, doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.08.220.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2019
HCV+ kidney transplants: Similar outcomes to HCV- regardless of recipient serostatus
Kidneys from donors with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection function well despite adverse quality assessment and are a valuable resource for transplantation candidates independent of HCV status, according to the findings of a large U.S. registry study.
A total of 260 HCV-viremic kidneys were transplanted in the first quarter of 2019, with 105 additional viremic kidneys being discarded, according to a report in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology by Vishnu S. Potluri, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
Donor HCV viremia was defined as an HCV nucleic acid test–positive result reported to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN). Donors who were HCV negative in this test were labeled as HCV nonviremic. Kidney transplantation recipients were defined as either HCV seropositive or seronegative based on HCV antibody testing.
During the first quarter of 2019, 74% of HCV-viremic kidneys were transplanted into seronegative recipients, which is a major change from how HCV-viremic kidneys were allocated a few years ago, according to the researchers. The results of small trials showing the benefits of such transplantations and the success of direct-acting antiviral therapy (DAA) on clearing HCV infections were indicated as likely responsible for the change.
HCV-viremic kidneys had similar function, compared with HCV-nonviremic kidneys, when matched on the donor elements included in the Kidney Profile Donor Index (KDPI), excluding HCV, they added. In addition, the 12-month estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was similar between the seropositive and seronegative recipients, respectively 65.4 and 71.1 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (P = .05), which suggests that recipient HCV serostatus does not negatively affect 1-year graft function using HCV-viremic kidneys in the era of DAA treatments, according to the authors.
Also, among HCV-seropositive recipients of HCV-viremic kidneys, seven (3.4%) died by 1 year post transplantation, while none of the HCV-seronegative recipients of HCV-viremic kidneys experienced graft failure or death.
“These striking results provide important additional evidence that the KDPI, with its current negative weighting for HCV status, does not accurately assess the quality of kidneys from HCV-viremic donors,” the authors wrote.
“HCV-viremic kidneys are a valuable resource for transplantation. Disincentives for accepting these organs should be addressed by the transplantation community,” Dr. Potluri and colleagues concluded.
This work was supported in part by the Health Resources and Services Administration of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The various authors reported grant funding and advisory board participation with a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Potluri VS et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30:1939-51.
Kidneys from donors with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection function well despite adverse quality assessment and are a valuable resource for transplantation candidates independent of HCV status, according to the findings of a large U.S. registry study.
A total of 260 HCV-viremic kidneys were transplanted in the first quarter of 2019, with 105 additional viremic kidneys being discarded, according to a report in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology by Vishnu S. Potluri, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
Donor HCV viremia was defined as an HCV nucleic acid test–positive result reported to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN). Donors who were HCV negative in this test were labeled as HCV nonviremic. Kidney transplantation recipients were defined as either HCV seropositive or seronegative based on HCV antibody testing.
During the first quarter of 2019, 74% of HCV-viremic kidneys were transplanted into seronegative recipients, which is a major change from how HCV-viremic kidneys were allocated a few years ago, according to the researchers. The results of small trials showing the benefits of such transplantations and the success of direct-acting antiviral therapy (DAA) on clearing HCV infections were indicated as likely responsible for the change.
HCV-viremic kidneys had similar function, compared with HCV-nonviremic kidneys, when matched on the donor elements included in the Kidney Profile Donor Index (KDPI), excluding HCV, they added. In addition, the 12-month estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was similar between the seropositive and seronegative recipients, respectively 65.4 and 71.1 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (P = .05), which suggests that recipient HCV serostatus does not negatively affect 1-year graft function using HCV-viremic kidneys in the era of DAA treatments, according to the authors.
Also, among HCV-seropositive recipients of HCV-viremic kidneys, seven (3.4%) died by 1 year post transplantation, while none of the HCV-seronegative recipients of HCV-viremic kidneys experienced graft failure or death.
“These striking results provide important additional evidence that the KDPI, with its current negative weighting for HCV status, does not accurately assess the quality of kidneys from HCV-viremic donors,” the authors wrote.
“HCV-viremic kidneys are a valuable resource for transplantation. Disincentives for accepting these organs should be addressed by the transplantation community,” Dr. Potluri and colleagues concluded.
This work was supported in part by the Health Resources and Services Administration of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The various authors reported grant funding and advisory board participation with a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Potluri VS et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30:1939-51.
Kidneys from donors with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection function well despite adverse quality assessment and are a valuable resource for transplantation candidates independent of HCV status, according to the findings of a large U.S. registry study.
A total of 260 HCV-viremic kidneys were transplanted in the first quarter of 2019, with 105 additional viremic kidneys being discarded, according to a report in the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology by Vishnu S. Potluri, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and colleagues.
Donor HCV viremia was defined as an HCV nucleic acid test–positive result reported to the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network (OPTN). Donors who were HCV negative in this test were labeled as HCV nonviremic. Kidney transplantation recipients were defined as either HCV seropositive or seronegative based on HCV antibody testing.
During the first quarter of 2019, 74% of HCV-viremic kidneys were transplanted into seronegative recipients, which is a major change from how HCV-viremic kidneys were allocated a few years ago, according to the researchers. The results of small trials showing the benefits of such transplantations and the success of direct-acting antiviral therapy (DAA) on clearing HCV infections were indicated as likely responsible for the change.
HCV-viremic kidneys had similar function, compared with HCV-nonviremic kidneys, when matched on the donor elements included in the Kidney Profile Donor Index (KDPI), excluding HCV, they added. In addition, the 12-month estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was similar between the seropositive and seronegative recipients, respectively 65.4 and 71.1 mL/min per 1.73 m2 (P = .05), which suggests that recipient HCV serostatus does not negatively affect 1-year graft function using HCV-viremic kidneys in the era of DAA treatments, according to the authors.
Also, among HCV-seropositive recipients of HCV-viremic kidneys, seven (3.4%) died by 1 year post transplantation, while none of the HCV-seronegative recipients of HCV-viremic kidneys experienced graft failure or death.
“These striking results provide important additional evidence that the KDPI, with its current negative weighting for HCV status, does not accurately assess the quality of kidneys from HCV-viremic donors,” the authors wrote.
“HCV-viremic kidneys are a valuable resource for transplantation. Disincentives for accepting these organs should be addressed by the transplantation community,” Dr. Potluri and colleagues concluded.
This work was supported in part by the Health Resources and Services Administration of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. The various authors reported grant funding and advisory board participation with a number of pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Potluri VS et al. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30:1939-51.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN SOCIETY OF NEPHROLOGY
Daratumumab approved in combo with VTd for transplant-eligible multiple myeloma
The Food and Drug Administration has approved daratumumab in combination with certain therapies for newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma who are eligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The approval specifies combination of this CD38-directed antibody with bortezomib (Velcade), thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd), according to an announcement from Janssen.
The approval is based on results from the CASSIOPEIA study. The first part of the study randomized 1,085 patients (median age, 58 years) and showed that, compared with VTd alone, the daratumumab-VTd combination had significantly better postconsolidation stringent complete response (29% vs. 20%; odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-2.12; P = .001) and a 53% reduction in risk of disease progression or death (hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.33-0.67; P = .0001).
The most frequent adverse reactions with 5% greater frequency in the daratumumab-VTd group were infusion reactions (including anaphylaxis), nausea, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, and bronchitis. Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the Janssen website.
Daratumumab was initially approved in 2015, and in June 2019, it received approval, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, for treatment of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved daratumumab in combination with certain therapies for newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma who are eligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The approval specifies combination of this CD38-directed antibody with bortezomib (Velcade), thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd), according to an announcement from Janssen.
The approval is based on results from the CASSIOPEIA study. The first part of the study randomized 1,085 patients (median age, 58 years) and showed that, compared with VTd alone, the daratumumab-VTd combination had significantly better postconsolidation stringent complete response (29% vs. 20%; odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-2.12; P = .001) and a 53% reduction in risk of disease progression or death (hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.33-0.67; P = .0001).
The most frequent adverse reactions with 5% greater frequency in the daratumumab-VTd group were infusion reactions (including anaphylaxis), nausea, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, and bronchitis. Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the Janssen website.
Daratumumab was initially approved in 2015, and in June 2019, it received approval, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, for treatment of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved daratumumab in combination with certain therapies for newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma who are eligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
The approval specifies combination of this CD38-directed antibody with bortezomib (Velcade), thalidomide, and dexamethasone (VTd), according to an announcement from Janssen.
The approval is based on results from the CASSIOPEIA study. The first part of the study randomized 1,085 patients (median age, 58 years) and showed that, compared with VTd alone, the daratumumab-VTd combination had significantly better postconsolidation stringent complete response (29% vs. 20%; odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.21-2.12; P = .001) and a 53% reduction in risk of disease progression or death (hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.33-0.67; P = .0001).
The most frequent adverse reactions with 5% greater frequency in the daratumumab-VTd group were infusion reactions (including anaphylaxis), nausea, pyrexia, upper respiratory tract infection, and bronchitis. Full prescribing information, including contraindications and warnings, can be found on the Janssen website.
Daratumumab was initially approved in 2015, and in June 2019, it received approval, in combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, for treatment of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who are ineligible for autologous stem cell transplant.
Ongoing research aims to improve transplant outcomes in sickle cell
Researchers are leading several studies designed to improve hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for patients with sickle cell disease (SCD), experts at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute reported during a recent webinar.
“HSCT offers a potential cure [for SCD], which may improve quantity and quality of life [for patients],” said Courtney D. Fitzhugh, MD, a Lasker Clinical Research Scholar in the Laboratory of Early Sickle Mortality Prevention at NHLBI.
Currently, HLA-matched sibling and matched unrelated donor sources provide the best outcomes for sickle cell patients undergoing allogeneic HSCT, she explained. Alternative stem cell sources include umbilical cord blood and haploidentical donors.
Over the past 2 years, the majority of novel transplant techniques have been primarily aimed at improving conditioning regimens and lowering rates of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Recent evidence
A recent international survey found high survival rates in patients with SCD who underwent HLA-matched sibling HSCT during 1986-2013. At 5-years, overall- and event-free survival rates were 92.9% and 91.4%, respectively, with even higher rates (95% and 93%) seen in children aged younger than 16 years.
With respect to safety, the cumulative incidence rates of acute and chronic GVHD were 14.8% and 14.3%, Dr. Fitzhugh reported.
Much of the success seen with HLA-matched sibling donors is attributable to recent data demonstrating that complete transformation of patient’s bone marrow is unnecessary to illicit a curative effect.
With donor myeloid chimerism levels of at least 20%, the sickle disease phenotype can be reversed, and there’s a reduced risk of GVHD, she said.
In mouse models, researchers have found that inclusion of sirolimus in HLA-matched pretransplant conditioning regimens leads to higher levels of donor cell engraftment. As a result, some conditioning regimens now administer sirolimus (target 10-15 ng/dL) one-day prior to transplantation.
In 55 patients transplanted using this technique, overall- and event-free survival rates of 93% and 87% have been reported, with no transplant-related mortality or evidence of GVHD. Other institutions have also begun to adopt this technique, and have reported similar findings, Dr. Fitzhugh reported.
“When you [administer high-dose] chemotherapy, you don’t expect that patients are able to have children, but we are excited to report that 8 of our patients have had 13 healthy babies post transplant,” Dr. Fitzhugh said.
As a whole, several recent studies have emphasized the importance of the conditioning regimen in successful transplantation for patients with SCD.
With HLA-matched sibling donors, myeloablative regimens that include antithymocyte globulin have demonstrated greater efficacy, she said.
In patients receiving a transplant from a matched unrelated donor, early use of alemtuzumab is linked to higher rates of GVHD, while ongoing studies are exploring whether abatacept reduces the risk of GVHD, she further explained.
With respect to haploidentical and unrelated umbilical cord donors, T-cell depletion and higher-intensity conditioning have been shown to reduce graft rejection rates, she said.
Dr. Fitzhugh acknowledged that long-term efficacy and safety of these novel conditioning regimens is largely unknown. Thus, ongoing follow-up is essential to monitor for potential late effects.
NHLBI-funded trials
Nancy L. DiFronzo, PhD, program director at NHLBI, explained that the agency has funded specific clinical studies evaluating allogeneic HSCT in patients with severe SCD.
“[Surprisingly], this treatment modality is [actually] quite rare, with [only] approximately 9,000 allogeneic transplants occurring in the United States each year,” she said.
One of the primary barriers to HSCT for SCD is a lack of compatible donors. Currently, fewer than 20% of sickle cell patients have a matched unrelated donor or HLA-matched sibling donor, she reported.
Another common barrier are the risks associated with the procedure, including treatment-related toxicities and death. Active participation in a clinical trial is one strategy that can mitigate these risks, she said.
The Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT CTN) is a group of transplant centers that are recognized experts in HSCT. Dr. DiFronzo explained that the consortium is cosponsored by the National Cancer Institute and NHLBI, with the goal of improving outcomes for both pediatric and adult patients with SCD undergoing HSCT.
At present, the BMT CTN has directly funded three multicenter clinical studies for SCD, including the SCURT study, which has now been completed, as well as the STRIDE2 and Haploidentical HCT trials, both of which are currently enrolling patients.
“The goal of these new approaches [being studied in these 3 trials] is cure, where individuals can live longer with a better quality of life,” Dr. DiFronzo said. “We’ve [specifically] adjusted regimens with [this goal] in mind.”
Dr. Fitzhugh and Dr. DiFronzo did not provide information on financial disclosures.
Researchers are leading several studies designed to improve hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for patients with sickle cell disease (SCD), experts at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute reported during a recent webinar.
“HSCT offers a potential cure [for SCD], which may improve quantity and quality of life [for patients],” said Courtney D. Fitzhugh, MD, a Lasker Clinical Research Scholar in the Laboratory of Early Sickle Mortality Prevention at NHLBI.
Currently, HLA-matched sibling and matched unrelated donor sources provide the best outcomes for sickle cell patients undergoing allogeneic HSCT, she explained. Alternative stem cell sources include umbilical cord blood and haploidentical donors.
Over the past 2 years, the majority of novel transplant techniques have been primarily aimed at improving conditioning regimens and lowering rates of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Recent evidence
A recent international survey found high survival rates in patients with SCD who underwent HLA-matched sibling HSCT during 1986-2013. At 5-years, overall- and event-free survival rates were 92.9% and 91.4%, respectively, with even higher rates (95% and 93%) seen in children aged younger than 16 years.
With respect to safety, the cumulative incidence rates of acute and chronic GVHD were 14.8% and 14.3%, Dr. Fitzhugh reported.
Much of the success seen with HLA-matched sibling donors is attributable to recent data demonstrating that complete transformation of patient’s bone marrow is unnecessary to illicit a curative effect.
With donor myeloid chimerism levels of at least 20%, the sickle disease phenotype can be reversed, and there’s a reduced risk of GVHD, she said.
In mouse models, researchers have found that inclusion of sirolimus in HLA-matched pretransplant conditioning regimens leads to higher levels of donor cell engraftment. As a result, some conditioning regimens now administer sirolimus (target 10-15 ng/dL) one-day prior to transplantation.
In 55 patients transplanted using this technique, overall- and event-free survival rates of 93% and 87% have been reported, with no transplant-related mortality or evidence of GVHD. Other institutions have also begun to adopt this technique, and have reported similar findings, Dr. Fitzhugh reported.
“When you [administer high-dose] chemotherapy, you don’t expect that patients are able to have children, but we are excited to report that 8 of our patients have had 13 healthy babies post transplant,” Dr. Fitzhugh said.
As a whole, several recent studies have emphasized the importance of the conditioning regimen in successful transplantation for patients with SCD.
With HLA-matched sibling donors, myeloablative regimens that include antithymocyte globulin have demonstrated greater efficacy, she said.
In patients receiving a transplant from a matched unrelated donor, early use of alemtuzumab is linked to higher rates of GVHD, while ongoing studies are exploring whether abatacept reduces the risk of GVHD, she further explained.
With respect to haploidentical and unrelated umbilical cord donors, T-cell depletion and higher-intensity conditioning have been shown to reduce graft rejection rates, she said.
Dr. Fitzhugh acknowledged that long-term efficacy and safety of these novel conditioning regimens is largely unknown. Thus, ongoing follow-up is essential to monitor for potential late effects.
NHLBI-funded trials
Nancy L. DiFronzo, PhD, program director at NHLBI, explained that the agency has funded specific clinical studies evaluating allogeneic HSCT in patients with severe SCD.
“[Surprisingly], this treatment modality is [actually] quite rare, with [only] approximately 9,000 allogeneic transplants occurring in the United States each year,” she said.
One of the primary barriers to HSCT for SCD is a lack of compatible donors. Currently, fewer than 20% of sickle cell patients have a matched unrelated donor or HLA-matched sibling donor, she reported.
Another common barrier are the risks associated with the procedure, including treatment-related toxicities and death. Active participation in a clinical trial is one strategy that can mitigate these risks, she said.
The Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT CTN) is a group of transplant centers that are recognized experts in HSCT. Dr. DiFronzo explained that the consortium is cosponsored by the National Cancer Institute and NHLBI, with the goal of improving outcomes for both pediatric and adult patients with SCD undergoing HSCT.
At present, the BMT CTN has directly funded three multicenter clinical studies for SCD, including the SCURT study, which has now been completed, as well as the STRIDE2 and Haploidentical HCT trials, both of which are currently enrolling patients.
“The goal of these new approaches [being studied in these 3 trials] is cure, where individuals can live longer with a better quality of life,” Dr. DiFronzo said. “We’ve [specifically] adjusted regimens with [this goal] in mind.”
Dr. Fitzhugh and Dr. DiFronzo did not provide information on financial disclosures.
Researchers are leading several studies designed to improve hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for patients with sickle cell disease (SCD), experts at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute reported during a recent webinar.
“HSCT offers a potential cure [for SCD], which may improve quantity and quality of life [for patients],” said Courtney D. Fitzhugh, MD, a Lasker Clinical Research Scholar in the Laboratory of Early Sickle Mortality Prevention at NHLBI.
Currently, HLA-matched sibling and matched unrelated donor sources provide the best outcomes for sickle cell patients undergoing allogeneic HSCT, she explained. Alternative stem cell sources include umbilical cord blood and haploidentical donors.
Over the past 2 years, the majority of novel transplant techniques have been primarily aimed at improving conditioning regimens and lowering rates of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
Recent evidence
A recent international survey found high survival rates in patients with SCD who underwent HLA-matched sibling HSCT during 1986-2013. At 5-years, overall- and event-free survival rates were 92.9% and 91.4%, respectively, with even higher rates (95% and 93%) seen in children aged younger than 16 years.
With respect to safety, the cumulative incidence rates of acute and chronic GVHD were 14.8% and 14.3%, Dr. Fitzhugh reported.
Much of the success seen with HLA-matched sibling donors is attributable to recent data demonstrating that complete transformation of patient’s bone marrow is unnecessary to illicit a curative effect.
With donor myeloid chimerism levels of at least 20%, the sickle disease phenotype can be reversed, and there’s a reduced risk of GVHD, she said.
In mouse models, researchers have found that inclusion of sirolimus in HLA-matched pretransplant conditioning regimens leads to higher levels of donor cell engraftment. As a result, some conditioning regimens now administer sirolimus (target 10-15 ng/dL) one-day prior to transplantation.
In 55 patients transplanted using this technique, overall- and event-free survival rates of 93% and 87% have been reported, with no transplant-related mortality or evidence of GVHD. Other institutions have also begun to adopt this technique, and have reported similar findings, Dr. Fitzhugh reported.
“When you [administer high-dose] chemotherapy, you don’t expect that patients are able to have children, but we are excited to report that 8 of our patients have had 13 healthy babies post transplant,” Dr. Fitzhugh said.
As a whole, several recent studies have emphasized the importance of the conditioning regimen in successful transplantation for patients with SCD.
With HLA-matched sibling donors, myeloablative regimens that include antithymocyte globulin have demonstrated greater efficacy, she said.
In patients receiving a transplant from a matched unrelated donor, early use of alemtuzumab is linked to higher rates of GVHD, while ongoing studies are exploring whether abatacept reduces the risk of GVHD, she further explained.
With respect to haploidentical and unrelated umbilical cord donors, T-cell depletion and higher-intensity conditioning have been shown to reduce graft rejection rates, she said.
Dr. Fitzhugh acknowledged that long-term efficacy and safety of these novel conditioning regimens is largely unknown. Thus, ongoing follow-up is essential to monitor for potential late effects.
NHLBI-funded trials
Nancy L. DiFronzo, PhD, program director at NHLBI, explained that the agency has funded specific clinical studies evaluating allogeneic HSCT in patients with severe SCD.
“[Surprisingly], this treatment modality is [actually] quite rare, with [only] approximately 9,000 allogeneic transplants occurring in the United States each year,” she said.
One of the primary barriers to HSCT for SCD is a lack of compatible donors. Currently, fewer than 20% of sickle cell patients have a matched unrelated donor or HLA-matched sibling donor, she reported.
Another common barrier are the risks associated with the procedure, including treatment-related toxicities and death. Active participation in a clinical trial is one strategy that can mitigate these risks, she said.
The Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trials Network (BMT CTN) is a group of transplant centers that are recognized experts in HSCT. Dr. DiFronzo explained that the consortium is cosponsored by the National Cancer Institute and NHLBI, with the goal of improving outcomes for both pediatric and adult patients with SCD undergoing HSCT.
At present, the BMT CTN has directly funded three multicenter clinical studies for SCD, including the SCURT study, which has now been completed, as well as the STRIDE2 and Haploidentical HCT trials, both of which are currently enrolling patients.
“The goal of these new approaches [being studied in these 3 trials] is cure, where individuals can live longer with a better quality of life,” Dr. DiFronzo said. “We’ve [specifically] adjusted regimens with [this goal] in mind.”
Dr. Fitzhugh and Dr. DiFronzo did not provide information on financial disclosures.
Several factors may affect immune suppression discontinuation after HCT
New research suggests several factors are associated with failure to discontinue immune suppression after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT).
Patients older than 50 years, those with advanced stage disease, patients with a mismatched unrelated donor, and those who received peripheral blood stem cells from an unrelated donor were less likely to discontinue immune suppression successfully, Joseph Pidala, MD, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., and colleagues reported in JAMA Oncology.
The researchers analyzed data from 827 patients in two national Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network studies (NCT00075816 and NCT00406393). These randomized, phase 3 trials enrolled patients with hematologic malignancies who received myeloablative conditioning before allogeneic HCT.
The patients’ median age at HCT was 44 years (range, less than 1 to 67 years), and 55.1% were male. The median follow-up was 72 months (range, 11-124 months).
At 5 years, 20% of patients (n = 168) had successfully discontinued immune suppression and were still alive. A total of 342 patients (41.4%) were able to stop immune suppression, but 127 of them had to resume it after developing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). There were an additional 47 patients who died or relapsed after stopping immune suppression.
The researchers identified several factors that were significantly associated with lower odds of discontinuing immune suppression and being free of GVHD, including:
- Being older than 50 years versus younger than 30 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.27; 99% confidence interval [CI], 0.14-0.50; P less than .001).
- Having a mismatched unrelated donor versus having a matched sibling (aOR, 0.37; 99% CI, 0.14-0.97; P = .008).
- Receiving peripheral blood stem cells versus bone marrow, from unrelated donors only (aOR, 0.46; 99% CI, 0.26-0.82; P less than .001).
- Having advanced stage disease versus early disease (aOR, 0.45; 99%CI, 0.23-0.86; P = .002).
The researchers also found that discontinuing immune suppression was not significantly associated with a decreased risk of relapse, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.95 (99% CI, 0.88-4.31; P = .03).
There was no significant association between acute GVHD–related variables and discontinuation of immune suppression. However, there were a few factors significantly associated with a lower likelihood of discontinuation after chronic GVHD, including:
- Current skin involvement (HR, 0.33; 99% CI, 0.14-0.80; P = .001).
- Unrelated well-matched donor versus matched sibling donor (HR, 0.29; 99% CI, 0.10-0.79; P = .001).
- Unrelated mismatched donor versus matched sibling donor (HR, 0.17; 99% CI, 0.03-0.95; P = .008).
In total, 127 patients had to resume immune suppression because of GVHD. Such failed attempts at discontinuing immune suppression were associated with receiving peripheral blood stem cells from an unrelated donor versus bone marrow from an unrelated donor, with an HR of 2.62 (99% CI, 1.30-5.29; P less than .001).
A history of acute or chronic GVHD was associated with failure to discontinue immune suppression, the researchers noted.
Lastly, the researchers developed dynamic prediction models for the probability of freedom from immune suppression and GVHD at 1, 3, and 5 years in the future. The team found that graft type, donor type, age, state history, and timing of immune suppression discontinuation were all associated with the likelihood of being free from immune suppression and GVHD at all three time points. Disease risk was only associated with freedom from immune suppression and GVHD at the 1-year mark.
The researchers said their findings must be validated in an independent cohort of patients and, after that, should be tested in a prospective trial.
The current study was funded by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Two of the researchers reported relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Pidala J et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2974.
New research suggests several factors are associated with failure to discontinue immune suppression after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT).
Patients older than 50 years, those with advanced stage disease, patients with a mismatched unrelated donor, and those who received peripheral blood stem cells from an unrelated donor were less likely to discontinue immune suppression successfully, Joseph Pidala, MD, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., and colleagues reported in JAMA Oncology.
The researchers analyzed data from 827 patients in two national Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network studies (NCT00075816 and NCT00406393). These randomized, phase 3 trials enrolled patients with hematologic malignancies who received myeloablative conditioning before allogeneic HCT.
The patients’ median age at HCT was 44 years (range, less than 1 to 67 years), and 55.1% were male. The median follow-up was 72 months (range, 11-124 months).
At 5 years, 20% of patients (n = 168) had successfully discontinued immune suppression and were still alive. A total of 342 patients (41.4%) were able to stop immune suppression, but 127 of them had to resume it after developing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). There were an additional 47 patients who died or relapsed after stopping immune suppression.
The researchers identified several factors that were significantly associated with lower odds of discontinuing immune suppression and being free of GVHD, including:
- Being older than 50 years versus younger than 30 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.27; 99% confidence interval [CI], 0.14-0.50; P less than .001).
- Having a mismatched unrelated donor versus having a matched sibling (aOR, 0.37; 99% CI, 0.14-0.97; P = .008).
- Receiving peripheral blood stem cells versus bone marrow, from unrelated donors only (aOR, 0.46; 99% CI, 0.26-0.82; P less than .001).
- Having advanced stage disease versus early disease (aOR, 0.45; 99%CI, 0.23-0.86; P = .002).
The researchers also found that discontinuing immune suppression was not significantly associated with a decreased risk of relapse, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.95 (99% CI, 0.88-4.31; P = .03).
There was no significant association between acute GVHD–related variables and discontinuation of immune suppression. However, there were a few factors significantly associated with a lower likelihood of discontinuation after chronic GVHD, including:
- Current skin involvement (HR, 0.33; 99% CI, 0.14-0.80; P = .001).
- Unrelated well-matched donor versus matched sibling donor (HR, 0.29; 99% CI, 0.10-0.79; P = .001).
- Unrelated mismatched donor versus matched sibling donor (HR, 0.17; 99% CI, 0.03-0.95; P = .008).
In total, 127 patients had to resume immune suppression because of GVHD. Such failed attempts at discontinuing immune suppression were associated with receiving peripheral blood stem cells from an unrelated donor versus bone marrow from an unrelated donor, with an HR of 2.62 (99% CI, 1.30-5.29; P less than .001).
A history of acute or chronic GVHD was associated with failure to discontinue immune suppression, the researchers noted.
Lastly, the researchers developed dynamic prediction models for the probability of freedom from immune suppression and GVHD at 1, 3, and 5 years in the future. The team found that graft type, donor type, age, state history, and timing of immune suppression discontinuation were all associated with the likelihood of being free from immune suppression and GVHD at all three time points. Disease risk was only associated with freedom from immune suppression and GVHD at the 1-year mark.
The researchers said their findings must be validated in an independent cohort of patients and, after that, should be tested in a prospective trial.
The current study was funded by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Two of the researchers reported relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Pidala J et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2974.
New research suggests several factors are associated with failure to discontinue immune suppression after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT).
Patients older than 50 years, those with advanced stage disease, patients with a mismatched unrelated donor, and those who received peripheral blood stem cells from an unrelated donor were less likely to discontinue immune suppression successfully, Joseph Pidala, MD, PhD, of Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla., and colleagues reported in JAMA Oncology.
The researchers analyzed data from 827 patients in two national Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network studies (NCT00075816 and NCT00406393). These randomized, phase 3 trials enrolled patients with hematologic malignancies who received myeloablative conditioning before allogeneic HCT.
The patients’ median age at HCT was 44 years (range, less than 1 to 67 years), and 55.1% were male. The median follow-up was 72 months (range, 11-124 months).
At 5 years, 20% of patients (n = 168) had successfully discontinued immune suppression and were still alive. A total of 342 patients (41.4%) were able to stop immune suppression, but 127 of them had to resume it after developing graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). There were an additional 47 patients who died or relapsed after stopping immune suppression.
The researchers identified several factors that were significantly associated with lower odds of discontinuing immune suppression and being free of GVHD, including:
- Being older than 50 years versus younger than 30 years (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.27; 99% confidence interval [CI], 0.14-0.50; P less than .001).
- Having a mismatched unrelated donor versus having a matched sibling (aOR, 0.37; 99% CI, 0.14-0.97; P = .008).
- Receiving peripheral blood stem cells versus bone marrow, from unrelated donors only (aOR, 0.46; 99% CI, 0.26-0.82; P less than .001).
- Having advanced stage disease versus early disease (aOR, 0.45; 99%CI, 0.23-0.86; P = .002).
The researchers also found that discontinuing immune suppression was not significantly associated with a decreased risk of relapse, with a hazard ratio (HR) of 1.95 (99% CI, 0.88-4.31; P = .03).
There was no significant association between acute GVHD–related variables and discontinuation of immune suppression. However, there were a few factors significantly associated with a lower likelihood of discontinuation after chronic GVHD, including:
- Current skin involvement (HR, 0.33; 99% CI, 0.14-0.80; P = .001).
- Unrelated well-matched donor versus matched sibling donor (HR, 0.29; 99% CI, 0.10-0.79; P = .001).
- Unrelated mismatched donor versus matched sibling donor (HR, 0.17; 99% CI, 0.03-0.95; P = .008).
In total, 127 patients had to resume immune suppression because of GVHD. Such failed attempts at discontinuing immune suppression were associated with receiving peripheral blood stem cells from an unrelated donor versus bone marrow from an unrelated donor, with an HR of 2.62 (99% CI, 1.30-5.29; P less than .001).
A history of acute or chronic GVHD was associated with failure to discontinue immune suppression, the researchers noted.
Lastly, the researchers developed dynamic prediction models for the probability of freedom from immune suppression and GVHD at 1, 3, and 5 years in the future. The team found that graft type, donor type, age, state history, and timing of immune suppression discontinuation were all associated with the likelihood of being free from immune suppression and GVHD at all three time points. Disease risk was only associated with freedom from immune suppression and GVHD at the 1-year mark.
The researchers said their findings must be validated in an independent cohort of patients and, after that, should be tested in a prospective trial.
The current study was funded by the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Two of the researchers reported relationships with more than 30 pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Pidala J et al. JAMA Oncol. 2019 Sep 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2974.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY