User login
JAK inhibitors emerge as promising alopecia treatment
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – After Brett King, MD, PhD, and his wife and collaborator, Brittany G. Craiglow, MD, published an index case of oral tofacitinib reversing alopecia universalis in a 25-year-old male patient back in 2014 (J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2988-90), they received hundreds of e-mails and phone calls from clinicians and patients.
“We also received quite a bit of media attention from around the world,” Dr. King recalled at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
After all, alopecia areata and its variants affect 1%-2% of the population and have a marked impact on health-related quality of life, with high rates of concomitant generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. “The health-related quality of life is similar to that of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, and there are no reliably effective therapies, especially for severe disease,” he said. “”
Currently available Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors include tofacitinib (Xeljanz), ruxolitinib (Jakafi), and baricitinib (Olumiant). “These medicines are not [Food and Drug Administration] approved for alopecia areata, though tofacitinib was recently approved for psoriatic arthritis, and so we have formal entry of this medicine into dermatology for the first time,” said Dr. King, who is a dermatologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Potential adverse effects of JAKs include nasopharyngitis, headache, diarrhea, elevated cholesterol, uncommonly herpes zoster, cytopenias, transaminitis, and rarely non-melanoma skin cancer, solid organ malignancy and lymphoma, and GI perforation. Tofacitinib has an FDA black box warning regarding serious infections and malignancies, and baricitinib has these plus an additional warning about thrombosis.
In an open label, two-center trial that followed the index patient report, Dr. King and his associates enrolled 66 patients aged 19-35 years who had greater than 50% scalp hair loss for at least 6 months to receive tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily for 3 months (JCI Insight. 2016; 1[15]:e89776). A primary outcome of interest was regrowth of hair as measured by the percent change in Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score. A SALT score of 100 indicates baldness, while a score of zero indicates no hair loss. Following 3 months of treatment, 32% of patients had a greater than 50% change in their SALT score, 32% had a change in the range of 5%-50%, while 36% had a change that was less than 5%.
“One of the interesting findings was that long duration of current episode of complete scalp hair loss was a negative predictor of treatment response, especially for those who have had hair loss greater than 10 years,” Dr. King said. Adverse events were “pretty bland,” with the most common being upper respiratory infection (17%), headache (8%), abdominal pain (8%), and acne (8%). Weight gain occurred in 1.5% of patients.
Next, Dr. King and colleagues reviewed the records of 90 patients aged 18 years or older who were treated with tofacitinib for at least 4 months (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76[1]:22-8). Patients had greater than 40% scalp hair loss, and the tofacitinib dose was up to 10 mg per day at the discretion of the physician. “About 43% of patients were treated with tofacitinib 5 mg” twice daily, Dr. King said. “Other patients had higher doses or the addition of prednisone for three doses to see if that would help.”
After treatment, 20% of patients had a greater than 90% change in their SALT score (complete scalp hair regrowth), while 38.4% had a change that ranged from 51%-90%. At the same time, 18% had a change in their SALT score that ranged from 6%-50%, while 23% had a change that was 5% or less. As observed in the earlier trial, researchers saw a negative correlation between duration of current episode of hair loss and latest percent change in SALT score.
“We believe that you have to catch people before they get to more than 10 years of complete scalp hair loss,” Dr. King said. “This is important for the pediatric age group. I just saw somebody who’s 13, and they’ve been bald for 8 years. You might make the argument that this person deserves treatment, at least for a period of time long enough to regrow their hair in order to reset the clock.”
The most common adverse events were acne and weight gain.
In a separate analysis, Dr. King, Dr. Craiglow, and Lucy Y. Liu, evaluated the use of tofacitinib for at least 2 months in 13 alopecia areata patients aged 12-17 years (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76[1]:29-32). They limited the analysis to those who had greater than 20% scalp hair loss, alopecia totalis, or alopecia universalis that was stable or worsening for 6 months or longer. Of the 13 patients, 9 (69%) were responders. Of the four non-responders, one had a very long duration of baldness. The percent change in SALT score was 93% overall, including 100% in the responder group over a median of 5 months and just 1% in the non-responder group over a median of 4 months. “This does not work every time,” Dr. King said.
While some preliminary studies of topical JAK inhibitors for alopecia areata show promise, it remains unclear if this approach will translate in a clinically meaningful way, he said. Clinical trials are currently under way.
Dr. King disclosed that he has received honoraria or consulting fees from Aclaris Therapeutics, Celgene, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Dermavant Sciences. He has also received funding support from The Ranjini and Ajay Poddar Resource Fund for Dermatologic Diseases Research.
dbrunk@mdedge.com
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – After Brett King, MD, PhD, and his wife and collaborator, Brittany G. Craiglow, MD, published an index case of oral tofacitinib reversing alopecia universalis in a 25-year-old male patient back in 2014 (J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2988-90), they received hundreds of e-mails and phone calls from clinicians and patients.
“We also received quite a bit of media attention from around the world,” Dr. King recalled at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
After all, alopecia areata and its variants affect 1%-2% of the population and have a marked impact on health-related quality of life, with high rates of concomitant generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. “The health-related quality of life is similar to that of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, and there are no reliably effective therapies, especially for severe disease,” he said. “”
Currently available Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors include tofacitinib (Xeljanz), ruxolitinib (Jakafi), and baricitinib (Olumiant). “These medicines are not [Food and Drug Administration] approved for alopecia areata, though tofacitinib was recently approved for psoriatic arthritis, and so we have formal entry of this medicine into dermatology for the first time,” said Dr. King, who is a dermatologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Potential adverse effects of JAKs include nasopharyngitis, headache, diarrhea, elevated cholesterol, uncommonly herpes zoster, cytopenias, transaminitis, and rarely non-melanoma skin cancer, solid organ malignancy and lymphoma, and GI perforation. Tofacitinib has an FDA black box warning regarding serious infections and malignancies, and baricitinib has these plus an additional warning about thrombosis.
In an open label, two-center trial that followed the index patient report, Dr. King and his associates enrolled 66 patients aged 19-35 years who had greater than 50% scalp hair loss for at least 6 months to receive tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily for 3 months (JCI Insight. 2016; 1[15]:e89776). A primary outcome of interest was regrowth of hair as measured by the percent change in Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score. A SALT score of 100 indicates baldness, while a score of zero indicates no hair loss. Following 3 months of treatment, 32% of patients had a greater than 50% change in their SALT score, 32% had a change in the range of 5%-50%, while 36% had a change that was less than 5%.
“One of the interesting findings was that long duration of current episode of complete scalp hair loss was a negative predictor of treatment response, especially for those who have had hair loss greater than 10 years,” Dr. King said. Adverse events were “pretty bland,” with the most common being upper respiratory infection (17%), headache (8%), abdominal pain (8%), and acne (8%). Weight gain occurred in 1.5% of patients.
Next, Dr. King and colleagues reviewed the records of 90 patients aged 18 years or older who were treated with tofacitinib for at least 4 months (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76[1]:22-8). Patients had greater than 40% scalp hair loss, and the tofacitinib dose was up to 10 mg per day at the discretion of the physician. “About 43% of patients were treated with tofacitinib 5 mg” twice daily, Dr. King said. “Other patients had higher doses or the addition of prednisone for three doses to see if that would help.”
After treatment, 20% of patients had a greater than 90% change in their SALT score (complete scalp hair regrowth), while 38.4% had a change that ranged from 51%-90%. At the same time, 18% had a change in their SALT score that ranged from 6%-50%, while 23% had a change that was 5% or less. As observed in the earlier trial, researchers saw a negative correlation between duration of current episode of hair loss and latest percent change in SALT score.
“We believe that you have to catch people before they get to more than 10 years of complete scalp hair loss,” Dr. King said. “This is important for the pediatric age group. I just saw somebody who’s 13, and they’ve been bald for 8 years. You might make the argument that this person deserves treatment, at least for a period of time long enough to regrow their hair in order to reset the clock.”
The most common adverse events were acne and weight gain.
In a separate analysis, Dr. King, Dr. Craiglow, and Lucy Y. Liu, evaluated the use of tofacitinib for at least 2 months in 13 alopecia areata patients aged 12-17 years (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76[1]:29-32). They limited the analysis to those who had greater than 20% scalp hair loss, alopecia totalis, or alopecia universalis that was stable or worsening for 6 months or longer. Of the 13 patients, 9 (69%) were responders. Of the four non-responders, one had a very long duration of baldness. The percent change in SALT score was 93% overall, including 100% in the responder group over a median of 5 months and just 1% in the non-responder group over a median of 4 months. “This does not work every time,” Dr. King said.
While some preliminary studies of topical JAK inhibitors for alopecia areata show promise, it remains unclear if this approach will translate in a clinically meaningful way, he said. Clinical trials are currently under way.
Dr. King disclosed that he has received honoraria or consulting fees from Aclaris Therapeutics, Celgene, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Dermavant Sciences. He has also received funding support from The Ranjini and Ajay Poddar Resource Fund for Dermatologic Diseases Research.
dbrunk@mdedge.com
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – After Brett King, MD, PhD, and his wife and collaborator, Brittany G. Craiglow, MD, published an index case of oral tofacitinib reversing alopecia universalis in a 25-year-old male patient back in 2014 (J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:2988-90), they received hundreds of e-mails and phone calls from clinicians and patients.
“We also received quite a bit of media attention from around the world,” Dr. King recalled at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
After all, alopecia areata and its variants affect 1%-2% of the population and have a marked impact on health-related quality of life, with high rates of concomitant generalized anxiety disorder and major depressive disorder. “The health-related quality of life is similar to that of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, and there are no reliably effective therapies, especially for severe disease,” he said. “”
Currently available Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors include tofacitinib (Xeljanz), ruxolitinib (Jakafi), and baricitinib (Olumiant). “These medicines are not [Food and Drug Administration] approved for alopecia areata, though tofacitinib was recently approved for psoriatic arthritis, and so we have formal entry of this medicine into dermatology for the first time,” said Dr. King, who is a dermatologist at Yale University, New Haven, Conn.
Potential adverse effects of JAKs include nasopharyngitis, headache, diarrhea, elevated cholesterol, uncommonly herpes zoster, cytopenias, transaminitis, and rarely non-melanoma skin cancer, solid organ malignancy and lymphoma, and GI perforation. Tofacitinib has an FDA black box warning regarding serious infections and malignancies, and baricitinib has these plus an additional warning about thrombosis.
In an open label, two-center trial that followed the index patient report, Dr. King and his associates enrolled 66 patients aged 19-35 years who had greater than 50% scalp hair loss for at least 6 months to receive tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily for 3 months (JCI Insight. 2016; 1[15]:e89776). A primary outcome of interest was regrowth of hair as measured by the percent change in Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) score. A SALT score of 100 indicates baldness, while a score of zero indicates no hair loss. Following 3 months of treatment, 32% of patients had a greater than 50% change in their SALT score, 32% had a change in the range of 5%-50%, while 36% had a change that was less than 5%.
“One of the interesting findings was that long duration of current episode of complete scalp hair loss was a negative predictor of treatment response, especially for those who have had hair loss greater than 10 years,” Dr. King said. Adverse events were “pretty bland,” with the most common being upper respiratory infection (17%), headache (8%), abdominal pain (8%), and acne (8%). Weight gain occurred in 1.5% of patients.
Next, Dr. King and colleagues reviewed the records of 90 patients aged 18 years or older who were treated with tofacitinib for at least 4 months (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76[1]:22-8). Patients had greater than 40% scalp hair loss, and the tofacitinib dose was up to 10 mg per day at the discretion of the physician. “About 43% of patients were treated with tofacitinib 5 mg” twice daily, Dr. King said. “Other patients had higher doses or the addition of prednisone for three doses to see if that would help.”
After treatment, 20% of patients had a greater than 90% change in their SALT score (complete scalp hair regrowth), while 38.4% had a change that ranged from 51%-90%. At the same time, 18% had a change in their SALT score that ranged from 6%-50%, while 23% had a change that was 5% or less. As observed in the earlier trial, researchers saw a negative correlation between duration of current episode of hair loss and latest percent change in SALT score.
“We believe that you have to catch people before they get to more than 10 years of complete scalp hair loss,” Dr. King said. “This is important for the pediatric age group. I just saw somebody who’s 13, and they’ve been bald for 8 years. You might make the argument that this person deserves treatment, at least for a period of time long enough to regrow their hair in order to reset the clock.”
The most common adverse events were acne and weight gain.
In a separate analysis, Dr. King, Dr. Craiglow, and Lucy Y. Liu, evaluated the use of tofacitinib for at least 2 months in 13 alopecia areata patients aged 12-17 years (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76[1]:29-32). They limited the analysis to those who had greater than 20% scalp hair loss, alopecia totalis, or alopecia universalis that was stable or worsening for 6 months or longer. Of the 13 patients, 9 (69%) were responders. Of the four non-responders, one had a very long duration of baldness. The percent change in SALT score was 93% overall, including 100% in the responder group over a median of 5 months and just 1% in the non-responder group over a median of 4 months. “This does not work every time,” Dr. King said.
While some preliminary studies of topical JAK inhibitors for alopecia areata show promise, it remains unclear if this approach will translate in a clinically meaningful way, he said. Clinical trials are currently under way.
Dr. King disclosed that he has received honoraria or consulting fees from Aclaris Therapeutics, Celgene, Concert Pharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and Dermavant Sciences. He has also received funding support from The Ranjini and Ajay Poddar Resource Fund for Dermatologic Diseases Research.
dbrunk@mdedge.com
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE SPD ANNUAL MEETING
So it’s pediatric onychomycosis. Now what?
CHICAGO – Though research shows that nail fungus occurs in just 0.3% of pediatric patients in the United States, that’s not what Sheila Friedlander, MD, is seeing in her southern California practice, where it’s not uncommon to see children whose nails, toe nails in particular, have fungal involvement.
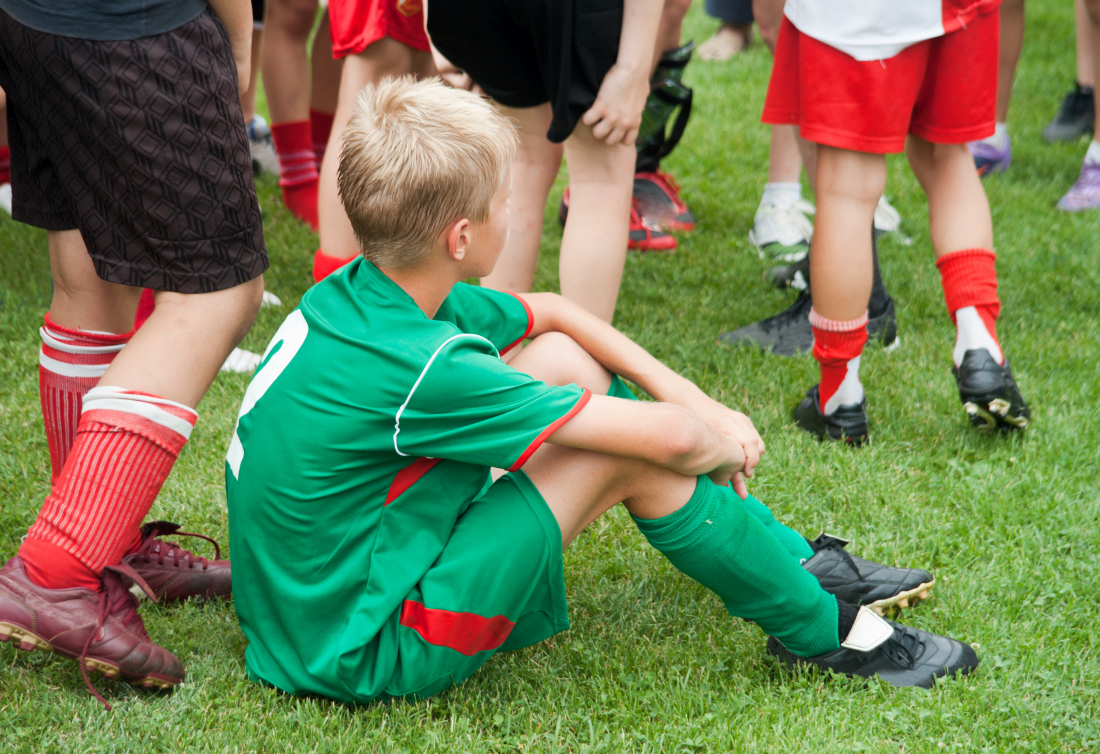
said Dr. Friedlander during a nail-focused session at the annual summer meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Dr. Friedlander, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, said that she suspects that more participation in organized sports at a young age may be contributing to the increase, with occlusive sports footwear replacing bare feet or sandals for more hours of the day, presenting more opportunities for toenail trauma in sports such as soccer.
When making the clinical call about a nail problem, bear in mind that the younger the child, the less likely a nail problem is fungal, Dr. Friedlander noted. “Little children are much less likely than older children to have nail fungus. Pediatric nails are thinner, and they are faster growing, with better blood supply to the matrix.”
And if frank onychomadesis is observed, think about the time of year, and ask about recent fevers and rashes, because coxsackievirus may be the culprit. “Be not afraid, and look everywhere if the nail is confusing to you,” she said. In all ages, the diagnosis is primarily clinical, “but I culture them, I ‘PAS’ [periodic acid-Schiff stain] them, too. If you do both, you’ll increase your yield,” Dr. Friedlander said, adding, “the beauty of PAS is you can use it to give your families an answer very soon.”
Once you’ve established that fungus is to blame for a nail problem, there’s a conundrum: There are no Food and Drug Administration-approved therapies, either topical or systemic, for pediatric onychomycosis, Dr. Friedlander said. She, along with coauthors and first author Aditya Gupta, MD, of Mediprobe Research, London, Ontario, Canada, recently published an article reviewing the safety and efficacy of antifungal agents in this age group (Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jun 26. doi: 10.1111/pde.13561).
Reviewing information available in the United States and Canada, Dr. Friedlander and her coauthors came up with three topical and four oral options for children, along with recommendations for dosage and duration.
In response to an audience question about the use of topical antifungal treatment for nail involvement, Dr. Friedlander responded, “I think topicals would be great for kids, but it’s for kids where there is no nail matrix involvement. Also, cost is a problem. Nobody will cover it. But some families are willing to do this to avoid systemic therapy,” and if the family budget can accommodate a topical choice, it’s a logical option, she said, noting that partial reimbursement via a coupon system is available from some pharmaceutical companies.
Where appropriate, ciclopirox 8%, efinaconazole 10%, and tavaborole 5% can each be considered. Dr. Friedlander cited one study she coauthored, which reported that 70% of pediatric participants with nonmatrix onychomycosis saw effective treatment, with a 71% mycological cure rate (P = .03), after 32 weeks of treatment with ciclopirox lacquer versus vehicle (Pediatr Dermatol. 2013 May-Jun;30[3]:316-22).
Systemic therapies – which, when studied, have been given at tinea capitis doses – could include griseofulvin, terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole.
In terms of oral options, Dr. Friedlander said, griseofulvin has some practical limitations. While prolonged treatment is required in any case, terbinafine may produce results in about 3 months, whereas griseofulvin may require up to 9 months of therapy. “I always try to use terbinafine … griseofulvin takes a year and a day,” she said.
She also shared some tips to improve pediatric adherence with oral antifungals: “You can tell parents to crush terbinafine tablets and mix in peanut butter or applesauce to improve adherence. Griseofulvin can be flavored by the pharmacy, but volumes are big with griseofulvin, so it’s a challenge to get kids to take it all,” she said.
Dr. Friedlander reported that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
koakes@mdedge.com
CHICAGO – Though research shows that nail fungus occurs in just 0.3% of pediatric patients in the United States, that’s not what Sheila Friedlander, MD, is seeing in her southern California practice, where it’s not uncommon to see children whose nails, toe nails in particular, have fungal involvement.
said Dr. Friedlander during a nail-focused session at the annual summer meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Dr. Friedlander, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, said that she suspects that more participation in organized sports at a young age may be contributing to the increase, with occlusive sports footwear replacing bare feet or sandals for more hours of the day, presenting more opportunities for toenail trauma in sports such as soccer.
When making the clinical call about a nail problem, bear in mind that the younger the child, the less likely a nail problem is fungal, Dr. Friedlander noted. “Little children are much less likely than older children to have nail fungus. Pediatric nails are thinner, and they are faster growing, with better blood supply to the matrix.”
And if frank onychomadesis is observed, think about the time of year, and ask about recent fevers and rashes, because coxsackievirus may be the culprit. “Be not afraid, and look everywhere if the nail is confusing to you,” she said. In all ages, the diagnosis is primarily clinical, “but I culture them, I ‘PAS’ [periodic acid-Schiff stain] them, too. If you do both, you’ll increase your yield,” Dr. Friedlander said, adding, “the beauty of PAS is you can use it to give your families an answer very soon.”
Once you’ve established that fungus is to blame for a nail problem, there’s a conundrum: There are no Food and Drug Administration-approved therapies, either topical or systemic, for pediatric onychomycosis, Dr. Friedlander said. She, along with coauthors and first author Aditya Gupta, MD, of Mediprobe Research, London, Ontario, Canada, recently published an article reviewing the safety and efficacy of antifungal agents in this age group (Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jun 26. doi: 10.1111/pde.13561).
Reviewing information available in the United States and Canada, Dr. Friedlander and her coauthors came up with three topical and four oral options for children, along with recommendations for dosage and duration.
In response to an audience question about the use of topical antifungal treatment for nail involvement, Dr. Friedlander responded, “I think topicals would be great for kids, but it’s for kids where there is no nail matrix involvement. Also, cost is a problem. Nobody will cover it. But some families are willing to do this to avoid systemic therapy,” and if the family budget can accommodate a topical choice, it’s a logical option, she said, noting that partial reimbursement via a coupon system is available from some pharmaceutical companies.
Where appropriate, ciclopirox 8%, efinaconazole 10%, and tavaborole 5% can each be considered. Dr. Friedlander cited one study she coauthored, which reported that 70% of pediatric participants with nonmatrix onychomycosis saw effective treatment, with a 71% mycological cure rate (P = .03), after 32 weeks of treatment with ciclopirox lacquer versus vehicle (Pediatr Dermatol. 2013 May-Jun;30[3]:316-22).
Systemic therapies – which, when studied, have been given at tinea capitis doses – could include griseofulvin, terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole.
In terms of oral options, Dr. Friedlander said, griseofulvin has some practical limitations. While prolonged treatment is required in any case, terbinafine may produce results in about 3 months, whereas griseofulvin may require up to 9 months of therapy. “I always try to use terbinafine … griseofulvin takes a year and a day,” she said.
She also shared some tips to improve pediatric adherence with oral antifungals: “You can tell parents to crush terbinafine tablets and mix in peanut butter or applesauce to improve adherence. Griseofulvin can be flavored by the pharmacy, but volumes are big with griseofulvin, so it’s a challenge to get kids to take it all,” she said.
Dr. Friedlander reported that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
koakes@mdedge.com
CHICAGO – Though research shows that nail fungus occurs in just 0.3% of pediatric patients in the United States, that’s not what Sheila Friedlander, MD, is seeing in her southern California practice, where it’s not uncommon to see children whose nails, toe nails in particular, have fungal involvement.
said Dr. Friedlander during a nail-focused session at the annual summer meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology. Dr. Friedlander, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California San Diego and Rady Children’s Hospital, said that she suspects that more participation in organized sports at a young age may be contributing to the increase, with occlusive sports footwear replacing bare feet or sandals for more hours of the day, presenting more opportunities for toenail trauma in sports such as soccer.
When making the clinical call about a nail problem, bear in mind that the younger the child, the less likely a nail problem is fungal, Dr. Friedlander noted. “Little children are much less likely than older children to have nail fungus. Pediatric nails are thinner, and they are faster growing, with better blood supply to the matrix.”
And if frank onychomadesis is observed, think about the time of year, and ask about recent fevers and rashes, because coxsackievirus may be the culprit. “Be not afraid, and look everywhere if the nail is confusing to you,” she said. In all ages, the diagnosis is primarily clinical, “but I culture them, I ‘PAS’ [periodic acid-Schiff stain] them, too. If you do both, you’ll increase your yield,” Dr. Friedlander said, adding, “the beauty of PAS is you can use it to give your families an answer very soon.”
Once you’ve established that fungus is to blame for a nail problem, there’s a conundrum: There are no Food and Drug Administration-approved therapies, either topical or systemic, for pediatric onychomycosis, Dr. Friedlander said. She, along with coauthors and first author Aditya Gupta, MD, of Mediprobe Research, London, Ontario, Canada, recently published an article reviewing the safety and efficacy of antifungal agents in this age group (Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jun 26. doi: 10.1111/pde.13561).
Reviewing information available in the United States and Canada, Dr. Friedlander and her coauthors came up with three topical and four oral options for children, along with recommendations for dosage and duration.
In response to an audience question about the use of topical antifungal treatment for nail involvement, Dr. Friedlander responded, “I think topicals would be great for kids, but it’s for kids where there is no nail matrix involvement. Also, cost is a problem. Nobody will cover it. But some families are willing to do this to avoid systemic therapy,” and if the family budget can accommodate a topical choice, it’s a logical option, she said, noting that partial reimbursement via a coupon system is available from some pharmaceutical companies.
Where appropriate, ciclopirox 8%, efinaconazole 10%, and tavaborole 5% can each be considered. Dr. Friedlander cited one study she coauthored, which reported that 70% of pediatric participants with nonmatrix onychomycosis saw effective treatment, with a 71% mycological cure rate (P = .03), after 32 weeks of treatment with ciclopirox lacquer versus vehicle (Pediatr Dermatol. 2013 May-Jun;30[3]:316-22).
Systemic therapies – which, when studied, have been given at tinea capitis doses – could include griseofulvin, terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole.
In terms of oral options, Dr. Friedlander said, griseofulvin has some practical limitations. While prolonged treatment is required in any case, terbinafine may produce results in about 3 months, whereas griseofulvin may require up to 9 months of therapy. “I always try to use terbinafine … griseofulvin takes a year and a day,” she said.
She also shared some tips to improve pediatric adherence with oral antifungals: “You can tell parents to crush terbinafine tablets and mix in peanut butter or applesauce to improve adherence. Griseofulvin can be flavored by the pharmacy, but volumes are big with griseofulvin, so it’s a challenge to get kids to take it all,” she said.
Dr. Friedlander reported that she had no relevant financial disclosures.
koakes@mdedge.com
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SUMMER AAD 2018
Alopecia areata linked to mental health disorders
Alopecia areata is associated with greater frequency of mental health disorders, according to a new analysis of U.S. hospitalizations.
Specifically, the analysis found, alopecia areata patients are at risk for any mental health disorder, anxiety disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, dementia, mood disorders, personality disorders, and suicide or intentionally self-inflicted injury. The report was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The researchers worked with 87,053,155 adult and child records from the 2002-2012 National Inpatient Sample, which represents 20% of U.S. hospitalizations.
Overall, 5,605 patients had alopecia areata, which was the secondary diagnosis more than 99% of the time. Compared with inpatients without alopecia areata, those with the disorder were more likely to be younger (42.2 vs. 47.9 years; P less than .0001), female (61.7% vs. 58.6%; P = .0297), and uninsured (8.1% vs. 5.5%; P less than .0001). In addition, inpatients with alopecia areata had a greater frequency of mental health disorders (32.8% vs. 20.0%; P less than .0001) and were more likely to have a primary mental health diagnosis (5.5% vs. 2.2%; P less than .0001), reported Vivek Singam of Northwestern University, Chicago, and his associates.
Among 15 mental health or classes of disorders examined, alopecia areata patients were at greater risk in 13 of them. The only exceptions were delirium/dementia/amnestic/cognitive disorders and disorders diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence.
Alopecia areata patients with a mental health disorder had a mean hospital stay of 6.0 days (95% confidence interval, 5.4.-6.6) and hospitalization cost of $11,907 (95% CI, $10,312-$13,503).
Previous studies had shown similar relationships. However, previous studies showed lower risk of alopecia areata and schizophrenia and no increased risk of ADHD, compared with the current study’s findings. The authors could offer no explanation for those differences.
The strengths of the current analysis include its use of a large-scale, nationally representative cohort and its large sample size, as well its inclusion of a broad range of mental health disorders. Because of its cross-sectional design, the study could not establish the temporal relationship between alopecia areata and mental health disorders.
It is unclear whether psychosocial stress might cause or exacerbate alopecia areata, or whether alopecia areata can lead to or worsen mental health disorders.
The researchers called for additional studies to understand this relationship and potential mechanisms.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Dermatology Foundation funded the study. The researchers declared having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Singam V et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Aug 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.044.
Alopecia areata is associated with greater frequency of mental health disorders, according to a new analysis of U.S. hospitalizations.
Specifically, the analysis found, alopecia areata patients are at risk for any mental health disorder, anxiety disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, dementia, mood disorders, personality disorders, and suicide or intentionally self-inflicted injury. The report was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The researchers worked with 87,053,155 adult and child records from the 2002-2012 National Inpatient Sample, which represents 20% of U.S. hospitalizations.
Overall, 5,605 patients had alopecia areata, which was the secondary diagnosis more than 99% of the time. Compared with inpatients without alopecia areata, those with the disorder were more likely to be younger (42.2 vs. 47.9 years; P less than .0001), female (61.7% vs. 58.6%; P = .0297), and uninsured (8.1% vs. 5.5%; P less than .0001). In addition, inpatients with alopecia areata had a greater frequency of mental health disorders (32.8% vs. 20.0%; P less than .0001) and were more likely to have a primary mental health diagnosis (5.5% vs. 2.2%; P less than .0001), reported Vivek Singam of Northwestern University, Chicago, and his associates.
Among 15 mental health or classes of disorders examined, alopecia areata patients were at greater risk in 13 of them. The only exceptions were delirium/dementia/amnestic/cognitive disorders and disorders diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence.
Alopecia areata patients with a mental health disorder had a mean hospital stay of 6.0 days (95% confidence interval, 5.4.-6.6) and hospitalization cost of $11,907 (95% CI, $10,312-$13,503).
Previous studies had shown similar relationships. However, previous studies showed lower risk of alopecia areata and schizophrenia and no increased risk of ADHD, compared with the current study’s findings. The authors could offer no explanation for those differences.
The strengths of the current analysis include its use of a large-scale, nationally representative cohort and its large sample size, as well its inclusion of a broad range of mental health disorders. Because of its cross-sectional design, the study could not establish the temporal relationship between alopecia areata and mental health disorders.
It is unclear whether psychosocial stress might cause or exacerbate alopecia areata, or whether alopecia areata can lead to or worsen mental health disorders.
The researchers called for additional studies to understand this relationship and potential mechanisms.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Dermatology Foundation funded the study. The researchers declared having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Singam V et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Aug 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.044.
Alopecia areata is associated with greater frequency of mental health disorders, according to a new analysis of U.S. hospitalizations.
Specifically, the analysis found, alopecia areata patients are at risk for any mental health disorder, anxiety disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, dementia, mood disorders, personality disorders, and suicide or intentionally self-inflicted injury. The report was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
The researchers worked with 87,053,155 adult and child records from the 2002-2012 National Inpatient Sample, which represents 20% of U.S. hospitalizations.
Overall, 5,605 patients had alopecia areata, which was the secondary diagnosis more than 99% of the time. Compared with inpatients without alopecia areata, those with the disorder were more likely to be younger (42.2 vs. 47.9 years; P less than .0001), female (61.7% vs. 58.6%; P = .0297), and uninsured (8.1% vs. 5.5%; P less than .0001). In addition, inpatients with alopecia areata had a greater frequency of mental health disorders (32.8% vs. 20.0%; P less than .0001) and were more likely to have a primary mental health diagnosis (5.5% vs. 2.2%; P less than .0001), reported Vivek Singam of Northwestern University, Chicago, and his associates.
Among 15 mental health or classes of disorders examined, alopecia areata patients were at greater risk in 13 of them. The only exceptions were delirium/dementia/amnestic/cognitive disorders and disorders diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence.
Alopecia areata patients with a mental health disorder had a mean hospital stay of 6.0 days (95% confidence interval, 5.4.-6.6) and hospitalization cost of $11,907 (95% CI, $10,312-$13,503).
Previous studies had shown similar relationships. However, previous studies showed lower risk of alopecia areata and schizophrenia and no increased risk of ADHD, compared with the current study’s findings. The authors could offer no explanation for those differences.
The strengths of the current analysis include its use of a large-scale, nationally representative cohort and its large sample size, as well its inclusion of a broad range of mental health disorders. Because of its cross-sectional design, the study could not establish the temporal relationship between alopecia areata and mental health disorders.
It is unclear whether psychosocial stress might cause or exacerbate alopecia areata, or whether alopecia areata can lead to or worsen mental health disorders.
The researchers called for additional studies to understand this relationship and potential mechanisms.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Dermatology Foundation funded the study. The researchers declared having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Singam V et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Aug 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.044.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Key clinical point: Alopecia areata patients should be monitored closely for mental health disorders.
Major finding: Overall, 32.8% of hospitalized alopecia areata patients had a mental health disorder, compared with 20.0% of controls.
Study details: Retrospective analysis of 87,053,155 U.S. adults and children.
Disclosures: The Agency for Healthcare Research & Quality and the Dermatology Foundation funded the study. The researchers declared having no conflicts of interest.
Source: Singam V et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Aug 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.07.044.
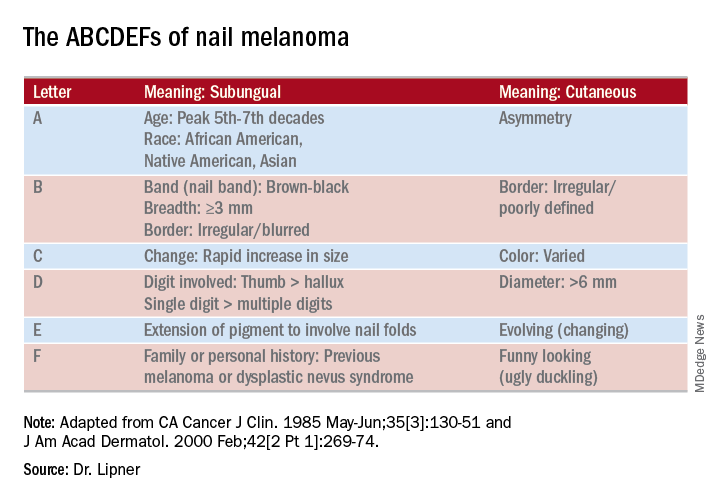
Longitudinal melanonychia: the good, the bad, and the confusing
CHICAGO – A discolored nail can give even seasoned dermatologists pause: Is the cause exogenous? Fungal or bacterial, perhaps? Could it be a subungual melanoma? Should it be followed, clipped, or biopsied? of the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
The session came after a recent nationwide survey performed by Dr. Lipner and her collaborators who asked dermatologists at different practice stages how confident they were in the diagnosis and management of melanonychia. “On the whole, they were not very confident at all,” said Dr. Lipner, director of the nail division at Cornell University, New York.
Of 142 dermatology residents, as well as 58 junior and 199 senior attending dermatologists, just 18.2% performed nail exams at each visit, and most (58%) only looked at nails during the total body skin exam. Over half (62%) of resident physicians reported feeling not confident about melanonychia diagnosis and management, while that figure dropped to 8.6% for senior attending physicians. Still, most senior physicians (64.3%) were just “fairly confident” in their melanonychia skills (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 May;76[5]:994-6).
Tools of the trade
Dermoscopy can be an invaluable tool for determining the cause of longitudinal melanonychia (LM). “Contact dermoscopy is helpful, so I always have ultrasound gel available,” Dr. Lipner said. “The gel makes the nail more of a flat surface,” which makes accurate viewing easier. Other useful tools include a double-action nail clipper, which, she said, is a worthwhile investment.
Because patients who are concerned about one of their nails will often come to their appointment with nail polish still on the other nails, Dr. Lipner always has polish remover pads available in the office. It’s important to be able to see all nails, she said, but she and her collaborators, including first author Pierre Halteh, MD, who was then a medical student at Cornell, discovered from their survey that “few physicians (32/402; 8%) asked their patients to remove nail polish at every visit.”
Nonmelanocytic causes of LM
Longitudinal melanonychias can have a nonmelanocytic etiology, which can range from subungual hematomas to pseudomonas and fungal infections to exogenous pigment.
Overall, subungual hematomas are the most common cause of melanonychia, although longitudinal hematomas are not commonly seen. The more remote the causative trauma, the darker the subungual discoloration, Dr. Lipner said. “Dermoscopy is very helpful” for subungual hematomas, which will usually show a homogeneous pattern, although “you can also see peripheral fadings, streaks, and periungual hemorrhages,” she added.
It is important to monitor these patients “because melanomas can bleed,” she said. In-office photography, or even pictures taken by patients, can be used to track the hematoma to resolution.
When thinking about exogenous sources of pigment, in addition to clues from the history, a tip-off can be that the proximal nail fold is also discolored, Dr. Lipner pointed out. A wide variety of common and less-common culprits may crop up, including from tar, tobacco, henna and other hair dyes, potassium permanganate, and even newspaper print, she said. With an exogenous source, careful clinical and dermoscopic examination may show that the pigment does not extend all the way proximally to the lunula, although it may follow the outline of the proximal nail fold.
When fungus is the cause of LM, the band is often wider proximally and tapers distally, Dr. Lipner noted. While Trichophyton rubrum var. nigricans is a known culprit, nondermatophytes, such as Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, can also cause an LM that often runs along the proximal and lateral nail folds. “To make the diagnosis, sending a clipping to the dermatopathologist is helpful,” she said. Hyphae can often be seen on staining and culture, she said. Polymerase chain reaction “is also possible and very helpful for these nondermatophytes.”
Bacterial colonization of the nail bed can be a cause of LM. Pathogens can include Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which will often show the characteristic greenish tint. Klebsiella and Proteus species may result in more of a grayish-black discoloration. A history of wet work, such as farming and other agricultural and dairy occupations, as well as housekeeping work, increases the risk for bacterial colonization.
Commonly, a bacterial etiology will result in discoloration beginning at the lateral nail fold or at the juncture of the proximal and lateral nail folds. Dermoscopy will show irregular fading of the discoloration toward the medial aspect of the nail, and gram staining of affected clippings will show gram-negative rods.
Melanocytic causes of longitudinal melanonychia
The melanotic macule, sometimes called melanocytic activation, is the most common subtype of melanin-derived LM in adults, Dr. Lipner said. This benign condition results from increased melanin synthesis without an increase in the number of melanocytes, which will be evident on histopathologic examination of the nail bed. Any of a variety of triggers can provoke the increased pigment, which can range from endocrine disruptions to inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis, to trauma (including nail biting or habit tics).
Pregnancy, normal ethnic variation, and chemotherapy administration are all also associated with melanotic macules. In any case, dermoscopy will show an LM characterized by a grayish background that contains darker grayish lines.
Melanocyte hyperplasia can also cause melanonychia, in which case the trick is sorting out which cases are benign and which are malignant, Dr. Lipner noted. And getting the diagnosis right in a timely fashion matters: “Ideally, we want to catch these melanomas in in situ stages where we can preserve the digit,” she said. “It’s been shown that there is no survival benefit for amputation versus en bloc excision for nail melanomas in situ.”
Nail matrix nevi are the most common cause of LM in children, Dr. Lipner said. Here, dermoscopy shows a brown background with brown lines, with regular color, thickness, and spacing.
On examination of a nail with a melanoma, “typically, we see features suggestive of melanoma but really no pathognomonic features,” she commented. Some signs that should prompt concern and a more thorough investigation, she said, include a dark brown or black band of LM; lack of homogeneity, such as the presence of lines of different colors; blurring of the borders of the pigmentation; and a triangular or wavering outline. Changes in the nail, such as fissuring or splitting, also are worrying, as is any associated discoloration of the periungual skin.
Dermoscopy may confirm the irregularity of the pigmentation pattern and show irregularly colored and spaced lines of varying thicknesses within the pigmented band. An LM caused by melanoma may also be marked by loss of parallelism within the pigmented band.
She pointed out that these concerning characteristics have been encapsulated in a mnemonic, first created in 2000, that’s meant to mirror the ABCDs of nonnail melanoma detection (J Am Acad Dermatol. Feb 2000;42[2 Pt 1]:269-74). Her survey found that overall, just one in four (24.8%) of respondents knew of the mnemonic for subungual melanomas.
Dr. Lipner reported that she has received research support from MOE Medical Devices and has served as a consultant to BAKO Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Lipner S. Summer AAD 2018, Presentation F004.
CHICAGO – A discolored nail can give even seasoned dermatologists pause: Is the cause exogenous? Fungal or bacterial, perhaps? Could it be a subungual melanoma? Should it be followed, clipped, or biopsied? of the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
The session came after a recent nationwide survey performed by Dr. Lipner and her collaborators who asked dermatologists at different practice stages how confident they were in the diagnosis and management of melanonychia. “On the whole, they were not very confident at all,” said Dr. Lipner, director of the nail division at Cornell University, New York.
Of 142 dermatology residents, as well as 58 junior and 199 senior attending dermatologists, just 18.2% performed nail exams at each visit, and most (58%) only looked at nails during the total body skin exam. Over half (62%) of resident physicians reported feeling not confident about melanonychia diagnosis and management, while that figure dropped to 8.6% for senior attending physicians. Still, most senior physicians (64.3%) were just “fairly confident” in their melanonychia skills (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 May;76[5]:994-6).
Tools of the trade

Dermoscopy can be an invaluable tool for determining the cause of longitudinal melanonychia (LM). “Contact dermoscopy is helpful, so I always have ultrasound gel available,” Dr. Lipner said. “The gel makes the nail more of a flat surface,” which makes accurate viewing easier. Other useful tools include a double-action nail clipper, which, she said, is a worthwhile investment.
Because patients who are concerned about one of their nails will often come to their appointment with nail polish still on the other nails, Dr. Lipner always has polish remover pads available in the office. It’s important to be able to see all nails, she said, but she and her collaborators, including first author Pierre Halteh, MD, who was then a medical student at Cornell, discovered from their survey that “few physicians (32/402; 8%) asked their patients to remove nail polish at every visit.”
Nonmelanocytic causes of LM
Longitudinal melanonychias can have a nonmelanocytic etiology, which can range from subungual hematomas to pseudomonas and fungal infections to exogenous pigment.
Overall, subungual hematomas are the most common cause of melanonychia, although longitudinal hematomas are not commonly seen. The more remote the causative trauma, the darker the subungual discoloration, Dr. Lipner said. “Dermoscopy is very helpful” for subungual hematomas, which will usually show a homogeneous pattern, although “you can also see peripheral fadings, streaks, and periungual hemorrhages,” she added.
It is important to monitor these patients “because melanomas can bleed,” she said. In-office photography, or even pictures taken by patients, can be used to track the hematoma to resolution.
When thinking about exogenous sources of pigment, in addition to clues from the history, a tip-off can be that the proximal nail fold is also discolored, Dr. Lipner pointed out. A wide variety of common and less-common culprits may crop up, including from tar, tobacco, henna and other hair dyes, potassium permanganate, and even newspaper print, she said. With an exogenous source, careful clinical and dermoscopic examination may show that the pigment does not extend all the way proximally to the lunula, although it may follow the outline of the proximal nail fold.
When fungus is the cause of LM, the band is often wider proximally and tapers distally, Dr. Lipner noted. While Trichophyton rubrum var. nigricans is a known culprit, nondermatophytes, such as Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, can also cause an LM that often runs along the proximal and lateral nail folds. “To make the diagnosis, sending a clipping to the dermatopathologist is helpful,” she said. Hyphae can often be seen on staining and culture, she said. Polymerase chain reaction “is also possible and very helpful for these nondermatophytes.”
Bacterial colonization of the nail bed can be a cause of LM. Pathogens can include Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which will often show the characteristic greenish tint. Klebsiella and Proteus species may result in more of a grayish-black discoloration. A history of wet work, such as farming and other agricultural and dairy occupations, as well as housekeeping work, increases the risk for bacterial colonization.
Commonly, a bacterial etiology will result in discoloration beginning at the lateral nail fold or at the juncture of the proximal and lateral nail folds. Dermoscopy will show irregular fading of the discoloration toward the medial aspect of the nail, and gram staining of affected clippings will show gram-negative rods.
Melanocytic causes of longitudinal melanonychia
The melanotic macule, sometimes called melanocytic activation, is the most common subtype of melanin-derived LM in adults, Dr. Lipner said. This benign condition results from increased melanin synthesis without an increase in the number of melanocytes, which will be evident on histopathologic examination of the nail bed. Any of a variety of triggers can provoke the increased pigment, which can range from endocrine disruptions to inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis, to trauma (including nail biting or habit tics).
Pregnancy, normal ethnic variation, and chemotherapy administration are all also associated with melanotic macules. In any case, dermoscopy will show an LM characterized by a grayish background that contains darker grayish lines.
Melanocyte hyperplasia can also cause melanonychia, in which case the trick is sorting out which cases are benign and which are malignant, Dr. Lipner noted. And getting the diagnosis right in a timely fashion matters: “Ideally, we want to catch these melanomas in in situ stages where we can preserve the digit,” she said. “It’s been shown that there is no survival benefit for amputation versus en bloc excision for nail melanomas in situ.”
Nail matrix nevi are the most common cause of LM in children, Dr. Lipner said. Here, dermoscopy shows a brown background with brown lines, with regular color, thickness, and spacing.
On examination of a nail with a melanoma, “typically, we see features suggestive of melanoma but really no pathognomonic features,” she commented. Some signs that should prompt concern and a more thorough investigation, she said, include a dark brown or black band of LM; lack of homogeneity, such as the presence of lines of different colors; blurring of the borders of the pigmentation; and a triangular or wavering outline. Changes in the nail, such as fissuring or splitting, also are worrying, as is any associated discoloration of the periungual skin.
Dermoscopy may confirm the irregularity of the pigmentation pattern and show irregularly colored and spaced lines of varying thicknesses within the pigmented band. An LM caused by melanoma may also be marked by loss of parallelism within the pigmented band.
She pointed out that these concerning characteristics have been encapsulated in a mnemonic, first created in 2000, that’s meant to mirror the ABCDs of nonnail melanoma detection (J Am Acad Dermatol. Feb 2000;42[2 Pt 1]:269-74). Her survey found that overall, just one in four (24.8%) of respondents knew of the mnemonic for subungual melanomas.
Dr. Lipner reported that she has received research support from MOE Medical Devices and has served as a consultant to BAKO Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Lipner S. Summer AAD 2018, Presentation F004.
CHICAGO – A discolored nail can give even seasoned dermatologists pause: Is the cause exogenous? Fungal or bacterial, perhaps? Could it be a subungual melanoma? Should it be followed, clipped, or biopsied? of the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
The session came after a recent nationwide survey performed by Dr. Lipner and her collaborators who asked dermatologists at different practice stages how confident they were in the diagnosis and management of melanonychia. “On the whole, they were not very confident at all,” said Dr. Lipner, director of the nail division at Cornell University, New York.
Of 142 dermatology residents, as well as 58 junior and 199 senior attending dermatologists, just 18.2% performed nail exams at each visit, and most (58%) only looked at nails during the total body skin exam. Over half (62%) of resident physicians reported feeling not confident about melanonychia diagnosis and management, while that figure dropped to 8.6% for senior attending physicians. Still, most senior physicians (64.3%) were just “fairly confident” in their melanonychia skills (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017 May;76[5]:994-6).
Tools of the trade

Dermoscopy can be an invaluable tool for determining the cause of longitudinal melanonychia (LM). “Contact dermoscopy is helpful, so I always have ultrasound gel available,” Dr. Lipner said. “The gel makes the nail more of a flat surface,” which makes accurate viewing easier. Other useful tools include a double-action nail clipper, which, she said, is a worthwhile investment.
Because patients who are concerned about one of their nails will often come to their appointment with nail polish still on the other nails, Dr. Lipner always has polish remover pads available in the office. It’s important to be able to see all nails, she said, but she and her collaborators, including first author Pierre Halteh, MD, who was then a medical student at Cornell, discovered from their survey that “few physicians (32/402; 8%) asked their patients to remove nail polish at every visit.”
Nonmelanocytic causes of LM
Longitudinal melanonychias can have a nonmelanocytic etiology, which can range from subungual hematomas to pseudomonas and fungal infections to exogenous pigment.
Overall, subungual hematomas are the most common cause of melanonychia, although longitudinal hematomas are not commonly seen. The more remote the causative trauma, the darker the subungual discoloration, Dr. Lipner said. “Dermoscopy is very helpful” for subungual hematomas, which will usually show a homogeneous pattern, although “you can also see peripheral fadings, streaks, and periungual hemorrhages,” she added.
It is important to monitor these patients “because melanomas can bleed,” she said. In-office photography, or even pictures taken by patients, can be used to track the hematoma to resolution.
When thinking about exogenous sources of pigment, in addition to clues from the history, a tip-off can be that the proximal nail fold is also discolored, Dr. Lipner pointed out. A wide variety of common and less-common culprits may crop up, including from tar, tobacco, henna and other hair dyes, potassium permanganate, and even newspaper print, she said. With an exogenous source, careful clinical and dermoscopic examination may show that the pigment does not extend all the way proximally to the lunula, although it may follow the outline of the proximal nail fold.
When fungus is the cause of LM, the band is often wider proximally and tapers distally, Dr. Lipner noted. While Trichophyton rubrum var. nigricans is a known culprit, nondermatophytes, such as Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, can also cause an LM that often runs along the proximal and lateral nail folds. “To make the diagnosis, sending a clipping to the dermatopathologist is helpful,” she said. Hyphae can often be seen on staining and culture, she said. Polymerase chain reaction “is also possible and very helpful for these nondermatophytes.”
Bacterial colonization of the nail bed can be a cause of LM. Pathogens can include Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which will often show the characteristic greenish tint. Klebsiella and Proteus species may result in more of a grayish-black discoloration. A history of wet work, such as farming and other agricultural and dairy occupations, as well as housekeeping work, increases the risk for bacterial colonization.
Commonly, a bacterial etiology will result in discoloration beginning at the lateral nail fold or at the juncture of the proximal and lateral nail folds. Dermoscopy will show irregular fading of the discoloration toward the medial aspect of the nail, and gram staining of affected clippings will show gram-negative rods.
Melanocytic causes of longitudinal melanonychia
The melanotic macule, sometimes called melanocytic activation, is the most common subtype of melanin-derived LM in adults, Dr. Lipner said. This benign condition results from increased melanin synthesis without an increase in the number of melanocytes, which will be evident on histopathologic examination of the nail bed. Any of a variety of triggers can provoke the increased pigment, which can range from endocrine disruptions to inflammatory conditions, such as psoriasis, to trauma (including nail biting or habit tics).
Pregnancy, normal ethnic variation, and chemotherapy administration are all also associated with melanotic macules. In any case, dermoscopy will show an LM characterized by a grayish background that contains darker grayish lines.
Melanocyte hyperplasia can also cause melanonychia, in which case the trick is sorting out which cases are benign and which are malignant, Dr. Lipner noted. And getting the diagnosis right in a timely fashion matters: “Ideally, we want to catch these melanomas in in situ stages where we can preserve the digit,” she said. “It’s been shown that there is no survival benefit for amputation versus en bloc excision for nail melanomas in situ.”
Nail matrix nevi are the most common cause of LM in children, Dr. Lipner said. Here, dermoscopy shows a brown background with brown lines, with regular color, thickness, and spacing.
On examination of a nail with a melanoma, “typically, we see features suggestive of melanoma but really no pathognomonic features,” she commented. Some signs that should prompt concern and a more thorough investigation, she said, include a dark brown or black band of LM; lack of homogeneity, such as the presence of lines of different colors; blurring of the borders of the pigmentation; and a triangular or wavering outline. Changes in the nail, such as fissuring or splitting, also are worrying, as is any associated discoloration of the periungual skin.
Dermoscopy may confirm the irregularity of the pigmentation pattern and show irregularly colored and spaced lines of varying thicknesses within the pigmented band. An LM caused by melanoma may also be marked by loss of parallelism within the pigmented band.
She pointed out that these concerning characteristics have been encapsulated in a mnemonic, first created in 2000, that’s meant to mirror the ABCDs of nonnail melanoma detection (J Am Acad Dermatol. Feb 2000;42[2 Pt 1]:269-74). Her survey found that overall, just one in four (24.8%) of respondents knew of the mnemonic for subungual melanomas.
Dr. Lipner reported that she has received research support from MOE Medical Devices and has served as a consultant to BAKO Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Lipner S. Summer AAD 2018, Presentation F004.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SUMMER AAD 2018
Tease out genetic and structural causes of children’s hair loss
according to Maria Hordinsky, MD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
The ectodermal dysplasias are a heterogeneous group of disorders in which a main feature is the absent, incomplete, or delayed development of one or more of the appendages derived from ectoderm, such as the hair follicle, Dr. Hordinsky said in a presentation at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s Women’s & Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
Patients with pure hair and nail ectodermal dysplasia generally present with absent or sparse eyebrows and eyelashes, as well as follicular papules on the scalp and fragile, irregular hair, Dr. Hordinsky said. The condition is caused by a mutation in a gene associated with the production of keratin. In another rare form of hereditary hair loss – hypotrichosis simplex – patients are born with normal hair but lose it gradually from the scalp during the middle of the first decade of life.
The inability to grow long hair characterizes short anagen syndrome, a congenital disorder not to be confused with loose anagen syndrome, Dr. Hordinsky said. Patients with short anagen syndrome experience an idiopathic short anagen phase and as a result, an increased number of hairs in the telogen phase. Children with short anagen syndrome have unusually short hair in early childhood. “Parents typically complain that their children exhibit short hair even though they have never had a haircut,” she explained.
Trichothiodystrophy, a rare autosomal recessive disease, is distinguished by hair that is brittle and sulfur deficient, Dr. Hordinsky said. She cited a review of 112 patients with trichothiodystrophy in which additional distinguishing features included developmental delay/intellectual impairment (86%), short stature (73%), and ichthyosis (65%).
Some cases of hair loss in children have a structural basis, Dr. Hordinsky noted. Structural hair abnormalities include fractures of the hair shaft, extraneous matter on the hair shaft, and hair shaft irregularities such as coiling or twisting, she said.
In trichoptilosis, extensive cuticle loss results in fraying and splitting of the hair shaft, while in patients with trichoclasis, a fractured hair is splinted by a partially intact cuticle.
In trichorrhexis nodosa, the most common type of structural hair abnormality, “intact nodes [of hair] resemble two paintbrushes thrust together,” Dr. Hordinsky explained. Trichorrhexis nodosa may be congenital or acquired, and occurs in children with mental retardation and argininosuccinic aciduria, she said.
A hair shaft abnormality is the culprit behind uncombable hair syndrome, which can be inherited or can occur sporadically, Dr. Hordinsky said. The key feature of the condition is unruly hair caused by a distinctive hair shaft defect, “possibly related to an abnormality in the inner root sheath.” Abnormal hairs usually become apparent at about 3-4 years of age, but eyebrows and eyelashes appear normal. Many patients have a silvery blonde tint to their hair because of how the abnormal hairs reflect light, she said.
Dr. Hordinsky is a consultant for P&G, Concert, Cassiopea, and BioAZ; and receives grant/research support from Aclaris, Allergan, and the National Alopecia Areata Foundation. SDEF and this news organization are owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
according to Maria Hordinsky, MD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
The ectodermal dysplasias are a heterogeneous group of disorders in which a main feature is the absent, incomplete, or delayed development of one or more of the appendages derived from ectoderm, such as the hair follicle, Dr. Hordinsky said in a presentation at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s Women’s & Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
Patients with pure hair and nail ectodermal dysplasia generally present with absent or sparse eyebrows and eyelashes, as well as follicular papules on the scalp and fragile, irregular hair, Dr. Hordinsky said. The condition is caused by a mutation in a gene associated with the production of keratin. In another rare form of hereditary hair loss – hypotrichosis simplex – patients are born with normal hair but lose it gradually from the scalp during the middle of the first decade of life.
The inability to grow long hair characterizes short anagen syndrome, a congenital disorder not to be confused with loose anagen syndrome, Dr. Hordinsky said. Patients with short anagen syndrome experience an idiopathic short anagen phase and as a result, an increased number of hairs in the telogen phase. Children with short anagen syndrome have unusually short hair in early childhood. “Parents typically complain that their children exhibit short hair even though they have never had a haircut,” she explained.
Trichothiodystrophy, a rare autosomal recessive disease, is distinguished by hair that is brittle and sulfur deficient, Dr. Hordinsky said. She cited a review of 112 patients with trichothiodystrophy in which additional distinguishing features included developmental delay/intellectual impairment (86%), short stature (73%), and ichthyosis (65%).
Some cases of hair loss in children have a structural basis, Dr. Hordinsky noted. Structural hair abnormalities include fractures of the hair shaft, extraneous matter on the hair shaft, and hair shaft irregularities such as coiling or twisting, she said.
In trichoptilosis, extensive cuticle loss results in fraying and splitting of the hair shaft, while in patients with trichoclasis, a fractured hair is splinted by a partially intact cuticle.
In trichorrhexis nodosa, the most common type of structural hair abnormality, “intact nodes [of hair] resemble two paintbrushes thrust together,” Dr. Hordinsky explained. Trichorrhexis nodosa may be congenital or acquired, and occurs in children with mental retardation and argininosuccinic aciduria, she said.
A hair shaft abnormality is the culprit behind uncombable hair syndrome, which can be inherited or can occur sporadically, Dr. Hordinsky said. The key feature of the condition is unruly hair caused by a distinctive hair shaft defect, “possibly related to an abnormality in the inner root sheath.” Abnormal hairs usually become apparent at about 3-4 years of age, but eyebrows and eyelashes appear normal. Many patients have a silvery blonde tint to their hair because of how the abnormal hairs reflect light, she said.
Dr. Hordinsky is a consultant for P&G, Concert, Cassiopea, and BioAZ; and receives grant/research support from Aclaris, Allergan, and the National Alopecia Areata Foundation. SDEF and this news organization are owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
according to Maria Hordinsky, MD, of the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
The ectodermal dysplasias are a heterogeneous group of disorders in which a main feature is the absent, incomplete, or delayed development of one or more of the appendages derived from ectoderm, such as the hair follicle, Dr. Hordinsky said in a presentation at Skin Disease Education Foundation’s Women’s & Pediatric Dermatology Seminar.
Patients with pure hair and nail ectodermal dysplasia generally present with absent or sparse eyebrows and eyelashes, as well as follicular papules on the scalp and fragile, irregular hair, Dr. Hordinsky said. The condition is caused by a mutation in a gene associated with the production of keratin. In another rare form of hereditary hair loss – hypotrichosis simplex – patients are born with normal hair but lose it gradually from the scalp during the middle of the first decade of life.
The inability to grow long hair characterizes short anagen syndrome, a congenital disorder not to be confused with loose anagen syndrome, Dr. Hordinsky said. Patients with short anagen syndrome experience an idiopathic short anagen phase and as a result, an increased number of hairs in the telogen phase. Children with short anagen syndrome have unusually short hair in early childhood. “Parents typically complain that their children exhibit short hair even though they have never had a haircut,” she explained.
Trichothiodystrophy, a rare autosomal recessive disease, is distinguished by hair that is brittle and sulfur deficient, Dr. Hordinsky said. She cited a review of 112 patients with trichothiodystrophy in which additional distinguishing features included developmental delay/intellectual impairment (86%), short stature (73%), and ichthyosis (65%).
Some cases of hair loss in children have a structural basis, Dr. Hordinsky noted. Structural hair abnormalities include fractures of the hair shaft, extraneous matter on the hair shaft, and hair shaft irregularities such as coiling or twisting, she said.
In trichoptilosis, extensive cuticle loss results in fraying and splitting of the hair shaft, while in patients with trichoclasis, a fractured hair is splinted by a partially intact cuticle.
In trichorrhexis nodosa, the most common type of structural hair abnormality, “intact nodes [of hair] resemble two paintbrushes thrust together,” Dr. Hordinsky explained. Trichorrhexis nodosa may be congenital or acquired, and occurs in children with mental retardation and argininosuccinic aciduria, she said.
A hair shaft abnormality is the culprit behind uncombable hair syndrome, which can be inherited or can occur sporadically, Dr. Hordinsky said. The key feature of the condition is unruly hair caused by a distinctive hair shaft defect, “possibly related to an abnormality in the inner root sheath.” Abnormal hairs usually become apparent at about 3-4 years of age, but eyebrows and eyelashes appear normal. Many patients have a silvery blonde tint to their hair because of how the abnormal hairs reflect light, she said.
Dr. Hordinsky is a consultant for P&G, Concert, Cassiopea, and BioAZ; and receives grant/research support from Aclaris, Allergan, and the National Alopecia Areata Foundation. SDEF and this news organization are owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
FROM SDEF WOMEN’S & PEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY SEMINAR
Plantar Ulcerative Lichen Planus: Rapid Improvement With a Novel Triple-Therapy Approach
Ulcerative lichen planus (ULP)(also called erosive) is a rare variant of lichen planus. Similar to classic lichen planus, the cause of ULP is largely unknown. Ulcerative lichen planus typically involves the oral mucosa or genitalia but rarely may present as ulcerations on the palms and soles. Clinical presentation usually involves a history of chronic ulcers that often have been previously misdiagnosed and resistant to treatment. Ulcerations on the plantar surfaces frequently cause severe pain and disability. Few cases have been reported and successful treatment is rare.
Case Report
A 56-year-old man was referred by podiatry to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of painful ulcerations involving the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the right great toe as well as the second to third digits. The ulcers had been ongoing for 8 years, treated mostly with local wound care without clinical improvement. His medical and family history was considered noncontributory as a possible etiology of the ulcers; however, he had been taking ibuprofen intermittently for years for general aches and pains, which raised the suspicion of a drug-induced etiology. Laboratory evaluation revealed positive hepatitis B serology but was otherwise unremarkable, including normal liver function tests and negative wound cultures.
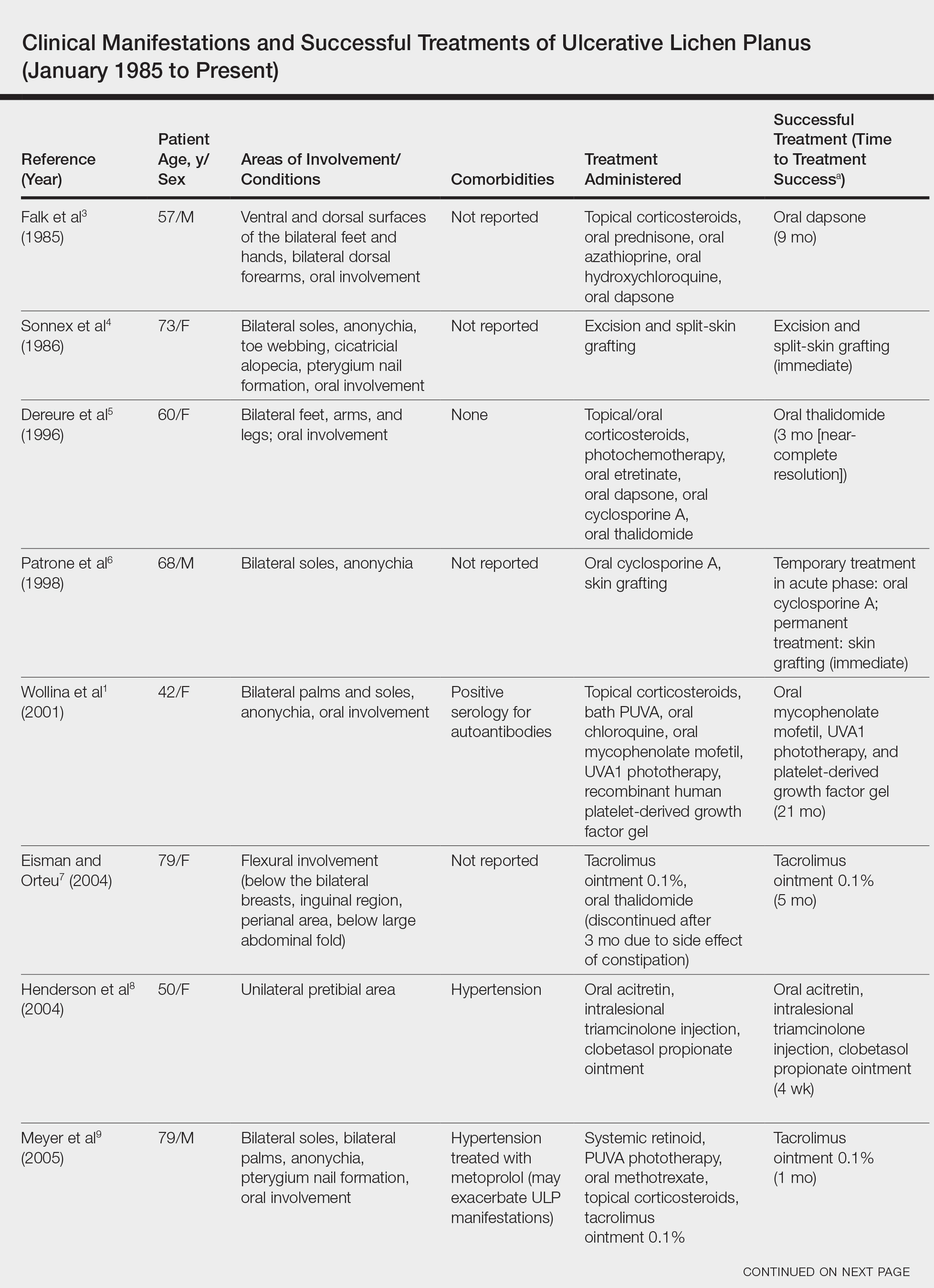
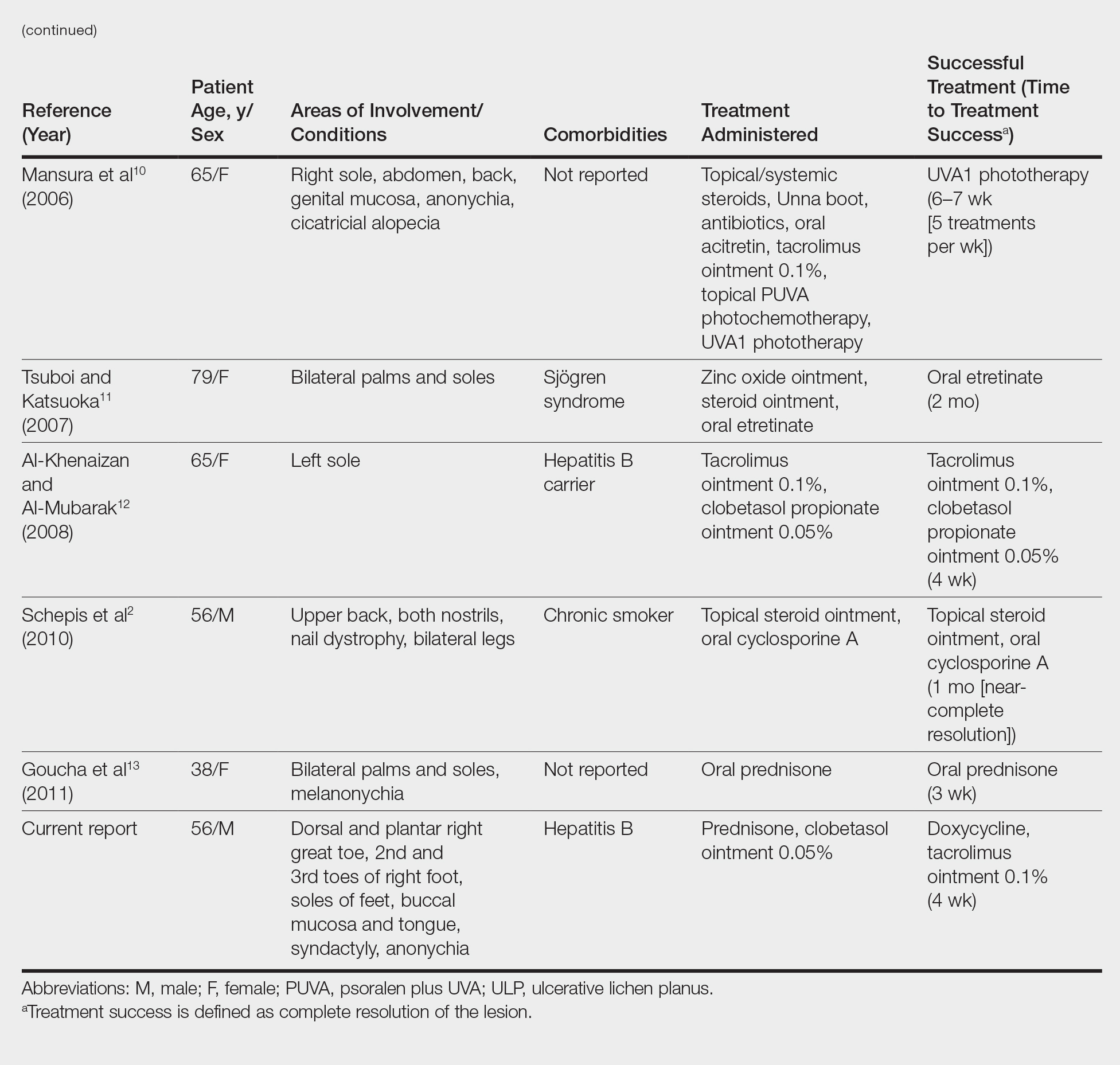
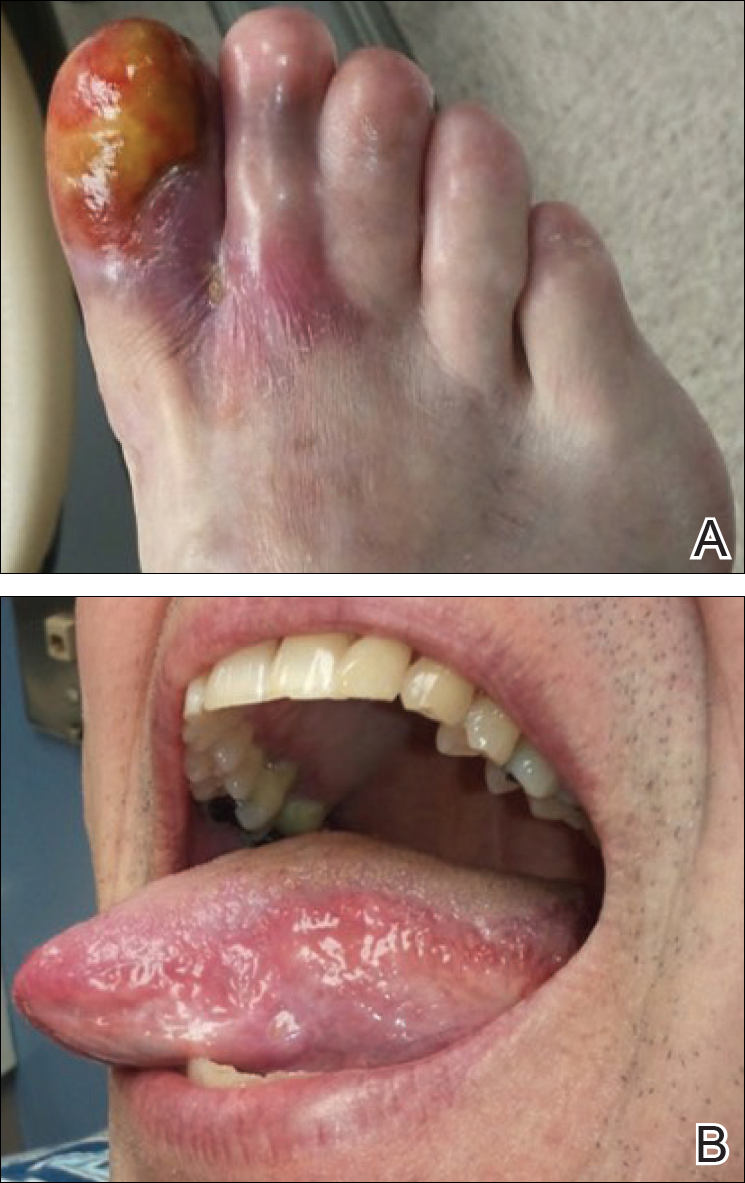
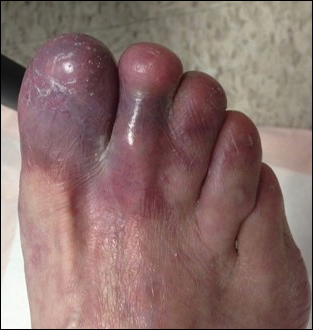
Physical examination revealed a beefy red, glazed ulceration involving the entire right great toe with extension onto the second and third toes. There was considerable scarring with syndactyly of the second and third toes and complete toenail loss of the right foot (Figure 1). On the insteps of the bilateral soles were a few scattered, pale, atrophic, violaceous papules with overlying thin lacy white streaks that were reflective of Wickham striae. Early dorsal pterygium formation also was noted on the bilateral third fingernails. Oral mucosal examination revealed lacy white plaques on the bilateral buccal mucosa with a large ulcer of the left lateral tongue (Figure 2). No genital or scalp lesions were present.

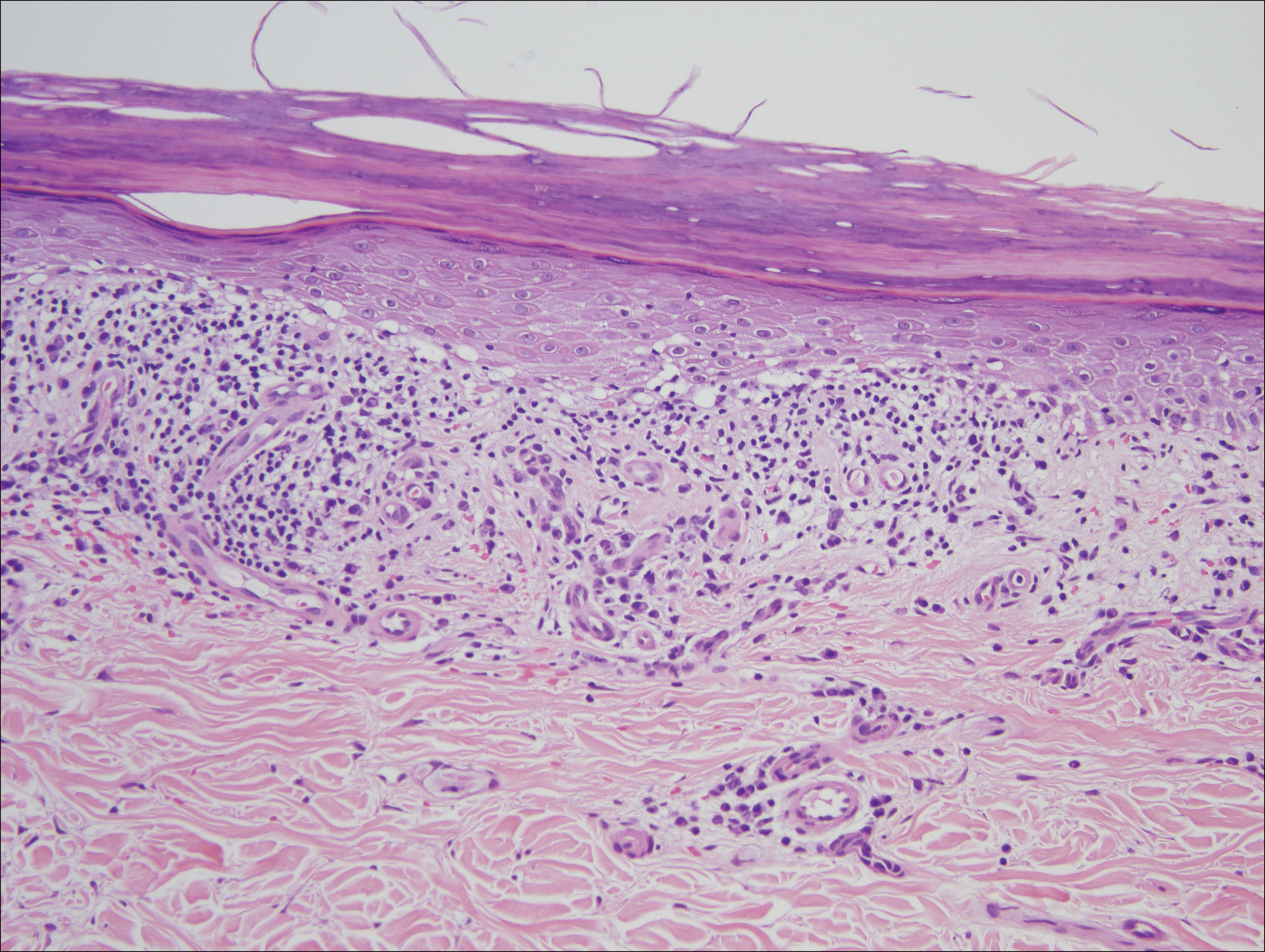
Histologic examination of a papule on the instep of the right sole demonstrated a dense lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis with basal vacuolar degeneration and early focal Max-Joseph space formation. Additionally, there was epidermal atrophy with mild hypergranulosis and scattered necrotic keratinocytes (Figure 3). A similar histologic picture was noted on a biopsy of the buccal mucosa overlying the right molar, albeit with epithelial acanthosis rather than atrophy.
Based on initial clinical suspicion for ULP, we suggested that our patient discontinue ibuprofen and started him on a regimen of oral prednisone 40 mg once daily and clobetasol ointment 0.05% applied twice daily to the plantar ulceration, both for 2 weeks. Dramatic improvement was noted after only 2 weeks of treatment. This regimen was then switched to oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily combined with tacrolimus ointment 0.1% applied twice daily to the plantar ulceration to avoid side effects of prolonged steroid use. Topical therapies were not used for the mucosal lesions. At 4-week follow-up, the patient continued to demonstrate notable clinical response with a greater than 70% physician-assessed improvement in ulcer severity (Figure 4) and near-complete resolution of the oral mucosal lesions. Our patient also reported almost complete resolution of pain. By 4-month follow-up, complete reepithelialization and resolution of the ulcers was noted (Figure 5). This improvement was sustained at additional follow-up 1 year after the initial presentation.
Comment
Ulcerative (or erosive) lichen planus is a rare form of lichen planus. Ulcerative lichen planus most commonly presents as erosive lesions of the oral and genital mucosae but rarely can involve other sites. The palms and soles are the most common sites of cutaneous involvement, with lesions frequently characterized by severe pain and limited mobility.2
We conducted a review of the Ovid MEDLINE database using the search terms ulcerative lichen planus and erosive lichen planus for articles from the last 30 years, focusing specifically on articles that reported cases of cutaneous involvement of ULP and successful therapeutic modalities. The Table provides a detailed summary of the cases from 1985 to present, representing a spectrum of clinical manifestations and successful treatments of ULP.1-13
Hepatitis C is a comorbidity commonly associated with classic lichen planus, while hepatitis B immunization has a well-described association with classic and oral ULP.12,14 Although hepatitis C was negative in our patient, we did find a chronic inactive carrier state for hepatitis B infection. Al-Khenaizan and Al-Mubarak12 reported the only other known case of ULP of the sole associated with positive serology for hepatitis B surface antigen.
Ulcerative lichen planus of the soles can be difficult to diagnose, especially when it is an isolated finding. It should be differentiated from localized bullous pemphigoid, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, ulcerative lupus erythematosus, and dermatitis artefacta.13 The characteristic associated clinical features of plantar ULP in our patient and lack of diagnostic immunofluorescence helped us to rule out these alternative diagnoses.4 Long-standing ulcerations of ULP also pose an increased risk for neoplastic transformation. Eisen15 noted a 0.4% to 5% frequency of malignant transformation into squamous cell carcinoma in those with oral ULP. Therefore, it is important to monitor previously ulcerated lesions long-term for such development.
Plantar ULP is difficult to treat and often is unresponsive to systemic and local treatment. Historically, surgical grafting of the affected areas was the treatment of choice, as reported by Patrone et al.6 Goucha et al13 reported complete healing of ulcerations within 3 weeks of starting oral prednisone 1 mg/kg once daily followed by a maintenance dosage of 5 mg once daily. Tacrolimus is a macrolide immunosuppressant that inhibits T-cell activation by forming a complex with FK506 binding protein in the cytoplasm of T cells that binds and inhibits calcineurin dephosphorylation of nuclear factor of activated T cells.12 Al-Khenaizan and Al-Mubarak12 reported resolution of plantar ULP ulcerations after 4 weeks of treatment with topical tacrolimus. Eisman and Orteu7 also achieved complete healing of ulcerations of plantar ULP using tacrolimus ointment 0.1%.
In our patient, doxycycline also was started at the time of initiating the topical tacrolimus. We chose this treatment to take advantage of its systemic anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antibacterial properties. Our case represents rapid and successful treatment of plantar ULP utilizing this specific combination of oral doxycycline and topical tacrolimus.
Conclusion
Ulcerative lichen planus is an uncommon variant of lichen planus, with cutaneous involvement only rarely reported in the literature. Physicians should be aware of this entity and should consider it in the differential diagnosis in patients presenting with chronic ulcers on the soles, especially when lesions have been unresponsive to appropriate wound care and antibiotic treatment or when cultures have been persistently negative for microbial growth. The possibility of drug-induced lichen planus also should not be overlooked, and one should consider discontinuation of all nonessential medications that could be potential culprits. In our patient ibuprofen was discontinued, but we can only speculate that it was contributory to his healing and only time will tell if resumption of this nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug causes a relapse in symptoms.
In our patient, a combination of systemic and topical steroids, topical tacrolimus, and oral doxycycline successfully treated his plantar ULP. Our findings provide further support for the use of topical tacrolimus as a steroid-sparing anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of plantar ULP. We also introduce the combination of topical tacrolimus and oral doxycycline as a novel therapeutic combination and relatively safer alternative to conventional immunosuppressive agents for long-term systemic anti-inflammatory effects.
- Wollina U, Konrad H, Graefe T. Ulcerative lichen planus: a case responding to recombinant platelet-derived growth factor BB and immunosuppression. Acta Derm Venereol. 2001;81:364-383.
- Schepis C, Lentini M, Siragusa M. Erosive lichen planus on an atypical site mimicking a factitial dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:185-186.
- Falk DK, Latour DL, King EL. Dapsone in the treatment of erosive lichen planus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:567-570.
- Sonnex TS, Eady RA, Sparrow GP, et al. Ulcerative lichen planus associated with webbing of the toes. J R Soc Med. 1986;79:363-365.
- Dereure O, Basset-Sequin N, Guilhou JJ. Erosive lichen planus: dramatic response to thalidomide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1392-1393.
- Patrone P, Stinco G, La Pia E, et al. Surgery and cyclosporine A in the treatment of erosive lichen planus of the feet. Eur J Dermatol. 1998;8:243-244.
- Eisman S, Orteu C. Recalcitrant erosive flexural lichen planus: successful treatment with a combination of thalidomide and 0.1% tacrolimus ointment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004;29:268-270.
- Henderson RL Jr, Williford PM, Molnar JA. Cutaneous ulcerative lichen planus exhibiting pathergy, response to acitretin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3:191-192.
- Meyer S, Burgdorf T, Szeimies R, et al. Management of erosive lichen planus with topical tacrolimus and recurrence secondary to metoprolol. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005;19:236-239.
- Mansura A, Alkalay R, Slodownik D, et al. Ultraviolet A-1 as a treatment for ulcerative lichen planus of the feet. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Pathomed. 2006;22:164-165.
- Tsuboi H, Katsuoka K. Ulcerative lichen planus associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. J Dermatol. 2007;34:131-134.
- Al-Khenaizan S, Al-Mubarak L. Ulcerative lichen planus of the sole: excellent response to topical tacrolimus. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:626-628.
- Goucha S, Khaled A, Rammeh S, et al. Erosive lichen planus of the soles: effective response to prednisone. Dermatol Ther. 2011;1:20-24.
- Binesh F, Parichehr K. Erosive lichen planus of the scalp and hepatitis C infection. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23:169.
- Eisen D. The clinical features, malignant potential, and systemic associations of oral lichen planus: a study of 723 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:207-214.
Ulcerative lichen planus (ULP)(also called erosive) is a rare variant of lichen planus. Similar to classic lichen planus, the cause of ULP is largely unknown. Ulcerative lichen planus typically involves the oral mucosa or genitalia but rarely may present as ulcerations on the palms and soles. Clinical presentation usually involves a history of chronic ulcers that often have been previously misdiagnosed and resistant to treatment. Ulcerations on the plantar surfaces frequently cause severe pain and disability. Few cases have been reported and successful treatment is rare.
Case Report
A 56-year-old man was referred by podiatry to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of painful ulcerations involving the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the right great toe as well as the second to third digits. The ulcers had been ongoing for 8 years, treated mostly with local wound care without clinical improvement. His medical and family history was considered noncontributory as a possible etiology of the ulcers; however, he had been taking ibuprofen intermittently for years for general aches and pains, which raised the suspicion of a drug-induced etiology. Laboratory evaluation revealed positive hepatitis B serology but was otherwise unremarkable, including normal liver function tests and negative wound cultures.
Physical examination revealed a beefy red, glazed ulceration involving the entire right great toe with extension onto the second and third toes. There was considerable scarring with syndactyly of the second and third toes and complete toenail loss of the right foot (Figure 1). On the insteps of the bilateral soles were a few scattered, pale, atrophic, violaceous papules with overlying thin lacy white streaks that were reflective of Wickham striae. Early dorsal pterygium formation also was noted on the bilateral third fingernails. Oral mucosal examination revealed lacy white plaques on the bilateral buccal mucosa with a large ulcer of the left lateral tongue (Figure 2). No genital or scalp lesions were present.


Histologic examination of a papule on the instep of the right sole demonstrated a dense lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis with basal vacuolar degeneration and early focal Max-Joseph space formation. Additionally, there was epidermal atrophy with mild hypergranulosis and scattered necrotic keratinocytes (Figure 3). A similar histologic picture was noted on a biopsy of the buccal mucosa overlying the right molar, albeit with epithelial acanthosis rather than atrophy.

Based on initial clinical suspicion for ULP, we suggested that our patient discontinue ibuprofen and started him on a regimen of oral prednisone 40 mg once daily and clobetasol ointment 0.05% applied twice daily to the plantar ulceration, both for 2 weeks. Dramatic improvement was noted after only 2 weeks of treatment. This regimen was then switched to oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily combined with tacrolimus ointment 0.1% applied twice daily to the plantar ulceration to avoid side effects of prolonged steroid use. Topical therapies were not used for the mucosal lesions. At 4-week follow-up, the patient continued to demonstrate notable clinical response with a greater than 70% physician-assessed improvement in ulcer severity (Figure 4) and near-complete resolution of the oral mucosal lesions. Our patient also reported almost complete resolution of pain. By 4-month follow-up, complete reepithelialization and resolution of the ulcers was noted (Figure 5). This improvement was sustained at additional follow-up 1 year after the initial presentation.


Comment
Ulcerative (or erosive) lichen planus is a rare form of lichen planus. Ulcerative lichen planus most commonly presents as erosive lesions of the oral and genital mucosae but rarely can involve other sites. The palms and soles are the most common sites of cutaneous involvement, with lesions frequently characterized by severe pain and limited mobility.2
We conducted a review of the Ovid MEDLINE database using the search terms ulcerative lichen planus and erosive lichen planus for articles from the last 30 years, focusing specifically on articles that reported cases of cutaneous involvement of ULP and successful therapeutic modalities. The Table provides a detailed summary of the cases from 1985 to present, representing a spectrum of clinical manifestations and successful treatments of ULP.1-13
Hepatitis C is a comorbidity commonly associated with classic lichen planus, while hepatitis B immunization has a well-described association with classic and oral ULP.12,14 Although hepatitis C was negative in our patient, we did find a chronic inactive carrier state for hepatitis B infection. Al-Khenaizan and Al-Mubarak12 reported the only other known case of ULP of the sole associated with positive serology for hepatitis B surface antigen.
Ulcerative lichen planus of the soles can be difficult to diagnose, especially when it is an isolated finding. It should be differentiated from localized bullous pemphigoid, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, ulcerative lupus erythematosus, and dermatitis artefacta.13 The characteristic associated clinical features of plantar ULP in our patient and lack of diagnostic immunofluorescence helped us to rule out these alternative diagnoses.4 Long-standing ulcerations of ULP also pose an increased risk for neoplastic transformation. Eisen15 noted a 0.4% to 5% frequency of malignant transformation into squamous cell carcinoma in those with oral ULP. Therefore, it is important to monitor previously ulcerated lesions long-term for such development.
Plantar ULP is difficult to treat and often is unresponsive to systemic and local treatment. Historically, surgical grafting of the affected areas was the treatment of choice, as reported by Patrone et al.6 Goucha et al13 reported complete healing of ulcerations within 3 weeks of starting oral prednisone 1 mg/kg once daily followed by a maintenance dosage of 5 mg once daily. Tacrolimus is a macrolide immunosuppressant that inhibits T-cell activation by forming a complex with FK506 binding protein in the cytoplasm of T cells that binds and inhibits calcineurin dephosphorylation of nuclear factor of activated T cells.12 Al-Khenaizan and Al-Mubarak12 reported resolution of plantar ULP ulcerations after 4 weeks of treatment with topical tacrolimus. Eisman and Orteu7 also achieved complete healing of ulcerations of plantar ULP using tacrolimus ointment 0.1%.
In our patient, doxycycline also was started at the time of initiating the topical tacrolimus. We chose this treatment to take advantage of its systemic anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antibacterial properties. Our case represents rapid and successful treatment of plantar ULP utilizing this specific combination of oral doxycycline and topical tacrolimus.
Conclusion
Ulcerative lichen planus is an uncommon variant of lichen planus, with cutaneous involvement only rarely reported in the literature. Physicians should be aware of this entity and should consider it in the differential diagnosis in patients presenting with chronic ulcers on the soles, especially when lesions have been unresponsive to appropriate wound care and antibiotic treatment or when cultures have been persistently negative for microbial growth. The possibility of drug-induced lichen planus also should not be overlooked, and one should consider discontinuation of all nonessential medications that could be potential culprits. In our patient ibuprofen was discontinued, but we can only speculate that it was contributory to his healing and only time will tell if resumption of this nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug causes a relapse in symptoms.
In our patient, a combination of systemic and topical steroids, topical tacrolimus, and oral doxycycline successfully treated his plantar ULP. Our findings provide further support for the use of topical tacrolimus as a steroid-sparing anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of plantar ULP. We also introduce the combination of topical tacrolimus and oral doxycycline as a novel therapeutic combination and relatively safer alternative to conventional immunosuppressive agents for long-term systemic anti-inflammatory effects.
Ulcerative lichen planus (ULP)(also called erosive) is a rare variant of lichen planus. Similar to classic lichen planus, the cause of ULP is largely unknown. Ulcerative lichen planus typically involves the oral mucosa or genitalia but rarely may present as ulcerations on the palms and soles. Clinical presentation usually involves a history of chronic ulcers that often have been previously misdiagnosed and resistant to treatment. Ulcerations on the plantar surfaces frequently cause severe pain and disability. Few cases have been reported and successful treatment is rare.
Case Report
A 56-year-old man was referred by podiatry to the dermatology clinic for evaluation of painful ulcerations involving the dorsal and plantar surfaces of the right great toe as well as the second to third digits. The ulcers had been ongoing for 8 years, treated mostly with local wound care without clinical improvement. His medical and family history was considered noncontributory as a possible etiology of the ulcers; however, he had been taking ibuprofen intermittently for years for general aches and pains, which raised the suspicion of a drug-induced etiology. Laboratory evaluation revealed positive hepatitis B serology but was otherwise unremarkable, including normal liver function tests and negative wound cultures.
Physical examination revealed a beefy red, glazed ulceration involving the entire right great toe with extension onto the second and third toes. There was considerable scarring with syndactyly of the second and third toes and complete toenail loss of the right foot (Figure 1). On the insteps of the bilateral soles were a few scattered, pale, atrophic, violaceous papules with overlying thin lacy white streaks that were reflective of Wickham striae. Early dorsal pterygium formation also was noted on the bilateral third fingernails. Oral mucosal examination revealed lacy white plaques on the bilateral buccal mucosa with a large ulcer of the left lateral tongue (Figure 2). No genital or scalp lesions were present.


Histologic examination of a papule on the instep of the right sole demonstrated a dense lichenoid lymphocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis with basal vacuolar degeneration and early focal Max-Joseph space formation. Additionally, there was epidermal atrophy with mild hypergranulosis and scattered necrotic keratinocytes (Figure 3). A similar histologic picture was noted on a biopsy of the buccal mucosa overlying the right molar, albeit with epithelial acanthosis rather than atrophy.

Based on initial clinical suspicion for ULP, we suggested that our patient discontinue ibuprofen and started him on a regimen of oral prednisone 40 mg once daily and clobetasol ointment 0.05% applied twice daily to the plantar ulceration, both for 2 weeks. Dramatic improvement was noted after only 2 weeks of treatment. This regimen was then switched to oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily combined with tacrolimus ointment 0.1% applied twice daily to the plantar ulceration to avoid side effects of prolonged steroid use. Topical therapies were not used for the mucosal lesions. At 4-week follow-up, the patient continued to demonstrate notable clinical response with a greater than 70% physician-assessed improvement in ulcer severity (Figure 4) and near-complete resolution of the oral mucosal lesions. Our patient also reported almost complete resolution of pain. By 4-month follow-up, complete reepithelialization and resolution of the ulcers was noted (Figure 5). This improvement was sustained at additional follow-up 1 year after the initial presentation.


Comment
Ulcerative (or erosive) lichen planus is a rare form of lichen planus. Ulcerative lichen planus most commonly presents as erosive lesions of the oral and genital mucosae but rarely can involve other sites. The palms and soles are the most common sites of cutaneous involvement, with lesions frequently characterized by severe pain and limited mobility.2
We conducted a review of the Ovid MEDLINE database using the search terms ulcerative lichen planus and erosive lichen planus for articles from the last 30 years, focusing specifically on articles that reported cases of cutaneous involvement of ULP and successful therapeutic modalities. The Table provides a detailed summary of the cases from 1985 to present, representing a spectrum of clinical manifestations and successful treatments of ULP.1-13
Hepatitis C is a comorbidity commonly associated with classic lichen planus, while hepatitis B immunization has a well-described association with classic and oral ULP.12,14 Although hepatitis C was negative in our patient, we did find a chronic inactive carrier state for hepatitis B infection. Al-Khenaizan and Al-Mubarak12 reported the only other known case of ULP of the sole associated with positive serology for hepatitis B surface antigen.
Ulcerative lichen planus of the soles can be difficult to diagnose, especially when it is an isolated finding. It should be differentiated from localized bullous pemphigoid, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, ulcerative lupus erythematosus, and dermatitis artefacta.13 The characteristic associated clinical features of plantar ULP in our patient and lack of diagnostic immunofluorescence helped us to rule out these alternative diagnoses.4 Long-standing ulcerations of ULP also pose an increased risk for neoplastic transformation. Eisen15 noted a 0.4% to 5% frequency of malignant transformation into squamous cell carcinoma in those with oral ULP. Therefore, it is important to monitor previously ulcerated lesions long-term for such development.
Plantar ULP is difficult to treat and often is unresponsive to systemic and local treatment. Historically, surgical grafting of the affected areas was the treatment of choice, as reported by Patrone et al.6 Goucha et al13 reported complete healing of ulcerations within 3 weeks of starting oral prednisone 1 mg/kg once daily followed by a maintenance dosage of 5 mg once daily. Tacrolimus is a macrolide immunosuppressant that inhibits T-cell activation by forming a complex with FK506 binding protein in the cytoplasm of T cells that binds and inhibits calcineurin dephosphorylation of nuclear factor of activated T cells.12 Al-Khenaizan and Al-Mubarak12 reported resolution of plantar ULP ulcerations after 4 weeks of treatment with topical tacrolimus. Eisman and Orteu7 also achieved complete healing of ulcerations of plantar ULP using tacrolimus ointment 0.1%.
In our patient, doxycycline also was started at the time of initiating the topical tacrolimus. We chose this treatment to take advantage of its systemic anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antibacterial properties. Our case represents rapid and successful treatment of plantar ULP utilizing this specific combination of oral doxycycline and topical tacrolimus.
Conclusion
Ulcerative lichen planus is an uncommon variant of lichen planus, with cutaneous involvement only rarely reported in the literature. Physicians should be aware of this entity and should consider it in the differential diagnosis in patients presenting with chronic ulcers on the soles, especially when lesions have been unresponsive to appropriate wound care and antibiotic treatment or when cultures have been persistently negative for microbial growth. The possibility of drug-induced lichen planus also should not be overlooked, and one should consider discontinuation of all nonessential medications that could be potential culprits. In our patient ibuprofen was discontinued, but we can only speculate that it was contributory to his healing and only time will tell if resumption of this nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug causes a relapse in symptoms.
In our patient, a combination of systemic and topical steroids, topical tacrolimus, and oral doxycycline successfully treated his plantar ULP. Our findings provide further support for the use of topical tacrolimus as a steroid-sparing anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of plantar ULP. We also introduce the combination of topical tacrolimus and oral doxycycline as a novel therapeutic combination and relatively safer alternative to conventional immunosuppressive agents for long-term systemic anti-inflammatory effects.
- Wollina U, Konrad H, Graefe T. Ulcerative lichen planus: a case responding to recombinant platelet-derived growth factor BB and immunosuppression. Acta Derm Venereol. 2001;81:364-383.
- Schepis C, Lentini M, Siragusa M. Erosive lichen planus on an atypical site mimicking a factitial dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:185-186.
- Falk DK, Latour DL, King EL. Dapsone in the treatment of erosive lichen planus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:567-570.
- Sonnex TS, Eady RA, Sparrow GP, et al. Ulcerative lichen planus associated with webbing of the toes. J R Soc Med. 1986;79:363-365.
- Dereure O, Basset-Sequin N, Guilhou JJ. Erosive lichen planus: dramatic response to thalidomide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1392-1393.
- Patrone P, Stinco G, La Pia E, et al. Surgery and cyclosporine A in the treatment of erosive lichen planus of the feet. Eur J Dermatol. 1998;8:243-244.
- Eisman S, Orteu C. Recalcitrant erosive flexural lichen planus: successful treatment with a combination of thalidomide and 0.1% tacrolimus ointment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004;29:268-270.
- Henderson RL Jr, Williford PM, Molnar JA. Cutaneous ulcerative lichen planus exhibiting pathergy, response to acitretin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3:191-192.
- Meyer S, Burgdorf T, Szeimies R, et al. Management of erosive lichen planus with topical tacrolimus and recurrence secondary to metoprolol. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005;19:236-239.
- Mansura A, Alkalay R, Slodownik D, et al. Ultraviolet A-1 as a treatment for ulcerative lichen planus of the feet. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Pathomed. 2006;22:164-165.
- Tsuboi H, Katsuoka K. Ulcerative lichen planus associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. J Dermatol. 2007;34:131-134.
- Al-Khenaizan S, Al-Mubarak L. Ulcerative lichen planus of the sole: excellent response to topical tacrolimus. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:626-628.
- Goucha S, Khaled A, Rammeh S, et al. Erosive lichen planus of the soles: effective response to prednisone. Dermatol Ther. 2011;1:20-24.
- Binesh F, Parichehr K. Erosive lichen planus of the scalp and hepatitis C infection. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23:169.
- Eisen D. The clinical features, malignant potential, and systemic associations of oral lichen planus: a study of 723 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:207-214.
- Wollina U, Konrad H, Graefe T. Ulcerative lichen planus: a case responding to recombinant platelet-derived growth factor BB and immunosuppression. Acta Derm Venereol. 2001;81:364-383.
- Schepis C, Lentini M, Siragusa M. Erosive lichen planus on an atypical site mimicking a factitial dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:185-186.
- Falk DK, Latour DL, King EL. Dapsone in the treatment of erosive lichen planus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;12:567-570.
- Sonnex TS, Eady RA, Sparrow GP, et al. Ulcerative lichen planus associated with webbing of the toes. J R Soc Med. 1986;79:363-365.
- Dereure O, Basset-Sequin N, Guilhou JJ. Erosive lichen planus: dramatic response to thalidomide. Arch Dermatol. 1996;132:1392-1393.
- Patrone P, Stinco G, La Pia E, et al. Surgery and cyclosporine A in the treatment of erosive lichen planus of the feet. Eur J Dermatol. 1998;8:243-244.
- Eisman S, Orteu C. Recalcitrant erosive flexural lichen planus: successful treatment with a combination of thalidomide and 0.1% tacrolimus ointment. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004;29:268-270.
- Henderson RL Jr, Williford PM, Molnar JA. Cutaneous ulcerative lichen planus exhibiting pathergy, response to acitretin. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004;3:191-192.
- Meyer S, Burgdorf T, Szeimies R, et al. Management of erosive lichen planus with topical tacrolimus and recurrence secondary to metoprolol. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005;19:236-239.
- Mansura A, Alkalay R, Slodownik D, et al. Ultraviolet A-1 as a treatment for ulcerative lichen planus of the feet. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Pathomed. 2006;22:164-165.
- Tsuboi H, Katsuoka K. Ulcerative lichen planus associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. J Dermatol. 2007;34:131-134.
- Al-Khenaizan S, Al-Mubarak L. Ulcerative lichen planus of the sole: excellent response to topical tacrolimus. Int J Dermatol. 2008;47:626-628.
- Goucha S, Khaled A, Rammeh S, et al. Erosive lichen planus of the soles: effective response to prednisone. Dermatol Ther. 2011;1:20-24.
- Binesh F, Parichehr K. Erosive lichen planus of the scalp and hepatitis C infection. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2013;23:169.
- Eisen D. The clinical features, malignant potential, and systemic associations of oral lichen planus: a study of 723 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;46:207-214.
Practice Points
- Consider ulcerative lichen planus (ULP) for chronic wounds on the soles.
- Topical therapeutic options may present a rapidly effective and relatively safe alternative to conventional immunosuppressive agents for long-term management of plantar ULP.
Foster cultural competence when examining hair, scalp of ethnic patients
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – The way Susan C. Taylor, MD, sees it,
At the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, Dr. Taylor, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, defined culturally competent care as a patient-centered approach in which clinicians establish a rapport with the patient and the caregiver. “It’s important that we ask the right questions,” she said. “In doing so, we have to be familiar with common hair care practices. It’s important that we respect our patients’ values, their goals, their health needs, and, of course, their cultural background. Finally, we have to engage in shared decision making. That’s where we can improve compliance and lead to an overall very satisfactory patient visit.”
To illustrate this point, she discussed the case of a four-year-old black female with a 9-month history of bad dandruff. The child’s mother reports thick flakes that never go away. She takes pride in caring for her daughter’s hair, and shampoos it every two weeks. “She tells me that during the 2.5 hours that it takes her on Saturdays to shampoo, detangle, and comb her daughter’s hair, which she then braids or cornrows and adorns with barrettes or balls, it is a great bonding experience for the two of them,” Dr. Taylor said. “The flakes are temporarily better after she ‘greases’ her daughter’s scalp, but after 2-3 days, they are back.”
In a case like this, Dr. Taylor recommends asking the parent or caregiver to join you while you examine the scalp. This way, the focus becomes the child’s scalp, and the parent is not just staring at your expressions. “The child also observes the pediatric dermatologist and parent/caregiver working together as a team,” she said. “You also want to ask the parent to remove the hair adornments. This makes the child feel more comfortable. It also allows you to observe how the hair is being managed. Are the adornments being removed gently? Is there aggressive pulling of the hair when they take out the braids? Is the child visibly wincing in pain? If the latter two happen this is a teachable moment. You can point out, ‘It looks like Susie is in pain. Let’s do it a little more gently. That might prevent further hair breakage.’ ”
The differential diagnosis of a scaly pediatric scalp includes infrequent shampooing, seborrheic dermatitis, tinea capitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis. The type of hairstyle also factors in. For example, cornrows are a popular hair styling option among ethnic patients. “These are very popular and very time consuming and may lead to infrequent shampooing,” she said. “If they’re put in very tightly or if they have beads or other adornments, it can lead to traction alopecia.” Twists, meanwhile, can create tension on the hair, while puffs can cause traction alopecia if they’re pulled too tightly. “Although dreadlocks are more common among adolescents, we’re seeing them more commonly in young children,” she said. “They can be very long and wavy and lead to traction alopecia.”
The time required to shampoo, detangle, and style tightly coiled African American hair can be significant. For example, in children with cornrows or braids with extensions, Dr. Taylor said that it might require 30 minutes to as long as 2 or 3 hours to remove their current hairstyle, followed by shampooing and conditioning. “Detangling can take at least 15 minutes. In tightly coiled African American hair, studies have demonstrated that detangling while the hair is wet is best, because you have fewer forces on that comb and the hair is less likely to break, as opposed to detangling when the hair is dry. After the wet hair is detangled and the conditioner is rinsed out, a leave-in conditioner is often applied. Then the hair is detangled again, which can take up to an hour, followed by styling, which can take 1-3 hours. That gives you some insight as to why there can often be infrequent shampooing.”
The recommended frequency of shampooing depends on the hairstyle selected. Many children with braids and extensions will have those braids and extensions taken out every six to 12 weeks, “but that doesn’t mean that the scalp can’t be shampooed,” Dr. Taylor said. “The scalp should be shampooed more often. Economics and socioeconomic status play into the frequency of shampooing. For example, if a parent or a caregiver sends a child to a hair stylist, that can range in price from $45 to $65 or more. Time also factors in. In the black community in particular, it’s a ritual on a Saturday to get your hair done. If the parent or caregiver works on weekends, that’s going to impact the frequency of shampooing.”
Dr. Taylor underscored the importance of framing the history-taking process to avoid common pitfall questions like “Do you wash the child’s hair every day or every other day?” or “Do you use dandruff shampoo every day?” It is important to remember that “the parent’s inherent perception is of a doctor who does not have my hair probably does not understand my hair or my child’s hair,” she said. “It’s unlikely that you’re going to find a parent who shampoos their child’s hair every day or every other day. Maybe once a week, probably biweekly. It’s important to ask culturally competent questions.”
She also advises against asking about shampooing when you’re examining the child’s hair, “because there’s going to be the perception that you may think the scalp is dirty,” Dr. Taylor explained. “You probably want to ask that when gathering the history of present illness. The culturally competent question is going to be, ‘Do you wash her/his hair weekly, every other week, monthly, or does it depend on the hair style?’ ”
Body language is also important. “Don’t lean in from afar when examining the patient,” she said. “Get up close and touch the child’s hair.” If you choose to wear surgical gloves for the exam “don’t hold your hands in the surgical scrub position,” she recommended. “Hold your hands in a more neutral position. I think it’s important to touch the hair.”
Referring back to the 4-year-old black child with bad dandruff, she said that a diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is unlikely since that condition usually occurs during puberty. “You should have a high index of suspicion for tinea capitis,” she said. “If the patient has occipital lymphadenopathy plus scaling of the scalp or alopecia, that’s enough to presumptively treat for tinea capitis. There are studies that support that.”
For established tinea capitis, Dr. Taylor advises parents to wash barrettes and other hair adornments in hot soapy water or in the dishwasher. She also recommends disposal of hair oil, pomade, and grease and shampooing the child’s hair with ketoconazole and use a conditioner to decrease household and patient spread, which decreases transmissible fungal spores. “There’s a misperception that the application of hair oils and grease can increase the rate of tinea capitis,” she noted. “That’s not true. However, if hair grease and hair oil is applied to the scalp within one week of culture, it could produce a false negative culture.”
For established seborrheic dermatitis, antifungal shampoos including ketoconazole, ciclopirox, and selenium sulfide may be too drying for ethnic hair, “which already has a propensity to break,” she said. “Instead, we recommend a 5-10 minute scalp contact time with the shampoo and avoid contact with strands of hair. Shampoo hair strands with a conditioning shampoo followed by a conditioner to limit hair breakage. We suggest once weekly or biweekly shampooing.”
Dr. Taylor disclosed that she has advisory board and/or investigator relationships with Aclaris Therapeutics, Allergan, Beiersdorf, Croma Pharmaceuticals, Galderma, Isdin, Johnson & Johnson, and Unilever. She also acknowledged Candrice R. Heath, MD, a dermatologist based in Newark, Delaware, for her assistance with the presentation content.
dbrunk@mdedge.com
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – The way Susan C. Taylor, MD, sees it,
At the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, Dr. Taylor, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, defined culturally competent care as a patient-centered approach in which clinicians establish a rapport with the patient and the caregiver. “It’s important that we ask the right questions,” she said. “In doing so, we have to be familiar with common hair care practices. It’s important that we respect our patients’ values, their goals, their health needs, and, of course, their cultural background. Finally, we have to engage in shared decision making. That’s where we can improve compliance and lead to an overall very satisfactory patient visit.”
To illustrate this point, she discussed the case of a four-year-old black female with a 9-month history of bad dandruff. The child’s mother reports thick flakes that never go away. She takes pride in caring for her daughter’s hair, and shampoos it every two weeks. “She tells me that during the 2.5 hours that it takes her on Saturdays to shampoo, detangle, and comb her daughter’s hair, which she then braids or cornrows and adorns with barrettes or balls, it is a great bonding experience for the two of them,” Dr. Taylor said. “The flakes are temporarily better after she ‘greases’ her daughter’s scalp, but after 2-3 days, they are back.”
In a case like this, Dr. Taylor recommends asking the parent or caregiver to join you while you examine the scalp. This way, the focus becomes the child’s scalp, and the parent is not just staring at your expressions. “The child also observes the pediatric dermatologist and parent/caregiver working together as a team,” she said. “You also want to ask the parent to remove the hair adornments. This makes the child feel more comfortable. It also allows you to observe how the hair is being managed. Are the adornments being removed gently? Is there aggressive pulling of the hair when they take out the braids? Is the child visibly wincing in pain? If the latter two happen this is a teachable moment. You can point out, ‘It looks like Susie is in pain. Let’s do it a little more gently. That might prevent further hair breakage.’ ”
The differential diagnosis of a scaly pediatric scalp includes infrequent shampooing, seborrheic dermatitis, tinea capitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis. The type of hairstyle also factors in. For example, cornrows are a popular hair styling option among ethnic patients. “These are very popular and very time consuming and may lead to infrequent shampooing,” she said. “If they’re put in very tightly or if they have beads or other adornments, it can lead to traction alopecia.” Twists, meanwhile, can create tension on the hair, while puffs can cause traction alopecia if they’re pulled too tightly. “Although dreadlocks are more common among adolescents, we’re seeing them more commonly in young children,” she said. “They can be very long and wavy and lead to traction alopecia.”
The time required to shampoo, detangle, and style tightly coiled African American hair can be significant. For example, in children with cornrows or braids with extensions, Dr. Taylor said that it might require 30 minutes to as long as 2 or 3 hours to remove their current hairstyle, followed by shampooing and conditioning. “Detangling can take at least 15 minutes. In tightly coiled African American hair, studies have demonstrated that detangling while the hair is wet is best, because you have fewer forces on that comb and the hair is less likely to break, as opposed to detangling when the hair is dry. After the wet hair is detangled and the conditioner is rinsed out, a leave-in conditioner is often applied. Then the hair is detangled again, which can take up to an hour, followed by styling, which can take 1-3 hours. That gives you some insight as to why there can often be infrequent shampooing.”
The recommended frequency of shampooing depends on the hairstyle selected. Many children with braids and extensions will have those braids and extensions taken out every six to 12 weeks, “but that doesn’t mean that the scalp can’t be shampooed,” Dr. Taylor said. “The scalp should be shampooed more often. Economics and socioeconomic status play into the frequency of shampooing. For example, if a parent or a caregiver sends a child to a hair stylist, that can range in price from $45 to $65 or more. Time also factors in. In the black community in particular, it’s a ritual on a Saturday to get your hair done. If the parent or caregiver works on weekends, that’s going to impact the frequency of shampooing.”
Dr. Taylor underscored the importance of framing the history-taking process to avoid common pitfall questions like “Do you wash the child’s hair every day or every other day?” or “Do you use dandruff shampoo every day?” It is important to remember that “the parent’s inherent perception is of a doctor who does not have my hair probably does not understand my hair or my child’s hair,” she said. “It’s unlikely that you’re going to find a parent who shampoos their child’s hair every day or every other day. Maybe once a week, probably biweekly. It’s important to ask culturally competent questions.”
She also advises against asking about shampooing when you’re examining the child’s hair, “because there’s going to be the perception that you may think the scalp is dirty,” Dr. Taylor explained. “You probably want to ask that when gathering the history of present illness. The culturally competent question is going to be, ‘Do you wash her/his hair weekly, every other week, monthly, or does it depend on the hair style?’ ”
Body language is also important. “Don’t lean in from afar when examining the patient,” she said. “Get up close and touch the child’s hair.” If you choose to wear surgical gloves for the exam “don’t hold your hands in the surgical scrub position,” she recommended. “Hold your hands in a more neutral position. I think it’s important to touch the hair.”
Referring back to the 4-year-old black child with bad dandruff, she said that a diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is unlikely since that condition usually occurs during puberty. “You should have a high index of suspicion for tinea capitis,” she said. “If the patient has occipital lymphadenopathy plus scaling of the scalp or alopecia, that’s enough to presumptively treat for tinea capitis. There are studies that support that.”
For established tinea capitis, Dr. Taylor advises parents to wash barrettes and other hair adornments in hot soapy water or in the dishwasher. She also recommends disposal of hair oil, pomade, and grease and shampooing the child’s hair with ketoconazole and use a conditioner to decrease household and patient spread, which decreases transmissible fungal spores. “There’s a misperception that the application of hair oils and grease can increase the rate of tinea capitis,” she noted. “That’s not true. However, if hair grease and hair oil is applied to the scalp within one week of culture, it could produce a false negative culture.”
For established seborrheic dermatitis, antifungal shampoos including ketoconazole, ciclopirox, and selenium sulfide may be too drying for ethnic hair, “which already has a propensity to break,” she said. “Instead, we recommend a 5-10 minute scalp contact time with the shampoo and avoid contact with strands of hair. Shampoo hair strands with a conditioning shampoo followed by a conditioner to limit hair breakage. We suggest once weekly or biweekly shampooing.”
Dr. Taylor disclosed that she has advisory board and/or investigator relationships with Aclaris Therapeutics, Allergan, Beiersdorf, Croma Pharmaceuticals, Galderma, Isdin, Johnson & Johnson, and Unilever. She also acknowledged Candrice R. Heath, MD, a dermatologist based in Newark, Delaware, for her assistance with the presentation content.
dbrunk@mdedge.com
LAKE TAHOE, CALIF. – The way Susan C. Taylor, MD, sees it,
At the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, Dr. Taylor, a dermatologist at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, defined culturally competent care as a patient-centered approach in which clinicians establish a rapport with the patient and the caregiver. “It’s important that we ask the right questions,” she said. “In doing so, we have to be familiar with common hair care practices. It’s important that we respect our patients’ values, their goals, their health needs, and, of course, their cultural background. Finally, we have to engage in shared decision making. That’s where we can improve compliance and lead to an overall very satisfactory patient visit.”
To illustrate this point, she discussed the case of a four-year-old black female with a 9-month history of bad dandruff. The child’s mother reports thick flakes that never go away. She takes pride in caring for her daughter’s hair, and shampoos it every two weeks. “She tells me that during the 2.5 hours that it takes her on Saturdays to shampoo, detangle, and comb her daughter’s hair, which she then braids or cornrows and adorns with barrettes or balls, it is a great bonding experience for the two of them,” Dr. Taylor said. “The flakes are temporarily better after she ‘greases’ her daughter’s scalp, but after 2-3 days, they are back.”
In a case like this, Dr. Taylor recommends asking the parent or caregiver to join you while you examine the scalp. This way, the focus becomes the child’s scalp, and the parent is not just staring at your expressions. “The child also observes the pediatric dermatologist and parent/caregiver working together as a team,” she said. “You also want to ask the parent to remove the hair adornments. This makes the child feel more comfortable. It also allows you to observe how the hair is being managed. Are the adornments being removed gently? Is there aggressive pulling of the hair when they take out the braids? Is the child visibly wincing in pain? If the latter two happen this is a teachable moment. You can point out, ‘It looks like Susie is in pain. Let’s do it a little more gently. That might prevent further hair breakage.’ ”
The differential diagnosis of a scaly pediatric scalp includes infrequent shampooing, seborrheic dermatitis, tinea capitis, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and sebopsoriasis. The type of hairstyle also factors in. For example, cornrows are a popular hair styling option among ethnic patients. “These are very popular and very time consuming and may lead to infrequent shampooing,” she said. “If they’re put in very tightly or if they have beads or other adornments, it can lead to traction alopecia.” Twists, meanwhile, can create tension on the hair, while puffs can cause traction alopecia if they’re pulled too tightly. “Although dreadlocks are more common among adolescents, we’re seeing them more commonly in young children,” she said. “They can be very long and wavy and lead to traction alopecia.”
The time required to shampoo, detangle, and style tightly coiled African American hair can be significant. For example, in children with cornrows or braids with extensions, Dr. Taylor said that it might require 30 minutes to as long as 2 or 3 hours to remove their current hairstyle, followed by shampooing and conditioning. “Detangling can take at least 15 minutes. In tightly coiled African American hair, studies have demonstrated that detangling while the hair is wet is best, because you have fewer forces on that comb and the hair is less likely to break, as opposed to detangling when the hair is dry. After the wet hair is detangled and the conditioner is rinsed out, a leave-in conditioner is often applied. Then the hair is detangled again, which can take up to an hour, followed by styling, which can take 1-3 hours. That gives you some insight as to why there can often be infrequent shampooing.”
The recommended frequency of shampooing depends on the hairstyle selected. Many children with braids and extensions will have those braids and extensions taken out every six to 12 weeks, “but that doesn’t mean that the scalp can’t be shampooed,” Dr. Taylor said. “The scalp should be shampooed more often. Economics and socioeconomic status play into the frequency of shampooing. For example, if a parent or a caregiver sends a child to a hair stylist, that can range in price from $45 to $65 or more. Time also factors in. In the black community in particular, it’s a ritual on a Saturday to get your hair done. If the parent or caregiver works on weekends, that’s going to impact the frequency of shampooing.”
Dr. Taylor underscored the importance of framing the history-taking process to avoid common pitfall questions like “Do you wash the child’s hair every day or every other day?” or “Do you use dandruff shampoo every day?” It is important to remember that “the parent’s inherent perception is of a doctor who does not have my hair probably does not understand my hair or my child’s hair,” she said. “It’s unlikely that you’re going to find a parent who shampoos their child’s hair every day or every other day. Maybe once a week, probably biweekly. It’s important to ask culturally competent questions.”
She also advises against asking about shampooing when you’re examining the child’s hair, “because there’s going to be the perception that you may think the scalp is dirty,” Dr. Taylor explained. “You probably want to ask that when gathering the history of present illness. The culturally competent question is going to be, ‘Do you wash her/his hair weekly, every other week, monthly, or does it depend on the hair style?’ ”
Body language is also important. “Don’t lean in from afar when examining the patient,” she said. “Get up close and touch the child’s hair.” If you choose to wear surgical gloves for the exam “don’t hold your hands in the surgical scrub position,” she recommended. “Hold your hands in a more neutral position. I think it’s important to touch the hair.”
Referring back to the 4-year-old black child with bad dandruff, she said that a diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is unlikely since that condition usually occurs during puberty. “You should have a high index of suspicion for tinea capitis,” she said. “If the patient has occipital lymphadenopathy plus scaling of the scalp or alopecia, that’s enough to presumptively treat for tinea capitis. There are studies that support that.”
For established tinea capitis, Dr. Taylor advises parents to wash barrettes and other hair adornments in hot soapy water or in the dishwasher. She also recommends disposal of hair oil, pomade, and grease and shampooing the child’s hair with ketoconazole and use a conditioner to decrease household and patient spread, which decreases transmissible fungal spores. “There’s a misperception that the application of hair oils and grease can increase the rate of tinea capitis,” she noted. “That’s not true. However, if hair grease and hair oil is applied to the scalp within one week of culture, it could produce a false negative culture.”
For established seborrheic dermatitis, antifungal shampoos including ketoconazole, ciclopirox, and selenium sulfide may be too drying for ethnic hair, “which already has a propensity to break,” she said. “Instead, we recommend a 5-10 minute scalp contact time with the shampoo and avoid contact with strands of hair. Shampoo hair strands with a conditioning shampoo followed by a conditioner to limit hair breakage. We suggest once weekly or biweekly shampooing.”
Dr. Taylor disclosed that she has advisory board and/or investigator relationships with Aclaris Therapeutics, Allergan, Beiersdorf, Croma Pharmaceuticals, Galderma, Isdin, Johnson & Johnson, and Unilever. She also acknowledged Candrice R. Heath, MD, a dermatologist based in Newark, Delaware, for her assistance with the presentation content.
dbrunk@mdedge.com
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE SPD ANNUAL MEETING
Taking the sting out of nail surgery: Postoperative pain pearls
CHICAGO – In a busy clinic it can be hard to find the time to stop, talk, and listen. But doing so will “pay dividends in time spent later – and in reduced complications” of nail surgery, according to Molly A. Hinshaw, MD.
Dr. Hinshaw, director of the nail clinic at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, shared her
“One pearl is the importance of patient education before we start,” Dr. Hinshaw said. Preoperatively, she takes time to talk through the entire surgery and expected postoperative course. Critically, she reassures patients that pain will be controlled; she also reviews in detail what the pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic pain control strategies will be.
In addition, it’s important to address patients’ natural anxiety about what the surgical site will look and feel like and how healing will progress, particularly in those first few days after surgery. “I offer a first dressing change in my practice, either at 24 or 48 hours. This can be very anxiolytic for the patient,” she said.
At the preoperative stage, Dr. Hinshaw also tells patients that, from a healing and pain management standpoint, to make sure they plan “to have a restful 48 hours after surgery.” Her patient instructions for the immediate postoperative period include keeping the limb elevated and avoiding unnecessary activity with the affected limb while the digit, whether a finger or toe, is still anesthetized. To stay on top of the pain, the appropriate oral pain medication should be started once sensation starts to return to the digit. She recommends patients also take a dose of their pain medication at bedtime, as this will help them get a restful night of sleep.
“One thing that I’ve learned over the years is that throbbing and a little bit of swelling after surgery is not uncommon,” said Dr. Hinshaw, who uses elastic self-adherent wrap for the top layer of wound dressings after nail surgery. She tells her patients, “if you’re feeling throbbing, you’re welcome to unwrap it and rewrap it more loosely.” Just giving the patient the ability to find a comfortable level of pressure on the affected digit is often enough to alleviate the throbbing, as opposed to treating that throbbing with pain medication.
Dr. Hinshaw said she’s learned to tailor her postoperative analgesia to the surgery and to the patient. With all patients, she is sure to make medication and dosing choices that take comorbidities and potential drug-drug interactions into account. She does not ask patients to stop anticoagulation before nail procedures.
For phenolization procedures and punch biopsies, she’ll advise patients to use acetaminophen or NSAIDs. Some procedures are going to have a more painful recovery course, said Dr. Hinshaw, so she’ll use an opioid such as hydrocodone with acetaminophen for shave excisions and fusiform longitudinal excisions.
The physician and patient can also plan ahead for a brief course of more potent opioids for some procedures. “Certainly for lateral longitudinal excisions, they will need narcotic pain management for at least 48 hours after surgery,” she noted. “It’s a painful surgery.”
Other procedures that will need more postoperative analgesia include flaps and nail unit grafts, she said. In general, NSAIDs are useful to add after the first 24 hours. In addition, “I always call my patients the day after surgery to see how they’re doing. This helps identify any issues and questions early and is comforting to the patient,” she added.
Dr. Hinshaw disclosed that she has an ownership stake in and sits on the board of directors of Accure Medical.
CHICAGO – In a busy clinic it can be hard to find the time to stop, talk, and listen. But doing so will “pay dividends in time spent later – and in reduced complications” of nail surgery, according to Molly A. Hinshaw, MD.
Dr. Hinshaw, director of the nail clinic at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, shared her
“One pearl is the importance of patient education before we start,” Dr. Hinshaw said. Preoperatively, she takes time to talk through the entire surgery and expected postoperative course. Critically, she reassures patients that pain will be controlled; she also reviews in detail what the pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic pain control strategies will be.
In addition, it’s important to address patients’ natural anxiety about what the surgical site will look and feel like and how healing will progress, particularly in those first few days after surgery. “I offer a first dressing change in my practice, either at 24 or 48 hours. This can be very anxiolytic for the patient,” she said.
At the preoperative stage, Dr. Hinshaw also tells patients that, from a healing and pain management standpoint, to make sure they plan “to have a restful 48 hours after surgery.” Her patient instructions for the immediate postoperative period include keeping the limb elevated and avoiding unnecessary activity with the affected limb while the digit, whether a finger or toe, is still anesthetized. To stay on top of the pain, the appropriate oral pain medication should be started once sensation starts to return to the digit. She recommends patients also take a dose of their pain medication at bedtime, as this will help them get a restful night of sleep.
“One thing that I’ve learned over the years is that throbbing and a little bit of swelling after surgery is not uncommon,” said Dr. Hinshaw, who uses elastic self-adherent wrap for the top layer of wound dressings after nail surgery. She tells her patients, “if you’re feeling throbbing, you’re welcome to unwrap it and rewrap it more loosely.” Just giving the patient the ability to find a comfortable level of pressure on the affected digit is often enough to alleviate the throbbing, as opposed to treating that throbbing with pain medication.
Dr. Hinshaw said she’s learned to tailor her postoperative analgesia to the surgery and to the patient. With all patients, she is sure to make medication and dosing choices that take comorbidities and potential drug-drug interactions into account. She does not ask patients to stop anticoagulation before nail procedures.
For phenolization procedures and punch biopsies, she’ll advise patients to use acetaminophen or NSAIDs. Some procedures are going to have a more painful recovery course, said Dr. Hinshaw, so she’ll use an opioid such as hydrocodone with acetaminophen for shave excisions and fusiform longitudinal excisions.
The physician and patient can also plan ahead for a brief course of more potent opioids for some procedures. “Certainly for lateral longitudinal excisions, they will need narcotic pain management for at least 48 hours after surgery,” she noted. “It’s a painful surgery.”
Other procedures that will need more postoperative analgesia include flaps and nail unit grafts, she said. In general, NSAIDs are useful to add after the first 24 hours. In addition, “I always call my patients the day after surgery to see how they’re doing. This helps identify any issues and questions early and is comforting to the patient,” she added.
Dr. Hinshaw disclosed that she has an ownership stake in and sits on the board of directors of Accure Medical.
CHICAGO – In a busy clinic it can be hard to find the time to stop, talk, and listen. But doing so will “pay dividends in time spent later – and in reduced complications” of nail surgery, according to Molly A. Hinshaw, MD.
Dr. Hinshaw, director of the nail clinic at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, shared her
“One pearl is the importance of patient education before we start,” Dr. Hinshaw said. Preoperatively, she takes time to talk through the entire surgery and expected postoperative course. Critically, she reassures patients that pain will be controlled; she also reviews in detail what the pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic pain control strategies will be.
In addition, it’s important to address patients’ natural anxiety about what the surgical site will look and feel like and how healing will progress, particularly in those first few days after surgery. “I offer a first dressing change in my practice, either at 24 or 48 hours. This can be very anxiolytic for the patient,” she said.
At the preoperative stage, Dr. Hinshaw also tells patients that, from a healing and pain management standpoint, to make sure they plan “to have a restful 48 hours after surgery.” Her patient instructions for the immediate postoperative period include keeping the limb elevated and avoiding unnecessary activity with the affected limb while the digit, whether a finger or toe, is still anesthetized. To stay on top of the pain, the appropriate oral pain medication should be started once sensation starts to return to the digit. She recommends patients also take a dose of their pain medication at bedtime, as this will help them get a restful night of sleep.
“One thing that I’ve learned over the years is that throbbing and a little bit of swelling after surgery is not uncommon,” said Dr. Hinshaw, who uses elastic self-adherent wrap for the top layer of wound dressings after nail surgery. She tells her patients, “if you’re feeling throbbing, you’re welcome to unwrap it and rewrap it more loosely.” Just giving the patient the ability to find a comfortable level of pressure on the affected digit is often enough to alleviate the throbbing, as opposed to treating that throbbing with pain medication.
Dr. Hinshaw said she’s learned to tailor her postoperative analgesia to the surgery and to the patient. With all patients, she is sure to make medication and dosing choices that take comorbidities and potential drug-drug interactions into account. She does not ask patients to stop anticoagulation before nail procedures.
For phenolization procedures and punch biopsies, she’ll advise patients to use acetaminophen or NSAIDs. Some procedures are going to have a more painful recovery course, said Dr. Hinshaw, so she’ll use an opioid such as hydrocodone with acetaminophen for shave excisions and fusiform longitudinal excisions.
The physician and patient can also plan ahead for a brief course of more potent opioids for some procedures. “Certainly for lateral longitudinal excisions, they will need narcotic pain management for at least 48 hours after surgery,” she noted. “It’s a painful surgery.”
Other procedures that will need more postoperative analgesia include flaps and nail unit grafts, she said. In general, NSAIDs are useful to add after the first 24 hours. In addition, “I always call my patients the day after surgery to see how they’re doing. This helps identify any issues and questions early and is comforting to the patient,” she added.
Dr. Hinshaw disclosed that she has an ownership stake in and sits on the board of directors of Accure Medical.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM SUMMER AAD 2018
Solitary Nodule on the Proximal Nail Fold
The Diagnosis: Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma
A shave biopsy revealed an uninvolved grenz zone and mildly cellular spindle cell dermal proliferation in a collagenous and myxoid background (Figure 1). Spindle cells were seen in a myxoid background among dense coarse collagen (Figure 2A). Spindle cells also were seen in a myxoid background with mast cells and capillary network (Figure 2B). Histopathologic examination of the biopsy specimen revealed spindle cells that were diffusely positive for CD34 (Figure 3); focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen; and negative for melanocytic markers, smooth muscle markers, and cytokeratin. A diagnosis of superficial acral fibromyxoma (SAFM) was made based on clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical findings.
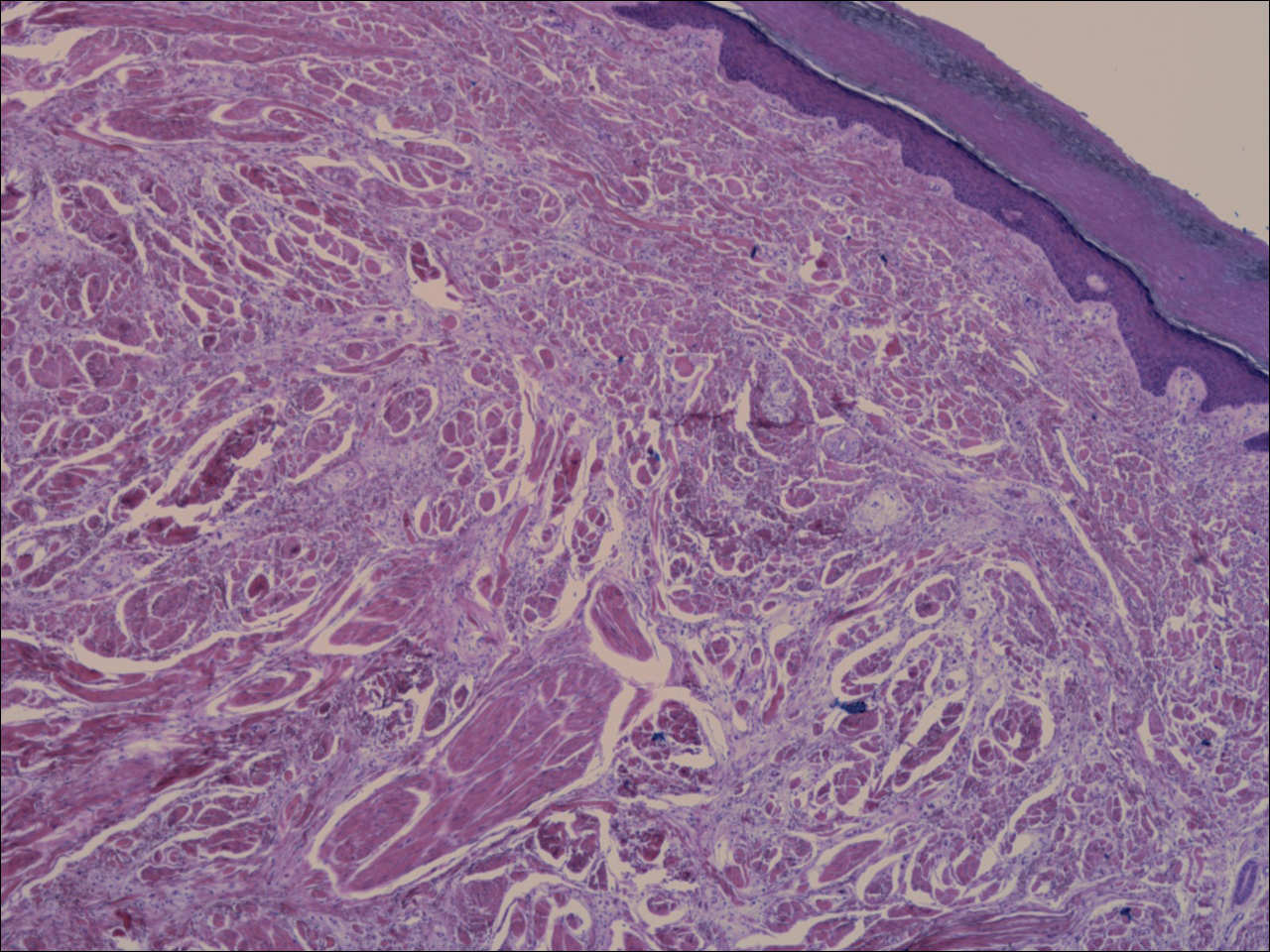
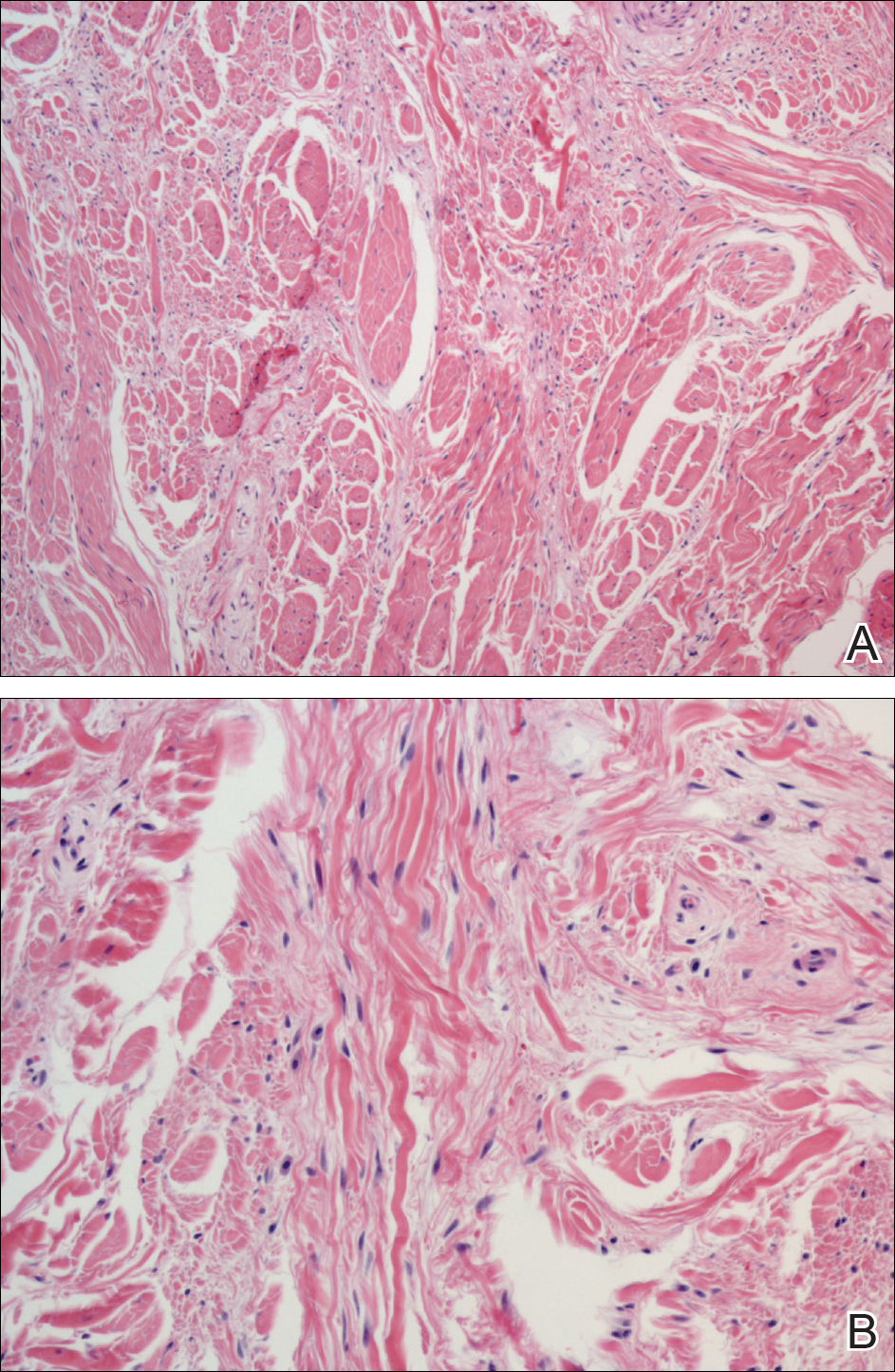
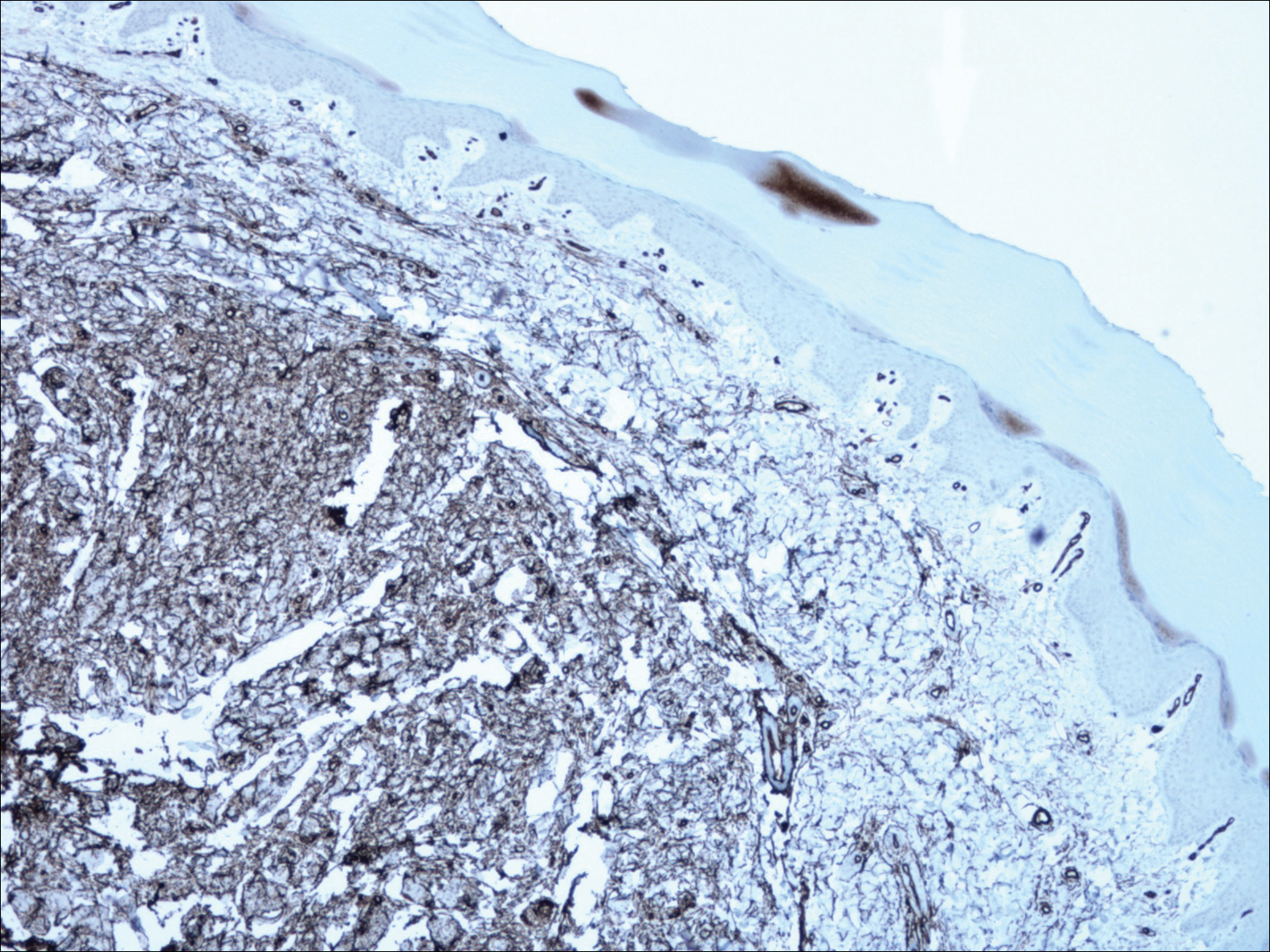
Superficial acral fibromyxomas, also known as digital fibromyxomas, are soft, slow-growing tumors that have a predilection for subungual or periungual regions of the hands and feet. Superficial acral fibromyxomas most frequently occur on the hallux and rarely occur on the ankle or leg. They can present as nodular, dome-shaped, polyploid, or verrucous masses. They can be soft to firm, gelatinous or solid, off-white to gray-white and can have fasciculate cut surfaces. Superficial acral fibromyxomas can be either painful or painless and present with a deformed nail in 9% of cases. Superficial acral fibromyxoma is a superficial lesion with frequent infiltration of the dermal collagen and subcutaneous tissue and may even erode or infiltrate into the underlying bone in rare cases.1-4 Although SAFMs are rare tumors, documented cases of SAFM have been reported at an increasing rate since the first published report by Fetsch et al2 in 2001.
Patients often delay seeking medical treatment and present with a solitary mass that has been slowly growing for months to years. In a study of 124 patients, Hollmann et al1 found that symptoms exist for a mean of 35 months and present with a small mass with a mean tumor size of 1.7 cm before biopsy or excision. Although the age range is broad, SAFM mostly affects middle-aged adults (median age, 49 years).1 Hollmann et al1 also reported a male predominance (1.3:1 ratio), and preexisting local trauma is reported in 25% of cases.2-4
The differential for SAFM should include dermatofibroma, keloid, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, acquired digital fibrokeratoma, infantile digital fibromatosis, neurolemmoma, sclerosing perineurioma, superficial angiomyxoma, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, and acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma.1-4
Superficial acral fibromyxomas are composed of CD34+ spindle or stellate-shaped cells that are embedded in a myxoid and/or dense hyalinized collagenous stroma in a random or loosely fascicular growth pattern. The spindle or stellate-shaped cells in SAFMs also have been found to be focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen and CD99. Lesions have accentuated microvasculature and increased mast cells.5-8
Conservative management is reasonable, but patients presenting with persistent pain and/or local deformity should be definitively treated with complete excision and follow-up. Hollmann et al1 found that 24% of tumors recurred locally upon incomplete excision after a mean interval of 27 months. All recurrent tumors had positive margins at excision or initial biopsy.1 To date, no reports of tumors metastasizing have been documented.1-4
- Hollmann TJ, Bovée JV, Fletcher CD. Digital fibromyxoma (superficial acral fibromyxoma): a detailed characterization of 124 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:789-798.
- Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Miettinen M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 37 cases of a distinctive soft tissue tumor with a predilection for the fingers and toes. Hum Pathol. 2001;32:704-714.
- Al-Daraji WI, Miettinen M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: a clinicopathological analysis of 32 tumors including 4 in the heel. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:1020-1026.
- Ashby-Richardson H, Rogers GS, Stadecker MJ. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: an overview. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:1064-1066.
- Quaba O, Evans A, Al-Nafussi AA, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:561-564.
- Oteo-Alvaro A, Meizoso T, Scarpellini A, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma of the toe, with erosion of the distal phalanx: a clinical report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128:271-274.
- Meyerle J, Keller RA, Krivda SJ. Superficial acral fibromyxoma of the index finger. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:134-136.
- Kazakov DV, Mentzel T, Buro G, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: report of two cases. Dermatology. 2002;205:285-288.
The Diagnosis: Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma
A shave biopsy revealed an uninvolved grenz zone and mildly cellular spindle cell dermal proliferation in a collagenous and myxoid background (Figure 1). Spindle cells were seen in a myxoid background among dense coarse collagen (Figure 2A). Spindle cells also were seen in a myxoid background with mast cells and capillary network (Figure 2B). Histopathologic examination of the biopsy specimen revealed spindle cells that were diffusely positive for CD34 (Figure 3); focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen; and negative for melanocytic markers, smooth muscle markers, and cytokeratin. A diagnosis of superficial acral fibromyxoma (SAFM) was made based on clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical findings.



Superficial acral fibromyxomas, also known as digital fibromyxomas, are soft, slow-growing tumors that have a predilection for subungual or periungual regions of the hands and feet. Superficial acral fibromyxomas most frequently occur on the hallux and rarely occur on the ankle or leg. They can present as nodular, dome-shaped, polyploid, or verrucous masses. They can be soft to firm, gelatinous or solid, off-white to gray-white and can have fasciculate cut surfaces. Superficial acral fibromyxomas can be either painful or painless and present with a deformed nail in 9% of cases. Superficial acral fibromyxoma is a superficial lesion with frequent infiltration of the dermal collagen and subcutaneous tissue and may even erode or infiltrate into the underlying bone in rare cases.1-4 Although SAFMs are rare tumors, documented cases of SAFM have been reported at an increasing rate since the first published report by Fetsch et al2 in 2001.
Patients often delay seeking medical treatment and present with a solitary mass that has been slowly growing for months to years. In a study of 124 patients, Hollmann et al1 found that symptoms exist for a mean of 35 months and present with a small mass with a mean tumor size of 1.7 cm before biopsy or excision. Although the age range is broad, SAFM mostly affects middle-aged adults (median age, 49 years).1 Hollmann et al1 also reported a male predominance (1.3:1 ratio), and preexisting local trauma is reported in 25% of cases.2-4
The differential for SAFM should include dermatofibroma, keloid, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, acquired digital fibrokeratoma, infantile digital fibromatosis, neurolemmoma, sclerosing perineurioma, superficial angiomyxoma, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, and acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma.1-4
Superficial acral fibromyxomas are composed of CD34+ spindle or stellate-shaped cells that are embedded in a myxoid and/or dense hyalinized collagenous stroma in a random or loosely fascicular growth pattern. The spindle or stellate-shaped cells in SAFMs also have been found to be focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen and CD99. Lesions have accentuated microvasculature and increased mast cells.5-8
Conservative management is reasonable, but patients presenting with persistent pain and/or local deformity should be definitively treated with complete excision and follow-up. Hollmann et al1 found that 24% of tumors recurred locally upon incomplete excision after a mean interval of 27 months. All recurrent tumors had positive margins at excision or initial biopsy.1 To date, no reports of tumors metastasizing have been documented.1-4
The Diagnosis: Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma
A shave biopsy revealed an uninvolved grenz zone and mildly cellular spindle cell dermal proliferation in a collagenous and myxoid background (Figure 1). Spindle cells were seen in a myxoid background among dense coarse collagen (Figure 2A). Spindle cells also were seen in a myxoid background with mast cells and capillary network (Figure 2B). Histopathologic examination of the biopsy specimen revealed spindle cells that were diffusely positive for CD34 (Figure 3); focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen; and negative for melanocytic markers, smooth muscle markers, and cytokeratin. A diagnosis of superficial acral fibromyxoma (SAFM) was made based on clinical, histopathologic, and immunohistochemical findings.



Superficial acral fibromyxomas, also known as digital fibromyxomas, are soft, slow-growing tumors that have a predilection for subungual or periungual regions of the hands and feet. Superficial acral fibromyxomas most frequently occur on the hallux and rarely occur on the ankle or leg. They can present as nodular, dome-shaped, polyploid, or verrucous masses. They can be soft to firm, gelatinous or solid, off-white to gray-white and can have fasciculate cut surfaces. Superficial acral fibromyxomas can be either painful or painless and present with a deformed nail in 9% of cases. Superficial acral fibromyxoma is a superficial lesion with frequent infiltration of the dermal collagen and subcutaneous tissue and may even erode or infiltrate into the underlying bone in rare cases.1-4 Although SAFMs are rare tumors, documented cases of SAFM have been reported at an increasing rate since the first published report by Fetsch et al2 in 2001.
Patients often delay seeking medical treatment and present with a solitary mass that has been slowly growing for months to years. In a study of 124 patients, Hollmann et al1 found that symptoms exist for a mean of 35 months and present with a small mass with a mean tumor size of 1.7 cm before biopsy or excision. Although the age range is broad, SAFM mostly affects middle-aged adults (median age, 49 years).1 Hollmann et al1 also reported a male predominance (1.3:1 ratio), and preexisting local trauma is reported in 25% of cases.2-4
The differential for SAFM should include dermatofibroma, keloid, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, acquired digital fibrokeratoma, infantile digital fibromatosis, neurolemmoma, sclerosing perineurioma, superficial angiomyxoma, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, and acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma.1-4
Superficial acral fibromyxomas are composed of CD34+ spindle or stellate-shaped cells that are embedded in a myxoid and/or dense hyalinized collagenous stroma in a random or loosely fascicular growth pattern. The spindle or stellate-shaped cells in SAFMs also have been found to be focally positive for epithelial membrane antigen and CD99. Lesions have accentuated microvasculature and increased mast cells.5-8
Conservative management is reasonable, but patients presenting with persistent pain and/or local deformity should be definitively treated with complete excision and follow-up. Hollmann et al1 found that 24% of tumors recurred locally upon incomplete excision after a mean interval of 27 months. All recurrent tumors had positive margins at excision or initial biopsy.1 To date, no reports of tumors metastasizing have been documented.1-4
- Hollmann TJ, Bovée JV, Fletcher CD. Digital fibromyxoma (superficial acral fibromyxoma): a detailed characterization of 124 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:789-798.
- Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Miettinen M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 37 cases of a distinctive soft tissue tumor with a predilection for the fingers and toes. Hum Pathol. 2001;32:704-714.
- Al-Daraji WI, Miettinen M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: a clinicopathological analysis of 32 tumors including 4 in the heel. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:1020-1026.
- Ashby-Richardson H, Rogers GS, Stadecker MJ. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: an overview. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:1064-1066.
- Quaba O, Evans A, Al-Nafussi AA, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:561-564.
- Oteo-Alvaro A, Meizoso T, Scarpellini A, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma of the toe, with erosion of the distal phalanx: a clinical report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128:271-274.
- Meyerle J, Keller RA, Krivda SJ. Superficial acral fibromyxoma of the index finger. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:134-136.
- Kazakov DV, Mentzel T, Buro G, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: report of two cases. Dermatology. 2002;205:285-288.
- Hollmann TJ, Bovée JV, Fletcher CD. Digital fibromyxoma (superficial acral fibromyxoma): a detailed characterization of 124 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:789-798.
- Fetsch JF, Laskin WB, Miettinen M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 37 cases of a distinctive soft tissue tumor with a predilection for the fingers and toes. Hum Pathol. 2001;32:704-714.
- Al-Daraji WI, Miettinen M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: a clinicopathological analysis of 32 tumors including 4 in the heel. J Cutan Pathol. 2008;35:1020-1026.
- Ashby-Richardson H, Rogers GS, Stadecker MJ. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: an overview. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2011;135:1064-1066.
- Quaba O, Evans A, Al-Nafussi AA, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. Br J Plast Surg. 2005;58:561-564.
- Oteo-Alvaro A, Meizoso T, Scarpellini A, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma of the toe, with erosion of the distal phalanx: a clinical report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128:271-274.
- Meyerle J, Keller RA, Krivda SJ. Superficial acral fibromyxoma of the index finger. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50:134-136.
- Kazakov DV, Mentzel T, Buro G, et al. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: report of two cases. Dermatology. 2002;205:285-288.
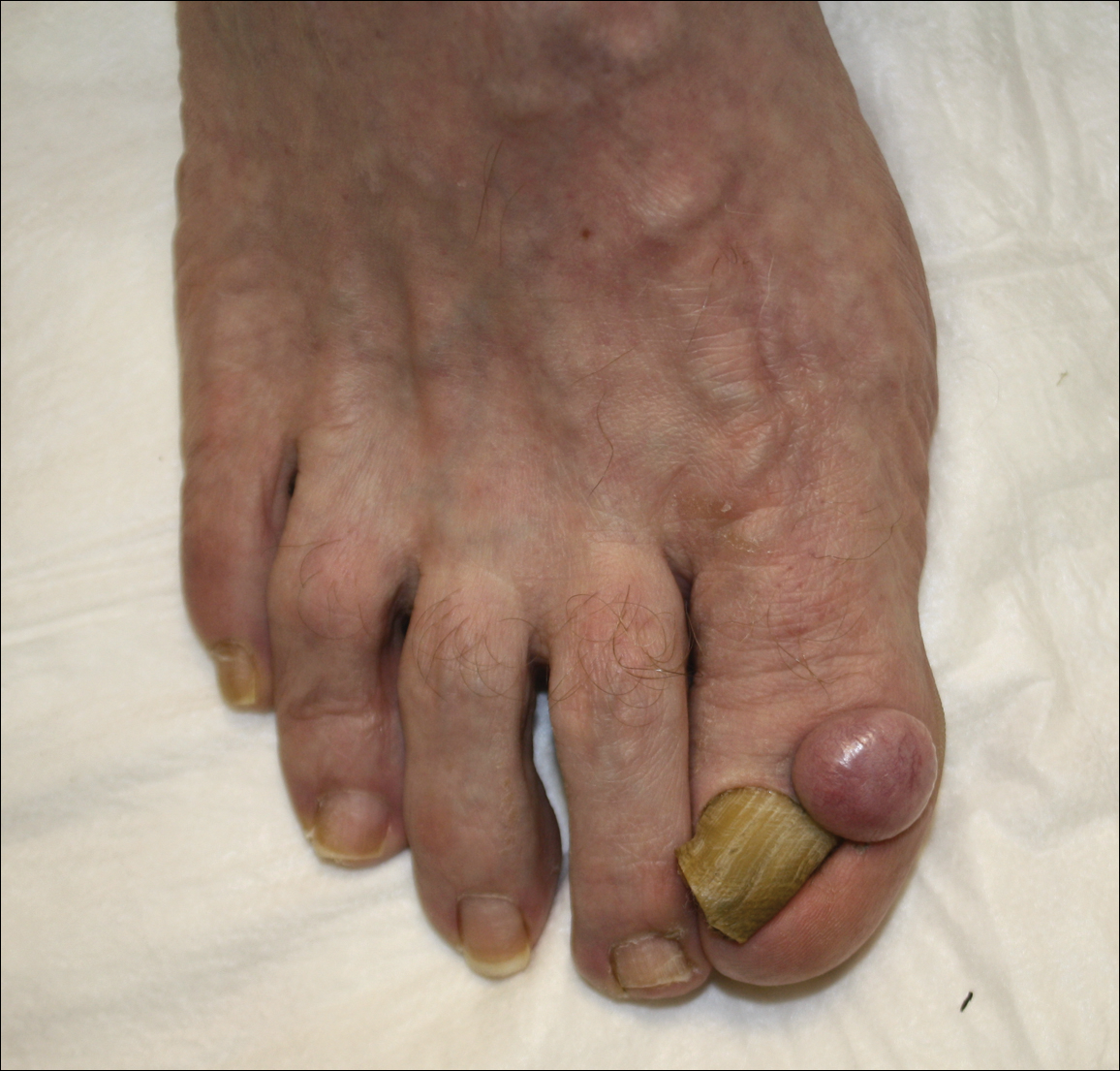
A 62-year-old man presented for evaluation of a slowly growing, nonpainful nodule on the first proximal toenail fold of the right foot of 6 years' duration. He reported that the nail plate of the affected toe was thickened and malaligned. He denied a history of trauma. Physical examination revealed a 2.0×1.6-cm, flesh-colored, nontender, well-defined, rubbery nodule with prominent overlying tortuous telangiectases on the medial aspect of the first proximal toenail fold of the right foot. The associated nail plate was yellow, thickened, and angled laterally into the second toe. Radiograph of the right hallux identified a soft tissue density contiguous with the dorsal aspect of the distal portion of the phalanx. There was no evidence of bony involvement. A shave saucerization biopsy specimen was obtained and sent for hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemical staining. The spindle cells were diffusely positive for CD34.
When fingernails are the clue to a bigger problem
CHICAGO – When a child or adolescent comes to the dermatologist’s office with a concern about fingernails or toenails, physician antennae may go up. “The world is different in the world of pediatrics – and even in the world of adolescents,” said Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD.
In adults, the most common cause of nail dystrophy is tinea, but for younger pediatric patients, less than 1% of nail problems are attributable to fungus, so dermatologists may need to look further.
“It’s so important in kids to do a good history and physical exam,” said Dr. Friedlander, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. History-taking should include determining whether the condition has been present since birth and how nail appearance has changed over time.
For Dr. Friedlander, the approach to nail abnormalities includes a full head and skin exam. “I always look at the teeth, the hair, the skin,” she said; underlying bony anomalies also may surface. A complete exam often will turn up important clues if a syndrome underpins the nail abnormalities, she said, speaking at the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
Her exemplar patient, she said, is a 19-year-old male who comes in with a parent because he’s bothered by his fingernails, which are dystrophic and small. A head-to-toe exam shows micronychia of both toes and fingers, with lunulae that are triangularly shaped. The hair, skin, and teeth of the patient all were normal in appearance. However, “The knees and elbows were odd,” Dr. Friedlander said.
This patient has nail-patella syndrome. “Even though it’s rare, I want you to think about it,” Dr. Friedlander said. The autosomal dominant condition is seen in about 1 in 50,000 patients. It’s thought to be caused by heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in gene LMX1B, she said, that codes for a LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta.
Though the small nails and triangular lunulae may be what brings the patient to the dermatologist’s office, a careful exam and one radiograph can pick up a tetrad of anomalies, Dr. Friedlander said. Abnormalities can be seen in both the knees and elbows; the patellae are often small, and may even be absent. In addition, a hip radiograph will show characteristic “horns” on the posterior iliac crests.
Coming back to the dermatologic exam, Dr. Friedlander said nails may be absent, hypoplastic, and dystrophic – but those are features that can be shared with other nail disorders, inherited and acquired. The pathognomonic finding for nail-patella syndrome is the presence of the triangular lunula, she said.
Now that the diagnosis has been made, Dr. Friedlander asked about this young man: “Where will you refer him?” Knowing the diagnosis means that there are a lot of calls for your staff to make, she said.
The patient with knee patella syndrome should be referred to an orthopedist to assess knees and elbows; radial head subluxation also is common in these patients, she said.
An ophthalmologic referral is important as well; hyperpigmentation of the pupillary margin – a “Lester iris” – can be seen, and increased rates of cataracts and glaucoma also are associated with nail-patella syndrome.
“,” Dr. Friedlander said. Up to half of nail-patella syndrome patients will have kidney involvement that initially presents with hematuria and proteinuria. Because the LMX1B mutation impairs how podocytes and glomerular filtration slits develop and function, up to 10% can develop end-stage renal failure, she said.
Parents also should be on the lookout for associated behavioral issues: “The other thing that’s interesting is that these kids have an increased risk of [attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder] and major depression,” Dr. Friedlander said.
Dr. Friedlander reported that she had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Friedlander, S. Summer AAD 2018. Session F004.
CHICAGO – When a child or adolescent comes to the dermatologist’s office with a concern about fingernails or toenails, physician antennae may go up. “The world is different in the world of pediatrics – and even in the world of adolescents,” said Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD.
In adults, the most common cause of nail dystrophy is tinea, but for younger pediatric patients, less than 1% of nail problems are attributable to fungus, so dermatologists may need to look further.
“It’s so important in kids to do a good history and physical exam,” said Dr. Friedlander, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. History-taking should include determining whether the condition has been present since birth and how nail appearance has changed over time.
For Dr. Friedlander, the approach to nail abnormalities includes a full head and skin exam. “I always look at the teeth, the hair, the skin,” she said; underlying bony anomalies also may surface. A complete exam often will turn up important clues if a syndrome underpins the nail abnormalities, she said, speaking at the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
Her exemplar patient, she said, is a 19-year-old male who comes in with a parent because he’s bothered by his fingernails, which are dystrophic and small. A head-to-toe exam shows micronychia of both toes and fingers, with lunulae that are triangularly shaped. The hair, skin, and teeth of the patient all were normal in appearance. However, “The knees and elbows were odd,” Dr. Friedlander said.
This patient has nail-patella syndrome. “Even though it’s rare, I want you to think about it,” Dr. Friedlander said. The autosomal dominant condition is seen in about 1 in 50,000 patients. It’s thought to be caused by heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in gene LMX1B, she said, that codes for a LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta.
Though the small nails and triangular lunulae may be what brings the patient to the dermatologist’s office, a careful exam and one radiograph can pick up a tetrad of anomalies, Dr. Friedlander said. Abnormalities can be seen in both the knees and elbows; the patellae are often small, and may even be absent. In addition, a hip radiograph will show characteristic “horns” on the posterior iliac crests.
Coming back to the dermatologic exam, Dr. Friedlander said nails may be absent, hypoplastic, and dystrophic – but those are features that can be shared with other nail disorders, inherited and acquired. The pathognomonic finding for nail-patella syndrome is the presence of the triangular lunula, she said.
Now that the diagnosis has been made, Dr. Friedlander asked about this young man: “Where will you refer him?” Knowing the diagnosis means that there are a lot of calls for your staff to make, she said.
The patient with knee patella syndrome should be referred to an orthopedist to assess knees and elbows; radial head subluxation also is common in these patients, she said.
An ophthalmologic referral is important as well; hyperpigmentation of the pupillary margin – a “Lester iris” – can be seen, and increased rates of cataracts and glaucoma also are associated with nail-patella syndrome.
“,” Dr. Friedlander said. Up to half of nail-patella syndrome patients will have kidney involvement that initially presents with hematuria and proteinuria. Because the LMX1B mutation impairs how podocytes and glomerular filtration slits develop and function, up to 10% can develop end-stage renal failure, she said.
Parents also should be on the lookout for associated behavioral issues: “The other thing that’s interesting is that these kids have an increased risk of [attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder] and major depression,” Dr. Friedlander said.
Dr. Friedlander reported that she had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Friedlander, S. Summer AAD 2018. Session F004.
CHICAGO – When a child or adolescent comes to the dermatologist’s office with a concern about fingernails or toenails, physician antennae may go up. “The world is different in the world of pediatrics – and even in the world of adolescents,” said Sheila Fallon Friedlander, MD.
In adults, the most common cause of nail dystrophy is tinea, but for younger pediatric patients, less than 1% of nail problems are attributable to fungus, so dermatologists may need to look further.
“It’s so important in kids to do a good history and physical exam,” said Dr. Friedlander, professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. History-taking should include determining whether the condition has been present since birth and how nail appearance has changed over time.
For Dr. Friedlander, the approach to nail abnormalities includes a full head and skin exam. “I always look at the teeth, the hair, the skin,” she said; underlying bony anomalies also may surface. A complete exam often will turn up important clues if a syndrome underpins the nail abnormalities, she said, speaking at the American Academy of Dermatology summer meeting.
Her exemplar patient, she said, is a 19-year-old male who comes in with a parent because he’s bothered by his fingernails, which are dystrophic and small. A head-to-toe exam shows micronychia of both toes and fingers, with lunulae that are triangularly shaped. The hair, skin, and teeth of the patient all were normal in appearance. However, “The knees and elbows were odd,” Dr. Friedlander said.
This patient has nail-patella syndrome. “Even though it’s rare, I want you to think about it,” Dr. Friedlander said. The autosomal dominant condition is seen in about 1 in 50,000 patients. It’s thought to be caused by heterozygous loss-of-function mutations in gene LMX1B, she said, that codes for a LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta.
Though the small nails and triangular lunulae may be what brings the patient to the dermatologist’s office, a careful exam and one radiograph can pick up a tetrad of anomalies, Dr. Friedlander said. Abnormalities can be seen in both the knees and elbows; the patellae are often small, and may even be absent. In addition, a hip radiograph will show characteristic “horns” on the posterior iliac crests.
Coming back to the dermatologic exam, Dr. Friedlander said nails may be absent, hypoplastic, and dystrophic – but those are features that can be shared with other nail disorders, inherited and acquired. The pathognomonic finding for nail-patella syndrome is the presence of the triangular lunula, she said.
Now that the diagnosis has been made, Dr. Friedlander asked about this young man: “Where will you refer him?” Knowing the diagnosis means that there are a lot of calls for your staff to make, she said.
The patient with knee patella syndrome should be referred to an orthopedist to assess knees and elbows; radial head subluxation also is common in these patients, she said.
An ophthalmologic referral is important as well; hyperpigmentation of the pupillary margin – a “Lester iris” – can be seen, and increased rates of cataracts and glaucoma also are associated with nail-patella syndrome.
“,” Dr. Friedlander said. Up to half of nail-patella syndrome patients will have kidney involvement that initially presents with hematuria and proteinuria. Because the LMX1B mutation impairs how podocytes and glomerular filtration slits develop and function, up to 10% can develop end-stage renal failure, she said.
Parents also should be on the lookout for associated behavioral issues: “The other thing that’s interesting is that these kids have an increased risk of [attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder] and major depression,” Dr. Friedlander said.
Dr. Friedlander reported that she had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Friedlander, S. Summer AAD 2018. Session F004.
REPORTING FROM SUMMER AAD 2018