User login
Two Cystic Duct Stents Appear Better Than One
according to a retrospective multicenter study.
These findings suggest that endoscopists should prioritize dual stent placement when feasible, and consider adding a second stent in patients who previously received a single stent, James D. Haddad, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and colleagues reported.
The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has recognized the role of endoscopic drainage in managing acute cholecystitis in high-risk patients, but specific guidance on optimal technique and follow-up remains unclear, the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
“Despite accumulating data and increased interest in this technique, clear guidance on the ideal strategy for ETGBD is lacking,” Dr. Haddad and colleagues wrote. “For example, the optimal size, number, and follow-up of cystic duct stents for patients undergoing ETGBD has not been well established.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators analyzed data from 75 patients at five academic medical centers who had undergone ETGBD between June 2013 and October 2022. Patients were divided into two groups based on whether they received one or two cystic duct stents.
The primary outcome was clinical success, defined as symptom resolution without requiring another drainage procedure. Secondary outcomes included technical success (defined as successful stent placement), along with rates of adverse events and unplanned reinterventions.
Out of the 75 patients, 59 received a single stent, while 16 received dual stents. The median follow-up time was 407 days overall, with a longer follow-up in the single-stent group (433 days), compared with the double-stent group (118 days).
Clinical success was reported in 81.3% of cases, which technical success was achieved in 88.2% of cases.
Patients who received two stents had significantly lower rates of unplanned reintervention, compared with those who received a single stent (0% vs 25.4%; P = .02). The median time to unplanned reintervention in the single-stent group was 210 days.
Use of a 7 French stent was strongly associated with placement of two stents (odd ratio [OR], 15.5; P = .01). Similarly, patients with a prior percutaneous cholecystostomy tube were significantly more likely to have two stents placed (OR, 10.8; P = .001).
Adverse event rates were uncommon and not statistically different between groups, with an overall rate of 6.7%. Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis was the most common adverse event, occurring in two patients in the single-stent group and one patient in the double-stent group. There were no reported cases of cystic duct or gallbladder perforation.
“In conclusion,” the investigators wrote, “ETGBD with dual transpapillary gallbladder stenting is associated with a lower rate of unplanned reinterventions, compared with that with single stenting, and has a low rate of adverse events. Endoscopists performing ETGBD should consider planned exchange of solitary transpapillary gallbladder stents or interval ERCP for reattempted placement of a second stent if placement of two stents is not possible at the index ERCP.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with Boston Scientific, Motus GI, and ConMed.
according to a retrospective multicenter study.
These findings suggest that endoscopists should prioritize dual stent placement when feasible, and consider adding a second stent in patients who previously received a single stent, James D. Haddad, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and colleagues reported.
The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has recognized the role of endoscopic drainage in managing acute cholecystitis in high-risk patients, but specific guidance on optimal technique and follow-up remains unclear, the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
“Despite accumulating data and increased interest in this technique, clear guidance on the ideal strategy for ETGBD is lacking,” Dr. Haddad and colleagues wrote. “For example, the optimal size, number, and follow-up of cystic duct stents for patients undergoing ETGBD has not been well established.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators analyzed data from 75 patients at five academic medical centers who had undergone ETGBD between June 2013 and October 2022. Patients were divided into two groups based on whether they received one or two cystic duct stents.
The primary outcome was clinical success, defined as symptom resolution without requiring another drainage procedure. Secondary outcomes included technical success (defined as successful stent placement), along with rates of adverse events and unplanned reinterventions.
Out of the 75 patients, 59 received a single stent, while 16 received dual stents. The median follow-up time was 407 days overall, with a longer follow-up in the single-stent group (433 days), compared with the double-stent group (118 days).
Clinical success was reported in 81.3% of cases, which technical success was achieved in 88.2% of cases.
Patients who received two stents had significantly lower rates of unplanned reintervention, compared with those who received a single stent (0% vs 25.4%; P = .02). The median time to unplanned reintervention in the single-stent group was 210 days.
Use of a 7 French stent was strongly associated with placement of two stents (odd ratio [OR], 15.5; P = .01). Similarly, patients with a prior percutaneous cholecystostomy tube were significantly more likely to have two stents placed (OR, 10.8; P = .001).
Adverse event rates were uncommon and not statistically different between groups, with an overall rate of 6.7%. Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis was the most common adverse event, occurring in two patients in the single-stent group and one patient in the double-stent group. There were no reported cases of cystic duct or gallbladder perforation.
“In conclusion,” the investigators wrote, “ETGBD with dual transpapillary gallbladder stenting is associated with a lower rate of unplanned reinterventions, compared with that with single stenting, and has a low rate of adverse events. Endoscopists performing ETGBD should consider planned exchange of solitary transpapillary gallbladder stents or interval ERCP for reattempted placement of a second stent if placement of two stents is not possible at the index ERCP.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with Boston Scientific, Motus GI, and ConMed.
according to a retrospective multicenter study.
These findings suggest that endoscopists should prioritize dual stent placement when feasible, and consider adding a second stent in patients who previously received a single stent, James D. Haddad, MD, of the University of Texas Southwestern, Dallas, and colleagues reported.
The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has recognized the role of endoscopic drainage in managing acute cholecystitis in high-risk patients, but specific guidance on optimal technique and follow-up remains unclear, the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
“Despite accumulating data and increased interest in this technique, clear guidance on the ideal strategy for ETGBD is lacking,” Dr. Haddad and colleagues wrote. “For example, the optimal size, number, and follow-up of cystic duct stents for patients undergoing ETGBD has not been well established.”
To address this knowledge gap, the investigators analyzed data from 75 patients at five academic medical centers who had undergone ETGBD between June 2013 and October 2022. Patients were divided into two groups based on whether they received one or two cystic duct stents.
The primary outcome was clinical success, defined as symptom resolution without requiring another drainage procedure. Secondary outcomes included technical success (defined as successful stent placement), along with rates of adverse events and unplanned reinterventions.
Out of the 75 patients, 59 received a single stent, while 16 received dual stents. The median follow-up time was 407 days overall, with a longer follow-up in the single-stent group (433 days), compared with the double-stent group (118 days).
Clinical success was reported in 81.3% of cases, which technical success was achieved in 88.2% of cases.
Patients who received two stents had significantly lower rates of unplanned reintervention, compared with those who received a single stent (0% vs 25.4%; P = .02). The median time to unplanned reintervention in the single-stent group was 210 days.
Use of a 7 French stent was strongly associated with placement of two stents (odd ratio [OR], 15.5; P = .01). Similarly, patients with a prior percutaneous cholecystostomy tube were significantly more likely to have two stents placed (OR, 10.8; P = .001).
Adverse event rates were uncommon and not statistically different between groups, with an overall rate of 6.7%. Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis was the most common adverse event, occurring in two patients in the single-stent group and one patient in the double-stent group. There were no reported cases of cystic duct or gallbladder perforation.
“In conclusion,” the investigators wrote, “ETGBD with dual transpapillary gallbladder stenting is associated with a lower rate of unplanned reinterventions, compared with that with single stenting, and has a low rate of adverse events. Endoscopists performing ETGBD should consider planned exchange of solitary transpapillary gallbladder stents or interval ERCP for reattempted placement of a second stent if placement of two stents is not possible at the index ERCP.”
The investigators disclosed relationships with Boston Scientific, Motus GI, and ConMed.
FROM TECHNIQUES AND INNOVATIONS IN GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
GLP-1 RAs Safe in the Perioperative Period: New Guidance
The new guidance, contrasting with earlier recommendations, says these incrementally used agents can be taken up until the day of surgery, but patients are advised to follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure. The decision to proceed with endoscopy and other procedures should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and interdisciplinary care teams in conjunction with minimization of the aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying, the guidance stresses.
The five endorsing organizations are the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), American Gastroenterological Association, International Society of Perioperative Care of Patients with Obesity, and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. The societies emphasize that the statement is intended as guidance only and is not an evidence-based formal guideline.
GLP-1 RAs are known to delay gastric emptying, raising concerns about regurgitation, aspiration, and airway compromise during anesthesia. Rare serious adverse events have also been observed, prompting the ASA in 2023 to recommend holding these agents for 1 week for the injectable form and 1 day for the oral form before all procedures requiring anesthesia.
That abundance of caution, however, had negative impacts of its own. “This guidance has led to cancellations and postponements of many endoscopic and surgical procedures or required patients to undergo general anesthesia who may otherwise have had their procedures performed under moderate sedation,” said guidance coauthor Allison R. Schulman, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine and surgery and chief of endoscopy at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “Nearly all institutions have been forced to revise preprocedural protocols, despite a lack of high-level evidence to suggest that these adjustments are necessary.”
“Studies have yielded mixed results as to whether patients on GLP-1s are at increased risk of these events, and the limited data available are inconsistent,” Schulman said. “As a result, there are inconsistencies in the recommendations from various societies leading to growing uncertainty with proceduralists on how to provide safe, effective, and timely procedural care to patients taking GLP-1 RAs.”
The new joint-society guidance may alleviate some of the uncertainty. Among the recommendations:
- Continuing GLP-1 RAs in the perioperative period should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and all care teams balancing the metabolic need for the GLP-1 RA with individual patient risk.
- Certain variables may increase the risk for delayed gastric emptying and aspiration with the periprocedural use of GLP-1 RAs: escalation phase — This phase vs the maintenance phase is associated with a higher risk for delayed gastric emptying; higher dose — the higher the dose, the greater the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) side effects; weekly dosing — GI side effects are more common with weekly vs daily formulations; presence of GI symptoms — nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and constipation may suggest delayed gastric emptying; and medical problems beyond GLP-1 RA indications with GI effects — assess for such conditions as bowel dysmotility, gastroparesis, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Risk factors should be assessed in advance to allow sufficient time to adjust preoperative care, including diet modification and medication bridging if GLP-1 RA cessation is deemed advisable.
- If retained gastric contents are a concern on the day of a procedure, point-of-care gastric ultrasound could be used to assess aspiration risk, resources permitting.
- The aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying should be minimized by preoperative diet modification and/or altering the anesthesia plan to consider rapid sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation. A 24-hour preoperative liquid diet, as before colonoscopy and bariatric surgery, can be utilized when delayed gastric emptying is a concern.
- When concern about retained gastric contents exists on procedure day, providers should engage patients in a shared decision-making model and consider the benefits and risks of rapid-sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation to minimize aspiration risk vs procedure cancellation.
“Safe continuation of surgery and gastrointestinal endoscopy, and prevention of procedure cancellation, for patients on GLP-1 RAs can be prioritized following the recommendations above, as would occur for other patient populations with gastroparesis,” the guidance panel wrote.
Commenting on the statement but not involved in it, David B. Purow, MD, managing director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwell Health/Huntington Hospital in Huntington, New York, said the recommendations will encourage clinicians to be more discerning about actual risk in individual cases rather than follow the previous blanket recommendation to stop these agents before procedures requiring sedation.
While GLP-1 RAs were prescribed for the relatively small number of patients with diabetes, he said, the risk was not apparent but became clearer with the widespread use of these agents for weight loss — often unregulated and undisclosed to care providers.
“The pendulum shifted too far the other way, and now it’s shifted back,” he said in an interview. “The new guidance is great because now we can be more thoughtful about managing individual patients.” He cited, for instance, the recommendations on the greater risk in patients in the dose escalation phase or on higher doses, and the risk-reducing measure of a liquid diet for 24 hours before surgery.
His center is already using point-of-care ultrasound and recently had a case in which a patient who forgot and took his GLP-1 RA before a scheduled procedure was found on ultrasound to have a full stomach. “In some cases, these drugs can cause an almost gastroparesis level of delayed emptying,” Purow said.
Purow thinks this early guidance will probably progress to firm guidelines within a year. Schulman is more cautious. “Our understanding of this complex topic is increasing rapidly, and ongoing clinical research will ultimately lead to evidence-based guidelines in this changing landscape,” she said.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Schulman is a consultant for Apollo Endosurgery, Boston Scientific, Olympus, Microtech, and Fractyl. Purow had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guidance, contrasting with earlier recommendations, says these incrementally used agents can be taken up until the day of surgery, but patients are advised to follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure. The decision to proceed with endoscopy and other procedures should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and interdisciplinary care teams in conjunction with minimization of the aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying, the guidance stresses.
The five endorsing organizations are the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), American Gastroenterological Association, International Society of Perioperative Care of Patients with Obesity, and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. The societies emphasize that the statement is intended as guidance only and is not an evidence-based formal guideline.
GLP-1 RAs are known to delay gastric emptying, raising concerns about regurgitation, aspiration, and airway compromise during anesthesia. Rare serious adverse events have also been observed, prompting the ASA in 2023 to recommend holding these agents for 1 week for the injectable form and 1 day for the oral form before all procedures requiring anesthesia.
That abundance of caution, however, had negative impacts of its own. “This guidance has led to cancellations and postponements of many endoscopic and surgical procedures or required patients to undergo general anesthesia who may otherwise have had their procedures performed under moderate sedation,” said guidance coauthor Allison R. Schulman, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine and surgery and chief of endoscopy at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “Nearly all institutions have been forced to revise preprocedural protocols, despite a lack of high-level evidence to suggest that these adjustments are necessary.”
“Studies have yielded mixed results as to whether patients on GLP-1s are at increased risk of these events, and the limited data available are inconsistent,” Schulman said. “As a result, there are inconsistencies in the recommendations from various societies leading to growing uncertainty with proceduralists on how to provide safe, effective, and timely procedural care to patients taking GLP-1 RAs.”
The new joint-society guidance may alleviate some of the uncertainty. Among the recommendations:
- Continuing GLP-1 RAs in the perioperative period should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and all care teams balancing the metabolic need for the GLP-1 RA with individual patient risk.
- Certain variables may increase the risk for delayed gastric emptying and aspiration with the periprocedural use of GLP-1 RAs: escalation phase — This phase vs the maintenance phase is associated with a higher risk for delayed gastric emptying; higher dose — the higher the dose, the greater the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) side effects; weekly dosing — GI side effects are more common with weekly vs daily formulations; presence of GI symptoms — nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and constipation may suggest delayed gastric emptying; and medical problems beyond GLP-1 RA indications with GI effects — assess for such conditions as bowel dysmotility, gastroparesis, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Risk factors should be assessed in advance to allow sufficient time to adjust preoperative care, including diet modification and medication bridging if GLP-1 RA cessation is deemed advisable.
- If retained gastric contents are a concern on the day of a procedure, point-of-care gastric ultrasound could be used to assess aspiration risk, resources permitting.
- The aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying should be minimized by preoperative diet modification and/or altering the anesthesia plan to consider rapid sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation. A 24-hour preoperative liquid diet, as before colonoscopy and bariatric surgery, can be utilized when delayed gastric emptying is a concern.
- When concern about retained gastric contents exists on procedure day, providers should engage patients in a shared decision-making model and consider the benefits and risks of rapid-sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation to minimize aspiration risk vs procedure cancellation.
“Safe continuation of surgery and gastrointestinal endoscopy, and prevention of procedure cancellation, for patients on GLP-1 RAs can be prioritized following the recommendations above, as would occur for other patient populations with gastroparesis,” the guidance panel wrote.
Commenting on the statement but not involved in it, David B. Purow, MD, managing director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwell Health/Huntington Hospital in Huntington, New York, said the recommendations will encourage clinicians to be more discerning about actual risk in individual cases rather than follow the previous blanket recommendation to stop these agents before procedures requiring sedation.
While GLP-1 RAs were prescribed for the relatively small number of patients with diabetes, he said, the risk was not apparent but became clearer with the widespread use of these agents for weight loss — often unregulated and undisclosed to care providers.
“The pendulum shifted too far the other way, and now it’s shifted back,” he said in an interview. “The new guidance is great because now we can be more thoughtful about managing individual patients.” He cited, for instance, the recommendations on the greater risk in patients in the dose escalation phase or on higher doses, and the risk-reducing measure of a liquid diet for 24 hours before surgery.
His center is already using point-of-care ultrasound and recently had a case in which a patient who forgot and took his GLP-1 RA before a scheduled procedure was found on ultrasound to have a full stomach. “In some cases, these drugs can cause an almost gastroparesis level of delayed emptying,” Purow said.
Purow thinks this early guidance will probably progress to firm guidelines within a year. Schulman is more cautious. “Our understanding of this complex topic is increasing rapidly, and ongoing clinical research will ultimately lead to evidence-based guidelines in this changing landscape,” she said.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Schulman is a consultant for Apollo Endosurgery, Boston Scientific, Olympus, Microtech, and Fractyl. Purow had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new guidance, contrasting with earlier recommendations, says these incrementally used agents can be taken up until the day of surgery, but patients are advised to follow a liquid diet for 24 hours before the procedure. The decision to proceed with endoscopy and other procedures should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and interdisciplinary care teams in conjunction with minimization of the aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying, the guidance stresses.
The five endorsing organizations are the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA), American Gastroenterological Association, International Society of Perioperative Care of Patients with Obesity, and Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons. The societies emphasize that the statement is intended as guidance only and is not an evidence-based formal guideline.
GLP-1 RAs are known to delay gastric emptying, raising concerns about regurgitation, aspiration, and airway compromise during anesthesia. Rare serious adverse events have also been observed, prompting the ASA in 2023 to recommend holding these agents for 1 week for the injectable form and 1 day for the oral form before all procedures requiring anesthesia.
That abundance of caution, however, had negative impacts of its own. “This guidance has led to cancellations and postponements of many endoscopic and surgical procedures or required patients to undergo general anesthesia who may otherwise have had their procedures performed under moderate sedation,” said guidance coauthor Allison R. Schulman, MD, MPH, an associate professor of medicine and surgery and chief of endoscopy at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. “Nearly all institutions have been forced to revise preprocedural protocols, despite a lack of high-level evidence to suggest that these adjustments are necessary.”
“Studies have yielded mixed results as to whether patients on GLP-1s are at increased risk of these events, and the limited data available are inconsistent,” Schulman said. “As a result, there are inconsistencies in the recommendations from various societies leading to growing uncertainty with proceduralists on how to provide safe, effective, and timely procedural care to patients taking GLP-1 RAs.”
The new joint-society guidance may alleviate some of the uncertainty. Among the recommendations:
- Continuing GLP-1 RAs in the perioperative period should be based on shared decision-making with the patient and all care teams balancing the metabolic need for the GLP-1 RA with individual patient risk.
- Certain variables may increase the risk for delayed gastric emptying and aspiration with the periprocedural use of GLP-1 RAs: escalation phase — This phase vs the maintenance phase is associated with a higher risk for delayed gastric emptying; higher dose — the higher the dose, the greater the risk for gastrointestinal (GI) side effects; weekly dosing — GI side effects are more common with weekly vs daily formulations; presence of GI symptoms — nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, and constipation may suggest delayed gastric emptying; and medical problems beyond GLP-1 RA indications with GI effects — assess for such conditions as bowel dysmotility, gastroparesis, and Parkinson’s disease.
- Risk factors should be assessed in advance to allow sufficient time to adjust preoperative care, including diet modification and medication bridging if GLP-1 RA cessation is deemed advisable.
- If retained gastric contents are a concern on the day of a procedure, point-of-care gastric ultrasound could be used to assess aspiration risk, resources permitting.
- The aspiration risk from delayed gastric emptying should be minimized by preoperative diet modification and/or altering the anesthesia plan to consider rapid sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation. A 24-hour preoperative liquid diet, as before colonoscopy and bariatric surgery, can be utilized when delayed gastric emptying is a concern.
- When concern about retained gastric contents exists on procedure day, providers should engage patients in a shared decision-making model and consider the benefits and risks of rapid-sequence induction of general anesthesia for tracheal intubation to minimize aspiration risk vs procedure cancellation.
“Safe continuation of surgery and gastrointestinal endoscopy, and prevention of procedure cancellation, for patients on GLP-1 RAs can be prioritized following the recommendations above, as would occur for other patient populations with gastroparesis,” the guidance panel wrote.
Commenting on the statement but not involved in it, David B. Purow, MD, managing director of the Digestive Health Center at Northwell Health/Huntington Hospital in Huntington, New York, said the recommendations will encourage clinicians to be more discerning about actual risk in individual cases rather than follow the previous blanket recommendation to stop these agents before procedures requiring sedation.
While GLP-1 RAs were prescribed for the relatively small number of patients with diabetes, he said, the risk was not apparent but became clearer with the widespread use of these agents for weight loss — often unregulated and undisclosed to care providers.
“The pendulum shifted too far the other way, and now it’s shifted back,” he said in an interview. “The new guidance is great because now we can be more thoughtful about managing individual patients.” He cited, for instance, the recommendations on the greater risk in patients in the dose escalation phase or on higher doses, and the risk-reducing measure of a liquid diet for 24 hours before surgery.
His center is already using point-of-care ultrasound and recently had a case in which a patient who forgot and took his GLP-1 RA before a scheduled procedure was found on ultrasound to have a full stomach. “In some cases, these drugs can cause an almost gastroparesis level of delayed emptying,” Purow said.
Purow thinks this early guidance will probably progress to firm guidelines within a year. Schulman is more cautious. “Our understanding of this complex topic is increasing rapidly, and ongoing clinical research will ultimately lead to evidence-based guidelines in this changing landscape,” she said.
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. Schulman is a consultant for Apollo Endosurgery, Boston Scientific, Olympus, Microtech, and Fractyl. Purow had no competing interests to declare.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Screening Options for Rare Malignancies
Dear colleagues,
As gastroenterologists and endoscopists, we spend significant time preventing and diagnosing GI malignancies.
For instance, is it worthwhile screening for pancreatic cancer, and, if so, how should this be done? Likewise, diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma is challenging; how best should one evaluate for this in higher risk populations, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis? And what about the costs, financial and otherwise, associated with screening?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Darshan Kothari and Dr. Daniel Bernstein discuss their approach to pancreatic cancer screening, including who is eligible, the preferred screening modalities, and the barriers to screening. In the accompanying perspective, Dr. Aparna Goel and Dr. Judah Kupferman focus on cholangiocarcinoma screening, identifying high-risk populations and discussing some of the concerns with screening, necessitating shared decision-making.
We welcome your thoughts on this issue. Share with us on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
An Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Screening
BY DANIEL A. BERNSTEIN, MD, AND DARSHAN KOTHARI, MD
Pancreatic cancer carries a dismal prognosis, now accounting for the third-most cancer-related mortality in the United States. A small proportion of patients are diagnosed at a local stage of disease, with over half found to have metastatic disease at presentation. Given the low overall incidence and lifetime risk in the general population, population-based screening is not justified.
About 10% of cases of pancreas cancer are associated with germ-line mutations and/or with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. Several academic societies and expert committees now recommend regular screening for pancreatic cancer in patients who are considered high-risk individuals, as they carry a fivefold relative risk for pancreatic cancer. Moreover, studies suggest that screening has the potential to identify early-stage resectable disease and decrease mortality in this patient population.
Patients who benefit from pancreatic cancer screening are those who carry an increased lifetime risk (in excess of 5%) of pancreatic cancer. High-risk individuals include those with germ-line mutations and/or those with a family history of pancreatic cancer in first-degree relatives. Consensus guidelines by the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening Consortium and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy provide medical centers with detailed recommendations on who and when to start screening.
High-risk individuals fall into three categories:
- Patients with high-risk germline mutations including: familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome (CDKN2A), hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes (BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (STK11), and hereditary pancreatitis (PRSS1 and SPINK1)
- Patients with low- to moderate-risk germ-line mutations with at least one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer: Lynch Syndrome (particularly MLH1 mutation), ataxia-telangiectasia (ATM), or Li-Fraumeni syndrome (p53)
- Patients with one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer who in turn has one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer (eg, a patient’s mother and maternal aunt or a patient’s father and patient’s sister)
Consistent with established guidelines, we recommend screening for high-risk patients beginning at age 50, or 10 years before the youngest age at which pancreas cancer was diagnosed in an affected relative. Screening is recommended earlier in patients with particularly high risk: at age 40 for patients with CDKN2A and STKI11 mutations and age 40 for patients with PRSS1 mutation or 20 years after the first attack of acute pancreatitis. For patients with a strong family history of pancreas cancer, we recommend comprehensive evaluation by a certified genetic counselor at a high-volume cancer center.
In practice, patients at our institution who are identified as high risk based on the above criteria are referred for an initial consultation at our pancreas center. In most cases, this should occur no sooner than 5 years prior to the recommended starting age for screening. All patients who are identified as high risk should be screened annually for diabetes given the growing evidence base supporting an association between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
After an initial visit and discussion of the risks and benefits of screening, most screening protocols start with a baseline endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance abdomen with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP), which will be repeated annually or sooner as the clinical condition warrants. A sooner-interval EUS should be considered for patients already undergoing screening who are newly found to have diabetes.
At our institution, we start with an in-person clinic evaluation followed by EUS. Thereafter, patients undergo MRI/MRCP (synchronized with a same-day clinic visit) alternating with EUS every 6 months to ensure patients are seen twice a year, though there is no specific data to support this approach. Non-diabetics also undergo yearly diabetes screening which will trigger an EUS if patients become diabetic.
We engage in shared decision-making with our high-risk individuals undergoing pancreatic cancer screening and at each visit we review their concurrent medical conditions and suitability to continue screening. We consider discontinuing screening after age 75, at the onset of any life-limiting illness, or after a discussion of risks and benefits if comorbidities lead to a substantial deterioration in a patient’s overall health status.
While a growing body of evidence exists to support the application of pancreatic cancer screening in high-risk individuals, this preventive service remains underutilized. Recent analysis of the screening cohort at our institution showed a demographically homogeneous group of mostly highly educated, high-income White females. These findings are consistent with the patient cohorts described in other pancreatic cancer screening programs and represent only a fraction of people who would qualify for pancreatic cancer screening.
A survey of patients undergoing screening at our institution identified cost, travel, and time associated with pancreatic cancer screening to be frequent challenges to participation. Further studies are needed to fully explore the barriers and psychological burden of pancreas cancer screening in high-risk individuals, and to identify ways to enrich the cohort of patients undergoing screening. This may involve novel methods to identify family members of patients with a new diagnosis of pancreas cancer and increasing health literacy around pancreatic cancer screening among patients and providers.
Pancreatic cancer screening has the potential to identify early-stage disease in patients who are at high risk because of germ-line mutations and/or family history. We recommend that patients engage in pancreatic cancer screening at high-volume centers with well-supported oncology, genetics, and research infrastructure.
Dr. Bernstein is a gastroenterology fellow at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina. Dr. Kothari is an associate professor of medicine in gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University School of Medicine.
Screening for Cholangiocarcinoma
BY JUDAH KUPFERMAN, MD, AND APARNA GOEL, MD
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive cancer of the bile ducts that poses many diagnostic challenges. Approximately 3% of gastrointestinal cancers are attributed to cholangiocarcinoma, and while the annual incidence of disease in the United States is about 1.26 per 100,000 people, the incidence of intrahepatic disease has been rising considerably.1,2 Screening for cholangiocarcinoma is reserved for high-risk individuals — such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC), and biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts or Caroli’s disease. The goal is to balance the benefits of early diagnosis with the costs and risks associated with screening, particularly given the limitations of available tools like MRI with cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which has a sensitivity of 70%-85%. In general, we recommend annual cholangiocarcinoma screening for high-risk individuals with MRI and MRCP as well as with cancer antigen (CA) 19-9. .
Screening in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
The lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with PSC is 10%-15% with an annual risk of 0.5%-1.5%. In our experience, this is often the most feared complication for PSC patients, even more so than the risk of liver transplantation. We recommend annual MRI with MRCP in addition to CA 19-9 for patients with PSC in the first decade of their diagnosis, as most cancers are diagnosed during this period. If a patient’s imaging has remained stable for over a decade and there is minimal hepatic fibrosis, we discuss the option of reducing screening frequency to every 2 years to minimize costs and exposure to MRI contrast risks.
If MRI reveals a concerning new large duct stricture, we will evaluate this with an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), as differentiating benign and malignant strictures is quite challenging with MRI. We generally recommend ERCP with brush cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization to improve diagnostic yield. Depending on imaging findings and location of the new large duct stricture, we may consider cholangioscopy during ERCP for direct visualization of the bile duct and directed tissue biopsies. Unfortunately, even in young, asymptomatic patients who undergo regular screening, cholangiocarcinoma is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Screening in Patients with Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Patients with SSC may develop cholangiocarcinoma because of chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes, such as IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, sarcoidosis, ischemic cholangiopathy, cystic fibrosis, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, severe sepsis (as recently seen from SARS-CoV-2), surgical complications, or other etiologies. When the condition is reversible, such as with IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, cancer screening may not be necessary. However, when irreversible damage occurs, the cancer risk increases, though it varies by disease type and severity. In most cases, we recommend routine screening for cholangiocarcinoma with MRI and CA 19-9 in this population.
Screening in Patients with Biliary Tract Disorders
Biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts and Caroli’s disease also harbor an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Choledochal cysts are congenital cystic dilations of the bile duct that have a 10%-30% lifetime risk of malignant transformation to cholangiocarcinoma. Surgical intervention to remove the cyst is often recommended because of this high risk. However, some patients may be unable or unwilling to undergo this surgery or they may have residual cysts. We recommend ongoing screening with MRI and CA 19-9 for these patients. Similarly, Caroli’s disease is a congenital disease associated with intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct cysts and associated with a 5%-15% lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma. MRI with MRCP and CA 19-9 should be performed routinely for patients with Caroli’s disease and syndrome.
Risks and Challenges in Cholangiocarcinoma Screening
While MRI with MRCP is the gold standard for cholangiocarcinoma screening, its limitations must be carefully considered. One growing concern is the potential for gadolinium retention in the brain, bones, or skin following repeated MRI scans. Though the long-term effects of gadolinium retention are not fully understood, we factor this into screening decisions, particularly for younger patients who may undergo decades of regular imaging.
MRI is not always feasible for certain patients, including those with metal implants, on hemodialysis, or with severe allergic reactions. In such cases, CT or ultrasound may serve as alternatives, though with lower sensitivity for detecting cholangiocarcinoma. Additionally, claustrophobia during MRI can be addressed with sedation, but this underscores the importance of shared decision-making.
From our perspective, cholangiocarcinoma screening in high-risk patients is crucial but not without challenges. Our current screening methods, while essential, are far from perfect, often missing early cancers or leading to unnecessary interventions. Because of these limitations, the window for treatment of localized disease can easily be missed. In our practice, we tailor screening strategies to each patient’s specific needs, weighing the potential benefits against the risks, costs, and the inherent uncertainty of early detection tools. We believe it is essential to involve patients in this decision-making process to provide a balanced, individualized approach that considers both clinical evidence and the personal preferences of each person.
Dr. Kupferman is a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford University School of Medicine in California. Dr. Goel is a transplant hepatologist and a clinical associate professor in gastroenterology & hepatology at Stanford.
References
1. Vithayathil M and Khan SA. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.022.
2. Patel N and Benipal B. Cureus. 2019 Jan. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3962.
Dear colleagues,
As gastroenterologists and endoscopists, we spend significant time preventing and diagnosing GI malignancies.
For instance, is it worthwhile screening for pancreatic cancer, and, if so, how should this be done? Likewise, diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma is challenging; how best should one evaluate for this in higher risk populations, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis? And what about the costs, financial and otherwise, associated with screening?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Darshan Kothari and Dr. Daniel Bernstein discuss their approach to pancreatic cancer screening, including who is eligible, the preferred screening modalities, and the barriers to screening. In the accompanying perspective, Dr. Aparna Goel and Dr. Judah Kupferman focus on cholangiocarcinoma screening, identifying high-risk populations and discussing some of the concerns with screening, necessitating shared decision-making.
We welcome your thoughts on this issue. Share with us on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
An Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Screening
BY DANIEL A. BERNSTEIN, MD, AND DARSHAN KOTHARI, MD
Pancreatic cancer carries a dismal prognosis, now accounting for the third-most cancer-related mortality in the United States. A small proportion of patients are diagnosed at a local stage of disease, with over half found to have metastatic disease at presentation. Given the low overall incidence and lifetime risk in the general population, population-based screening is not justified.
About 10% of cases of pancreas cancer are associated with germ-line mutations and/or with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. Several academic societies and expert committees now recommend regular screening for pancreatic cancer in patients who are considered high-risk individuals, as they carry a fivefold relative risk for pancreatic cancer. Moreover, studies suggest that screening has the potential to identify early-stage resectable disease and decrease mortality in this patient population.
Patients who benefit from pancreatic cancer screening are those who carry an increased lifetime risk (in excess of 5%) of pancreatic cancer. High-risk individuals include those with germ-line mutations and/or those with a family history of pancreatic cancer in first-degree relatives. Consensus guidelines by the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening Consortium and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy provide medical centers with detailed recommendations on who and when to start screening.
High-risk individuals fall into three categories:
- Patients with high-risk germline mutations including: familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome (CDKN2A), hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes (BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (STK11), and hereditary pancreatitis (PRSS1 and SPINK1)
- Patients with low- to moderate-risk germ-line mutations with at least one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer: Lynch Syndrome (particularly MLH1 mutation), ataxia-telangiectasia (ATM), or Li-Fraumeni syndrome (p53)
- Patients with one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer who in turn has one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer (eg, a patient’s mother and maternal aunt or a patient’s father and patient’s sister)
Consistent with established guidelines, we recommend screening for high-risk patients beginning at age 50, or 10 years before the youngest age at which pancreas cancer was diagnosed in an affected relative. Screening is recommended earlier in patients with particularly high risk: at age 40 for patients with CDKN2A and STKI11 mutations and age 40 for patients with PRSS1 mutation or 20 years after the first attack of acute pancreatitis. For patients with a strong family history of pancreas cancer, we recommend comprehensive evaluation by a certified genetic counselor at a high-volume cancer center.
In practice, patients at our institution who are identified as high risk based on the above criteria are referred for an initial consultation at our pancreas center. In most cases, this should occur no sooner than 5 years prior to the recommended starting age for screening. All patients who are identified as high risk should be screened annually for diabetes given the growing evidence base supporting an association between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
After an initial visit and discussion of the risks and benefits of screening, most screening protocols start with a baseline endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance abdomen with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP), which will be repeated annually or sooner as the clinical condition warrants. A sooner-interval EUS should be considered for patients already undergoing screening who are newly found to have diabetes.
At our institution, we start with an in-person clinic evaluation followed by EUS. Thereafter, patients undergo MRI/MRCP (synchronized with a same-day clinic visit) alternating with EUS every 6 months to ensure patients are seen twice a year, though there is no specific data to support this approach. Non-diabetics also undergo yearly diabetes screening which will trigger an EUS if patients become diabetic.
We engage in shared decision-making with our high-risk individuals undergoing pancreatic cancer screening and at each visit we review their concurrent medical conditions and suitability to continue screening. We consider discontinuing screening after age 75, at the onset of any life-limiting illness, or after a discussion of risks and benefits if comorbidities lead to a substantial deterioration in a patient’s overall health status.
While a growing body of evidence exists to support the application of pancreatic cancer screening in high-risk individuals, this preventive service remains underutilized. Recent analysis of the screening cohort at our institution showed a demographically homogeneous group of mostly highly educated, high-income White females. These findings are consistent with the patient cohorts described in other pancreatic cancer screening programs and represent only a fraction of people who would qualify for pancreatic cancer screening.
A survey of patients undergoing screening at our institution identified cost, travel, and time associated with pancreatic cancer screening to be frequent challenges to participation. Further studies are needed to fully explore the barriers and psychological burden of pancreas cancer screening in high-risk individuals, and to identify ways to enrich the cohort of patients undergoing screening. This may involve novel methods to identify family members of patients with a new diagnosis of pancreas cancer and increasing health literacy around pancreatic cancer screening among patients and providers.
Pancreatic cancer screening has the potential to identify early-stage disease in patients who are at high risk because of germ-line mutations and/or family history. We recommend that patients engage in pancreatic cancer screening at high-volume centers with well-supported oncology, genetics, and research infrastructure.
Dr. Bernstein is a gastroenterology fellow at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina. Dr. Kothari is an associate professor of medicine in gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University School of Medicine.
Screening for Cholangiocarcinoma
BY JUDAH KUPFERMAN, MD, AND APARNA GOEL, MD
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive cancer of the bile ducts that poses many diagnostic challenges. Approximately 3% of gastrointestinal cancers are attributed to cholangiocarcinoma, and while the annual incidence of disease in the United States is about 1.26 per 100,000 people, the incidence of intrahepatic disease has been rising considerably.1,2 Screening for cholangiocarcinoma is reserved for high-risk individuals — such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC), and biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts or Caroli’s disease. The goal is to balance the benefits of early diagnosis with the costs and risks associated with screening, particularly given the limitations of available tools like MRI with cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which has a sensitivity of 70%-85%. In general, we recommend annual cholangiocarcinoma screening for high-risk individuals with MRI and MRCP as well as with cancer antigen (CA) 19-9. .
Screening in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
The lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with PSC is 10%-15% with an annual risk of 0.5%-1.5%. In our experience, this is often the most feared complication for PSC patients, even more so than the risk of liver transplantation. We recommend annual MRI with MRCP in addition to CA 19-9 for patients with PSC in the first decade of their diagnosis, as most cancers are diagnosed during this period. If a patient’s imaging has remained stable for over a decade and there is minimal hepatic fibrosis, we discuss the option of reducing screening frequency to every 2 years to minimize costs and exposure to MRI contrast risks.
If MRI reveals a concerning new large duct stricture, we will evaluate this with an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), as differentiating benign and malignant strictures is quite challenging with MRI. We generally recommend ERCP with brush cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization to improve diagnostic yield. Depending on imaging findings and location of the new large duct stricture, we may consider cholangioscopy during ERCP for direct visualization of the bile duct and directed tissue biopsies. Unfortunately, even in young, asymptomatic patients who undergo regular screening, cholangiocarcinoma is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Screening in Patients with Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Patients with SSC may develop cholangiocarcinoma because of chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes, such as IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, sarcoidosis, ischemic cholangiopathy, cystic fibrosis, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, severe sepsis (as recently seen from SARS-CoV-2), surgical complications, or other etiologies. When the condition is reversible, such as with IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, cancer screening may not be necessary. However, when irreversible damage occurs, the cancer risk increases, though it varies by disease type and severity. In most cases, we recommend routine screening for cholangiocarcinoma with MRI and CA 19-9 in this population.
Screening in Patients with Biliary Tract Disorders
Biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts and Caroli’s disease also harbor an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Choledochal cysts are congenital cystic dilations of the bile duct that have a 10%-30% lifetime risk of malignant transformation to cholangiocarcinoma. Surgical intervention to remove the cyst is often recommended because of this high risk. However, some patients may be unable or unwilling to undergo this surgery or they may have residual cysts. We recommend ongoing screening with MRI and CA 19-9 for these patients. Similarly, Caroli’s disease is a congenital disease associated with intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct cysts and associated with a 5%-15% lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma. MRI with MRCP and CA 19-9 should be performed routinely for patients with Caroli’s disease and syndrome.
Risks and Challenges in Cholangiocarcinoma Screening
While MRI with MRCP is the gold standard for cholangiocarcinoma screening, its limitations must be carefully considered. One growing concern is the potential for gadolinium retention in the brain, bones, or skin following repeated MRI scans. Though the long-term effects of gadolinium retention are not fully understood, we factor this into screening decisions, particularly for younger patients who may undergo decades of regular imaging.
MRI is not always feasible for certain patients, including those with metal implants, on hemodialysis, or with severe allergic reactions. In such cases, CT or ultrasound may serve as alternatives, though with lower sensitivity for detecting cholangiocarcinoma. Additionally, claustrophobia during MRI can be addressed with sedation, but this underscores the importance of shared decision-making.
From our perspective, cholangiocarcinoma screening in high-risk patients is crucial but not without challenges. Our current screening methods, while essential, are far from perfect, often missing early cancers or leading to unnecessary interventions. Because of these limitations, the window for treatment of localized disease can easily be missed. In our practice, we tailor screening strategies to each patient’s specific needs, weighing the potential benefits against the risks, costs, and the inherent uncertainty of early detection tools. We believe it is essential to involve patients in this decision-making process to provide a balanced, individualized approach that considers both clinical evidence and the personal preferences of each person.
Dr. Kupferman is a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford University School of Medicine in California. Dr. Goel is a transplant hepatologist and a clinical associate professor in gastroenterology & hepatology at Stanford.
References
1. Vithayathil M and Khan SA. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.022.
2. Patel N and Benipal B. Cureus. 2019 Jan. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3962.
Dear colleagues,
As gastroenterologists and endoscopists, we spend significant time preventing and diagnosing GI malignancies.
For instance, is it worthwhile screening for pancreatic cancer, and, if so, how should this be done? Likewise, diagnosing cholangiocarcinoma is challenging; how best should one evaluate for this in higher risk populations, such as primary sclerosing cholangitis? And what about the costs, financial and otherwise, associated with screening?
In this issue of Perspectives, Dr. Darshan Kothari and Dr. Daniel Bernstein discuss their approach to pancreatic cancer screening, including who is eligible, the preferred screening modalities, and the barriers to screening. In the accompanying perspective, Dr. Aparna Goel and Dr. Judah Kupferman focus on cholangiocarcinoma screening, identifying high-risk populations and discussing some of the concerns with screening, necessitating shared decision-making.
We welcome your thoughts on this issue. Share with us on X at @AGA_GIHN.
Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, MSc, is associate professor of medicine, Yale University, New Haven, and chief of endoscopy at West Haven VA Medical Center, both in Connecticut. He is an associate editor for GI & Hepatology News.
An Approach to Pancreatic Cancer Screening
BY DANIEL A. BERNSTEIN, MD, AND DARSHAN KOTHARI, MD
Pancreatic cancer carries a dismal prognosis, now accounting for the third-most cancer-related mortality in the United States. A small proportion of patients are diagnosed at a local stage of disease, with over half found to have metastatic disease at presentation. Given the low overall incidence and lifetime risk in the general population, population-based screening is not justified.
About 10% of cases of pancreas cancer are associated with germ-line mutations and/or with a strong family history of pancreatic cancer. Several academic societies and expert committees now recommend regular screening for pancreatic cancer in patients who are considered high-risk individuals, as they carry a fivefold relative risk for pancreatic cancer. Moreover, studies suggest that screening has the potential to identify early-stage resectable disease and decrease mortality in this patient population.
Patients who benefit from pancreatic cancer screening are those who carry an increased lifetime risk (in excess of 5%) of pancreatic cancer. High-risk individuals include those with germ-line mutations and/or those with a family history of pancreatic cancer in first-degree relatives. Consensus guidelines by the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening Consortium and the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy provide medical centers with detailed recommendations on who and when to start screening.
High-risk individuals fall into three categories:
- Patients with high-risk germline mutations including: familial atypical multiple mole melanoma syndrome (CDKN2A), hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes (BRCA1, BRCA2, and PALB2), Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (STK11), and hereditary pancreatitis (PRSS1 and SPINK1)
- Patients with low- to moderate-risk germ-line mutations with at least one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer: Lynch Syndrome (particularly MLH1 mutation), ataxia-telangiectasia (ATM), or Li-Fraumeni syndrome (p53)
- Patients with one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer who in turn has one first-degree relative with pancreatic cancer (eg, a patient’s mother and maternal aunt or a patient’s father and patient’s sister)
Consistent with established guidelines, we recommend screening for high-risk patients beginning at age 50, or 10 years before the youngest age at which pancreas cancer was diagnosed in an affected relative. Screening is recommended earlier in patients with particularly high risk: at age 40 for patients with CDKN2A and STKI11 mutations and age 40 for patients with PRSS1 mutation or 20 years after the first attack of acute pancreatitis. For patients with a strong family history of pancreas cancer, we recommend comprehensive evaluation by a certified genetic counselor at a high-volume cancer center.
In practice, patients at our institution who are identified as high risk based on the above criteria are referred for an initial consultation at our pancreas center. In most cases, this should occur no sooner than 5 years prior to the recommended starting age for screening. All patients who are identified as high risk should be screened annually for diabetes given the growing evidence base supporting an association between new-onset diabetes and pancreatic cancer.
After an initial visit and discussion of the risks and benefits of screening, most screening protocols start with a baseline endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance abdomen with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRI/MRCP), which will be repeated annually or sooner as the clinical condition warrants. A sooner-interval EUS should be considered for patients already undergoing screening who are newly found to have diabetes.
At our institution, we start with an in-person clinic evaluation followed by EUS. Thereafter, patients undergo MRI/MRCP (synchronized with a same-day clinic visit) alternating with EUS every 6 months to ensure patients are seen twice a year, though there is no specific data to support this approach. Non-diabetics also undergo yearly diabetes screening which will trigger an EUS if patients become diabetic.
We engage in shared decision-making with our high-risk individuals undergoing pancreatic cancer screening and at each visit we review their concurrent medical conditions and suitability to continue screening. We consider discontinuing screening after age 75, at the onset of any life-limiting illness, or after a discussion of risks and benefits if comorbidities lead to a substantial deterioration in a patient’s overall health status.
While a growing body of evidence exists to support the application of pancreatic cancer screening in high-risk individuals, this preventive service remains underutilized. Recent analysis of the screening cohort at our institution showed a demographically homogeneous group of mostly highly educated, high-income White females. These findings are consistent with the patient cohorts described in other pancreatic cancer screening programs and represent only a fraction of people who would qualify for pancreatic cancer screening.
A survey of patients undergoing screening at our institution identified cost, travel, and time associated with pancreatic cancer screening to be frequent challenges to participation. Further studies are needed to fully explore the barriers and psychological burden of pancreas cancer screening in high-risk individuals, and to identify ways to enrich the cohort of patients undergoing screening. This may involve novel methods to identify family members of patients with a new diagnosis of pancreas cancer and increasing health literacy around pancreatic cancer screening among patients and providers.
Pancreatic cancer screening has the potential to identify early-stage disease in patients who are at high risk because of germ-line mutations and/or family history. We recommend that patients engage in pancreatic cancer screening at high-volume centers with well-supported oncology, genetics, and research infrastructure.
Dr. Bernstein is a gastroenterology fellow at Duke University School of Medicine, Durham, North Carolina. Dr. Kothari is an associate professor of medicine in gastroenterology and hepatology at Duke University School of Medicine.
Screening for Cholangiocarcinoma
BY JUDAH KUPFERMAN, MD, AND APARNA GOEL, MD
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive cancer of the bile ducts that poses many diagnostic challenges. Approximately 3% of gastrointestinal cancers are attributed to cholangiocarcinoma, and while the annual incidence of disease in the United States is about 1.26 per 100,000 people, the incidence of intrahepatic disease has been rising considerably.1,2 Screening for cholangiocarcinoma is reserved for high-risk individuals — such as those with primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), secondary sclerosing cholangitis (SSC), and biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts or Caroli’s disease. The goal is to balance the benefits of early diagnosis with the costs and risks associated with screening, particularly given the limitations of available tools like MRI with cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which has a sensitivity of 70%-85%. In general, we recommend annual cholangiocarcinoma screening for high-risk individuals with MRI and MRCP as well as with cancer antigen (CA) 19-9. .
Screening in Patients with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
The lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma in patients with PSC is 10%-15% with an annual risk of 0.5%-1.5%. In our experience, this is often the most feared complication for PSC patients, even more so than the risk of liver transplantation. We recommend annual MRI with MRCP in addition to CA 19-9 for patients with PSC in the first decade of their diagnosis, as most cancers are diagnosed during this period. If a patient’s imaging has remained stable for over a decade and there is minimal hepatic fibrosis, we discuss the option of reducing screening frequency to every 2 years to minimize costs and exposure to MRI contrast risks.
If MRI reveals a concerning new large duct stricture, we will evaluate this with an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), as differentiating benign and malignant strictures is quite challenging with MRI. We generally recommend ERCP with brush cytology and fluorescence in situ hybridization to improve diagnostic yield. Depending on imaging findings and location of the new large duct stricture, we may consider cholangioscopy during ERCP for direct visualization of the bile duct and directed tissue biopsies. Unfortunately, even in young, asymptomatic patients who undergo regular screening, cholangiocarcinoma is frequently diagnosed at an advanced stage.
Screening in Patients with Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Patients with SSC may develop cholangiocarcinoma because of chronic inflammatory and fibrotic processes, such as IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, sarcoidosis, ischemic cholangiopathy, cystic fibrosis, recurrent pyogenic cholangitis, severe sepsis (as recently seen from SARS-CoV-2), surgical complications, or other etiologies. When the condition is reversible, such as with IgG4-associated cholangiopathy, cancer screening may not be necessary. However, when irreversible damage occurs, the cancer risk increases, though it varies by disease type and severity. In most cases, we recommend routine screening for cholangiocarcinoma with MRI and CA 19-9 in this population.
Screening in Patients with Biliary Tract Disorders
Biliary tract disorders such as choledochal cysts and Caroli’s disease also harbor an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma. Choledochal cysts are congenital cystic dilations of the bile duct that have a 10%-30% lifetime risk of malignant transformation to cholangiocarcinoma. Surgical intervention to remove the cyst is often recommended because of this high risk. However, some patients may be unable or unwilling to undergo this surgery or they may have residual cysts. We recommend ongoing screening with MRI and CA 19-9 for these patients. Similarly, Caroli’s disease is a congenital disease associated with intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct cysts and associated with a 5%-15% lifetime risk of cholangiocarcinoma. MRI with MRCP and CA 19-9 should be performed routinely for patients with Caroli’s disease and syndrome.
Risks and Challenges in Cholangiocarcinoma Screening
While MRI with MRCP is the gold standard for cholangiocarcinoma screening, its limitations must be carefully considered. One growing concern is the potential for gadolinium retention in the brain, bones, or skin following repeated MRI scans. Though the long-term effects of gadolinium retention are not fully understood, we factor this into screening decisions, particularly for younger patients who may undergo decades of regular imaging.
MRI is not always feasible for certain patients, including those with metal implants, on hemodialysis, or with severe allergic reactions. In such cases, CT or ultrasound may serve as alternatives, though with lower sensitivity for detecting cholangiocarcinoma. Additionally, claustrophobia during MRI can be addressed with sedation, but this underscores the importance of shared decision-making.
From our perspective, cholangiocarcinoma screening in high-risk patients is crucial but not without challenges. Our current screening methods, while essential, are far from perfect, often missing early cancers or leading to unnecessary interventions. Because of these limitations, the window for treatment of localized disease can easily be missed. In our practice, we tailor screening strategies to each patient’s specific needs, weighing the potential benefits against the risks, costs, and the inherent uncertainty of early detection tools. We believe it is essential to involve patients in this decision-making process to provide a balanced, individualized approach that considers both clinical evidence and the personal preferences of each person.
Dr. Kupferman is a gastroenterology fellow at Stanford University School of Medicine in California. Dr. Goel is a transplant hepatologist and a clinical associate professor in gastroenterology & hepatology at Stanford.
References
1. Vithayathil M and Khan SA. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.022.
2. Patel N and Benipal B. Cureus. 2019 Jan. doi: 10.7759/cureus.3962.
AI Tool Helps Detect, Differentiate Pancreatic Lesions During Endoscopic Ultrasound
PHILADELPHIA —
This was a transatlantic collaborative effort involving researchers in Portugal, Spain, the United States, and Brazil, and the AI tool “works on different platforms and different devices,” Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD, with Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Porto, Portugal, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Mascarenhas noted that pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) are a common incidental finding during imaging and are differentiated by whether they’re mucinous PCLs (M-PCLs) or non-mucinous PCLs (NM-PCLs). The malignancy risk is almost exclusive of PCL with a mucinous phenotype.
Pancreatic solid lesions are also prevalent, and differentiation is challenging. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (P-DAC) is the most common pancreatic solid lesion and has a poor prognosis because of late-stage disease at diagnosis. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (P-NETs) are less common but have malignant potential.
EUS is the “gold standard” for pancreatic lesion evaluation, but its diagnostic accuracy is suboptimal, particularly for lesions < 10 mm, Mascarenhas noted.
With an eye toward improving diagnostic accuracy, he and colleagues developed a convolutional neural network for detecting and differentiating cystic (M-PCL and NM-PCL) and solid (P-DAC and P-NET) pancreatic lesions.
They leveraged data from 378 EUS exams with 126,000 still images — 19,528 M-PCL, 8175 NM-PCL, 64,286 P-DAC, 29,153 P-NET, and 4858 normal pancreas images.
The AI tool demonstrated 99.1% accuracy for identifying normal pancreatic tissue, and it showed 99% and 99.8% accuracy for M-PCL and NM-PCL, respectively.
For pancreatic solid lesions, P-DAC and P-NET were distinguished with 94% accuracy, with 98.7% and 83.6% sensitivity for P-DAC and P-NET, respectively.
Real-Time Validation Next
“AI is delivering promising results throughout medicine, but particularly in gastroenterology, which is one of the most fertile areas of AI research. This comes mostly from the deployment of deep-learning models, most of them convolutional neural networks, which are highly efficient for image analysis,” Mascarenhas told attendees.
This is the “first worldwide convolutional neural network” capable of detecting and differentiating both cystic and solid pancreatic lesions. The use of a large dataset from four centers in two continents helps minimize the impact of demographic bias, Mascarenhas added.
The study is based on still images, not full videos, he noted. As a next step, the team is conducting a multicenter study focused on real-time clinical validation of the model during EUS procedures.
“AI has the potential to improve the diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound. We’re just on the tip of the iceberg. There is enormous potential to harness AI, and we welcome all the groups that might want to join our research,” Mascarenhas said.
Brennan Spiegel, MD, MSHS, AGAF, director of Health Services Research at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, who wasn’t involved in the study, is optimistic about emerging applications for AI.
“AI holds incredible promise in gastroenterology, especially for diagnosing complex pancreatic lesions where early, accurate differentiation can be lifesaving,” Spiegel said in an interview.
“This study’s high accuracy across diverse datasets is encouraging; however, as a retrospective analysis, it leaves the real-time clinical impact still to be proven. Prospective studies will be essential to confirm AI’s role in enhancing our diagnostic capabilities,” Spiegel cautioned.
“More generally, AI is rapidly transforming gastroenterology by enhancing our ability to detect, differentiate, and monitor conditions with unprecedented precision. From improving early cancer detection to guiding complex diagnostic procedures, AI stands to become an invaluable tool that complements clinical expertise. As we refine these technologies, the potential for AI to elevate both diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes in GI is truly remarkable,” Spiegel said.
The study had no specific funding. Mascarenhas and Spiegel have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA —
This was a transatlantic collaborative effort involving researchers in Portugal, Spain, the United States, and Brazil, and the AI tool “works on different platforms and different devices,” Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD, with Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Porto, Portugal, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Mascarenhas noted that pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) are a common incidental finding during imaging and are differentiated by whether they’re mucinous PCLs (M-PCLs) or non-mucinous PCLs (NM-PCLs). The malignancy risk is almost exclusive of PCL with a mucinous phenotype.
Pancreatic solid lesions are also prevalent, and differentiation is challenging. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (P-DAC) is the most common pancreatic solid lesion and has a poor prognosis because of late-stage disease at diagnosis. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (P-NETs) are less common but have malignant potential.
EUS is the “gold standard” for pancreatic lesion evaluation, but its diagnostic accuracy is suboptimal, particularly for lesions < 10 mm, Mascarenhas noted.
With an eye toward improving diagnostic accuracy, he and colleagues developed a convolutional neural network for detecting and differentiating cystic (M-PCL and NM-PCL) and solid (P-DAC and P-NET) pancreatic lesions.
They leveraged data from 378 EUS exams with 126,000 still images — 19,528 M-PCL, 8175 NM-PCL, 64,286 P-DAC, 29,153 P-NET, and 4858 normal pancreas images.
The AI tool demonstrated 99.1% accuracy for identifying normal pancreatic tissue, and it showed 99% and 99.8% accuracy for M-PCL and NM-PCL, respectively.
For pancreatic solid lesions, P-DAC and P-NET were distinguished with 94% accuracy, with 98.7% and 83.6% sensitivity for P-DAC and P-NET, respectively.
Real-Time Validation Next
“AI is delivering promising results throughout medicine, but particularly in gastroenterology, which is one of the most fertile areas of AI research. This comes mostly from the deployment of deep-learning models, most of them convolutional neural networks, which are highly efficient for image analysis,” Mascarenhas told attendees.
This is the “first worldwide convolutional neural network” capable of detecting and differentiating both cystic and solid pancreatic lesions. The use of a large dataset from four centers in two continents helps minimize the impact of demographic bias, Mascarenhas added.
The study is based on still images, not full videos, he noted. As a next step, the team is conducting a multicenter study focused on real-time clinical validation of the model during EUS procedures.
“AI has the potential to improve the diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound. We’re just on the tip of the iceberg. There is enormous potential to harness AI, and we welcome all the groups that might want to join our research,” Mascarenhas said.
Brennan Spiegel, MD, MSHS, AGAF, director of Health Services Research at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, who wasn’t involved in the study, is optimistic about emerging applications for AI.
“AI holds incredible promise in gastroenterology, especially for diagnosing complex pancreatic lesions where early, accurate differentiation can be lifesaving,” Spiegel said in an interview.
“This study’s high accuracy across diverse datasets is encouraging; however, as a retrospective analysis, it leaves the real-time clinical impact still to be proven. Prospective studies will be essential to confirm AI’s role in enhancing our diagnostic capabilities,” Spiegel cautioned.
“More generally, AI is rapidly transforming gastroenterology by enhancing our ability to detect, differentiate, and monitor conditions with unprecedented precision. From improving early cancer detection to guiding complex diagnostic procedures, AI stands to become an invaluable tool that complements clinical expertise. As we refine these technologies, the potential for AI to elevate both diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes in GI is truly remarkable,” Spiegel said.
The study had no specific funding. Mascarenhas and Spiegel have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
PHILADELPHIA —
This was a transatlantic collaborative effort involving researchers in Portugal, Spain, the United States, and Brazil, and the AI tool “works on different platforms and different devices,” Miguel Mascarenhas, MD, PhD, with Centro Hospitalar Universitário de São João, Porto, Portugal, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Mascarenhas noted that pancreatic cystic lesions (PCLs) are a common incidental finding during imaging and are differentiated by whether they’re mucinous PCLs (M-PCLs) or non-mucinous PCLs (NM-PCLs). The malignancy risk is almost exclusive of PCL with a mucinous phenotype.
Pancreatic solid lesions are also prevalent, and differentiation is challenging. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (P-DAC) is the most common pancreatic solid lesion and has a poor prognosis because of late-stage disease at diagnosis. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (P-NETs) are less common but have malignant potential.
EUS is the “gold standard” for pancreatic lesion evaluation, but its diagnostic accuracy is suboptimal, particularly for lesions < 10 mm, Mascarenhas noted.
With an eye toward improving diagnostic accuracy, he and colleagues developed a convolutional neural network for detecting and differentiating cystic (M-PCL and NM-PCL) and solid (P-DAC and P-NET) pancreatic lesions.
They leveraged data from 378 EUS exams with 126,000 still images — 19,528 M-PCL, 8175 NM-PCL, 64,286 P-DAC, 29,153 P-NET, and 4858 normal pancreas images.
The AI tool demonstrated 99.1% accuracy for identifying normal pancreatic tissue, and it showed 99% and 99.8% accuracy for M-PCL and NM-PCL, respectively.
For pancreatic solid lesions, P-DAC and P-NET were distinguished with 94% accuracy, with 98.7% and 83.6% sensitivity for P-DAC and P-NET, respectively.
Real-Time Validation Next
“AI is delivering promising results throughout medicine, but particularly in gastroenterology, which is one of the most fertile areas of AI research. This comes mostly from the deployment of deep-learning models, most of them convolutional neural networks, which are highly efficient for image analysis,” Mascarenhas told attendees.
This is the “first worldwide convolutional neural network” capable of detecting and differentiating both cystic and solid pancreatic lesions. The use of a large dataset from four centers in two continents helps minimize the impact of demographic bias, Mascarenhas added.
The study is based on still images, not full videos, he noted. As a next step, the team is conducting a multicenter study focused on real-time clinical validation of the model during EUS procedures.
“AI has the potential to improve the diagnostic accuracy of endoscopic ultrasound. We’re just on the tip of the iceberg. There is enormous potential to harness AI, and we welcome all the groups that might want to join our research,” Mascarenhas said.
Brennan Spiegel, MD, MSHS, AGAF, director of Health Services Research at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, who wasn’t involved in the study, is optimistic about emerging applications for AI.
“AI holds incredible promise in gastroenterology, especially for diagnosing complex pancreatic lesions where early, accurate differentiation can be lifesaving,” Spiegel said in an interview.
“This study’s high accuracy across diverse datasets is encouraging; however, as a retrospective analysis, it leaves the real-time clinical impact still to be proven. Prospective studies will be essential to confirm AI’s role in enhancing our diagnostic capabilities,” Spiegel cautioned.
“More generally, AI is rapidly transforming gastroenterology by enhancing our ability to detect, differentiate, and monitor conditions with unprecedented precision. From improving early cancer detection to guiding complex diagnostic procedures, AI stands to become an invaluable tool that complements clinical expertise. As we refine these technologies, the potential for AI to elevate both diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes in GI is truly remarkable,” Spiegel said.
The study had no specific funding. Mascarenhas and Spiegel have declared no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACG 2024
Baveno VI Criteria Appear Cost-Effective for Detecting Varices in Cirrhosis
Compared with endoscopy, , according to new research.
Although upper gastrointestinal endoscopy continues to be the gold standard for detecting varices, the Baveno VI criteria combine liver stiffness and platelet count values to rule out high-risk varices, which can save on endoscopy costs.
“The Baveno VI criteria can reduce the need for endoscopies in patients with cirrhosis, but it is important to ascertain if they are also cost-effective,” said senior author Emmanuel Tsochatzis, MD, professor of hepatology at the University College London Institute for Liver and Digestive Health and Royal Free Hospital in London.
“Our findings confirm that the application of these criteria is highly cost-effective, and given the fact that they are also safe, should be considered for widespread implementation,” he said.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Baveno VI Criteria Analysis
On the basis of the Baveno VI Consensus, endoscopy screening can be avoided in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease and Child-Pugh A cirrhosis who have a platelet count > 150,000/mm3 and a liver stiffness measurement < 20 kPa.
In addition, expanded Baveno VI criteria have suggested optimized cut-off values to avoid even more endoscopies — at a platelet value of > 110,000/mm3 and a liver stiffness < 25 kPa.
Previous research indicates that the expanded criteria could avoid double the number of endoscopies, the authors wrote, with a risk of missing high-risk varices in 1.6% of patients with the criteria and 0.6% of overall study participants. Both criteria have been validated in large groups of patients with compensated cirrhosis of different etiologies, but the cost-effectiveness hasn’t been analyzed.
Dr. Tsochatzis and colleagues created an analytical decision model to estimate the costs and benefits of using the Baveno VI criteria as compared with endoscopy as the standard of care among a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients with Child-Pugh A cirrhosis. The research team looked at costs and clinical outcomes based on the United Kingdom National Health Service perspective at 1 year from diagnosis and then estimated the expected costs and outcomes at 5 years and 20 years, including factors such as liver disease progression and variceal bleeding.
As part of the model, the Baveno VI criteria were implemented at annual screenings with targeted endoscopy for patients who met the criteria, as compared with endoscopy as a biannual screening using esophagogastroduodenoscopy for everyone.
In general, the Baveno VI criteria were cost-effective compared with endoscopy in all analyses, including all time points, as well as deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses. The cost of using the criteria was £67 per patient, as compared with £411 per patient for esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
For the 1000 patients, the criteria produced 0.16 additional quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) per patient at an incremental cost of £326, or about $443, over 5 years. This resulted in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of £2081, or $2830, per additional QALY gained.
In addition, the incremental net monetary benefit of the Baveno VI criteria was £2808, or $3819, over 5 years per patient.
The results were also consistent and cost-effective in Canada and Spain using relevant cost inputs from those countries. In Canada, the ICER per QALY estimates were €3535, or $3712, over 5 years and €4610, or $4841, over 20 years. In Spain, the ICER per QALY estimates were €1966, or $2064, over 5 years and €2225, or $2336, over 20 years.
Baveno VI Considerations
Despite the small risk of false negatives, the Baveno VI criteria could avoid unnecessary endoscopies and provide significant cost savings, the study authors wrote.
“It should be mentioned, however, that sparing endoscopies could result in missing the incidental detection of esophageal and gastric cancers, particularly in patients with higher risk, such as those who misuse alcohol,” Dr. Tsochatzis said.
Future studies could investigate ways to broaden the applicability of the Baveno VI criteria to other patient subgroups, identify optimal cut-off points, and incorporate patients with systemic therapies.
“Baveno VI criteria can be safely used to avoid endoscopy in a substantial proportion of patients with compensated cirrhosis,” said Wayne Bai, MBChB, a gastroenterologist at Waikato Hospital and the University of Auckland in New Zealand.
Dr. Bai, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched the Baveno VI criteria and participated in Baveno VII criteria meetings. In an analysis of more than two dozen studies, he and colleagues found that the Baveno VI criteria had a pooled 99% negative predictive value for ruling out high-risk varices and weren’t affected by the cause of cirrhosis. However, expanding the criteria had suboptimal performance in some cases.
“The progressive change in approach to the management of compensated cirrhosis, progressively focusing on treating portal hypertension with beta-blockers independently of the presence of varices, might render these criteria less relevant,” he said.
The authors were supported by funds from the National Institute for Health and Care Research Applied Research Collaboration North Thames, the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, and the European Union’s European Regional Development Fund and European Social Fund. Dr Bai reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Compared with endoscopy, , according to new research.
Although upper gastrointestinal endoscopy continues to be the gold standard for detecting varices, the Baveno VI criteria combine liver stiffness and platelet count values to rule out high-risk varices, which can save on endoscopy costs.
“The Baveno VI criteria can reduce the need for endoscopies in patients with cirrhosis, but it is important to ascertain if they are also cost-effective,” said senior author Emmanuel Tsochatzis, MD, professor of hepatology at the University College London Institute for Liver and Digestive Health and Royal Free Hospital in London.
“Our findings confirm that the application of these criteria is highly cost-effective, and given the fact that they are also safe, should be considered for widespread implementation,” he said.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Baveno VI Criteria Analysis
On the basis of the Baveno VI Consensus, endoscopy screening can be avoided in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease and Child-Pugh A cirrhosis who have a platelet count > 150,000/mm3 and a liver stiffness measurement < 20 kPa.
In addition, expanded Baveno VI criteria have suggested optimized cut-off values to avoid even more endoscopies — at a platelet value of > 110,000/mm3 and a liver stiffness < 25 kPa.
Previous research indicates that the expanded criteria could avoid double the number of endoscopies, the authors wrote, with a risk of missing high-risk varices in 1.6% of patients with the criteria and 0.6% of overall study participants. Both criteria have been validated in large groups of patients with compensated cirrhosis of different etiologies, but the cost-effectiveness hasn’t been analyzed.
Dr. Tsochatzis and colleagues created an analytical decision model to estimate the costs and benefits of using the Baveno VI criteria as compared with endoscopy as the standard of care among a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients with Child-Pugh A cirrhosis. The research team looked at costs and clinical outcomes based on the United Kingdom National Health Service perspective at 1 year from diagnosis and then estimated the expected costs and outcomes at 5 years and 20 years, including factors such as liver disease progression and variceal bleeding.
As part of the model, the Baveno VI criteria were implemented at annual screenings with targeted endoscopy for patients who met the criteria, as compared with endoscopy as a biannual screening using esophagogastroduodenoscopy for everyone.
In general, the Baveno VI criteria were cost-effective compared with endoscopy in all analyses, including all time points, as well as deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses. The cost of using the criteria was £67 per patient, as compared with £411 per patient for esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
For the 1000 patients, the criteria produced 0.16 additional quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) per patient at an incremental cost of £326, or about $443, over 5 years. This resulted in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of £2081, or $2830, per additional QALY gained.
In addition, the incremental net monetary benefit of the Baveno VI criteria was £2808, or $3819, over 5 years per patient.
The results were also consistent and cost-effective in Canada and Spain using relevant cost inputs from those countries. In Canada, the ICER per QALY estimates were €3535, or $3712, over 5 years and €4610, or $4841, over 20 years. In Spain, the ICER per QALY estimates were €1966, or $2064, over 5 years and €2225, or $2336, over 20 years.
Baveno VI Considerations
Despite the small risk of false negatives, the Baveno VI criteria could avoid unnecessary endoscopies and provide significant cost savings, the study authors wrote.
“It should be mentioned, however, that sparing endoscopies could result in missing the incidental detection of esophageal and gastric cancers, particularly in patients with higher risk, such as those who misuse alcohol,” Dr. Tsochatzis said.
Future studies could investigate ways to broaden the applicability of the Baveno VI criteria to other patient subgroups, identify optimal cut-off points, and incorporate patients with systemic therapies.
“Baveno VI criteria can be safely used to avoid endoscopy in a substantial proportion of patients with compensated cirrhosis,” said Wayne Bai, MBChB, a gastroenterologist at Waikato Hospital and the University of Auckland in New Zealand.
Dr. Bai, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched the Baveno VI criteria and participated in Baveno VII criteria meetings. In an analysis of more than two dozen studies, he and colleagues found that the Baveno VI criteria had a pooled 99% negative predictive value for ruling out high-risk varices and weren’t affected by the cause of cirrhosis. However, expanding the criteria had suboptimal performance in some cases.
“The progressive change in approach to the management of compensated cirrhosis, progressively focusing on treating portal hypertension with beta-blockers independently of the presence of varices, might render these criteria less relevant,” he said.
The authors were supported by funds from the National Institute for Health and Care Research Applied Research Collaboration North Thames, the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, and the European Union’s European Regional Development Fund and European Social Fund. Dr Bai reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Compared with endoscopy, , according to new research.
Although upper gastrointestinal endoscopy continues to be the gold standard for detecting varices, the Baveno VI criteria combine liver stiffness and platelet count values to rule out high-risk varices, which can save on endoscopy costs.
“The Baveno VI criteria can reduce the need for endoscopies in patients with cirrhosis, but it is important to ascertain if they are also cost-effective,” said senior author Emmanuel Tsochatzis, MD, professor of hepatology at the University College London Institute for Liver and Digestive Health and Royal Free Hospital in London.
“Our findings confirm that the application of these criteria is highly cost-effective, and given the fact that they are also safe, should be considered for widespread implementation,” he said.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Baveno VI Criteria Analysis
On the basis of the Baveno VI Consensus, endoscopy screening can be avoided in patients with compensated advanced chronic liver disease and Child-Pugh A cirrhosis who have a platelet count > 150,000/mm3 and a liver stiffness measurement < 20 kPa.
In addition, expanded Baveno VI criteria have suggested optimized cut-off values to avoid even more endoscopies — at a platelet value of > 110,000/mm3 and a liver stiffness < 25 kPa.
Previous research indicates that the expanded criteria could avoid double the number of endoscopies, the authors wrote, with a risk of missing high-risk varices in 1.6% of patients with the criteria and 0.6% of overall study participants. Both criteria have been validated in large groups of patients with compensated cirrhosis of different etiologies, but the cost-effectiveness hasn’t been analyzed.
Dr. Tsochatzis and colleagues created an analytical decision model to estimate the costs and benefits of using the Baveno VI criteria as compared with endoscopy as the standard of care among a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients with Child-Pugh A cirrhosis. The research team looked at costs and clinical outcomes based on the United Kingdom National Health Service perspective at 1 year from diagnosis and then estimated the expected costs and outcomes at 5 years and 20 years, including factors such as liver disease progression and variceal bleeding.
As part of the model, the Baveno VI criteria were implemented at annual screenings with targeted endoscopy for patients who met the criteria, as compared with endoscopy as a biannual screening using esophagogastroduodenoscopy for everyone.
In general, the Baveno VI criteria were cost-effective compared with endoscopy in all analyses, including all time points, as well as deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses. The cost of using the criteria was £67 per patient, as compared with £411 per patient for esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
For the 1000 patients, the criteria produced 0.16 additional quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) per patient at an incremental cost of £326, or about $443, over 5 years. This resulted in an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of £2081, or $2830, per additional QALY gained.
In addition, the incremental net monetary benefit of the Baveno VI criteria was £2808, or $3819, over 5 years per patient.
The results were also consistent and cost-effective in Canada and Spain using relevant cost inputs from those countries. In Canada, the ICER per QALY estimates were €3535, or $3712, over 5 years and €4610, or $4841, over 20 years. In Spain, the ICER per QALY estimates were €1966, or $2064, over 5 years and €2225, or $2336, over 20 years.
Baveno VI Considerations
Despite the small risk of false negatives, the Baveno VI criteria could avoid unnecessary endoscopies and provide significant cost savings, the study authors wrote.
“It should be mentioned, however, that sparing endoscopies could result in missing the incidental detection of esophageal and gastric cancers, particularly in patients with higher risk, such as those who misuse alcohol,” Dr. Tsochatzis said.
Future studies could investigate ways to broaden the applicability of the Baveno VI criteria to other patient subgroups, identify optimal cut-off points, and incorporate patients with systemic therapies.
“Baveno VI criteria can be safely used to avoid endoscopy in a substantial proportion of patients with compensated cirrhosis,” said Wayne Bai, MBChB, a gastroenterologist at Waikato Hospital and the University of Auckland in New Zealand.
Dr. Bai, who wasn’t involved with this study, has researched the Baveno VI criteria and participated in Baveno VII criteria meetings. In an analysis of more than two dozen studies, he and colleagues found that the Baveno VI criteria had a pooled 99% negative predictive value for ruling out high-risk varices and weren’t affected by the cause of cirrhosis. However, expanding the criteria had suboptimal performance in some cases.
“The progressive change in approach to the management of compensated cirrhosis, progressively focusing on treating portal hypertension with beta-blockers independently of the presence of varices, might render these criteria less relevant,” he said.
The authors were supported by funds from the National Institute for Health and Care Research Applied Research Collaboration North Thames, the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, and the European Union’s European Regional Development Fund and European Social Fund. Dr Bai reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
ACG/ASGE Task Force Identifies 19 Indicators for Achieving Quality GI Endoscopy
— most of which have a performance target > 98%, implying they should be achieved in nearly every case.
The task force’s work was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
“The purpose of this paper is to delineate all of the steps that the endoscopist should be thinking about before they perform any endoscopy,” task force member Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview.
“Some of these are straightforward — for instance, did we get informed consent? Others are more nuanced — did we appropriately plan for sedation for the procedure, or did we give the right antibiotics before the procedure to prevent an infectious complication after?
“While the vast majority of endoscopists do these measures with every procedure, especially in unusual circumstances or when the procedure is an emergency, they can be overlooked. Having these quality indicators listed in one place should minimize these omissions,” Dr. Shaheen said.
Four Priority Indicators
The update represents the third iteration of the ACG/ASGE quality indicators on GI endoscopic procedures, the most recent of which was published nearly a decade ago.
As in preceding versions, the task force “prioritized indicators that have wide-ranging clinical implications and have been validated in clinical studies.” There are 19 in total, divided into three time periods: Preprocedure (8), intraprocedure (4), and postprocedure (7).
While all 19 indicators are intended to serve as a framework for continual quality improvement efforts among endoscopists and units, the task force recognized a subset of 4 they identified as being a particular priority:
- Frequency with which endoscopy is performed for an indication that is included in a published standard list of appropriate indications and the indication is documented (performance target > 95%)
- Frequency with which prophylactic antibiotics are administered for appropriate indications (performance target > 98%)
- Frequency with which a plan for the management of antithrombotic therapy is formulated and documented before the procedure (performance target = 95%)
- Frequency with which adverse events are documented (performance target > 98%)
Room for Improvement
There remains a lack of compliance with some of these indicators, the task force said.
“Procedures are still performed for questionable indications, adverse events are not always captured and documented, and communication between the endoscopist and patient and/or involved clinicians is sometimes lacking.
“For these reasons, strict attention to the quality indicators in this document and an active plan for improvement in areas of measured deficiency should be a central pillar of the successful practice of endoscopy,” they wrote.
The task force advised that quality improvement efforts initially focus on the four priority indicators and then progress to include other indicators once it is determined that endoscopists are performing above recommended thresholds, either at baseline or after corrective interventions.
Reached for comment, Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MD, MPH, AGAF, a gastroenterologist with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview that these updated recommendations are “important and commonsense standard procedures that should be followed for all procedures.”
“We recognize endoscopic evaluation plays an important role in the assessment of GI illnesses, but there are also both risks and costs to this as a diagnostic and therapeutic intervention. Thus, it is important to make sure these standards are met, to optimize the outcomes of our patients,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan, who was not involved in this work.
In a separate statement, the American Gastroenterological Association affirmed that is committed to supporting gastroenterologists in providing high-quality care via improved patients outcomes, increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness. AGA encouraged GIs to visit gastro.org/quality to learn more and find quality measures on topics including Barrett’s esophagus, inflammatory bowel disease, acute pancreatitis, and gastric intestinal metaplasia.
This work had no financial support. Dr. Shaheen and Dr. Ananthakrishnan disclosed having no relevant competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
— most of which have a performance target > 98%, implying they should be achieved in nearly every case.
The task force’s work was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
“The purpose of this paper is to delineate all of the steps that the endoscopist should be thinking about before they perform any endoscopy,” task force member Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview.
“Some of these are straightforward — for instance, did we get informed consent? Others are more nuanced — did we appropriately plan for sedation for the procedure, or did we give the right antibiotics before the procedure to prevent an infectious complication after?
“While the vast majority of endoscopists do these measures with every procedure, especially in unusual circumstances or when the procedure is an emergency, they can be overlooked. Having these quality indicators listed in one place should minimize these omissions,” Dr. Shaheen said.
Four Priority Indicators
The update represents the third iteration of the ACG/ASGE quality indicators on GI endoscopic procedures, the most recent of which was published nearly a decade ago.
As in preceding versions, the task force “prioritized indicators that have wide-ranging clinical implications and have been validated in clinical studies.” There are 19 in total, divided into three time periods: Preprocedure (8), intraprocedure (4), and postprocedure (7).
While all 19 indicators are intended to serve as a framework for continual quality improvement efforts among endoscopists and units, the task force recognized a subset of 4 they identified as being a particular priority:
- Frequency with which endoscopy is performed for an indication that is included in a published standard list of appropriate indications and the indication is documented (performance target > 95%)
- Frequency with which prophylactic antibiotics are administered for appropriate indications (performance target > 98%)
- Frequency with which a plan for the management of antithrombotic therapy is formulated and documented before the procedure (performance target = 95%)
- Frequency with which adverse events are documented (performance target > 98%)
Room for Improvement
There remains a lack of compliance with some of these indicators, the task force said.
“Procedures are still performed for questionable indications, adverse events are not always captured and documented, and communication between the endoscopist and patient and/or involved clinicians is sometimes lacking.
“For these reasons, strict attention to the quality indicators in this document and an active plan for improvement in areas of measured deficiency should be a central pillar of the successful practice of endoscopy,” they wrote.
The task force advised that quality improvement efforts initially focus on the four priority indicators and then progress to include other indicators once it is determined that endoscopists are performing above recommended thresholds, either at baseline or after corrective interventions.
Reached for comment, Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MD, MPH, AGAF, a gastroenterologist with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview that these updated recommendations are “important and commonsense standard procedures that should be followed for all procedures.”
“We recognize endoscopic evaluation plays an important role in the assessment of GI illnesses, but there are also both risks and costs to this as a diagnostic and therapeutic intervention. Thus, it is important to make sure these standards are met, to optimize the outcomes of our patients,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan, who was not involved in this work.
In a separate statement, the American Gastroenterological Association affirmed that is committed to supporting gastroenterologists in providing high-quality care via improved patients outcomes, increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness. AGA encouraged GIs to visit gastro.org/quality to learn more and find quality measures on topics including Barrett’s esophagus, inflammatory bowel disease, acute pancreatitis, and gastric intestinal metaplasia.
This work had no financial support. Dr. Shaheen and Dr. Ananthakrishnan disclosed having no relevant competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
— most of which have a performance target > 98%, implying they should be achieved in nearly every case.
The task force’s work was published online in The American Journal of Gastroenterology.
“The purpose of this paper is to delineate all of the steps that the endoscopist should be thinking about before they perform any endoscopy,” task force member Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, said in an interview.
“Some of these are straightforward — for instance, did we get informed consent? Others are more nuanced — did we appropriately plan for sedation for the procedure, or did we give the right antibiotics before the procedure to prevent an infectious complication after?
“While the vast majority of endoscopists do these measures with every procedure, especially in unusual circumstances or when the procedure is an emergency, they can be overlooked. Having these quality indicators listed in one place should minimize these omissions,” Dr. Shaheen said.
Four Priority Indicators
The update represents the third iteration of the ACG/ASGE quality indicators on GI endoscopic procedures, the most recent of which was published nearly a decade ago.
As in preceding versions, the task force “prioritized indicators that have wide-ranging clinical implications and have been validated in clinical studies.” There are 19 in total, divided into three time periods: Preprocedure (8), intraprocedure (4), and postprocedure (7).
While all 19 indicators are intended to serve as a framework for continual quality improvement efforts among endoscopists and units, the task force recognized a subset of 4 they identified as being a particular priority:
- Frequency with which endoscopy is performed for an indication that is included in a published standard list of appropriate indications and the indication is documented (performance target > 95%)
- Frequency with which prophylactic antibiotics are administered for appropriate indications (performance target > 98%)
- Frequency with which a plan for the management of antithrombotic therapy is formulated and documented before the procedure (performance target = 95%)
- Frequency with which adverse events are documented (performance target > 98%)
Room for Improvement
There remains a lack of compliance with some of these indicators, the task force said.
“Procedures are still performed for questionable indications, adverse events are not always captured and documented, and communication between the endoscopist and patient and/or involved clinicians is sometimes lacking.
“For these reasons, strict attention to the quality indicators in this document and an active plan for improvement in areas of measured deficiency should be a central pillar of the successful practice of endoscopy,” they wrote.
The task force advised that quality improvement efforts initially focus on the four priority indicators and then progress to include other indicators once it is determined that endoscopists are performing above recommended thresholds, either at baseline or after corrective interventions.
Reached for comment, Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan, MD, MPH, AGAF, a gastroenterologist with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, Massachusetts, said in an interview that these updated recommendations are “important and commonsense standard procedures that should be followed for all procedures.”
“We recognize endoscopic evaluation plays an important role in the assessment of GI illnesses, but there are also both risks and costs to this as a diagnostic and therapeutic intervention. Thus, it is important to make sure these standards are met, to optimize the outcomes of our patients,” said Dr. Ananthakrishnan, who was not involved in this work.
In a separate statement, the American Gastroenterological Association affirmed that is committed to supporting gastroenterologists in providing high-quality care via improved patients outcomes, increased efficiency and cost-effectiveness. AGA encouraged GIs to visit gastro.org/quality to learn more and find quality measures on topics including Barrett’s esophagus, inflammatory bowel disease, acute pancreatitis, and gastric intestinal metaplasia.
This work had no financial support. Dr. Shaheen and Dr. Ananthakrishnan disclosed having no relevant competing interests.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY
Automated ERCP Report Card Offers High Accuracy, Minimal Work
offering a real-time gauge of both individual- and institutional-level quality indicators, according to the developers.
The tool boasts an accuracy level exceeding 96%, integrates with multiple electronic health records, and requires minimal additional work time, reported Anmol Singh, MD, of TriStar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
“Implementation of quality indicator tracking remains difficult due to the complexity of ERCP as compared with other endoscopic procedures, resulting in significant limitations in the extraction and synthesis of these data,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “Manual extraction methods such as self-assessment forms and chart reviews are both time intensive and error prone, and current automated extraction methods, such as natural language processing, can require substantial resources to implement and undesirably complicate the endoscopy work flow.”
To overcome these challenges, Dr. Singh and colleagues designed an analytics tool that automatically collects ERCP quality indicators from endoscopy reports with “minimal input” from the endoscopist, and is compatible with “any electronic reporting system.”
Development relied upon endoscopy records from 2,146 ERCPs performed by 12 endoscopists at four facilities. The most common reason for ERCP was choledocholithiasis, followed by malignant and benign biliary stricture. Most common procedures were stent placement and sphincterotomy.
Data were aggregated in a Health Level–7 (HL-7) interface, an international standard system that enables compatibility between different types of electronic health records. Some inputs were entered by the performing endoscopist via drop-down menus.
Next, data were shifted into an analytics suite, which evaluated quality indicators, including cannulation difficulty and success rate, and administration of post-ERCP pancreatitis prophylaxis.
Manual review showed that this approach yielded an accuracy of 96.5%-100%.
Beyond this high level of accuracy, Dr. Singh and colleagues described several reasons why their tool may be superior to previous attempts at an automated ERCP report card.
“Our HL-7–based tool offers several advantages, including versatility via compatibility with multiple types of commercial reporting software and flexibility in customizing the type and aesthetic of the data displayed,” they wrote. “These features improve the user interface, keep costs down, and allow for integration into smaller or nonacademic practice settings.”
They also highlighted how the tool measures quality in relation to procedure indication and difficulty at the provider level.
“Unlike in colonoscopy, where metrics such as adenoma detection rate can be ubiquitously applied to all screening procedures, the difficulty and risk profile of ERCP is inextricably dependent on patient and procedural factors such as indication of the procedure, history of interventions, or history of altered anatomy,” Dr. Singh and colleagues wrote. “Prior studies have shown that both the cost-effectiveness and complication rates of procedures are influenced by procedural indication and complexity. As such, benchmarking an individual provider’s performance necessarily requires the correct procedural context.”
With further optimization, this tool can be integrated into various types of existing endoscopy reporting software at a reasonable cost, and with minimal impact on routine work flow, the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Boston Scientific, Organon, and others.
offering a real-time gauge of both individual- and institutional-level quality indicators, according to the developers.
The tool boasts an accuracy level exceeding 96%, integrates with multiple electronic health records, and requires minimal additional work time, reported Anmol Singh, MD, of TriStar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
“Implementation of quality indicator tracking remains difficult due to the complexity of ERCP as compared with other endoscopic procedures, resulting in significant limitations in the extraction and synthesis of these data,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “Manual extraction methods such as self-assessment forms and chart reviews are both time intensive and error prone, and current automated extraction methods, such as natural language processing, can require substantial resources to implement and undesirably complicate the endoscopy work flow.”
To overcome these challenges, Dr. Singh and colleagues designed an analytics tool that automatically collects ERCP quality indicators from endoscopy reports with “minimal input” from the endoscopist, and is compatible with “any electronic reporting system.”
Development relied upon endoscopy records from 2,146 ERCPs performed by 12 endoscopists at four facilities. The most common reason for ERCP was choledocholithiasis, followed by malignant and benign biliary stricture. Most common procedures were stent placement and sphincterotomy.
Data were aggregated in a Health Level–7 (HL-7) interface, an international standard system that enables compatibility between different types of electronic health records. Some inputs were entered by the performing endoscopist via drop-down menus.
Next, data were shifted into an analytics suite, which evaluated quality indicators, including cannulation difficulty and success rate, and administration of post-ERCP pancreatitis prophylaxis.
Manual review showed that this approach yielded an accuracy of 96.5%-100%.
Beyond this high level of accuracy, Dr. Singh and colleagues described several reasons why their tool may be superior to previous attempts at an automated ERCP report card.
“Our HL-7–based tool offers several advantages, including versatility via compatibility with multiple types of commercial reporting software and flexibility in customizing the type and aesthetic of the data displayed,” they wrote. “These features improve the user interface, keep costs down, and allow for integration into smaller or nonacademic practice settings.”
They also highlighted how the tool measures quality in relation to procedure indication and difficulty at the provider level.
“Unlike in colonoscopy, where metrics such as adenoma detection rate can be ubiquitously applied to all screening procedures, the difficulty and risk profile of ERCP is inextricably dependent on patient and procedural factors such as indication of the procedure, history of interventions, or history of altered anatomy,” Dr. Singh and colleagues wrote. “Prior studies have shown that both the cost-effectiveness and complication rates of procedures are influenced by procedural indication and complexity. As such, benchmarking an individual provider’s performance necessarily requires the correct procedural context.”
With further optimization, this tool can be integrated into various types of existing endoscopy reporting software at a reasonable cost, and with minimal impact on routine work flow, the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Boston Scientific, Organon, and others.
offering a real-time gauge of both individual- and institutional-level quality indicators, according to the developers.
The tool boasts an accuracy level exceeding 96%, integrates with multiple electronic health records, and requires minimal additional work time, reported Anmol Singh, MD, of TriStar Centennial Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, and colleagues.
“Implementation of quality indicator tracking remains difficult due to the complexity of ERCP as compared with other endoscopic procedures, resulting in significant limitations in the extraction and synthesis of these data,” the investigators wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. “Manual extraction methods such as self-assessment forms and chart reviews are both time intensive and error prone, and current automated extraction methods, such as natural language processing, can require substantial resources to implement and undesirably complicate the endoscopy work flow.”
To overcome these challenges, Dr. Singh and colleagues designed an analytics tool that automatically collects ERCP quality indicators from endoscopy reports with “minimal input” from the endoscopist, and is compatible with “any electronic reporting system.”
Development relied upon endoscopy records from 2,146 ERCPs performed by 12 endoscopists at four facilities. The most common reason for ERCP was choledocholithiasis, followed by malignant and benign biliary stricture. Most common procedures were stent placement and sphincterotomy.
Data were aggregated in a Health Level–7 (HL-7) interface, an international standard system that enables compatibility between different types of electronic health records. Some inputs were entered by the performing endoscopist via drop-down menus.
Next, data were shifted into an analytics suite, which evaluated quality indicators, including cannulation difficulty and success rate, and administration of post-ERCP pancreatitis prophylaxis.
Manual review showed that this approach yielded an accuracy of 96.5%-100%.
Beyond this high level of accuracy, Dr. Singh and colleagues described several reasons why their tool may be superior to previous attempts at an automated ERCP report card.
“Our HL-7–based tool offers several advantages, including versatility via compatibility with multiple types of commercial reporting software and flexibility in customizing the type and aesthetic of the data displayed,” they wrote. “These features improve the user interface, keep costs down, and allow for integration into smaller or nonacademic practice settings.”
They also highlighted how the tool measures quality in relation to procedure indication and difficulty at the provider level.
“Unlike in colonoscopy, where metrics such as adenoma detection rate can be ubiquitously applied to all screening procedures, the difficulty and risk profile of ERCP is inextricably dependent on patient and procedural factors such as indication of the procedure, history of interventions, or history of altered anatomy,” Dr. Singh and colleagues wrote. “Prior studies have shown that both the cost-effectiveness and complication rates of procedures are influenced by procedural indication and complexity. As such, benchmarking an individual provider’s performance necessarily requires the correct procedural context.”
With further optimization, this tool can be integrated into various types of existing endoscopy reporting software at a reasonable cost, and with minimal impact on routine work flow, the investigators concluded.
The investigators disclosed relationships with AbbVie, Boston Scientific, Organon, and others.
FROM TECHNIQUES AND INNOVATIONS IN GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
Advanced Tissue Resection in Gastroenterology: Indications, Role, and Outcomes
Endoscopists are often faced with unique challenges in the management and resection of various gastrointestinal tract lesions. These challenges could be lesion-related, endoscopist-related, or practice-related (see Table 1). (ATR). Not only does this organ-sparing approach offer a less invasive alternative to surgery, but it has also proved to have outcomes comparable to those of surgical standard of practice in specific scenarios. 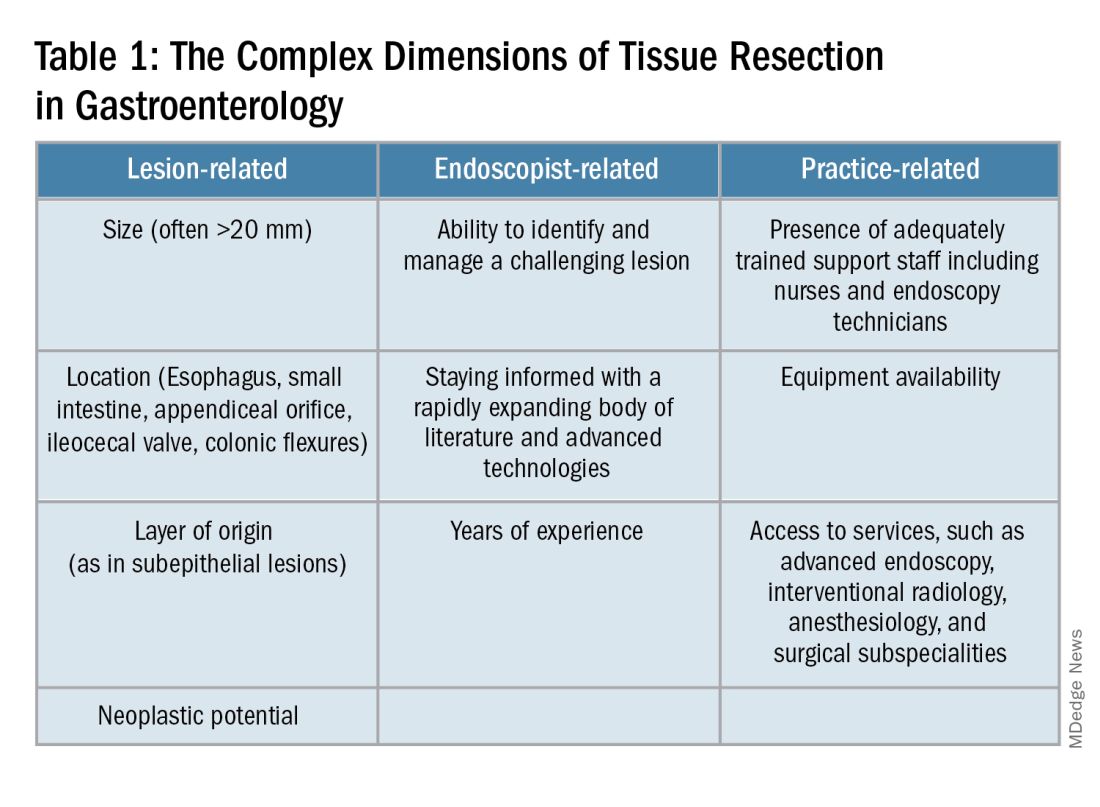
When Do You Refer to an Advanced Endoscopist?
One of the most critical steps in caring for patients with complex lesions is the ability to accurately determine whether a referral to an advanced endoscopist is warranted. The initial assessment of a lesion should always involve a careful assessment that risk stratifies the lesion depending on the location, size, neoplastic potential, and the feasibility of standard endoscopic resection compared to the need for surgical input.
A practical example in the case of colonic polyps is highlighted by the American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) guidelines recommending the referral of patients with polyps’ size ≥ 20 mm, challenging polypectomy location, or recurrent polyp at a prior polypectomy site to an endoscopic referral center.1 In the case of subepithelial lesions without endoscopic characteristics of benign etiology (i.e., lipomas, pancreatic rests, etc.), the threshold for referral to advanced endoscopists for further diagnostic testing by means of endoscopic ultrasonography or for therapeutic ATR should be lower.
Endoscopic tissue resection follows a spectrum, which often involves deeper layers of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) as we progress along this spectrum (see Figure 1). 
ATR, a term encompassing a variety of endoscopic techniques ranging from endoscopic mucosal resection to full thickness resection, has gained traction over the last years given the ability to effectively remove various lesions in a precise time and cost-effective manner while maintaining the integrity of the GIT and avoiding major surgery. The indications for ATR vary depending on the technique, but generally include the presence of large or poorly positioned lesions, particularly in high-risk areas of the GIT such as the esophagus and small intestine, lesions extending beyond the mucosal layer or originating from deeper layers, and when en bloc resection of select lesions is necessary.
For providers referring patients for ATR, we recommend a few important endoscopic pearls when caring for these patients.
1) Biopsy the lesion if there is concern for malignancy — While some studies have noted increased fibrosis during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and some guidelines recommend against biopsies pre ESD, we believe that when there is high pretest probability for malignancy, a biopsy should be obtained. This should involve the area that is most concerning for malignancy (at the margin or center).2
2) While marking a lesion with tattoo is helpful for surgical planning and for lesions difficult to locate endoscopically, we stress the importance of placing tattoos 3 to 5 centimeters distal to the lesion and avoiding tattooing the lesion itself, which has been shown to induce fibrosis and can make resection challenging. Based on an international Delphi consensus, expert recommendations on when and how to endoscopically tattoo a lesion can be instrumental in adequately localizing the lesion, allowing for endoscopic resection, and preventing unnecessary surgeries.3
3) If you encounter a lesion that you are not sure can be resected safely and efficaciously, we recommend against attempting resection that may result in partial resection. This can also induce fibrosis and scarring and limit future attempts at resection.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
EMR is currently utilized for curative treatment of a wide array of GIT lesions limited to the mucosal layer, whether metaplastic, dysplastic, or even in cases with early mucosal cancer, where the risk of submucosal and lymphatic invasion is minimal.4 This makes EMR a versatile and proven therapy, often serving as the first-line treatment for many GIT lesions.
EMR has various techniques that could be categorized into suction or non-suction (lift and cut) techniques. In the suction technique, devices like multiband mucosectomy (MBM) are commonly used, especially in nodular Barrett’s dysplasia, forming a pseudopolyp for subsequent resection. The procedure is characterized by its safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to its widespread adoption in clinical practice. In the lift and cut approach, a submucosal injection is utilized to separate the muscularis propria from the lesion, thereby reducing the risk of perforation. Different solutions, such as normal saline, hypertonic saline, 50% dextrose, or proprietary submucosal injection solutions, are employed for submucosal injection.5
The non-suction technique using a snare to resect polyps after injection is more often used in colonic and small intestinal EMR. Resection can be done via thermal energy in the form of cut or coagulation; however, there is rising data on the use of piecemeal cold snare resection for select flat polyps of the colon.6 There is also promising data on the role of underwater EMR, a common technique employed for colonic lesions, particularly if the lesion does not lift well with submucosal injection.7
Adverse events associated with EMR include bleeding (7%-8%) and perforation (0.9%-2%).8-9 Adequate submucosal fluid injection is crucial to prevent perforations. However, the main limitation of EMR is the piecemeal nature of resections for lesions larger than 20 mm, leading to compromised histopathologic evaluation for complete excision, especially in cases with superficial submucosal invasion (SMI). This can result in residual or recurrent tissue, reportedly 8% to 20%.10 Despite this limitation, EMR remains a reliable strategy, and recurrent lesions are generally manageable through repeat sessions. The importance of EMR as a therapeutic modality lies in its role in addressing lesions with favorable characteristics, where the risk of SMI is low.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
ESD is an evolving technique that can be utilized for submucosal lesions of the GIT, lesions not amenable to EMR due to submucosal fibrosis, when en bloc removal of a lesion is needed for accurate histopathological diagnosis, and when other techniques fail.11-12
ESD was only recently adopted in the United States, requires specialized training, and usually is a lengthier procedure than EMR.13 Compared to EMR, it has higher en bloc resection rates and lower recurrence rates, making it curative for lesions with superficial SMI and favorable histologic features.4,14 The safety profile of ESD appears favorable, with most of the adverse events managed successfully by endoscopic methods. Major complications include intraoperative and delayed perforation, intraoperative and delayed bleeding, aspiration pneumonia, thromboembolism, and stricture formation in the case of circumferential lesions.15
Despite being technically challenging, ESD may provide a cost-effective long-term solution by avoiding surgery, reducing the need for additional interventions by minimizing recurrence rates. Given the technical complexity of ESD, particularly the submucosal dissection portion, techniques such as hybrid ESD developed. Hybrid ESD combines snaring with circumferential mucosal incision and partial submucosal dissection. Although it promises shorter procedure times, reduced complication rates like perforation, and similar recurrence rates compared to traditional ESD, studies have shown lower success rates in en bloc resection.16-17
Both EMR and ESD are considered complementary strategies, and the choice between them should be dictated by lesion characteristics, patient preferences, and local expertise.
Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection (STER)
STER has emerged as a well-established technique for the endoscopic resection of GI subepithelial tumors (SETs) originating from the muscularis propria layer. The standard STER procedure involves a series of steps including submucosal elevation proximal to the SET, mucosotomy, creation of a submucosal tunnel, dissection of the SET within the tunnel, enucleation from the deep muscle layer, and subsequent specimen retrieval followed by mucosal closure.
This technique is typically recommended for SETs smaller than 3.5 cm, particularly those located in the mid or distal esophagus, cardia, or along the greater curvature of the gastric body.18 However, STER may pose technical challenges for larger SETs or lesions in anatomically difficult locations, where surgical resection is recommended instead.19 Notably, recent large-scale meta-analyses have showcased the favorable complete resection and en bloc resection rates of STER in treating GI SETs.20
Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection (EFTR)
EFTR has emerged as a valuable technique in the endoscopic management of gastrointestinal lesions, particularly SETs and lesions not amenable to EMR or ESD due to fibrosis. EFTR involves the resection of all layers of the GIT from mucosa to serosa, and therefore is well-suited for SETs arising from the muscularis propria (MP).20
EFTR entails two main concepts: tissue resection and complete defect closure. Conventional EFTR consists of several steps, which include mucosal and submucosal pre-cutting, circumferential incision, and dissection through the MP or serosa. This results in a full thickness defect, for which closure of the wall defect is achieved using standard endoscopic clips or a combination of clips and endoloops or endoscopic suturing.21 For lesions less than 2 cm, EFTR can be performed in a single step using a cap-mounted full thickness resection device (FTRD). This results in deployment of over-the-scope clip over the target lesion followed by snaring the lesions above the clip.21
Location of the SET generally dictates the specific modality of ATR. For example, esophageal SETs may be more amenable to STER given that the lesion typically runs parallel with the lumen of the tubular esophagus, which allows for easier dissection without the need of full or partial retroflexion. While gastric SETs can be resected with STER, it may be challenging and more effectively addressed with EFTR, particularly when the entire lesion can be grasped into the full-thickness resection device.22 Limited data exists for duodenal EFTR, and colorectal SETs closure is particularly challenging.
Conclusion
It is key to emphasize that ATR cannot be safely established in practice without the incorporation of a multidisciplinary team (surgeons, radiologists, etc.), specialized tools, and trained personnel. This requires dedicated endoscopic rooms, careful patient selection, and a comprehensive approach to patient care before, during, and after these procedures.
Moreover, it is important to note that some patients may require post-procedure hospitalization for observation to ensure no early complications are encountered. Optimal surveillance strategies after ATR rely heavily on the potential for residual or recurrent disease, underlying pathology, and the expertise of the advanced endoscopist. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and technological advances of devices will further enhance the efficacy and safety of ATR in gastroenterology.
Dr. Madi (@MahMadi90) is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri. Dr. Rengarajan (@ArvindRenga) and Dr. Bazarbashi (@AhmadBazarbashi) are based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and no funding was required for this project.
References
1. Copland AP, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on appropriate and tailored polypectomy: Expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.012.
2. Lee SP, et al. Effect of preceding biopsy on the results of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal laterally spreading tumor. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05625-3.
3. Medina-Prado L, et al. When and how to use endoscopic tattooing in the colon: An international Delphi agreement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.024.
4. Rashid MU, et al. EMR and ESD: Indications, techniques and results. Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101742.
5. Castro R, et al. Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.777.
6. Rex DK. Best practices for resection of diminutive and small polyps in the colorectum. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2019.06.004.
7. Lv XH, et al. Underwater EMR for nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.10.044.
8. Fujiya M, et al. Efficacy and adverse events of EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colon neoplasms: a meta-analysis of studies comparing EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.034.
9. Kandel P, Wallace MB. Colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.05.006.
10. Kemper G, et al; ENDOCARE Study Group. Endoscopic techniques to reduce recurrence rates after colorectal EMR: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08574-z.
11. Goto O, et al. Expanding indications for ESD: submucosal disease (SMT/carcinoid tumors). Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.11.006.
12. Wang K, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection, indication, methods and perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1111/den.14474.
13. Herreros de Tejada A. ESD training: A challenging path to excellence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014 Apr 16. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i4.112.
14. Chiba H, et al. Safety and efficacy of simultaneous colorectal ESD for large synchronous colorectal lesions. Endosc Int Open. 2017 Jul. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-110567.
15. Mannath J, Ragunath K. Endoscopic mucosal resection: who and how? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep. doi: 10.1177/1756283X10388683.
16. Wang XY, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: An alternative resection modality for large laterally spreading tumors in the cecum? BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01766-w.
17. McCarty TR, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) compared with conventional ESD for colorectal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1055/a-1266-1855.
18. Jain D, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria. Ann Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.20524/aog.2017.0128.
19. Lv XH, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017 Jan. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4978-7.
20. Cao B, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021 Jan. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.6989/2020.
21. Cai M, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.12.013.
22. Brigic A, et al. A systematic review regarding the feasibility and safety of endoscopic full thickness resection (EFTR) for colonic lesions. Surg Endosc. 2013 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2946-z.
Endoscopists are often faced with unique challenges in the management and resection of various gastrointestinal tract lesions. These challenges could be lesion-related, endoscopist-related, or practice-related (see Table 1). (ATR). Not only does this organ-sparing approach offer a less invasive alternative to surgery, but it has also proved to have outcomes comparable to those of surgical standard of practice in specific scenarios. 
When Do You Refer to an Advanced Endoscopist?
One of the most critical steps in caring for patients with complex lesions is the ability to accurately determine whether a referral to an advanced endoscopist is warranted. The initial assessment of a lesion should always involve a careful assessment that risk stratifies the lesion depending on the location, size, neoplastic potential, and the feasibility of standard endoscopic resection compared to the need for surgical input.
A practical example in the case of colonic polyps is highlighted by the American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) guidelines recommending the referral of patients with polyps’ size ≥ 20 mm, challenging polypectomy location, or recurrent polyp at a prior polypectomy site to an endoscopic referral center.1 In the case of subepithelial lesions without endoscopic characteristics of benign etiology (i.e., lipomas, pancreatic rests, etc.), the threshold for referral to advanced endoscopists for further diagnostic testing by means of endoscopic ultrasonography or for therapeutic ATR should be lower.
Endoscopic tissue resection follows a spectrum, which often involves deeper layers of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) as we progress along this spectrum (see Figure 1). 
ATR, a term encompassing a variety of endoscopic techniques ranging from endoscopic mucosal resection to full thickness resection, has gained traction over the last years given the ability to effectively remove various lesions in a precise time and cost-effective manner while maintaining the integrity of the GIT and avoiding major surgery. The indications for ATR vary depending on the technique, but generally include the presence of large or poorly positioned lesions, particularly in high-risk areas of the GIT such as the esophagus and small intestine, lesions extending beyond the mucosal layer or originating from deeper layers, and when en bloc resection of select lesions is necessary.
For providers referring patients for ATR, we recommend a few important endoscopic pearls when caring for these patients.
1) Biopsy the lesion if there is concern for malignancy — While some studies have noted increased fibrosis during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and some guidelines recommend against biopsies pre ESD, we believe that when there is high pretest probability for malignancy, a biopsy should be obtained. This should involve the area that is most concerning for malignancy (at the margin or center).2
2) While marking a lesion with tattoo is helpful for surgical planning and for lesions difficult to locate endoscopically, we stress the importance of placing tattoos 3 to 5 centimeters distal to the lesion and avoiding tattooing the lesion itself, which has been shown to induce fibrosis and can make resection challenging. Based on an international Delphi consensus, expert recommendations on when and how to endoscopically tattoo a lesion can be instrumental in adequately localizing the lesion, allowing for endoscopic resection, and preventing unnecessary surgeries.3
3) If you encounter a lesion that you are not sure can be resected safely and efficaciously, we recommend against attempting resection that may result in partial resection. This can also induce fibrosis and scarring and limit future attempts at resection.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
EMR is currently utilized for curative treatment of a wide array of GIT lesions limited to the mucosal layer, whether metaplastic, dysplastic, or even in cases with early mucosal cancer, where the risk of submucosal and lymphatic invasion is minimal.4 This makes EMR a versatile and proven therapy, often serving as the first-line treatment for many GIT lesions.
EMR has various techniques that could be categorized into suction or non-suction (lift and cut) techniques. In the suction technique, devices like multiband mucosectomy (MBM) are commonly used, especially in nodular Barrett’s dysplasia, forming a pseudopolyp for subsequent resection. The procedure is characterized by its safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to its widespread adoption in clinical practice. In the lift and cut approach, a submucosal injection is utilized to separate the muscularis propria from the lesion, thereby reducing the risk of perforation. Different solutions, such as normal saline, hypertonic saline, 50% dextrose, or proprietary submucosal injection solutions, are employed for submucosal injection.5
The non-suction technique using a snare to resect polyps after injection is more often used in colonic and small intestinal EMR. Resection can be done via thermal energy in the form of cut or coagulation; however, there is rising data on the use of piecemeal cold snare resection for select flat polyps of the colon.6 There is also promising data on the role of underwater EMR, a common technique employed for colonic lesions, particularly if the lesion does not lift well with submucosal injection.7
Adverse events associated with EMR include bleeding (7%-8%) and perforation (0.9%-2%).8-9 Adequate submucosal fluid injection is crucial to prevent perforations. However, the main limitation of EMR is the piecemeal nature of resections for lesions larger than 20 mm, leading to compromised histopathologic evaluation for complete excision, especially in cases with superficial submucosal invasion (SMI). This can result in residual or recurrent tissue, reportedly 8% to 20%.10 Despite this limitation, EMR remains a reliable strategy, and recurrent lesions are generally manageable through repeat sessions. The importance of EMR as a therapeutic modality lies in its role in addressing lesions with favorable characteristics, where the risk of SMI is low.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
ESD is an evolving technique that can be utilized for submucosal lesions of the GIT, lesions not amenable to EMR due to submucosal fibrosis, when en bloc removal of a lesion is needed for accurate histopathological diagnosis, and when other techniques fail.11-12
ESD was only recently adopted in the United States, requires specialized training, and usually is a lengthier procedure than EMR.13 Compared to EMR, it has higher en bloc resection rates and lower recurrence rates, making it curative for lesions with superficial SMI and favorable histologic features.4,14 The safety profile of ESD appears favorable, with most of the adverse events managed successfully by endoscopic methods. Major complications include intraoperative and delayed perforation, intraoperative and delayed bleeding, aspiration pneumonia, thromboembolism, and stricture formation in the case of circumferential lesions.15
Despite being technically challenging, ESD may provide a cost-effective long-term solution by avoiding surgery, reducing the need for additional interventions by minimizing recurrence rates. Given the technical complexity of ESD, particularly the submucosal dissection portion, techniques such as hybrid ESD developed. Hybrid ESD combines snaring with circumferential mucosal incision and partial submucosal dissection. Although it promises shorter procedure times, reduced complication rates like perforation, and similar recurrence rates compared to traditional ESD, studies have shown lower success rates in en bloc resection.16-17
Both EMR and ESD are considered complementary strategies, and the choice between them should be dictated by lesion characteristics, patient preferences, and local expertise.
Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection (STER)
STER has emerged as a well-established technique for the endoscopic resection of GI subepithelial tumors (SETs) originating from the muscularis propria layer. The standard STER procedure involves a series of steps including submucosal elevation proximal to the SET, mucosotomy, creation of a submucosal tunnel, dissection of the SET within the tunnel, enucleation from the deep muscle layer, and subsequent specimen retrieval followed by mucosal closure.
This technique is typically recommended for SETs smaller than 3.5 cm, particularly those located in the mid or distal esophagus, cardia, or along the greater curvature of the gastric body.18 However, STER may pose technical challenges for larger SETs or lesions in anatomically difficult locations, where surgical resection is recommended instead.19 Notably, recent large-scale meta-analyses have showcased the favorable complete resection and en bloc resection rates of STER in treating GI SETs.20
Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection (EFTR)
EFTR has emerged as a valuable technique in the endoscopic management of gastrointestinal lesions, particularly SETs and lesions not amenable to EMR or ESD due to fibrosis. EFTR involves the resection of all layers of the GIT from mucosa to serosa, and therefore is well-suited for SETs arising from the muscularis propria (MP).20
EFTR entails two main concepts: tissue resection and complete defect closure. Conventional EFTR consists of several steps, which include mucosal and submucosal pre-cutting, circumferential incision, and dissection through the MP or serosa. This results in a full thickness defect, for which closure of the wall defect is achieved using standard endoscopic clips or a combination of clips and endoloops or endoscopic suturing.21 For lesions less than 2 cm, EFTR can be performed in a single step using a cap-mounted full thickness resection device (FTRD). This results in deployment of over-the-scope clip over the target lesion followed by snaring the lesions above the clip.21
Location of the SET generally dictates the specific modality of ATR. For example, esophageal SETs may be more amenable to STER given that the lesion typically runs parallel with the lumen of the tubular esophagus, which allows for easier dissection without the need of full or partial retroflexion. While gastric SETs can be resected with STER, it may be challenging and more effectively addressed with EFTR, particularly when the entire lesion can be grasped into the full-thickness resection device.22 Limited data exists for duodenal EFTR, and colorectal SETs closure is particularly challenging.
Conclusion
It is key to emphasize that ATR cannot be safely established in practice without the incorporation of a multidisciplinary team (surgeons, radiologists, etc.), specialized tools, and trained personnel. This requires dedicated endoscopic rooms, careful patient selection, and a comprehensive approach to patient care before, during, and after these procedures.
Moreover, it is important to note that some patients may require post-procedure hospitalization for observation to ensure no early complications are encountered. Optimal surveillance strategies after ATR rely heavily on the potential for residual or recurrent disease, underlying pathology, and the expertise of the advanced endoscopist. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and technological advances of devices will further enhance the efficacy and safety of ATR in gastroenterology.
Dr. Madi (@MahMadi90) is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri. Dr. Rengarajan (@ArvindRenga) and Dr. Bazarbashi (@AhmadBazarbashi) are based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and no funding was required for this project.
References
1. Copland AP, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on appropriate and tailored polypectomy: Expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.012.
2. Lee SP, et al. Effect of preceding biopsy on the results of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal laterally spreading tumor. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05625-3.
3. Medina-Prado L, et al. When and how to use endoscopic tattooing in the colon: An international Delphi agreement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.024.
4. Rashid MU, et al. EMR and ESD: Indications, techniques and results. Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101742.
5. Castro R, et al. Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.777.
6. Rex DK. Best practices for resection of diminutive and small polyps in the colorectum. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2019.06.004.
7. Lv XH, et al. Underwater EMR for nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.10.044.
8. Fujiya M, et al. Efficacy and adverse events of EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colon neoplasms: a meta-analysis of studies comparing EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.034.
9. Kandel P, Wallace MB. Colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.05.006.
10. Kemper G, et al; ENDOCARE Study Group. Endoscopic techniques to reduce recurrence rates after colorectal EMR: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08574-z.
11. Goto O, et al. Expanding indications for ESD: submucosal disease (SMT/carcinoid tumors). Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.11.006.
12. Wang K, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection, indication, methods and perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1111/den.14474.
13. Herreros de Tejada A. ESD training: A challenging path to excellence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014 Apr 16. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i4.112.
14. Chiba H, et al. Safety and efficacy of simultaneous colorectal ESD for large synchronous colorectal lesions. Endosc Int Open. 2017 Jul. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-110567.
15. Mannath J, Ragunath K. Endoscopic mucosal resection: who and how? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep. doi: 10.1177/1756283X10388683.
16. Wang XY, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: An alternative resection modality for large laterally spreading tumors in the cecum? BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01766-w.
17. McCarty TR, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) compared with conventional ESD for colorectal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1055/a-1266-1855.
18. Jain D, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria. Ann Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.20524/aog.2017.0128.
19. Lv XH, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017 Jan. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4978-7.
20. Cao B, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021 Jan. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.6989/2020.
21. Cai M, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.12.013.
22. Brigic A, et al. A systematic review regarding the feasibility and safety of endoscopic full thickness resection (EFTR) for colonic lesions. Surg Endosc. 2013 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2946-z.
Endoscopists are often faced with unique challenges in the management and resection of various gastrointestinal tract lesions. These challenges could be lesion-related, endoscopist-related, or practice-related (see Table 1). (ATR). Not only does this organ-sparing approach offer a less invasive alternative to surgery, but it has also proved to have outcomes comparable to those of surgical standard of practice in specific scenarios. 
When Do You Refer to an Advanced Endoscopist?
One of the most critical steps in caring for patients with complex lesions is the ability to accurately determine whether a referral to an advanced endoscopist is warranted. The initial assessment of a lesion should always involve a careful assessment that risk stratifies the lesion depending on the location, size, neoplastic potential, and the feasibility of standard endoscopic resection compared to the need for surgical input.
A practical example in the case of colonic polyps is highlighted by the American Gastroenterology Association (AGA) guidelines recommending the referral of patients with polyps’ size ≥ 20 mm, challenging polypectomy location, or recurrent polyp at a prior polypectomy site to an endoscopic referral center.1 In the case of subepithelial lesions without endoscopic characteristics of benign etiology (i.e., lipomas, pancreatic rests, etc.), the threshold for referral to advanced endoscopists for further diagnostic testing by means of endoscopic ultrasonography or for therapeutic ATR should be lower.
Endoscopic tissue resection follows a spectrum, which often involves deeper layers of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) as we progress along this spectrum (see Figure 1). 
ATR, a term encompassing a variety of endoscopic techniques ranging from endoscopic mucosal resection to full thickness resection, has gained traction over the last years given the ability to effectively remove various lesions in a precise time and cost-effective manner while maintaining the integrity of the GIT and avoiding major surgery. The indications for ATR vary depending on the technique, but generally include the presence of large or poorly positioned lesions, particularly in high-risk areas of the GIT such as the esophagus and small intestine, lesions extending beyond the mucosal layer or originating from deeper layers, and when en bloc resection of select lesions is necessary.
For providers referring patients for ATR, we recommend a few important endoscopic pearls when caring for these patients.
1) Biopsy the lesion if there is concern for malignancy — While some studies have noted increased fibrosis during endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and some guidelines recommend against biopsies pre ESD, we believe that when there is high pretest probability for malignancy, a biopsy should be obtained. This should involve the area that is most concerning for malignancy (at the margin or center).2
2) While marking a lesion with tattoo is helpful for surgical planning and for lesions difficult to locate endoscopically, we stress the importance of placing tattoos 3 to 5 centimeters distal to the lesion and avoiding tattooing the lesion itself, which has been shown to induce fibrosis and can make resection challenging. Based on an international Delphi consensus, expert recommendations on when and how to endoscopically tattoo a lesion can be instrumental in adequately localizing the lesion, allowing for endoscopic resection, and preventing unnecessary surgeries.3
3) If you encounter a lesion that you are not sure can be resected safely and efficaciously, we recommend against attempting resection that may result in partial resection. This can also induce fibrosis and scarring and limit future attempts at resection.
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR)
EMR is currently utilized for curative treatment of a wide array of GIT lesions limited to the mucosal layer, whether metaplastic, dysplastic, or even in cases with early mucosal cancer, where the risk of submucosal and lymphatic invasion is minimal.4 This makes EMR a versatile and proven therapy, often serving as the first-line treatment for many GIT lesions.
EMR has various techniques that could be categorized into suction or non-suction (lift and cut) techniques. In the suction technique, devices like multiband mucosectomy (MBM) are commonly used, especially in nodular Barrett’s dysplasia, forming a pseudopolyp for subsequent resection. The procedure is characterized by its safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness, contributing to its widespread adoption in clinical practice. In the lift and cut approach, a submucosal injection is utilized to separate the muscularis propria from the lesion, thereby reducing the risk of perforation. Different solutions, such as normal saline, hypertonic saline, 50% dextrose, or proprietary submucosal injection solutions, are employed for submucosal injection.5
The non-suction technique using a snare to resect polyps after injection is more often used in colonic and small intestinal EMR. Resection can be done via thermal energy in the form of cut or coagulation; however, there is rising data on the use of piecemeal cold snare resection for select flat polyps of the colon.6 There is also promising data on the role of underwater EMR, a common technique employed for colonic lesions, particularly if the lesion does not lift well with submucosal injection.7
Adverse events associated with EMR include bleeding (7%-8%) and perforation (0.9%-2%).8-9 Adequate submucosal fluid injection is crucial to prevent perforations. However, the main limitation of EMR is the piecemeal nature of resections for lesions larger than 20 mm, leading to compromised histopathologic evaluation for complete excision, especially in cases with superficial submucosal invasion (SMI). This can result in residual or recurrent tissue, reportedly 8% to 20%.10 Despite this limitation, EMR remains a reliable strategy, and recurrent lesions are generally manageable through repeat sessions. The importance of EMR as a therapeutic modality lies in its role in addressing lesions with favorable characteristics, where the risk of SMI is low.
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
ESD is an evolving technique that can be utilized for submucosal lesions of the GIT, lesions not amenable to EMR due to submucosal fibrosis, when en bloc removal of a lesion is needed for accurate histopathological diagnosis, and when other techniques fail.11-12
ESD was only recently adopted in the United States, requires specialized training, and usually is a lengthier procedure than EMR.13 Compared to EMR, it has higher en bloc resection rates and lower recurrence rates, making it curative for lesions with superficial SMI and favorable histologic features.4,14 The safety profile of ESD appears favorable, with most of the adverse events managed successfully by endoscopic methods. Major complications include intraoperative and delayed perforation, intraoperative and delayed bleeding, aspiration pneumonia, thromboembolism, and stricture formation in the case of circumferential lesions.15
Despite being technically challenging, ESD may provide a cost-effective long-term solution by avoiding surgery, reducing the need for additional interventions by minimizing recurrence rates. Given the technical complexity of ESD, particularly the submucosal dissection portion, techniques such as hybrid ESD developed. Hybrid ESD combines snaring with circumferential mucosal incision and partial submucosal dissection. Although it promises shorter procedure times, reduced complication rates like perforation, and similar recurrence rates compared to traditional ESD, studies have shown lower success rates in en bloc resection.16-17
Both EMR and ESD are considered complementary strategies, and the choice between them should be dictated by lesion characteristics, patient preferences, and local expertise.
Submucosal Tunneling Endoscopic Resection (STER)
STER has emerged as a well-established technique for the endoscopic resection of GI subepithelial tumors (SETs) originating from the muscularis propria layer. The standard STER procedure involves a series of steps including submucosal elevation proximal to the SET, mucosotomy, creation of a submucosal tunnel, dissection of the SET within the tunnel, enucleation from the deep muscle layer, and subsequent specimen retrieval followed by mucosal closure.
This technique is typically recommended for SETs smaller than 3.5 cm, particularly those located in the mid or distal esophagus, cardia, or along the greater curvature of the gastric body.18 However, STER may pose technical challenges for larger SETs or lesions in anatomically difficult locations, where surgical resection is recommended instead.19 Notably, recent large-scale meta-analyses have showcased the favorable complete resection and en bloc resection rates of STER in treating GI SETs.20
Endoscopic Full Thickness Resection (EFTR)
EFTR has emerged as a valuable technique in the endoscopic management of gastrointestinal lesions, particularly SETs and lesions not amenable to EMR or ESD due to fibrosis. EFTR involves the resection of all layers of the GIT from mucosa to serosa, and therefore is well-suited for SETs arising from the muscularis propria (MP).20
EFTR entails two main concepts: tissue resection and complete defect closure. Conventional EFTR consists of several steps, which include mucosal and submucosal pre-cutting, circumferential incision, and dissection through the MP or serosa. This results in a full thickness defect, for which closure of the wall defect is achieved using standard endoscopic clips or a combination of clips and endoloops or endoscopic suturing.21 For lesions less than 2 cm, EFTR can be performed in a single step using a cap-mounted full thickness resection device (FTRD). This results in deployment of over-the-scope clip over the target lesion followed by snaring the lesions above the clip.21
Location of the SET generally dictates the specific modality of ATR. For example, esophageal SETs may be more amenable to STER given that the lesion typically runs parallel with the lumen of the tubular esophagus, which allows for easier dissection without the need of full or partial retroflexion. While gastric SETs can be resected with STER, it may be challenging and more effectively addressed with EFTR, particularly when the entire lesion can be grasped into the full-thickness resection device.22 Limited data exists for duodenal EFTR, and colorectal SETs closure is particularly challenging.
Conclusion
It is key to emphasize that ATR cannot be safely established in practice without the incorporation of a multidisciplinary team (surgeons, radiologists, etc.), specialized tools, and trained personnel. This requires dedicated endoscopic rooms, careful patient selection, and a comprehensive approach to patient care before, during, and after these procedures.
Moreover, it is important to note that some patients may require post-procedure hospitalization for observation to ensure no early complications are encountered. Optimal surveillance strategies after ATR rely heavily on the potential for residual or recurrent disease, underlying pathology, and the expertise of the advanced endoscopist. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing research and technological advances of devices will further enhance the efficacy and safety of ATR in gastroenterology.
Dr. Madi (@MahMadi90) is based in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Saint Louis, Missouri. Dr. Rengarajan (@ArvindRenga) and Dr. Bazarbashi (@AhmadBazarbashi) are based in the Division of Gastroenterology, Washington University in St. Louis. The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose, and no funding was required for this project.
References
1. Copland AP, et al. AGA Clinical Practice Update on appropriate and tailored polypectomy: Expert review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.10.012.
2. Lee SP, et al. Effect of preceding biopsy on the results of endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal laterally spreading tumor. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05625-3.
3. Medina-Prado L, et al. When and how to use endoscopic tattooing in the colon: An international Delphi agreement. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.01.024.
4. Rashid MU, et al. EMR and ESD: Indications, techniques and results. Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2022.101742.
5. Castro R, et al. Solutions for submucosal injection: What to choose and how to do it. World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i7.777.
6. Rex DK. Best practices for resection of diminutive and small polyps in the colorectum. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2019 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2019.06.004.
7. Lv XH, et al. Underwater EMR for nonpedunculated colorectal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2022.10.044.
8. Fujiya M, et al. Efficacy and adverse events of EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection for the treatment of colon neoplasms: a meta-analysis of studies comparing EMR and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2014.07.034.
9. Kandel P, Wallace MB. Colorectal endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2017.05.006.
10. Kemper G, et al; ENDOCARE Study Group. Endoscopic techniques to reduce recurrence rates after colorectal EMR: systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-021-08574-z.
11. Goto O, et al. Expanding indications for ESD: submucosal disease (SMT/carcinoid tumors). Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2014 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2013.11.006.
12. Wang K, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection, indication, methods and perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2023 Jan. doi: 10.1111/den.14474.
13. Herreros de Tejada A. ESD training: A challenging path to excellence. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2014 Apr 16. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v6.i4.112.
14. Chiba H, et al. Safety and efficacy of simultaneous colorectal ESD for large synchronous colorectal lesions. Endosc Int Open. 2017 Jul. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-110567.
15. Mannath J, Ragunath K. Endoscopic mucosal resection: who and how? Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep. doi: 10.1177/1756283X10388683.
16. Wang XY, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection: An alternative resection modality for large laterally spreading tumors in the cecum? BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 May. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01766-w.
17. McCarty TR, et al. Hybrid endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) compared with conventional ESD for colorectal lesions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2021 Oct. doi: 10.1055/a-1266-1855.
18. Jain D, et al. Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection of upper gastrointestinal tract tumors arising from muscularis propria. Ann Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb. doi: 10.20524/aog.2017.0128.
19. Lv XH, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for upper gastrointestinal submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017 Jan. doi: 10.1007/s00464-016-4978-7.
20. Cao B, et al. Efficacy and safety of submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection for gastric submucosal tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2021 Jan. doi: 10.17235/reed.2020.6989/2020.
21. Cai M, et al. Endoscopic full-thickness resection (EFTR) for gastrointestinal subepithelial tumors. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.giec.2015.12.013.
22. Brigic A, et al. A systematic review regarding the feasibility and safety of endoscopic full thickness resection (EFTR) for colonic lesions. Surg Endosc. 2013 Oct. doi: 10.1007/s00464-013-2946-z.
Fluid Management in Acute Pancreatitis
Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS; American College of Gastroenterology. American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis [published correction appears in Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(2):302]. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(9):1400-1415. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.218
de-Madaria E, Buxbaum JL, Maisonneuve P, et al. Aggressive or moderate fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(11):989-1000. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2202884
Zhao G, Zhang JG, Wu HS, et al. Effects of different resuscitation fluid on severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(13):2044-2052. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2044
Guzmán-Calderón E, Diaz-Arocutipa C, Monge E. Lactate Ringer's versus normal saline in the management of acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Dig Dis Sci. 2022;67(8):4131-4139. doi:10.1007/s10620-021-07269-8
Hoste EA, Maitland K, Brudney CS, et al; ADQI XII Investigators Group. Four phases of intravenous fluid therapy: a conceptual model. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113(5):740-747. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu300
Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2013;13(4 suppl 2):e1-e15. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063
Machicado JD, Papachristou GI. Pharmacologic management and prevention of acute pancreatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2019;35(5):460-467. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000563
Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS; American College of Gastroenterology. American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis [published correction appears in Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(2):302]. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(9):1400-1415. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.218
de-Madaria E, Buxbaum JL, Maisonneuve P, et al. Aggressive or moderate fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(11):989-1000. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2202884
Zhao G, Zhang JG, Wu HS, et al. Effects of different resuscitation fluid on severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(13):2044-2052. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2044
Guzmán-Calderón E, Diaz-Arocutipa C, Monge E. Lactate Ringer's versus normal saline in the management of acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Dig Dis Sci. 2022;67(8):4131-4139. doi:10.1007/s10620-021-07269-8
Hoste EA, Maitland K, Brudney CS, et al; ADQI XII Investigators Group. Four phases of intravenous fluid therapy: a conceptual model. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113(5):740-747. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu300
Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2013;13(4 suppl 2):e1-e15. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063
Machicado JD, Papachristou GI. Pharmacologic management and prevention of acute pancreatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2019;35(5):460-467. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000563
Tenner S, Baillie J, DeWitt J, Vege SS; American College of Gastroenterology. American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis [published correction appears in Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109(2):302]. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(9):1400-1415. doi:10.1038/ajg.2013.218
de-Madaria E, Buxbaum JL, Maisonneuve P, et al. Aggressive or moderate fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(11):989-1000. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2202884
Zhao G, Zhang JG, Wu HS, et al. Effects of different resuscitation fluid on severe acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(13):2044-2052. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i13.2044
Guzmán-Calderón E, Diaz-Arocutipa C, Monge E. Lactate Ringer's versus normal saline in the management of acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Dig Dis Sci. 2022;67(8):4131-4139. doi:10.1007/s10620-021-07269-8
Hoste EA, Maitland K, Brudney CS, et al; ADQI XII Investigators Group. Four phases of intravenous fluid therapy: a conceptual model. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113(5):740-747. doi:10.1093/bja/aeu300
Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2013;13(4 suppl 2):e1-e15. doi:10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063
Machicado JD, Papachristou GI. Pharmacologic management and prevention of acute pancreatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2019;35(5):460-467. doi:10.1097/MOG.0000000000000563
May 2024 – ICYMI
Gastroenterology
January 2024
Hirano I, et al; ASCENT WORKING GROUP. Ascending to New Heights for Novel Therapeutics for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690772; PMCID: PMC10872872.
Åkerström JH, et al. Antireflux Surgery Versus Antireflux Medication and Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):132-138.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.050. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690771.
Barnes EL, et al; AGA Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Pouchitis and Inflammatory Pouch Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):59-85. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.015. PMID: 38128971.
February 2024
Yoo HW, et al. Helicobacter pylori Treatment and Gastric Cancer Risk After Endoscopic Resection of Dysplasia: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):313-322.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37863270.
Yang J, et al. High Soluble Fiber Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):323-337.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37858797.
Young E, et al. Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging Improves Colonic Adenoma Detection: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):338-340.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Oct 14. PMID: 37839498.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
January 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; Dutch Familial Pancreatic Cancer Surveillance Study work group. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms in High-Risk Individuals: Incidence, Growth Rate, and Malignancy Risk. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):62-71.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.03.035. Epub 2023 Apr 7. PMID: 37031711.
Reddy CA, et al. Achalasia is Strongly Associated With Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Other Allergic Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):34-41.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.06.013. Epub 2023 Jun 28. PMID: 37391057; PMCID: PMC10753026.
Thiruvengadam NR, et al. The Clinical Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Surveillance of Incidentally Detected Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: A Microsimulation Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.05.028. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 19;: PMID: 37302442.
February 2024
Goodoory VC, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Mesalamine in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):243-251.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Feb 27. PMID: 36858143.
Brenner DM, et al. Development and Current State of Digital Therapeutics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.013. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743035.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
January 2024
Ramirez PR, et al. Gaps and Improvement Opportunities in Post-Colonoscopy Communication. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1):90-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 22.
Gonzaga ER, et al. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the Management of Gastroparesis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan; 26(1): 46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 13.
Wang D, et al. Sphincterotomy vs Sham Procedure for Pain Relief in Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1): 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Nov 8.
Gastro Hep Advances
January 2024
Adeniran E, et al. Intense and Sustained Alcohol Consumption Associated With Acute Pancreatitis Warrants Early Intervention. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1):61-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.017. Epub 2023 Sep 2.
Alkhouri N, et al. A Novel Prescription Digital Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.019. Epub 2023 Oct 1.
Gastroenterology
January 2024
Hirano I, et al; ASCENT WORKING GROUP. Ascending to New Heights for Novel Therapeutics for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690772; PMCID: PMC10872872.
Åkerström JH, et al. Antireflux Surgery Versus Antireflux Medication and Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):132-138.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.050. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690771.
Barnes EL, et al; AGA Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Pouchitis and Inflammatory Pouch Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):59-85. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.015. PMID: 38128971.
February 2024
Yoo HW, et al. Helicobacter pylori Treatment and Gastric Cancer Risk After Endoscopic Resection of Dysplasia: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):313-322.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37863270.
Yang J, et al. High Soluble Fiber Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):323-337.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37858797.
Young E, et al. Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging Improves Colonic Adenoma Detection: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):338-340.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Oct 14. PMID: 37839498.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
January 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; Dutch Familial Pancreatic Cancer Surveillance Study work group. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms in High-Risk Individuals: Incidence, Growth Rate, and Malignancy Risk. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):62-71.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.03.035. Epub 2023 Apr 7. PMID: 37031711.
Reddy CA, et al. Achalasia is Strongly Associated With Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Other Allergic Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):34-41.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.06.013. Epub 2023 Jun 28. PMID: 37391057; PMCID: PMC10753026.
Thiruvengadam NR, et al. The Clinical Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Surveillance of Incidentally Detected Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: A Microsimulation Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.05.028. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 19;: PMID: 37302442.
February 2024
Goodoory VC, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Mesalamine in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):243-251.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Feb 27. PMID: 36858143.
Brenner DM, et al. Development and Current State of Digital Therapeutics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.013. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743035.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
January 2024
Ramirez PR, et al. Gaps and Improvement Opportunities in Post-Colonoscopy Communication. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1):90-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 22.
Gonzaga ER, et al. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the Management of Gastroparesis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan; 26(1): 46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 13.
Wang D, et al. Sphincterotomy vs Sham Procedure for Pain Relief in Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1): 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Nov 8.
Gastro Hep Advances
January 2024
Adeniran E, et al. Intense and Sustained Alcohol Consumption Associated With Acute Pancreatitis Warrants Early Intervention. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1):61-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.017. Epub 2023 Sep 2.
Alkhouri N, et al. A Novel Prescription Digital Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.019. Epub 2023 Oct 1.
Gastroenterology
January 2024
Hirano I, et al; ASCENT WORKING GROUP. Ascending to New Heights for Novel Therapeutics for Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):1-10. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.09.004. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690772; PMCID: PMC10872872.
Åkerström JH, et al. Antireflux Surgery Versus Antireflux Medication and Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma in Patients With Barrett’s Esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):132-138.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.08.050. Epub 2023 Sep 9. PMID: 37690771.
Barnes EL, et al; AGA Clinical Guidelines Committee. AGA Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Pouchitis and Inflammatory Pouch Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2024 Jan;166(1):59-85. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.015. PMID: 38128971.
February 2024
Yoo HW, et al. Helicobacter pylori Treatment and Gastric Cancer Risk After Endoscopic Resection of Dysplasia: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):313-322.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.013. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37863270.
Yang J, et al. High Soluble Fiber Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis Through Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Mice. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):323-337.e7. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.012. Epub 2023 Oct 18. PMID: 37858797.
Young E, et al. Texture and Color Enhancement Imaging Improves Colonic Adenoma Detection: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Gastroenterology. 2024 Feb;166(2):338-340.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Oct 14. PMID: 37839498.
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology
January 2024
Overbeek KA, et al; Dutch Familial Pancreatic Cancer Surveillance Study work group. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms in High-Risk Individuals: Incidence, Growth Rate, and Malignancy Risk. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):62-71.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.03.035. Epub 2023 Apr 7. PMID: 37031711.
Reddy CA, et al. Achalasia is Strongly Associated With Eosinophilic Esophagitis and Other Allergic Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):34-41.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.06.013. Epub 2023 Jun 28. PMID: 37391057; PMCID: PMC10753026.
Thiruvengadam NR, et al. The Clinical Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of Surveillance of Incidentally Detected Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia: A Microsimulation Analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan;22(1):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.05.028. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Erratum in: Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 19;: PMID: 37302442.
February 2024
Goodoory VC, et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Efficacy of Mesalamine in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):243-251.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.02.014. Epub 2023 Feb 27. PMID: 36858143.
Brenner DM, et al. Development and Current State of Digital Therapeutics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Feb;22(2):222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2023.09.013. Epub 2023 Sep 22. PMID: 37743035.
Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
January 2024
Ramirez PR, et al. Gaps and Improvement Opportunities in Post-Colonoscopy Communication. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1):90-92. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 22.
Gonzaga ER, et al. Gastric Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (G-POEM) for the Management of Gastroparesis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan; 26(1): 46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.09.002. Epub 2023 Oct 13.
Wang D, et al. Sphincterotomy vs Sham Procedure for Pain Relief in Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Tech Innov Gastrointest Endosc. 2024 Jan;26(1): 30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.tige.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Nov 8.
Gastro Hep Advances
January 2024
Adeniran E, et al. Intense and Sustained Alcohol Consumption Associated With Acute Pancreatitis Warrants Early Intervention. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1):61-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.017. Epub 2023 Sep 2.
Alkhouri N, et al. A Novel Prescription Digital Therapeutic Option for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Gastro Hep Advances. 2024 Jan;3(1): 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.gastha.2023.08.019. Epub 2023 Oct 1.