User login
Geographic Clusters Show Uneven Cancer Screening in the US
Geographic Clusters Show Uneven Cancer Screening in the US
TOPLINE:
An analysis of 3142 US counties revealed that county-level screening for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer increased overall between 1997 and 2019; however, despite the reduced geographic variation, persistently high-screening clusters remained in the Northeast, whereas persistently low-screening clusters remained in the Southwest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Cancer screening reduces mortality. Despite guideline recommendation, the uptake of breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer screening in the US falls short of national goals and varies across sociodemographic groups. To date, only a few studies have examined geographic and temporal patterns of screening.
- To address this gap, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using an ecological panel design to analyze county-level screening prevalence across 3142 US mainland counties from 1997 to 2019, deriving prevalence estimates from Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) data over 3- to 5-year periods.
- Spatial autocorrelation analyses, including Global Moran I and the bivariate local indicator of spatial autocorrelation, were performed to assess geographic clusters of cancer screening within each period. Four types of local geographic clusters of county-level cancer screening were identified: counties with persistently high screening rates, counties with persistently low screening rates, counties in which screening rates decreased from high to low, and counties in which screening rates increased from low to high.
- Screening prevalence was compared across multiple time windows for different modalities (mammography, a Papanicolaou test, colonoscopy, colorectal cancer test, endoscopy, and a fecal occult blood test [FOBT]). Overall, 3101 counties were analyzed for mammography and the Papanicolaou test, 3107 counties for colonoscopy, 3100 counties for colorectal cancer test, 3089 counties for endoscopy, and 3090 counties for the FOBT.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall screening prevalence increased from 1997 to 2019, and global spatial autocorrelation declined over time. For instance, the distribution of mammography screening became 83% more uniform in more recent years (Moran I, 0.57 in 1997-1999 vs 0.10 in 2017-2019). Similarly, Papanicolaou test screening became more uniform in more recent years (Moran I, 0.44 vs. 0.07). These changes indicate reduced geographic heterogeneity.
- Colonoscopy and endoscopy use increased, surpassing a 50% prevalence in many counties for 2010; however, FOBT use declined. Spatial clustering also attenuated, with a 23.4% declined in Moran I for colonoscopy from 2011-2016 to 2017-2019, a 12.3% decline in the colorectal cancer test from 2004-2007 to 2008-2010, and a 14.0% decline for endoscopy from 2004-2007 to 2008-2010.
- Persistently high-/high-screening clusters were concentrated in the Northeast for mammography and colorectal cancer screening and in the East for Papanicolaou test screening, whereas persistently low-/low-screening clusters were concentrated in the Southwest for the same modalities.
- Clusters of low- and high-screening counties were more disadvantaged -- with lower socioeconomic status and a higher proportion of non-White residents -- than other cluster types, suggesting some improvement in screening uptake in more disadvantaged areas. Counties with persistently low screening exhibited greater socioeconomic disadvantages -- lower media household income, higher poverty, lower home values, and lower educational attainment -- than those with persistently high screening.
IN PRACTICE:
"This cross-sectional study found that despite secular increases that reduced geographic variation in screening, local clusters of high and low screening persisted in the Northeast and Southwest US, respectively. Future studies could incorporate health care access characteristics to explain why areas of low screening did not catch up to optimize cancer screening practice," the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Pranoti Pradhan, PhD, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The county-level estimates were modeled using BRFSS, NHIS, and US Census data, which might be susceptible to sampling biases despite corrections for nonresponse and noncoverage. Researchers lacked data on specific health systems characteristics that may have directly driven changes in prevalence and were restricted to using screening time intervals available from the Small Area Estimates for Cancer-Relates Measures from the National Cancer Institute, rather than those according to US Preventive Services Task Force guidelines. Additionally, the spatial cluster method was sensitive to county size and arrangement, which may have influenced local cluster detection.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported by the T32 Cancer Prevention and Control Funding Fellowship and T32 Cancer Epidemiology Fellowship at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An analysis of 3142 US counties revealed that county-level screening for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer increased overall between 1997 and 2019; however, despite the reduced geographic variation, persistently high-screening clusters remained in the Northeast, whereas persistently low-screening clusters remained in the Southwest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Cancer screening reduces mortality. Despite guideline recommendation, the uptake of breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer screening in the US falls short of national goals and varies across sociodemographic groups. To date, only a few studies have examined geographic and temporal patterns of screening.
- To address this gap, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using an ecological panel design to analyze county-level screening prevalence across 3142 US mainland counties from 1997 to 2019, deriving prevalence estimates from Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) data over 3- to 5-year periods.
- Spatial autocorrelation analyses, including Global Moran I and the bivariate local indicator of spatial autocorrelation, were performed to assess geographic clusters of cancer screening within each period. Four types of local geographic clusters of county-level cancer screening were identified: counties with persistently high screening rates, counties with persistently low screening rates, counties in which screening rates decreased from high to low, and counties in which screening rates increased from low to high.
- Screening prevalence was compared across multiple time windows for different modalities (mammography, a Papanicolaou test, colonoscopy, colorectal cancer test, endoscopy, and a fecal occult blood test [FOBT]). Overall, 3101 counties were analyzed for mammography and the Papanicolaou test, 3107 counties for colonoscopy, 3100 counties for colorectal cancer test, 3089 counties for endoscopy, and 3090 counties for the FOBT.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall screening prevalence increased from 1997 to 2019, and global spatial autocorrelation declined over time. For instance, the distribution of mammography screening became 83% more uniform in more recent years (Moran I, 0.57 in 1997-1999 vs 0.10 in 2017-2019). Similarly, Papanicolaou test screening became more uniform in more recent years (Moran I, 0.44 vs. 0.07). These changes indicate reduced geographic heterogeneity.
- Colonoscopy and endoscopy use increased, surpassing a 50% prevalence in many counties for 2010; however, FOBT use declined. Spatial clustering also attenuated, with a 23.4% declined in Moran I for colonoscopy from 2011-2016 to 2017-2019, a 12.3% decline in the colorectal cancer test from 2004-2007 to 2008-2010, and a 14.0% decline for endoscopy from 2004-2007 to 2008-2010.
- Persistently high-/high-screening clusters were concentrated in the Northeast for mammography and colorectal cancer screening and in the East for Papanicolaou test screening, whereas persistently low-/low-screening clusters were concentrated in the Southwest for the same modalities.
- Clusters of low- and high-screening counties were more disadvantaged -- with lower socioeconomic status and a higher proportion of non-White residents -- than other cluster types, suggesting some improvement in screening uptake in more disadvantaged areas. Counties with persistently low screening exhibited greater socioeconomic disadvantages -- lower media household income, higher poverty, lower home values, and lower educational attainment -- than those with persistently high screening.
IN PRACTICE:
"This cross-sectional study found that despite secular increases that reduced geographic variation in screening, local clusters of high and low screening persisted in the Northeast and Southwest US, respectively. Future studies could incorporate health care access characteristics to explain why areas of low screening did not catch up to optimize cancer screening practice," the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Pranoti Pradhan, PhD, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The county-level estimates were modeled using BRFSS, NHIS, and US Census data, which might be susceptible to sampling biases despite corrections for nonresponse and noncoverage. Researchers lacked data on specific health systems characteristics that may have directly driven changes in prevalence and were restricted to using screening time intervals available from the Small Area Estimates for Cancer-Relates Measures from the National Cancer Institute, rather than those according to US Preventive Services Task Force guidelines. Additionally, the spatial cluster method was sensitive to county size and arrangement, which may have influenced local cluster detection.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported by the T32 Cancer Prevention and Control Funding Fellowship and T32 Cancer Epidemiology Fellowship at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
An analysis of 3142 US counties revealed that county-level screening for breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer increased overall between 1997 and 2019; however, despite the reduced geographic variation, persistently high-screening clusters remained in the Northeast, whereas persistently low-screening clusters remained in the Southwest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Cancer screening reduces mortality. Despite guideline recommendation, the uptake of breast, cervical, and colorectal cancer screening in the US falls short of national goals and varies across sociodemographic groups. To date, only a few studies have examined geographic and temporal patterns of screening.
- To address this gap, researchers conducted a cross-sectional study using an ecological panel design to analyze county-level screening prevalence across 3142 US mainland counties from 1997 to 2019, deriving prevalence estimates from Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) data over 3- to 5-year periods.
- Spatial autocorrelation analyses, including Global Moran I and the bivariate local indicator of spatial autocorrelation, were performed to assess geographic clusters of cancer screening within each period. Four types of local geographic clusters of county-level cancer screening were identified: counties with persistently high screening rates, counties with persistently low screening rates, counties in which screening rates decreased from high to low, and counties in which screening rates increased from low to high.
- Screening prevalence was compared across multiple time windows for different modalities (mammography, a Papanicolaou test, colonoscopy, colorectal cancer test, endoscopy, and a fecal occult blood test [FOBT]). Overall, 3101 counties were analyzed for mammography and the Papanicolaou test, 3107 counties for colonoscopy, 3100 counties for colorectal cancer test, 3089 counties for endoscopy, and 3090 counties for the FOBT.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall screening prevalence increased from 1997 to 2019, and global spatial autocorrelation declined over time. For instance, the distribution of mammography screening became 83% more uniform in more recent years (Moran I, 0.57 in 1997-1999 vs 0.10 in 2017-2019). Similarly, Papanicolaou test screening became more uniform in more recent years (Moran I, 0.44 vs. 0.07). These changes indicate reduced geographic heterogeneity.
- Colonoscopy and endoscopy use increased, surpassing a 50% prevalence in many counties for 2010; however, FOBT use declined. Spatial clustering also attenuated, with a 23.4% declined in Moran I for colonoscopy from 2011-2016 to 2017-2019, a 12.3% decline in the colorectal cancer test from 2004-2007 to 2008-2010, and a 14.0% decline for endoscopy from 2004-2007 to 2008-2010.
- Persistently high-/high-screening clusters were concentrated in the Northeast for mammography and colorectal cancer screening and in the East for Papanicolaou test screening, whereas persistently low-/low-screening clusters were concentrated in the Southwest for the same modalities.
- Clusters of low- and high-screening counties were more disadvantaged -- with lower socioeconomic status and a higher proportion of non-White residents -- than other cluster types, suggesting some improvement in screening uptake in more disadvantaged areas. Counties with persistently low screening exhibited greater socioeconomic disadvantages -- lower media household income, higher poverty, lower home values, and lower educational attainment -- than those with persistently high screening.
IN PRACTICE:
"This cross-sectional study found that despite secular increases that reduced geographic variation in screening, local clusters of high and low screening persisted in the Northeast and Southwest US, respectively. Future studies could incorporate health care access characteristics to explain why areas of low screening did not catch up to optimize cancer screening practice," the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study, led by Pranoti Pradhan, PhD, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
The county-level estimates were modeled using BRFSS, NHIS, and US Census data, which might be susceptible to sampling biases despite corrections for nonresponse and noncoverage. Researchers lacked data on specific health systems characteristics that may have directly driven changes in prevalence and were restricted to using screening time intervals available from the Small Area Estimates for Cancer-Relates Measures from the National Cancer Institute, rather than those according to US Preventive Services Task Force guidelines. Additionally, the spatial cluster method was sensitive to county size and arrangement, which may have influenced local cluster detection.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported by the T32 Cancer Prevention and Control Funding Fellowship and T32 Cancer Epidemiology Fellowship at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The authors declared having no conflicts of interest.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Geographic Clusters Show Uneven Cancer Screening in the US
Geographic Clusters Show Uneven Cancer Screening in the US
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – A 70-year-old Vietnam veteran with oropharyngeal cancer presented challenges beyond his disease.
He couldn’t afford transportation for daily radiation treatments and had lost > 10% of his body weight due to pain and eating difficulties, recalled radiation oncologist Vinita Takiar, MD, PhD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
To make matters more difficult, his wife held medical power of attorney despite his apparent competence to make decisions, said Takiar, who formerly worked with the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Cincinnati Healthcare System and is now chair of radiation oncology at Penn State University.
All these factors would likely have derailed his treatment if not for a coordinated team intervention, Takiar said. Fortunately, the clinic launched a multifaceted effort involving representatives from the social work, dentistry, ethics, nutrition, and chaplaincy departments.
When surgery became impossible because the patient couldn’t lie on the operating table for adequate tumor exposure, she said, the existing team framework enabled a seamless and rapid transition to radiation with concurrent chemotherapy.
The patient completed treatment with an excellent response, offering a lesson in the importance of multidisciplinary care in head-and-neck cancers, she said.
In fact, when it comes to these forms of cancer, coordinated care “is probably more impactful than any treatment that we’re going to come up with,” she said. “The data show that when we do multidisciplinary care and we do it well, it actually improves the patient experience and outcomes.”
As Takiar noted, teamwork matters in many ways. It leads to better logistics and can address disparities, reduce financial burden and stigma, and even increase clinical trial involvement.
She pointed to studies linking teamwork to better outcomes, support for patients, and overall survival.
Takiar highlighted different parts of teams headed by radiation oncologists who act as “a node to improve multimodal care delivery.”
Speech and swallowing specialists, for example, are helpful in head-and-neck cancer because “there’s an impact on speech, swallowing, and appearance. Our patients don’t want to go out to dinner with friends because they can’t do it.”
Dentists and prosthodontists are key team members too: “I have dentists who have my cell phone number. They just call me: ‘Can I do this extraction? Was this in your radiation field? What was the dose?’”
Other team members include ear, nose, and throat specialists, palliative and supportive care specialists, medical oncologists, nurses, pathologists, transportation workers, and service connection specialists. She noted that previous military experience can affect radiation therapy. For example, the physical restraints required during treatment present particular challenges for veterans who’ve had wartime trauma. These patients may require therapy adjustments.
What’s next on the horizon? Takiar highlighted precision oncology and molecular profiling, artificial intelligence in care decisions and in radiation planning, telemedicine and virtual tumor boards, and expanded survivorship programs.
As for now, she urged colleagues to not be afraid to chat with radiation oncologists. “Please talk to us. We prioritize open communication and shared decision-making with the entire team,” she said. “If you see something and think your radiation oncologist should know about it, you think it was caused by the radiation, you should reach out to us.”
Takiar reported no disclosures.
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Team-Based Care is Crucial for Head-and-Neck Cancer Cases
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
ATLANTA —Jacqueline Lee, MD, a reproductive endocrinologist at Emory School of Medicine, frequently treats patients with cancer. Recently, she treated 4 women in their 30s with histories of colon cancer, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer. A young man in his 20s sought her care, to discuss his case of lymphoma.
All these patients sought guidance from Lee because they want to protect their ability to have children. At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology, Lee explained that plenty of patients are finding themselves in similar straits due in part to recent trends.
Cancer rates in the US have been rising among people aged 15 to 39 years, who now account for 4.2% of all cancer cases. An estimated 84,100 people in this age group are expected to be diagnosed with cancer this year. Meanwhile, women are having children later in life-birth rates are up among those aged 25 to 49 years-making it more likely that they have histories of cancer.
Although it's difficult to predict how cancer will affect fertility, Lee emphasized that many chemotherapy medications, including cisplatin and carboplatin, are cytotoxic. "It's hard to always predict what someone's arc of care is going to be," she said, "so I really have a low threshold for recommending fertility preservation in patients who have a strong desire to have future childbearing."
For women with cancer, egg preservation isn't the only strategy. Clinicians can also try to protect ovarian tissue from pelvic radiation through surgical reposition of the ovaries, Lee noted. In addition goserelin, a hormone-suppressing therapy, may protect the ovaries from chemotherapy, though its effectiveness in boosting pregnancy rates is still unclear.
"When I mentioned this option, it's usually for patients who can't preserve fertility via egg or embryo preservation, or we don't have the luxury of that kind of time," Lee said. "I say that if helps at all, it might help you resume menses after treatment. But infertility is still very common."
For some patients, freezing eggs is an easy decision. "They don't have a reproductive partner they're ready to make embryos with, so we proceed with egg preservation. It's no longer considered experimental and comes with lower upfront costs since the costs of actually making embryos are deferred until the future."
In addition, she said, freezing eggs also avoids the touchy topic of disposing of embryos. Lee cautions patients that retrieving eggs is a 2-week process that requires any initiation of cancer care to be delayed. However, the retrieval process can be adjusted in patients with special needs due to the type of cancer they have.
For prepubertal girls with cancer, ovarian tissue can be removed and frozen as a fertility preservation option. However, this is not considered standard of care. "We don't do it," she said. "We refer out if needed. Hopefully we'll develop a program in the future."
As for the 5 patients that Lee mentioned, with details changed to protect their privacy, their outcomes were as follows:
- The woman with colon cancer, who had undergone a hemicolectomy, chose to defer fertility preservation.
- The woman with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, who was taking depo-Lupron, had undetectable anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. Lee discussed the possibility of IVF with a donor egg.
- The woman with breast cancer, who was newly diagnosed, deferred fertility preservation.
- The man with lymphoma (Hodgkin's), who was awaiting chemotherapy, had his sperm frozen.
- The woman with lymphoma (new diagnosis) had 27 eggs frozen.
Lee had no disclosures to report.
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
Rising Cancer Rates Among Young People Spur New Fertility Preservation Options
VA Cancer Clinical Trials as a Strategy for Increasing Accrual of Racial and Ethnic Underrepresented Groups
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.
Background
Cancer clinical trials (CCTs) are central to improving cancer care. However, generalizability of findings from CCTs is difficult due to the lack of diversity in most United States CCTs. Clinical trial accrual of underrepresented groups, is low throughout the United States and is approximately 4-5% in most CCTs. Reasons for low accrual in this population are multifactorial. Despite numerous factors related to accruing racial and ethnic underrepresented groups, many institutions have sought to address these barriers. We conducted a scoping review to identify evidence-based approaches to increase participation in cancer treatment clinical trials.
Methods
We reviewed the Salisbury VA Medical Center Oncology clinical trial database from October 2019 to June 2024. The participants in these clinical trials required consent. These clinical trials included treatment interventional as well as non-treatment interventional. Fifteen studies were included and over 260 Veterans participated.
Results
Key themes emerged that included a focus on patient education, cultural competency, and building capacity in the clinics to care for the Veteran population at three separate sites in the Salisbury VA system. The Black Veteran accrual rate of 29% was achieved. This accrual rate is representative of our VA catchment population of 33% for Black Veterans, and is five times the national average.
Conclusions
The research team’s success in enrolling Black Veterans in clinical trials is attributed to several factors. The demographic composition of Veterans served by the Salisbury, Charlotte, and Kernersville VA provided a diverse population that included a 33% Black group. The type of clinical trials focused on patients who were most impacted by the disease. The VA did afford less barriers to access to health care.

Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
In 2020, the US Multi-Society Task Force (USMSTF) on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) increased the recommended colon polyp surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas from 5 to 10 years to 7 to 10 years.1 This change was prompted by emerging research indicating that rates of CRC and advanced neoplasia among patients with a history of only 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas are lower than initially estimated.2,3 This extension provides an opportunity to increase endoscopy capacity and improve access to colonoscopies by retroactively applying the 2020 guidelines to surveillance interval recommendations made before their introduction. For example, based on the updated guidelines, patients previously recommended to undergo colon polyp surveillance colonoscopy 5 years after an index colonoscopy could extend their surveillance interval by 2 to 5 years. Increasing endoscopic capacity could address the growing demand for colonoscopies from new screening guidelines that reduced the age of initial CRC screening from 50 years to 45 years and the backlog of procedures due to COVID-19 restrictions.4
As part of a project to increase endoscopic capacity at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS), this study assessed the potential impact of retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity. These results may be informative for other VA and private-sector health care systems seeking to identify strategies to improve endoscopy capacity.
Methods
VAPHS is an integrated health care system in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) serving 85,000 patients across 8 health care institutions in Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. VAPHS manages colorectal screening recommendations for patients receiving medical care in the health care system regardless of whether their prior colonoscopy was performed at VAPHS or external facilities. The VA maintains a national CRC screening and surveillance electronic medical record reminder that prompts health care practitioners to order colon polyp surveillance based on interval recommendations from the index colonoscopy. This study reviewed all patients from the VAPHS panel with a reminder to undergo colonoscopy for screening for CRC or surveillance of colon polyps within 12 months from September 1, 2022.
Among patients with a reminder, 3 investigators reviewed index colonoscopy and pathology reports to identify CRC risk category, colonoscopy indication, procedural quality, and recommended repeat colonoscopy interval. Per the USMSTF guidelines, patients with incomplete colonoscopy or pathology records, high-risk indications (ie, personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, personal history of CRC, or family history of CRC), or inadequate bowel preparation (Boston Bowel Preparation Score < 6) were excluded. Additionally, patients who had CRC screening or surveillance discontinued due to age or comorbidities, had completed a subsequent follow-up colonoscopy, or were deceased at the time of review were excluded.
Retroactive Interval Reclassification
Among eligible patients, this study compared the repeat colonoscopy interval recommended by the prior endoscopist with those from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines. In cases where the interval was documented as a range of years, the lower end was considered the recommendation. Similarly, the lower end of the range from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was used for the reclassified surveillance interval. Years extended per patient were quantified relative to September 1, 2023 (ie, 1 year after the review date). For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2016, the initial surveillance recommendation was 5 years, and the reclassified recommendation was 7 years, the interval extension beyond September 1, 2023, was 0 years.
Furthermore, because index surveillance recommendations are not always guideline concordant, the years extended per patient were calculated by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s recommendations with the guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy.5 For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2018, and the endoscopist recommended a 5-year follow-up for a patient with average risk for CRC, adequate bowel preparation, and no colorectal polyps, that patient is eligible to extend their colonoscopy to September 1, 2028, based on guideline recommendations at the time of index endoscopy recommending that the next colonoscopy occur in 10 years. In this analysis the 2012 USMSTF guidelines were applied to all index colonoscopies completed in 2021 or earlier to allow time for adoption of the 2020 guidelines.
This project fulfilled a facility mandate to increase capacity to conduct endoscopic procedures. Institutional review board approval was not required by VAPHS policy relating to clinical operations projects. Approval for publication of clinical operations activity was obtained from the VAPHS facility director.
Results
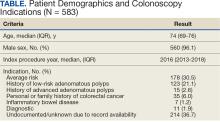
Within 1 year of the September 1, 2022, review date, 637 patients receiving care at VAPHS had clinical reminders for an upcoming colonoscopy. Of these, 54 (8.4%) were already up to date or were deceased at the time of review. Of the 583 eligible patients, 96% were male, the median age was 74 years, the median index colonoscopy year was 2016, and 178 (30.5%) had an average-risk CRC screening indication at the index colonoscopy (Table).
Of the 583 patients due for colonoscopy, 331 (56.7%) had both colonoscopy and pathology reports available. The majority of those with incomplete records had the index colonoscopy completed outside VAPHS. Among these patients, 222 (67.0%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of those with adequate bowel preparation, 43 were not eligible for interval extension because of high-risk conditions and 13 were not eligible because there was no index surveillance interval recommendation from the index endoscopist. Of the patients due for colonoscopy, 166 (28.4%) were potentially eligible for surveillance interval extension (Figure).
Sixty-five (39.2%) of the 166 patients had 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas on their index colonoscopy. Sixty-two patients were eligible for interval extension to 7 years, but this only resulted in ≥ 1 year of extension beyond the review date for 36 (6% of all 583 patients due for colonoscopy). The 36 patients were extended 63 years. By harmonizing the index endoscopists’ surveillance interval recommendation with the guideline at the time of the index colonoscopy, 29 additional patients could have their colonoscopy extended by ≥ 1 year. Harmonization extended colonoscopy intervals by 93 years. Retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines and harmonizing recommendations to guidelines extended the time of index colonoscopy by 153 years.
Discussion
With retroactive application of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines, 6% of patients due for an upcoming colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year by extending the surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas to 7 years. An additional 5% of patients could extend their interval by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s interval recommendation with polyp surveillance guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy. These findings are consistent with the results of 2 studies that demonstrated that about 14% of patients due for colonoscopy could have their interval extended.6,7 The current study enhances those insights by separating the contribution of 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines from the contribution of harmonizing surveillance intervals with guidelines for other polyp histologies. This study found that there is an opportunity to improve endoscopic capacity by harmonizing recommendations with guidelines. This complements a 2023 study showing that even when knowledgeable about guidelines, clinicians do not necessarily follow recommendations.8 While this and previous research have identified that 11% to 14% of patients are eligible for extension, these individuals would also have to be willing to have their polyp surveillance intervals extended for there to be a real-world impact on endoscopic capacity. A 2024 study found that only 19% to 37% of patients with 1 to 2 small tubular adenomas were willing to have polyps surveillance interval extension.9 This suggests the actual effect on capacity may be even lower than reported.
Limitations
The overall impact of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity was blunted by the high prevalence of incomplete index colonoscopy records among the study population. Without data on bowel preparation quality or procedure indications, this study could not assess whether 43% of patients were eligible for surveillance interval extension. Most index colonoscopies with incomplete documentation were completed at community-care gastroenterology facilities. This high rate of incomplete documentation is likely generalizable to other VA health care systems—especially in the era of the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, which increased veteran access to non-VA community care.10 Veterans due for colon polyp surveillance colonoscopies are more likely to have had their prior colonoscopy in community care compared with prior eras.11 Furthermore, because the VHA is among the most established integrated health care systems offering primary and subspecialty care in the US, private sector health care systems may have even greater rates of care fragmentation for longitudinal CRC screening and colon polyp surveillance, as these systems have only begun to regionally integrate recently.12,13
Another limitation is that nearly one-third of the individuals with documentation had inadequate bowel preparation for surveillance recommendations. This results in shorter surveillance follow-up colonoscopies and increases downstream demand for future colonoscopies. The low yield of extending colon polyp surveillance interval in this study emphasizes that improved efforts to obtain colonoscopy and pathology reports from community care, right-sizing the colon polyp surveillance intervals recommended by endoscopists, and improving quality of bowel preparation could have downstream health care system benefits in the future. These efforts could increase colonoscopy capacity at VA health care systems, thereby shortening colonoscopy wait times, decreasing fragmentation of care, and increasing the number of veterans who receive high-quality colonoscopies at VA health care systems.14
Conclusions
Eleven percent of patients in this study due for a colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year. About half of these extensions were directly due to the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance interval extension for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas. The rest resulted from harmonizing recommendations with guidelines at the time of the procedure. To determine whether retroactively applying polyp surveillance guidelines to follow-up interval recommendations will result in improved endoscopic capacity, health care system administrators should consider the degree of CRC screening care fragmentation in their patient population. Greater long-term gains in endoscopic capacity may be achieved by proactively supporting endoscopists in making guideline-concordant screening recommendations at the time of colonoscopy.
Gupta S, Lieberman D, Anderson JC, et al. Recommendations for follow-up after colonoscopy and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:463-485. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.01.014
Dubé C, Yakubu M, McCurdy BR, et al. Risk of advanced adenoma, colorectal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality in people with low-risk adenomas at baseline colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1790-1801. doi:10.1038/ajg.2017.360
Click B, Pinsky PF, Hickey T, Doroudi M, Shoen RE. Association of colonoscopy adenoma findings with long-term colorectal cancer incidence. JAMA. 2018;319:2021-2031. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.5809
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
Djinbachian R, Dubé AJ, Durand M, et al. Adherence to post-polypectomy surveillance guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2019;51:673-683. doi:10.1055/a-0865-2082
Gawron AJ, Kaltenbach T, Dominitz JA. The impact of the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic on access to endoscopy procedures in the VA healthcare system. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1216-1220.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.033
Xiao AH, Chang SY, Stevoff CG, Komanduri S, Pandolfino JE, Keswani RN. Adoption of multi-society guidelines facilitates value-based reduction in screening and surveillance colonoscopy volume during COVID-19 pandemic. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:2578-2584. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06539-1
Dong J, Wang LF, Ardolino E, Feuerstein JD. Real-world compliance with the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer polypectomy surveillance guidelines: an observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023;97:350-356.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.020
Lee JK, Koripella PC, Jensen CD, et al. Randomized trial of patient outreach approaches to de-implement outdated colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22:1315-1322.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.027
Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, HR 3230, 113th Cong (2014). Accessed September 8, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/113th-congress/house-bill/3230
Dueker JM, Khalid A. Performance of the Veterans Choice Program for improving access to colonoscopy at a tertiary VA facility. Fed Pract. 2020;37:224-228.
Oliver A. The Veterans Health Administration: an American success story? Milbank Q. 2007;85:5-35. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0009.2007.00475.x
Furukawa MF, Machta RM, Barrett KA, et al. Landscape of health systems in the United States. Med Care Res Rev. 2020;77:357-366. doi:10.1177/1077558718823130
Petros V, Tsambikos E, Madhoun M, Tierney WM. Impact of community referral on colonoscopy quality metrics in a Veterans Affairs Medical Center. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13:e00460. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000460
In 2020, the US Multi-Society Task Force (USMSTF) on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) increased the recommended colon polyp surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas from 5 to 10 years to 7 to 10 years.1 This change was prompted by emerging research indicating that rates of CRC and advanced neoplasia among patients with a history of only 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas are lower than initially estimated.2,3 This extension provides an opportunity to increase endoscopy capacity and improve access to colonoscopies by retroactively applying the 2020 guidelines to surveillance interval recommendations made before their introduction. For example, based on the updated guidelines, patients previously recommended to undergo colon polyp surveillance colonoscopy 5 years after an index colonoscopy could extend their surveillance interval by 2 to 5 years. Increasing endoscopic capacity could address the growing demand for colonoscopies from new screening guidelines that reduced the age of initial CRC screening from 50 years to 45 years and the backlog of procedures due to COVID-19 restrictions.4
As part of a project to increase endoscopic capacity at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS), this study assessed the potential impact of retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity. These results may be informative for other VA and private-sector health care systems seeking to identify strategies to improve endoscopy capacity.
Methods
VAPHS is an integrated health care system in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) serving 85,000 patients across 8 health care institutions in Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. VAPHS manages colorectal screening recommendations for patients receiving medical care in the health care system regardless of whether their prior colonoscopy was performed at VAPHS or external facilities. The VA maintains a national CRC screening and surveillance electronic medical record reminder that prompts health care practitioners to order colon polyp surveillance based on interval recommendations from the index colonoscopy. This study reviewed all patients from the VAPHS panel with a reminder to undergo colonoscopy for screening for CRC or surveillance of colon polyps within 12 months from September 1, 2022.
Among patients with a reminder, 3 investigators reviewed index colonoscopy and pathology reports to identify CRC risk category, colonoscopy indication, procedural quality, and recommended repeat colonoscopy interval. Per the USMSTF guidelines, patients with incomplete colonoscopy or pathology records, high-risk indications (ie, personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, personal history of CRC, or family history of CRC), or inadequate bowel preparation (Boston Bowel Preparation Score < 6) were excluded. Additionally, patients who had CRC screening or surveillance discontinued due to age or comorbidities, had completed a subsequent follow-up colonoscopy, or were deceased at the time of review were excluded.
Retroactive Interval Reclassification
Among eligible patients, this study compared the repeat colonoscopy interval recommended by the prior endoscopist with those from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines. In cases where the interval was documented as a range of years, the lower end was considered the recommendation. Similarly, the lower end of the range from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was used for the reclassified surveillance interval. Years extended per patient were quantified relative to September 1, 2023 (ie, 1 year after the review date). For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2016, the initial surveillance recommendation was 5 years, and the reclassified recommendation was 7 years, the interval extension beyond September 1, 2023, was 0 years.
Furthermore, because index surveillance recommendations are not always guideline concordant, the years extended per patient were calculated by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s recommendations with the guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy.5 For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2018, and the endoscopist recommended a 5-year follow-up for a patient with average risk for CRC, adequate bowel preparation, and no colorectal polyps, that patient is eligible to extend their colonoscopy to September 1, 2028, based on guideline recommendations at the time of index endoscopy recommending that the next colonoscopy occur in 10 years. In this analysis the 2012 USMSTF guidelines were applied to all index colonoscopies completed in 2021 or earlier to allow time for adoption of the 2020 guidelines.
This project fulfilled a facility mandate to increase capacity to conduct endoscopic procedures. Institutional review board approval was not required by VAPHS policy relating to clinical operations projects. Approval for publication of clinical operations activity was obtained from the VAPHS facility director.
Results
Within 1 year of the September 1, 2022, review date, 637 patients receiving care at VAPHS had clinical reminders for an upcoming colonoscopy. Of these, 54 (8.4%) were already up to date or were deceased at the time of review. Of the 583 eligible patients, 96% were male, the median age was 74 years, the median index colonoscopy year was 2016, and 178 (30.5%) had an average-risk CRC screening indication at the index colonoscopy (Table).
Of the 583 patients due for colonoscopy, 331 (56.7%) had both colonoscopy and pathology reports available. The majority of those with incomplete records had the index colonoscopy completed outside VAPHS. Among these patients, 222 (67.0%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of those with adequate bowel preparation, 43 were not eligible for interval extension because of high-risk conditions and 13 were not eligible because there was no index surveillance interval recommendation from the index endoscopist. Of the patients due for colonoscopy, 166 (28.4%) were potentially eligible for surveillance interval extension (Figure).
Sixty-five (39.2%) of the 166 patients had 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas on their index colonoscopy. Sixty-two patients were eligible for interval extension to 7 years, but this only resulted in ≥ 1 year of extension beyond the review date for 36 (6% of all 583 patients due for colonoscopy). The 36 patients were extended 63 years. By harmonizing the index endoscopists’ surveillance interval recommendation with the guideline at the time of the index colonoscopy, 29 additional patients could have their colonoscopy extended by ≥ 1 year. Harmonization extended colonoscopy intervals by 93 years. Retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines and harmonizing recommendations to guidelines extended the time of index colonoscopy by 153 years.
Discussion
With retroactive application of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines, 6% of patients due for an upcoming colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year by extending the surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas to 7 years. An additional 5% of patients could extend their interval by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s interval recommendation with polyp surveillance guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy. These findings are consistent with the results of 2 studies that demonstrated that about 14% of patients due for colonoscopy could have their interval extended.6,7 The current study enhances those insights by separating the contribution of 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines from the contribution of harmonizing surveillance intervals with guidelines for other polyp histologies. This study found that there is an opportunity to improve endoscopic capacity by harmonizing recommendations with guidelines. This complements a 2023 study showing that even when knowledgeable about guidelines, clinicians do not necessarily follow recommendations.8 While this and previous research have identified that 11% to 14% of patients are eligible for extension, these individuals would also have to be willing to have their polyp surveillance intervals extended for there to be a real-world impact on endoscopic capacity. A 2024 study found that only 19% to 37% of patients with 1 to 2 small tubular adenomas were willing to have polyps surveillance interval extension.9 This suggests the actual effect on capacity may be even lower than reported.
Limitations
The overall impact of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity was blunted by the high prevalence of incomplete index colonoscopy records among the study population. Without data on bowel preparation quality or procedure indications, this study could not assess whether 43% of patients were eligible for surveillance interval extension. Most index colonoscopies with incomplete documentation were completed at community-care gastroenterology facilities. This high rate of incomplete documentation is likely generalizable to other VA health care systems—especially in the era of the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, which increased veteran access to non-VA community care.10 Veterans due for colon polyp surveillance colonoscopies are more likely to have had their prior colonoscopy in community care compared with prior eras.11 Furthermore, because the VHA is among the most established integrated health care systems offering primary and subspecialty care in the US, private sector health care systems may have even greater rates of care fragmentation for longitudinal CRC screening and colon polyp surveillance, as these systems have only begun to regionally integrate recently.12,13
Another limitation is that nearly one-third of the individuals with documentation had inadequate bowel preparation for surveillance recommendations. This results in shorter surveillance follow-up colonoscopies and increases downstream demand for future colonoscopies. The low yield of extending colon polyp surveillance interval in this study emphasizes that improved efforts to obtain colonoscopy and pathology reports from community care, right-sizing the colon polyp surveillance intervals recommended by endoscopists, and improving quality of bowel preparation could have downstream health care system benefits in the future. These efforts could increase colonoscopy capacity at VA health care systems, thereby shortening colonoscopy wait times, decreasing fragmentation of care, and increasing the number of veterans who receive high-quality colonoscopies at VA health care systems.14
Conclusions
Eleven percent of patients in this study due for a colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year. About half of these extensions were directly due to the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance interval extension for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas. The rest resulted from harmonizing recommendations with guidelines at the time of the procedure. To determine whether retroactively applying polyp surveillance guidelines to follow-up interval recommendations will result in improved endoscopic capacity, health care system administrators should consider the degree of CRC screening care fragmentation in their patient population. Greater long-term gains in endoscopic capacity may be achieved by proactively supporting endoscopists in making guideline-concordant screening recommendations at the time of colonoscopy.
In 2020, the US Multi-Society Task Force (USMSTF) on Colorectal Cancer (CRC) increased the recommended colon polyp surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas from 5 to 10 years to 7 to 10 years.1 This change was prompted by emerging research indicating that rates of CRC and advanced neoplasia among patients with a history of only 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas are lower than initially estimated.2,3 This extension provides an opportunity to increase endoscopy capacity and improve access to colonoscopies by retroactively applying the 2020 guidelines to surveillance interval recommendations made before their introduction. For example, based on the updated guidelines, patients previously recommended to undergo colon polyp surveillance colonoscopy 5 years after an index colonoscopy could extend their surveillance interval by 2 to 5 years. Increasing endoscopic capacity could address the growing demand for colonoscopies from new screening guidelines that reduced the age of initial CRC screening from 50 years to 45 years and the backlog of procedures due to COVID-19 restrictions.4
As part of a project to increase endoscopic capacity at the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pittsburgh Healthcare System (VAPHS), this study assessed the potential impact of retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity. These results may be informative for other VA and private-sector health care systems seeking to identify strategies to improve endoscopy capacity.
Methods
VAPHS is an integrated health care system in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) serving 85,000 patients across 8 health care institutions in Pennsylvania, Ohio, and West Virginia. VAPHS manages colorectal screening recommendations for patients receiving medical care in the health care system regardless of whether their prior colonoscopy was performed at VAPHS or external facilities. The VA maintains a national CRC screening and surveillance electronic medical record reminder that prompts health care practitioners to order colon polyp surveillance based on interval recommendations from the index colonoscopy. This study reviewed all patients from the VAPHS panel with a reminder to undergo colonoscopy for screening for CRC or surveillance of colon polyps within 12 months from September 1, 2022.
Among patients with a reminder, 3 investigators reviewed index colonoscopy and pathology reports to identify CRC risk category, colonoscopy indication, procedural quality, and recommended repeat colonoscopy interval. Per the USMSTF guidelines, patients with incomplete colonoscopy or pathology records, high-risk indications (ie, personal history of inflammatory bowel disease, personal history of CRC, or family history of CRC), or inadequate bowel preparation (Boston Bowel Preparation Score < 6) were excluded. Additionally, patients who had CRC screening or surveillance discontinued due to age or comorbidities, had completed a subsequent follow-up colonoscopy, or were deceased at the time of review were excluded.
Retroactive Interval Reclassification
Among eligible patients, this study compared the repeat colonoscopy interval recommended by the prior endoscopist with those from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines. In cases where the interval was documented as a range of years, the lower end was considered the recommendation. Similarly, the lower end of the range from the 2020 USMSTF guidelines was used for the reclassified surveillance interval. Years extended per patient were quantified relative to September 1, 2023 (ie, 1 year after the review date). For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2016, the initial surveillance recommendation was 5 years, and the reclassified recommendation was 7 years, the interval extension beyond September 1, 2023, was 0 years.
Furthermore, because index surveillance recommendations are not always guideline concordant, the years extended per patient were calculated by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s recommendations with the guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy.5 For example, if the index colonoscopy was completed on September 1, 2018, and the endoscopist recommended a 5-year follow-up for a patient with average risk for CRC, adequate bowel preparation, and no colorectal polyps, that patient is eligible to extend their colonoscopy to September 1, 2028, based on guideline recommendations at the time of index endoscopy recommending that the next colonoscopy occur in 10 years. In this analysis the 2012 USMSTF guidelines were applied to all index colonoscopies completed in 2021 or earlier to allow time for adoption of the 2020 guidelines.
This project fulfilled a facility mandate to increase capacity to conduct endoscopic procedures. Institutional review board approval was not required by VAPHS policy relating to clinical operations projects. Approval for publication of clinical operations activity was obtained from the VAPHS facility director.
Results
Within 1 year of the September 1, 2022, review date, 637 patients receiving care at VAPHS had clinical reminders for an upcoming colonoscopy. Of these, 54 (8.4%) were already up to date or were deceased at the time of review. Of the 583 eligible patients, 96% were male, the median age was 74 years, the median index colonoscopy year was 2016, and 178 (30.5%) had an average-risk CRC screening indication at the index colonoscopy (Table).
Of the 583 patients due for colonoscopy, 331 (56.7%) had both colonoscopy and pathology reports available. The majority of those with incomplete records had the index colonoscopy completed outside VAPHS. Among these patients, 222 (67.0%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of those with adequate bowel preparation, 43 were not eligible for interval extension because of high-risk conditions and 13 were not eligible because there was no index surveillance interval recommendation from the index endoscopist. Of the patients due for colonoscopy, 166 (28.4%) were potentially eligible for surveillance interval extension (Figure).
Sixty-five (39.2%) of the 166 patients had 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas on their index colonoscopy. Sixty-two patients were eligible for interval extension to 7 years, but this only resulted in ≥ 1 year of extension beyond the review date for 36 (6% of all 583 patients due for colonoscopy). The 36 patients were extended 63 years. By harmonizing the index endoscopists’ surveillance interval recommendation with the guideline at the time of the index colonoscopy, 29 additional patients could have their colonoscopy extended by ≥ 1 year. Harmonization extended colonoscopy intervals by 93 years. Retroactively applying the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines and harmonizing recommendations to guidelines extended the time of index colonoscopy by 153 years.
Discussion
With retroactive application of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines, 6% of patients due for an upcoming colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year by extending the surveillance interval for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas to 7 years. An additional 5% of patients could extend their interval by harmonizing the index endoscopist’s interval recommendation with polyp surveillance guidelines at the time of the index colonoscopy. These findings are consistent with the results of 2 studies that demonstrated that about 14% of patients due for colonoscopy could have their interval extended.6,7 The current study enhances those insights by separating the contribution of 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines from the contribution of harmonizing surveillance intervals with guidelines for other polyp histologies. This study found that there is an opportunity to improve endoscopic capacity by harmonizing recommendations with guidelines. This complements a 2023 study showing that even when knowledgeable about guidelines, clinicians do not necessarily follow recommendations.8 While this and previous research have identified that 11% to 14% of patients are eligible for extension, these individuals would also have to be willing to have their polyp surveillance intervals extended for there to be a real-world impact on endoscopic capacity. A 2024 study found that only 19% to 37% of patients with 1 to 2 small tubular adenomas were willing to have polyps surveillance interval extension.9 This suggests the actual effect on capacity may be even lower than reported.
Limitations
The overall impact of the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance guidelines on endoscopic capacity was blunted by the high prevalence of incomplete index colonoscopy records among the study population. Without data on bowel preparation quality or procedure indications, this study could not assess whether 43% of patients were eligible for surveillance interval extension. Most index colonoscopies with incomplete documentation were completed at community-care gastroenterology facilities. This high rate of incomplete documentation is likely generalizable to other VA health care systems—especially in the era of the Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, which increased veteran access to non-VA community care.10 Veterans due for colon polyp surveillance colonoscopies are more likely to have had their prior colonoscopy in community care compared with prior eras.11 Furthermore, because the VHA is among the most established integrated health care systems offering primary and subspecialty care in the US, private sector health care systems may have even greater rates of care fragmentation for longitudinal CRC screening and colon polyp surveillance, as these systems have only begun to regionally integrate recently.12,13
Another limitation is that nearly one-third of the individuals with documentation had inadequate bowel preparation for surveillance recommendations. This results in shorter surveillance follow-up colonoscopies and increases downstream demand for future colonoscopies. The low yield of extending colon polyp surveillance interval in this study emphasizes that improved efforts to obtain colonoscopy and pathology reports from community care, right-sizing the colon polyp surveillance intervals recommended by endoscopists, and improving quality of bowel preparation could have downstream health care system benefits in the future. These efforts could increase colonoscopy capacity at VA health care systems, thereby shortening colonoscopy wait times, decreasing fragmentation of care, and increasing the number of veterans who receive high-quality colonoscopies at VA health care systems.14
Conclusions
Eleven percent of patients in this study due for a colonoscopy could extend their follow-up by ≥ 1 year. About half of these extensions were directly due to the 2020 USMSTF polyp surveillance interval extension for 1 to 2 subcentimeter tubular adenomas. The rest resulted from harmonizing recommendations with guidelines at the time of the procedure. To determine whether retroactively applying polyp surveillance guidelines to follow-up interval recommendations will result in improved endoscopic capacity, health care system administrators should consider the degree of CRC screening care fragmentation in their patient population. Greater long-term gains in endoscopic capacity may be achieved by proactively supporting endoscopists in making guideline-concordant screening recommendations at the time of colonoscopy.
Gupta S, Lieberman D, Anderson JC, et al. Recommendations for follow-up after colonoscopy and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:463-485. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.01.014
Dubé C, Yakubu M, McCurdy BR, et al. Risk of advanced adenoma, colorectal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality in people with low-risk adenomas at baseline colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1790-1801. doi:10.1038/ajg.2017.360
Click B, Pinsky PF, Hickey T, Doroudi M, Shoen RE. Association of colonoscopy adenoma findings with long-term colorectal cancer incidence. JAMA. 2018;319:2021-2031. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.5809
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
Djinbachian R, Dubé AJ, Durand M, et al. Adherence to post-polypectomy surveillance guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2019;51:673-683. doi:10.1055/a-0865-2082
Gawron AJ, Kaltenbach T, Dominitz JA. The impact of the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic on access to endoscopy procedures in the VA healthcare system. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1216-1220.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.033
Xiao AH, Chang SY, Stevoff CG, Komanduri S, Pandolfino JE, Keswani RN. Adoption of multi-society guidelines facilitates value-based reduction in screening and surveillance colonoscopy volume during COVID-19 pandemic. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:2578-2584. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06539-1
Dong J, Wang LF, Ardolino E, Feuerstein JD. Real-world compliance with the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer polypectomy surveillance guidelines: an observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023;97:350-356.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.020
Lee JK, Koripella PC, Jensen CD, et al. Randomized trial of patient outreach approaches to de-implement outdated colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22:1315-1322.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.027
Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, HR 3230, 113th Cong (2014). Accessed September 8, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/113th-congress/house-bill/3230
Dueker JM, Khalid A. Performance of the Veterans Choice Program for improving access to colonoscopy at a tertiary VA facility. Fed Pract. 2020;37:224-228.
Oliver A. The Veterans Health Administration: an American success story? Milbank Q. 2007;85:5-35. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0009.2007.00475.x
Furukawa MF, Machta RM, Barrett KA, et al. Landscape of health systems in the United States. Med Care Res Rev. 2020;77:357-366. doi:10.1177/1077558718823130
Petros V, Tsambikos E, Madhoun M, Tierney WM. Impact of community referral on colonoscopy quality metrics in a Veterans Affairs Medical Center. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13:e00460. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000460
Gupta S, Lieberman D, Anderson JC, et al. Recommendations for follow-up after colonoscopy and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020;91:463-485. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2020.01.014
Dubé C, Yakubu M, McCurdy BR, et al. Risk of advanced adenoma, colorectal cancer, and colorectal cancer mortality in people with low-risk adenomas at baseline colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1790-1801. doi:10.1038/ajg.2017.360
Click B, Pinsky PF, Hickey T, Doroudi M, Shoen RE. Association of colonoscopy adenoma findings with long-term colorectal cancer incidence. JAMA. 2018;319:2021-2031. doi:10.1001/jama.2018.5809
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325:1965-1977. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.6238
Djinbachian R, Dubé AJ, Durand M, et al. Adherence to post-polypectomy surveillance guidelines: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2019;51:673-683. doi:10.1055/a-0865-2082
Gawron AJ, Kaltenbach T, Dominitz JA. The impact of the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic on access to endoscopy procedures in the VA healthcare system. Gastroenterology. 2020;159:1216-1220.e1. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.07.033
Xiao AH, Chang SY, Stevoff CG, Komanduri S, Pandolfino JE, Keswani RN. Adoption of multi-society guidelines facilitates value-based reduction in screening and surveillance colonoscopy volume during COVID-19 pandemic. Dig Dis Sci. 2021;66:2578-2584. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06539-1
Dong J, Wang LF, Ardolino E, Feuerstein JD. Real-world compliance with the 2020 U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer polypectomy surveillance guidelines: an observational study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2023;97:350-356.e3. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2022.08.020
Lee JK, Koripella PC, Jensen CD, et al. Randomized trial of patient outreach approaches to de-implement outdated colonoscopy surveillance intervals. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;22:1315-1322.e7. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.12.027
Veterans Access, Choice, and Accountability Act of 2014, HR 3230, 113th Cong (2014). Accessed September 8, 2025. https://www.congress.gov/bill/113th-congress/house-bill/3230
Dueker JM, Khalid A. Performance of the Veterans Choice Program for improving access to colonoscopy at a tertiary VA facility. Fed Pract. 2020;37:224-228.
Oliver A. The Veterans Health Administration: an American success story? Milbank Q. 2007;85:5-35. doi:10.1111/j.1468-0009.2007.00475.x
Furukawa MF, Machta RM, Barrett KA, et al. Landscape of health systems in the United States. Med Care Res Rev. 2020;77:357-366. doi:10.1177/1077558718823130
Petros V, Tsambikos E, Madhoun M, Tierney WM. Impact of community referral on colonoscopy quality metrics in a Veterans Affairs Medical Center. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022;13:e00460. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000460
Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
Impact of Retroactive Application of Updated Surveillance Guidelines on Endoscopy Center Capacity at a Large VA Health Care System
mRNA Cancer Vaccines: Pipeline Insights for Clinicians
Since 1965, messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines have been studied for cancer treatment, but it was the technological advances in vaccines during the COVID pandemic that helped accelerate research. Currently, no vaccine has been approved for tumor treatment, although many clinical studies are ongoing worldwide. According to experts consulted by Medscape’s Portuguese edition, the outlook is very promising, and these studies are expected to open doors for personalized therapies.
In cancer treatment, the vaccine would function as an immunotherapy, in which the immune system can be “trained” to act against an invader. Just as with pathogens, the platform would use parts of the tumor — which have altered proteins or are expressed at abnormal levels — to teach the body to defend itself against cancer.
Vladmir Lima, MD, PhD, clinical oncologist at A.C. Camargo Cancer Center, São Paulo, Brazil, explained that with this technology it will be possible to produce personalized vaccines, which prevents, for example, large-scale manufacturing. “In theory, these vaccines can be developed for any tumor type, but this does not mean that efficacy will be the same for all,” he said. Because cancer has specific characteristics in each individual, it is difficult to envision a single vaccine that works for all cancers.
Current evidence suggests the vaccine could be administered after chemotherapy or radiotherapy, with the goal of reducing tumor mass and increasing the effectiveness of mRNA-based treatment, according to Ana Paula Lepique, professor and researcher in tumor immunology at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, University of São Paulo, São Paulo.
“There is also a study with pancreatic cancer patients, in which the vaccine was administered after surgery,” she explained. “It would not work, for example, to give chemotherapy or radiotherapy while the immune response is being triggered by the vaccine. This would make the vaccine ineffective, since chemotherapy and radiotherapy are toxic to lymphocytes.”
Lepique also clarified that it is possible to combine the vaccine with immunotherapy targeting immune regulatory molecules. “In this case, in addition to administering the mRNA with the antigen, a strategy is used to improve the patient’s immune response.”
Challenges With mRNA Vaccines
Despite being a promising technology, there are challenges, warned Lepique. mRNA molecules degrade quickly when injected into the body, which can compromise vaccine efficacy. To overcome this, researchers have developed nanoencapsulation technologies that protect the molecules and allow safe use in vaccines. “Another alternative is transferring the mRNA into dendritic cells, known as antigen-presenting cells, and then administering these cells to the patient,” she explained.
Global Research Status
According to a study published this year in Med, over 120 clinical trials are exploring mRNA vaccines to treat lung, breast, prostate, and pancreatic tumors, as well as melanoma.
Lepique noted that the countries leading this research are the US, UK, Germany, China, and Japan. “Unfortunately, the US government recently cut funding for mRNA vaccine development and testing, which will likely have significant consequences,” she said.
Lepique reported that Brazilian researchers are collaborating with international institutions to develop these vaccines. “The Brazilian government, through the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation, recently announced investments in mRNA technologies for vaccines. While not specifically targeting cancer, these investments could also benefit this field,” she clarified.
Leading Studies
Lepique highlighted the most advanced studies to date:
- Pancreatic cancer: A study published in Nature in February demonstrated that a personalized mRNA vaccine reduced the risk for recurrence after surgery in 16 patients, with 3 years of follow-up.
- Melanoma: A study published in The Lancet reported improved survival in melanoma patients after mRNA vaccine administration combined with the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab applied after surgical tumor resection.
- Universal vaccine: A study in Nature Biomedical Engineering described the creation of a “generic” vaccine capable of activating the patient’s immune system and inducing tumor regression. Lepique explained that this vaccine acts more as an immune response modulator than a classical neoantigen-specific vaccine. “Because it is not limited to a single neoantigen, it could potentially be universal, though further testing is needed to determine efficacy across all cancer types,” she added.
Lima highlighted a 2024 study being conducted by MSD and Moderna against lung cancer, with results yet to be published. “Patients first receive immunotherapy after surgery. Once the vaccine is ready, it is added to the ongoing immunotherapy,” he explained. The global phase 3 study involves 868 patients with resected lung cancer who previously underwent chemotherapy. Participants receive the vaccine (1 mg every 3 weeks, up to nine doses) alongside pembrolizumab (400 mg every 6 weeks, up to nine cycles) over approximately 1 year.
Other mRNA vaccines remain in early-stage development. For example, in May 2024, the UK National Health Service recruited participants for a personalized colorectal cancer mRNA vaccine trial.
Advantages of mRNA Technology
Experts noted that mRNA-based cancer vaccines are considered safer for patients because the tumor mRNA is synthesized in the laboratory. According to Lepique, these vaccines are more specific than many other cancer therapies, and therefore carry a lower risk for serious side effects.
“Clinical studies have shown that these vaccines can generate immunological memory, meaning lymphocytes that recognize tumor antigens remain in the body and can respond to recurrence,” she explained.
It is also possible to combine multiple mRNA molecules in a single vaccine, creating a platform that targets several tumor antigens simultaneously. “Formulations can additionally include adjuvants to further enhance immune responses against tumors,” she said. However, as a personalized therapy, costs are high, and vaccine formulation requires considerable time.
Lima emphasized the customization advantage: “We can take a portion of the patient’s tumor, sequence it to identify alterations, and develop a vaccine specifically for that tumor.” He also highlighted safety data, noting that the platform has been widely used in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development, providing confidence in large-scale application. “The potential exists to achieve more personalized, tumor-directed immunotherapy with greater scalability,” he explained.
Outlook and Limitations
Lima noted that although the projected efficacy is promising, definitive results are still pending.
“We have very positive expectations, but we must wait for study outcomes. Efficacy may vary across scenarios and among patients. The immune system may also respond against the vaccine itself, potentially reducing effectiveness at times,” he explained.
According to Lima, mRNA vaccines are expected to complement current treatments, enhancing outcomes without replacing conventional approaches entirely.
“It will not be a panacea. These vaccines are likely to add to and improve strategies we already use, but they will not work for all patients in every scenario,” he concluded.
Lepique highlighted the promise of combination strategies. “The outlook is positive, particularly because multiple mRNA types can be combined in a single formulation and used alongside drugs that enhance immune responses,” she explained.
Although mRNA vaccine research has been ongoing for many years, prior results have brought both progress and setbacks. “This new protocol appears more effective [and] capable of generating immunological memory and is also safe,” she noted. Still, she cautioned that cancer presents unique challenges: “The disease has multiple mechanisms to evade immune responses. Additionally, some tumors are naturally unrecognized by the immune system, the so-called ‘cold tumors.’”
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Since 1965, messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines have been studied for cancer treatment, but it was the technological advances in vaccines during the COVID pandemic that helped accelerate research. Currently, no vaccine has been approved for tumor treatment, although many clinical studies are ongoing worldwide. According to experts consulted by Medscape’s Portuguese edition, the outlook is very promising, and these studies are expected to open doors for personalized therapies.
In cancer treatment, the vaccine would function as an immunotherapy, in which the immune system can be “trained” to act against an invader. Just as with pathogens, the platform would use parts of the tumor — which have altered proteins or are expressed at abnormal levels — to teach the body to defend itself against cancer.
Vladmir Lima, MD, PhD, clinical oncologist at A.C. Camargo Cancer Center, São Paulo, Brazil, explained that with this technology it will be possible to produce personalized vaccines, which prevents, for example, large-scale manufacturing. “In theory, these vaccines can be developed for any tumor type, but this does not mean that efficacy will be the same for all,” he said. Because cancer has specific characteristics in each individual, it is difficult to envision a single vaccine that works for all cancers.
Current evidence suggests the vaccine could be administered after chemotherapy or radiotherapy, with the goal of reducing tumor mass and increasing the effectiveness of mRNA-based treatment, according to Ana Paula Lepique, professor and researcher in tumor immunology at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, University of São Paulo, São Paulo.
“There is also a study with pancreatic cancer patients, in which the vaccine was administered after surgery,” she explained. “It would not work, for example, to give chemotherapy or radiotherapy while the immune response is being triggered by the vaccine. This would make the vaccine ineffective, since chemotherapy and radiotherapy are toxic to lymphocytes.”
Lepique also clarified that it is possible to combine the vaccine with immunotherapy targeting immune regulatory molecules. “In this case, in addition to administering the mRNA with the antigen, a strategy is used to improve the patient’s immune response.”
Challenges With mRNA Vaccines
Despite being a promising technology, there are challenges, warned Lepique. mRNA molecules degrade quickly when injected into the body, which can compromise vaccine efficacy. To overcome this, researchers have developed nanoencapsulation technologies that protect the molecules and allow safe use in vaccines. “Another alternative is transferring the mRNA into dendritic cells, known as antigen-presenting cells, and then administering these cells to the patient,” she explained.
Global Research Status
According to a study published this year in Med, over 120 clinical trials are exploring mRNA vaccines to treat lung, breast, prostate, and pancreatic tumors, as well as melanoma.
Lepique noted that the countries leading this research are the US, UK, Germany, China, and Japan. “Unfortunately, the US government recently cut funding for mRNA vaccine development and testing, which will likely have significant consequences,” she said.
Lepique reported that Brazilian researchers are collaborating with international institutions to develop these vaccines. “The Brazilian government, through the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation, recently announced investments in mRNA technologies for vaccines. While not specifically targeting cancer, these investments could also benefit this field,” she clarified.
Leading Studies
Lepique highlighted the most advanced studies to date:
- Pancreatic cancer: A study published in Nature in February demonstrated that a personalized mRNA vaccine reduced the risk for recurrence after surgery in 16 patients, with 3 years of follow-up.
- Melanoma: A study published in The Lancet reported improved survival in melanoma patients after mRNA vaccine administration combined with the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab applied after surgical tumor resection.
- Universal vaccine: A study in Nature Biomedical Engineering described the creation of a “generic” vaccine capable of activating the patient’s immune system and inducing tumor regression. Lepique explained that this vaccine acts more as an immune response modulator than a classical neoantigen-specific vaccine. “Because it is not limited to a single neoantigen, it could potentially be universal, though further testing is needed to determine efficacy across all cancer types,” she added.
Lima highlighted a 2024 study being conducted by MSD and Moderna against lung cancer, with results yet to be published. “Patients first receive immunotherapy after surgery. Once the vaccine is ready, it is added to the ongoing immunotherapy,” he explained. The global phase 3 study involves 868 patients with resected lung cancer who previously underwent chemotherapy. Participants receive the vaccine (1 mg every 3 weeks, up to nine doses) alongside pembrolizumab (400 mg every 6 weeks, up to nine cycles) over approximately 1 year.
Other mRNA vaccines remain in early-stage development. For example, in May 2024, the UK National Health Service recruited participants for a personalized colorectal cancer mRNA vaccine trial.
Advantages of mRNA Technology
Experts noted that mRNA-based cancer vaccines are considered safer for patients because the tumor mRNA is synthesized in the laboratory. According to Lepique, these vaccines are more specific than many other cancer therapies, and therefore carry a lower risk for serious side effects.
“Clinical studies have shown that these vaccines can generate immunological memory, meaning lymphocytes that recognize tumor antigens remain in the body and can respond to recurrence,” she explained.
It is also possible to combine multiple mRNA molecules in a single vaccine, creating a platform that targets several tumor antigens simultaneously. “Formulations can additionally include adjuvants to further enhance immune responses against tumors,” she said. However, as a personalized therapy, costs are high, and vaccine formulation requires considerable time.
Lima emphasized the customization advantage: “We can take a portion of the patient’s tumor, sequence it to identify alterations, and develop a vaccine specifically for that tumor.” He also highlighted safety data, noting that the platform has been widely used in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development, providing confidence in large-scale application. “The potential exists to achieve more personalized, tumor-directed immunotherapy with greater scalability,” he explained.
Outlook and Limitations
Lima noted that although the projected efficacy is promising, definitive results are still pending.
“We have very positive expectations, but we must wait for study outcomes. Efficacy may vary across scenarios and among patients. The immune system may also respond against the vaccine itself, potentially reducing effectiveness at times,” he explained.
According to Lima, mRNA vaccines are expected to complement current treatments, enhancing outcomes without replacing conventional approaches entirely.
“It will not be a panacea. These vaccines are likely to add to and improve strategies we already use, but they will not work for all patients in every scenario,” he concluded.
Lepique highlighted the promise of combination strategies. “The outlook is positive, particularly because multiple mRNA types can be combined in a single formulation and used alongside drugs that enhance immune responses,” she explained.
Although mRNA vaccine research has been ongoing for many years, prior results have brought both progress and setbacks. “This new protocol appears more effective [and] capable of generating immunological memory and is also safe,” she noted. Still, she cautioned that cancer presents unique challenges: “The disease has multiple mechanisms to evade immune responses. Additionally, some tumors are naturally unrecognized by the immune system, the so-called ‘cold tumors.’”
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Since 1965, messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines have been studied for cancer treatment, but it was the technological advances in vaccines during the COVID pandemic that helped accelerate research. Currently, no vaccine has been approved for tumor treatment, although many clinical studies are ongoing worldwide. According to experts consulted by Medscape’s Portuguese edition, the outlook is very promising, and these studies are expected to open doors for personalized therapies.
In cancer treatment, the vaccine would function as an immunotherapy, in which the immune system can be “trained” to act against an invader. Just as with pathogens, the platform would use parts of the tumor — which have altered proteins or are expressed at abnormal levels — to teach the body to defend itself against cancer.
Vladmir Lima, MD, PhD, clinical oncologist at A.C. Camargo Cancer Center, São Paulo, Brazil, explained that with this technology it will be possible to produce personalized vaccines, which prevents, for example, large-scale manufacturing. “In theory, these vaccines can be developed for any tumor type, but this does not mean that efficacy will be the same for all,” he said. Because cancer has specific characteristics in each individual, it is difficult to envision a single vaccine that works for all cancers.
Current evidence suggests the vaccine could be administered after chemotherapy or radiotherapy, with the goal of reducing tumor mass and increasing the effectiveness of mRNA-based treatment, according to Ana Paula Lepique, professor and researcher in tumor immunology at the Institute of Biomedical Sciences, University of São Paulo, São Paulo.
“There is also a study with pancreatic cancer patients, in which the vaccine was administered after surgery,” she explained. “It would not work, for example, to give chemotherapy or radiotherapy while the immune response is being triggered by the vaccine. This would make the vaccine ineffective, since chemotherapy and radiotherapy are toxic to lymphocytes.”
Lepique also clarified that it is possible to combine the vaccine with immunotherapy targeting immune regulatory molecules. “In this case, in addition to administering the mRNA with the antigen, a strategy is used to improve the patient’s immune response.”
Challenges With mRNA Vaccines
Despite being a promising technology, there are challenges, warned Lepique. mRNA molecules degrade quickly when injected into the body, which can compromise vaccine efficacy. To overcome this, researchers have developed nanoencapsulation technologies that protect the molecules and allow safe use in vaccines. “Another alternative is transferring the mRNA into dendritic cells, known as antigen-presenting cells, and then administering these cells to the patient,” she explained.
Global Research Status
According to a study published this year in Med, over 120 clinical trials are exploring mRNA vaccines to treat lung, breast, prostate, and pancreatic tumors, as well as melanoma.
Lepique noted that the countries leading this research are the US, UK, Germany, China, and Japan. “Unfortunately, the US government recently cut funding for mRNA vaccine development and testing, which will likely have significant consequences,” she said.
Lepique reported that Brazilian researchers are collaborating with international institutions to develop these vaccines. “The Brazilian government, through the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation, recently announced investments in mRNA technologies for vaccines. While not specifically targeting cancer, these investments could also benefit this field,” she clarified.
Leading Studies
Lepique highlighted the most advanced studies to date:
- Pancreatic cancer: A study published in Nature in February demonstrated that a personalized mRNA vaccine reduced the risk for recurrence after surgery in 16 patients, with 3 years of follow-up.
- Melanoma: A study published in The Lancet reported improved survival in melanoma patients after mRNA vaccine administration combined with the checkpoint inhibitor pembrolizumab applied after surgical tumor resection.
- Universal vaccine: A study in Nature Biomedical Engineering described the creation of a “generic” vaccine capable of activating the patient’s immune system and inducing tumor regression. Lepique explained that this vaccine acts more as an immune response modulator than a classical neoantigen-specific vaccine. “Because it is not limited to a single neoantigen, it could potentially be universal, though further testing is needed to determine efficacy across all cancer types,” she added.
Lima highlighted a 2024 study being conducted by MSD and Moderna against lung cancer, with results yet to be published. “Patients first receive immunotherapy after surgery. Once the vaccine is ready, it is added to the ongoing immunotherapy,” he explained. The global phase 3 study involves 868 patients with resected lung cancer who previously underwent chemotherapy. Participants receive the vaccine (1 mg every 3 weeks, up to nine doses) alongside pembrolizumab (400 mg every 6 weeks, up to nine cycles) over approximately 1 year.
Other mRNA vaccines remain in early-stage development. For example, in May 2024, the UK National Health Service recruited participants for a personalized colorectal cancer mRNA vaccine trial.
Advantages of mRNA Technology
Experts noted that mRNA-based cancer vaccines are considered safer for patients because the tumor mRNA is synthesized in the laboratory. According to Lepique, these vaccines are more specific than many other cancer therapies, and therefore carry a lower risk for serious side effects.
“Clinical studies have shown that these vaccines can generate immunological memory, meaning lymphocytes that recognize tumor antigens remain in the body and can respond to recurrence,” she explained.
It is also possible to combine multiple mRNA molecules in a single vaccine, creating a platform that targets several tumor antigens simultaneously. “Formulations can additionally include adjuvants to further enhance immune responses against tumors,” she said. However, as a personalized therapy, costs are high, and vaccine formulation requires considerable time.
Lima emphasized the customization advantage: “We can take a portion of the patient’s tumor, sequence it to identify alterations, and develop a vaccine specifically for that tumor.” He also highlighted safety data, noting that the platform has been widely used in SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development, providing confidence in large-scale application. “The potential exists to achieve more personalized, tumor-directed immunotherapy with greater scalability,” he explained.
Outlook and Limitations
Lima noted that although the projected efficacy is promising, definitive results are still pending.
“We have very positive expectations, but we must wait for study outcomes. Efficacy may vary across scenarios and among patients. The immune system may also respond against the vaccine itself, potentially reducing effectiveness at times,” he explained.
According to Lima, mRNA vaccines are expected to complement current treatments, enhancing outcomes without replacing conventional approaches entirely.
“It will not be a panacea. These vaccines are likely to add to and improve strategies we already use, but they will not work for all patients in every scenario,” he concluded.
Lepique highlighted the promise of combination strategies. “The outlook is positive, particularly because multiple mRNA types can be combined in a single formulation and used alongside drugs that enhance immune responses,” she explained.
Although mRNA vaccine research has been ongoing for many years, prior results have brought both progress and setbacks. “This new protocol appears more effective [and] capable of generating immunological memory and is also safe,” she noted. Still, she cautioned that cancer presents unique challenges: “The disease has multiple mechanisms to evade immune responses. Additionally, some tumors are naturally unrecognized by the immune system, the so-called ‘cold tumors.’”
This story was translated from Medscape’s Portuguese edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Hepatitis D Virus Classified as Carcinogenic: Implications
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of the World Health Organization has classified hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic, citing sufficient evidence and placing it alongside hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Individuals with HBV-HDV coinfection face an elevated risk for liver cancer, highlighting the need for HBV vaccination, systematic screening, and early antiviral treatment to reduce the progression to cirrhosis and HCC.
About 12 million people globally have HBV-HDV coinfection, representing 5% of all chronic HBV cases. The prevalence of this condition varies regionally, with a likely underdiagnosis. True coinfection rates may reach 13%-14%, the highest in Europe’s Mediterranean region.
Virus Biology
HDV is an incomplete virus that infects hepatocytes and requires the envelope protein of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for cell exit. Infection occurs only with chronic HBV infection, either as a superinfection or simultaneous acquisition. Humans are the only known natural host.
HDV coinfection worsens HBV-induced hepatic inflammation and prognosis, and up to 80% of patients develop cirrhosis. Triple infection with the HBV virus, HDV, and HIV further increases this risk, and the global prevalence is likely underestimated.
Cancer Risk
HDV infection significantly increases the risk for HCC compared with HBV infection alone. Many patients die from decompensated cirrhosis or HCC, reflecting the aggressive nature of coinfection.
The molecular mechanisms underlying HDV oncogenesis remain unclear. Research conducted over the past 15 years has provided insights that could inform the development of more effective treatments.
Early vaccination prophylaxis is critical for reducing the risk for HCC, despite limited options.
Treatment Options
Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated antiviral efficacy for:
- Pegylated interferon alpha (Peg-IFN) is approved for HBV and is active against HDV.
- Bulevirtide, a synthetic myristoylated lipopeptide entry inhibitor, is used alone or in combination with Peg-IFN.
Suppression of HBV remains central. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs, such as entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, significantly reduce HCC progression in treated patients compared with untreated patients at risk.
Promising therapeutics include lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor that blocks HDV particle formation, and nucleic acid polymers targeting the host chaperone DNAJB12 to inhibit HBV and HDV replication.
Guideline Updates
The 2023 addendum to the S3 guidelines covers the prophylaxis, diagnosis, and treatment of HBV, including HDV management.
IARC experts also re-evaluated the human cytomegalovirus and Merkel cell polyomavirus. Complete assessments are expected in the next edition of IARC Monographs.
HBV Vaccination
HBV vaccination is the only effective prophylaxis against HBV and HDV. Introduced in 1982 for high-risk groups, it reduced chronic infections, with the WHO expanding its recommendations from 1992 onward.
Infants and young children are at the highest risk of developing this disease. Acute HBV infection often resolves in adults, but infants face up to a 90% risk of developing chronic infection. Newborns of mothers with chronic or undiagnosed HBV infections are particularly vulnerable.
Routine infant immunization includes three doses, with the first dose administered within 12 hours of birth. In Germany, the Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) recommends the administration of combination vaccines, with the hexavalent vaccine administered at 2, 4, and 11 months in a 2 + 1 schedule.
Timely vaccination is crucial because undetected chronic infections often lead to late-stage HCC diagnosis. Adults in high-risk groups should receive HBV vaccination counseling.
STIKO recommends vaccination for close contacts of individuals who are HBsAg-positive, individuals with high-risk sexual contacts, immunocompromised persons, and those with preexisting conditions that increase the risk for severe HBV infection.
Since 2021, insured adults aged 35 years or older in Germany have undergone one-time HBV and HCV screening. HDV testing is recommended for all HBsAg-positive patients. Current frameworks may miss cases, and additional or personalized screening could improve the detection of previously unrecognized infections.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of the World Health Organization has classified hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic, citing sufficient evidence and placing it alongside hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Individuals with HBV-HDV coinfection face an elevated risk for liver cancer, highlighting the need for HBV vaccination, systematic screening, and early antiviral treatment to reduce the progression to cirrhosis and HCC.
About 12 million people globally have HBV-HDV coinfection, representing 5% of all chronic HBV cases. The prevalence of this condition varies regionally, with a likely underdiagnosis. True coinfection rates may reach 13%-14%, the highest in Europe’s Mediterranean region.
Virus Biology
HDV is an incomplete virus that infects hepatocytes and requires the envelope protein of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for cell exit. Infection occurs only with chronic HBV infection, either as a superinfection or simultaneous acquisition. Humans are the only known natural host.
HDV coinfection worsens HBV-induced hepatic inflammation and prognosis, and up to 80% of patients develop cirrhosis. Triple infection with the HBV virus, HDV, and HIV further increases this risk, and the global prevalence is likely underestimated.
Cancer Risk
HDV infection significantly increases the risk for HCC compared with HBV infection alone. Many patients die from decompensated cirrhosis or HCC, reflecting the aggressive nature of coinfection.
The molecular mechanisms underlying HDV oncogenesis remain unclear. Research conducted over the past 15 years has provided insights that could inform the development of more effective treatments.
Early vaccination prophylaxis is critical for reducing the risk for HCC, despite limited options.
Treatment Options
Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated antiviral efficacy for:
- Pegylated interferon alpha (Peg-IFN) is approved for HBV and is active against HDV.
- Bulevirtide, a synthetic myristoylated lipopeptide entry inhibitor, is used alone or in combination with Peg-IFN.
Suppression of HBV remains central. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs, such as entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, significantly reduce HCC progression in treated patients compared with untreated patients at risk.
Promising therapeutics include lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor that blocks HDV particle formation, and nucleic acid polymers targeting the host chaperone DNAJB12 to inhibit HBV and HDV replication.
Guideline Updates
The 2023 addendum to the S3 guidelines covers the prophylaxis, diagnosis, and treatment of HBV, including HDV management.
IARC experts also re-evaluated the human cytomegalovirus and Merkel cell polyomavirus. Complete assessments are expected in the next edition of IARC Monographs.
HBV Vaccination
HBV vaccination is the only effective prophylaxis against HBV and HDV. Introduced in 1982 for high-risk groups, it reduced chronic infections, with the WHO expanding its recommendations from 1992 onward.
Infants and young children are at the highest risk of developing this disease. Acute HBV infection often resolves in adults, but infants face up to a 90% risk of developing chronic infection. Newborns of mothers with chronic or undiagnosed HBV infections are particularly vulnerable.
Routine infant immunization includes three doses, with the first dose administered within 12 hours of birth. In Germany, the Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) recommends the administration of combination vaccines, with the hexavalent vaccine administered at 2, 4, and 11 months in a 2 + 1 schedule.
Timely vaccination is crucial because undetected chronic infections often lead to late-stage HCC diagnosis. Adults in high-risk groups should receive HBV vaccination counseling.
STIKO recommends vaccination for close contacts of individuals who are HBsAg-positive, individuals with high-risk sexual contacts, immunocompromised persons, and those with preexisting conditions that increase the risk for severe HBV infection.
Since 2021, insured adults aged 35 years or older in Germany have undergone one-time HBV and HCV screening. HDV testing is recommended for all HBsAg-positive patients. Current frameworks may miss cases, and additional or personalized screening could improve the detection of previously unrecognized infections.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) of the World Health Organization has classified hepatitis D virus (HDV) as carcinogenic, citing sufficient evidence and placing it alongside hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Individuals with HBV-HDV coinfection face an elevated risk for liver cancer, highlighting the need for HBV vaccination, systematic screening, and early antiviral treatment to reduce the progression to cirrhosis and HCC.
About 12 million people globally have HBV-HDV coinfection, representing 5% of all chronic HBV cases. The prevalence of this condition varies regionally, with a likely underdiagnosis. True coinfection rates may reach 13%-14%, the highest in Europe’s Mediterranean region.
Virus Biology
HDV is an incomplete virus that infects hepatocytes and requires the envelope protein of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) for cell exit. Infection occurs only with chronic HBV infection, either as a superinfection or simultaneous acquisition. Humans are the only known natural host.
HDV coinfection worsens HBV-induced hepatic inflammation and prognosis, and up to 80% of patients develop cirrhosis. Triple infection with the HBV virus, HDV, and HIV further increases this risk, and the global prevalence is likely underestimated.
Cancer Risk
HDV infection significantly increases the risk for HCC compared with HBV infection alone. Many patients die from decompensated cirrhosis or HCC, reflecting the aggressive nature of coinfection.
The molecular mechanisms underlying HDV oncogenesis remain unclear. Research conducted over the past 15 years has provided insights that could inform the development of more effective treatments.
Early vaccination prophylaxis is critical for reducing the risk for HCC, despite limited options.
Treatment Options
Randomized controlled trials have demonstrated antiviral efficacy for:
- Pegylated interferon alpha (Peg-IFN) is approved for HBV and is active against HDV.
- Bulevirtide, a synthetic myristoylated lipopeptide entry inhibitor, is used alone or in combination with Peg-IFN.
Suppression of HBV remains central. Nucleoside and nucleotide analogs, such as entecavir, tenofovir alafenamide fumarate, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, significantly reduce HCC progression in treated patients compared with untreated patients at risk.
Promising therapeutics include lonafarnib, a farnesyltransferase inhibitor that blocks HDV particle formation, and nucleic acid polymers targeting the host chaperone DNAJB12 to inhibit HBV and HDV replication.
Guideline Updates
The 2023 addendum to the S3 guidelines covers the prophylaxis, diagnosis, and treatment of HBV, including HDV management.
IARC experts also re-evaluated the human cytomegalovirus and Merkel cell polyomavirus. Complete assessments are expected in the next edition of IARC Monographs.
HBV Vaccination
HBV vaccination is the only effective prophylaxis against HBV and HDV. Introduced in 1982 for high-risk groups, it reduced chronic infections, with the WHO expanding its recommendations from 1992 onward.
Infants and young children are at the highest risk of developing this disease. Acute HBV infection often resolves in adults, but infants face up to a 90% risk of developing chronic infection. Newborns of mothers with chronic or undiagnosed HBV infections are particularly vulnerable.
Routine infant immunization includes three doses, with the first dose administered within 12 hours of birth. In Germany, the Standing Committee on Vaccination (STIKO) recommends the administration of combination vaccines, with the hexavalent vaccine administered at 2, 4, and 11 months in a 2 + 1 schedule.
Timely vaccination is crucial because undetected chronic infections often lead to late-stage HCC diagnosis. Adults in high-risk groups should receive HBV vaccination counseling.
STIKO recommends vaccination for close contacts of individuals who are HBsAg-positive, individuals with high-risk sexual contacts, immunocompromised persons, and those with preexisting conditions that increase the risk for severe HBV infection.
Since 2021, insured adults aged 35 years or older in Germany have undergone one-time HBV and HCV screening. HDV testing is recommended for all HBsAg-positive patients. Current frameworks may miss cases, and additional or personalized screening could improve the detection of previously unrecognized infections.
This story was translated from Univadis Germany.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
PHOENIX – Medications used in oncology clinical trials pose unique challenges in areas such as labeling, packaging, and administration, a US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) pharmacist cautioned colleagues, and placebos have special needs too.
Even basic safety protections can be lacking when a drug is investigational, said Emily Hennes, PharmD, BCOP, clinical pharmacy specialist for research at William S. Middleton Memorial Veterans Hospital in Shorewood Hills, Wisconsin, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology.
“All of the safety features that we have come to know and love in dispensing commercial drugs are absent. There’s no Tall Man lettering, there's no color differentiation, and there's no barcoding, because these are not registered drugs," she said.
A 2017 report found that 81% of pharmacists surveyed indicated some level of concern regarding the safety risk in using investigational drugs. At the same time, Hennes noted, the Joint Commission has mandated that pharmacists must control the storage, dispensing, labeling, and distribution of investigational medications.
Here are things to know about the use of investigational cancer drugs:
Drug Interactions Are Common
Hennes highlighted a 2023 study of medication reconciliation of 501 patients in 79 clinical trials that found alarming levels of drug interactions:
• 360 clinically relevant drug-drug interactions were identified among 189 patients, including 158 therapies that were prohibited by protocols. Of these, 57.7% involved cytochrome P450 enzymes, which are involved in metabolism.
• Reconciliation revealed that 35.2% of medications were not otherwise known or documented.
• A median of 2 previously unknown therapies per patient was discovered in 74% of patients.
• Alternative medicine products such as supplements and over-the-counter drugs were implicated in 60% of identified drug interactions.
• Only 41% of oncologists discussed alternative medicine use with patients, which Hennes attributed to “lack of familiarity with many alternative medicine products or insufficient training.”
To make things more complicated, “We sometimes don’t know the full pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile of an investigational agent,” she said.
Naming and Labeling May Not Be Standard
Investigational products may not have genetic names and instead have an alphanumeric identifier such as INV54826 that can be quite similar to other products, she said. Investigational drugs may even go through name changes, forcing pharmacists to be alerted to protect patients.
In addition, labeling may not be standardized. Drugs may arrive unlabeled, with the wrong volume and size, and lack of barcoding. In some cases, pharmacists choose to put new, patient-friendly labels on these products, Hennes said.
Information Distribution is Key
“Something that comes up in our practice quite a bit is that there’s no standard drug reference regarding investigational drugs,” Hennes said. “Finding ways to get key information to staff at the point of care is really critical to make sure we’re able to safely treat our patients.”
Precautions May Be Needed to Maintain Blinding Protocols
Hennes explained that pharmacists must use opaque brown bag covers to maintain blinding when parenteral products have distinctive colors. Lines may have to be covered too, which can create challenges during administration.
“Pumps aren’t meant to run lines that are covered,” she said, which can lead to jams. “If you don’t do education with your point of care staff, it can cause a lot of confusion.”
It’s also important for blinding purposes to keep an eye on how long it takes to prepare a treatment, she said. A study’s integrity, for example, could be violated if a complex investigational product takes an hour to equilibrate to room temperature and 20-30 minutes to prepare, while a placebo only requires “drawing a few mils of saline out of a bag and labeling it.”
Education for Patients Can Be Useful
Hennes urged colleagues to remind patients to save investigational medication at the end of each cycle and return it to the clinic site for accountability.
She also suggested creating treatment calendars/reminders for patients and discussing
Hennes reported no disclosures.
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Don't Treat Investigational Cancer Drugs Like Other Medications
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
TOPLINE:
The incidence of skin cancer in England varied by ethnicity: White individuals had higher rates of melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma than Asian or Black individuals. In contrast, acral lentiginous melanoma was most common among Black individuals, whereas cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Kaposi sarcoma were highest among those in the "Other" ethnic group.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analysed all cases of cutaneous melanoma (melanoma and acral lentiginous melanoma), basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and Kaposi sarcoma using data from the NHS National Disease Registration Service cancer registry between 2013 and 2020.
- Data collection incorporated ethnicity information from multiple health care datasets, including Clinical Outcomes and Services Dataset, Patient Administration System, Radiotherapy Dataset, Diagnostic Imaging Dataset, and Hospital Episode Statistics.
- A population analysis categorised patients into 7 standardised ethnic groups (on the basis of Office for National Statistics classifications): White, Asian, Chinese, Black, mixed, other, and unknown groups, with ethnicity data being self-reported by patients.
- Outcomes included European age-standardised rates calculated using the 2013 European Standard Population and reported per 100,000 person-years (PYs).
TAKEAWAY:
- White Individuals had 13-fold higher rates of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (61.75 per 100,000 PYs), 26-fold and 27-fold higher rates of basal cell carcinoma (153.69 per 100,000 PYs), and 33-fold and 16-fold higher rates of cutaneous melanoma (27.29 per 100,000 PYs) than Asian and Black individuals, respectively.
- Black individuals had the highest incidence of acral lentiginous melanoma (0.85 per 100,000 PYs), and those in the other ethnic group had the highest incidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (1.74 per 100,000 PYs) and Kaposi sarcoma (1.57 per 100,000 PYs).
- The presentation of early-stage melanoma was low among Asian (53.5%), Black (62.4%), mixed (62.5%), and other (76.4%) ethnic groups compared to that among White ethnicities (79.8%).
- Acral lentiginous melanomas were less likely to get urgent suspected cancer pathway referrals than overall melanoma (40.1% vs 44.6%; P < .001) and more likely to be diagnosed late than overall melanoma (stage I/II at diagnosis; 72% vs 80%; P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE:
"The findings emphasise the need for better, targeted ethnicity data collection strategies to address incidence, outcomes and health care equity for not just skin cancer but all health conditions in underserved populations," the authors wrote. "While projects like the Global Burden of Disease have improved global health care reporting, continuous audit and improvement of collected data are essential to provide better care across people of all ethnicities."
SOURCE:
This study was led by Shehnaz Ahmed, British Association of Dermatologists, London, England. It was published online on September 10, 2025, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Census data collection after every 10 years could have contributed to inaccurate population estimates and incidence rates. Small sample sizes in certain ethnic groups could have led to potential confounders, requiring a cautious interpretation of relative incidence. The NHS data included only self-reported ethnicity data with no available details of skin phototypes, skin tones, or racial ancestry. This study lacked granular ethnicity census data and stage data for basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous small cell carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported through a partnership between the British Association of Dermatologists and NHS England's National Disease Registration Service. Two authors reported being employees of the British Association of Dermatologists.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The incidence of skin cancer in England varied by ethnicity: White individuals had higher rates of melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma than Asian or Black individuals. In contrast, acral lentiginous melanoma was most common among Black individuals, whereas cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Kaposi sarcoma were highest among those in the "Other" ethnic group.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analysed all cases of cutaneous melanoma (melanoma and acral lentiginous melanoma), basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and Kaposi sarcoma using data from the NHS National Disease Registration Service cancer registry between 2013 and 2020.
- Data collection incorporated ethnicity information from multiple health care datasets, including Clinical Outcomes and Services Dataset, Patient Administration System, Radiotherapy Dataset, Diagnostic Imaging Dataset, and Hospital Episode Statistics.
- A population analysis categorised patients into 7 standardised ethnic groups (on the basis of Office for National Statistics classifications): White, Asian, Chinese, Black, mixed, other, and unknown groups, with ethnicity data being self-reported by patients.
- Outcomes included European age-standardised rates calculated using the 2013 European Standard Population and reported per 100,000 person-years (PYs).
TAKEAWAY:
- White Individuals had 13-fold higher rates of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (61.75 per 100,000 PYs), 26-fold and 27-fold higher rates of basal cell carcinoma (153.69 per 100,000 PYs), and 33-fold and 16-fold higher rates of cutaneous melanoma (27.29 per 100,000 PYs) than Asian and Black individuals, respectively.
- Black individuals had the highest incidence of acral lentiginous melanoma (0.85 per 100,000 PYs), and those in the other ethnic group had the highest incidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (1.74 per 100,000 PYs) and Kaposi sarcoma (1.57 per 100,000 PYs).
- The presentation of early-stage melanoma was low among Asian (53.5%), Black (62.4%), mixed (62.5%), and other (76.4%) ethnic groups compared to that among White ethnicities (79.8%).
- Acral lentiginous melanomas were less likely to get urgent suspected cancer pathway referrals than overall melanoma (40.1% vs 44.6%; P < .001) and more likely to be diagnosed late than overall melanoma (stage I/II at diagnosis; 72% vs 80%; P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE:
"The findings emphasise the need for better, targeted ethnicity data collection strategies to address incidence, outcomes and health care equity for not just skin cancer but all health conditions in underserved populations," the authors wrote. "While projects like the Global Burden of Disease have improved global health care reporting, continuous audit and improvement of collected data are essential to provide better care across people of all ethnicities."
SOURCE:
This study was led by Shehnaz Ahmed, British Association of Dermatologists, London, England. It was published online on September 10, 2025, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Census data collection after every 10 years could have contributed to inaccurate population estimates and incidence rates. Small sample sizes in certain ethnic groups could have led to potential confounders, requiring a cautious interpretation of relative incidence. The NHS data included only self-reported ethnicity data with no available details of skin phototypes, skin tones, or racial ancestry. This study lacked granular ethnicity census data and stage data for basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous small cell carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported through a partnership between the British Association of Dermatologists and NHS England's National Disease Registration Service. Two authors reported being employees of the British Association of Dermatologists.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The incidence of skin cancer in England varied by ethnicity: White individuals had higher rates of melanoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma than Asian or Black individuals. In contrast, acral lentiginous melanoma was most common among Black individuals, whereas cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and Kaposi sarcoma were highest among those in the "Other" ethnic group.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analysed all cases of cutaneous melanoma (melanoma and acral lentiginous melanoma), basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and Kaposi sarcoma using data from the NHS National Disease Registration Service cancer registry between 2013 and 2020.
- Data collection incorporated ethnicity information from multiple health care datasets, including Clinical Outcomes and Services Dataset, Patient Administration System, Radiotherapy Dataset, Diagnostic Imaging Dataset, and Hospital Episode Statistics.
- A population analysis categorised patients into 7 standardised ethnic groups (on the basis of Office for National Statistics classifications): White, Asian, Chinese, Black, mixed, other, and unknown groups, with ethnicity data being self-reported by patients.
- Outcomes included European age-standardised rates calculated using the 2013 European Standard Population and reported per 100,000 person-years (PYs).
TAKEAWAY:
- White Individuals had 13-fold higher rates of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (61.75 per 100,000 PYs), 26-fold and 27-fold higher rates of basal cell carcinoma (153.69 per 100,000 PYs), and 33-fold and 16-fold higher rates of cutaneous melanoma (27.29 per 100,000 PYs) than Asian and Black individuals, respectively.
- Black individuals had the highest incidence of acral lentiginous melanoma (0.85 per 100,000 PYs), and those in the other ethnic group had the highest incidence of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (1.74 per 100,000 PYs) and Kaposi sarcoma (1.57 per 100,000 PYs).
- The presentation of early-stage melanoma was low among Asian (53.5%), Black (62.4%), mixed (62.5%), and other (76.4%) ethnic groups compared to that among White ethnicities (79.8%).
- Acral lentiginous melanomas were less likely to get urgent suspected cancer pathway referrals than overall melanoma (40.1% vs 44.6%; P < .001) and more likely to be diagnosed late than overall melanoma (stage I/II at diagnosis; 72% vs 80%; P < .0001).
IN PRACTICE:
"The findings emphasise the need for better, targeted ethnicity data collection strategies to address incidence, outcomes and health care equity for not just skin cancer but all health conditions in underserved populations," the authors wrote. "While projects like the Global Burden of Disease have improved global health care reporting, continuous audit and improvement of collected data are essential to provide better care across people of all ethnicities."
SOURCE:
This study was led by Shehnaz Ahmed, British Association of Dermatologists, London, England. It was published online on September 10, 2025, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Census data collection after every 10 years could have contributed to inaccurate population estimates and incidence rates. Small sample sizes in certain ethnic groups could have led to potential confounders, requiring a cautious interpretation of relative incidence. The NHS data included only self-reported ethnicity data with no available details of skin phototypes, skin tones, or racial ancestry. This study lacked granular ethnicity census data and stage data for basal cell carcinoma, cutaneous small cell carcinoma, and Kaposi sarcoma.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was supported through a partnership between the British Association of Dermatologists and NHS England's National Disease Registration Service. Two authors reported being employees of the British Association of Dermatologists.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
Does Ethnicity Affect Skin Cancer Risk?
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
PHOENIX – Three decades after he initiated the transformation of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) into a model research and clinical health care system, former US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Under Secretary of Health Kenneth W. Kizer, MD, MPH, urged cancer specialists to embrace this challenging moment as an opportunity for bold innovation.
At the annual meeting of the Association of VA Hematology/Oncology (AVAHO), Kizer acknowledged that the VA faces an “uncertain and turbulent time” in areas such as funding, staffing, community care implementation, and the rollout of a new electronic health record system.
He also noted the grim rise of global instability, economic turmoil, climate change, infectious diseases, political violence, and mass shootings.
“This can be stressful. It can create negative energy. But this uncertainty can also be liberating, and it can prompt positive energy and innovation, depending on choices that we make,” said Kizer, who also has served as California’s top health official prior to leading the VHA from 1994 to 1999.
From “Bloated Bureaucracy’ to High-Quality Health Care System
Kizer has been credited with revitalizing VHA care through a greater commitment to quality, and harkened to his work with the VA as an example of how bold goals can lead to bold innovation.
“What were the perceptions of VA health care in 1994? Well, they weren’t very good, frankly,” Kizer recalled. He described the VA as having a reputation at that time as “highly dysfunctional” with “a very bloated and entrenched bureaucracy.” As for quality of care, it “wasn’t viewed as very good.”
The system’s problems were so severe that patients would park motorhomes in VA medical center parking lots as they waited for care. “While they might have an appointment for one day, they may not be seen for 3 or 4 or 5 days. So they would stay in their motorhome until they finally got into their clinic appointment,” Kizer said.
Overall, “the public viewed the VA as this bleak backwater of incompetence and difference and inefficiency, and there were very strong calls to privatize the VA,” Kizer said.
Kizer asked colleagues about what he should do after he was asked to take the under secretary job. “With one exception, they all said, don’t go near it. Don’t touch it. Walk away. That it’s impossible to change the organization.
“I looked at the VA and I saw an opportunity. When I told [members of the President Bill] Clinton [Administration] yes, my bold aim was that I would like to pursue this was to make VHA a model of excellent health care, an exemplary health care system. Most everyone else thought that I was totally delusional, but sometimes it’s good to be delusional.”
Revolutionary Changes Despite Opposition
Kizer sought reforms in 5 major strategic objectives, all without explicit congressional approval: creating an accountable management structure, decentralizing decision-making, integrating care, implementing universal primary care, and pursuing eligibility reform to create the current 8-tier VA system.
One major innovation was the implementation of community-based outpatient clinics (CBOCs): “Those were strongly opposed initially,” Kizer said. “Everyone, the veteran community in particular, had been led to believe that the only good care was in the hospital.”
The resistance was substantial. “There was a lot of opposition when we said we’re going to move out into the community where you live to make [care] easier to access,” Kizer said.
To make things more difficult, Congress wouldn’t fund the project: “For the first 3 years, every CBOC had to be funded by redirected savings from other things that we could do within the system,” he said. “All of this was through redirected savings and finding ways to save and reinvest.”
Innovation From the Ground Up
Kizer emphasized that many breakthrough innovations came from frontline staff rather than executive mandates. He cited the example of Barcode Medication Administration, which originated from a nurse in Topeka, Kan.
The nurse saw a barcode scanner put to work at a rental car company where it was used to check cars in and out. She wondered, “Why can’t we do this with medications when they’re given on the floor? We followed up on it, pursued those things, tested it out, it worked.”
The results were dramatic. “I was told at a meeting that they had achieved close to 80% reduction in medication errors,” Kizer said. After verifying the results personally, he “authorized $20 million, and we moved forward with it systemwide.”
This experience reinforced his belief in harvesting ideas from staff at all levels.
Innovation remains part of the VA’s culture “despite what some people would have you believe,” Kizer said. Recently, the VA has made major advances in areas such as patient transportation and the climate crisis, he said.
Inside the Recipe for Innovation
Boldness, persistence, adaptability, and tolerance for risk are necessary ingredients for high-risk goals, Kizer said. Ambition is also part of the picture.
He highlighted examples such as the Apollo moon landing, the first sub-4-minute mile, and the first swim across the English Channel by a woman.
In medicine, Kizer pointed to a national patient safety campaign that saved an estimated 122,000 lives. He also mentioned recent progress in organ transplantation such as recommendations from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine to establish national performance goals and the Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network’s target of 60,000 deceased donor transplants by 2026.
Bold doesn’t mean being reckless or careless, Kizer said. “But it does require innovation. And it does require that you try some new things, some of which aren’t going to work out.”
The key mindset, he explained, is to “embrace the unknown” because “you often really don’t know how you will accomplish the aim when you start. But you’ll figure it out as you go.”
Kizer highlighted 2 opposing strategies to handling challenging times.
According to him, the “negative energy” approach focuses on frustrations, limitations, and asking “Why is this happening to me?”
In contrast, a “positive energy” approach expects problems, focuses on available resources and capabilities, and asks, “What are the opportunities that these changes are creating for me?”
Kizer made it crystal clear which option he prefers.
Dr. Kizer disclosed that his comments represent his opinions only, and he noted his ongoing connections to the VA.
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty
Architect of VA Transformation Urges Innovation Amid Uncertainty