User login
AGA News
Receive $300,000 for your research in health disparities
Applications for the research scholar award are due by Nov. 9, 2020.
The American Gastroenterological Association Research Foundation is pleased to announce an important addition to its prestigious awards portfolio. The AGA Research Scholar Award in Digestive Disease Health Disparities supports early-career faculty dedicated to investigating digestive diseases or disorders that disproportionately affect racial or ethnic minority populations in North America.
Applicants must have a full-time faculty (or equivalent) position and may be performing any type of research (clinical, basic, or translational). Awardees will receive a total of $300,000 over 3 years with funding to commence in July 2021. The deadline to apply is Nov. 9, 2020.
This award is just one example of how AGA is helping to improve patient care for those who need it most. Support AGA Giving Day and learn more about the AGA Equity Project – a multiyear effort spanning all aspects of our organization to achieve equity and eradicate disparities in digestive diseases.
Save the date for DDW Virtual™
In 2021, Digestive Disease Week® moves online as a fully virtual meeting with slightly new dates: May 21-23, 2021.
For more than 50 years, the digestive disease community has connected over the best science, education, and networking at DDW, and we’re confident this year will be no exception. In fact, we’re excited by opportunities the new format provides to learn, share, and connect with each other.
Watch the DDW website for more information as it becomes available. In the meantime, check out our FAQs about DDW Virtual™. If you have a question we didn’t answer, please submit a ticket to our help desk.
DDW is jointly sponsored by AGA, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
Virtual 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress® now open for registration
Help forge the roadmap to advance prevention, treatments, and cures for all patients living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Join the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation, AGA, and a true community of friends and colleagues at the premier conference on IBD. The fourth annual Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, taking place virtually Jan. 21-24, 2021, is now open for registration.
The 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress virtual experience will look a little different but will still bring you all the benefits and quality programming you have come to expect. The Congress will offer 4 days of learning, with more than 100 speakers and more than 200 expected abstracts – all from the safety of your home or work. Now at an even more affordable price, access from anywhere, and the ability to hear from the top leaders in the IBD field – this is a unique opportunity to join us as we come together virtually.
By moving our event online, we can now pass on greater savings to you. Registration for the conference provides you with substantial savings over last year and access to all sessions and networking opportunities. This virtual experience will bring our community of IBD professionals together in an engaging, interactive setting which will include breakout rooms, receptions, and much more.
The 2021 congress committee chair David T. Rubin, MD, AGAF, University of Chicago, and cochair Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, AGAF, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, lead a faculty that includes thought leaders in the fields of GI, research investigation, surgery, pediatrics, advanced practice, IBD nursing, diet and nutrition, mental health, radiology, pathology, and more.
Register and get inspired to improve skills and patient outcomes, learn practical information you can immediately implement, hear what’s on the horizon in potential IBD treatments, discover fresh perspectives from multidisciplinary faculty and attendees.
You don’t want to miss the 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, connecting virtually on Jan. 21-24, 2021.
Register today to save before the early bird deadline of Friday, Nov. 6.
Learn more, submit an abstract, and register by visiting crohnscolitiscongress.org.
AGA releases largest real-world report on safety and effectiveness of fecal microbiota transplantation
About 90% of patients tracked in the AGA FMT National Registry were cured of Clostridioides difficile infection with few serious side effects.
AGA has released the first results from the NIH-funded AGA Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) National Registry, the largest real-world study on the safety and effectiveness of FMT. Published in Gastroenterology, the registry reported that FMT led to a cure of C. difficile infection in 90% of patients across 20 North American FMT practice sites. Few serious side effects were reported.
“While the value of fecal microbiota transplantation for treating recurrent C. difficile infection is clear from research studies, the potential long-term consequences of altering a patient’s gut microbiota are not fully known,” says Colleen R. Kelly, MD, AGAF, associate professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I. and coprincipal investigator of the AGA FMT National Registry. “Releasing the initial results of the AGA FMT National Registry is an important step toward understanding the true risks and benefits of microbiota therapeutics in a real-world setting.”
This new report details effectiveness and safety outcomes from the first 259 patients enrolled in the registry between December 2017 and September 2019. Almost all participants received FMT using an unknown donor from stool banks. The most common method of FMT delivery was colonoscopy followed by upper endoscopy. Of the 222 participants who returned for the 1-month follow-up, 200 participants (90%) had their C. difficile infection cured with 197 of those requiring only a single FMT. Infections were reported in 11 participants, but only 2 were thought to be possibly related to the procedure. FMT response was deemed durable, with recurrence of C. difficile infection in the 6 months after successful FMT occurring in only 4% of participants. This data includes patients with comorbidities, such as IBD and immunocompromised status, who are typically excluded from FMT clinical trials.
“These initial results show a high success rate of FMT in the real-world setting. We’ll continue to track these patients for 10 years to assess long-term safety, which will be critical to determining the full safety profile of FMT,” added Dr. Kelly.
AGA raises concerns about recent executive order
We are speaking out to ensure a brighter and more equitable future.
AGA is concerned by the Executive Order on Combating Race and Sex Stereotyping issued on Sept. 22, 2020. This order, while confirming that training of the federal workforce to create an inclusive workspace is beneficial, also leads to a misguided perception of the purpose and outcomes of this type of training. In addition, it may have unintended ramifications for institutions receiving federal research funding.
We believe it is critical and necessary to understand both the positive and negative realities of our nation’s history, so that together we can forge forward into a brighter, and more equitable future.
As highlighted in AGA’s commentary published in Gastroenterology, AGA believes that equity is defined by fair treatment, access, opportunity, and advancement for all, acknowledging that there are historically underserved and underrepresented populations. Equity requires identifying and eliminating barriers that have created unbalanced conditions and prevented the full participation of some groups in order to provide equal opportunity for all groups.
By default, teaching and practicing equity, diversity and inclusion aims not to place any group above or below any other group, or to create division. It rather seeks to achieve fairness and understanding, and fully recognize the dignity of all groups, identities, and individuals.
AGA stands with the Association of American Medical Colleges in our commitment to being a diverse, inclusive, equitable, and antiracist organization.
Our commitment to this issue is manifest in the AGA Equity Project.
Receive $300,000 for your research in health disparities
Applications for the research scholar award are due by Nov. 9, 2020.
The American Gastroenterological Association Research Foundation is pleased to announce an important addition to its prestigious awards portfolio. The AGA Research Scholar Award in Digestive Disease Health Disparities supports early-career faculty dedicated to investigating digestive diseases or disorders that disproportionately affect racial or ethnic minority populations in North America.
Applicants must have a full-time faculty (or equivalent) position and may be performing any type of research (clinical, basic, or translational). Awardees will receive a total of $300,000 over 3 years with funding to commence in July 2021. The deadline to apply is Nov. 9, 2020.
This award is just one example of how AGA is helping to improve patient care for those who need it most. Support AGA Giving Day and learn more about the AGA Equity Project – a multiyear effort spanning all aspects of our organization to achieve equity and eradicate disparities in digestive diseases.
Save the date for DDW Virtual™
In 2021, Digestive Disease Week® moves online as a fully virtual meeting with slightly new dates: May 21-23, 2021.
For more than 50 years, the digestive disease community has connected over the best science, education, and networking at DDW, and we’re confident this year will be no exception. In fact, we’re excited by opportunities the new format provides to learn, share, and connect with each other.
Watch the DDW website for more information as it becomes available. In the meantime, check out our FAQs about DDW Virtual™. If you have a question we didn’t answer, please submit a ticket to our help desk.
DDW is jointly sponsored by AGA, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
Virtual 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress® now open for registration
Help forge the roadmap to advance prevention, treatments, and cures for all patients living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Join the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation, AGA, and a true community of friends and colleagues at the premier conference on IBD. The fourth annual Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, taking place virtually Jan. 21-24, 2021, is now open for registration.
The 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress virtual experience will look a little different but will still bring you all the benefits and quality programming you have come to expect. The Congress will offer 4 days of learning, with more than 100 speakers and more than 200 expected abstracts – all from the safety of your home or work. Now at an even more affordable price, access from anywhere, and the ability to hear from the top leaders in the IBD field – this is a unique opportunity to join us as we come together virtually.
By moving our event online, we can now pass on greater savings to you. Registration for the conference provides you with substantial savings over last year and access to all sessions and networking opportunities. This virtual experience will bring our community of IBD professionals together in an engaging, interactive setting which will include breakout rooms, receptions, and much more.
The 2021 congress committee chair David T. Rubin, MD, AGAF, University of Chicago, and cochair Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, AGAF, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, lead a faculty that includes thought leaders in the fields of GI, research investigation, surgery, pediatrics, advanced practice, IBD nursing, diet and nutrition, mental health, radiology, pathology, and more.
Register and get inspired to improve skills and patient outcomes, learn practical information you can immediately implement, hear what’s on the horizon in potential IBD treatments, discover fresh perspectives from multidisciplinary faculty and attendees.
You don’t want to miss the 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, connecting virtually on Jan. 21-24, 2021.
Register today to save before the early bird deadline of Friday, Nov. 6.
Learn more, submit an abstract, and register by visiting crohnscolitiscongress.org.
AGA releases largest real-world report on safety and effectiveness of fecal microbiota transplantation
About 90% of patients tracked in the AGA FMT National Registry were cured of Clostridioides difficile infection with few serious side effects.
AGA has released the first results from the NIH-funded AGA Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) National Registry, the largest real-world study on the safety and effectiveness of FMT. Published in Gastroenterology, the registry reported that FMT led to a cure of C. difficile infection in 90% of patients across 20 North American FMT practice sites. Few serious side effects were reported.
“While the value of fecal microbiota transplantation for treating recurrent C. difficile infection is clear from research studies, the potential long-term consequences of altering a patient’s gut microbiota are not fully known,” says Colleen R. Kelly, MD, AGAF, associate professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I. and coprincipal investigator of the AGA FMT National Registry. “Releasing the initial results of the AGA FMT National Registry is an important step toward understanding the true risks and benefits of microbiota therapeutics in a real-world setting.”
This new report details effectiveness and safety outcomes from the first 259 patients enrolled in the registry between December 2017 and September 2019. Almost all participants received FMT using an unknown donor from stool banks. The most common method of FMT delivery was colonoscopy followed by upper endoscopy. Of the 222 participants who returned for the 1-month follow-up, 200 participants (90%) had their C. difficile infection cured with 197 of those requiring only a single FMT. Infections were reported in 11 participants, but only 2 were thought to be possibly related to the procedure. FMT response was deemed durable, with recurrence of C. difficile infection in the 6 months after successful FMT occurring in only 4% of participants. This data includes patients with comorbidities, such as IBD and immunocompromised status, who are typically excluded from FMT clinical trials.
“These initial results show a high success rate of FMT in the real-world setting. We’ll continue to track these patients for 10 years to assess long-term safety, which will be critical to determining the full safety profile of FMT,” added Dr. Kelly.
AGA raises concerns about recent executive order
We are speaking out to ensure a brighter and more equitable future.
AGA is concerned by the Executive Order on Combating Race and Sex Stereotyping issued on Sept. 22, 2020. This order, while confirming that training of the federal workforce to create an inclusive workspace is beneficial, also leads to a misguided perception of the purpose and outcomes of this type of training. In addition, it may have unintended ramifications for institutions receiving federal research funding.
We believe it is critical and necessary to understand both the positive and negative realities of our nation’s history, so that together we can forge forward into a brighter, and more equitable future.
As highlighted in AGA’s commentary published in Gastroenterology, AGA believes that equity is defined by fair treatment, access, opportunity, and advancement for all, acknowledging that there are historically underserved and underrepresented populations. Equity requires identifying and eliminating barriers that have created unbalanced conditions and prevented the full participation of some groups in order to provide equal opportunity for all groups.
By default, teaching and practicing equity, diversity and inclusion aims not to place any group above or below any other group, or to create division. It rather seeks to achieve fairness and understanding, and fully recognize the dignity of all groups, identities, and individuals.
AGA stands with the Association of American Medical Colleges in our commitment to being a diverse, inclusive, equitable, and antiracist organization.
Our commitment to this issue is manifest in the AGA Equity Project.
Receive $300,000 for your research in health disparities
Applications for the research scholar award are due by Nov. 9, 2020.
The American Gastroenterological Association Research Foundation is pleased to announce an important addition to its prestigious awards portfolio. The AGA Research Scholar Award in Digestive Disease Health Disparities supports early-career faculty dedicated to investigating digestive diseases or disorders that disproportionately affect racial or ethnic minority populations in North America.
Applicants must have a full-time faculty (or equivalent) position and may be performing any type of research (clinical, basic, or translational). Awardees will receive a total of $300,000 over 3 years with funding to commence in July 2021. The deadline to apply is Nov. 9, 2020.
This award is just one example of how AGA is helping to improve patient care for those who need it most. Support AGA Giving Day and learn more about the AGA Equity Project – a multiyear effort spanning all aspects of our organization to achieve equity and eradicate disparities in digestive diseases.
Save the date for DDW Virtual™
In 2021, Digestive Disease Week® moves online as a fully virtual meeting with slightly new dates: May 21-23, 2021.
For more than 50 years, the digestive disease community has connected over the best science, education, and networking at DDW, and we’re confident this year will be no exception. In fact, we’re excited by opportunities the new format provides to learn, share, and connect with each other.
Watch the DDW website for more information as it becomes available. In the meantime, check out our FAQs about DDW Virtual™. If you have a question we didn’t answer, please submit a ticket to our help desk.
DDW is jointly sponsored by AGA, the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract.
Virtual 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress® now open for registration
Help forge the roadmap to advance prevention, treatments, and cures for all patients living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Join the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation, AGA, and a true community of friends and colleagues at the premier conference on IBD. The fourth annual Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, taking place virtually Jan. 21-24, 2021, is now open for registration.
The 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress virtual experience will look a little different but will still bring you all the benefits and quality programming you have come to expect. The Congress will offer 4 days of learning, with more than 100 speakers and more than 200 expected abstracts – all from the safety of your home or work. Now at an even more affordable price, access from anywhere, and the ability to hear from the top leaders in the IBD field – this is a unique opportunity to join us as we come together virtually.
By moving our event online, we can now pass on greater savings to you. Registration for the conference provides you with substantial savings over last year and access to all sessions and networking opportunities. This virtual experience will bring our community of IBD professionals together in an engaging, interactive setting which will include breakout rooms, receptions, and much more.
The 2021 congress committee chair David T. Rubin, MD, AGAF, University of Chicago, and cochair Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS, AGAF, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, lead a faculty that includes thought leaders in the fields of GI, research investigation, surgery, pediatrics, advanced practice, IBD nursing, diet and nutrition, mental health, radiology, pathology, and more.
Register and get inspired to improve skills and patient outcomes, learn practical information you can immediately implement, hear what’s on the horizon in potential IBD treatments, discover fresh perspectives from multidisciplinary faculty and attendees.
You don’t want to miss the 2021 Crohn’s & Colitis Congress, connecting virtually on Jan. 21-24, 2021.
Register today to save before the early bird deadline of Friday, Nov. 6.
Learn more, submit an abstract, and register by visiting crohnscolitiscongress.org.
AGA releases largest real-world report on safety and effectiveness of fecal microbiota transplantation
About 90% of patients tracked in the AGA FMT National Registry were cured of Clostridioides difficile infection with few serious side effects.
AGA has released the first results from the NIH-funded AGA Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT) National Registry, the largest real-world study on the safety and effectiveness of FMT. Published in Gastroenterology, the registry reported that FMT led to a cure of C. difficile infection in 90% of patients across 20 North American FMT practice sites. Few serious side effects were reported.
“While the value of fecal microbiota transplantation for treating recurrent C. difficile infection is clear from research studies, the potential long-term consequences of altering a patient’s gut microbiota are not fully known,” says Colleen R. Kelly, MD, AGAF, associate professor of medicine at Brown University, Providence, R.I. and coprincipal investigator of the AGA FMT National Registry. “Releasing the initial results of the AGA FMT National Registry is an important step toward understanding the true risks and benefits of microbiota therapeutics in a real-world setting.”
This new report details effectiveness and safety outcomes from the first 259 patients enrolled in the registry between December 2017 and September 2019. Almost all participants received FMT using an unknown donor from stool banks. The most common method of FMT delivery was colonoscopy followed by upper endoscopy. Of the 222 participants who returned for the 1-month follow-up, 200 participants (90%) had their C. difficile infection cured with 197 of those requiring only a single FMT. Infections were reported in 11 participants, but only 2 were thought to be possibly related to the procedure. FMT response was deemed durable, with recurrence of C. difficile infection in the 6 months after successful FMT occurring in only 4% of participants. This data includes patients with comorbidities, such as IBD and immunocompromised status, who are typically excluded from FMT clinical trials.
“These initial results show a high success rate of FMT in the real-world setting. We’ll continue to track these patients for 10 years to assess long-term safety, which will be critical to determining the full safety profile of FMT,” added Dr. Kelly.
AGA raises concerns about recent executive order
We are speaking out to ensure a brighter and more equitable future.
AGA is concerned by the Executive Order on Combating Race and Sex Stereotyping issued on Sept. 22, 2020. This order, while confirming that training of the federal workforce to create an inclusive workspace is beneficial, also leads to a misguided perception of the purpose and outcomes of this type of training. In addition, it may have unintended ramifications for institutions receiving federal research funding.
We believe it is critical and necessary to understand both the positive and negative realities of our nation’s history, so that together we can forge forward into a brighter, and more equitable future.
As highlighted in AGA’s commentary published in Gastroenterology, AGA believes that equity is defined by fair treatment, access, opportunity, and advancement for all, acknowledging that there are historically underserved and underrepresented populations. Equity requires identifying and eliminating barriers that have created unbalanced conditions and prevented the full participation of some groups in order to provide equal opportunity for all groups.
By default, teaching and practicing equity, diversity and inclusion aims not to place any group above or below any other group, or to create division. It rather seeks to achieve fairness and understanding, and fully recognize the dignity of all groups, identities, and individuals.
AGA stands with the Association of American Medical Colleges in our commitment to being a diverse, inclusive, equitable, and antiracist organization.
Our commitment to this issue is manifest in the AGA Equity Project.
Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic fluid collections
Pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are common after acute pancreatitis but almost always resolve spontaneously. Persistent collections that cause symptoms, become infected, and/or compress vital structures require treatment. Open surgery had traditionally been considered the standard method for this indication;1 Given its inherently less invasive nature, endoscopic transmural drainage (ETMD) has become a mainstay of this step-up philosophy – it is now the dominant strategy for pseudocyst drainage and, on the basis of emerging randomized trial data, compares very favorably with surgery for the treatment of walled-off necrosis (WON).
According to the step-up approach, the initial treatment of symptomatic and/or infected collections that are within 4 weeks of an attack of pancreatitis involves conservative management because the wall of the collection is typically immature; the systemic inflammation may be significantly exacerbated by definitive drainage, particularly surgery. In this early phase, failure of conservative management is addressed by percutaneous catheter placement, stepping up to a minimally invasive operation if the response to percutaneous drainage and antibiotics is insufficient.
Collections that are at least 4 weeks from the onset of acute pancreatitis are considered mature and termed pseudocysts or WONs depending on whether they contain pure fluid or necrotic tissue. In this phase, endoscopic treatment plays a primary management role because these collections are generally adherent to the stomach or duodenal wall and their capsule is organized enough to withstand endoscopic intervention. If treatment can be held off until this phase, then percutaneous and surgical drainage can often be avoided.
In practice, the 4-week rule holds true for most, but not all, PFCs. ETMD can be performed in some particularly mature collections prior to 4 weeks if the indication is strong and the collection appears to have a mature wall. However, the potential for cyst wall perforation is higher and should be considered in the risk-benefit discussion. Conversely, some collections beyond 4 weeks lack an adequately organized wall and require additional time for maturation.
While endoscopic drainage of pseudocysts has essentially supplanted surgery, the management of WON is more complex and remains multidisciplinary. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated no difference in major complications and/or death between a surgical and endoscopic step-up strategy for WON.2,3 Rates of pancreatic fistulae, hospital stay, and overall treatment costs, however, favored endoscopy. Nevertheless, defining the ideal strategy for many of these patients with complexity requires multidisciplinary discussion. Surgery continues to play a primary role in several scenarios, including collections that are not close to the upper GI tract, those that are particularly complex and extend caudally, and situations in which the endoscopic progress is too slow.
The three most important questions when deciding to embark on ETMD are: (1) whether drainage is indicated (that is, is the patient symptomatic or is there evidence that the PFC is infected?), (2) whether the wall of the collection is adequately mature and apposed to the GI tract wall; and (3) whether the collection contains necrosis? This last question has critical implications in the technical approach to drainage. While CT scan with IV contrast is accurate for assessing wall maturity, it is inadequate to evaluate the presence or quantity of necrosum. Transabdominal ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound, and MRI (on a T2 sequence) are all superior for this purpose. MRI has the additional benefit of assessing the pancreatic duct integrity, which may influence subsequent management.
Pseudocysts can be managed by cyst-gastrostomy or cyst-duodenostomy alone, whereas most WONs require the additional step of endoscopic necrosectomy – the process of entering the cyst cavity to mechanically debride necrotic tissue. Because of a higher rate of technical success, endoscopic ultrasound–directed creation of the transmural drainage pathway has become standard practice. In addition, it is likely safer, allowing for the identification and avoidance of interceding vessels and other vital structures. The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with pancreatic stent placement as primary therapy for PFCs is limited to the drainage of small collections (<5 cm), for which it is the preferred treatment strategy. It is as effective as ETMD, which may not be feasible or safe for small PFCs.
Plastic double-pigtail stents have traditionally been used to maintain the transmural tract for both pseudocyst and WON. Recently, however, metallic stents have become more popular. Fully covered biliary self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) are easier to place, have a larger lumen, and are associated with improved outcomes, compared with plastic stents in observational studies of pseudocyst drainage. Lumen-apposing metallic stents (LAMS) have become the preferred prosthesis for WON drainage given the ability to near-simultaneously establish access and deploy the stent, as well as their much larger caliber lumen which permits seamless entry into the cavity with an endoscope. Based on ease and efficiency of use, LAMS are also commonly employed for pseudocyst drainage, although entry into the cavity is unnecessary.
Plastic stents have been shown to be more cost effective than LAMS for pseudocyst drainage, although the economics around biliary SEMS in this context have not been explored. Robust comparative effectiveness data defining the optimal prostheses for pseudocysts are needed. The literature comparing LAMS to plastic stents for the management of WON is mixed. Studies have shown LAMS to be more cost effective, but a small randomized trial demonstrated no difference in clinical success or in the number of procedures to achieve WON resolution.4 We generally favor LAMS for WON since large-caliber balloon dilation of the tract seems safer within the lumen of the LAMS (which could seal small perforations and tamponade bleeding vessels) than within a freshly created tract.
Secondary infection of the cavity, usually because of stent occlusion, and bleeding are the most common complications of ETMD. Even in the absence of stent occlusion, contamination of the collection after ETMD is ubiquitous and, as such, we prescribe prophylactic antibiotics for 1-2 weeks after the procedure, although this practice is not evidence based. Hemorrhage appears to be increasing in frequency with the diffusion of LAMS; this has been postulated to be due to particularly rapid cyst cavity collapse resulting in erosion of the stent into contralateral cyst wall vessels. CT angiography followed by an embolization procedure for a possible pseudoaneurysm is the mainstay of treatment. Serious venous bleeding is more challenging to address because angiographic options are limited.
Despite tremendous recent advances, several important controversies in the endoscopic management of PFCs persist. The optimal prosthesis, the importance of first-session endoscopic necroscopy (compared with stepping up to endoscopic necroscopy only if necessary), the roles of adjunctive drain placement and chemical debridement (such as hydrogen peroxide), the need for concomitant pancreatic stent placement, and the preferred long-term management of a disconnected pancreatic duct are areas for which additional research is sorely needed. We further discuss these questions and many additional technical considerations pertaining to endoscopic drainage in a recent review.5
In summary, endoscopic transmural drainage of mature PFCs is effective and safe. Existing evidence supports its use as the favored treatment modality in appropriate candidates and has rendered it a mainstay of the therapeutic armamentarium for this disease. Further studies are needed to address critical unanswered questions and to develop a uniform endoscopic management paradigm.
References
1. van Santvoort HC et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(16):1491-502.
2. van Brunschot S et al. Lancet. 2018;391(10115):51-8.
3. Bang JY et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1027-40.
4. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019;68(7):1200-9.
5. Elmunzer BJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(12):1851-63.
Dr. Moran is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; Dr. Elmunzer is the Peter Cotton Professor of Medicine and Endoscopic Innovation, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina. The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this review.
Pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are common after acute pancreatitis but almost always resolve spontaneously. Persistent collections that cause symptoms, become infected, and/or compress vital structures require treatment. Open surgery had traditionally been considered the standard method for this indication;1 Given its inherently less invasive nature, endoscopic transmural drainage (ETMD) has become a mainstay of this step-up philosophy – it is now the dominant strategy for pseudocyst drainage and, on the basis of emerging randomized trial data, compares very favorably with surgery for the treatment of walled-off necrosis (WON).
According to the step-up approach, the initial treatment of symptomatic and/or infected collections that are within 4 weeks of an attack of pancreatitis involves conservative management because the wall of the collection is typically immature; the systemic inflammation may be significantly exacerbated by definitive drainage, particularly surgery. In this early phase, failure of conservative management is addressed by percutaneous catheter placement, stepping up to a minimally invasive operation if the response to percutaneous drainage and antibiotics is insufficient.
Collections that are at least 4 weeks from the onset of acute pancreatitis are considered mature and termed pseudocysts or WONs depending on whether they contain pure fluid or necrotic tissue. In this phase, endoscopic treatment plays a primary management role because these collections are generally adherent to the stomach or duodenal wall and their capsule is organized enough to withstand endoscopic intervention. If treatment can be held off until this phase, then percutaneous and surgical drainage can often be avoided.
In practice, the 4-week rule holds true for most, but not all, PFCs. ETMD can be performed in some particularly mature collections prior to 4 weeks if the indication is strong and the collection appears to have a mature wall. However, the potential for cyst wall perforation is higher and should be considered in the risk-benefit discussion. Conversely, some collections beyond 4 weeks lack an adequately organized wall and require additional time for maturation.
While endoscopic drainage of pseudocysts has essentially supplanted surgery, the management of WON is more complex and remains multidisciplinary. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated no difference in major complications and/or death between a surgical and endoscopic step-up strategy for WON.2,3 Rates of pancreatic fistulae, hospital stay, and overall treatment costs, however, favored endoscopy. Nevertheless, defining the ideal strategy for many of these patients with complexity requires multidisciplinary discussion. Surgery continues to play a primary role in several scenarios, including collections that are not close to the upper GI tract, those that are particularly complex and extend caudally, and situations in which the endoscopic progress is too slow.
The three most important questions when deciding to embark on ETMD are: (1) whether drainage is indicated (that is, is the patient symptomatic or is there evidence that the PFC is infected?), (2) whether the wall of the collection is adequately mature and apposed to the GI tract wall; and (3) whether the collection contains necrosis? This last question has critical implications in the technical approach to drainage. While CT scan with IV contrast is accurate for assessing wall maturity, it is inadequate to evaluate the presence or quantity of necrosum. Transabdominal ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound, and MRI (on a T2 sequence) are all superior for this purpose. MRI has the additional benefit of assessing the pancreatic duct integrity, which may influence subsequent management.
Pseudocysts can be managed by cyst-gastrostomy or cyst-duodenostomy alone, whereas most WONs require the additional step of endoscopic necrosectomy – the process of entering the cyst cavity to mechanically debride necrotic tissue. Because of a higher rate of technical success, endoscopic ultrasound–directed creation of the transmural drainage pathway has become standard practice. In addition, it is likely safer, allowing for the identification and avoidance of interceding vessels and other vital structures. The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with pancreatic stent placement as primary therapy for PFCs is limited to the drainage of small collections (<5 cm), for which it is the preferred treatment strategy. It is as effective as ETMD, which may not be feasible or safe for small PFCs.
Plastic double-pigtail stents have traditionally been used to maintain the transmural tract for both pseudocyst and WON. Recently, however, metallic stents have become more popular. Fully covered biliary self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) are easier to place, have a larger lumen, and are associated with improved outcomes, compared with plastic stents in observational studies of pseudocyst drainage. Lumen-apposing metallic stents (LAMS) have become the preferred prosthesis for WON drainage given the ability to near-simultaneously establish access and deploy the stent, as well as their much larger caliber lumen which permits seamless entry into the cavity with an endoscope. Based on ease and efficiency of use, LAMS are also commonly employed for pseudocyst drainage, although entry into the cavity is unnecessary.
Plastic stents have been shown to be more cost effective than LAMS for pseudocyst drainage, although the economics around biliary SEMS in this context have not been explored. Robust comparative effectiveness data defining the optimal prostheses for pseudocysts are needed. The literature comparing LAMS to plastic stents for the management of WON is mixed. Studies have shown LAMS to be more cost effective, but a small randomized trial demonstrated no difference in clinical success or in the number of procedures to achieve WON resolution.4 We generally favor LAMS for WON since large-caliber balloon dilation of the tract seems safer within the lumen of the LAMS (which could seal small perforations and tamponade bleeding vessels) than within a freshly created tract.
Secondary infection of the cavity, usually because of stent occlusion, and bleeding are the most common complications of ETMD. Even in the absence of stent occlusion, contamination of the collection after ETMD is ubiquitous and, as such, we prescribe prophylactic antibiotics for 1-2 weeks after the procedure, although this practice is not evidence based. Hemorrhage appears to be increasing in frequency with the diffusion of LAMS; this has been postulated to be due to particularly rapid cyst cavity collapse resulting in erosion of the stent into contralateral cyst wall vessels. CT angiography followed by an embolization procedure for a possible pseudoaneurysm is the mainstay of treatment. Serious venous bleeding is more challenging to address because angiographic options are limited.
Despite tremendous recent advances, several important controversies in the endoscopic management of PFCs persist. The optimal prosthesis, the importance of first-session endoscopic necroscopy (compared with stepping up to endoscopic necroscopy only if necessary), the roles of adjunctive drain placement and chemical debridement (such as hydrogen peroxide), the need for concomitant pancreatic stent placement, and the preferred long-term management of a disconnected pancreatic duct are areas for which additional research is sorely needed. We further discuss these questions and many additional technical considerations pertaining to endoscopic drainage in a recent review.5
In summary, endoscopic transmural drainage of mature PFCs is effective and safe. Existing evidence supports its use as the favored treatment modality in appropriate candidates and has rendered it a mainstay of the therapeutic armamentarium for this disease. Further studies are needed to address critical unanswered questions and to develop a uniform endoscopic management paradigm.
References
1. van Santvoort HC et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(16):1491-502.
2. van Brunschot S et al. Lancet. 2018;391(10115):51-8.
3. Bang JY et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1027-40.
4. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019;68(7):1200-9.
5. Elmunzer BJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(12):1851-63.
Dr. Moran is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; Dr. Elmunzer is the Peter Cotton Professor of Medicine and Endoscopic Innovation, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina. The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this review.
Pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) are common after acute pancreatitis but almost always resolve spontaneously. Persistent collections that cause symptoms, become infected, and/or compress vital structures require treatment. Open surgery had traditionally been considered the standard method for this indication;1 Given its inherently less invasive nature, endoscopic transmural drainage (ETMD) has become a mainstay of this step-up philosophy – it is now the dominant strategy for pseudocyst drainage and, on the basis of emerging randomized trial data, compares very favorably with surgery for the treatment of walled-off necrosis (WON).
According to the step-up approach, the initial treatment of symptomatic and/or infected collections that are within 4 weeks of an attack of pancreatitis involves conservative management because the wall of the collection is typically immature; the systemic inflammation may be significantly exacerbated by definitive drainage, particularly surgery. In this early phase, failure of conservative management is addressed by percutaneous catheter placement, stepping up to a minimally invasive operation if the response to percutaneous drainage and antibiotics is insufficient.
Collections that are at least 4 weeks from the onset of acute pancreatitis are considered mature and termed pseudocysts or WONs depending on whether they contain pure fluid or necrotic tissue. In this phase, endoscopic treatment plays a primary management role because these collections are generally adherent to the stomach or duodenal wall and their capsule is organized enough to withstand endoscopic intervention. If treatment can be held off until this phase, then percutaneous and surgical drainage can often be avoided.
In practice, the 4-week rule holds true for most, but not all, PFCs. ETMD can be performed in some particularly mature collections prior to 4 weeks if the indication is strong and the collection appears to have a mature wall. However, the potential for cyst wall perforation is higher and should be considered in the risk-benefit discussion. Conversely, some collections beyond 4 weeks lack an adequately organized wall and require additional time for maturation.
While endoscopic drainage of pseudocysts has essentially supplanted surgery, the management of WON is more complex and remains multidisciplinary. Two recent randomized trials demonstrated no difference in major complications and/or death between a surgical and endoscopic step-up strategy for WON.2,3 Rates of pancreatic fistulae, hospital stay, and overall treatment costs, however, favored endoscopy. Nevertheless, defining the ideal strategy for many of these patients with complexity requires multidisciplinary discussion. Surgery continues to play a primary role in several scenarios, including collections that are not close to the upper GI tract, those that are particularly complex and extend caudally, and situations in which the endoscopic progress is too slow.
The three most important questions when deciding to embark on ETMD are: (1) whether drainage is indicated (that is, is the patient symptomatic or is there evidence that the PFC is infected?), (2) whether the wall of the collection is adequately mature and apposed to the GI tract wall; and (3) whether the collection contains necrosis? This last question has critical implications in the technical approach to drainage. While CT scan with IV contrast is accurate for assessing wall maturity, it is inadequate to evaluate the presence or quantity of necrosum. Transabdominal ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound, and MRI (on a T2 sequence) are all superior for this purpose. MRI has the additional benefit of assessing the pancreatic duct integrity, which may influence subsequent management.
Pseudocysts can be managed by cyst-gastrostomy or cyst-duodenostomy alone, whereas most WONs require the additional step of endoscopic necrosectomy – the process of entering the cyst cavity to mechanically debride necrotic tissue. Because of a higher rate of technical success, endoscopic ultrasound–directed creation of the transmural drainage pathway has become standard practice. In addition, it is likely safer, allowing for the identification and avoidance of interceding vessels and other vital structures. The role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with pancreatic stent placement as primary therapy for PFCs is limited to the drainage of small collections (<5 cm), for which it is the preferred treatment strategy. It is as effective as ETMD, which may not be feasible or safe for small PFCs.
Plastic double-pigtail stents have traditionally been used to maintain the transmural tract for both pseudocyst and WON. Recently, however, metallic stents have become more popular. Fully covered biliary self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) are easier to place, have a larger lumen, and are associated with improved outcomes, compared with plastic stents in observational studies of pseudocyst drainage. Lumen-apposing metallic stents (LAMS) have become the preferred prosthesis for WON drainage given the ability to near-simultaneously establish access and deploy the stent, as well as their much larger caliber lumen which permits seamless entry into the cavity with an endoscope. Based on ease and efficiency of use, LAMS are also commonly employed for pseudocyst drainage, although entry into the cavity is unnecessary.
Plastic stents have been shown to be more cost effective than LAMS for pseudocyst drainage, although the economics around biliary SEMS in this context have not been explored. Robust comparative effectiveness data defining the optimal prostheses for pseudocysts are needed. The literature comparing LAMS to plastic stents for the management of WON is mixed. Studies have shown LAMS to be more cost effective, but a small randomized trial demonstrated no difference in clinical success or in the number of procedures to achieve WON resolution.4 We generally favor LAMS for WON since large-caliber balloon dilation of the tract seems safer within the lumen of the LAMS (which could seal small perforations and tamponade bleeding vessels) than within a freshly created tract.
Secondary infection of the cavity, usually because of stent occlusion, and bleeding are the most common complications of ETMD. Even in the absence of stent occlusion, contamination of the collection after ETMD is ubiquitous and, as such, we prescribe prophylactic antibiotics for 1-2 weeks after the procedure, although this practice is not evidence based. Hemorrhage appears to be increasing in frequency with the diffusion of LAMS; this has been postulated to be due to particularly rapid cyst cavity collapse resulting in erosion of the stent into contralateral cyst wall vessels. CT angiography followed by an embolization procedure for a possible pseudoaneurysm is the mainstay of treatment. Serious venous bleeding is more challenging to address because angiographic options are limited.
Despite tremendous recent advances, several important controversies in the endoscopic management of PFCs persist. The optimal prosthesis, the importance of first-session endoscopic necroscopy (compared with stepping up to endoscopic necroscopy only if necessary), the roles of adjunctive drain placement and chemical debridement (such as hydrogen peroxide), the need for concomitant pancreatic stent placement, and the preferred long-term management of a disconnected pancreatic duct are areas for which additional research is sorely needed. We further discuss these questions and many additional technical considerations pertaining to endoscopic drainage in a recent review.5
In summary, endoscopic transmural drainage of mature PFCs is effective and safe. Existing evidence supports its use as the favored treatment modality in appropriate candidates and has rendered it a mainstay of the therapeutic armamentarium for this disease. Further studies are needed to address critical unanswered questions and to develop a uniform endoscopic management paradigm.
References
1. van Santvoort HC et al. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(16):1491-502.
2. van Brunschot S et al. Lancet. 2018;391(10115):51-8.
3. Bang JY et al. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(4):1027-40.
4. Bang JY et al. Gut. 2019;68(7):1200-9.
5. Elmunzer BJ. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(12):1851-63.
Dr. Moran is assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston; Dr. Elmunzer is the Peter Cotton Professor of Medicine and Endoscopic Innovation, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, Medical University of South Carolina. The authors have no conflicts of interest pertaining to this review.
Fellowship procedure logs: A word of advice for fellows and a call to action for fellowship programs
As a GI fellow, I never would have imagined I would be writing an article on GI fellowship procedure logs. At the time, in my naiveté, I looked at the procedure log as a necessary evil and part of the “red tape” imposed on fellowship programs by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME). While the importance of keeping a log was highlighted and enforced by my program, the large majority of the recommended numbers were easily achievable. As a result, even my sporadic tracking of completed procedures was sufficient to meet the requirements. My poor compliance wasn’t because I was lazy or careless, but rather because of the absence of a formal system, which resulted in homegrown methods that were highly inaccurate. I wasn’t alone in my follies. As I discussed this issue with fellows across the nation, I learned that these sentiments were universally shared. It seemed that everyone had come up with their own unique way of keeping a log – from Word and Excel documents, to a binder of patient stickers, to a daily folded sheet of paper with scribbled technical notes – all of which were an inconvenience to trainees already stretched thin. However, when the time came for employee credentialing, I came to realize the importance of keeping an accurate record. This once-neglected document would become the ultimate record of my capabilities for independent practice. The pitfalls and shortcomings of how we currently log procedures is why it was the first thing I worked on improving once I was an academic faculty member. There had to be a better way!
I started by reviewing what ACGME actually mandates trainees in GI to track, and to my surprise, they no longer set minimum procedure requirements, but rather competencies. The current requirements state that “Fellows must demonstrate competence in performance of ... procedures”1 and specifically state that competence should “not be based solely on a minimum number of procedures performed.” So, where does the need for a procedure log and minimum numbers come from? Your fellowship programs’ review committee. Programs recognize that, in order to approve requests for independent practice privileges, they need to substantiate the competency of the fellow, which ultimately is best evidenced through procedure logs. Therefore, the committee sets the minimum number of cases they believe is necessary for trainees to practice safely and independently.2 Our program leadership at UConn Health in Farmington, Conn., annually assesses our procedure activity and, over the years, has settled on the procedure guideline numbers provided to fellows at orientation and reviewed with them semiannually.
Once I understood exactly why we need procedure logs, I started looking at how other specialties handle them, particularly surgical programs in which accurate procedure logs are vitally important. It turns out that they universally use, and look favorably on, the ACGME Case Log System - an online, all encompassing, tracking software. This system is provided to surgical programs despite ACGME’s focus on competencies rather than numbers. Why this system is not offered for GI programs is unclear. However, in my endeavor, I was able to find the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Procedure Log system. When we reviewed the system in 2015 for use in our program, it was more of a concept than an all-encompassing tool. Fortunately, the AGA Information Technology (IT) and Training departments were kind enough to work with us to develop a complete online tracking tool that could be used nationally by all trainees in GI. Finally, we had a system to keep an accurate, secure log online and in real time.
A plea to fellows
With this, understand that in today’s document driven and litigious world, your procedure log is as vital to endoscopy as the scope itself. Without it, you may not be granted permission to do x, y, or z procedure. Indirectly, it can lead to delays in patient care and may prevent you from performing certain tasks and ultimately lead to repetitive training. Treat it as an official legal document of what you’ve done and what you are capable of doing. Recognize that it will be used by your mentors as supporting evidence regarding your competency for independent practice. Ask your training program to provide a clear list of expectations and requirements for graduation and a method for you to accurately track them, such as the AGA Procedure Log. An online, mobile system will allow you to document cases immediately after you finish while the procedure is fresh in your mind. Taking an extra minute after each case will prevent headaches down the road. The faculty and your cofellows all know of the end of the year “procedure scavenger” (i.e., the fellow who searches for procedures and takes them from others to make sure they meet their numbers for graduation). Please don’t be that person.
A request for program directors
As GI educators, we all know the mention of procedure logs to fellows is typically accompanied by eye rolls. It doesn’t have to be that way. Provide your fellows with clear expectations and a quick, easy, and accurate way to track their accomplishments. Help them recognize the importance of an accurate and complete procedure log. Consider an online tracking system such as the AGA Procedure Log. Studies have demonstrated that a computer-based system increases compliance and accuracy.3 Not providing one will surely lead to difficulties in the long run and is a disservice to those we work to empower, educate, and prepare for success.
References
1. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Gastroenterology. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. 2020 Jul 1. pp 21, 28. Accessed Sept. 13, 2020. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramRequirements/144_Gastroenterology_2020.pdf.
2. Steven J et al. J Grad Med Educat. 2012;4(2):257-60.
3. Rowe BH et al. Can Fam Physician. 1995;41:2113–20.
Dr. Rezaizadeh is an assistant professor of medicine, associate program director, gastroenterology fellowship program, UConn Health, Farmington, Conn.
As a GI fellow, I never would have imagined I would be writing an article on GI fellowship procedure logs. At the time, in my naiveté, I looked at the procedure log as a necessary evil and part of the “red tape” imposed on fellowship programs by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME). While the importance of keeping a log was highlighted and enforced by my program, the large majority of the recommended numbers were easily achievable. As a result, even my sporadic tracking of completed procedures was sufficient to meet the requirements. My poor compliance wasn’t because I was lazy or careless, but rather because of the absence of a formal system, which resulted in homegrown methods that were highly inaccurate. I wasn’t alone in my follies. As I discussed this issue with fellows across the nation, I learned that these sentiments were universally shared. It seemed that everyone had come up with their own unique way of keeping a log – from Word and Excel documents, to a binder of patient stickers, to a daily folded sheet of paper with scribbled technical notes – all of which were an inconvenience to trainees already stretched thin. However, when the time came for employee credentialing, I came to realize the importance of keeping an accurate record. This once-neglected document would become the ultimate record of my capabilities for independent practice. The pitfalls and shortcomings of how we currently log procedures is why it was the first thing I worked on improving once I was an academic faculty member. There had to be a better way!
I started by reviewing what ACGME actually mandates trainees in GI to track, and to my surprise, they no longer set minimum procedure requirements, but rather competencies. The current requirements state that “Fellows must demonstrate competence in performance of ... procedures”1 and specifically state that competence should “not be based solely on a minimum number of procedures performed.” So, where does the need for a procedure log and minimum numbers come from? Your fellowship programs’ review committee. Programs recognize that, in order to approve requests for independent practice privileges, they need to substantiate the competency of the fellow, which ultimately is best evidenced through procedure logs. Therefore, the committee sets the minimum number of cases they believe is necessary for trainees to practice safely and independently.2 Our program leadership at UConn Health in Farmington, Conn., annually assesses our procedure activity and, over the years, has settled on the procedure guideline numbers provided to fellows at orientation and reviewed with them semiannually.
Once I understood exactly why we need procedure logs, I started looking at how other specialties handle them, particularly surgical programs in which accurate procedure logs are vitally important. It turns out that they universally use, and look favorably on, the ACGME Case Log System - an online, all encompassing, tracking software. This system is provided to surgical programs despite ACGME’s focus on competencies rather than numbers. Why this system is not offered for GI programs is unclear. However, in my endeavor, I was able to find the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Procedure Log system. When we reviewed the system in 2015 for use in our program, it was more of a concept than an all-encompassing tool. Fortunately, the AGA Information Technology (IT) and Training departments were kind enough to work with us to develop a complete online tracking tool that could be used nationally by all trainees in GI. Finally, we had a system to keep an accurate, secure log online and in real time.
A plea to fellows
With this, understand that in today’s document driven and litigious world, your procedure log is as vital to endoscopy as the scope itself. Without it, you may not be granted permission to do x, y, or z procedure. Indirectly, it can lead to delays in patient care and may prevent you from performing certain tasks and ultimately lead to repetitive training. Treat it as an official legal document of what you’ve done and what you are capable of doing. Recognize that it will be used by your mentors as supporting evidence regarding your competency for independent practice. Ask your training program to provide a clear list of expectations and requirements for graduation and a method for you to accurately track them, such as the AGA Procedure Log. An online, mobile system will allow you to document cases immediately after you finish while the procedure is fresh in your mind. Taking an extra minute after each case will prevent headaches down the road. The faculty and your cofellows all know of the end of the year “procedure scavenger” (i.e., the fellow who searches for procedures and takes them from others to make sure they meet their numbers for graduation). Please don’t be that person.
A request for program directors
As GI educators, we all know the mention of procedure logs to fellows is typically accompanied by eye rolls. It doesn’t have to be that way. Provide your fellows with clear expectations and a quick, easy, and accurate way to track their accomplishments. Help them recognize the importance of an accurate and complete procedure log. Consider an online tracking system such as the AGA Procedure Log. Studies have demonstrated that a computer-based system increases compliance and accuracy.3 Not providing one will surely lead to difficulties in the long run and is a disservice to those we work to empower, educate, and prepare for success.
References
1. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Gastroenterology. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. 2020 Jul 1. pp 21, 28. Accessed Sept. 13, 2020. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramRequirements/144_Gastroenterology_2020.pdf.
2. Steven J et al. J Grad Med Educat. 2012;4(2):257-60.
3. Rowe BH et al. Can Fam Physician. 1995;41:2113–20.
Dr. Rezaizadeh is an assistant professor of medicine, associate program director, gastroenterology fellowship program, UConn Health, Farmington, Conn.
As a GI fellow, I never would have imagined I would be writing an article on GI fellowship procedure logs. At the time, in my naiveté, I looked at the procedure log as a necessary evil and part of the “red tape” imposed on fellowship programs by the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education (ACGME). While the importance of keeping a log was highlighted and enforced by my program, the large majority of the recommended numbers were easily achievable. As a result, even my sporadic tracking of completed procedures was sufficient to meet the requirements. My poor compliance wasn’t because I was lazy or careless, but rather because of the absence of a formal system, which resulted in homegrown methods that were highly inaccurate. I wasn’t alone in my follies. As I discussed this issue with fellows across the nation, I learned that these sentiments were universally shared. It seemed that everyone had come up with their own unique way of keeping a log – from Word and Excel documents, to a binder of patient stickers, to a daily folded sheet of paper with scribbled technical notes – all of which were an inconvenience to trainees already stretched thin. However, when the time came for employee credentialing, I came to realize the importance of keeping an accurate record. This once-neglected document would become the ultimate record of my capabilities for independent practice. The pitfalls and shortcomings of how we currently log procedures is why it was the first thing I worked on improving once I was an academic faculty member. There had to be a better way!
I started by reviewing what ACGME actually mandates trainees in GI to track, and to my surprise, they no longer set minimum procedure requirements, but rather competencies. The current requirements state that “Fellows must demonstrate competence in performance of ... procedures”1 and specifically state that competence should “not be based solely on a minimum number of procedures performed.” So, where does the need for a procedure log and minimum numbers come from? Your fellowship programs’ review committee. Programs recognize that, in order to approve requests for independent practice privileges, they need to substantiate the competency of the fellow, which ultimately is best evidenced through procedure logs. Therefore, the committee sets the minimum number of cases they believe is necessary for trainees to practice safely and independently.2 Our program leadership at UConn Health in Farmington, Conn., annually assesses our procedure activity and, over the years, has settled on the procedure guideline numbers provided to fellows at orientation and reviewed with them semiannually.
Once I understood exactly why we need procedure logs, I started looking at how other specialties handle them, particularly surgical programs in which accurate procedure logs are vitally important. It turns out that they universally use, and look favorably on, the ACGME Case Log System - an online, all encompassing, tracking software. This system is provided to surgical programs despite ACGME’s focus on competencies rather than numbers. Why this system is not offered for GI programs is unclear. However, in my endeavor, I was able to find the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) Procedure Log system. When we reviewed the system in 2015 for use in our program, it was more of a concept than an all-encompassing tool. Fortunately, the AGA Information Technology (IT) and Training departments were kind enough to work with us to develop a complete online tracking tool that could be used nationally by all trainees in GI. Finally, we had a system to keep an accurate, secure log online and in real time.
A plea to fellows
With this, understand that in today’s document driven and litigious world, your procedure log is as vital to endoscopy as the scope itself. Without it, you may not be granted permission to do x, y, or z procedure. Indirectly, it can lead to delays in patient care and may prevent you from performing certain tasks and ultimately lead to repetitive training. Treat it as an official legal document of what you’ve done and what you are capable of doing. Recognize that it will be used by your mentors as supporting evidence regarding your competency for independent practice. Ask your training program to provide a clear list of expectations and requirements for graduation and a method for you to accurately track them, such as the AGA Procedure Log. An online, mobile system will allow you to document cases immediately after you finish while the procedure is fresh in your mind. Taking an extra minute after each case will prevent headaches down the road. The faculty and your cofellows all know of the end of the year “procedure scavenger” (i.e., the fellow who searches for procedures and takes them from others to make sure they meet their numbers for graduation). Please don’t be that person.
A request for program directors
As GI educators, we all know the mention of procedure logs to fellows is typically accompanied by eye rolls. It doesn’t have to be that way. Provide your fellows with clear expectations and a quick, easy, and accurate way to track their accomplishments. Help them recognize the importance of an accurate and complete procedure log. Consider an online tracking system such as the AGA Procedure Log. Studies have demonstrated that a computer-based system increases compliance and accuracy.3 Not providing one will surely lead to difficulties in the long run and is a disservice to those we work to empower, educate, and prepare for success.
References
1. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Gastroenterology. Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education. 2020 Jul 1. pp 21, 28. Accessed Sept. 13, 2020. https://www.acgme.org/Portals/0/PFAssets/ProgramRequirements/144_Gastroenterology_2020.pdf.
2. Steven J et al. J Grad Med Educat. 2012;4(2):257-60.
3. Rowe BH et al. Can Fam Physician. 1995;41:2113–20.
Dr. Rezaizadeh is an assistant professor of medicine, associate program director, gastroenterology fellowship program, UConn Health, Farmington, Conn.
Breaking the glass ceiling in interventional endoscopy: Practical considerations for women
Subspecialty training in advanced endoscopy has become increasingly appealing to GI fellows. The allure of an ever-evolving and innovative field is demonstrated by a substantial increase in the number of training programs over the last 2 decades, from 10 in the year 2000 to over 100 currently.1 Despite its increasing popularity, women interventionalists have been a glaring absence in this phenomenon.
For the 2018-2019 academic year, women represented only 12% of incoming advanced endoscopy fellows who matched through the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) match program. Perhaps more concerning, studies have found that the percentage of female trainees interested in advanced endoscopy diminishes as general GI fellowship progresses.2
Several potential contributors have been cited that elucidate this disparity including work-life balance, radiation exposure, and lack of mentorship.2 Implicit bias also undoubtedly plays a role.
Choosing a career path: Academia vs. private practice
The decision to pursue academia versus private practice in the field of advanced endoscopy is not always straightforward. For a relatively saturated subspecialty, geographic constraints and availability of positions may limit one path or another. Although an interventional practice is best supported by a tertiary care center, there is a known opportunity conflict between the number of advanced endoscopy trainees and the availability of academic positions.3
Although private practice may offer more autonomy in scheduling and fewer nonclinical responsibilities, there may be increased pressure to retain high clinical volumes with direct financial consequences, as well as limitations in overall career advancement. Pursuing an academic path, however, may lead to less flexibility in scheduling, more travel involved with speaking engagements, and teaching and/or research responsibilities disrupting a favorable work-life balance.3 Regardless of career path, the best environment to thrive as an advanced endoscopist and a mother is one in which there is recognition and support of the challenging early family years.
Family planning
Given the long and arduous training, along with the pressures of the early faculty/clinical years, there is no perfect time for a pregnancy. Even when a pregnancy is planned, there is no certainty it will follow the intended course. The challenges specific to a career in advanced endoscopy are not well described.
Considerations during a pregnancy
When to divulge
For female interventionalists, determining when to divulge a pregnancy and the duration of maternity leave can be elusive. There is a fine balance between revealing prematurely given the risk of miscarriage and waiting so long that appropriate precautions are forsaken. One might consider disclosing the pregnancy to a few key personnel in the endoscopy unit and/or a radiation safety officer to optimize early measures to prevent occupational hazards.
Maternity leave
Every institution and practice differ in the details of maternity leave policies. These details should be reviewed and negotiated in advance. At a minimum, they are guided by the federal Family and Medical Leave Act, which entitles employees to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave.4 Each pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum period is unique and unpredictable. While early planning and consideration of coverage are crucial, it is imperative to be realistic and fluid about the postpartum journey. The unpredictable need for an extended leave has the potential to lead to career stagnancy. It is important to remember that this is a small fraction of time in the context of an entire career.
Fluoroscopy exposure
The exposure to fluoroscopy and potential adverse effects on a pregnancy has been cited frequently by women as a barrier to pursuing advanced endoscopy.2 Given the paucity of women in this field, there has yet to be definitive data on the management of fluoroscopy risk while pregnant. The ASGE Quality Assurance Endoscopy Committee has acknowledged the importance of such data and is currently preparing guidelines for radiation safety that will address the risks for pregnant endoscopists and strategies to minimize fetal exposure. The use of a fetal monitor and an early discussion with the institution’s radiation safety officer are essential to minimize fetal exposure.
Optimizing ergonomics
There have been several publications demonstrating the deleterious musculoskeletal impacts of poor ergonomics while performing endoscopy, with women being at greater risk.5The New Gastroenterologist has also published a primer on this topic. In addition to inadequate education on biomechanics and inconsistent implementation of preventative safeguards, poor endoscope design has been shown to contribute. This can be accentuated for women in advanced endoscopy who perform complex procedures with therapeutic endoscopes equipped with suboptimal handle size and dial placement.
The potential for musculoskeletal injury increases during pregnancy. The standard measures to optimize biomechanics include screen at eye level, bed at hip height, a cushioned mat, and an athletic stance.6 In addition, back injury during pregnancy in advanced endoscopy is not uncommon. Several considerations should be entertained including use of double lead versus standard two-piece 0.5-mm lead with shielding curtains and walls, sitting during procedures when possible, and incorporating short breaks in the endoscopy schedule. Furthermore, more focus and innovation are required from endoscope manufacturers to tailor toward female hand anatomy. Until then, these small but meaningful measures may help to ensure optimal biomechanics to prevent injury.
Breastfeeding/pumping
Breastfeeding in the field of advanced endoscopy has traditionally been challenging. Navigating the collection and storage of breast milk during a busy day of interventional cases can be overwhelming. The previously stagnant industry of electric breast pumps has recently been revolutionized by the innovation of wearable breast pumps. Women are no longer required to find private space to connect to a loud, wired, contraption at least 30 minutes at a time, several times a day. In the context of a busy endoscopy schedule, this antiquated ritual is nearly incompatible with the continuation of breast feeding after returning to work. With relatively silent, wearable breast pumps, it is now possible to continue patient care whether in the clinic or in the endoscopy suite with minimal disruption to a productive day.
Resources
Although there continues to be a void for dedicated mentorship for female interventionalists, there have been many organizational initiatives to unite female gastroenterologists and promote the advancement of women. Several specific initiatives have been particularly effective. Women in Endoscopy (WIE) is a global organization that champions the advancement of women in GI through education, professional growth, and leadership development. In collaboration with the American Gastroenterological Association, they have recently held a virtual event focused on career advancement in the context of unique challenges for women, “Cross Your T’s to Success: How to Deliver a Great Talk, Get Your New Title and Seize Your Next Career Twist.” WIE has also recently launched a webinar series, “Women in Advanced Endoscopy: Fellows Educational Series,” that highlights practicing female interventionalists and illuminating the path to entering the field for trainees. In addition, the ASGE Leadership Education and Development (LEAD) Program has had longstanding success in providing young female gastroenterologists an opportunity to enhance their career advancement skills and facilitate the path to leadership positions. The popularity and success of the LEAD program has led the ASGE to create a special interest group known as ASGE Women in Endoscopy (AWE) with a mission to develop resources for career development during the first 5 years after fellowship. The American College of Gastroenterology also has a unique networking platform for women known as the Women in GI Circle. Furthermore, social media platforms such as Facebook’s Physician Moms Group (PMG) and Ladies of the Gut (LOG; group accessible by invitation only) have proved powerful in connecting female endoscopists and providing a great resource for quick guidance, encouragement, and commiseration. There are also multiple Facebook groups for breastfeeding physicians including Dr. Milk and other pump-specific groups. These online communities have facilitated the dissemination of high-quality resources for troubleshooting and general camaraderie.
Conclusion
Women remain a minority in GI, and especially in advanced endoscopy. Compared with surgical subspecialties that have witnessed substantial progress in the recruitment of women over the past decade, advanced endoscopy seems to be lagging far behind. Recent studies have shown that unified efforts from the surgical societies, such as establishing mentorship programs for trainees, have managed to increase the rates of women in general surgery programs from 14% in 2001 to 40% in 2017.7,8 As the barriers for women entering advanced endoscopy are further understood, the underlying concern of reconciling a challenging field and motherhood has emerged as a common thread. While the practical information presented here cannot overcome the cultural constructs and implicit biases in which women practice advanced endoscopy, the hope is to provide a pragmatic approach to the perceived barriers and promote dialogue among women so that they, too, can pursue and thrive in the field of advanced endoscopy.
References
1. Trindade AJ et al. Characteristics, goals, and motivations of applicants pursuing a fourth-year advanced endoscopy fellowship. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76(5):939-44.
2. Pollack MJ et al. Gender disparities and gastroenterology trainee attitudes toward advanced endoscopic training. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(5):1111.
3. Granato CM et al. Career prospects and professional landscape after advanced endoscopy fellowship training: a survey assessing graduates from 2009 to 2013. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;84(2):266-71.
4. Family and Medical Leave Act. US Department of Labor. Accessed May 15, 2020. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla.
5. Pedrosa MC et al. Minimizing occupational hazards in endoscopy: Personal protective equipment, radiation safety, and ergonomics. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(2):227-35.
6. Singla M et al. Training the endo-athlete: An update in ergonomics in endoscopy. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2018;16(7):1003-6.
7. Aziz HB et al. 2018 ACS Governors Survey: Gender inequality and harassment remain a challenge in surgery. Bulletin of the American College of Surgeons. Accessed August 22, 2020. https://bulletin.facs.org/2019/09/2018-acs-governors-survey-gender-inequality-and-harassment-remain-a-challenge-in-surgery/
8. Abelson JS et al. The climb to break the glass ceiling in surgery: trends in women progressing from medical school to surgical training and academic leadership from 1994 to 2015. Am J Surg. 2016;212(4):566-72.e1.
Dr. Hasan is director of interventional endoscopy, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, NorthBay Healthcare Group; Dr. Schulman is an assistant professor, director of bariatric endoscopy, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Subspecialty training in advanced endoscopy has become increasingly appealing to GI fellows. The allure of an ever-evolving and innovative field is demonstrated by a substantial increase in the number of training programs over the last 2 decades, from 10 in the year 2000 to over 100 currently.1 Despite its increasing popularity, women interventionalists have been a glaring absence in this phenomenon.
For the 2018-2019 academic year, women represented only 12% of incoming advanced endoscopy fellows who matched through the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) match program. Perhaps more concerning, studies have found that the percentage of female trainees interested in advanced endoscopy diminishes as general GI fellowship progresses.2
Several potential contributors have been cited that elucidate this disparity including work-life balance, radiation exposure, and lack of mentorship.2 Implicit bias also undoubtedly plays a role.
Choosing a career path: Academia vs. private practice
The decision to pursue academia versus private practice in the field of advanced endoscopy is not always straightforward. For a relatively saturated subspecialty, geographic constraints and availability of positions may limit one path or another. Although an interventional practice is best supported by a tertiary care center, there is a known opportunity conflict between the number of advanced endoscopy trainees and the availability of academic positions.3
Although private practice may offer more autonomy in scheduling and fewer nonclinical responsibilities, there may be increased pressure to retain high clinical volumes with direct financial consequences, as well as limitations in overall career advancement. Pursuing an academic path, however, may lead to less flexibility in scheduling, more travel involved with speaking engagements, and teaching and/or research responsibilities disrupting a favorable work-life balance.3 Regardless of career path, the best environment to thrive as an advanced endoscopist and a mother is one in which there is recognition and support of the challenging early family years.
Family planning
Given the long and arduous training, along with the pressures of the early faculty/clinical years, there is no perfect time for a pregnancy. Even when a pregnancy is planned, there is no certainty it will follow the intended course. The challenges specific to a career in advanced endoscopy are not well described.
Considerations during a pregnancy
When to divulge
For female interventionalists, determining when to divulge a pregnancy and the duration of maternity leave can be elusive. There is a fine balance between revealing prematurely given the risk of miscarriage and waiting so long that appropriate precautions are forsaken. One might consider disclosing the pregnancy to a few key personnel in the endoscopy unit and/or a radiation safety officer to optimize early measures to prevent occupational hazards.
Maternity leave
Every institution and practice differ in the details of maternity leave policies. These details should be reviewed and negotiated in advance. At a minimum, they are guided by the federal Family and Medical Leave Act, which entitles employees to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave.4 Each pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum period is unique and unpredictable. While early planning and consideration of coverage are crucial, it is imperative to be realistic and fluid about the postpartum journey. The unpredictable need for an extended leave has the potential to lead to career stagnancy. It is important to remember that this is a small fraction of time in the context of an entire career.
Fluoroscopy exposure
The exposure to fluoroscopy and potential adverse effects on a pregnancy has been cited frequently by women as a barrier to pursuing advanced endoscopy.2 Given the paucity of women in this field, there has yet to be definitive data on the management of fluoroscopy risk while pregnant. The ASGE Quality Assurance Endoscopy Committee has acknowledged the importance of such data and is currently preparing guidelines for radiation safety that will address the risks for pregnant endoscopists and strategies to minimize fetal exposure. The use of a fetal monitor and an early discussion with the institution’s radiation safety officer are essential to minimize fetal exposure.
Optimizing ergonomics
There have been several publications demonstrating the deleterious musculoskeletal impacts of poor ergonomics while performing endoscopy, with women being at greater risk.5The New Gastroenterologist has also published a primer on this topic. In addition to inadequate education on biomechanics and inconsistent implementation of preventative safeguards, poor endoscope design has been shown to contribute. This can be accentuated for women in advanced endoscopy who perform complex procedures with therapeutic endoscopes equipped with suboptimal handle size and dial placement.
The potential for musculoskeletal injury increases during pregnancy. The standard measures to optimize biomechanics include screen at eye level, bed at hip height, a cushioned mat, and an athletic stance.6 In addition, back injury during pregnancy in advanced endoscopy is not uncommon. Several considerations should be entertained including use of double lead versus standard two-piece 0.5-mm lead with shielding curtains and walls, sitting during procedures when possible, and incorporating short breaks in the endoscopy schedule. Furthermore, more focus and innovation are required from endoscope manufacturers to tailor toward female hand anatomy. Until then, these small but meaningful measures may help to ensure optimal biomechanics to prevent injury.
Breastfeeding/pumping
Breastfeeding in the field of advanced endoscopy has traditionally been challenging. Navigating the collection and storage of breast milk during a busy day of interventional cases can be overwhelming. The previously stagnant industry of electric breast pumps has recently been revolutionized by the innovation of wearable breast pumps. Women are no longer required to find private space to connect to a loud, wired, contraption at least 30 minutes at a time, several times a day. In the context of a busy endoscopy schedule, this antiquated ritual is nearly incompatible with the continuation of breast feeding after returning to work. With relatively silent, wearable breast pumps, it is now possible to continue patient care whether in the clinic or in the endoscopy suite with minimal disruption to a productive day.
Resources
Although there continues to be a void for dedicated mentorship for female interventionalists, there have been many organizational initiatives to unite female gastroenterologists and promote the advancement of women. Several specific initiatives have been particularly effective. Women in Endoscopy (WIE) is a global organization that champions the advancement of women in GI through education, professional growth, and leadership development. In collaboration with the American Gastroenterological Association, they have recently held a virtual event focused on career advancement in the context of unique challenges for women, “Cross Your T’s to Success: How to Deliver a Great Talk, Get Your New Title and Seize Your Next Career Twist.” WIE has also recently launched a webinar series, “Women in Advanced Endoscopy: Fellows Educational Series,” that highlights practicing female interventionalists and illuminating the path to entering the field for trainees. In addition, the ASGE Leadership Education and Development (LEAD) Program has had longstanding success in providing young female gastroenterologists an opportunity to enhance their career advancement skills and facilitate the path to leadership positions. The popularity and success of the LEAD program has led the ASGE to create a special interest group known as ASGE Women in Endoscopy (AWE) with a mission to develop resources for career development during the first 5 years after fellowship. The American College of Gastroenterology also has a unique networking platform for women known as the Women in GI Circle. Furthermore, social media platforms such as Facebook’s Physician Moms Group (PMG) and Ladies of the Gut (LOG; group accessible by invitation only) have proved powerful in connecting female endoscopists and providing a great resource for quick guidance, encouragement, and commiseration. There are also multiple Facebook groups for breastfeeding physicians including Dr. Milk and other pump-specific groups. These online communities have facilitated the dissemination of high-quality resources for troubleshooting and general camaraderie.
Conclusion
Women remain a minority in GI, and especially in advanced endoscopy. Compared with surgical subspecialties that have witnessed substantial progress in the recruitment of women over the past decade, advanced endoscopy seems to be lagging far behind. Recent studies have shown that unified efforts from the surgical societies, such as establishing mentorship programs for trainees, have managed to increase the rates of women in general surgery programs from 14% in 2001 to 40% in 2017.7,8 As the barriers for women entering advanced endoscopy are further understood, the underlying concern of reconciling a challenging field and motherhood has emerged as a common thread. While the practical information presented here cannot overcome the cultural constructs and implicit biases in which women practice advanced endoscopy, the hope is to provide a pragmatic approach to the perceived barriers and promote dialogue among women so that they, too, can pursue and thrive in the field of advanced endoscopy.
References
1. Trindade AJ et al. Characteristics, goals, and motivations of applicants pursuing a fourth-year advanced endoscopy fellowship. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76(5):939-44.
2. Pollack MJ et al. Gender disparities and gastroenterology trainee attitudes toward advanced endoscopic training. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(5):1111.
3. Granato CM et al. Career prospects and professional landscape after advanced endoscopy fellowship training: a survey assessing graduates from 2009 to 2013. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;84(2):266-71.
4. Family and Medical Leave Act. US Department of Labor. Accessed May 15, 2020. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla.
5. Pedrosa MC et al. Minimizing occupational hazards in endoscopy: Personal protective equipment, radiation safety, and ergonomics. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(2):227-35.
6. Singla M et al. Training the endo-athlete: An update in ergonomics in endoscopy. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2018;16(7):1003-6.
7. Aziz HB et al. 2018 ACS Governors Survey: Gender inequality and harassment remain a challenge in surgery. Bulletin of the American College of Surgeons. Accessed August 22, 2020. https://bulletin.facs.org/2019/09/2018-acs-governors-survey-gender-inequality-and-harassment-remain-a-challenge-in-surgery/
8. Abelson JS et al. The climb to break the glass ceiling in surgery: trends in women progressing from medical school to surgical training and academic leadership from 1994 to 2015. Am J Surg. 2016;212(4):566-72.e1.
Dr. Hasan is director of interventional endoscopy, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, NorthBay Healthcare Group; Dr. Schulman is an assistant professor, director of bariatric endoscopy, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Subspecialty training in advanced endoscopy has become increasingly appealing to GI fellows. The allure of an ever-evolving and innovative field is demonstrated by a substantial increase in the number of training programs over the last 2 decades, from 10 in the year 2000 to over 100 currently.1 Despite its increasing popularity, women interventionalists have been a glaring absence in this phenomenon.
For the 2018-2019 academic year, women represented only 12% of incoming advanced endoscopy fellows who matched through the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) match program. Perhaps more concerning, studies have found that the percentage of female trainees interested in advanced endoscopy diminishes as general GI fellowship progresses.2
Several potential contributors have been cited that elucidate this disparity including work-life balance, radiation exposure, and lack of mentorship.2 Implicit bias also undoubtedly plays a role.
Choosing a career path: Academia vs. private practice
The decision to pursue academia versus private practice in the field of advanced endoscopy is not always straightforward. For a relatively saturated subspecialty, geographic constraints and availability of positions may limit one path or another. Although an interventional practice is best supported by a tertiary care center, there is a known opportunity conflict between the number of advanced endoscopy trainees and the availability of academic positions.3
Although private practice may offer more autonomy in scheduling and fewer nonclinical responsibilities, there may be increased pressure to retain high clinical volumes with direct financial consequences, as well as limitations in overall career advancement. Pursuing an academic path, however, may lead to less flexibility in scheduling, more travel involved with speaking engagements, and teaching and/or research responsibilities disrupting a favorable work-life balance.3 Regardless of career path, the best environment to thrive as an advanced endoscopist and a mother is one in which there is recognition and support of the challenging early family years.
Family planning
Given the long and arduous training, along with the pressures of the early faculty/clinical years, there is no perfect time for a pregnancy. Even when a pregnancy is planned, there is no certainty it will follow the intended course. The challenges specific to a career in advanced endoscopy are not well described.
Considerations during a pregnancy
When to divulge
For female interventionalists, determining when to divulge a pregnancy and the duration of maternity leave can be elusive. There is a fine balance between revealing prematurely given the risk of miscarriage and waiting so long that appropriate precautions are forsaken. One might consider disclosing the pregnancy to a few key personnel in the endoscopy unit and/or a radiation safety officer to optimize early measures to prevent occupational hazards.
Maternity leave
Every institution and practice differ in the details of maternity leave policies. These details should be reviewed and negotiated in advance. At a minimum, they are guided by the federal Family and Medical Leave Act, which entitles employees to 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave.4 Each pregnancy, delivery, and postpartum period is unique and unpredictable. While early planning and consideration of coverage are crucial, it is imperative to be realistic and fluid about the postpartum journey. The unpredictable need for an extended leave has the potential to lead to career stagnancy. It is important to remember that this is a small fraction of time in the context of an entire career.
Fluoroscopy exposure
The exposure to fluoroscopy and potential adverse effects on a pregnancy has been cited frequently by women as a barrier to pursuing advanced endoscopy.2 Given the paucity of women in this field, there has yet to be definitive data on the management of fluoroscopy risk while pregnant. The ASGE Quality Assurance Endoscopy Committee has acknowledged the importance of such data and is currently preparing guidelines for radiation safety that will address the risks for pregnant endoscopists and strategies to minimize fetal exposure. The use of a fetal monitor and an early discussion with the institution’s radiation safety officer are essential to minimize fetal exposure.
Optimizing ergonomics
There have been several publications demonstrating the deleterious musculoskeletal impacts of poor ergonomics while performing endoscopy, with women being at greater risk.5The New Gastroenterologist has also published a primer on this topic. In addition to inadequate education on biomechanics and inconsistent implementation of preventative safeguards, poor endoscope design has been shown to contribute. This can be accentuated for women in advanced endoscopy who perform complex procedures with therapeutic endoscopes equipped with suboptimal handle size and dial placement.
The potential for musculoskeletal injury increases during pregnancy. The standard measures to optimize biomechanics include screen at eye level, bed at hip height, a cushioned mat, and an athletic stance.6 In addition, back injury during pregnancy in advanced endoscopy is not uncommon. Several considerations should be entertained including use of double lead versus standard two-piece 0.5-mm lead with shielding curtains and walls, sitting during procedures when possible, and incorporating short breaks in the endoscopy schedule. Furthermore, more focus and innovation are required from endoscope manufacturers to tailor toward female hand anatomy. Until then, these small but meaningful measures may help to ensure optimal biomechanics to prevent injury.
Breastfeeding/pumping
Breastfeeding in the field of advanced endoscopy has traditionally been challenging. Navigating the collection and storage of breast milk during a busy day of interventional cases can be overwhelming. The previously stagnant industry of electric breast pumps has recently been revolutionized by the innovation of wearable breast pumps. Women are no longer required to find private space to connect to a loud, wired, contraption at least 30 minutes at a time, several times a day. In the context of a busy endoscopy schedule, this antiquated ritual is nearly incompatible with the continuation of breast feeding after returning to work. With relatively silent, wearable breast pumps, it is now possible to continue patient care whether in the clinic or in the endoscopy suite with minimal disruption to a productive day.
Resources
Although there continues to be a void for dedicated mentorship for female interventionalists, there have been many organizational initiatives to unite female gastroenterologists and promote the advancement of women. Several specific initiatives have been particularly effective. Women in Endoscopy (WIE) is a global organization that champions the advancement of women in GI through education, professional growth, and leadership development. In collaboration with the American Gastroenterological Association, they have recently held a virtual event focused on career advancement in the context of unique challenges for women, “Cross Your T’s to Success: How to Deliver a Great Talk, Get Your New Title and Seize Your Next Career Twist.” WIE has also recently launched a webinar series, “Women in Advanced Endoscopy: Fellows Educational Series,” that highlights practicing female interventionalists and illuminating the path to entering the field for trainees. In addition, the ASGE Leadership Education and Development (LEAD) Program has had longstanding success in providing young female gastroenterologists an opportunity to enhance their career advancement skills and facilitate the path to leadership positions. The popularity and success of the LEAD program has led the ASGE to create a special interest group known as ASGE Women in Endoscopy (AWE) with a mission to develop resources for career development during the first 5 years after fellowship. The American College of Gastroenterology also has a unique networking platform for women known as the Women in GI Circle. Furthermore, social media platforms such as Facebook’s Physician Moms Group (PMG) and Ladies of the Gut (LOG; group accessible by invitation only) have proved powerful in connecting female endoscopists and providing a great resource for quick guidance, encouragement, and commiseration. There are also multiple Facebook groups for breastfeeding physicians including Dr. Milk and other pump-specific groups. These online communities have facilitated the dissemination of high-quality resources for troubleshooting and general camaraderie.
Conclusion
Women remain a minority in GI, and especially in advanced endoscopy. Compared with surgical subspecialties that have witnessed substantial progress in the recruitment of women over the past decade, advanced endoscopy seems to be lagging far behind. Recent studies have shown that unified efforts from the surgical societies, such as establishing mentorship programs for trainees, have managed to increase the rates of women in general surgery programs from 14% in 2001 to 40% in 2017.7,8 As the barriers for women entering advanced endoscopy are further understood, the underlying concern of reconciling a challenging field and motherhood has emerged as a common thread. While the practical information presented here cannot overcome the cultural constructs and implicit biases in which women practice advanced endoscopy, the hope is to provide a pragmatic approach to the perceived barriers and promote dialogue among women so that they, too, can pursue and thrive in the field of advanced endoscopy.
References
1. Trindade AJ et al. Characteristics, goals, and motivations of applicants pursuing a fourth-year advanced endoscopy fellowship. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;76(5):939-44.
2. Pollack MJ et al. Gender disparities and gastroenterology trainee attitudes toward advanced endoscopic training. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(5):1111.
3. Granato CM et al. Career prospects and professional landscape after advanced endoscopy fellowship training: a survey assessing graduates from 2009 to 2013. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;84(2):266-71.
4. Family and Medical Leave Act. US Department of Labor. Accessed May 15, 2020. https://www.dol.gov/agencies/whd/fmla.
5. Pedrosa MC et al. Minimizing occupational hazards in endoscopy: Personal protective equipment, radiation safety, and ergonomics. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72(2):227-35.
6. Singla M et al. Training the endo-athlete: An update in ergonomics in endoscopy. Clin Gastro Hepatol. 2018;16(7):1003-6.
7. Aziz HB et al. 2018 ACS Governors Survey: Gender inequality and harassment remain a challenge in surgery. Bulletin of the American College of Surgeons. Accessed August 22, 2020. https://bulletin.facs.org/2019/09/2018-acs-governors-survey-gender-inequality-and-harassment-remain-a-challenge-in-surgery/
8. Abelson JS et al. The climb to break the glass ceiling in surgery: trends in women progressing from medical school to surgical training and academic leadership from 1994 to 2015. Am J Surg. 2016;212(4):566-72.e1.
Dr. Hasan is director of interventional endoscopy, department of gastroenterology and hepatology, NorthBay Healthcare Group; Dr. Schulman is an assistant professor, director of bariatric endoscopy, division of gastroenterology and hepatology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
Evaluating a paper: Take care not to be confounded
In an earlier article, we looked at the meaning of the P value.1 This time we will look at another crucial statistical concept: that of confounding.
Confounding, as the name implies, is the recognition that crude associations may not reflect reality, but may instead be the result of outside factors. To illustrate, imagine that you want to study whether smoking increases the risk of death (in statistical terms, smoking is the exposure, and death is the outcome). You follow 5,000 people who smoke and 5,000 people who do not smoke for 10 years. At the end of the follow-up you find that about 40% of nonsmokers died, compared with only 10% of smokers. What do you conclude? At face value it would seem that smoking prevents death. However, before reaching this conclusion you might want to look at other factors. A look at the dataset shows that the average baseline age among nonsmokers was 60 years, whereas among smokers was 40 years. Could this be the cause of the results? You repeat the analysis based on strata of age (i.e., you compare smokers who were aged 60-70 years at baseline with nonsmokers who were aged 60-70 years, smokers who were aged 50-60 years with nonsmokers who were aged 50-60 years, and so on). What you find is that, for each category of age, the percentage of death among smokers was higher. Hence, you now reach the opposite conclusion, namely that smoking does increase the risk of death.
What happened? Why the different result? The answer is that, in this case, age was a confounder. What we initially thought was the effect of smoking was, in reality, at least in part, the effect of age. Overall, more deaths occurred among nonsmokers in the first analysis because they were older at baseline. When we compare people with similar age but who differ on smoking status, then the difference in mortality between them is not because of age (they have the same age) but smoking. Thus, in the second analysis we took age into account, or, in statistical terms, we adjusted for age, whereas the first analysis was, in statistical terms, an unadjusted or crude analysis. We should always be aware of studies with only crude results, because they might be biased/misleading.2
In the example above, age is not the only factor that might influence mortality. Alcohol or drug use, cancer or heart disease, body mass index, or physical activity can also influence death, independently of smoking. How to adjust for all these factors? We cannot do stratified analyses as we did above, because the strata would be too many. The solution is to do a multivariable regression analysis. This is a statistical tool to adjust for multiple factors (or variables) at the same time. When we adjust for all these factors, we are comparing the effect of smoking in people who are the same with regard to all these factors but who differ on smoking status. In statistical terms, we study the effect of smoking, keeping everything else constant. In this way we “isolate” the effect of smoking on death by taking into account all other factors, or, in statistical terms, we study the effect of smoking independently of other factors.
How many factors should be included in a multivariable analysis? As a general rule, the more the better, to reduce confounding. However, the number of variables to include in a regression model is limited by the sample size. The general rule of thumb is that, for every 10 events (for dichotomous outcomes) or 10 people (for continuous outcomes), we can add one variable in the model. If we add more variables than that, then in statistical terms the model becomes overfitted (i.e., it gives results that are specific to that dataset, but may not be applicable to other datasets). Overfitted models can be as biased/misleading as crude models.3
What are we to do about other factors that may affect mortality independently of smoking (e.g., diet), but which are not found in our dataset? Unfortunately, nothing. Since we do not have that information, we cannot adjust for it. In this case, diet is in statistical terms an unmeasured confounder. Unfortunately, in all observational studies there is always at least some degree of unmeasured confounding, because there may be many factors that can influence the outcome (and the exposure) which are not part of the dataset. While some statistical tools have been developed to estimate unmeasured confounding, and therefore interpret the results in its light, unmeasured confounding remains one of the major limitations of observational studies.4
Randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) on the other side do not have this problem in theory. With properly designed RCTs, all confounders, both measured and unmeasured, will be balanced between the two groups. For example, imagine an RCT where some patients are randomized to take drug A or drug B. Because patients are randomly allocated to one group or the other, it is assumed that all other factors are also randomly distributed. Hence, the two groups should be equal to each other with respect to all other factors except our active intervention, namely the type of drug they are taking (A or B). For this reason, in RCTs there is no need to adjust for multiple factors with a multivariable regression analysis, and crude unadjusted results can be presented as unbiased.
There is however a caveat. What happens if one patient who was randomized to take drug A takes drug B instead? Should she still be counted in analysis under drug A (as randomized) or under drug B (as she took it)? The usual practice is to do this and present both. In the first case, we will have the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, and in the second case, the per-protocol analysis (PPA). The advantage of the ITT is that it keeps the strength of randomization, namely the balancing of confounders, and therefore can present unbiased results. The advantage of the PPA is that it measures what was actually done in reality. However, in this case there is a departure from the original randomization, and hence there is the possibility of introducing confounding, because now patients are not randomly allocated to one treatment or the other. The larger the departure from randomization, the more probable the introduction of bias/confounding. For example, what if patients with more severe disease took drug A, even though they were randomized to take drug B? That will have an influence the outcome. For this reason, outcomes of the ITT analysis are considered the main results of RCTs, because PPA results can be confounded.
In summary, when reading studies, do not simply accept the results as they are presented, but rather ask yourself: “Could they be confounded by other factors, and therefore be unreliable? What steps did the authors take to reduce confounding? If they presented only crude analyses, and this was not justified by a RCT design, do they recognize it as a major limitation?” There are many nuances in every paper that can be appreciated only through a careful reading of the methods section. Hopefully, this article can shed some light on these issues and help the readers to not be confounded.
References
1. The P value: What to make of it? A simple guide for the uninitiated. GI and Hepatology News. 2019 Sep 23. https://www.mdedge.com/gihepnews/article/208601/mixed-topics/p-value-what-make-it-simple-guide-uninitiated
2. VanderWeele TJ et al. Ann Stat. 2013 Feb;41(1):196-220.
3. Concato J et al. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Feb 1;118(3):201-10.
4. VanderWeele TJ et al. Ann Intern Med. 2017 Aug 15;167(4):268-74.
Dr. Jovani is a therapeutic endoscopy fellow in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
In an earlier article, we looked at the meaning of the P value.1 This time we will look at another crucial statistical concept: that of confounding.
Confounding, as the name implies, is the recognition that crude associations may not reflect reality, but may instead be the result of outside factors. To illustrate, imagine that you want to study whether smoking increases the risk of death (in statistical terms, smoking is the exposure, and death is the outcome). You follow 5,000 people who smoke and 5,000 people who do not smoke for 10 years. At the end of the follow-up you find that about 40% of nonsmokers died, compared with only 10% of smokers. What do you conclude? At face value it would seem that smoking prevents death. However, before reaching this conclusion you might want to look at other factors. A look at the dataset shows that the average baseline age among nonsmokers was 60 years, whereas among smokers was 40 years. Could this be the cause of the results? You repeat the analysis based on strata of age (i.e., you compare smokers who were aged 60-70 years at baseline with nonsmokers who were aged 60-70 years, smokers who were aged 50-60 years with nonsmokers who were aged 50-60 years, and so on). What you find is that, for each category of age, the percentage of death among smokers was higher. Hence, you now reach the opposite conclusion, namely that smoking does increase the risk of death.
What happened? Why the different result? The answer is that, in this case, age was a confounder. What we initially thought was the effect of smoking was, in reality, at least in part, the effect of age. Overall, more deaths occurred among nonsmokers in the first analysis because they were older at baseline. When we compare people with similar age but who differ on smoking status, then the difference in mortality between them is not because of age (they have the same age) but smoking. Thus, in the second analysis we took age into account, or, in statistical terms, we adjusted for age, whereas the first analysis was, in statistical terms, an unadjusted or crude analysis. We should always be aware of studies with only crude results, because they might be biased/misleading.2
In the example above, age is not the only factor that might influence mortality. Alcohol or drug use, cancer or heart disease, body mass index, or physical activity can also influence death, independently of smoking. How to adjust for all these factors? We cannot do stratified analyses as we did above, because the strata would be too many. The solution is to do a multivariable regression analysis. This is a statistical tool to adjust for multiple factors (or variables) at the same time. When we adjust for all these factors, we are comparing the effect of smoking in people who are the same with regard to all these factors but who differ on smoking status. In statistical terms, we study the effect of smoking, keeping everything else constant. In this way we “isolate” the effect of smoking on death by taking into account all other factors, or, in statistical terms, we study the effect of smoking independently of other factors.
How many factors should be included in a multivariable analysis? As a general rule, the more the better, to reduce confounding. However, the number of variables to include in a regression model is limited by the sample size. The general rule of thumb is that, for every 10 events (for dichotomous outcomes) or 10 people (for continuous outcomes), we can add one variable in the model. If we add more variables than that, then in statistical terms the model becomes overfitted (i.e., it gives results that are specific to that dataset, but may not be applicable to other datasets). Overfitted models can be as biased/misleading as crude models.3
What are we to do about other factors that may affect mortality independently of smoking (e.g., diet), but which are not found in our dataset? Unfortunately, nothing. Since we do not have that information, we cannot adjust for it. In this case, diet is in statistical terms an unmeasured confounder. Unfortunately, in all observational studies there is always at least some degree of unmeasured confounding, because there may be many factors that can influence the outcome (and the exposure) which are not part of the dataset. While some statistical tools have been developed to estimate unmeasured confounding, and therefore interpret the results in its light, unmeasured confounding remains one of the major limitations of observational studies.4
Randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) on the other side do not have this problem in theory. With properly designed RCTs, all confounders, both measured and unmeasured, will be balanced between the two groups. For example, imagine an RCT where some patients are randomized to take drug A or drug B. Because patients are randomly allocated to one group or the other, it is assumed that all other factors are also randomly distributed. Hence, the two groups should be equal to each other with respect to all other factors except our active intervention, namely the type of drug they are taking (A or B). For this reason, in RCTs there is no need to adjust for multiple factors with a multivariable regression analysis, and crude unadjusted results can be presented as unbiased.
There is however a caveat. What happens if one patient who was randomized to take drug A takes drug B instead? Should she still be counted in analysis under drug A (as randomized) or under drug B (as she took it)? The usual practice is to do this and present both. In the first case, we will have the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, and in the second case, the per-protocol analysis (PPA). The advantage of the ITT is that it keeps the strength of randomization, namely the balancing of confounders, and therefore can present unbiased results. The advantage of the PPA is that it measures what was actually done in reality. However, in this case there is a departure from the original randomization, and hence there is the possibility of introducing confounding, because now patients are not randomly allocated to one treatment or the other. The larger the departure from randomization, the more probable the introduction of bias/confounding. For example, what if patients with more severe disease took drug A, even though they were randomized to take drug B? That will have an influence the outcome. For this reason, outcomes of the ITT analysis are considered the main results of RCTs, because PPA results can be confounded.
In summary, when reading studies, do not simply accept the results as they are presented, but rather ask yourself: “Could they be confounded by other factors, and therefore be unreliable? What steps did the authors take to reduce confounding? If they presented only crude analyses, and this was not justified by a RCT design, do they recognize it as a major limitation?” There are many nuances in every paper that can be appreciated only through a careful reading of the methods section. Hopefully, this article can shed some light on these issues and help the readers to not be confounded.
References
1. The P value: What to make of it? A simple guide for the uninitiated. GI and Hepatology News. 2019 Sep 23. https://www.mdedge.com/gihepnews/article/208601/mixed-topics/p-value-what-make-it-simple-guide-uninitiated
2. VanderWeele TJ et al. Ann Stat. 2013 Feb;41(1):196-220.
3. Concato J et al. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Feb 1;118(3):201-10.
4. VanderWeele TJ et al. Ann Intern Med. 2017 Aug 15;167(4):268-74.
Dr. Jovani is a therapeutic endoscopy fellow in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
In an earlier article, we looked at the meaning of the P value.1 This time we will look at another crucial statistical concept: that of confounding.
Confounding, as the name implies, is the recognition that crude associations may not reflect reality, but may instead be the result of outside factors. To illustrate, imagine that you want to study whether smoking increases the risk of death (in statistical terms, smoking is the exposure, and death is the outcome). You follow 5,000 people who smoke and 5,000 people who do not smoke for 10 years. At the end of the follow-up you find that about 40% of nonsmokers died, compared with only 10% of smokers. What do you conclude? At face value it would seem that smoking prevents death. However, before reaching this conclusion you might want to look at other factors. A look at the dataset shows that the average baseline age among nonsmokers was 60 years, whereas among smokers was 40 years. Could this be the cause of the results? You repeat the analysis based on strata of age (i.e., you compare smokers who were aged 60-70 years at baseline with nonsmokers who were aged 60-70 years, smokers who were aged 50-60 years with nonsmokers who were aged 50-60 years, and so on). What you find is that, for each category of age, the percentage of death among smokers was higher. Hence, you now reach the opposite conclusion, namely that smoking does increase the risk of death.
What happened? Why the different result? The answer is that, in this case, age was a confounder. What we initially thought was the effect of smoking was, in reality, at least in part, the effect of age. Overall, more deaths occurred among nonsmokers in the first analysis because they were older at baseline. When we compare people with similar age but who differ on smoking status, then the difference in mortality between them is not because of age (they have the same age) but smoking. Thus, in the second analysis we took age into account, or, in statistical terms, we adjusted for age, whereas the first analysis was, in statistical terms, an unadjusted or crude analysis. We should always be aware of studies with only crude results, because they might be biased/misleading.2
In the example above, age is not the only factor that might influence mortality. Alcohol or drug use, cancer or heart disease, body mass index, or physical activity can also influence death, independently of smoking. How to adjust for all these factors? We cannot do stratified analyses as we did above, because the strata would be too many. The solution is to do a multivariable regression analysis. This is a statistical tool to adjust for multiple factors (or variables) at the same time. When we adjust for all these factors, we are comparing the effect of smoking in people who are the same with regard to all these factors but who differ on smoking status. In statistical terms, we study the effect of smoking, keeping everything else constant. In this way we “isolate” the effect of smoking on death by taking into account all other factors, or, in statistical terms, we study the effect of smoking independently of other factors.
How many factors should be included in a multivariable analysis? As a general rule, the more the better, to reduce confounding. However, the number of variables to include in a regression model is limited by the sample size. The general rule of thumb is that, for every 10 events (for dichotomous outcomes) or 10 people (for continuous outcomes), we can add one variable in the model. If we add more variables than that, then in statistical terms the model becomes overfitted (i.e., it gives results that are specific to that dataset, but may not be applicable to other datasets). Overfitted models can be as biased/misleading as crude models.3
What are we to do about other factors that may affect mortality independently of smoking (e.g., diet), but which are not found in our dataset? Unfortunately, nothing. Since we do not have that information, we cannot adjust for it. In this case, diet is in statistical terms an unmeasured confounder. Unfortunately, in all observational studies there is always at least some degree of unmeasured confounding, because there may be many factors that can influence the outcome (and the exposure) which are not part of the dataset. While some statistical tools have been developed to estimate unmeasured confounding, and therefore interpret the results in its light, unmeasured confounding remains one of the major limitations of observational studies.4
Randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) on the other side do not have this problem in theory. With properly designed RCTs, all confounders, both measured and unmeasured, will be balanced between the two groups. For example, imagine an RCT where some patients are randomized to take drug A or drug B. Because patients are randomly allocated to one group or the other, it is assumed that all other factors are also randomly distributed. Hence, the two groups should be equal to each other with respect to all other factors except our active intervention, namely the type of drug they are taking (A or B). For this reason, in RCTs there is no need to adjust for multiple factors with a multivariable regression analysis, and crude unadjusted results can be presented as unbiased.
There is however a caveat. What happens if one patient who was randomized to take drug A takes drug B instead? Should she still be counted in analysis under drug A (as randomized) or under drug B (as she took it)? The usual practice is to do this and present both. In the first case, we will have the intention-to-treat (ITT) analysis, and in the second case, the per-protocol analysis (PPA). The advantage of the ITT is that it keeps the strength of randomization, namely the balancing of confounders, and therefore can present unbiased results. The advantage of the PPA is that it measures what was actually done in reality. However, in this case there is a departure from the original randomization, and hence there is the possibility of introducing confounding, because now patients are not randomly allocated to one treatment or the other. The larger the departure from randomization, the more probable the introduction of bias/confounding. For example, what if patients with more severe disease took drug A, even though they were randomized to take drug B? That will have an influence the outcome. For this reason, outcomes of the ITT analysis are considered the main results of RCTs, because PPA results can be confounded.
In summary, when reading studies, do not simply accept the results as they are presented, but rather ask yourself: “Could they be confounded by other factors, and therefore be unreliable? What steps did the authors take to reduce confounding? If they presented only crude analyses, and this was not justified by a RCT design, do they recognize it as a major limitation?” There are many nuances in every paper that can be appreciated only through a careful reading of the methods section. Hopefully, this article can shed some light on these issues and help the readers to not be confounded.
References
1. The P value: What to make of it? A simple guide for the uninitiated. GI and Hepatology News. 2019 Sep 23. https://www.mdedge.com/gihepnews/article/208601/mixed-topics/p-value-what-make-it-simple-guide-uninitiated
2. VanderWeele TJ et al. Ann Stat. 2013 Feb;41(1):196-220.
3. Concato J et al. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Feb 1;118(3):201-10.
4. VanderWeele TJ et al. Ann Intern Med. 2017 Aug 15;167(4):268-74.
Dr. Jovani is a therapeutic endoscopy fellow in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore.
A practical approach to utilizing cannabis as adjuvant therapy in inflammatory bowel disease
Case 1
A 30 year-old female with longstanding ulcerative colitis who has a history of medically refractory steroid-dependent disease and was able to achieve remission with vedolizumab for the last 5 years. Most recent objective assessment showed histologic remission. She has been using daily cannabis medicinally for the last year (high CBD:THC [cannabidiol:delta-9-tetracannabidol] concentration). She notes that she has felt better in the last year since introducing cannabis (improved stool frequency/formation, sleep quality). She inquires about discontinuing her biologic therapy in the hope of using cannabis alone to maintain remission.

Figure 1.
Case 2
A 22-year-old male with ileocolonic inflammatory Crohn’s disease escalated to adalimumab requiring an intensification of therapy to weekly dosing to normalize C-reactive protein (CRP). A recent colonoscopy showed endoscopic improvement (colonic normalization and rare aphthae in ileum). He notes clear clinical improvement, but he continues to experience diarrhea and abdominal cramping (no relationship to meals). Declines addition of immunomodulator (nervous about returning to college during the COVID-19 pandemic). He wonders whether cannabis could be effective in controlling his symptoms as he has had improvement in symptoms during his sporadic recreational cannabis exposure.
Discussion
These cases outline the challenges that providers face when managing patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when a patient would like to either substitute or incorporate cannabis into their treatment plan. Studies have shown a high prevalence of cannabis use among patients with IBD. With the restrictions surrounding the use of cannabis – either medically or recreationally – being liberalized in many states, these conversations are likely to become more frequent in your practice. However, one of the first challenges that providers face surrounding cannabis is that many patients who use cannabis do not disclose use to their health care team for fear of being judged negatively. In addition, many providers do not routinely ask about cannabis use during office visits. This might be directly related to being unprepared to have a knowledge-based discussion on the risks and benefits of cannabis use in IBD, with the same confidence present during discussion of biologic therapies.
For background, Cannabis sativa (cannabis) is composed of hundreds of phytocannabinoids, the two most common are THC and CBD. These cannabinoids act at the endocannabinoid receptors, which are expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems and immune cells/tissues, and help explain the clinical changes experienced by cannabis users. Both THC and CBD have been studied in varying doses and routes of administration in patients with IBD, making it challenging to translate into real-world recommendations for patients. Some of the most common reported benefits of cannabis use (particularly in an IBD population) are improvement in pain, diarrhea, nausea, and joint pain. Some studies have shown overall improvement in quality of life (Figure 1).
Some common questions that arise surrounding cannabis use in IBD patients include:
1. Is it possible to stop traditional medical therapy and replace it with cannabis therapy?
No studies have directly addressed this exact question. The small studies, both randomized controlled trials and retrospective ones, have studied the effects of cannabis as adjuvant therapy only. None of the data available to date suggest that cannabis has any anti-inflammatory properties with absence of improvement in biomarkers or endoscopic measures of inflammation. In effect, any attempt to discontinue standard therapy with substitution of cannabis-based therapy should be seen as no different than simply discontinuing standard therapy. There exists the argument that – among those with moderate to severe disease – cannabis might suppress the investigation of mild symptoms which may herald a flare of disease, thus lulling the patient into a state of false stability. We do not advocate the substitution of cannabis products in place of standard medical therapy.
2. Is there a role for cannabis as adjuvant therapy in patients with IBD?
Studies to date have included only symptomatic patients with objective evidence of inflammation and assessed clinical, biochemical, or endoscopic endpoints. In Crohn’s disease, two studies showed no improvement in clinical remission rates but showed improvement in clinical response; a third study showed both improvement in clinical remission/response as well as improved quality of life. No study showed a change in disease markers of activity including CRP, fecal calprotectin, or endoscopic scoring. In one study, all patients relapsed shortly after cannabis discontinuation suggesting that, while there was benefit in symptom control, there was no improvement of the underlying chronic inflammation.
In patients with ulcerative colitis, there were two studies. One study showed no improvement and high rates of intolerance in the treatment group, while the other study reported improved disease activity but no objective improvement. The variation in results between disease states and between studies might be because of cannabis formulations. In patients with persistent symptoms despite current medical therapy, there might be a role in those patients for adjuvant therapy for improvement symptom control but not disease control. Optimization of medical therapy would still be indicated.
3. What dose and formulation of cannabis should I recommend to a patient as adjuvant therapy?
This is an excellent question and one that unfortunately we do not have the answer to. As mentioned previously, the studies have looked at varying formulations (THC alone, CBD:THC with varying percentages of THC, CBD alone) and varying routes of administration (sublingual, oral, inhalation). The IBD studies looking at CBD-alone formulations lacked clinical efficacy. In states where cannabis products have been accessible to IBD patients, no data on the product type (THC:CBD), method of administration, or prescriber preferences have been published.
4. What risks should I advise my patients about with cannabis use?
The challenge is that we don’t have large population-based studies in IBD looking at long-term risks of cannabis use. However, in the small RCT studies there were minimal reported side effects and no major adverse events over 8-10 weeks. Larger IBD population-based studies have shown that cannabis users were more likely to discontinue traditional medical therapy, and there is an increased risk for surgery in patients with Crohn’s disease. Larger studies in non-IBD patients have shown risk for addiction to other substances, diminished life achievement, increased motor vehicle accidents, chronic bronchitis, psychiatric disturbances and cannabis dependence, and cannabis hyperemesis syndrome (with an uncanny presentation resembling Crohn’s disease flare with partial small bowel obstruction). Patients should also be advised about legal implications of use (given its continued classification as a federal schedule 1 drug), possible drug interactions, and special considerations in pediatric patients (increased risk of addiction), elderly patients (increased risk of neuropsychological effects), and during pregnancy (with national obstetric society guidelines warning against use because of fetal exposure and increased risk of stillbirth).
5. What are the legal implications for providers? Patients?
As of July 2020, cannabis is available for recreational use in 12 states, for medicinal use in 28 states, and illegal in 11 states. So the answer really depends on what state the patient lives in. As a provider who might certify patients (in some medicinal states) or recommend cannabis to patients, you should consider legal and licensing implications. Again, this might vary state to state, and you should also take into account federal status. Providers acting in compliance with state laws are unlikely to have federal consequences. However, remember that malpractice insurance only covers FDA-approved medical therapies. Patients should be advised to consider the potential (although highly unlikely) to face federal prosecution and implications of use for employment, school, camp, or travel, and driving restrictions.
Take home points
- Inquire about cannabis to start the conversation.
- Know your state’s legalization status surrounding cannabis.
- Patients with IBD report improvement in symptoms and quality of life with adjuvant cannabis use; however, there is no change in disease activity.
- Encourage your patients to continue and optimize their maintenance therapy.
- Educate your patients about the legal considerations and known risks.
In conclusion, the use of cannabis in IBD patients has increased in recent years. It is important to be able to discuss the risks and benefits of use with your IBD patients. Focus on the lack of data showing that cannabis improves disease activity, and has shown benefit only in improving IBD-associated symptoms. In some patients there might be a role for adjuvant cannabis therapy to improve overall symptom control and quality of life.
Dr. Kinnucan is an assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor; Dr. Swaminath is an associate professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Lenox Hill Hospital, Northwell Health, New York.
Case 1
A 30 year-old female with longstanding ulcerative colitis who has a history of medically refractory steroid-dependent disease and was able to achieve remission with vedolizumab for the last 5 years. Most recent objective assessment showed histologic remission. She has been using daily cannabis medicinally for the last year (high CBD:THC [cannabidiol:delta-9-tetracannabidol] concentration). She notes that she has felt better in the last year since introducing cannabis (improved stool frequency/formation, sleep quality). She inquires about discontinuing her biologic therapy in the hope of using cannabis alone to maintain remission.

Figure 1.
Case 2
A 22-year-old male with ileocolonic inflammatory Crohn’s disease escalated to adalimumab requiring an intensification of therapy to weekly dosing to normalize C-reactive protein (CRP). A recent colonoscopy showed endoscopic improvement (colonic normalization and rare aphthae in ileum). He notes clear clinical improvement, but he continues to experience diarrhea and abdominal cramping (no relationship to meals). Declines addition of immunomodulator (nervous about returning to college during the COVID-19 pandemic). He wonders whether cannabis could be effective in controlling his symptoms as he has had improvement in symptoms during his sporadic recreational cannabis exposure.
Discussion
These cases outline the challenges that providers face when managing patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when a patient would like to either substitute or incorporate cannabis into their treatment plan. Studies have shown a high prevalence of cannabis use among patients with IBD. With the restrictions surrounding the use of cannabis – either medically or recreationally – being liberalized in many states, these conversations are likely to become more frequent in your practice. However, one of the first challenges that providers face surrounding cannabis is that many patients who use cannabis do not disclose use to their health care team for fear of being judged negatively. In addition, many providers do not routinely ask about cannabis use during office visits. This might be directly related to being unprepared to have a knowledge-based discussion on the risks and benefits of cannabis use in IBD, with the same confidence present during discussion of biologic therapies.
For background, Cannabis sativa (cannabis) is composed of hundreds of phytocannabinoids, the two most common are THC and CBD. These cannabinoids act at the endocannabinoid receptors, which are expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems and immune cells/tissues, and help explain the clinical changes experienced by cannabis users. Both THC and CBD have been studied in varying doses and routes of administration in patients with IBD, making it challenging to translate into real-world recommendations for patients. Some of the most common reported benefits of cannabis use (particularly in an IBD population) are improvement in pain, diarrhea, nausea, and joint pain. Some studies have shown overall improvement in quality of life (Figure 1).
Some common questions that arise surrounding cannabis use in IBD patients include:
1. Is it possible to stop traditional medical therapy and replace it with cannabis therapy?
No studies have directly addressed this exact question. The small studies, both randomized controlled trials and retrospective ones, have studied the effects of cannabis as adjuvant therapy only. None of the data available to date suggest that cannabis has any anti-inflammatory properties with absence of improvement in biomarkers or endoscopic measures of inflammation. In effect, any attempt to discontinue standard therapy with substitution of cannabis-based therapy should be seen as no different than simply discontinuing standard therapy. There exists the argument that – among those with moderate to severe disease – cannabis might suppress the investigation of mild symptoms which may herald a flare of disease, thus lulling the patient into a state of false stability. We do not advocate the substitution of cannabis products in place of standard medical therapy.
2. Is there a role for cannabis as adjuvant therapy in patients with IBD?
Studies to date have included only symptomatic patients with objective evidence of inflammation and assessed clinical, biochemical, or endoscopic endpoints. In Crohn’s disease, two studies showed no improvement in clinical remission rates but showed improvement in clinical response; a third study showed both improvement in clinical remission/response as well as improved quality of life. No study showed a change in disease markers of activity including CRP, fecal calprotectin, or endoscopic scoring. In one study, all patients relapsed shortly after cannabis discontinuation suggesting that, while there was benefit in symptom control, there was no improvement of the underlying chronic inflammation.
In patients with ulcerative colitis, there were two studies. One study showed no improvement and high rates of intolerance in the treatment group, while the other study reported improved disease activity but no objective improvement. The variation in results between disease states and between studies might be because of cannabis formulations. In patients with persistent symptoms despite current medical therapy, there might be a role in those patients for adjuvant therapy for improvement symptom control but not disease control. Optimization of medical therapy would still be indicated.
3. What dose and formulation of cannabis should I recommend to a patient as adjuvant therapy?
This is an excellent question and one that unfortunately we do not have the answer to. As mentioned previously, the studies have looked at varying formulations (THC alone, CBD:THC with varying percentages of THC, CBD alone) and varying routes of administration (sublingual, oral, inhalation). The IBD studies looking at CBD-alone formulations lacked clinical efficacy. In states where cannabis products have been accessible to IBD patients, no data on the product type (THC:CBD), method of administration, or prescriber preferences have been published.
4. What risks should I advise my patients about with cannabis use?
The challenge is that we don’t have large population-based studies in IBD looking at long-term risks of cannabis use. However, in the small RCT studies there were minimal reported side effects and no major adverse events over 8-10 weeks. Larger IBD population-based studies have shown that cannabis users were more likely to discontinue traditional medical therapy, and there is an increased risk for surgery in patients with Crohn’s disease. Larger studies in non-IBD patients have shown risk for addiction to other substances, diminished life achievement, increased motor vehicle accidents, chronic bronchitis, psychiatric disturbances and cannabis dependence, and cannabis hyperemesis syndrome (with an uncanny presentation resembling Crohn’s disease flare with partial small bowel obstruction). Patients should also be advised about legal implications of use (given its continued classification as a federal schedule 1 drug), possible drug interactions, and special considerations in pediatric patients (increased risk of addiction), elderly patients (increased risk of neuropsychological effects), and during pregnancy (with national obstetric society guidelines warning against use because of fetal exposure and increased risk of stillbirth).
5. What are the legal implications for providers? Patients?
As of July 2020, cannabis is available for recreational use in 12 states, for medicinal use in 28 states, and illegal in 11 states. So the answer really depends on what state the patient lives in. As a provider who might certify patients (in some medicinal states) or recommend cannabis to patients, you should consider legal and licensing implications. Again, this might vary state to state, and you should also take into account federal status. Providers acting in compliance with state laws are unlikely to have federal consequences. However, remember that malpractice insurance only covers FDA-approved medical therapies. Patients should be advised to consider the potential (although highly unlikely) to face federal prosecution and implications of use for employment, school, camp, or travel, and driving restrictions.
Take home points
- Inquire about cannabis to start the conversation.
- Know your state’s legalization status surrounding cannabis.
- Patients with IBD report improvement in symptoms and quality of life with adjuvant cannabis use; however, there is no change in disease activity.
- Encourage your patients to continue and optimize their maintenance therapy.
- Educate your patients about the legal considerations and known risks.
In conclusion, the use of cannabis in IBD patients has increased in recent years. It is important to be able to discuss the risks and benefits of use with your IBD patients. Focus on the lack of data showing that cannabis improves disease activity, and has shown benefit only in improving IBD-associated symptoms. In some patients there might be a role for adjuvant cannabis therapy to improve overall symptom control and quality of life.
Dr. Kinnucan is an assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor; Dr. Swaminath is an associate professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Lenox Hill Hospital, Northwell Health, New York.
Case 1
A 30 year-old female with longstanding ulcerative colitis who has a history of medically refractory steroid-dependent disease and was able to achieve remission with vedolizumab for the last 5 years. Most recent objective assessment showed histologic remission. She has been using daily cannabis medicinally for the last year (high CBD:THC [cannabidiol:delta-9-tetracannabidol] concentration). She notes that she has felt better in the last year since introducing cannabis (improved stool frequency/formation, sleep quality). She inquires about discontinuing her biologic therapy in the hope of using cannabis alone to maintain remission.

Figure 1.
Case 2
A 22-year-old male with ileocolonic inflammatory Crohn’s disease escalated to adalimumab requiring an intensification of therapy to weekly dosing to normalize C-reactive protein (CRP). A recent colonoscopy showed endoscopic improvement (colonic normalization and rare aphthae in ileum). He notes clear clinical improvement, but he continues to experience diarrhea and abdominal cramping (no relationship to meals). Declines addition of immunomodulator (nervous about returning to college during the COVID-19 pandemic). He wonders whether cannabis could be effective in controlling his symptoms as he has had improvement in symptoms during his sporadic recreational cannabis exposure.
Discussion
These cases outline the challenges that providers face when managing patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) when a patient would like to either substitute or incorporate cannabis into their treatment plan. Studies have shown a high prevalence of cannabis use among patients with IBD. With the restrictions surrounding the use of cannabis – either medically or recreationally – being liberalized in many states, these conversations are likely to become more frequent in your practice. However, one of the first challenges that providers face surrounding cannabis is that many patients who use cannabis do not disclose use to their health care team for fear of being judged negatively. In addition, many providers do not routinely ask about cannabis use during office visits. This might be directly related to being unprepared to have a knowledge-based discussion on the risks and benefits of cannabis use in IBD, with the same confidence present during discussion of biologic therapies.
For background, Cannabis sativa (cannabis) is composed of hundreds of phytocannabinoids, the two most common are THC and CBD. These cannabinoids act at the endocannabinoid receptors, which are expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems and immune cells/tissues, and help explain the clinical changes experienced by cannabis users. Both THC and CBD have been studied in varying doses and routes of administration in patients with IBD, making it challenging to translate into real-world recommendations for patients. Some of the most common reported benefits of cannabis use (particularly in an IBD population) are improvement in pain, diarrhea, nausea, and joint pain. Some studies have shown overall improvement in quality of life (Figure 1).
Some common questions that arise surrounding cannabis use in IBD patients include:
1. Is it possible to stop traditional medical therapy and replace it with cannabis therapy?
No studies have directly addressed this exact question. The small studies, both randomized controlled trials and retrospective ones, have studied the effects of cannabis as adjuvant therapy only. None of the data available to date suggest that cannabis has any anti-inflammatory properties with absence of improvement in biomarkers or endoscopic measures of inflammation. In effect, any attempt to discontinue standard therapy with substitution of cannabis-based therapy should be seen as no different than simply discontinuing standard therapy. There exists the argument that – among those with moderate to severe disease – cannabis might suppress the investigation of mild symptoms which may herald a flare of disease, thus lulling the patient into a state of false stability. We do not advocate the substitution of cannabis products in place of standard medical therapy.
2. Is there a role for cannabis as adjuvant therapy in patients with IBD?
Studies to date have included only symptomatic patients with objective evidence of inflammation and assessed clinical, biochemical, or endoscopic endpoints. In Crohn’s disease, two studies showed no improvement in clinical remission rates but showed improvement in clinical response; a third study showed both improvement in clinical remission/response as well as improved quality of life. No study showed a change in disease markers of activity including CRP, fecal calprotectin, or endoscopic scoring. In one study, all patients relapsed shortly after cannabis discontinuation suggesting that, while there was benefit in symptom control, there was no improvement of the underlying chronic inflammation.
In patients with ulcerative colitis, there were two studies. One study showed no improvement and high rates of intolerance in the treatment group, while the other study reported improved disease activity but no objective improvement. The variation in results between disease states and between studies might be because of cannabis formulations. In patients with persistent symptoms despite current medical therapy, there might be a role in those patients for adjuvant therapy for improvement symptom control but not disease control. Optimization of medical therapy would still be indicated.
3. What dose and formulation of cannabis should I recommend to a patient as adjuvant therapy?
This is an excellent question and one that unfortunately we do not have the answer to. As mentioned previously, the studies have looked at varying formulations (THC alone, CBD:THC with varying percentages of THC, CBD alone) and varying routes of administration (sublingual, oral, inhalation). The IBD studies looking at CBD-alone formulations lacked clinical efficacy. In states where cannabis products have been accessible to IBD patients, no data on the product type (THC:CBD), method of administration, or prescriber preferences have been published.
4. What risks should I advise my patients about with cannabis use?
The challenge is that we don’t have large population-based studies in IBD looking at long-term risks of cannabis use. However, in the small RCT studies there were minimal reported side effects and no major adverse events over 8-10 weeks. Larger IBD population-based studies have shown that cannabis users were more likely to discontinue traditional medical therapy, and there is an increased risk for surgery in patients with Crohn’s disease. Larger studies in non-IBD patients have shown risk for addiction to other substances, diminished life achievement, increased motor vehicle accidents, chronic bronchitis, psychiatric disturbances and cannabis dependence, and cannabis hyperemesis syndrome (with an uncanny presentation resembling Crohn’s disease flare with partial small bowel obstruction). Patients should also be advised about legal implications of use (given its continued classification as a federal schedule 1 drug), possible drug interactions, and special considerations in pediatric patients (increased risk of addiction), elderly patients (increased risk of neuropsychological effects), and during pregnancy (with national obstetric society guidelines warning against use because of fetal exposure and increased risk of stillbirth).
5. What are the legal implications for providers? Patients?
As of July 2020, cannabis is available for recreational use in 12 states, for medicinal use in 28 states, and illegal in 11 states. So the answer really depends on what state the patient lives in. As a provider who might certify patients (in some medicinal states) or recommend cannabis to patients, you should consider legal and licensing implications. Again, this might vary state to state, and you should also take into account federal status. Providers acting in compliance with state laws are unlikely to have federal consequences. However, remember that malpractice insurance only covers FDA-approved medical therapies. Patients should be advised to consider the potential (although highly unlikely) to face federal prosecution and implications of use for employment, school, camp, or travel, and driving restrictions.
Take home points
- Inquire about cannabis to start the conversation.
- Know your state’s legalization status surrounding cannabis.
- Patients with IBD report improvement in symptoms and quality of life with adjuvant cannabis use; however, there is no change in disease activity.
- Encourage your patients to continue and optimize their maintenance therapy.
- Educate your patients about the legal considerations and known risks.
In conclusion, the use of cannabis in IBD patients has increased in recent years. It is important to be able to discuss the risks and benefits of use with your IBD patients. Focus on the lack of data showing that cannabis improves disease activity, and has shown benefit only in improving IBD-associated symptoms. In some patients there might be a role for adjuvant cannabis therapy to improve overall symptom control and quality of life.
Dr. Kinnucan is an assistant professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor; Dr. Swaminath is an associate professor of medicine, division of gastroenterology, Lenox Hill Hospital, Northwell Health, New York.
Staying financially well in the time of COVID-19
As COVID-19 continues to threaten the United States and the world, individuals in every profession have been challenged to examine their financial situation. At Fidelity Investments, we recently conducted a national survey asking people how current events have affected their opinions and behaviors when it comes to their money. The results showed that six in 10 Americans are concerned about household finances over the next 6 months. Unfortunately, we’ve seen that even health care professionals have not been financially spared, with salaries or benefits cut or, worse, furloughs and layoffs as hospital systems struggle. I work with many physicians, including gastroenterologists, in my role as a wealth planner for Fidelity Investments and have received quite a few questions related to shoring up family finances during these difficult times.
Luckily, the financial best practices that I share in “good” times ring true even in today’s world, with a few additions given the health and economic risks created by COVID-19.
1. Review your budget. It’s one thing to know that your budget is generally balanced (the dollars you spend are less than the dollars you earn). But it’s worth taking a closer look to see just where those dollars are going. In times of uncertainty, cutting back on expenses that aren’t necessary or don’t provide meaningful value to your life can be worthwhile. If you or your family have lost income because of the pandemic, you might consider these seven simple tips to help boost your cash flow.
2. Tackle (or find relief from) student loan debt. Doctors today graduate medical school with a median debt of just under $195,000.1 Repaying these loans is daunting, particularly during the COVID-19 crisis. The recent passing of the CARES Act recognizes these difficult times: in fact, it automatically suspended required minimum loan payments and interest accrual on federal student loans until Sept. 30, 2020. This only applies to federal student loans, not private student loans. Beyond this period, if you are still struggling with payments, you may explore the possibility of refinancing, by taking out a lower-interest private loan and using that to pay off student loans (although this may extend the life of your loan). Borrowers could also consider other programs, such as REPAYE (Revised Pay As You Earn) through which your monthly payment tops out at 10% of your monthly income, or Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) if you work for a not-for-profit hospital or other qualifying employer. This program forgives the remaining balance on your direct loans after you have made 120 qualifying monthly payments while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
Additionally, borrowers could look for opportunities to reduce accrued interest, either by refinancing to a lower rate or making payments every 2 weeks rather than once each month.
3. Evaluate your emergency fund. It’s a good idea to keep 3-6 months’ of essential expenses in cash or cash-like investments. If you don’t yet have this 3- to 6-month cushion saved, now is a good time to work to reduce your expenses and stash away any extra cash.
4. Save early and often for retirement. You can borrow money to support many of life’s needs, from housing, to cars, to college. But you can’t borrow for retirement. That is why I encourage clients to put retirement savings at the top of the list, after accounting for day-to-day needs of their families. People often ask me whether it makes sense to continue saving for retirement, often a far-off goal for younger doctors, especially in these uncertain times. My answer? Yes. If you are able to save, continue to save: the earlier you begin to make contributions to your retirement account, and the longer you continue to do so, the more your retirement account(s) have the potential to grow over time.
Another question I receive is whether to take distributions from a retirement account early if you find yourself in a precarious financial situation because of the COVID-19 crisis. The CARES Act provides options allowing Americans to take a withdrawal or loan from a participating retirement plan if you, your spouse, or your dependent have a COVID-19 related illness or you’re experiencing a loss of income related to the COVID-19 pandemic. Try to look at alternative sources of income before tapping your hard-earned retirement savings. If you can find a way to continue saving and avoid drawing down your retirement accounts, your future self will thank you.
5. If you have a high-deductible health plan that offers it, explore a Health Savings Account (HSA). One of the most important factors in a solid financial plan is knowing how to pay for health care expenses, both now and as we age. HSAs are a tax-advantaged account that can be used to save money for qualified medical expenses. They are considered to provide a “triple-tax advantage” since contributions, qualified withdrawals, and investment growth are all tax-free.2 The dollars in these accounts can stay there over time, so in years with low expenses you could use these to save for health care in retirement, while in other years they can be used to pay necessary medical bills. HSAs require the participant to be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan, so you would first need to verify that your employer provides this option.
6. Be prepared to protect yourself, your practice, and your family. Typically, I encourage the medical professionals I work with to review their current insurance plans (such as disability, life, and malpractice) to determine whether they have the right levels of coverage for their situation. With COVID-19 layered on top of the usual level of risk, it’s important to consider reviewing or updating other key elements of your family’s plan, like your health care proxies and a living will.
7. Put your income to work. When your disposable income grows, and you’ve covered all of the foundational elements of a financial plan (a rainy-day fund, contingency planning for health care costs, and so on), it might be the right time to consider investing for something other than retirement. As you do that, be sure you are invested in a diversified strategy with a balance of risk and return that is comfortable for you.
Recent market volatility can bring nerves that make it difficult to stay invested. However, as long as your risk tolerance and time horizon reflect your asset allocation – the mix of stock, bonds, and cash (which a financial planner can help with) – you can take comfort in knowing that historically every severe downturn has eventually given way to further growth.
During uncertain times like these, I think the best guidance is to focus on what you can control. The considerations above are a great place to start building a financial plan to solidify you and your family’s future. A Fidelity survey found that 44% of Americans are now working to build up their emergency savings, and one-third (34%) are rethinking how they manage their money because of the COVID-19 crisis.3 Despite the stresses we all face, there is no time like the present to start or revisit your financial plan.
Footnotes
1. Barron D. Why Doctors Are Drowning in Medical School Debt. Scientific American. July 15, 2019.
2. With respect to federal taxation only. Contributions, investment earnings, and distributions may or may not be subject to state taxation. The triple tax advantages are only applicable if the money is used to pay for qualified medical expenses as described in IRS Publication 969.
3. Fidelity Market Sentiment Study presents the findings of a nationwide online survey consisting of 3,012 adults, at least 18 years of age, from which 1,591 respondents qualified as having at least one investment account. The study was fielded April 1-8, 2020, by ENGINE INSIGHTS, an independent research firm not affiliated with Fidelity Investments. The results of this survey may not be representative of all adults meeting the same criteria as those surveyed for this study. For the purposes of this study, the generations are defined as follows: Millennials (aged 24-39 years); Generation X (aged 40-55 years); Baby Boomers (aged 56-74 years).
Mr. Tudor is Vice President, Wealth Planning Consultant at Fidelity Investments.
As COVID-19 continues to threaten the United States and the world, individuals in every profession have been challenged to examine their financial situation. At Fidelity Investments, we recently conducted a national survey asking people how current events have affected their opinions and behaviors when it comes to their money. The results showed that six in 10 Americans are concerned about household finances over the next 6 months. Unfortunately, we’ve seen that even health care professionals have not been financially spared, with salaries or benefits cut or, worse, furloughs and layoffs as hospital systems struggle. I work with many physicians, including gastroenterologists, in my role as a wealth planner for Fidelity Investments and have received quite a few questions related to shoring up family finances during these difficult times.
Luckily, the financial best practices that I share in “good” times ring true even in today’s world, with a few additions given the health and economic risks created by COVID-19.
1. Review your budget. It’s one thing to know that your budget is generally balanced (the dollars you spend are less than the dollars you earn). But it’s worth taking a closer look to see just where those dollars are going. In times of uncertainty, cutting back on expenses that aren’t necessary or don’t provide meaningful value to your life can be worthwhile. If you or your family have lost income because of the pandemic, you might consider these seven simple tips to help boost your cash flow.
2. Tackle (or find relief from) student loan debt. Doctors today graduate medical school with a median debt of just under $195,000.1 Repaying these loans is daunting, particularly during the COVID-19 crisis. The recent passing of the CARES Act recognizes these difficult times: in fact, it automatically suspended required minimum loan payments and interest accrual on federal student loans until Sept. 30, 2020. This only applies to federal student loans, not private student loans. Beyond this period, if you are still struggling with payments, you may explore the possibility of refinancing, by taking out a lower-interest private loan and using that to pay off student loans (although this may extend the life of your loan). Borrowers could also consider other programs, such as REPAYE (Revised Pay As You Earn) through which your monthly payment tops out at 10% of your monthly income, or Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) if you work for a not-for-profit hospital or other qualifying employer. This program forgives the remaining balance on your direct loans after you have made 120 qualifying monthly payments while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
Additionally, borrowers could look for opportunities to reduce accrued interest, either by refinancing to a lower rate or making payments every 2 weeks rather than once each month.
3. Evaluate your emergency fund. It’s a good idea to keep 3-6 months’ of essential expenses in cash or cash-like investments. If you don’t yet have this 3- to 6-month cushion saved, now is a good time to work to reduce your expenses and stash away any extra cash.
4. Save early and often for retirement. You can borrow money to support many of life’s needs, from housing, to cars, to college. But you can’t borrow for retirement. That is why I encourage clients to put retirement savings at the top of the list, after accounting for day-to-day needs of their families. People often ask me whether it makes sense to continue saving for retirement, often a far-off goal for younger doctors, especially in these uncertain times. My answer? Yes. If you are able to save, continue to save: the earlier you begin to make contributions to your retirement account, and the longer you continue to do so, the more your retirement account(s) have the potential to grow over time.
Another question I receive is whether to take distributions from a retirement account early if you find yourself in a precarious financial situation because of the COVID-19 crisis. The CARES Act provides options allowing Americans to take a withdrawal or loan from a participating retirement plan if you, your spouse, or your dependent have a COVID-19 related illness or you’re experiencing a loss of income related to the COVID-19 pandemic. Try to look at alternative sources of income before tapping your hard-earned retirement savings. If you can find a way to continue saving and avoid drawing down your retirement accounts, your future self will thank you.
5. If you have a high-deductible health plan that offers it, explore a Health Savings Account (HSA). One of the most important factors in a solid financial plan is knowing how to pay for health care expenses, both now and as we age. HSAs are a tax-advantaged account that can be used to save money for qualified medical expenses. They are considered to provide a “triple-tax advantage” since contributions, qualified withdrawals, and investment growth are all tax-free.2 The dollars in these accounts can stay there over time, so in years with low expenses you could use these to save for health care in retirement, while in other years they can be used to pay necessary medical bills. HSAs require the participant to be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan, so you would first need to verify that your employer provides this option.
6. Be prepared to protect yourself, your practice, and your family. Typically, I encourage the medical professionals I work with to review their current insurance plans (such as disability, life, and malpractice) to determine whether they have the right levels of coverage for their situation. With COVID-19 layered on top of the usual level of risk, it’s important to consider reviewing or updating other key elements of your family’s plan, like your health care proxies and a living will.
7. Put your income to work. When your disposable income grows, and you’ve covered all of the foundational elements of a financial plan (a rainy-day fund, contingency planning for health care costs, and so on), it might be the right time to consider investing for something other than retirement. As you do that, be sure you are invested in a diversified strategy with a balance of risk and return that is comfortable for you.
Recent market volatility can bring nerves that make it difficult to stay invested. However, as long as your risk tolerance and time horizon reflect your asset allocation – the mix of stock, bonds, and cash (which a financial planner can help with) – you can take comfort in knowing that historically every severe downturn has eventually given way to further growth.
During uncertain times like these, I think the best guidance is to focus on what you can control. The considerations above are a great place to start building a financial plan to solidify you and your family’s future. A Fidelity survey found that 44% of Americans are now working to build up their emergency savings, and one-third (34%) are rethinking how they manage their money because of the COVID-19 crisis.3 Despite the stresses we all face, there is no time like the present to start or revisit your financial plan.
Footnotes
1. Barron D. Why Doctors Are Drowning in Medical School Debt. Scientific American. July 15, 2019.
2. With respect to federal taxation only. Contributions, investment earnings, and distributions may or may not be subject to state taxation. The triple tax advantages are only applicable if the money is used to pay for qualified medical expenses as described in IRS Publication 969.
3. Fidelity Market Sentiment Study presents the findings of a nationwide online survey consisting of 3,012 adults, at least 18 years of age, from which 1,591 respondents qualified as having at least one investment account. The study was fielded April 1-8, 2020, by ENGINE INSIGHTS, an independent research firm not affiliated with Fidelity Investments. The results of this survey may not be representative of all adults meeting the same criteria as those surveyed for this study. For the purposes of this study, the generations are defined as follows: Millennials (aged 24-39 years); Generation X (aged 40-55 years); Baby Boomers (aged 56-74 years).
Mr. Tudor is Vice President, Wealth Planning Consultant at Fidelity Investments.
As COVID-19 continues to threaten the United States and the world, individuals in every profession have been challenged to examine their financial situation. At Fidelity Investments, we recently conducted a national survey asking people how current events have affected their opinions and behaviors when it comes to their money. The results showed that six in 10 Americans are concerned about household finances over the next 6 months. Unfortunately, we’ve seen that even health care professionals have not been financially spared, with salaries or benefits cut or, worse, furloughs and layoffs as hospital systems struggle. I work with many physicians, including gastroenterologists, in my role as a wealth planner for Fidelity Investments and have received quite a few questions related to shoring up family finances during these difficult times.
Luckily, the financial best practices that I share in “good” times ring true even in today’s world, with a few additions given the health and economic risks created by COVID-19.
1. Review your budget. It’s one thing to know that your budget is generally balanced (the dollars you spend are less than the dollars you earn). But it’s worth taking a closer look to see just where those dollars are going. In times of uncertainty, cutting back on expenses that aren’t necessary or don’t provide meaningful value to your life can be worthwhile. If you or your family have lost income because of the pandemic, you might consider these seven simple tips to help boost your cash flow.
2. Tackle (or find relief from) student loan debt. Doctors today graduate medical school with a median debt of just under $195,000.1 Repaying these loans is daunting, particularly during the COVID-19 crisis. The recent passing of the CARES Act recognizes these difficult times: in fact, it automatically suspended required minimum loan payments and interest accrual on federal student loans until Sept. 30, 2020. This only applies to federal student loans, not private student loans. Beyond this period, if you are still struggling with payments, you may explore the possibility of refinancing, by taking out a lower-interest private loan and using that to pay off student loans (although this may extend the life of your loan). Borrowers could also consider other programs, such as REPAYE (Revised Pay As You Earn) through which your monthly payment tops out at 10% of your monthly income, or Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) if you work for a not-for-profit hospital or other qualifying employer. This program forgives the remaining balance on your direct loans after you have made 120 qualifying monthly payments while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
Additionally, borrowers could look for opportunities to reduce accrued interest, either by refinancing to a lower rate or making payments every 2 weeks rather than once each month.
3. Evaluate your emergency fund. It’s a good idea to keep 3-6 months’ of essential expenses in cash or cash-like investments. If you don’t yet have this 3- to 6-month cushion saved, now is a good time to work to reduce your expenses and stash away any extra cash.
4. Save early and often for retirement. You can borrow money to support many of life’s needs, from housing, to cars, to college. But you can’t borrow for retirement. That is why I encourage clients to put retirement savings at the top of the list, after accounting for day-to-day needs of their families. People often ask me whether it makes sense to continue saving for retirement, often a far-off goal for younger doctors, especially in these uncertain times. My answer? Yes. If you are able to save, continue to save: the earlier you begin to make contributions to your retirement account, and the longer you continue to do so, the more your retirement account(s) have the potential to grow over time.
Another question I receive is whether to take distributions from a retirement account early if you find yourself in a precarious financial situation because of the COVID-19 crisis. The CARES Act provides options allowing Americans to take a withdrawal or loan from a participating retirement plan if you, your spouse, or your dependent have a COVID-19 related illness or you’re experiencing a loss of income related to the COVID-19 pandemic. Try to look at alternative sources of income before tapping your hard-earned retirement savings. If you can find a way to continue saving and avoid drawing down your retirement accounts, your future self will thank you.
5. If you have a high-deductible health plan that offers it, explore a Health Savings Account (HSA). One of the most important factors in a solid financial plan is knowing how to pay for health care expenses, both now and as we age. HSAs are a tax-advantaged account that can be used to save money for qualified medical expenses. They are considered to provide a “triple-tax advantage” since contributions, qualified withdrawals, and investment growth are all tax-free.2 The dollars in these accounts can stay there over time, so in years with low expenses you could use these to save for health care in retirement, while in other years they can be used to pay necessary medical bills. HSAs require the participant to be enrolled in a high-deductible health plan, so you would first need to verify that your employer provides this option.
6. Be prepared to protect yourself, your practice, and your family. Typically, I encourage the medical professionals I work with to review their current insurance plans (such as disability, life, and malpractice) to determine whether they have the right levels of coverage for their situation. With COVID-19 layered on top of the usual level of risk, it’s important to consider reviewing or updating other key elements of your family’s plan, like your health care proxies and a living will.
7. Put your income to work. When your disposable income grows, and you’ve covered all of the foundational elements of a financial plan (a rainy-day fund, contingency planning for health care costs, and so on), it might be the right time to consider investing for something other than retirement. As you do that, be sure you are invested in a diversified strategy with a balance of risk and return that is comfortable for you.
Recent market volatility can bring nerves that make it difficult to stay invested. However, as long as your risk tolerance and time horizon reflect your asset allocation – the mix of stock, bonds, and cash (which a financial planner can help with) – you can take comfort in knowing that historically every severe downturn has eventually given way to further growth.
During uncertain times like these, I think the best guidance is to focus on what you can control. The considerations above are a great place to start building a financial plan to solidify you and your family’s future. A Fidelity survey found that 44% of Americans are now working to build up their emergency savings, and one-third (34%) are rethinking how they manage their money because of the COVID-19 crisis.3 Despite the stresses we all face, there is no time like the present to start or revisit your financial plan.
Footnotes
1. Barron D. Why Doctors Are Drowning in Medical School Debt. Scientific American. July 15, 2019.
2. With respect to federal taxation only. Contributions, investment earnings, and distributions may or may not be subject to state taxation. The triple tax advantages are only applicable if the money is used to pay for qualified medical expenses as described in IRS Publication 969.
3. Fidelity Market Sentiment Study presents the findings of a nationwide online survey consisting of 3,012 adults, at least 18 years of age, from which 1,591 respondents qualified as having at least one investment account. The study was fielded April 1-8, 2020, by ENGINE INSIGHTS, an independent research firm not affiliated with Fidelity Investments. The results of this survey may not be representative of all adults meeting the same criteria as those surveyed for this study. For the purposes of this study, the generations are defined as follows: Millennials (aged 24-39 years); Generation X (aged 40-55 years); Baby Boomers (aged 56-74 years).
Mr. Tudor is Vice President, Wealth Planning Consultant at Fidelity Investments.
Web-based fellowship interviews in the era of COVID 19: Tips and tricks
Fellowship interviews are an essential step – arguably the most important step – in the process of matching candidates to training programs. Until recently, most programs relied exclusively on on-site face-to face interviews. Since the appearance of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical field has utilized web-based platforms. Despite inherent limitations, virtual meetings appear to be effective in providing patient care and in conducting administrative meetings.1,2
Because of uncertainty related to the pandemic, including changing guidelines regarding social distancing and travel restrictions, fellowship programs are expected to comply with CDC,3 state, and federal recommendations to avoid nonessential travel. Therefore, conducting web-based interviews exclusively will likely become a necessity.
While there may be some disadvantages to web-based interviews, many candidates find the overall experience satisfactory, thereby allowing them to understand the programs, express themselves, and comfortably rank the programs, as two studies have shown.4,5 Programs and candidates are encouraged to adapt to this new reality in order to achieve a successful match. After all, there are many potential advantages of web-based interviews. In addition to eliminating the risk of COVID-19 acquisition, web-based interviews have been described as helping to improve scheduling flexibility, reduce the financial burden, and allow conducting more interviews for candidates and programs (Table 1).6-8
There are different styles to the web-based interview.9 Some programs choose to offer a single group interview (or the so-called panel interview) in which all the interviewing faculties invite each candidate at a time. Alternatively, programs might choose to conduct separate interviews by each faculty in which the candidates would alternate. For the latter option, the program could use a single invitation link or multiple invitation links for each session.
General tips for a successful interview:9
1. Be pleasant and professional: Your communication with the program should reflect excellent manners and a professional attitude with everyone (i.e., faculties, coordinators, and fellows).
2. Know yourself and what you want: Review your CV and personal statement and reflect on your achievements, strengths and weaknesses. Identify examples from your experience that would speak well of you as a person and as a physician.
3. Communication is key:
- Respond to the interview invitations promptly.
- Send a brief thank you email to the interviewers and the coordinator. Avoid being generic; mention specific points of discussion and show your interest in the program.
- Proofread your emails carefully. Well-written emails that are devoid of grammatical or spelling errors send a positive message about the candidate.
4. Do your homework:
- Read the information posted on the website carefully and take notes. This should provide you with useful information to use when you rank the programs and could lead to questions that you might want to ask your interviewers. Besides, asking questions that are answered on the website reflects poorly on the candidate.
- Pay attention to various clues that could reflect how organized and how academically oriented a program is. For example, a program that provides details about their didactic lectures sends a message that quality teaching is a priority. On the other hand, a program that has a website that hasn’t been updated for years could dissuade rather than recruit applicants.
- Read about the faculty, their areas of interests, and publications. Learn how their names are pronounced and use them during the interview.
- Read about the city where the program is. It shows interest in the area where you might be living and will help you to stand out among candidates.
5. Be prepared for the classics; be honest, genuine, and authentic. Think about these common prompts:
- Tell me about yourself.
- Why did you choose gastroenterology?
- Where do you see yourself in 5 years?
- Why would you like to come to the city where the program is?
- Are there any certain areas in gastroenterology that you’re interested in more (e.g., hepatology, motility, IBD, advanced endoscopy)?
6. It is likely your interviewer will ask if you have questions. Ask questions that further allow you to assess the program and your fit into the program.
- What aspects of the program are you most proud of?
- Where would you like to see this program in 5 years?
- What keeps you at this program?
Tips for a successful web-based interview9,10 (Table 2):
1. Pay attention to the time zone of the city of the program. Be ready at least 10 minutes before the interview.
2. Ensure a fast and stable Internet service for an uninterrupted interview experience. Consider using an ethernet cable. Have a back-up plan such as using a phone as a hotspot.
3. Use a quiet and private room, preferably at home. Be aware of the background. A simple decoration is acceptable.
4. Consider recording yourself using the same device you’ll use for the interview to make sure audio and video are functioning properly.
5. When scheduling more than one interview in 1 day, allow at least 2 hours between interviews to avoid scheduling conflicts caused by unanticipated delays related to technical issues.
6. Have immediate access to the invitation link(s) that you received. Add the interviews to your device’s calendar. Note that sometimes a new invitation link is generated last minute because of technical issues.
7. While the advice for physical interviews is to turn off your phone (and smart watch), you’ll have to keep your phone on but on silent for the virtual interviews. Sometimes, you’ll receive a phone call from the program to update you about any last-minute changes.
7. It is recommended that a laptop or a tablet with a camera with good resolution and a microphone be used rather than using a phone. A wide screen allows better communication. Disable notification on that device to avoid interruptions.
8. Sit comfortably with the device being at or just below eye level. Avoid distractions and maintain eye contact.
9. Familiarize yourself with the platform used and its functions. Double check the audio and video before each interview.
10. Put your device on a desk or table to improve stability; don’t hold it in your hand.
11. Find a place where the view is best and your face appears in the middle of the screen; not too far or too close. Use a well-lit room but don’t have a source of light behind you. Many platforms allow you to select a background or blur the background. A background that is monochromatic and not distracting is recommended.
12. Use a pen and a paper to take notes during the interview. You would use these notes to generate “thank you” or “interest in program” emails. Additionally, they will be a helpful reference when ranking programs.
13. Do not type. Typing is much louder to the interviewer and can be distracting.
14. Dress professionally, just as you dress for an on-site interview. You never know when you might have to stand up during the interview for unplanned reasons.
15. Do a practice interview. Have a colleague set up a virtual web session using any available platform. This will allow you to get feedback on your dress, background, acoustics, and general ability to answer questions.
References
1. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:1150-7.
2. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e016242.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus and Travel in the United States, 2020.
4. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99:e114.
5. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:155-9.
6. West J Emerg Med. 2018;19:80-6.
7. Int J Med Educ. 2016;7:102-8.
8. Aparajit Naram M. How COVID-19 changed our fellowship interview process for the better. KevinMD.com. April 17, 2020.
9. Association of American Medical Colleges. Virtual interviews: Tips for medical school applicants, 2020. Updated May 14, 2020.
10. Top 5 video interviewing tips for residency and fellowship programs. Thalamus: Connecting the Docs. April 2, 2020, 2020.
Dr. Kiwan is chief fellow in gastroenterology, division of gastroenterology, at Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center, John D. Dingell VA Medical Center, all in Detroit. Dr. Judd is an assistant professor and associate program director in the division of gastroenterology, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center, John D. Dingell VA Medical Center. Dr. Al Masalmeh is in the department of internal medicine, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center. Dr. Levine is professor and the vice chair for education, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center.
Fellowship interviews are an essential step – arguably the most important step – in the process of matching candidates to training programs. Until recently, most programs relied exclusively on on-site face-to face interviews. Since the appearance of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical field has utilized web-based platforms. Despite inherent limitations, virtual meetings appear to be effective in providing patient care and in conducting administrative meetings.1,2
Because of uncertainty related to the pandemic, including changing guidelines regarding social distancing and travel restrictions, fellowship programs are expected to comply with CDC,3 state, and federal recommendations to avoid nonessential travel. Therefore, conducting web-based interviews exclusively will likely become a necessity.
While there may be some disadvantages to web-based interviews, many candidates find the overall experience satisfactory, thereby allowing them to understand the programs, express themselves, and comfortably rank the programs, as two studies have shown.4,5 Programs and candidates are encouraged to adapt to this new reality in order to achieve a successful match. After all, there are many potential advantages of web-based interviews. In addition to eliminating the risk of COVID-19 acquisition, web-based interviews have been described as helping to improve scheduling flexibility, reduce the financial burden, and allow conducting more interviews for candidates and programs (Table 1).6-8
There are different styles to the web-based interview.9 Some programs choose to offer a single group interview (or the so-called panel interview) in which all the interviewing faculties invite each candidate at a time. Alternatively, programs might choose to conduct separate interviews by each faculty in which the candidates would alternate. For the latter option, the program could use a single invitation link or multiple invitation links for each session.
General tips for a successful interview:9
1. Be pleasant and professional: Your communication with the program should reflect excellent manners and a professional attitude with everyone (i.e., faculties, coordinators, and fellows).
2. Know yourself and what you want: Review your CV and personal statement and reflect on your achievements, strengths and weaknesses. Identify examples from your experience that would speak well of you as a person and as a physician.
3. Communication is key:
- Respond to the interview invitations promptly.
- Send a brief thank you email to the interviewers and the coordinator. Avoid being generic; mention specific points of discussion and show your interest in the program.
- Proofread your emails carefully. Well-written emails that are devoid of grammatical or spelling errors send a positive message about the candidate.
4. Do your homework:
- Read the information posted on the website carefully and take notes. This should provide you with useful information to use when you rank the programs and could lead to questions that you might want to ask your interviewers. Besides, asking questions that are answered on the website reflects poorly on the candidate.
- Pay attention to various clues that could reflect how organized and how academically oriented a program is. For example, a program that provides details about their didactic lectures sends a message that quality teaching is a priority. On the other hand, a program that has a website that hasn’t been updated for years could dissuade rather than recruit applicants.
- Read about the faculty, their areas of interests, and publications. Learn how their names are pronounced and use them during the interview.
- Read about the city where the program is. It shows interest in the area where you might be living and will help you to stand out among candidates.
5. Be prepared for the classics; be honest, genuine, and authentic. Think about these common prompts:
- Tell me about yourself.
- Why did you choose gastroenterology?
- Where do you see yourself in 5 years?
- Why would you like to come to the city where the program is?
- Are there any certain areas in gastroenterology that you’re interested in more (e.g., hepatology, motility, IBD, advanced endoscopy)?
6. It is likely your interviewer will ask if you have questions. Ask questions that further allow you to assess the program and your fit into the program.
- What aspects of the program are you most proud of?
- Where would you like to see this program in 5 years?
- What keeps you at this program?
Tips for a successful web-based interview9,10 (Table 2):
1. Pay attention to the time zone of the city of the program. Be ready at least 10 minutes before the interview.
2. Ensure a fast and stable Internet service for an uninterrupted interview experience. Consider using an ethernet cable. Have a back-up plan such as using a phone as a hotspot.
3. Use a quiet and private room, preferably at home. Be aware of the background. A simple decoration is acceptable.
4. Consider recording yourself using the same device you’ll use for the interview to make sure audio and video are functioning properly.
5. When scheduling more than one interview in 1 day, allow at least 2 hours between interviews to avoid scheduling conflicts caused by unanticipated delays related to technical issues.
6. Have immediate access to the invitation link(s) that you received. Add the interviews to your device’s calendar. Note that sometimes a new invitation link is generated last minute because of technical issues.
7. While the advice for physical interviews is to turn off your phone (and smart watch), you’ll have to keep your phone on but on silent for the virtual interviews. Sometimes, you’ll receive a phone call from the program to update you about any last-minute changes.
7. It is recommended that a laptop or a tablet with a camera with good resolution and a microphone be used rather than using a phone. A wide screen allows better communication. Disable notification on that device to avoid interruptions.
8. Sit comfortably with the device being at or just below eye level. Avoid distractions and maintain eye contact.
9. Familiarize yourself with the platform used and its functions. Double check the audio and video before each interview.
10. Put your device on a desk or table to improve stability; don’t hold it in your hand.
11. Find a place where the view is best and your face appears in the middle of the screen; not too far or too close. Use a well-lit room but don’t have a source of light behind you. Many platforms allow you to select a background or blur the background. A background that is monochromatic and not distracting is recommended.
12. Use a pen and a paper to take notes during the interview. You would use these notes to generate “thank you” or “interest in program” emails. Additionally, they will be a helpful reference when ranking programs.
13. Do not type. Typing is much louder to the interviewer and can be distracting.
14. Dress professionally, just as you dress for an on-site interview. You never know when you might have to stand up during the interview for unplanned reasons.
15. Do a practice interview. Have a colleague set up a virtual web session using any available platform. This will allow you to get feedback on your dress, background, acoustics, and general ability to answer questions.
References
1. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:1150-7.
2. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e016242.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus and Travel in the United States, 2020.
4. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99:e114.
5. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:155-9.
6. West J Emerg Med. 2018;19:80-6.
7. Int J Med Educ. 2016;7:102-8.
8. Aparajit Naram M. How COVID-19 changed our fellowship interview process for the better. KevinMD.com. April 17, 2020.
9. Association of American Medical Colleges. Virtual interviews: Tips for medical school applicants, 2020. Updated May 14, 2020.
10. Top 5 video interviewing tips for residency and fellowship programs. Thalamus: Connecting the Docs. April 2, 2020, 2020.
Dr. Kiwan is chief fellow in gastroenterology, division of gastroenterology, at Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center, John D. Dingell VA Medical Center, all in Detroit. Dr. Judd is an assistant professor and associate program director in the division of gastroenterology, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center, John D. Dingell VA Medical Center. Dr. Al Masalmeh is in the department of internal medicine, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center. Dr. Levine is professor and the vice chair for education, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center.
Fellowship interviews are an essential step – arguably the most important step – in the process of matching candidates to training programs. Until recently, most programs relied exclusively on on-site face-to face interviews. Since the appearance of the COVID-19 pandemic, the medical field has utilized web-based platforms. Despite inherent limitations, virtual meetings appear to be effective in providing patient care and in conducting administrative meetings.1,2
Because of uncertainty related to the pandemic, including changing guidelines regarding social distancing and travel restrictions, fellowship programs are expected to comply with CDC,3 state, and federal recommendations to avoid nonessential travel. Therefore, conducting web-based interviews exclusively will likely become a necessity.
While there may be some disadvantages to web-based interviews, many candidates find the overall experience satisfactory, thereby allowing them to understand the programs, express themselves, and comfortably rank the programs, as two studies have shown.4,5 Programs and candidates are encouraged to adapt to this new reality in order to achieve a successful match. After all, there are many potential advantages of web-based interviews. In addition to eliminating the risk of COVID-19 acquisition, web-based interviews have been described as helping to improve scheduling flexibility, reduce the financial burden, and allow conducting more interviews for candidates and programs (Table 1).6-8
There are different styles to the web-based interview.9 Some programs choose to offer a single group interview (or the so-called panel interview) in which all the interviewing faculties invite each candidate at a time. Alternatively, programs might choose to conduct separate interviews by each faculty in which the candidates would alternate. For the latter option, the program could use a single invitation link or multiple invitation links for each session.
General tips for a successful interview:9
1. Be pleasant and professional: Your communication with the program should reflect excellent manners and a professional attitude with everyone (i.e., faculties, coordinators, and fellows).
2. Know yourself and what you want: Review your CV and personal statement and reflect on your achievements, strengths and weaknesses. Identify examples from your experience that would speak well of you as a person and as a physician.
3. Communication is key:
- Respond to the interview invitations promptly.
- Send a brief thank you email to the interviewers and the coordinator. Avoid being generic; mention specific points of discussion and show your interest in the program.
- Proofread your emails carefully. Well-written emails that are devoid of grammatical or spelling errors send a positive message about the candidate.
4. Do your homework:
- Read the information posted on the website carefully and take notes. This should provide you with useful information to use when you rank the programs and could lead to questions that you might want to ask your interviewers. Besides, asking questions that are answered on the website reflects poorly on the candidate.
- Pay attention to various clues that could reflect how organized and how academically oriented a program is. For example, a program that provides details about their didactic lectures sends a message that quality teaching is a priority. On the other hand, a program that has a website that hasn’t been updated for years could dissuade rather than recruit applicants.
- Read about the faculty, their areas of interests, and publications. Learn how their names are pronounced and use them during the interview.
- Read about the city where the program is. It shows interest in the area where you might be living and will help you to stand out among candidates.
5. Be prepared for the classics; be honest, genuine, and authentic. Think about these common prompts:
- Tell me about yourself.
- Why did you choose gastroenterology?
- Where do you see yourself in 5 years?
- Why would you like to come to the city where the program is?
- Are there any certain areas in gastroenterology that you’re interested in more (e.g., hepatology, motility, IBD, advanced endoscopy)?
6. It is likely your interviewer will ask if you have questions. Ask questions that further allow you to assess the program and your fit into the program.
- What aspects of the program are you most proud of?
- Where would you like to see this program in 5 years?
- What keeps you at this program?
Tips for a successful web-based interview9,10 (Table 2):
1. Pay attention to the time zone of the city of the program. Be ready at least 10 minutes before the interview.
2. Ensure a fast and stable Internet service for an uninterrupted interview experience. Consider using an ethernet cable. Have a back-up plan such as using a phone as a hotspot.
3. Use a quiet and private room, preferably at home. Be aware of the background. A simple decoration is acceptable.
4. Consider recording yourself using the same device you’ll use for the interview to make sure audio and video are functioning properly.
5. When scheduling more than one interview in 1 day, allow at least 2 hours between interviews to avoid scheduling conflicts caused by unanticipated delays related to technical issues.
6. Have immediate access to the invitation link(s) that you received. Add the interviews to your device’s calendar. Note that sometimes a new invitation link is generated last minute because of technical issues.
7. While the advice for physical interviews is to turn off your phone (and smart watch), you’ll have to keep your phone on but on silent for the virtual interviews. Sometimes, you’ll receive a phone call from the program to update you about any last-minute changes.
7. It is recommended that a laptop or a tablet with a camera with good resolution and a microphone be used rather than using a phone. A wide screen allows better communication. Disable notification on that device to avoid interruptions.
8. Sit comfortably with the device being at or just below eye level. Avoid distractions and maintain eye contact.
9. Familiarize yourself with the platform used and its functions. Double check the audio and video before each interview.
10. Put your device on a desk or table to improve stability; don’t hold it in your hand.
11. Find a place where the view is best and your face appears in the middle of the screen; not too far or too close. Use a well-lit room but don’t have a source of light behind you. Many platforms allow you to select a background or blur the background. A background that is monochromatic and not distracting is recommended.
12. Use a pen and a paper to take notes during the interview. You would use these notes to generate “thank you” or “interest in program” emails. Additionally, they will be a helpful reference when ranking programs.
13. Do not type. Typing is much louder to the interviewer and can be distracting.
14. Dress professionally, just as you dress for an on-site interview. You never know when you might have to stand up during the interview for unplanned reasons.
15. Do a practice interview. Have a colleague set up a virtual web session using any available platform. This will allow you to get feedback on your dress, background, acoustics, and general ability to answer questions.
References
1. Dig Dis Sci. 2019;64:1150-7.
2. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e016242.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coronavirus and Travel in the United States, 2020.
4. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99:e114.
5. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:155-9.
6. West J Emerg Med. 2018;19:80-6.
7. Int J Med Educ. 2016;7:102-8.
8. Aparajit Naram M. How COVID-19 changed our fellowship interview process for the better. KevinMD.com. April 17, 2020.
9. Association of American Medical Colleges. Virtual interviews: Tips for medical school applicants, 2020. Updated May 14, 2020.
10. Top 5 video interviewing tips for residency and fellowship programs. Thalamus: Connecting the Docs. April 2, 2020, 2020.
Dr. Kiwan is chief fellow in gastroenterology, division of gastroenterology, at Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center, John D. Dingell VA Medical Center, all in Detroit. Dr. Judd is an assistant professor and associate program director in the division of gastroenterology, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center, John D. Dingell VA Medical Center. Dr. Al Masalmeh is in the department of internal medicine, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center. Dr. Levine is professor and the vice chair for education, Wayne State University, Detroit Medical Center.
Eosinophilic esophagitis: Frequently asked questions (and answers) for the early-career gastroenterologist
Introduction
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) has transformed over the past 3 decades from a rarely encountered entity to one of the most common causes of dysphagia in adults.1 Given the marked rise in prevalence, the early-career gastroenterologist will undoubtedly be involved with managing this disease.2 The typical presentation includes a young, atopic male presenting with dysphagia in the outpatient setting or, more acutely, with a food impaction when on call. As every fellow is keenly aware, the calls often come late at night as patients commonly have meat impactions while consuming dinner. Current management focuses on symptomatic, histologic, and endoscopic improvement with medication, dietary, and mechanical (i.e., dilation) modalities.
EoE is defined by the presence of esophageal dysfunction and esophageal eosinophilic inflammation with ≥15 eosinophils/high-powered field (eos/hpf) required for the diagnosis. With better understanding of the pathogenesis of EoE involving the complex interaction of environmental, host, and genetic factors, advancements have been made as it relates to the diagnostic criteria, endoscopic evaluation, and therapeutic options. In this article, we review the current management of adult patients with EoE and offer practical guidance to key questions for the young gastroenterologist as well as insights into future areas of interest.
What should I consider when diagnosing EoE?
Symptoms are central to the diagnosis and clinical presentation of EoE. In assessing symptoms, clinicians should be aware of adaptive “IMPACT” strategies patients often subconsciously develop in response to their chronic and progressive condition: Imbibing fluids with meals, modifying foods by cutting or pureeing, prolonging meal times, avoiding harder texture foods, chewing excessively, and turning away tablets/pills.3 Failure to query such adaptive behaviors may lead to an underestimation of disease activity and severity.
An important aspect to confirming the diagnosis of EoE is to exclude other causes of esophageal eosinophilia. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is known to cause esophageal eosinophilia and historically has been viewed as a distinct disease process. In fact, initial guidelines included lack of response to a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) trial or normal esophageal pH monitoring as diagnostic criteria.4 However, as experience was garnered, it became clear that PPI therapy was effective at improving inflammation in 30%-50% of patients with clinical presentations and histologic features consistent with EoE. As such, the concept of PPI–responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE) was introduced in 2011.5 Further investigation then highlighted that PPI-REE and EoE had nearly identical clinical, endoscopic, and histologic features as well as eosinophil biomarker and gene expression profiles. Hence, recent international guidelines no longer necessitate a PPI trial to establish a diagnosis of EoE.6
The young gastroenterologist should also be mindful of other issues related to the initial diagnosis of EoE. EoE may present concomitantly with other disease entities including GERD, “extra-esophageal” eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases, concomitant IgE-mediated food allergy, hypereosinophilic syndromes, connective tissue disorders, autoimmune diseases, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.3 It has been speculated that some of these disorders share common aspects of genetic and environmental predisposing factors as well as shared pathogenesis. Careful history taking should include a full review of atopic conditions and GI-related symptoms and endoscopy should carefully inspect not only the esophagus, but also gastric and duodenal mucosa. The endoscopic features almost always reveal edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and strictures and can be assessed using the EoE Endoscopic Reference Scoring system (EREFS).7 EREFS allows for systematic identification of abnormalities that can inform decisions regarding treatment efficacy and decisions on the need for esophageal dilation. When the esophageal mucosa is evaluated for biopsies, furrows and exudates should be targeted, if present, and multiple biopsies (minimum of five to six) should be taken throughout the esophagus given the patchy nature of the disease.
How do I choose an initial therapy?
The choice of initial therapy considers patient preferences, medication availability, disease severity, impact on quality of life, and need for repeated endoscopies. While there are many novel agents currently being investigated in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials, the current mainstays of treatment include PPI therapy, topical steroids, dietary therapy, and dilation. Of note, there have been no head-to-head trials comparing these different modalities. A recent systematic review reported that PPIs can induce histologic remission in 42% of patients.8 The ease of use and availability of PPI therapy make this an attractive first choice for patients. Pooled estimates show that topical steroids can induce remission in 66% of patients.8 It is important to note that there is currently no Food and Drug Administration–approved formulation of steroids for the treatment of EoE. As such, there are several practical aspects to consider when instructing patients to use agents not designed for esophageal delivery (Figure 1).
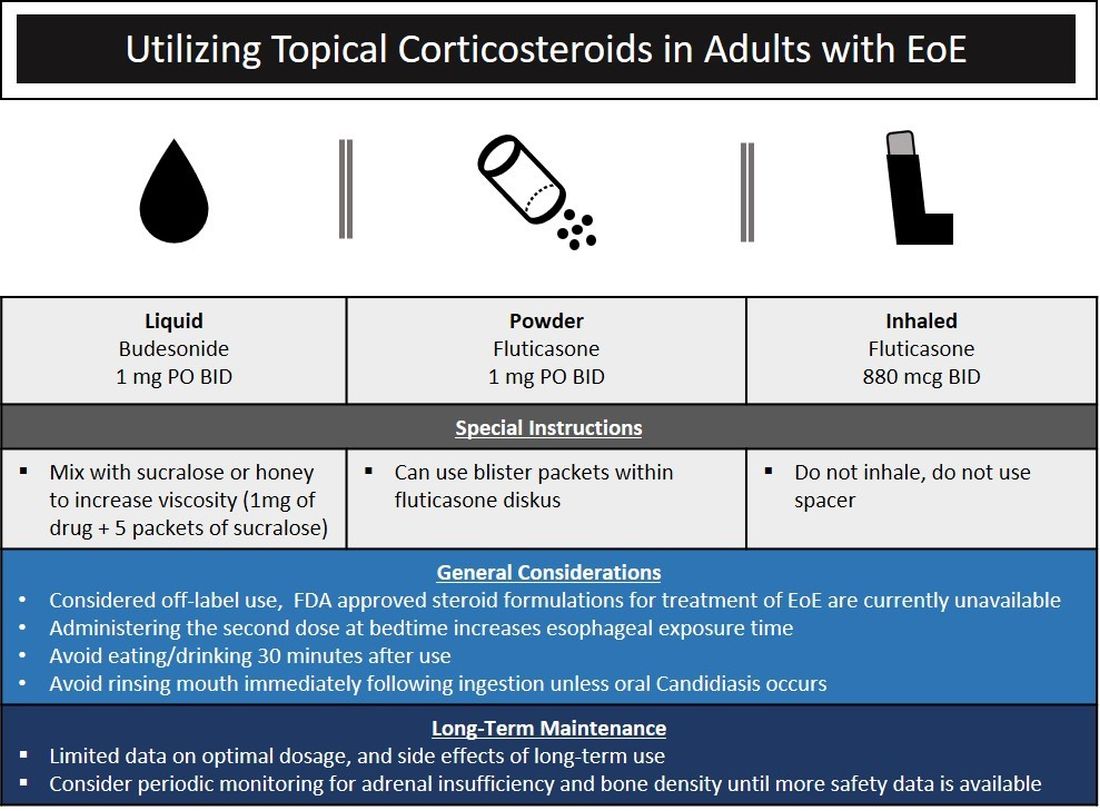
Source: Dr. Patel, Dr. Hirano
Lack of insurance coverage for topical steroids can make cost of a prescription a deterrent to use. While topical steroids are well tolerated, concerns for candidiasis and adrenal insufficiency are being monitored in prospective, long-term clinical trials. Concomitant use of steroids with PPI would be appropriate for EoE patients with coexisting GERD (severe heartburn, erosive esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus). In addition, we often combine steroids with PPI therapy for EoE patients who demonstrate a convincing but incomplete response to PPI monotherapy (i.e., reduction of baseline inflammation from 75 eos/hpf to 20 eos/hpf).
Diet therapy is a popular choice for management of EoE by patients, given the ability to remove food triggers that initiate the immune dysregulation and to avoid chronic medication use. Three dietary options have been described including an elemental, amino acid–based diet which eliminates all common food allergens, allergy testing–directed elimination diet, and an empiric elimination diet. Though elemental diets have shown the most efficacy, practical aspects of implementing, maintaining, and identifying triggers restrict their adoption by most patients and clinicians.9 Allergy-directed elimination diets, where allergens are eliminated based on office-based allergy testing, initially seemed promising, though studies have shown limited histologic remission, compared with other diet therapies as well as the inability to identify true food triggers. Advancement of office-based testing to identify food triggers is needed to streamline this dietary approach. In the adult patient, the empiric elimination diet remains an attractive choice of the available dietary therapies. In this dietary approach, which has shown efficacy in both children and adults, the most common food allergens (milk, wheat, soy, egg, nuts, and seafood) are eliminated.9
How do I make dietary therapy work in clinical practice?
Before dietary therapy is initiated, it is important that your practice is situated to support this approach and that patients fully understand the process. A multidisciplinary approach optimizes dietary therapy. Dietitians provide expert guidance on eliminating trigger foods, maintaining nutrition, and avoiding inadvertent cross-contamination. Patient questions may include the safety of consumption of non–cow-based cheese/milk, alcoholic beverages, wheat alternatives, and restaurant food. Allergists address concerns for a concomitant IgE food allergy based on a clinical history or previous testing. Patients should be informed that identifying a food trigger often takes several months and multiple endoscopies. Clinicians should be aware of potential food cost and accessibility issues as well as the reported, albeit uncommon, development of de novo IgE-mediated food allergy during reintroduction. Timing of diet therapy is also a factor in success. Patients should avoid starting diets during major holidays, family celebrations, college years, and busy travel months.
Particularly empiric elimination diets, frequently used in adults, several approaches have been described (Figure 2).
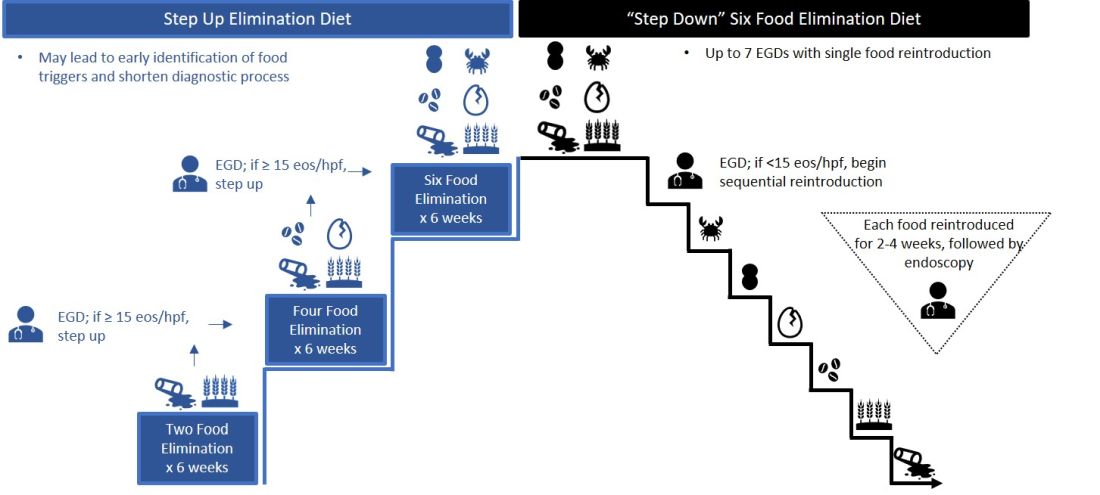
Source: Dr. Patel, Dr. Hirano
Initially, a step-down approach was described, with patients pursuing a six-food elimination diet (SFED), which eliminates the six most common triggers: milk, wheat, soy/legumes, egg, nuts, and seafood. Once in histologic remission, patients then systematically reintroduce foods in order to identify a causative trigger. Given that many patients have only one or two identified food triggers, other approaches were created including a single-food elimination diet eliminating milk, the two-food elimination diet (TFED) eliminating milk and wheat, and the four-food elimination diet (FFED) eliminating milk, wheat, soy/legumes, and eggs. A novel step-up approach has also now been described where patients start with the TFED and progress to the FFED and then potentially SFED based on histologic response.10 This approach has the potential to more readily identify triggers, decrease diagnostic time, and reduce endoscopic interventions. There are pros and cons to each elimination diet approach that should be discussed with patients. Many patients may find a one- or two-food elimination diet more feasible than a full SFED.
What should I consider when performing dilation?
Esophageal dilation is frequently used to address the fibrostenotic complications of EoE that do not as readily respond to PPI, steroid, or diet therapy. The majority of patients note symptomatic improvement following dilation, though dilation alone does not address the inflammatory component of disease.8 With a conservative approach, the complication rates of esophageal dilation in EoE are similar to that of benign, esophageal strictures. Endoscopists should be aware that endoscopy alone can miss strictures and consider both practical and technical aspects when performing dilations (Table 1).11,12
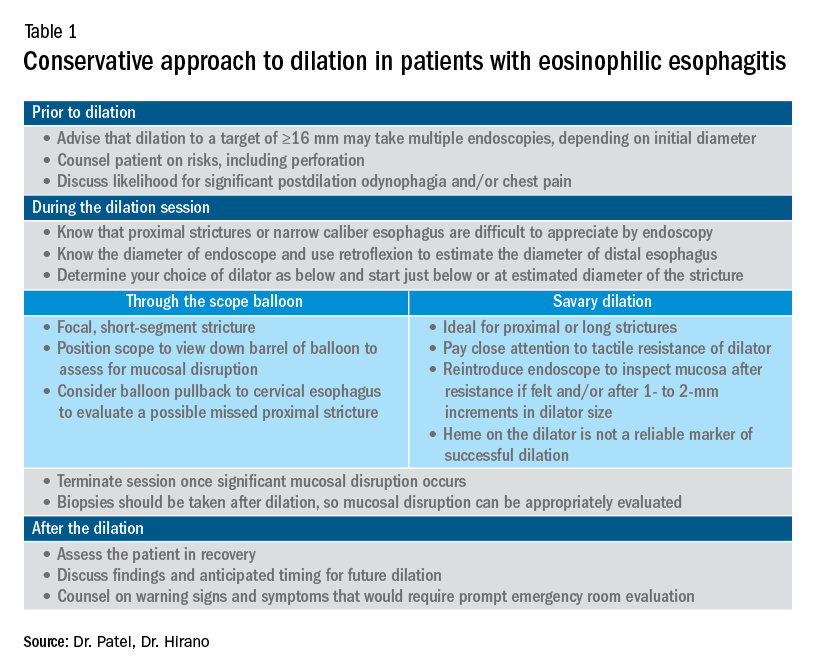
When should an allergist be consulted?
The role of the allergist in the management of patients with EoE varies by patient and practice. IgE serologic or skin testing have limited accuracy in identifying food triggers for EoE. Nevertheless, the majority of patients with EoE have an atopic condition which may include asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, or IgE-mediated food allergy. Although EoE is thought to primarily occur from an immune response to ingested oral allergens, aeroallergens may exacerbate disease as evidenced by the seasonal variation in EoE symptoms in some patients. The allergist provides treatment for these “extraesophageal” atopic conditions which may, in turn, have synergistic effects on the treatment of EoE. Furthermore, allergists may prescribe biologic therapies that are FDA approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. While not approved for EoE, several of these agents have shown efficacy in phase 2 clinical trials in EoE. In some practice settings, allergists primarily manage EoE patients with the assistance of gastroenterologists for periodic endoscopic activity assessment.
What are the key aspects of maintenance therapy?
The goals of treatment focus on symptomatic, histologic, and endoscopic improvement, and the prevention of future or ongoing fibrostenotic complications.2 Because of the adaptive eating behaviors discussed above, symptom response may not reliably correlate with histologic and/or endoscopic improvement. Moreover, dysphagia is related to strictures that often do not resolve in spite of resolution of mucosal inflammation. As such, histology and endoscopy are more objective and reliable targets of a successful response to therapy. Though studies have used variable esophageal density levels for response, using a cutoff of <15 eos/hpf as a therapeutic endpoint is reasonable for both initial response to therapy and long-term monitoring.13 We advocate for standardization of reporting endoscopic findings to better track change over time using the EREFS scoring system.7 While inflammatory features improve, the fibrostenotic features may persist despite improvement in histology. Dilation is often performed in these situations, especially for symptomatic individuals.
During clinical follow-up, the frequency of monitoring as it relates to symptom and endoscopic assessment is not well defined. It is reasonable to repeat endoscopic intervention following changes in therapy (i.e., reduction in steroid dosing or reintroduction of putative food triggers) or in symptoms.13 It is unclear if patients benefit from repeated endoscopies at set intervals without symptom change and after histologic response has been confirmed. In our practice, endoscopies are often considered on an annual basis. This interval is increased for patients with demonstrated stability of disease.
For patients who opt for dietary therapy and have one or two food triggers identified, long-term maintenance therapy can be straightforward with ongoing food avoidance. Limited data exist regarding long-term effectiveness of dietary therapy but loss of initial response has been reported that is often attributed to problems with adherence. Use of “diet holidays” or “planned cheats” to allow for intermittent consumption of trigger foods, often under the cover of short-term use of steroids, may improve the long-term feasibility of diet approaches.
In the recent American Gastroenterological Association guidelines, continuation of swallowed, topical steroids is recommended following remission with short-term treatment. The recurrence of both symptoms and inflammation following medication withdrawal supports this practice. Furthermore, natural history studies demonstrate progression of esophageal strictures with untreated disease.
There are no clear guidelines for long-term dosage and use of PPI or topical steroid therapy. Our practice is to down-titrate the dose of PPI or steroid following remission with short-term therapy, often starting with a reduction from twice a day to daily dosing. Although topical steroid therapy has fewer side effects, compared with systemic steroids, patients should be aware of the potential for adrenal suppression especially in an atopic population who may be exposed to multiple forms of topical steroids. Shared decision-making between patients and providers is recommended to determine comfort level with long-term use of prescription medications and dosage.
What’s on the horizon?
Several areas of development are underway to better assess and manage EoE. Novel histologic scoring tools now assess characteristics on pathology beyond eosinophil density, office-based testing modalities have been developed to assess inflammatory activity and thereby obviate the need for endoscopy, new technology can provide measures of esophageal remodeling and provide assessment of disease severity, and several biologic agents are being studied that target specific allergic mediators of the immune response in EoE.3,14-18 These novel tools, technologies, and therapies will undoubtedly change the management approach to EoE. Referral of patients into ongoing clinical trials will help inform advances in the field.
Conclusion
As an increasingly prevalent disease with a high degree of upper GI morbidity, EoE has transitioned from a rare entity to a commonly encountered disease. The new gastroenterologist will confront both straightforward as well as complex patients with EoE, and we offer several practical aspects on management. In the years ahead, the care of patients with EoE will continue to evolve to a more streamlined, effective, and personalized approach.
References
1. Kidambi T et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:4335-41.
2. Dellon ES et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:319-32 e3.
3. Hirano I et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:840-51.
4. Furuta GT et al. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342-63.
5. Liacouras CA et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3-20 e6; quiz 1-2.
6. Dellon ES et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:1022-33 e10.
7. Hirano I et al. Gut. 2013;62:489-95.
8. Rank MA et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1789-810 e15.
9. Arias A et al. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1639-48.
10. Molina-Infante J et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1365-72.
11. Gentile N et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:1333-40.
12. Hirano I. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:601-6.
13. Hirano I et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1776-86.
14. Collins MH et al. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30:1-8.
15. Furuta GT et al. Gut. 2013;62:1395-405.
16. Katzka DA et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:77-83 e2.
17. Kwiatek MA et al. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:82-90.
18. Nicodeme F et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1101-7 e1.
Introduction
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) has transformed over the past 3 decades from a rarely encountered entity to one of the most common causes of dysphagia in adults.1 Given the marked rise in prevalence, the early-career gastroenterologist will undoubtedly be involved with managing this disease.2 The typical presentation includes a young, atopic male presenting with dysphagia in the outpatient setting or, more acutely, with a food impaction when on call. As every fellow is keenly aware, the calls often come late at night as patients commonly have meat impactions while consuming dinner. Current management focuses on symptomatic, histologic, and endoscopic improvement with medication, dietary, and mechanical (i.e., dilation) modalities.
EoE is defined by the presence of esophageal dysfunction and esophageal eosinophilic inflammation with ≥15 eosinophils/high-powered field (eos/hpf) required for the diagnosis. With better understanding of the pathogenesis of EoE involving the complex interaction of environmental, host, and genetic factors, advancements have been made as it relates to the diagnostic criteria, endoscopic evaluation, and therapeutic options. In this article, we review the current management of adult patients with EoE and offer practical guidance to key questions for the young gastroenterologist as well as insights into future areas of interest.
What should I consider when diagnosing EoE?
Symptoms are central to the diagnosis and clinical presentation of EoE. In assessing symptoms, clinicians should be aware of adaptive “IMPACT” strategies patients often subconsciously develop in response to their chronic and progressive condition: Imbibing fluids with meals, modifying foods by cutting or pureeing, prolonging meal times, avoiding harder texture foods, chewing excessively, and turning away tablets/pills.3 Failure to query such adaptive behaviors may lead to an underestimation of disease activity and severity.
An important aspect to confirming the diagnosis of EoE is to exclude other causes of esophageal eosinophilia. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is known to cause esophageal eosinophilia and historically has been viewed as a distinct disease process. In fact, initial guidelines included lack of response to a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) trial or normal esophageal pH monitoring as diagnostic criteria.4 However, as experience was garnered, it became clear that PPI therapy was effective at improving inflammation in 30%-50% of patients with clinical presentations and histologic features consistent with EoE. As such, the concept of PPI–responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE) was introduced in 2011.5 Further investigation then highlighted that PPI-REE and EoE had nearly identical clinical, endoscopic, and histologic features as well as eosinophil biomarker and gene expression profiles. Hence, recent international guidelines no longer necessitate a PPI trial to establish a diagnosis of EoE.6
The young gastroenterologist should also be mindful of other issues related to the initial diagnosis of EoE. EoE may present concomitantly with other disease entities including GERD, “extra-esophageal” eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases, concomitant IgE-mediated food allergy, hypereosinophilic syndromes, connective tissue disorders, autoimmune diseases, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.3 It has been speculated that some of these disorders share common aspects of genetic and environmental predisposing factors as well as shared pathogenesis. Careful history taking should include a full review of atopic conditions and GI-related symptoms and endoscopy should carefully inspect not only the esophagus, but also gastric and duodenal mucosa. The endoscopic features almost always reveal edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and strictures and can be assessed using the EoE Endoscopic Reference Scoring system (EREFS).7 EREFS allows for systematic identification of abnormalities that can inform decisions regarding treatment efficacy and decisions on the need for esophageal dilation. When the esophageal mucosa is evaluated for biopsies, furrows and exudates should be targeted, if present, and multiple biopsies (minimum of five to six) should be taken throughout the esophagus given the patchy nature of the disease.
How do I choose an initial therapy?
The choice of initial therapy considers patient preferences, medication availability, disease severity, impact on quality of life, and need for repeated endoscopies. While there are many novel agents currently being investigated in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials, the current mainstays of treatment include PPI therapy, topical steroids, dietary therapy, and dilation. Of note, there have been no head-to-head trials comparing these different modalities. A recent systematic review reported that PPIs can induce histologic remission in 42% of patients.8 The ease of use and availability of PPI therapy make this an attractive first choice for patients. Pooled estimates show that topical steroids can induce remission in 66% of patients.8 It is important to note that there is currently no Food and Drug Administration–approved formulation of steroids for the treatment of EoE. As such, there are several practical aspects to consider when instructing patients to use agents not designed for esophageal delivery (Figure 1).

Source: Dr. Patel, Dr. Hirano
Lack of insurance coverage for topical steroids can make cost of a prescription a deterrent to use. While topical steroids are well tolerated, concerns for candidiasis and adrenal insufficiency are being monitored in prospective, long-term clinical trials. Concomitant use of steroids with PPI would be appropriate for EoE patients with coexisting GERD (severe heartburn, erosive esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus). In addition, we often combine steroids with PPI therapy for EoE patients who demonstrate a convincing but incomplete response to PPI monotherapy (i.e., reduction of baseline inflammation from 75 eos/hpf to 20 eos/hpf).
Diet therapy is a popular choice for management of EoE by patients, given the ability to remove food triggers that initiate the immune dysregulation and to avoid chronic medication use. Three dietary options have been described including an elemental, amino acid–based diet which eliminates all common food allergens, allergy testing–directed elimination diet, and an empiric elimination diet. Though elemental diets have shown the most efficacy, practical aspects of implementing, maintaining, and identifying triggers restrict their adoption by most patients and clinicians.9 Allergy-directed elimination diets, where allergens are eliminated based on office-based allergy testing, initially seemed promising, though studies have shown limited histologic remission, compared with other diet therapies as well as the inability to identify true food triggers. Advancement of office-based testing to identify food triggers is needed to streamline this dietary approach. In the adult patient, the empiric elimination diet remains an attractive choice of the available dietary therapies. In this dietary approach, which has shown efficacy in both children and adults, the most common food allergens (milk, wheat, soy, egg, nuts, and seafood) are eliminated.9
How do I make dietary therapy work in clinical practice?
Before dietary therapy is initiated, it is important that your practice is situated to support this approach and that patients fully understand the process. A multidisciplinary approach optimizes dietary therapy. Dietitians provide expert guidance on eliminating trigger foods, maintaining nutrition, and avoiding inadvertent cross-contamination. Patient questions may include the safety of consumption of non–cow-based cheese/milk, alcoholic beverages, wheat alternatives, and restaurant food. Allergists address concerns for a concomitant IgE food allergy based on a clinical history or previous testing. Patients should be informed that identifying a food trigger often takes several months and multiple endoscopies. Clinicians should be aware of potential food cost and accessibility issues as well as the reported, albeit uncommon, development of de novo IgE-mediated food allergy during reintroduction. Timing of diet therapy is also a factor in success. Patients should avoid starting diets during major holidays, family celebrations, college years, and busy travel months.
Particularly empiric elimination diets, frequently used in adults, several approaches have been described (Figure 2).

Source: Dr. Patel, Dr. Hirano
Initially, a step-down approach was described, with patients pursuing a six-food elimination diet (SFED), which eliminates the six most common triggers: milk, wheat, soy/legumes, egg, nuts, and seafood. Once in histologic remission, patients then systematically reintroduce foods in order to identify a causative trigger. Given that many patients have only one or two identified food triggers, other approaches were created including a single-food elimination diet eliminating milk, the two-food elimination diet (TFED) eliminating milk and wheat, and the four-food elimination diet (FFED) eliminating milk, wheat, soy/legumes, and eggs. A novel step-up approach has also now been described where patients start with the TFED and progress to the FFED and then potentially SFED based on histologic response.10 This approach has the potential to more readily identify triggers, decrease diagnostic time, and reduce endoscopic interventions. There are pros and cons to each elimination diet approach that should be discussed with patients. Many patients may find a one- or two-food elimination diet more feasible than a full SFED.
What should I consider when performing dilation?
Esophageal dilation is frequently used to address the fibrostenotic complications of EoE that do not as readily respond to PPI, steroid, or diet therapy. The majority of patients note symptomatic improvement following dilation, though dilation alone does not address the inflammatory component of disease.8 With a conservative approach, the complication rates of esophageal dilation in EoE are similar to that of benign, esophageal strictures. Endoscopists should be aware that endoscopy alone can miss strictures and consider both practical and technical aspects when performing dilations (Table 1).11,12

When should an allergist be consulted?
The role of the allergist in the management of patients with EoE varies by patient and practice. IgE serologic or skin testing have limited accuracy in identifying food triggers for EoE. Nevertheless, the majority of patients with EoE have an atopic condition which may include asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, or IgE-mediated food allergy. Although EoE is thought to primarily occur from an immune response to ingested oral allergens, aeroallergens may exacerbate disease as evidenced by the seasonal variation in EoE symptoms in some patients. The allergist provides treatment for these “extraesophageal” atopic conditions which may, in turn, have synergistic effects on the treatment of EoE. Furthermore, allergists may prescribe biologic therapies that are FDA approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. While not approved for EoE, several of these agents have shown efficacy in phase 2 clinical trials in EoE. In some practice settings, allergists primarily manage EoE patients with the assistance of gastroenterologists for periodic endoscopic activity assessment.
What are the key aspects of maintenance therapy?
The goals of treatment focus on symptomatic, histologic, and endoscopic improvement, and the prevention of future or ongoing fibrostenotic complications.2 Because of the adaptive eating behaviors discussed above, symptom response may not reliably correlate with histologic and/or endoscopic improvement. Moreover, dysphagia is related to strictures that often do not resolve in spite of resolution of mucosal inflammation. As such, histology and endoscopy are more objective and reliable targets of a successful response to therapy. Though studies have used variable esophageal density levels for response, using a cutoff of <15 eos/hpf as a therapeutic endpoint is reasonable for both initial response to therapy and long-term monitoring.13 We advocate for standardization of reporting endoscopic findings to better track change over time using the EREFS scoring system.7 While inflammatory features improve, the fibrostenotic features may persist despite improvement in histology. Dilation is often performed in these situations, especially for symptomatic individuals.
During clinical follow-up, the frequency of monitoring as it relates to symptom and endoscopic assessment is not well defined. It is reasonable to repeat endoscopic intervention following changes in therapy (i.e., reduction in steroid dosing or reintroduction of putative food triggers) or in symptoms.13 It is unclear if patients benefit from repeated endoscopies at set intervals without symptom change and after histologic response has been confirmed. In our practice, endoscopies are often considered on an annual basis. This interval is increased for patients with demonstrated stability of disease.
For patients who opt for dietary therapy and have one or two food triggers identified, long-term maintenance therapy can be straightforward with ongoing food avoidance. Limited data exist regarding long-term effectiveness of dietary therapy but loss of initial response has been reported that is often attributed to problems with adherence. Use of “diet holidays” or “planned cheats” to allow for intermittent consumption of trigger foods, often under the cover of short-term use of steroids, may improve the long-term feasibility of diet approaches.
In the recent American Gastroenterological Association guidelines, continuation of swallowed, topical steroids is recommended following remission with short-term treatment. The recurrence of both symptoms and inflammation following medication withdrawal supports this practice. Furthermore, natural history studies demonstrate progression of esophageal strictures with untreated disease.
There are no clear guidelines for long-term dosage and use of PPI or topical steroid therapy. Our practice is to down-titrate the dose of PPI or steroid following remission with short-term therapy, often starting with a reduction from twice a day to daily dosing. Although topical steroid therapy has fewer side effects, compared with systemic steroids, patients should be aware of the potential for adrenal suppression especially in an atopic population who may be exposed to multiple forms of topical steroids. Shared decision-making between patients and providers is recommended to determine comfort level with long-term use of prescription medications and dosage.
What’s on the horizon?
Several areas of development are underway to better assess and manage EoE. Novel histologic scoring tools now assess characteristics on pathology beyond eosinophil density, office-based testing modalities have been developed to assess inflammatory activity and thereby obviate the need for endoscopy, new technology can provide measures of esophageal remodeling and provide assessment of disease severity, and several biologic agents are being studied that target specific allergic mediators of the immune response in EoE.3,14-18 These novel tools, technologies, and therapies will undoubtedly change the management approach to EoE. Referral of patients into ongoing clinical trials will help inform advances in the field.
Conclusion
As an increasingly prevalent disease with a high degree of upper GI morbidity, EoE has transitioned from a rare entity to a commonly encountered disease. The new gastroenterologist will confront both straightforward as well as complex patients with EoE, and we offer several practical aspects on management. In the years ahead, the care of patients with EoE will continue to evolve to a more streamlined, effective, and personalized approach.
References
1. Kidambi T et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:4335-41.
2. Dellon ES et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:319-32 e3.
3. Hirano I et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:840-51.
4. Furuta GT et al. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342-63.
5. Liacouras CA et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3-20 e6; quiz 1-2.
6. Dellon ES et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:1022-33 e10.
7. Hirano I et al. Gut. 2013;62:489-95.
8. Rank MA et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1789-810 e15.
9. Arias A et al. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1639-48.
10. Molina-Infante J et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1365-72.
11. Gentile N et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:1333-40.
12. Hirano I. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:601-6.
13. Hirano I et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1776-86.
14. Collins MH et al. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30:1-8.
15. Furuta GT et al. Gut. 2013;62:1395-405.
16. Katzka DA et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:77-83 e2.
17. Kwiatek MA et al. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:82-90.
18. Nicodeme F et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1101-7 e1.
Introduction
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) has transformed over the past 3 decades from a rarely encountered entity to one of the most common causes of dysphagia in adults.1 Given the marked rise in prevalence, the early-career gastroenterologist will undoubtedly be involved with managing this disease.2 The typical presentation includes a young, atopic male presenting with dysphagia in the outpatient setting or, more acutely, with a food impaction when on call. As every fellow is keenly aware, the calls often come late at night as patients commonly have meat impactions while consuming dinner. Current management focuses on symptomatic, histologic, and endoscopic improvement with medication, dietary, and mechanical (i.e., dilation) modalities.
EoE is defined by the presence of esophageal dysfunction and esophageal eosinophilic inflammation with ≥15 eosinophils/high-powered field (eos/hpf) required for the diagnosis. With better understanding of the pathogenesis of EoE involving the complex interaction of environmental, host, and genetic factors, advancements have been made as it relates to the diagnostic criteria, endoscopic evaluation, and therapeutic options. In this article, we review the current management of adult patients with EoE and offer practical guidance to key questions for the young gastroenterologist as well as insights into future areas of interest.
What should I consider when diagnosing EoE?
Symptoms are central to the diagnosis and clinical presentation of EoE. In assessing symptoms, clinicians should be aware of adaptive “IMPACT” strategies patients often subconsciously develop in response to their chronic and progressive condition: Imbibing fluids with meals, modifying foods by cutting or pureeing, prolonging meal times, avoiding harder texture foods, chewing excessively, and turning away tablets/pills.3 Failure to query such adaptive behaviors may lead to an underestimation of disease activity and severity.
An important aspect to confirming the diagnosis of EoE is to exclude other causes of esophageal eosinophilia. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is known to cause esophageal eosinophilia and historically has been viewed as a distinct disease process. In fact, initial guidelines included lack of response to a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) trial or normal esophageal pH monitoring as diagnostic criteria.4 However, as experience was garnered, it became clear that PPI therapy was effective at improving inflammation in 30%-50% of patients with clinical presentations and histologic features consistent with EoE. As such, the concept of PPI–responsive esophageal eosinophilia (PPI-REE) was introduced in 2011.5 Further investigation then highlighted that PPI-REE and EoE had nearly identical clinical, endoscopic, and histologic features as well as eosinophil biomarker and gene expression profiles. Hence, recent international guidelines no longer necessitate a PPI trial to establish a diagnosis of EoE.6
The young gastroenterologist should also be mindful of other issues related to the initial diagnosis of EoE. EoE may present concomitantly with other disease entities including GERD, “extra-esophageal” eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases, concomitant IgE-mediated food allergy, hypereosinophilic syndromes, connective tissue disorders, autoimmune diseases, celiac disease, and inflammatory bowel disease.3 It has been speculated that some of these disorders share common aspects of genetic and environmental predisposing factors as well as shared pathogenesis. Careful history taking should include a full review of atopic conditions and GI-related symptoms and endoscopy should carefully inspect not only the esophagus, but also gastric and duodenal mucosa. The endoscopic features almost always reveal edema, rings, exudates, furrows, and strictures and can be assessed using the EoE Endoscopic Reference Scoring system (EREFS).7 EREFS allows for systematic identification of abnormalities that can inform decisions regarding treatment efficacy and decisions on the need for esophageal dilation. When the esophageal mucosa is evaluated for biopsies, furrows and exudates should be targeted, if present, and multiple biopsies (minimum of five to six) should be taken throughout the esophagus given the patchy nature of the disease.
How do I choose an initial therapy?
The choice of initial therapy considers patient preferences, medication availability, disease severity, impact on quality of life, and need for repeated endoscopies. While there are many novel agents currently being investigated in phase 2 and 3 clinical trials, the current mainstays of treatment include PPI therapy, topical steroids, dietary therapy, and dilation. Of note, there have been no head-to-head trials comparing these different modalities. A recent systematic review reported that PPIs can induce histologic remission in 42% of patients.8 The ease of use and availability of PPI therapy make this an attractive first choice for patients. Pooled estimates show that topical steroids can induce remission in 66% of patients.8 It is important to note that there is currently no Food and Drug Administration–approved formulation of steroids for the treatment of EoE. As such, there are several practical aspects to consider when instructing patients to use agents not designed for esophageal delivery (Figure 1).

Source: Dr. Patel, Dr. Hirano
Lack of insurance coverage for topical steroids can make cost of a prescription a deterrent to use. While topical steroids are well tolerated, concerns for candidiasis and adrenal insufficiency are being monitored in prospective, long-term clinical trials. Concomitant use of steroids with PPI would be appropriate for EoE patients with coexisting GERD (severe heartburn, erosive esophagitis, Barrett’s esophagus). In addition, we often combine steroids with PPI therapy for EoE patients who demonstrate a convincing but incomplete response to PPI monotherapy (i.e., reduction of baseline inflammation from 75 eos/hpf to 20 eos/hpf).
Diet therapy is a popular choice for management of EoE by patients, given the ability to remove food triggers that initiate the immune dysregulation and to avoid chronic medication use. Three dietary options have been described including an elemental, amino acid–based diet which eliminates all common food allergens, allergy testing–directed elimination diet, and an empiric elimination diet. Though elemental diets have shown the most efficacy, practical aspects of implementing, maintaining, and identifying triggers restrict their adoption by most patients and clinicians.9 Allergy-directed elimination diets, where allergens are eliminated based on office-based allergy testing, initially seemed promising, though studies have shown limited histologic remission, compared with other diet therapies as well as the inability to identify true food triggers. Advancement of office-based testing to identify food triggers is needed to streamline this dietary approach. In the adult patient, the empiric elimination diet remains an attractive choice of the available dietary therapies. In this dietary approach, which has shown efficacy in both children and adults, the most common food allergens (milk, wheat, soy, egg, nuts, and seafood) are eliminated.9
How do I make dietary therapy work in clinical practice?
Before dietary therapy is initiated, it is important that your practice is situated to support this approach and that patients fully understand the process. A multidisciplinary approach optimizes dietary therapy. Dietitians provide expert guidance on eliminating trigger foods, maintaining nutrition, and avoiding inadvertent cross-contamination. Patient questions may include the safety of consumption of non–cow-based cheese/milk, alcoholic beverages, wheat alternatives, and restaurant food. Allergists address concerns for a concomitant IgE food allergy based on a clinical history or previous testing. Patients should be informed that identifying a food trigger often takes several months and multiple endoscopies. Clinicians should be aware of potential food cost and accessibility issues as well as the reported, albeit uncommon, development of de novo IgE-mediated food allergy during reintroduction. Timing of diet therapy is also a factor in success. Patients should avoid starting diets during major holidays, family celebrations, college years, and busy travel months.
Particularly empiric elimination diets, frequently used in adults, several approaches have been described (Figure 2).

Source: Dr. Patel, Dr. Hirano
Initially, a step-down approach was described, with patients pursuing a six-food elimination diet (SFED), which eliminates the six most common triggers: milk, wheat, soy/legumes, egg, nuts, and seafood. Once in histologic remission, patients then systematically reintroduce foods in order to identify a causative trigger. Given that many patients have only one or two identified food triggers, other approaches were created including a single-food elimination diet eliminating milk, the two-food elimination diet (TFED) eliminating milk and wheat, and the four-food elimination diet (FFED) eliminating milk, wheat, soy/legumes, and eggs. A novel step-up approach has also now been described where patients start with the TFED and progress to the FFED and then potentially SFED based on histologic response.10 This approach has the potential to more readily identify triggers, decrease diagnostic time, and reduce endoscopic interventions. There are pros and cons to each elimination diet approach that should be discussed with patients. Many patients may find a one- or two-food elimination diet more feasible than a full SFED.
What should I consider when performing dilation?
Esophageal dilation is frequently used to address the fibrostenotic complications of EoE that do not as readily respond to PPI, steroid, or diet therapy. The majority of patients note symptomatic improvement following dilation, though dilation alone does not address the inflammatory component of disease.8 With a conservative approach, the complication rates of esophageal dilation in EoE are similar to that of benign, esophageal strictures. Endoscopists should be aware that endoscopy alone can miss strictures and consider both practical and technical aspects when performing dilations (Table 1).11,12

When should an allergist be consulted?
The role of the allergist in the management of patients with EoE varies by patient and practice. IgE serologic or skin testing have limited accuracy in identifying food triggers for EoE. Nevertheless, the majority of patients with EoE have an atopic condition which may include asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, or IgE-mediated food allergy. Although EoE is thought to primarily occur from an immune response to ingested oral allergens, aeroallergens may exacerbate disease as evidenced by the seasonal variation in EoE symptoms in some patients. The allergist provides treatment for these “extraesophageal” atopic conditions which may, in turn, have synergistic effects on the treatment of EoE. Furthermore, allergists may prescribe biologic therapies that are FDA approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, asthma, and allergic rhinitis. While not approved for EoE, several of these agents have shown efficacy in phase 2 clinical trials in EoE. In some practice settings, allergists primarily manage EoE patients with the assistance of gastroenterologists for periodic endoscopic activity assessment.
What are the key aspects of maintenance therapy?
The goals of treatment focus on symptomatic, histologic, and endoscopic improvement, and the prevention of future or ongoing fibrostenotic complications.2 Because of the adaptive eating behaviors discussed above, symptom response may not reliably correlate with histologic and/or endoscopic improvement. Moreover, dysphagia is related to strictures that often do not resolve in spite of resolution of mucosal inflammation. As such, histology and endoscopy are more objective and reliable targets of a successful response to therapy. Though studies have used variable esophageal density levels for response, using a cutoff of <15 eos/hpf as a therapeutic endpoint is reasonable for both initial response to therapy and long-term monitoring.13 We advocate for standardization of reporting endoscopic findings to better track change over time using the EREFS scoring system.7 While inflammatory features improve, the fibrostenotic features may persist despite improvement in histology. Dilation is often performed in these situations, especially for symptomatic individuals.
During clinical follow-up, the frequency of monitoring as it relates to symptom and endoscopic assessment is not well defined. It is reasonable to repeat endoscopic intervention following changes in therapy (i.e., reduction in steroid dosing or reintroduction of putative food triggers) or in symptoms.13 It is unclear if patients benefit from repeated endoscopies at set intervals without symptom change and after histologic response has been confirmed. In our practice, endoscopies are often considered on an annual basis. This interval is increased for patients with demonstrated stability of disease.
For patients who opt for dietary therapy and have one or two food triggers identified, long-term maintenance therapy can be straightforward with ongoing food avoidance. Limited data exist regarding long-term effectiveness of dietary therapy but loss of initial response has been reported that is often attributed to problems with adherence. Use of “diet holidays” or “planned cheats” to allow for intermittent consumption of trigger foods, often under the cover of short-term use of steroids, may improve the long-term feasibility of diet approaches.
In the recent American Gastroenterological Association guidelines, continuation of swallowed, topical steroids is recommended following remission with short-term treatment. The recurrence of both symptoms and inflammation following medication withdrawal supports this practice. Furthermore, natural history studies demonstrate progression of esophageal strictures with untreated disease.
There are no clear guidelines for long-term dosage and use of PPI or topical steroid therapy. Our practice is to down-titrate the dose of PPI or steroid following remission with short-term therapy, often starting with a reduction from twice a day to daily dosing. Although topical steroid therapy has fewer side effects, compared with systemic steroids, patients should be aware of the potential for adrenal suppression especially in an atopic population who may be exposed to multiple forms of topical steroids. Shared decision-making between patients and providers is recommended to determine comfort level with long-term use of prescription medications and dosage.
What’s on the horizon?
Several areas of development are underway to better assess and manage EoE. Novel histologic scoring tools now assess characteristics on pathology beyond eosinophil density, office-based testing modalities have been developed to assess inflammatory activity and thereby obviate the need for endoscopy, new technology can provide measures of esophageal remodeling and provide assessment of disease severity, and several biologic agents are being studied that target specific allergic mediators of the immune response in EoE.3,14-18 These novel tools, technologies, and therapies will undoubtedly change the management approach to EoE. Referral of patients into ongoing clinical trials will help inform advances in the field.
Conclusion
As an increasingly prevalent disease with a high degree of upper GI morbidity, EoE has transitioned from a rare entity to a commonly encountered disease. The new gastroenterologist will confront both straightforward as well as complex patients with EoE, and we offer several practical aspects on management. In the years ahead, the care of patients with EoE will continue to evolve to a more streamlined, effective, and personalized approach.
References
1. Kidambi T et al. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:4335-41.
2. Dellon ES et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:319-32 e3.
3. Hirano I et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:840-51.
4. Furuta GT et al. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342-63.
5. Liacouras CA et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3-20 e6; quiz 1-2.
6. Dellon ES et al. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:1022-33 e10.
7. Hirano I et al. Gut. 2013;62:489-95.
8. Rank MA et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1789-810 e15.
9. Arias A et al. Gastroenterology. 2014;146:1639-48.
10. Molina-Infante J et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141:1365-72.
11. Gentile N et al. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014;40:1333-40.
12. Hirano I. Gastroenterology. 2018;155:601-6.
13. Hirano I et al. Gastroenterology. 2020;158:1776-86.
14. Collins MH et al. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30:1-8.
15. Furuta GT et al. Gut. 2013;62:1395-405.
16. Katzka DA et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:77-83 e2.
17. Kwiatek MA et al. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:82-90.
18. Nicodeme F et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1101-7 e1.
New realities
Dear colleagues,
The August issue of The New Gastroenterologist has arrived! The summer of 2020 certainly looks different from years past, as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on and we continue to adjust to the new realities of our personal and professional lives. Our third-year fellows have graduated amidst these unusual circumstances, some facing an uncertain job landscape. Yet their hard work is not lost upon us – as we must step back to recognize their achievements and bid them congratulations on the culmination of several years of training.
The pandemic has been pervasive in medical education with a profound effect on our training programs. Two very resourceful fellows, Indira Bhavsar-Burke and Claire Jansson-Knodell (Indiana University), share their experience with COVID-19 and how they used this time to create an online curriculum for medical students who were pulled from their gastroenterology clinical rotations.
As we remain socially distanced, connecting through virtual platforms and social media seems more important than ever, but digital media can be difficult to navigate as physicians. Austin Chiang (Thomas Jefferson University) offers a candid snapshot of the benefits and pitfalls of social media as a gastroenterologist, with advice on how to optimize one’s professional presence online.
This quarter’s “In Focus” feature is an excellent, high-yield review of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ronak Vashi Patel and Ikuo Hirano (Northwestern University) seek to answer frequently asked questions about diagnostic considerations and the approach to management by reviewing therapeutic options – a truly valuable clinical piece to guide any young gastroenterologist.
Our medical ethics series features a poignant piece written by Diana Anderson (University of California, San Francisco) and David Seres (Columbia University) on the role of nutritional support in patients with restrictive eating disorders. The article addresses the complex interplay between certain diagnoses and our emotive response as clinicians – a critical piece of patient care that is seldom discussed. The authors implore us to consider this difficult question: Could our unconscious partiality as physicians be worse than intentional harm?
Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa (Harvard University) discusses how her interest in health equity and health care policy led her to the Commonwealth Fund Fellowship in Minority Health Policy. Her passion for health care delivery reform and the care of vulnerable populations shines through as she describes how this post-GI fellowship pathway has been formative in shaping her career as a dynamic new gastroenterologist.
For those interested in serving as an expert witness, seasoned malpractice attorneys Daniel Mills and Courtney Lindbert (Cunningham, Meyer & Vedrine P.C.) offer a salient list of the “do’s and don’ts” of the medical expert. Finally, this summer’s DHPA Private Practice Perspectives article, written by Michael Weinstein (Capital Digestive Care), offers important considerations for evaluating independent GI practices and how their response to COVID-19 can dictate their preparedness for future crises.
If you have interest in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (vijayarao@medicine.bsd.uchicago.edu), or Ryan Farrell (rfarrell@gastro.org), managing editor of TNG.
Stay well,
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant professor of medicine, University of Chicago, section of gastroenterology, hepatology & nutrition
Dear colleagues,
The August issue of The New Gastroenterologist has arrived! The summer of 2020 certainly looks different from years past, as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on and we continue to adjust to the new realities of our personal and professional lives. Our third-year fellows have graduated amidst these unusual circumstances, some facing an uncertain job landscape. Yet their hard work is not lost upon us – as we must step back to recognize their achievements and bid them congratulations on the culmination of several years of training.
The pandemic has been pervasive in medical education with a profound effect on our training programs. Two very resourceful fellows, Indira Bhavsar-Burke and Claire Jansson-Knodell (Indiana University), share their experience with COVID-19 and how they used this time to create an online curriculum for medical students who were pulled from their gastroenterology clinical rotations.
As we remain socially distanced, connecting through virtual platforms and social media seems more important than ever, but digital media can be difficult to navigate as physicians. Austin Chiang (Thomas Jefferson University) offers a candid snapshot of the benefits and pitfalls of social media as a gastroenterologist, with advice on how to optimize one’s professional presence online.
This quarter’s “In Focus” feature is an excellent, high-yield review of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ronak Vashi Patel and Ikuo Hirano (Northwestern University) seek to answer frequently asked questions about diagnostic considerations and the approach to management by reviewing therapeutic options – a truly valuable clinical piece to guide any young gastroenterologist.
Our medical ethics series features a poignant piece written by Diana Anderson (University of California, San Francisco) and David Seres (Columbia University) on the role of nutritional support in patients with restrictive eating disorders. The article addresses the complex interplay between certain diagnoses and our emotive response as clinicians – a critical piece of patient care that is seldom discussed. The authors implore us to consider this difficult question: Could our unconscious partiality as physicians be worse than intentional harm?
Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa (Harvard University) discusses how her interest in health equity and health care policy led her to the Commonwealth Fund Fellowship in Minority Health Policy. Her passion for health care delivery reform and the care of vulnerable populations shines through as she describes how this post-GI fellowship pathway has been formative in shaping her career as a dynamic new gastroenterologist.
For those interested in serving as an expert witness, seasoned malpractice attorneys Daniel Mills and Courtney Lindbert (Cunningham, Meyer & Vedrine P.C.) offer a salient list of the “do’s and don’ts” of the medical expert. Finally, this summer’s DHPA Private Practice Perspectives article, written by Michael Weinstein (Capital Digestive Care), offers important considerations for evaluating independent GI practices and how their response to COVID-19 can dictate their preparedness for future crises.
If you have interest in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (vijayarao@medicine.bsd.uchicago.edu), or Ryan Farrell (rfarrell@gastro.org), managing editor of TNG.
Stay well,
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant professor of medicine, University of Chicago, section of gastroenterology, hepatology & nutrition
Dear colleagues,
The August issue of The New Gastroenterologist has arrived! The summer of 2020 certainly looks different from years past, as the COVID-19 pandemic rages on and we continue to adjust to the new realities of our personal and professional lives. Our third-year fellows have graduated amidst these unusual circumstances, some facing an uncertain job landscape. Yet their hard work is not lost upon us – as we must step back to recognize their achievements and bid them congratulations on the culmination of several years of training.
The pandemic has been pervasive in medical education with a profound effect on our training programs. Two very resourceful fellows, Indira Bhavsar-Burke and Claire Jansson-Knodell (Indiana University), share their experience with COVID-19 and how they used this time to create an online curriculum for medical students who were pulled from their gastroenterology clinical rotations.
As we remain socially distanced, connecting through virtual platforms and social media seems more important than ever, but digital media can be difficult to navigate as physicians. Austin Chiang (Thomas Jefferson University) offers a candid snapshot of the benefits and pitfalls of social media as a gastroenterologist, with advice on how to optimize one’s professional presence online.
This quarter’s “In Focus” feature is an excellent, high-yield review of eosinophilic esophagitis. Ronak Vashi Patel and Ikuo Hirano (Northwestern University) seek to answer frequently asked questions about diagnostic considerations and the approach to management by reviewing therapeutic options – a truly valuable clinical piece to guide any young gastroenterologist.
Our medical ethics series features a poignant piece written by Diana Anderson (University of California, San Francisco) and David Seres (Columbia University) on the role of nutritional support in patients with restrictive eating disorders. The article addresses the complex interplay between certain diagnoses and our emotive response as clinicians – a critical piece of patient care that is seldom discussed. The authors implore us to consider this difficult question: Could our unconscious partiality as physicians be worse than intentional harm?
Adjoa Anyane-Yeboa (Harvard University) discusses how her interest in health equity and health care policy led her to the Commonwealth Fund Fellowship in Minority Health Policy. Her passion for health care delivery reform and the care of vulnerable populations shines through as she describes how this post-GI fellowship pathway has been formative in shaping her career as a dynamic new gastroenterologist.
For those interested in serving as an expert witness, seasoned malpractice attorneys Daniel Mills and Courtney Lindbert (Cunningham, Meyer & Vedrine P.C.) offer a salient list of the “do’s and don’ts” of the medical expert. Finally, this summer’s DHPA Private Practice Perspectives article, written by Michael Weinstein (Capital Digestive Care), offers important considerations for evaluating independent GI practices and how their response to COVID-19 can dictate their preparedness for future crises.
If you have interest in contributing or have ideas for future TNG topics, please contact me (vijayarao@medicine.bsd.uchicago.edu), or Ryan Farrell (rfarrell@gastro.org), managing editor of TNG.
Stay well,
Vijaya L. Rao, MD
Editor-in-Chief
Assistant professor of medicine, University of Chicago, section of gastroenterology, hepatology & nutrition
























