User login
The current and future state of uterus transplantation
Since the first baby was born after a uterus transplantation in Sweden in 2014, uterus transplantation has been rapidly transitioning toward clinical reality.1 Several teams in the United States and multiple teams worldwide have performed the procedure, with the total number of worldwide surgeries performed nearing 100.
Uterus transplantation is the first and only true treatment for women with absolute uterine factor infertility – estimated to affect 1 in 500 women – and is filling an unmet need for this population of women. Women who have sought participation in uterus transplantation research have had complex and meaningful reasons and motivations for doing so.2 Combined with an accumulation of successful pregnancies, this makes continued research and technical improvement a worthy endeavor.
Most of the births thus far have occurred through the living-donor model; the initial Swedish trial involved nine women, seven of whom completed the procedure with viable transplants from living donors, and gave birth to eight healthy children. (Two required hysterectomy prior to attempted embryo transfer.3)
The Cleveland Clinic opted to build its first – and still ongoing – trial focusing on deceased-donor uterus transplants on the premise that such an approach obviates any risk to the donor and presents the fewest ethical challenges at the current time. Of eight uterus transplants performed thus far at the Cleveland Clinic, there have been three live births and two graft failures. As of early 2021, there was one ongoing pregnancy and two patients in preparation for embryo transfer.
Thus far, neither the living- nor deceased-donor model of uterus transplantation has been demonstrated to be superior. However, as data accrues from deceased donor studies, we will be able to more directly compare outcomes.
In the meantime, alongside a rapid ascent of clinical landmarks – the first live birth in the United States from living-donor uterus transplantation in 2017 at Baylor University Medical Center in Houston,4 for instance, and the first live birth in the United States from deceased-donor uterus transplantation in 2019 at the Cleveland Clinic – there have been significant improvements in surgical retrieval of the uterus and in the optimization of graft performance.5
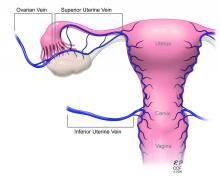
Most notably, the utero-ovarian vein has been used successfully in living donors to achieve venous drainage of the graft. This has lessened the risks of deep pelvic dissection in the living donor and made the transition to laparoscopic and robotic approaches in the living donor much easier.
Donor procurement, venous drainage
Adequate circulatory inflow and outflow for the transplanted uterus are essential both for the prevention of ischemia and thrombosis, which have been major causes of graft failure, and for meeting the increased demands of blood flow during pregnancy. Of the two, the outflow is the more challenging component.
Venous drainage traditionally has been accomplished through the use of the uterine veins, which drain into the internal iliac veins; often the vascular graft will include a portion of the internal iliac vessel which can be connected via anastomoses to the external iliac vein classically in deceased donors. Typically, the gynecologic surgeon on the team performs the vaginal anastomosis and suspension of the uterus, while the transplant surgeons perform the venous and arterial anastomoses.
In the living-donor model, procurement and dissection of these often unpredictable and tortuous complexes in the deep pelvis – particularly the branching uterine veins that lie in close proximity to the ureter, bladder, other blood vessels, and rectum – can be risky. The anatomic variants in the uterine vein are numerous, and even in one patient, a comprehensive dissection on one side cannot be expected to be mirrored on the contralateral side.
In addition to the risk of injury to the donor, the anastomosis may be unsuccessful as the veins are thinly walled and challenging to suture. As such, multiple modifications have been developed, often adapted to the donor’s anatomy and the caliber and accessibility of vessels. Preoperative vascular imaging with CT and/or MRI may help to identify suitable candidates and also may facilitate presurgical planning of which vessels may be selected for use.
Recently, surgeons performing living-donor transplantations have successfully used the more accessible and less risky ovarian and/or utero-ovarian veins for venous anastomosis. In 2019, for instance, a team in Pune, India, reported laparoscopically dissecting the donor ovarian veins and a portion of the internal iliac artery, and completing anastomosis with bilateral donor internal iliac arteries to recipient internal iliac arteries, and bilateral donor ovarian veins to recipient external iliac veins.6 It is significant that these smaller-caliber vessels were found to able to support the uterus through pregnancy.
We must be cautious, however, to avoid removing donors’ ovaries. Oophorectomy for women in their 40s can result in significant long-term medical sequelae. Surgeons at Baylor have achieved at least one live birth after harvesting the donor’s utero-ovarian veins while conserving the ovaries – a significant advancement for the living-donor model.4
There is tremendous interest in developing minimally invasive approaches to further reduce living-donor risk. The Swedish team has completed a series of eight robotic hysterectomies in living-donor uterus transplantations as part of a second trial. Addressing the reality of a learning curve, their study was designed around a step-wise approach, mastering initial steps first – e.g., dissections of the uterovaginal fossa, arteries, and ureters – and ultimately converting to laparotomy.7 In the United States, Baylor University has now completed at least five completely robotic living-donor hysterectomies with complete vaginal extraction.
Published data on robotic surgery suggests that surgical access and perioperative visualization of the vessels may be improved. And as minimally invasive approaches are adopted and improved, the length of donor surgery – 10-13 hours of operating room time in the original Swedish series – should diminish, as should the morbidity associated with laparotomy.
Surgical acquisition of a uterine graft from a deceased donor diminishes concerns for injury to nearby structures. Therefore, although it is a technically similar procedure, a deceased-donor model allows more flexibility with the length, caliber, and number of vessels that can be used for anastomosis. The internal iliac vessels and even portions of the external iliac vessels and ovarian vessels can be used to allow maximum flexibility.8
Surgical technique for uterus recipients
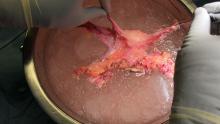
For the recipient surgery, entry is achieved via a midline, vertical laparotomy. The external iliac vessels are exposed, and the sites of vascular anastomoses are identified. The peritoneal reflection of the bladder is identified and dissected away to expose the anterior vagina, and the vagina is opened to a diameter that matches the donor, typically using a monopolar electrosurgical cutting instrument.
The vault of the donor vagina will be attached to the recipient’s existing vagina or vaginal pouch. It is important to identify recipient vaginal mucosa and incorporate it into the vaginal anastomosis to reduce the risk of vaginal stricture. We recommend that the vaginal mucosa be tagged with PDS II sutures or grasped with allis clamps to prevent retraction.
Surgical teams have taken multiple approaches to vaginal anastomosis. The Cleveland Clinic has used both a running suture as well as a horizontal mattress stitch for closure. For the latter, a 30-inch double-armed 2.0 Vicryl allows for complete suturing of the recipient vagina – with eight stitches placed circumferentially – before the uterus is placed. Both ends of the suture are passed intra-abdominal to intravaginal in the recipient.9
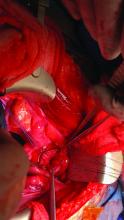
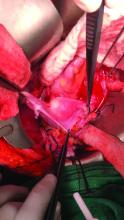
Once the donor uterus is suspended, attention focuses on vascular anastomosis, with bilateral end-to-side anastomosis between the donor anterior division of the internal iliac arteries and the external iliac vessels of the recipient, and with venous drainage commonly achieved through the uterine veins draining into the internal or external iliac vein of the recipient. As mentioned, recent cases involving living donors have also demonstrated success with the use of ovarian and/or utero-ovarian veins. Care should be taken to avoid having tension or twisting across the anastomosis.
After adequate graft perfusion is confirmed, with the uterus turning from a dusky color to a pink and well-perfused organ, the vaginal anastomosis is completed, with the arms of the double-armed suture passed through the donor vagina, from intravaginal to intra-abdominal. Tension should be evenly spread along the recipient and donor vagina in order to reduce the formation of granulation tissue and the severity of future vaginal stricturing.
For uterine fixation, polypropylene sutures are placed between the graft uterosacral ligaments and recipient uterine rudiments, and between the graft round ligaments and the recipient pelvic side wall at the level of the deep inguinal ring.
Current uterus transplantation protocols require removal of the uterus after one or two live births are achieved, so that recipients will not be exposed to long-term immunosuppression.
Complications and controversies
Postoperative vaginal strictures can make embryo transfer difficult and are a common complication in both living- and deceased-donor models. The Cleveland Clinic team has applied techniques from vaginal reconstructive surgery to try to reduce the occurrence of postoperative strictures – mainly increasing attention paid to anastomosis tissue–site preparation and closure of the anastomosis using a tension-free interrupted suture technique, as described above.9 The jury is out on whether such changes are sufficient, and a more complete understanding of the causes of vaginal stricture is needed.
Other perioperative complications include infection and graft thrombosis, both of which typically result in urgent graft hysterectomy. During pregnancy, one of our patients experienced abnormal placentation, though this was not thought to be related to uterus transplantation.5
The U.S. Uterus Transplant Consortium (USUTC) is a group of active programs that are sharing ideas and outcomes and advocating for continued research in this rapidly developing field. Uterine transplants require collaboration with transplant surgery, transplant medicine, infectious disease, gynecologic surgery, high-risk obstetrics, and other specialties. While significant progress has been made in a short period of time, uterine transplantation is still in its early stages, and transplants should be done in institutions that have the capacity for mentorship, bioethical oversight, and long-term follow-up of donors, recipients, and offspring.
The USUTC has recently proposed guidelines for nomenclature related to operative technique, vascular anatomy, and uterine transplantation outcomes.10 It proposes standardizing the names for the four veins originating from the uterus (to eliminate current inconsistency), which will be important as optimal strategies for vascular anastomoses are discussed and determined.
In addition, the consortium is creating a registry for the rigorous collection of data on procedures and outcomes (from menstruation and pregnancy through delivery, graft removal, and long-term follow-up). A registry has also been proposed by the International Society for Uterine Transplantation.
A major question remains in our field: Is the living-donor or deceased-donor uterus transplant the best approach? Knowledge of the quality of the uterus is greater preoperatively within a living-donor model, but no matter how minimally invasive the technique, the donor still assumes some risk of prolonged surgery and extensive pelvic dissection for a transplant that is not lifesaving.
On the other hand, deceased-donor transplants require additional layers of organization and coordination, and the availability of suitable deceased-donor uteri will likely not be sufficient to meet the current demand. Many of us in the field believe that the future of uterine transplantation will involve some combination of living- and deceased-donor transplants – similar to other solid organ transplant programs.
Dr. Flyckt and Dr. Richards reported that they have no relevant financial disclosures.
Correction, 2/2/21: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Richards' name in the photo caption.
References
1. Lancet. 2015;14:385:607-16.
2. AJOB Empir Bioeth. 2019;10(1):23-5.
3. Transplantation. 2020;104(7):1312-5.
4. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(5):1270-4.
5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223(2):143-51.
6. J Minimally Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:628-35.
7. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020;99(9):1222-9.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(1):183.
9. Fertil Steril. 2020 Jul 16. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.05.017
10 Am J Transplant. 2020;20(12):3319-25.
Since the first baby was born after a uterus transplantation in Sweden in 2014, uterus transplantation has been rapidly transitioning toward clinical reality.1 Several teams in the United States and multiple teams worldwide have performed the procedure, with the total number of worldwide surgeries performed nearing 100.
Uterus transplantation is the first and only true treatment for women with absolute uterine factor infertility – estimated to affect 1 in 500 women – and is filling an unmet need for this population of women. Women who have sought participation in uterus transplantation research have had complex and meaningful reasons and motivations for doing so.2 Combined with an accumulation of successful pregnancies, this makes continued research and technical improvement a worthy endeavor.
Most of the births thus far have occurred through the living-donor model; the initial Swedish trial involved nine women, seven of whom completed the procedure with viable transplants from living donors, and gave birth to eight healthy children. (Two required hysterectomy prior to attempted embryo transfer.3)
The Cleveland Clinic opted to build its first – and still ongoing – trial focusing on deceased-donor uterus transplants on the premise that such an approach obviates any risk to the donor and presents the fewest ethical challenges at the current time. Of eight uterus transplants performed thus far at the Cleveland Clinic, there have been three live births and two graft failures. As of early 2021, there was one ongoing pregnancy and two patients in preparation for embryo transfer.
Thus far, neither the living- nor deceased-donor model of uterus transplantation has been demonstrated to be superior. However, as data accrues from deceased donor studies, we will be able to more directly compare outcomes.
In the meantime, alongside a rapid ascent of clinical landmarks – the first live birth in the United States from living-donor uterus transplantation in 2017 at Baylor University Medical Center in Houston,4 for instance, and the first live birth in the United States from deceased-donor uterus transplantation in 2019 at the Cleveland Clinic – there have been significant improvements in surgical retrieval of the uterus and in the optimization of graft performance.5
Most notably, the utero-ovarian vein has been used successfully in living donors to achieve venous drainage of the graft. This has lessened the risks of deep pelvic dissection in the living donor and made the transition to laparoscopic and robotic approaches in the living donor much easier.
Donor procurement, venous drainage
Adequate circulatory inflow and outflow for the transplanted uterus are essential both for the prevention of ischemia and thrombosis, which have been major causes of graft failure, and for meeting the increased demands of blood flow during pregnancy. Of the two, the outflow is the more challenging component.
Venous drainage traditionally has been accomplished through the use of the uterine veins, which drain into the internal iliac veins; often the vascular graft will include a portion of the internal iliac vessel which can be connected via anastomoses to the external iliac vein classically in deceased donors. Typically, the gynecologic surgeon on the team performs the vaginal anastomosis and suspension of the uterus, while the transplant surgeons perform the venous and arterial anastomoses.
In the living-donor model, procurement and dissection of these often unpredictable and tortuous complexes in the deep pelvis – particularly the branching uterine veins that lie in close proximity to the ureter, bladder, other blood vessels, and rectum – can be risky. The anatomic variants in the uterine vein are numerous, and even in one patient, a comprehensive dissection on one side cannot be expected to be mirrored on the contralateral side.
In addition to the risk of injury to the donor, the anastomosis may be unsuccessful as the veins are thinly walled and challenging to suture. As such, multiple modifications have been developed, often adapted to the donor’s anatomy and the caliber and accessibility of vessels. Preoperative vascular imaging with CT and/or MRI may help to identify suitable candidates and also may facilitate presurgical planning of which vessels may be selected for use.
Recently, surgeons performing living-donor transplantations have successfully used the more accessible and less risky ovarian and/or utero-ovarian veins for venous anastomosis. In 2019, for instance, a team in Pune, India, reported laparoscopically dissecting the donor ovarian veins and a portion of the internal iliac artery, and completing anastomosis with bilateral donor internal iliac arteries to recipient internal iliac arteries, and bilateral donor ovarian veins to recipient external iliac veins.6 It is significant that these smaller-caliber vessels were found to able to support the uterus through pregnancy.
We must be cautious, however, to avoid removing donors’ ovaries. Oophorectomy for women in their 40s can result in significant long-term medical sequelae. Surgeons at Baylor have achieved at least one live birth after harvesting the donor’s utero-ovarian veins while conserving the ovaries – a significant advancement for the living-donor model.4
There is tremendous interest in developing minimally invasive approaches to further reduce living-donor risk. The Swedish team has completed a series of eight robotic hysterectomies in living-donor uterus transplantations as part of a second trial. Addressing the reality of a learning curve, their study was designed around a step-wise approach, mastering initial steps first – e.g., dissections of the uterovaginal fossa, arteries, and ureters – and ultimately converting to laparotomy.7 In the United States, Baylor University has now completed at least five completely robotic living-donor hysterectomies with complete vaginal extraction.
Published data on robotic surgery suggests that surgical access and perioperative visualization of the vessels may be improved. And as minimally invasive approaches are adopted and improved, the length of donor surgery – 10-13 hours of operating room time in the original Swedish series – should diminish, as should the morbidity associated with laparotomy.
Surgical acquisition of a uterine graft from a deceased donor diminishes concerns for injury to nearby structures. Therefore, although it is a technically similar procedure, a deceased-donor model allows more flexibility with the length, caliber, and number of vessels that can be used for anastomosis. The internal iliac vessels and even portions of the external iliac vessels and ovarian vessels can be used to allow maximum flexibility.8
Surgical technique for uterus recipients
For the recipient surgery, entry is achieved via a midline, vertical laparotomy. The external iliac vessels are exposed, and the sites of vascular anastomoses are identified. The peritoneal reflection of the bladder is identified and dissected away to expose the anterior vagina, and the vagina is opened to a diameter that matches the donor, typically using a monopolar electrosurgical cutting instrument.
The vault of the donor vagina will be attached to the recipient’s existing vagina or vaginal pouch. It is important to identify recipient vaginal mucosa and incorporate it into the vaginal anastomosis to reduce the risk of vaginal stricture. We recommend that the vaginal mucosa be tagged with PDS II sutures or grasped with allis clamps to prevent retraction.
Surgical teams have taken multiple approaches to vaginal anastomosis. The Cleveland Clinic has used both a running suture as well as a horizontal mattress stitch for closure. For the latter, a 30-inch double-armed 2.0 Vicryl allows for complete suturing of the recipient vagina – with eight stitches placed circumferentially – before the uterus is placed. Both ends of the suture are passed intra-abdominal to intravaginal in the recipient.9
Once the donor uterus is suspended, attention focuses on vascular anastomosis, with bilateral end-to-side anastomosis between the donor anterior division of the internal iliac arteries and the external iliac vessels of the recipient, and with venous drainage commonly achieved through the uterine veins draining into the internal or external iliac vein of the recipient. As mentioned, recent cases involving living donors have also demonstrated success with the use of ovarian and/or utero-ovarian veins. Care should be taken to avoid having tension or twisting across the anastomosis.
After adequate graft perfusion is confirmed, with the uterus turning from a dusky color to a pink and well-perfused organ, the vaginal anastomosis is completed, with the arms of the double-armed suture passed through the donor vagina, from intravaginal to intra-abdominal. Tension should be evenly spread along the recipient and donor vagina in order to reduce the formation of granulation tissue and the severity of future vaginal stricturing.
For uterine fixation, polypropylene sutures are placed between the graft uterosacral ligaments and recipient uterine rudiments, and between the graft round ligaments and the recipient pelvic side wall at the level of the deep inguinal ring.
Current uterus transplantation protocols require removal of the uterus after one or two live births are achieved, so that recipients will not be exposed to long-term immunosuppression.
Complications and controversies
Postoperative vaginal strictures can make embryo transfer difficult and are a common complication in both living- and deceased-donor models. The Cleveland Clinic team has applied techniques from vaginal reconstructive surgery to try to reduce the occurrence of postoperative strictures – mainly increasing attention paid to anastomosis tissue–site preparation and closure of the anastomosis using a tension-free interrupted suture technique, as described above.9 The jury is out on whether such changes are sufficient, and a more complete understanding of the causes of vaginal stricture is needed.
Other perioperative complications include infection and graft thrombosis, both of which typically result in urgent graft hysterectomy. During pregnancy, one of our patients experienced abnormal placentation, though this was not thought to be related to uterus transplantation.5
The U.S. Uterus Transplant Consortium (USUTC) is a group of active programs that are sharing ideas and outcomes and advocating for continued research in this rapidly developing field. Uterine transplants require collaboration with transplant surgery, transplant medicine, infectious disease, gynecologic surgery, high-risk obstetrics, and other specialties. While significant progress has been made in a short period of time, uterine transplantation is still in its early stages, and transplants should be done in institutions that have the capacity for mentorship, bioethical oversight, and long-term follow-up of donors, recipients, and offspring.
The USUTC has recently proposed guidelines for nomenclature related to operative technique, vascular anatomy, and uterine transplantation outcomes.10 It proposes standardizing the names for the four veins originating from the uterus (to eliminate current inconsistency), which will be important as optimal strategies for vascular anastomoses are discussed and determined.
In addition, the consortium is creating a registry for the rigorous collection of data on procedures and outcomes (from menstruation and pregnancy through delivery, graft removal, and long-term follow-up). A registry has also been proposed by the International Society for Uterine Transplantation.
A major question remains in our field: Is the living-donor or deceased-donor uterus transplant the best approach? Knowledge of the quality of the uterus is greater preoperatively within a living-donor model, but no matter how minimally invasive the technique, the donor still assumes some risk of prolonged surgery and extensive pelvic dissection for a transplant that is not lifesaving.
On the other hand, deceased-donor transplants require additional layers of organization and coordination, and the availability of suitable deceased-donor uteri will likely not be sufficient to meet the current demand. Many of us in the field believe that the future of uterine transplantation will involve some combination of living- and deceased-donor transplants – similar to other solid organ transplant programs.
Dr. Flyckt and Dr. Richards reported that they have no relevant financial disclosures.
Correction, 2/2/21: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Richards' name in the photo caption.
References
1. Lancet. 2015;14:385:607-16.
2. AJOB Empir Bioeth. 2019;10(1):23-5.
3. Transplantation. 2020;104(7):1312-5.
4. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(5):1270-4.
5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223(2):143-51.
6. J Minimally Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:628-35.
7. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020;99(9):1222-9.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(1):183.
9. Fertil Steril. 2020 Jul 16. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.05.017
10 Am J Transplant. 2020;20(12):3319-25.
Since the first baby was born after a uterus transplantation in Sweden in 2014, uterus transplantation has been rapidly transitioning toward clinical reality.1 Several teams in the United States and multiple teams worldwide have performed the procedure, with the total number of worldwide surgeries performed nearing 100.
Uterus transplantation is the first and only true treatment for women with absolute uterine factor infertility – estimated to affect 1 in 500 women – and is filling an unmet need for this population of women. Women who have sought participation in uterus transplantation research have had complex and meaningful reasons and motivations for doing so.2 Combined with an accumulation of successful pregnancies, this makes continued research and technical improvement a worthy endeavor.
Most of the births thus far have occurred through the living-donor model; the initial Swedish trial involved nine women, seven of whom completed the procedure with viable transplants from living donors, and gave birth to eight healthy children. (Two required hysterectomy prior to attempted embryo transfer.3)
The Cleveland Clinic opted to build its first – and still ongoing – trial focusing on deceased-donor uterus transplants on the premise that such an approach obviates any risk to the donor and presents the fewest ethical challenges at the current time. Of eight uterus transplants performed thus far at the Cleveland Clinic, there have been three live births and two graft failures. As of early 2021, there was one ongoing pregnancy and two patients in preparation for embryo transfer.
Thus far, neither the living- nor deceased-donor model of uterus transplantation has been demonstrated to be superior. However, as data accrues from deceased donor studies, we will be able to more directly compare outcomes.
In the meantime, alongside a rapid ascent of clinical landmarks – the first live birth in the United States from living-donor uterus transplantation in 2017 at Baylor University Medical Center in Houston,4 for instance, and the first live birth in the United States from deceased-donor uterus transplantation in 2019 at the Cleveland Clinic – there have been significant improvements in surgical retrieval of the uterus and in the optimization of graft performance.5
Most notably, the utero-ovarian vein has been used successfully in living donors to achieve venous drainage of the graft. This has lessened the risks of deep pelvic dissection in the living donor and made the transition to laparoscopic and robotic approaches in the living donor much easier.
Donor procurement, venous drainage
Adequate circulatory inflow and outflow for the transplanted uterus are essential both for the prevention of ischemia and thrombosis, which have been major causes of graft failure, and for meeting the increased demands of blood flow during pregnancy. Of the two, the outflow is the more challenging component.
Venous drainage traditionally has been accomplished through the use of the uterine veins, which drain into the internal iliac veins; often the vascular graft will include a portion of the internal iliac vessel which can be connected via anastomoses to the external iliac vein classically in deceased donors. Typically, the gynecologic surgeon on the team performs the vaginal anastomosis and suspension of the uterus, while the transplant surgeons perform the venous and arterial anastomoses.
In the living-donor model, procurement and dissection of these often unpredictable and tortuous complexes in the deep pelvis – particularly the branching uterine veins that lie in close proximity to the ureter, bladder, other blood vessels, and rectum – can be risky. The anatomic variants in the uterine vein are numerous, and even in one patient, a comprehensive dissection on one side cannot be expected to be mirrored on the contralateral side.
In addition to the risk of injury to the donor, the anastomosis may be unsuccessful as the veins are thinly walled and challenging to suture. As such, multiple modifications have been developed, often adapted to the donor’s anatomy and the caliber and accessibility of vessels. Preoperative vascular imaging with CT and/or MRI may help to identify suitable candidates and also may facilitate presurgical planning of which vessels may be selected for use.
Recently, surgeons performing living-donor transplantations have successfully used the more accessible and less risky ovarian and/or utero-ovarian veins for venous anastomosis. In 2019, for instance, a team in Pune, India, reported laparoscopically dissecting the donor ovarian veins and a portion of the internal iliac artery, and completing anastomosis with bilateral donor internal iliac arteries to recipient internal iliac arteries, and bilateral donor ovarian veins to recipient external iliac veins.6 It is significant that these smaller-caliber vessels were found to able to support the uterus through pregnancy.
We must be cautious, however, to avoid removing donors’ ovaries. Oophorectomy for women in their 40s can result in significant long-term medical sequelae. Surgeons at Baylor have achieved at least one live birth after harvesting the donor’s utero-ovarian veins while conserving the ovaries – a significant advancement for the living-donor model.4
There is tremendous interest in developing minimally invasive approaches to further reduce living-donor risk. The Swedish team has completed a series of eight robotic hysterectomies in living-donor uterus transplantations as part of a second trial. Addressing the reality of a learning curve, their study was designed around a step-wise approach, mastering initial steps first – e.g., dissections of the uterovaginal fossa, arteries, and ureters – and ultimately converting to laparotomy.7 In the United States, Baylor University has now completed at least five completely robotic living-donor hysterectomies with complete vaginal extraction.
Published data on robotic surgery suggests that surgical access and perioperative visualization of the vessels may be improved. And as minimally invasive approaches are adopted and improved, the length of donor surgery – 10-13 hours of operating room time in the original Swedish series – should diminish, as should the morbidity associated with laparotomy.
Surgical acquisition of a uterine graft from a deceased donor diminishes concerns for injury to nearby structures. Therefore, although it is a technically similar procedure, a deceased-donor model allows more flexibility with the length, caliber, and number of vessels that can be used for anastomosis. The internal iliac vessels and even portions of the external iliac vessels and ovarian vessels can be used to allow maximum flexibility.8
Surgical technique for uterus recipients
For the recipient surgery, entry is achieved via a midline, vertical laparotomy. The external iliac vessels are exposed, and the sites of vascular anastomoses are identified. The peritoneal reflection of the bladder is identified and dissected away to expose the anterior vagina, and the vagina is opened to a diameter that matches the donor, typically using a monopolar electrosurgical cutting instrument.
The vault of the donor vagina will be attached to the recipient’s existing vagina or vaginal pouch. It is important to identify recipient vaginal mucosa and incorporate it into the vaginal anastomosis to reduce the risk of vaginal stricture. We recommend that the vaginal mucosa be tagged with PDS II sutures or grasped with allis clamps to prevent retraction.
Surgical teams have taken multiple approaches to vaginal anastomosis. The Cleveland Clinic has used both a running suture as well as a horizontal mattress stitch for closure. For the latter, a 30-inch double-armed 2.0 Vicryl allows for complete suturing of the recipient vagina – with eight stitches placed circumferentially – before the uterus is placed. Both ends of the suture are passed intra-abdominal to intravaginal in the recipient.9
Once the donor uterus is suspended, attention focuses on vascular anastomosis, with bilateral end-to-side anastomosis between the donor anterior division of the internal iliac arteries and the external iliac vessels of the recipient, and with venous drainage commonly achieved through the uterine veins draining into the internal or external iliac vein of the recipient. As mentioned, recent cases involving living donors have also demonstrated success with the use of ovarian and/or utero-ovarian veins. Care should be taken to avoid having tension or twisting across the anastomosis.
After adequate graft perfusion is confirmed, with the uterus turning from a dusky color to a pink and well-perfused organ, the vaginal anastomosis is completed, with the arms of the double-armed suture passed through the donor vagina, from intravaginal to intra-abdominal. Tension should be evenly spread along the recipient and donor vagina in order to reduce the formation of granulation tissue and the severity of future vaginal stricturing.
For uterine fixation, polypropylene sutures are placed between the graft uterosacral ligaments and recipient uterine rudiments, and between the graft round ligaments and the recipient pelvic side wall at the level of the deep inguinal ring.
Current uterus transplantation protocols require removal of the uterus after one or two live births are achieved, so that recipients will not be exposed to long-term immunosuppression.
Complications and controversies
Postoperative vaginal strictures can make embryo transfer difficult and are a common complication in both living- and deceased-donor models. The Cleveland Clinic team has applied techniques from vaginal reconstructive surgery to try to reduce the occurrence of postoperative strictures – mainly increasing attention paid to anastomosis tissue–site preparation and closure of the anastomosis using a tension-free interrupted suture technique, as described above.9 The jury is out on whether such changes are sufficient, and a more complete understanding of the causes of vaginal stricture is needed.
Other perioperative complications include infection and graft thrombosis, both of which typically result in urgent graft hysterectomy. During pregnancy, one of our patients experienced abnormal placentation, though this was not thought to be related to uterus transplantation.5
The U.S. Uterus Transplant Consortium (USUTC) is a group of active programs that are sharing ideas and outcomes and advocating for continued research in this rapidly developing field. Uterine transplants require collaboration with transplant surgery, transplant medicine, infectious disease, gynecologic surgery, high-risk obstetrics, and other specialties. While significant progress has been made in a short period of time, uterine transplantation is still in its early stages, and transplants should be done in institutions that have the capacity for mentorship, bioethical oversight, and long-term follow-up of donors, recipients, and offspring.
The USUTC has recently proposed guidelines for nomenclature related to operative technique, vascular anatomy, and uterine transplantation outcomes.10 It proposes standardizing the names for the four veins originating from the uterus (to eliminate current inconsistency), which will be important as optimal strategies for vascular anastomoses are discussed and determined.
In addition, the consortium is creating a registry for the rigorous collection of data on procedures and outcomes (from menstruation and pregnancy through delivery, graft removal, and long-term follow-up). A registry has also been proposed by the International Society for Uterine Transplantation.
A major question remains in our field: Is the living-donor or deceased-donor uterus transplant the best approach? Knowledge of the quality of the uterus is greater preoperatively within a living-donor model, but no matter how minimally invasive the technique, the donor still assumes some risk of prolonged surgery and extensive pelvic dissection for a transplant that is not lifesaving.
On the other hand, deceased-donor transplants require additional layers of organization and coordination, and the availability of suitable deceased-donor uteri will likely not be sufficient to meet the current demand. Many of us in the field believe that the future of uterine transplantation will involve some combination of living- and deceased-donor transplants – similar to other solid organ transplant programs.
Dr. Flyckt and Dr. Richards reported that they have no relevant financial disclosures.
Correction, 2/2/21: An earlier version of this article misstated Dr. Richards' name in the photo caption.
References
1. Lancet. 2015;14:385:607-16.
2. AJOB Empir Bioeth. 2019;10(1):23-5.
3. Transplantation. 2020;104(7):1312-5.
4. Am J Transplant. 2018;18(5):1270-4.
5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;223(2):143-51.
6. J Minimally Invasive Gynecol. 2019;26:628-35.
7. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020;99(9):1222-9.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018;110(1):183.
9. Fertil Steril. 2020 Jul 16. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2020.05.017
10 Am J Transplant. 2020;20(12):3319-25.
Uterus transplantation for absolute uterine factor infertility
Until the advent of uterus transplantation, there was no restorative procedure available to a woman presenting with an absent uterus or nonfunctioning uterus; that is, absolute uterine factor infertility (AUFI). It is estimated that 1 in 500 women of childbearing age are affected by AUFI.1,2 An absent uterus may be secondary to uterine agenesis or Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH), which occurs in 1 in 4,500 women.3,4 (Because women with MRKH have a normal karyotype, their children can be normal, without urogenital malformations.5)
Given the fact that roughly 240,000 hysterectomies are performed in the United States each year for women aged under 44 years, hysterectomy is the most common cause of acquired AUFI.6AUFI may also be secondary to a uterus that will not support a viable pregnancy; that is, a nonfunctional uterus. In this case, medical or surgical treatment is impossible to enable normal physiological uterine function to produce a successful pregnancy. Causal factors include Müllerian anomalies, severe intrauterine adhesions/Asherman syndrome, uterine fibroids not amendable to surgical therapy, and radiation injury not responsive to medical therapy.
Prior to uterus transplantation, parenthood could only be achieved via adoption, foster parenting, or gestational carrier. While utilizing a gestational carrier is legal in most U.S. states, most countries of western Europe as well as Brazil and Japan, to name a few, do not allow the use of gestational carriers. For some women, moreover, the desire is not only to have a baby, but to carry a child as well.
For this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted the assistance of Rebecca Flyckt, MD, division chief of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and associate professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Elliott G. Richards, MD, director of reproductive endocrinology and infertility research at the Cleveland Clinic, to discuss the current and future state of uterus transplantation.
Dr. Flyckt and Dr. Richards have both contributed to the uterus transplantation team at the Cleveland Clinic and are founding members of the U.S. Uterus Transplant Consortium. They are well published in the field of minimally invasive gynecology and reproductive endocrinology and infertility. It is truly a pleasure to welcome them both to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
References
1. Fertil Steril. 2014 May;101(5):1228-36.
2. Acta Biomater. 2014 Dec;10(12):5034-42.
3. Hum Reprod Update. Mar-Apr 2001;7(2):161-74.
4. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2000 Oct;55(10):644-9.
5. Fertil Steril. 1997 Feb;67(2):387-9
6. Am J Public Health. 2003 Feb;93(2):307-12.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. Dr. Miller reported that he has no disclosures relevant to this Master Class. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Until the advent of uterus transplantation, there was no restorative procedure available to a woman presenting with an absent uterus or nonfunctioning uterus; that is, absolute uterine factor infertility (AUFI). It is estimated that 1 in 500 women of childbearing age are affected by AUFI.1,2 An absent uterus may be secondary to uterine agenesis or Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH), which occurs in 1 in 4,500 women.3,4 (Because women with MRKH have a normal karyotype, their children can be normal, without urogenital malformations.5)
Given the fact that roughly 240,000 hysterectomies are performed in the United States each year for women aged under 44 years, hysterectomy is the most common cause of acquired AUFI.6AUFI may also be secondary to a uterus that will not support a viable pregnancy; that is, a nonfunctional uterus. In this case, medical or surgical treatment is impossible to enable normal physiological uterine function to produce a successful pregnancy. Causal factors include Müllerian anomalies, severe intrauterine adhesions/Asherman syndrome, uterine fibroids not amendable to surgical therapy, and radiation injury not responsive to medical therapy.
Prior to uterus transplantation, parenthood could only be achieved via adoption, foster parenting, or gestational carrier. While utilizing a gestational carrier is legal in most U.S. states, most countries of western Europe as well as Brazil and Japan, to name a few, do not allow the use of gestational carriers. For some women, moreover, the desire is not only to have a baby, but to carry a child as well.
For this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted the assistance of Rebecca Flyckt, MD, division chief of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and associate professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Elliott G. Richards, MD, director of reproductive endocrinology and infertility research at the Cleveland Clinic, to discuss the current and future state of uterus transplantation.
Dr. Flyckt and Dr. Richards have both contributed to the uterus transplantation team at the Cleveland Clinic and are founding members of the U.S. Uterus Transplant Consortium. They are well published in the field of minimally invasive gynecology and reproductive endocrinology and infertility. It is truly a pleasure to welcome them both to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
References
1. Fertil Steril. 2014 May;101(5):1228-36.
2. Acta Biomater. 2014 Dec;10(12):5034-42.
3. Hum Reprod Update. Mar-Apr 2001;7(2):161-74.
4. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2000 Oct;55(10):644-9.
5. Fertil Steril. 1997 Feb;67(2):387-9
6. Am J Public Health. 2003 Feb;93(2):307-12.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. Dr. Miller reported that he has no disclosures relevant to this Master Class. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Until the advent of uterus transplantation, there was no restorative procedure available to a woman presenting with an absent uterus or nonfunctioning uterus; that is, absolute uterine factor infertility (AUFI). It is estimated that 1 in 500 women of childbearing age are affected by AUFI.1,2 An absent uterus may be secondary to uterine agenesis or Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH), which occurs in 1 in 4,500 women.3,4 (Because women with MRKH have a normal karyotype, their children can be normal, without urogenital malformations.5)
Given the fact that roughly 240,000 hysterectomies are performed in the United States each year for women aged under 44 years, hysterectomy is the most common cause of acquired AUFI.6AUFI may also be secondary to a uterus that will not support a viable pregnancy; that is, a nonfunctional uterus. In this case, medical or surgical treatment is impossible to enable normal physiological uterine function to produce a successful pregnancy. Causal factors include Müllerian anomalies, severe intrauterine adhesions/Asherman syndrome, uterine fibroids not amendable to surgical therapy, and radiation injury not responsive to medical therapy.
Prior to uterus transplantation, parenthood could only be achieved via adoption, foster parenting, or gestational carrier. While utilizing a gestational carrier is legal in most U.S. states, most countries of western Europe as well as Brazil and Japan, to name a few, do not allow the use of gestational carriers. For some women, moreover, the desire is not only to have a baby, but to carry a child as well.
For this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted the assistance of Rebecca Flyckt, MD, division chief of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center and associate professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, and Elliott G. Richards, MD, director of reproductive endocrinology and infertility research at the Cleveland Clinic, to discuss the current and future state of uterus transplantation.
Dr. Flyckt and Dr. Richards have both contributed to the uterus transplantation team at the Cleveland Clinic and are founding members of the U.S. Uterus Transplant Consortium. They are well published in the field of minimally invasive gynecology and reproductive endocrinology and infertility. It is truly a pleasure to welcome them both to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
References
1. Fertil Steril. 2014 May;101(5):1228-36.
2. Acta Biomater. 2014 Dec;10(12):5034-42.
3. Hum Reprod Update. Mar-Apr 2001;7(2):161-74.
4. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2000 Oct;55(10):644-9.
5. Fertil Steril. 1997 Feb;67(2):387-9
6. Am J Public Health. 2003 Feb;93(2):307-12.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, Ill. Dr. Miller reported that he has no disclosures relevant to this Master Class. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
The fourth trimester: Achieving improved postpartum care
The field of ob.gyn. has long focused significantly more attention on the prenatal period – on determining the optimal frequency of ultrasound examinations, for instance, and on screening for diabetes and other conditions – than on women’s health and well-being after delivery.
The traditional 6-week postpartum visit has too often been a quick and cursory visit, with new mothers typically navigating the preceding postpartum transitions on their own.
The need to redefine postpartum care was a central message of Haywood Brown, MD, who in 2017 served as the president of the America College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Dr. Brown established a task force whose work resulted in important guidance for taking a more comprehensive and patient-centered approach to postpartum care.1
Improved care in the “fourth trimester,” as it has come to be known, is comprehensive and includes ensuring that our patients have a solid transition to health care beyond the pregnancy. We also hope that it will help us to reduce maternal mortality, given that more than half of pregnancy-related deaths occur after delivery.
Timing and frequency of contact
Historically, we’ve had a single 6-week postpartum visit, with little or no maternal support or patient contact before this visit unless the patient reported a complication. In the new paradigm, as described in the ACOG committee opinion on optimizing postpartum care, maternal care should be an ongoing process.1
so that any questions or concerns may be addressed and support can be provided.
This should be followed by individualized, ongoing care until a comprehensive postpartum visit covering physical, social, and psychological well-being is conducted by 12 weeks after birth – anytime between 4 and 12 weeks.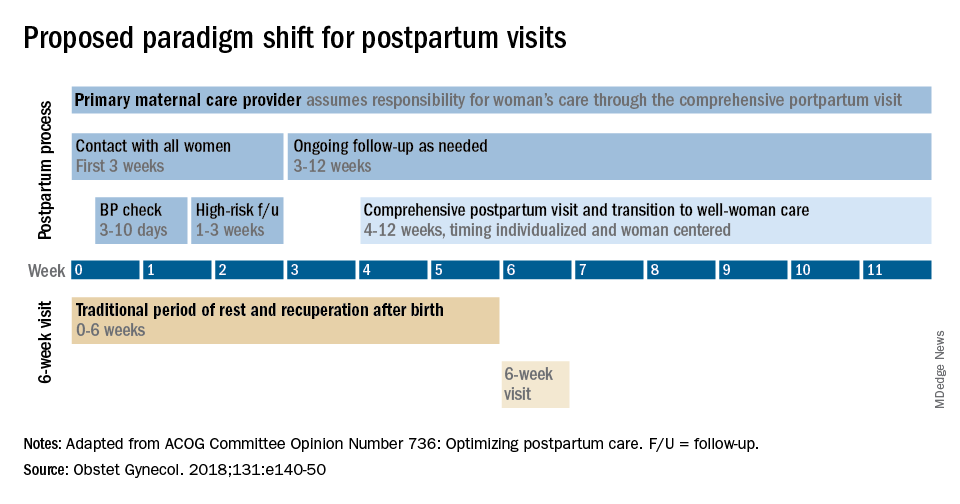
By stressing the importance of postpartum care during prenatal visits – and by talking about some of its key elements such as mental health, breastfeeding, and chronic disease management – we can let our patients know that postpartum care is not just an afterthought, but that it involves planning backed by evidence and expert opinion. Currently, as many as 40% of women do not attend a postpartum visit; early discussion, it is hoped, will increase attendance.
Certain high-risk groups should be seen or screened earlier than 3 weeks post partum. For instance, women who have hypertensive disorders of pregnancy should be evaluated no later than 7-10 days post partum, and women with severe hypertension should be seen within 72 hours, according to ACOG.
Early blood pressure checks – and follow-up as necessary – are critical for reducing the risk of postpartum stroke and other complications. I advocate uniformly checking blood pressure within several days after hospital discharge for all women who have hypertension at the end of their pregnancy.
Other high-risk conditions requiring early follow-up include diabetes and autoimmune conditions such as lupus, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis that may flare in the postpartum period. Women with a history of postpartum depression similarly may benefit from early contact; they are at higher risk of having depression again, and there are clearly effective treatments, both medication and psychotherapy based.
In between the initial early contact (by 7-10 days post partum or by 3 weeks post partum) and the comprehensive visit between 4 and 12 weeks, the need for and timing of patient contact can be individualized. Some women will need only a brief contact and a visit at 8-10 weeks, while others will need much more. Our goal, as in all of medicine, is to provide individualized, patient-centered care.
Methods of contact
With the exception of the final comprehensive visit, postpartum care need not occur in person. Some conditions require an early office visit, but in general, as ACOG states, the usefulness of an in-person visit should be weighed against the burden of traveling to and attending that visit.
For many women, in-person visits are difficult, and we must be creative in utilizing telemedicine and phone support, text messaging, and app-based support. Having practiced during this pandemic, we are better positioned than ever before to make it relatively easy for new mothers to obtain ongoing postpartum care.
Notably, research is demonstrating that the use of technology may allow us to provide improved care and monitoring of hypertension in the postpartum period. For example, a randomized trial published in 2018 of over 200 women with a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy found that text-based surveillance with home blood pressure monitoring was more effective than usual in-person blood pressure checks in meeting clinical guidelines for postpartum monitoring.2
Women in the texting group were significantly more likely to have a single blood pressure obtained in the first 10 days post partum than women in the office group.
Postpartum care is also not a completely physician-driven endeavor. Much of what is needed to help women successfully navigate the fourth trimester can be provided by certified nurse midwives, advanced practice nurses, and other members of our maternal care teams.
Components of postpartum care
The postpartum care plan should be comprehensive, and having a checklist to guide one through initial and comprehensive visits may be helpful. The ACOG committee opinion categorizes the components of postpartum care into seven domains: mood and emotional well-being; infant care and feeding; sexuality, contraception, and birth spacing; sleep and fatigue; physical recovery from birth; chronic disease management; and health maintenance.1
The importance of screening for depression and anxiety cannot be emphasized enough. Perinatal depression is highly prevalent: It affects as many as one in seven women and can result in adverse short- and long-term effects on both the mother and child.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has offered guidance for years, most recently in 2019 with its recommendations that clinicians refer pregnant and postpartum women who are at increased risk for depression to counseling interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy.3 There is evidence that some form of treatment for women who screen positive reduces the risk of perinatal depression.
Additionally, there is emerging evidence that postpartum PTSD may be as prevalent as postpartum depression.4 As ACOG points out, trauma is “in the eye of the beholder,” and an estimated 3%-16% of women have PTSD related to a traumatic birth experience. Complications like shoulder dystocia or postpartum hemorrhage, in which delivery processes rapidly change course, can be experienced as traumatic by women even though they and their infants are healthy. The risk of posttraumatic stress should be on our radar screen.
Interpregnancy intervals similarly are not discussed enough. We do not commonly talk to patients about how pregnancy and breastfeeding are nutritionally depleting and how it takes time to replenish these stores – yet birth spacing is so important.
Compared with interpregnancy intervals of at least 18 months, intervals shorter than 6 months were associated in a meta-analysis with increased risks of preterm birth, low birth weight, and small for gestational age.5 Optimal birth spacing is one of the few low-cost interventions available for reducing pregnancy complications in the future.
Finally, that chronic disease management is a domain of postpartum care warrants emphasis. We must work to ensure that patients have a solid plan of care in place for their diabetes, hypertension, lupus, or other chronic conditions. This includes who will provide that ongoing care, as well as when medical management should be restarted.
Some women are aware of the importance of timely care – of not waiting for 12 months, for instance, to see an internist or specialist – but others are not.
Again, certain health conditions such as multiple sclerosis and RA necessitate follow-up within a couple weeks after delivery so that medications can be restarted or dose adjustments made. The need for early postpartum follow-up can be discussed during prenatal visits, along with anticipatory guidance about breastfeeding, the signs and symptoms of perinatal depression and anxiety, and other components of the fourth trimester.
Dr. Macones has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 May;131(5):e140-50.
2. BMJ Qual Saf. 2018 Apr 27;27(11):871-7.
3. JAMA. 2019 Feb 12;321(6):580-7.
4. Clin Psychol Rev. 2014 Jul;34:389-401.JAMA. 2006 Apr 19;295(15):1809-23.
The field of ob.gyn. has long focused significantly more attention on the prenatal period – on determining the optimal frequency of ultrasound examinations, for instance, and on screening for diabetes and other conditions – than on women’s health and well-being after delivery.
The traditional 6-week postpartum visit has too often been a quick and cursory visit, with new mothers typically navigating the preceding postpartum transitions on their own.
The need to redefine postpartum care was a central message of Haywood Brown, MD, who in 2017 served as the president of the America College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Dr. Brown established a task force whose work resulted in important guidance for taking a more comprehensive and patient-centered approach to postpartum care.1
Improved care in the “fourth trimester,” as it has come to be known, is comprehensive and includes ensuring that our patients have a solid transition to health care beyond the pregnancy. We also hope that it will help us to reduce maternal mortality, given that more than half of pregnancy-related deaths occur after delivery.
Timing and frequency of contact
Historically, we’ve had a single 6-week postpartum visit, with little or no maternal support or patient contact before this visit unless the patient reported a complication. In the new paradigm, as described in the ACOG committee opinion on optimizing postpartum care, maternal care should be an ongoing process.1
so that any questions or concerns may be addressed and support can be provided.
This should be followed by individualized, ongoing care until a comprehensive postpartum visit covering physical, social, and psychological well-being is conducted by 12 weeks after birth – anytime between 4 and 12 weeks.
By stressing the importance of postpartum care during prenatal visits – and by talking about some of its key elements such as mental health, breastfeeding, and chronic disease management – we can let our patients know that postpartum care is not just an afterthought, but that it involves planning backed by evidence and expert opinion. Currently, as many as 40% of women do not attend a postpartum visit; early discussion, it is hoped, will increase attendance.
Certain high-risk groups should be seen or screened earlier than 3 weeks post partum. For instance, women who have hypertensive disorders of pregnancy should be evaluated no later than 7-10 days post partum, and women with severe hypertension should be seen within 72 hours, according to ACOG.
Early blood pressure checks – and follow-up as necessary – are critical for reducing the risk of postpartum stroke and other complications. I advocate uniformly checking blood pressure within several days after hospital discharge for all women who have hypertension at the end of their pregnancy.
Other high-risk conditions requiring early follow-up include diabetes and autoimmune conditions such as lupus, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis that may flare in the postpartum period. Women with a history of postpartum depression similarly may benefit from early contact; they are at higher risk of having depression again, and there are clearly effective treatments, both medication and psychotherapy based.
In between the initial early contact (by 7-10 days post partum or by 3 weeks post partum) and the comprehensive visit between 4 and 12 weeks, the need for and timing of patient contact can be individualized. Some women will need only a brief contact and a visit at 8-10 weeks, while others will need much more. Our goal, as in all of medicine, is to provide individualized, patient-centered care.
Methods of contact
With the exception of the final comprehensive visit, postpartum care need not occur in person. Some conditions require an early office visit, but in general, as ACOG states, the usefulness of an in-person visit should be weighed against the burden of traveling to and attending that visit.
For many women, in-person visits are difficult, and we must be creative in utilizing telemedicine and phone support, text messaging, and app-based support. Having practiced during this pandemic, we are better positioned than ever before to make it relatively easy for new mothers to obtain ongoing postpartum care.
Notably, research is demonstrating that the use of technology may allow us to provide improved care and monitoring of hypertension in the postpartum period. For example, a randomized trial published in 2018 of over 200 women with a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy found that text-based surveillance with home blood pressure monitoring was more effective than usual in-person blood pressure checks in meeting clinical guidelines for postpartum monitoring.2
Women in the texting group were significantly more likely to have a single blood pressure obtained in the first 10 days post partum than women in the office group.
Postpartum care is also not a completely physician-driven endeavor. Much of what is needed to help women successfully navigate the fourth trimester can be provided by certified nurse midwives, advanced practice nurses, and other members of our maternal care teams.
Components of postpartum care
The postpartum care plan should be comprehensive, and having a checklist to guide one through initial and comprehensive visits may be helpful. The ACOG committee opinion categorizes the components of postpartum care into seven domains: mood and emotional well-being; infant care and feeding; sexuality, contraception, and birth spacing; sleep and fatigue; physical recovery from birth; chronic disease management; and health maintenance.1
The importance of screening for depression and anxiety cannot be emphasized enough. Perinatal depression is highly prevalent: It affects as many as one in seven women and can result in adverse short- and long-term effects on both the mother and child.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has offered guidance for years, most recently in 2019 with its recommendations that clinicians refer pregnant and postpartum women who are at increased risk for depression to counseling interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy.3 There is evidence that some form of treatment for women who screen positive reduces the risk of perinatal depression.
Additionally, there is emerging evidence that postpartum PTSD may be as prevalent as postpartum depression.4 As ACOG points out, trauma is “in the eye of the beholder,” and an estimated 3%-16% of women have PTSD related to a traumatic birth experience. Complications like shoulder dystocia or postpartum hemorrhage, in which delivery processes rapidly change course, can be experienced as traumatic by women even though they and their infants are healthy. The risk of posttraumatic stress should be on our radar screen.
Interpregnancy intervals similarly are not discussed enough. We do not commonly talk to patients about how pregnancy and breastfeeding are nutritionally depleting and how it takes time to replenish these stores – yet birth spacing is so important.
Compared with interpregnancy intervals of at least 18 months, intervals shorter than 6 months were associated in a meta-analysis with increased risks of preterm birth, low birth weight, and small for gestational age.5 Optimal birth spacing is one of the few low-cost interventions available for reducing pregnancy complications in the future.
Finally, that chronic disease management is a domain of postpartum care warrants emphasis. We must work to ensure that patients have a solid plan of care in place for their diabetes, hypertension, lupus, or other chronic conditions. This includes who will provide that ongoing care, as well as when medical management should be restarted.
Some women are aware of the importance of timely care – of not waiting for 12 months, for instance, to see an internist or specialist – but others are not.
Again, certain health conditions such as multiple sclerosis and RA necessitate follow-up within a couple weeks after delivery so that medications can be restarted or dose adjustments made. The need for early postpartum follow-up can be discussed during prenatal visits, along with anticipatory guidance about breastfeeding, the signs and symptoms of perinatal depression and anxiety, and other components of the fourth trimester.
Dr. Macones has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 May;131(5):e140-50.
2. BMJ Qual Saf. 2018 Apr 27;27(11):871-7.
3. JAMA. 2019 Feb 12;321(6):580-7.
4. Clin Psychol Rev. 2014 Jul;34:389-401.JAMA. 2006 Apr 19;295(15):1809-23.
The field of ob.gyn. has long focused significantly more attention on the prenatal period – on determining the optimal frequency of ultrasound examinations, for instance, and on screening for diabetes and other conditions – than on women’s health and well-being after delivery.
The traditional 6-week postpartum visit has too often been a quick and cursory visit, with new mothers typically navigating the preceding postpartum transitions on their own.
The need to redefine postpartum care was a central message of Haywood Brown, MD, who in 2017 served as the president of the America College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Dr. Brown established a task force whose work resulted in important guidance for taking a more comprehensive and patient-centered approach to postpartum care.1
Improved care in the “fourth trimester,” as it has come to be known, is comprehensive and includes ensuring that our patients have a solid transition to health care beyond the pregnancy. We also hope that it will help us to reduce maternal mortality, given that more than half of pregnancy-related deaths occur after delivery.
Timing and frequency of contact
Historically, we’ve had a single 6-week postpartum visit, with little or no maternal support or patient contact before this visit unless the patient reported a complication. In the new paradigm, as described in the ACOG committee opinion on optimizing postpartum care, maternal care should be an ongoing process.1
so that any questions or concerns may be addressed and support can be provided.
This should be followed by individualized, ongoing care until a comprehensive postpartum visit covering physical, social, and psychological well-being is conducted by 12 weeks after birth – anytime between 4 and 12 weeks.
By stressing the importance of postpartum care during prenatal visits – and by talking about some of its key elements such as mental health, breastfeeding, and chronic disease management – we can let our patients know that postpartum care is not just an afterthought, but that it involves planning backed by evidence and expert opinion. Currently, as many as 40% of women do not attend a postpartum visit; early discussion, it is hoped, will increase attendance.
Certain high-risk groups should be seen or screened earlier than 3 weeks post partum. For instance, women who have hypertensive disorders of pregnancy should be evaluated no later than 7-10 days post partum, and women with severe hypertension should be seen within 72 hours, according to ACOG.
Early blood pressure checks – and follow-up as necessary – are critical for reducing the risk of postpartum stroke and other complications. I advocate uniformly checking blood pressure within several days after hospital discharge for all women who have hypertension at the end of their pregnancy.
Other high-risk conditions requiring early follow-up include diabetes and autoimmune conditions such as lupus, multiple sclerosis, and psoriasis that may flare in the postpartum period. Women with a history of postpartum depression similarly may benefit from early contact; they are at higher risk of having depression again, and there are clearly effective treatments, both medication and psychotherapy based.
In between the initial early contact (by 7-10 days post partum or by 3 weeks post partum) and the comprehensive visit between 4 and 12 weeks, the need for and timing of patient contact can be individualized. Some women will need only a brief contact and a visit at 8-10 weeks, while others will need much more. Our goal, as in all of medicine, is to provide individualized, patient-centered care.
Methods of contact
With the exception of the final comprehensive visit, postpartum care need not occur in person. Some conditions require an early office visit, but in general, as ACOG states, the usefulness of an in-person visit should be weighed against the burden of traveling to and attending that visit.
For many women, in-person visits are difficult, and we must be creative in utilizing telemedicine and phone support, text messaging, and app-based support. Having practiced during this pandemic, we are better positioned than ever before to make it relatively easy for new mothers to obtain ongoing postpartum care.
Notably, research is demonstrating that the use of technology may allow us to provide improved care and monitoring of hypertension in the postpartum period. For example, a randomized trial published in 2018 of over 200 women with a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy found that text-based surveillance with home blood pressure monitoring was more effective than usual in-person blood pressure checks in meeting clinical guidelines for postpartum monitoring.2
Women in the texting group were significantly more likely to have a single blood pressure obtained in the first 10 days post partum than women in the office group.
Postpartum care is also not a completely physician-driven endeavor. Much of what is needed to help women successfully navigate the fourth trimester can be provided by certified nurse midwives, advanced practice nurses, and other members of our maternal care teams.
Components of postpartum care
The postpartum care plan should be comprehensive, and having a checklist to guide one through initial and comprehensive visits may be helpful. The ACOG committee opinion categorizes the components of postpartum care into seven domains: mood and emotional well-being; infant care and feeding; sexuality, contraception, and birth spacing; sleep and fatigue; physical recovery from birth; chronic disease management; and health maintenance.1
The importance of screening for depression and anxiety cannot be emphasized enough. Perinatal depression is highly prevalent: It affects as many as one in seven women and can result in adverse short- and long-term effects on both the mother and child.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has offered guidance for years, most recently in 2019 with its recommendations that clinicians refer pregnant and postpartum women who are at increased risk for depression to counseling interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy.3 There is evidence that some form of treatment for women who screen positive reduces the risk of perinatal depression.
Additionally, there is emerging evidence that postpartum PTSD may be as prevalent as postpartum depression.4 As ACOG points out, trauma is “in the eye of the beholder,” and an estimated 3%-16% of women have PTSD related to a traumatic birth experience. Complications like shoulder dystocia or postpartum hemorrhage, in which delivery processes rapidly change course, can be experienced as traumatic by women even though they and their infants are healthy. The risk of posttraumatic stress should be on our radar screen.
Interpregnancy intervals similarly are not discussed enough. We do not commonly talk to patients about how pregnancy and breastfeeding are nutritionally depleting and how it takes time to replenish these stores – yet birth spacing is so important.
Compared with interpregnancy intervals of at least 18 months, intervals shorter than 6 months were associated in a meta-analysis with increased risks of preterm birth, low birth weight, and small for gestational age.5 Optimal birth spacing is one of the few low-cost interventions available for reducing pregnancy complications in the future.
Finally, that chronic disease management is a domain of postpartum care warrants emphasis. We must work to ensure that patients have a solid plan of care in place for their diabetes, hypertension, lupus, or other chronic conditions. This includes who will provide that ongoing care, as well as when medical management should be restarted.
Some women are aware of the importance of timely care – of not waiting for 12 months, for instance, to see an internist or specialist – but others are not.
Again, certain health conditions such as multiple sclerosis and RA necessitate follow-up within a couple weeks after delivery so that medications can be restarted or dose adjustments made. The need for early postpartum follow-up can be discussed during prenatal visits, along with anticipatory guidance about breastfeeding, the signs and symptoms of perinatal depression and anxiety, and other components of the fourth trimester.
Dr. Macones has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2018 May;131(5):e140-50.
2. BMJ Qual Saf. 2018 Apr 27;27(11):871-7.
3. JAMA. 2019 Feb 12;321(6):580-7.
4. Clin Psychol Rev. 2014 Jul;34:389-401.JAMA. 2006 Apr 19;295(15):1809-23.
The fourth trimester
As we approach the end of this year, one of the most surreal times in human history, we will look back on the many things we taught ourselves, the many things we took for granted, the many things we were grateful for, the many things we missed, and the many things we plan to do once we can do things again. Among the many things 2020 taught us to appreciate was the very real manifestation of the old adage, “prevention is the best medicine.” To prevent transmission of SARS-CoV-2, we wore masks, we sanitized everything, we avoided crowds, we traded in-person meetings for virtual meetings, we learned how to homeschool our children, and we delayed seeing relatives and friends.
Ob.gyns. in small and large practices around the world had the tremendous challenge of balancing necessary in-person prenatal care services with keeping their patients and babies safe. Labor and delivery units had even greater demands to keep women and neonates free of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Practices quickly put into place new treatment protocols and new management strategies to maintain the health of their staff while ensuring a high quality of care.
While we have focused much of our attention on greater precautions during pregnancy and childbirth, an important component of care is the immediate postpartum period – colloquially referred to as the “fourth trimester” – which remains critical to maintaining physical and mental health and well-being.
Despite concerns regarding COVID-19 safety, we should continue monitoring our patients during these crucial first weeks after childbirth. This year of social isolation, financial strain, and incredible uncertainty has created additional stress in many women’s lives. The usual support that some women would receive from family members, friends, and other mothers in the early days post partum may not be available. The pandemic also has further highlighted inequities in access to health care for vulnerable groups. In addition, restrictions have increased the incidence of intimate partner violence as many women and children have needed to shelter with their abusers. Perhaps now more than any time previously, ob.gyns. must be attuned to their patients’ needs and be ready to provide compassionate and sensitive care.
In this final month of the year, we have invited George A. Macones, MD, professor and chair of the department of women’s health at the University of Texas, Austin, to address the importance of care in the final “trimester” of pregnancy – the first 3 months post partum.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at obnews@mdedge.com.
*This version has been updated to correct an erroneous byline, photo, and bio.
As we approach the end of this year, one of the most surreal times in human history, we will look back on the many things we taught ourselves, the many things we took for granted, the many things we were grateful for, the many things we missed, and the many things we plan to do once we can do things again. Among the many things 2020 taught us to appreciate was the very real manifestation of the old adage, “prevention is the best medicine.” To prevent transmission of SARS-CoV-2, we wore masks, we sanitized everything, we avoided crowds, we traded in-person meetings for virtual meetings, we learned how to homeschool our children, and we delayed seeing relatives and friends.
Ob.gyns. in small and large practices around the world had the tremendous challenge of balancing necessary in-person prenatal care services with keeping their patients and babies safe. Labor and delivery units had even greater demands to keep women and neonates free of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Practices quickly put into place new treatment protocols and new management strategies to maintain the health of their staff while ensuring a high quality of care.
While we have focused much of our attention on greater precautions during pregnancy and childbirth, an important component of care is the immediate postpartum period – colloquially referred to as the “fourth trimester” – which remains critical to maintaining physical and mental health and well-being.
Despite concerns regarding COVID-19 safety, we should continue monitoring our patients during these crucial first weeks after childbirth. This year of social isolation, financial strain, and incredible uncertainty has created additional stress in many women’s lives. The usual support that some women would receive from family members, friends, and other mothers in the early days post partum may not be available. The pandemic also has further highlighted inequities in access to health care for vulnerable groups. In addition, restrictions have increased the incidence of intimate partner violence as many women and children have needed to shelter with their abusers. Perhaps now more than any time previously, ob.gyns. must be attuned to their patients’ needs and be ready to provide compassionate and sensitive care.
In this final month of the year, we have invited George A. Macones, MD, professor and chair of the department of women’s health at the University of Texas, Austin, to address the importance of care in the final “trimester” of pregnancy – the first 3 months post partum.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at obnews@mdedge.com.
*This version has been updated to correct an erroneous byline, photo, and bio.
As we approach the end of this year, one of the most surreal times in human history, we will look back on the many things we taught ourselves, the many things we took for granted, the many things we were grateful for, the many things we missed, and the many things we plan to do once we can do things again. Among the many things 2020 taught us to appreciate was the very real manifestation of the old adage, “prevention is the best medicine.” To prevent transmission of SARS-CoV-2, we wore masks, we sanitized everything, we avoided crowds, we traded in-person meetings for virtual meetings, we learned how to homeschool our children, and we delayed seeing relatives and friends.
Ob.gyns. in small and large practices around the world had the tremendous challenge of balancing necessary in-person prenatal care services with keeping their patients and babies safe. Labor and delivery units had even greater demands to keep women and neonates free of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Practices quickly put into place new treatment protocols and new management strategies to maintain the health of their staff while ensuring a high quality of care.
While we have focused much of our attention on greater precautions during pregnancy and childbirth, an important component of care is the immediate postpartum period – colloquially referred to as the “fourth trimester” – which remains critical to maintaining physical and mental health and well-being.
Despite concerns regarding COVID-19 safety, we should continue monitoring our patients during these crucial first weeks after childbirth. This year of social isolation, financial strain, and incredible uncertainty has created additional stress in many women’s lives. The usual support that some women would receive from family members, friends, and other mothers in the early days post partum may not be available. The pandemic also has further highlighted inequities in access to health care for vulnerable groups. In addition, restrictions have increased the incidence of intimate partner violence as many women and children have needed to shelter with their abusers. Perhaps now more than any time previously, ob.gyns. must be attuned to their patients’ needs and be ready to provide compassionate and sensitive care.
In this final month of the year, we have invited George A. Macones, MD, professor and chair of the department of women’s health at the University of Texas, Austin, to address the importance of care in the final “trimester” of pregnancy – the first 3 months post partum.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at obnews@mdedge.com.
*This version has been updated to correct an erroneous byline, photo, and bio.
Adenomyosis: An update on imaging, medical, and surgical treatment
Adenomyosis is a benign disorder, present in 20%-35% of women and characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. The ectopic endometrial tissue appears to cause hypertrophy in the myometrium, resulting in an enlarged globular uterus.
Adenomyosis may present as diffuse or focal involvement within the uterus. When the focal lesion appears to be well defined, it is referred to as an adenomyoma. It is not encapsulated like a fibroid. There may be involvement of the junctional zone of the myometrium – the area between the subendometrial myometrium and the outer myometrium. While the pathogenesis of adenomyosis is unknown, two rigorous theories exist: endomyometrial invagination of the endometrium and de novo from Müllerian rests.
For this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted Keith B. Isaacson, MD, to discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of adenomyosis.
Dr. Isaacson is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, Newton, Mass., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is currently in practice specializing in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, where he is the director of the AAGL Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery. Dr. Isaacson is a past president of both the AAGL and the Society of Reproductive Surgeons, as well as a published clinical researcher and surgical innovator.
It is a true honor to welcome Dr. Isaacson to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant disclosures. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Adenomyosis is a benign disorder, present in 20%-35% of women and characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. The ectopic endometrial tissue appears to cause hypertrophy in the myometrium, resulting in an enlarged globular uterus.
Adenomyosis may present as diffuse or focal involvement within the uterus. When the focal lesion appears to be well defined, it is referred to as an adenomyoma. It is not encapsulated like a fibroid. There may be involvement of the junctional zone of the myometrium – the area between the subendometrial myometrium and the outer myometrium. While the pathogenesis of adenomyosis is unknown, two rigorous theories exist: endomyometrial invagination of the endometrium and de novo from Müllerian rests.
For this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted Keith B. Isaacson, MD, to discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of adenomyosis.
Dr. Isaacson is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, Newton, Mass., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is currently in practice specializing in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, where he is the director of the AAGL Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery. Dr. Isaacson is a past president of both the AAGL and the Society of Reproductive Surgeons, as well as a published clinical researcher and surgical innovator.
It is a true honor to welcome Dr. Isaacson to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant disclosures. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Adenomyosis is a benign disorder, present in 20%-35% of women and characterized by the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within the myometrium. The ectopic endometrial tissue appears to cause hypertrophy in the myometrium, resulting in an enlarged globular uterus.
Adenomyosis may present as diffuse or focal involvement within the uterus. When the focal lesion appears to be well defined, it is referred to as an adenomyoma. It is not encapsulated like a fibroid. There may be involvement of the junctional zone of the myometrium – the area between the subendometrial myometrium and the outer myometrium. While the pathogenesis of adenomyosis is unknown, two rigorous theories exist: endomyometrial invagination of the endometrium and de novo from Müllerian rests.
For this installment of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery, I have enlisted Keith B. Isaacson, MD, to discuss the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and medical and surgical treatment of adenomyosis.
Dr. Isaacson is the director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, Newton, Mass., and associate professor of obstetrics and gynecology at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He is currently in practice specializing in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery and infertility at Newton-Wellesley Hospital, where he is the director of the AAGL Fellowship in Minimally Invasive Gynecologic Surgery. Dr. Isaacson is a past president of both the AAGL and the Society of Reproductive Surgeons, as well as a published clinical researcher and surgical innovator.
It is a true honor to welcome Dr. Isaacson to this edition of the Master Class in Gynecologic Surgery.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the Department of Clinical Sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant disclosures. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Adenomyosis: While a last resort, surgery remains an option
Adenomyosis causing severe dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and heavy menstrual bleeding has been thought to affect primarily multiparous women in their mid- to late 40s. Often women who experience pain and heavy bleeding will tolerate their symptoms until they are done with childbearing, at which point they often go on to have a hysterectomy to relieve them of these symptoms. Tissue histology obtained at the time of hysterectomy confirms the diagnosis of adenomyosis.
Because the diagnosis is made at the time of hysterectomy, the published incidence and prevalence of adenomyosis is more a reflection of a risk for hysterectomy and not for the disease itself. MRI has been used to evaluate the junctional zone in patients with symptoms of endometriosis. This screen tool is an expensive one, however, and has not been used extensively to evaluate women with symptoms of adenomyosis who are not candidates for a hysterectomy.
Ultrasound studies
Over the past 5-7 years, numerous studies have been performed that demonstrate ultrasound changes consistent with adenomyosis within the uterus. These changes include asymmetry and heterogeneity of the anterior and posterior myometrium, cystic lesions in the myometrium, ultrasound striations, and streaking and irregular junctional zone thickening seen on 3-D scans.
Our newfound ability to demonstrate changes consistent with adenomyosis by ultrasound – a tool that is much less expensive than MRI and more available to patients – means that we can and should consider adenomyosis in patients suffering from dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, dyspareunia, and infertility – regardless of the patient’s age.
In the last 5 years, adenomyosis has been increasingly recognized as a disorder affecting women of all reproductive ages, including teenagers whose dysmenorrhea disrupts their education and young women undergoing infertility evaluations. In one study, 12% of adolescent girls and young women aged 14–20 years lost days of school or work each month because of dysmenorrhea.1 This disruption is not “normal.”
Several meta-analyses have also demonstrated that ultrasound and MRI changes consistent with adenomyosis can affect embryo implantation rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. The implantation rates can be as low as one half the expected rate without adenomyosis. Additionally, adenomyosis has been shown to increase the risk of miscarriage and preterm delivery.2,3
The clinicians who order and carefully look at the ultrasound themselves, rather than rely on the radiologist to make the diagnosis, will be able to see the changes consistent with adenomyosis. Over time – I anticipate the next several years – a standardized radiologic definition for adenomyosis will evolve, and radiologists will become more familiar with these changes. In the meantime, our patients should not have missed diagnoses.
Considerations for surgery
For the majority of younger patients who are not trying to conceive but want to maintain their fertility, medical treatment with oral contraceptives, progestins, or the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (Mirena) will relieve symptoms. The Mirena IUD has been found in studies of 6-36 months’ treatment duration to decrease the size of the uterus by 25%4 and improve dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia with a low profile of adverse effects in most women.
The Mirena IUD should be considered as a first-line therapy for all women with heavy menstrual bleeding and dyspareunia who want to preserve their fertility.
Patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate medical therapy, and do not want to preserve their fertility, may consider hysterectomy, long regarded as the preferred method of treatment. Endometrial ablation can also be considered in those who no longer desire to preserve fertility and are experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding. Those with extensive adenomyosis, however, often experience poor results with endometrial ablation and may ultimately require hysterectomy. Endometrial ablation has a history of a high failure rate in women younger than 45 years old.
Patients with adenomyosis who wish to preserve their fertility and cannot tolerate or are unresponsive to hormonal therapy, or those with infertility thought to be caused by adenomyosis, should consider these three management options:
- Do nothing. The embryo implantation rate is not zero with adenomyosis, and we have no data on the number of patients who conceive with adenomyotic changes detected by MRI or ultrasound.
- Pretreat with a GnRH agonist for 2-3 months prior to a frozen embryo transfer (FET). Suppressing the disease prior to an FET seems to increase the implantation rate to what is expected for that patient given her age and other fertility factors.3 While this approach is often successful, an estimated 15%-20% of patients are unable to tolerate GnRH agonist treatment because of its side effects.
- Seek surgical resection of adenomyosis. Unlike uterine fibroids, adenomyosis has no pseudocapsule. When resecting the disease via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or hysteroscopy, the process is more of a debulking procedure. Surgical resection should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate hormonal suppression or have failed the other two options.
Surgical approaches
Surgical excision can be challenging because adenomyosis burrows its way through the muscle, is often diffuse, and cannot necessarily be resected with clean margins as can a fibroid. Yet, as demonstrated in a systematic review of 27 observational studies of conservative surgery for adenomyosis – 10 prospective and 17 retrospective studies with a total of almost 1,400 patients and all with adenomyosis confirmed histopathologically – surgery can improve pain, menorrhagia, and adenomyosis-related infertility in a significant number of cases.5
Disease may be resected through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or as we are currently doing with focal disease that is close to the endometrium, hysteroscopy. The type of surgery will depend on the location and characteristics of the disease, and on the surgeon’s skills. The principles are the same with all three approaches: to remove as much diseased tissue – and preserve as much healthy myometrial tissue – as possible and to reconstruct the uterine wall so that it maintains its integrity and can sustain a pregnancy.
The open approach known as the Osada procedure, after Hisao Osada, MD, PhD, in Tokyo, is well described in the literature, with a relatively large number of cases reported in prospective studies. Dr. Osada performs a radical adenomyosis excision with a triple flap method of uterine wall reconstruction. The uterus is bisected in the mid-sagittal plane all the way down through the adenomyosis until the uterine cavity is reached. Excision of the adenomyotic tissue is guided by palpation with the index finger, and a myometrial thickness of 1 cm from the serosa and the endometrium is preserved.
The endometrium is closed, and the myometrial defect is closed with a triple flap method that avoids overlapping suture lines. On one side of the uterus, the myometrium and serosa are sutured in the antero-posterior plane. The seromuscular layer of the opposite side of the uterine wall is then brought over the first seromuscular suture line.6
Others, such as Grigoris H. Grimbizis, MD, PhD, in Greece, have used a laparoscopic approach and closed the myometrium in layers similar to those of a myomectomy.7 There are no comparative trials that demonstrate one technique is superior to the other.
While there are no textbook techniques published for resecting adenomyotic tissue laparoscopically or hysteroscopically from the normal myometrium, there are some general principals the surgeon should keep in mind. Adenomyosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within myometrium, but biopsy studies have demonstrated that there are relatively few glands and stroma within the diseased tissue. Mostly, the adenomyotic tissue we encounter comprises smooth muscle hyperplasia and fibrosis.
Since there is no pseudocapsule surrounding adenomyotic tissue, the visual cue for the cytoreductive procedure is the presence of normal-appearing myometrium. The normal myometrium can be delineated by palpation with laparoscopic instruments or hysteroscopic loops as it clearly feels less fibrotic and firm than the adenomyotic tissue. For this reason, the adenomyotic tissue is removed in a piecemeal fashion until normal tissue is encountered. (This same philosophy can be applied to removing fibrotic, glandular, or cystic tissue hysteroscopically.)
If the disease involves the inner myometrium, it should resected as this may be very important to restoring normal uterine contractions needed for embryo implantation and development, even if it means entering the cavity laparoscopically.
Hysteroscopically, there is no ability to suture a myometrial defect. This limitation is concerning because the adenomyosis is thought to invade the myometrium and not displace it as seen with monoclonal uterine fibroids. There are no case reports of uterine rupture after hysteroscopic resection of adenomyosis, but the number of cases reported with this type of resection in general is very small.
Laparoscopically, the myometrial defect should be repaired similarly to a myomectomy defect. Chromic or polydioxanone (PDS) suture is appropriate. We have used 2-0 PDS V-loc and a 2-3 layer closure in our laparoscopic cases.
Diffuse adenomyosis can involve the entire anterior or posterior wall of the uterus or both. The surgeon should not attempt to remove all of the disease in this situation and must leave enough tissue, even diseased, to allow for structural integrity during pregnancy. Uterine rupture has not been reported in all published case series and studies, but overall, it is a concern with surgical excision of adenomyosis. An analysis of over 2,000 cases of adenomyomectomies reported worldwide since 1990 shows a uterine rupture rate in the 6% rate, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 7%-72%.8
When the disease is focal and close to the endometrium, as opposed to diffuse and affecting the entire back wall of the uterus, hysteroscopic excision may be an appropriate, less invasive approach.
One of the patients for whom we’ve taken this approach was a 37-year-old patient who presented with a history of six miscarriages, a negative work-up for recurrent pregnancy loss, an enlarged uterus, 8 years of heavy menstrual bleeding, and only mild dysmenorrhea. She had undergone in vitro fertilization with failed embryo transfers but normal genetic screens of the embryos. She was referred with a suspicion of fibroids. An MRI and ultrasound showed heterogeneous myometrium adjacent to the endometrium. This tissue was resected using a bipolar loop electrode until normal myometrium was encountered.
Hysteroscopic resections are currently described in the literature through case reports rather than larger prospective or retrospective studies, and much more research is needed to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of this approach.
At this point in time, while surgery to excise adenomyosis is a last resort and best methods are deliberated, it is still important to appreciate that surgery is an option. Continued infertility is not the only choice, nor is hysterectomy.
References
1. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2014;27:258-65.
2. Minerva Ginecol. 2018 Jun;70(3):295-302.
3. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3):483-490.e3.
4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(4):373.e1-7.
5. J. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018 Feb;25:265-76.
6. Reproductive BioMed Online. 2011 Jan;22(1):94-9.
7. Fertil Steril. 2014 Feb;101(2):472-87.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018 Mar;109(3):406-17.
Adenomyosis causing severe dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and heavy menstrual bleeding has been thought to affect primarily multiparous women in their mid- to late 40s. Often women who experience pain and heavy bleeding will tolerate their symptoms until they are done with childbearing, at which point they often go on to have a hysterectomy to relieve them of these symptoms. Tissue histology obtained at the time of hysterectomy confirms the diagnosis of adenomyosis.
Because the diagnosis is made at the time of hysterectomy, the published incidence and prevalence of adenomyosis is more a reflection of a risk for hysterectomy and not for the disease itself. MRI has been used to evaluate the junctional zone in patients with symptoms of endometriosis. This screen tool is an expensive one, however, and has not been used extensively to evaluate women with symptoms of adenomyosis who are not candidates for a hysterectomy.
Ultrasound studies
Over the past 5-7 years, numerous studies have been performed that demonstrate ultrasound changes consistent with adenomyosis within the uterus. These changes include asymmetry and heterogeneity of the anterior and posterior myometrium, cystic lesions in the myometrium, ultrasound striations, and streaking and irregular junctional zone thickening seen on 3-D scans.
Our newfound ability to demonstrate changes consistent with adenomyosis by ultrasound – a tool that is much less expensive than MRI and more available to patients – means that we can and should consider adenomyosis in patients suffering from dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, dyspareunia, and infertility – regardless of the patient’s age.
In the last 5 years, adenomyosis has been increasingly recognized as a disorder affecting women of all reproductive ages, including teenagers whose dysmenorrhea disrupts their education and young women undergoing infertility evaluations. In one study, 12% of adolescent girls and young women aged 14–20 years lost days of school or work each month because of dysmenorrhea.1 This disruption is not “normal.”
Several meta-analyses have also demonstrated that ultrasound and MRI changes consistent with adenomyosis can affect embryo implantation rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. The implantation rates can be as low as one half the expected rate without adenomyosis. Additionally, adenomyosis has been shown to increase the risk of miscarriage and preterm delivery.2,3
The clinicians who order and carefully look at the ultrasound themselves, rather than rely on the radiologist to make the diagnosis, will be able to see the changes consistent with adenomyosis. Over time – I anticipate the next several years – a standardized radiologic definition for adenomyosis will evolve, and radiologists will become more familiar with these changes. In the meantime, our patients should not have missed diagnoses.
Considerations for surgery
For the majority of younger patients who are not trying to conceive but want to maintain their fertility, medical treatment with oral contraceptives, progestins, or the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (Mirena) will relieve symptoms. The Mirena IUD has been found in studies of 6-36 months’ treatment duration to decrease the size of the uterus by 25%4 and improve dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia with a low profile of adverse effects in most women.
The Mirena IUD should be considered as a first-line therapy for all women with heavy menstrual bleeding and dyspareunia who want to preserve their fertility.
Patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate medical therapy, and do not want to preserve their fertility, may consider hysterectomy, long regarded as the preferred method of treatment. Endometrial ablation can also be considered in those who no longer desire to preserve fertility and are experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding. Those with extensive adenomyosis, however, often experience poor results with endometrial ablation and may ultimately require hysterectomy. Endometrial ablation has a history of a high failure rate in women younger than 45 years old.
Patients with adenomyosis who wish to preserve their fertility and cannot tolerate or are unresponsive to hormonal therapy, or those with infertility thought to be caused by adenomyosis, should consider these three management options:
- Do nothing. The embryo implantation rate is not zero with adenomyosis, and we have no data on the number of patients who conceive with adenomyotic changes detected by MRI or ultrasound.
- Pretreat with a GnRH agonist for 2-3 months prior to a frozen embryo transfer (FET). Suppressing the disease prior to an FET seems to increase the implantation rate to what is expected for that patient given her age and other fertility factors.3 While this approach is often successful, an estimated 15%-20% of patients are unable to tolerate GnRH agonist treatment because of its side effects.
- Seek surgical resection of adenomyosis. Unlike uterine fibroids, adenomyosis has no pseudocapsule. When resecting the disease via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or hysteroscopy, the process is more of a debulking procedure. Surgical resection should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate hormonal suppression or have failed the other two options.
Surgical approaches
Surgical excision can be challenging because adenomyosis burrows its way through the muscle, is often diffuse, and cannot necessarily be resected with clean margins as can a fibroid. Yet, as demonstrated in a systematic review of 27 observational studies of conservative surgery for adenomyosis – 10 prospective and 17 retrospective studies with a total of almost 1,400 patients and all with adenomyosis confirmed histopathologically – surgery can improve pain, menorrhagia, and adenomyosis-related infertility in a significant number of cases.5
Disease may be resected through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or as we are currently doing with focal disease that is close to the endometrium, hysteroscopy. The type of surgery will depend on the location and characteristics of the disease, and on the surgeon’s skills. The principles are the same with all three approaches: to remove as much diseased tissue – and preserve as much healthy myometrial tissue – as possible and to reconstruct the uterine wall so that it maintains its integrity and can sustain a pregnancy.
The open approach known as the Osada procedure, after Hisao Osada, MD, PhD, in Tokyo, is well described in the literature, with a relatively large number of cases reported in prospective studies. Dr. Osada performs a radical adenomyosis excision with a triple flap method of uterine wall reconstruction. The uterus is bisected in the mid-sagittal plane all the way down through the adenomyosis until the uterine cavity is reached. Excision of the adenomyotic tissue is guided by palpation with the index finger, and a myometrial thickness of 1 cm from the serosa and the endometrium is preserved.
The endometrium is closed, and the myometrial defect is closed with a triple flap method that avoids overlapping suture lines. On one side of the uterus, the myometrium and serosa are sutured in the antero-posterior plane. The seromuscular layer of the opposite side of the uterine wall is then brought over the first seromuscular suture line.6
Others, such as Grigoris H. Grimbizis, MD, PhD, in Greece, have used a laparoscopic approach and closed the myometrium in layers similar to those of a myomectomy.7 There are no comparative trials that demonstrate one technique is superior to the other.
While there are no textbook techniques published for resecting adenomyotic tissue laparoscopically or hysteroscopically from the normal myometrium, there are some general principals the surgeon should keep in mind. Adenomyosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within myometrium, but biopsy studies have demonstrated that there are relatively few glands and stroma within the diseased tissue. Mostly, the adenomyotic tissue we encounter comprises smooth muscle hyperplasia and fibrosis.
Since there is no pseudocapsule surrounding adenomyotic tissue, the visual cue for the cytoreductive procedure is the presence of normal-appearing myometrium. The normal myometrium can be delineated by palpation with laparoscopic instruments or hysteroscopic loops as it clearly feels less fibrotic and firm than the adenomyotic tissue. For this reason, the adenomyotic tissue is removed in a piecemeal fashion until normal tissue is encountered. (This same philosophy can be applied to removing fibrotic, glandular, or cystic tissue hysteroscopically.)
If the disease involves the inner myometrium, it should resected as this may be very important to restoring normal uterine contractions needed for embryo implantation and development, even if it means entering the cavity laparoscopically.
Hysteroscopically, there is no ability to suture a myometrial defect. This limitation is concerning because the adenomyosis is thought to invade the myometrium and not displace it as seen with monoclonal uterine fibroids. There are no case reports of uterine rupture after hysteroscopic resection of adenomyosis, but the number of cases reported with this type of resection in general is very small.
Laparoscopically, the myometrial defect should be repaired similarly to a myomectomy defect. Chromic or polydioxanone (PDS) suture is appropriate. We have used 2-0 PDS V-loc and a 2-3 layer closure in our laparoscopic cases.
Diffuse adenomyosis can involve the entire anterior or posterior wall of the uterus or both. The surgeon should not attempt to remove all of the disease in this situation and must leave enough tissue, even diseased, to allow for structural integrity during pregnancy. Uterine rupture has not been reported in all published case series and studies, but overall, it is a concern with surgical excision of adenomyosis. An analysis of over 2,000 cases of adenomyomectomies reported worldwide since 1990 shows a uterine rupture rate in the 6% rate, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 7%-72%.8
When the disease is focal and close to the endometrium, as opposed to diffuse and affecting the entire back wall of the uterus, hysteroscopic excision may be an appropriate, less invasive approach.
One of the patients for whom we’ve taken this approach was a 37-year-old patient who presented with a history of six miscarriages, a negative work-up for recurrent pregnancy loss, an enlarged uterus, 8 years of heavy menstrual bleeding, and only mild dysmenorrhea. She had undergone in vitro fertilization with failed embryo transfers but normal genetic screens of the embryos. She was referred with a suspicion of fibroids. An MRI and ultrasound showed heterogeneous myometrium adjacent to the endometrium. This tissue was resected using a bipolar loop electrode until normal myometrium was encountered.
Hysteroscopic resections are currently described in the literature through case reports rather than larger prospective or retrospective studies, and much more research is needed to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of this approach.
At this point in time, while surgery to excise adenomyosis is a last resort and best methods are deliberated, it is still important to appreciate that surgery is an option. Continued infertility is not the only choice, nor is hysterectomy.
References
1. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2014;27:258-65.
2. Minerva Ginecol. 2018 Jun;70(3):295-302.
3. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3):483-490.e3.
4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(4):373.e1-7.
5. J. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018 Feb;25:265-76.
6. Reproductive BioMed Online. 2011 Jan;22(1):94-9.
7. Fertil Steril. 2014 Feb;101(2):472-87.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018 Mar;109(3):406-17.
Adenomyosis causing severe dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and heavy menstrual bleeding has been thought to affect primarily multiparous women in their mid- to late 40s. Often women who experience pain and heavy bleeding will tolerate their symptoms until they are done with childbearing, at which point they often go on to have a hysterectomy to relieve them of these symptoms. Tissue histology obtained at the time of hysterectomy confirms the diagnosis of adenomyosis.
Because the diagnosis is made at the time of hysterectomy, the published incidence and prevalence of adenomyosis is more a reflection of a risk for hysterectomy and not for the disease itself. MRI has been used to evaluate the junctional zone in patients with symptoms of endometriosis. This screen tool is an expensive one, however, and has not been used extensively to evaluate women with symptoms of adenomyosis who are not candidates for a hysterectomy.
Ultrasound studies
Over the past 5-7 years, numerous studies have been performed that demonstrate ultrasound changes consistent with adenomyosis within the uterus. These changes include asymmetry and heterogeneity of the anterior and posterior myometrium, cystic lesions in the myometrium, ultrasound striations, and streaking and irregular junctional zone thickening seen on 3-D scans.
Our newfound ability to demonstrate changes consistent with adenomyosis by ultrasound – a tool that is much less expensive than MRI and more available to patients – means that we can and should consider adenomyosis in patients suffering from dysmenorrhea, heavy menstrual bleeding, back pain, dyspareunia, and infertility – regardless of the patient’s age.
In the last 5 years, adenomyosis has been increasingly recognized as a disorder affecting women of all reproductive ages, including teenagers whose dysmenorrhea disrupts their education and young women undergoing infertility evaluations. In one study, 12% of adolescent girls and young women aged 14–20 years lost days of school or work each month because of dysmenorrhea.1 This disruption is not “normal.”
Several meta-analyses have also demonstrated that ultrasound and MRI changes consistent with adenomyosis can affect embryo implantation rates in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. The implantation rates can be as low as one half the expected rate without adenomyosis. Additionally, adenomyosis has been shown to increase the risk of miscarriage and preterm delivery.2,3
The clinicians who order and carefully look at the ultrasound themselves, rather than rely on the radiologist to make the diagnosis, will be able to see the changes consistent with adenomyosis. Over time – I anticipate the next several years – a standardized radiologic definition for adenomyosis will evolve, and radiologists will become more familiar with these changes. In the meantime, our patients should not have missed diagnoses.
Considerations for surgery
For the majority of younger patients who are not trying to conceive but want to maintain their fertility, medical treatment with oral contraceptives, progestins, or the levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine device (Mirena) will relieve symptoms. The Mirena IUD has been found in studies of 6-36 months’ treatment duration to decrease the size of the uterus by 25%4 and improve dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia with a low profile of adverse effects in most women.
The Mirena IUD should be considered as a first-line therapy for all women with heavy menstrual bleeding and dyspareunia who want to preserve their fertility.
Patients who do not respond to or cannot tolerate medical therapy, and do not want to preserve their fertility, may consider hysterectomy, long regarded as the preferred method of treatment. Endometrial ablation can also be considered in those who no longer desire to preserve fertility and are experiencing heavy menstrual bleeding. Those with extensive adenomyosis, however, often experience poor results with endometrial ablation and may ultimately require hysterectomy. Endometrial ablation has a history of a high failure rate in women younger than 45 years old.
Patients with adenomyosis who wish to preserve their fertility and cannot tolerate or are unresponsive to hormonal therapy, or those with infertility thought to be caused by adenomyosis, should consider these three management options:
- Do nothing. The embryo implantation rate is not zero with adenomyosis, and we have no data on the number of patients who conceive with adenomyotic changes detected by MRI or ultrasound.
- Pretreat with a GnRH agonist for 2-3 months prior to a frozen embryo transfer (FET). Suppressing the disease prior to an FET seems to increase the implantation rate to what is expected for that patient given her age and other fertility factors.3 While this approach is often successful, an estimated 15%-20% of patients are unable to tolerate GnRH agonist treatment because of its side effects.
- Seek surgical resection of adenomyosis. Unlike uterine fibroids, adenomyosis has no pseudocapsule. When resecting the disease via laparotomy, laparoscopy, or hysteroscopy, the process is more of a debulking procedure. Surgical resection should be reserved for those who cannot tolerate hormonal suppression or have failed the other two options.
Surgical approaches
Surgical excision can be challenging because adenomyosis burrows its way through the muscle, is often diffuse, and cannot necessarily be resected with clean margins as can a fibroid. Yet, as demonstrated in a systematic review of 27 observational studies of conservative surgery for adenomyosis – 10 prospective and 17 retrospective studies with a total of almost 1,400 patients and all with adenomyosis confirmed histopathologically – surgery can improve pain, menorrhagia, and adenomyosis-related infertility in a significant number of cases.5
Disease may be resected through laparotomy, laparoscopy, or as we are currently doing with focal disease that is close to the endometrium, hysteroscopy. The type of surgery will depend on the location and characteristics of the disease, and on the surgeon’s skills. The principles are the same with all three approaches: to remove as much diseased tissue – and preserve as much healthy myometrial tissue – as possible and to reconstruct the uterine wall so that it maintains its integrity and can sustain a pregnancy.
The open approach known as the Osada procedure, after Hisao Osada, MD, PhD, in Tokyo, is well described in the literature, with a relatively large number of cases reported in prospective studies. Dr. Osada performs a radical adenomyosis excision with a triple flap method of uterine wall reconstruction. The uterus is bisected in the mid-sagittal plane all the way down through the adenomyosis until the uterine cavity is reached. Excision of the adenomyotic tissue is guided by palpation with the index finger, and a myometrial thickness of 1 cm from the serosa and the endometrium is preserved.
The endometrium is closed, and the myometrial defect is closed with a triple flap method that avoids overlapping suture lines. On one side of the uterus, the myometrium and serosa are sutured in the antero-posterior plane. The seromuscular layer of the opposite side of the uterine wall is then brought over the first seromuscular suture line.6
Others, such as Grigoris H. Grimbizis, MD, PhD, in Greece, have used a laparoscopic approach and closed the myometrium in layers similar to those of a myomectomy.7 There are no comparative trials that demonstrate one technique is superior to the other.
While there are no textbook techniques published for resecting adenomyotic tissue laparoscopically or hysteroscopically from the normal myometrium, there are some general principals the surgeon should keep in mind. Adenomyosis is defined as the presence of endometrial glands and stroma within myometrium, but biopsy studies have demonstrated that there are relatively few glands and stroma within the diseased tissue. Mostly, the adenomyotic tissue we encounter comprises smooth muscle hyperplasia and fibrosis.
Since there is no pseudocapsule surrounding adenomyotic tissue, the visual cue for the cytoreductive procedure is the presence of normal-appearing myometrium. The normal myometrium can be delineated by palpation with laparoscopic instruments or hysteroscopic loops as it clearly feels less fibrotic and firm than the adenomyotic tissue. For this reason, the adenomyotic tissue is removed in a piecemeal fashion until normal tissue is encountered. (This same philosophy can be applied to removing fibrotic, glandular, or cystic tissue hysteroscopically.)
If the disease involves the inner myometrium, it should resected as this may be very important to restoring normal uterine contractions needed for embryo implantation and development, even if it means entering the cavity laparoscopically.
Hysteroscopically, there is no ability to suture a myometrial defect. This limitation is concerning because the adenomyosis is thought to invade the myometrium and not displace it as seen with monoclonal uterine fibroids. There are no case reports of uterine rupture after hysteroscopic resection of adenomyosis, but the number of cases reported with this type of resection in general is very small.
Laparoscopically, the myometrial defect should be repaired similarly to a myomectomy defect. Chromic or polydioxanone (PDS) suture is appropriate. We have used 2-0 PDS V-loc and a 2-3 layer closure in our laparoscopic cases.
Diffuse adenomyosis can involve the entire anterior or posterior wall of the uterus or both. The surgeon should not attempt to remove all of the disease in this situation and must leave enough tissue, even diseased, to allow for structural integrity during pregnancy. Uterine rupture has not been reported in all published case series and studies, but overall, it is a concern with surgical excision of adenomyosis. An analysis of over 2,000 cases of adenomyomectomies reported worldwide since 1990 shows a uterine rupture rate in the 6% rate, with a pregnancy rate ranging from 7%-72%.8
When the disease is focal and close to the endometrium, as opposed to diffuse and affecting the entire back wall of the uterus, hysteroscopic excision may be an appropriate, less invasive approach.
One of the patients for whom we’ve taken this approach was a 37-year-old patient who presented with a history of six miscarriages, a negative work-up for recurrent pregnancy loss, an enlarged uterus, 8 years of heavy menstrual bleeding, and only mild dysmenorrhea. She had undergone in vitro fertilization with failed embryo transfers but normal genetic screens of the embryos. She was referred with a suspicion of fibroids. An MRI and ultrasound showed heterogeneous myometrium adjacent to the endometrium. This tissue was resected using a bipolar loop electrode until normal myometrium was encountered.
Hysteroscopic resections are currently described in the literature through case reports rather than larger prospective or retrospective studies, and much more research is needed to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of this approach.
At this point in time, while surgery to excise adenomyosis is a last resort and best methods are deliberated, it is still important to appreciate that surgery is an option. Continued infertility is not the only choice, nor is hysterectomy.
References
1. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2014;27:258-65.
2. Minerva Ginecol. 2018 Jun;70(3):295-302.
3. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(3):483-490.e3.
4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;198(4):373.e1-7.
5. J. Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2018 Feb;25:265-76.
6. Reproductive BioMed Online. 2011 Jan;22(1):94-9.
7. Fertil Steril. 2014 Feb;101(2):472-87.
8. Fertil Steril. 2018 Mar;109(3):406-17.
Breast cancer screening complexities
Breast cancer in women remains one of the most common types of cancer in the United States, affecting about one in eight women1 over the course of their lifetime. Despite its pervasiveness, the 5-year survival rate for women with breast cancer remains high, estimated at around 90%2 based on data from 2010-2016, in large part because of early detection and treatment through screening. However, many organizations disagree on when to start and how often to screen women at average risk.
Important to discussions about breast cancer screening is the trend that many women delay childbirth until their 30s and 40s. In 2018 the birth rate increased for women ages 35-44, and the mean age of first birth increased from the prior year across all racial and ethnic groups.3 Therefore, ob.gyns. may need to consider that their patients not only may have increased risk of developing breast cancer based on age alone – women aged 35-44 have four times greater risk of disease than women aged 20-342 – but that the pregnancy itself may further exacerbate risk in older women. A 2019 pooled analysis found that women who were older at first birth had a greater chance of developing breast cancer compared with women with no children.4
In addition, ob.gyns. should consider that their patients may have received a breast cancer diagnosis prior to initiation or completion of their family plans or that their patients are cancer survivors – in 2013-2017, breast cancer was the most common form of cancer in adolescents and young adults.5 Thus, practitioners should be prepared to discuss not only options for fertility preservation but the evidence regarding cancer recurrence after pregnancy.
We have invited Dr. Katherine Tkaczuk, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland School of Medicine* and director of the breast evaluation and treatment program at the Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center, to discuss the vital role of screening in the shared decision-making process of breast cancer prevention.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore,* as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Correction, 1/8/21: *An earlier version of this article misstated the university affiliations for Dr. Tkaczuk and Dr. Reece.
References
1. U.S. Breast Cancer Statistics. breastcancer.org.
2. “Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer,” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
3. Martin JA et al. “Births: Final Data for 2018.” National Vital Statistics Reports. 2019 Nov 27;68(13):1-46.
4. Nichols HB et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jan;170(1):22-30.
5. “Cancer Stat Facts: Cancer Among Adolescents and Young Adults (AYAs) (Ages 15-39),” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
Breast cancer in women remains one of the most common types of cancer in the United States, affecting about one in eight women1 over the course of their lifetime. Despite its pervasiveness, the 5-year survival rate for women with breast cancer remains high, estimated at around 90%2 based on data from 2010-2016, in large part because of early detection and treatment through screening. However, many organizations disagree on when to start and how often to screen women at average risk.
Important to discussions about breast cancer screening is the trend that many women delay childbirth until their 30s and 40s. In 2018 the birth rate increased for women ages 35-44, and the mean age of first birth increased from the prior year across all racial and ethnic groups.3 Therefore, ob.gyns. may need to consider that their patients not only may have increased risk of developing breast cancer based on age alone – women aged 35-44 have four times greater risk of disease than women aged 20-342 – but that the pregnancy itself may further exacerbate risk in older women. A 2019 pooled analysis found that women who were older at first birth had a greater chance of developing breast cancer compared with women with no children.4
In addition, ob.gyns. should consider that their patients may have received a breast cancer diagnosis prior to initiation or completion of their family plans or that their patients are cancer survivors – in 2013-2017, breast cancer was the most common form of cancer in adolescents and young adults.5 Thus, practitioners should be prepared to discuss not only options for fertility preservation but the evidence regarding cancer recurrence after pregnancy.
We have invited Dr. Katherine Tkaczuk, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland School of Medicine* and director of the breast evaluation and treatment program at the Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center, to discuss the vital role of screening in the shared decision-making process of breast cancer prevention.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore,* as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Correction, 1/8/21: *An earlier version of this article misstated the university affiliations for Dr. Tkaczuk and Dr. Reece.
References
1. U.S. Breast Cancer Statistics. breastcancer.org.
2. “Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer,” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
3. Martin JA et al. “Births: Final Data for 2018.” National Vital Statistics Reports. 2019 Nov 27;68(13):1-46.
4. Nichols HB et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jan;170(1):22-30.
5. “Cancer Stat Facts: Cancer Among Adolescents and Young Adults (AYAs) (Ages 15-39),” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
Breast cancer in women remains one of the most common types of cancer in the United States, affecting about one in eight women1 over the course of their lifetime. Despite its pervasiveness, the 5-year survival rate for women with breast cancer remains high, estimated at around 90%2 based on data from 2010-2016, in large part because of early detection and treatment through screening. However, many organizations disagree on when to start and how often to screen women at average risk.
Important to discussions about breast cancer screening is the trend that many women delay childbirth until their 30s and 40s. In 2018 the birth rate increased for women ages 35-44, and the mean age of first birth increased from the prior year across all racial and ethnic groups.3 Therefore, ob.gyns. may need to consider that their patients not only may have increased risk of developing breast cancer based on age alone – women aged 35-44 have four times greater risk of disease than women aged 20-342 – but that the pregnancy itself may further exacerbate risk in older women. A 2019 pooled analysis found that women who were older at first birth had a greater chance of developing breast cancer compared with women with no children.4
In addition, ob.gyns. should consider that their patients may have received a breast cancer diagnosis prior to initiation or completion of their family plans or that their patients are cancer survivors – in 2013-2017, breast cancer was the most common form of cancer in adolescents and young adults.5 Thus, practitioners should be prepared to discuss not only options for fertility preservation but the evidence regarding cancer recurrence after pregnancy.
We have invited Dr. Katherine Tkaczuk, professor of medicine at the University of Maryland School of Medicine* and director of the breast evaluation and treatment program at the Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center, to discuss the vital role of screening in the shared decision-making process of breast cancer prevention.
Dr. Reece, who specializes in maternal-fetal medicine, is executive vice president for medical affairs at the University of Maryland, Baltimore,* as well as the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and dean of the school of medicine. He is the medical editor of this column. He said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Contact him at obnews@mdedge.com.
Correction, 1/8/21: *An earlier version of this article misstated the university affiliations for Dr. Tkaczuk and Dr. Reece.
References
1. U.S. Breast Cancer Statistics. breastcancer.org.
2. “Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer,” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
3. Martin JA et al. “Births: Final Data for 2018.” National Vital Statistics Reports. 2019 Nov 27;68(13):1-46.
4. Nichols HB et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jan;170(1):22-30.
5. “Cancer Stat Facts: Cancer Among Adolescents and Young Adults (AYAs) (Ages 15-39),” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
An oncologist’s view on screening mammography
Screening mammography has contributed to the lowering of mortality from breast cancer by facilitating earlier diagnosis and a lower stage at diagnosis. With more effective treatment options for women who are diagnosed with lower-stage breast cancer, the current 5-year survival rate has risen to 90% – significantly higher than the 5-year survival rate of 75% in 1975.1
Women who are at much higher risk for developing breast cancer – mainly because of family history, certain genetic mutations, or a history of radiation therapy to the chest – will benefit the most from earlier and more frequent screening mammography as well as enhanced screening with non-x-ray methods of breast imaging. It is important that ob.gyns. help to identify these women.
However, the majority of women who are screened with mammography are at “average risk,” with a lifetime risk for developing breast cancer of 12.9%, based on 2015-2017 data from the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER).1 The median age at diagnosis of breast cancer in the U.S. is 62 years,1 and advancing age is the most important risk factor for these women.
A 20% relative risk reduction in breast cancer mortality with screening mammography has been demonstrated both in systematic reviews of randomized and observational studies2 and in a meta-analysis of 11 randomized trials comparing screening and no screening.3 Even though the majority of randomized trials were done in the age of film mammography, experts believe that we still see at least a 20% reduction today.
Among average-risk women, those aged 50-74 with a life expectancy of at least 10 years will benefit the most from regular screening. According to the 2016 screening guideline of the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), relative risk reductions in breast cancer mortality from mammography screening, by age group, are 0.88 (confidence interval, 0.73-1.003) for ages 39-49; 0.86 (CI, 0.68-0.97) for ages 50-59; 0.67 (CI, 0.55-0.91) for ages 60-69; and 0.80 (CI, 0.51 to 1.28) for ages 70-74.2
For women aged 40-49 years, most of the guidelines in the United States recommend individualized screening every 1 or 2 years – screening that is guided by shared decision-making that takes into account each woman’s values regarding relative harms and benefits. This is because their risk of developing breast cancer is relatively low while the risk of false-positive results can be higher.
A few exceptions include guidelines by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the American College of Radiology, which recommend annual screening mammography starting at age 40 years for all average-risk women. In our program, we adhere to these latter recommendations and advise annual digital 3-D mammograms starting at age 40 and continuing until age 74, or longer if the woman is otherwise healthy with a life expectancy greater than 10 years.
Screening and overdiagnosis
Overdiagnosis – the diagnosis of cancers that may not actually cause mortality or may not even have become apparent without screening – is a concern for all women undergoing routine screening for breast cancer. There is significant uncertainty about its frequency, however.
Research cited by the USPSTF suggests that as many as one in five women diagnosed with breast cancer over approximately 10 years will be overdiagnosed. Other modeling studies have estimated one in eight overdiagnoses, for women aged 50-75 years specifically. By the more conservative estimate, according to the USPSTF, one breast cancer death will be prevented for every 2-3 cases of unnecessary treatment.2
Ductal carcinoma in situ is confined to the mammary ductal-lobular system and lacks the classic characteristics of cancer. Technically, it should not metastasize. But we do not know with certainty which cases of DCIS will or will not progress to invasive cancer. Therefore these women often are offered surgical approaches mirroring invasive cancer treatments (lumpectomy with radiation or even mastectomy in some cases), while for some, such treatments may be unnecessary.
Screening younger women (40-49)
Shared decision-making is always important for breast cancer screening, but in our program we routinely recommend annual screening in average-risk women starting at age 40 for several reasons. For one, younger women may present with more aggressive types of breast cancer such as triple-negative breast cancer. These are much less common than hormone-receptor positive breast cancers – they represent 15%-20% of all breast cancers – but they are faster growing and may develop in the interim if women are screened less often (at 2-year intervals).
In addition, finding an invasive breast cancer early is almost always beneficial. Earlier diagnosis (lower stage at diagnosis) is associated with increased breast cancer-specific and overall survival, as well as less-aggressive treatment approaches.
As a medical oncologist who treats women with breast cancer, I see these benefits firsthand. With earlier diagnosis, we are more likely to offer less aggressive surgical approaches such as partial mastectomy (lumpectomy) and sentinel lymph node biopsy as opposed to total mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection, the latter of which is more likely to be associated with lymphedema and which can lead to postmastectomy chest wall pain syndromes.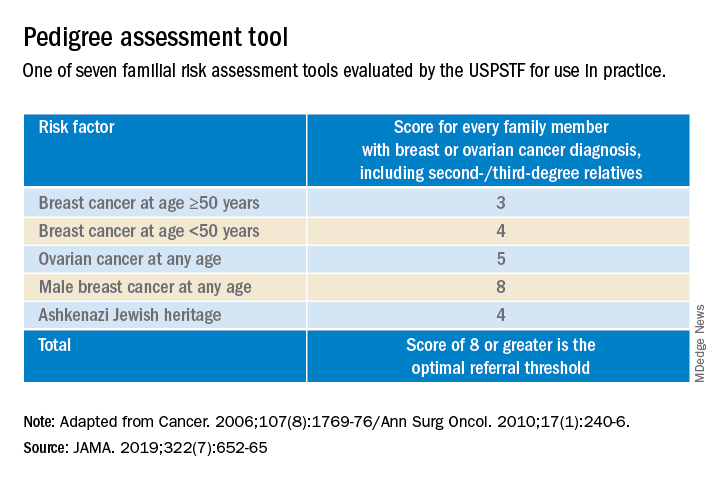
We also are able to use less aggressive radiation therapy approaches such as partial breast radiation, and less aggressive breast cancer–specific systemic treatments for women with a lower stage of breast cancer at diagnosis. In some cases, adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy may not be needed – and when it is necessary, shorter courses of chemotherapy or targeted chemotherapeutic regimens may be offered. This means lower systemic toxicities, both early and late, such as less cytopenias, risk of infections, mucositis, hair loss, cardiotoxicity, secondary malignancies/leukemia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
It is important to note that Black women in the United States have the highest death rate from breast cancer – 27.3 per 100,000 per year, versus 19.6 per 100,000 per year for White women1 – and that younger Black women appear to have a higher risk of developing triple-negative breast cancer, a more aggressive type of breast cancer. The higher breast cancer mortality in Black women is likely multifactorial and may be attributed partly to disparities in health care and partly to tumor biology. The case for annual screening in this population thus seems especially strong.
Screening modalities
Digital 3-D mammography, or digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), is widely considered to be a more sensitive screening tool than conventional digital mammography alone. The NCCN recommends DBT for women with an average risk of developing breast cancer starting at age 40,4,5 and the USPSTF, while offering no recommendation on DBT as a primary screening method (“insufficient evidence”), says that DBT appears to increase cancer detection rates.2 So, I do routinely recommend it.
DBT may be especially beneficial for women with dense breast tissue (determined mammographically), who are most often premenopausal women – particularly non-Hispanic White women. Dense breast tissue itself can contribute to an increased risk of breast cancer – an approximately 20% higher relative risk in an average-risk woman with heterogeneously dense breast tissue, and an approximately 100% higher relative risk in a woman with extremely dense breasts6 – but unfortunately it affects the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
I do not recommend routine supplemental screening with other methods (breast ultrasonography or MRI) for women at average risk of breast cancer who have dense breasts. MRI with gadolinium contrast is recommended as an adjunct to mammography for women who have a lifetime risk of developing breast cancer of more than 20%-25% (e.g., women with known BRCA1/2 mutations or radiation to breast tissue), and can be done annually at the same time as the screening mammogram is done. Some clinicians and patients prefer to alternate these two tests – one every 6 months.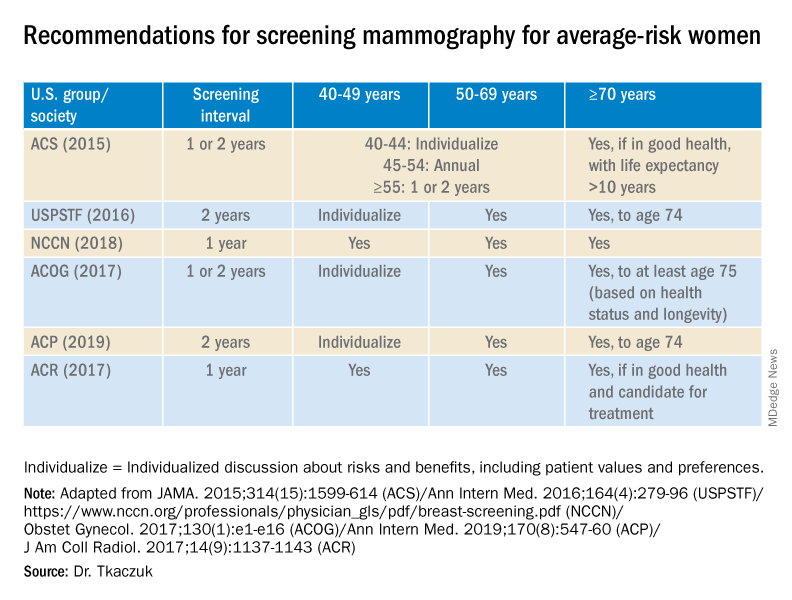
Screening breast MRI is more sensitive but less specific than mammography; combining the two screening modalities leads to overall increased sensitivity and specificity in high-risk populations.
Risk assessment
Identifying higher-risk women who need to be sent to a genetic counselor is critically important. The USPSTF recommends that women who have family members with breast, ovarian, tubal or peritoneal cancer, or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations, be assessed with a brief familial risk assessment tool such as the Pedigree Assessment Tool. This and other validated tools have been evaluated by the USPSTF and can be used to guide referrals to genetic counseling for more definitive risk assessment.7
These tools are different from general breast cancer risk assessment models, such as the NCI’s Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool,8 which are designed to calculate the 5-year and lifetime risk of developing invasive breast cancer for an average-risk woman but not to identify BRCA-related cancer risk. (The NCI’s tool is based on the Gail model, which has been widely used over the years.)
The general risk assessment models use a women’s personal medical and reproductive history as well as the history of breast cancer among her first-degree relatives to estimate her risk.
Dr. Tkaczuk reported that she has no disclosures.
References
1. “Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer.” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
2. Siu AL et al. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Feb 16. doi: 10.7326/M15-2886.
3. Independent UK Panel on Breast Cancer Screening. Lancet. 2012 Nov 17;380(9855):1778-86.
4. NCCN guidelines for Detection, Prevention, & Risk Reduction: Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
5. NCCN guidelines for Detection, Prevention, & Risk Reduction: Breast Cancer Risk Reduction. National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
6. Ziv E et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13(12):2090-5.
7. USPSTF. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65.
8. The Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool. National Cancer Institute.
Screening mammography has contributed to the lowering of mortality from breast cancer by facilitating earlier diagnosis and a lower stage at diagnosis. With more effective treatment options for women who are diagnosed with lower-stage breast cancer, the current 5-year survival rate has risen to 90% – significantly higher than the 5-year survival rate of 75% in 1975.1
Women who are at much higher risk for developing breast cancer – mainly because of family history, certain genetic mutations, or a history of radiation therapy to the chest – will benefit the most from earlier and more frequent screening mammography as well as enhanced screening with non-x-ray methods of breast imaging. It is important that ob.gyns. help to identify these women.
However, the majority of women who are screened with mammography are at “average risk,” with a lifetime risk for developing breast cancer of 12.9%, based on 2015-2017 data from the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER).1 The median age at diagnosis of breast cancer in the U.S. is 62 years,1 and advancing age is the most important risk factor for these women.
A 20% relative risk reduction in breast cancer mortality with screening mammography has been demonstrated both in systematic reviews of randomized and observational studies2 and in a meta-analysis of 11 randomized trials comparing screening and no screening.3 Even though the majority of randomized trials were done in the age of film mammography, experts believe that we still see at least a 20% reduction today.
Among average-risk women, those aged 50-74 with a life expectancy of at least 10 years will benefit the most from regular screening. According to the 2016 screening guideline of the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), relative risk reductions in breast cancer mortality from mammography screening, by age group, are 0.88 (confidence interval, 0.73-1.003) for ages 39-49; 0.86 (CI, 0.68-0.97) for ages 50-59; 0.67 (CI, 0.55-0.91) for ages 60-69; and 0.80 (CI, 0.51 to 1.28) for ages 70-74.2
For women aged 40-49 years, most of the guidelines in the United States recommend individualized screening every 1 or 2 years – screening that is guided by shared decision-making that takes into account each woman’s values regarding relative harms and benefits. This is because their risk of developing breast cancer is relatively low while the risk of false-positive results can be higher.
A few exceptions include guidelines by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the American College of Radiology, which recommend annual screening mammography starting at age 40 years for all average-risk women. In our program, we adhere to these latter recommendations and advise annual digital 3-D mammograms starting at age 40 and continuing until age 74, or longer if the woman is otherwise healthy with a life expectancy greater than 10 years.
Screening and overdiagnosis
Overdiagnosis – the diagnosis of cancers that may not actually cause mortality or may not even have become apparent without screening – is a concern for all women undergoing routine screening for breast cancer. There is significant uncertainty about its frequency, however.
Research cited by the USPSTF suggests that as many as one in five women diagnosed with breast cancer over approximately 10 years will be overdiagnosed. Other modeling studies have estimated one in eight overdiagnoses, for women aged 50-75 years specifically. By the more conservative estimate, according to the USPSTF, one breast cancer death will be prevented for every 2-3 cases of unnecessary treatment.2
Ductal carcinoma in situ is confined to the mammary ductal-lobular system and lacks the classic characteristics of cancer. Technically, it should not metastasize. But we do not know with certainty which cases of DCIS will or will not progress to invasive cancer. Therefore these women often are offered surgical approaches mirroring invasive cancer treatments (lumpectomy with radiation or even mastectomy in some cases), while for some, such treatments may be unnecessary.
Screening younger women (40-49)
Shared decision-making is always important for breast cancer screening, but in our program we routinely recommend annual screening in average-risk women starting at age 40 for several reasons. For one, younger women may present with more aggressive types of breast cancer such as triple-negative breast cancer. These are much less common than hormone-receptor positive breast cancers – they represent 15%-20% of all breast cancers – but they are faster growing and may develop in the interim if women are screened less often (at 2-year intervals).
In addition, finding an invasive breast cancer early is almost always beneficial. Earlier diagnosis (lower stage at diagnosis) is associated with increased breast cancer-specific and overall survival, as well as less-aggressive treatment approaches.
As a medical oncologist who treats women with breast cancer, I see these benefits firsthand. With earlier diagnosis, we are more likely to offer less aggressive surgical approaches such as partial mastectomy (lumpectomy) and sentinel lymph node biopsy as opposed to total mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection, the latter of which is more likely to be associated with lymphedema and which can lead to postmastectomy chest wall pain syndromes.
We also are able to use less aggressive radiation therapy approaches such as partial breast radiation, and less aggressive breast cancer–specific systemic treatments for women with a lower stage of breast cancer at diagnosis. In some cases, adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy may not be needed – and when it is necessary, shorter courses of chemotherapy or targeted chemotherapeutic regimens may be offered. This means lower systemic toxicities, both early and late, such as less cytopenias, risk of infections, mucositis, hair loss, cardiotoxicity, secondary malignancies/leukemia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
It is important to note that Black women in the United States have the highest death rate from breast cancer – 27.3 per 100,000 per year, versus 19.6 per 100,000 per year for White women1 – and that younger Black women appear to have a higher risk of developing triple-negative breast cancer, a more aggressive type of breast cancer. The higher breast cancer mortality in Black women is likely multifactorial and may be attributed partly to disparities in health care and partly to tumor biology. The case for annual screening in this population thus seems especially strong.
Screening modalities
Digital 3-D mammography, or digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), is widely considered to be a more sensitive screening tool than conventional digital mammography alone. The NCCN recommends DBT for women with an average risk of developing breast cancer starting at age 40,4,5 and the USPSTF, while offering no recommendation on DBT as a primary screening method (“insufficient evidence”), says that DBT appears to increase cancer detection rates.2 So, I do routinely recommend it.
DBT may be especially beneficial for women with dense breast tissue (determined mammographically), who are most often premenopausal women – particularly non-Hispanic White women. Dense breast tissue itself can contribute to an increased risk of breast cancer – an approximately 20% higher relative risk in an average-risk woman with heterogeneously dense breast tissue, and an approximately 100% higher relative risk in a woman with extremely dense breasts6 – but unfortunately it affects the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
I do not recommend routine supplemental screening with other methods (breast ultrasonography or MRI) for women at average risk of breast cancer who have dense breasts. MRI with gadolinium contrast is recommended as an adjunct to mammography for women who have a lifetime risk of developing breast cancer of more than 20%-25% (e.g., women with known BRCA1/2 mutations or radiation to breast tissue), and can be done annually at the same time as the screening mammogram is done. Some clinicians and patients prefer to alternate these two tests – one every 6 months.
Screening breast MRI is more sensitive but less specific than mammography; combining the two screening modalities leads to overall increased sensitivity and specificity in high-risk populations.
Risk assessment
Identifying higher-risk women who need to be sent to a genetic counselor is critically important. The USPSTF recommends that women who have family members with breast, ovarian, tubal or peritoneal cancer, or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations, be assessed with a brief familial risk assessment tool such as the Pedigree Assessment Tool. This and other validated tools have been evaluated by the USPSTF and can be used to guide referrals to genetic counseling for more definitive risk assessment.7
These tools are different from general breast cancer risk assessment models, such as the NCI’s Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool,8 which are designed to calculate the 5-year and lifetime risk of developing invasive breast cancer for an average-risk woman but not to identify BRCA-related cancer risk. (The NCI’s tool is based on the Gail model, which has been widely used over the years.)
The general risk assessment models use a women’s personal medical and reproductive history as well as the history of breast cancer among her first-degree relatives to estimate her risk.
Dr. Tkaczuk reported that she has no disclosures.
References
1. “Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer.” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
2. Siu AL et al. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Feb 16. doi: 10.7326/M15-2886.
3. Independent UK Panel on Breast Cancer Screening. Lancet. 2012 Nov 17;380(9855):1778-86.
4. NCCN guidelines for Detection, Prevention, & Risk Reduction: Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
5. NCCN guidelines for Detection, Prevention, & Risk Reduction: Breast Cancer Risk Reduction. National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
6. Ziv E et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13(12):2090-5.
7. USPSTF. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65.
8. The Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool. National Cancer Institute.
Screening mammography has contributed to the lowering of mortality from breast cancer by facilitating earlier diagnosis and a lower stage at diagnosis. With more effective treatment options for women who are diagnosed with lower-stage breast cancer, the current 5-year survival rate has risen to 90% – significantly higher than the 5-year survival rate of 75% in 1975.1
Women who are at much higher risk for developing breast cancer – mainly because of family history, certain genetic mutations, or a history of radiation therapy to the chest – will benefit the most from earlier and more frequent screening mammography as well as enhanced screening with non-x-ray methods of breast imaging. It is important that ob.gyns. help to identify these women.
However, the majority of women who are screened with mammography are at “average risk,” with a lifetime risk for developing breast cancer of 12.9%, based on 2015-2017 data from the National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program (SEER).1 The median age at diagnosis of breast cancer in the U.S. is 62 years,1 and advancing age is the most important risk factor for these women.
A 20% relative risk reduction in breast cancer mortality with screening mammography has been demonstrated both in systematic reviews of randomized and observational studies2 and in a meta-analysis of 11 randomized trials comparing screening and no screening.3 Even though the majority of randomized trials were done in the age of film mammography, experts believe that we still see at least a 20% reduction today.
Among average-risk women, those aged 50-74 with a life expectancy of at least 10 years will benefit the most from regular screening. According to the 2016 screening guideline of the United States Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF), relative risk reductions in breast cancer mortality from mammography screening, by age group, are 0.88 (confidence interval, 0.73-1.003) for ages 39-49; 0.86 (CI, 0.68-0.97) for ages 50-59; 0.67 (CI, 0.55-0.91) for ages 60-69; and 0.80 (CI, 0.51 to 1.28) for ages 70-74.2
For women aged 40-49 years, most of the guidelines in the United States recommend individualized screening every 1 or 2 years – screening that is guided by shared decision-making that takes into account each woman’s values regarding relative harms and benefits. This is because their risk of developing breast cancer is relatively low while the risk of false-positive results can be higher.
A few exceptions include guidelines by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) and the American College of Radiology, which recommend annual screening mammography starting at age 40 years for all average-risk women. In our program, we adhere to these latter recommendations and advise annual digital 3-D mammograms starting at age 40 and continuing until age 74, or longer if the woman is otherwise healthy with a life expectancy greater than 10 years.
Screening and overdiagnosis
Overdiagnosis – the diagnosis of cancers that may not actually cause mortality or may not even have become apparent without screening – is a concern for all women undergoing routine screening for breast cancer. There is significant uncertainty about its frequency, however.
Research cited by the USPSTF suggests that as many as one in five women diagnosed with breast cancer over approximately 10 years will be overdiagnosed. Other modeling studies have estimated one in eight overdiagnoses, for women aged 50-75 years specifically. By the more conservative estimate, according to the USPSTF, one breast cancer death will be prevented for every 2-3 cases of unnecessary treatment.2
Ductal carcinoma in situ is confined to the mammary ductal-lobular system and lacks the classic characteristics of cancer. Technically, it should not metastasize. But we do not know with certainty which cases of DCIS will or will not progress to invasive cancer. Therefore these women often are offered surgical approaches mirroring invasive cancer treatments (lumpectomy with radiation or even mastectomy in some cases), while for some, such treatments may be unnecessary.
Screening younger women (40-49)
Shared decision-making is always important for breast cancer screening, but in our program we routinely recommend annual screening in average-risk women starting at age 40 for several reasons. For one, younger women may present with more aggressive types of breast cancer such as triple-negative breast cancer. These are much less common than hormone-receptor positive breast cancers – they represent 15%-20% of all breast cancers – but they are faster growing and may develop in the interim if women are screened less often (at 2-year intervals).
In addition, finding an invasive breast cancer early is almost always beneficial. Earlier diagnosis (lower stage at diagnosis) is associated with increased breast cancer-specific and overall survival, as well as less-aggressive treatment approaches.
As a medical oncologist who treats women with breast cancer, I see these benefits firsthand. With earlier diagnosis, we are more likely to offer less aggressive surgical approaches such as partial mastectomy (lumpectomy) and sentinel lymph node biopsy as opposed to total mastectomy with axillary lymph node dissection, the latter of which is more likely to be associated with lymphedema and which can lead to postmastectomy chest wall pain syndromes.
We also are able to use less aggressive radiation therapy approaches such as partial breast radiation, and less aggressive breast cancer–specific systemic treatments for women with a lower stage of breast cancer at diagnosis. In some cases, adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy may not be needed – and when it is necessary, shorter courses of chemotherapy or targeted chemotherapeutic regimens may be offered. This means lower systemic toxicities, both early and late, such as less cytopenias, risk of infections, mucositis, hair loss, cardiotoxicity, secondary malignancies/leukemia, and peripheral sensory neuropathy.
It is important to note that Black women in the United States have the highest death rate from breast cancer – 27.3 per 100,000 per year, versus 19.6 per 100,000 per year for White women1 – and that younger Black women appear to have a higher risk of developing triple-negative breast cancer, a more aggressive type of breast cancer. The higher breast cancer mortality in Black women is likely multifactorial and may be attributed partly to disparities in health care and partly to tumor biology. The case for annual screening in this population thus seems especially strong.
Screening modalities
Digital 3-D mammography, or digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), is widely considered to be a more sensitive screening tool than conventional digital mammography alone. The NCCN recommends DBT for women with an average risk of developing breast cancer starting at age 40,4,5 and the USPSTF, while offering no recommendation on DBT as a primary screening method (“insufficient evidence”), says that DBT appears to increase cancer detection rates.2 So, I do routinely recommend it.
DBT may be especially beneficial for women with dense breast tissue (determined mammographically), who are most often premenopausal women – particularly non-Hispanic White women. Dense breast tissue itself can contribute to an increased risk of breast cancer – an approximately 20% higher relative risk in an average-risk woman with heterogeneously dense breast tissue, and an approximately 100% higher relative risk in a woman with extremely dense breasts6 – but unfortunately it affects the sensitivity and specificity of screening mammography.
I do not recommend routine supplemental screening with other methods (breast ultrasonography or MRI) for women at average risk of breast cancer who have dense breasts. MRI with gadolinium contrast is recommended as an adjunct to mammography for women who have a lifetime risk of developing breast cancer of more than 20%-25% (e.g., women with known BRCA1/2 mutations or radiation to breast tissue), and can be done annually at the same time as the screening mammogram is done. Some clinicians and patients prefer to alternate these two tests – one every 6 months.
Screening breast MRI is more sensitive but less specific than mammography; combining the two screening modalities leads to overall increased sensitivity and specificity in high-risk populations.
Risk assessment
Identifying higher-risk women who need to be sent to a genetic counselor is critically important. The USPSTF recommends that women who have family members with breast, ovarian, tubal or peritoneal cancer, or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations, be assessed with a brief familial risk assessment tool such as the Pedigree Assessment Tool. This and other validated tools have been evaluated by the USPSTF and can be used to guide referrals to genetic counseling for more definitive risk assessment.7
These tools are different from general breast cancer risk assessment models, such as the NCI’s Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool,8 which are designed to calculate the 5-year and lifetime risk of developing invasive breast cancer for an average-risk woman but not to identify BRCA-related cancer risk. (The NCI’s tool is based on the Gail model, which has been widely used over the years.)
The general risk assessment models use a women’s personal medical and reproductive history as well as the history of breast cancer among her first-degree relatives to estimate her risk.
Dr. Tkaczuk reported that she has no disclosures.
References
1. “Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer.” Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. National Cancer Institute.
2. Siu AL et al. Ann Intern Med. 2016 Feb 16. doi: 10.7326/M15-2886.
3. Independent UK Panel on Breast Cancer Screening. Lancet. 2012 Nov 17;380(9855):1778-86.
4. NCCN guidelines for Detection, Prevention, & Risk Reduction: Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
5. NCCN guidelines for Detection, Prevention, & Risk Reduction: Breast Cancer Risk Reduction. National Comprehensive Cancer Network.
6. Ziv E et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13(12):2090-5.
7. USPSTF. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65.
8. The Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool. National Cancer Institute.
Identifying ovarian malignancy is not so easy
When an ovarian mass is anticipated or known, following evaluation of a patient’s history and physician examination, imaging via transvaginal and often abdominal ultrasound is the very next step. This evaluation likely will include both gray-scale and color Doppler examination. The initial concern always must be to identify ovarian malignancy.
Despite morphological scoring systems as well as the use of Doppler ultrasonography, there remains a lack of agreement and acceptance. In a 2008 multicenter study, Timmerman and colleagues evaluated 1,066 patients with 1,233 persistent adnexal tumors via transvaginal grayscale and Doppler ultrasound; 73% were benign tumors, and 27% were malignant tumors. Information on 42 gray-scale ultrasound variables and 6 Doppler variables was collected and evaluated to determine which variables had the highest positive predictive value for a malignant tumor and for a benign mass (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365).
Five simple rules were selected that best predict malignancy (M-rules), as follows:
- Irregular solid tumor.
- Ascites.
- At least four papillary projections.
- Irregular multilocular-solid tumor with a greatest diameter greater than or equal to 10 cm.
- Very high color content on Doppler exam.
The following five simple rules suggested that a mass is benign (B-rules):
- Unilocular cyst.
- Largest solid component less than 7 mm.
- Acoustic shadows.
- Smooth multilocular tumor less than 10 cm.
- No detectable blood flow with Doppler exam.
Unfortunately, despite a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 90%, and a positive and negative predictive value of 80% and 97%, these 10 simple rules were applicable to only 76% of tumors.
To assist those of us who are not gynecologic oncologists and who are often faced with having to determine whether surgery is recommended, I have elicited the expertise of Jubilee Brown, MD, professor and associate director of gynecologic oncology at the Levine Cancer Institute, Carolinas HealthCare System, in Charlotte, N.C., and the current president of the AAGL, to lead us in a review of evaluating an ovarian mass.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, Ill., and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
When an ovarian mass is anticipated or known, following evaluation of a patient’s history and physician examination, imaging via transvaginal and often abdominal ultrasound is the very next step. This evaluation likely will include both gray-scale and color Doppler examination. The initial concern always must be to identify ovarian malignancy.
Despite morphological scoring systems as well as the use of Doppler ultrasonography, there remains a lack of agreement and acceptance. In a 2008 multicenter study, Timmerman and colleagues evaluated 1,066 patients with 1,233 persistent adnexal tumors via transvaginal grayscale and Doppler ultrasound; 73% were benign tumors, and 27% were malignant tumors. Information on 42 gray-scale ultrasound variables and 6 Doppler variables was collected and evaluated to determine which variables had the highest positive predictive value for a malignant tumor and for a benign mass (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365).
Five simple rules were selected that best predict malignancy (M-rules), as follows:
- Irregular solid tumor.
- Ascites.
- At least four papillary projections.
- Irregular multilocular-solid tumor with a greatest diameter greater than or equal to 10 cm.
- Very high color content on Doppler exam.
The following five simple rules suggested that a mass is benign (B-rules):
- Unilocular cyst.
- Largest solid component less than 7 mm.
- Acoustic shadows.
- Smooth multilocular tumor less than 10 cm.
- No detectable blood flow with Doppler exam.
Unfortunately, despite a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 90%, and a positive and negative predictive value of 80% and 97%, these 10 simple rules were applicable to only 76% of tumors.
To assist those of us who are not gynecologic oncologists and who are often faced with having to determine whether surgery is recommended, I have elicited the expertise of Jubilee Brown, MD, professor and associate director of gynecologic oncology at the Levine Cancer Institute, Carolinas HealthCare System, in Charlotte, N.C., and the current president of the AAGL, to lead us in a review of evaluating an ovarian mass.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, Ill., and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
When an ovarian mass is anticipated or known, following evaluation of a patient’s history and physician examination, imaging via transvaginal and often abdominal ultrasound is the very next step. This evaluation likely will include both gray-scale and color Doppler examination. The initial concern always must be to identify ovarian malignancy.
Despite morphological scoring systems as well as the use of Doppler ultrasonography, there remains a lack of agreement and acceptance. In a 2008 multicenter study, Timmerman and colleagues evaluated 1,066 patients with 1,233 persistent adnexal tumors via transvaginal grayscale and Doppler ultrasound; 73% were benign tumors, and 27% were malignant tumors. Information on 42 gray-scale ultrasound variables and 6 Doppler variables was collected and evaluated to determine which variables had the highest positive predictive value for a malignant tumor and for a benign mass (Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365).
Five simple rules were selected that best predict malignancy (M-rules), as follows:
- Irregular solid tumor.
- Ascites.
- At least four papillary projections.
- Irregular multilocular-solid tumor with a greatest diameter greater than or equal to 10 cm.
- Very high color content on Doppler exam.
The following five simple rules suggested that a mass is benign (B-rules):
- Unilocular cyst.
- Largest solid component less than 7 mm.
- Acoustic shadows.
- Smooth multilocular tumor less than 10 cm.
- No detectable blood flow with Doppler exam.
Unfortunately, despite a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 90%, and a positive and negative predictive value of 80% and 97%, these 10 simple rules were applicable to only 76% of tumors.
To assist those of us who are not gynecologic oncologists and who are often faced with having to determine whether surgery is recommended, I have elicited the expertise of Jubilee Brown, MD, professor and associate director of gynecologic oncology at the Levine Cancer Institute, Carolinas HealthCare System, in Charlotte, N.C., and the current president of the AAGL, to lead us in a review of evaluating an ovarian mass.
Dr. Miller is professor of obstetrics & gynecology in the department of clinical sciences, Rosalind Franklin University, North Chicago, Ill., and director of minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at Advocate Lutheran General Hospital, Park Ridge, both in Illinois. Email him at obnews@mdedge.com.
How to evaluate a suspicious ovarian mass
Ovarian masses are common in women of all ages. It is important not to miss even one ovarian cancer, but we must also identify masses that will resolve on their own over time to avoid overtreatment. These concurrent goals of excluding malignancy while not overtreating patients are the basis for management of the pelvic mass. Additionally, fertility preservation is important when surgery is performed in a reproductive-aged woman.
An ovarian mass may be anything from a simple functional or physiologic cyst to an endometrioma to an epithelial carcinoma, a germ-cell tumor, or a stromal tumor (the latter three of which may metastasize). Across the general population, women have a 5%-10% lifetime risk of needing surgery for a suspected ovarian mass and a 1.4% (1 in 70) risk that this mass is cancerous. The majority of ovarian cysts or masses therefore are benign.
A thorough history – including family history – and physical examination with appropriate laboratory testing and directed imaging are important first steps for the ob.gyn. Fortunately, we have guidelines and criteria governing not only when observation or surgery is warranted but also when patients should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist. By following these guidelines,1 we are able to achieve the best outcomes.
Transvaginal ultrasound
A 2007 groundbreaking study led by Barbara Goff, MD, demonstrated that there are warning signs for ovarian cancer – symptoms that are significantly associated with malignancy. Dr. Goff and her coinvestigators evaluated the charts of hundreds of patients, including about 150 with ovarian cancer, and found that pelvic/abdominal pressure or pain, bloating, increase in abdominal size, and difficulty eating or feeling full were significantly and independently associated with cancer if these symptoms were present for less than a year and occurred at least 12 times per month.2
A pelvic examination is an integral part of evaluating every patient who has such concerns. That said, pelvic exams have limited ability to identify adnexal masses, especially in women who are obese – and that’s where imaging becomes especially important.
Masses generally can be considered simple or complex based on their appearance. A simple cyst is fluid-filled with thin, smooth walls and the absence of solid components or septations; it is significantly more likely to resolve on its own and is less likely to imply malignancy than a complex cyst, especially in a premenopausal woman. A complex cyst is multiseptated and/or solid – possibly with papillary projections – and is more concerning, especially if there is increased, new vascularity. Making this distinction helps us determine the risk of malignancy.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is the preferred method for imaging, and our threshold for obtaining a TVUS should be very low. Women who have symptoms or concerns that can’t be attributed to a particular condition, and women in whom a mass can be palpated (even if asymptomatic) should have a TVUS. The imaging modality is cost effective and well tolerated by patients, does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, and should generally be considered first-line imaging.3,4
Size is not predictive of malignancy, but it is important for determining whether surgery is warranted. In our experience, a mass of 8-10 cm or larger on TVUS is at risk of torsion and is unlikely to resolve on its own, even in a premenopausal woman. While large masses generally require surgery, patients of any age who have simple cysts smaller than 8-10 cm generally can be followed with serial exams and ultrasound; spontaneous regression is common.
Doppler ultrasonography is useful for evaluating blood flow in and around an ovarian mass and can be helpful for confirming suspected characteristics of a mass.
Recent studies from the radiology community have looked at the utility of the resistive index – a measure of the impedance and velocity of blood flow – as a predictor of ovarian malignancy. However, we caution against using Doppler to determine whether a mass is benign or malignant, or to determine the necessity of surgery. An abnormal ovary may have what is considered to be a normal resistive index, and the resistive index of a normal ovary may fall within the abnormal range. Doppler flow can be helpful, but it must be combined with other predictive features, like solid components with flow or papillary projections within a cyst, to define a decision about surgery.4,5
Magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in differentiating a fibroid from an ovarian mass, and a CT scan can be helpful in looking for disseminated disease when ovarian cancer is suspected based on ultrasound imaging, physical and history, and serum markers. A CT is useful, for instance, in a patient whose ovary is distended with ascites or who has upper abdominal complaints and a complex cyst. CT, PET, and MRI are not recommended in the initial evaluation of an ovarian mass.
The utility of serum biomarkers
Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) testing may be helpful – in combination with other findings – for decision-making regarding the likelihood of malignancy and the need to refer patients. CA-125 is like Doppler in that a normal CA-125 cannot eliminate the possibility of cancer, and an abnormal CA-125 does not in and of itself imply malignancy. It’s far from a perfect cancer screening test.
CA-125 is a protein associated with epithelial ovarian malignancies, the type of ovarian cancer most commonly seen in postmenopausal women with genetic predispositions. Its specificity and positive predictive value are much higher in postmenopausal women than in average-risk premenopausal women (those without a family history or a known mutation that predisposes them to ovarian cancer). Levels of the marker are elevated in association with many nonmalignant conditions in premenopausal women – endometriosis, fibroids, and various inflammatory conditions, for instance – so the marker’s utility in this population is limited.
For women who have a family history of ovarian cancer or a known breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) or BRCA2 mutation, there are some data that suggest that monitoring with CA-125 measurements and TVUS may be a good approach to following patients prior to the age at which risk-reducing surgery can best be performed.
In an adolescent girl or a woman of reproductive age, we think less about epithelial cancer and more about germ-cell and stromal tumors. When a solid mass is palpated or visualized on imaging, we therefore will utilize a different set of markers; alpha-fetoprotein, L-lactate dehydrogenase, and beta-HCG, for instance, have much higher specificity than CA-125 does for germ-cell tumors in this age group and may be helpful in the evaluation. Similarly, in cases of a very large mass resembling a mucinous tumor, a carcinoembryonic antigen may be helpful.
A number of proprietary profiling technologies have been developed to determine the risk of a diagnosed mass being malignant. For instance, the OVA1 assay looks at five serum markers and scores the results, and the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) combines the results of three serum markers with menopausal status into a numerical score. Both have Food and Drug Administration approval for use in women in whom surgery has been deemed necessary. These panels can be fairly predictive of risk and may be helpful – especially in rural areas – in determining which women should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist for surgery.
It is important to appreciate that an ovarian cyst or mass should never be biopsied or aspirated lest a malignant tumor confined to one ovary be potentially spread to the peritoneum.
Referral to a gynecologic oncologist
Postmenopausal women with a CA-125 greater than 35 U/mL should be referred, as should postmenopausal women with ascites, those with a nodular or fixed pelvic mass, and those with suspected abdominal or distant metastases (per a CT scan, for instance).
In premenopausal women, ascites, a nodular or fixed mass, and evidence of metastases also are reasons for referral to a gynecologic oncologist. CA-125, again, is much more likely to be elevated for reasons other than malignancy and therefore is not as strong a driver for referral as in postmenopausal women. Patients with markedly elevated levels, however, should probably be referred – particularly when other clinical factors also suggest the need for consultation. While there is no evidence-based threshold for CA-125 in premenopausal women, a CA-125 greater than 200 U/mL is a good cutoff for referral.
For any patient, family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer – especially in a first-degree relative – raises the risk of malignancy and should figure prominently into decision-making regarding referral. Criteria for referral are among the points discussed in the ACOG 2016 Practice Bulletin on Evaluation and Management of Adnexal Masses.1
A note on BRCA mutations
As the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says in its practice bulletin, the most important personal risk factor for ovarian cancer is a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer. Women with such a family history can undergo genetic testing for BRCA mutations and have the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancers when mutations are detected. This simple blood test can save lives.
A modeling study we recently completed – not yet published – shows that it actually would be cost effective to do population screening with BRCA testing performed on every woman at age 30 years.
According to the National Cancer Institute website (last review: 2018), it is estimated that about 44% of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation, and about 17% of those who inherit a BRAC2 mutation, will develop ovarian cancer by the age of 80 years. By identifying those mutations, women may undergo risk-reducing surgery at designated ages after childbearing is complete and bring their risk down to under 5%.
An international take on managing adnexal masses
- Pelvic ultrasound should include the transvaginal approach. Use Doppler imaging as indicated.
- Although simple ovarian cysts are not precursor lesions to a malignant ovarian cancer, perform a high-quality examination to make sure there are no solid/papillary structures before classifying a cyst as a simple cyst. The risk of progression to malignancy is extremely low, but some follow-up is prudent.
- The most accurate method of characterizing an ovarian mass currently is real-time pattern recognition sonography in the hands of an experienced imager.
- Pattern recognition sonography or a risk model such as the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis (IOTA) Simple Rules can be used to initially characterize an ovarian mass.
- When an ovarian lesion is classified as benign, the patient may be followed conservatively, or if indicated, surgery can be performed by a general gynecologist.
- Serial sonography can be beneficial, but there are limited prospective data to support an exact interval and duration.
- Fewer surgical interventions may result in an increase in sonographic surveillance.
- When an ovarian lesion is considered indeterminate on initial sonography, and after appropriate clinical evaluation, a “second-step” evaluation may include referral to an expert sonologist, serial sonography, application of established risk-prediction models, correlation with serum biomarkers, correlation with MRI, or referral to a gynecologic oncologist for further evaluation.
From the First International Consensus Report on Adnexal Masses: Management Recommendations
Source: Glanc P et al. J Ultrasound Med. 2017 May;36(5):849-63.
Dr. Brown reported that she had received an earlier grant from Aspira Labs, the company that developed the OVA1 assay. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Nov. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001768.
2. Cancer. 2007 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22371.
3. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000083.
4. Ultrasound Q. 2013 Mar. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3182814d9b.
5. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365.
Ovarian masses are common in women of all ages. It is important not to miss even one ovarian cancer, but we must also identify masses that will resolve on their own over time to avoid overtreatment. These concurrent goals of excluding malignancy while not overtreating patients are the basis for management of the pelvic mass. Additionally, fertility preservation is important when surgery is performed in a reproductive-aged woman.
An ovarian mass may be anything from a simple functional or physiologic cyst to an endometrioma to an epithelial carcinoma, a germ-cell tumor, or a stromal tumor (the latter three of which may metastasize). Across the general population, women have a 5%-10% lifetime risk of needing surgery for a suspected ovarian mass and a 1.4% (1 in 70) risk that this mass is cancerous. The majority of ovarian cysts or masses therefore are benign.
A thorough history – including family history – and physical examination with appropriate laboratory testing and directed imaging are important first steps for the ob.gyn. Fortunately, we have guidelines and criteria governing not only when observation or surgery is warranted but also when patients should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist. By following these guidelines,1 we are able to achieve the best outcomes.
Transvaginal ultrasound
A 2007 groundbreaking study led by Barbara Goff, MD, demonstrated that there are warning signs for ovarian cancer – symptoms that are significantly associated with malignancy. Dr. Goff and her coinvestigators evaluated the charts of hundreds of patients, including about 150 with ovarian cancer, and found that pelvic/abdominal pressure or pain, bloating, increase in abdominal size, and difficulty eating or feeling full were significantly and independently associated with cancer if these symptoms were present for less than a year and occurred at least 12 times per month.2
A pelvic examination is an integral part of evaluating every patient who has such concerns. That said, pelvic exams have limited ability to identify adnexal masses, especially in women who are obese – and that’s where imaging becomes especially important.
Masses generally can be considered simple or complex based on their appearance. A simple cyst is fluid-filled with thin, smooth walls and the absence of solid components or septations; it is significantly more likely to resolve on its own and is less likely to imply malignancy than a complex cyst, especially in a premenopausal woman. A complex cyst is multiseptated and/or solid – possibly with papillary projections – and is more concerning, especially if there is increased, new vascularity. Making this distinction helps us determine the risk of malignancy.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is the preferred method for imaging, and our threshold for obtaining a TVUS should be very low. Women who have symptoms or concerns that can’t be attributed to a particular condition, and women in whom a mass can be palpated (even if asymptomatic) should have a TVUS. The imaging modality is cost effective and well tolerated by patients, does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, and should generally be considered first-line imaging.3,4
Size is not predictive of malignancy, but it is important for determining whether surgery is warranted. In our experience, a mass of 8-10 cm or larger on TVUS is at risk of torsion and is unlikely to resolve on its own, even in a premenopausal woman. While large masses generally require surgery, patients of any age who have simple cysts smaller than 8-10 cm generally can be followed with serial exams and ultrasound; spontaneous regression is common.
Doppler ultrasonography is useful for evaluating blood flow in and around an ovarian mass and can be helpful for confirming suspected characteristics of a mass.
Recent studies from the radiology community have looked at the utility of the resistive index – a measure of the impedance and velocity of blood flow – as a predictor of ovarian malignancy. However, we caution against using Doppler to determine whether a mass is benign or malignant, or to determine the necessity of surgery. An abnormal ovary may have what is considered to be a normal resistive index, and the resistive index of a normal ovary may fall within the abnormal range. Doppler flow can be helpful, but it must be combined with other predictive features, like solid components with flow or papillary projections within a cyst, to define a decision about surgery.4,5
Magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in differentiating a fibroid from an ovarian mass, and a CT scan can be helpful in looking for disseminated disease when ovarian cancer is suspected based on ultrasound imaging, physical and history, and serum markers. A CT is useful, for instance, in a patient whose ovary is distended with ascites or who has upper abdominal complaints and a complex cyst. CT, PET, and MRI are not recommended in the initial evaluation of an ovarian mass.
The utility of serum biomarkers
Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) testing may be helpful – in combination with other findings – for decision-making regarding the likelihood of malignancy and the need to refer patients. CA-125 is like Doppler in that a normal CA-125 cannot eliminate the possibility of cancer, and an abnormal CA-125 does not in and of itself imply malignancy. It’s far from a perfect cancer screening test.
CA-125 is a protein associated with epithelial ovarian malignancies, the type of ovarian cancer most commonly seen in postmenopausal women with genetic predispositions. Its specificity and positive predictive value are much higher in postmenopausal women than in average-risk premenopausal women (those without a family history or a known mutation that predisposes them to ovarian cancer). Levels of the marker are elevated in association with many nonmalignant conditions in premenopausal women – endometriosis, fibroids, and various inflammatory conditions, for instance – so the marker’s utility in this population is limited.
For women who have a family history of ovarian cancer or a known breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) or BRCA2 mutation, there are some data that suggest that monitoring with CA-125 measurements and TVUS may be a good approach to following patients prior to the age at which risk-reducing surgery can best be performed.
In an adolescent girl or a woman of reproductive age, we think less about epithelial cancer and more about germ-cell and stromal tumors. When a solid mass is palpated or visualized on imaging, we therefore will utilize a different set of markers; alpha-fetoprotein, L-lactate dehydrogenase, and beta-HCG, for instance, have much higher specificity than CA-125 does for germ-cell tumors in this age group and may be helpful in the evaluation. Similarly, in cases of a very large mass resembling a mucinous tumor, a carcinoembryonic antigen may be helpful.
A number of proprietary profiling technologies have been developed to determine the risk of a diagnosed mass being malignant. For instance, the OVA1 assay looks at five serum markers and scores the results, and the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) combines the results of three serum markers with menopausal status into a numerical score. Both have Food and Drug Administration approval for use in women in whom surgery has been deemed necessary. These panels can be fairly predictive of risk and may be helpful – especially in rural areas – in determining which women should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist for surgery.
It is important to appreciate that an ovarian cyst or mass should never be biopsied or aspirated lest a malignant tumor confined to one ovary be potentially spread to the peritoneum.
Referral to a gynecologic oncologist
Postmenopausal women with a CA-125 greater than 35 U/mL should be referred, as should postmenopausal women with ascites, those with a nodular or fixed pelvic mass, and those with suspected abdominal or distant metastases (per a CT scan, for instance).
In premenopausal women, ascites, a nodular or fixed mass, and evidence of metastases also are reasons for referral to a gynecologic oncologist. CA-125, again, is much more likely to be elevated for reasons other than malignancy and therefore is not as strong a driver for referral as in postmenopausal women. Patients with markedly elevated levels, however, should probably be referred – particularly when other clinical factors also suggest the need for consultation. While there is no evidence-based threshold for CA-125 in premenopausal women, a CA-125 greater than 200 U/mL is a good cutoff for referral.
For any patient, family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer – especially in a first-degree relative – raises the risk of malignancy and should figure prominently into decision-making regarding referral. Criteria for referral are among the points discussed in the ACOG 2016 Practice Bulletin on Evaluation and Management of Adnexal Masses.1
A note on BRCA mutations
As the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says in its practice bulletin, the most important personal risk factor for ovarian cancer is a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer. Women with such a family history can undergo genetic testing for BRCA mutations and have the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancers when mutations are detected. This simple blood test can save lives.
A modeling study we recently completed – not yet published – shows that it actually would be cost effective to do population screening with BRCA testing performed on every woman at age 30 years.
According to the National Cancer Institute website (last review: 2018), it is estimated that about 44% of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation, and about 17% of those who inherit a BRAC2 mutation, will develop ovarian cancer by the age of 80 years. By identifying those mutations, women may undergo risk-reducing surgery at designated ages after childbearing is complete and bring their risk down to under 5%.
An international take on managing adnexal masses
- Pelvic ultrasound should include the transvaginal approach. Use Doppler imaging as indicated.
- Although simple ovarian cysts are not precursor lesions to a malignant ovarian cancer, perform a high-quality examination to make sure there are no solid/papillary structures before classifying a cyst as a simple cyst. The risk of progression to malignancy is extremely low, but some follow-up is prudent.
- The most accurate method of characterizing an ovarian mass currently is real-time pattern recognition sonography in the hands of an experienced imager.
- Pattern recognition sonography or a risk model such as the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis (IOTA) Simple Rules can be used to initially characterize an ovarian mass.
- When an ovarian lesion is classified as benign, the patient may be followed conservatively, or if indicated, surgery can be performed by a general gynecologist.
- Serial sonography can be beneficial, but there are limited prospective data to support an exact interval and duration.
- Fewer surgical interventions may result in an increase in sonographic surveillance.
- When an ovarian lesion is considered indeterminate on initial sonography, and after appropriate clinical evaluation, a “second-step” evaluation may include referral to an expert sonologist, serial sonography, application of established risk-prediction models, correlation with serum biomarkers, correlation with MRI, or referral to a gynecologic oncologist for further evaluation.
From the First International Consensus Report on Adnexal Masses: Management Recommendations
Source: Glanc P et al. J Ultrasound Med. 2017 May;36(5):849-63.
Dr. Brown reported that she had received an earlier grant from Aspira Labs, the company that developed the OVA1 assay. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Nov. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001768.
2. Cancer. 2007 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22371.
3. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000083.
4. Ultrasound Q. 2013 Mar. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3182814d9b.
5. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365.
Ovarian masses are common in women of all ages. It is important not to miss even one ovarian cancer, but we must also identify masses that will resolve on their own over time to avoid overtreatment. These concurrent goals of excluding malignancy while not overtreating patients are the basis for management of the pelvic mass. Additionally, fertility preservation is important when surgery is performed in a reproductive-aged woman.
An ovarian mass may be anything from a simple functional or physiologic cyst to an endometrioma to an epithelial carcinoma, a germ-cell tumor, or a stromal tumor (the latter three of which may metastasize). Across the general population, women have a 5%-10% lifetime risk of needing surgery for a suspected ovarian mass and a 1.4% (1 in 70) risk that this mass is cancerous. The majority of ovarian cysts or masses therefore are benign.
A thorough history – including family history – and physical examination with appropriate laboratory testing and directed imaging are important first steps for the ob.gyn. Fortunately, we have guidelines and criteria governing not only when observation or surgery is warranted but also when patients should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist. By following these guidelines,1 we are able to achieve the best outcomes.
Transvaginal ultrasound
A 2007 groundbreaking study led by Barbara Goff, MD, demonstrated that there are warning signs for ovarian cancer – symptoms that are significantly associated with malignancy. Dr. Goff and her coinvestigators evaluated the charts of hundreds of patients, including about 150 with ovarian cancer, and found that pelvic/abdominal pressure or pain, bloating, increase in abdominal size, and difficulty eating or feeling full were significantly and independently associated with cancer if these symptoms were present for less than a year and occurred at least 12 times per month.2
A pelvic examination is an integral part of evaluating every patient who has such concerns. That said, pelvic exams have limited ability to identify adnexal masses, especially in women who are obese – and that’s where imaging becomes especially important.
Masses generally can be considered simple or complex based on their appearance. A simple cyst is fluid-filled with thin, smooth walls and the absence of solid components or septations; it is significantly more likely to resolve on its own and is less likely to imply malignancy than a complex cyst, especially in a premenopausal woman. A complex cyst is multiseptated and/or solid – possibly with papillary projections – and is more concerning, especially if there is increased, new vascularity. Making this distinction helps us determine the risk of malignancy.
Transvaginal ultrasound (TVUS) is the preferred method for imaging, and our threshold for obtaining a TVUS should be very low. Women who have symptoms or concerns that can’t be attributed to a particular condition, and women in whom a mass can be palpated (even if asymptomatic) should have a TVUS. The imaging modality is cost effective and well tolerated by patients, does not expose the patient to ionizing radiation, and should generally be considered first-line imaging.3,4
Size is not predictive of malignancy, but it is important for determining whether surgery is warranted. In our experience, a mass of 8-10 cm or larger on TVUS is at risk of torsion and is unlikely to resolve on its own, even in a premenopausal woman. While large masses generally require surgery, patients of any age who have simple cysts smaller than 8-10 cm generally can be followed with serial exams and ultrasound; spontaneous regression is common.
Doppler ultrasonography is useful for evaluating blood flow in and around an ovarian mass and can be helpful for confirming suspected characteristics of a mass.
Recent studies from the radiology community have looked at the utility of the resistive index – a measure of the impedance and velocity of blood flow – as a predictor of ovarian malignancy. However, we caution against using Doppler to determine whether a mass is benign or malignant, or to determine the necessity of surgery. An abnormal ovary may have what is considered to be a normal resistive index, and the resistive index of a normal ovary may fall within the abnormal range. Doppler flow can be helpful, but it must be combined with other predictive features, like solid components with flow or papillary projections within a cyst, to define a decision about surgery.4,5
Magnetic resonance imaging can be useful in differentiating a fibroid from an ovarian mass, and a CT scan can be helpful in looking for disseminated disease when ovarian cancer is suspected based on ultrasound imaging, physical and history, and serum markers. A CT is useful, for instance, in a patient whose ovary is distended with ascites or who has upper abdominal complaints and a complex cyst. CT, PET, and MRI are not recommended in the initial evaluation of an ovarian mass.
The utility of serum biomarkers
Cancer antigen 125 (CA-125) testing may be helpful – in combination with other findings – for decision-making regarding the likelihood of malignancy and the need to refer patients. CA-125 is like Doppler in that a normal CA-125 cannot eliminate the possibility of cancer, and an abnormal CA-125 does not in and of itself imply malignancy. It’s far from a perfect cancer screening test.
CA-125 is a protein associated with epithelial ovarian malignancies, the type of ovarian cancer most commonly seen in postmenopausal women with genetic predispositions. Its specificity and positive predictive value are much higher in postmenopausal women than in average-risk premenopausal women (those without a family history or a known mutation that predisposes them to ovarian cancer). Levels of the marker are elevated in association with many nonmalignant conditions in premenopausal women – endometriosis, fibroids, and various inflammatory conditions, for instance – so the marker’s utility in this population is limited.
For women who have a family history of ovarian cancer or a known breast cancer gene 1 (BRCA1) or BRCA2 mutation, there are some data that suggest that monitoring with CA-125 measurements and TVUS may be a good approach to following patients prior to the age at which risk-reducing surgery can best be performed.
In an adolescent girl or a woman of reproductive age, we think less about epithelial cancer and more about germ-cell and stromal tumors. When a solid mass is palpated or visualized on imaging, we therefore will utilize a different set of markers; alpha-fetoprotein, L-lactate dehydrogenase, and beta-HCG, for instance, have much higher specificity than CA-125 does for germ-cell tumors in this age group and may be helpful in the evaluation. Similarly, in cases of a very large mass resembling a mucinous tumor, a carcinoembryonic antigen may be helpful.
A number of proprietary profiling technologies have been developed to determine the risk of a diagnosed mass being malignant. For instance, the OVA1 assay looks at five serum markers and scores the results, and the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm (ROMA) combines the results of three serum markers with menopausal status into a numerical score. Both have Food and Drug Administration approval for use in women in whom surgery has been deemed necessary. These panels can be fairly predictive of risk and may be helpful – especially in rural areas – in determining which women should be referred to a gynecologic oncologist for surgery.
It is important to appreciate that an ovarian cyst or mass should never be biopsied or aspirated lest a malignant tumor confined to one ovary be potentially spread to the peritoneum.
Referral to a gynecologic oncologist
Postmenopausal women with a CA-125 greater than 35 U/mL should be referred, as should postmenopausal women with ascites, those with a nodular or fixed pelvic mass, and those with suspected abdominal or distant metastases (per a CT scan, for instance).
In premenopausal women, ascites, a nodular or fixed mass, and evidence of metastases also are reasons for referral to a gynecologic oncologist. CA-125, again, is much more likely to be elevated for reasons other than malignancy and therefore is not as strong a driver for referral as in postmenopausal women. Patients with markedly elevated levels, however, should probably be referred – particularly when other clinical factors also suggest the need for consultation. While there is no evidence-based threshold for CA-125 in premenopausal women, a CA-125 greater than 200 U/mL is a good cutoff for referral.
For any patient, family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer – especially in a first-degree relative – raises the risk of malignancy and should figure prominently into decision-making regarding referral. Criteria for referral are among the points discussed in the ACOG 2016 Practice Bulletin on Evaluation and Management of Adnexal Masses.1
A note on BRCA mutations
As the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says in its practice bulletin, the most important personal risk factor for ovarian cancer is a strong family history of breast or ovarian cancer. Women with such a family history can undergo genetic testing for BRCA mutations and have the opportunity to prevent ovarian cancers when mutations are detected. This simple blood test can save lives.
A modeling study we recently completed – not yet published – shows that it actually would be cost effective to do population screening with BRCA testing performed on every woman at age 30 years.
According to the National Cancer Institute website (last review: 2018), it is estimated that about 44% of women who inherit a BRCA1 mutation, and about 17% of those who inherit a BRAC2 mutation, will develop ovarian cancer by the age of 80 years. By identifying those mutations, women may undergo risk-reducing surgery at designated ages after childbearing is complete and bring their risk down to under 5%.
An international take on managing adnexal masses
- Pelvic ultrasound should include the transvaginal approach. Use Doppler imaging as indicated.
- Although simple ovarian cysts are not precursor lesions to a malignant ovarian cancer, perform a high-quality examination to make sure there are no solid/papillary structures before classifying a cyst as a simple cyst. The risk of progression to malignancy is extremely low, but some follow-up is prudent.
- The most accurate method of characterizing an ovarian mass currently is real-time pattern recognition sonography in the hands of an experienced imager.
- Pattern recognition sonography or a risk model such as the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis (IOTA) Simple Rules can be used to initially characterize an ovarian mass.
- When an ovarian lesion is classified as benign, the patient may be followed conservatively, or if indicated, surgery can be performed by a general gynecologist.
- Serial sonography can be beneficial, but there are limited prospective data to support an exact interval and duration.
- Fewer surgical interventions may result in an increase in sonographic surveillance.
- When an ovarian lesion is considered indeterminate on initial sonography, and after appropriate clinical evaluation, a “second-step” evaluation may include referral to an expert sonologist, serial sonography, application of established risk-prediction models, correlation with serum biomarkers, correlation with MRI, or referral to a gynecologic oncologist for further evaluation.
From the First International Consensus Report on Adnexal Masses: Management Recommendations
Source: Glanc P et al. J Ultrasound Med. 2017 May;36(5):849-63.
Dr. Brown reported that she had received an earlier grant from Aspira Labs, the company that developed the OVA1 assay. Dr. Miller reported that he has no relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Nov. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001768.
2. Cancer. 2007 Jan 15. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22371.
3. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Mar. doi: 10.1097/GRF.0000000000000083.
4. Ultrasound Q. 2013 Mar. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3182814d9b.
5. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun. doi: 10.1002/uog.5365.