User login
MDedge conference coverage features onsite reporting of the latest study results and expert perspectives from leading researchers.
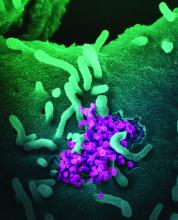
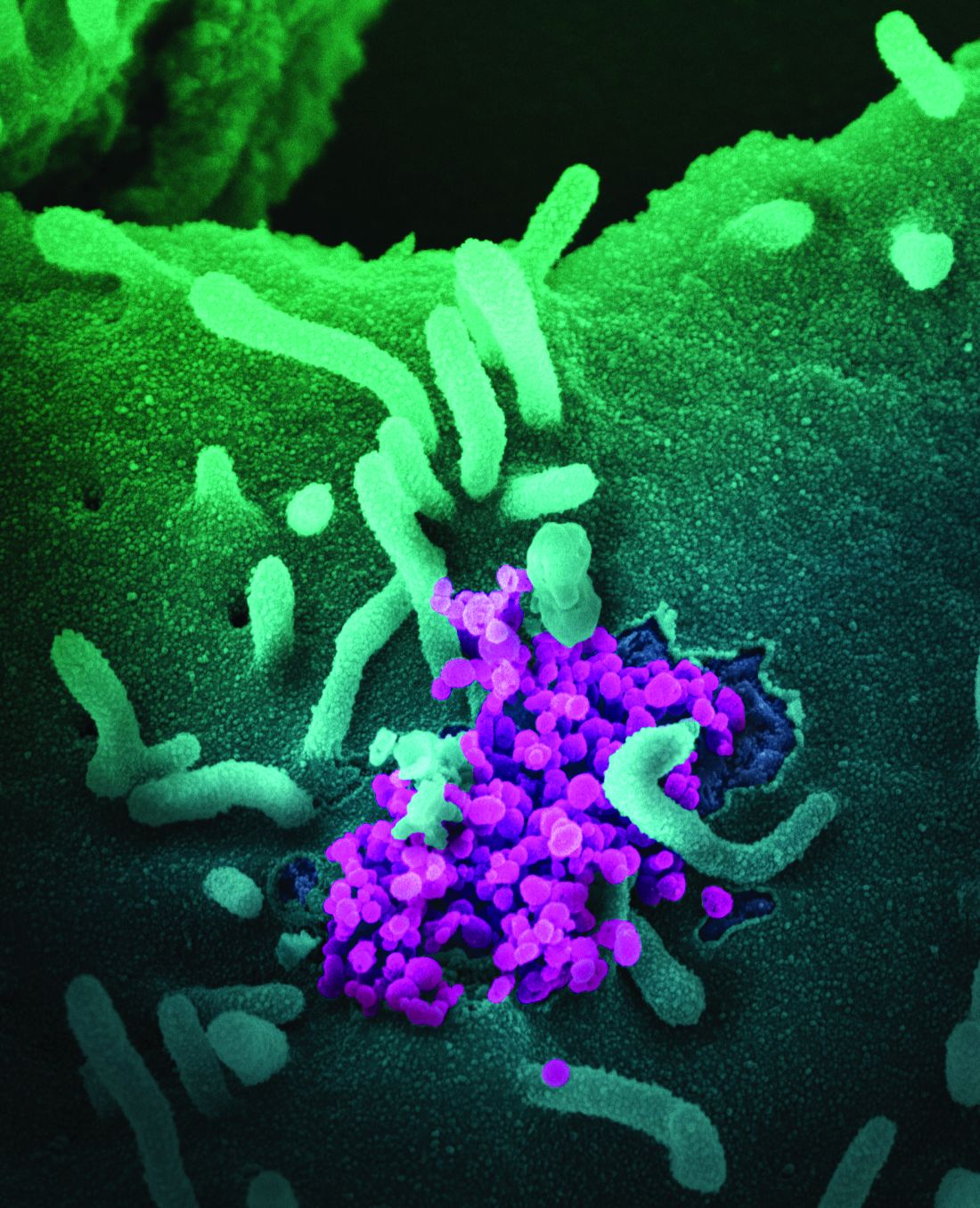
PPE protected critical care staff from COVID-19 transmission
, a new study has found.
“Other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection,” said lead author Kate El Bouzidi, MRCP, South London Specialist Virology Centre, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London.
She noted that 60% of critical care staff were symptomatic during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic and 20% were antibody positive, with 10% asymptomatic. “Staff acquisition peaked 3 weeks before the peak of COVID-19 ICU admission, and personal protective equipment (PPE) was effective at preventing transmission from patients.” Working in other areas of the hospital was associated with higher seroprevalence, Dr. El Bouzidi noted.
The findings were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The novel coronavirus was spreading around the world, and when it reached northern Italy, medical authorities began to think in terms of how it might overwhelm the health care system in the United Kingdom, explained Dr. El Bouzidi.
“There was a lot of interest at this time about health care workers who were particularly vulnerable and also about the allocation of resources and rationing of care, particularly in intensive care,” she said. “And this only intensified when our prime minister was admitted to intensive care. About this time, antibody testing also became available.”
The goal of their study was to determine the SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in critical care staff, as well as look at the correlation between antibody status, prior swab testing, and COVID-19 symptoms.
The survey was conducted at Kings College Hospital in London, which is a tertiary-care teaching center. The critical care department is one of the largest in the United Kingdom. The authors estimate that more than 800 people worked in the critical care units, and between March and April 2020, more than 2,000 patients with COVID-19 were admitted, of whom 180 required care in the ICU.
“There was good PPE available in the ICU units right from the start,” she said, “and staff testing was available.”
All staff working in the critical care department participated in the study, which required serum samples and completion of a questionnaire. The samples were tested via six different assays to measure receptor-binding domain, nucleoprotein, and tri-spike, with one antibody result determined for each sample.
Of the 625 staff members, 384 (61.4%) had previously reported experiencing symptoms and 124 (19.8%) had sent a swab for testing. COVID-19 infection had been confirmed in 37 of those health care workers (29.8%).
Overall, 21% were positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, of whom 9.9% had been asymptomatic.
“We were surprised to find that 61% of staff reported symptoms they felt could be consistent with COVID-19,” she said, noting that fatigue, headache, and cough were the most common symptoms reported. “Seroprevalence was reported in 31% of symptomatic staff and in 5% of those without symptoms.”
Seroprevalence differed by role in a critical care unit, although it did not significantly differ by factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, or underlying conditions. Consultants, who are senior physicians, were twice as likely to test positive, compared with junior doctors. The reason for this finding is not clear, but it may lie in the nature of their work responsibilities, such as performing more aerosol-generating procedures in the ICU or in other departments.
The investigators looked at the timing of infections and found that they preceded peak of patient admissions by 3 weeks, with peak onset of staff symptoms in early March. At this time, Dr. El Bouzidi noted, there were very few patients with COVID-19 in the hospital, and good PPE was available throughout this time period.
“Staff were unlikely to be infected by ICU patients, and therefore PPE was largely effective,” she said. “Other sources of infection were more likely to be the cause, such as interactions with other staff, meetings, or contact in break rooms. Routine mask-wearing throughout the hospital was only encouraged as of June 15.”
There were several limitations to the study, such as the cross-sectional design, reliance on response/recall, the fact that antibody tests are unlikely to detect all previous infections, and no genomic data were available to confirm infections. Even though the study had limitations, Dr. El Bouzidi concluded that ICU staff are unlikely to contract COVID-19 from patients but that other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection.
These findings, she added, demonstrate that PPE was effective at preventing transmission from patients and that protective measures need to be maintained when staff is away from the bedside.
In commenting on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that, even though the study was conducted almost a year ago, the results are still relevant with regard to the effectiveness of PPE.
“There was a huge amount of uncertainty about PPE – what was most effective, could we reuse it, how to sterilize it, what about surfaces, and so on,” he said. “Even for people who work in ICU and who are familiar with the environment and familiar with the patients, there was 1,000 times more uncertainty about everything they were doing.”
Dr. Martin believes that the situation has improved. “It’s not that we take COVID more lightly, but I think the staff is more comfortable dealing with it,” he said. “They now know what they need to do on an hourly and daily basis to stay safe. The PPE had become second nature to them now, with all the other precautions.”
, a new study has found.
“Other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection,” said lead author Kate El Bouzidi, MRCP, South London Specialist Virology Centre, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London.
She noted that 60% of critical care staff were symptomatic during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic and 20% were antibody positive, with 10% asymptomatic. “Staff acquisition peaked 3 weeks before the peak of COVID-19 ICU admission, and personal protective equipment (PPE) was effective at preventing transmission from patients.” Working in other areas of the hospital was associated with higher seroprevalence, Dr. El Bouzidi noted.
The findings were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The novel coronavirus was spreading around the world, and when it reached northern Italy, medical authorities began to think in terms of how it might overwhelm the health care system in the United Kingdom, explained Dr. El Bouzidi.
“There was a lot of interest at this time about health care workers who were particularly vulnerable and also about the allocation of resources and rationing of care, particularly in intensive care,” she said. “And this only intensified when our prime minister was admitted to intensive care. About this time, antibody testing also became available.”
The goal of their study was to determine the SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in critical care staff, as well as look at the correlation between antibody status, prior swab testing, and COVID-19 symptoms.
The survey was conducted at Kings College Hospital in London, which is a tertiary-care teaching center. The critical care department is one of the largest in the United Kingdom. The authors estimate that more than 800 people worked in the critical care units, and between March and April 2020, more than 2,000 patients with COVID-19 were admitted, of whom 180 required care in the ICU.
“There was good PPE available in the ICU units right from the start,” she said, “and staff testing was available.”
All staff working in the critical care department participated in the study, which required serum samples and completion of a questionnaire. The samples were tested via six different assays to measure receptor-binding domain, nucleoprotein, and tri-spike, with one antibody result determined for each sample.
Of the 625 staff members, 384 (61.4%) had previously reported experiencing symptoms and 124 (19.8%) had sent a swab for testing. COVID-19 infection had been confirmed in 37 of those health care workers (29.8%).
Overall, 21% were positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, of whom 9.9% had been asymptomatic.
“We were surprised to find that 61% of staff reported symptoms they felt could be consistent with COVID-19,” she said, noting that fatigue, headache, and cough were the most common symptoms reported. “Seroprevalence was reported in 31% of symptomatic staff and in 5% of those without symptoms.”
Seroprevalence differed by role in a critical care unit, although it did not significantly differ by factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, or underlying conditions. Consultants, who are senior physicians, were twice as likely to test positive, compared with junior doctors. The reason for this finding is not clear, but it may lie in the nature of their work responsibilities, such as performing more aerosol-generating procedures in the ICU or in other departments.
The investigators looked at the timing of infections and found that they preceded peak of patient admissions by 3 weeks, with peak onset of staff symptoms in early March. At this time, Dr. El Bouzidi noted, there were very few patients with COVID-19 in the hospital, and good PPE was available throughout this time period.
“Staff were unlikely to be infected by ICU patients, and therefore PPE was largely effective,” she said. “Other sources of infection were more likely to be the cause, such as interactions with other staff, meetings, or contact in break rooms. Routine mask-wearing throughout the hospital was only encouraged as of June 15.”
There were several limitations to the study, such as the cross-sectional design, reliance on response/recall, the fact that antibody tests are unlikely to detect all previous infections, and no genomic data were available to confirm infections. Even though the study had limitations, Dr. El Bouzidi concluded that ICU staff are unlikely to contract COVID-19 from patients but that other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection.
These findings, she added, demonstrate that PPE was effective at preventing transmission from patients and that protective measures need to be maintained when staff is away from the bedside.
In commenting on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that, even though the study was conducted almost a year ago, the results are still relevant with regard to the effectiveness of PPE.
“There was a huge amount of uncertainty about PPE – what was most effective, could we reuse it, how to sterilize it, what about surfaces, and so on,” he said. “Even for people who work in ICU and who are familiar with the environment and familiar with the patients, there was 1,000 times more uncertainty about everything they were doing.”
Dr. Martin believes that the situation has improved. “It’s not that we take COVID more lightly, but I think the staff is more comfortable dealing with it,” he said. “They now know what they need to do on an hourly and daily basis to stay safe. The PPE had become second nature to them now, with all the other precautions.”
, a new study has found.
“Other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection,” said lead author Kate El Bouzidi, MRCP, South London Specialist Virology Centre, King’s College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, London.
She noted that 60% of critical care staff were symptomatic during the first wave of the coronavirus pandemic and 20% were antibody positive, with 10% asymptomatic. “Staff acquisition peaked 3 weeks before the peak of COVID-19 ICU admission, and personal protective equipment (PPE) was effective at preventing transmission from patients.” Working in other areas of the hospital was associated with higher seroprevalence, Dr. El Bouzidi noted.
The findings were presented at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
The novel coronavirus was spreading around the world, and when it reached northern Italy, medical authorities began to think in terms of how it might overwhelm the health care system in the United Kingdom, explained Dr. El Bouzidi.
“There was a lot of interest at this time about health care workers who were particularly vulnerable and also about the allocation of resources and rationing of care, particularly in intensive care,” she said. “And this only intensified when our prime minister was admitted to intensive care. About this time, antibody testing also became available.”
The goal of their study was to determine the SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in critical care staff, as well as look at the correlation between antibody status, prior swab testing, and COVID-19 symptoms.
The survey was conducted at Kings College Hospital in London, which is a tertiary-care teaching center. The critical care department is one of the largest in the United Kingdom. The authors estimate that more than 800 people worked in the critical care units, and between March and April 2020, more than 2,000 patients with COVID-19 were admitted, of whom 180 required care in the ICU.
“There was good PPE available in the ICU units right from the start,” she said, “and staff testing was available.”
All staff working in the critical care department participated in the study, which required serum samples and completion of a questionnaire. The samples were tested via six different assays to measure receptor-binding domain, nucleoprotein, and tri-spike, with one antibody result determined for each sample.
Of the 625 staff members, 384 (61.4%) had previously reported experiencing symptoms and 124 (19.8%) had sent a swab for testing. COVID-19 infection had been confirmed in 37 of those health care workers (29.8%).
Overall, 21% were positive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, of whom 9.9% had been asymptomatic.
“We were surprised to find that 61% of staff reported symptoms they felt could be consistent with COVID-19,” she said, noting that fatigue, headache, and cough were the most common symptoms reported. “Seroprevalence was reported in 31% of symptomatic staff and in 5% of those without symptoms.”
Seroprevalence differed by role in a critical care unit, although it did not significantly differ by factors such as age, sex, ethnicity, or underlying conditions. Consultants, who are senior physicians, were twice as likely to test positive, compared with junior doctors. The reason for this finding is not clear, but it may lie in the nature of their work responsibilities, such as performing more aerosol-generating procedures in the ICU or in other departments.
The investigators looked at the timing of infections and found that they preceded peak of patient admissions by 3 weeks, with peak onset of staff symptoms in early March. At this time, Dr. El Bouzidi noted, there were very few patients with COVID-19 in the hospital, and good PPE was available throughout this time period.
“Staff were unlikely to be infected by ICU patients, and therefore PPE was largely effective,” she said. “Other sources of infection were more likely to be the cause, such as interactions with other staff, meetings, or contact in break rooms. Routine mask-wearing throughout the hospital was only encouraged as of June 15.”
There were several limitations to the study, such as the cross-sectional design, reliance on response/recall, the fact that antibody tests are unlikely to detect all previous infections, and no genomic data were available to confirm infections. Even though the study had limitations, Dr. El Bouzidi concluded that ICU staff are unlikely to contract COVID-19 from patients but that other staff, other areas of the hospital, and the wider community are more likely sources of infection.
These findings, she added, demonstrate that PPE was effective at preventing transmission from patients and that protective measures need to be maintained when staff is away from the bedside.
In commenting on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that, even though the study was conducted almost a year ago, the results are still relevant with regard to the effectiveness of PPE.
“There was a huge amount of uncertainty about PPE – what was most effective, could we reuse it, how to sterilize it, what about surfaces, and so on,” he said. “Even for people who work in ICU and who are familiar with the environment and familiar with the patients, there was 1,000 times more uncertainty about everything they were doing.”
Dr. Martin believes that the situation has improved. “It’s not that we take COVID more lightly, but I think the staff is more comfortable dealing with it,” he said. “They now know what they need to do on an hourly and daily basis to stay safe. The PPE had become second nature to them now, with all the other precautions.”
FROM CCC50
‘Unprecedented’ long-term survival after immunotherapy in pretreated NSCLC
Longer-term survival with immunotherapy for patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is once again being applauded by experts in the field.
This time, the data come from trials that tested immunotherapy in the second-line setting for patients who had experienced disease progression with platinum-based chemotherapy. The latest 5-year follow-up from two landmark trials, one with pembrolizumab, the other with nivolumab, show that the survival benefit can persist for years after treatment is stopped.
“These are unprecedented data,” Fred R. Hirsch, MD, PhD, executive director of the Center for Thoracic Oncology at the Tisch Cancer Institute, New York, said in an interview. He was not involved in either trial and was approached for comment.
Pembrolizumab survival data
The new longer-term data on pembrolizumab come from the KEYNOTE-010 trial, which included more than 1,000 patients with advanced NSCLC who had previously undergone treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. The patients were randomly assigned to receive either pembrolizumab or docetaxel for 2 years.
This is the latest update on data from this trial, which has been described as “really extraordinary.”
The 5-year overall survival rates were more than doubled in the pembrolizumab groups, compared with the docetaxel group, reported Roy Herbst, MD, PhD, department of medical oncology, Yale Comprehensive Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn.. He was presenting the new data at the recent World Conference on Lung Cancer 2020.
Overall results for patients with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) expression greater than 1% show that 15.6% of the pembrolizumab group were still alive at 5 years versus 6.5% of the docetaxel group.
The results were even better among patients who had high PD-L1 TPS expression (>50%): in this subgroup, 25% of the patients who received pembrolizumab were still alive versus 8.2% of those who received docetaxel.
In addition, at 5 years, 9.4% of patients who received pembrolizumab were disease free versus 0.7% of the patients who received docetaxel, Dr. Herbst reported.
Dr. Hirsch commented that the 5-year survival rate of 25% among patients with high PD-L1 expression who underwent treatment with pembrolizumab is “great progress in lung cancer treatment, there is no doubt about it.”
He noted that the results also show that “numerically,” it matters whether patients have low PD-L1 expression. “We know from first-line studies that pembrolizumab monotherapy is effective in high PD-L1–expressing tumors, so these data fit very well,” he said.
At the meeting, Dr. Herbst summarized his presentation on pembrolizumab for patients with NSCLC who had previously undergone treatment, saying that, “with 5 years of follow-up, we continue to see a clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival and PFS [progression-free survival].
“Pembrolizumab monotherapy is a standard of care in patients with immunotherapy-naive or previously treated PD-L1–positive advanced non–small cell lung cancer,” Herbst stated.
Dr. Hirsch was largely in agreement. He believes that, for patients with a PD-L1 TPS of at least 50%, the standard of care “is practically pembrolizumab monotherapy, unless there are certain circumstances where you would add chemotherapy,” such as for patients with a high tumor volume, “where you want to see a very quick response.”
Dr. Hirsch pointed out, however, that currently most patients with high PD-L1–expressing tumors are given pembrolizumab in the first line, which begs the question as to what to give those who experience disease progression after immunotherapy.
“That is an open space,” he said. “There is a lot of studies going on in what we call the immunotherapy-refractory patients.
“We don’t have clear guidance for clinical practice yet,” he commented. He noted that there are several options: “Do you continue with chemotherapy? Do you continue with chemotherapy plus another immunotherapy? Do you switch to another immunotherapy?”
Commenting on Twitter, Stephen V. Liu, MD, director of thoracic oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, said the results were “very exciting.”
However, he wondered whether the results suggest that patients with high PD-L1 expression “may be able to stop” receiving pembrolizumab, whereas those with disease of lower expression “may need longer therapy.”
H. Jack West, MD, medical director of the thoracic oncology program, Swedish Cancer Institute, Seattle, said on Twitter that, to him, the “most impressive” aspect was the “new insight about patients stopping pembro after 2 years but still having two-thirds with sustained response.”
He added that he would “love to learn which patients can stop therapy and when, or whether we can do infrequent maintenance IO [immunotherapy].”
Nivolumab survival data
The data on nivolumab come from a pooled analysis of 5-year data on 854 patients from CheckMate 057 and CheckMate 017. The analysis was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology on Jan. 15, 2021.
Both of these trials compared nivolumab with docetaxel for patients with NSCLC who had experienced disease progression with platinum-based chemotherapy.
The pooled analysis showed that the 5-year overall survival rate was more than fivefold greater with nivolumab than with docetaxel, at 13.4% versus 2.6%.
Moreover, more than 80% of patients who had not experienced progression with the immunotherapy at 2 years were still alive at 5 years. The percentage rose to more than 90% among those who had not experienced progression at 3 years.
Lead author Julie R. Brahmer, MD, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues said the results “demonstrate that nivolumab can provide long-term survival benefit with durable responses and a tolerable safety profile in patients with previously treated, advanced NSCLC.
“Furthermore, some patients appear to maintain prolonged disease control even after stopping systemic therapy,” they noted.
Dr. Hirsch commented that, although the survival rates with nivolumab were slightly lower than reported with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-010, they could still be “within the range.” He added that “I wouldn’t conclude that pembrolizumab is better than nivolumab.”
Many factors may account for these differences, he suggested, including differences in the patient populations or simply differences in the numbers of patients included.
For him, the “main point” of the new data from both trials is that immunotherapy has shown “tremendous progress, compared to chemotherapy.”
KEYNOTE-010 was sponsored by Merck Sharp & Dohme. CheckMate 017 and CheckMate057 were sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Herbst has relationships with Jun Shi Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Merck, Pfizer, AbbVie, Biodesix, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Heat Biologics, Loxo, Nektar, NextCure, Novartis, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Shire, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Symphogen, Tesaro, Neon Therapeutics, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Armo Biosciences, Genmab, Halozyme, and Tocagen. Dr. Brahmer has relationships with Roche/Genentech, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Celgene, Syndax, Janssen Oncology, Merck, Amgen, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Incyte, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Revolution, and Roche/Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Longer-term survival with immunotherapy for patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is once again being applauded by experts in the field.
This time, the data come from trials that tested immunotherapy in the second-line setting for patients who had experienced disease progression with platinum-based chemotherapy. The latest 5-year follow-up from two landmark trials, one with pembrolizumab, the other with nivolumab, show that the survival benefit can persist for years after treatment is stopped.
“These are unprecedented data,” Fred R. Hirsch, MD, PhD, executive director of the Center for Thoracic Oncology at the Tisch Cancer Institute, New York, said in an interview. He was not involved in either trial and was approached for comment.
Pembrolizumab survival data
The new longer-term data on pembrolizumab come from the KEYNOTE-010 trial, which included more than 1,000 patients with advanced NSCLC who had previously undergone treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. The patients were randomly assigned to receive either pembrolizumab or docetaxel for 2 years.
This is the latest update on data from this trial, which has been described as “really extraordinary.”
The 5-year overall survival rates were more than doubled in the pembrolizumab groups, compared with the docetaxel group, reported Roy Herbst, MD, PhD, department of medical oncology, Yale Comprehensive Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn.. He was presenting the new data at the recent World Conference on Lung Cancer 2020.
Overall results for patients with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) expression greater than 1% show that 15.6% of the pembrolizumab group were still alive at 5 years versus 6.5% of the docetaxel group.
The results were even better among patients who had high PD-L1 TPS expression (>50%): in this subgroup, 25% of the patients who received pembrolizumab were still alive versus 8.2% of those who received docetaxel.
In addition, at 5 years, 9.4% of patients who received pembrolizumab were disease free versus 0.7% of the patients who received docetaxel, Dr. Herbst reported.
Dr. Hirsch commented that the 5-year survival rate of 25% among patients with high PD-L1 expression who underwent treatment with pembrolizumab is “great progress in lung cancer treatment, there is no doubt about it.”
He noted that the results also show that “numerically,” it matters whether patients have low PD-L1 expression. “We know from first-line studies that pembrolizumab monotherapy is effective in high PD-L1–expressing tumors, so these data fit very well,” he said.
At the meeting, Dr. Herbst summarized his presentation on pembrolizumab for patients with NSCLC who had previously undergone treatment, saying that, “with 5 years of follow-up, we continue to see a clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival and PFS [progression-free survival].
“Pembrolizumab monotherapy is a standard of care in patients with immunotherapy-naive or previously treated PD-L1–positive advanced non–small cell lung cancer,” Herbst stated.
Dr. Hirsch was largely in agreement. He believes that, for patients with a PD-L1 TPS of at least 50%, the standard of care “is practically pembrolizumab monotherapy, unless there are certain circumstances where you would add chemotherapy,” such as for patients with a high tumor volume, “where you want to see a very quick response.”
Dr. Hirsch pointed out, however, that currently most patients with high PD-L1–expressing tumors are given pembrolizumab in the first line, which begs the question as to what to give those who experience disease progression after immunotherapy.
“That is an open space,” he said. “There is a lot of studies going on in what we call the immunotherapy-refractory patients.
“We don’t have clear guidance for clinical practice yet,” he commented. He noted that there are several options: “Do you continue with chemotherapy? Do you continue with chemotherapy plus another immunotherapy? Do you switch to another immunotherapy?”
Commenting on Twitter, Stephen V. Liu, MD, director of thoracic oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, said the results were “very exciting.”
However, he wondered whether the results suggest that patients with high PD-L1 expression “may be able to stop” receiving pembrolizumab, whereas those with disease of lower expression “may need longer therapy.”
H. Jack West, MD, medical director of the thoracic oncology program, Swedish Cancer Institute, Seattle, said on Twitter that, to him, the “most impressive” aspect was the “new insight about patients stopping pembro after 2 years but still having two-thirds with sustained response.”
He added that he would “love to learn which patients can stop therapy and when, or whether we can do infrequent maintenance IO [immunotherapy].”
Nivolumab survival data
The data on nivolumab come from a pooled analysis of 5-year data on 854 patients from CheckMate 057 and CheckMate 017. The analysis was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology on Jan. 15, 2021.
Both of these trials compared nivolumab with docetaxel for patients with NSCLC who had experienced disease progression with platinum-based chemotherapy.
The pooled analysis showed that the 5-year overall survival rate was more than fivefold greater with nivolumab than with docetaxel, at 13.4% versus 2.6%.
Moreover, more than 80% of patients who had not experienced progression with the immunotherapy at 2 years were still alive at 5 years. The percentage rose to more than 90% among those who had not experienced progression at 3 years.
Lead author Julie R. Brahmer, MD, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues said the results “demonstrate that nivolumab can provide long-term survival benefit with durable responses and a tolerable safety profile in patients with previously treated, advanced NSCLC.
“Furthermore, some patients appear to maintain prolonged disease control even after stopping systemic therapy,” they noted.
Dr. Hirsch commented that, although the survival rates with nivolumab were slightly lower than reported with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-010, they could still be “within the range.” He added that “I wouldn’t conclude that pembrolizumab is better than nivolumab.”
Many factors may account for these differences, he suggested, including differences in the patient populations or simply differences in the numbers of patients included.
For him, the “main point” of the new data from both trials is that immunotherapy has shown “tremendous progress, compared to chemotherapy.”
KEYNOTE-010 was sponsored by Merck Sharp & Dohme. CheckMate 017 and CheckMate057 were sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Herbst has relationships with Jun Shi Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Merck, Pfizer, AbbVie, Biodesix, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Heat Biologics, Loxo, Nektar, NextCure, Novartis, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Shire, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Symphogen, Tesaro, Neon Therapeutics, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Armo Biosciences, Genmab, Halozyme, and Tocagen. Dr. Brahmer has relationships with Roche/Genentech, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Celgene, Syndax, Janssen Oncology, Merck, Amgen, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Incyte, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Revolution, and Roche/Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Longer-term survival with immunotherapy for patients with non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is once again being applauded by experts in the field.
This time, the data come from trials that tested immunotherapy in the second-line setting for patients who had experienced disease progression with platinum-based chemotherapy. The latest 5-year follow-up from two landmark trials, one with pembrolizumab, the other with nivolumab, show that the survival benefit can persist for years after treatment is stopped.
“These are unprecedented data,” Fred R. Hirsch, MD, PhD, executive director of the Center for Thoracic Oncology at the Tisch Cancer Institute, New York, said in an interview. He was not involved in either trial and was approached for comment.
Pembrolizumab survival data
The new longer-term data on pembrolizumab come from the KEYNOTE-010 trial, which included more than 1,000 patients with advanced NSCLC who had previously undergone treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy. The patients were randomly assigned to receive either pembrolizumab or docetaxel for 2 years.
This is the latest update on data from this trial, which has been described as “really extraordinary.”
The 5-year overall survival rates were more than doubled in the pembrolizumab groups, compared with the docetaxel group, reported Roy Herbst, MD, PhD, department of medical oncology, Yale Comprehensive Cancer Center, New Haven, Conn.. He was presenting the new data at the recent World Conference on Lung Cancer 2020.
Overall results for patients with programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) expression greater than 1% show that 15.6% of the pembrolizumab group were still alive at 5 years versus 6.5% of the docetaxel group.
The results were even better among patients who had high PD-L1 TPS expression (>50%): in this subgroup, 25% of the patients who received pembrolizumab were still alive versus 8.2% of those who received docetaxel.
In addition, at 5 years, 9.4% of patients who received pembrolizumab were disease free versus 0.7% of the patients who received docetaxel, Dr. Herbst reported.
Dr. Hirsch commented that the 5-year survival rate of 25% among patients with high PD-L1 expression who underwent treatment with pembrolizumab is “great progress in lung cancer treatment, there is no doubt about it.”
He noted that the results also show that “numerically,” it matters whether patients have low PD-L1 expression. “We know from first-line studies that pembrolizumab monotherapy is effective in high PD-L1–expressing tumors, so these data fit very well,” he said.
At the meeting, Dr. Herbst summarized his presentation on pembrolizumab for patients with NSCLC who had previously undergone treatment, saying that, “with 5 years of follow-up, we continue to see a clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival and PFS [progression-free survival].
“Pembrolizumab monotherapy is a standard of care in patients with immunotherapy-naive or previously treated PD-L1–positive advanced non–small cell lung cancer,” Herbst stated.
Dr. Hirsch was largely in agreement. He believes that, for patients with a PD-L1 TPS of at least 50%, the standard of care “is practically pembrolizumab monotherapy, unless there are certain circumstances where you would add chemotherapy,” such as for patients with a high tumor volume, “where you want to see a very quick response.”
Dr. Hirsch pointed out, however, that currently most patients with high PD-L1–expressing tumors are given pembrolizumab in the first line, which begs the question as to what to give those who experience disease progression after immunotherapy.
“That is an open space,” he said. “There is a lot of studies going on in what we call the immunotherapy-refractory patients.
“We don’t have clear guidance for clinical practice yet,” he commented. He noted that there are several options: “Do you continue with chemotherapy? Do you continue with chemotherapy plus another immunotherapy? Do you switch to another immunotherapy?”
Commenting on Twitter, Stephen V. Liu, MD, director of thoracic oncology at Georgetown University, Washington, said the results were “very exciting.”
However, he wondered whether the results suggest that patients with high PD-L1 expression “may be able to stop” receiving pembrolizumab, whereas those with disease of lower expression “may need longer therapy.”
H. Jack West, MD, medical director of the thoracic oncology program, Swedish Cancer Institute, Seattle, said on Twitter that, to him, the “most impressive” aspect was the “new insight about patients stopping pembro after 2 years but still having two-thirds with sustained response.”
He added that he would “love to learn which patients can stop therapy and when, or whether we can do infrequent maintenance IO [immunotherapy].”
Nivolumab survival data
The data on nivolumab come from a pooled analysis of 5-year data on 854 patients from CheckMate 057 and CheckMate 017. The analysis was published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology on Jan. 15, 2021.
Both of these trials compared nivolumab with docetaxel for patients with NSCLC who had experienced disease progression with platinum-based chemotherapy.
The pooled analysis showed that the 5-year overall survival rate was more than fivefold greater with nivolumab than with docetaxel, at 13.4% versus 2.6%.
Moreover, more than 80% of patients who had not experienced progression with the immunotherapy at 2 years were still alive at 5 years. The percentage rose to more than 90% among those who had not experienced progression at 3 years.
Lead author Julie R. Brahmer, MD, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues said the results “demonstrate that nivolumab can provide long-term survival benefit with durable responses and a tolerable safety profile in patients with previously treated, advanced NSCLC.
“Furthermore, some patients appear to maintain prolonged disease control even after stopping systemic therapy,” they noted.
Dr. Hirsch commented that, although the survival rates with nivolumab were slightly lower than reported with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-010, they could still be “within the range.” He added that “I wouldn’t conclude that pembrolizumab is better than nivolumab.”
Many factors may account for these differences, he suggested, including differences in the patient populations or simply differences in the numbers of patients included.
For him, the “main point” of the new data from both trials is that immunotherapy has shown “tremendous progress, compared to chemotherapy.”
KEYNOTE-010 was sponsored by Merck Sharp & Dohme. CheckMate 017 and CheckMate057 were sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Herbst has relationships with Jun Shi Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Genentech, Merck, Pfizer, AbbVie, Biodesix, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, EMD Serono, Heat Biologics, Loxo, Nektar, NextCure, Novartis, Sanofi, Seattle Genetics, Shire, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Symphogen, Tesaro, Neon Therapeutics, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Armo Biosciences, Genmab, Halozyme, and Tocagen. Dr. Brahmer has relationships with Roche/Genentech, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Lilly, Celgene, Syndax, Janssen Oncology, Merck, Amgen, Genentech, AstraZeneca, Incyte, Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Revolution, and Roche/Genentech.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vedolizumab looks safer than anti-TNF drugs in older adults with IBD
A large analysis of Medicare data from all 50 states suggests that vedolizumab may be just as effective as anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) agents in controlling inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in patients aged over 65 years, with fewer infectious disease hospitalizations.
The study was prompted by the fact that older adults are greatly underrepresented in clinical trials of approved IBD medications. There is a second peak in IBD diagnosis among people in their 50s and 60s, and IBD patients are living longer with more effective medications. So although a significant number of IBD patients are aged 65 years or older, that group encompasses less than 1% of adults in clinical trials, Bharati Kochar, MD, reported at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Therefore, we don’t know how well these medications work and how safe they are specifically in older adults,” said Dr. Kochar, a gastroenterologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The data largely support what had been known mechanistically about vedolizumab. “It suggests that both drugs work well enough to prevent [IBD-related] hospitalizations, but clearly there was a benefit toward the safer medication, Entyvio [vedolizumab], in the infection-related hospitalizations. That’s not the only readout in infections, but it is an important readout because infections that get hospitalized are the ones that predict mortality and disability,” said Matthew Ciorba, MD, who attended the session. Dr. Ciorba is director of the IBD Center at Washington University in St. Louis and was not involved in the study.
“I think this study is reassuring to clinicians. It provides important clinical data that support what we know about the mechanisms of vedolizumab. The safety data we predicted is borne out in this large and well-done study,” said Dr. Ciorba.
The researchers collected a 20% random sample from a 50-state Medicare claims database, including patients who were aged 65 years or older, who had two or more codes for Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, and had 18 months of continuous enrollment. It excluded Medicare Part C patients; those who used ustekinumab, natalizumab, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus during the look back and study period; and those with two or more codes for rheumatoid arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis during the study period.
Among those included, 480 patients were on vedolizumab, while 1,152 were on anti-TNF medications. The two groups were broadly similar in their characteristics: Twenty-nine percent of both groups took budesonide, although the anti-TNF group had a higher frequency use of systemic corticosteroids (68% vs. 57%), 5-ASA drugs (62% vs. 42%), and immunomodulators (32% vs. 28%).
There were no significant differences between the two groups with respect to frequency of IBD-related hospitalizations, IBD-related surgery, steroid prescription rate after induction, or all-cause hospitalization. However, infection-related hospitalizations were less frequent in the vedolizumab group (crude incidence, 0.03 vs. 0.05 per person-year; adjusted hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.86).
“I think it’s important to use your clinical judgment to treat the patient in front of you, and these data should simply help contextualize risk for older IBD patients newly initiating vedolizumab and anti-TNF agents,” said Dr. Kochar. However, recognizing the limitations of any retrospective study based on administrative data, she called for additional research. “There is a vast need for additional large and robust comparative effectiveness and safety studies in older adults of the rapidly proliferating arsenal of IBD medications,” Dr. Kochar concluded.
Dr. Kochar and Dr. Ciorba have no relevant financial disclosures.
A large analysis of Medicare data from all 50 states suggests that vedolizumab may be just as effective as anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) agents in controlling inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in patients aged over 65 years, with fewer infectious disease hospitalizations.
The study was prompted by the fact that older adults are greatly underrepresented in clinical trials of approved IBD medications. There is a second peak in IBD diagnosis among people in their 50s and 60s, and IBD patients are living longer with more effective medications. So although a significant number of IBD patients are aged 65 years or older, that group encompasses less than 1% of adults in clinical trials, Bharati Kochar, MD, reported at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Therefore, we don’t know how well these medications work and how safe they are specifically in older adults,” said Dr. Kochar, a gastroenterologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The data largely support what had been known mechanistically about vedolizumab. “It suggests that both drugs work well enough to prevent [IBD-related] hospitalizations, but clearly there was a benefit toward the safer medication, Entyvio [vedolizumab], in the infection-related hospitalizations. That’s not the only readout in infections, but it is an important readout because infections that get hospitalized are the ones that predict mortality and disability,” said Matthew Ciorba, MD, who attended the session. Dr. Ciorba is director of the IBD Center at Washington University in St. Louis and was not involved in the study.
“I think this study is reassuring to clinicians. It provides important clinical data that support what we know about the mechanisms of vedolizumab. The safety data we predicted is borne out in this large and well-done study,” said Dr. Ciorba.
The researchers collected a 20% random sample from a 50-state Medicare claims database, including patients who were aged 65 years or older, who had two or more codes for Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, and had 18 months of continuous enrollment. It excluded Medicare Part C patients; those who used ustekinumab, natalizumab, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus during the look back and study period; and those with two or more codes for rheumatoid arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis during the study period.
Among those included, 480 patients were on vedolizumab, while 1,152 were on anti-TNF medications. The two groups were broadly similar in their characteristics: Twenty-nine percent of both groups took budesonide, although the anti-TNF group had a higher frequency use of systemic corticosteroids (68% vs. 57%), 5-ASA drugs (62% vs. 42%), and immunomodulators (32% vs. 28%).
There were no significant differences between the two groups with respect to frequency of IBD-related hospitalizations, IBD-related surgery, steroid prescription rate after induction, or all-cause hospitalization. However, infection-related hospitalizations were less frequent in the vedolizumab group (crude incidence, 0.03 vs. 0.05 per person-year; adjusted hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.86).
“I think it’s important to use your clinical judgment to treat the patient in front of you, and these data should simply help contextualize risk for older IBD patients newly initiating vedolizumab and anti-TNF agents,” said Dr. Kochar. However, recognizing the limitations of any retrospective study based on administrative data, she called for additional research. “There is a vast need for additional large and robust comparative effectiveness and safety studies in older adults of the rapidly proliferating arsenal of IBD medications,” Dr. Kochar concluded.
Dr. Kochar and Dr. Ciorba have no relevant financial disclosures.
A large analysis of Medicare data from all 50 states suggests that vedolizumab may be just as effective as anti–tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) agents in controlling inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in patients aged over 65 years, with fewer infectious disease hospitalizations.
The study was prompted by the fact that older adults are greatly underrepresented in clinical trials of approved IBD medications. There is a second peak in IBD diagnosis among people in their 50s and 60s, and IBD patients are living longer with more effective medications. So although a significant number of IBD patients are aged 65 years or older, that group encompasses less than 1% of adults in clinical trials, Bharati Kochar, MD, reported at the annual congress of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association.
“Therefore, we don’t know how well these medications work and how safe they are specifically in older adults,” said Dr. Kochar, a gastroenterologist at Massachusetts General Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
The data largely support what had been known mechanistically about vedolizumab. “It suggests that both drugs work well enough to prevent [IBD-related] hospitalizations, but clearly there was a benefit toward the safer medication, Entyvio [vedolizumab], in the infection-related hospitalizations. That’s not the only readout in infections, but it is an important readout because infections that get hospitalized are the ones that predict mortality and disability,” said Matthew Ciorba, MD, who attended the session. Dr. Ciorba is director of the IBD Center at Washington University in St. Louis and was not involved in the study.
“I think this study is reassuring to clinicians. It provides important clinical data that support what we know about the mechanisms of vedolizumab. The safety data we predicted is borne out in this large and well-done study,” said Dr. Ciorba.
The researchers collected a 20% random sample from a 50-state Medicare claims database, including patients who were aged 65 years or older, who had two or more codes for Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, and had 18 months of continuous enrollment. It excluded Medicare Part C patients; those who used ustekinumab, natalizumab, cyclosporine, or tacrolimus during the look back and study period; and those with two or more codes for rheumatoid arthritis, plaque psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis during the study period.
Among those included, 480 patients were on vedolizumab, while 1,152 were on anti-TNF medications. The two groups were broadly similar in their characteristics: Twenty-nine percent of both groups took budesonide, although the anti-TNF group had a higher frequency use of systemic corticosteroids (68% vs. 57%), 5-ASA drugs (62% vs. 42%), and immunomodulators (32% vs. 28%).
There were no significant differences between the two groups with respect to frequency of IBD-related hospitalizations, IBD-related surgery, steroid prescription rate after induction, or all-cause hospitalization. However, infection-related hospitalizations were less frequent in the vedolizumab group (crude incidence, 0.03 vs. 0.05 per person-year; adjusted hazard ratio, 0.47; 95% confidence interval, 0.25-0.86).
“I think it’s important to use your clinical judgment to treat the patient in front of you, and these data should simply help contextualize risk for older IBD patients newly initiating vedolizumab and anti-TNF agents,” said Dr. Kochar. However, recognizing the limitations of any retrospective study based on administrative data, she called for additional research. “There is a vast need for additional large and robust comparative effectiveness and safety studies in older adults of the rapidly proliferating arsenal of IBD medications,” Dr. Kochar concluded.
Dr. Kochar and Dr. Ciorba have no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE CROHN’S & COLITIS CONGRESS
Women and ACS: Focus on typical symptoms to improve outcomes
There are some differences in how women relative to men report symptoms of an acute coronary syndrome (ACS), but they should not be permitted to get in the way of prompt diagnosis and treatment, according to an expert review at the virtual Going Back to the Heart of Cardiology meeting.
“We need to get away from the idea that symptoms of a myocardial infarction in women are atypical, because women are also having typical symptoms,” said Martha Gulati, MD, chief of cardiology at the University of Arizona, Phoenix.
Sexes share key symptoms, but not treatment
Although “women are more likely to report additional symptoms,” chest pain “is pretty much equal between men and women” presenting with an ACS, according to Dr. Gulati.
There are several studies that have shown this, including the Variation in Recovery: Role of Gender on Outcomes of Young AMI patients (VIRGO). In VIRGO, which looked at ACS symptom presentation in younger patients (ages 18-55 years), 87.0% of women versus 89.5% of men presented with chest pain defined as pain, pressure, tightness, or discomfort.
Even among those who recognize that more women die of cardiovascular disease (CVD) disease than any other cause, nothing seems to erase the bias that women in an ED are less likely than men to be having a heart attack. About 60 million women in the United States have CVD, so no threat imposes a higher toll in morbidity and mortality.
In comparison, there are only about 3.5 million women with breast cancer. Even though this is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in women, it is dwarfed by CVD, according to statistics cited by Dr. Gulati. Yet, the data show women get inferior care by guideline-based standards.
“After a myocardial infarction, women relative to men are less likely to get aspirin or beta-blockers within 24 hours, they are less likely to undergo any type of invasive procedure, and they are less likely to meet the door-to-balloon time or receive any reperfusion therapy,” Dr. Gulati said. After a CVD event, “the only thing women do better is to die.”
Additional symptoms may muddy the diagnostic waters
In the setting of ACS, the problem is not that women fail to report symptoms that should lead clinicians to consider CVD, but that they report additional symptoms. For the clinician less inclined to consider CVD in women, particularly younger women, there is a greater risk of going down the wrong diagnostic pathway.
In other words, women report symptoms consistent with CVD, “but it is a question of whether we are hearing it,” Dr. Gulati said.
In the VIRGO study, 61.9% of women versus 54.8% of men (P < .001) presented three or more symptoms in addition to chest pain, such as epigastric symptoms, discomfort in the arms or neck, or palpitations. Women were more likely than men to attribute the symptoms to stress or anxiety (20.9% vs. 11.8%; P < .001), while less likely to consider them a result of muscle pain (15.4% vs. 21.2%; P = .029).
There are other gender differences for ACS. For example, women are more likely than men to presented ischemia without obstruction, but Dr. Gulati emphasized that lack of obstruction is not a reason to dismiss the potential for an underlying CV cause.
‘Yentl syndrome’ persists
“Women should not need to present exactly like men to be taken seriously,” she said, describing the “Yentl syndrome,” which now has its own Wikipedia page. A cardiovascular version of this syndrome was first described 30 years ago. Based on a movie of a woman who cross dresses in order to be allowed to undertake Jewish studies, the term captures the societal failure to adapt care for women who do not present disease the same way that men do.
Overall, inadequate urgency to pursue potential symptoms of ACS in women is just another manifestation of the “bikini approach to women’s health,” according to Dr. Gulati. This describes the focus on the breast and reproductive system to the exclusion or other organs and anatomy. Dr. Gulati speculated that this might be the reason that clinicians have failed to apply ACS guidelines to women with the same rigor that they apply to men.
This is hardly a new issue. Calls for improving cardiovascular care in women have been increasing in volume for more than past 20 years, but the issue has proven persistent, according to Dr. Gulati. As an example, she noted that the same types of gaps in care and in outcome reported in a 2008 registry study had not much changed in an article published 8 years later.
The solution is not complex, according to Dr. Gulati. In the ED, guideline-directed diagnostic tests should be offered to any man or woman, including younger women, who present with chest pain, ignoring gender bias that threatens misinterpretation of patient history and symptoms. Once CVD is diagnosed as promptly in women as it is in men, guideline-directed intervention would be expected to reduce the gender gap in outcomes.
“By applying standardized protocols, it will help us to the same for women as we do for men,” Dr. Gulati said.
The meeting was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
There are some differences in how women relative to men report symptoms of an acute coronary syndrome (ACS), but they should not be permitted to get in the way of prompt diagnosis and treatment, according to an expert review at the virtual Going Back to the Heart of Cardiology meeting.
“We need to get away from the idea that symptoms of a myocardial infarction in women are atypical, because women are also having typical symptoms,” said Martha Gulati, MD, chief of cardiology at the University of Arizona, Phoenix.
Sexes share key symptoms, but not treatment
Although “women are more likely to report additional symptoms,” chest pain “is pretty much equal between men and women” presenting with an ACS, according to Dr. Gulati.
There are several studies that have shown this, including the Variation in Recovery: Role of Gender on Outcomes of Young AMI patients (VIRGO). In VIRGO, which looked at ACS symptom presentation in younger patients (ages 18-55 years), 87.0% of women versus 89.5% of men presented with chest pain defined as pain, pressure, tightness, or discomfort.
Even among those who recognize that more women die of cardiovascular disease (CVD) disease than any other cause, nothing seems to erase the bias that women in an ED are less likely than men to be having a heart attack. About 60 million women in the United States have CVD, so no threat imposes a higher toll in morbidity and mortality.
In comparison, there are only about 3.5 million women with breast cancer. Even though this is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in women, it is dwarfed by CVD, according to statistics cited by Dr. Gulati. Yet, the data show women get inferior care by guideline-based standards.
“After a myocardial infarction, women relative to men are less likely to get aspirin or beta-blockers within 24 hours, they are less likely to undergo any type of invasive procedure, and they are less likely to meet the door-to-balloon time or receive any reperfusion therapy,” Dr. Gulati said. After a CVD event, “the only thing women do better is to die.”
Additional symptoms may muddy the diagnostic waters
In the setting of ACS, the problem is not that women fail to report symptoms that should lead clinicians to consider CVD, but that they report additional symptoms. For the clinician less inclined to consider CVD in women, particularly younger women, there is a greater risk of going down the wrong diagnostic pathway.
In other words, women report symptoms consistent with CVD, “but it is a question of whether we are hearing it,” Dr. Gulati said.
In the VIRGO study, 61.9% of women versus 54.8% of men (P < .001) presented three or more symptoms in addition to chest pain, such as epigastric symptoms, discomfort in the arms or neck, or palpitations. Women were more likely than men to attribute the symptoms to stress or anxiety (20.9% vs. 11.8%; P < .001), while less likely to consider them a result of muscle pain (15.4% vs. 21.2%; P = .029).
There are other gender differences for ACS. For example, women are more likely than men to presented ischemia without obstruction, but Dr. Gulati emphasized that lack of obstruction is not a reason to dismiss the potential for an underlying CV cause.
‘Yentl syndrome’ persists
“Women should not need to present exactly like men to be taken seriously,” she said, describing the “Yentl syndrome,” which now has its own Wikipedia page. A cardiovascular version of this syndrome was first described 30 years ago. Based on a movie of a woman who cross dresses in order to be allowed to undertake Jewish studies, the term captures the societal failure to adapt care for women who do not present disease the same way that men do.
Overall, inadequate urgency to pursue potential symptoms of ACS in women is just another manifestation of the “bikini approach to women’s health,” according to Dr. Gulati. This describes the focus on the breast and reproductive system to the exclusion or other organs and anatomy. Dr. Gulati speculated that this might be the reason that clinicians have failed to apply ACS guidelines to women with the same rigor that they apply to men.
This is hardly a new issue. Calls for improving cardiovascular care in women have been increasing in volume for more than past 20 years, but the issue has proven persistent, according to Dr. Gulati. As an example, she noted that the same types of gaps in care and in outcome reported in a 2008 registry study had not much changed in an article published 8 years later.
The solution is not complex, according to Dr. Gulati. In the ED, guideline-directed diagnostic tests should be offered to any man or woman, including younger women, who present with chest pain, ignoring gender bias that threatens misinterpretation of patient history and symptoms. Once CVD is diagnosed as promptly in women as it is in men, guideline-directed intervention would be expected to reduce the gender gap in outcomes.
“By applying standardized protocols, it will help us to the same for women as we do for men,” Dr. Gulati said.
The meeting was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
There are some differences in how women relative to men report symptoms of an acute coronary syndrome (ACS), but they should not be permitted to get in the way of prompt diagnosis and treatment, according to an expert review at the virtual Going Back to the Heart of Cardiology meeting.
“We need to get away from the idea that symptoms of a myocardial infarction in women are atypical, because women are also having typical symptoms,” said Martha Gulati, MD, chief of cardiology at the University of Arizona, Phoenix.
Sexes share key symptoms, but not treatment
Although “women are more likely to report additional symptoms,” chest pain “is pretty much equal between men and women” presenting with an ACS, according to Dr. Gulati.
There are several studies that have shown this, including the Variation in Recovery: Role of Gender on Outcomes of Young AMI patients (VIRGO). In VIRGO, which looked at ACS symptom presentation in younger patients (ages 18-55 years), 87.0% of women versus 89.5% of men presented with chest pain defined as pain, pressure, tightness, or discomfort.
Even among those who recognize that more women die of cardiovascular disease (CVD) disease than any other cause, nothing seems to erase the bias that women in an ED are less likely than men to be having a heart attack. About 60 million women in the United States have CVD, so no threat imposes a higher toll in morbidity and mortality.
In comparison, there are only about 3.5 million women with breast cancer. Even though this is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in women, it is dwarfed by CVD, according to statistics cited by Dr. Gulati. Yet, the data show women get inferior care by guideline-based standards.
“After a myocardial infarction, women relative to men are less likely to get aspirin or beta-blockers within 24 hours, they are less likely to undergo any type of invasive procedure, and they are less likely to meet the door-to-balloon time or receive any reperfusion therapy,” Dr. Gulati said. After a CVD event, “the only thing women do better is to die.”
Additional symptoms may muddy the diagnostic waters
In the setting of ACS, the problem is not that women fail to report symptoms that should lead clinicians to consider CVD, but that they report additional symptoms. For the clinician less inclined to consider CVD in women, particularly younger women, there is a greater risk of going down the wrong diagnostic pathway.
In other words, women report symptoms consistent with CVD, “but it is a question of whether we are hearing it,” Dr. Gulati said.
In the VIRGO study, 61.9% of women versus 54.8% of men (P < .001) presented three or more symptoms in addition to chest pain, such as epigastric symptoms, discomfort in the arms or neck, or palpitations. Women were more likely than men to attribute the symptoms to stress or anxiety (20.9% vs. 11.8%; P < .001), while less likely to consider them a result of muscle pain (15.4% vs. 21.2%; P = .029).
There are other gender differences for ACS. For example, women are more likely than men to presented ischemia without obstruction, but Dr. Gulati emphasized that lack of obstruction is not a reason to dismiss the potential for an underlying CV cause.
‘Yentl syndrome’ persists
“Women should not need to present exactly like men to be taken seriously,” she said, describing the “Yentl syndrome,” which now has its own Wikipedia page. A cardiovascular version of this syndrome was first described 30 years ago. Based on a movie of a woman who cross dresses in order to be allowed to undertake Jewish studies, the term captures the societal failure to adapt care for women who do not present disease the same way that men do.
Overall, inadequate urgency to pursue potential symptoms of ACS in women is just another manifestation of the “bikini approach to women’s health,” according to Dr. Gulati. This describes the focus on the breast and reproductive system to the exclusion or other organs and anatomy. Dr. Gulati speculated that this might be the reason that clinicians have failed to apply ACS guidelines to women with the same rigor that they apply to men.
This is hardly a new issue. Calls for improving cardiovascular care in women have been increasing in volume for more than past 20 years, but the issue has proven persistent, according to Dr. Gulati. As an example, she noted that the same types of gaps in care and in outcome reported in a 2008 registry study had not much changed in an article published 8 years later.
The solution is not complex, according to Dr. Gulati. In the ED, guideline-directed diagnostic tests should be offered to any man or woman, including younger women, who present with chest pain, ignoring gender bias that threatens misinterpretation of patient history and symptoms. Once CVD is diagnosed as promptly in women as it is in men, guideline-directed intervention would be expected to reduce the gender gap in outcomes.
“By applying standardized protocols, it will help us to the same for women as we do for men,” Dr. Gulati said.
The meeting was sponsored by MedscapeLive. MedscapeLive and this news organization are owned by the same parent company.
FROM GOING BACK TO THE HEART OF CARDIOLOGY
Combo disappoints in metastatic, castration-resistant prostate cancer
In a phase 1/2 study, adding saracatinib to docetaxel increased toxicity without improving progression-free or overall survival.
“Although we could safely combine the Src kinase inhibitor saracatinib with docetaxel, it did not show any improvement in outcomes, when compared with docetaxel plus placebo. We therefore do not recommend proceeding to a phase 3 trial,” said investigator Robert J. Jones, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Cancer Sciences at the University of Glasgow, Scotland.
Dr. Jones presented the phase 1/2 trial results at the 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium (Abstract 107).
He explained that saracatinib targets Src family members, and Src activity is increased during the acquisition of castration resistance and during taxane resistance. Dr. Jones and colleagues therefore theorized that saracatinib could be beneficial for patients with mCRPC.
The team tested their theory with the phase 1/2 trial, enrolling patients with mCRPC who had not previously received taxanes or radionucleotides. Dr. Jones reported results for 10 patients in the phase 1 portion of the trial and 140 patients in the phase 2 portion.
In phase 1, patients received saracatinib at 50 mg, 125 mg, or 175 mg daily plus docetaxel at 75 mg/m2.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities or pharmacokinetic interactions in these patients, so the phase 2 dose of saracatinib was 175 mg daily.
In phase 2, patients were randomized to receive saracatinib plus docetaxel or placebo plus docetaxel.
Results: Safety and efficacy
“In terms of efficacy, the trial failed to meet its primary endpoint of demonstrating an improvement in progression-free survival. Indeed, there was a trend toward an improvement in progression-free survival for patients receiving placebo,” Dr. Jones said. “Similarly, in this key secondary endpoint of overall survival, there was no benefit from the addition of saracatinib. And again, there was a trend toward an improved survival in patients receiving placebo.”
The median progression-free survival was 19 weeks with saracatinib and 29 weeks with placebo (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.348).
The median overall survival was 62 weeks with saracatinib and 83 weeks with placebo (adjusted HR, 1.422).
Furthermore, there were no significant differences between the treatment arms for two other efficacy endpoints – maximum absolute change in prostate-specific antigen levels and absolute change in circulating tumor cell count from baseline to cycle three.
However, grade 3 or higher adverse events were more common in the saracatinib arm than in the placebo arm – 59% (41/69) and 41% (29/71), respectively.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the saracatinib and placebo arms, respectively) were neutropenia (25% vs. 8%), diarrhea (12% vs. 4%), and fatigue (6% vs. 4%).
This research was funded by the UK National Health Service and Cancer Research UK. Dr. Jones disclosed relationships with Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a number of other companies.
In a phase 1/2 study, adding saracatinib to docetaxel increased toxicity without improving progression-free or overall survival.
“Although we could safely combine the Src kinase inhibitor saracatinib with docetaxel, it did not show any improvement in outcomes, when compared with docetaxel plus placebo. We therefore do not recommend proceeding to a phase 3 trial,” said investigator Robert J. Jones, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Cancer Sciences at the University of Glasgow, Scotland.
Dr. Jones presented the phase 1/2 trial results at the 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium (Abstract 107).
He explained that saracatinib targets Src family members, and Src activity is increased during the acquisition of castration resistance and during taxane resistance. Dr. Jones and colleagues therefore theorized that saracatinib could be beneficial for patients with mCRPC.
The team tested their theory with the phase 1/2 trial, enrolling patients with mCRPC who had not previously received taxanes or radionucleotides. Dr. Jones reported results for 10 patients in the phase 1 portion of the trial and 140 patients in the phase 2 portion.
In phase 1, patients received saracatinib at 50 mg, 125 mg, or 175 mg daily plus docetaxel at 75 mg/m2.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities or pharmacokinetic interactions in these patients, so the phase 2 dose of saracatinib was 175 mg daily.
In phase 2, patients were randomized to receive saracatinib plus docetaxel or placebo plus docetaxel.
Results: Safety and efficacy
“In terms of efficacy, the trial failed to meet its primary endpoint of demonstrating an improvement in progression-free survival. Indeed, there was a trend toward an improvement in progression-free survival for patients receiving placebo,” Dr. Jones said. “Similarly, in this key secondary endpoint of overall survival, there was no benefit from the addition of saracatinib. And again, there was a trend toward an improved survival in patients receiving placebo.”
The median progression-free survival was 19 weeks with saracatinib and 29 weeks with placebo (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.348).
The median overall survival was 62 weeks with saracatinib and 83 weeks with placebo (adjusted HR, 1.422).
Furthermore, there were no significant differences between the treatment arms for two other efficacy endpoints – maximum absolute change in prostate-specific antigen levels and absolute change in circulating tumor cell count from baseline to cycle three.
However, grade 3 or higher adverse events were more common in the saracatinib arm than in the placebo arm – 59% (41/69) and 41% (29/71), respectively.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the saracatinib and placebo arms, respectively) were neutropenia (25% vs. 8%), diarrhea (12% vs. 4%), and fatigue (6% vs. 4%).
This research was funded by the UK National Health Service and Cancer Research UK. Dr. Jones disclosed relationships with Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a number of other companies.
In a phase 1/2 study, adding saracatinib to docetaxel increased toxicity without improving progression-free or overall survival.
“Although we could safely combine the Src kinase inhibitor saracatinib with docetaxel, it did not show any improvement in outcomes, when compared with docetaxel plus placebo. We therefore do not recommend proceeding to a phase 3 trial,” said investigator Robert J. Jones, MD, PhD, of the Institute of Cancer Sciences at the University of Glasgow, Scotland.
Dr. Jones presented the phase 1/2 trial results at the 2021 Genitourinary Cancers Symposium (Abstract 107).
He explained that saracatinib targets Src family members, and Src activity is increased during the acquisition of castration resistance and during taxane resistance. Dr. Jones and colleagues therefore theorized that saracatinib could be beneficial for patients with mCRPC.
The team tested their theory with the phase 1/2 trial, enrolling patients with mCRPC who had not previously received taxanes or radionucleotides. Dr. Jones reported results for 10 patients in the phase 1 portion of the trial and 140 patients in the phase 2 portion.
In phase 1, patients received saracatinib at 50 mg, 125 mg, or 175 mg daily plus docetaxel at 75 mg/m2.
There were no dose-limiting toxicities or pharmacokinetic interactions in these patients, so the phase 2 dose of saracatinib was 175 mg daily.
In phase 2, patients were randomized to receive saracatinib plus docetaxel or placebo plus docetaxel.
Results: Safety and efficacy
“In terms of efficacy, the trial failed to meet its primary endpoint of demonstrating an improvement in progression-free survival. Indeed, there was a trend toward an improvement in progression-free survival for patients receiving placebo,” Dr. Jones said. “Similarly, in this key secondary endpoint of overall survival, there was no benefit from the addition of saracatinib. And again, there was a trend toward an improved survival in patients receiving placebo.”
The median progression-free survival was 19 weeks with saracatinib and 29 weeks with placebo (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.348).
The median overall survival was 62 weeks with saracatinib and 83 weeks with placebo (adjusted HR, 1.422).
Furthermore, there were no significant differences between the treatment arms for two other efficacy endpoints – maximum absolute change in prostate-specific antigen levels and absolute change in circulating tumor cell count from baseline to cycle three.
However, grade 3 or higher adverse events were more common in the saracatinib arm than in the placebo arm – 59% (41/69) and 41% (29/71), respectively.
The most common grade 3 or higher adverse events (in the saracatinib and placebo arms, respectively) were neutropenia (25% vs. 8%), diarrhea (12% vs. 4%), and fatigue (6% vs. 4%).
This research was funded by the UK National Health Service and Cancer Research UK. Dr. Jones disclosed relationships with Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a number of other companies.
FROM GUCS 2021
Burnout rates in ICU staff fueled by shortages, overtime
Health care professionals working in critical care settings have been overburdened because of the plethora of COVID-19 cases, which has led to symptoms of burnout in both physicians and nurses, findings from a new study show.
“Overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout,” said lead study author Niek Kok, MSc, of IQ healthcare, Radboud University Medical Center, Radboud Institute for Health Sciences, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. “All ICU professionals are at the risk of this, and in our study, the incidence of physicians experiencing burnout was significantly higher than that of nurses in June 2020.”
This burnout can be explained by conditions caused by the pandemic, he noted, such as the scarcity of staff and resources and having to work with colleagues who were not qualified to work in critical care but who were there out of necessity.
Mr. Kok presented the findings of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Burnout highest among critical care physicians
The ICU can be a stressful environment for both patients and health care personnel, and burnout is not uncommon among ICU clinicians. However, COVID-19 has amplified the degree of burnout being experienced by clinicians working in this setting. Critical care physicians now top the list of physicians experiencing burnout, at 51%, up from 44% last year, according to the Medscape report ‘Death by 1000 Thousand Cuts’: Physician Burnout and Suicide Report 2021.
The Medscape Nurse Career Satisfaction Report 2020, while not restricted to those working in critical care, also reported higher rates of burnout, compared with the prepandemic period. The percentage of nurses reporting being “very burned out” prior to the pandemic was 4%. Six months into the pandemic, that percentage soared to 18%.
In this study, Mr. Kok and colleagues examined the prevalence and incidence of burnout symptoms and moral distress in health care professionals working in the ICU, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“When the COVID-19 pandemic surfaced in the Netherlands, the health care professionals in our hospitals were motivated to do everything they could to provide the best care possible,” said Mr. Kok. “Many of the ICU professionals immediately realized that they would have to work longer hours.”
However, the health care professionals that he spoke with did have mixed feelings. Some were afraid of being infected with the virus, while others said that “it was very interesting times for them and that gave them extra motivation to do the work.
“Some physicians [and] the WHO warned that COVID-19 is not going to weathered by a heroic sprint – it is an arduous marathon that is going to go hand in hand with burnout symptoms,” Mr. Kok added. “It will eat away at our qualified ICU staff.”
Before and after data on burnout
It was widely believed that the COVID-19 pandemic would increase burnout symptoms, as had been demonstrated in studies of previous pandemics. However, Mr. Kok emphasized that there are no before and after measurements that transcend cross-sectional designs.
“The claim [has been] that it increases burnout – but there are no assessments of how it progresses in ICU professionals through time,” he said. “So what we really need is a comparison [of] before and after the pandemic.”
It is quite difficult to obtain this type of information because disruptive events like the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be predicted, he said. Thus, it is challenging to get a baseline measurement. But Mr. Kok pointed out that the study has both “before and after” measurements.
“By coincidence really, we had baseline data to measure the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and had information that was collected before the pandemic,” he said.
In January 2020, a study began looking at the effects of ethics meetings on moral distress in ICU professionals. Data had been collected on moral distress and burnout on ICU professionals in December 2019. The first COVID-19 cases appeared in the Netherlands in February 2020.
A follow-up study was then conducted in May and June 2020, several months into the pandemic.
The longitudinal open cohort study included all ICU personnel who were working in five units within a single university medical center, plus another adult ICU that was based in a separate teaching hospital.
A total of 352 health care professionals responded to a baseline survey in October through December 2019, and then 233 responded to a follow-up survey sent in May and June 2020. The authors measured burnout symptoms and moral distress with the Maslach Burnout Inventory and the Moral Distress Scale, respectively.
Findings
The overall prevalence of burnout symptoms was 23.0% prior to the pandemic, and that jumped to 36.1% at post-peak time. Higher rates of burnout were reported by nurses (38.0%) than physicians (28.6%).
However, the incidence rate of new burnout cases was higher among physicians, compared with nurses (26.7% vs 21.9%). Not surprisingly, a higher prevalence of burnout symptoms was observed in the post-peak period for all clinicians (odds ratio, 1.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.53), and was higher for nurses (odds ratio, 1.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-3.04), for those working overtime (OR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.48-3.02), and for personnel who directly engaged in patient care (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.35-2.60).
Physicians in general were much more likely to develop burnout symptoms related to the pandemic, compared with nurses (OR, 3.56; 95% CI, 1.06-12.21).
When looking at findings on moral distress, Kok pointed out that it often arises in situations when the health care professional knows the right thing to do but is prevented from doing so. “Morally distressful situations all rose from December to June,” said Mr. Kok. “Scarcity was the most distressing. The other was where colleagues were perceived to be less skilled, and this had to do with the recruitment of people from outside of the ICU to provide care.”
Moral distress from scarcity and unskilled colleagues were both significantly related to burnout, he noted.
In the final model, working in a COVID-19 unit, stress from scarcity of resources and people, stress from unskilled colleagues, and stress from unsafe conditions were all related to burnout. “The stress of physicians was significantly higher,” said Kok. “Even though nurses had higher baseline burnout, it became less pronounced in June 2020. This indicates that burnout was significantly higher in physicians.”
Thus, Mr. Kok and colleagues concluded that overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout, and all ICU workers are at risk.
Burnout rates higher in physicians
Weighing in on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that the differences observed between physicians and nurses may have to do with the fact that “nurses have been smoldering all along and experiencing higher rates of burnout.
“They may have adapted better to the pandemic conditions, since they are more used to working overtime and short staffed, and spending far more time at the bedside,” he said. “Because of the volume of patients, physicians may be spending more hours doing patient care and are experiencing more burnout.”
For physicians, this may be a more significant change in the workload, as well as the complexity of the situation because of the pandemic. “Many things layer into it, such as [the fact] that there are no families present to give patients support, the complexity of care of these patients, and things like lack of PPE,” Dr. Martin said.
The study did not differentiate among physician groups, so it is unclear if the affected physicians were residents, fellows, or more senior staff. “Residents are often quite busy already, and don’t usually have the capacity to add more to their schedules, and maybe attendings were having to spend more time doing patient care,” Dr. Martin said. “In the United States, at least some personnel were restricted from working with COVID-19 patients. Medical students were removed in many places as well as nonessential staff, so that may have also added to their burnout.”
The study was conducted in the Netherlands, so there may be differences in the work environment, responsibilities of nurses vs. physicians, staffing, and so on. “But it still shows that burnout is very real among doctors and nurses working in the ICU in pandemic conditions,” he said.
Health care professionals working in critical care settings have been overburdened because of the plethora of COVID-19 cases, which has led to symptoms of burnout in both physicians and nurses, findings from a new study show.
“Overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout,” said lead study author Niek Kok, MSc, of IQ healthcare, Radboud University Medical Center, Radboud Institute for Health Sciences, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. “All ICU professionals are at the risk of this, and in our study, the incidence of physicians experiencing burnout was significantly higher than that of nurses in June 2020.”
This burnout can be explained by conditions caused by the pandemic, he noted, such as the scarcity of staff and resources and having to work with colleagues who were not qualified to work in critical care but who were there out of necessity.
Mr. Kok presented the findings of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Burnout highest among critical care physicians
The ICU can be a stressful environment for both patients and health care personnel, and burnout is not uncommon among ICU clinicians. However, COVID-19 has amplified the degree of burnout being experienced by clinicians working in this setting. Critical care physicians now top the list of physicians experiencing burnout, at 51%, up from 44% last year, according to the Medscape report ‘Death by 1000 Thousand Cuts’: Physician Burnout and Suicide Report 2021.
The Medscape Nurse Career Satisfaction Report 2020, while not restricted to those working in critical care, also reported higher rates of burnout, compared with the prepandemic period. The percentage of nurses reporting being “very burned out” prior to the pandemic was 4%. Six months into the pandemic, that percentage soared to 18%.
In this study, Mr. Kok and colleagues examined the prevalence and incidence of burnout symptoms and moral distress in health care professionals working in the ICU, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“When the COVID-19 pandemic surfaced in the Netherlands, the health care professionals in our hospitals were motivated to do everything they could to provide the best care possible,” said Mr. Kok. “Many of the ICU professionals immediately realized that they would have to work longer hours.”
However, the health care professionals that he spoke with did have mixed feelings. Some were afraid of being infected with the virus, while others said that “it was very interesting times for them and that gave them extra motivation to do the work.
“Some physicians [and] the WHO warned that COVID-19 is not going to weathered by a heroic sprint – it is an arduous marathon that is going to go hand in hand with burnout symptoms,” Mr. Kok added. “It will eat away at our qualified ICU staff.”
Before and after data on burnout
It was widely believed that the COVID-19 pandemic would increase burnout symptoms, as had been demonstrated in studies of previous pandemics. However, Mr. Kok emphasized that there are no before and after measurements that transcend cross-sectional designs.
“The claim [has been] that it increases burnout – but there are no assessments of how it progresses in ICU professionals through time,” he said. “So what we really need is a comparison [of] before and after the pandemic.”
It is quite difficult to obtain this type of information because disruptive events like the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be predicted, he said. Thus, it is challenging to get a baseline measurement. But Mr. Kok pointed out that the study has both “before and after” measurements.
“By coincidence really, we had baseline data to measure the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and had information that was collected before the pandemic,” he said.
In January 2020, a study began looking at the effects of ethics meetings on moral distress in ICU professionals. Data had been collected on moral distress and burnout on ICU professionals in December 2019. The first COVID-19 cases appeared in the Netherlands in February 2020.
A follow-up study was then conducted in May and June 2020, several months into the pandemic.
The longitudinal open cohort study included all ICU personnel who were working in five units within a single university medical center, plus another adult ICU that was based in a separate teaching hospital.
A total of 352 health care professionals responded to a baseline survey in October through December 2019, and then 233 responded to a follow-up survey sent in May and June 2020. The authors measured burnout symptoms and moral distress with the Maslach Burnout Inventory and the Moral Distress Scale, respectively.
Findings
The overall prevalence of burnout symptoms was 23.0% prior to the pandemic, and that jumped to 36.1% at post-peak time. Higher rates of burnout were reported by nurses (38.0%) than physicians (28.6%).
However, the incidence rate of new burnout cases was higher among physicians, compared with nurses (26.7% vs 21.9%). Not surprisingly, a higher prevalence of burnout symptoms was observed in the post-peak period for all clinicians (odds ratio, 1.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.53), and was higher for nurses (odds ratio, 1.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-3.04), for those working overtime (OR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.48-3.02), and for personnel who directly engaged in patient care (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.35-2.60).
Physicians in general were much more likely to develop burnout symptoms related to the pandemic, compared with nurses (OR, 3.56; 95% CI, 1.06-12.21).
When looking at findings on moral distress, Kok pointed out that it often arises in situations when the health care professional knows the right thing to do but is prevented from doing so. “Morally distressful situations all rose from December to June,” said Mr. Kok. “Scarcity was the most distressing. The other was where colleagues were perceived to be less skilled, and this had to do with the recruitment of people from outside of the ICU to provide care.”
Moral distress from scarcity and unskilled colleagues were both significantly related to burnout, he noted.
In the final model, working in a COVID-19 unit, stress from scarcity of resources and people, stress from unskilled colleagues, and stress from unsafe conditions were all related to burnout. “The stress of physicians was significantly higher,” said Kok. “Even though nurses had higher baseline burnout, it became less pronounced in June 2020. This indicates that burnout was significantly higher in physicians.”
Thus, Mr. Kok and colleagues concluded that overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout, and all ICU workers are at risk.
Burnout rates higher in physicians
Weighing in on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that the differences observed between physicians and nurses may have to do with the fact that “nurses have been smoldering all along and experiencing higher rates of burnout.
“They may have adapted better to the pandemic conditions, since they are more used to working overtime and short staffed, and spending far more time at the bedside,” he said. “Because of the volume of patients, physicians may be spending more hours doing patient care and are experiencing more burnout.”
For physicians, this may be a more significant change in the workload, as well as the complexity of the situation because of the pandemic. “Many things layer into it, such as [the fact] that there are no families present to give patients support, the complexity of care of these patients, and things like lack of PPE,” Dr. Martin said.
The study did not differentiate among physician groups, so it is unclear if the affected physicians were residents, fellows, or more senior staff. “Residents are often quite busy already, and don’t usually have the capacity to add more to their schedules, and maybe attendings were having to spend more time doing patient care,” Dr. Martin said. “In the United States, at least some personnel were restricted from working with COVID-19 patients. Medical students were removed in many places as well as nonessential staff, so that may have also added to their burnout.”
The study was conducted in the Netherlands, so there may be differences in the work environment, responsibilities of nurses vs. physicians, staffing, and so on. “But it still shows that burnout is very real among doctors and nurses working in the ICU in pandemic conditions,” he said.
Health care professionals working in critical care settings have been overburdened because of the plethora of COVID-19 cases, which has led to symptoms of burnout in both physicians and nurses, findings from a new study show.
“Overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout,” said lead study author Niek Kok, MSc, of IQ healthcare, Radboud University Medical Center, Radboud Institute for Health Sciences, Nijmegen, the Netherlands. “All ICU professionals are at the risk of this, and in our study, the incidence of physicians experiencing burnout was significantly higher than that of nurses in June 2020.”
This burnout can be explained by conditions caused by the pandemic, he noted, such as the scarcity of staff and resources and having to work with colleagues who were not qualified to work in critical care but who were there out of necessity.
Mr. Kok presented the findings of the study at the Critical Care Congress sponsored by the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Burnout highest among critical care physicians
The ICU can be a stressful environment for both patients and health care personnel, and burnout is not uncommon among ICU clinicians. However, COVID-19 has amplified the degree of burnout being experienced by clinicians working in this setting. Critical care physicians now top the list of physicians experiencing burnout, at 51%, up from 44% last year, according to the Medscape report ‘Death by 1000 Thousand Cuts’: Physician Burnout and Suicide Report 2021.
The Medscape Nurse Career Satisfaction Report 2020, while not restricted to those working in critical care, also reported higher rates of burnout, compared with the prepandemic period. The percentage of nurses reporting being “very burned out” prior to the pandemic was 4%. Six months into the pandemic, that percentage soared to 18%.
In this study, Mr. Kok and colleagues examined the prevalence and incidence of burnout symptoms and moral distress in health care professionals working in the ICU, both before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
“When the COVID-19 pandemic surfaced in the Netherlands, the health care professionals in our hospitals were motivated to do everything they could to provide the best care possible,” said Mr. Kok. “Many of the ICU professionals immediately realized that they would have to work longer hours.”
However, the health care professionals that he spoke with did have mixed feelings. Some were afraid of being infected with the virus, while others said that “it was very interesting times for them and that gave them extra motivation to do the work.
“Some physicians [and] the WHO warned that COVID-19 is not going to weathered by a heroic sprint – it is an arduous marathon that is going to go hand in hand with burnout symptoms,” Mr. Kok added. “It will eat away at our qualified ICU staff.”
Before and after data on burnout
It was widely believed that the COVID-19 pandemic would increase burnout symptoms, as had been demonstrated in studies of previous pandemics. However, Mr. Kok emphasized that there are no before and after measurements that transcend cross-sectional designs.
“The claim [has been] that it increases burnout – but there are no assessments of how it progresses in ICU professionals through time,” he said. “So what we really need is a comparison [of] before and after the pandemic.”
It is quite difficult to obtain this type of information because disruptive events like the COVID-19 pandemic cannot be predicted, he said. Thus, it is challenging to get a baseline measurement. But Mr. Kok pointed out that the study has both “before and after” measurements.
“By coincidence really, we had baseline data to measure the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and had information that was collected before the pandemic,” he said.
In January 2020, a study began looking at the effects of ethics meetings on moral distress in ICU professionals. Data had been collected on moral distress and burnout on ICU professionals in December 2019. The first COVID-19 cases appeared in the Netherlands in February 2020.
A follow-up study was then conducted in May and June 2020, several months into the pandemic.
The longitudinal open cohort study included all ICU personnel who were working in five units within a single university medical center, plus another adult ICU that was based in a separate teaching hospital.
A total of 352 health care professionals responded to a baseline survey in October through December 2019, and then 233 responded to a follow-up survey sent in May and June 2020. The authors measured burnout symptoms and moral distress with the Maslach Burnout Inventory and the Moral Distress Scale, respectively.
Findings
The overall prevalence of burnout symptoms was 23.0% prior to the pandemic, and that jumped to 36.1% at post-peak time. Higher rates of burnout were reported by nurses (38.0%) than physicians (28.6%).
However, the incidence rate of new burnout cases was higher among physicians, compared with nurses (26.7% vs 21.9%). Not surprisingly, a higher prevalence of burnout symptoms was observed in the post-peak period for all clinicians (odds ratio, 1.83; 95% confidence interval, 1.32-2.53), and was higher for nurses (odds ratio, 1.77; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-3.04), for those working overtime (OR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.48-3.02), and for personnel who directly engaged in patient care (OR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.35-2.60).
Physicians in general were much more likely to develop burnout symptoms related to the pandemic, compared with nurses (OR, 3.56; 95% CI, 1.06-12.21).
When looking at findings on moral distress, Kok pointed out that it often arises in situations when the health care professional knows the right thing to do but is prevented from doing so. “Morally distressful situations all rose from December to June,” said Mr. Kok. “Scarcity was the most distressing. The other was where colleagues were perceived to be less skilled, and this had to do with the recruitment of people from outside of the ICU to provide care.”
Moral distress from scarcity and unskilled colleagues were both significantly related to burnout, he noted.
In the final model, working in a COVID-19 unit, stress from scarcity of resources and people, stress from unskilled colleagues, and stress from unsafe conditions were all related to burnout. “The stress of physicians was significantly higher,” said Kok. “Even though nurses had higher baseline burnout, it became less pronounced in June 2020. This indicates that burnout was significantly higher in physicians.”
Thus, Mr. Kok and colleagues concluded that overburdening ICU professionals during an extended period of time leads to burnout, and all ICU workers are at risk.
Burnout rates higher in physicians
Weighing in on the study, Greg S. Martin, MD, FCCP, professor of medicine in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, noted that the differences observed between physicians and nurses may have to do with the fact that “nurses have been smoldering all along and experiencing higher rates of burnout.
“They may have adapted better to the pandemic conditions, since they are more used to working overtime and short staffed, and spending far more time at the bedside,” he said. “Because of the volume of patients, physicians may be spending more hours doing patient care and are experiencing more burnout.”
For physicians, this may be a more significant change in the workload, as well as the complexity of the situation because of the pandemic. “Many things layer into it, such as [the fact] that there are no families present to give patients support, the complexity of care of these patients, and things like lack of PPE,” Dr. Martin said.
The study did not differentiate among physician groups, so it is unclear if the affected physicians were residents, fellows, or more senior staff. “Residents are often quite busy already, and don’t usually have the capacity to add more to their schedules, and maybe attendings were having to spend more time doing patient care,” Dr. Martin said. “In the United States, at least some personnel were restricted from working with COVID-19 patients. Medical students were removed in many places as well as nonessential staff, so that may have also added to their burnout.”
The study was conducted in the Netherlands, so there may be differences in the work environment, responsibilities of nurses vs. physicians, staffing, and so on. “But it still shows that burnout is very real among doctors and nurses working in the ICU in pandemic conditions,” he said.
FROM CCC50
Psychiatrist recounts haunting ordeal with an anonymous stalker
Looking back on his experience of being stalked by a former patient for nearly 1 year, William J. Newman, MD, regrets not reaching out to colleagues about the patient boundary violations earlier than he did.
“My mindset was: ‘Maybe I did something wrong that created this,’ ” Dr. Newman, professor and interim chair of psychiatry at Saint Louis University, said during an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “That’s a common theme among victims of stalking, being kind of embarrassed and not wanting to share it with other people.”
Dr. Newman’s ordeal began in August 2014, when the first of several threatening emails messages were sent to his account at the University of California, Davis, where he held a faculty post and worked on the teaching service at the Sacramento Mental Health Treatment Center, a county hospital that serves mainly uninsured or underinsured populations. The messages always contained a nonspecific email recipient name and the first wasn’t terribly worrisome, Dr. Newman said. It basically read (profanities excluded): “What is wrong with you? Leave me alone. All I want is some privacy.”
About 3 months later, he received another message in a similar writing pattern, but the name of the sender was “god devil,” which raised a red flag to him. “Once you start to get religious concepts, people are compelled to commit acts when they believe they’re doing so beyond the laws of the land and are doing so for a religious purpose,” said Dr. Newman, who is immediate past president of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law.
The content of the message contained the first name of a coworker and phrasing inferring suicide, which gave Dr. Newman a hint that it was someone he had cared for at the mental health treatment center, “but as anybody who has worked on a busy inpatient service can tell you, you encounter several suicidal patients, and this didn’t really narrow it down,” he said. “This told me the person had presented after a suicide attempt. In some ways, that made me a little more concerned, because because they don’t really worry about the consequences of being shot by law enforcement or dying in an attack.”
Dr. Newman contacted the university’s information technology team, which was able to trace all messages to an IP address from a computer located at a downtown branch of the public library, which had surveillance video. Armed with this information, he contacted the Sacramento Police Department to see if they would help. He had “what I can only describe as an unsatisfying and somewhat condescending conversation with an officer, who said: ‘Sir, we can’t just go around asking people questions without knowing they did something wrong. There’s nothing we’re going to do.’ ”
Between November 2014 and May 2015, Dr. Newman continued to receive periodic messages from the individual of varied length and intensity.
“Some messages were more disorganized and difficult to follow, while others were very intense and pointed about my imminent death,” he recalled. “I started to ignore these messages as much as possible, tried to put my head in the sand and move forward.”
However, one phrase contained in a message read “you won’t even recognize me,” which gave Dr. Newman pause. “It highlighted the idea that because I don’t know who this is, they could walk up to me on the sidewalk, and I would have no idea, which in its own right is somewhat terrorizing.”
At this point, he contacted the police again, telling them he was fearful for his imminent safety. He also met with his department chair and administrators, who helped Dr. Newman develop a plan to enter and exit the hospital at different times. Then, in May 2015, the stalker sent Dr. Newman another email message threatening not only his life, but the lives of his colleagues at the hospital.
“This was viewed as a terroristic threat, because [it inferred that] other people were going to be shot other than just me,” he said.
After this, Dr. Newman’s administrators contacted the police about the threat, who identified the individual through video surveillance footage at the public library and began to search for him. It was a patient who had been on testosterone and previously had sent similar messages to another mental health provider in town and wound up showing up at that person’s office with a loaded firearm.
“At that point, the police were called to the scene, picked the individual up, and took him to a local emergency room where he was placed on an involuntary 5150 psychiatric hold,” he said. “It was frustrating to me that this was very much minimized and kind of put to the side.”
Once he learned the stalker’s name, Dr. Newman had no recollection of the individual. “The patient had presented after a carbon monoxide overdose, had been sent to a local emergency room and came to my service,” he said. “It was a very nonconfrontational hospitalization, nothing out of the ordinary.”
At this point, the stalker was still at large, so Dr. Newman wrote farewell notes to his wife, children, and loved ones, “just in case,” he said. “I had those tucked away. That wasn’t an overly pleasant experience.” He also lived away from his family outside of Sacramento while police searched for his stalker.
In late May 2015, police located and arrested the individual, and Dr. Newman began a series of conversations with the District Attorney’s office. “They told me there were seven terroristic threat charges that had been levied. They said they were taking this very seriously and [that the case] would be going to trial.” About 1 year later, after Dr. Newman’s move to Missouri, the District Attorney indicated that there would be a court trial and that Dr. Newman would be asked to serve as a fact witness. “I gave them all the information I had, talked to investigators, and the process was moving along for about a year to the point that they had an anticipated trial date,” he said. About 1 year later, he received an automated phone message which stated that the individual had been released from jail. He called the District Attorney to ask what happened.
“He said the judge didn’t really want to deal with this [case] anymore, and accepted a plea with time served and released him,” Dr. Newman said. “That was the outcome of the situation.”
According to a 1997 study of 100 stalking victims, 94% made major lifestyle changes after their ordeal, 82% modified usual activities, 73% increased security measures, 70% curtailed social outings, 53% decreased/stopped work or school, and 39% relocated. “You do change a lot of what you do and how you do it in your life when you’ve had this experience, especially when it’s been a chronic experience for months or years,” said Dr. Newman, who is also medical director of adult psychiatric inpatient services for Saint Louis University. “To this day I get antsy any time I think about the story or prepare to talk about it. It remains uncomfortable even 6 years later, even without an ongoing direct threat at this point.”
The physiological impact of chronic stalking also takes its toll. The body releases adrenaline and cortisol as part of the fight or flight response, while chronic stress “is when you feel an increased stress response and have adrenaline and cortisol elevated for an extended period of time,” he said. “There are negative impacts in terms of increased inflammation in the body and in the brain. I have spoken to several professionals who have been stalked by former patients. Commonly, they have been diagnosed in the period after that with an autoimmune illness or a cancer. Less than a year after my stalking situation ended, I was diagnosed with a metastatic cancer and had to start chemotherapy. I would not at all be surprised that those things are highly related to one another.”
When patient boundary violations start to become problematic or worrisome, Dr. Newman advised reaching out to colleagues and law enforcement for help. “Don’t let it go on insidiously for an extended period of time,” he said. “I think that was the biggest lesson I learned.”
He reported having no financial disclosures.
Looking back on his experience of being stalked by a former patient for nearly 1 year, William J. Newman, MD, regrets not reaching out to colleagues about the patient boundary violations earlier than he did.
“My mindset was: ‘Maybe I did something wrong that created this,’ ” Dr. Newman, professor and interim chair of psychiatry at Saint Louis University, said during an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “That’s a common theme among victims of stalking, being kind of embarrassed and not wanting to share it with other people.”
Dr. Newman’s ordeal began in August 2014, when the first of several threatening emails messages were sent to his account at the University of California, Davis, where he held a faculty post and worked on the teaching service at the Sacramento Mental Health Treatment Center, a county hospital that serves mainly uninsured or underinsured populations. The messages always contained a nonspecific email recipient name and the first wasn’t terribly worrisome, Dr. Newman said. It basically read (profanities excluded): “What is wrong with you? Leave me alone. All I want is some privacy.”
About 3 months later, he received another message in a similar writing pattern, but the name of the sender was “god devil,” which raised a red flag to him. “Once you start to get religious concepts, people are compelled to commit acts when they believe they’re doing so beyond the laws of the land and are doing so for a religious purpose,” said Dr. Newman, who is immediate past president of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law.
The content of the message contained the first name of a coworker and phrasing inferring suicide, which gave Dr. Newman a hint that it was someone he had cared for at the mental health treatment center, “but as anybody who has worked on a busy inpatient service can tell you, you encounter several suicidal patients, and this didn’t really narrow it down,” he said. “This told me the person had presented after a suicide attempt. In some ways, that made me a little more concerned, because because they don’t really worry about the consequences of being shot by law enforcement or dying in an attack.”
Dr. Newman contacted the university’s information technology team, which was able to trace all messages to an IP address from a computer located at a downtown branch of the public library, which had surveillance video. Armed with this information, he contacted the Sacramento Police Department to see if they would help. He had “what I can only describe as an unsatisfying and somewhat condescending conversation with an officer, who said: ‘Sir, we can’t just go around asking people questions without knowing they did something wrong. There’s nothing we’re going to do.’ ”
Between November 2014 and May 2015, Dr. Newman continued to receive periodic messages from the individual of varied length and intensity.
“Some messages were more disorganized and difficult to follow, while others were very intense and pointed about my imminent death,” he recalled. “I started to ignore these messages as much as possible, tried to put my head in the sand and move forward.”
However, one phrase contained in a message read “you won’t even recognize me,” which gave Dr. Newman pause. “It highlighted the idea that because I don’t know who this is, they could walk up to me on the sidewalk, and I would have no idea, which in its own right is somewhat terrorizing.”
At this point, he contacted the police again, telling them he was fearful for his imminent safety. He also met with his department chair and administrators, who helped Dr. Newman develop a plan to enter and exit the hospital at different times. Then, in May 2015, the stalker sent Dr. Newman another email message threatening not only his life, but the lives of his colleagues at the hospital.
“This was viewed as a terroristic threat, because [it inferred that] other people were going to be shot other than just me,” he said.
After this, Dr. Newman’s administrators contacted the police about the threat, who identified the individual through video surveillance footage at the public library and began to search for him. It was a patient who had been on testosterone and previously had sent similar messages to another mental health provider in town and wound up showing up at that person’s office with a loaded firearm.
“At that point, the police were called to the scene, picked the individual up, and took him to a local emergency room where he was placed on an involuntary 5150 psychiatric hold,” he said. “It was frustrating to me that this was very much minimized and kind of put to the side.”
Once he learned the stalker’s name, Dr. Newman had no recollection of the individual. “The patient had presented after a carbon monoxide overdose, had been sent to a local emergency room and came to my service,” he said. “It was a very nonconfrontational hospitalization, nothing out of the ordinary.”
At this point, the stalker was still at large, so Dr. Newman wrote farewell notes to his wife, children, and loved ones, “just in case,” he said. “I had those tucked away. That wasn’t an overly pleasant experience.” He also lived away from his family outside of Sacramento while police searched for his stalker.
In late May 2015, police located and arrested the individual, and Dr. Newman began a series of conversations with the District Attorney’s office. “They told me there were seven terroristic threat charges that had been levied. They said they were taking this very seriously and [that the case] would be going to trial.” About 1 year later, after Dr. Newman’s move to Missouri, the District Attorney indicated that there would be a court trial and that Dr. Newman would be asked to serve as a fact witness. “I gave them all the information I had, talked to investigators, and the process was moving along for about a year to the point that they had an anticipated trial date,” he said. About 1 year later, he received an automated phone message which stated that the individual had been released from jail. He called the District Attorney to ask what happened.
“He said the judge didn’t really want to deal with this [case] anymore, and accepted a plea with time served and released him,” Dr. Newman said. “That was the outcome of the situation.”
According to a 1997 study of 100 stalking victims, 94% made major lifestyle changes after their ordeal, 82% modified usual activities, 73% increased security measures, 70% curtailed social outings, 53% decreased/stopped work or school, and 39% relocated. “You do change a lot of what you do and how you do it in your life when you’ve had this experience, especially when it’s been a chronic experience for months or years,” said Dr. Newman, who is also medical director of adult psychiatric inpatient services for Saint Louis University. “To this day I get antsy any time I think about the story or prepare to talk about it. It remains uncomfortable even 6 years later, even without an ongoing direct threat at this point.”
The physiological impact of chronic stalking also takes its toll. The body releases adrenaline and cortisol as part of the fight or flight response, while chronic stress “is when you feel an increased stress response and have adrenaline and cortisol elevated for an extended period of time,” he said. “There are negative impacts in terms of increased inflammation in the body and in the brain. I have spoken to several professionals who have been stalked by former patients. Commonly, they have been diagnosed in the period after that with an autoimmune illness or a cancer. Less than a year after my stalking situation ended, I was diagnosed with a metastatic cancer and had to start chemotherapy. I would not at all be surprised that those things are highly related to one another.”
When patient boundary violations start to become problematic or worrisome, Dr. Newman advised reaching out to colleagues and law enforcement for help. “Don’t let it go on insidiously for an extended period of time,” he said. “I think that was the biggest lesson I learned.”
He reported having no financial disclosures.
Looking back on his experience of being stalked by a former patient for nearly 1 year, William J. Newman, MD, regrets not reaching out to colleagues about the patient boundary violations earlier than he did.
“My mindset was: ‘Maybe I did something wrong that created this,’ ” Dr. Newman, professor and interim chair of psychiatry at Saint Louis University, said during an annual psychopharmacology update held by the Nevada Psychiatric Association. “That’s a common theme among victims of stalking, being kind of embarrassed and not wanting to share it with other people.”
Dr. Newman’s ordeal began in August 2014, when the first of several threatening emails messages were sent to his account at the University of California, Davis, where he held a faculty post and worked on the teaching service at the Sacramento Mental Health Treatment Center, a county hospital that serves mainly uninsured or underinsured populations. The messages always contained a nonspecific email recipient name and the first wasn’t terribly worrisome, Dr. Newman said. It basically read (profanities excluded): “What is wrong with you? Leave me alone. All I want is some privacy.”
About 3 months later, he received another message in a similar writing pattern, but the name of the sender was “god devil,” which raised a red flag to him. “Once you start to get religious concepts, people are compelled to commit acts when they believe they’re doing so beyond the laws of the land and are doing so for a religious purpose,” said Dr. Newman, who is immediate past president of the American Academy of Psychiatry and the Law.
The content of the message contained the first name of a coworker and phrasing inferring suicide, which gave Dr. Newman a hint that it was someone he had cared for at the mental health treatment center, “but as anybody who has worked on a busy inpatient service can tell you, you encounter several suicidal patients, and this didn’t really narrow it down,” he said. “This told me the person had presented after a suicide attempt. In some ways, that made me a little more concerned, because because they don’t really worry about the consequences of being shot by law enforcement or dying in an attack.”
Dr. Newman contacted the university’s information technology team, which was able to trace all messages to an IP address from a computer located at a downtown branch of the public library, which had surveillance video. Armed with this information, he contacted the Sacramento Police Department to see if they would help. He had “what I can only describe as an unsatisfying and somewhat condescending conversation with an officer, who said: ‘Sir, we can’t just go around asking people questions without knowing they did something wrong. There’s nothing we’re going to do.’ ”
Between November 2014 and May 2015, Dr. Newman continued to receive periodic messages from the individual of varied length and intensity.
“Some messages were more disorganized and difficult to follow, while others were very intense and pointed about my imminent death,” he recalled. “I started to ignore these messages as much as possible, tried to put my head in the sand and move forward.”
However, one phrase contained in a message read “you won’t even recognize me,” which gave Dr. Newman pause. “It highlighted the idea that because I don’t know who this is, they could walk up to me on the sidewalk, and I would have no idea, which in its own right is somewhat terrorizing.”
At this point, he contacted the police again, telling them he was fearful for his imminent safety. He also met with his department chair and administrators, who helped Dr. Newman develop a plan to enter and exit the hospital at different times. Then, in May 2015, the stalker sent Dr. Newman another email message threatening not only his life, but the lives of his colleagues at the hospital.
“This was viewed as a terroristic threat, because [it inferred that] other people were going to be shot other than just me,” he said.
After this, Dr. Newman’s administrators contacted the police about the threat, who identified the individual through video surveillance footage at the public library and began to search for him. It was a patient who had been on testosterone and previously had sent similar messages to another mental health provider in town and wound up showing up at that person’s office with a loaded firearm.
“At that point, the police were called to the scene, picked the individual up, and took him to a local emergency room where he was placed on an involuntary 5150 psychiatric hold,” he said. “It was frustrating to me that this was very much minimized and kind of put to the side.”
Once he learned the stalker’s name, Dr. Newman had no recollection of the individual. “The patient had presented after a carbon monoxide overdose, had been sent to a local emergency room and came to my service,” he said. “It was a very nonconfrontational hospitalization, nothing out of the ordinary.”
At this point, the stalker was still at large, so Dr. Newman wrote farewell notes to his wife, children, and loved ones, “just in case,” he said. “I had those tucked away. That wasn’t an overly pleasant experience.” He also lived away from his family outside of Sacramento while police searched for his stalker.
In late May 2015, police located and arrested the individual, and Dr. Newman began a series of conversations with the District Attorney’s office. “They told me there were seven terroristic threat charges that had been levied. They said they were taking this very seriously and [that the case] would be going to trial.” About 1 year later, after Dr. Newman’s move to Missouri, the District Attorney indicated that there would be a court trial and that Dr. Newman would be asked to serve as a fact witness. “I gave them all the information I had, talked to investigators, and the process was moving along for about a year to the point that they had an anticipated trial date,” he said. About 1 year later, he received an automated phone message which stated that the individual had been released from jail. He called the District Attorney to ask what happened.
“He said the judge didn’t really want to deal with this [case] anymore, and accepted a plea with time served and released him,” Dr. Newman said. “That was the outcome of the situation.”
According to a 1997 study of 100 stalking victims, 94% made major lifestyle changes after their ordeal, 82% modified usual activities, 73% increased security measures, 70% curtailed social outings, 53% decreased/stopped work or school, and 39% relocated. “You do change a lot of what you do and how you do it in your life when you’ve had this experience, especially when it’s been a chronic experience for months or years,” said Dr. Newman, who is also medical director of adult psychiatric inpatient services for Saint Louis University. “To this day I get antsy any time I think about the story or prepare to talk about it. It remains uncomfortable even 6 years later, even without an ongoing direct threat at this point.”
The physiological impact of chronic stalking also takes its toll. The body releases adrenaline and cortisol as part of the fight or flight response, while chronic stress “is when you feel an increased stress response and have adrenaline and cortisol elevated for an extended period of time,” he said. “There are negative impacts in terms of increased inflammation in the body and in the brain. I have spoken to several professionals who have been stalked by former patients. Commonly, they have been diagnosed in the period after that with an autoimmune illness or a cancer. Less than a year after my stalking situation ended, I was diagnosed with a metastatic cancer and had to start chemotherapy. I would not at all be surprised that those things are highly related to one another.”
When patient boundary violations start to become problematic or worrisome, Dr. Newman advised reaching out to colleagues and law enforcement for help. “Don’t let it go on insidiously for an extended period of time,” he said. “I think that was the biggest lesson I learned.”
He reported having no financial disclosures.
FROM NPA 2021
Expert calls for paradigm shift in lab monitoring of some dermatology drugs
From time to time, Joslyn Kirby, MD, asks other physicians about their experience with certain medications used in dermatology, especially when something new hits the market.
“Sometimes I get an answer like, ‘The last time I used that medicine, my patient needed a liver transplant,’ ” Dr. Kirby, associate professor of dermatology, Penn State University, Hershey, said during the Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference. “It’s typically a story of something rare, uncommon, and awful. The challenge with an anecdote is that for all its power, it has a lower level of evidence. But it sticks with us and influences us more than a better level of evidence because it’s a situation and a story that we might relate to.”
Dr. Kirby said that when she thinks about managing side effects from drugs used in dermatology, it usually relates to something common and low-risk such as sore, dry skin with isotretinoin use. In contrast, if there is an uncommon but serious side effect, then mitigation rather than management is key. “I want to mitigate the risk – meaning warn my patient about it or be careful about how I select my patients when it is a serious side effect that happens infrequently,” she said. “The worst combination is a frequent and severe side effect. That is something we should avoid, for sure.”
Isotretinoin
But another aspect of prescribing a new drug for patients can be less clear-cut, Dr. Kirby continued, such as the rationale for routine lab monitoring. She began by discussing one of her male patients with moderate to severe acne. After he failed oral antibiotics and topical retinoids, she recommended isotretinoin, which carries a risk of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis. “Early in my career, I was getting a lot of monthly labs in patients on this drug that were totally normal and not influencing my practice,” Dr. Kirby recalled. “We’ve seen studies coming out on isotretinoin lab monitoring, showing us that we can keep our patients safe and that we really don’t need to be checking labs as often, because lab changes are infrequent.”
In one of those studies, researchers evaluated 1,863 patients treated with isotretinoin for acne between Jan. 1, 2008, and June 30, 2017 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82[1]:72-9).Over time, fewer than 1% of patients screened developed grade 3 or greater triglyceride testing abnormalities, while fewer than 0.5% developed liver function testing (LFT) abnormalities. Authors of a separate systematic review concluded that for patients on isotretinoin therapy without elevated baseline triglycerides, or risk thereof, monitoring triglycerides is of little value (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:960-6). Of the 25 patients in the analysis who developed pancreatitis on isotretinoin, only 3 had elevated triglycerides at baseline.
“I was taught that I need to check triglycerides frequently due to the risk of pancreatitis developing with isotretinoin use,” Dr. Kirby said. “Lipid changes on therapy are expected, but they tend to peak early, meaning the first 3 months of treatment when we’re ramping up from a starting dose to a maintenance dose. It’s rare for somebody to be a late bloomer, meaning that they have totally normal labs in the first 3 months and then suddenly develop an abnormality. People are either going to demonstrate an abnormality early or not have one at all.”
When Dr. Kirby starts patients on isotretinoin, she orders baseline LFTs and a lipid panel and repeats them 60 days later. “If everything is fine or only mildly high, we don’t do more testing, only a review of systems,” she said. “This is valuable to our patients because fear of needles and fainting peak during adolescence.”
Spironolactone
The clinical use of regularly monitoring potassium levels in young women taking spironolactone for acne has also been questioned. The drug has been linked to an increased risk for hyperkalemia, but the prevalence is unclear. “I got a lot of normal potassium levels in these patients [when] I was in training and I really questioned, ‘Why am I doing this? What is the rationale?’ ” Dr. Kirby said.
In a study that informed her own practice, researchers reviewed the rate of hyperkalemia in 974 healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne or for an endocrine disorder with associated acne between Dec. 1, 2000, and March 31, 2014 (JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Sep;151[9]:941-4). Of the total of 1,802 serum potassium measurements taken during treatment, 13 (0.72%) were mildly elevated levels and none of the patients had a potassium level above 5.5 mEq/L. Retesting within 1 to 3 weeks in 6 of 13 patients with elevated levels found that potassium levels were normal. “The recommendation for spironolactone in healthy women is not to check the potassium level,” Dr. Kirby said, adding that she does counsel patients about the risk of breast tenderness (which can occur 5% to 40% of the time) and spotting (which can occur in 10% to 20% of patients). Gynecomastia can occur in 10% to 30% of men, which is one of the reasons she does not use spironolactone in male patients.
TB testing and biologics
Whether or not to test for TB in patients with psoriasis taking biologic therapies represents another conundrum, she continued. Patients taking biologics are at risk of reactivation of latent TB infection, but in her experience, package inserts contain language like “perform TB testing at baseline, then periodically,” or “use at baseline, then with active TB symptoms,” and “after treatment is discontinued.”
“What the inserts didn’t recommend was to perform TB testing every year, which is what my routine had been,” Dr. Kirby said. “In the United States, thankfully we don’t have a lot of TB.” In a study that informed her own practice, researchers at a single academic medical center retrospectively reviewed the TB seroconversion rate among 316 patients treated with second-generation biologics (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Oct 1;S0190-9622[20]32676-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.075). It found that only six patients (2%) converted and had a positive TB test later during treatment with the biologic. “Of these six people, all had grown up outside the U.S., had traveled outside of the U.S., or were in a group living situation,” said Dr. Kirby, who was not affiliated with the study.
“This informs our rationale for how we can do this testing. If insurance requires it every year, fine. But if they don’t, I ask patients about travel, about their living situation, and how they’re feeling. If everything’s going great, I don’t order TB testing. I do favor the interferon-gamma release assays because they’re a lot more effective than PPDs [purified protein derivative skin tests]. Also, PPDs are difficult for patients who have a low rate of returning to have that test read.”
Terbinafine for onychomycosis
Dr. Kirby also discussed the rationale for ordering regular LFTs in patients taking terbinafine for onychomycosis. “There is a risk of drug-induced liver injury from taking terbinafine, but it’s rare,” she said. “Can we be thoughtful about which patients we expose?”
Evidence suggests that patients with hyperkeratosis greater than 2 mm, with nail matrix involvement, with 50% or more of the nail involved, or having concomitant peripheral vascular disease and diabetes are recalcitrant to treatment with terbinafine
(J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Apr;80[4]:853-67). “If we can frame this risk, then we can frame it for our patients,” she said. “We’re more likely to cause liver injury with an antibiotic. When it comes to an oral antifungal, itraconazole is more likely than terbinafine to cause liver injury. The rate of liver injury with terbinafine is only about 2 out of 100,000. It’s five times more likely with itraconazole and 21 times more likely with Augmentin.”
She recommends obtaining a baseline LFT in patients starting terbinafine therapy “to make sure their liver is normal from the start.” In addition, she advised, “let them know that there is a TB seroconversion risk of about 1 in 50,000 people, and that if it happens there would be symptomatic changes. They would maybe notice pruritus and have a darkening in their urine, and they’d have some flu-like symptoms, which would mean stop the drug and get some care.”
Dr. Kirby emphasized that a patient’s propensity for developing drug-induced liver injury from terbinafine use is not predictable from LFT monitoring. “What you’re more likely to find is an asymptomatic LFT rise in about 1% of people,” she said.
She disclosed that she has received honoraria from AbbVie, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB Pharma.
From time to time, Joslyn Kirby, MD, asks other physicians about their experience with certain medications used in dermatology, especially when something new hits the market.
“Sometimes I get an answer like, ‘The last time I used that medicine, my patient needed a liver transplant,’ ” Dr. Kirby, associate professor of dermatology, Penn State University, Hershey, said during the Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference. “It’s typically a story of something rare, uncommon, and awful. The challenge with an anecdote is that for all its power, it has a lower level of evidence. But it sticks with us and influences us more than a better level of evidence because it’s a situation and a story that we might relate to.”
Dr. Kirby said that when she thinks about managing side effects from drugs used in dermatology, it usually relates to something common and low-risk such as sore, dry skin with isotretinoin use. In contrast, if there is an uncommon but serious side effect, then mitigation rather than management is key. “I want to mitigate the risk – meaning warn my patient about it or be careful about how I select my patients when it is a serious side effect that happens infrequently,” she said. “The worst combination is a frequent and severe side effect. That is something we should avoid, for sure.”
Isotretinoin
But another aspect of prescribing a new drug for patients can be less clear-cut, Dr. Kirby continued, such as the rationale for routine lab monitoring. She began by discussing one of her male patients with moderate to severe acne. After he failed oral antibiotics and topical retinoids, she recommended isotretinoin, which carries a risk of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis. “Early in my career, I was getting a lot of monthly labs in patients on this drug that were totally normal and not influencing my practice,” Dr. Kirby recalled. “We’ve seen studies coming out on isotretinoin lab monitoring, showing us that we can keep our patients safe and that we really don’t need to be checking labs as often, because lab changes are infrequent.”
In one of those studies, researchers evaluated 1,863 patients treated with isotretinoin for acne between Jan. 1, 2008, and June 30, 2017 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82[1]:72-9).Over time, fewer than 1% of patients screened developed grade 3 or greater triglyceride testing abnormalities, while fewer than 0.5% developed liver function testing (LFT) abnormalities. Authors of a separate systematic review concluded that for patients on isotretinoin therapy without elevated baseline triglycerides, or risk thereof, monitoring triglycerides is of little value (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:960-6). Of the 25 patients in the analysis who developed pancreatitis on isotretinoin, only 3 had elevated triglycerides at baseline.
“I was taught that I need to check triglycerides frequently due to the risk of pancreatitis developing with isotretinoin use,” Dr. Kirby said. “Lipid changes on therapy are expected, but they tend to peak early, meaning the first 3 months of treatment when we’re ramping up from a starting dose to a maintenance dose. It’s rare for somebody to be a late bloomer, meaning that they have totally normal labs in the first 3 months and then suddenly develop an abnormality. People are either going to demonstrate an abnormality early or not have one at all.”
When Dr. Kirby starts patients on isotretinoin, she orders baseline LFTs and a lipid panel and repeats them 60 days later. “If everything is fine or only mildly high, we don’t do more testing, only a review of systems,” she said. “This is valuable to our patients because fear of needles and fainting peak during adolescence.”
Spironolactone
The clinical use of regularly monitoring potassium levels in young women taking spironolactone for acne has also been questioned. The drug has been linked to an increased risk for hyperkalemia, but the prevalence is unclear. “I got a lot of normal potassium levels in these patients [when] I was in training and I really questioned, ‘Why am I doing this? What is the rationale?’ ” Dr. Kirby said.
In a study that informed her own practice, researchers reviewed the rate of hyperkalemia in 974 healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne or for an endocrine disorder with associated acne between Dec. 1, 2000, and March 31, 2014 (JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Sep;151[9]:941-4). Of the total of 1,802 serum potassium measurements taken during treatment, 13 (0.72%) were mildly elevated levels and none of the patients had a potassium level above 5.5 mEq/L. Retesting within 1 to 3 weeks in 6 of 13 patients with elevated levels found that potassium levels were normal. “The recommendation for spironolactone in healthy women is not to check the potassium level,” Dr. Kirby said, adding that she does counsel patients about the risk of breast tenderness (which can occur 5% to 40% of the time) and spotting (which can occur in 10% to 20% of patients). Gynecomastia can occur in 10% to 30% of men, which is one of the reasons she does not use spironolactone in male patients.
TB testing and biologics
Whether or not to test for TB in patients with psoriasis taking biologic therapies represents another conundrum, she continued. Patients taking biologics are at risk of reactivation of latent TB infection, but in her experience, package inserts contain language like “perform TB testing at baseline, then periodically,” or “use at baseline, then with active TB symptoms,” and “after treatment is discontinued.”
“What the inserts didn’t recommend was to perform TB testing every year, which is what my routine had been,” Dr. Kirby said. “In the United States, thankfully we don’t have a lot of TB.” In a study that informed her own practice, researchers at a single academic medical center retrospectively reviewed the TB seroconversion rate among 316 patients treated with second-generation biologics (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Oct 1;S0190-9622[20]32676-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.075). It found that only six patients (2%) converted and had a positive TB test later during treatment with the biologic. “Of these six people, all had grown up outside the U.S., had traveled outside of the U.S., or were in a group living situation,” said Dr. Kirby, who was not affiliated with the study.
“This informs our rationale for how we can do this testing. If insurance requires it every year, fine. But if they don’t, I ask patients about travel, about their living situation, and how they’re feeling. If everything’s going great, I don’t order TB testing. I do favor the interferon-gamma release assays because they’re a lot more effective than PPDs [purified protein derivative skin tests]. Also, PPDs are difficult for patients who have a low rate of returning to have that test read.”
Terbinafine for onychomycosis
Dr. Kirby also discussed the rationale for ordering regular LFTs in patients taking terbinafine for onychomycosis. “There is a risk of drug-induced liver injury from taking terbinafine, but it’s rare,” she said. “Can we be thoughtful about which patients we expose?”
Evidence suggests that patients with hyperkeratosis greater than 2 mm, with nail matrix involvement, with 50% or more of the nail involved, or having concomitant peripheral vascular disease and diabetes are recalcitrant to treatment with terbinafine
(J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Apr;80[4]:853-67). “If we can frame this risk, then we can frame it for our patients,” she said. “We’re more likely to cause liver injury with an antibiotic. When it comes to an oral antifungal, itraconazole is more likely than terbinafine to cause liver injury. The rate of liver injury with terbinafine is only about 2 out of 100,000. It’s five times more likely with itraconazole and 21 times more likely with Augmentin.”
She recommends obtaining a baseline LFT in patients starting terbinafine therapy “to make sure their liver is normal from the start.” In addition, she advised, “let them know that there is a TB seroconversion risk of about 1 in 50,000 people, and that if it happens there would be symptomatic changes. They would maybe notice pruritus and have a darkening in their urine, and they’d have some flu-like symptoms, which would mean stop the drug and get some care.”
Dr. Kirby emphasized that a patient’s propensity for developing drug-induced liver injury from terbinafine use is not predictable from LFT monitoring. “What you’re more likely to find is an asymptomatic LFT rise in about 1% of people,” she said.
She disclosed that she has received honoraria from AbbVie, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB Pharma.
From time to time, Joslyn Kirby, MD, asks other physicians about their experience with certain medications used in dermatology, especially when something new hits the market.
“Sometimes I get an answer like, ‘The last time I used that medicine, my patient needed a liver transplant,’ ” Dr. Kirby, associate professor of dermatology, Penn State University, Hershey, said during the Orlando Dermatology Aesthetic and Clinical Conference. “It’s typically a story of something rare, uncommon, and awful. The challenge with an anecdote is that for all its power, it has a lower level of evidence. But it sticks with us and influences us more than a better level of evidence because it’s a situation and a story that we might relate to.”
Dr. Kirby said that when she thinks about managing side effects from drugs used in dermatology, it usually relates to something common and low-risk such as sore, dry skin with isotretinoin use. In contrast, if there is an uncommon but serious side effect, then mitigation rather than management is key. “I want to mitigate the risk – meaning warn my patient about it or be careful about how I select my patients when it is a serious side effect that happens infrequently,” she said. “The worst combination is a frequent and severe side effect. That is something we should avoid, for sure.”
Isotretinoin
But another aspect of prescribing a new drug for patients can be less clear-cut, Dr. Kirby continued, such as the rationale for routine lab monitoring. She began by discussing one of her male patients with moderate to severe acne. After he failed oral antibiotics and topical retinoids, she recommended isotretinoin, which carries a risk of hypertriglyceridemia-associated pancreatitis. “Early in my career, I was getting a lot of monthly labs in patients on this drug that were totally normal and not influencing my practice,” Dr. Kirby recalled. “We’ve seen studies coming out on isotretinoin lab monitoring, showing us that we can keep our patients safe and that we really don’t need to be checking labs as often, because lab changes are infrequent.”
In one of those studies, researchers evaluated 1,863 patients treated with isotretinoin for acne between Jan. 1, 2008, and June 30, 2017 (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jan;82[1]:72-9).Over time, fewer than 1% of patients screened developed grade 3 or greater triglyceride testing abnormalities, while fewer than 0.5% developed liver function testing (LFT) abnormalities. Authors of a separate systematic review concluded that for patients on isotretinoin therapy without elevated baseline triglycerides, or risk thereof, monitoring triglycerides is of little value (Br J Dermatol. 2017 Oct;177[4]:960-6). Of the 25 patients in the analysis who developed pancreatitis on isotretinoin, only 3 had elevated triglycerides at baseline.
“I was taught that I need to check triglycerides frequently due to the risk of pancreatitis developing with isotretinoin use,” Dr. Kirby said. “Lipid changes on therapy are expected, but they tend to peak early, meaning the first 3 months of treatment when we’re ramping up from a starting dose to a maintenance dose. It’s rare for somebody to be a late bloomer, meaning that they have totally normal labs in the first 3 months and then suddenly develop an abnormality. People are either going to demonstrate an abnormality early or not have one at all.”
When Dr. Kirby starts patients on isotretinoin, she orders baseline LFTs and a lipid panel and repeats them 60 days later. “If everything is fine or only mildly high, we don’t do more testing, only a review of systems,” she said. “This is valuable to our patients because fear of needles and fainting peak during adolescence.”
Spironolactone
The clinical use of regularly monitoring potassium levels in young women taking spironolactone for acne has also been questioned. The drug has been linked to an increased risk for hyperkalemia, but the prevalence is unclear. “I got a lot of normal potassium levels in these patients [when] I was in training and I really questioned, ‘Why am I doing this? What is the rationale?’ ” Dr. Kirby said.
In a study that informed her own practice, researchers reviewed the rate of hyperkalemia in 974 healthy young women taking spironolactone for acne or for an endocrine disorder with associated acne between Dec. 1, 2000, and March 31, 2014 (JAMA Dermatol. 2015 Sep;151[9]:941-4). Of the total of 1,802 serum potassium measurements taken during treatment, 13 (0.72%) were mildly elevated levels and none of the patients had a potassium level above 5.5 mEq/L. Retesting within 1 to 3 weeks in 6 of 13 patients with elevated levels found that potassium levels were normal. “The recommendation for spironolactone in healthy women is not to check the potassium level,” Dr. Kirby said, adding that she does counsel patients about the risk of breast tenderness (which can occur 5% to 40% of the time) and spotting (which can occur in 10% to 20% of patients). Gynecomastia can occur in 10% to 30% of men, which is one of the reasons she does not use spironolactone in male patients.
TB testing and biologics
Whether or not to test for TB in patients with psoriasis taking biologic therapies represents another conundrum, she continued. Patients taking biologics are at risk of reactivation of latent TB infection, but in her experience, package inserts contain language like “perform TB testing at baseline, then periodically,” or “use at baseline, then with active TB symptoms,” and “after treatment is discontinued.”
“What the inserts didn’t recommend was to perform TB testing every year, which is what my routine had been,” Dr. Kirby said. “In the United States, thankfully we don’t have a lot of TB.” In a study that informed her own practice, researchers at a single academic medical center retrospectively reviewed the TB seroconversion rate among 316 patients treated with second-generation biologics (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Oct 1;S0190-9622[20]32676-1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.09.075). It found that only six patients (2%) converted and had a positive TB test later during treatment with the biologic. “Of these six people, all had grown up outside the U.S., had traveled outside of the U.S., or were in a group living situation,” said Dr. Kirby, who was not affiliated with the study.
“This informs our rationale for how we can do this testing. If insurance requires it every year, fine. But if they don’t, I ask patients about travel, about their living situation, and how they’re feeling. If everything’s going great, I don’t order TB testing. I do favor the interferon-gamma release assays because they’re a lot more effective than PPDs [purified protein derivative skin tests]. Also, PPDs are difficult for patients who have a low rate of returning to have that test read.”
Terbinafine for onychomycosis
Dr. Kirby also discussed the rationale for ordering regular LFTs in patients taking terbinafine for onychomycosis. “There is a risk of drug-induced liver injury from taking terbinafine, but it’s rare,” she said. “Can we be thoughtful about which patients we expose?”
Evidence suggests that patients with hyperkeratosis greater than 2 mm, with nail matrix involvement, with 50% or more of the nail involved, or having concomitant peripheral vascular disease and diabetes are recalcitrant to treatment with terbinafine
(J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Apr;80[4]:853-67). “If we can frame this risk, then we can frame it for our patients,” she said. “We’re more likely to cause liver injury with an antibiotic. When it comes to an oral antifungal, itraconazole is more likely than terbinafine to cause liver injury. The rate of liver injury with terbinafine is only about 2 out of 100,000. It’s five times more likely with itraconazole and 21 times more likely with Augmentin.”
She recommends obtaining a baseline LFT in patients starting terbinafine therapy “to make sure their liver is normal from the start.” In addition, she advised, “let them know that there is a TB seroconversion risk of about 1 in 50,000 people, and that if it happens there would be symptomatic changes. They would maybe notice pruritus and have a darkening in their urine, and they’d have some flu-like symptoms, which would mean stop the drug and get some care.”
Dr. Kirby emphasized that a patient’s propensity for developing drug-induced liver injury from terbinafine use is not predictable from LFT monitoring. “What you’re more likely to find is an asymptomatic LFT rise in about 1% of people,” she said.
She disclosed that she has received honoraria from AbbVie, ChemoCentryx, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, and UCB Pharma.
FROM ODAC 2021
Molecular insights suggest novel therapies for hidradenitis suppurativa
at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented highlights of a multicenter translational study, which utilized whole transcriptome analysis of lesional and nonlesional skin from patients with HS and normal controls along with quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. The purpose was to further define the molecular taxonomy of this inflammatory disease. And while this objective was achieved, the results also underscored a truism regarding the painful and scarring disease: “HS is characterized by an ever-growing complexity, which translates into multiple potential mechanistic drivers,” observed Dr. da Costa, head of immunology precision medicine at AstraZeneca in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Indeed, the study identified a panel of immune-related drivers in HS that influence innate immunity and cell differentiation in follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The research by Dr. da Costa and coinvestigators identified a broad array of promising novel therapeutic targets in HS.
“Our findings provide evidence of an inflammatory process coupled with impaired barrier function, altered epidermal cell differentiation, and possibly abnormal microbiome activity which can be seen at the follicular and epidermal keratinocytes and also to a minor degree at the level of the skin glands,” Dr. da Costa said.
There is a huge unmet need for new therapies for HS, since at present adalimumab (Humira) is the only approved medication for this debilitating inflammatory disease. Some good news that emerged from this translational study is that some of the novel molecular mediators implicated in HS are targeted by multiple Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies that have other indications. From a drug development standpoint, repurposing a commercially available drug for a novel indication is a much more efficient and less costly endeavor than is necessary to establish the safety and efficacy of an unproven new agent.
The translational work demonstrated that the proteins calgranulin-A and -B and serpin-B4 were strongly expressed in the hair root sheaths of patients with HS. Connexin-32 and koebnerisin were present in stratum granulosum, matrix metallopeptidase-9 was strongly expressed in resident monocytes, small prolin-rich protein 3 in apocrine sweat glands and ducts as well as in sebaceous glands and ducts, and transcobalamin-1 was prominent in stratum spinosum.
Of the 19 key molecular mediators of HS identified in the study, FDA-approved agents are already available that target 12 of them. For example, apremilast (Otezla) targets interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Gentamicin targets growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6) and interleukin-17 (IL-17). Secukinumab (Cosentyx) and ixekizumab (Taltz) target IL-17A, and brodalumab (Siliq) more broadly targets IL-17A as well as all the other IL-17 receptors. Thalidomide targets hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and TNF-alpha. Spironolactone targets androgen receptor (AR) and TNF-alpha. Colchicine targets tubulin. Anakinra (Kineret) homes in on the IL-1 receptor. And prednisone targets NFxB.
Other key molecular mediators of HS, which are targeted by commercially available drugs, include epidermal growth factor (EGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), epiregulin (EREG), fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1), FGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), and IL-6, according to Dr. da Costa.
In addition, clinical trials are underway in HS involving totally investigational agents, including several Janus kinase inhibitors and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors.
The work described by Dr. da Costa had multiple funding sources, including the European Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation, the University of Copenhagen, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, AstraZeneca, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. da Costa is an employee of AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden.
at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented highlights of a multicenter translational study, which utilized whole transcriptome analysis of lesional and nonlesional skin from patients with HS and normal controls along with quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. The purpose was to further define the molecular taxonomy of this inflammatory disease. And while this objective was achieved, the results also underscored a truism regarding the painful and scarring disease: “HS is characterized by an ever-growing complexity, which translates into multiple potential mechanistic drivers,” observed Dr. da Costa, head of immunology precision medicine at AstraZeneca in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Indeed, the study identified a panel of immune-related drivers in HS that influence innate immunity and cell differentiation in follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The research by Dr. da Costa and coinvestigators identified a broad array of promising novel therapeutic targets in HS.
“Our findings provide evidence of an inflammatory process coupled with impaired barrier function, altered epidermal cell differentiation, and possibly abnormal microbiome activity which can be seen at the follicular and epidermal keratinocytes and also to a minor degree at the level of the skin glands,” Dr. da Costa said.
There is a huge unmet need for new therapies for HS, since at present adalimumab (Humira) is the only approved medication for this debilitating inflammatory disease. Some good news that emerged from this translational study is that some of the novel molecular mediators implicated in HS are targeted by multiple Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies that have other indications. From a drug development standpoint, repurposing a commercially available drug for a novel indication is a much more efficient and less costly endeavor than is necessary to establish the safety and efficacy of an unproven new agent.
The translational work demonstrated that the proteins calgranulin-A and -B and serpin-B4 were strongly expressed in the hair root sheaths of patients with HS. Connexin-32 and koebnerisin were present in stratum granulosum, matrix metallopeptidase-9 was strongly expressed in resident monocytes, small prolin-rich protein 3 in apocrine sweat glands and ducts as well as in sebaceous glands and ducts, and transcobalamin-1 was prominent in stratum spinosum.
Of the 19 key molecular mediators of HS identified in the study, FDA-approved agents are already available that target 12 of them. For example, apremilast (Otezla) targets interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Gentamicin targets growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6) and interleukin-17 (IL-17). Secukinumab (Cosentyx) and ixekizumab (Taltz) target IL-17A, and brodalumab (Siliq) more broadly targets IL-17A as well as all the other IL-17 receptors. Thalidomide targets hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and TNF-alpha. Spironolactone targets androgen receptor (AR) and TNF-alpha. Colchicine targets tubulin. Anakinra (Kineret) homes in on the IL-1 receptor. And prednisone targets NFxB.
Other key molecular mediators of HS, which are targeted by commercially available drugs, include epidermal growth factor (EGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), epiregulin (EREG), fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1), FGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), and IL-6, according to Dr. da Costa.
In addition, clinical trials are underway in HS involving totally investigational agents, including several Janus kinase inhibitors and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors.
The work described by Dr. da Costa had multiple funding sources, including the European Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation, the University of Copenhagen, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, AstraZeneca, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. da Costa is an employee of AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden.
at the virtual annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
He presented highlights of a multicenter translational study, which utilized whole transcriptome analysis of lesional and nonlesional skin from patients with HS and normal controls along with quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry. The purpose was to further define the molecular taxonomy of this inflammatory disease. And while this objective was achieved, the results also underscored a truism regarding the painful and scarring disease: “HS is characterized by an ever-growing complexity, which translates into multiple potential mechanistic drivers,” observed Dr. da Costa, head of immunology precision medicine at AstraZeneca in Gothenburg, Sweden.
Indeed, the study identified a panel of immune-related drivers in HS that influence innate immunity and cell differentiation in follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The research by Dr. da Costa and coinvestigators identified a broad array of promising novel therapeutic targets in HS.
“Our findings provide evidence of an inflammatory process coupled with impaired barrier function, altered epidermal cell differentiation, and possibly abnormal microbiome activity which can be seen at the follicular and epidermal keratinocytes and also to a minor degree at the level of the skin glands,” Dr. da Costa said.
There is a huge unmet need for new therapies for HS, since at present adalimumab (Humira) is the only approved medication for this debilitating inflammatory disease. Some good news that emerged from this translational study is that some of the novel molecular mediators implicated in HS are targeted by multiple Food and Drug Administration–approved therapies that have other indications. From a drug development standpoint, repurposing a commercially available drug for a novel indication is a much more efficient and less costly endeavor than is necessary to establish the safety and efficacy of an unproven new agent.
The translational work demonstrated that the proteins calgranulin-A and -B and serpin-B4 were strongly expressed in the hair root sheaths of patients with HS. Connexin-32 and koebnerisin were present in stratum granulosum, matrix metallopeptidase-9 was strongly expressed in resident monocytes, small prolin-rich protein 3 in apocrine sweat glands and ducts as well as in sebaceous glands and ducts, and transcobalamin-1 was prominent in stratum spinosum.
Of the 19 key molecular mediators of HS identified in the study, FDA-approved agents are already available that target 12 of them. For example, apremilast (Otezla) targets interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Gentamicin targets growth arrest-specific 6 (GAS6) and interleukin-17 (IL-17). Secukinumab (Cosentyx) and ixekizumab (Taltz) target IL-17A, and brodalumab (Siliq) more broadly targets IL-17A as well as all the other IL-17 receptors. Thalidomide targets hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and TNF-alpha. Spironolactone targets androgen receptor (AR) and TNF-alpha. Colchicine targets tubulin. Anakinra (Kineret) homes in on the IL-1 receptor. And prednisone targets NFxB.
Other key molecular mediators of HS, which are targeted by commercially available drugs, include epidermal growth factor (EGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (MCSF), epiregulin (EREG), fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1), FGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2), and IL-6, according to Dr. da Costa.
In addition, clinical trials are underway in HS involving totally investigational agents, including several Janus kinase inhibitors and tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitors.
The work described by Dr. da Costa had multiple funding sources, including the European Hidradenitis Suppurativa Foundation, the University of Copenhagen, the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, AstraZeneca, and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Dr. da Costa is an employee of AstraZeneca, Gothenburg, Sweden.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
Anybody for a nanobody? Novel psoriasis therapy impresses in phase 2b
in a phase 2b randomized trial, Kim A. Papp, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
A nanobody is a tiny antibody fragment with a much smaller molecular weight than the monoclonal antibodies utilized today in treating psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. The sonelokinab nanobody, derived from animals in the camel family, is a recombinant sequence-optimized nanobody specific for human IL-17F, IL-17A, the heterodimer IL-17A/F, and serum albumin. The binding to serum albumin give sonelokinab a lengthy half-life of 10-12 hours, which may be therapeutically relevant, explained Dr. Papp, president and founder of Probity Medical Research in Waterloo, Ont.
He presented the 24-week results of a multicenter, double-blind, double-dummy randomized trial including 313 North American and European adults with an average 18-year history of psoriasis and a baseline Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of about 21. They were randomized to one of six treatment arms for the first 12 weeks: subcutaneous injection of sonelokinab at 30, 60, or 120 mg at weeks 0, 2, 4, and 8; enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab at 120 mg every 2 weeks through week 10; the IL-17A inhibitor secukinumab (Cosentyx) at its standard dosing as an active comparator; or placebo. Data analysis was by rigorous nonresponder imputation, meaning anyone who didn’t complete the study was scored as a nonresponder.
“This yields a conservative data analysis somewhat biased against sonelokinab,” the dermatologist pointed out.
The primary outcome in the trial was the week-12 rate of an Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 0 or 1, indicative of clear or almost clear skin. This was achieved in 88.2% of patients in the highest-dose arm of sonelokinab. That group also had a week-12 PASI 90 response rate of 76.5% and a PASI 100 response rate of 33.3%. By comparison, patients on standard-dose secukinumab had a less robust week-12 IGA 0/1 rate of 77.4%, a PASI 90 of 64.2%, and a PASI 100 of 28.3%. Of note, however, this secukinumab performance was better than seen in the 30-mg sonelokinab group, and comparable to outcomes with 60 mg of sonelokinab.
Dose escalation was performed from weeks 12-24. Patients with a week-12 IGA score greater than 1 after being on sonelokinab at 30 or 60 mg were upgraded to 120 mg at week 12 and again every 4 weeks thereafter. Placebo-treated controls were switched to 120 mg at weeks 12, 14, 16, and every 4 weeks thereafter. The group on the enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab moved to 120 mg every 4 weeks, while those who had gotten four doses of sonelokinab at 120 mg during the first 12 weeks were switched to 120 mg every 8 weeks. The secukinumab group remained on the approved dosing through week 24.
At week 24, superior outcomes were seen in the enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab group, with an IGA 0/1 response rate of 94.2%, a PASI 90 of 90.4%, and a PASI 100 of 56.9%. The corresponding week-24 rates in patients on 120 mg of sonelokinab every 8 weeks from week 12 on were 80.4%, 79.2%, and 40.4%, outcomes similar to those seen with secukinumab.
The rapidity of response to sonelokinab at 120 mg was striking, with approximately one-third of treated patients achieving a PASI 90 response by week 4.
“This could reflect the smaller molecular profile. There is possibly rapid increased absorption or bioavailability, quicker time to achieving serum half-life, better penetration into target tissue, and perhaps more effective engagement at the target. All of those things are possibilities. These are things that are yet to be explored, but it’s very enticing to see that uncharacteristically rapid initial response. It’s all very gratifying – and tantalizing,” Dr. Papp said in response to an audience question.
The safety profile of sonelokinab was reassuring. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis in 13.5% of patients and pruritus in 6.7%, with most cases being mild or moderate. As with other IL-17 blockers, there was an increase in oral candidiasis. This side effect appeared to occur in dose-dependent fashion: The incidence was zero in the 30-mg group, 1.9% with 60 mg, 3.8% with sonelokinab at 120 mg without an enhanced loading dose, and 5.9% with the enhanced loading dose.
The study was conducted by Avillion in partnership with Merck. Dr. Papp reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to those and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
in a phase 2b randomized trial, Kim A. Papp, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
A nanobody is a tiny antibody fragment with a much smaller molecular weight than the monoclonal antibodies utilized today in treating psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. The sonelokinab nanobody, derived from animals in the camel family, is a recombinant sequence-optimized nanobody specific for human IL-17F, IL-17A, the heterodimer IL-17A/F, and serum albumin. The binding to serum albumin give sonelokinab a lengthy half-life of 10-12 hours, which may be therapeutically relevant, explained Dr. Papp, president and founder of Probity Medical Research in Waterloo, Ont.
He presented the 24-week results of a multicenter, double-blind, double-dummy randomized trial including 313 North American and European adults with an average 18-year history of psoriasis and a baseline Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of about 21. They were randomized to one of six treatment arms for the first 12 weeks: subcutaneous injection of sonelokinab at 30, 60, or 120 mg at weeks 0, 2, 4, and 8; enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab at 120 mg every 2 weeks through week 10; the IL-17A inhibitor secukinumab (Cosentyx) at its standard dosing as an active comparator; or placebo. Data analysis was by rigorous nonresponder imputation, meaning anyone who didn’t complete the study was scored as a nonresponder.
“This yields a conservative data analysis somewhat biased against sonelokinab,” the dermatologist pointed out.
The primary outcome in the trial was the week-12 rate of an Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 0 or 1, indicative of clear or almost clear skin. This was achieved in 88.2% of patients in the highest-dose arm of sonelokinab. That group also had a week-12 PASI 90 response rate of 76.5% and a PASI 100 response rate of 33.3%. By comparison, patients on standard-dose secukinumab had a less robust week-12 IGA 0/1 rate of 77.4%, a PASI 90 of 64.2%, and a PASI 100 of 28.3%. Of note, however, this secukinumab performance was better than seen in the 30-mg sonelokinab group, and comparable to outcomes with 60 mg of sonelokinab.
Dose escalation was performed from weeks 12-24. Patients with a week-12 IGA score greater than 1 after being on sonelokinab at 30 or 60 mg were upgraded to 120 mg at week 12 and again every 4 weeks thereafter. Placebo-treated controls were switched to 120 mg at weeks 12, 14, 16, and every 4 weeks thereafter. The group on the enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab moved to 120 mg every 4 weeks, while those who had gotten four doses of sonelokinab at 120 mg during the first 12 weeks were switched to 120 mg every 8 weeks. The secukinumab group remained on the approved dosing through week 24.
At week 24, superior outcomes were seen in the enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab group, with an IGA 0/1 response rate of 94.2%, a PASI 90 of 90.4%, and a PASI 100 of 56.9%. The corresponding week-24 rates in patients on 120 mg of sonelokinab every 8 weeks from week 12 on were 80.4%, 79.2%, and 40.4%, outcomes similar to those seen with secukinumab.
The rapidity of response to sonelokinab at 120 mg was striking, with approximately one-third of treated patients achieving a PASI 90 response by week 4.
“This could reflect the smaller molecular profile. There is possibly rapid increased absorption or bioavailability, quicker time to achieving serum half-life, better penetration into target tissue, and perhaps more effective engagement at the target. All of those things are possibilities. These are things that are yet to be explored, but it’s very enticing to see that uncharacteristically rapid initial response. It’s all very gratifying – and tantalizing,” Dr. Papp said in response to an audience question.
The safety profile of sonelokinab was reassuring. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis in 13.5% of patients and pruritus in 6.7%, with most cases being mild or moderate. As with other IL-17 blockers, there was an increase in oral candidiasis. This side effect appeared to occur in dose-dependent fashion: The incidence was zero in the 30-mg group, 1.9% with 60 mg, 3.8% with sonelokinab at 120 mg without an enhanced loading dose, and 5.9% with the enhanced loading dose.
The study was conducted by Avillion in partnership with Merck. Dr. Papp reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to those and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
in a phase 2b randomized trial, Kim A. Papp, MD, PhD, reported at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
A nanobody is a tiny antibody fragment with a much smaller molecular weight than the monoclonal antibodies utilized today in treating psoriasis or atopic dermatitis. The sonelokinab nanobody, derived from animals in the camel family, is a recombinant sequence-optimized nanobody specific for human IL-17F, IL-17A, the heterodimer IL-17A/F, and serum albumin. The binding to serum albumin give sonelokinab a lengthy half-life of 10-12 hours, which may be therapeutically relevant, explained Dr. Papp, president and founder of Probity Medical Research in Waterloo, Ont.
He presented the 24-week results of a multicenter, double-blind, double-dummy randomized trial including 313 North American and European adults with an average 18-year history of psoriasis and a baseline Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score of about 21. They were randomized to one of six treatment arms for the first 12 weeks: subcutaneous injection of sonelokinab at 30, 60, or 120 mg at weeks 0, 2, 4, and 8; enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab at 120 mg every 2 weeks through week 10; the IL-17A inhibitor secukinumab (Cosentyx) at its standard dosing as an active comparator; or placebo. Data analysis was by rigorous nonresponder imputation, meaning anyone who didn’t complete the study was scored as a nonresponder.
“This yields a conservative data analysis somewhat biased against sonelokinab,” the dermatologist pointed out.
The primary outcome in the trial was the week-12 rate of an Investigator’s Global Assessment score of 0 or 1, indicative of clear or almost clear skin. This was achieved in 88.2% of patients in the highest-dose arm of sonelokinab. That group also had a week-12 PASI 90 response rate of 76.5% and a PASI 100 response rate of 33.3%. By comparison, patients on standard-dose secukinumab had a less robust week-12 IGA 0/1 rate of 77.4%, a PASI 90 of 64.2%, and a PASI 100 of 28.3%. Of note, however, this secukinumab performance was better than seen in the 30-mg sonelokinab group, and comparable to outcomes with 60 mg of sonelokinab.
Dose escalation was performed from weeks 12-24. Patients with a week-12 IGA score greater than 1 after being on sonelokinab at 30 or 60 mg were upgraded to 120 mg at week 12 and again every 4 weeks thereafter. Placebo-treated controls were switched to 120 mg at weeks 12, 14, 16, and every 4 weeks thereafter. The group on the enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab moved to 120 mg every 4 weeks, while those who had gotten four doses of sonelokinab at 120 mg during the first 12 weeks were switched to 120 mg every 8 weeks. The secukinumab group remained on the approved dosing through week 24.
At week 24, superior outcomes were seen in the enhanced–loading-dose sonelokinab group, with an IGA 0/1 response rate of 94.2%, a PASI 90 of 90.4%, and a PASI 100 of 56.9%. The corresponding week-24 rates in patients on 120 mg of sonelokinab every 8 weeks from week 12 on were 80.4%, 79.2%, and 40.4%, outcomes similar to those seen with secukinumab.
The rapidity of response to sonelokinab at 120 mg was striking, with approximately one-third of treated patients achieving a PASI 90 response by week 4.
“This could reflect the smaller molecular profile. There is possibly rapid increased absorption or bioavailability, quicker time to achieving serum half-life, better penetration into target tissue, and perhaps more effective engagement at the target. All of those things are possibilities. These are things that are yet to be explored, but it’s very enticing to see that uncharacteristically rapid initial response. It’s all very gratifying – and tantalizing,” Dr. Papp said in response to an audience question.
The safety profile of sonelokinab was reassuring. The most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis in 13.5% of patients and pruritus in 6.7%, with most cases being mild or moderate. As with other IL-17 blockers, there was an increase in oral candidiasis. This side effect appeared to occur in dose-dependent fashion: The incidence was zero in the 30-mg group, 1.9% with 60 mg, 3.8% with sonelokinab at 120 mg without an enhanced loading dose, and 5.9% with the enhanced loading dose.
The study was conducted by Avillion in partnership with Merck. Dr. Papp reported receiving research funding from and serving as a consultant to those and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
FROM the eadv congress