User login
Children and COVID: New-case counts offer dueling narratives
New COVID-19 cases in children jumped by 66% during the first 2 weeks of December after an 8-week steady period lasting through October and November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
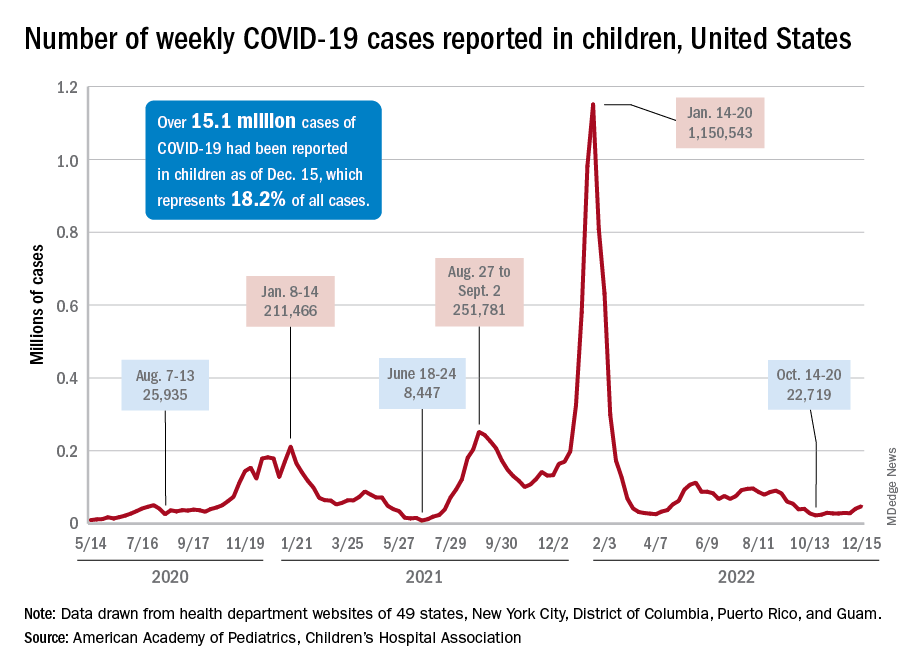
and totaling less than 29,000 for the week of Nov. 25 to Dec. 1. That increase of almost 19,000 cases is the largest over a 2-week period since late July, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report based on data collected from state and territorial health department websites.
[This publication has been following the AAP/CHA report since the summer of 2020 and continues to share the data for the sake of consistency, but it must be noted that a number of states are no longer updating their public COVID dashboards. As a result, there is now a considerable discrepancy between the AAP/CHA weekly figures and those reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has no such limitations on state data.]
The situation involving new cases over the last 2 weeks is quite different from the CDC’s perspective. The agency does not publish a weekly count, instead offering cumulative cases, which stood at almost 16.1 million as of Dec. 14. Calculating a 2-week total puts the new-case count for Dec. 1-14 at 113,572 among children aged 0-17 years. That is higher than the AAP/CHA count (88,629) for roughly the same period, but it is actually lower than the CDC’s figure (161,832) for the last 2 weeks of November.
The CDC data, in other words, suggest that new cases have gone down in the last 2 weeks, while the AAP and CHA, with their somewhat limited perspective, announced that new cases have gone up.
One COVID-related measure from the CDC that is not contradicted by other sources is hospitalization rates, which had climbed from 0.16 new admissions in children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID per 100,000 population on Oct. 22 to 0.29 per 100,000 on Dec. 9. Visits to the emergency department with diagnosed COVID, meanwhile, have been fairly steady so far through December in children, according to the CDC.
New COVID-19 cases in children jumped by 66% during the first 2 weeks of December after an 8-week steady period lasting through October and November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

and totaling less than 29,000 for the week of Nov. 25 to Dec. 1. That increase of almost 19,000 cases is the largest over a 2-week period since late July, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report based on data collected from state and territorial health department websites.
[This publication has been following the AAP/CHA report since the summer of 2020 and continues to share the data for the sake of consistency, but it must be noted that a number of states are no longer updating their public COVID dashboards. As a result, there is now a considerable discrepancy between the AAP/CHA weekly figures and those reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has no such limitations on state data.]
The situation involving new cases over the last 2 weeks is quite different from the CDC’s perspective. The agency does not publish a weekly count, instead offering cumulative cases, which stood at almost 16.1 million as of Dec. 14. Calculating a 2-week total puts the new-case count for Dec. 1-14 at 113,572 among children aged 0-17 years. That is higher than the AAP/CHA count (88,629) for roughly the same period, but it is actually lower than the CDC’s figure (161,832) for the last 2 weeks of November.
The CDC data, in other words, suggest that new cases have gone down in the last 2 weeks, while the AAP and CHA, with their somewhat limited perspective, announced that new cases have gone up.
One COVID-related measure from the CDC that is not contradicted by other sources is hospitalization rates, which had climbed from 0.16 new admissions in children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID per 100,000 population on Oct. 22 to 0.29 per 100,000 on Dec. 9. Visits to the emergency department with diagnosed COVID, meanwhile, have been fairly steady so far through December in children, according to the CDC.
New COVID-19 cases in children jumped by 66% during the first 2 weeks of December after an 8-week steady period lasting through October and November, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

and totaling less than 29,000 for the week of Nov. 25 to Dec. 1. That increase of almost 19,000 cases is the largest over a 2-week period since late July, the AAP and CHA said in their weekly COVID report based on data collected from state and territorial health department websites.
[This publication has been following the AAP/CHA report since the summer of 2020 and continues to share the data for the sake of consistency, but it must be noted that a number of states are no longer updating their public COVID dashboards. As a result, there is now a considerable discrepancy between the AAP/CHA weekly figures and those reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which has no such limitations on state data.]
The situation involving new cases over the last 2 weeks is quite different from the CDC’s perspective. The agency does not publish a weekly count, instead offering cumulative cases, which stood at almost 16.1 million as of Dec. 14. Calculating a 2-week total puts the new-case count for Dec. 1-14 at 113,572 among children aged 0-17 years. That is higher than the AAP/CHA count (88,629) for roughly the same period, but it is actually lower than the CDC’s figure (161,832) for the last 2 weeks of November.
The CDC data, in other words, suggest that new cases have gone down in the last 2 weeks, while the AAP and CHA, with their somewhat limited perspective, announced that new cases have gone up.
One COVID-related measure from the CDC that is not contradicted by other sources is hospitalization rates, which had climbed from 0.16 new admissions in children aged 0-17 years with confirmed COVID per 100,000 population on Oct. 22 to 0.29 per 100,000 on Dec. 9. Visits to the emergency department with diagnosed COVID, meanwhile, have been fairly steady so far through December in children, according to the CDC.
COVID booster shot poll: People ‘don’t think they need one’
Now, a new poll shows why so few people are willing to roll up their sleeves again.
The most common reasons people give for not getting the latest booster shot is that they “don’t think they need one” (44%) and they “don’t think the benefits are worth it” (37%), according to poll results from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
The data comes amid announcements by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that boosters reduced COVID-19 hospitalizations by up to 57% for U.S. adults and by up to 84% for people age 65 and older. Those figures are just the latest in a mountain of research reporting the public health benefits of COVID-19 vaccines.
Despite all of the statistical data, health officials’ recent vaccination campaigns have proven far from compelling.
So far, just 15% of people age 12 and older have gotten the latest booster, and 36% of people age 65 and older have gotten it, the CDC’s vaccination trackershows.
Since the start of the pandemic, 1.1 million people in the U.S. have died from COVID-19, with the number of deaths currently rising by 400 per day, The New York Times COVID tracker shows.
Many experts continue to note the need for everyone to get booster shots regularly, but some advocate that perhaps a change in strategy is in order.
“What the administration should do is push for vaccinating people in high-risk groups, including those who are older, those who are immunocompromised and those who have comorbidities,” Paul Offitt, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told CNN.
Federal regulators have announced they will meet Jan. 26 with a panel of vaccine advisors to examine the current recommended vaccination schedule as well as look at the effectiveness and composition of current vaccines and boosters, with an eye toward the make-up of next-generation shots.
Vaccines are the “best available protection” against hospitalization and death caused by COVID-19, said Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, in a statement announcing the planned meeting.
“Since the initial authorizations of these vaccines, we have learned that protection wanes over time, especially as the virus rapidly mutates and new variants and subvariants emerge,” he said. “Therefore, it’s important to continue discussions about the optimal composition of COVID-19 vaccines for primary and booster vaccination, as well as the optimal interval for booster vaccination.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Now, a new poll shows why so few people are willing to roll up their sleeves again.
The most common reasons people give for not getting the latest booster shot is that they “don’t think they need one” (44%) and they “don’t think the benefits are worth it” (37%), according to poll results from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
The data comes amid announcements by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that boosters reduced COVID-19 hospitalizations by up to 57% for U.S. adults and by up to 84% for people age 65 and older. Those figures are just the latest in a mountain of research reporting the public health benefits of COVID-19 vaccines.
Despite all of the statistical data, health officials’ recent vaccination campaigns have proven far from compelling.
So far, just 15% of people age 12 and older have gotten the latest booster, and 36% of people age 65 and older have gotten it, the CDC’s vaccination trackershows.
Since the start of the pandemic, 1.1 million people in the U.S. have died from COVID-19, with the number of deaths currently rising by 400 per day, The New York Times COVID tracker shows.
Many experts continue to note the need for everyone to get booster shots regularly, but some advocate that perhaps a change in strategy is in order.
“What the administration should do is push for vaccinating people in high-risk groups, including those who are older, those who are immunocompromised and those who have comorbidities,” Paul Offitt, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told CNN.
Federal regulators have announced they will meet Jan. 26 with a panel of vaccine advisors to examine the current recommended vaccination schedule as well as look at the effectiveness and composition of current vaccines and boosters, with an eye toward the make-up of next-generation shots.
Vaccines are the “best available protection” against hospitalization and death caused by COVID-19, said Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, in a statement announcing the planned meeting.
“Since the initial authorizations of these vaccines, we have learned that protection wanes over time, especially as the virus rapidly mutates and new variants and subvariants emerge,” he said. “Therefore, it’s important to continue discussions about the optimal composition of COVID-19 vaccines for primary and booster vaccination, as well as the optimal interval for booster vaccination.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Now, a new poll shows why so few people are willing to roll up their sleeves again.
The most common reasons people give for not getting the latest booster shot is that they “don’t think they need one” (44%) and they “don’t think the benefits are worth it” (37%), according to poll results from the Kaiser Family Foundation.
The data comes amid announcements by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention that boosters reduced COVID-19 hospitalizations by up to 57% for U.S. adults and by up to 84% for people age 65 and older. Those figures are just the latest in a mountain of research reporting the public health benefits of COVID-19 vaccines.
Despite all of the statistical data, health officials’ recent vaccination campaigns have proven far from compelling.
So far, just 15% of people age 12 and older have gotten the latest booster, and 36% of people age 65 and older have gotten it, the CDC’s vaccination trackershows.
Since the start of the pandemic, 1.1 million people in the U.S. have died from COVID-19, with the number of deaths currently rising by 400 per day, The New York Times COVID tracker shows.
Many experts continue to note the need for everyone to get booster shots regularly, but some advocate that perhaps a change in strategy is in order.
“What the administration should do is push for vaccinating people in high-risk groups, including those who are older, those who are immunocompromised and those who have comorbidities,” Paul Offitt, MD, director of the Vaccine Education Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, told CNN.
Federal regulators have announced they will meet Jan. 26 with a panel of vaccine advisors to examine the current recommended vaccination schedule as well as look at the effectiveness and composition of current vaccines and boosters, with an eye toward the make-up of next-generation shots.
Vaccines are the “best available protection” against hospitalization and death caused by COVID-19, said Peter Marks, MD, PhD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, in a statement announcing the planned meeting.
“Since the initial authorizations of these vaccines, we have learned that protection wanes over time, especially as the virus rapidly mutates and new variants and subvariants emerge,” he said. “Therefore, it’s important to continue discussions about the optimal composition of COVID-19 vaccines for primary and booster vaccination, as well as the optimal interval for booster vaccination.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Rise of ‘alarming’ subvariants of COVID ‘worrisome’ for winter
It’s a story perhaps more appropriate for Halloween than for the festive holiday season, given its scary implications.
Not too dire so far, until the researchers’ other findings are considered.
The BQ.1, BQ1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 subvariants are the most resistant to neutralizing antibodies, researcher Qian Wang, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online in the journal Cell. This means people have no or “markedly reduced” protection against infection from these four strains, even if they’ve already had COVID-19 or are vaccinated and boosted multiple times, including with a bivalent vaccine.
On top of that, all available monoclonal antibody treatments are mostly or completely ineffective against these subvariants.
What does that mean for the immediate future? The findings are definitely “worrisome,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Translational Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
But evidence from other countries, specifically Singapore and France, show that at least two of these variants turned out not to be as damaging as expected, likely because of high numbers of people vaccinated or who survived previous infections, he said.
Still, there is little to celebrate in the new findings, except that COVID-19 vaccinations and prior infections can still reduce the risk for serious outcomes such as hospitalization and death, the researchers wrote.
In fact, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data released on Dec. 16 shows that people who have received four shots of the original COVID-19 vaccines as well as the bivalent booster were 57% less likely to visit an urgent care clinic or emergency room, regardless of age.
It comes at a time when BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 account for about 70% of the circulating variants, data show. In addition, hospitalizations are up 18% over the past 2 weeks and COVID-19 deaths are up 50% nationwide, The New York Times reported.
Globally, in many places, an “immunity wall” that has been built, Dr. Topol said. That may not be the case in the United States.
“The problem in the United States, making it harder to predict, is that we have a very low rate of recent boosters, in the past 6 months, especially in seniors,” he said. For example, only 36% of Americans aged 65 years and older, the group with highest risk, have received an updated bivalent booster.
An evolving virus
The subvariants are successfully replacing BA.5, which reigned as one of the most common Omicron variants over the past year. The latest CDC data show that BA.5 now accounts for only about 10% of the circulating virus. The researchers wrote: “This rapid replacement of virus strains is raising the specter of yet another wave of infections in the coming months.”
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 evolved directly from BA.5 – adding more and some novel mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. XBB and XBB.1 are the “offspring” of a combination of two other strains, known as BJ.1 and BA.2.75.
The story sounds familiar to the researchers. “The rapid rise of these subvariants and their extensive array of spike mutations are reminiscent of the appearance of the first Omicron variant last year, thus raising concerns that they may further compromise the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines and monoclonal antibody therapeutics,” they wrote. “We now report findings that indicate that such concerns are, sadly, justified, especially so for the XBB and XBB.1 subvariants.”
To figure out how effective existing antibodies could be against these newer subvariants, Dr. Wang and colleagues used blood samples from five groups of people. They tested serum from people who had three doses of the original COVID-19 vaccine, four doses of the original vaccine, those who received a bivalent booster, people who experienced a breakthrough infection with the BA.2 Omicron variant, and those who had a breakthrough with a BA.4 or BA.5 variant.
Adding the new subvariants to these serum samples revealed that the existing antibodies in the blood were ineffective at wiping out or neutralizing BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.
The BQ.1 subvariant was six times more resistant to antibodies than BA.5, its parent strain, and XBB.1 was 63 times more resistant compared with its predecessor, BA.2.
This shift in the ability of vaccines to stop the subvariants “is particularly concerning,” the researchers wrote.
Wiping out treatments too
Dr. Wang and colleagues also tested how well a panel of 23 different monoclonal antibody drugs might work against the four subvariants. The therapies all worked well against the original Omicron variant and included some approved for use through the Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization (EUA) program at the time of the study.
They found that 19 of these 23 monoclonal antibodies lost effectiveness “greatly or completely” against XBB and XBB.1, for example.
This is not the first time that monoclonal antibody therapies have gone from effective to ineffective. Previous variants have come out that no longer responded to treatment with bamlanivimab, etesevimab, imdevimab, casirivimab, tixagevimab, cilgavimab, and sotrovimab. Bebtelovimab now joins this list and is no longer available from Eli Lilly under EUA because of this lack of effectiveness.
The lack of an effective monoclonal antibody treatment “poses a serious problem for millions of immunocompromised individuals who do not respond robustly to COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers wrote, adding that “the urgent need to develop active monoclonal antibodies for clinical use is obvious.”
A limitation of the study is that the work is done in blood samples. The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination against the BQ and XBB subvariants should be evaluated in people in clinical studies, the authors noted.
Also, the current study looked at how well antibodies could neutralize the viral strains, but future research, they added, should look at how well “cellular immunity” or other aspects of the immune system might protect people.
Going forward, the challenge remains to develop vaccines and treatments that offer broad protection as the coronavirus continues to evolve.
In an alarming ending, the researchers wrote: “We have collectively chased after SARS-CoV-2 variants for over 2 years, and yet, the virus continues to evolve and evade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a story perhaps more appropriate for Halloween than for the festive holiday season, given its scary implications.
Not too dire so far, until the researchers’ other findings are considered.
The BQ.1, BQ1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 subvariants are the most resistant to neutralizing antibodies, researcher Qian Wang, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online in the journal Cell. This means people have no or “markedly reduced” protection against infection from these four strains, even if they’ve already had COVID-19 or are vaccinated and boosted multiple times, including with a bivalent vaccine.
On top of that, all available monoclonal antibody treatments are mostly or completely ineffective against these subvariants.
What does that mean for the immediate future? The findings are definitely “worrisome,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Translational Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
But evidence from other countries, specifically Singapore and France, show that at least two of these variants turned out not to be as damaging as expected, likely because of high numbers of people vaccinated or who survived previous infections, he said.
Still, there is little to celebrate in the new findings, except that COVID-19 vaccinations and prior infections can still reduce the risk for serious outcomes such as hospitalization and death, the researchers wrote.
In fact, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data released on Dec. 16 shows that people who have received four shots of the original COVID-19 vaccines as well as the bivalent booster were 57% less likely to visit an urgent care clinic or emergency room, regardless of age.
It comes at a time when BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 account for about 70% of the circulating variants, data show. In addition, hospitalizations are up 18% over the past 2 weeks and COVID-19 deaths are up 50% nationwide, The New York Times reported.
Globally, in many places, an “immunity wall” that has been built, Dr. Topol said. That may not be the case in the United States.
“The problem in the United States, making it harder to predict, is that we have a very low rate of recent boosters, in the past 6 months, especially in seniors,” he said. For example, only 36% of Americans aged 65 years and older, the group with highest risk, have received an updated bivalent booster.
An evolving virus
The subvariants are successfully replacing BA.5, which reigned as one of the most common Omicron variants over the past year. The latest CDC data show that BA.5 now accounts for only about 10% of the circulating virus. The researchers wrote: “This rapid replacement of virus strains is raising the specter of yet another wave of infections in the coming months.”
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 evolved directly from BA.5 – adding more and some novel mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. XBB and XBB.1 are the “offspring” of a combination of two other strains, known as BJ.1 and BA.2.75.
The story sounds familiar to the researchers. “The rapid rise of these subvariants and their extensive array of spike mutations are reminiscent of the appearance of the first Omicron variant last year, thus raising concerns that they may further compromise the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines and monoclonal antibody therapeutics,” they wrote. “We now report findings that indicate that such concerns are, sadly, justified, especially so for the XBB and XBB.1 subvariants.”
To figure out how effective existing antibodies could be against these newer subvariants, Dr. Wang and colleagues used blood samples from five groups of people. They tested serum from people who had three doses of the original COVID-19 vaccine, four doses of the original vaccine, those who received a bivalent booster, people who experienced a breakthrough infection with the BA.2 Omicron variant, and those who had a breakthrough with a BA.4 or BA.5 variant.
Adding the new subvariants to these serum samples revealed that the existing antibodies in the blood were ineffective at wiping out or neutralizing BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.
The BQ.1 subvariant was six times more resistant to antibodies than BA.5, its parent strain, and XBB.1 was 63 times more resistant compared with its predecessor, BA.2.
This shift in the ability of vaccines to stop the subvariants “is particularly concerning,” the researchers wrote.
Wiping out treatments too
Dr. Wang and colleagues also tested how well a panel of 23 different monoclonal antibody drugs might work against the four subvariants. The therapies all worked well against the original Omicron variant and included some approved for use through the Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization (EUA) program at the time of the study.
They found that 19 of these 23 monoclonal antibodies lost effectiveness “greatly or completely” against XBB and XBB.1, for example.
This is not the first time that monoclonal antibody therapies have gone from effective to ineffective. Previous variants have come out that no longer responded to treatment with bamlanivimab, etesevimab, imdevimab, casirivimab, tixagevimab, cilgavimab, and sotrovimab. Bebtelovimab now joins this list and is no longer available from Eli Lilly under EUA because of this lack of effectiveness.
The lack of an effective monoclonal antibody treatment “poses a serious problem for millions of immunocompromised individuals who do not respond robustly to COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers wrote, adding that “the urgent need to develop active monoclonal antibodies for clinical use is obvious.”
A limitation of the study is that the work is done in blood samples. The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination against the BQ and XBB subvariants should be evaluated in people in clinical studies, the authors noted.
Also, the current study looked at how well antibodies could neutralize the viral strains, but future research, they added, should look at how well “cellular immunity” or other aspects of the immune system might protect people.
Going forward, the challenge remains to develop vaccines and treatments that offer broad protection as the coronavirus continues to evolve.
In an alarming ending, the researchers wrote: “We have collectively chased after SARS-CoV-2 variants for over 2 years, and yet, the virus continues to evolve and evade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It’s a story perhaps more appropriate for Halloween than for the festive holiday season, given its scary implications.
Not too dire so far, until the researchers’ other findings are considered.
The BQ.1, BQ1.1, XBB, and XBB.1 subvariants are the most resistant to neutralizing antibodies, researcher Qian Wang, PhD, and colleagues wrote in a study published online in the journal Cell. This means people have no or “markedly reduced” protection against infection from these four strains, even if they’ve already had COVID-19 or are vaccinated and boosted multiple times, including with a bivalent vaccine.
On top of that, all available monoclonal antibody treatments are mostly or completely ineffective against these subvariants.
What does that mean for the immediate future? The findings are definitely “worrisome,” said Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Translational Research Institute in La Jolla, Calif.
But evidence from other countries, specifically Singapore and France, show that at least two of these variants turned out not to be as damaging as expected, likely because of high numbers of people vaccinated or who survived previous infections, he said.
Still, there is little to celebrate in the new findings, except that COVID-19 vaccinations and prior infections can still reduce the risk for serious outcomes such as hospitalization and death, the researchers wrote.
In fact, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data released on Dec. 16 shows that people who have received four shots of the original COVID-19 vaccines as well as the bivalent booster were 57% less likely to visit an urgent care clinic or emergency room, regardless of age.
It comes at a time when BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 account for about 70% of the circulating variants, data show. In addition, hospitalizations are up 18% over the past 2 weeks and COVID-19 deaths are up 50% nationwide, The New York Times reported.
Globally, in many places, an “immunity wall” that has been built, Dr. Topol said. That may not be the case in the United States.
“The problem in the United States, making it harder to predict, is that we have a very low rate of recent boosters, in the past 6 months, especially in seniors,” he said. For example, only 36% of Americans aged 65 years and older, the group with highest risk, have received an updated bivalent booster.
An evolving virus
The subvariants are successfully replacing BA.5, which reigned as one of the most common Omicron variants over the past year. The latest CDC data show that BA.5 now accounts for only about 10% of the circulating virus. The researchers wrote: “This rapid replacement of virus strains is raising the specter of yet another wave of infections in the coming months.”
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 evolved directly from BA.5 – adding more and some novel mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 virus. XBB and XBB.1 are the “offspring” of a combination of two other strains, known as BJ.1 and BA.2.75.
The story sounds familiar to the researchers. “The rapid rise of these subvariants and their extensive array of spike mutations are reminiscent of the appearance of the first Omicron variant last year, thus raising concerns that they may further compromise the efficacy of current COVID-19 vaccines and monoclonal antibody therapeutics,” they wrote. “We now report findings that indicate that such concerns are, sadly, justified, especially so for the XBB and XBB.1 subvariants.”
To figure out how effective existing antibodies could be against these newer subvariants, Dr. Wang and colleagues used blood samples from five groups of people. They tested serum from people who had three doses of the original COVID-19 vaccine, four doses of the original vaccine, those who received a bivalent booster, people who experienced a breakthrough infection with the BA.2 Omicron variant, and those who had a breakthrough with a BA.4 or BA.5 variant.
Adding the new subvariants to these serum samples revealed that the existing antibodies in the blood were ineffective at wiping out or neutralizing BQ.1, BQ.1.1, XBB, and XBB.1.
The BQ.1 subvariant was six times more resistant to antibodies than BA.5, its parent strain, and XBB.1 was 63 times more resistant compared with its predecessor, BA.2.
This shift in the ability of vaccines to stop the subvariants “is particularly concerning,” the researchers wrote.
Wiping out treatments too
Dr. Wang and colleagues also tested how well a panel of 23 different monoclonal antibody drugs might work against the four subvariants. The therapies all worked well against the original Omicron variant and included some approved for use through the Food and Drug Administration emergency use authorization (EUA) program at the time of the study.
They found that 19 of these 23 monoclonal antibodies lost effectiveness “greatly or completely” against XBB and XBB.1, for example.
This is not the first time that monoclonal antibody therapies have gone from effective to ineffective. Previous variants have come out that no longer responded to treatment with bamlanivimab, etesevimab, imdevimab, casirivimab, tixagevimab, cilgavimab, and sotrovimab. Bebtelovimab now joins this list and is no longer available from Eli Lilly under EUA because of this lack of effectiveness.
The lack of an effective monoclonal antibody treatment “poses a serious problem for millions of immunocompromised individuals who do not respond robustly to COVID-19 vaccines,” the researchers wrote, adding that “the urgent need to develop active monoclonal antibodies for clinical use is obvious.”
A limitation of the study is that the work is done in blood samples. The effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccination against the BQ and XBB subvariants should be evaluated in people in clinical studies, the authors noted.
Also, the current study looked at how well antibodies could neutralize the viral strains, but future research, they added, should look at how well “cellular immunity” or other aspects of the immune system might protect people.
Going forward, the challenge remains to develop vaccines and treatments that offer broad protection as the coronavirus continues to evolve.
In an alarming ending, the researchers wrote: “We have collectively chased after SARS-CoV-2 variants for over 2 years, and yet, the virus continues to evolve and evade.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CELL
As COVID treatments dwindle, are new ones waiting in the wings?
It was the last monoclonal antibody treatment standing. But less than 10 months after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration gave bebtelovimab its emergency use authorization (EUA) to fight COVID-19, it earlier this month de-authorized it, just as it had for other monoclonal antibody treatments, and for the same reason:
Bebtelovimab couldn’t neutralize the Omicron subvariants BQ.1 and BQ.1.1, the cause of nearly 60% of COVID cases nationally as of November 30.
Next on the chopping block, some predict, will be Evusheld, the combination of tixagevimab and cilgavimab given as a preventive monoclonal antibody to people who are immunocompromised and at high risk of contracting COVID and to those who can’t take the vaccine. In October, the FDA warned that Evusheld was not neutralizing circulating COVID variants.
As the options for treating and preventing COVID decline, will companies rally quickly to develop new ones, or cut their losses in developing treatments that may work for only a few months, given the speed of viral mutations?
But although monoclonal antibody treatments are off the table, at least for now, antiviral drugs – including Paxlovid – are still very much available, and some say underused.
Others suggest it’s time to resurrect interest in convalescent plasma, a treatment used early in the pandemic before drugs or vaccines were here and still authorized for use in those who are immunosuppressed or receiving immunosuppressive treatment.
And on the prevention front, staying up to date with booster vaccines, masking, and taking other precautions should be stressed more, others say, regardless of the number of treatment options, and especially now, as cases rise and people gather for the winter holidays.
‘A major setback’
The bebtelovimab de-authorization was “a major setback,” but an understandable one, said Arturo Casadevall, MD, PhD, professor and chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. “Monoclonal antibodies are great drugs. We are in an unfortunate situation in that they are vulnerable to changes in the virus” and can’t offer long-lasting protection.
Supplies of bebtelovimab will be retained, according to the FDA, in case variants susceptible to it return.
“What happened to bebtelovimab is no surprise,” agreed Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. “This is what is going to happen when you are targeting a virus that mutates a lot.”
Monoclonal antibodies work by binding to the spike protein on the virus surface to prevent it from entering cells.
However, Dr. Adalja doesn’t view the disappearance of monoclonal antibody treatments as a major setback. Monoclonal antibodies were not the primary way COVID was treated, he said.
While he does believe it’s important that more monoclonal antibody treatments be developed, “I think it’s important to remember we still have Paxlovid while everyone is lamenting the loss of bebtelovimab.’’
Antivirals: What’s here, what’s coming
Compared with monoclonal antibodies, “Paxlovid remains a much easier drug to give,” Dr. Adalja told this news organization, because it is taken orally, not intravenously.
And it’s effective. In a recent study, researchers found that adults diagnosed with COVID given Paxlovid within 5 days of diagnosis had a 51% lower hospitalization rate within the next 30 days than those not given it. Another study shows it could also reduce a person’s risk of developing long COVID by 26%.
Paxlovid is underused, Dr. Adalja said, partly because the rebound potential got more press than the effectiveness. When a celebrity got rebound from Paxlovid, he said, that would make the news, overshadowing the research on its effectiveness.
Besides Paxlovid, the antivirals remdesivir (Veklury), given intravenously for 3 days, and molnupiravir (Lagevrio), taken orally, are also still available. Antivirals work by targeting specific parts of the virus to prevent it from multiplying.
In the lab, remdesivir, molnupiravir, and another antiviral, nirmatrelvir, all appear to be effective against both BQ.1.1 (a BA.5 subvariant) and XBB (a BA.2 subvariant), both rapidly rising in the United States, according to a report last week in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers also tested several monoclonal antibodies and found they did not neutralize either of the subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB.
A new oral antiviral, Xocova (ensitrelvir fumaric acid), from Japanese manufacturer Shionogi, received emergency approval in Japan on November 22. It’s taken once a day for 5 days. The goal is to expand access to it globally, according to the company.
Pardes Biosciences launched a phase 2 trial in September for its oral antiviral drug (PBI-0451), under study as a treatment and preventive for COVID. It expects data by the first quarter of 2023.
Pfizer, which makes Paxlovid, has partnered with Clear Creek Bio to develop another oral antiviral COVID drug.
Other approaches
A receptor protein known as ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) is the main “doorway” that SARS-CoV-2 uses to enter and infect cells.
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists are developing a “decoy” drug that works by mimicking the ACE2 receptor on the surface of cells; when the virus tries to bind to it, the spike protein is destroyed. Human trials have not yet started.
Other researchers are investigating whether an already-approved drug used to treat a liver disease, Actigall (UDCA/ursodeoxycholic acid), could protect against COVID infection by reducing ACE2.
So far, the researchers have found in early research that people taking UDCA for liver conditions were less likely than those not taking the drug to have severe COVID. They also found that UDCA reduced SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lungs maintained outside the body.
Monoclonal antibody treatments?
After the FDA decision to withdraw the bebtelovimab EUA, which Eli Lilly said it agreed with, the company issued a statement, promising it wasn’t giving up on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“Lilly will continue to search and evaluate monoclonal antibodies to identify potential candidates for clinical development against new variants,” it read in part.
AstraZeneca, which makes Evusheld, is also continuing to work on monoclonal antibody development. According to a spokesperson, “We are also developing a new long-acting antibody combination – AZD5156 – which has been shown in the lab to neutralize emerging new variants and all known variants to date. We are working to accelerate the development of AZD5156 to make it available at the end of 2023.”
The AstraZeneca spokesperson said he could share no more information about what the combination would include.
A convalescent plasma comeback?
Although Paxlovid can help, there are many contraindications to it, such as drug-drug interactions, Dr. Casadevall told this news organization. And now that the monoclonal antibody treatments have been paused, convalescent plasma “is the only antibody-based therapy that is reliably available. Convalescent plasma includes thousands of different antibodies.”
With his colleagues, Dr. Casadevall evaluated plasma samples from 740 patients. Some had received booster vaccines and been infected with Omicron, others had received boosters and not been infected, and still others had not been vaccinated and became infected.
In a report (not yet peer-reviewed), they found the plasma from those who had been infected or boosted within the past 6 months neutralized the new Omicron variants BQ.1.1, XBB.1, and BF.7.
A push for boosters, masks
To get through the coming months, taking precautions like masking and distancing and staying up to date on booster vaccinations, especially for older adults, can make a difference, other experts say.
In a Twitter thread in early December, Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics and molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, urged people to take COVID seriously as holiday parties and gatherings occur.
“The single most impactful thing you can do is get your bivalent booster,” he tweeted, as well as give your kids the booster, citing preliminary research that the bivalent mRNA booster broadens immunity against the Omicron subvariants.
For seniors, he said, ‘‘if you get breakthrough COVID, [it’s] really important to get Paxlovid.” Masks will help not only for COVID but also influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other conditions.
Mitigation measures have largely been abandoned, according to Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. In an op-ed in the Los Angeles Times, and on his Twitter feed, he reminds people about masking and urges people to get the bivalent booster.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Dec. 8, only 13.5% of people aged 5 and older have gotten an updated booster, despite research that shows an increase in antibodies to BQ.1.1. Recent research has found that the bivalent booster increases antibodies to BQ.1.1 by up to 10-fold, Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja is on advisory boards for Shionogi, GSK, and Pardes. Dr. Casadevall reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It was the last monoclonal antibody treatment standing. But less than 10 months after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration gave bebtelovimab its emergency use authorization (EUA) to fight COVID-19, it earlier this month de-authorized it, just as it had for other monoclonal antibody treatments, and for the same reason:
Bebtelovimab couldn’t neutralize the Omicron subvariants BQ.1 and BQ.1.1, the cause of nearly 60% of COVID cases nationally as of November 30.
Next on the chopping block, some predict, will be Evusheld, the combination of tixagevimab and cilgavimab given as a preventive monoclonal antibody to people who are immunocompromised and at high risk of contracting COVID and to those who can’t take the vaccine. In October, the FDA warned that Evusheld was not neutralizing circulating COVID variants.
As the options for treating and preventing COVID decline, will companies rally quickly to develop new ones, or cut their losses in developing treatments that may work for only a few months, given the speed of viral mutations?
But although monoclonal antibody treatments are off the table, at least for now, antiviral drugs – including Paxlovid – are still very much available, and some say underused.
Others suggest it’s time to resurrect interest in convalescent plasma, a treatment used early in the pandemic before drugs or vaccines were here and still authorized for use in those who are immunosuppressed or receiving immunosuppressive treatment.
And on the prevention front, staying up to date with booster vaccines, masking, and taking other precautions should be stressed more, others say, regardless of the number of treatment options, and especially now, as cases rise and people gather for the winter holidays.
‘A major setback’
The bebtelovimab de-authorization was “a major setback,” but an understandable one, said Arturo Casadevall, MD, PhD, professor and chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. “Monoclonal antibodies are great drugs. We are in an unfortunate situation in that they are vulnerable to changes in the virus” and can’t offer long-lasting protection.
Supplies of bebtelovimab will be retained, according to the FDA, in case variants susceptible to it return.
“What happened to bebtelovimab is no surprise,” agreed Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. “This is what is going to happen when you are targeting a virus that mutates a lot.”
Monoclonal antibodies work by binding to the spike protein on the virus surface to prevent it from entering cells.
However, Dr. Adalja doesn’t view the disappearance of monoclonal antibody treatments as a major setback. Monoclonal antibodies were not the primary way COVID was treated, he said.
While he does believe it’s important that more monoclonal antibody treatments be developed, “I think it’s important to remember we still have Paxlovid while everyone is lamenting the loss of bebtelovimab.’’
Antivirals: What’s here, what’s coming
Compared with monoclonal antibodies, “Paxlovid remains a much easier drug to give,” Dr. Adalja told this news organization, because it is taken orally, not intravenously.
And it’s effective. In a recent study, researchers found that adults diagnosed with COVID given Paxlovid within 5 days of diagnosis had a 51% lower hospitalization rate within the next 30 days than those not given it. Another study shows it could also reduce a person’s risk of developing long COVID by 26%.
Paxlovid is underused, Dr. Adalja said, partly because the rebound potential got more press than the effectiveness. When a celebrity got rebound from Paxlovid, he said, that would make the news, overshadowing the research on its effectiveness.
Besides Paxlovid, the antivirals remdesivir (Veklury), given intravenously for 3 days, and molnupiravir (Lagevrio), taken orally, are also still available. Antivirals work by targeting specific parts of the virus to prevent it from multiplying.
In the lab, remdesivir, molnupiravir, and another antiviral, nirmatrelvir, all appear to be effective against both BQ.1.1 (a BA.5 subvariant) and XBB (a BA.2 subvariant), both rapidly rising in the United States, according to a report last week in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers also tested several monoclonal antibodies and found they did not neutralize either of the subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB.
A new oral antiviral, Xocova (ensitrelvir fumaric acid), from Japanese manufacturer Shionogi, received emergency approval in Japan on November 22. It’s taken once a day for 5 days. The goal is to expand access to it globally, according to the company.
Pardes Biosciences launched a phase 2 trial in September for its oral antiviral drug (PBI-0451), under study as a treatment and preventive for COVID. It expects data by the first quarter of 2023.
Pfizer, which makes Paxlovid, has partnered with Clear Creek Bio to develop another oral antiviral COVID drug.
Other approaches
A receptor protein known as ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) is the main “doorway” that SARS-CoV-2 uses to enter and infect cells.
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists are developing a “decoy” drug that works by mimicking the ACE2 receptor on the surface of cells; when the virus tries to bind to it, the spike protein is destroyed. Human trials have not yet started.
Other researchers are investigating whether an already-approved drug used to treat a liver disease, Actigall (UDCA/ursodeoxycholic acid), could protect against COVID infection by reducing ACE2.
So far, the researchers have found in early research that people taking UDCA for liver conditions were less likely than those not taking the drug to have severe COVID. They also found that UDCA reduced SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lungs maintained outside the body.
Monoclonal antibody treatments?
After the FDA decision to withdraw the bebtelovimab EUA, which Eli Lilly said it agreed with, the company issued a statement, promising it wasn’t giving up on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“Lilly will continue to search and evaluate monoclonal antibodies to identify potential candidates for clinical development against new variants,” it read in part.
AstraZeneca, which makes Evusheld, is also continuing to work on monoclonal antibody development. According to a spokesperson, “We are also developing a new long-acting antibody combination – AZD5156 – which has been shown in the lab to neutralize emerging new variants and all known variants to date. We are working to accelerate the development of AZD5156 to make it available at the end of 2023.”
The AstraZeneca spokesperson said he could share no more information about what the combination would include.
A convalescent plasma comeback?
Although Paxlovid can help, there are many contraindications to it, such as drug-drug interactions, Dr. Casadevall told this news organization. And now that the monoclonal antibody treatments have been paused, convalescent plasma “is the only antibody-based therapy that is reliably available. Convalescent plasma includes thousands of different antibodies.”
With his colleagues, Dr. Casadevall evaluated plasma samples from 740 patients. Some had received booster vaccines and been infected with Omicron, others had received boosters and not been infected, and still others had not been vaccinated and became infected.
In a report (not yet peer-reviewed), they found the plasma from those who had been infected or boosted within the past 6 months neutralized the new Omicron variants BQ.1.1, XBB.1, and BF.7.
A push for boosters, masks
To get through the coming months, taking precautions like masking and distancing and staying up to date on booster vaccinations, especially for older adults, can make a difference, other experts say.
In a Twitter thread in early December, Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics and molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, urged people to take COVID seriously as holiday parties and gatherings occur.
“The single most impactful thing you can do is get your bivalent booster,” he tweeted, as well as give your kids the booster, citing preliminary research that the bivalent mRNA booster broadens immunity against the Omicron subvariants.
For seniors, he said, ‘‘if you get breakthrough COVID, [it’s] really important to get Paxlovid.” Masks will help not only for COVID but also influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other conditions.
Mitigation measures have largely been abandoned, according to Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. In an op-ed in the Los Angeles Times, and on his Twitter feed, he reminds people about masking and urges people to get the bivalent booster.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Dec. 8, only 13.5% of people aged 5 and older have gotten an updated booster, despite research that shows an increase in antibodies to BQ.1.1. Recent research has found that the bivalent booster increases antibodies to BQ.1.1 by up to 10-fold, Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja is on advisory boards for Shionogi, GSK, and Pardes. Dr. Casadevall reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It was the last monoclonal antibody treatment standing. But less than 10 months after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration gave bebtelovimab its emergency use authorization (EUA) to fight COVID-19, it earlier this month de-authorized it, just as it had for other monoclonal antibody treatments, and for the same reason:
Bebtelovimab couldn’t neutralize the Omicron subvariants BQ.1 and BQ.1.1, the cause of nearly 60% of COVID cases nationally as of November 30.
Next on the chopping block, some predict, will be Evusheld, the combination of tixagevimab and cilgavimab given as a preventive monoclonal antibody to people who are immunocompromised and at high risk of contracting COVID and to those who can’t take the vaccine. In October, the FDA warned that Evusheld was not neutralizing circulating COVID variants.
As the options for treating and preventing COVID decline, will companies rally quickly to develop new ones, or cut their losses in developing treatments that may work for only a few months, given the speed of viral mutations?
But although monoclonal antibody treatments are off the table, at least for now, antiviral drugs – including Paxlovid – are still very much available, and some say underused.
Others suggest it’s time to resurrect interest in convalescent plasma, a treatment used early in the pandemic before drugs or vaccines were here and still authorized for use in those who are immunosuppressed or receiving immunosuppressive treatment.
And on the prevention front, staying up to date with booster vaccines, masking, and taking other precautions should be stressed more, others say, regardless of the number of treatment options, and especially now, as cases rise and people gather for the winter holidays.
‘A major setback’
The bebtelovimab de-authorization was “a major setback,” but an understandable one, said Arturo Casadevall, MD, PhD, professor and chair of molecular microbiology and immunology at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health in Baltimore. “Monoclonal antibodies are great drugs. We are in an unfortunate situation in that they are vulnerable to changes in the virus” and can’t offer long-lasting protection.
Supplies of bebtelovimab will be retained, according to the FDA, in case variants susceptible to it return.
“What happened to bebtelovimab is no surprise,” agreed Amesh Adalja, MD, senior scholar at Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. “This is what is going to happen when you are targeting a virus that mutates a lot.”
Monoclonal antibodies work by binding to the spike protein on the virus surface to prevent it from entering cells.
However, Dr. Adalja doesn’t view the disappearance of monoclonal antibody treatments as a major setback. Monoclonal antibodies were not the primary way COVID was treated, he said.
While he does believe it’s important that more monoclonal antibody treatments be developed, “I think it’s important to remember we still have Paxlovid while everyone is lamenting the loss of bebtelovimab.’’
Antivirals: What’s here, what’s coming
Compared with monoclonal antibodies, “Paxlovid remains a much easier drug to give,” Dr. Adalja told this news organization, because it is taken orally, not intravenously.
And it’s effective. In a recent study, researchers found that adults diagnosed with COVID given Paxlovid within 5 days of diagnosis had a 51% lower hospitalization rate within the next 30 days than those not given it. Another study shows it could also reduce a person’s risk of developing long COVID by 26%.
Paxlovid is underused, Dr. Adalja said, partly because the rebound potential got more press than the effectiveness. When a celebrity got rebound from Paxlovid, he said, that would make the news, overshadowing the research on its effectiveness.
Besides Paxlovid, the antivirals remdesivir (Veklury), given intravenously for 3 days, and molnupiravir (Lagevrio), taken orally, are also still available. Antivirals work by targeting specific parts of the virus to prevent it from multiplying.
In the lab, remdesivir, molnupiravir, and another antiviral, nirmatrelvir, all appear to be effective against both BQ.1.1 (a BA.5 subvariant) and XBB (a BA.2 subvariant), both rapidly rising in the United States, according to a report last week in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The researchers also tested several monoclonal antibodies and found they did not neutralize either of the subvariants BQ.1.1 and XBB.
A new oral antiviral, Xocova (ensitrelvir fumaric acid), from Japanese manufacturer Shionogi, received emergency approval in Japan on November 22. It’s taken once a day for 5 days. The goal is to expand access to it globally, according to the company.
Pardes Biosciences launched a phase 2 trial in September for its oral antiviral drug (PBI-0451), under study as a treatment and preventive for COVID. It expects data by the first quarter of 2023.
Pfizer, which makes Paxlovid, has partnered with Clear Creek Bio to develop another oral antiviral COVID drug.
Other approaches
A receptor protein known as ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2) is the main “doorway” that SARS-CoV-2 uses to enter and infect cells.
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists are developing a “decoy” drug that works by mimicking the ACE2 receptor on the surface of cells; when the virus tries to bind to it, the spike protein is destroyed. Human trials have not yet started.
Other researchers are investigating whether an already-approved drug used to treat a liver disease, Actigall (UDCA/ursodeoxycholic acid), could protect against COVID infection by reducing ACE2.
So far, the researchers have found in early research that people taking UDCA for liver conditions were less likely than those not taking the drug to have severe COVID. They also found that UDCA reduced SARS-CoV-2 infection in human lungs maintained outside the body.
Monoclonal antibody treatments?
After the FDA decision to withdraw the bebtelovimab EUA, which Eli Lilly said it agreed with, the company issued a statement, promising it wasn’t giving up on monoclonal antibody treatments.
“Lilly will continue to search and evaluate monoclonal antibodies to identify potential candidates for clinical development against new variants,” it read in part.
AstraZeneca, which makes Evusheld, is also continuing to work on monoclonal antibody development. According to a spokesperson, “We are also developing a new long-acting antibody combination – AZD5156 – which has been shown in the lab to neutralize emerging new variants and all known variants to date. We are working to accelerate the development of AZD5156 to make it available at the end of 2023.”
The AstraZeneca spokesperson said he could share no more information about what the combination would include.
A convalescent plasma comeback?
Although Paxlovid can help, there are many contraindications to it, such as drug-drug interactions, Dr. Casadevall told this news organization. And now that the monoclonal antibody treatments have been paused, convalescent plasma “is the only antibody-based therapy that is reliably available. Convalescent plasma includes thousands of different antibodies.”
With his colleagues, Dr. Casadevall evaluated plasma samples from 740 patients. Some had received booster vaccines and been infected with Omicron, others had received boosters and not been infected, and still others had not been vaccinated and became infected.
In a report (not yet peer-reviewed), they found the plasma from those who had been infected or boosted within the past 6 months neutralized the new Omicron variants BQ.1.1, XBB.1, and BF.7.
A push for boosters, masks
To get through the coming months, taking precautions like masking and distancing and staying up to date on booster vaccinations, especially for older adults, can make a difference, other experts say.
In a Twitter thread in early December, Peter Hotez, MD, PhD, professor of pediatrics and molecular virology and microbiology at Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, urged people to take COVID seriously as holiday parties and gatherings occur.
“The single most impactful thing you can do is get your bivalent booster,” he tweeted, as well as give your kids the booster, citing preliminary research that the bivalent mRNA booster broadens immunity against the Omicron subvariants.
For seniors, he said, ‘‘if you get breakthrough COVID, [it’s] really important to get Paxlovid.” Masks will help not only for COVID but also influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and other conditions.
Mitigation measures have largely been abandoned, according to Eric Topol, MD, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute, La Jolla, Calif., and editor-in-chief of Medscape. In an op-ed in the Los Angeles Times, and on his Twitter feed, he reminds people about masking and urges people to get the bivalent booster.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, as of Dec. 8, only 13.5% of people aged 5 and older have gotten an updated booster, despite research that shows an increase in antibodies to BQ.1.1. Recent research has found that the bivalent booster increases antibodies to BQ.1.1 by up to 10-fold, Dr. Topol said.
Dr. Adalja is on advisory boards for Shionogi, GSK, and Pardes. Dr. Casadevall reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Paxlovid has been free so far. Next year, sticker shock awaits
Nearly 6 million Americans have taken Paxlovid for free, courtesy of the federal government. The Pfizer pill has helped prevent many people infected with COVID-19 from being hospitalized or dying, and it may even reduce the risk of developing long COVID.
And that means fewer people will get the potentially lifesaving treatments, experts said.
“I think the numbers will go way down,” said Jill Rosenthal, director of public health policy at the Center for American Progress, a left-leaning think tank. A bill for several hundred dollars or more would lead many people to decide the medication isn’t worth the price, she said.
In response to the unprecedented public health crisis caused by COVID, the federal government spent billions of dollars on developing new vaccines and treatments, to swift success: Less than a year after the pandemic was declared, medical workers got their first vaccines. But as many people have refused the shots and stopped wearing masks, the virus still rages and mutates. In 2022 alone, 250,000 Americans have died from COVID, more than from strokes or diabetes.
But soon the Department of Health & Human Services will stop supplying COVID treatments, and pharmacies will purchase and bill for them the same way they do for antibiotic pills or asthma inhalers. Paxlovid is expected to hit the private market in mid-2023, according to HHS plans shared in an October meeting with state health officials and clinicians. Merck’s Lagevrio, a less-effective COVID treatment pill, and AstraZeneca’s Evusheld, a preventive therapy for the immunocompromised, are on track to be commercialized sooner, sometime in the winter.
The U.S. government has so far purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid, priced at about $530 each, a discount for buying in bulk that Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla called “really very attractive” to the federal government in a July earnings call. The drug will cost far more on the private market, although in a statement to Kaiser Health News, Pfizer declined to share the planned price. The government will also stop paying for the company’s COVID vaccine next year – those shots will quadruple in price, from the discount rate the government pays of $30 to about $120.
Mr. Bourla told investors in November that he expects the move will make Paxlovid and its COVID vaccine “a multibillion-dollars franchise.”
Nearly 9 in 10 people dying from the virus now are 65 or older. Yet federal law restricts Medicare Part D – the prescription drug program that covers nearly 50 million seniors – from covering the COVID treatment pills. The medications are meant for those most at risk of serious illness, including seniors.
Paxlovid and the other treatments are currently available under an emergency use authorization from the FDA, a fast-track review used in extraordinary situations. Although Pfizer applied for full approval in June, the process can take anywhere from several months to years. And Medicare Part D can’t cover any medications without that full stamp of approval.
Paying out-of-pocket would be “a substantial barrier” for seniors on Medicare – the very people who would benefit most from the drug, wrote federal health experts.
“From a public health perspective, and even from a health care capacity and cost perspective, it would just defy reason to not continue to make these drugs readily available,” said Dr. Larry Madoff, medical director of Massachusetts’s Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Sciences. He’s hopeful that the federal health agency will find a way to set aside unused doses for seniors and people without insurance.
In mid-November, the White House requested that Congress approve an additional $2.5 billion for COVID therapeutics and vaccines to make sure people can afford the medications when they’re no longer free. But there’s little hope it will be approved – the Senate voted that same day to end the public health emergency and denied similar requests in recent months.
Many Americans have already faced hurdles just getting a prescription for COVID treatment. Although the federal government doesn’t track who’s gotten the drug, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study using data from 30 medical centers found that Black and Hispanic patients with COVID were much less likely to receive Paxlovid than White patients. (Hispanic people can be of any race or combination of races.) And when the government is no longer picking up the tab, experts predict that these gaps by race, income, and geography will widen.
People in Northeastern states used the drug far more often than those in the rest of the country, according to a KHN analysis of Paxlovid use in September and October. But it wasn’t because people in the region were getting sick from COVID at much higher rates – instead, many of those states offered better access to health care to begin with and created special programs to get Paxlovid to their residents.
About 10 mostly Democratic states and several large counties in the Northeast and elsewhere created free “test-to-treat” programs that allow their residents to get an immediate doctor visit and prescription for treatment after testing positive for COVID. In Massachusetts, more than 20,000 residents have used the state’s video and phone hotline, which is available 7 days a week in 13 languages. Massachusetts, which has the highest insurance rate in the country and relatively low travel times to pharmacies, had the second-highest Paxlovid usage rate among states this fall.
States with higher COVID death rates, like Florida and Kentucky, where residents must travel farther for health care and are more likely to be uninsured, used the drug less often. Without no-cost test-to-treat options, residents have struggled to get prescriptions even though the drug itself is still free.
“If you look at access to medications for people who are uninsured, I think that there’s no question that will widen those disparities,” Ms. Rosenthal said.
People who get insurance through their jobs could face high copays at the register, too, just as they do for insulin and other expensive or brand-name drugs.
Most private insurance companies will end up covering COVID therapeutics to some extent, said Sabrina Corlette, a research professor at Georgetown University’s Center on Health Insurance Reforms. After all, the pills are cheaper than a hospital stay. But for most people who get insurance through their jobs, there are “really no rules at all,” she said. Some insurers could take months to add the drugs to their plans or decide not to pay for them.
And the additional cost means many people will go without the medication. “We know from lots of research that when people face cost sharing for these drugs that they need to take, they will often forgo or cut back,” Ms. Corlette said.
One group doesn’t need to worry about sticker shock. Medicaid, the public insurance program for low-income adults and children, will cover the treatments in full until at least early 2024.
HHS officials could set aside any leftover taxpayer-funded medication for people who can’t afford to pay the full cost, but they haven’t shared any concrete plans to do so. The government purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid and 3 million of Lagevrio. Fewer than a third have been used, and usage has fallen in recent months, according to KHN’s analysis of the data from HHS.
Sixty percent of the government’s supply of Evusheld is also still available, although the COVID prevention therapy is less effective against new strains of the virus. The health department in one state, New Mexico, has recommended against using it.
HHS did not make officials available for an interview or answer written questions about the commercialization plans.
The government created a potential workaround when they moved bebtelovimab, another COVID treatment, to the private market this summer. It now retails for $2,100 per patient. The agency set aside the remaining 60,000 government-purchased doses that hospitals could use to treat uninsured patients in a convoluted dose-replacement process. But it’s hard to tell how well that setup would work for Paxlovid: Bebtelovimab was already much less popular, and the FDA halted its use on Nov. 30 because it’s less effective against current strains of the virus.
Federal officials and insurance companies would have good reason to make sure patients can continue to afford COVID drugs: They’re far cheaper than if patients land in the emergency room.
“The medications are so worthwhile,” said Dr. Madoff, the Massachusetts health official. “They’re not expensive in the grand scheme of health care costs.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Nearly 6 million Americans have taken Paxlovid for free, courtesy of the federal government. The Pfizer pill has helped prevent many people infected with COVID-19 from being hospitalized or dying, and it may even reduce the risk of developing long COVID.
And that means fewer people will get the potentially lifesaving treatments, experts said.
“I think the numbers will go way down,” said Jill Rosenthal, director of public health policy at the Center for American Progress, a left-leaning think tank. A bill for several hundred dollars or more would lead many people to decide the medication isn’t worth the price, she said.
In response to the unprecedented public health crisis caused by COVID, the federal government spent billions of dollars on developing new vaccines and treatments, to swift success: Less than a year after the pandemic was declared, medical workers got their first vaccines. But as many people have refused the shots and stopped wearing masks, the virus still rages and mutates. In 2022 alone, 250,000 Americans have died from COVID, more than from strokes or diabetes.
But soon the Department of Health & Human Services will stop supplying COVID treatments, and pharmacies will purchase and bill for them the same way they do for antibiotic pills or asthma inhalers. Paxlovid is expected to hit the private market in mid-2023, according to HHS plans shared in an October meeting with state health officials and clinicians. Merck’s Lagevrio, a less-effective COVID treatment pill, and AstraZeneca’s Evusheld, a preventive therapy for the immunocompromised, are on track to be commercialized sooner, sometime in the winter.
The U.S. government has so far purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid, priced at about $530 each, a discount for buying in bulk that Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla called “really very attractive” to the federal government in a July earnings call. The drug will cost far more on the private market, although in a statement to Kaiser Health News, Pfizer declined to share the planned price. The government will also stop paying for the company’s COVID vaccine next year – those shots will quadruple in price, from the discount rate the government pays of $30 to about $120.
Mr. Bourla told investors in November that he expects the move will make Paxlovid and its COVID vaccine “a multibillion-dollars franchise.”
Nearly 9 in 10 people dying from the virus now are 65 or older. Yet federal law restricts Medicare Part D – the prescription drug program that covers nearly 50 million seniors – from covering the COVID treatment pills. The medications are meant for those most at risk of serious illness, including seniors.
Paxlovid and the other treatments are currently available under an emergency use authorization from the FDA, a fast-track review used in extraordinary situations. Although Pfizer applied for full approval in June, the process can take anywhere from several months to years. And Medicare Part D can’t cover any medications without that full stamp of approval.
Paying out-of-pocket would be “a substantial barrier” for seniors on Medicare – the very people who would benefit most from the drug, wrote federal health experts.
“From a public health perspective, and even from a health care capacity and cost perspective, it would just defy reason to not continue to make these drugs readily available,” said Dr. Larry Madoff, medical director of Massachusetts’s Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Sciences. He’s hopeful that the federal health agency will find a way to set aside unused doses for seniors and people without insurance.
In mid-November, the White House requested that Congress approve an additional $2.5 billion for COVID therapeutics and vaccines to make sure people can afford the medications when they’re no longer free. But there’s little hope it will be approved – the Senate voted that same day to end the public health emergency and denied similar requests in recent months.
Many Americans have already faced hurdles just getting a prescription for COVID treatment. Although the federal government doesn’t track who’s gotten the drug, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study using data from 30 medical centers found that Black and Hispanic patients with COVID were much less likely to receive Paxlovid than White patients. (Hispanic people can be of any race or combination of races.) And when the government is no longer picking up the tab, experts predict that these gaps by race, income, and geography will widen.
People in Northeastern states used the drug far more often than those in the rest of the country, according to a KHN analysis of Paxlovid use in September and October. But it wasn’t because people in the region were getting sick from COVID at much higher rates – instead, many of those states offered better access to health care to begin with and created special programs to get Paxlovid to their residents.
About 10 mostly Democratic states and several large counties in the Northeast and elsewhere created free “test-to-treat” programs that allow their residents to get an immediate doctor visit and prescription for treatment after testing positive for COVID. In Massachusetts, more than 20,000 residents have used the state’s video and phone hotline, which is available 7 days a week in 13 languages. Massachusetts, which has the highest insurance rate in the country and relatively low travel times to pharmacies, had the second-highest Paxlovid usage rate among states this fall.
States with higher COVID death rates, like Florida and Kentucky, where residents must travel farther for health care and are more likely to be uninsured, used the drug less often. Without no-cost test-to-treat options, residents have struggled to get prescriptions even though the drug itself is still free.
“If you look at access to medications for people who are uninsured, I think that there’s no question that will widen those disparities,” Ms. Rosenthal said.
People who get insurance through their jobs could face high copays at the register, too, just as they do for insulin and other expensive or brand-name drugs.
Most private insurance companies will end up covering COVID therapeutics to some extent, said Sabrina Corlette, a research professor at Georgetown University’s Center on Health Insurance Reforms. After all, the pills are cheaper than a hospital stay. But for most people who get insurance through their jobs, there are “really no rules at all,” she said. Some insurers could take months to add the drugs to their plans or decide not to pay for them.
And the additional cost means many people will go without the medication. “We know from lots of research that when people face cost sharing for these drugs that they need to take, they will often forgo or cut back,” Ms. Corlette said.
One group doesn’t need to worry about sticker shock. Medicaid, the public insurance program for low-income adults and children, will cover the treatments in full until at least early 2024.
HHS officials could set aside any leftover taxpayer-funded medication for people who can’t afford to pay the full cost, but they haven’t shared any concrete plans to do so. The government purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid and 3 million of Lagevrio. Fewer than a third have been used, and usage has fallen in recent months, according to KHN’s analysis of the data from HHS.
Sixty percent of the government’s supply of Evusheld is also still available, although the COVID prevention therapy is less effective against new strains of the virus. The health department in one state, New Mexico, has recommended against using it.
HHS did not make officials available for an interview or answer written questions about the commercialization plans.
The government created a potential workaround when they moved bebtelovimab, another COVID treatment, to the private market this summer. It now retails for $2,100 per patient. The agency set aside the remaining 60,000 government-purchased doses that hospitals could use to treat uninsured patients in a convoluted dose-replacement process. But it’s hard to tell how well that setup would work for Paxlovid: Bebtelovimab was already much less popular, and the FDA halted its use on Nov. 30 because it’s less effective against current strains of the virus.
Federal officials and insurance companies would have good reason to make sure patients can continue to afford COVID drugs: They’re far cheaper than if patients land in the emergency room.
“The medications are so worthwhile,” said Dr. Madoff, the Massachusetts health official. “They’re not expensive in the grand scheme of health care costs.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Nearly 6 million Americans have taken Paxlovid for free, courtesy of the federal government. The Pfizer pill has helped prevent many people infected with COVID-19 from being hospitalized or dying, and it may even reduce the risk of developing long COVID.
And that means fewer people will get the potentially lifesaving treatments, experts said.
“I think the numbers will go way down,” said Jill Rosenthal, director of public health policy at the Center for American Progress, a left-leaning think tank. A bill for several hundred dollars or more would lead many people to decide the medication isn’t worth the price, she said.
In response to the unprecedented public health crisis caused by COVID, the federal government spent billions of dollars on developing new vaccines and treatments, to swift success: Less than a year after the pandemic was declared, medical workers got their first vaccines. But as many people have refused the shots and stopped wearing masks, the virus still rages and mutates. In 2022 alone, 250,000 Americans have died from COVID, more than from strokes or diabetes.
But soon the Department of Health & Human Services will stop supplying COVID treatments, and pharmacies will purchase and bill for them the same way they do for antibiotic pills or asthma inhalers. Paxlovid is expected to hit the private market in mid-2023, according to HHS plans shared in an October meeting with state health officials and clinicians. Merck’s Lagevrio, a less-effective COVID treatment pill, and AstraZeneca’s Evusheld, a preventive therapy for the immunocompromised, are on track to be commercialized sooner, sometime in the winter.
The U.S. government has so far purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid, priced at about $530 each, a discount for buying in bulk that Pfizer CEO Albert Bourla called “really very attractive” to the federal government in a July earnings call. The drug will cost far more on the private market, although in a statement to Kaiser Health News, Pfizer declined to share the planned price. The government will also stop paying for the company’s COVID vaccine next year – those shots will quadruple in price, from the discount rate the government pays of $30 to about $120.
Mr. Bourla told investors in November that he expects the move will make Paxlovid and its COVID vaccine “a multibillion-dollars franchise.”
Nearly 9 in 10 people dying from the virus now are 65 or older. Yet federal law restricts Medicare Part D – the prescription drug program that covers nearly 50 million seniors – from covering the COVID treatment pills. The medications are meant for those most at risk of serious illness, including seniors.
Paxlovid and the other treatments are currently available under an emergency use authorization from the FDA, a fast-track review used in extraordinary situations. Although Pfizer applied for full approval in June, the process can take anywhere from several months to years. And Medicare Part D can’t cover any medications without that full stamp of approval.
Paying out-of-pocket would be “a substantial barrier” for seniors on Medicare – the very people who would benefit most from the drug, wrote federal health experts.
“From a public health perspective, and even from a health care capacity and cost perspective, it would just defy reason to not continue to make these drugs readily available,” said Dr. Larry Madoff, medical director of Massachusetts’s Bureau of Infectious Disease and Laboratory Sciences. He’s hopeful that the federal health agency will find a way to set aside unused doses for seniors and people without insurance.
In mid-November, the White House requested that Congress approve an additional $2.5 billion for COVID therapeutics and vaccines to make sure people can afford the medications when they’re no longer free. But there’s little hope it will be approved – the Senate voted that same day to end the public health emergency and denied similar requests in recent months.
Many Americans have already faced hurdles just getting a prescription for COVID treatment. Although the federal government doesn’t track who’s gotten the drug, a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention study using data from 30 medical centers found that Black and Hispanic patients with COVID were much less likely to receive Paxlovid than White patients. (Hispanic people can be of any race or combination of races.) And when the government is no longer picking up the tab, experts predict that these gaps by race, income, and geography will widen.
People in Northeastern states used the drug far more often than those in the rest of the country, according to a KHN analysis of Paxlovid use in September and October. But it wasn’t because people in the region were getting sick from COVID at much higher rates – instead, many of those states offered better access to health care to begin with and created special programs to get Paxlovid to their residents.
About 10 mostly Democratic states and several large counties in the Northeast and elsewhere created free “test-to-treat” programs that allow their residents to get an immediate doctor visit and prescription for treatment after testing positive for COVID. In Massachusetts, more than 20,000 residents have used the state’s video and phone hotline, which is available 7 days a week in 13 languages. Massachusetts, which has the highest insurance rate in the country and relatively low travel times to pharmacies, had the second-highest Paxlovid usage rate among states this fall.
States with higher COVID death rates, like Florida and Kentucky, where residents must travel farther for health care and are more likely to be uninsured, used the drug less often. Without no-cost test-to-treat options, residents have struggled to get prescriptions even though the drug itself is still free.
“If you look at access to medications for people who are uninsured, I think that there’s no question that will widen those disparities,” Ms. Rosenthal said.
People who get insurance through their jobs could face high copays at the register, too, just as they do for insulin and other expensive or brand-name drugs.
Most private insurance companies will end up covering COVID therapeutics to some extent, said Sabrina Corlette, a research professor at Georgetown University’s Center on Health Insurance Reforms. After all, the pills are cheaper than a hospital stay. But for most people who get insurance through their jobs, there are “really no rules at all,” she said. Some insurers could take months to add the drugs to their plans or decide not to pay for them.
And the additional cost means many people will go without the medication. “We know from lots of research that when people face cost sharing for these drugs that they need to take, they will often forgo or cut back,” Ms. Corlette said.
One group doesn’t need to worry about sticker shock. Medicaid, the public insurance program for low-income adults and children, will cover the treatments in full until at least early 2024.
HHS officials could set aside any leftover taxpayer-funded medication for people who can’t afford to pay the full cost, but they haven’t shared any concrete plans to do so. The government purchased 20 million courses of Paxlovid and 3 million of Lagevrio. Fewer than a third have been used, and usage has fallen in recent months, according to KHN’s analysis of the data from HHS.
Sixty percent of the government’s supply of Evusheld is also still available, although the COVID prevention therapy is less effective against new strains of the virus. The health department in one state, New Mexico, has recommended against using it.
HHS did not make officials available for an interview or answer written questions about the commercialization plans.
The government created a potential workaround when they moved bebtelovimab, another COVID treatment, to the private market this summer. It now retails for $2,100 per patient. The agency set aside the remaining 60,000 government-purchased doses that hospitals could use to treat uninsured patients in a convoluted dose-replacement process. But it’s hard to tell how well that setup would work for Paxlovid: Bebtelovimab was already much less popular, and the FDA halted its use on Nov. 30 because it’s less effective against current strains of the virus.
Federal officials and insurance companies would have good reason to make sure patients can continue to afford COVID drugs: They’re far cheaper than if patients land in the emergency room.
“The medications are so worthwhile,” said Dr. Madoff, the Massachusetts health official. “They’re not expensive in the grand scheme of health care costs.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Vaccination cuts long COVID risk for rheumatic disease patients
Patients with rheumatic disease are at least half as likely to develop long COVID after a SARS-CoV-2 infection if they have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, according to research published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases (2022 Nov 28. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223439).
“Moreover, those who were vaccinated prior to getting COVID-19 had less pain and fatigue after their infection,” Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a study author, said in an interview. “These findings reinforce the importance of vaccination in this population.”
Messaging around the value of COVID vaccination has been confusing for some with rheumatic disease “because our concern regarding a blunted response to vaccination has led many patients to think that they do not provide much benefit if they are on immunosuppression,” Dr. Wallace said. “In our cohort, which included many patients on immunosuppression of varying degrees, being vaccinated was quite beneficial.”
Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that the study is an “extremely important contribution to our understanding of COVID-19 and its pattern of recovery in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases [IMIDs].” Remaining unanswered questions are “whether patients with IMIDs develop more frequent PASC [post–acute sequelae of COVID-19] from COVID-19 and, if so, is it milder or more severe, and does it differ in its clinical phenotype?”
Long COVID risk assessed at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection
The researchers prospectively tracked 280 adult patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in the greater Boston area who had systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases and had an acute COVID-19 infection between March 2020 and July 2022. Patients were an average 53 years old, and most were White (82%) and female (80%). More than half (59%) had inflammatory arthritis, a quarter (24%) had connective tissue disease, and most others had a vasculitis condition or multiple conditions.
A total of 11% of patients were unvaccinated, 28% were partially vaccinated with one mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, and 41% were fully vaccinated with two mRNA vaccine doses or one Johnson & Johnson dose. The 116 fully vaccinated patients were considered to have a breakthrough infection while the other 164 were considered to have a nonbreakthrough infection. The breakthrough and nonbreakthrough groups were similar in terms of age, sex, race, ethnicity, smoking status, and type of rheumatic disease. Comorbidities were also similar, except obesity, which was more common in the non–breakthrough infection group (25%) than the breakthrough infection group (10%).
The researchers queried patients on their COVID-19 symptoms, how long symptoms lasted, treatments they received, and hospitalization details. COVID-19 symptoms assessed included fever, sore throat, new cough, nasal congestion/rhinorrhea, dyspnea, chest pain, rash, myalgia, fatigue/malaise, headache, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, anosmia, dysgeusia, and joint pain.
Patients completed surveys about symptoms at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection. Long COVID, or PASC, was defined as any persistent symptom at the times assessed.
Vaccinated patients fared better across outcomes
At 4 weeks after infection, 41% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 54% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P = .04). At 3 months after infection, 21% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 41% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P < .0001).
Vaccinated patients were half as likely to have long COVID at 4 weeks after infection (adjusted odds ratio, 0.49) and 90% less likely to have long COVID 3 months after infection (aOR, 0.1), after adjustment for age, sex, race, comorbidities, and use of any of four immune-suppressing medications (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or glucocorticoids).
Fully vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections had an average 21 additional days without symptoms during follow-up, compared with unvaccinated and partially vaccinated patients (P = .04).
Reduced risk of long COVID did not change for vaccinated patients after sensitivity analyses for those who did not receive nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) or monoclonal antibodies, those who didn’t receive any COVID-19-related treatment, those who completed their questionnaires within 6 months after infection, and those who were not hospitalized.
“One important message is that among those who did get PASC, the severity appears similar among those with and without a breakthrough infection,” Dr. Wallace said. “This highlights the need for ongoing research to improve recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of PASC.”
Many more breakthrough infections (72%) than nonbreakthrough infections (2%) occurred during Omicron. The authors acknowledged that different variants might play a role in different long COVID risks but said such potential confounding is unlikely to fully explain the results.
“Even with data suggesting that the Omicron variants may be intrinsically less severe, vaccination still has an impact on severity of infection, rates of hospitalization, and other outcomes and thus may play a role in the risk of PASC,” lead author Naomi Patel, MD, an instructor at Harvard Medical School and a rheumatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “A study evaluating the proportions with PASC by vaccination status during the time in which a single variant is predominant, such as the early Omicron era, could help to better assess the more isolated impact of vaccination on PASC.”
Dr. Calabrese said he is convinced that Omicron infections are less likely to result in more severe forms of acute COVID than pre-Omicron infections, and he suspects Omicron infections are also less likely to result in long COVID, although less evidence currently supports this hypothesis.
Hospitalization was more common in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients than in vaccinated patients (27% vs. 5%; P = .001). Although pain and fatigue were lower in those with breakthrough infections, functional scores and health-related quality of life were similar in both groups.
Some symptoms significantly differed between vaccinated and unvaccinated/partly vaccinated groups, possibly caused partly by different variants. Nasal congestion was more common (73%) in those with breakthrough infections than in those with nonbreakthrough infections (46%; P < .0001). Those who were unvaccinated/partly vaccinated were significantly more likely to have loss of smell (46% vs. 22%) or taste (45% vs. 28%) or to have joint pain (11% vs. 4%).
Treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was also more common in vaccinated patients (12%) than in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients (1%; P < .0001), as was treatment with monoclonal antibodies (34% vs. 8%; P < .0001).
The study was limited by its low diversity and being at a single health care system, the authors said. Study coauthor Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, said in an interview that the group is planning additional studies as their cohort grows, including “investigating the relationships between COVID-19 and specific rheumatic diseases and immunomodulating medications, expansion of autoimmunity and systemic inflammation, and lung damage among specific patient populations.”
Dr. Calabrese said it will be important for follow-up study of the symptomatic patients to “determine how many of these patients will fit the clinical picture of long COVID or long-haul phenotypes over the months and years ahead, including documenting exertional malaise and quality of life.
This study only assessed patients who received zero, one, or two doses of a vaccine, but many patients with rheumatic disease today will likely have received booster doses. However, Dr. Calabrese said it would be difficult to quantify whether a third, fourth, or fifth dose offers additional protection from long-term COVID complications after full vaccination or hybrid vaccination.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Wallace has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Principia/Sanofi and consulting fees from Zenas BioPharma, Horizon, Sanofi, Shionogi, Viela Bio, and Medpace. Dr. Sparks has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Inova Diagnostics, Janssen, Optum, and Pfizer. Dr. Patel has received consulting fees from FVC Health. Calabrese has consulted for Genentech, Sanofi-Regeneron, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic disease are at least half as likely to develop long COVID after a SARS-CoV-2 infection if they have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, according to research published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases (2022 Nov 28. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223439).
“Moreover, those who were vaccinated prior to getting COVID-19 had less pain and fatigue after their infection,” Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a study author, said in an interview. “These findings reinforce the importance of vaccination in this population.”
Messaging around the value of COVID vaccination has been confusing for some with rheumatic disease “because our concern regarding a blunted response to vaccination has led many patients to think that they do not provide much benefit if they are on immunosuppression,” Dr. Wallace said. “In our cohort, which included many patients on immunosuppression of varying degrees, being vaccinated was quite beneficial.”
Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that the study is an “extremely important contribution to our understanding of COVID-19 and its pattern of recovery in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases [IMIDs].” Remaining unanswered questions are “whether patients with IMIDs develop more frequent PASC [post–acute sequelae of COVID-19] from COVID-19 and, if so, is it milder or more severe, and does it differ in its clinical phenotype?”
Long COVID risk assessed at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection
The researchers prospectively tracked 280 adult patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in the greater Boston area who had systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases and had an acute COVID-19 infection between March 2020 and July 2022. Patients were an average 53 years old, and most were White (82%) and female (80%). More than half (59%) had inflammatory arthritis, a quarter (24%) had connective tissue disease, and most others had a vasculitis condition or multiple conditions.
A total of 11% of patients were unvaccinated, 28% were partially vaccinated with one mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, and 41% were fully vaccinated with two mRNA vaccine doses or one Johnson & Johnson dose. The 116 fully vaccinated patients were considered to have a breakthrough infection while the other 164 were considered to have a nonbreakthrough infection. The breakthrough and nonbreakthrough groups were similar in terms of age, sex, race, ethnicity, smoking status, and type of rheumatic disease. Comorbidities were also similar, except obesity, which was more common in the non–breakthrough infection group (25%) than the breakthrough infection group (10%).
The researchers queried patients on their COVID-19 symptoms, how long symptoms lasted, treatments they received, and hospitalization details. COVID-19 symptoms assessed included fever, sore throat, new cough, nasal congestion/rhinorrhea, dyspnea, chest pain, rash, myalgia, fatigue/malaise, headache, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, anosmia, dysgeusia, and joint pain.
Patients completed surveys about symptoms at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection. Long COVID, or PASC, was defined as any persistent symptom at the times assessed.
Vaccinated patients fared better across outcomes
At 4 weeks after infection, 41% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 54% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P = .04). At 3 months after infection, 21% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 41% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P < .0001).
Vaccinated patients were half as likely to have long COVID at 4 weeks after infection (adjusted odds ratio, 0.49) and 90% less likely to have long COVID 3 months after infection (aOR, 0.1), after adjustment for age, sex, race, comorbidities, and use of any of four immune-suppressing medications (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or glucocorticoids).
Fully vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections had an average 21 additional days without symptoms during follow-up, compared with unvaccinated and partially vaccinated patients (P = .04).
Reduced risk of long COVID did not change for vaccinated patients after sensitivity analyses for those who did not receive nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) or monoclonal antibodies, those who didn’t receive any COVID-19-related treatment, those who completed their questionnaires within 6 months after infection, and those who were not hospitalized.
“One important message is that among those who did get PASC, the severity appears similar among those with and without a breakthrough infection,” Dr. Wallace said. “This highlights the need for ongoing research to improve recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of PASC.”
Many more breakthrough infections (72%) than nonbreakthrough infections (2%) occurred during Omicron. The authors acknowledged that different variants might play a role in different long COVID risks but said such potential confounding is unlikely to fully explain the results.
“Even with data suggesting that the Omicron variants may be intrinsically less severe, vaccination still has an impact on severity of infection, rates of hospitalization, and other outcomes and thus may play a role in the risk of PASC,” lead author Naomi Patel, MD, an instructor at Harvard Medical School and a rheumatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “A study evaluating the proportions with PASC by vaccination status during the time in which a single variant is predominant, such as the early Omicron era, could help to better assess the more isolated impact of vaccination on PASC.”
Dr. Calabrese said he is convinced that Omicron infections are less likely to result in more severe forms of acute COVID than pre-Omicron infections, and he suspects Omicron infections are also less likely to result in long COVID, although less evidence currently supports this hypothesis.
Hospitalization was more common in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients than in vaccinated patients (27% vs. 5%; P = .001). Although pain and fatigue were lower in those with breakthrough infections, functional scores and health-related quality of life were similar in both groups.
Some symptoms significantly differed between vaccinated and unvaccinated/partly vaccinated groups, possibly caused partly by different variants. Nasal congestion was more common (73%) in those with breakthrough infections than in those with nonbreakthrough infections (46%; P < .0001). Those who were unvaccinated/partly vaccinated were significantly more likely to have loss of smell (46% vs. 22%) or taste (45% vs. 28%) or to have joint pain (11% vs. 4%).
Treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was also more common in vaccinated patients (12%) than in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients (1%; P < .0001), as was treatment with monoclonal antibodies (34% vs. 8%; P < .0001).
The study was limited by its low diversity and being at a single health care system, the authors said. Study coauthor Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, said in an interview that the group is planning additional studies as their cohort grows, including “investigating the relationships between COVID-19 and specific rheumatic diseases and immunomodulating medications, expansion of autoimmunity and systemic inflammation, and lung damage among specific patient populations.”
Dr. Calabrese said it will be important for follow-up study of the symptomatic patients to “determine how many of these patients will fit the clinical picture of long COVID or long-haul phenotypes over the months and years ahead, including documenting exertional malaise and quality of life.
This study only assessed patients who received zero, one, or two doses of a vaccine, but many patients with rheumatic disease today will likely have received booster doses. However, Dr. Calabrese said it would be difficult to quantify whether a third, fourth, or fifth dose offers additional protection from long-term COVID complications after full vaccination or hybrid vaccination.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Wallace has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Principia/Sanofi and consulting fees from Zenas BioPharma, Horizon, Sanofi, Shionogi, Viela Bio, and Medpace. Dr. Sparks has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Inova Diagnostics, Janssen, Optum, and Pfizer. Dr. Patel has received consulting fees from FVC Health. Calabrese has consulted for Genentech, Sanofi-Regeneron, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with rheumatic disease are at least half as likely to develop long COVID after a SARS-CoV-2 infection if they have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, according to research published in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases (2022 Nov 28. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223439).
“Moreover, those who were vaccinated prior to getting COVID-19 had less pain and fatigue after their infection,” Zachary S. Wallace, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and a study author, said in an interview. “These findings reinforce the importance of vaccination in this population.”
Messaging around the value of COVID vaccination has been confusing for some with rheumatic disease “because our concern regarding a blunted response to vaccination has led many patients to think that they do not provide much benefit if they are on immunosuppression,” Dr. Wallace said. “In our cohort, which included many patients on immunosuppression of varying degrees, being vaccinated was quite beneficial.”
Leonard H. Calabrese, DO, director of the R.J. Fasenmyer Center for Clinical Immunology and a professor of medicine at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that the study is an “extremely important contribution to our understanding of COVID-19 and its pattern of recovery in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases [IMIDs].” Remaining unanswered questions are “whether patients with IMIDs develop more frequent PASC [post–acute sequelae of COVID-19] from COVID-19 and, if so, is it milder or more severe, and does it differ in its clinical phenotype?”
Long COVID risk assessed at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection
The researchers prospectively tracked 280 adult patients in the Mass General Brigham health care system in the greater Boston area who had systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases and had an acute COVID-19 infection between March 2020 and July 2022. Patients were an average 53 years old, and most were White (82%) and female (80%). More than half (59%) had inflammatory arthritis, a quarter (24%) had connective tissue disease, and most others had a vasculitis condition or multiple conditions.
A total of 11% of patients were unvaccinated, 28% were partially vaccinated with one mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose, and 41% were fully vaccinated with two mRNA vaccine doses or one Johnson & Johnson dose. The 116 fully vaccinated patients were considered to have a breakthrough infection while the other 164 were considered to have a nonbreakthrough infection. The breakthrough and nonbreakthrough groups were similar in terms of age, sex, race, ethnicity, smoking status, and type of rheumatic disease. Comorbidities were also similar, except obesity, which was more common in the non–breakthrough infection group (25%) than the breakthrough infection group (10%).
The researchers queried patients on their COVID-19 symptoms, how long symptoms lasted, treatments they received, and hospitalization details. COVID-19 symptoms assessed included fever, sore throat, new cough, nasal congestion/rhinorrhea, dyspnea, chest pain, rash, myalgia, fatigue/malaise, headache, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea, anosmia, dysgeusia, and joint pain.
Patients completed surveys about symptoms at 4 weeks and 3 months after infection. Long COVID, or PASC, was defined as any persistent symptom at the times assessed.
Vaccinated patients fared better across outcomes
At 4 weeks after infection, 41% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 54% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P = .04). At 3 months after infection, 21% of fully vaccinated patients had at least one persistent symptom, compared with 41% of unvaccinated or partially vaccinated patients (P < .0001).
Vaccinated patients were half as likely to have long COVID at 4 weeks after infection (adjusted odds ratio, 0.49) and 90% less likely to have long COVID 3 months after infection (aOR, 0.1), after adjustment for age, sex, race, comorbidities, and use of any of four immune-suppressing medications (anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies, methotrexate, mycophenolate, or glucocorticoids).
Fully vaccinated patients with breakthrough infections had an average 21 additional days without symptoms during follow-up, compared with unvaccinated and partially vaccinated patients (P = .04).
Reduced risk of long COVID did not change for vaccinated patients after sensitivity analyses for those who did not receive nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) or monoclonal antibodies, those who didn’t receive any COVID-19-related treatment, those who completed their questionnaires within 6 months after infection, and those who were not hospitalized.
“One important message is that among those who did get PASC, the severity appears similar among those with and without a breakthrough infection,” Dr. Wallace said. “This highlights the need for ongoing research to improve recognition, diagnosis, and treatment of PASC.”
Many more breakthrough infections (72%) than nonbreakthrough infections (2%) occurred during Omicron. The authors acknowledged that different variants might play a role in different long COVID risks but said such potential confounding is unlikely to fully explain the results.
“Even with data suggesting that the Omicron variants may be intrinsically less severe, vaccination still has an impact on severity of infection, rates of hospitalization, and other outcomes and thus may play a role in the risk of PASC,” lead author Naomi Patel, MD, an instructor at Harvard Medical School and a rheumatologist at Massachusetts General Hospital, said in an interview. “A study evaluating the proportions with PASC by vaccination status during the time in which a single variant is predominant, such as the early Omicron era, could help to better assess the more isolated impact of vaccination on PASC.”
Dr. Calabrese said he is convinced that Omicron infections are less likely to result in more severe forms of acute COVID than pre-Omicron infections, and he suspects Omicron infections are also less likely to result in long COVID, although less evidence currently supports this hypothesis.
Hospitalization was more common in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients than in vaccinated patients (27% vs. 5%; P = .001). Although pain and fatigue were lower in those with breakthrough infections, functional scores and health-related quality of life were similar in both groups.
Some symptoms significantly differed between vaccinated and unvaccinated/partly vaccinated groups, possibly caused partly by different variants. Nasal congestion was more common (73%) in those with breakthrough infections than in those with nonbreakthrough infections (46%; P < .0001). Those who were unvaccinated/partly vaccinated were significantly more likely to have loss of smell (46% vs. 22%) or taste (45% vs. 28%) or to have joint pain (11% vs. 4%).
Treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir was also more common in vaccinated patients (12%) than in unvaccinated/partly vaccinated patients (1%; P < .0001), as was treatment with monoclonal antibodies (34% vs. 8%; P < .0001).
The study was limited by its low diversity and being at a single health care system, the authors said. Study coauthor Jeffrey A. Sparks, MD, MMSc, an assistant professor of medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, said in an interview that the group is planning additional studies as their cohort grows, including “investigating the relationships between COVID-19 and specific rheumatic diseases and immunomodulating medications, expansion of autoimmunity and systemic inflammation, and lung damage among specific patient populations.”
Dr. Calabrese said it will be important for follow-up study of the symptomatic patients to “determine how many of these patients will fit the clinical picture of long COVID or long-haul phenotypes over the months and years ahead, including documenting exertional malaise and quality of life.
This study only assessed patients who received zero, one, or two doses of a vaccine, but many patients with rheumatic disease today will likely have received booster doses. However, Dr. Calabrese said it would be difficult to quantify whether a third, fourth, or fifth dose offers additional protection from long-term COVID complications after full vaccination or hybrid vaccination.
The research was funded by the Rheumatology Research Foundation, the National Institutes of Health, the R. Bruce and Joan M. Mickey Research Scholar Fund, and the Llura Gund Award for Rheumatoid Arthritis Research and Care. Dr. Wallace has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Principia/Sanofi and consulting fees from Zenas BioPharma, Horizon, Sanofi, Shionogi, Viela Bio, and Medpace. Dr. Sparks has received research support from Bristol-Myers Squibb and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Inova Diagnostics, Janssen, Optum, and Pfizer. Dr. Patel has received consulting fees from FVC Health. Calabrese has consulted for Genentech, Sanofi-Regeneron, AstraZeneca, and GlaxoSmithKline.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF THE RHEUMATIC DISEASES
Children and COVID: Hospitalizations provide a tale of two sources
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.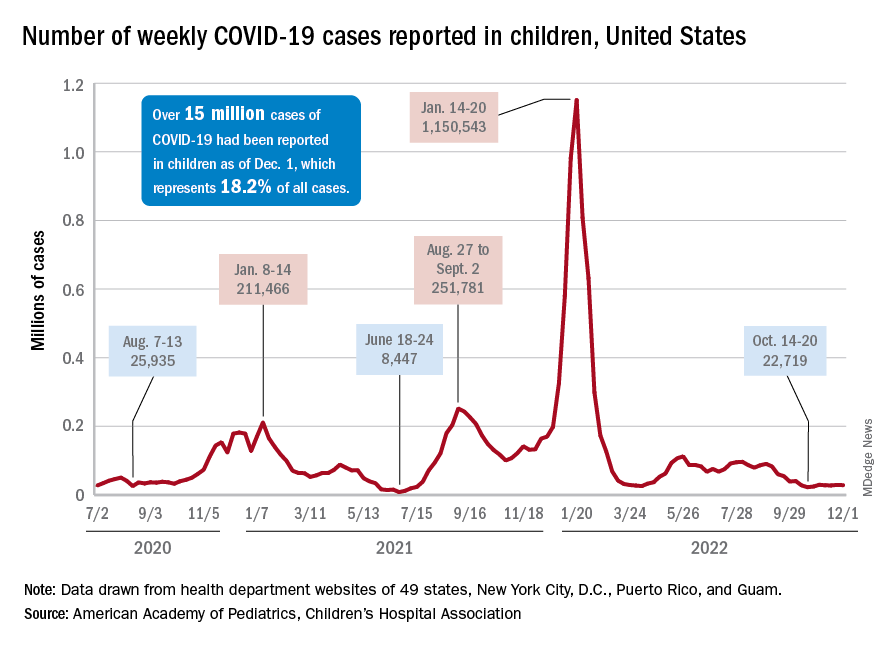
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
New cases of COVID-19 in children largely held steady over the Thanksgiving holiday, but hospital admissions are telling a somewhat different story.
New pediatric COVID cases for the week ending on Thanksgiving (11/18-11/24) were up by 5.3% over the previous week, but in the most recent week (11/25-12/1) new cases dropped by 2.6%, according to state data collected by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
In both weeks, though, the total case count stayed below 30,000 – a streak that has now lasted 8 weeks – so the actual number of weekly cases remained fairly low, the AAP/CHA weekly report indicates.
The nation’s emergency departments also experienced a small Thanksgiving bump, as the proportion of visits with diagnosed COVID went from 1.0% of all ED visits for children aged 0-11 years on Nov. 14 to 2.0% on Nov. 27, just 3 days after the official holiday, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The rate was down to 1.5% on Dec. 1, and similar patterns can be seen for children aged 12-15 and 16-17 years.
New hospital admissions, on the other hand, seem to be following a different path, at least according to the CDC. The hospitalization rate for children aged 0-17 years bottomed out at 0.16 new admissions per 100,000 population back on Oct. 21 and has climbed fairly steadily since then. It was up to 0.20 per 100,000 by Nov. 14, had reached 0.22 per 100,000 on Thanksgiving day (11/24), and then continued to 0.26 per 100,000 by Dec. 2, the latest date for which CDC data are available.
The hospitalization story, however, offers yet another twist. The New York Times, using data from the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, reports that new COVID-related admissions have held steady at 1.0 per 100,000 since Nov. 18. The rate is much higher than has been reported by the CDC, but no increase can be seen in recent weeks among children, which is not the case for Americans overall, Medscape recently reported.
Study comparing surgical and N95 masks sparks concern
The study’s senior author is John Conly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and professor at the University of Calgary (Alta.), and Alberta Health Services. The findings are not consistent with those of many other studies on this topic.
Commenting about Dr. Conly’s study, Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, wrote: “It’s woefully underpowered but ruled out a doubling of hazard for use of medical masks.”
The study, which was partially funded by the World Health Organization, was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This is not the first time that Dr. Conly, who also advises the WHO, has been the subject of controversy. He previously denied that COVID-19 is airborne – a position that is contradicted by strong evidence. In 2021, Dr. Conly made headlines with his controversial claim that N95 respirators can cause harms, including oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide retention.
A detailed examination by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, pointed out numerous scientific flaws in the study, including inconsistent use of both types of masks. The study also examined health care workers in four very different countries (Canada, Israel, Egypt, and Pakistan) during different periods of the pandemic, which may have affected the results. Furthermore, the study did not account for vaccination status and lacked a control group. CIDRAP receives funding from 3M, which makes N95 respirators.
In a commentary published alongside the study, Roger Chou, MD, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that the results were “not definitive,” with “a generous noninferiority threshold” that is actually “consistent with up to a relative 70% increased risk ... which may be unacceptable to many health workers.”
Lead study author Mark Loeb, MD, professor of infectious diseases at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., defended the findings. “The confidence intervals around this, that is, what the possible results could be if the trial was repeated many times, range from −2.5% to 4.9%,” he told this news organization. “This means that the risk of a COVID-19 infection in those using the medical masks could have ranged from anywhere from 2.5% reduction in risk to a 4.9% increase in risk. Readers and policy makers can decide for themselves about this.”
“There is no point continuing to run underpowered, poorly designed studies that are designed to confirm existing biases,” Raina MacIntyre, PhD, professor of global biosecurity and head of the Biosecurity Program at the Kirby Institute, Sydney, said in an interview. “The new study in Annals of Internal Medicine is entirely consistent with our finding that to prevent infection, you need an N95, and it needs to be worn throughout the whole shift. A surgical mask and intermittent use of N95 are equally ineffective. This should not surprise anyone, given a surgical mask is not designed as respiratory protection but is designed to prevent splash or spray of liquid on the face. Only a respirator is designed as respiratory protection through both the seal around the face and the filter of the face piece to prevent inhalation of virus laden aerosols, but you need to wear it continually in a high-risk environment like a hospital.”
“It makes zero sense to do a randomized trial on something you can measure directly,” said Kimberly Prather, PhD, an atmospheric chemist, professor, and director of the NSF Center for Aerosol Impacts on Chemistry of the Environment at the University of California, San Diego. “In fact, many studies have shown aerosols leaking out of surgical masks. Surgical masks are designed to block large spray droplets. Aerosols (0.5-3 mcm), which have been shown to contain infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus, travel with the air flow, and escape.”
“This study ... will be used to justify policies of supplying health care workers, and perhaps patients and visitors, too, with inadequate protection,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“These authors have been pushing back against treating COVID as airborne for 3 years,” David Fisman, MD, an epidemiologist and infectious disease specialist at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “So, you’ll see these folks brandishing this very flawed trial to justify continuing the infection control practices that have been so disastrous throughout the pandemic.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Juravinski Research Institute. Dr. Conly reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Pfizer, and the WHO. Dr. Chou disclosed being a methodologist for WHO guidelines on infection prevention and control measures for COVID-19. Dr. Loeb disclosed payment for expert testimony on personal protective equipment from the government of Manitoba and the Peel District School Board. Dr. MacIntyre has led a large body of research on masks and respirators in health workers, including four randomized clinical trials. She is the author of a book, “Dark Winter: An insider’s guide to pandemics and biosecurity” (Syndey: NewSouth Publishing, 2022), which covers the history and politics of the controversies around N95 and masks. Dr. Prather reported no disclosures. Dr. Greenhalgh is a member of Independent SAGE and an unpaid adviser to the philanthropic fund Balvi. Dr. Fisman has served as a paid legal expert for the Ontario Nurses’ Association in their challenge to Directive 5, which restricted access to N95 masks in health care. He also served as a paid legal expert for the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario in its efforts to make schools safer in Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study’s senior author is John Conly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and professor at the University of Calgary (Alta.), and Alberta Health Services. The findings are not consistent with those of many other studies on this topic.
Commenting about Dr. Conly’s study, Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, wrote: “It’s woefully underpowered but ruled out a doubling of hazard for use of medical masks.”
The study, which was partially funded by the World Health Organization, was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This is not the first time that Dr. Conly, who also advises the WHO, has been the subject of controversy. He previously denied that COVID-19 is airborne – a position that is contradicted by strong evidence. In 2021, Dr. Conly made headlines with his controversial claim that N95 respirators can cause harms, including oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide retention.
A detailed examination by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, pointed out numerous scientific flaws in the study, including inconsistent use of both types of masks. The study also examined health care workers in four very different countries (Canada, Israel, Egypt, and Pakistan) during different periods of the pandemic, which may have affected the results. Furthermore, the study did not account for vaccination status and lacked a control group. CIDRAP receives funding from 3M, which makes N95 respirators.
In a commentary published alongside the study, Roger Chou, MD, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that the results were “not definitive,” with “a generous noninferiority threshold” that is actually “consistent with up to a relative 70% increased risk ... which may be unacceptable to many health workers.”
Lead study author Mark Loeb, MD, professor of infectious diseases at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., defended the findings. “The confidence intervals around this, that is, what the possible results could be if the trial was repeated many times, range from −2.5% to 4.9%,” he told this news organization. “This means that the risk of a COVID-19 infection in those using the medical masks could have ranged from anywhere from 2.5% reduction in risk to a 4.9% increase in risk. Readers and policy makers can decide for themselves about this.”
“There is no point continuing to run underpowered, poorly designed studies that are designed to confirm existing biases,” Raina MacIntyre, PhD, professor of global biosecurity and head of the Biosecurity Program at the Kirby Institute, Sydney, said in an interview. “The new study in Annals of Internal Medicine is entirely consistent with our finding that to prevent infection, you need an N95, and it needs to be worn throughout the whole shift. A surgical mask and intermittent use of N95 are equally ineffective. This should not surprise anyone, given a surgical mask is not designed as respiratory protection but is designed to prevent splash or spray of liquid on the face. Only a respirator is designed as respiratory protection through both the seal around the face and the filter of the face piece to prevent inhalation of virus laden aerosols, but you need to wear it continually in a high-risk environment like a hospital.”
“It makes zero sense to do a randomized trial on something you can measure directly,” said Kimberly Prather, PhD, an atmospheric chemist, professor, and director of the NSF Center for Aerosol Impacts on Chemistry of the Environment at the University of California, San Diego. “In fact, many studies have shown aerosols leaking out of surgical masks. Surgical masks are designed to block large spray droplets. Aerosols (0.5-3 mcm), which have been shown to contain infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus, travel with the air flow, and escape.”
“This study ... will be used to justify policies of supplying health care workers, and perhaps patients and visitors, too, with inadequate protection,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“These authors have been pushing back against treating COVID as airborne for 3 years,” David Fisman, MD, an epidemiologist and infectious disease specialist at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “So, you’ll see these folks brandishing this very flawed trial to justify continuing the infection control practices that have been so disastrous throughout the pandemic.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Juravinski Research Institute. Dr. Conly reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Pfizer, and the WHO. Dr. Chou disclosed being a methodologist for WHO guidelines on infection prevention and control measures for COVID-19. Dr. Loeb disclosed payment for expert testimony on personal protective equipment from the government of Manitoba and the Peel District School Board. Dr. MacIntyre has led a large body of research on masks and respirators in health workers, including four randomized clinical trials. She is the author of a book, “Dark Winter: An insider’s guide to pandemics and biosecurity” (Syndey: NewSouth Publishing, 2022), which covers the history and politics of the controversies around N95 and masks. Dr. Prather reported no disclosures. Dr. Greenhalgh is a member of Independent SAGE and an unpaid adviser to the philanthropic fund Balvi. Dr. Fisman has served as a paid legal expert for the Ontario Nurses’ Association in their challenge to Directive 5, which restricted access to N95 masks in health care. He also served as a paid legal expert for the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario in its efforts to make schools safer in Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study’s senior author is John Conly, MD, an infectious disease specialist and professor at the University of Calgary (Alta.), and Alberta Health Services. The findings are not consistent with those of many other studies on this topic.
Commenting about Dr. Conly’s study, Eric Topol, MD, editor-in-chief of Medscape, wrote: “It’s woefully underpowered but ruled out a doubling of hazard for use of medical masks.”
The study, which was partially funded by the World Health Organization, was published online in Annals of Internal Medicine.
This is not the first time that Dr. Conly, who also advises the WHO, has been the subject of controversy. He previously denied that COVID-19 is airborne – a position that is contradicted by strong evidence. In 2021, Dr. Conly made headlines with his controversial claim that N95 respirators can cause harms, including oxygen depletion and carbon dioxide retention.
A detailed examination by the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, pointed out numerous scientific flaws in the study, including inconsistent use of both types of masks. The study also examined health care workers in four very different countries (Canada, Israel, Egypt, and Pakistan) during different periods of the pandemic, which may have affected the results. Furthermore, the study did not account for vaccination status and lacked a control group. CIDRAP receives funding from 3M, which makes N95 respirators.
In a commentary published alongside the study, Roger Chou, MD, professor of medicine at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, said that the results were “not definitive,” with “a generous noninferiority threshold” that is actually “consistent with up to a relative 70% increased risk ... which may be unacceptable to many health workers.”
Lead study author Mark Loeb, MD, professor of infectious diseases at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., defended the findings. “The confidence intervals around this, that is, what the possible results could be if the trial was repeated many times, range from −2.5% to 4.9%,” he told this news organization. “This means that the risk of a COVID-19 infection in those using the medical masks could have ranged from anywhere from 2.5% reduction in risk to a 4.9% increase in risk. Readers and policy makers can decide for themselves about this.”
“There is no point continuing to run underpowered, poorly designed studies that are designed to confirm existing biases,” Raina MacIntyre, PhD, professor of global biosecurity and head of the Biosecurity Program at the Kirby Institute, Sydney, said in an interview. “The new study in Annals of Internal Medicine is entirely consistent with our finding that to prevent infection, you need an N95, and it needs to be worn throughout the whole shift. A surgical mask and intermittent use of N95 are equally ineffective. This should not surprise anyone, given a surgical mask is not designed as respiratory protection but is designed to prevent splash or spray of liquid on the face. Only a respirator is designed as respiratory protection through both the seal around the face and the filter of the face piece to prevent inhalation of virus laden aerosols, but you need to wear it continually in a high-risk environment like a hospital.”
“It makes zero sense to do a randomized trial on something you can measure directly,” said Kimberly Prather, PhD, an atmospheric chemist, professor, and director of the NSF Center for Aerosol Impacts on Chemistry of the Environment at the University of California, San Diego. “In fact, many studies have shown aerosols leaking out of surgical masks. Surgical masks are designed to block large spray droplets. Aerosols (0.5-3 mcm), which have been shown to contain infectious SARS-CoV-2 virus, travel with the air flow, and escape.”
“This study ... will be used to justify policies of supplying health care workers, and perhaps patients and visitors, too, with inadequate protection,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, professor of primary care health sciences at the University of Oxford (England), told this news organization.
“These authors have been pushing back against treating COVID as airborne for 3 years,” David Fisman, MD, an epidemiologist and infectious disease specialist at the University of Toronto, said in an interview. “So, you’ll see these folks brandishing this very flawed trial to justify continuing the infection control practices that have been so disastrous throughout the pandemic.”
The study was funded by the World Health Organization, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and the Juravinski Research Institute. Dr. Conly reported receiving grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research, Pfizer, and the WHO. Dr. Chou disclosed being a methodologist for WHO guidelines on infection prevention and control measures for COVID-19. Dr. Loeb disclosed payment for expert testimony on personal protective equipment from the government of Manitoba and the Peel District School Board. Dr. MacIntyre has led a large body of research on masks and respirators in health workers, including four randomized clinical trials. She is the author of a book, “Dark Winter: An insider’s guide to pandemics and biosecurity” (Syndey: NewSouth Publishing, 2022), which covers the history and politics of the controversies around N95 and masks. Dr. Prather reported no disclosures. Dr. Greenhalgh is a member of Independent SAGE and an unpaid adviser to the philanthropic fund Balvi. Dr. Fisman has served as a paid legal expert for the Ontario Nurses’ Association in their challenge to Directive 5, which restricted access to N95 masks in health care. He also served as a paid legal expert for the Elementary Teachers’ Federation of Ontario in its efforts to make schools safer in Ontario.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
FDA pulls U.S. authorization for Eli Lilly’s COVID drug bebtelovimab
the Food and Drug Administration said, citing it is not expected to neutralize the dominant BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 subvariants of Omicron.
The announcement on Nov. 30 takes away authorization from the last COVID-19 monoclonal antibody treatment, leaving Pfizer’s antiviral drug Paxlovid, Merck’s Lagevrio, and Gilead Sciences’ Veklury as treatments for the disease, besides convalescent plasma for some patients.
AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody Evusheld is also authorized for protection against COVID-19 infection in some people.
Eli Lilly and its authorized distributors have paused commercial distribution of the monoclonal antibody until further notice from the agency, while the U.S. government has also paused fulfillment of any pending requests under its scheme to help uninsured and underinsured Americans access the drug.
The drug, which was discovered by Abcellera and commercialized by Eli Lilly, received an authorization from the FDA in February.
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 have become the dominant strains in the United States after a steady increase in prevalence over the last 2 months, surpassing Omicron’s BA.5 subvariant, which had driven cases earlier in the year.
The subvariants accounted for around 57% of the cases nationally, as per government data last week.
Reuters Health Information © 2022
the Food and Drug Administration said, citing it is not expected to neutralize the dominant BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 subvariants of Omicron.
The announcement on Nov. 30 takes away authorization from the last COVID-19 monoclonal antibody treatment, leaving Pfizer’s antiviral drug Paxlovid, Merck’s Lagevrio, and Gilead Sciences’ Veklury as treatments for the disease, besides convalescent plasma for some patients.
AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody Evusheld is also authorized for protection against COVID-19 infection in some people.
Eli Lilly and its authorized distributors have paused commercial distribution of the monoclonal antibody until further notice from the agency, while the U.S. government has also paused fulfillment of any pending requests under its scheme to help uninsured and underinsured Americans access the drug.
The drug, which was discovered by Abcellera and commercialized by Eli Lilly, received an authorization from the FDA in February.
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 have become the dominant strains in the United States after a steady increase in prevalence over the last 2 months, surpassing Omicron’s BA.5 subvariant, which had driven cases earlier in the year.
The subvariants accounted for around 57% of the cases nationally, as per government data last week.
Reuters Health Information © 2022
the Food and Drug Administration said, citing it is not expected to neutralize the dominant BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 subvariants of Omicron.
The announcement on Nov. 30 takes away authorization from the last COVID-19 monoclonal antibody treatment, leaving Pfizer’s antiviral drug Paxlovid, Merck’s Lagevrio, and Gilead Sciences’ Veklury as treatments for the disease, besides convalescent plasma for some patients.
AstraZeneca’s monoclonal antibody Evusheld is also authorized for protection against COVID-19 infection in some people.
Eli Lilly and its authorized distributors have paused commercial distribution of the monoclonal antibody until further notice from the agency, while the U.S. government has also paused fulfillment of any pending requests under its scheme to help uninsured and underinsured Americans access the drug.
The drug, which was discovered by Abcellera and commercialized by Eli Lilly, received an authorization from the FDA in February.
BQ.1 and BQ.1.1 have become the dominant strains in the United States after a steady increase in prevalence over the last 2 months, surpassing Omicron’s BA.5 subvariant, which had driven cases earlier in the year.
The subvariants accounted for around 57% of the cases nationally, as per government data last week.
Reuters Health Information © 2022
RSV surge stuns parents and strains providers, but doctors offer help
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
RSV cases peaked in mid-November, according to the latest Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data, with RSV-associated hospitalizations in the United States among patients 0-4 years having maxed out five times higher than they were at the same time in 2021. These surges strained providers and left parents scrambling for care. Fortunately, pediatric hospitalizations appear to be subsiding.
In interviews, the parents of the child who had a severe case of RSV reflected on their son’s bout with the illness, and doctors described challenges to dealing with the surge in RSV cases this season. The physicians also offered advice on how recognize and respond to future cases of the virus.
Sebastian Witt’s story
“I didn’t even know what RSV was,” said Malte Witt, whose son, Sebastian, 2, was recently hospitalized for RSV in Denver.
Mr. Witt and his wife, Emily Witt, both 32, thought they were dealing with a typical cold until Sebastian’s condition dramatically deteriorated about 36 hours after symptom onset.
“He basically just slumped over and collapsed, coughing uncontrollably,” Mr. Witt said in an interview. “He couldn’t catch his breath.”
The Witts rushed Sebastian to the ED at Children’s Hospital Colorado, expecting to see a doctor immediately. Instead, they spent the night in an overcrowded waiting room alongside many other families in the same situation.
“There was no room for anyone to sit anywhere,” Mr. Witt said. “There were people sitting on the floor. I counted maybe six children hooked up to oxygen when we walked in.”
After waiting approximately 45 minutes, a nurse checked Sebastian’s oxygen saturation. The readings were 79%-83%. This range is significantly below thresholds for supplemental oxygen described by most pediatric guidelines, which range from 90 to 94%.
The nurse connected Sebastian to bottled oxygen in the waiting room, and a recheck 4 hours later showed that his oxygen saturation had improved.
But the improvement didn’t last.
“At roughly hour 10 in the waiting room – it was 4 in the morning – you could tell that Seb was exhausted, really not acting like himself,” Mr. Witt said. “We thought maybe it’s just late at night, he hasn’t really slept. But then Emily noticed that his oxygen tank had run out.”
Mr. Witt told a nurse, and after another check revealed low oxygen saturation, Sebastian was finally admitted.
Early RSV surge strains pediatric providers
With RSV-associated hospitalizations peaking at 48 per 100,000 children, Colorado has been among the states hardest hit by the virus. New Mexico – where hospitalizations peaked at 56.4 per 100,000 children – comes in second. Even in states like California, where hospitalization rates have been almost 10-fold lower than New Mexico, pediatric providers have been stretched to their limits.
“Many hospitals are really being overwhelmed with admissions for RSV, both routine RSV – relatively mild hospitalizations with bronchiolitis – as well as kids in the ICU with more severe cases,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at UC Davis Health, Sacramento, said in an interview.
Dr. Blumberg believes the severity of the 2022-2023 RSV season is likely COVID related.
“All community-associated respiratory viral infections are out of whack because of the pandemic, and all the masking and social distancing that was occurring,” he said.
This may also explain why older kids are coming down with more severe cases of RSV.
“Some children are getting RSV for the first time as older children,” Dr. Blumberg said, noting that, historically, most children were infected in the first 2 years of life. “There are reports of children 3 or 4 years of age being admitted with their first episode of RSV because of the [COVID] pandemic.”
This year’s RSV season is also notable for arriving early, potentially catching the community off guard, according to Jennifer D. Kusma, MD, a primary care pediatrician at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago.
“People who should have been protected often weren’t protected yet,” Dr. Kusma said in an interview.
Treatments new, old, and unproven
On Nov. 17, in the midst of the RSV surge, the American Academy of Pediatrics issued updated guidance for palivizumab, an RSV-targeting monoclonal antibody labeled for children at risk of severe RSV, including those with pre-existing lung or heart conditions, and infants with a history of premature birth (less than or equal to 35 weeks’ gestational age).
“If RSV disease activity persists at high levels in a given region through the fall and winter, the AAP supports providing more than five consecutive doses of palivizumab to eligible children,” the update stated.
Insurance companies appear to be responding in kind, covering additional doses for children in need.
“[Payers] have agreed that, if [palivizumab] needs to be given for an additional month or 2 or 3, then they’re making a commitment that they’ll reimburse hospitals for providing that,” Dr. Blumberg said.
For ineligible patients, such as Sebastian, who was born prematurely at 36 weeks – 1 week shy of the label requirement – treatment relies upon supportive care with oxygen and IV fluids.
At home, parents are left with simpler options.
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma recommended keeping children hydrated, maintaining humidified air, and using saline nose drops with bulb suction to clear mucus.
In the Witts’ experience, that last step may be easier said than done.
“Every time a nurse would walk into the room, Sebastian would yell: ‘Go away, doctor! I don’t want snot sucker!’” Mr. Witt said.
“If you over snot-suck, that’s really uncomfortable for the kid, and really hard for you,” Ms. Witt said. “And it doesn’t make much of a difference. It’s just very hard to find a middle ground, where you’re helping and keeping them comfortable.”
Some parents are turning to novel strategies, such as nebulized hypertonic saline, currently marketed on Amazon for children with RSV.
Although the AAP offers a weak recommendation for nebulized hypertonic saline in children hospitalized more than 72 hours, they advise against it in the emergency setting, citing inconsistent findings in clinical trials.
To any parents tempted by thousands of positive Amazon reviews, Dr. Blumberg said, “I wouldn’t waste my money on that.”
Dr. Kusma agreed.
“[Nebulized hypertonic saline] can be irritating,” she said. “It’s saltwater, essentially. If a parent is in the position where they’re worried about their child’s breathing to the point that they think they need to use it, I would err on the side of calling your pediatrician and being seen.”
Going in, coming home
Dr. Kusma said parents should seek medical attention if a child is breathing faster and working harder to get air. Increased work of breathing is characterized by pulling of the skin at the notch where the throat meets the chest bone (tracheal tugging), and flattening of the belly that makes the ribcage more prominent.
Mr. Witt saw these signs in Sebastian. He knew they were significant, because a friend who is a nurse had previously shown him some examples of children who exhibited these symptoms online.
“That’s how I knew that things were actually really dangerous,” Mr. Witt said. “Had she not shown me those videos a month and a half before this happened, I don’t know that we would have hit the alarm bell as quickly as we did.”
After spending their second night and the following day in a cramped preoperative room converted to manage overflow from the emergency department, Sebastian’s condition improved, and he was discharged. The Witts are relieved to be home, but frustrations from their ordeal remain, especially considering the estimated $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs they expect to pay.
“How is this our health care system?” Ms. Witt asked. “This is unbelievable.”
An optimistic outlook
RSV seasons typically demonstrate a clear peak, followed by a decline through the rest of the season, suggesting better times lie ahead; however, this season has been anything but typical.
“I’m hopeful that it will just go away and stay away,” Dr. Kusma said, citing this trend. “But I can’t know for sure.”
To anxious parents, Dr. Blumberg offered an optimistic view of RSV seasons to come.
“There’s hope,” he said. “There are vaccines that are being developed that are very close to FDA approval. So, it’s possible that this time next year, we might have widespread RSV vaccination available for children so that we don’t have to go through this nightmare again.”
Dr. Blumberg and Dr. Kusma disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.